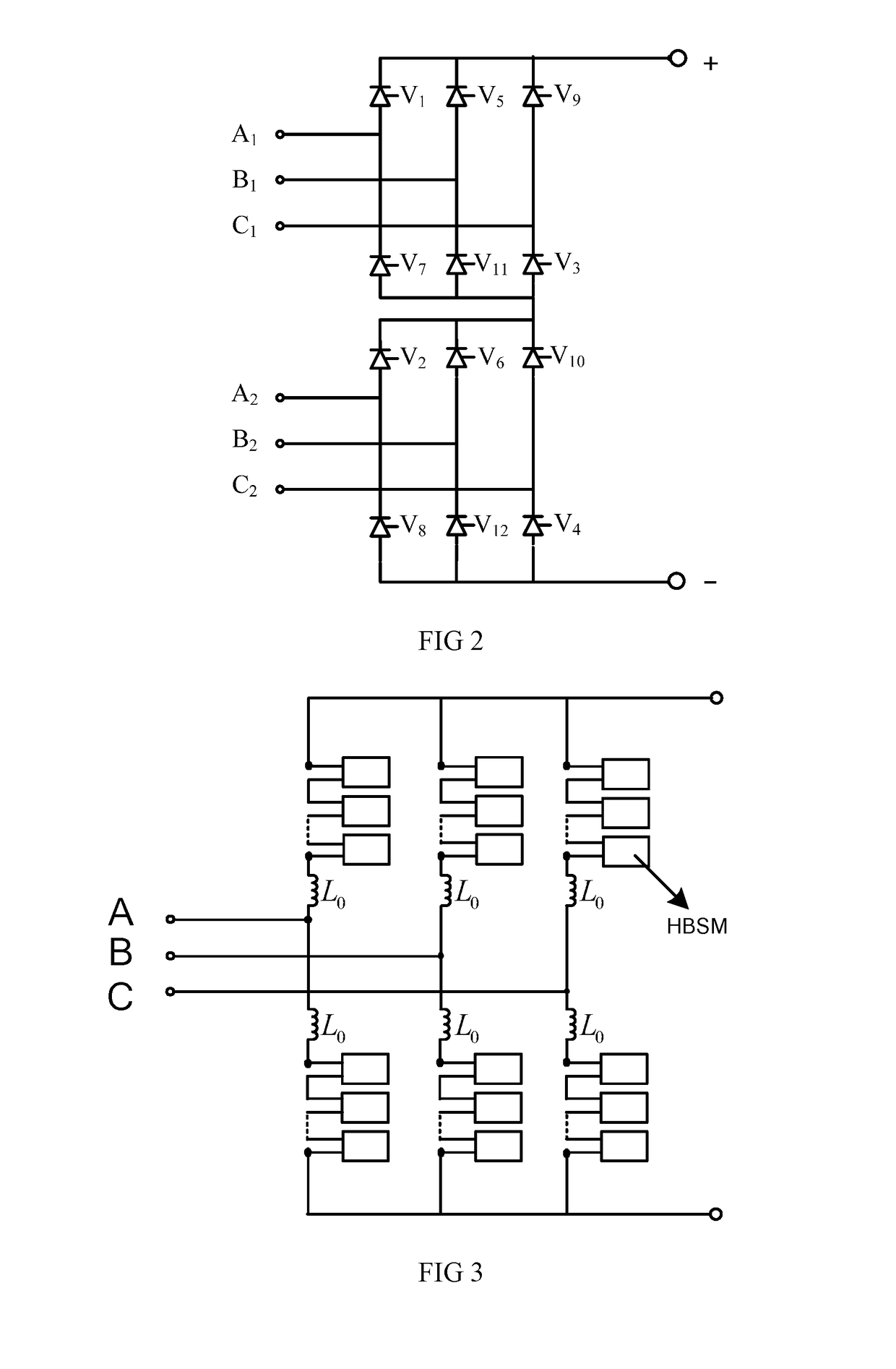
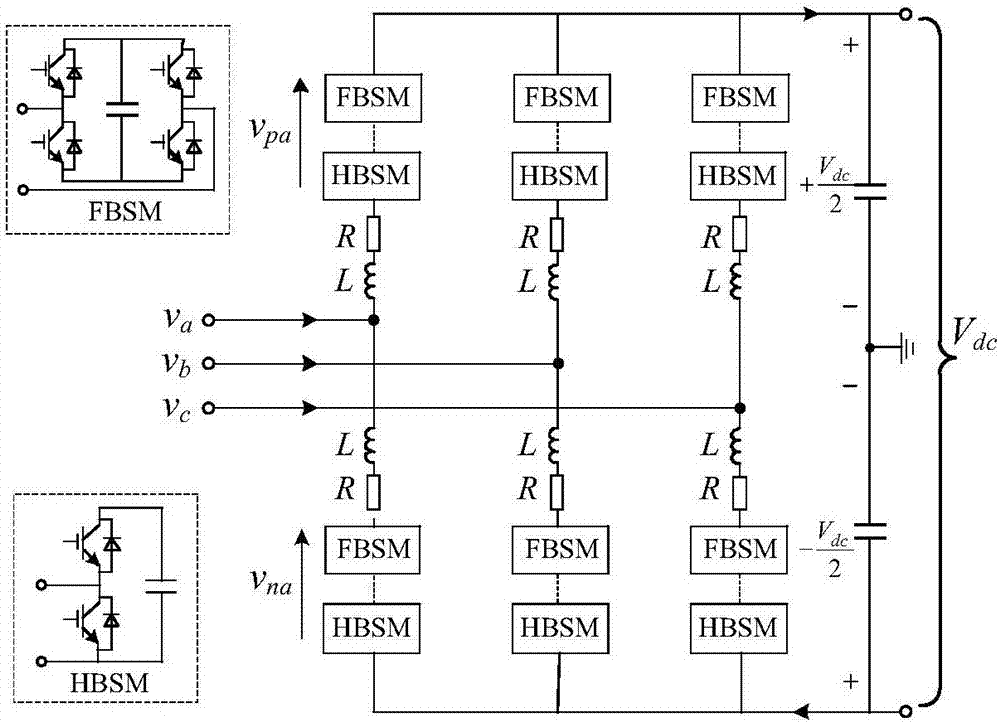
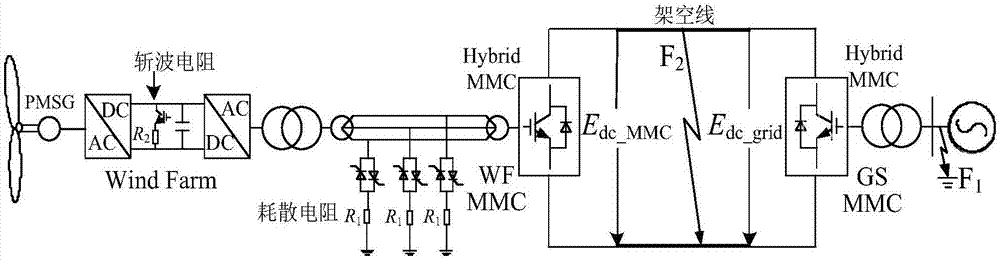
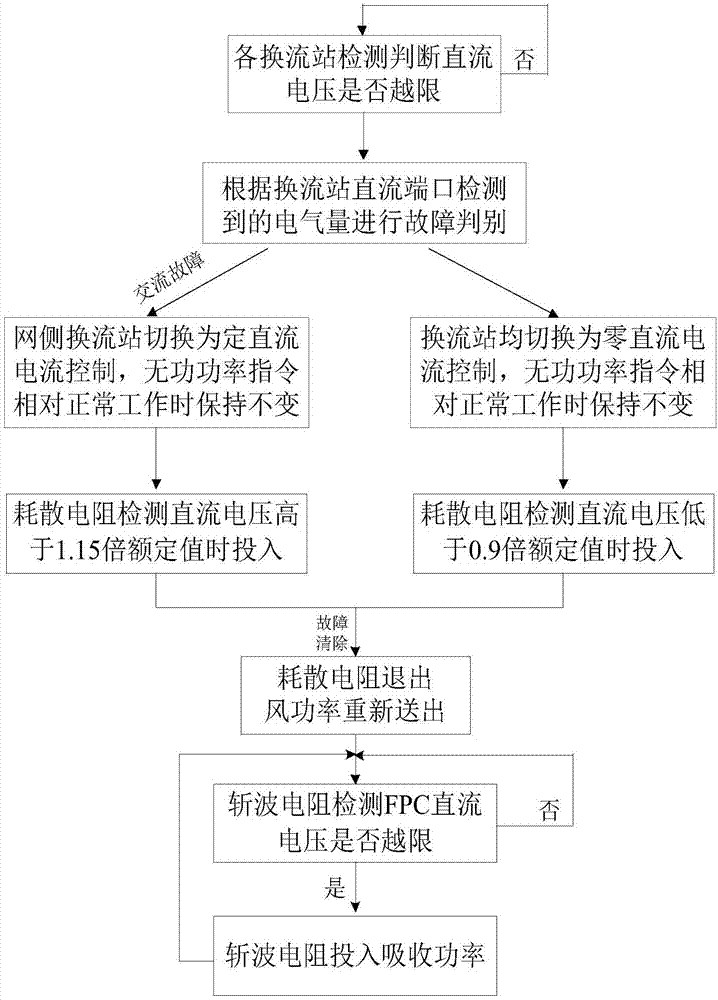
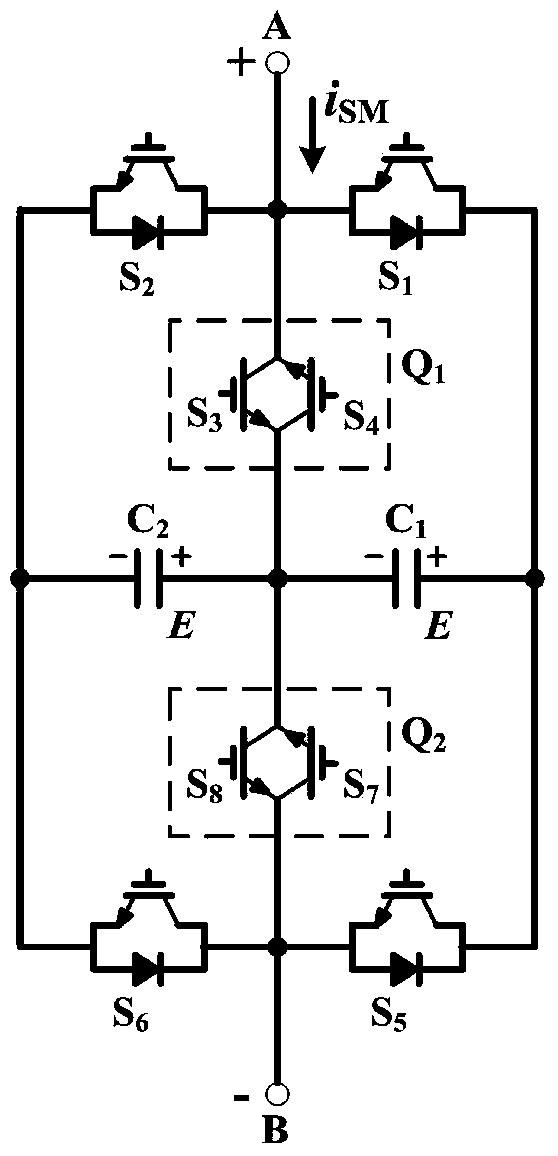
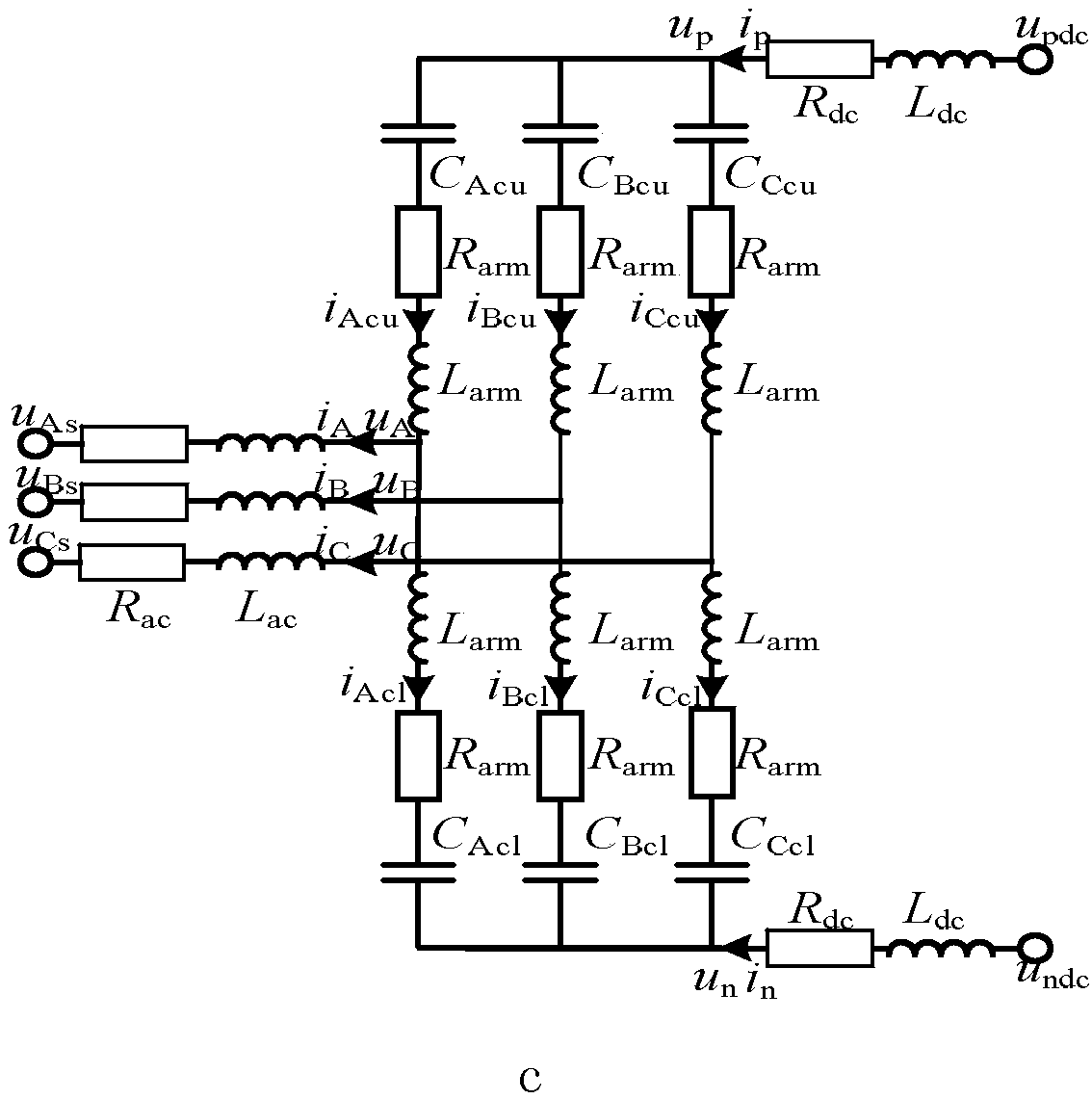
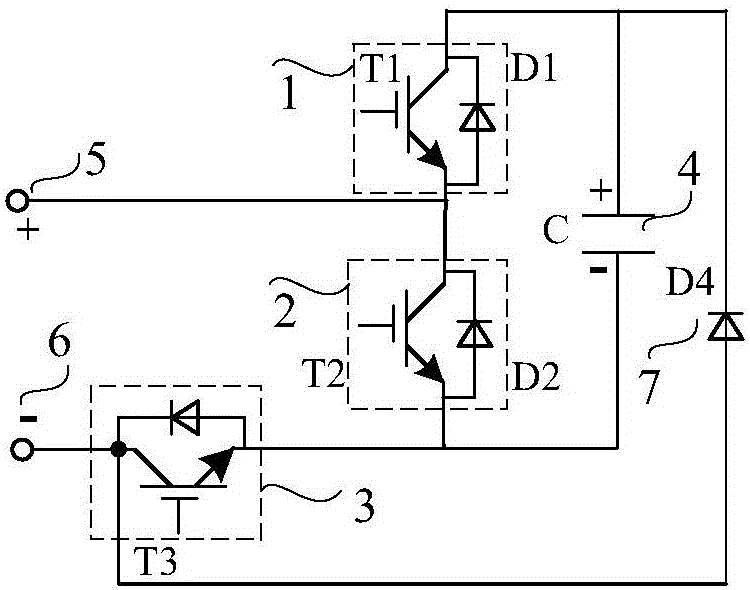
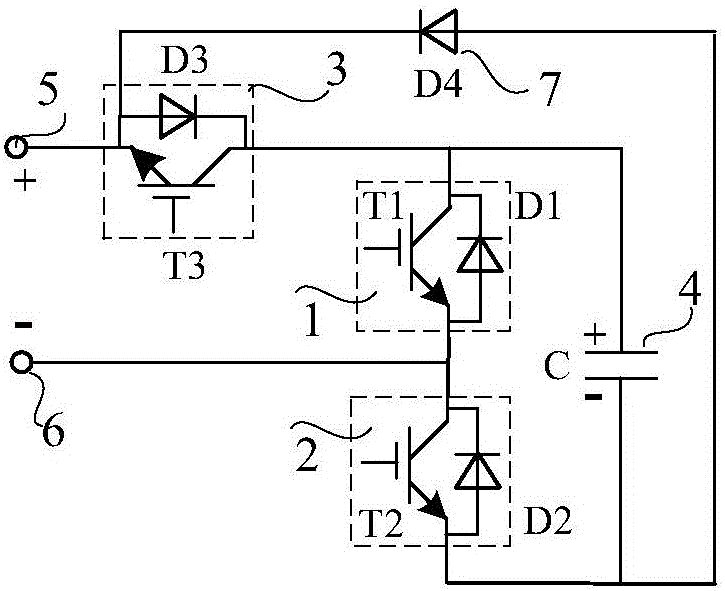
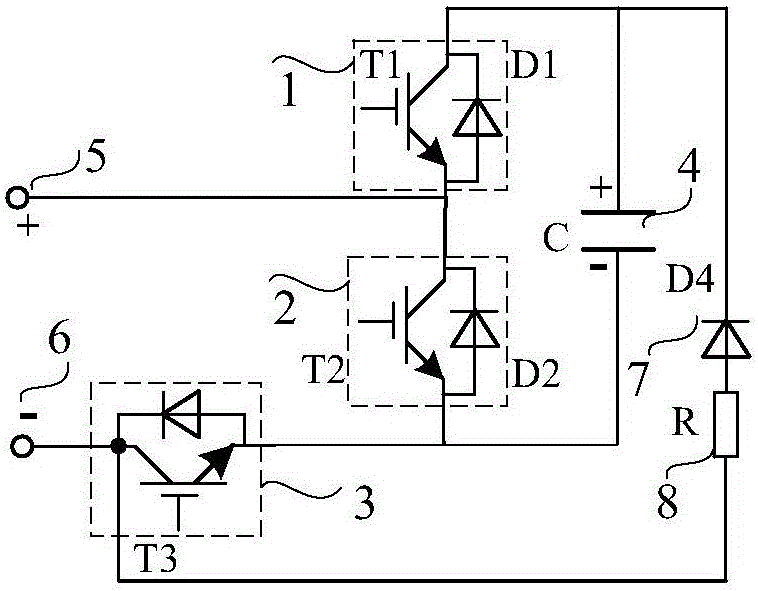
Patents
Literature
381 results about "Dc fault" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fault arc detection method and protection device adopting same
ActiveCN101696986AFast operationExpand the scope of protectionCurrent/voltage measurementEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionEmbedded systemElectrical current
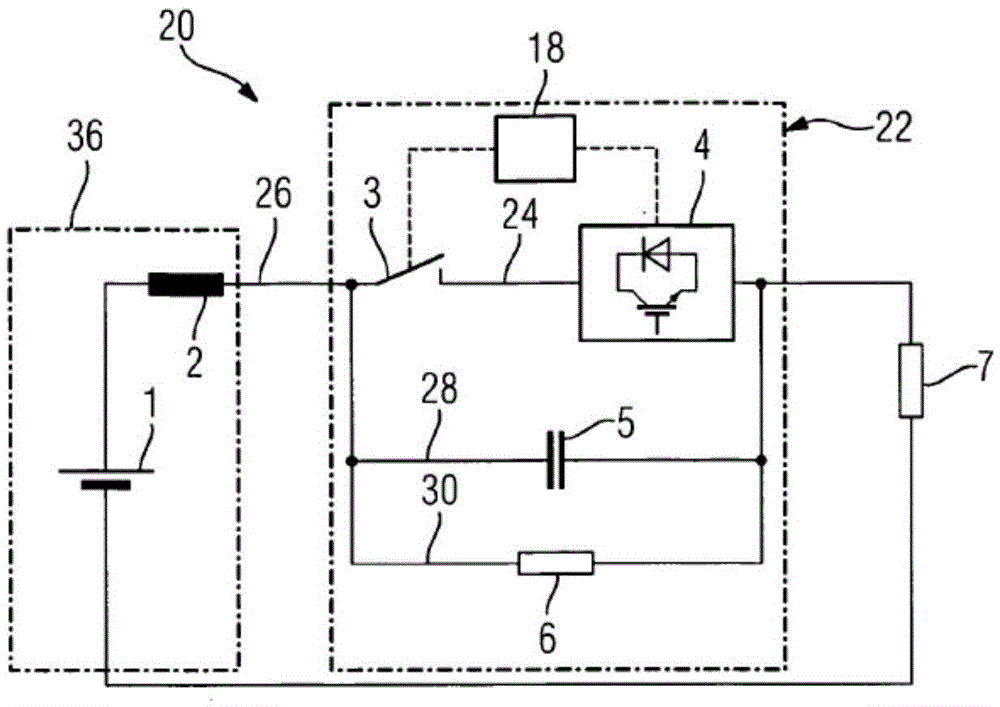
The invention discloses a fault arc detection method which comprises the following steps of: sampling a current signal to acquire a sampling signal, then separating a high-frequency part from the sampling signal, identifying electric arcs by detecting the energy mutation of the high-frequency part and recording the appearance frequency of the electric arcs, and finally identifying a fault arc by detecting the frequency of the electric arcs. By utilizing the characteristic that the fault arc waveform contains high-frequency disturbance as a judgment condition for identify the electric arcs, the method effectively detects the alterative-current resistant load and the direct-current fault arc. The invention also discloses a protection device adopting the method, which can effectively recognize various fault arcs and takes corresponding protection measures.
Owner:JIANGSU KAILONG ELECTRONICS
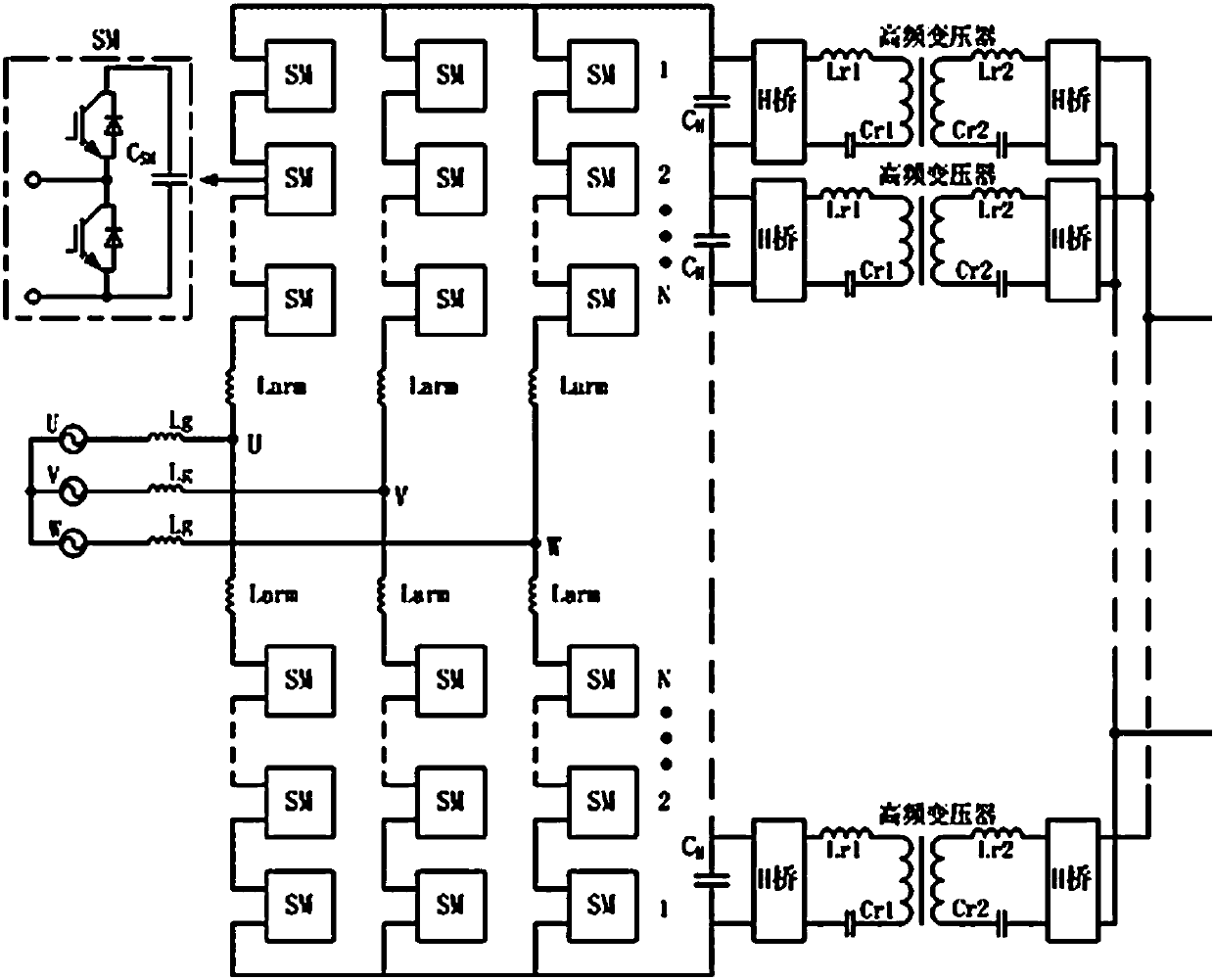
Modular multilevel DC-DC converter and associated method of use
ActiveUS9893633B1Increase flexibilityHigh operating requirementsEfficient power electronics conversionElectric power transfer ac networkGrid faultDc dc converter
In one embodiment, a current-fed modular multilevel dual active-bridge DC-DC converter suitable for medium voltage direct current (MVDC) grid or high voltage direct current (HVDC) grid integration is described. The DAB modular converter and the current-fed DAB converter are soft-switched modular multilevel dual-active-bridge (DAB) converters having DC fault ride-through capability. In an additional embodiment a voltage-fed isolated modular dual active-bridge DC-DC converter for medium voltage direct current (MVDC) or high voltage direct current (HVDC) grids or systems is described. In specific embodiments, the converters may be coupled to a battery energy storage system (BESS), wherein the BESS comprises split-battery units and the interface of the isolated DC-DC converter connects the split-battery units to the MVDC or HVDC system. The converters can be implemented in single-phase or poly-phase configurations and can be controlled to maintain a desired DC output current under both normal and DC grid fault condition.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
An lcc and mmc series-connected HVDC system with DC fault ride-through capability
ActiveUS20170331390A1High-quality output voltageSmall footprintAc-dc conversionElectric power transfer ac networkElectric power transmissionModular transformation
The present invention discloses an LCC and MMC series-connected HVDC system with DC fault ride-through capacity, comprising rectifier and inverter linked by DC transmission line; Both the positive pole and the negative pole of the rectifier and the inverter consist of line-commutated converter and modular converter in series-connection; the modular converter adopts one MMC or several parallel-connected MMCs. The present invention has the advantage of low cost, low power loss and high reliability of the LCC, as well as flexible control, low harmonics and AC voltage support of the MMC. Further, the present invention is able to deal with DC fault by itself, hence additional DC fault clearing equipment is not needed. As a result, the present invention is suitable for the field of long-distance large-capacity power transmission and has broad development potential.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
AC/DC fault ride-through and energy dissipation method for wind power flexible direct grid connection
InactiveCN107994613AEasy to controlGuaranteed safe operationSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsWind energy generationElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention discloses an AC / DC fault ride-through and energy dissipation method for wind power flexible direct grid connection. A system is mainly formed by a direct-drive permanent magnet synchronous generator, a full-power frequency converter, a hybrid MMC and a dissipative resistor. An AC and DC are controlled respectively through the hybrid MMC; during direct current faults, the MMC operatesnear a zero direct voltage through a negative input full-bridge sub-module, and DC fault ride-through can be achieved without needing to block MMC. In order to ensure the safety of a converter valveduring the fault, the dissipative resistor is used to absorb energy during the fault so that a wind farm is disconnected with a grid during the fault and still maintains normal operation.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +2
Discrimination algorithm for aviation fault arc detection
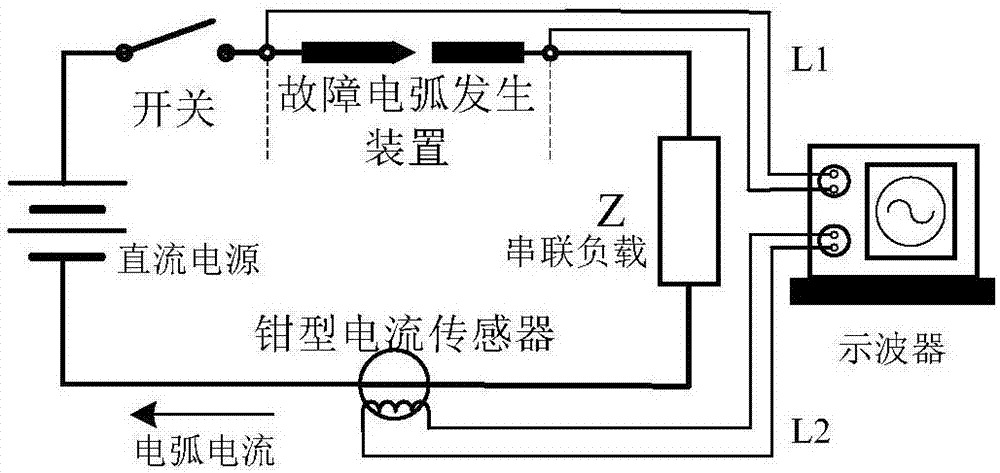
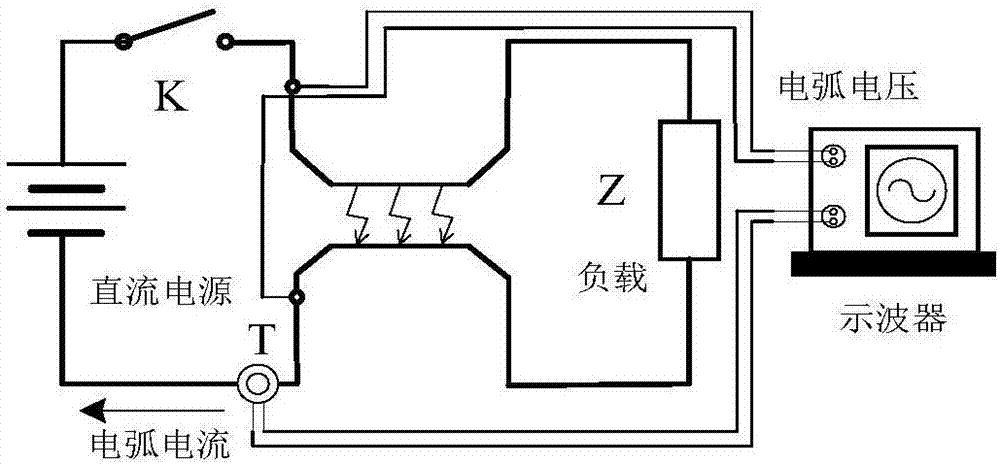
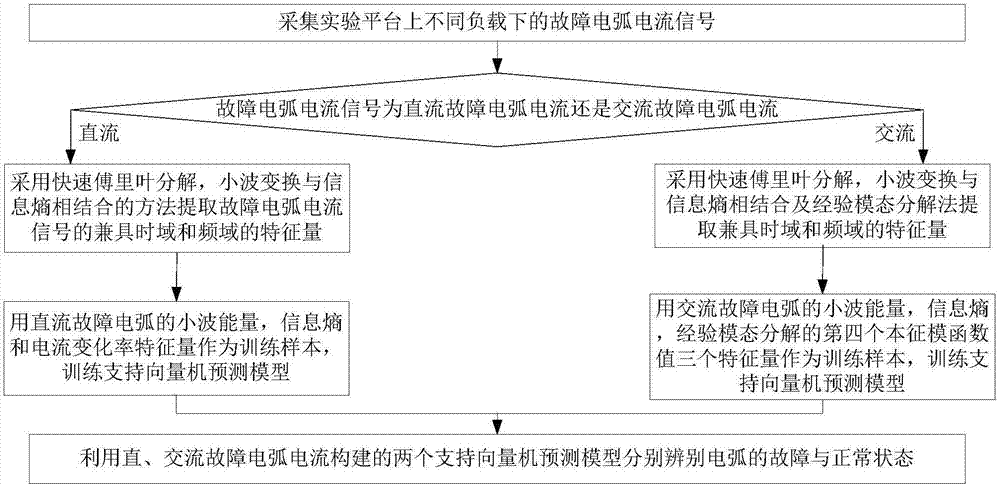
InactiveCN107064752AImprove accuracyReduce chanceTesting dielectric strengthCharacter and pattern recognitionSupport vector machineTime domain
The invention discloses a discrimination algorithm for aviation fault arc detection and belongs to a field of aviation fault arc detection. The algorithm specifically includes collecting fault arc current signals in conditions with different loads on a test platform; judging whether the fault arc current signals are DC fault arc current or AC fault arc current and extracting characteristic quantities with both time domain and frequency domain; aiming at wavelet energy of DC fault arcs, information entropy and current change rate and wavelet energy of AC fault arcs, training a support vector machine predication model by taking the information entropy and a fourth eigenmode function value obtained through empirical mode decomposition; and distinguishing fault and normal states of arcs by utilizing two support vector machine predication models. According to the invention, a plurality of characteristic quantities are selected, fault characteristic contingency is reduced and discrimination accuracy is increased. Intelligent discrimination is performed on characteristics in a fault and normal critical range and randomness is reduced.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Capacitive charging DC breaker and application thereof
ActiveCN105656019AEliminates Inductor-Capacitor Resonance ProblemsEliminate resonanceDc network circuit arrangementsEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionCapacitanceDc current
The invention discloses a capacitive charging DC breaker. The capacitive charging DC breaker comprises an auxiliary branch and a primary branch, which are connected with each other in parallel, wherein the auxiliary branch is formed by connecting a first mechanical switch and a power electronic device valve bank in series; and the primary branch is formed by connecting DC capacitors and a diode valve bank in series. A DC fault current is isolated through the charging effect of a DC to each DC capacitor during a DC fault period. A reclosing instruction is sent out only when the condition that a line side current of the DC breaker is higher than a threshold is detected in the reclosing process. The invention further discloses the DC breaker. The primary branch is formed by connecting multiple groups of DC capacitors which are connected with one another in series and the mechanical switches in parallel. The invention further discloses a control method for carrying out fast reclosing on the DC breaker correspondingly. The defect that inductance-capacitance oscillation is easily formed by the DC capacitors and line inductor of the existing DC breaker can be avoided; opening and closing of the DC fault current are stable and reliable; and fast reclosing can be achieved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
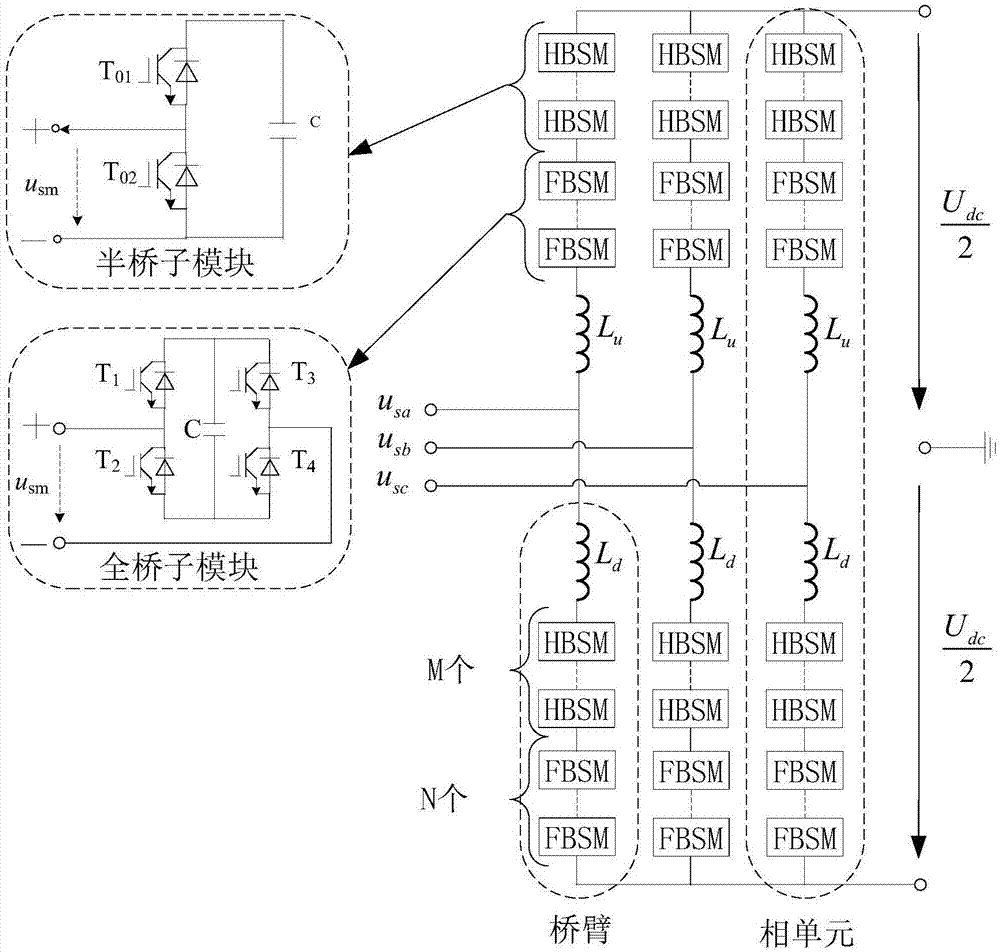
Fault-tolerance-capability-equipped MMC sub-module structure capable of realizing DC fault self-protection, and MMC modulation method thereof
ActiveCN104410260AImprove level integrationReduce on-state lossElectric power transfer ac networkDc-ac conversion without reversalThree levelFault tolerance
The invention discloses a fault-tolerance-capability-equipped MMC sub-module structure capable of realizing DC fault self-protection. Current stress balance of two capacitors and eight power switch tubes in a sub-module are adjusted through redundant switch states; three level can be output at a normal mode, and the level integration of the sub-module is improved; under the condition of a locking mode, the capacitors of the sub-module are completely invested into legs, the capacitors of the sub-module are charged, a reverse electromotive force is generated, and a function of isolating DC-side faults is realized. According to the invention, when the sub-module structure is applied to an MMC-HVDC system, self-protection of the DC-side faults can be realized. Due to the symmetry of the structure, the output characteristics of sub-module structure, under the condition of the locking mode, are symmetrical about a current direction, and good symmetry helps to maintain the current stress balance of the power devices and the capacitors in the sub-module; and when the MMC sub-module structure is applied to an HCMC-HVDC system, the MMC sub-module structure is lower in conduction loss than a full-bridge sub-module structure and higher in system operation efficiency.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Photovoltaic system DC side arc fault detection system and detection method thereof
PendingCN110417351AReduce false detection rateImprove detection accuracyPhotovoltaic monitoringPhotovoltaic energy generationCapacitanceGenerative adversarial network
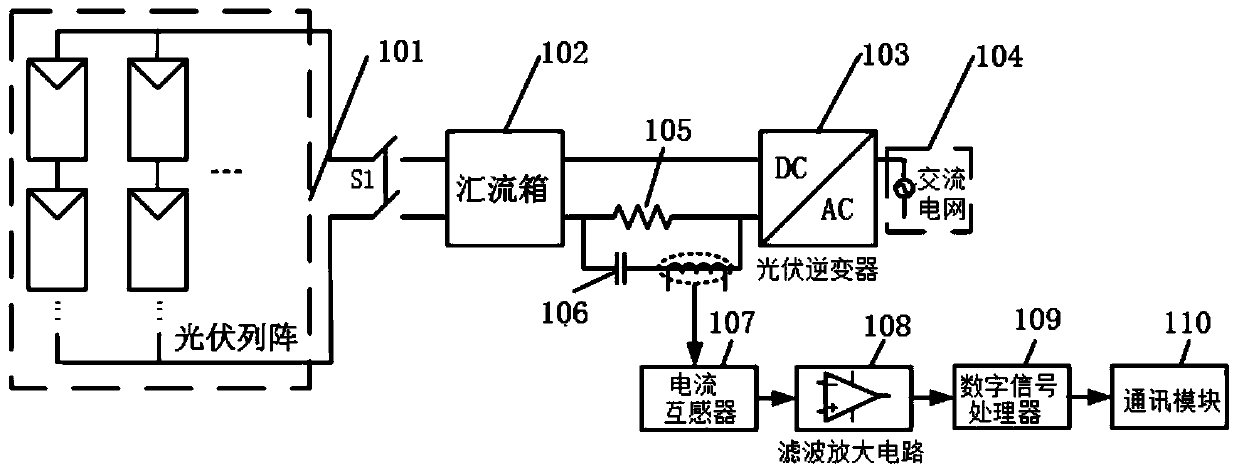
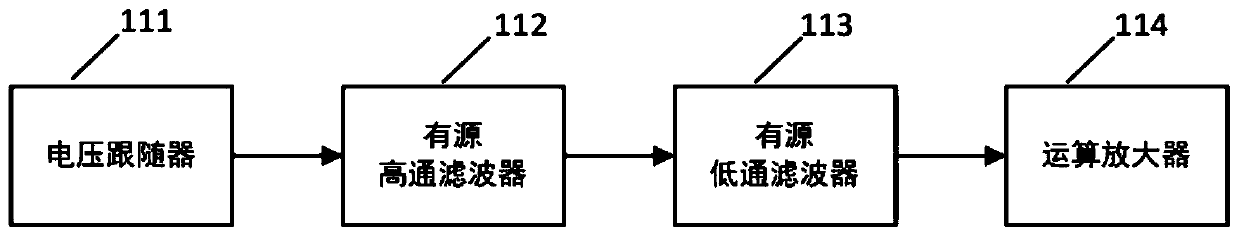
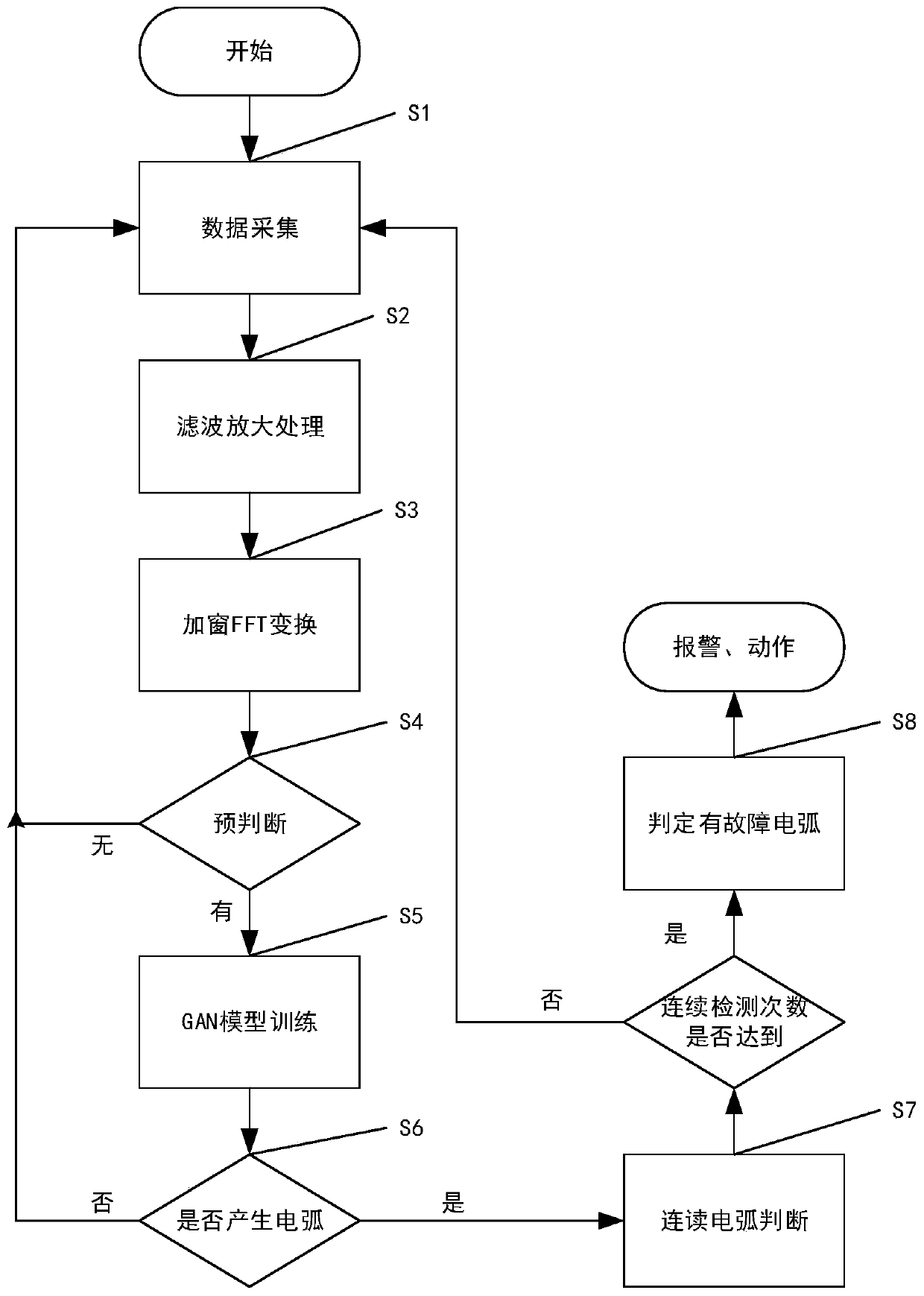
The invention relates to a photovoltaic system DC side arc fault detection system and a detection method thereof. According to the invention, a sampling inductor is connected in series on a circuit from the output of a combiner box to an inverter, a capacitor is connected in series with a primary side winding of a current transformer and then connected in parallel with two ends of the sampling inductor, a secondary side winding of the current transformer collects a characteristic alternating current signal of the DC side arc and sends the characteristic alternating current signal to a filtering and amplification circuit, and a current signal outputted and processed by the filtering and amplification circuit is sent to a digital signal processor for judgment, and then a judgment result is outputted and then transmitted through a communication module. The detection method comprises the steps of collecting an alternating current signal at the DC side of the photovoltaic system, and extracting signal characteristics in the frequency domain; pre-judging the signal; training a GAN (Generative Adversarial Network) model; and judging a DC fault arc and sending alarm information. In order to reduce the false detection rate and improve the robustness of the detection system, the generative adversarial network is introduced into the judgment of the fault arc. The false detection rate of the DC fault arc can be reduced, the detection rate is improved, and the safe and stable operation of the photovoltaic system at the DC side is ensured.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Symmetrical bipolar MMC DC-side single-pole ground fault ride-through and recovery method
ActiveCN107069679AReduce shockReduce power deficitEmergency protective circuit arrangementsRecovery methodDc circuit breaker
The invention provides a symmetrical bipolar MMC DC-side single-pole ground fault ride-through and recovery method. Through cooperation of a DC circuit breaker and a converter, DC fault current cut-off and power recovery are realized, and safe operation of the converter is protected. Through cooperation of active power and reactive power of the sound pole and the faulty pole, the active power deficiency of a converter station in the failure period is reduced. Rated reactive power is supplied to the grid, and therefore, the impact of a fault to an AC system is reduced. By actively controlling the common-mode components of the reference voltages of the upper and lower bridge arms of the converter, the risk brought to the safe operation of the system by excessive current surge stress of the converter due to reclosing failure is avoided. Based on the fact that a dual-pole short-circuit fault at the DC side of a symmetrical bipolar MMC can be regarded as a special case of single-pole ground faults of both positive and negative DC buses, the method of the invention can be used to handle a dual-pole short-circuit fault at the DC side of a symmetrical bipolar MMC.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
AC/DC decoupling control method of modular multi-level current converter and application thereof
ActiveCN106505641AAvoid damageSimple and reliable control processElectrical apparatusCapacitanceDc current
The invention discloses an AC / DC decoupling control method of a modular multi-level current converter. The method comprises the steps of adding DC current control in current inner-loop control so that current inner-loop control comprises AC current control and DC current control, thereby using output of the AC current control and output of the DC current control as main components of an output voltage reference value of each phase leg of the modular multi-level current converter; respectively controlling reference values of the AC current control and the DC current control, and simultaneously controlling outputs of the AC current control and the DC current control, thereby realizing control on main components, and furthermore preventing current converter locking because of a leg overcurrent in DC fault. The invention further discloses application of the method in a flexible DC power transmission system. The AC current and the DC current of each current converter station and capacitance and voltage of each submodule are controlled into a safe range, thereby realizing DC fault crossing of the flexible DC power transmission system.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Flexible DC network DC short-circuit fault ride through method
ActiveCN105048488AGuaranteed uptimeFlexible and controllable DC fault currentElectric power transfer ac networkDc circuit breakerEngineering
The invention discloses a flexible DC network DC short-circuit fault ride through method realized by cooperative control of an MMC with negative level output capability and a mechanical DC circuit breaker, and belongs to the field of flexible DC network DC fault protection. There are three means for processing a DC fault in the prior art mainly, including cut-off of connection with a DC system by means of AC equipment, DC fault elimination by means of a current converter and DC fault isolation by means of DC equipment, while the three methods cannot effectively realize flexible DC network DC fault protection. The MMC comprises submodules with negative level output capability, and voltage of the DC port of the current converter is enabled to be negative-level by flexibly regulating output voltage of upper and lower bridge arms so that objectives that DC short-circuit fault current is controllable and is rapidly reduced to zero can be achieved, and the requirement of isolating the DC fault can be met by the mechanical DC circuit breaker.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
DC fault electric arc detection method and system
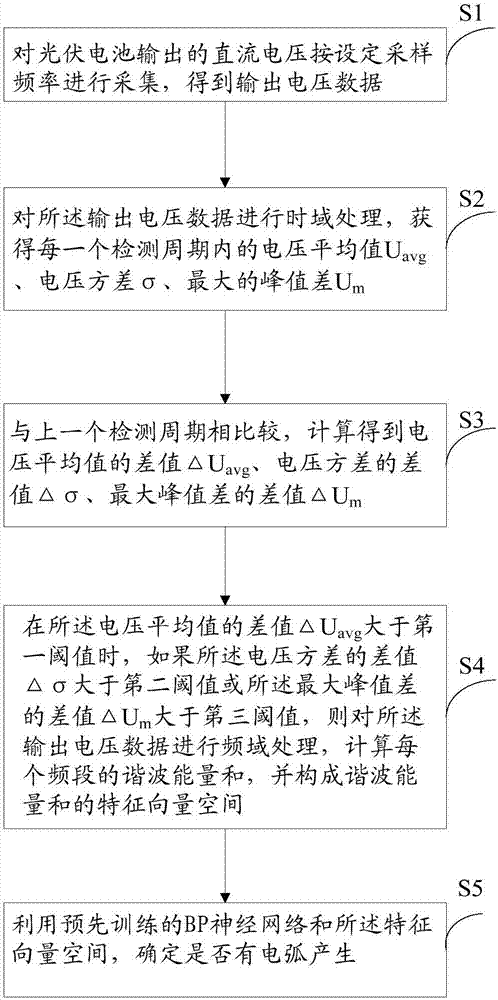
The invention relates to a DC fault arc detection method and system The DC fault arc detection method comprises steps of performing collection on DC voltage outputted by a photovoltaic battery according to set sampling frequency to obtain output voltage data, performing time domain processing on output voltage data, obtaining a voltage average value Uavg, a voltage variance sigma and a maximum peak value difference Um in each detection cycle, comparing with a last detection cycle, when a difference value delta Uavg of a voltage average value is greater than a first threshold value, if the difference value delta sigma of the voltage variance is greater than a second threshold value or a biggest peak value difference value delta Um is greater than a third threshold value, performing time domain processing on output voltage data, calculating a harmonic wave energy sum of each frequency band, constructing a characteristic vector space of the harmonic wave energy sum, and using a pre-trained BP nerve network and the characteristic vector space to determine whether an electric arc is generated. The DC fault arc detection method and system solve problems that the current fault arc detection is not accurate and high in misjudgment, and can improve safety of a photovoltaic power generation system.
Owner:ANHUI JIANGHUAI AUTOMOBILE GRP CORP LTD
DC fault arc detection method
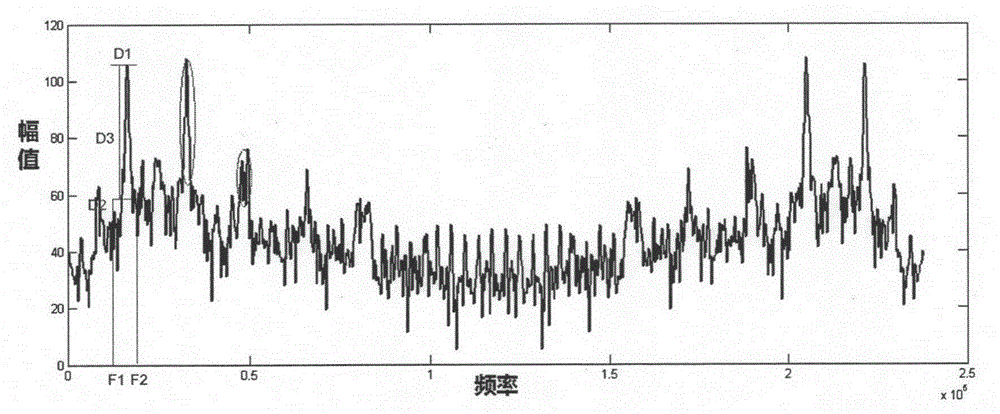
InactiveCN105093082ATesting dielectric strengthPhotovoltaic monitoringFrequency spectrumHigh frequency power
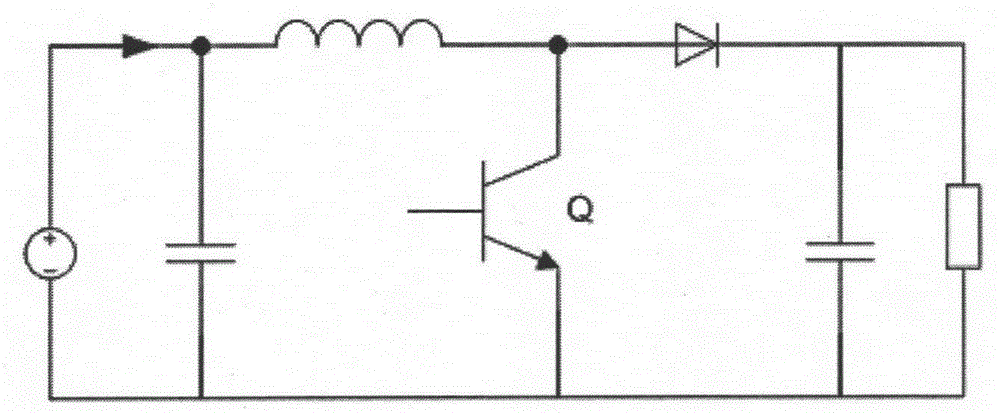
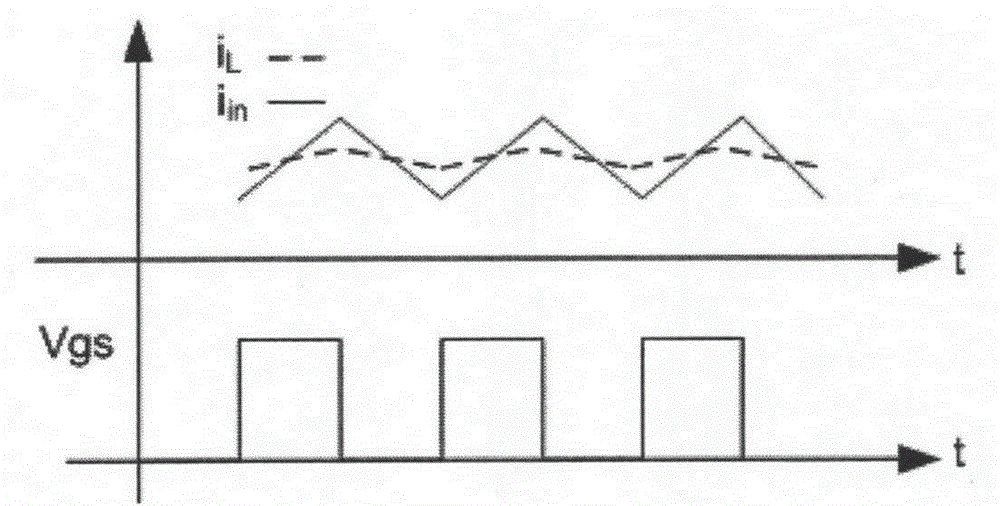
The invention relates to a DC fault arc detection method. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of 1, sampling, filtering and conducting the fast Fourier transformation on an input current of a high-frequency power electronic converter to obtain an amplitude-versus-frequency curve for the high-frequency components of the current; 2, selecting at least one frequency band containing a switching frequency or a multiple frequency from the amplitude-versus-frequency curve, and calculating the peak value D1 of the magnitude of the curve and the mean value D2 of the magnitude of the curve within the selected frequency band. Based on the change of the distance between the peak value D1 and the mean value D2, whether an arc is generated or not can be judged. If the mean value D2 gets closer to the peak value D1, the arc is judged to be generated. Otherwise, no arc is generated. According to the novel DC fault arc detection method, based on the own characteristics of the converter, noise signals are generated by the high-frequency components of the direct current at the frequency multiplication points of the switching frequency of the converter. By utilizing the noise signals, the arc spectrum of an arc fault can be analyzed and calculated. In this way, whether the arc fault occurs or not can be detected.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHINT POWER SYST
Sub-module, protection unit, converter, and control method thereof
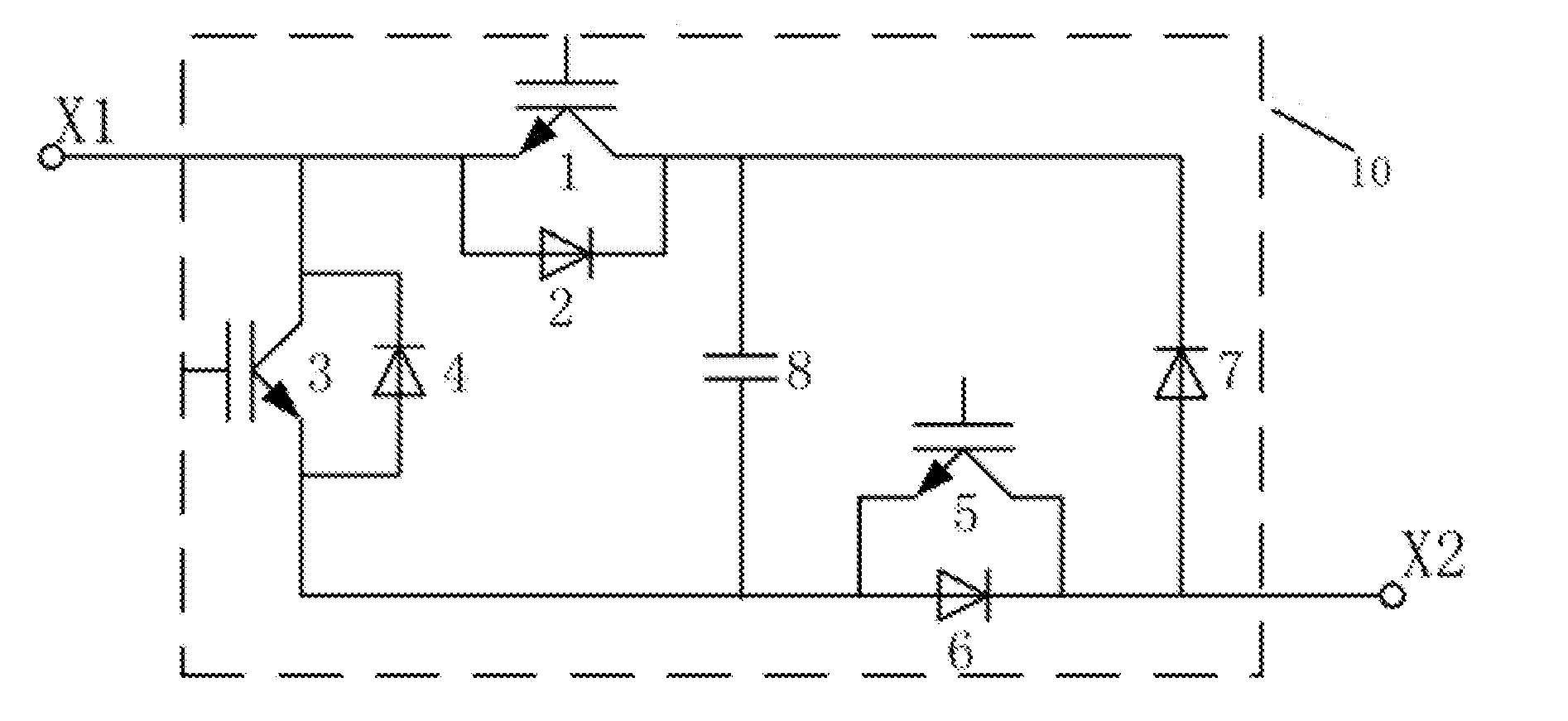
InactiveUS20160126827A1Inhibit currentEmergency protective circuit arrangementsAc-dc conversionEnergy storageResistor
Disclosed are a submodule structure formed of an energy storage element, a first turn-off device, a second turn-off device, a third turn-off device, a freewheeling diode, a series resistor, and diodes respectively in antiparallel connection with the turn-off devices, and a converter completely or partially formed of the submodules. Also disclosed are a relevant protection unit and a control method for the converter. The converter can be locked when a direct current (DC) fault occurs to prevent an alternating current (AC) system from injecting a fault current into a DC network, so that a transient fault of the DC network can be removed without tripping an AC line switch, thereby rapidly restarting the system. A charging resistor is comprised in the submodule so that a charging resistor disposed at an AC side of the converter can be reduced and even may not be disposed.
Owner:NR ELECTRIC CO LTD +1
DC line fault protection method utilizing current converter active injection and traveling-wave coupling
ActiveCN108551161AGuaranteed uptimeReduce outage timeElectric power transfer ac networkEmergency protective circuit arrangementsEngineeringSelf adaptive
The invention discloses a DC line fault protection method utilizing current converter active injection and traveling-wave coupling. The DC line fault protection method comprises the steps of utilizinga health pole current converter additional control strategy to inject a feature signal into a DC line within an interval after fault pole DC line fault clearing / isolation and before current converterrestarting / reclosing of a DC power transmission system, wherein propagation properties of the feature signal are different when a DC line fault exists and disappears, utilizing the difference to realize fault property determination of the DC fault line, and further controlling a fault pole power transmission system not to restart / reclose a circuit breaker, thereby realizing DC line fault protection. The DC line fault protection method realizes self-adaptive restarting / reclosing of the DC system in an overhead line power transmission occasion, shortens the power outage duration, ensures the safe and reliable operation of the DC system, and has remarkable direct benefits and indirect benefits.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +2
Hybrid DC power transmission system having DC fault blocking capacity and control method thereof
ActiveCN105914772AReduce in quantityReduce switching lossesElectric power transfer ac networkWind energy generationPower compensationHybrid type
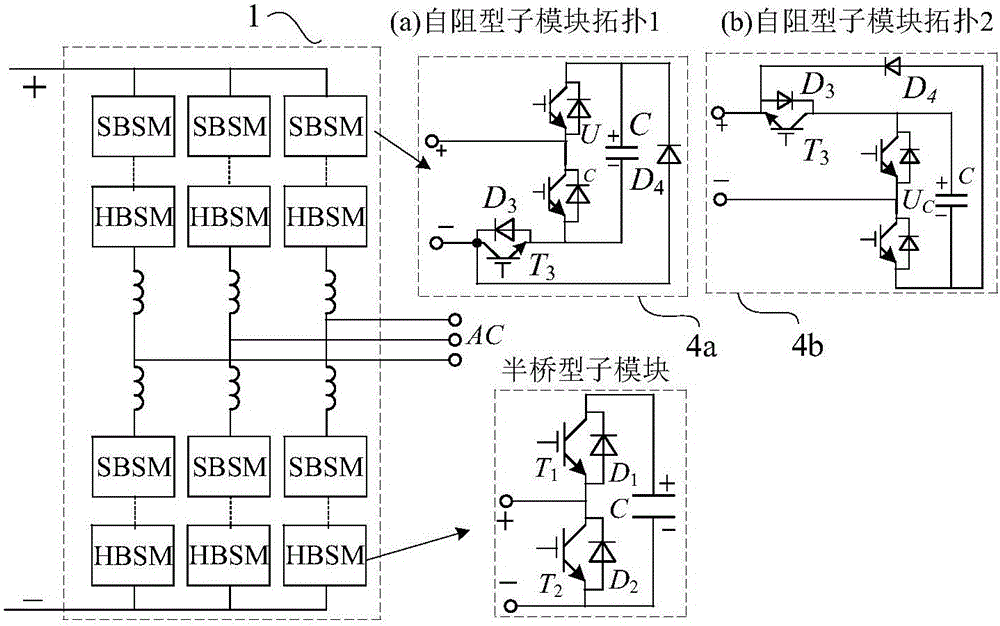
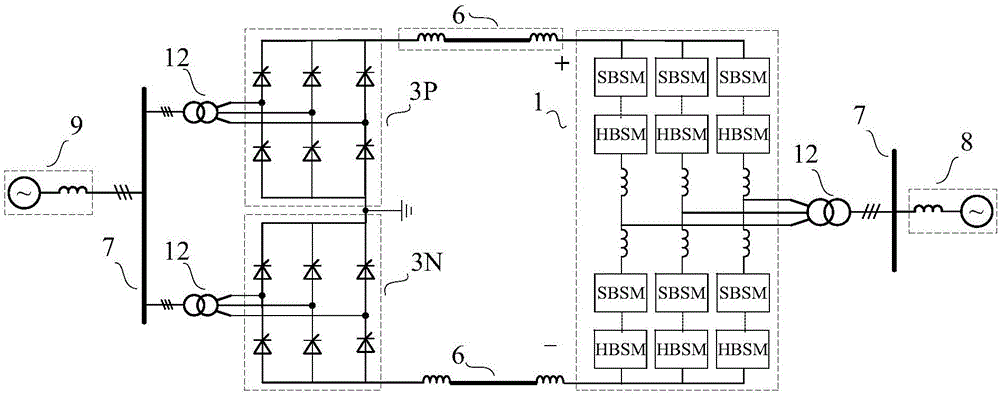
The invention discloses a hybrid DC power transmission system. The power transmission system comprises a phase controlled rectifier which is arranged at a transmitting end and a self-resistance modularized multilevel converter which is arranged at a receiving end, or comprises the self-resistance modularized multilevel converter which is arranged at the transmitting end and the phase controlled rectifier which is arranged at the receiving end. The transmitting end and a first AC system are connected at the AC bus of the transmitting end, the receiving end and a second AC system are connected at the AC bus of the receiving end through an AC transformer, and the controlled rectifier and DC port of the self-resistance modularized multilevel converter are connected through a corresponding DC power transmission line. The invention also discloses a corresponding control method of the hybrid DC power transmission system. The problems that a phase controlled converter cannot connect a weak AC power grid and is liable to fail in phase commutation can be solved; or the phase controlled converter can directly connect a wind power plant with no requirement for installing of a reactive power compensation device so that the hybrid power transmission system is enabled to have a DC fault isolation function at the minimum cost.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
DC superconducting fault current limiter
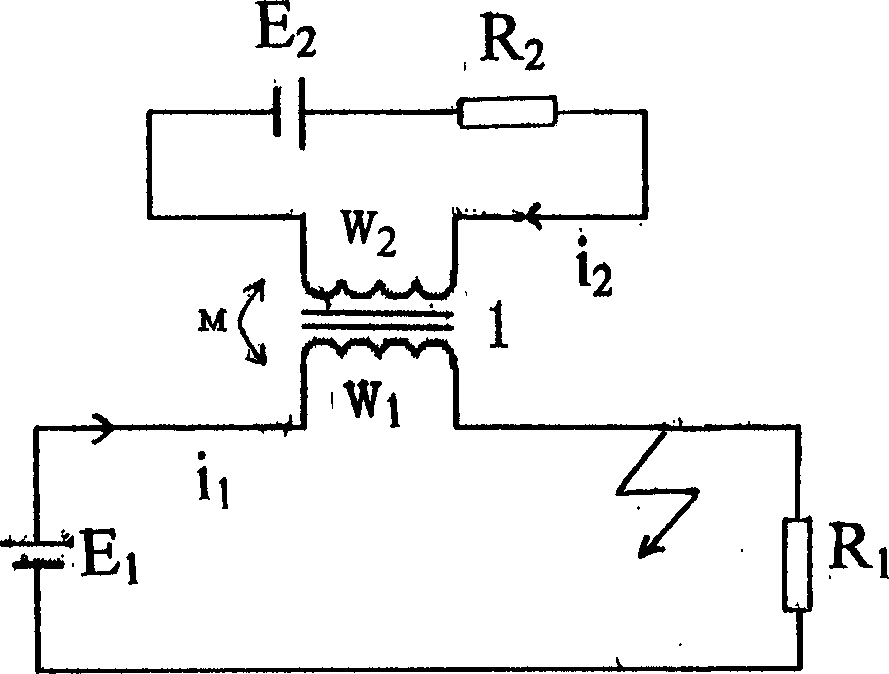
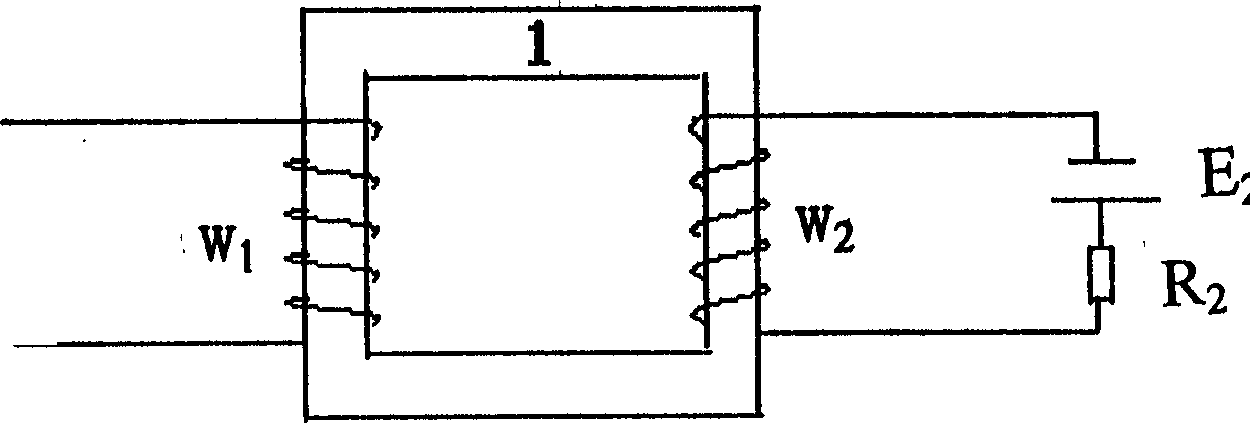
InactiveCN1595583ALow energy storageShort response timeEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionProtective switch operating/release mechanismsStored energyElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention supplies a DC superconduction fault current limiter, whose structure is: two superconduction coupling coil w1 and w2, has the same inductance wrapped on ring shaped core and one superconduction coil w1 is current limiting inductor whose two ends are connected to load loop, and another superconduction coil w2 as bias winding is connected to DC power source E2 and resistor R2 in series, w1 and w2 cooled by cooling device current limiting effect. The invention has advantages is: notable current limiting effect and low loss; short response time and high reliability, when the system operates normally, superconduction coil has very small stored energy and won't create overvoltage after accident protection; detecting, triggering and current limiting are integrated without need of adding control circuit, simple structure and small volume. The invention can satisfy DC fault protective device of individual system such as ship, plane, oil platform, mobile communication station and electric automobile.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
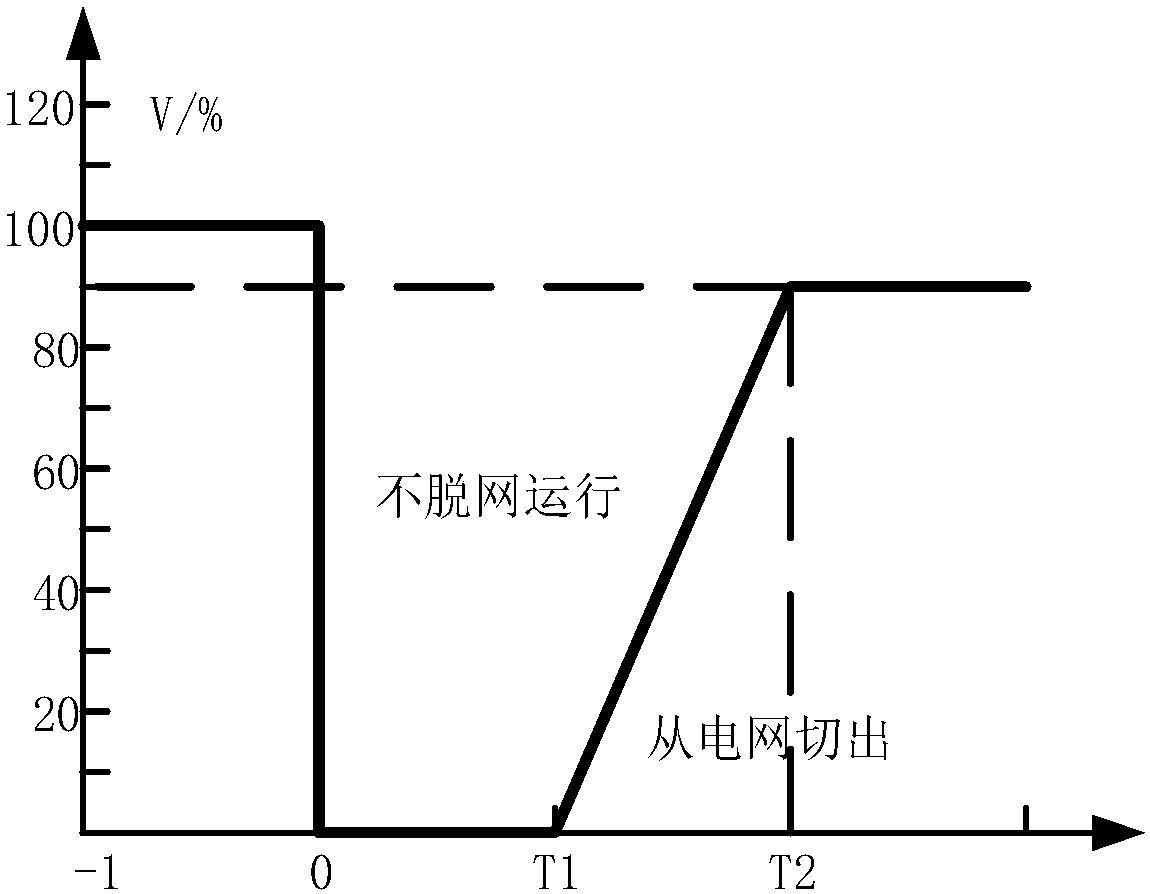
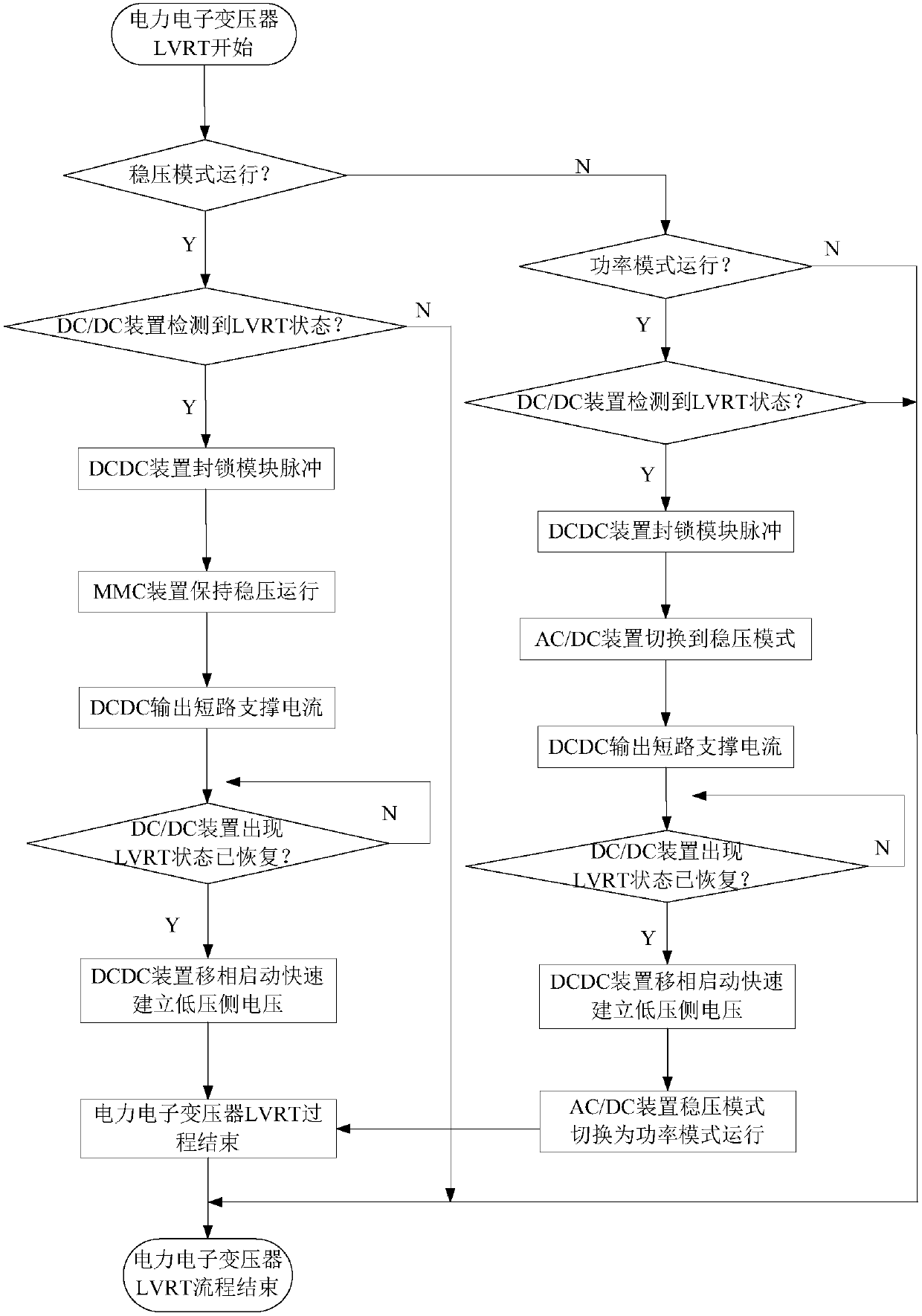
DC fault ride-through method for power electronic transformer
ActiveCN107947221AImprove stabilityReduce power supply reliabilityElectric power transfer ac networkEmergency protective circuit arrangementsMicrogridLow voltage
Owner:XIAN XJ POWER ELECTRONICS TECH
MMC sub module with direct-current fault blocking capability
ActiveCN108306501AImprove economyImprove performanceElectric power transfer ac networkEmergency protective circuit arrangementsReverse currentCapacitance
Provided in the invention is an MMC sub module with the direct-current fault blocking capability. The MMC sub module comprises a power electronic device and a capacitor. A hybrid bridge arm formed bya plurality of MMC sub modules form a flexible direct-current power transmission converter; and a rectification or inversion function can be realized in normal operation. When a direct-current bus short-circuit fault occurs at a direct-current side of the converter, a power electronic switch is turned off and the capacitor is connected in series to a clamping diode in a reverse direction to realize direct-current bus fault isolation. Therefore, the short-circuit reverse current fault isolation capability of the flexible direct-current power transmission direct-current side based on a damping dual-sub-unit module is improved.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +2
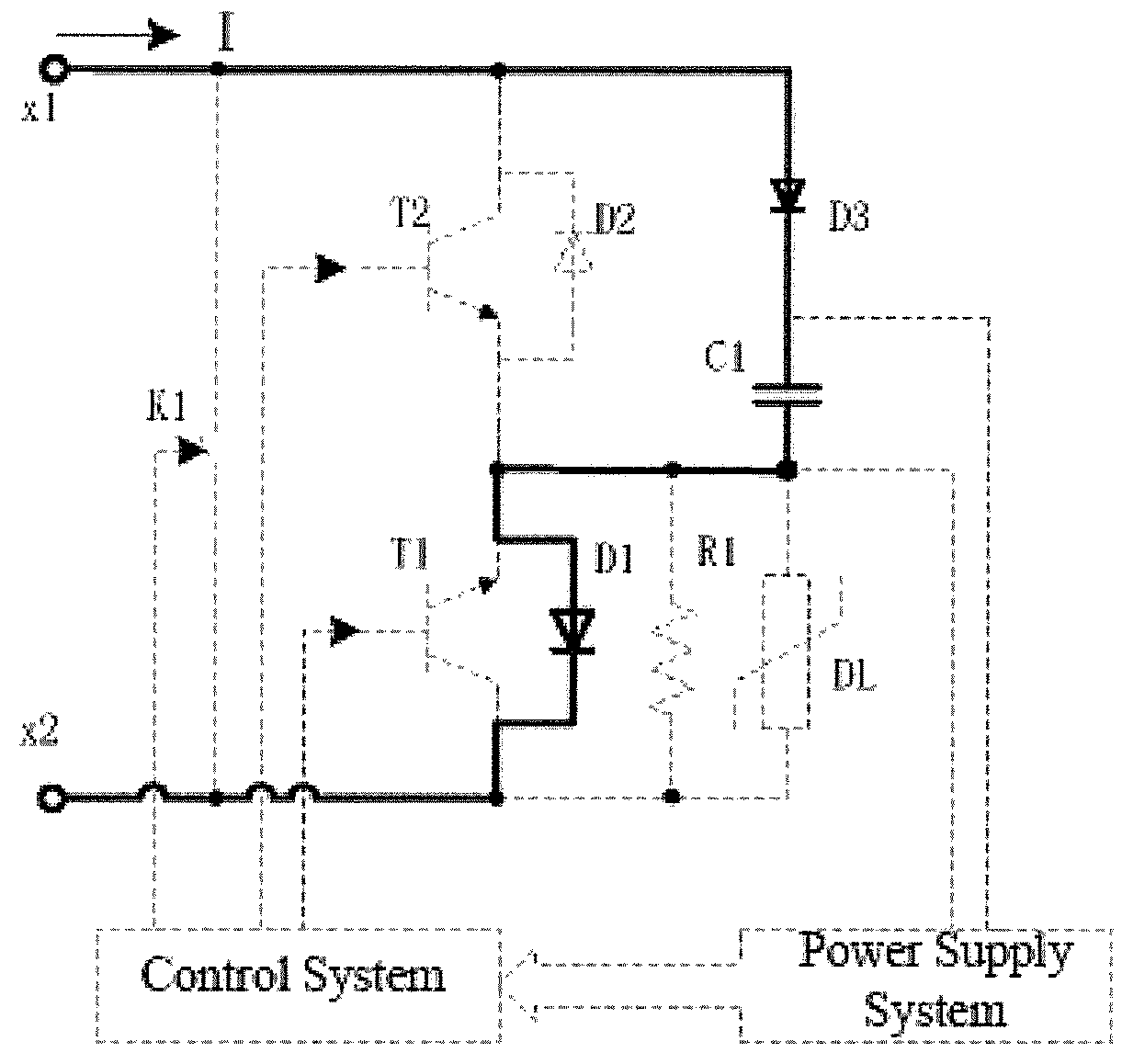
Fault current-suppressing damper topology circuit and control method thereof and converter
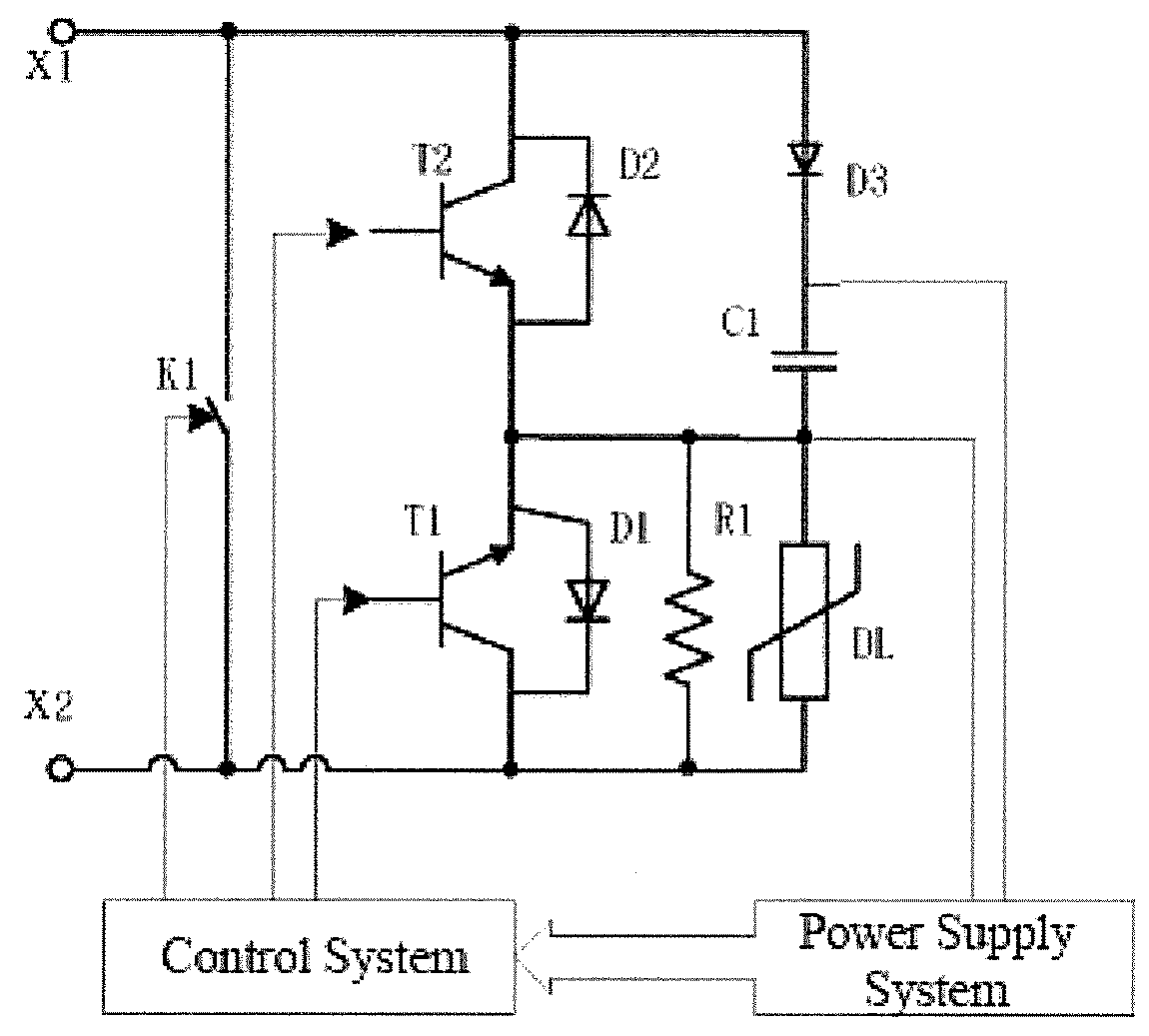
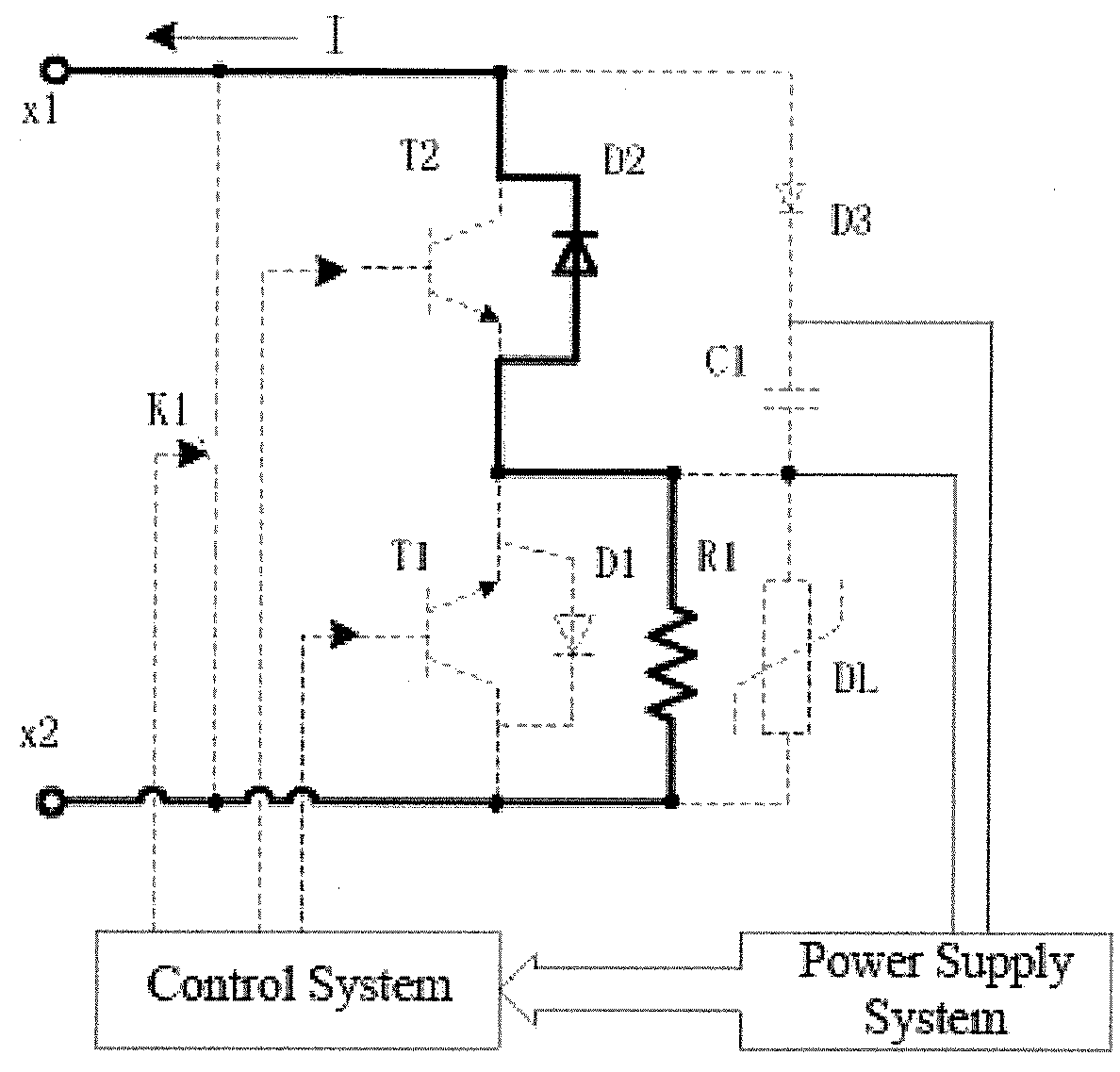
ActiveUS20180183231A1Effectively protects safetyFaster delayTransistorAc-dc conversionEngineeringVoltage source
Disclosed are a fault current-suppressing damper topology circuit and a control method thereof and a converter. An anode of a separate diode is connected to a positive electrode of a second switch module, a cathode of the separate diode is connected to one end of an energy storage capacitor, and the other end of the energy storage capacitor is connected to a negative electrode of a first switch module; a damping resistor is connected in parallel with an arrester and then with the first switch module; a bypass switch is connected in parallel between a terminal x1 and a terminal x2 of the damper topology circuit; a power supply system acquires energy from the energy storage capacitor and supplies power to a control system; and the control system controls an operating state of the damper topology circuit by controlling the bypass switch, the first switch module and the second switch module. The fault current-suppressing damper topology circuit is applied to voltage source converters. In case of a DC fault, stress resulting from fault currents is reduced by use of a damping resistor, thereby avoiding damages to a device and achieving self-power supply, modularization and independent control. The fault current-suppressing damper topology circuit can be flexibly applied to various types of voltage source converters and has outstanding economic efficiency and technicality.
Owner:NR ELECTRIC CO LTD +1
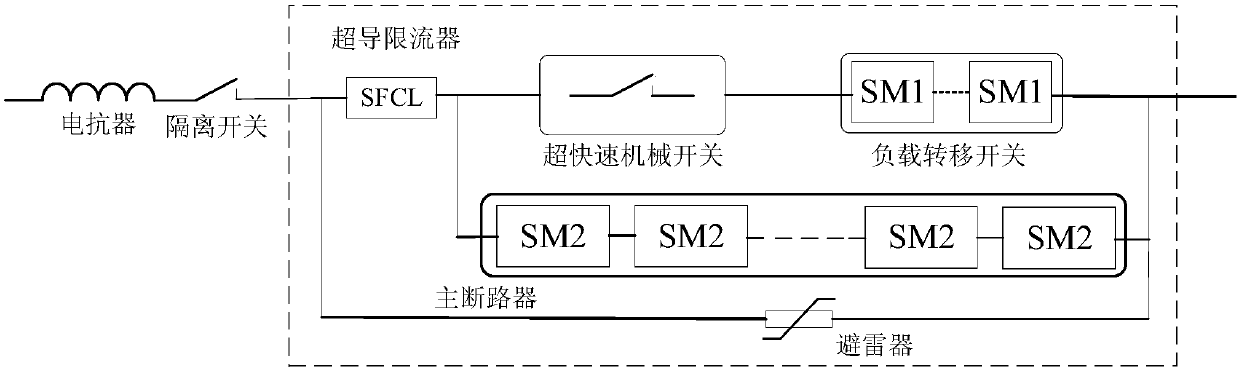
Direct current circuit breaker with opening current reducing effect and direct current fault treatment strategy thereof
InactiveCN107785867AReduce in quantityReduce lossEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentStrong referenceDc circuit breaker
The invention discloses a direct current circuit breaker with opening current reducing effect and a direct current fault treatment strategy thereof. The direct current circuit breaker comprises a normal current flowing branch circuit, a current opening branch circuit, an energy consumption branch circuit, a super-conduction current limiter, a reactor and an isolation switch, wherein the normal current flowing branch circuit is formed by connecting a super-quick mechanical switch and a load transfer switch in series; the current opening branch circuit consists of a main circuit breaker; the energy consumption branch circuit consists of a lightning arrester; the load transfer switch is formed by connecting a plurality of submodules with bidirectional current flowing ability in series and parallel; the main circuit breaker is formed by connecting a plurality of enhanced semi-bridge submodules in series and parallel. The direct current circuit breaker has the advantages that the ascendingspeed and amplitude of the fault current are inhibited by the super-conduction current limiter, and then the opening current of the circuit breaker is reduced; the number of the submodules of the maincircuit breaker is greatly reduced, the engineering cost and operation loss are greatly reduced, and the strong reference meaning and use value in the engineering are realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +3
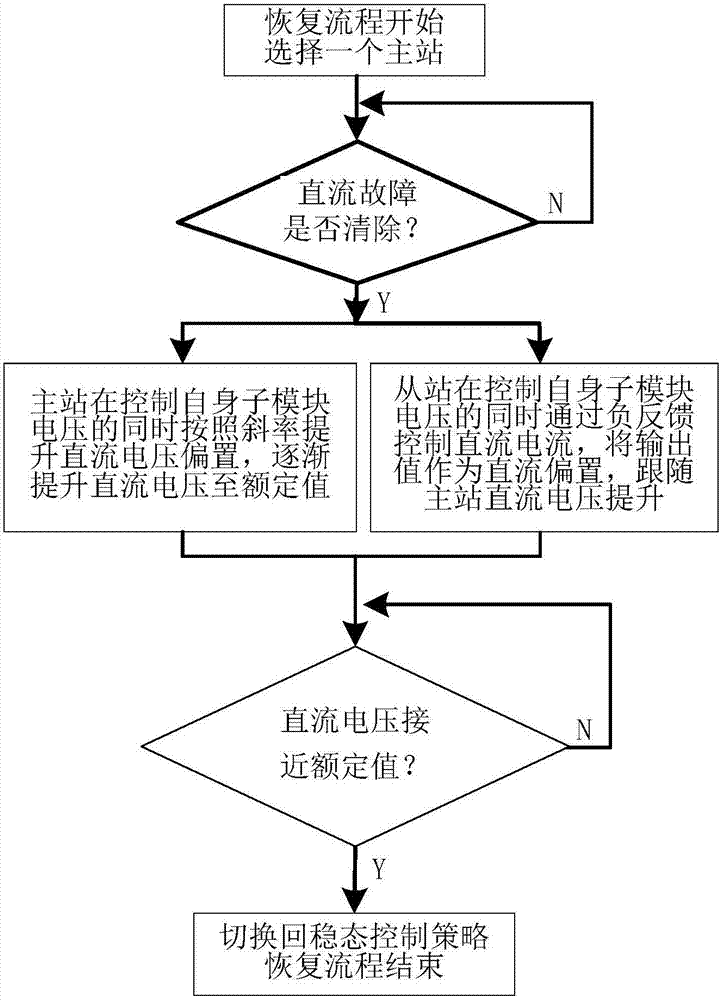
Method and device for recovering direct-current short-circuit failure of hybrid modular multilevel converter
ActiveCN106953347APromote recoveryStable recoveryElectric power transfer ac networkContigency dealing ac circuit arrangementsDc currentMaster station
The invention relates to a method and device for recovering the direct-current short-circuit failure of a hybrid modular multilevel converter. The convertor station control mode needing to be recovered is divided into a master station mode and a slave station mode; when one convertor station is selected as the master station, other convertor stations are used as the slave stations; and, when the master station gradually rises direct-current voltage to a rated value, the slave stations track the direct-current voltage of the master station through the difference between a direct-current feedback value and a direct-current reference value, so that synchronous rising of the direct-current voltage is realized. By means of the method and device for recovering the direct-current short-circuit failure of the hybrid modular multilevel converter disclosed by the invention, inter-station communication is not needed in the whole recovery process; cooperation of a circuit breaker is not needed; the convertor stations can recover the direct-current voltage rapidly and stably after the direct-current short-circuit failure is ended, and can recover the direct-current voltage to the normal operation state before the direct-current failure according to a pre-set process and detection of the own electrical quantity; impact current does not exist in the recovery process; and the grid-connected state can be continuously kept.
Owner:XUJI GRP +4
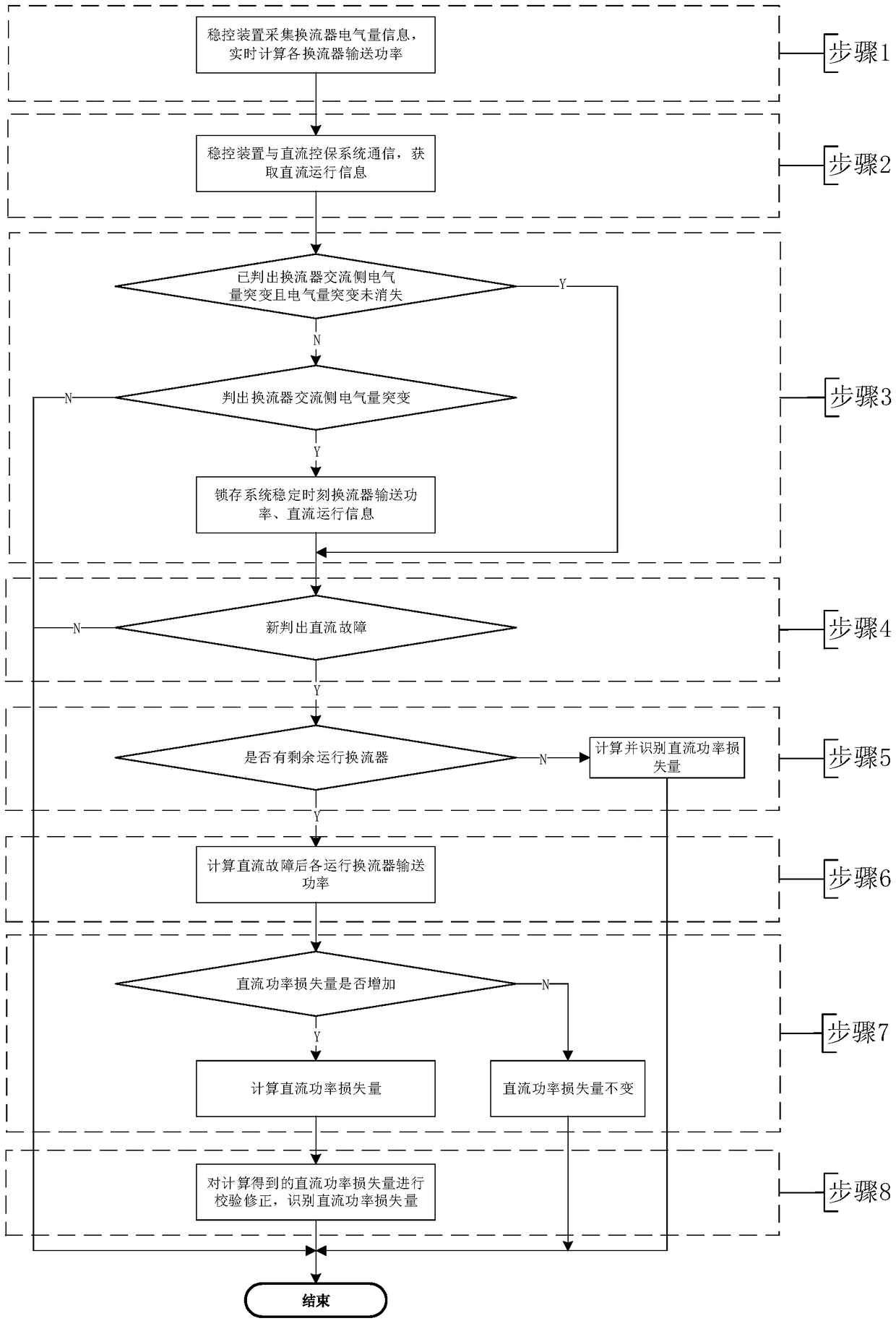
Method and system for identifying power loss of UHVDC by stability control device
ActiveCN108879755AIdentify the amount of power lossGuaranteed accuracyElectric power transfer ac networkElectric power systemPower grid
The present invention discloses a method and a system for identifying power loss of UHVDC by a stability control device, and belongs to the field of electric power systems and automation thereof. DC transmission power loss that the stability control device needs to identify is mainly divided into two cases: DC power speed dropping and blocking of a converter. Each time the stability control deviceidentifies DC power speed dropping or blocking of the converter, calculating transmission power of the converter after a DC fault, and identifying direct current transmission power loss by using total transmission DC power during normal operation of the system. According to the method and the system for identifying power loss of UHVDC by the stability control device, accurateness and effectiveness in identification of the DC power transmission power loss under condition of single or sequential fault of the UHVDC is ensured, safety and stability in operation of a AC / DC power grid is ensuredby further adoption of corresponding control measures.
Owner:NARI TECH CO LTD +2
MMC submodule topological structure based on H-bridge
ActiveCN105356770AReduce capacitanceReduce volumeAc-dc conversion without reversalDc-dc conversionCapacitanceDc capacitor
The invention discloses an MMC submodule topological structure based on an H-bridge. The objective is that DC fault protection capacity of the H-bridge is inherited, the capacitance value of a DC capacitor is reduced, the module size is reduced and power density is enhanced. The adopted technical scheme is that the MMC submodule topological structure based on the H-bridge comprises four IBGT transistors which are connected in turn. A diode is connected on each of the four IBGT transistors in an antiparallel way. The H-bridge is formed by the four IBGT transistors and the diodes. The bus of the H-bridge is connected with the DC capacitor (Cdc). The H-bridge comprises two half-bridge structures. The midpoints of the two half-bridge structures are output of MMC submodules. Any one half-bridge structure of the two half-bridge structures is connected with an LC network. The loop of the LC network is connected with high level or low level of the H-bridge.
Owner:TBEA SUNOASIS +2
An AC/DC fault identification and protection coordination method in a converter station
ActiveCN109038520AEmergency protective circuit arrangementsElectric power transfer ac networkHarmonicEngineering
The invention discloses an AC / DC fault identification and protection coordination method in a converter station belonging to the technical field of safe operation of an AC / DC hybrid transmission system. According to the characteristics of DC second harmonic current and AC negative sequence current before and after the converter lockout, the invention puts forward the converter station differentialcurrent protection, which can distinguish AC from DC faults, determine the fault area, and the coordination and cooperation scheme of AC and DC protection. Finally, combined with PSCAD / EMTDC model ofPV / DC convergent access system, the feasibility of differential protection and the reliability of AC / DC protection coordination scheme are verified. The results show that the proposed method can effectively identify AC and DC faults, and is less affected by the transition resistance.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Self-blocking sub-module with energy-consuming resistor and application thereof
InactiveCN105763089ASmall time constantFast blockingDc-ac conversion without reversalDc capacitorEngineering
The invention discloses a self-blocking sub-module topological structure with an energy-consuming resistor. The sub-module topological structure comprises two switch modules connected in series, a DC capacitor, a third switch module, a diode, and the energy-consuming resistor. Each of the two switch modules is composed of a full-controlled device and a diode in inverse parallel connection. The negative end of the first switch module is connected with the positive end of the second switch module. The positive pole and the negative pole of the DC capacitor are connected with the positive end of the first switch module and the negative end of the second switch module respectively. The third switch module is electrically connected with the first switch module or the second switch module. The diode is electrically connected with the third switch module and the DC capacitor. The energy-consuming resistor and the diode are connected in series to form a series connection assembly. The invention further discloses a modular multi-level converter containing the self-blocking sub-module topological structure. The self-blocking sub-module topological structure may inhibit an increase in the voltage of a sub-module DC capacitor for the duration of blocking a DC fault, and guarantees system operation safety.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A method for clearing DC faults in a current transfer multilevel converter topology
ActiveCN109217265AClear DC Fault QuicklyDC fault fastEmergency protective circuit arrangementsElectric power transfer ac networkModularityDc fault
A method for clearing DC faults in a current transfer multilevel convert topology belongs to the field of flexible HVDC technology, based on the topology of half-bridge multilevel converter, A current transfer type modular multilevel converter topology is established by using the energy absorption branch and the bridge arm transfer branch. The converter is quickly disconnected from the fault linethrough the cut-off branch, and then the fault current is absorbed through the bridge arm transfer branch and the energy absorption branch, so that the DC fault can be quickly cleared. The method transfers and clears the DC side short-circuit fault current of the converter through the cooperation of each branch in the current transfer type modular multi-level converter topology, and has good economy and strong practicability.
Owner:NORTHEAST DIANLI UNIVERSITY
Multi-port current-limiting circuit breaker suitable for direct-current power grid
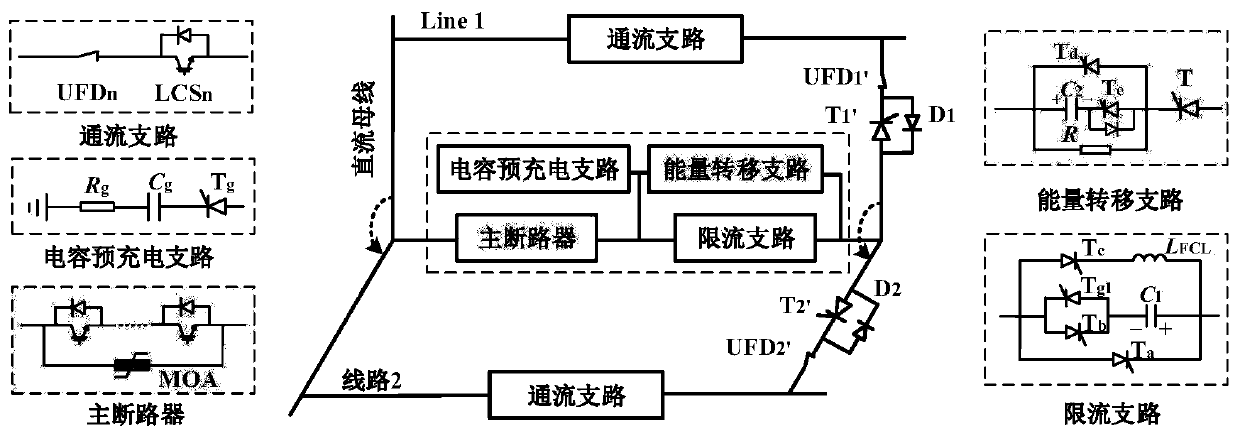
PendingCN110994568ASimple logicImprove economyEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentCapacitancePower grid
The invention provides a multi-port current-limiting circuit breaker topology suitable for a direct-current power grid and a control method of the multi-port current-limiting circuit breaker topology.The topological structure is composed of a through-current branch, a current-limiting branch, a capacitor pre-charging branch, a main circuit breaker and an energy transfer branch. A single main circuit breaker is adopted to protect a plurality of direct-current lines, a thyristor with high through-current capability is used as a control unit between the main circuit breaker and the direct-current lines, a capacitor pre-charging branch fully utilizes a direct-current system to charge a capacitor of a current-limiting branch, and an energy transfer branch is used for shielding current-limitingreactance. The invention provides a control method of a multi-port direct-current circuit breaker. The multi-port direct-current circuit breaker is controlled under the three conditions of normal operation of a line where the multi-port direct-current circuit breaker is located, circuit breaking after a direct-current fault of one line is detected and energy consumption after the current of a fault line is reduced to zero.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
MMC dual sub-module topology with DC-side fault self-clearing capability
InactiveCN110429843AWith DC side fault self-clearing capabilityImprove versatilityAc-dc conversionElectric power transfer ac networkCapacitanceDc fault
The present invention discloses an MMC dual sub-module topology with a DC-side fault self-clearing capability. Two half-bridge modules are connected in series by a connecting circuit, the input end ofthe output end of the dual sub-module are connected in parallel with a reverse blocking circuit. The connecting circuit in the dual sub-module is formed by connecting an insulated gate bipolar transistor and a diode in anti-parallel mode; and the reverse blocking circuit is formed by connecting a capacitor and a diode in series. When a fault occurs on the DC side, the reverse blocking circuit hasan effect for clearing a fault current, the dual sub-module has good universality, can be used for hybrid sub-module topology to allow the converter to have a DC fault clearing capability so as to ensure the safe and reliable operation of the MMC-HVDC system.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +1
DC fault reclosing strategy for flexible DC power transmission system
InactiveCN106026007AAvoid dischargeAvoid secondary overcurrent impactEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionOperation modeEngineering
The invention discloses a DC fault reclosing strategy of a flexible direct current transmission system, which clears the DC fault current through a blocking converter and completes deionization; after that, puts all SBSMs into a similar half-bridge blocking mode; uses the SBSM-like half-bridge blocking mode realizes the operation mode of SBSM‑MMC uncontrolled rectifier bridge; if the DC line no longer has current, it is judged that the fault has disappeared, enters the system restart operation mode, and resumes normal operation under the restart control strategy; if the DC line appears current again, then Indicates that the fault still exists, it is judged as a permanent fault, and the converter is blocked immediately. Compared with the prior art, the present invention can realize reclosing judgment only by judging whether the current exists or not. When the reclosing is a permanent fault, the converter can be quickly re-blocked under the condition of a small line current, effectively avoiding It prevents the secondary overcurrent impact caused by reclosing to the system, and has the positive effect of low current hazard.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com