Patents
Literature
3285 results about "Detonator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
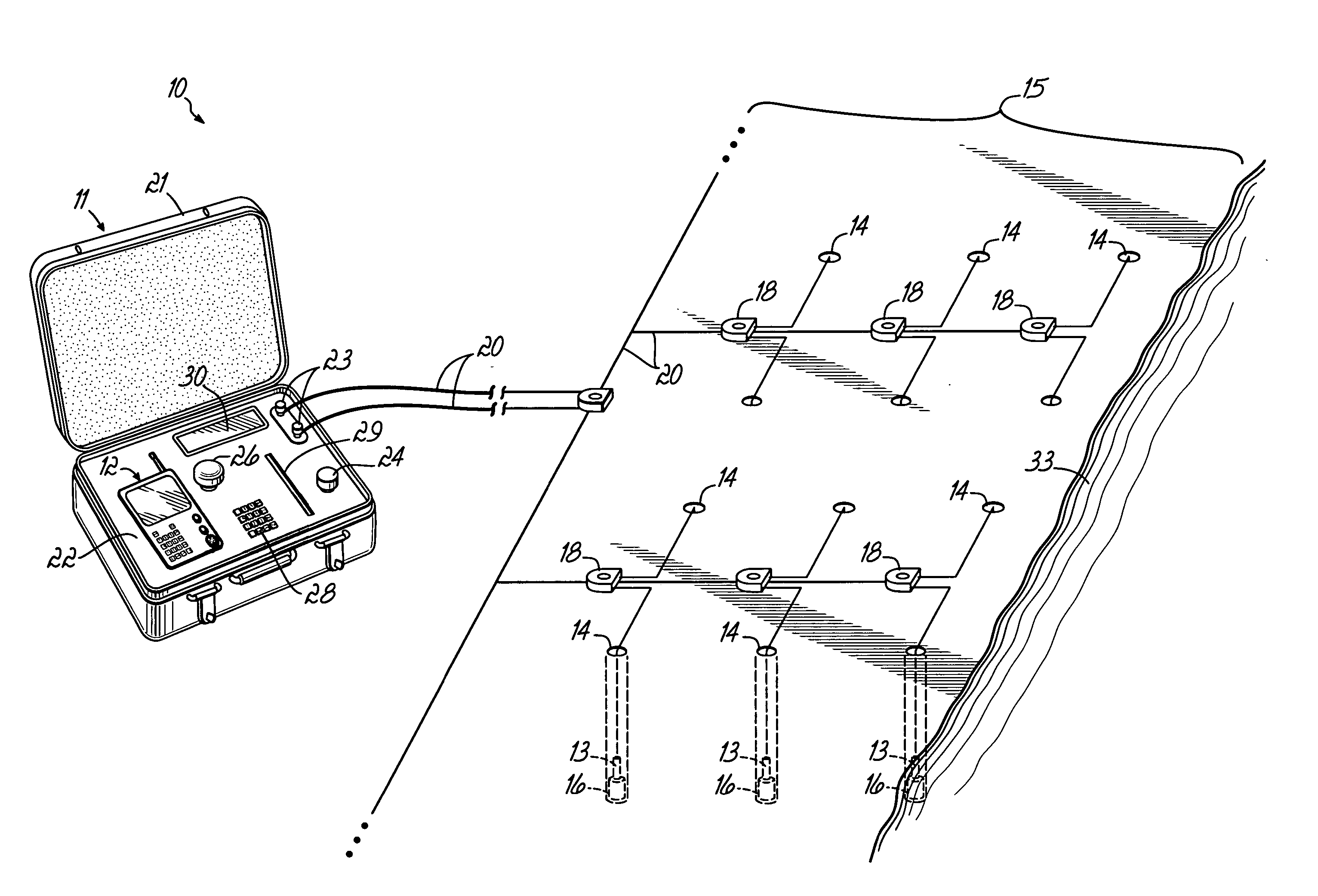
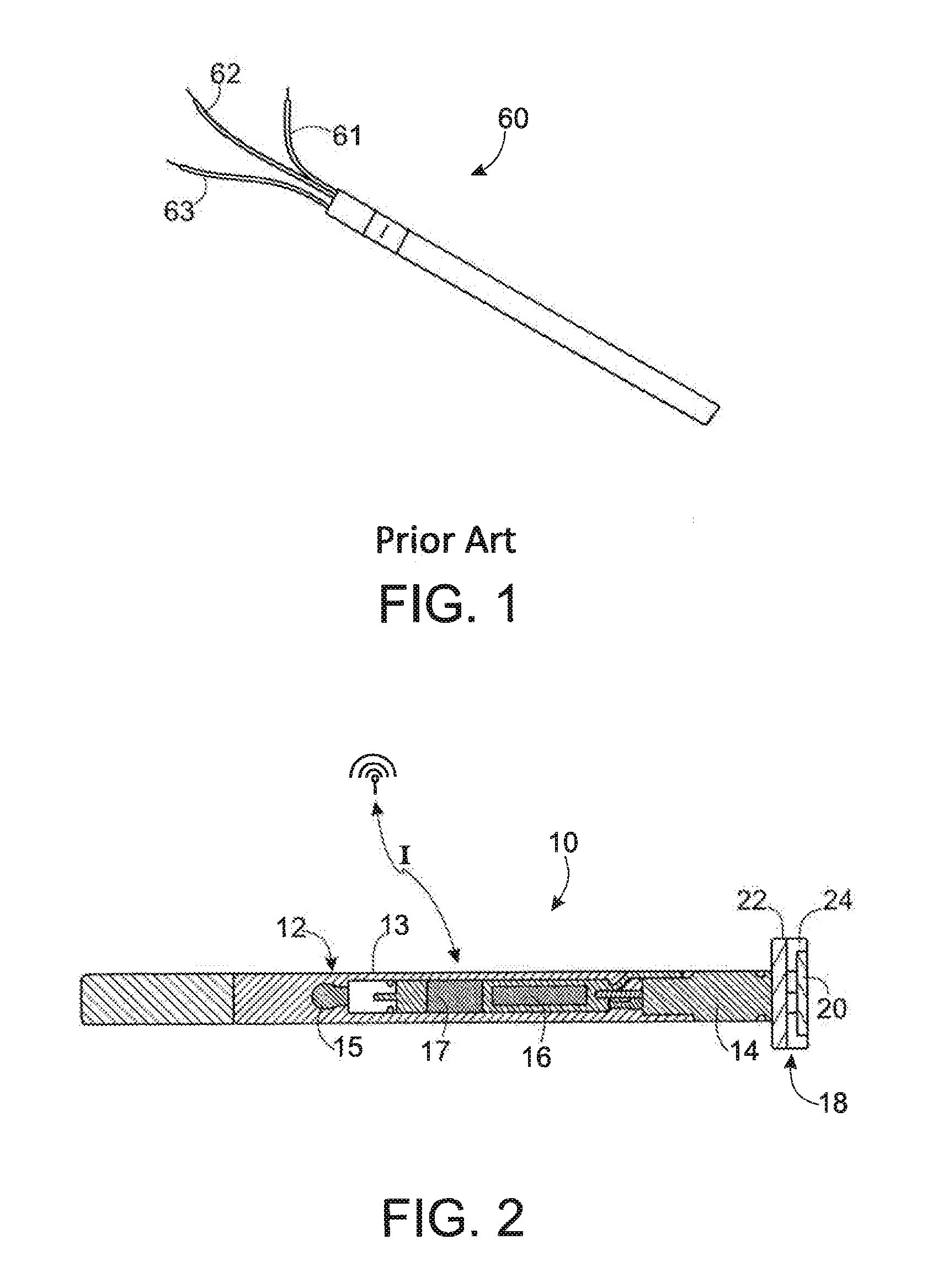
A detonator, frequently a blasting cap, is a device used to trigger an explosive device. Detonators can be chemically, mechanically, or electrically initiated, the latter two being the most common. The commercial use of explosives uses electrical detonators or the capped fuse which is a length of safety fuse to which an ordinary detonator has been joined. Many detonators' primary explosive is a material called ASA compound. This compound is formed from lead azide, lead styphnate and aluminium and is pressed into place above the base charge, usually TNT or tetryl in military detonators and PETN in commercial detonators.
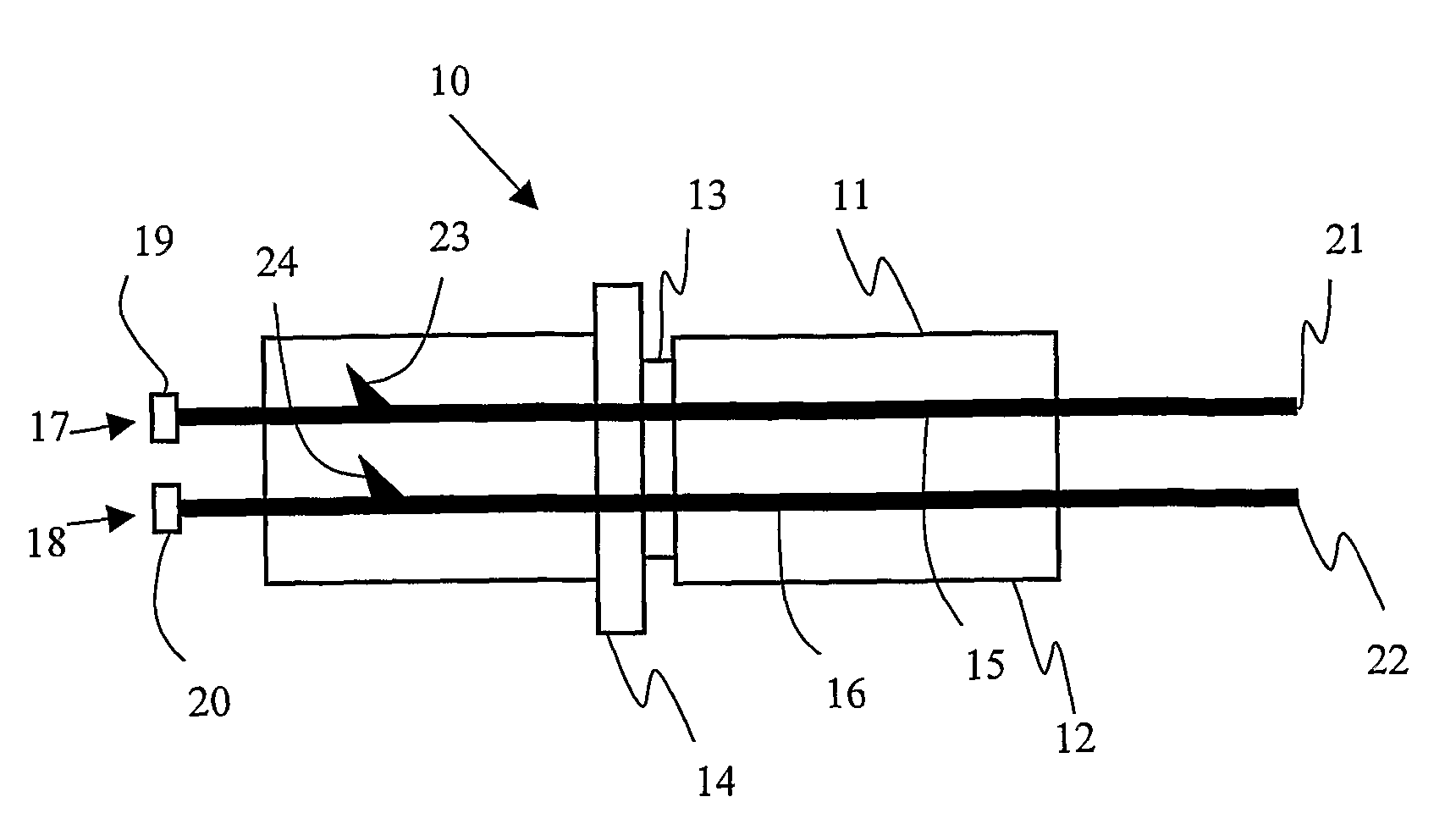
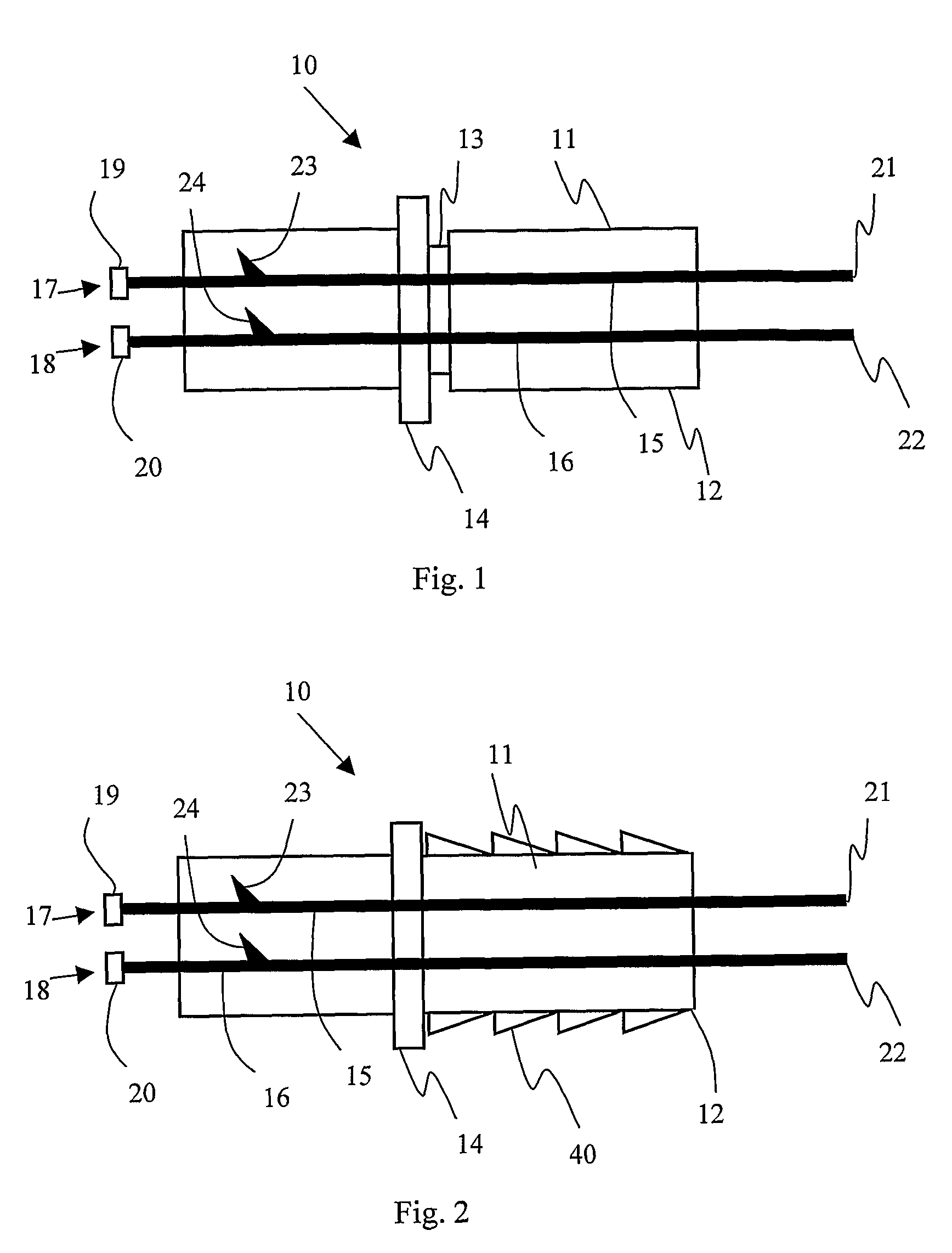
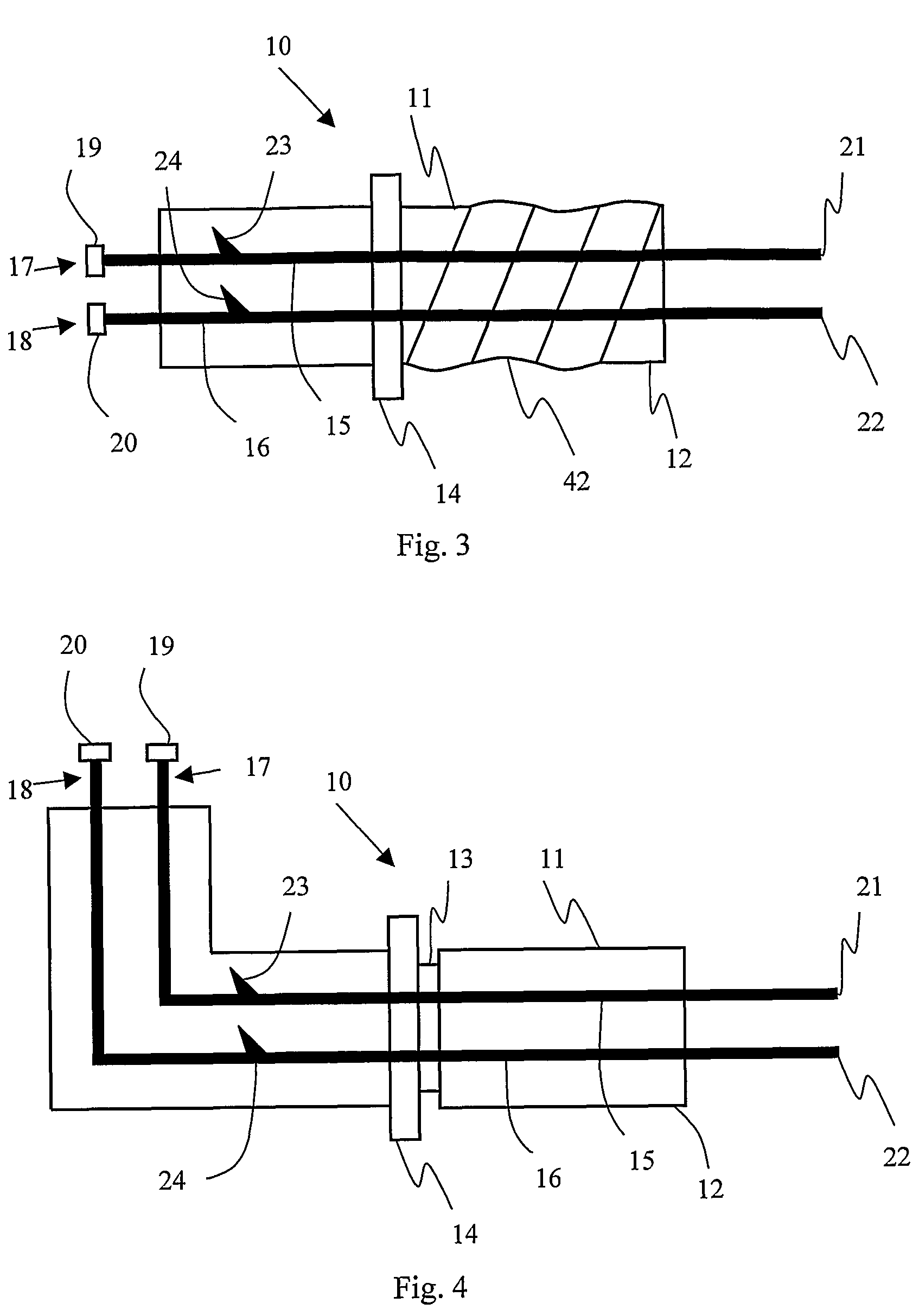
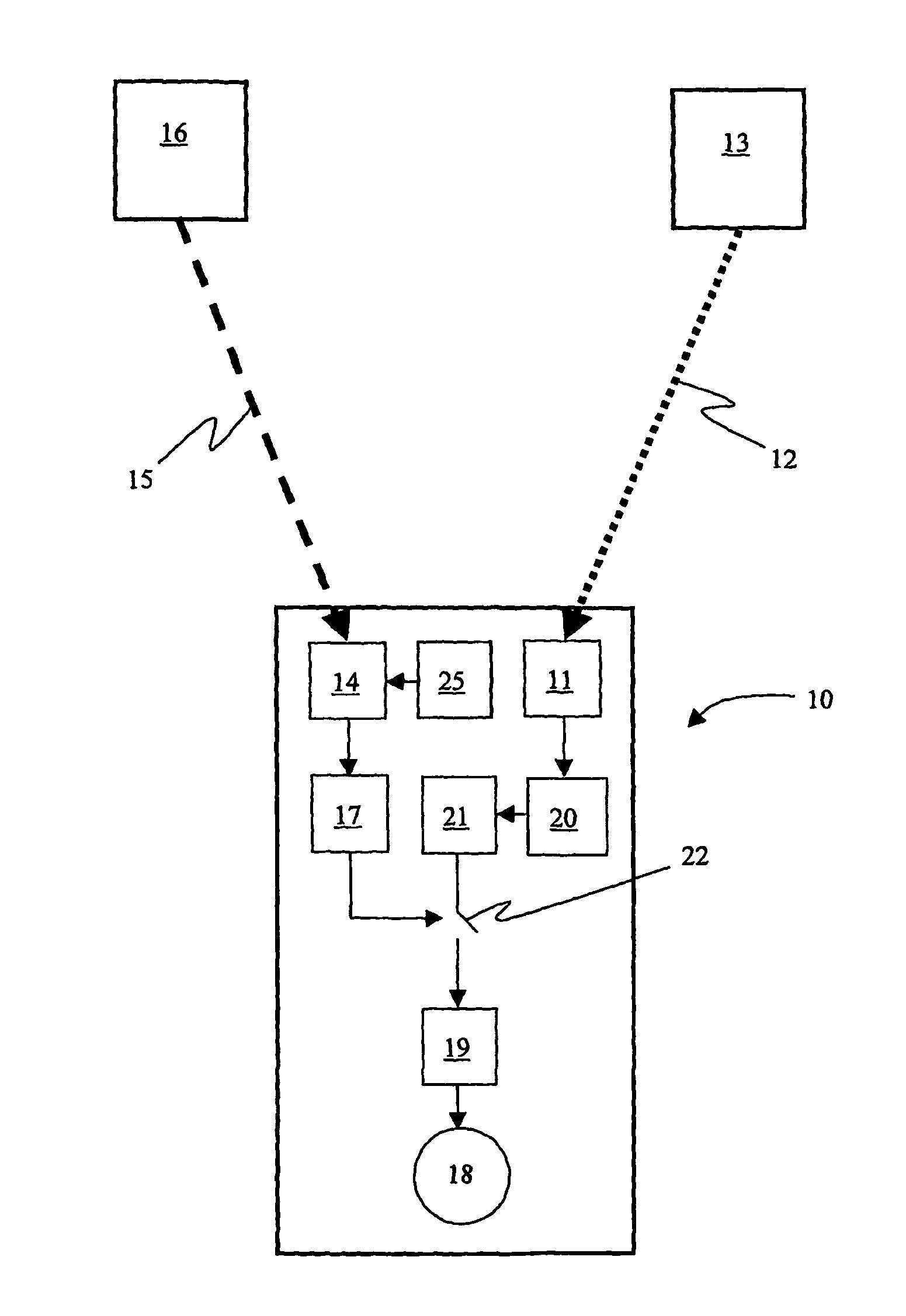
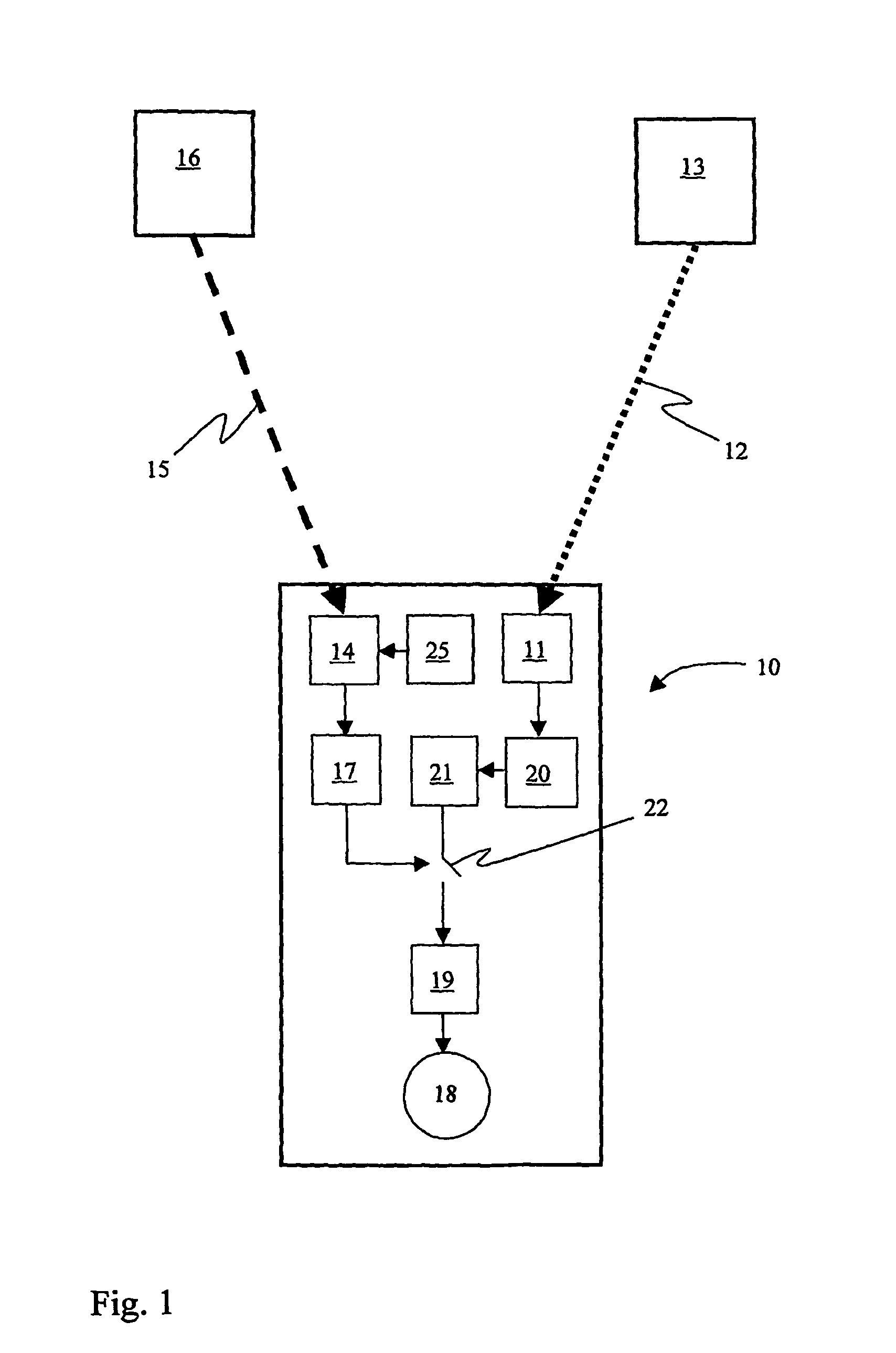
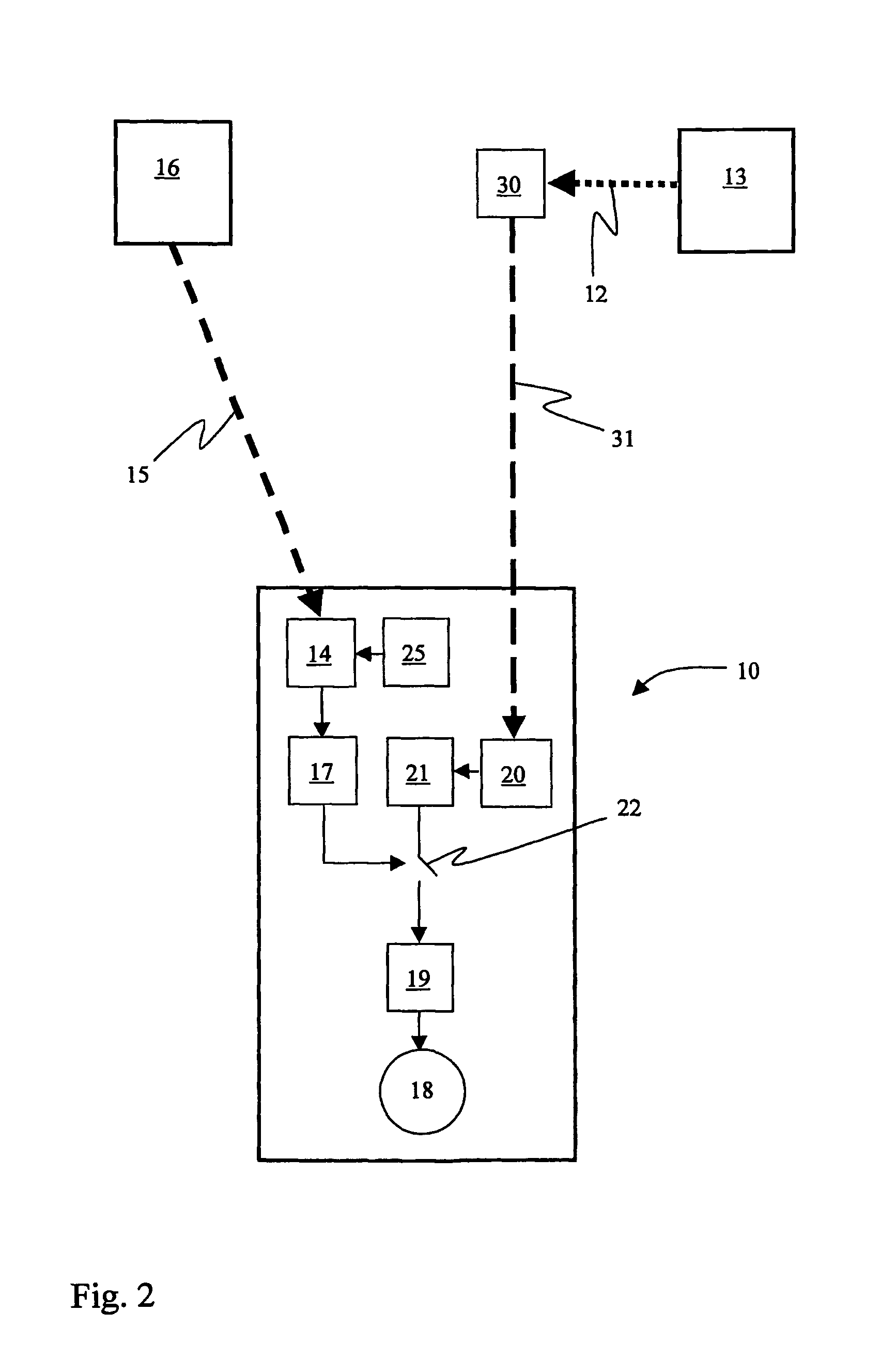
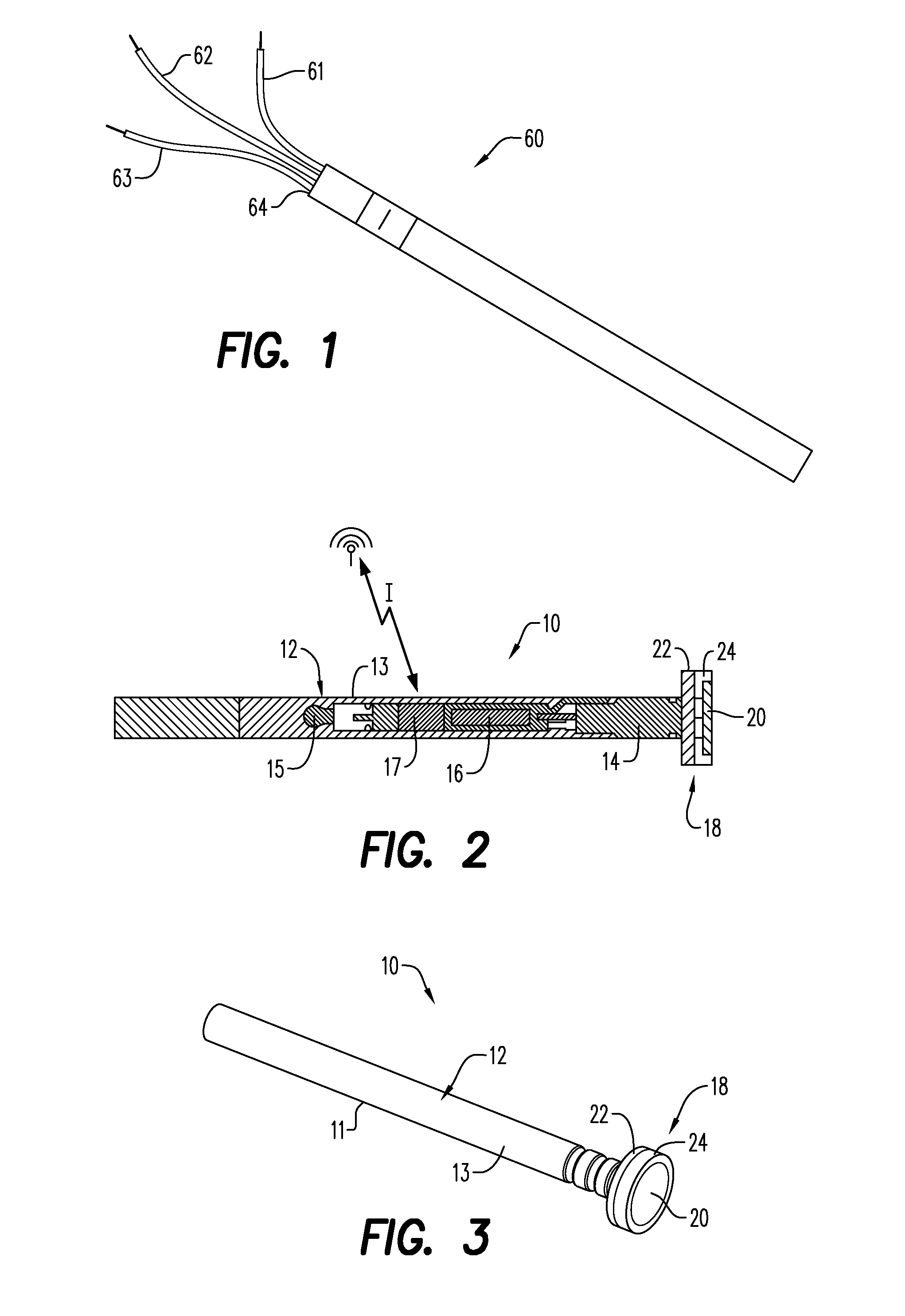
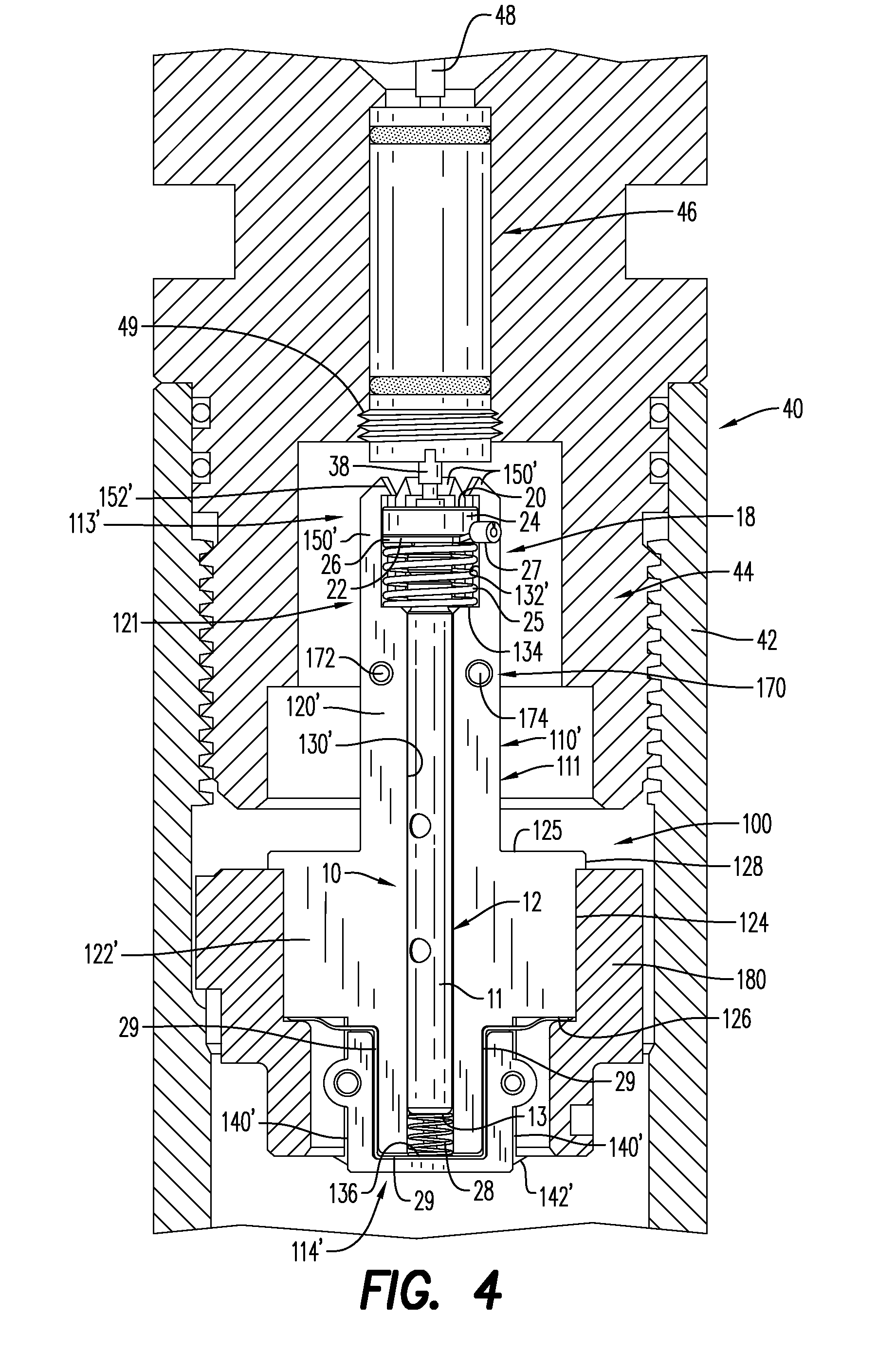
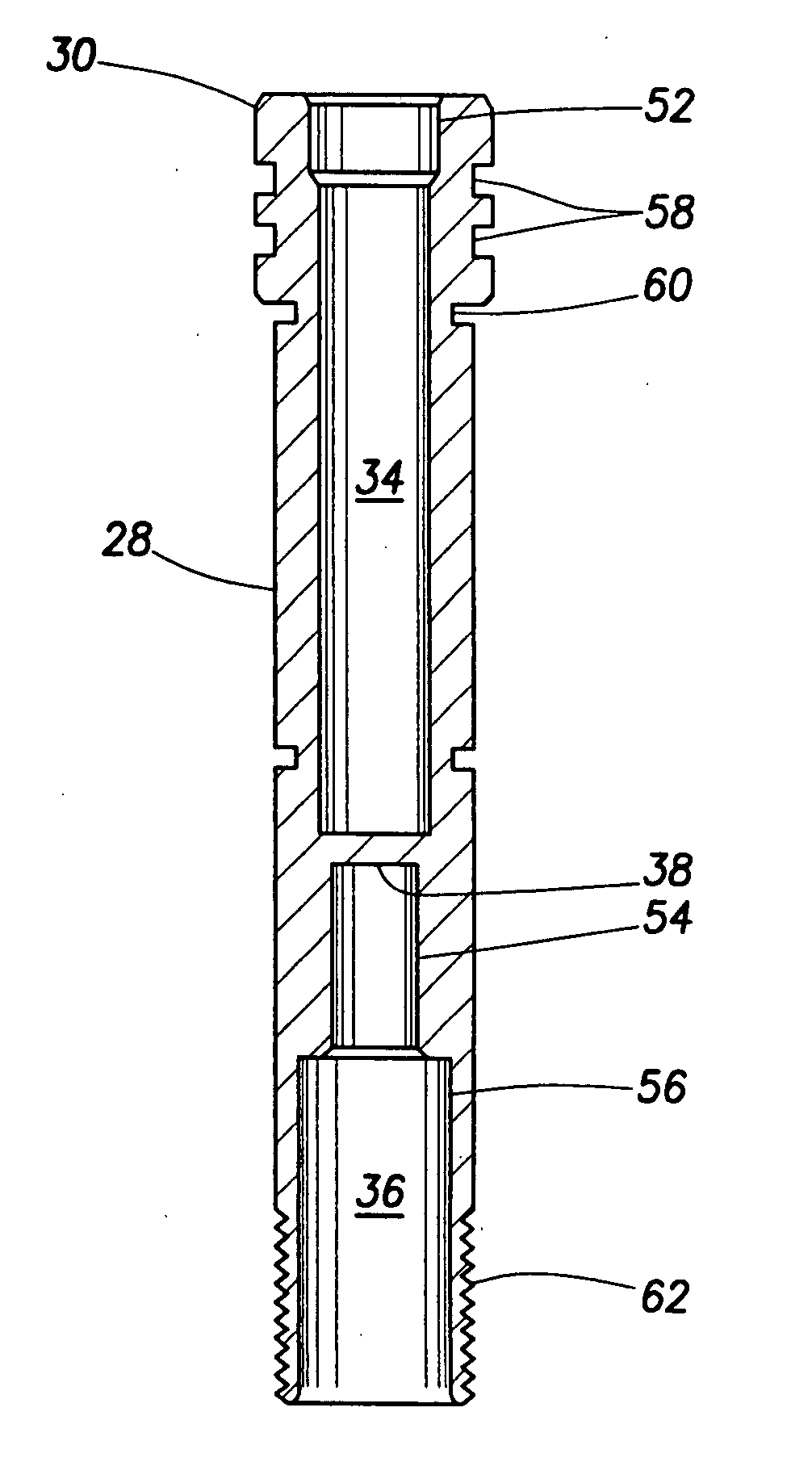
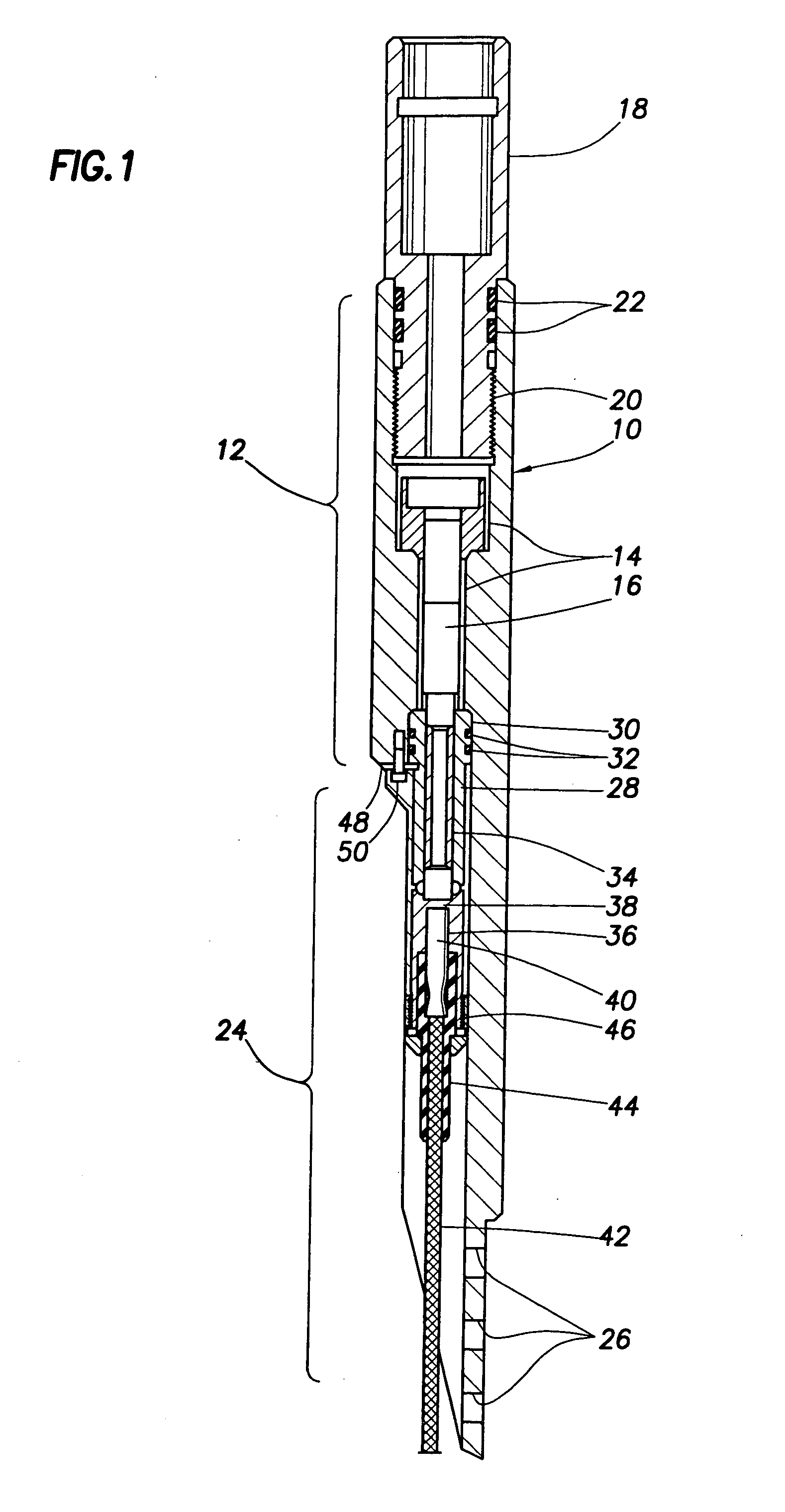
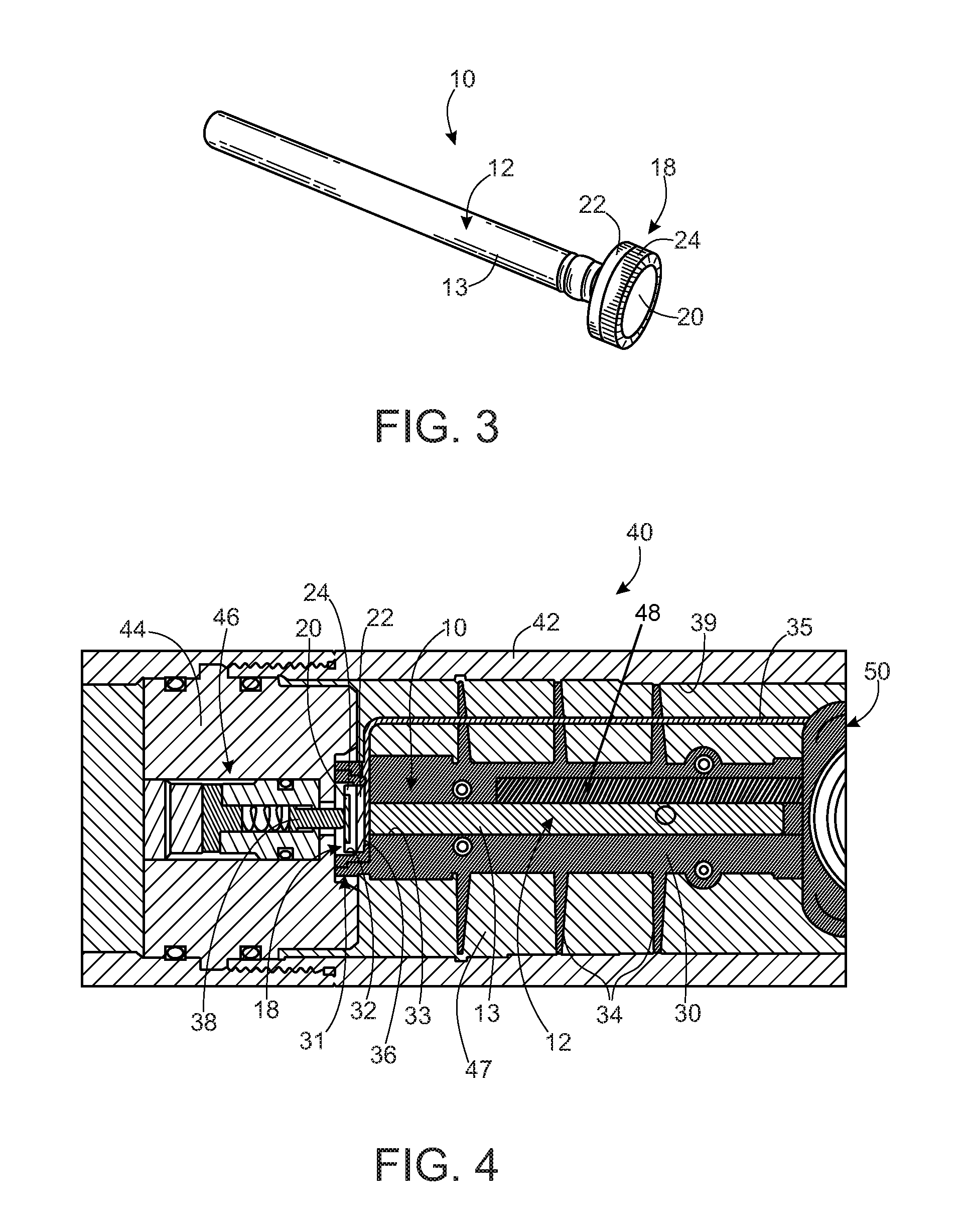
Integrated detonators for use with explosive devices
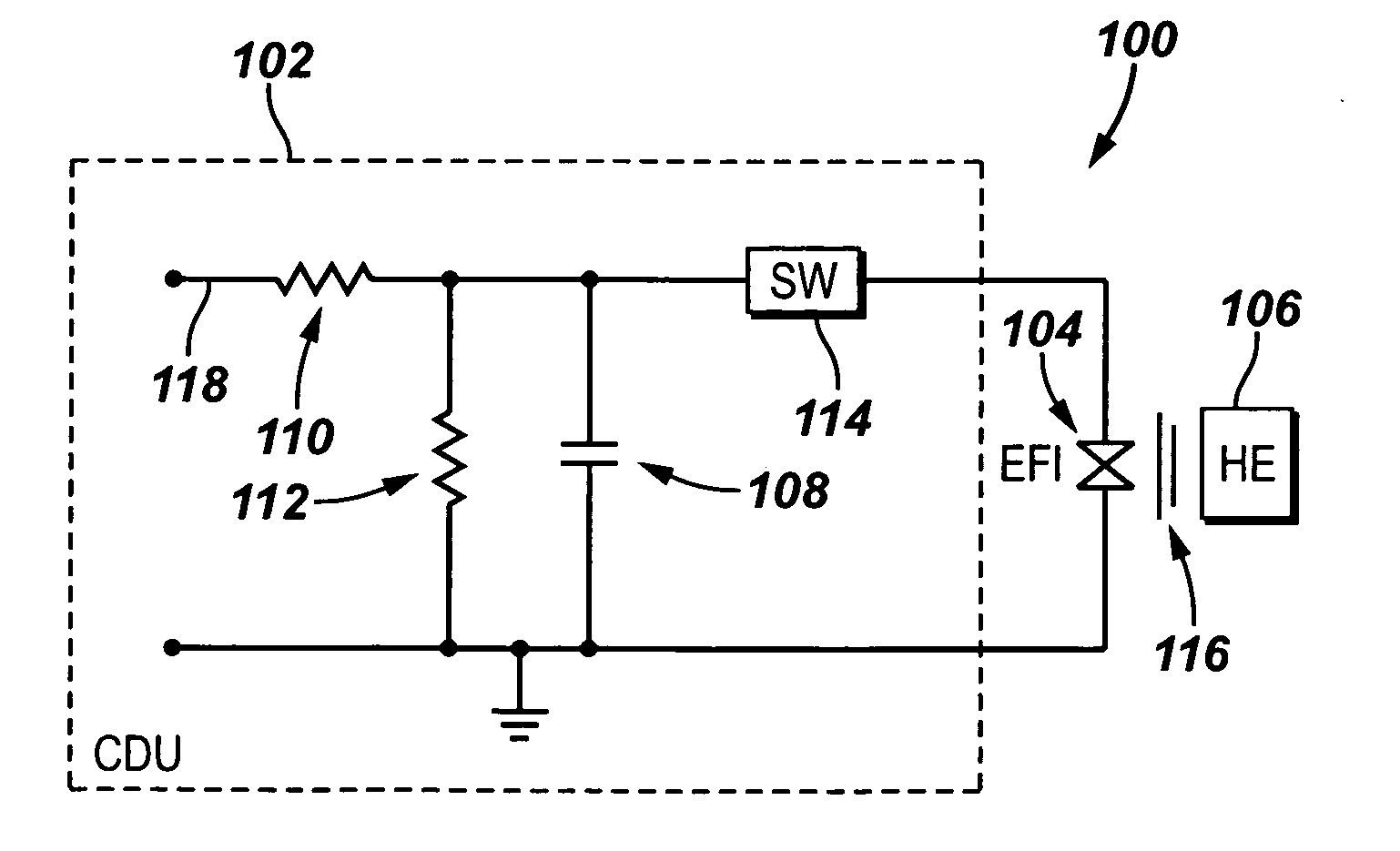
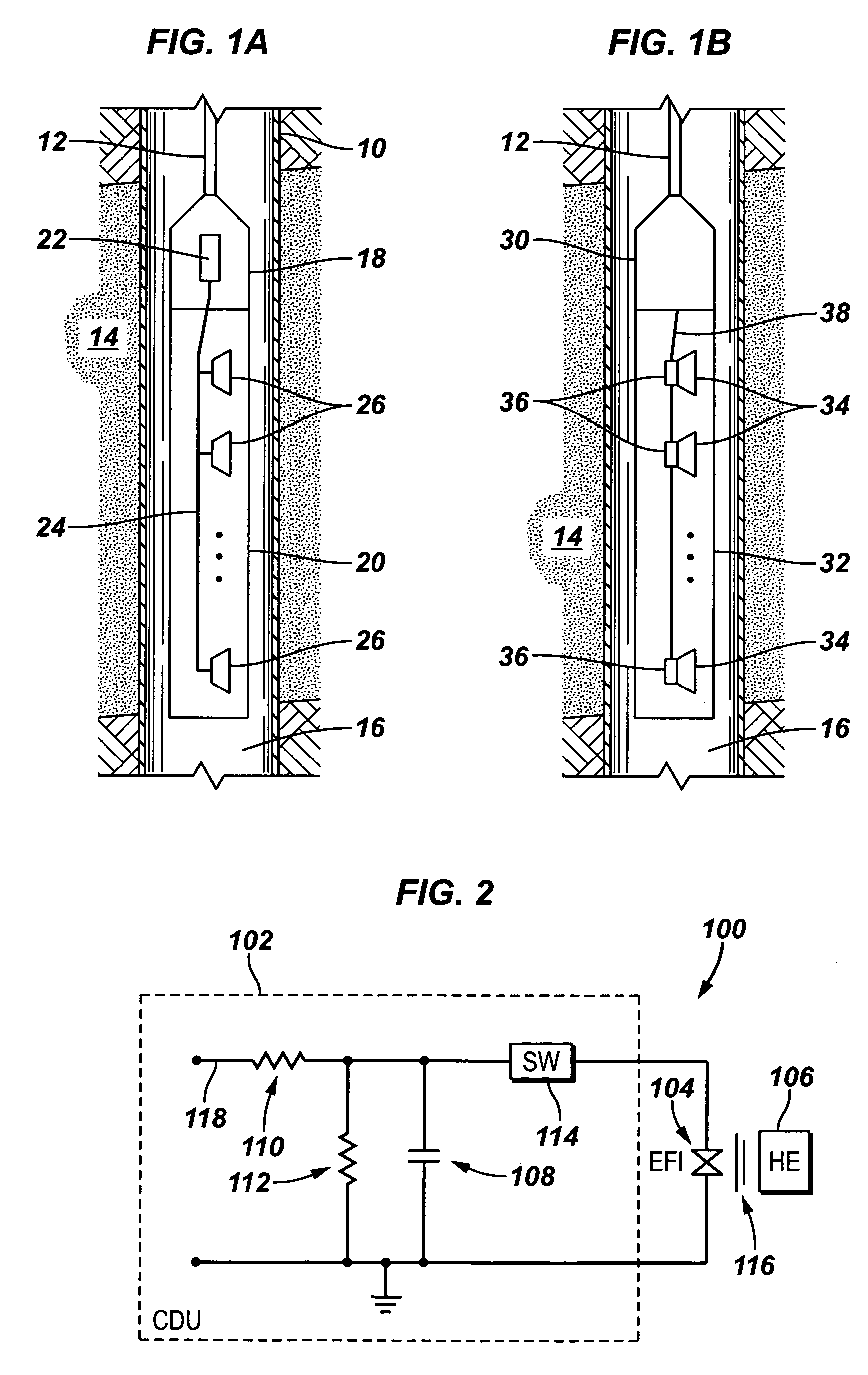
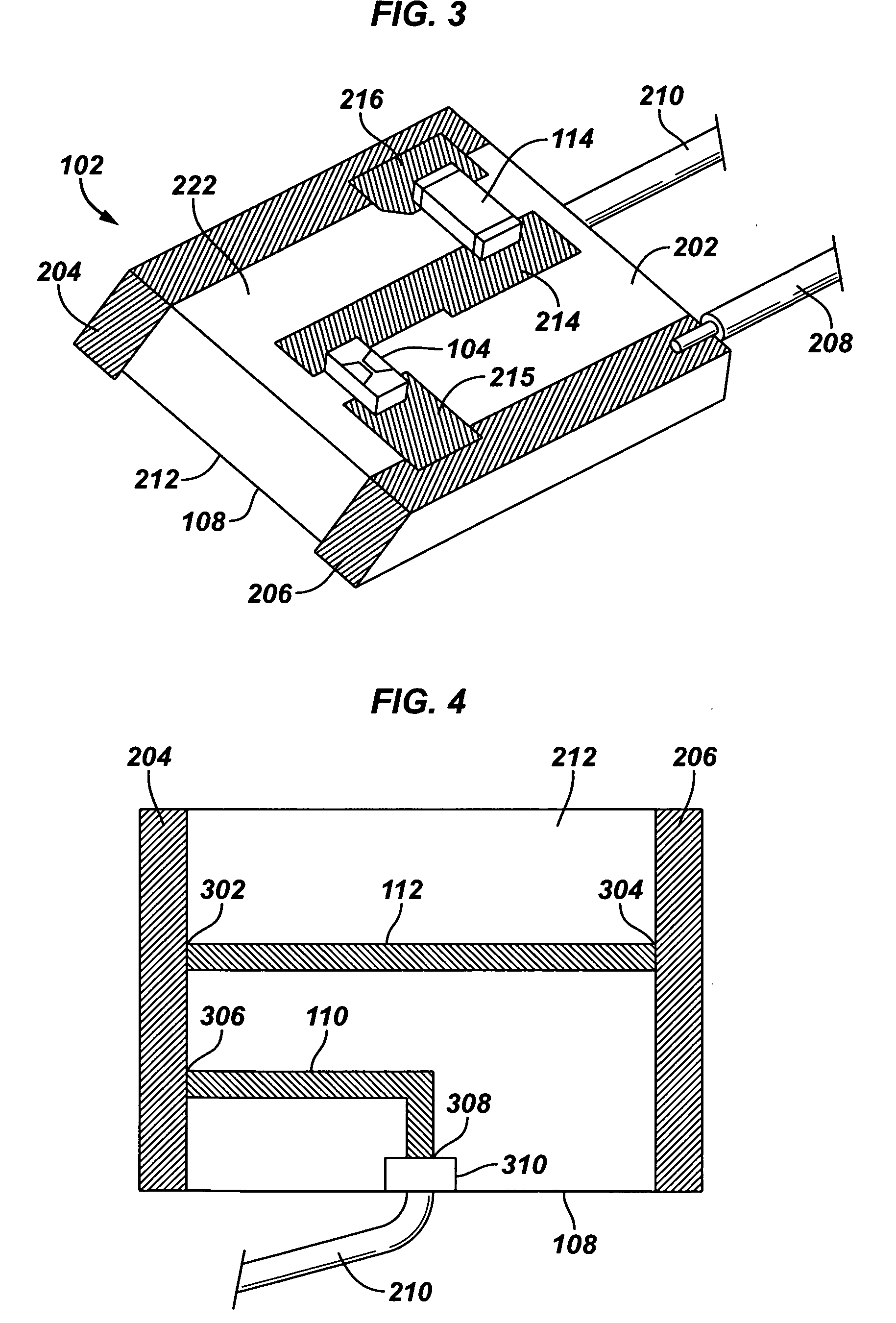
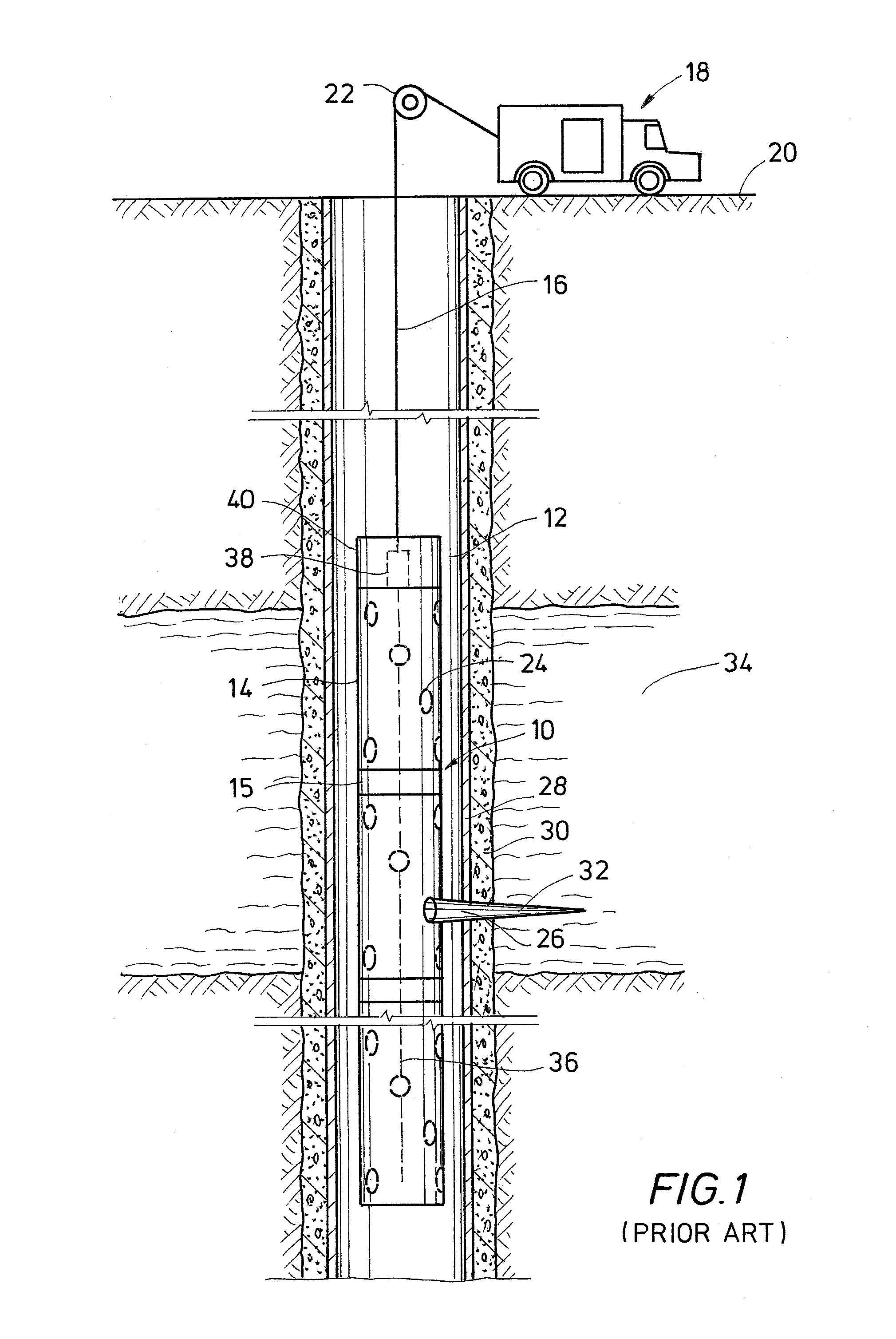
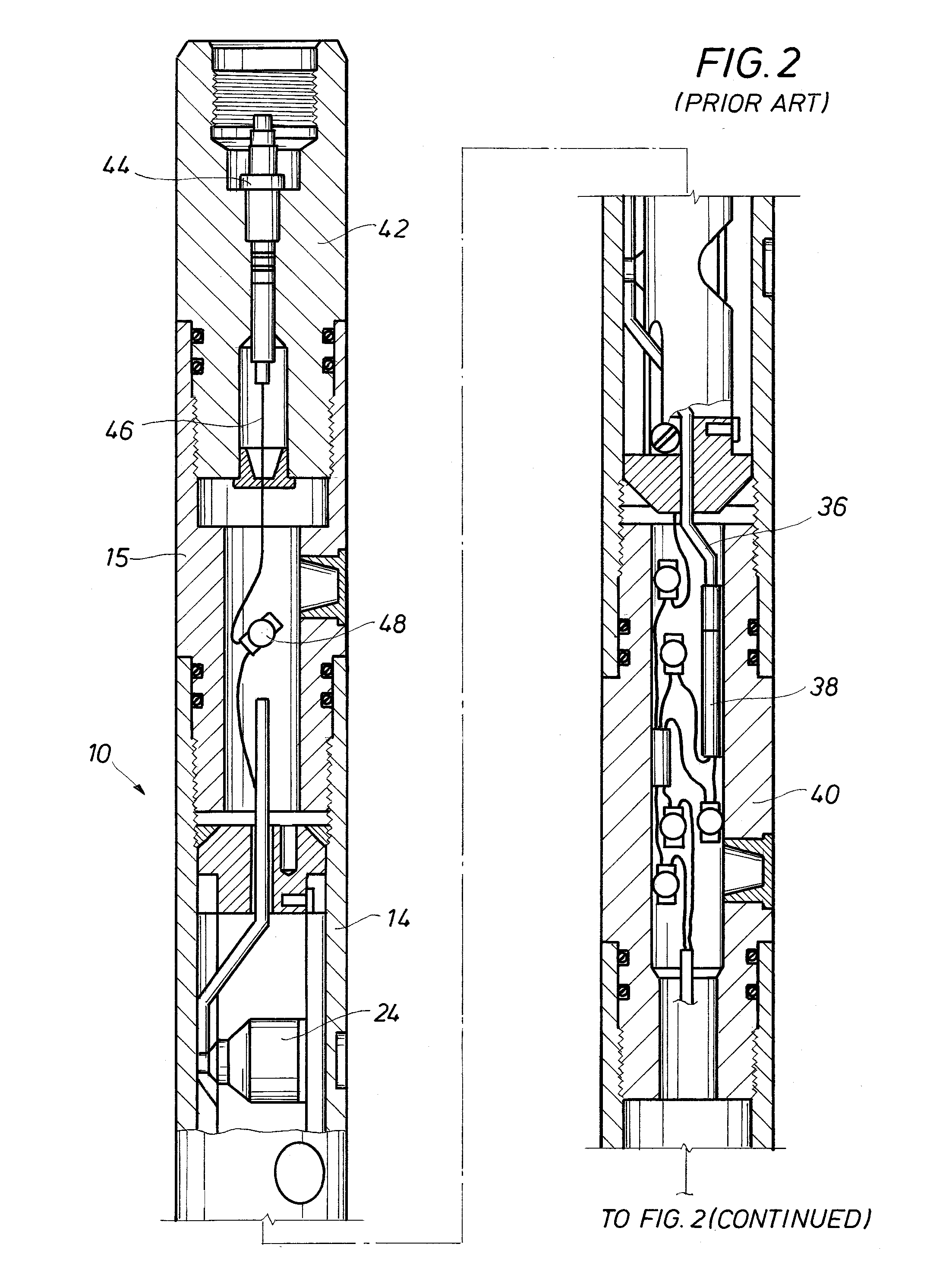
A detonator assembly is provided for use in oilfield operations to detonate an explosive downhole including a capacitor discharge unit and initiator electrically connected together to form a single unit. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract, which will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Connection cartridge for downhole string
A cartridge assembly for use with a perforating system having a contact terminal that connects to a perforating signal line when inserted into a receptacle end of a perforating gun. A detonator may be included in an end of the cartridge assembly for initiating a detonating cord in the perforating gun. The cartridge assembly is a modular unit that replaces the manual connections made when assembling a string of perforating guns. The cartridge assembly may optionally include a controller switch for controlling current flow through the cartridge assembly.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
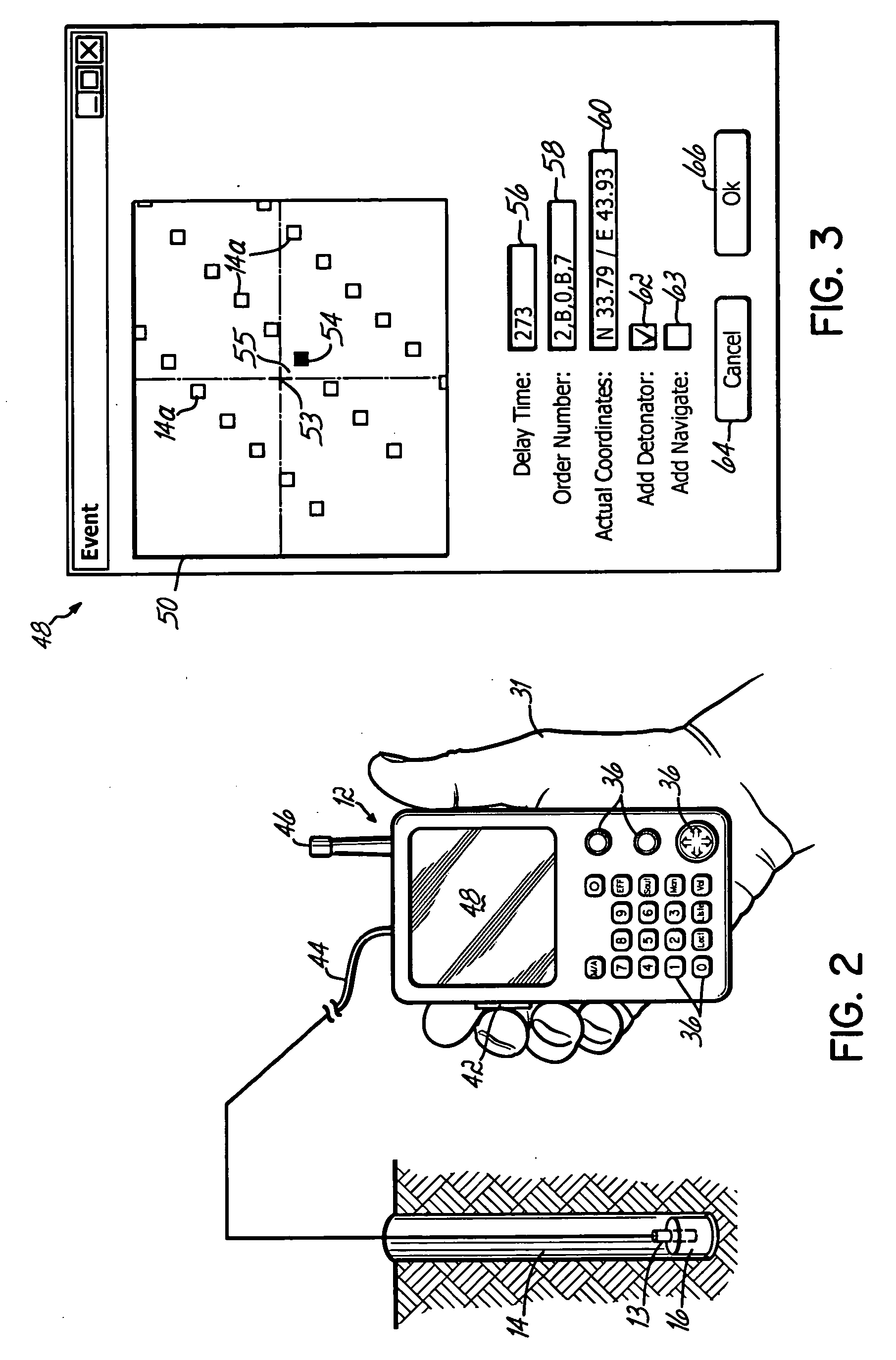
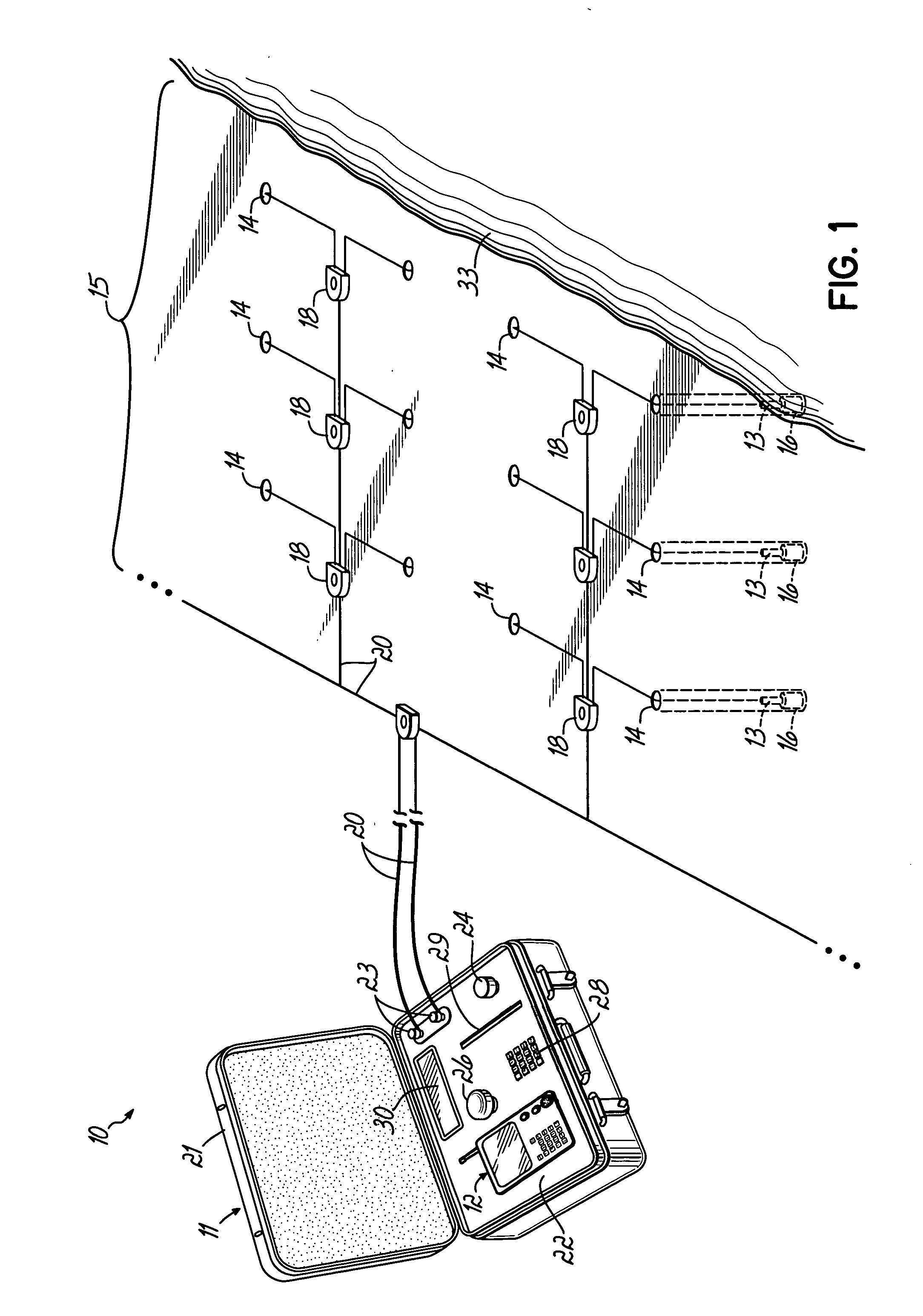
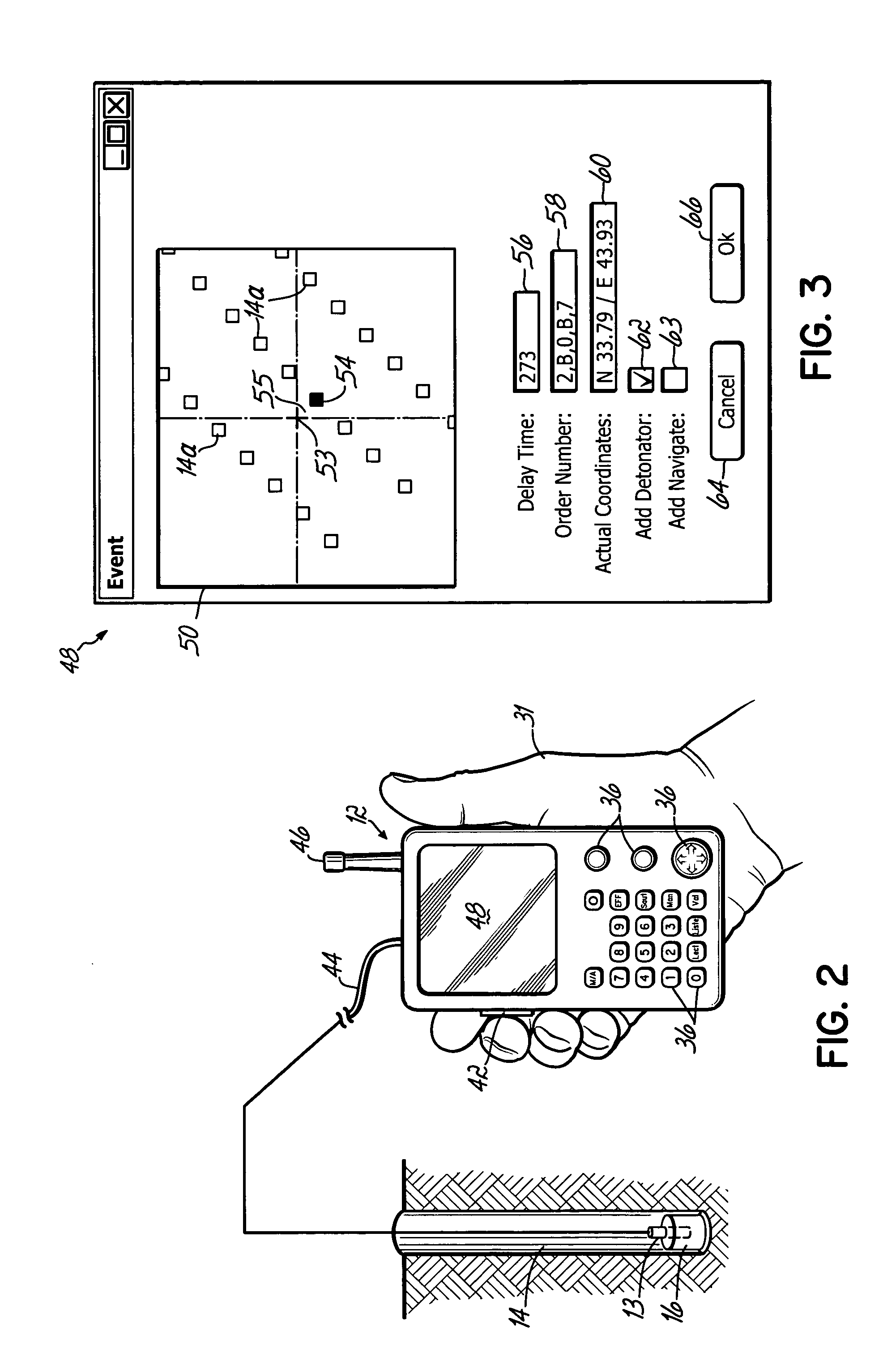
Positional blasting system
InactiveUS20050217525A1Easy to useAccurate locationBlasting cartridgesBlastingDetonatorLocation detection
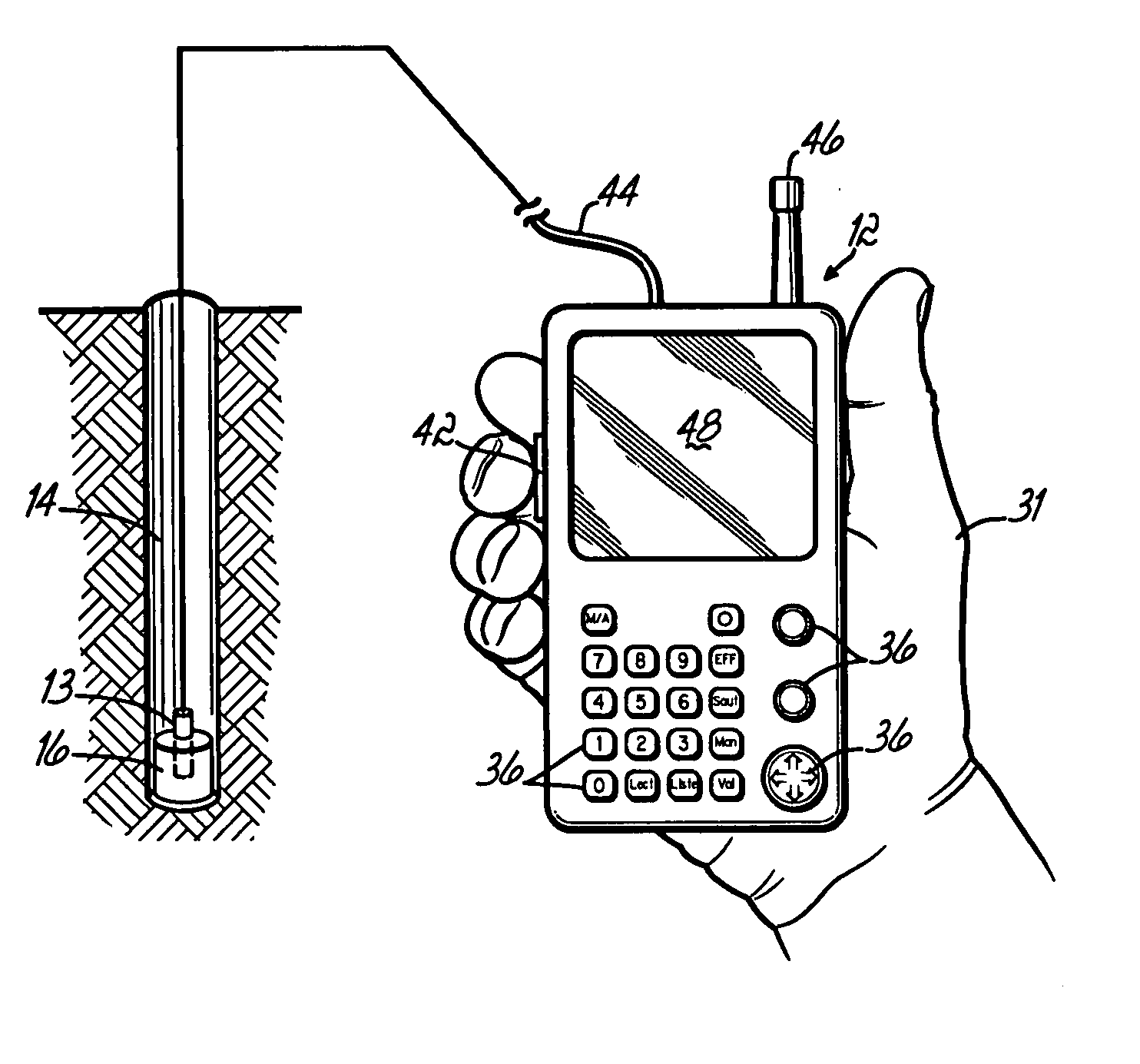
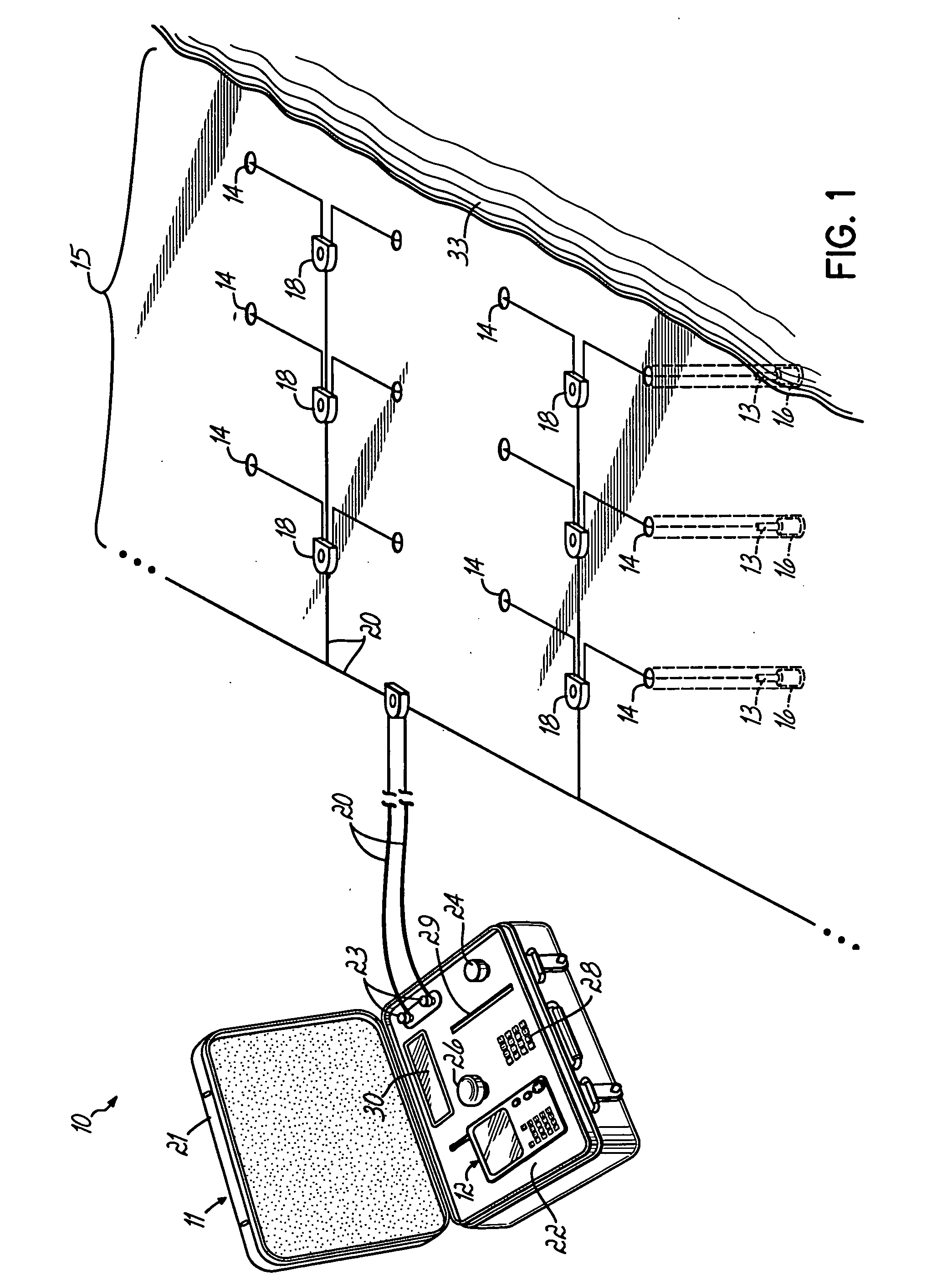
A blasting system facilitates the actuation of a plurality of programmable detonators according to a desired blasting pattern, to cause the discharge of a plurality of associated charges, by downloading to the detonators blasting information that can be automatically determined by a portable handheld unit that incorporates a positional detecting device, such as a GPS device. The blasting information for any given detonator can be determined by the handheld unit as a function of the distance and the direction of the movement of the unit to the detonator, and / or by the actual GPS location while at the site of the detonator. This automatic determination of blasting information, and particularly the delay times, based on the movement of the unit to the detonator, eliminates error prone human calculations of the delay times needed for multiple detonators at a blasting site. This simplifies the operations and procedures needed for achieving a desired blasting pattern, without sacrificing safety or quality.
Owner:DAVEY BICKFORD USA
Positional blasting system
A blasting system facilitates the actuation of a plurality of programmable detonators according to a desired blasting pattern, to cause the discharge of a plurality of associated charges, by downloading to the detonators blasting information that can be automatically determined by a portable handheld unit that incorporates a positional detecting device, such as a GPS device. The blasting information for any given detonator can be determined by the handheld unit as a function of the distance and the direction of the movement of the unit to the detonator, and / or by the actual GPS location while at the site of the detonator. This automatic determination of blasting information, and particularly the delay times, based on the movement of the unit to the detonator, eliminates error prone human calculations of the delay times needed for multiple detonators at a blasting site. This simplifies the operations and procedures needed for achieving a desired blasting pattern, without sacrificing safety or quality.
Owner:DAVEY BICKFORD USA
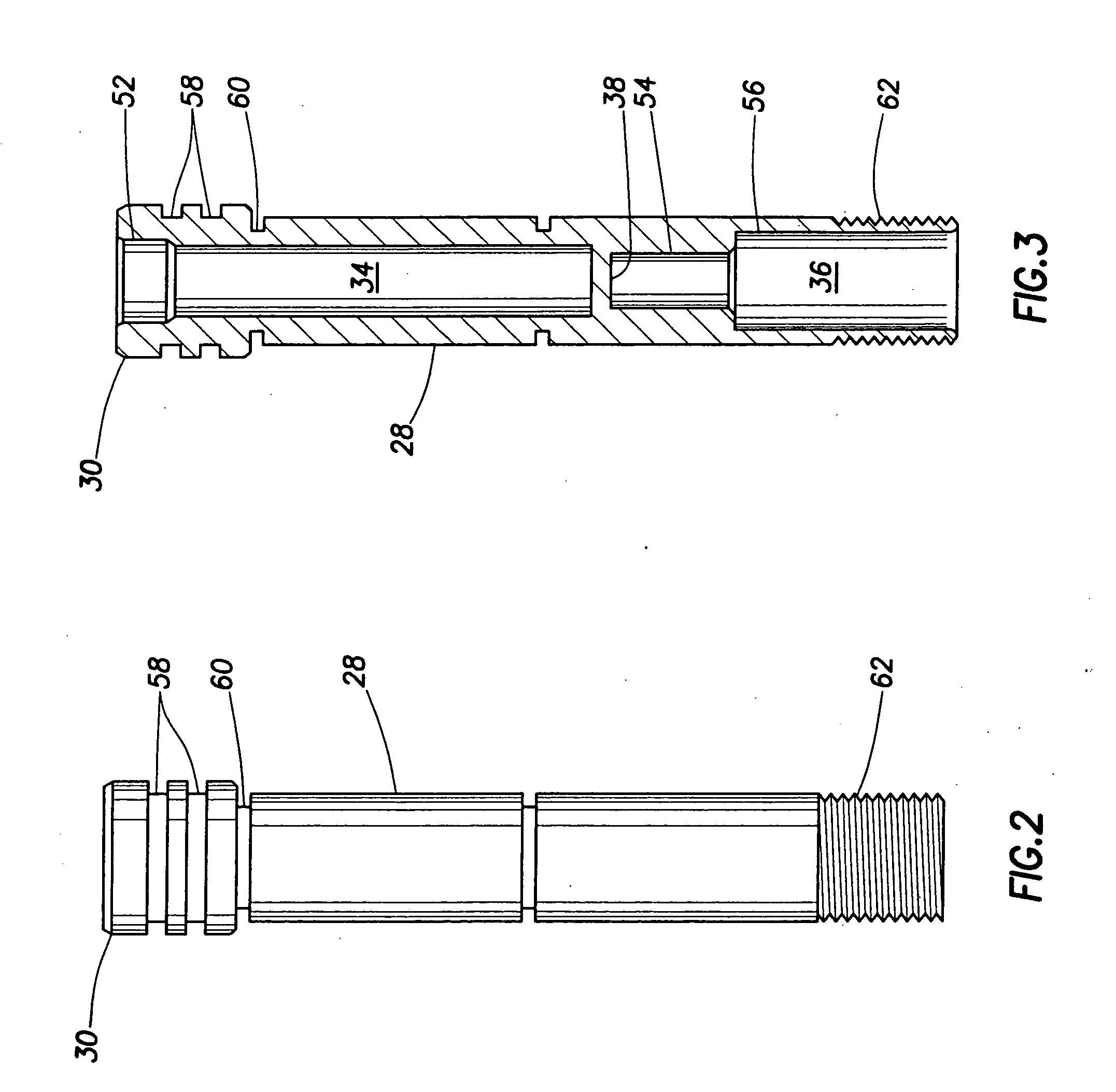
Electromechanical assembly for connecting a series of guns used in the perforation of wells
ActiveUS8875787B2Big economyImprove securityFluid removalDrilling machines and methodsDetonatorCharge carrier
An electromechanical assembly for a series of guns used in the perforation of petroleum producing wells. Each gun is a cylindrical housing having a charge-carrier loaded with explosive charges in contact with a detonating cord which contacts an electronically activated detonator. The guns are joined by intermediary joints and terminate in a bottom sub on its lower end and a firing head at its upper end. The charge-carrier of each gun is detonated, beginning with the bottommost gun. Insulating end plates are on the lower and upper ends of the carrier for centering and anchoring the charge-carriers. An electrical wire runs from a retractable contact pin in each carrier, through the intermediary joint which has a changeover switch sensitive to the high pressures produced by the explosion in the carrier located in the gun immediately beneath it, rupturing a mechanical fuse and allowing the switch to close.
Owner:TASSAROLI
Forty millimeter caliber exercise bullet
ActiveUS20120180685A1Safely securedAvoid failureAmmunition projectilesTraining ammunitionDetonatorCentrifugal force
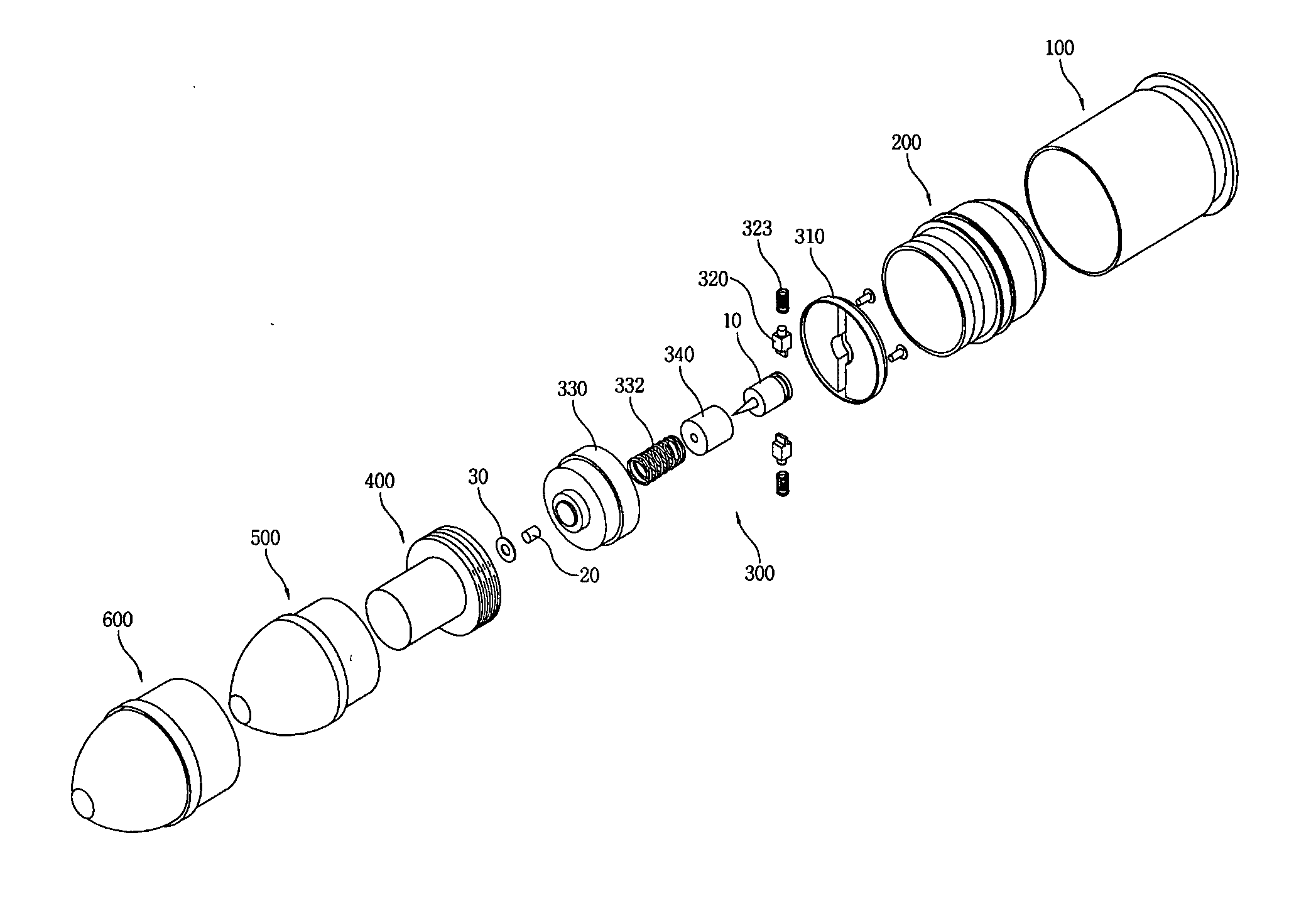
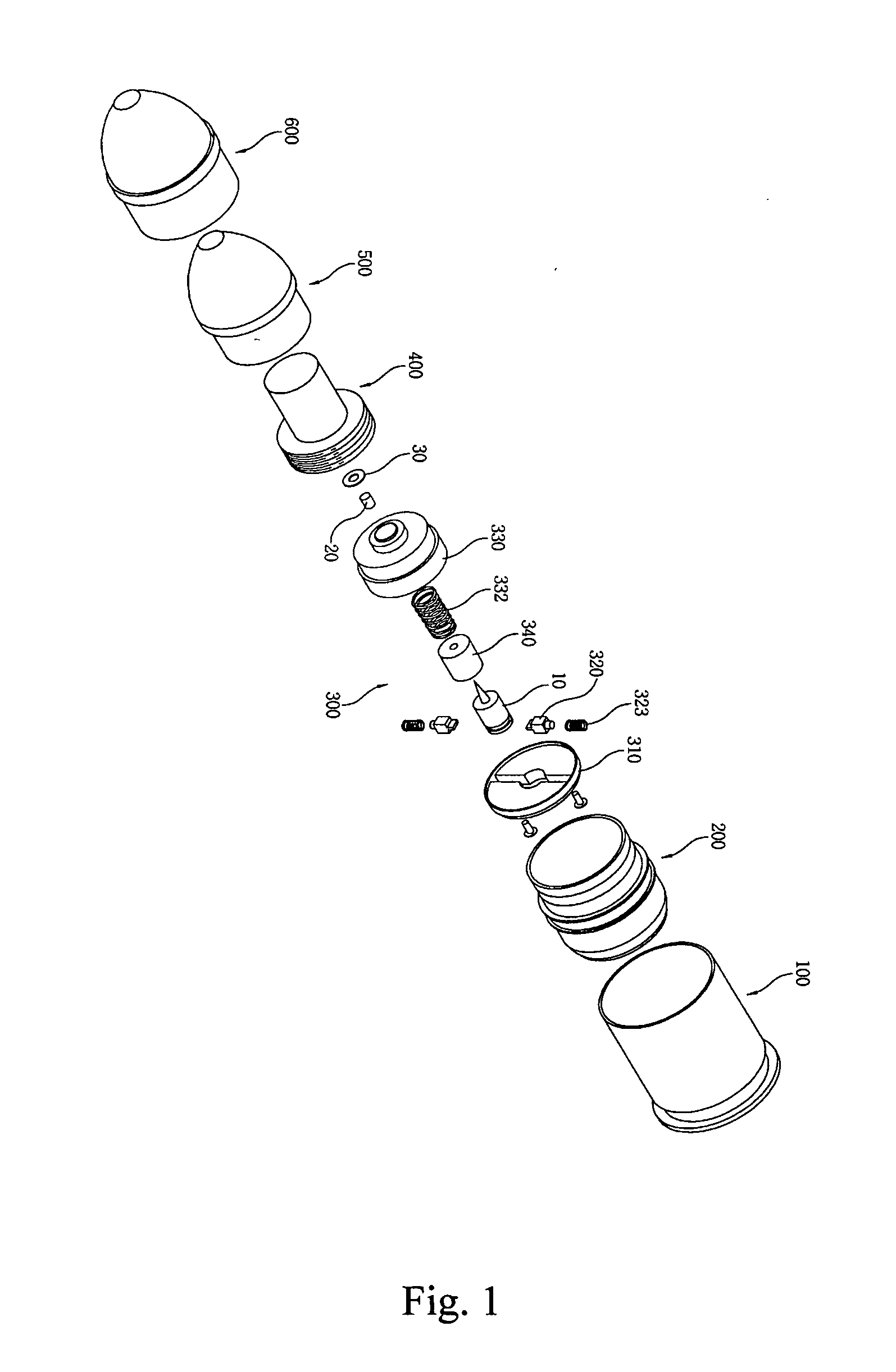
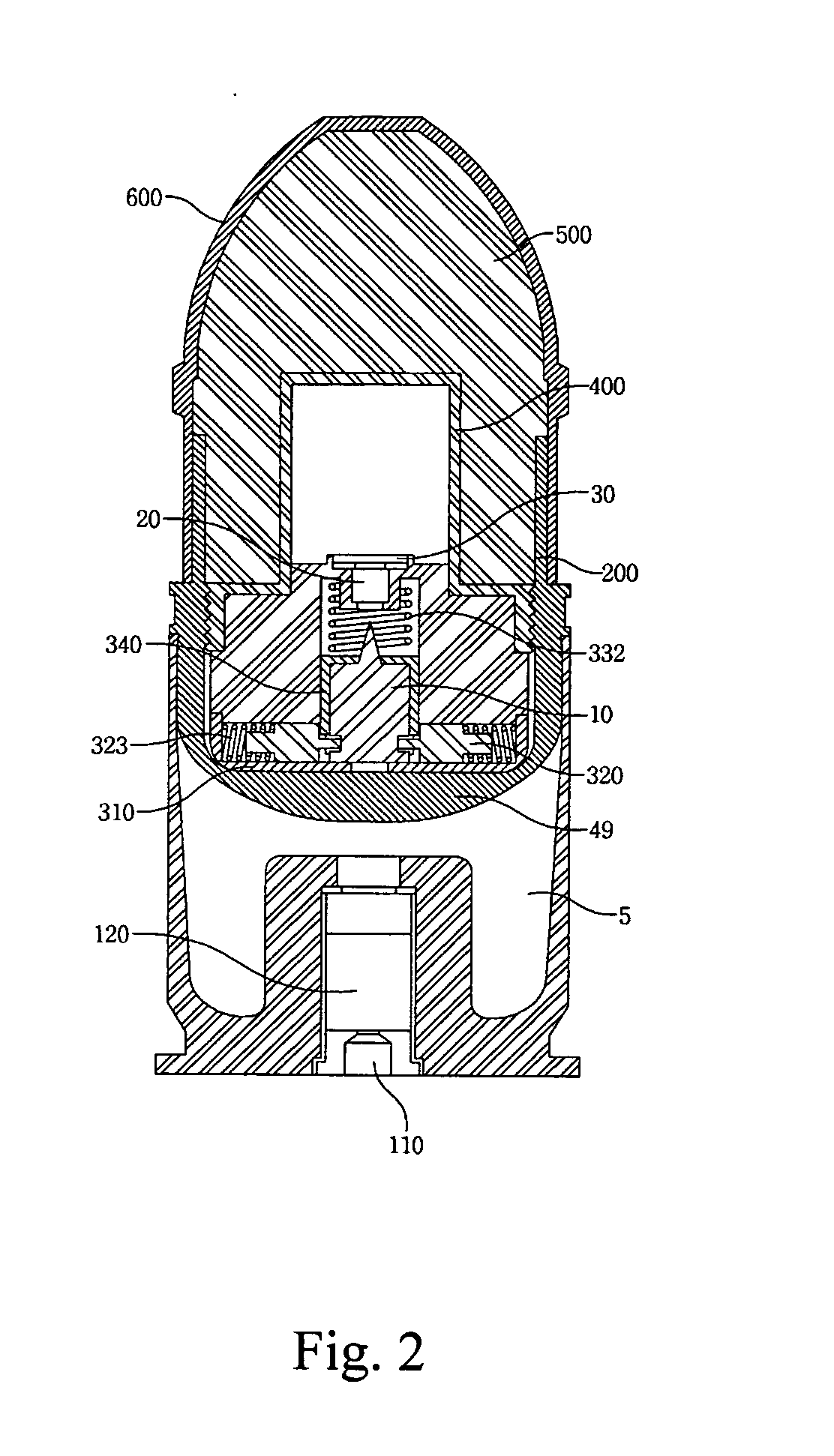
A forty millimeter caliber exercise bullet has improved for properly exploding on a target, and securely maintaining the unloaded status during ordinary time. The improved exercise bullet comprising that; a skirt (200), a striking pin (10), a safety device assembly (300) consisting a detent cover (310) with a central mounting groove (311) and a pair of mounting grooves (312), a detent (320) for retaining the striking pin (10) by engaging or disengaging into the circumferential groove (11) by springs (323), a detonator cap (330) forming a hollow pocket (331) to insert a detonator trigger (20), a washer (30), and a press-spring (332) for pressing a guiding cap (340), an explosion pipe (400), a smoke shell (500), and an ogive (600). When the bullet is fired, the rotation of bullet generates centrifugal force to slide the retainer outward for disengaging the circumferential groove, then the striking pin moves upward to impact the detonator trigger when it hit on the target.
Owner:C N O TECH KOREA
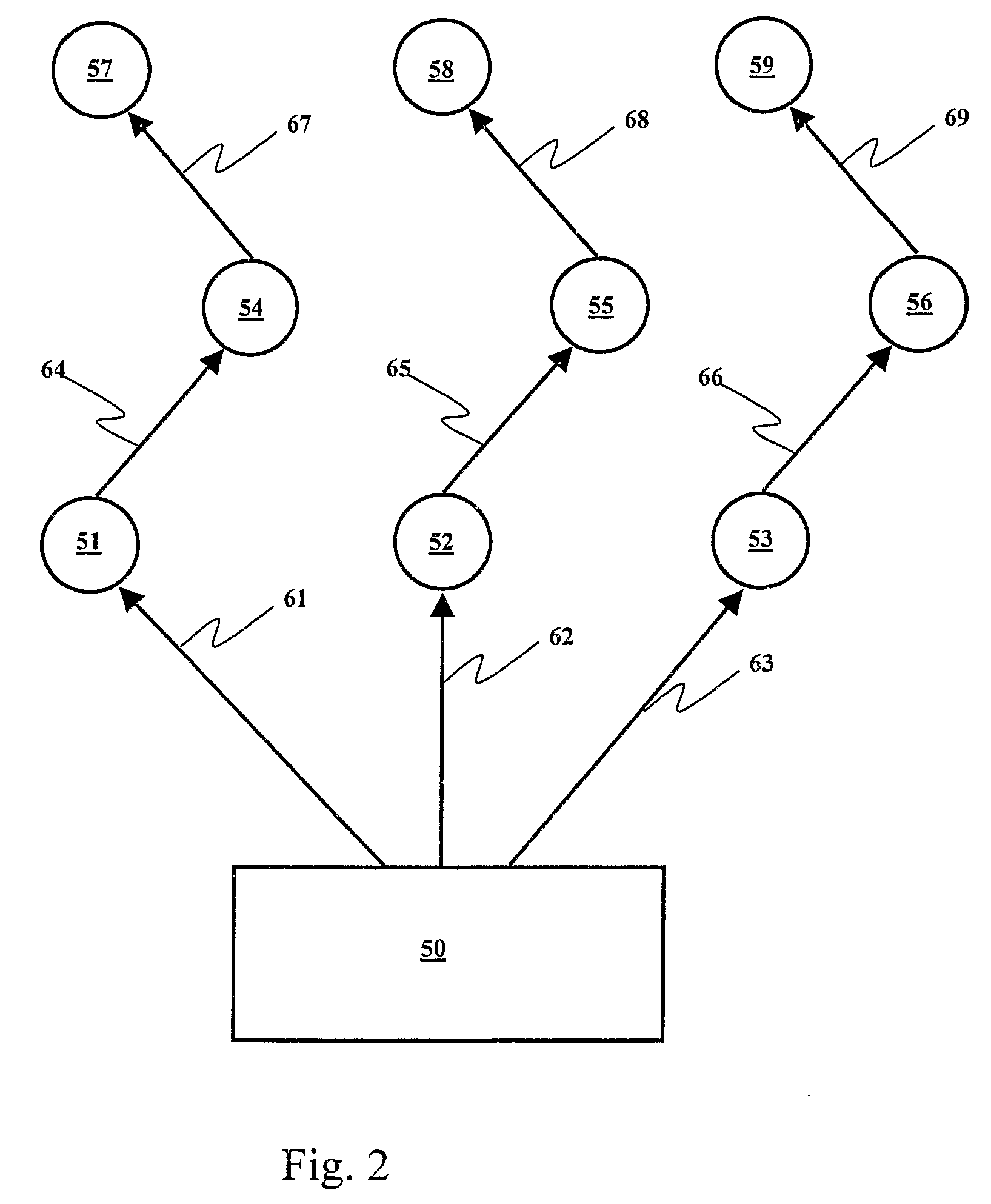
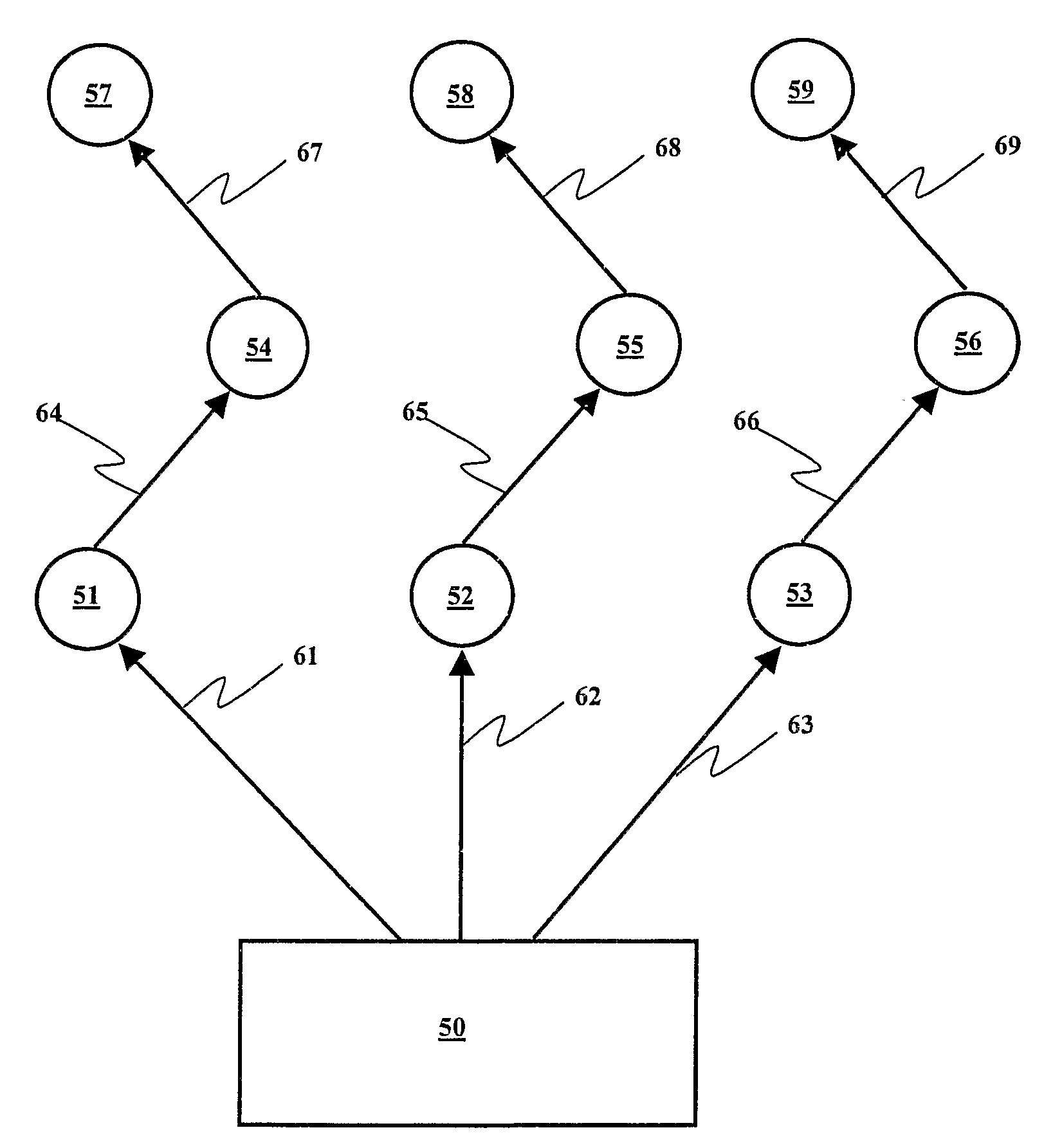
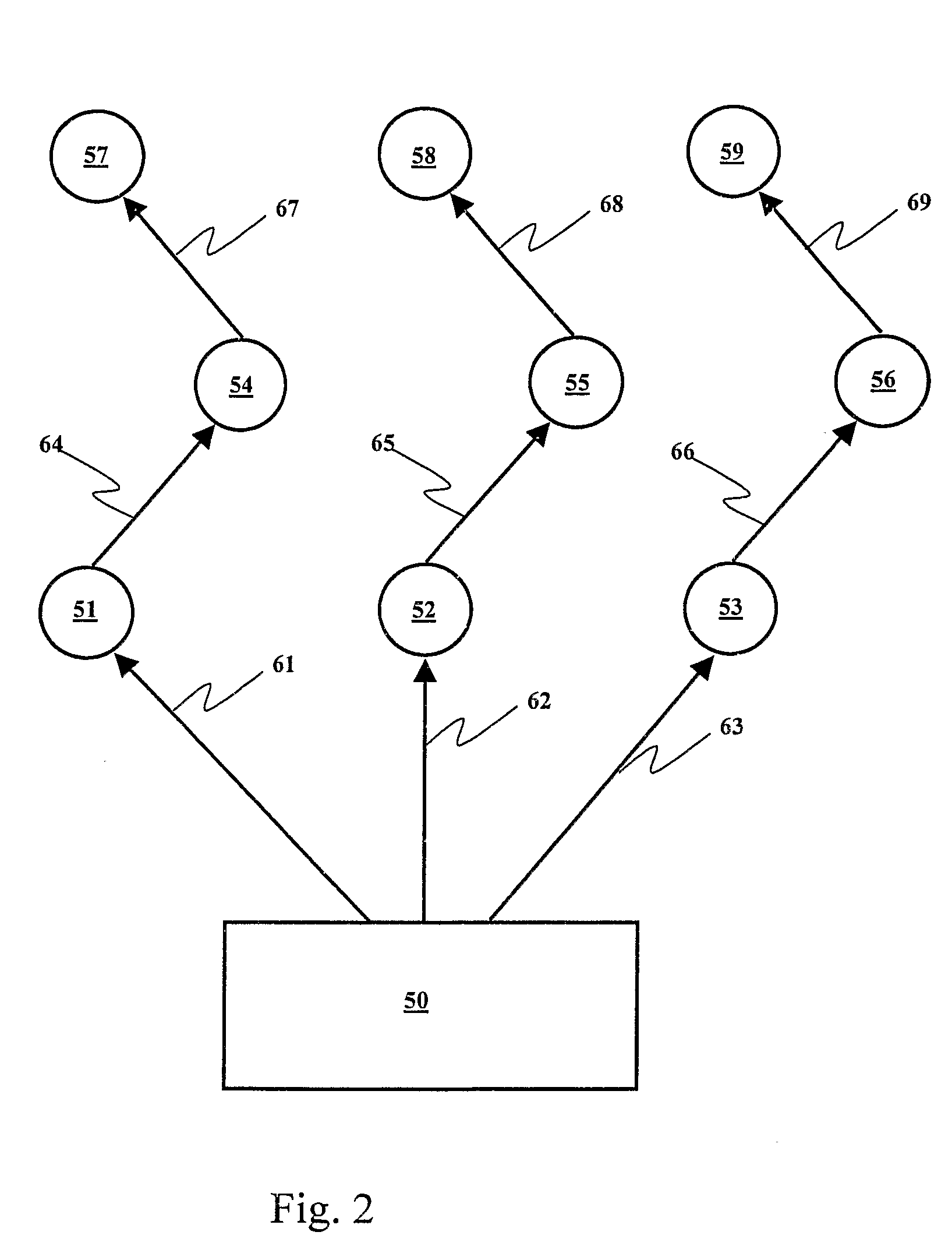
Wireless detonator assemblies, and corresponding networks
Wireless detonator assemblies (51-59) in use, form a cross-communicating network of wireless “detonator assemblies, such that communication of each wireless detonator assembly (57-59) with an associated blasting machine (50) can occur either directly, or via relay of signals (61-69) between other wireless detonator assemblies (51-56) in the network. Wireless detonator assemblies (51-59) can disseminate information (such as status information, identity information, firing codes, delay times and environmental conditions) among all of the wireless detonator assemblies in the network, while compensating for signal transmission relay delays at nodes in the network, thereby enabling the wireless detonator assemblies to detonate the explosive charges in accordance with the delay times. Various wireless detonator assemblies and corresponding blasting apparatus are disclosed and claimed. Methods of blasting using the wireless detonator assemblies and blasting apparatus are also disclosed and claimed.
Owner:ORICA EXPLOSIVES TECH PTY LTD
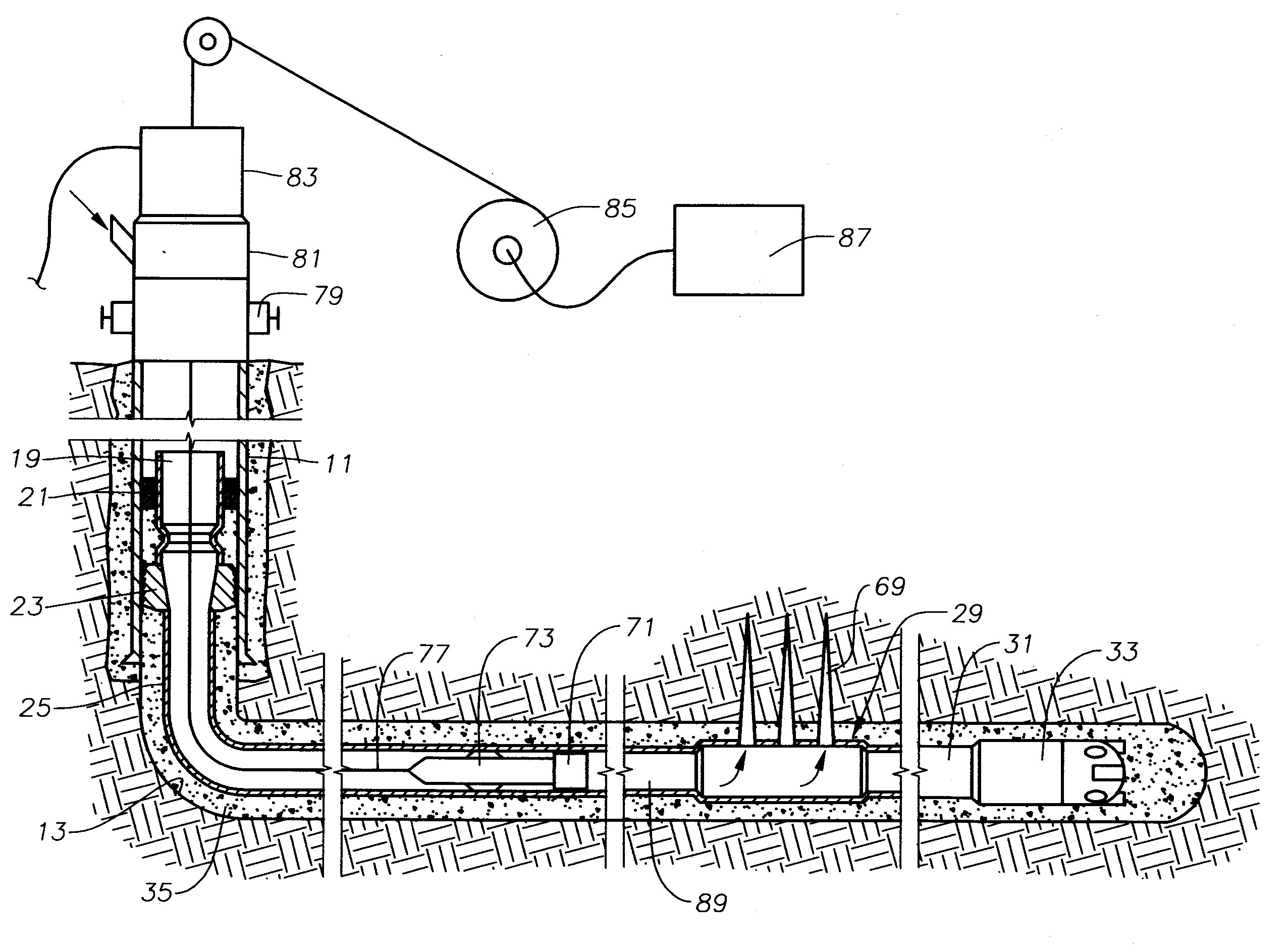
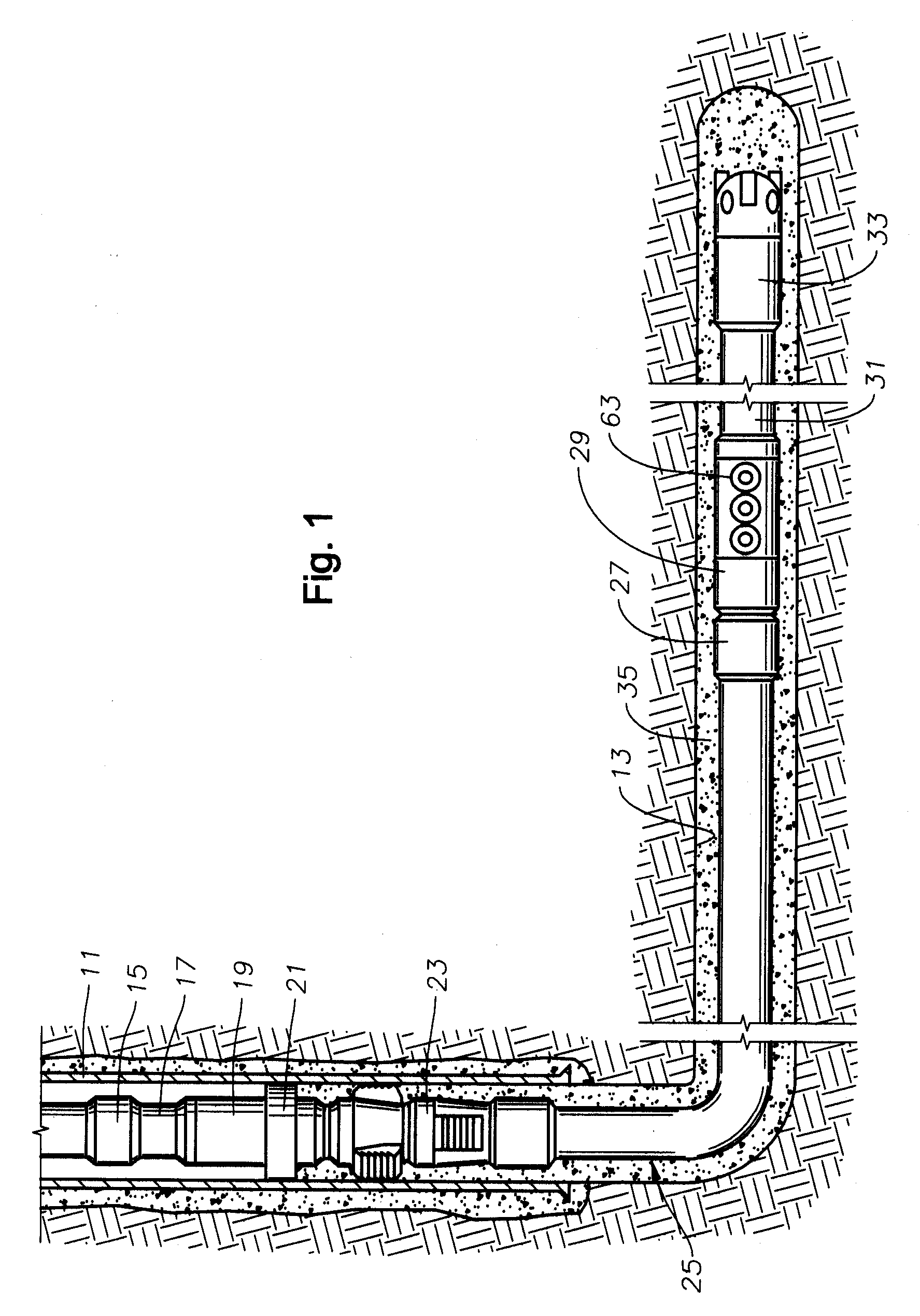
Wellbore gun perforating system and method
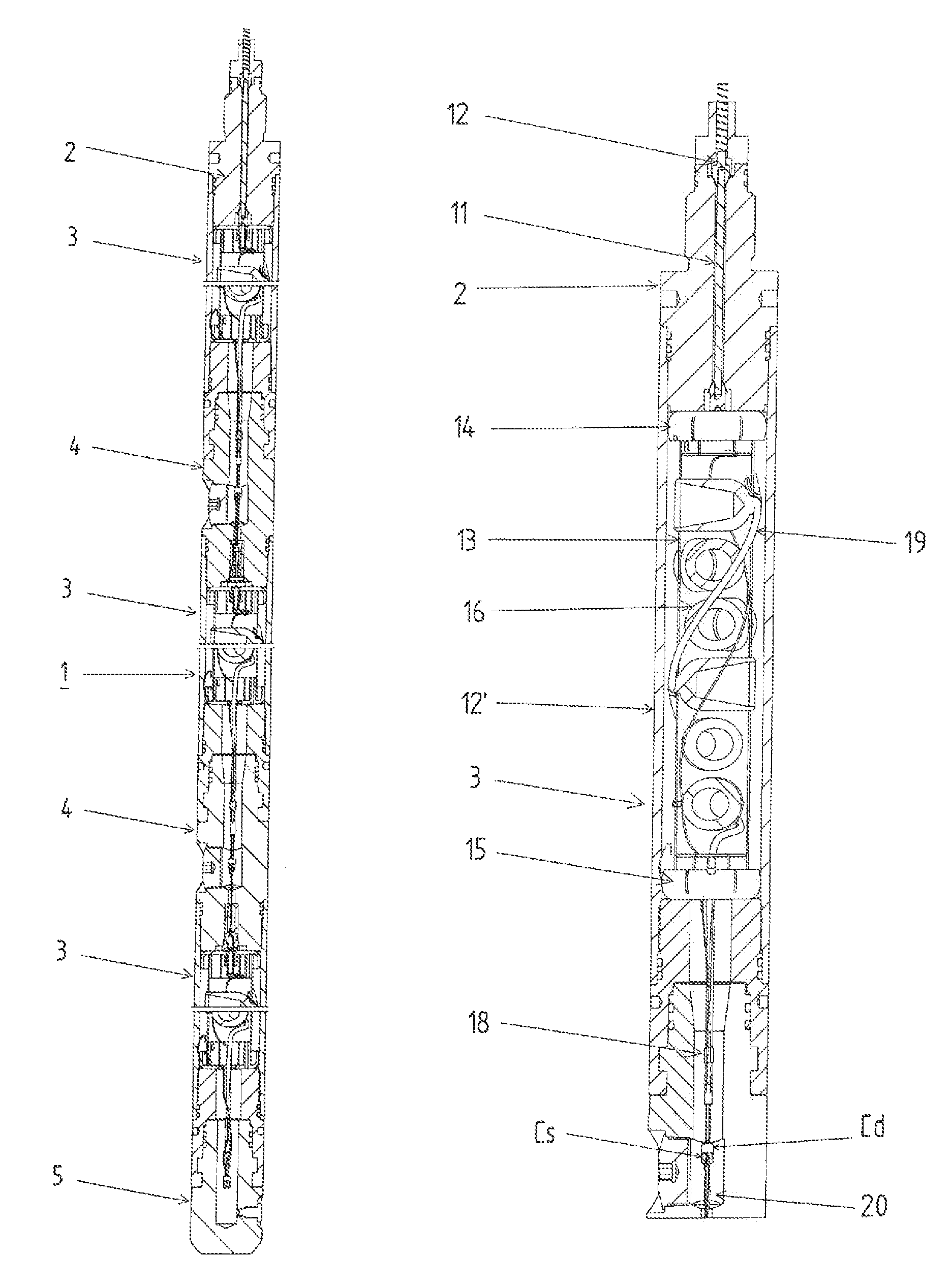
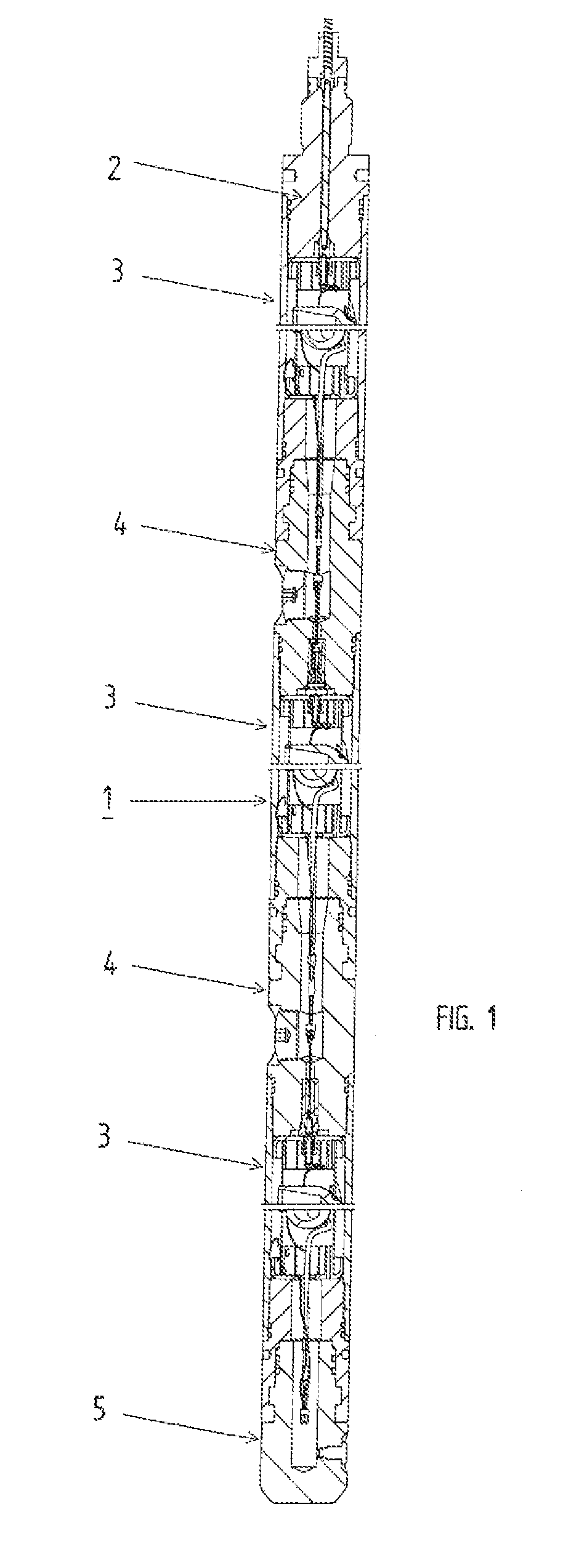
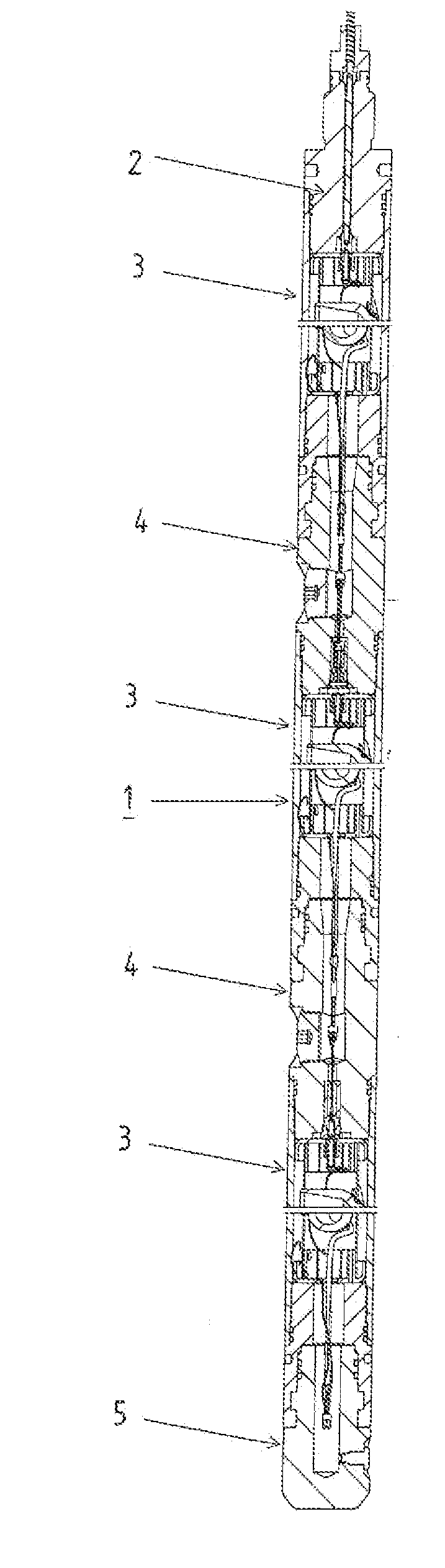
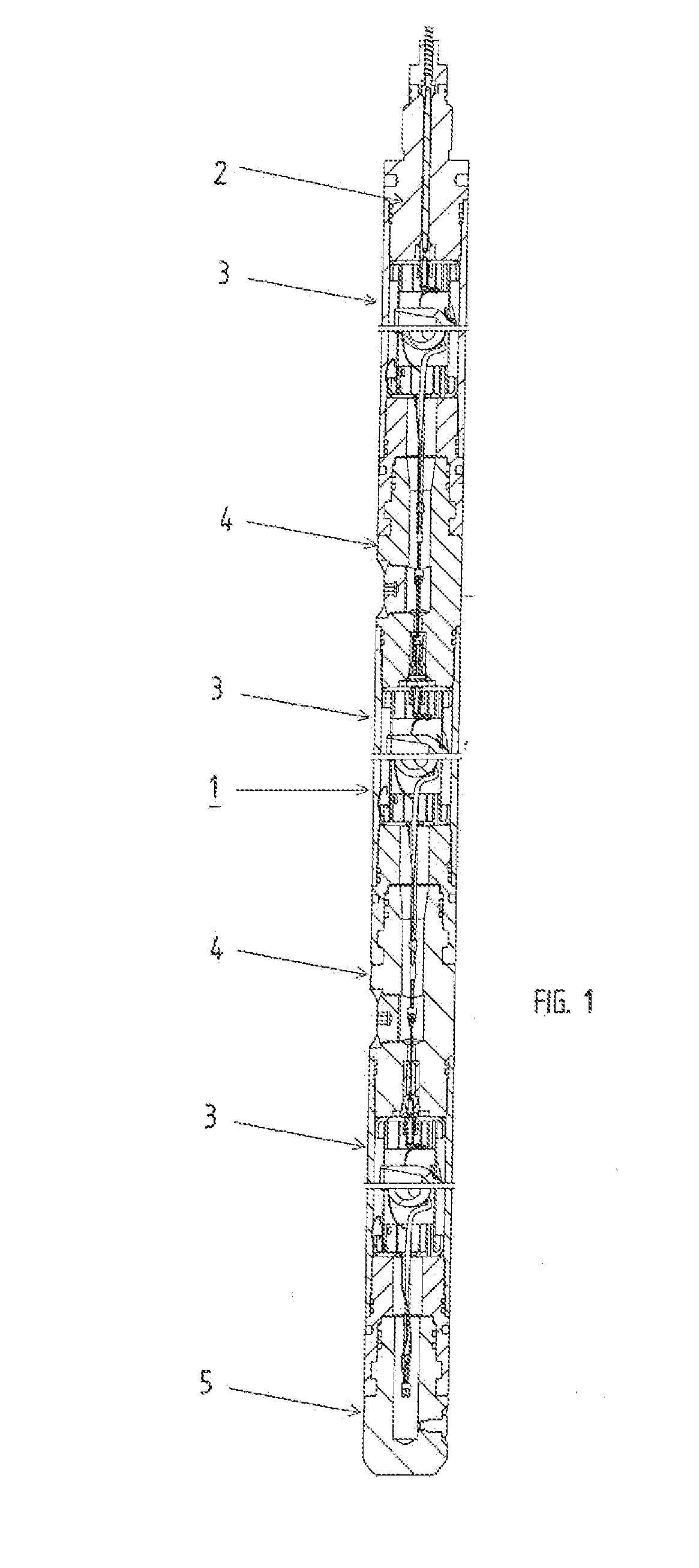
A wellbore perforating system and method with reliable and safer connections in a perforating gun assembly is disclosed. The system / method includes a gun string assembly (GSA) deployed in a wellbore with multiple perforating guns attached to plural switch subs. The perforating guns are pre-wired with a cable having multi conductors; the multi conductors are connected to electrical ring contacts on either end of the perforating guns. The switch subs are configured with electrical contacts that are attached to the electrical contacts of the perforating guns without the need for manual electrical connections and assembly in the field of operations. The system further includes detonating with a detonator that is positioned upstream of the perforating gun. The detonator is wired to a switch that is positioned downstream of the perforating gun.
Owner:WELLS FARGO BANK NAT ASSOC +1
Electric and Ballistic Connection Through A Field Joint
ActiveUS20110024116A1Engagement/disengagement of coupling partsTwo pole connectionsDetonatorDetonation
A perforating system having annular connectors for attachment between adjacent perforating guns and connectors. The connectors include male and female connectors with respective outer and inner contact surfaces. The connectors also include attachment for electrical detonators and / or booster charges for transferring ballistic detonations between the perforating gun and connector sub.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Connection cartridge for downhole string
A cartridge assembly for use with a perforating system having a contact terminal that connects to a perforating signal line when inserted into a receptacle end of a perforating gun. A detonator may be included in an end of the cartridge assembly for initiating a detonating cord in the perforating gun. The cartridge assembly is a modular unit that replaces the manual connections made when assembling a string of perforating guns. The cartridge assembly may optionally include a controller switch for controlling current flow through the cartridge assembly.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Using a Combination of a Perforating Gun with an Inflatable to Complete Multiple Zones in a Single Trip
A one trip system for perforating and fracking multiple intervals uses a releasable barrier. The barrier can be an inflatable. A pressure booster system is associated with the BHA so that the existing hydrostatic pressure is boosted when the gun or portions thereof are fired. After firing in one interval, the BHA is raised and the barrier is redeployed and the pattern repeats. Instruments allow sensing the conditions in the interval for optimal placement of the gun therein and for monitoring flow, pressure and formation conditions during the fracturing. Circulation between gun firings cleans up the hole. If run in on wireline a water saving tool can be associated with the BHA to rapidly position it where desired. A multitude of perforation charges mounted in the BHA can be selectively fired by selected corresponding detonator based on a predetermined sequence or surface telemetry command.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
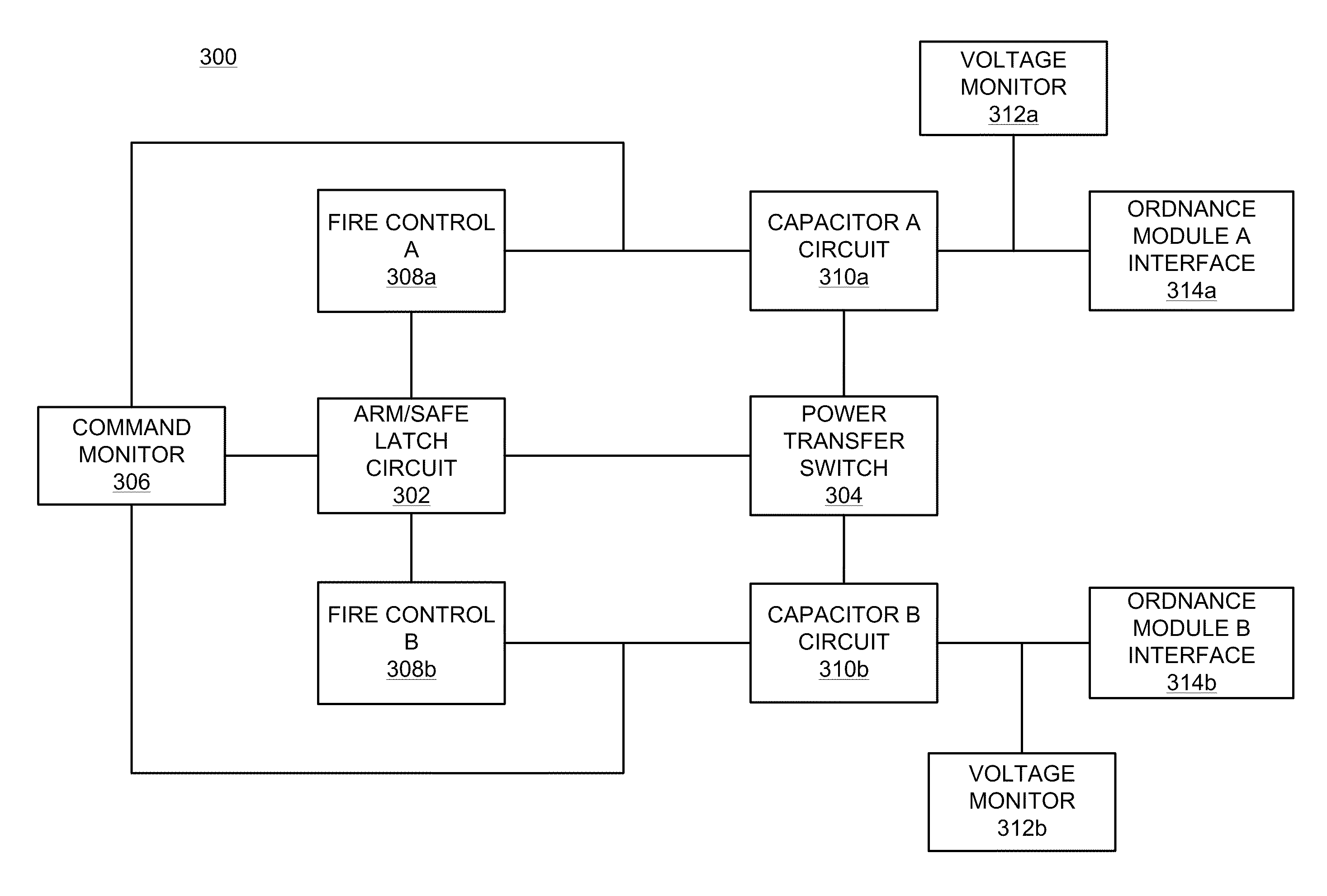
Ordnance firing system
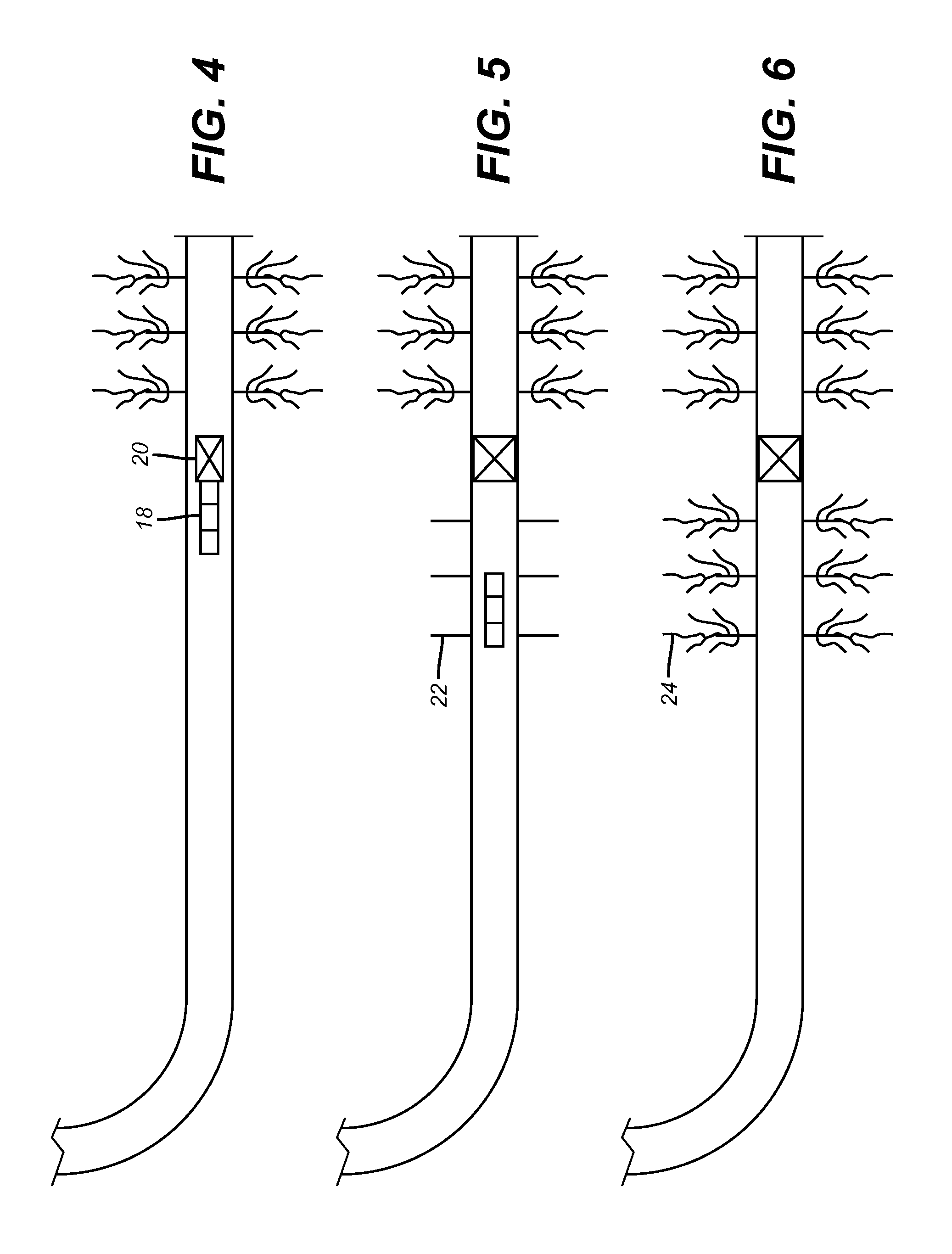
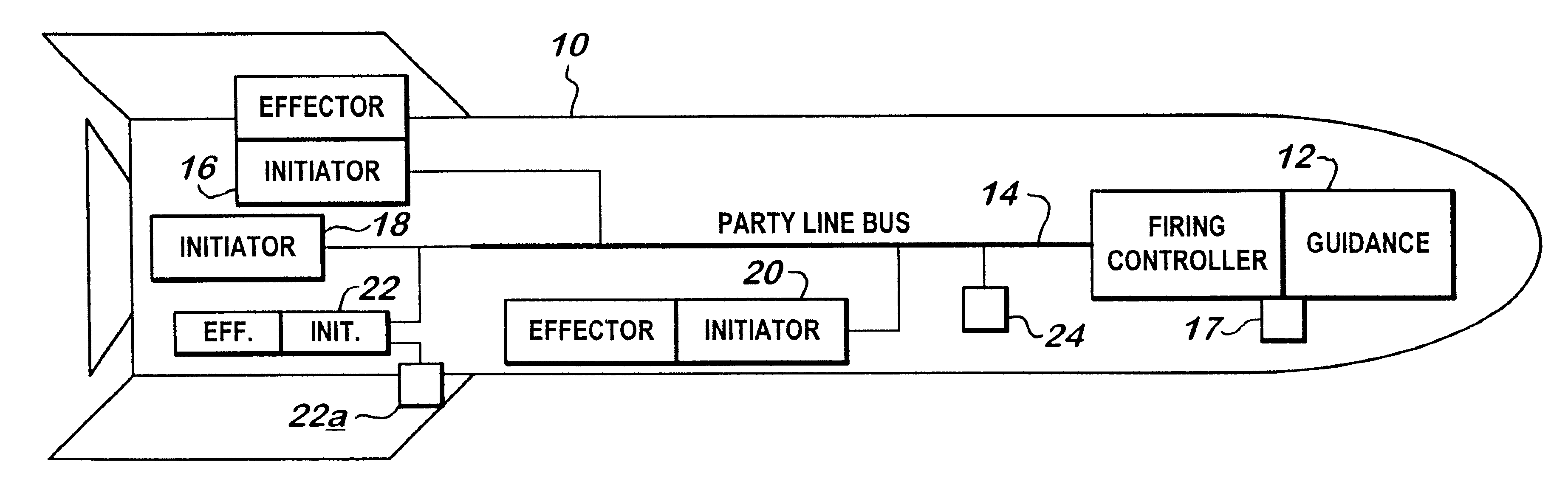
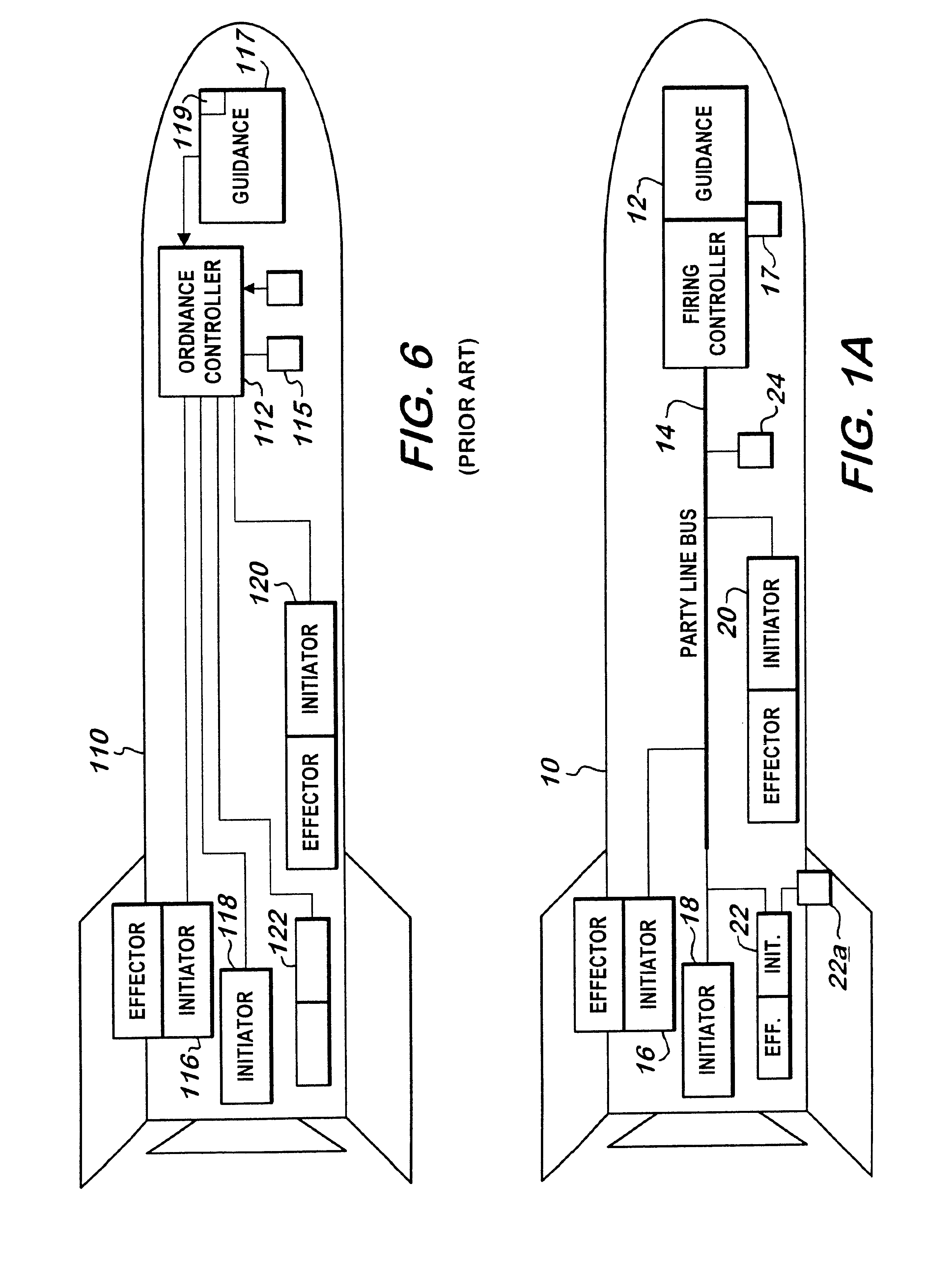
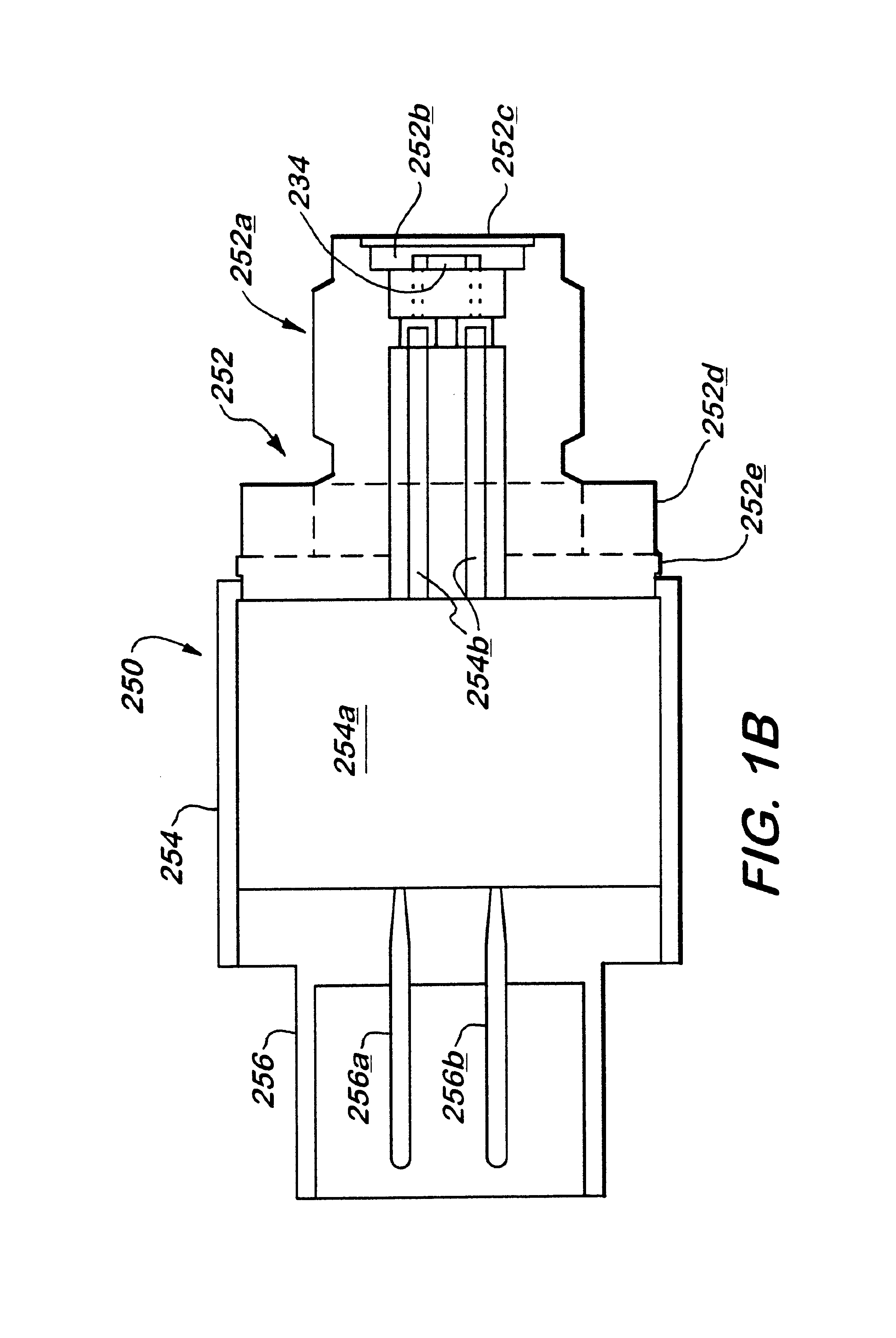
An ordnance system of the present invention may include or feature any one or more of: a control unit, one or more effectors (detonators, initiators, shaped charges and the like), and a two-, three- or four-wire communication bus between the control unit and the effectors; an addressable system in which all the effectors can be connected to the same communication bus and the control unit can issue coded signals on the bus addressed to a specific effector; inductive coupling between the effectors and the communication bus; and a multi-voltage level communication system in which communication signals are carried at a first voltage and arming signals are provided at a second, higher voltage. Other features may include two-way communication between effectors and the control unit and the de-centralization of firing control so that the control unit does not have exclusive control over whether the effectors function. As a result, the individual effectors possess decision-making ability and, for purposes of this invention, may be referred to as "intelligent" effectors. To participate in the decision-making process, effectors of this invention may be equipped with sensors or other diagnostic circuitry whose condition is checked for satisfactory output before functioning is permitted to occur.
Owner:ENSIGN BICKFORD AEROSPACE & DEFENSE
Perforating gun assembly and method for creating perforation cavities
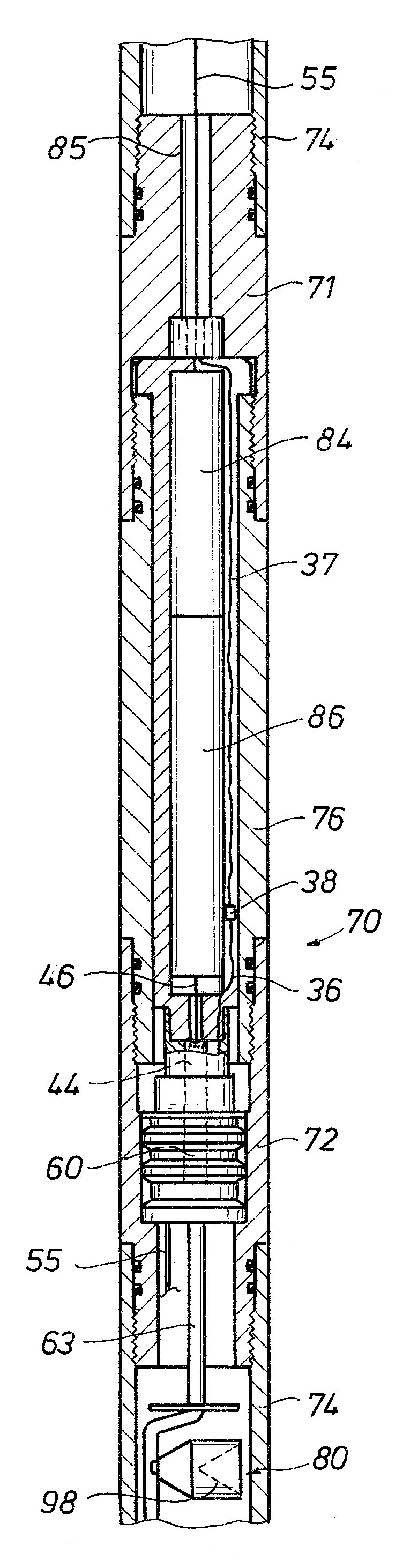
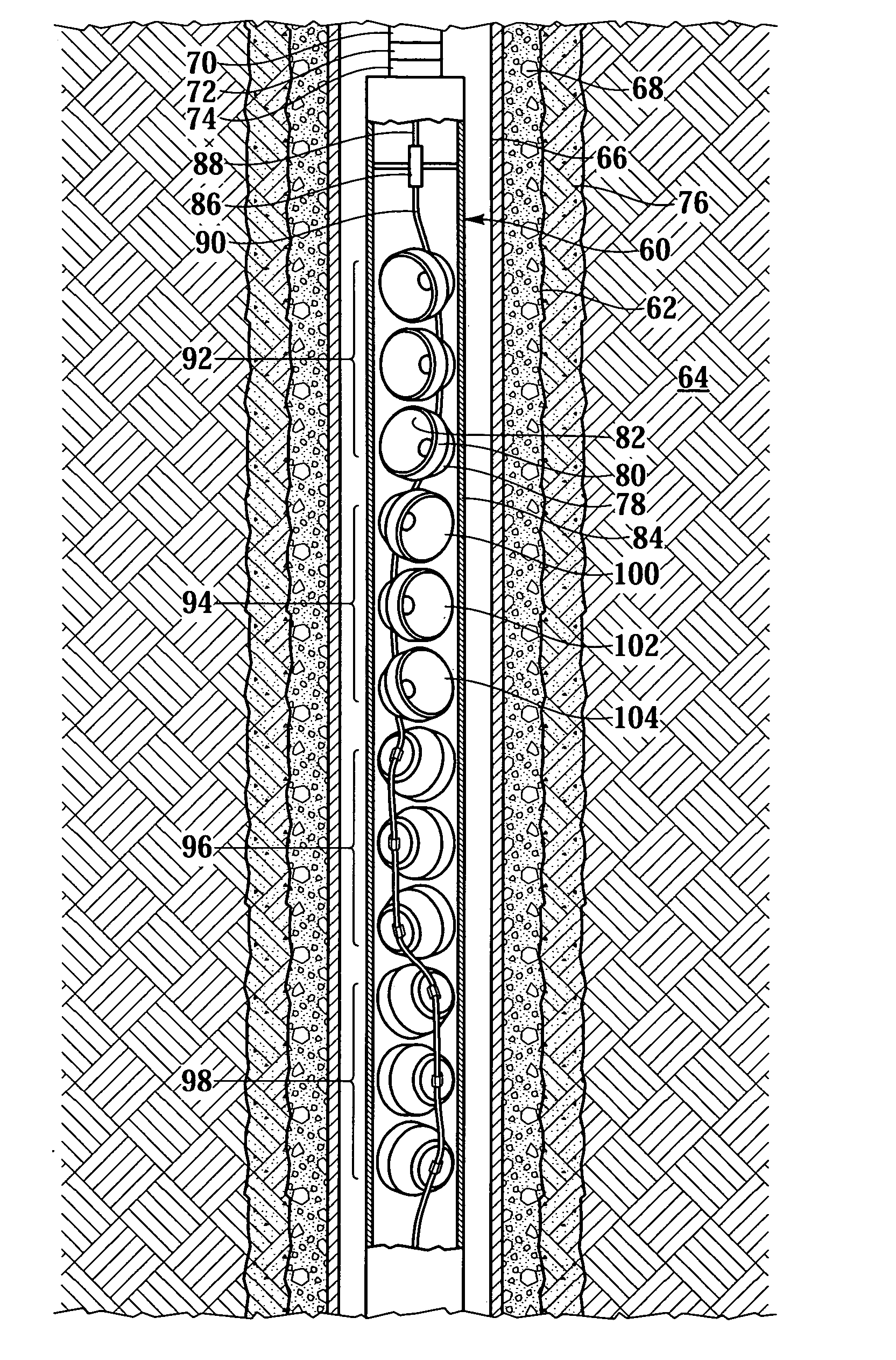
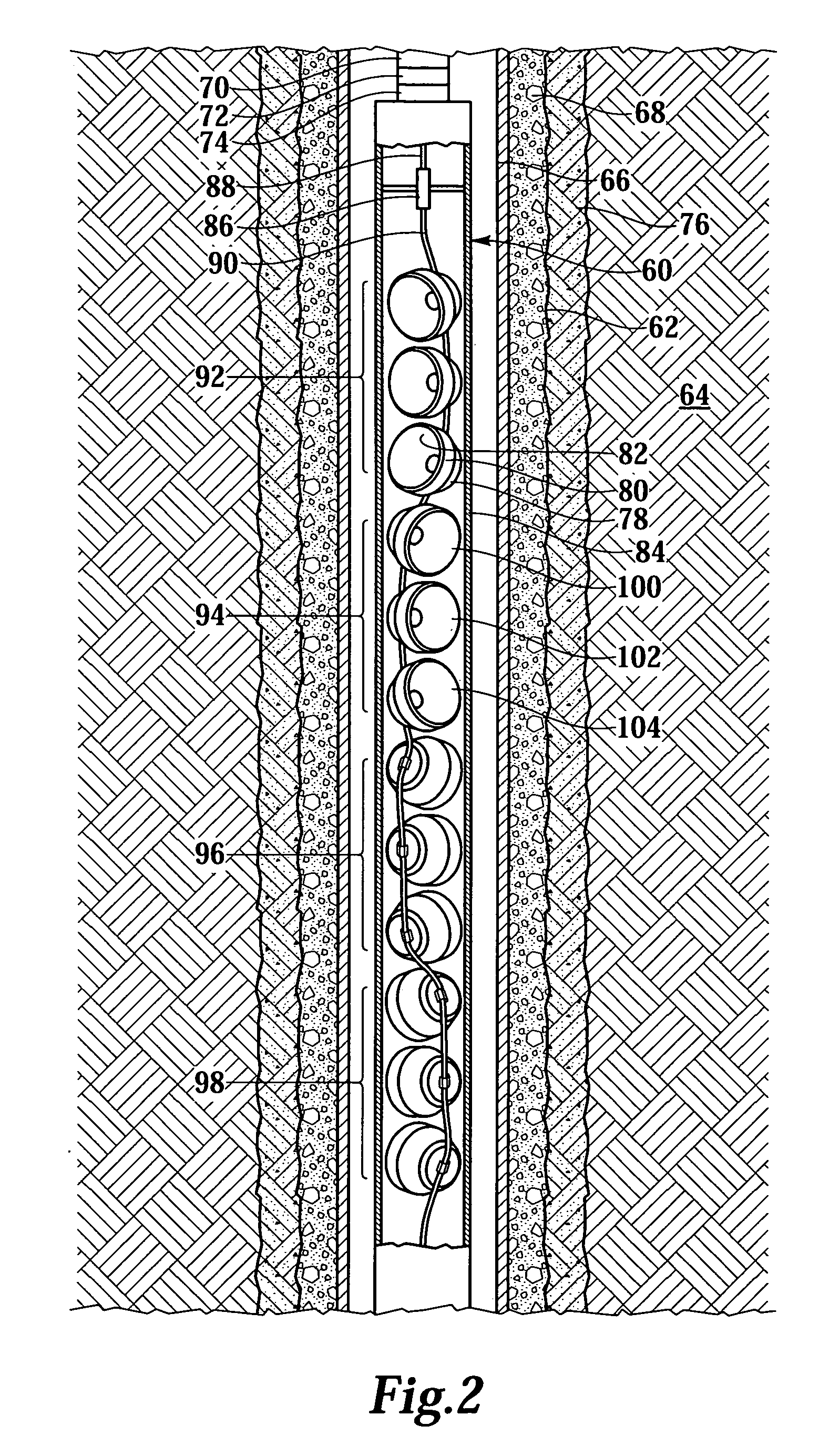
A perforating gun assembly (60) for creating communication paths for fluid between a formation (64) and a cased wellbore (66) includes a housing (84), a detonator (86) positioned within the housing (84) and a detonating cord (90) operably associated with the detonator (86). The perforating gun assembly (60) also includes one or more substantially axially oriented collections (92, 94, 96, 98) of shaped charges. Each of the shaped charges in the collections (92, 94, 96, 98) is operably associated with the detonating cord (90). In addition, adjacent shaped charges in each collection (92, 94, 96, 98) of shaped charges are oriented to converge toward one another such that upon detonation, the shaped charges in each collection (92, 94, 96, 98) form jets that interact with one another to create perforation cavities in the formation (64).
Owner:WELL BALLISTICS +2
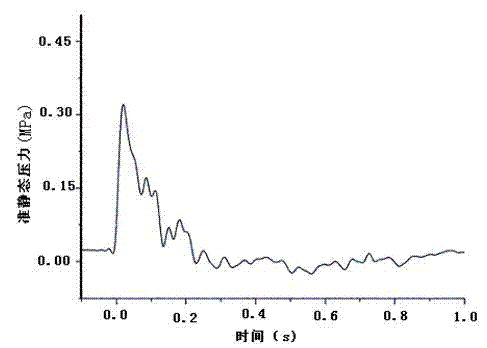
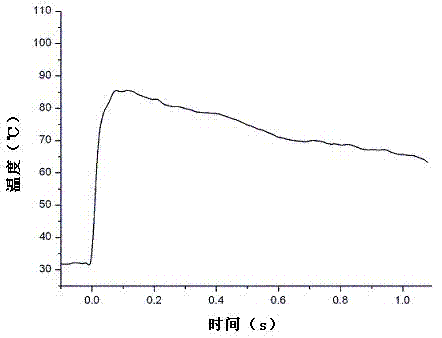
Detonation performance test method for high-energy imploding explosive
InactiveCN102253083AFlexible simulationRealize synchronized measurementsMaterial exposibilityDetonatorExplosive Agents
The invention discloses a detonation performance test method for high-energy imploding explosive. The method is characterized in that: a explosive grain with a detonator is placed in a sealed explosion vessel; quasi-static pressure of the explosive, transient temperature of the explosive, detonation velocity of the explosive and gas components of the explosive are detected; a temperature sensor is arranged on the sealed explosion vessel, and is provided for monitoring the temperature changing in the sealed explosion vessel during the test process, a pressure sensor is arranged on the sealed explosion vessel, and is provided for monitoring the pressure changing in the sealed explosion vessel during the test process; the sealed explosion vessel is further connected with a gas collection andtest system, a firing device, a detonation velocity test device, a mechanical vacuum pump and a gas cylinder. The method is applicable for the performance tests of various imploding explosives, and can be provided for performing laboratory quantitative evaluation to the gas expansion working.
Owner:XIAN MODERN CHEM RES INST
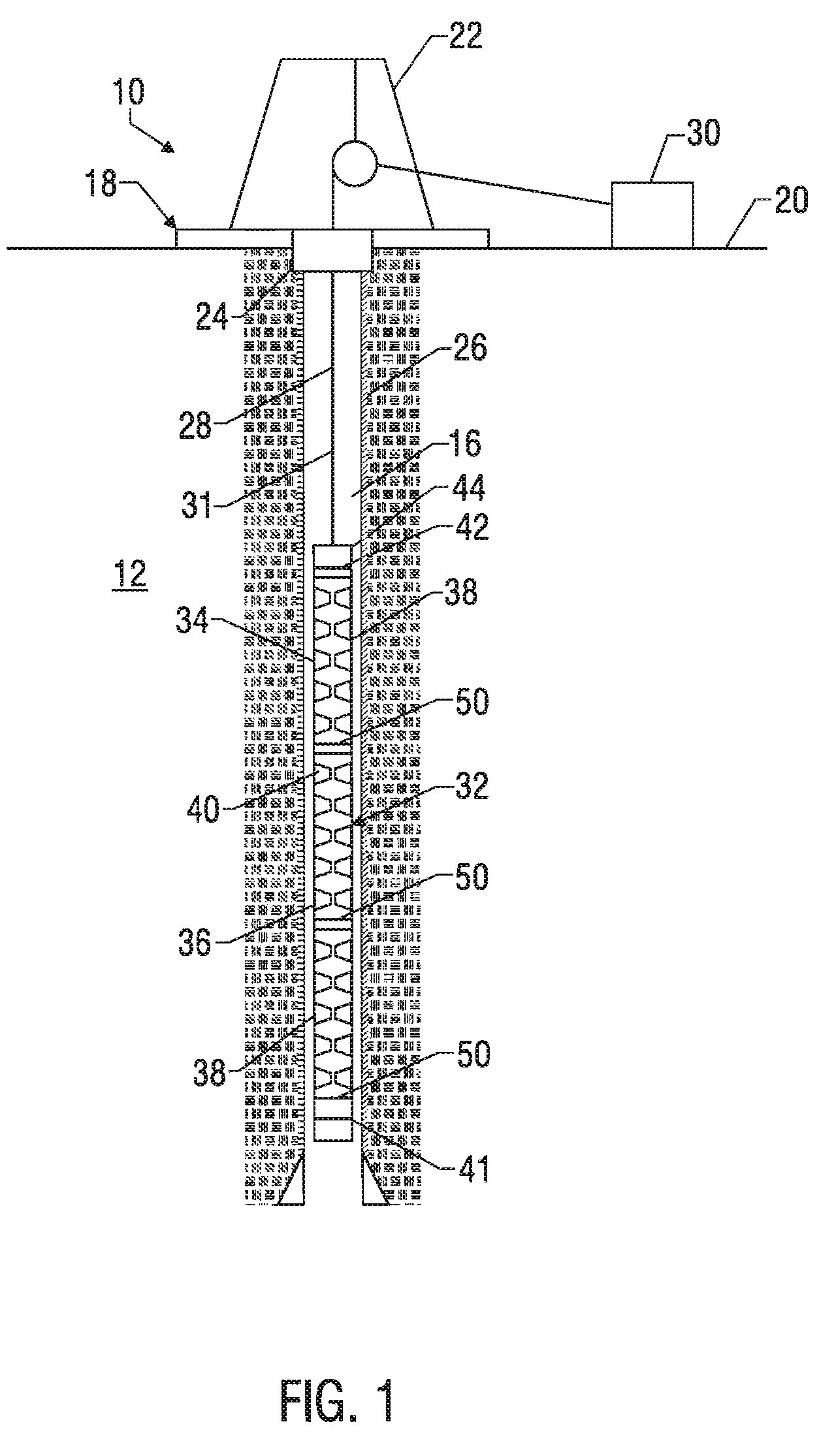
Method and Apparatus for Completing a Horizontal Well
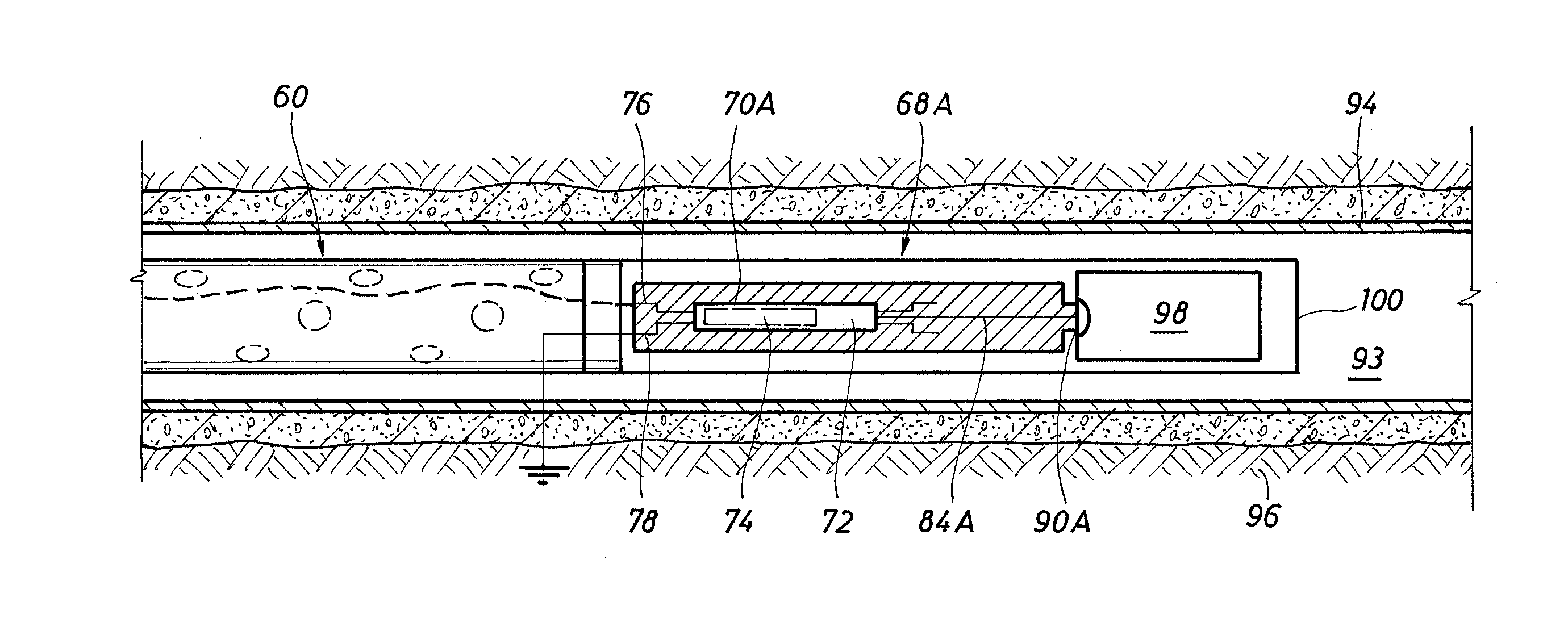
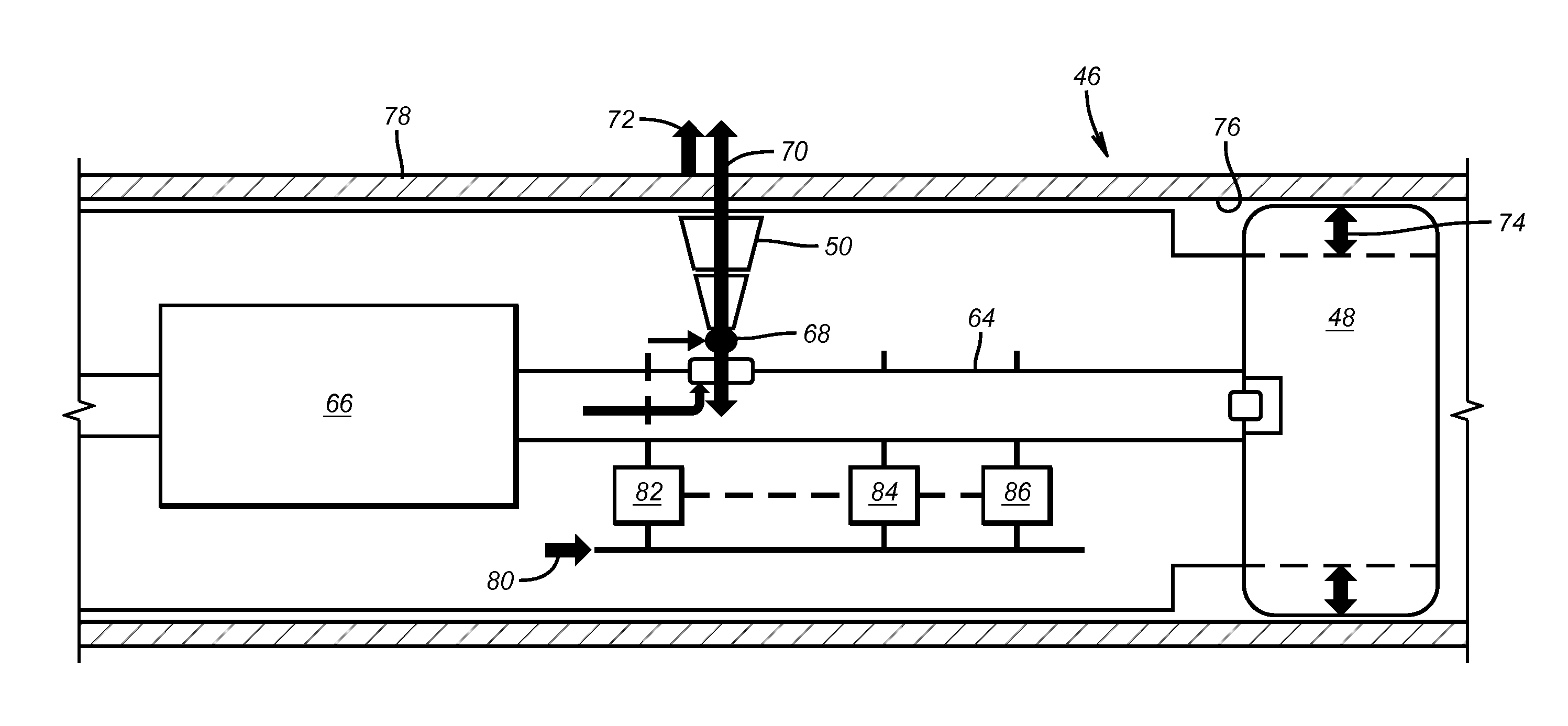
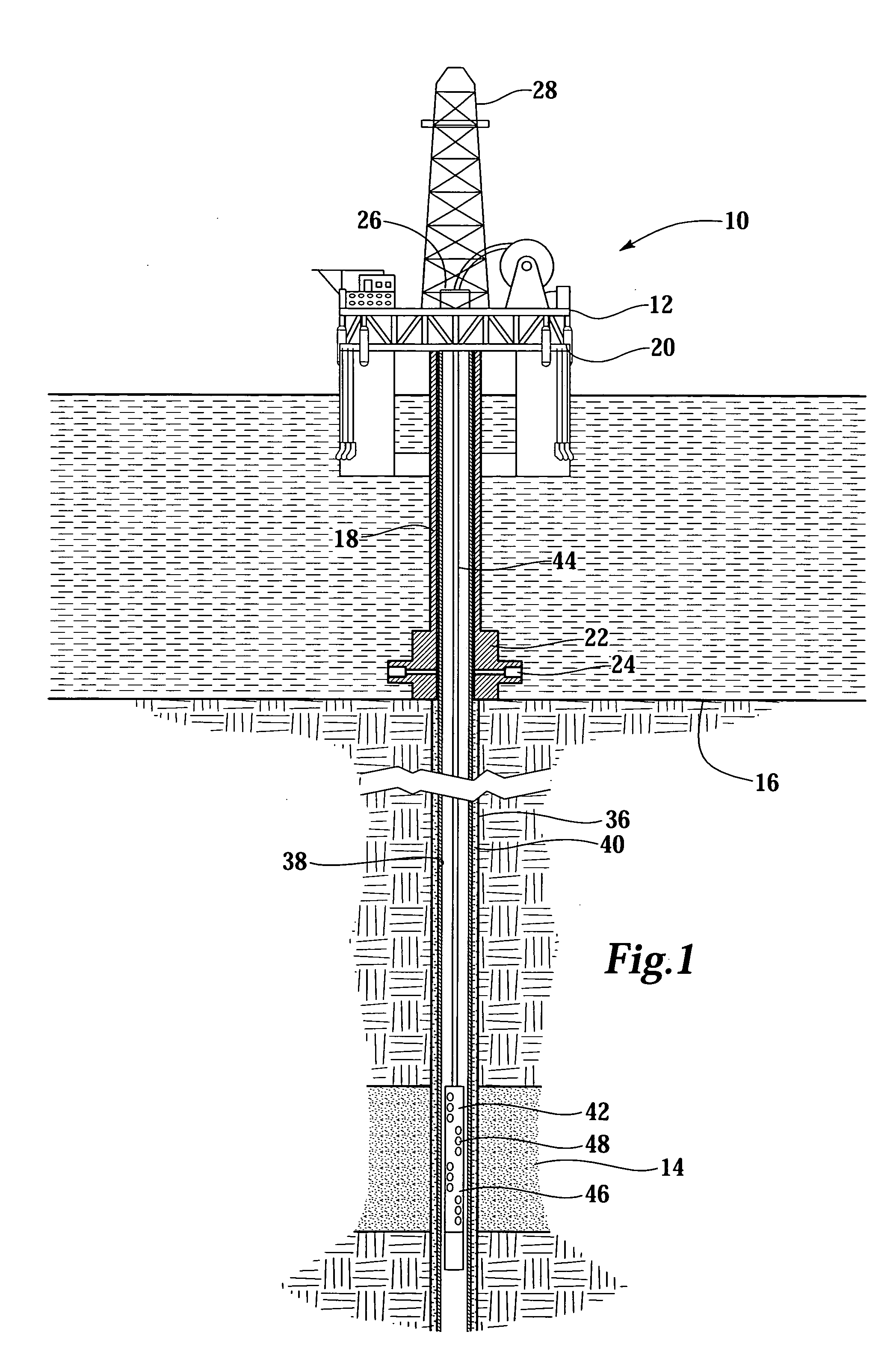
A firing head assembly has a sealed chamber containing a piston, a firing pin, and an impact detonator. The firing head assembly and a perforating charge are installed within a sub and the sub is secured into a string of conduit being lowered into a wellbore. After cementing the conduit, the operator drills out the cement in the conduit, disintegrating the chamber and exposing the sealed chamber to the fluid pressure of the drilling fluid in the conduit. The drilling fluid pressure causes the piston to drive the firing pin against the detonator, which detonates the perforating charge. The operator then pumps down a logging tool to survey the well. Fluid in the conduit below the pump-down head can flow out the displacement perforation into the earth formation while the logging tool is moving downward.
Owner:TOLSON JET PERFORATORS
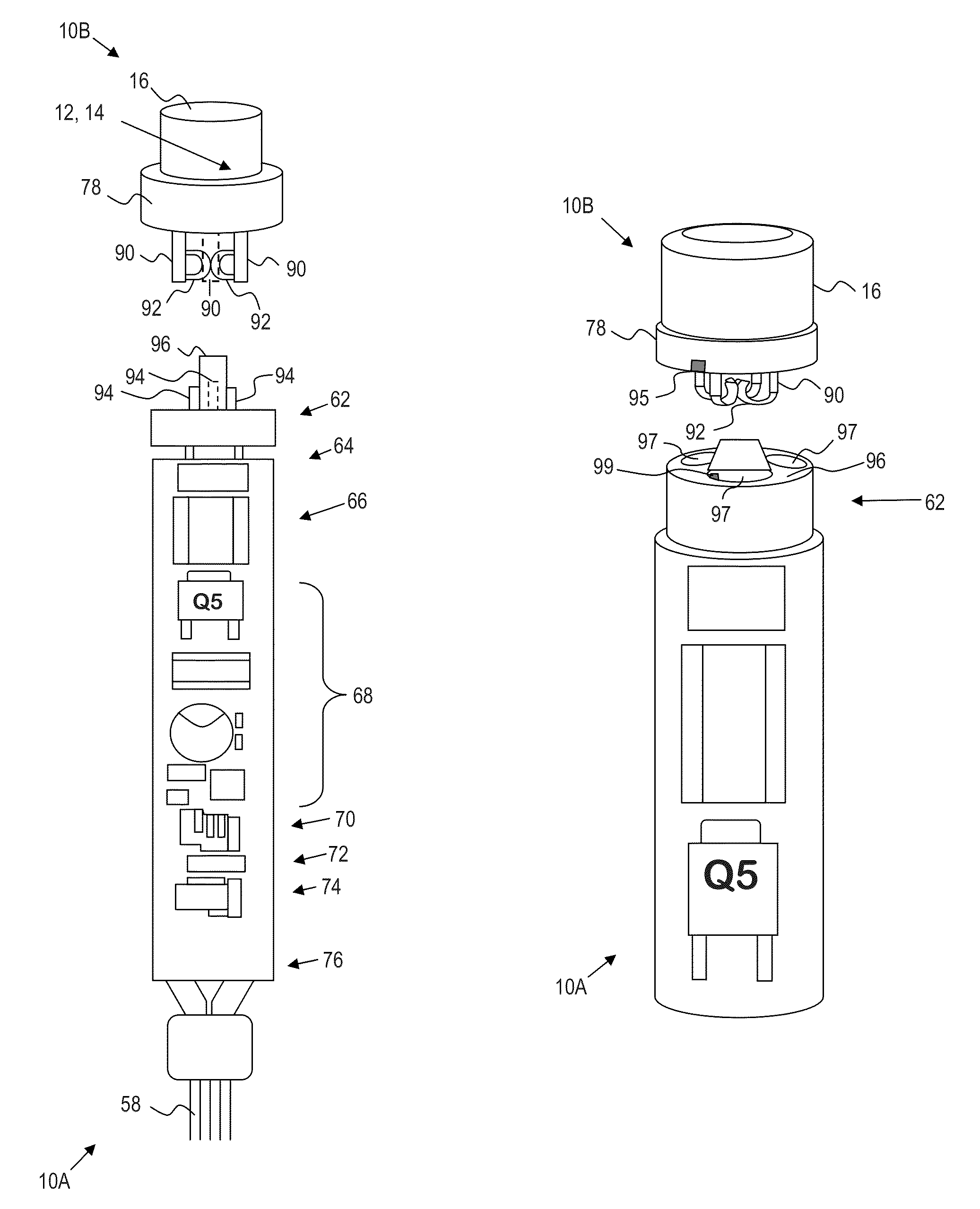
Electronic safe/arm system and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20110277620A1Low impedance connectionGood adhesionCosmonautic vehiclesIncandescent ignitionDetonatorElectricity
An ordnance firing system is disclosed that includes a reusable electronics module and an ordnance module, each enclosed in a separate, sealed housing. The electronics module housing encloses firing electronics for electrically triggering initiation of a detonator in the ordnance module. The electronics module detachably connects to the ordnance modules via a connector which extends away from the electronics module housing. The housing of the ordnance module is constructed to be blast-resistant to prevent detonation of the detonator from rendering the electronics module inoperable.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Electromechanical assembly for connecting a series of guns used in the perforation of wells
ActiveUS20130043074A1Big economyImprove securityFluid removalDrilling machines and methodsDetonatorElectricity
Electromechanical assembly for connecting a series of guns used in the perforation of petroleum producing wells. Each gun has a cylindrical housing for a charge-carrier loaded with explosive shaped-charges set in radial fashion. The charges are in contact with a detonating cord that is in contact with an electronically activated detonator. The series of guns are joined firmly by intermediary joints and terminate in a bottom sub on its lower extreme, where the series is initiated by a firing head which is connected to the surface with an electrical connection. It is possible to detonate the charge-carrier of each gun, beginning with the bottommost gun that remains active.
Owner:TASSAROLI
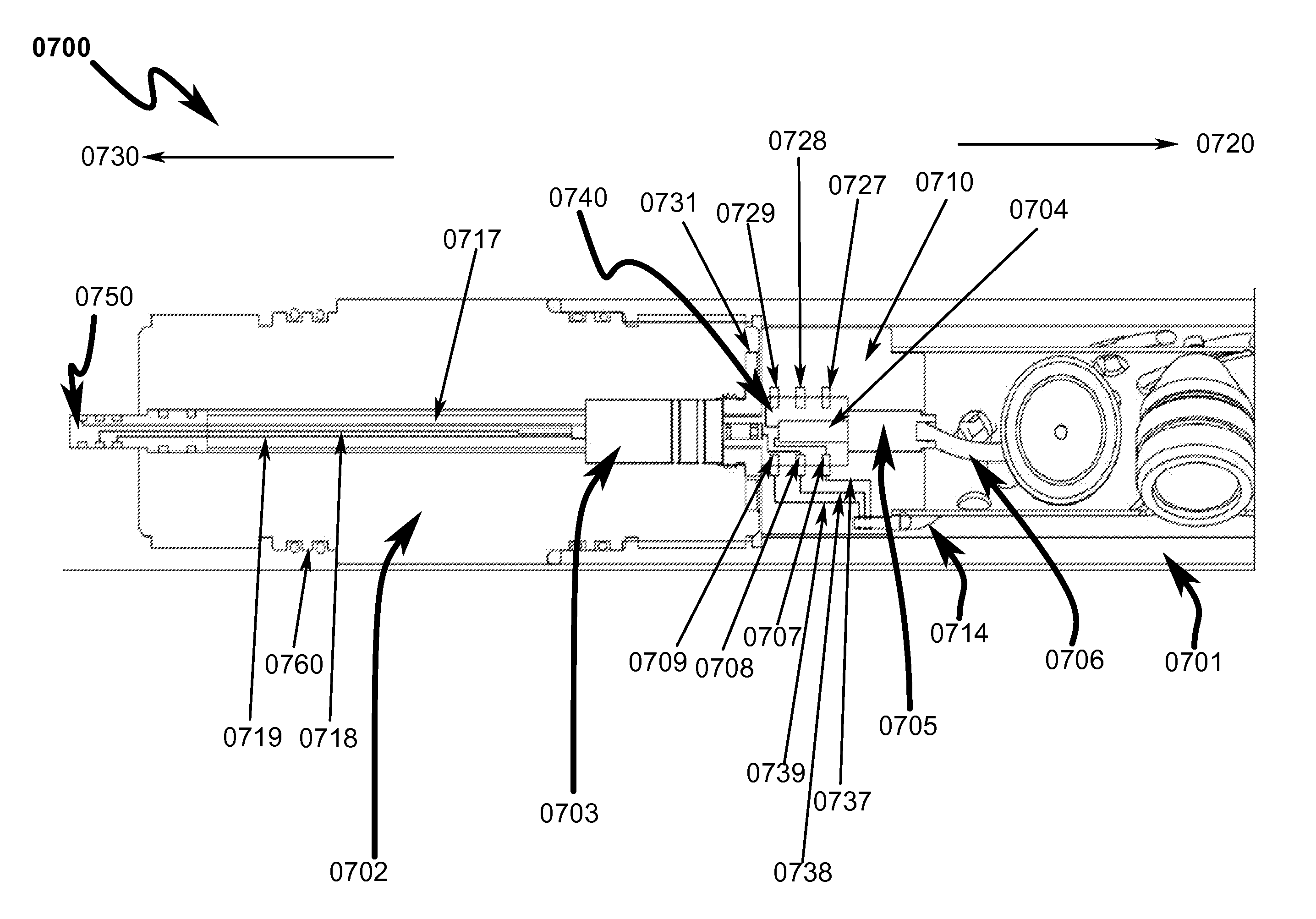
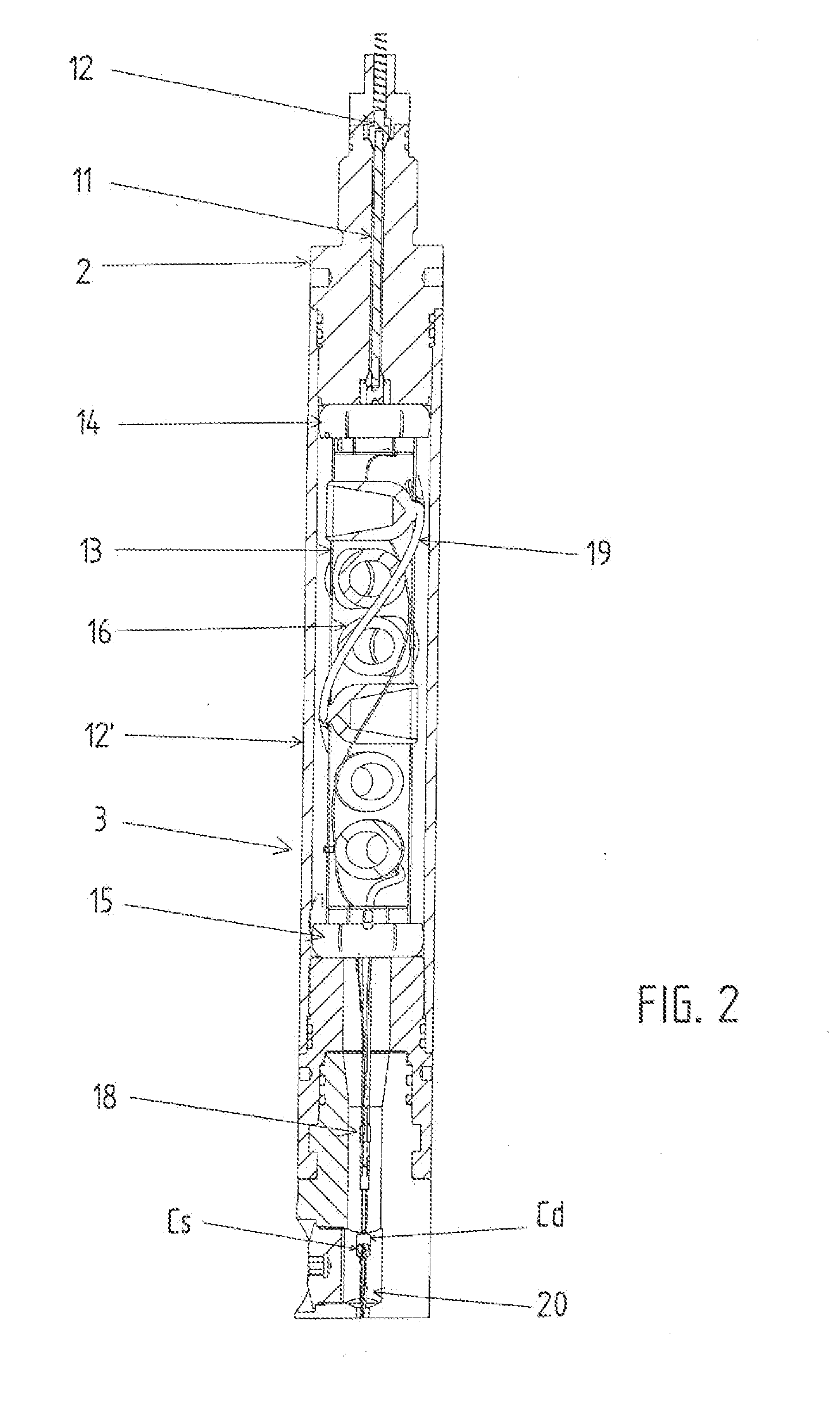
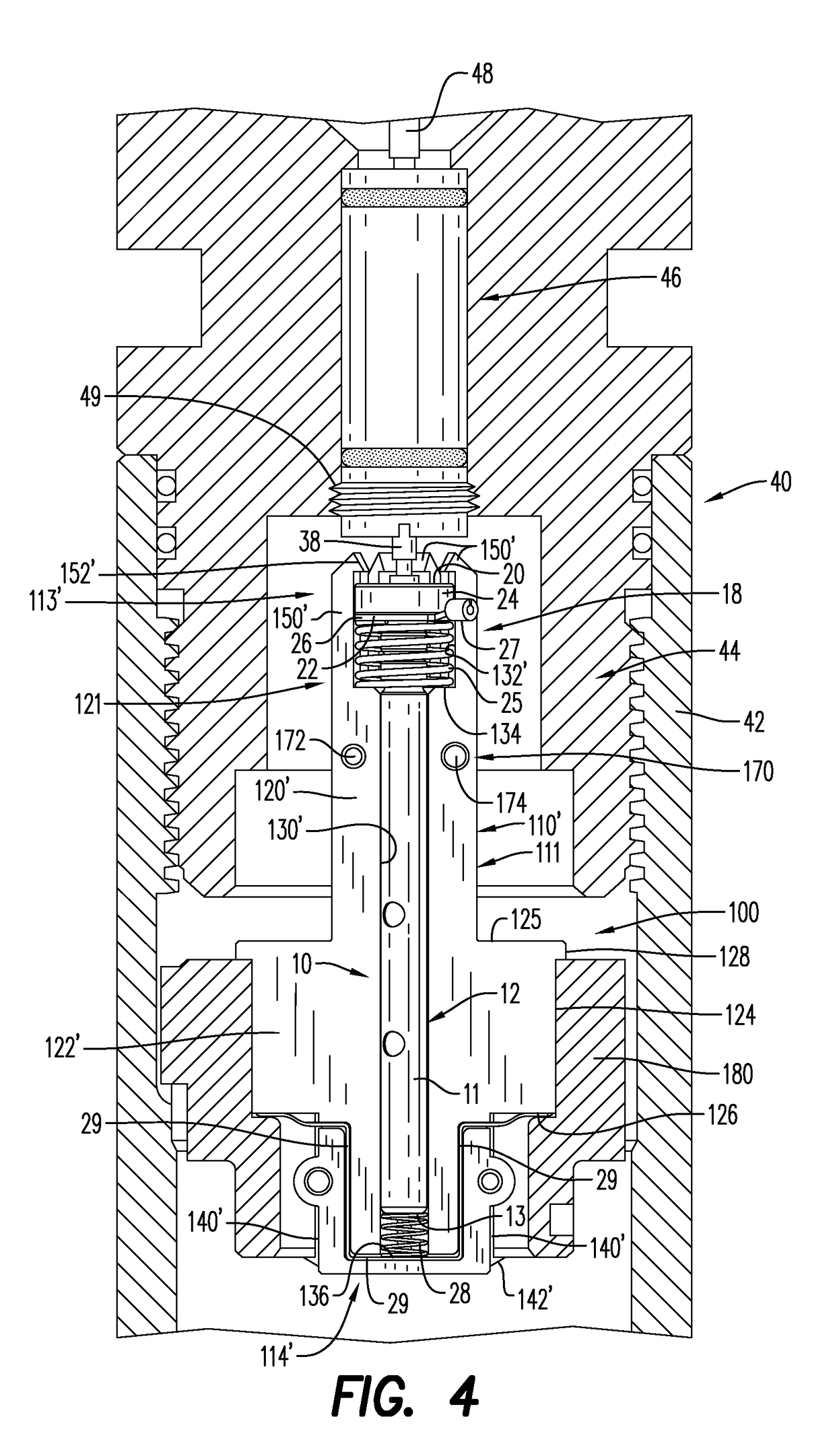
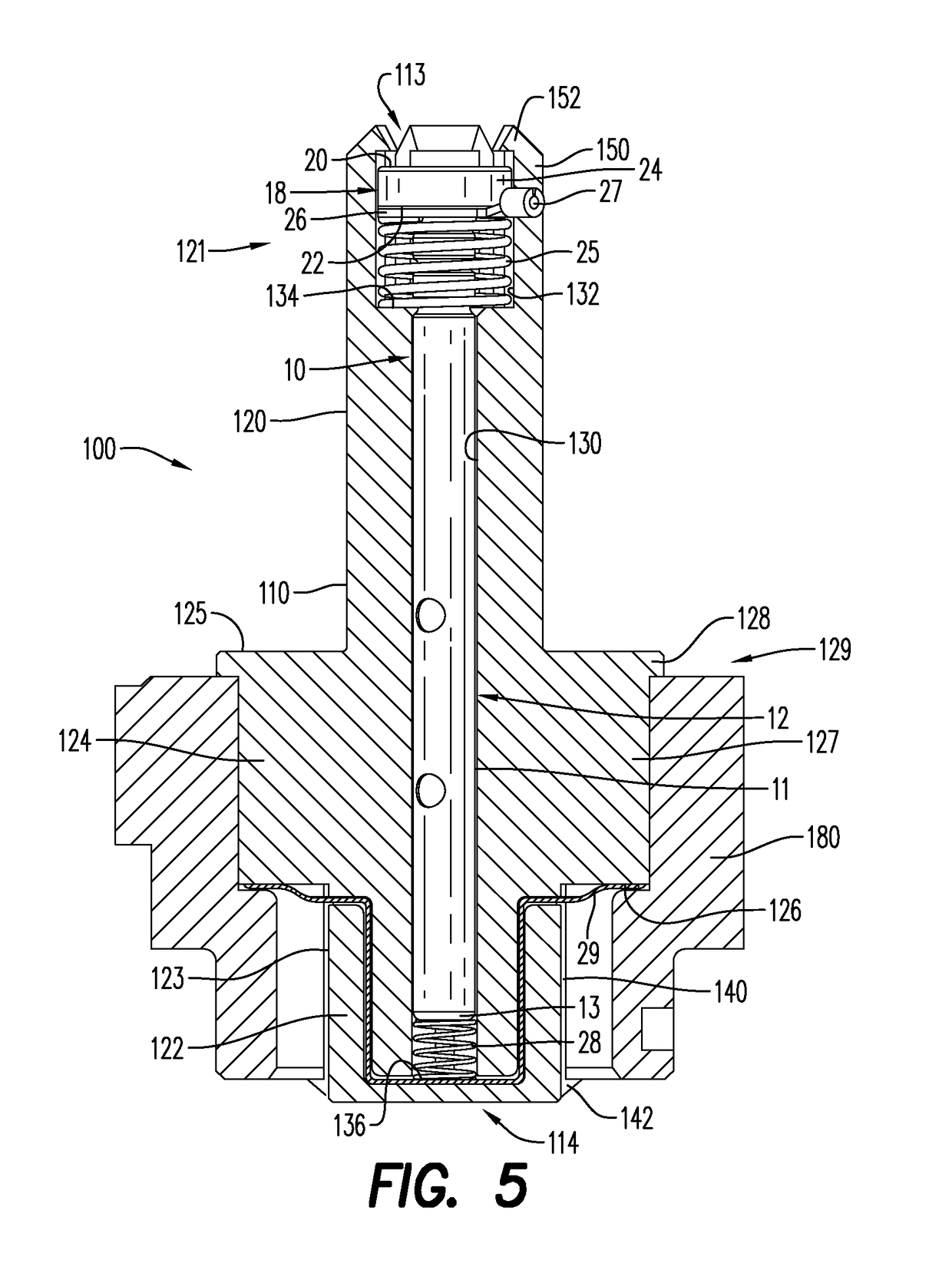
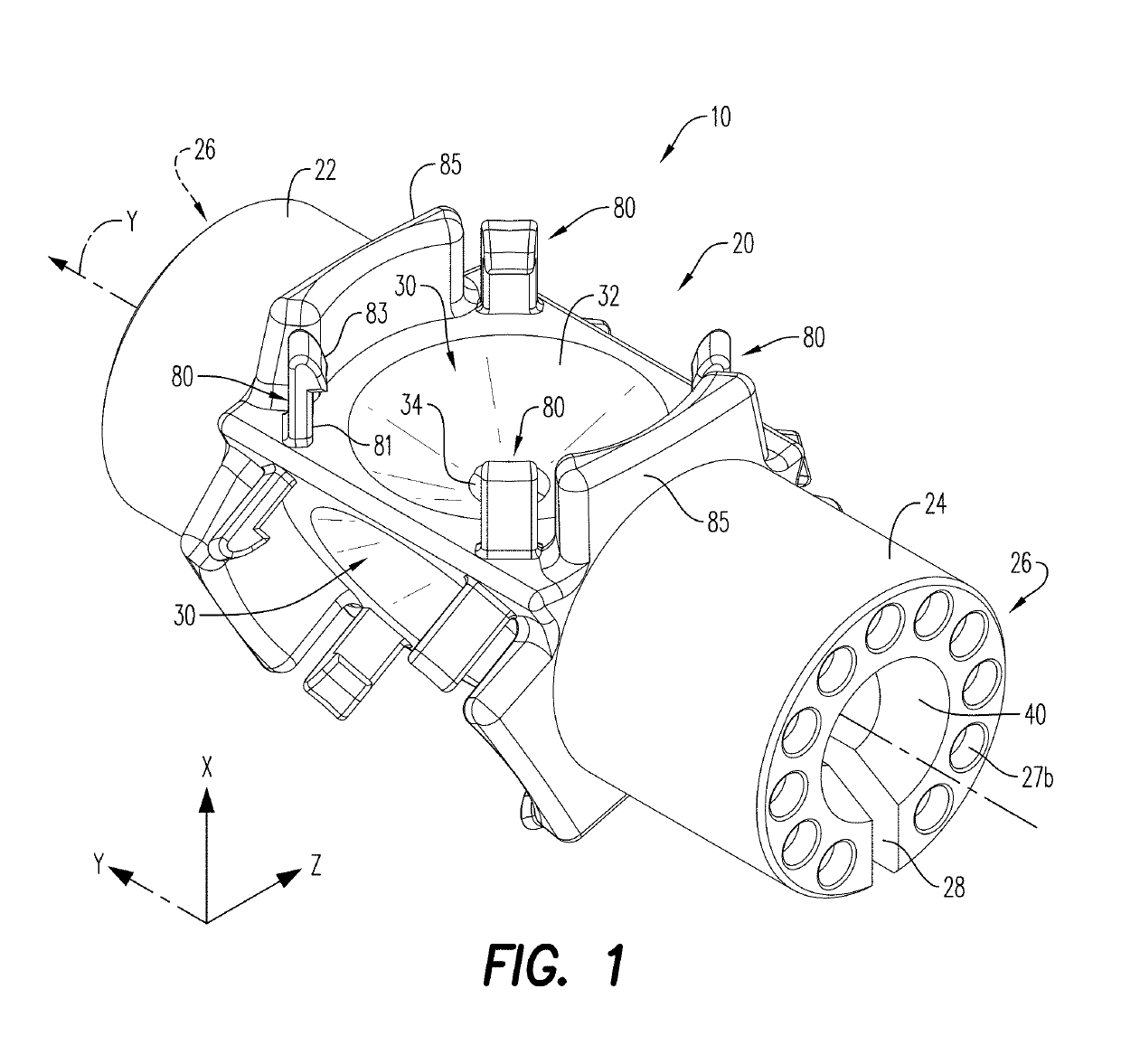
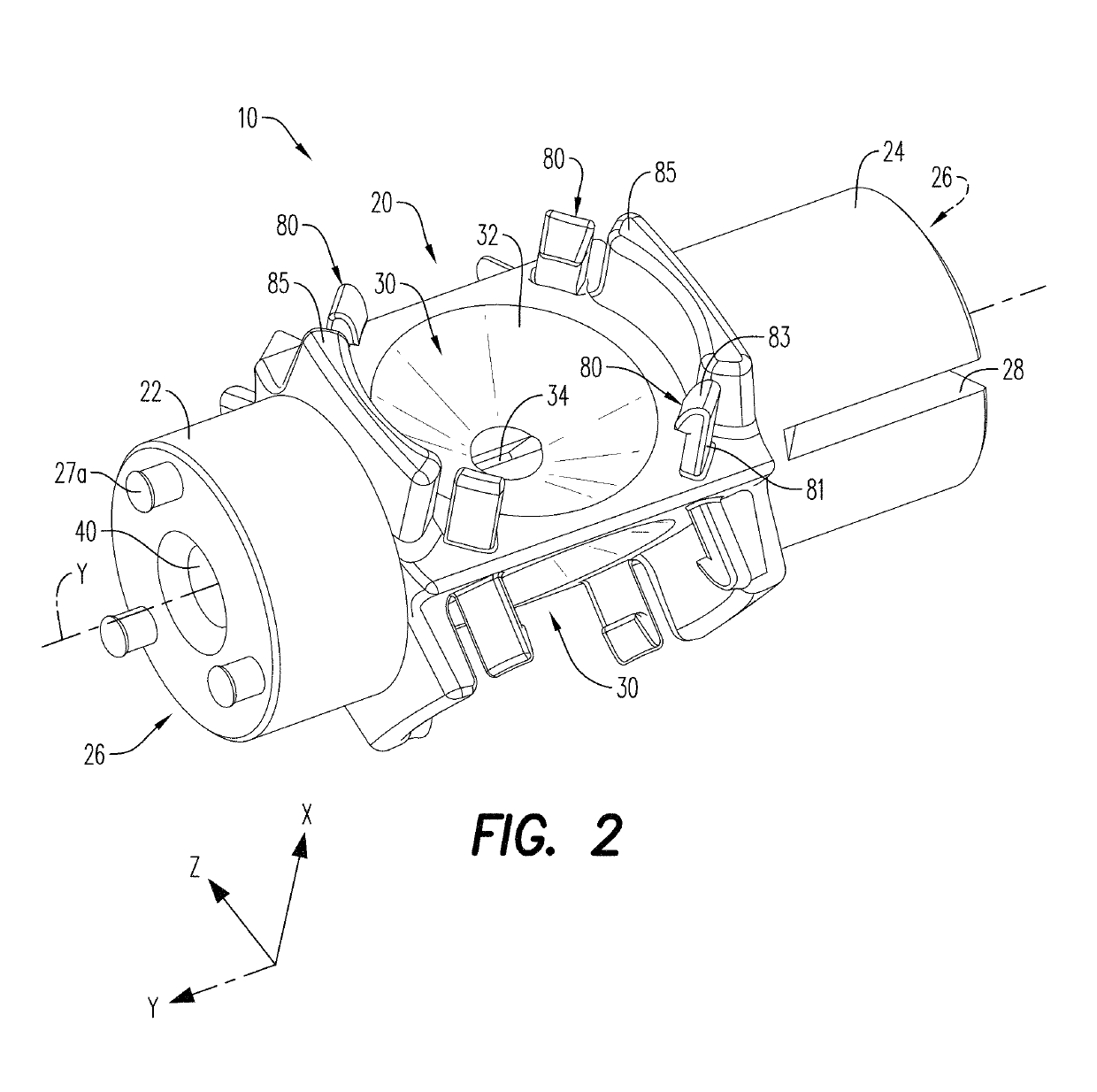
Device and method for positioning a detonator within a perforating gun assembly
Owner:DYNAENERGETICS US INC +1
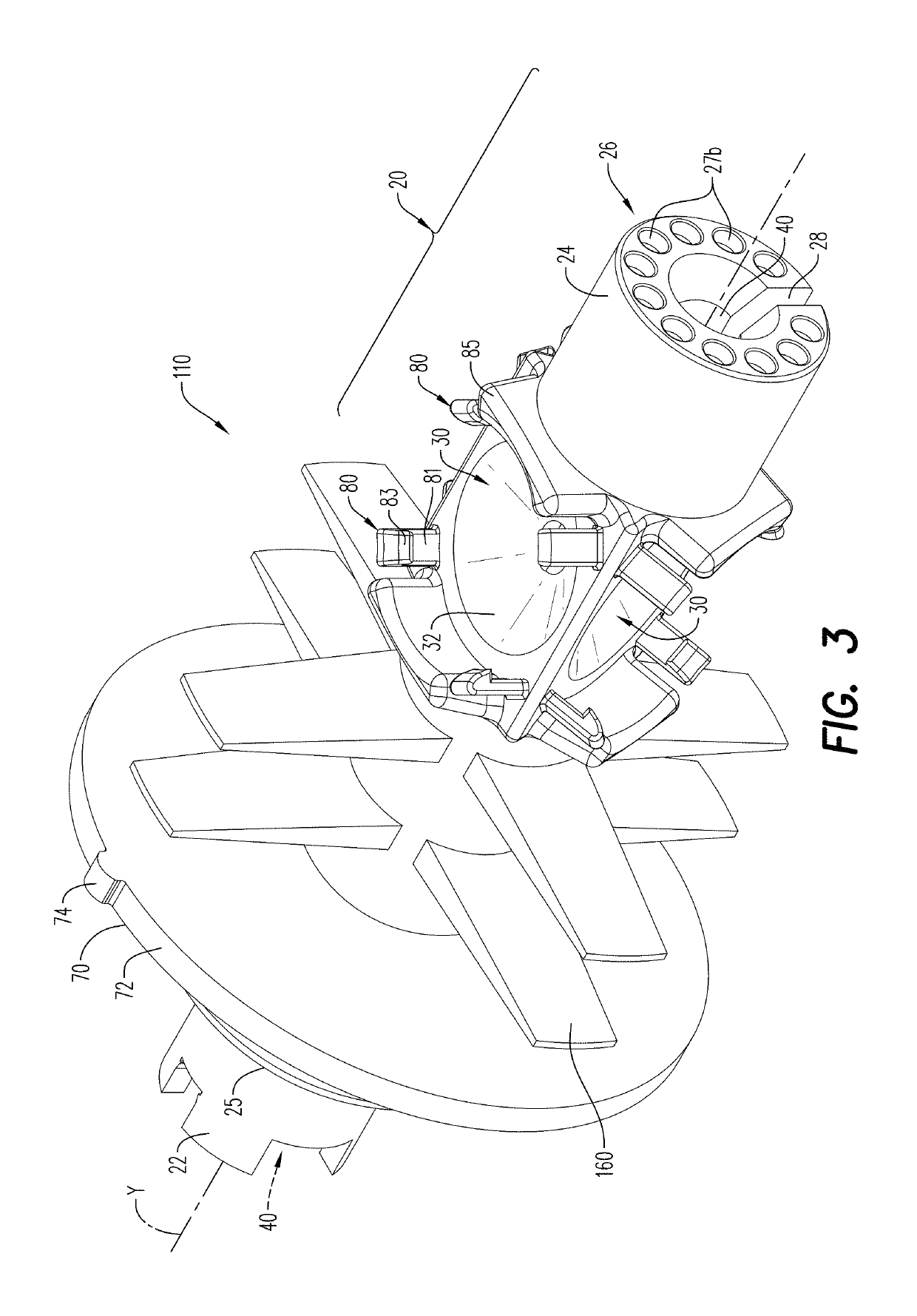
Positioning device for shaped charges in a perforating gun module
ActiveUS10458213B1Increase flow rateFacilitates direct and simultaneous initiationSurveyFluid removalDetonatorShaped charge
A positioning device includes a shaped charge holder. A plurality of shaped charge receptacles formed in the shaped charge holder are configured to arrange a plurality of shaped charges in a desired orientation. The shaped charges are detonated by a detonator in response to an initiation signal. The positioning device may be secured in a perforating gun module, with vertical and horizontal movement of the positioning being inhibited in the perforating gun module.
Owner:DYNAENERGETICS
Apparatus and method for selective actuation of downhole tools
The present invention provides systems, methods and devices for selectively firing a gun train formed of a plurality of guns. Conventionally, the guns each include a detonator assembly that detonates upon receiving a firing signal transmitted by a surface source. In one embodiment of the present invention, an operator provided in the gun train selectively couples one or more of the guns to the signal transmission medium. The operator has an safe state wherein the operator isolates the gun from the firing signal and an armed state wherein the operator enable the transmission of the firing signal to the gun. A control signal is used to move operator between the safe state and the armed state. In some embodiments, two or more guns are each provided with a separate operator. In other embodiments, one operator can selectively engage two or more guns.
Owner:OWEN OIL TOOLS
Connector for electronic detonators
ActiveUS8069789B2Avoid unnecessary distractionsImprove connection securityRelieving strain on wire connectionBlasting cartridgesDetonatorElectricity
Fire, arm, and disarm signals are typically transmitted to electronic detonators via signal transmission lines. Traditionally, such signal transmission lines include wires wherein one end of each wire is soldered directly to printed circuit boards and / or other signal processing components retained within the shell of a detonator. Other ‘modular’ blasting apparatuses of the prior art provide means to connect signal transmission lines to detonators in the field. Signal transmission line / detonator contacts are susceptible to disruption, particularly when the signal transmission lines are subject to inadvertent tugging or tensile forces at the blast site. The present application discloses an electrical connector that enables secure connection between a signal transmission line and any detonator adapted to receive and optionally process electrical signals from the signal transmission line. Specifically, the electrical connector can be affixed to the signal input end of a detonator, and includes at least one bridge element to provide electrical contact between a signal transmission line, and internal electrical component(s) of the detonator.
Owner:ORICA EXPLOSIVES TECH PTY LTD
Hollow-hole rhombic parallel cut blasting damping method
InactiveCN102914226AReduce blasting vibration velocityReduce the impactBlastingDetonatorUnderground tunnel
The invention relates to a hollow-hole rhombic parallel cut blasting damping method. Blasting tunneling is performed on the tunnel face of an underground tunnel. The construction method comprises using a down-the-hole drill to drill a hollow hole with the diameter of 90mm to 180mm at the position of the middle of the tunnel face of the tunnel; using a hammerdrill to drill a plurality of blast holes, enabling the blast holes to comprise cut holes, auxiliary holes, periphery holes and base plate holes which are expanded around the hollow hole; filling explosives and detonators, using stemming to seal the blast holes, adopting rock emulsion explosives, and using ordinary millisecond nonel detonators or high-precison millisecond nonel detonators; and detonating the explosives according to blast hole arranging orders and detonator delay time. The hollow-hole rhombic parallel cut blasting damping method has the advantages that when an urban subway underneath passes buildings at a close range in a granite stratum and old resident houses, the blast vibration speed can be effectively controlled, influences of blast vibration on the buildings and life of residents are reduced, and compared with a traditional wedge cut blasting scheme, the hollow-hole rhombic parallel cut blasting damping method enables the maximum blasting vibration speed to be reduced by 50%.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
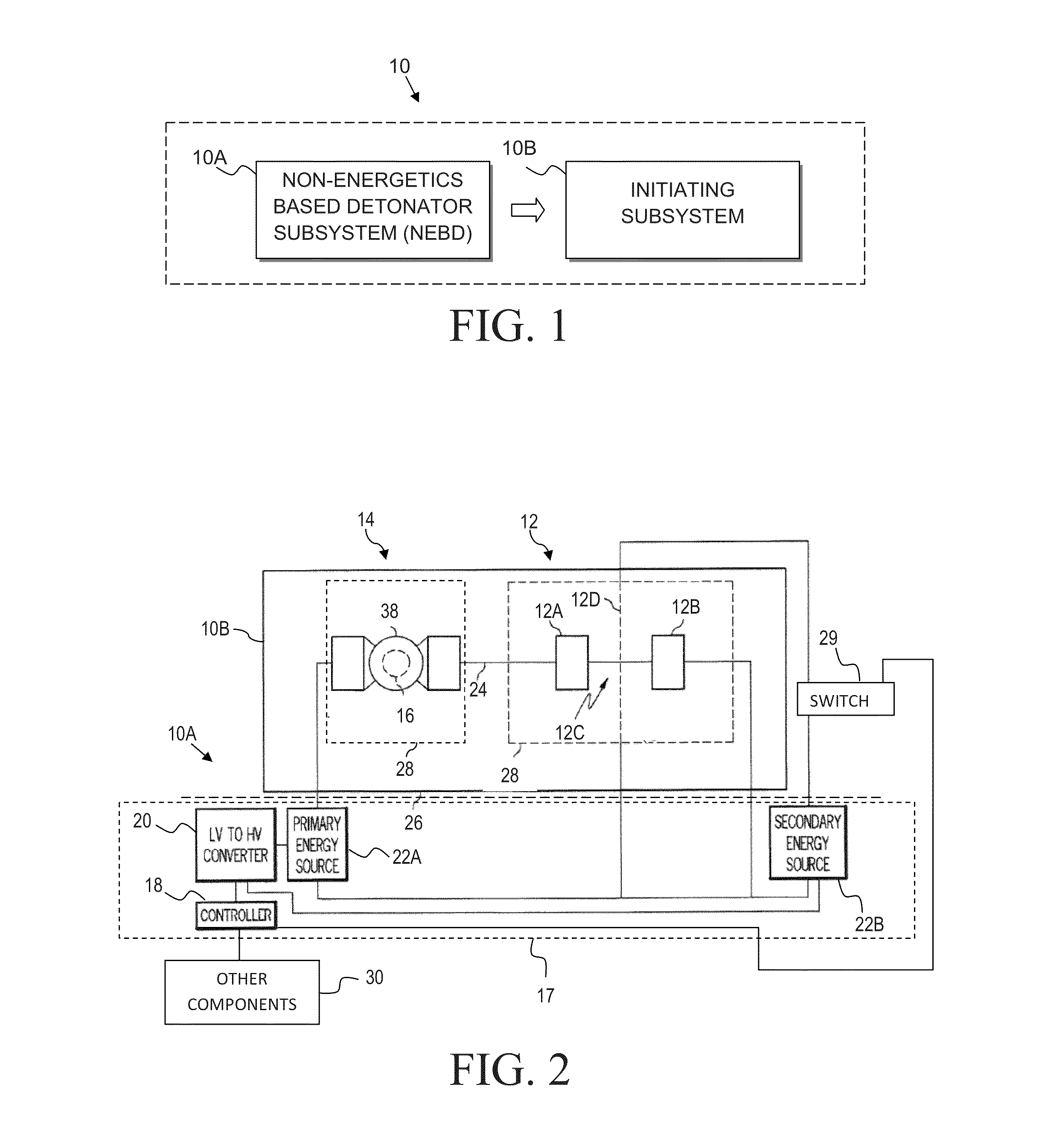
Non-energetics based detonator
A detonator system is provided for use with explosives that utilizes two subsystems. A first subsystem functions as a non-explosives based detonator, which does not contain any explosives. The second subsystem is an initiating subsystem, which includes an initiating pellet. To set off an explosive event, the non-energetics based detonator is coupled to the initiating subsystem and the non-energetics based detonator is commanded to provide a suitable signal to the initiating subsystem that is sufficient to function the initiating pellet. Further, the initiating subsystem can be integrated directly into an associated explosive such as a booster that has been configured to receive the initiator subsystem without changing the hazard class of the booster.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Wireless detonator assemblies, corresponding blasting apparatuses, and methods of blasting
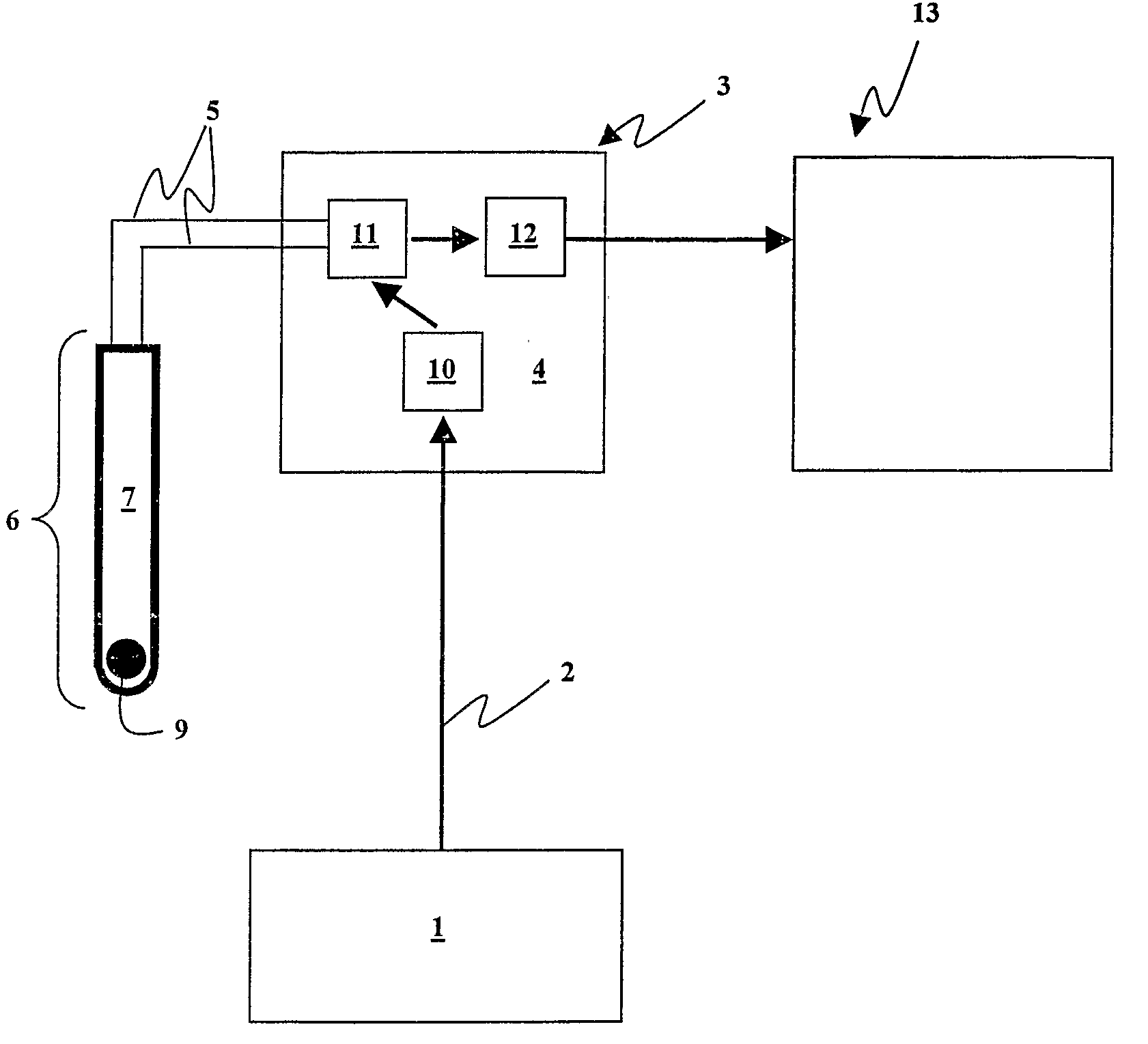
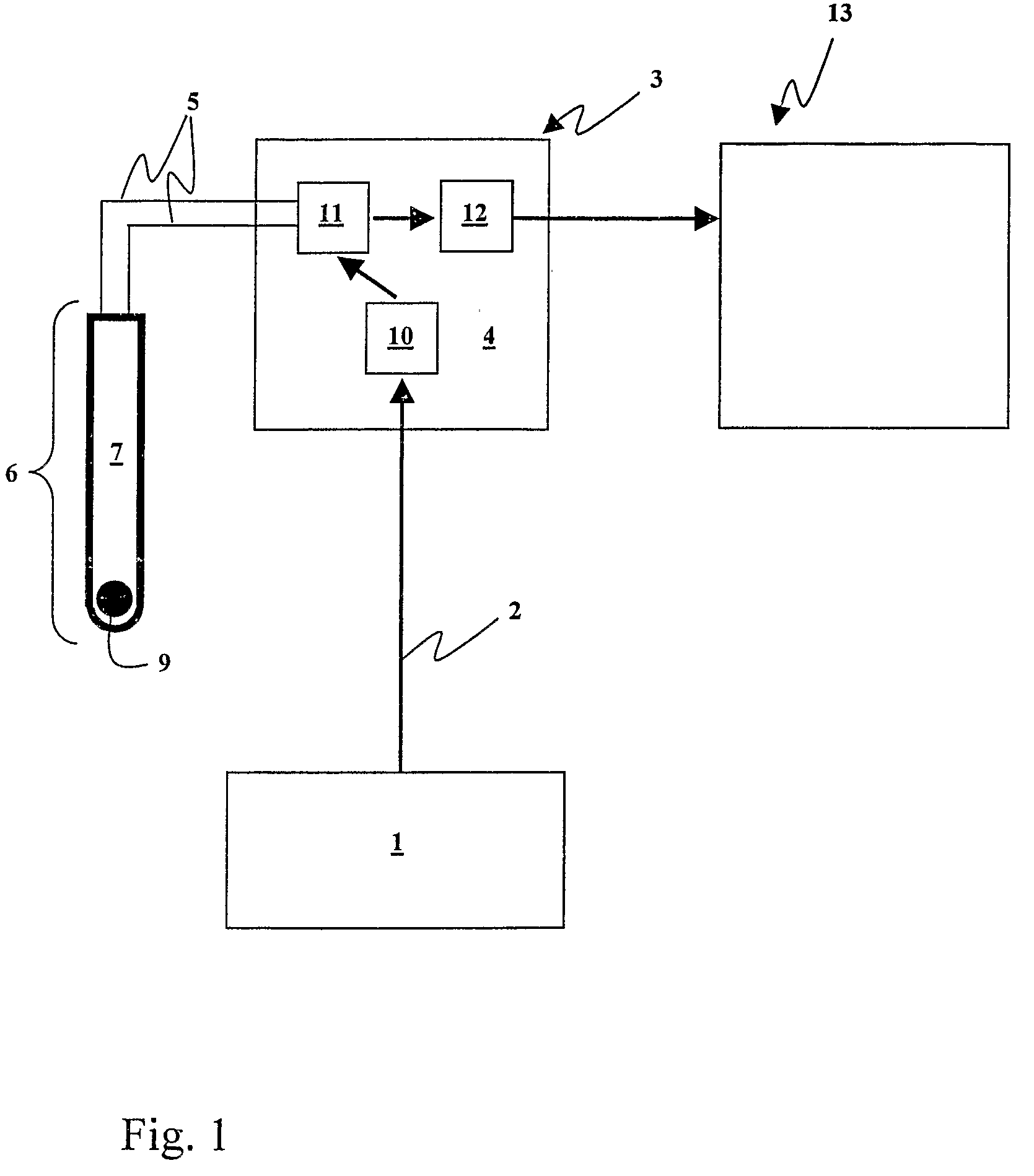
A wireless or partially wireless detonator assembly (10) and corresponding blasting apparatus, that may be “powered Up” by a remote source of power (13) that is entirely distinct from the energy used for general command signal communications (16). In one embodiment, the detonator assembly (10) may include an active power source (25) with sufficient power for communications, but insufficient power to cause intentional or inadvertent actuation of the detonator (10).
Owner:ORICA EXPLOSIVES TECH PTY LTD
Device and method for positioning a detonator within a perforating gun assembly
According to an aspect, a detonator positioning device is provided for use with a wireless detonator in a perforating gun assembly. The detonator positioning device includes a single mechanism for physical electrical connection, while the remaining electrical connections are made via electrically contactable components. A method of assembling the perforating gun assembly is also provided, including a detonator positioning device configured to receive and hold the wireless detonator.
Owner:DYNAENERGETICS US INC +1
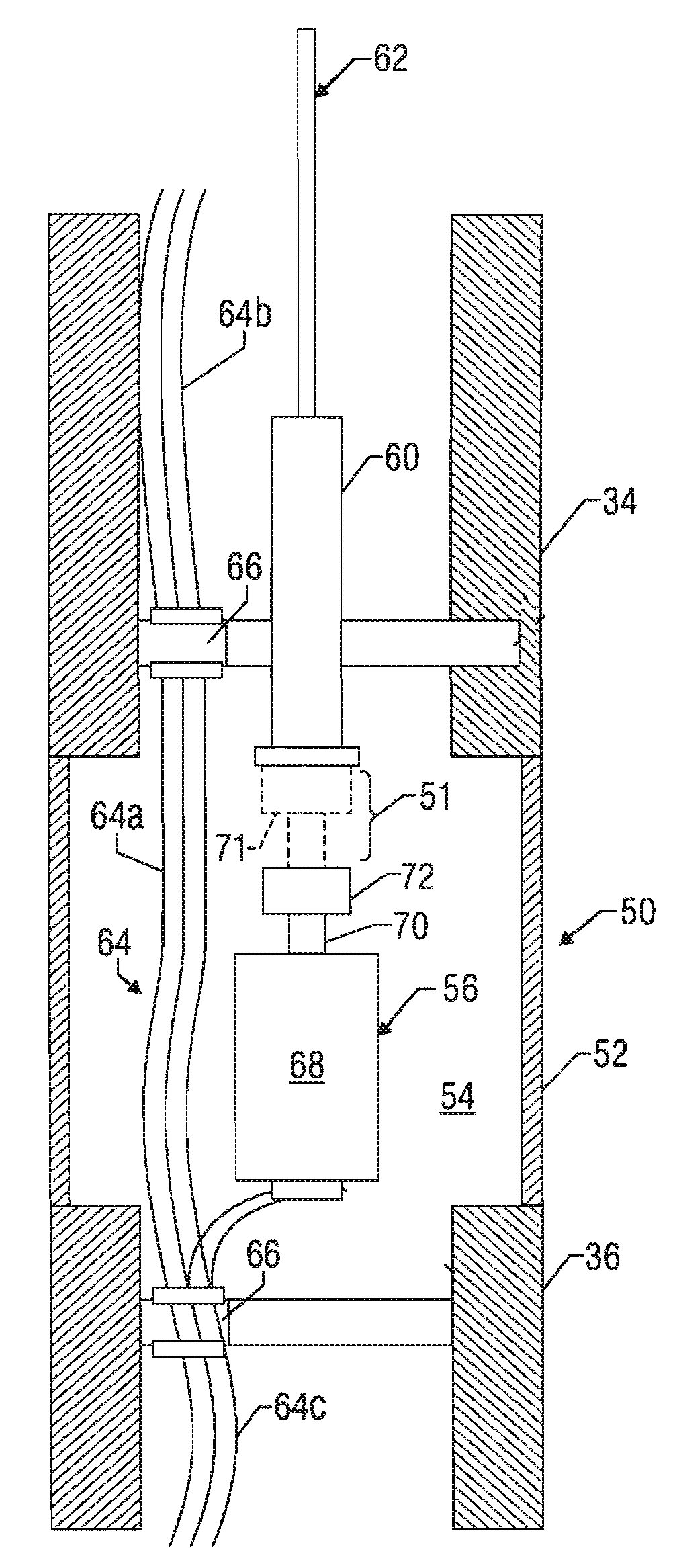
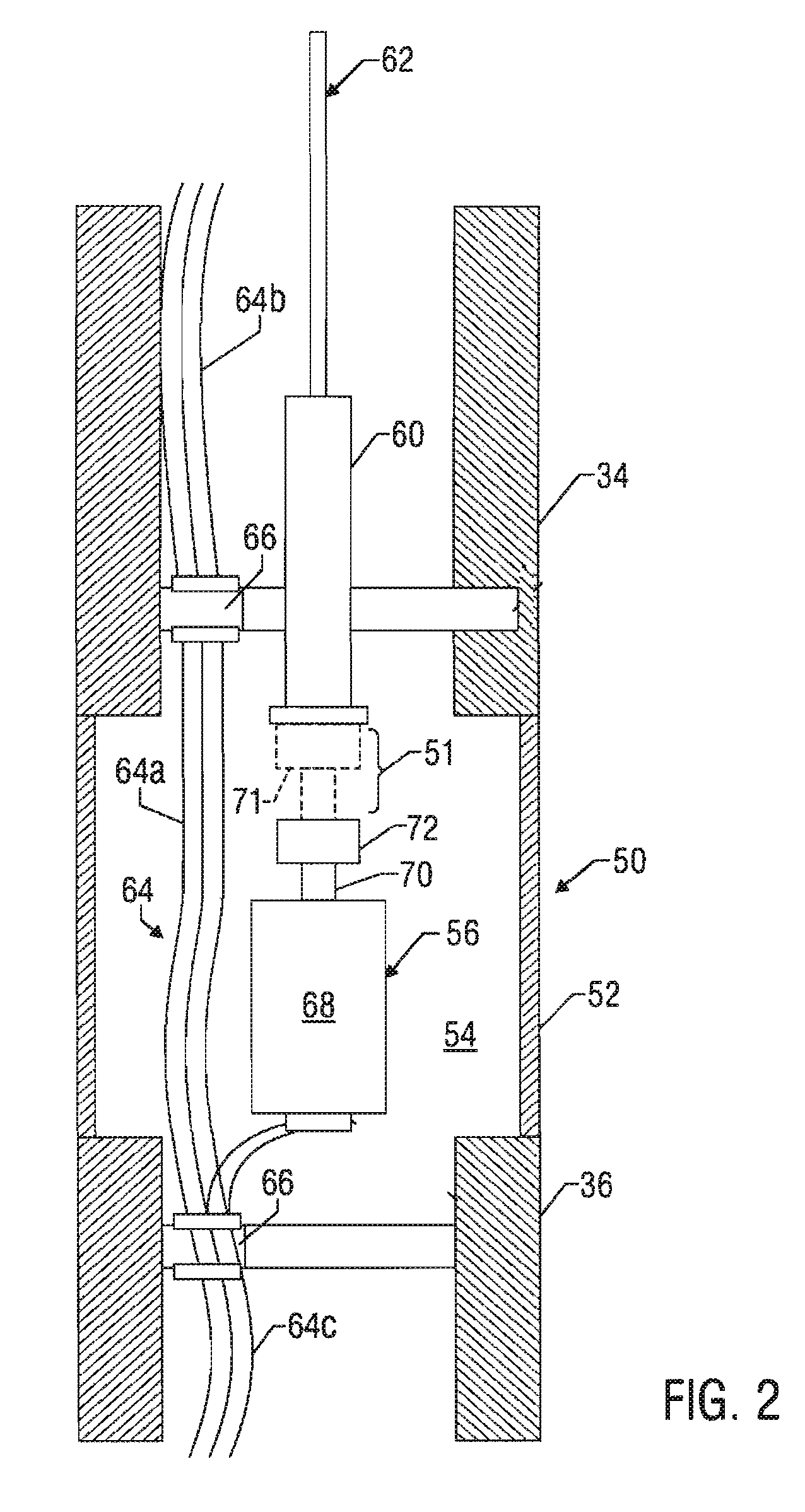
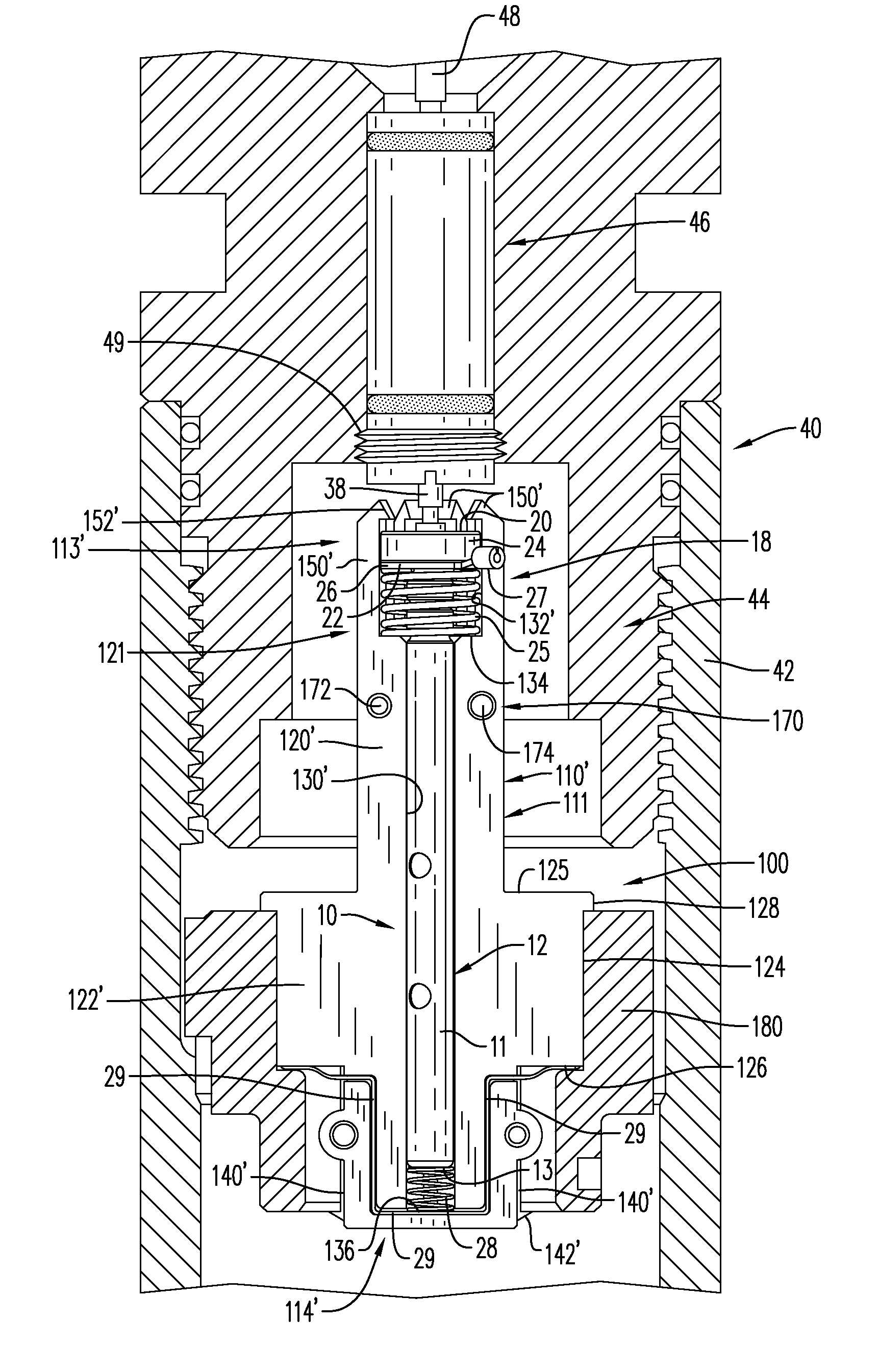
High pressure exposed detonating cord detonator system
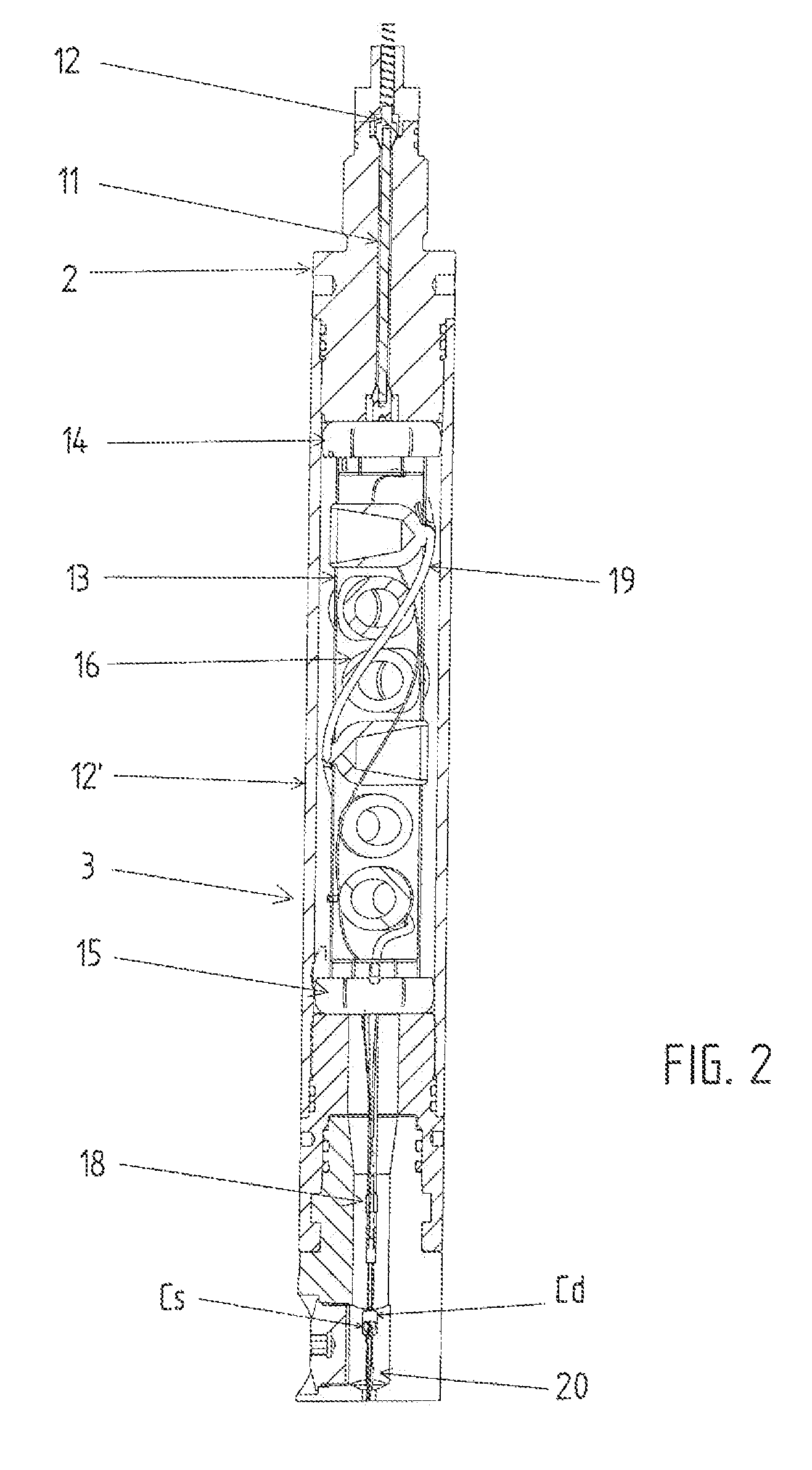
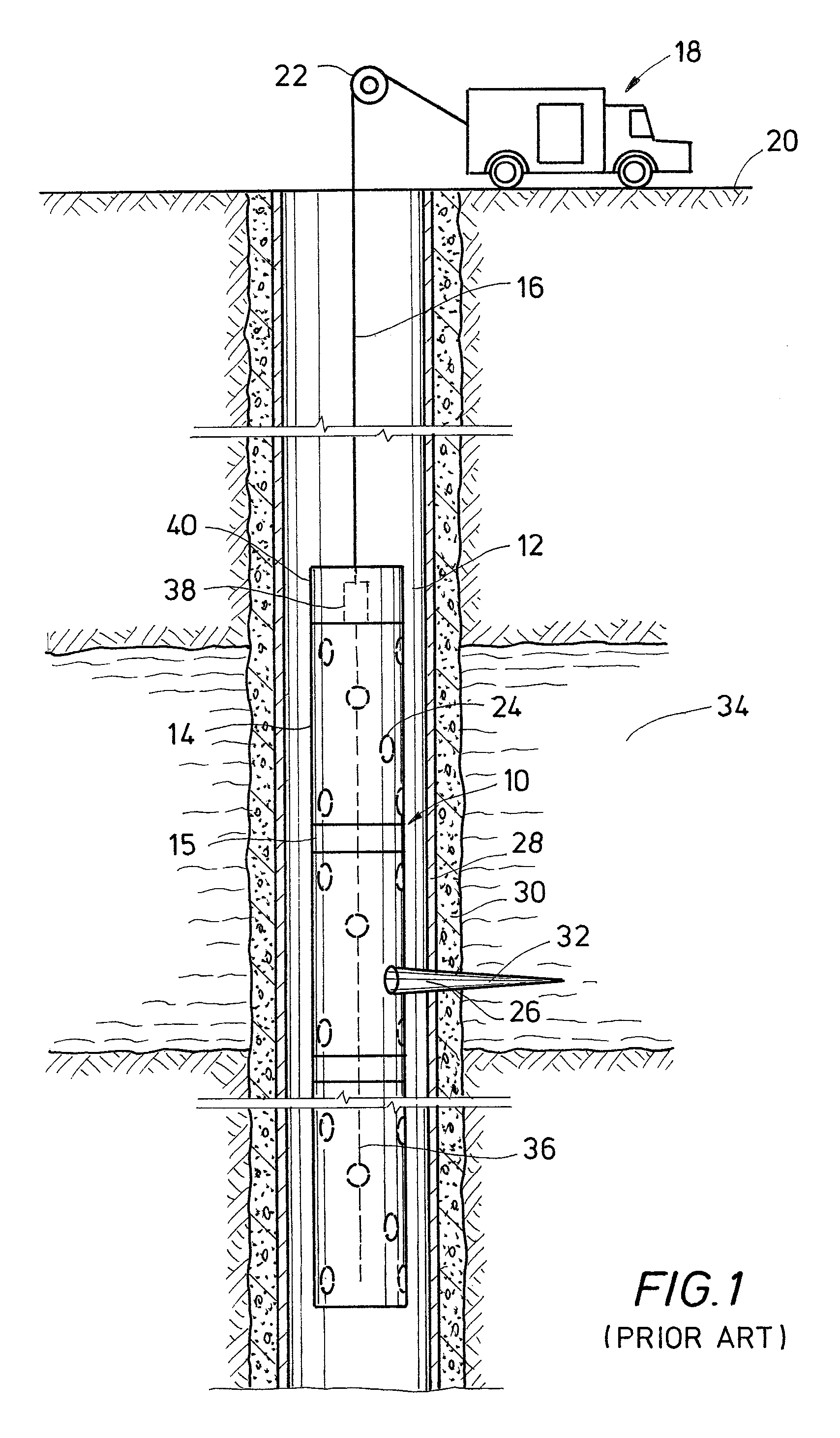
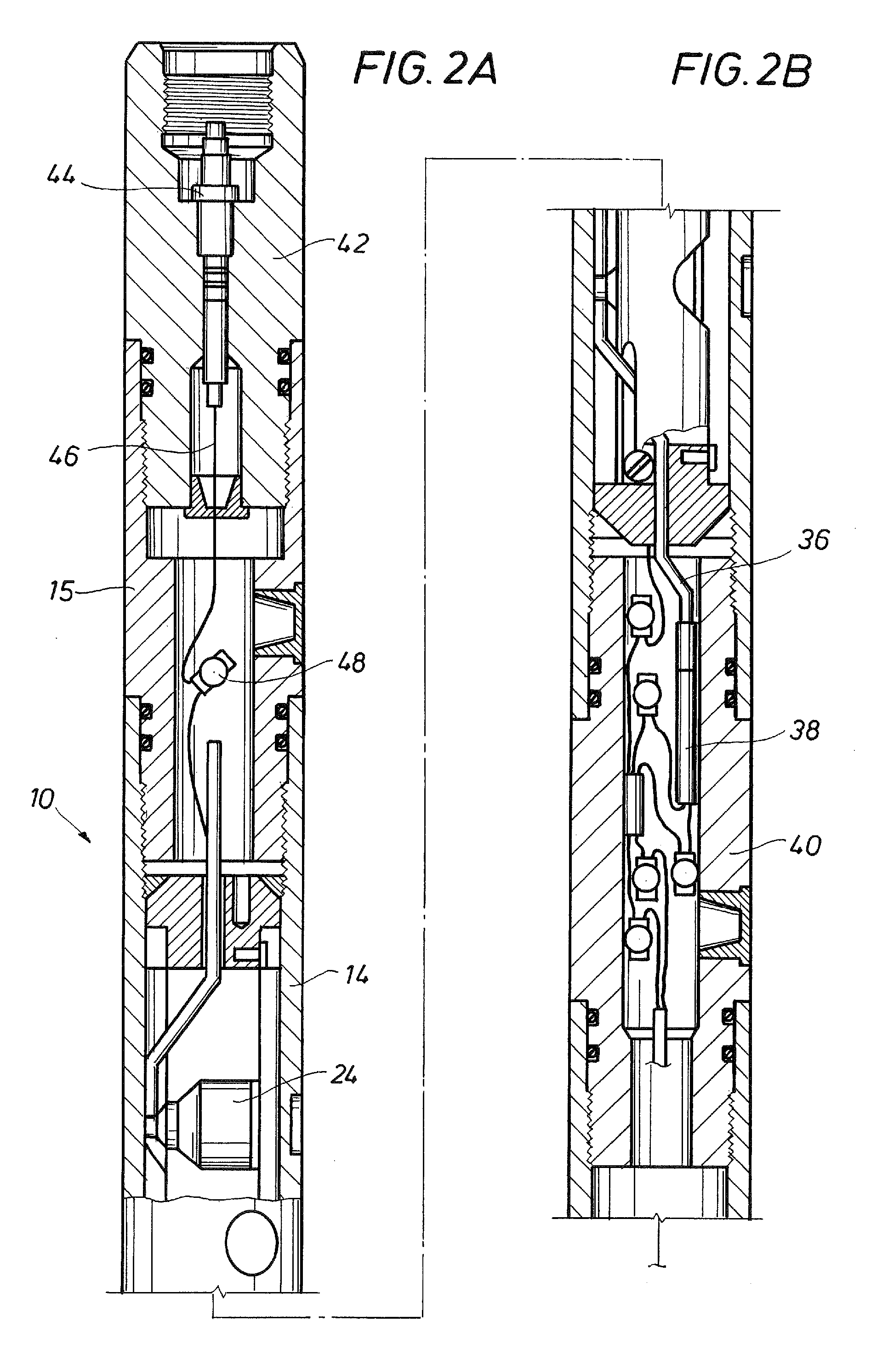
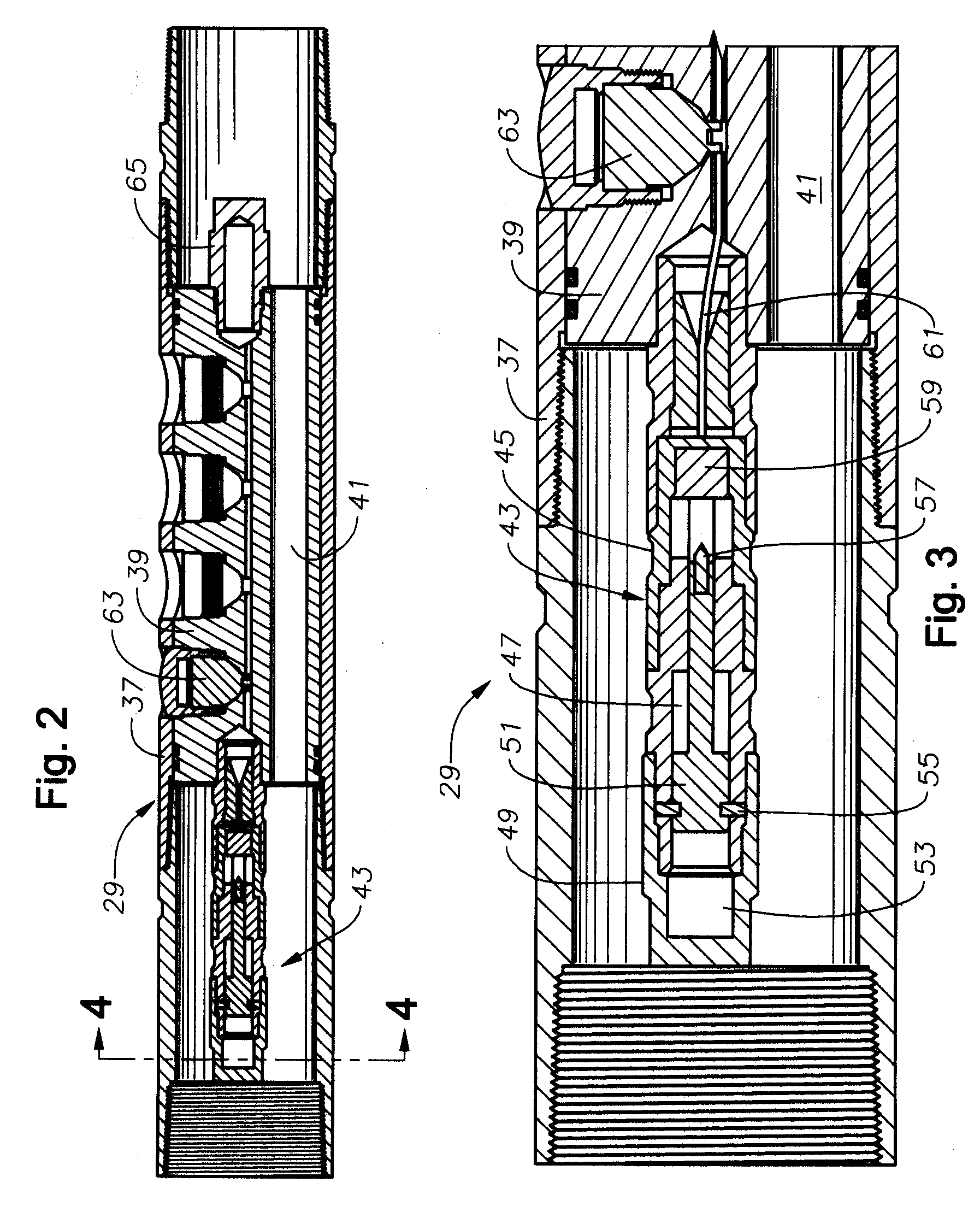
A detonator system for borehole systems which include detonating cord exposed to borehole fluids, pressures and temperatures. A firing head has a sealed chamber for an electrically fired detonator and has a booster charge holder forming part of the seal. The chamber is sealed by a wire line firing sub and by the booster holder. The charge holder includes a bulkhead separating the detonator chamber from a booster charge chamber and providing part of the detonator chamber seal. The detonator explosive and the booster charge are positioned on opposite sides of the bulkhead so that upon detonation of the detonator, the bulkhead is ruptured and the explosion transfers to the booster charge and from it to the detonating cord. The firing head includes holes for attachment of borehole tools such as perforating guns or back off tools to be fired by the detonating cord.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Wireless Detonator Assemblies, and Corresponding Networks
Wireless detonator assemblies (51-59) in use, form a cross-communicating network of wireless “detonator assemblies, such that communication of each wireless detonator assembly (57-59) with an associated blasting machine (50) can occur either directly, or via relay of signals (61-69) between other wireless detonator assemblies (51-56) in the network. Wireless detonator assemblies (51-59) can disseminate information (such as status information, identity information, firing codes, delay times and environmental conditions) among all of the wireless detonator assemblies in the network, while compensating for signal transmission relay delays at nodes in the network, thereby enabling the wireless detonator assemblies to detonate the explosive charges in accordance with the delay times. Various wireless detonator assemblies and corresponding blasting apparatus are disclosed and claimed. Methods of blasting using the wireless detonator assemblies and blasting apparatus are also disclosed and claimed.
Owner:ORICA EXPLOSIVES TECH PTY LTD
Perforating gun and detonator assembly
According to an aspect, a perforating gun assembly and a detonator assembly is provided. The detonator assembly includes at least a shell, means for selective detonation, and more than one electrically contactable component that is configured for being electrically contactably received by the perforating gun assembly without using a wired electrical connection, but rather forms the electrical connection merely by contact with at least one of the more than one electrically contactable components. A method of assembling the perforating gun assembly including the detonator assembly is also provided.
Owner:DYNAENERGETICS
Perforating gun and detonator assembly
According to an aspect, a perforating gun assembly and a detonator assembly are provided. The detonator assembly includes at least a shell, and more than one electrically contactable component that is configured for being electrically contactably received by the perforating gun assembly without using a wired electrical connection, but rather forms the electrical connection merely by contact with at least one of the more than one electrically contactable components. According to an aspect, the detonator assembly includes a selective detonator assembly. A method of assembling the perforating gun assembly including the detonator assembly is also provided.
Owner:DYNAENERGETICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com