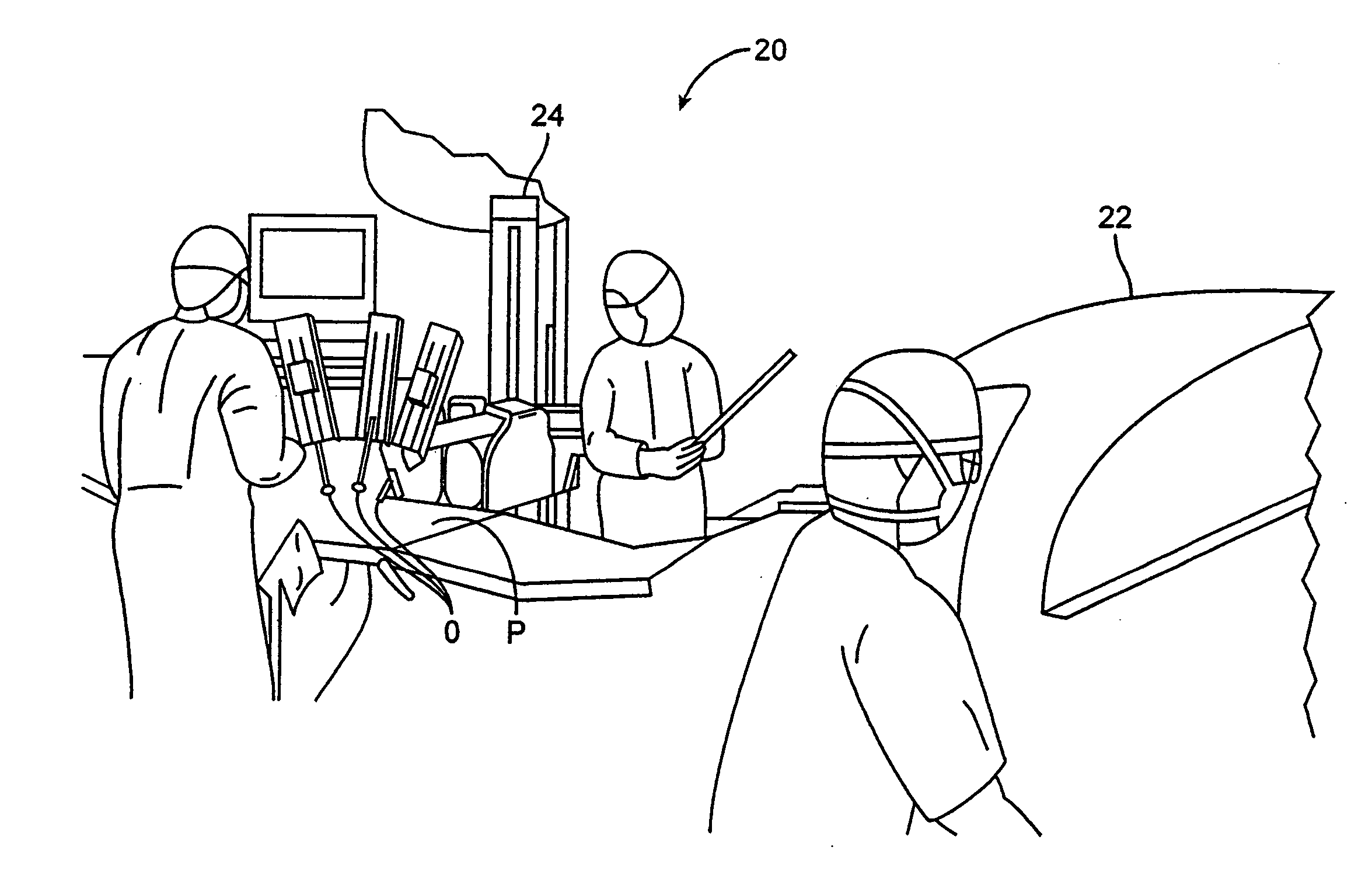
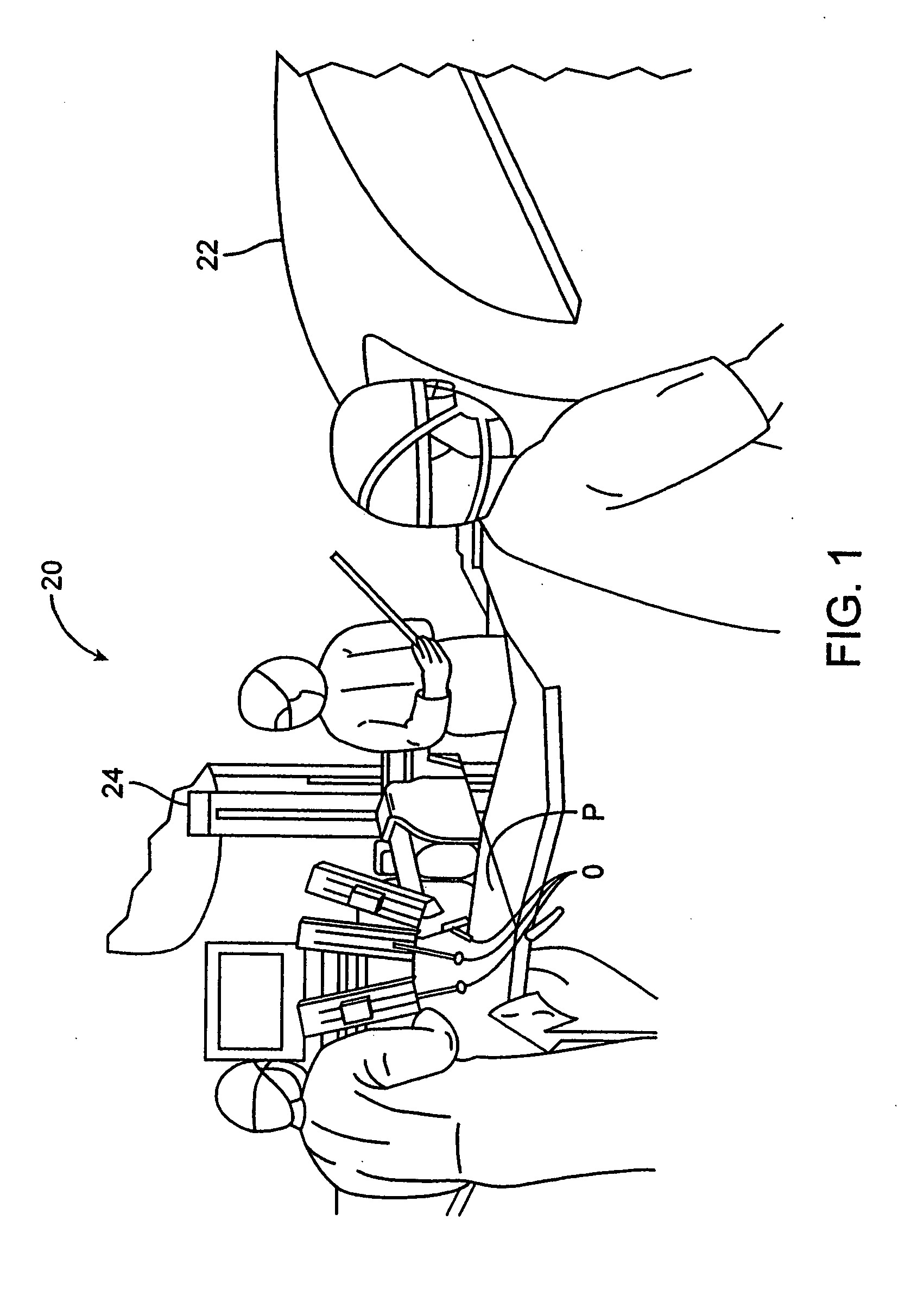
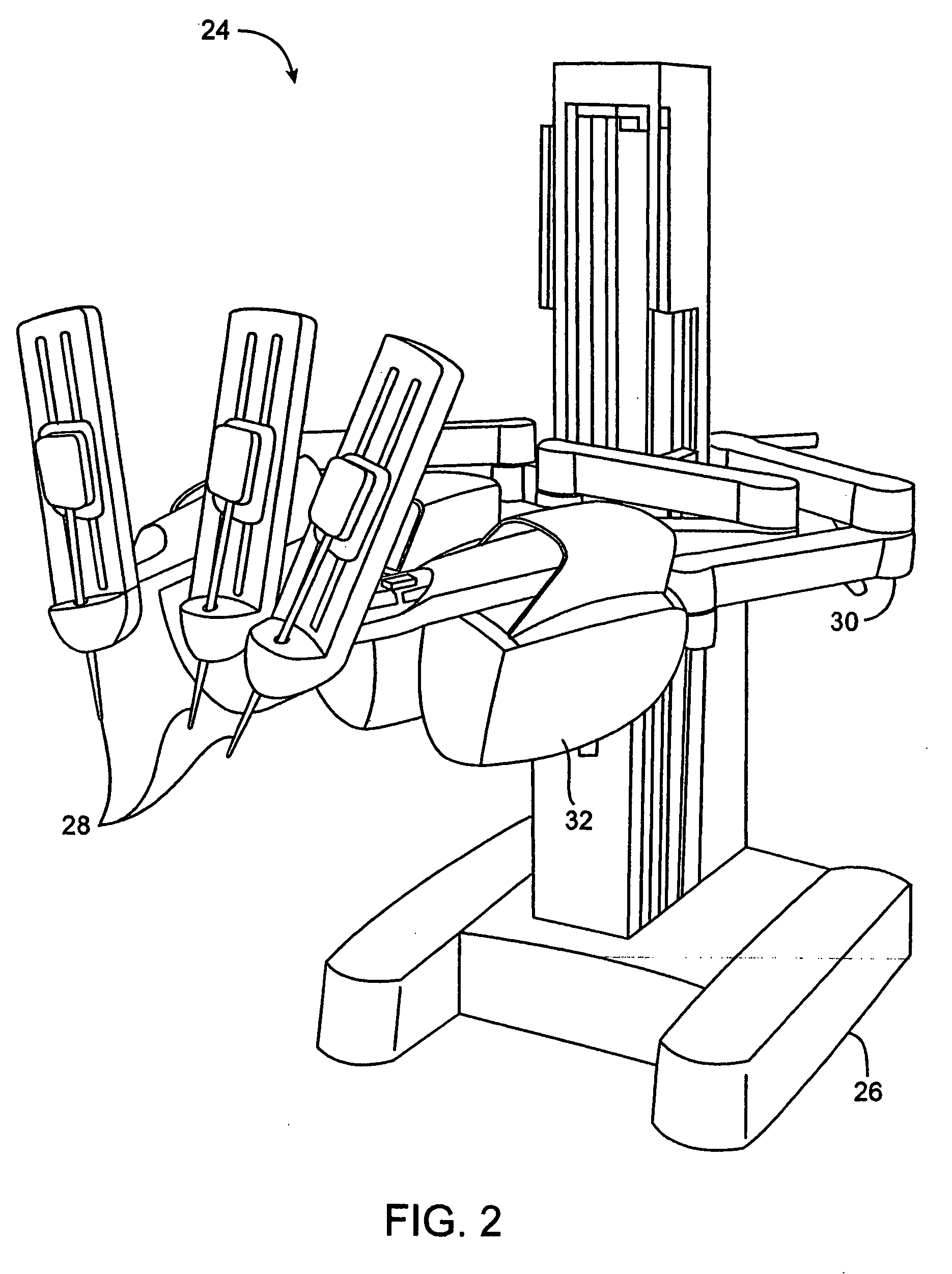
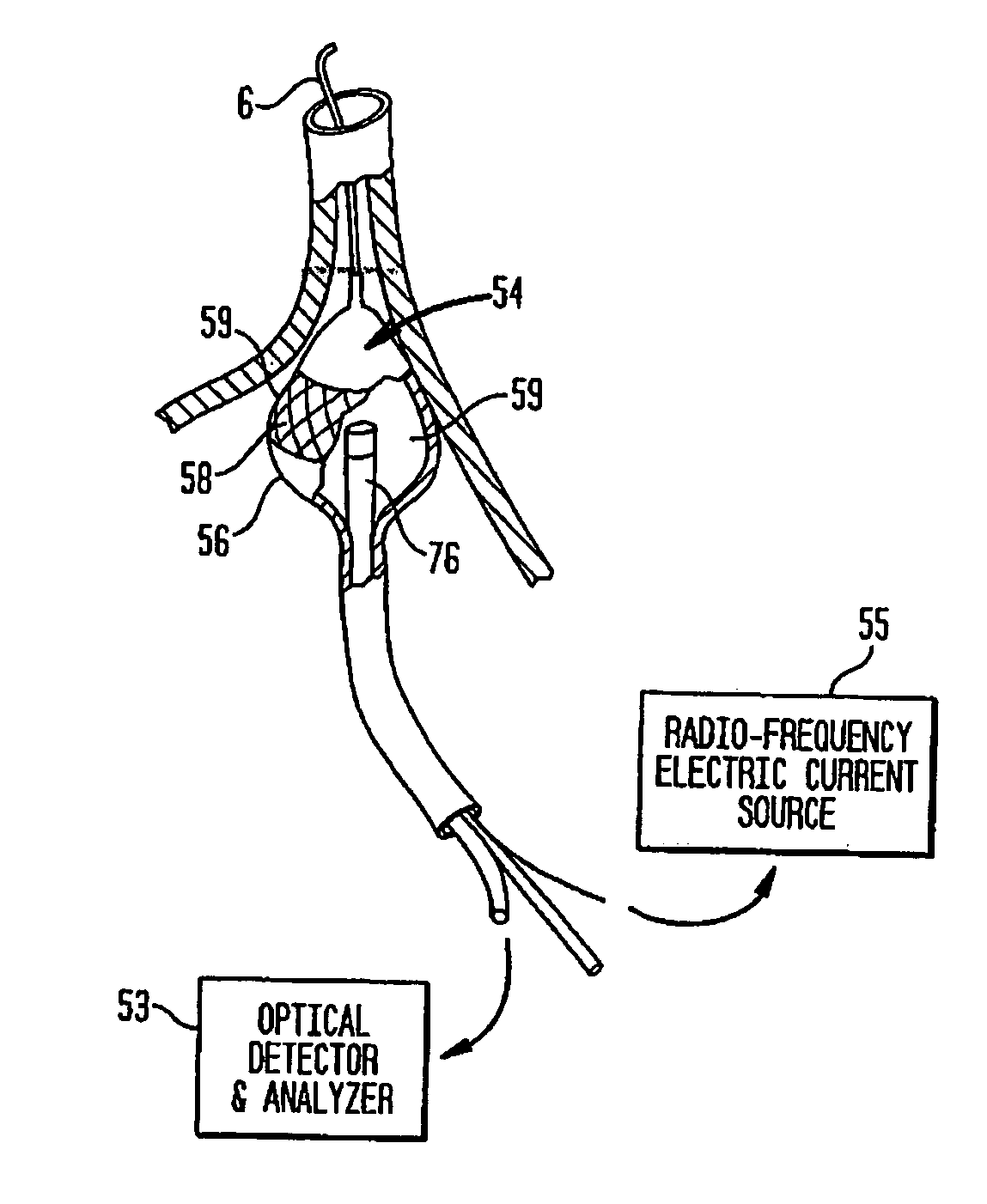
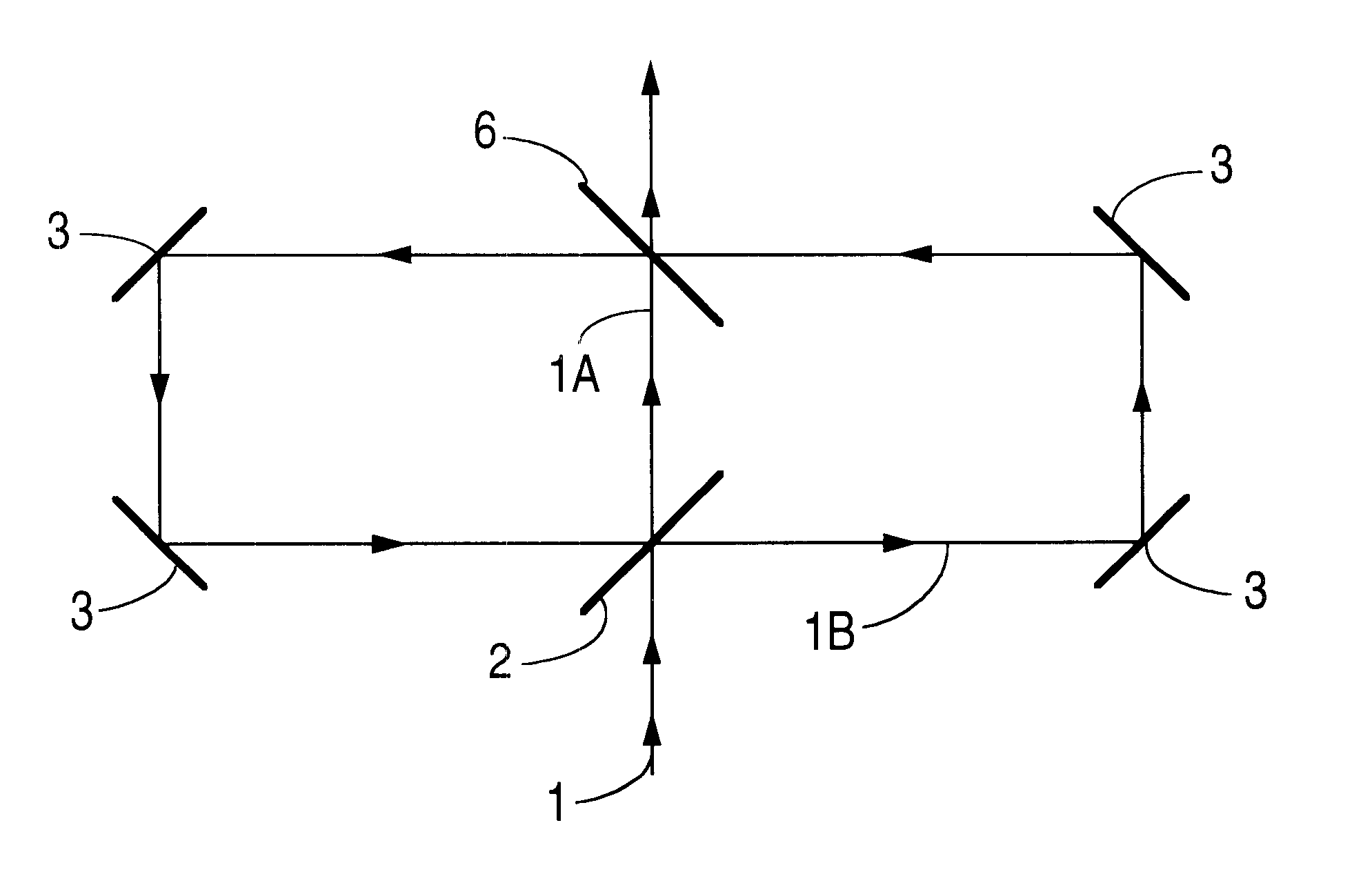
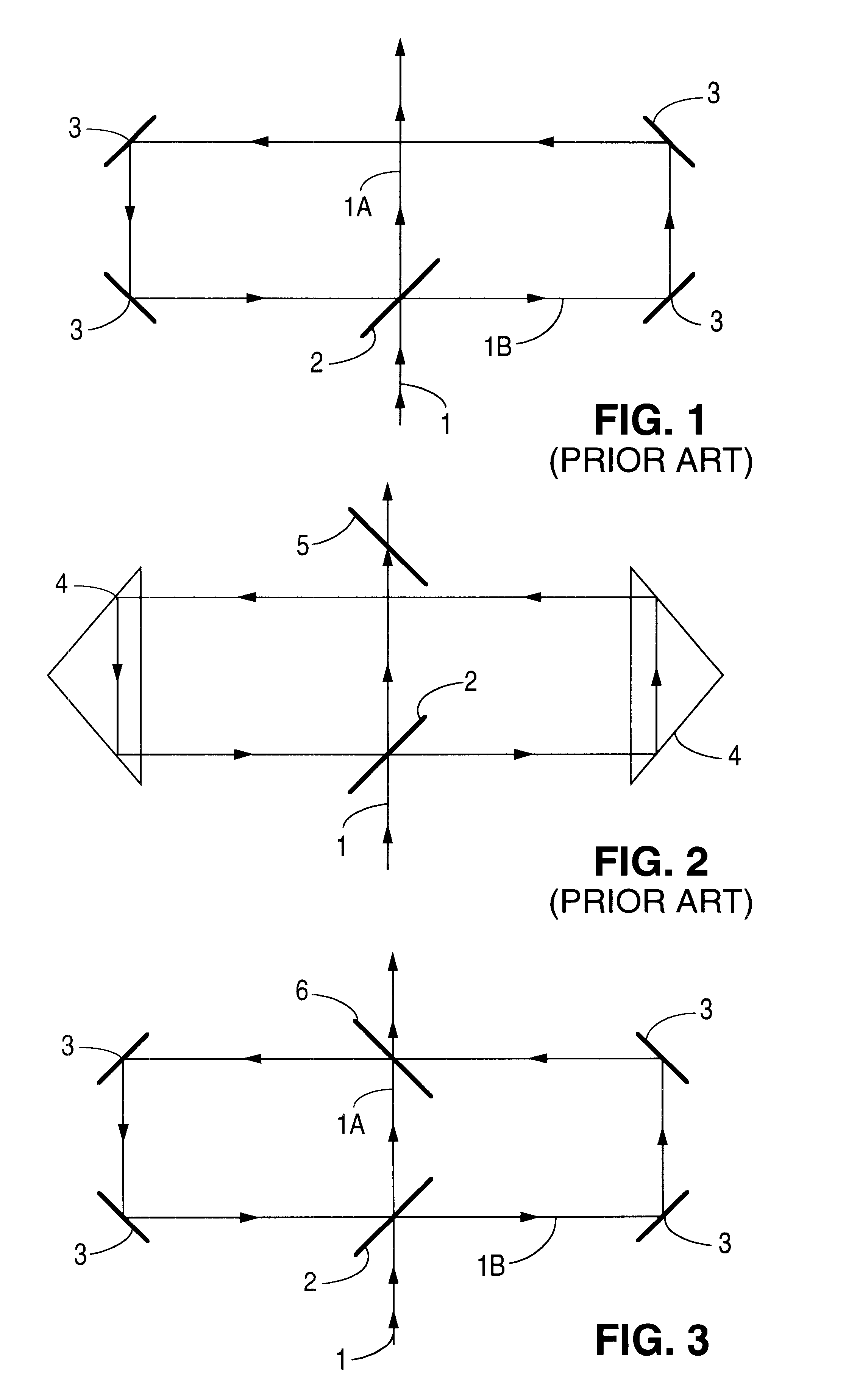
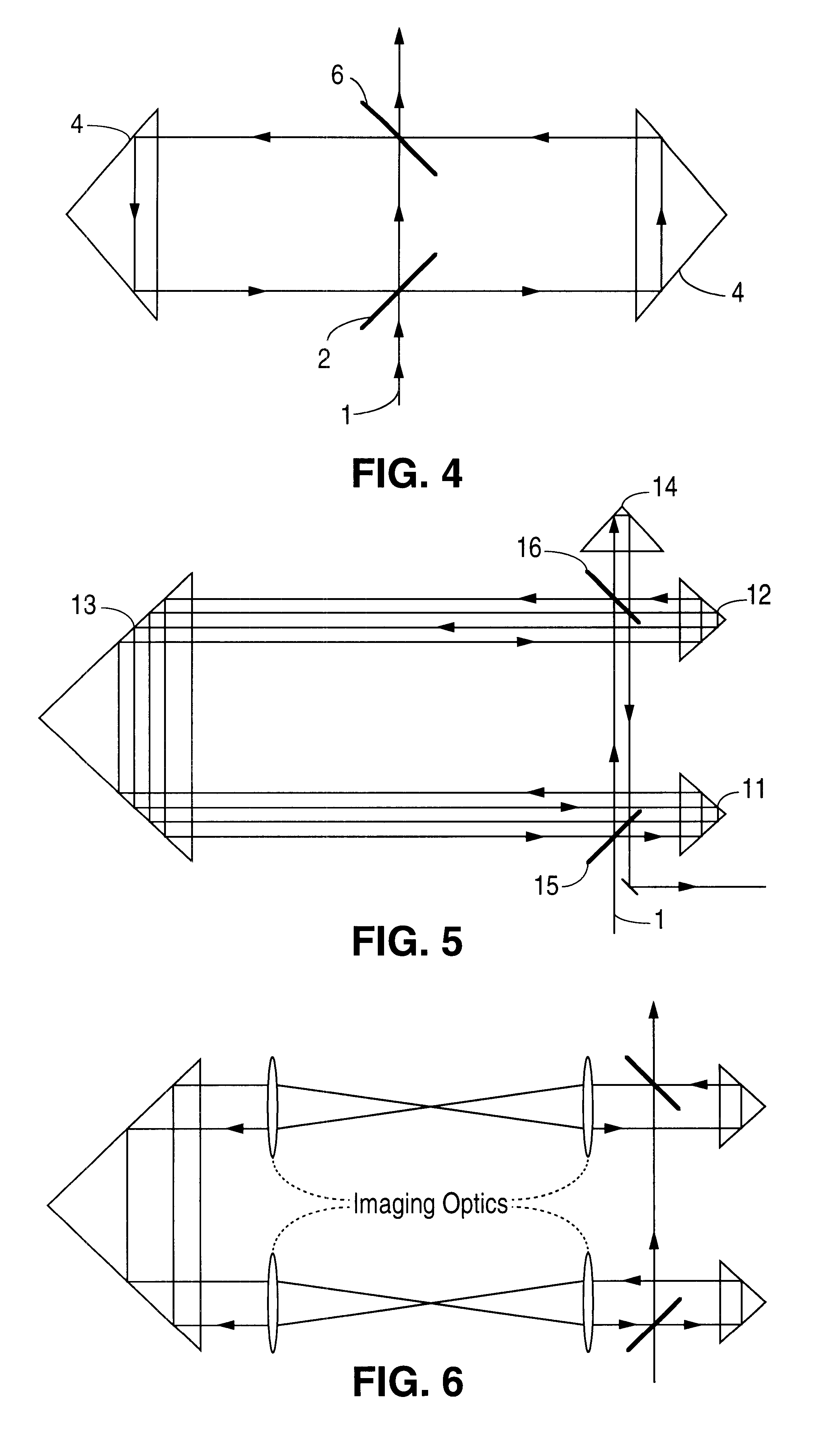
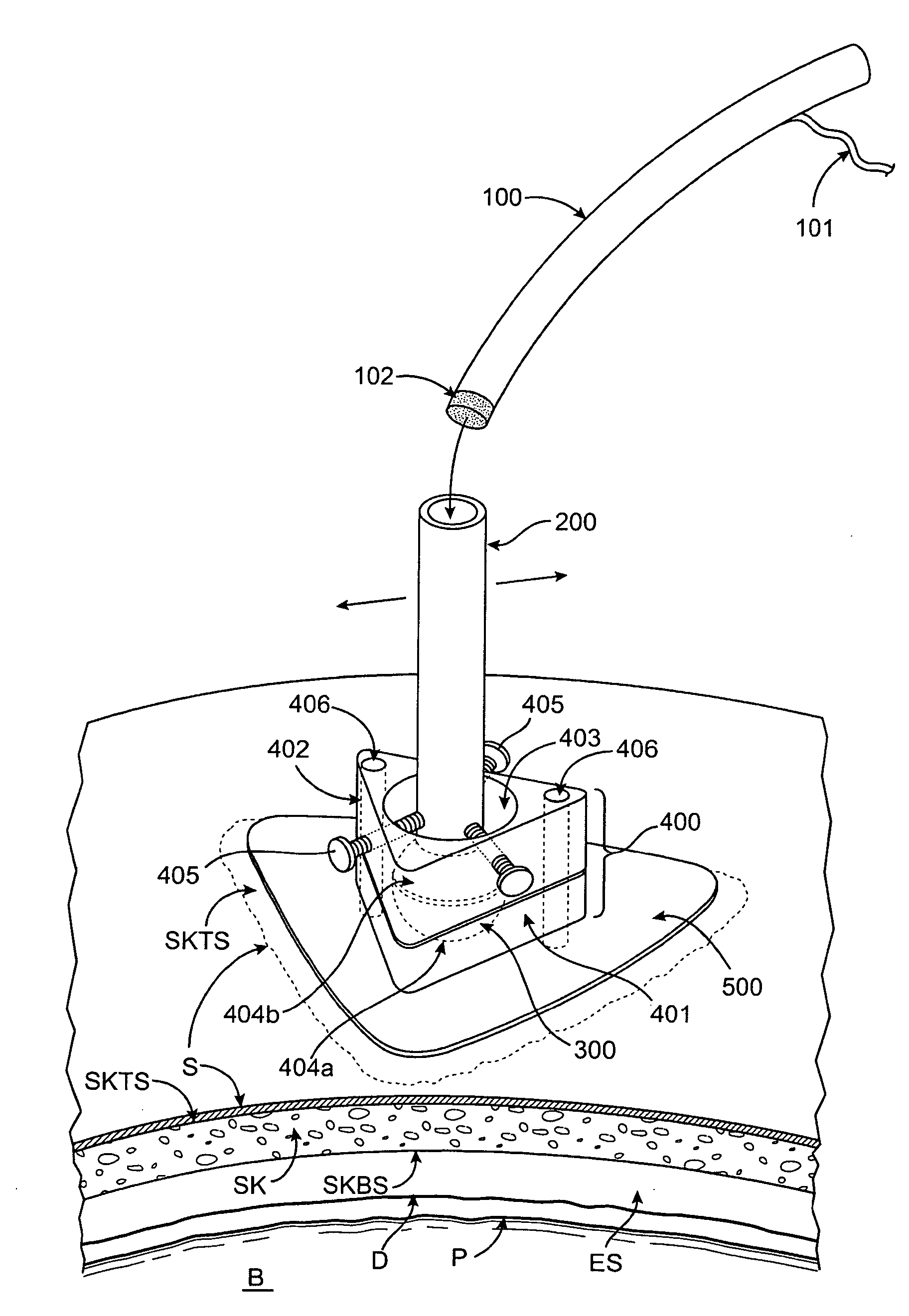
Patents
Literature
368results about How to "Improve energy transfer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
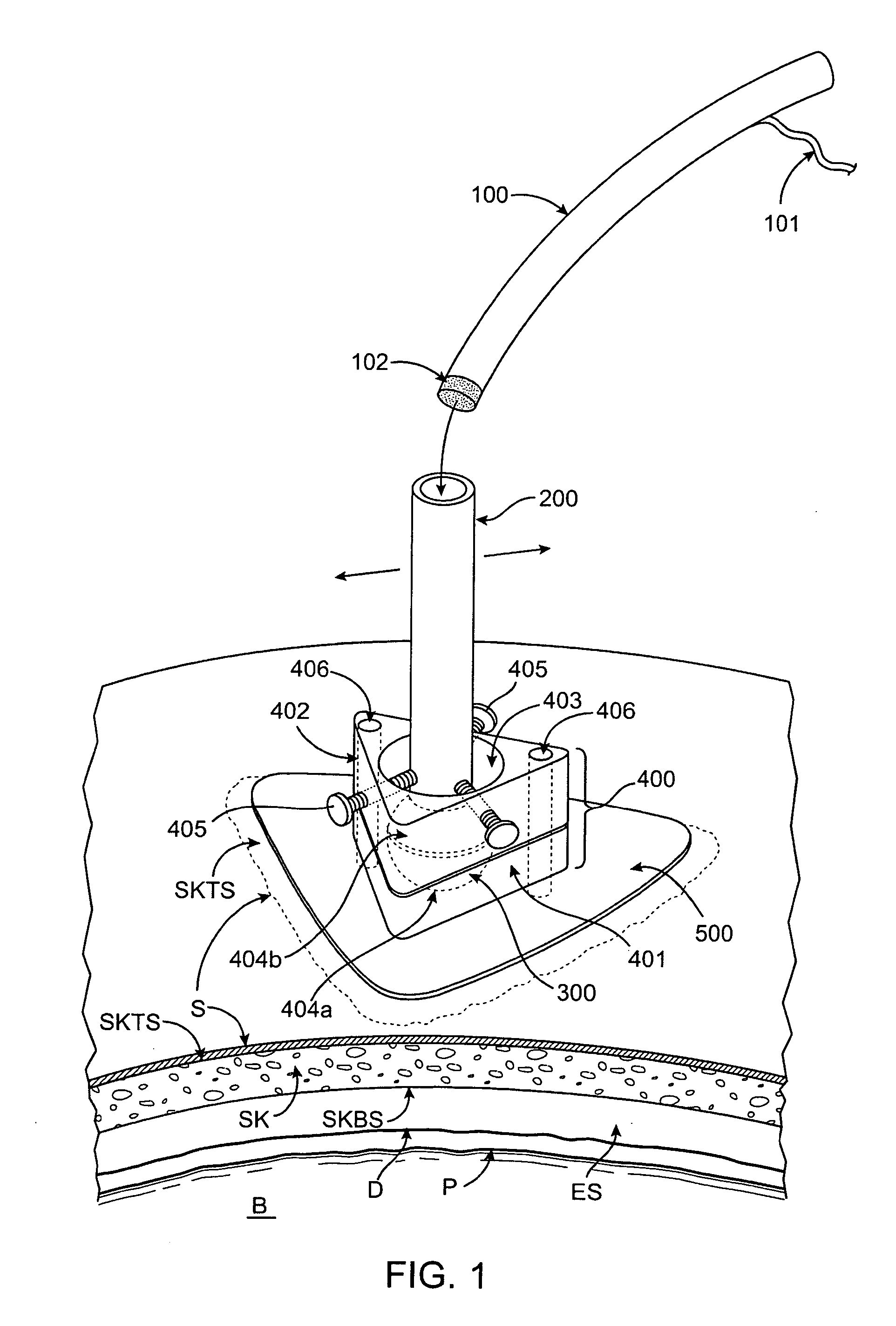
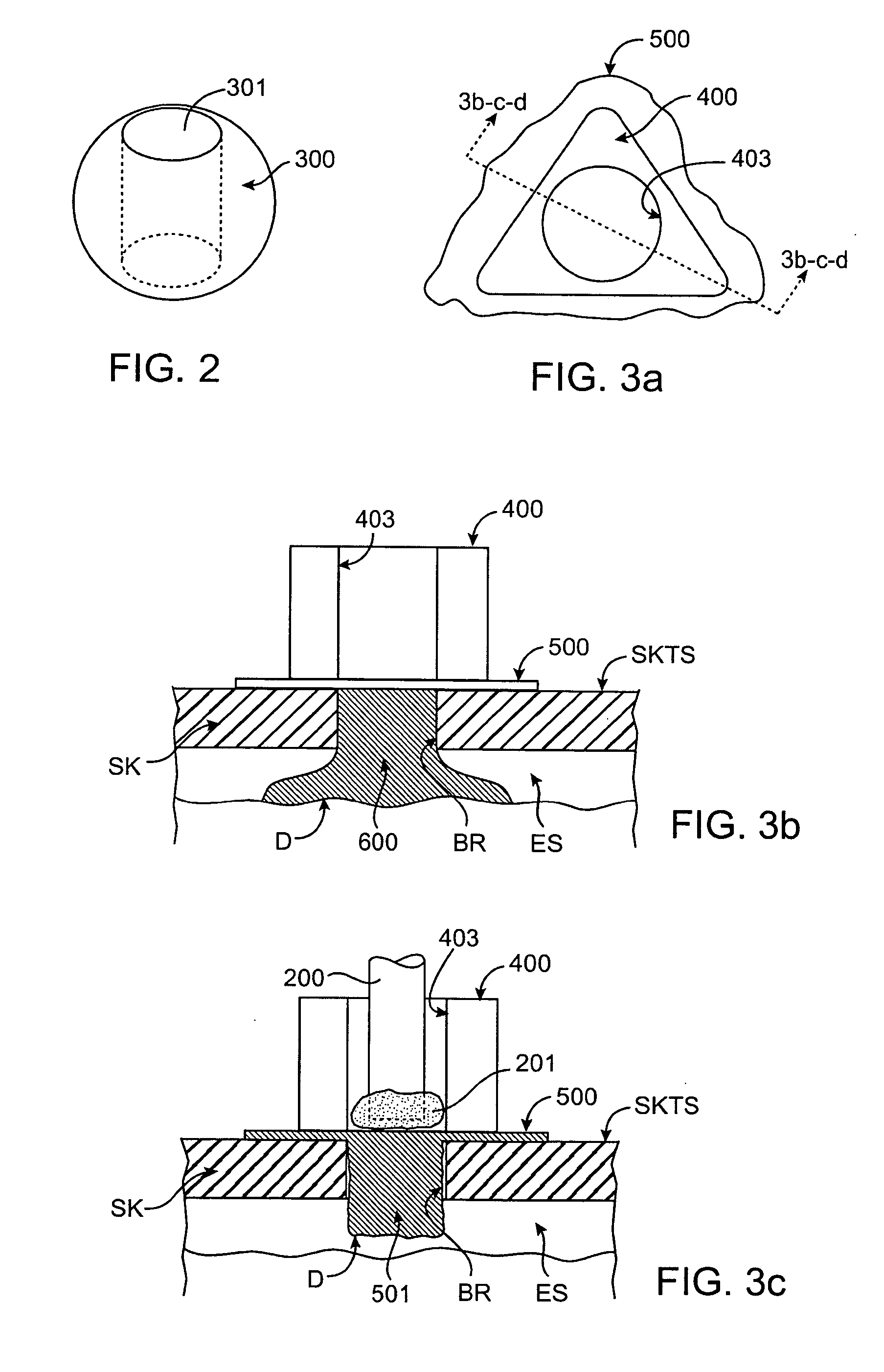
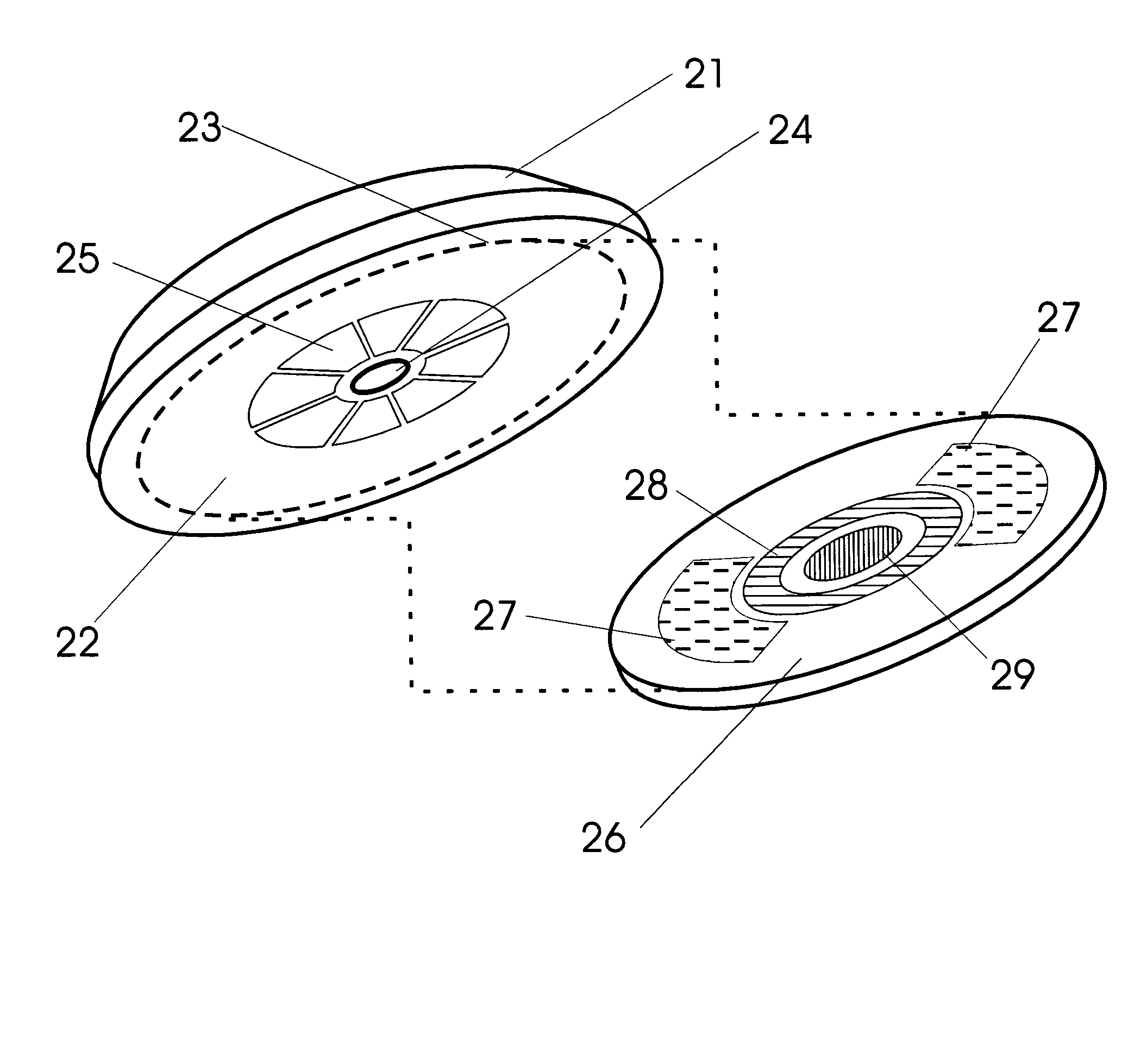
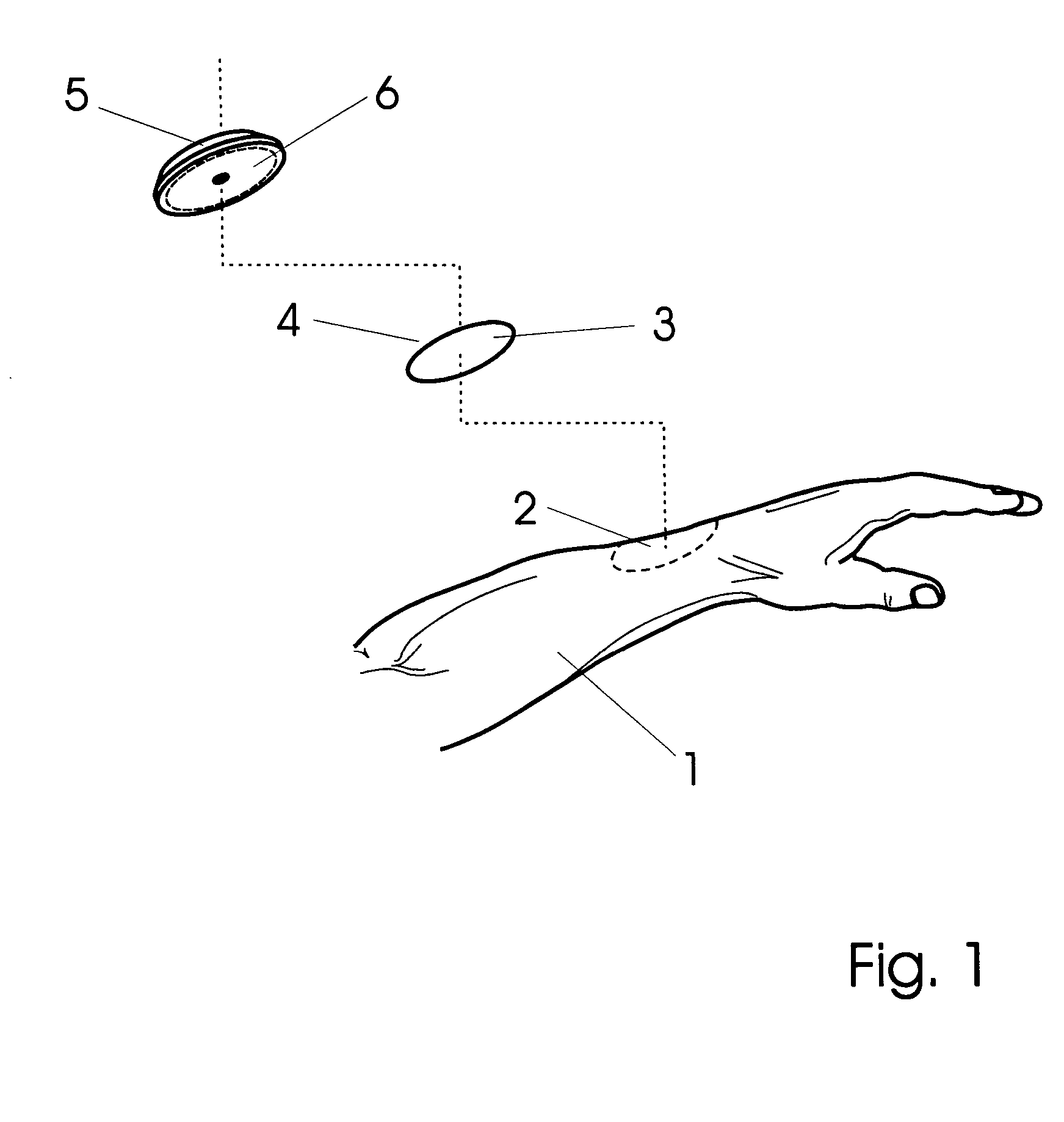
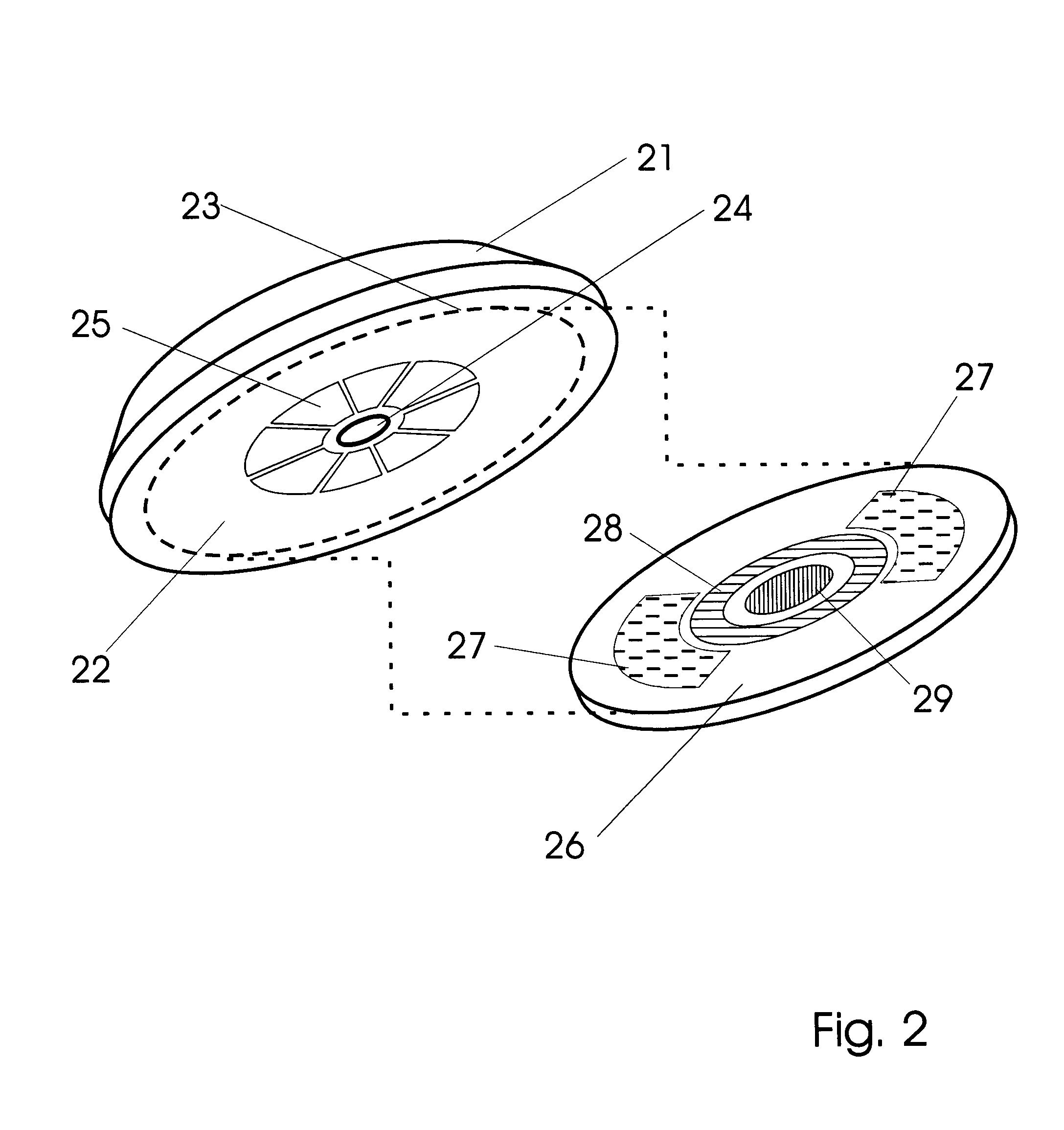
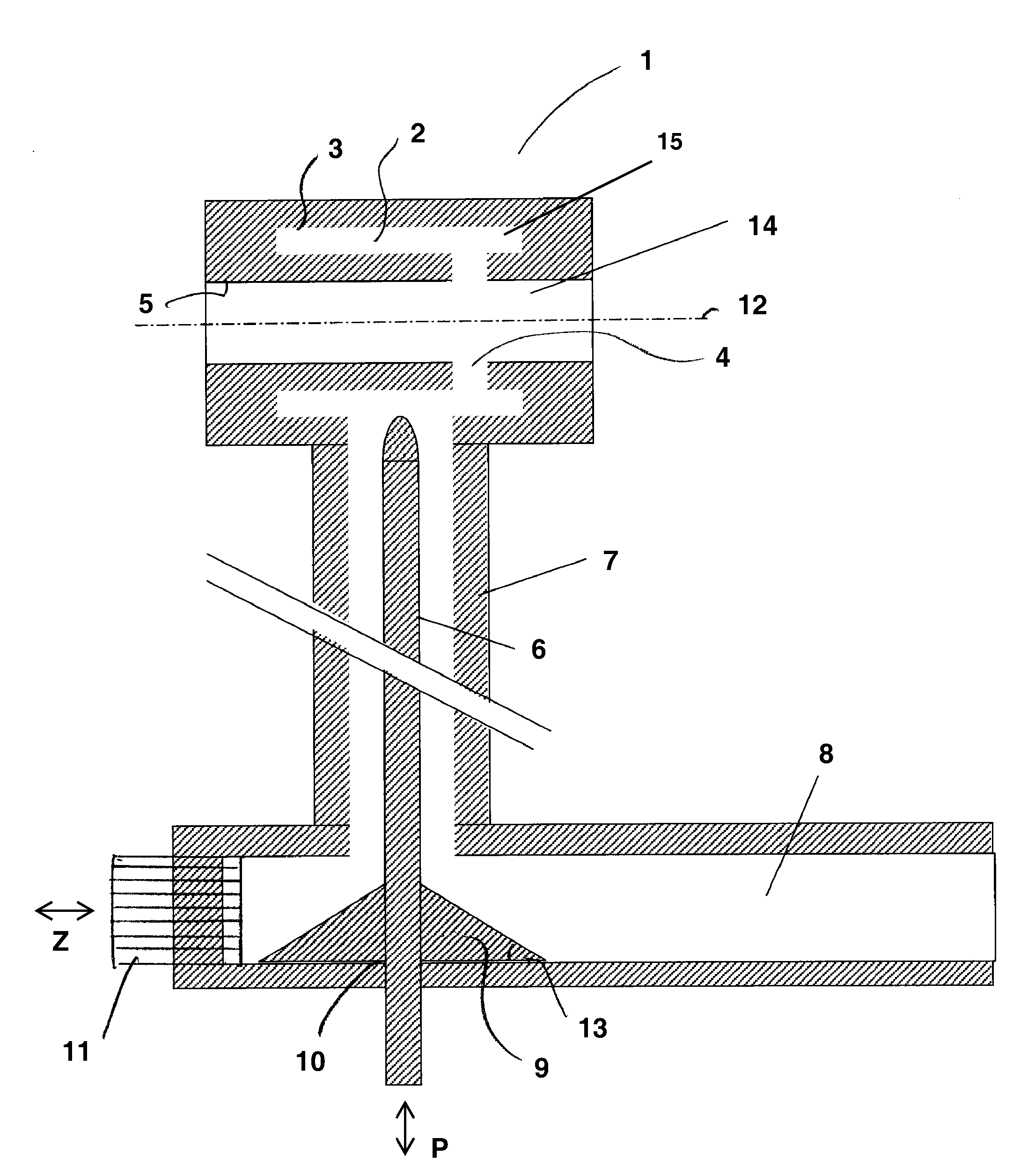
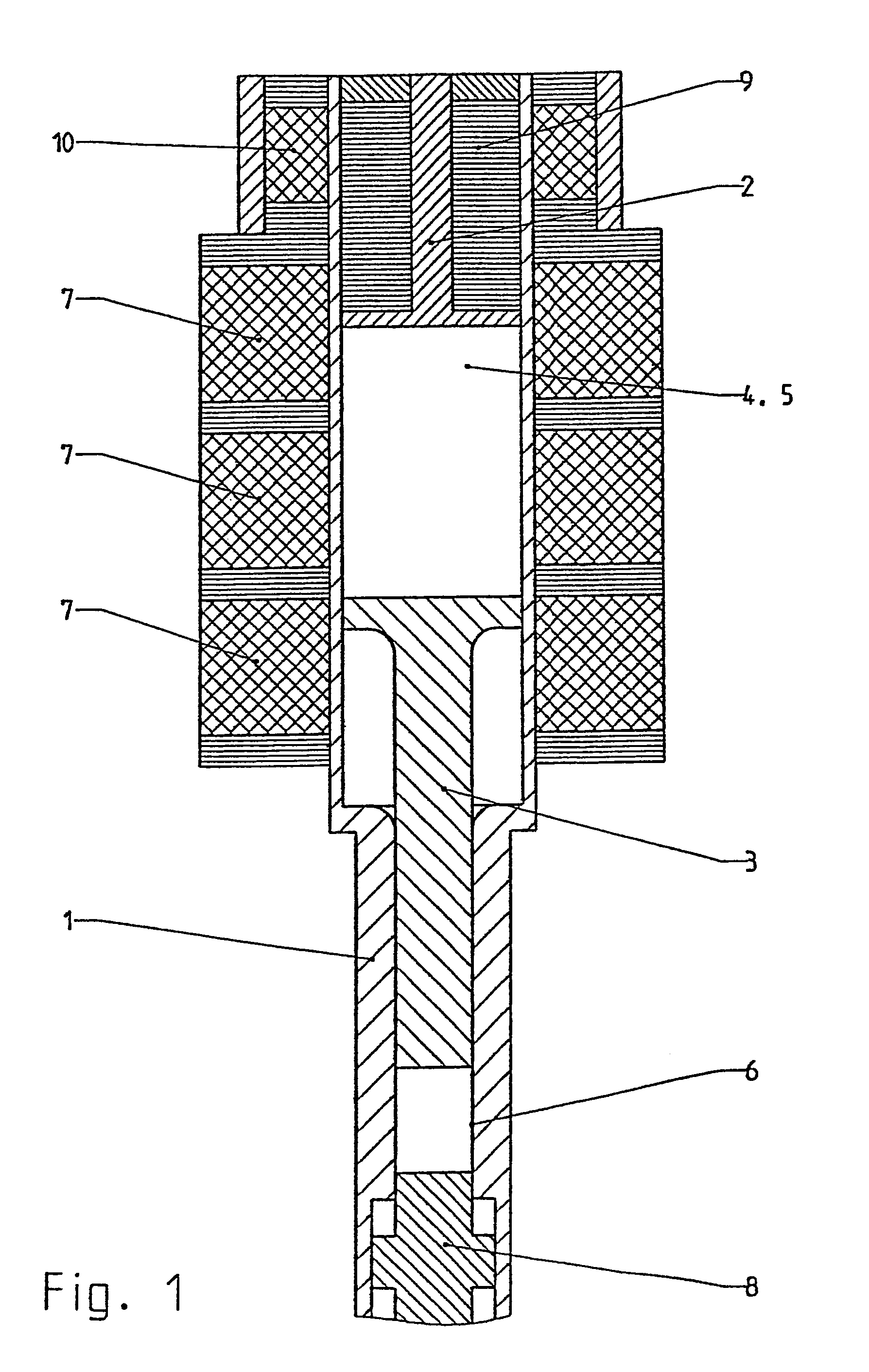
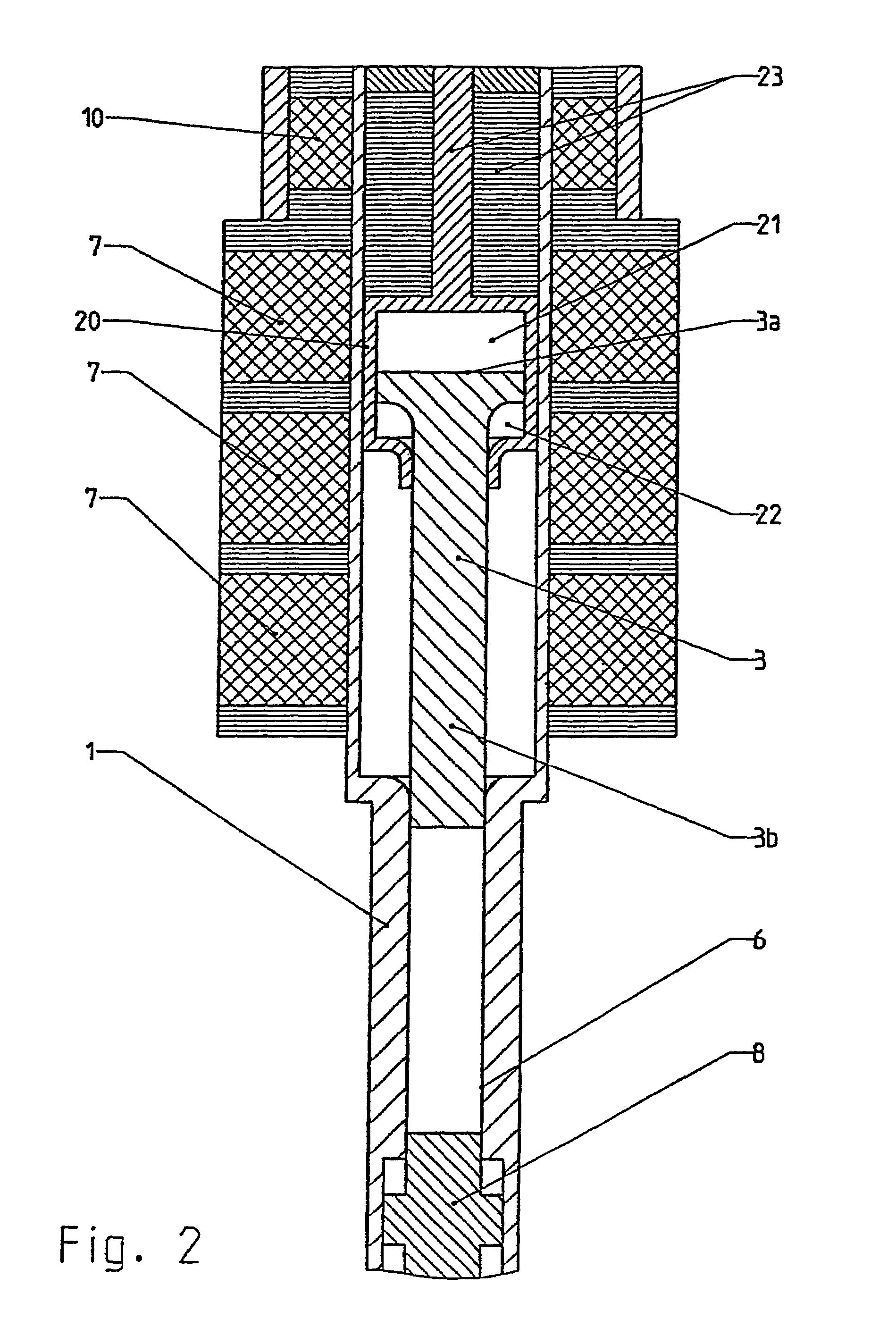
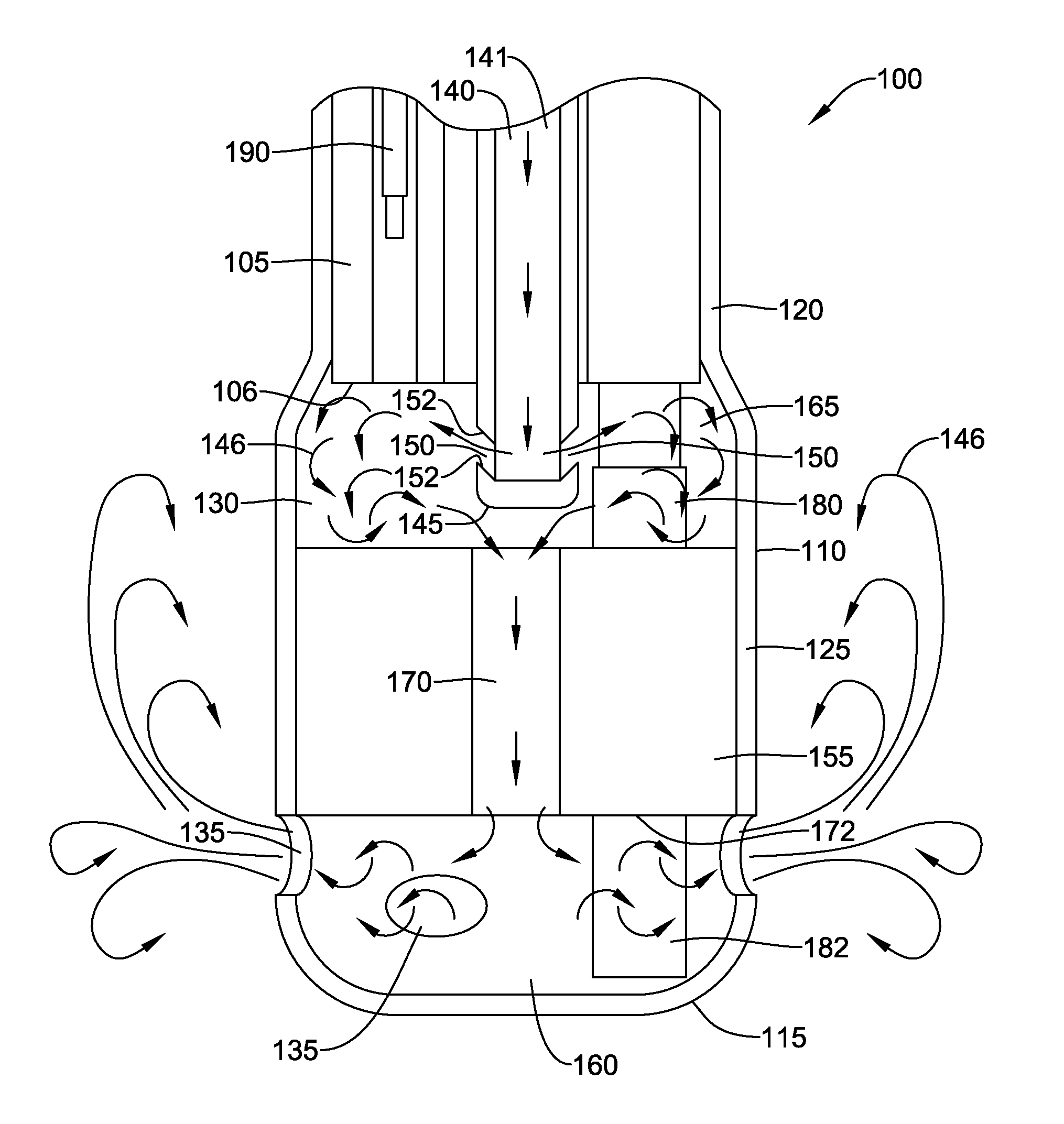
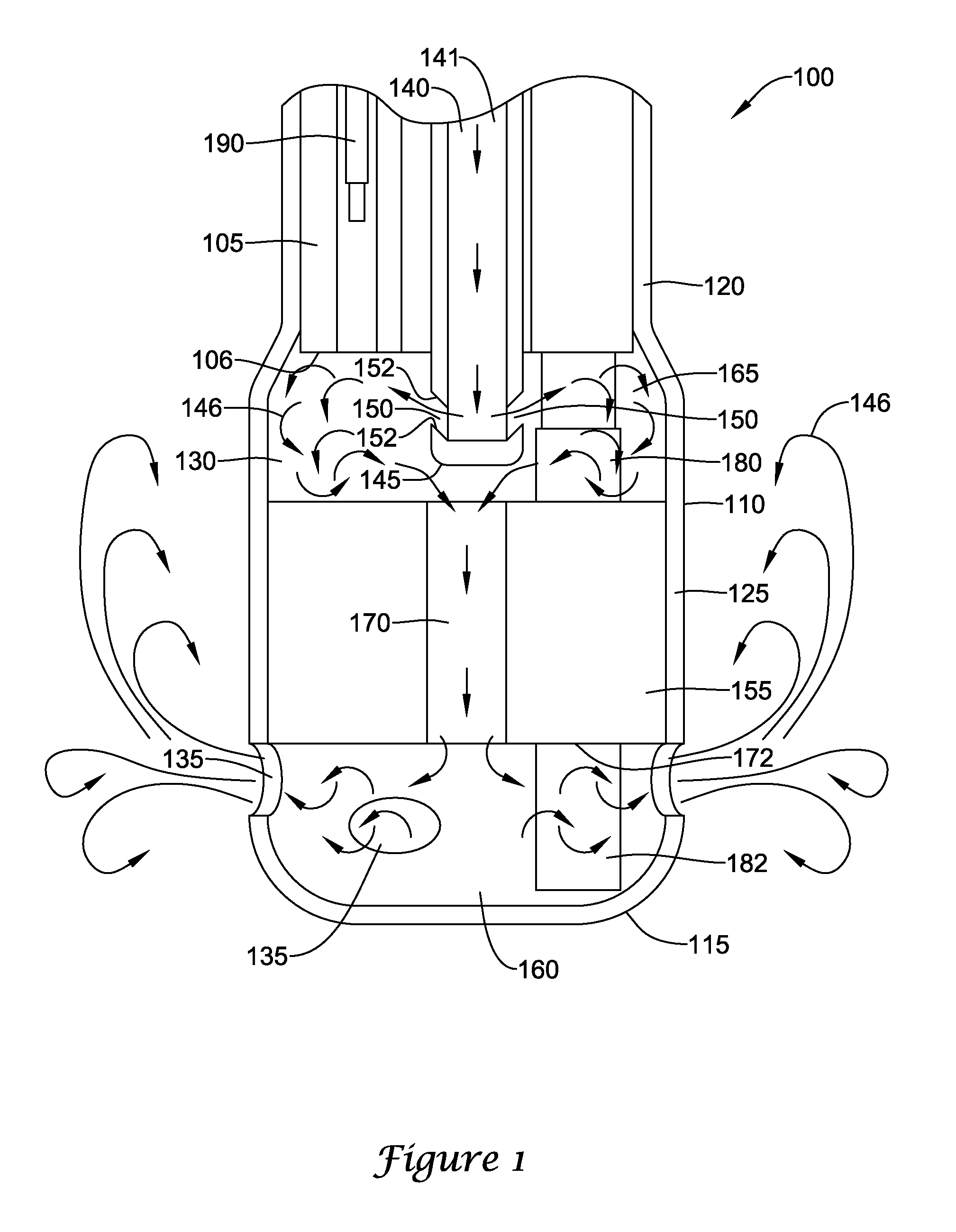
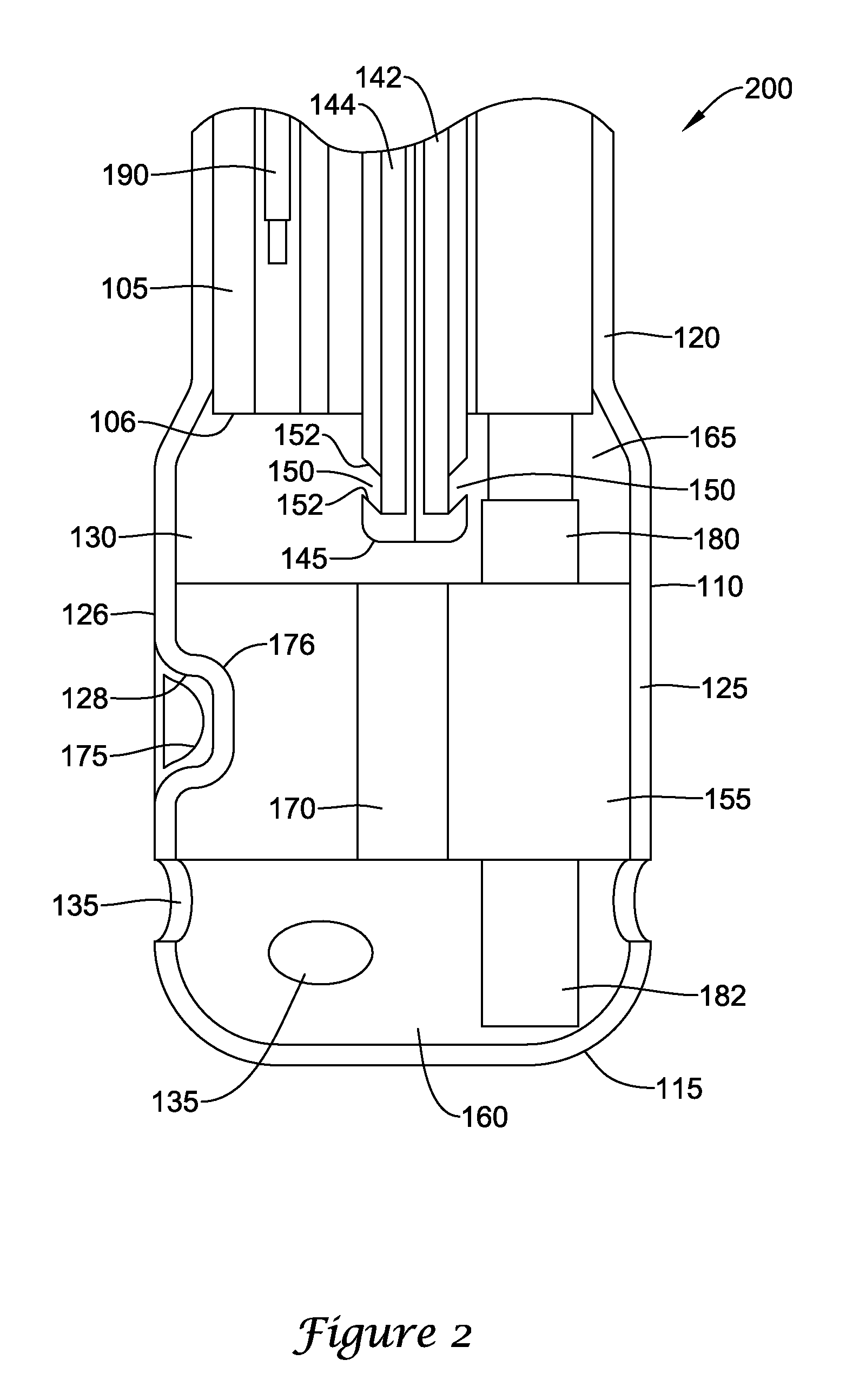
Bipolar cauterizing instrument
A bipolar surgical instrument that includes opposing grips that can engage the tissue. A current is delivered from an electrosurgical power source to electrodes disposed on the grips to cauterize the tissue. The electrode configurations provide efficient cauterization of the tissue. In some embodiments, the positive and negative electrodes will be offset from each other to prevent shorting and to provide a thin line of coagulation heating to the gripped tissue. In some embodiments the electrodes are removably coupled to the grips through nonconductive sleeves. In some embodiments, the first electrode is disposed in a groove and the second electrode is disposed on a boss.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL
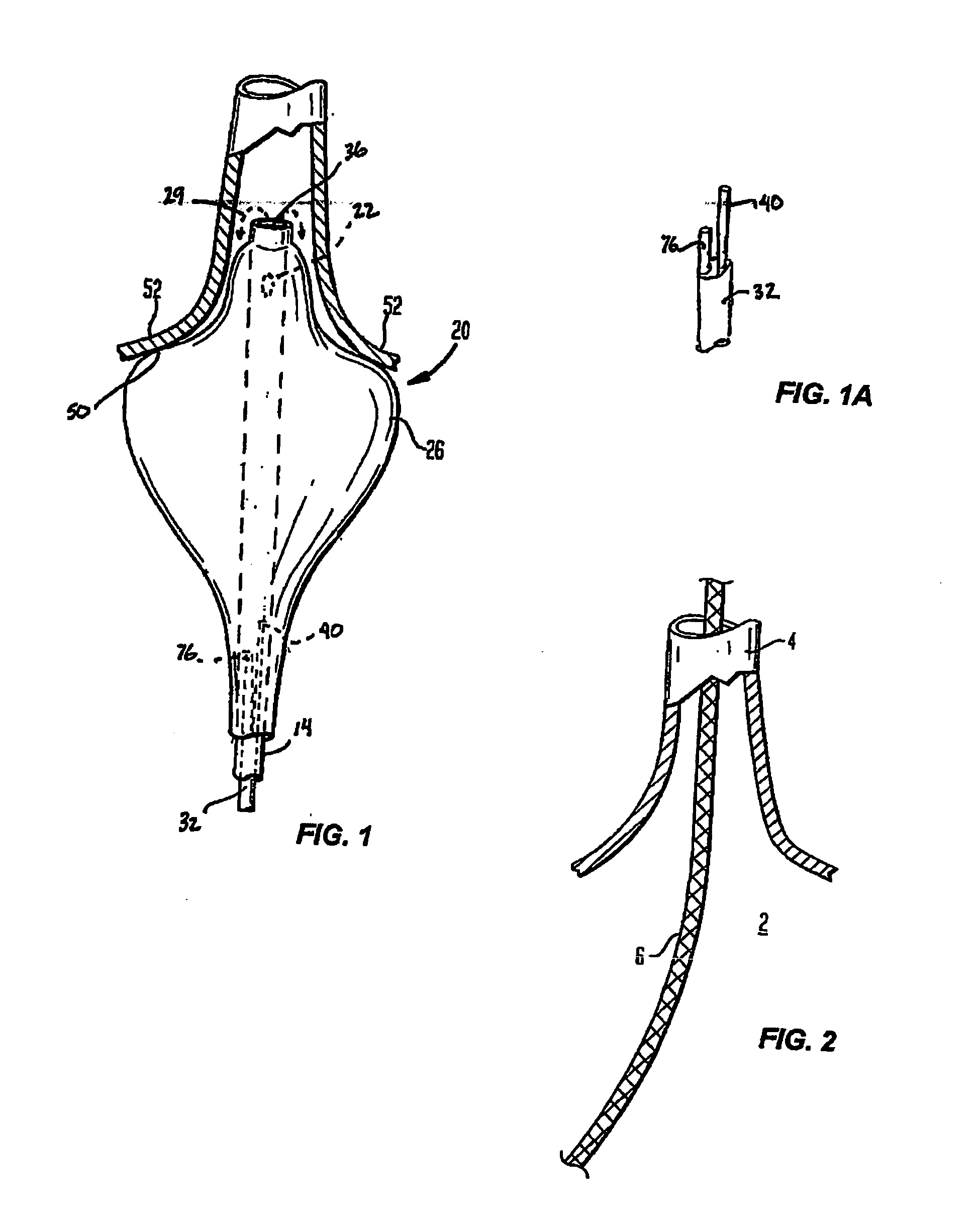
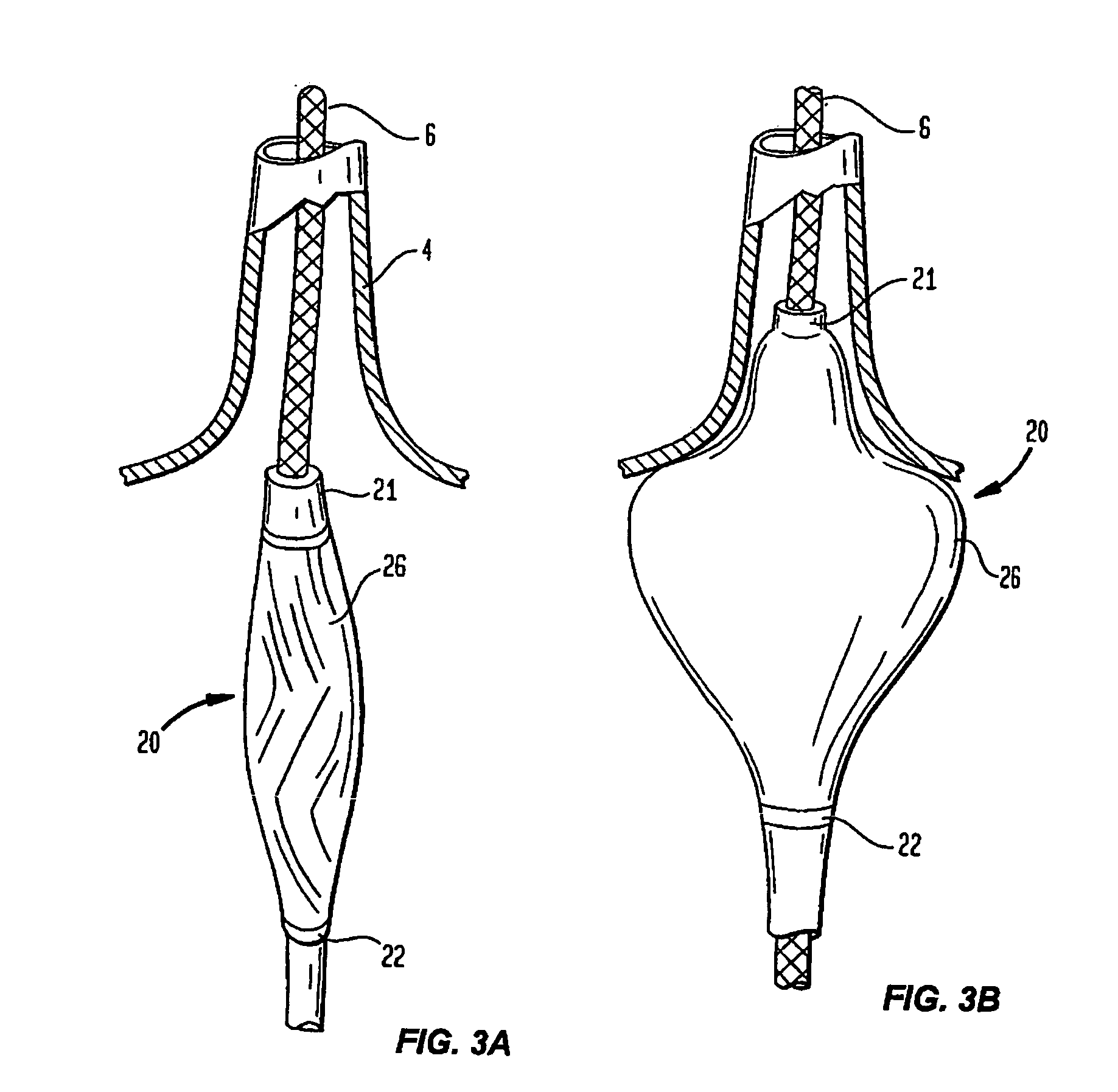
Guided cardiac ablation catheters
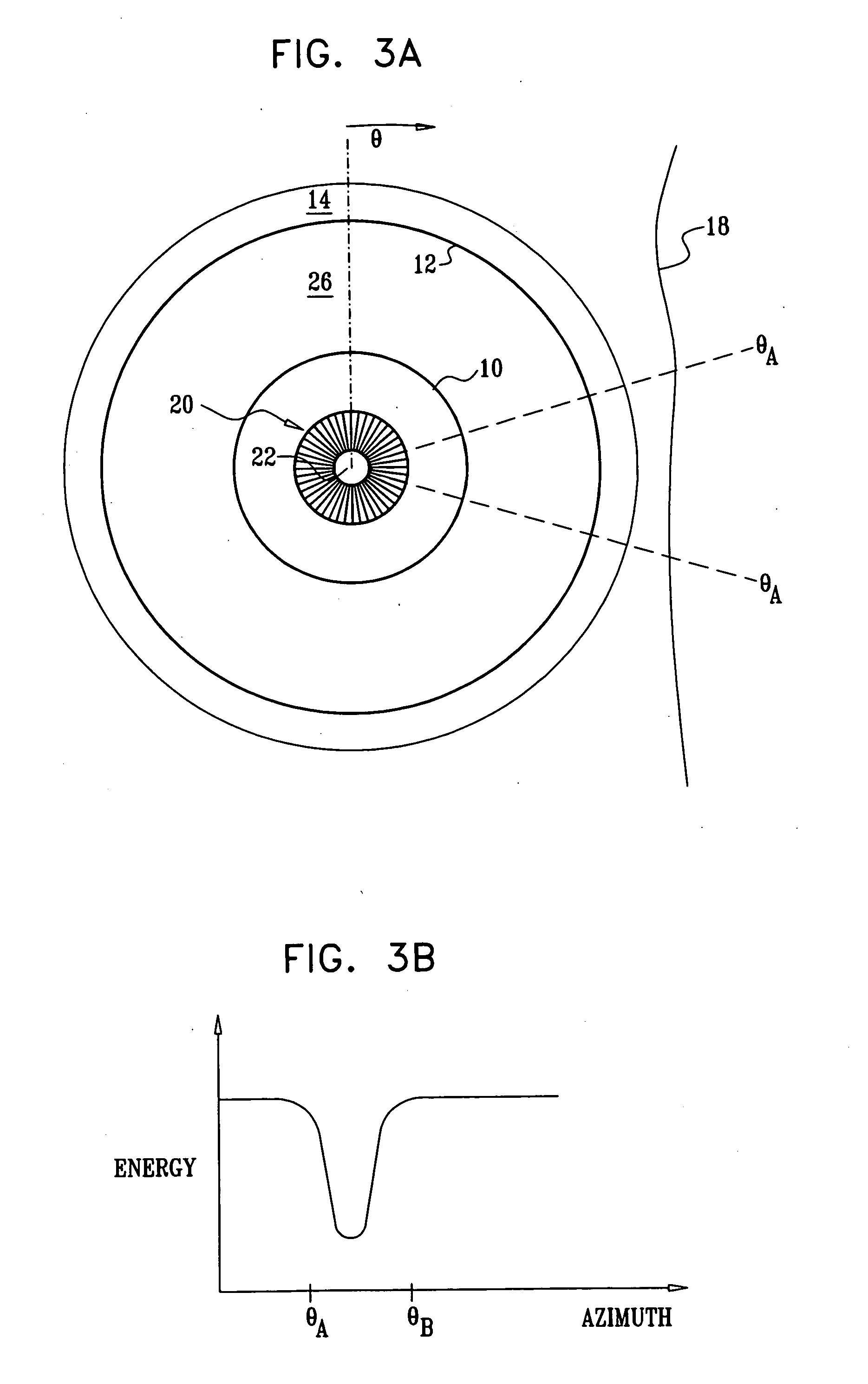
InactiveUS20050065504A1Improve energy transferEnhance the imageUltrasound therapyLaproscopesLight sourceCardiac Ablation
Owner:CARDIOFOCUS INC
Golf club face flexure control system
InactiveUS6979270B1High modulusImprove energy transferGolf clubsRacket sportsControl systemGolf Ball
An improved line of golf clubs tailored to the golfer. The face wall firstly is designed so that the face wall modulus of elasticity increases from a low modulus for the low swing speed range to progressively higher modula for the higher swing speed ranges. Face modulus can be altered by a variety of techniques including face wall thinning, material selection and heat treatment or a combination thereof. In each of the swing speed range clubs, the face has a first modulus of elasticity determined by the face itself and after the face deflects to a predetermined value, the face modulus is significantly increased by a secondary wall parallel to and closely spaced behind the face wall.
Owner:KARSTEN MFG CORP
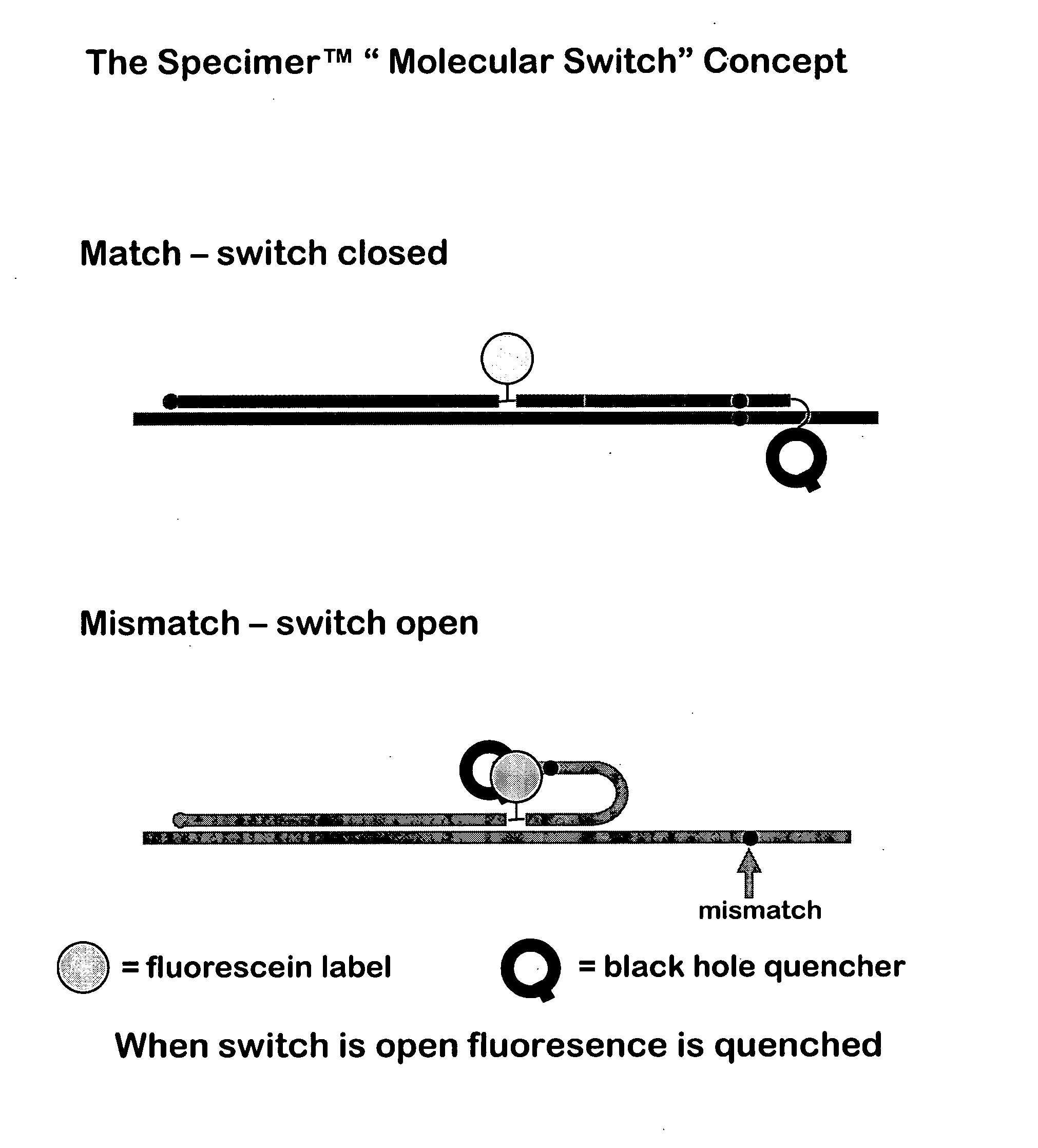
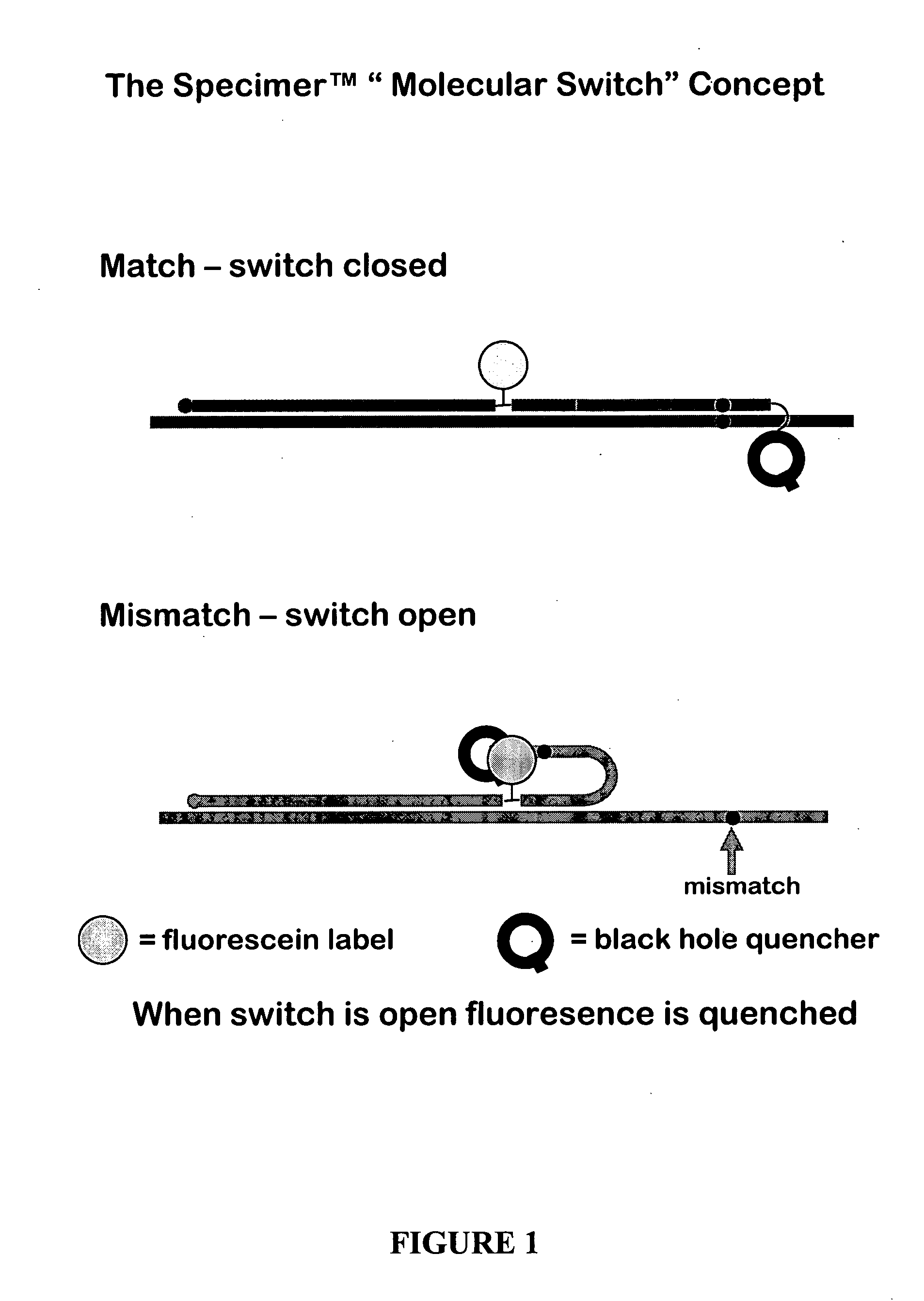
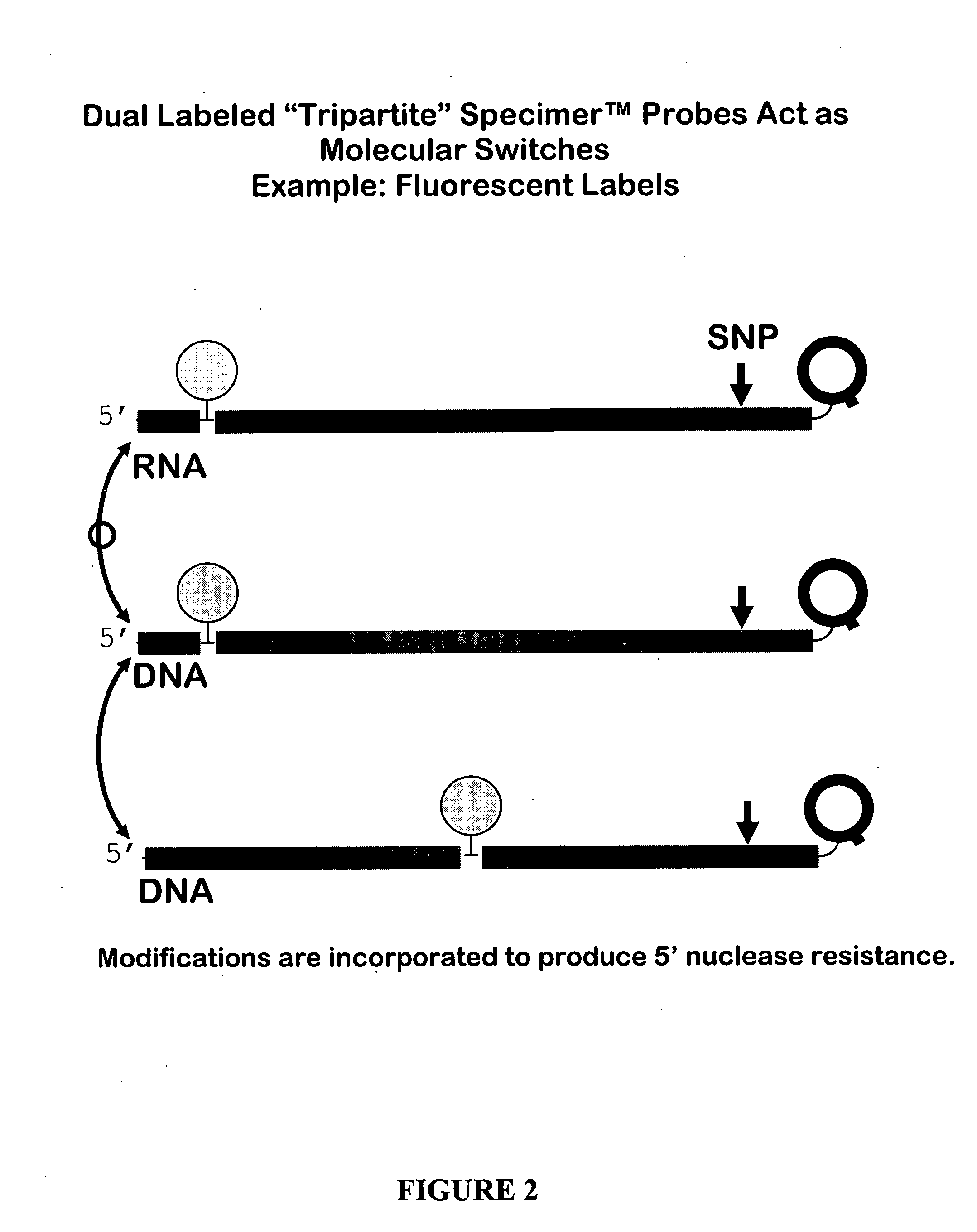
Oligonucleotides comprising a molecular switch
ActiveUS20050042638A1Strong specificityGuaranteed positioningSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBinding domainMolecular switch
This invention relates to oligonucleotides comprising a molecular switch which may exist in an “open” or “closed” position. The molecular switch portion of the probe is particularly sensitive to the identity of sequences complementary to the molecular switch. Oligonucleotides containing a molecular switch are applicable to all kinds of hybridization processes. Due to the sensitivity of the switch domain of the oligonucleotide, probes containing a molecular switch are particularly useful in the identification of single point mismatches. More specifically, a portion, but not all, of the oligonucleotide becomes unbound from a mismatched target. The invention further relates to methods of using said oligonucleotides for research reagents, and clinical diagnostics. An exemplary oligonucleotide comprises a first hybridizable domain, a second bridging block domain, and a third binding domain.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
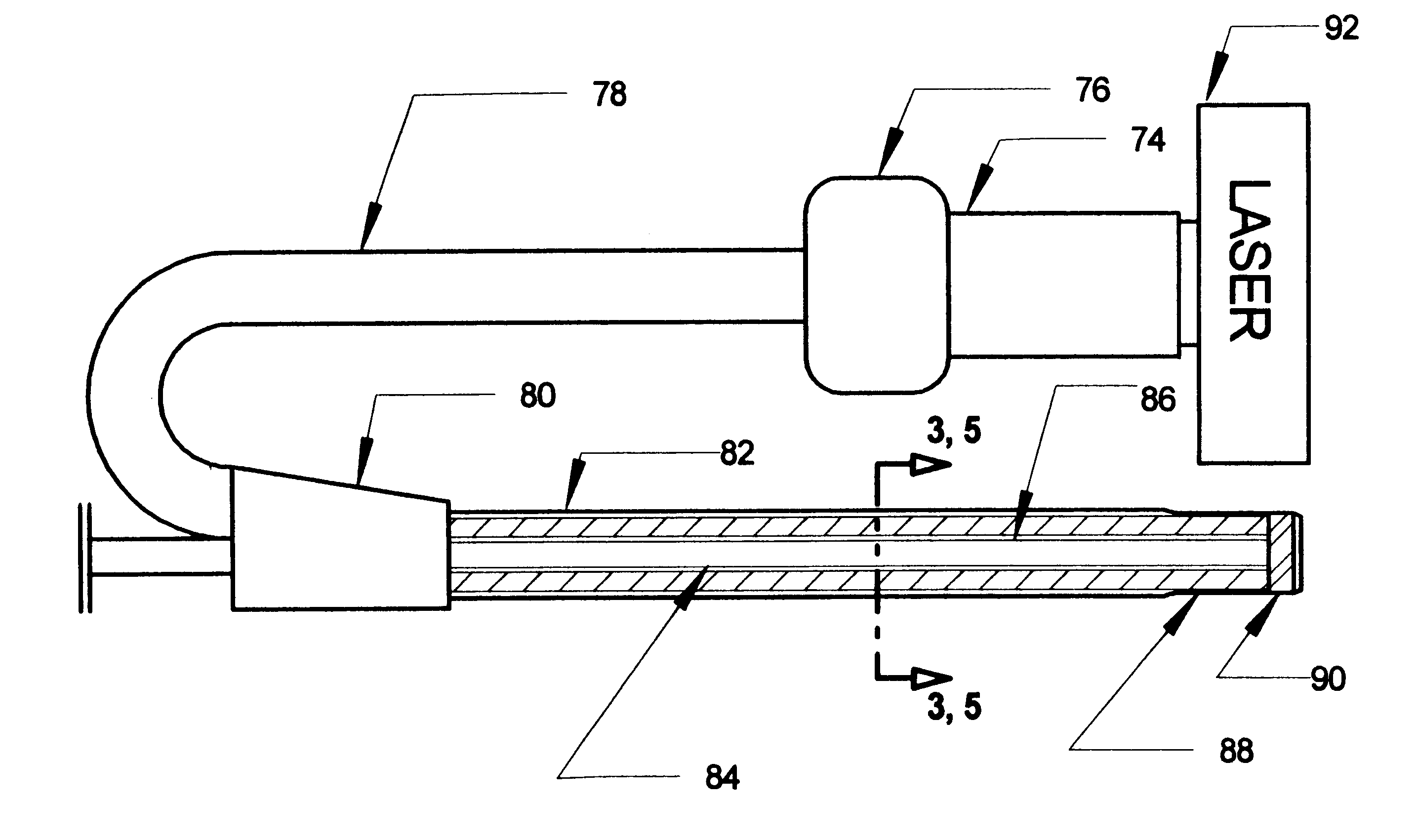
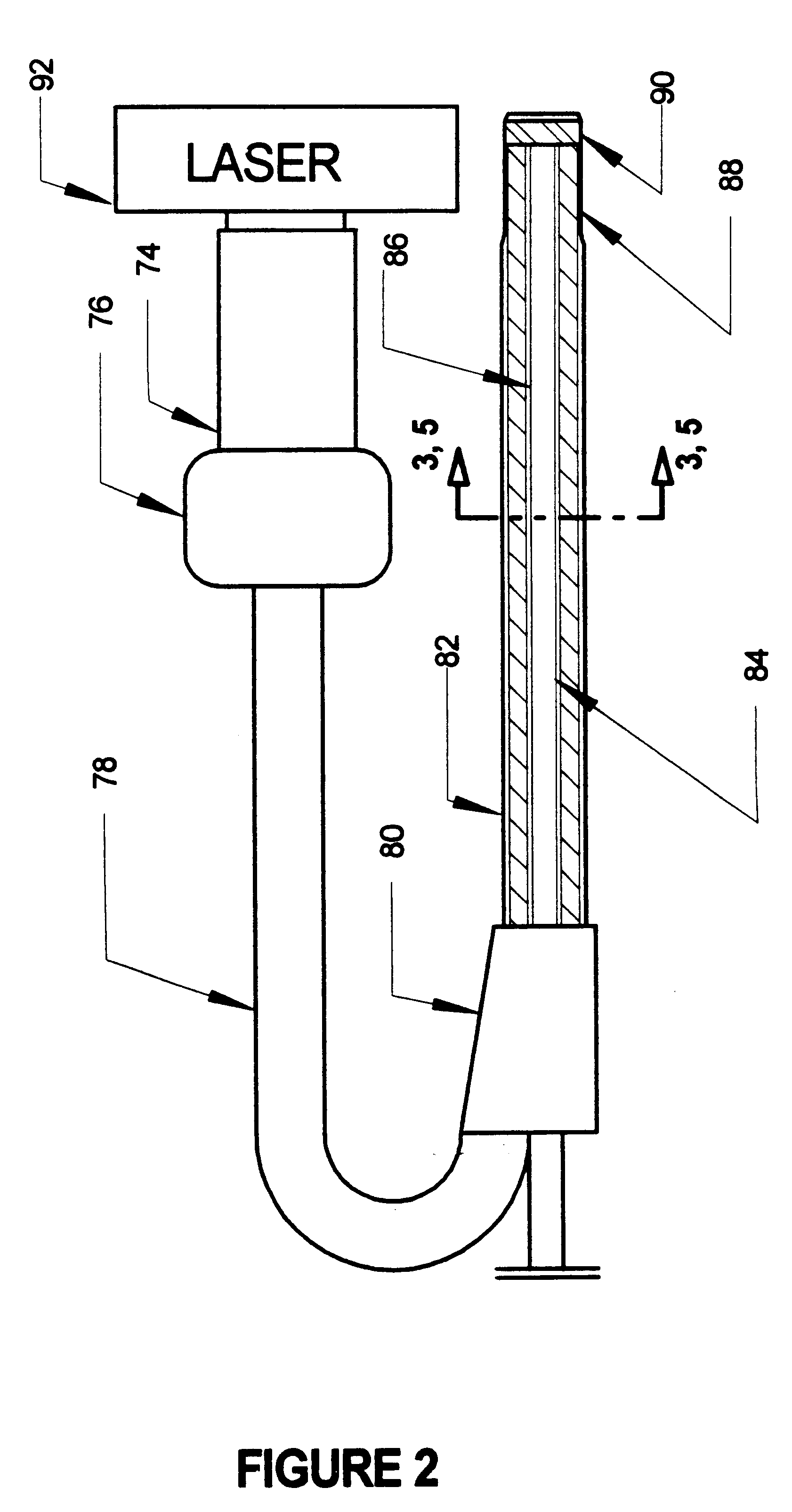
Excimer laser catheter
InactiveUS6440125B1Reduce the possibilityHigh energy laserDiagnosticsCatheterEndovascular therapyAtheroma
A method and apparatus of providing endovascular therapy. The steps include arranging optical fibers within a catheter, the catheter having a tip whose length is at least 1 cm and whose diameter of less than 1 millimeter, connecting an excimer laser to the optical fibers; and delivering laser energy from the excimer laser in excess of 60 fluence at 40 Hertz through the optical fibers. The delivering of the laser energy may be to non-calcified or calcified deposits of an atherosclerotic lesion to ablate the same. The method also includes the step of inserting the catheter through an artery by pushing the same until the tip is in within laser energy striking distance of the atherosclerotic lesion.
Owner:RENTROP PETER
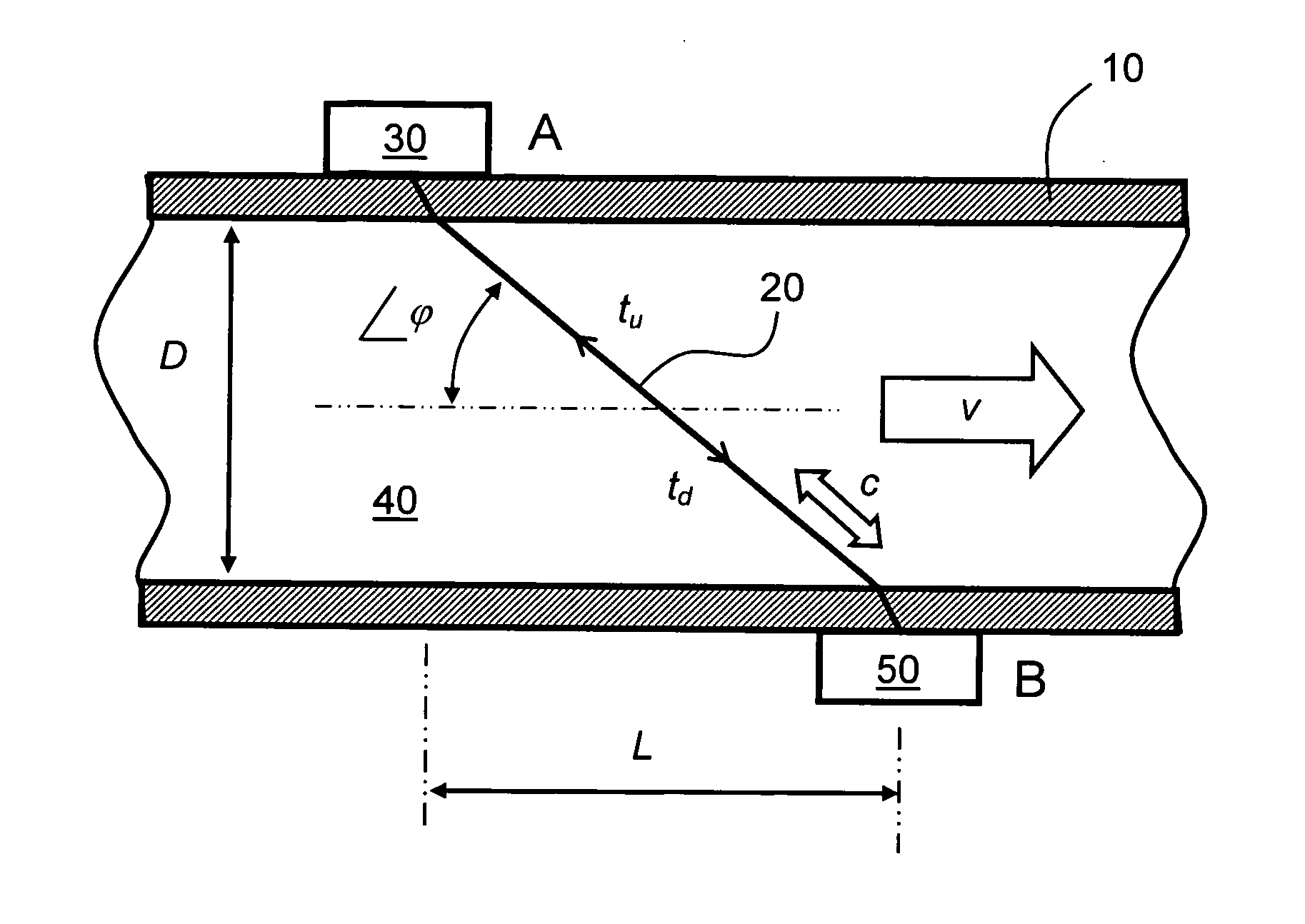
Flow measuring apparatus
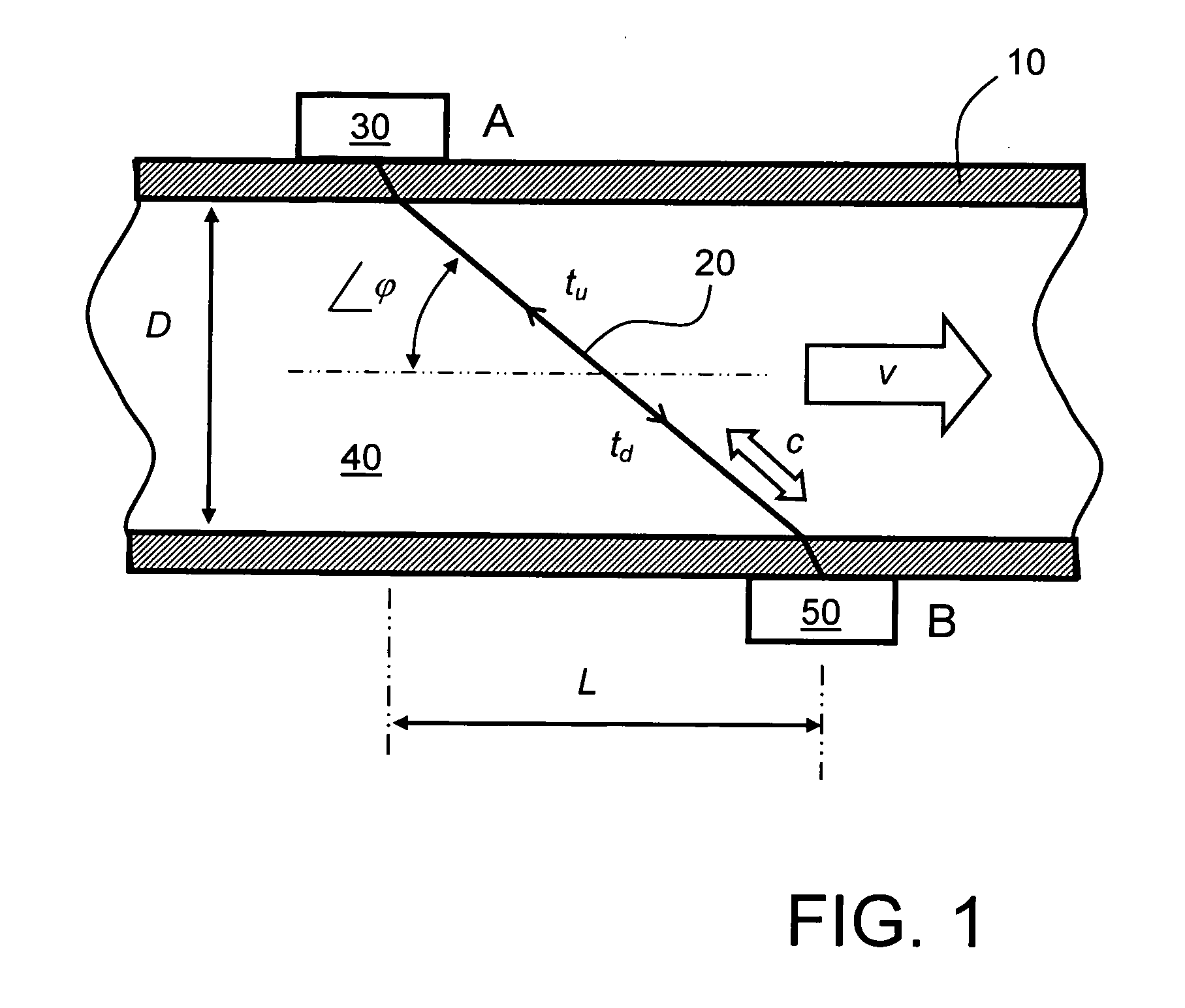
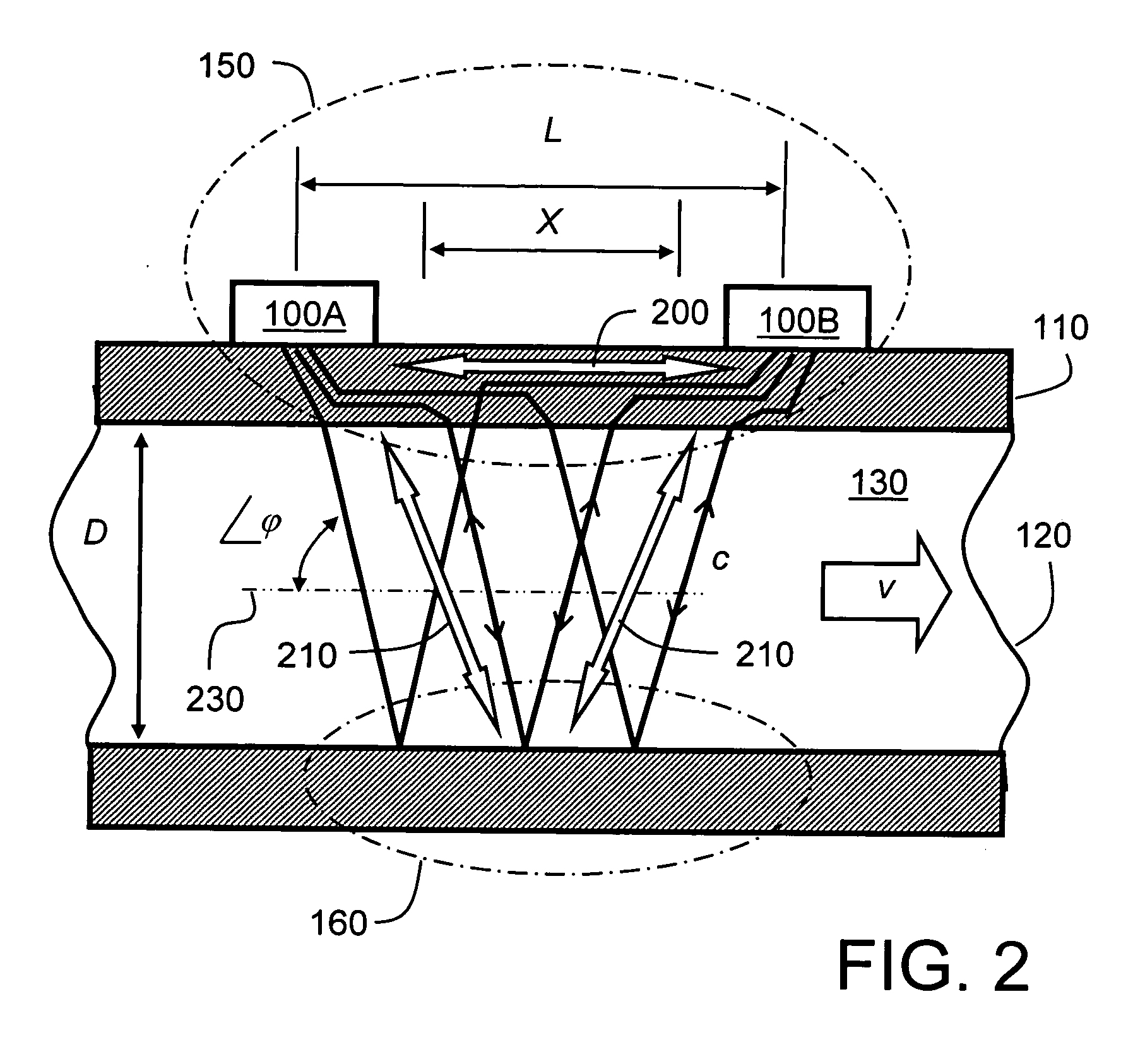
ActiveUS20110271769A1Reliable and accurate measurementImprove energy transferFlow propertiesVolume flow measuring devicesPropagation timeUltrasonic radiation
A flow measuring apparatus (300, 500) measures a fluid flow (130) within a conduit (120) including a wall (110). The apparatus (300, 500) includes a transducer arrangement including at least two transducers (100A, 100B) for alternately emitting and receiving ultrasonic radiation through the conduit wall (110) and the flow (130). The apparatus (300, 500) also includes a signal processing arrangement (310) for generating signals to excite the transducer arrangement (100A, 100B) and for processing received signals provided by the transducer arrangement (100A, 100B) for generating output signals from the signal processing arrangement (310) indicative of properties of the flow. The transducer arrangement (100A, 100B) in cooperation with the conduit (120) provides a first path (200) for Lamb-wave ultrasonic radiation coupling directly from a first of the at least two transducers (100A, 100B), to a second of said at least two transducers to generate a first received signal. The transducer arrangement (100A, 100B) in cooperation with the conduit (120) provides at least one second path (210) for ultrasonic propagation along the wall (100) via Lamb waves coupling to at least a portion of the flow (130) from a first of the at least two transducers (100A, 100B) to a second of the at least two transducers (100A, 100B) to generate a second received signal. The signal processing arrangement (310) determines from said first and second received signals ultrasonic radiation propagation time periods through the first path (200) and through the at least one second path (210), and to perform computational operations on the propagation time periods to determine properties of the flow including, but not limited to, at least one of: fluid flow velocity (v) in the conduit (120), a sound velocity (c) through the fluid (130).
Owner:XSENS
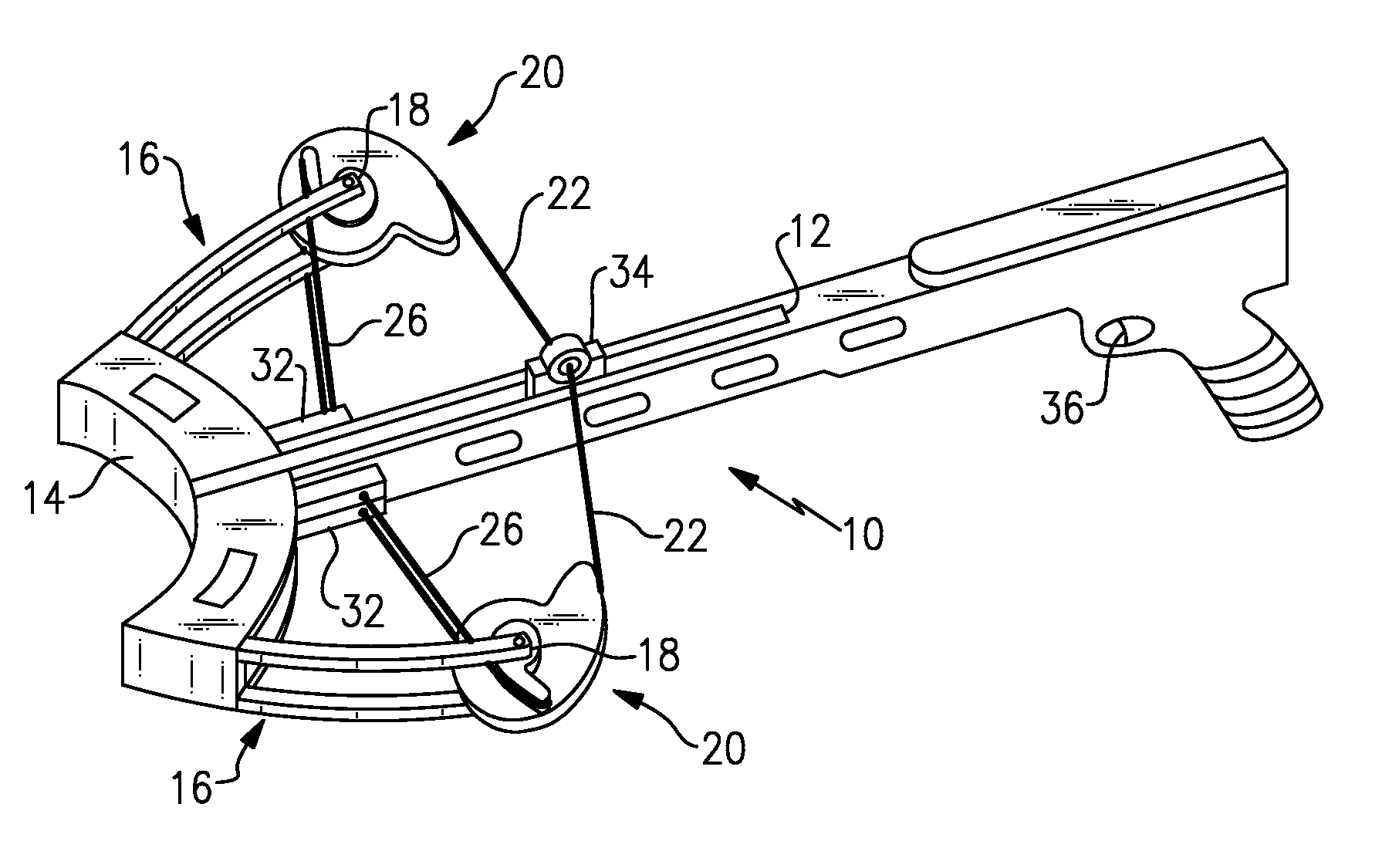
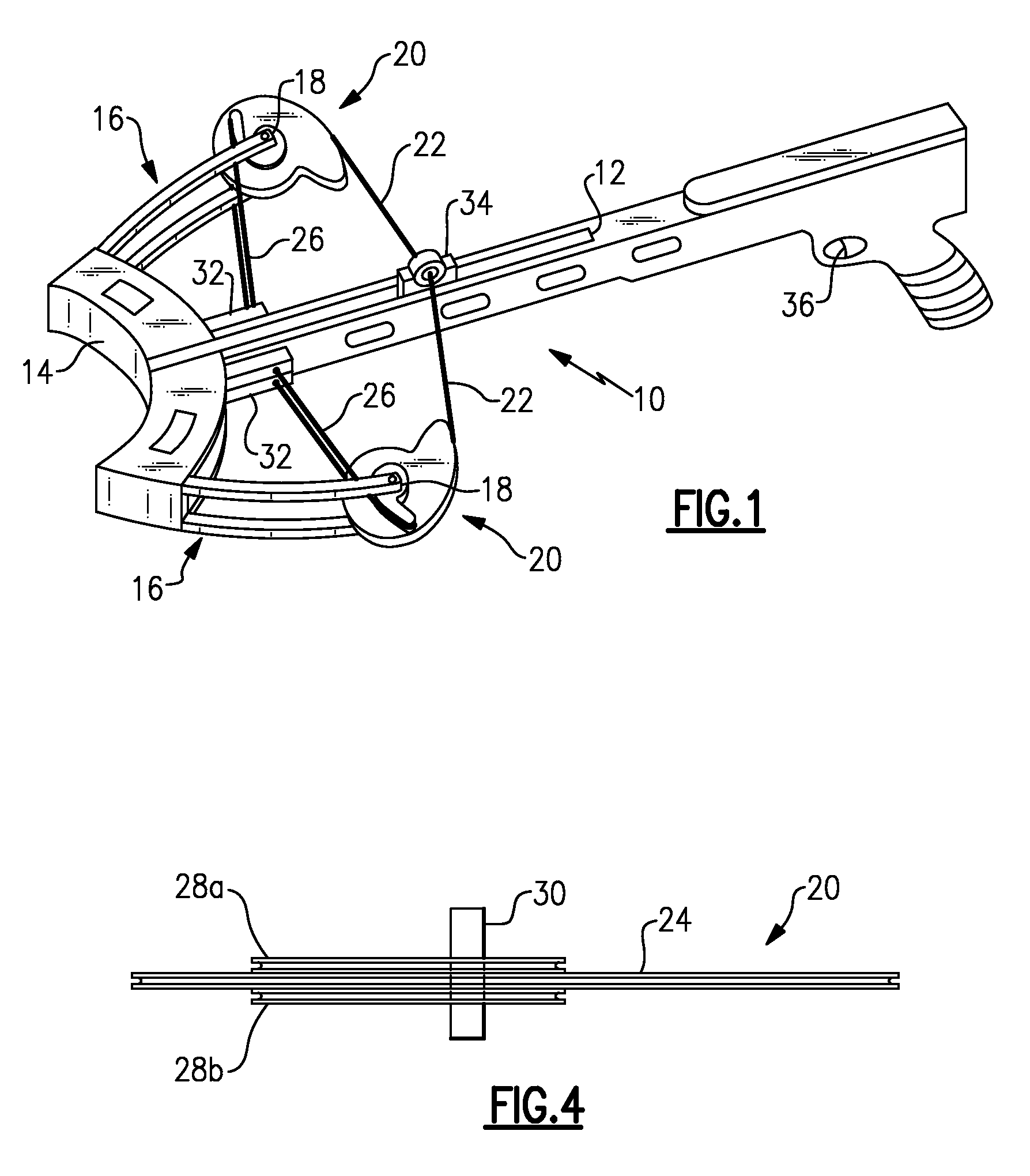
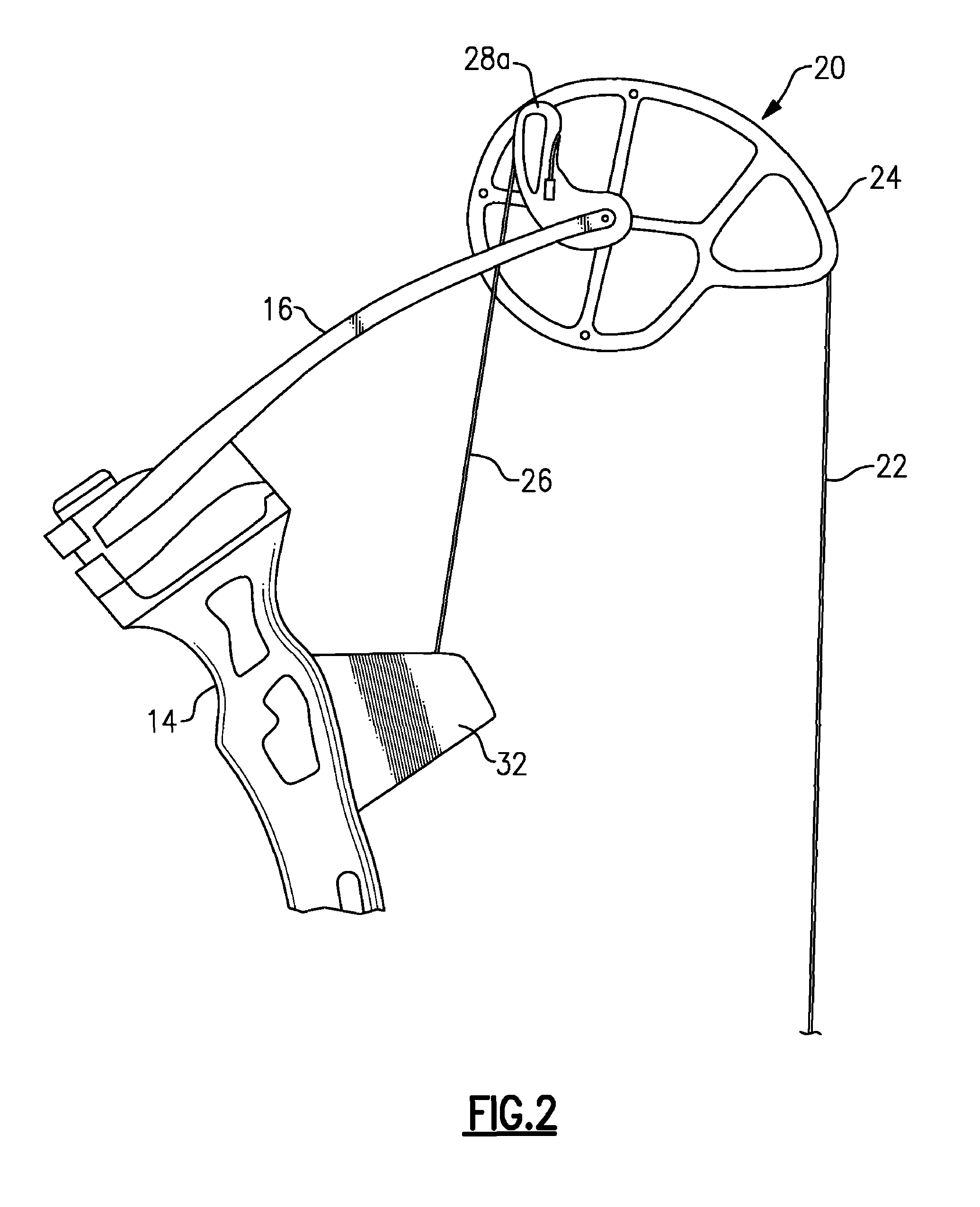
Bowstring cam arrangement for compound crossbow
A compound bow or crossbow employs bowstring cams with bowstring cam grooves and power cord cam grooves. Preferably a pair of generally identical power cord cam grooves are positioned axially above and below the bowstring cam groove. The power cords are anchored to a fixed anchor point, e.g., a pylon, on the near end of the riser or on the near side of the crossbow bar or stock. The power cords do not cross over to the other limb. The reduction in the number of cam wheels and pulleys and in the number of strings or cords results in greater efficiency and higher transfer of energy from the bow to the arrow or bolt. There is no drop-off in pull weight at full draw. The bolt or arrow accelerates throughout the travel of the bowstring, resulting in significantly higher velocity.
Owner:RAVIN CROSSBOWS
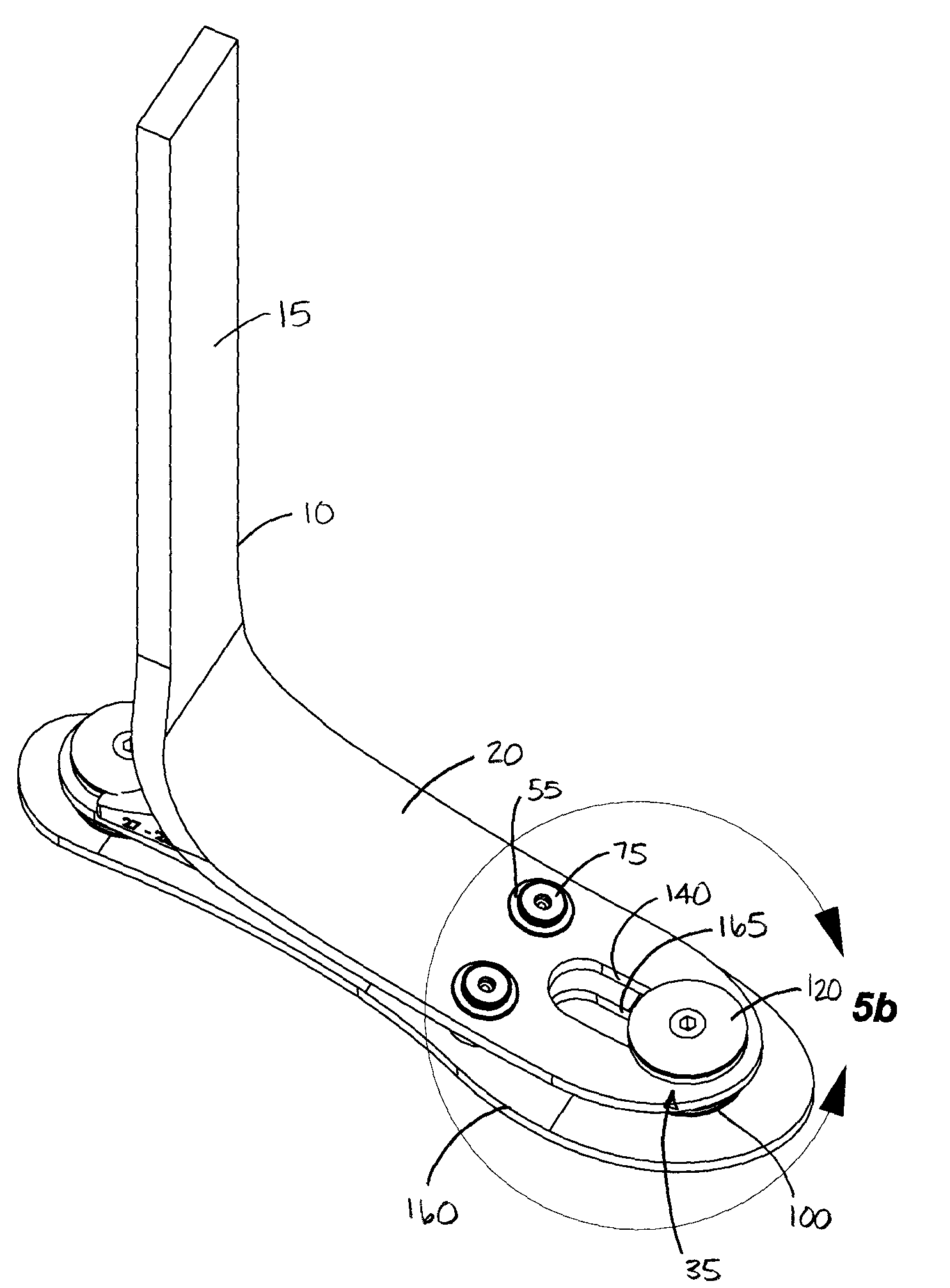
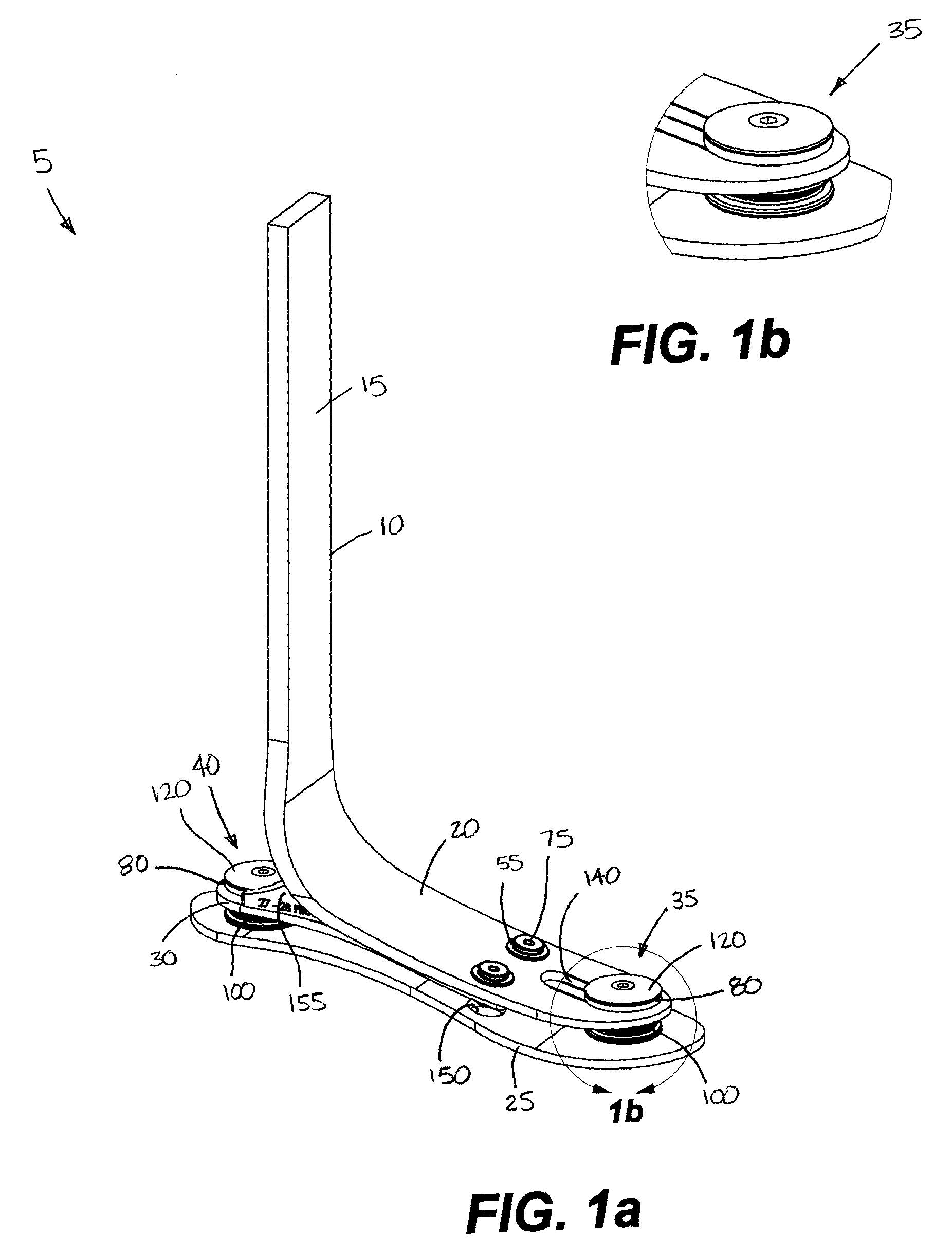
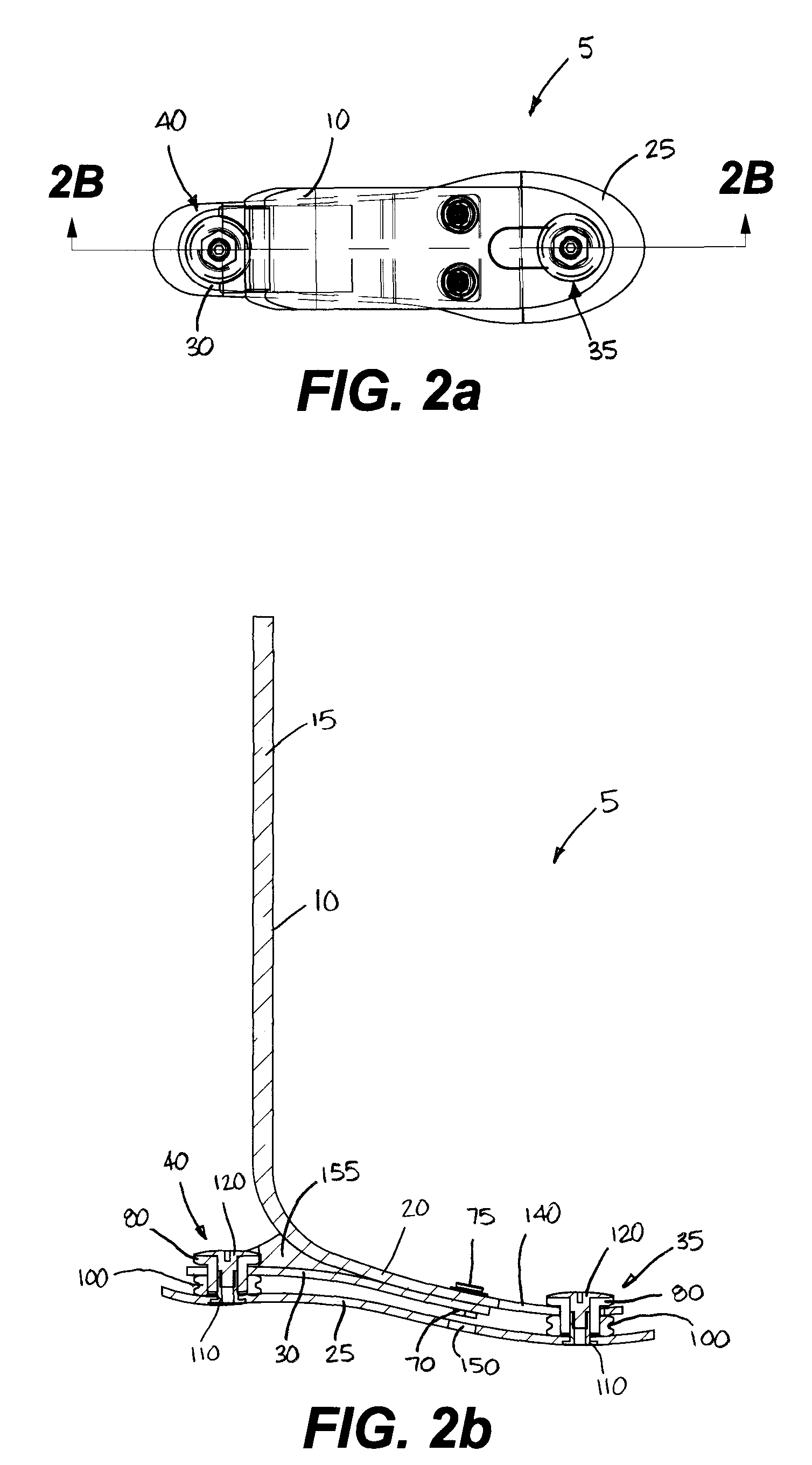
Prosthetic foot
ActiveUS20100042228A1Improve energy transferIncreased spring lengthArtificial legsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationHeel strike
A stable shock absorbing prosthetic foot that transfers energy between heel strike and toe-off. A toe plate is separated from one or more other plates by a bumper assembly located at each of the toe end and heel end of the foot. Certain embodiments of the shock absorbing foot of the present invention are designed for use with a prosthetic ankle. A torsion adapter may also be used to attach a prosthetic foot of the present invention to the remainder of a prosthesis.
Owner:WILLOWWOOD GLOBAL LLC
Optical pulse stretching and smoothing for ArF and F2 lithography excimer lasers
InactiveUS6389045B1Easy to stretchFlat shapeOptical resonator shape and constructionGenerators/motorsOptical reflectionLithographic artist
A method and apparatus are provided for temporally stretching and smoothing of the pulses of an output beam of excimer and lithography lasers. The method and apparatus are based upon providing an optical delay line or circuit having a plurality of optical reflectors and a plurality of beam recombiners or splitters so arranged as to divide the pulse into numerous portions which vary in their travel time through the circuit. As a result, the energy of the incident pulse is greatly stretched and smoothed.
Owner:COHERENT GMBH
Methods and systems for ultrasound delivery through a cranial aperture
InactiveUS20070038100A1Reduce and minimize effectImprove energy transferUltrasound therapyDiagnostic probe attachmentUltrasound deviceRadiology
A method for delivering ultrasound energy to a patient's intracranial space includes forming at least one aperture in the patient's skull, introducing at least one acoustically conductive medium into the intracranial space to contact brain tissue of the patient, advancing an ultrasound device at least partially through the aperture in the skull, and transmitting ultrasound energy to the intracranial space, using the ultrasound device. In some embodiments, the acoustically conductive medium may be cooled to help regulate the temperature of the patient's brain tissue.
Owner:PENUMBRA
Phased-array for tissue treatment
ActiveUS20050215990A1Convenient treatmentWeaken energyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyTarget tissuePhased array
Apparatus is provided for ablating tissue of a patient by applying ultrasound energy to the tissue. The apparatus is typically delivered to the targeted tissue via a catheter and includes an ultrasound array, which is adapted to be driven as a phased array to concentrate the ultrasound energy on the targeted tissue while avoiding surrounding tissue.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
Cardiac ablation catheters for forming overlapping lesions
InactiveUS20090299354A1Improve energy transferEnhance the imageUltrasound therapyDiagnosticsCardiac AblationTarget tissue
Methods and instruments are disclosed for creating lesions in tissue, especially cardiac tissue, for treatment of arrhythmias and the like, by employing an elastic balloon and an energy emitter, which is independently positionable within the lumen of the instrument and adapted to project a series of spots of ablative energy through a transmissive region of the balloon to a target tissue site. The energy emitter preferably is configured such the spots of energy result in a series of lesions formed in the target tissue region when the emitter is activated, the lesions having an average area ranging from about 5 mm2 to about 100 mm2. In one aspect of the invention, percutaneous ablation instruments are disclosed in the form of catheter bodies having one or more balloon structures at the distal end region of the instrument and an energy emitting element, which is independently positionable and rotatable within a lumen of the instrument and adapted to project ablative energy through a transmissive region of the balloon to a target tissue site in contact with, or proximal to, the balloon surface.
Owner:CARDIOFOCUS INC
Disposable couplings for biometric instruments
InactiveUS20050090725A1Improve energy transferGood of laser lightUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostics using lightAcoustic energyOpto electronic
Photoacoustic measurement system are configured with a special view towards efficient coupling of optical and acoustic energy between respective transducers and a tissue test site. In particular, a disposable substrate provides support for advanced optical paths including, for example, windows, lenses, and index matching gels or fluids. In addition, substrates may also accommodate arrays of coupling sites corresponding to a plurality of acoustic detectors spatially separated. These substrates may additionally include means to affix and secure the device to a measurement head having optoelectronic and electromechanical transducers therein. Further, these substrates include mechanisms which help to affix the substrates to test sites in stabile and secure fashion.
Owner:PAGE JOSEPH +1
Apparatus for Effecting Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition (PCVD)
ActiveUS20070289532A1Increase power levelIncrease deposition rateGlass making apparatusElectric discharge tubesChemical vapor depositionSilicon dioxide
The present invention relates to an apparatus for carrying out a plasma chemical vapor deposition process by which one or more layers of doped or undoped silica can be deposited on the interior of an elongated glass substrate tube. The present invention further relates to a method for manufacturing an optical fiber using such an apparatus.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
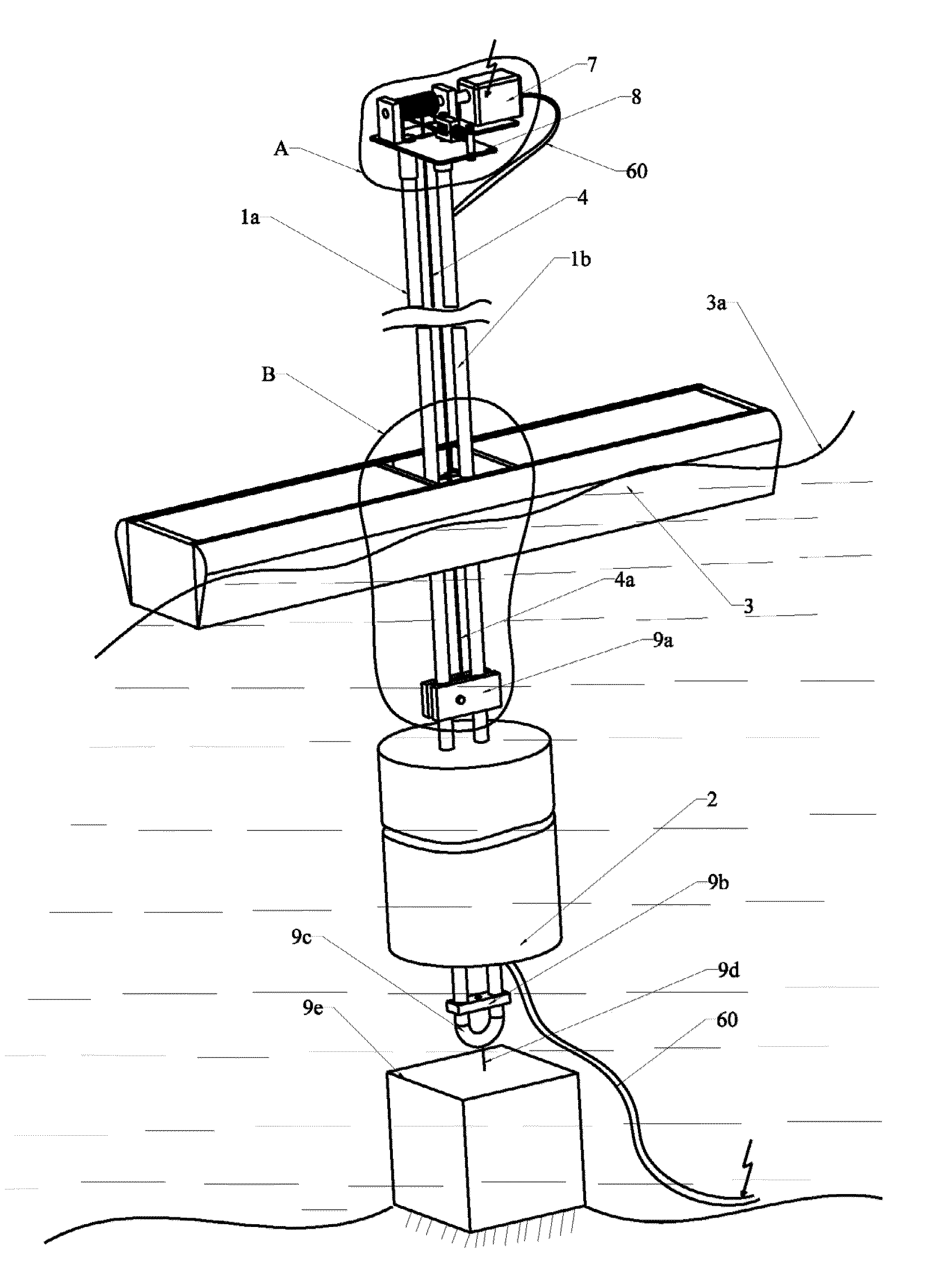
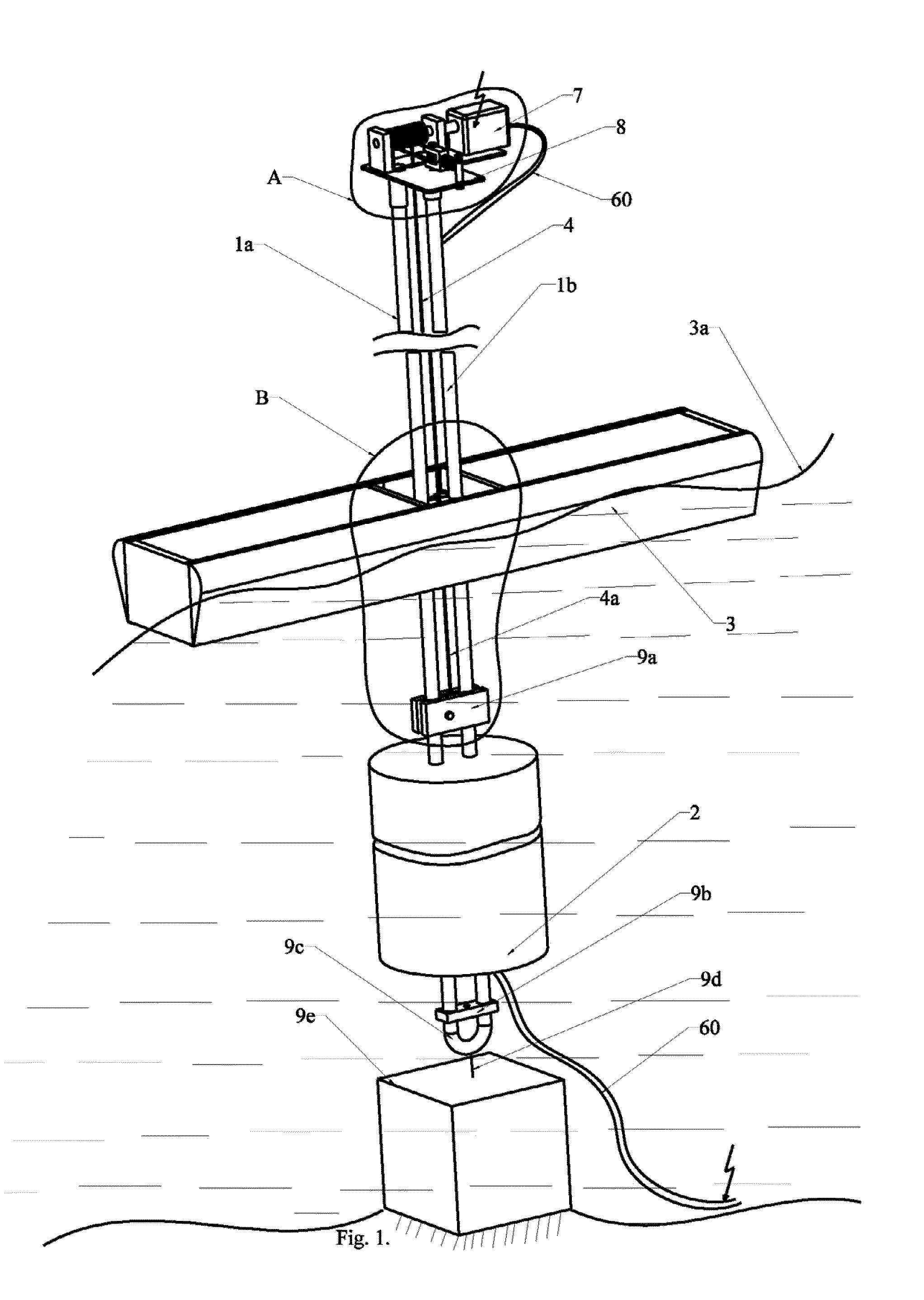
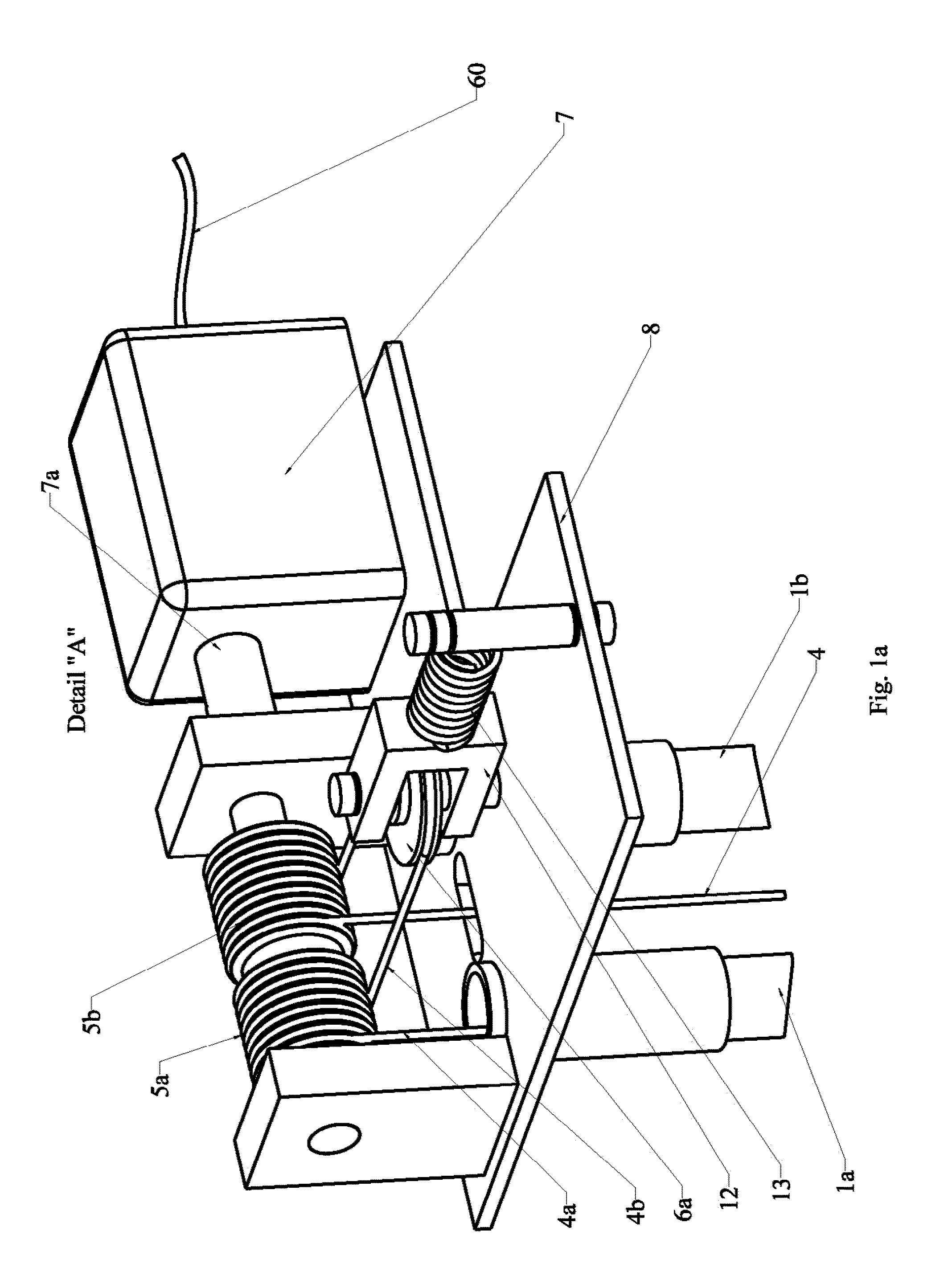
Ocean wave power plant
ActiveUS20130127168A1Reduced maintenance needsReduce lossesEngine fuctionsMachines/enginesPower stationSea waves
An ocean wave power plant provided for by respective interconnected functional units comprising a support structure (1a, 1b) is disclosed. The support structure (1a, 1b) is terminated in a lower end with a fastening bracket (9c) which can be anchored in a single point to a mass (9e) when deployed in the sea. A submergible uplift floating body (2) is providing buoyancy for the ocean wave power plant when deployed in the sea. The a uplift floating body (2) is attached to the support structure (1a, 1b), an electric power generating subsystem (A) supported by a platform (8) is terminating the support structure (1a, 1b) in an upper end of the support structure. A transmission member (4, 4a, 18) is attached in one end to a floating body (3) and in another end to the power generating subsystem (A) transferring wave motion from the floating body (3) to the power generating subsystem (A).
Owner:DRAGIC MILE
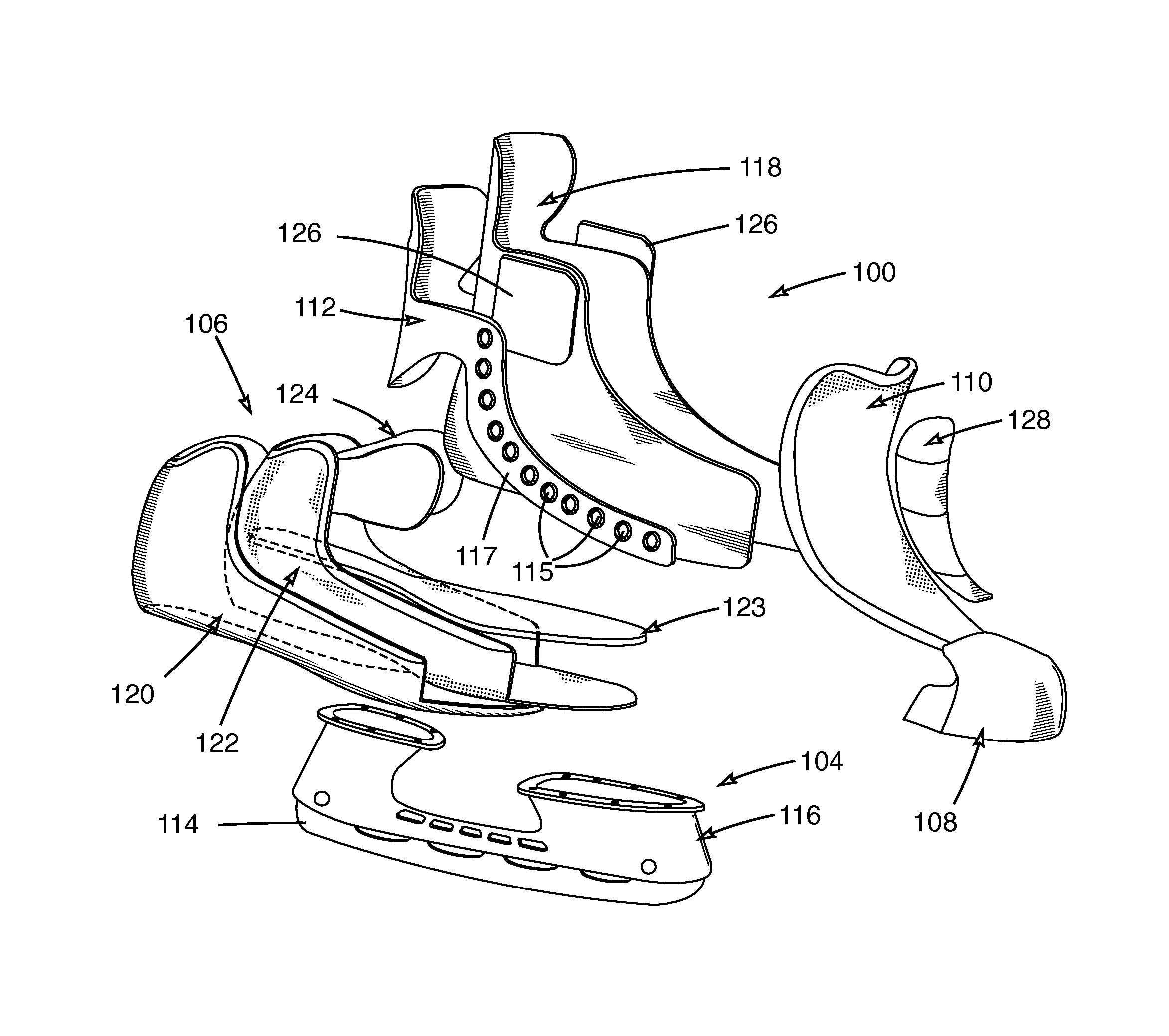
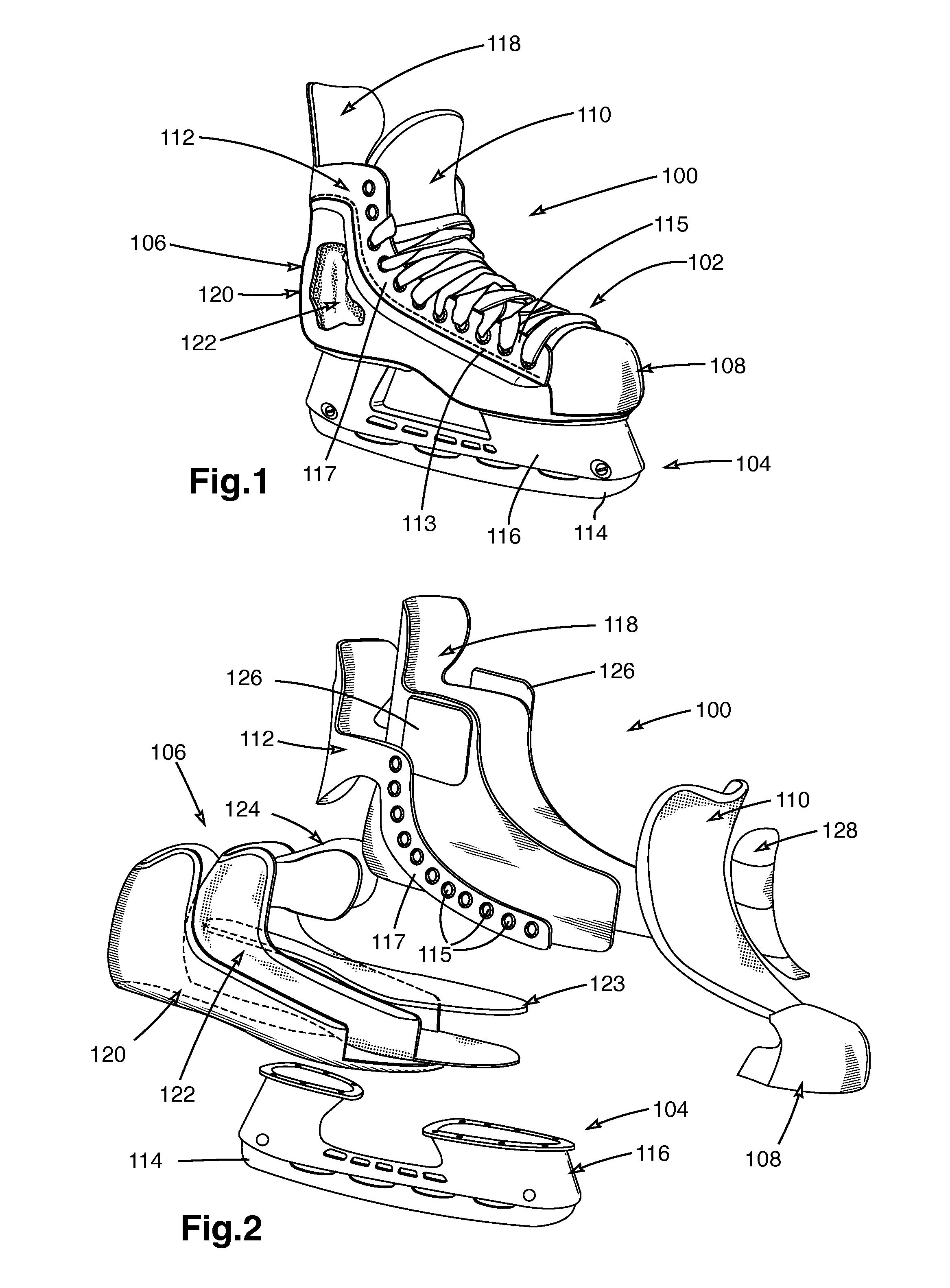
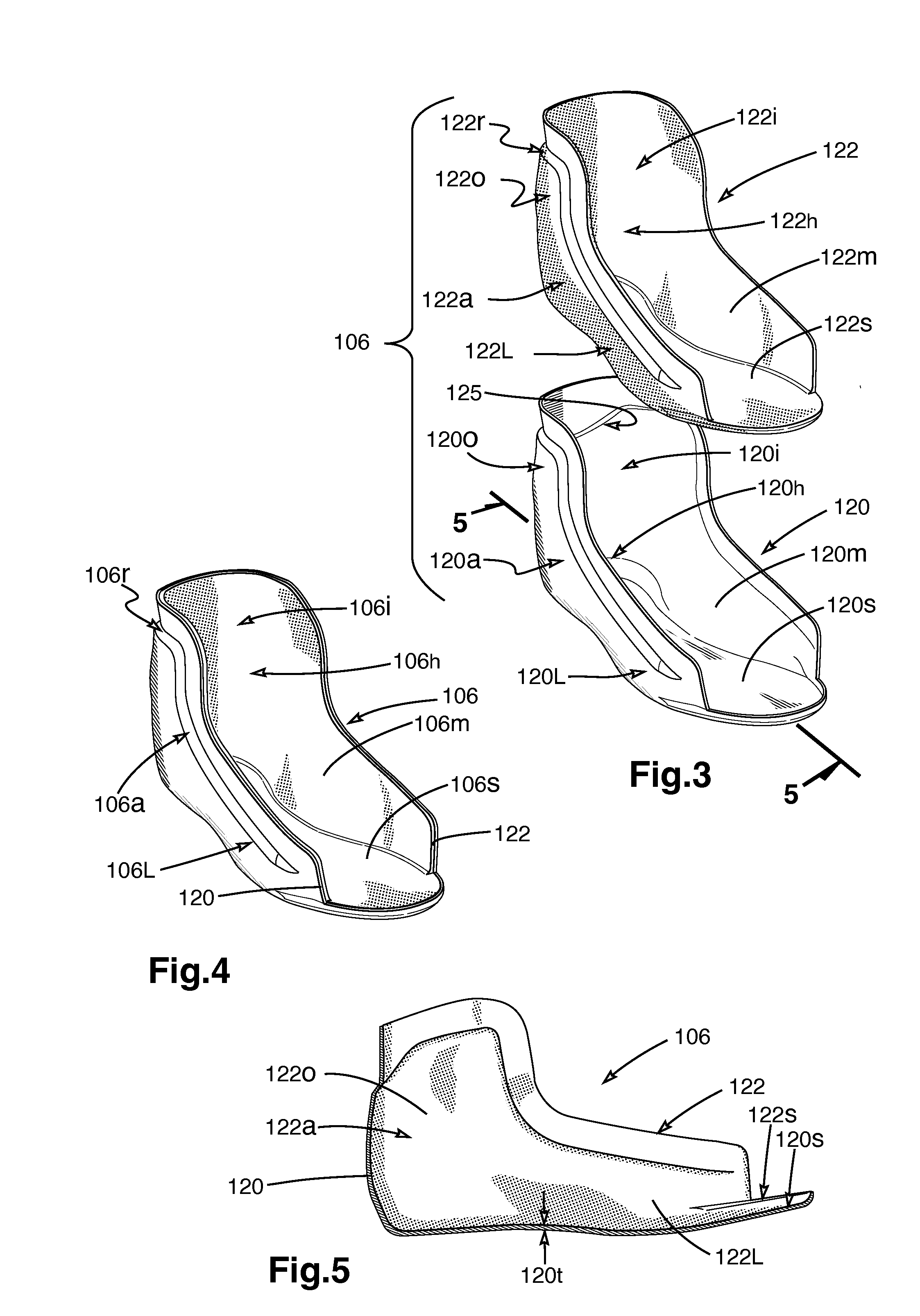
Skate
A skate having a skate boot with a non-lasted boot shell, the shell having a first non-lasted three-dimensional sub-shell and a second non-lasted three-dimensional sub-shell, the second sub-shell being interior to and adjoining the first sub-shell, the first sub-shell comprising a first material having a first density and the second sub-shell comprising a second material having a second density, the second density being less than the first density, the shell being shaped so as to have a heel portion, an ankle portion, a lateral portion, a medial portion, and a sole portion; and a ground-engaging assembly disposed on an underside of the skate. Additional sub-shells are possible. Methods of manufacturing the skate boot shell, including molding and build-up, are also disclosed.
Owner:SPORT MASKA
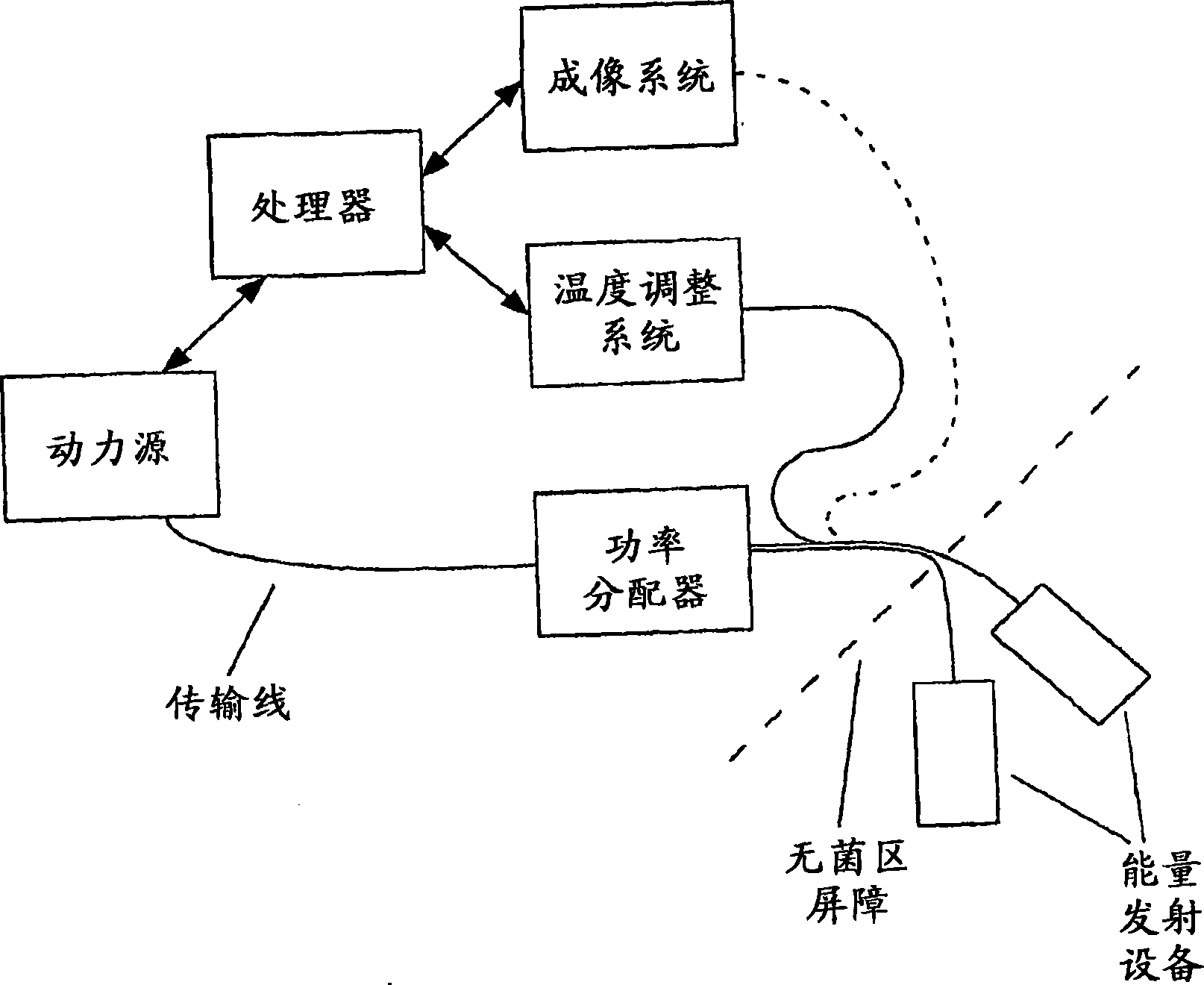
Energy delivery systems and uses thereof
ActiveCN101511295AImprove energy transferSurgical needlesSurgical instruments using microwavesVascular thrombosisThrombus
The present invention relates to comprehensive systems, devices and methods for delivering energy to tissue for a wide variety of applications, including medical procedures (e.g., tissue ablation, resection, cautery, vascular thrombosis, treatment of cardiac arrhythmias and dysrhythmias, electrosurgery, tissue harvest, etc.). In certain embodiments, systems, devices, and methods are provided for treating a tissue region (e.g., a tumor) through application of energy.
Owner:NEUWAVE MEDICAL
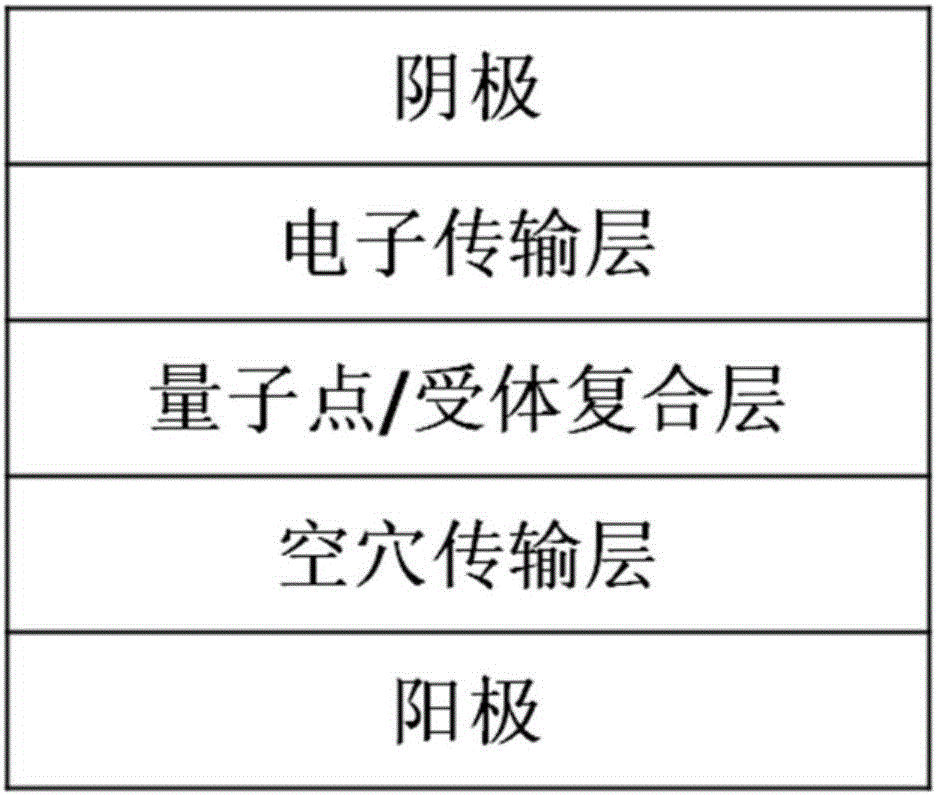
Light emitting diode including quantum dots and energy transfer molecules and fabrication method and display device thereof
InactiveCN106356462AImprove injection abilityImprove energy transferSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFluorescenceClick chemistry
The invention provides a light emitting diode. The light emitting diode comprises a substrate, positive pole, hole transfer layer, emitting layer, electron transport layer and negative pole. The emitting layer comprises quantum dots and energy transfer molecules. The energy transfer molecules crosslink with the quantum dots by click chemistry. The energy transfer molecules, as dispersion medium of the quantum dots, have high electron / hole carrier injection ability, which can promote the production of excitons in energy transfer molecules and realize effective energy transfer from energy transfer molecules to fluorescent quantum dots. At certain voltage, the device can emit within the wavelength range of 380-900nm, with the maximum emitting peak covering ultraviolet to dark red light range. The invention further discloses the fabrication method and electronic display equipment of a light emitting diode.
Owner:SUZHOU XINGSHUO NANOTECH CO LTD
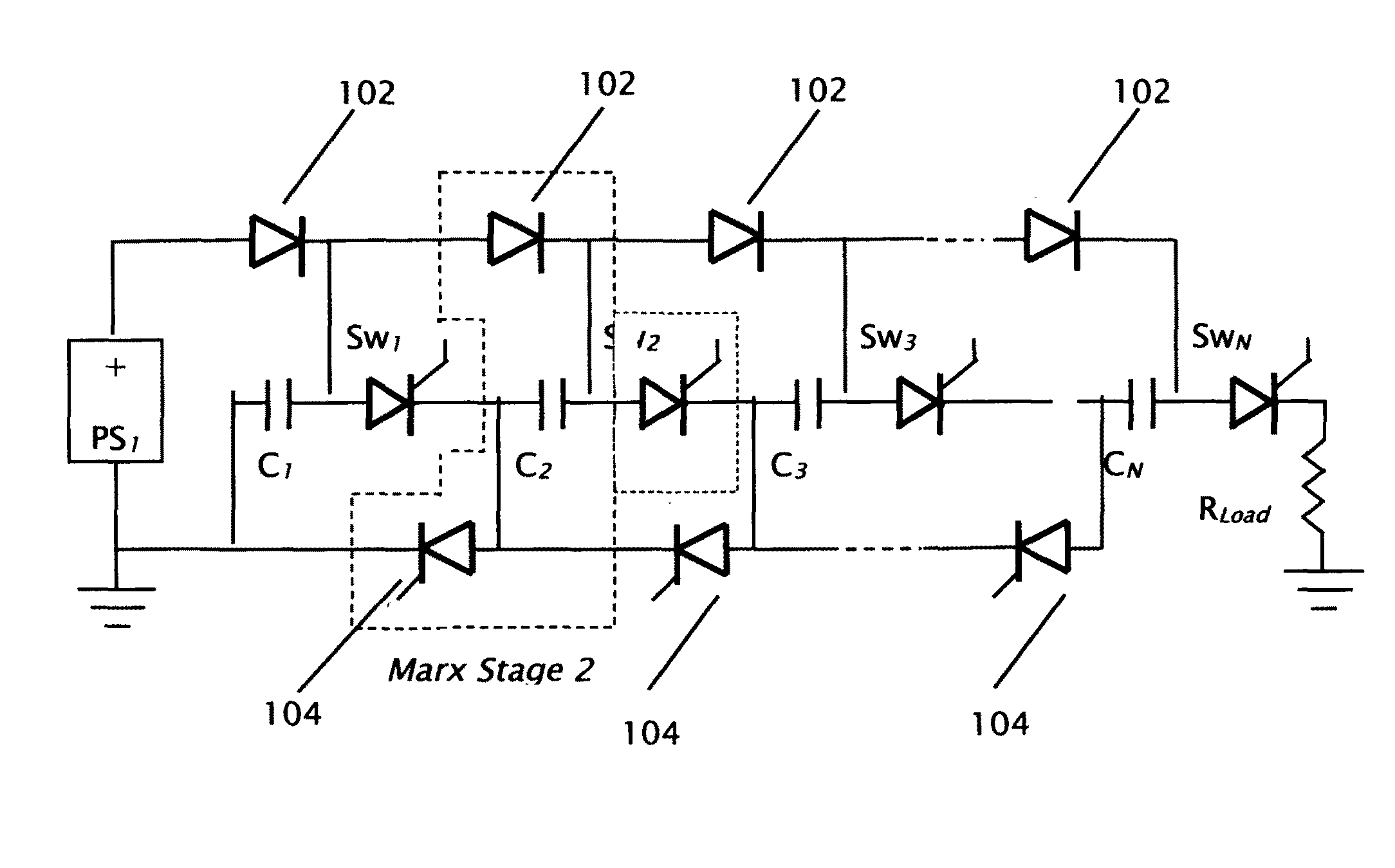
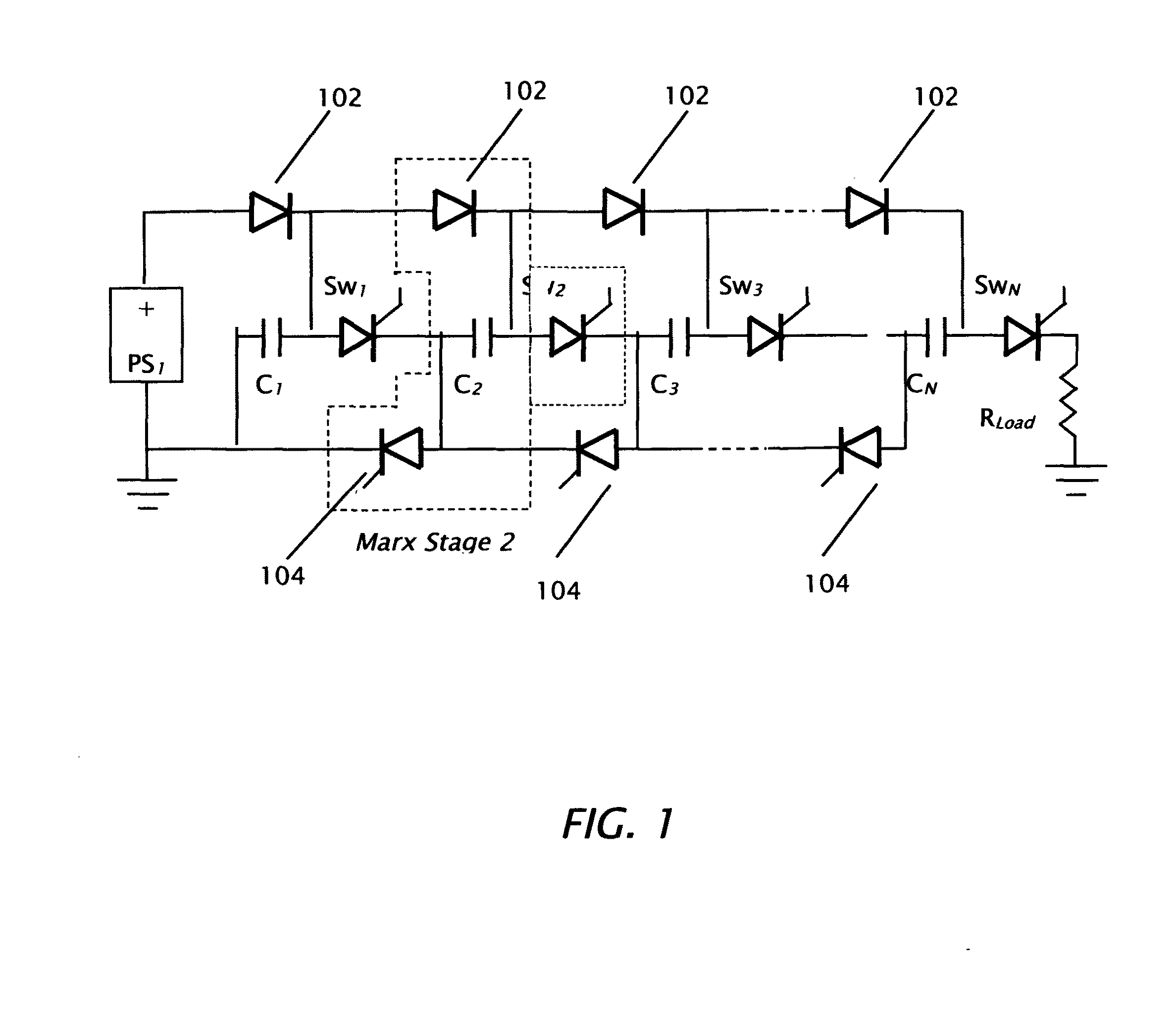
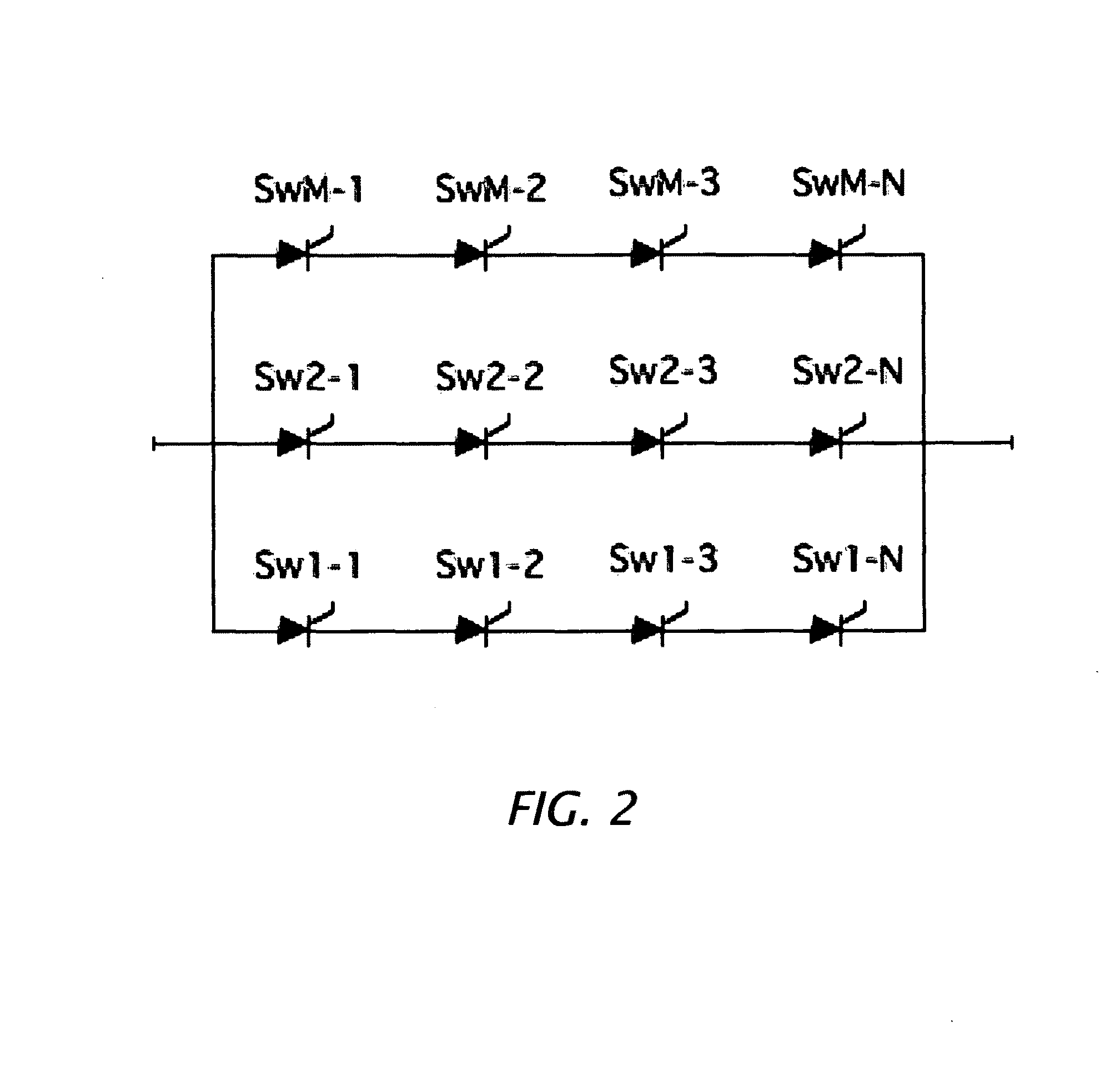
Photon initiated marxed modulators
InactiveUS7989987B2Improve rate performanceSolution to short lifeApparatus without intermediate ac conversionPulse generation by energy-accumulating elementThyratronHigh voltage pulse
The features of this invention allow construction and operation of a variety of high voltage, high repetition rated pulse generators of the Marx type that are switched with photon initiated semiconductor switches of the closing type. The photon initiated semiconductor switches can be constructed with bulk materials or in layered devices such as thyristors. Variations on the invention permit the formation of shaped high voltage pulses; particularly those that are nearly rectangular: with controlled rise and fall times, minimal or no overshoot, and minimal voltage ripple.
Owner:MCDONALD KENNETH FOX
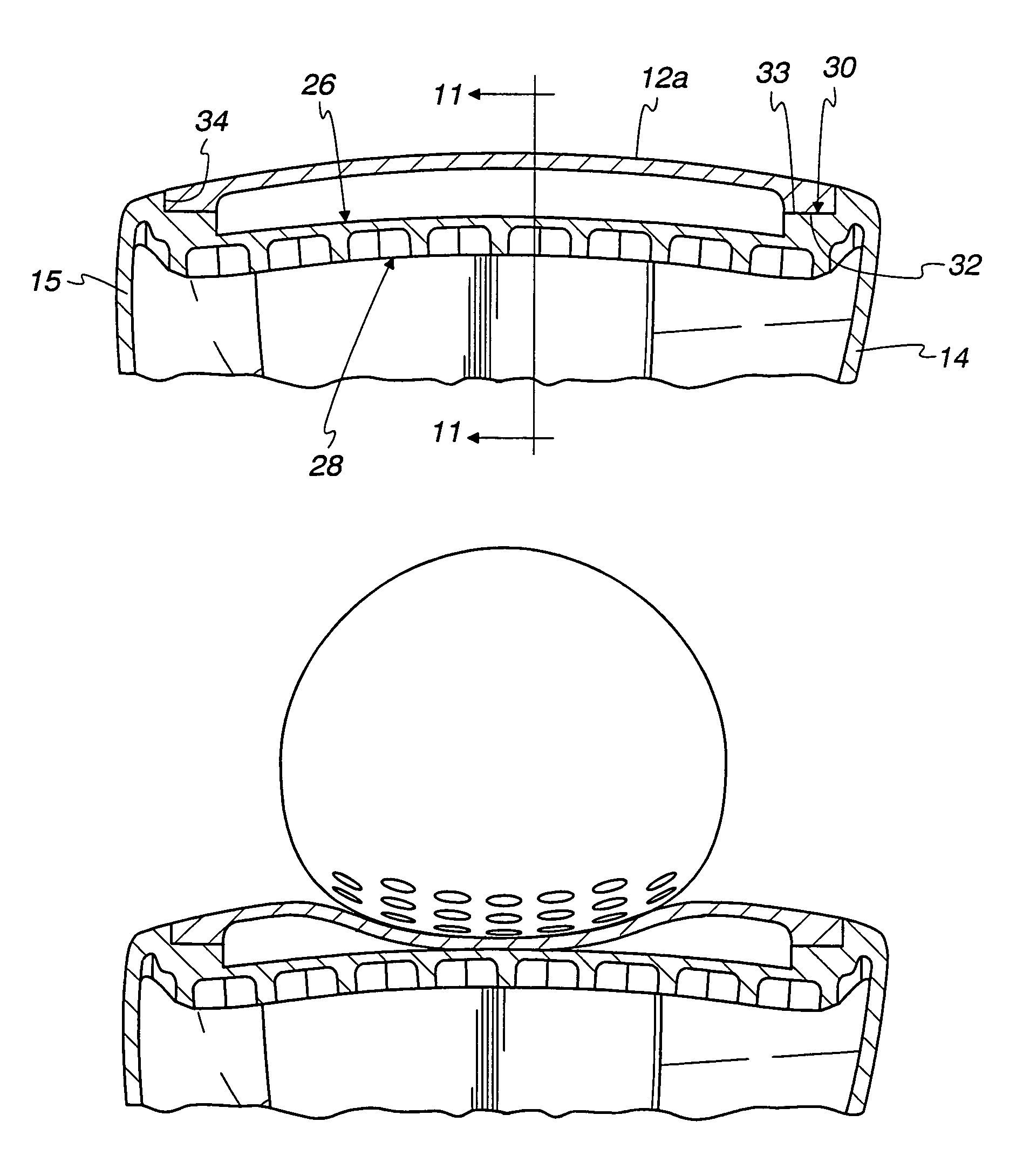
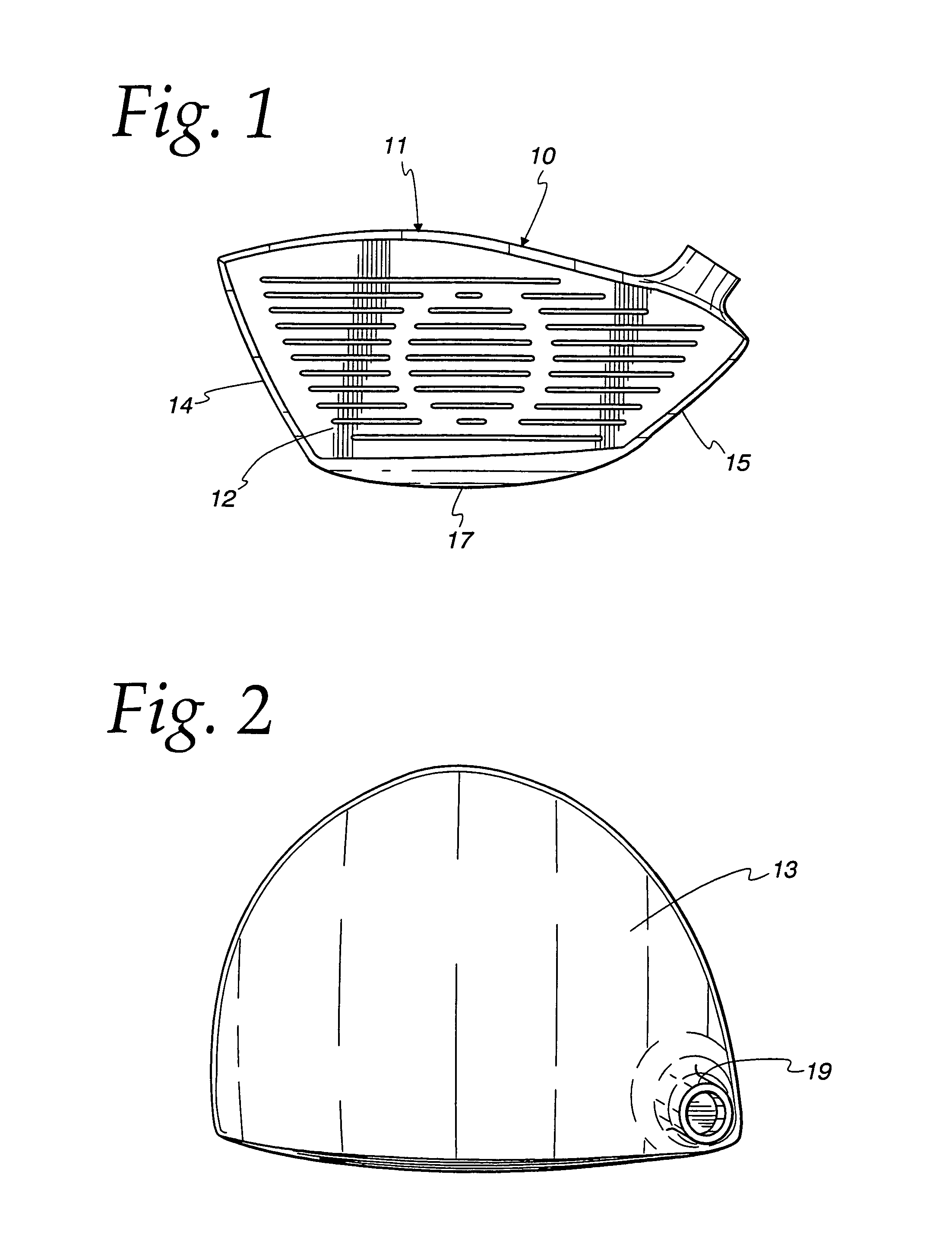
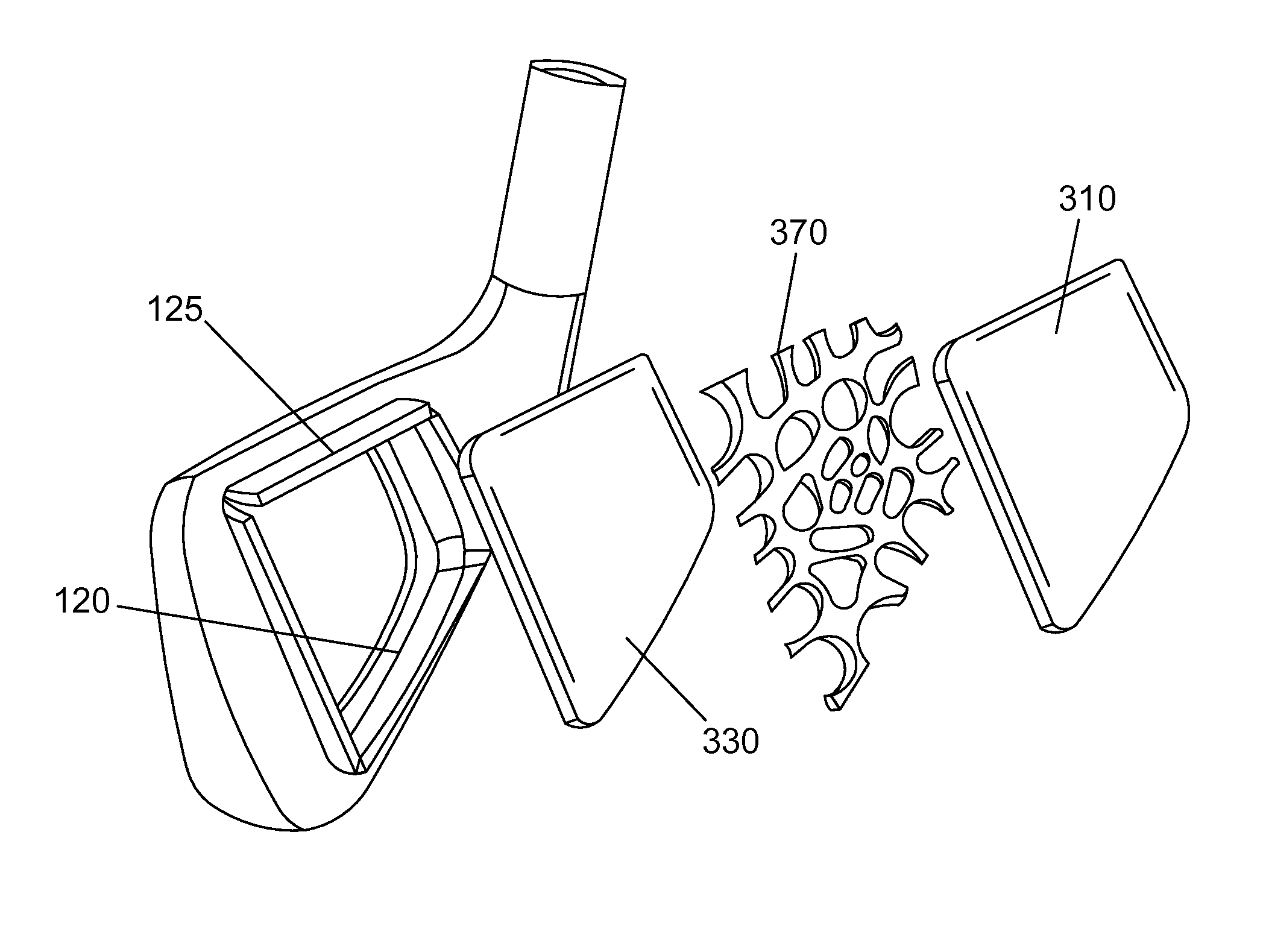
Golf club head comprising multiple materials
ActiveUS9370697B2Increase the lengthStraighter trajectoryGolf clubsRacket sportsEngineeringGolf Ball
A golf club head having an insert mechanically coupled to a frame. The construction allows a golf club head to be fabricated with a combination of dissimilar materials, resulting in a club head with improved performance. In some embodiments, the insert comprises an outer insert material, an inner insert material, and a sandwiched material. The sandwiched material may be constructed with a plurality of voids having a varying distribution, thereby resembling a biological structure. Methods for forming a golf club having an insert mechanically coupled to a frame are also disclosed.
Owner:COBRA GOLF
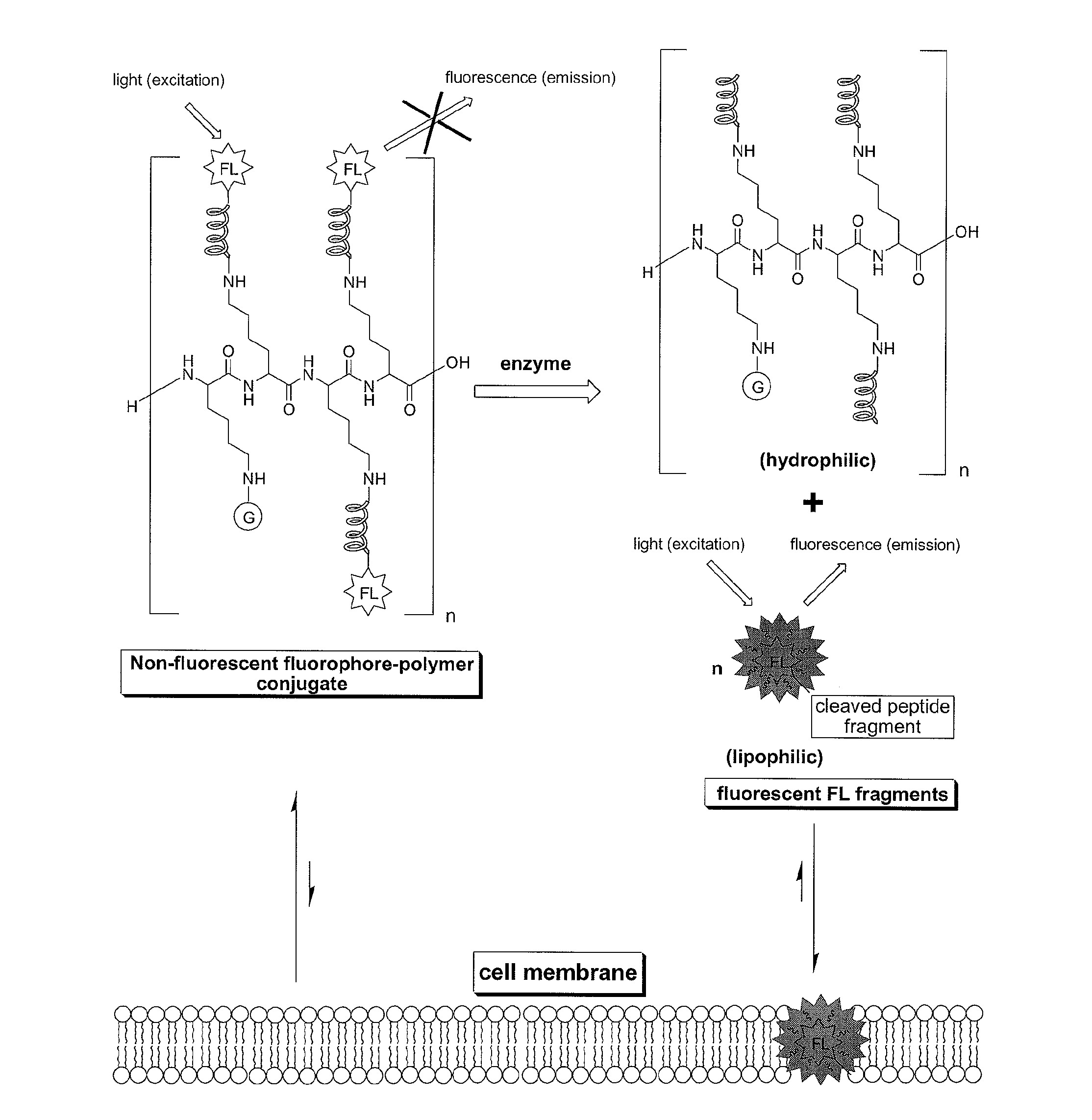
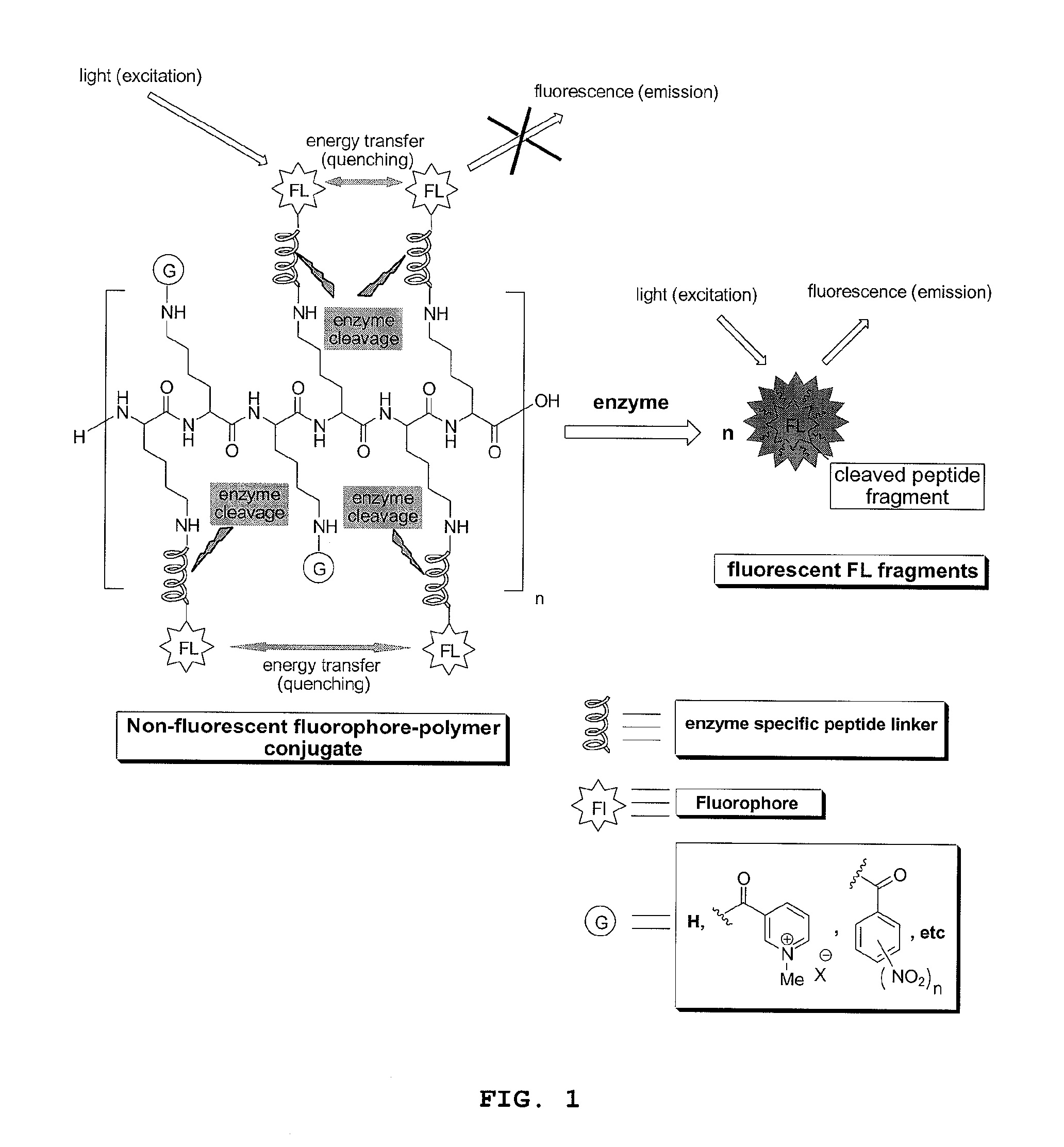
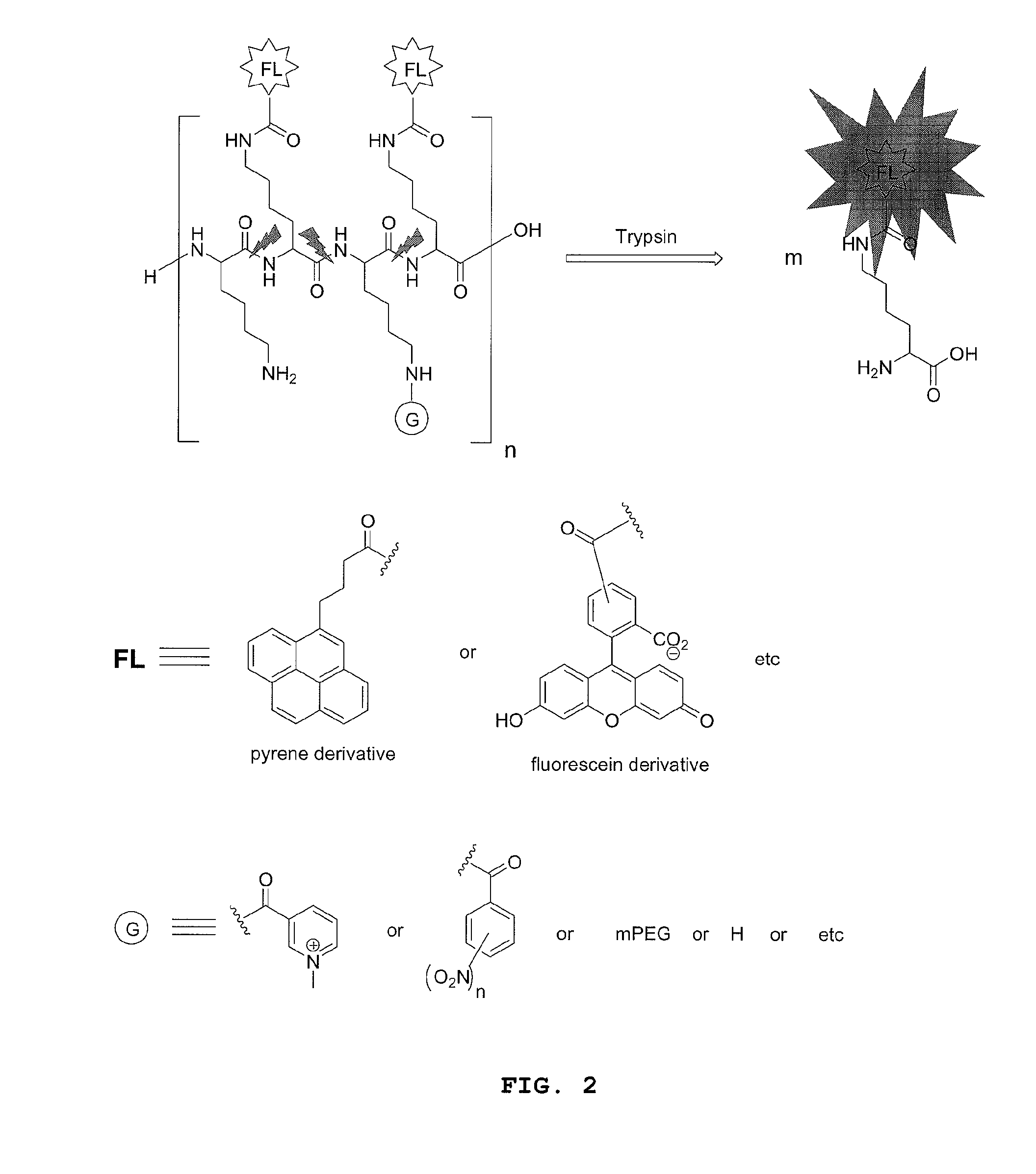
Compounds for fluorescence imaging
InactiveUS20100278745A1Improved propertyReduce diffuseUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMicrobiological testing/measurementIonSolid phases
Methods and compositions involving enzyme-activatable fluorophore polymer imaging agents for photodetection of specific tissues and / or human diseases and disorders are provided. In certain embodiments, the imaging agent comprises a hydrophilic polymer backbone (e.g., poly(L)lysine), a hydrophobic fluorophore, and a hydrophilic solubilizing agent. The solubilizing agent may comprise a quarternary ammonium group (e.g., a 1-methylnicotinic group) to enhance self-quenching of the fluorophore. Various methods for the generation and purification of imaging agents are also provided, including methods involving solid phase probe extraction or ion exchange purification.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GENEVA
Golf club head comprising multiple materials
ActiveUS20140323237A1Improved drive lengthStraighter trajectoryGolf clubsRacket sportsMulti materialEngineering
A golf club head having an insert mechanically coupled to a frame. The construction allows a golf club head to be fabricated with a combination of dissimilar materials, resulting in a club head with improved performance. In some embodiments, the insert comprises an outer insert material, an inner insert material, and a sandwiched material. The sandwiched material may be constructed with a plurality of voids having a varying distribution, thereby resembling a biological structure. Methods for forming a golf club having an insert mechanically coupled to a frame are also disclosed.
Owner:COBRA GOLF
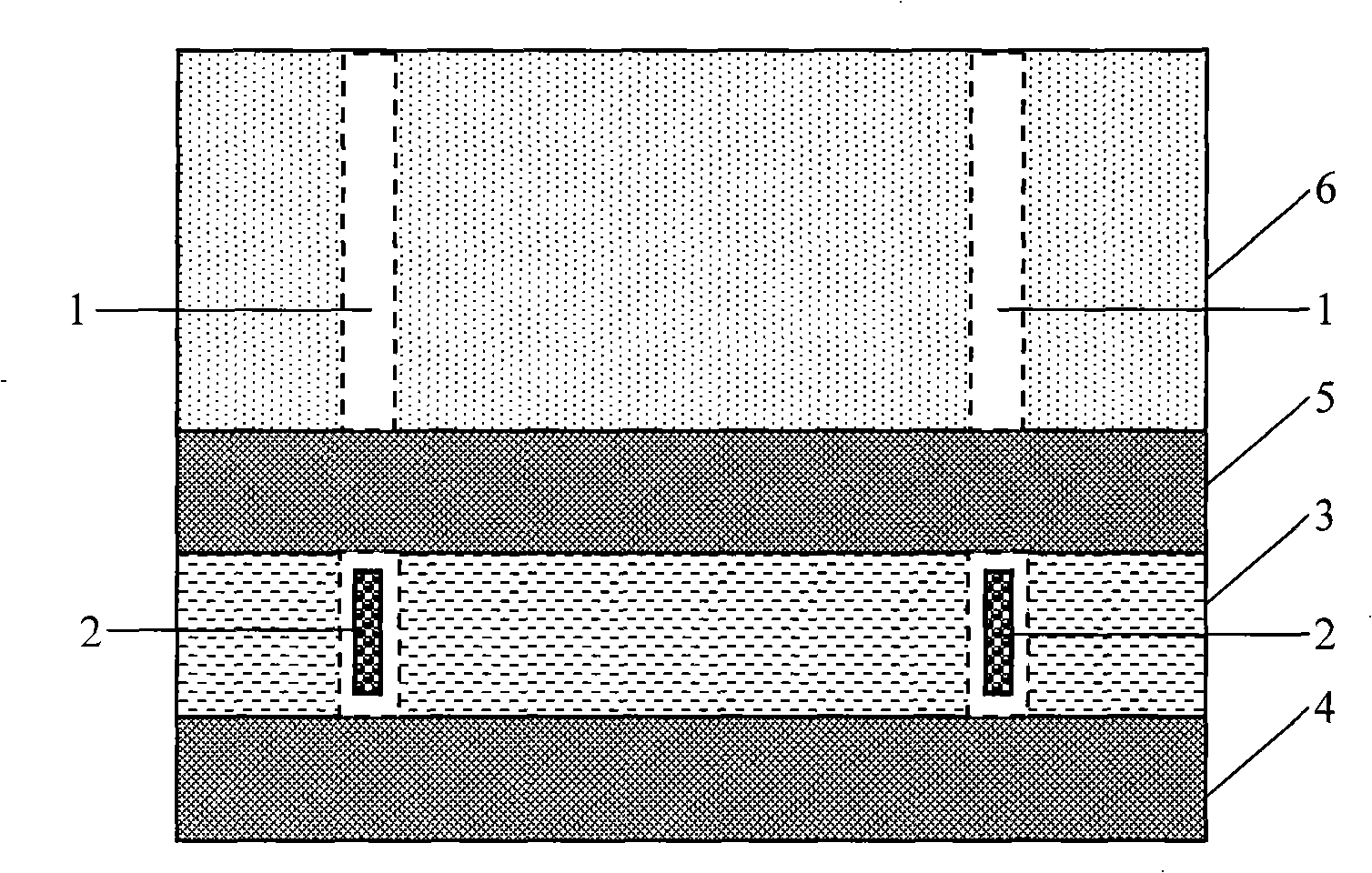
Bulletproof composite board
The invention discloses a bulletproof composite board comprising an buffer layer as the external layer, an absorption layer connected with the buffer layer, and a barrier layer connected with the absorption layer, wherein the buffer layer comprises a plurality of disks superposed into a scalelike structure, and the disks are provided with a convex surface towards the external layer; the absorption layer comprises weftless fabric pressure layers and knitted fabrics, which are superposed, and the weftless fabric pressure layers and the knitted fabrics comprise fibers of which the strength is atleast 15 cN / dtex and the modulus is at least 390 cN / dtex; and the barrier layer comprises a metal plate of which the tensile strength is greater than 1000 MPa. A bullet is deflected under the action of the convex surface of the disks, and the penetrating capability of the bullet is reduced; under the alternate actions of the weftless fabrics and the knitted fabrics, the energy of the bullet is quickly transferred and absorbed; and finally, the bullet is effectively prevented when getting into contact with the barrier layer with high strength.
Owner:杨珍芬
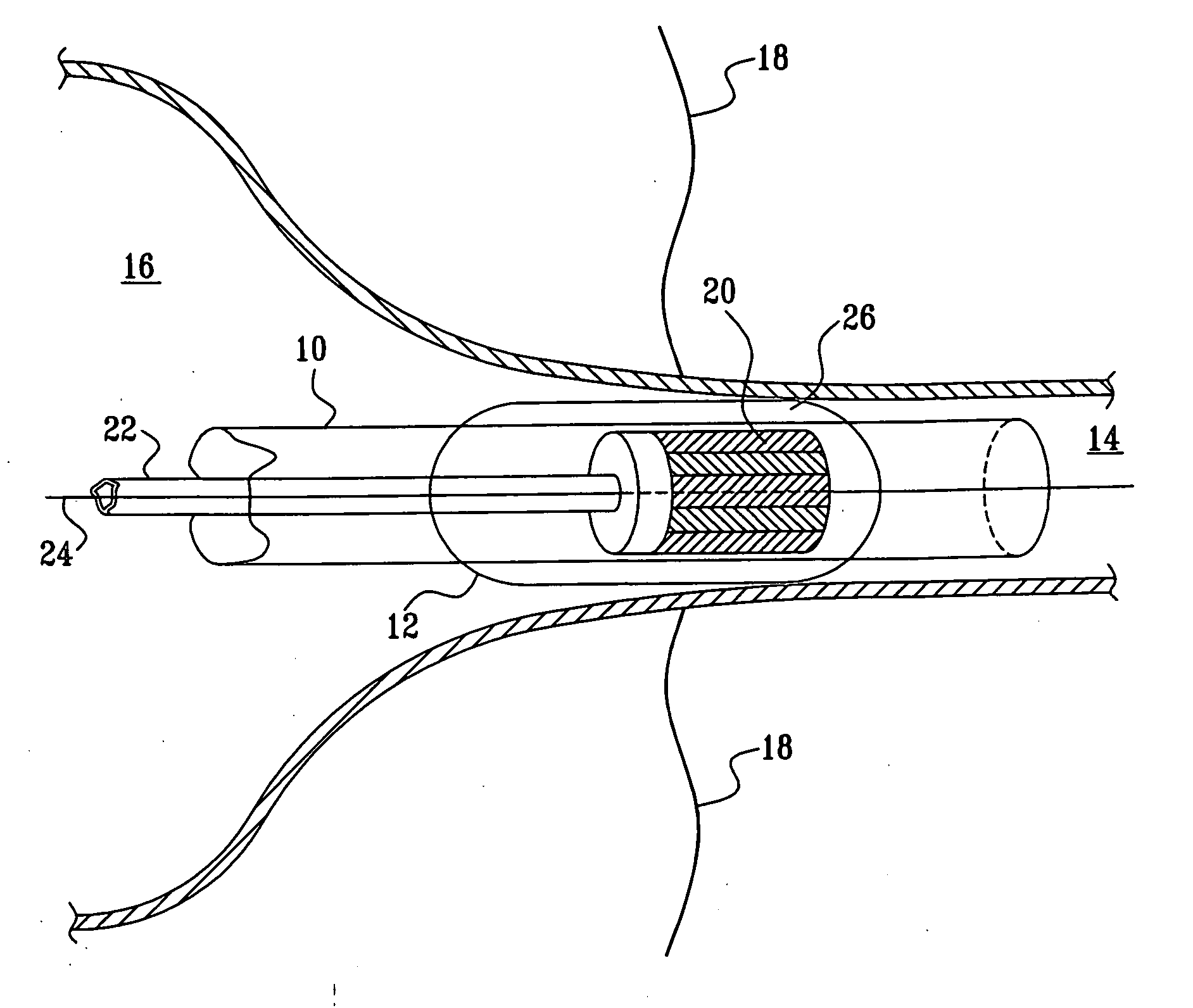
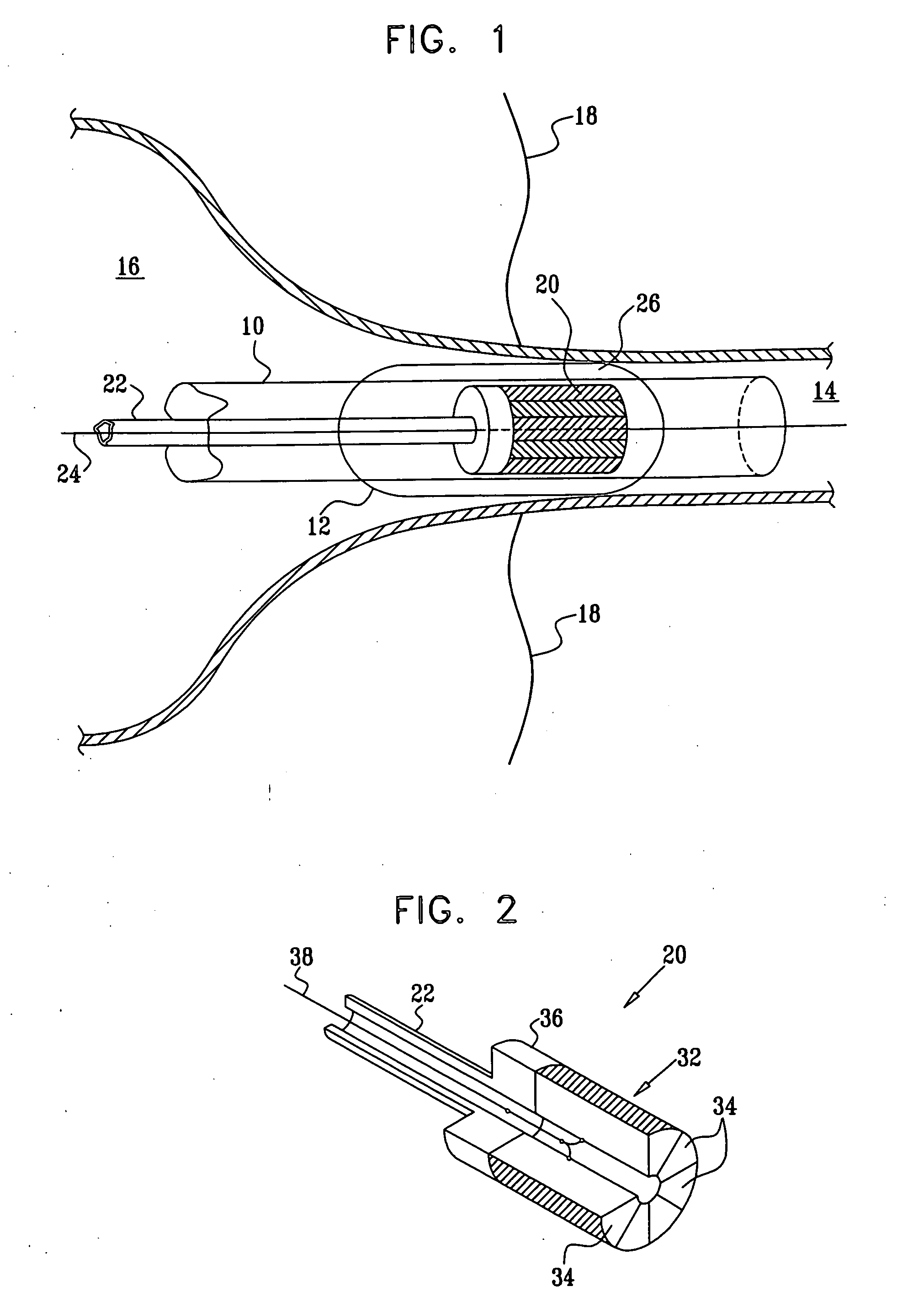
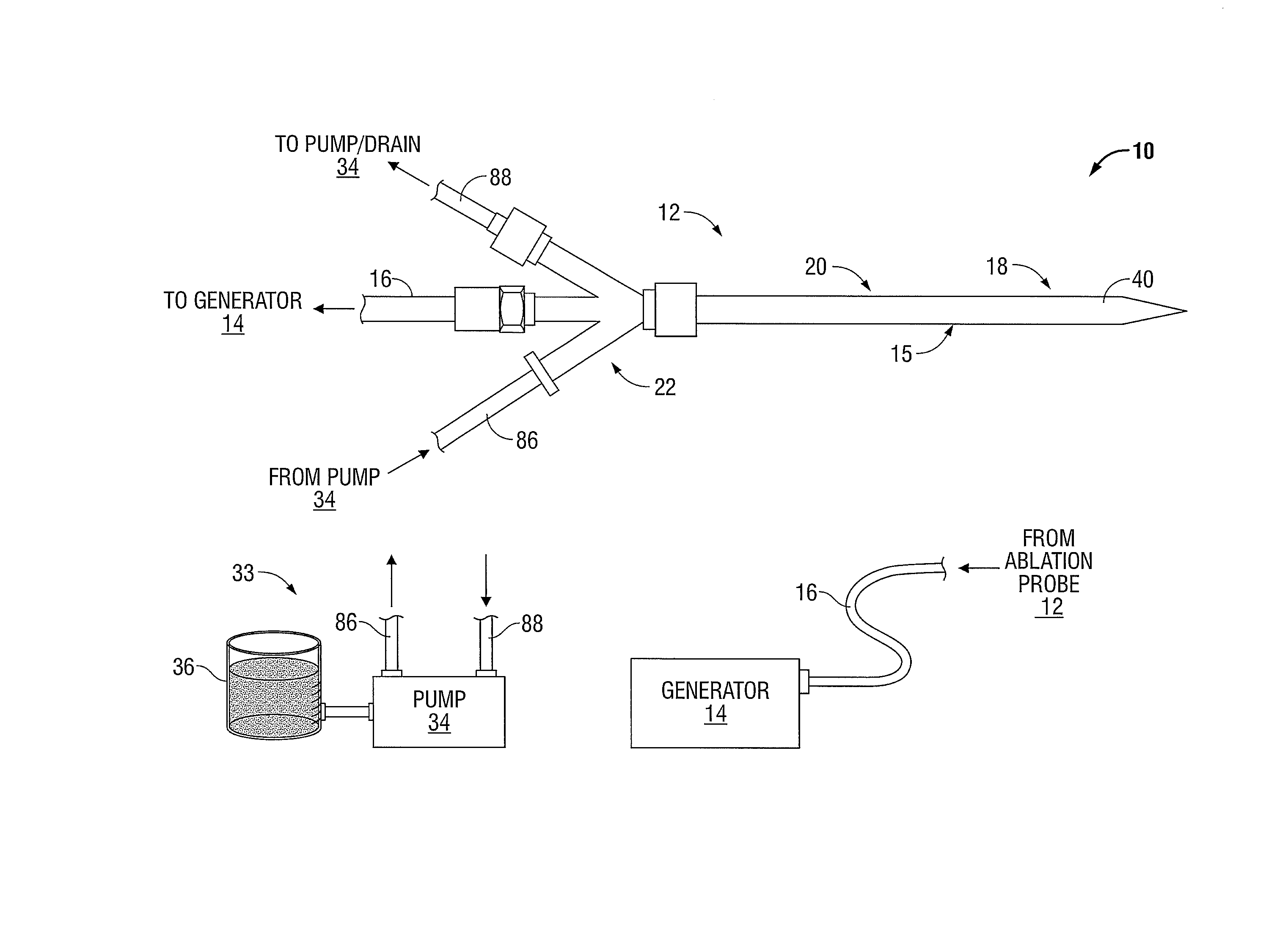
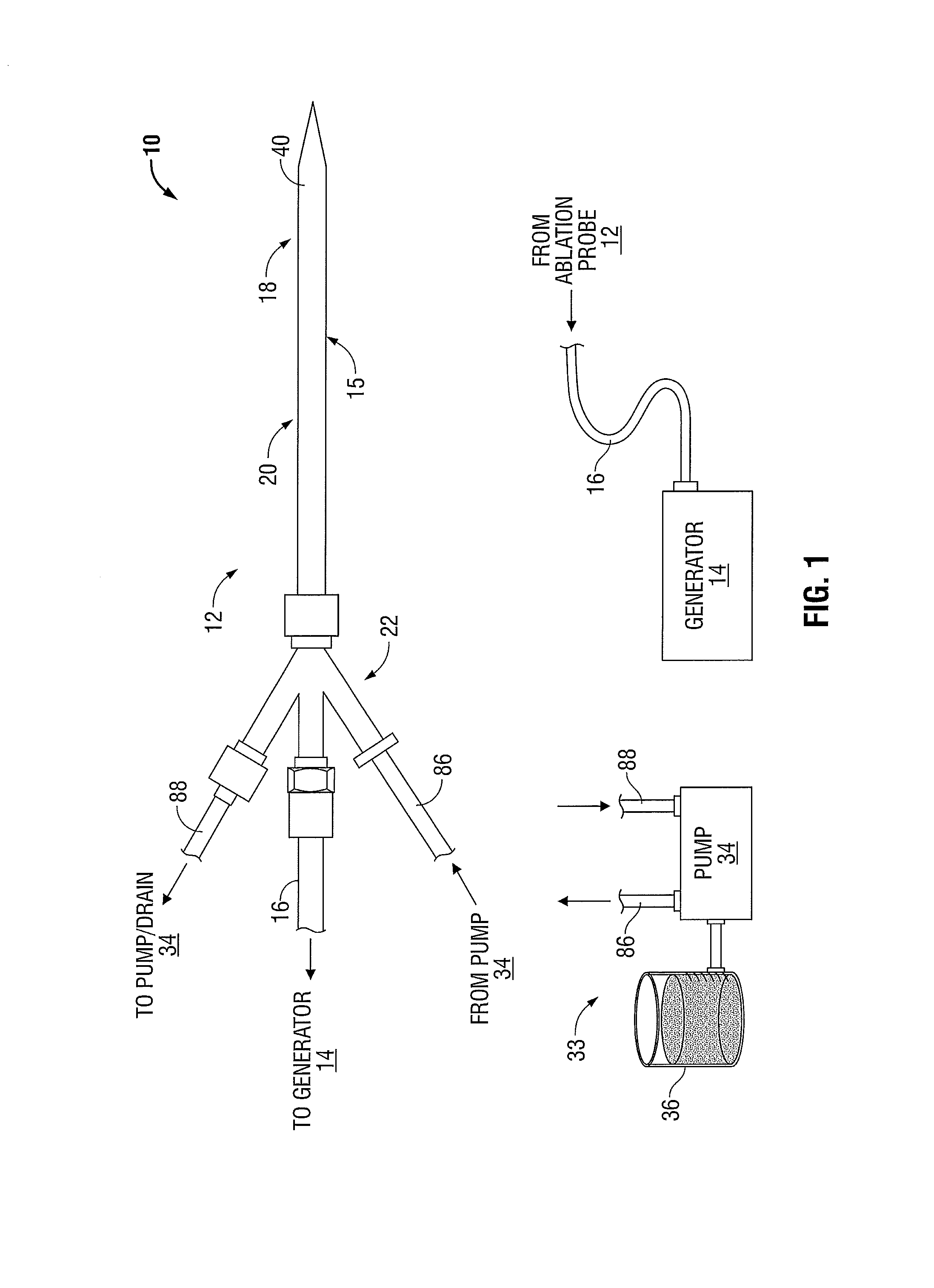
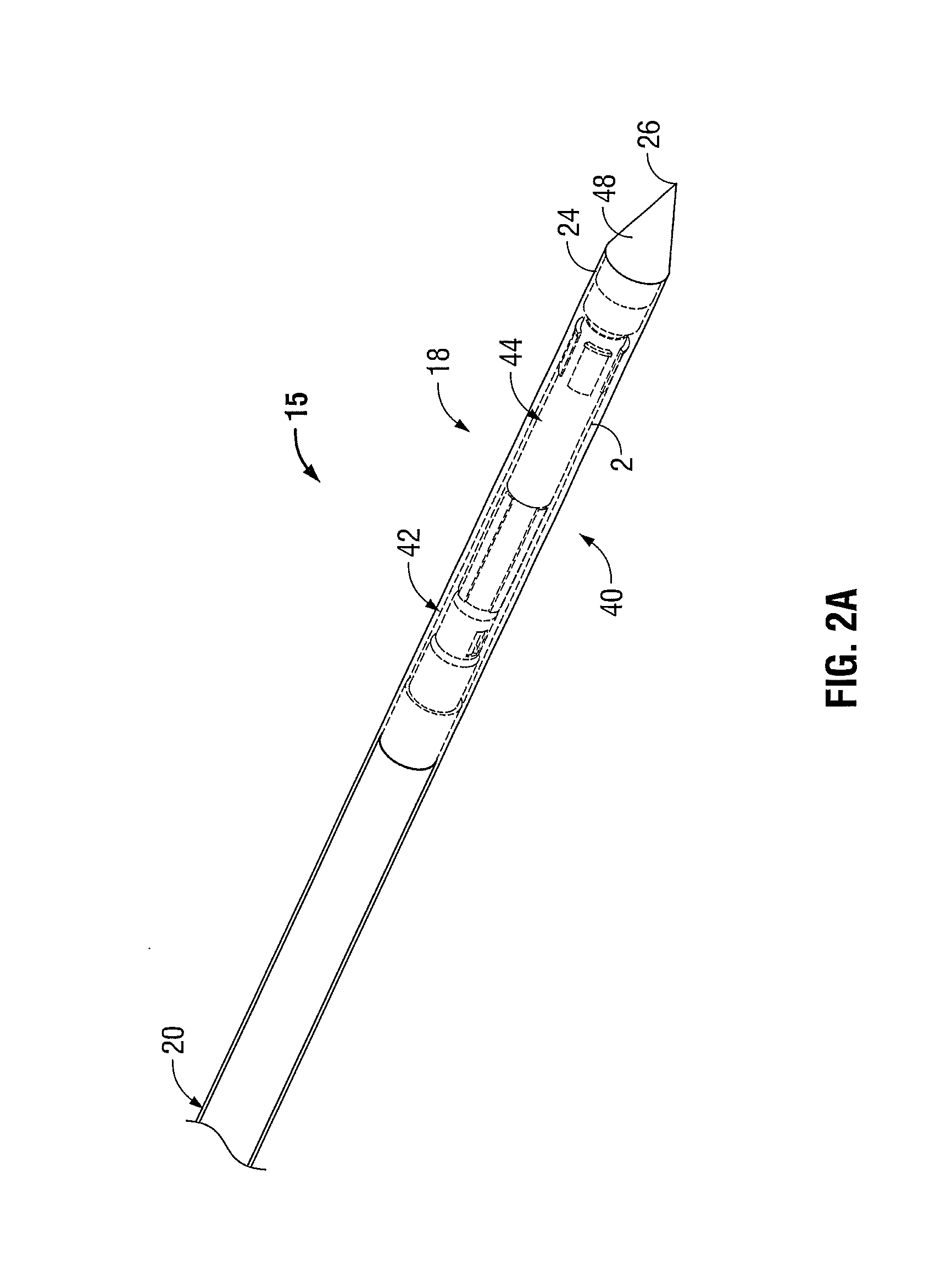
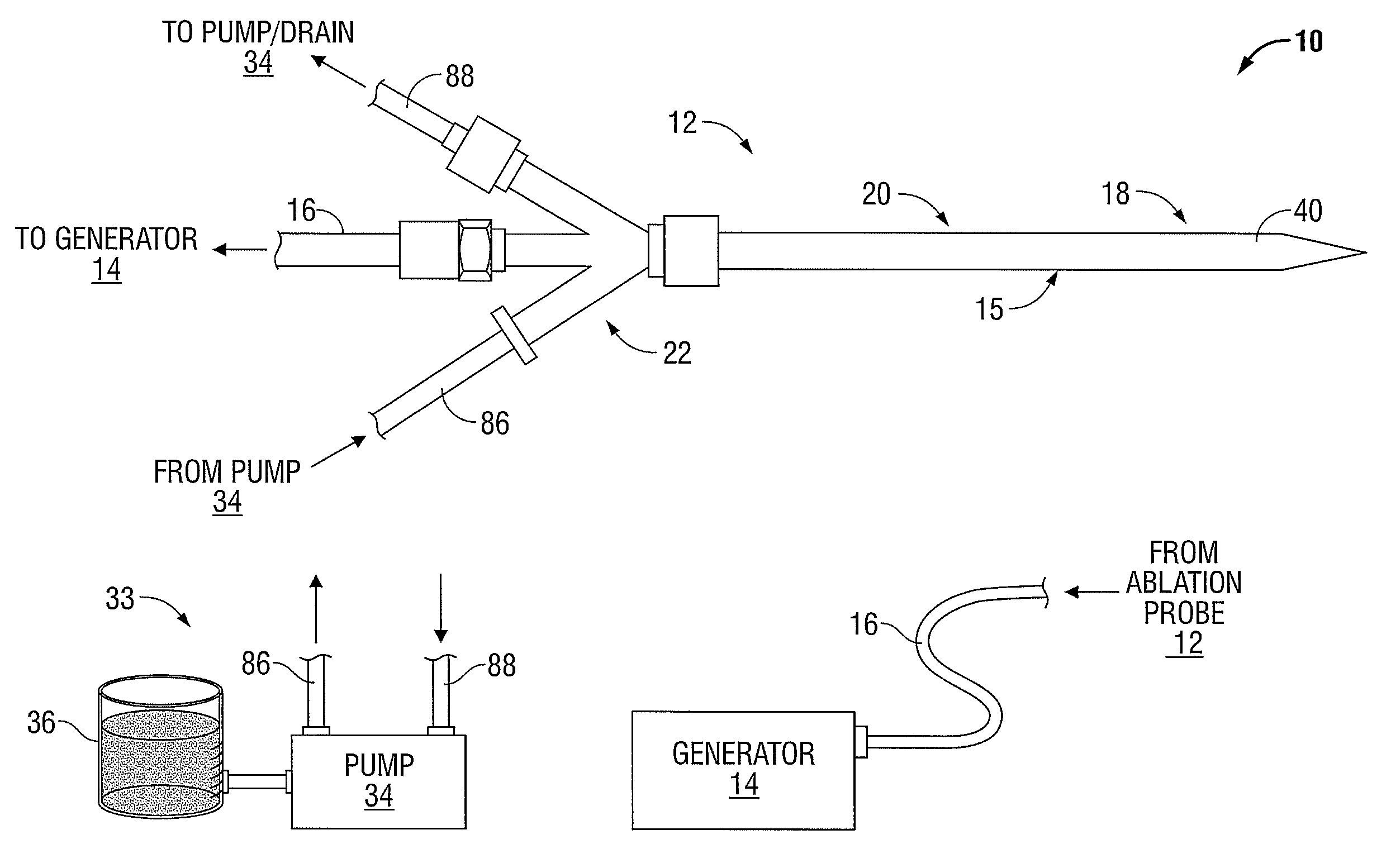
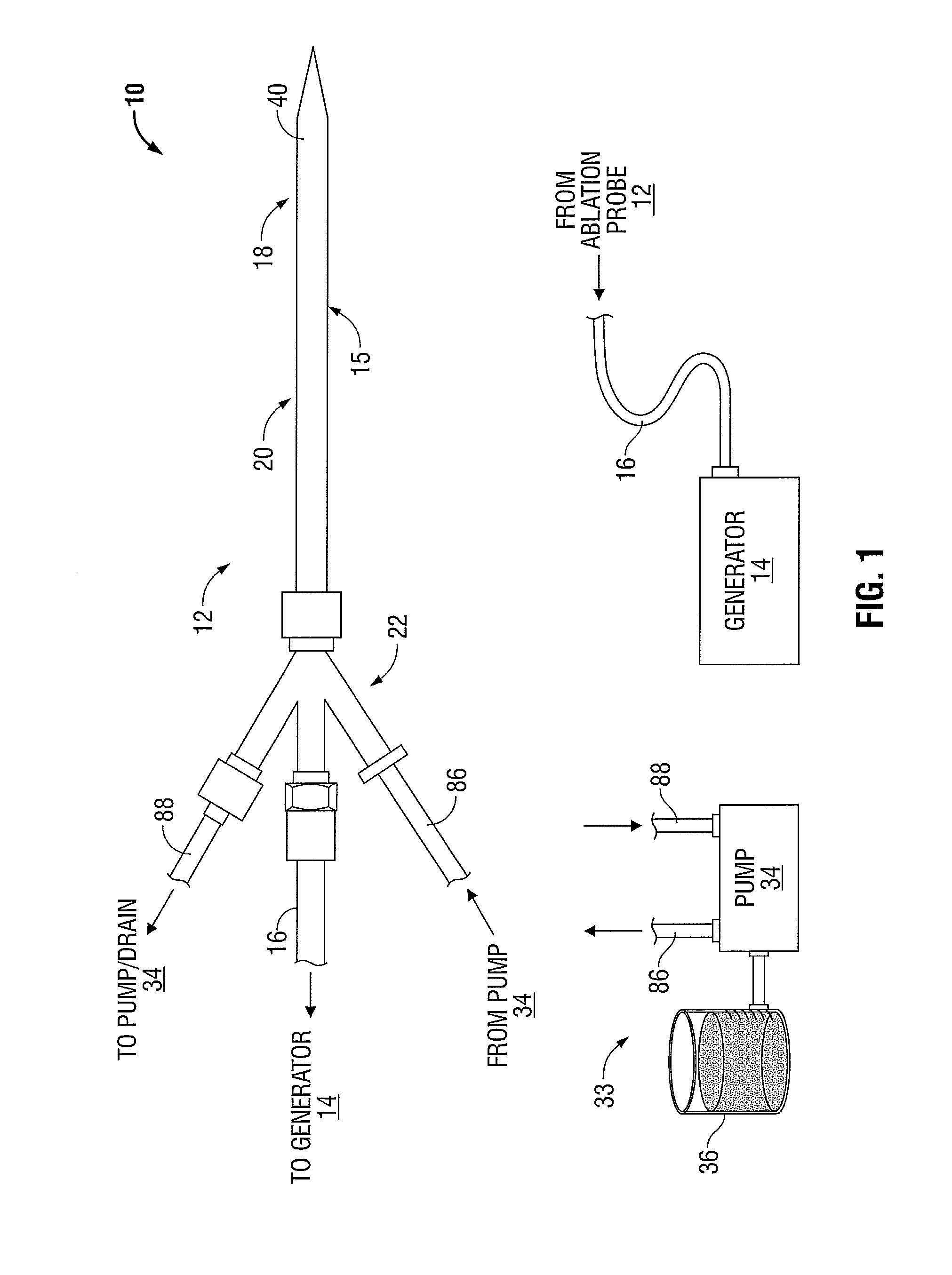
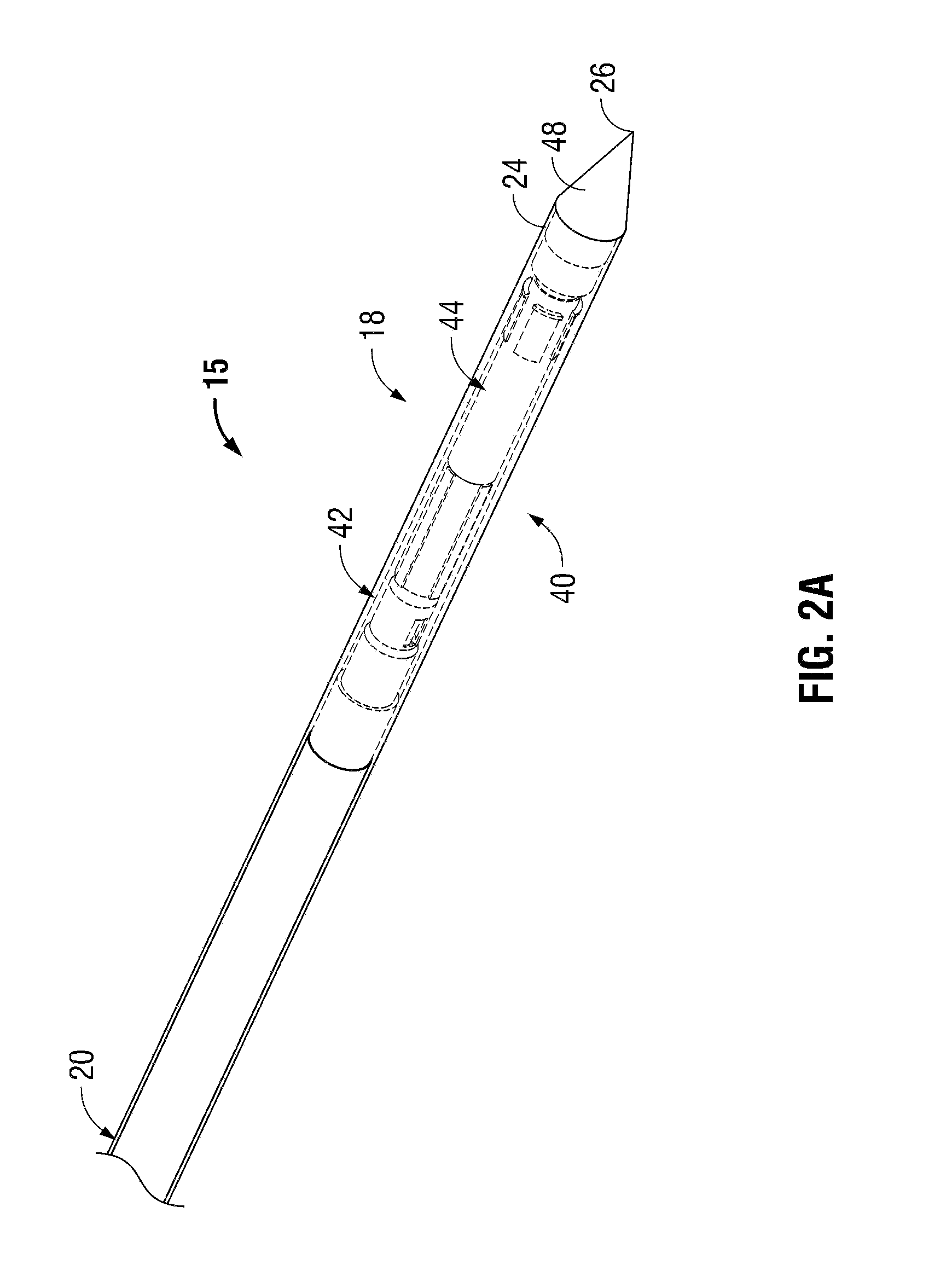
Ablation Systems, Probes, and Methods for Reducing Radiation from an Ablation Probe into the Environment
ActiveUS20130178842A1Reduce eliminateChangeSurgical needlesSurgical instruments for heatingCatheterBiomedical engineering
The ablation systems, ablation probes, and corresponding methods according to the present disclosure reduce or eliminate energy radiating from an ablation probe into the environment. Some ablation probes include a retractable sheath that shields at least the radiating portion of the ablation probe. The retractable sheath and / or the ablation probe may include conduits through which a fluid may flow to shield the radiating portion and to drive the retractable sheath to an extended state. Other ablation probes include apertures defined in the probe walls through which the fluid can flow to expand a balloon surrounding the radiating portion. Yet other ablation probes include a thermal indicator to indicate the temperature of the ablation probe to a user. The ablation systems include fluid circuits and associated mechanical controls for varying the contents and / or flow rate of the fluid provided to the radiating portion of the ablation probe.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Pneumatic spring percussion mechanism with an electro-dynamically actuated driving piston
InactiveUS7025183B2Easy to carryLong channelReciprocating drilling machinesConstructionsEngineeringLinear motor
The invention relates to a pneumatic spring percussion mechanism comprising a driving piston moving back and forth in a housing of the percussion mechanism and a percussion piston, wherein a pneumatic spring is configured between the driving piston and the percussion piston. The movement of the driving piston can be transmitted to a percussion piston by means of said pneumatic spring. The driving piston can be driven by an electric linear motor and is connected to an aromatic of the linear motor, forming a single piece therewith. This arrangement makes it possible to eliminate the use of a conventional rotary motor and a crank mechanism to drive the driving piston.
Owner:WACKER NEUSON SE
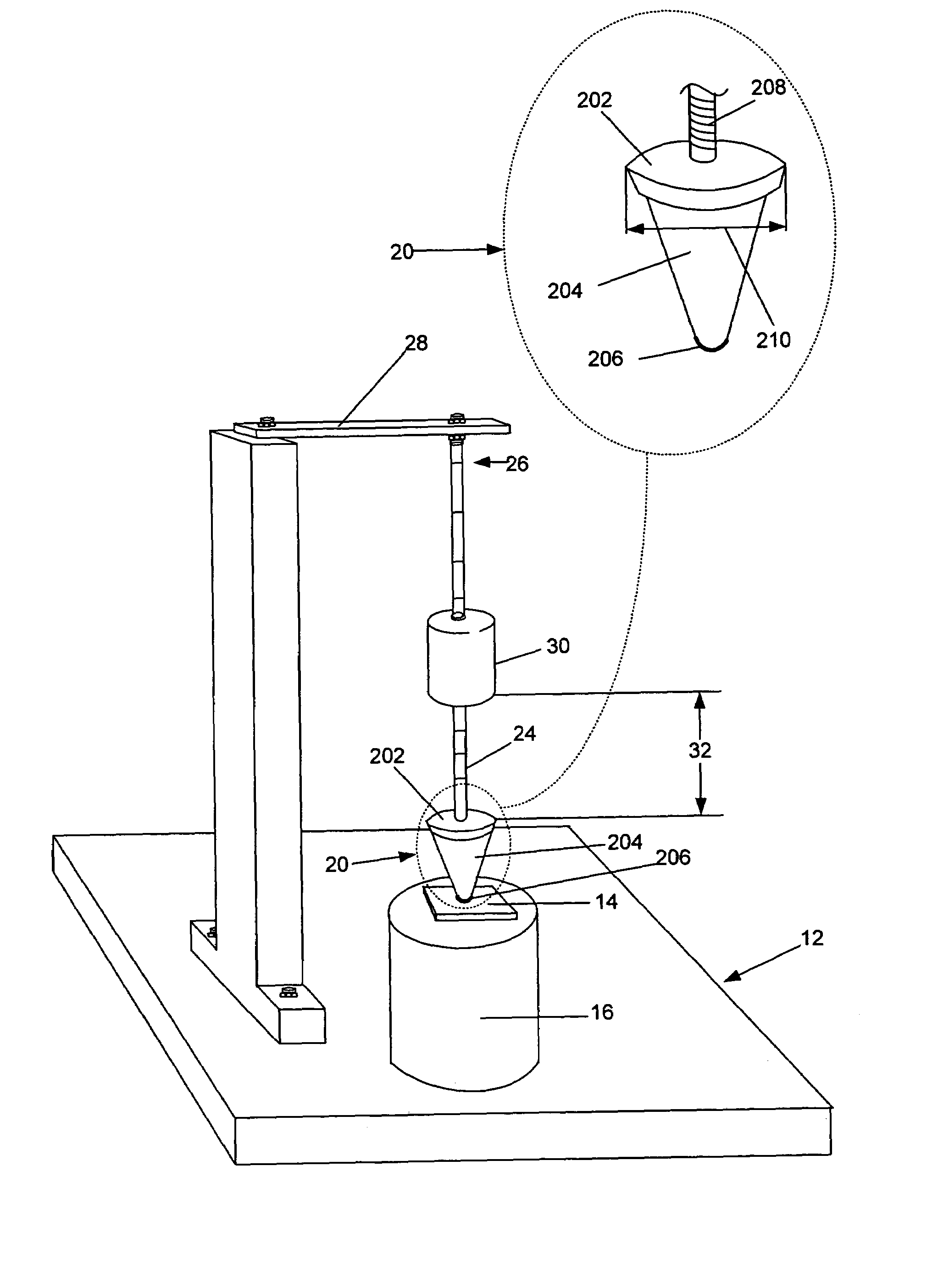
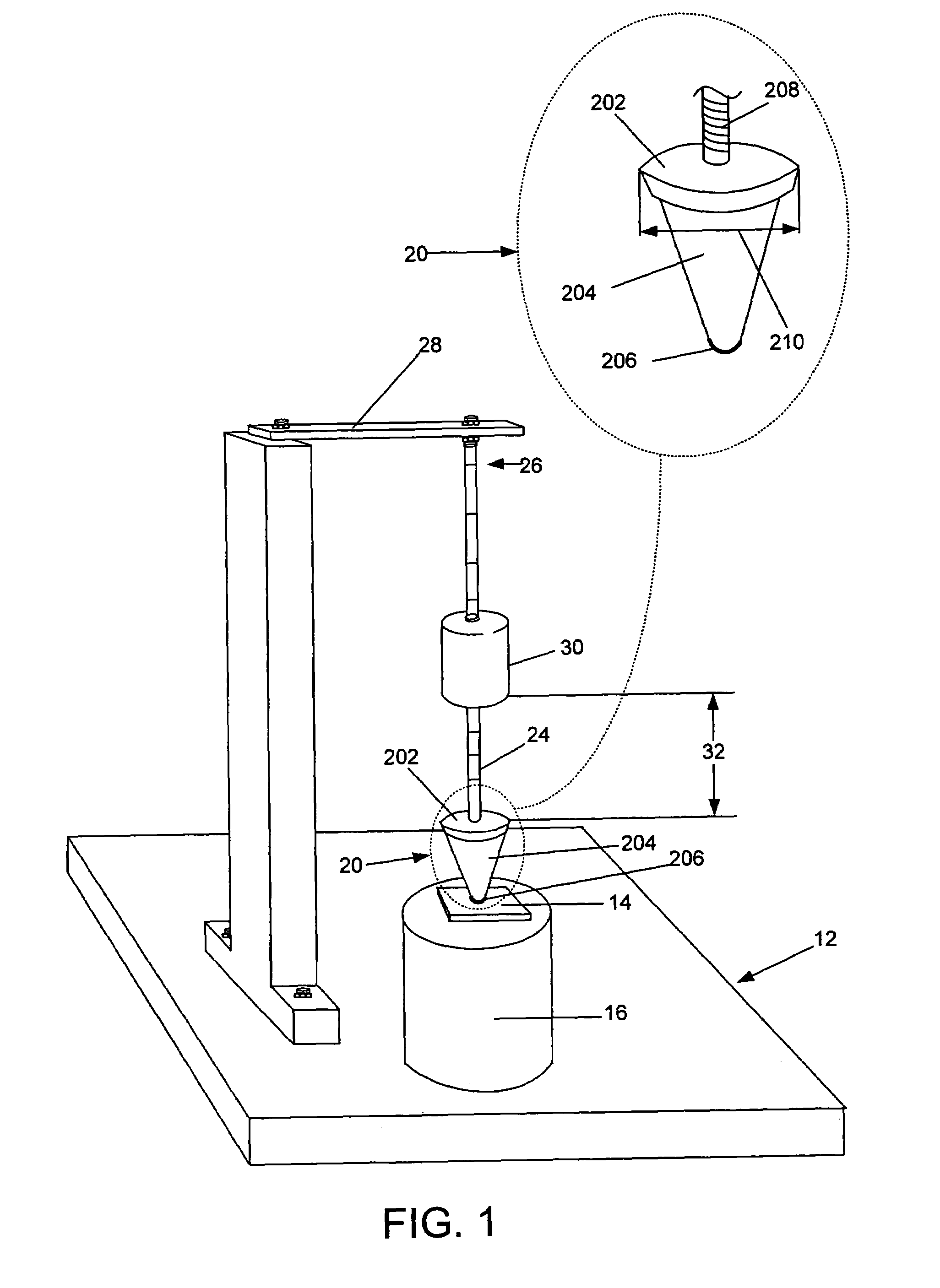
Method and apparatus for dynamic impact testing
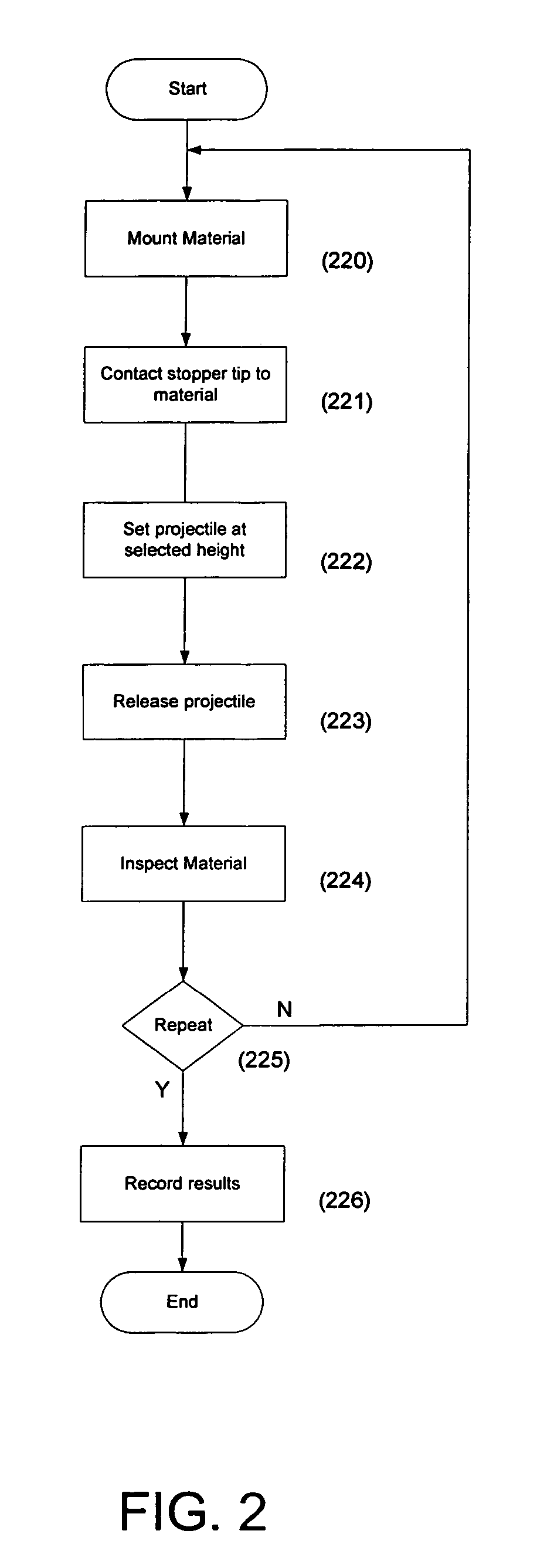
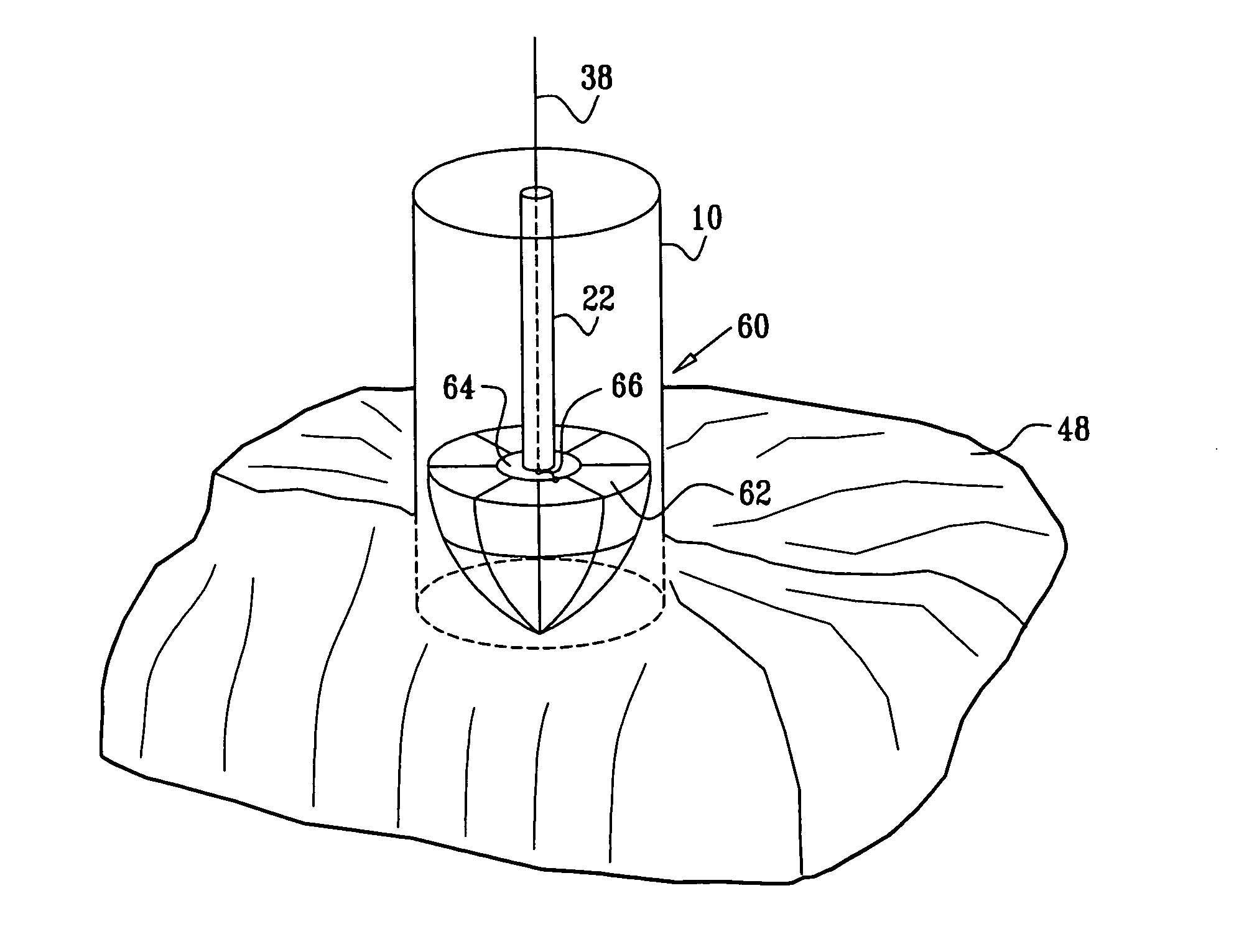
InactiveUS7412870B2Good adhesionEasy to removeAcceleration measurementMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesTest materialImpact testing
A method and apparatus wherein a material or object to be tested is placed on a base support. A stopper assembly having a stopper tip on one end in contact with the test material or object, and a washer on the opposite end attached to a rod. A projectile is propelled with a selected level of force along the rod and impacts the washer, which transmits the force of impact through the stopper tip to the test material or object. The level of propelling force, the mass of the projectile, the construction of the stopper assembly and the location of impact on the test material or object may be precisely adjusted to simulate real-life impacts.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Phased-array for tissue treatment
ActiveUS7854733B2Weaken energyFocusUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyTarget tissuePhased array
Apparatus is provided for ablating tissue of a patient by applying ultrasound energy to the tissue. The apparatus is typically delivered to the targeted tissue via a catheter and includes an ultrasound array, which is adapted to be driven as a phased array to concentrate the ultrasound energy on the targeted tissue while avoiding surrounding tissue.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
Open irrigated ablation catheter
ActiveUS9456867B2Reduce the possibilityPreventing or reducing impedance rise of tissue in contactElectrocardiographySurgical instruments for heatingMedicineMedical device
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method for blasting seepage enhancement for low infiltration sandrock -type uranium deposit
The invention discloses a method for explosion and leakage increase of a low permeability sandstone uranium deposit, which includes steps as follows: A. blast holes are drilled through the overburden, the top rock of occurrence terrane to the proper position of the occurrence terrane from surface. An underreamer is used to locally ream the blast holes at the occurrence terrane to meet charging requirement; B. blasting cartridges are arranged in the blast holes in an uncoupling way; the detonator is waterproof; uncoupling charge for explosion comprises radial uncoupling charge and axial uncoupling charge; C. after the blasting cartridges are arranged properly, hole seal measures shall be taken to build up the blast holes; D. the blasting cartridges are initiated through short delay blasting which comprises short delay blasting inside the blast holes and short delay blasting between the blast holes. The recovery factor and the yield per unit of in-situ Uranium leaching are improved; the uranium deposit resource of low permeability sandstone type is used completely, thus alleviating the shortages of uranium resources.
Owner:INST OF ROCK AND SOIL MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Ablation systems, probes, and methods for reducing radiation from an ablation probe into the environment
InactiveUS9113930B2Reduce and eliminate radiationChangeSurgical needlesSurgical instruments for heatingCatheterBiomedical engineering
The ablation systems, ablation probes, and corresponding methods according to the present disclosure reduce or eliminate energy radiating from an ablation probe into the environment. Some ablation probes include a retractable sheath that shields at least the radiating portion of the ablation probe. The retractable sheath and / or the ablation probe may include conduits through which a fluid may flow to shield the radiating portion and to drive the retractable sheath to an extended state. Other ablation probes include apertures defined in the probe walls through which the fluid can flow to expand a balloon surrounding the radiating portion. Yet other ablation probes include a thermal indicator to indicate the temperature of the ablation probe to a user. The ablation systems include fluid circuits and associated mechanical controls for varying the contents and / or flow rate of the fluid provided to the radiating portion of the ablation probe.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com