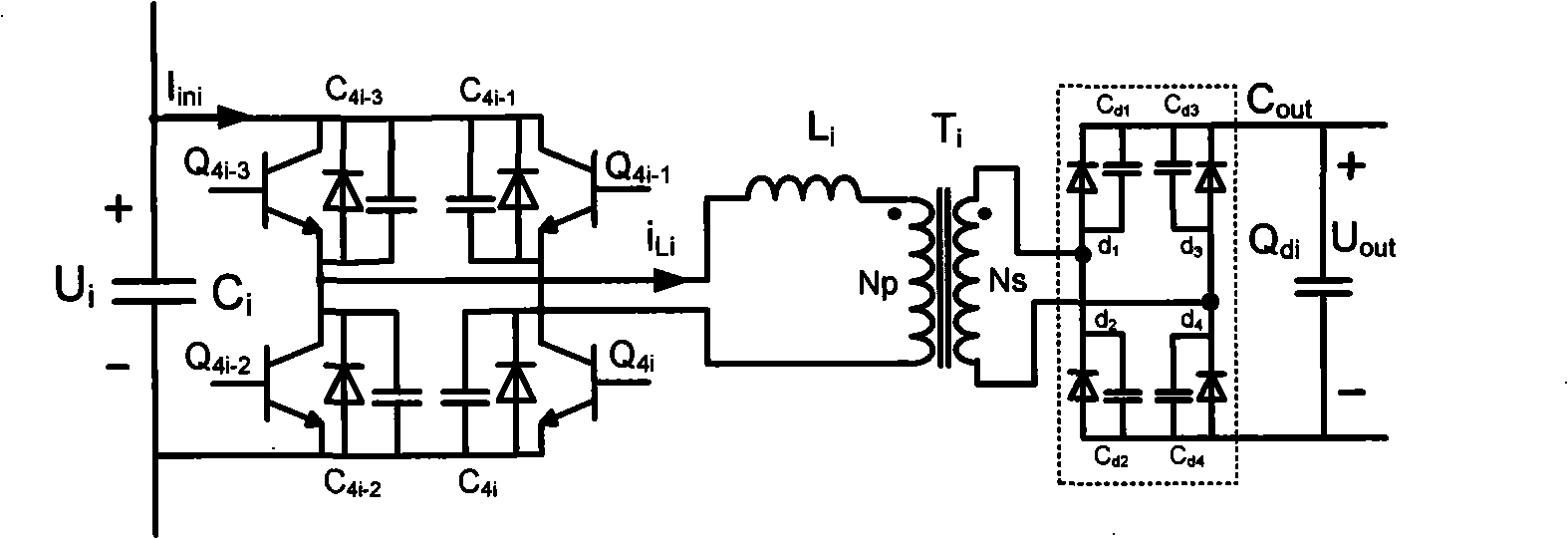
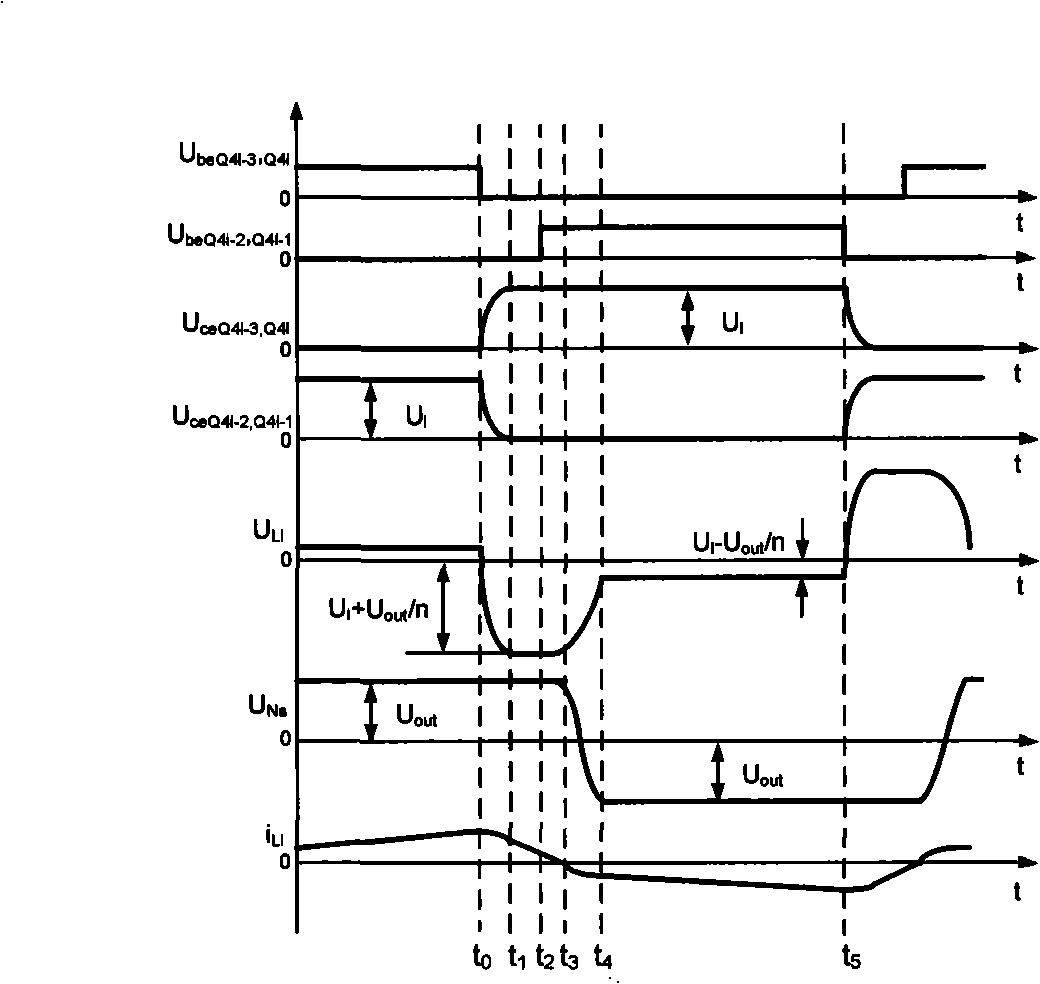
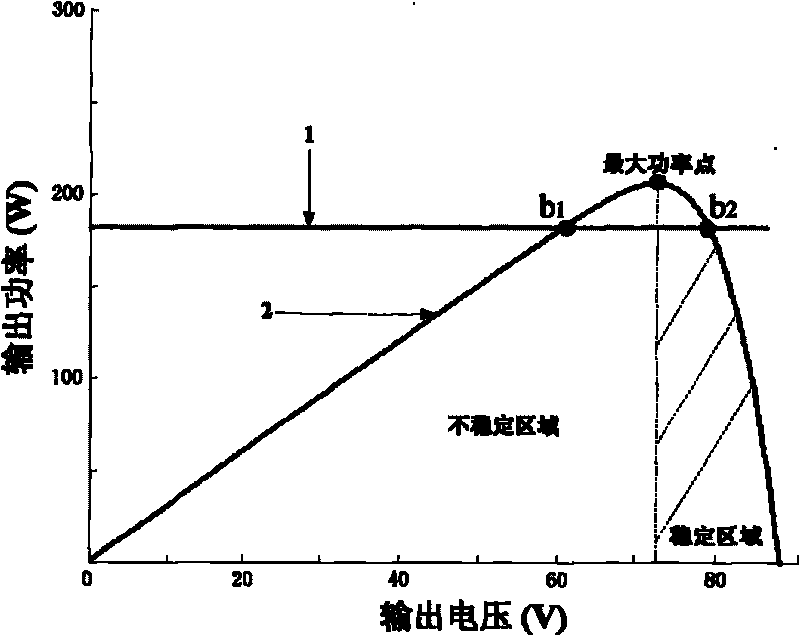
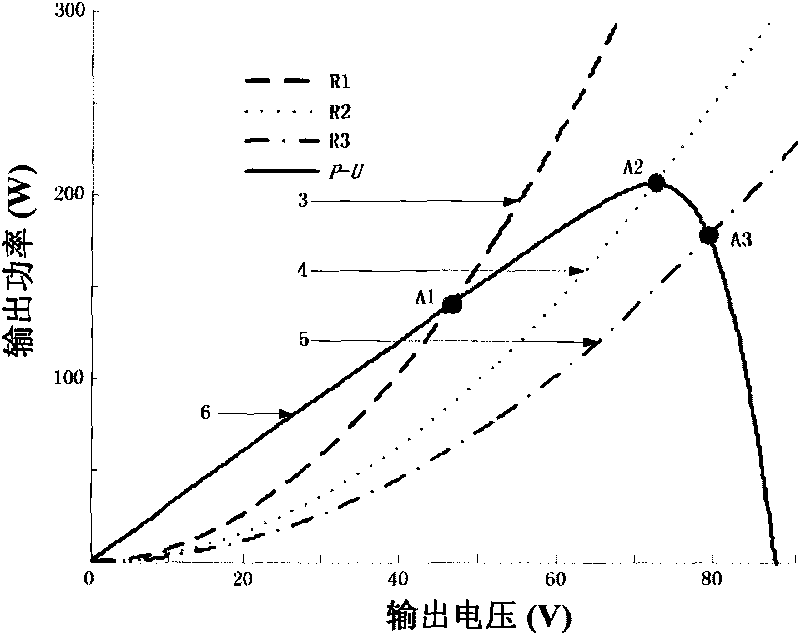
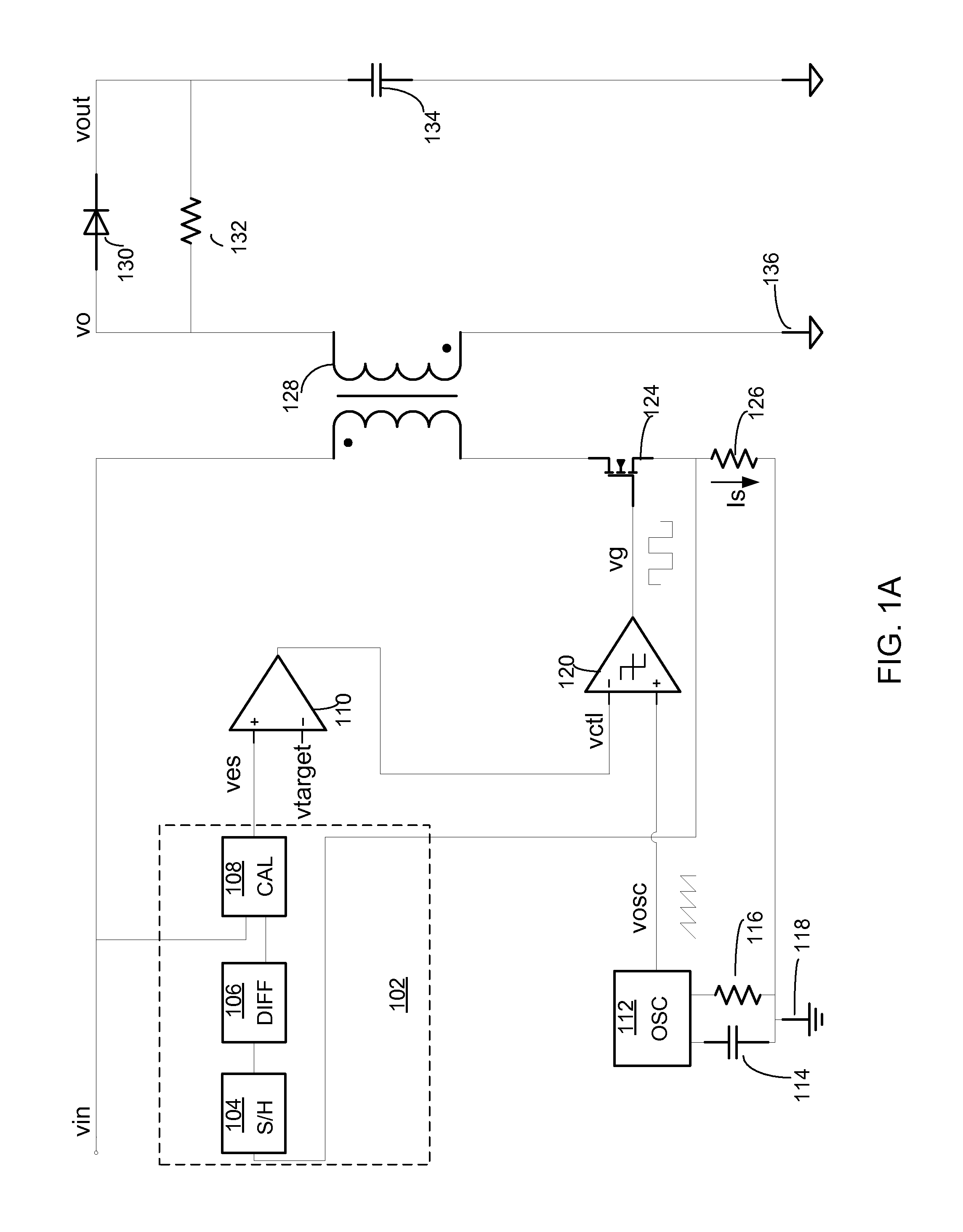
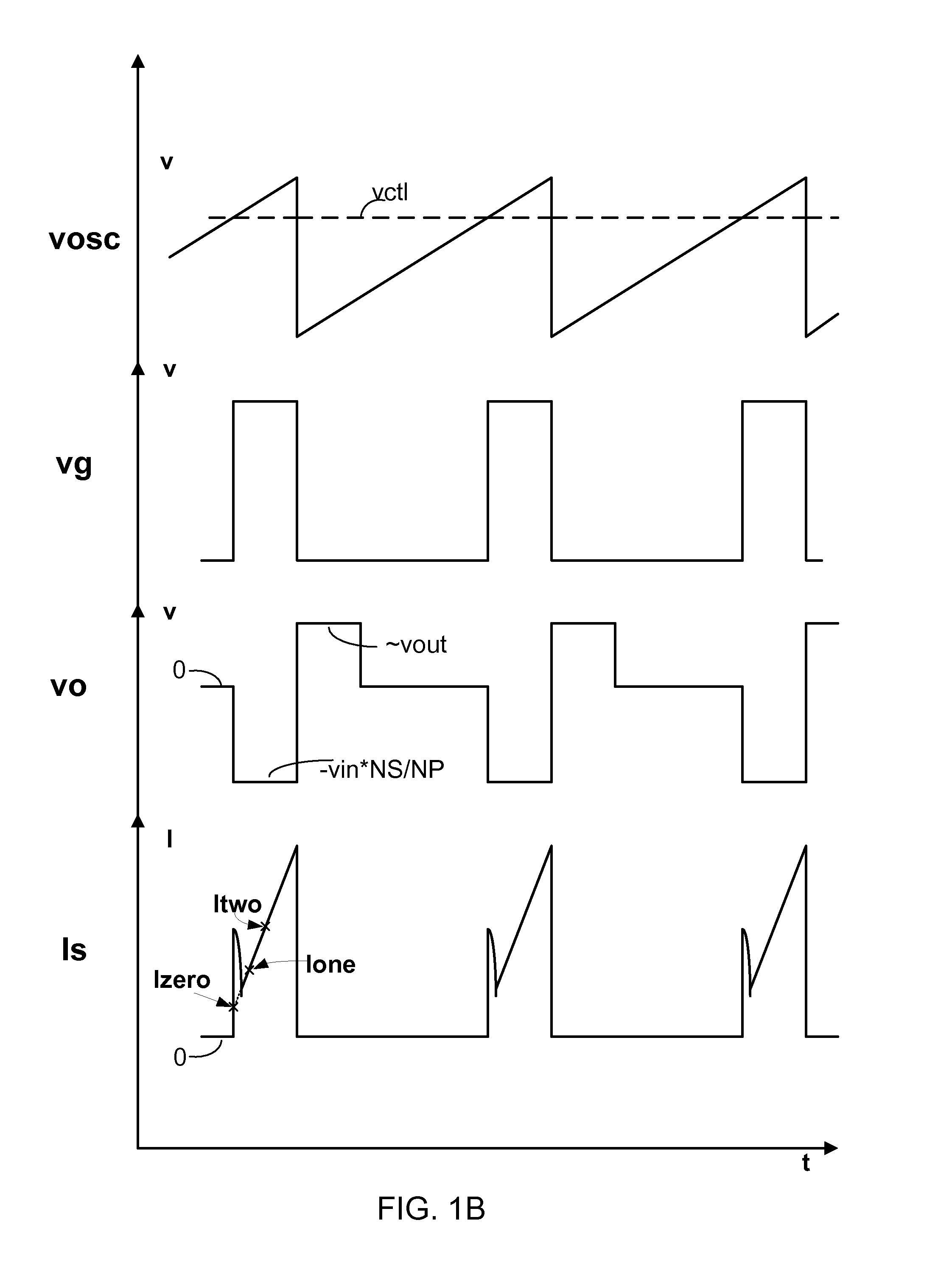
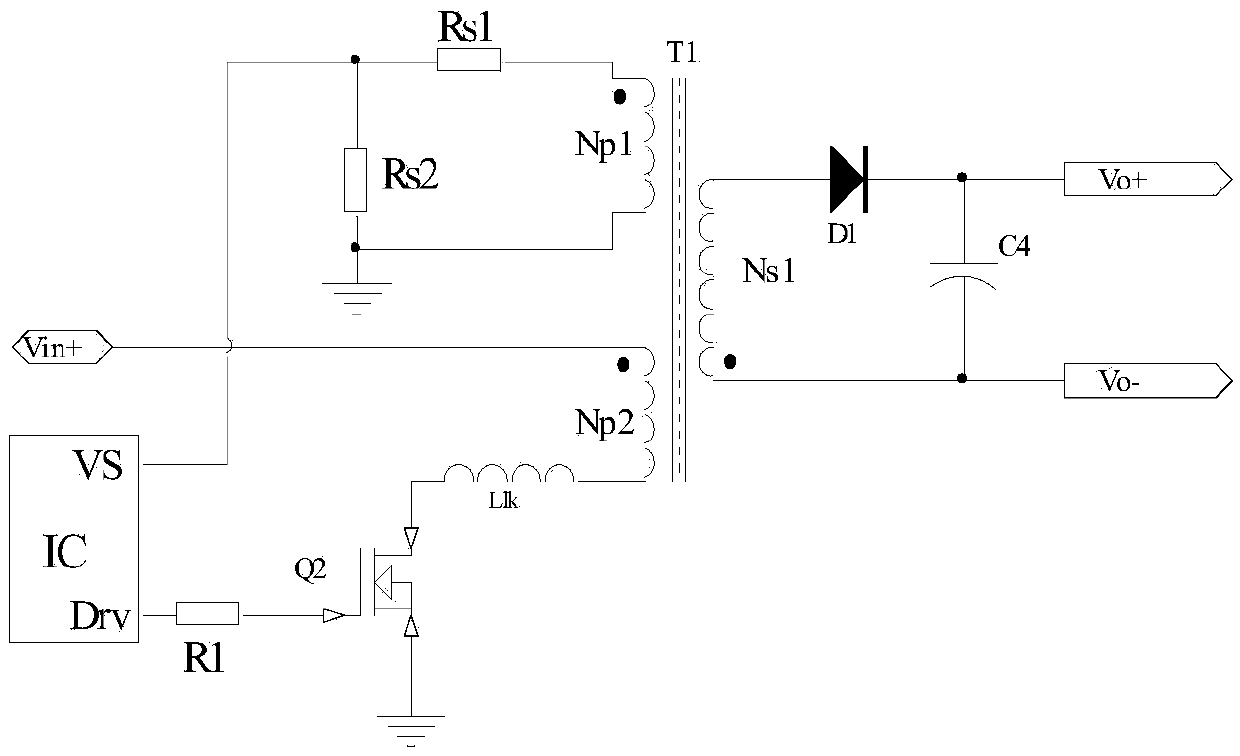
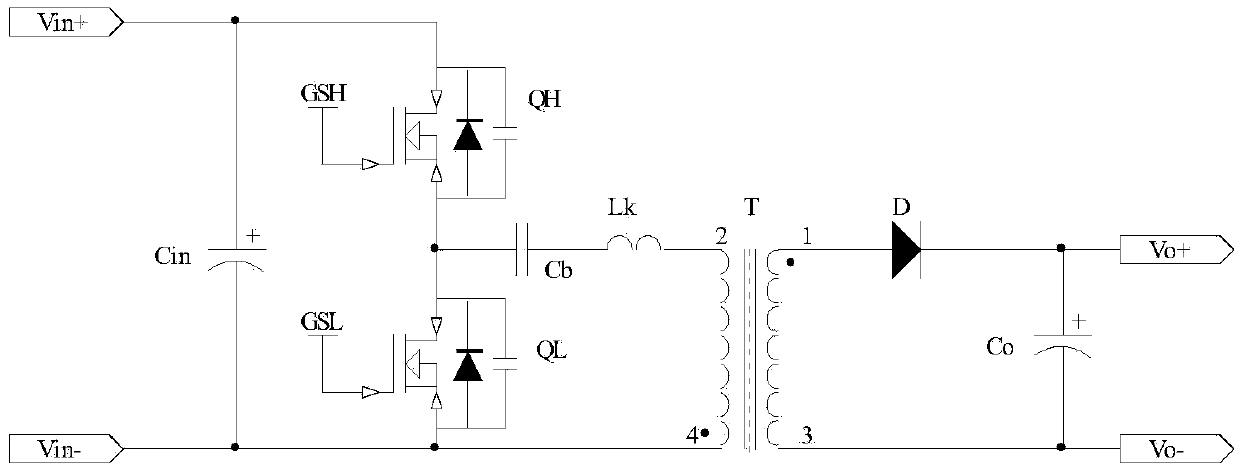
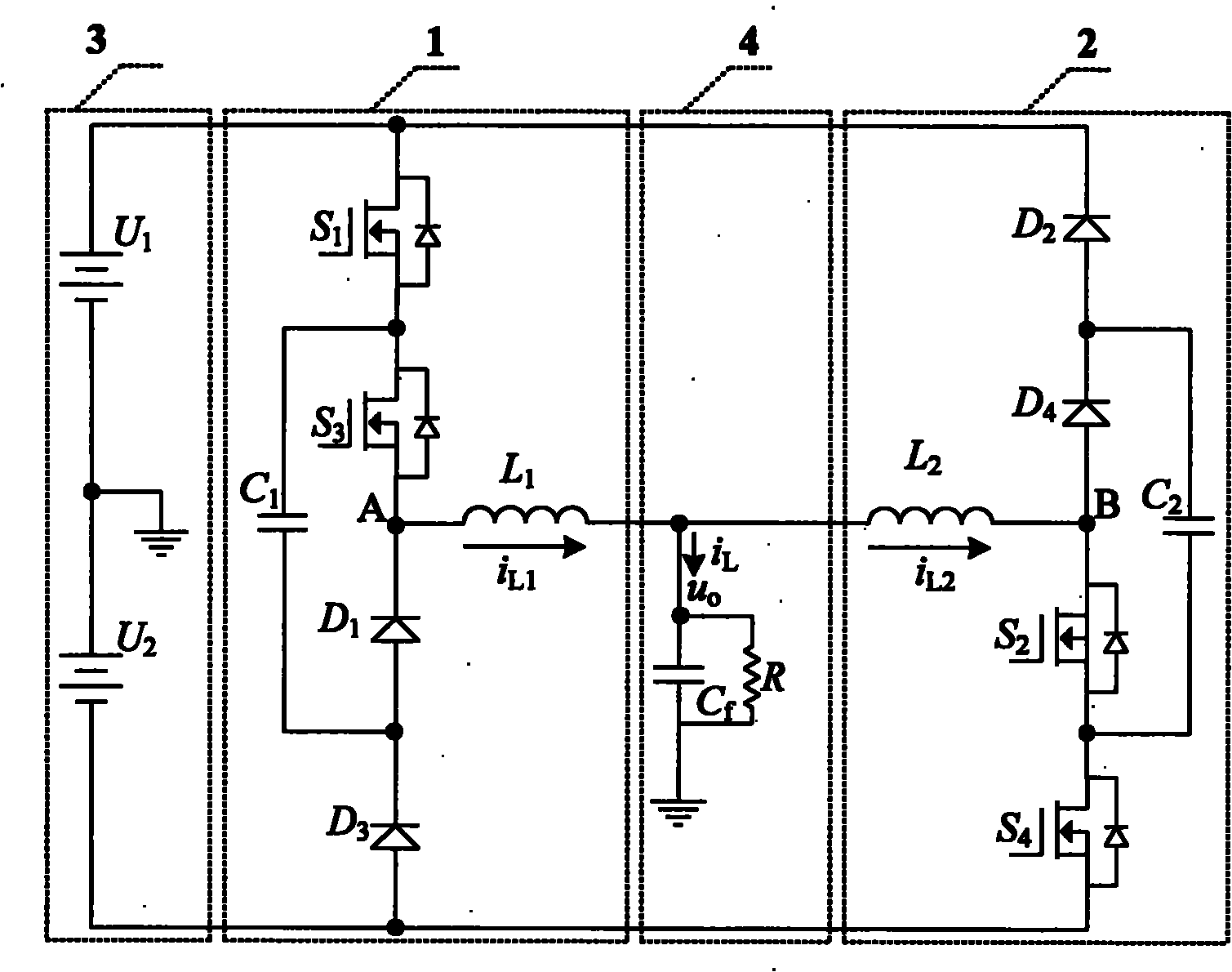
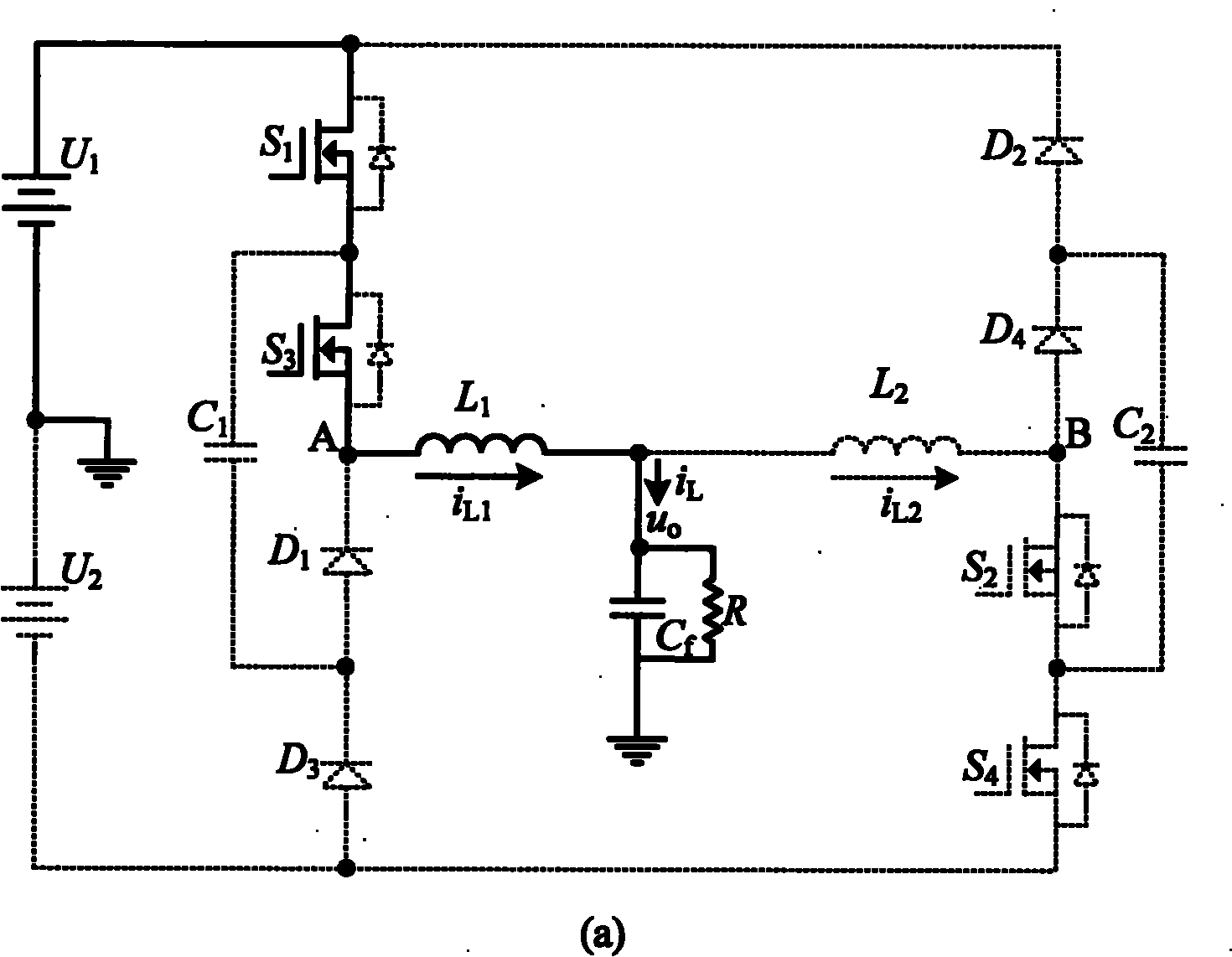
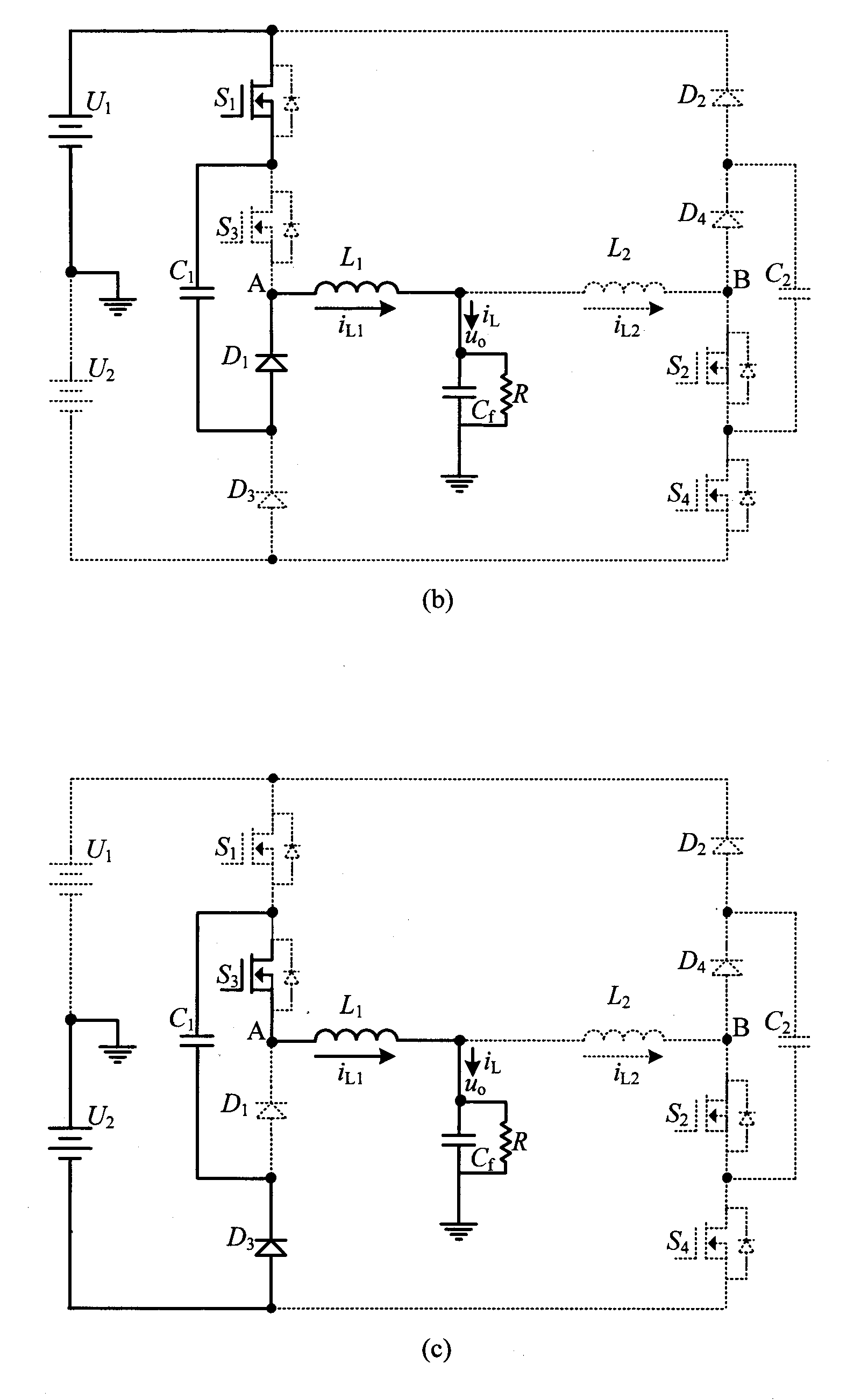
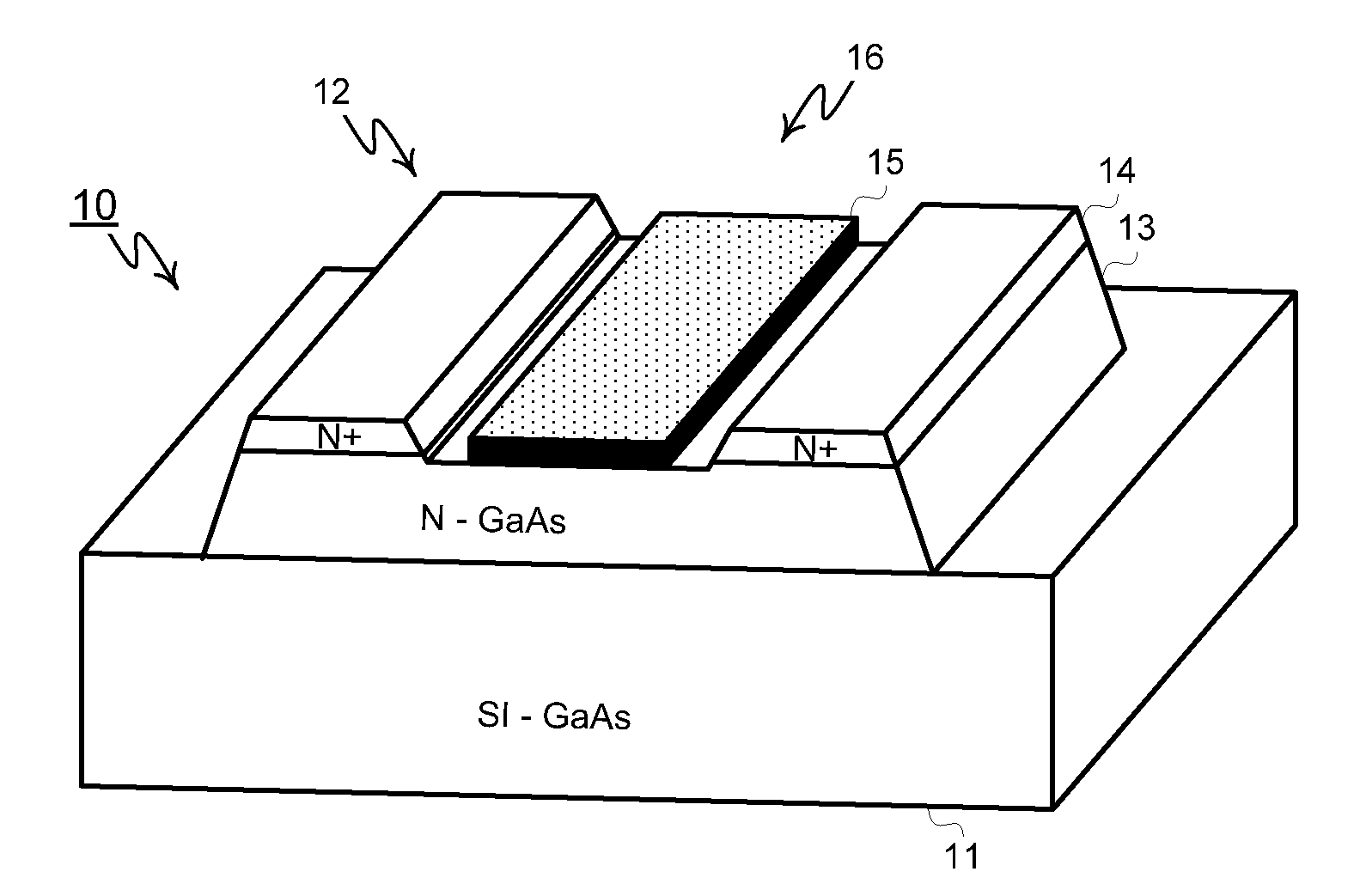
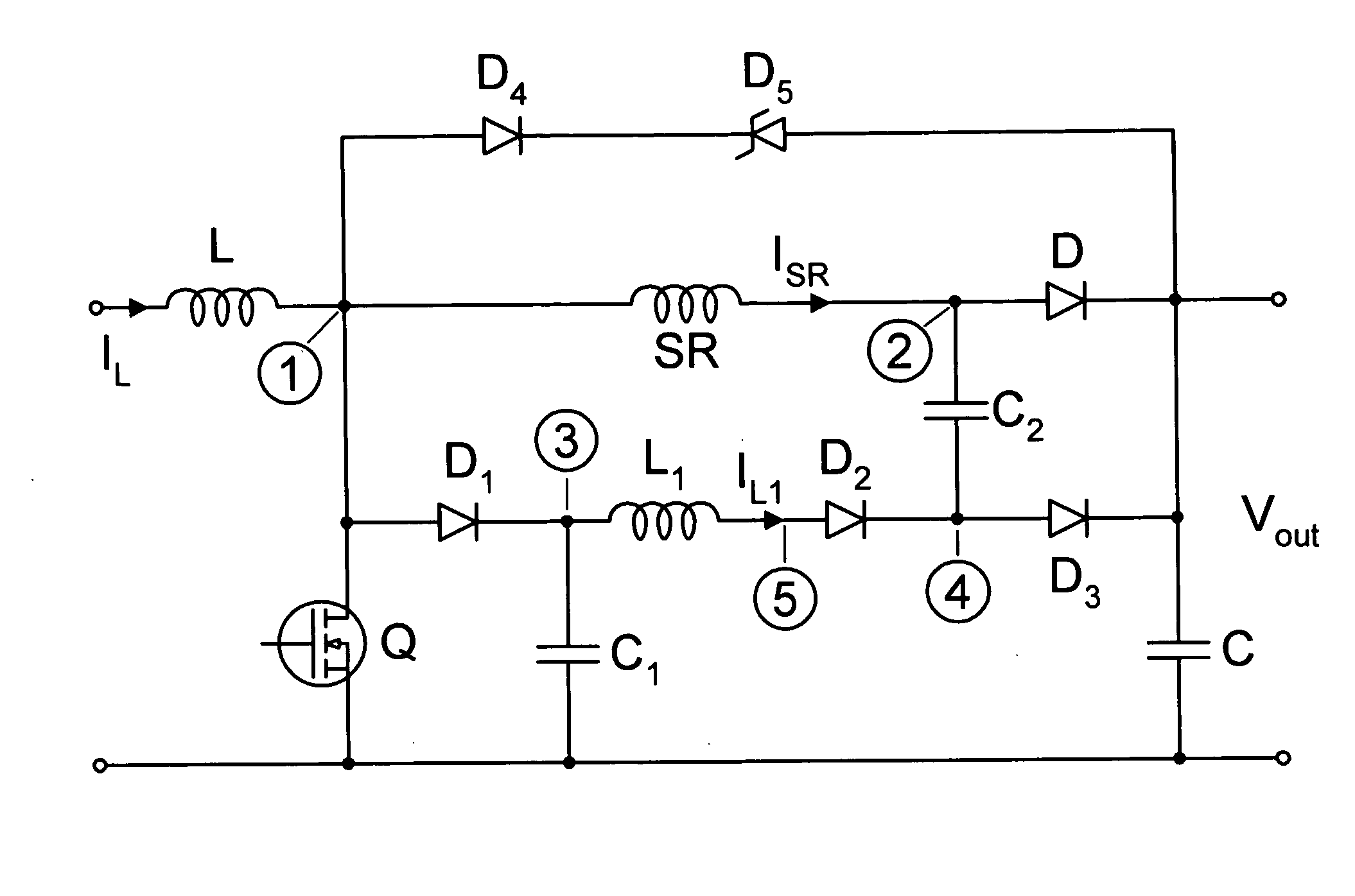
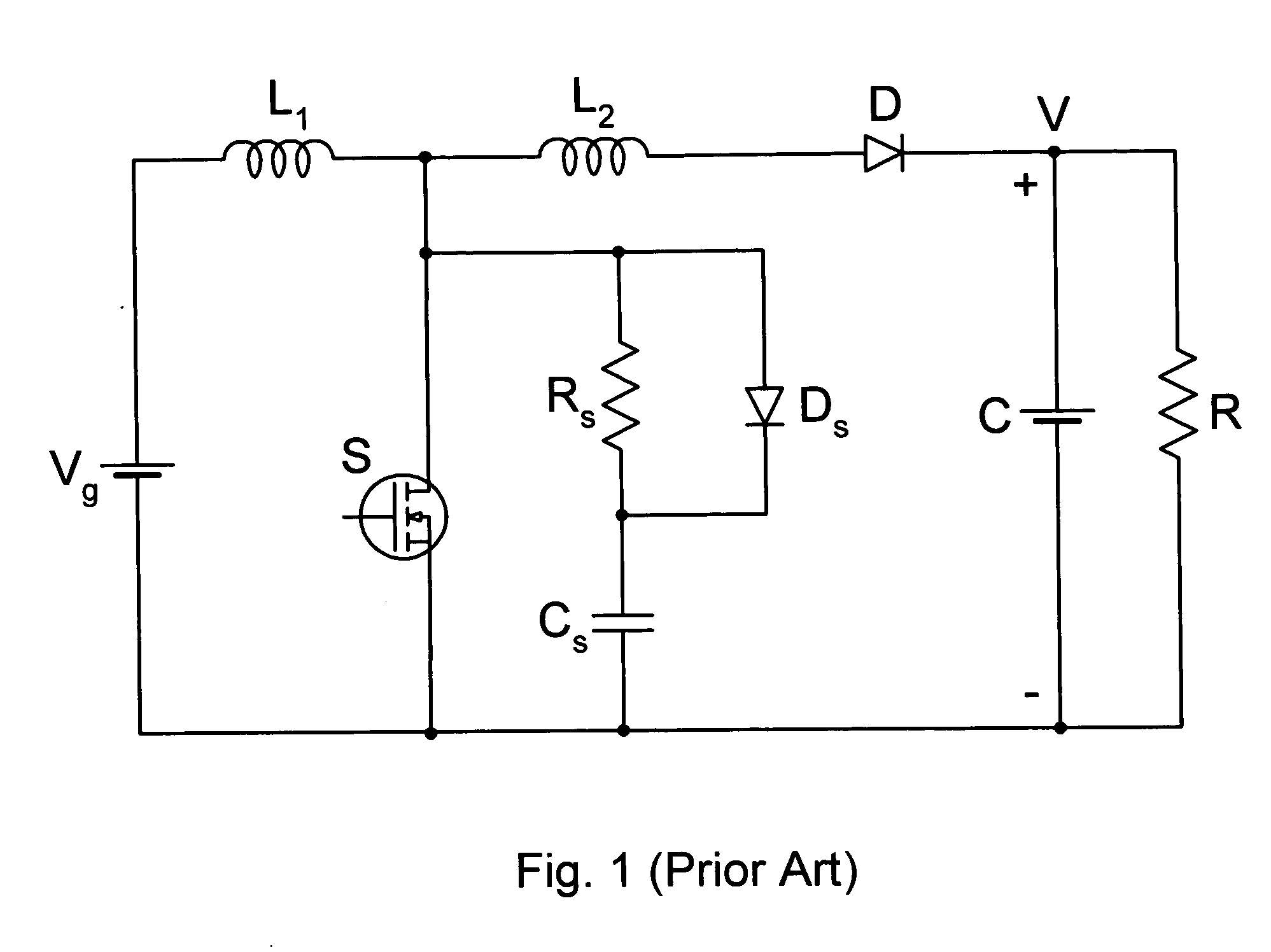
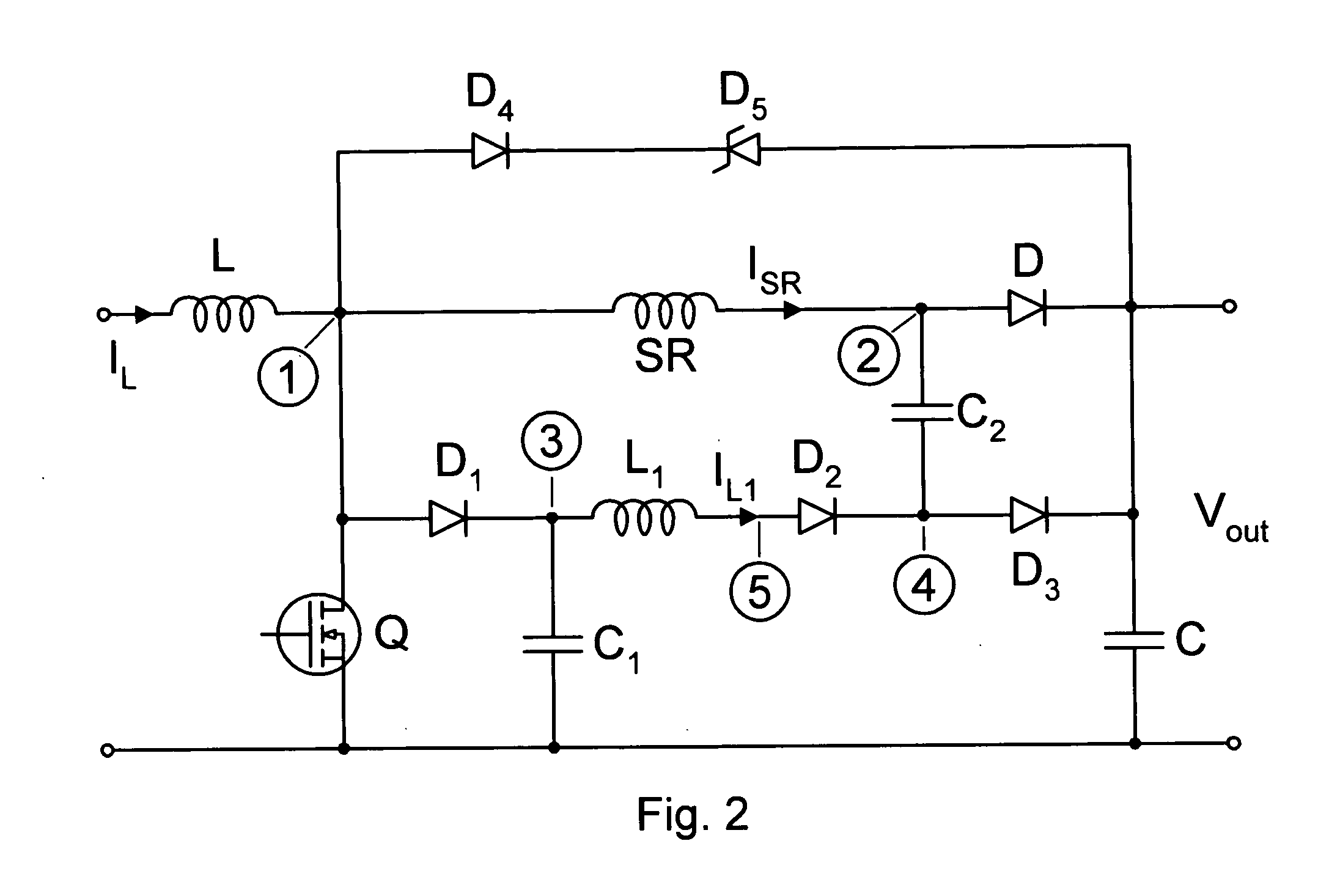
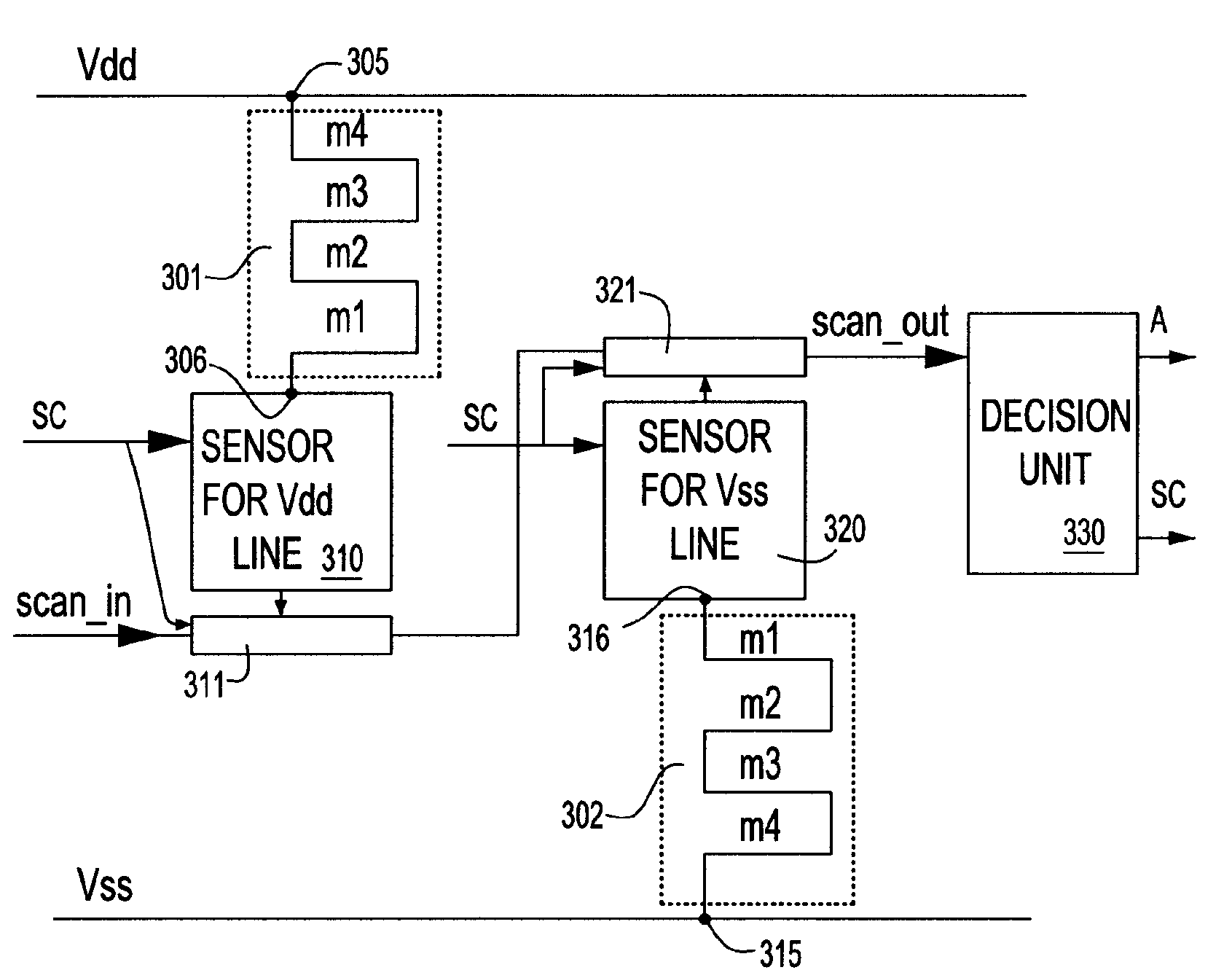
Patents
Literature
1108results about How to "Reduce voltage stress" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
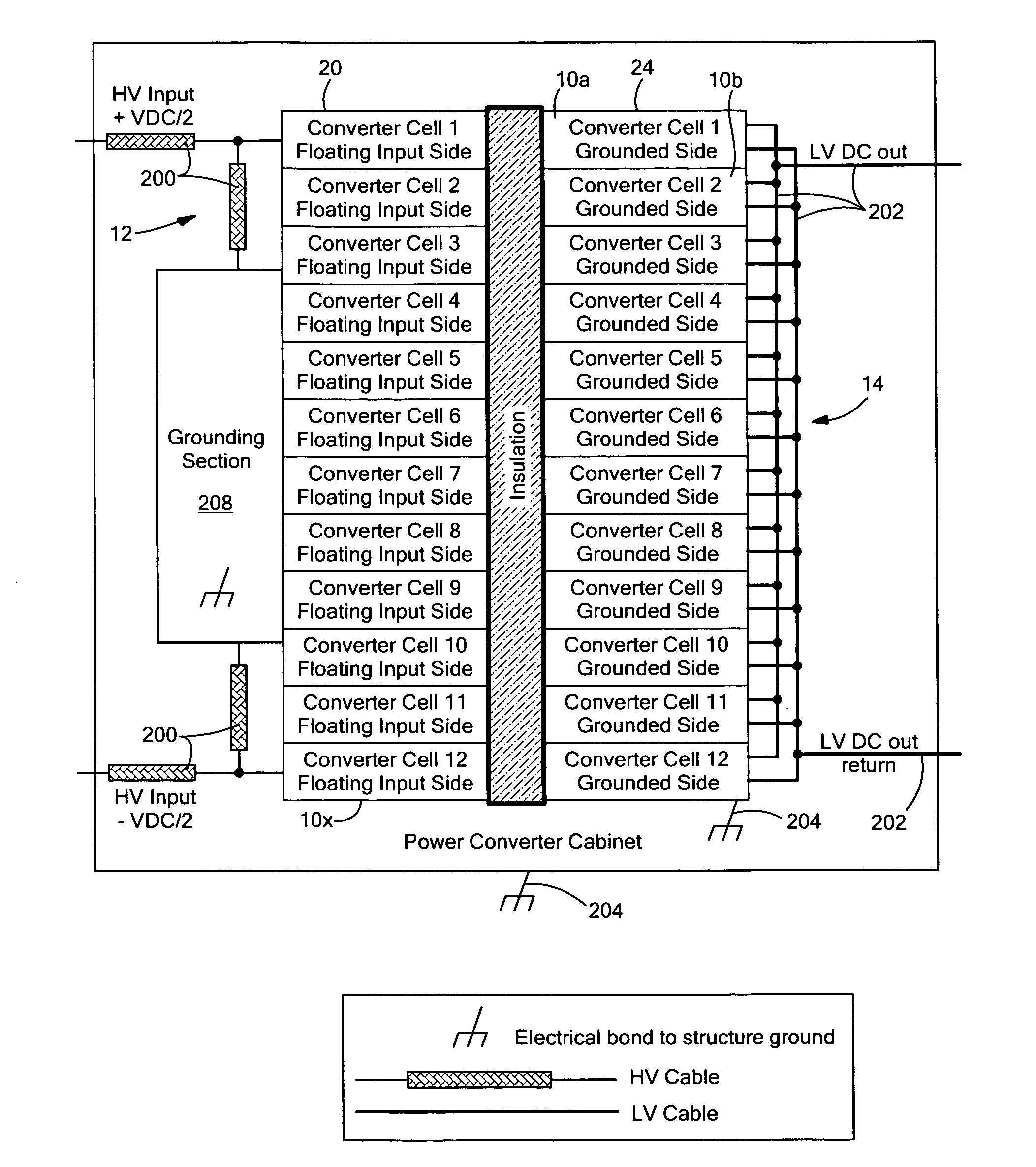
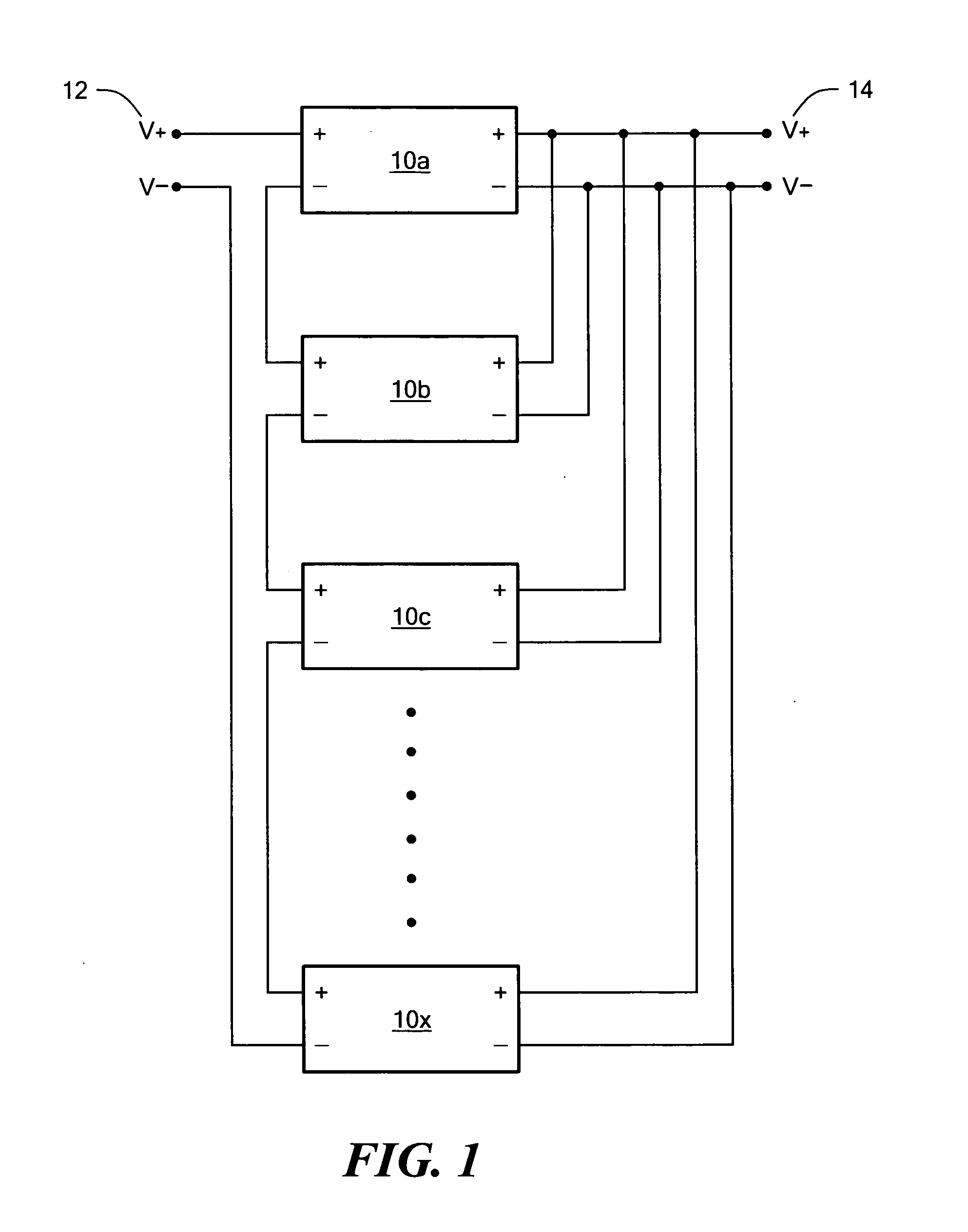
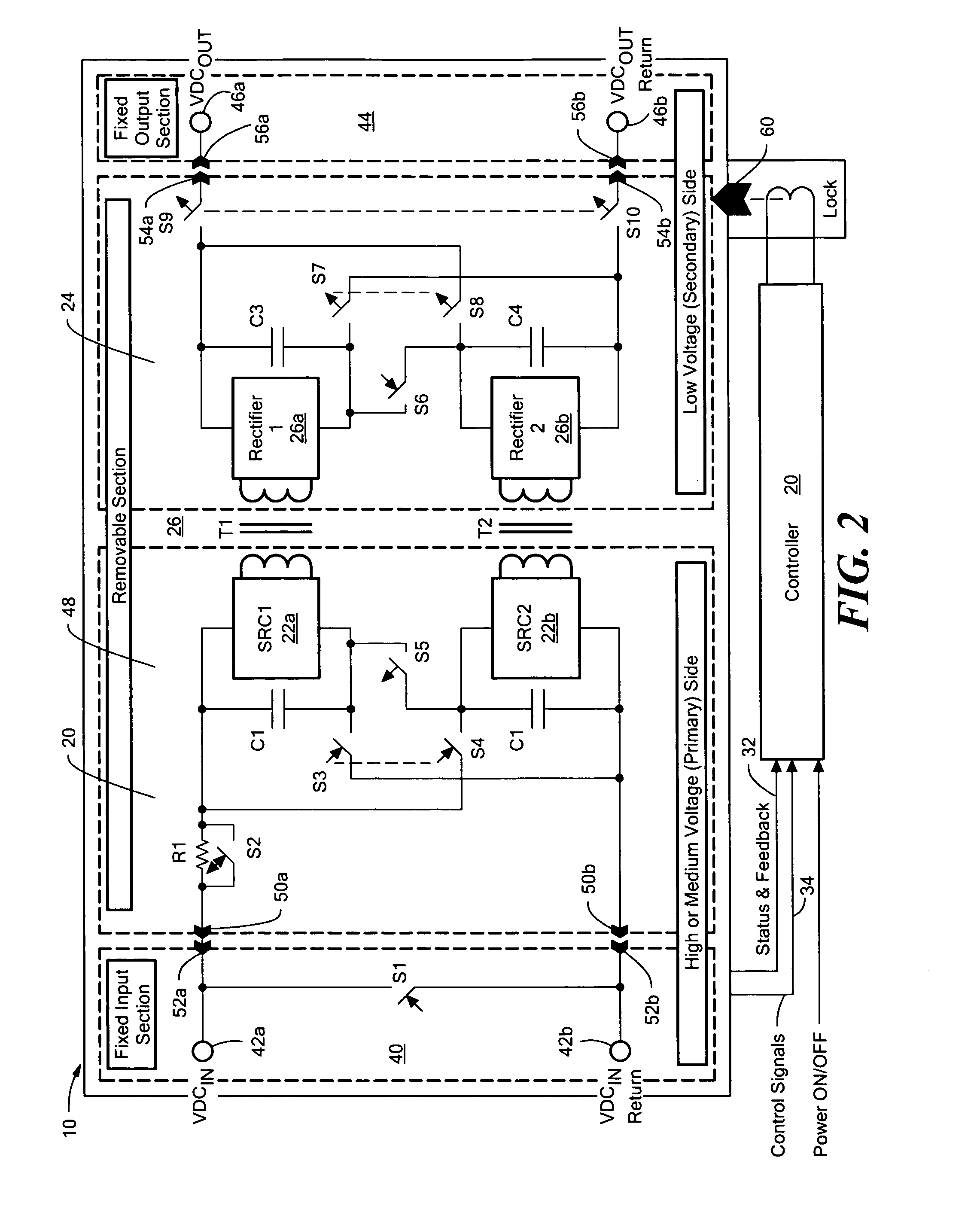
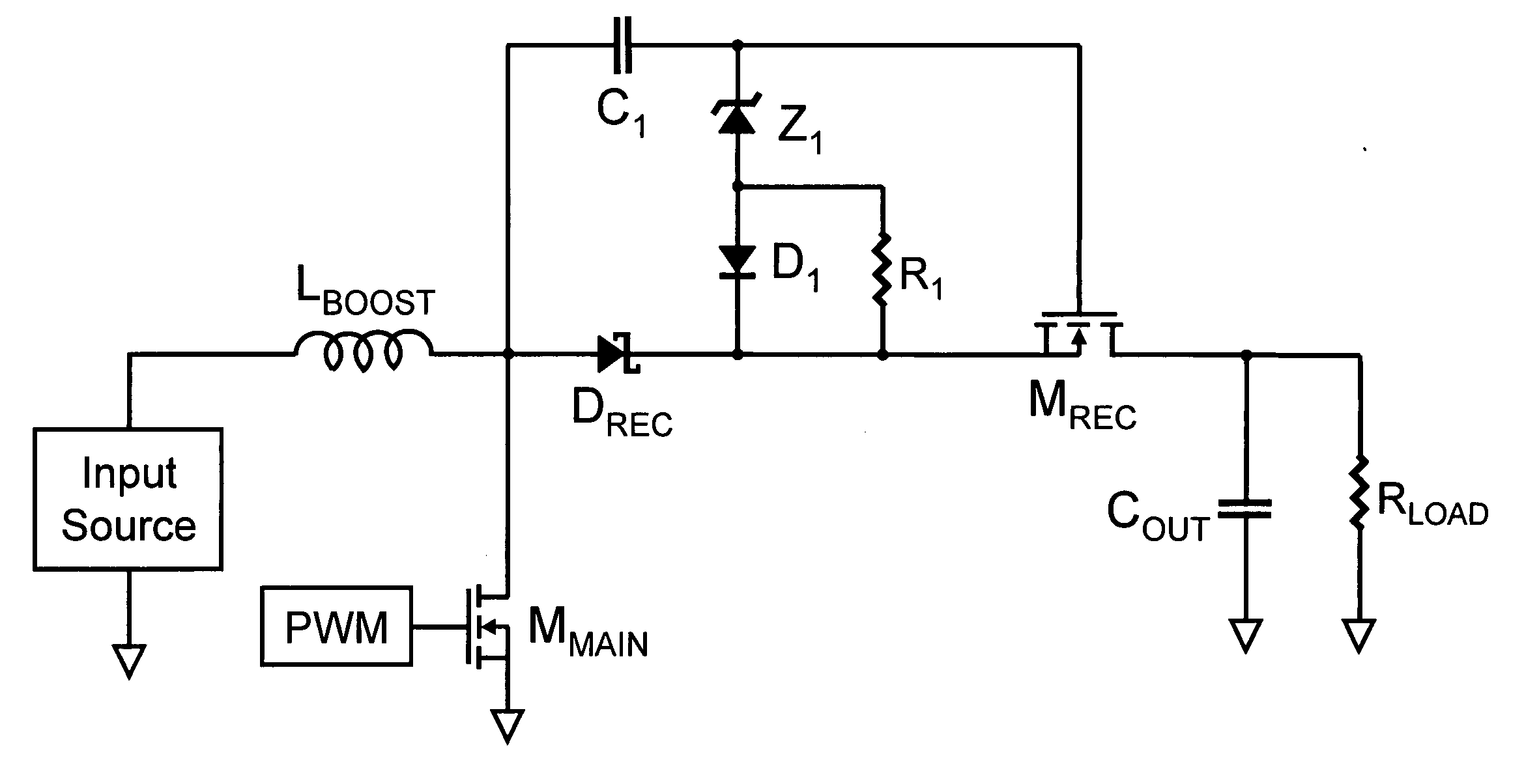
Circuit for maintaining hold-up time while reducing bulk capacitor size and improving efficiency in a power supply
InactiveUS20050030772A1Improve efficiencyReducing voltage operating rangeEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus with intermediate ac conversionCapacitanceDc dc converter
Owner:ASTEC INT LTD
Active-clamp current-source push-pull dc-dc converter
InactiveUS20070247877A1Improve power conversion efficiencyReduce voltage stressEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionFull wavePush pull
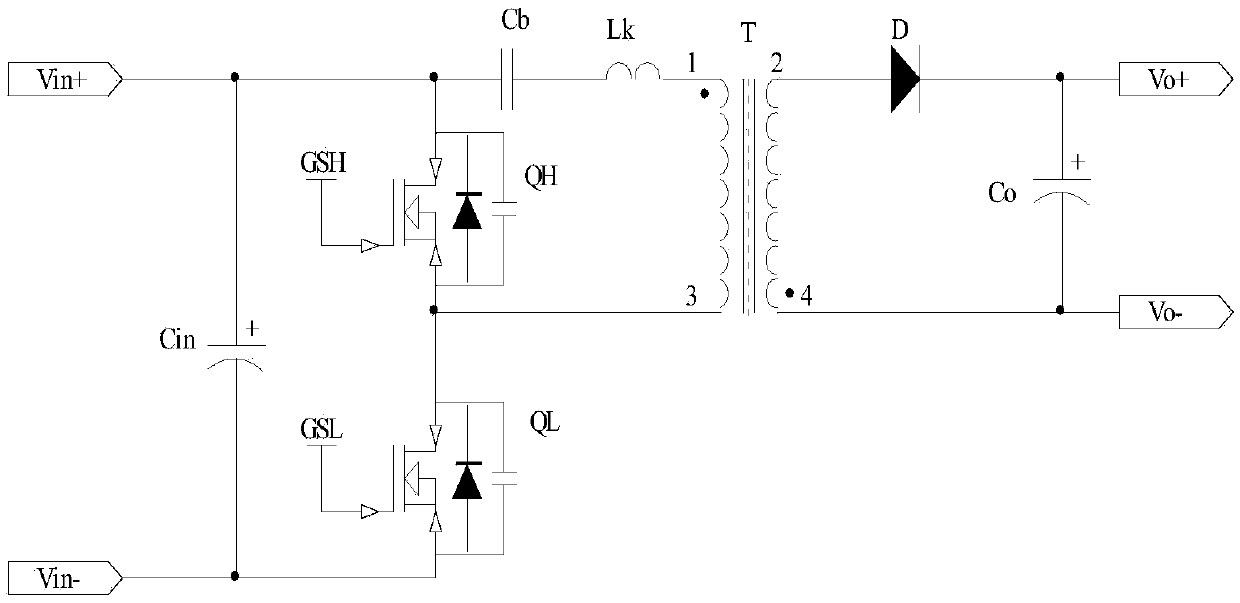
Provided is a current-source push-pull DC-DC converter using an active clamp circuit for reusing energy of leakage inductances by not only diodes on a secondary side of a transformer being zero-current switched using a series-resonant full-wave rectifier, but also the active clamp circuit on a primary side of the transformer, which provides a discharge path of the energy stored in the leakage inductances, increases power conversion efficiency even for a wide input voltage range and reduces a switch voltage stress as compared to a conventional current-source push-pull circuit by operating even for a duty ratio below 0.5 by flowing a current of an input inductor through capacitors of the active clamp circuit when both main switches are off.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
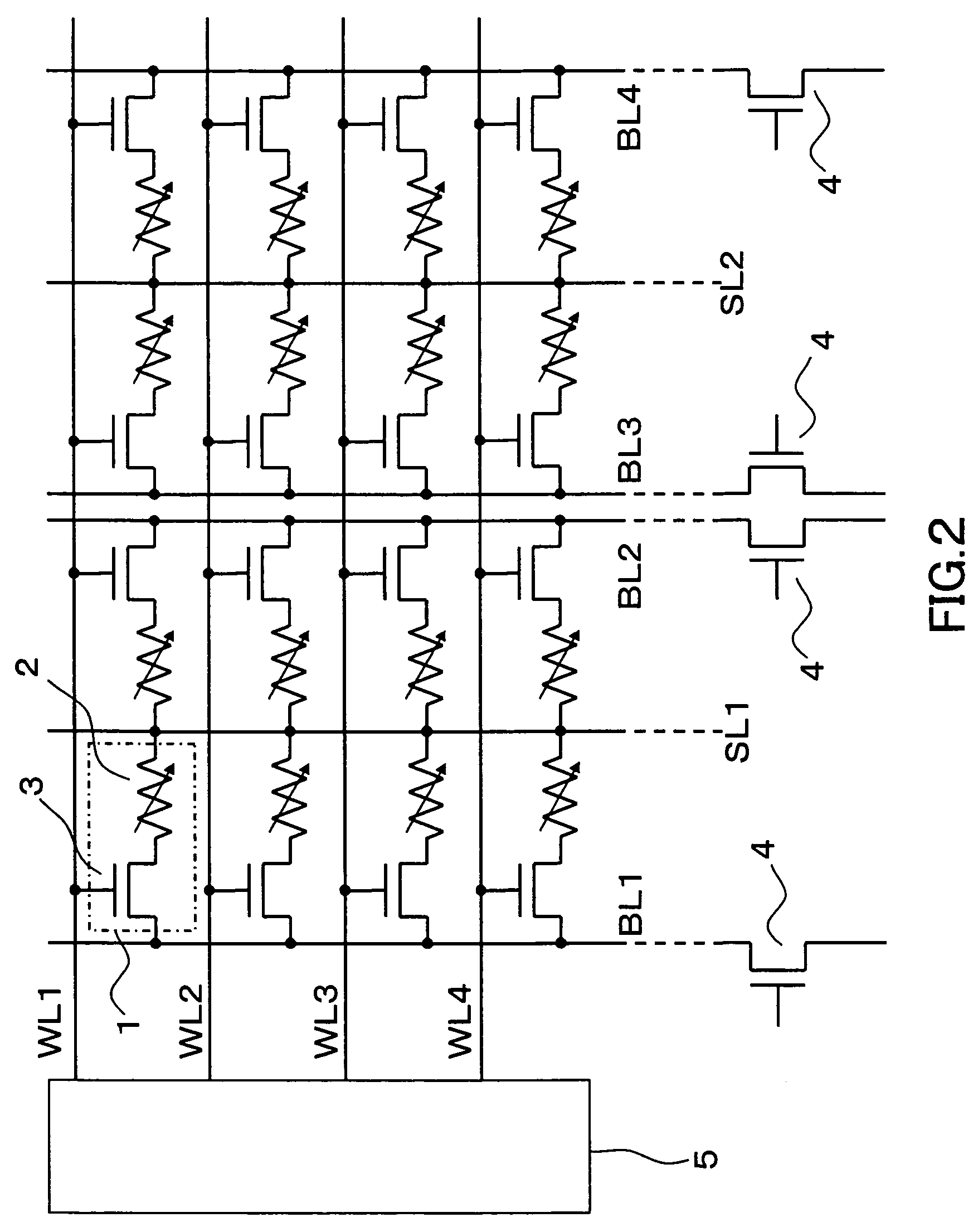
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device
ActiveUS7016222B2Higher-reliability data retention characteristicReduce voltage stressSolid-state devicesDigital storageComputer architectureCommon word
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
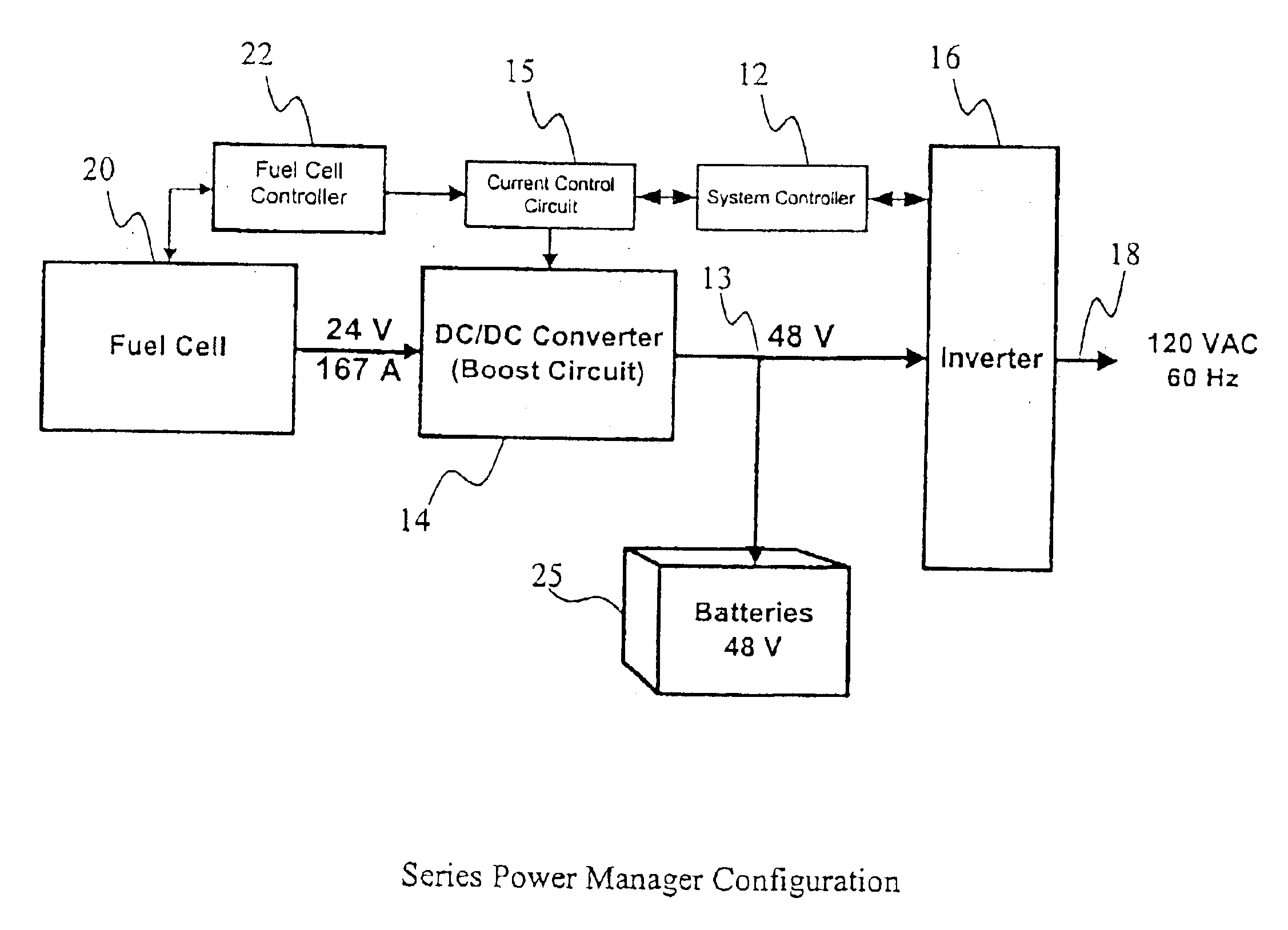
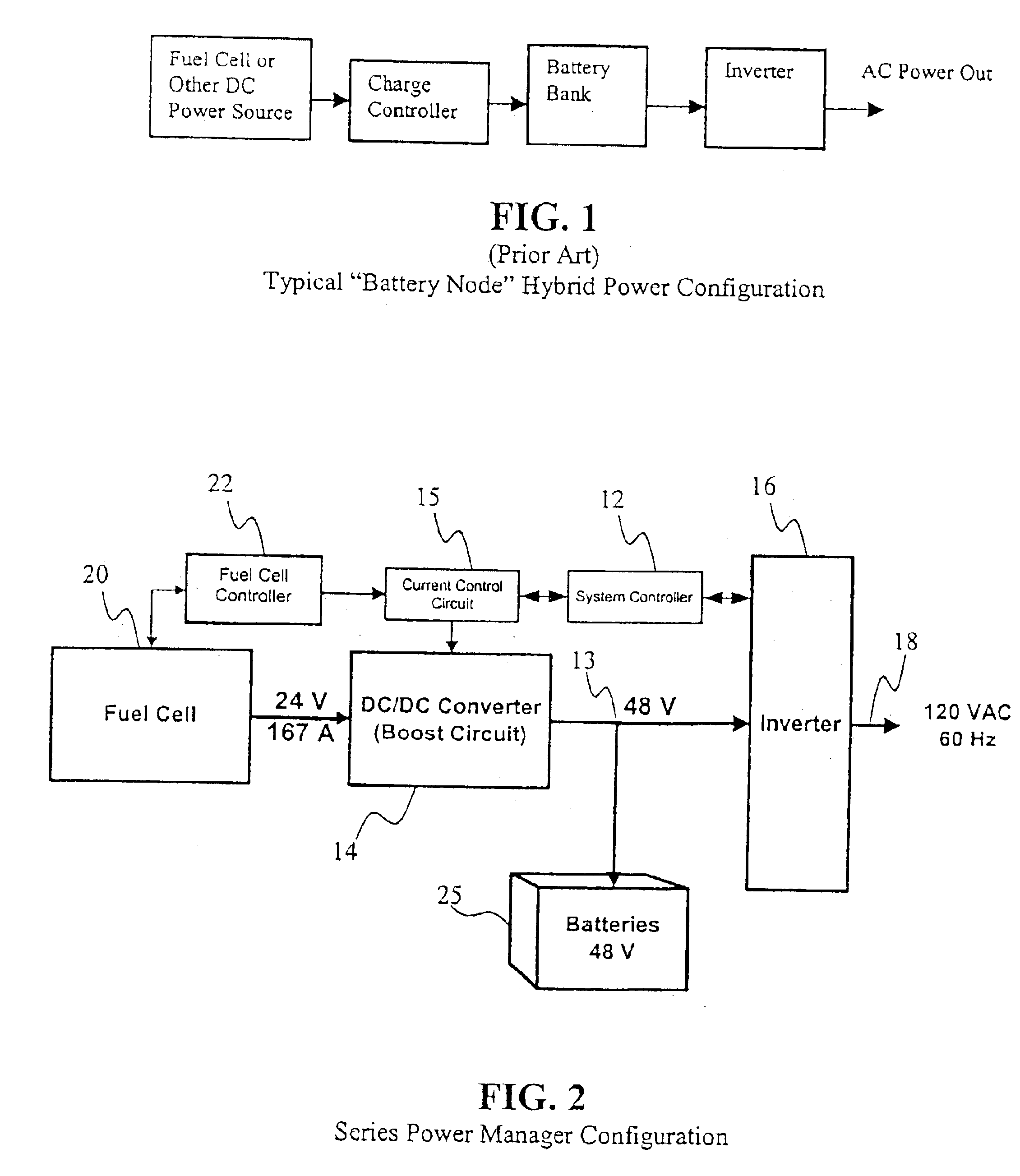
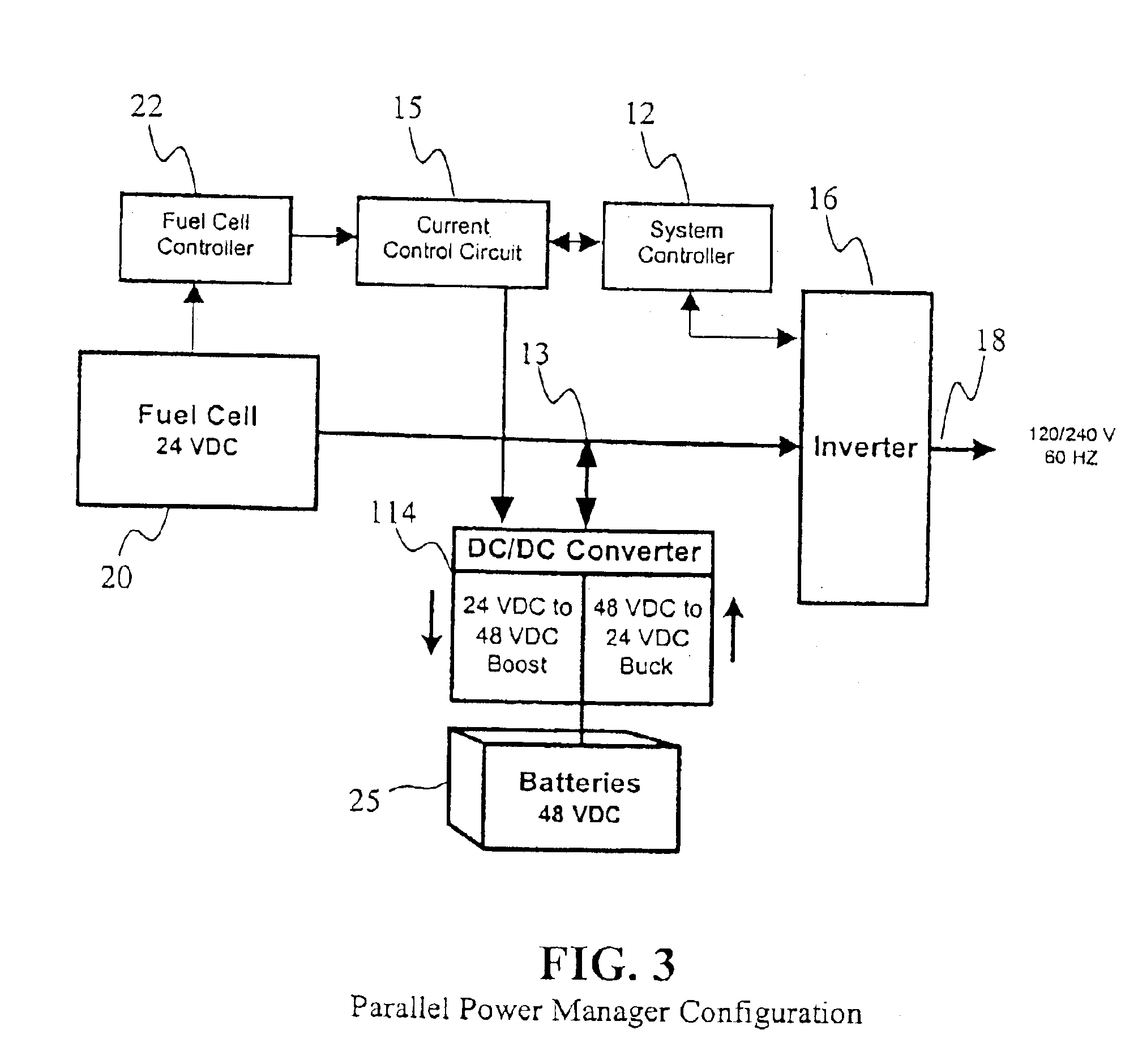
DC to DC converter and power management system
InactiveUS6882063B2Reduce noise and ripple currentReduce voltage stressDc network circuit arrangementsBatteries circuit arrangementsElectrical energy storageDC-BUS
A DC to DC Converter includes an electrical circuit that allows batteries and other electrical energy storage devices to be charged from or to discharge to a variable voltage DC bus. This electrical circuit also enables seamless integration with other energy storage devices and / or DC power sources, such as fuel cells, to provide DC power for a Power Management System. A Power Management System preferably provides both full power source management and power conditioning. The Power Management System is able to manage power flow to and from multiple, isolated power sources and energy storage devices to deliver high quality alternating current (“AC”) power to a load.
Owner:INT POWER SYST
Modular multilevel DC-DC converter and associated method of use
ActiveUS9893633B1Increase flexibilityHigh operating requirementsEfficient power electronics conversionElectric power transfer ac networkGrid faultDc dc converter
In one embodiment, a current-fed modular multilevel dual active-bridge DC-DC converter suitable for medium voltage direct current (MVDC) grid or high voltage direct current (HVDC) grid integration is described. The DAB modular converter and the current-fed DAB converter are soft-switched modular multilevel dual-active-bridge (DAB) converters having DC fault ride-through capability. In an additional embodiment a voltage-fed isolated modular dual active-bridge DC-DC converter for medium voltage direct current (MVDC) or high voltage direct current (HVDC) grids or systems is described. In specific embodiments, the converters may be coupled to a battery energy storage system (BESS), wherein the BESS comprises split-battery units and the interface of the isolated DC-DC converter connects the split-battery units to the MVDC or HVDC system. The converters can be implemented in single-phase or poly-phase configurations and can be controlled to maintain a desired DC output current under both normal and DC grid fault condition.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
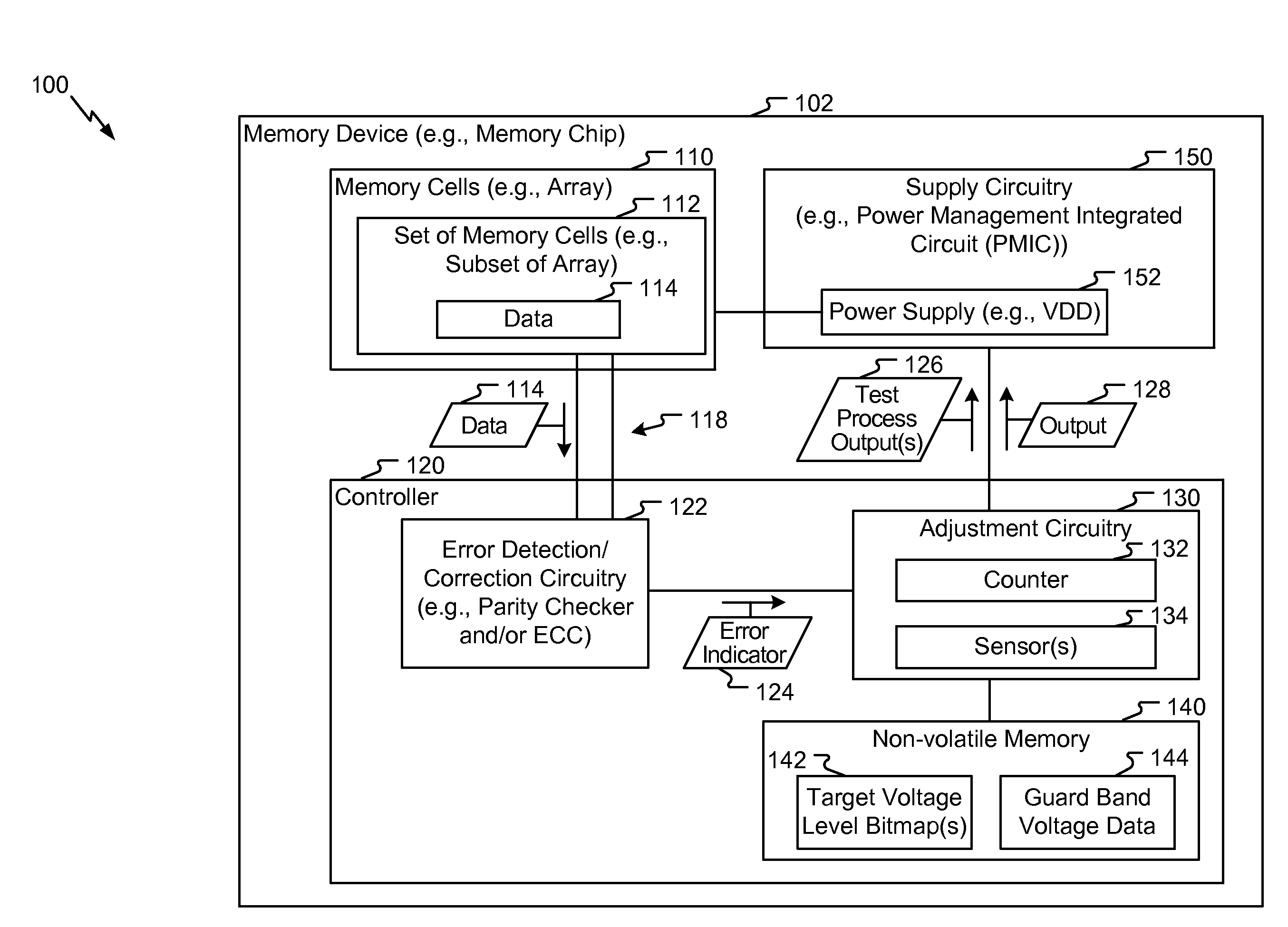
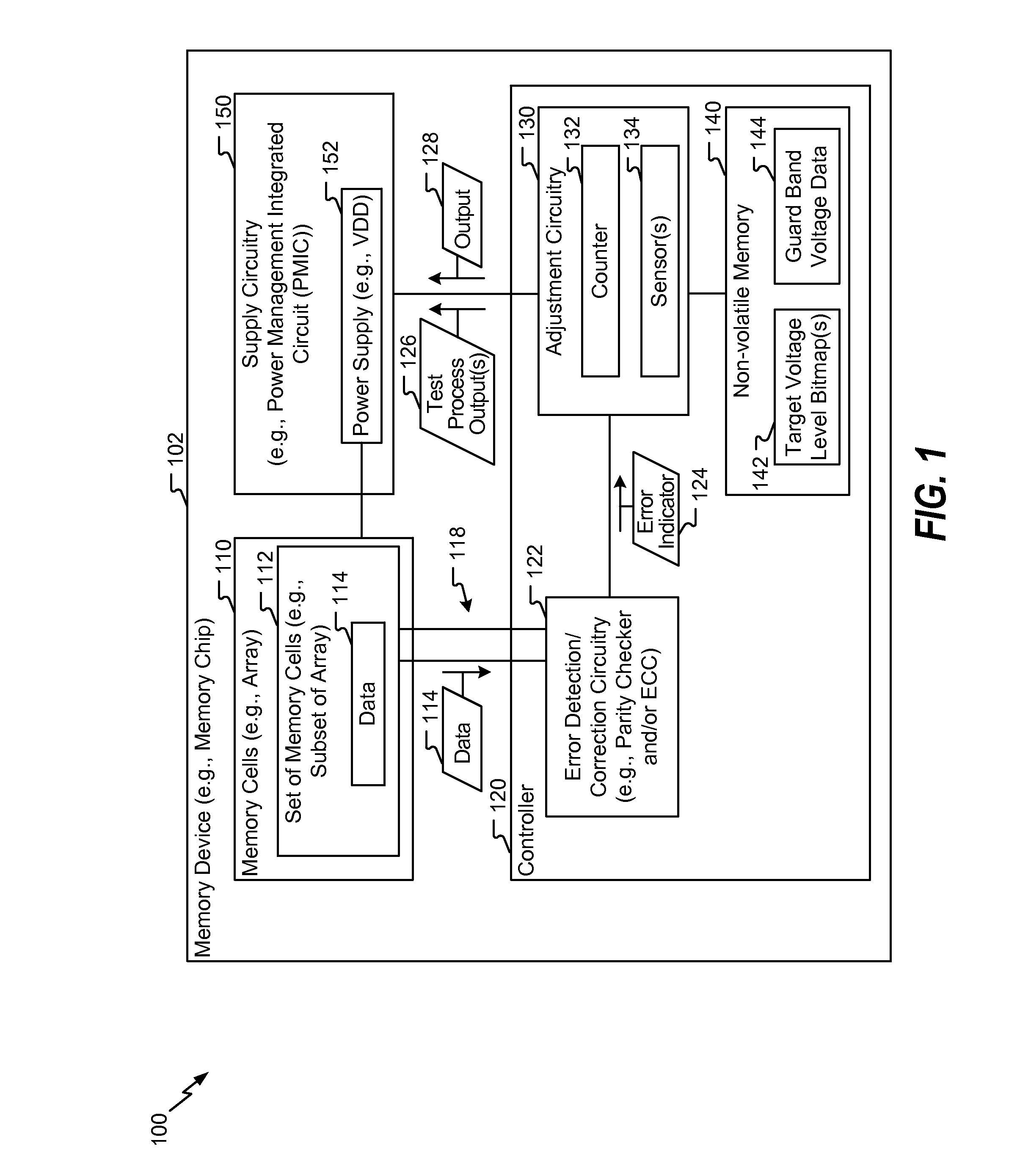
Memory device with adaptive voltage scaling based on error information
ActiveUS20160225436A1Reduce impactOperation margin is reducedDigital storageNon-redundant fault processingEngineeringSelf adaptive
A method of operation of a memory device includes, for each operating frequency of multiple operating frequencies, determining a target voltage level of a supply voltage. For example, a first target voltage level for a first operating frequency of the multiple operating frequencies is determined. The method includes accessing first data from the memory device while the memory device is operating at the first operating frequency and is powered by the supply voltage having a first voltage level. The method includes determining a first number of errors associated with the first data. The method further includes, in response to the first number of errors satisfying a threshold, adjusting the supply voltage to a second voltage level that is greater than the first voltage level.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Bidirectional dc-dc converter
InactiveUS20150097546A1Improve conversion rateLow switching voltageEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionDc dc converterVoltage source
A bidirectional converter circuit includes a voltage source which provides an input voltage, an energy storage set connected to the voltage source and receives the input voltage, a switch set connected to the energy storage set, wherein the switch set includes a first switch and a second switch; an operating switch set connected to the switch set, wherein the operating switch set includes a first operating switch, a second operating switch, a third operating switch and a fourth operating switch. The bidirectional converter further includes a blocking capacitor set and a (input / output) capacitor set. Wherein, the blocking capacitor set is connected to the switch set and the operating switch set. The first operating switch and the second operating switch are driven complementarily with the first switch, and the third operating switch and the fourth operating switch are driven complementarily with the second switch.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device
ActiveUS20040130939A1Securing higher-reliability data retention characteristicReduce voltage stressSolid-state devicesDigital storageComputer architectureCommon word
A memory cell array is included which is constituted by arranging the plurality of nonvolatile memory cells in a row direction and column direction respectively and arranging the plurality of word lines (WL) and the plurality of bit lines (BL) in the row direction and the column direction respectively in order to select a predetermined memory cell or a memory cell group out of the arranged nonvolatile memory cells, in which the memory cells are respectively constituted by connecting one end of a variable resistive element for storing information in accordance with a change of electrical resistances with the source of a selection transistor while in the memory cell array, the drain of the selection transistor is connected with a common bit line (BL) along the column direction, the other end of the variable resistive element is connected with a source line (SL), and the gate of the selection transistor is connected with the common word line (WL) along the row direction. According to the above memory cell configuration, it is possible to provide a nonvolatile semiconductor memory device capable of reducing voltage stresses applied to the variable resistive element of an unselected memory cell at the time of the reading and programming operations and securing a higher-reliability data holding characteristic.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Reconfigurable multi-cell power converter
ActiveUS20100314937A1Simple to reconfigureSimple and fast isolation and replacementElectric signal transmission systemsBatteries circuit arrangementsEngineeringVoltage
A reconfigurable multi-cell power converter and method wherein a set of cells are connected between an input bus and a load in an input series output parallel configuration or in an input parallel output series configuration. Each cell includes a primary side reconfigurable between series and parallel operation and a secondary side also reconfigurable between series and parallel operation. Switching circuitry is configured to reconfigure the primary side of each cell between series and parallel operation and vice versa and also to reconfigure the secondary side of each cell between series and parallel operation and vice versa. A controller is configured to actuate the switching circuitry depending a voltage on the input bus and / or cell condition to reconfigure all the cell primary sides and / or secondary sides while maintaining a desired input series output parallel or input parallel output series connection for the set of cells.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
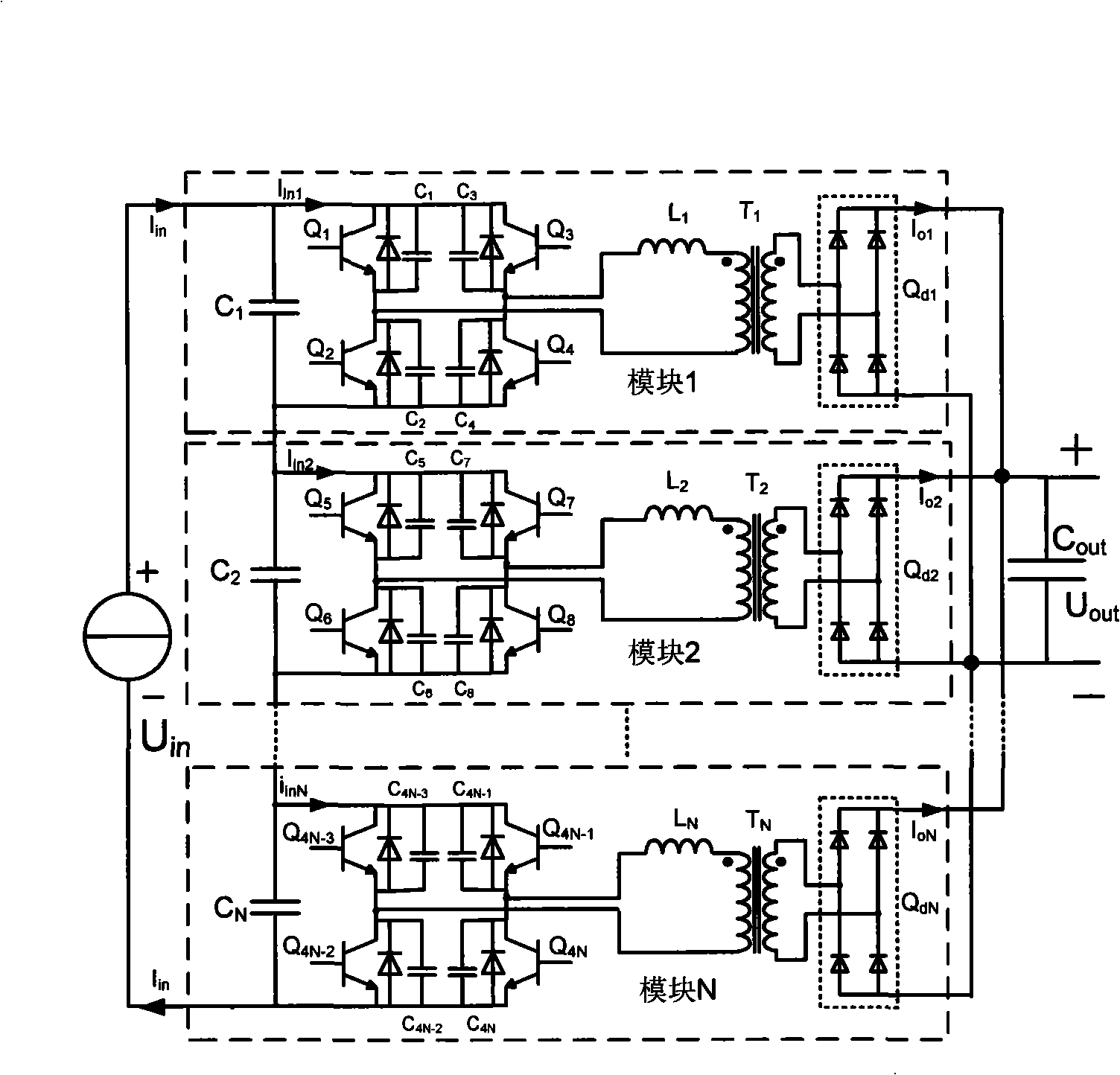
Input-series-output-parallel automatic voltage equalizing DC transformer based on full-bridge topological structure
InactiveCN101345473AReduce voltage stressReduce volumeApparatus without intermediate ac conversionCapacitanceFull bridge
The invention provides an input-series-output-parallel auto balanced voltage transformer based on a full-bridge topology belonging to the dc transformer field. The dc transformer is composed of N dc transformers with a full-bridge topology structure (N is natural number), wherein the input ends of the dc transformer power modules are mutual in-series and connected to the positive and negative terminals of a dc voltage source, the output ends are mutual parallel and connected to two ends of an output filter capacitor. Each power module of the full-bridge topology structure dc transformer comprises an input capacitance, a full-bridge circuit, a series inductance, a high frequency isolating transformer and an output rectifier circuit. The full-bridge circuit comprises a full-bridge circuit formed by four switch tubes, each power module works in the same work frequency or a different work frequency at a duty cycle near to 0.5. The balance voltage at each input side of the power module is auto realized using the input-series-output-parallel structure and secondary side clamping action of the transformer. The transformer provided by the invention not only can be applied in the occasion that no voltage adjustment is needed during the input and output high voltage, but also the occasion of different input voltage grades, which has a good application flexibility and has certain application prospects in the high voltage input and high power occasions.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
High-efficiency stable multifunctional single-stage photovoltaic single-phase grid-connected control method
InactiveCN101714763AReduce Harmonic Distortion RateImprove power qualitySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationPower factorClosed loop
The invention discloses a high-efficiency stable multifunctional single-stage photovoltaic single-phase grid-connected control method, and belongs to the technical field of photovoltaic power generation control. The method is characterized in that: the method adopts a high-speed digital signal processor and applies a C language dynamic fixed-point algorithm to form a high-performance control algorithm of a whole grid-connected control system; the method adopts a single-stage grid-connected control structure and a quick smooth maximum power point tracking method to directly transmit the maximum energy sent by a photovoltaic array to a local urban power grid through first-stage DC / AC transformation; the harmonic and idle work produced by a local load can be compensated by adopting an FBD method, so the method is favorable for improving the electrical energy quality of the local power grid; and a proportional resonant converter is used to implement precise closed-loop control for the grid-connected current so that the photovoltaic grid-connected current and the commercial single-phase voltage are totally synchronous while implementing maximum power point tracking of the photovoltaic array. The power factor is high, the system efficiency is high, the operation of the whole system is safe and reliable, and the aberration rate of the grid-connected current harmonic is lower than 3 percent.
Owner:WUXI SLD POWER TECH
High voltage gain bidirectional DC-DC (direct current-direct current) converter based on switching capacitors and coupling inductors
InactiveCN104218798ASmall rippleReduce the size of the inductorDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationCapacitanceHigh frequency power
The invention discloses a high voltage gain bidirectional DC-DC (direct current-direct current) converter based on switching capacitors and coupling inductors. The high voltage gain bidirectional DC-DC converter based on the switching capacitors and the coupling inductors is formed by combining Boost convertors, the coupling inductors and the switching capacitors in interleaved mode. An electric circuit of the high voltage gain bidirectional DC-DC converter based on the switching capacitors and the coupling inductors comprises n / 2 coupling inductors T1[L1, L2], T2[L3, L4]... T(n / 2)[L(n-1), Ln], 2n high frequency power switches S1, S2... Sn and Q1, Q2... Qn, N-1 high frequency switching capacitors C1, C2... C(n-1) and two input and output filter capacitors CL and CH. The high voltage gain bidirectional DC-DC converter based on the switching capacitors and the coupling inductors can effectively reduce current stress of a low voltage side power device and voltage stress of a high voltage side power device, further reduces the ripple of an input current and decrease the inductor size by using the coupling inductors, improves efficiency of an exchanger, and achieves bidirectional DC-DC conversion high in efficiency and high in voltage gain. According to high voltage gain bidirectional DC-DC converter based on the switching capacitors and the coupling inductors, an interleaved technology, a magnetic integration technology and a switching capacitor technology are combined, and therefore novel topology of the high voltage gain bidirectional DC-DC converter based on the switching capacitors and the coupling inductors not only has characteristics of being low in ripple of the input current and easy to design in EMT mode of an interleaved converter, but also achieves the purposes that a transformation ratio of input voltage and output voltage is large and switch voltage stress is low.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
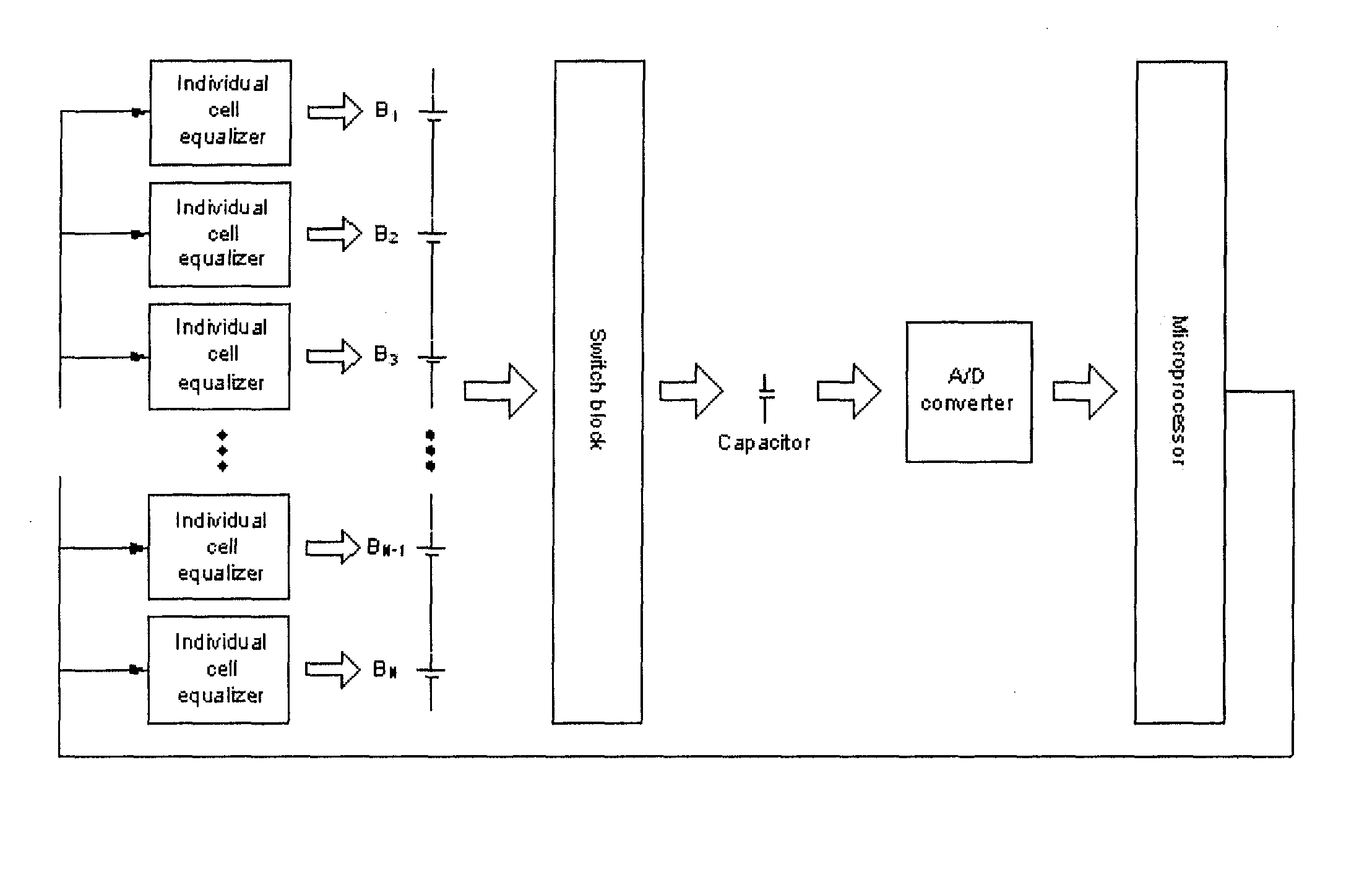
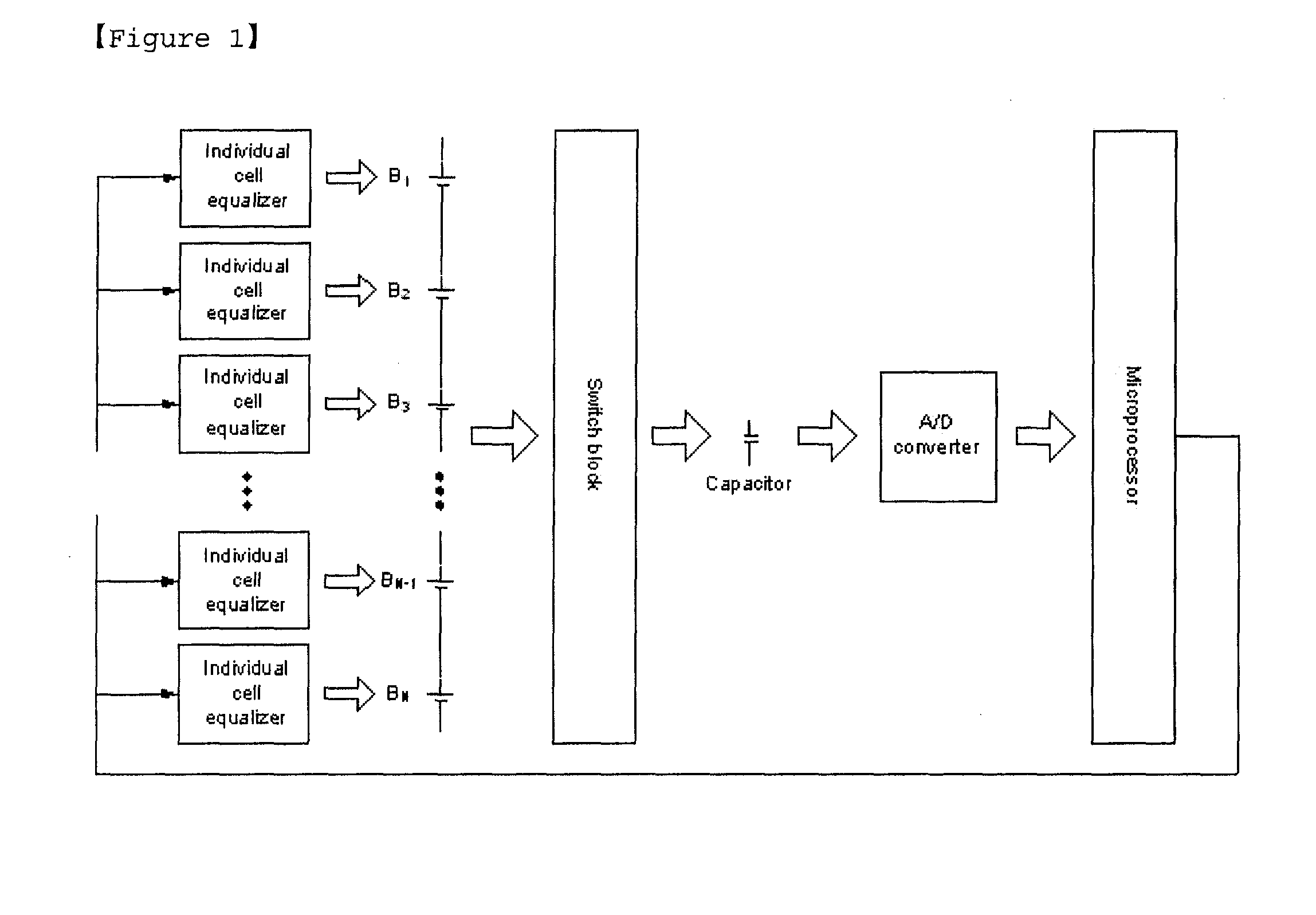
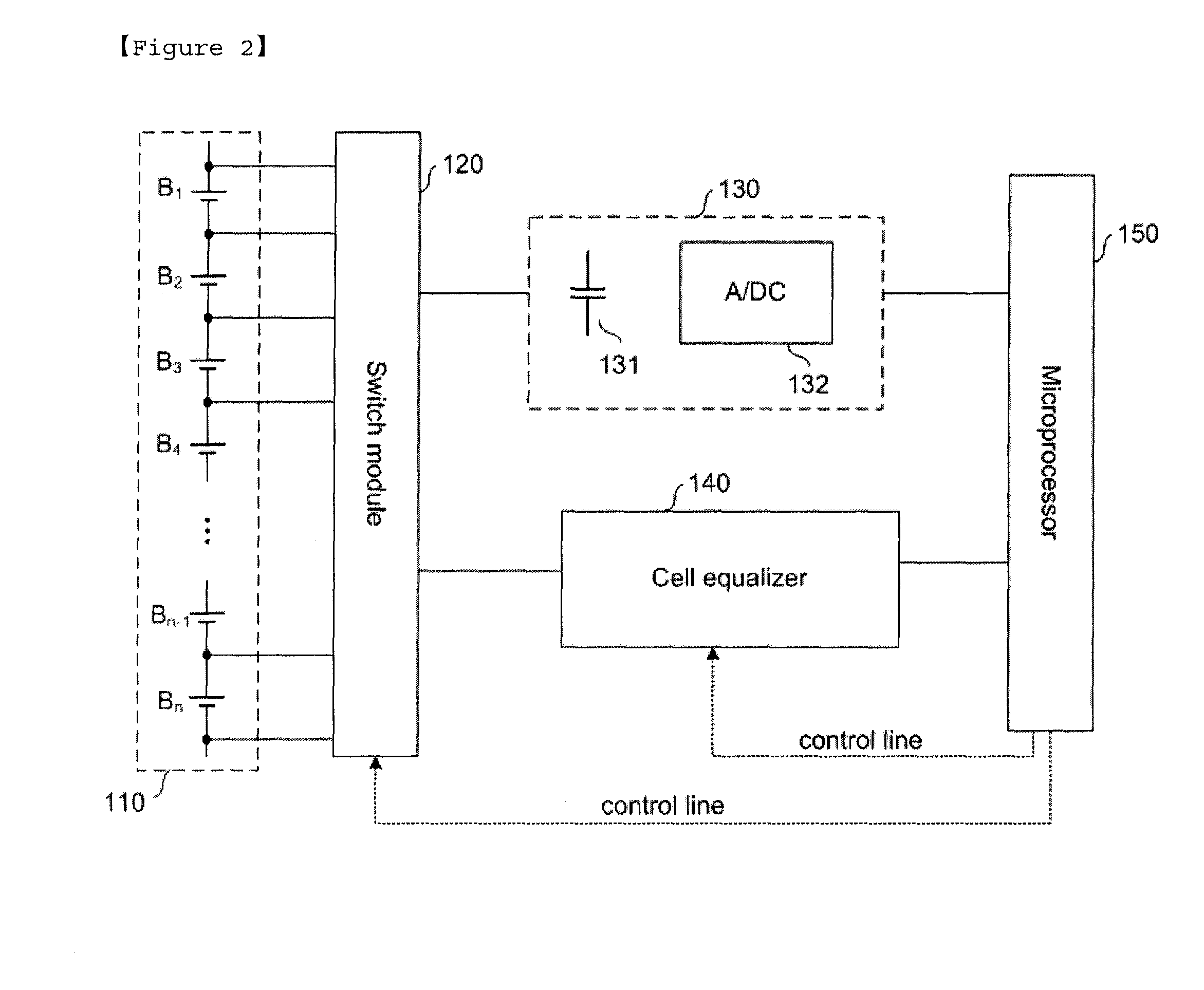
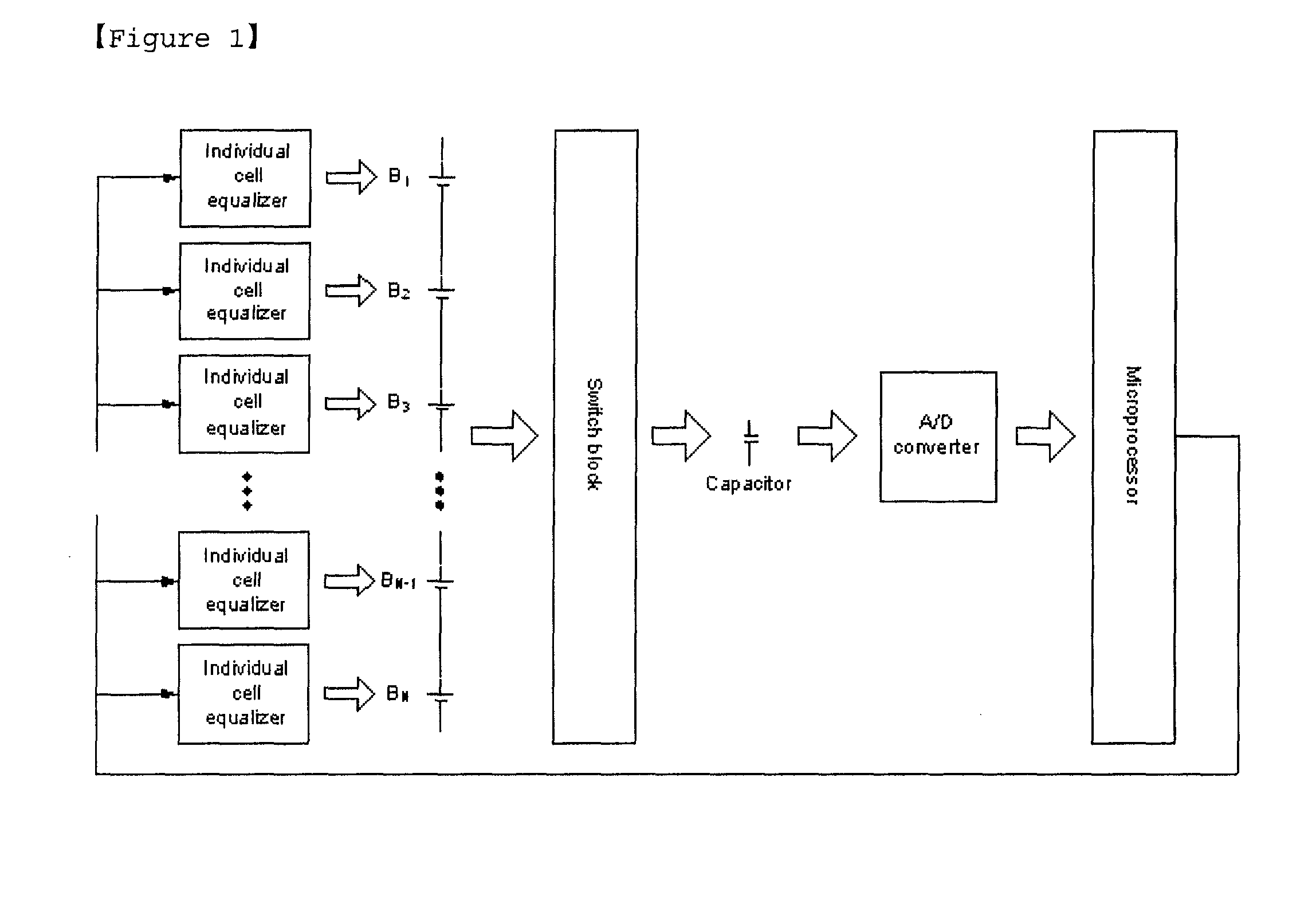
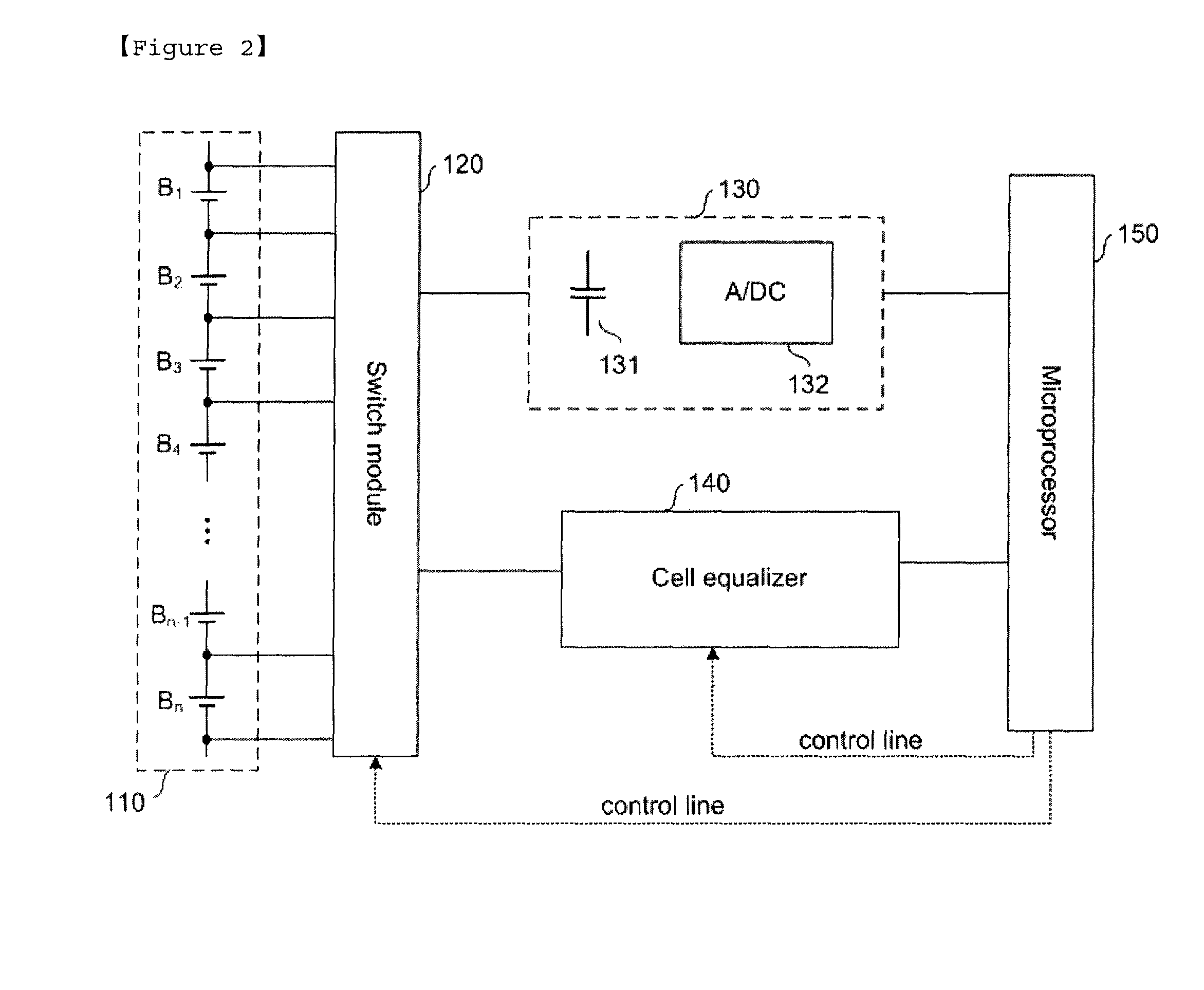
Battery Management System with Integration of Voltage Sensor and Charge Equalizer
ActiveUS20100231166A1Reduce volumeReduce chargeCharge equalisation circuitCircuit monitoring/indicationVoltage sensorBattery management systems
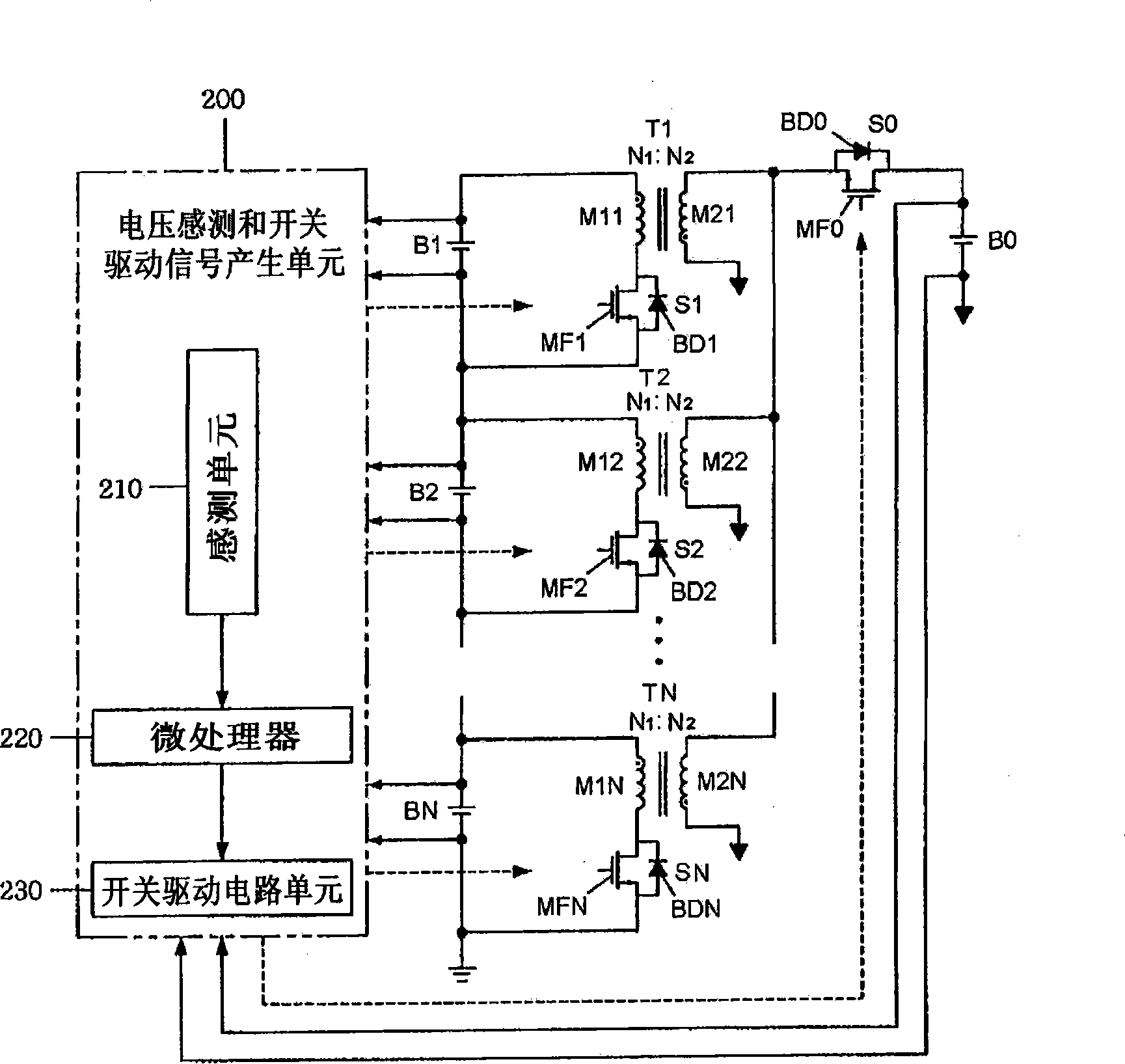
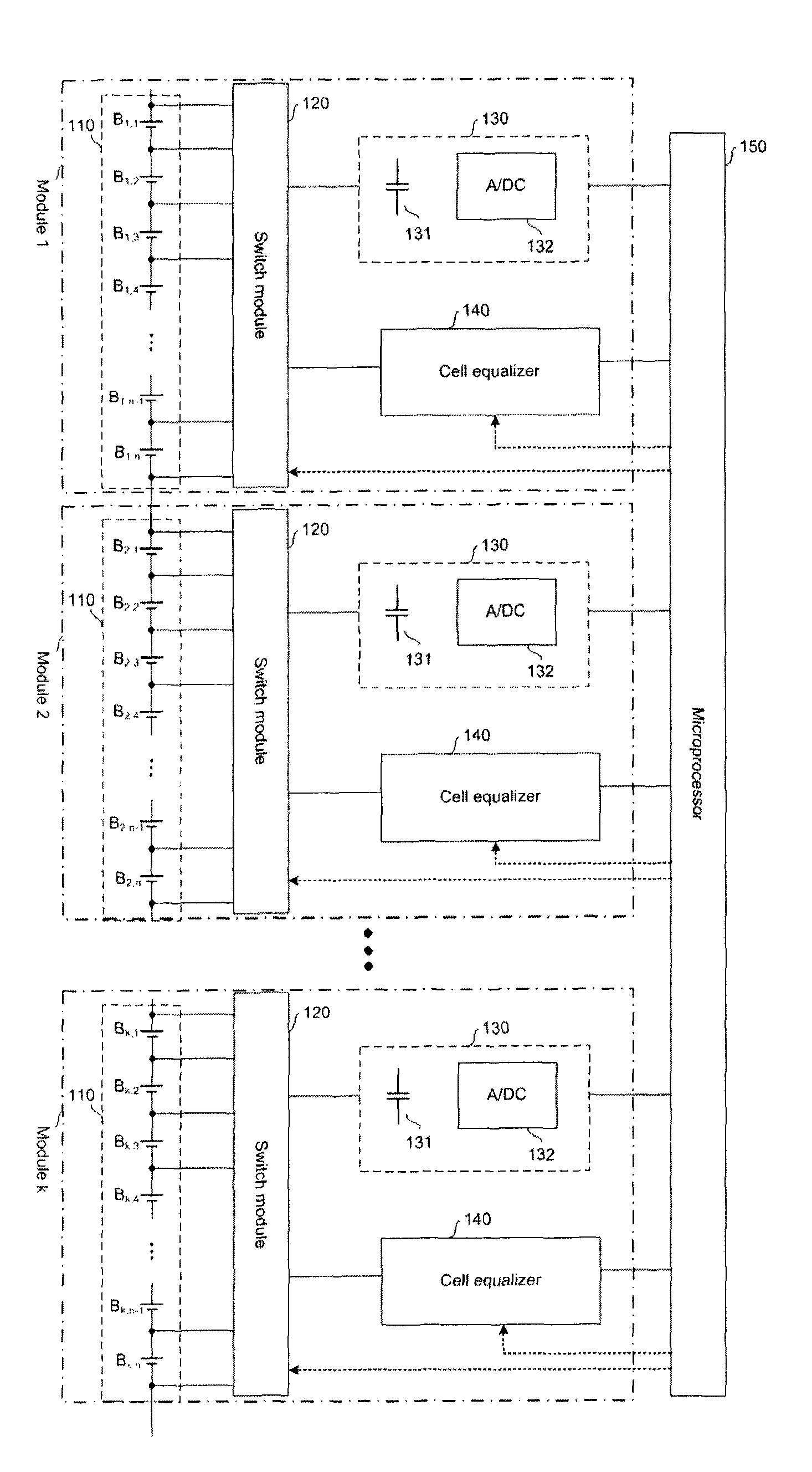
A battery management system according to the present invention comprises a battery module consisted of a plurality of batteries connected in series; a switch module connected in parallel to the battery module; a voltage sensor measuring a voltage of each battery composing the battery module; a charge equalizer causing each battery composing the battery module to be charged, discharged or charged / discharged; and a microprocessor controlling the switch module to determine whether to charge or discharge each battery composing the battery module according to the voltage values measured by the voltage sensor and; wherein the voltage sensor and the charge equalizer are connected in parallel to each battery composing the battery module by the switch module.
Owner:SK ON CO LTD +1
High efficiency power conversion circuits
InactiveUS20060062026A1Easy to handleReduce winding voltage stress stressEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionLevel shiftingFull bridge
A composite high voltage schottky rectifier is revealed that provides a forward voltage slightly larger than a low voltage schottky rectifier combined with a high voltage breakdown capability. The composite rectifier can be formed from the combination of a low voltage schottky rectifier, a high voltage mosfet, and a few small passive components. A quarter bridge primary switching network similar in some ways to a half bridge primary switching network is revealed. The quarter bridge network consists of four switches with voltage stress equal to half the line voltage and the network applies one quarter of the line voltage to a primary magnetic circuit element network thereby reducing the number of primary winding turns required to one quarter by comparison to a common full bridge network. A synchronously switched buck post regulator is revealed for multi-output forward converters. The synchronously switched buck post regulator accomplishes precise independent load regulation for each output and reduced magnetics volume by using a coupled inductor with a common core for all outputs plus a second smaller inductor for each output except the highest voltage output. An improved capacitor coupled floating gate drive circuit is revealed that provides an effective drive mechanism for a floating or high side switch without the use of level shifting circuits or magnetic coupling. The capacitor coupled floating gate drive circuit is an improvement over prior art capacitor coupled floating gate drive circuits in that the new circuit uses a positive current feedback mechanism to reject slowly changing voltage variations that cause unintentional switch state changes in prior art capacitor coupled floating gate drive circuits.
Owner:TECHN WITTS
Cascade megawatt photovoltaic grid-connected inverter
InactiveCN102097966AReduce volumeReduce weightDc-dc conversionPhotovoltaic energy generationHigh energyTransformer
The invention provides a cascade megawatt photovoltaic grid-connected inverter, wherein a topology structure of the cascade megawatt photovoltaic grid-connected inverter is composed of two levels, namely a DC / DC (direct current / direct current) isolation level and a DC / AC (direct current / alternating current) output level; the structures of three phases of circuits are the same; the output ends of a power inverter group of each single-phase of DC / DC output level are connected in a star shape; the input sides of power units of each single-phase level are provided with independent PV (photovoltaic) modules of the same structure; the DC / DC isolation level comprises high-frequency DC / AC, a high-frequency transformer and high-frequency AC / DC nodes of each single-phase for realizing isolation and boosting, and reducing the consumption of a switch tube via action of a resonant soft switch; the output level power transformer set adopts a bridge type inverter circuit; and the single-phase output level power units are connected with each other in a cascade mode. Based output cascade, the device can realize megawatt grid connection; as a high-frequency chain technology is used, the traditional low frequency transformer is omitted, and the power density is high; and compared with the existing photovoltaic grid-connected inverter structure, the device provided by the invention has the advantages of high energy conversion efficiency, excellent output energy quality, certain fault-tolerant capability and the like.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Novel efficient and reliable DC/AC converter for fuel cell power conditioning
InactiveUS20050141248A1Reduce conduction lossReduced Thermal Management RequirementsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsDc circuit to reduce harmonics/ripplesFuel cellsWork status
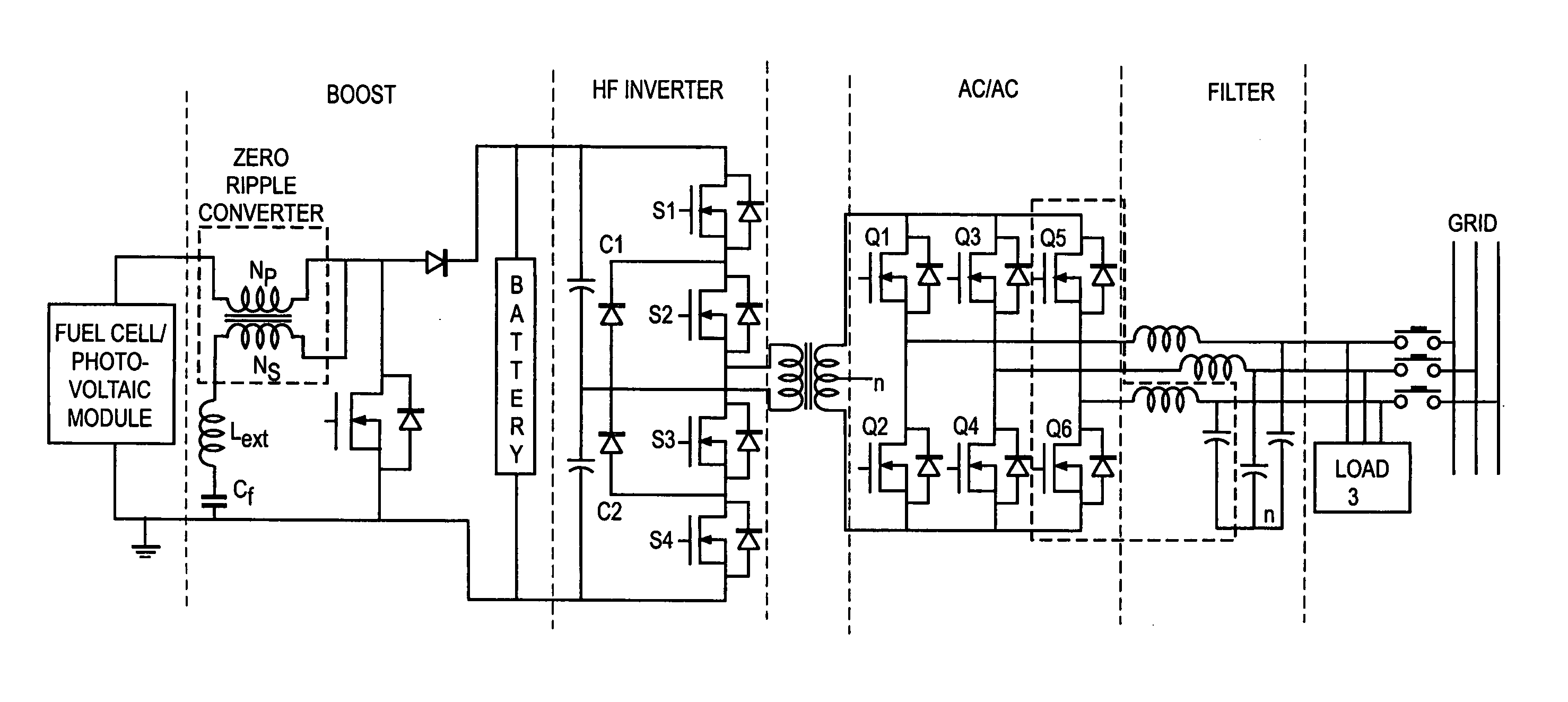
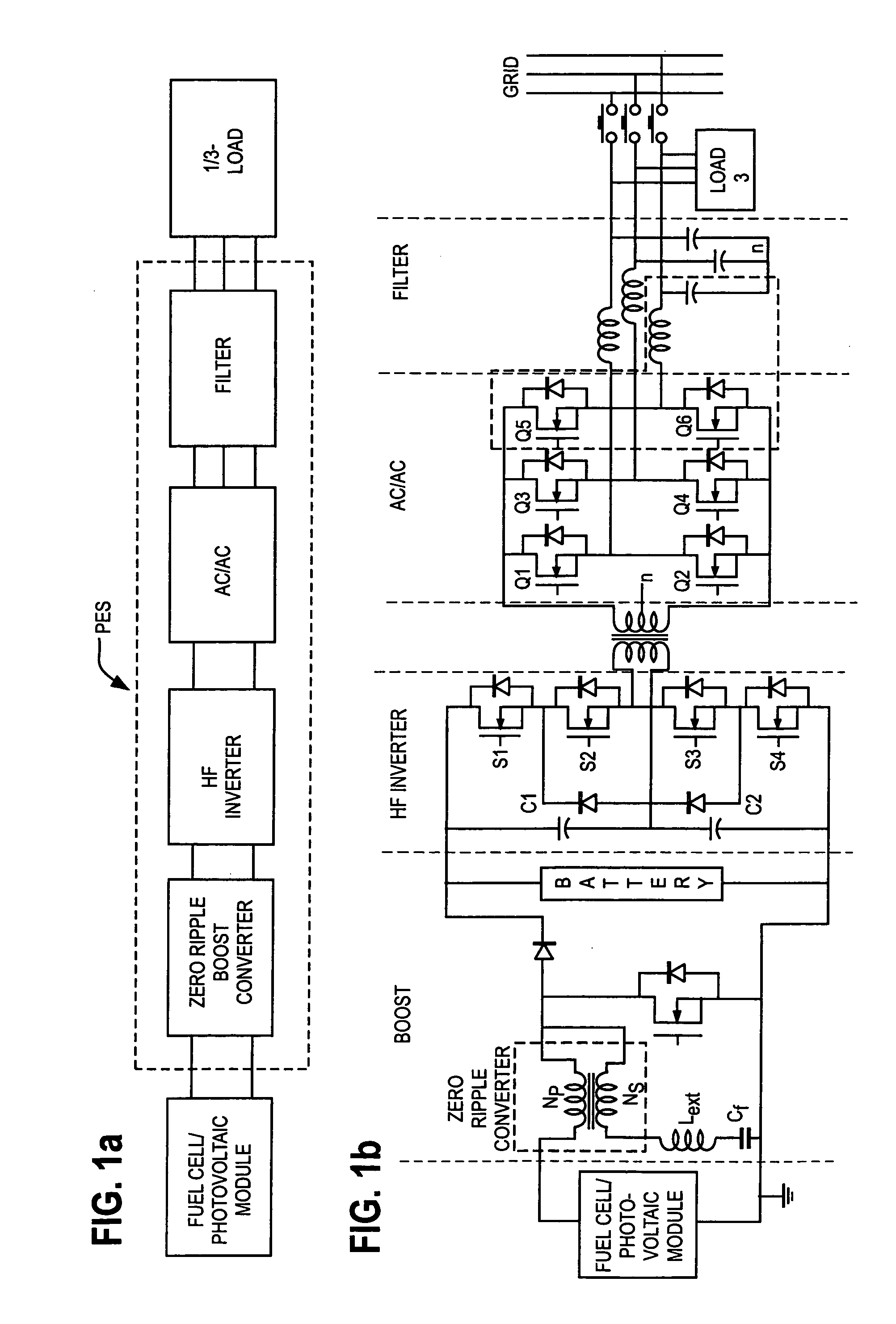
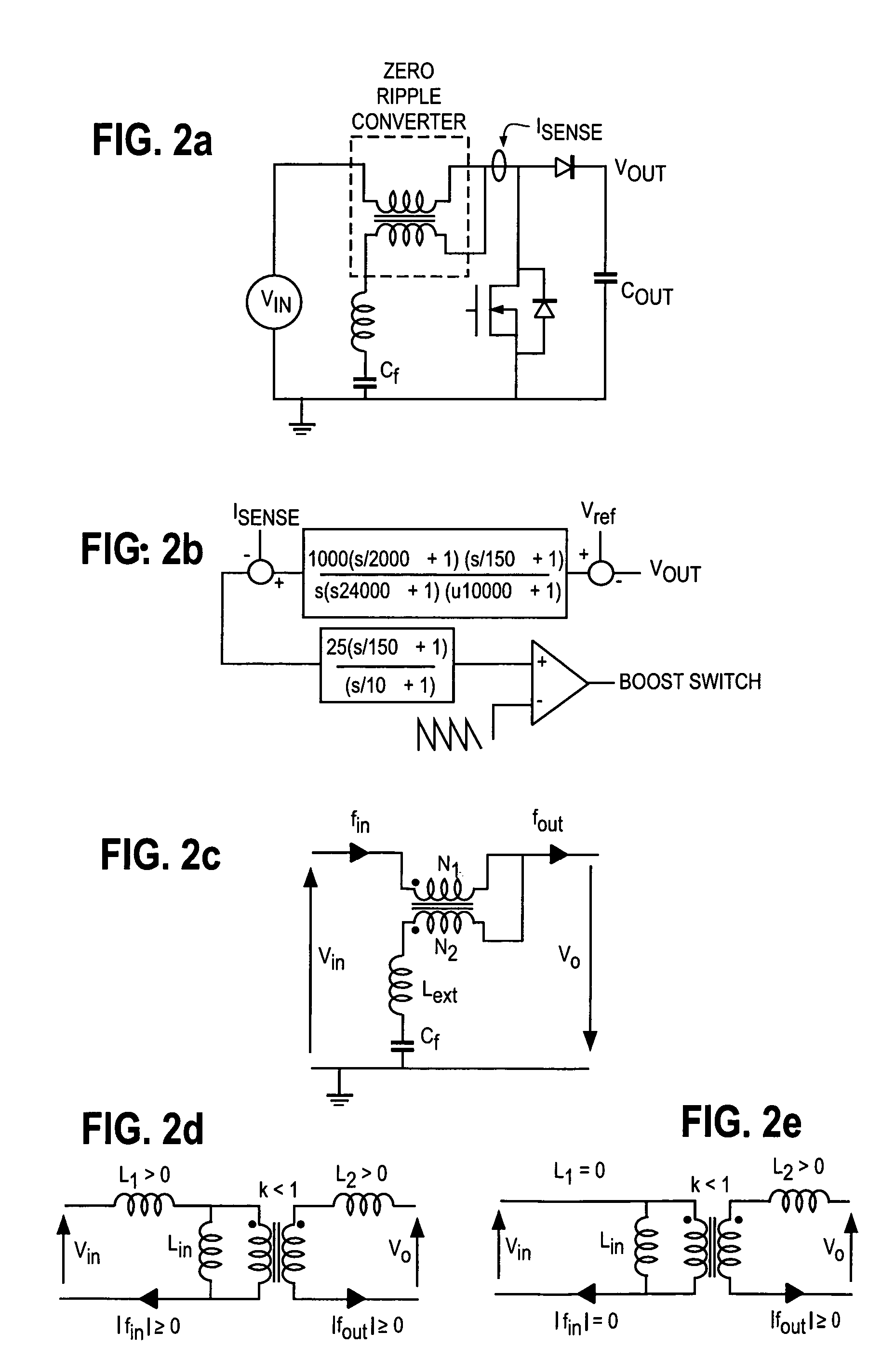
A novel power conditioning converter which provides a significant reduction in input current ripple (<1%), with efficiency above 90% and reduced thermal management is proposed. The converter in discussion has a sort-switched, multilevel, high frequency converter, which acts as an interface between the dc / dc boost and the ac / ac converter. This paper presents a detailed description of the operation of the converter and highlights the important features and advantages. SABER simulation results are presented to provide an improved understanding of the switching mechanisms. A discussion on the implementation of the converter and the status of ongoing work is presented.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Charge equalization apparatus with parallel connection of secondary windings of multiple transformers
ActiveCN101467324AImprove balanceImprove uniformityCharge equalisation circuitElectric powerTransformerEngineering
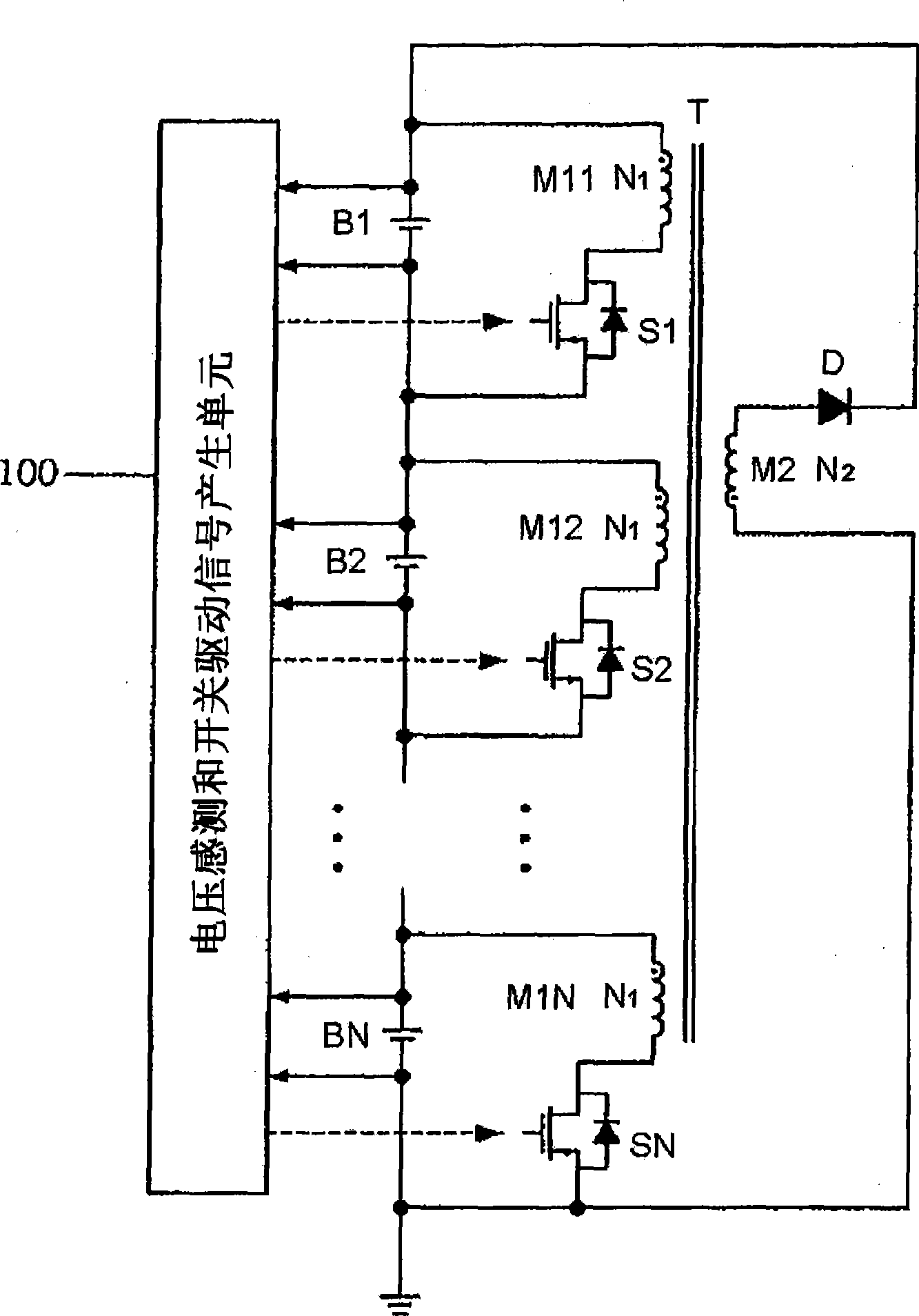
The present invention relates, in general, to a charge equalization apparatus with series-connected battery cells and, more particularly, to a charge equalization apparatus, in which series-connected battery cells (Bl to BN) are connected in parallel with the primary windings (Mi l to MlN) of transformers (Tl to TN), switches (Sl to SN) for controlling the flow of current of the primary windings are connected in series with the primary windings (Ml 1 to MlN), and multiple secondary windings (M21 to M2N) corresponding to the primary windings are connected in parallel with each other.
Owner:SK ON CO LTD +1
Battery management system with integration of voltage sensor and charge equalizer
ActiveUS8253378B2Reduce volumeReduce chargeCharge equalisation circuitCircuit monitoring/indicationElectrical batteryEngineering
A battery management system according to the present invention comprises a battery module consisted of a plurality of batteries connected in series; a switch module connected in parallel to the battery module; a voltage sensor measuring a voltage of each battery composing the battery module; a charge equalizer causing each battery composing the battery module to be charged, discharged or charged / discharged; and a microprocessor controlling the switch module to determine whether to charge or discharge each battery composing the battery module according to the voltage values measured by the voltage sensor and; wherein the voltage sensor and the charge equalizer are connected in parallel to each battery composing the battery module by the switch module.
Owner:SK ON CO LTD +1
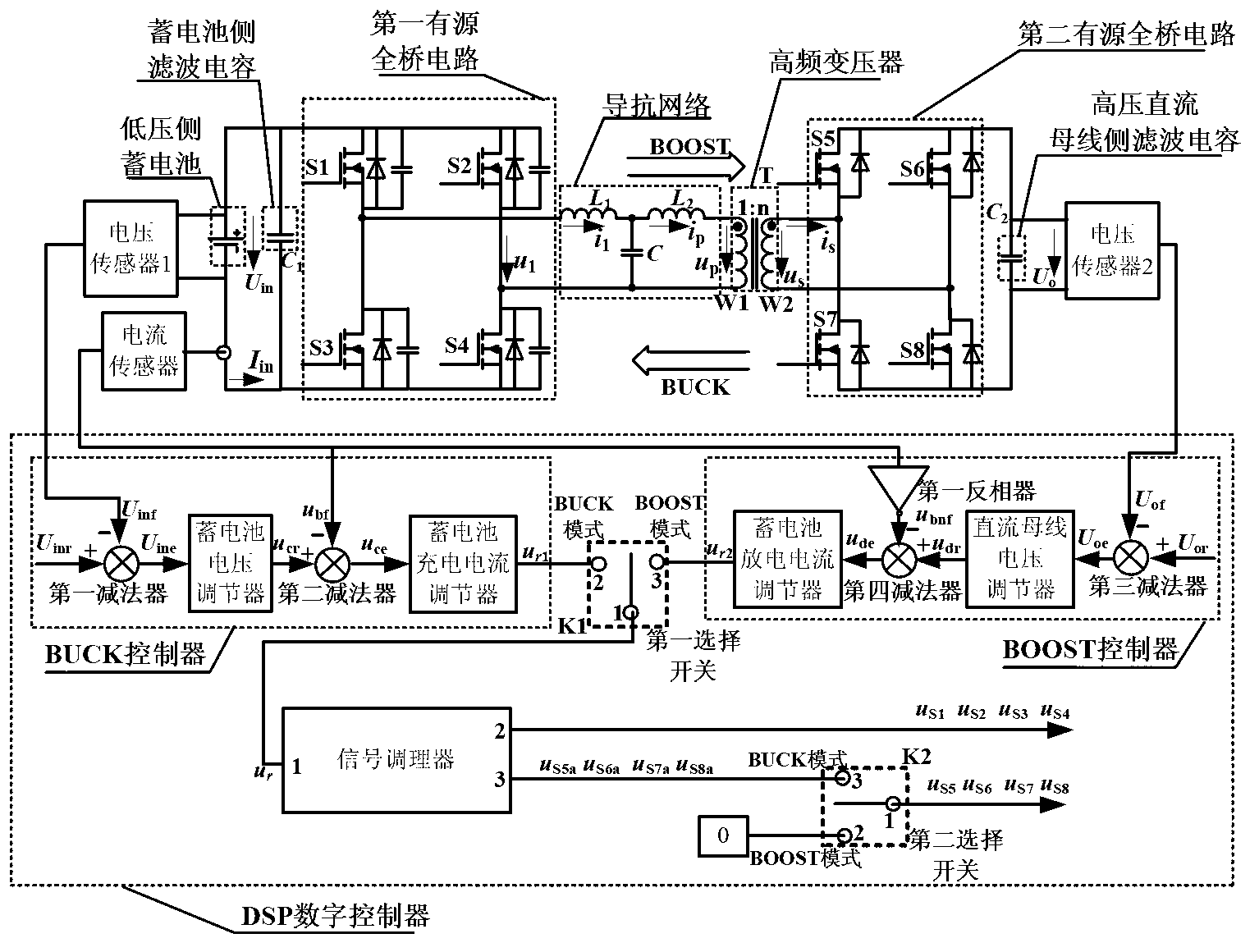
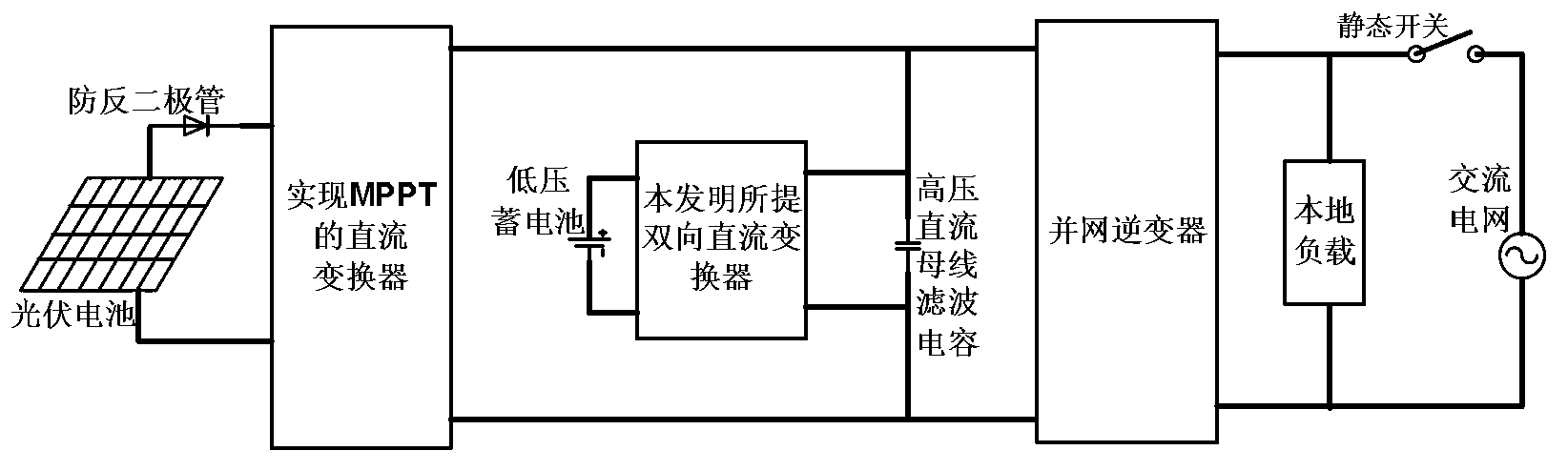
Bidirectional direct current converter based on immittance network, and digital control system and method of bidirectional direct current converter
InactiveCN103187879AReduce voltage stressReduce current stressDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationCapacitanceDigital signal processing
The invention discloses a bidirectional direct current converter based on an immittance network, and a digital control system and a digital control method of the bidirectional direct current converter. The bidirectional direct current converter based on the immittance network comprises a storage battery, a low-voltage-side filter capacitor, a first active full-bridge circuit, the immittance network, a high-frequency transformer, a second active full-bridge circuit and a high-voltage-bus-side filter capacitor. The digital control system comprises a first voltage sensor, a second voltage sensor, a current sensor and a digital signal processing (DSP) digital controller, wherein the DSP digital controller comprises a BUCK controller, a BOOST controller, a signal conditioner, a first selective switch and a second selective switch. According to the basic characteristics of the immittance network, the two active full-bridge circuits in the bidirectional direct current converter can operate with high power factor, and the current stress of a switching tube can be greatly reduced. By the adoption of the system and the method, according to the characteristics of the immittance network, the zero-current turn on and zero-current turn off of all switching devices of a high-voltage-side active full-bridge circuit are realized, and the efficiency of the converter is improved.
Owner:YANCHENG INST OF TECH
High-gain interleaving boost converter
ActiveCN102946194ASimple topologyReduce voltage stressApparatus without intermediate ac conversionCapacitanceConverters
The invention provides a high-gain interleaving boost converter. The high-gain interleaving boost converter comprises two inductors, two power switches, an output diode and voltage-multiplying units, wherein the voltage-multiplying units form a three-port unit by a diode and a capacitor; the first port is connected with one end of the capacitor, the other end of the capacitor and the node of the diode cathode are used as the second port; and the anode of the diode is used as the third port. The base gain is doubled on the basis of the gain of the original circuit by adding one voltage-multiplying unit in the circuit each time, i.e. the gain ratio of the circuit is (n+1) times that of the base boost converter by adding n voltage-multiplying units in the circuit. Compared with the conventional high-gain boost converters, the high-gain interleaving boost converter disclosed by the invention has simple circuit topology and no coupling inductance (EMI (Electro-Magnetic Interference) small), and can greatly reduce voltage stress of a switching element, so that the integral working efficiency of the converter is improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Dc converter
ActiveCN101197540ASmall output ripple noiseReduce voltage stressApparatus with intermediate ac conversionElectric variable regulationCapacitanceLow voltage
The invention provides a DC converter which overcomes the shortcoming in the prior art that an isolating main voltage stress is high, the utilization rate of a transformer is low and the wave noise of the output voltage is high and so forth. The invention comprises a PWM controller, an adjustment converter for receiving an output controlling pulse signal of the PWM controller and an isolating converter; the adjustment converter can adjust the input voltage to a relatively stable bus voltage, the isolating converter is provided with a fixed air space ratio, which can transform the bus voltage into the output voltage required and transfer the power rate, the transformer auxiliary side of the isolating converter is provided with a rectifying circuit comprising two switch tubes, the rectifying circuit comprises two groups of driving wave-shaping circuit comprising two sets of diode and capacitors, which are respectively connected with the two switch tubes to form a staggered and parallel first branch and a second branch. The invention has the advantageous performance of high efficiency, dynamic reaction, better wave noise and EMC, which can meet the requirement of a low voltage current DC converter.
Owner:EMERSON NETWORK POWER CO LTD
Isolated Switched-mode Power Supply With Output Regulation From Primary Side
InactiveUS20090067201A1Reduce voltage stressShorten the counting processDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationSwitched-mode power supply
Embodiments disclosed herein describe an isolated switched-mode power supply with its output regulated from the primary side, by generating a sensing current using a sensing element coupled to the output of the power supply, and measuring a scaled version of the sensing current which depends on the output voltage, and calculating an estimate voltage representing the output voltage, and regulating the output of the isolated switched-mode power supply based on the estimate voltage.
Owner:CAI JUN
Feedback control method, feedback control method based control method for asymmetric half bridge type flyback converter, and realization circuits for two methods
ActiveCN105375783AHigh precisionIncrease profitDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationResonance oscillationParasitic capacitance
The invention aims to realize that a control mode of primary side feedback is added into an asymmetric half bridge type flyback converter in a non-complementary DCM mode. For the asymmetric half bridge type flyback converter working in the non-complementary DCM mode, primary side inductance is released and is not clamped by an output end at the moment of finishing primary side excitation energy resetting. At the time, the primary side inductance, resonant capacitance, leakage inductance, and parasitic capacitance between the drain and the source of an MOS transistor start resonance oscillation; and at the moment of oscillation starting, a voltage between the drain and the source of the MOS transistor forms an "inflection point", voltages on two ends of the primary side inductance reflect voltage changes of the output end, voltages ontwo ends of an auxiliary winding have similar changes, an oscillation starting direction is just opposite to the direction of the voltages on the two ends of the primary side inductance due to a dotted terminal winding relationship, and if the inflection point is detected through the auxiliary winding and inflection point information is transmitted to a controller, the detection and control of an output voltage can be realized. Compared with the prior art, relatively high output voltage precision, linear adjustment rate and load adjustment rate of the converter can be ensured; and meanwhile, zero voltage switching (ZVS) of a primary side switch tube can be realized, the working frequency of the converter can be increased, the efficiency of the converter can be improved, and the volume of a complete machine is reduced.
Owner:MORNSUN GUANGZHOU SCI & TECH
Two-Stage Charge Equalization Method and Apparatus for Series-Connected Battery String
ActiveUS20100207579A1Reduce voltage stressEfficient charge equalizationCharge equalisation circuitElectric powerEngineeringDc converter
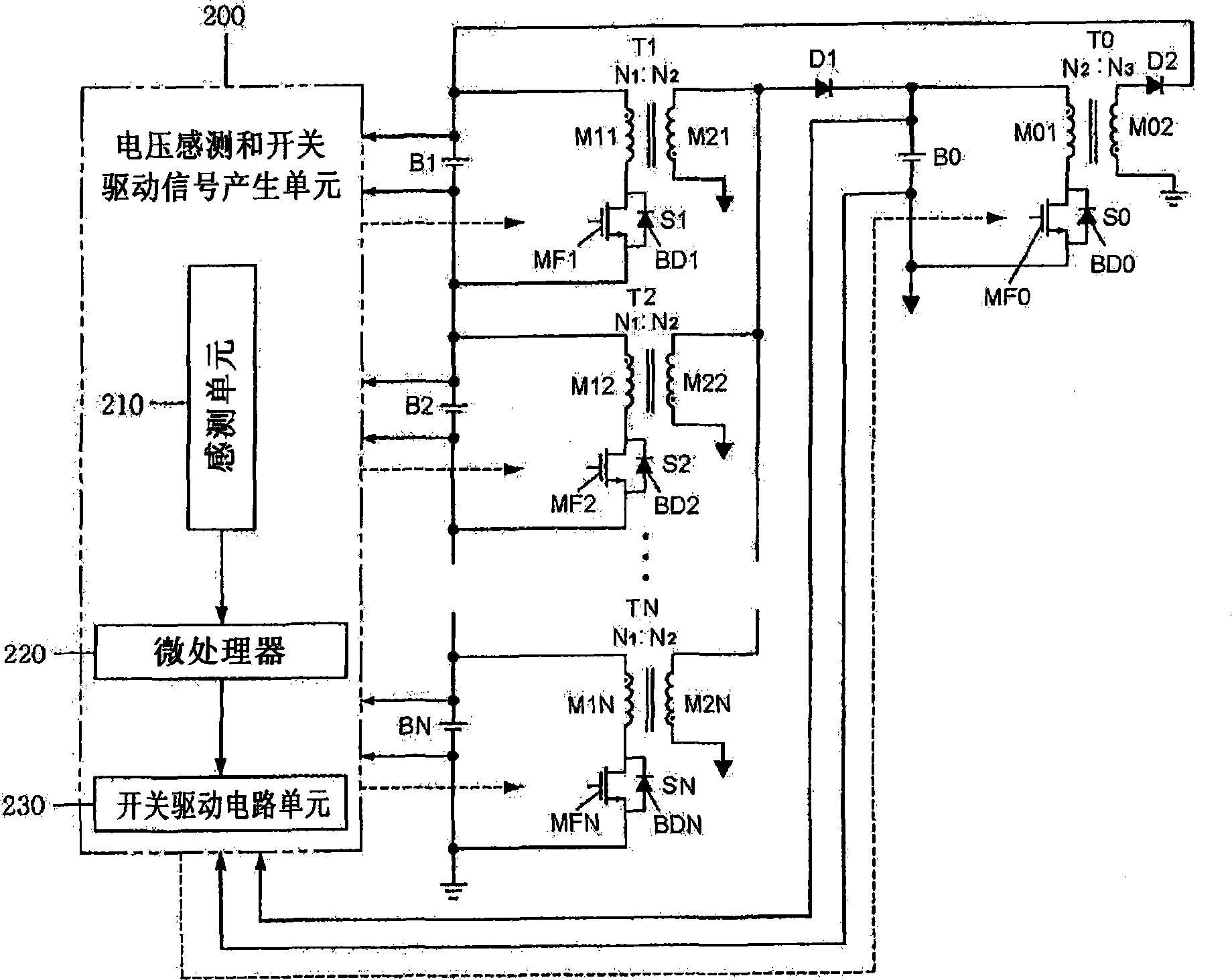
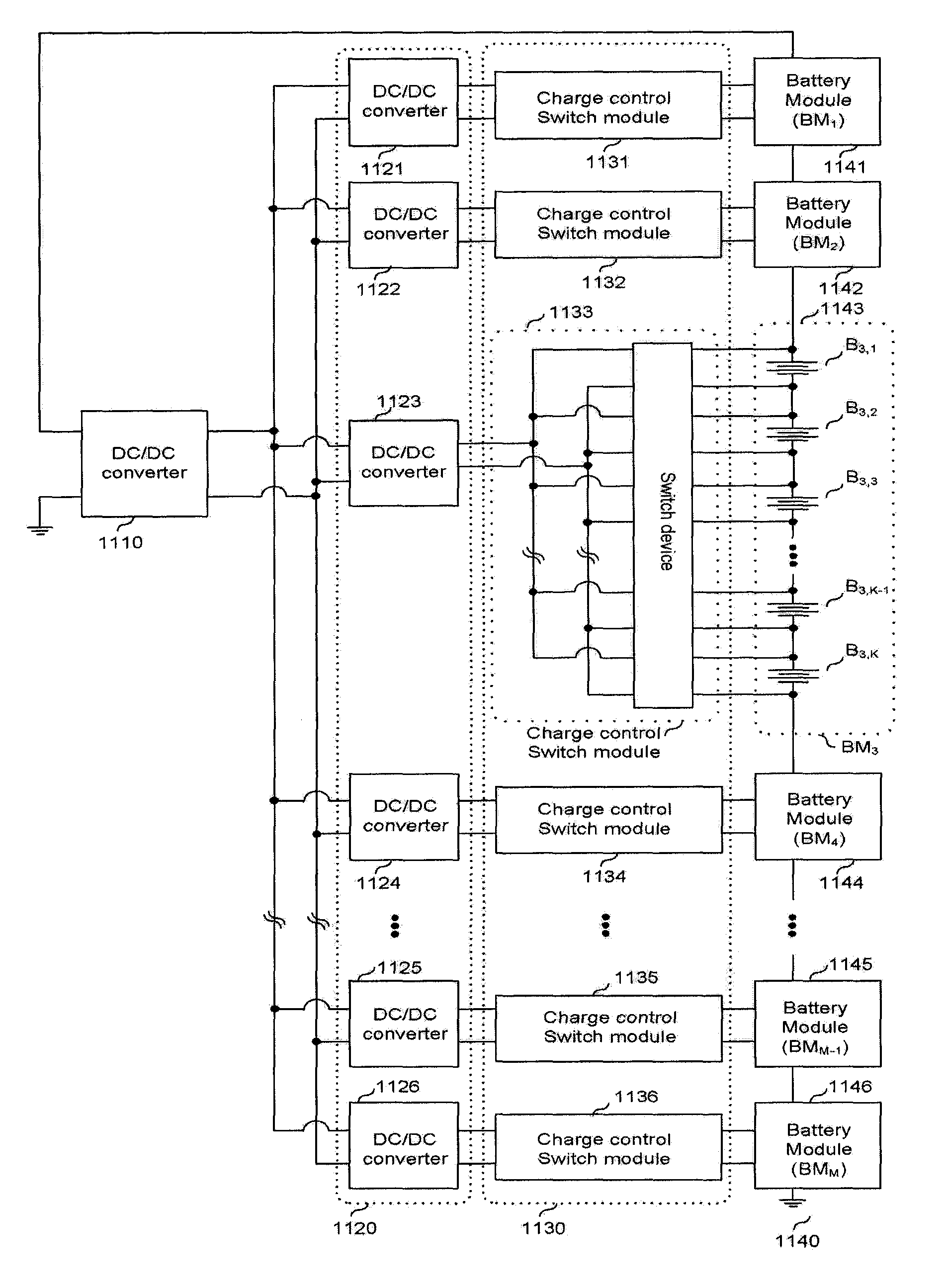
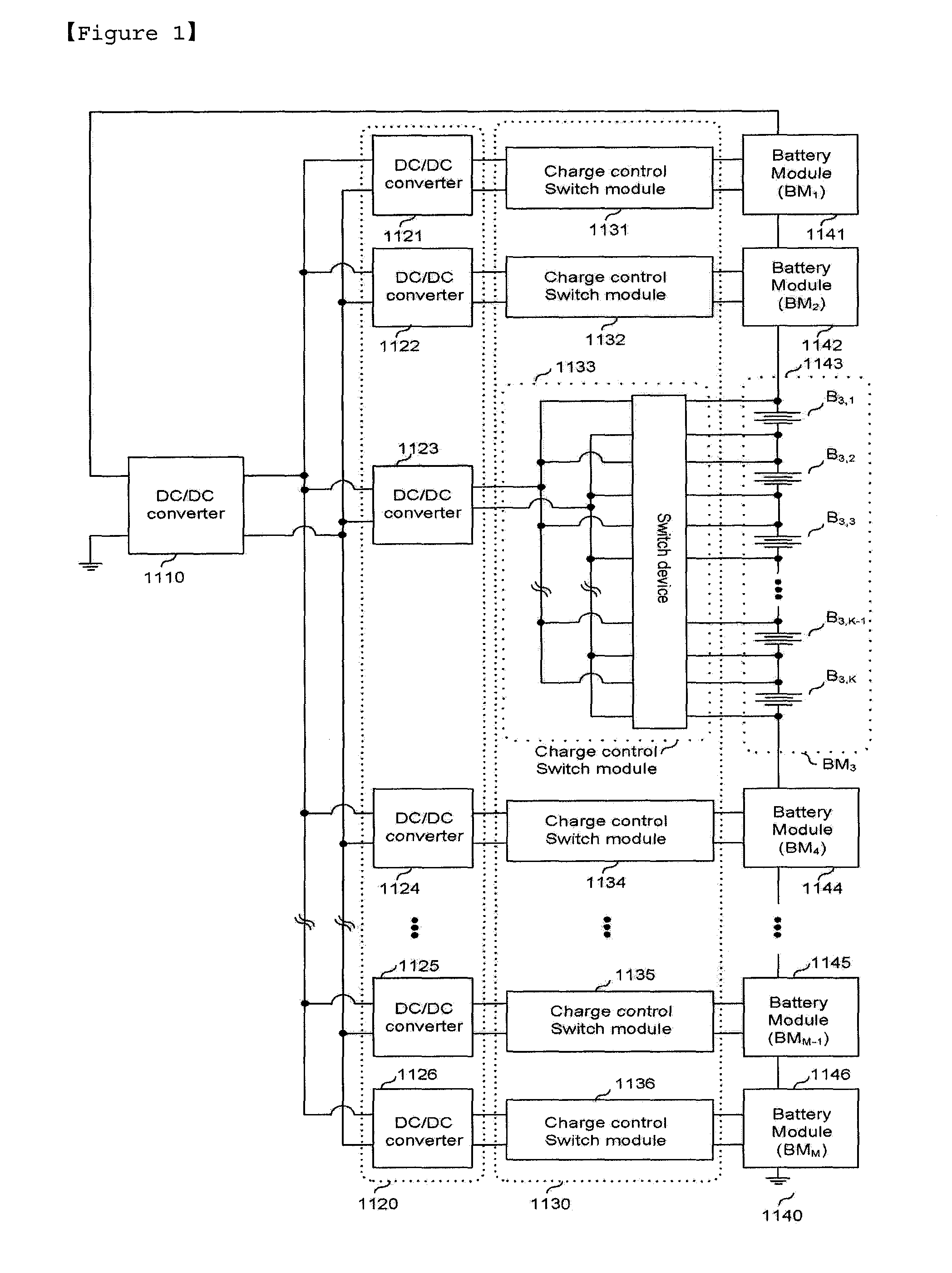
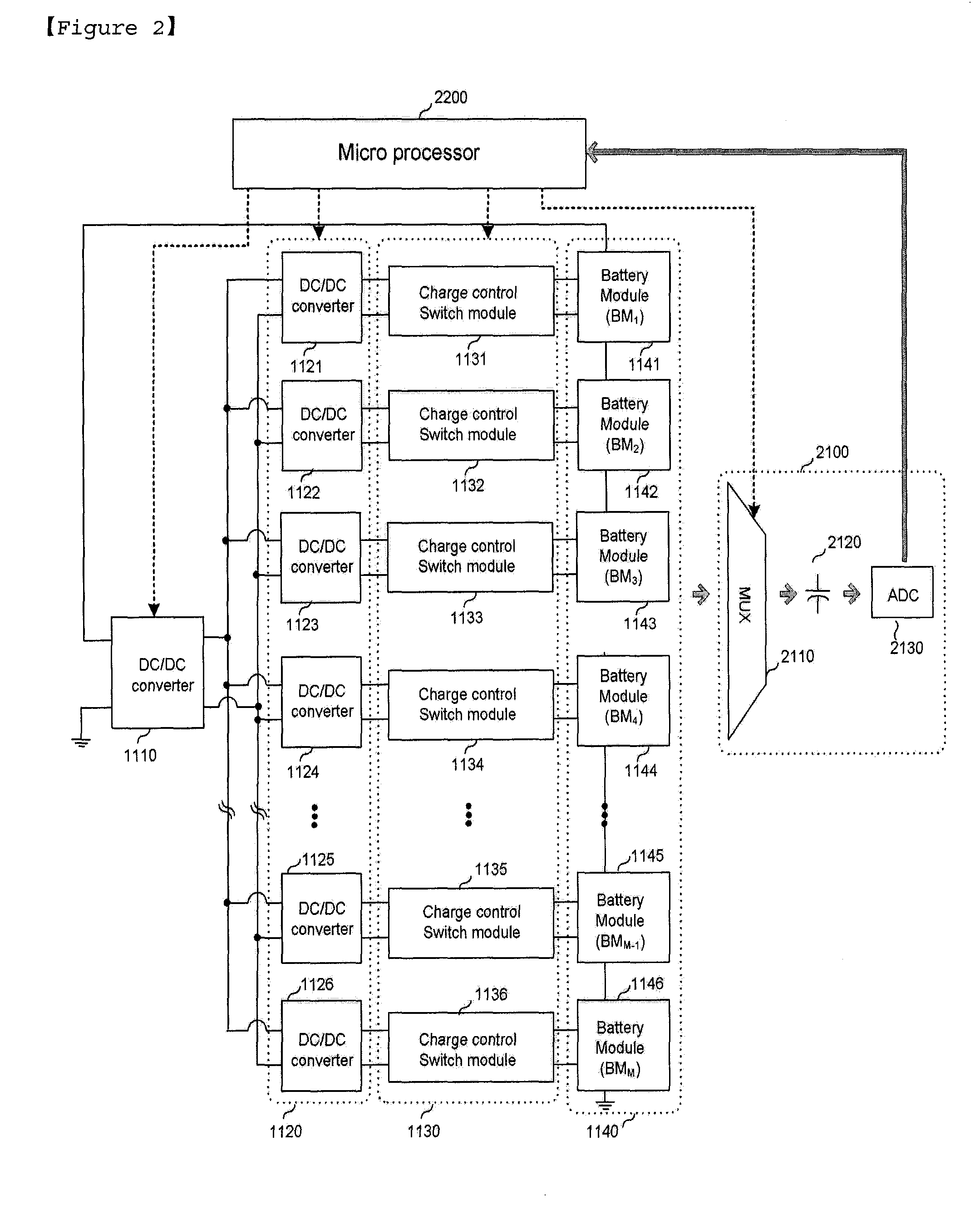
A two-stage charge equalization apparatus for a series-connected battery string comprises a battery module having a plurality of batteries connected in series; a battery string having M (M≧2) battery modules connected in series; M charge control switch modules connected in parallel to each of the M battery modules; M second DC / DC converters connected to each of the M charge control switch modules; a single first DC / DC converter connected to the M second DC / DC converter; and a microprocessor controlling the charge control switch module, wherein the first DC / DC converter is inputted with an overall potential of the battery string and outputs a potential lower than the potential inputted and each of batteries composing the battery module shares the second DC / DC converter using the charge control switch module.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH +1
Capacitor-clamped three-level dual-buck half-bridge inverter
InactiveCN101902143ASimple structureReduce switching frequencyAc-dc conversionLoad circuitThree level
The invention discloses a capacitor-clamped three-level dual-buck half-bridge inverter which comprises a first three-level duck circuit, a second three-level duck circuit, a direct-current power-supply input circuit and a load circuit, wherein each three-level duck circuit comprises two power switching tubes, two power diodes, a clamping capacitor and an inductor, and +1, -1 and 0 three-state levels are output by an inverter bridge under the actions of controlling the switching tubes and clamping the clamping capacitor, thereby realizing the three-level dual-buck half-bridge inverter. The invention has the advantages that the advantage that a DBI circuit has not problems of through bridge arms or backward recovery of switching tube body diodes is inherited; the advantage that a three-level convertor per se has small output voltage harmonic content is reserved; compared with a traditional half-bridge inverter, the voltage stress of power devices is reduced; and the whole circuit structure is simpler and easy to realize.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Merged and Isolated Power MESFET Devices
InactiveUS20070131938A1Maximize efficiencyReduce conduction lossTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringMESFET
A first type of merged power MESFET device includes two monolithically integrated MESFETS. The MESFETS share common sources and gates, and are sized so that one MESFET may be used as a power device while the other is used as a current-sense device. A second type of merged power MESFET device includes two monolithically integrated MESFETS. The MESFETS share a common region which serves as the source for one MESFET and the drain for the second MESFET. This allows the two MESFETS to function as the high and low-side switches for a buck or boost regulator. A third type of merged power MESFET device combines the high and low-side switches with a current-sensing device.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
Control method and device for alternating-current solid-state power controller with current limiting function
ActiveCN103916112AIncrease loadAllowable capacity increaseElectronic switchingCapacitanceMain branch
The invention discloses a control method and device for an alternating-current solid-state power controller with a current limiting function. Through control over a first power tube and a second power tube of a main branch circuit and a third power tube and a fourth power tube of a current limiting branch circuit, when loads are normally started, natural zero-voltage turn-on and natural zero-current turnoff of the alternating-current solid-state power controller are achieved within a half of power source period, when large-capacity capacitive loads or rectifier bridge loads with large-capacity filtering capacitance are started, current-limiting charging is firstly performed through the current-limiting branch circuit, and then the alternating-current solid-state power controlled is completely turned on; when a short circuit fault happens on the alternating-current solid-state power controller, the main branch circuit is firstly turned off to perform fault current limiting, and then the alternating-current solid-state power controller is turned off. Natural zero-voltage on-off of the alternating-current SSPC is achieved within the half of the power source period, besides, the control method and device have a high-power current-limiting function, capacity for carrying the capacitive loads and the rectifier bridge loads of the alternating-current SSPC is improved, and anti-interference capacity of short circuit protection of the alternating-current SSPC is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Liquid crystal display apparatus having pixels with low leakage current
InactiveUS7212183B2Reduce voltage stressCurrent be suppressCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsLow leakageLiquid-crystal display
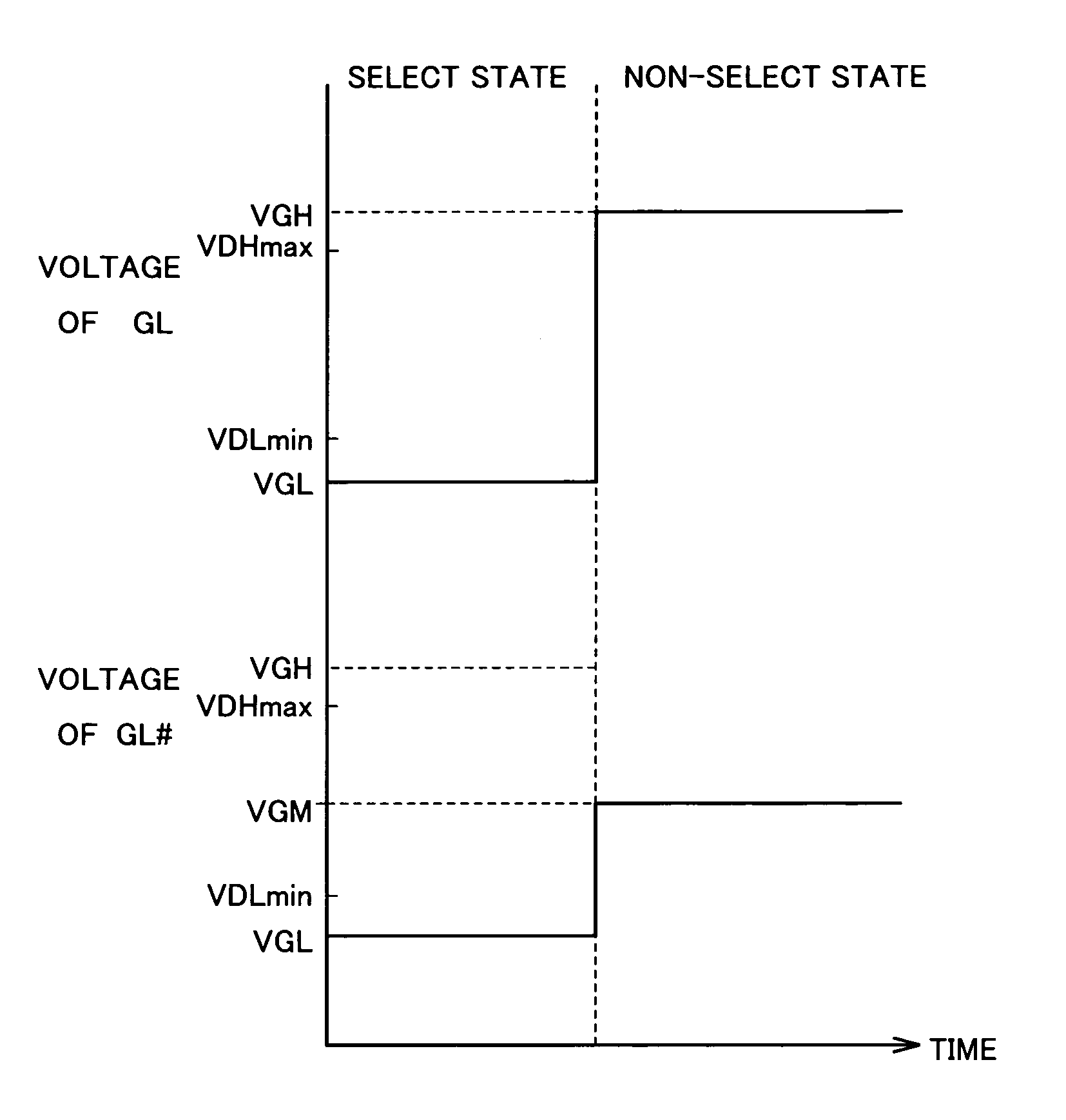
A pixel has first to third N-type TFT elements serially connected between a data line and a pixel electrode node. Each gate of the first and second TFT elements is connected to a first gate line, while the gate of the third TFT element is connected to a second gate line. The first and second gate lines in a select state each set to a high voltage that can fully turn-on the first to third TFT elements. The first gate line in a non-select state is set to a low voltage that can fully turn-off the first and second TFT elements, while the second gate line in the non-select state is set to an intermediate voltage between the maximum and the minimum voltages being transmitted on the data line.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Non dissipative snubber circuit with saturable reactor
InactiveUS20060262577A1Unnecessary dissipationLeast circuit complexityEfficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsLow voltageActive power factor correction
A new type of the passive non-dissipative snubber with a single saturable reactor improves the performance of the boost converter used as a front-end active Power Factor Correction (PFC) in two critical areas: excess voltage stresses caused by high voltage spikes on input high voltage switching transistor of the boost converter is eliminated and EMI noise is much reduced. The high voltage spike energy instead of being dissipated as in a dissipative snubber circuits is recovered resulting in increased conversion efficiency. High voltage spike elimination also allows use of lower voltage rated devices with lower ON resistance, hence further increasing the efficiency of the PFC boost converter.
Owner:TESLACO
On-chip electromigration monitoring system
ActiveUS7394273B2Improve system performanceReduce voltage stressSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMonitoring systemVoltage drop
A packaged semiconductor chip is provided which includes a semiconductor chip and a package element. The semiconductor chip includes a plurality of semiconductor devices and a plurality of conductive features disposed at an exterior face of the semiconductor chip. The package element has a plurality of external features conductively connected to the plurality of conductive features of the semiconductor chip. The semiconductor chip includes a monitored element including a conductive interconnect that conductively interconnects a first node of the semiconductor chip to a second node of the semiconductor chip. A detection circuit in the semiconductor chip is operable to compare a variable voltage drop across the monitored element with a reference voltage drop across a reference element on the chip at a plurality of different times during a lifetime of the packaged semiconductor chip so as to detect when the resistance of the monitored element is over threshold.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com