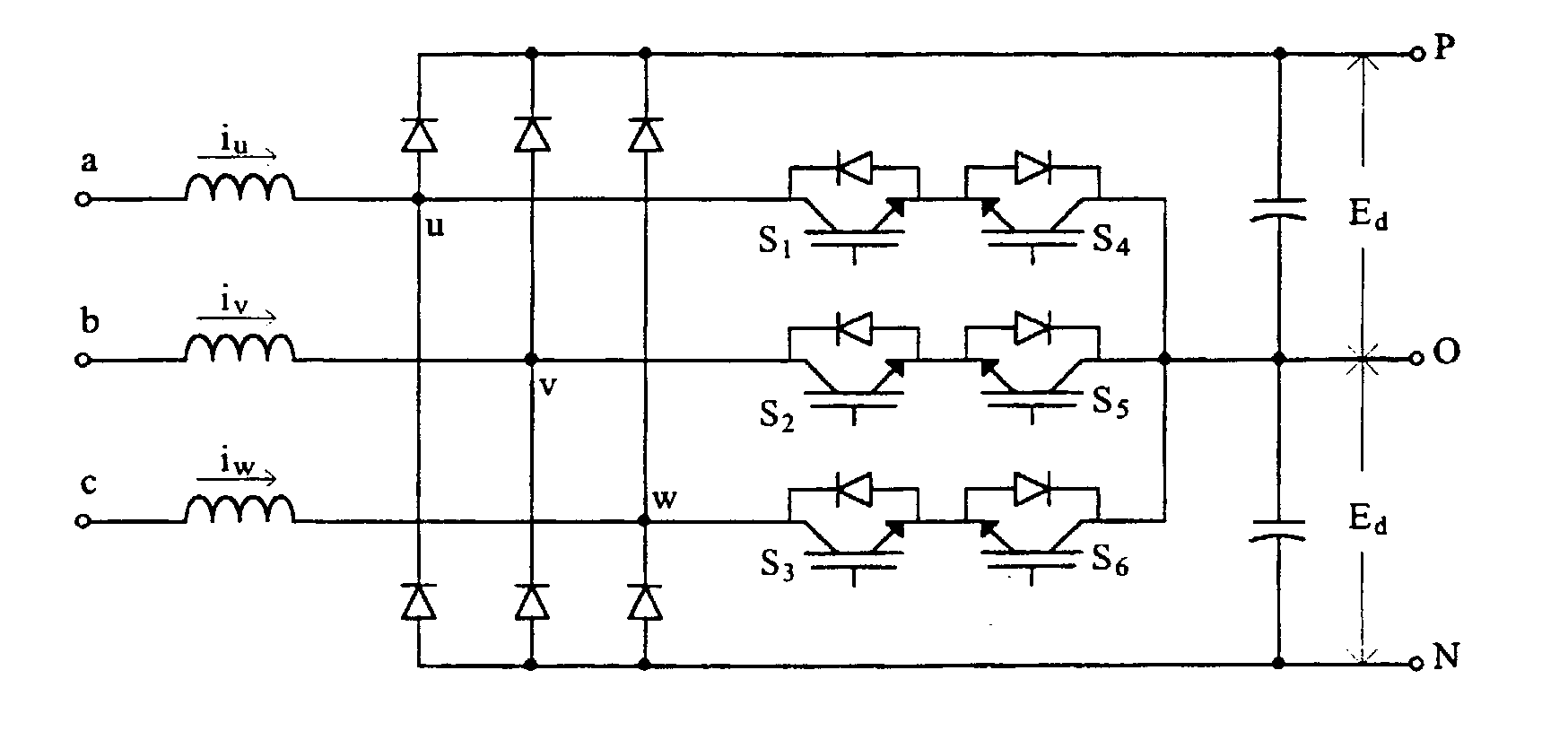
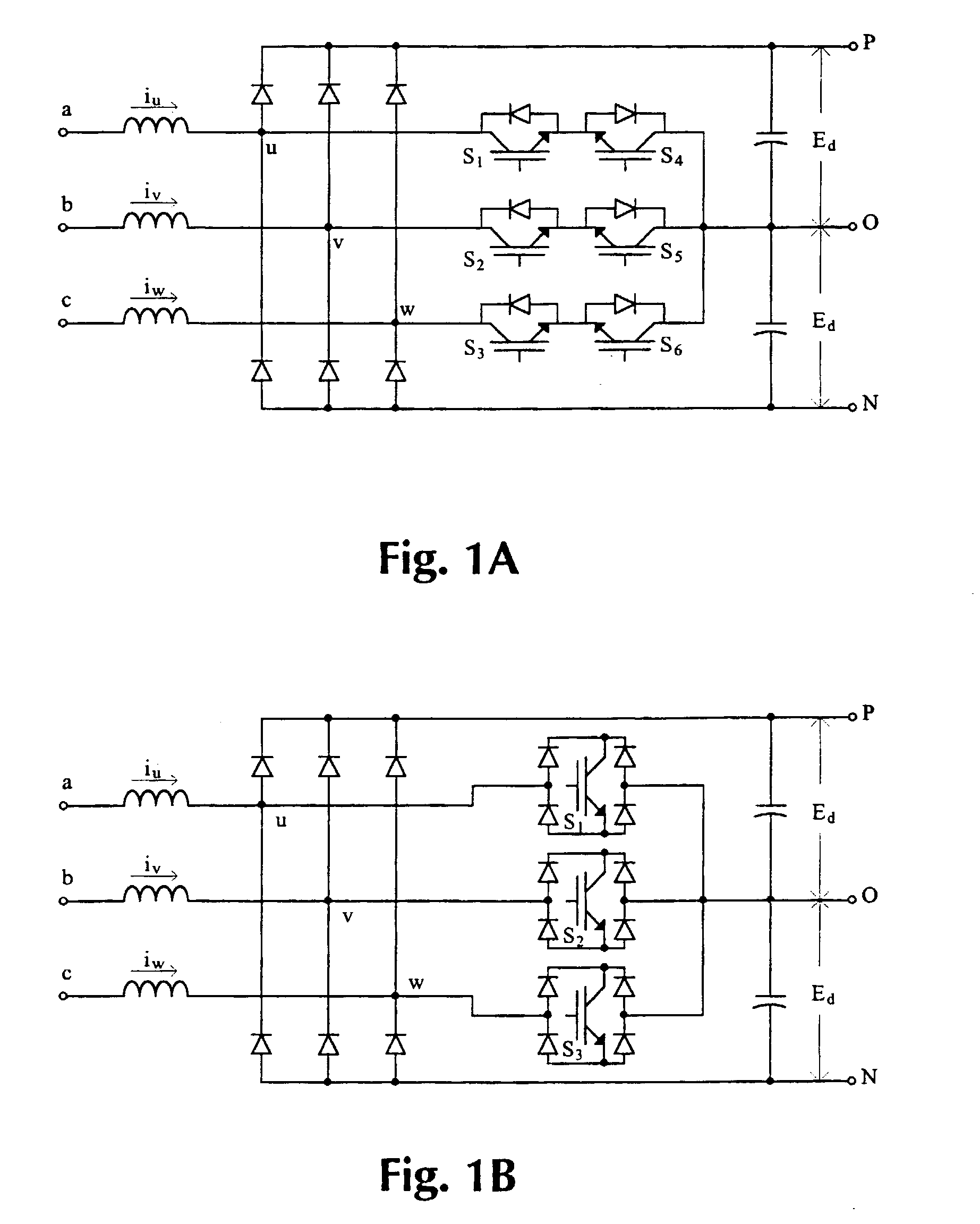
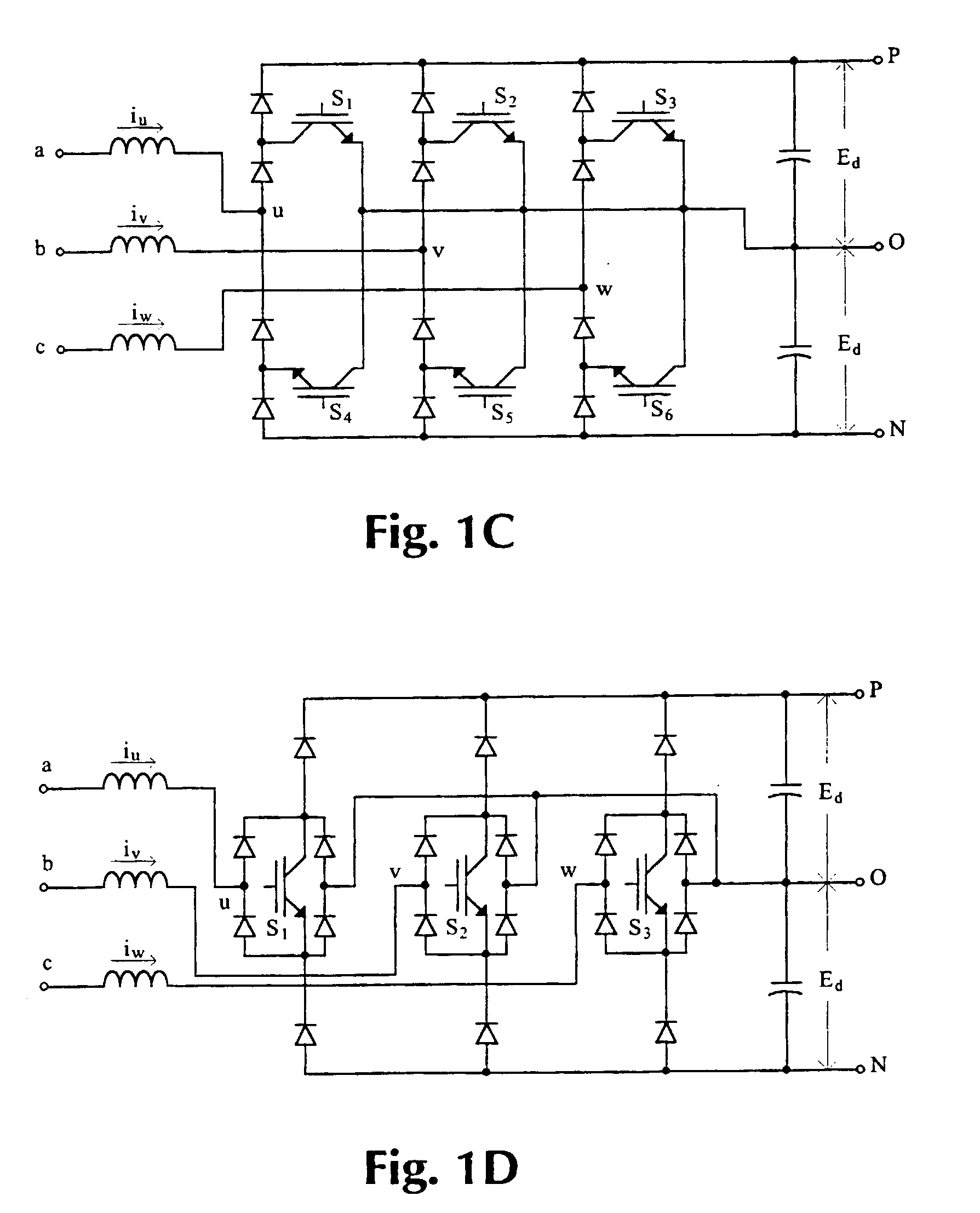
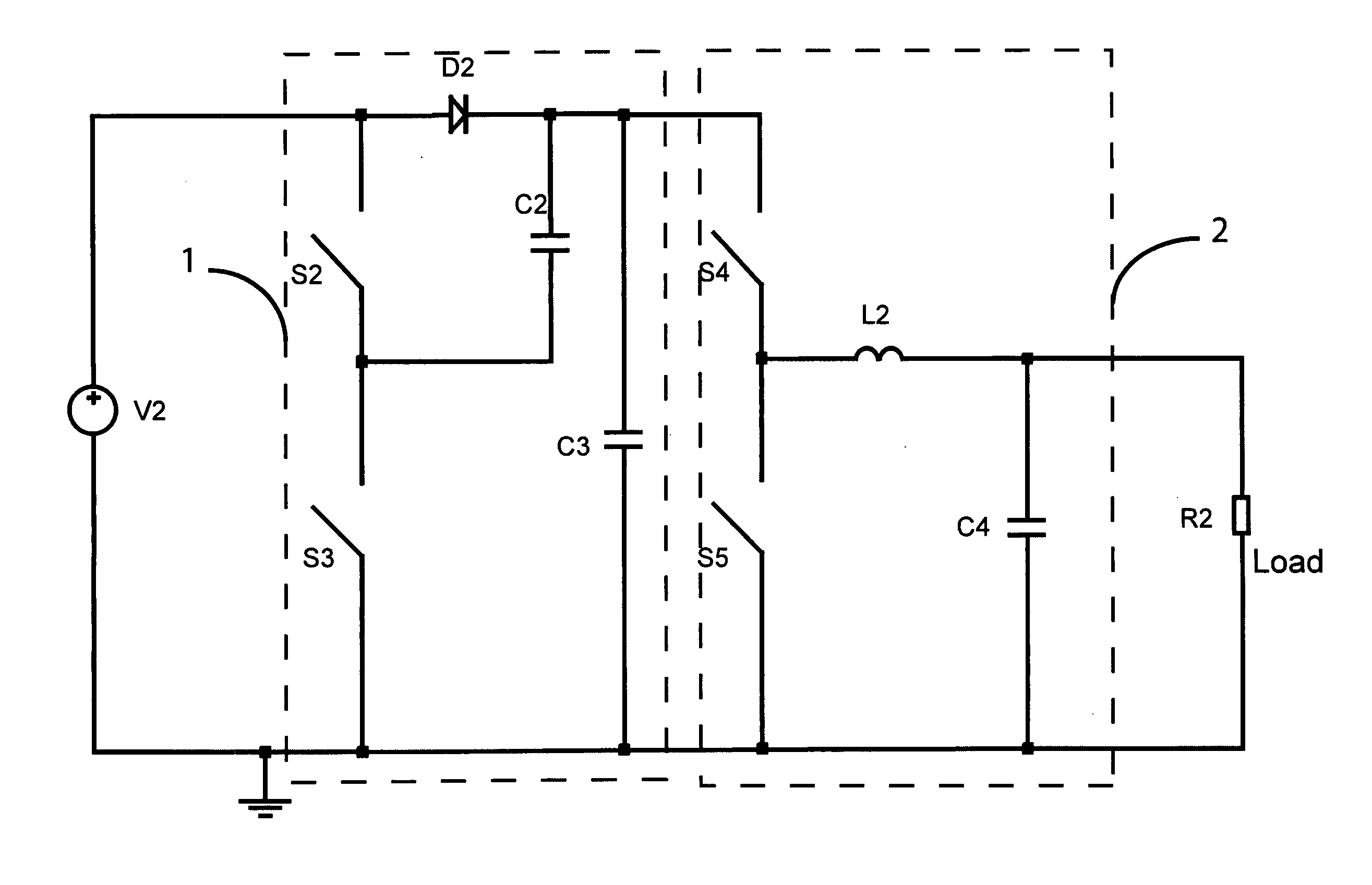
Patents
Literature
5738 results about "Switching frequency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In electronics, switching frequency refers to the rate at which an electronic switch performs its function.
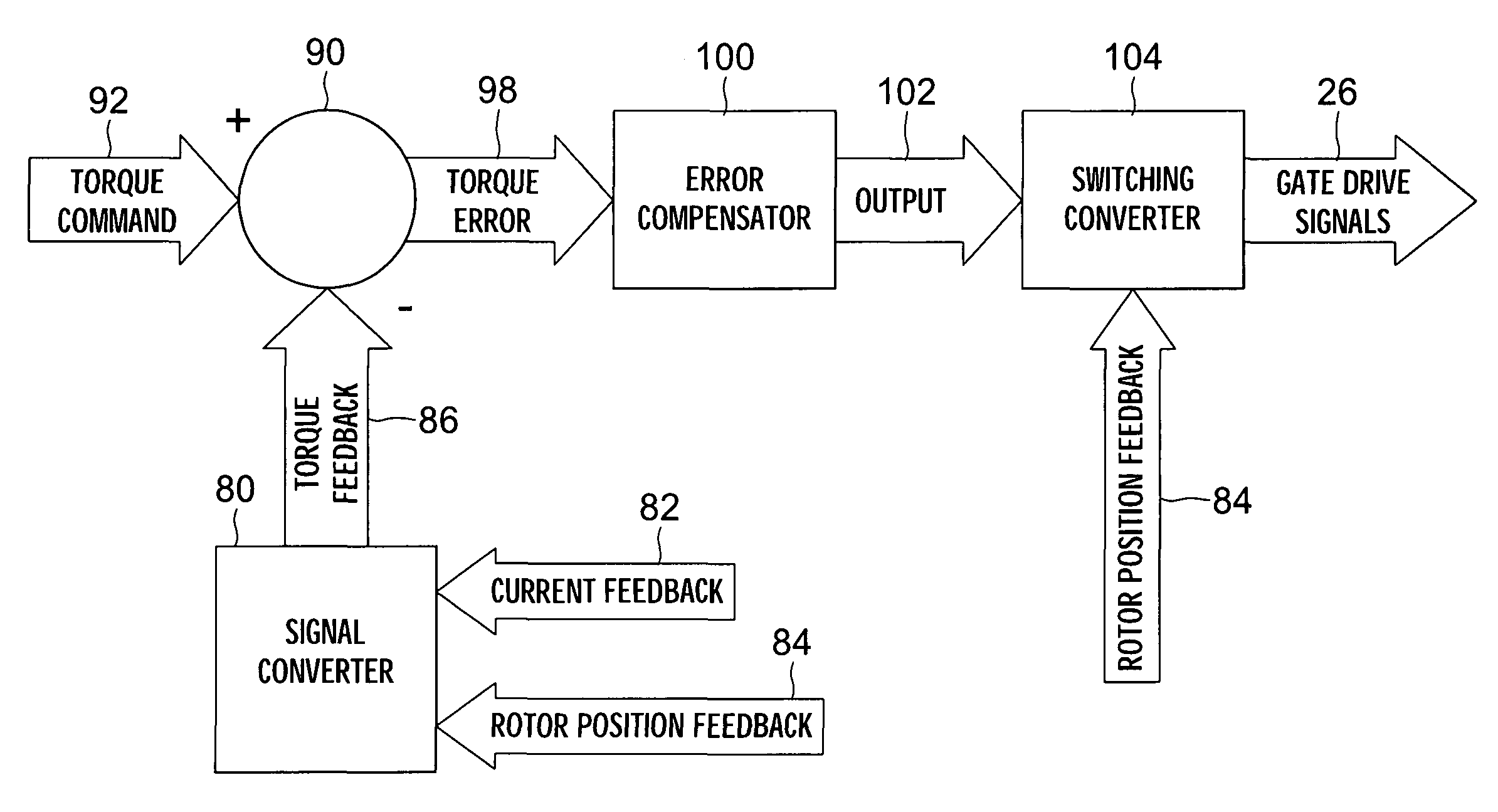
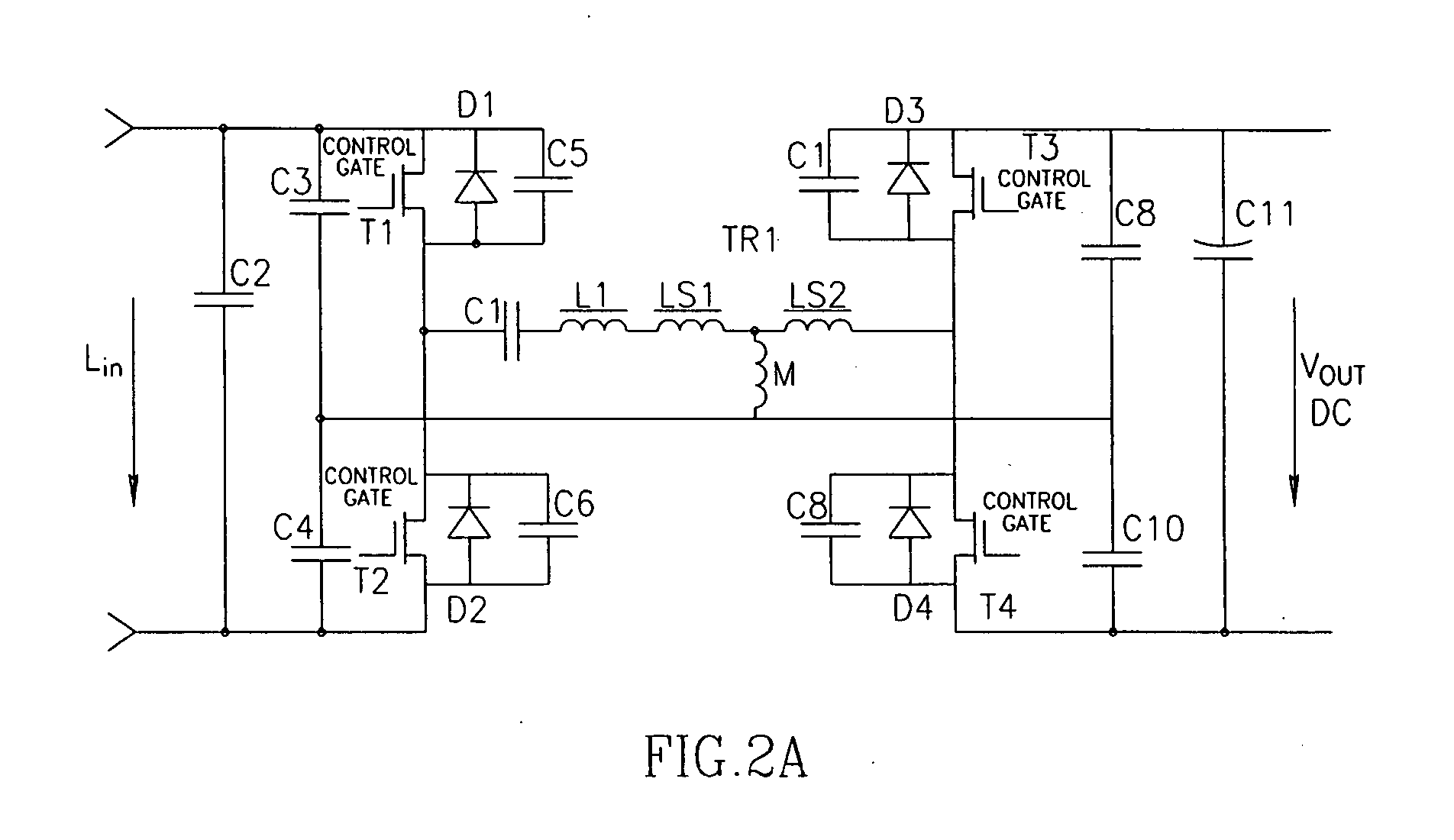
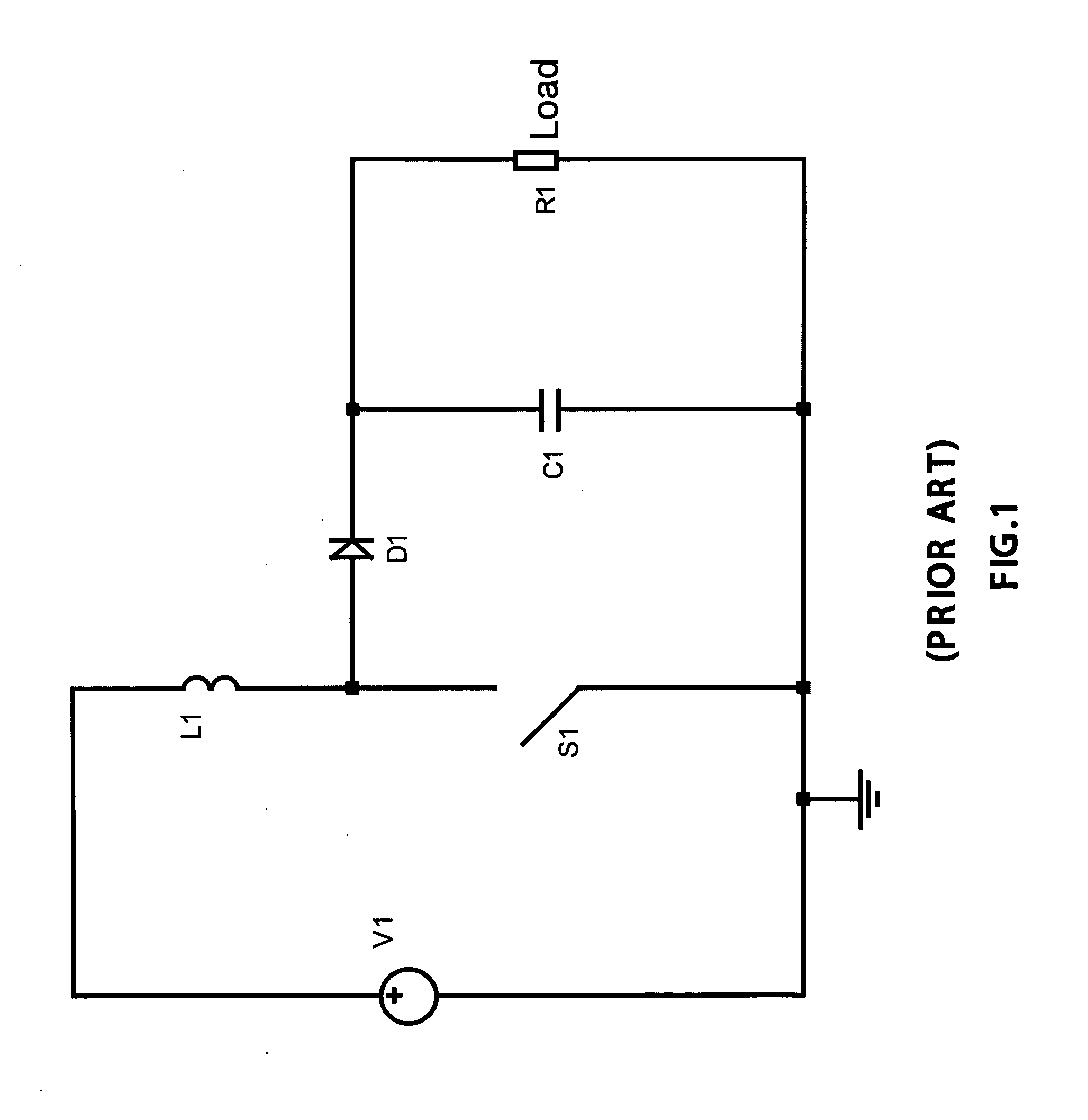
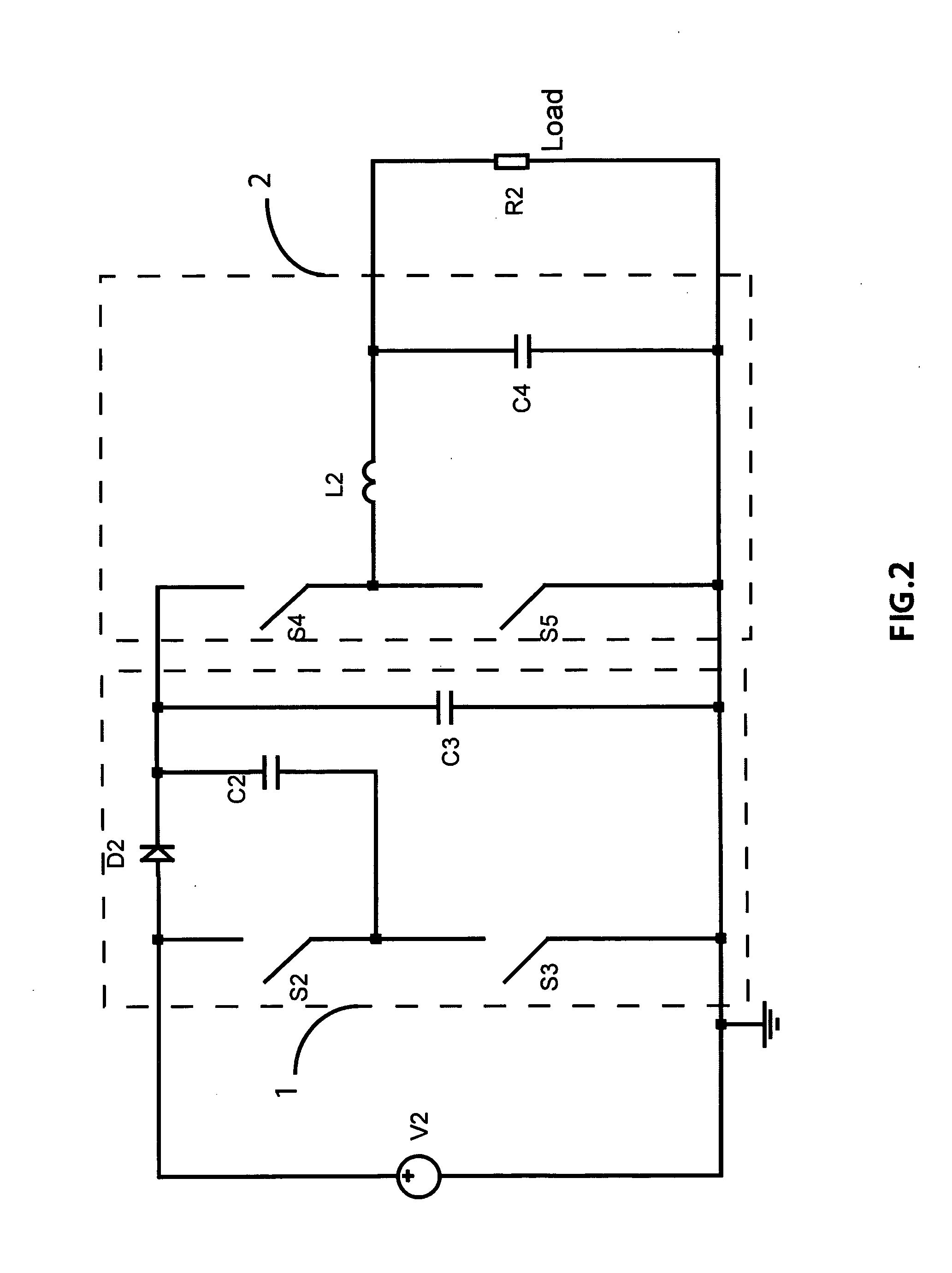
Torque controller in an electric motor
ActiveUS7898198B2Motor control for very low speedsDC motor speed/torque controlMaximum torqueSlow rotation
The torque of a motor operated by an inverter circuit is controlled to allow maximum torque in the motor when the motor is stalled or at low rotation speeds. Control is accomplished by providing a switching frequency to the motor at a first switching frequency, detecting a rotation speed of the motor, and switching the current to the motor to a second switching frequency when the rotation speed of the motor drops to a predetermined slow rotation speed. The second switching frequency is less than the first switching frequency.
Owner:DRS NETWORK & IMAGING SYST
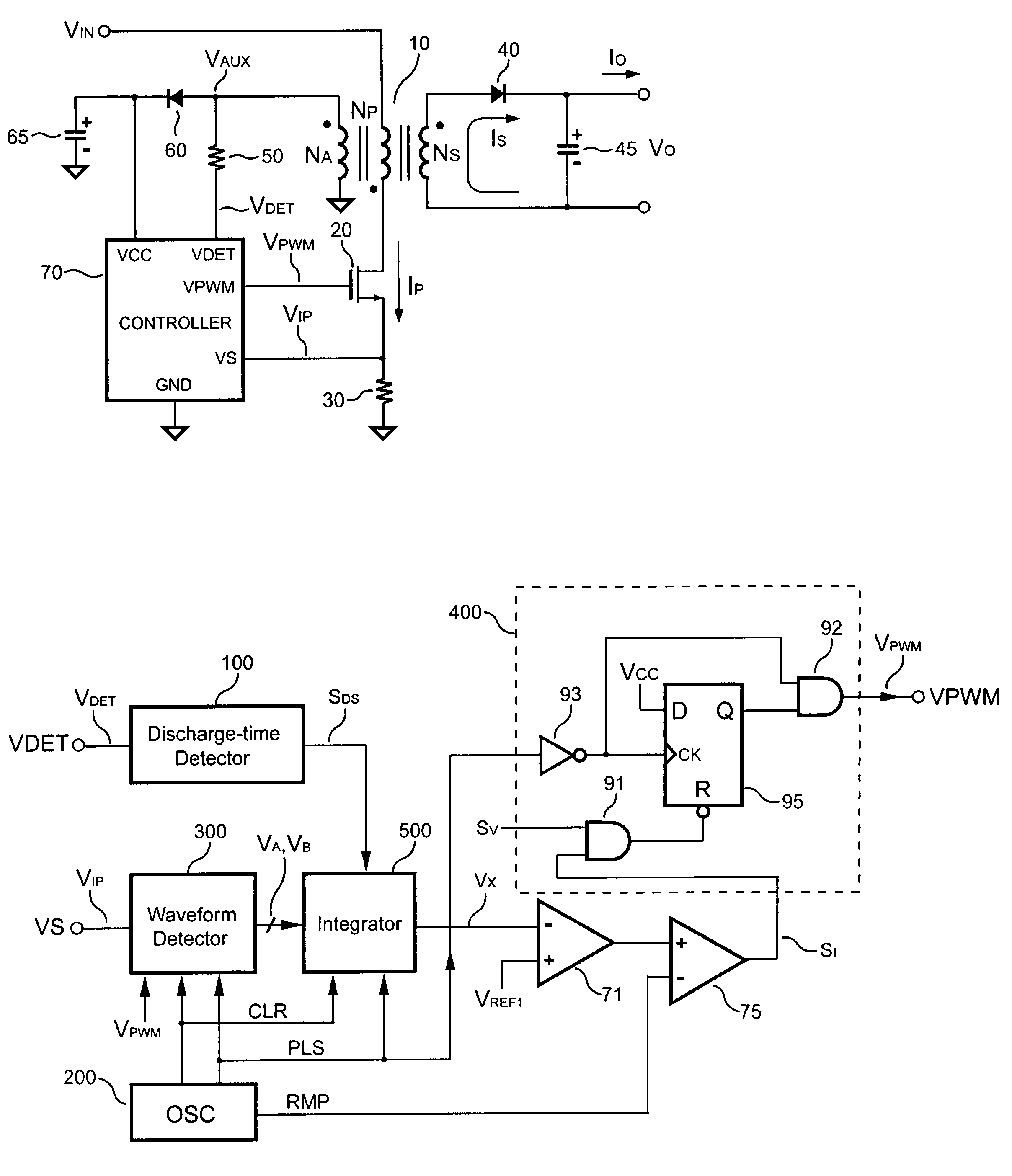
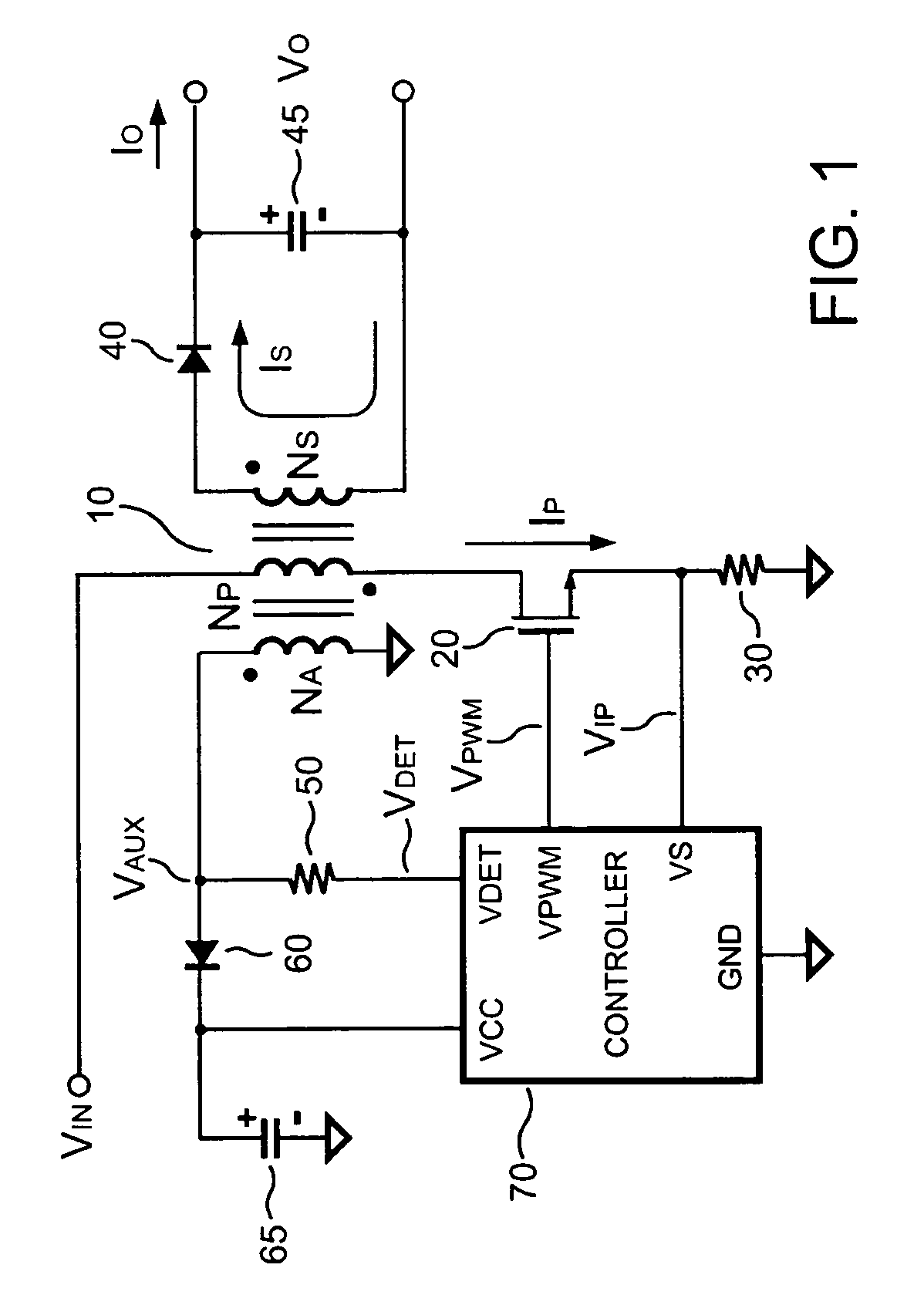
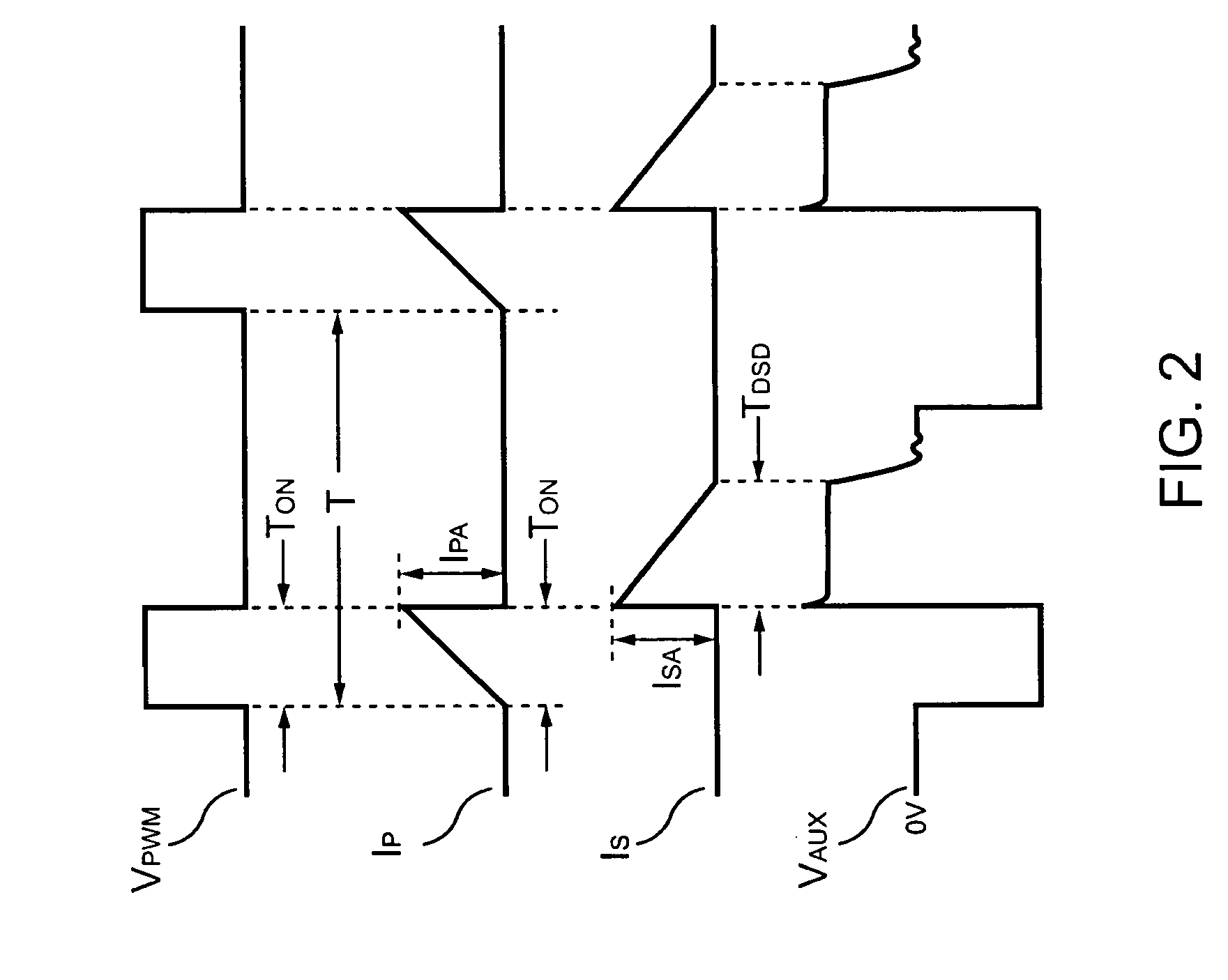
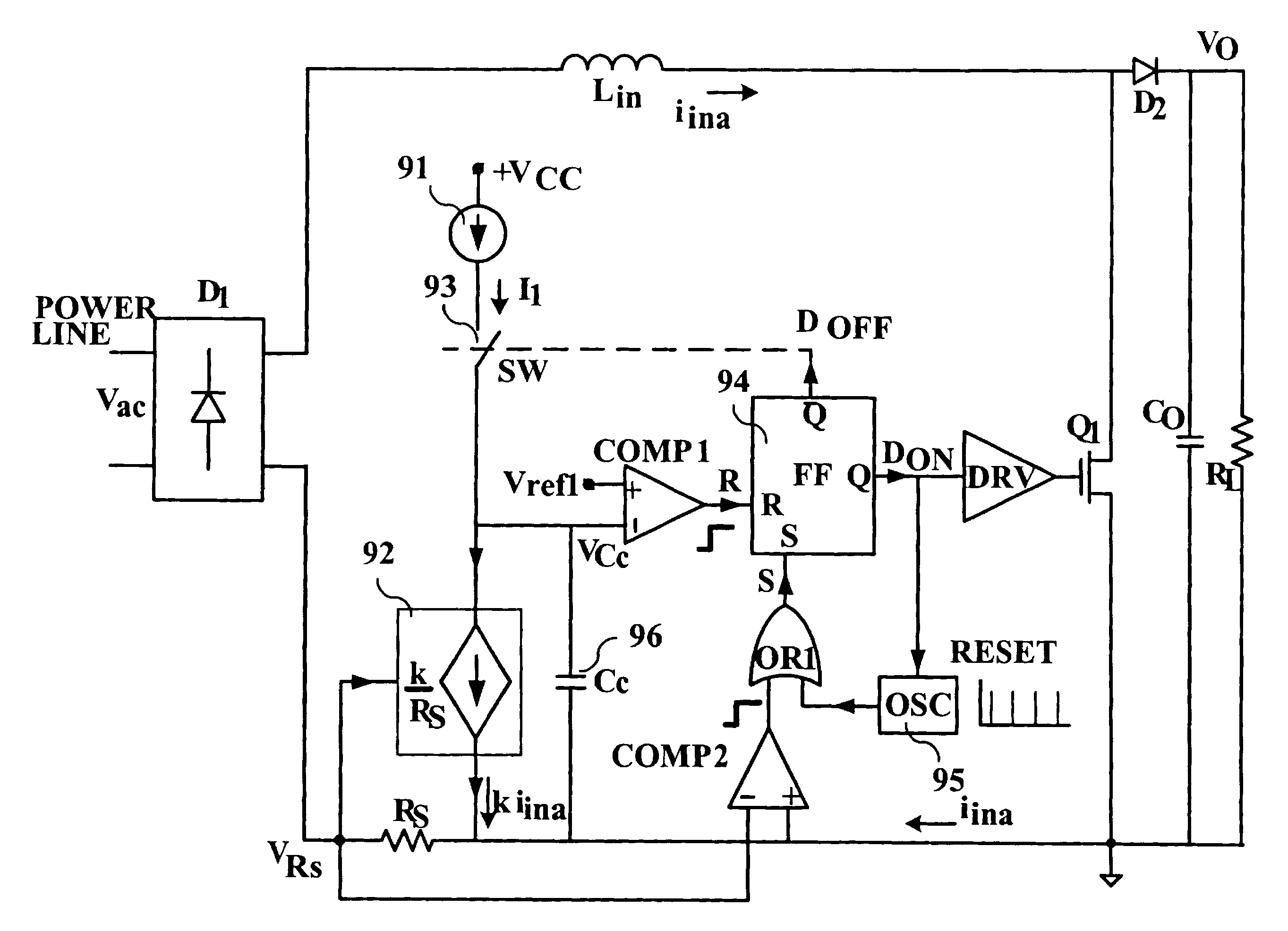
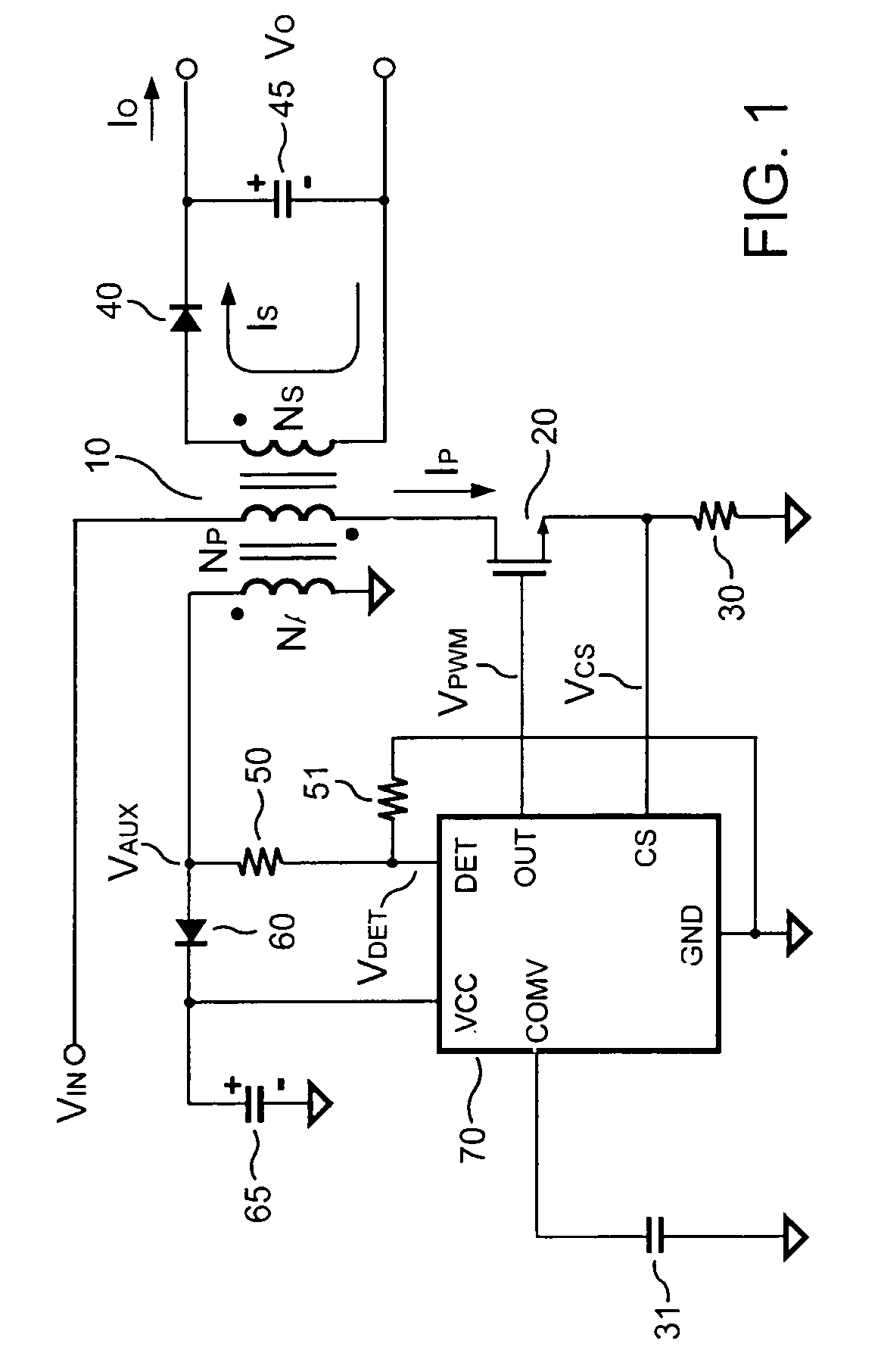
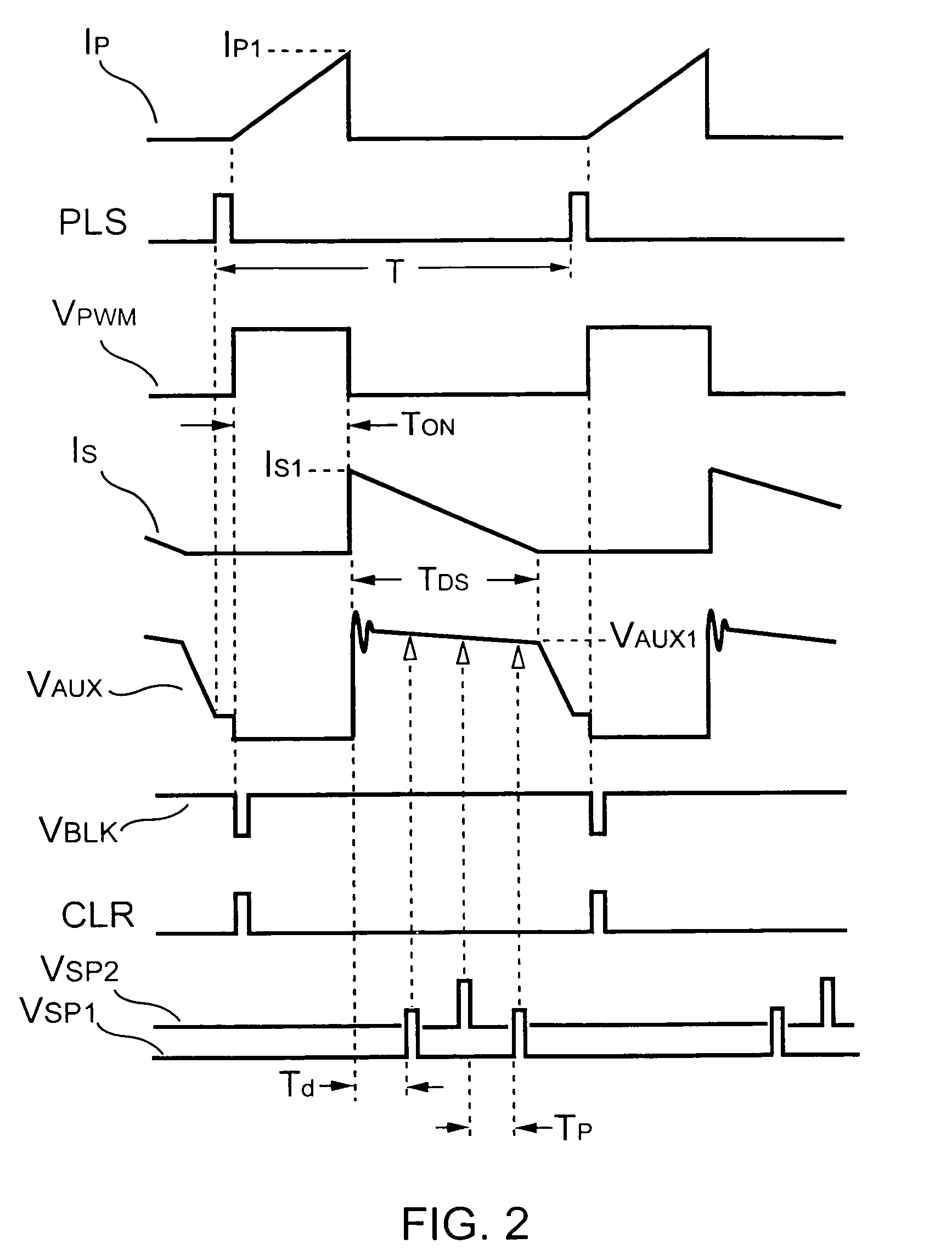
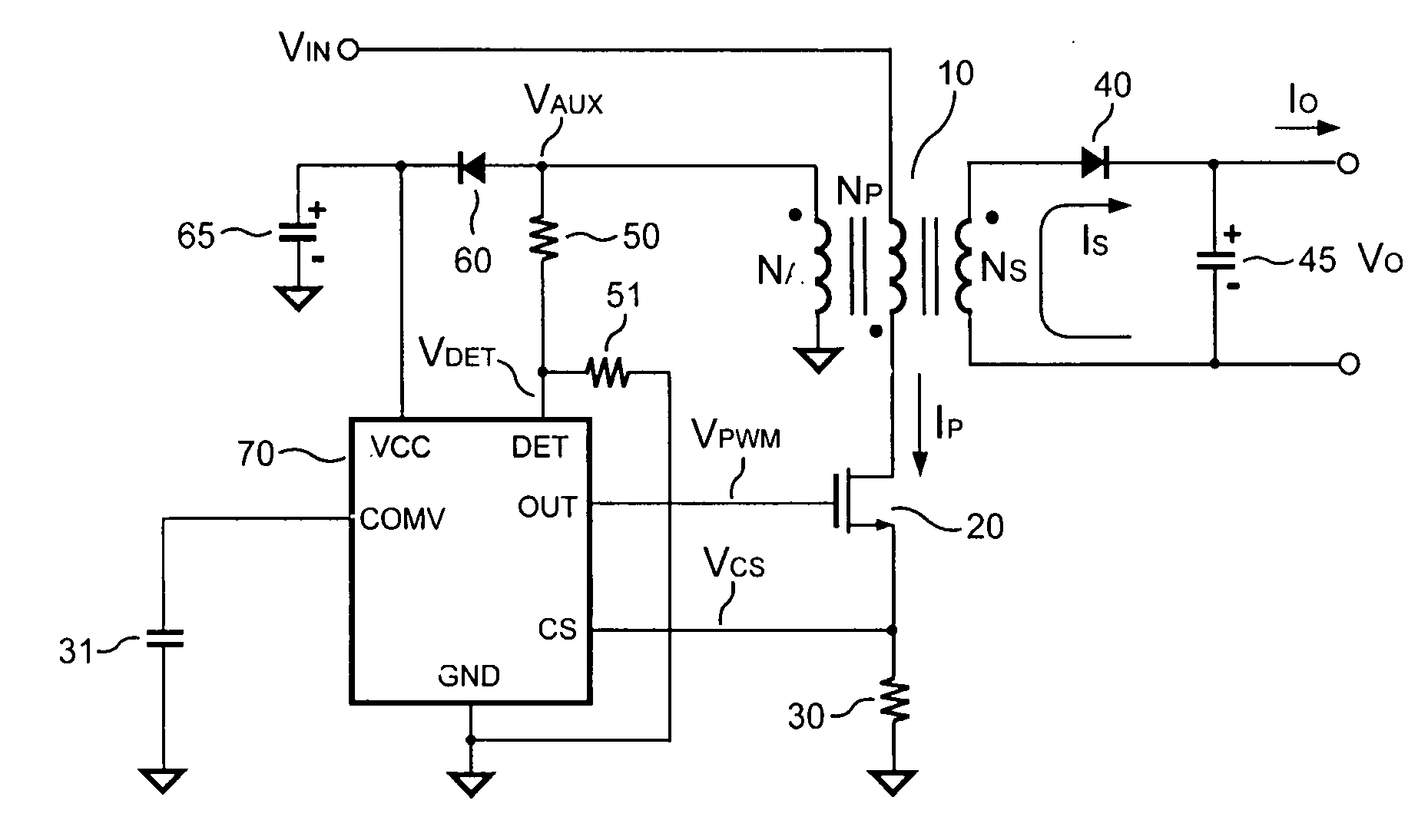
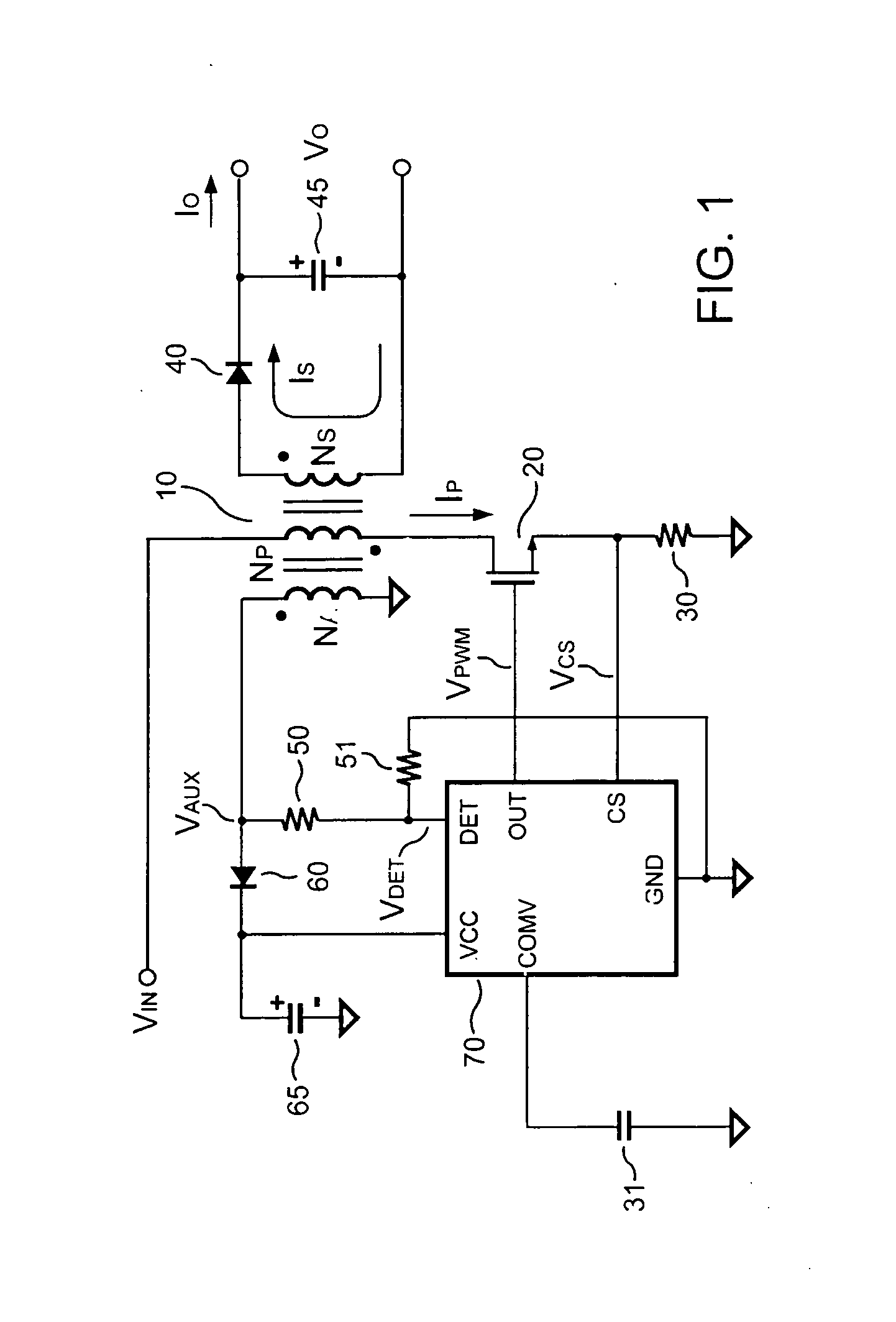
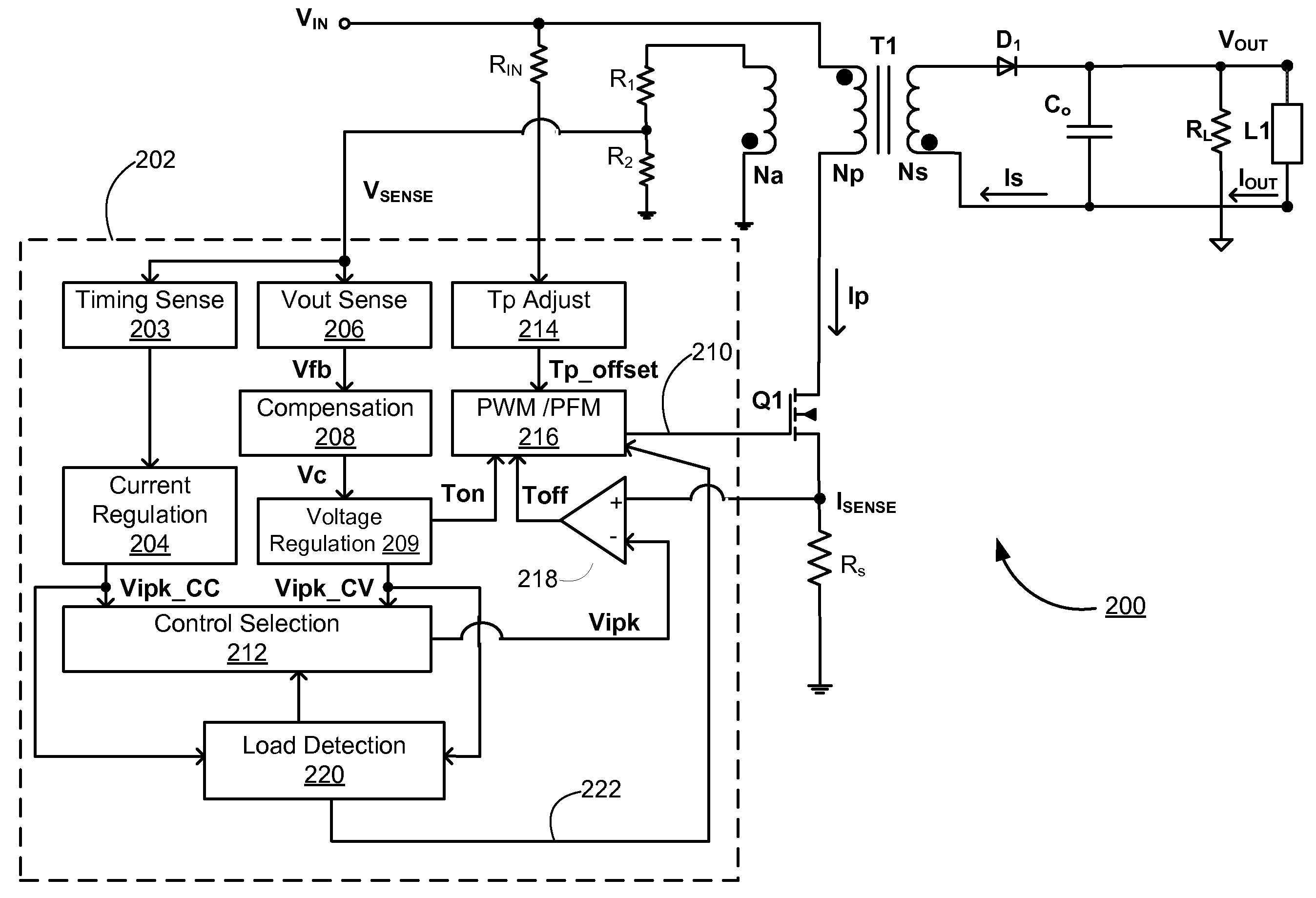
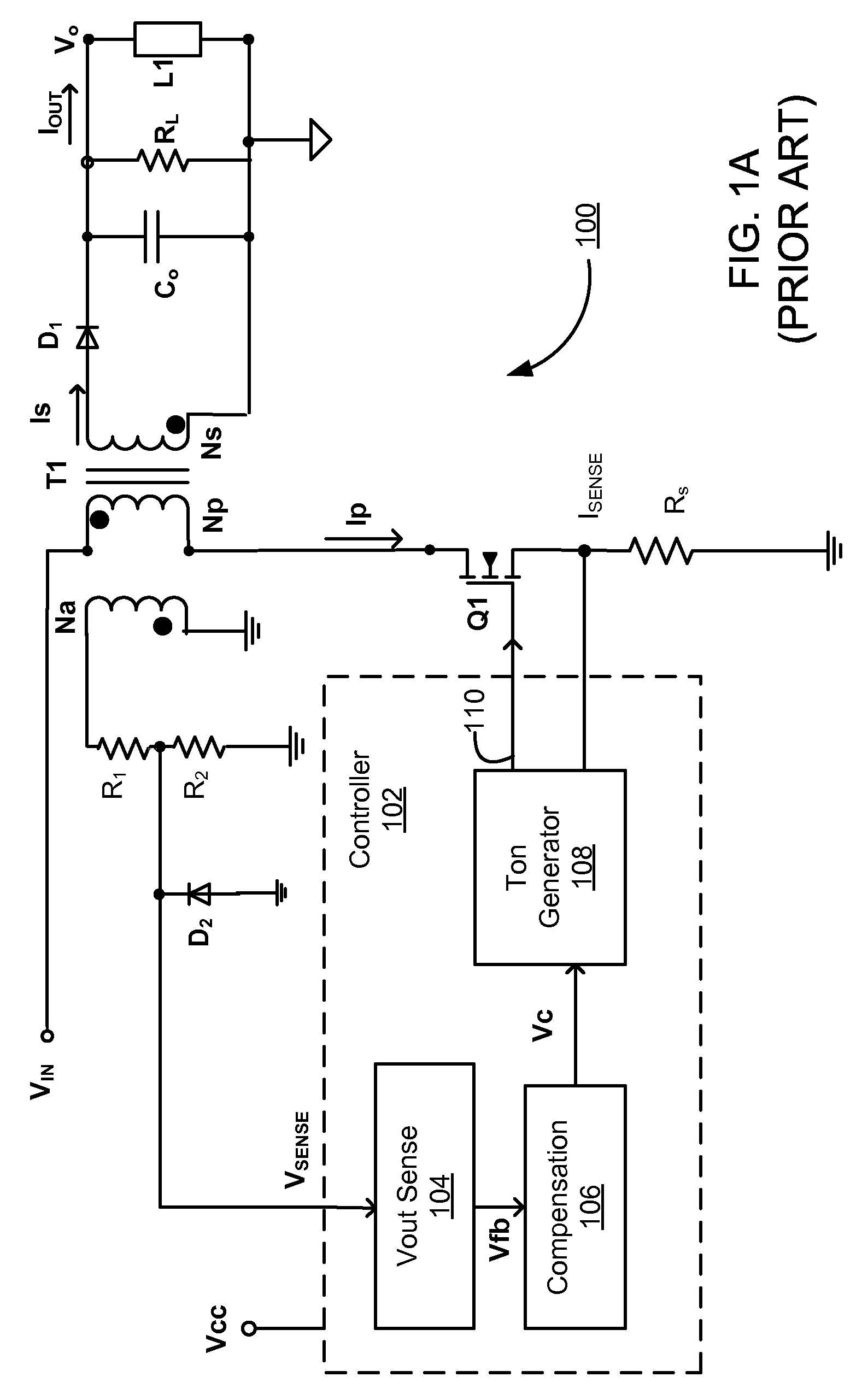
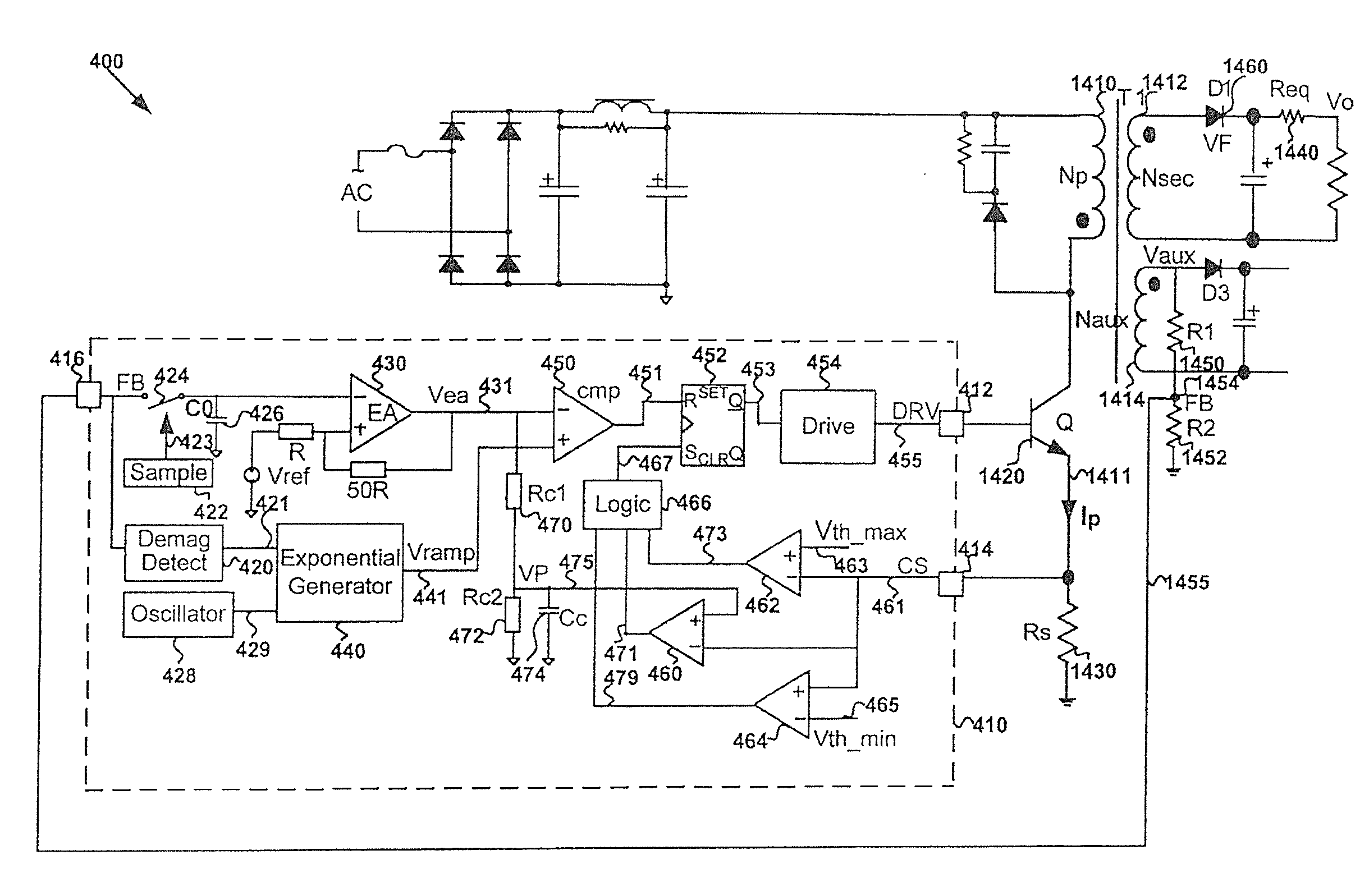
Control circuit for controlling output current at the primary side of a power converter
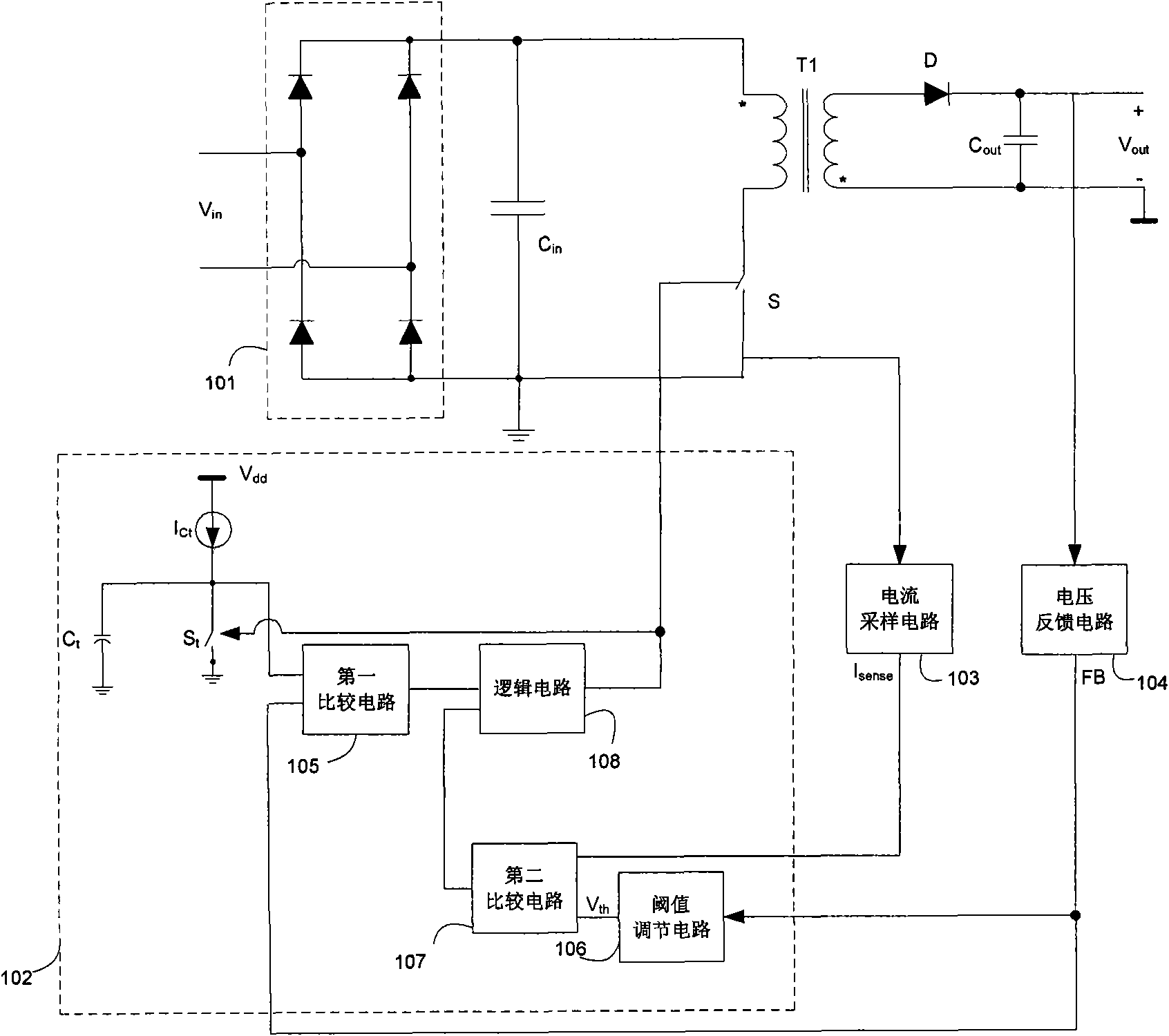
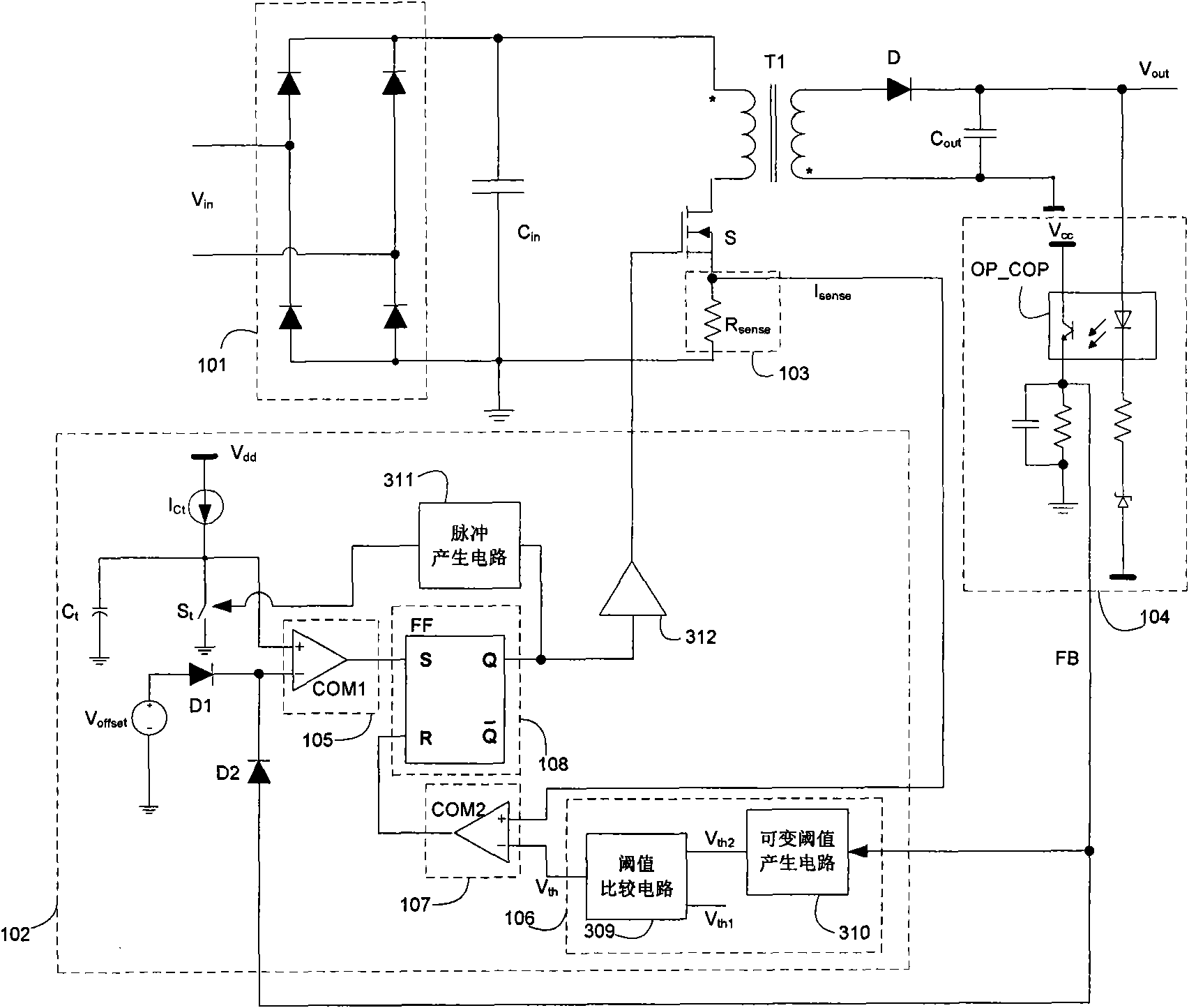
A control circuit controlling output current at the primary side of a power converter is provided. A waveform detector generates a current-waveform signal. A discharge-time detector detects a discharge-time of a secondary side switching current. An oscillator generates an oscillation signal for determining the switching frequency of the switching signal. An integrator generates an integrated signal by integrating an average current signal with the discharge-time. The average current signal is generated in response to the current-waveform signal. The time constant of the integrator is correlated with the switching period of the switching signal, therefore the integrated signal is proportional to the output current. An error amplifier amplifies the integrated signal and provides a loop gain for output current control. A comparator controls the pulse width of the switching signal in reference to the output of the error amplifier. Therefore, the output current of the power converter can be regulated.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
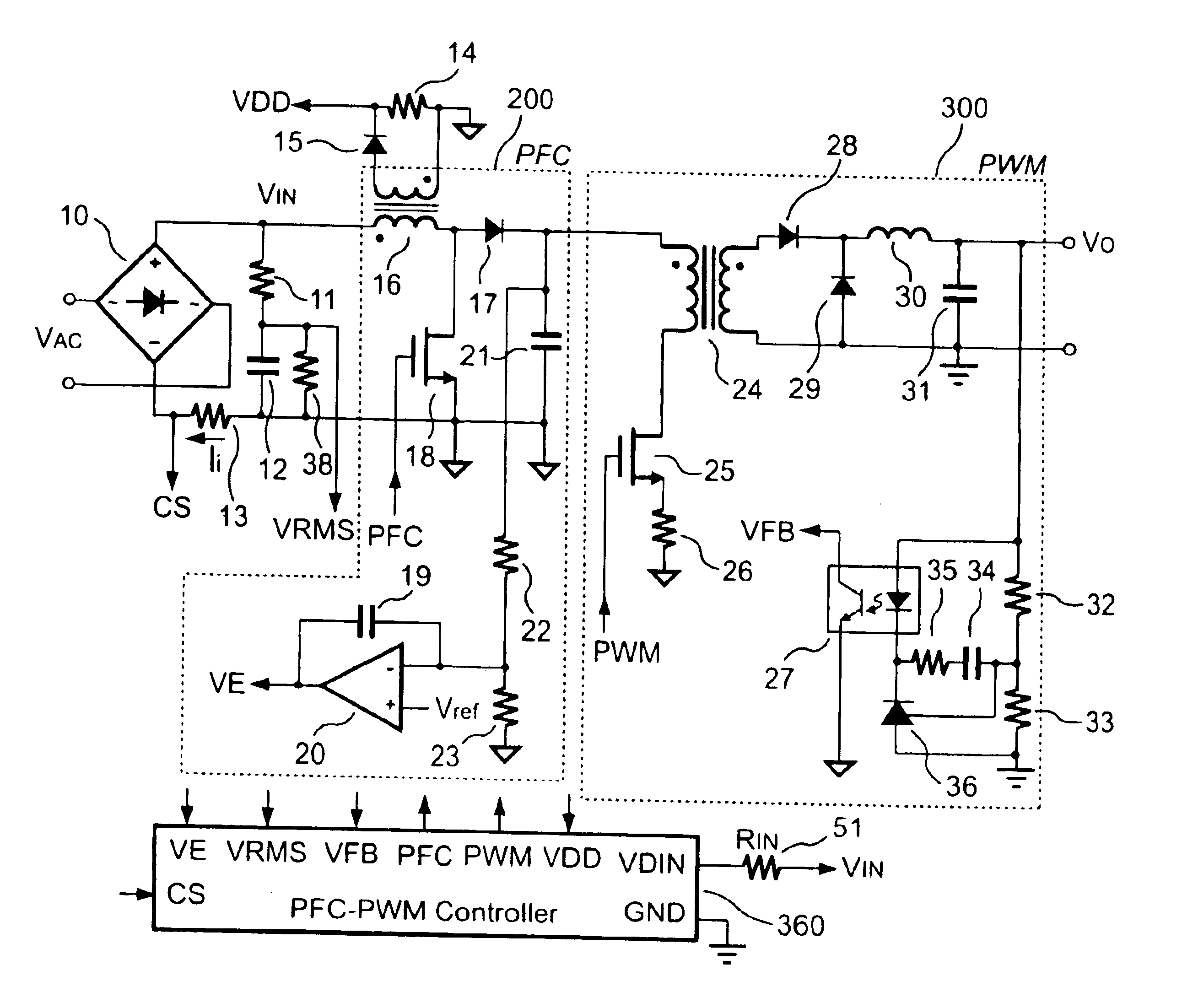
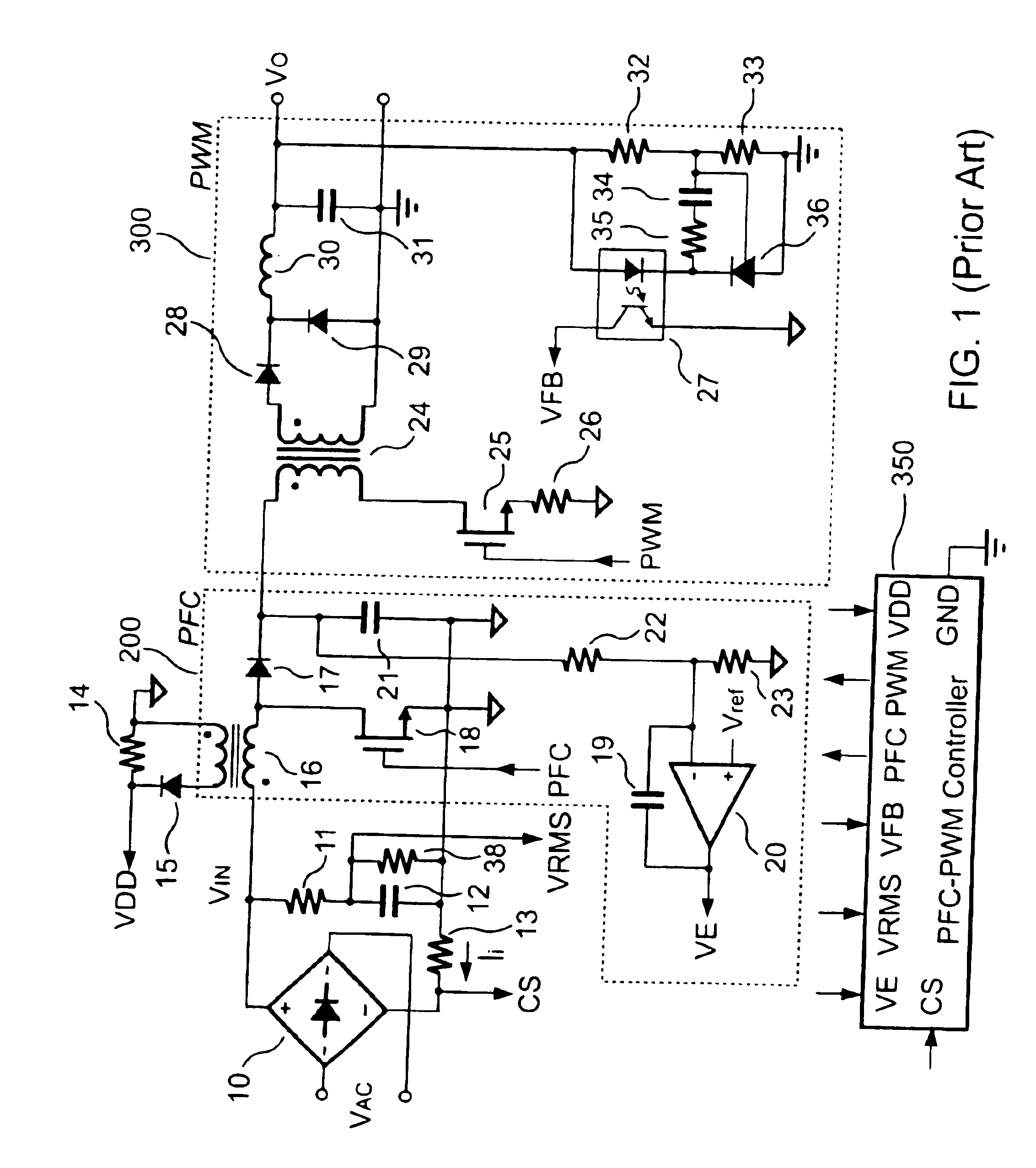
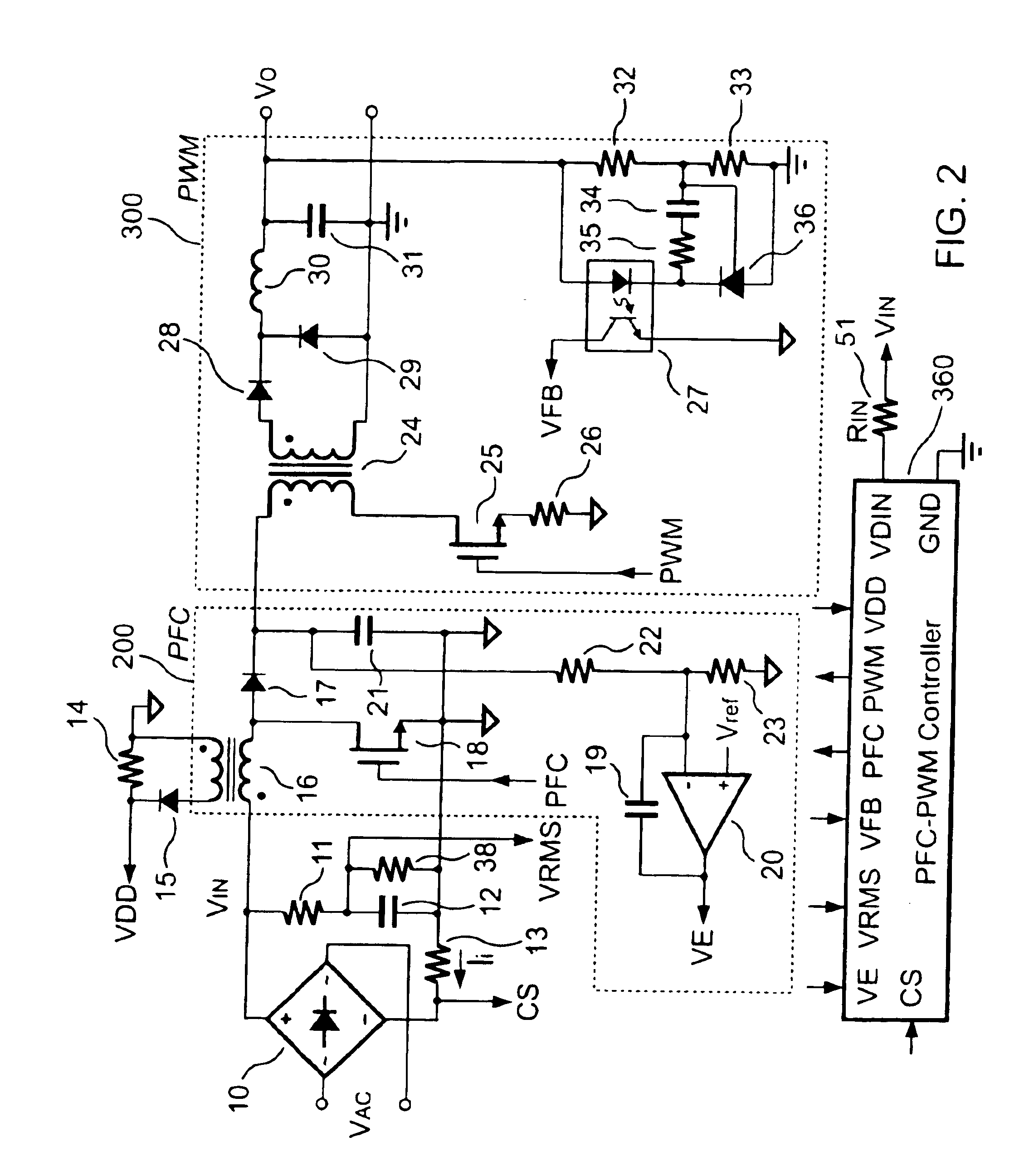
PFC-PWM controller having a power saving means
InactiveUS6839247B1Stable deliveryImprove transmission efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcSwitching signalEngineering
A PFC-PWM controller with a power saving means is disclosed. A built-in current synthesizer generates a bias current in response to feedback voltages sampled from the PWM circuit and the PFC circuit. The bias current modulates the oscillation frequency to further reduce the switching frequencies of the PWM signal and the PFC signal under light-load and zero-load conditions. Thus, power consumption is greatly reduced. The PFC and the PWM switching signals interleave each other, so that power can be transferred more smoothly from the PFC circuit to the PWM circuit. The saturation of the switching components can be avoided by limiting the maximum on-time of the PWM signal. Further, an external resistor is used to start up the PFC-PWM controller and provide an AC template signal for PFC control.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
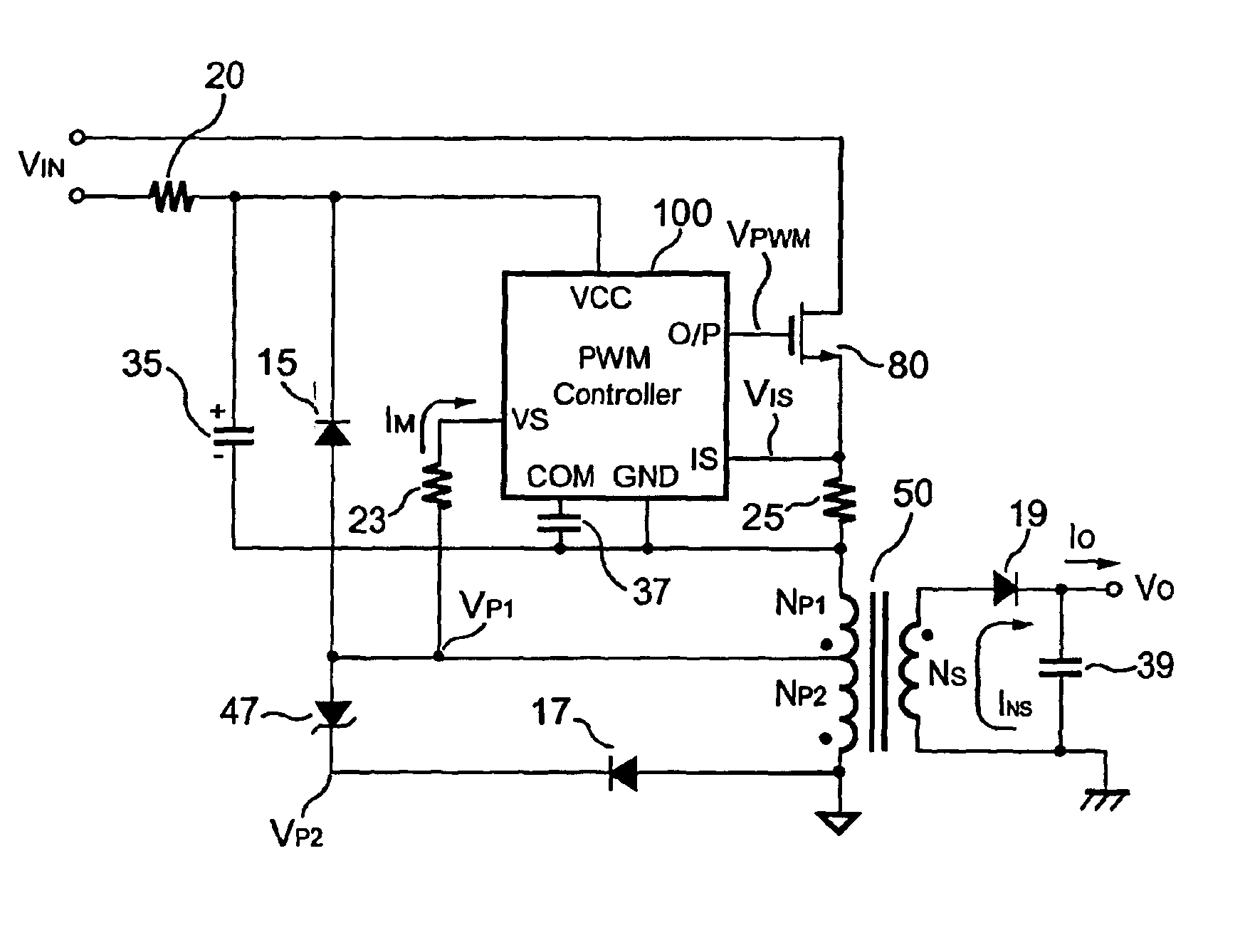
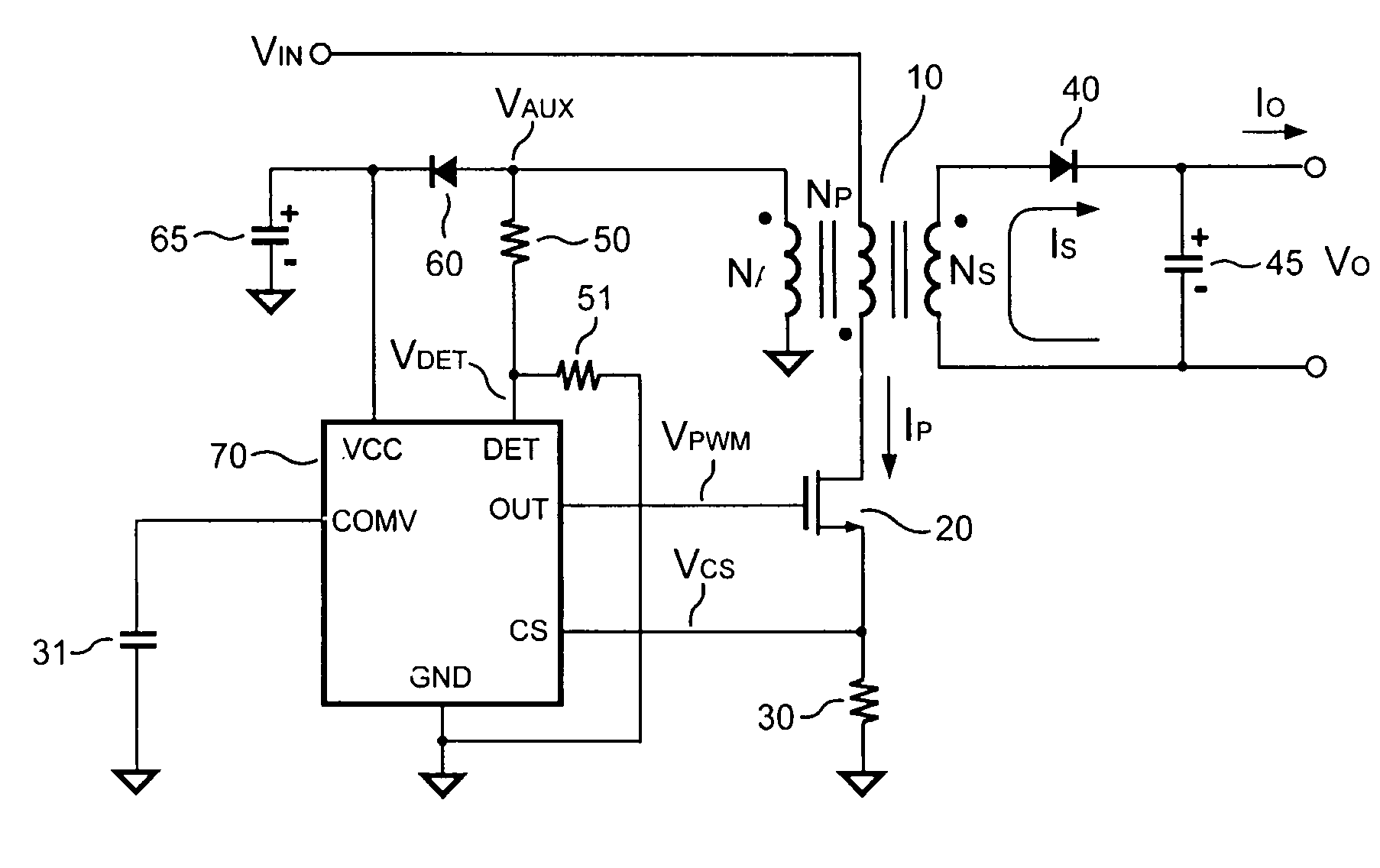
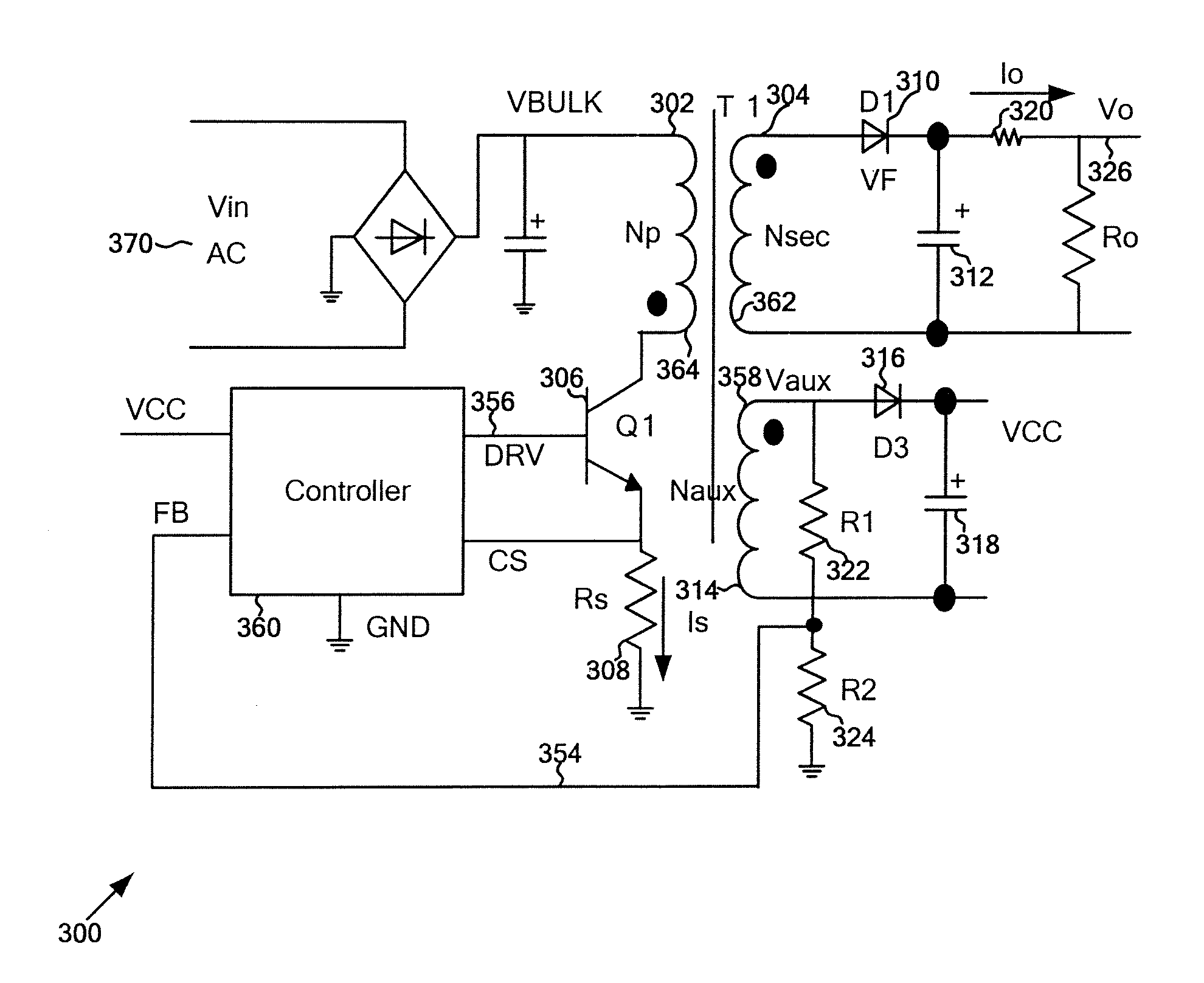
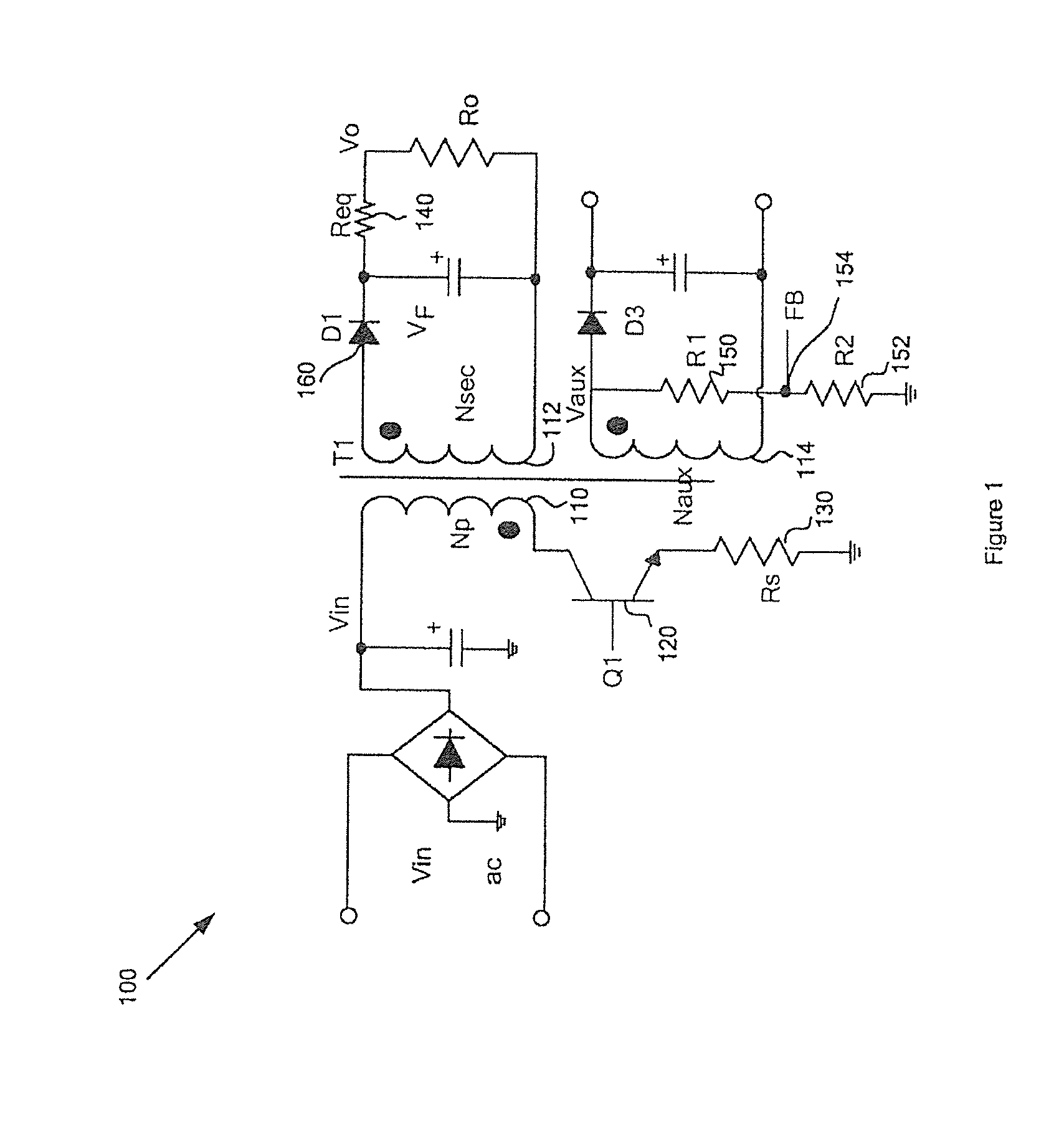
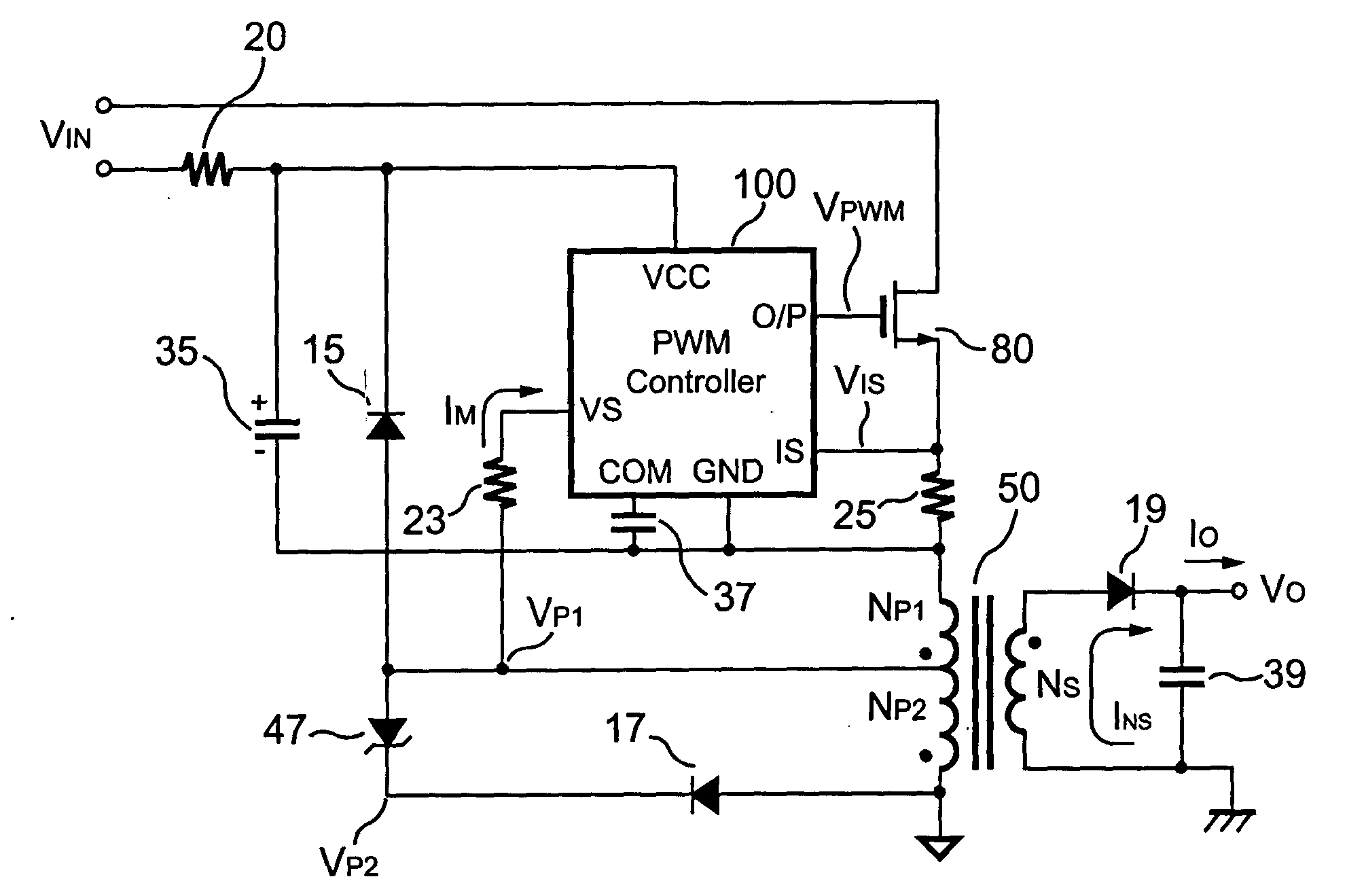
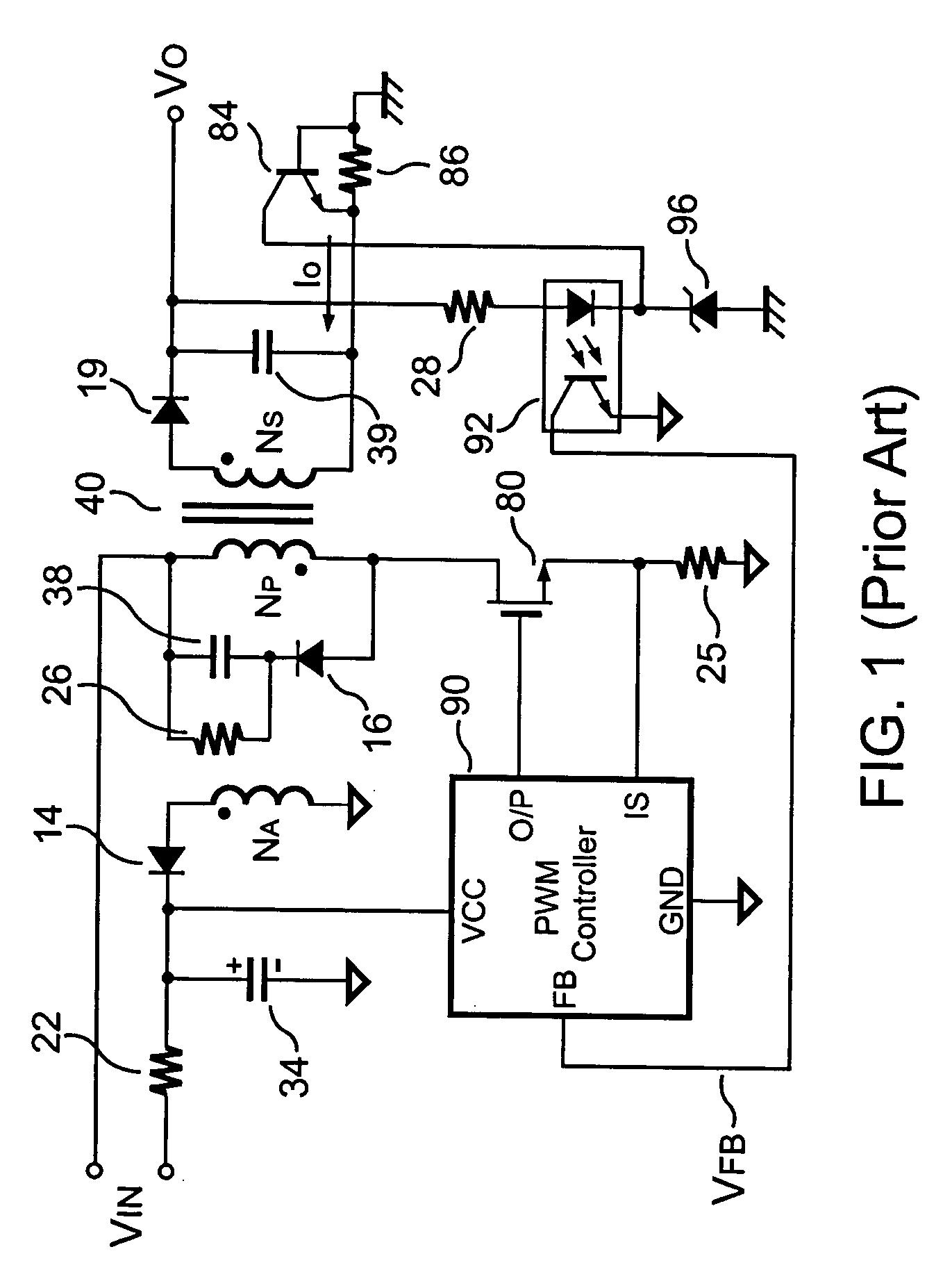
Primary-side controlled flyback power converter
InactiveUS6853563B1Low costSmall sizeEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionTransformerSwitching frequency
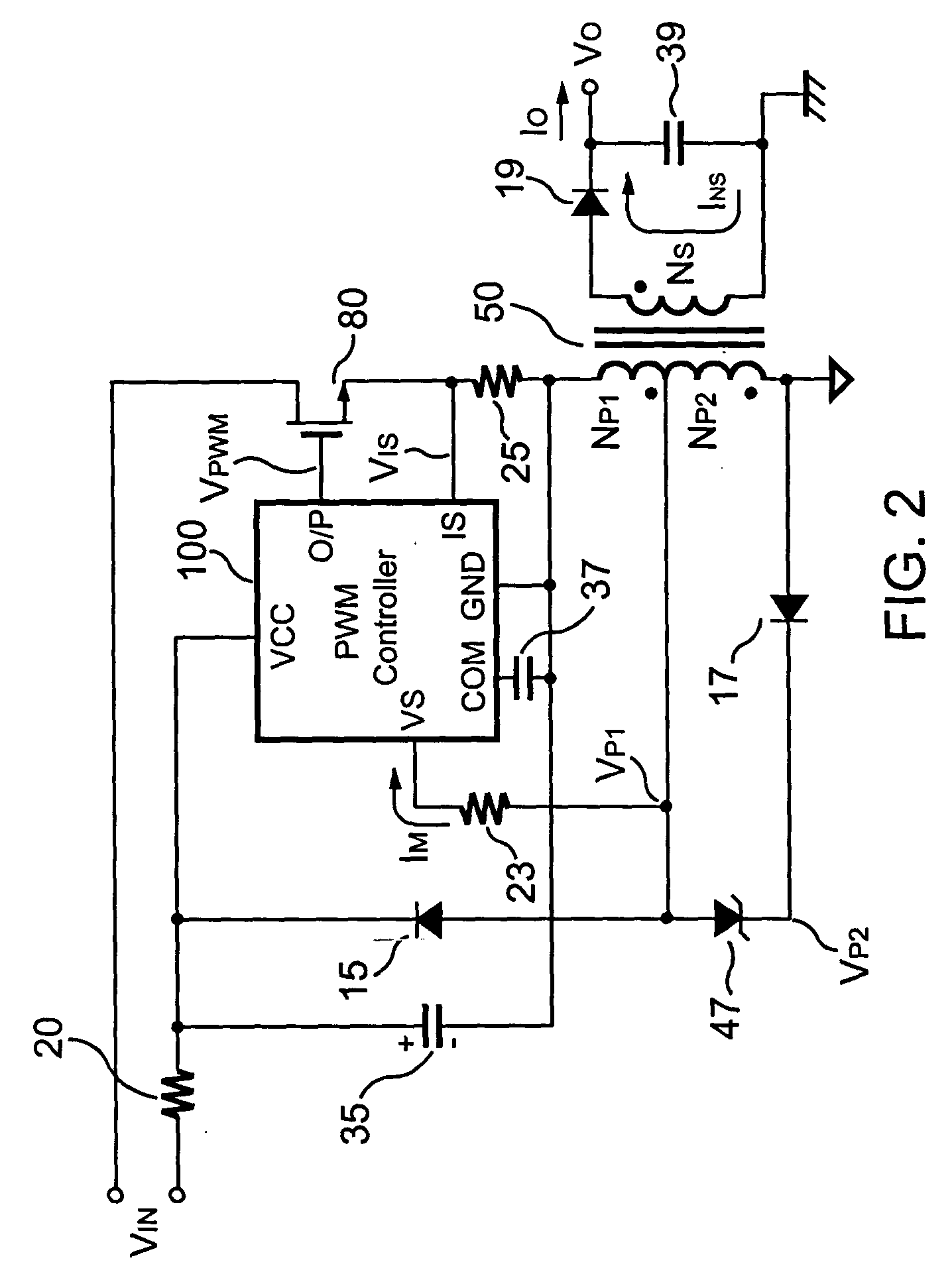
The present invention provides a primary-side flyback power converter that supplies a constant voltage output and a constant current output. To generate a well-regulated output voltage under varying load conditions, a PWM controller is included in the power converter in order to generate a PWM signal controlling a switching transistor in response to a flyback voltage sampled from a first primary winding of the power supply transformer. Several improvements are included in this present invention to overcome the disadvantages of prior-art flyback power converters. Firstly, the flyback energy of the first primary winding is used as a DC power source for the PWM controller in order to reduce power consumption. A double sample amplifier samples the flyback voltage just before the transformer current drops to zero. Moreover, an offset current is pulled from a detection input of the double sample amplifier in order to generate a more accurate DC output voltage. The offset current is generated in response to the temperature in order to compensate for temperature-induced voltage fluctuations across the output rectifier. Ultimately, in order to maintain a constant output current, the PWM controller modulates the switching frequency in response to the output voltage.
Owner:FAIRCHILD TAIWAN
Contactless electrical energy transmission system having a primary side current feedback control and soft-switched secondary side rectifier
ActiveUS6934167B2Energy can transferEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcSwitching frequencyEngineering
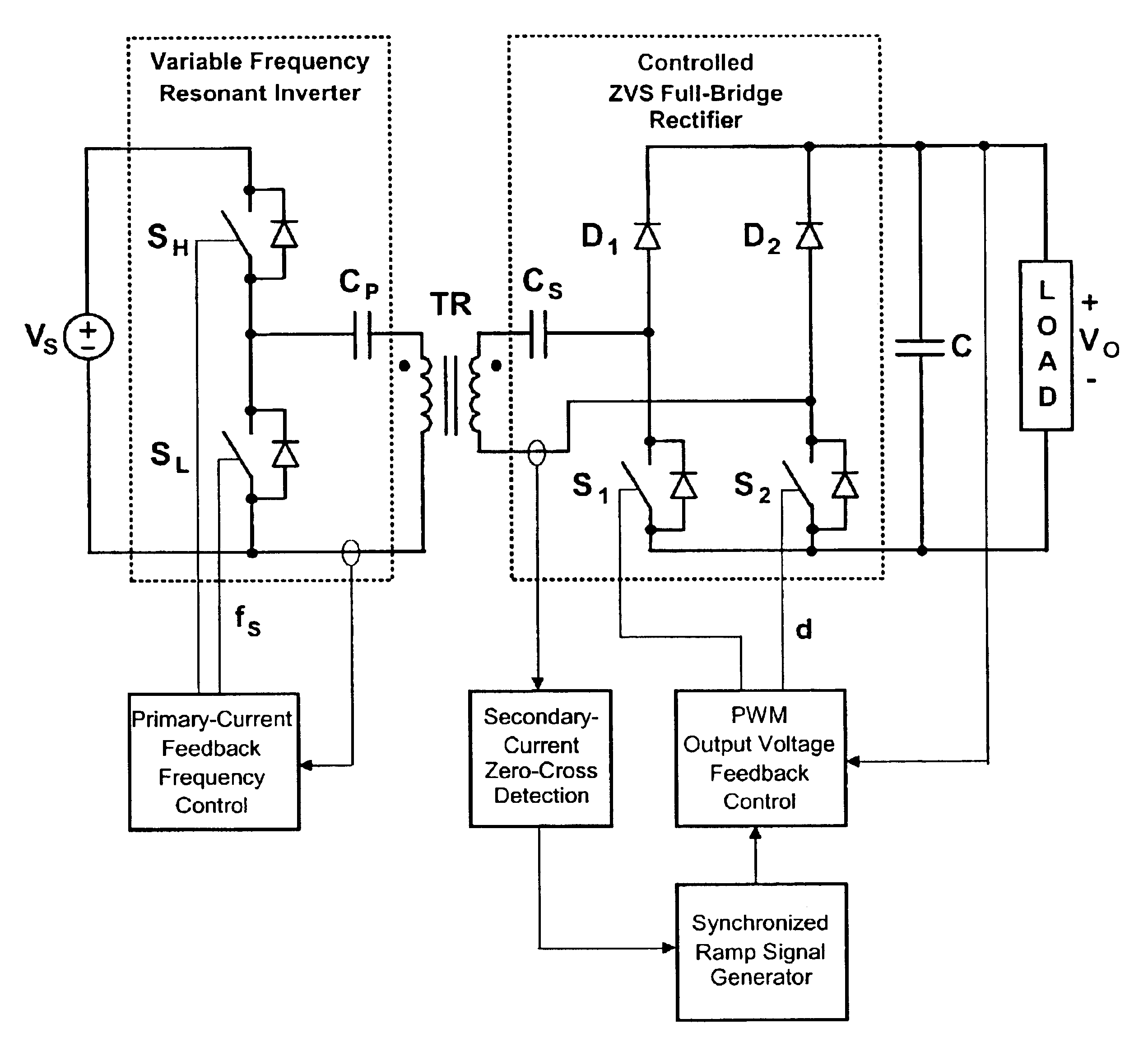
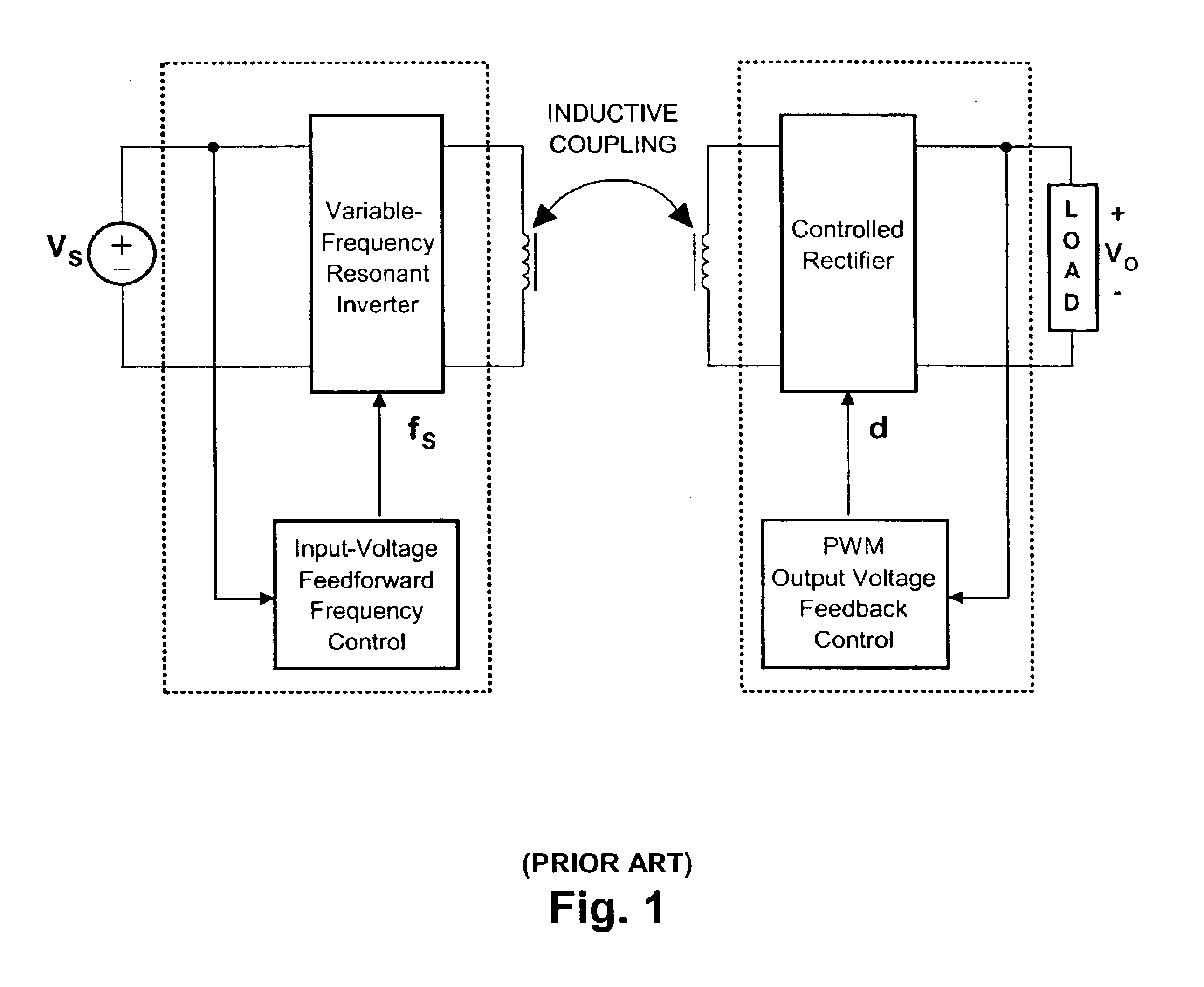
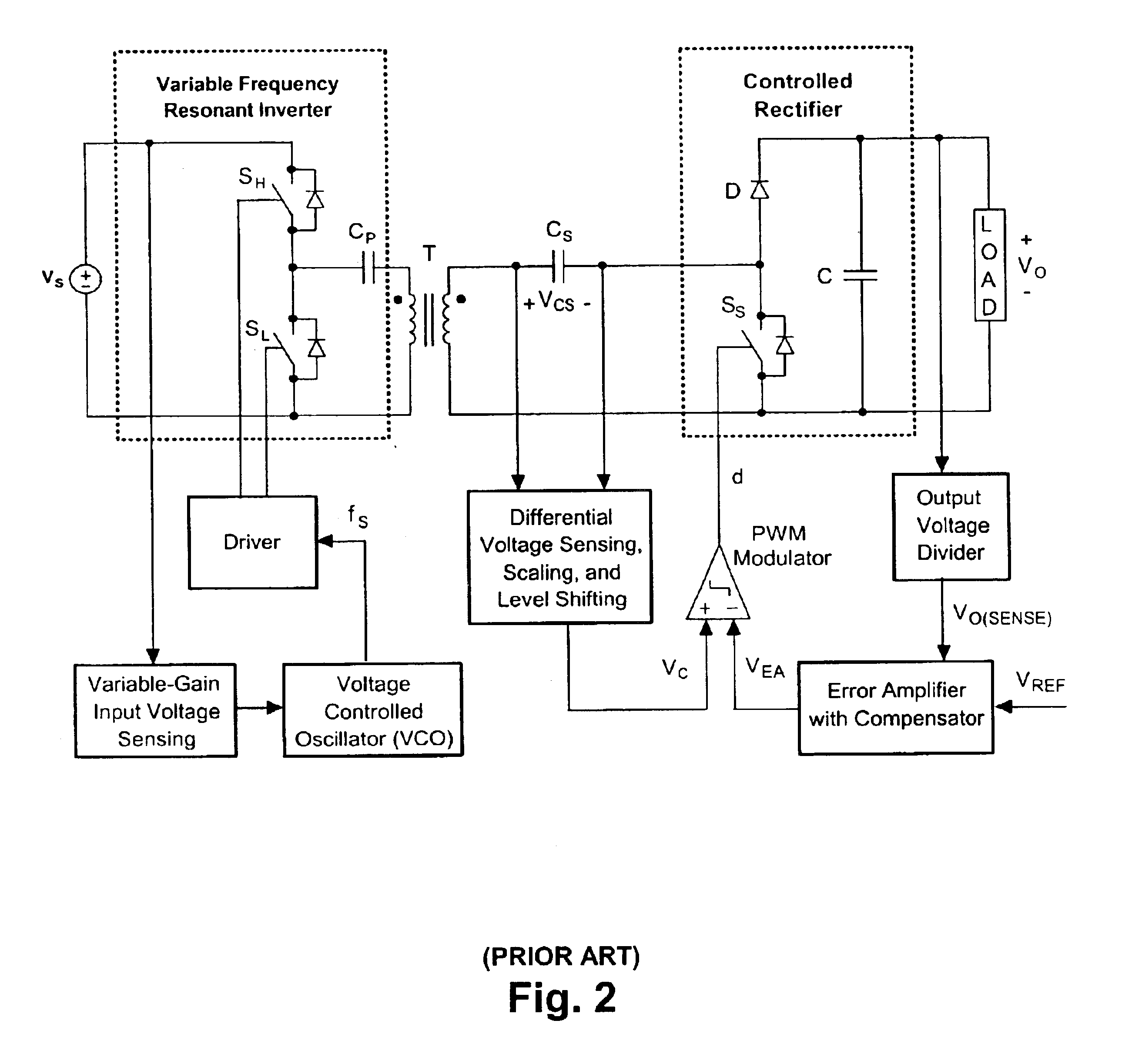
A contactless electrical energy transmission system includes a transformer having a primary winding that is coupled to a power source through a primary resonant circuit and a secondary winding that is coupled to a load through a secondary resonant circuit. The primary and secondary resonant circuits are inductively coupled to each other. A primary control circuit detects current changes through the primary resonant circuit to control the switching frequency of a controllable switching device for maintaining a substantially constant energy transfer between the primary winding and secondary winding in response to at least one of a power source voltage change and a load change. As a result, excessive circulating energy of the CEET system is minimized providing a tight regulation of the output voltage over the entire load and input voltage ranges without any feedback connection between the primary side and the secondary side.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Synchronous Rectifier Design for Wireless Power Receiver
InactiveUS20150326143A1Lower forward voltage dropImprove efficiencyBatteries circuit arrangementsAc-dc conversion without reversalDelay-locked loopSwitching frequency
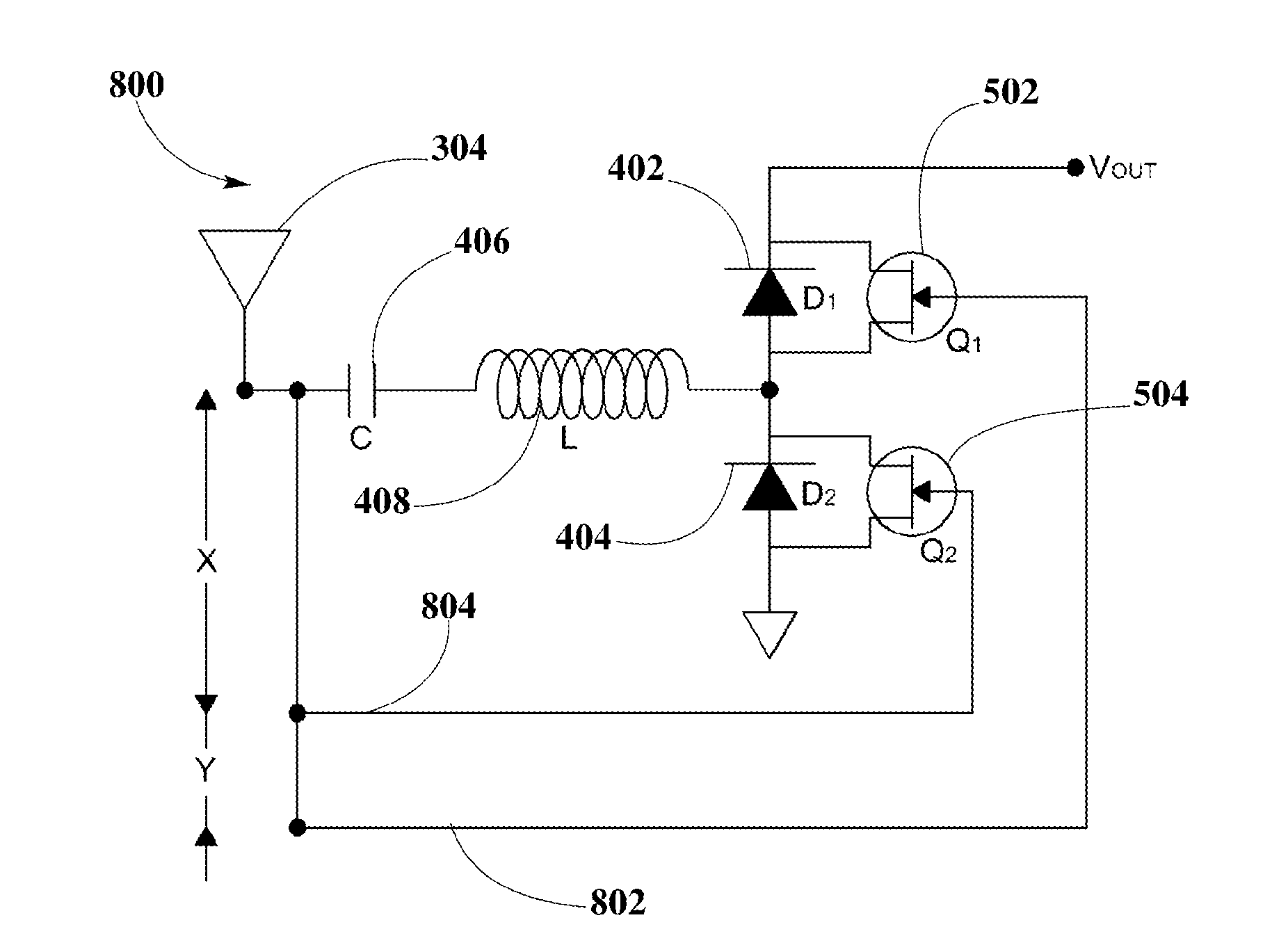
Synchronous rectifier circuit topologies for a wireless power receiver receiving a supply of power from a wireless transmitter are disclosed. The synchronous rectifier circuit topologies include a half-bridge diode-FET transistor rectifier for rectifying the wireless power into power including a DC waveform, using a control scheme that may be provided by a delay-locked loop clock, or phase shifters, or wavelength links to control conduction of FET transistors in the synchronous rectifier circuit topology, and maintaining a constant switching frequency to have the diodes, coupled to FET transistors, to allow current to flow through each one respectively at the appropriate timing, focusing on high conduction times. The synchronous rectifier circuit topologies may enable power transfer of high-frequency signals at enhanced efficiency due to significant reduction of forward voltage drop and lossless switching.
Owner:ENERGOUS CORPORATION
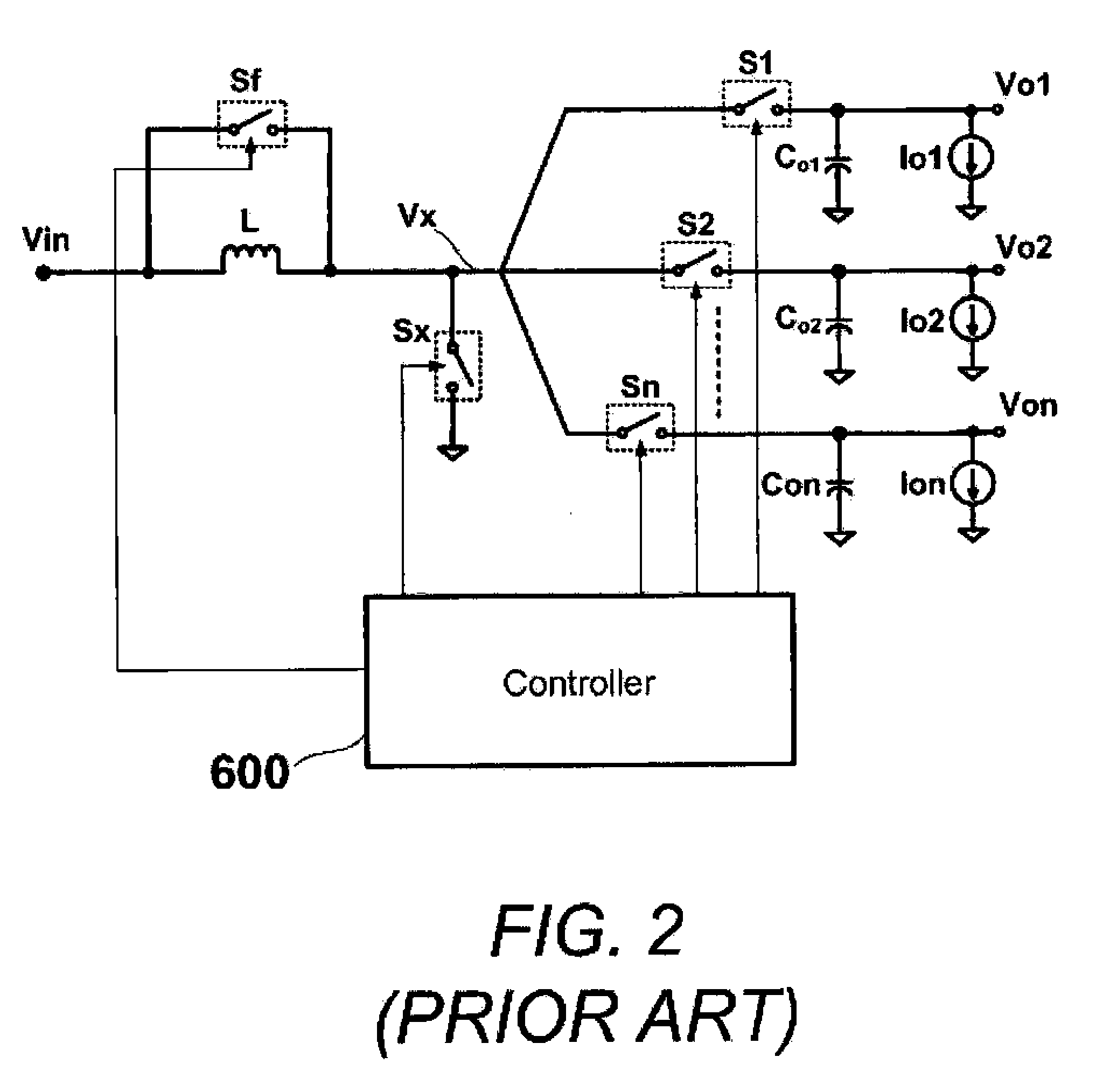
Multiple-Output DC-DC Converter
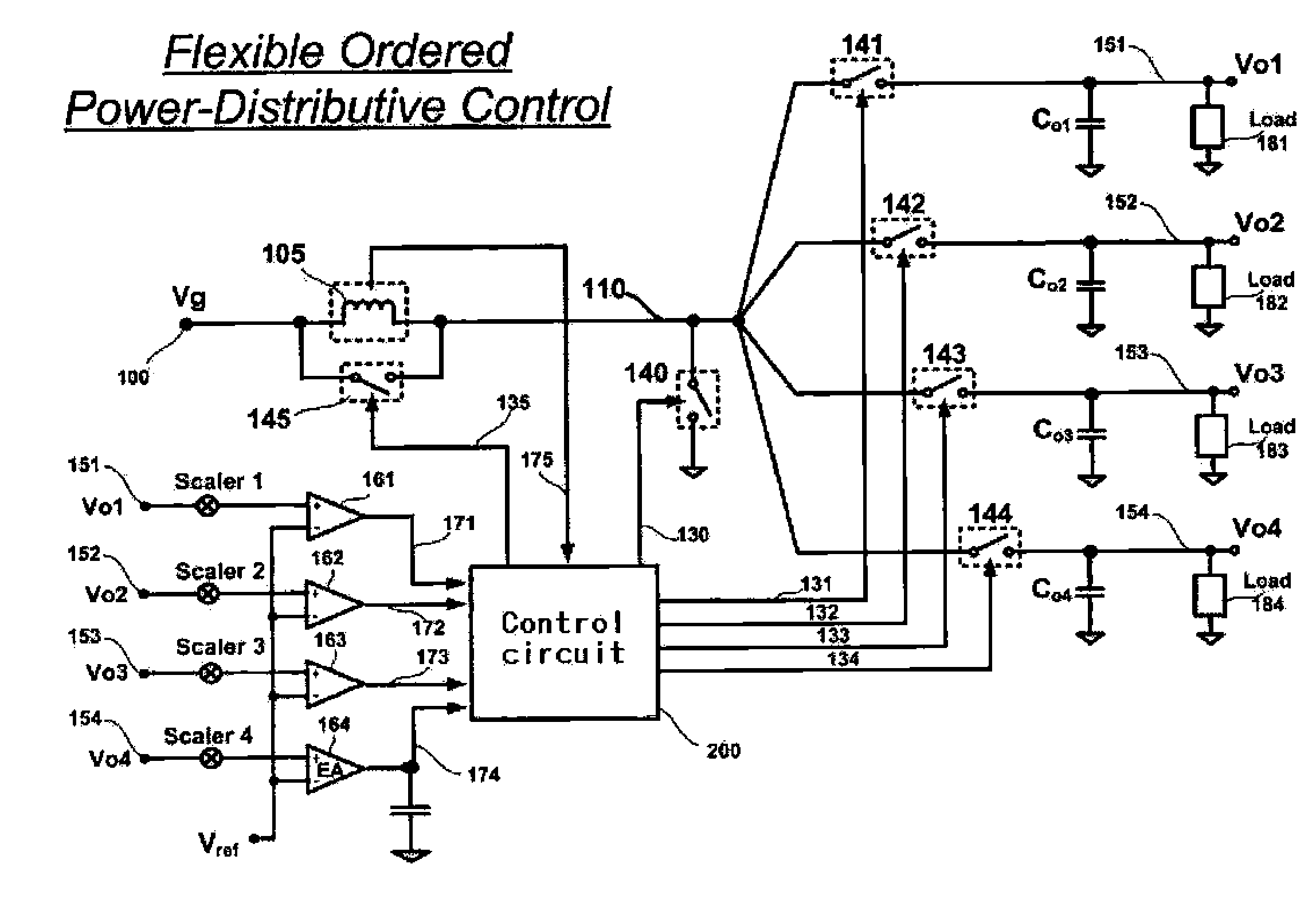
The invention relates to a DC / DC converter design. The converter requires only one single inductor to draw energy from one input source and distribute it to more than one outputs, employing Flexible-Order Power-Distributive Control (FOPDC). It include a single inductor, a number of power switches, comparators, only one error amplifier, a detecting circuit and a control block to regulate outputs. This converter can correctly regulate multiple outputs with fast transient response, low cross regulation, and effective switching frequency for each output. It can work in both discontinuous conduction mode (DCM) and continuous conduction mode (CCM). Moreover, with FOPDC, future output extension is simple, making a shorter time-to-market process for next versions of the converter. The design can be applied to different types of DC-DC converter.
Owner:JDA TECH
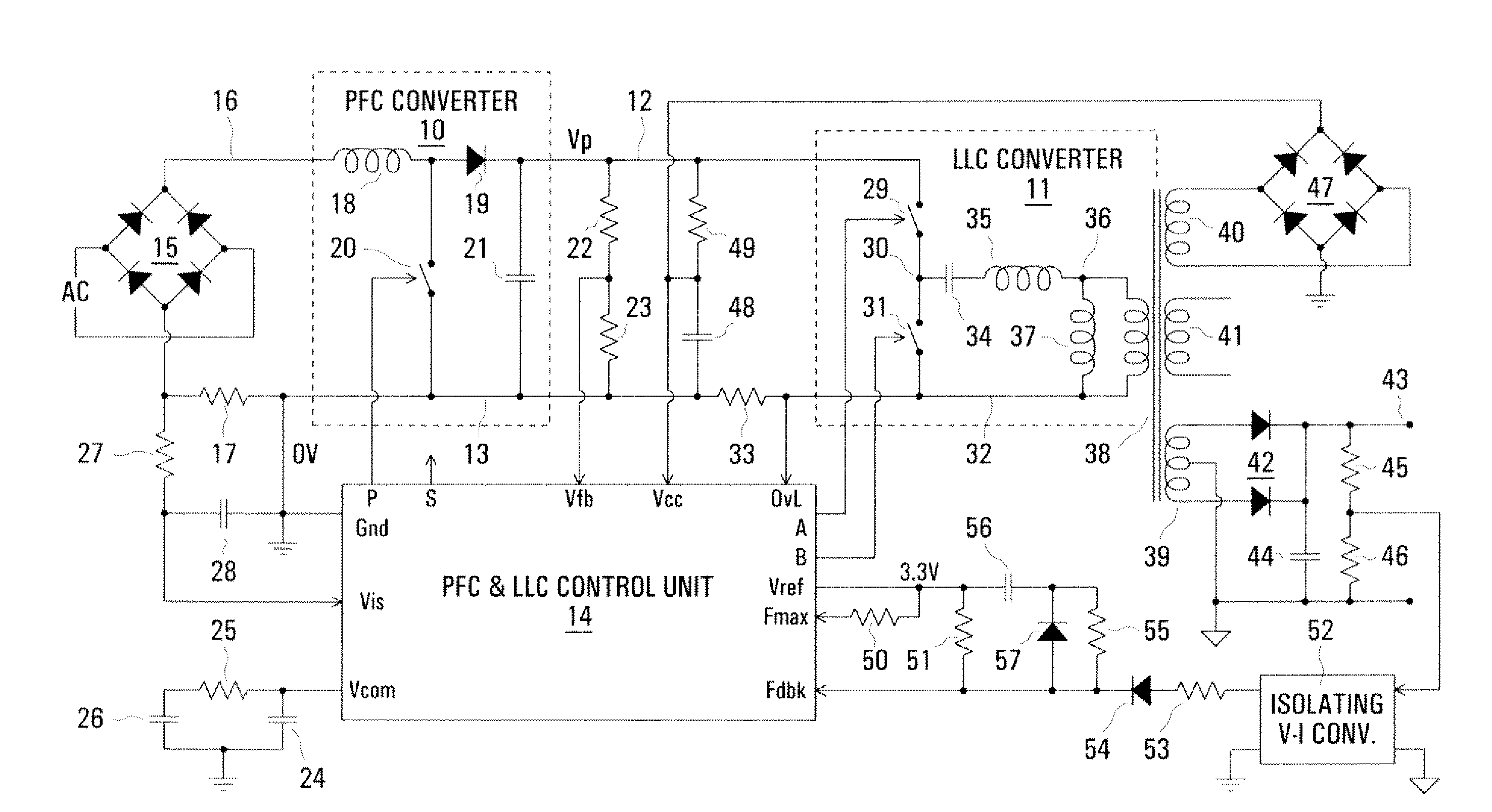
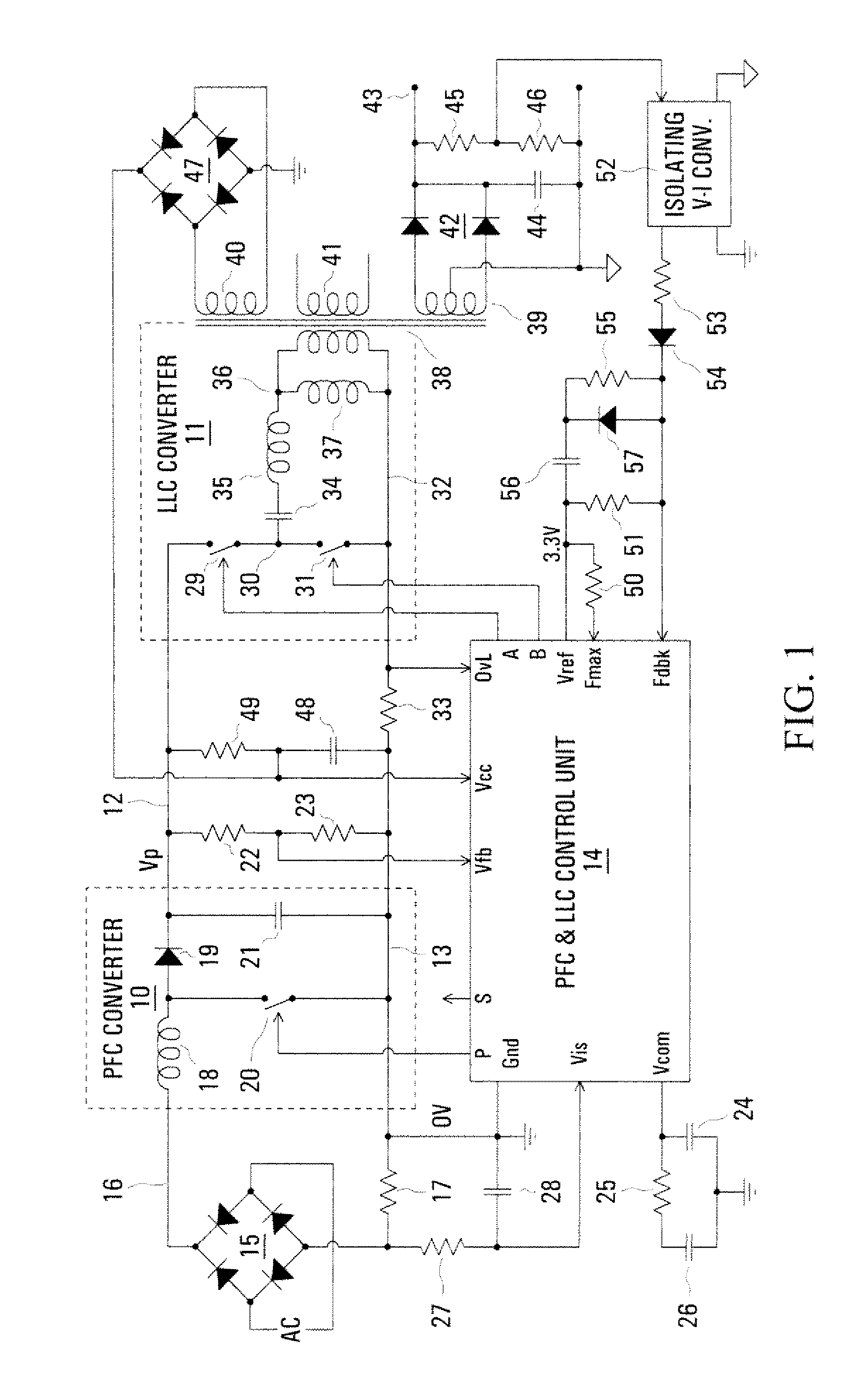
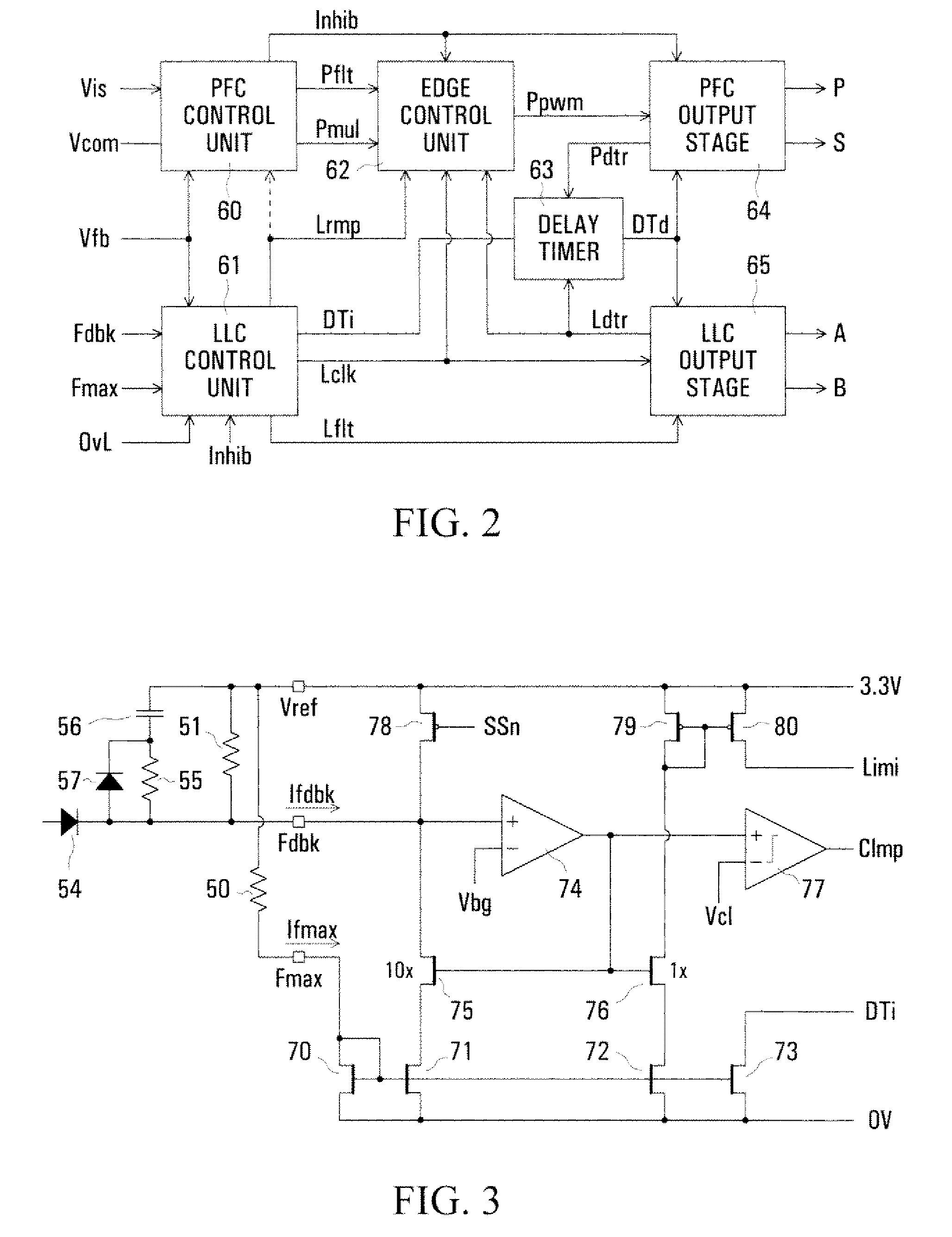
Control arrangement for a resonant mode power converter
InactiveUS20080198638A1Minimize such dead timeMinimize timeEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionCharge currentControl signal
The switching frequency of an LLC converter is controlled by a control unit to which a feedback circuit provides a first current dependent upon the output voltage of the converter. An oscillator circuit produces a sawtooth waveform at a frequency dependent upon the first current, up to a limit equal to a second current set by a resistor. Two complementary switch control signals are produced for controlling two switches of the converter for conduction in alternate cycles of the sawtooth waveform. A timer produces dead times between the two complementary switch control signals in dependence upon the second current. Another resistor provides a current constituting a minimum value of the first current, and a charging current of a capacitor in series with a resistor modifies the first current for soft starting of the converter.
Owner:POWER INTEGRATIONS INC
PFC apparatus for a converter operating in the borderline conduction mode
InactiveUS6469917B1Ac-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionHemt circuitsEngineering
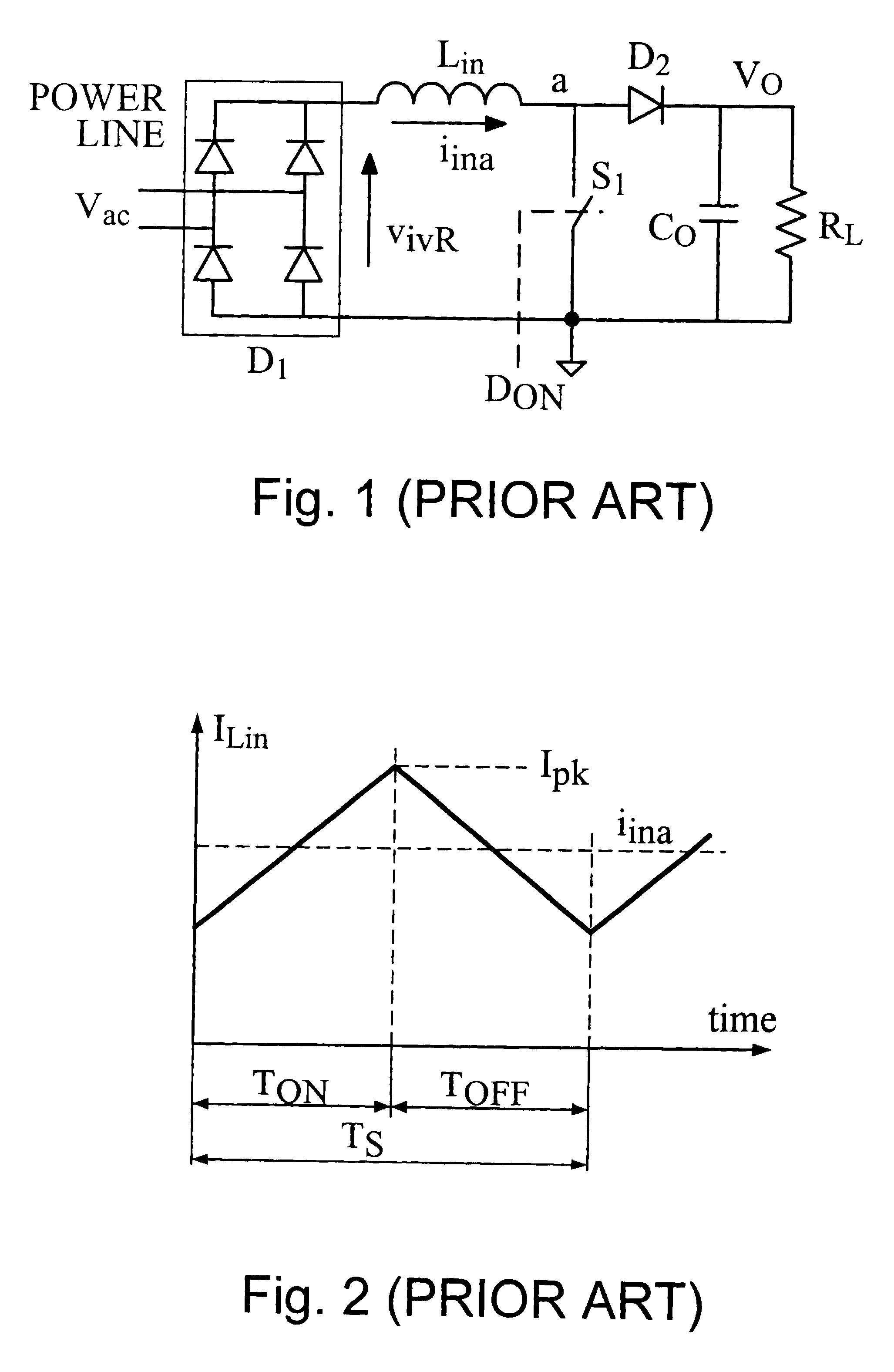
Power factor correction apparatus, for a switching power supply fed by an array of rectifying diodes and consisting of at least an input inductor, a contact of which is connected in series with a contact of the array, and of a power switch connected between the other contact of the array and the other contact of the input inductor that comprises circuitry for identifying, in each cycle determined by the switching frequency of the power supply, whenever the instantaneous value of the current through the inductor reaches a minimal value; circuitry for switching the power switch to its conducting state in response to the minimal current through the inductor; circuitry for reflecting the current flowing through the inductor by a measurable or simulated parameter; and circuitry for providing indication, in each cycle, by using the parameter, the indication being related to the timing until the peak value of the current, that corresponds to a specific load, has been essentially reached, or to the time from the moment that the current reaches the minimal value until the timing, and for switching the power switch to its non-conducting state in response to the indication.
Owner:GREEN POWER TECH LTD
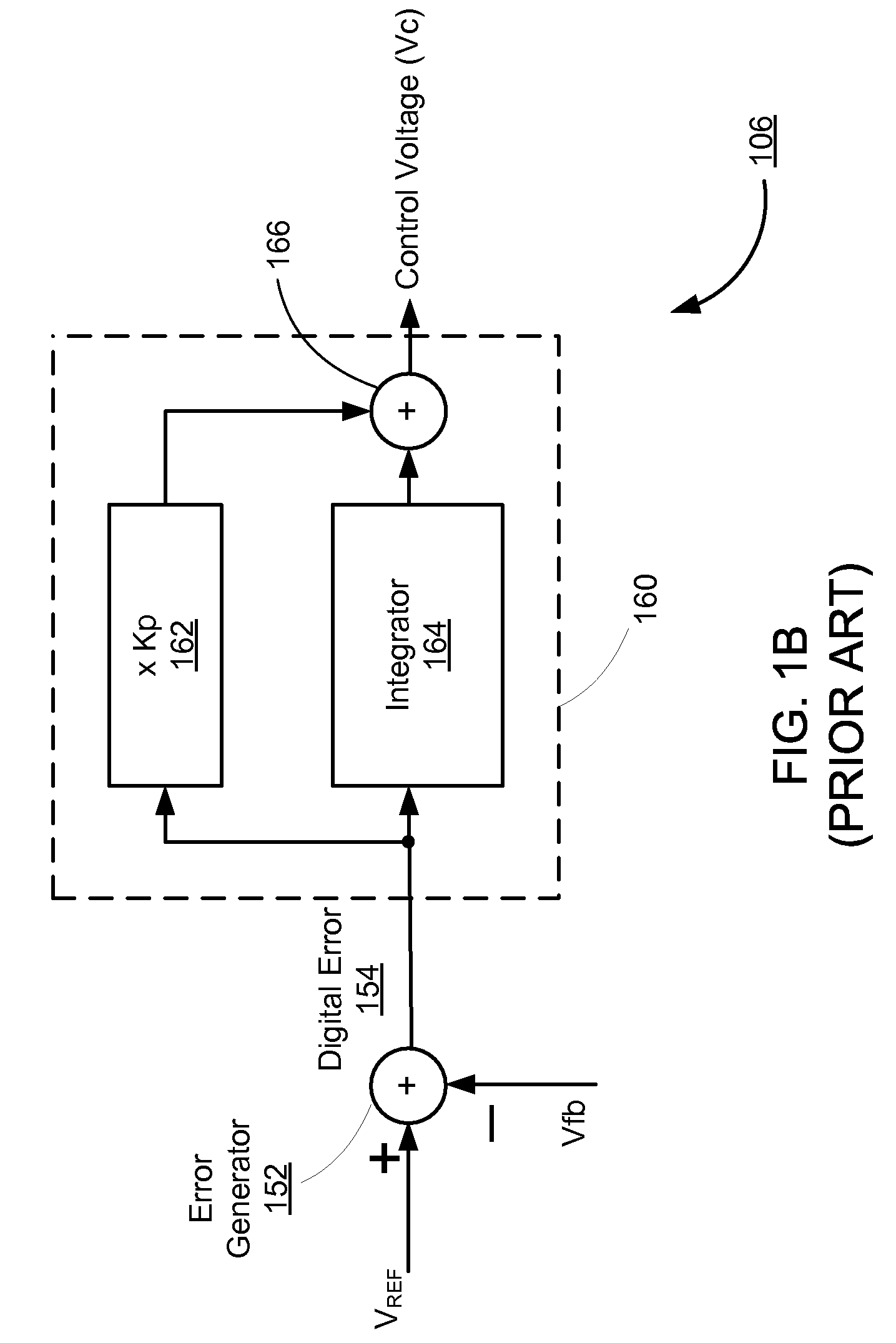
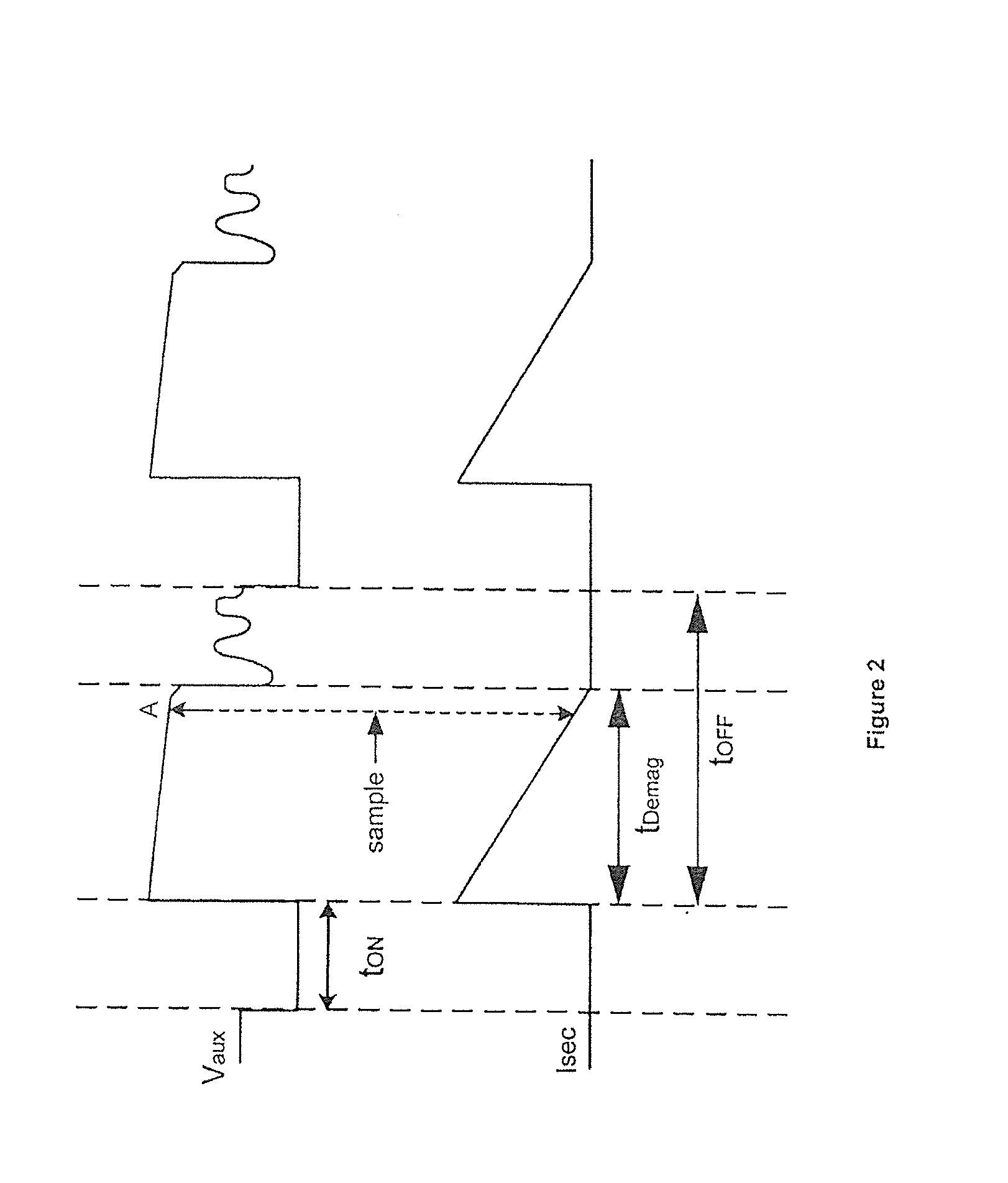
Switching control circuit having off-time modulation to improve efficiency of primary-side controlled power supply
ActiveUS7362593B2Save power consumptionLight load conditionEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionAudio power amplifierControl signal
A voltage-waveform detector produces a voltage-feedback signal and a discharge-time signal by multi-sampling a voltage signal of a transformer. The discharge-time signal represents a discharge time of a secondary-side switching current. A voltage-loop error amplifier amplifies the voltage-feedback signal and generates a control signal. An off-time modulator correspondingly generates a discharge-current signal and a standby signal in response to the control signal and an under-voltage signal. The under-voltage signal indicates a low supply voltage of the controller. An oscillator produces a pulse signal in response to the discharge-current signal. The pulse signal determines the off-time of the switching signal. A PWM circuit generates the switching signal in response to the pulse signal and the standby signal. The standby signal further controls the off-time of the switching signal and maintains a minimum switching frequency. The switching signal is used for regulating the output of the power supply.
Owner:FAIRCHILD SEMICON CORP
Switching control circuit having off-time modulation to improve efficiency of primary-side controlled power supply
ActiveUS20060055433A1Save power consumptionLight load conditionEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionControl signalSwitching frequency
A voltage-waveform detector produces a voltage-feedback signal and a discharge-time signal by multi-sampling a voltage signal of a transformer. The discharge-time signal represents a discharge time of a secondary-side switching current. A voltage-loop error amplifier amplifies the voltage-feedback signal and generates a control signal. An off-time modulator correspondingly generates a discharge-current signal and a standby signal in response to the control signal and an under-voltage signal. The under-voltage signal indicates a low supply voltage of the controller. An oscillator produces a pulse signal in response to the discharge-current signal. The pulse signal determines the off-time of the switching signal. A PWM circuit generates the switching signal in response to the pulse signal and the standby signal. The standby signal further controls the off-time of the switching signal and maintains a minimum switching frequency. The switching signal is used for regulating the output of the power supply.
Owner:FAIRCHILD SEMICON CORP
System and method for controlling an electric arc welder
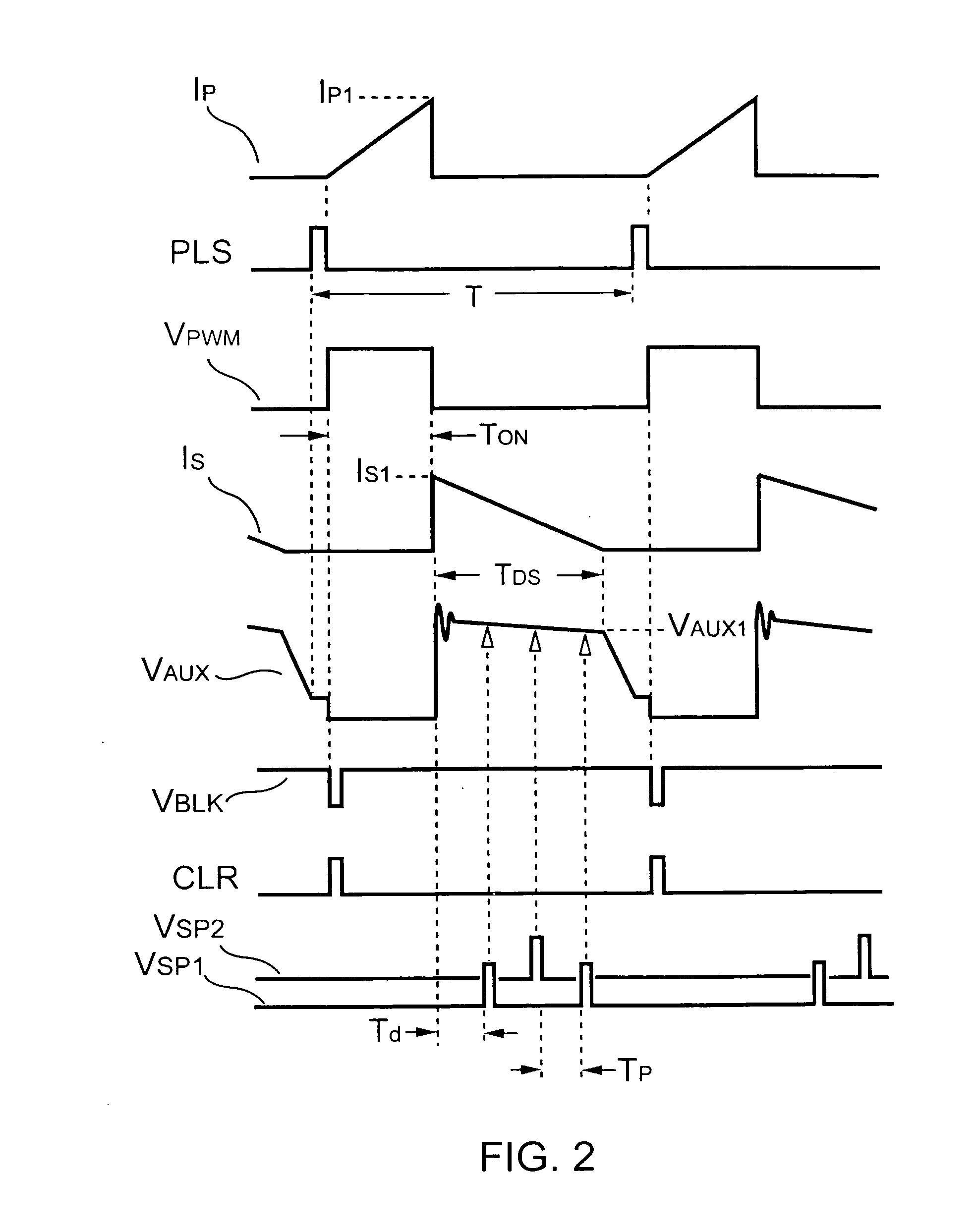
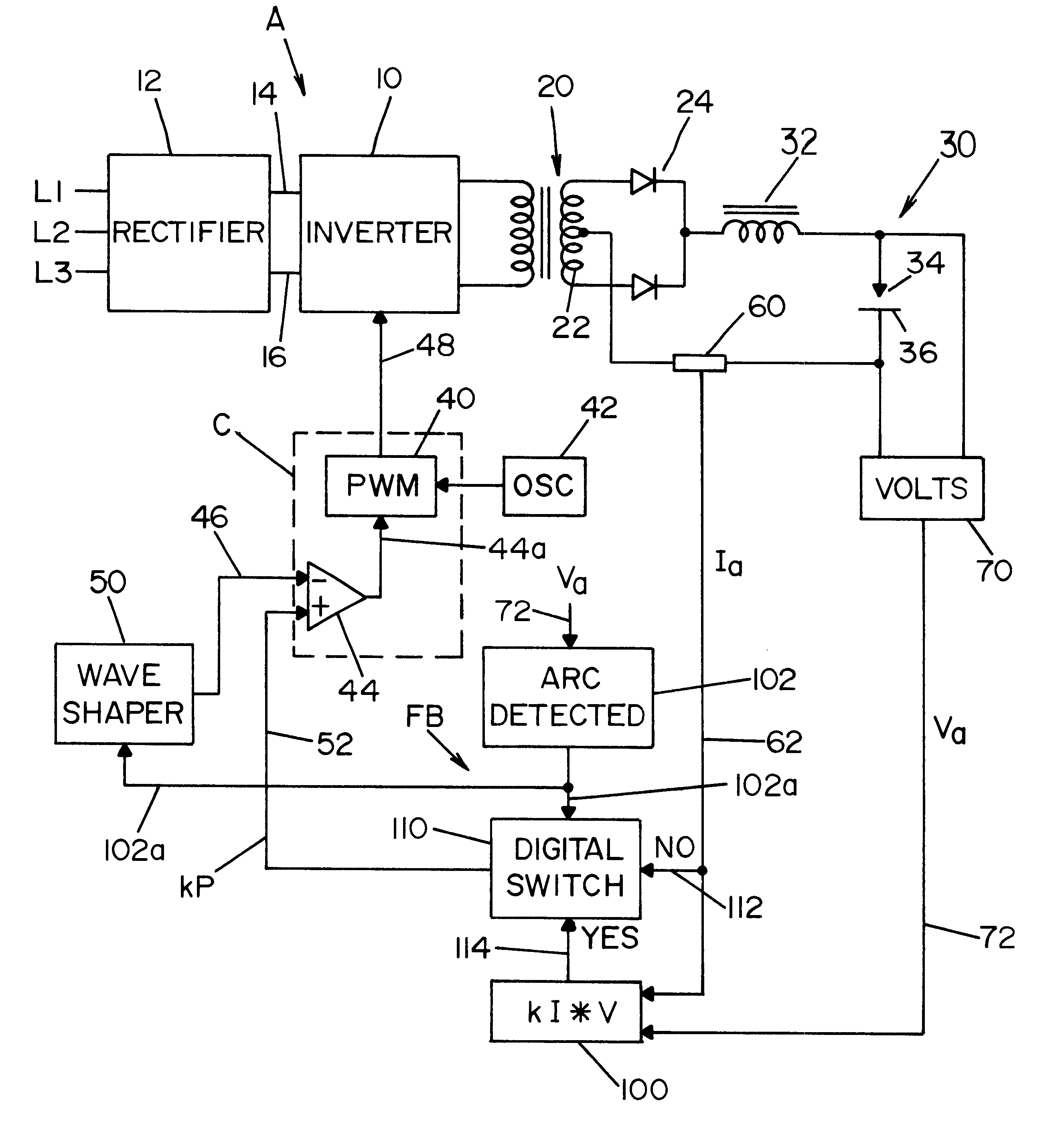
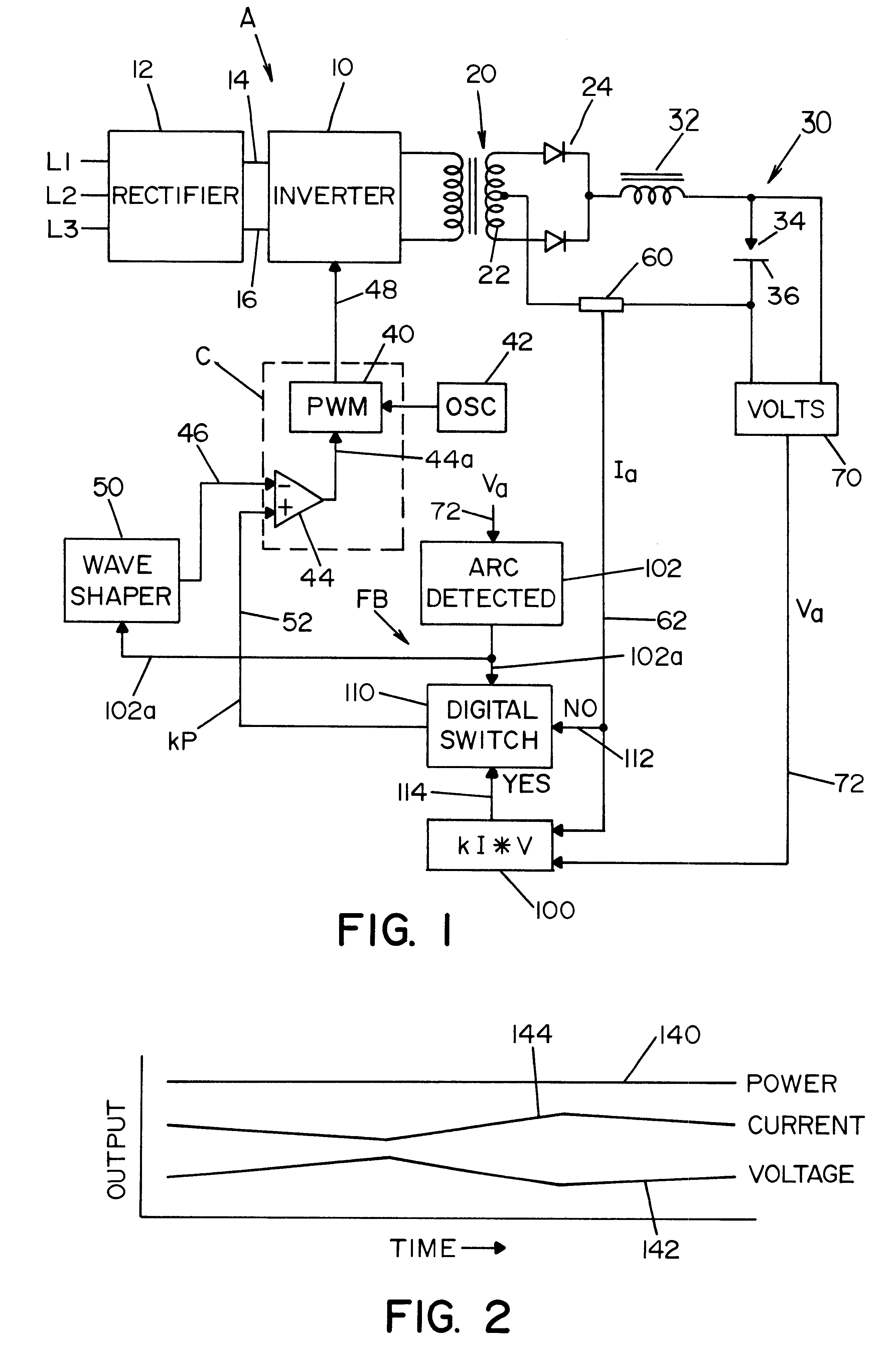
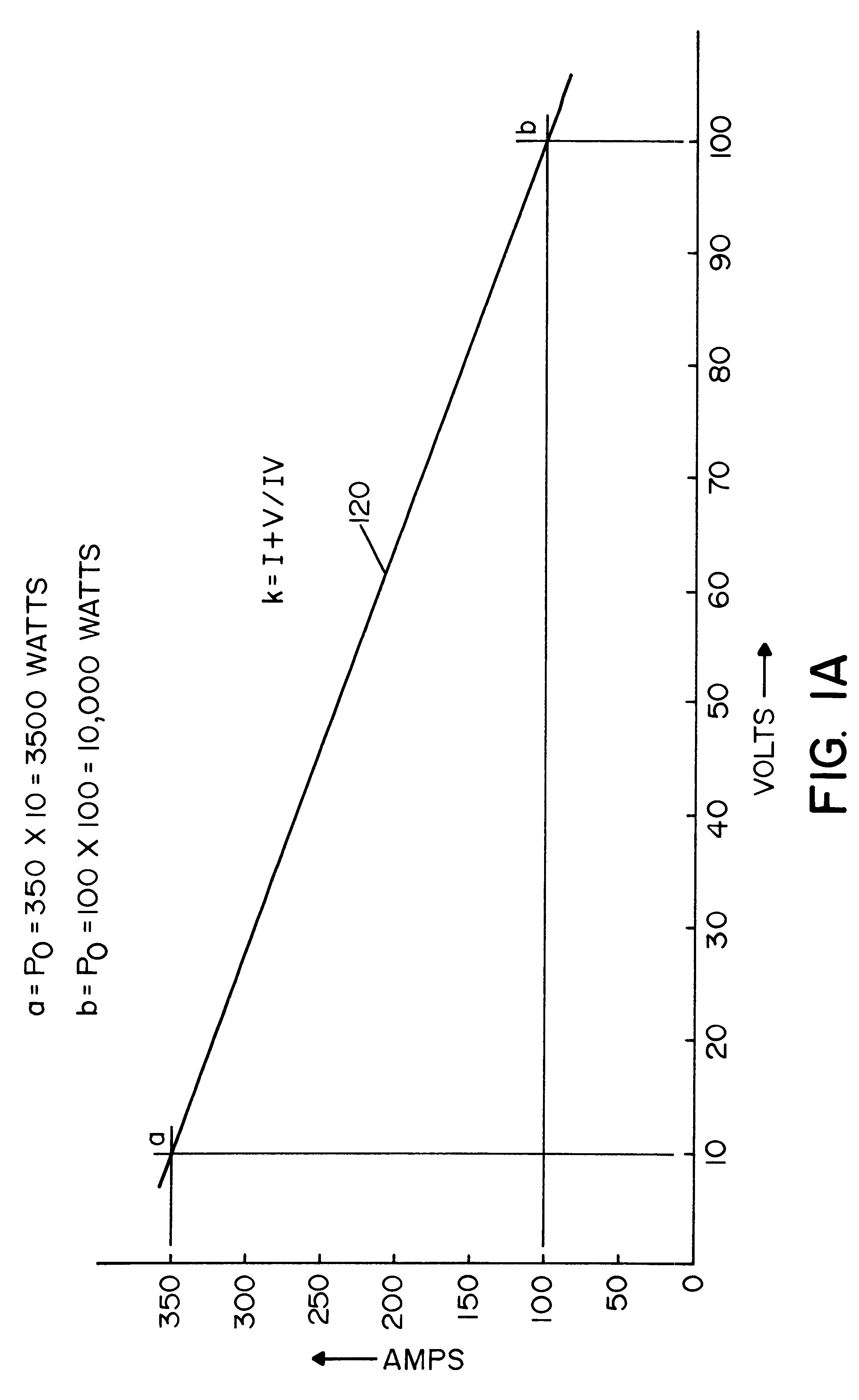
InactiveUS6498321B1Inhibit currentRealize automatic adjustmentArc welding apparatusControl signalControl system
A control system for an electric arc welder performing a welding process between an electrode and a workpiece, which system comprises: a high speed switching type power supply with a controller operated at a switching frequency of at least about 10 kHz with an input current control signal to adjust the output current of the power supply; a first sensor sensing the actual arc voltage; a second sensor sensing the actual arc current; a first circuit for creating a power signal representing the desired real time power level at progressive times during the welding process; a second circuit for creating a function of the sensed actual voltage and the sensed actual current; and a third circuit for adjusting the current control signal in accordance with the difference between the power signal and the function of the actual voltage and current, preferably arc power.
Owner:LINCOLN GLOBAL INC
Detecting Light Load Conditions and Improving Light Load Efficiency in a Switching Power Converter
ActiveUS20100208500A1Minimize switching lossesReduce switching frequencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionLow loadVoltage regulation
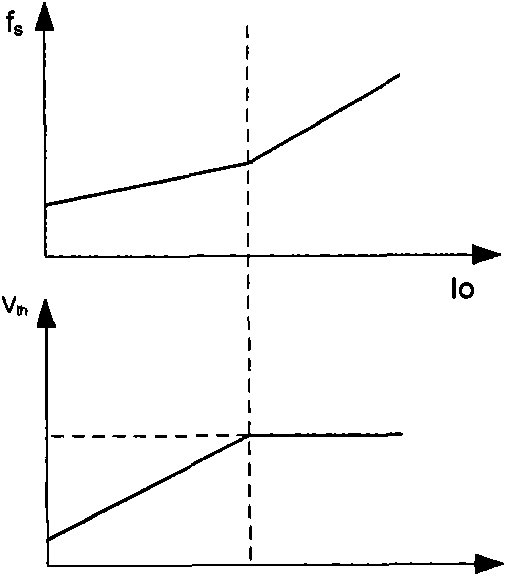
A switching power converter detects low load conditions based on the ratio of a first peak current value for peak current switching in constant voltage regulation mode to a second peak current value for peak current switching in constant current regulation mode. The power supply load is considered to have a low load if the ratio is lower than a predetermined threshold. Once a low load condition is detected, the switching frequency of the switching power converter is reduced to a level that minimizes switching loss in the power converter. In addition, the switching power converter also adjusts the switching frequency according to the sensed input line voltage. An offset is added to the switching period to reduce the switching frequency of the switching power converter, as the input line voltage is increased.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR INC
Resonant converters and control methods thereof
ActiveUS20150229225A1Improve performanceReducing switching-frequency rangeEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionTime delaysEngineering
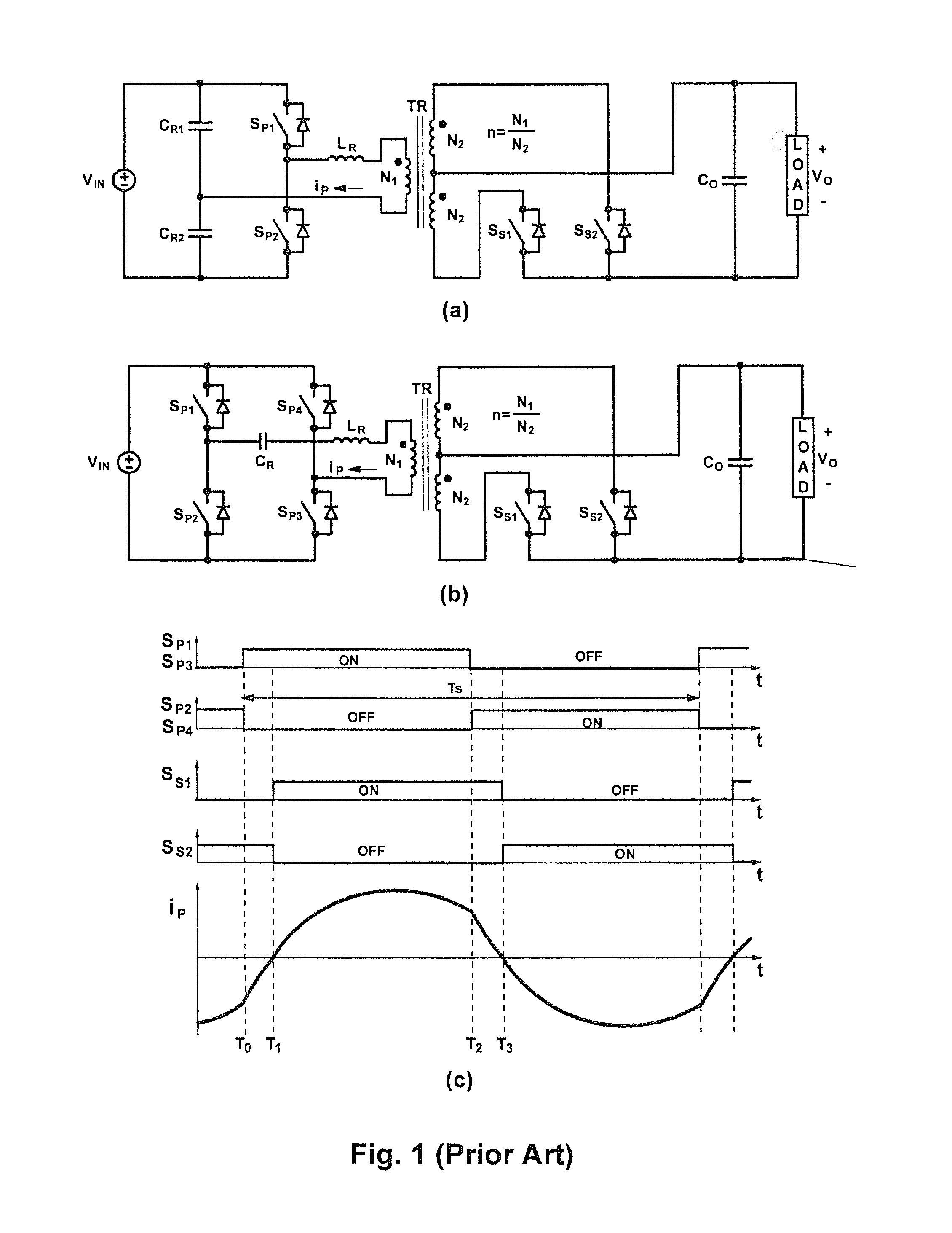
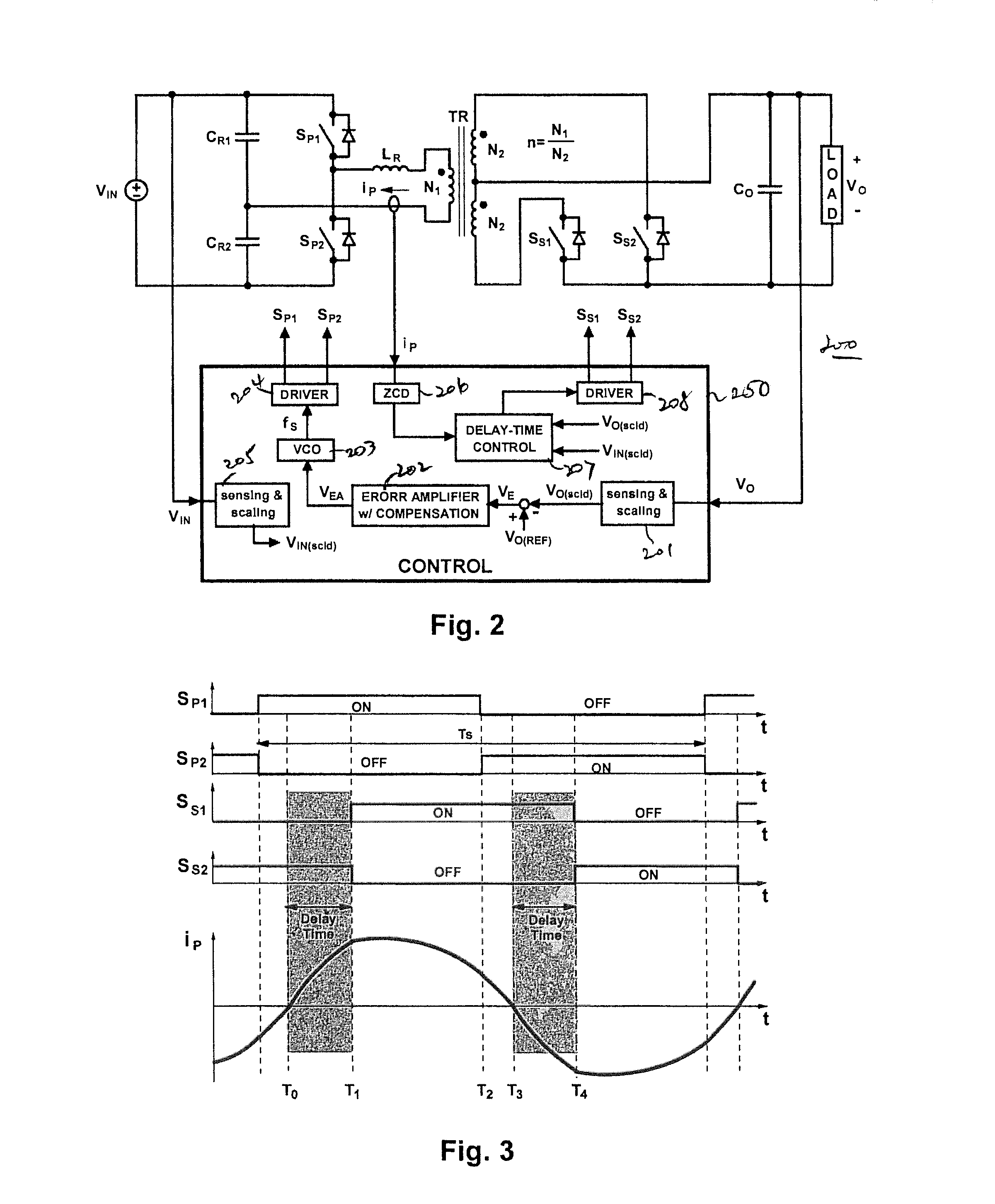
Control methods for resonant converters offer improved performance in resonant converters that operate with a wide input-voltage range or a wide output-voltage range (or both) by substantially reducing the switching-frequency range. Reduction in the switching frequency range is achieved by controlling the output voltage with a combination of variable-frequency control and time-delay control. Variable-frequency control may be used to control the primary switches of an isolated resonant converter, while delay-time control may be used to control secondary-side rectifier switches provided in place of diode rectifiers. The secondary-side control may be implemented by sensing the secondary current or the primary current (or both) and by delaying the turning-off of the corresponding secondary switch with respect to the zero crossings in the secondary current or the primary current.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Apparatus and method for high efficiency isolated power converter
InactiveUS20090034299A1Improve efficiencyLow conductiveDc network circuit arrangementsEfficient power electronics conversionDc dc converterFull bridge
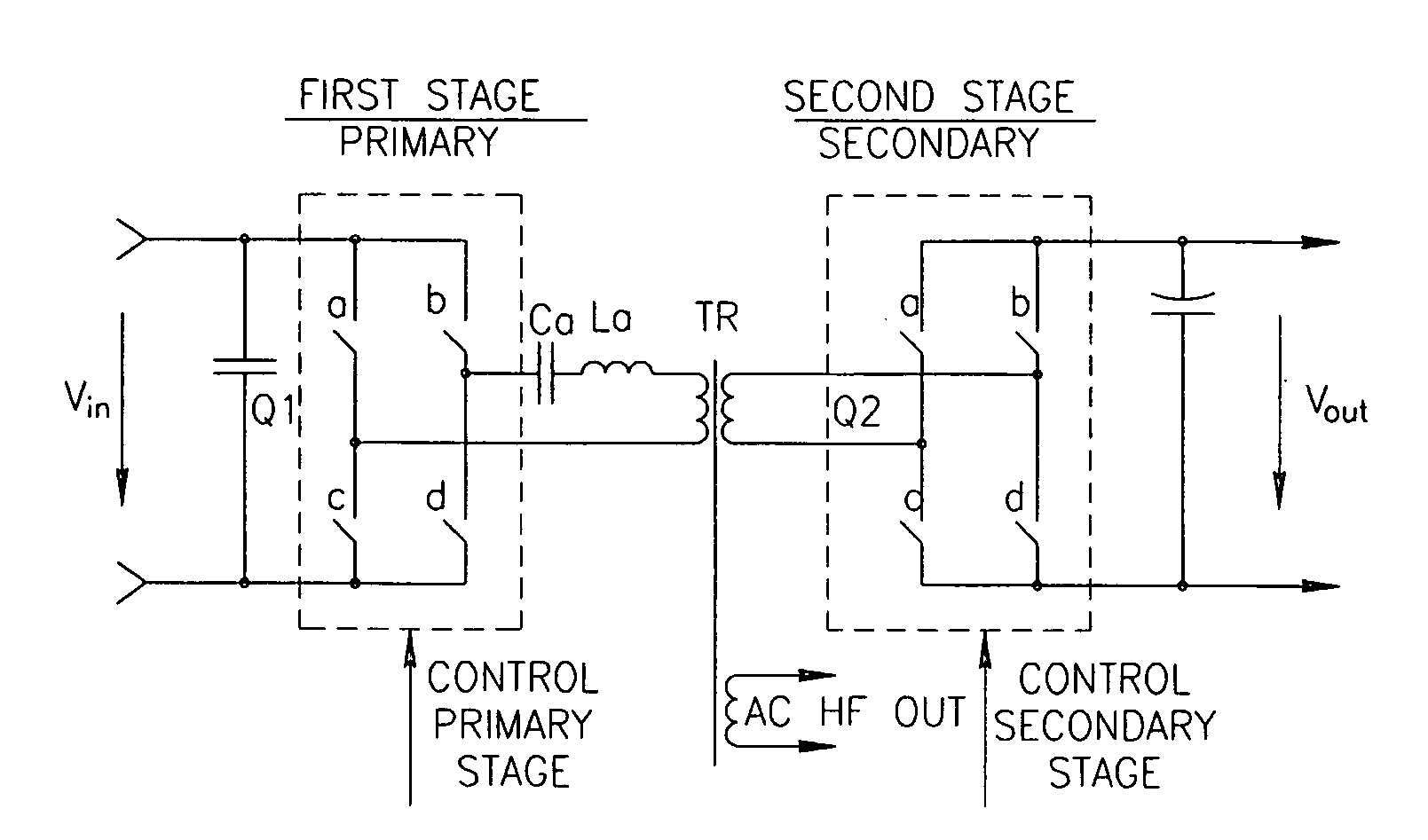
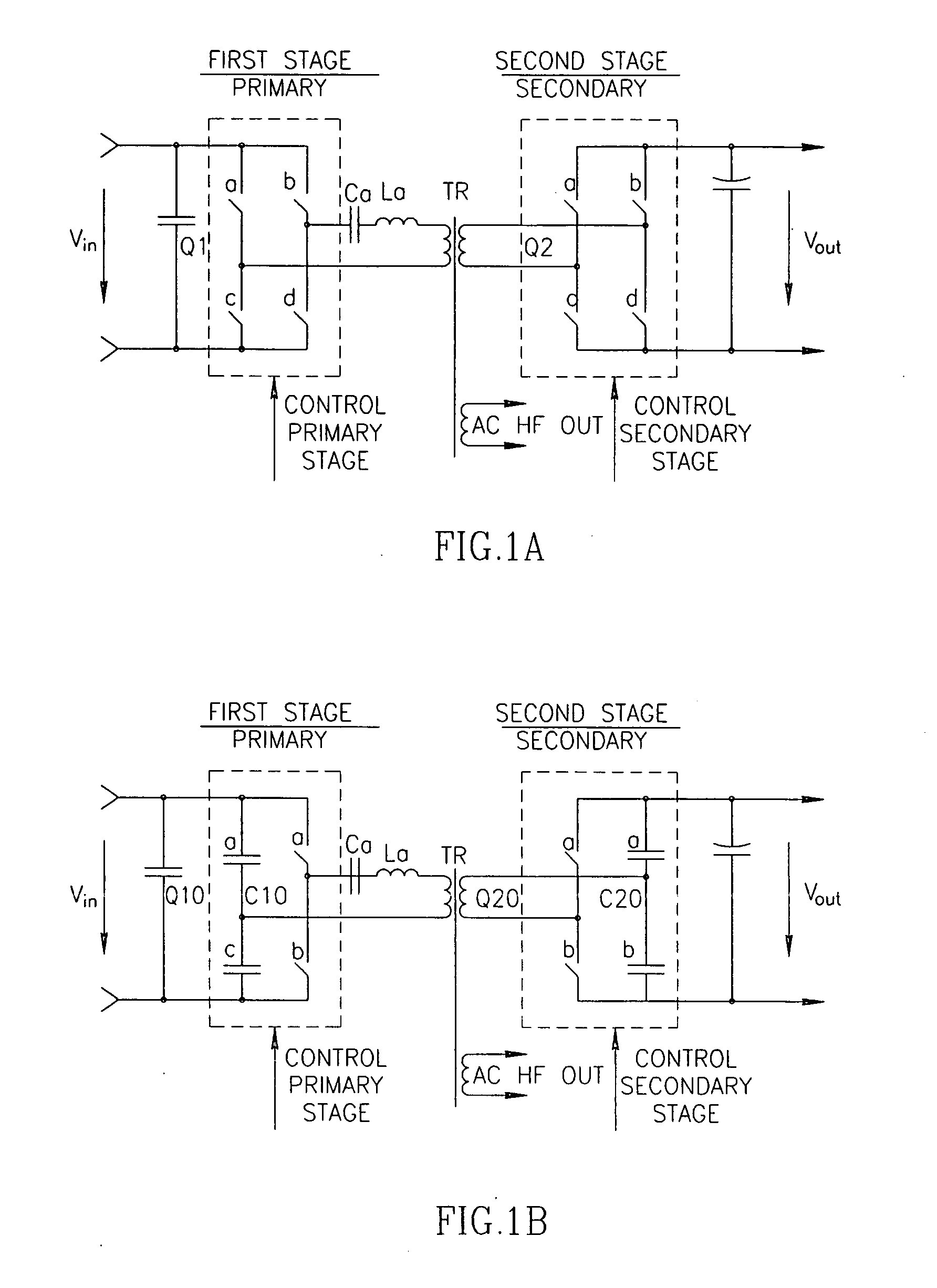
A DC-DC converter apparatus comprising half or full bridge, two-stage resonant converter, which may include series resonant (inductor, capacitor) devices. An isolated transformer having primary and secondary winding supplies current to full-wave secondary stage-bridge through the use of primary winding resonant devices employing primary stage-bridge. The magnetizing of said devices employs zero-current, zero-voltage resonant-transition switching technology, which reduces switching losses at all switching frequencies to almost zero. The regulation of output voltage at all loads and input voltages achieved by the control of the switching frequency and the phase between signals for primary and secondary stages. The proper intermittent of the frequency and the phase allows achieving the value of efficiency up to 97%.
Owner:LUMENIS LTD
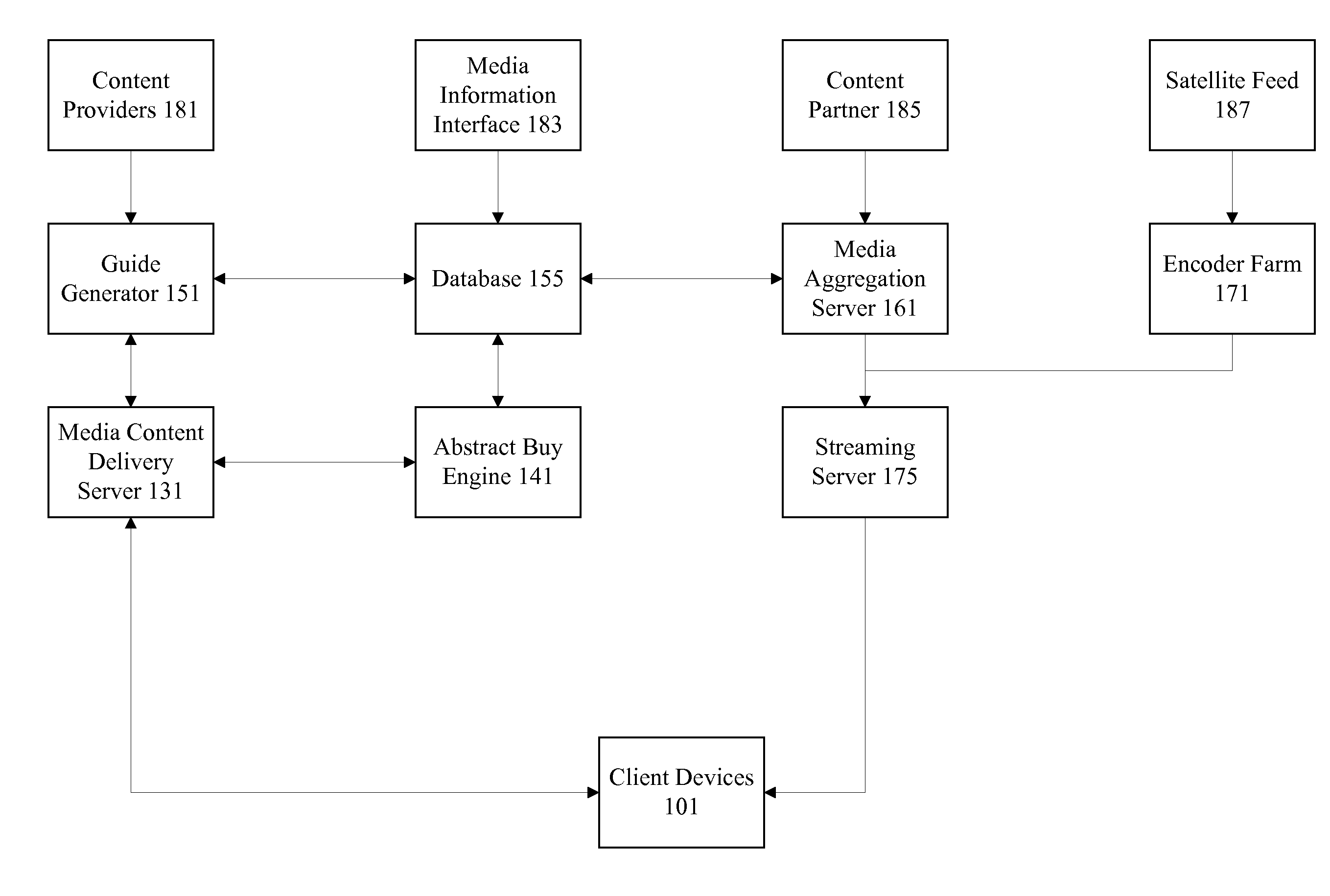
Implicit mechanism for determining user response to media
ActiveUS20110072448A1Analogue secracy/subscription systemsBroadcast information monitoringSwitching frequencyTime duration
Mechanisms are provided for implicitly determining user response to media content. User response may include satisfaction, interest, and engagement levels. User response is determined implicitly by measuring channel switching, channel switching frequency, duration of viewing time, content duration, etc. in a linear or non-linear manner. In one example, the viewing duration evaluated with the media content duration to generate an interest factor. A relative interest factor for the media content is generated by referencing interest factors for the user for other pieces of media content for the user. User responses can be analyzed to determine user attention span, make content recommendations, deliver selected versions of content, customize advertising for a user, etc.
Owner:TIVO CORP
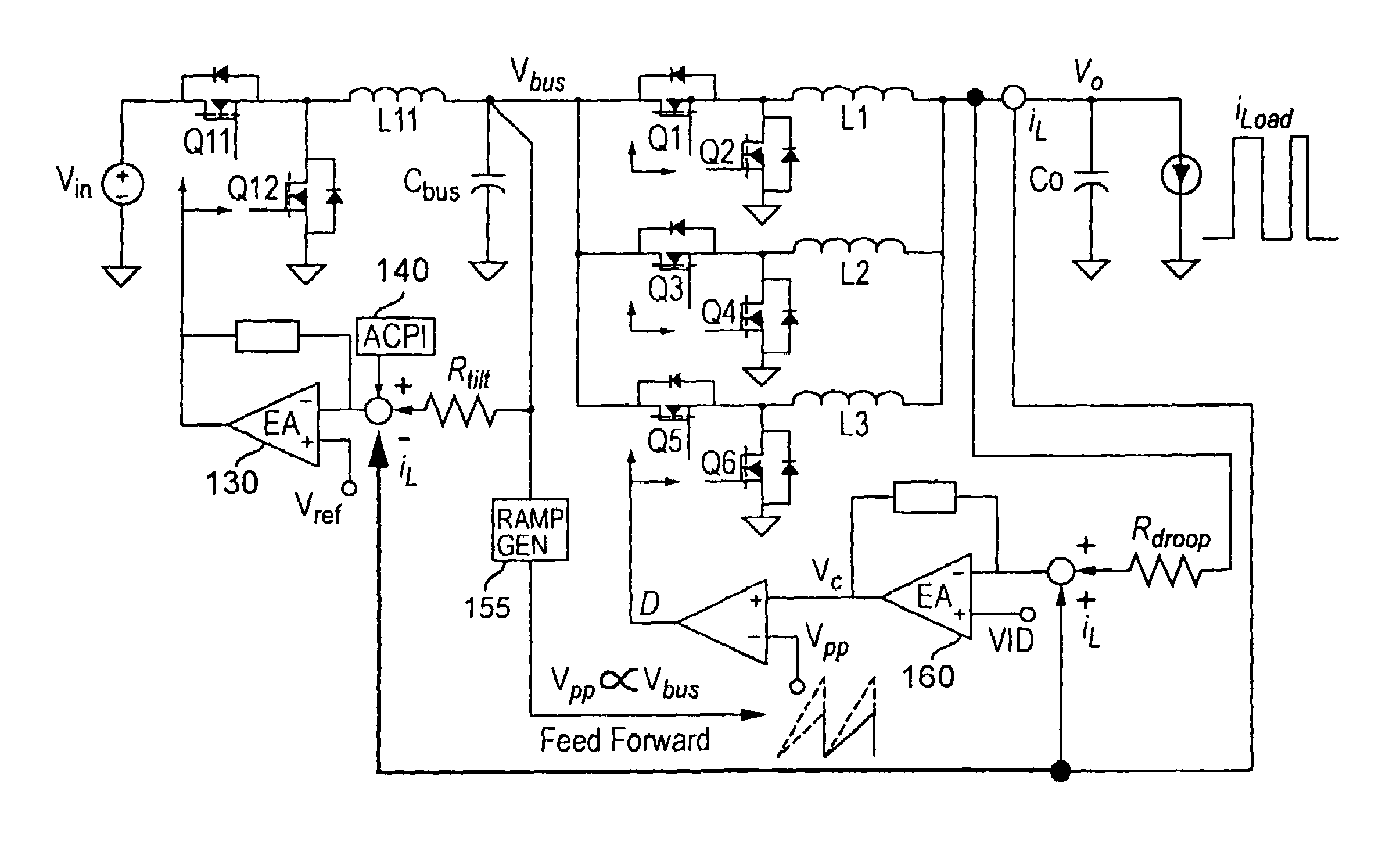
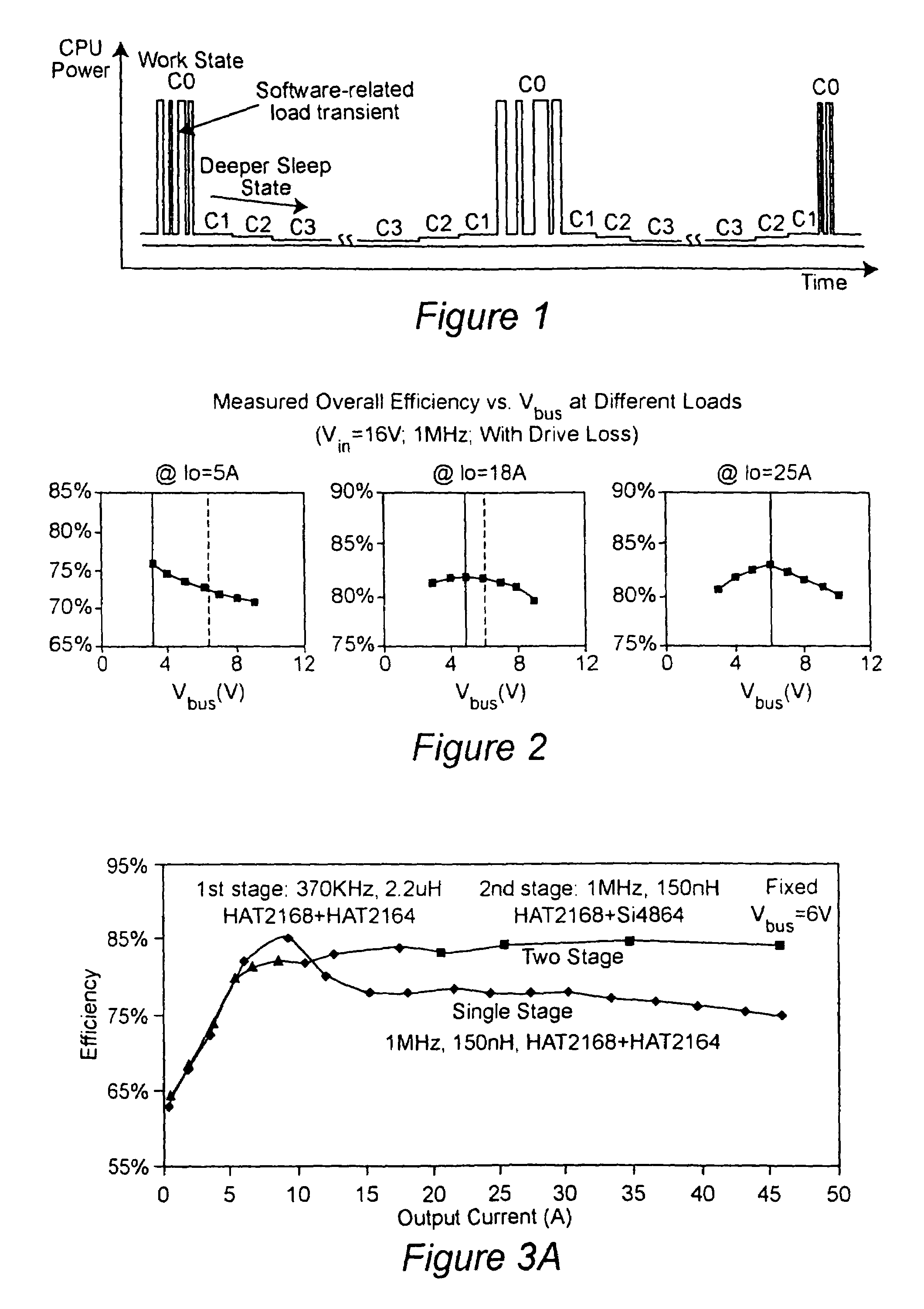
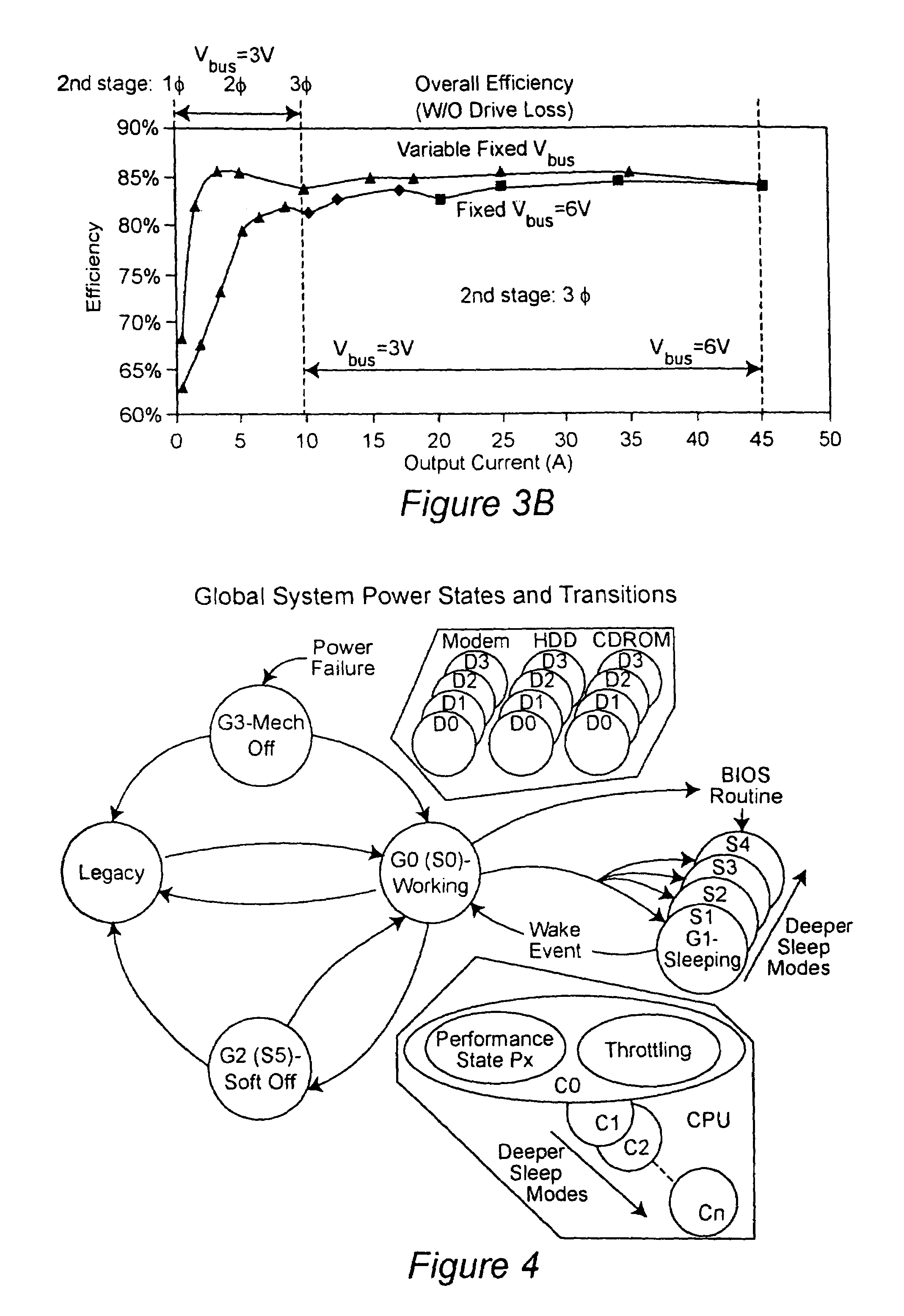
Two-stage voltage regulators with adjustable intermediate bus voltage, adjustable switching frequency, and adjustable number of active phases
InactiveUS7071660B2Improve efficiencyWide variationEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionBuck converterSwitching frequency
A two-stage power converter that dynamically adjusts to output current requirements includes a first stage regulator that provides power to a second stage regulator. The first stage can be a buck converter, and the second stage can be a multiple-phase buck converter. The output voltage of the first stage (intermediate bus voltage Vbus) is varied according to the load current to optimize conversion efficiency. To provide maximum efficiency, the Vbus voltage is increased as load current increases. The Vbus voltage provided by the first stage can be varied by duty cycle or operating frequency control. In another embodiment, the switching frequency of the second stage is varied as output current changes so that output current ripple is held constant. In an embodiment employing a multiple-phase buck converter in the second stage, the number of operating phases are varied as output current changes.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Active power factor correction circuit and control method thereof
InactiveUS7295452B1Reduce Higher Harmonic DistortionReduce switching lossesEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcDriver circuitPower switching
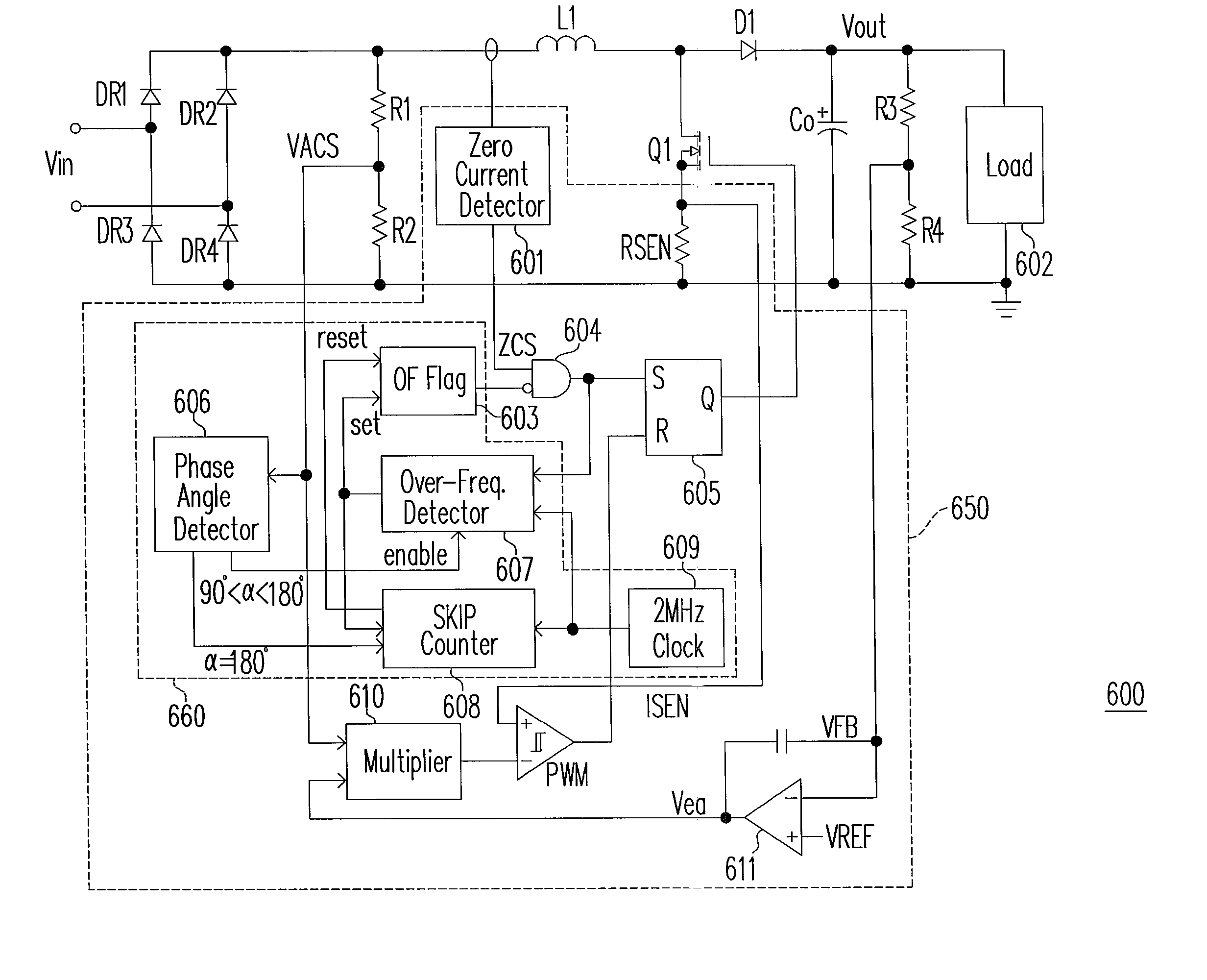
An active power factor correction (PFC) circuit and its controlling method are provided. The method comprises the following steps. Drive the power switch of the circuit so that the average inductor current waveform follows the rectified input voltage waveform. Suspend the operation of the power switch at a first moment in a first line cycle of the rectified input voltage and then resume the operation of the power switch at a second moment in a second line cycle of the rectified input voltage. The first moment is when the phase angle of the rectified input voltage exceeds a predetermined angle and the switching frequency of the power switch exceeds a predetermined frequency. The time span from the first moment to the end of the first line cycle is substantially as long as the time span from the beginning of the second line cycle to the second moment.
Owner:GREEN MARK TECH
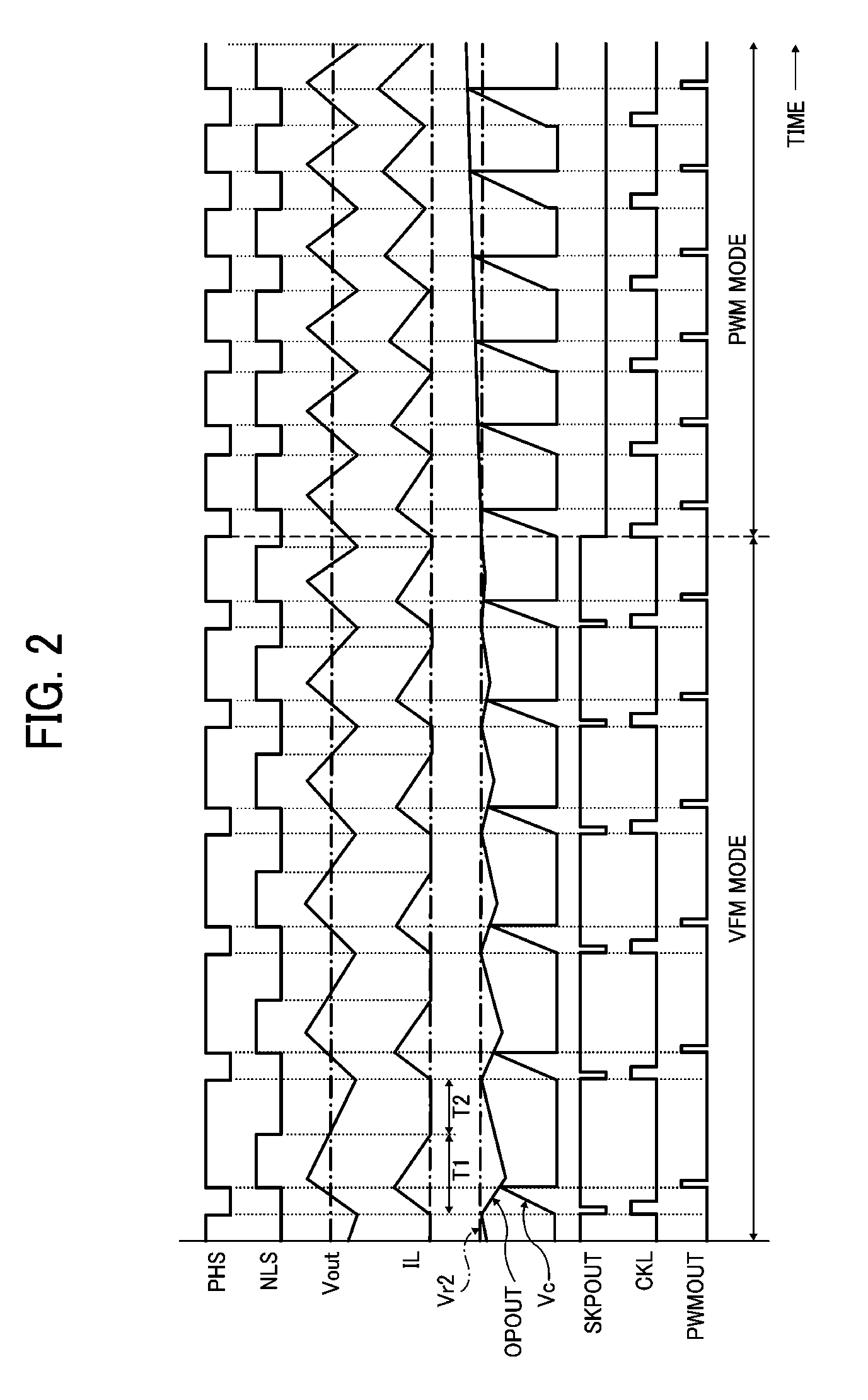
Dc-dc converter
InactiveUS20100066328A1Increase currentReduce switching frequencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionDc dc converterEngineering
A non-isolated DC-DC converter that converts a voltage input to an input terminal to output a constant output voltage to a load terminal while switching control mode between a PWM mode and a VFM mode depending on a current output to the load terminal. The DC-DC converter includes an inductor, a switching circuit, and a control circuit. The inductor stores electric energy for supply to the load terminal. The switching circuit switches on and off current flow at a switching frequency to alternately charge and discharge the inductor. The control circuit increases an electric current flowing to the load terminal through the inductor per one operational cycle as the switching frequency decreases during VFM control mode operation.
Owner:RICOH ELECTRONIC DEVICES CO LTD
Systems and methods for voltage control and current control of power conversion systems with multiple operation modes
ActiveUS20140078790A1Improve efficiencyReduce switching lossesEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionSwitching frequencySystem controller
System and method for regulating a power conversion system. A system controller for regulating a power conversion system includes an operation-mode-selection component and a driving component. The operation-mode-selection component is configured to receive a first signal related to an output load of the power conversion system and a second signal related to an input signal received by the power conversion system and output a mode-selection signal based on at least information associated with the first signal and the second signal. The driving component is configured to receive the mode-selection signal and generate a drive signal based on at least information associated with the mode-selection signal, the driving signal corresponding to a switching frequency.
Owner:ON BRIGHT ELECTRONICS SHANGHAI
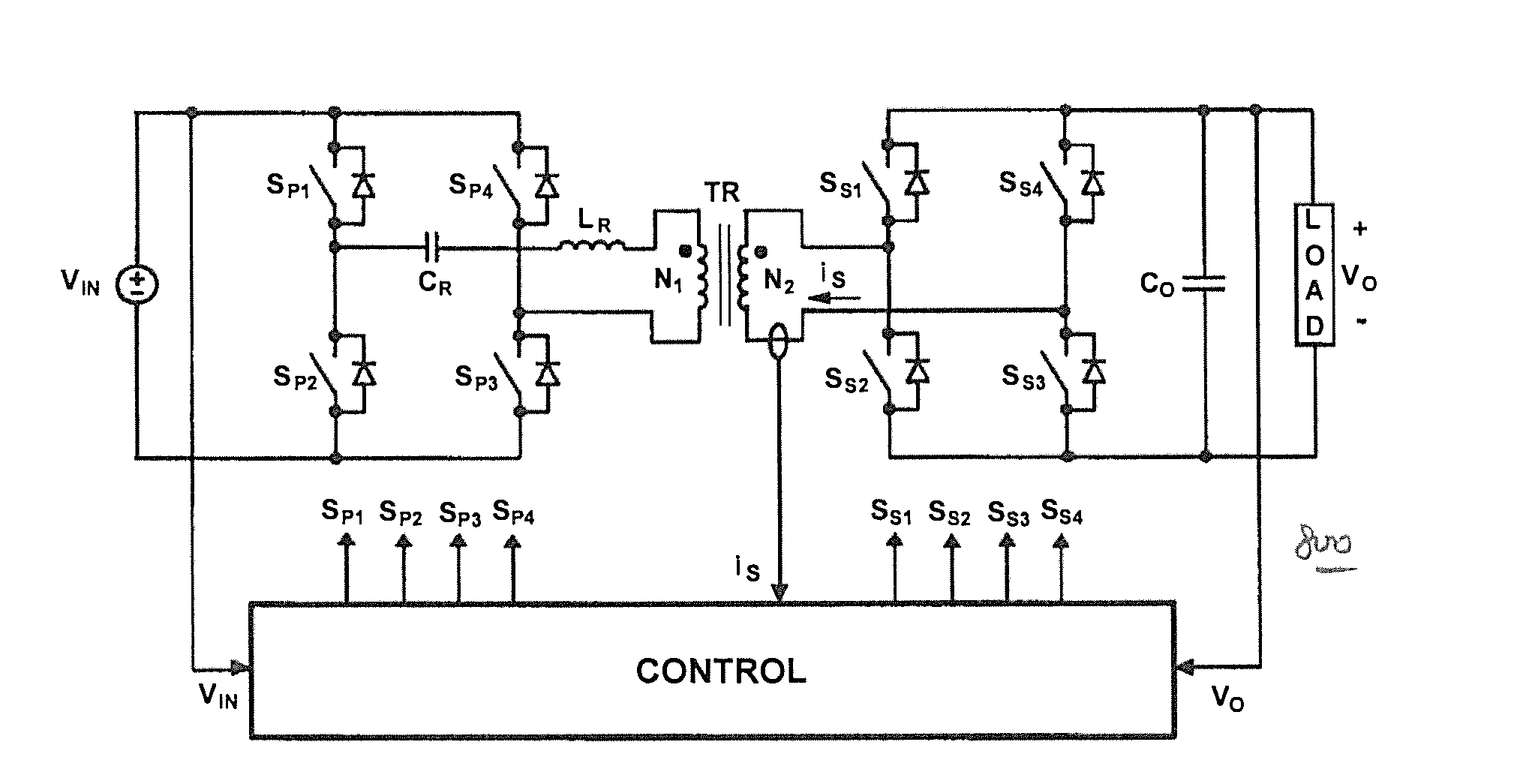
Method and control circuitry for a three-phase three-level boost-type rectifier
InactiveUS20030128563A1Easy to analyzePoor waveform qualityAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionThree levelDynamic balance
A synchronized control method for a three-phase three-level boost-type rectifier with reduced input current ripple and balanced output voltages is disclosed. The proposed control allows simplifying the control circuit as much as possible without compromising the rectifier performance. In fact, besides simplicity, the control method featured synchronized command signals to de switching devices, minimized input current ripple, full controllability of the output voltage, dynamic balance of the output center point, constant switching frequency, simplified design of EMC filters, good transient and steady state performance, and low cost. The invention described first the most important configurations that the three-phase three-level boost-type rectifier may assume and studied the converter's operation. The concept involved for output voltage, input current, neutral point balance and control system design was presented.
Owner:VERTIV CORP
Hysteretic CL power converter
ActiveUS20120170334A1Reduce the valueSmall sizeEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionĆuk converterSwitching frequency
A novel switching hysteretic power converter is presented. The power converter combines the function of a capacitive charge pump with the function of an inductive step down converter to obtain a switching boost converter with a much simpler control method with respect to conventional inductive boost power converters. The hysteretic control provides stable operation in all conditions with excellent load transient response. Furthermore the hysteretic control allows high frequency switching reducing the size and cost of the passive components. The Discontinuous Conduction Mode of operation provides very high efficiency even at light loads. The presented power converter can be operated as a boost converter or as a buck converter simply by changing the switching phase of one switch. In both types of operation the efficiency of the hysteretic power converter can be quite high even at high switching frequencies.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
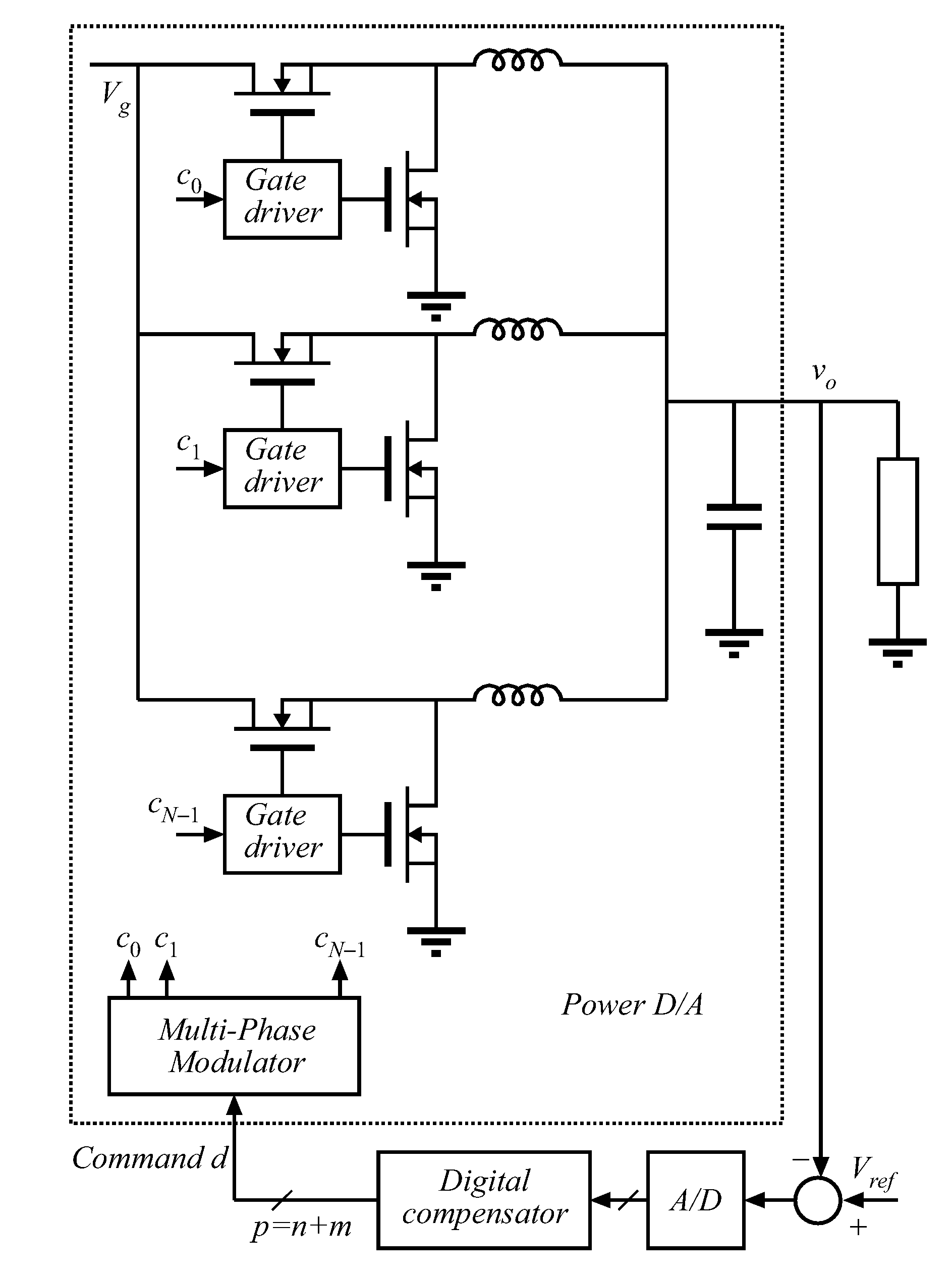
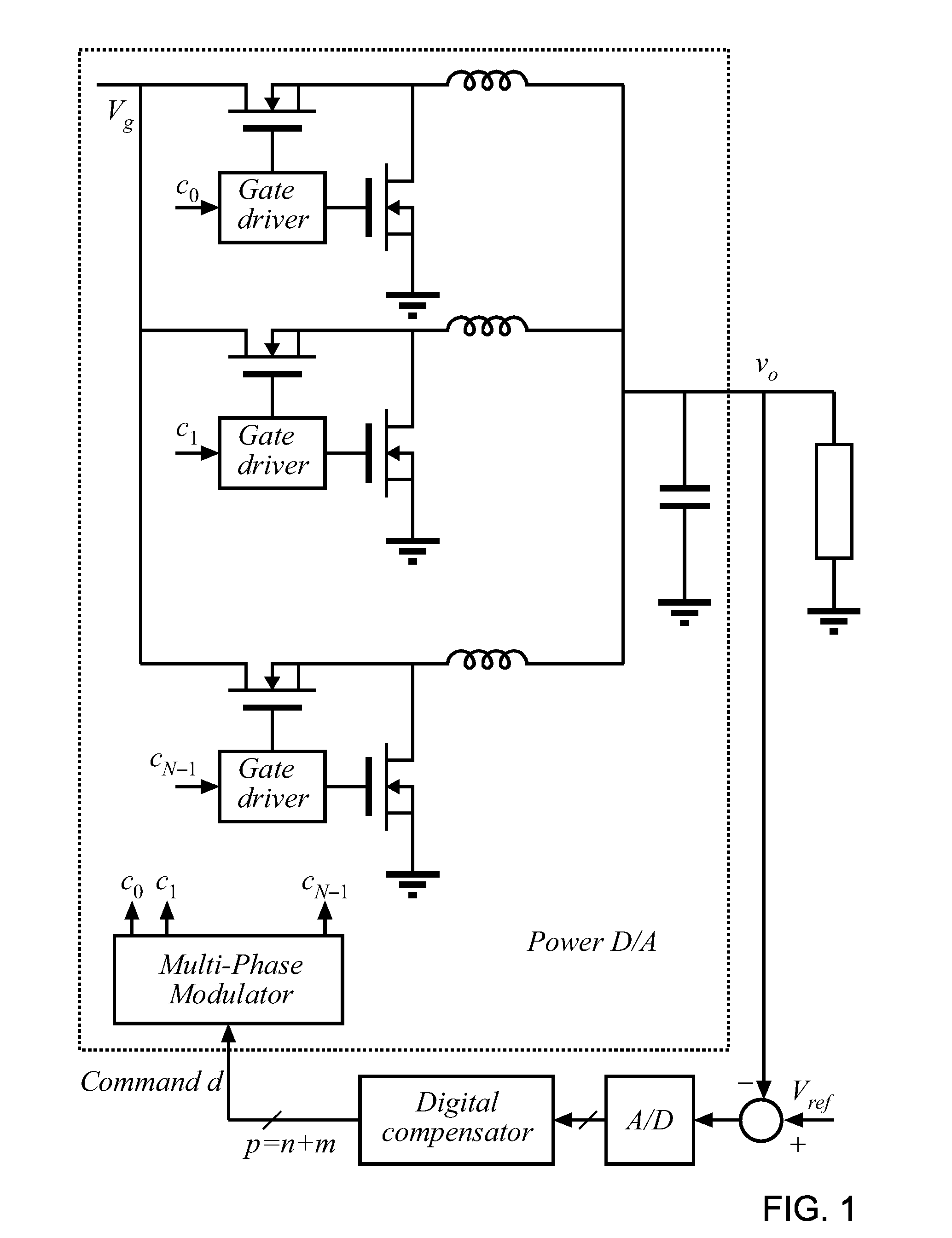
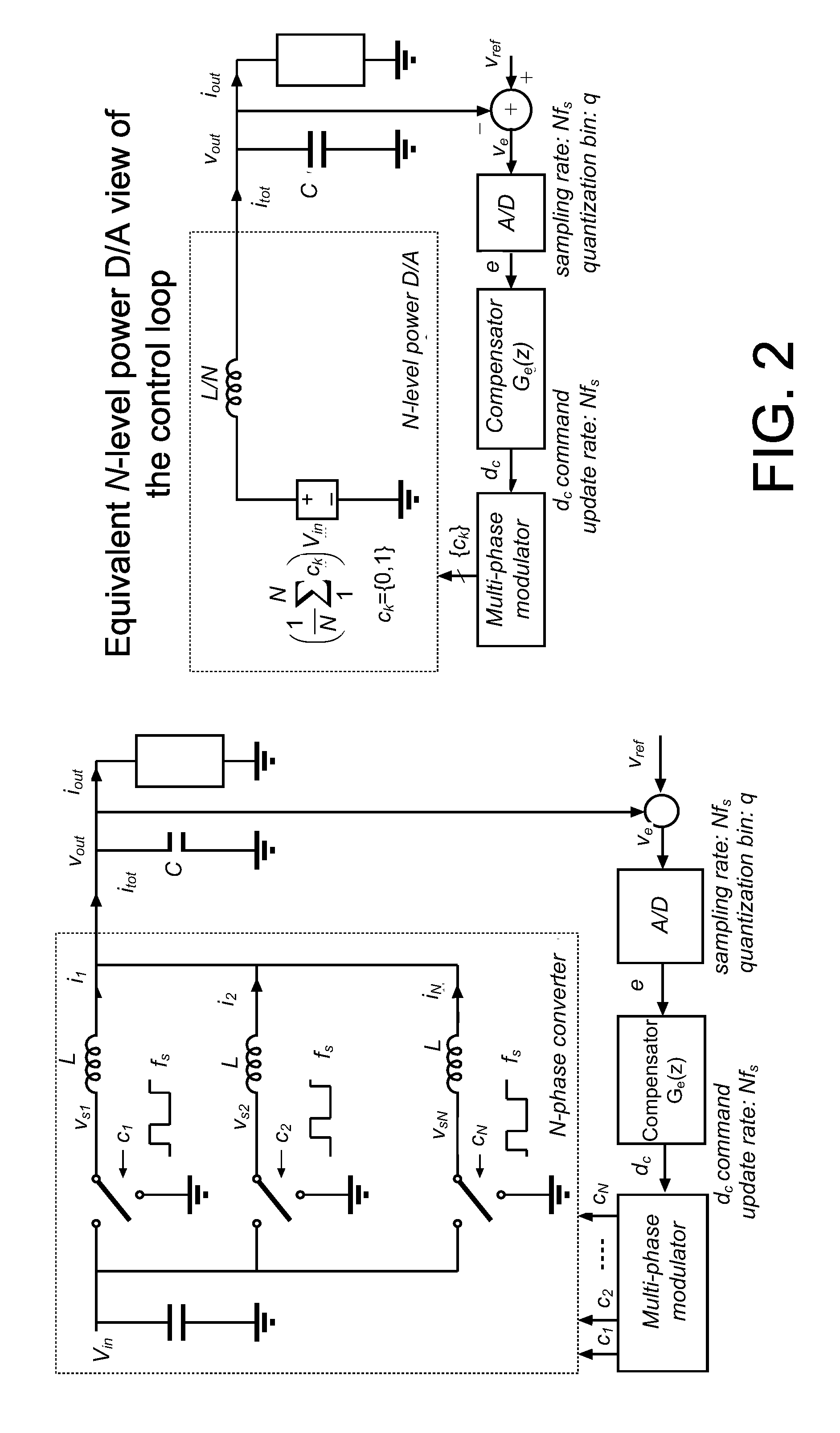
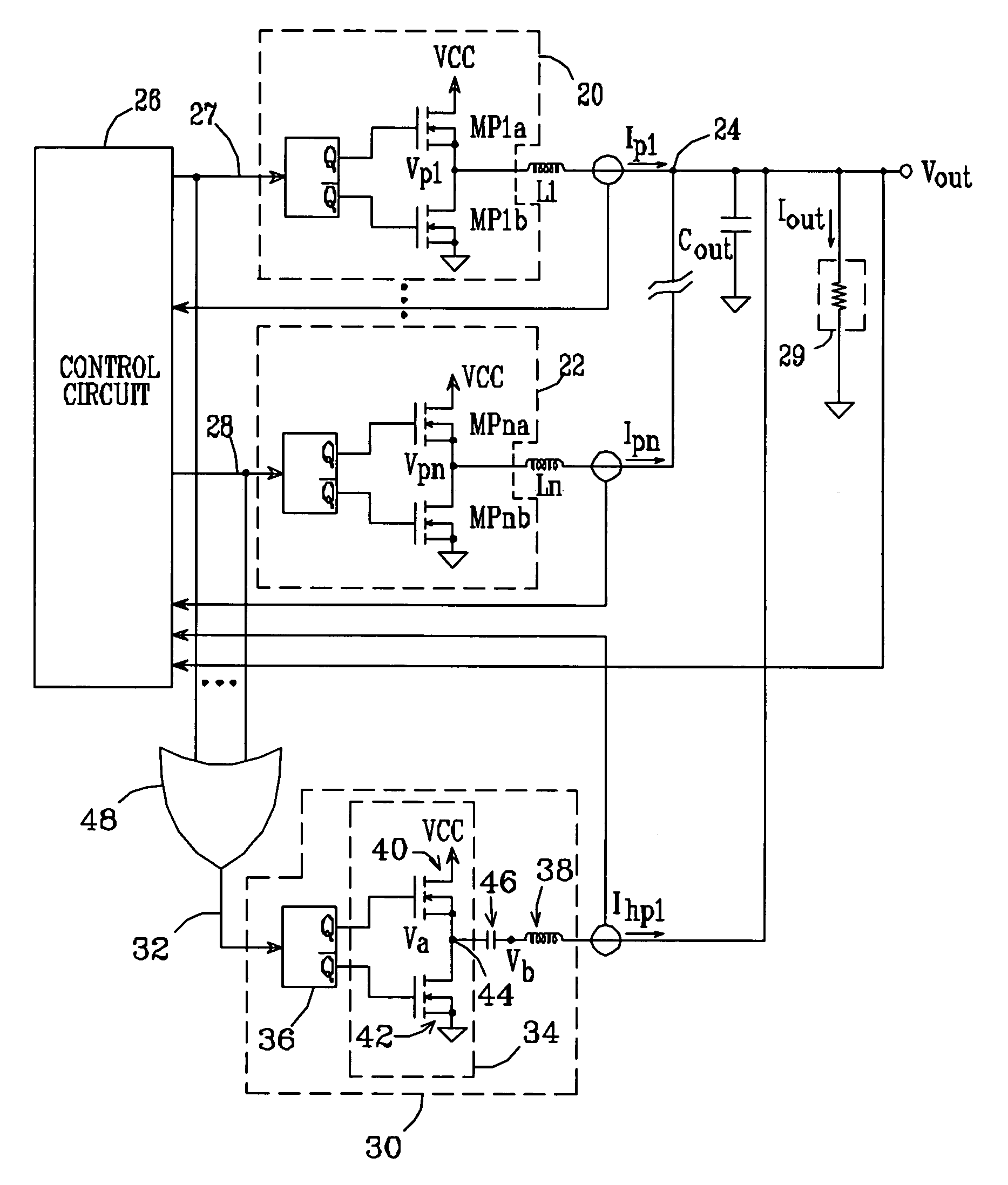
Multi-phase modulator
ActiveUS20080310200A1Dc-dc conversionDc source parallel operationResolution enhancement technologiesImage resolution
An architecture is described for digital multi-phase modulators (MPM) that leads to an efficient, high performance hardware realization. The combined modulator, switching phases and output filter can be viewed as a multi-level digital to analog converter with high power output, or a power D / A, and concepts used in D / A converters are leveraged to achieve high performance and hardware efficiency. The modulator can be split into three functional blocks including a decoder that determines how many phases are on at any time, a selector that determines which phases are on at any time, and a single high resolution module that is time shared among all phases. The resulting architecture scales favorably with a large number of phases, fs, facilitates fast update rates of the input command well above the single phase switching frequency and is compatible with a wide range of known DPWM techniques for the LSB module and resolution-enhancement techniques such as dithering or Σ-Δ modulation.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
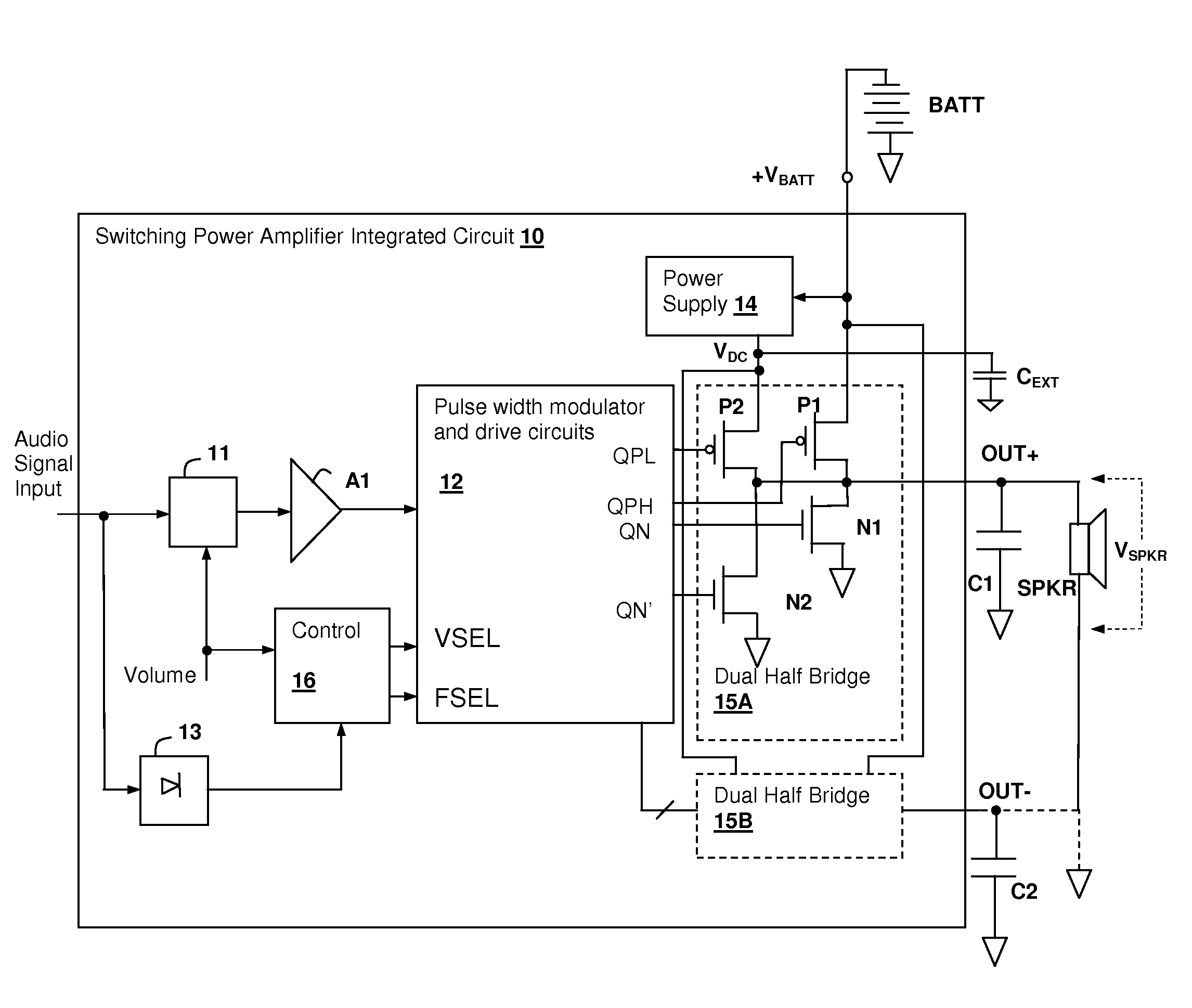
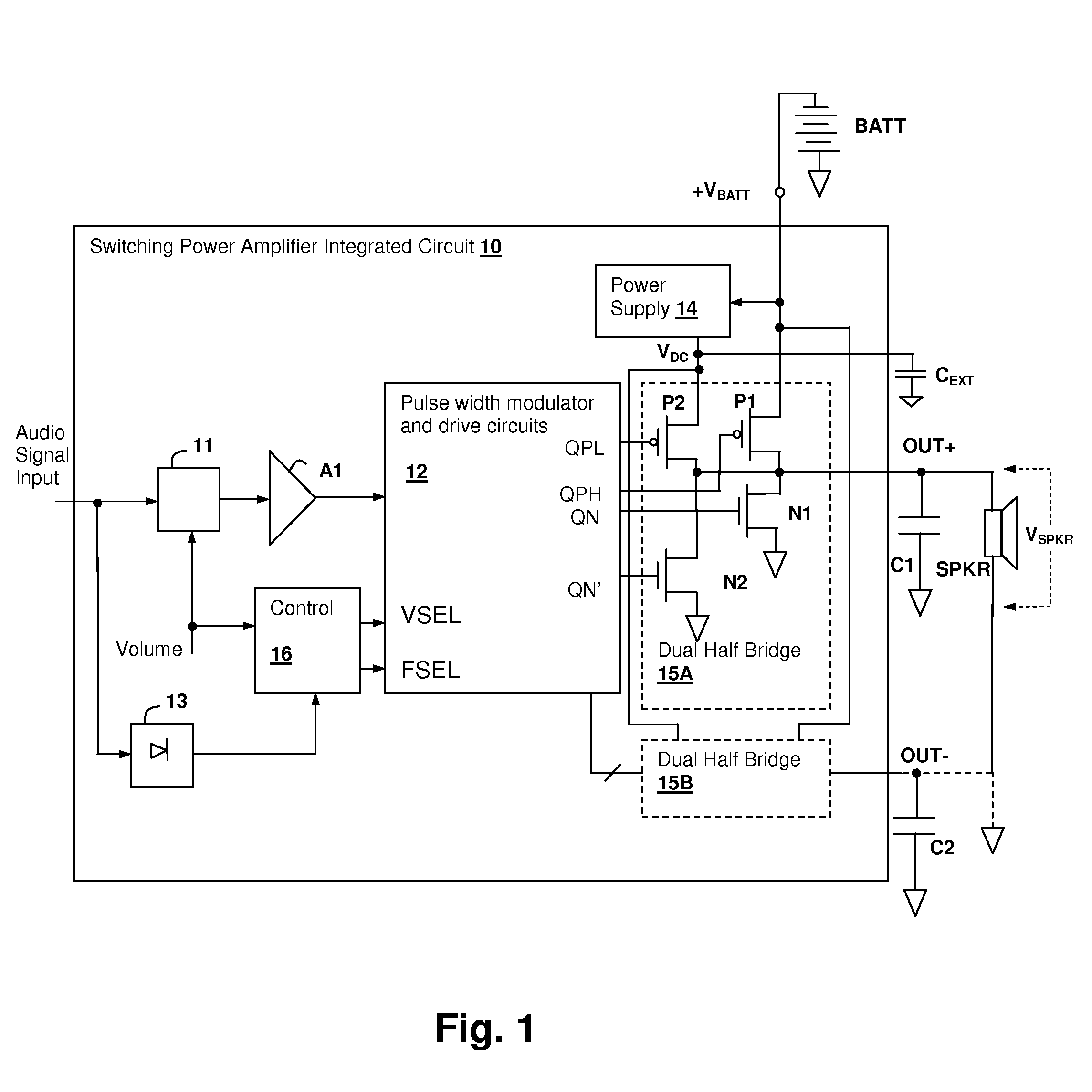
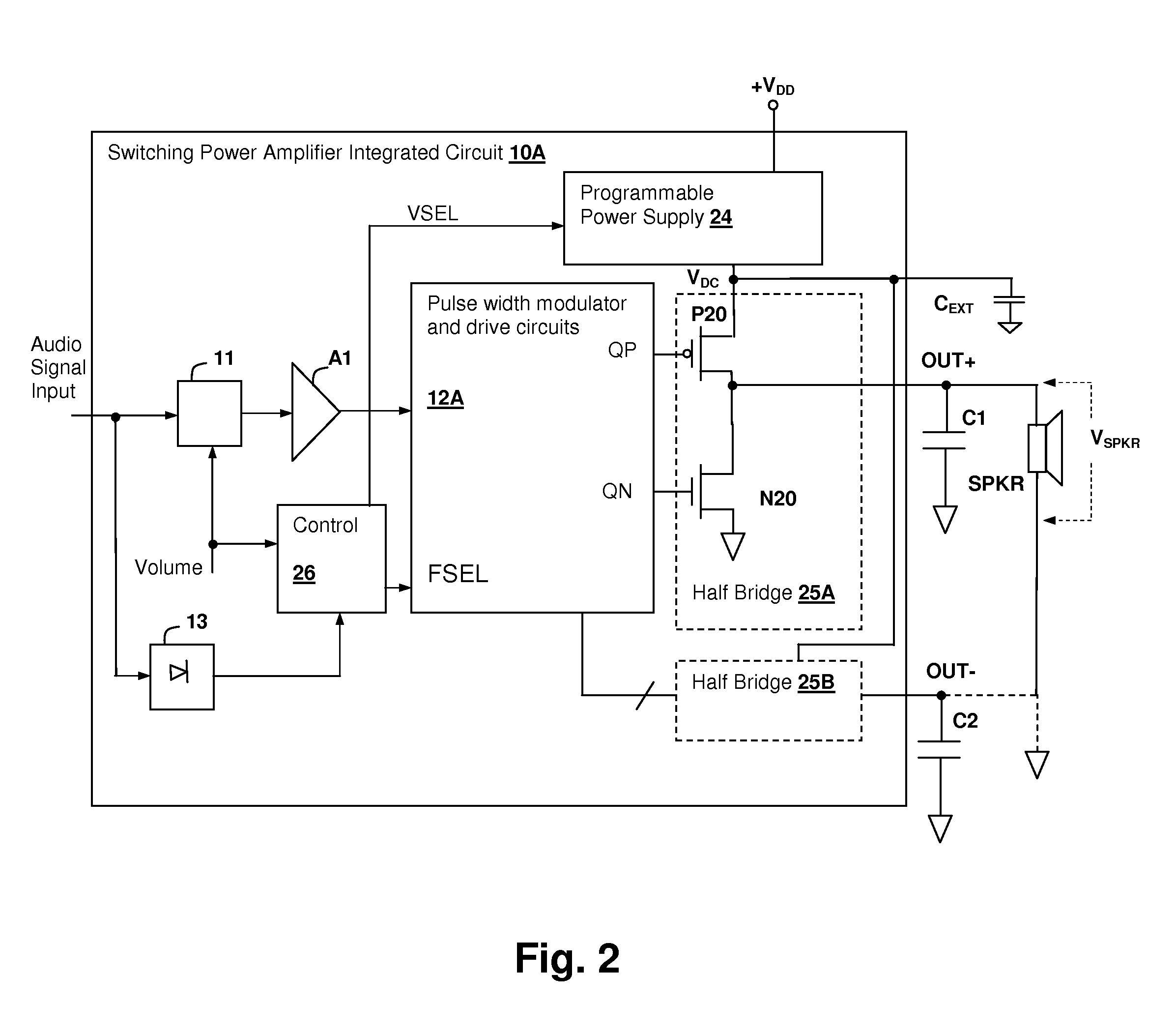
Pulse-width modulated (PWM) audio power amplifier having output signal magnitude controlled pulse voltage and switching frequency
ActiveUS8093951B1Reduce switching frequencyAudio amplifierAmplifiers with semiconductor devices onlyClass-D amplifierSwitching frequency
An audio switching power amplifier having an output pulse voltage selected in conformity with an indication of the output signal amplitude provides lower electromagnetic interference (EMI) in class-D amplifier implementations, in particular, in inductor-less designs. The output pulse voltage may be selected by providing multiple switching circuits, such as half or fully bridge switches, with each switching circuit connected to a different power supply. One of the switching circuits is activated by the switching controller, while the others are disabled, providing selection of the output pulse voltage. Selection of a lower pulse voltage, when the maximum voltage is not required, reduces the generated EMI. The switching frequency of the class-D amplifier may also be controlled in conformity with the output signal amplitude, so that at higher output levels a lower switching rate is selected, reducing the generated EMI.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Systems and methods for flyback power converters with switching frequency and peak current adjustments based on changes in feedback signals
ActiveUS20130033905A1Increase frequencyIncreasing magnitudeEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionPeak currentEngineering
System and method for regulating a power converter. The system includes a first comparator configured to receive a first input signal and a second input signal and generate a first comparison signal based on at least information associated with the first input signal and the second input signal, a pulse-width-modulation generator configured to receive at least the first comparison signal and generate a modulation signal based on at least information associated with the first comparison signal, a driver component configured to receive the modulation signal and output a drive signal to a switch to adjust a primary current flowing through a primary winding of the power converter, and a voltage-change-rate detection component configured to sample the feedback signal to generate a first sampled signal for a first modulation period and to sample the feedback signal to generate a second sampled signal for a second modulation period.
Owner:ON BRIGHT ELECTRONICS SHANGHAI
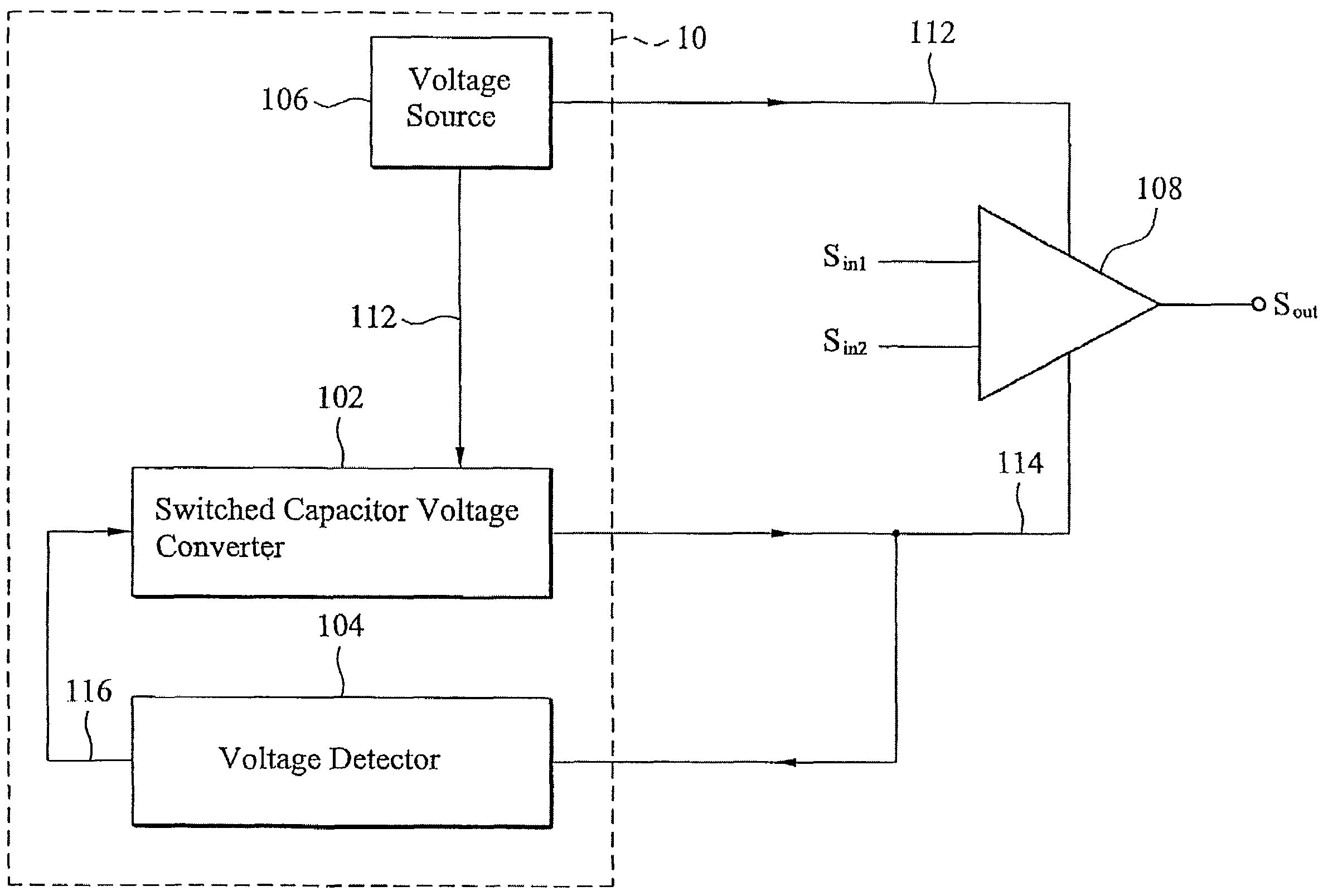
Voltage generating apparatus and methods
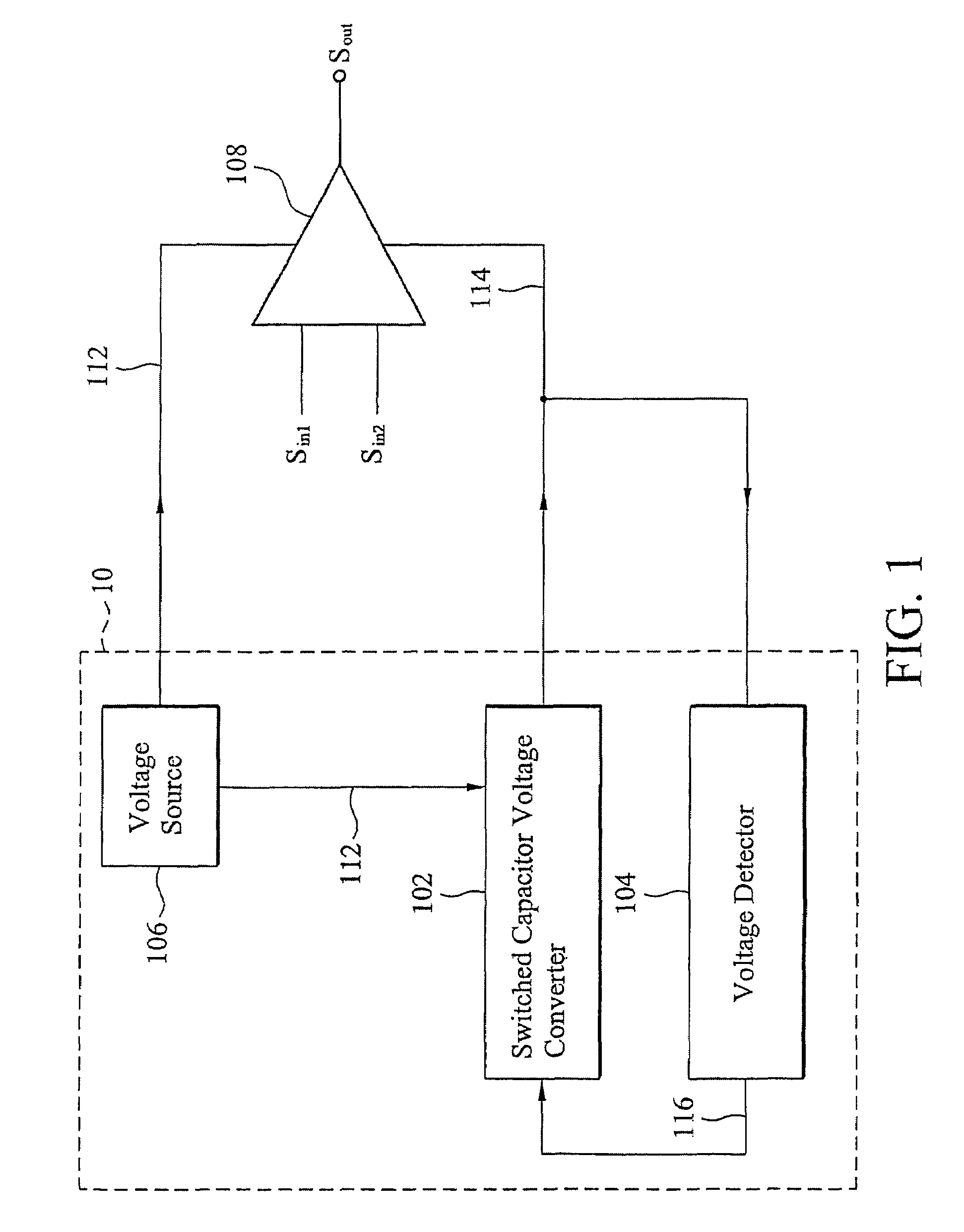
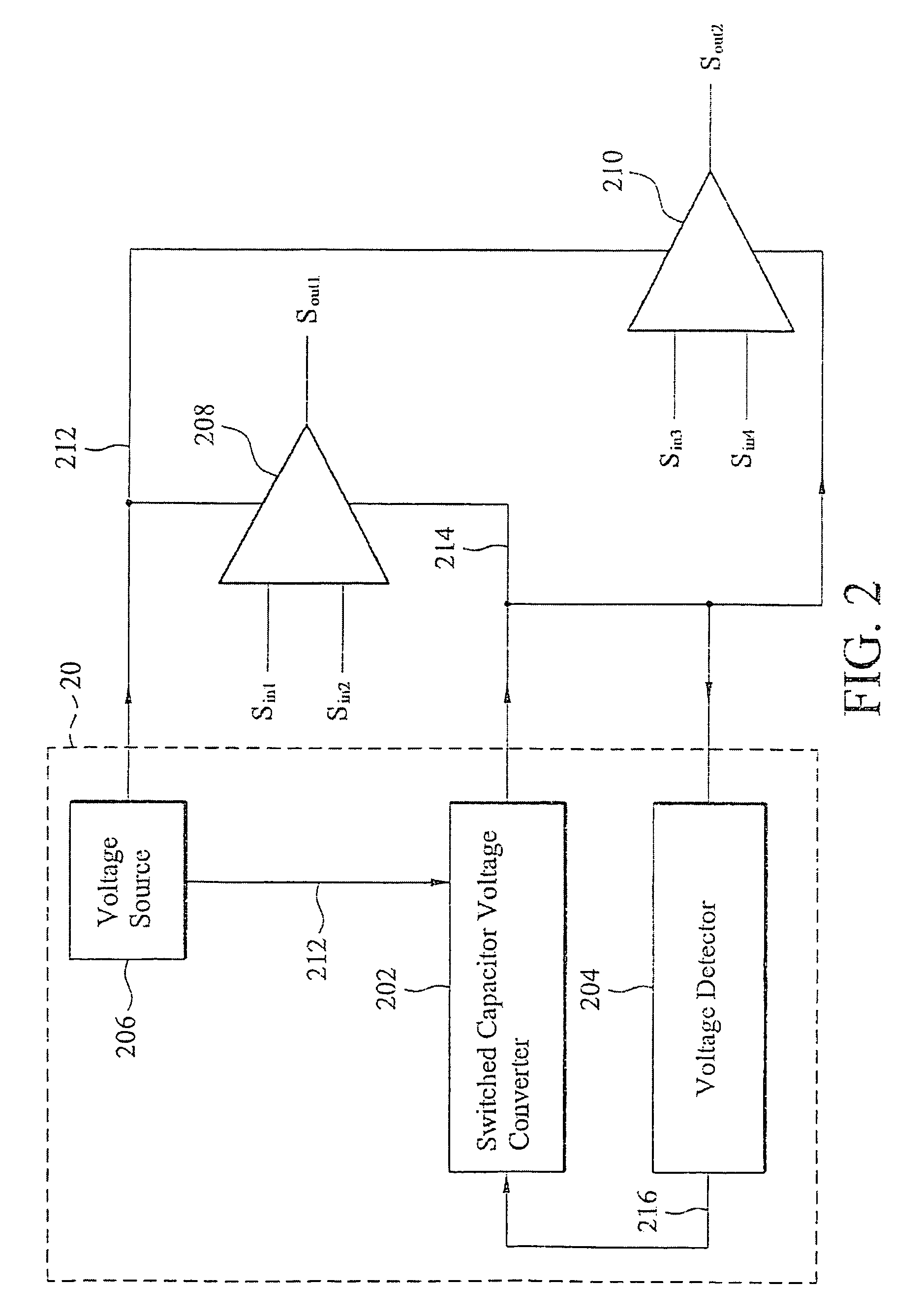
InactiveUS7609114B2Amplifier detailsAmplifiers with semiconductor devices onlyVoltage converterAudio power amplifier
The invention provides a voltage generating apparatus for powering at least one amplifier. The voltage generating apparatus comprises a voltage source, a switched capacitor voltage converter and a voltage detector. The voltage source supplies a first voltage to a positive voltage input terminal of the at least one amplifier. The first voltage is a positive DC voltage. The switched capacitor voltage converter is coupled to the voltage source for outputting an output voltage to a negative voltage input terminal of the at least one amplifier according to the first voltage and a predetermined voltage. The output voltage is a negative DC voltage. The voltage detector is coupled to the switched capacitor voltage converter for determining a switching frequency corresponding to the predetermined voltage according to the output voltage. The switched capacitor voltage converter increases the output voltage when the switching frequency is decreased and decreases the output voltage when the switching frequency is increased.
Owner:UPI SEMICON CORP
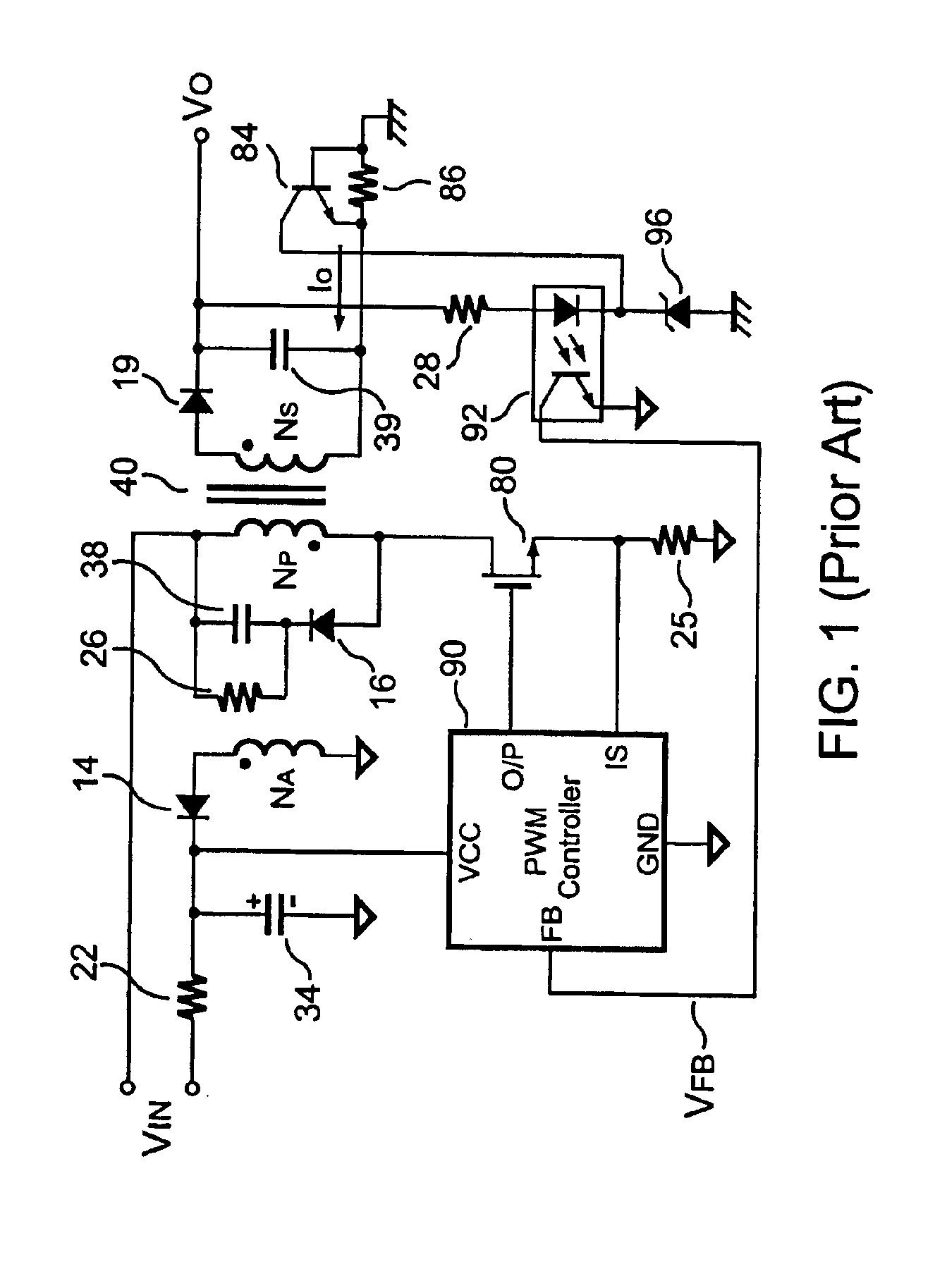
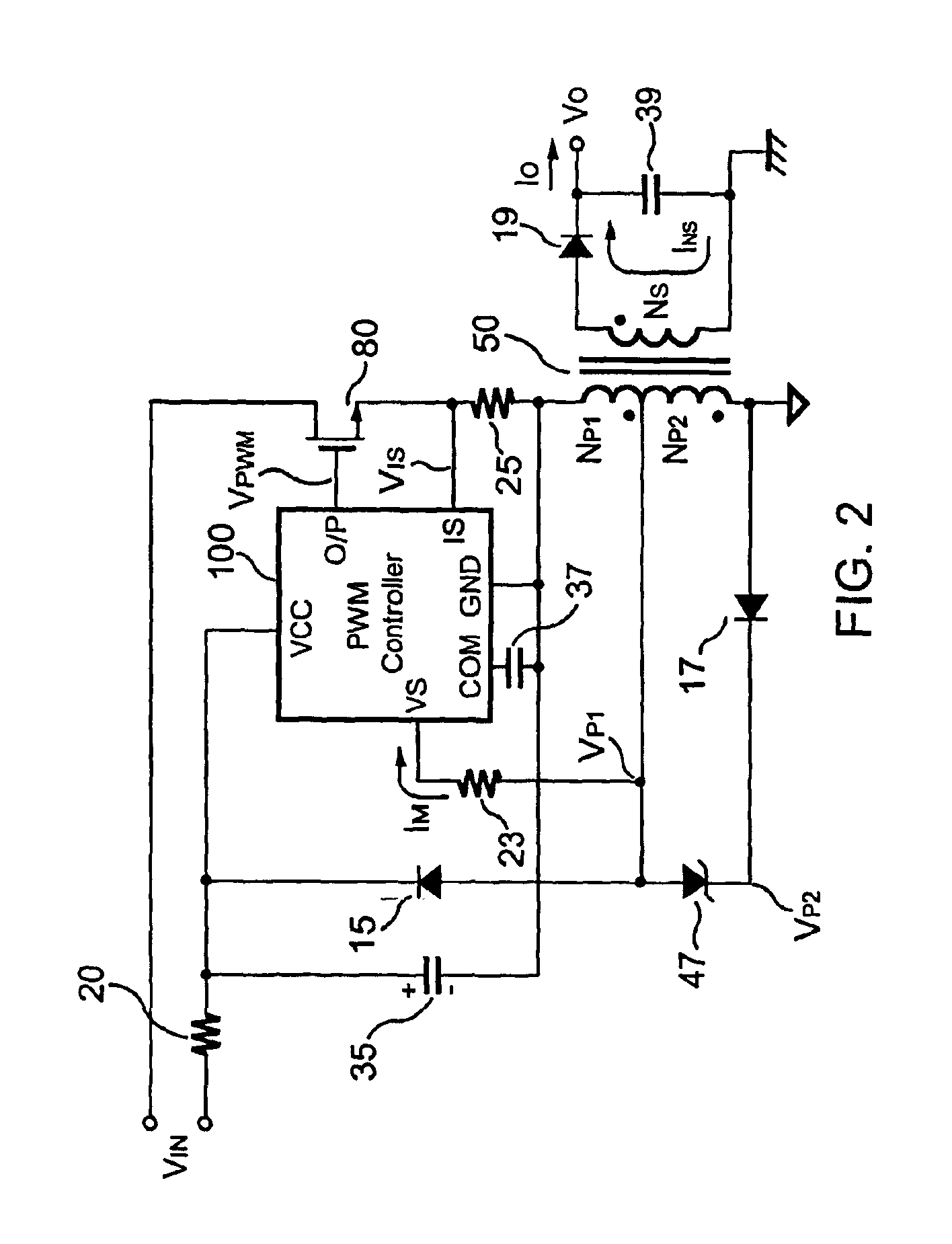
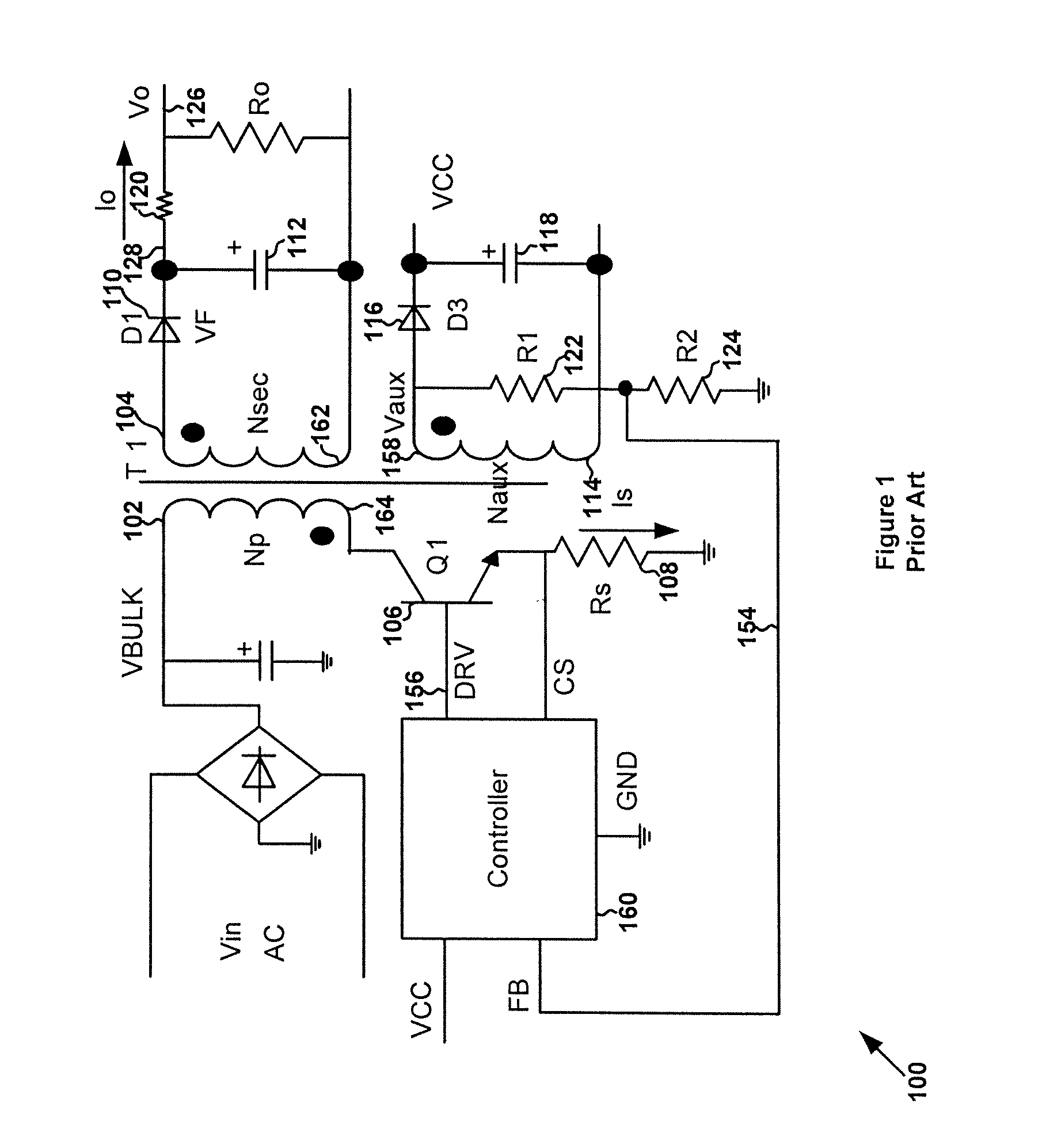
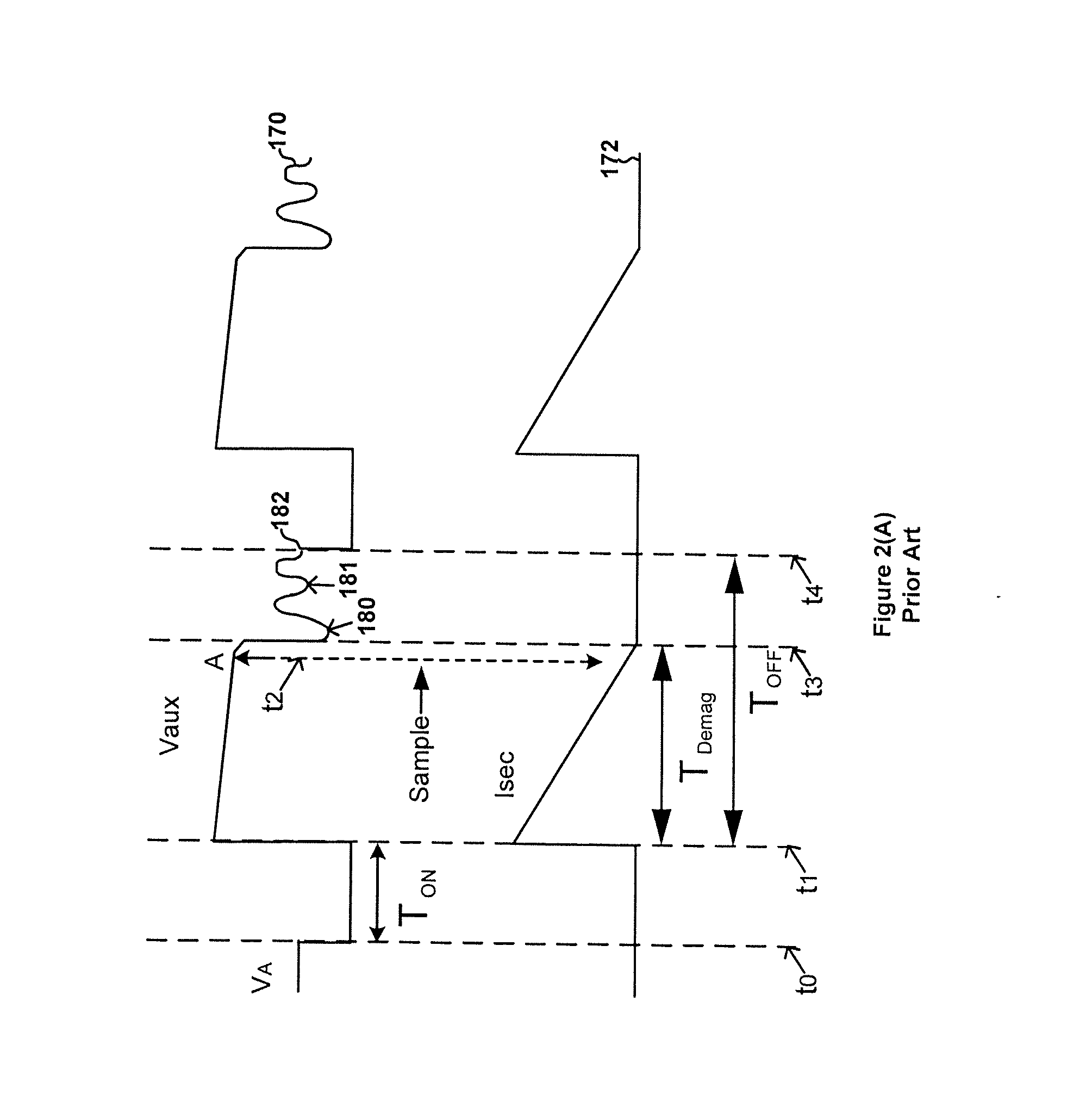
Primary-side controlled flyback power converter
InactiveUS20050024898A1Save power costSmall sizeEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionTransformerSwitching frequency
The present invention provides a primary-side flyback power converter that supplies a constant voltage output and a constant current output. To generate a well-regulated output voltage under varying load conditions, a PWM controller is included in the power converter in order to generate a PWM signal controlling a switching transistor in response to a flyback voltage sampled from a first primary winding of the power supply transformer. Several improvements are included in this present invention to overcome the disadvantages of prior-art flyback power converters. Firstly, the flyback energy of the first primary winding is used as a DC power source for the PWM controller in order to reduce power consumption. A double sample amplifier samples the flyback voltage just before the transformer current drops to zero. Moreover, an offset current is pulled from a detection input of the double sample amplifier in order to generate a more accurate DC output voltage. The offset current is generated in response to the temperature in order to compensate for temperature-induced voltage fluctuations across the output rectifier. Ultimately, in order to maintain a constant output current, the PWM controller modulates the switching frequency in response to the output voltage.
Owner:FAIRCHILD TAIWAN
Switch voltage-stabilizing circuit and control method thereof
ActiveCN101552560APrevent fallingAvoid audio noiseDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationStored energyElectricity
The invention discloses a switch voltage-stabilizing circuit which can regulate switching frequency as well as current peak, has high efficiency and has no audio-frequency noise generated in a state of light load, and method thereof. The switch voltage-stabilizing circuit comprises an energy storage component capable of storing energy; a switch electrically coupled to the energy storage component, wherein the energy storage component can store energy when the switch is on, and the energy stored in the energy storage component is transmitted to a load when the switch is off; a control circuit electrically coupled to the switch, wherein the control circuit compares current flowing through the switch with a current threshold, when the current flowing through the switch is more than the current threshold, the switch is off, and the control circuit determines on and off time of the switch according to the load of the switch voltage-stabilizing circuit, when the load becomes big, the on and off time of the switch is reduced, and when the load becomes small, the on and off time of the switch is increased. The current threshold is constant when the circuit has no light load and becomes low with the load reduced when the circuit has light load.
Owner:CHENGDU MONOLITHIC POWER SYST
Current resonant dc-dc converter of multi-output type
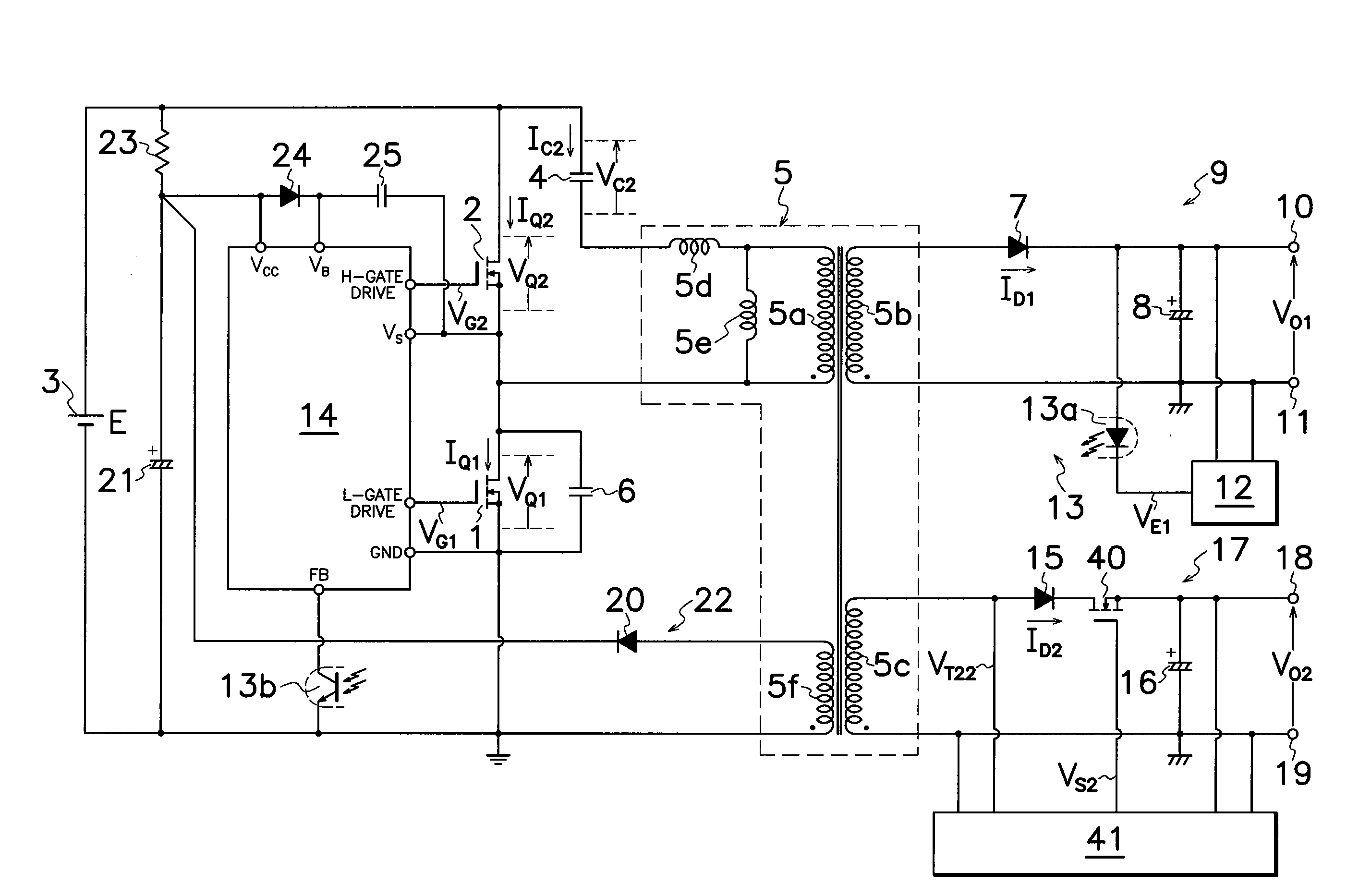
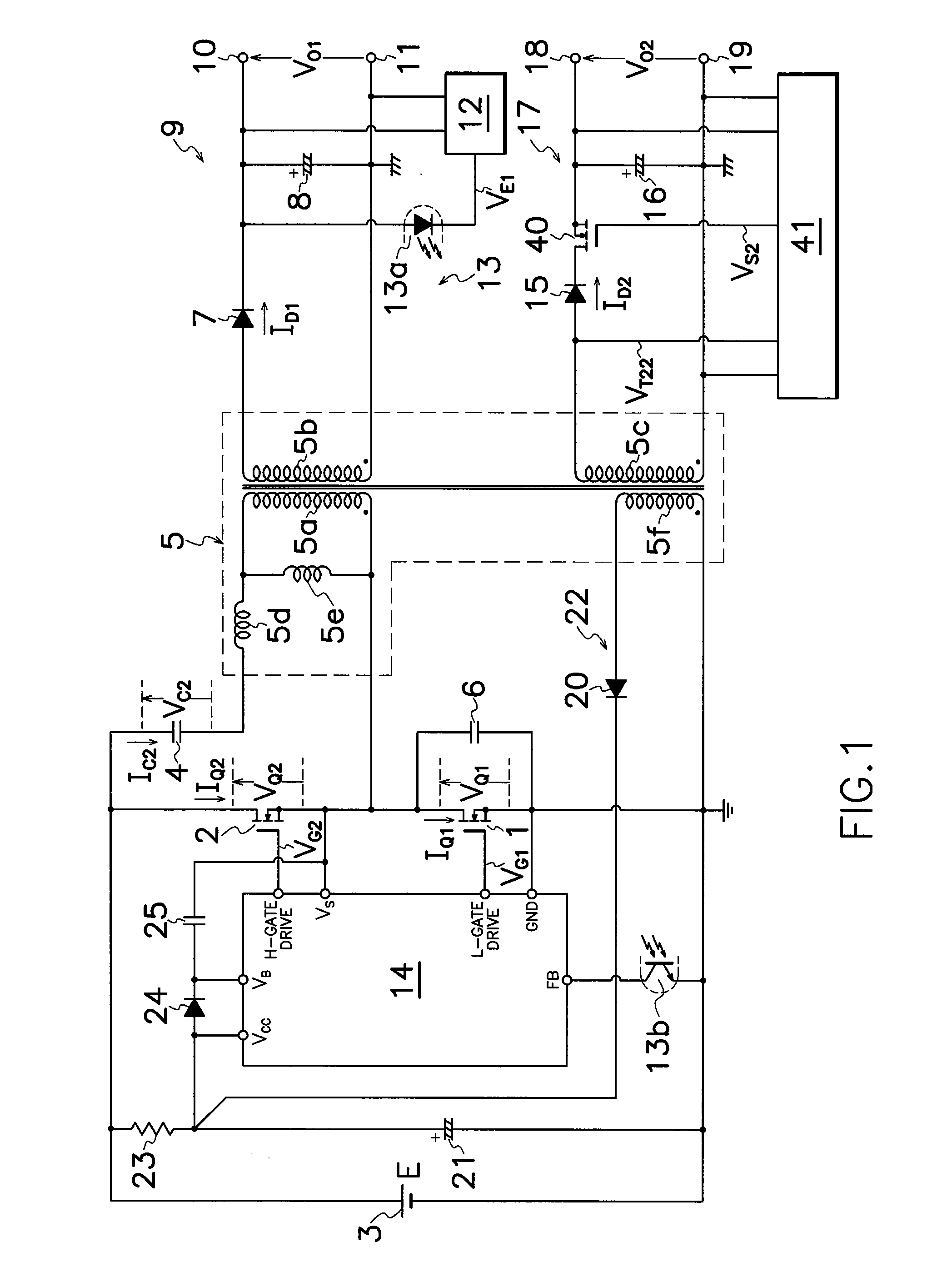
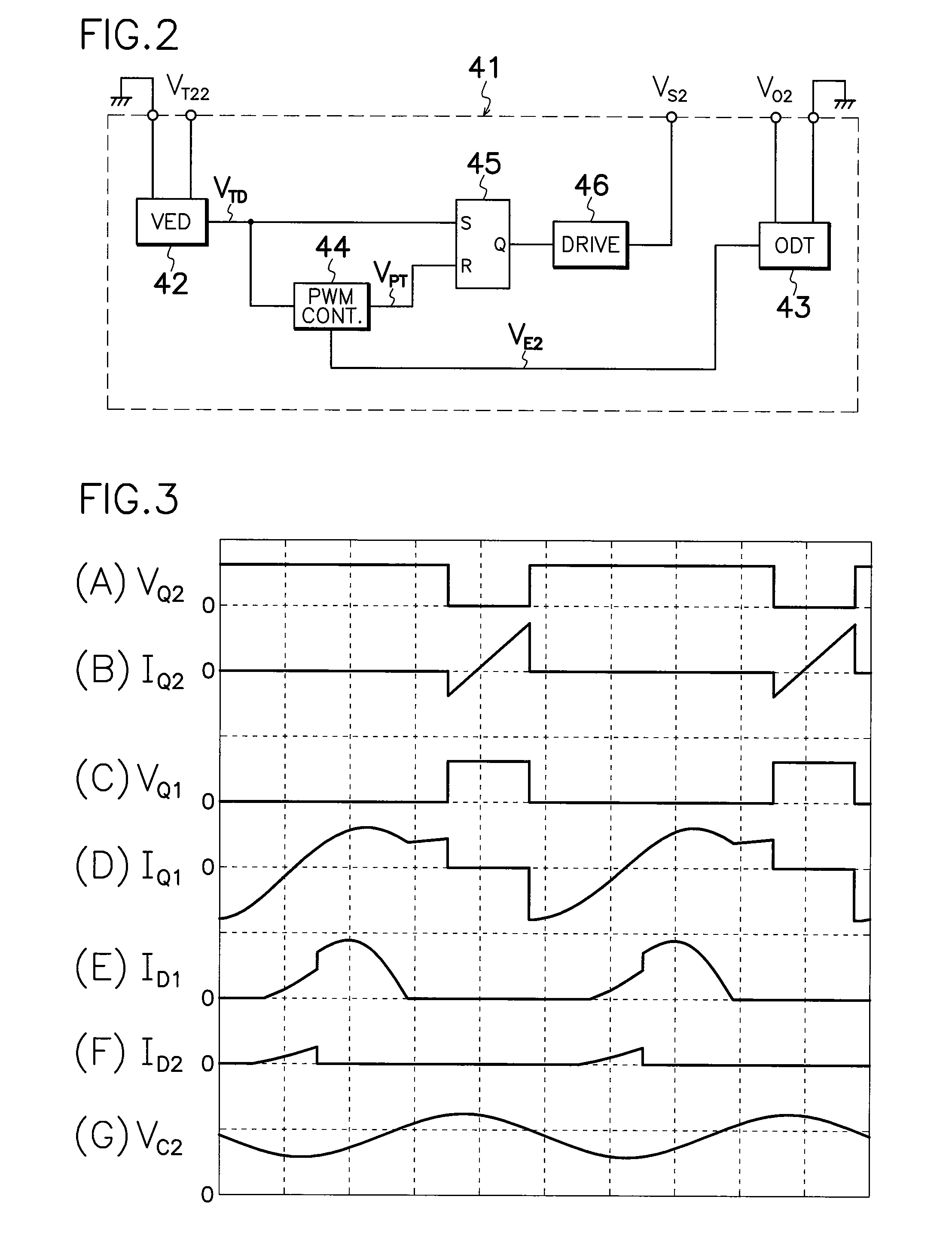
InactiveUS20090251925A1Extended service lifeImprove power conversion efficiencyAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionDc dc converterTransformer
A current resonant DC-DC converter of multi-output type is provided which comprises an output-regulatory MOS-FET 40 connected between a secondary winding 5c of a transformer 5 and a smoothing capacitor 16 in a second rectifying smoother 17, and an output control circuit 41 for controlling the on-off operation of output-regulatory MOS-FET 40 based on voltage VO2 from smoothing capacitor 16 in second rectifying smoother 17. By turning the on-off operation of output-regulatory MOS-FET 40 in synchronization with switching frequency of first or second MOS-FETs 1, 2, an ideal cross regulation among respective DC outputs can be obtained, providing the inexpensive converter with simple circuit alteration capable of producing highly stable DC outputs with high power conversion efficiency, high accuracy and less power conversion loss.
Owner:SANKEN ELECTRIC CO LTD
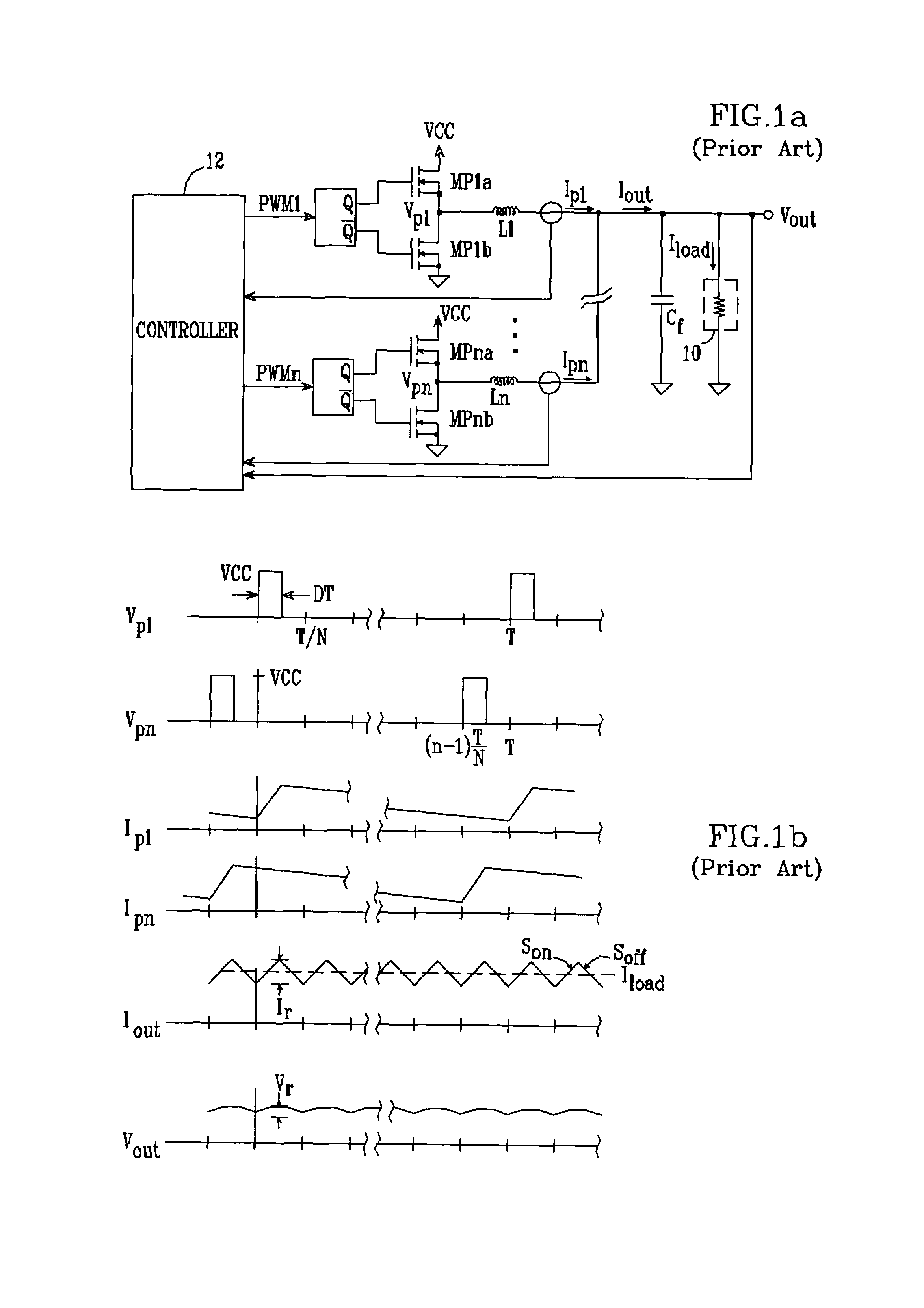
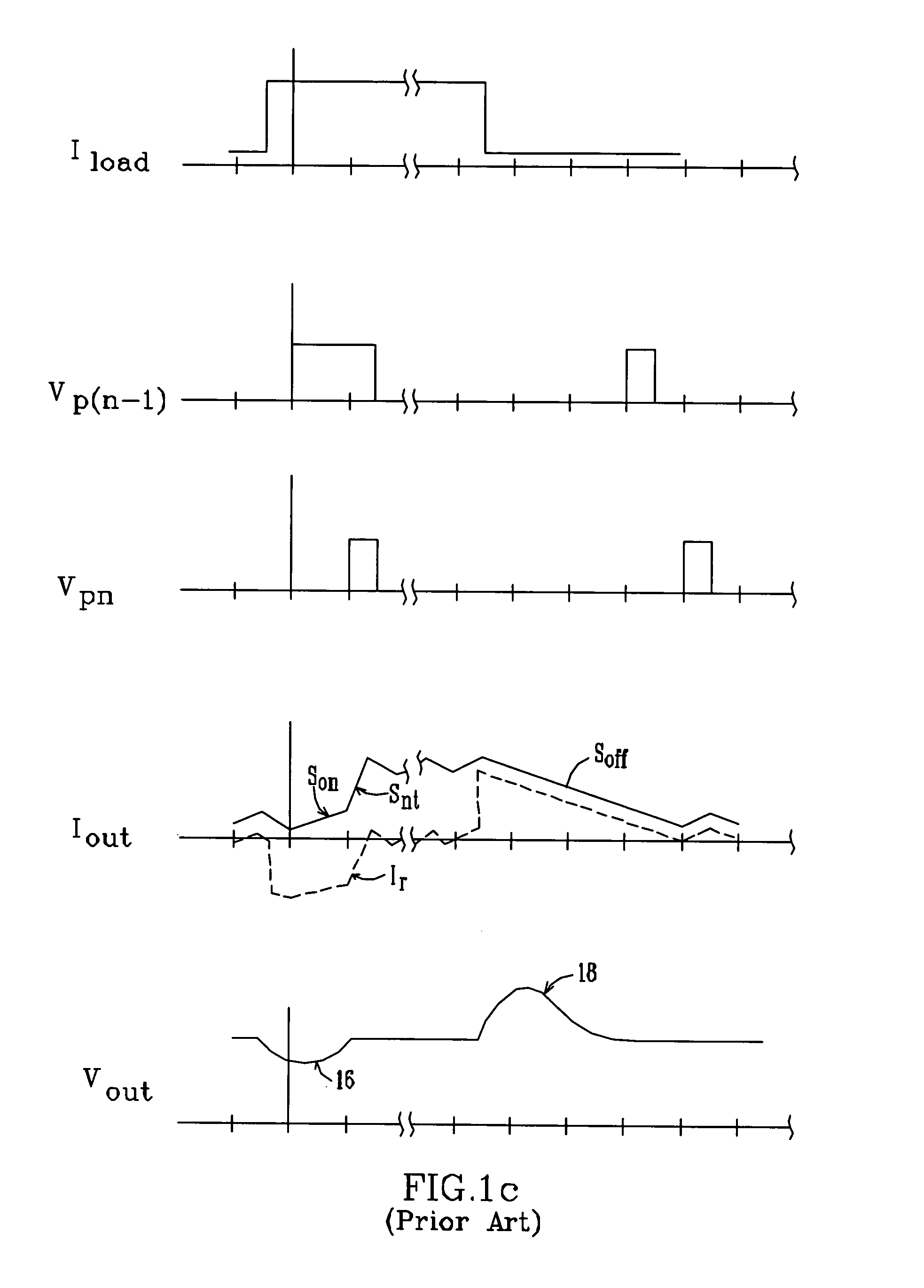
Multiple-phase DC-DC converter topology
ActiveUS6943535B1Improve responseIncrease speedDc-dc conversionAc network voltage adjustmentPhase currentsDc dc converter
A multiple-phase DC—DC converter adds at least one additional phase to an N-phase DC—DC converter to improve the converter's response to changes in load. In one embodiment, an additional phase operates at a switching frequency greater than that of the N phases, to generate a current which is added to the N phase currents to improve the converter's response to changes in load. In another embodiment, an additional phase is configured to improve the converter's response to a load release. Here, the additional phase is kept off during load increase and steady-state conditions. However, when a load release occurs, the additional phase is turned on and acts to extract current from the converter's output terminal while the N phase currents slowly fall, to reduce the magnitude of output voltage overshoot that occurs on load release.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com