Patents
Literature
933results about "Training ammunition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
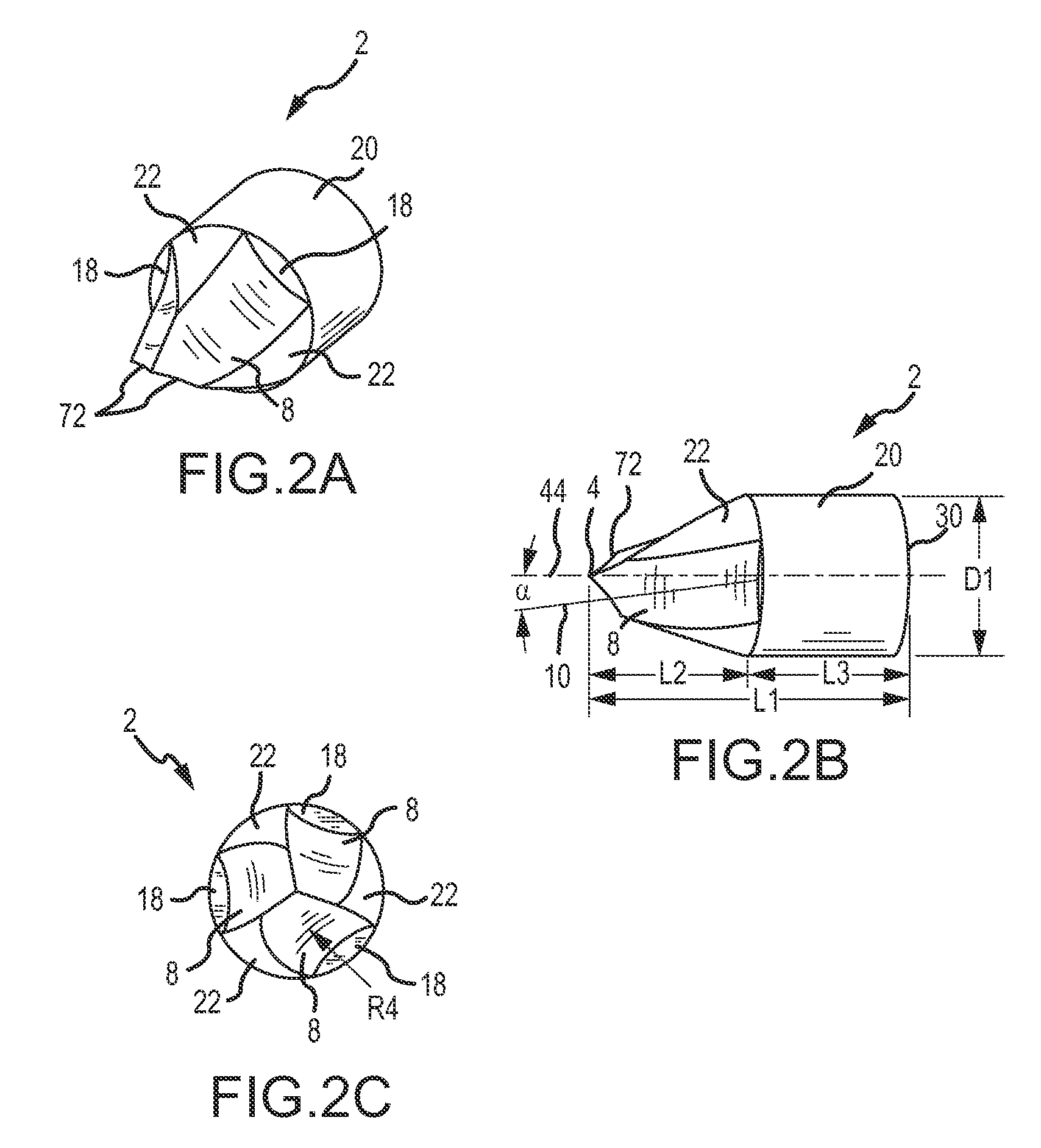
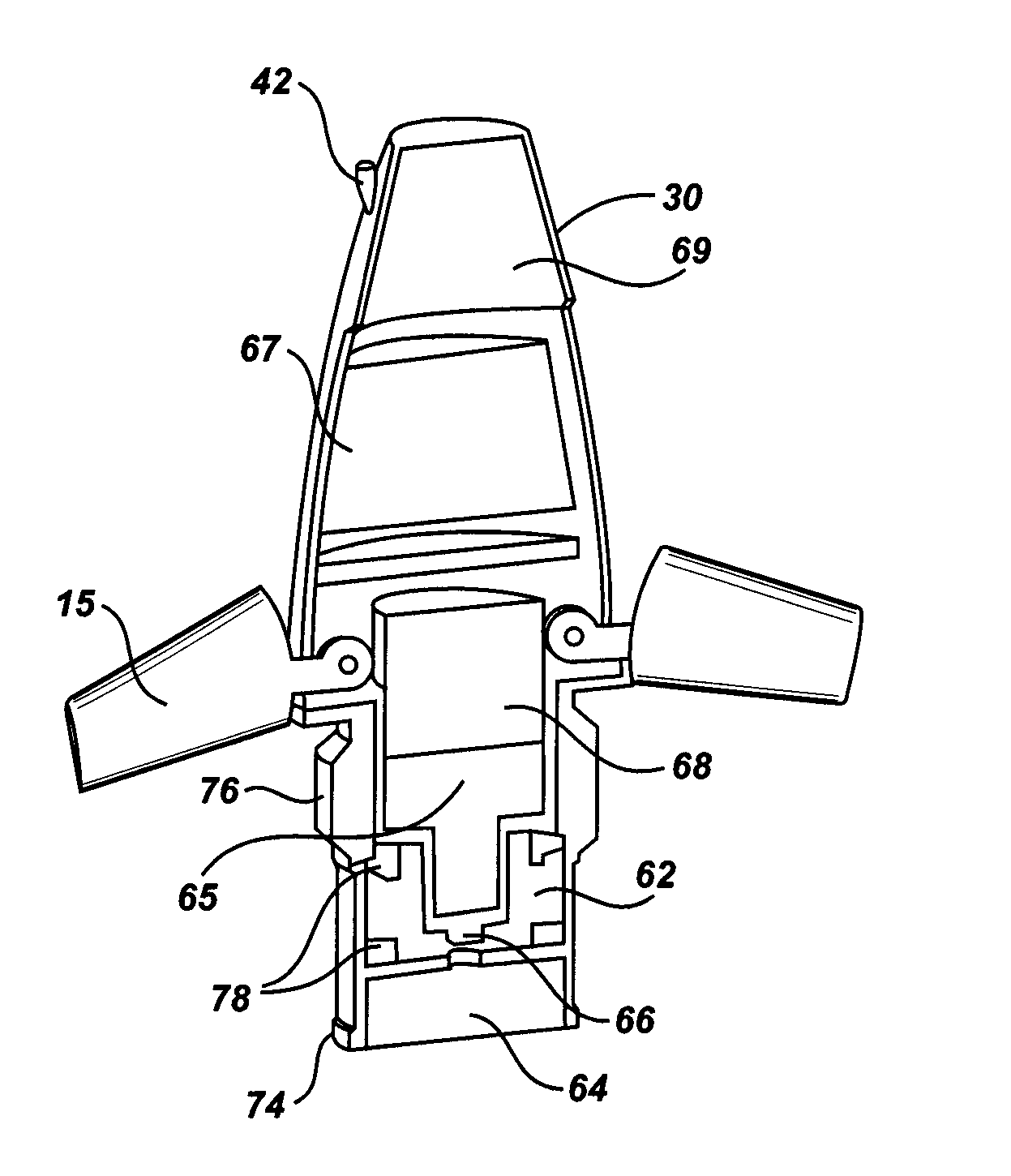
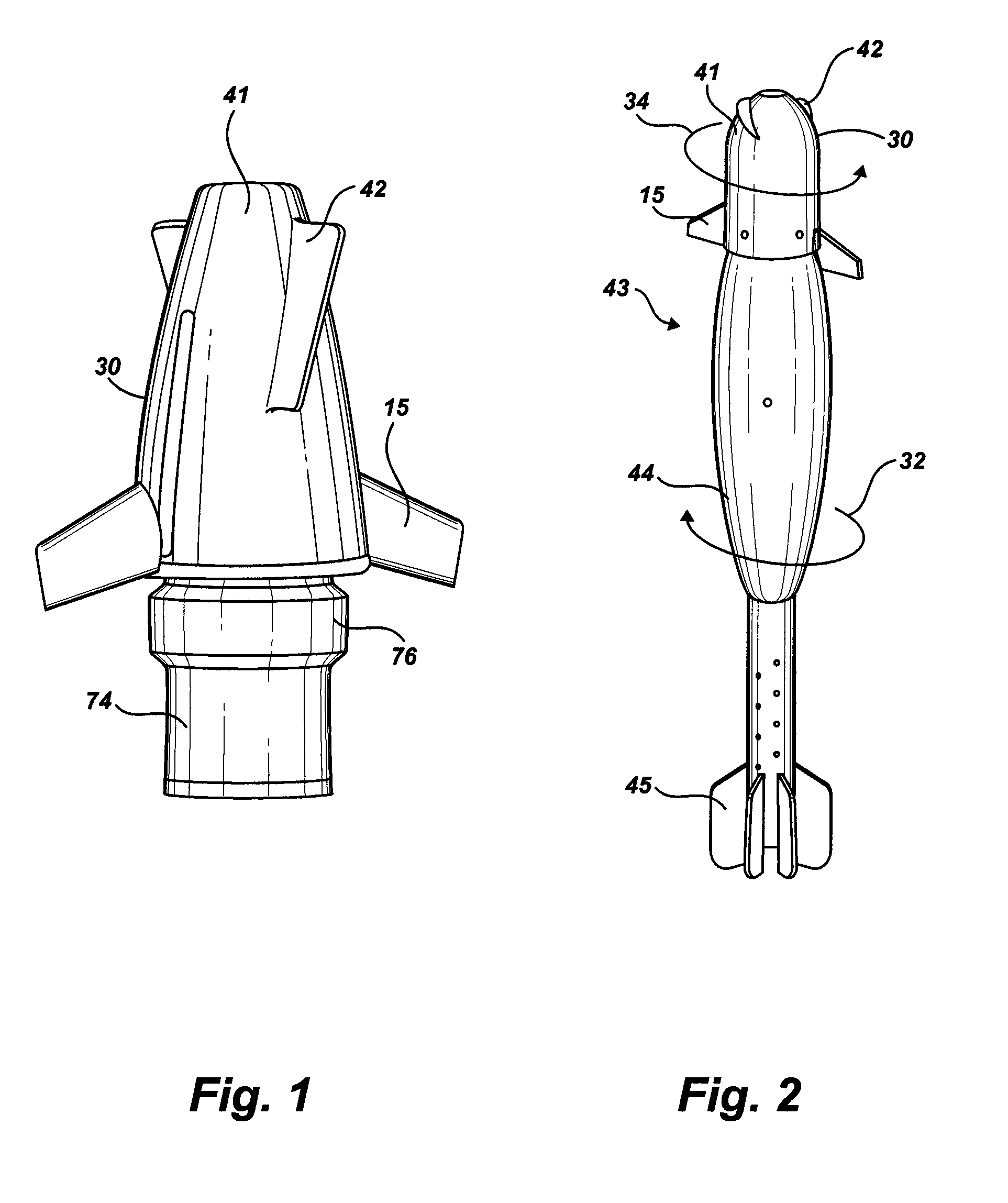
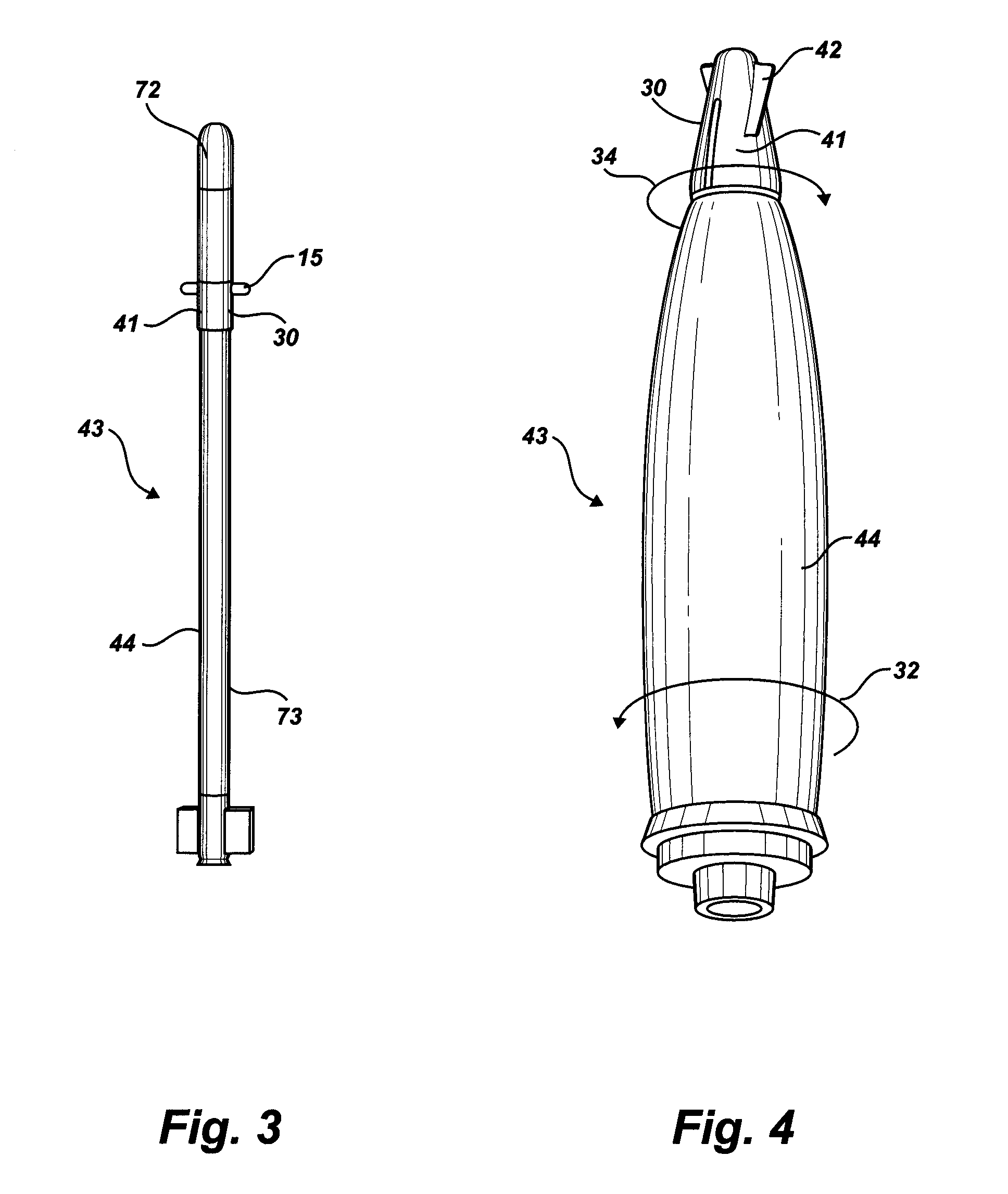
High accuracy projectile
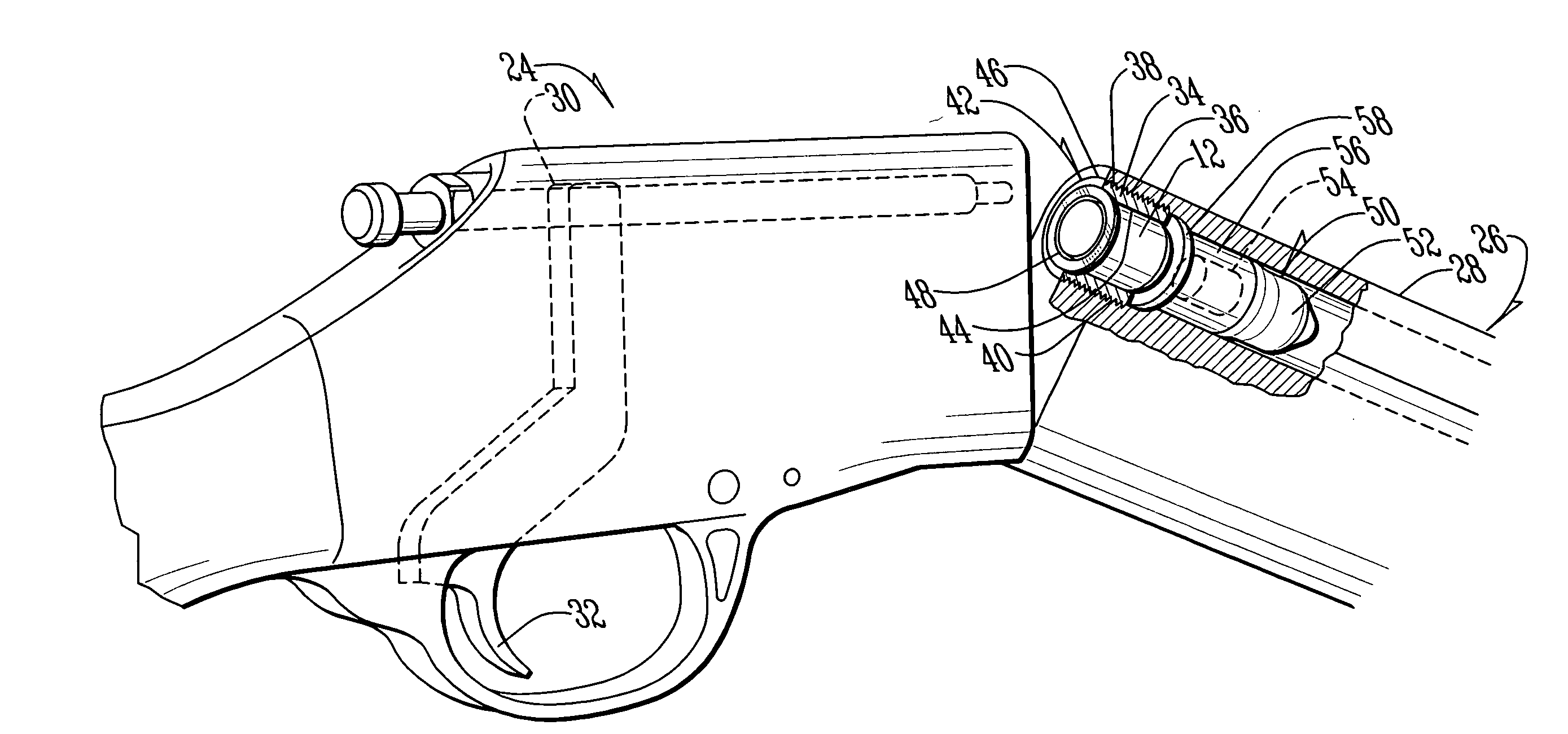
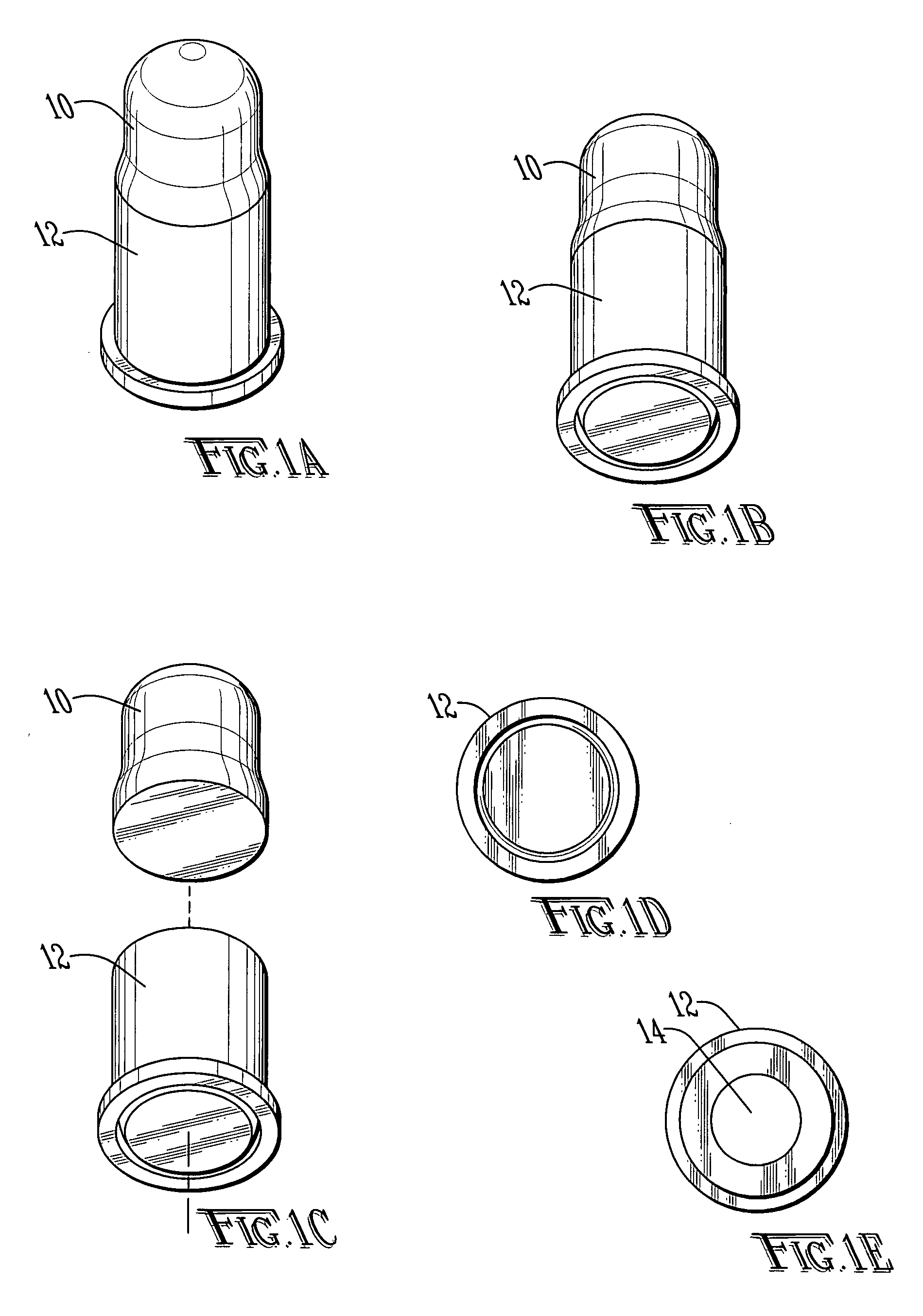
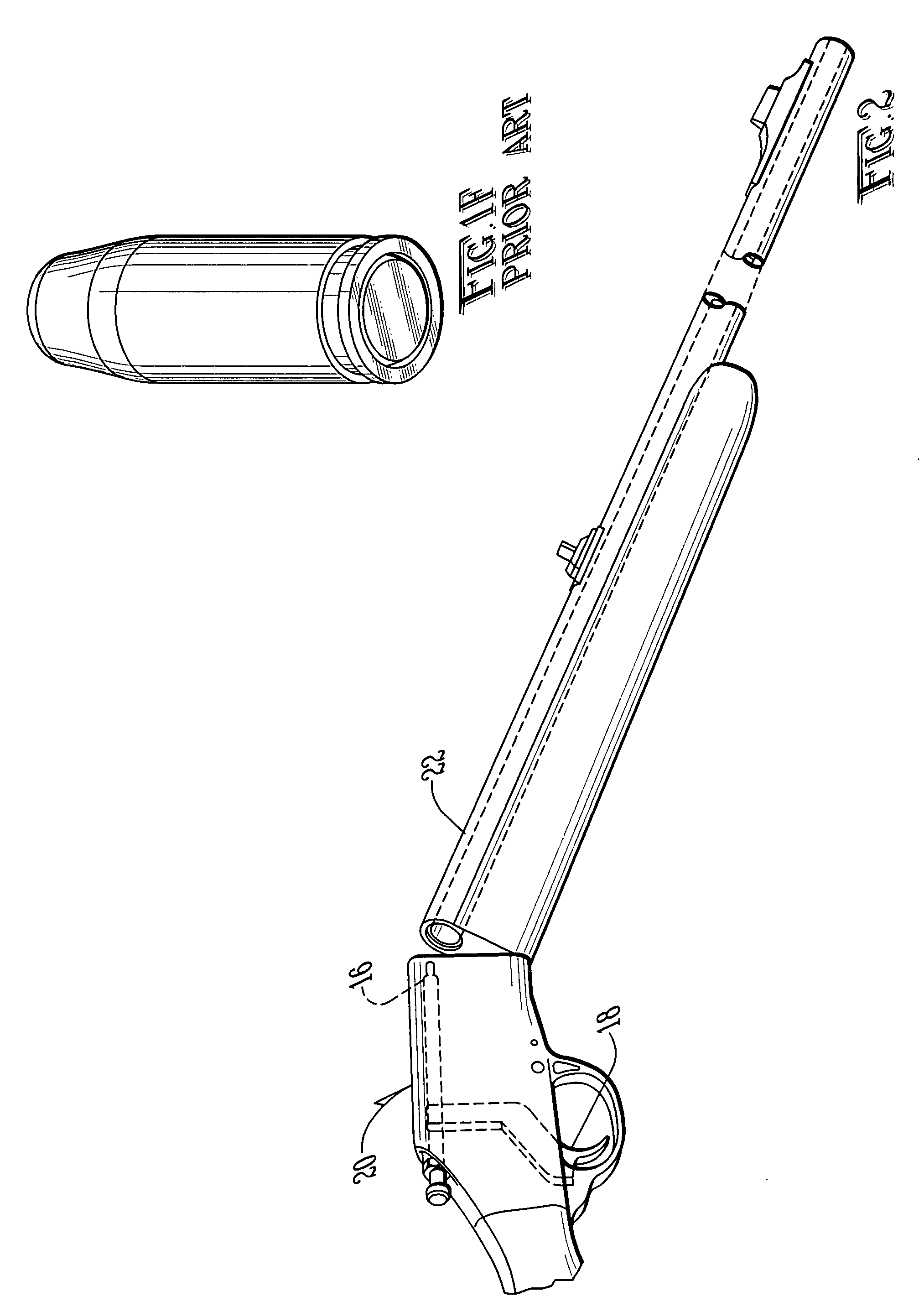
InactiveUS6070532AMinimizes bullet jumpImprove accuracyAmmunition projectilesTraining ammunitionEngineeringGun barrel
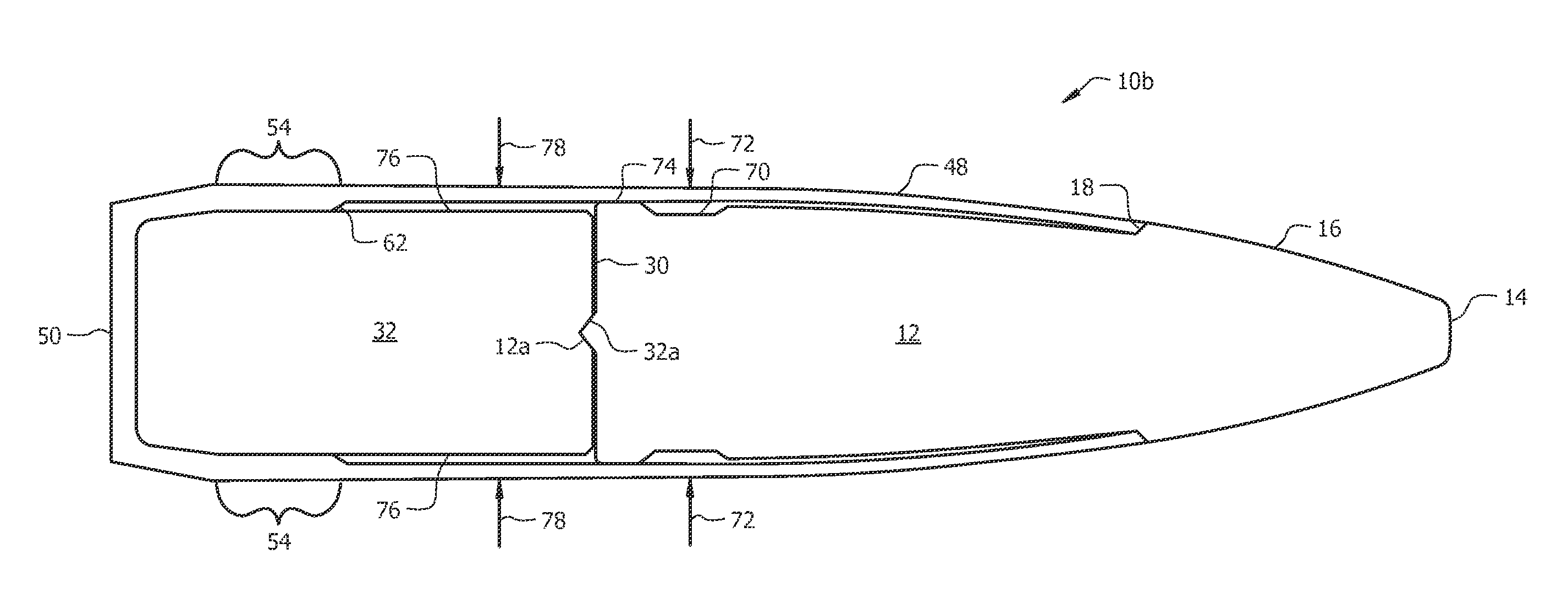
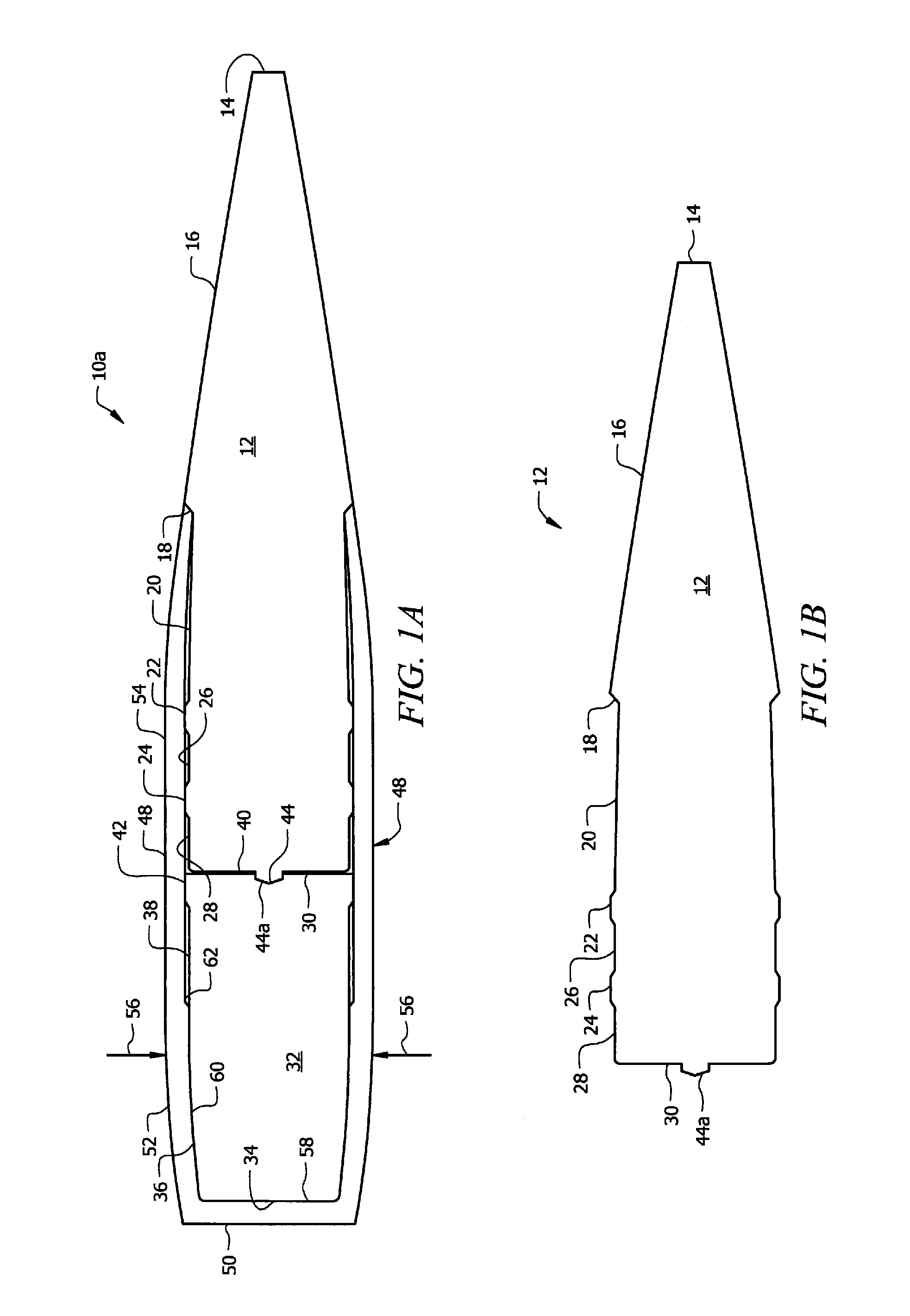
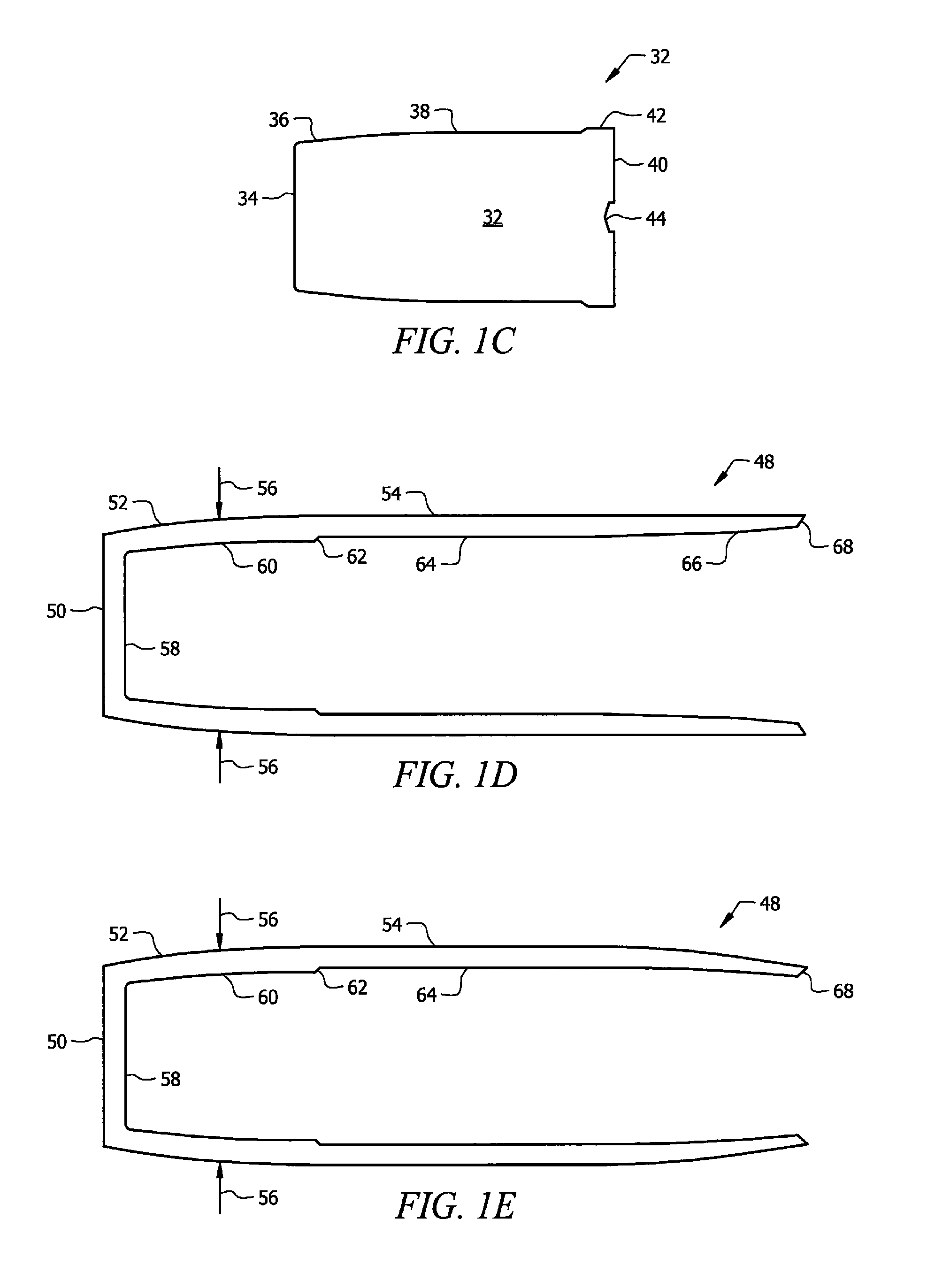
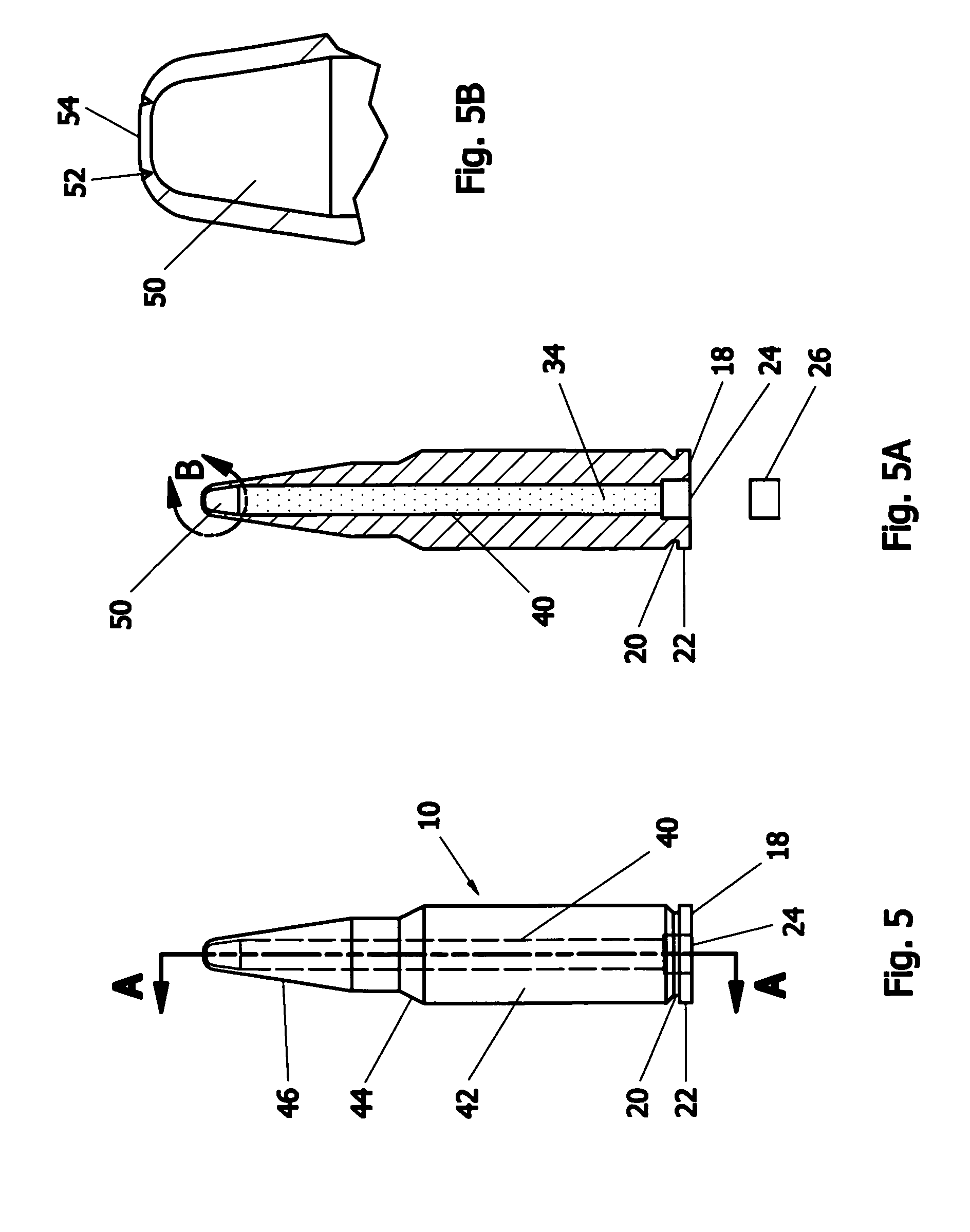
A projectile having improved accuracy when fired over long ranges is formed from a monolithic block of a copper alloy. Proceeding from a nose to a heel of the projectile, is a fore portion with arcuate side walls, a body portion of substantially constant cross-sectional area that minimally contacts a rifled gun barrel, a drive band having a diameter effective to seal propellant gases and an aft portion that continuously decreases in diameter terminating at the heel. A cylindrical bore extends from an opened end at the nose to a closed end proximate to a transition plane between the fore portion and the body portion.
Owner:OLIN CORP
Projectile for fire arms
InactiveUS8511233B2Maximal gas pressureVelocity increasesAmmunition projectilesTraining ammunitionPower beltEngineering
A projectile for fire arms formed in such a way that it includes a front portion of essentially convex axial cross-section that via a transition transforms into a rear portion of essentially cylindrical radial cross-section, which rear portion acts as a power belt for the projectile.
Owner:NORMA PRECISION AB
Composite projectile and cartridge with composite projectile
A projectile includes: (a) a cured, toughened polymer resin; and (b) a particulate filler distributed through the resin, the filler having a density greater than a density of the resin, wherein the projectile has average density less than the density of lead.
Owner:GFY PROD LLC
High volume multiple component projectile assembly
A projectile includes a head, a tail, and an interface that interconnects the head and tail. Multiple sections of the interface are deformed by being compressed radially inwardly into respective annular recesses formed between the interface and the head and tail during manufacturing or by rifling when the projectile is fired. The amount of deformation is controlled by the depth of each of the annular recesses. In all embodiments, annular ridges formed in the head, the tail, or both, define the longitudinal extent of the annular recesses. The interface includes an annular obturation region and has a beveled open leading end to facilitate insertion of the head and tail into the interface.
Owner:LIBERTY OPCO LLC
Intercept vehicle for airborne nuclear, chemical and biological weapons of mass destruction
InactiveUS6626077B1Minimize damageHigh probability of successfully capturing a weaponAmmunition projectilesAircraft componentsRadiological weaponEngineering
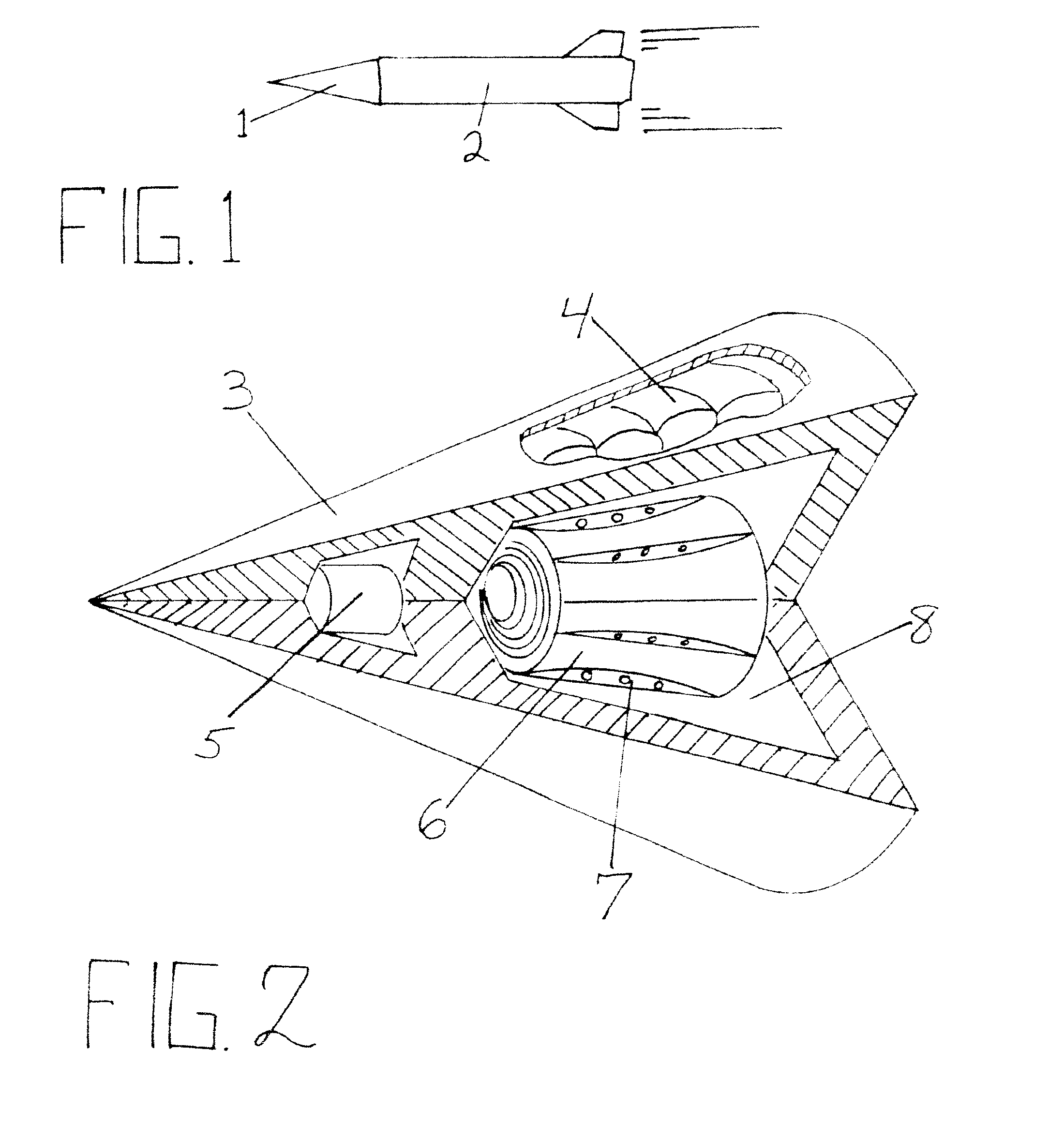
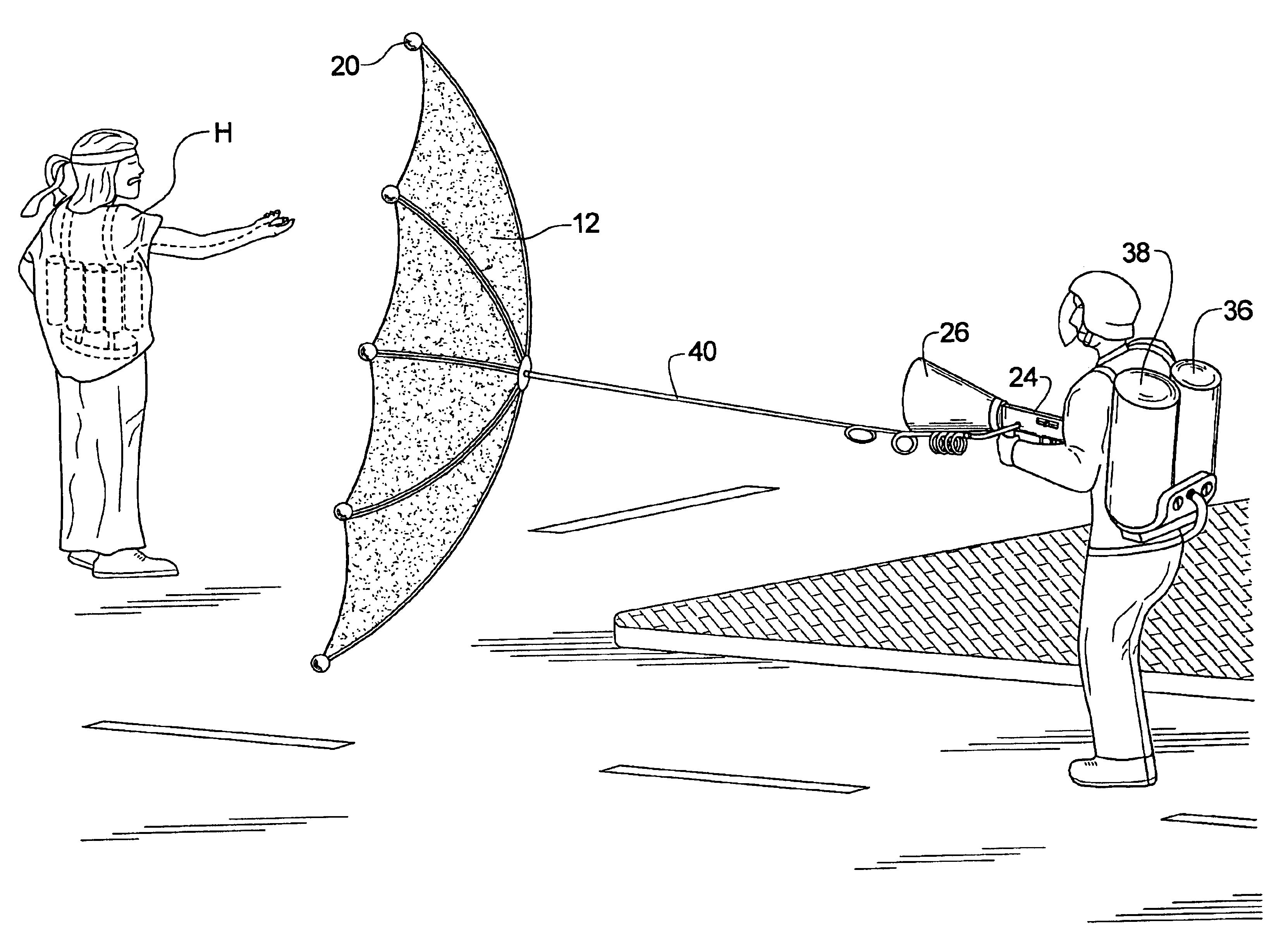
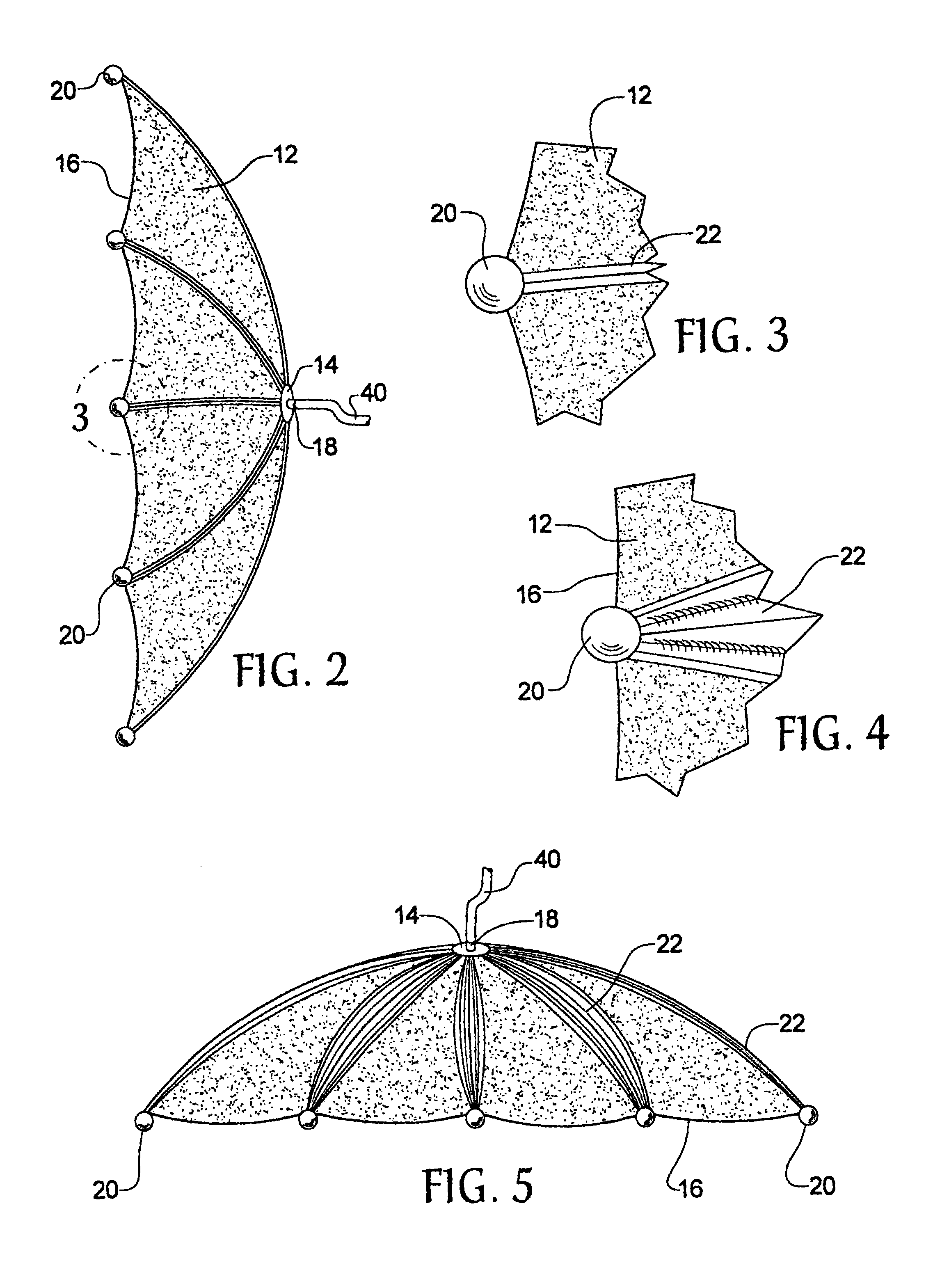
An intercept device for flying objects made of a light-weight, packable structure made of a pliable, tear resistant material that can be expanded to a large web-like structure by means of a deployment device, into the path of a flying weapon. To capture, hold and reduce the velocity of intercepted flying objects, activatable resistance bodies are incorporated into uniformly distributed masses that are connected to the perimeter of the web like structure. Contractable sections of the web, made of cable-like structures, connected to perimeter masses, act as drawstrings upon collision with flying object. This causes closure of the web around the flying object as a result of the mass's inertia and added resistance from deployable resistance structures that place tension on drawstring structures of the web. The flying object is subsequently captured within the web, held secure and it's velocity rapidly reduced.
Owner:GILBERT MARK DAVID
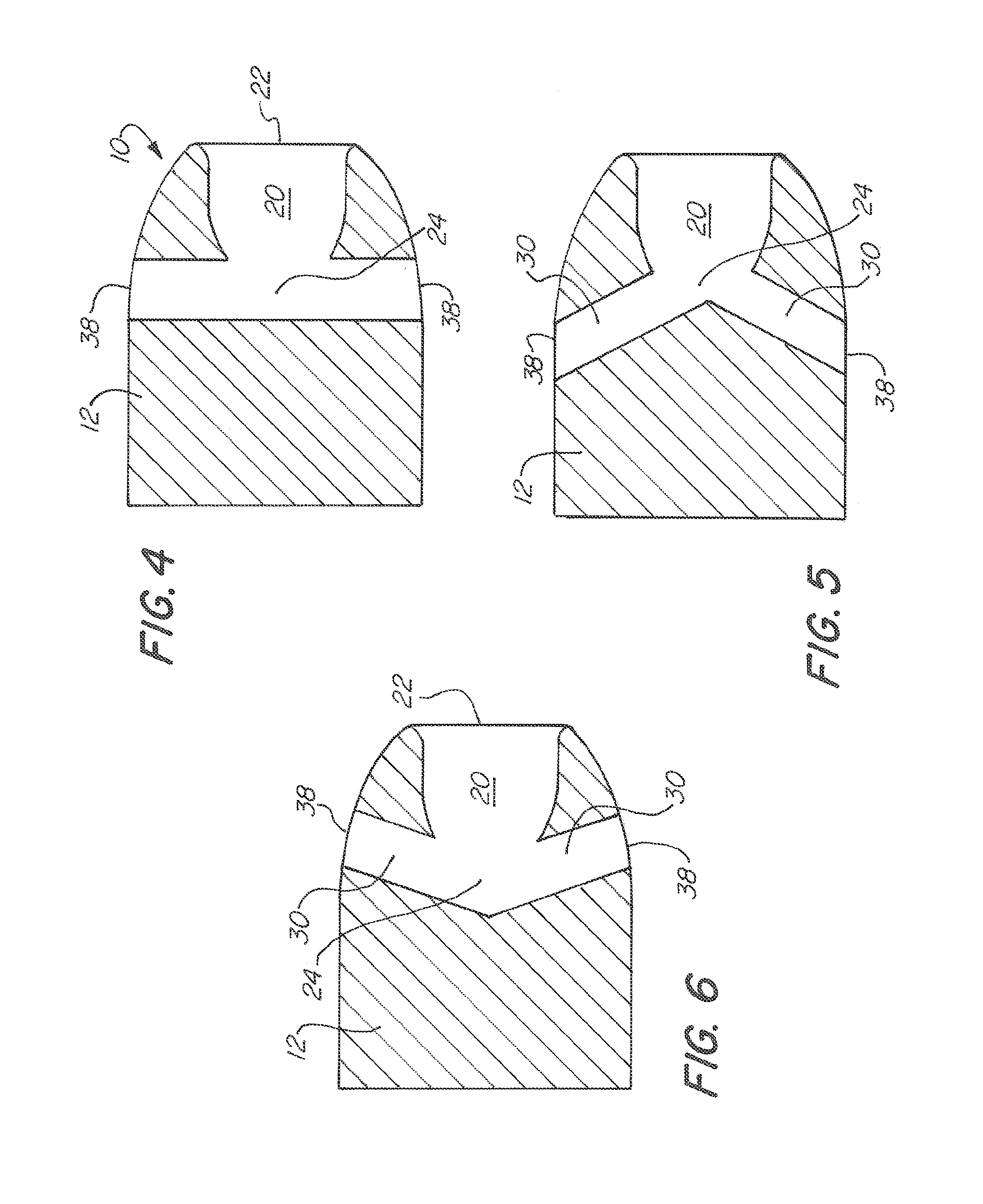
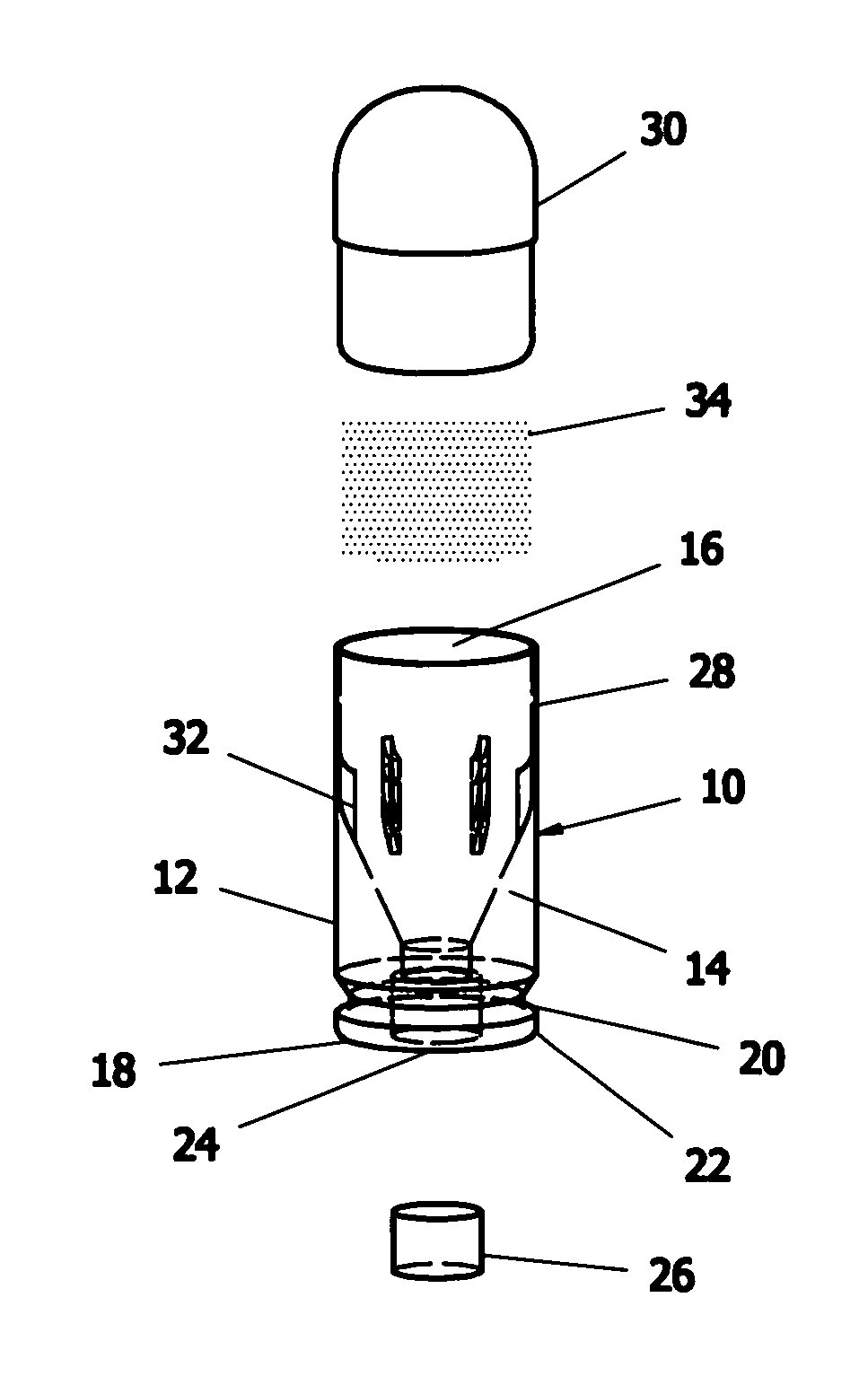
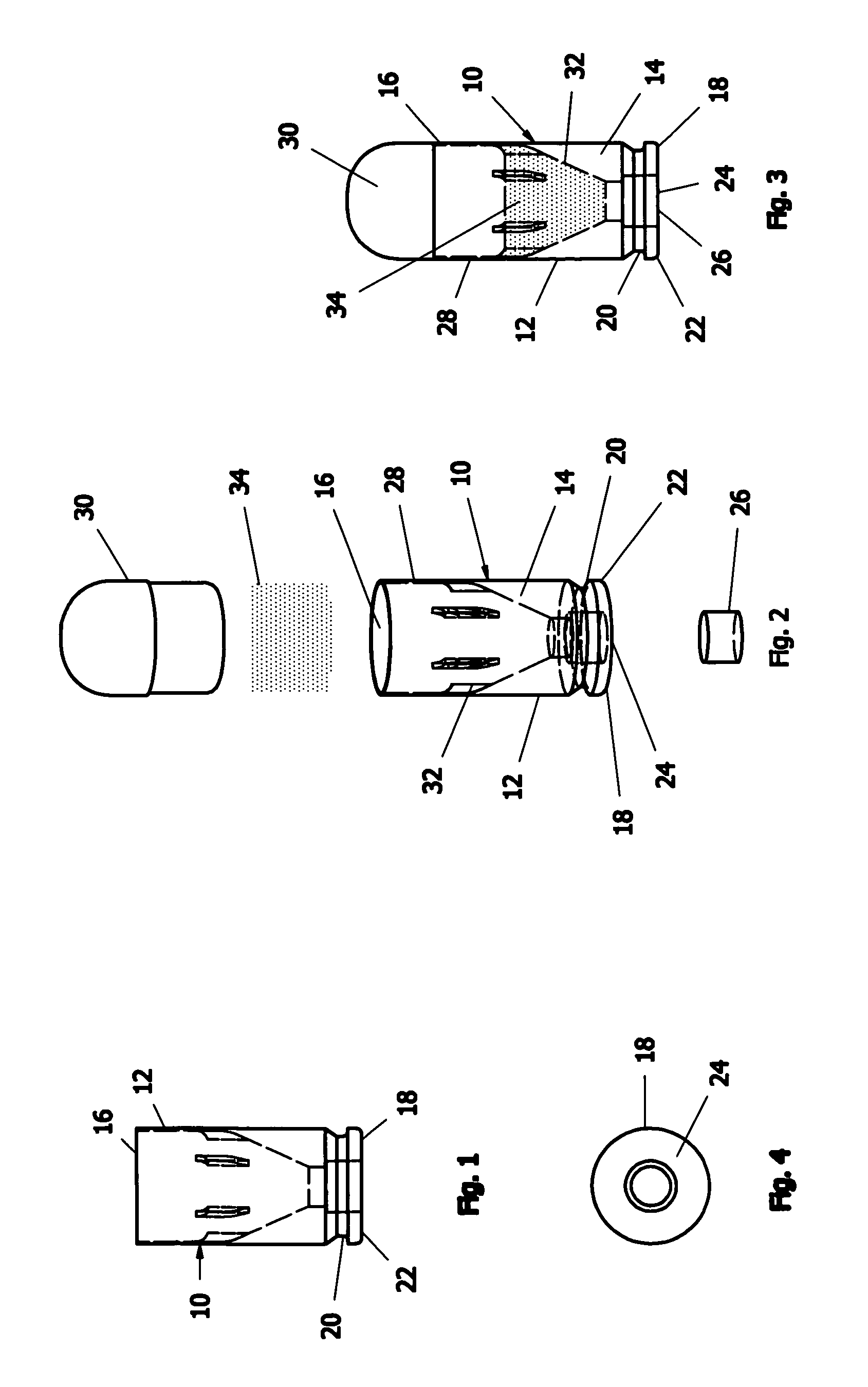
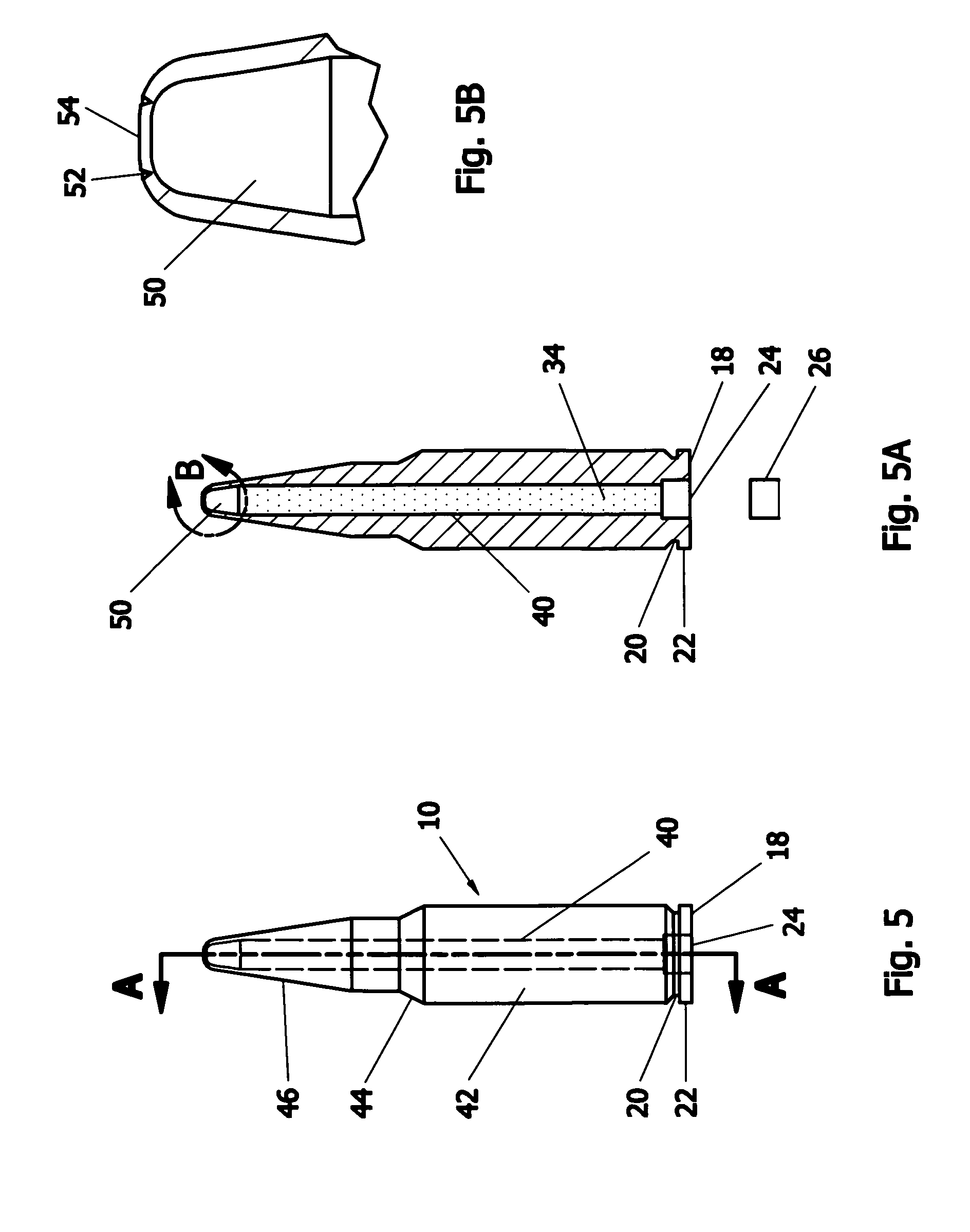
Large caliber frangible projectile
A large caliber, frangible, training projectile imitates, for training purposes, the corresponding tactical projectile. To enable fragmentation of the training projectile at impact, some embodiments of the frangible projectile are partially or entirely made of a material with a lower yield strength than the material used in the counterpart tactical projectile. Some embodiments of the frangible projectile may include portions that are sectioned, welded, or provided with stress risers. Some embodiments of the frangible projectile may include high density particles suspended in a weaker medium. The fragmentation methods may be applied to the overall mass of the projectile, or to a portion of the projectile.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
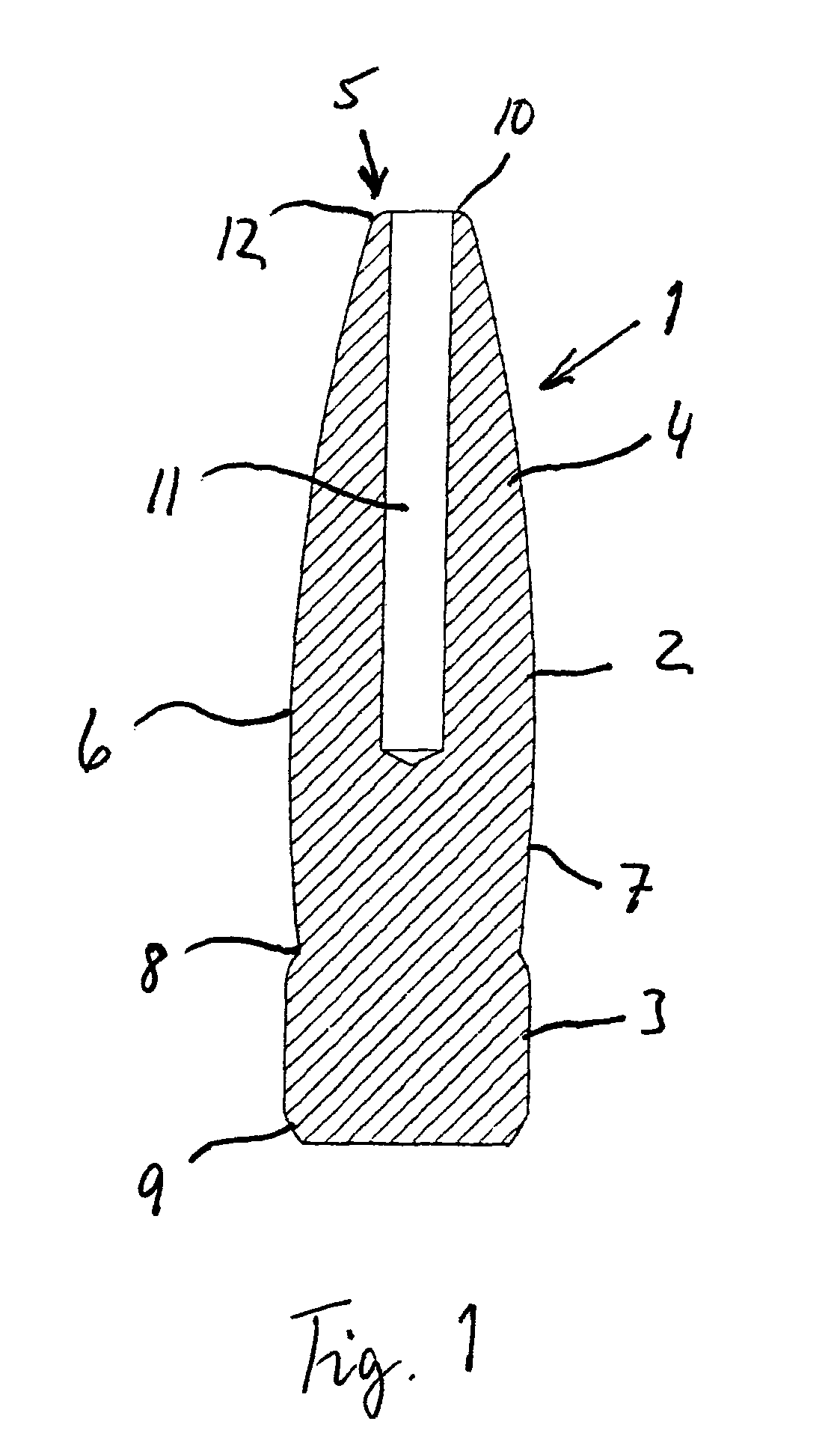
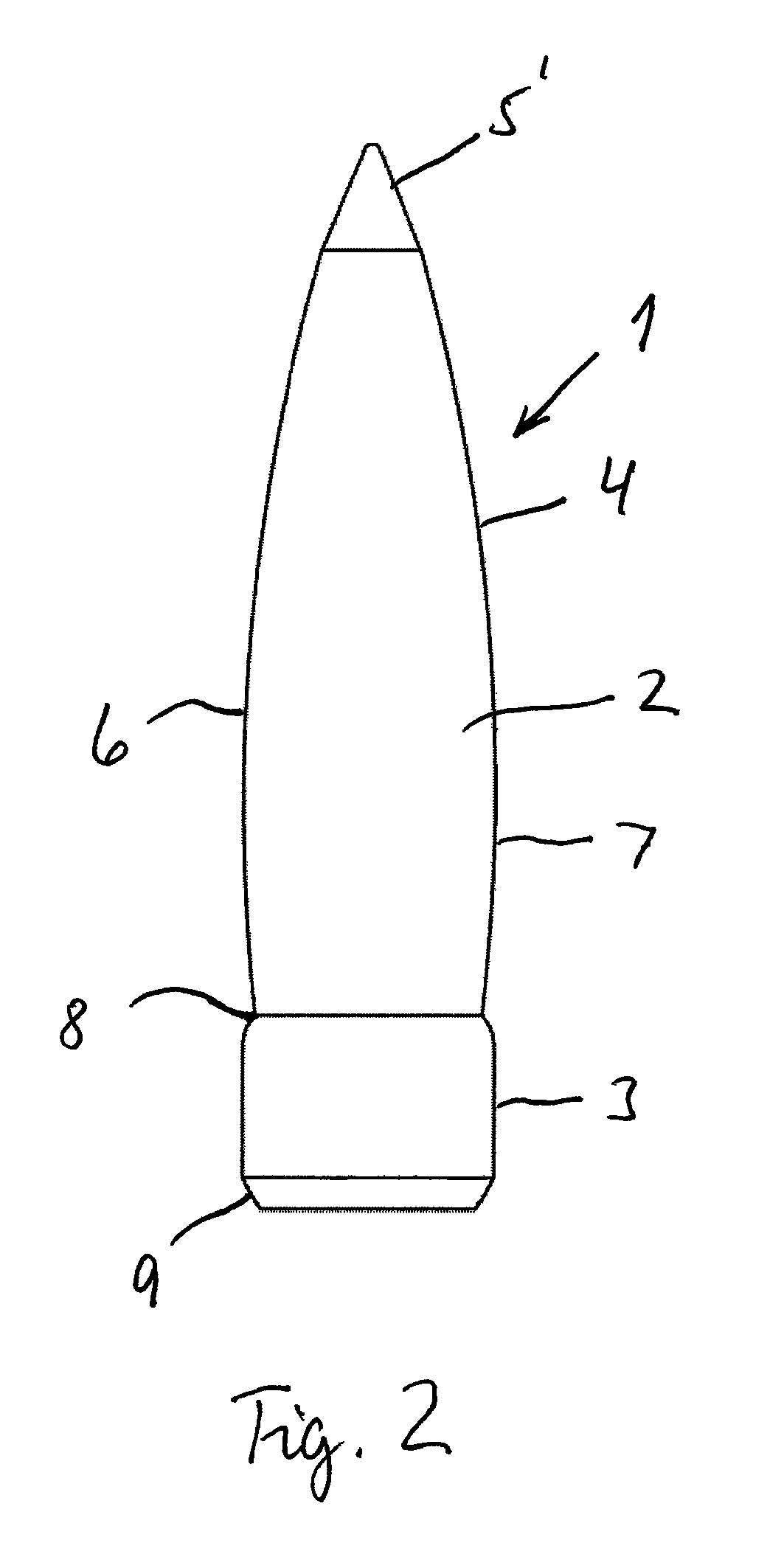
Projectile
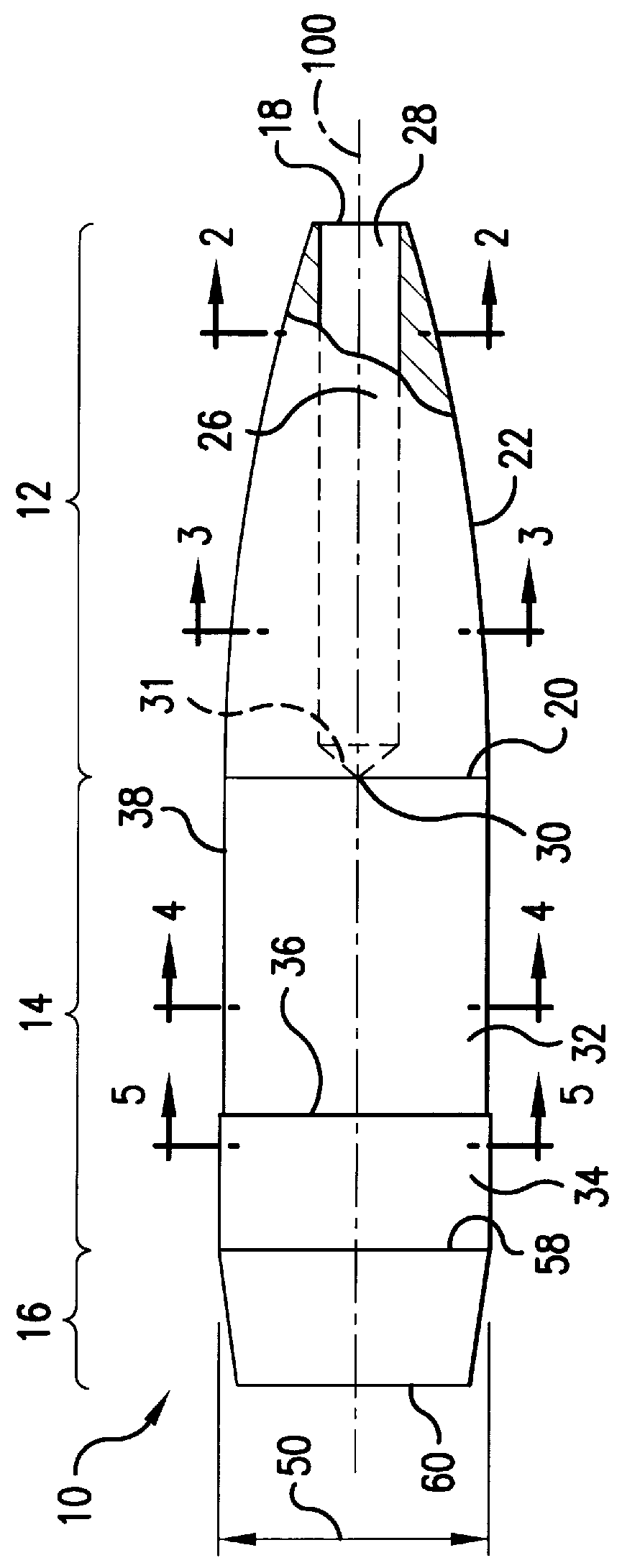
ActiveUS8893621B1Superior flight stability characteristicHighly effectiveAmmunition projectilesTraining ammunitionEngineeringBearing surface
A projectile comprised of an ogive section, a bearing surface section and a boattail section. A cavity is formed inside the projectile from an aperture on the aft end of the boattail section and forward to about the transition point (shoulder) between the ogive section and bearing surface section. The cavity is centered about the centerline of the projectile and open on the aft end of the projectile.
Owner:ESCOBAR ROLANDO
Muzzleloading firearm projectile
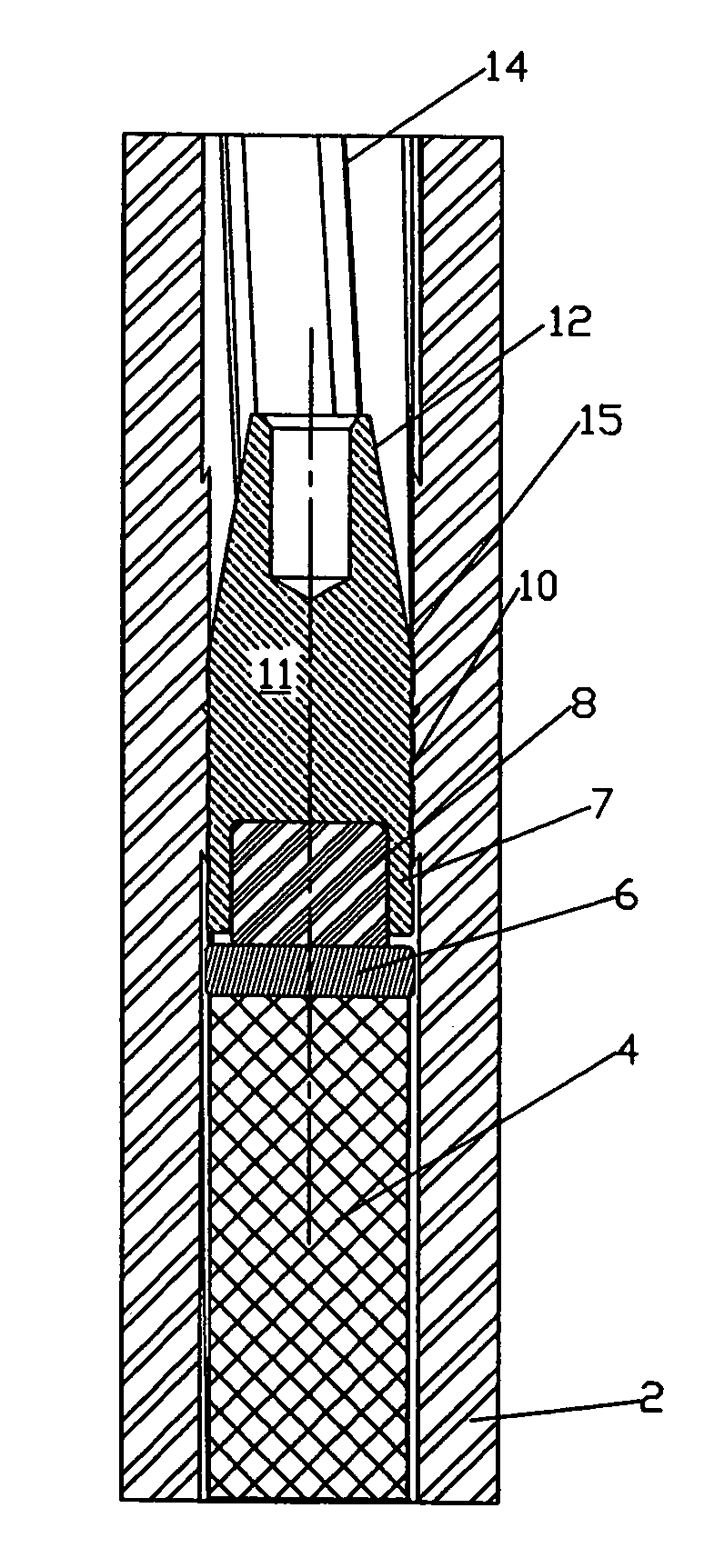
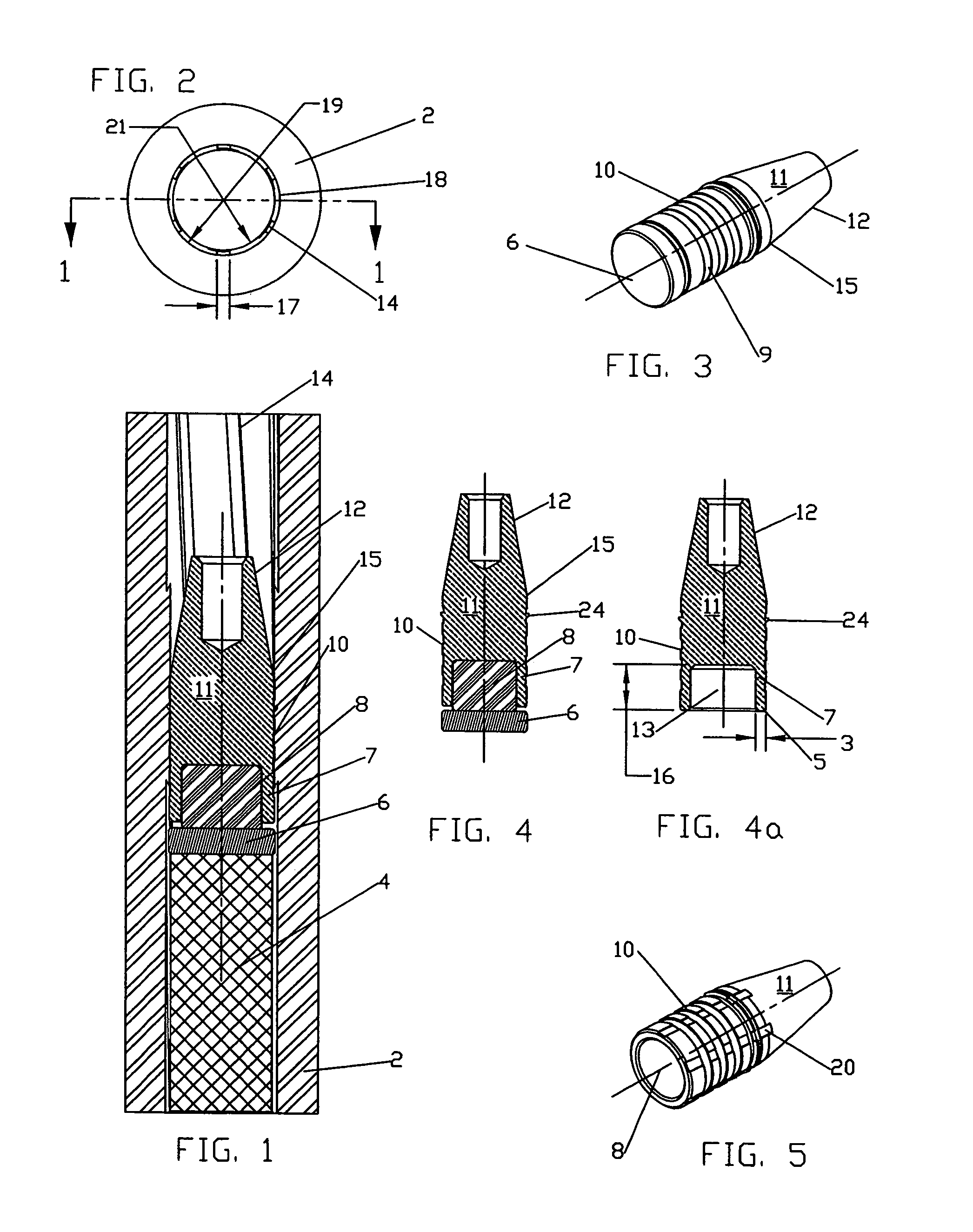
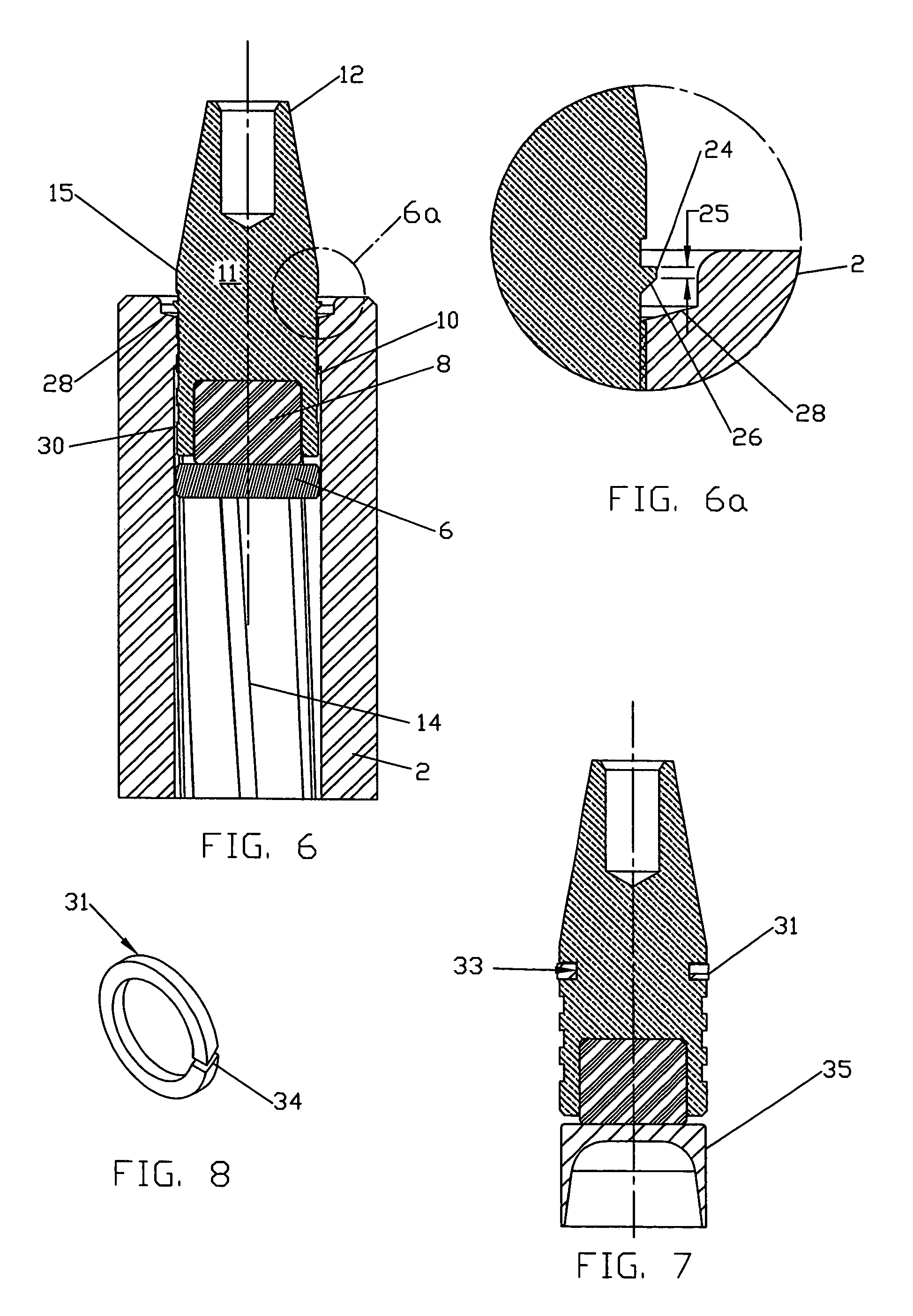
InactiveUS7380505B1Easy loadingReasonable alignmentAmmunition projectilesTraining ammunitionEngineeringCopper
A muzzle loading firearm projectile is disclosed that is composed of a multi diameter, hollow base solid copper bullet, the rear cavity filled with a material of low-density, and a gas pressure seal that separates the bullet from the powder charge. The majority of the bullet shank has a diameter less than the bore diameter of the firearm barrel to allow for ease of loading and alignment of the barrel and bullet axis; a narrow ring of material larger than the barrel bore diameter but less than the groove diameter is located at the junction of the bullet shank and nose profile that centers the bullet in the barrel and positively positions the bullet over the powder charge regardless of orientation of the firearm. The low-density material filling the rear cavity of the bullet acts as an expansion medium when impacted by the rear gas seal during the firing process causing the hollow shank of the bullet to expand and lock into the barrel rifling.
Owner:SHIERY JEFFREY C
System and method for processing ferrotungsten and other tungsten alloys, articles formed therefrom and methods for detecting the same
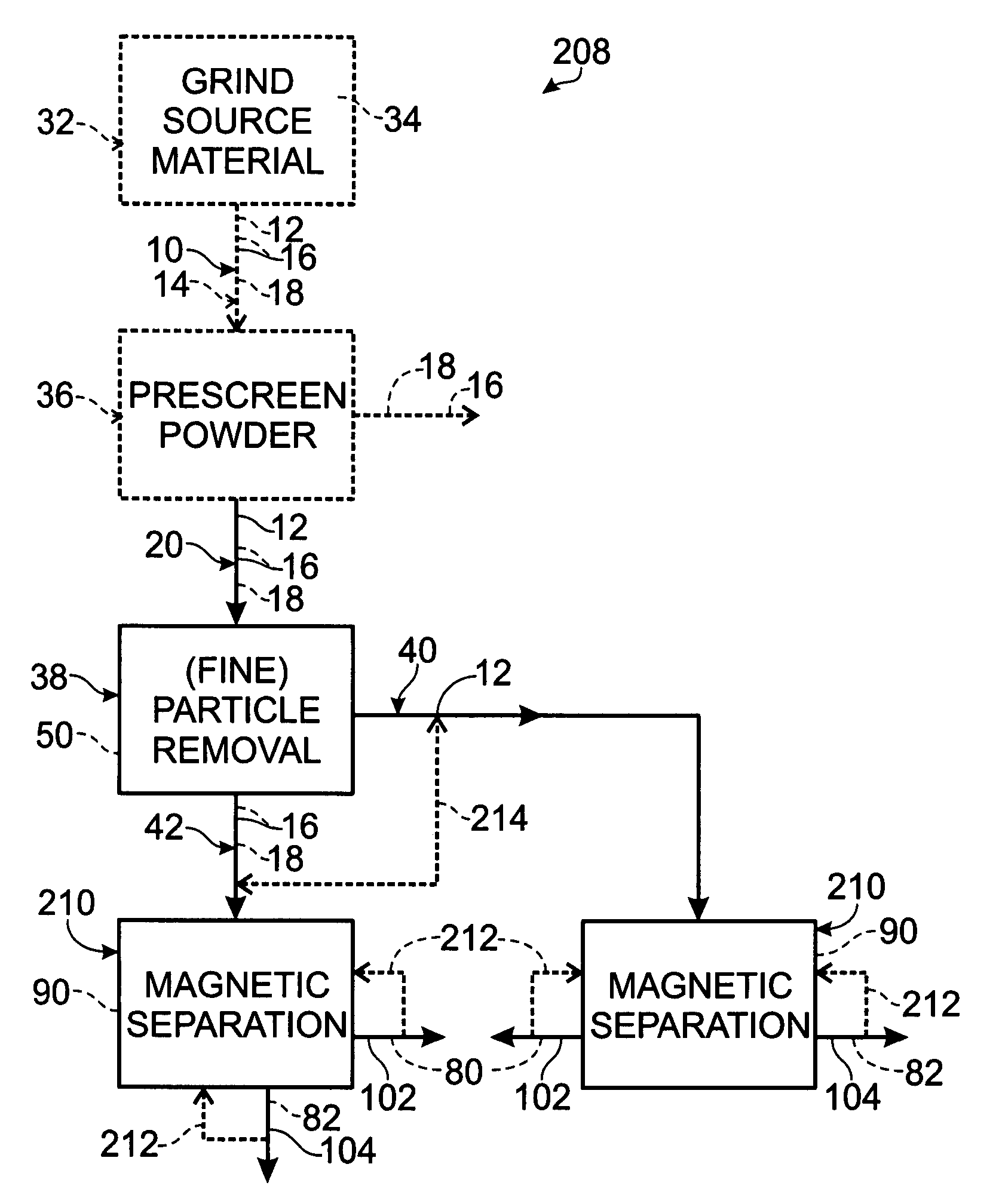
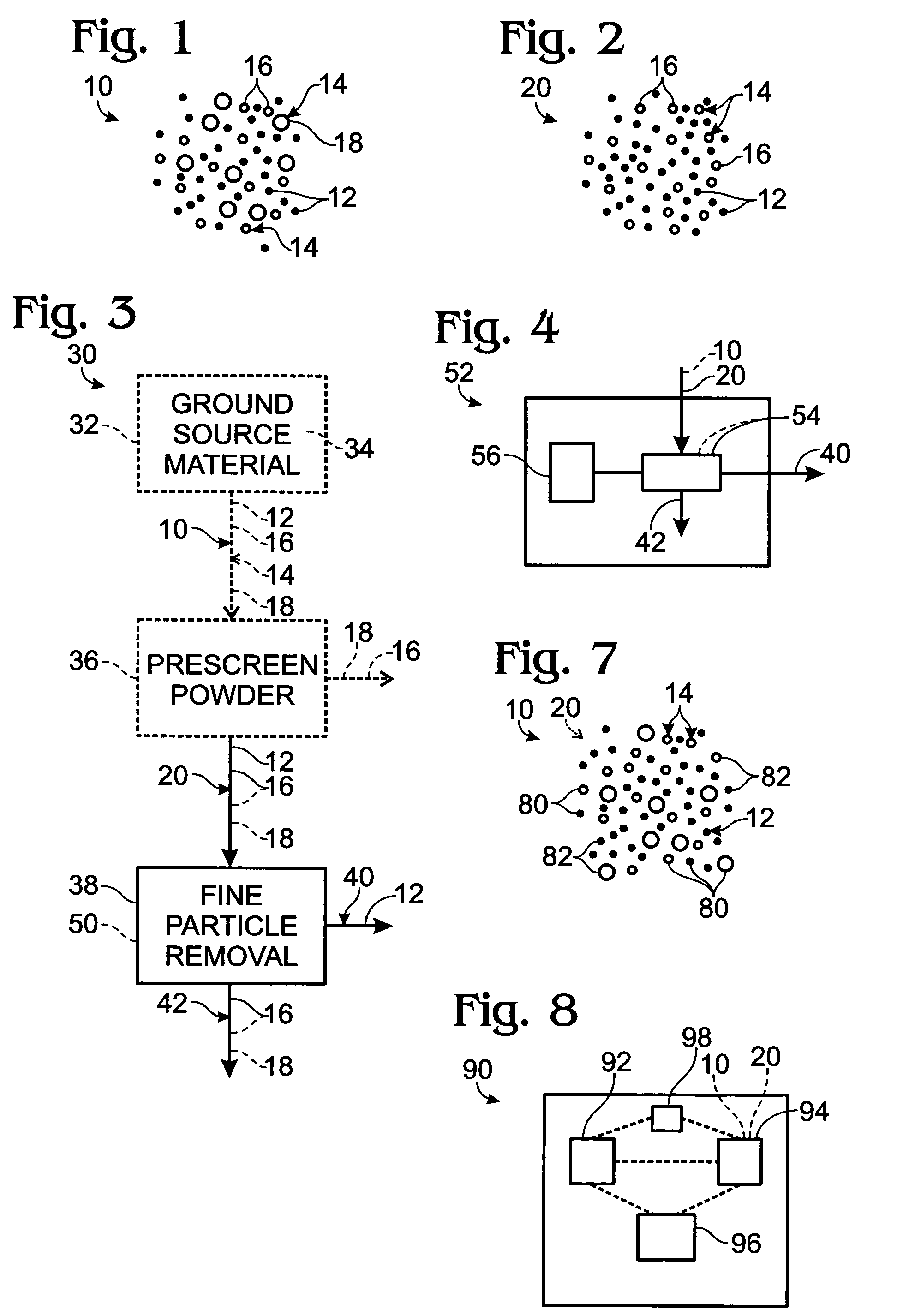
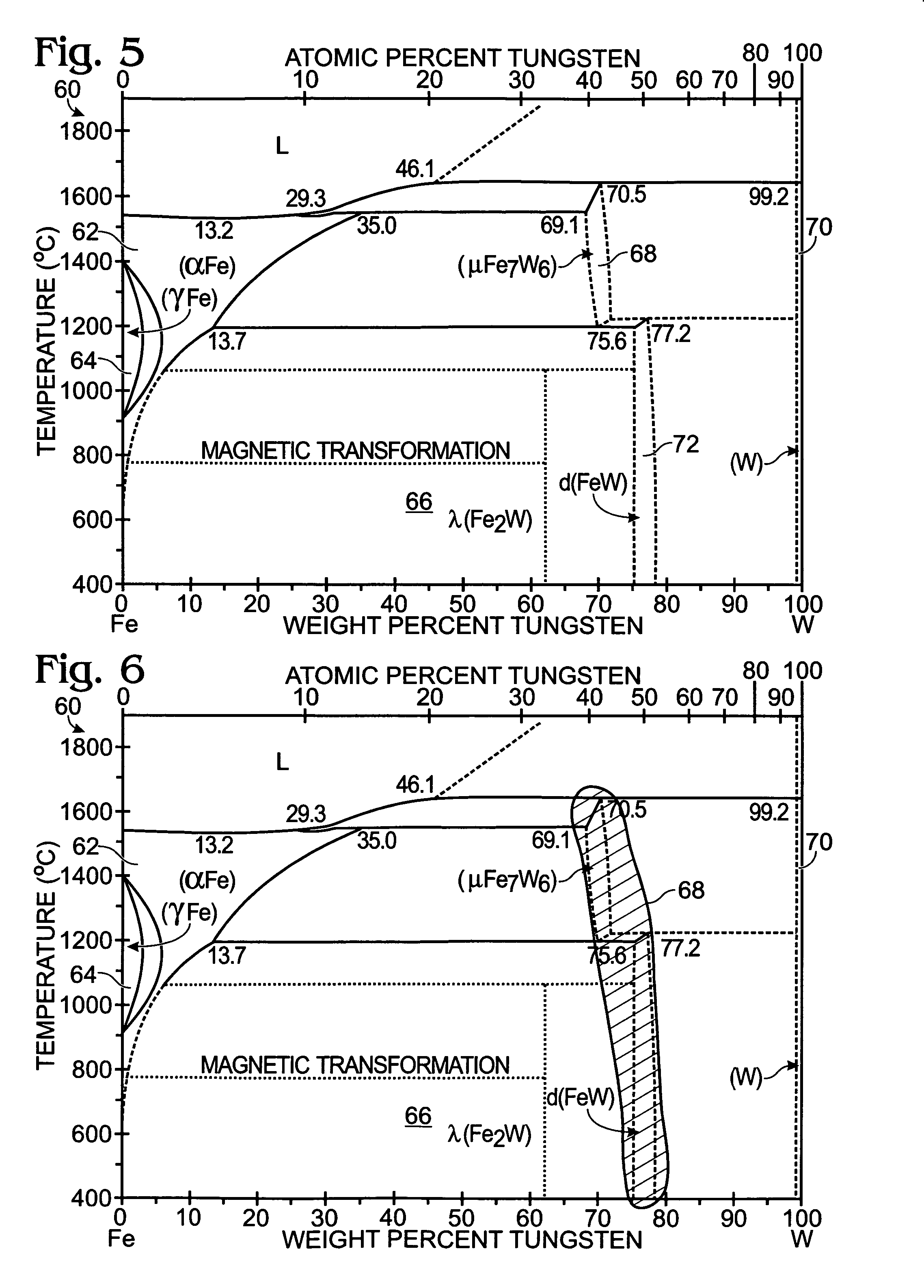
Systems and methods for refining or otherwise processing tungsten alloys, including ferrotungsten powder and articles formed therefrom, and methods for detecting the presence of the same. The methods include at least one of magnetically-separating and particle-size-separating ferrotungsten or ferrotungsten-containing powder. In some embodiments, powder may be separated to remove fine particles, and optionally to separate the remaining particles into fractions containing selected particle size distributions. The powder additionally or alternatively may be separated into at least magnetic and non-magnetic fractions. In some embodiments, portions of two or more size and / or magnetism fractions are mixed to provide a ferrotungsten-containing feedstock. Selected fractions resulting from the size and magnetism separation steps may be utilized to provide a ferrotungsten-containing feedstock from which articles are produced and which may include additional components.
Owner:AMICK FAMILY REVOCABLE LIVING TRUST
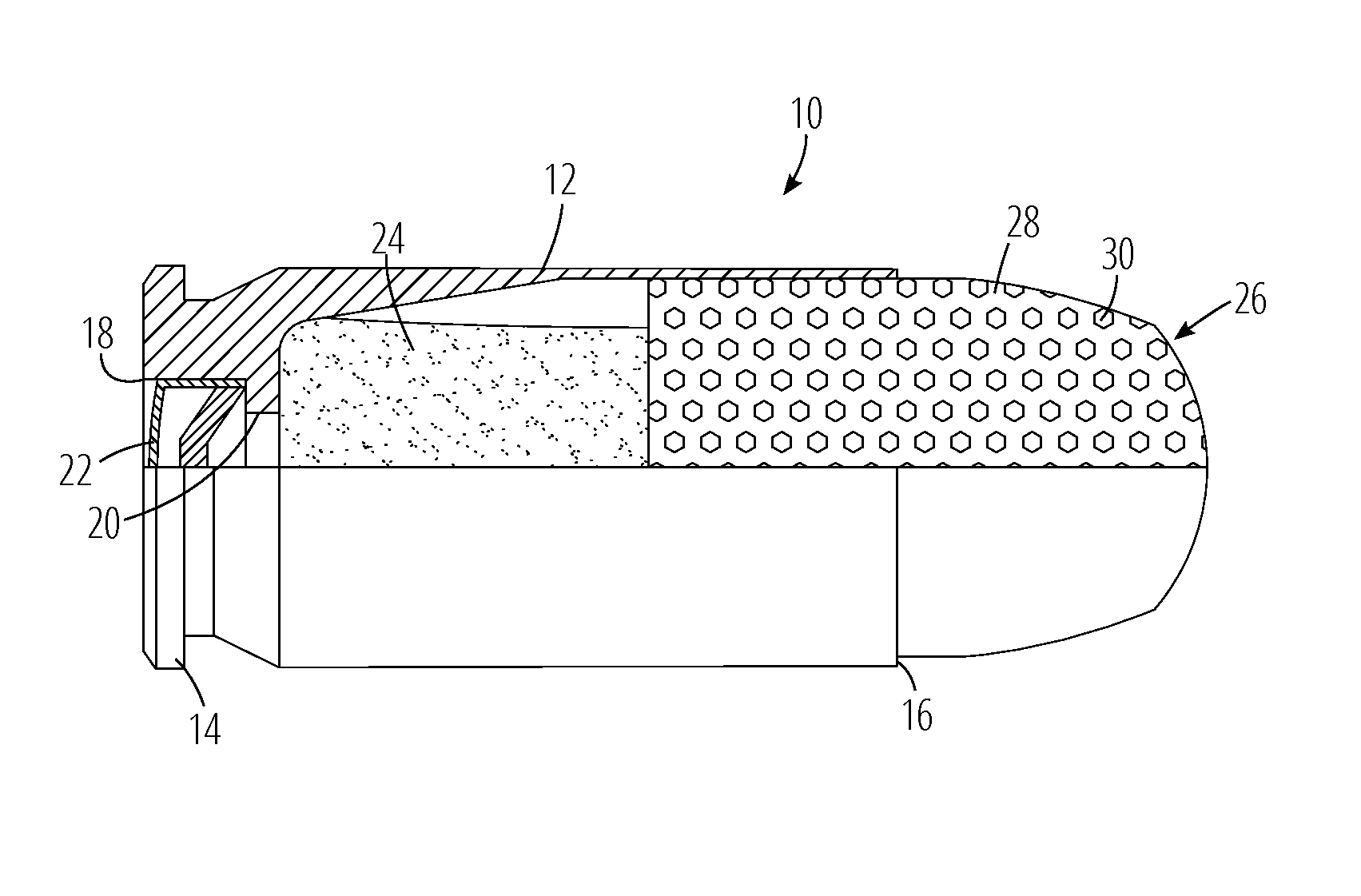
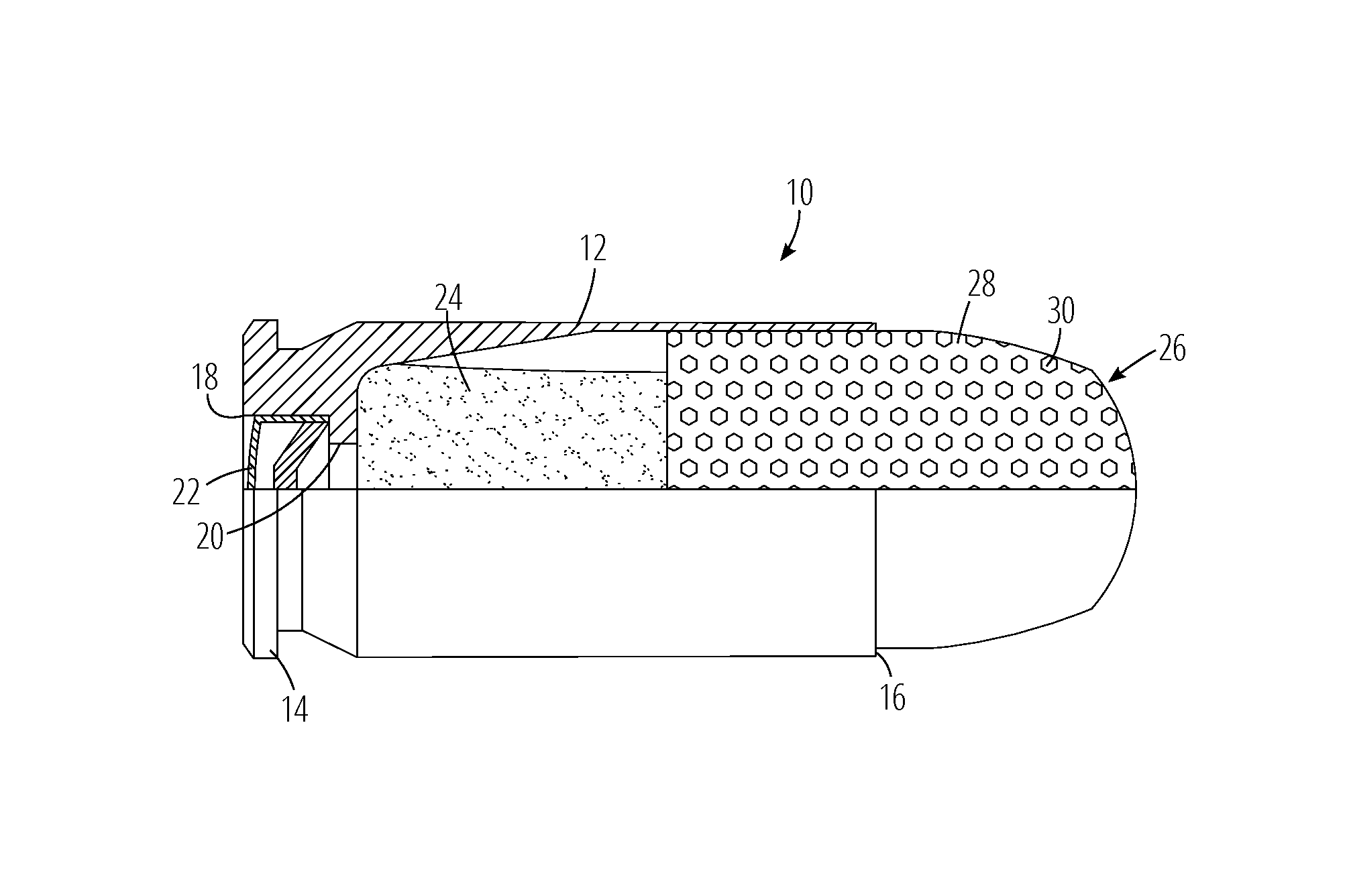
Bullets With Lateral Damage Stopping Power
ActiveUS20140261044A1Raise the possibilityGood stopping effectAmmunition projectilesTraining ammunitionElastomerEngineering
Ammunition which includes a bullet having an effective caliber that is larger than its nominal caliber, comprised of a bullet body with a longitudinal cavity in the forward end, and one or more bores extending from the cavity to bore openings on the exterior of the bullet. In use, target media is gathered in the cavity and ejected under force through the bore openings, increasing the damage done by the bullet. Preferably, the bullet cavity and bores are filled with a polymeric or elastomeric material.
Owner:BRANCA CHRISTOPHER +2
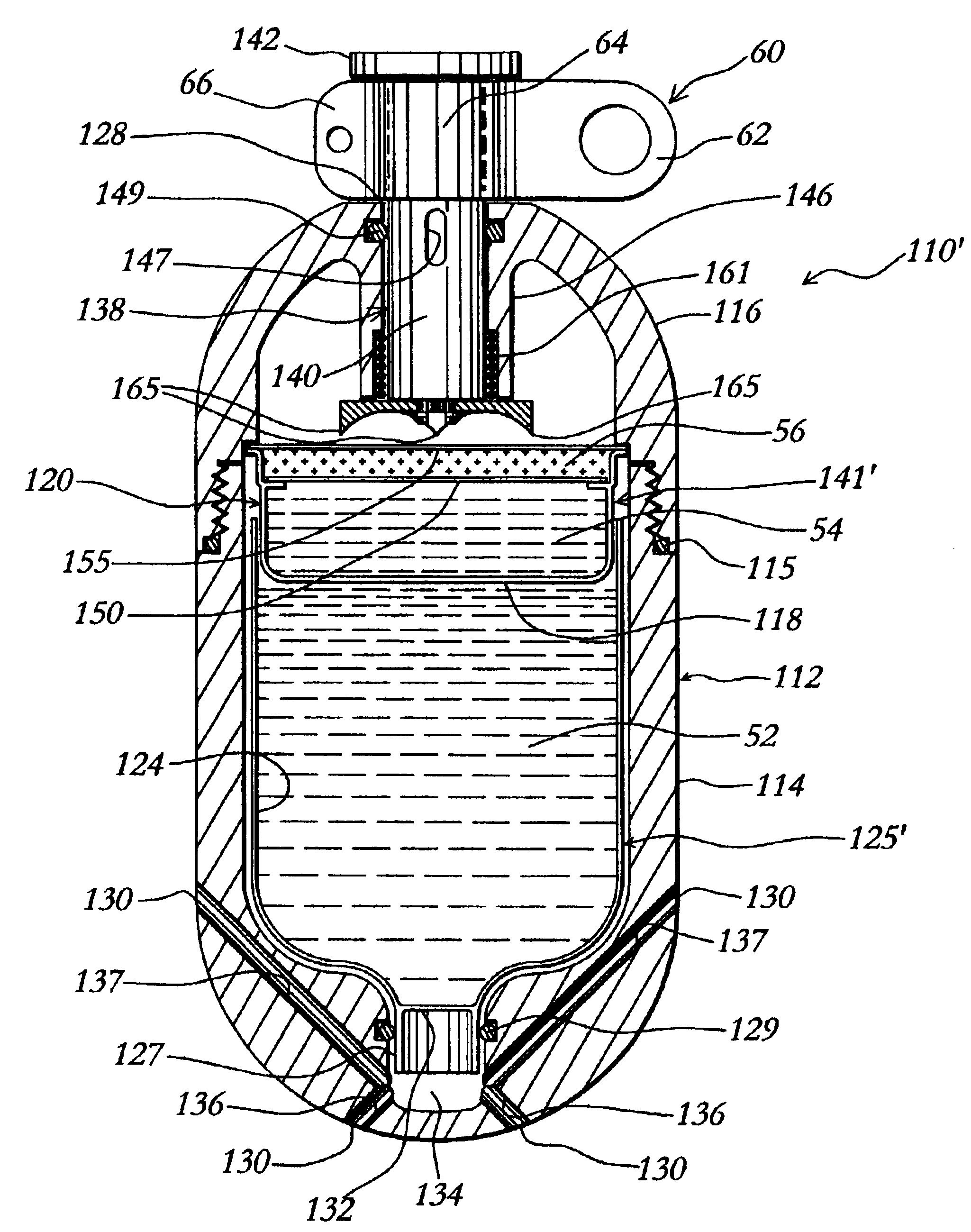
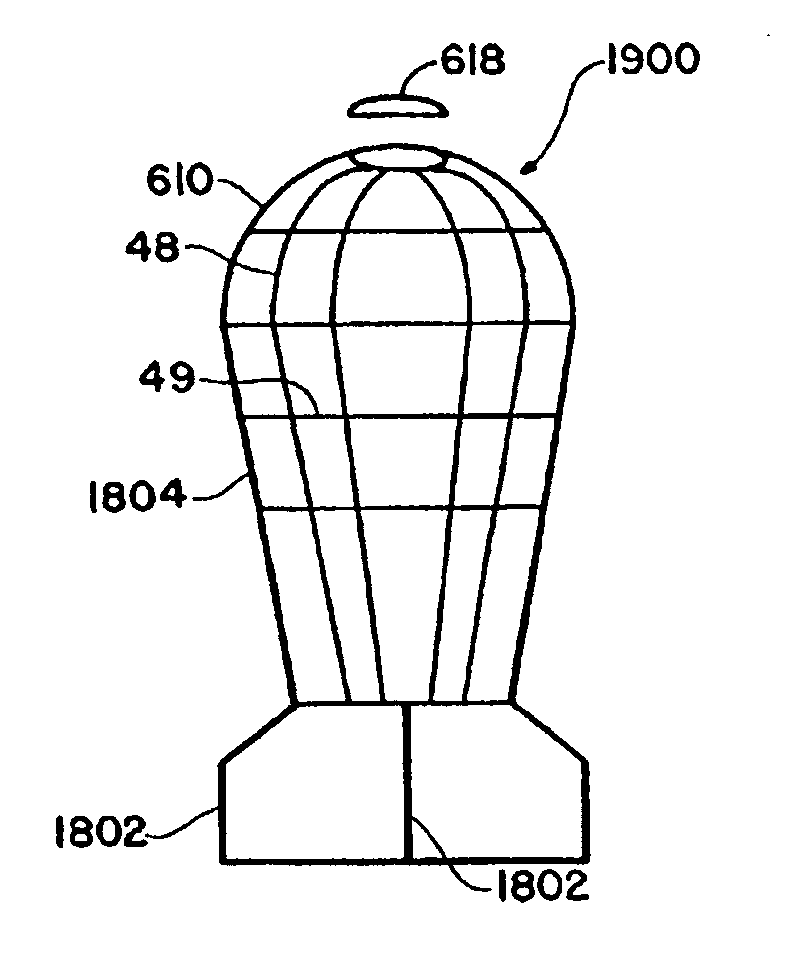
Spin Stabilized And/ Or Drag Stabilized, Blunt Impact Non-Lethal Projectile
InactiveUS20120291655A1Large deformationExcessive compressionAmmunition projectilesTraining ammunitionCrowd controlSpins
A spin stabilized and drag-stabilized, blunt impact, non-lethal projectile is provided, having a rigid base and rigid windscreen, with a compressible body therebetween, thereby enabling use thereof in high pressure / compression firing mechanisms, but yet operable to compress / deform upon impact with a target. In particular, a spin stabilized, blunt impact, non-lethal projectile is provided having a rigid windscreen and base, with a compressible body therebetween which compresses / deforms upon impact with a target. In addition, a drag-stabilized version thereof is provided, having canted fins thereon so as to control flight of the projectile via the imposition of drag thereon. Additionally, the projectile is capable of carrying agents, such as crowd control and marking agents, in an agent reservoir, and ejecting same onto a target upon impact.
Owner:JONES KENNETH R
Method and apparatus for propelling a pellet or BB using a shock-sensitive explosive cap
A method and apparatus for expelling a projection from an air gun by striking a primer cap filled with a shock-sensitive explosive compound, causing the cap to explode, which in turn rapidly compresses a volume of air located between the projectile and the cap, causing the projectile to exit from the barrel of the air gun at a high rate of speed.
Owner:GUNSANDMORE INFO
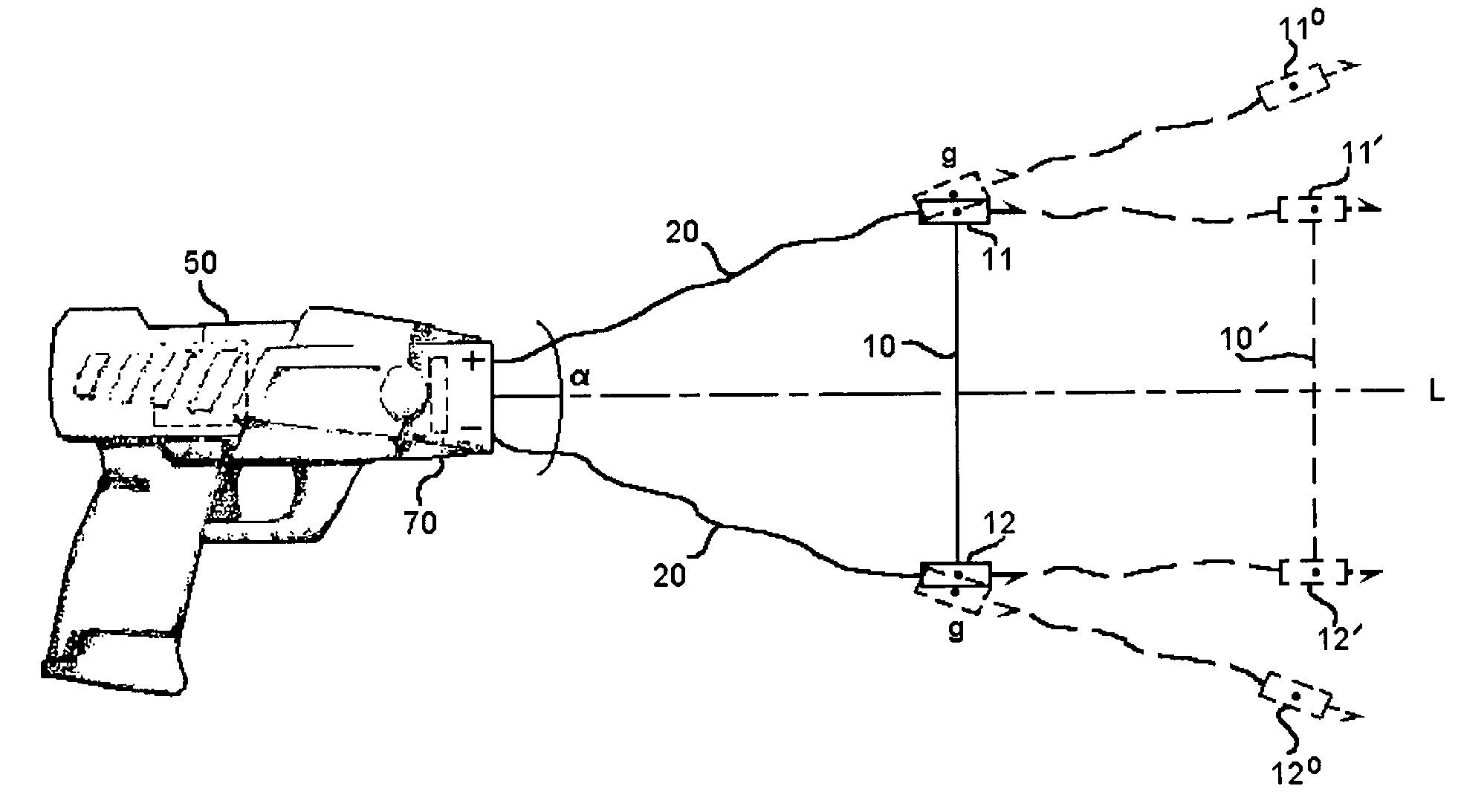
Apparatus and method for electrical immobilization weapon
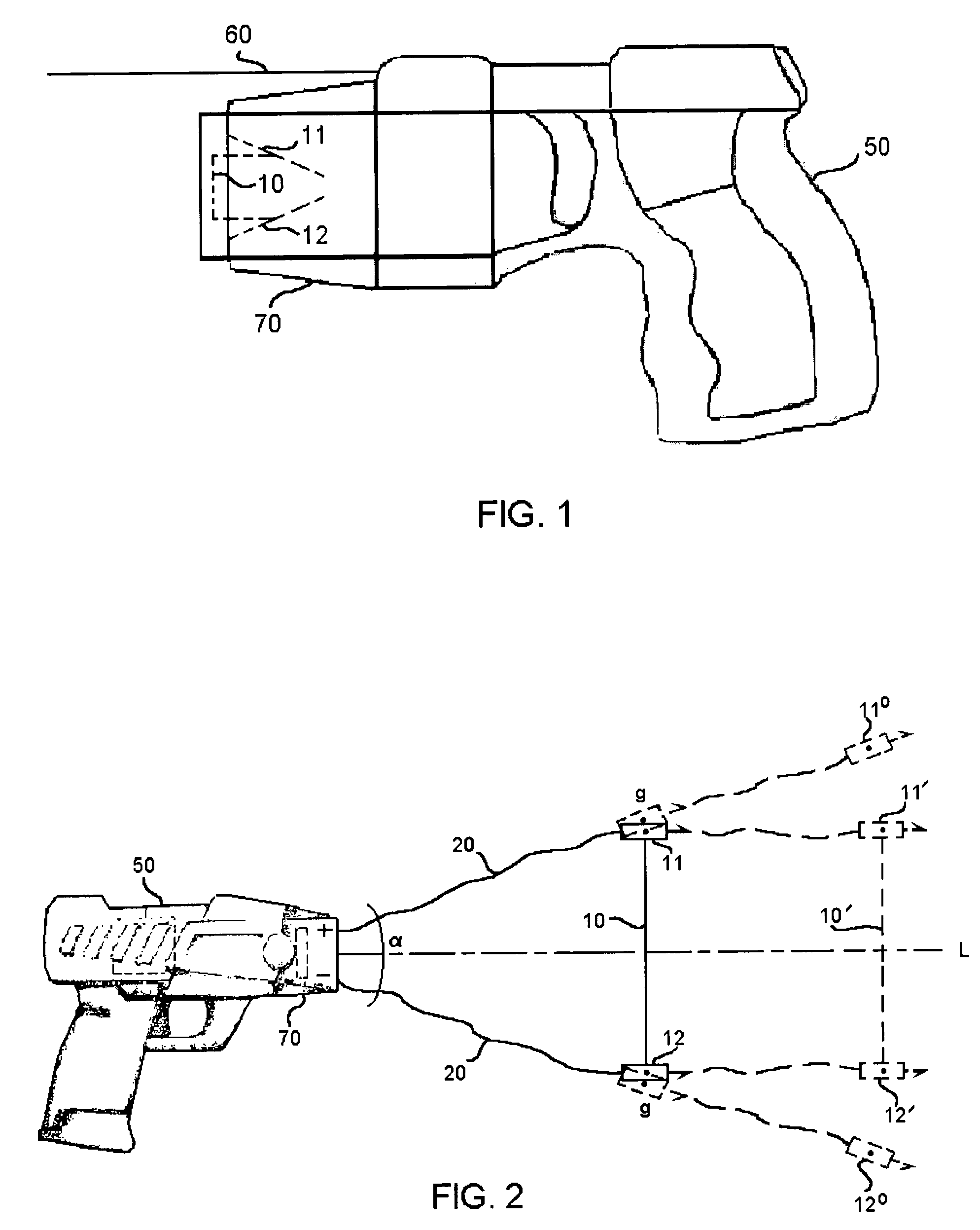
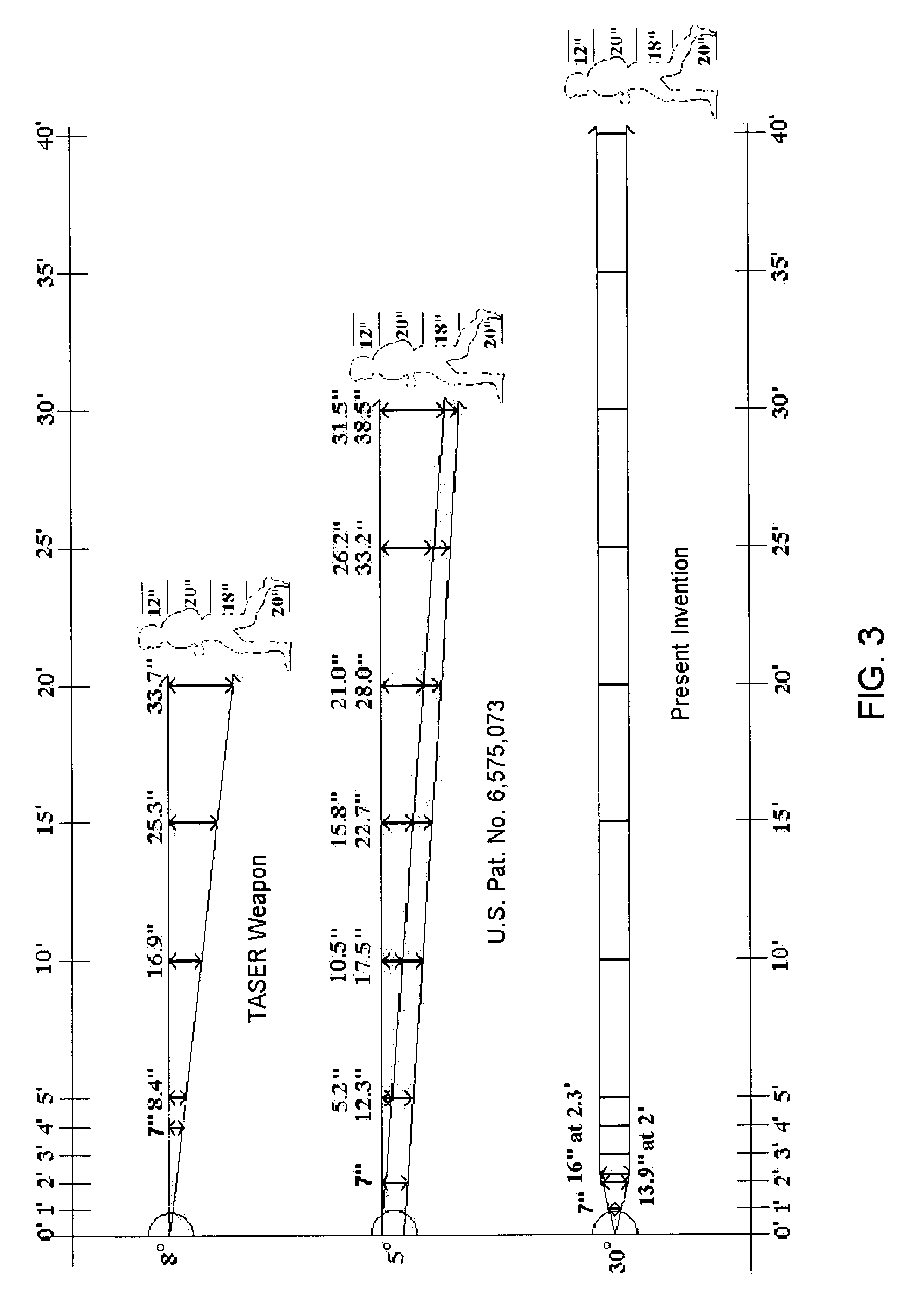
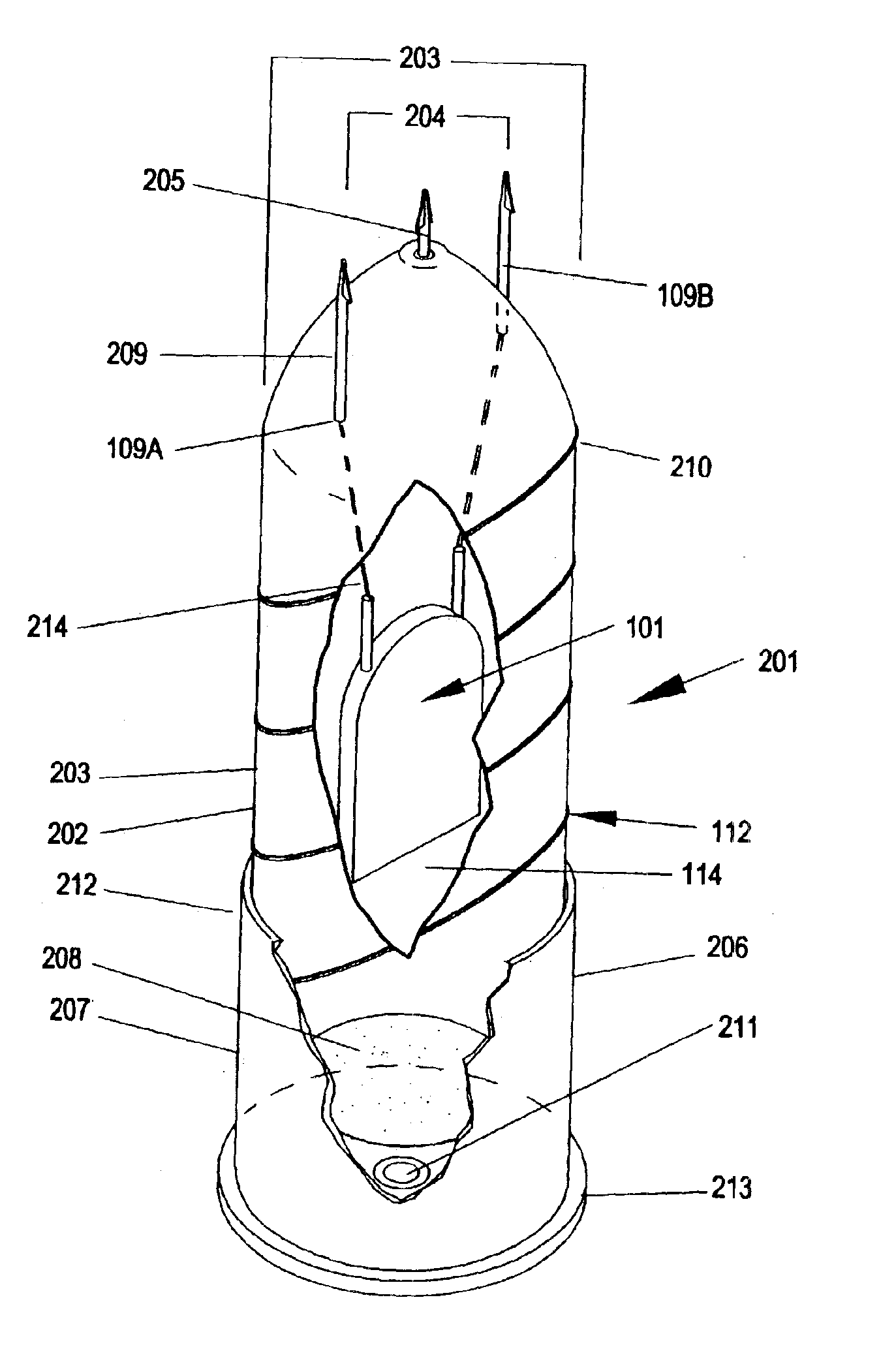
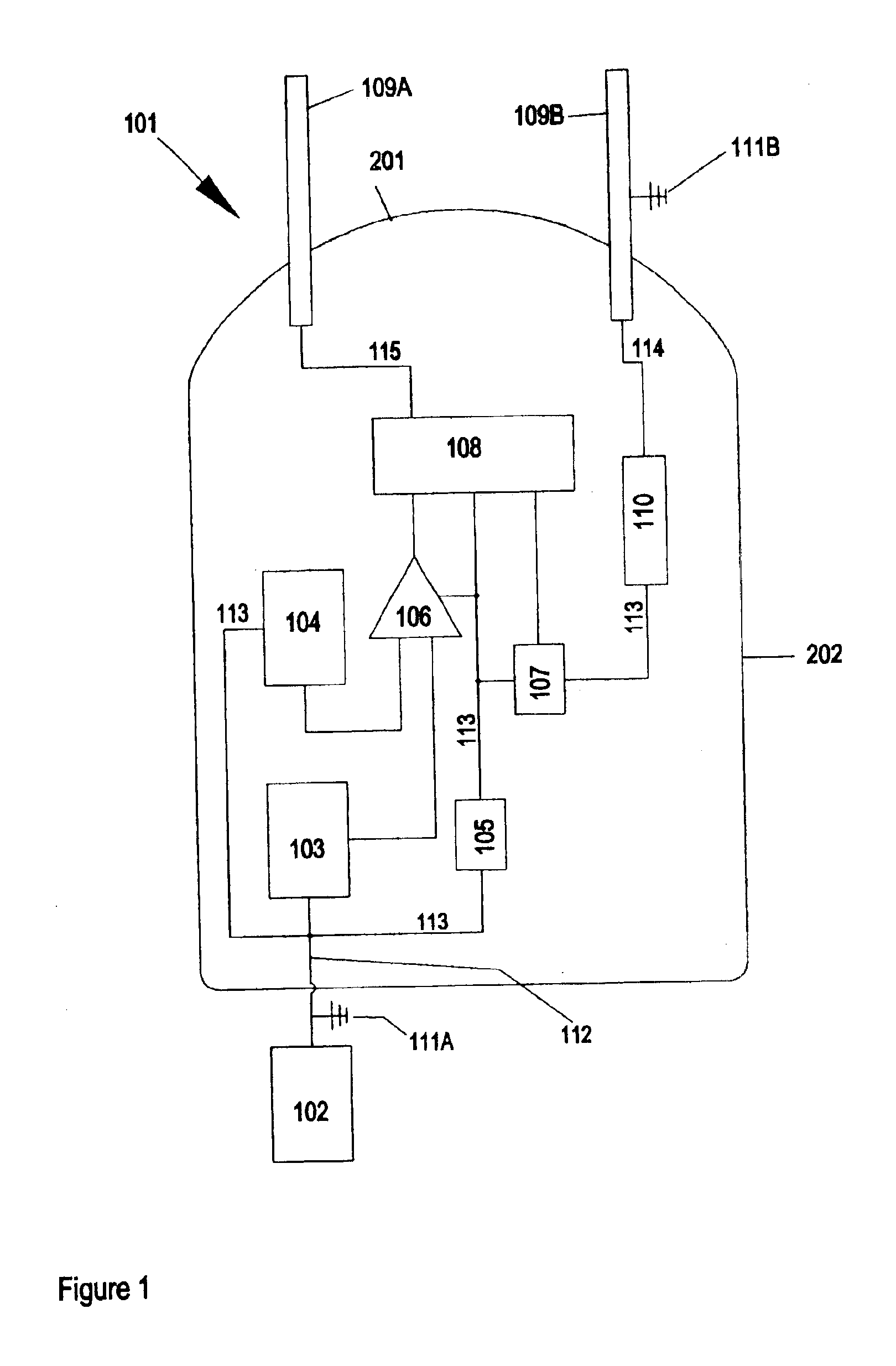
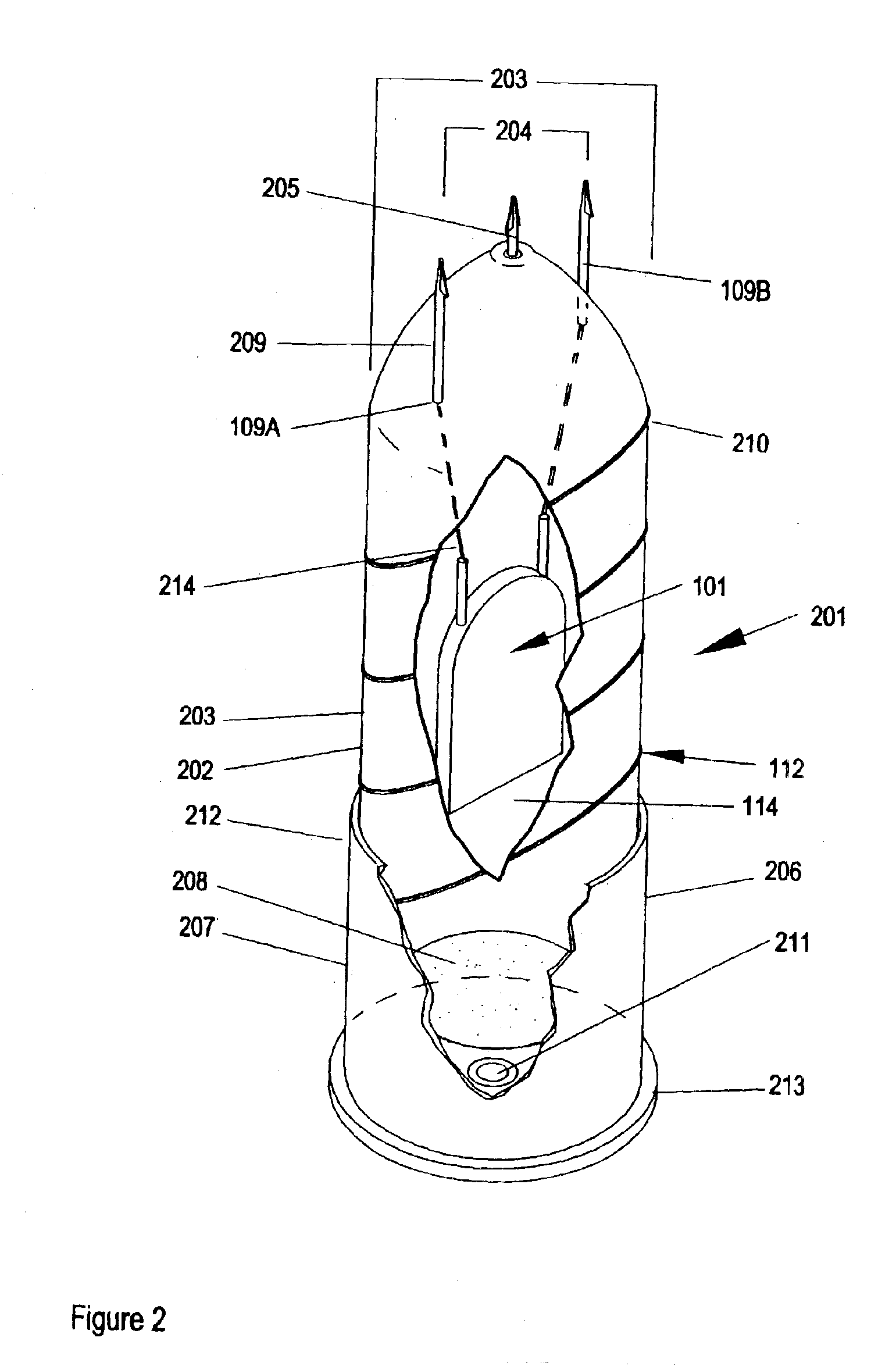
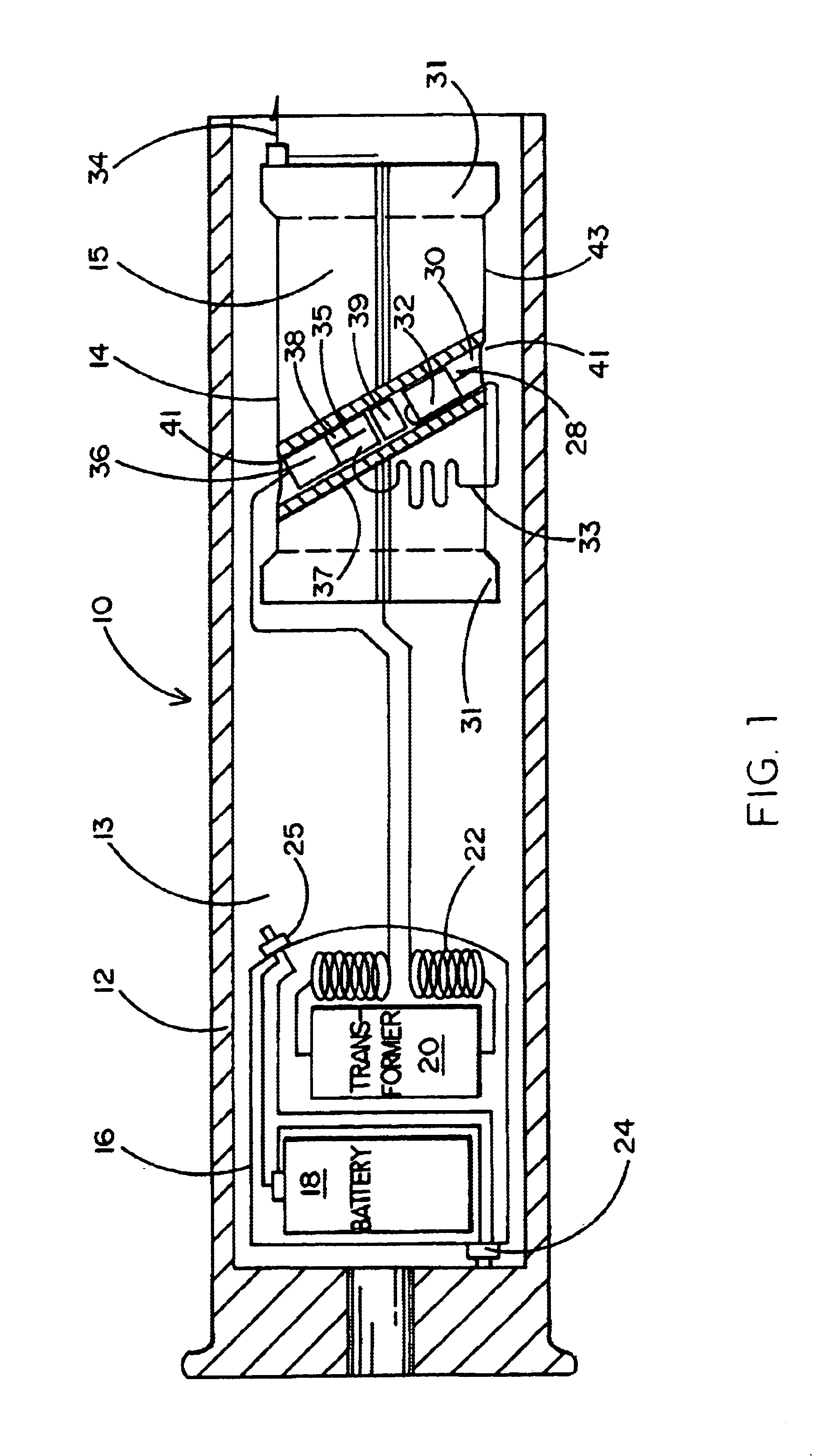
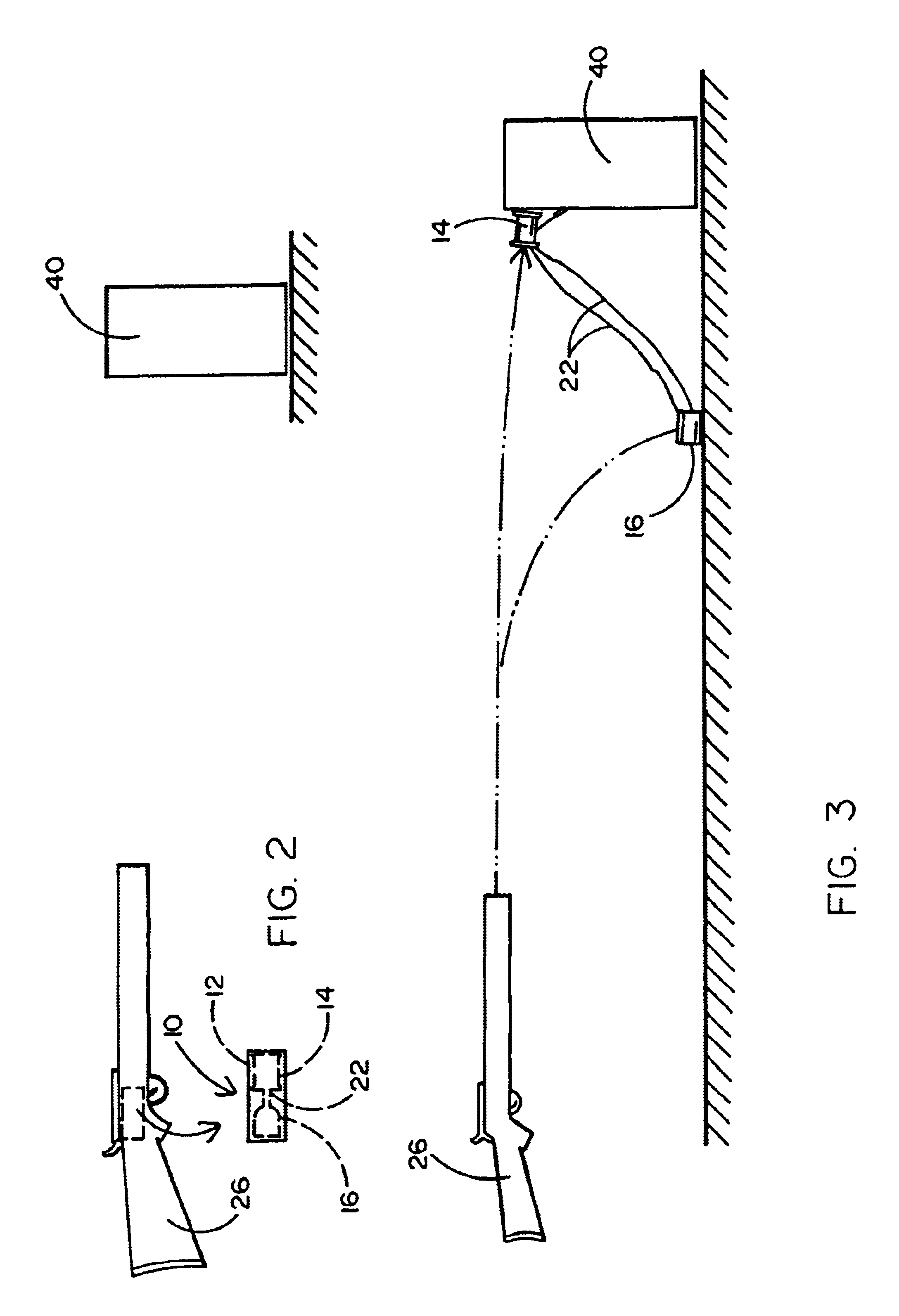
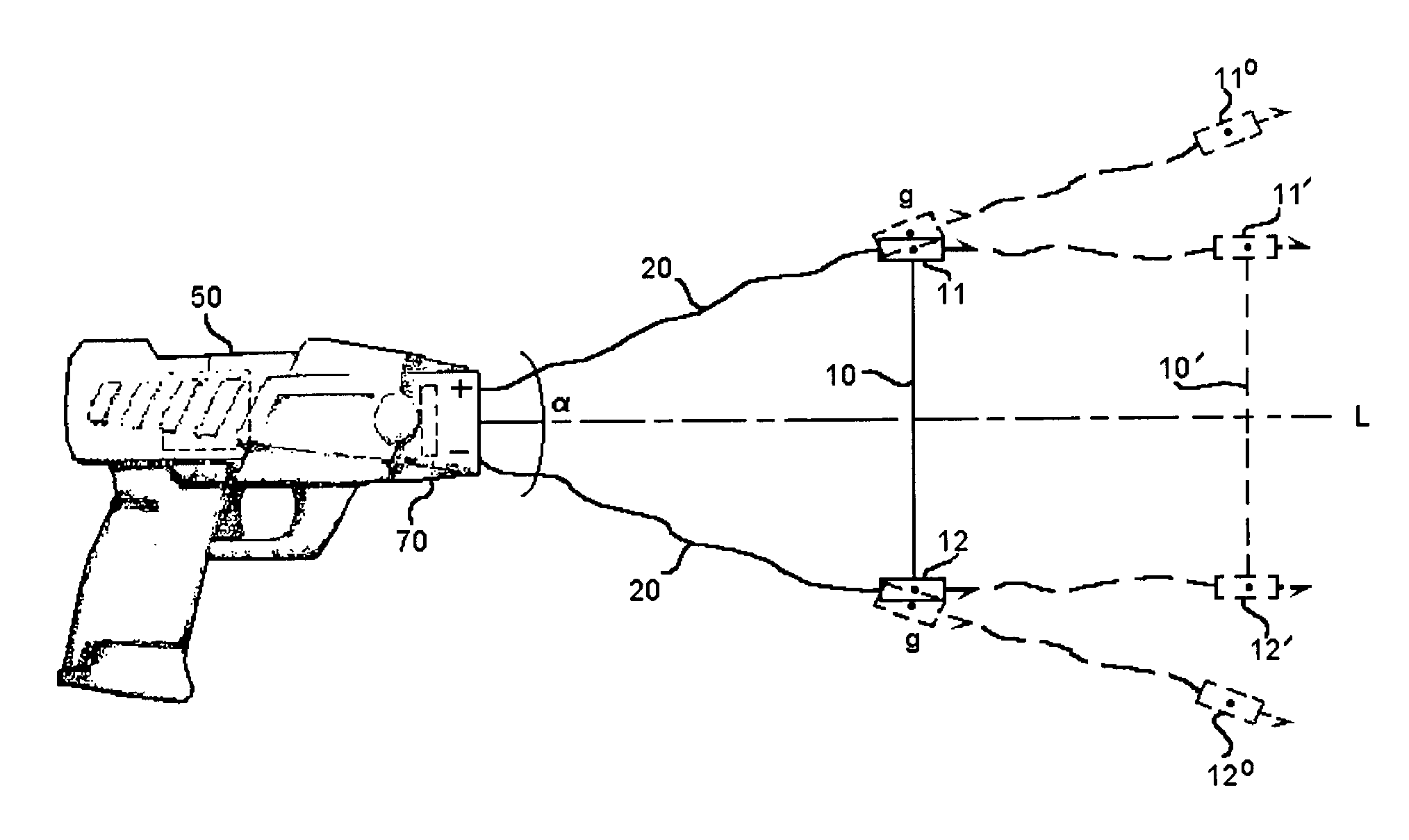
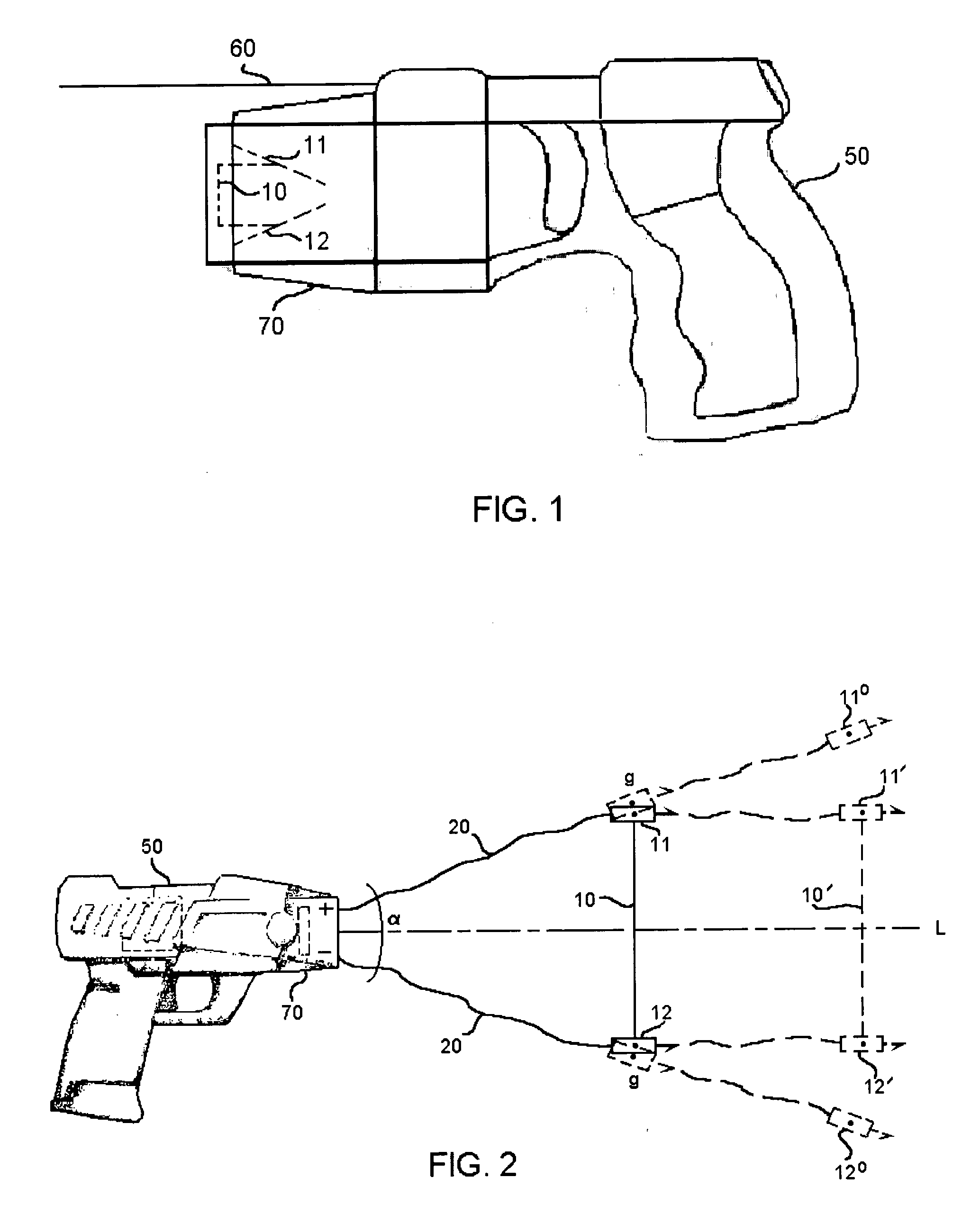
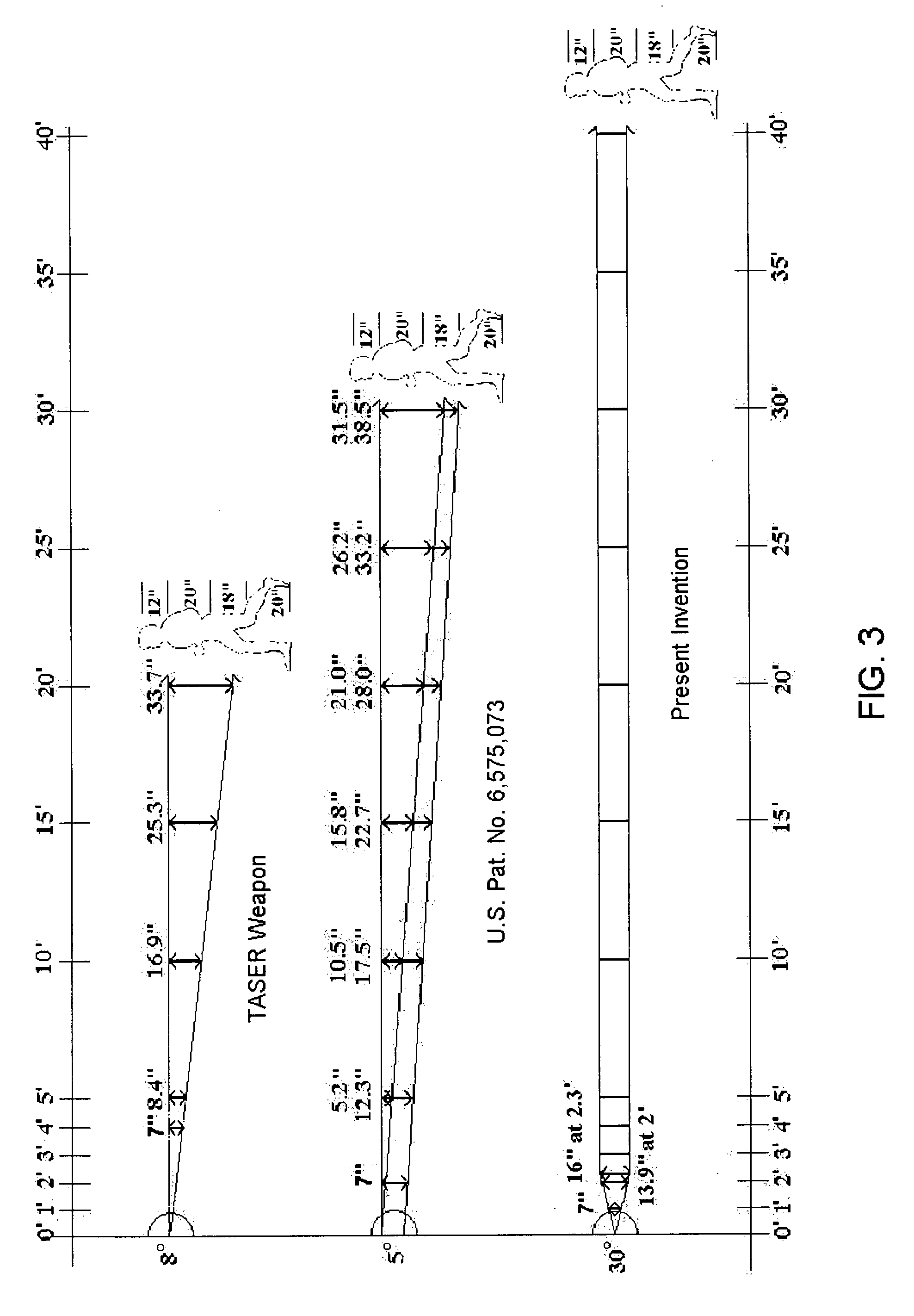
ActiveUS7314007B2Suitable for useEffective shooting rangeAmmunition projectilesElectric shock equipmentsInvolved musclesTaser
An electrical immobilization weapon having a prolonged range of effectiveness and improved accuracy compared to conventional Taser weapons, while being compact in structure and lightweight. The weapon having a replaceable cartridge which, when employed, can space a pair of electrodes to a specific critical area on a remote target, so the electrical energy carried by the electrodes can induce the involuntary contraction of the involved muscles through the critical area within a significant range of length between the electrodes for effective immobilization. The electrical energy generated by a power source of the weapon completes an electrical circuit through a minimum path being a length of at least 5 inches between the two points on the target.
Owner:VOLGER INT AB
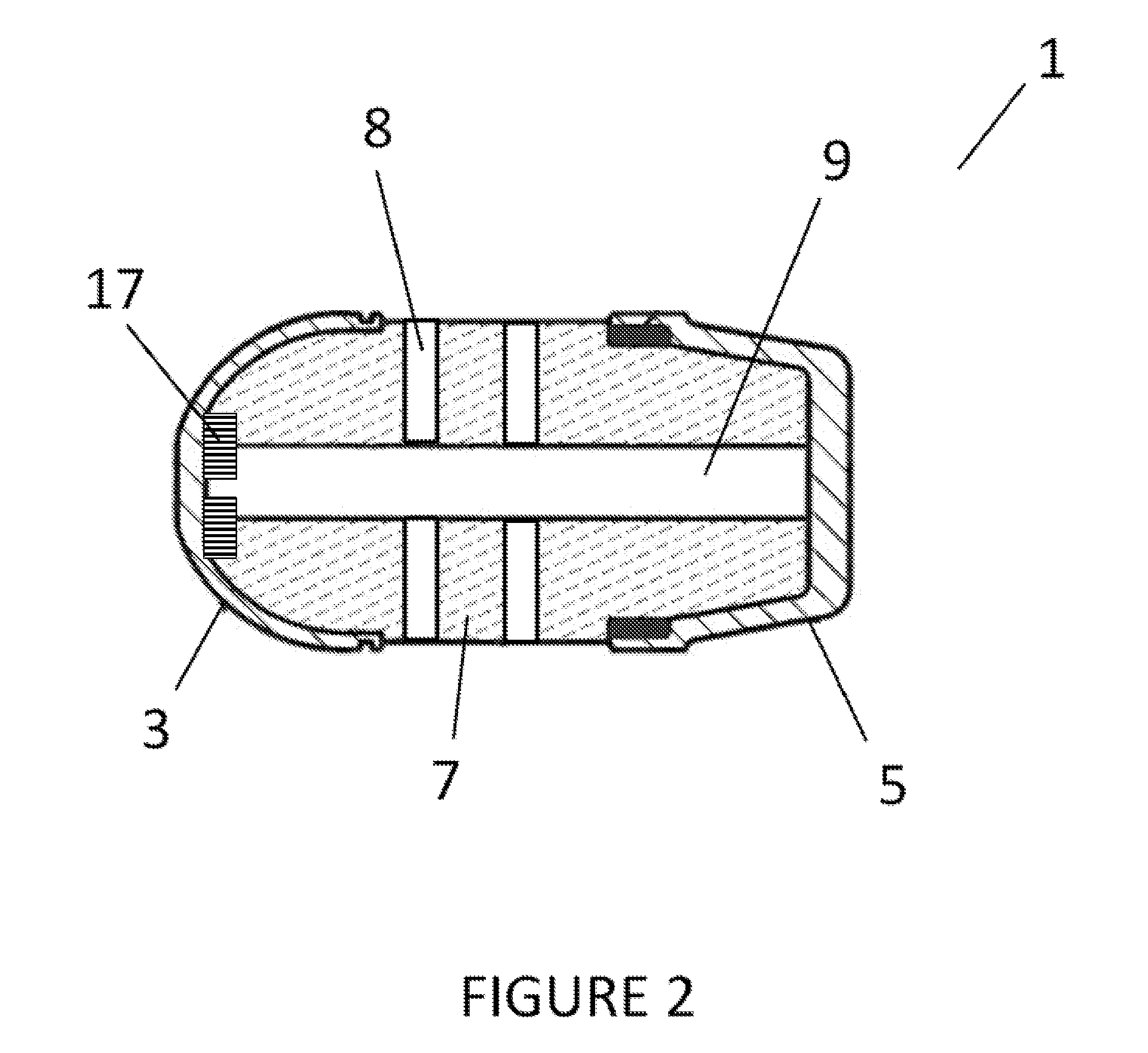
Forty millimeter caliber exercise bullet
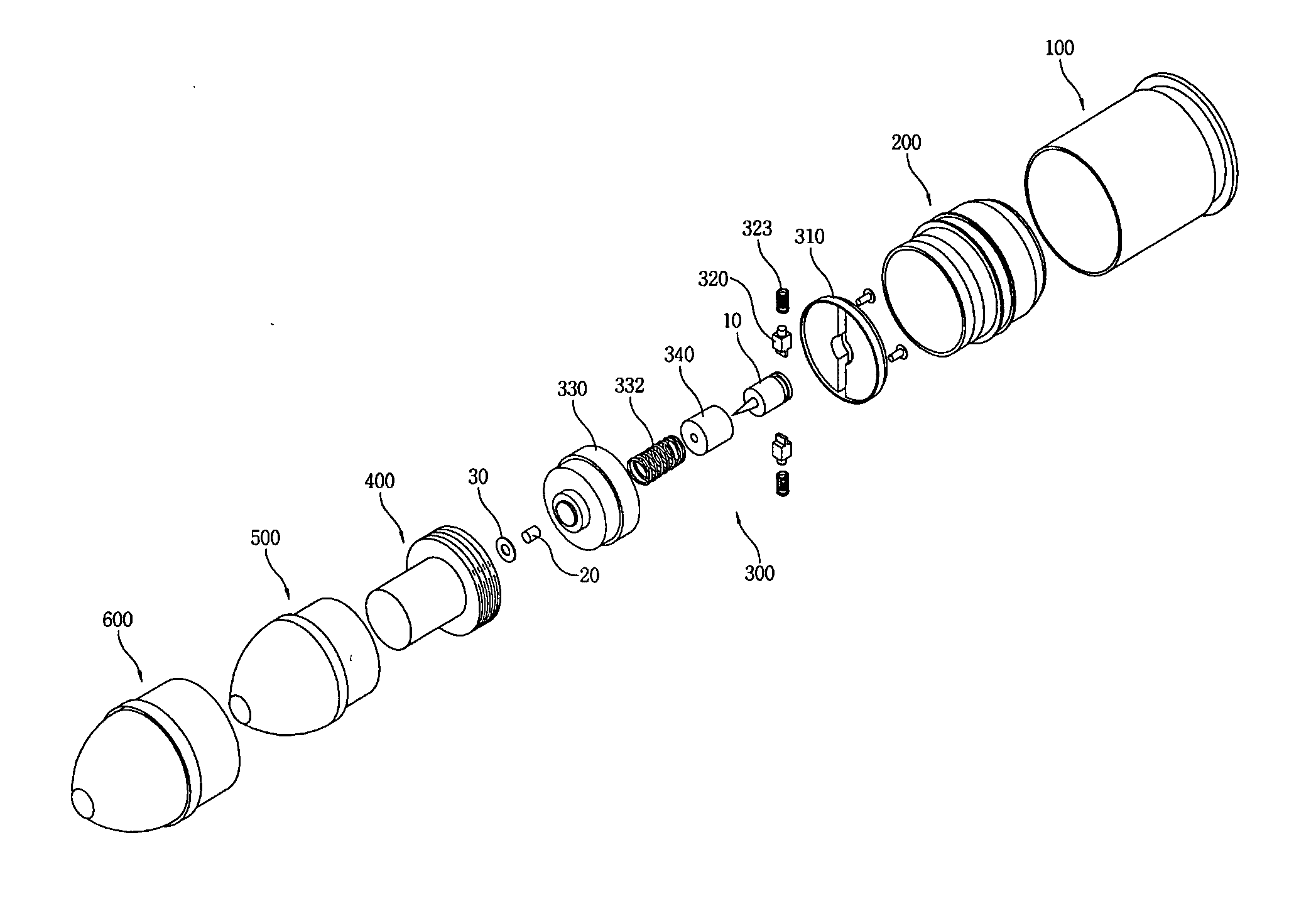
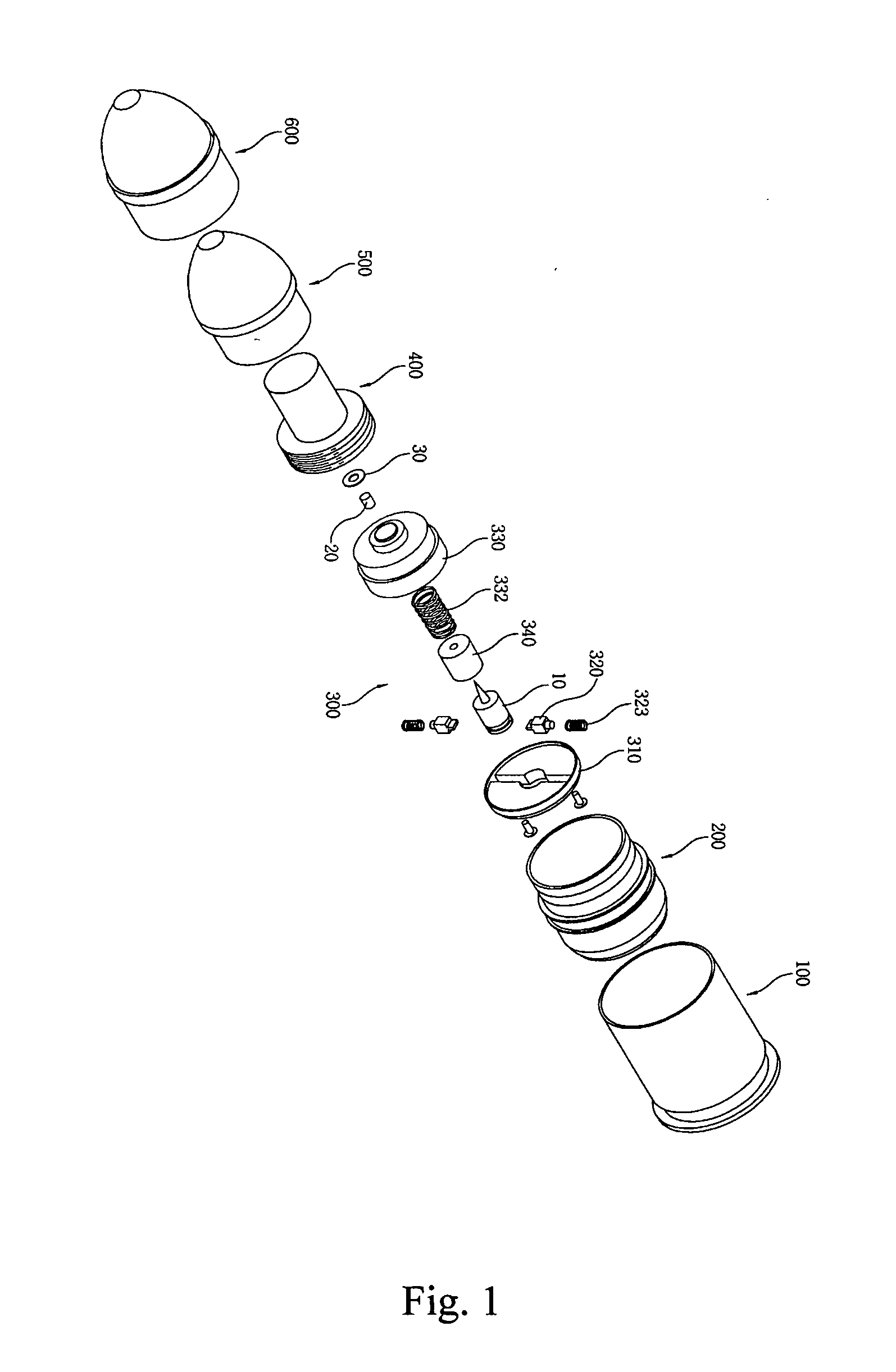
ActiveUS20120180685A1Safely securedAvoid failureAmmunition projectilesTraining ammunitionDetonatorCentrifugal force
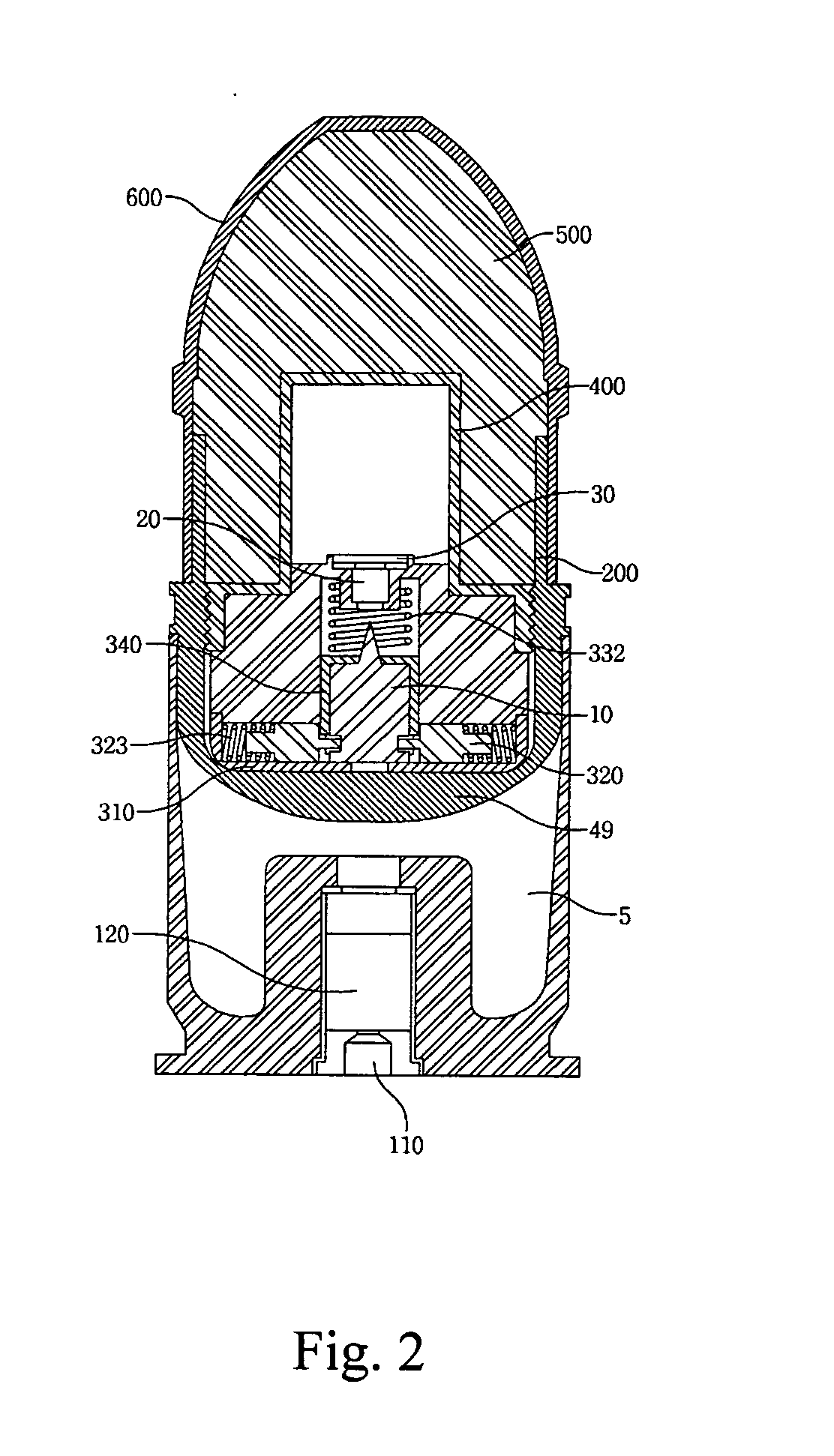
A forty millimeter caliber exercise bullet has improved for properly exploding on a target, and securely maintaining the unloaded status during ordinary time. The improved exercise bullet comprising that; a skirt (200), a striking pin (10), a safety device assembly (300) consisting a detent cover (310) with a central mounting groove (311) and a pair of mounting grooves (312), a detent (320) for retaining the striking pin (10) by engaging or disengaging into the circumferential groove (11) by springs (323), a detonator cap (330) forming a hollow pocket (331) to insert a detonator trigger (20), a washer (30), and a press-spring (332) for pressing a guiding cap (340), an explosion pipe (400), a smoke shell (500), and an ogive (600). When the bullet is fired, the rotation of bullet generates centrifugal force to slide the retainer outward for disengaging the circumferential groove, then the striking pin moves upward to impact the detonator trigger when it hit on the target.
Owner:C N O TECH KOREA
Explosion containment net
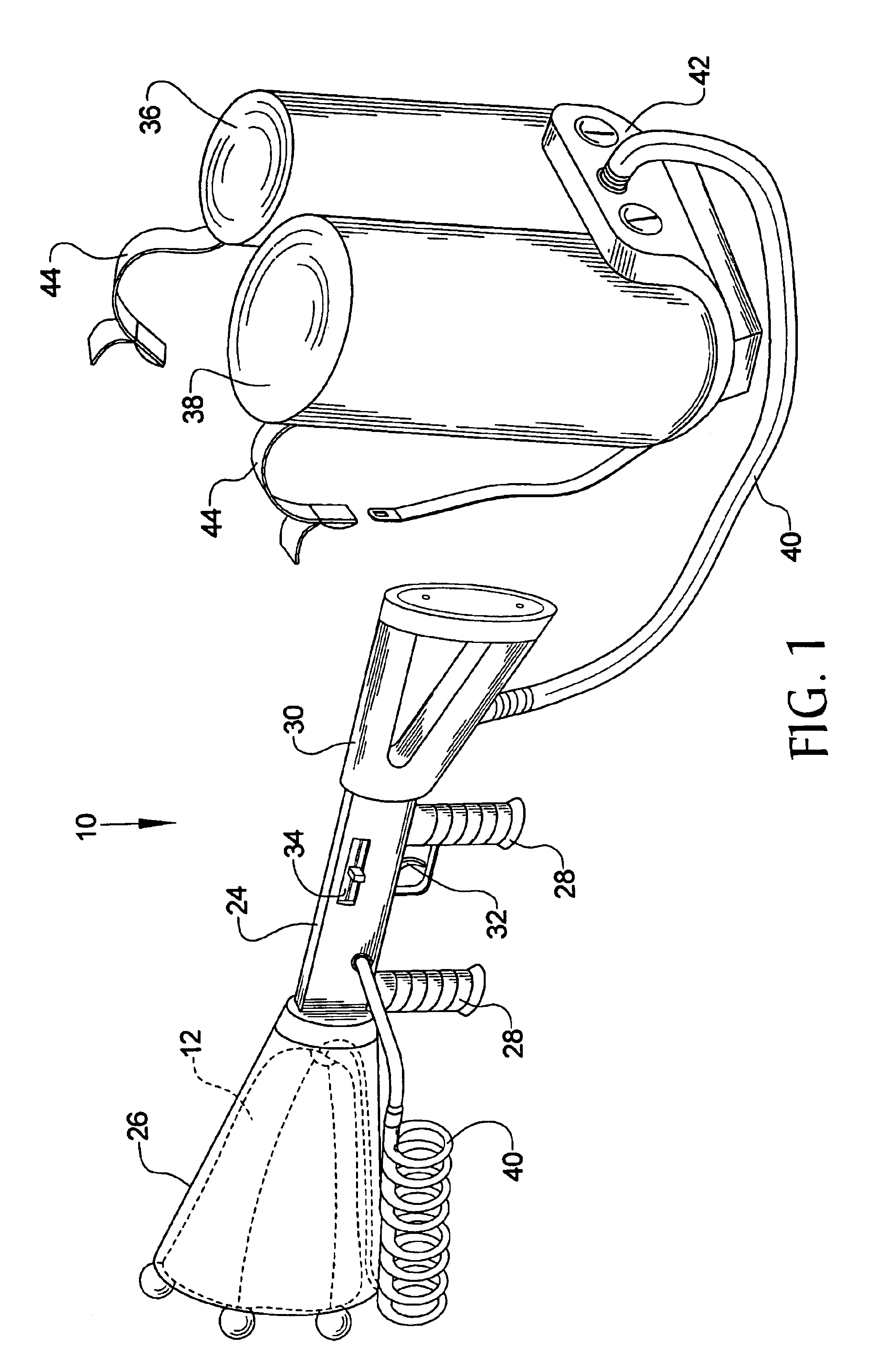
InactiveUS6854374B1Minimize and contain explosive blastPrevent serious injuryAmmunition projectilesTraining ammunitionHigh densityEngineering
A net is made from an explosive resistant material such as KEVLAR and is thrown over an explosive-laden device such that the net helps contain the blast force of the explosive-laden device. The net also has a nozzle that is fluid connected to a fire suppressant agent as well as a high density foam, each of which are discharged through the nozzle once the net is thrown over the explosive-laden device, the fire suppressant agent and the high density foam each helping to minimize the blast force of the explosive-laden device. The net can be thrown manually or can be fired from a gun that uses either pneumatic force or a firing cartridge to propel the net at its target.
Owner:BREAZEALE O ALAN
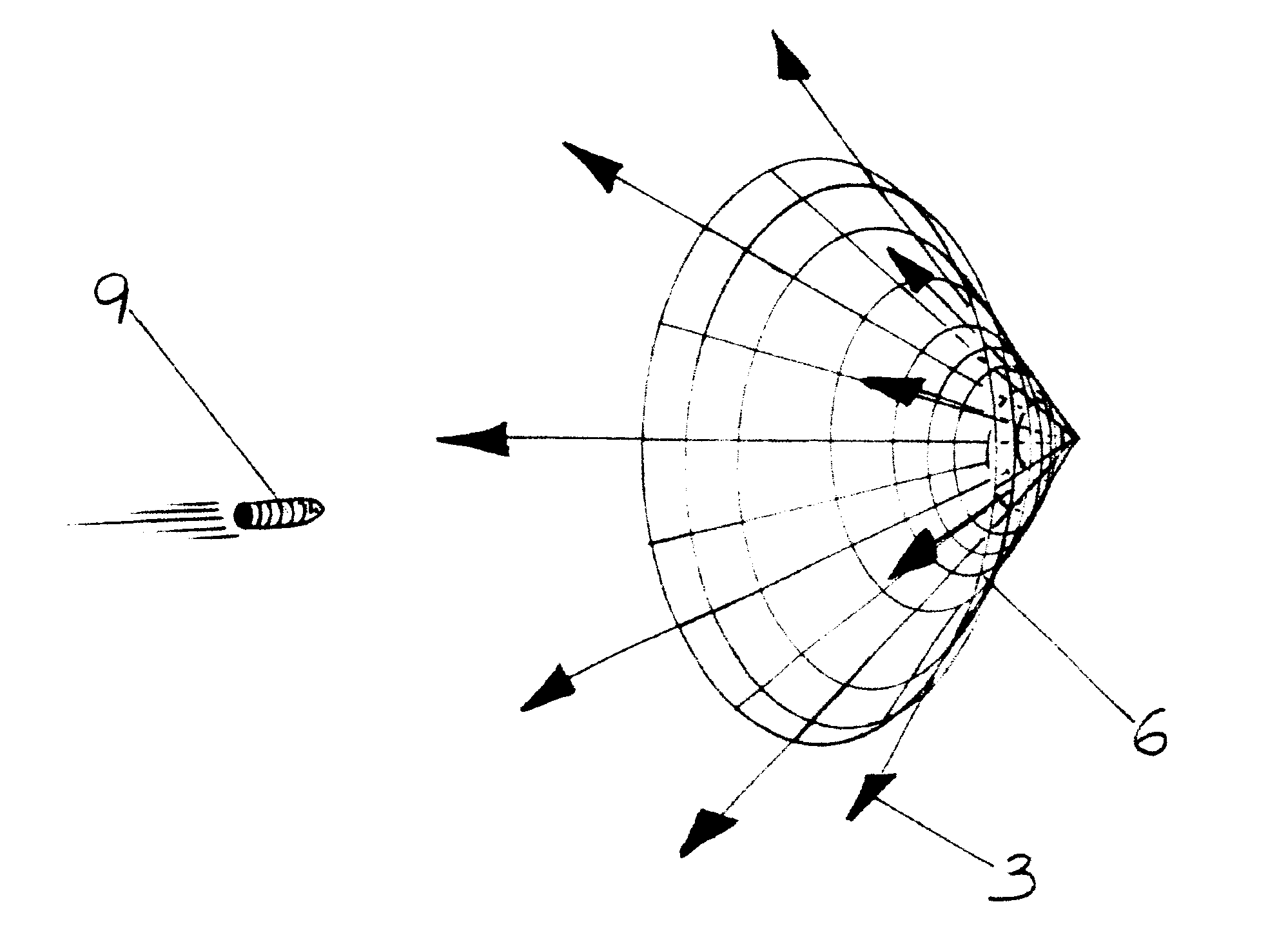
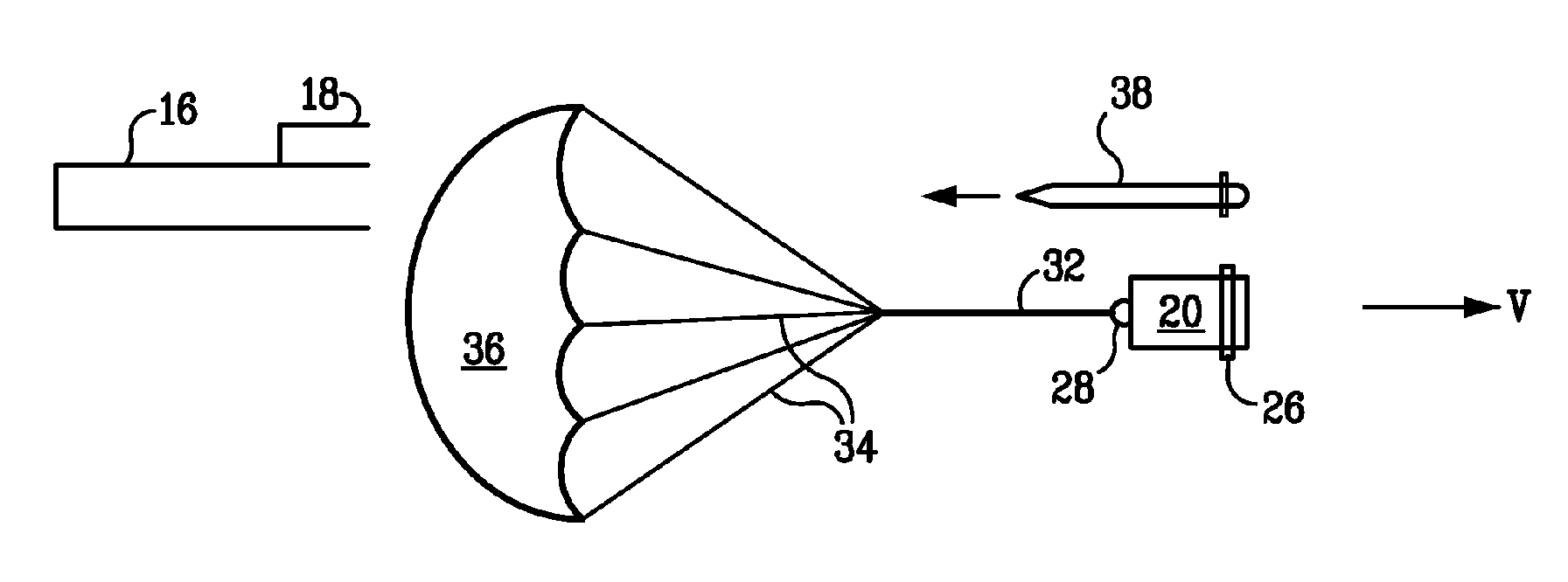
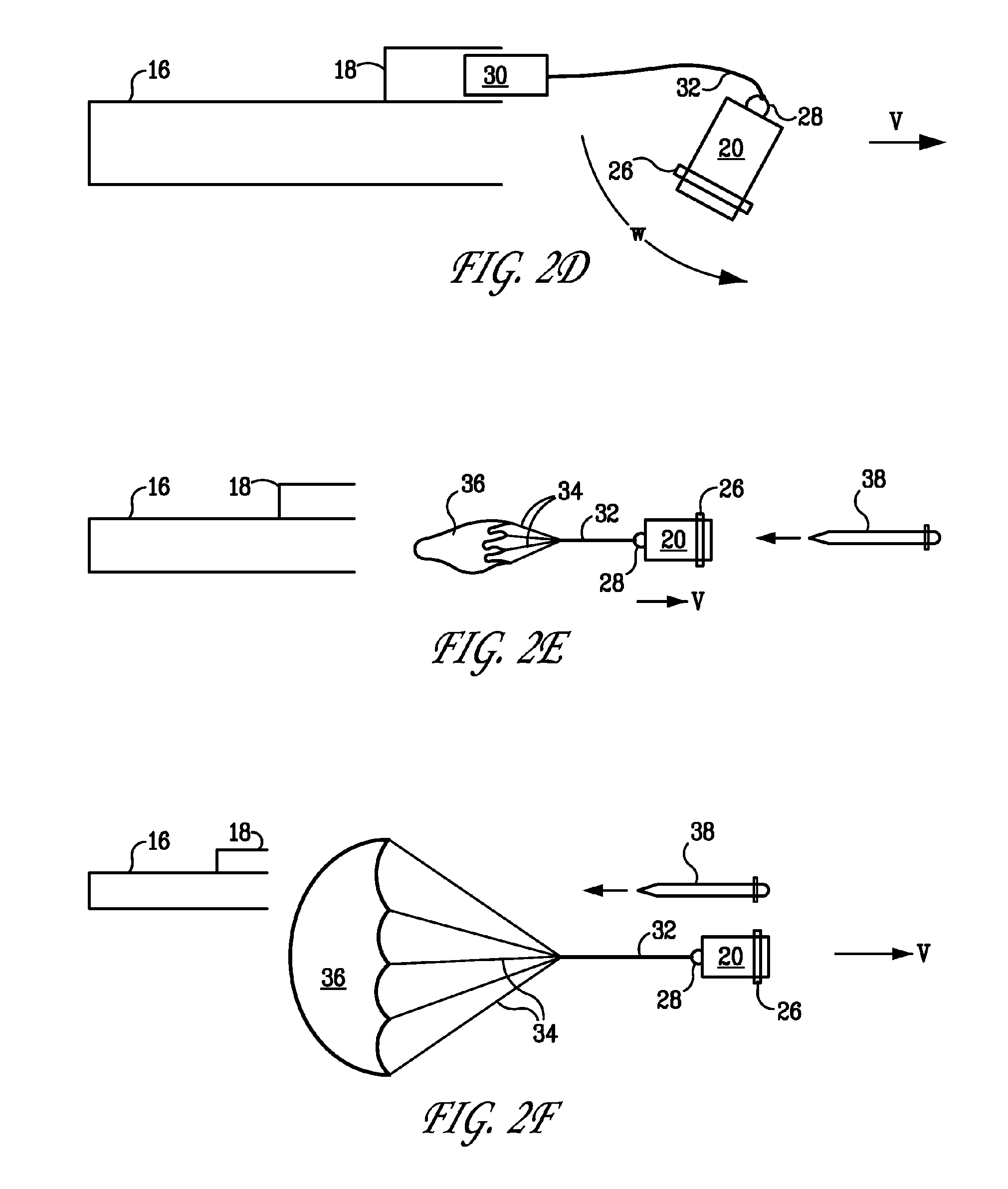
Parachute active protection apparatus
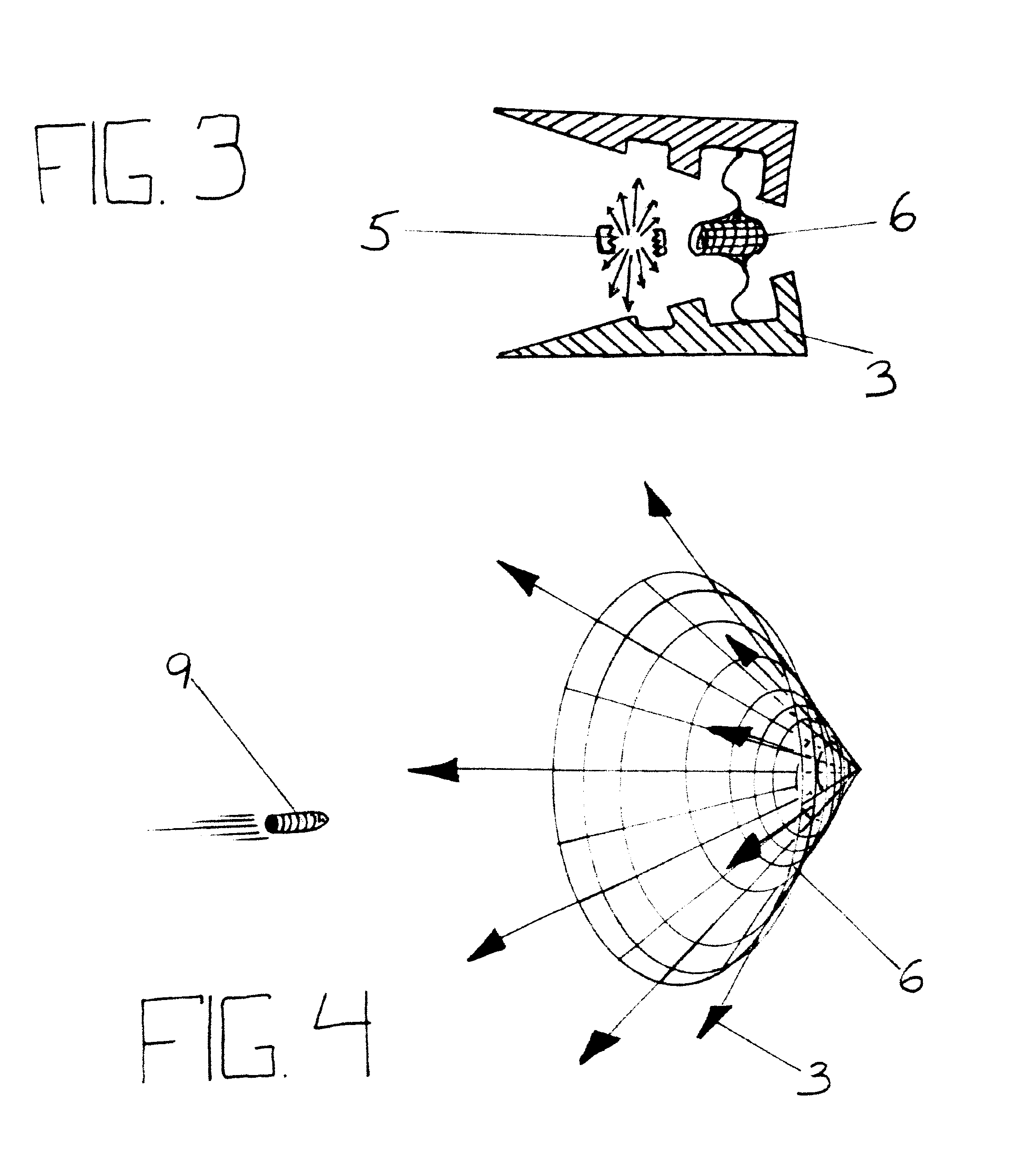
An apparatus for protecting an object from an incoming munition includes a tracking apparatus mounted on the object, for tracking the incoming munition; a firing solution computer connected to the tracking apparatus; a plurality of launch tubes mounted on the object, the plurality of launch tubes pointing in different directions so as to maximize coverage of an area surrounding the object; a parachute container attached to each launch tube; an igniter disposed in a rear of each launch tube and connected to the firing solution computer; a propelling charge disposed in front of each igniter; a mass disposed in front of each propelling charge; a connecting ring attached to a front of each mass; a parachute disposed in the parachute container; and a cable connecting the connecting ring and the parachute.
Owner:US ARMY AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
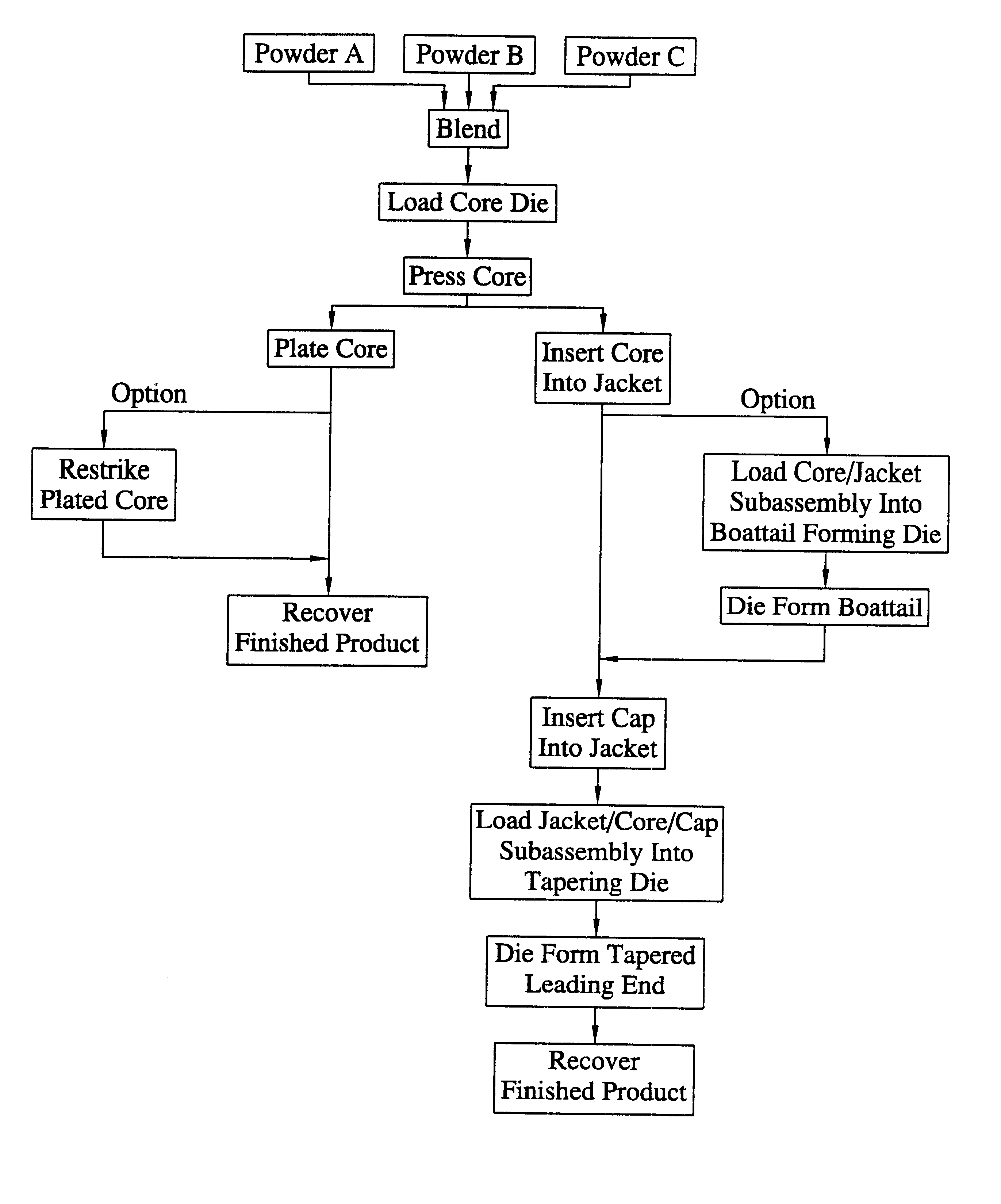
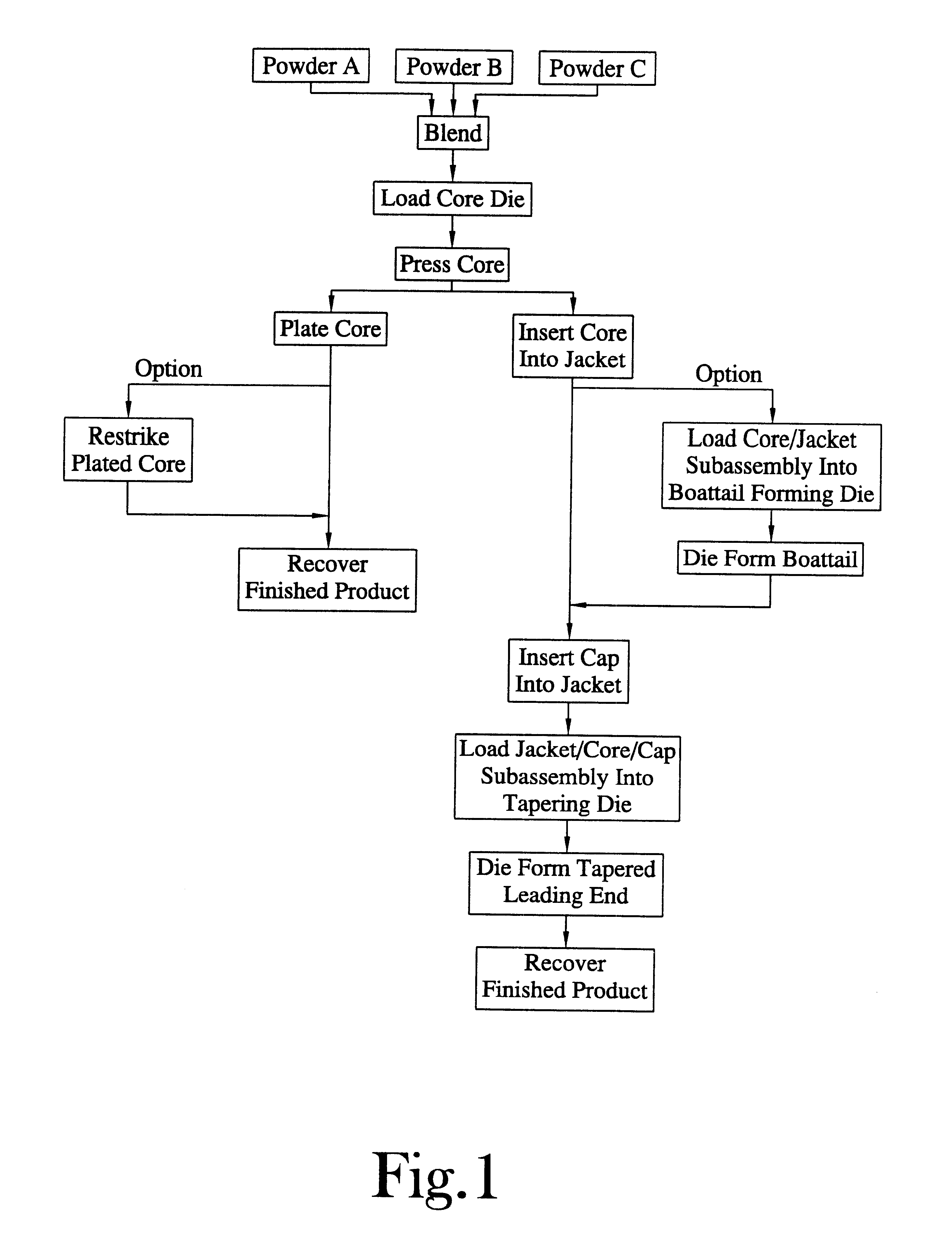
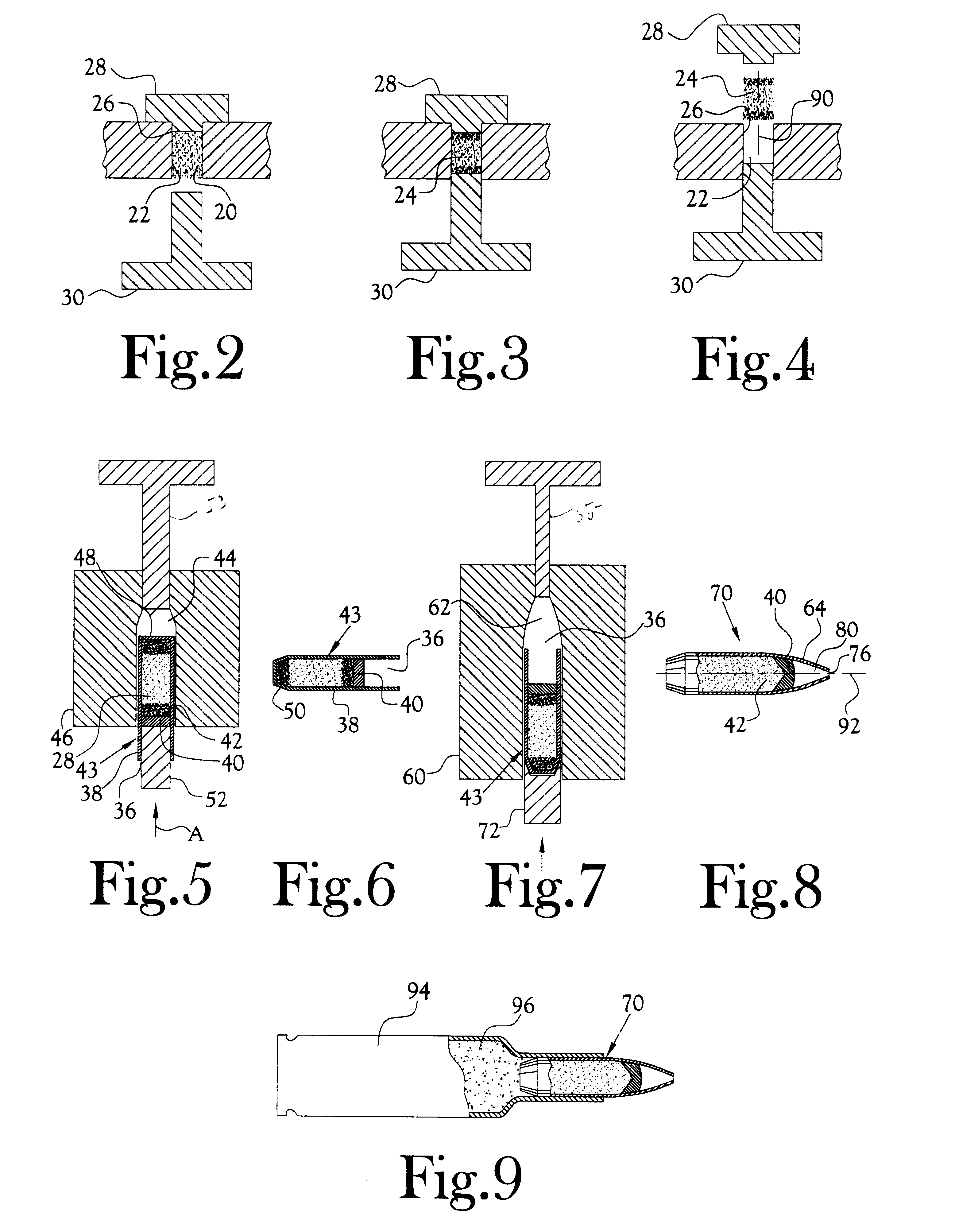
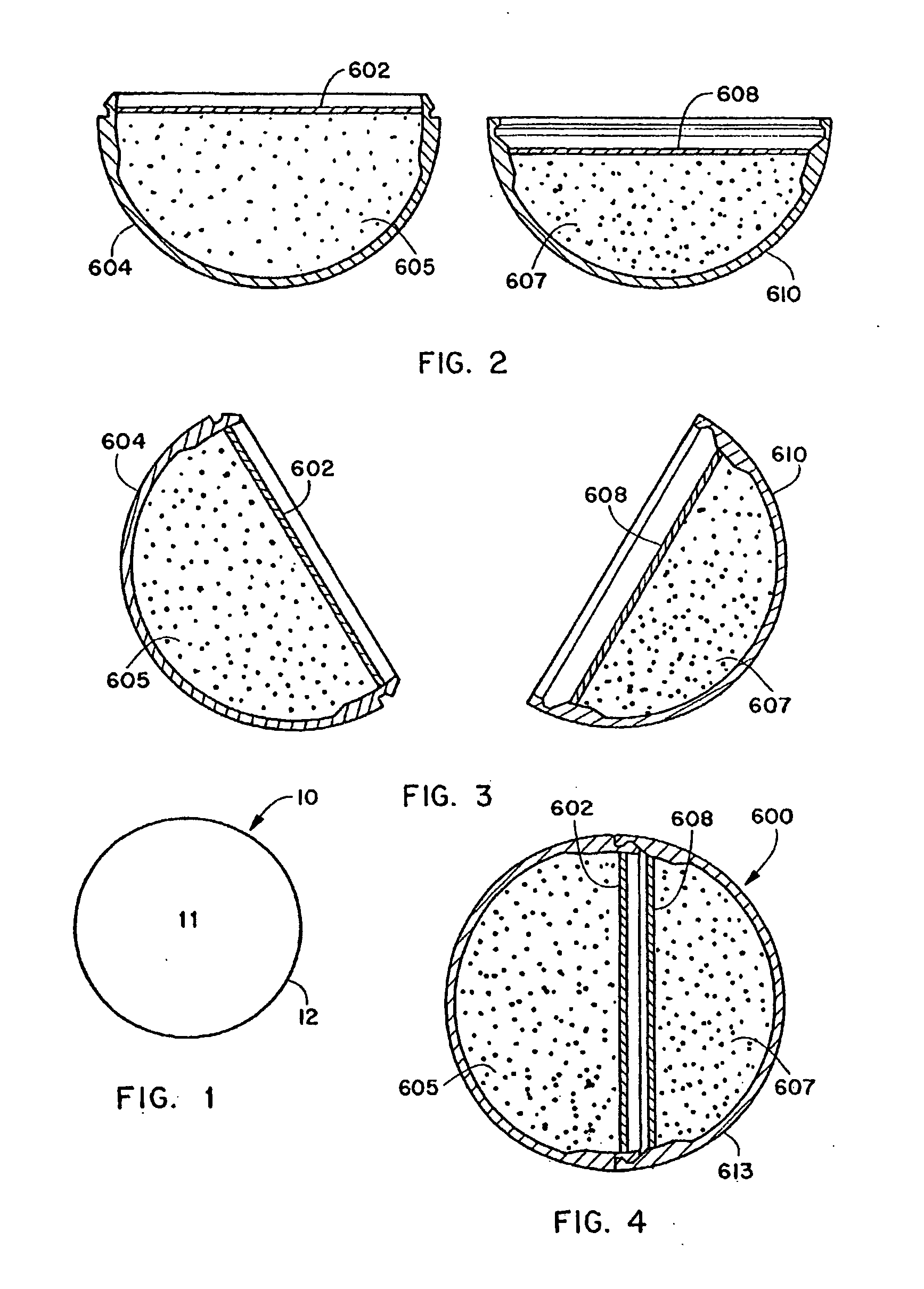
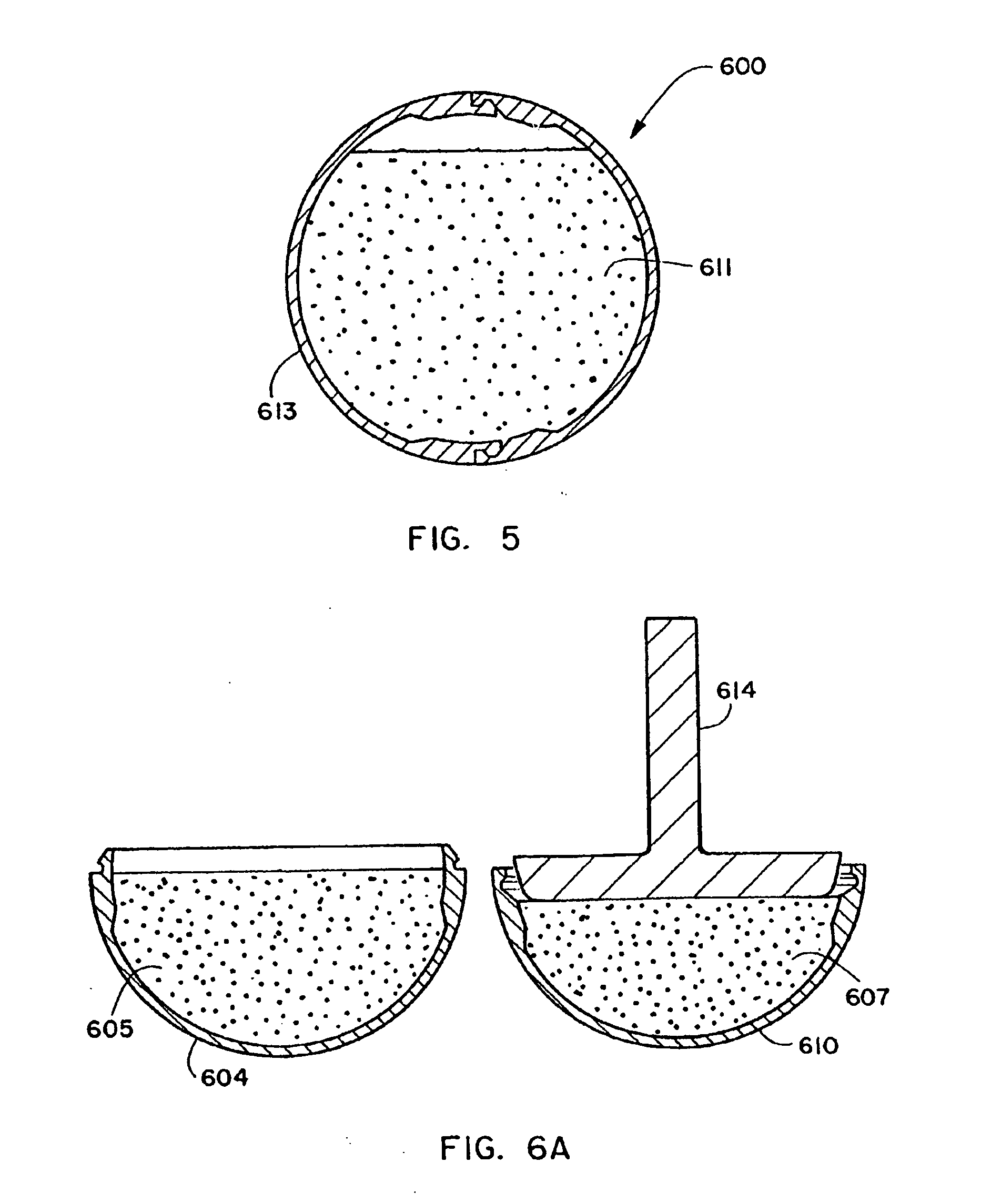
Method for the manufacture of a frangible nonsintered powder-based projectile for use in gun ammunition and product obtained thereby
InactiveUS6457417B1Easy and inexpensive to manufactureAmmunition projectilesTraining ammunitionSemi solidRicochet
A method for the manufacture of heavy metal powder-based frangible projectiles which are relatively easy and inexpensive to manufacture and which exhibit a selectable variety of desirable physical and / or performance properties. The projectiles of the present invention are powder-based, preferably including predominately tungsten powder as a heavy metal, particularly a tungsten powder which includes a predominate portion of finely sized particles. Lighter metal powders, also preferably having a predominate portion of finely sized particles, may be employed in combination with the tungsten to achieve certain desired results. Importantly, the present inventor has found that inclusion of a non-metal matrix powder, also of finely sized particles, in a mixture of a heavy metal powder, such as tungsten powder, and a light metal powder, may be employed in a variety of combinations to produce a projectile which is fully frangible upon striking a target (no ricochet), or which is frangible after either partial or full penetration of a selected target, either a semi-solid (e.g., a gel block) or a solid (e.g., a ¼ inch thick cold rolled steel plate at an angle of about 90 degrees).
Owner:COVE CORP +1
Projectile with Enhanced Ballistics
ActiveUS20160153757A1Flatter and faster external ballisticsImproved target penetrationAmmunition projectilesTraining ammunitionProximal pointEngineering
The present invention provides a projectile device and a method of manufacture of a projectile device and in particular, to a pistol bullet and a rifle bullet and method of manufacture of same. In one embodiment, the projectile apparatus has a cylindrical body portion having a diameter, a front nose section tapering from a most proximal point of the projectile to the cylindrical body portion, and a rear tail section connected to the body portion and extending to the most distal point of the projectile, in which the front nose portion comprises a plurality of twisting depressions forming troughs.
Owner:G9 HLDG LLC
Plastic ammunition casing and method
Ammunition having an integrally formed, polymeric casing is provided. Plastic casings for ammunition may be made using injection molding processes for combat ammunition, target ammunition and blanks. The casings, in one embodiment, include a hollow tubular member with an open end and a closed end having an aperture for a primer cap. The base of the casing includes a conical shape within the tube that narrows toward the base. An annular groove and an annular rim are disposed about an outer periphery of the base. Plastic casings may be utilized for ammunition cartridges used in pistols, rifles and shotguns, and are lighter and less expensive to manufacture than traditional brass casings. Further, the polymeric casings may include any desired colorants to distinguish different calibers of ammunition by color, and the spent casings may be recyclable.
Owner:TRIVETTE ROGER BLAINE
Sub-lethal, wireless projectile and accessories
InactiveUS6880466B2Increase energy levelReduce power levelAmmunition projectilesElectric shock equipmentsSTUNElectric discharge
The invention is a circuit capable of being positioned in a variety of wireless projectile and of delivering a series of pulsed electric discharges in two wave frequencies so as to stun and disable a target individual. The projectiles are adapted to be discharged from a different types of devices and powered by explosive, pneumatic, or manual means. At least one mode includes the ability to deliver a stunning physical blow in addition to the electric shock. The device is sub-lethal, but totally disabling in effects on a target individual.
Owner:CSA ENERGY
Reusable paint grenade
A reusable paint dispersing grenade of the type employed in paint ball games is constructed in such a manner as to avoid the use of any combustible materials, and also to avoid the requirement for access to a source of compressed air for operation. The paint grenade of the invention has a hollow, fluid-tight casing defining an enclosed cavity that is divided internally into a marking paint chamber, a first propellant component chamber, and a second propellant component chamber. The propellant component chambers are each filled separately with propellant components, but remain isolated from each other until the paint dispersing grenade is used. At that time the propellant components chemically react with each other in a noncombustible manner to produce a quantity of gas under pressure. The expanding gas produced by the chemical reaction builds to a pressure sufficient to break a paint seal in the casing or a gas seal initially separating the gas from the paint, whereupon the gas under pressure forces the paint out through one or more paint expulsion ports. The device may be recharged with marking paint and the chemically reactive propellant components any number of times.
Owner:ESTRELLA RANDALL P
Plastic ammunition casing and method
InactiveUS20100275804A1Ammunition projectilesShotgun ammunitionShotgun pelletInjection molding process
Ammunition having an integrally formed, polymeric casing is provided. Plastic casings for ammunition may be made using injection molding processes for combat ammunition, target ammunition and blanks. The casings, in one embodiment, include a hollow tubular member with an open end and a closed end having an aperture for a primer cap. The base of the casing includes a conical shape within the tube that narrows toward the base. An annular groove and an annular rim are disposed about an outer periphery of the base. Plastic casings may be utilized for ammunition cartridges used in pistols, rifles and shotguns, and are lighter and less expensive to manufacture than traditional brass casings. Further, the polymeric casings may include any desired colorants to distinguish different calibers of ammunition by color, and the spent casings may be recyclable.
Owner:TRIVETTE ROGER BLAINE
Non-lethal projectile systems
InactiveUS20050188886A1Maximize effectivenessImprove efficiencyAmmunition projectilesTraining ammunitionEngineeringProjectile
A non-lethal projectile system for non-lethally inhibiting a living target, multi-functional launching devices for delivering the non-lethal projectile systems to a target, methods of assembling the non-lethal projectiles, and tactical methods of the use of the non-lethal projectile, the non-lethal projectile consists of a projectile body to be impacted with a living target and an inhibiting substance within the projectile body, wherein upon impact with the target, the inhibiting substance is dispersed on and about the target. In a variation, the projectile body ruptures upon impact releasing the substance. In another variation, the inhibiting substance is a powdered substance comprising a powdered pepper derived substance, for example, oleoresin capsicum or capsaicin.
Owner:PEPPERBALL TECH
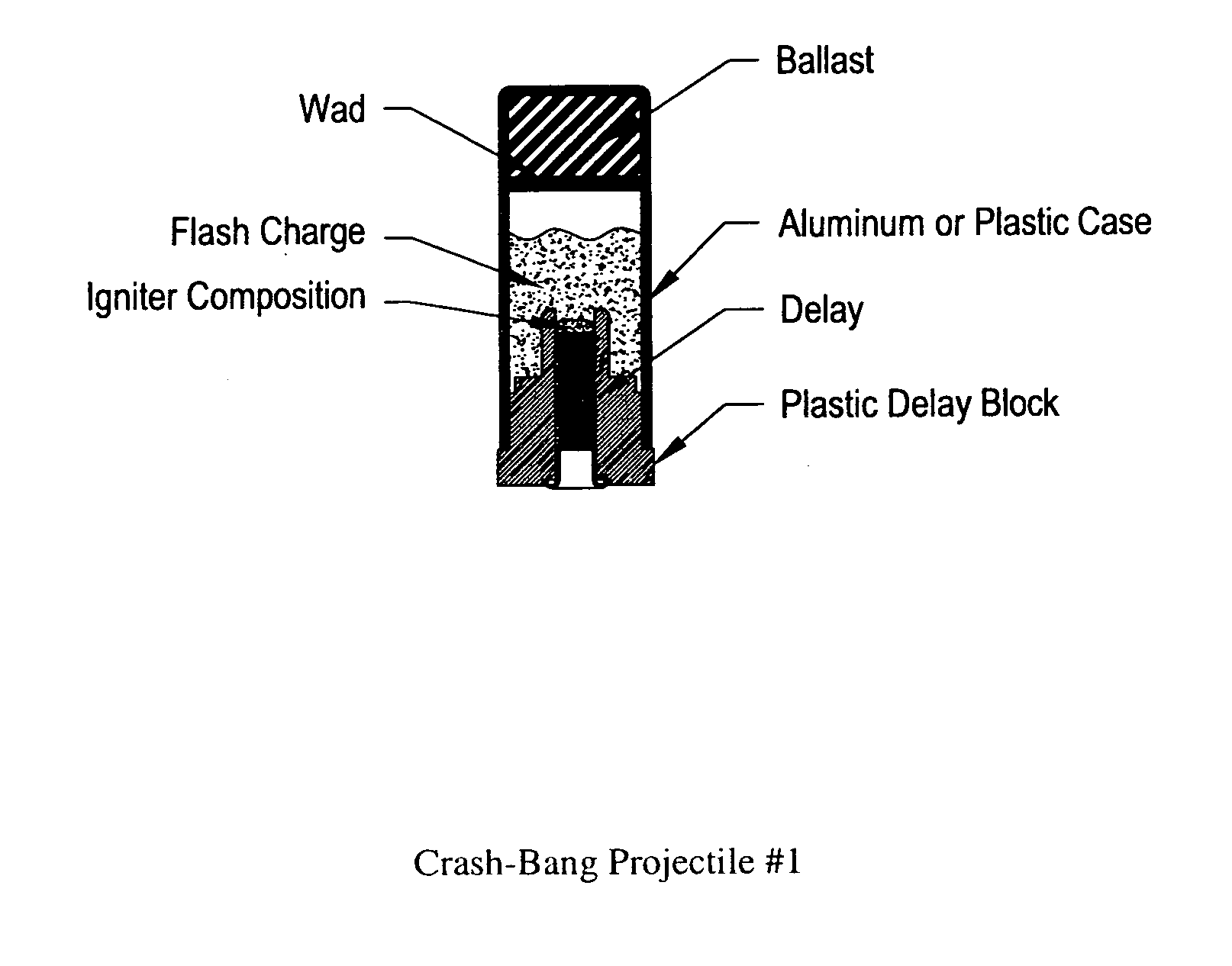
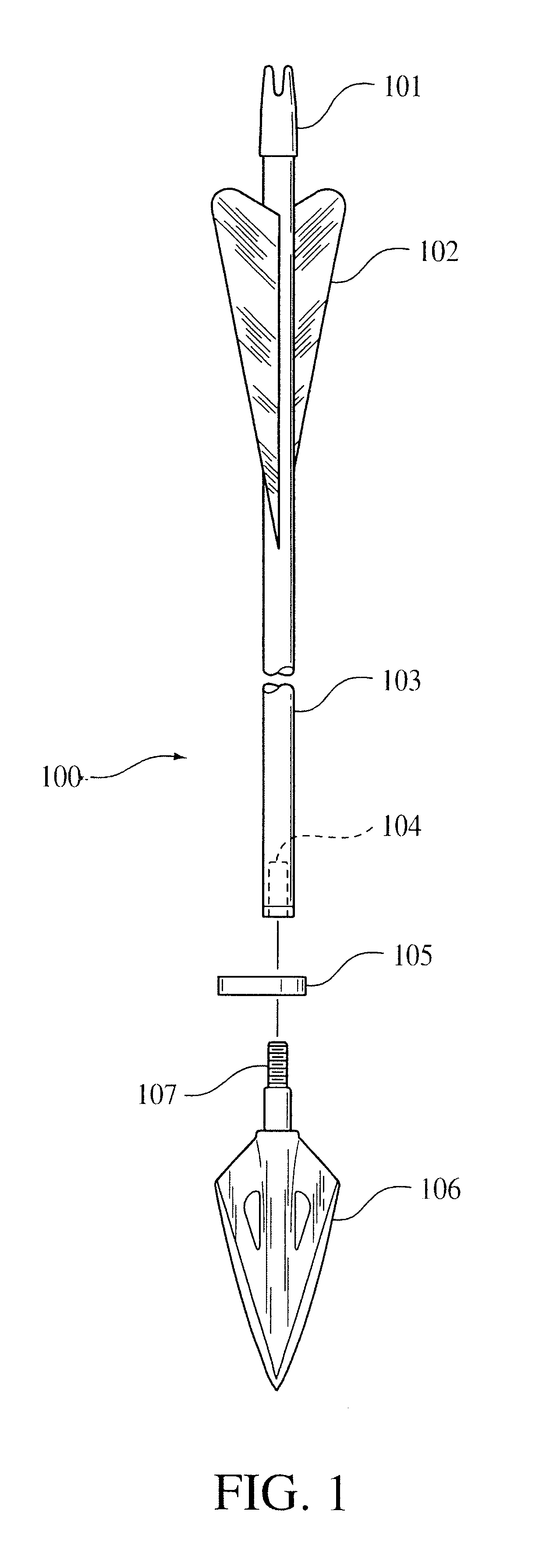
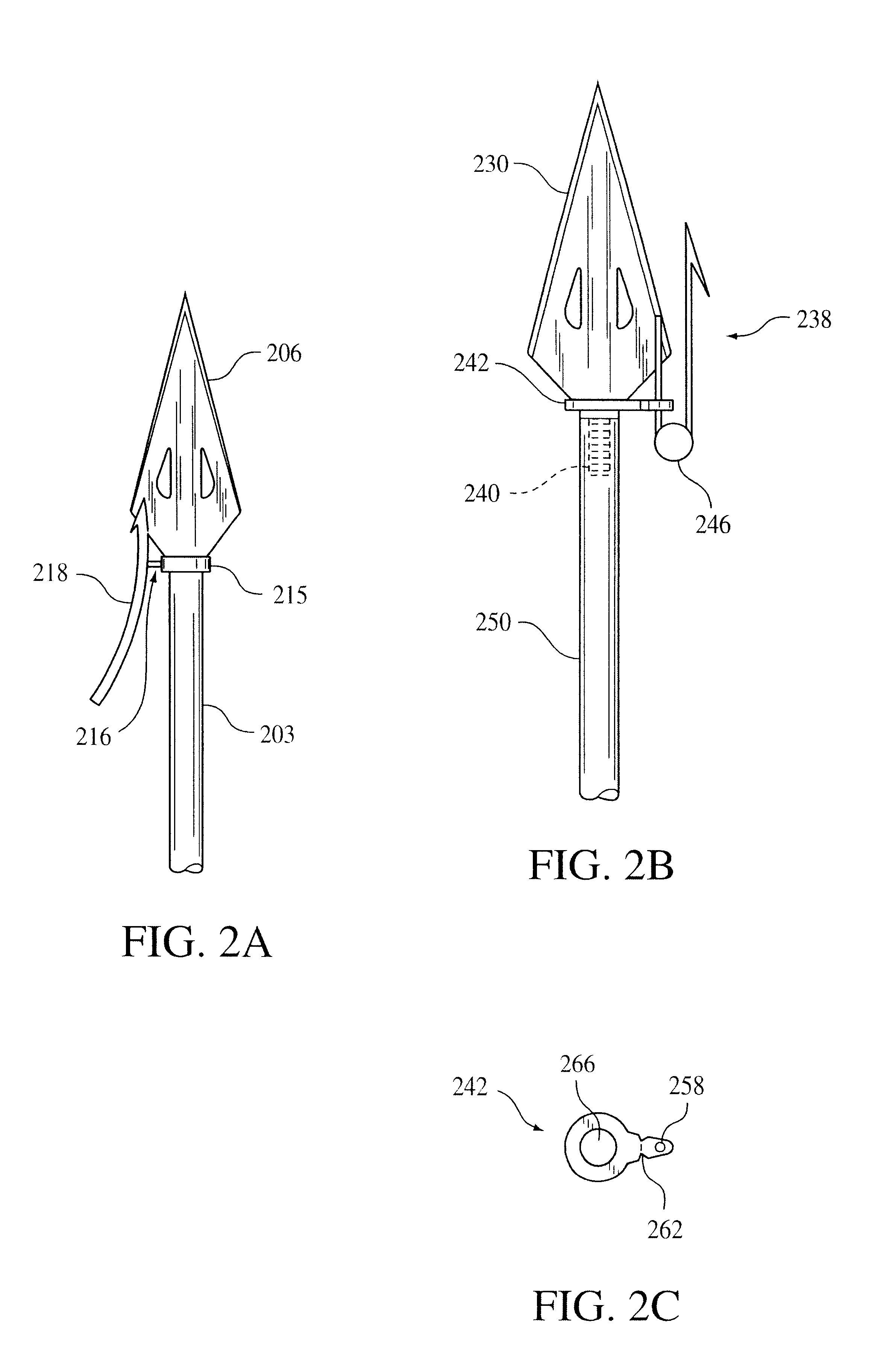
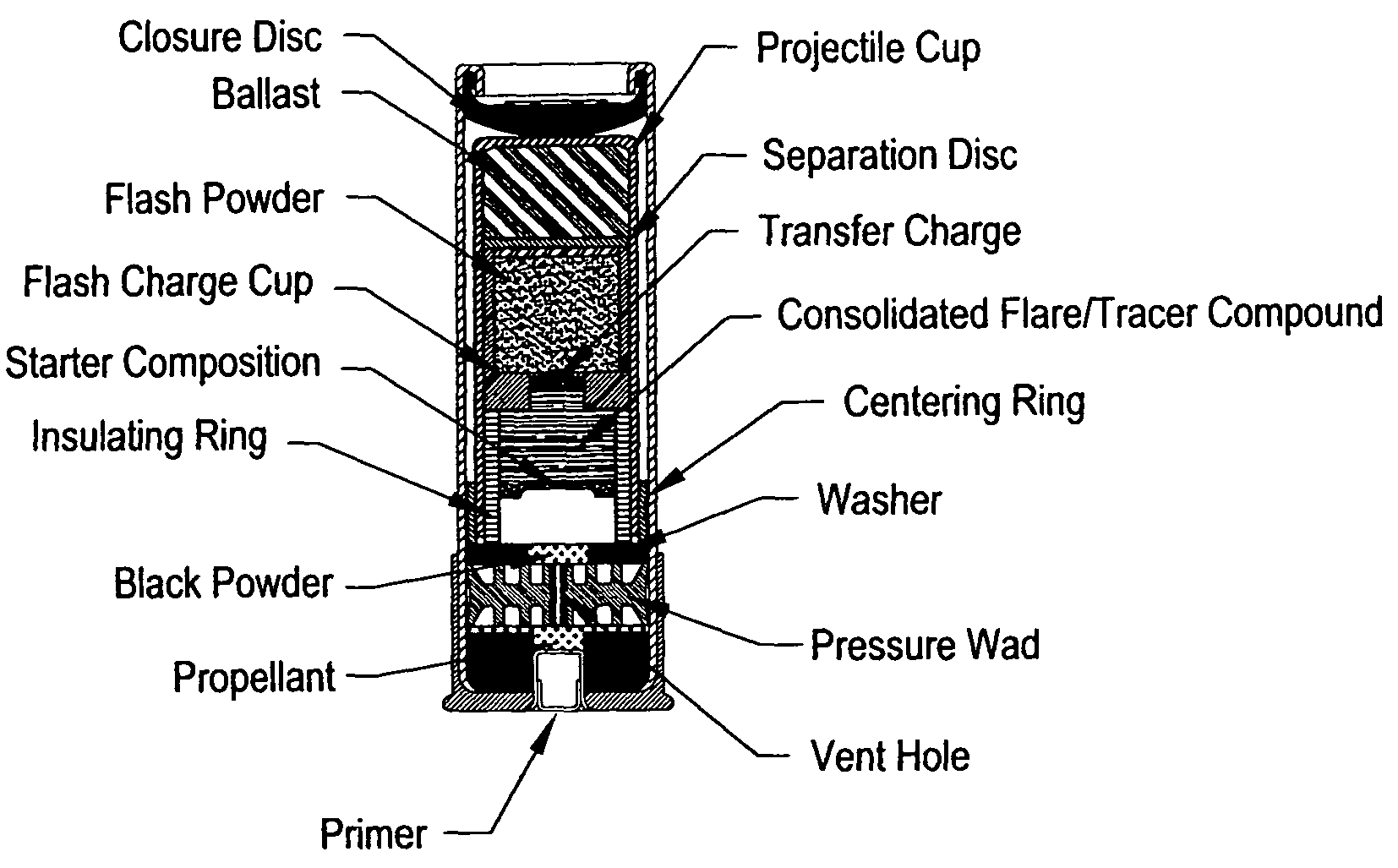
Flare-bang projectile
ActiveUS20100212533A1Improve stabilityImprove accuracyAmmunition projectilesFirework flares/torchesLeading edgeFlare
A flare-bang projectile is comprised of a weighty ballast in the front leading edge, a flash-bang charge, a transfer charge and a flare charge that is lit by a starter composition located at the rear of the flare charge. When the flare charge is ignited such that it burns during the flight of the projectile, an the projectile path is indicated to thereby provide warning signaling.
Owner:COMBINED SYST
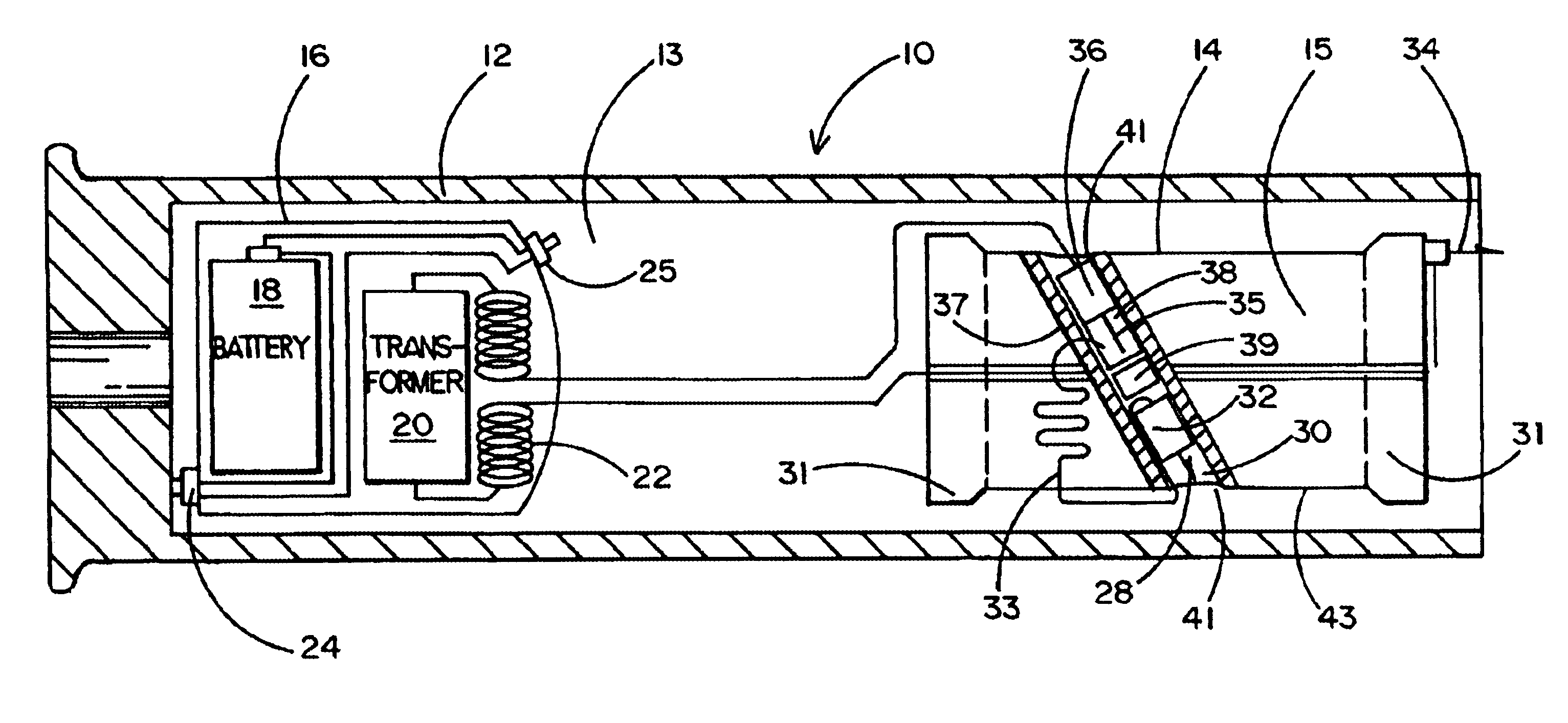
Multi-stage projectile weapon for immobilization and capture
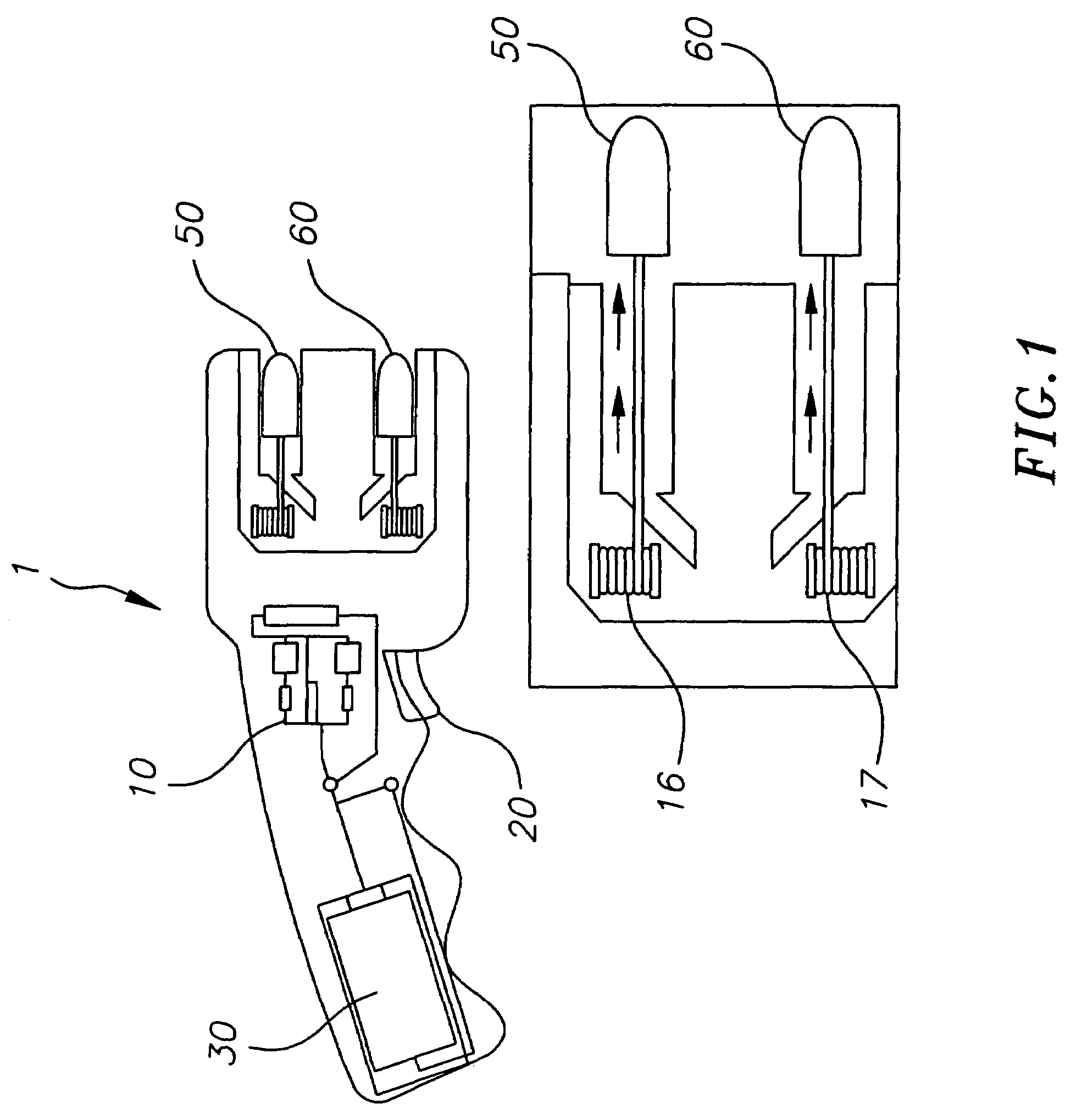
InactiveUS6877434B1Improved versionAmmunition projectilesAircraft componentsTransformerHigh voltage pulse
Two distinct projectile stages are employed in a projectile configured to be fired at a remote target from a rifle, grenade launcher, gas gun or the like. A first stage comprises a pair of wire tethered contact darts for applying an immobilizing electrical discharge to the target. The second stage comprises a battery, circuits, transformer and wires used to generate a high voltage pulsed signal and apply it to the contact darts in the first stage. The higher mass of the second stage impacts the lower mass first stage at launch causing the first stage to be propelled to the target while the slower second stage hits the ground short of the target.
Owner:SAFARILAND
Projectile for an electrical discharge weapon
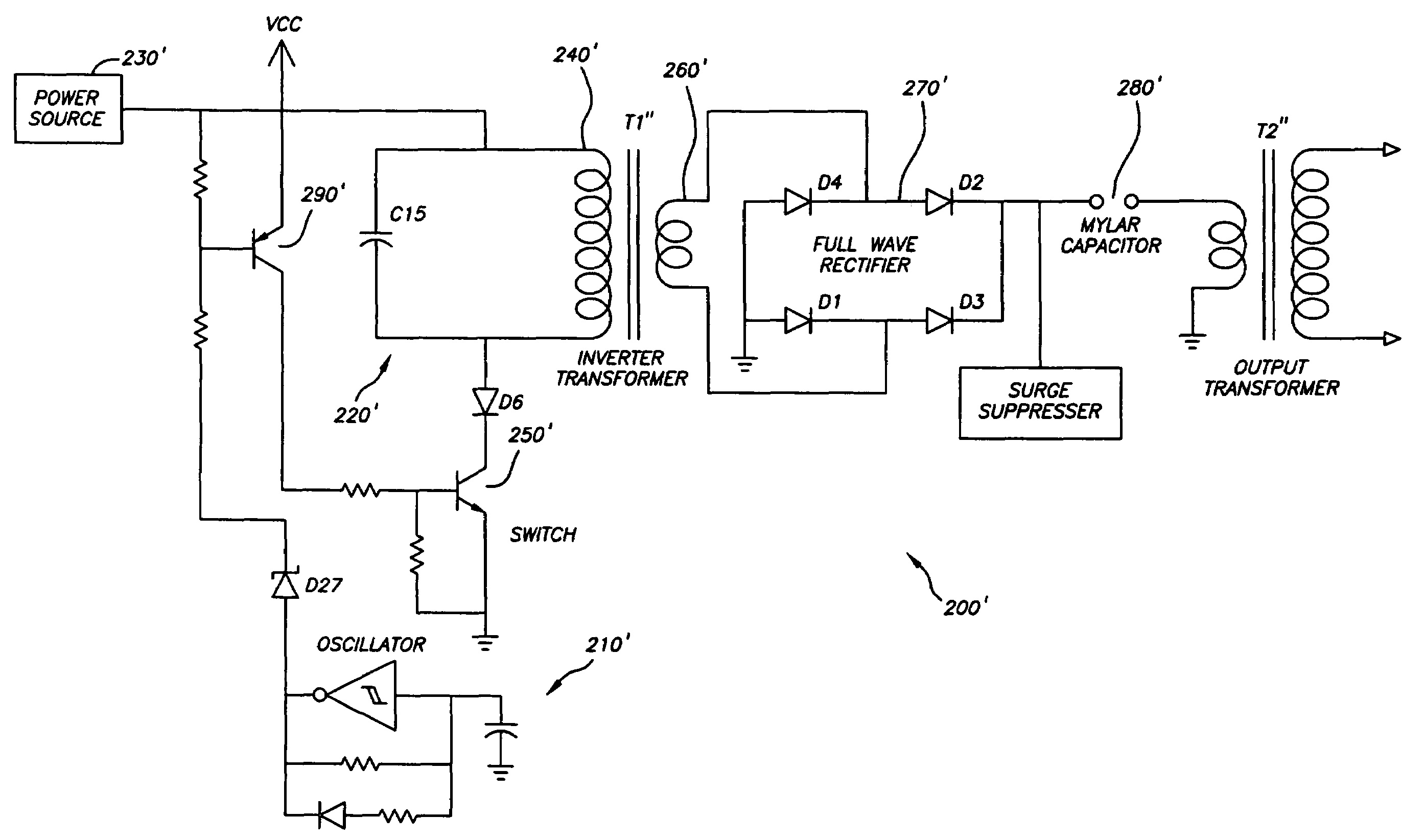
ActiveUS7237352B2Reduce power consumptionImprove power efficiencyAmmunition projectilesElectrical apparatusEngineeringElectrical discharge machining
An electrical discharge weapon projectile for immobilizing a live target that includes a shock circuit having a low power consumption, a high power efficiency, and / or a low weight. In one embodiment, the projectile includes a high efficiency circuit that would reduce the weights of shock circuits while providing a more effective and safer power level, so that the circuits may be entirely contained within the projectile to eliminate the need for range limiting trailing wires.
Owner:VIEVU +1
Electrical immobilization weapon
ActiveUS20060187610A1Vibration minimizationImprove efficiencyAmmunition projectilesElectrical apparatusEngineeringProjectile
A cartridge for an electrical immobilization weapon for optimized effectiveness and accuracy, comprising: a housing means for accommodating first and second projectiles adapted for being spaced within a targeted portion, having a length of at least from 5 inches to 25 inches, of a human body and for transmitting the electrical energy to the target; connecting means having at least one such length for interconnecting the first and second projectiles and available outside the housing means for retaining the projectiles within the said length in between thereof; means including the housing means for separating the first and second projectiles for immediately achieving a said length in between after leaving the housing means; means secured to the housing means for propelling the projectiles from the housing means for reaching the targeted portion; and means for coupling the projectiles to the electrical energy of the weapon's power supply.
Owner:VOLGER INT AB
Projectile trajectory control system
ActiveUS7354017B2Reduce time and energyReduce weightAmmunition projectilesDirection controllersAviationVehicle frame
Trajectory is controlled by a control system having fins that de-spin a section of the control system relative to a projectile or missile. The control system also includes aero-surfaces that produce a lift when brought to rotation speed of about 0 Hz relative to a reference frame and a brake that couples the guidance package to the rotational inertia of the projectile or missile. In one example, no electric motor is used in the trajectory control system, saving weight and increasing reliability.
Owner:GEN DYNAMICS ORDNANCE & TACTICAL SYST
Tracking system, apparatus and method
A remotely-locatable tracking device and system is presented for use with a projectile that contacts a mobile target. The device is particularly useful with hunting arrows that contact a target animal. The device detaches from the arrow and attaches to the animal upon impact. The device is preferably comprised of a passive transponder and the system preferably uses a handheld transceiver to locate the transponder attached to the target animal.
Owner:HILLIARD RANDY
Flare-bang projectile
ActiveUS7908972B2Improve stabilityImprove accuracyAmmunition projectilesFirework flares/torchesLeading edgeFlare
A flare-bang projectile is comprised of a weighty ballast in the front leading edge, a flash-bang charge, a transfer charge and a flare charge that is lit by a starter composition located at the rear of the flare charge. When the flare charge is ignited such that it burns during the flight of the projectile, an the projectile path is indicated to thereby provide warning signaling.
Owner:COMBINED SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com