Patents
Literature
69results about How to "Minimize switching losses" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
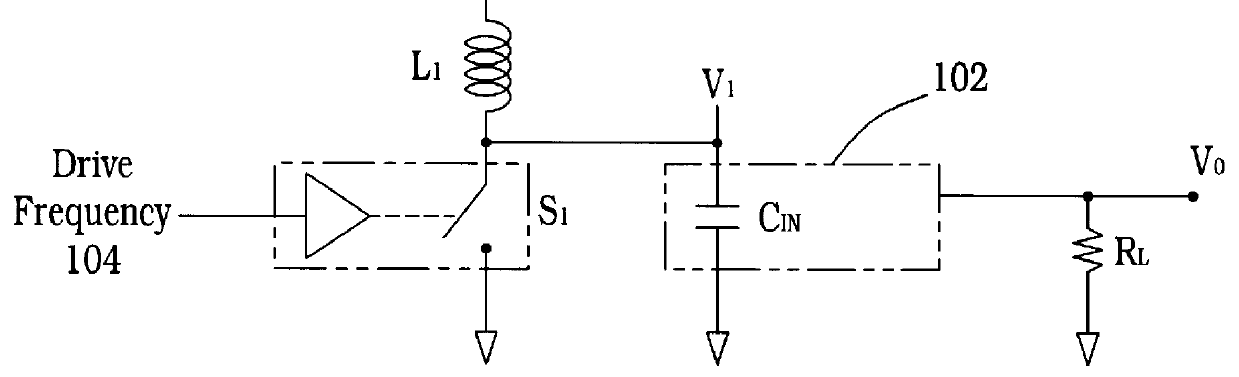
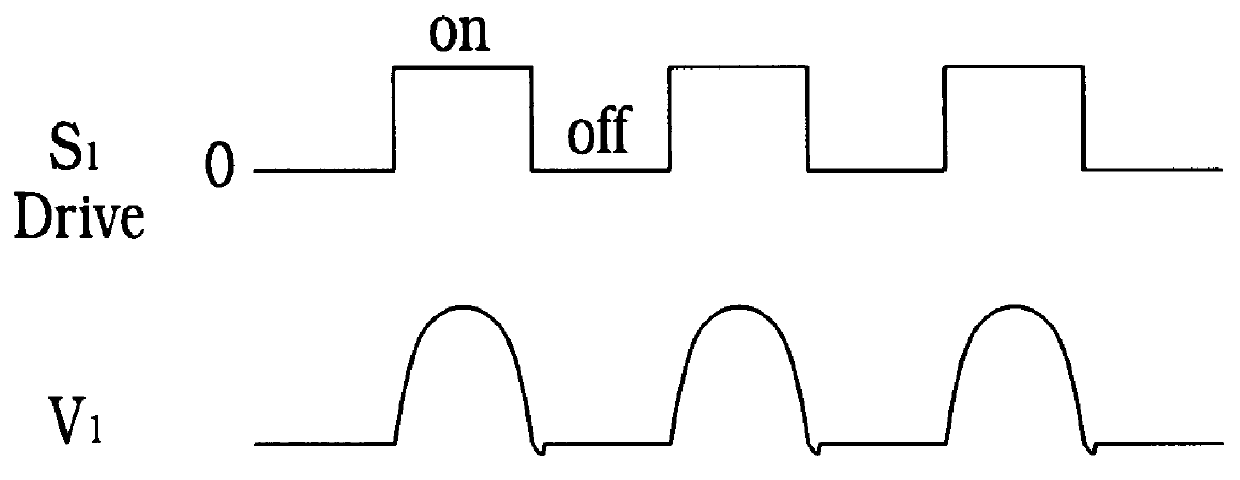
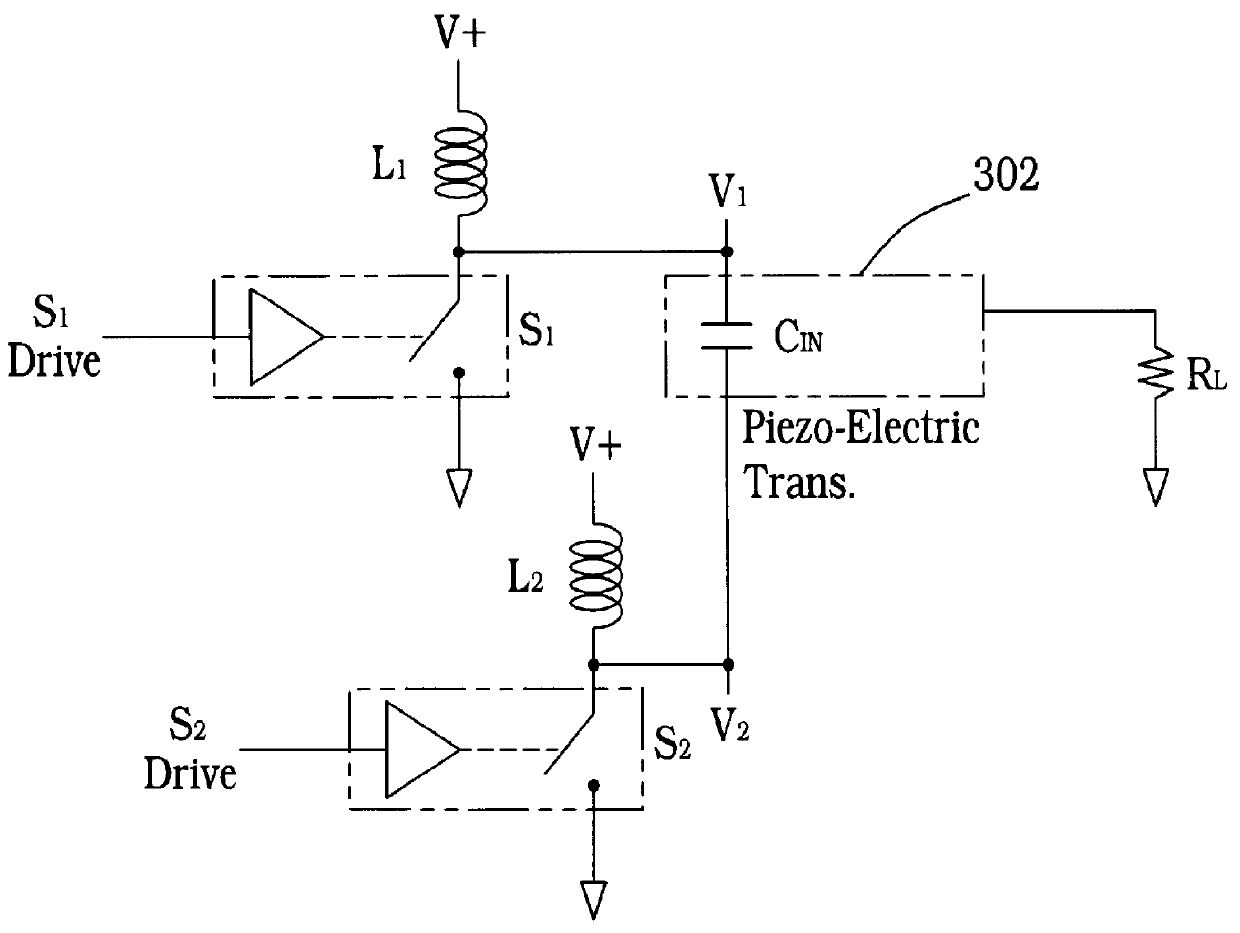
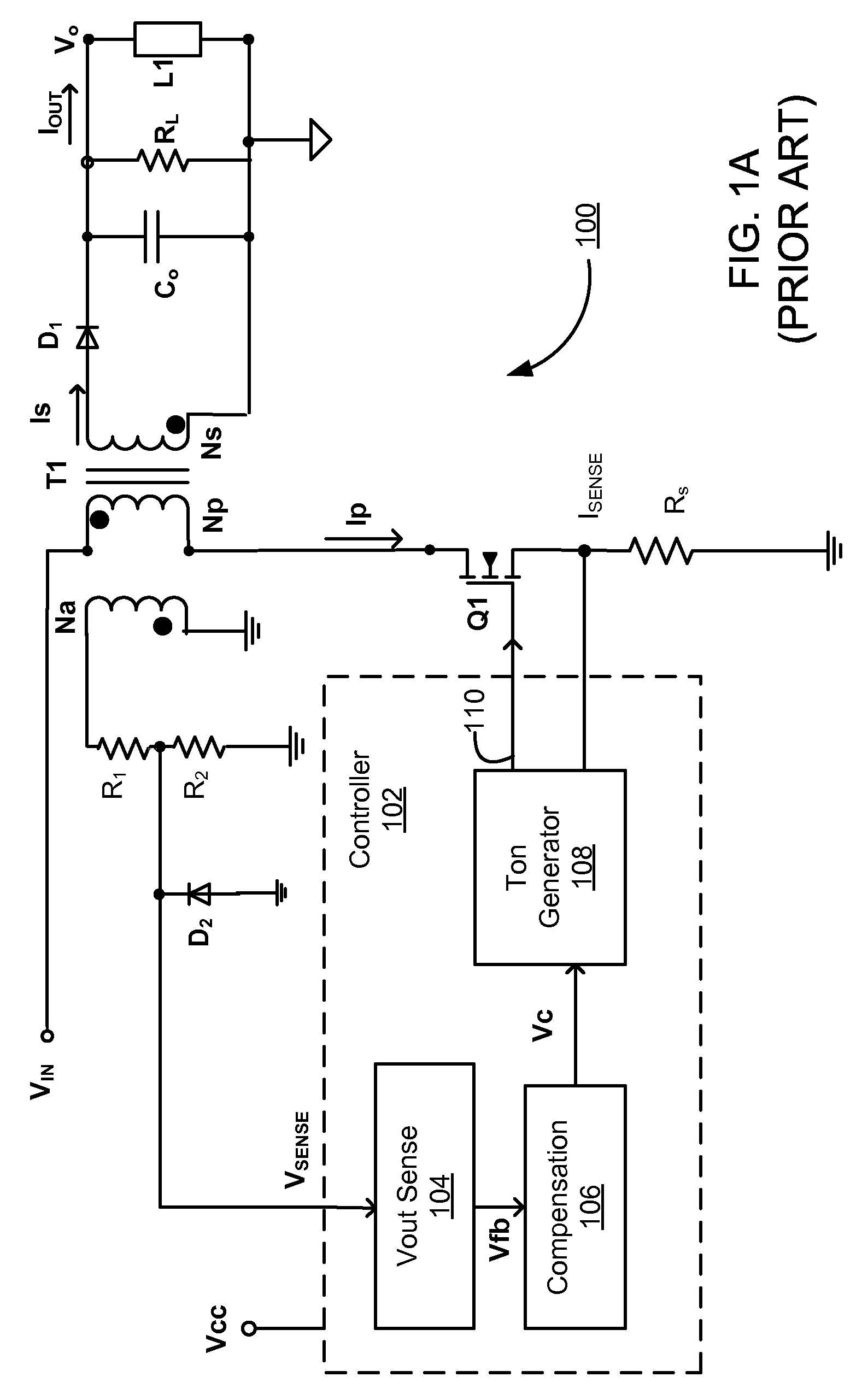
Pulse frequency modulation drive circuit for piezoelectric transformer
InactiveUS6016052AInhibits "mode-hopping" or operationIncreases effective step-up ratioPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesStatic indicating devicesInductorOut of phase
A pulse frequency modulation drive circuit (1114) for a piezoelectric transformer (1102) is provided. Circuit (1114) includes a piezoelectric transformer (1102) having a resonant frequency and an input and an output section. A frequency feedback network connected to the piezoelectric transformer (1102) and an output level sense (1112) connected to the piezoelectric transformer (1102) is also provided. A drive circuit (1114) has a first switch (S1) and a third switch (S3) having a capacitance (1118) therebetween. A second switch (S2) and a fourth switch (S4) connect a supply voltage (VIN) to each of a pair of inductors (L1 and L2) and the second switch (S2) and the fourth switch (S4) are driven 180 DEG out of phase at the resonant frequency of the piezoelectric transformer (1102).
Owner:CTS CORP ELKHART
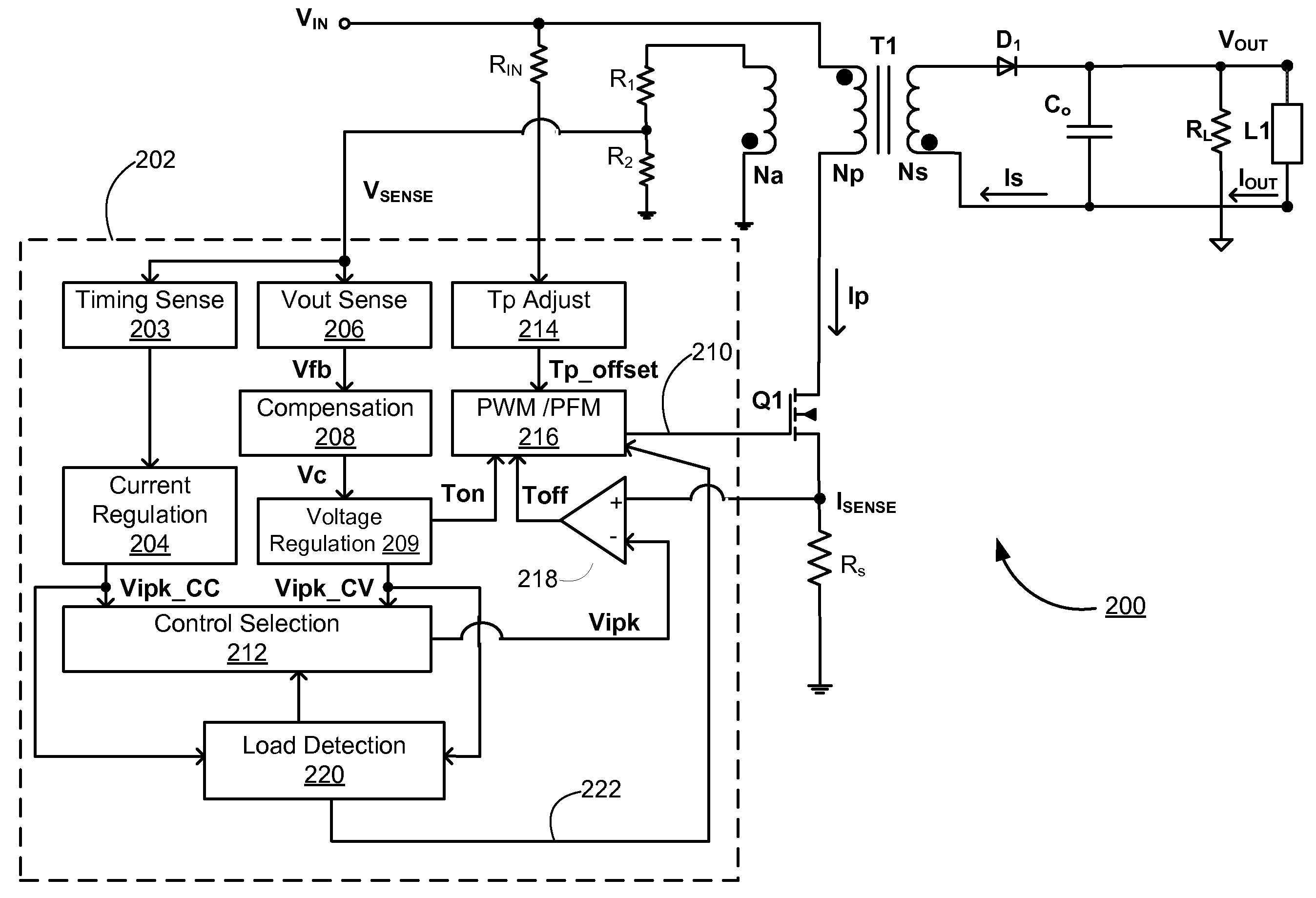
Detecting Light Load Conditions and Improving Light Load Efficiency in a Switching Power Converter
ActiveUS20100208500A1Minimize switching lossesReduce switching frequencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionLow loadVoltage regulation
A switching power converter detects low load conditions based on the ratio of a first peak current value for peak current switching in constant voltage regulation mode to a second peak current value for peak current switching in constant current regulation mode. The power supply load is considered to have a low load if the ratio is lower than a predetermined threshold. Once a low load condition is detected, the switching frequency of the switching power converter is reduced to a level that minimizes switching loss in the power converter. In addition, the switching power converter also adjusts the switching frequency according to the sensed input line voltage. An offset is added to the switching period to reduce the switching frequency of the switching power converter, as the input line voltage is increased.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR INC
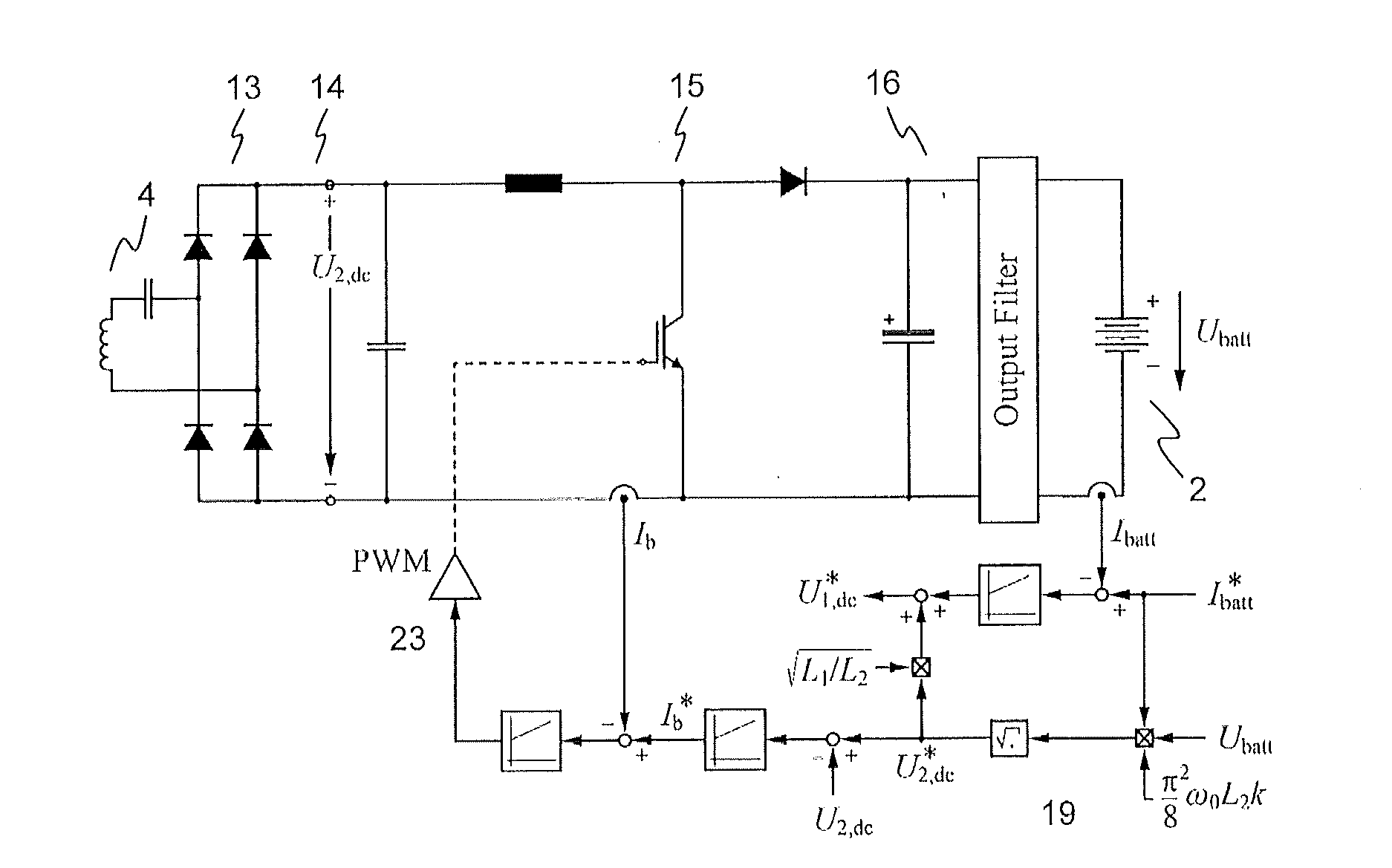
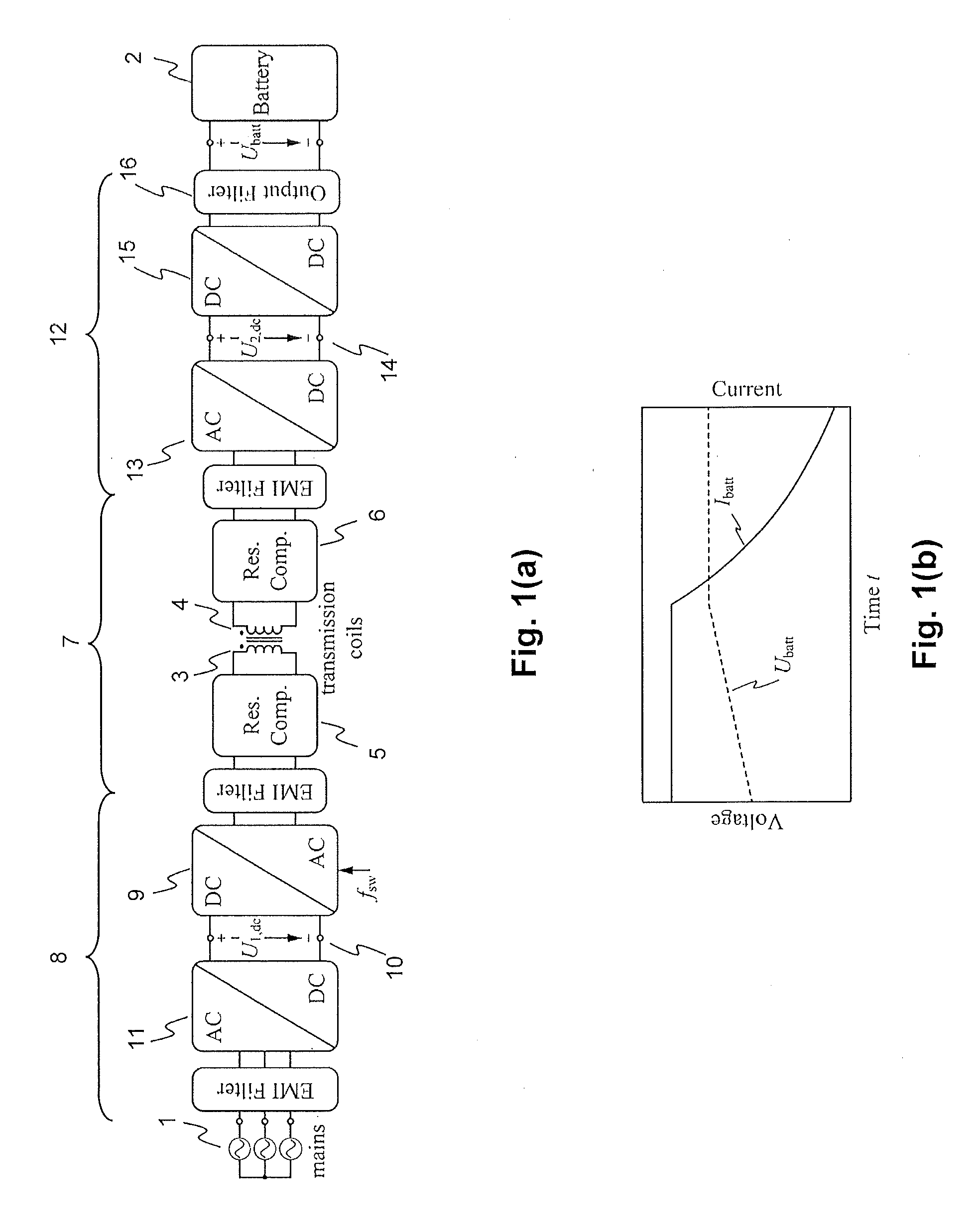
Inductive power transfer system and method for operating an inductive power transfer system
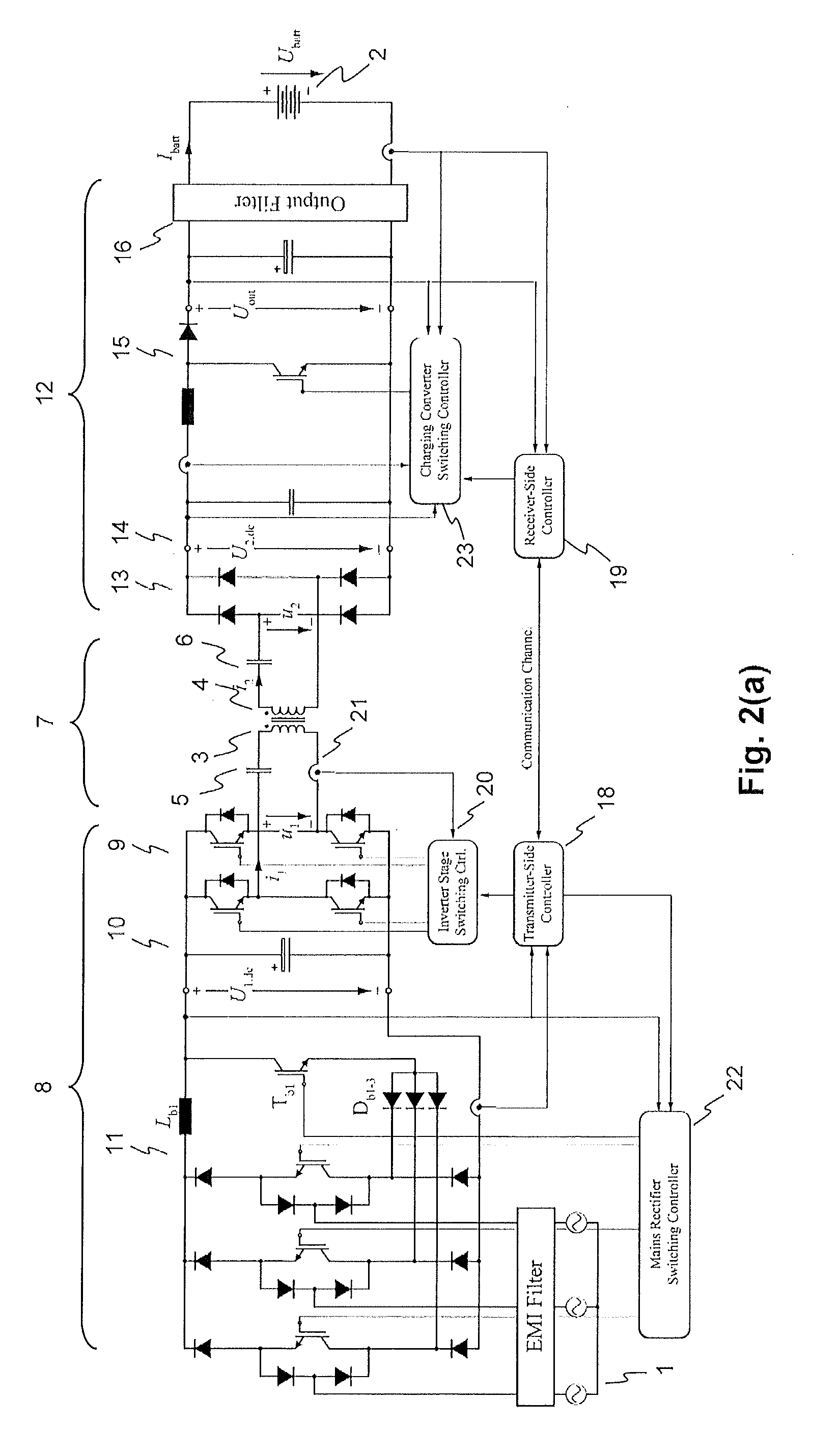
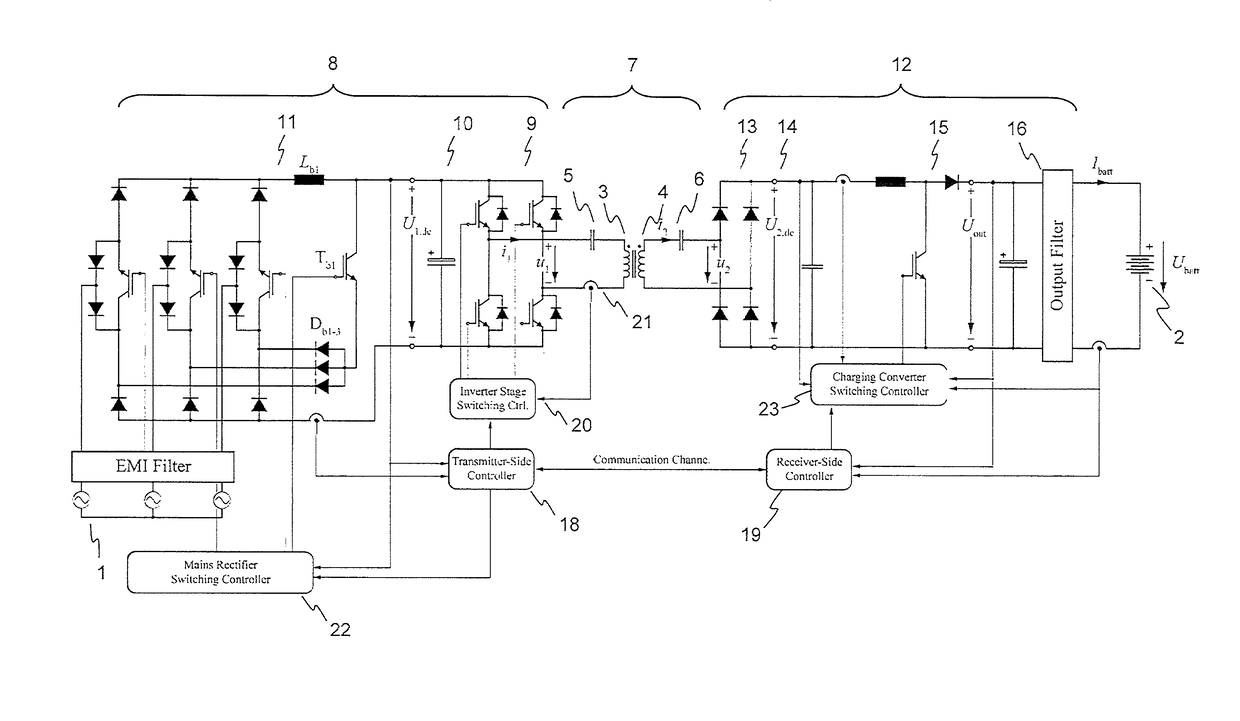
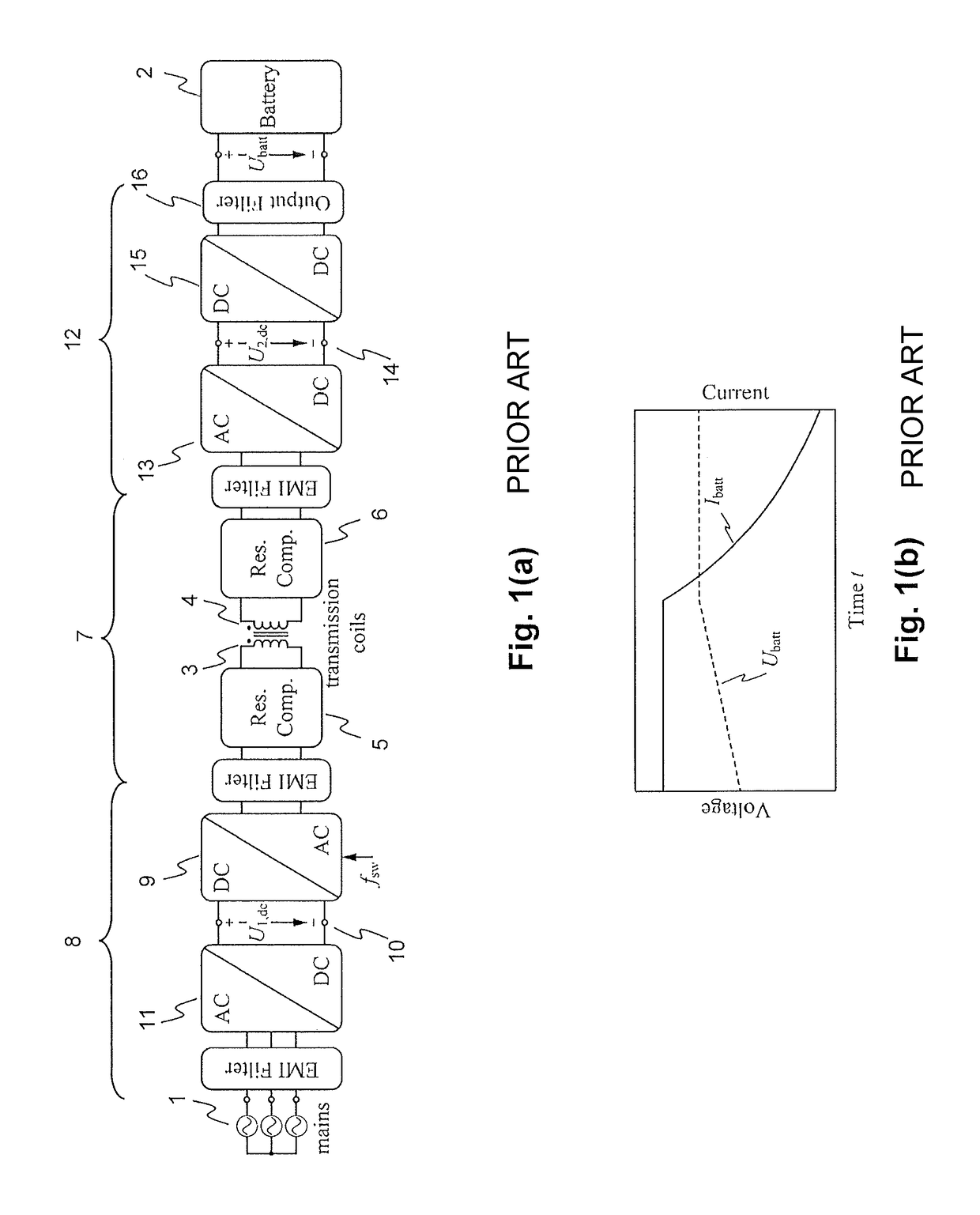
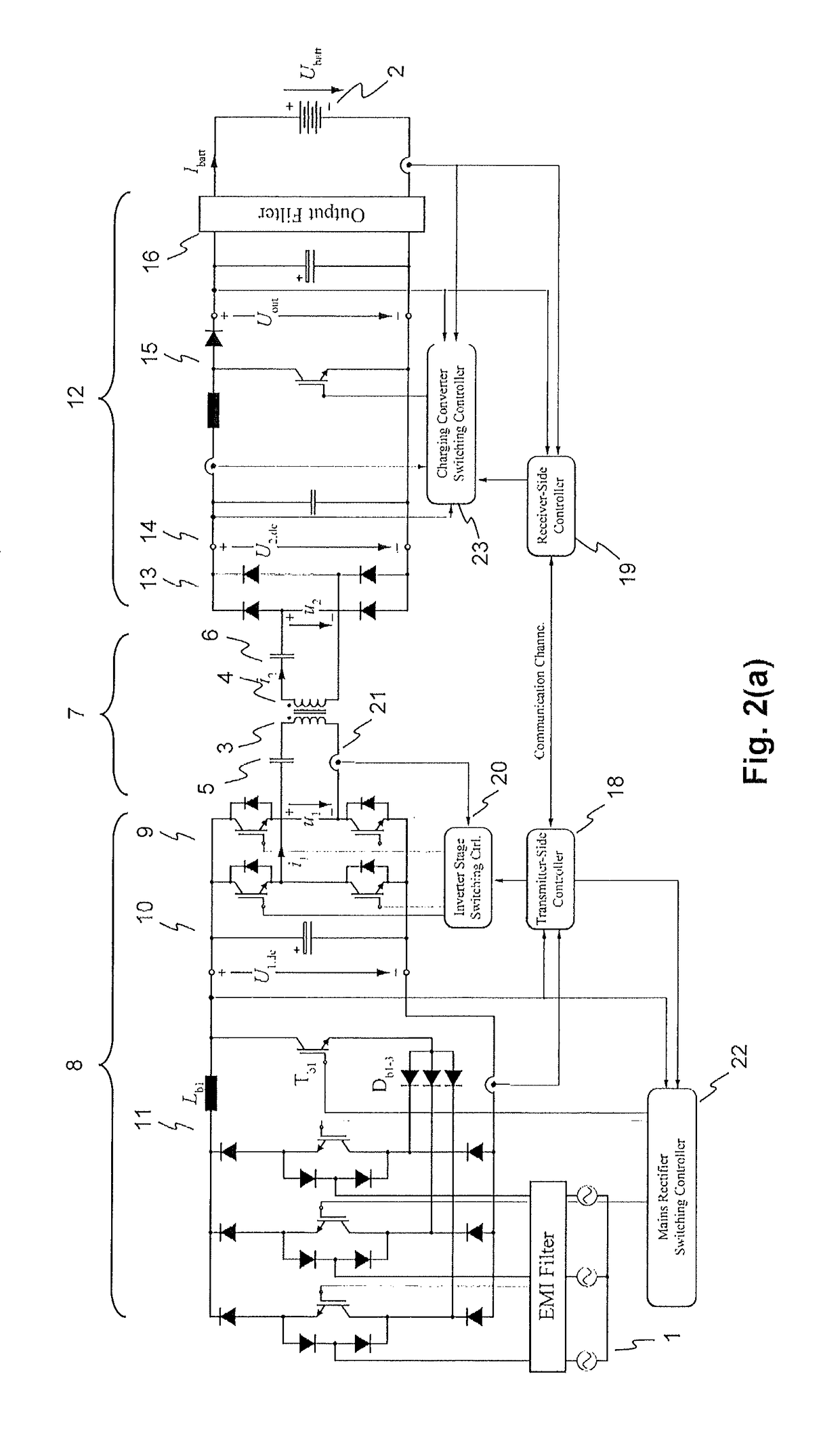
InactiveUS20150280455A1Minimize switching lossesBatteries circuit arrangementsCharging stationsTransmitter coilEngineering
An exemplary inductive power transfer system having a transmitter coil and a receiver coil. A transmitter-side power converter having a mains rectifier stage powering a transmitter-side dc-bus and controlling a transmitter-side dc-bus voltage U1,dc. A transmitter-side inverter stage with a switching frequency fsw supplies the transmitter coil with an alternating current. A receiver-side power converter having a receiver-side rectifier stage that rectifies a voltage induced in the receiver coil and powering a receiver-side dc-bus and a receiver-side charging converter controlling a receiver-side dc-bus voltage U2,dc. Power controllers that determine from a power transfer efficiency of the power transfer, reference values U1,dc*, U2,dc* for the transmitter and receiver side dc-bus voltages. An inverter stage switching controller controls the switching frequency fsw to reduce losses in the transmitter-side inverter stage.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
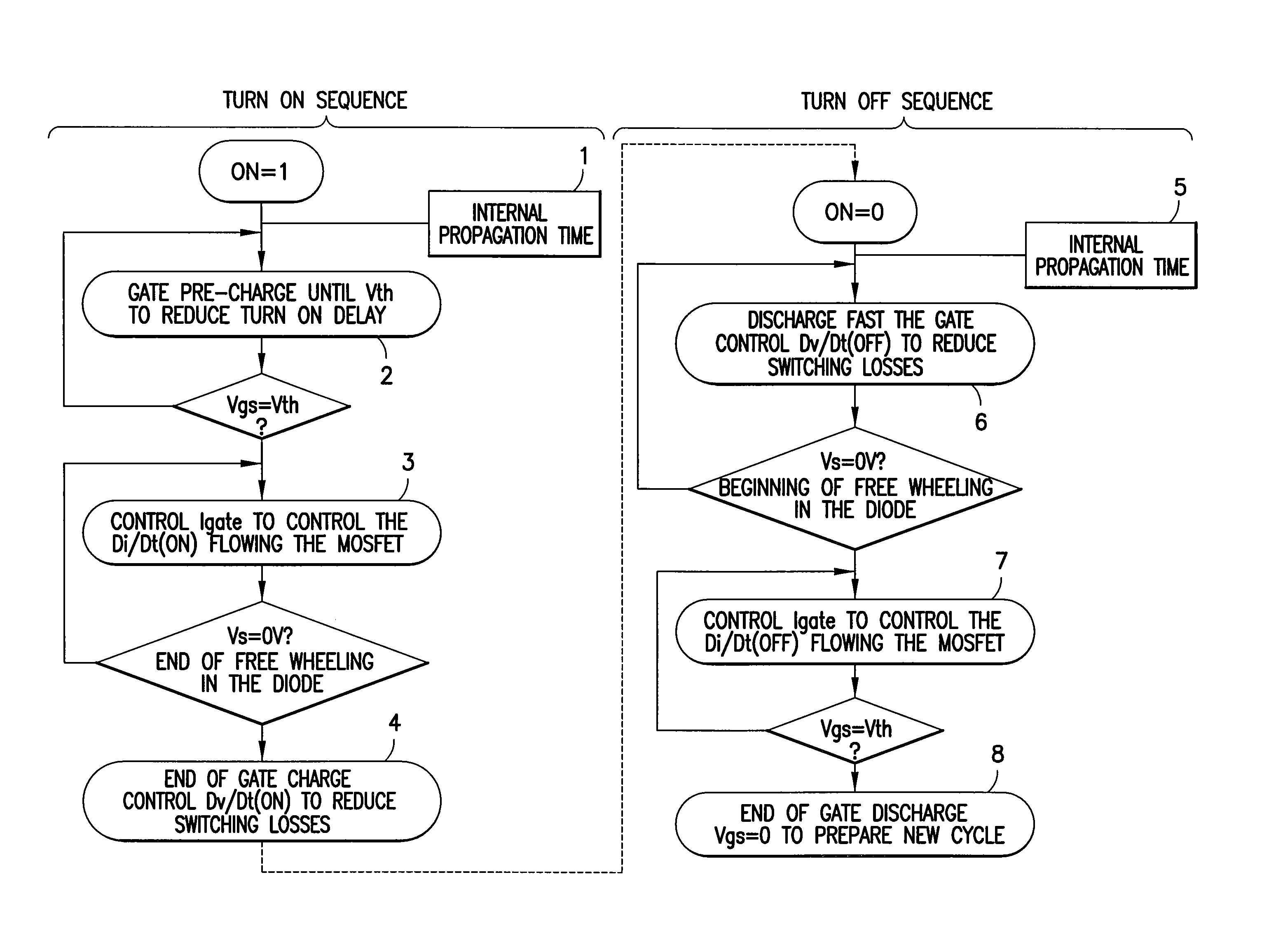
DC brushed motor drive with circuit to reduce di/dt and emi, for mosfet vth detection, voltage source detection, and overpower protection
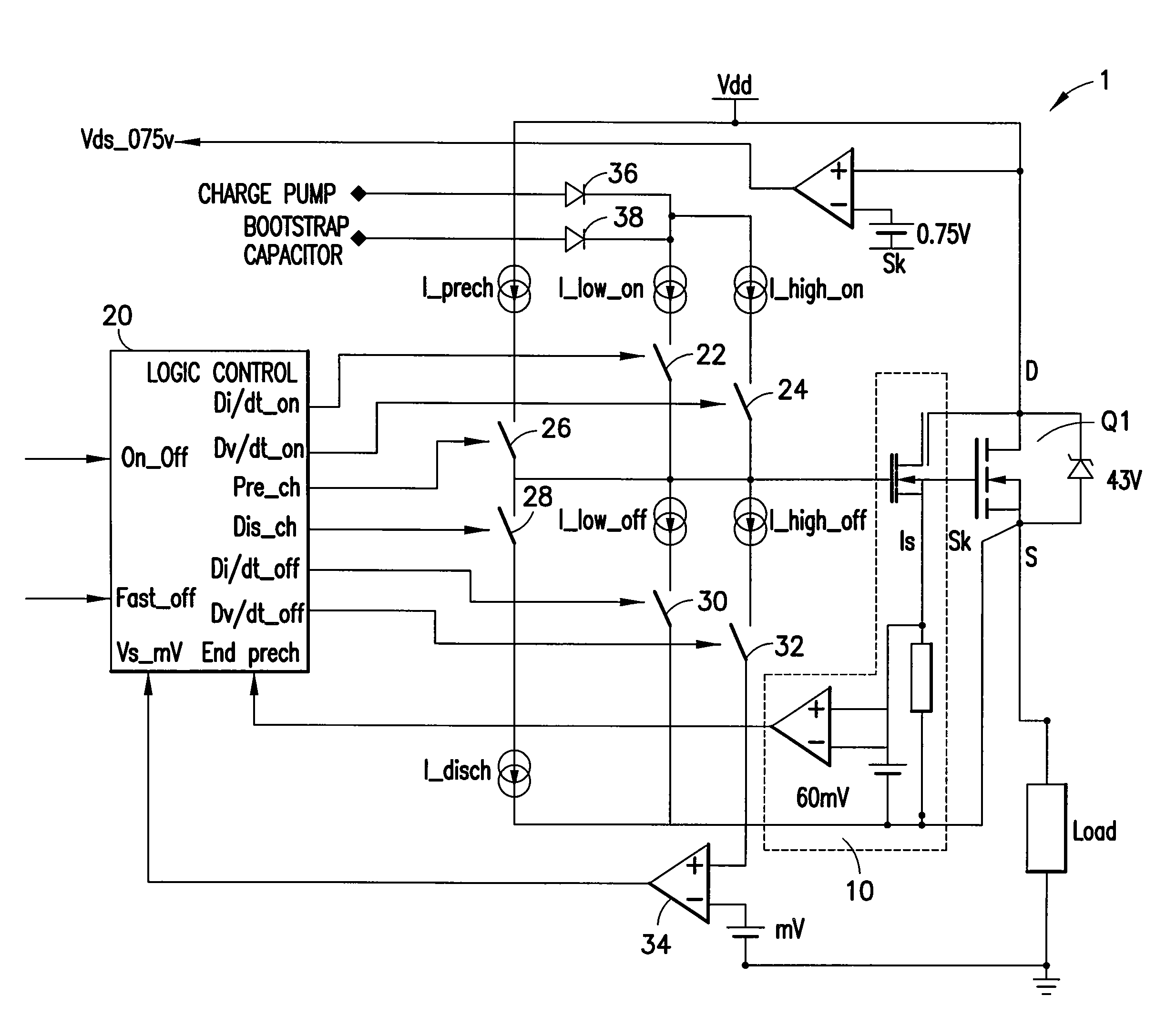
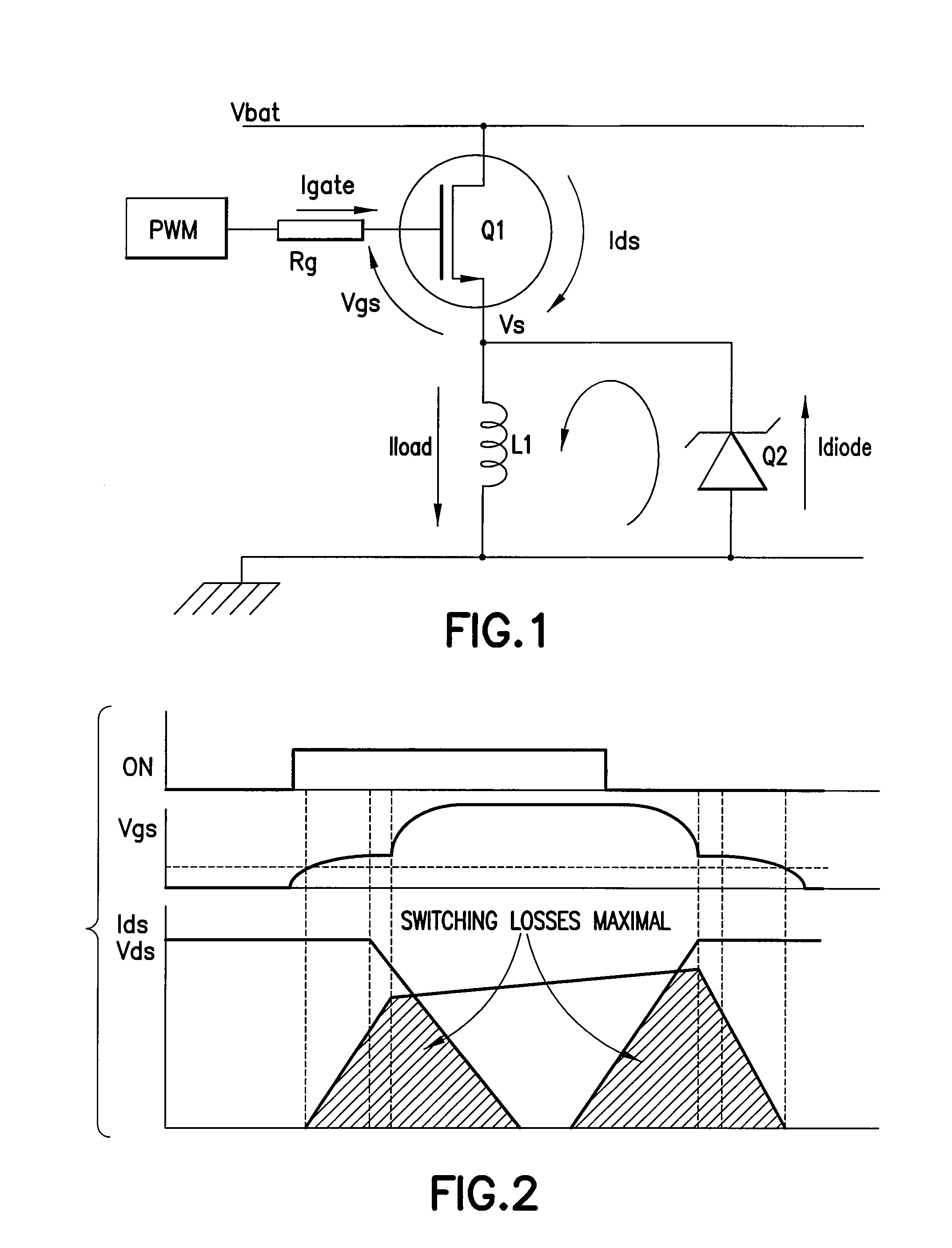
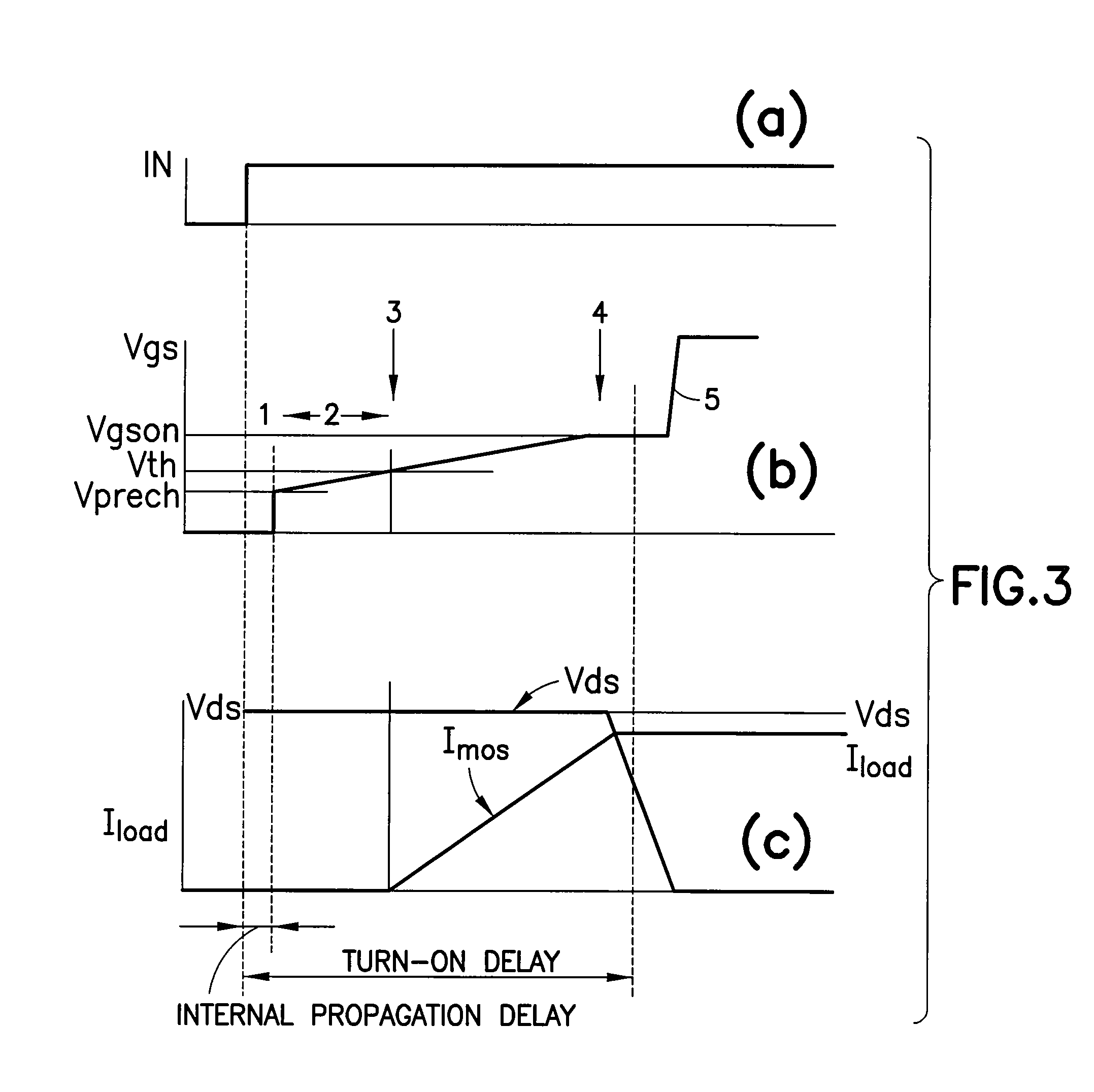
ActiveUS20090027096A1Reduce electromagnetic interferenceMinimize switching lossesTransistorElectronic switchingMOSFETPulse control
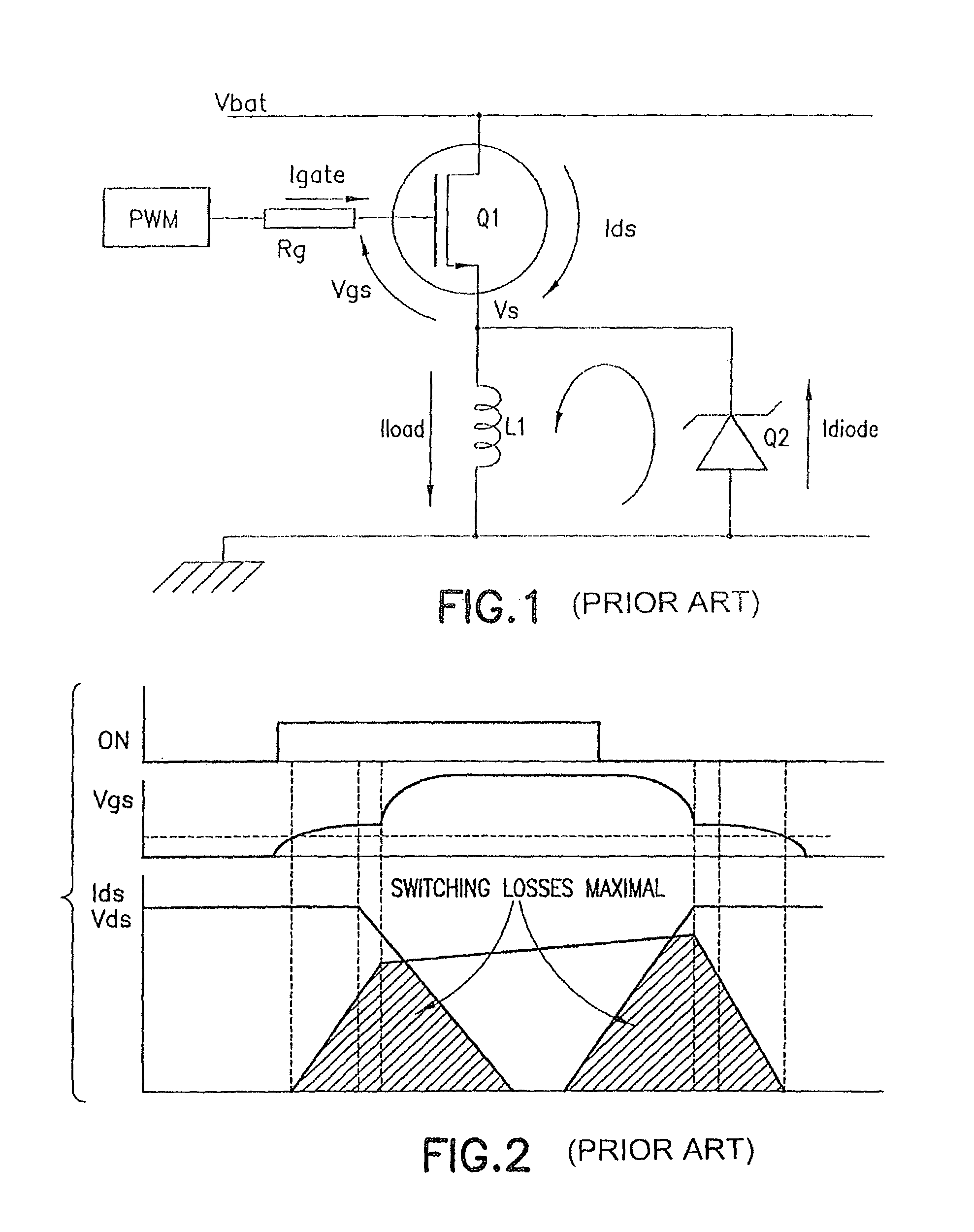
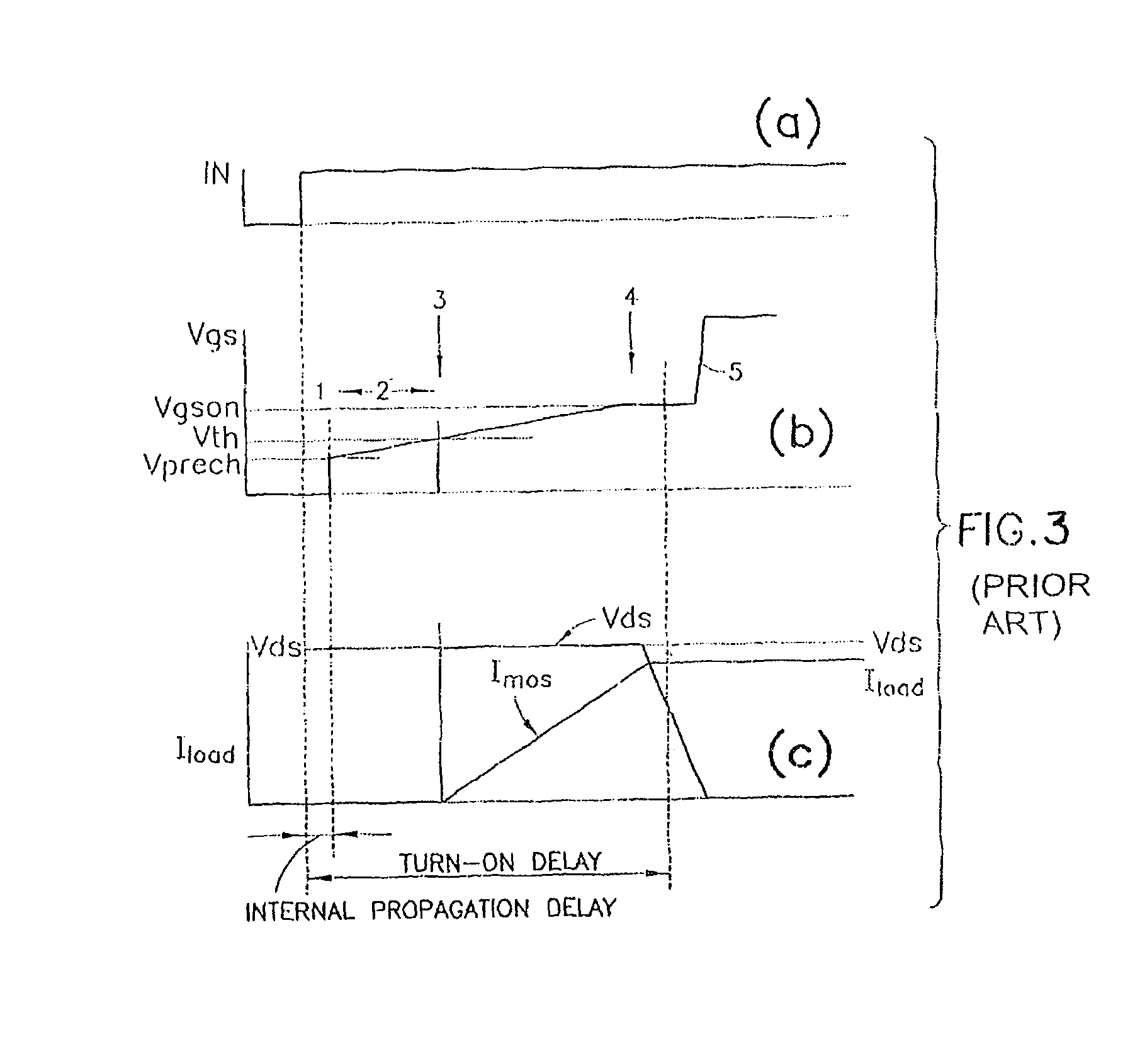
A gate driver for performing gate shaping on a first transistor of having gate, source, and drain terminals, the first transistor being selected from a switching stage of a power switching circuit having high- and low-side transistors series connected at a switching node for driving a load. The gate driver includes the following steps: upon receipt of an ON pulse pre-charging the gate terminal until gate to source terminal voltage equals Vth, controlling the di / dt(ON) flowing in the first transistor while free wheeling current is flowing in a second transistor of the switching stage, and controlling the dv / dt(ON) of the first transistor while a charge on the gate terminal is present; and upon receipt of an OFF pulse controlling the dv / dt(OFF) of the first transistor until free wheeling current is flowing in the second transistor, and controlling the di / dt(OFF) flowing in the first transistor while the gate to source terminal voltage equals Vth.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
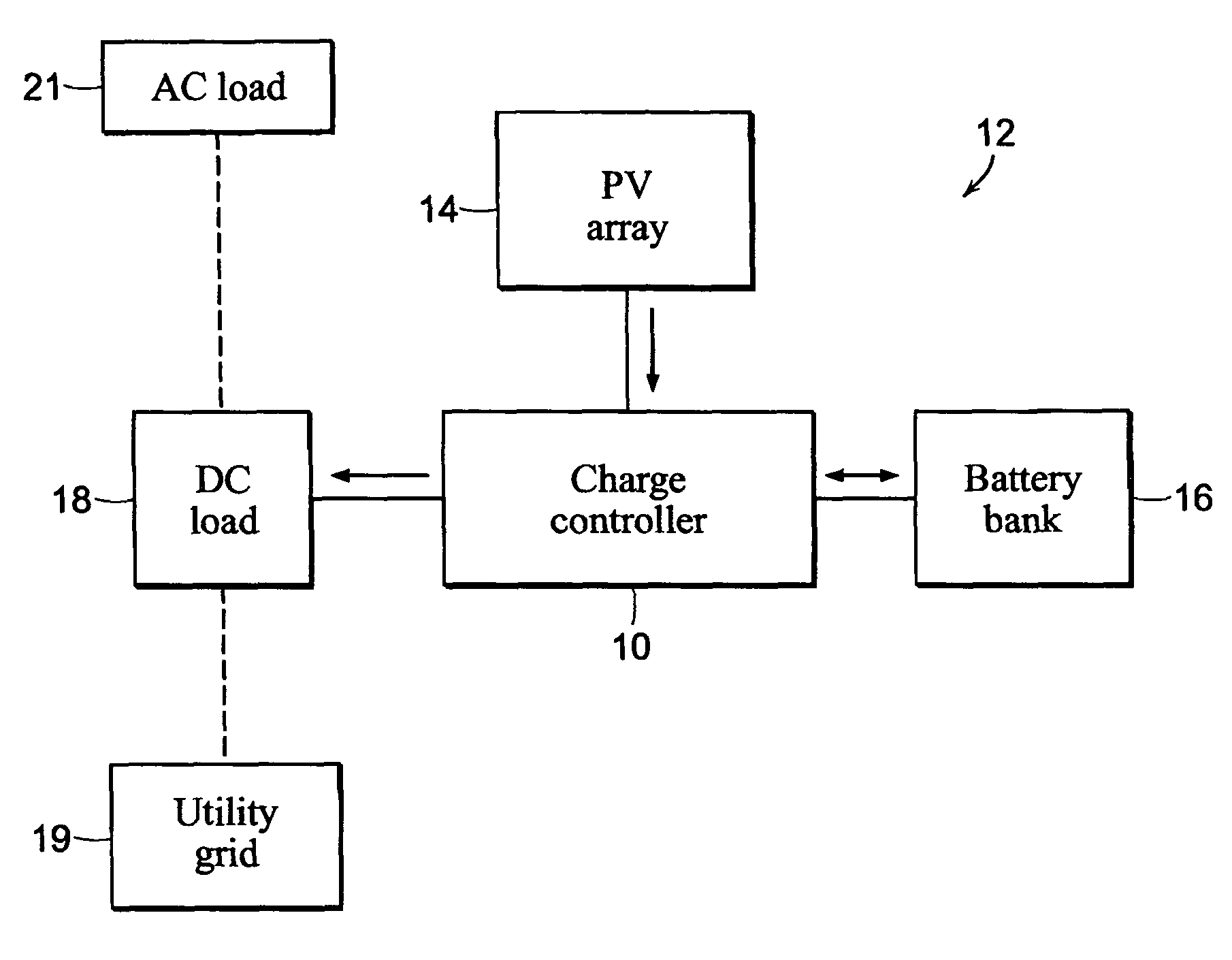
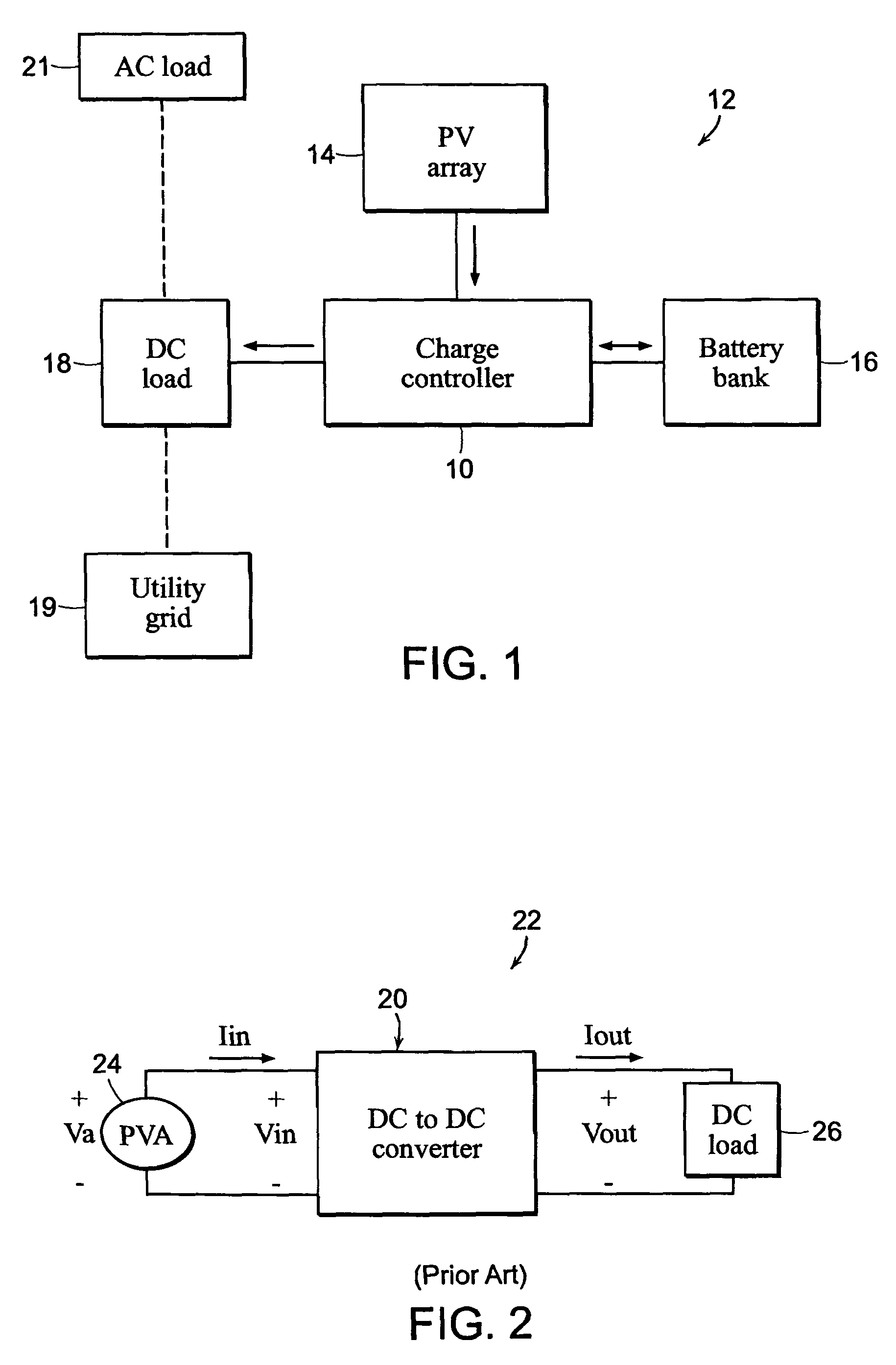
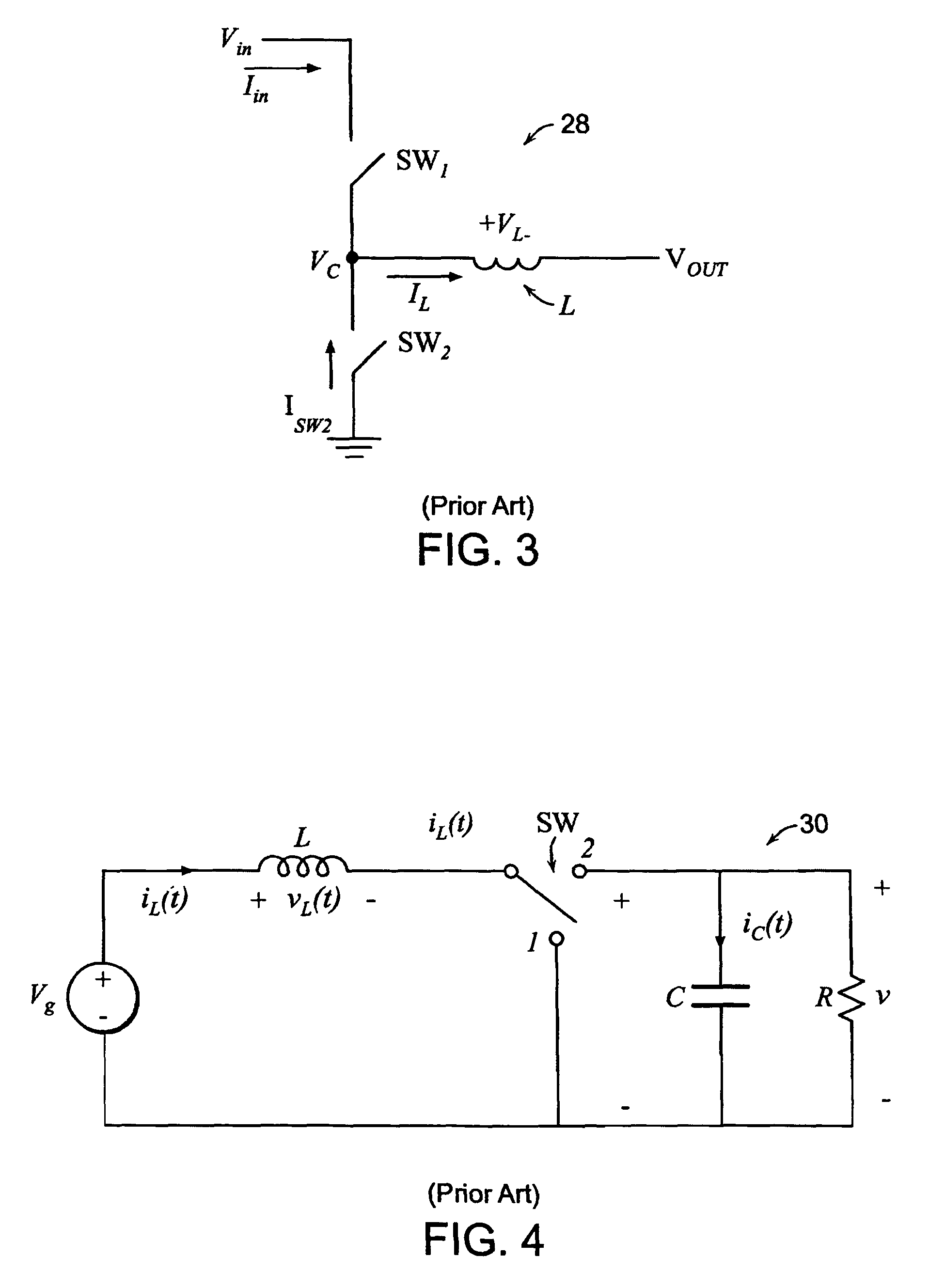
Modulation control scheme for power converters in photovoltaic system charge controllers
ActiveUS8970161B1Maximize efficiencyConduction loss can be minimizedEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionEngineeringMaximum power point tracking
A modulation control scheme for a series-connected dual active bridge (DAB) DC to DC converter in a maximum power point tracking charge controller used in a photovoltaic system controls operation of the converter in a forward direction power flow mode to control charging of a battery bank with electricity produced by the photovoltaic array. The modulation control scheme is also capable of operating the converter in a reverse direction power flow mode to control the flow of electricity from the battery bank to a DC load. The modulation control scheme divides the converter's operating range in each mode into five main cases of minimum root mean square (M-RMS) operating regions and seven main cases of full zero-voltage switching (F-ZVS) operating regions, as well as transition operating regions between adjacent main cases, based on applicable power level and value of voltage differential.
Owner:CUADROS CARLOS
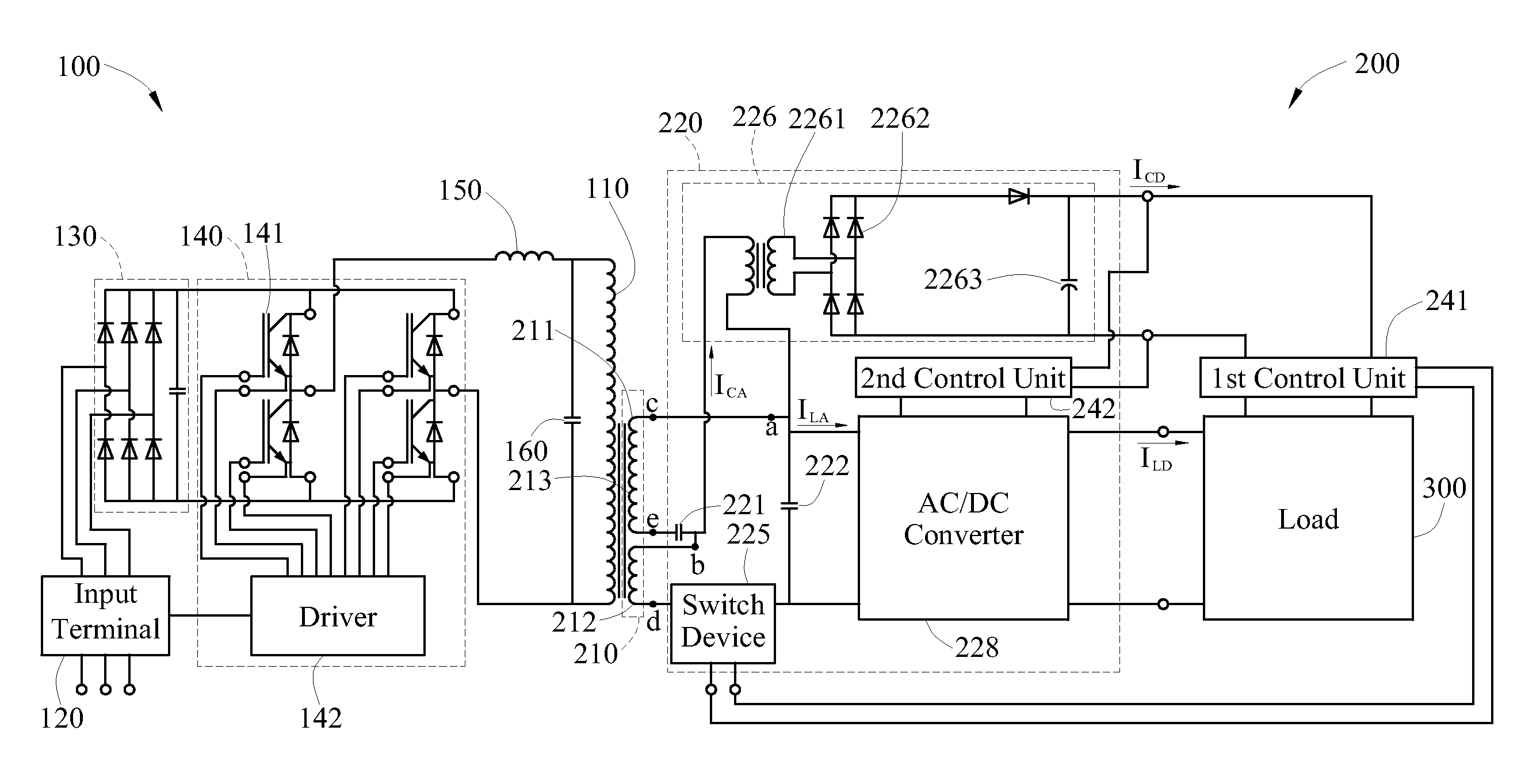
Induction power system
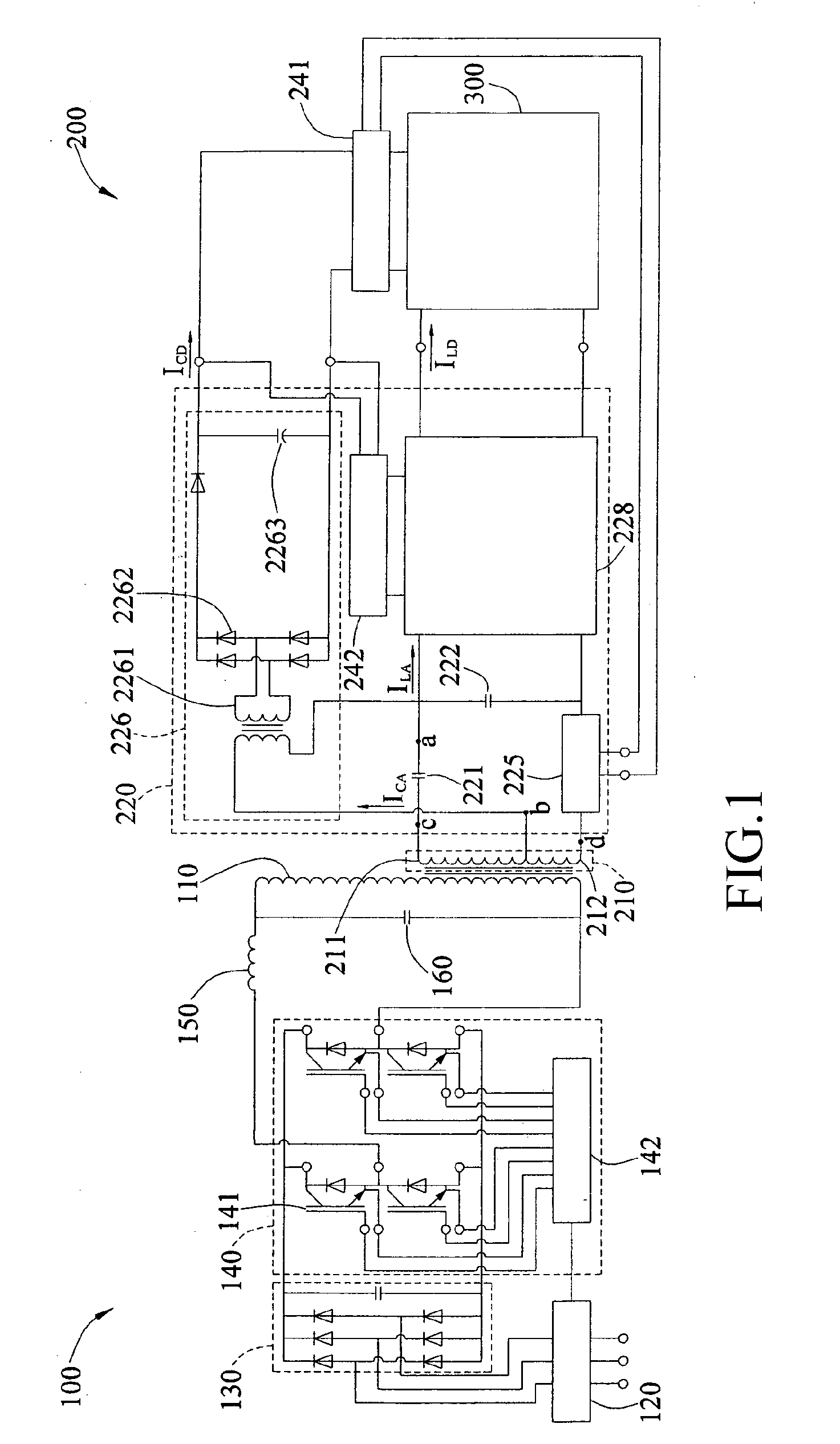
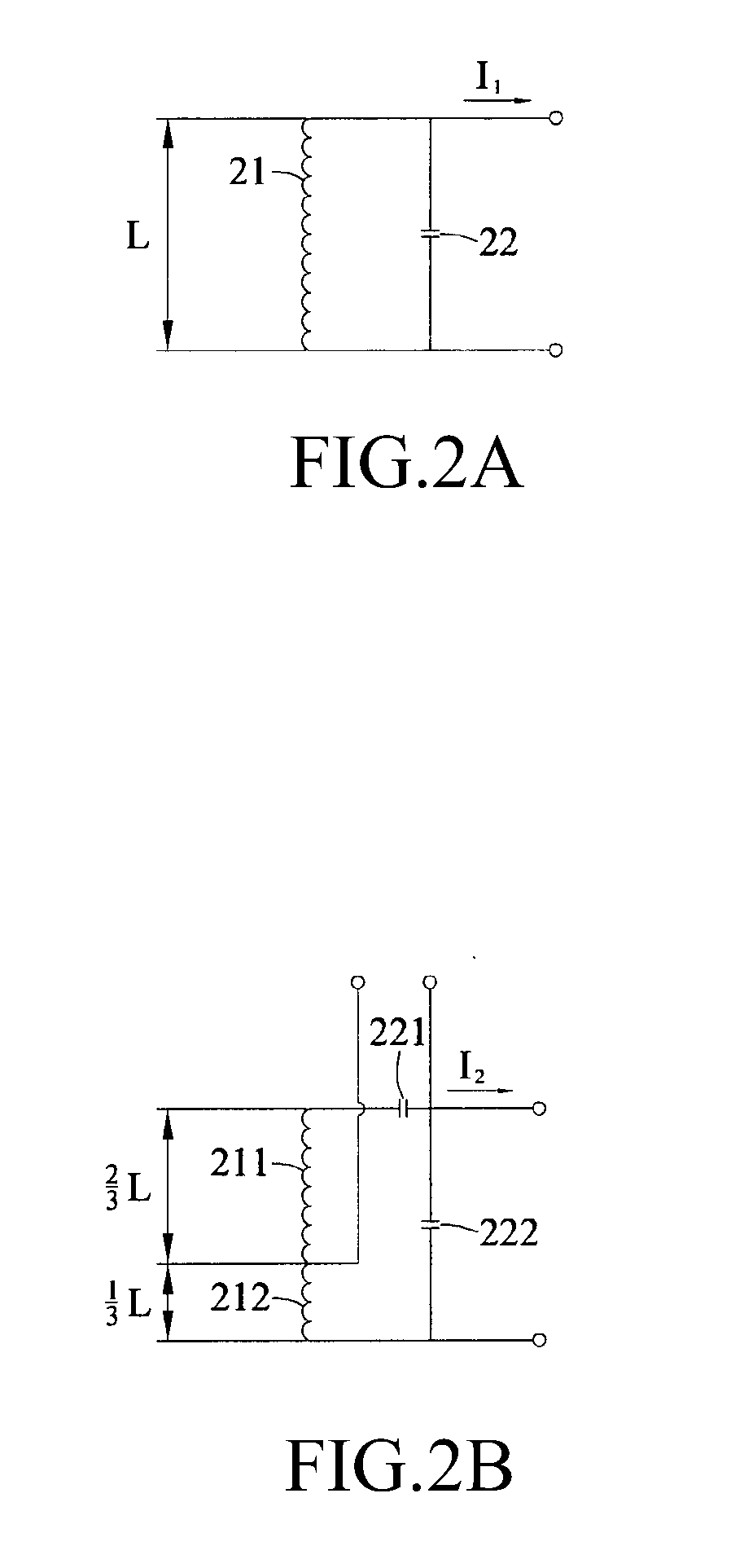
ActiveUS20100097830A1Minimize switching lossesReduce power wasteAc-dc conversion without reversalElectromagnetic wave systemInductorEngineering
An induced power system for being connected with and driving loads (300) includes a primary circuit (100) and a secondary circuit (200). The primary circuit (100) is provided with a primary inductor (110) for generating current induced magnetic filed. The secondary circuit (200) is provided with an induce generation portion (210) and a power distribution portion (220). The induce generation portion (210) is provided with a first inductor (211) and a second inductor (212) connected in series with each other and adjacent with the primary inductor (110), for generating induced alter current. The power distribution portion (220) is provided with a first capacitor (221), a second capacitor (222) and a switching device (225), in which the first capacitor (221) is connected with the first inductor (211) in series to generate series resonance, thus to provide a control power supply. The second capacitor (222) is connected with the first, the second inductors (211, 212) and the first capacitor (221) in parallel to generate parallel resonance, thus to provide a load power supply. When the switching device (225) is on, the load power supply is provided to the loads (300).
Owner:AMIDOF TECH
Zvs voltage source inverter
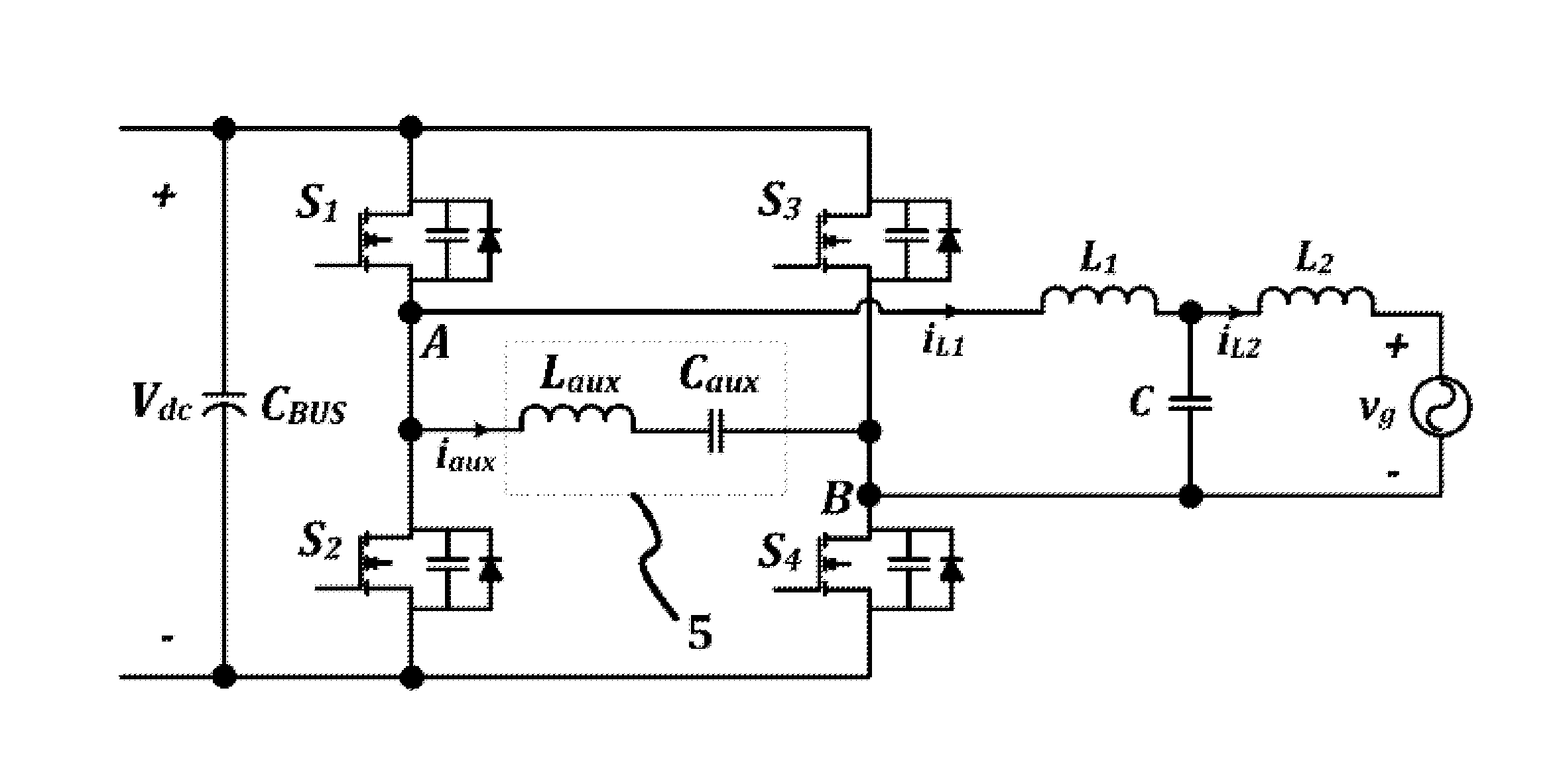
ActiveUS20150194909A1Eliminate switching lossesRemoves reverse recovery lossEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionZ-source inverterFull bridge
Systems and methods relating to zero voltage switching for inverters. A full bridge inverter is used in conjunction with a passive auxiliary circuit and an output filter. A control system controls the current by way of the auxiliary circuit and injects a high quality current to a power grid. The control system adjusts the duty ratio and switching frequency of the gate pulses applied to the power semiconductors in the full-bridge inverter. As well, the control system adjusts the phase shift between gate pulses for both the leading leg and lagging leg power semiconductors to control the current passing through the auxiliary circuit.
Owner:SPARQ SYST INC
Power Supplying Apparatus
InactiveUS20100026262A1Minimize switching lossesControl power can be decreasedEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionLower limitSleep state
A first-order feedback control power supply apparatus being arranged in such a manner that when the apparatus is driven under light load condition, a current flowing through an inductor is detected by employing a second CR smoothing filter; when the present load condition is judged as a light load condition based upon the detected inductor current, both upper-sided / lower-sided power MOSFETs and a PWM oscillator are turned OFF so as to be brought into sleep states; when an output voltage of the power supply apparatus is lowered and the lowered output voltage reaches a lower limit threshold of a transient variation detecting circuit, the upper-sided power MOSFET is turned ON to recover the output voltage; and when the output voltage of the power supply voltage reaches a predetermined voltage, the upper-sided power MOSFET is turned OFF so as to be again brought into the sleep state.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Hysteretic switching regulator
InactiveUS7714562B2Less interactionShort response timeDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationLow-pass filterBand-pass filter
A switching regulator circuit including a high-side switch and a low-side switch; an inductor having a first terminal coupled to a common terminal between the high-side switch and the low-side switch, and a second terminal coupled to an output terminal of the switching regulator circuit; a low-pass filter coupled to the first terminal of the inductor, where the low-pass filter is operative for generating a ramp signal based on the voltage signal present at the first terminal of the inductor; and a hysteretic comparator coupled to the low pass filter, where the hysteretic comparator receives the ramp signal as an input signal, and generates an output signal which is operative for controlling the operation of the high-side switch and the low-side switch.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
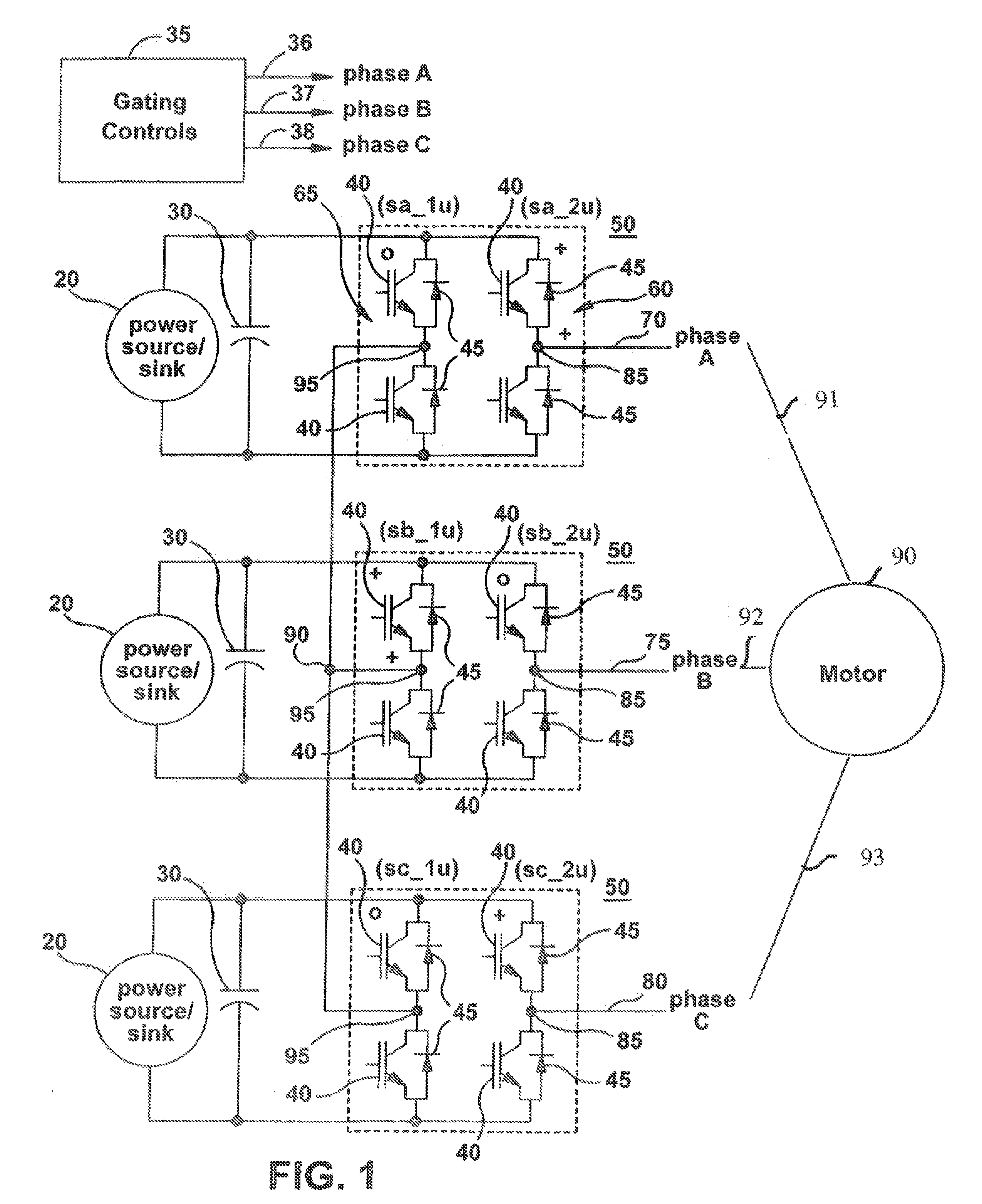
Zero-current notch waveform for control of a three-phase, wye-connected H-bridge converter for powering a high-speed electric motor
InactiveUS7847507B2Minimize switching lossesMaximize output power capabilityAC motor controlElectric motor controlTotal harmonic distortionThree-phase
A zero-current, synchronous switching waveform is provided for a three-phase, wye-connected H-Bridge to power an electric motor. The switching waveform includes two notches per cycle on the switching waveform provided to each of the semiconductor switches to minimize total harmonic distortion and switching loss. Positioning of the notch with respect to the zero-current crossing is optimized to reduce switching loss and minimize total harmonic distortion.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
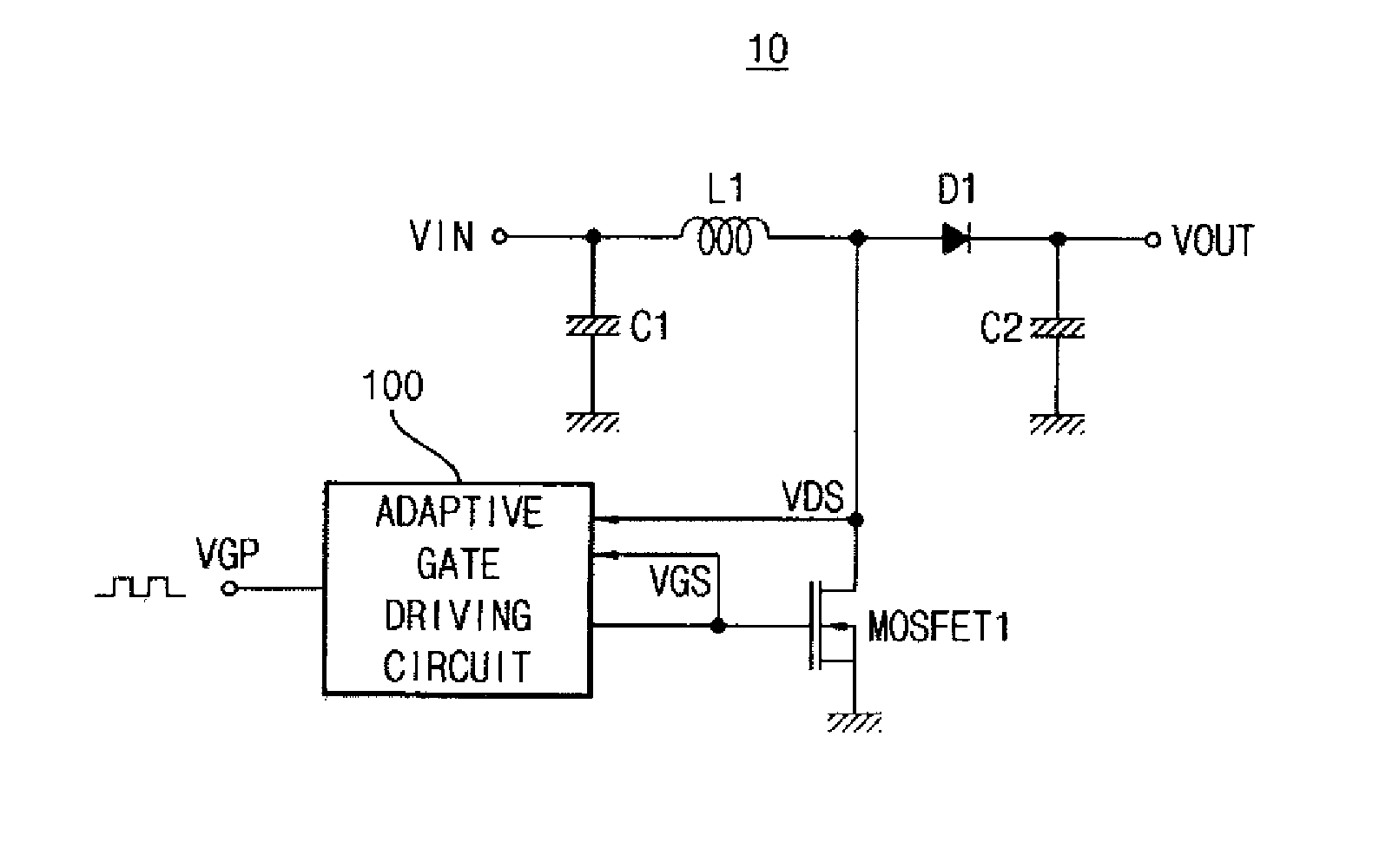
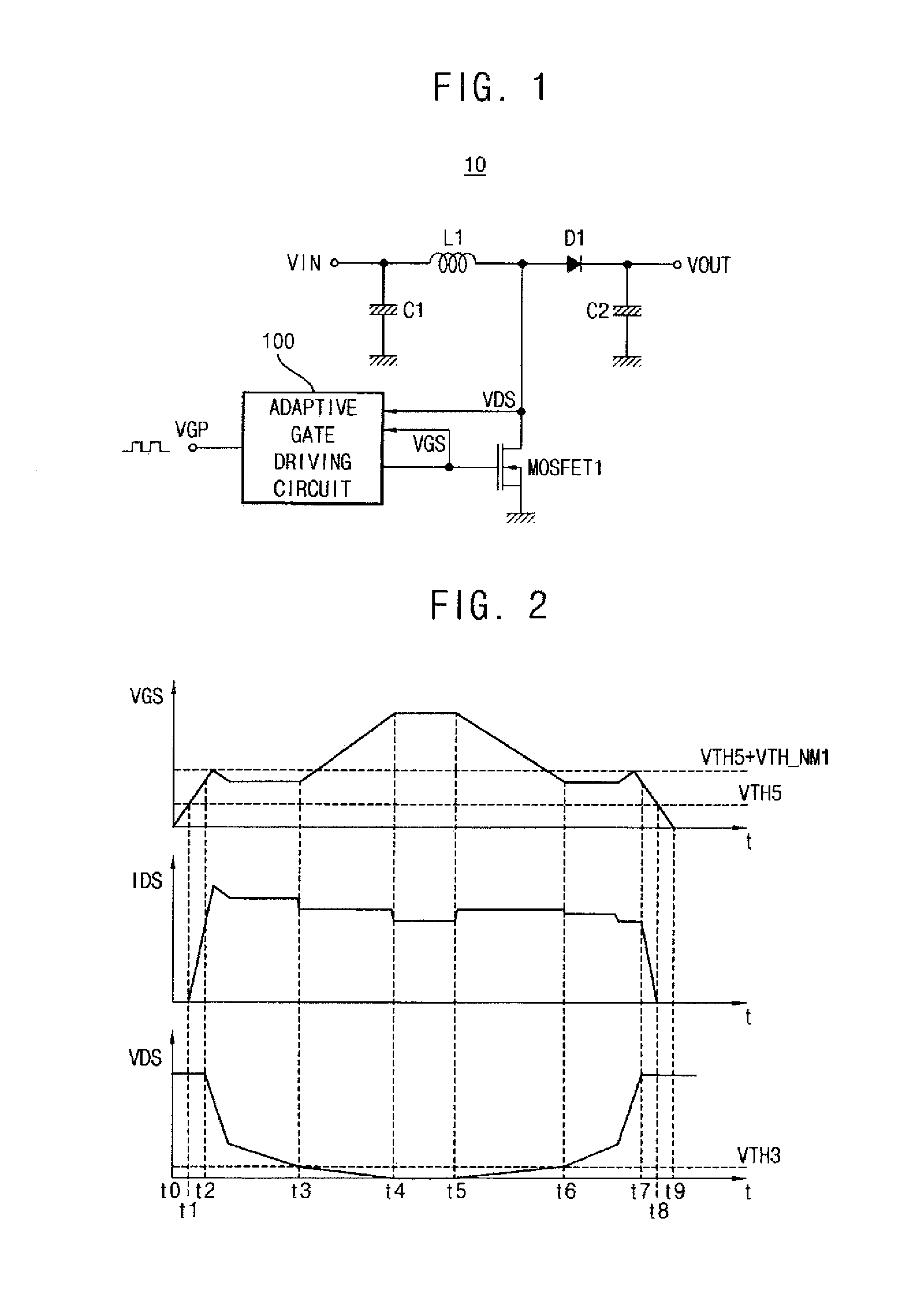
Circuit for driving gate of power mos transistor
ActiveUS20140015501A1EMI suppressionAvoid failureDc-dc conversionElectronic switchingDriver circuitTransistor
A circuit for driving a gate of a power MOS transistor includes an adaptive pull-up unit and an adaptive pull-down unit. The adaptive pull-up unit is connected between a first power source voltage and the gate of the power MOS transistor. The adaptive pull-up unit maximizes pull-up current driving ability. The adaptive pull-down unit is connected between a second power source voltage and the gate of the power MOS transistor. The adaptive pull-down unit maximizes pull-down current driving ability.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Miniature high-voltage power supplies
ActiveUS8058861B2Minimize power consumptionMinimize switching lossesTelevision system detailsAc-dc conversionHigh resistanceCapacitance
The present invention provides a system comprising a high-voltage capacitive device and a power circuit electrically coupled to the capacitive device, wherein the power circuit is configured for stepping up a lower DC source voltage to a higher DC output voltage, wherein the source voltage is less than about 5 V, and wherein the output voltage is at least about 1.25 kV, and wherein the power circuit comprises a magnetic component and a switching component for charging and discharging the magnetic component, wherein the switching component has a high resistance of at least about 5 ohms.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL +1
Modulated power supply
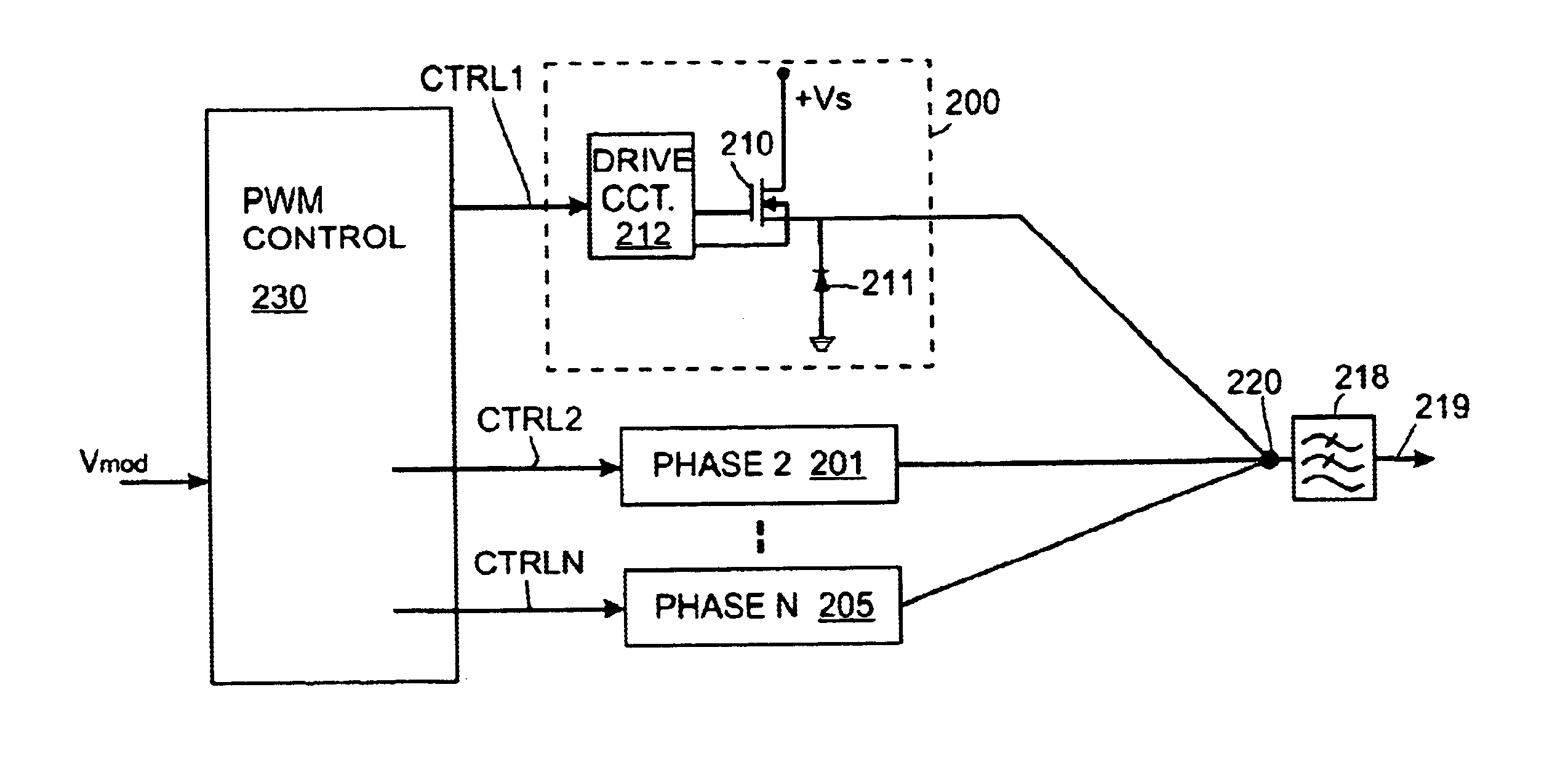
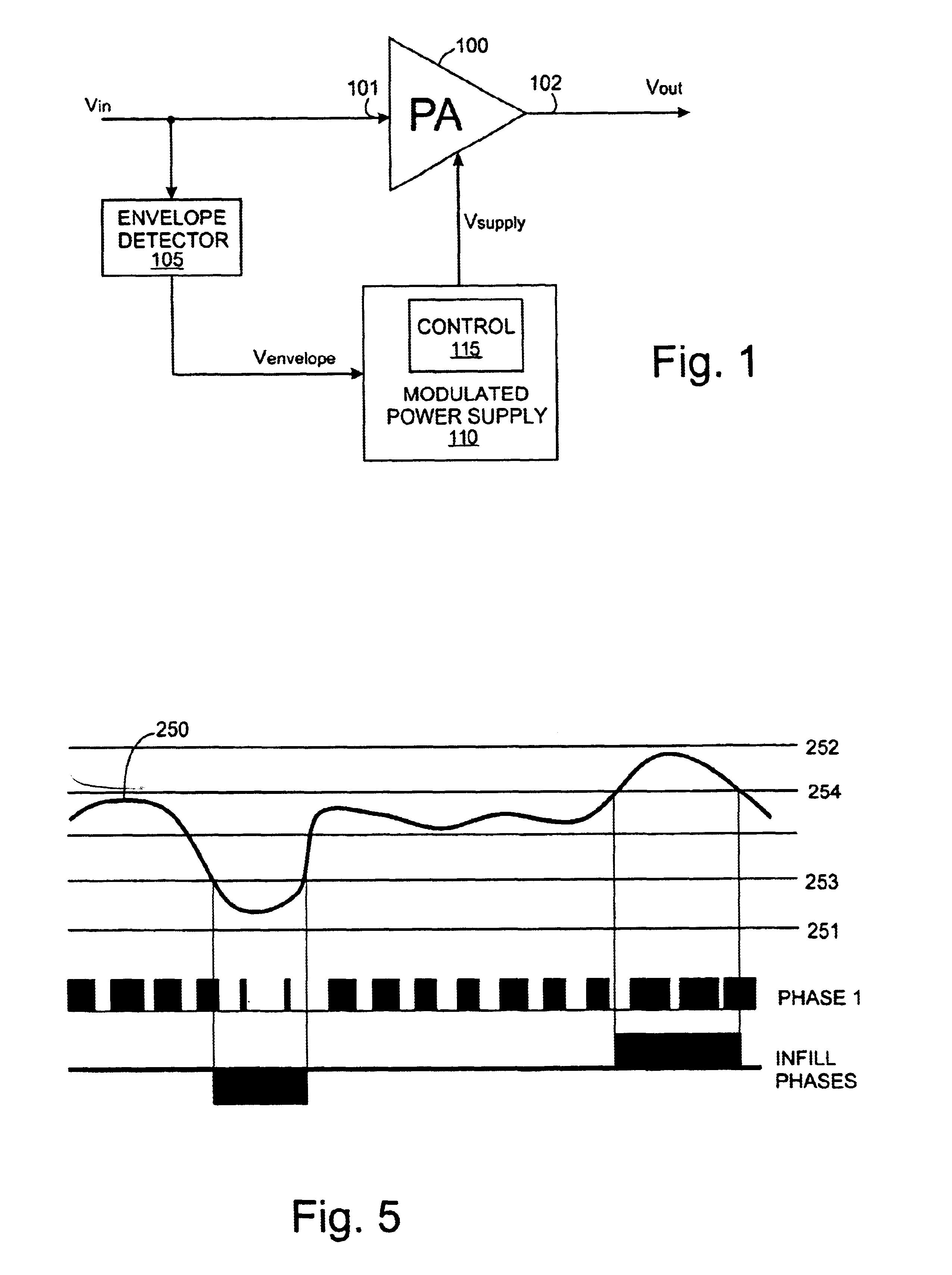
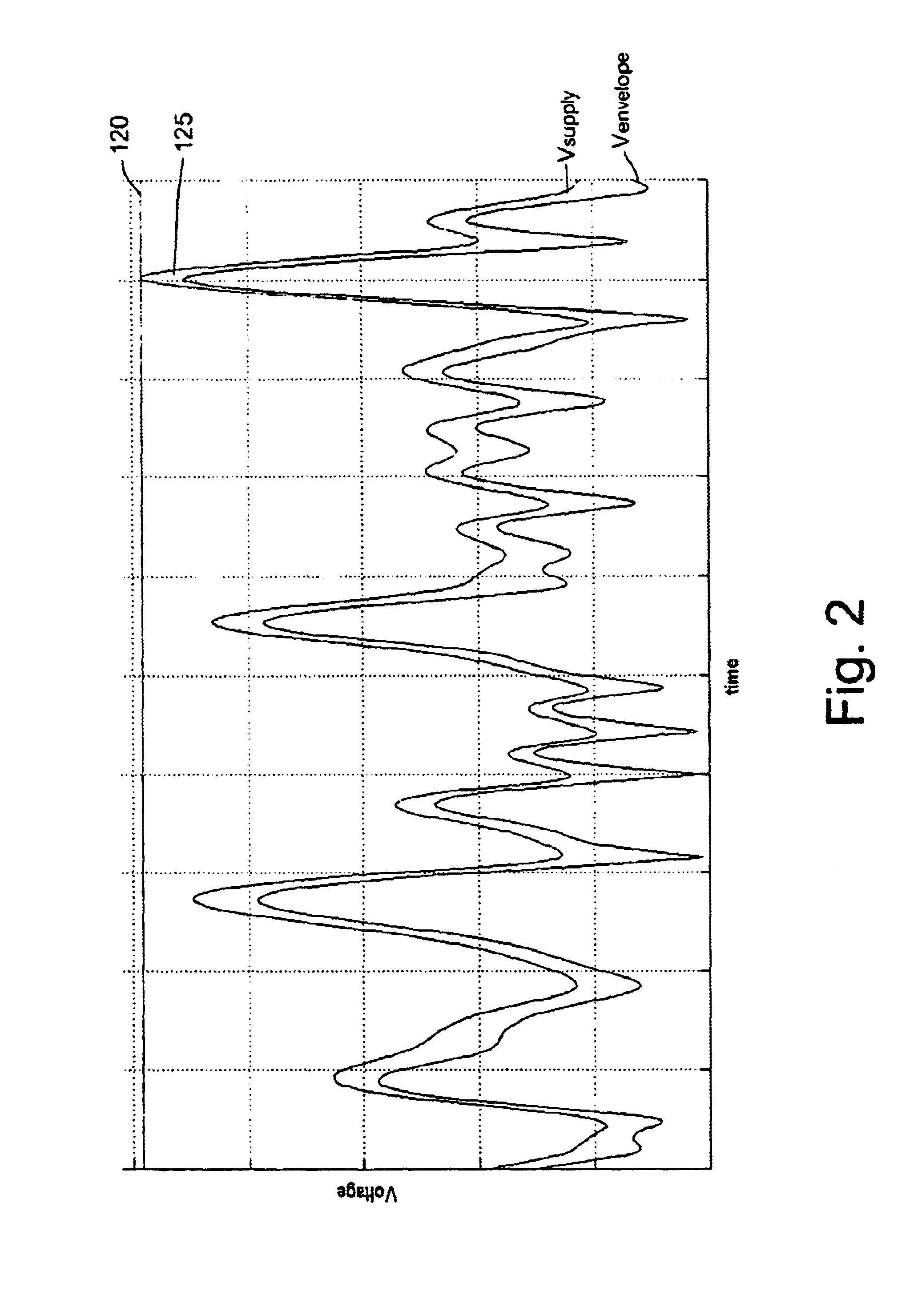
InactiveUS6894559B1Reduce power consumptionReduce switching lossesAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyDc amplifiers with modulator-demodulatorPower switchingPeak value
A modulated power supply comprises a converter having a primary power switching device and a secondary power switching device. The outputs of the primary and secondary power switching devices are combined to provide an output. A controller controls operation of the switching devices in response to a modulating input signal. Only the primary power switching device is operated while a property of the input signal lies within a first predetermined range and both the primary and the secondary power switching devices are operated while the property of the input signal lies outside the first predetermined range. This can reduce switching losses in comparison to operating the full array of switches. This is particularly well-suited to peaky signals. The property of the modulating input signal which causes the controller to bring secondary power switching devices into operation can be amplitude or rate of change of amplitude.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
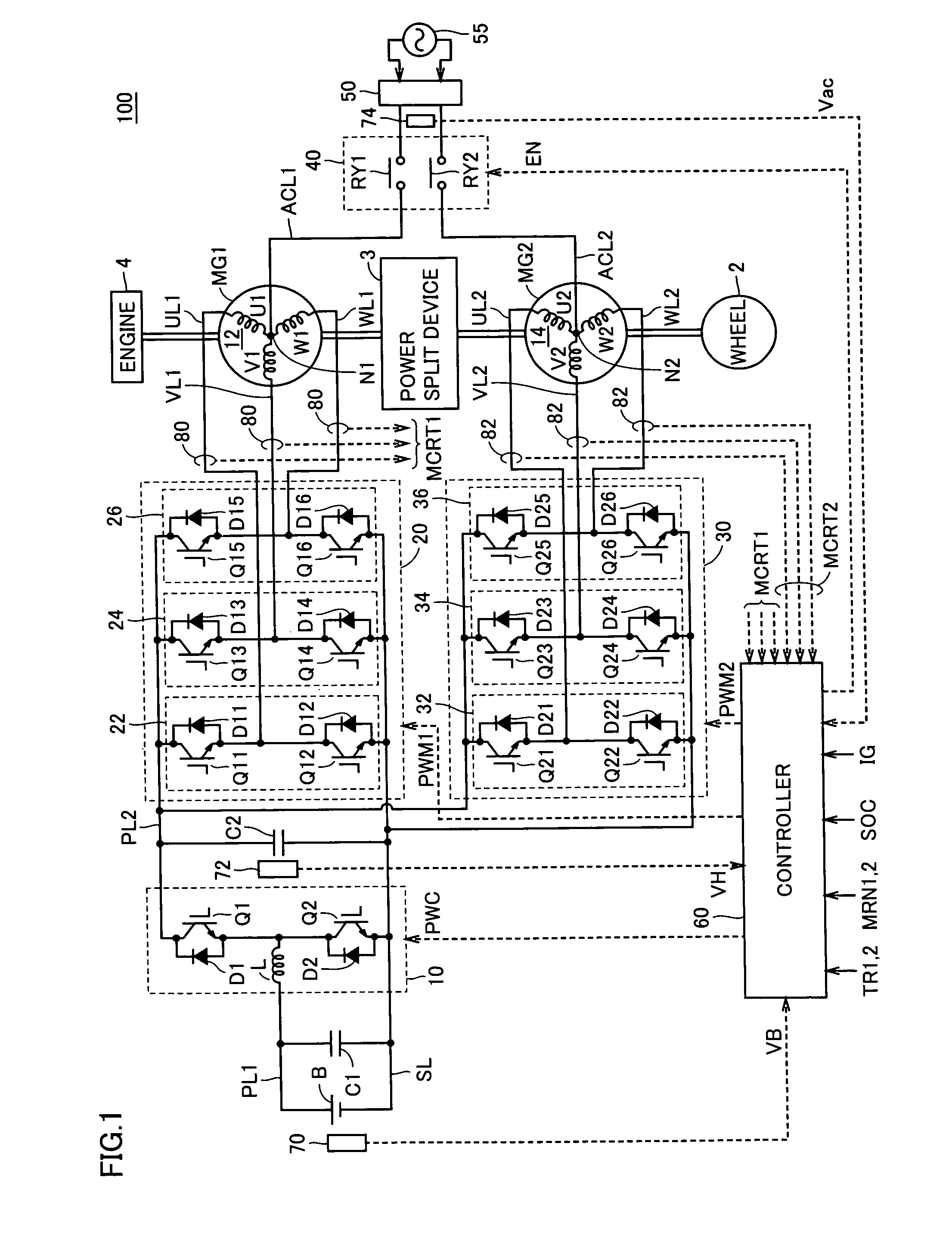
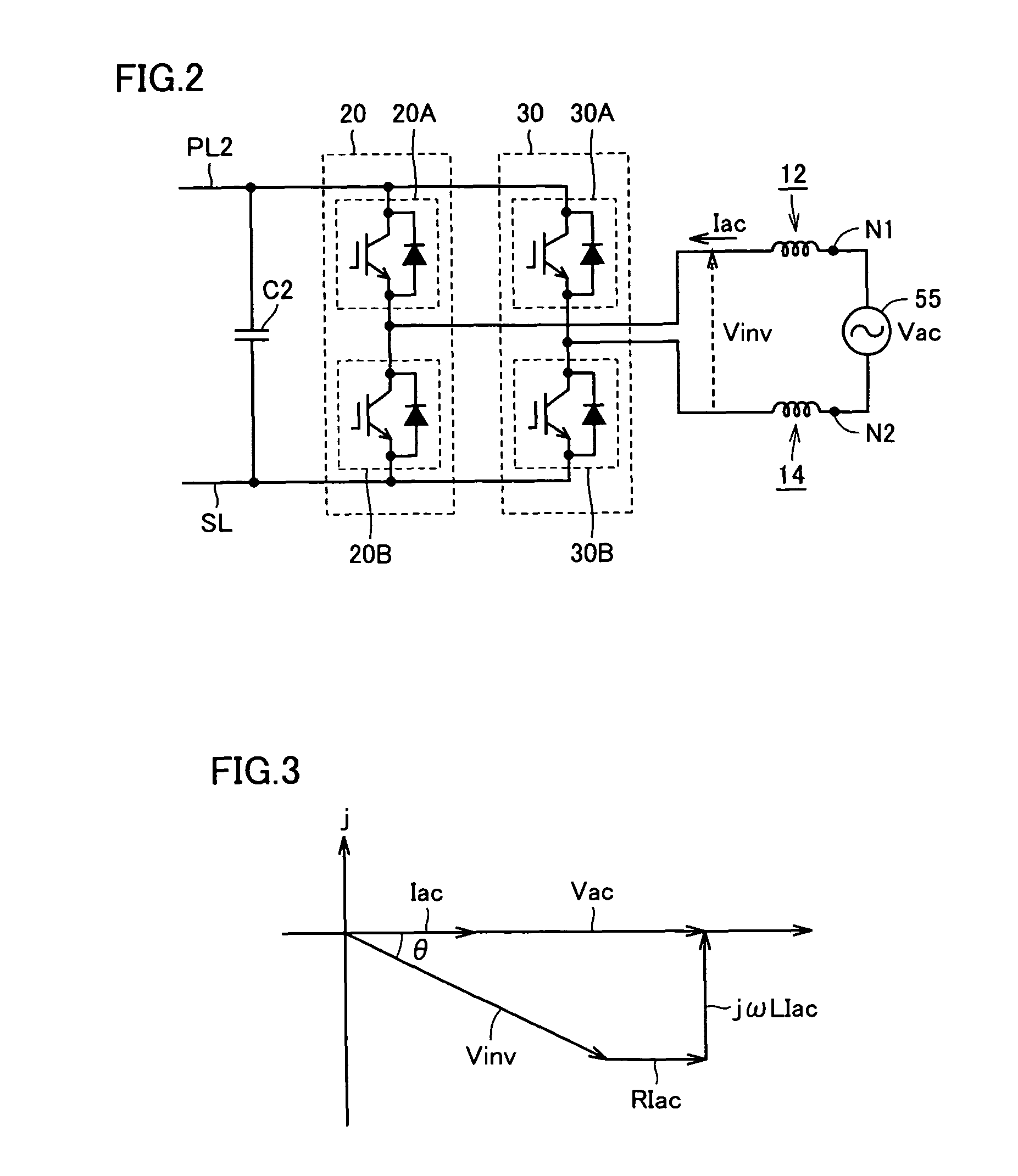
Charge control apparatus, electrically powered vehicle and electric storage charge control method
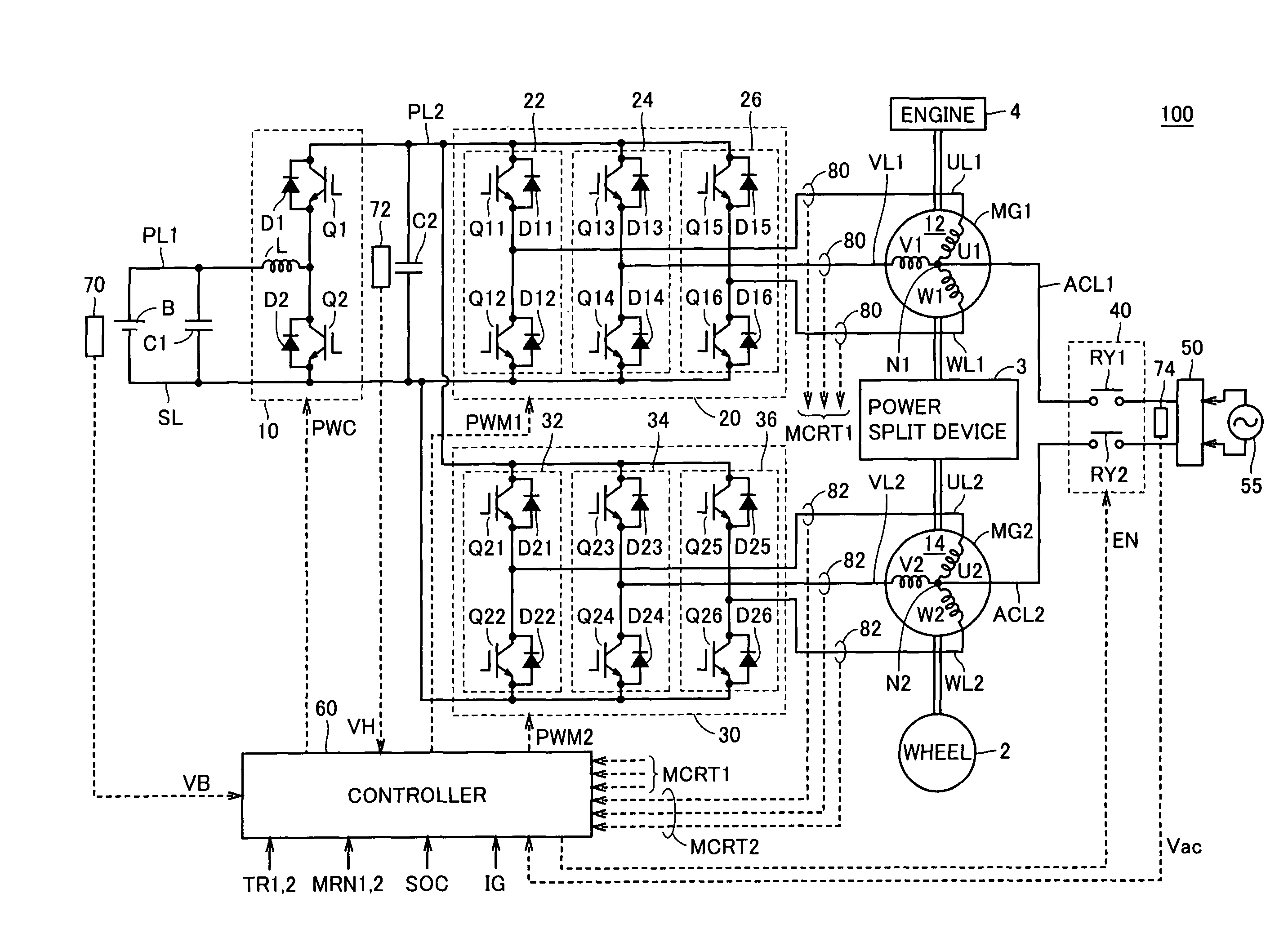
InactiveUS7859201B2Easy to set upMinimize switching lossesHybrid vehiclesBatteries circuit arrangementsControl objectiveCharge control
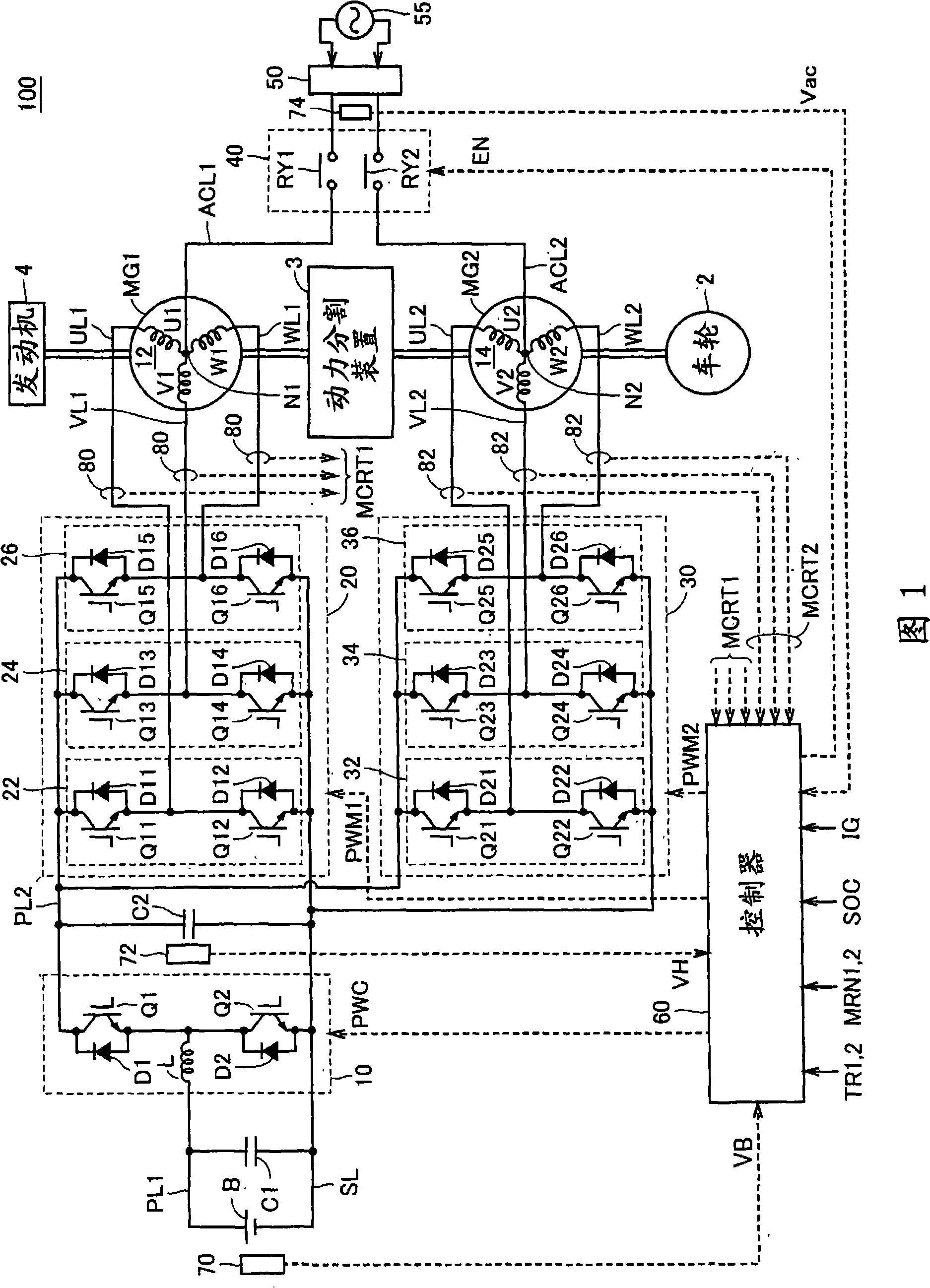
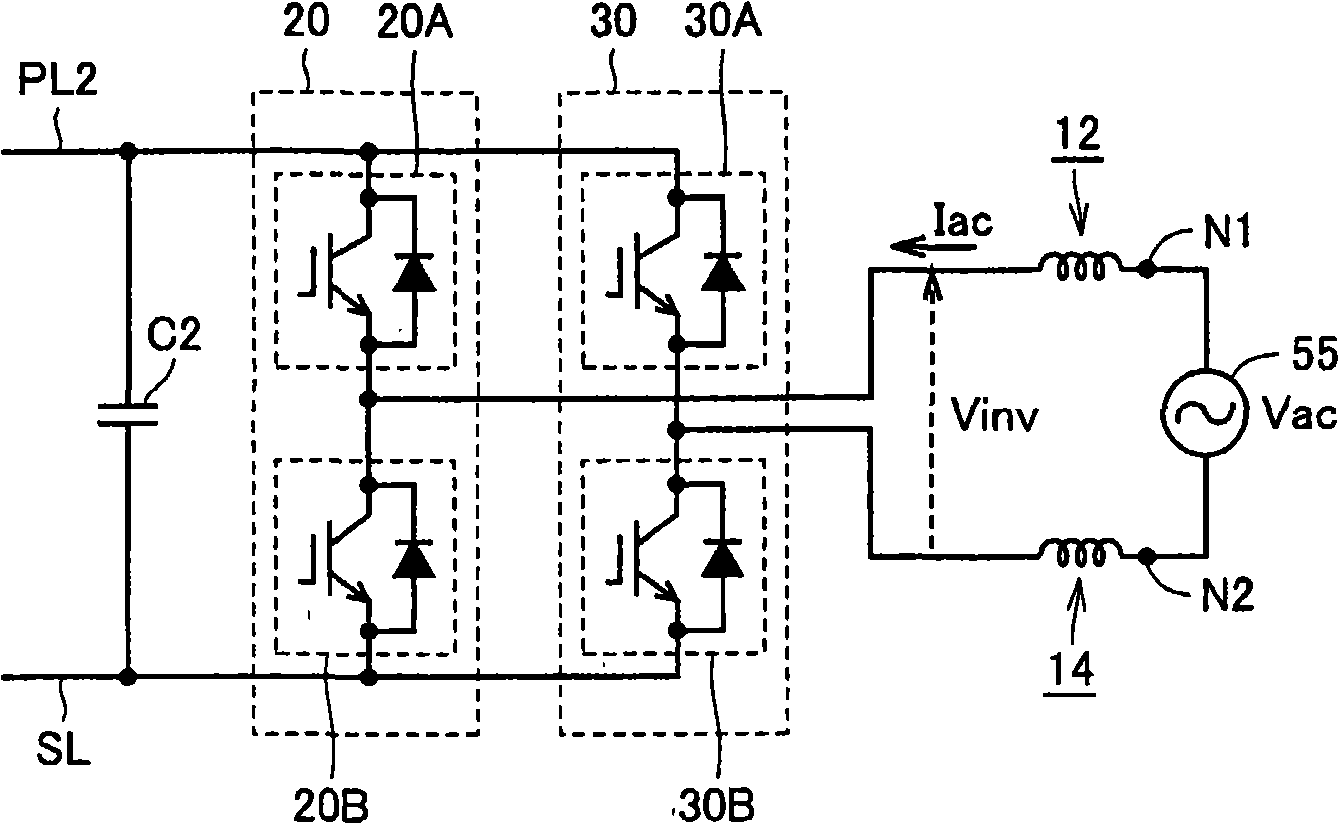
When it is determined that an electric storage is to be charged from a commercial power source, a controller sets a control target of a voltage of a power line to be controlled by a boost converter, based on a voltage of the commercial power source. Specifically, the controller sets the control target of the voltage to a level approximately equal to the crest value of voltage. Then, the controller outputs an input permission command to a relay circuit, and controls inverters to execute charging of the electric storage.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Hysteretic switching regulator
InactiveUS20070145965A1Easy to understandLess interactionDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationLow-pass filterEngineering
A switching regulator circuit including a high-side switch and a low-side switch; an inductor having a first terminal coupled to a common terminal between the high-side switch and the low-side switch, and a second terminal coupled to an output terminal of the switching regulator circuit; a low-pass filter coupled to the first terminal of the inductor, where the low-pass filter is operative for generating a ramp signal based on the voltage signal present at the first terminal of the inductor; and a hysteretic comparator coupled to the low pass filter, where the hysteretic comparator receives the ramp signal as an input signal, and generates an output signal which is operative for controlling the operation of the high-side switch and the low-side switch.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
Detecting light load conditions and improving light load efficiency in a switching power converter
ActiveUS8199537B2Minimize switching lossesReduce switching frequencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionVoltage regulationPeak value
A switching power converter detects low load conditions based on the ratio of a first peak current value for peak current switching in constant voltage regulation mode to a second peak current value for peak current switching in constant current regulation mode. The power supply load is considered to have a low load if the ratio is lower than a predetermined threshold. Once a low load condition is detected, the switching frequency of the switching power converter is reduced to a level that minimizes switching loss in the power converter. In addition, the switching power converter also adjusts the switching frequency according to the sensed input line voltage. An offset is added to the switching period to reduce the switching frequency of the switching power converter, as the input line voltage is increased.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR INC
Power converter with high efficiency in operation
ActiveUS20120099348A1Avoid flowReduce switching lossesEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcTransformerEngineering
A power converter includes a main switch to which a capacitor is connected through a sub-diode. A primary coil of a transformer and a sub-switch are joined parallel to the capacitor. A main diode is coupled in series with the main switch. A sub-diode and a secondary coil of the transformer are connected parallel to the main diode. The rate of a rise in voltage across the main switch when turned off is suppressed by the rate of charging of the capacitor. Subsequently, by turning on the sub-switch, the current flowing through the main diode to be delivered to the transformer, thereby causing the current flowing through the main switch when turned on to be decreased by the sub-inductor.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Polyphase Voltage Converter Control Method
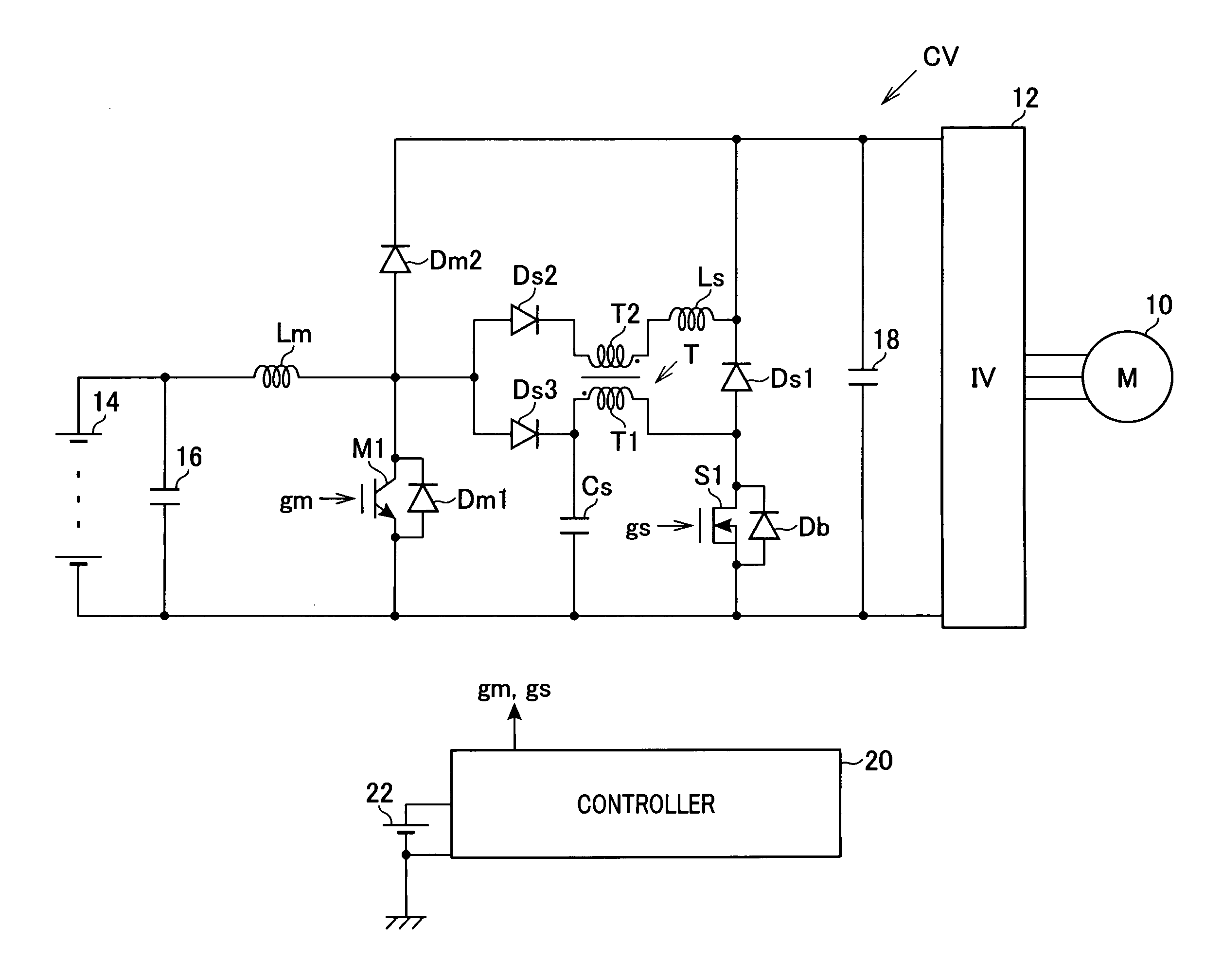
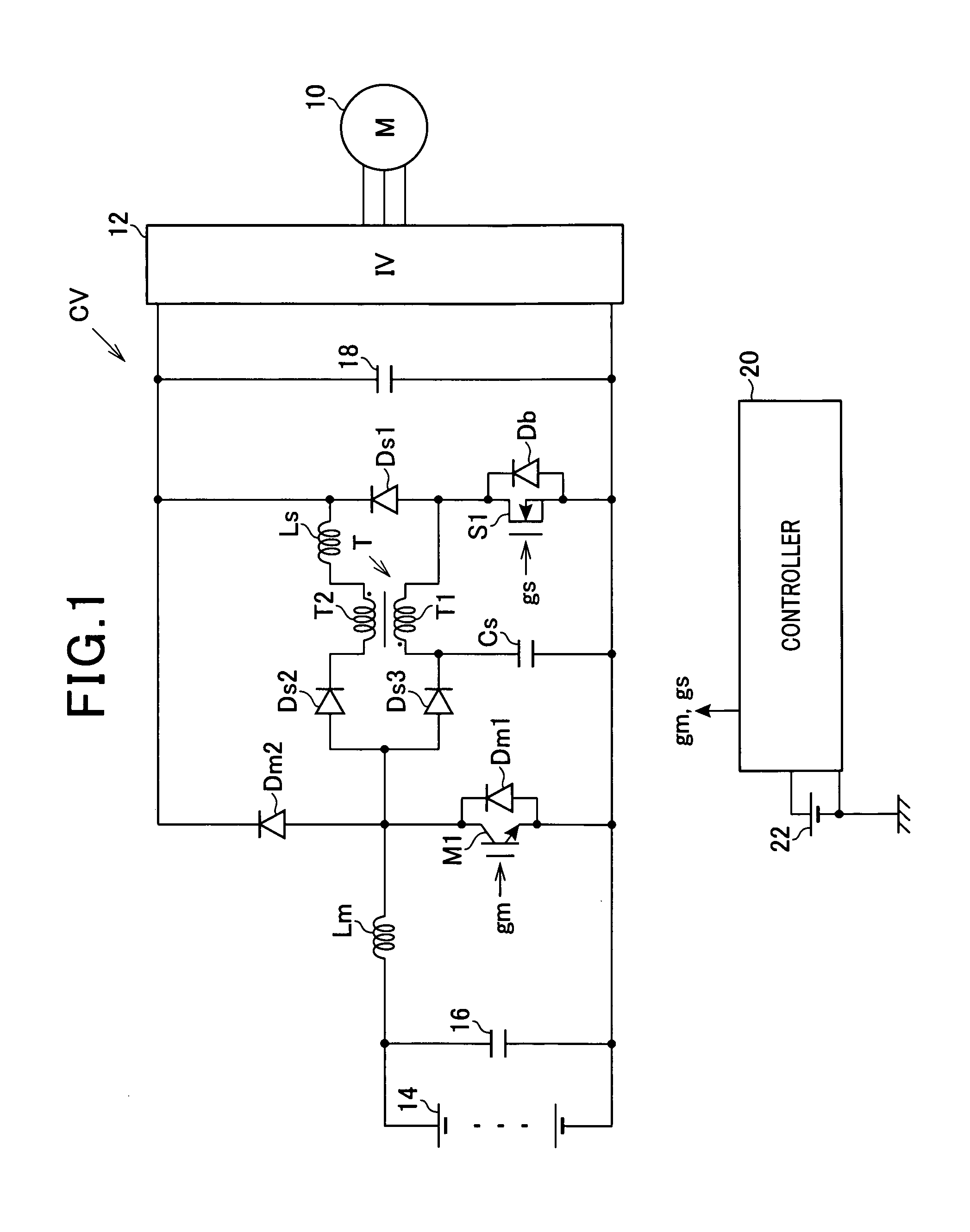
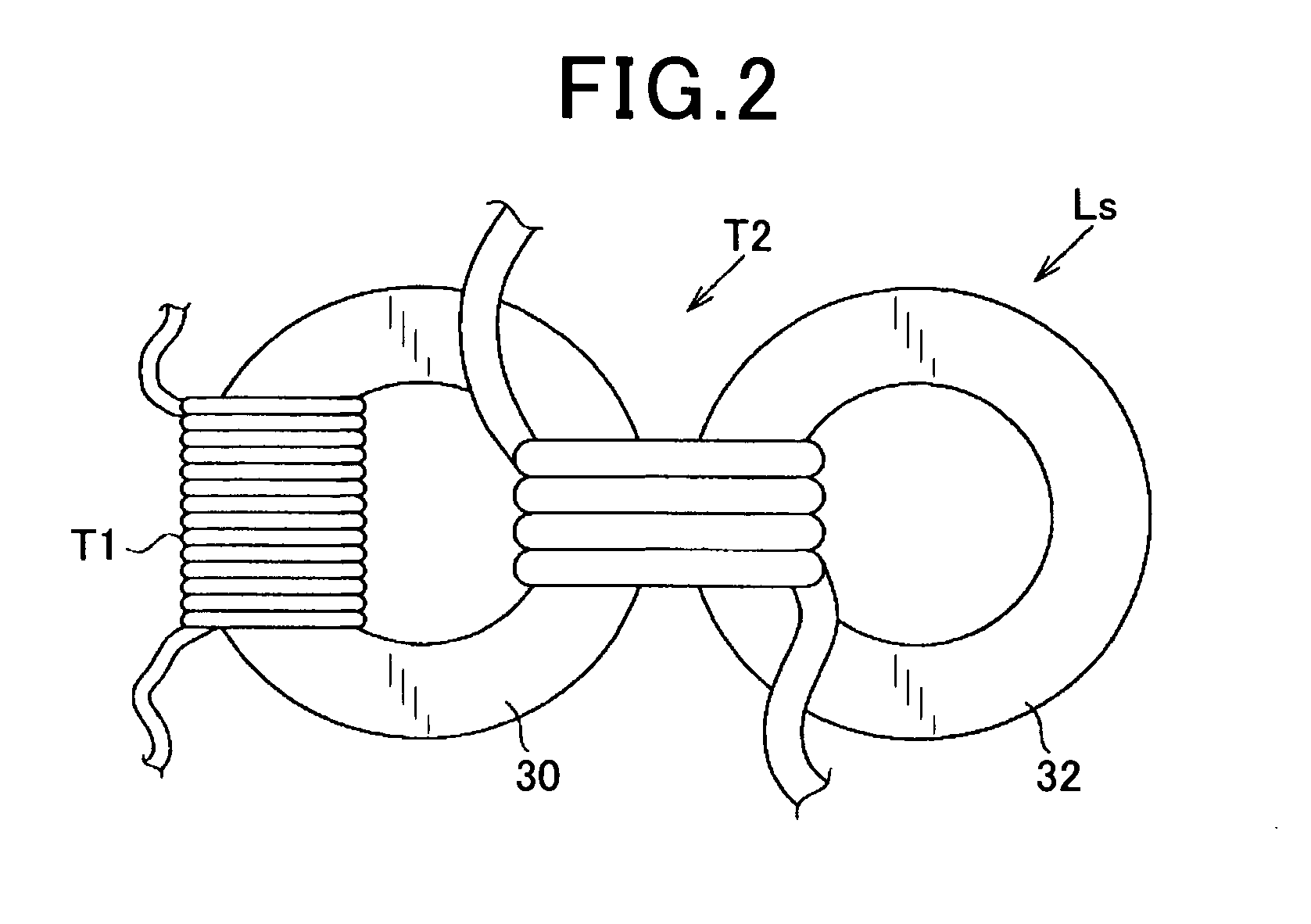
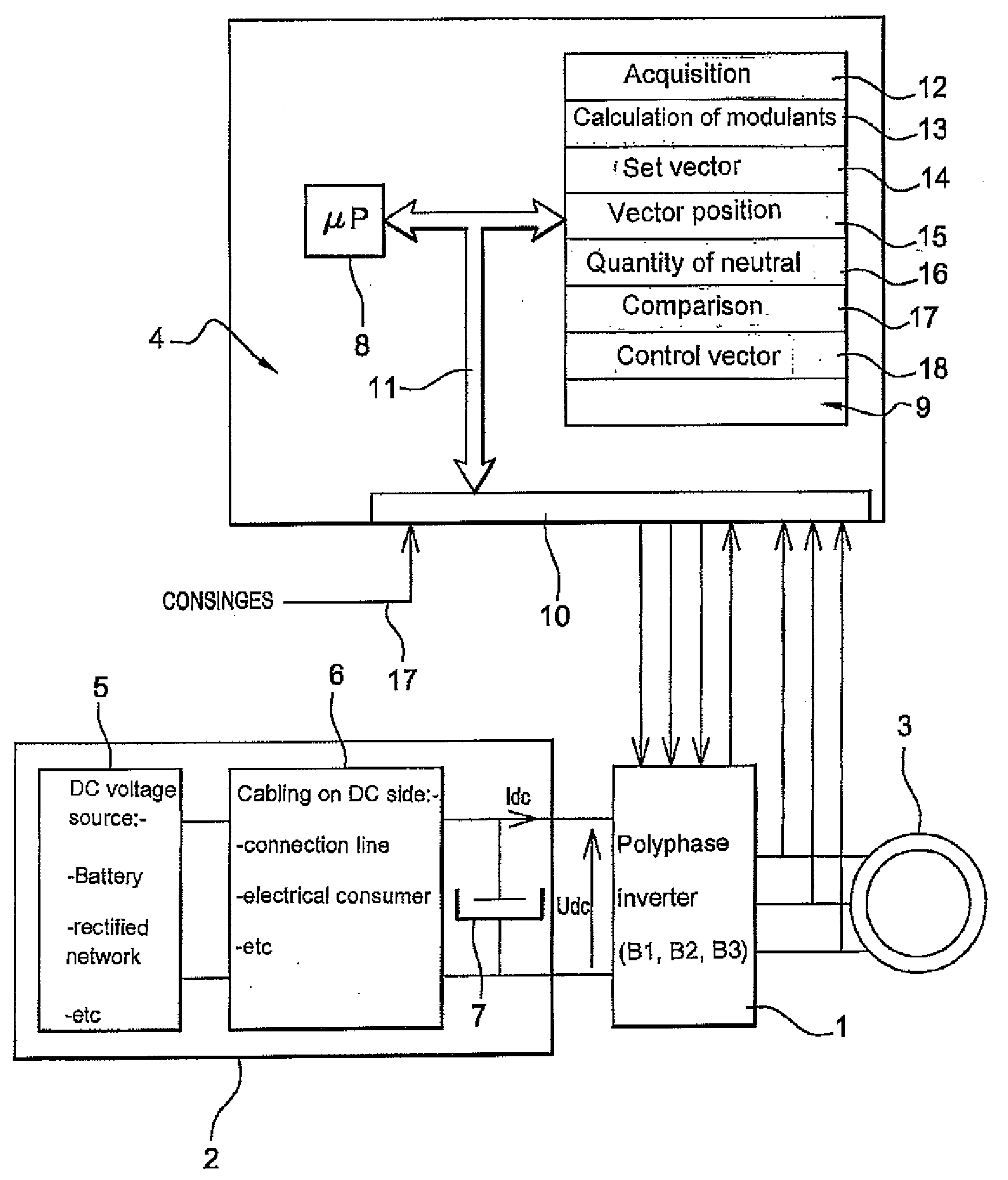
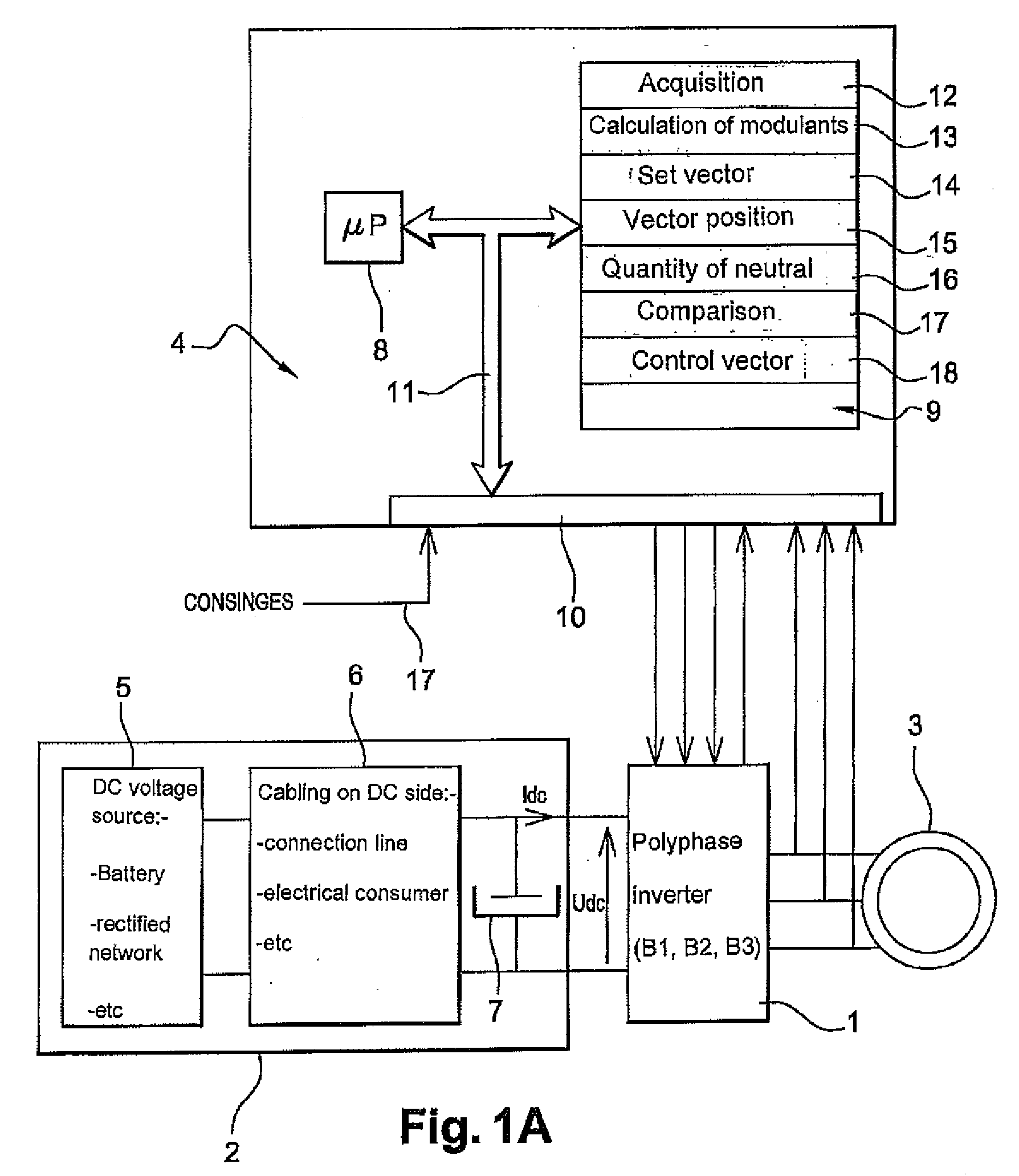
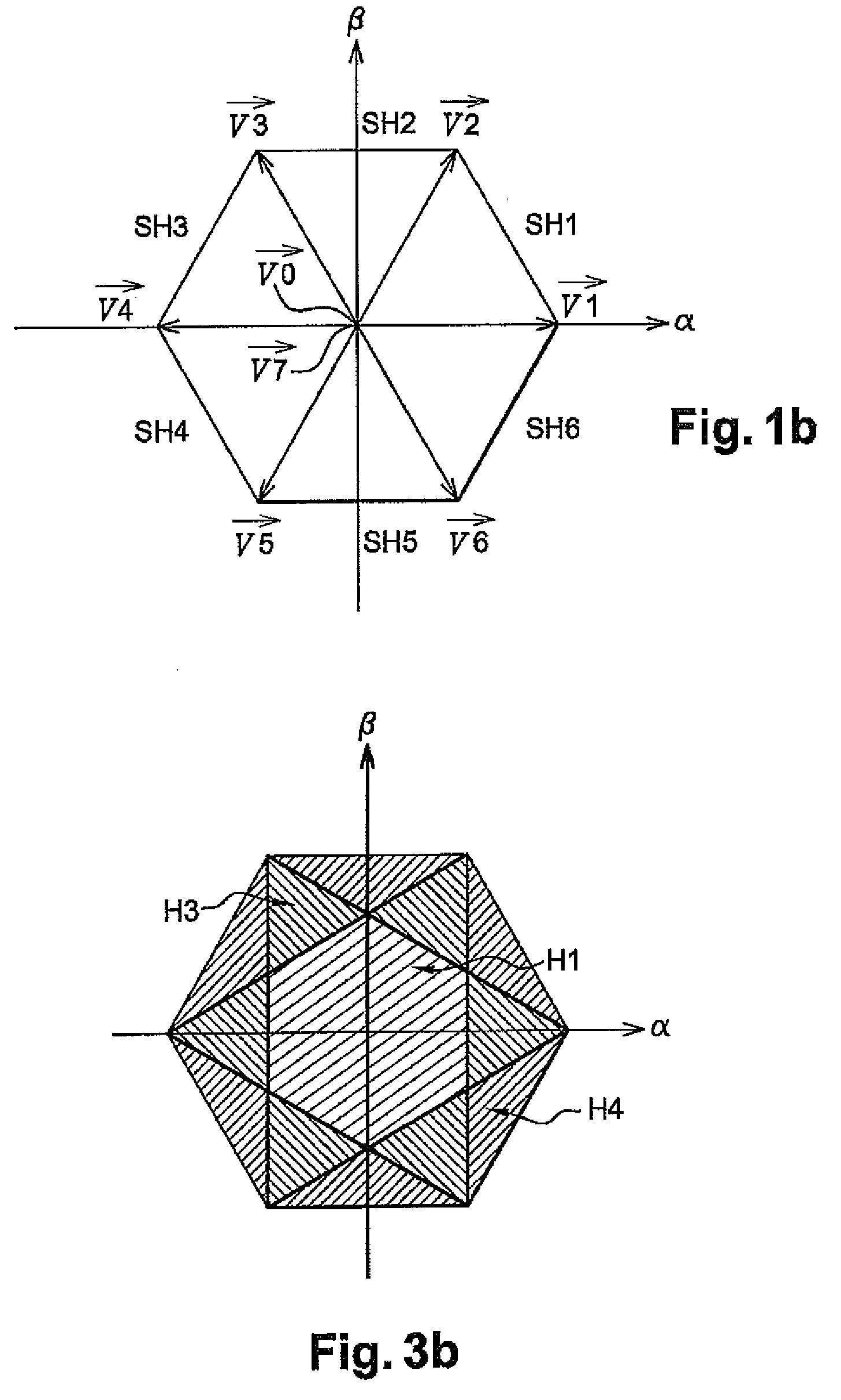
ActiveUS20080266918A1Minimises switch lossReduce effective currentSingle-phase induction motor startersMotor/generator/converter stoppersVoltage converterVoltage reference
A method for driving a power bridge (1) which is used for controlling a multiphase electric load (3), connectable to said electric load (3) via several arms and drivable by switching functions which determine free wheel controlling vectors and are active for controlling the load. The inventive method consists in selecting a first switching function production method which produces a reduced number of combinations of switching functions corresponding to the free wheel control vectors or a second switching function production method which produces combinations of switching functions corresponding only to the active control vectors, wherein said method are defined according to a given reference voltage vector and in applying said selected for producing a sequence of control vectors from the produced combinations of switching functions.
Owner:VALEO EQUIP ELECTRIC MOTEUR
Switching power source apparatus
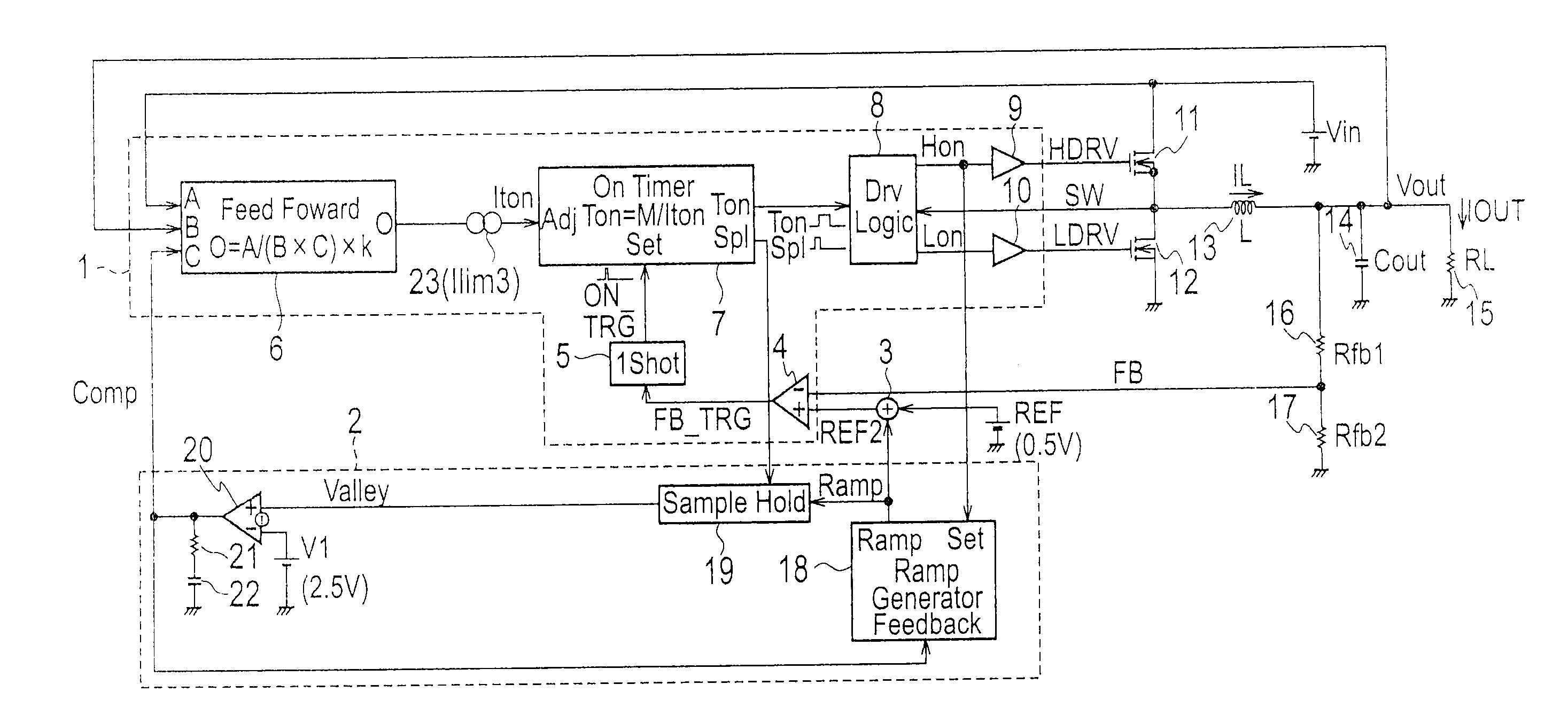
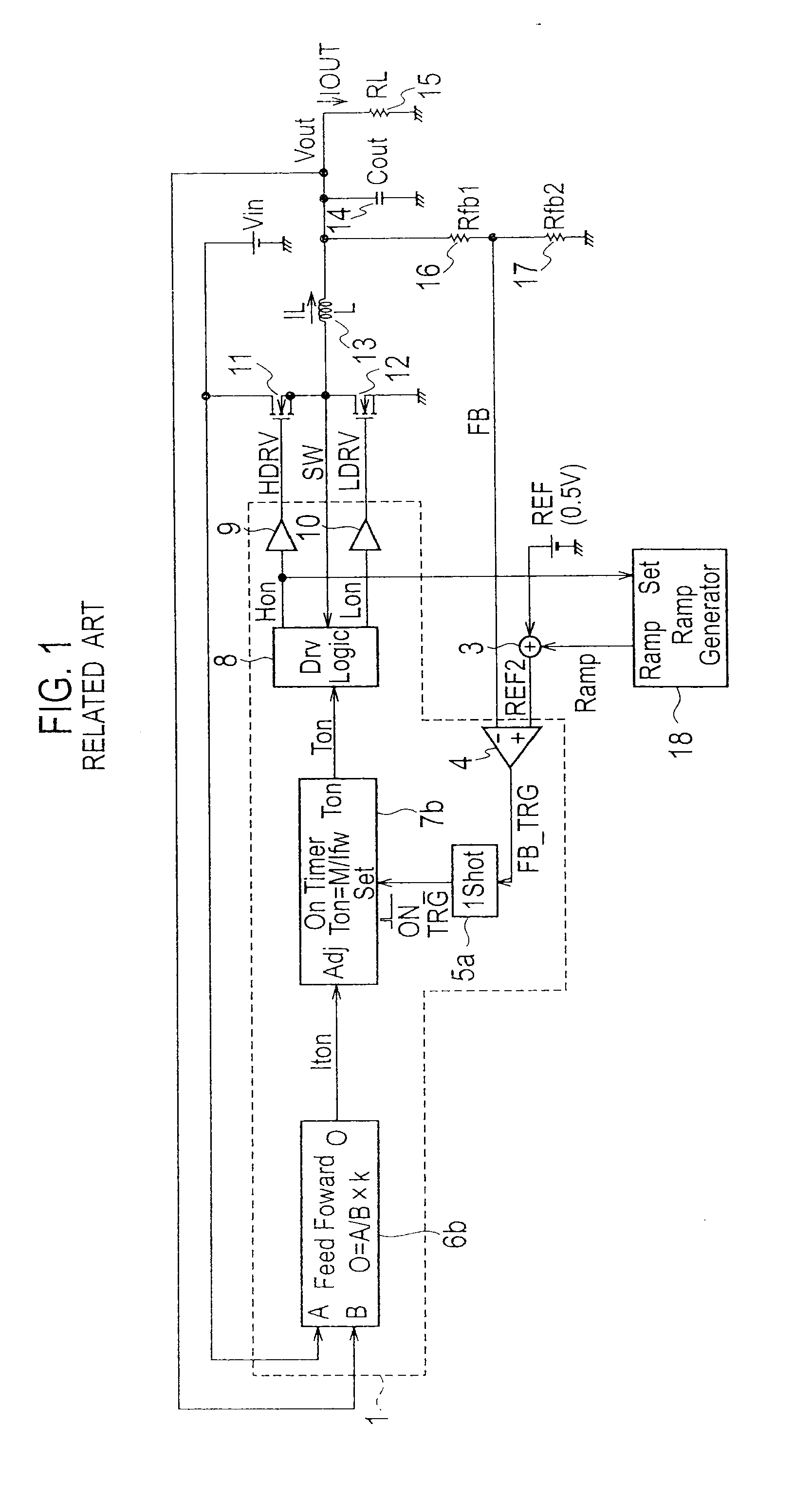
InactiveUS20120043949A1Improve efficiencyReduce in quantityEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus with intermediate ac conversionMOSFETFeedback controller
A switching power source apparatus includes a high-side MOSFET 11, a ramp generator 18 to generate a ramp signal, an amplitude signal generator (second feedback controller 2) to generate an amplitude signal Comp corresponding to an amplitude of the ramp signal, and a first feedback controller 1 to control the ON timing of the high-side MOSFET 11 according to the ramp signal, a feedback signal FB, and a first reference voltage REF and control the ON width of the high-side MOSFET 11 according to the amplitude signal Comp. The ramp generator 18 controls the inclination of the ramp signal so that the ramp signal maintains a predetermined amplitude. The first feedback controller 1 controls the ON width of the high-side MOSFET 11 so that the ON width does not become narrower than a predetermined limit value.
Owner:SANKEN ELECTRIC CO LTD
Charger for vehicles
ActiveUS20160288660A1Weakening rangeConduction loss can be minimizedBatteries circuit arrangementsCharging stationsBattery chargeElectrical battery
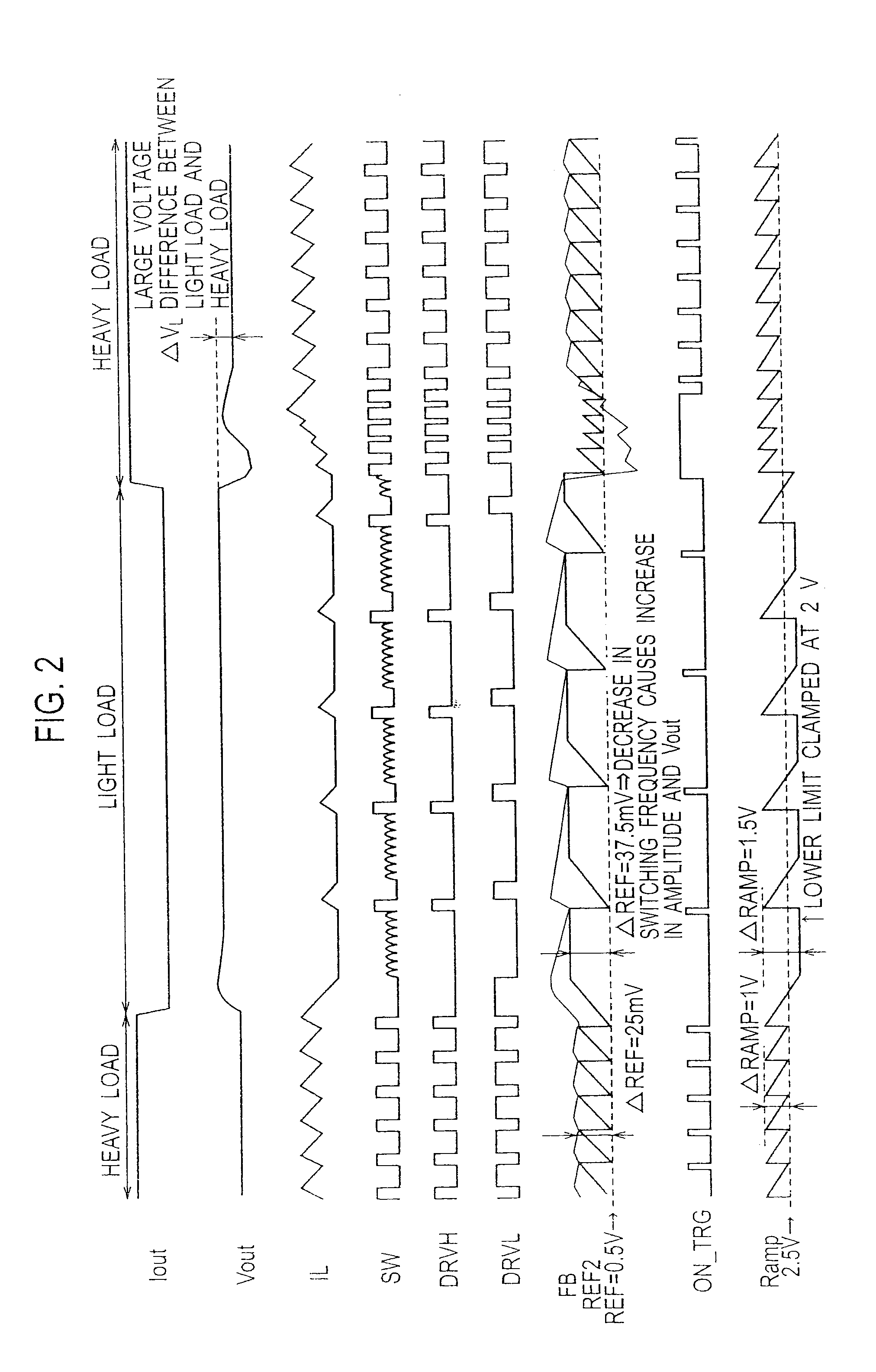
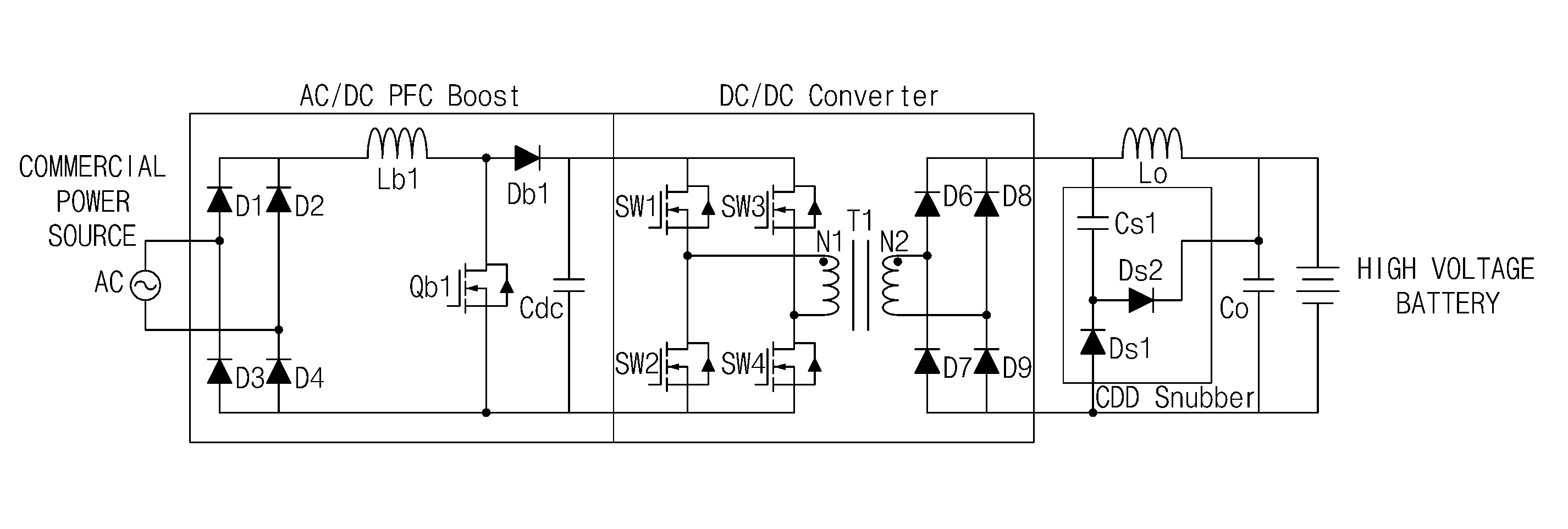
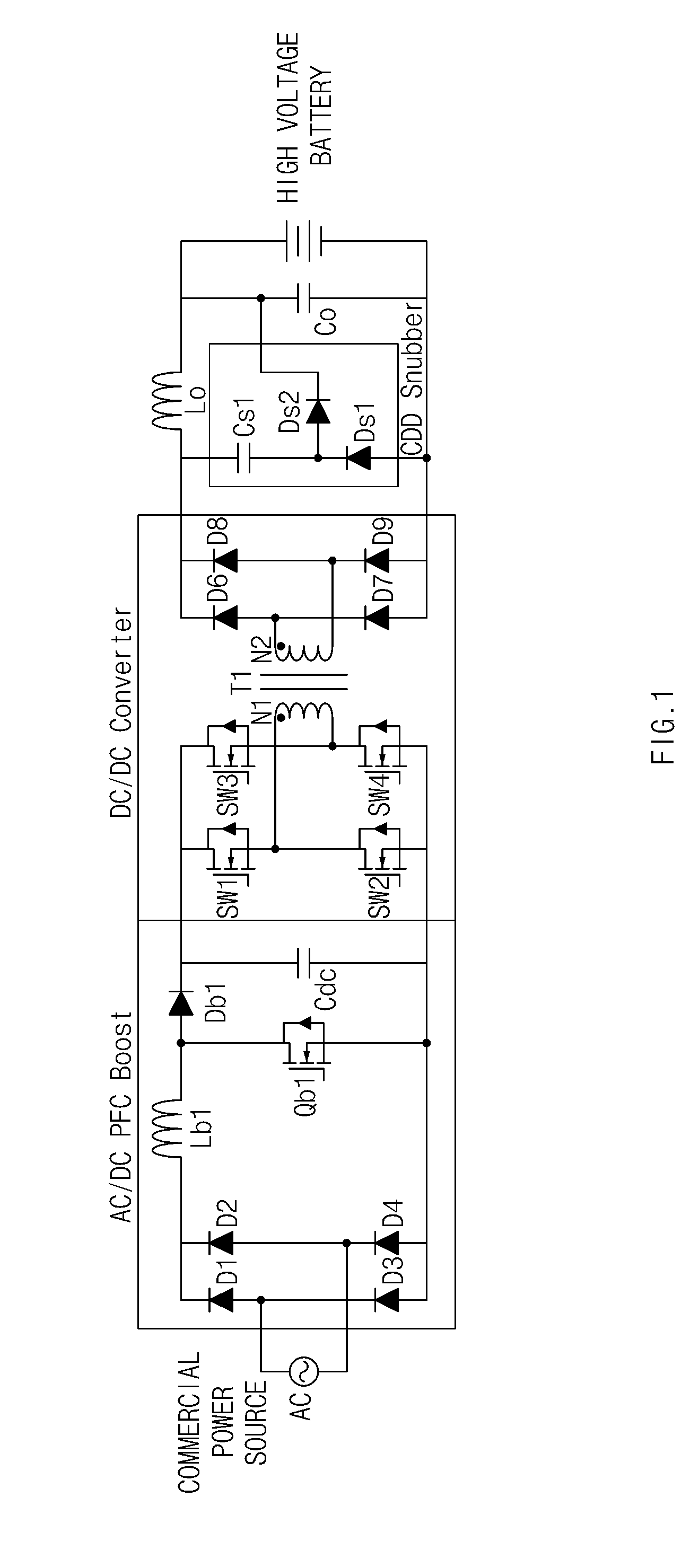
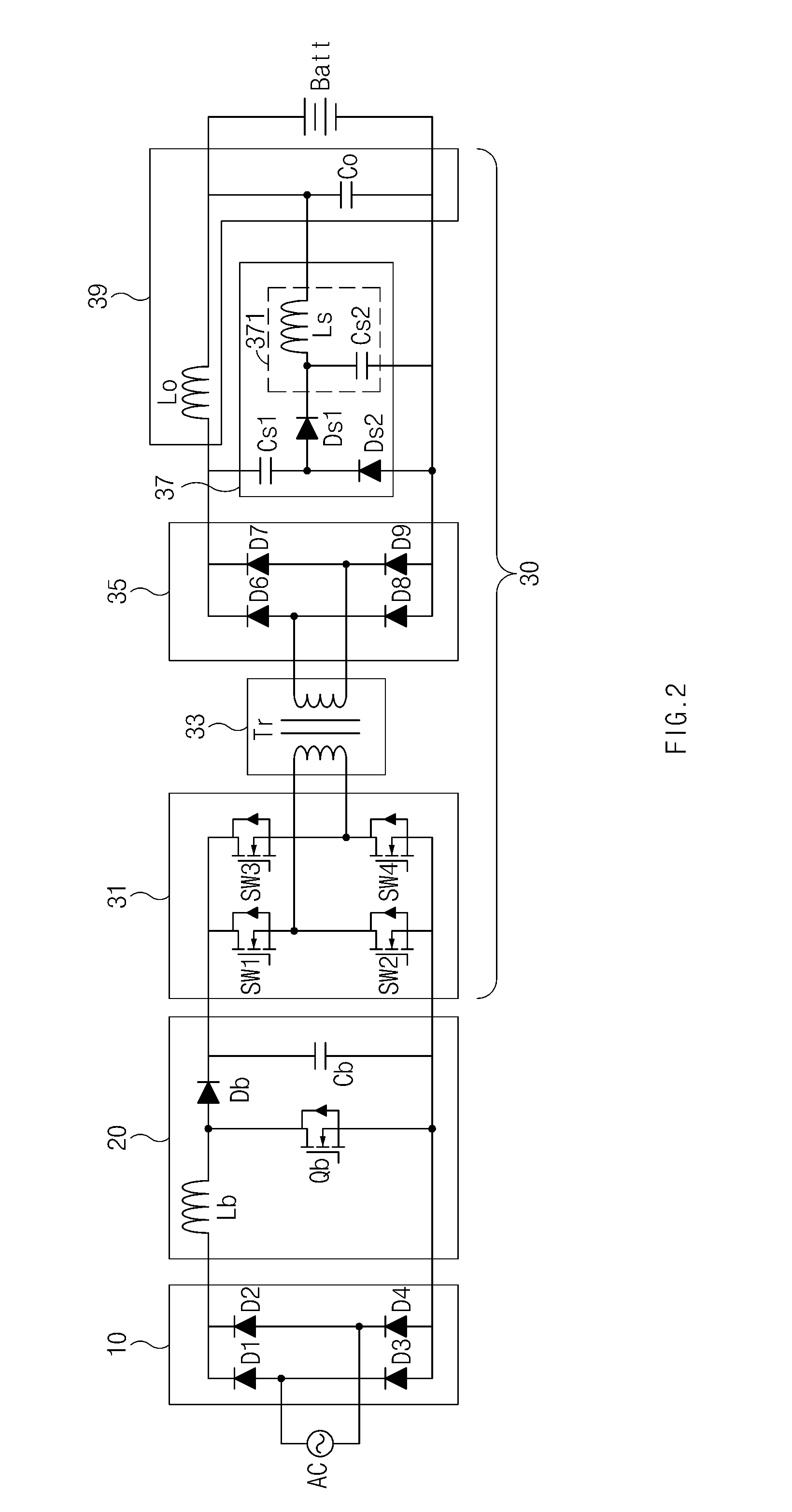
A device and method are provided for a charger for vehicles. In particular, the charger includes, an AC / DC converter configured to convert a commercial alternating current power source to a direct current power source and a DC / DC converter configured to convert the direct current power source applied from the AC / DC converter to a battery charging power source. The direct current power source is supplied to a battery. The DC / DC converter includes a snubber circuit that reduces the magnitude of a ripple current of the charging power source.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Inductive power transfer system and method for operating an inductive power transfer system
InactiveUS9843199B2Minimize switching lossesBatteries circuit arrangementsCharging stationsTransmitter coilPower inverter
An exemplary inductive power transfer system having a transmitter coil and a receiver coil. A transmitter-side power converter having a mains rectifier stage powering a transmitter-side dc-bus and controlling a transmitter-side dc-bus voltage U1,dc. A transmitter-side inverter stage with a switching frequency fsw supplies the transmitter coil with an alternating current. A receiver-side power converter having a receiver-side rectifier stage that rectifies a voltage induced in the receiver coil and powering a receiver-side dc-bus and a receiver-side charging converter controlling a receiver-side dc-bus voltage U2,dc. Power controllers that determine from a power transfer efficiency of the power transfer, reference values U1,dc*, U2,dc* for the transmitter and receiver side dc-bus voltages. An inverter stage switching controller controls the switching frequency fsw to reduce losses in the transmitter-side inverter stage.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
DC brushed motor drive with circuit to reduce di/dt and EMI, for MOSFET Vth detection, voltage source detection, and overpower protection
ActiveUS8102192B2Minimize switching lossesReduce electromagnetic interferenceTransistorElectronic switchingMOSFETPulse control
A gate driver for performing gate shaping on a first transistor of having gate, source, and drain terminals, the first transistor being selected from a switching stage of a power switching circuit having high- and low-side transistors series connected at a switching node for driving a load. The gate driver includes the following steps: upon receipt of an ON pulse pre-charging the gate terminal until gate to source terminal voltage equals Vth, controlling the di / dt(ON) flowing in the first transistor while free wheeling current is flowing in a second transistor of the switching stage, and controlling the dv / dt(ON) of the first transistor while a charge on the gate terminal is present; and upon receipt of an OFF pulse controlling the dv / dt(OFF) of the first transistor until free wheeling current is flowing in the second transistor, and controlling the di / dt(OFF) flowing in the first transistor while the gate to source terminal voltage equals Vth.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
High power factor, electrolytic capacitor-less driver circuit for light-emitting diode lamps
ActiveUS20140285102A1Minimize turn-on switching lossImprove reliabilityElectroluminescent light sourcesElectric light circuit arrangementTransformerElectrolytic capacitor
A driver circuit for use with LED lamps. The driver circuit uses a rectifier, a power factor correction subcircuit, a voltage conversion subcircuit, and a semiconductor switch. The power factor correction subcircuit uses a film capacitor instead of an electrolytic capacitor. As well, the power factor correction subcircuit uses either an inductor or a transformer to shape the incoming current to a substantially sinusoidal waveform that is in phase with the input AC current. The semiconductor switch provides a high frequency pulsating triangular current at the output of the rectifier.
Owner:JAIN PRAVEEN K +1
Charger for vehicles
ActiveUS9789774B2Weakening rangeConduction loss can be minimizedBatteries circuit arrangementsCharging stationsBattery chargePower flow
A device and method are provided for a charger for vehicles. In particular, the charger includes, an AC / DC converter configured to convert a commercial alternating current power source to a direct current power source and a DC / DC converter configured to convert the direct current power source applied from the AC / DC converter to a battery charging power source. The direct current power source is supplied to a battery. The DC / DC converter includes a snubber circuit that reduces the magnitude of a ripple current of the charging power source.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Charge control apparatus, electrically powered vehicle and electric storage charge control method
InactiveCN101277839ASmall sizeReduce weightHybrid vehiclesBatteries circuit arrangementsControl objectiveCharge control
When it is determined that an electric storage (B) is to be charged from a commercial power source (55), a controller (60) sets a control target of a voltage VH of a power line (PL2) to be controlled by a boost converter (10), based on a voltage Vac of the commercial power source (55). Specifically, the controller (60) sets the control target of the voltage VH to a level approximately equal to the crest value of voltage Vac. Then, the controller (60) outputs an input permission command (EN) to a relay circuit (40), and controls inverters (20, 30) to execute charging of the electric storage (B).
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Synchronous rectification circuit with dead time regulation
InactiveUS20050174819A1Minimize such dead timeKeep for a long timeEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionEngineeringDeadband
A synchronous rectification circuit with dead time regulation being adapted for a forward power supply to regulate a dead time of a switch circuit is described. The synchronous rectification circuit has a first switch control circuit connected with a first switch to control ON / OFF of the first switch, a dead time regulation circuit connected with the first switch control circuit to produce a dead time regulation signal, and a second switch control circuit connected with a second switch and the dead time regulation circuit to control ON / OFF of the second switch.
Owner:NIKO SEMICON
Miniature high-voltage power supplies
ActiveUS20080304290A1Minimize power dissipationMinimize switching lossTelevision system detailsDc network circuit arrangementsEngineeringHigh pressure
The present invention provides miniature power supplies and circuitry for powering high-voltage devices.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL +1
Switching power supply device
InactiveUS7405951B2Minimize switching lossesEliminate switching lossesDc network circuit arrangementsTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsLeakage inductanceEngineering
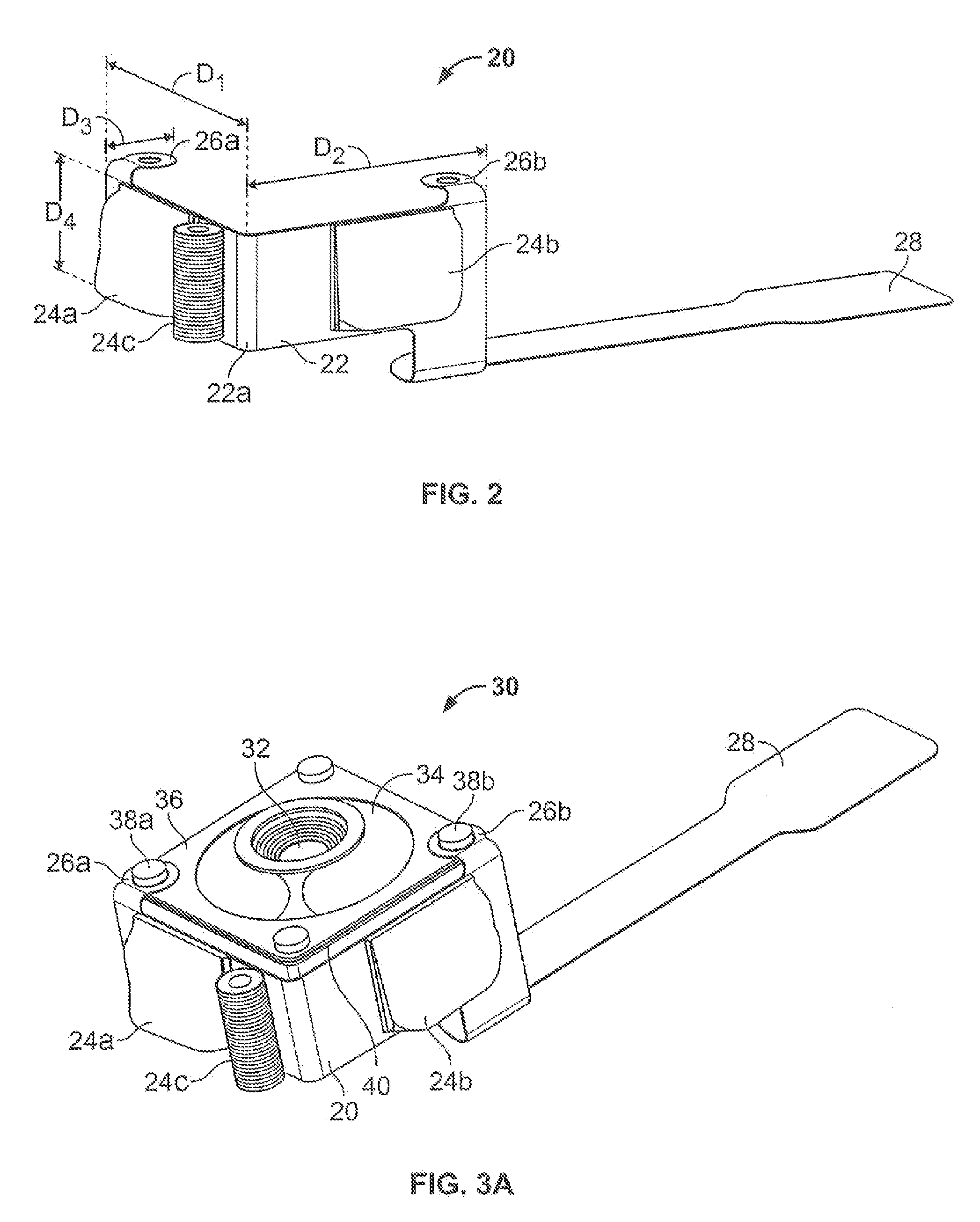
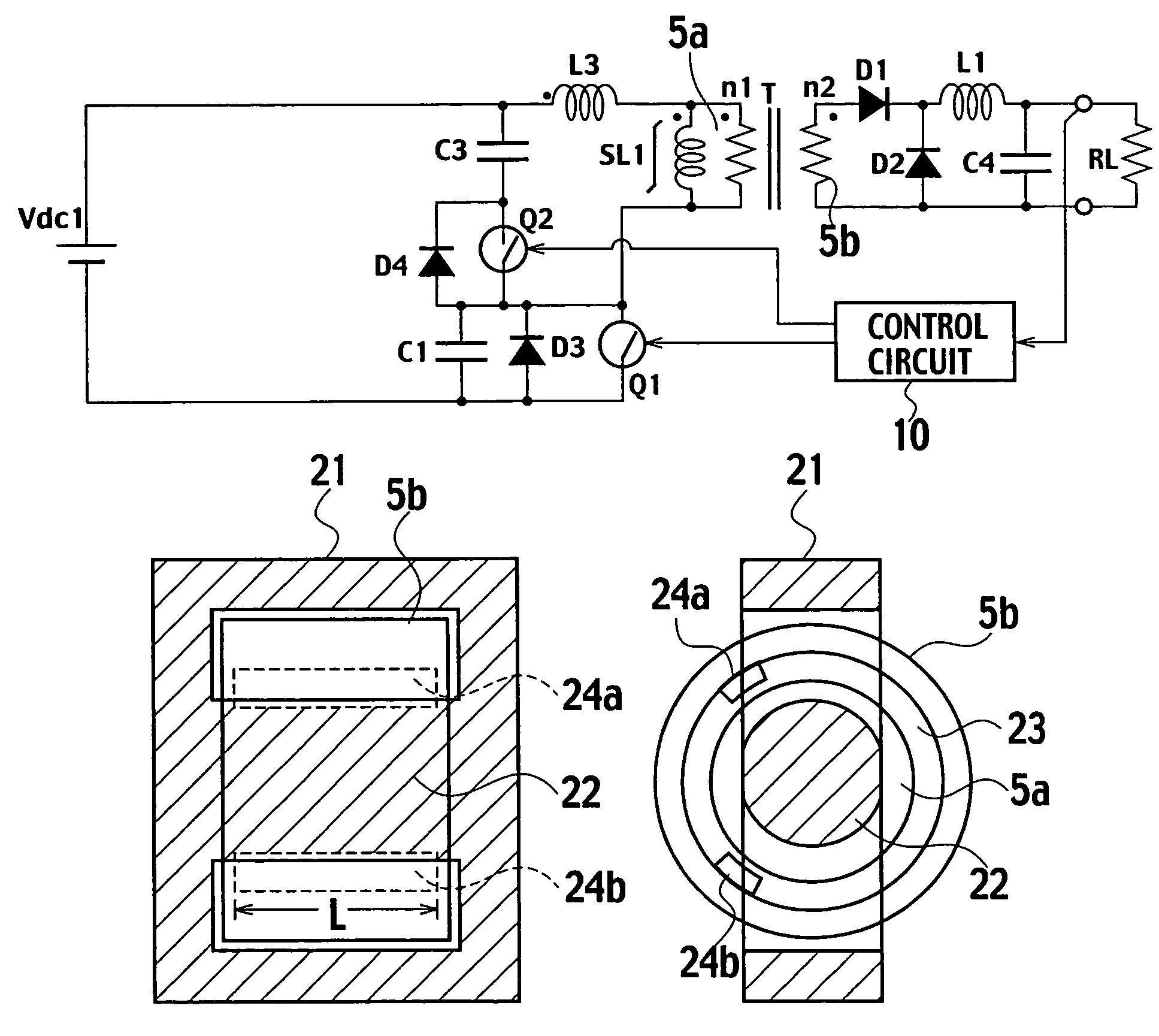
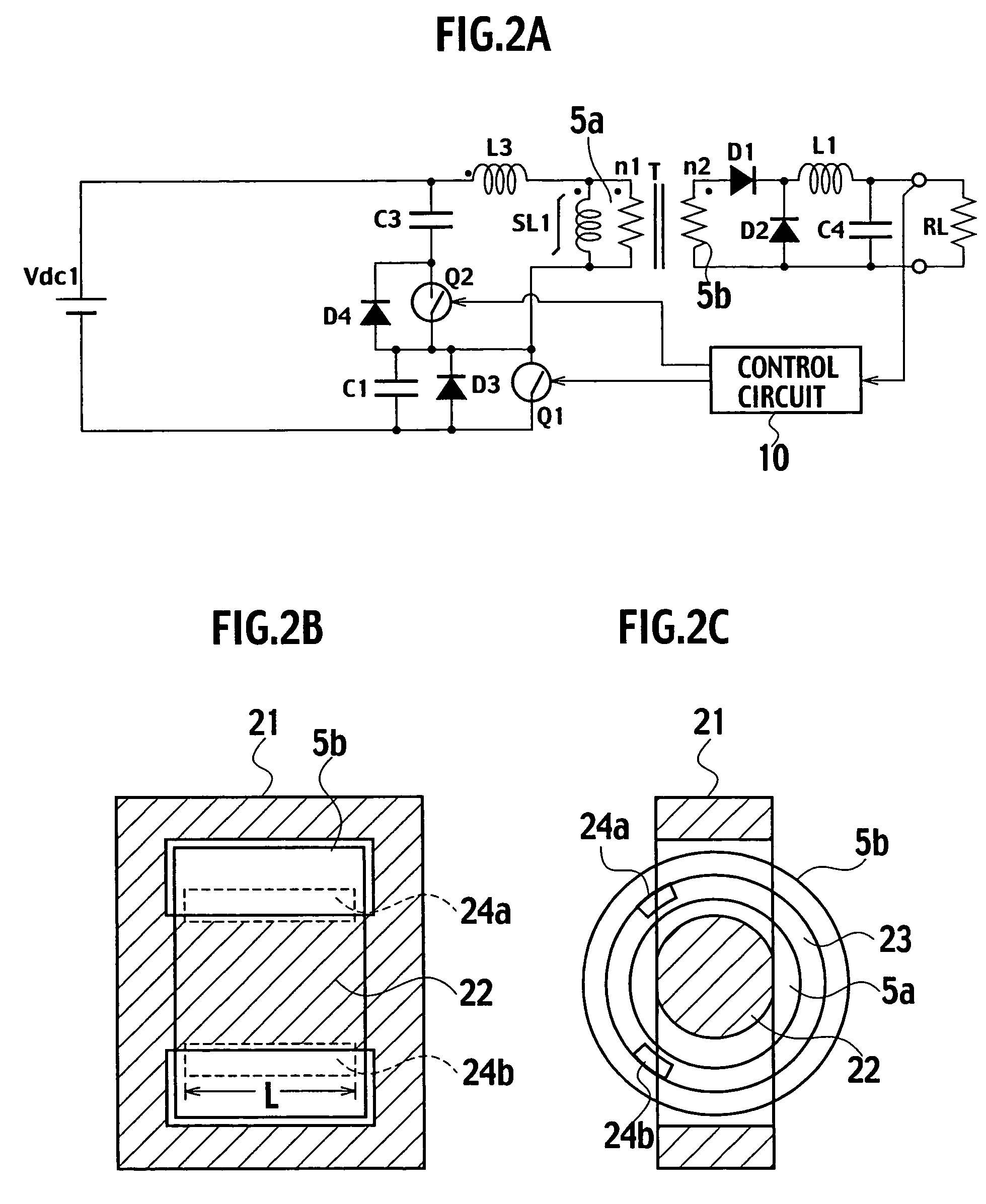
A switching power supply includes: a first series circuit, connected to both terminals of a direct current power supply Vdc1, in which a primary winding 5a of a transformer T, a reactor L3 and a first switch Q1 are connected in series; a second series circuit, connected to both terminals of the primary winding 5a and the reactor L3, which includes a switch Q2 and a capacitor C3; a smoothing circuit D1, D2, L1, C4; and a control circuit 10 alternately turning on and turning off the switches Q1, Q2. The transformer T includes: a main core 21, formed with a magnetic circuit, on which the primary and secondary windings 5a, 5b are wound with a given gap 23; and a plurality of auxiliary cores 24a, 24b disposed in the given gap 23 with a given distance in a circumferential direction of the primary winding 5a. Further, the reactor L3 is formed of a leakage inductance of the transformer T.
Owner:SANKEN ELECTRIC CO LTD
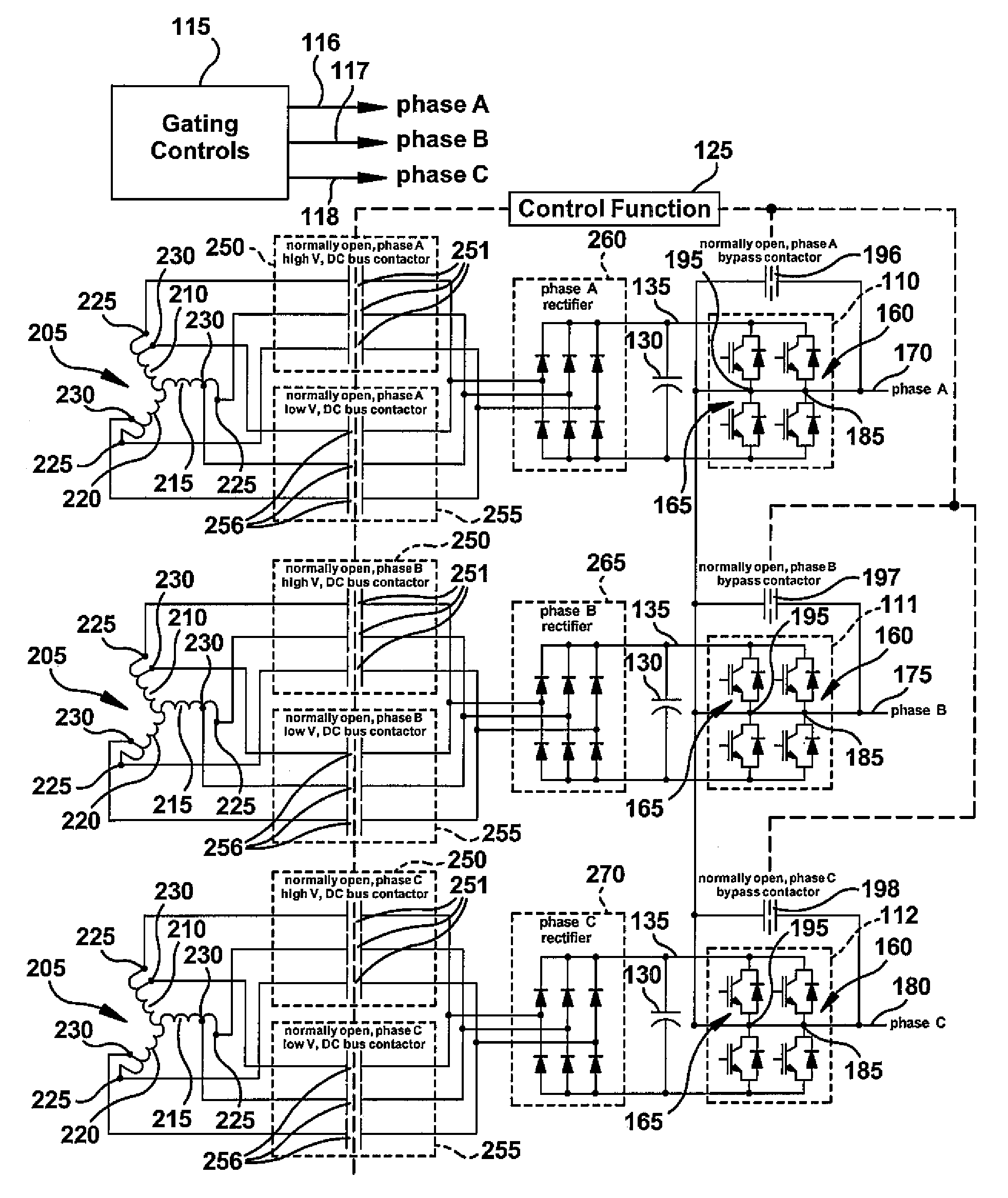
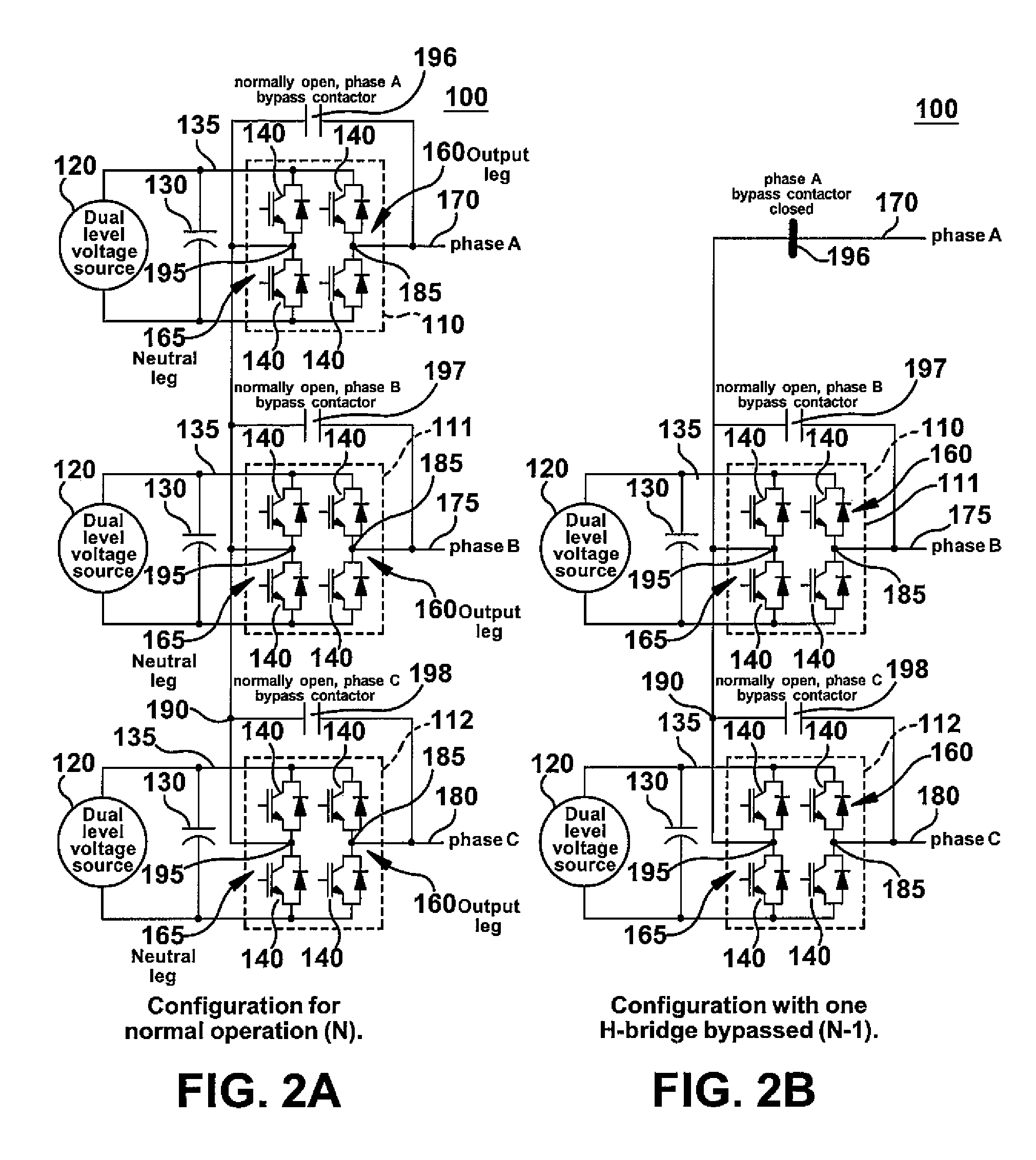
Dual voltage wye-connected H-bridge converter topology for powering a high-speed electric motor
InactiveUS7643318B2High voltageMinimize switching lossesAc-dc conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsLow voltageEngineering
A topology for a three-phase, wye-connected H-bridge converter allowing continued operation when one H-bridge phase has failed by bypassing the failed H-bridge, increasing dc-bus voltage to provide the required output load voltage, and decreasing switching frequency to reduce power losses in semiconductor switches. In normal operation, the dc-bus voltage is operated at a lower voltage, improving the reliability of power semiconductor devices. When an H-bridge is bypassed, the dc-bus is operated at a higher voltage but lower effective switching frequency, reducing semiconductor losses, allowing the converter to put out more current with the same temperature rise in the power switches.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
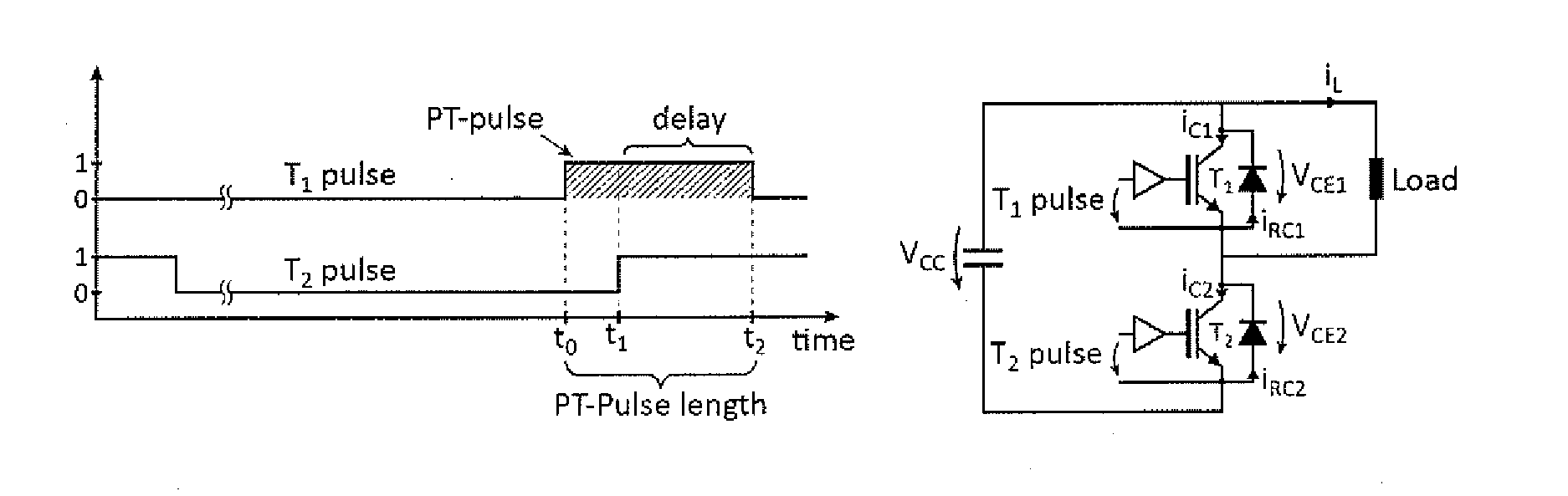
Control of reverse-conducting IGBT
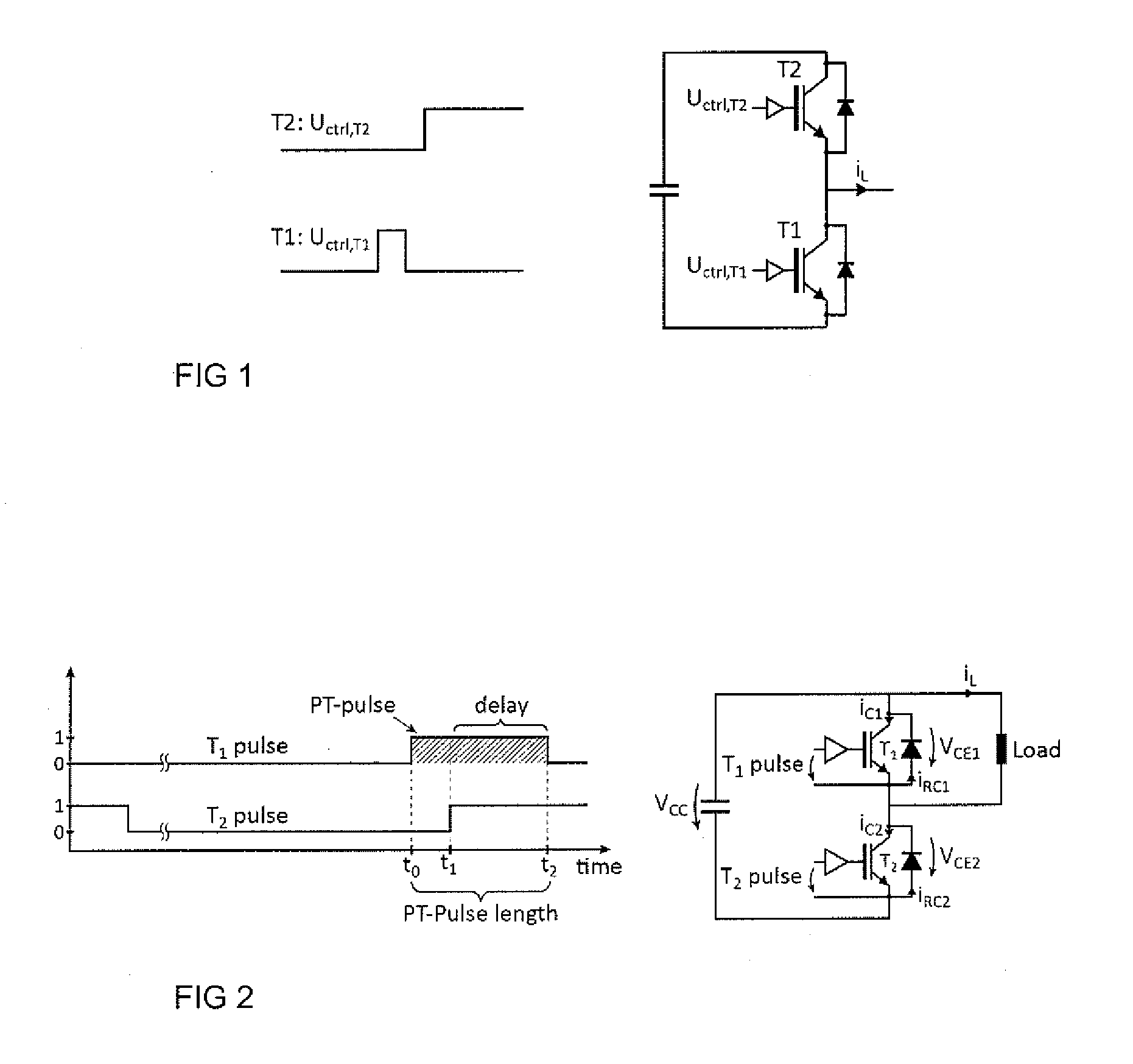
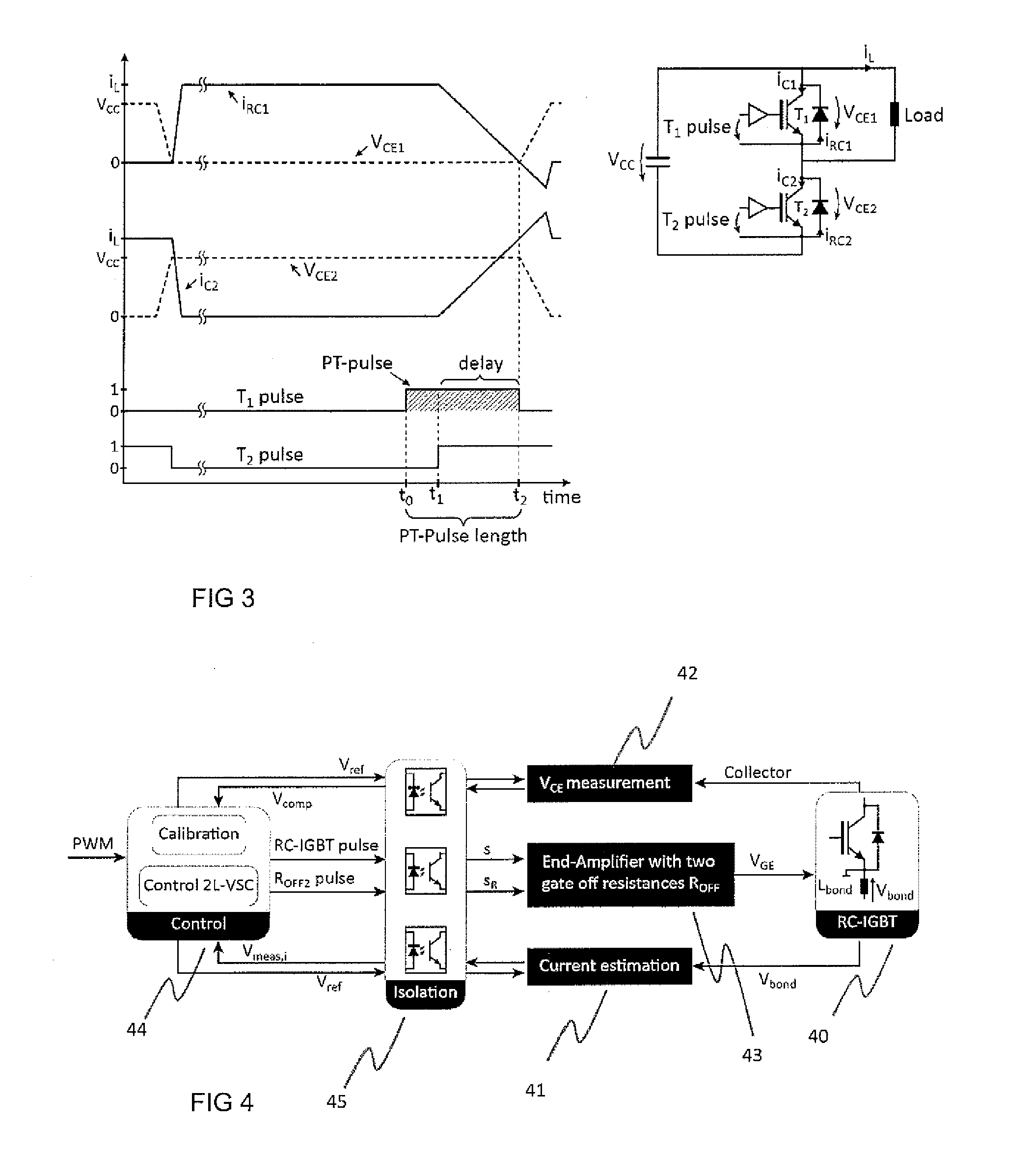
A method and an arrangement of controlling a reverse-conducting IGBT (RC-IGBT) component in a circuit comprising a series connection of controllable switch components where at least one of the controllable switch components is an RC-IGBT and the other component is to be controlled to a conductive state. The method comprising applying a pre-trigger pulse to the gate electrode of the RC-IGBT during reverse conduction of the RC-IGBT at a first time instant (t1), the pre-trigger pulse corresponding to a turn-on gate pulse, applying a turn-on gate pulse at a second time instant (t2) to the other controllable switch component of the series connection for controlling the other controllable switch component to a conductive state such that the pre-trigger pulse and the turn-on gate pulse overlap, and ending the pre-trigger pulse after a delay time at the third time instant (t3), the delay time being the time period when the turn-on gate pulse and the pre-trigger pulse overlap.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com