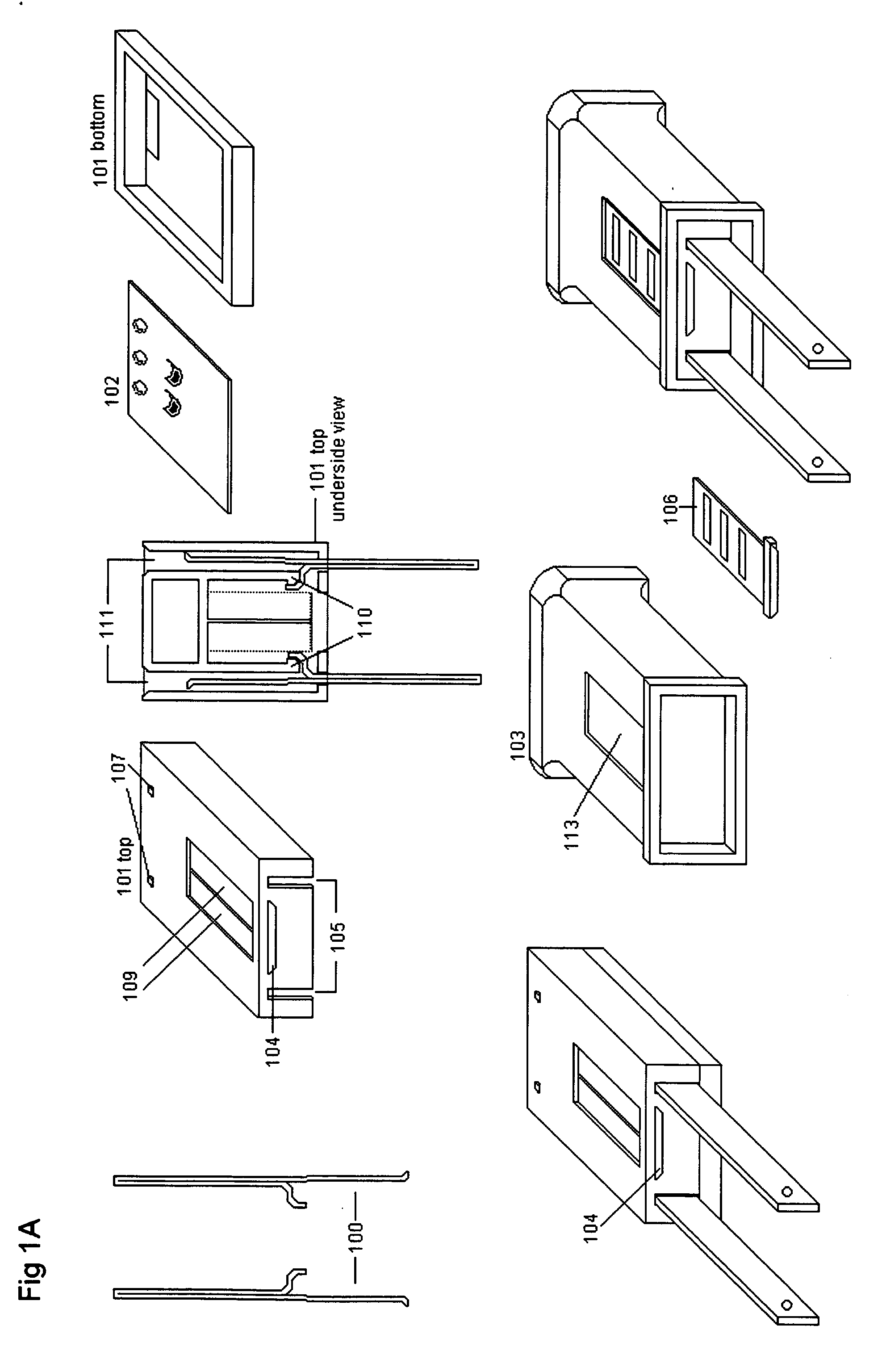
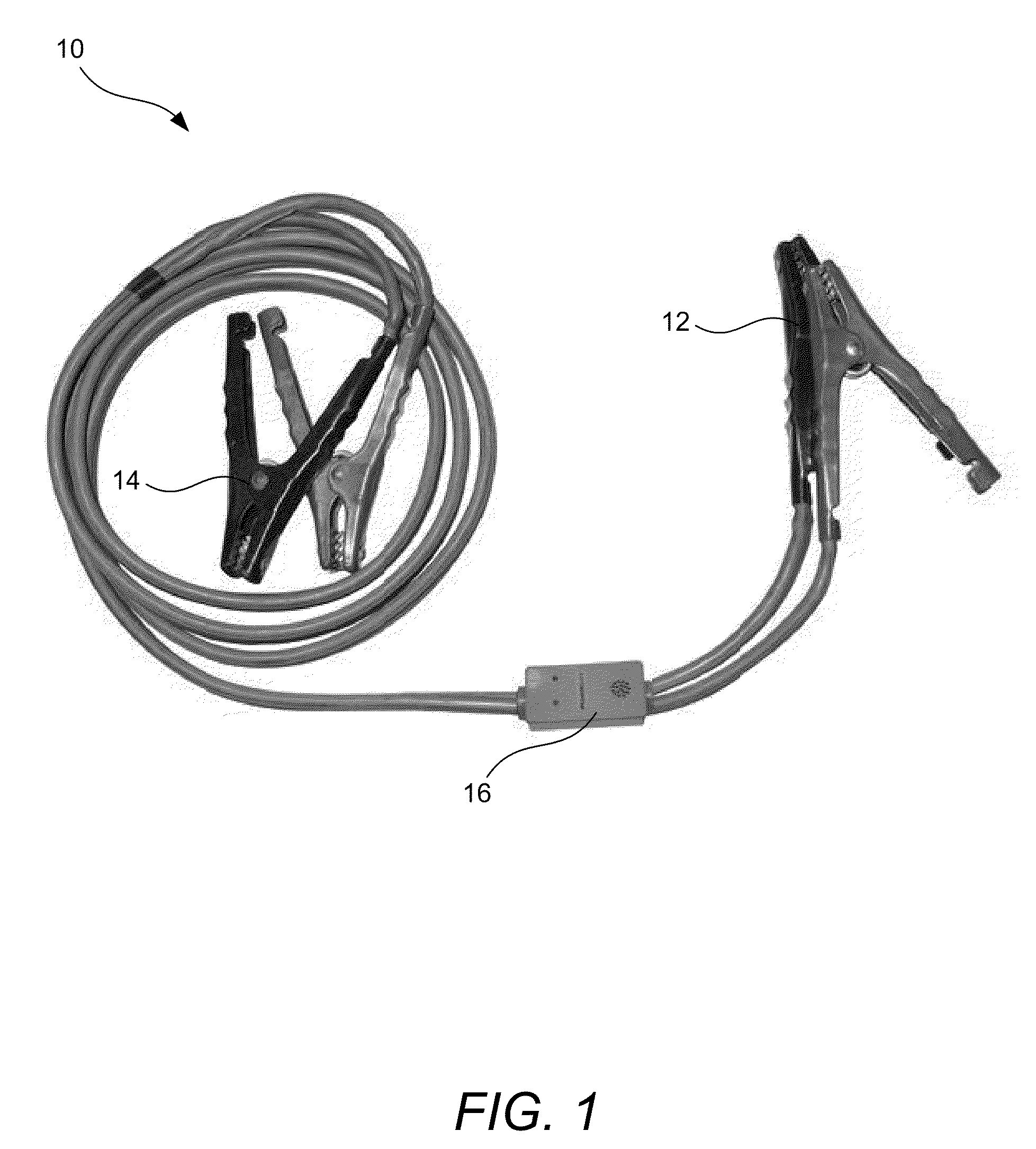Patents
Literature
534 results about "Voltage spike" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In electrical engineering, spikes are fast, short duration electrical transients in voltage (voltage spikes), current (current spikes), or transferred energy (energy spikes) in an electrical circuit.
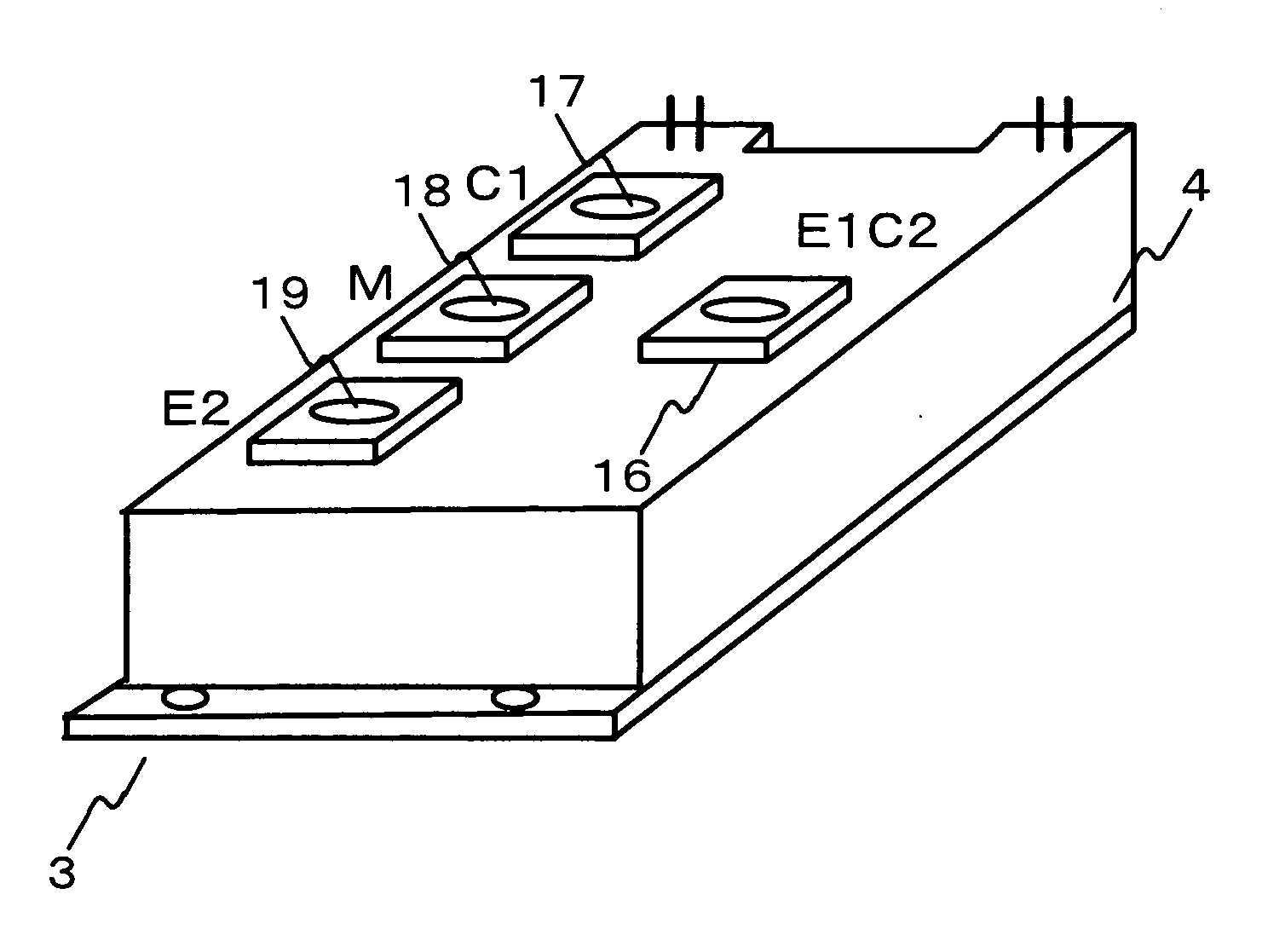
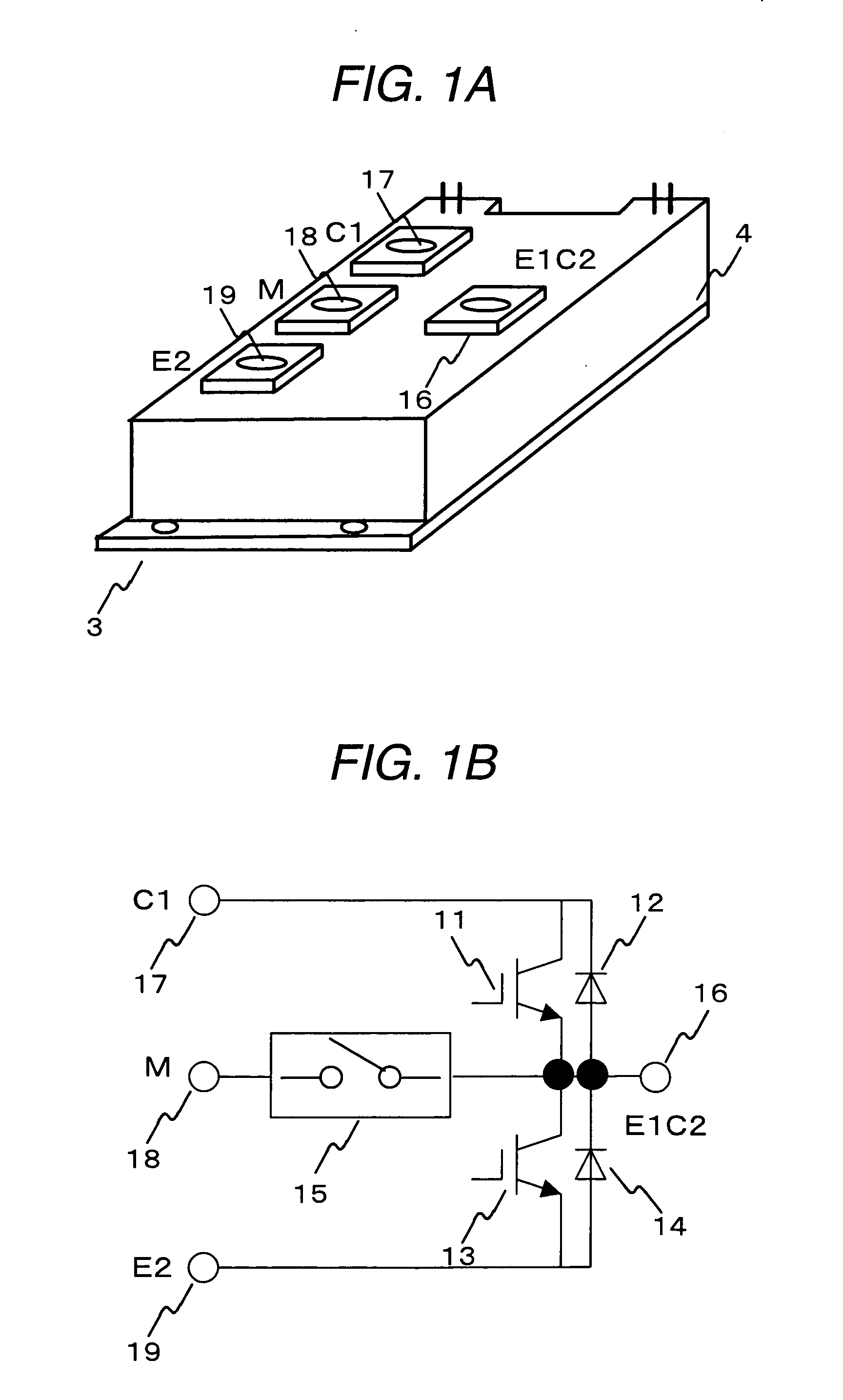
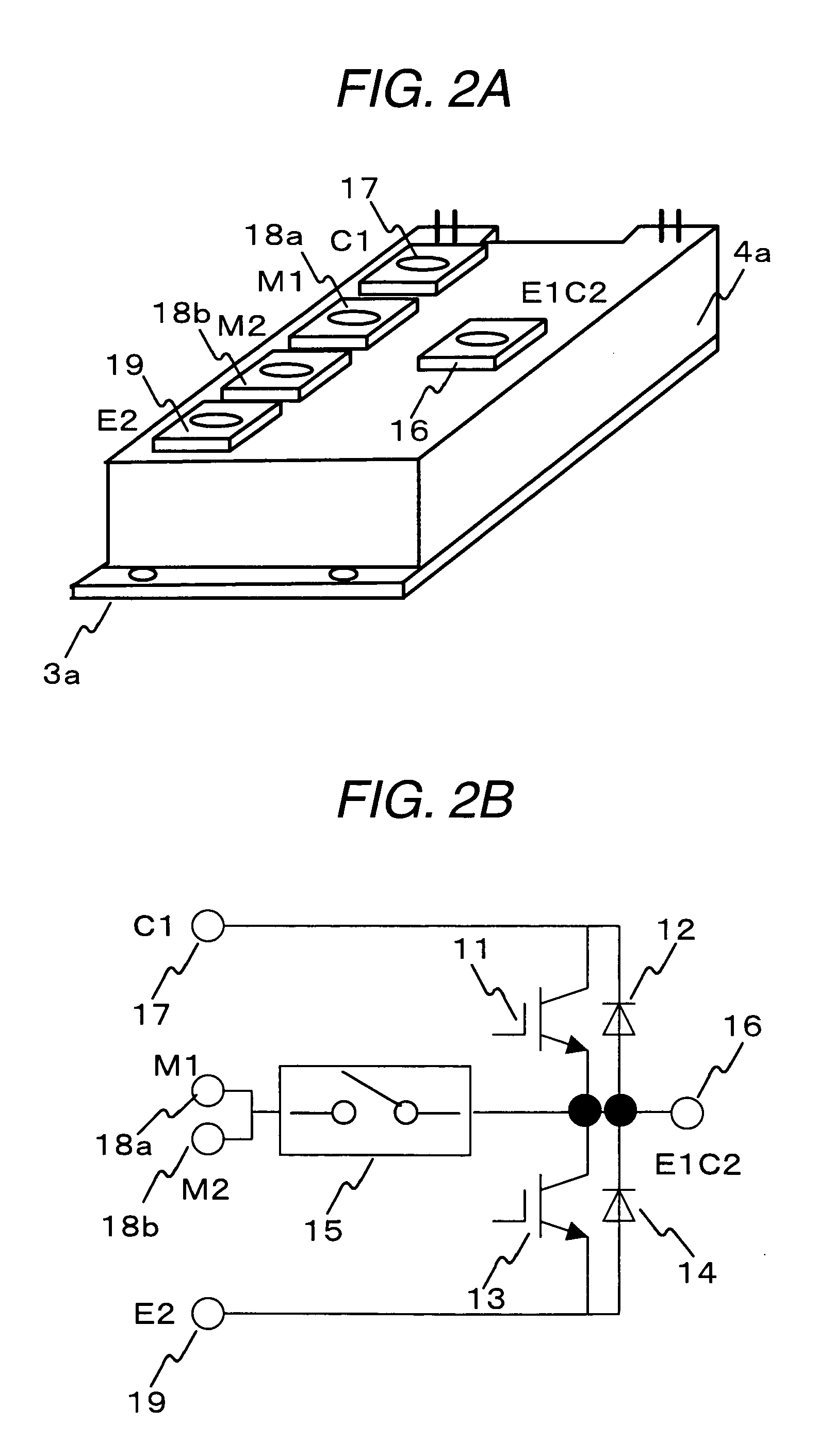
Enhanced ZScreen modulator techniques
Owner:REAID INC
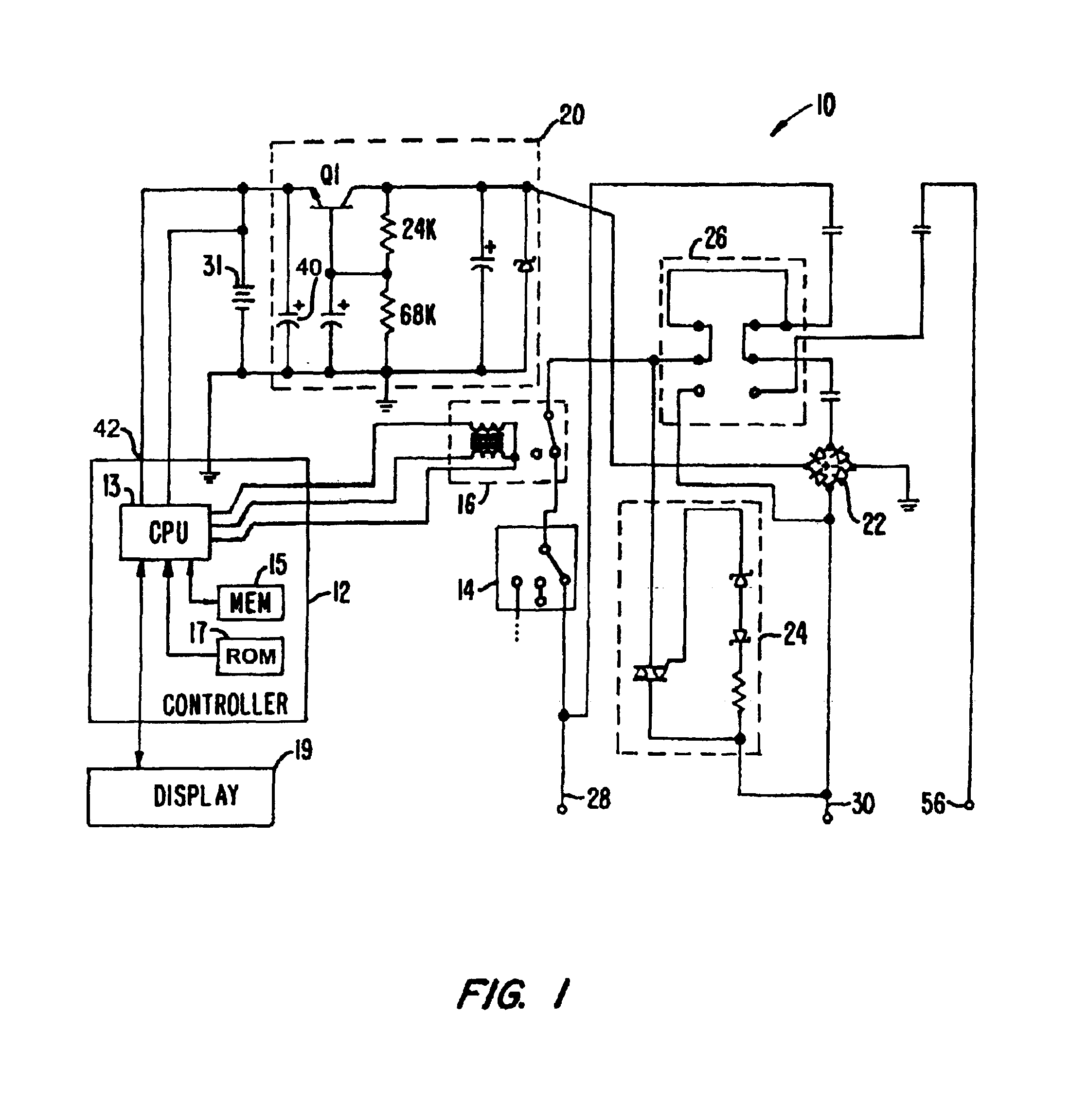
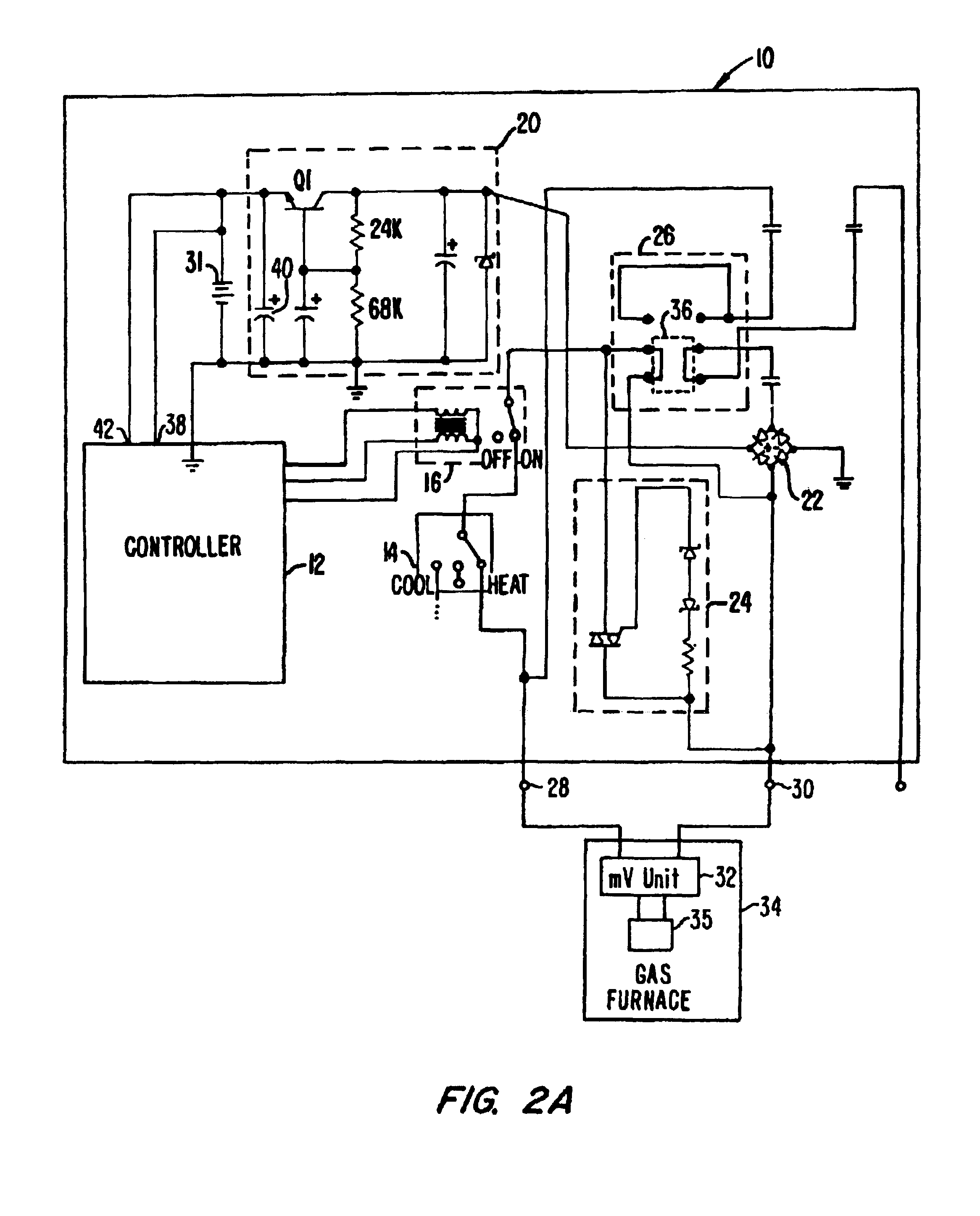
Thermostat operable from various power sources
InactiveUS6886754B2Fluid heatersTemperature control using electric meansVoltage spikeOperating point
A thermostat is operable from battery, common-wire (“C-wire”), or furnace relay power. The thermostat includes a power source selector, such as a jumper wire, that is set when the thermostat is installed in a heating system. In a gas millivolt heating system, the thermostat operates off of battery power. In heating systems having a C-wire, a diode bridge converter converts alternating-current voltage to direct-current voltage to provide operating power to the thermostat. In heating systems without a C-wire and having sufficient furnace relay current, a triac converter in series with the furnace relay provides voltage spikes to the diode bridge converter to provide operating power to the thermostat when the furnace is on, and the diode bridge converts AC to DC voltage when the furnace is not on. The thermostat can also be used in cooling systems and heating, ventilation, and air-conditioning systems. Thus, the thermostat can be used in a wide variety of applications.
Owner:TIM SIMON
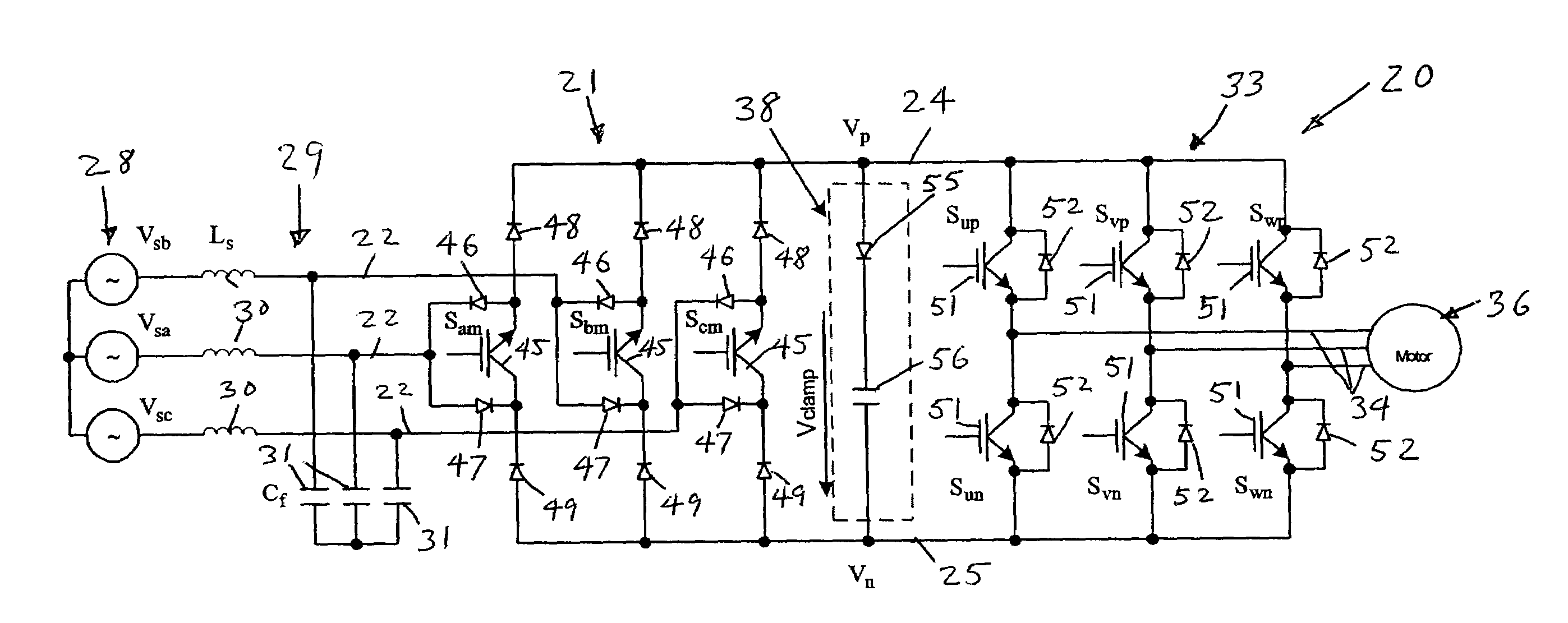
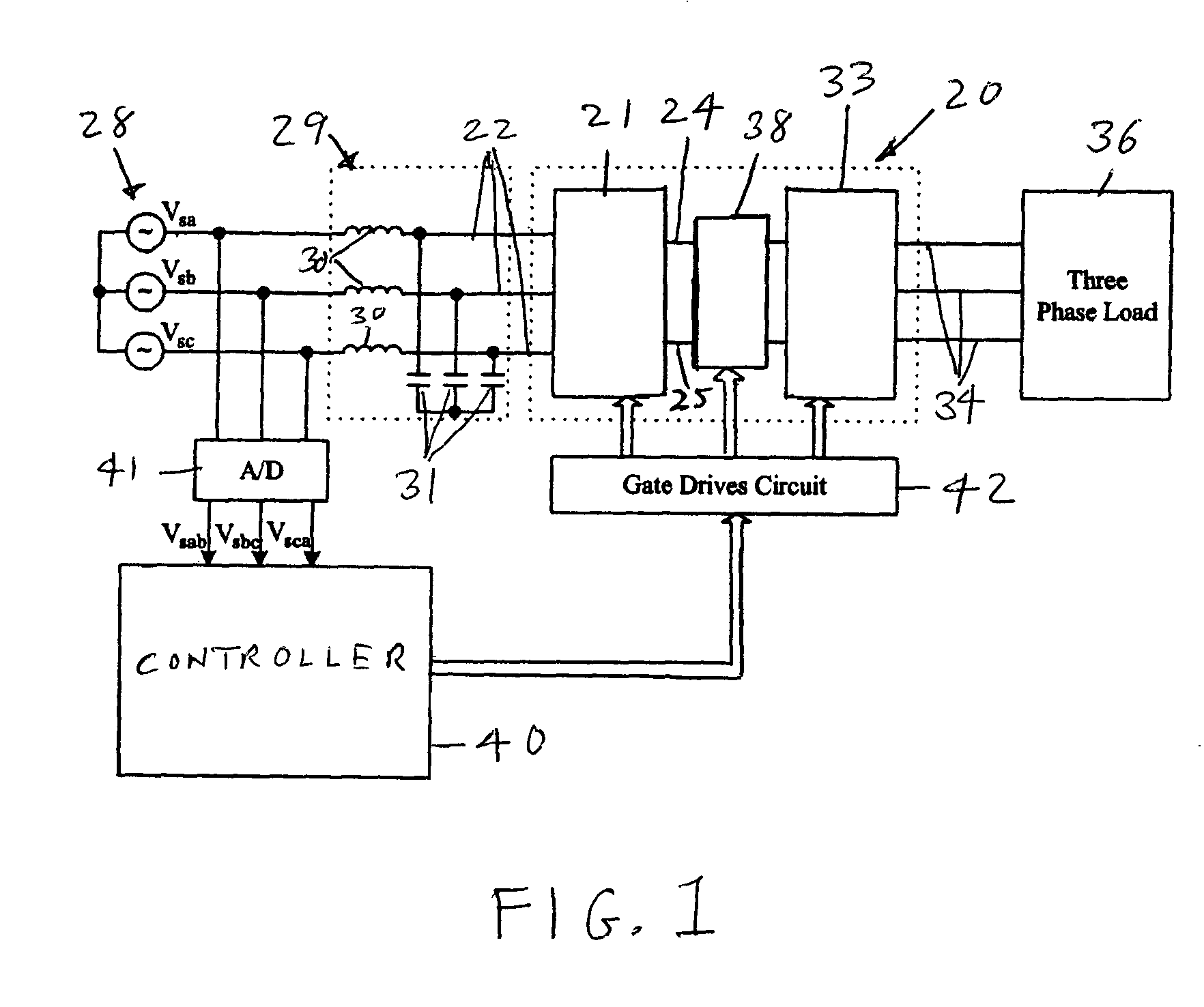
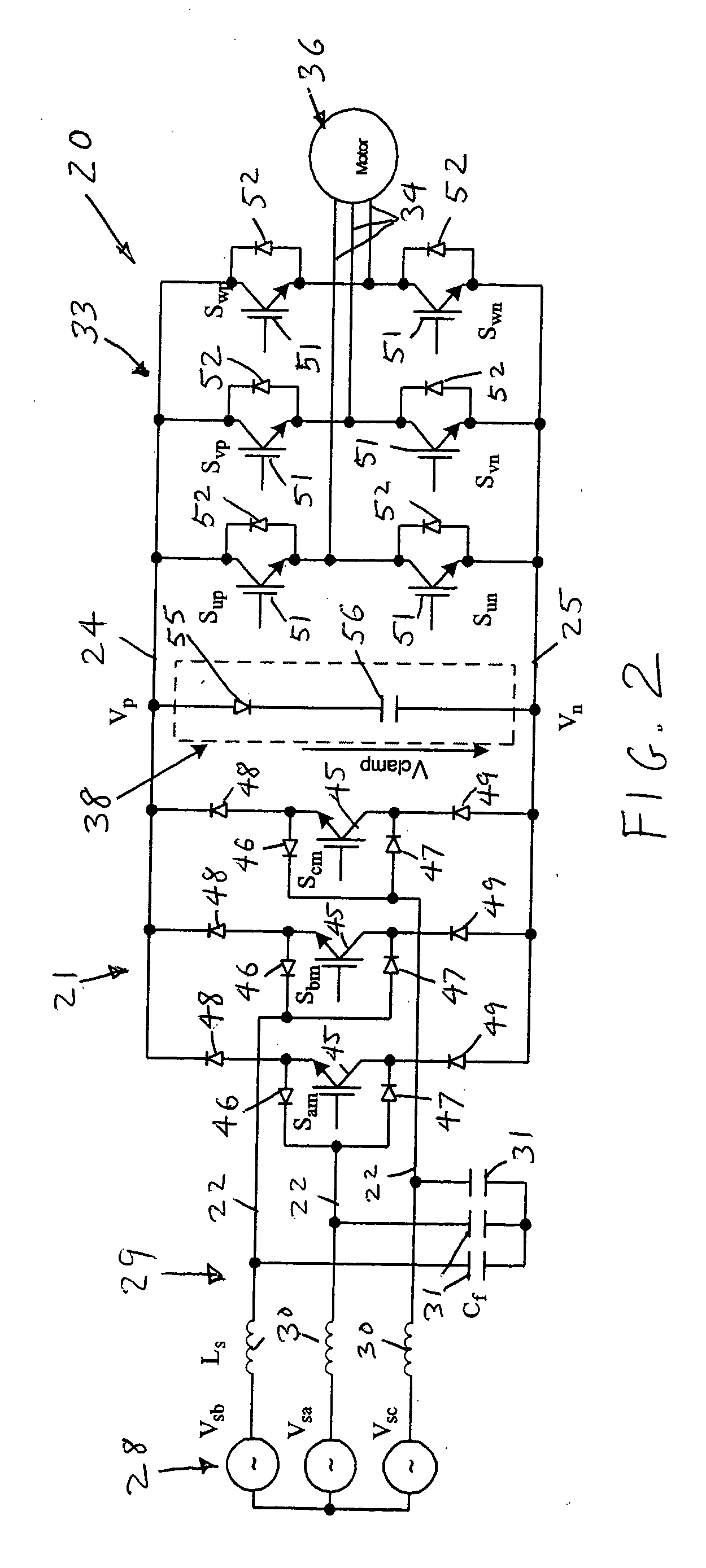
Dual bridge matrix converter
ActiveUS6995992B2Reduce and eliminate voltage spikeSmall and inexpensiveConversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc circuit to reduce harmonics/ripplesMatrix convertersClamp capacitor
A dual bridge matrix converter has a line-side converter with controllable switches that receives AC power and provides unidirectional power to high and low DC link lines, and a load-side converter which receives the power from the DC link lines and provides AC power to output lines. A clamp circuit is connected across the DC link lines and includes a series connected diode and a capacitor. Negative DC link current will be conducted through the clamp diode to charge the clamp capacitor to avoid voltage spikes on the DC link lines. A controllable switch may be connected in parallel with the clamp diode and is turned on when the voltage across the clamp capacitor is above a threshold that is greater than the normal peak-to-peak AC input voltage. The switch is turned off when the voltage across the clamp capacitor is lower than the threshold voltage.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Apparatus and method for electrostatic spray coating of medical devices
ActiveUS20050175772A1Increased ionization increases the fraction of coating spray attractedIncrease electrode surface areaLiquid spraying plantsElectric shock equipmentsVoltage spikeSpray coating
An apparatus and method for electrostatic spray deposition of small targets, such as medical devices like stents. The apparatus includes a target holder which applies a first electrical potential to the target, and an electrostatic dispensing nozzle which applies a second potential sufficient to attract the coating fluid from the nozzle toward the target. Because the entire dispensing nozzle is conductive, the coating fluid may receive a greater charge than may be obtained with internal electrode-type nozzles. Electrostatic attraction of the coating fluid to the target is enhanced by the combination of higher charge density imparted to the coating fluid by the conductive nozzle, and application of a momentary voltage spike to the target to provide consistent conductivity between the target and its holder, thereby ensuring the target is presents the full first potential applied to the holder. The voltage spike may also be used independently of the conductive nozzle.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Semiconductor module for use in power supply
ActiveUS20100039843A1Reduce withstand voltageLow costConversion constructional detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsVoltage spikeComputer module
A series connection circuit of IGBTs and an AC switch are contained in one package. The series connection circuit is connected between the positive and negative terminals of a DC power source, and the AC switch is connected between a neutral point of the DC power source and a series connection point between the IGBTs. Straight conductor strips can be used to connect terminals on the package to the DC power source, thereby reducing inductance and thus also reducing voltage spikes.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Apparatus and method for electrostatic spray coating of medical devices
ActiveUS7241344B2Increased ionization increases the fraction of coating spray attractedIncrease electrode surface areaLiquid spraying plantsElectric shock equipmentsVoltage spikeSpray coating
An apparatus and method for electrostatic spray deposition of small targets, such as medical devices like stents. The apparatus includes a target holder which applies a first electrical potential to the target, and an electrostatic dispensing nozzle which applies a second potential sufficient to attract the coating fluid from the nozzle toward the target. Because the entire dispensing nozzle is conductive, the coating fluid may receive a greater charge than may be obtained with internal electrode-type nozzles. Electrostatic attraction of the coating fluid to the target is enhanced by the combination of higher charge density imparted to the coating fluid by the conductive nozzle, and application of a momentary voltage spike to the target to provide consistent conductivity between the target and its holder, thereby ensuring the target is presents the full first potential applied to the holder. The voltage spike may also be used independently of the conductive nozzle.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Plug and cord connector set with integrated circuitry
ActiveUS20060270250A1Eliminate needElectricity consumption is minimizedSubstation/switching arrangement detailsTwo pole connectionsVoltage spikeFull wave
A plug and / or a plug and cord connector set that is easily mass produced and includes integrated circuitry for use with decorative lighting products such as Christmas lights and rope lights. The integrated circuitry included in the plug and / or plug and cord connector combination can serve to reduce or limit current, provide full-wave AC to DC rectification, provide overload protection, reduce voltage, protect against voltage spikes, add blinking or flashing functions, or any combination thereof. An optional intermediate circuit is included for the manufacture of light strings employing multiple series connections.
Owner:FIBER OPTIC DESIGNS
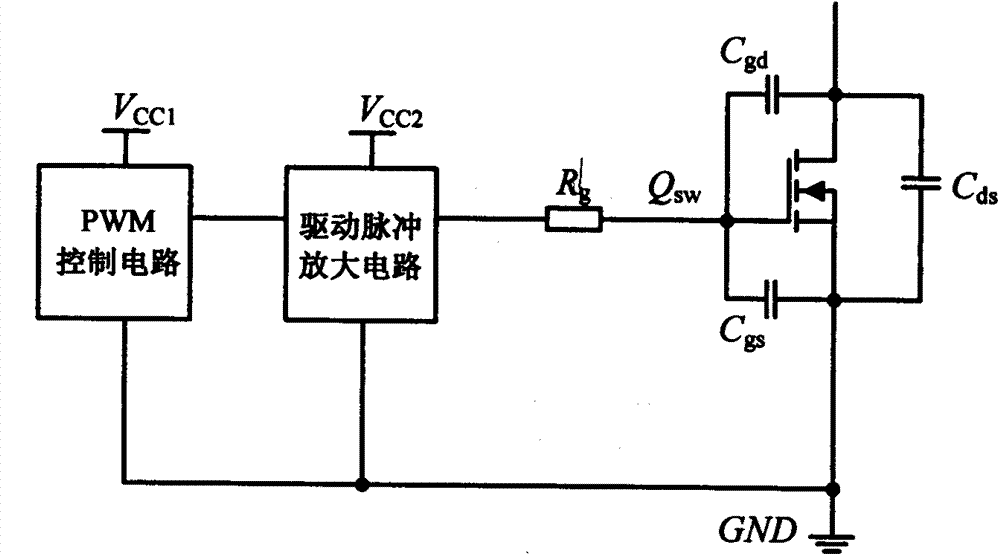
High-reliability MOSFET drive circuit
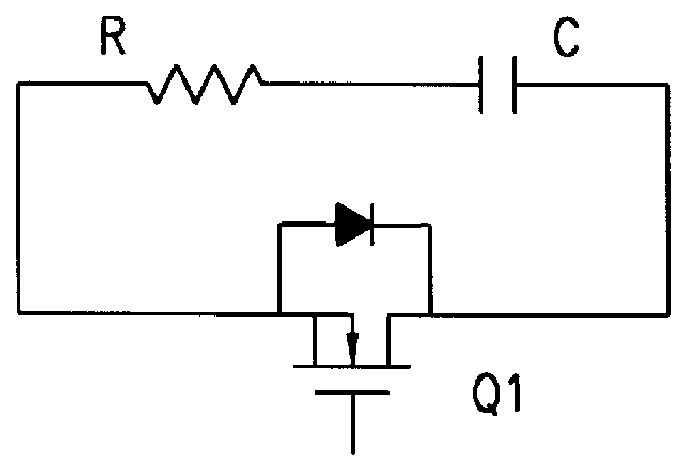
The invention relates to a drive circuit applied to a power switch tube MOSFET, in particular to a drive circuit of a silicon carbide MOSFET, and belongs to the technical field of drive circuits. The drive circuit aims to solve the problem that when an MOSFET in an existing drive circuit is turned off, the reliability is poor. The drive circuit comprises a PWM control circuit, a drive pulse amplifying circuit, a drive resistor Rg, a first diode D1, a resistor R1, a PNP triode Qoff, a second diode D2 and a capacitor C. According to the drive circuit, the PNP triode Qoff, the resistor R1 and the capacitor C form an MOSFET turn-off circuit; when the MOSFET is turned off quickly, a gate pole positive voltage spike caused by Miller currents is effectively suppressed; meanwhile, a gate pole negative voltage spike can also be suppressed through the second diode D2 and the capacitor C, it is guaranteed that the MOSFET is turned off safely and reliably, and the performance advantages of the silicon carbide MOSFET can be given to full play.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Multimeter with filtered measurement mode
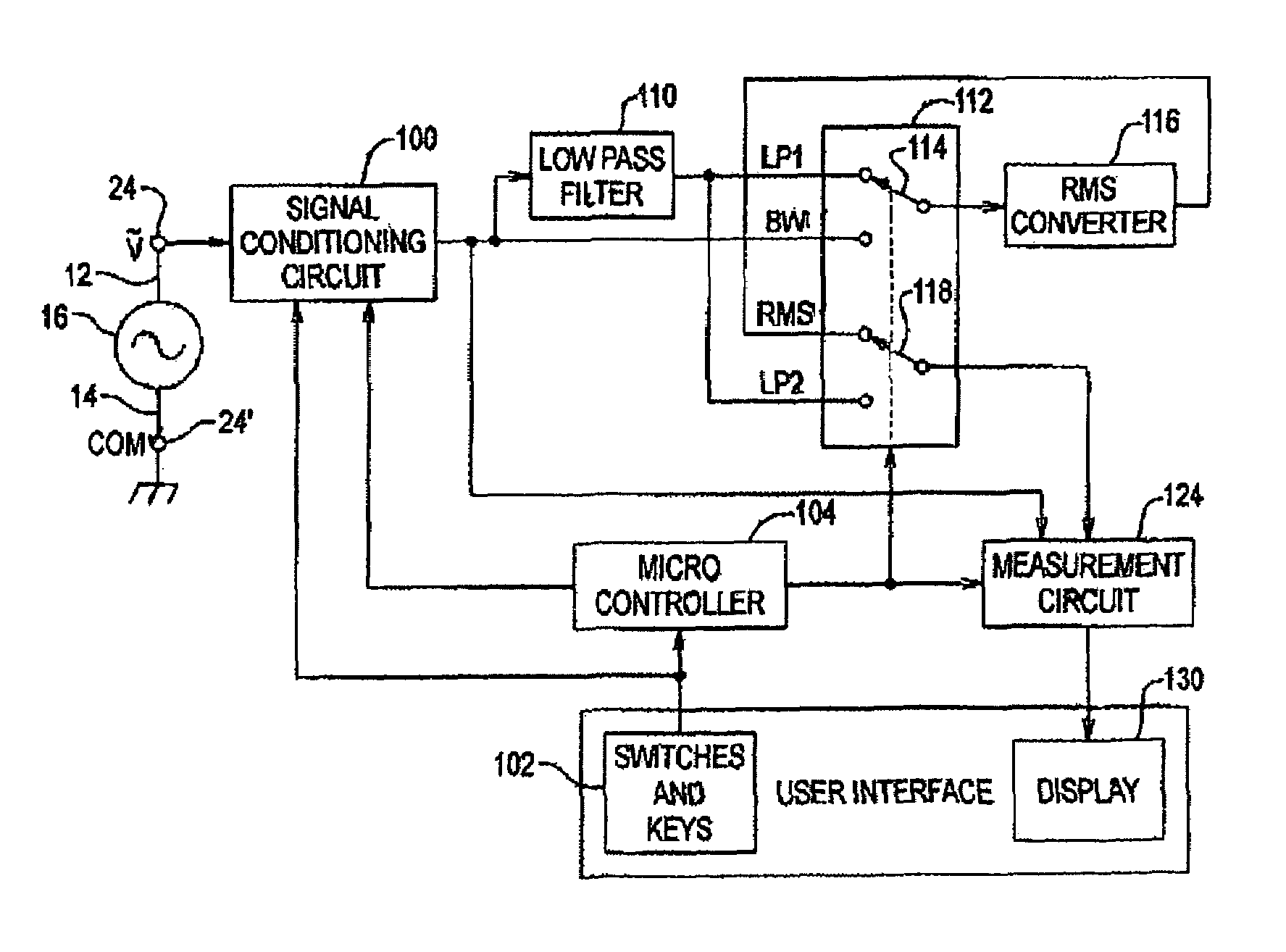
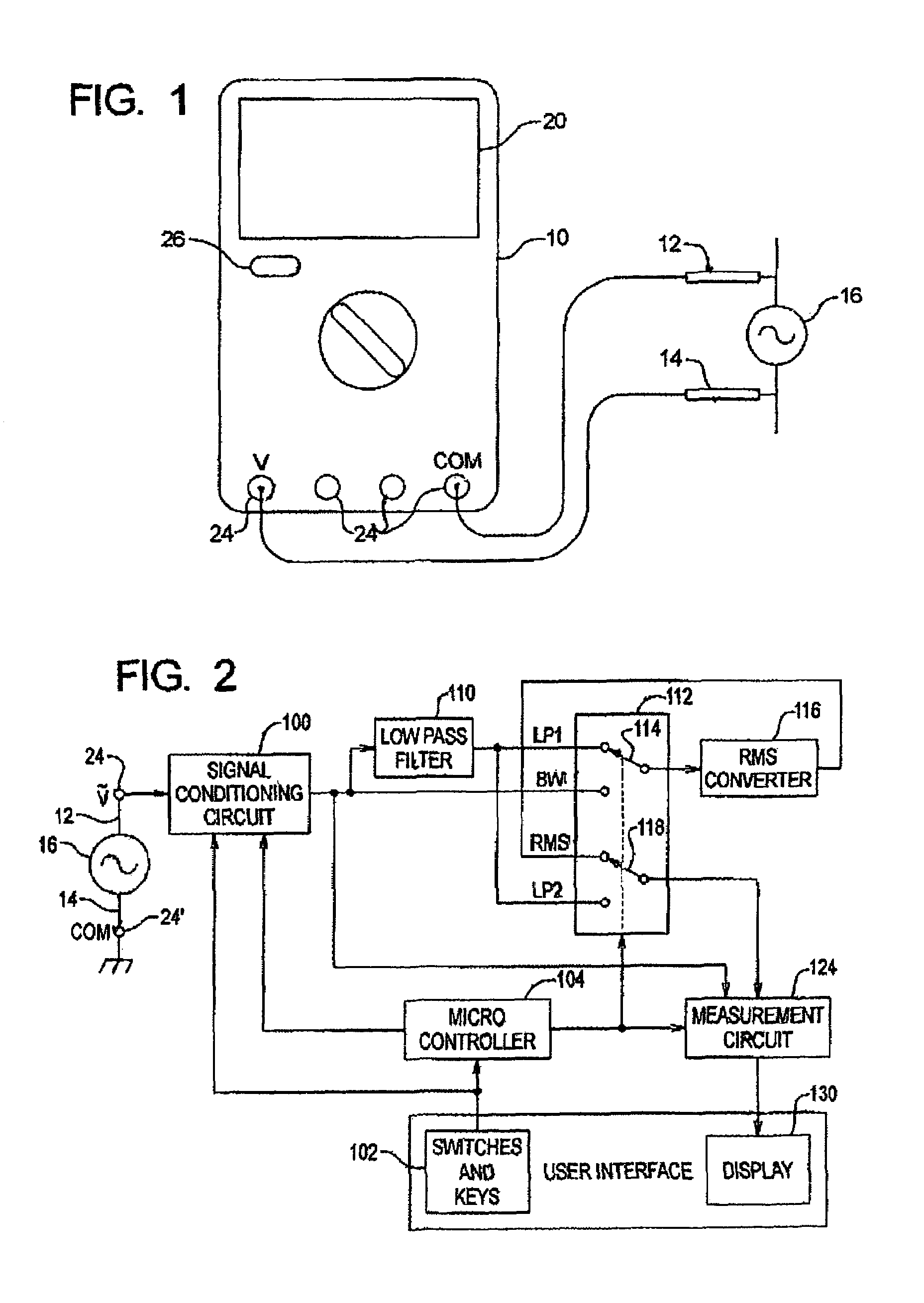
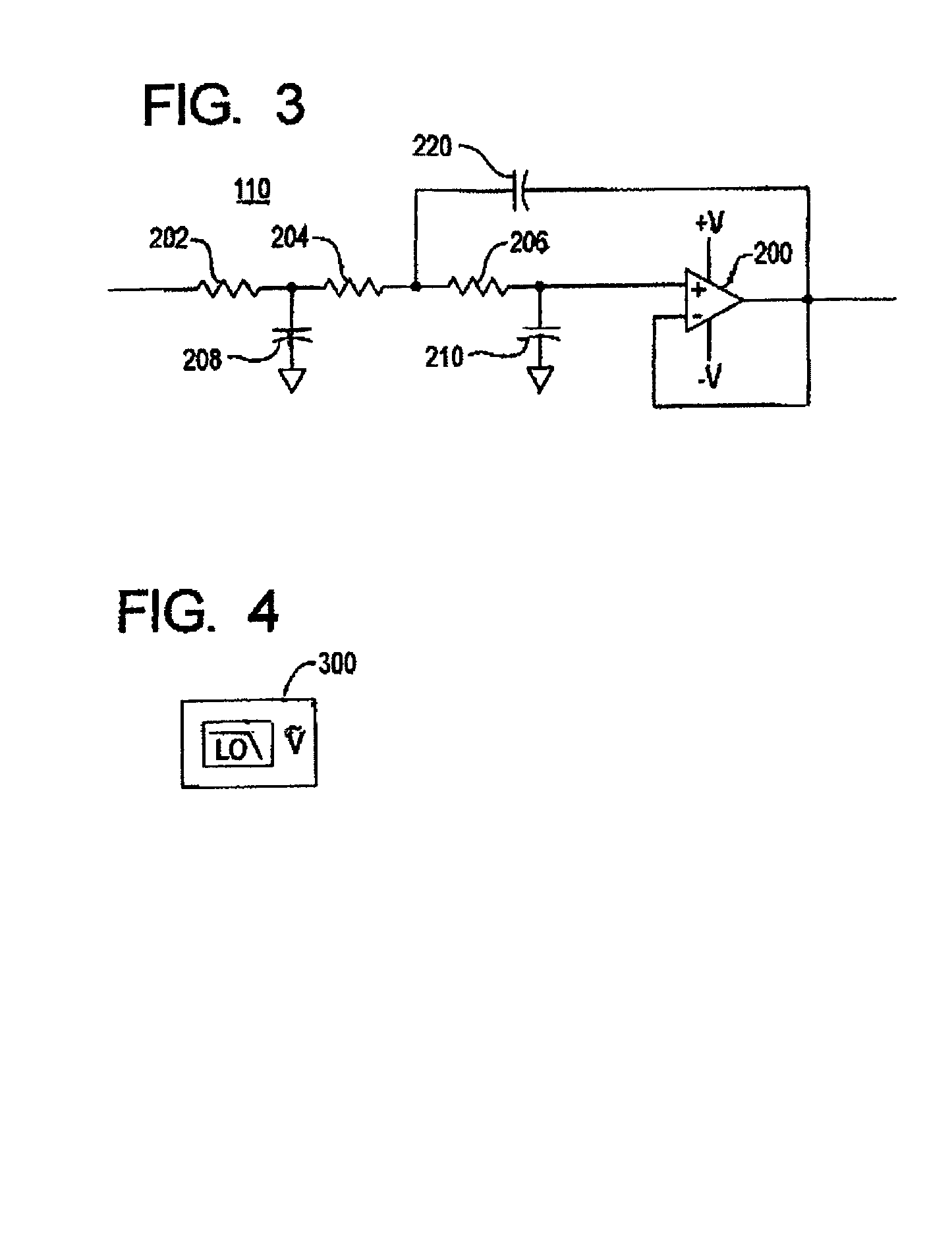
ActiveUS7034517B2Improve abilitiesSpecial tariff metersDynamo-electric motor metersVoltage spikeMotor drive
A multimeter with a filtered measurement mode. By pressing a single button or key, a low-pass filter is switched into the signal path to filter voltage spikes, noise, and switching transients from pulse-width modulated pulses, or lower frequency sinusoidal signals with higher frequency components, and at the same time an on-screen icon indicates to a user that the filtered mode has been selected. The user can switch back and forth between filtered and unfiltered modes. The filtered measurement mode is useful in measuring the outputs of modern adjustable-speed motor drives, uninterruptible power sources, and switch power supplies.
Owner:JOHN FLUKE MFG CO INC
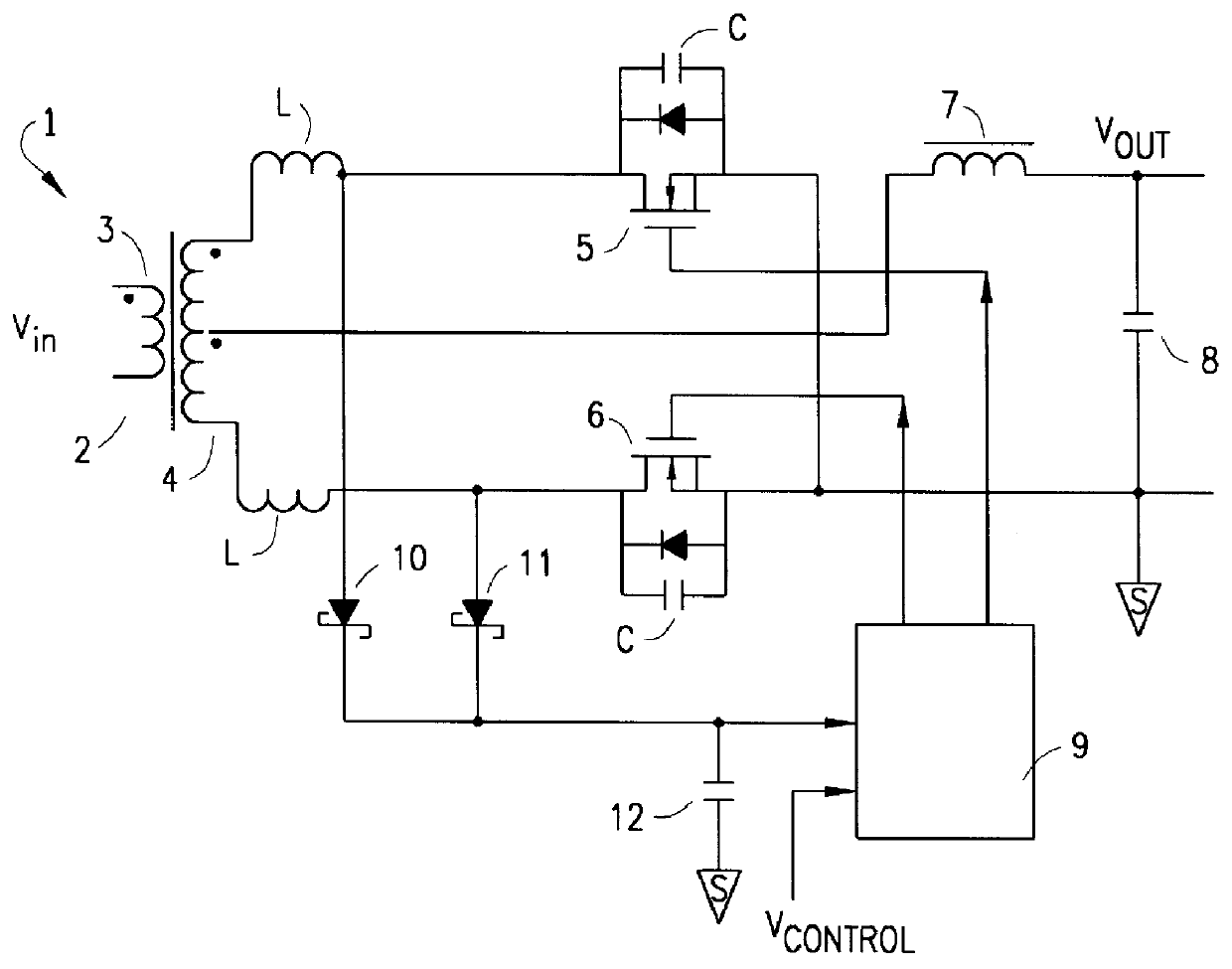
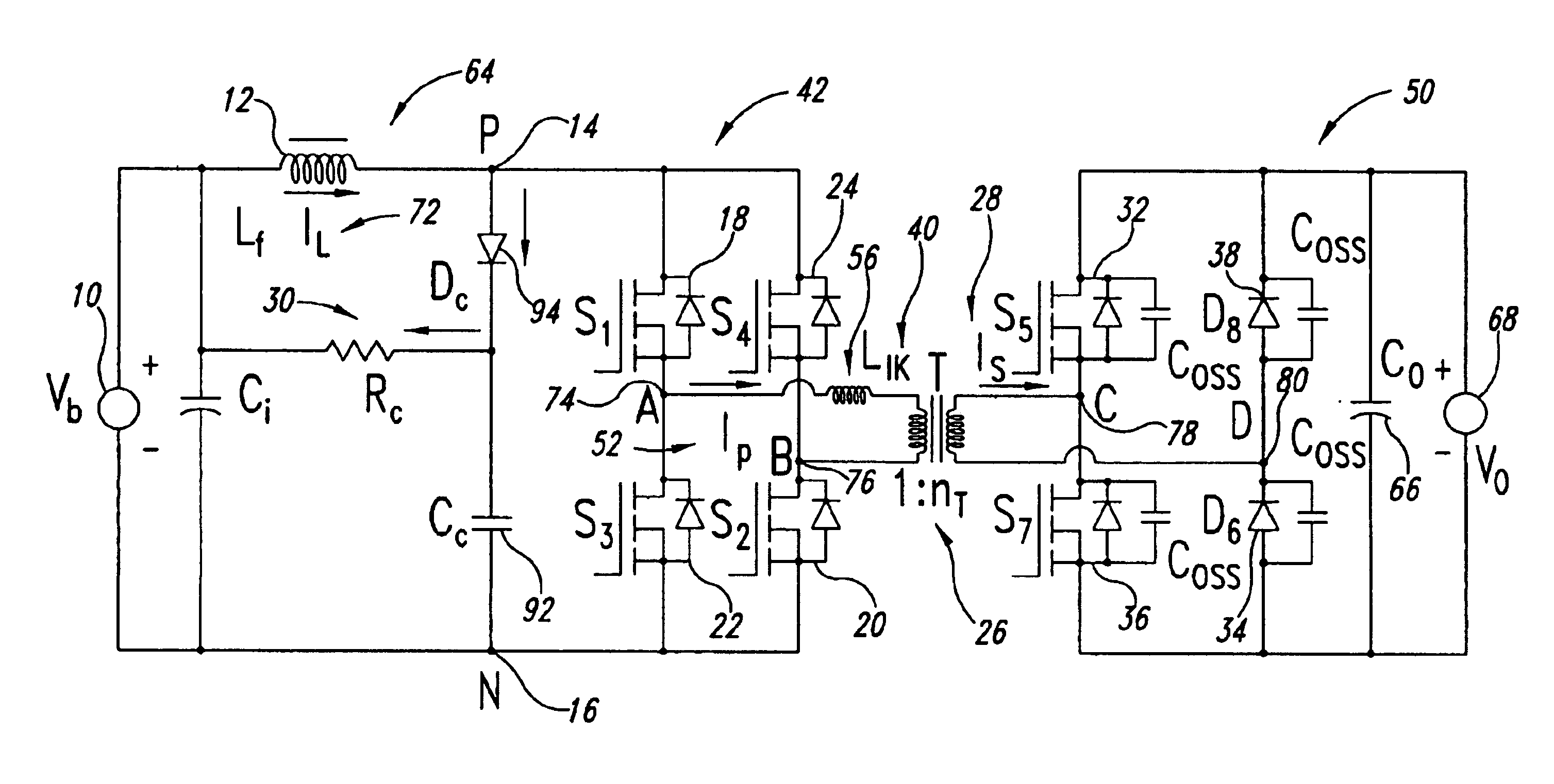
Accelerated commutation for passive clamp isolated boost converters
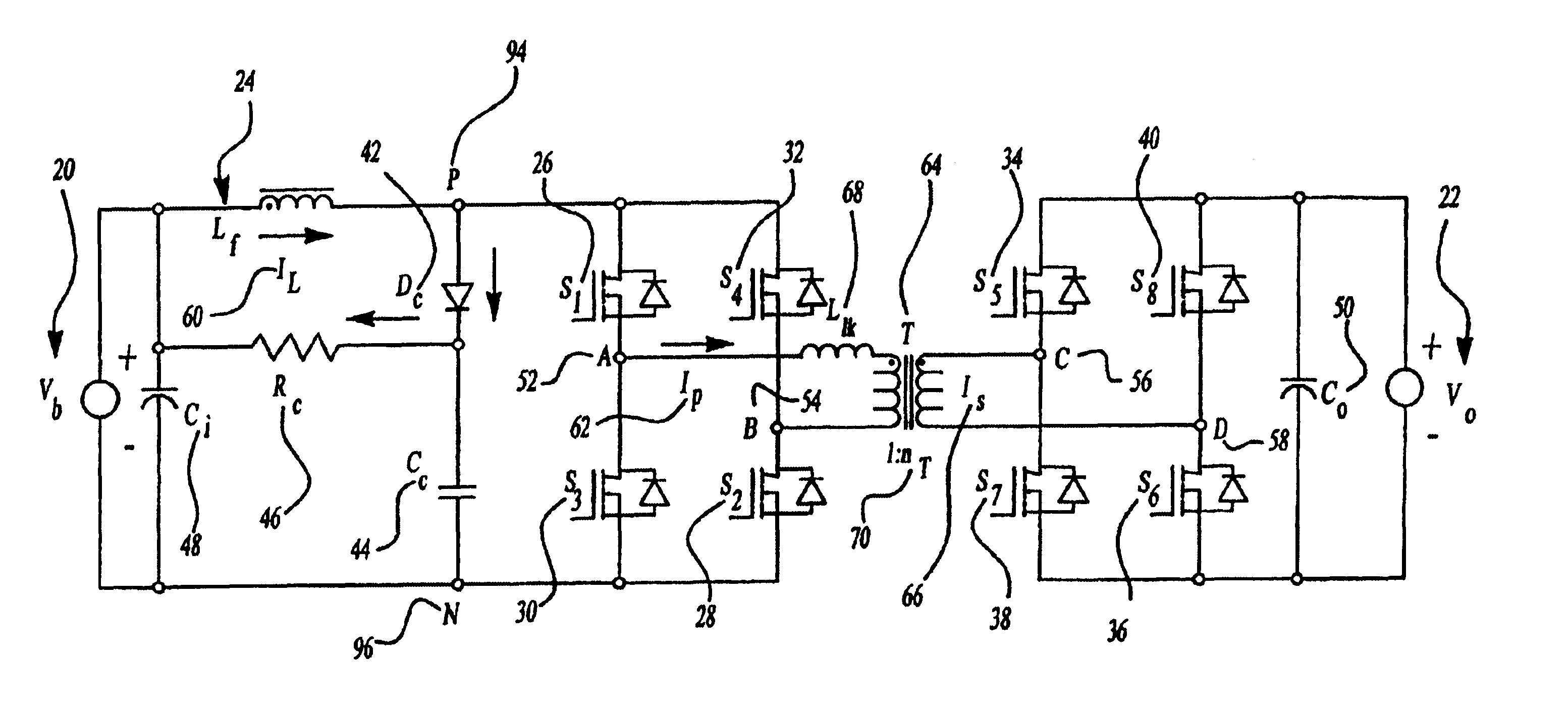
InactiveUS6876556B2Efficient and cost-effectiveImprove efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsVoltage spikeBuck converter
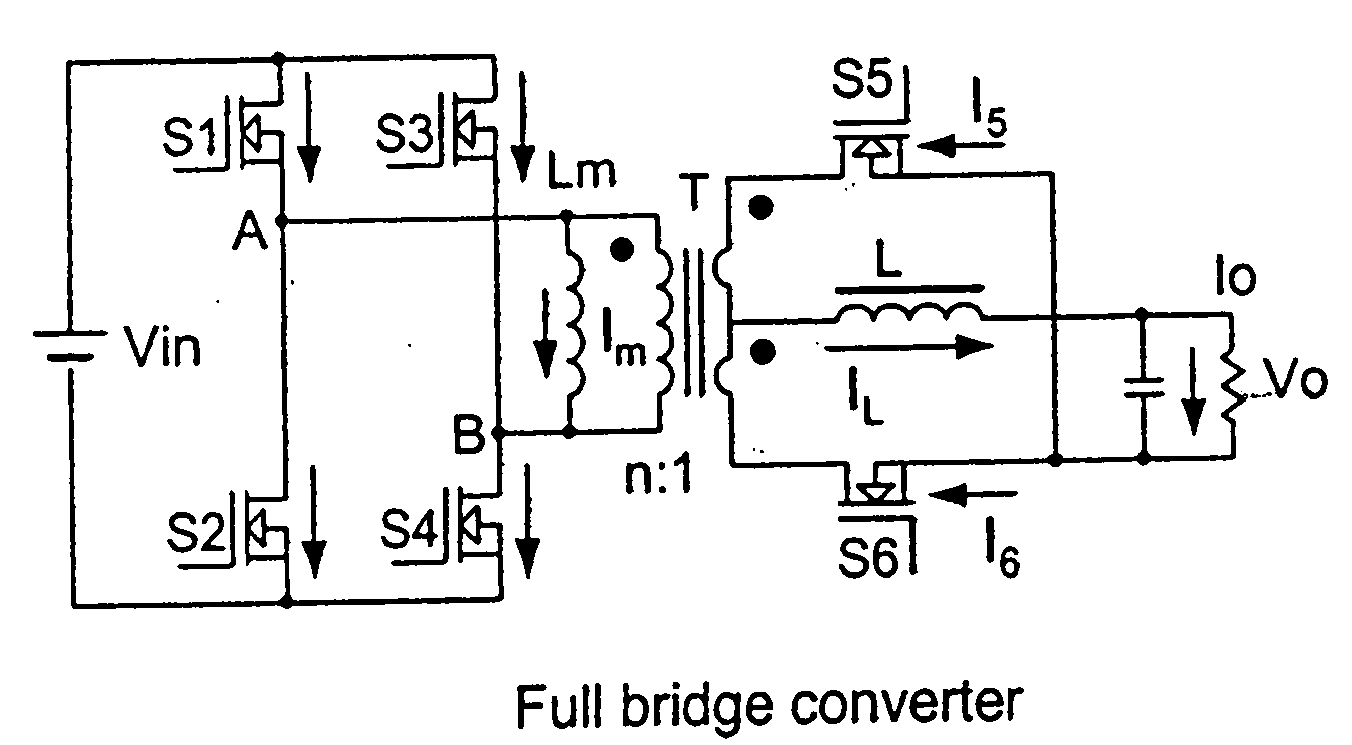
An efficient and cost effective bidirectional DC / DC converter reduces switch voltage stress via accelerated commutation allowing use of a low-cost passive clamp circuit in boost mode. The converter includes a primary circuit, transformer and secondary circuit. The primary circuit takes the form of a “full bridge converter,” a “push-pull converter,” or an “L-type converter.”. The primary circuit may include a dissipator such as a snubber circuit or small buck converter. A secondary side of the transformer is momentarily shorted by the secondary circuit by, for example, turning on at least two switches in the secondary circuit simultaneously for a minimal calibratable period when a pair of primary circuit controllers turn off to protect the primary circuit switches from voltage spikes during switching conditions.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
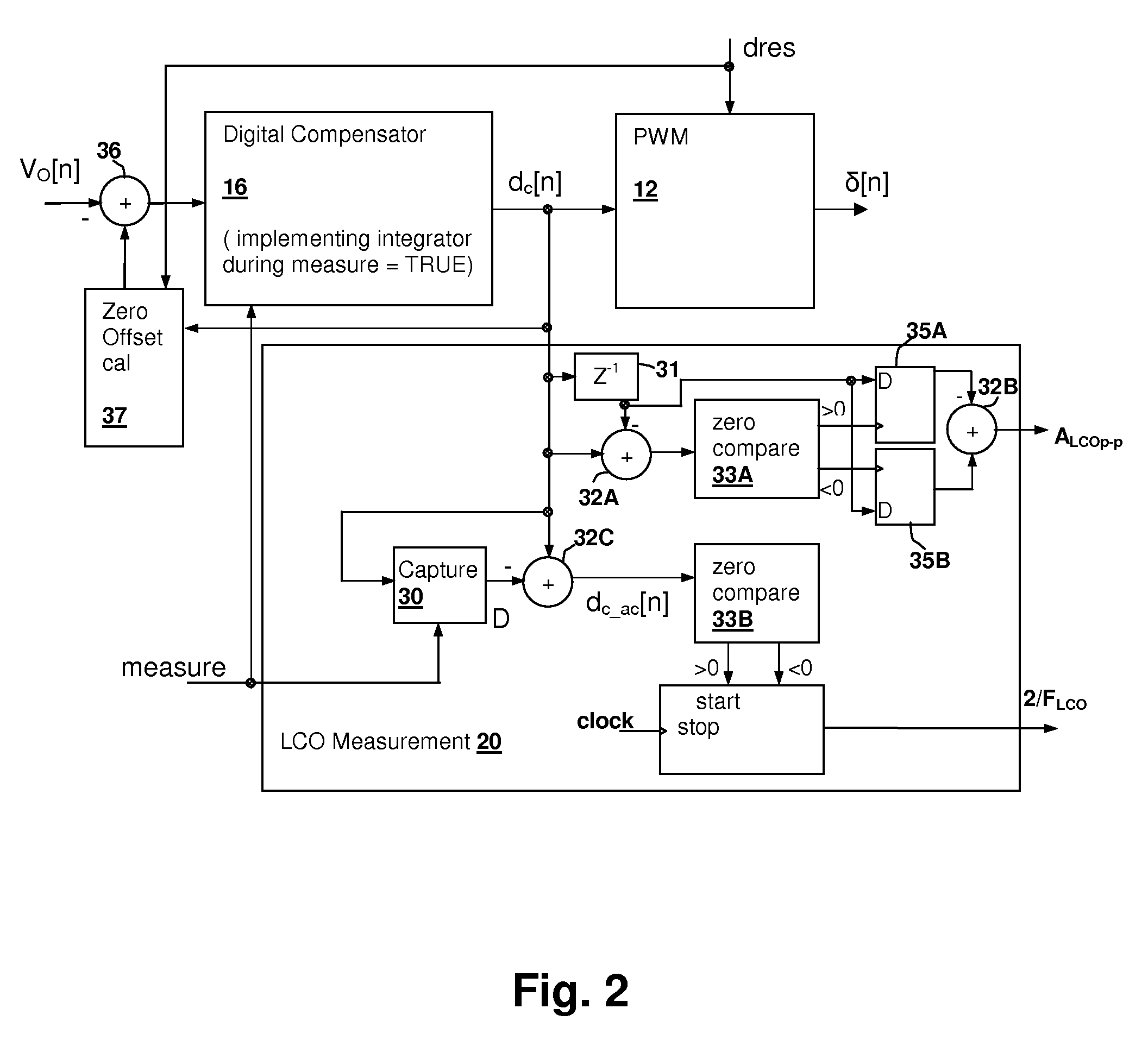
Switch-mode power supply (SMPS) with auto-tuning using limit-cycle oscillation response evaluation
A switch-mode power supply (SMPS) with auto-tuning using limit-cycle oscillation response evaluation provides optimized performance with reduced capacitance and inductance requirements for a given design. During operation of the SMPS, parameters of the converter are extracted, and the feedback and / or feed-forward compensation is adjusted to either hold the loop bandwidth of the converter near the critical bandwidth of the output capacitors, or maintain output voltage transients within a specified limit. The compensator response is either periodically updated, or is updated in response to an event, such as detection of a transient voltage spike having a characteristic that exceeds one or more predetermined thresholds.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
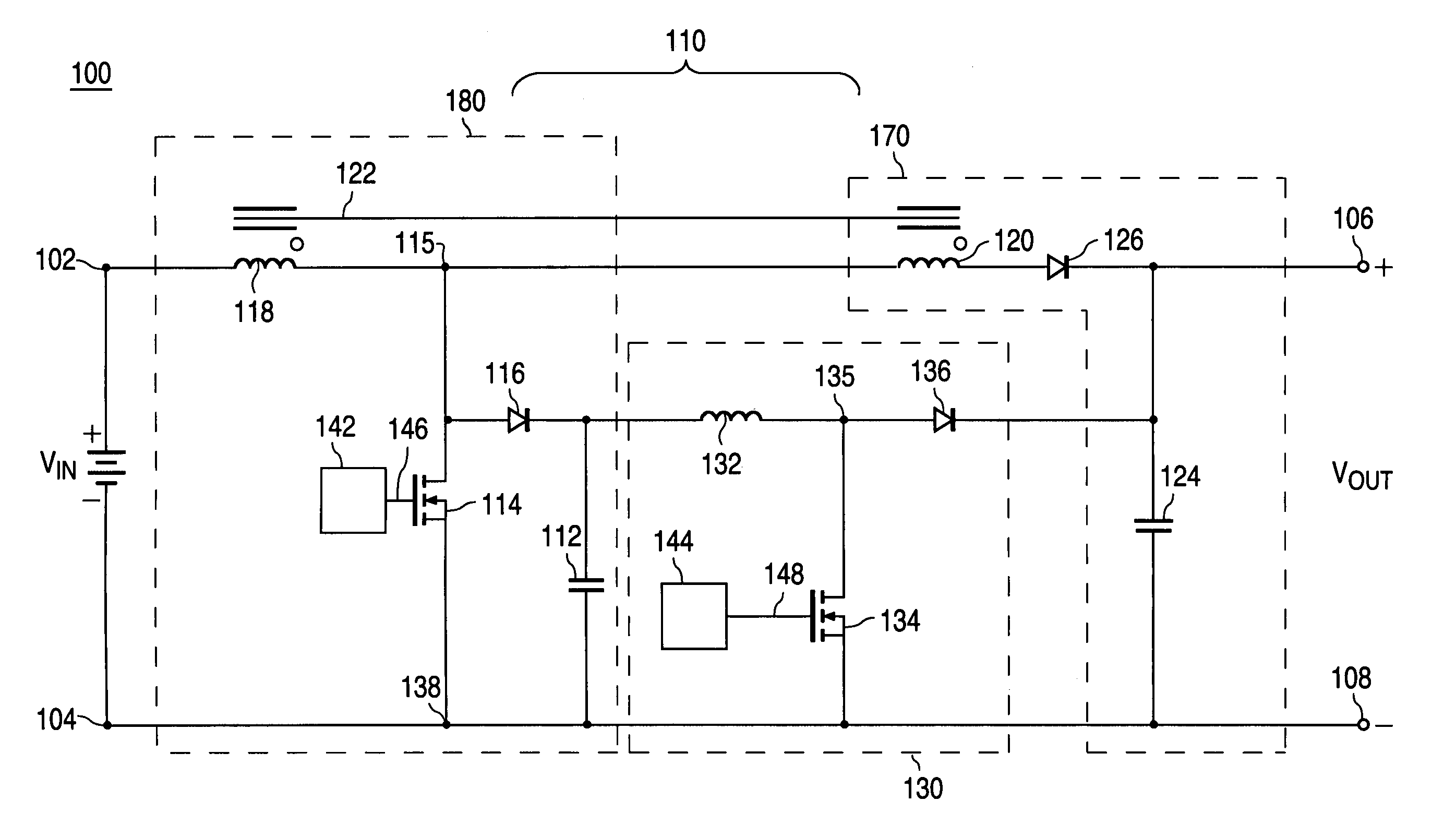
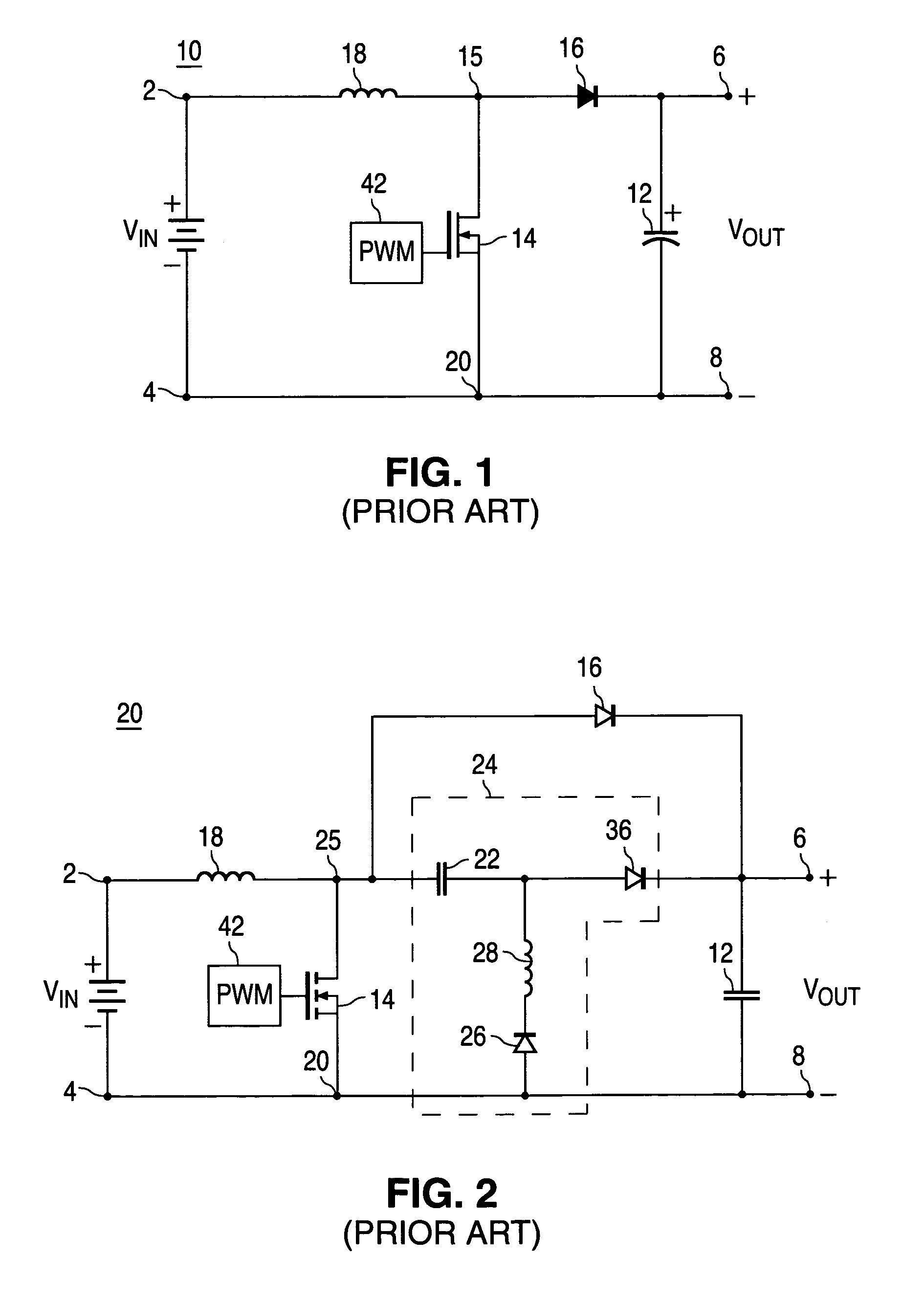
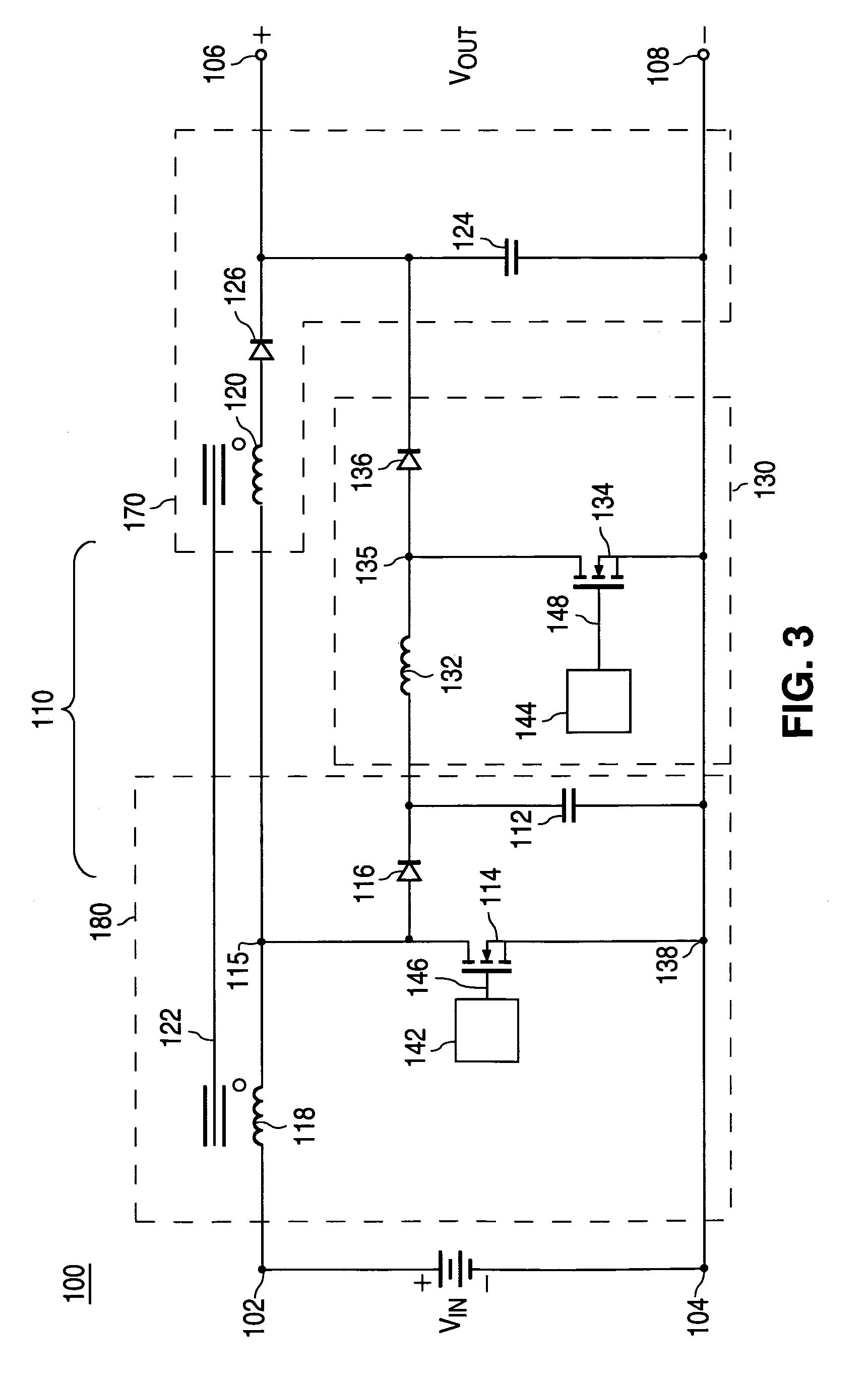
Two stage boost converter topology
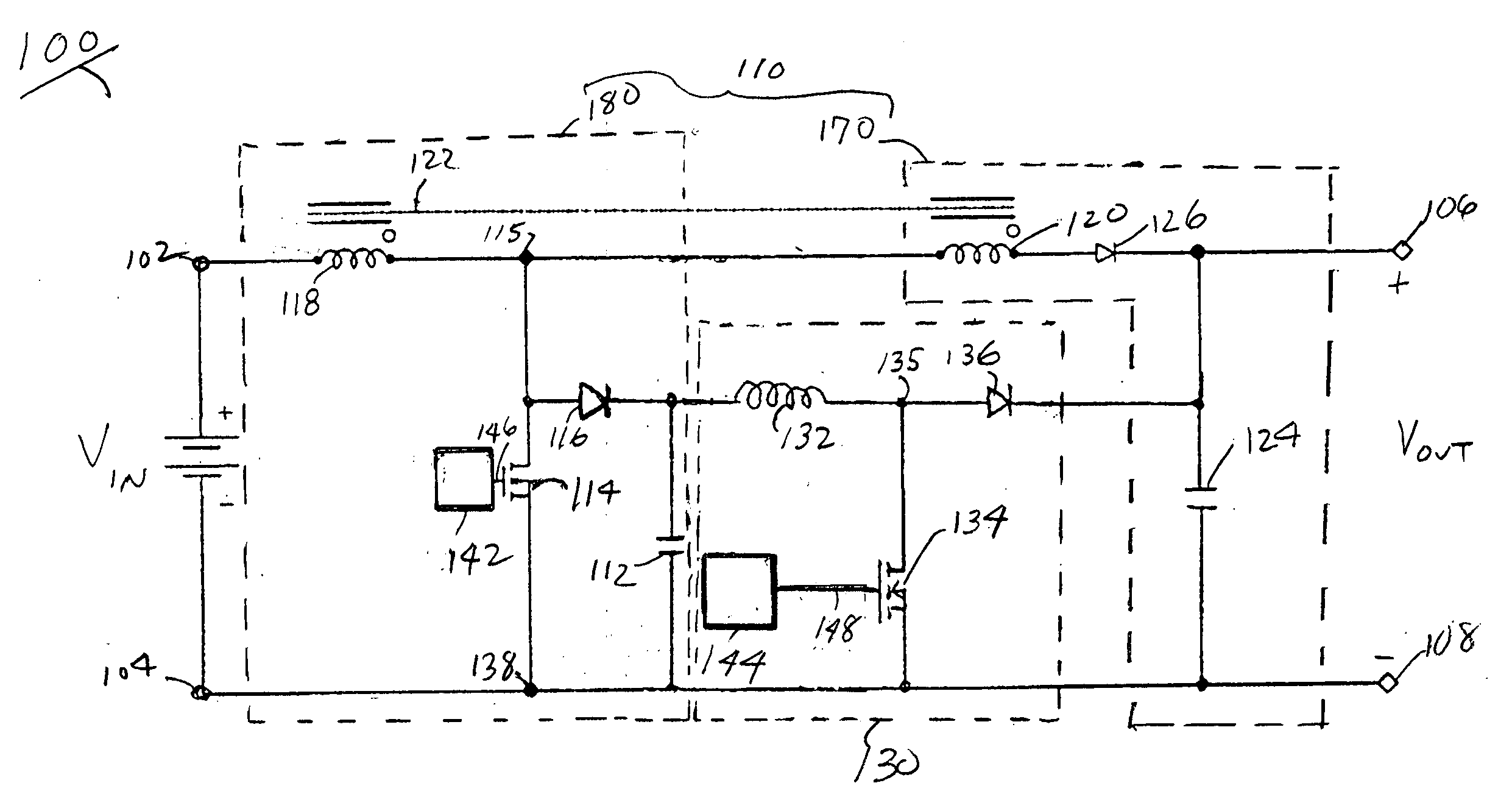
ActiveUS7023186B2Reduce voltageSmall and less-costlyDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationMOSFETVoltage spike
A power converter having a two stage boost circuit and a small boost converter. The main power flow for the power converter is via the two stage booster circuit having a single switch. The voltage spike of the switch is clamped by a diode and a capacitor. The energy at the capacitor is transferred to the power converter's output terminals by the small boost converter. The two stage boost converter topology enables the use of much lower voltage and Rdson MOSFET switches so as to reduce cost, switch conduction loss and turn on loss.
Owner:ASTEC INT LTD
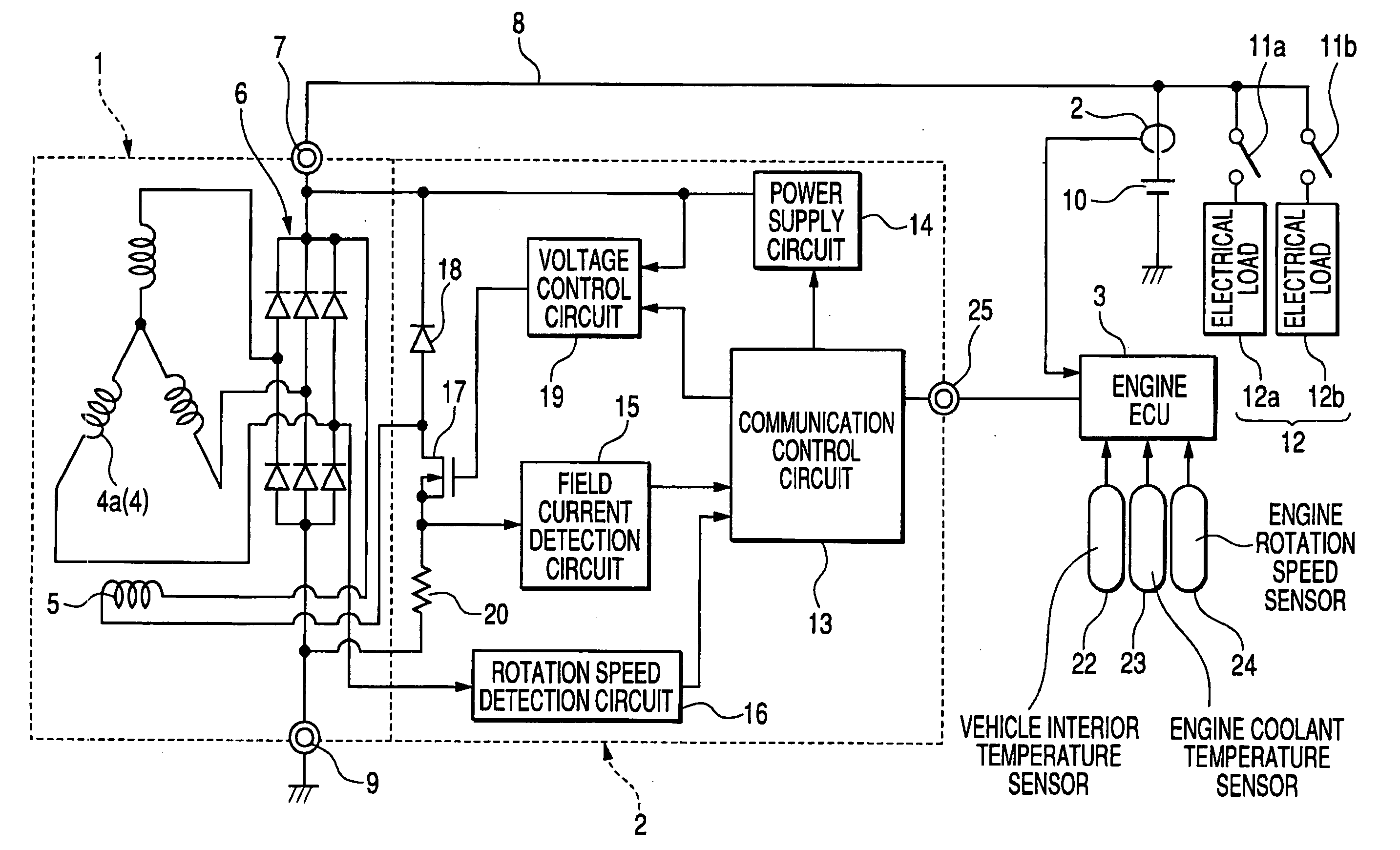
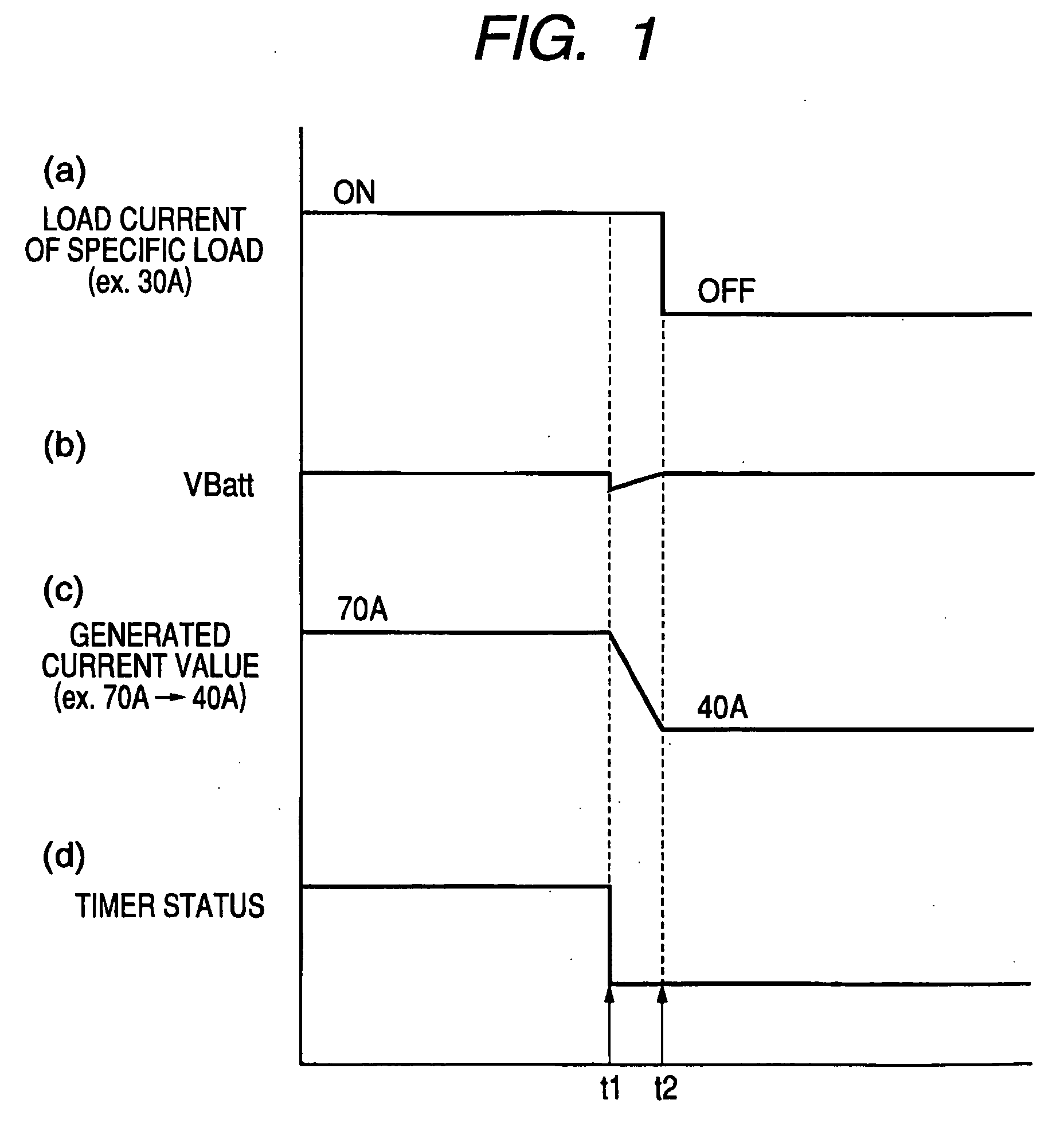
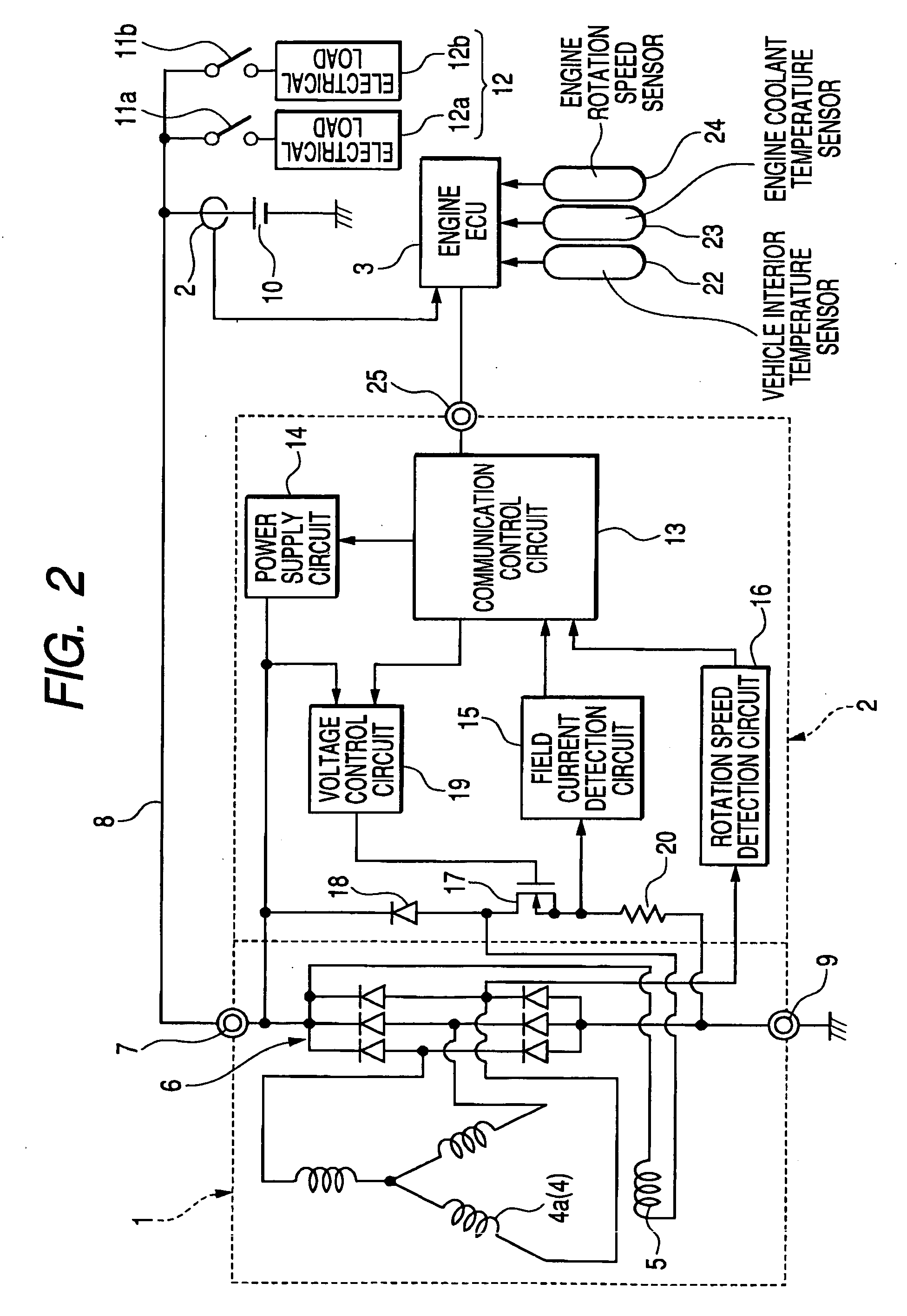
Vehicle-mounted electrical generator control system enabling suppression of supply voltage spikes that result from disconnecting electrical loads
ActiveUS20050269880A1Avoid voltage spikesTotal current dropBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric devicesElectricityVoltage spike
A vehicle generator control system detects a time point at which an electrical load is to be disconnected from the generator output, with the detection being achieved prior to that disconnection time point, and initiates a lowering of the generated current of the generator by an amount equal to the load current of that electrical load. The generated current of the generator is thereby reduced, by the time of the disconnection, to a value whereby substantially no voltage spike is produced in the generator output voltage.
Owner:DENSO CORP
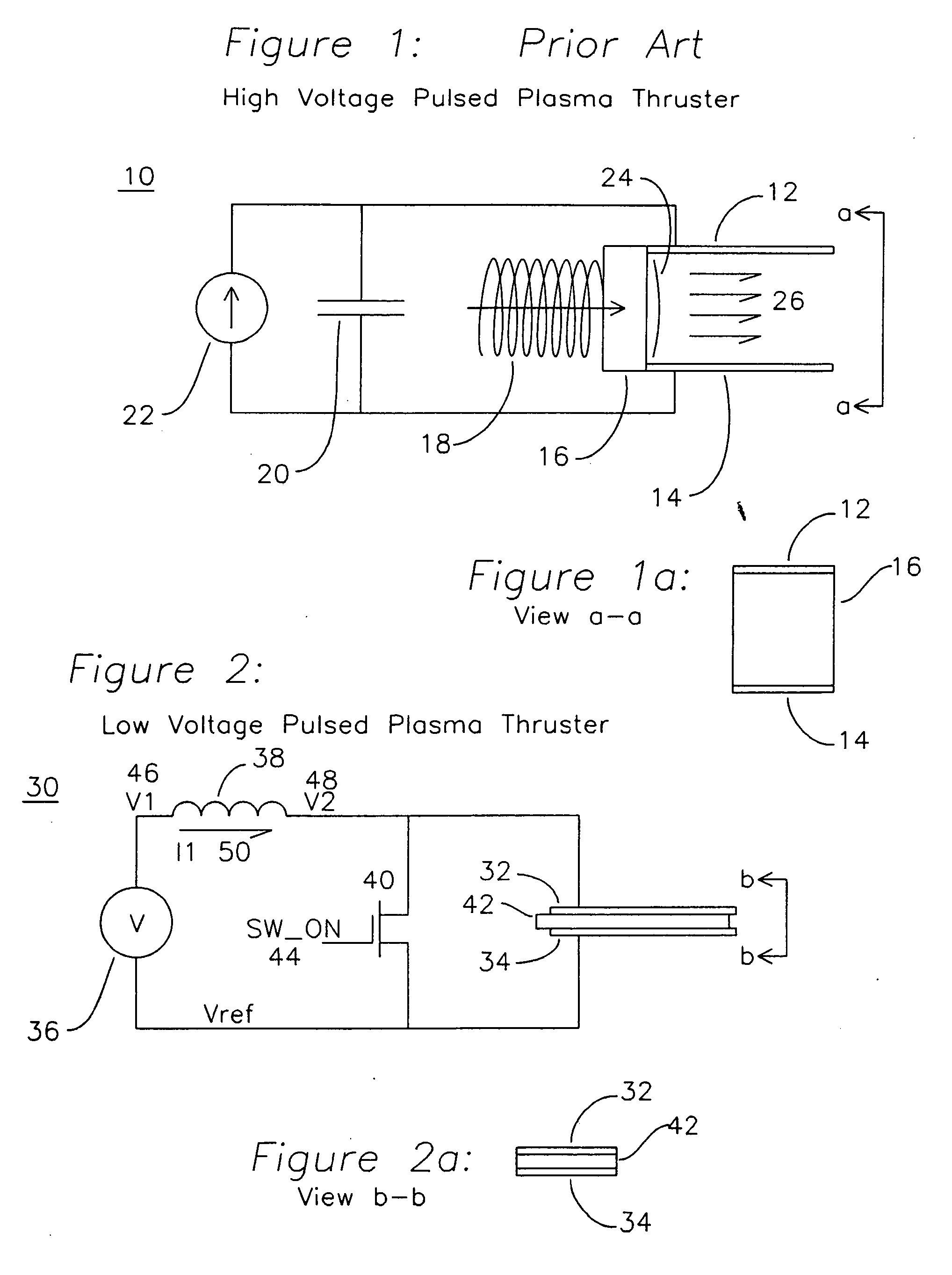
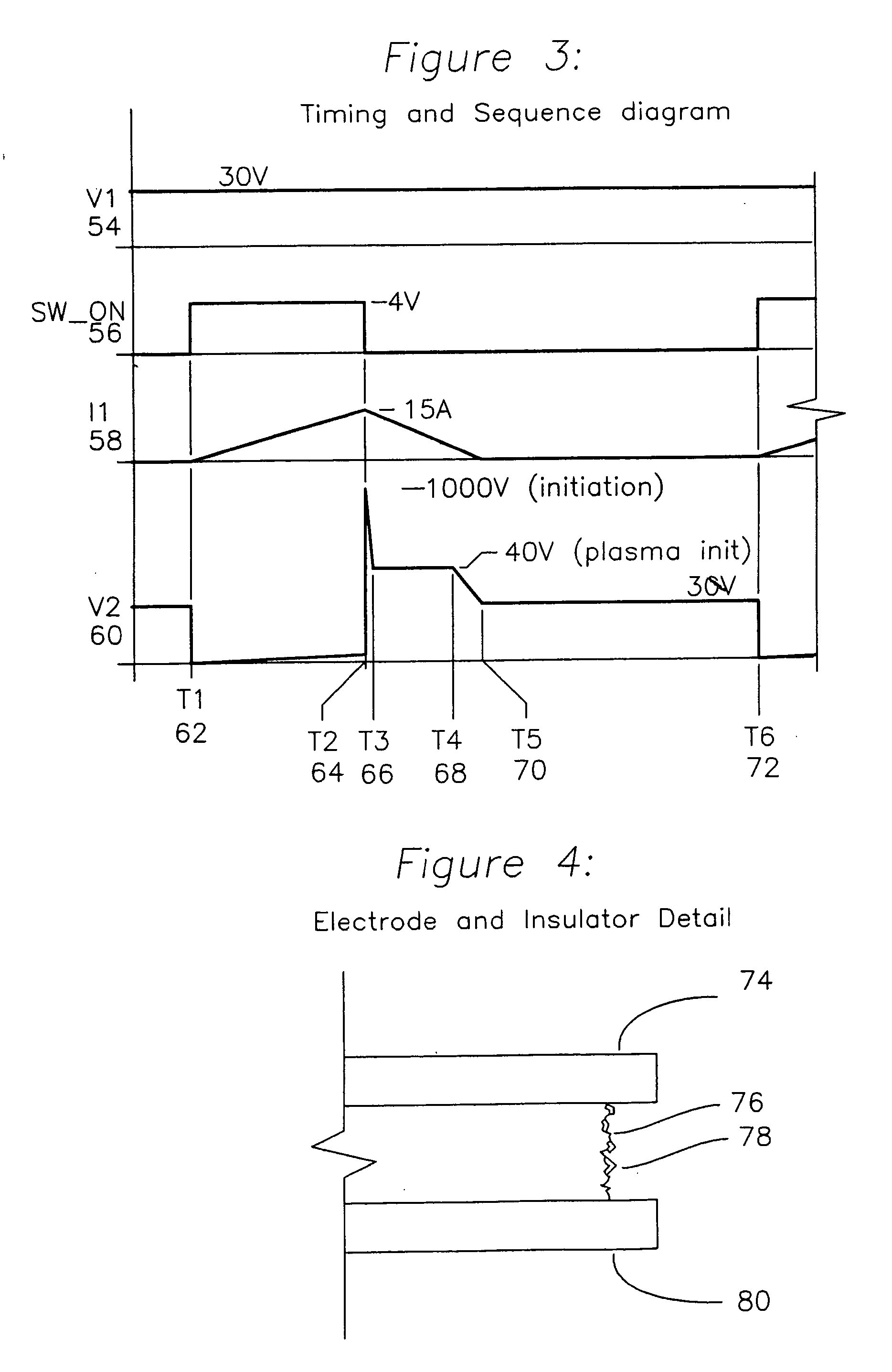
Vacuum arc plasma thrusters with inductive energy storage driver
InactiveUS20070045248A1Effective “ throttle ”High resistivityArc welding apparatusMachines/enginesVoltage spikeLow voltage
An apparatus for producing a vacuum arc plasma source device using a low mass, compact inductive energy storage circuit powered by a low voltage DC supply acts as a vacuum arc plasma thruster. An inductor is charged through a switch, subsequently the switch is opened and a voltage spike of Ldi / dt is produced initiating plasma across a resistive path separating anode and cathode. The plasma is subsequently maintained by energy stored in the inductor. Plasma is produced from cathode material, which allows for any electrically conductive material to be used. A planar structure, a tubular structure, and a coaxial structure allow for consumption of cathode material feed and thereby long lifetime of the thruster for long durations of time.
Owner:KRISHNAN MAHADEVAN
Dual bridge matrix converter
ActiveUS20050099829A1Reduce and eliminate high voltage spikeSmall and inexpensiveConversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc circuit to reduce harmonics/ripplesMatrix convertersClamp capacitor
A dual bridge matrix converter has a line-side converter with controllable switches that receives AC power and provides unidirectional power to high and low DC link lines, and a load-side converter which receives the power from the DC link lines and provides AC power to output lines. A clamp circuit is connected across the DC link lines and includes a series connected diode and a capacitor. Negative DC link current will be conducted through the clamp diode to charge the clamp capacitor to avoid voltage spikes on the DC link lines. A controllable switch may be connected in parallel with the clamp diode and is turned on when the voltage across the clamp capacitor is above a threshold that is greater than the normal peak-to-peak AC input voltage. The switch is turned off when the voltage across the clamp capacitor is lower than the threshold voltage.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
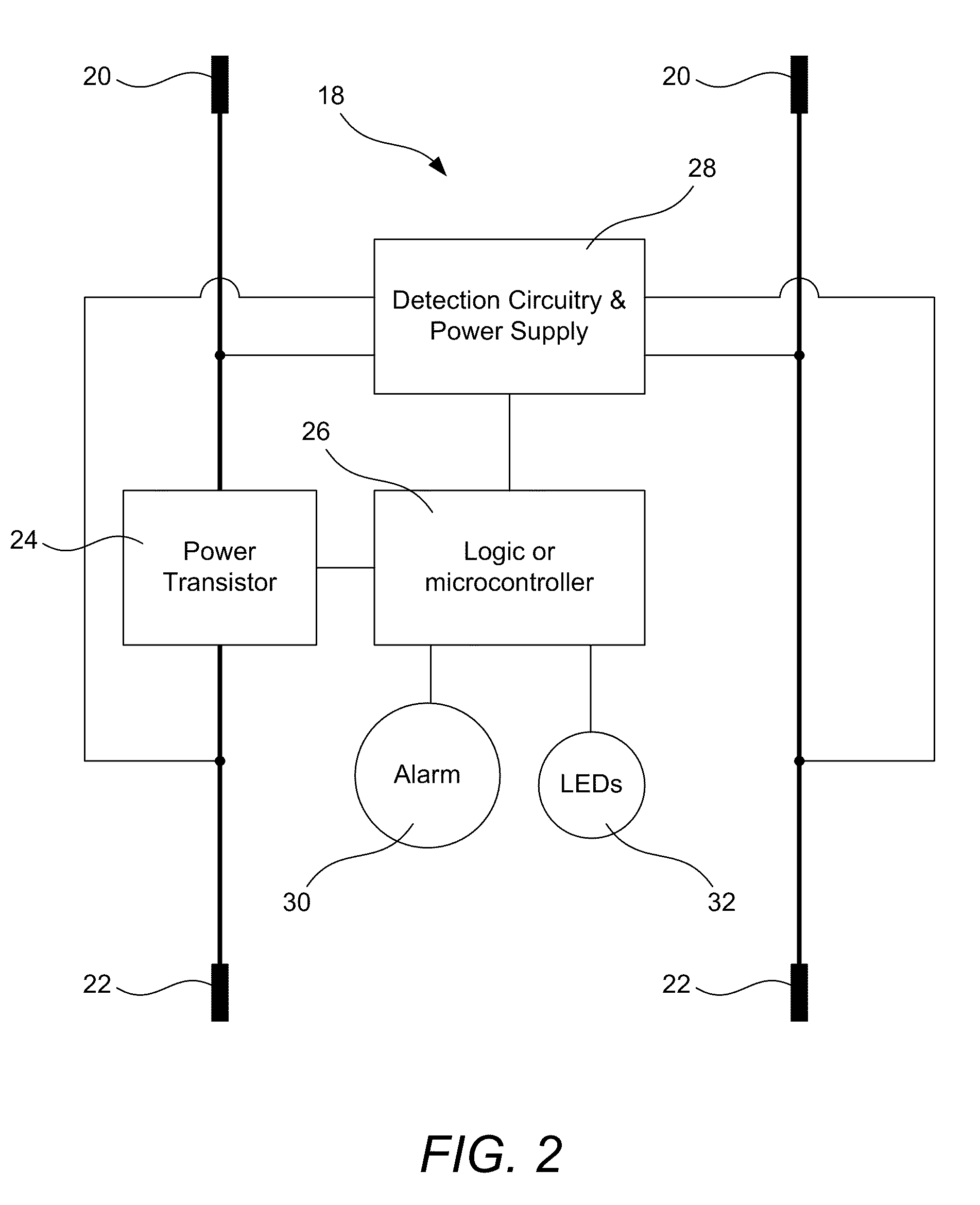
Low-voltage connection with safety circuit and method for determining proper connection polarity
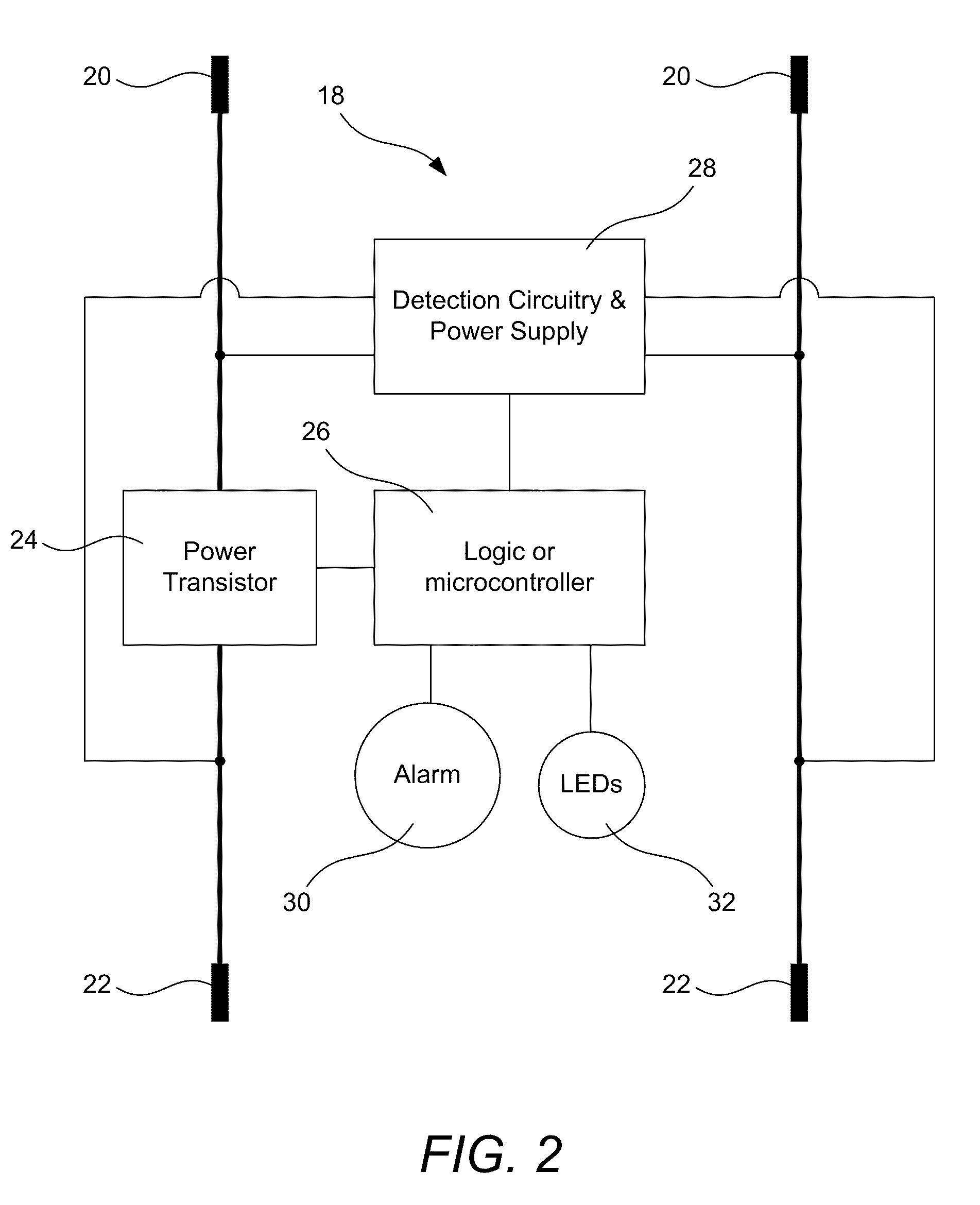
InactiveUS8199024B2Reduces and prevents damageReduces and prevents voltage spikeCoupling device detailsEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionVoltage spikeUnsafe condition
A safety circuit used in low-voltage connecting systems leaves the two low-voltage systems disconnected until it determines that it is safe to make a connection. When the safety circuit determines that no unsafe conditions exist and that it is safe to connect the two low-voltage systems, the safety circuit may connect the two systems by way of a “soft start” that provides a connection between the two systems over a period of time that reduces or prevents inductive voltage spikes on one or more of the low-voltage systems. When one of the low-voltage systems has a completely-discharged battery incorporated into it, a method is used for detection of proper polarity of the connections between the low-voltage systems. The polarity of the discharged battery is determined by passing one or more test currents through it and determining whether a corresponding voltage rise is observed.
Owner:ENERGY SAFE TECH
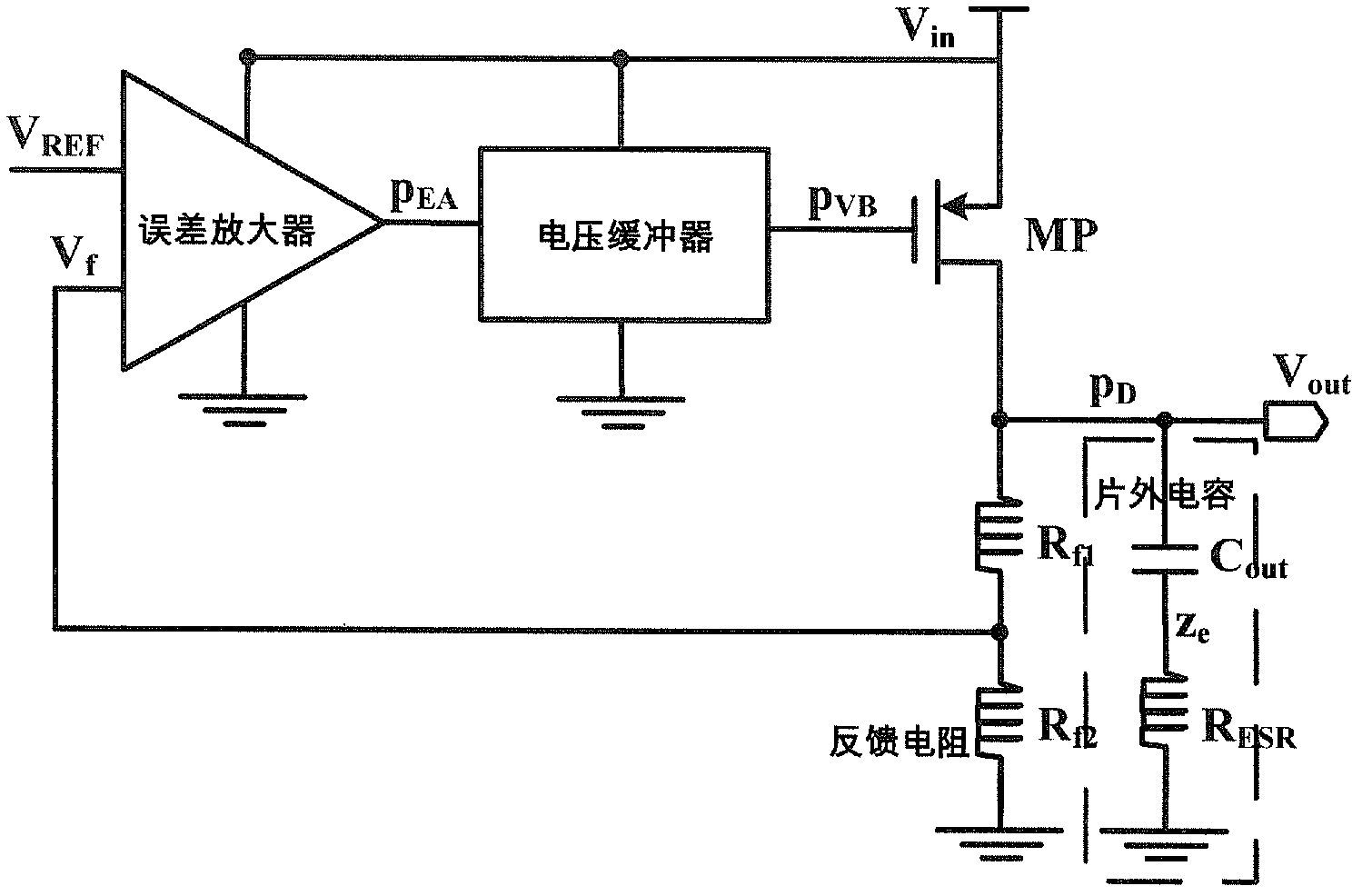
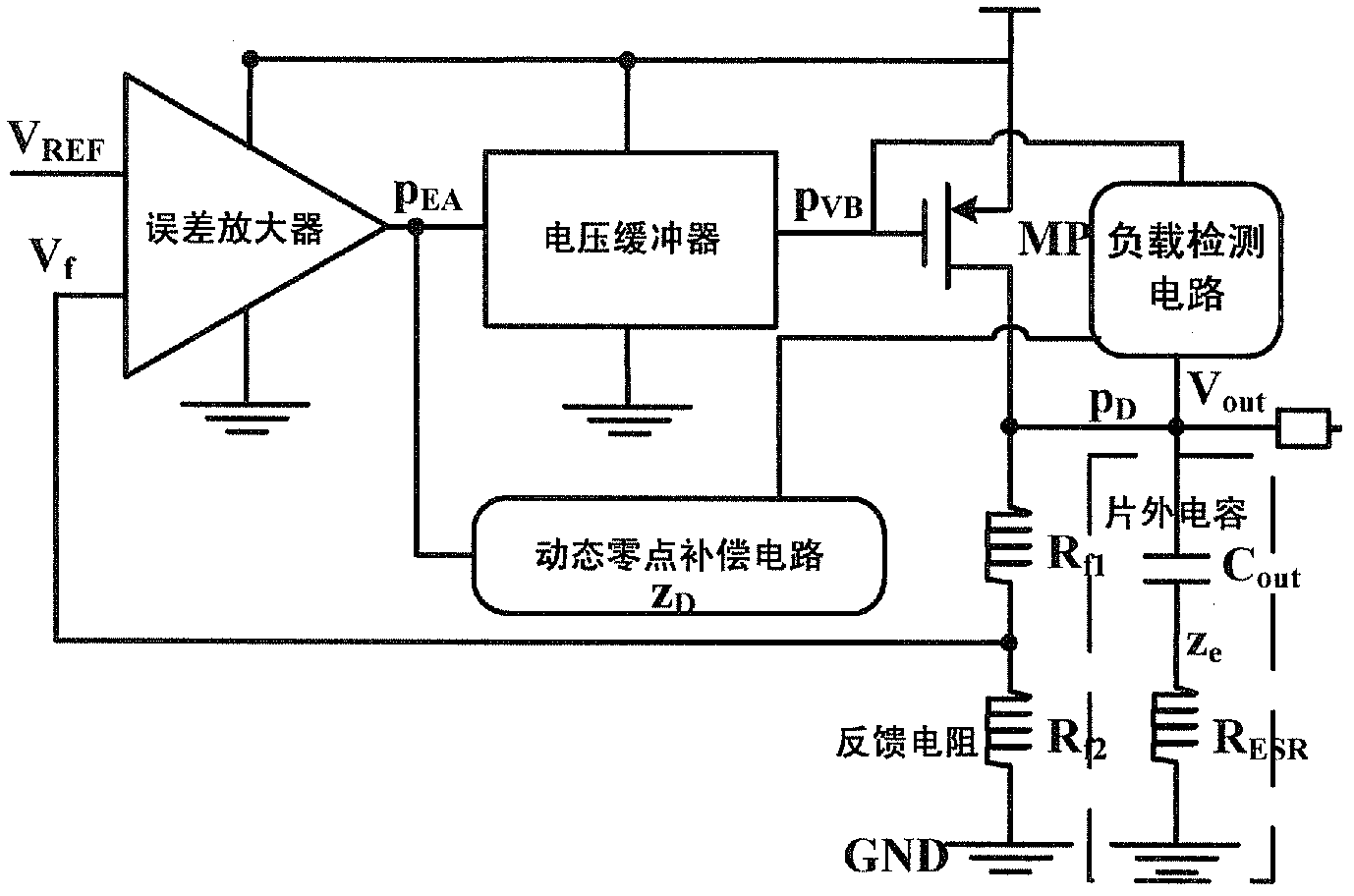
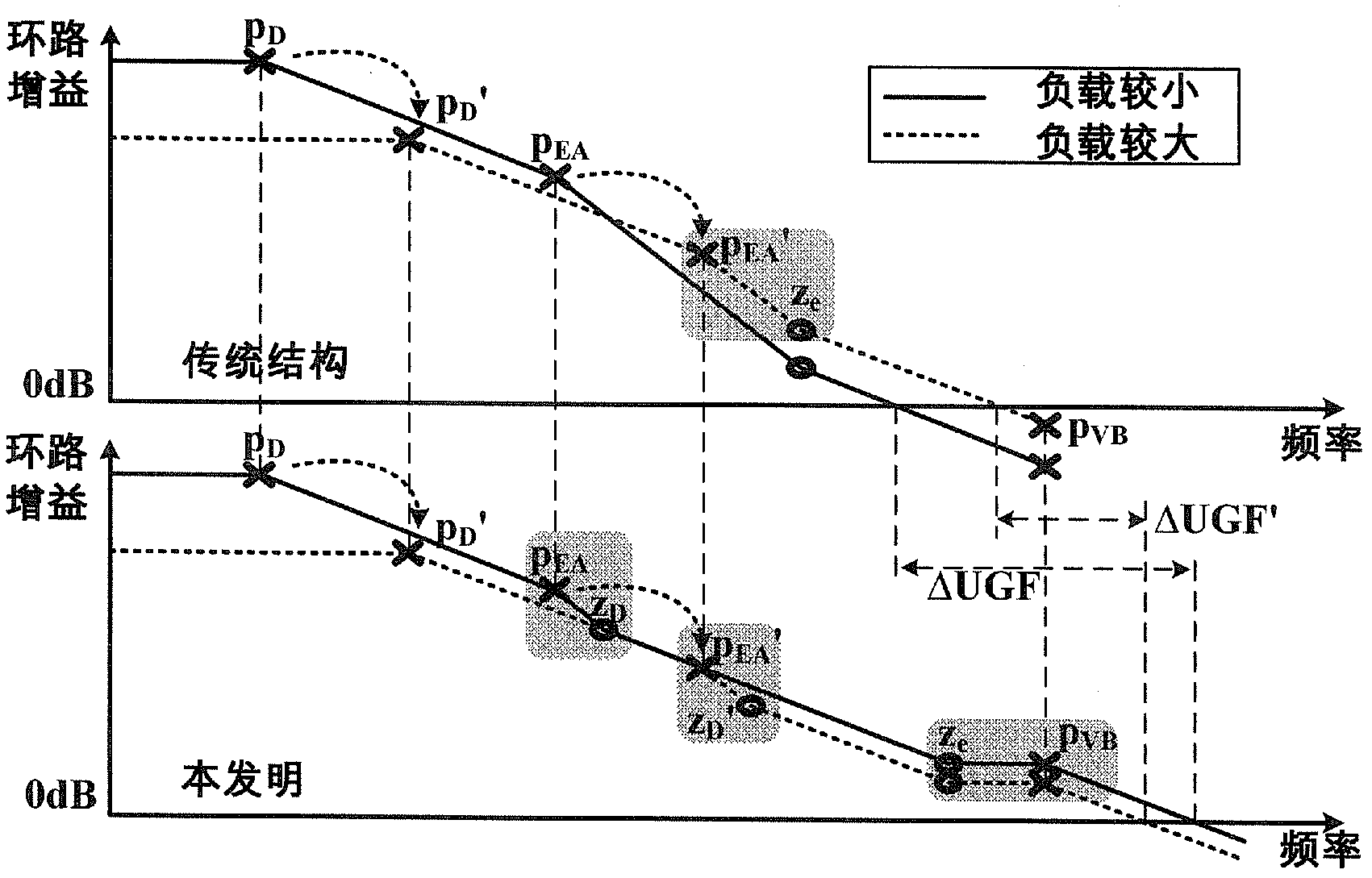
Linear voltage regulator with load detection circuit and dynamic zero compensation circuit
InactiveCN103105883AImprove transient response performanceNo effect on current efficiencyElectric variable regulationElectrical resistance and conductanceVoltage spike
The invention discloses a linear voltage regulator with a load detection circuit and a dynamic zero compensation circuit. The linear voltage regulator comprises an error amplifier, a voltage bumper, a power tube P-channel metal oxide semiconductor (PMOS), a first feedback resistance Rf1, a second feedback resistance Rf2, a load detection circuit and a dynamic zero compensation circuit, the load detection circuit is connected between an output end of the low-dropout linear voltage regulator and the voltage bumper, and the dynamic zero compensation circuit is connected between the output end of the low-dropout linear voltage regulator and the error amplifier. The load detection circuit is used for detecting the change of the load current, and then the load detection circuit controls the dynamic zero compensation circuit to produce dynamic zero zD to track and compensate a first non-dominant pole pEA of the linear voltage regulator. The dynamic compensation technology enables the low-dropout linear voltage regulator to have a better transient response performance and a smaller voltage spike for the load change compared with conventional structures. The load detection circuit and the dynamic zero compensation circuit have no static power consumption and no influence for the current efficiency of the whole low-dropout linear voltage regulator.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Clamping circuit and method for synchronous rectification
InactiveUS6128206ASuppress high voltage spikeReduce peak voltageAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionVoltage spikeTransformer
A rectifier circuit having voltage clamping circuitry is disclosed. The rectifier circuit includes a transformer having a primary winding and a secondary winding and transistor switches each being connected to an end of the secondary winding of the transformer. The rectifier circuit further includes a first diode having an anode terminal connected to a first end of the secondary winding and a second diode having an anode terminal connected to a second end of the secondary winding. The cathode terminals of the first and second diodes are coupled to a capacitor. The energy stemming from voltage spikes and / or high frequency ringing appearing at the transistor switches due to parasitic effects is effectively absorbed by the first and second diodes and collected in the capacitor. The collected energy is recycled to control the operation of the transistor switches.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
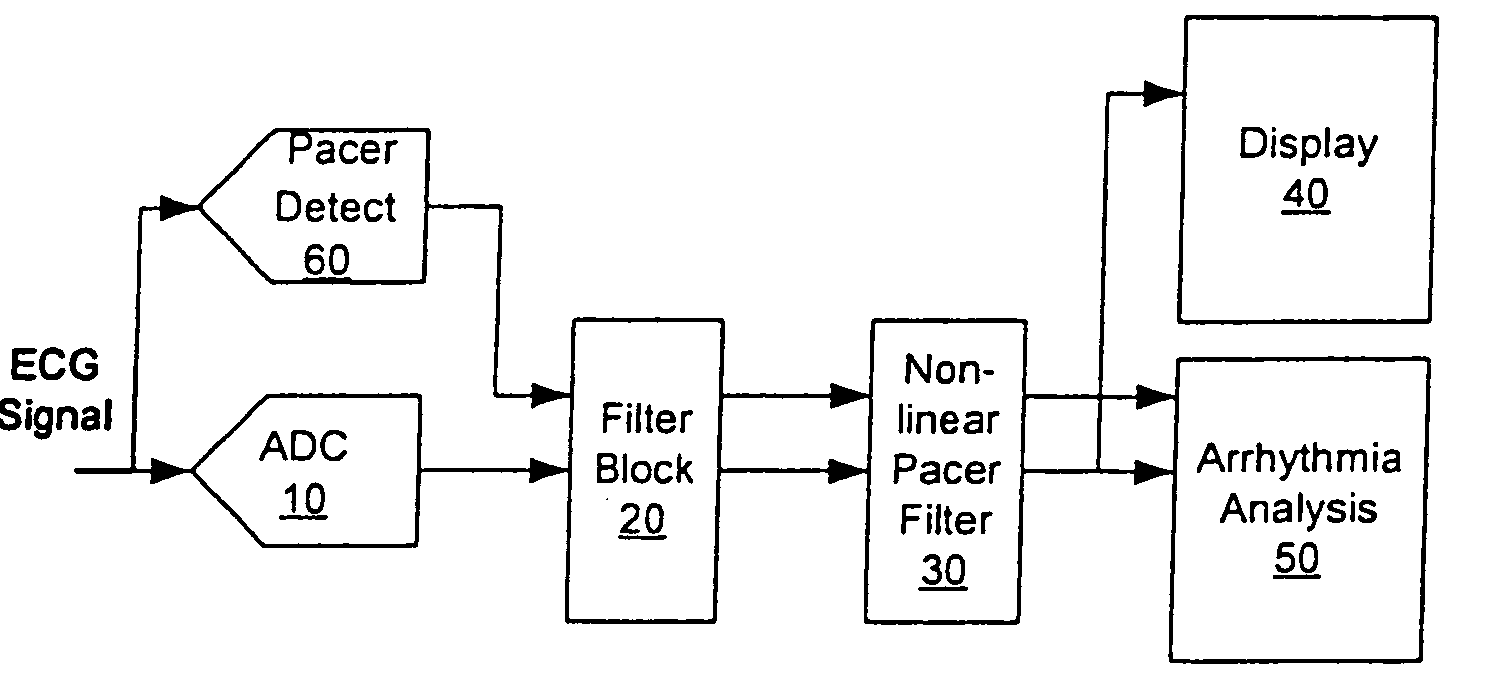
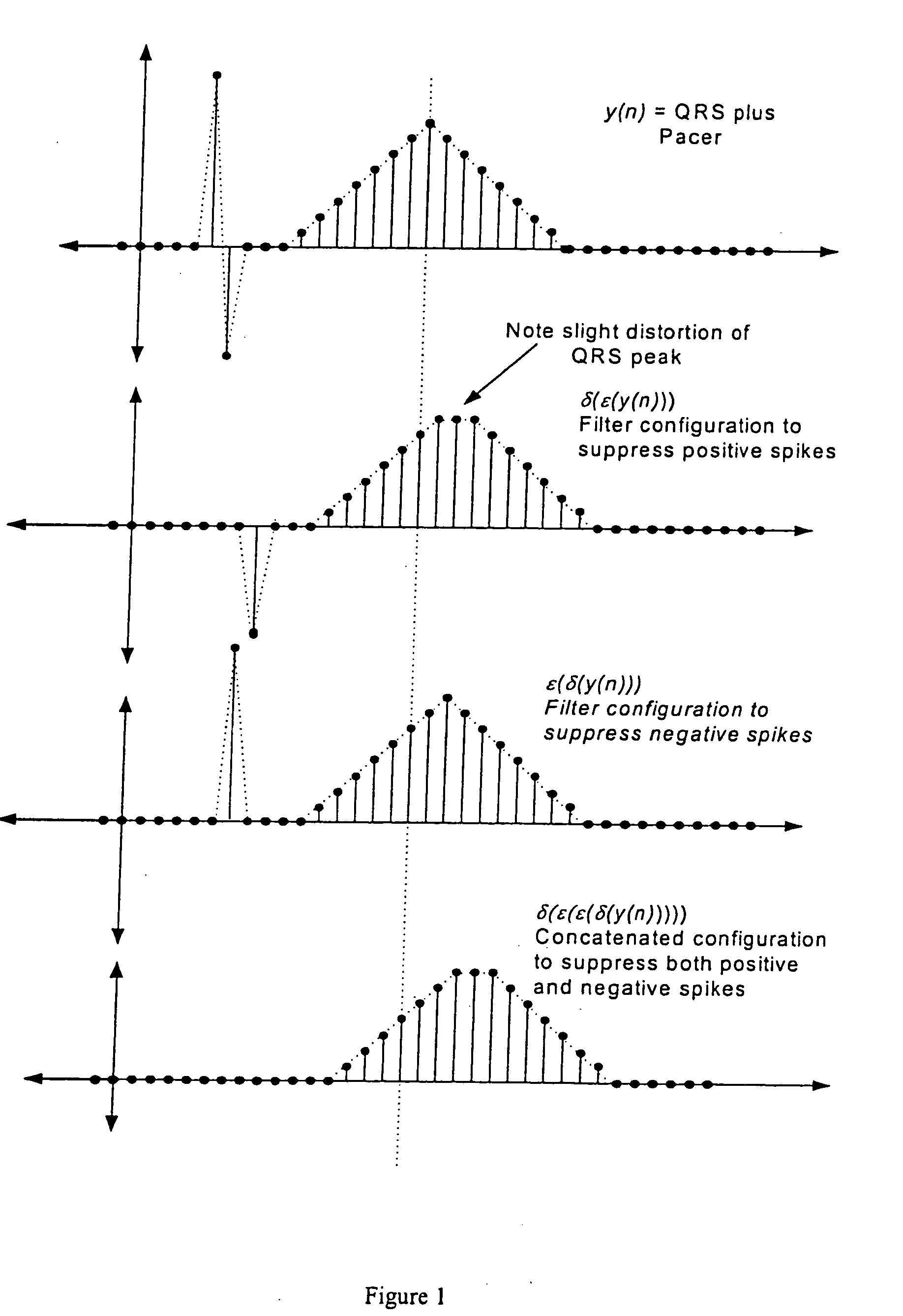
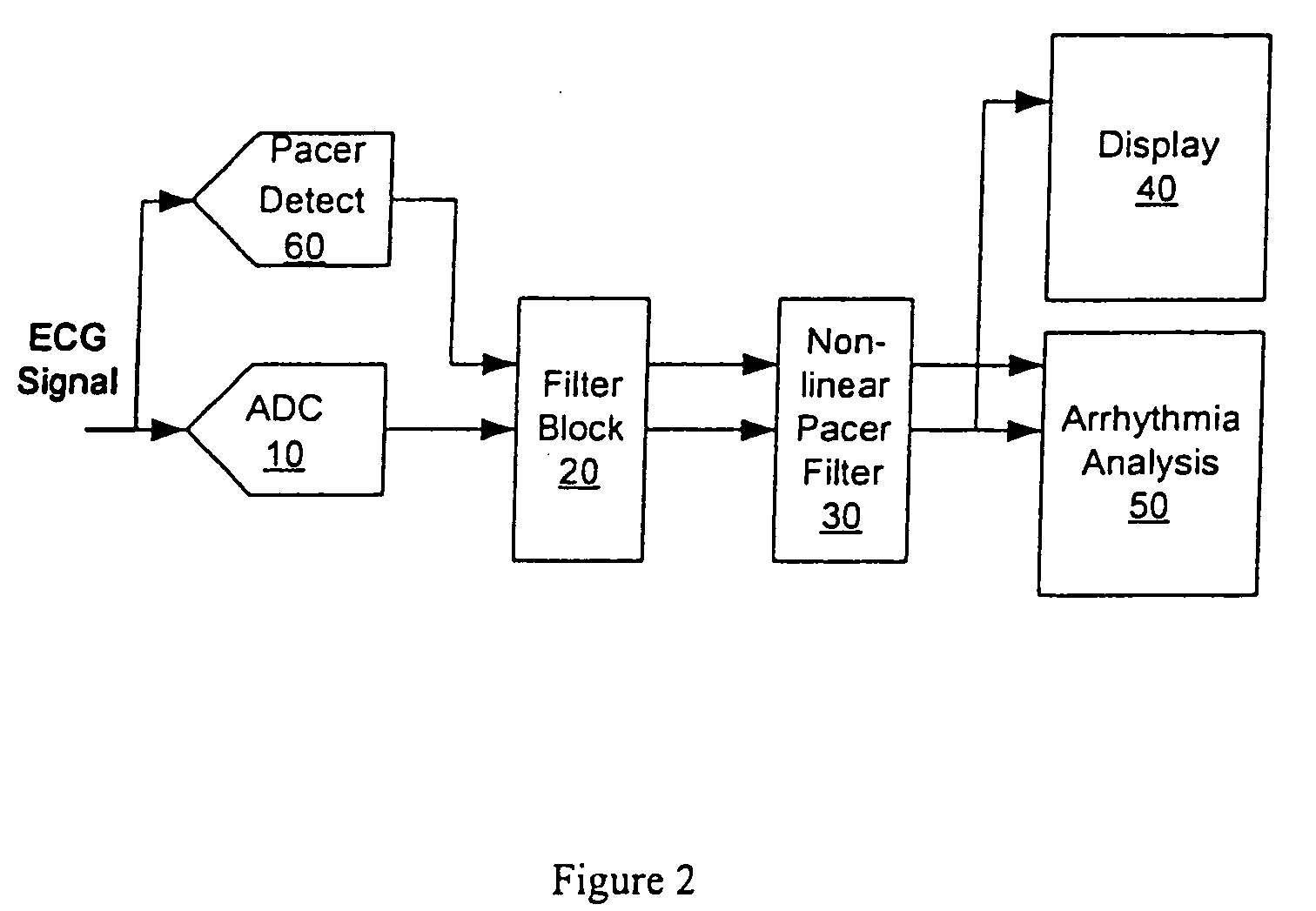
Nonlinear method and apparatus for electrocardiogram pacemaker signal filtering
InactiveUS20050234361A1Overcome limitationsProvide benefitsElectrocardiographyDigital technique networkNonlinear methodsEcg signal
Signal “peak” and “valley” removal properties of mathematical morphology operators are exploited in a method and apparatus for detecting, removing, or improving fidelity of pacemaker signal components of the Electrocardiogram (ECG) at sampling rates well below the pacemaker signal Nyquist rate. The method works for the wide variability in pacemaker signal amplitude, width, firing frequency, and other characteristics encountered in practice, and it works for malfunctioning pacemakers that may fire at any point relative to the QRS complex of the ECG signal. Filtering operations require minimal digital storage and are computationally inexpensive (no multiplications), mainly involving “maximum” and “minimum” type signal detections over a finite time history of the input signal. This implies that the method can be inexpensively implemented on small instruments in either hardware or software. The method may also be used to estimate the height and polarity of the pacemaker voltage spike, even though the base sampling period may be longer than the width of the spike.
Owner:WELCH ALLYN INC
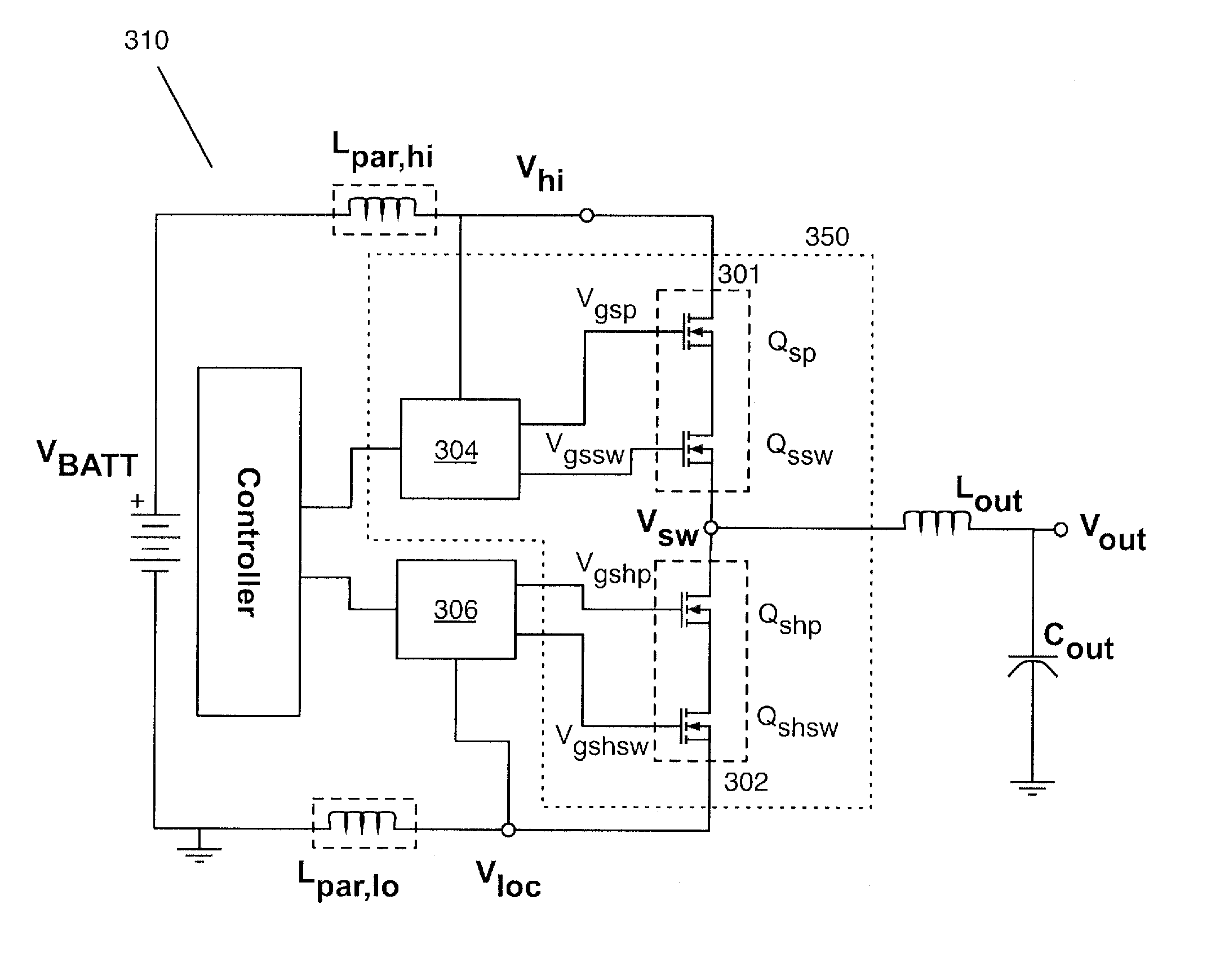
Over Voltage Protection of a Switching Converter
Embodiments for at least one method and apparatus of generating a regulated voltage are disclosed. One apparatus includes a voltage regulator. The voltage regulator includes regulator circuitry for generating a regulated voltage from a first power supply and a second power supply, and voltage spike protection circuitry for voltage-spike-protecting the regulator circuitry, wherein the voltage spike protection circuitry includes a dissipative element and a charge-storage circuit. One method includes a method of generating a regulated voltage. The method includes regulator circuitry generating a regulated voltage from an input voltage, and voltage-spike-protecting the regulator circuitry with voltage spike protection circuitry, wherein the voltage spike protection circuitry includes a dissipative element and a charge-storage circuit.
Owner:R2 SEMICON
High-efficiency, overvoltage-protected, light-emitting semiconductor device
ActiveUS20070284606A1Improve efficiencyLess likely to breakSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesOvervoltageVoltage spike
An LED comprises a multilayered light-generating semiconductor region grown on one of a pair of opposite major surfaces of a semiconducting silicon substrate, a bonding pad overlying the light-generating semiconductor region and received in part in a cavity formed centrally therein, and a substrate electrode on the other major surface of the substrate. For protecting the LED from voltage spikes or like transients, an overvoltage protector such as a Schottky barrier diode is interposed between the bonding pad and the substrate. Further, for a uniform current distribution throughout the light-generating semiconductor region, a current-spreading film of electrically conducting, optically transparent material overlies the light-generating semiconductor region and itself covered by a transparent overlay of electrically insulating material. The bonding pad is electrically coupled to the current-spreading film via a plurality of connector strips extending radially from the pad over the transparent overlay. The connector strips have ribs depending therefrom and extending through radial slits in the transparent overlay into electrical contact with the current-spreading film.
Owner:SANKEN ELECTRIC CO LTD
Active clamping forward-flyback converter
ActiveCN101692595AReduce voltage stressIncrease profitApparatus with intermediate ac conversionElectric variable regulationCapacitanceVoltage spike
The invention discloses an active clamping forward-flyback converter, which is provided with a primary side clamping resonant circuit comprising a series branch consisting of a clamping switching tube and a primary side clamping capacitor, wherein the series branch is connected with an original-level winding of the primary side of an isolation transformer in parallel or is connected in serial between a start end of the original-level winding of the primary side of the isolation transformer and a negative terminal of a direct current power supply; and a contravariant switching tube works in a ZVS state, and a secondary rectification circuit is one of a forward-flyback working rectification loop and a flyback working rectification loop. The active clamping forward-flyback converter can enter two different operation modes to achieve a large adjustment range of input and output voltages, reduce reverse steady-state voltages and reverse recovery resonance voltage spikes of a primary side switching tube and a secondary rectifier diode and the voltage stress and the switching loss of the primary side switching tube, and improve the efficiency. The active clamping forward-flyback converter is particularly suitable to be widely applied in the occasions with a very wide input voltage fluctuation range and a wide and high output voltage, in which semiconductors cannot withstand high voltages.
Owner:SANTAK ELECTRONICS SHENZHEN
Methods of preparing and using electrostatically treated fluids
InactiveUS6974561B1Measurably betterIncrease crop yieldElectrolysis componentsLiquid separation by electricityWater basedVoltage spike
The present invention includes an improved electrostatic device for energizing fluids, in particular water based fluids, which will be used to provide a benefit to living organisms, machinery, processes and substances. The improved device of the invention will include an electrostatic voltage spike signal generator, two or more radio frequency signal generators, one or more antennas, optional one or more signal boosters and a fluid conduit. When fluid is treated with the improved device of the invention, the fluid will become energized and can be used to provide significant benefits in applications such as milk production, flower production, fruit production, crop production, vegetable production, shrimp production, egg production, meat production, gasoline combustion, waste fluid combustion, scale removal, water purification, fluid tracking, fluid sterilization and more.
Owner:COMPLETE WATER SYST L L C
Device and method of commutation control for an isolated boost converter
InactiveUS6937483B2Reduce wasteImprove efficiencyDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationVoltage spikeReverse recovery
A device and method of commutation control for an isolated boost converter provides a unique commutation logic to limit voltage spikes by utilizing switches on the secondary side to minimize a mismatch between current in the inductor and current in the leakage inductance of the transformer when commutation takes places. To minimize this mismatch, the current in the leakage inductance is preset at a certain level that approaches the current in the inductor prior to the commutation, thus significantly reducing the power rating for a clamp circuit and enabling use of a simple passive clamp circuit. In addition, through unique timing of the turn-on of the secondary switches, soft switching conditions are created that eliminate turn-on losses and the reverse recovery problems of free-wheeling diodes.
Owner:VITESCO TECH USA LLC
Plug and cord connector set with integrated circuitry
ActiveUS7377802B2Total current dropEliminate needSubstation/switching arrangement detailsTwo pole connectionsVoltage spikeRope light
A plug and / or a plug and cord connector set that includes integrated circuitry for use with decorative lighting products such as Christmas lights and rope lights. The integrated circuitry included in the plug and / or plug and cord connector combination can serve to reduce or limit current, provide full-wave AC to DC rectification, provide overload protection, reduce voltage, protect against voltage spikes, add blinking or flashing functions, or any combination thereof. An optional intermediate circuit is included for the manufacture of light strings employing multiple series connections.
Owner:FIBER OPTIC DESIGNS
Low-Voltage Connection with Safety Circuit and Method for Determining Proper Connection Polarity
InactiveUS20100283623A1Reduces and prevents inductive voltage spikeReduces and prevents damageCoupling device detailsEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionVoltage spikeUnsafe condition
A safety circuit used in low-voltage connecting systems leaves the two low-voltage systems disconnected until it determines that it is safe to make a connection. When the safety circuit determines that no unsafe conditions exist and that it is safe to connect the two low-voltage systems, the safety circuit may connect the two systems by way of a “soft start” that provides a connection between the two systems over a period of time that reduces or prevents inductive voltage spikes on one or more of the low-voltage systems. When one of the low-voltage systems has a completely-discharged battery incorporated into it, a method is used for detection of proper polarity of the connections between the low-voltage systems. The polarity of the discharged battery is determined by passing one or more test currents through it and determining whether a corresponding voltage rise is observed.
Owner:ENERGY SAFE TECH
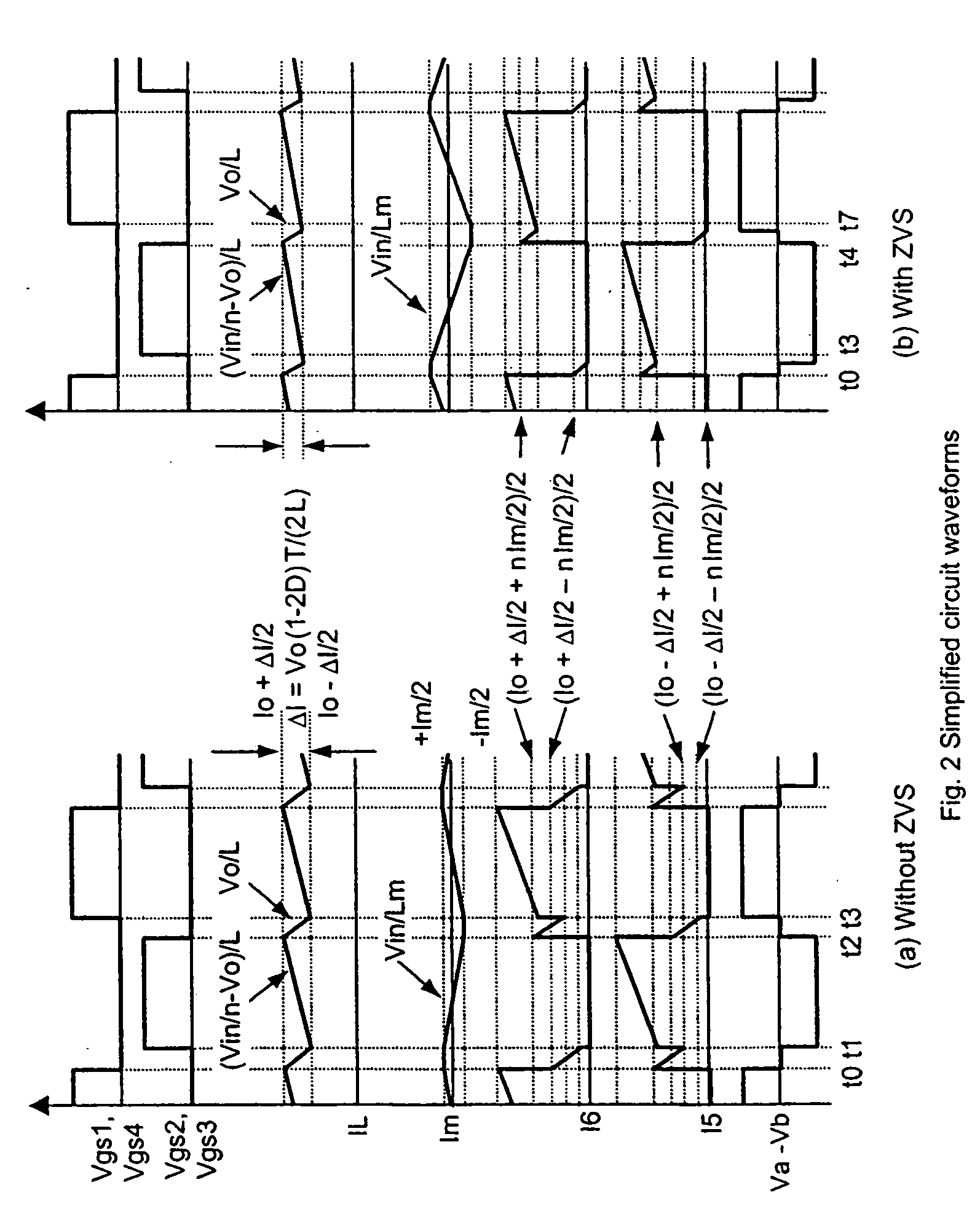
Simple zero voltage switching full-bridge DC bus converters
InactiveUS20060279966A1Increasing magnetizing currentIncrease currentEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionMOSFETCapacitance
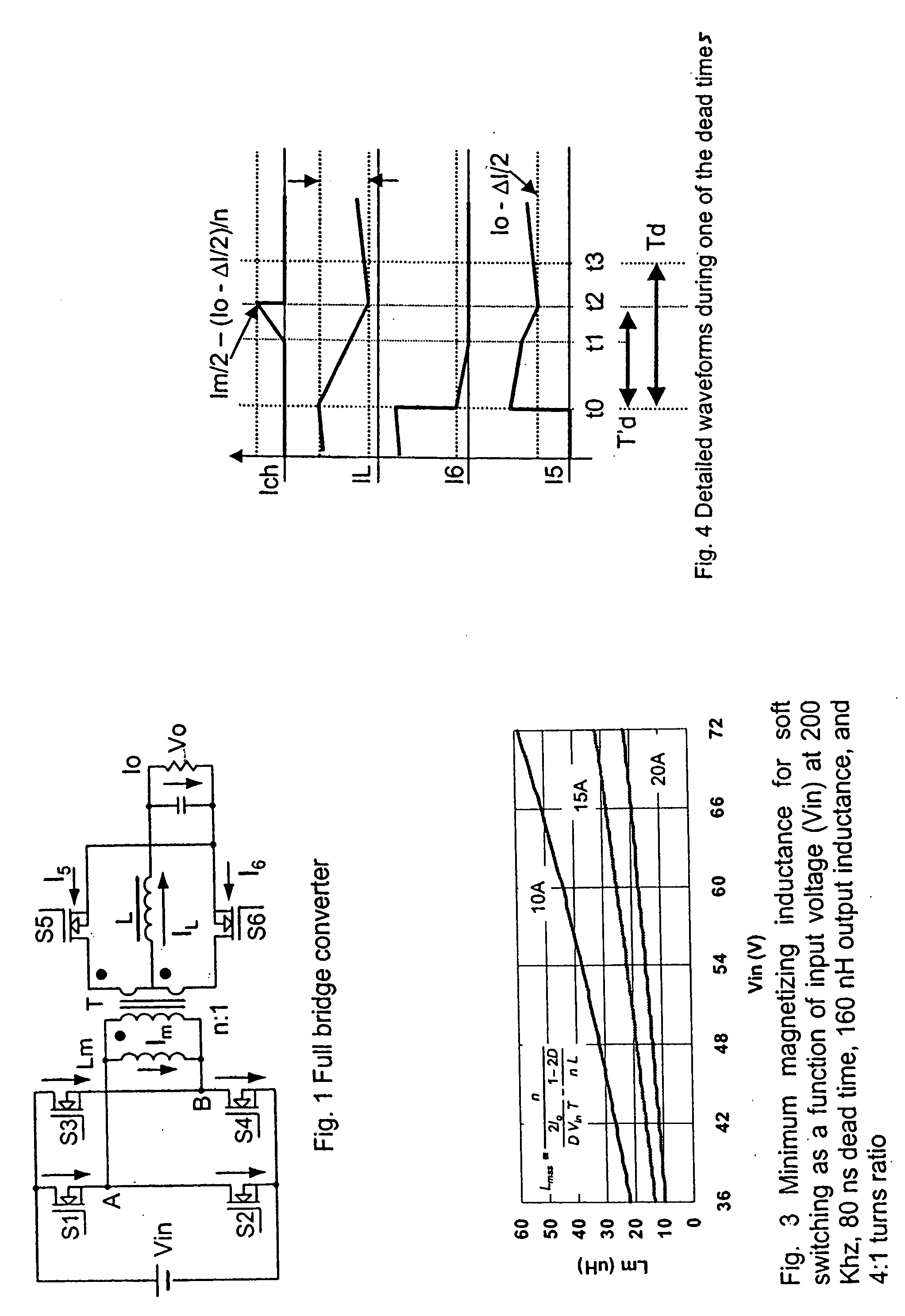
A method and circuit arrangement for achieving zero voltage switching (ZVS) in a 50% duty cycle full-bridge DC bus converter. The ZVS is obtained by increasing the transformer magnetizing current. During the small dead time between conductions of the two bridge legs, the increased magnetizing current supports the output inductor current, and resonates with MOSFET output capacitance, resulting in ZVS operation. With ZVS operation, body diode conduction and voltage spikes across the secondary synchronous rectifiers are reduced, full load efficiency is increased, and transformer flux balance is enhanced.
Owner:INTERNATIONAL RECTIFIER COEP
Water-cooled three-phase diode-clamped three-level inverted power module
ActiveCN101741227AImprove power densityEasy to installConversion constructional detailsCooling/ventilation/heating modificationsCapacitanceThree level
The invention discloses a water-cooled power module of three-phase diode-clamped three-level inverted topology. The water-cooled power module comprises a support frame, an electrolytic capacitor set, a second laminated bus bar, a water-cooled radiator, a first laminated bus bar, a power device, a balance resistor, a voltage sensor and first absorption capacitor sets, wherein the electrolytic capacitor set is positioned on the support frame; the second laminated bus bar is paved on the electrolytic capacitor set; the water-cooled radiator is spanned above the second laminated bus bar; a first laminated bus bar is spanned above the water-cooled radiator, and corresponding toothed connecting terminals between the first laminated bus bar and the second laminated bus bar are connected through a second absorption capacitor set; the power device, the balance resistor and the voltage sensor are fixed on the upper surface of the water-cooled radiator and are interconnected through the first laminated bus bar; and the first absorption capacitor sets are positioned above the first laminated bus bar and are interconnected through the first laminated bus bar. The water-cooled power module is arranged on the integral water-cooled radiator, so the power density is greatly improved, and the water-cooled power module can be applied to the places which are narrow or closed or have explosion-proof requirements; and the turn-off voltage spike is small, the electrolytic capacitor is difficult to emit heat, and the water-cooled power module is easy to mount and maintain.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Two stage boost converter topology
ActiveUS20060028186A1Reduces switch conductionReduces turn lossDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationMOSFETVoltage spike
A power converter having a two stage boost circuit and a small boost converter. The main power flow for the power converter is via the two stage booster circuit having a single switch. The voltage spike of the switch is clamped by a diode and a capacitor. The energy at the capacitor is transferred to the power converter's output terminals by the small boost converter. The two stage boost converter topology enables the use of much lower voltage and Rdson MOSFET switches so as to reduce cost, switch conduction loss and turn on loss.
Owner:ASTEC INT LTD
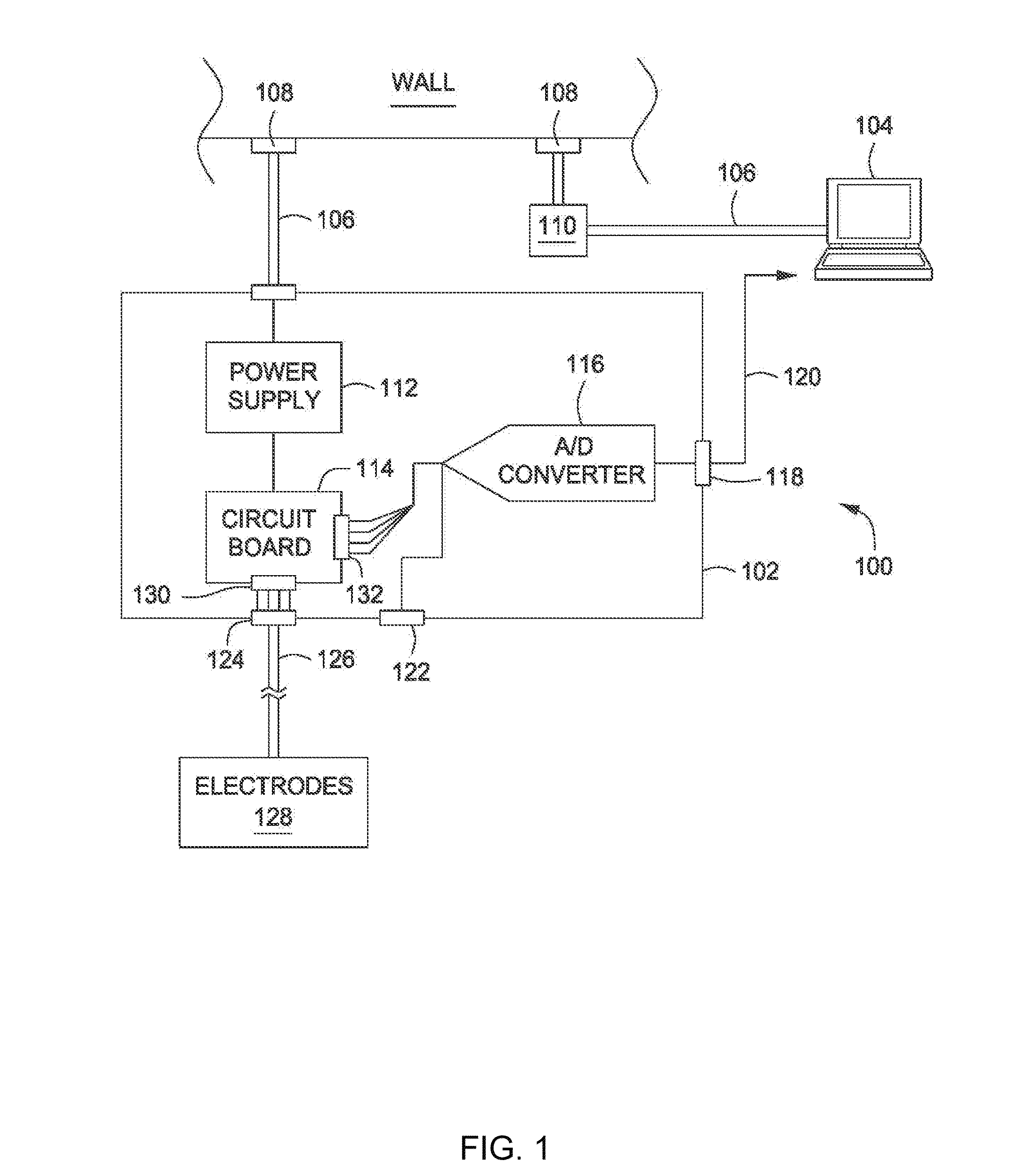
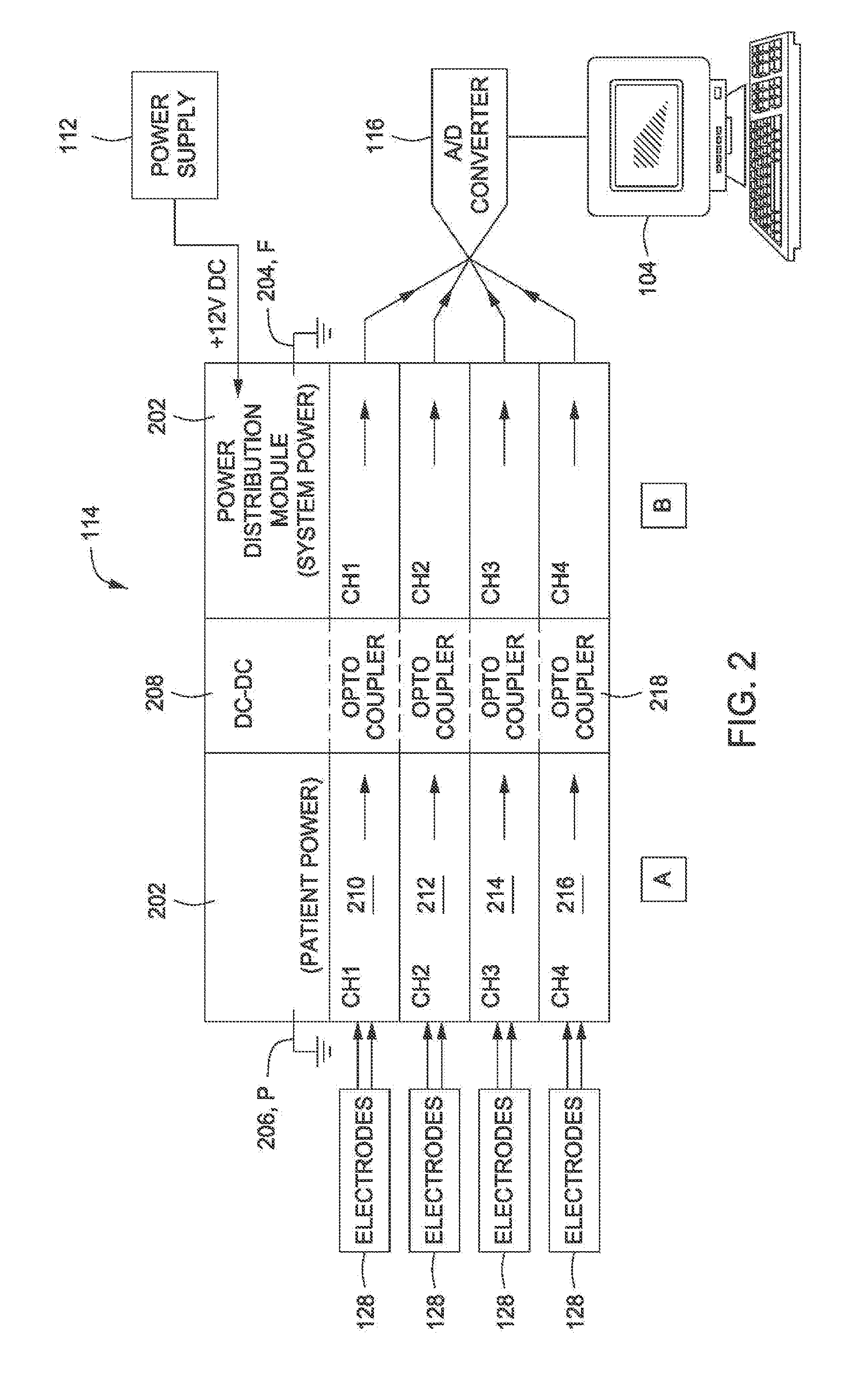
Noninvasive measurement of uterine emg propagation and power spectrum frequency to predict true preterm labor and delivery
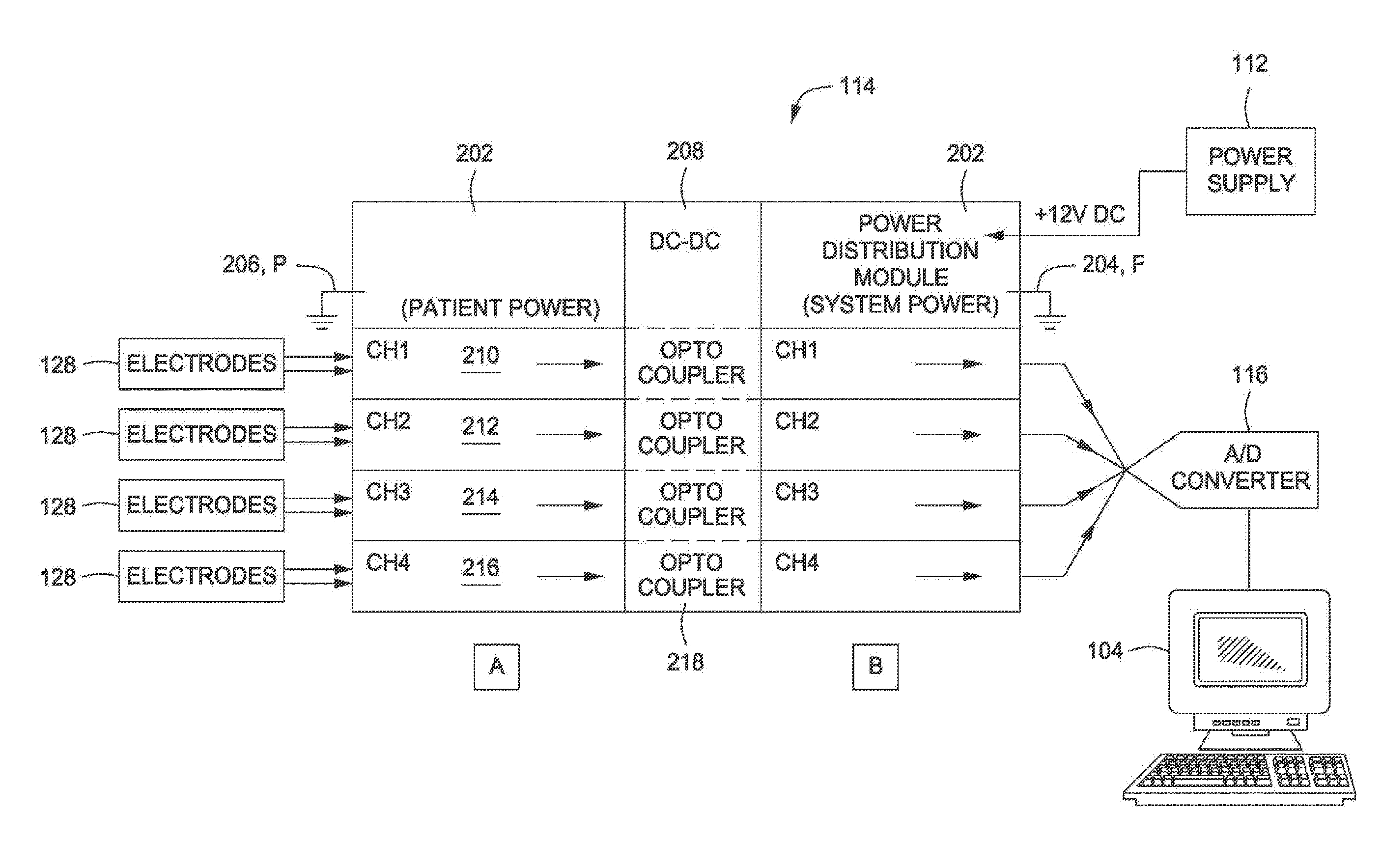
InactiveUS20110237972A1Understand clearlyLabor for correctingHealth-index calculationElectromyographyObstetricsVoltage spike
A method operable to more accurately predict true preterm labor and delivery is provided. Trans-abdominal uterine electromyography (EMG) and power spectrum (PS) analysis can identify electrical signals characteristic of labor at term and preterm with relatively high positive and negative predictive values. The use of propagation velocity (PV) of uterine EMG signals may either be done independently or in conjunction with PS analysis. This method involves applying at least two pairs of electrodes to a maternal abdomen. The time associated with measuring a voltage spike of a propagating myometrial wave traveling through the pairs of electrodes allows the amount of time required for the propagating myometrial wave to transverse the distance between electrodes to be determined. With this information a propagation velocity (PV) of the propagating myometrial wave may be determined. This PV may be compared to a labor positive predictive value (PPV). A favorable comparison indicates an increased probability of true preterm labor and delivery.
Owner:REPRODIVE RES TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com