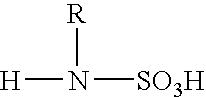Patents
Literature
775results about "Electric shock equipments" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
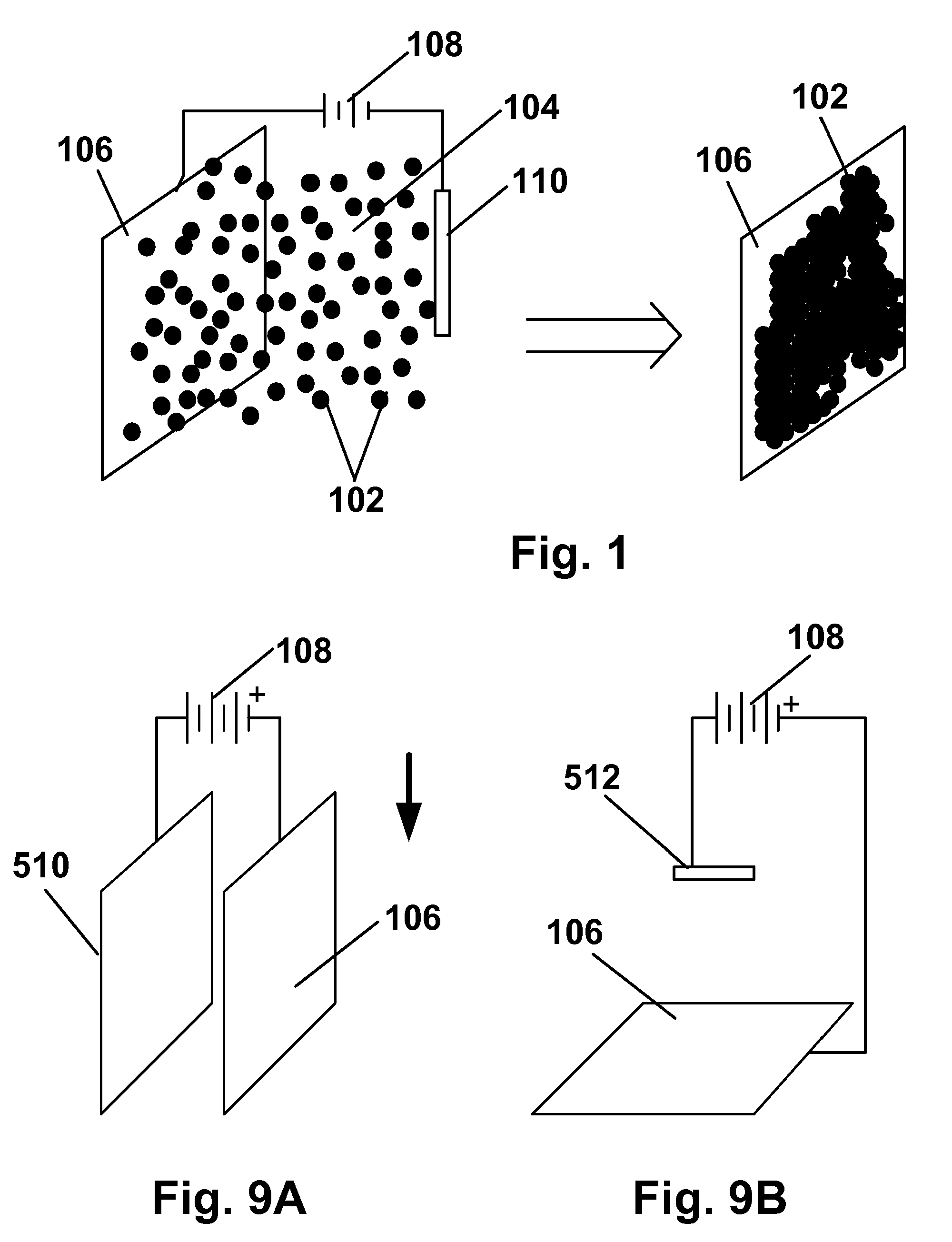
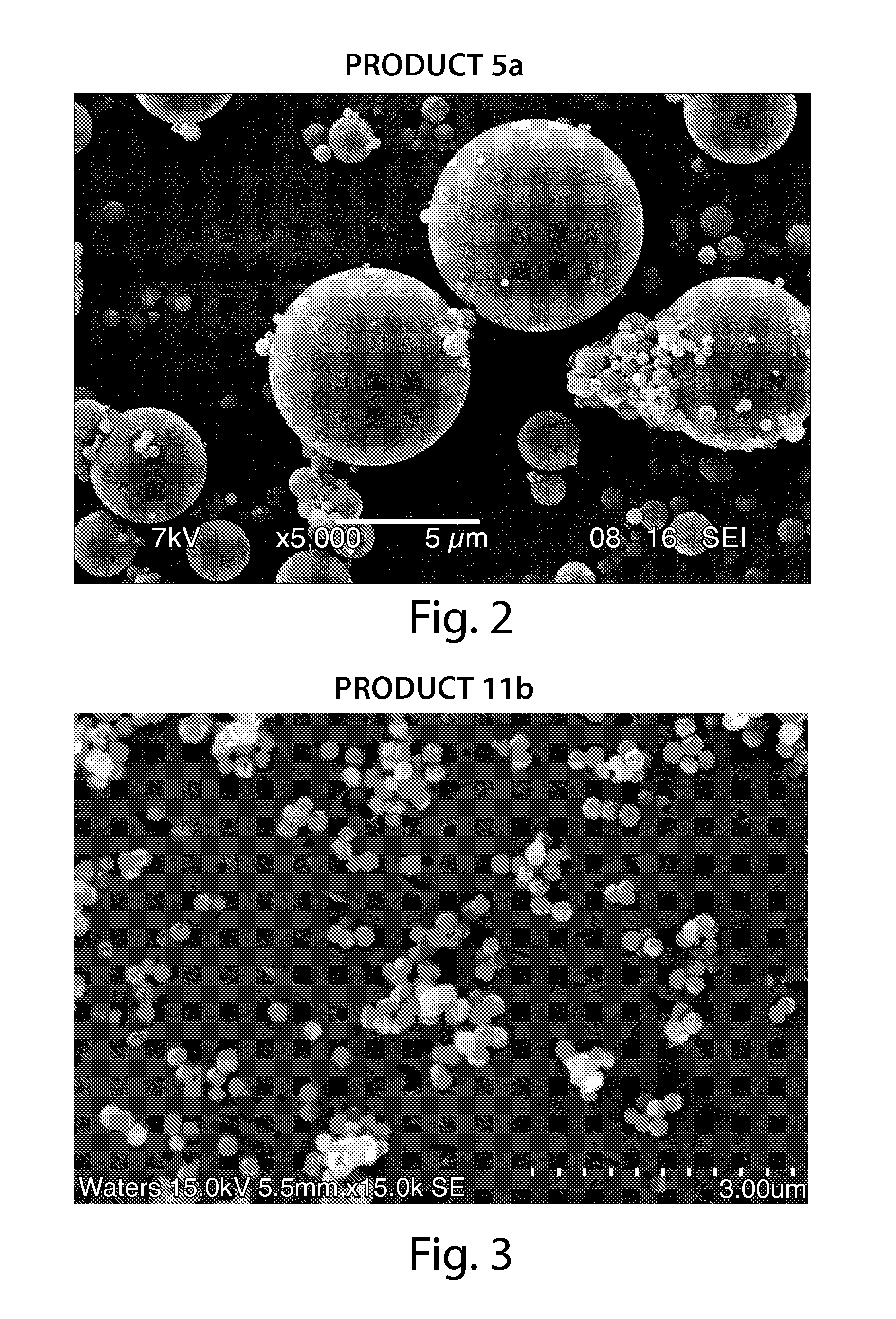
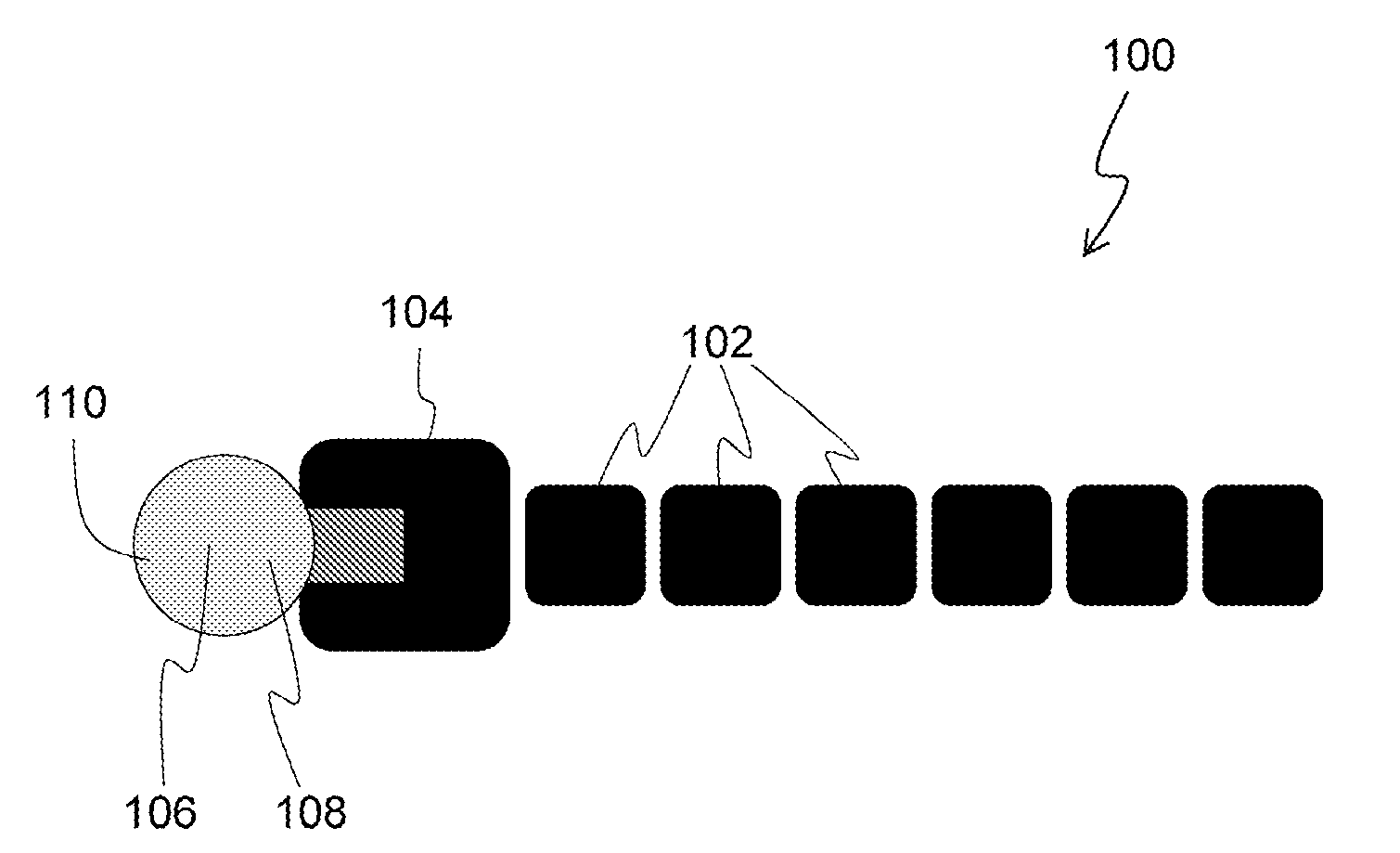
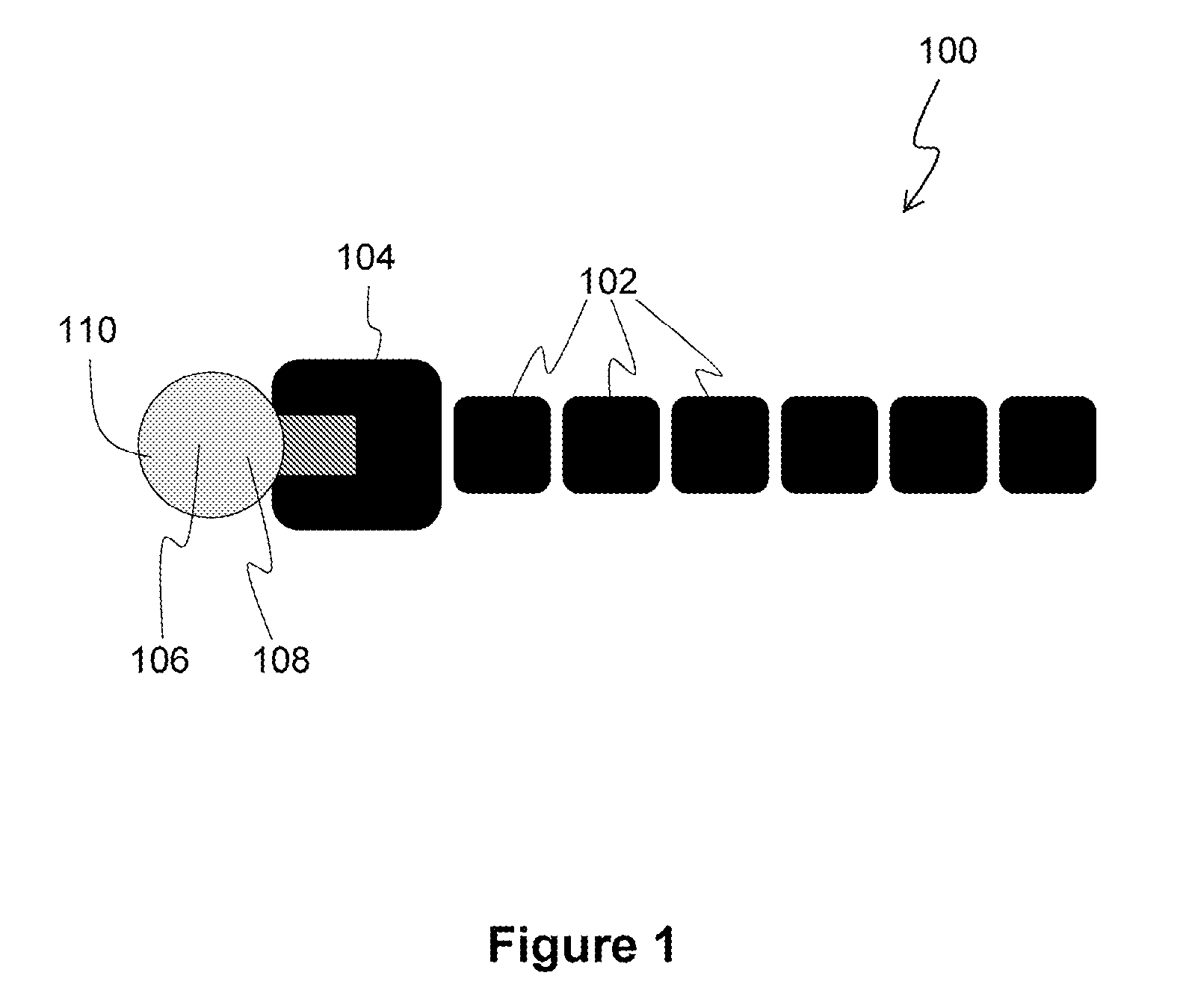
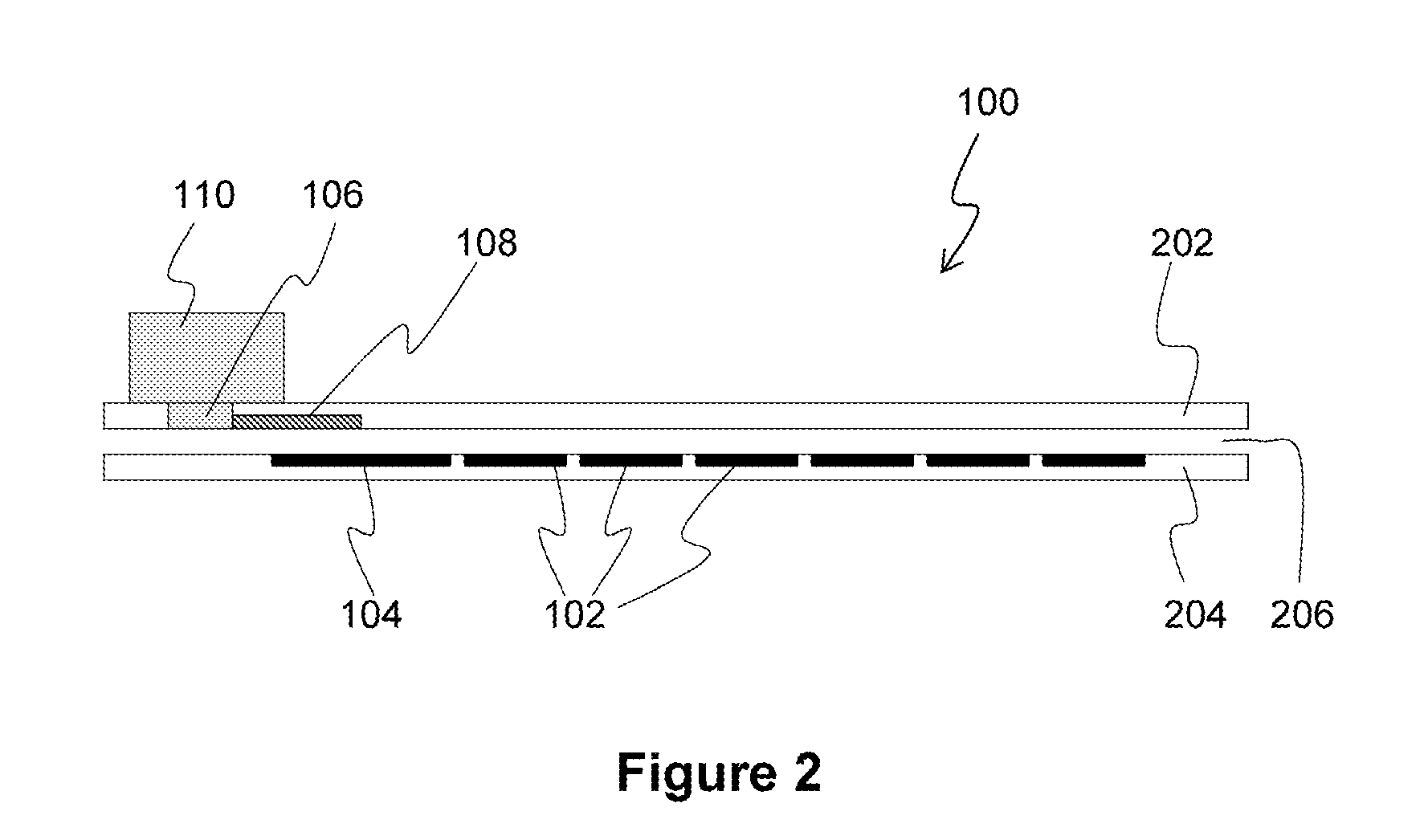
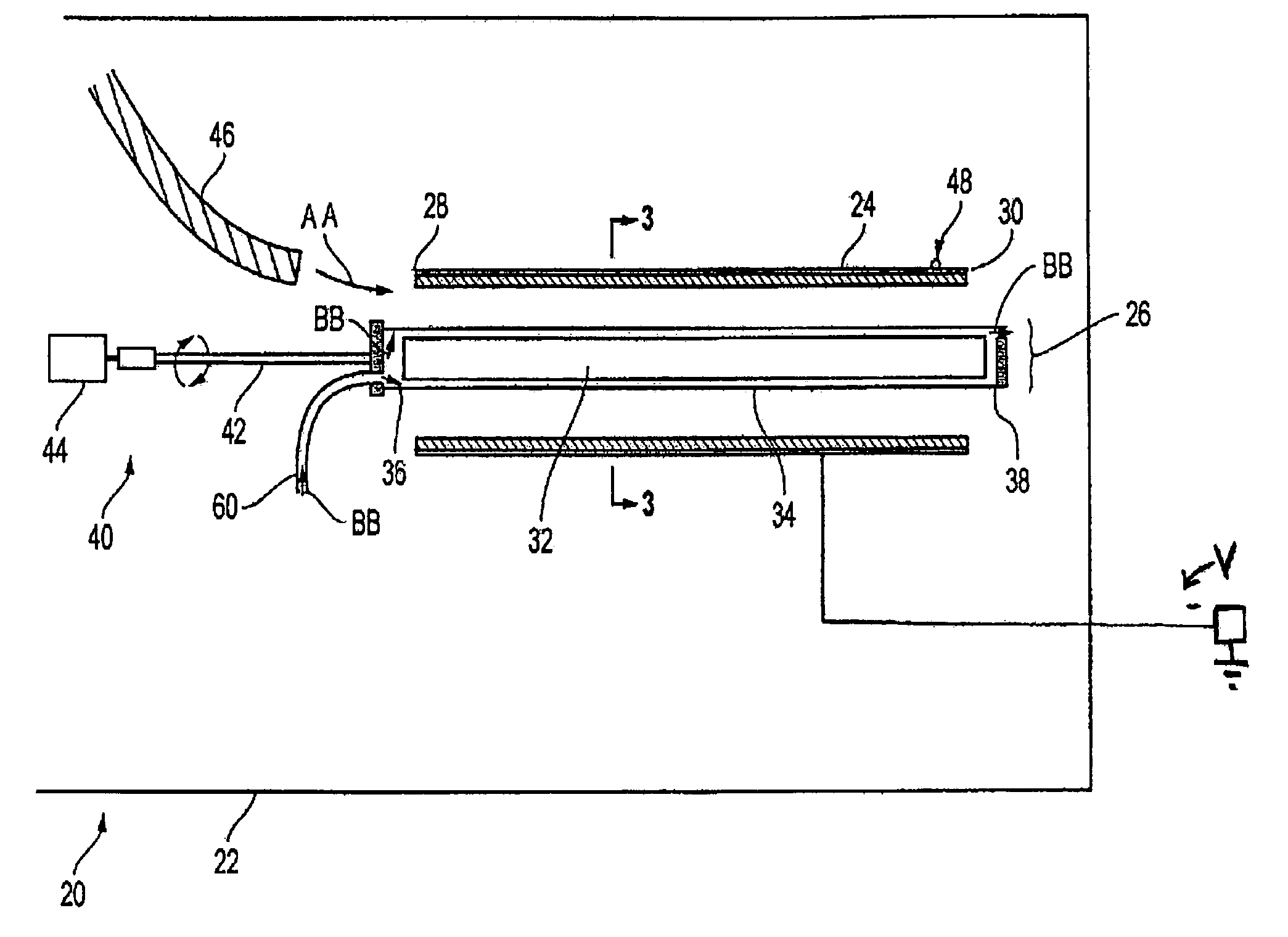
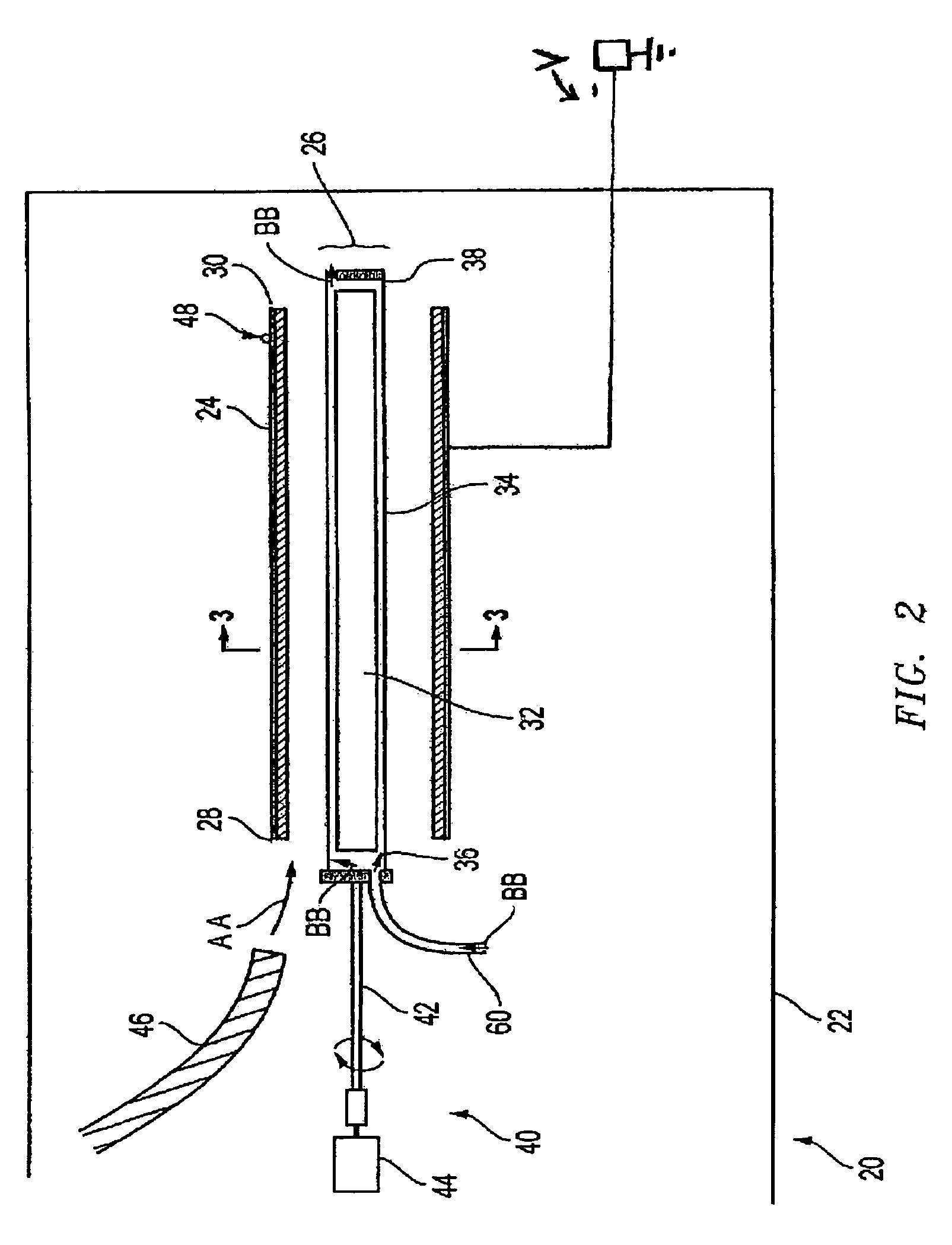
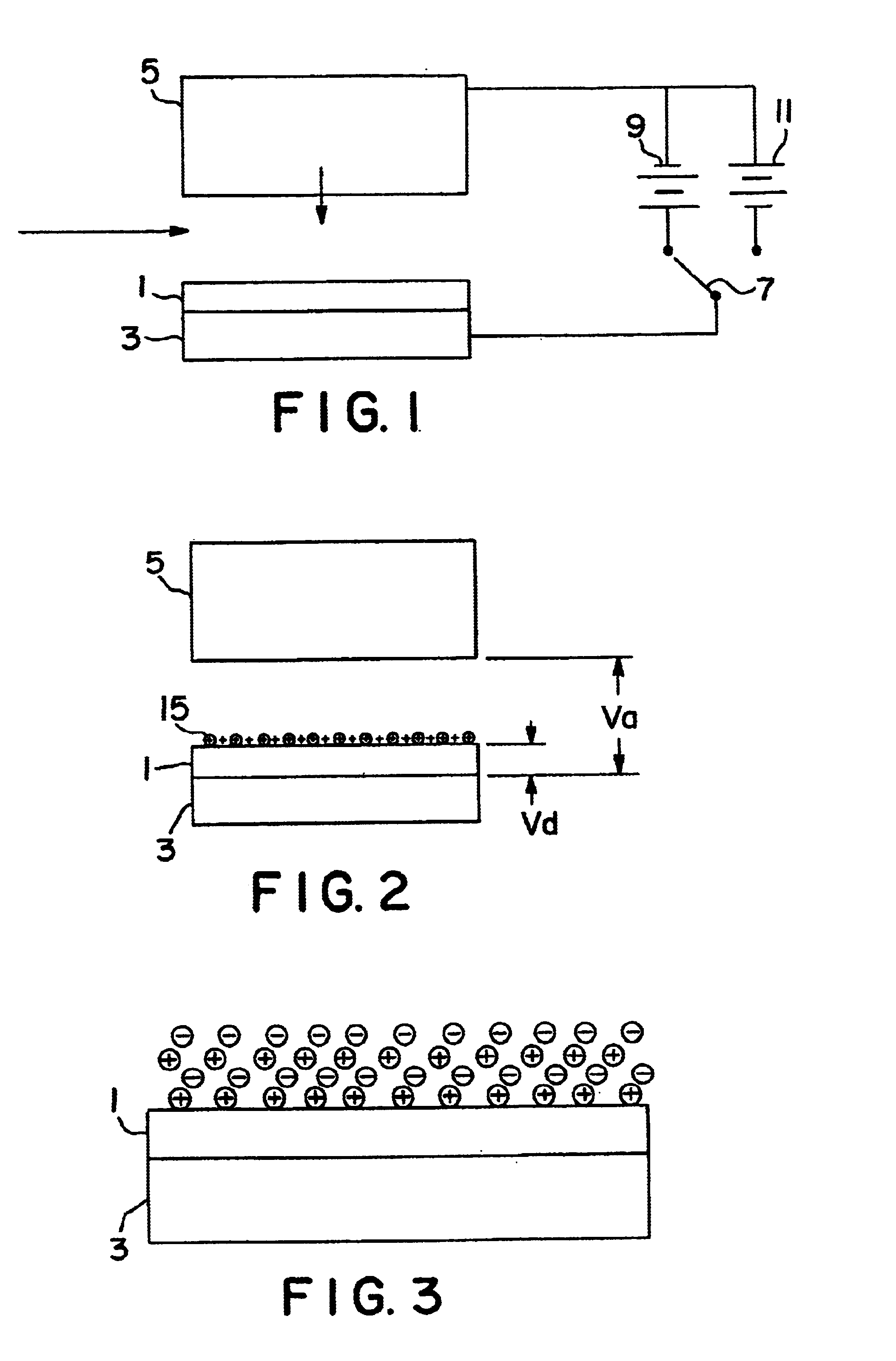
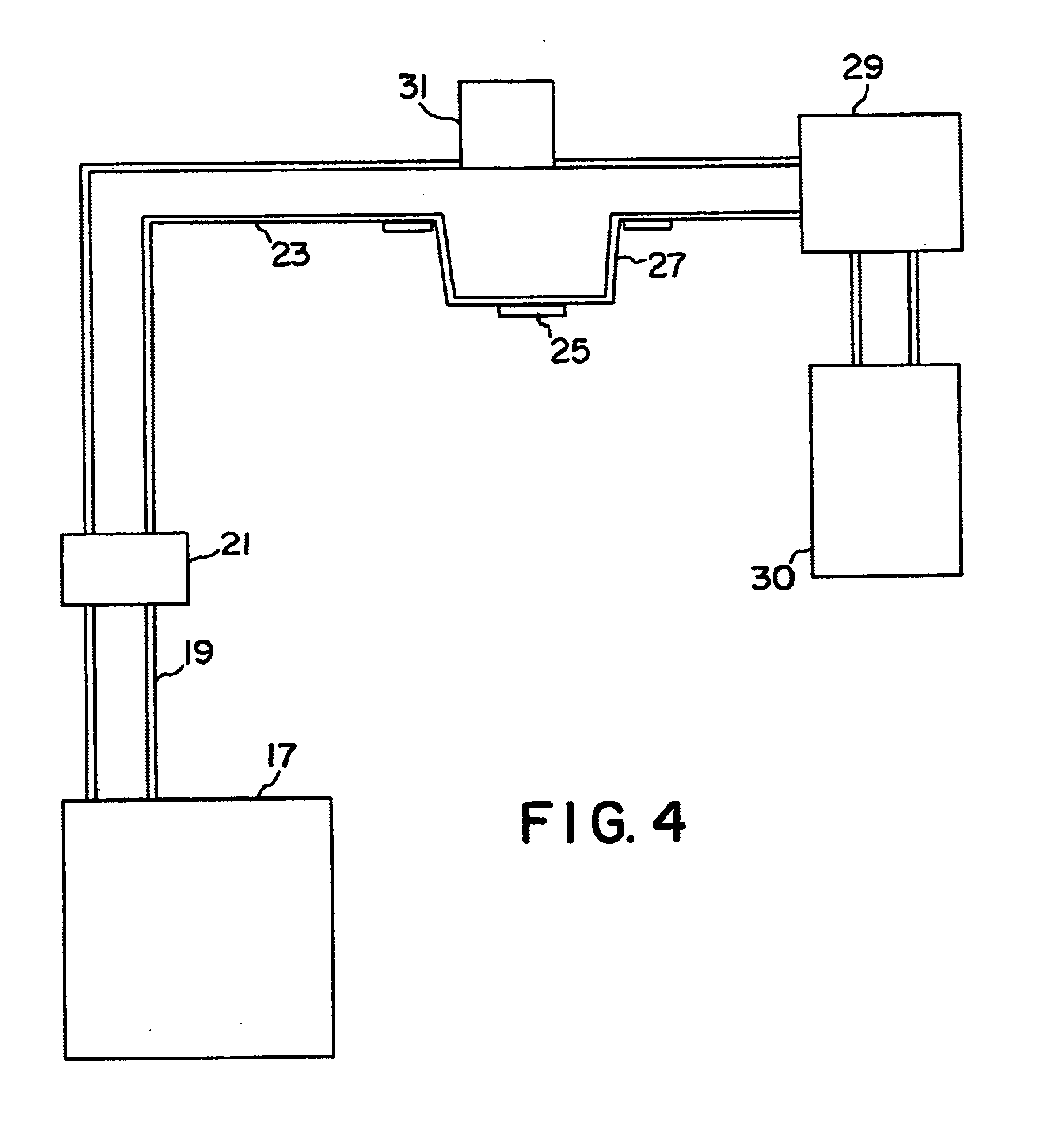
Processes for the production of electrophoretic displays
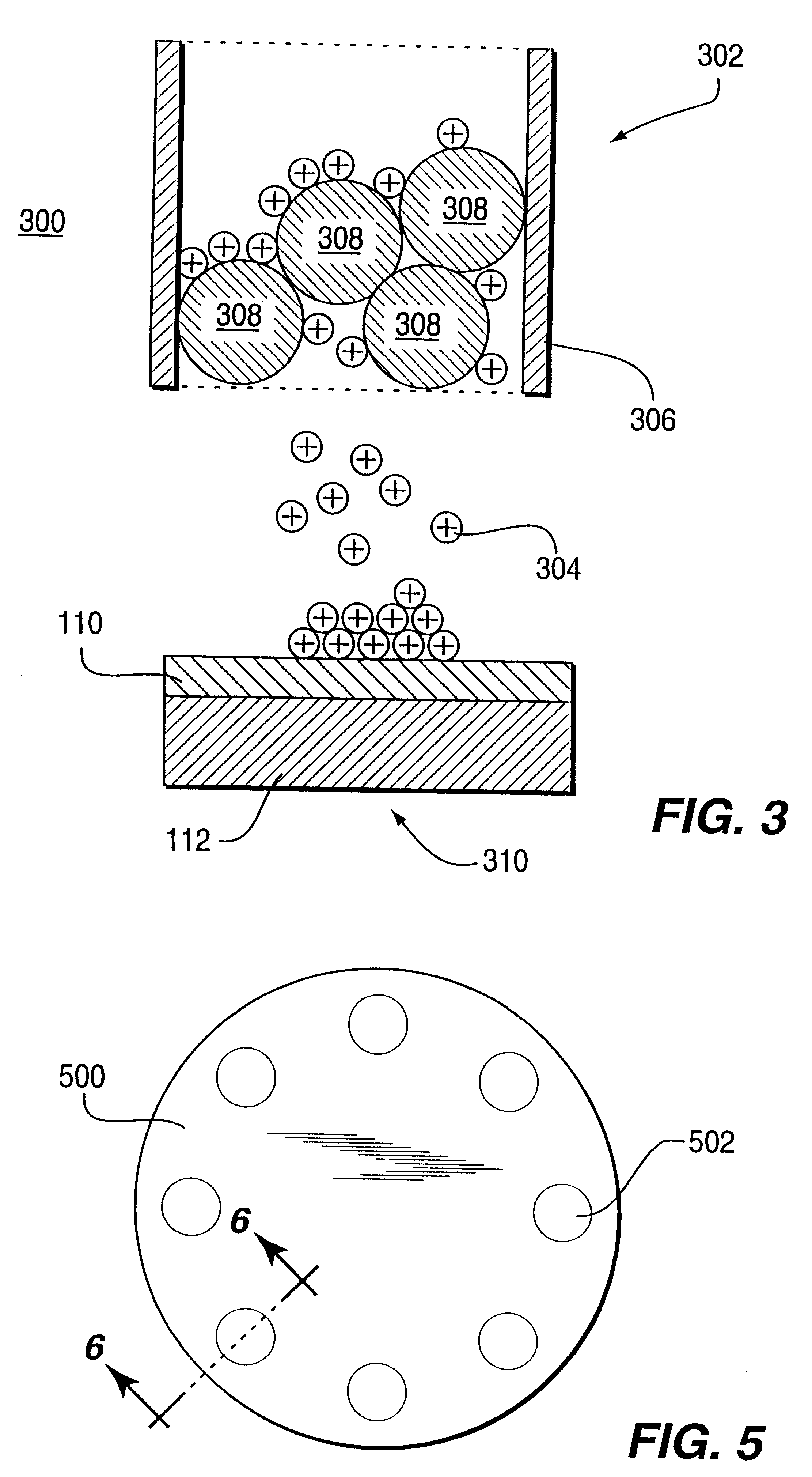
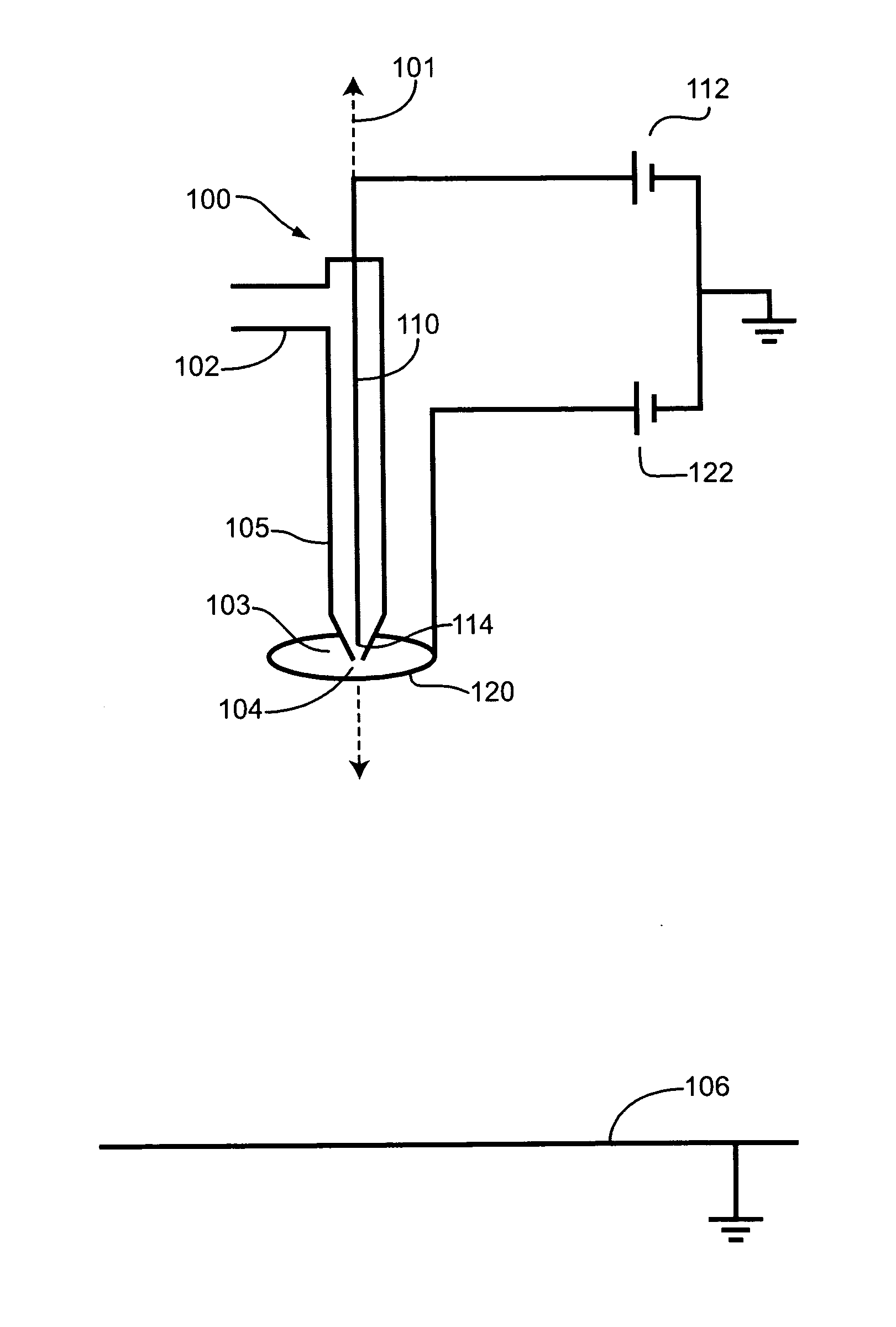
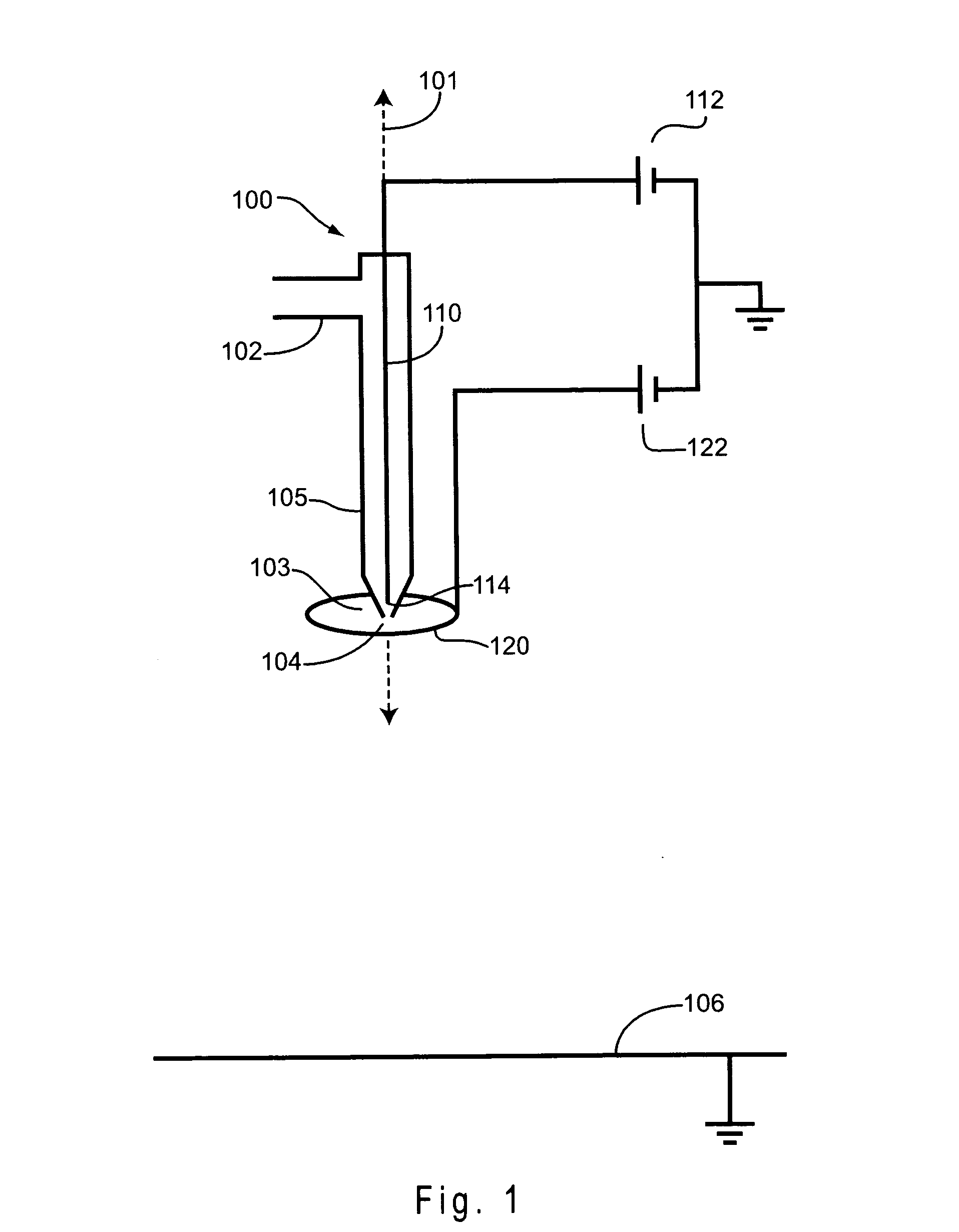
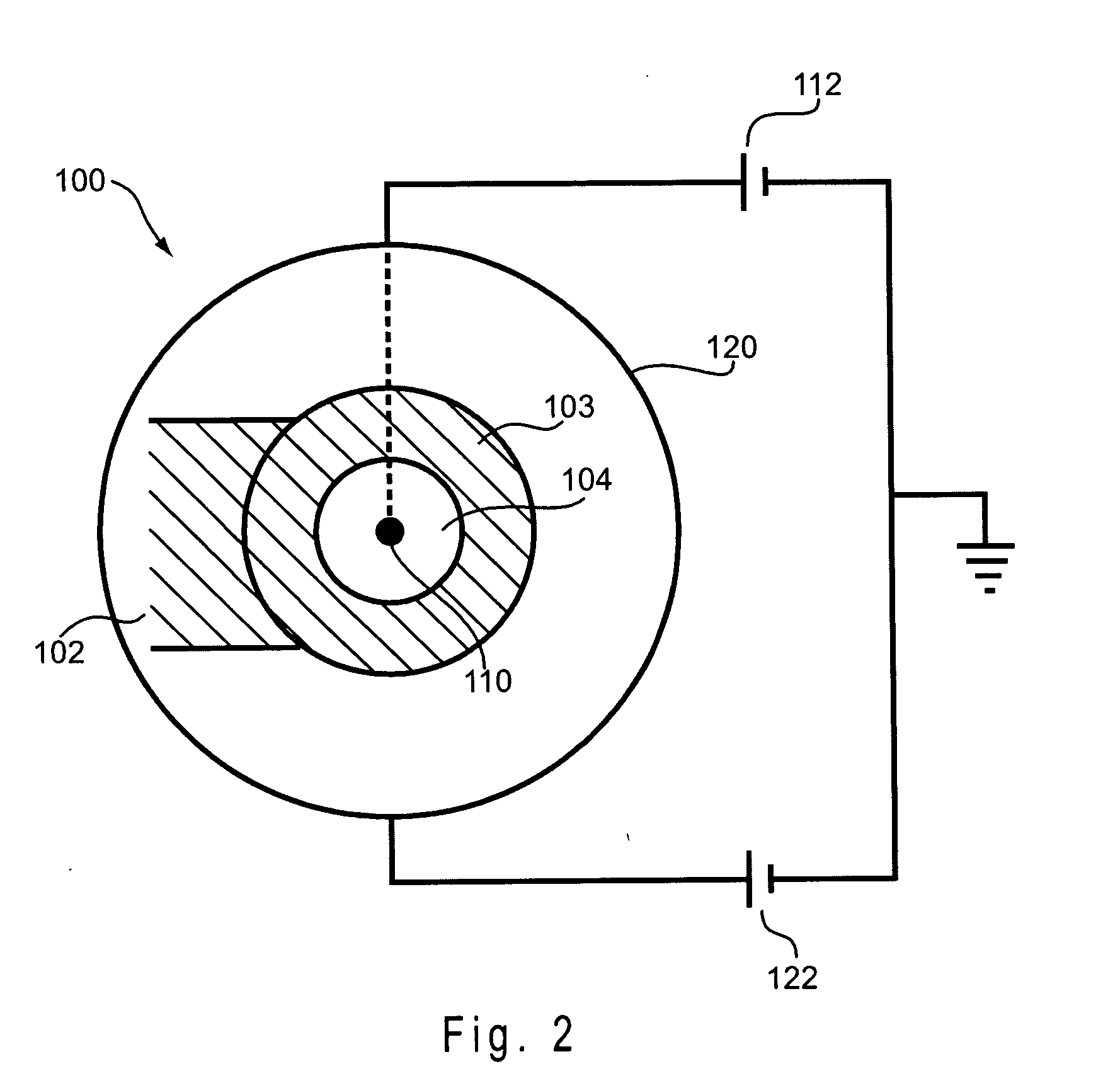
ActiveUS7339715B2Electric shock equipmentsElectrophoretic coatingsElectrophoresisPotential difference
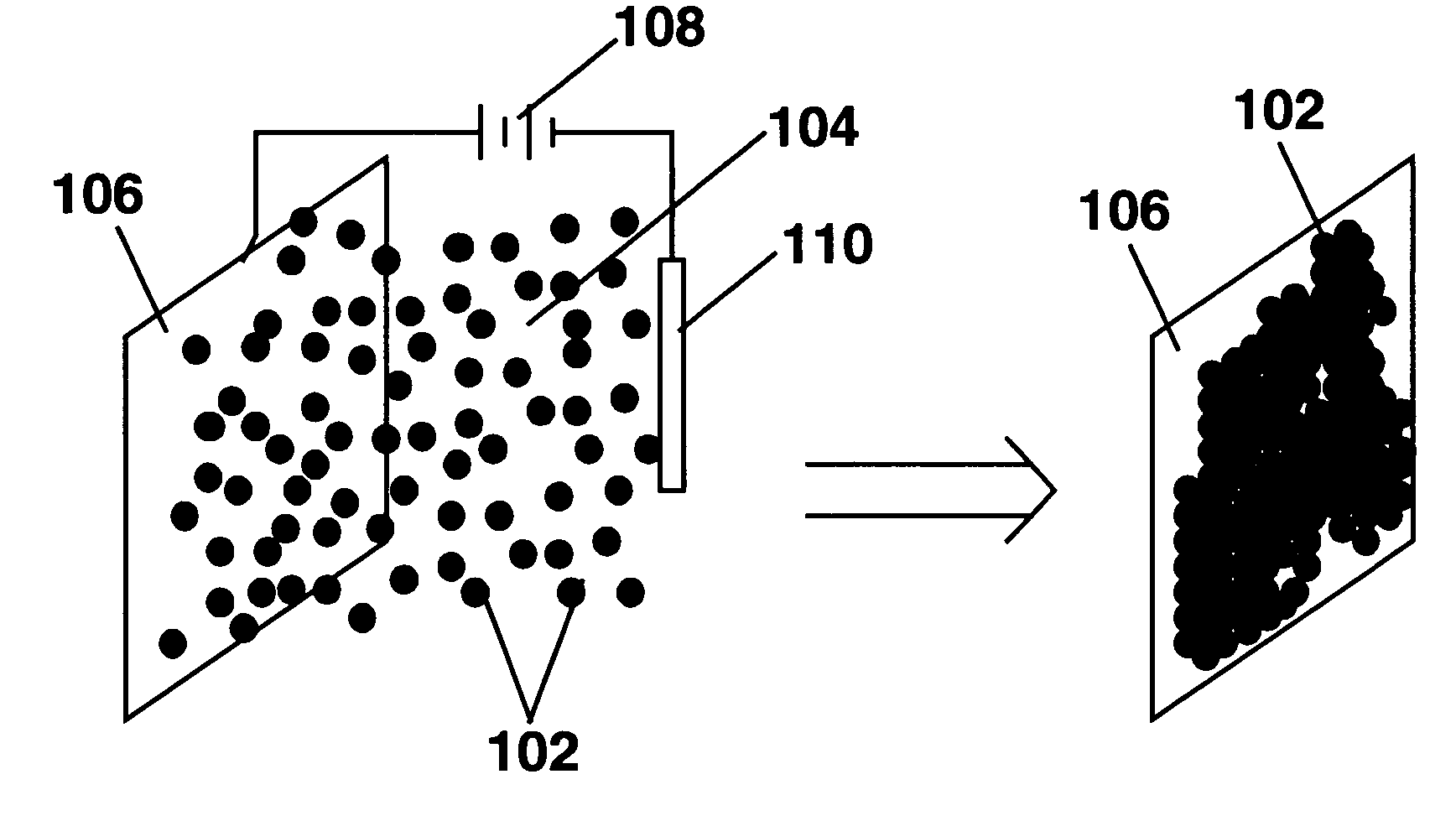
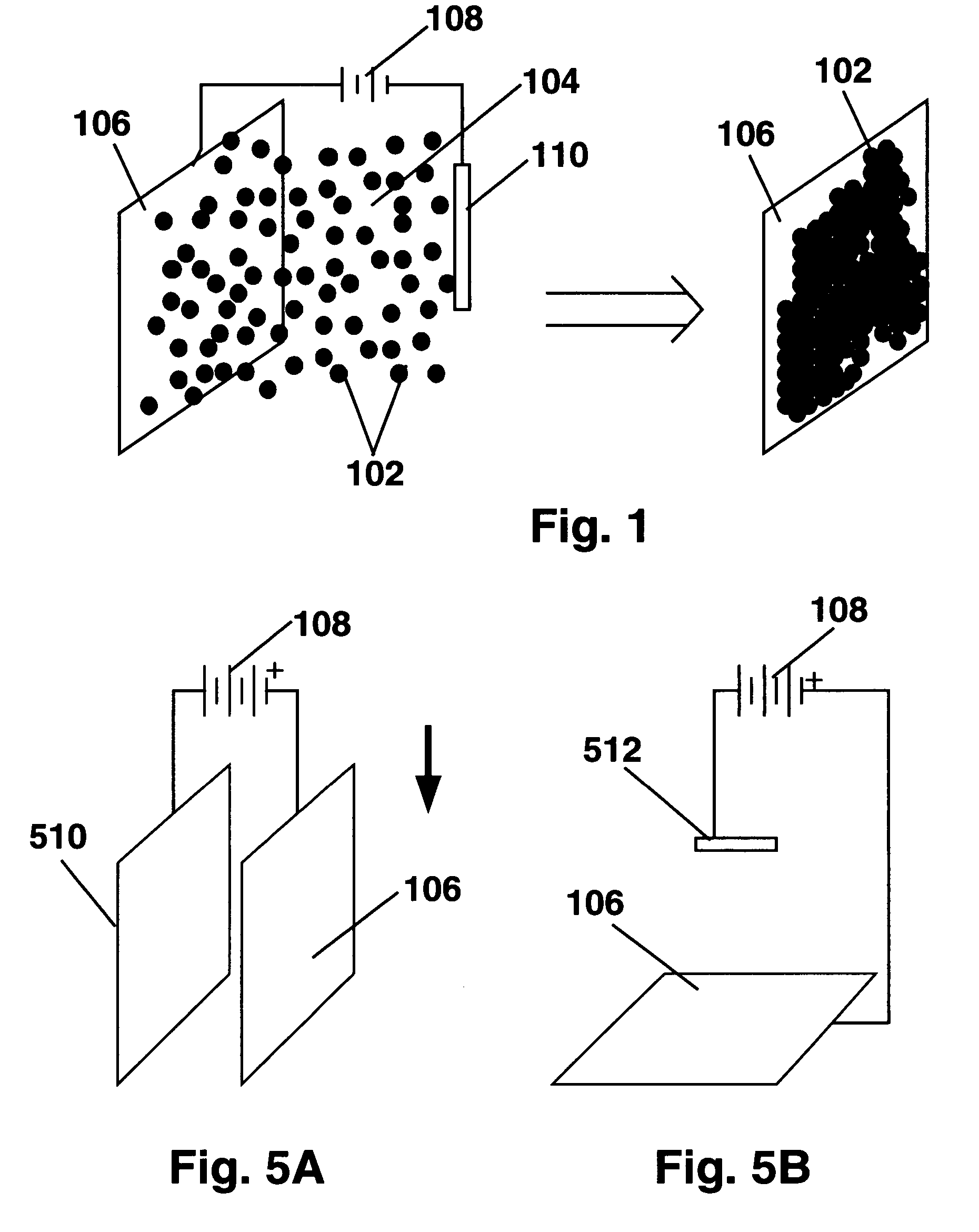
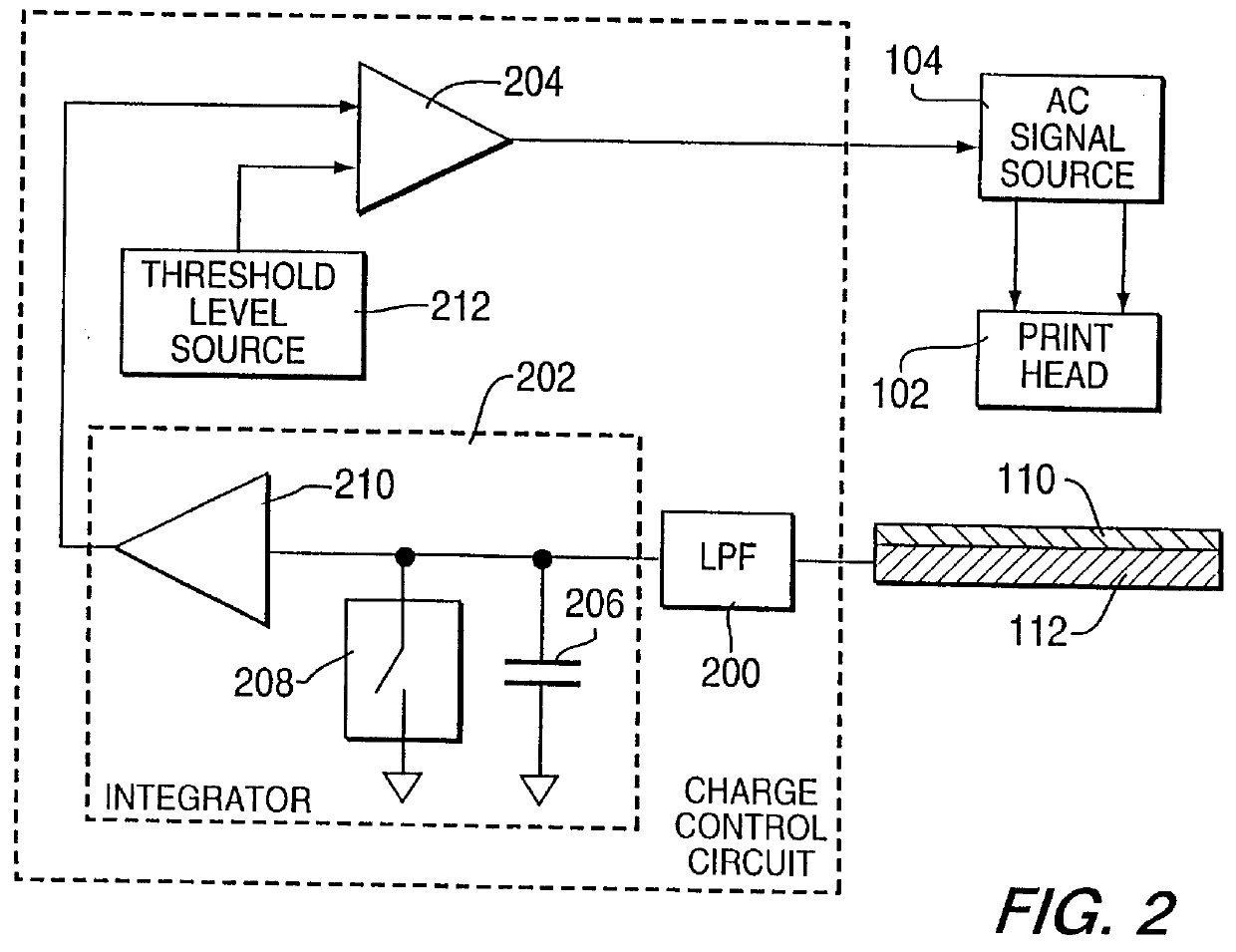
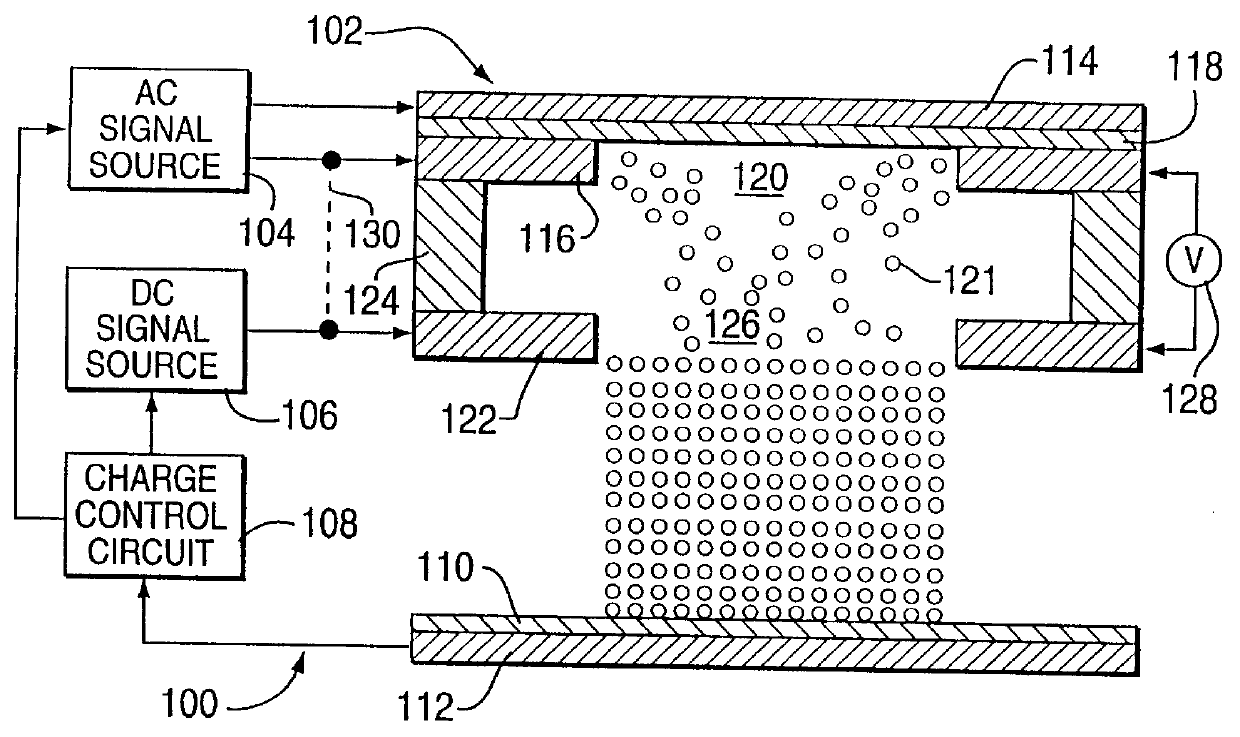
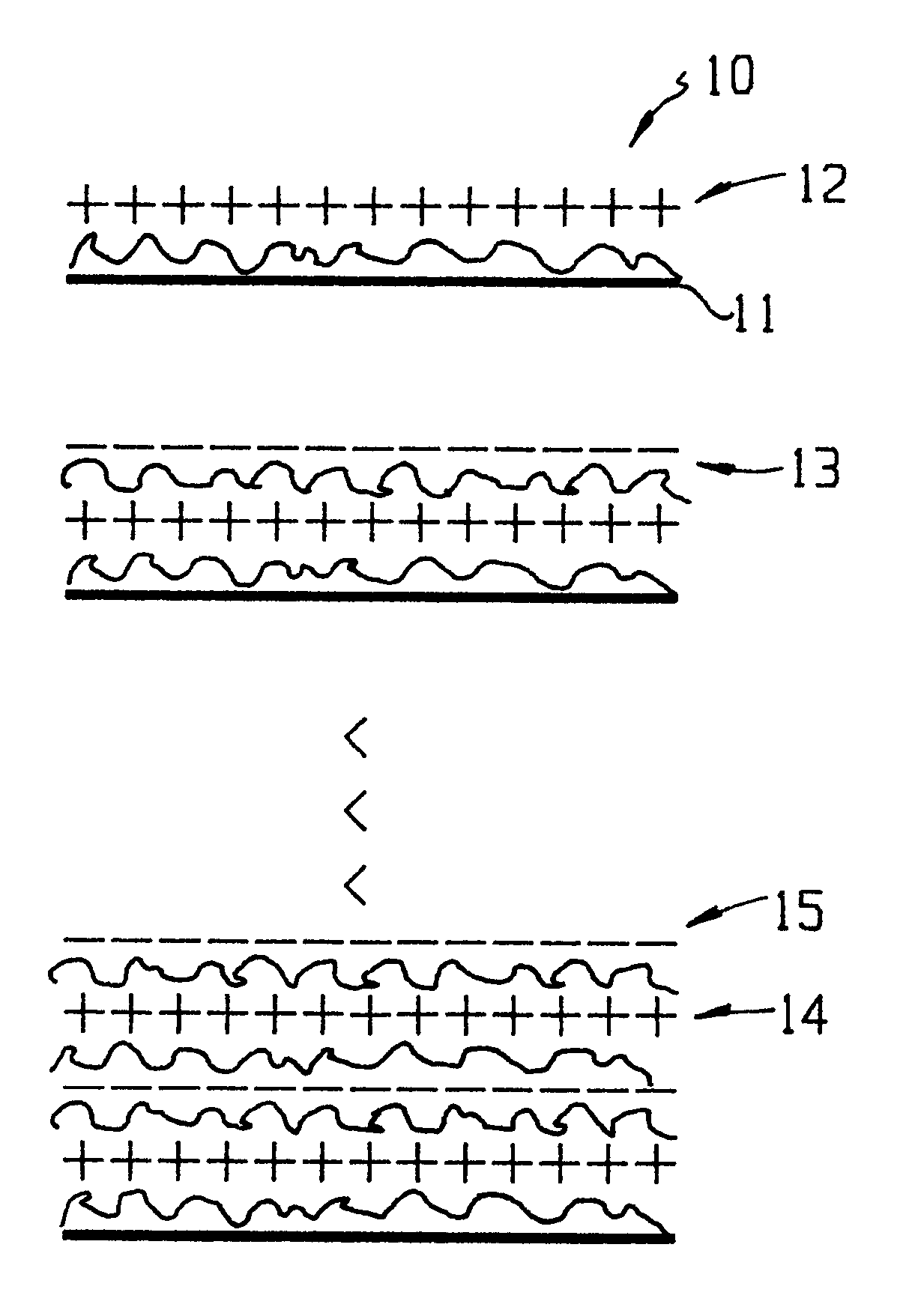
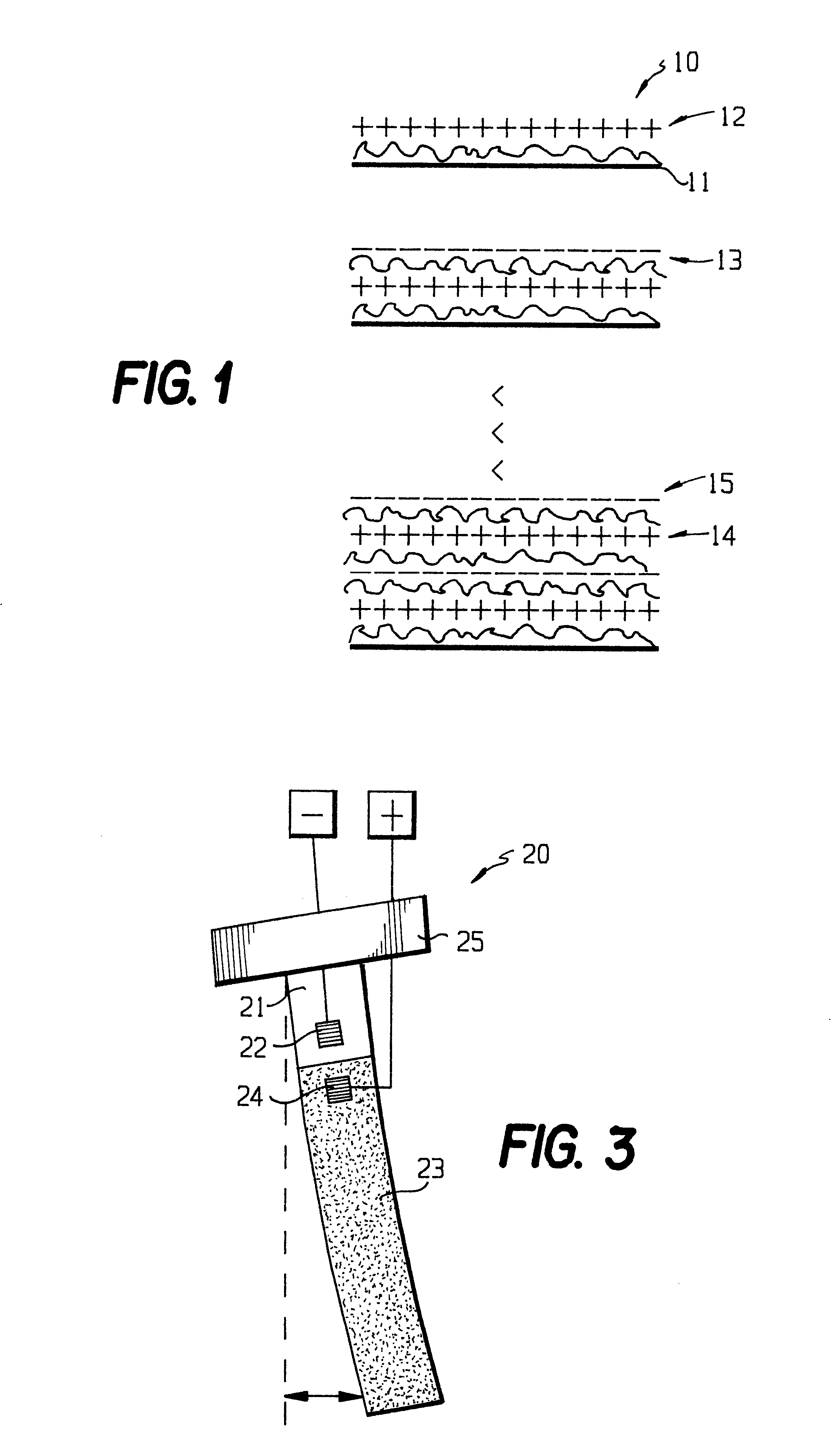
A coating of an encapsulated electrophoretic medium is formed on a substrate (106) by dispersing in a fluid (104) a plurality of electrophoretic capsules (102), contacting at least a portion of a substrate (106) with the fluid (104); and applying a potential difference between at least a part of the portion of the substrate (106) contacting the fluid (104) and a counter-electrode (110) in electrical contact with the fluid (104), thereby causing capsules (102) to be deposited upon at least part of the portion of the substrate (106) contacting the fluid (102). Patterned coatings of capsules containing different colors may be deposited in registration with electrodes using multiple capsule deposition steps. Alternatively, a patterned coating may be deposited upon a substrate containing a conductive layer by varying the conductivity of the conductive layer by radiation exposure or by coating portions of the conductive layer with an insulating layer, typically a photoresist.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
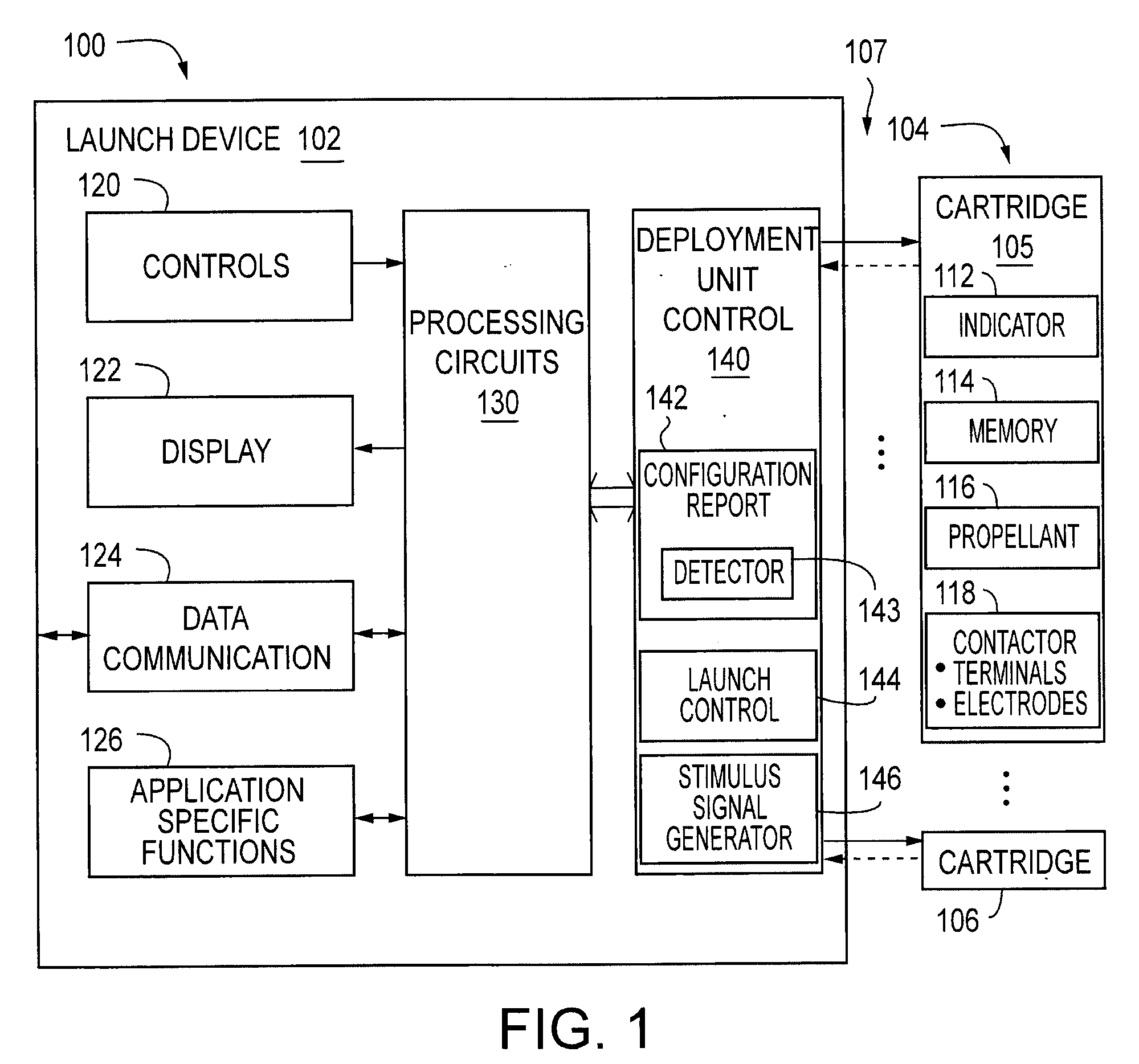
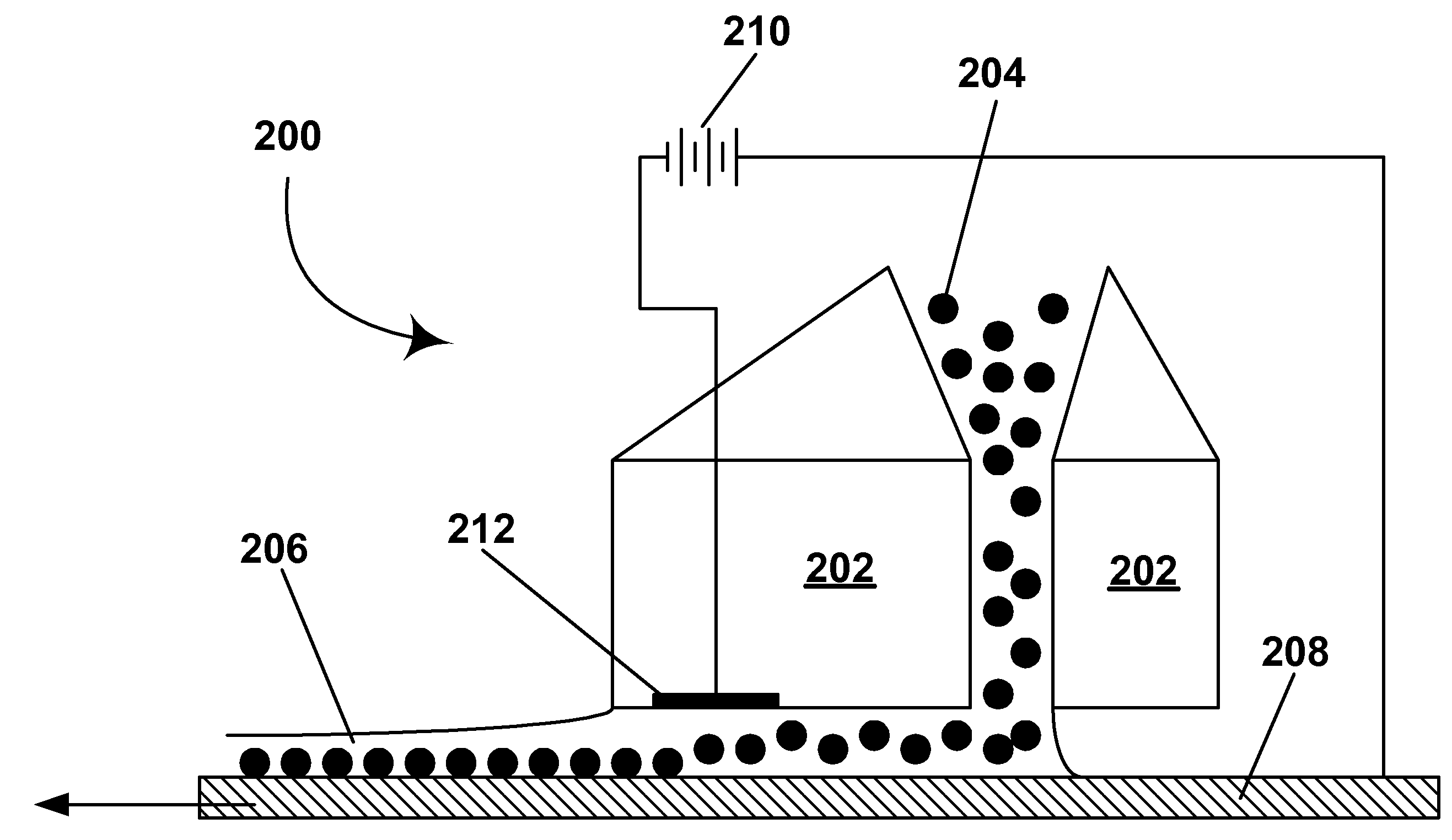
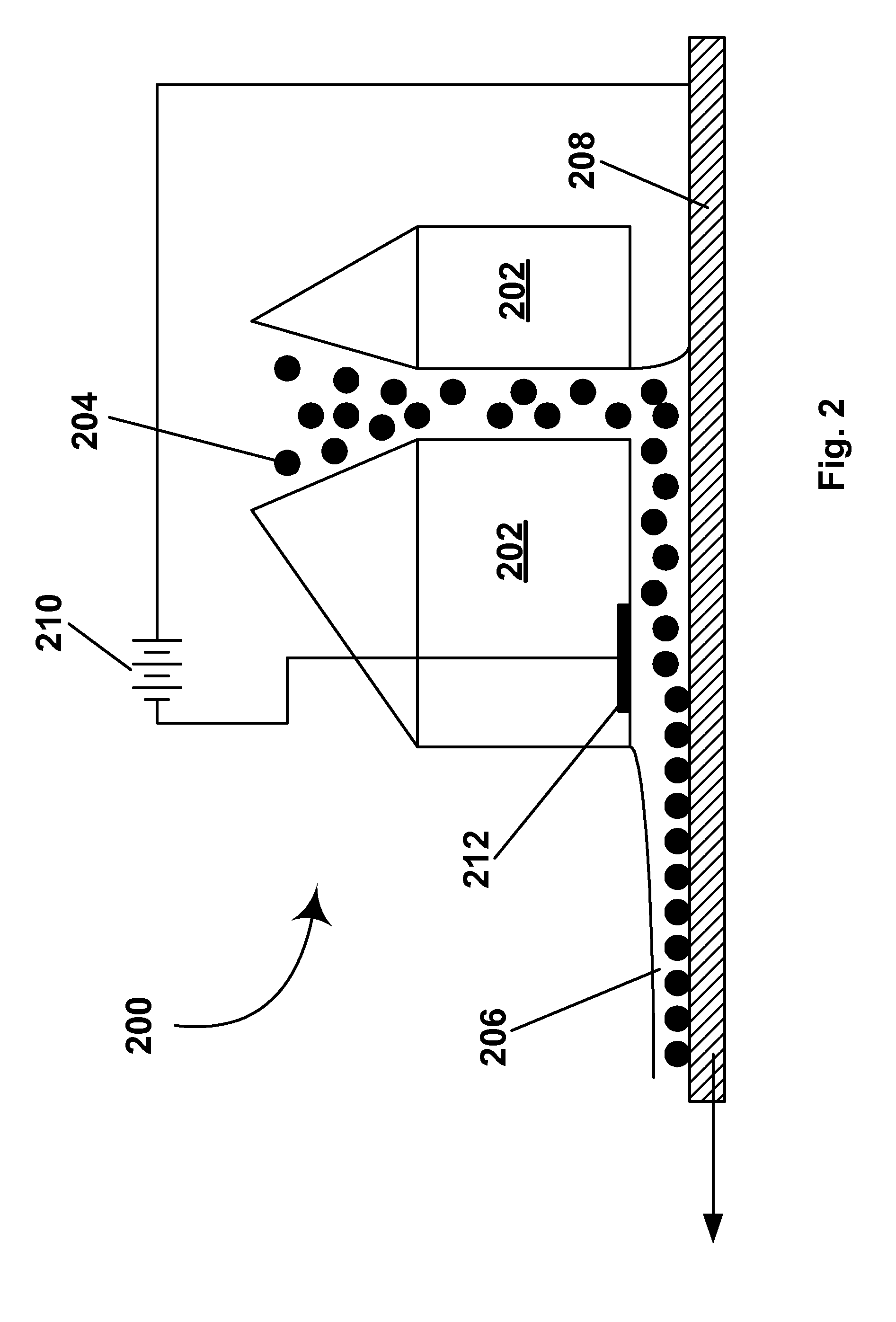
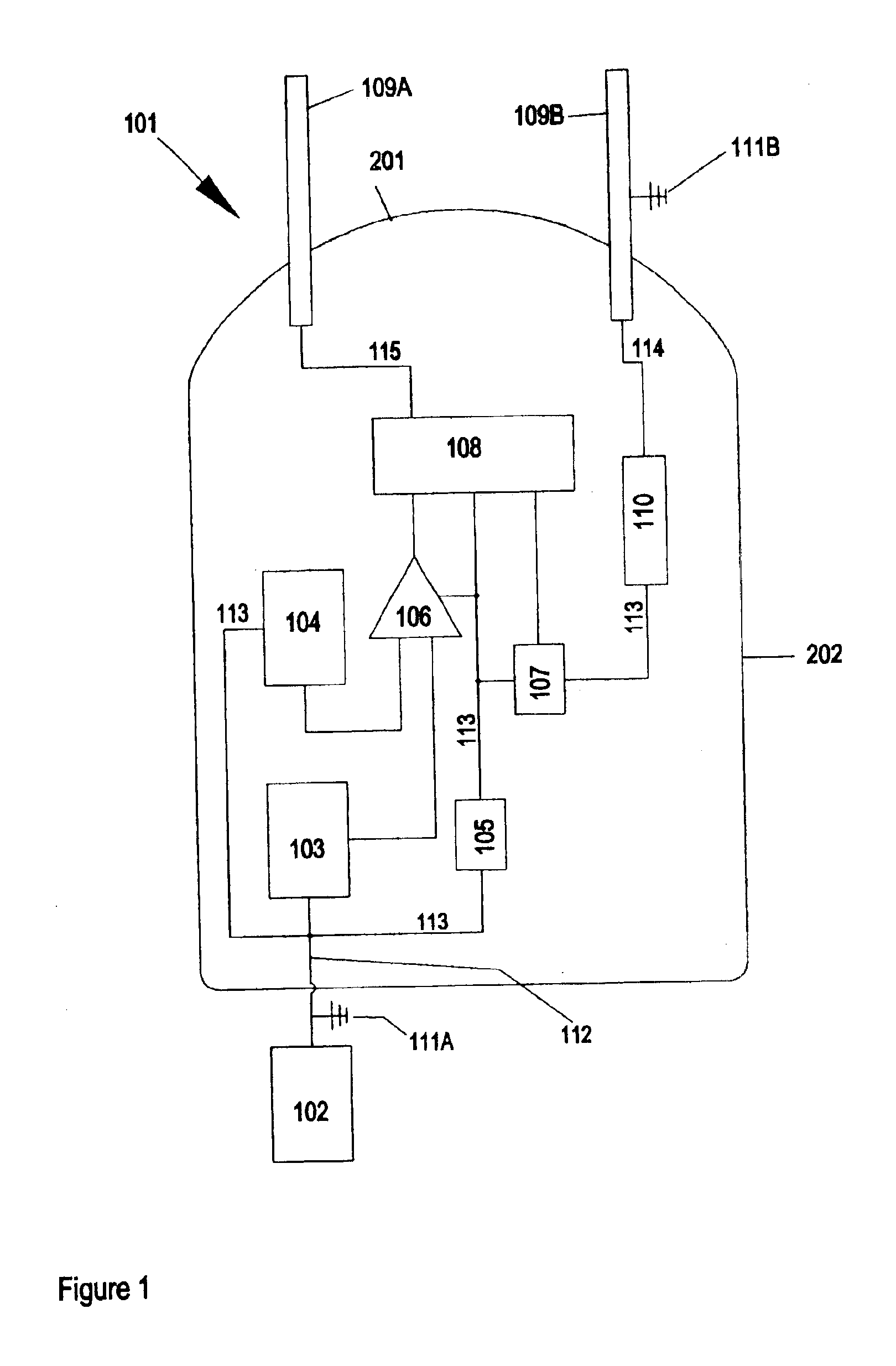
Systems and Methods for Modular Electronic Weaponry
ActiveUS20070070574A1Easy to operateSafety arrangementElectric shock equipmentsModularityEmbedded system
An apparatus produces contractions in skeletal muscles of a target to impede locomotion by the target. The apparatus is used with a provided deployment unit that deploys an electrode away from the apparatus. The electrode conducts a current through the target. The apparatus includes a bus; a plurality of ports, and a controller. Each port couples a module to the bus. The controller is coupled to the bus to communicate with each module to determine a description of each module.
Owner:AXON ENTERPRISE INC
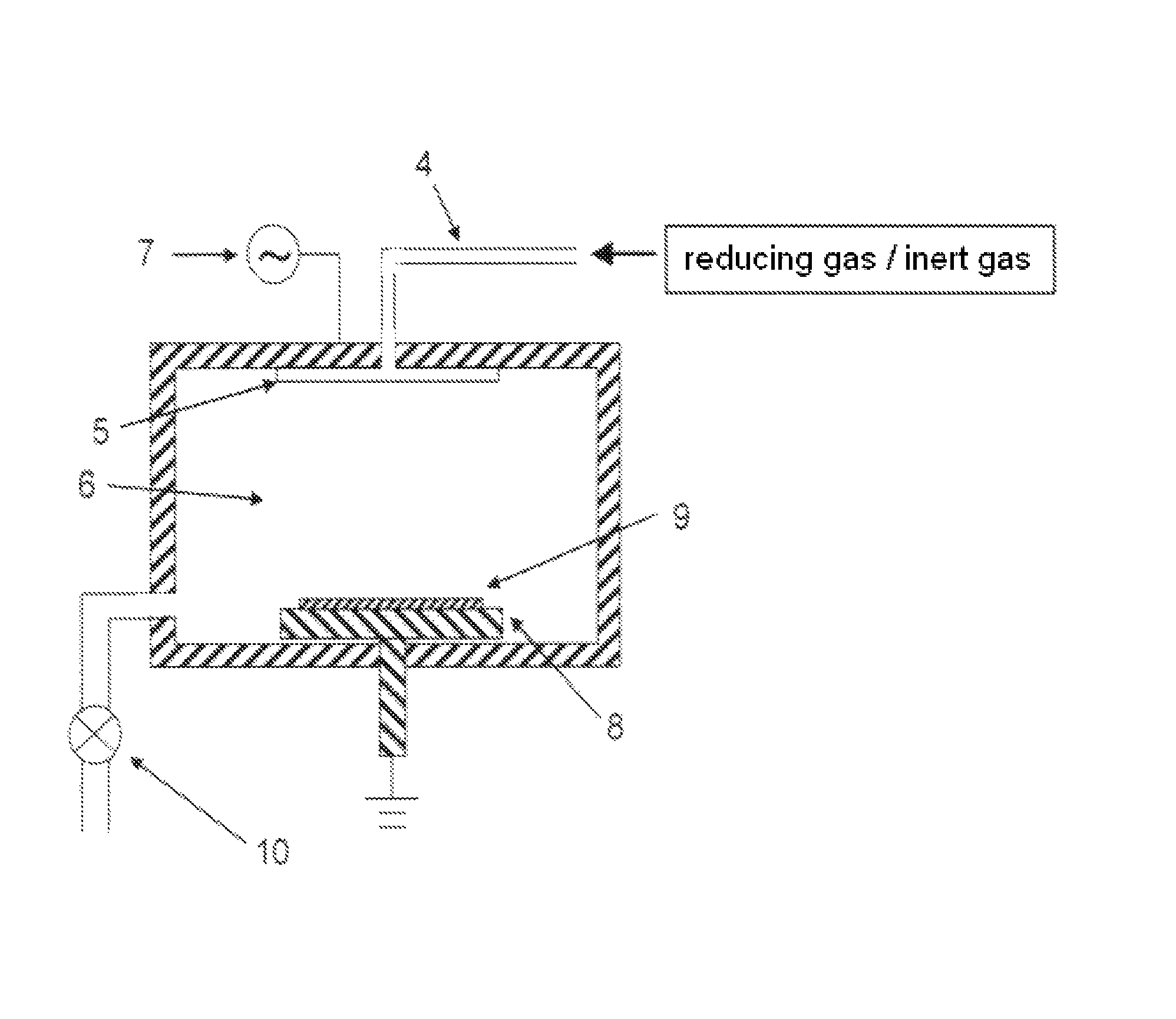
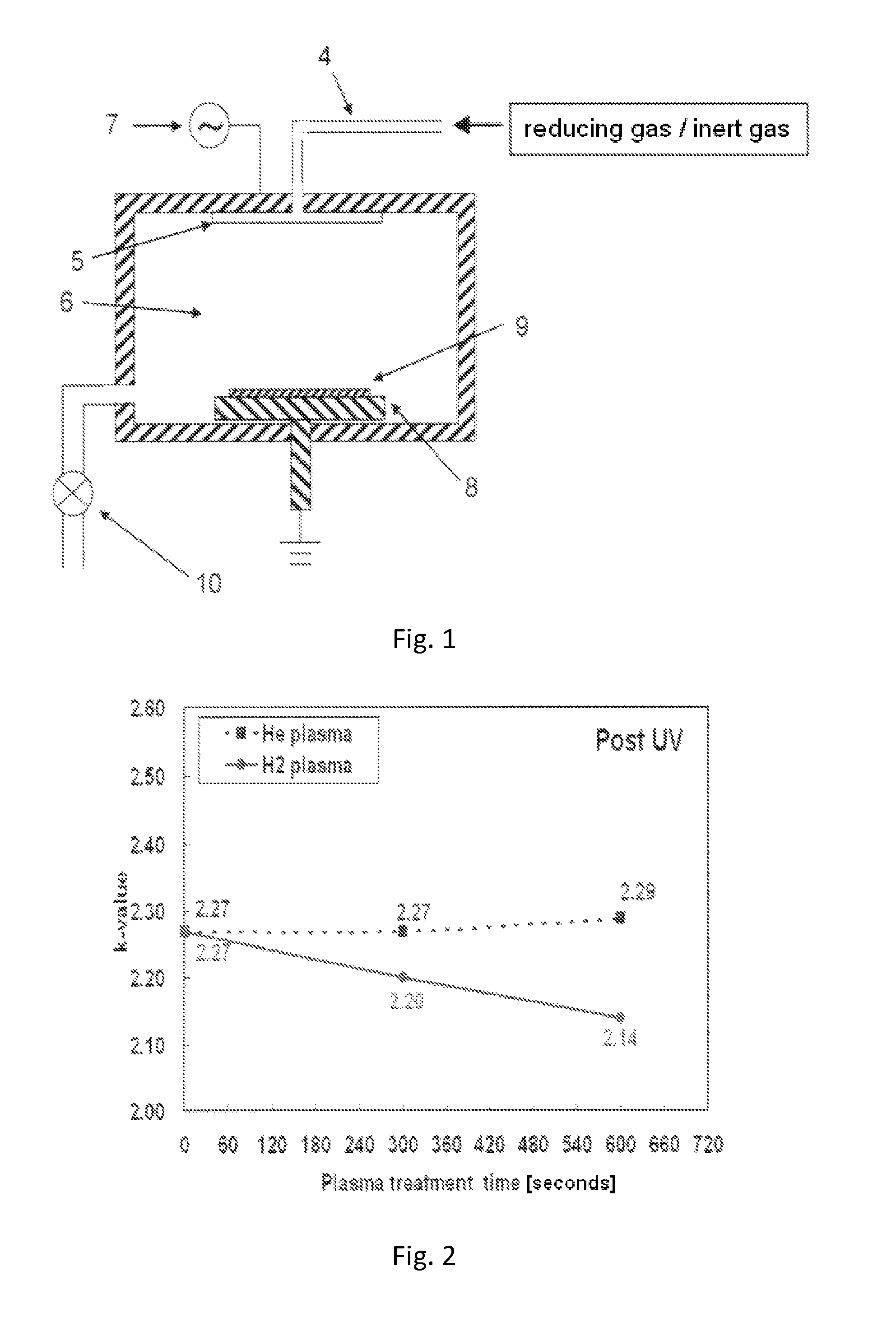
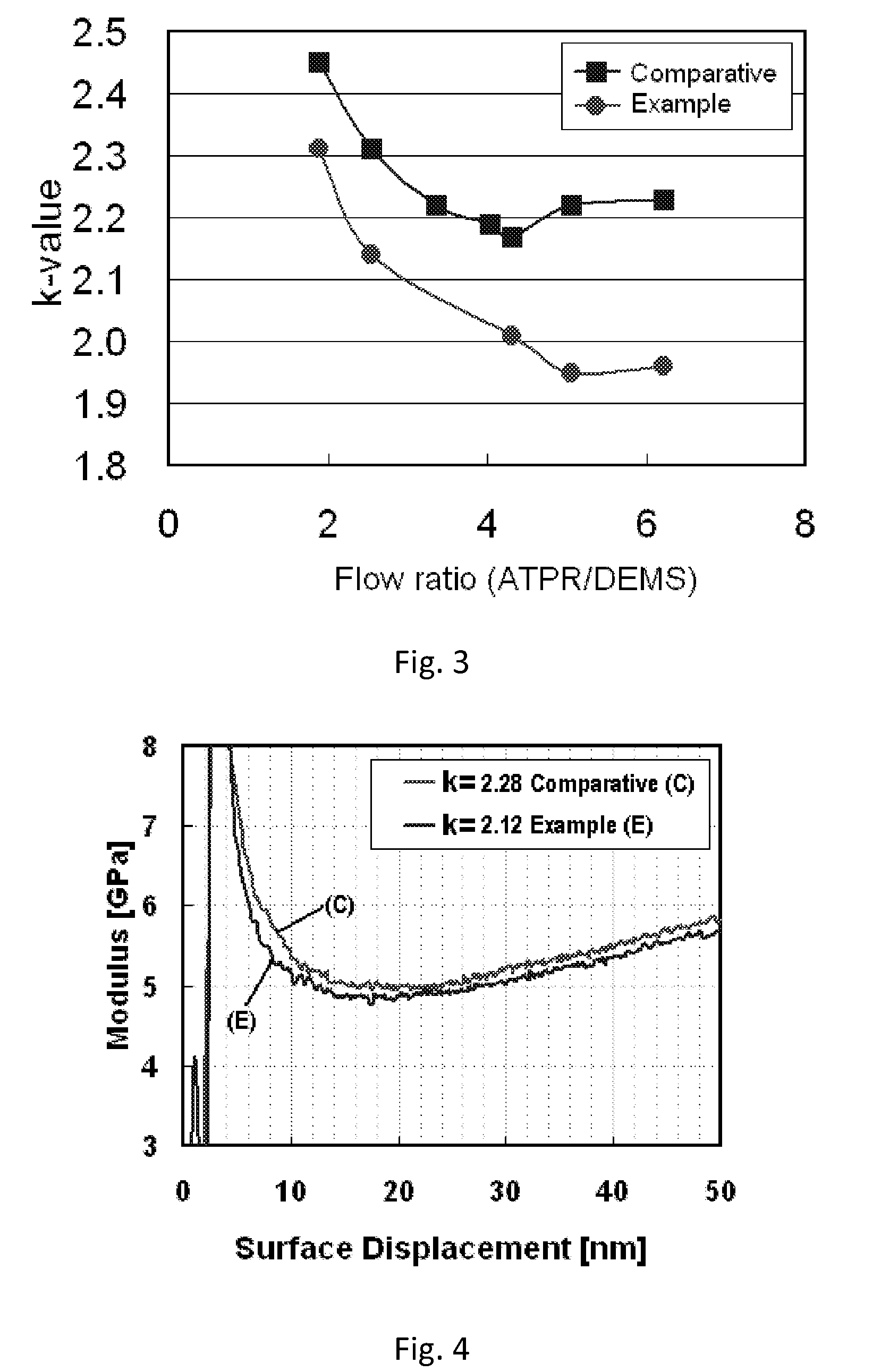
Method for reducing dielectric constant of film using direct plasma of hydrogen
ActiveUS8551892B2Low dielectric constantMaintain mechanical strengthElectric shock equipmentsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDielectricCapacitance
A method for reducing a dielectric constant of a film includes (i) forming a dielectric film on a substrate; (ii) treating a surface of the film without film formation, and (III) curing the film. Step (i) includes providing a dielectric film containing a porous matrix and a porogen on a substrate, step (ii) includes, prior to or subsequent to step (iii), treating the dielectric film with charged species of hydrogen generated by capacitively-coupled plasma without film deposition to reduce a dielectric constant of the dielectric film, and step (iii) includes UV-curing the dielectric film to remove at least partially the porogen from the film.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Processes for the production of electrophoretic displays
ActiveUS7910175B2Electric shock equipmentsElectrophoretic coatingsPotential differenceElectrophoresis
A coating of an encapsulated electrophoretic medium is formed on a substrate (106) by dispersing in a fluid (104) a plurality of electrophoretic capsules (102), contacting at least a portion of a substrate (106) with the fluid (104); and applying a potential difference between at least a part of the portion of the substrate (106) contacting the fluid (104) and a counter-electrode (110) in electrical contact with the fluid (104), thereby causing capsules (102) to be deposited upon at least part of the portion of the substrate (106) contacting the fluid (102). Patterned coatings of capsules containing different colors may be deposited in registration with electrodes using multiple capsule deposition steps. Alternatively, patterned coatings of capsules may be formed by applying a fluid form of an electrophoretic medium to a substrate, and applying a temporally varying voltage between an electrode and the substrate. The process may be repeated to allow for deposition of full color displays.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Method for electrostatically depositing a medicament powder upon predefined regions of a substrate
Method for electrostatically depositing select doses of medicament powder at select locations on a substrate. Specifically, the apparatus contains a charged particle emitter for generating charged particles that charge a predefined region of a substrate and a charge accumulation control circuit for computing the amount of charge accumulated upon the substrate and deactivating the emitter when a selected quantity of charge has accumulated. Additionally, a triboelectric charging apparatus charges the medicament powder and forms a charged medicament cloud proximate the charged region of the substrate. The medicament particles within the medicament cloud electrostatically adhere to the charged region. The quantity of charge accumulated on the substrate at the predefined region and the charge-to-mass ratio of the medicament powder in the cloud control the amount (dose) of medicament deposited and retained by the substrate. Consequently, this apparatus accurately controls both medicament dosage and deposition location. Furthermore, since the substrate can be of any dielectric material that retains an electrostatic charge, the apparatus can be used to deposit medicament on substrates that are presently used in oral medicament consumption, e.g., substrates that are used to fabricate suppositories, inhalants, tablets, capsules and the like.
Owner:DELSYS PHARMA
Methods and systems for making electrodes having at least one functional gradient therein and devices resulting therefrom
InactiveUS20110123866A1Improve performanceElectrode manufacturing processesElectric shock equipmentsHigh fluxEngineering
The invention disclosed herein provides for methods and apparatuses that yield electrodes having at least one functional gradient therein. In many embodiments, the electrodes comprise an electrode matrix having a plurality of layers, where at least two of the layers differs functionally, in composition, structure, or, organization. High-throughput electrode screening apparatuses are disclosed that include array formers and testers. Electrodes and battery cells arising from the methods and apparatuses disclosed herein are likewise disclosed. The methods, apparatuses, and resulting electrode and cell devices are, in some embodiments, ideally suited for use in lithium-ion batteries.
Owner:MOLECULAR NANOSYST
Method and apparatus for electrostatically depositing a medicament powder upon predefined regions of a substrate
A method for electrostatically depositing select doses of medicament powder at select locations on a substrate. Specifically, an apparatus contains a charged particle emitter for generating charged particles that charge a predefined region of a substrate and a charge accumulation control circuit for computing the amount of charge accumulated upon the substrate and deactivating the emitter when a selected quantity of charge has accumulated. Additionally, a triboelectric charging apparatus charges the medicament powder and forms a charged medicament cloud proximate the charged region of the substrate. The medicament particles within the medicament cloud electrostatically adhere to the charged region. The quantity of charge accumulated on the substrate at the predefined region and the charge-to-mass ratio of the medicament powder in the cloud control the amount (dose) of medicament deposited and retained by the substrate. Consequently, this apparatus accurately controls both medicament dosage and deposition location. Furthermore, since the substrate can be of any dielectric material that retains an electrostatic charge, the apparatus can be used to deposit medicament on substrates that are presently used in oral medicament consumption, e.g., substrates that are used to fabricate suppositories, inhalants, tablets, capsules and the like.
Owner:DELSYS PHARMA
Method and apparatus for coating medical implants
InactiveUS20070031607A1Reduce unevennessMinimize volume chargeLiquid spraying plantsLiquid surface applicatorsFiberBiomedical engineering
A method of coating a non-rotary object with an electrospun coat, the method comprising, dispensing a charged liquefied polymer through at least one dispensing element within an electric field to thereby form a jet of polymer fibers, and moving the dispensing element relative to the object so as to coat the object with the electrospun coat.
Owner:NICAST LTD
Electrostrictive and piezoelectric thin film assemblies and method of fabrication therefor
InactiveUS6447887B1Avoid misalignmentUniform propertyAnodisationMaterial nanotechnologyMolecular levelEngineering
An electrostatic self-assembly method of fabricating electrostrictive and piezoelectric thin film assemblies not only provides a thinner film than is attainable by conventional methods, but provides excellent molecular-level uniformity and precise structural control, and thus large, effective piezoelectric coefficients. The method produces a thin film assembly including (a) a substrate, and (b) a film having one or a plurality of layers disposed upon the substrate, wherein at least one of the layers includes a dipolar material, and this layer of dipolar material has a uniform thickness of at most 500 nm.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Methods and apparatus for forming uniform particle layers of phosphor material on a surface
InactiveUS20100291313A1Easy to controlHigh bulk densityLiquid surface applicatorsElectric shock equipmentsPhosphorStatic electricity
A method for forming a layer of an LED phosphor material includes disposing a first surface in a proximity of a powder that includes an LED phosphor material, forming electrostatic charges on the first surface, and forming a layer of the LED phosphor material on the first surface at least partially by using the electrostatic charges. In an embodiment, the method includes disposing the first surface in an interior of a chamber and forming an airborne distribution of the powder in the interior of the chamber in a vicinity of the first surface. In another embodiment, the method includes providing a reservoir of the powder and applying to said phosphor powder an electrostatic charge opposite to that of said electrostatic charge on the first surface.
Owner:ACHROLUX
Hydrophilic polymer treatment of an activated polymeric material and use thereof
InactiveUS6830782B2Simple materialImprove nucleationRadiation applicationsFibre typesFiberMicroorganism
A method of modifying a polymeric material which comprises the steps of activation-treatment and a hydrophilic polymer-treatment, or comprises the steps of activation-treatment, a hydrophilic polymer-treatment, and monomer grafting in this order, or comprises the step of a solvent-treatment followed by these steps. Thus, the polymeric material, e.g., polyolefin, is improved in hydrophilicity, adhesion, etc. without lowering the practical strength thereof. The polymeric material thus improved in adhesion and other properties can be used in many applications where water absorption and adhesion are required, such as an absorption material, e.g., a wiping / cleansing material, a water retention material, a material for microorganism culture media, a separator for batteries (or cells), a synthetic paper, a filter medium, a textile product for clothing, a medical / sanitary / cosmetic supply, and reinforcing fibers for composite materials.
Owner:KB INT
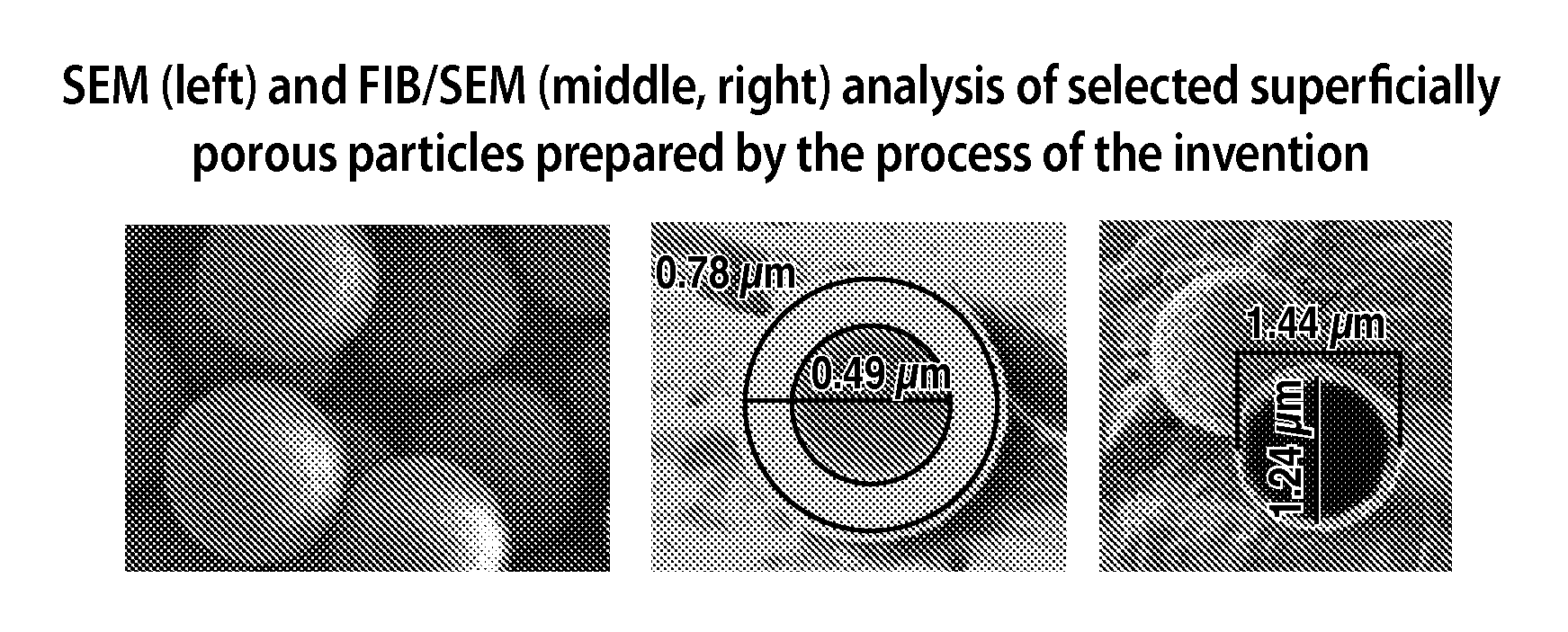
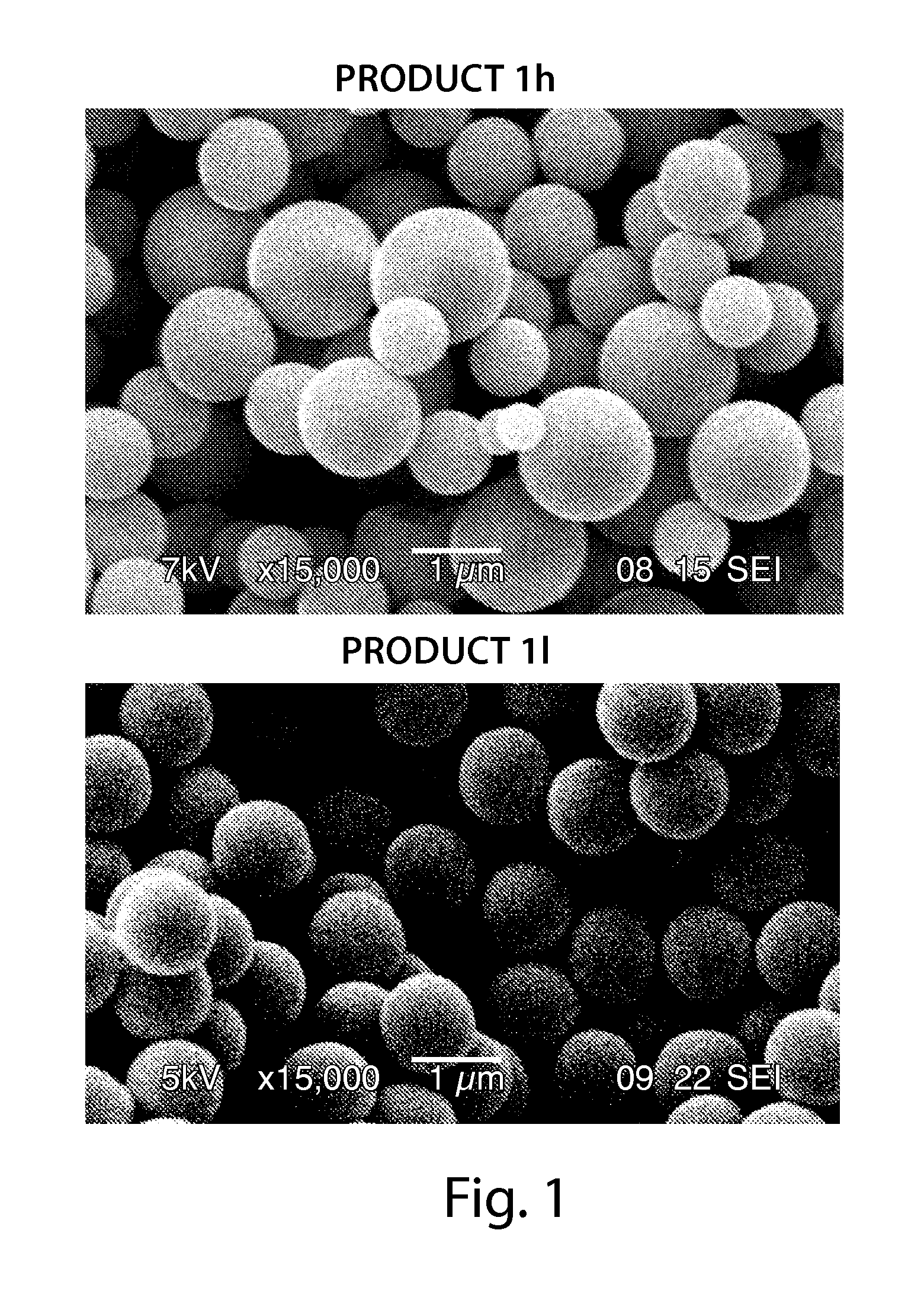
Superficially porous materials comprising a substantially nonporous core having narrow particle size distribution; process for the preparation thereof; and use thereof for chromatographic separations
InactiveUS20130112605A1Prevent fine generationInhibit aggregationIon-exchanger regenerationPretreated surfacesChromatographic separationHybrid material
Novel chromatographic materials for chromatographic separations, columns, kits, and methods for preparation and separations with a superficially porous material comprising a substantially nonporous core and one or more layers of a porous shell material surrounding the core. The material of the invention is comprised of superficially porous particles and a narrow particle size distrution. The material of the invention is comprised of a superficially porous monolith, the substantially nonporous core material is silica; silica coated with an inorganic / organic hybrid surrounding material; a magnetic core material; a magnetic core material coated with silica; a high thermal conductivity core material; a high thermal conductivity core material coated with silica; a composite material; an inorganic / organic hybrid surrounding material; a composite material coated with silica; a magnetic core material coated with an inorganic / organic hybrid surrounding material; or a high thermal conductivity core material coated with an inorganic / organic hybrid surrounding material.
Owner:WATERS TECH CORP
Surface Assisted Fluid Loading and Droplet Dispensing
InactiveUS20090304944A1Easy to useFacilitates of propertyLiquid surface applicatorsElectric shock equipmentsMicro actuatorFluid loading
The present invention relates to surface assisted fluid loading and droplet dispensing on a droplet micro actuator. A droplet actuator is provided and includes one or more electrodes configured for conducting one or more droplet operations on a droplet operations surface of the substrate. The droplet actuator further includes a wettable surface defining a path from a fluid reservoir into a locus which is sufficiently near to one or more of the electrodes that activation of the one or more electrodes results in a droplet operation. Methods and systems are also provided.
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC
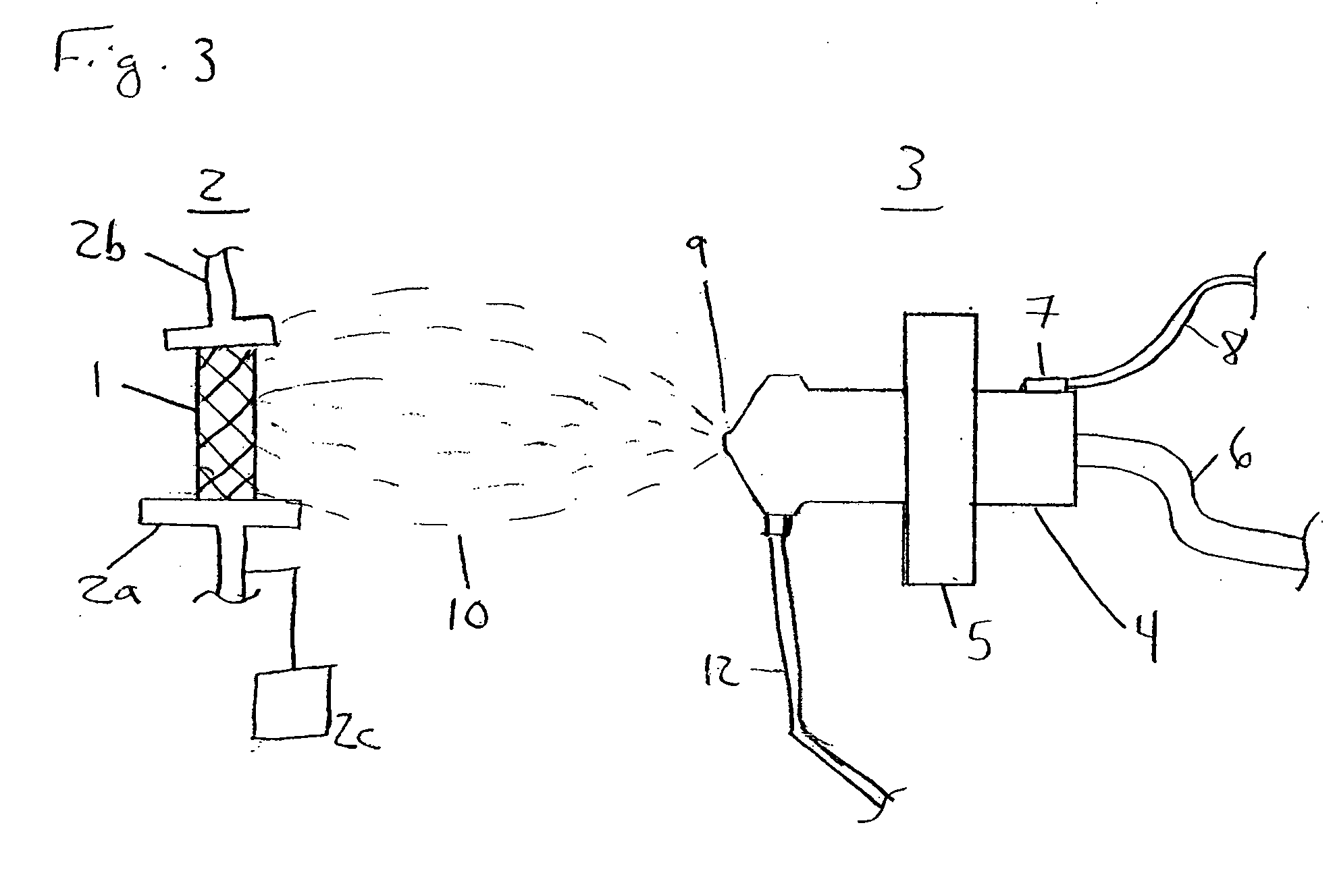
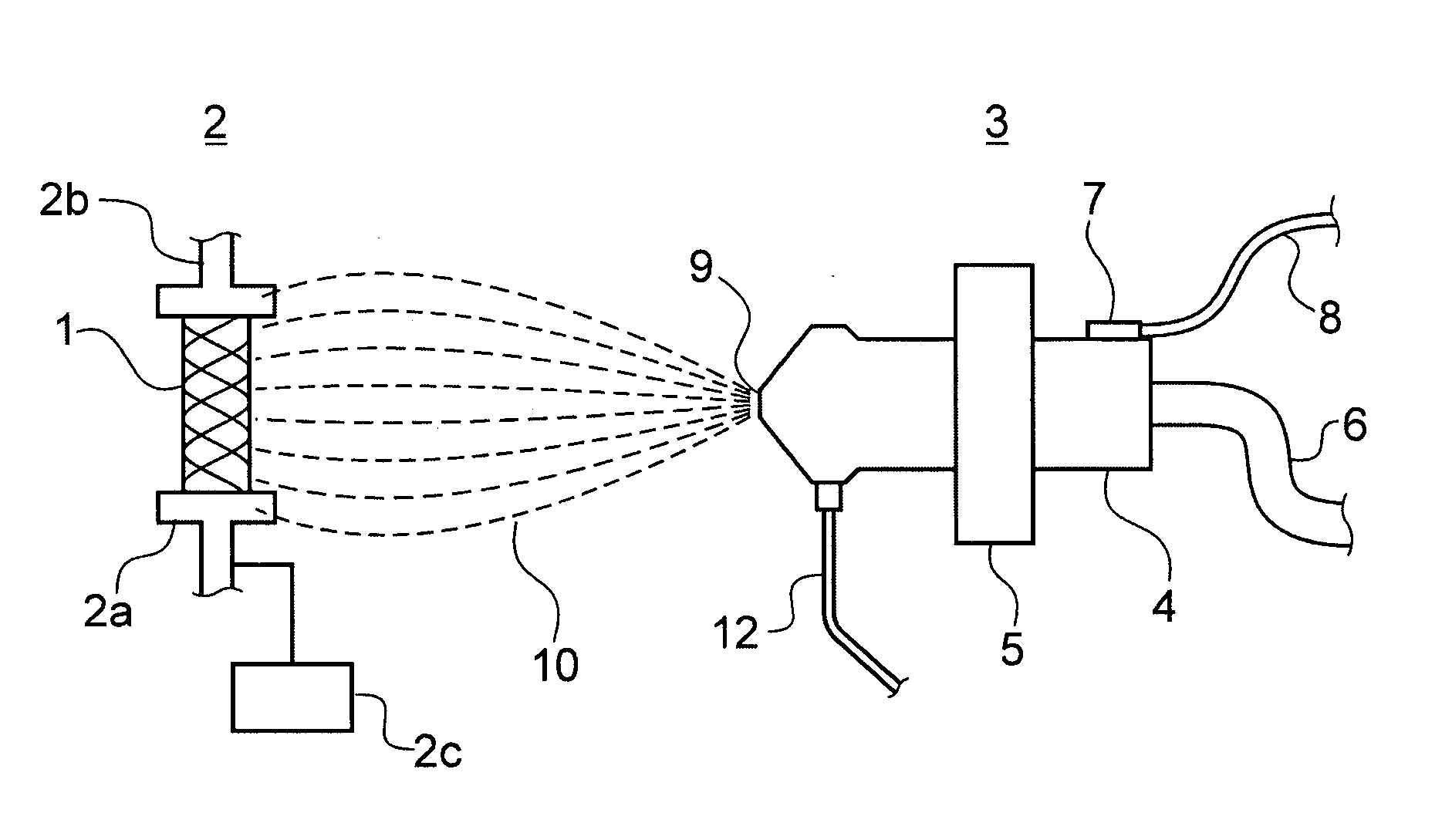
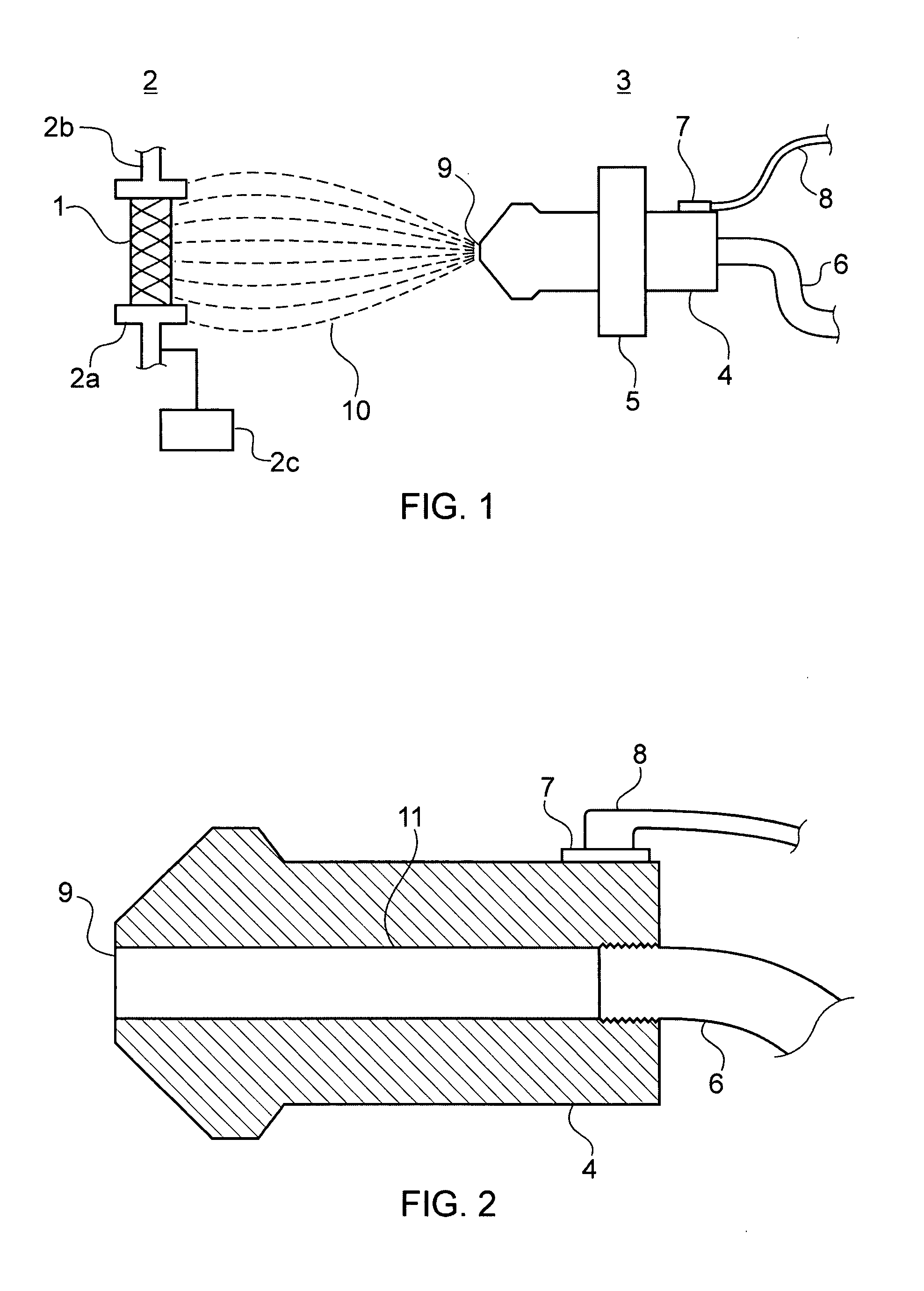
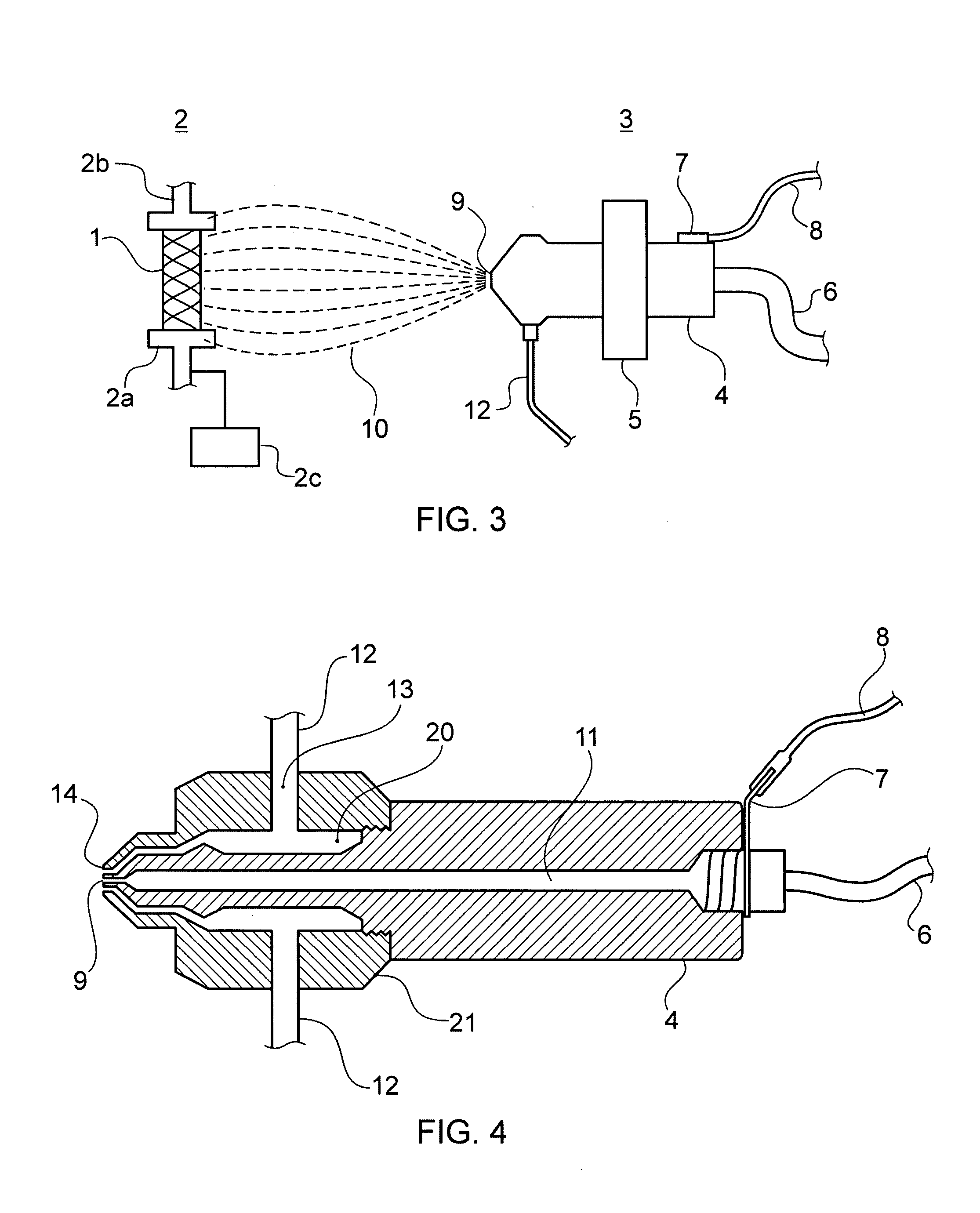
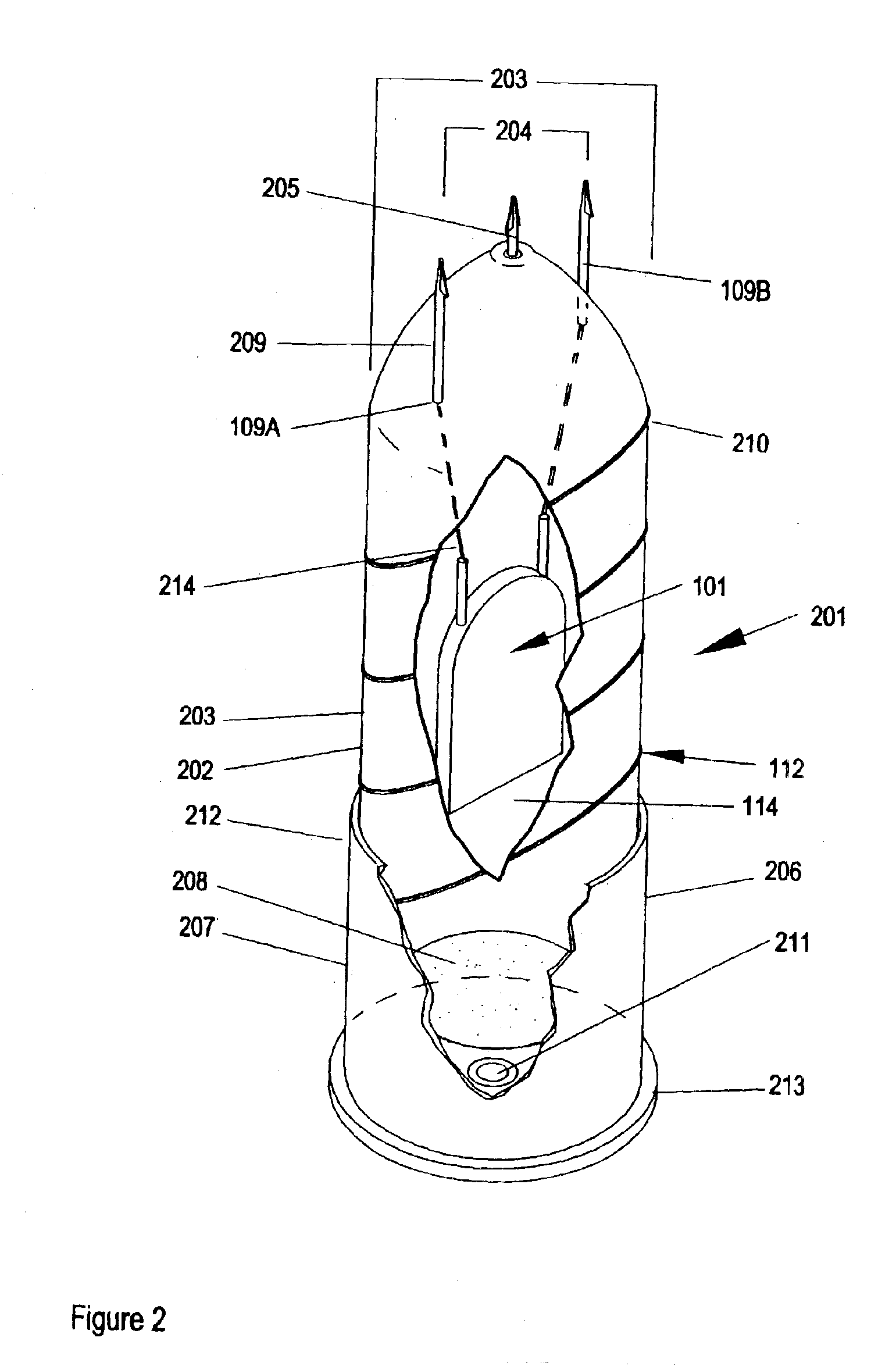
Apparatus and method for electrical immobilization weapon
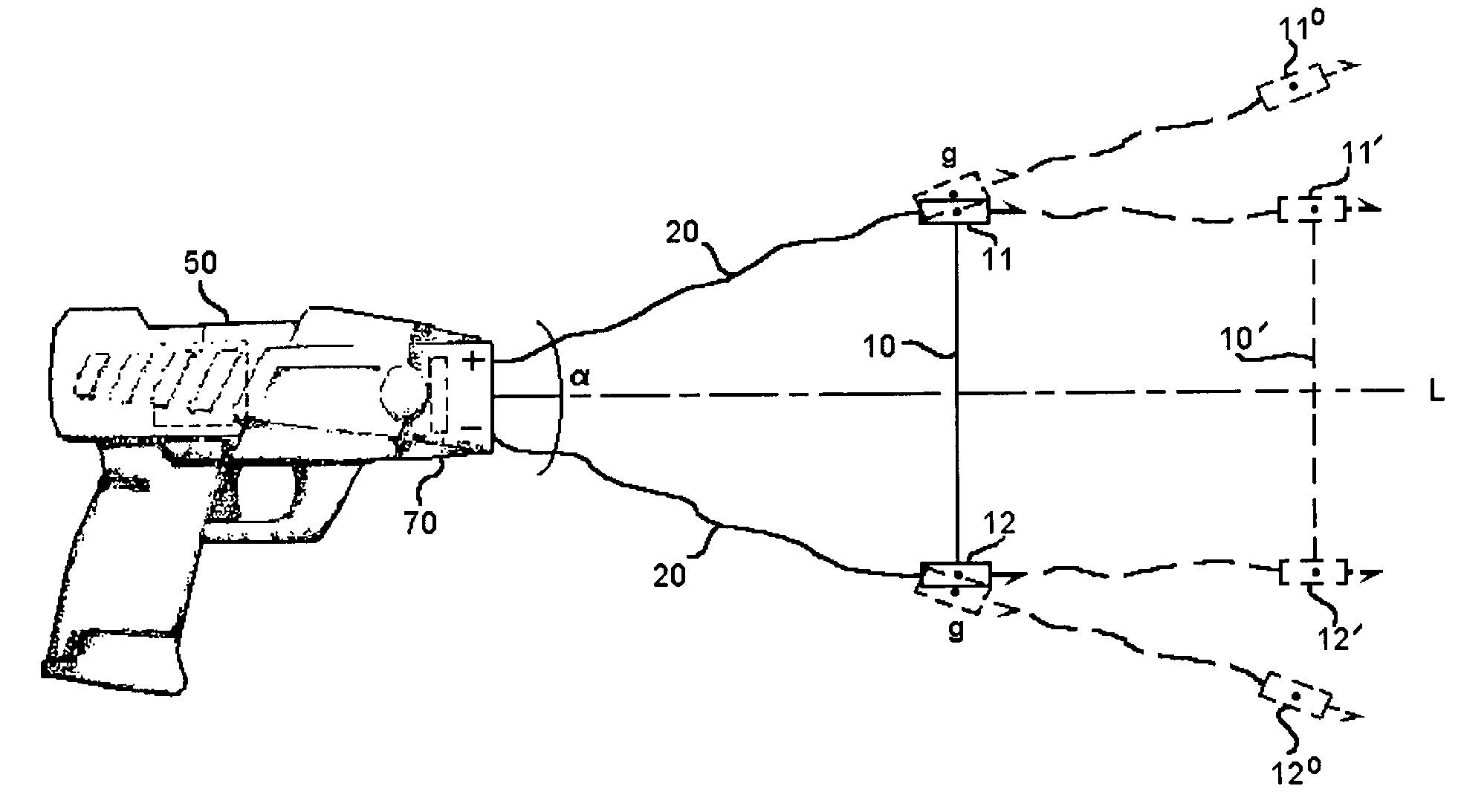
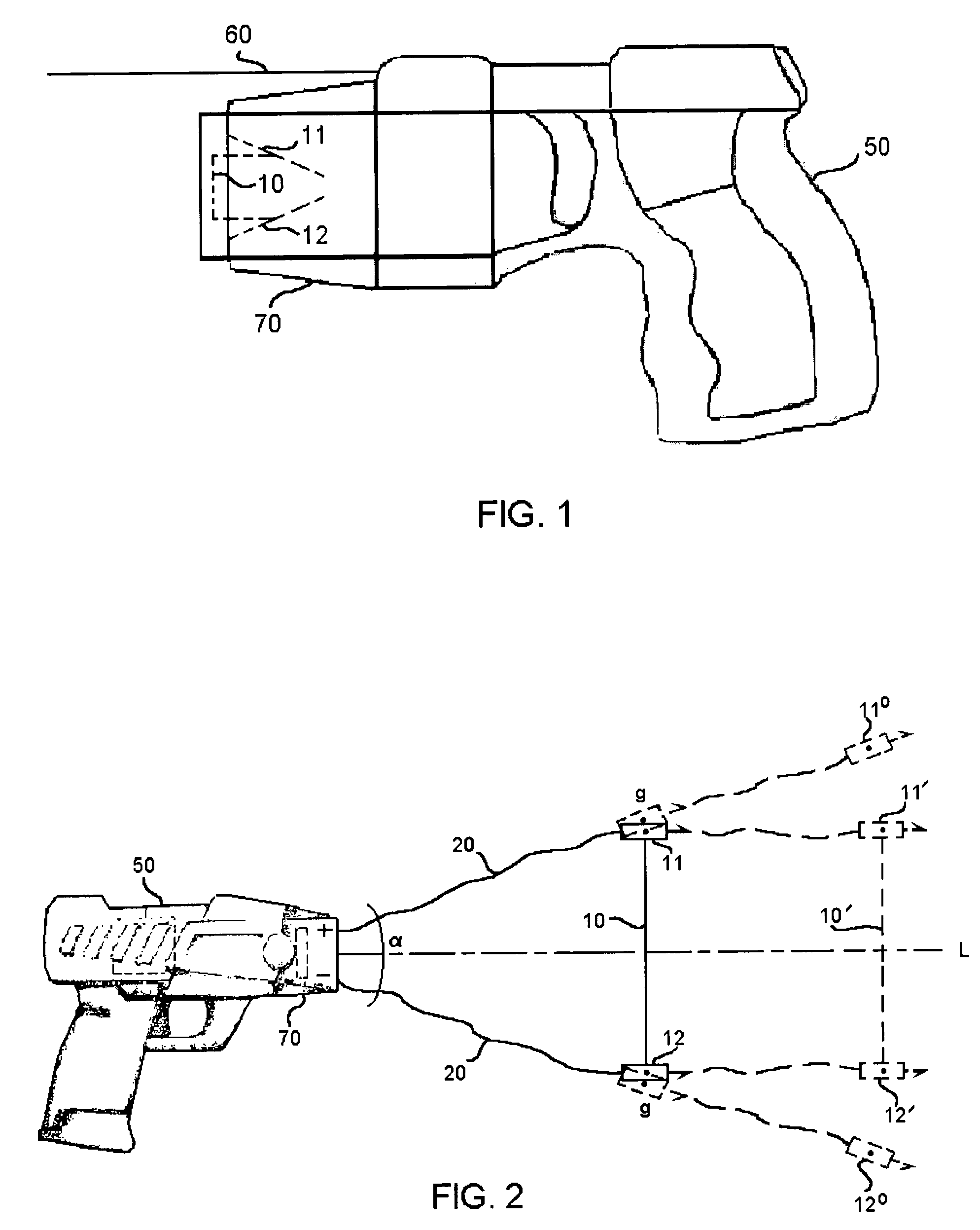
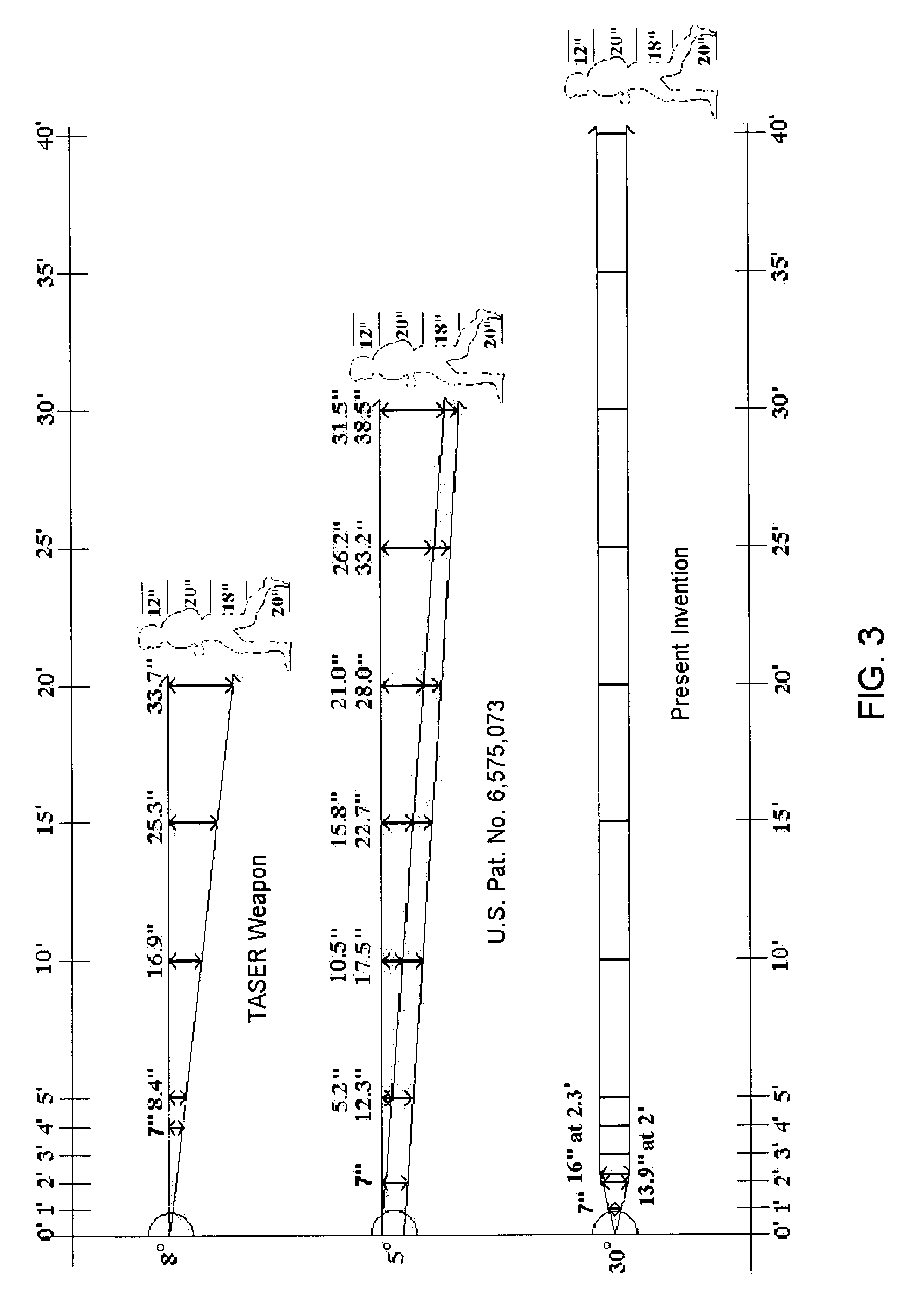
ActiveUS7314007B2Suitable for useEffective shooting rangeAmmunition projectilesElectric shock equipmentsInvolved musclesTaser
An electrical immobilization weapon having a prolonged range of effectiveness and improved accuracy compared to conventional Taser weapons, while being compact in structure and lightweight. The weapon having a replaceable cartridge which, when employed, can space a pair of electrodes to a specific critical area on a remote target, so the electrical energy carried by the electrodes can induce the involuntary contraction of the involved muscles through the critical area within a significant range of length between the electrodes for effective immobilization. The electrical energy generated by a power source of the weapon completes an electrical circuit through a minimum path being a length of at least 5 inches between the two points on the target.
Owner:VOLGER INT AB
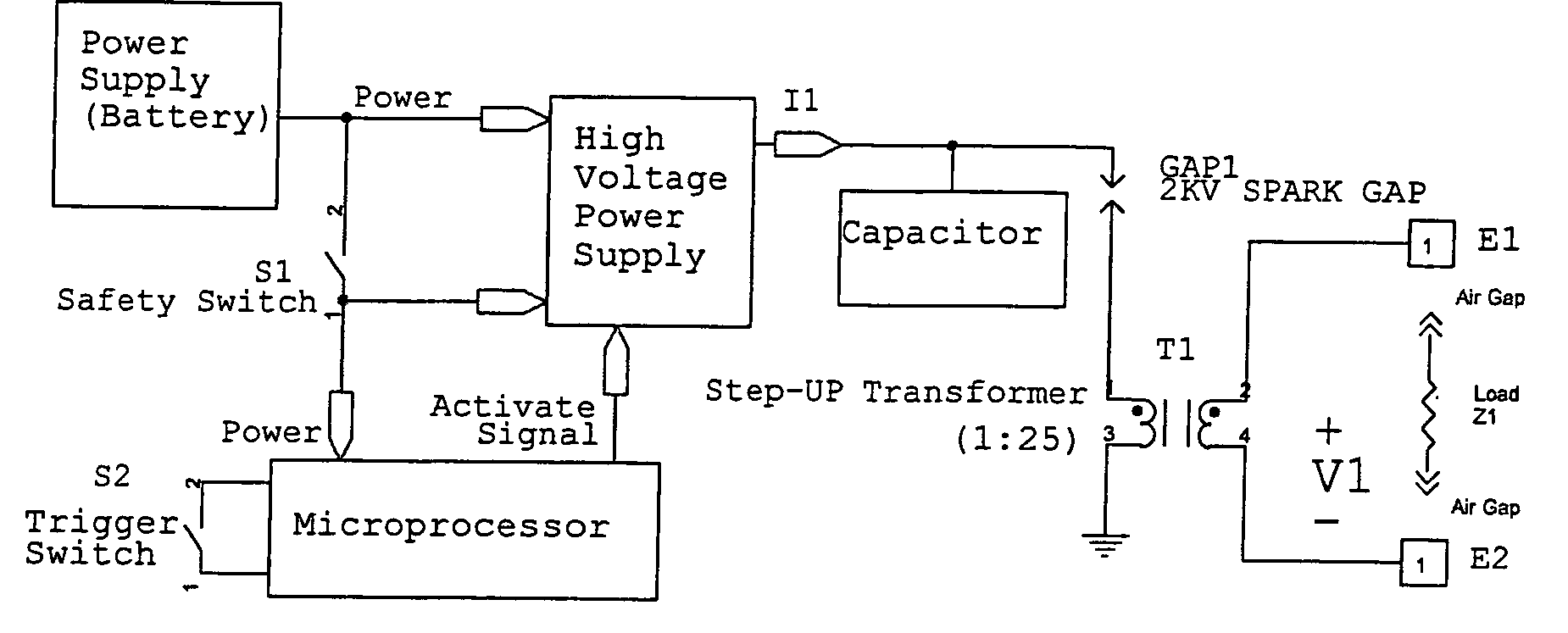
Dual operating mode electronic disabling device for generating a time-sequenced, shaped voltage output waveform
InactiveUS6999295B2Increase the air gapHigh impedanceElectric shock equipmentsPistolsLow voltageEngineering
Owner:AXON ENTERPRISE INC
Apparatus and method for electrostatic spray coating of medical devices
ActiveUS20050175772A1Increased ionization increases the fraction of coating spray attractedIncrease electrode surface areaLiquid spraying plantsElectric shock equipmentsVoltage spikeSpray coating
An apparatus and method for electrostatic spray deposition of small targets, such as medical devices like stents. The apparatus includes a target holder which applies a first electrical potential to the target, and an electrostatic dispensing nozzle which applies a second potential sufficient to attract the coating fluid from the nozzle toward the target. Because the entire dispensing nozzle is conductive, the coating fluid may receive a greater charge than may be obtained with internal electrode-type nozzles. Electrostatic attraction of the coating fluid to the target is enhanced by the combination of higher charge density imparted to the coating fluid by the conductive nozzle, and application of a momentary voltage spike to the target to provide consistent conductivity between the target and its holder, thereby ensuring the target is presents the full first potential applied to the holder. The voltage spike may also be used independently of the conductive nozzle.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Two-step method of coating an article for security printing
ActiveUS20060194040A1Electric shock equipmentsSynthetic resin layered productsEngineeringSecurity printing
A two-step method of making of a security printed image is disclosed and includes coating of the surface of a substrate with a predetermined image shape with an ink containing flaked magnetic pigment in a predetermined concentration, exposing a wet printed image to a magnetic field to align magnetic particles in a predetermined manner, allowing the ink to cure, and coating the substrate with a second printed image on the top of the first image. The second printed image with the same or different image shape is printed with another ink containing clear or dyed ink vehicle mixed with flaked magnetic pigment in a low concentration, exposed to the magnetic field of the same or different configuration as the first printed image and cured until the ink is dry.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
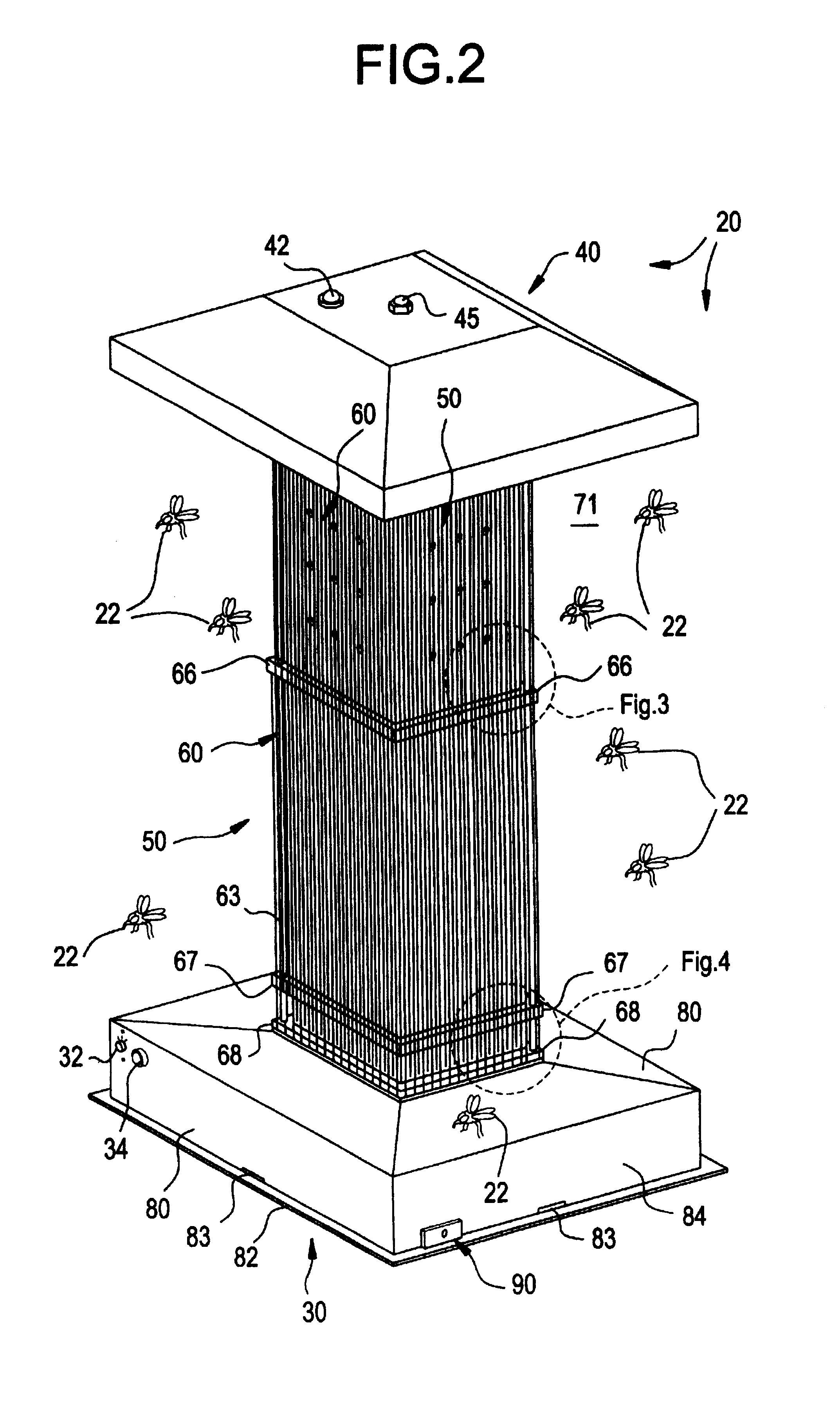
Insect trap
InactiveUS6886292B2Easy to mountEasy to removeElectric shock equipmentsInsect catchers and killersEngineeringInsect attractants
An insect trap which includes a base having a rear surface and a front surface, a housing mounted to cover at least a portion of the front surface of the base, an insect attractant such as a light located at least partially within the housing, an insect neutralizer such as an adhesive surface located at least partially within the housing, and an electrical plug protruding from the rear surface of the base whereby the insect trap may be mounted to an electrical socket by inserting the electrical plug into the electrical socket. The insect trap can be easily mounted and removed, making it suitable for intermittent, seasonal, or temporary use.
Owner:GARDNER MFG CO INC
Method for fabricating nanoscale patterns in light curable compositions using an electric field
InactiveUS6964793B2High aspect ratioElectric shock equipmentsDecorative surface effectsLithography processImage resolution
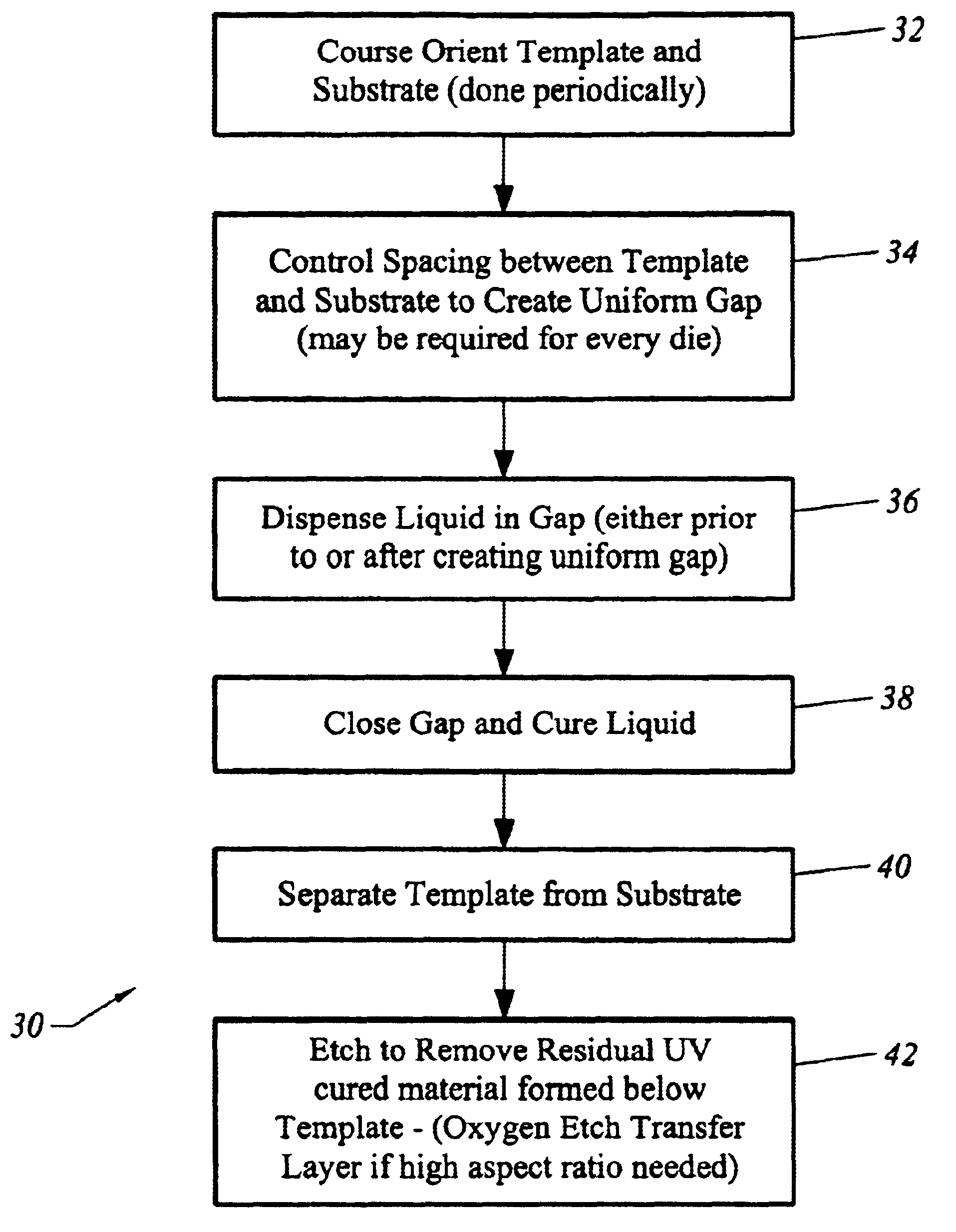
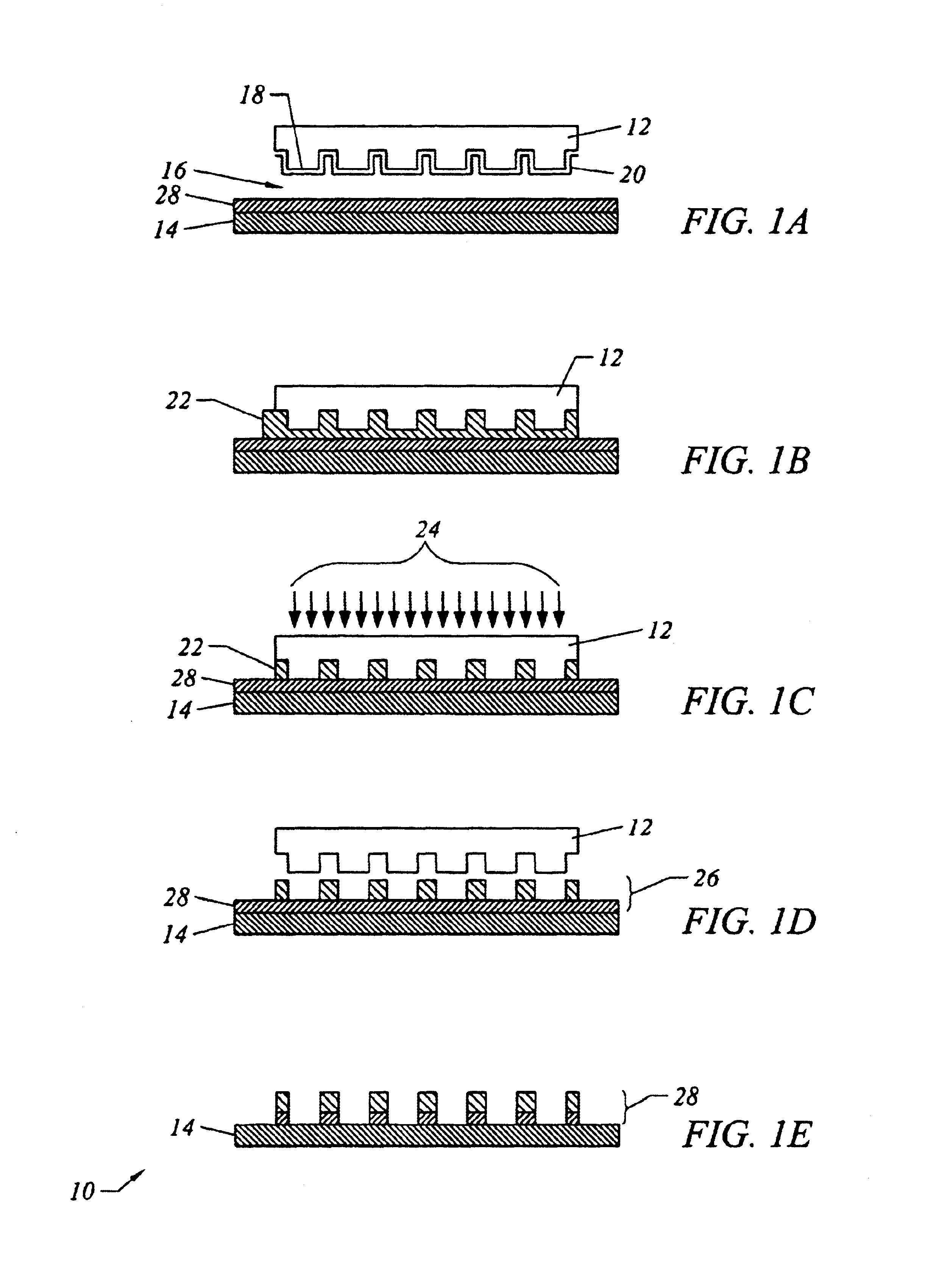
A high-throughput lithography process for creating high-resolution patterns in a polymerizable composition using carefully controlled electric field followed by curing of the polymerizable composition is described. The process involves the use of a template that includes the desired patterns. This template is brought into close proximity to the polymerizable composition on the substrate. An external electric file is applied to the template-substrate interface while maintaining a uniform, carefully controlled gap between the template and substrate. This causes the polymerizable composition to be attracted to the raised portions of the template. By appropriately choosing the various process parameters such as the viscosity of the polymerizable composition, the magnitude of the electric field, and the distance between the template and substrate, the resolution of the structures formed in the liquid may be controlled to conform to that of the template.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Electrohydrodynamic spraying system
An electrohydrodynamic spray apparatus includes a liquid inlet and a spray nozzle in fluid communication with the liquid inlet, where the spray nozzle has an opening downstream of the liquid inlet. An inner electrode is situated at least partially inside the spray nozzle. An outer electrode is situated external to the spray nozzle and within about 100 mm of the opening of the nozzle. The electrohydrodynamic spray apparatus can be combined with a substrate to form an electrohydrodynamic spray system. The electrohydrodynamic spray apparatus or system can be used to form nanostructures such as nanodrops, nanoparticles and thin films.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
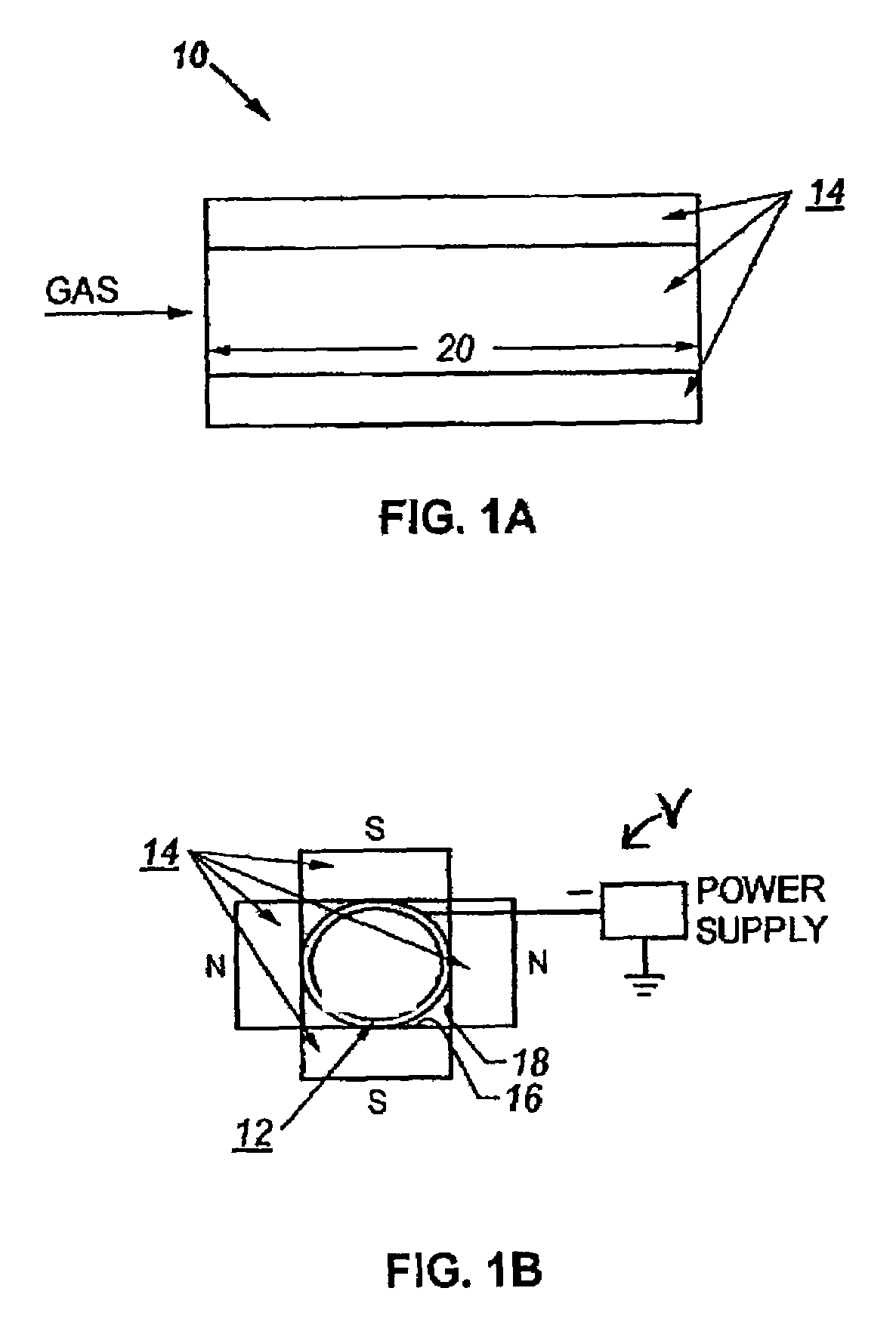
Method for depositing coatings on the interior surfaces of tubular structures
A method is disclosed for substantially uniformly coating an interior surface of a ferromagnetic tubular structure such as a ferromagnetic tube having a high aspect ratio. The method entails inducing a magnetic field of a given magnitude within the tubular structure. Further, a bias is applied at a given voltage to the tubular structure. Then, the interior surface of the tubular structure is exposed to a gaseous precursor material under conditions effective to convert a quantity of the gaseous precursor material to ionize gaseous precursor material. The given magnitude and voltage is such that it is effective to deposit the ionized the gaseous precursor material onto the interior surface and converts the ionized gaseous precursor material to a substantially uniform protective coating in the interior surface.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
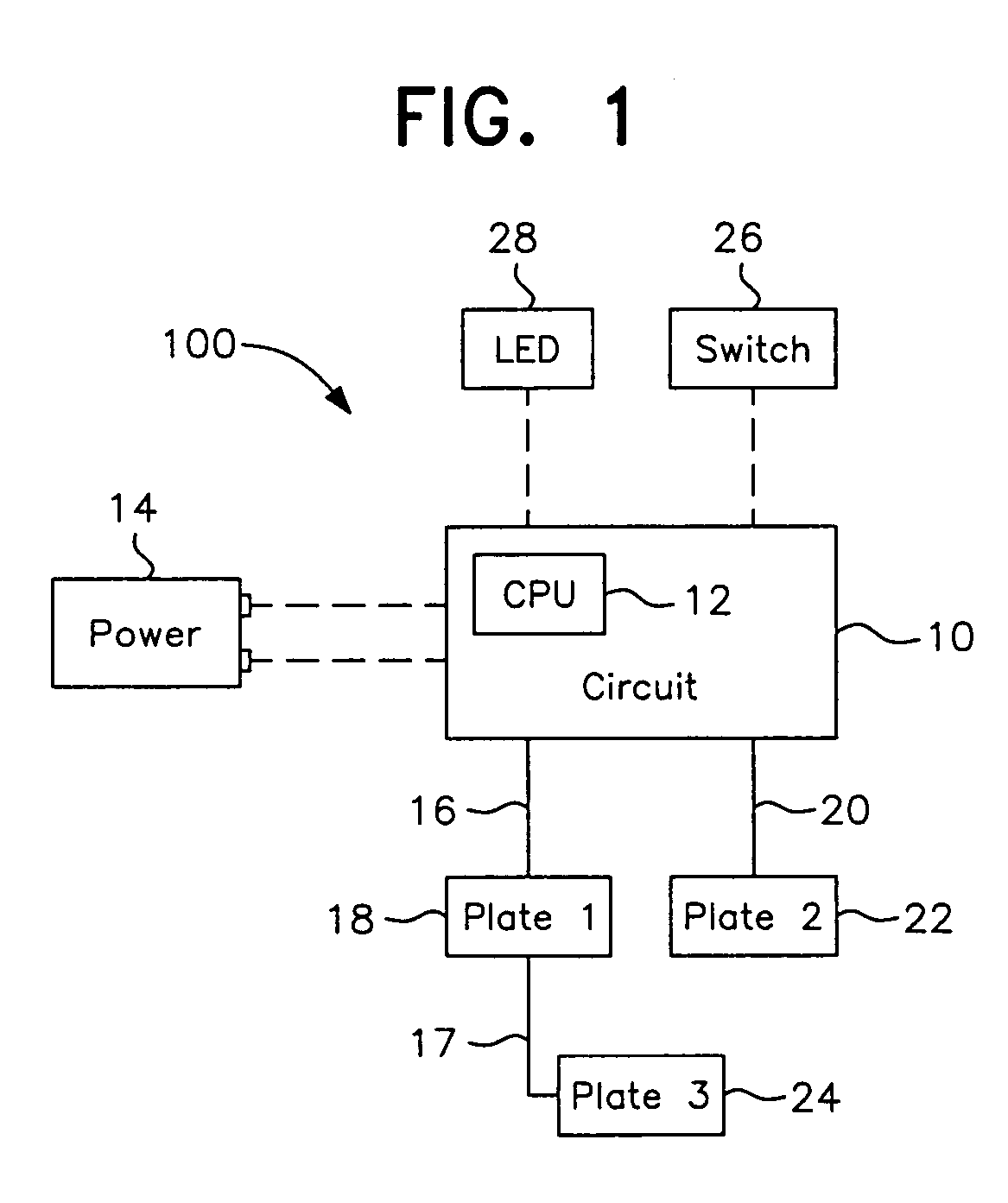
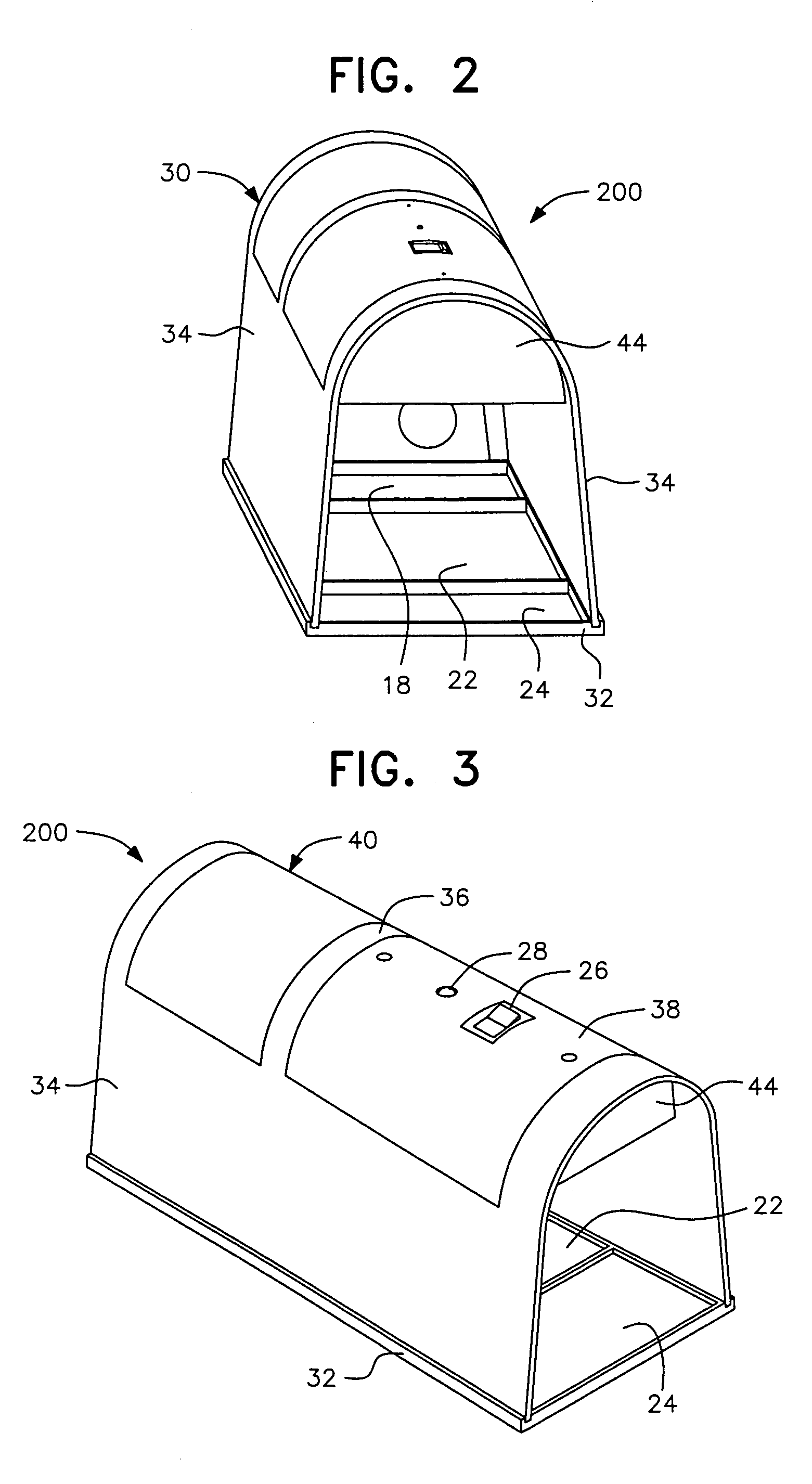
CPU-controlled, rearming electronic animal trap with three-killing-plate configuration
InactiveUS7219466B2Power capabilityReduce the possibilityAnimal huntingElectric shock equipmentsElectricityTrapping
An electronic animal trap with a CPU-controlled, rearming, three-killing-plate configuration and extended killing cycle for trapping and exterminating larger rodents such as rats. The high-voltage output circuit is connected to a pair of killing plates which are activated with a high-voltage pulse train for a killing cycle when a pest of known impedance is sensed across said pair of plates. A third killing plate, electrically coupled to a first plate of said pair of plates, is brought to the voltage level of the first plate within approximately 1 msec of circuit activation for increased kill and escape-prevention capabilities.
Owner:WOODSTREAM CORP
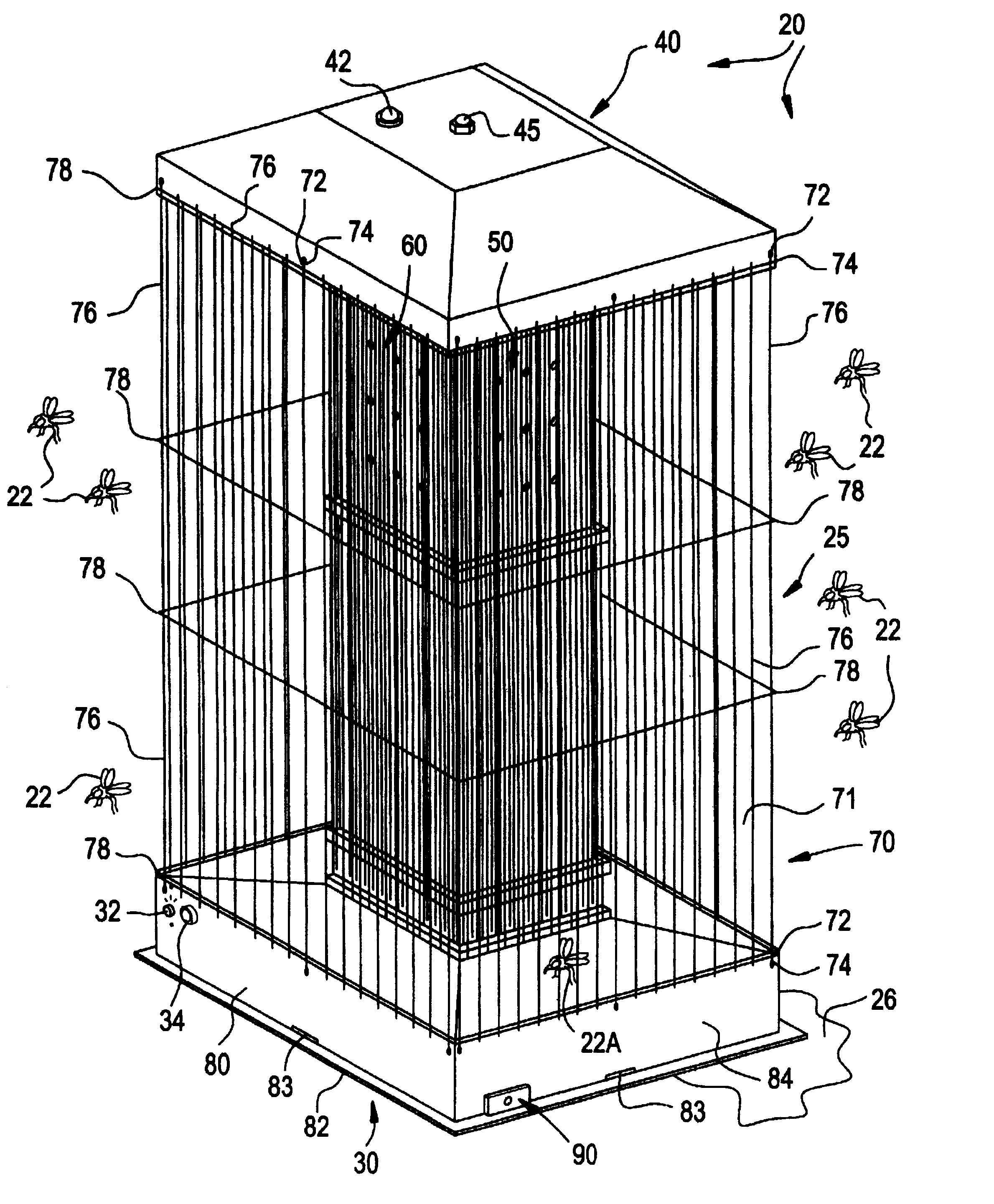
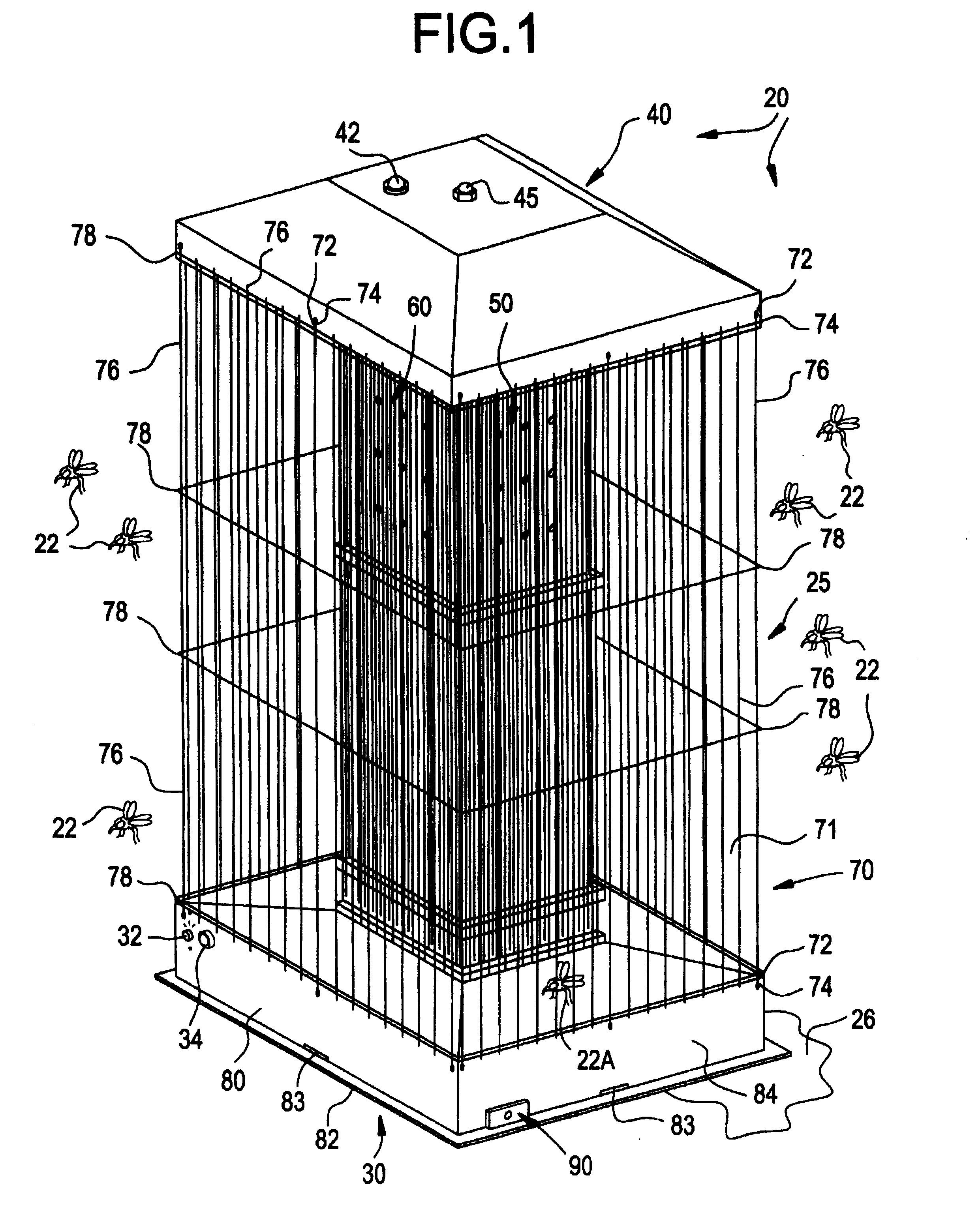
Mosquito killing system
InactiveUS6568124B1Electric shock equipmentsInsect catchers and killersEngineeringPressure difference
An insect killing system optimized for mosquitoes uses multiple thermal gradients to simulate the breathing and body heat from animals, including human beings and fowl, to attract insects for subsequent electrocution. The system comprises an elongated, generally parallelepiped housing supported upon a lower base. A heating tower shrouded by the housing supports a spaced apart, generally pyramidal roof. Several slits penetrate the base to permit air entry. An internal fan draws air into the base where the air mixes with scents, pheromones, and / or moisture. Mixed air is blown into and through the heating tower. An internal baffle divides the tower interior into separate, spaced apart compartments. A lower compartment houses a heater, and an adjacent upper compartment vents warmed air to atmosphere, creating numerous separate streams of warmed air that, to an insect, emulate human breathing. The baffle restricts air flow to create a pressure differential while ensuring adequate residence time to sufficiently warm the air. Heated air traversing the upper compartment is expelled through a plurality of discharge orifices. The resulting multitude of warm air currents creates an infrared signature emulating human breathing to attract mosquitoes. Additionally, a motorized mechanism provides movement of the apparatus to create motion simulating a living creature, which provides a further attractant to mosquitoes.
Owner:SHRADER TIFFANY +1
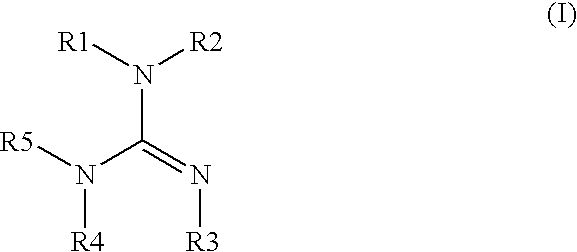
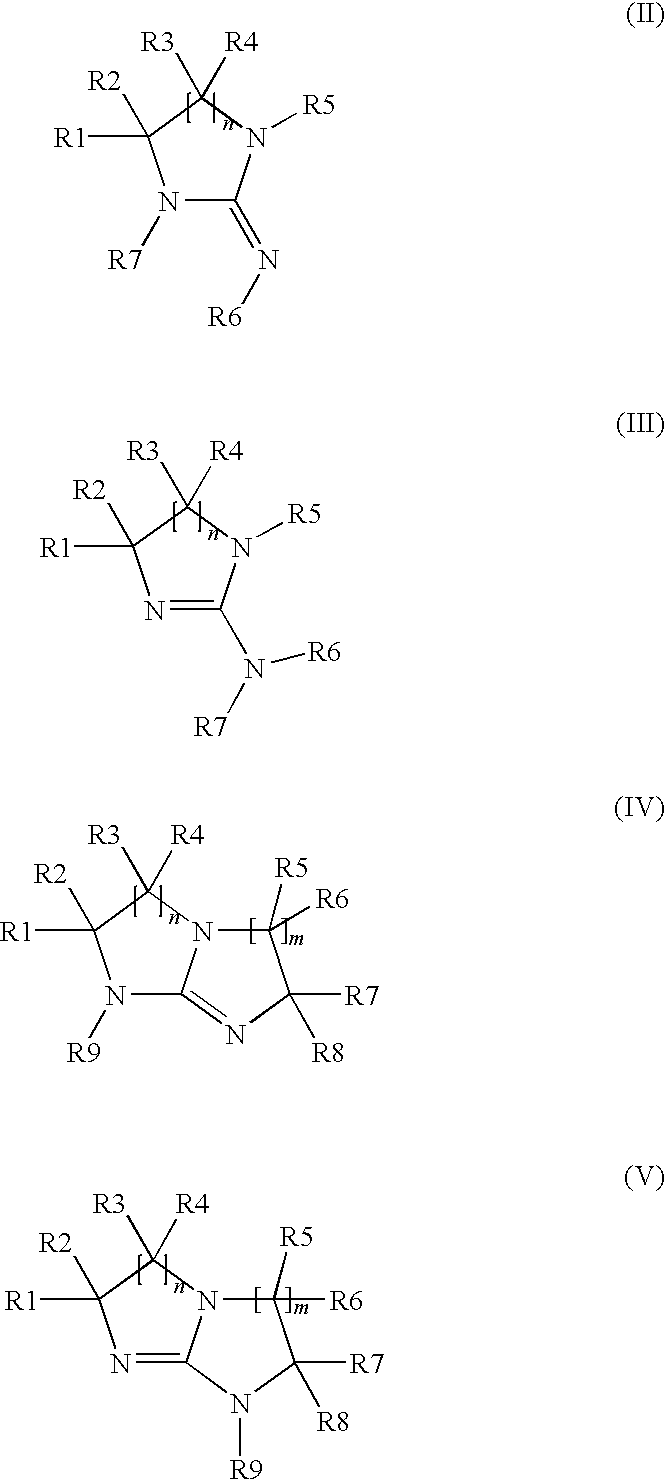
Electrodepositable coating composition containing a cyclic guanidine
The present invention is directed towards an electrocoating composition comprising a cyclic guanidine.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
Apparatus and method for electrostatic spray coating of medical devices
ActiveUS7241344B2Increased ionization increases the fraction of coating spray attractedIncrease electrode surface areaLiquid spraying plantsElectric shock equipmentsVoltage spikeSpray coating
An apparatus and method for electrostatic spray deposition of small targets, such as medical devices like stents. The apparatus includes a target holder which applies a first electrical potential to the target, and an electrostatic dispensing nozzle which applies a second potential sufficient to attract the coating fluid from the nozzle toward the target. Because the entire dispensing nozzle is conductive, the coating fluid may receive a greater charge than may be obtained with internal electrode-type nozzles. Electrostatic attraction of the coating fluid to the target is enhanced by the combination of higher charge density imparted to the coating fluid by the conductive nozzle, and application of a momentary voltage spike to the target to provide consistent conductivity between the target and its holder, thereby ensuring the target is presents the full first potential applied to the holder. The voltage spike may also be used independently of the conductive nozzle.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
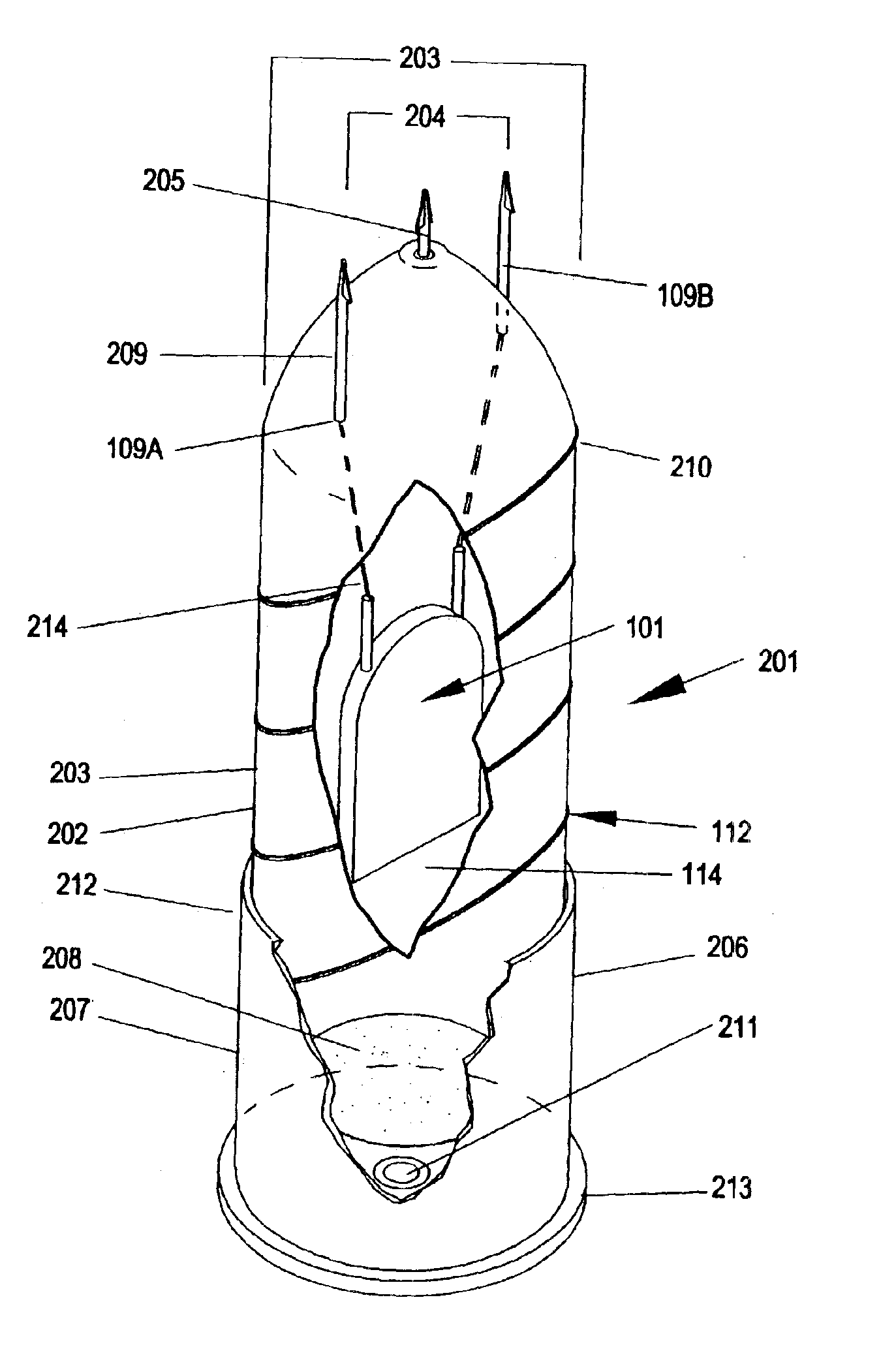
Sub-lethal, wireless projectile and accessories
InactiveUS6880466B2Increase energy levelReduce power levelAmmunition projectilesElectric shock equipmentsSTUNElectric discharge
The invention is a circuit capable of being positioned in a variety of wireless projectile and of delivering a series of pulsed electric discharges in two wave frequencies so as to stun and disable a target individual. The projectiles are adapted to be discharged from a different types of devices and powered by explosive, pneumatic, or manual means. At least one mode includes the ability to deliver a stunning physical blow in addition to the electric shock. The device is sub-lethal, but totally disabling in effects on a target individual.
Owner:CSA ENERGY
Method for depositing particles onto a substrate using an alternating electric field
InactiveUS6923979B2Quality improvementAvoid charge accumulationPowder deliveryPretreated surfacesElectrical polarityElectric field
Owner:MICRODOSE THERAPEUTX INC
Diffuser with light emitting diode nightlight
An electrically operated diffuser has a fragrance-emitting element (8) for facilitating diffusion of an active material, and at least one light emitting diode (7). The at least one light emitting diode (7) serves as a nightlight and has a luminous intensity rating of at least about 5000 mcd at 20 mA. Also, the at least one light emitting diode (7) may be positioned at a back surface of the diffuser, such that when an active material is received in the compartment the at least one light emitting diode (7) shines through the active material. The diffuser may include a remote-use assembly to supply power to the diffuser from a wall socket remote from the diffuser. The diffuser may also include a light controller to change one or more of the color and the intensity of the at least one light emitting diode (7).
Owner:SC JOHNSON & SON INC
Ordered vertically oriented porous inorganic films produced through solution processing
InactiveUS20060278158A1Easy to produceFrom gel statePhotosensitive materialsPatterned substrateSelf-assembly
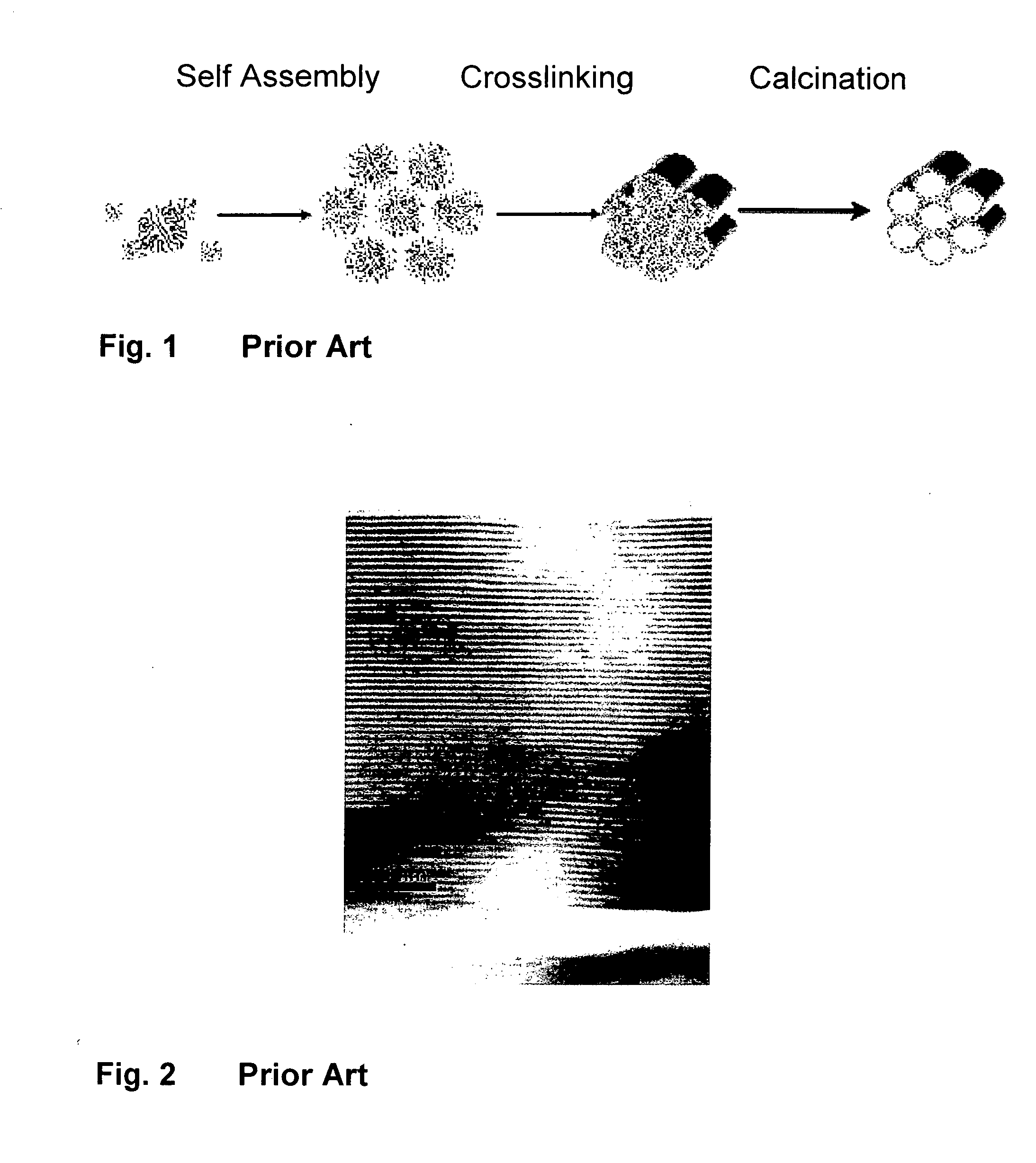
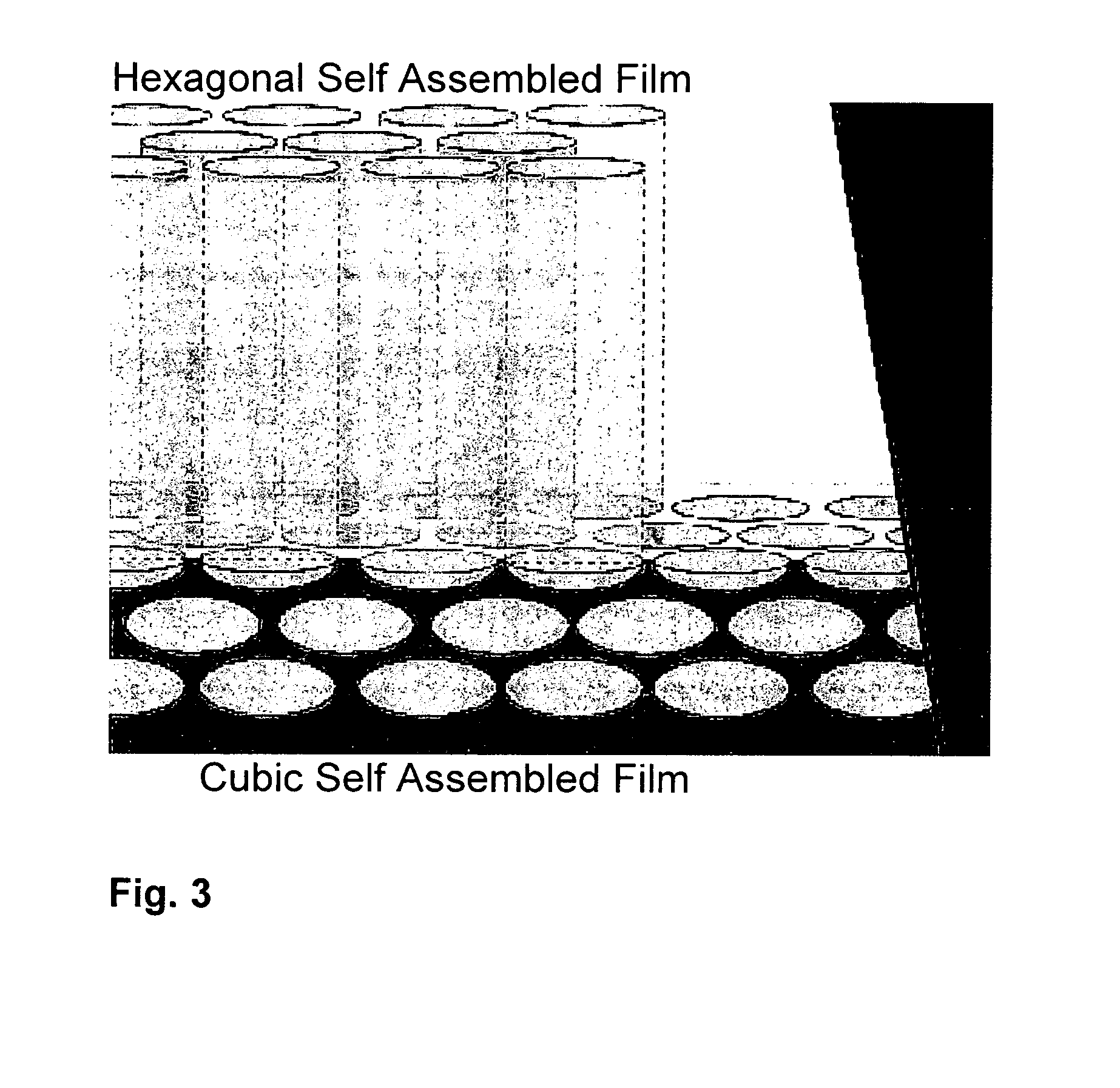
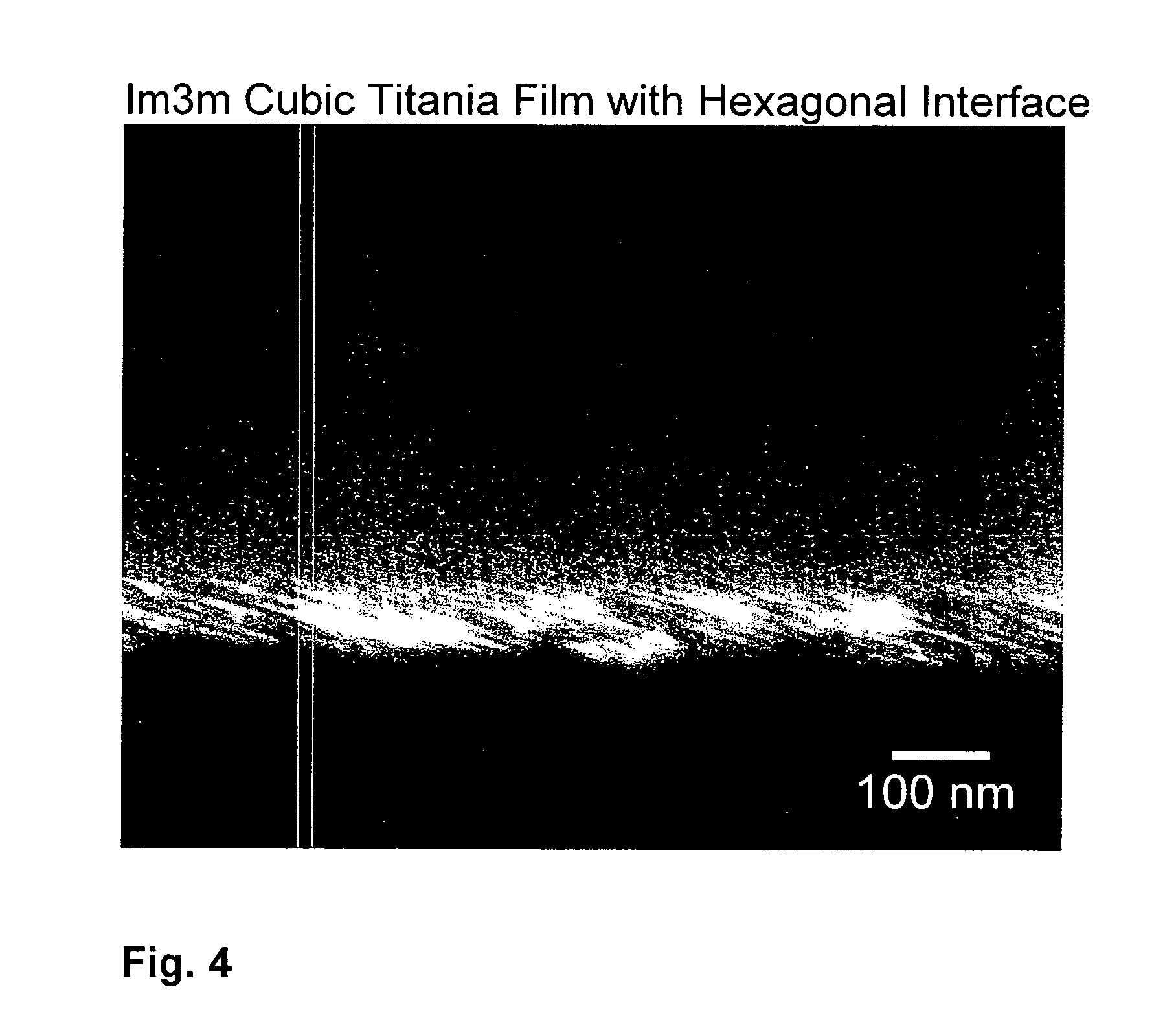
Porous films with straight pores oriented normal to the plane of the films are produced through solution processing techniques. The production takes advantage of inorganic-surfactant or inorganic-polymer co-assembly and a patterned substrate. The patterned substrate, which is also produced via solution phase self-assembly, forces vertical orientation in a hexagonal cylinder system with no practical limits in substrate size or type. This provides a route to vertically oriented inorganic pores with a pitch ranging from 3 nm to over 15 nm and pore sizes ranging from 2 nm to over 12 nm. The size is tuned by choice the choice of organic templating agents and the deposition conditions. The pores can be produced with or without a capping layer which can be used to seal the nanopores.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Cable covered in solid lubricant
The invention relates to apparatus for depositing a lubricant coating on a cable, the cable including a sheath made by means of an extruder followed by a cooling vessel. Downstream from the cooling vessel, the apparatus includes a heater member followed by a deposition chamber for depositing a lubricant material.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com