Patents
Literature
9919 results about "Charge control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Charge control is a technology that lets an electric utility control, in real time, the charging of a gridable (plug-in) vehicle, such as a plug-in hybrid (PHEV) or a battery electric vehicle (BEV). Through charge control, the utility is able to postpone charging of the vehicle during time of peak demand. Additionally, this technology may enable the owner and the power company to track the vehicle's usage and performance, while on the road and while charging.
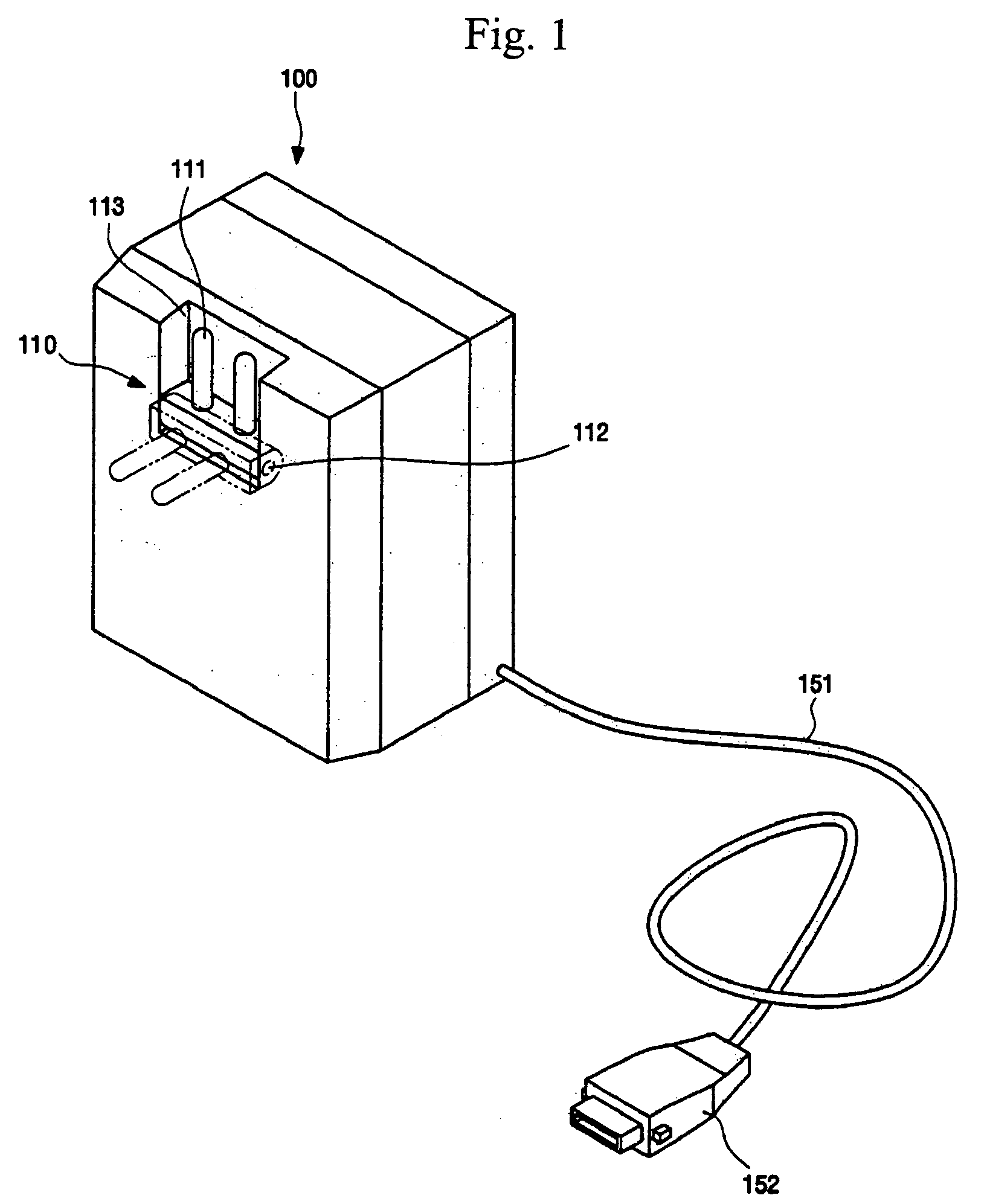
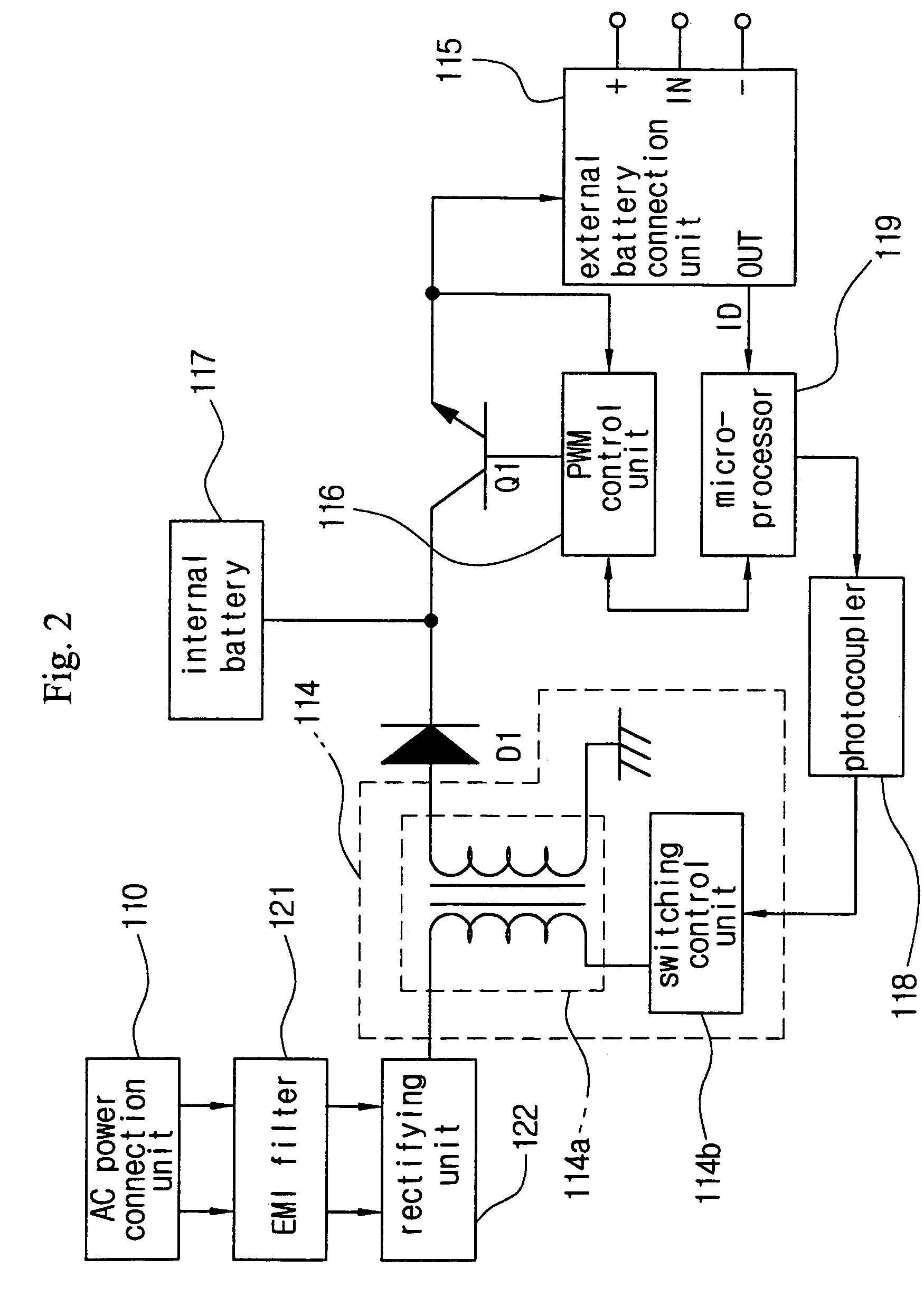
Wireless power charging timing and charging control
ActiveUS20100213895A1Control moreReduce energy costsElectromagnetic wave systemMobile unit charging stationsEnergy rateTime schedule
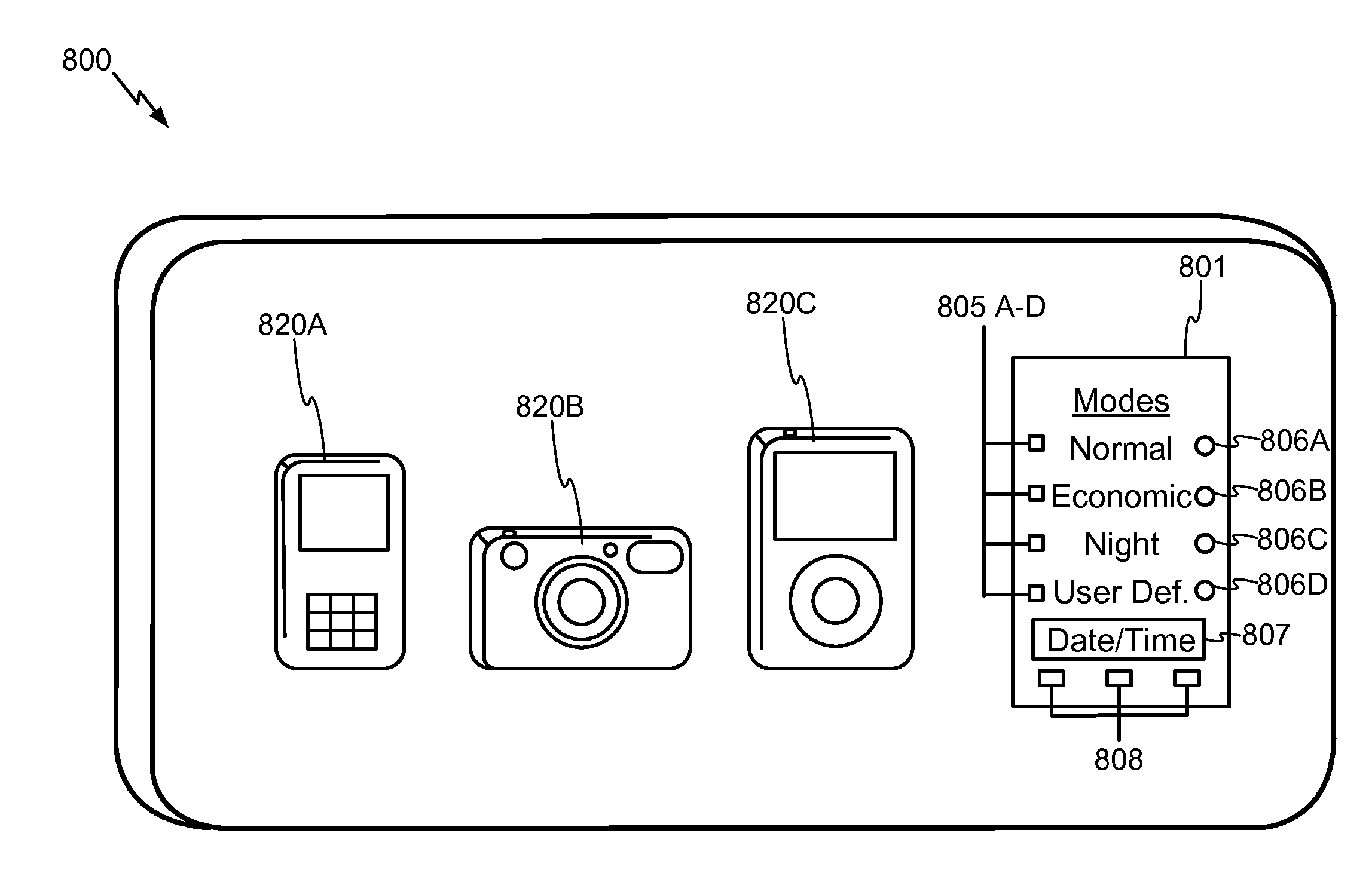
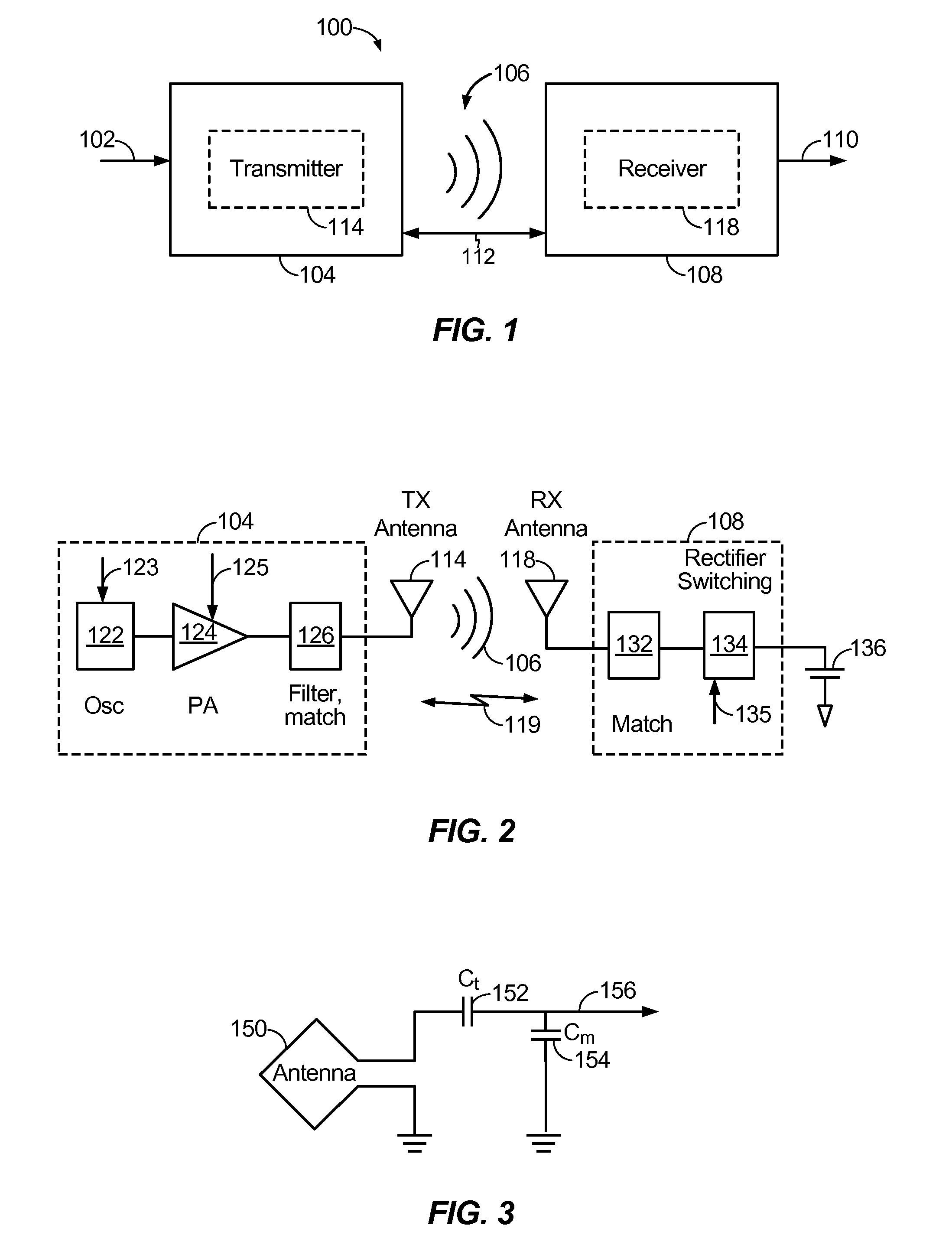
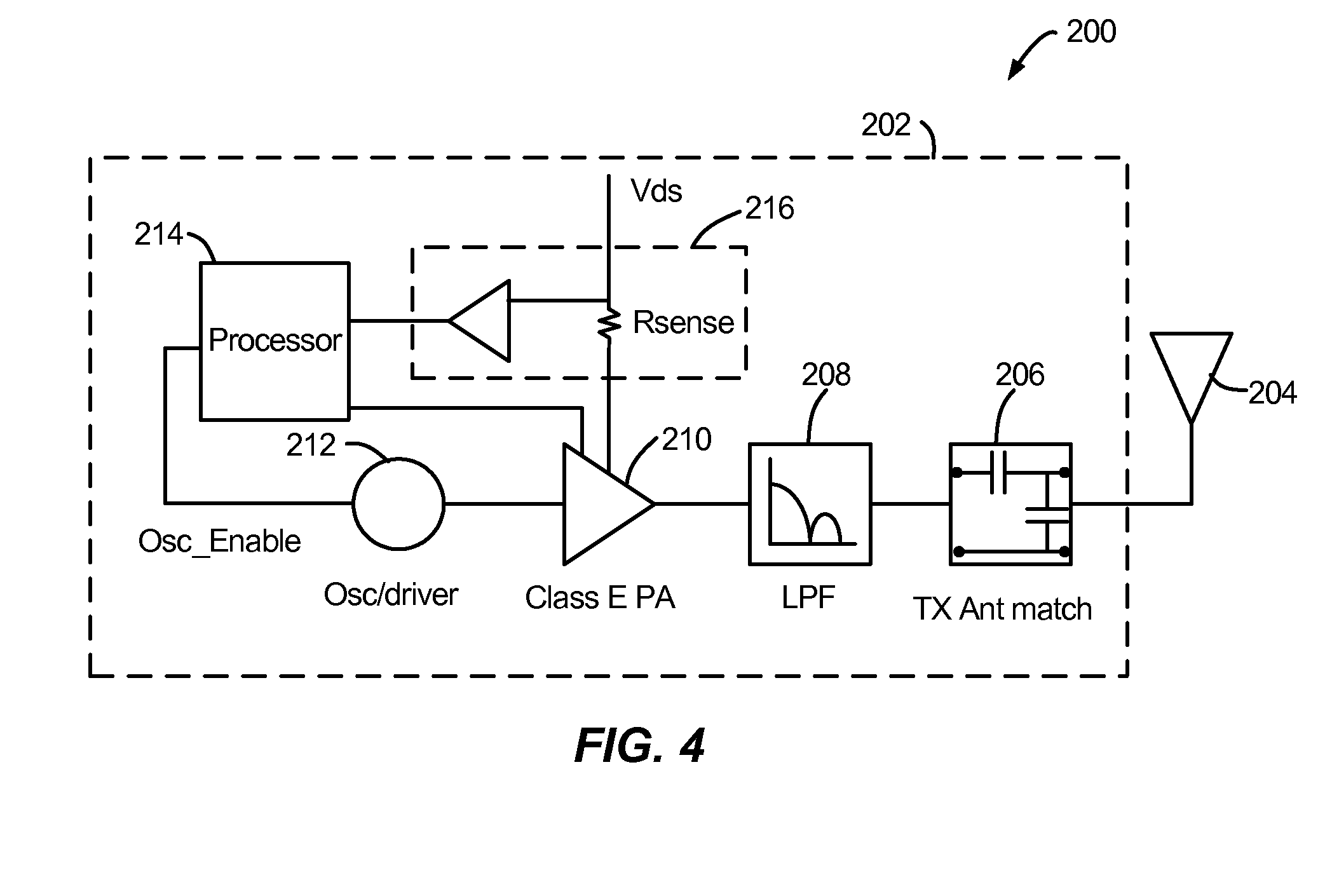
Exemplary embodiments are directed to timing and control of wireless power transfer. A wireless power charging device includes at least one transmitter and a processor in communication with the at least one transmitter. The transmitter is configured for transmitting wireless power to one or more electronic devices, and the processor is configured to deactivate the transmitter during a pre-determined time interval. The charging device may include charging modes that a user may select between from an interface of the charging device. Charging modes may be related to times of operation such as those based on a user schedule, based on energy rates, or with modes programmed by a user. A charging schedule may be created by a user through the interface of the charging device or from an external device in communication with the charging device.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
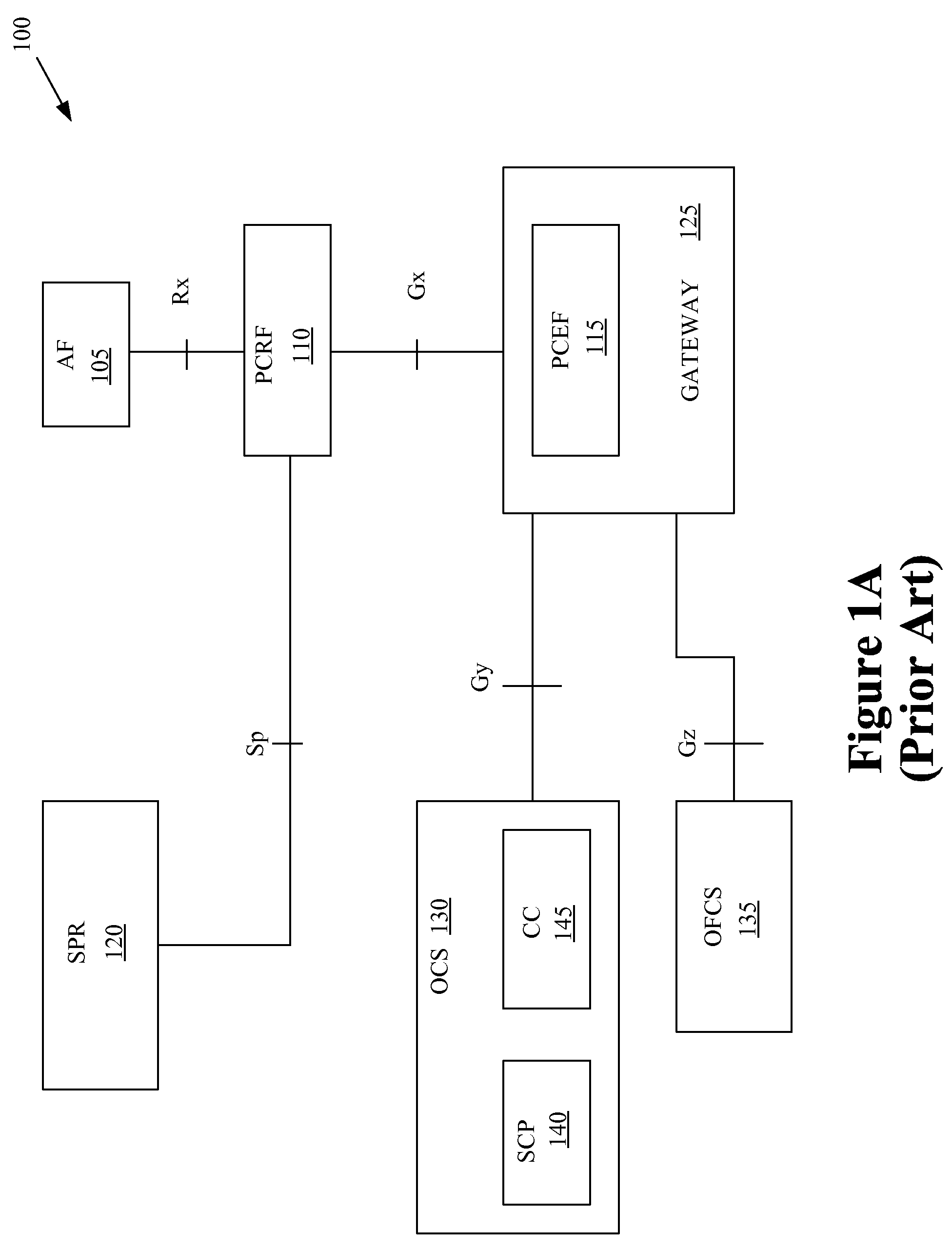
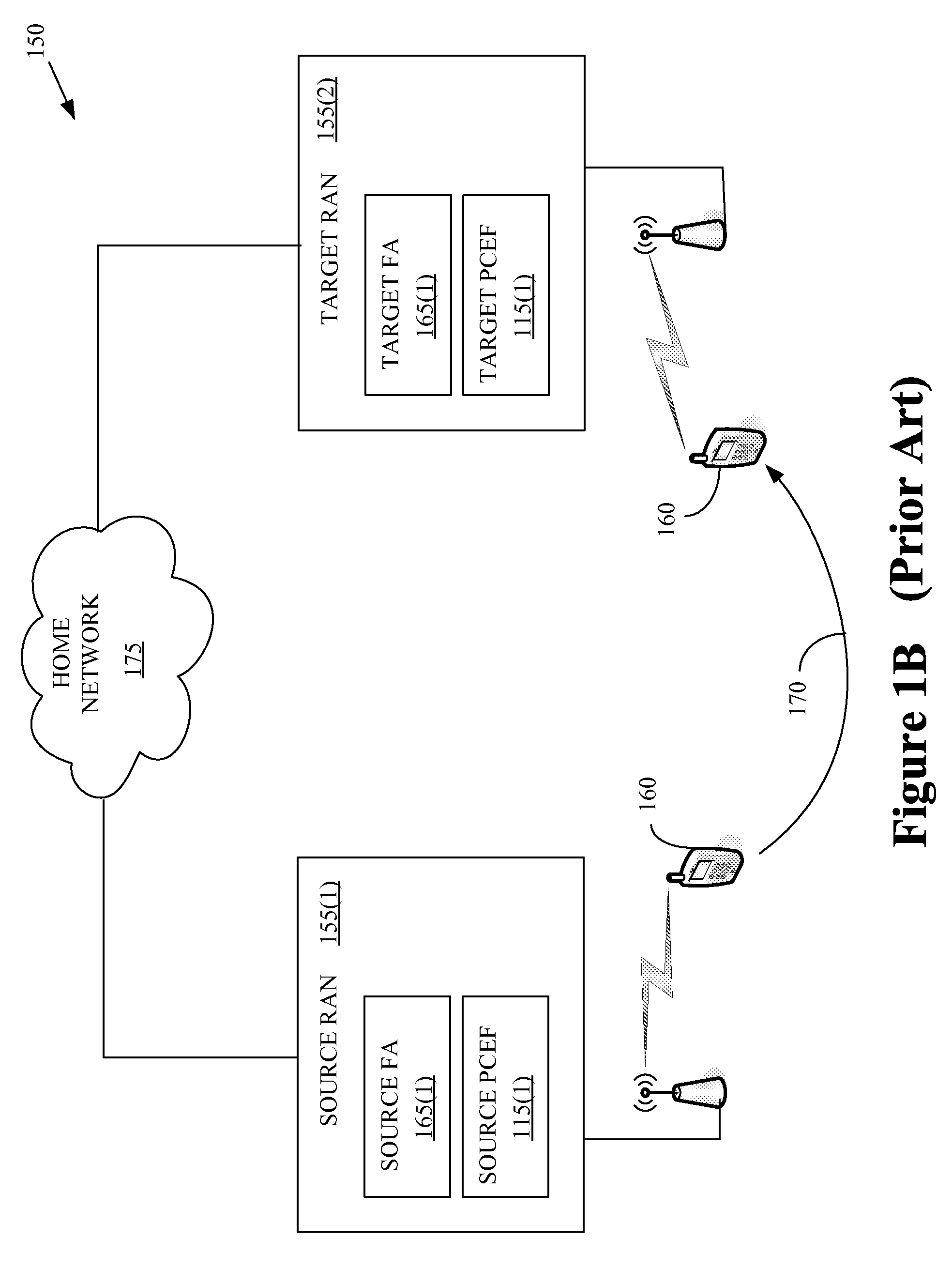
Mobility Aware Policy and Charging Control in a Wireless Communication Network
ActiveUS20080229385A1Metering/charging/biilling arrangementsTelephonic communicationAccess networkCommunications system
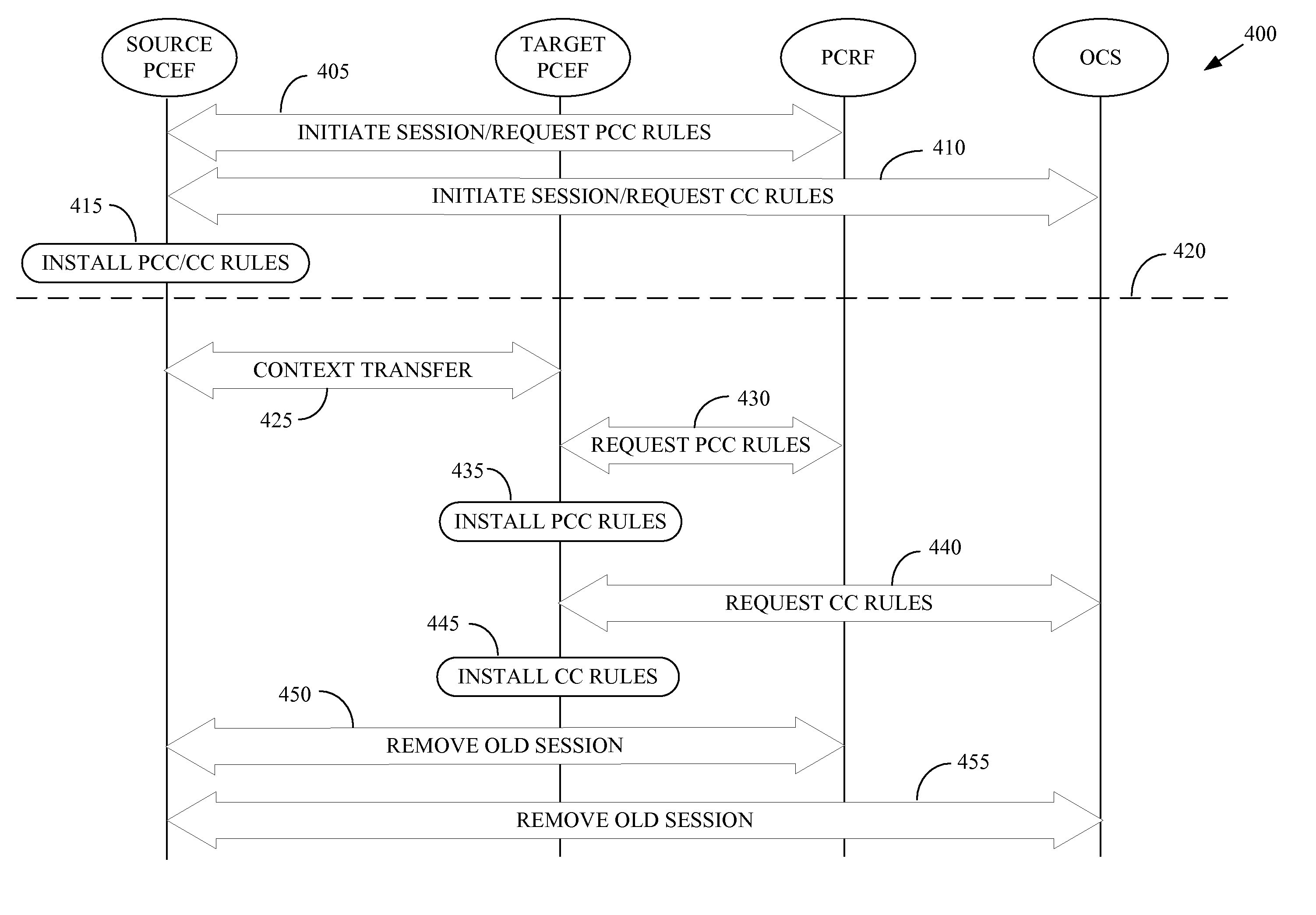
One embodiment of the present invention provides a method for implementation in a policy control and charging rules functional entity in a wireless communication system. The method includes receiving, from at least one of a source policy and charging enforcement function in a source access network or a target policy and charging enforcement function in a target access network, information indicative of a mobile unit that has handed off from the source access network to the target access network. The method also includes establishing a first session for communicating policy and charging rules associated with the mobile unit. The first session is concurrent with a second session for communicating policy and charging rules associated with the mobile unit. The second session was previously established with the source policy and charging enforcement function in the source access network. The method further includes transmitting at least one policy and charging rule to the target policy and charging enforcement function using the first session.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
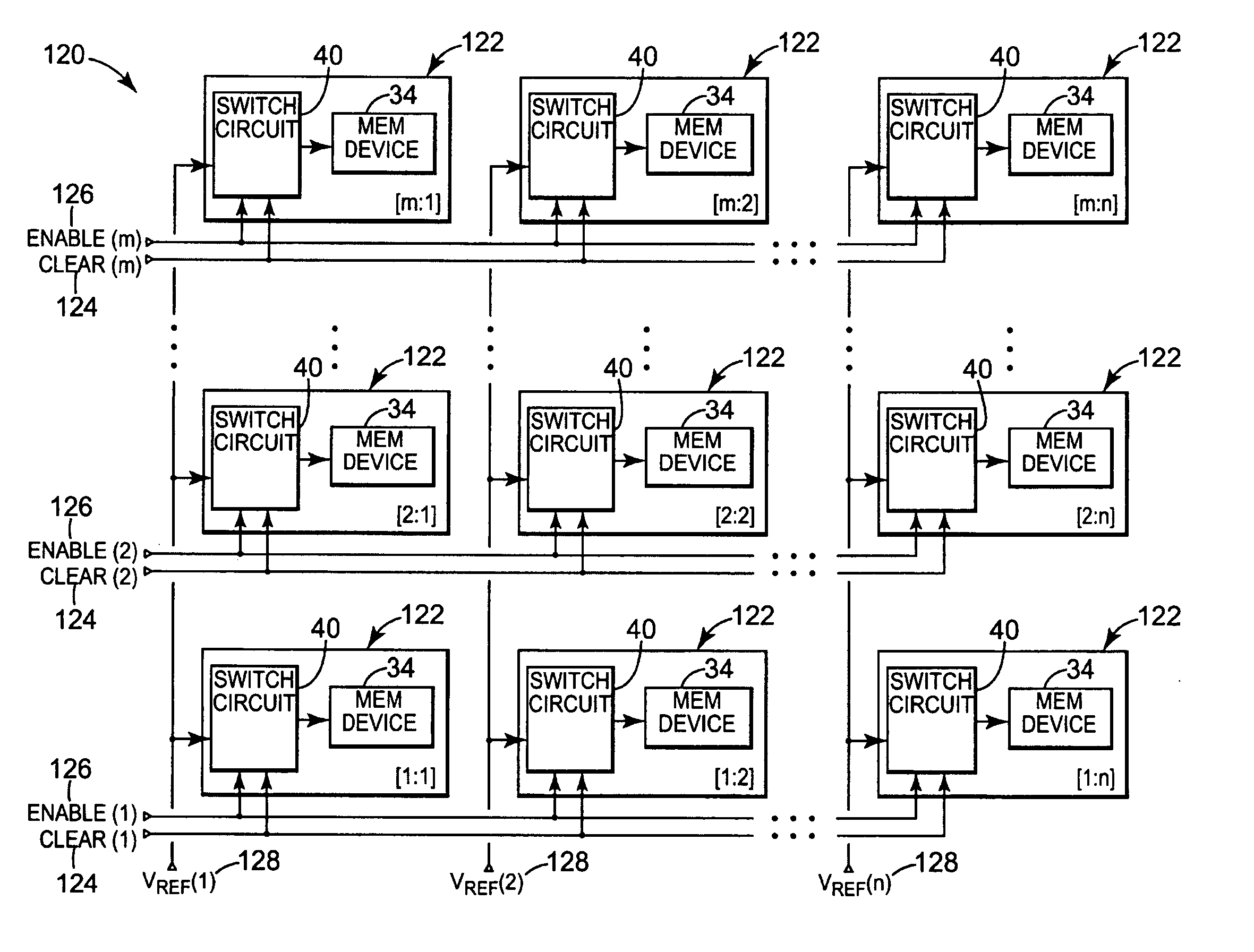
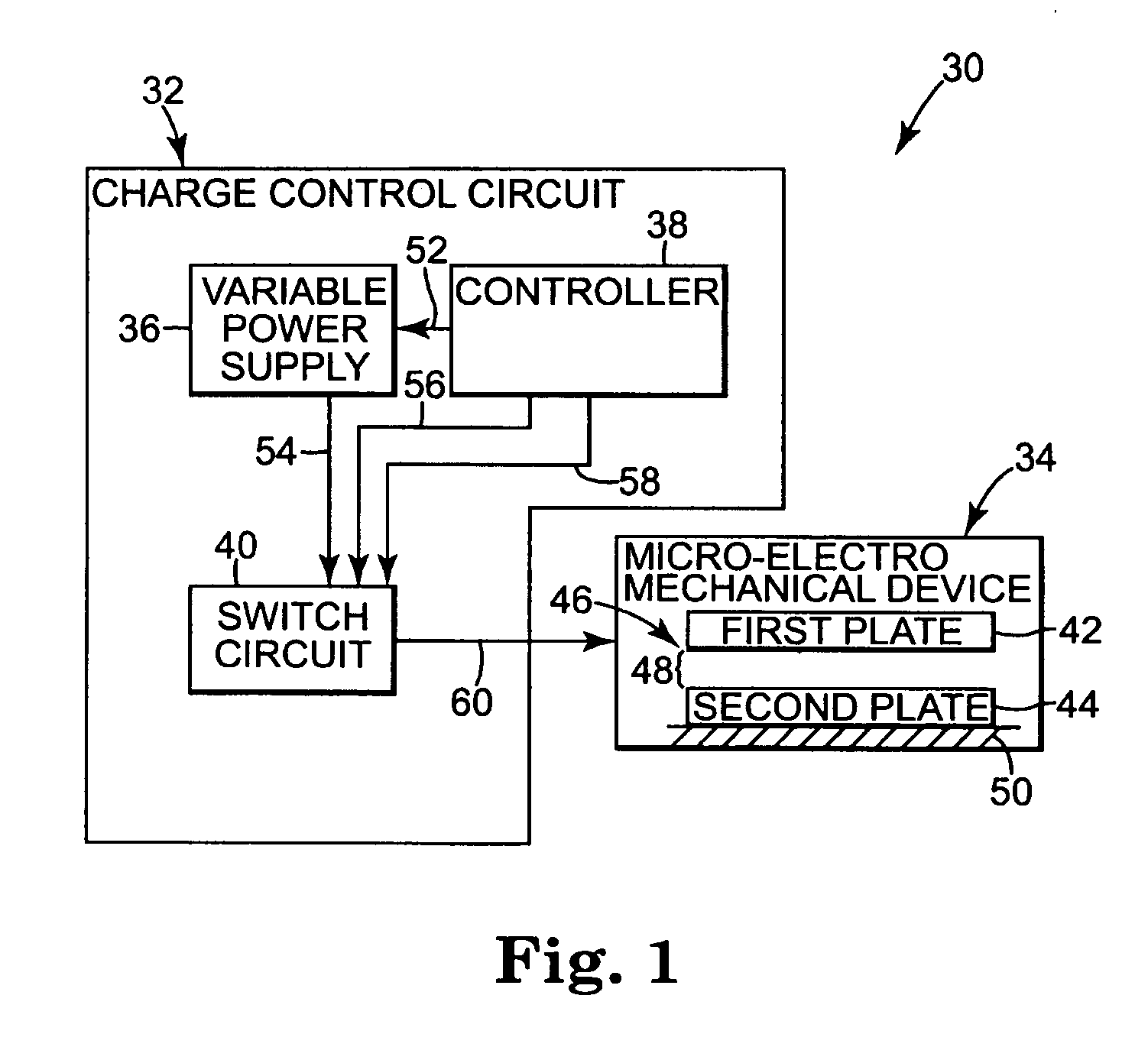
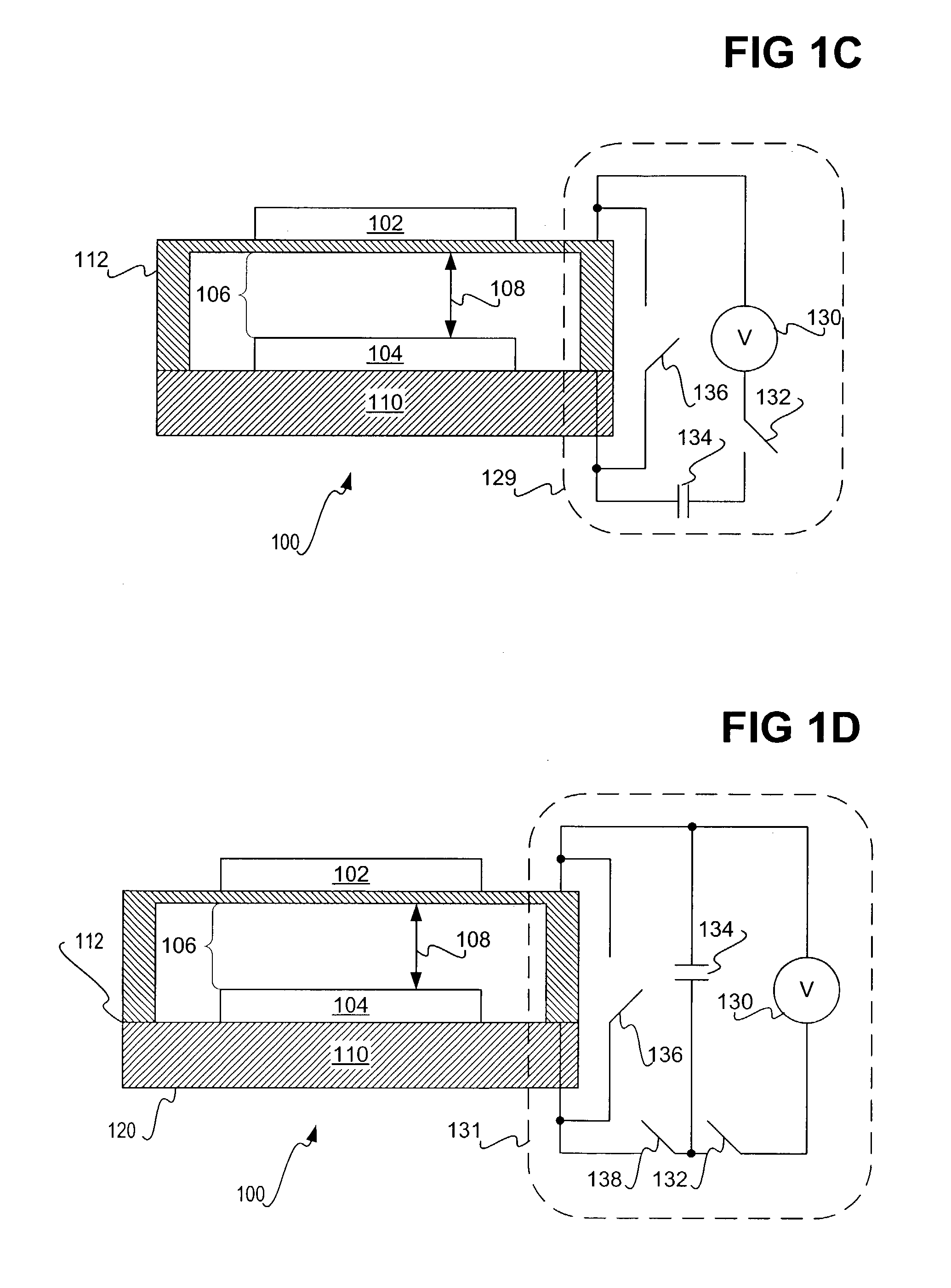
Charge control of micro-electromechanical device
InactiveUS20050001828A1Capacitor with electrode distance variationPolarising elementsElectricityCharge control
A charge control circuit for controlling a micro-electromechanical system (MEMS) device having variable capacitor formed by first conductive plate and a second conductive plate separated by a variable gap distance. The charge control circuit comprises a switch circuit configured to receive a reference voltage having a selected voltage level and configured to respond to an enable signal having a duration at least as long as an electrical time constant constant of the MEMS device, but shorter than a mechanical time constant of the MEMS device, to apply the selected voltage level across the first and second plates for the duration to thereby cause a stored charge having a desired magnitude to accumulate on the variable capacitor, wherein the variable gap distance is a function of the magnitude of the stored charge.
Owner:MARTIN ERIC T +5
Electric charger and power supply device for portable terminal
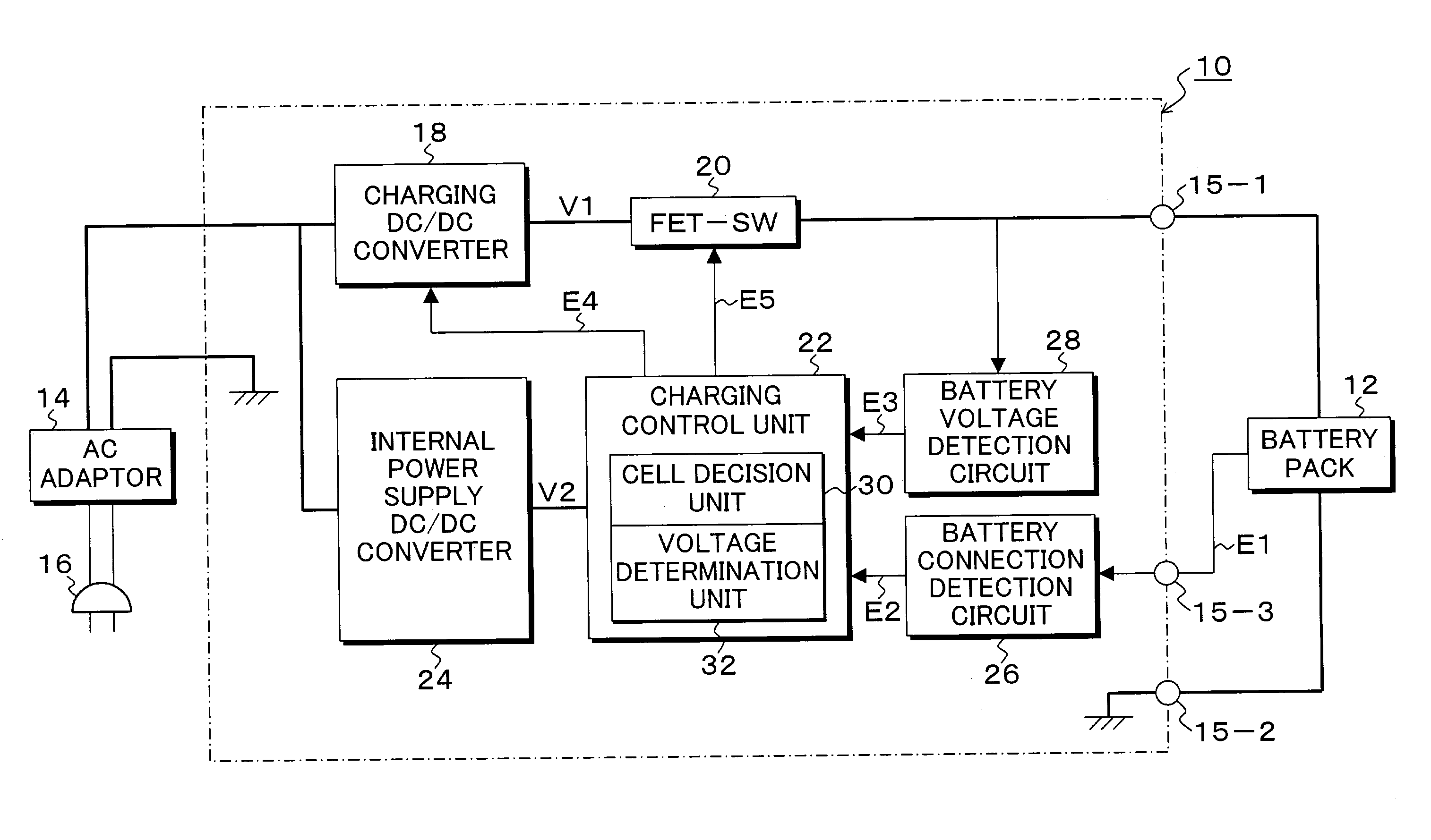
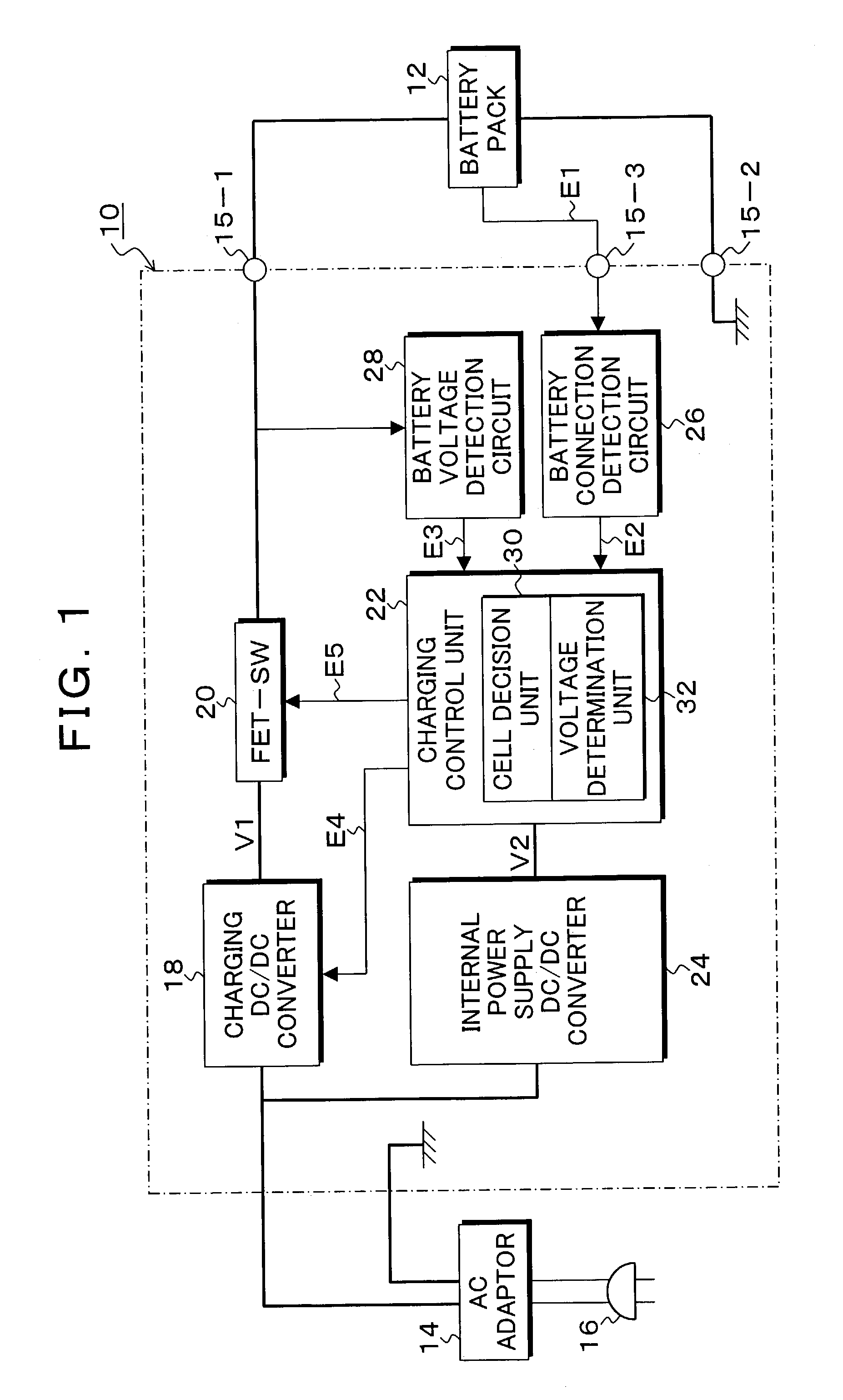
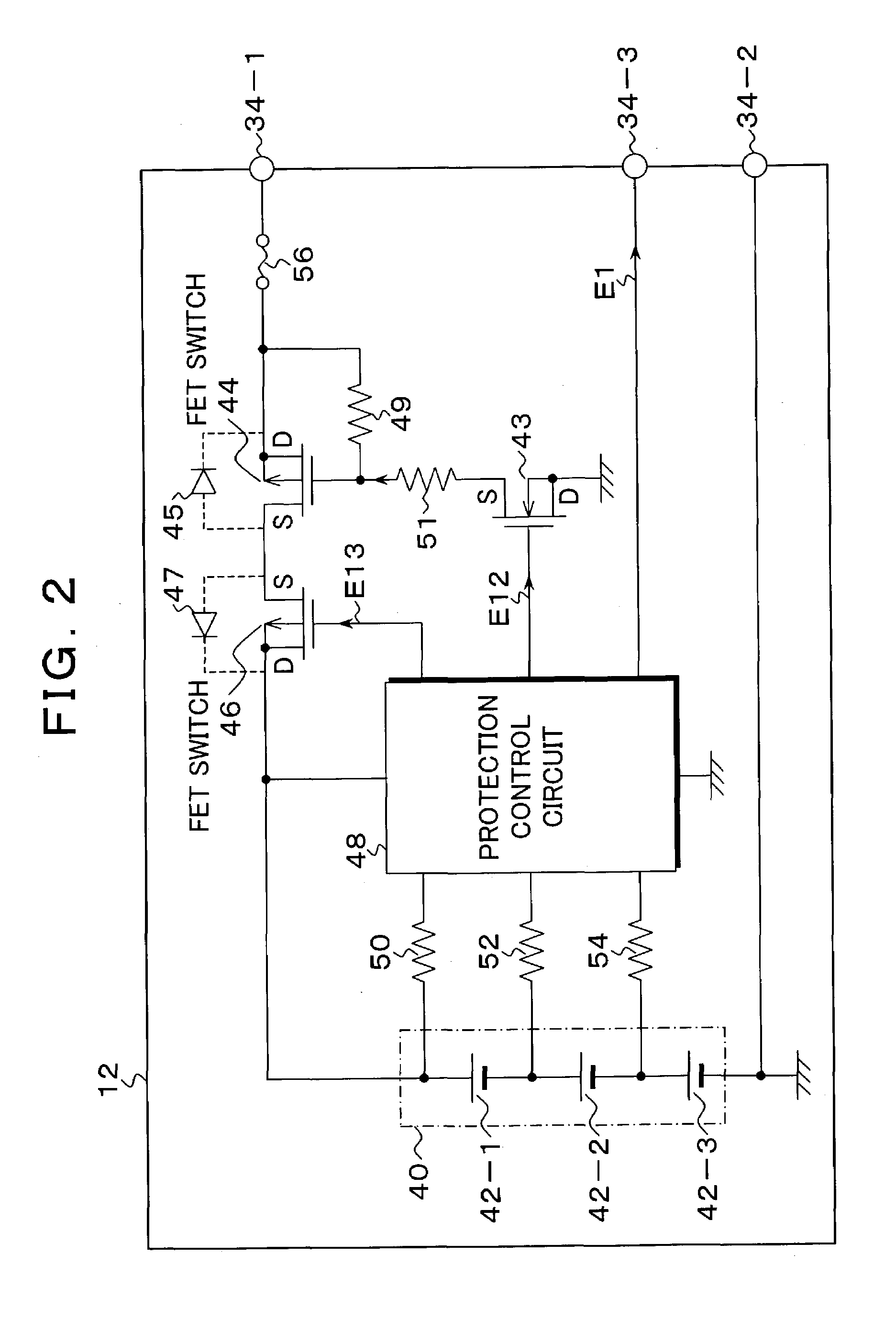
InactiveUS7183748B1Prevents wasteful power consumptionCancel a battery cutoff operationElectric powerArrangements for several simultaneous batteriesCharge controlBattery cell
A charging control unit decides the number of battery cells on the basis of an output voltage of a battery pack, and an output voltage of a charging circuit is determined in accordance with the decided number of battery cells. Even though supply of an external power supply is detected, when a battery connection is not detected, the power supply circuit of the charging control unit is set in a stop state. In addition, when disconnection of the battery is detected, a canceling voltage for canceling a cutoff state caused by overdischarging of the battery is output. In a power supply device for a portable terminal, a capacitor electrically charged by an output voltage of main DC / DC converter is connected as an auxiliary power supply of a backup DC / DC converter to make exchange of the auxiliary battery unnecessary.
Owner:FUJITSU FRONTECH LTD
Portable charger for mobile phone
InactiveUS7166987B2Easy to carryGood adhesionTravelling carriersHoldersCapacitanceElectrical battery
Owner:R F TECH
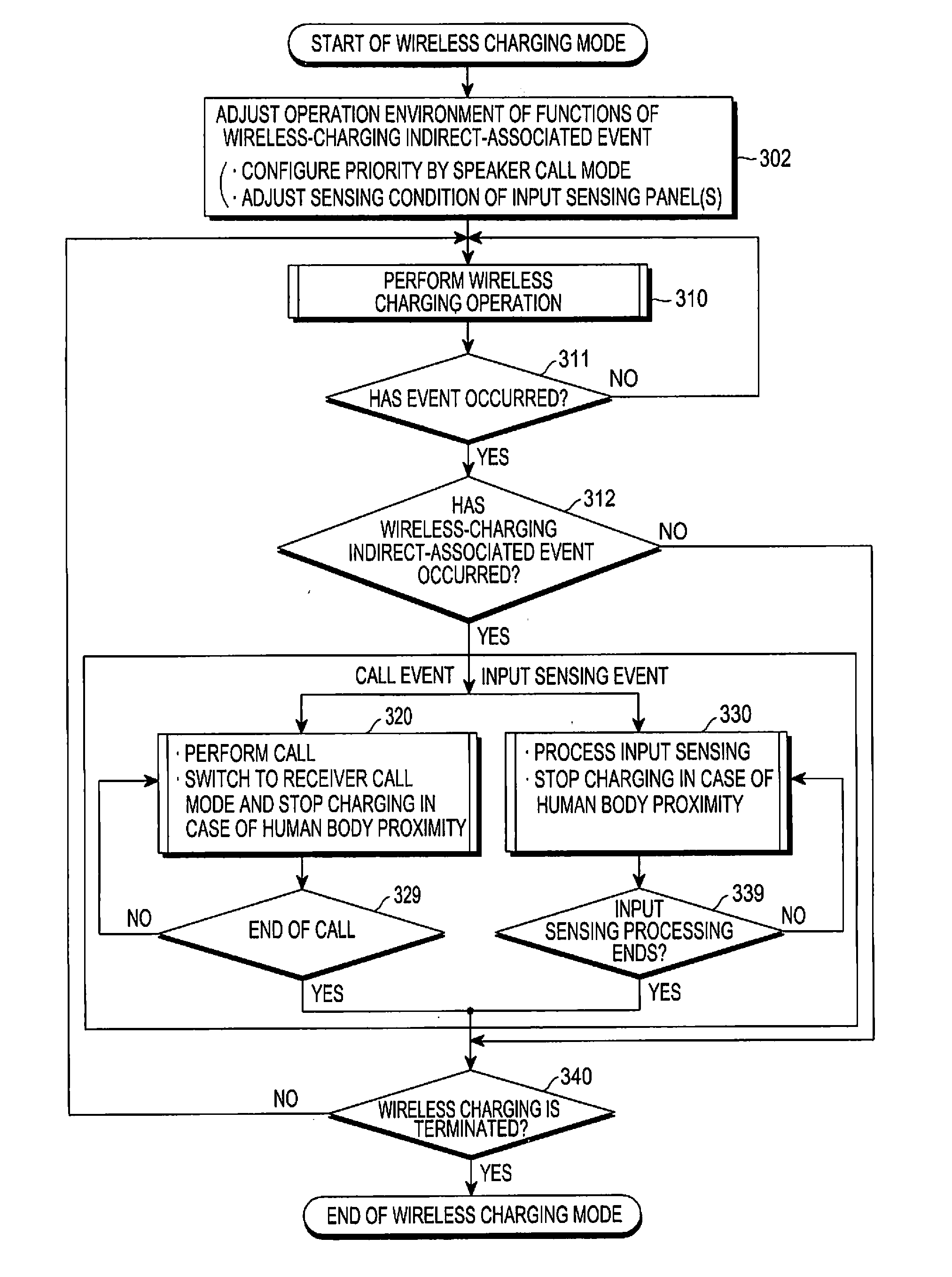
Wireless charging control method and apparatus in wireless power transmission system
ActiveUS20160204642A1Reduce the impactImprove user convenienceCircuit authenticationElectric powerCharge controlElectric power
The present disclosure provides a wireless charging control method. The wireless charging control method in an apparatus having a wireless power reception module, includes sensing an event in a wireless charging mode, determining whether the sensed event is a predetermined wireless-charging indirect-associated event, when the sensed event is a predetermined wireless-charging indirect-associated event, identifying a wireless charging operation corresponding to the wireless-charging indirect-associated event and controlling wireless charging according to the identified wireless charging operation.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
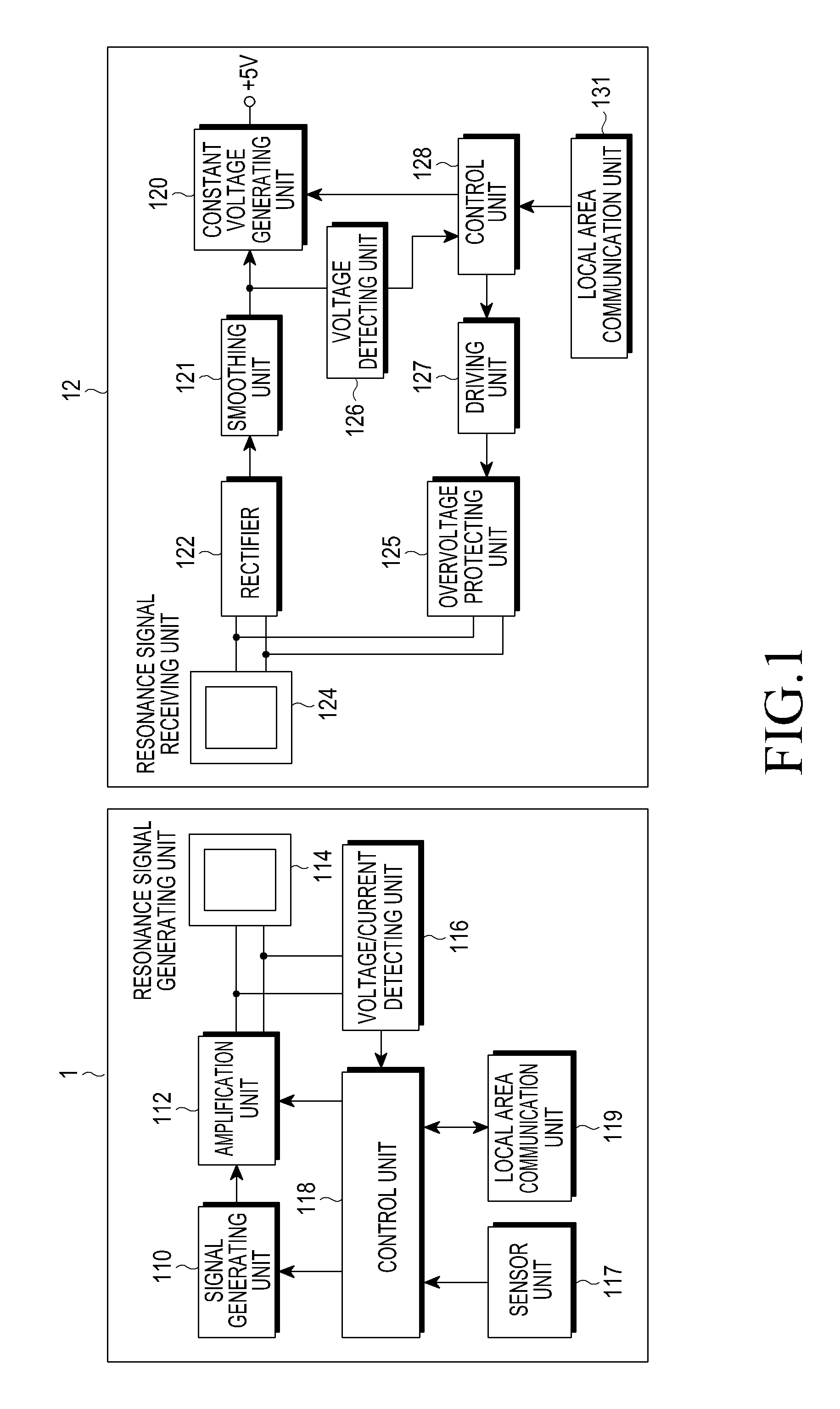
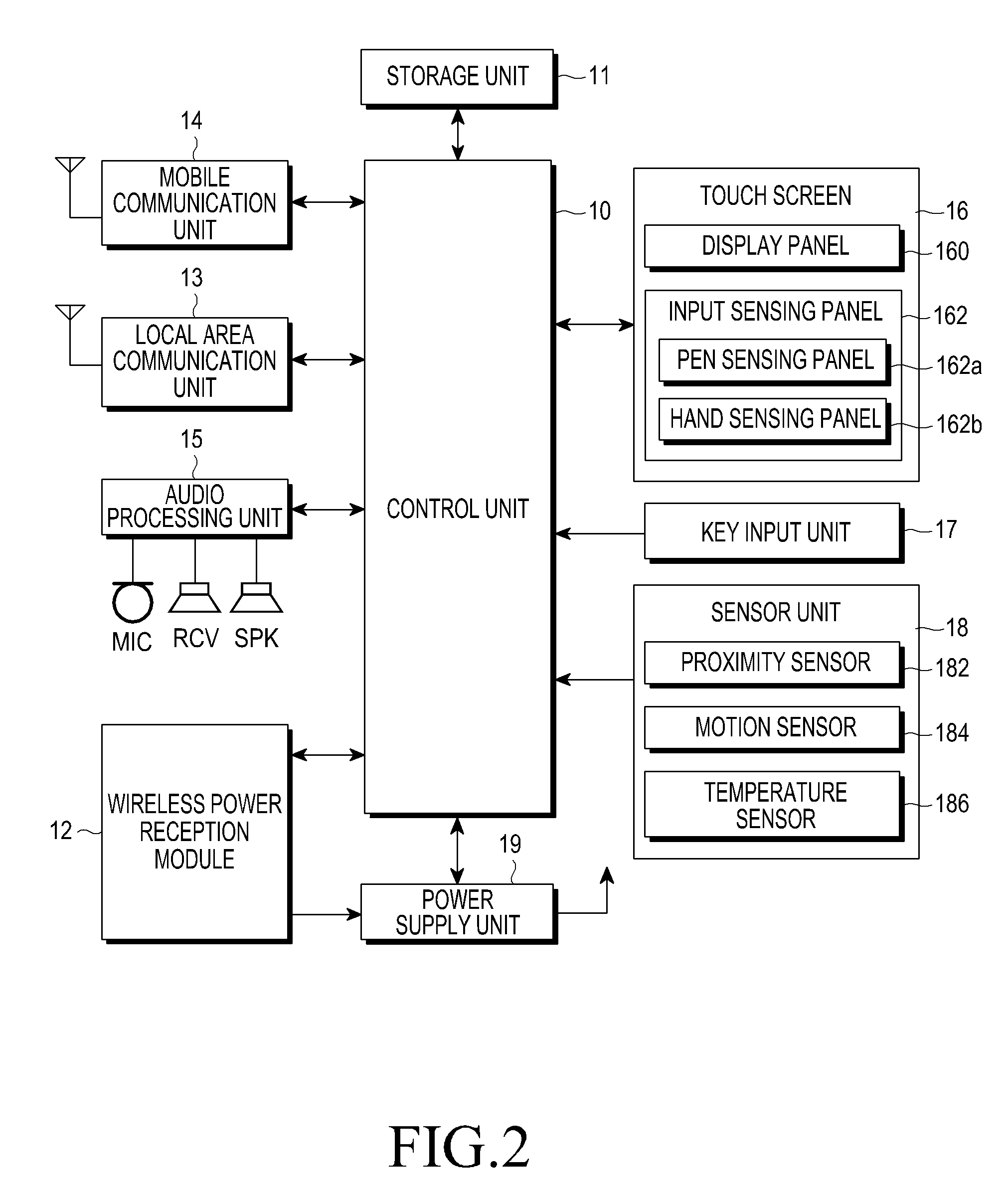
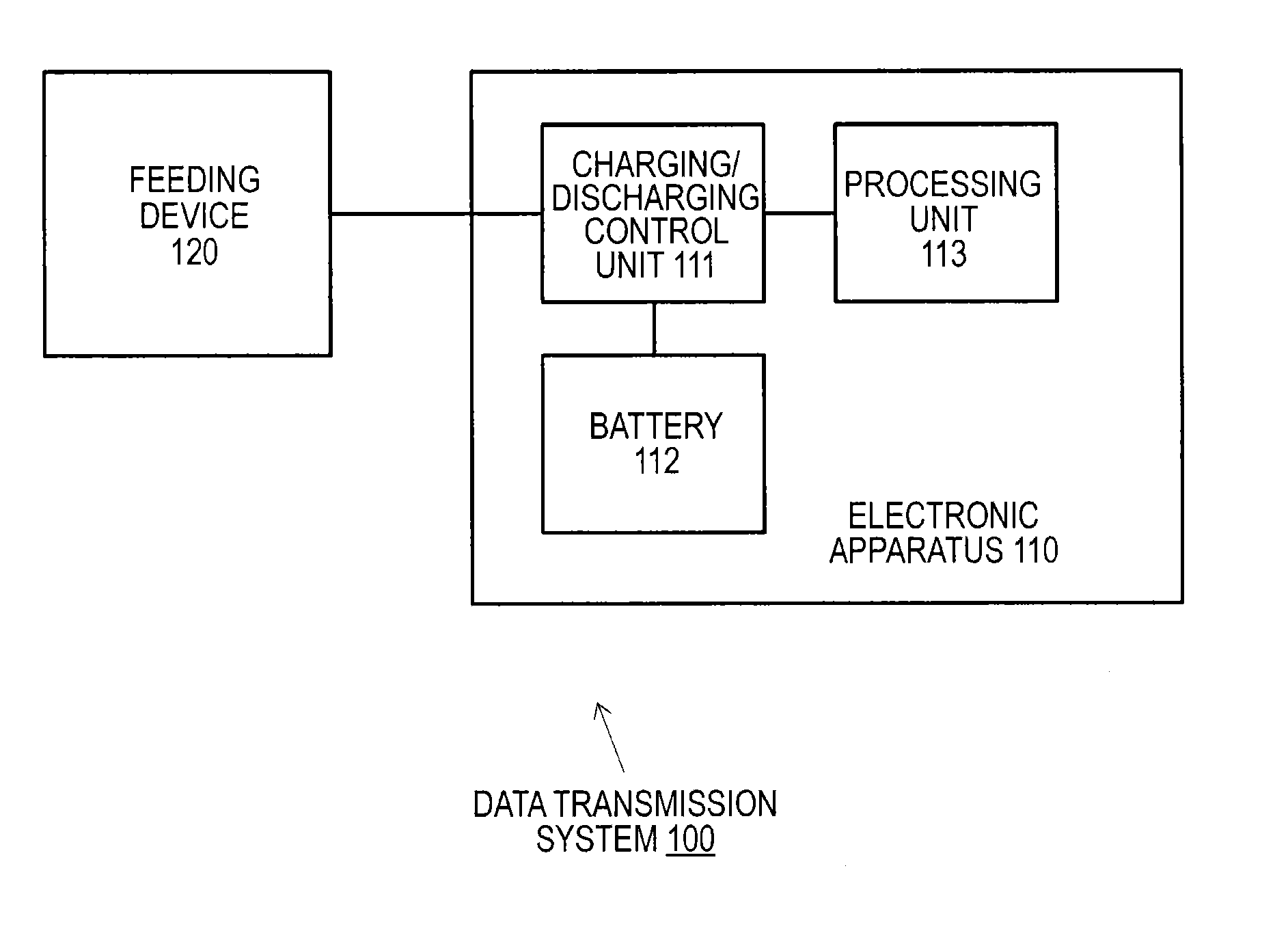
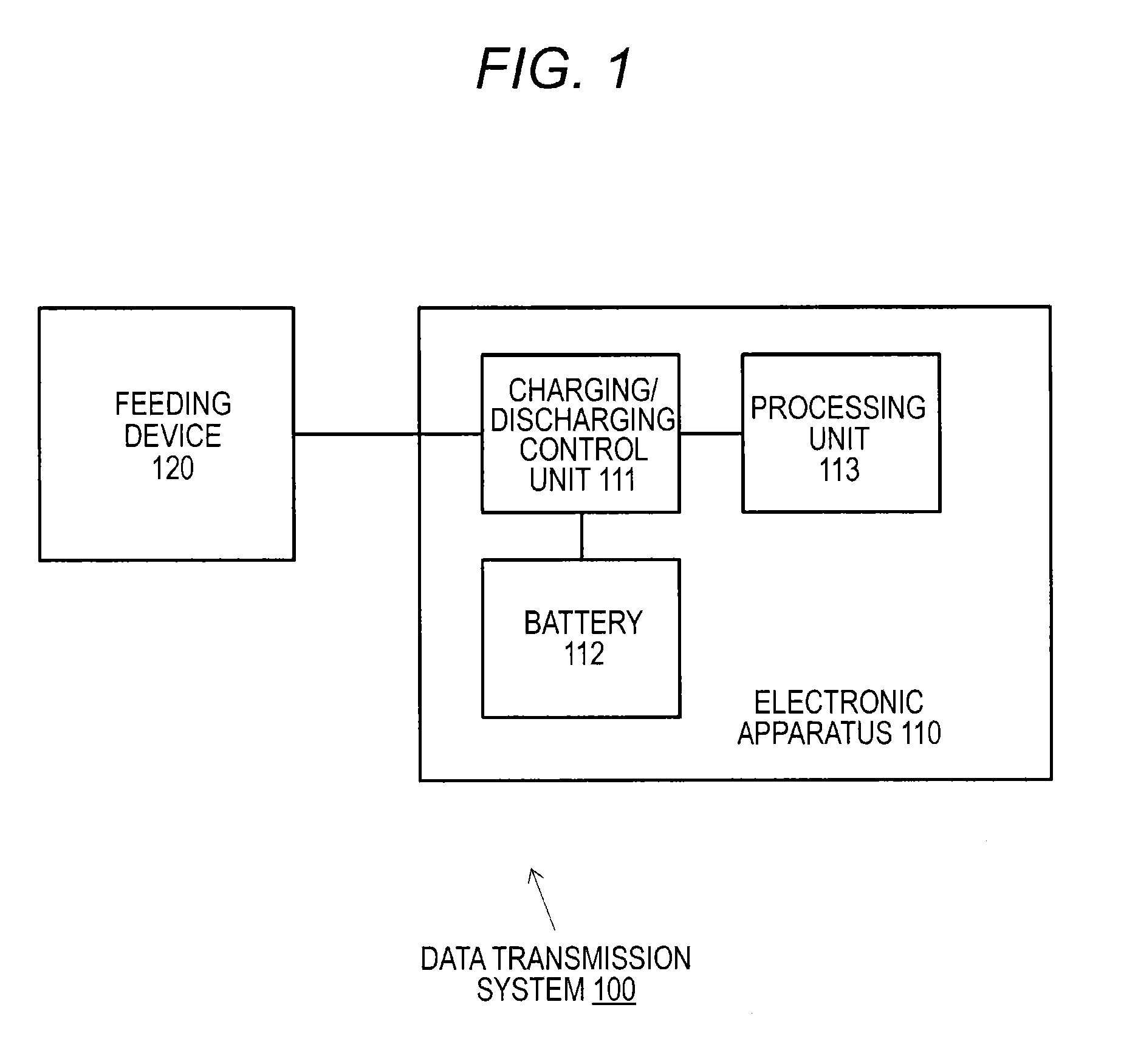
Electronic apparatus, charging control method, charging system, and data transmission system
ActiveUS20140245036A1Efficient chargingMaintain charging efficiencyCircuit monitoring/indicationNear-field systems using receiversElectrical batteryCharge control
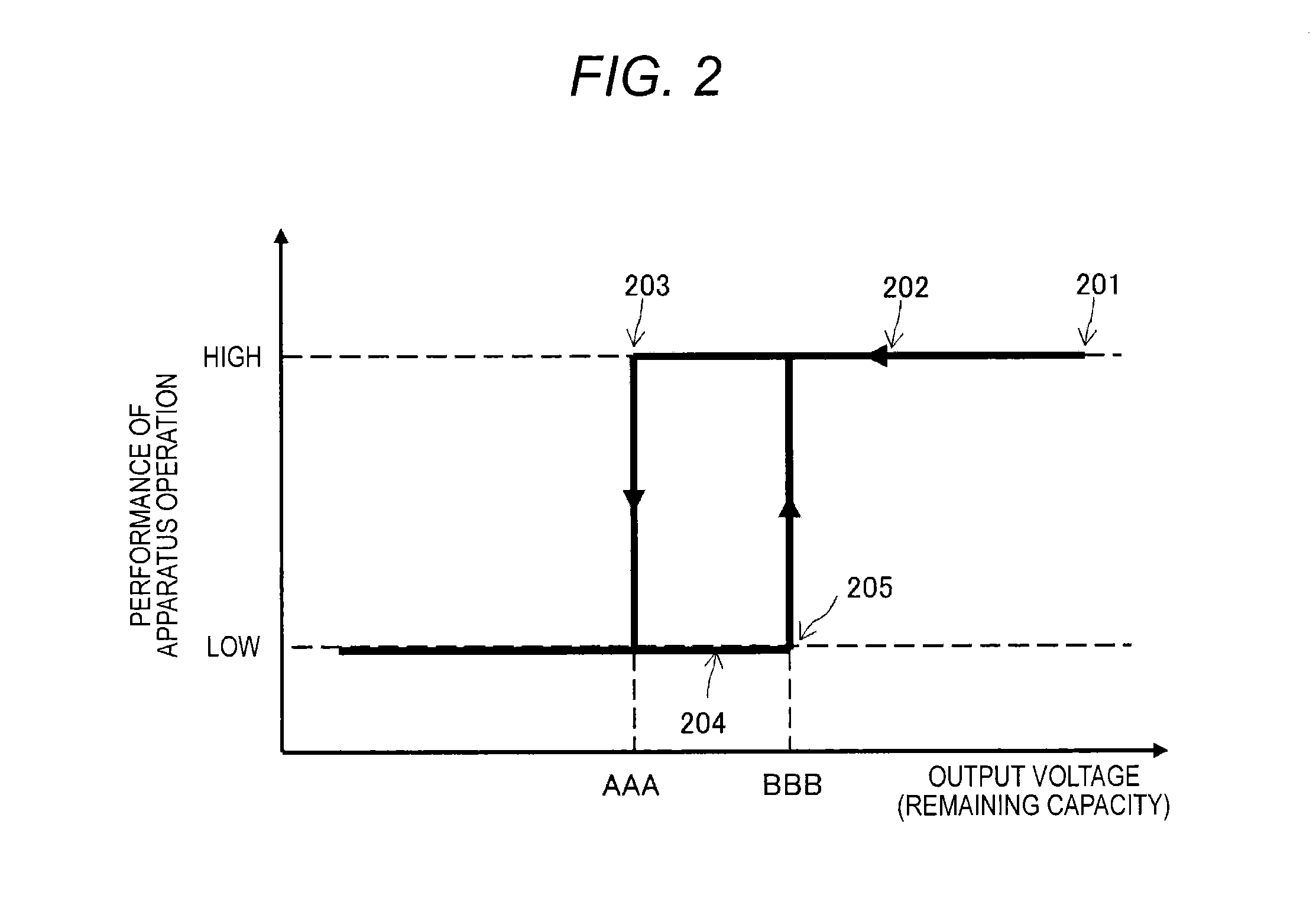
Even in a state in which the remaining capacity of a battery decreases, an apparatus operation is appropriately executed while charging efficiency of the battery is maintained.A processing unit 103 has a first operation mode in which an operation is enabled using only external power from a feeding device 120 and a second operation mode in which the operation is enabled by feeding from a battery 102 in addition to the external power from the feeding device 120. When the remaining capacity of the battery 102 is sufficient, the processing unit 103 executes an apparatus operation in the second operation mode. However, when the remaining capacity of the battery 102 decreases, the processing unit 103 changes an operation mode to the first operation mode and executes charging of the battery 102 while continuously executing the apparatus operation.
Owner:SONY CORP
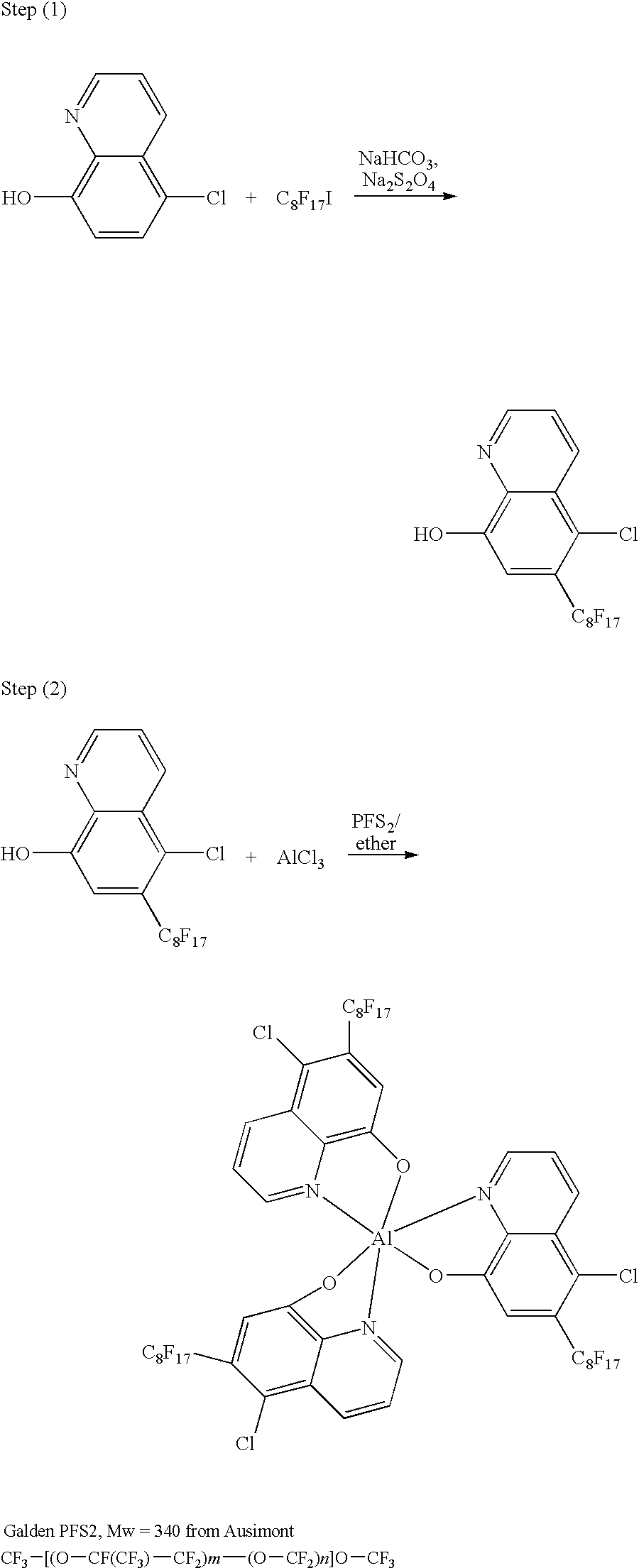
Electrophoretic dispersion with a fluorinated solvent and a charge controlling agent
ActiveUS7110162B2Improve adsorption capacityImprove surface activityStatic indicating devicesAzo dyesElectrophoresisCharge control
The invention relates to a novel electrophoretic dispersion comprising a fluorinated solvent as the continuous phase, charged pigment particles or pigment containing microcapsules as the dispersed phase, and the charge of the pigment particles is provided by a charge controlling agent comprising:(i) a soluble fluorinated electron accepting or proton donating compound or polymer in the continuous phase and an electron donating or proton accepting compound or polymer in the dispersed phase; or(ii) a soluble fluorinated electron donating or proton accepting compound or polymer in the continuous phase and an electron accepting or proton donating compound or polymer in the dispersed phase.
Owner:E INK CALIFORNIA
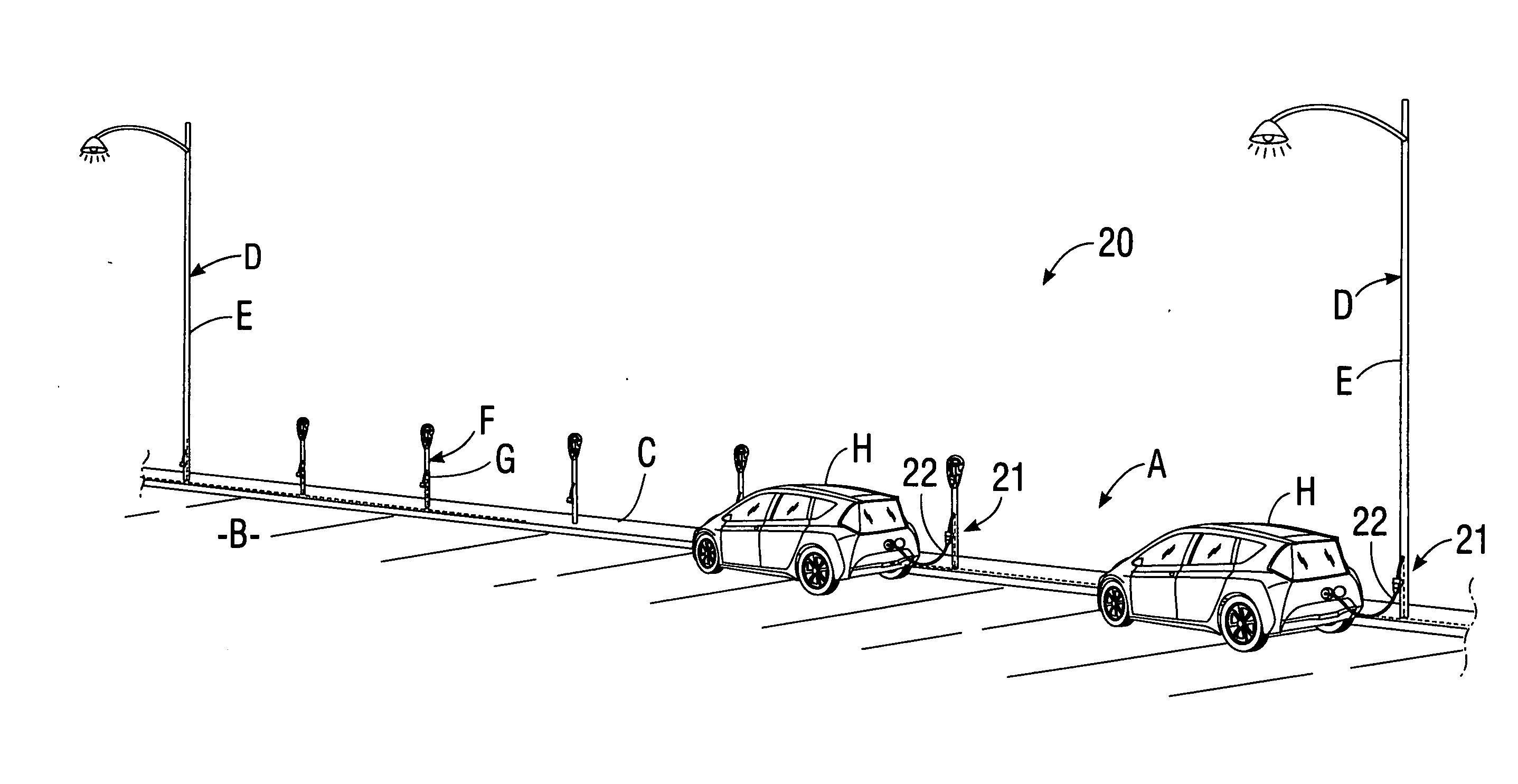
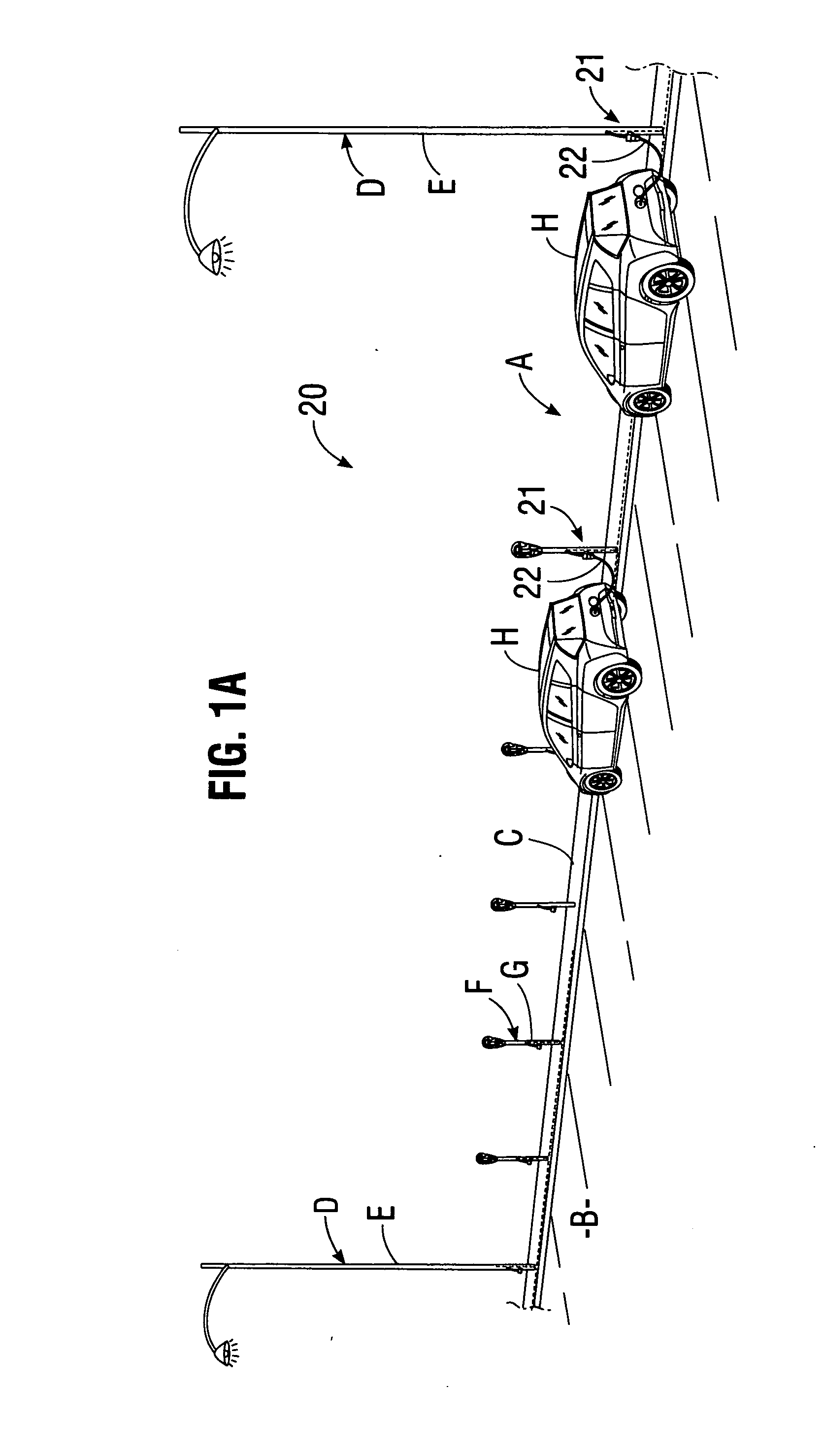
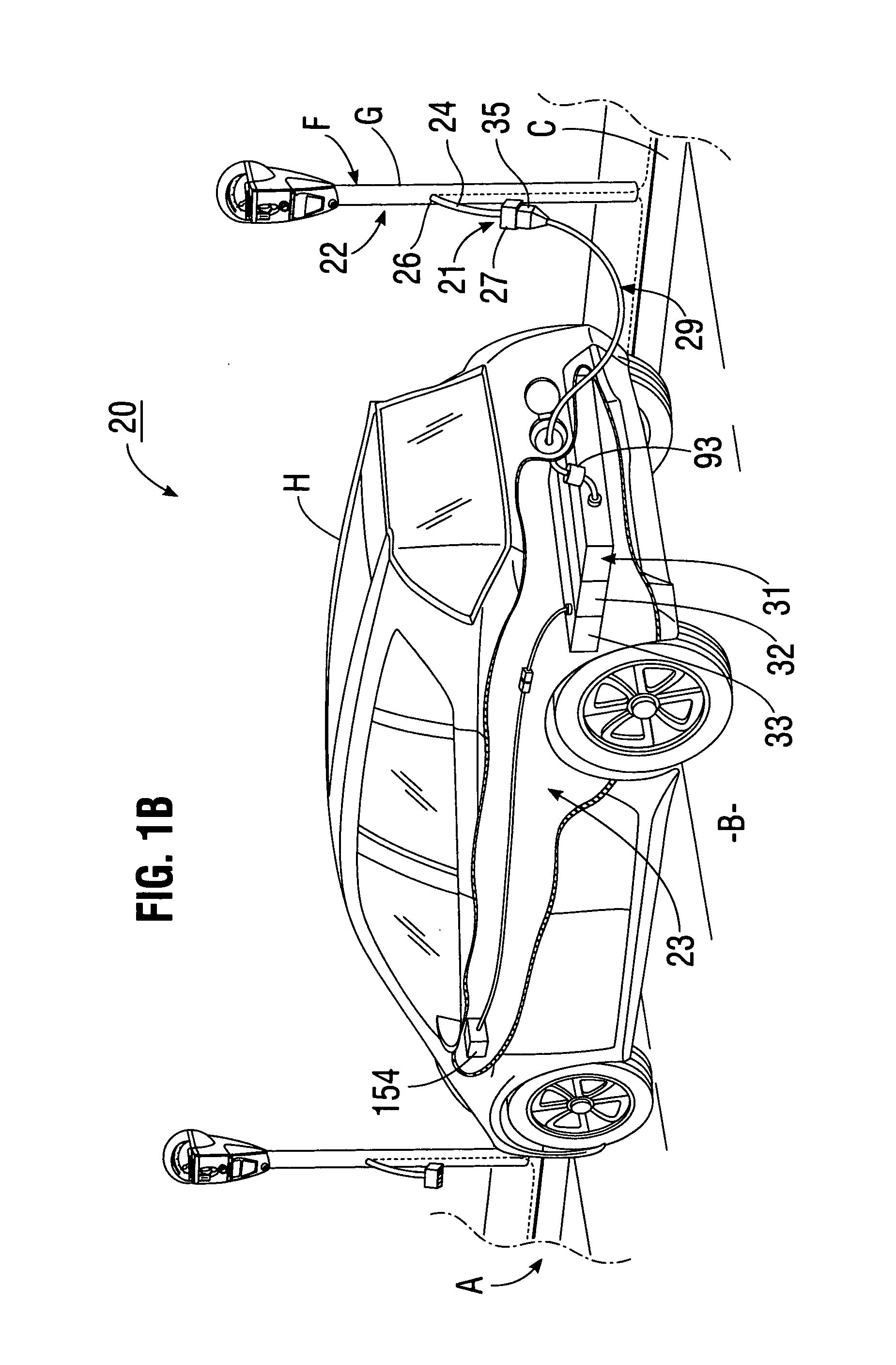
System for charging electric vehicle batteries from street lights and parking meters
InactiveUS20120229085A1Easy to modifyAvoid flowBatteries circuit arrangementsPlural diverse prime-mover propulsion mountingEngineeringCard reader
A system for charging batteries of electric vehicles from public fixtures such as street lights and parking meters includes modifying the fixture to convert it to a vehicle battery charging station using a power interface module having a novel keyed electrical power output receptacle connectable to power mains powering the fixture. The system includes a complementarily coded, keyed plug which must be inserted into the power output receptacle to access electrical power from the receptacle, the plug being located at the input end of vehicle charger cable terminated at output end thereof by a vehicle-mounted charge control system which will actuate a charging current contactor permitting charging current to flow from the receptacle to batteries within the vehicle only if a pre-paid charge authorization payment device, such as a magnetically or electronically encoded charge card is inserted into a charger station access enable device such as card reader mounted in the vehicle.
Owner:CHAPIN WILLIAM L MR
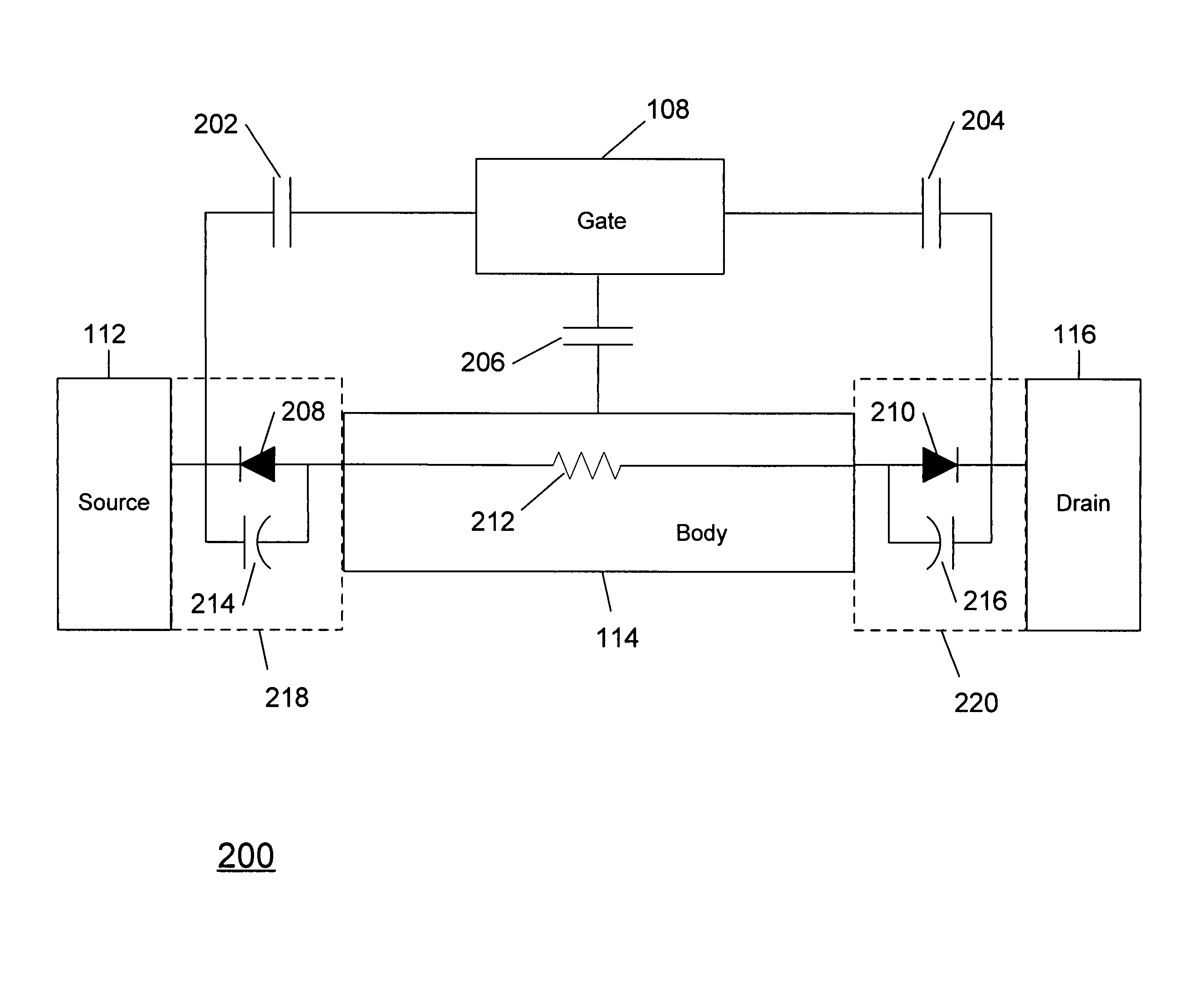
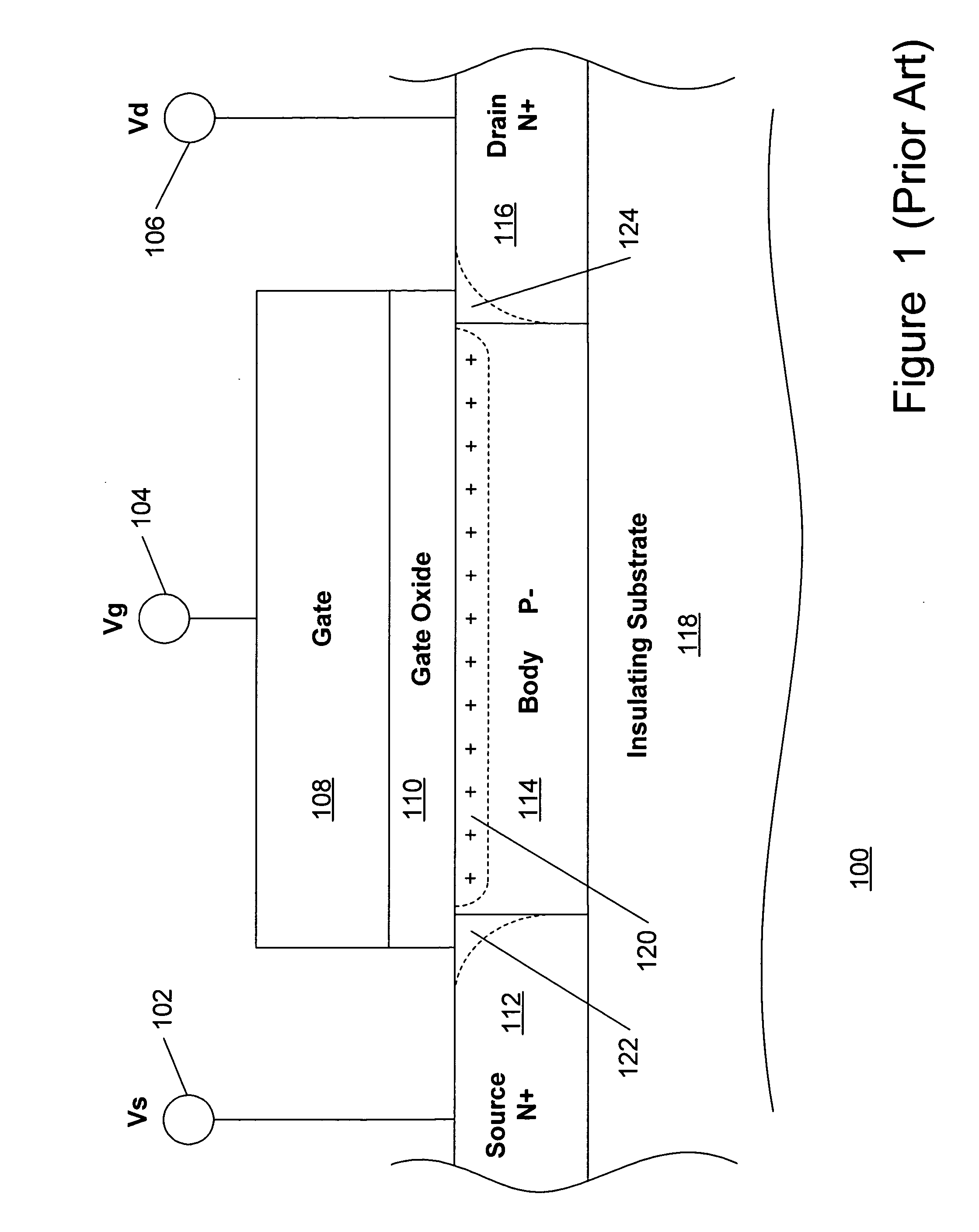
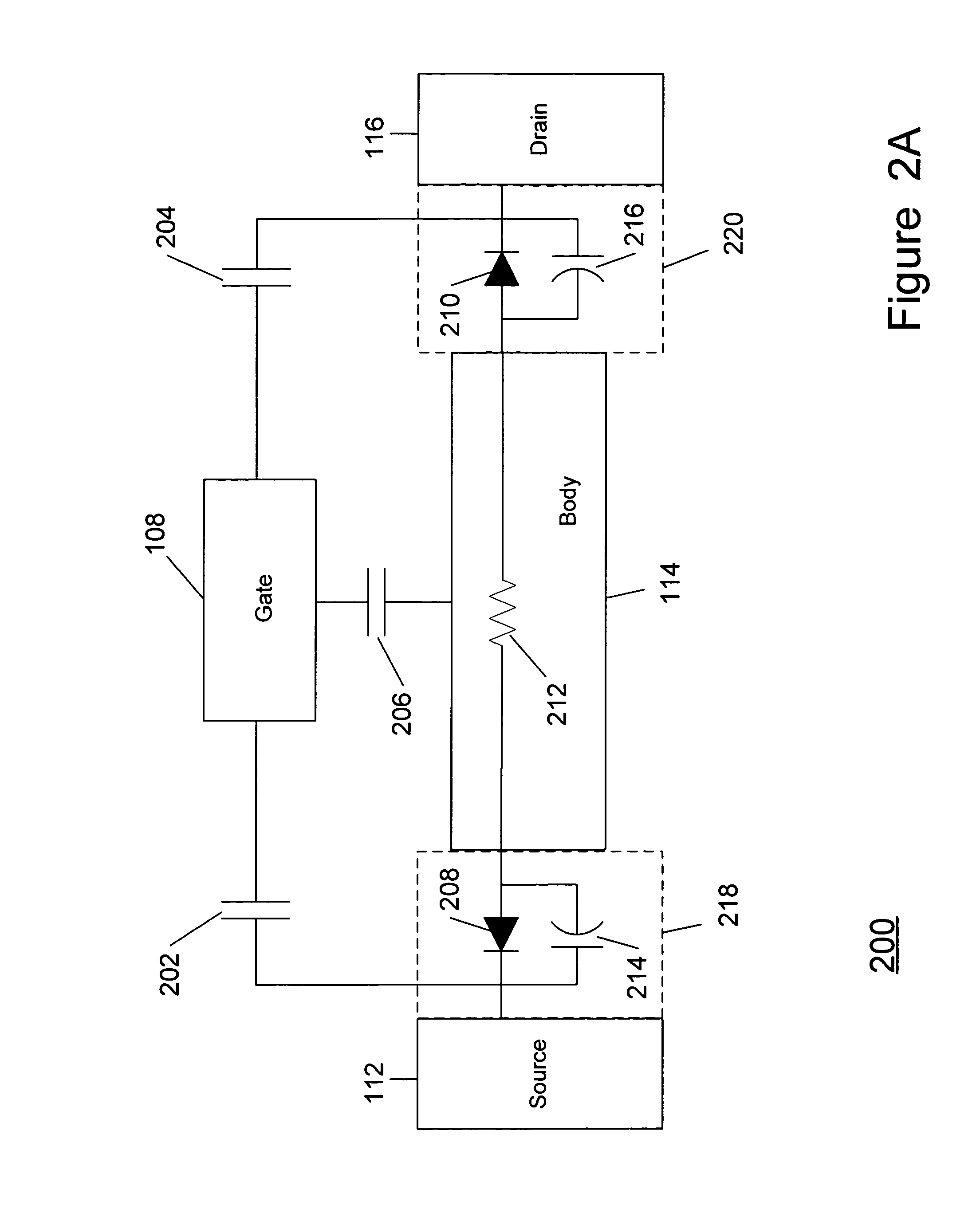
Method and apparatus improving gate oxide reliability by controlling accumulated charge
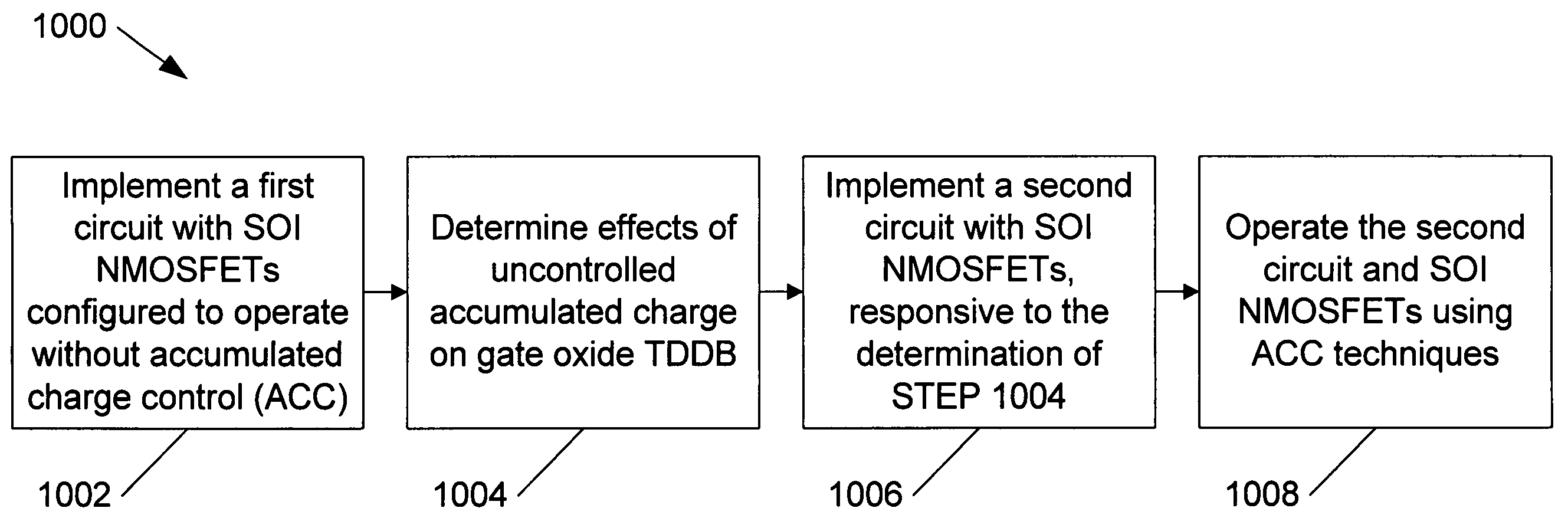
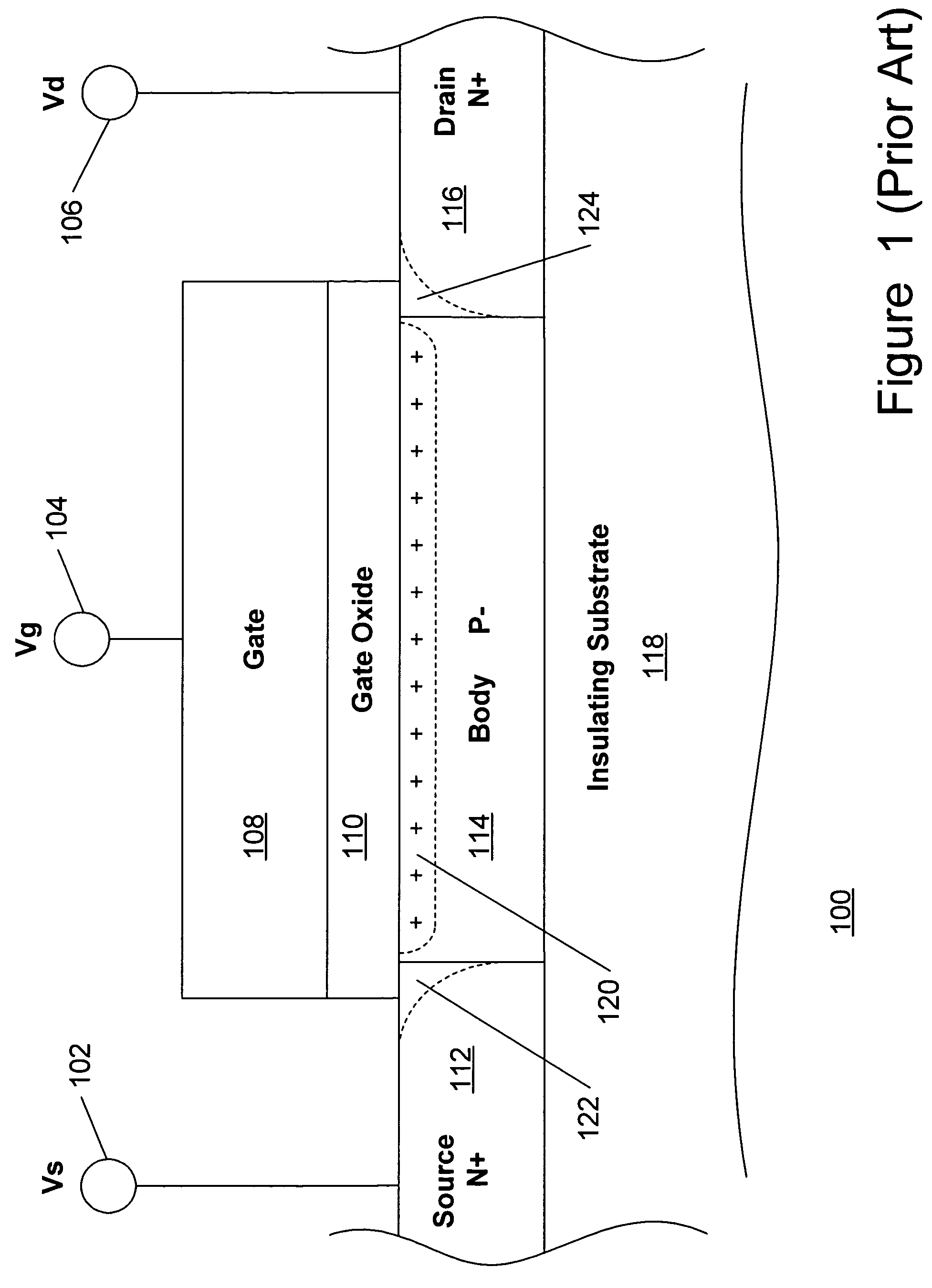
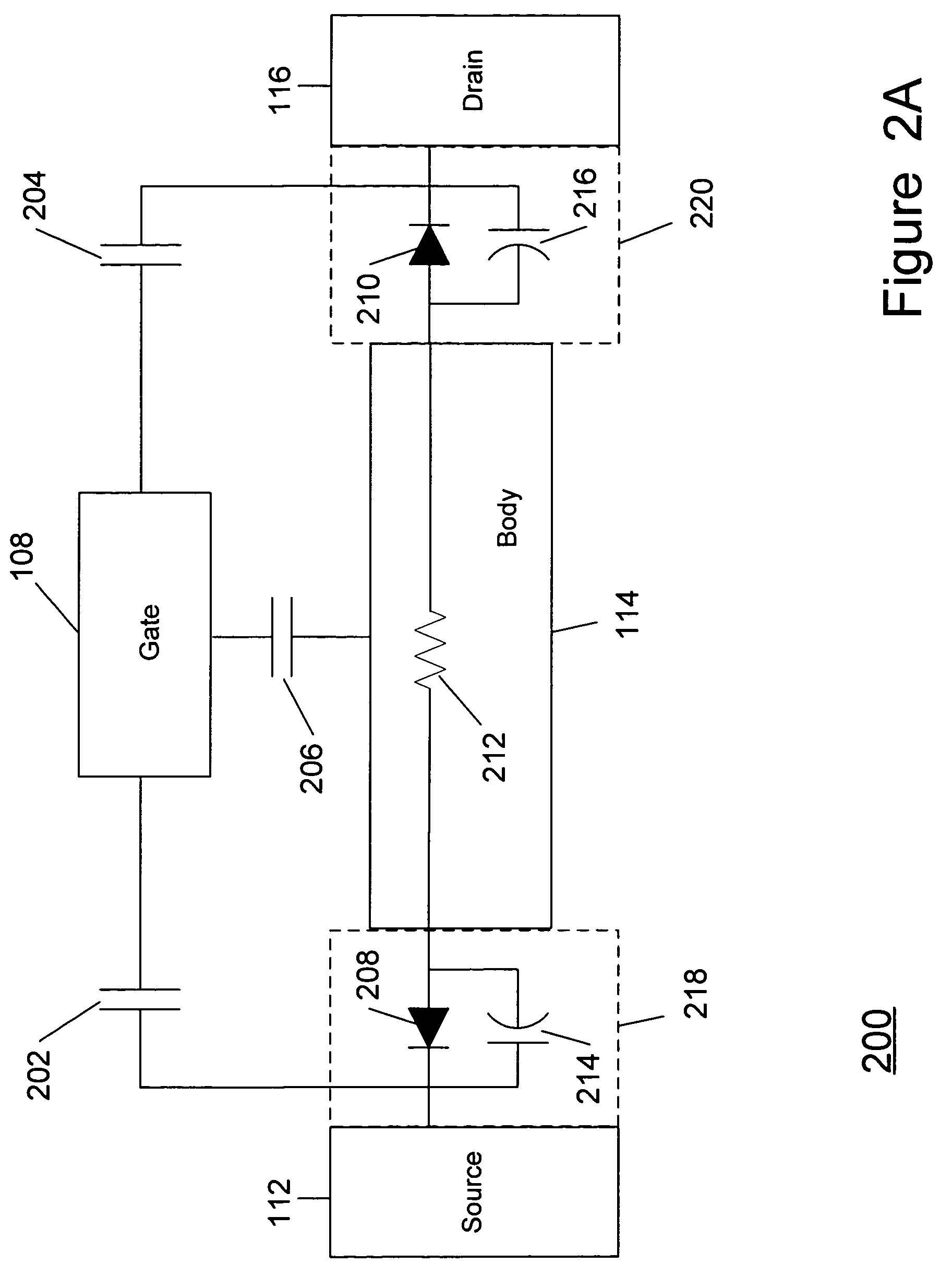
ActiveUS20070069291A1Improving nonlinear responses and harmonic and intermodulaton distortion effectsReduce non-linearitySolid-state devicesElectronic switchingMOSFETDielectric
A method and apparatus are disclosed for use in improving the gate oxide reliability of semiconductor-on-insulator (SOI) metal-oxide-silicon field effect transistor (MOSFET) devices using accumulated charge control (ACC) techniques. The method and apparatus are adapted to remove, reduce, or otherwise control accumulated charge in SOI MOSFETs, thereby yielding improvements in FET performance characteristics. In one embodiment, a circuit comprises a MOSFET, operating in an accumulated charge regime, and means for controlling the accumulated charge, operatively coupled to the SOI MOSFET. A first determination is made of the effects of an uncontrolled accumulated charge on time dependent dielectric breakdown (TDDB) of the gate oxide of the SOI MOSFET. A second determination is made of the effects of a controlled accumulated charge on TDDB of the gate oxide of the SOI MOSFET. The SOI MOSFET is adapted to have a selected average time-to-breakdown, responsive to the first and second determinations, and the circuit is operated using techniques for accumulated charge control operatively coupled to the SOI MOSFET. In one embodiment, the accumulated charge control techniques include using an accumulated charge sink operatively coupled to the SOI MOSFET body.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Optical interference pixel display with charge control
An electronic device of an embodiment of the invention is for at least partially displaying a pixel of a displayable image. The electronic device includes a first reflector and a second reflector that define an optical cavity therebetween, and which is selective of a visible wavelength at an intensity by optical interference. The electronic device also includes a charge-controlling mechanism to allow optical properties of the optical cavity to be varied by controlling a predetermined amount of charge stored on the first and the second reflectors. The visible wavelength and / or the intensity are thus variably selectable in correspondence with the pixel of the displayable image.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
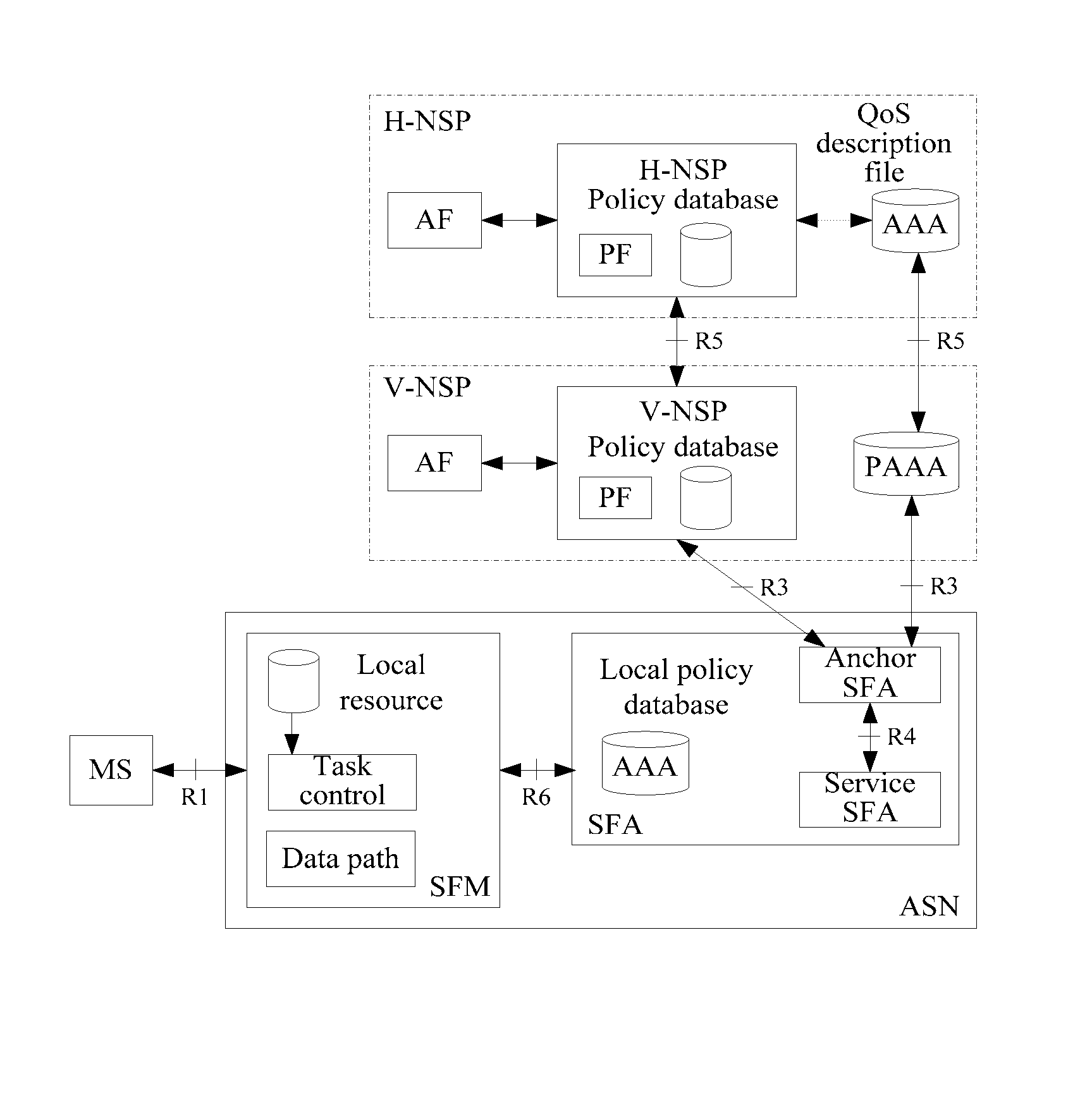
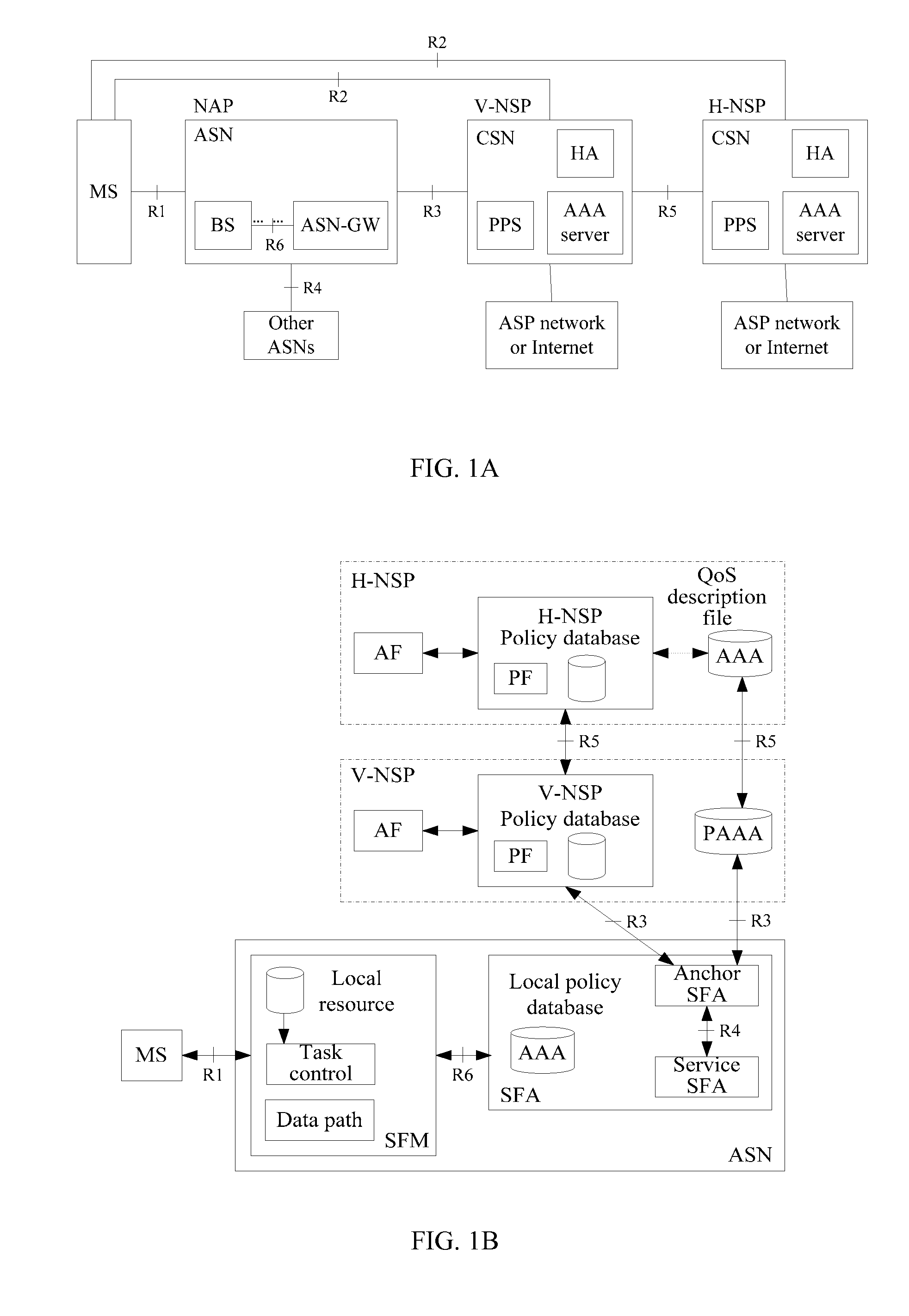
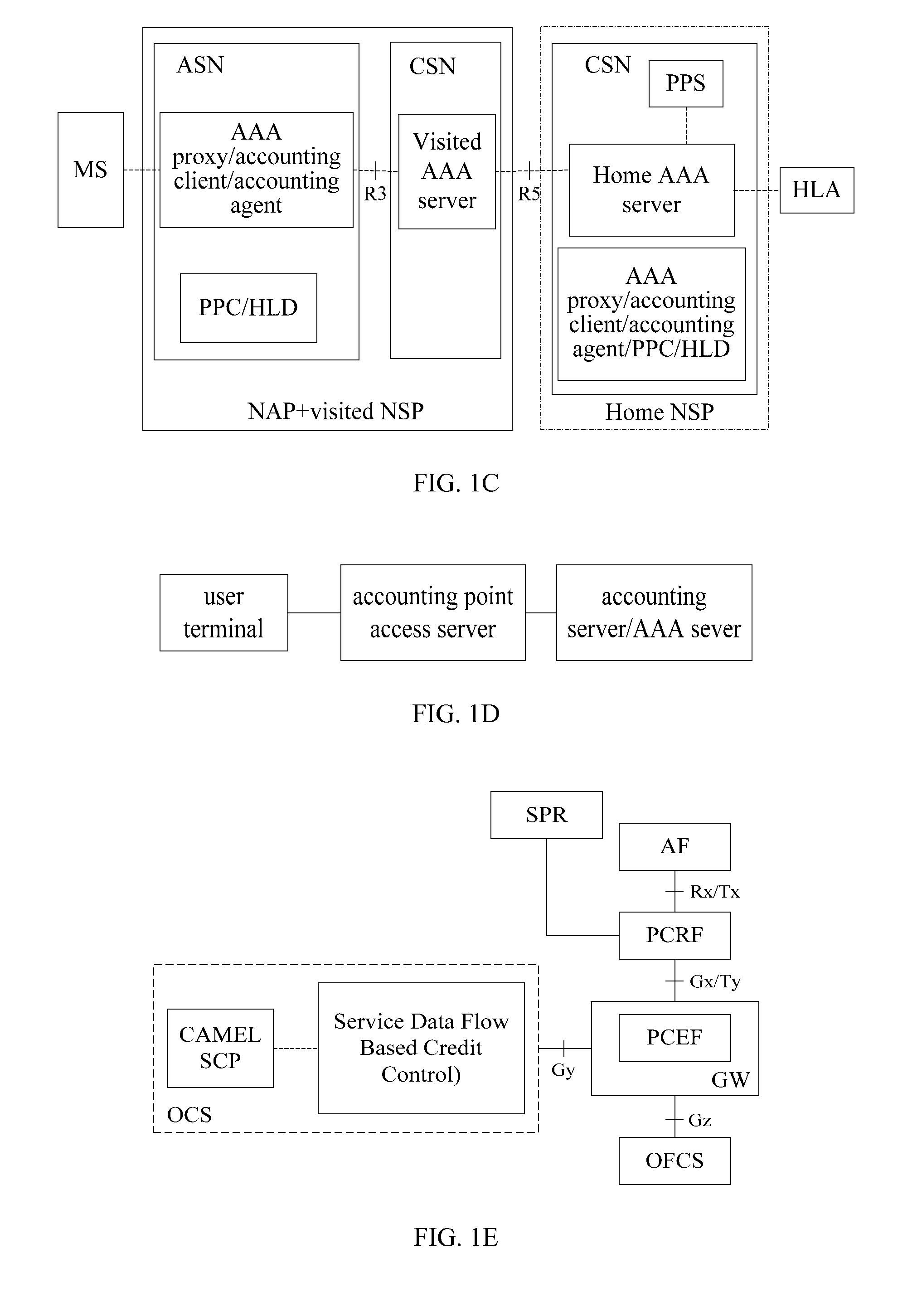
System and charging control method of network convergence policy and charging control architecture
ActiveUS20090228956A1Digital data processing detailsSpecial service for subscribersNetwork ConvergenceService flow
A system and charging control method of network convergence policy and charging control architecture are disclosed, based on the QoS parameter, charging policy and user subscribing information granted by the service layer, the PCRF confirms PCC rule, and provides the PCC rule to the policy distribution function PDF. As the interface between the PCRF and PCC policy performing entity, the PDF performs the protocol conversion and information distribution. Based on the PCC rule, the PCC policy performing entity performs QoS policy of the service data flow and the detecting and charging of the service flow.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
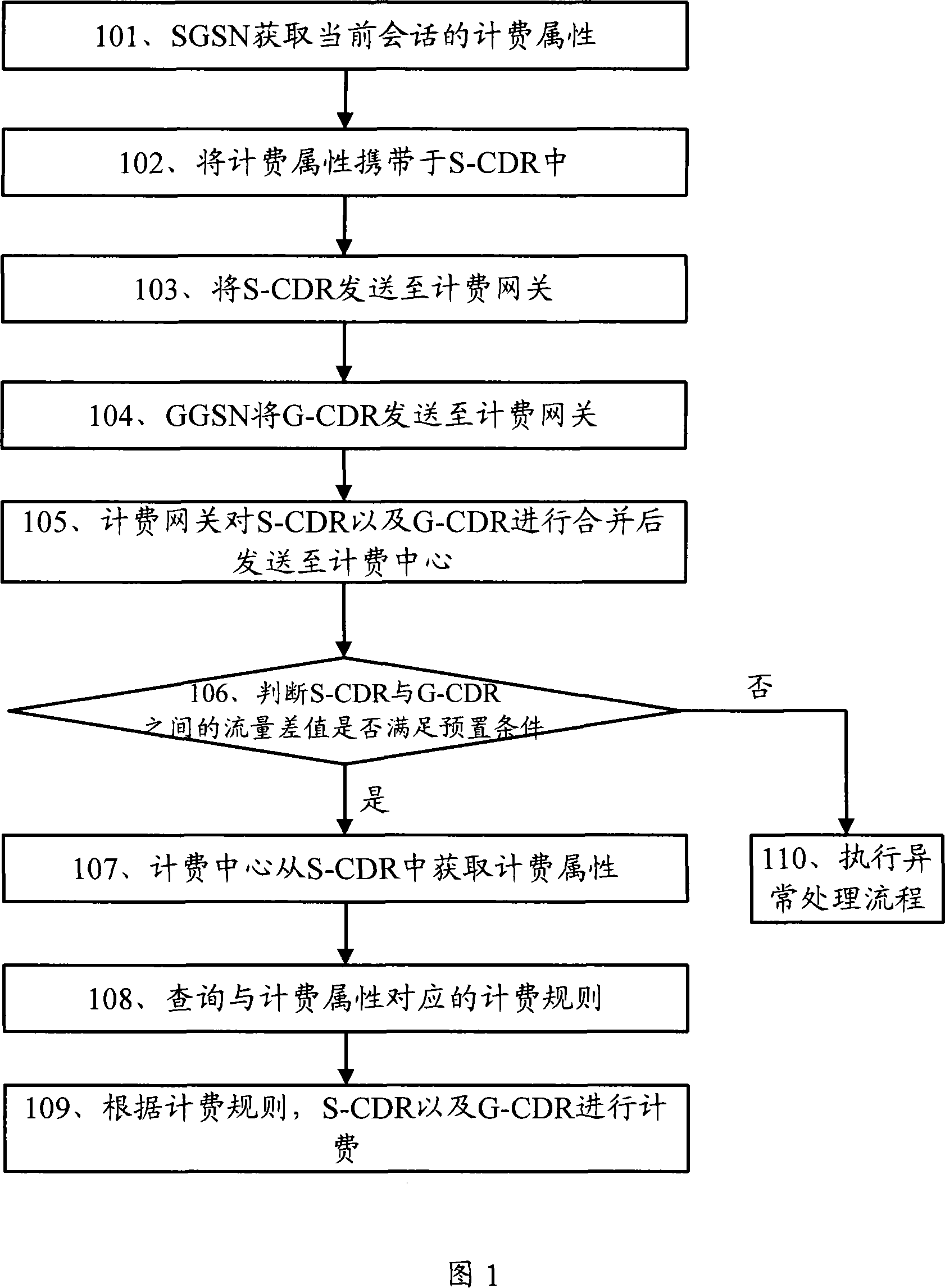
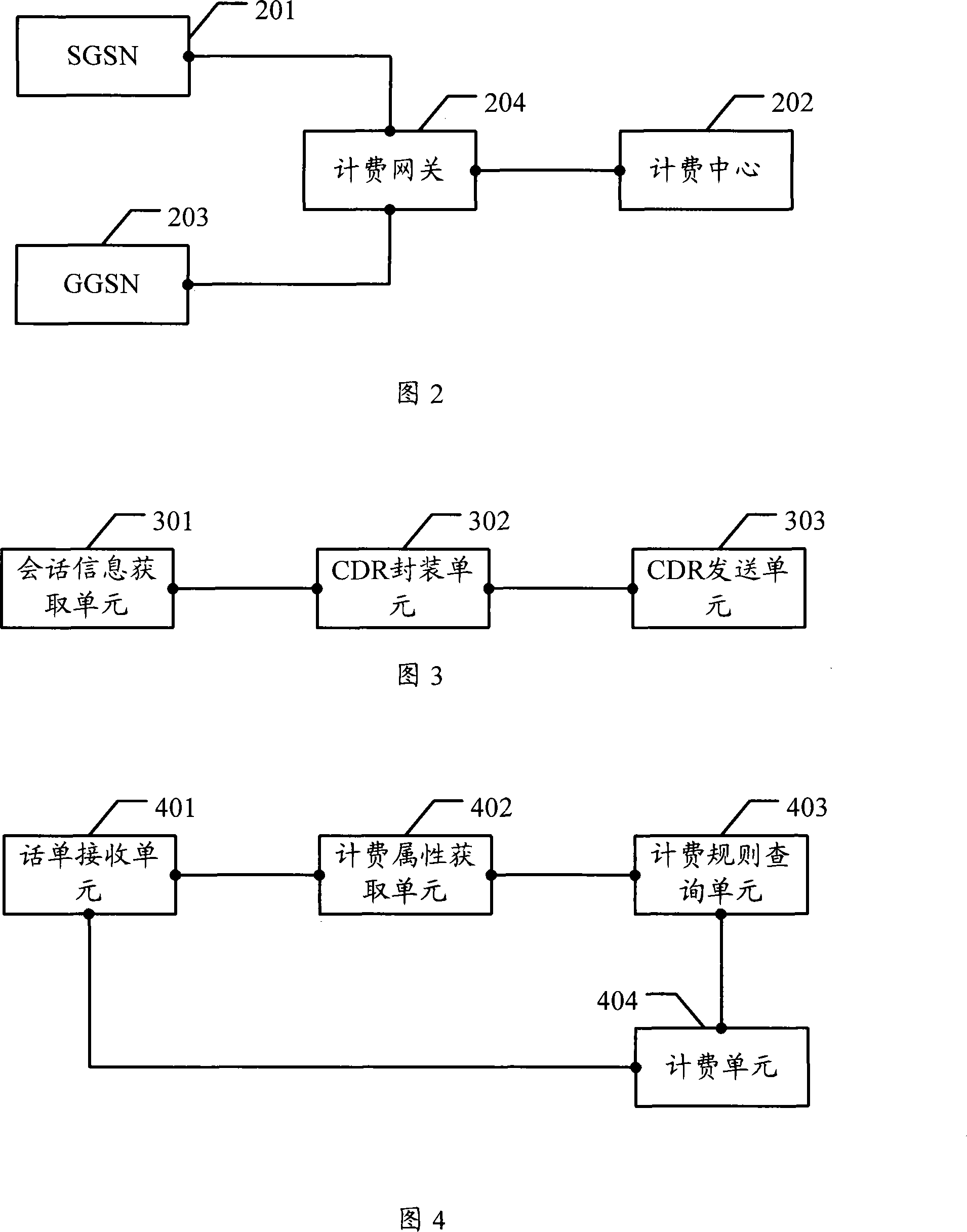
Charging control method, charging center and related equipment
InactiveCN101183958ABilling attributes do not affectWill not affect judgmentMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsGeneral Packet Radio ServiceRelevant information
The invention discloses a charging control method, a charging center and the relative equipment for the purpose of improving the charging accuracy. The method of the invention comprises the following steps: the charging attribute of the current conversation is obtained by the general grouping wireless service supporting node GSN; the charging attribute carried by each CDR is used to instruct the relative information to the tunnel of the CDR; the CDR is sent to the charging center; the charging attribute of the CDR is obtained by the charging center according to the information of the CDR; the charging center accounts according to the CDR and the charging attribute; the invention also provides the charging center and the relative equipment. The invention has an advantage of increasing the charging accuracy effectively.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
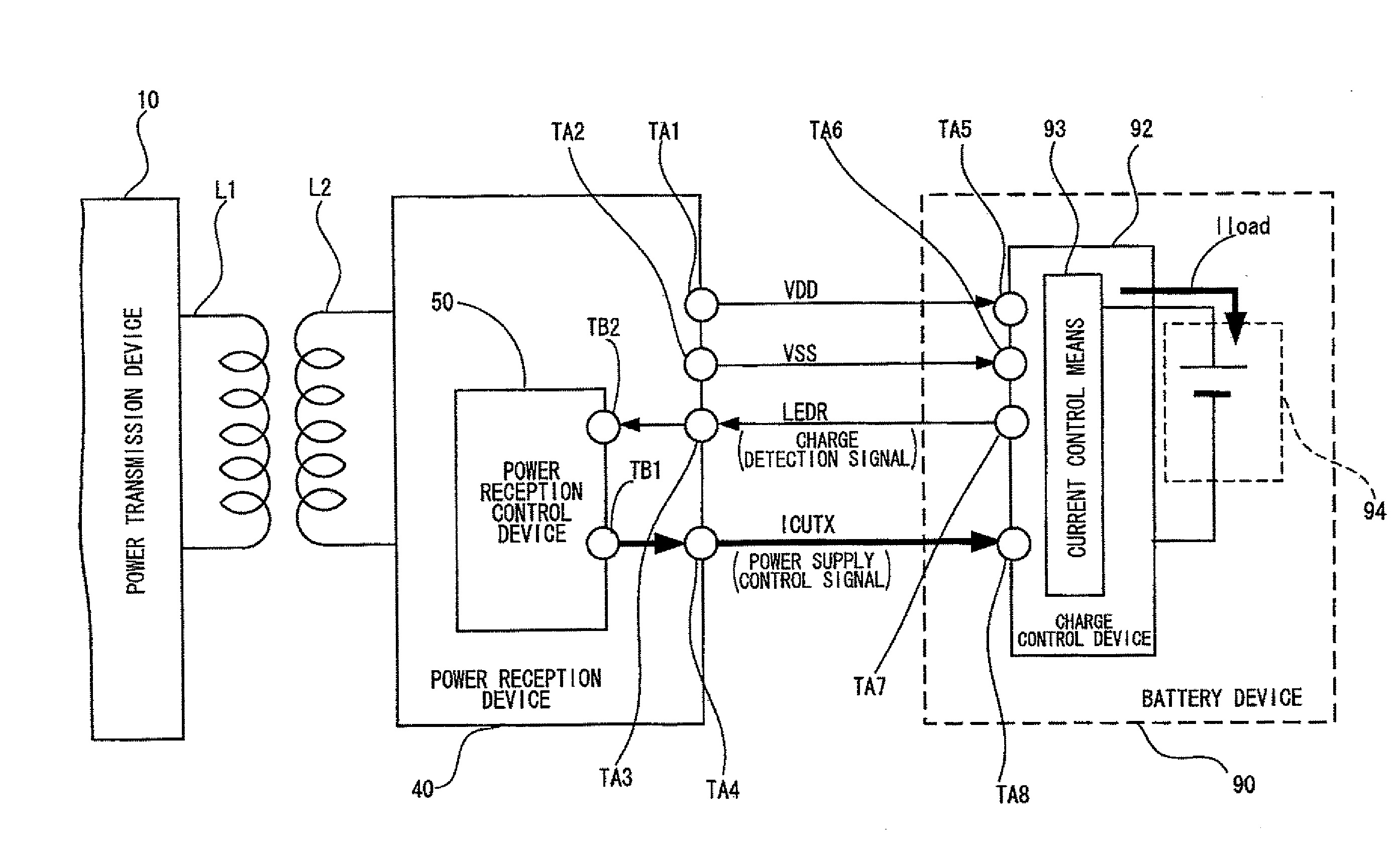
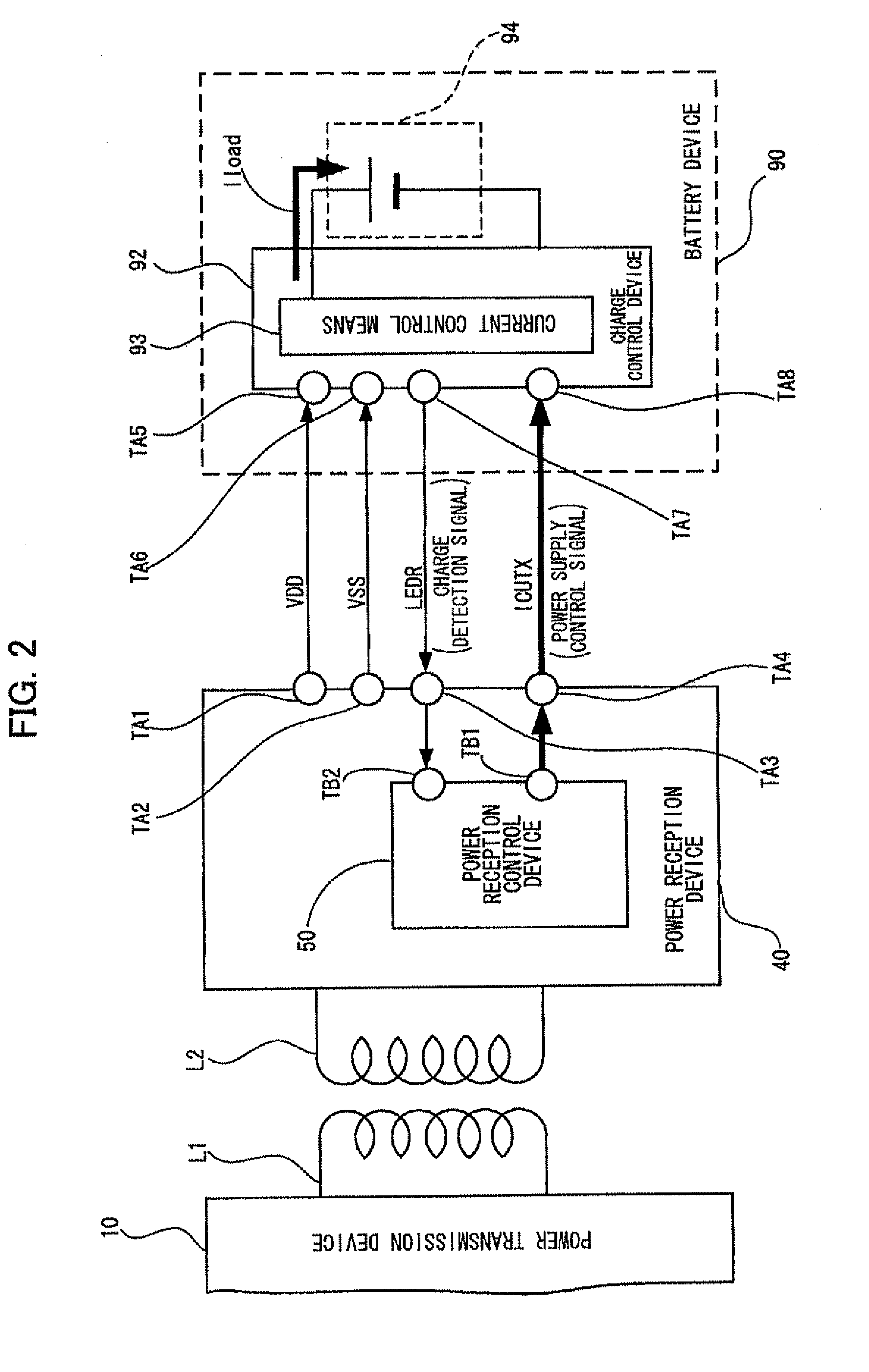
Power reception control device, power reception device, non-contact power transmission system, charge control device, battery device, and electronic instrument
ActiveUS20090021219A1Circuit authenticationNear-field transmissionElectric power transmissionTransport system
A power reception control device provided in a power reception device of a non-contact power transmission system includes a power-reception-side control circuit that controls an operation of the power reception device, and a power supply control signal output terminal that supplies a power supply control signal to a charge control device, the power supply control signal controlling power supply to a battery. The power-reception-side control circuit controls a timing at which the power supply control signal (ICUTX) is output from the power supply control signal output terminal. The operation of the charge control device is compulsorily controlled using the power supply control signal (ICUTX).
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
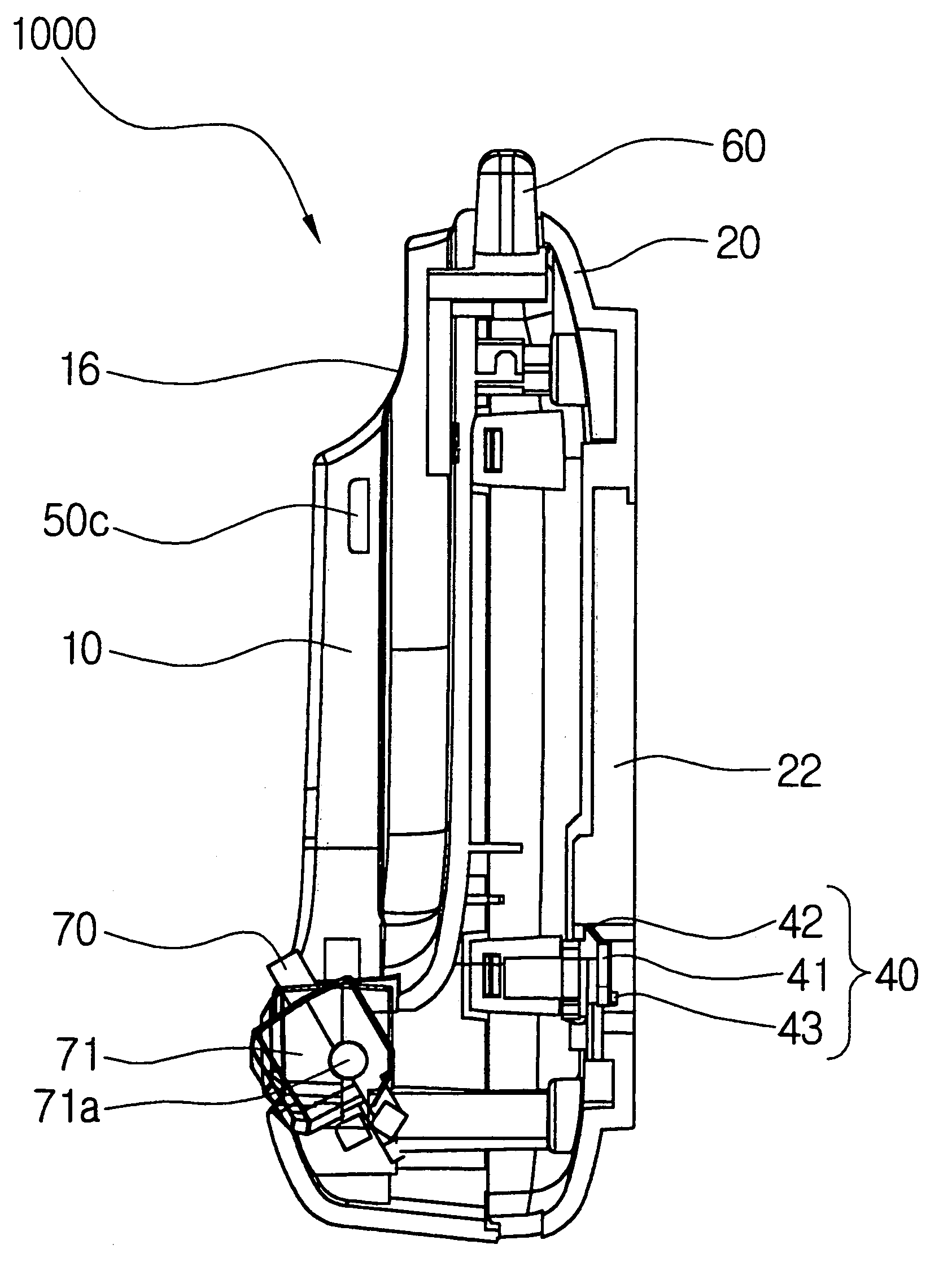
Contact-Less Chargeable Battery and Charging Device, Battery Charging Set, and Charging Control Method Thereof
ActiveUS20080303479A1Avoid internal damageAc-dc conversion without reversalCircuit monitoring/indicationBattery chargeRechargeable cell
The present invention relates to a wireless charger for a mobile communication terminal, which allows charging a plurality of batteries in a conveniently way without any terminal connection of the batteries to chargers for various mobile communication terminals such as a cellular phone and PDA and also allows intercepting electromagnetic waves while the charger is used, by means of Faraday's law.The wireless charger of the present invention includes a charger body having an electromagnetic wave intercepting means; a charging pad received in the charger body; and at least one battery that is to be charged by means of induced electromotive force generated by the charging pad, wherein the charger body includes a power supply means, a housing having a receiver for receiving the charging pad and connected to the power supply means, and a cover hinged to the housing.
Owner:LS CABLE & SYST LTD
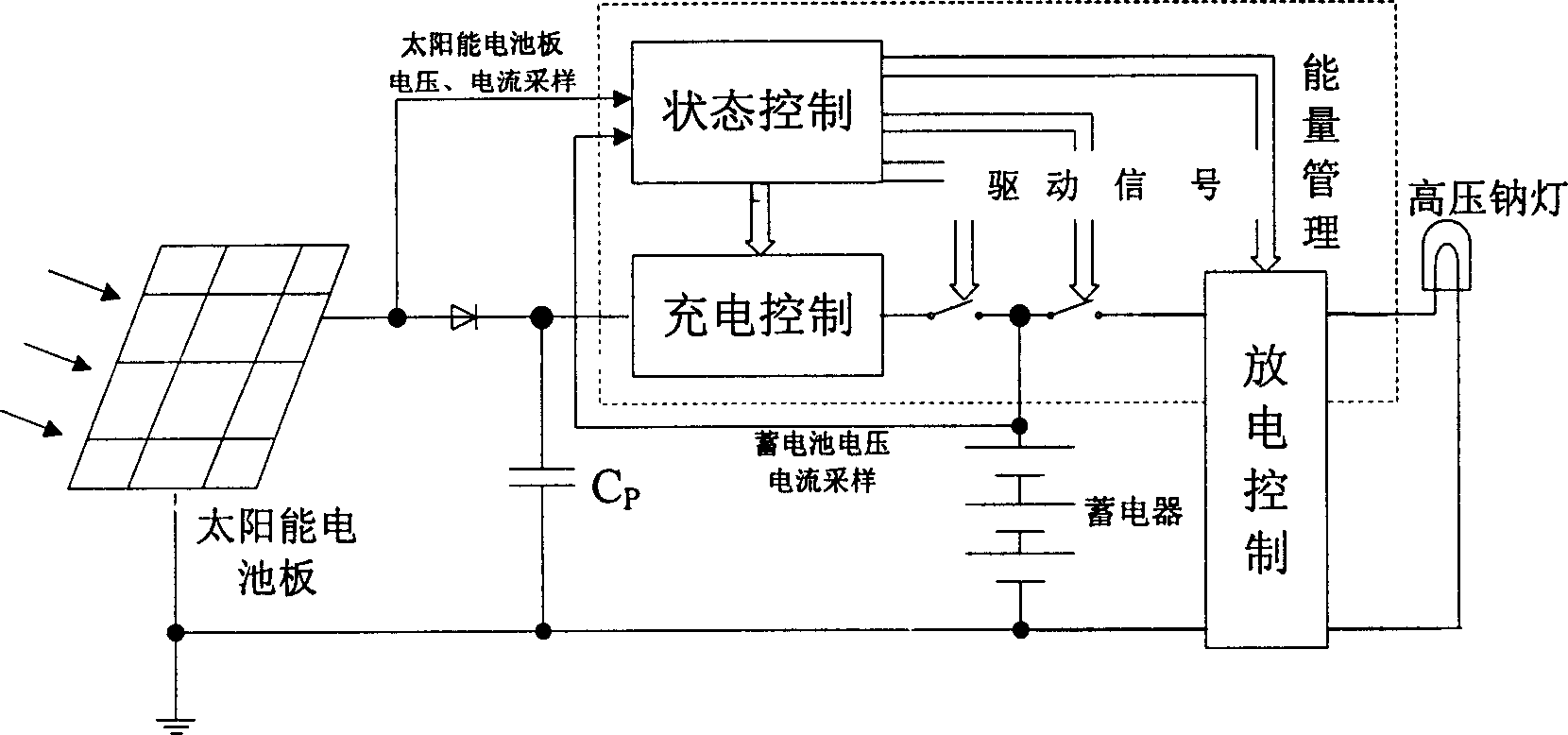
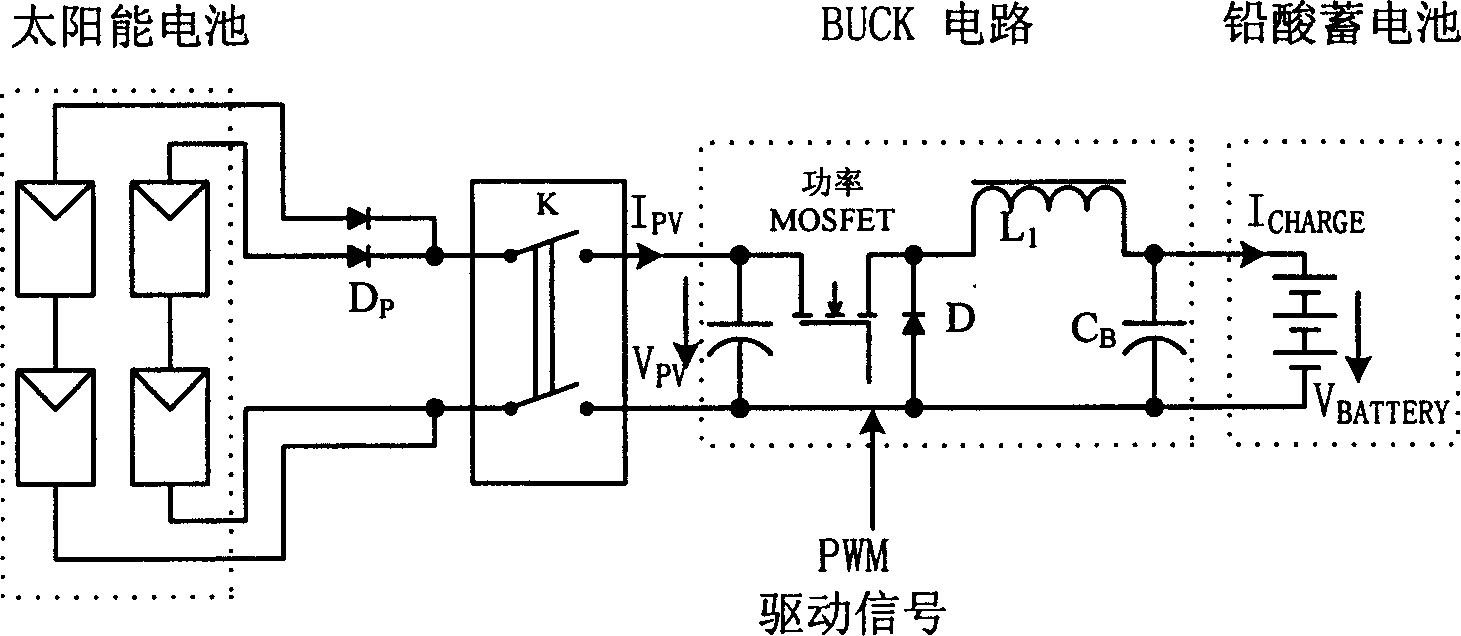
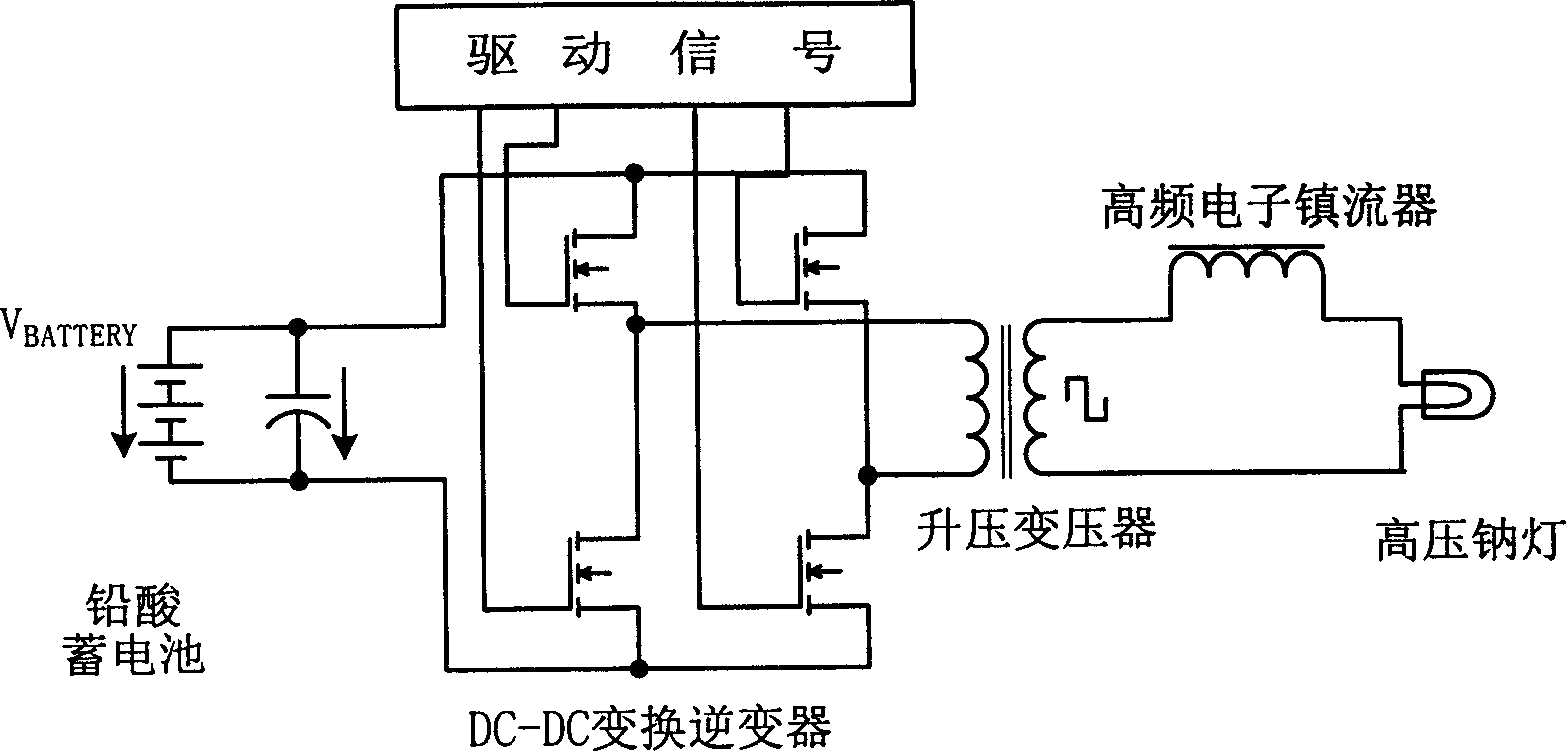
Solar energy high voltage sodium lamp controller based on single stage inverter
InactiveCN1787717ARealize intelligent controlImproved and enhanced charge and discharge capabilitiesBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric lighting sourcesMicrocontrollerEngineering
This invention relates to a solar energy high pressure Na-lamp controller based on a single stage inverter characterizing in applying a sectional charge control and a frequency conversion output control, in which, the hardware includes a singlechip control circuit, a single-stage total bridge inversion circuit, a storage battery charge circuit, a high frequency electronic ballast circuit, a solar energy cell, storage batteries and luminaries, the controller is charged by MPPT to increase the system efficiency and applies frequency conversion output to control the current of the lamp, besides, a design of machine-card separation is applied to the controller on the structure to meet the needs of different luminaries and lamination, the control structure is integrated in a control card suitable for software upgrading.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
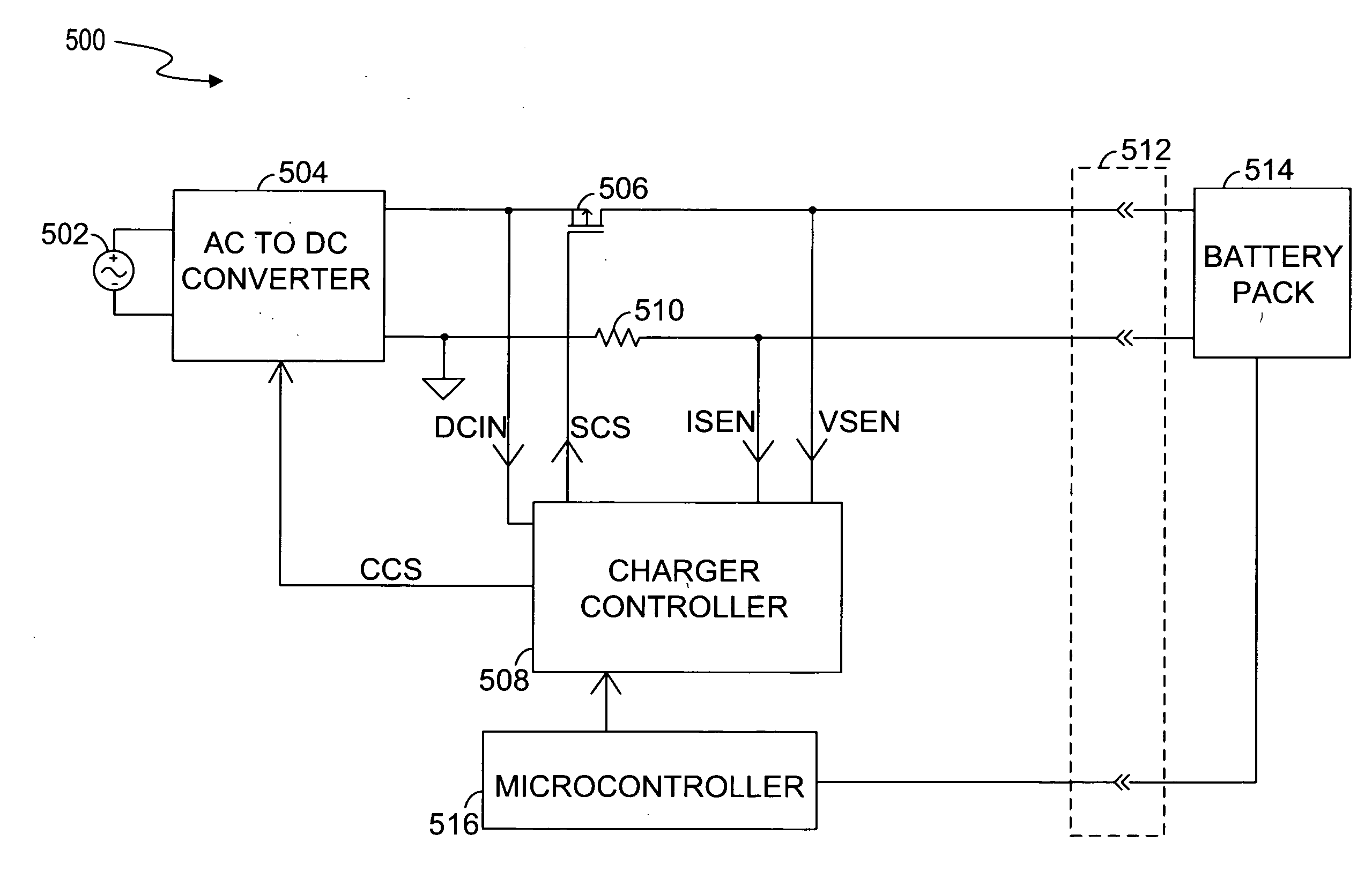
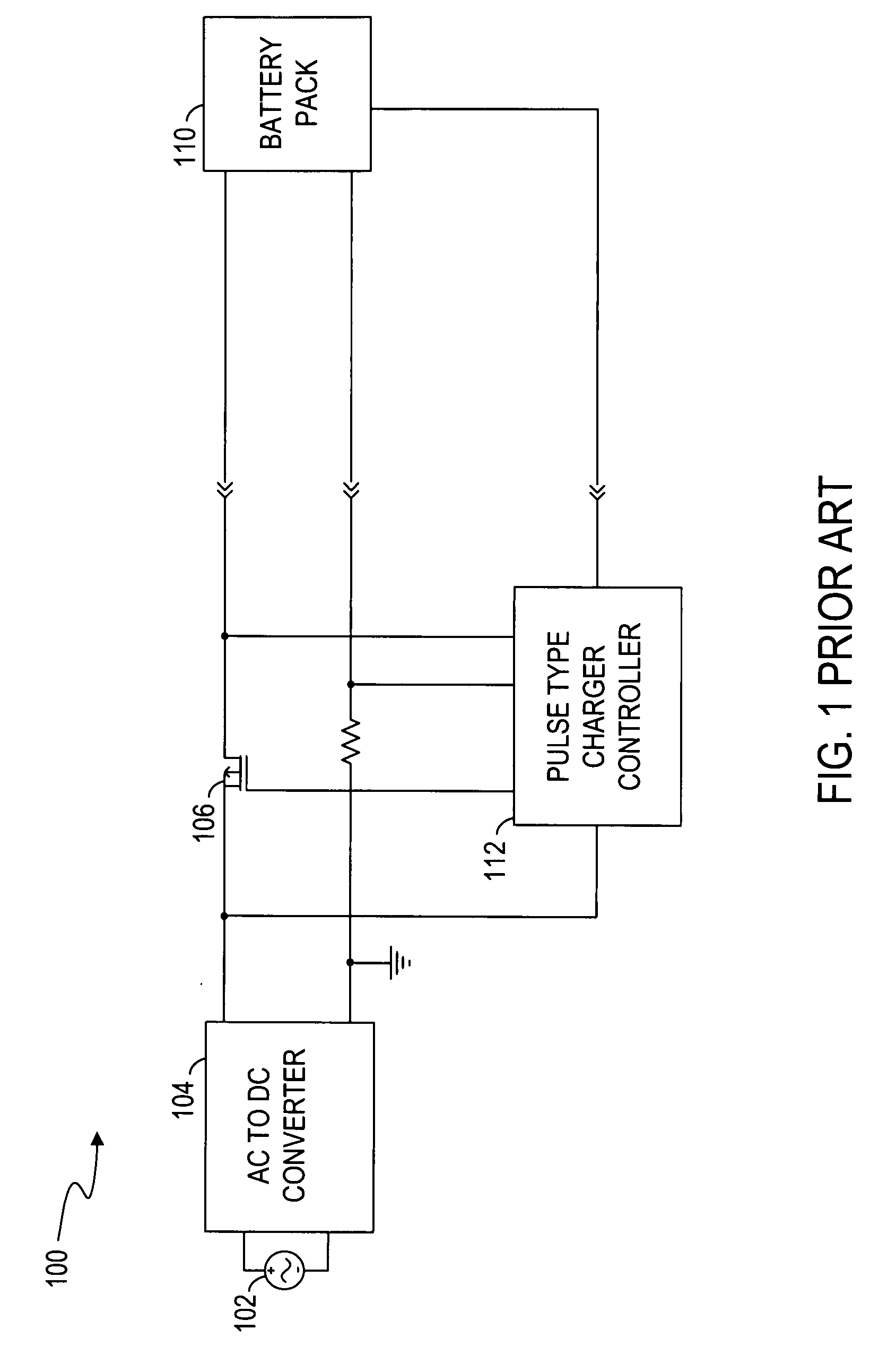
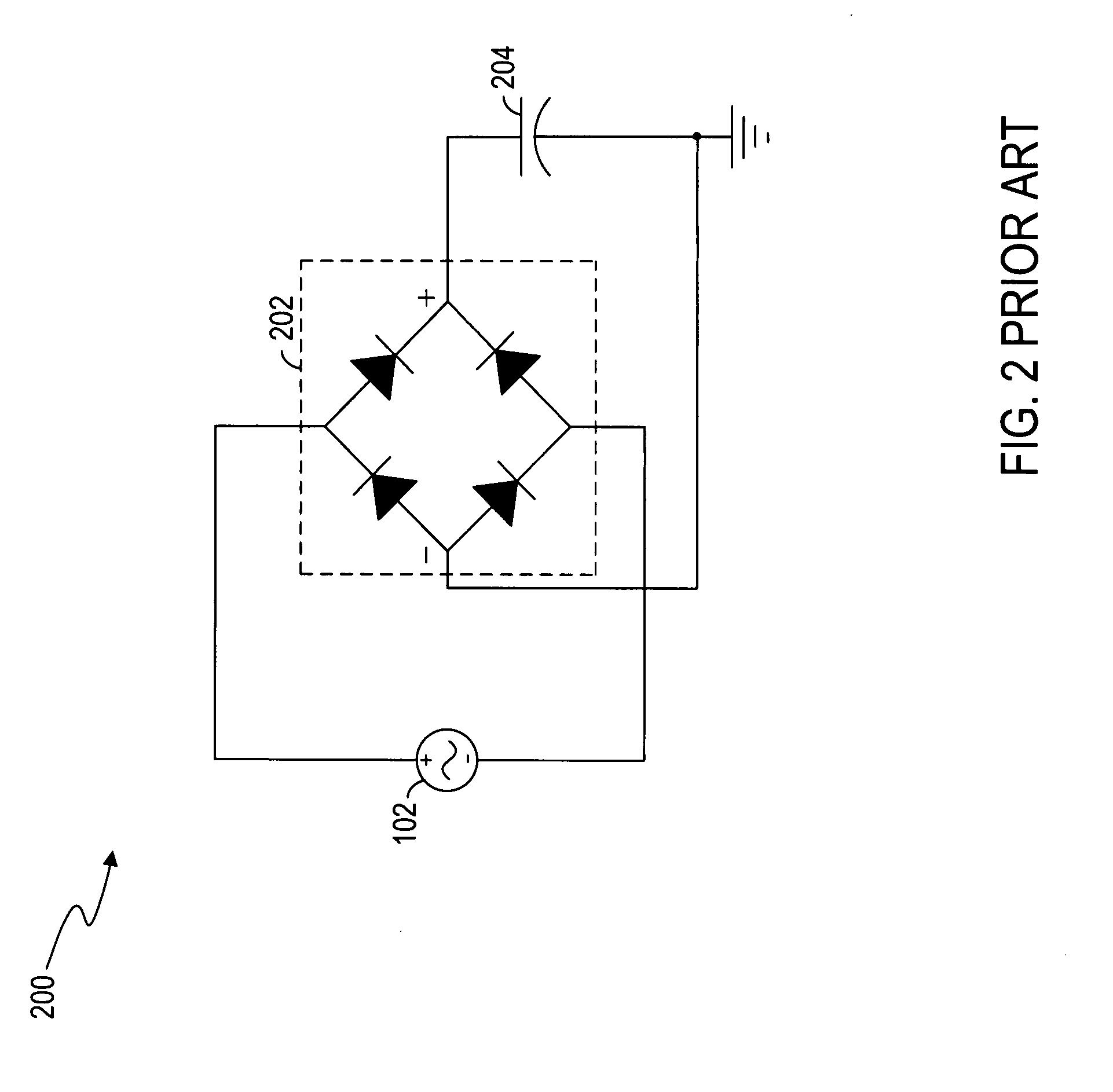
Circuits and methods for battery charging
ActiveUS20080197811A1Batteries circuit arrangementsSecondary cells charging/dischargingBattery chargeCharge control
Circuits and methods for battery charging are disclosed. In one embodiment, the battery charging circuit comprises an AC to DC converter, a charging control switch, and a charger controller. The AC to DC converter provides a charging power to a battery pack. The charging control switch is coupled between the AC to DC converter and the battery pack. The charging control switch transfers the charging power to the battery pack. The charger controller detects a battery status of the battery pack and controls the charging control switch to charge the battery pack in a continuous charging mode or a pulse charging mode according to the battery status. The charger controller also controls the AC to DC converter to regulate the charging power according to the battery status.
Owner:O2 MICRO INT LTD
Storage battery system and automobile
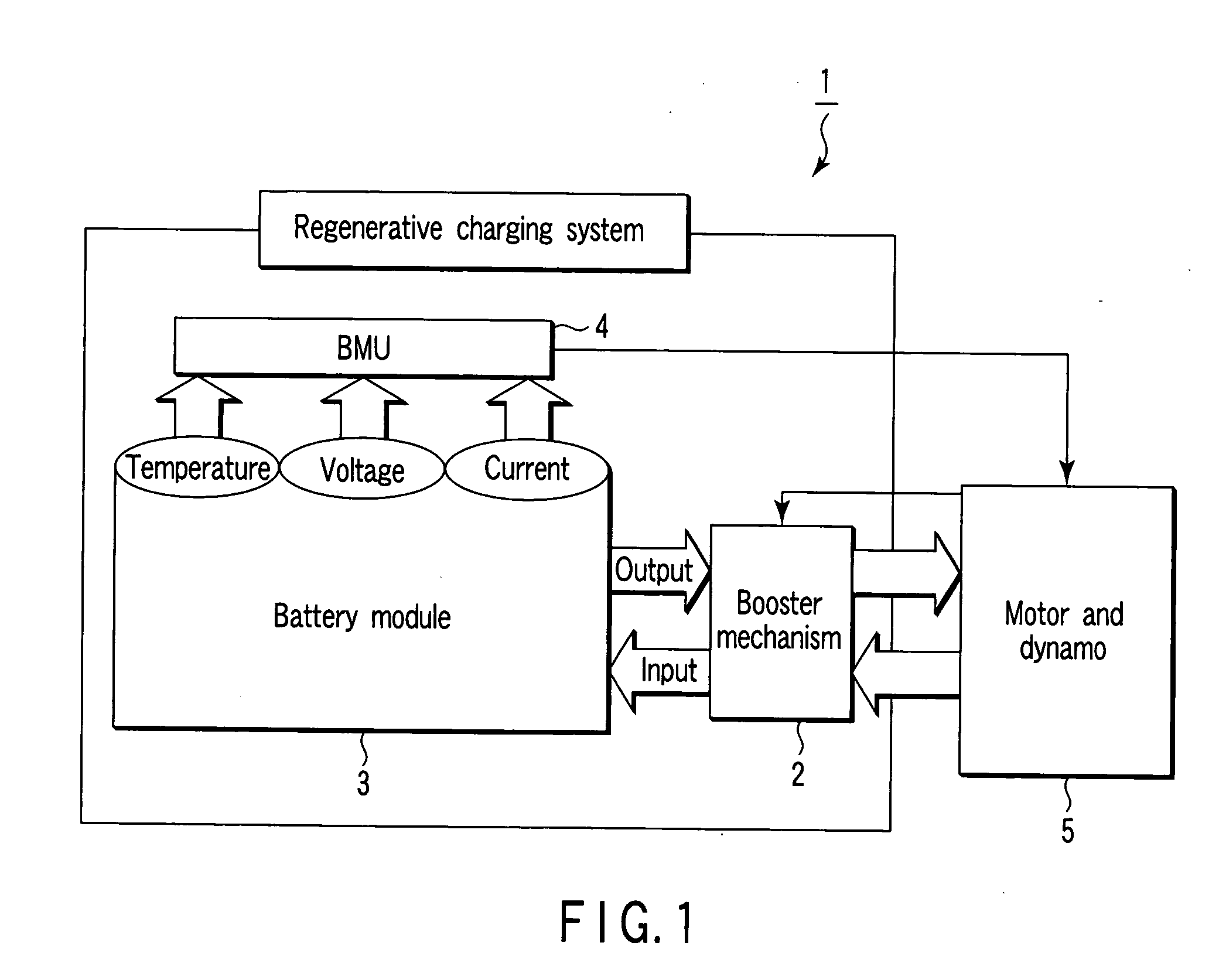
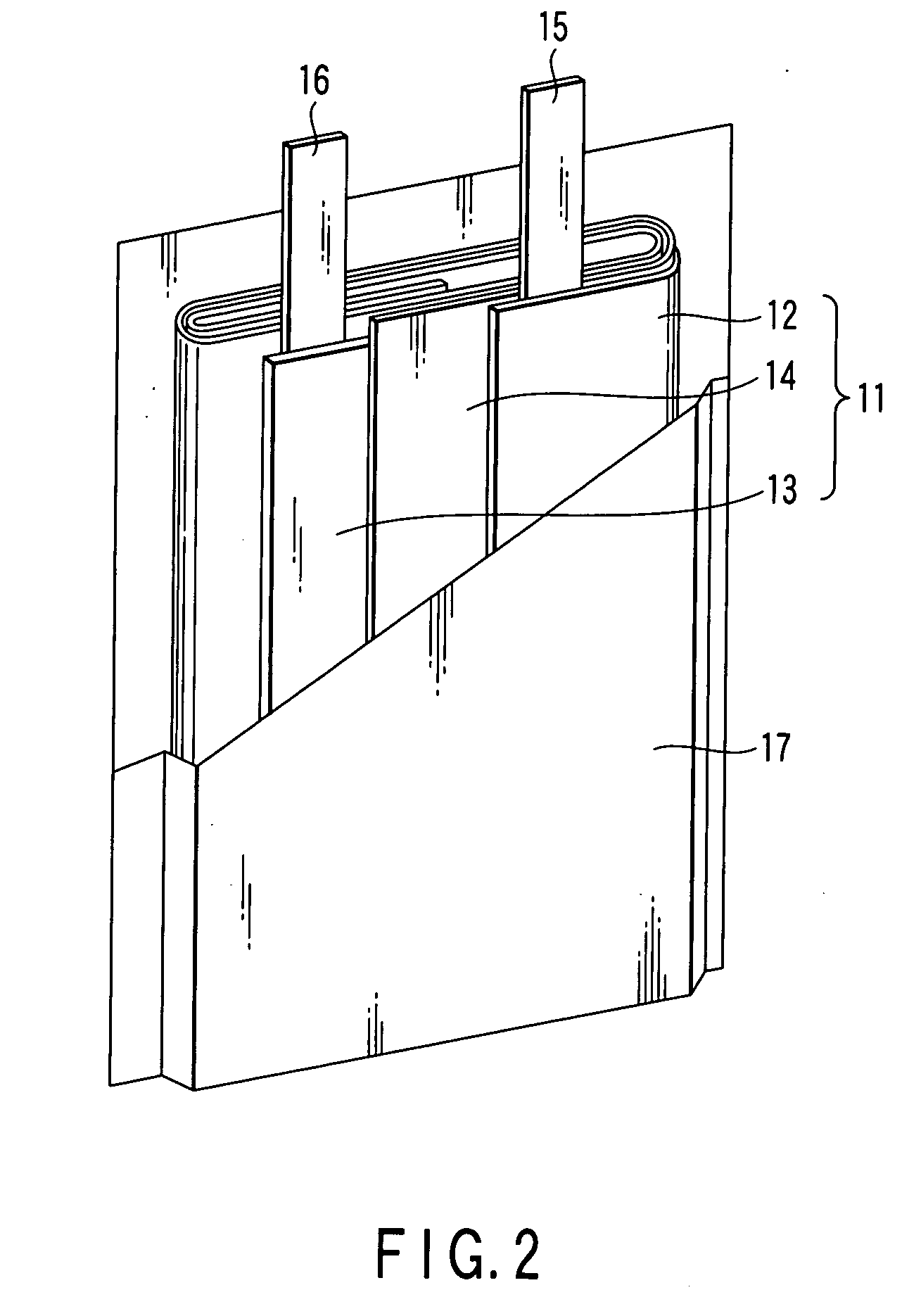
InactiveUS20060068272A1Suppressing swellingBatteries circuit arrangementsCell temperature controlVoltmeterCharge control
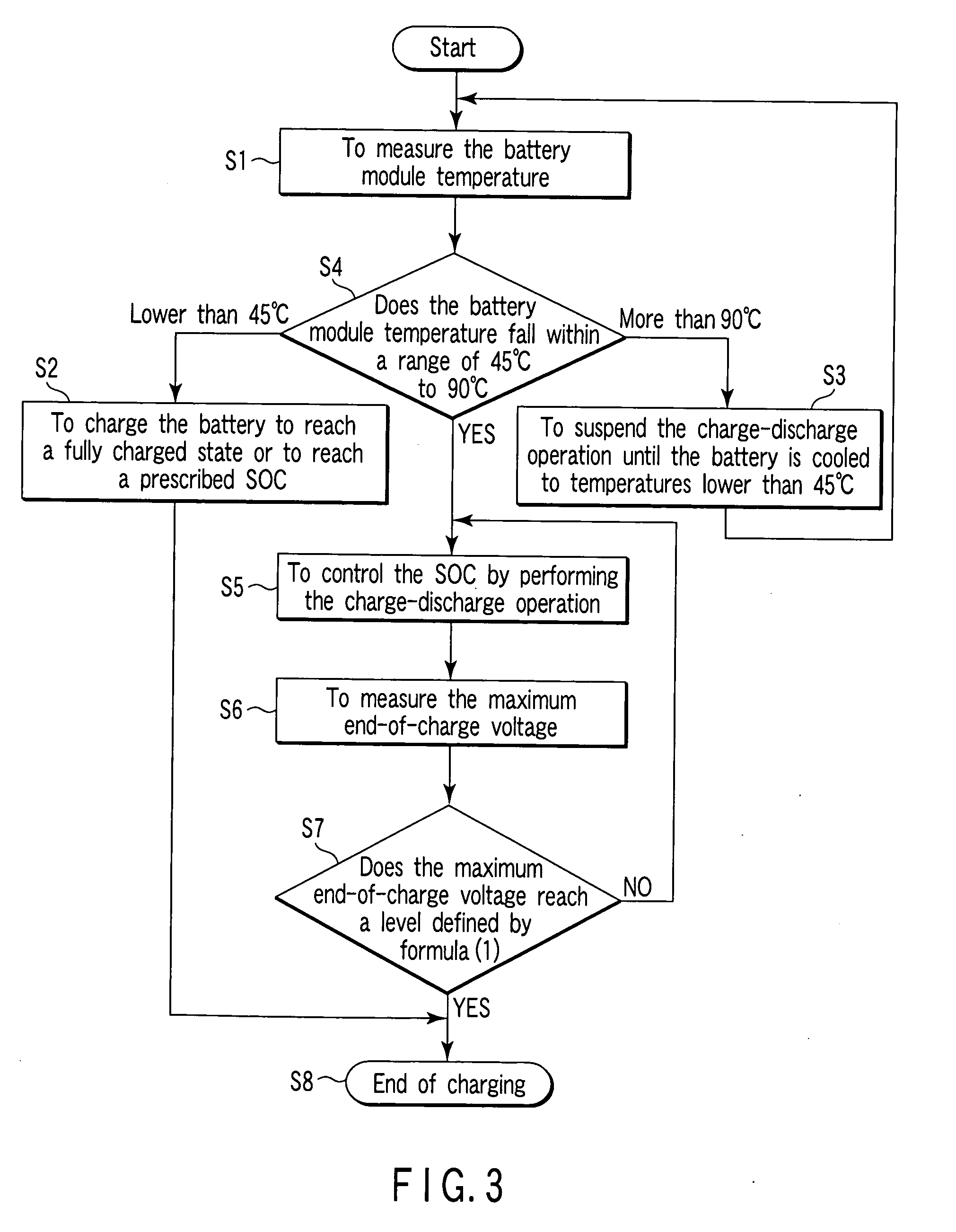
A storage battery system includes a battery module including nonaqueous electrolyte secondary batteries. The storage battery system further includes a temperature sensor which measures a temperature of the battery module, a voltmeter which measures a voltage of each of the nonaqueous electrolyte secondary batteries and a charge control unit which controls a maximum end-of-charge voltage V1 (V) of the nonaqueous electrolyte secondary batteries to fall within the range defined in formula (1) given below when the temperature of the battery module is not lower than 45° C. and is not higher than 90° C.: 0.85×V0≦V1≦0.96×V0 (1)
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Electronic Cigarette Casing and Electronic Cigarette Device
InactiveUS20140083443A1Safe and reliable to and dischargeFast chargingBatteries circuit arrangementsTobacco pipesElectrical batteryControl system
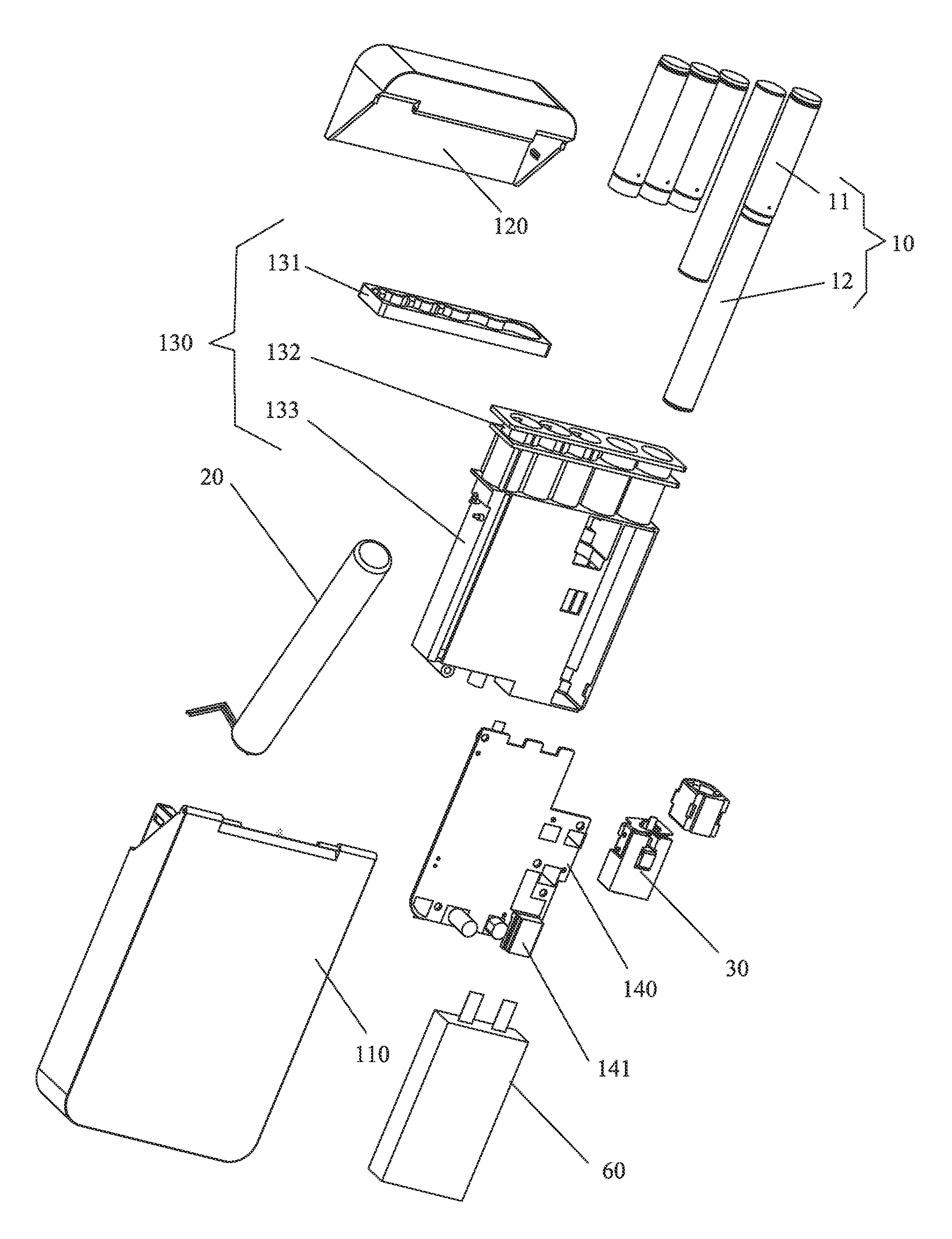
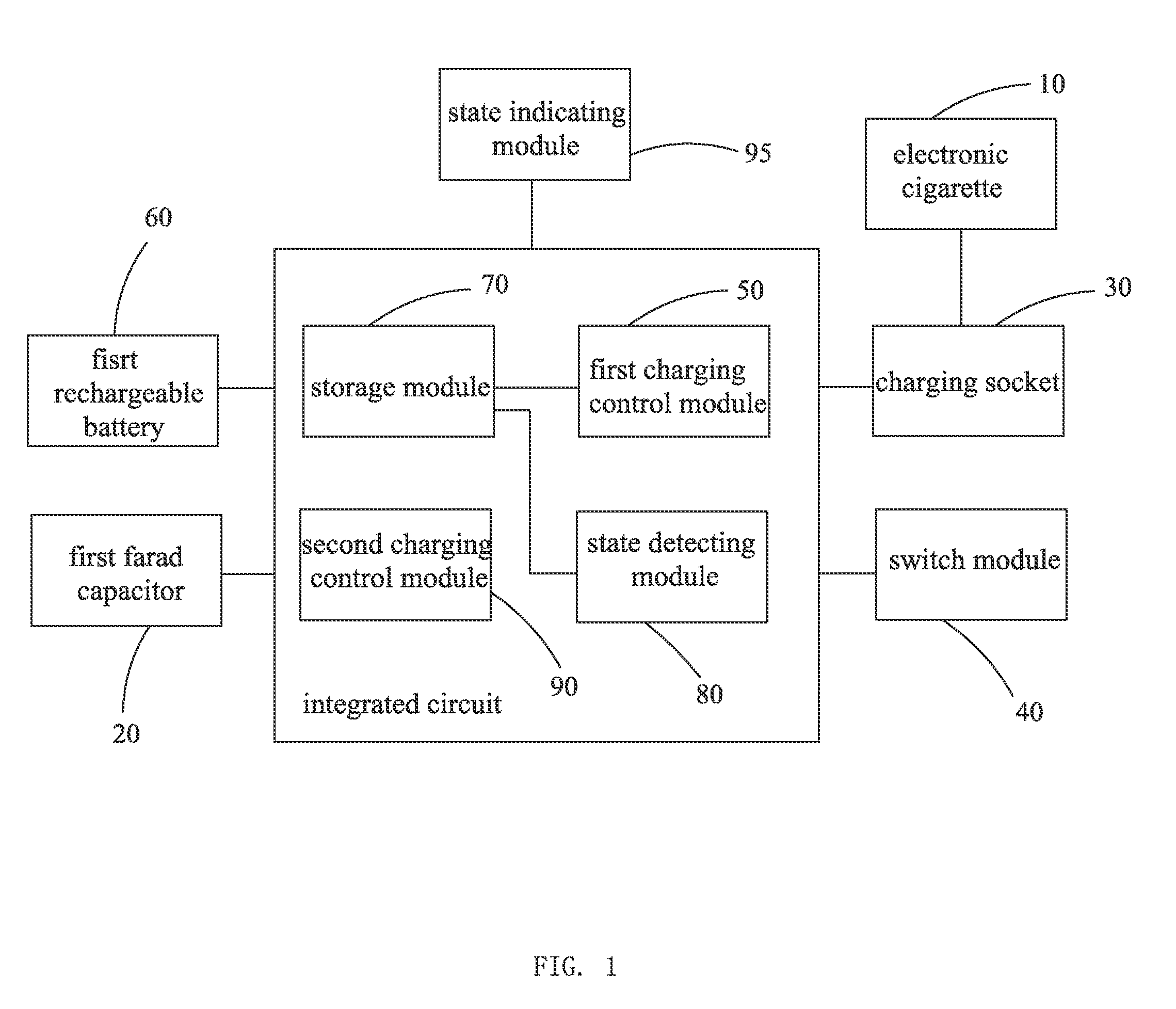
The invention provides an electronic cigarette casing and an electronic cigarette device, the electronic cigarette casing comprises a case body for accommodating electronic cigarettes, a first power supply configured in the case body and a charging control system for controlling the first power supply to charge the electronic cigarettes, the first power supply comprises a farad capacitor. The electronic cigarette casing using the farad capacitor instead of the traditional batteries to supply electrical power, can achieve the technical effects of safe and reliable charging / discharging, rapid charging, and more charging and discharging times.
Owner:HUIZHOU KIMREE TECH
Method and apparatus improving gate oxide reliability by controlling accumulated charge
ActiveUS7890891B2Improving nonlinear responses and harmonic and intermodulaton distortion effectsReduce non-linearitySolid-state devicesElectronic switchingMOSFETDielectric
A method and apparatus are disclosed for use in improving the gate oxide reliability of semiconductor-on-insulator (SOI) metal-oxide-silicon field effect transistor (MOSFET) devices using accumulated charge control (ACC) techniques. The method and apparatus are adapted to remove, reduce, or otherwise control accumulated charge in SOI MOSFETs, thereby yielding improvements in FET performance characteristics. In one embodiment, a circuit comprises a MOSFET, operating in an accumulated charge regime, and means for controlling the accumulated charge, operatively coupled to the SOI MOSFET. A first determination is made of the effects of an uncontrolled accumulated charge on time dependent dielectric breakdown (TDDB) of the gate oxide of the SOI MOSFET. A second determination is made of the effects of a controlled accumulated charge on TDDB of the gate oxide of the SOI MOSFET. The SOI MOSFET is adapted to have a selected average time-to-breakdown, responsive to the first and second determinations, and the circuit is operated using techniques for accumulated charge control operatively coupled to the SOI MOSFET. In one embodiment, the accumulated charge control techniques include using an accumulated charge sink operatively coupled to the SOI MOSFET body.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
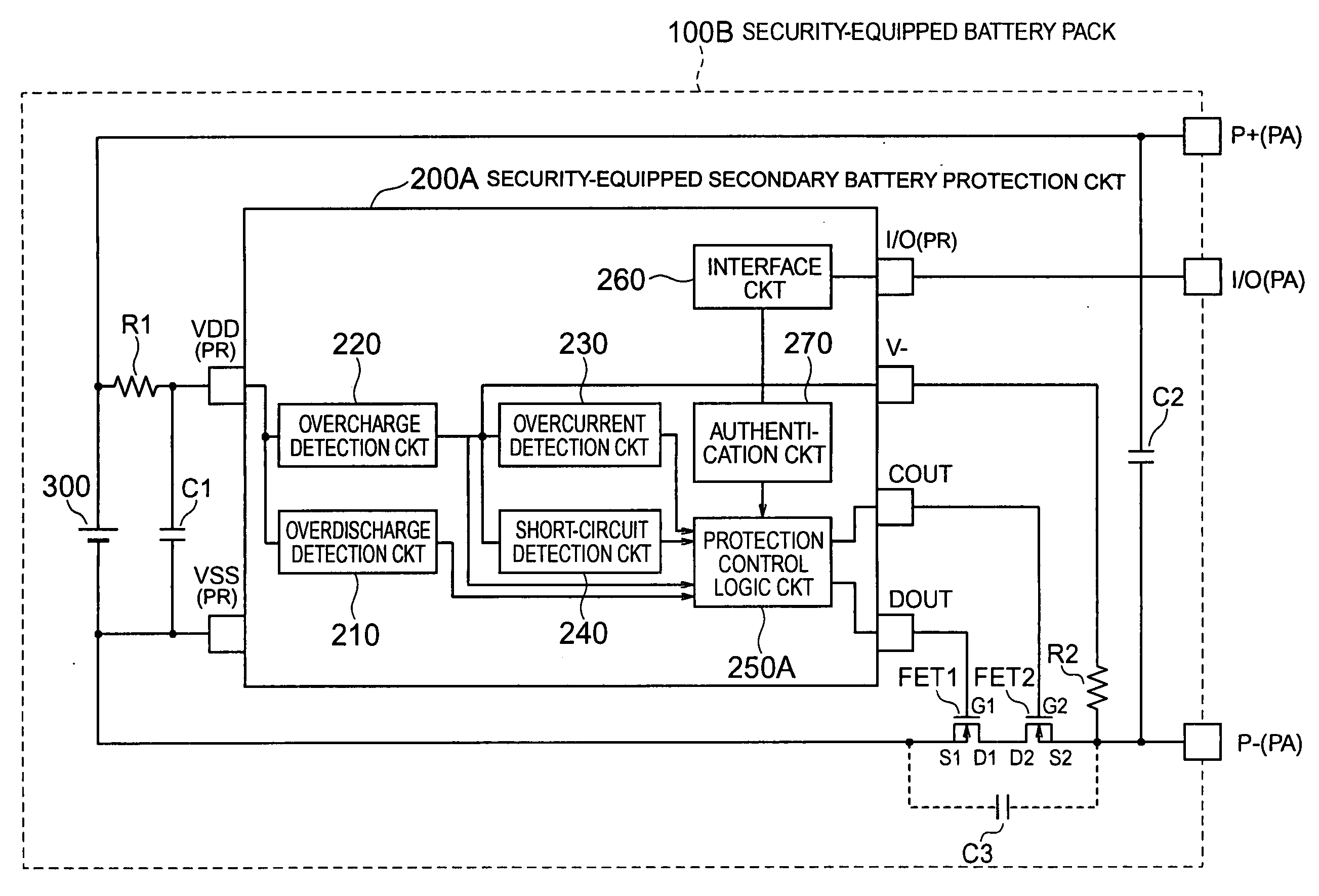
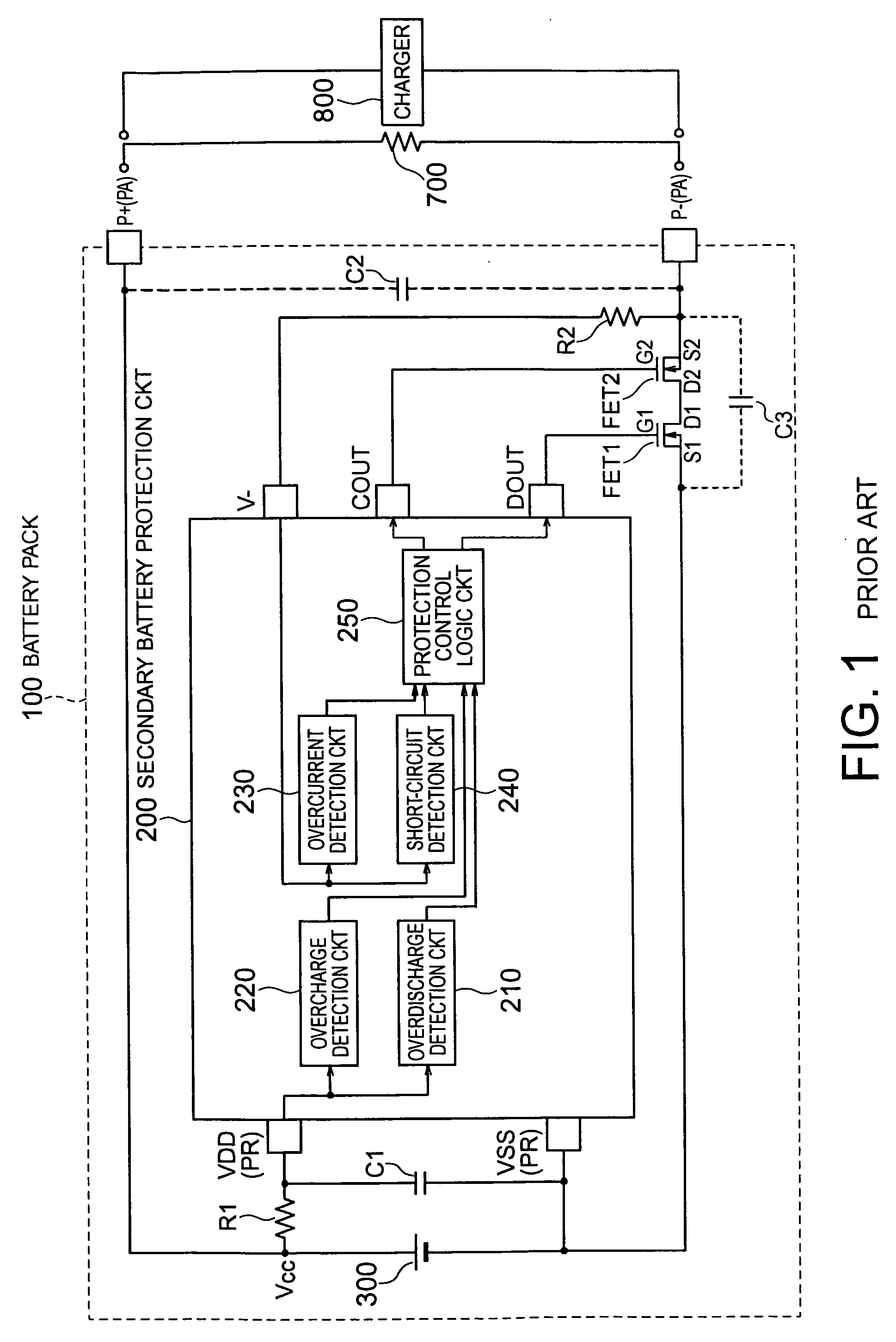
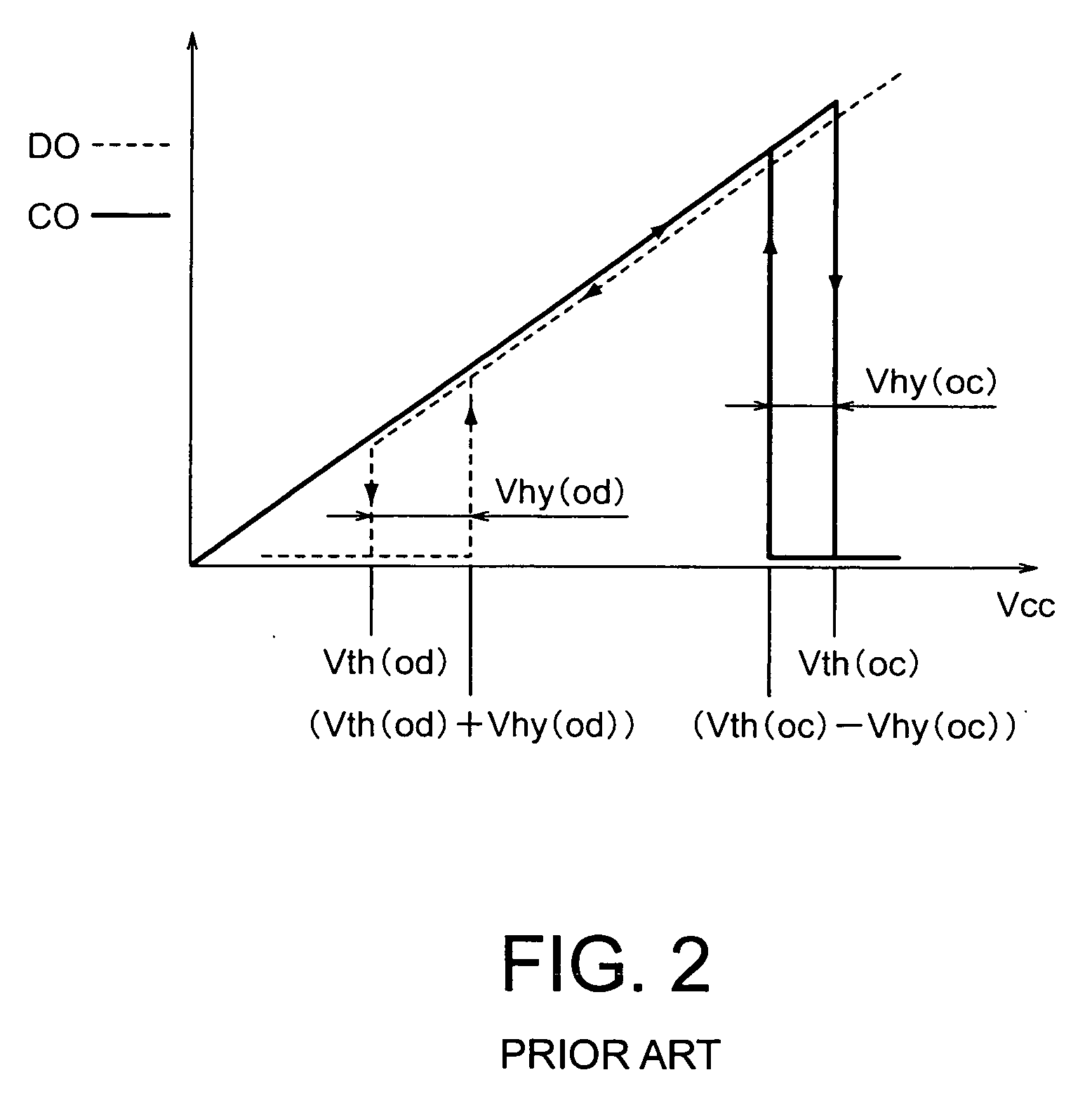
Secondary battery protection circuit comprising a security arrangement
InactiveUS20060208850A1Low overall parts countLow part-countProgramme controlElectric signal transmission systemsCharge controlControl switch
In a secondary battery protection circuit (200A) having a protection arrangement (210, 220, 230, 240, 250A) for protecting a secondary battery (300), by turning a discharge control switch (FET1) and a charge control switch (FET2) on and off, so as to prevent the secondary battery from overdischarging and overcharging, the secondary battery protection circuit further has a security arrangement (260, 270) for precluding counterfeit goods of a secondary pack. The security arrangement has an interface circuit (260) for interfacing to a portable unit body (500) and an authentication circuit (270) for calculating an identifier obtained by encrypting a random number received from the portable unit body to return the identifier to the portable unit body.
Owner:MITSUMI ELECTRIC CO LTD
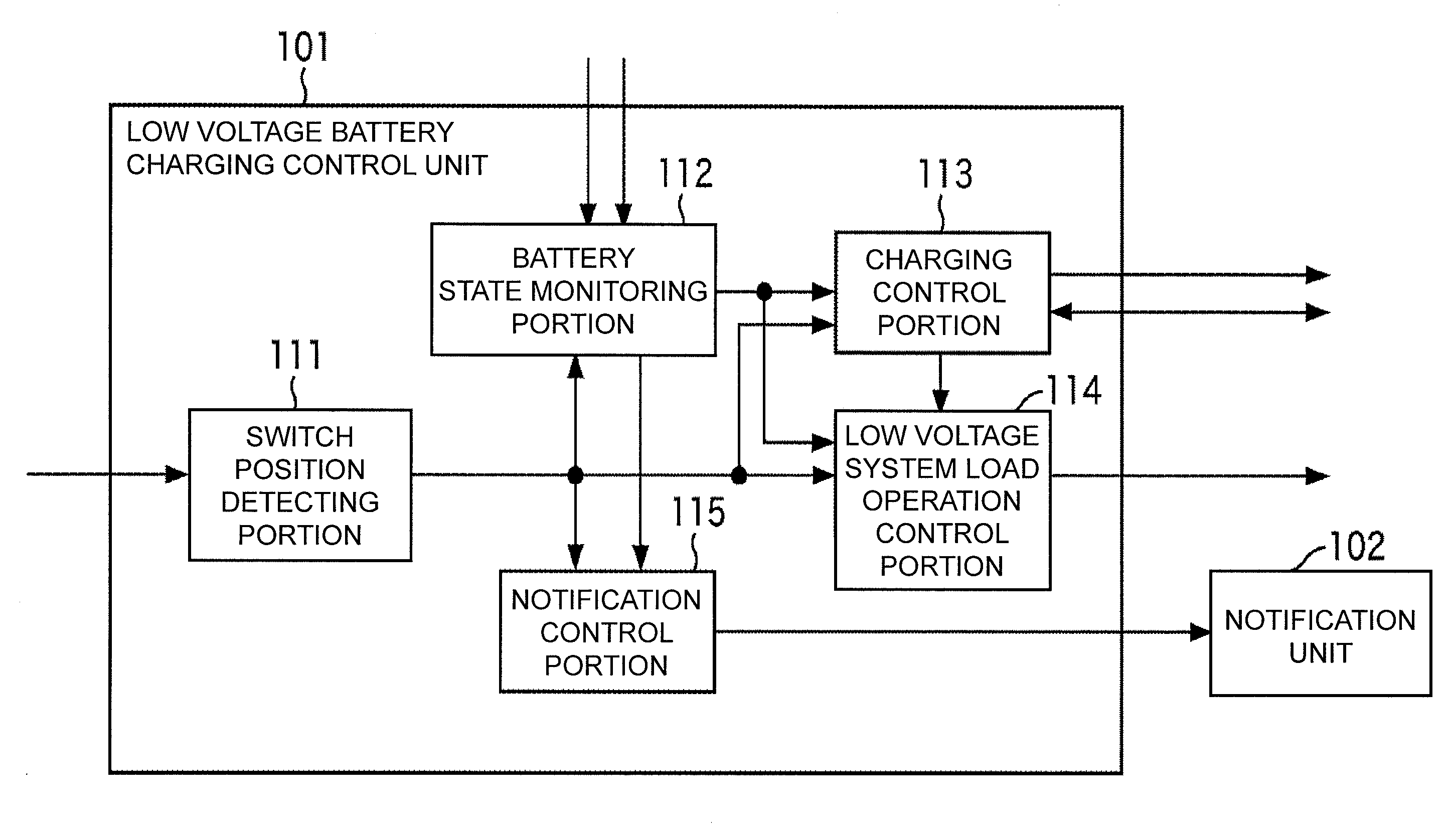
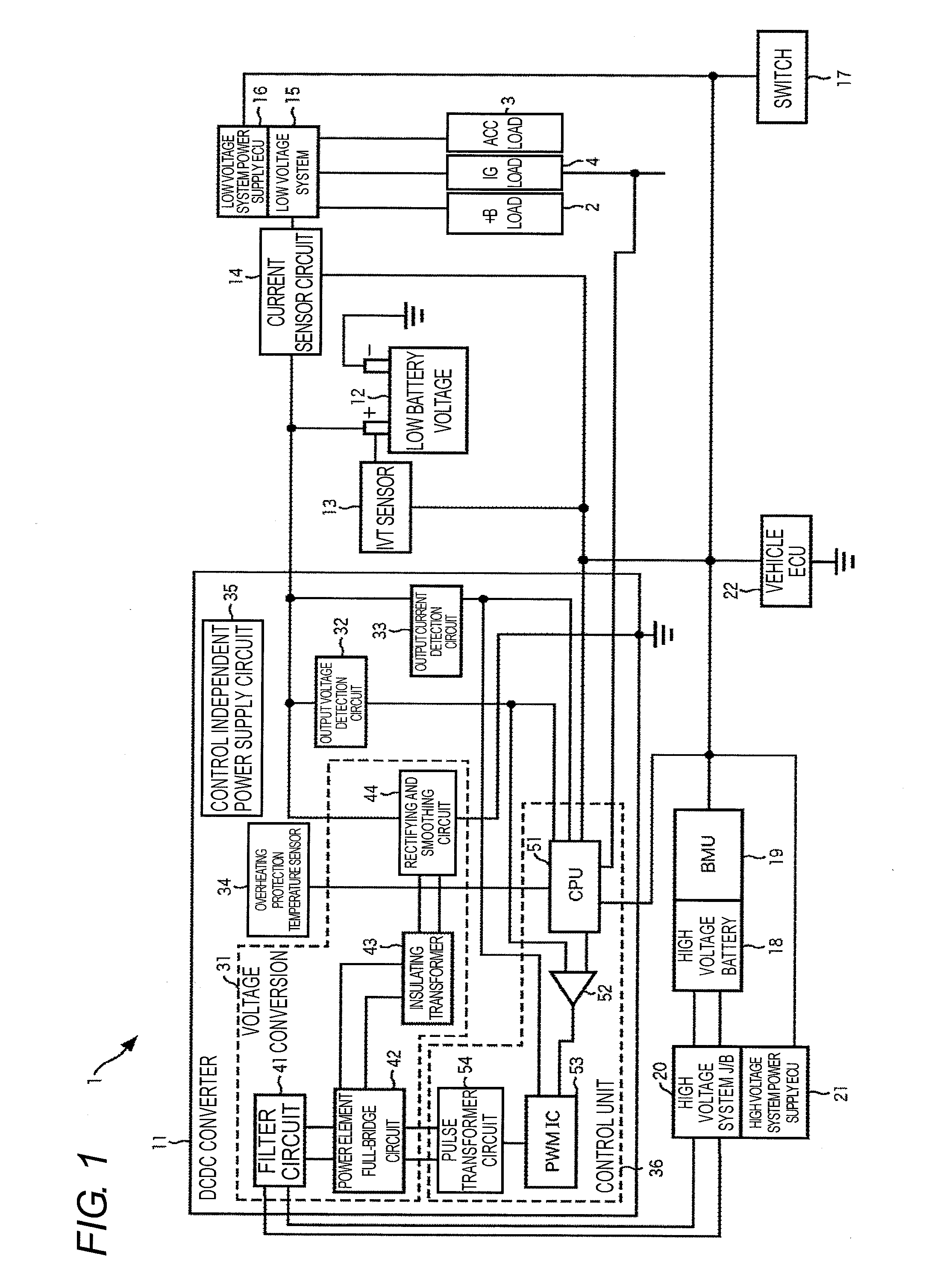
Charging control device and method, charging device, as well as program
InactiveUS20100244782A1Prevent low running outLower runHybrid vehiclesCircuit monitoring/indicationLow voltageElectrical battery
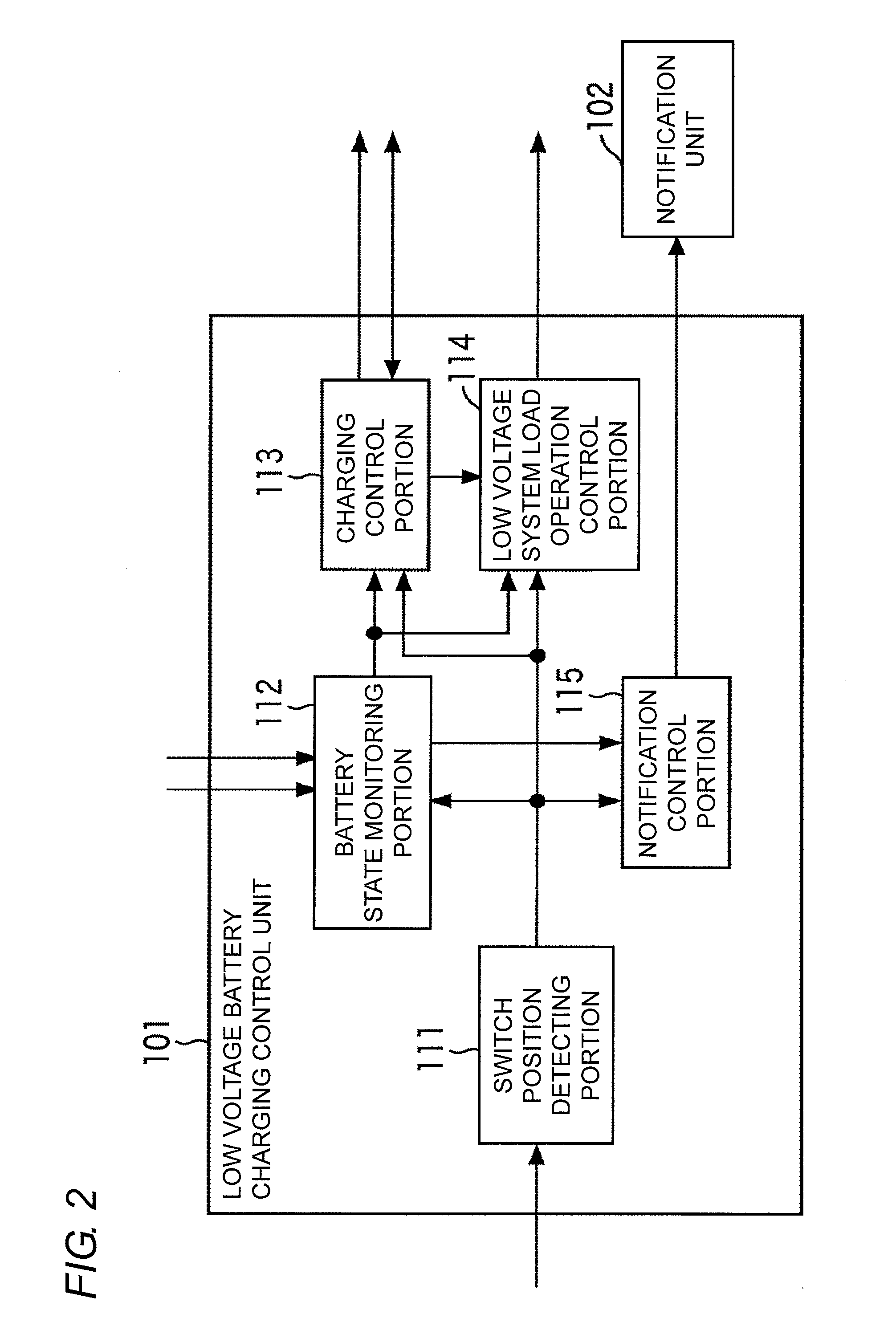
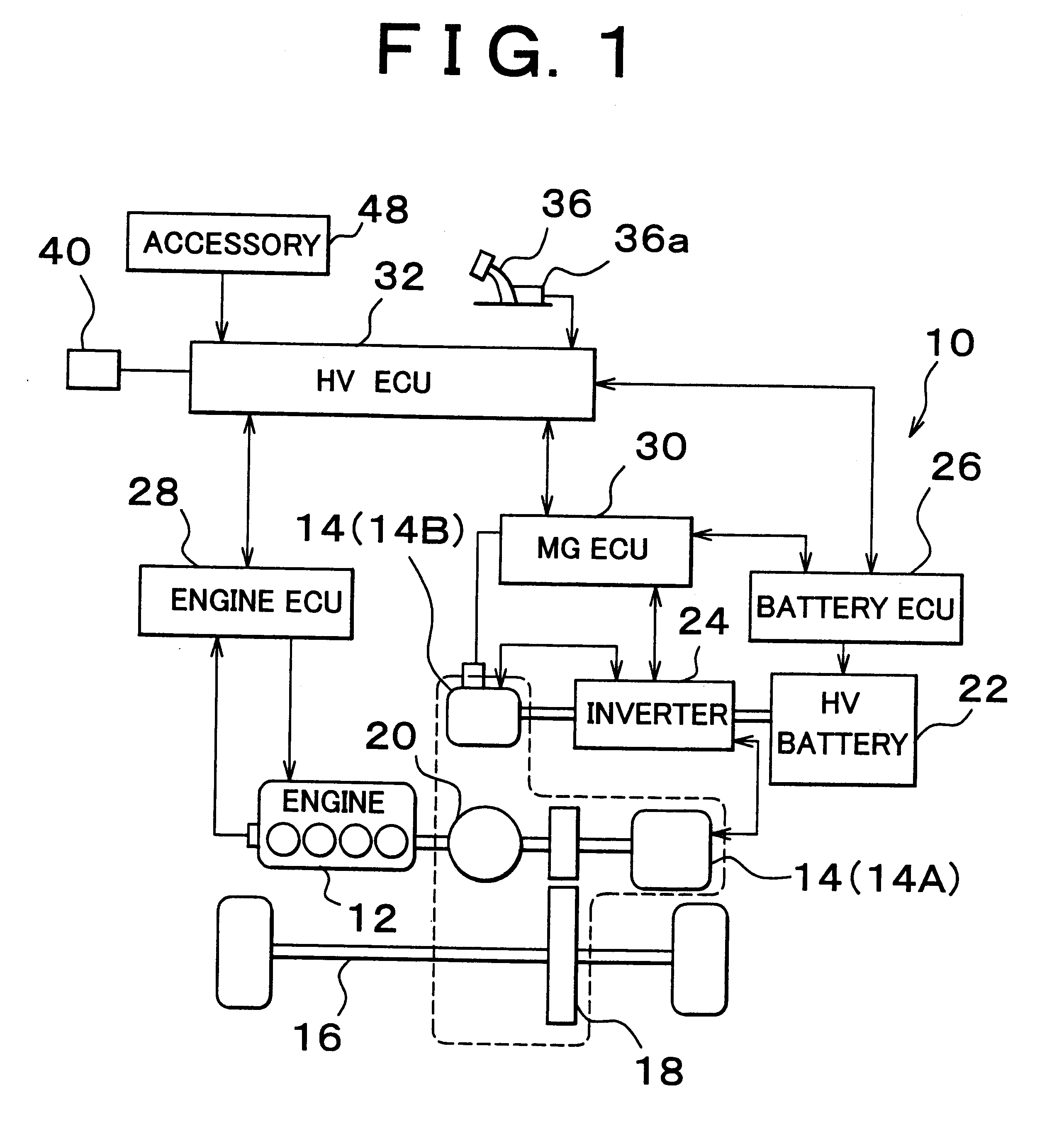
A battery state monitoring portion intermittently monitors the low voltage battery for supplying power to electrical components arranged in a vehicle while the power supply to the low voltage system load other than a +B load is stopped, a DCDC converter is stopped, and a +B power supply mode in which the vehicle cannot travel is set. A charging control portion starts up the DCDC converter and charges the low voltage battery with the power of a high voltage battery as a power source of the vehicle through the DCDC converter when the voltage of the low voltage battery becomes lower than or equal to a charging start voltage when the +B power supply mode is set. The present invention can be applied to a charging device of a battery of an electric vehicle.
Owner:OMRON AUTOMOTIVE ELECTRONICS CO LTD
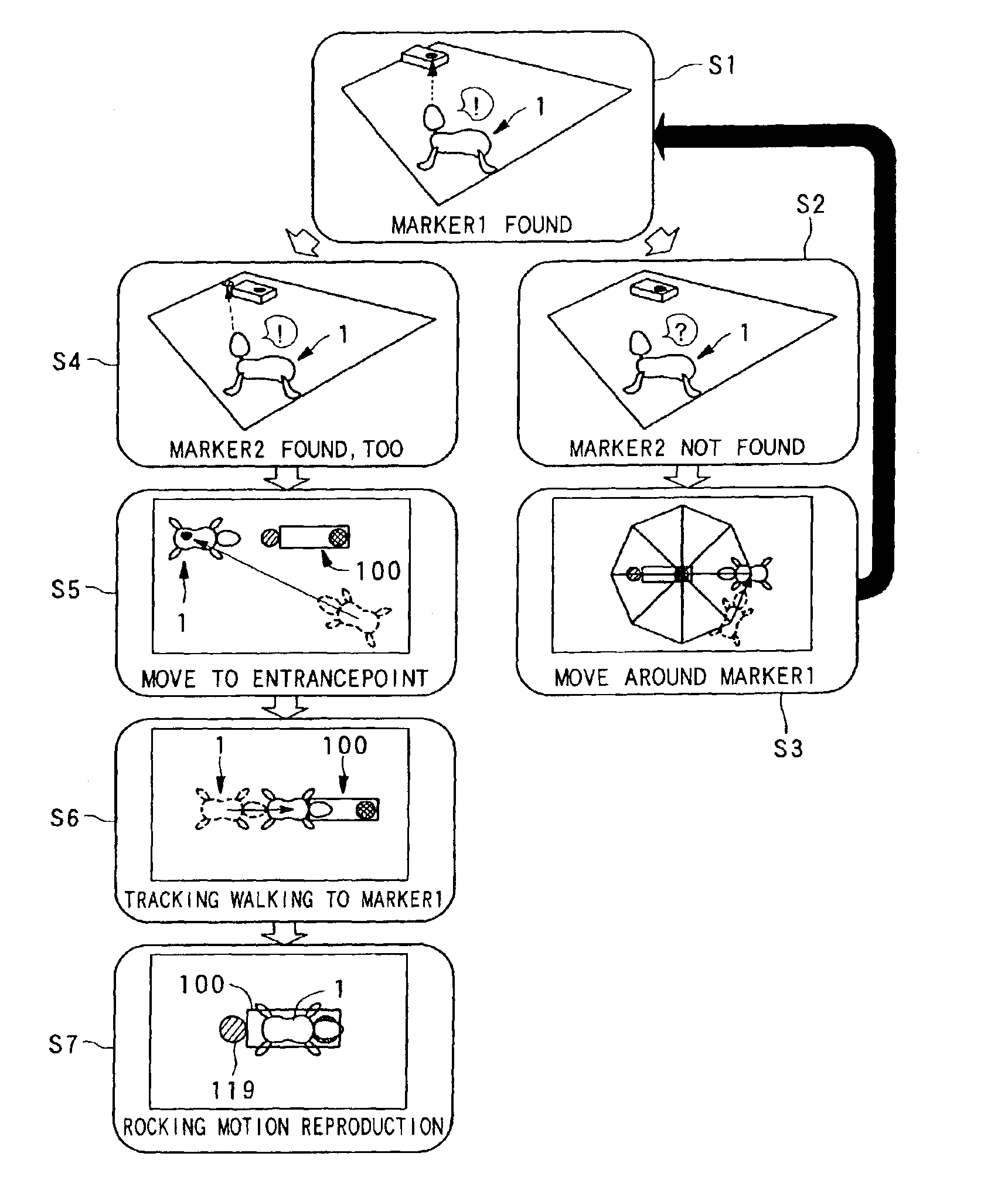
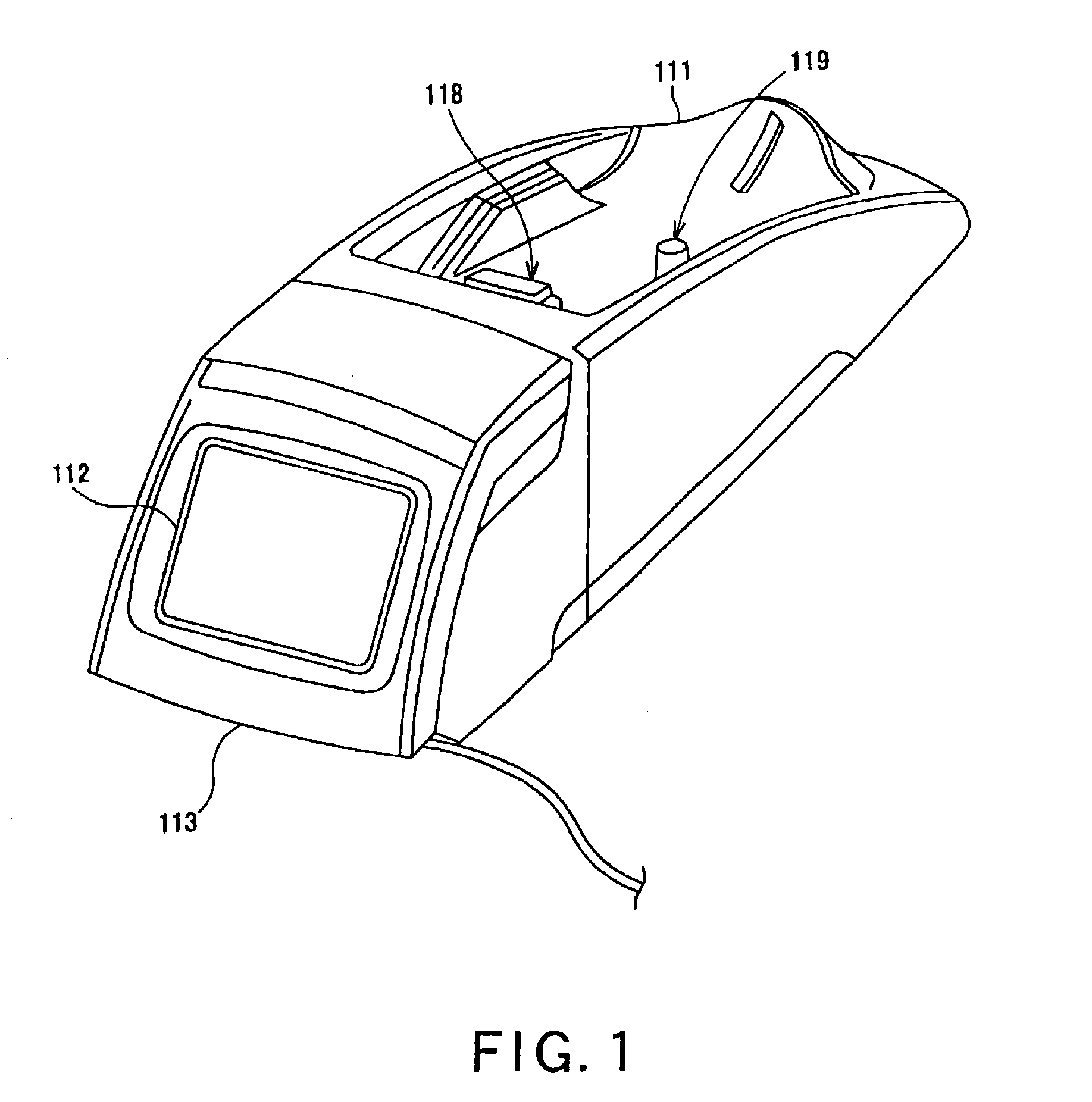
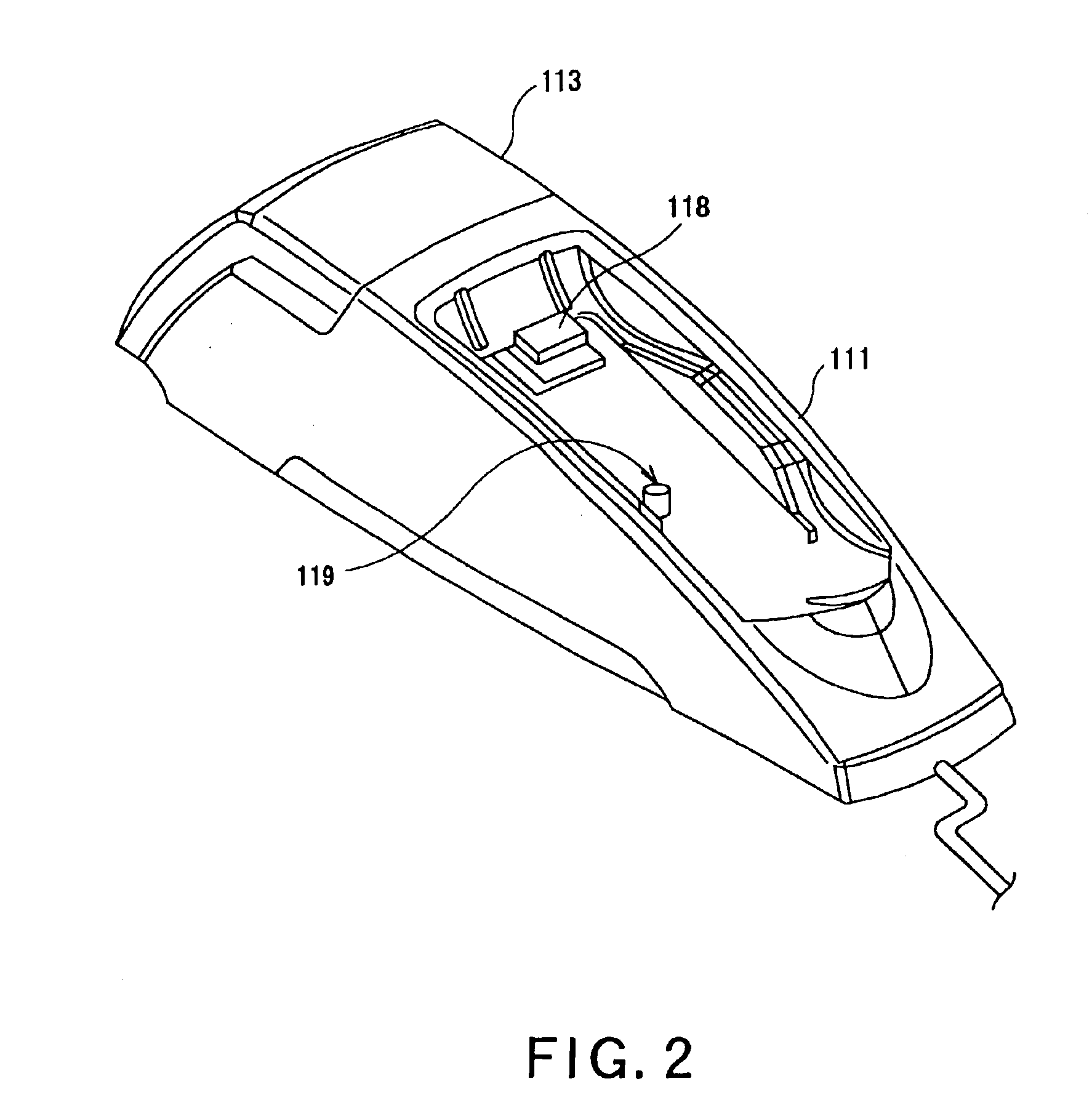
Electrical charging system, electrical charging controlling method, robot apparatus, electrical charging device, electrical charging controlling program and recording medium
A robot apparatus 1 is to be electrically charged autonomously. An electrical charging device 100 is provided with two markers, namely a main marker 118 and a sub-marker 119, and the heights of the markers are pre-stored in the robot apparatus. When the robot apparatus 1 is to find the direction and the distance to the electrical charging device 100, a CCD camera 20 finds the direction vector of the marker from the photographed image. This direction vector is transformed into a position vector of a camera coordinate system {c} and further into a position vector of the robot coordinate system {b}. The coordinate in the height-wise direction in the robot coordinate system {b} is compared to the pre-stored height to find the distance between the markers and the robot apparatus and the direction of the robot apparatus.
Owner:SONY CORP
Charge controller and navigation device for plug-in vehicle
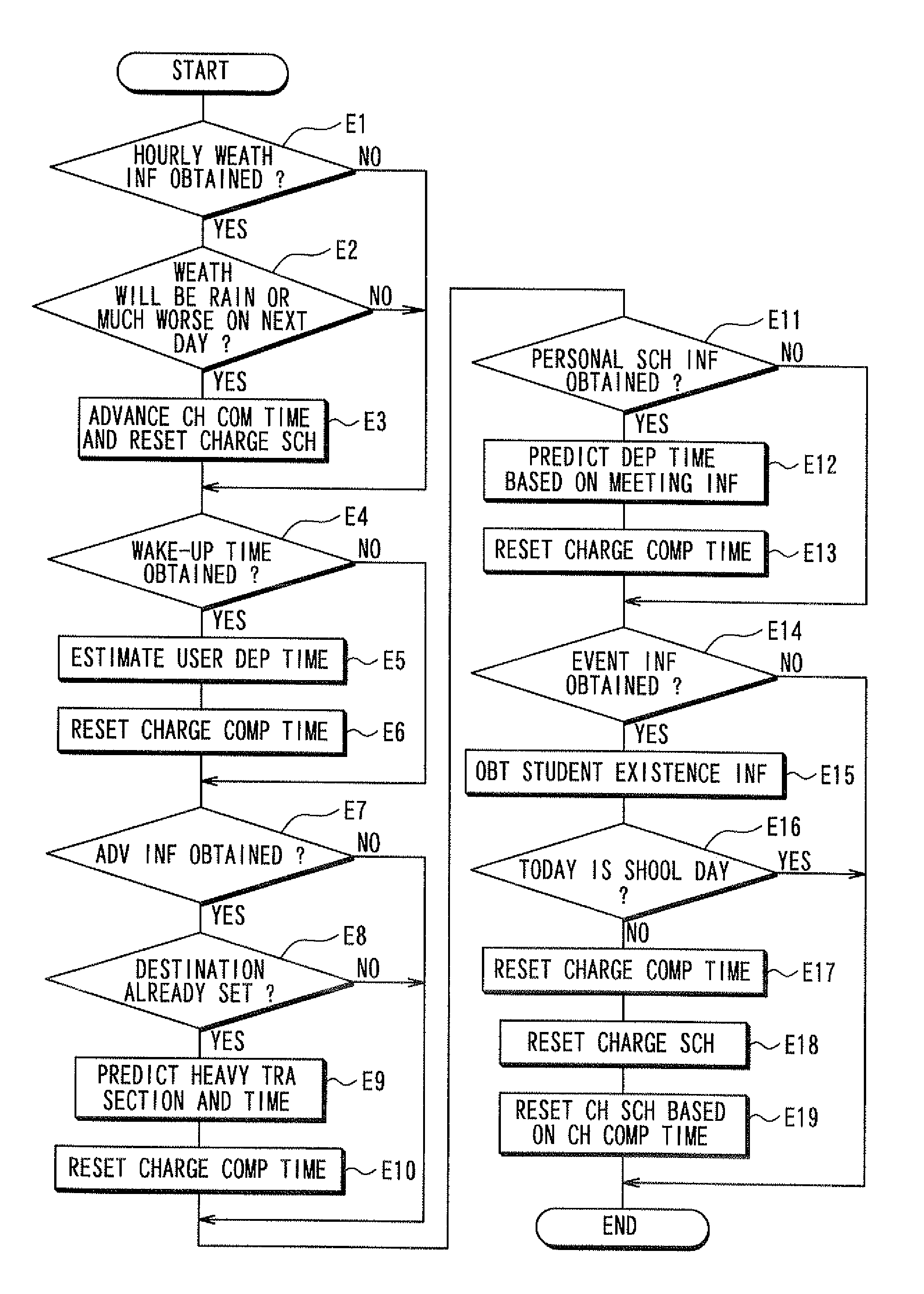
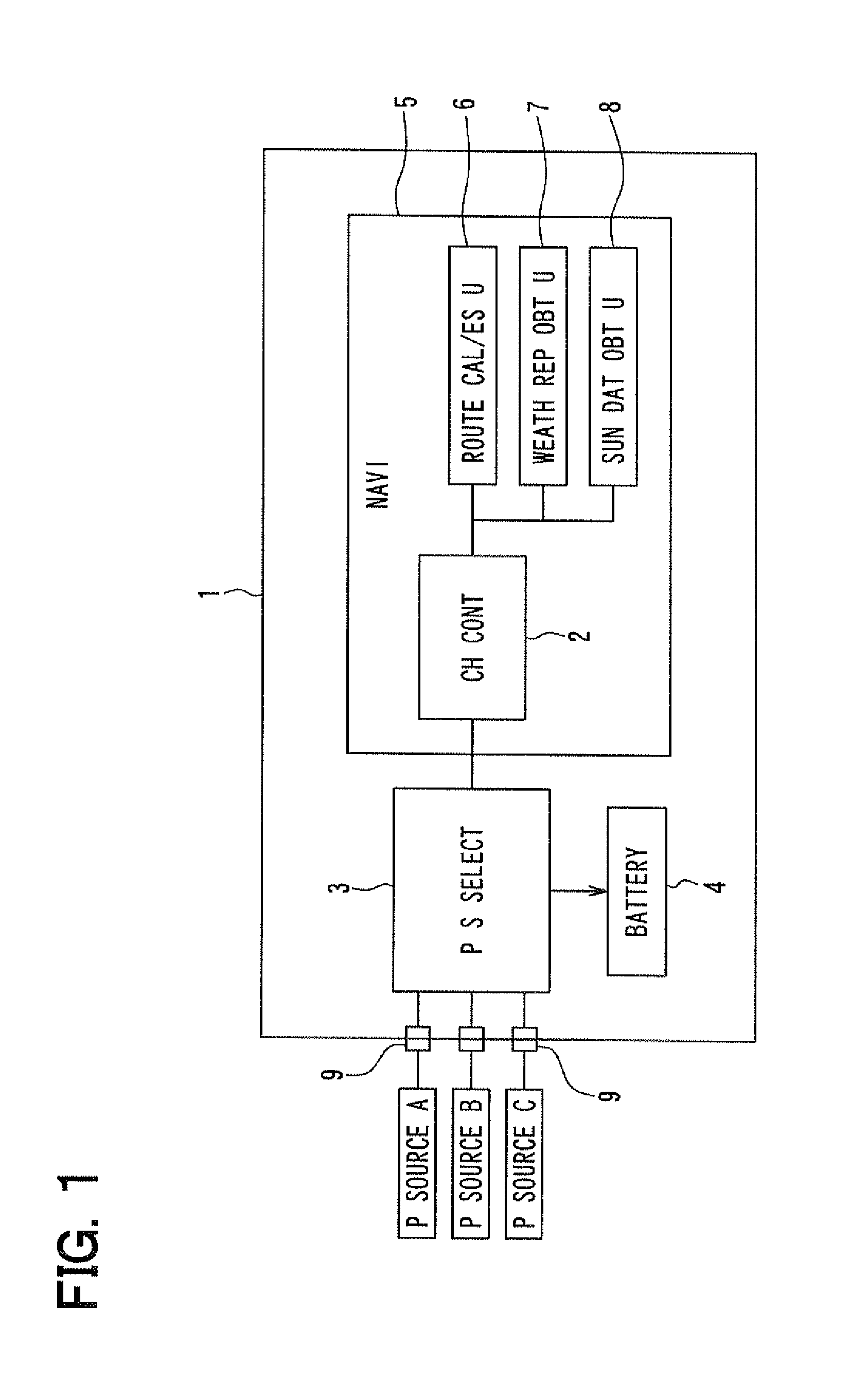
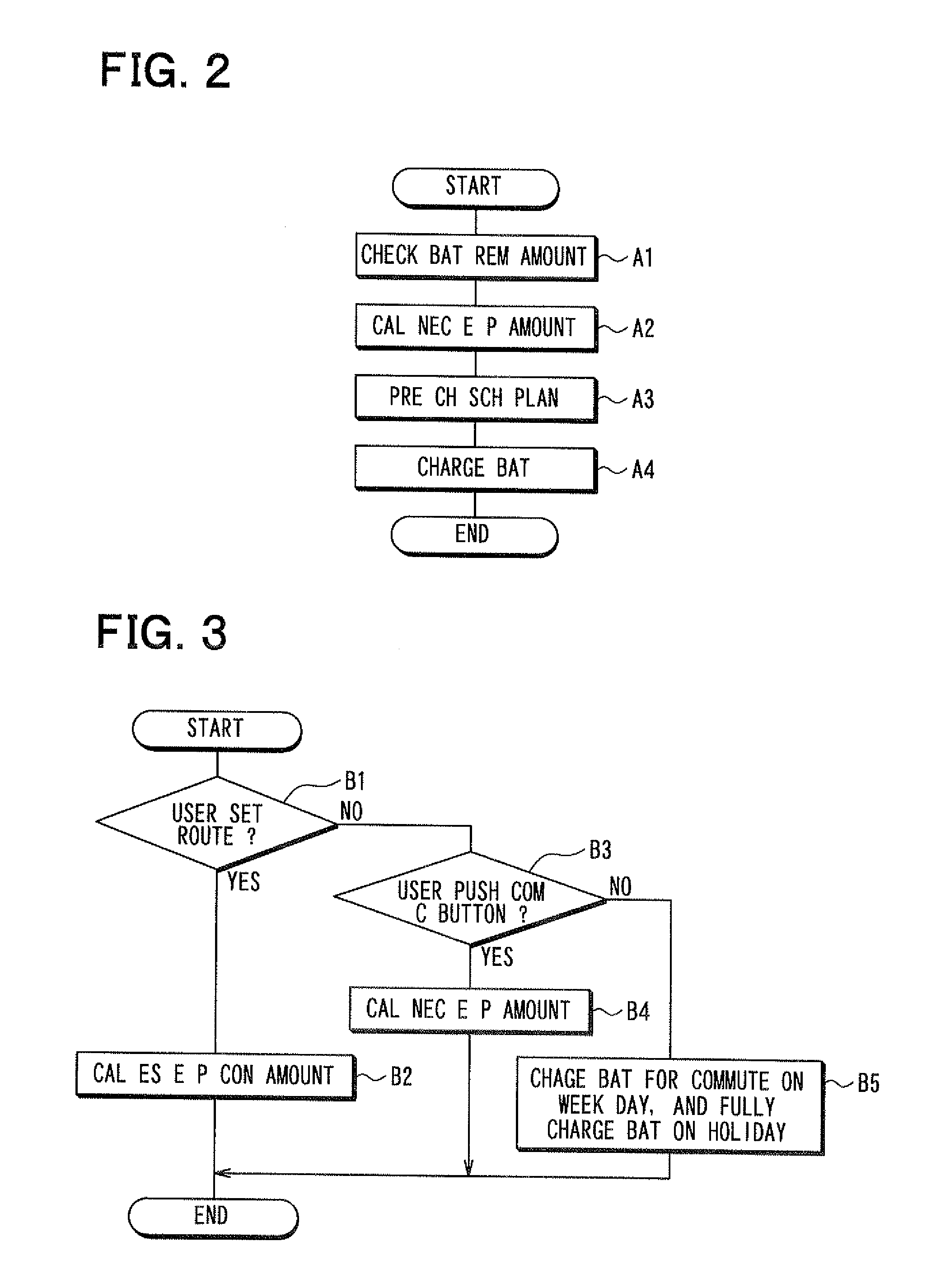
ActiveUS20110202221A1Reduce charging costsFully chargedHybrid vehiclesBatteries circuit arrangementsElectrical batteryElectric power system
A charge controller for charging a battery of a plug-in vehicle with a plurality of electric power sources includes: a driving route estimation element; an estimated electric power consumption amount calculator; a weather information obtaining element; a sunshine information obtaining element; a solar photovoltaic generation electric power amount calculator; an electric power shortage amount calculator for calculating an electric power shortage amount when the solar photovoltaic generation electric power amount is smaller than an estimated electric power consumption amount; a charge schedule preparation element for preparing a charge schedule, which represents a first charge time for charging the battery with a solar photovoltaic generation system and a second charge time for charging the battery by the electric power shortage amount with another electric power source; and a charge control element for controlling to charge the battery according to the charge schedule.
Owner:DENSO CORP
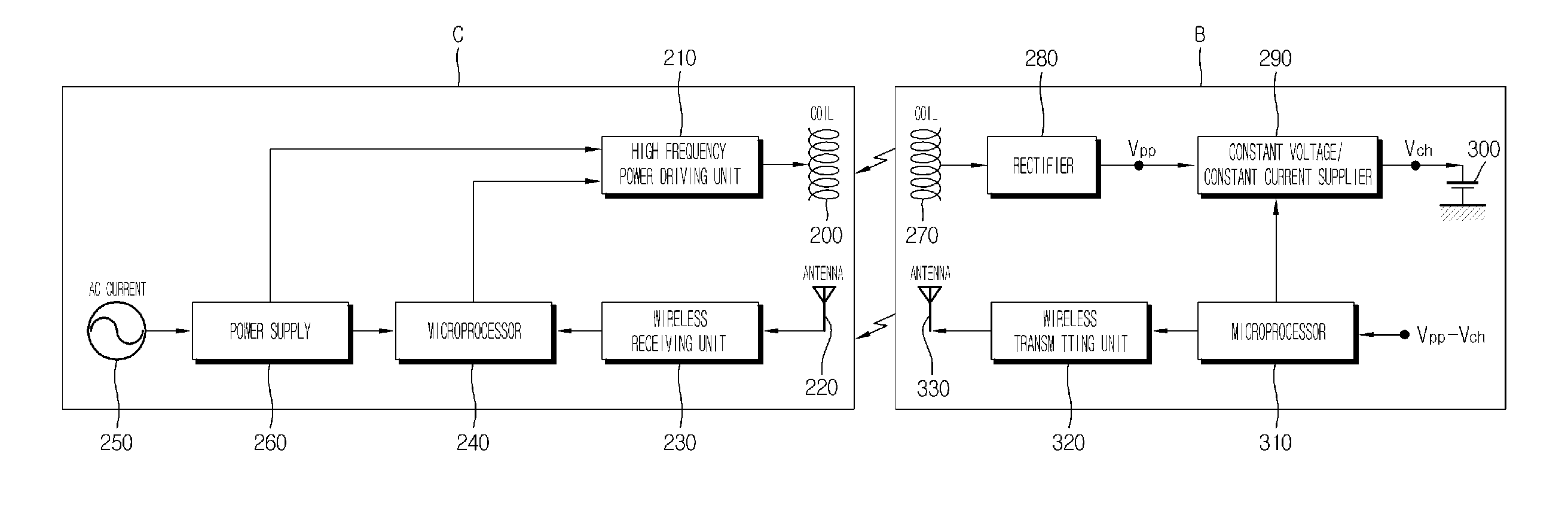
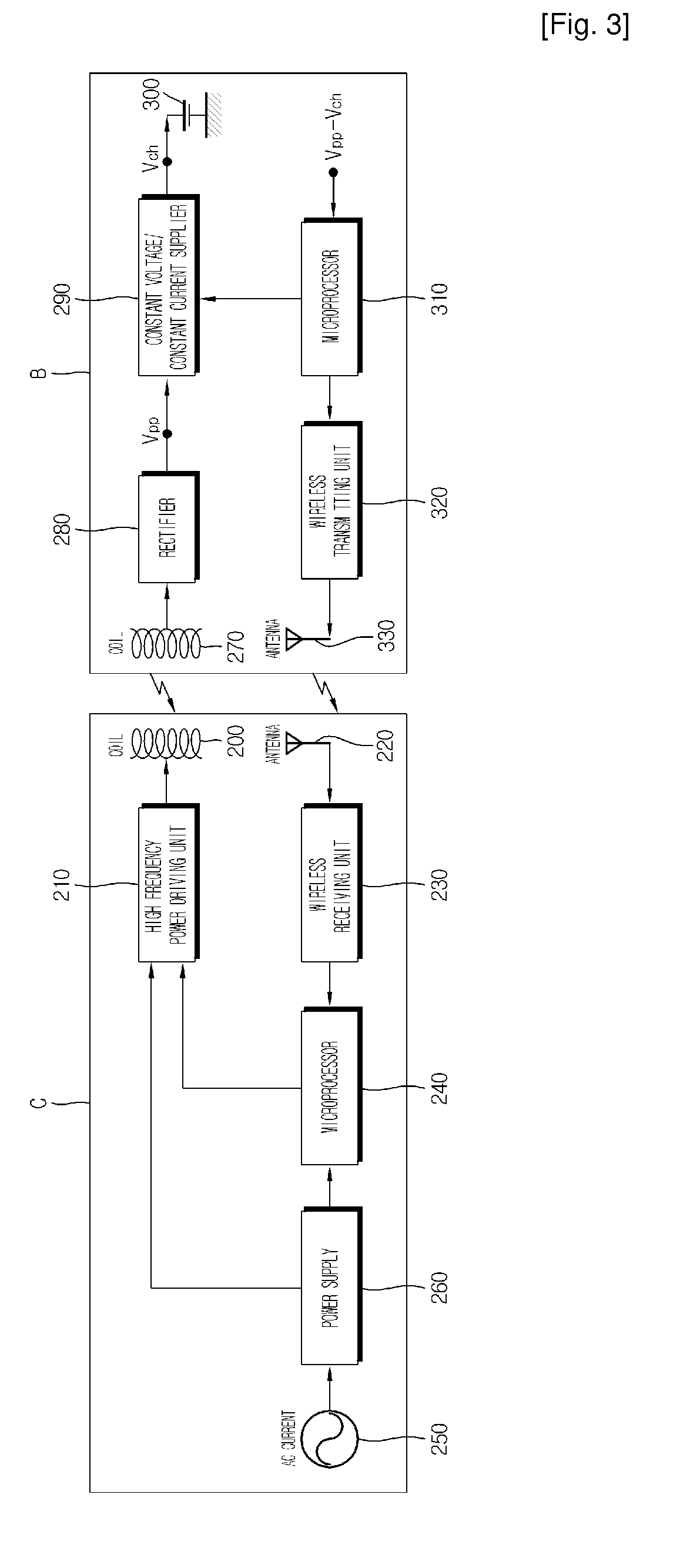
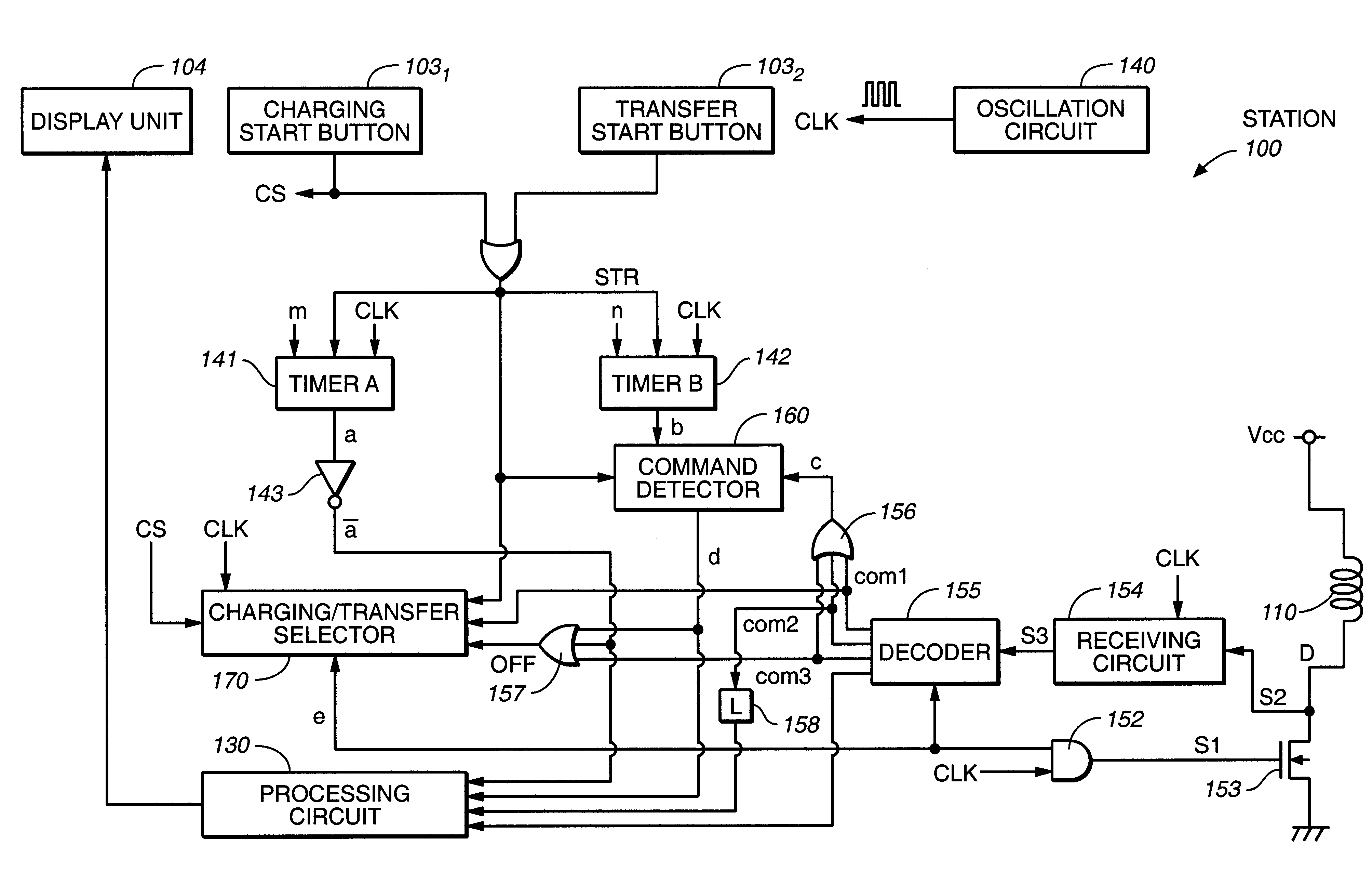
Electronic device, control method for electronic device, recharge-rate estimating method for secondary battery, and charging control method for secondary battery
A first circuit having a first coil electrically charges a second circuit having a second coil through electromagnetic coupling of the two coils. When data signals are to be transferred between the first and second circuits, signal transfer is started only after the second circuit has been charged for a predetermined period of time. The position relationship between the coils is also detected, and a charging / transfer selector changes a duty ratio between charge transfer and data transfer in accordance with the detected result. The charge is transferred in an intermittent manner, and the charging rate is adjusted according to the difference between the voltage of a secondary battery observed during a charging phase and the voltage of the secondary battery observed a certain time after interruption of the charging phase, or vice versa.
Owner:CHAMIRAUX MANAGEMENT LLC
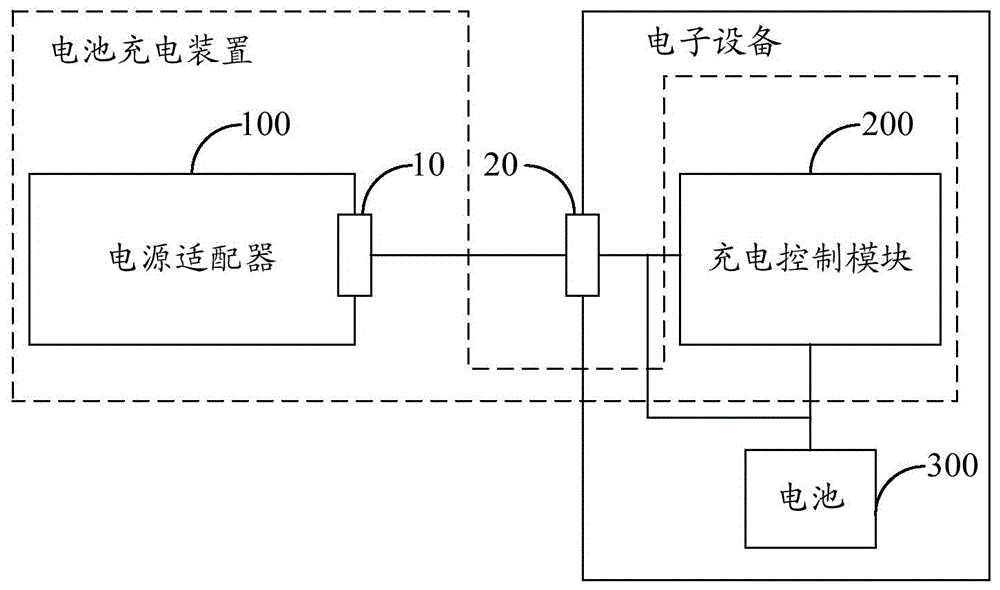
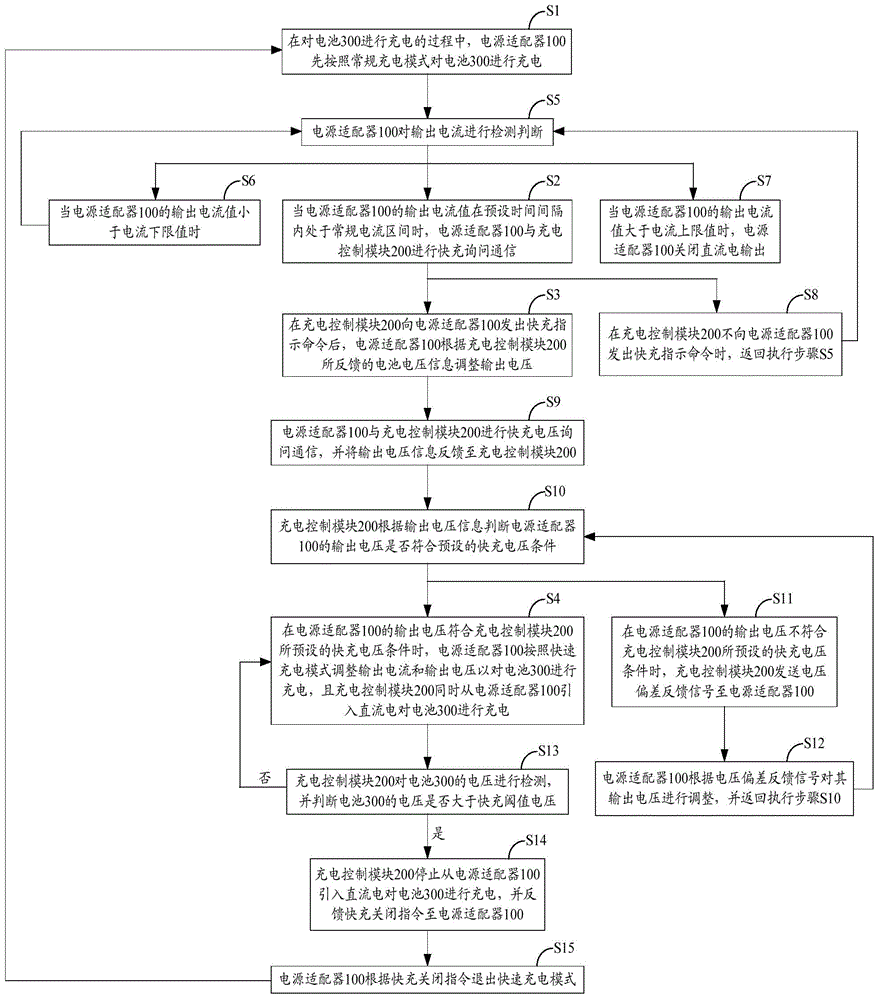
Cell charging device and method
ActiveCN104810877AShorten charging timeSecondary cells charging/dischargingElectric powerCurrent rangeCharge control
The invention belongs to the technical field of charging and provides a cell charging device and method. In the process of charging a cell by utilizing the cell charging device comprising a power adapter and a charging control module, the power adapter charges the cell in a conventional charging mode first; when the output current value of the power adapter is in a conventional current range in a preset time interval, the power adapter is in quick charge inquiry communication with the charging control module; after the charging control module sends a quick charge instruction command to the power adapter, the power adapter adjusts output voltage according to the cell voltage information fed back by the charging control module; when the output voltage accords with the preset quick charge voltage condition of the charging control module, the power adapter adjusts output current and output voltage according to the quick charge mode so as to charge the cell; and meanwhile, the charging control module introduces a direct current from the power adapter to charge the cell, and thus the purpose of reducing charging time by carrying out quick charge on the cell is realized.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
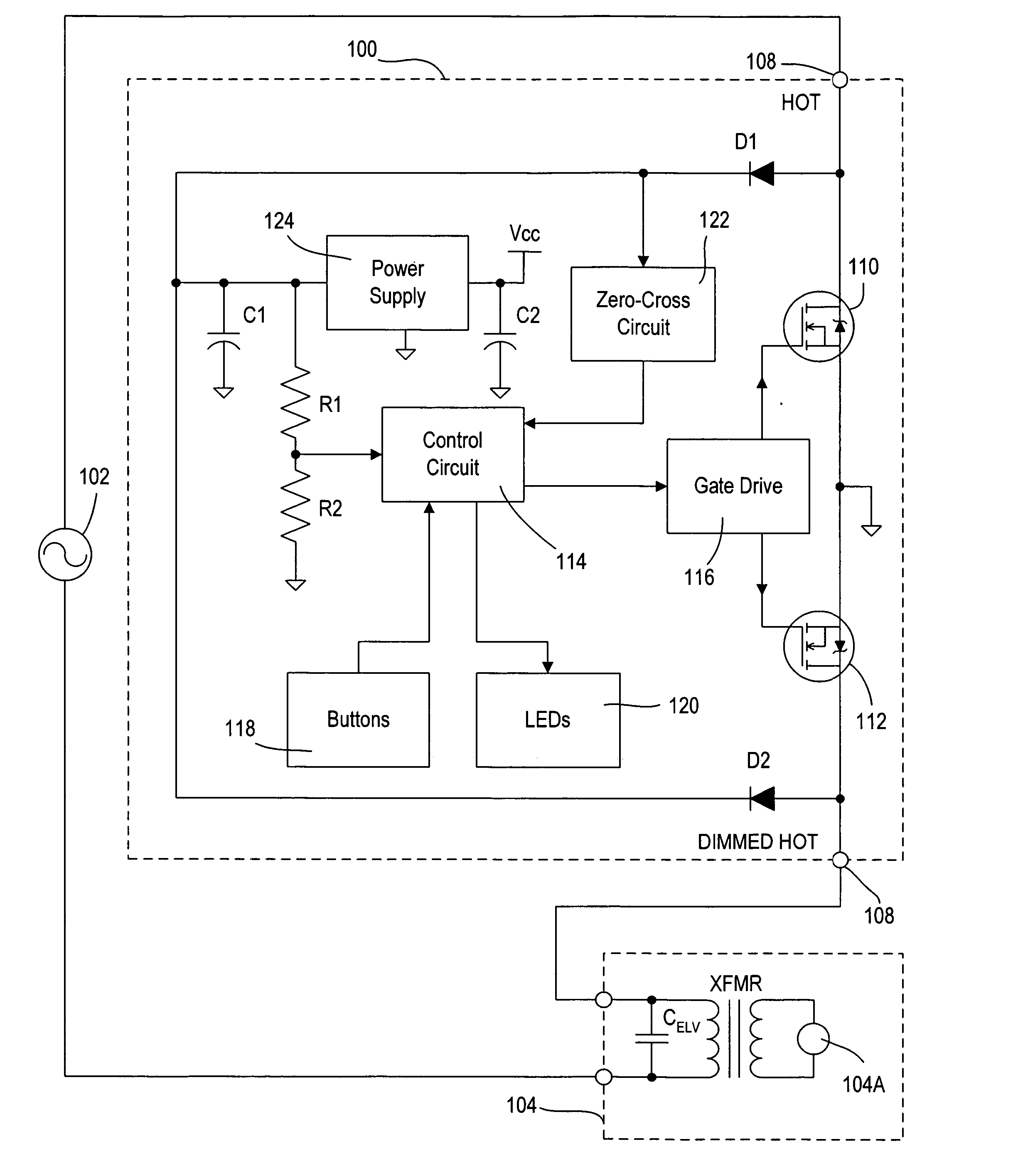
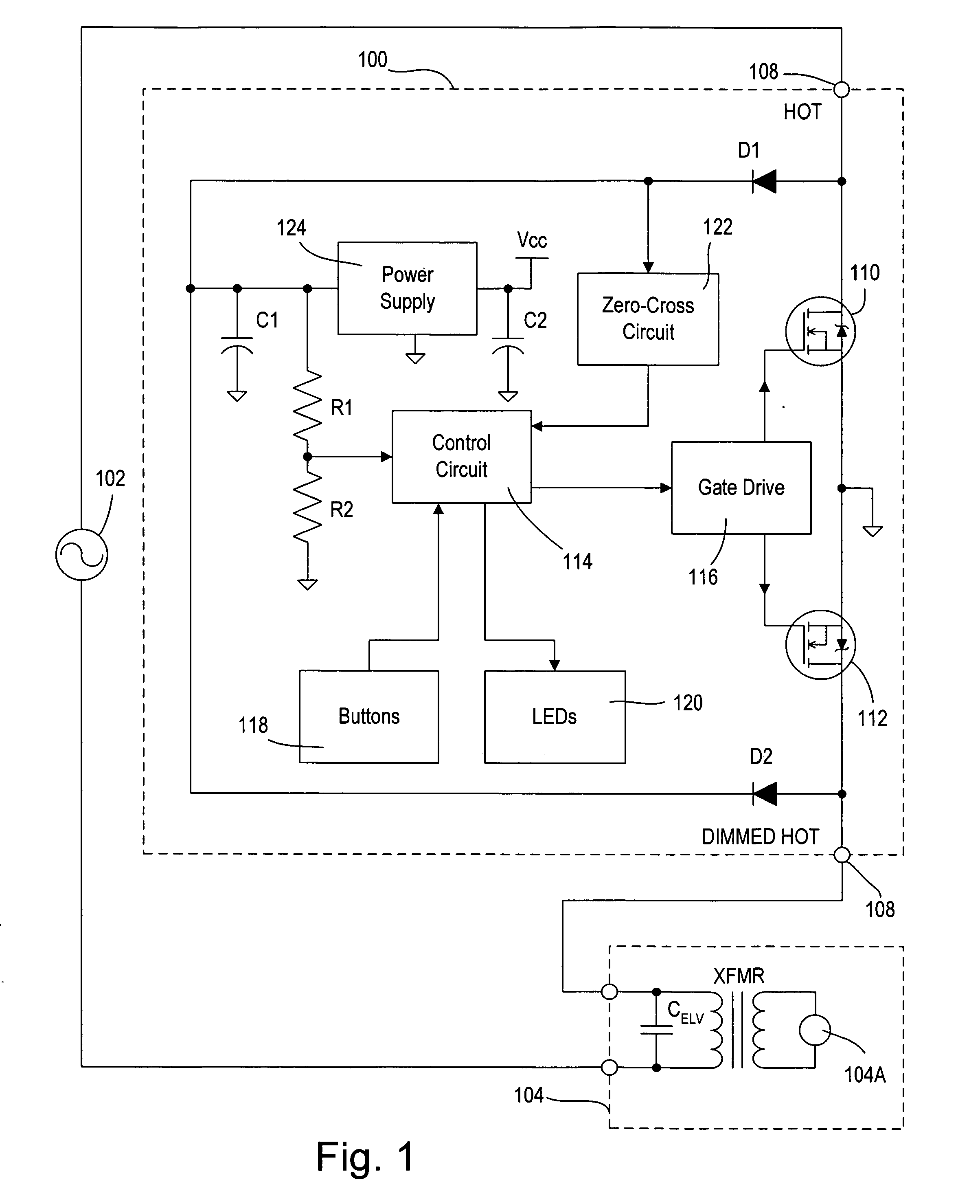
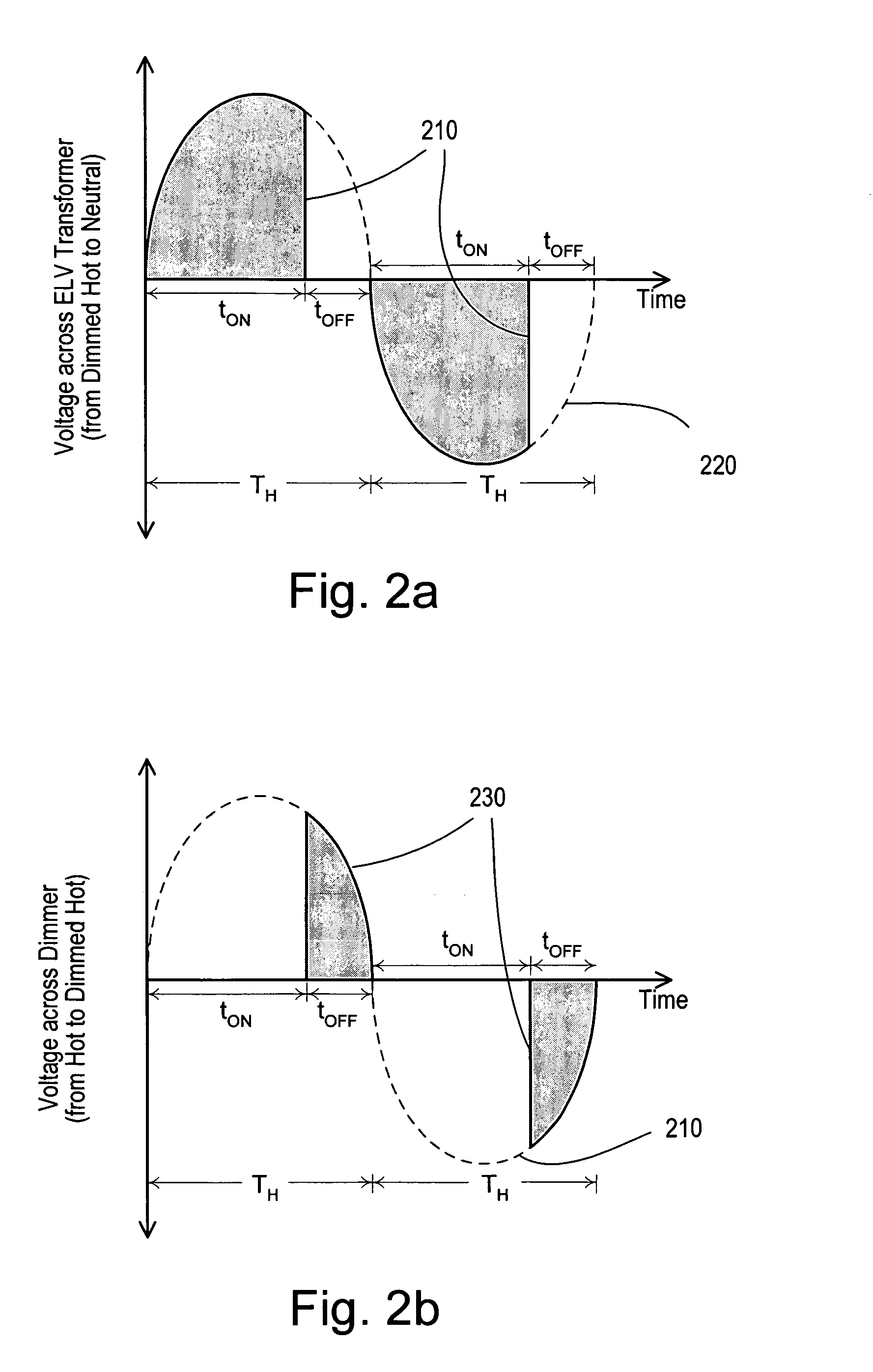
Dimmer having a power supply monitoring circuit
ActiveUS20060255745A1Decrease on-timeExtended on-timeElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementCapacitanceEffect light
A two-wire dimmer for control of a lighting load from an alternating-current (AC) power source includes a semiconductor switch, a power supply, and a control circuit. The power supply includes an energy storage input capacitor that is able to charge only when the semiconductor switch is non-conductive. The control circuit continuously monitors the voltage on the input capacitor and automatically decreases the maximum allowable conduction time of the semiconductor switch when the voltage falls to a level that will not guarantee proper operation of the power supply. The dimmer of the present invention is able to provide the maximum possible conduction time of the semiconductor switch at high end (i.e., maximum light intensity) while simultaneously ensuring sufficient charging time for proper operation of the power supply, and hence, the dimmer.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
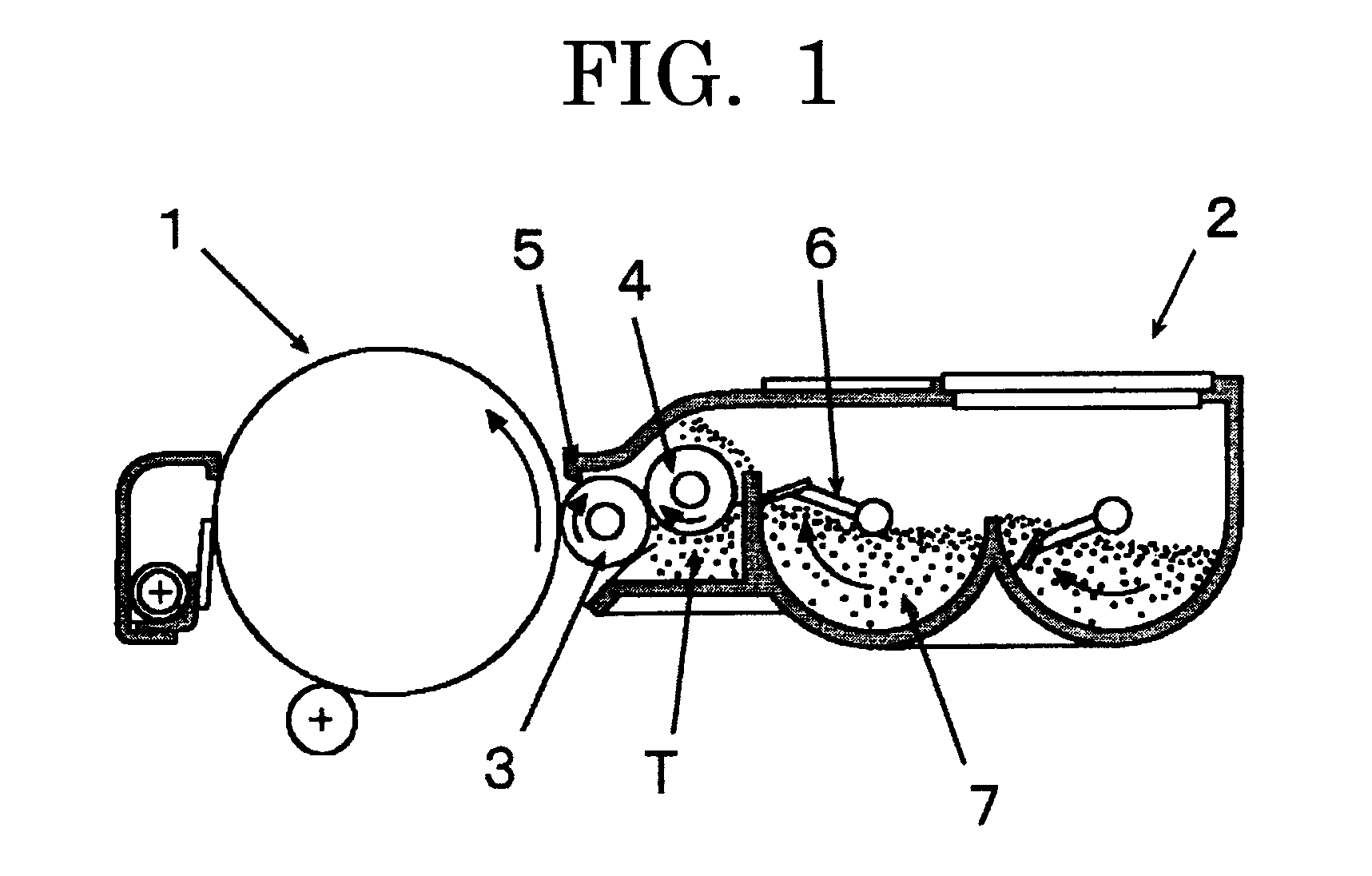
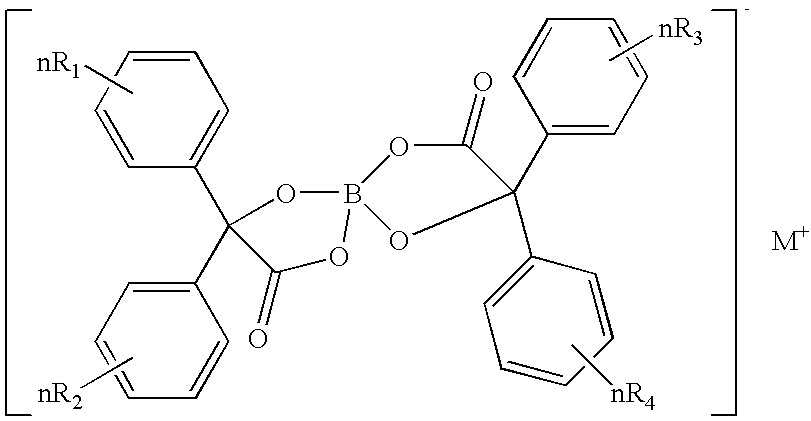
Toner and image forming method
InactiveUS20070207399A1Improve stabilityUniformly and efficiently chargingElectrographic process apparatusDevelopersImage transferLatent image
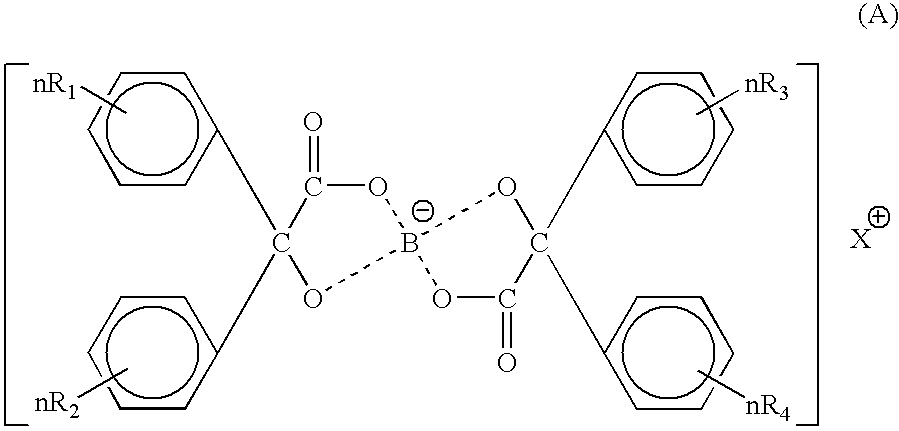
Toner for electrostatic charge development wherein no scumming occurs, and toner leakage caused by charge defect of the toner on a developing roller can be inhibited, and an excellent image stability is obtained is provided.The toner used for an image forming method having a latent electrostatic image forming step of forming a latent electrostatic image on a latent electrostatic image bearing member primarily charged, a developing step of developing the latent electrostatic image by each toner which multiple developing devices have to form a toner image on the latent electrostatic image bearing member, a transferring step of transferring the toner image with respective colors formed on the latent electrostatic image bearing member onto a recording material and a fixing step of fixing the toner image transferred onto the recording material, wherein the toner comprises a colorant and a resin and contains an organic boron compound represented by a following chemical formula (A) as a charge controlling agent, further the toner is treated with an inorganic fine particle and at least one of the inorganic particles is a magnesium silicate compound represented by a following general formula [2] is provided.wherein X is an alkali metal, R1, R2, R3 or R4 each represents a hydrogen atom, an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, an alkoxy group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, or a halogen atom.MgxSiyO(x+2y) [2]wherein x and y are integers.
Owner:RICOH KK
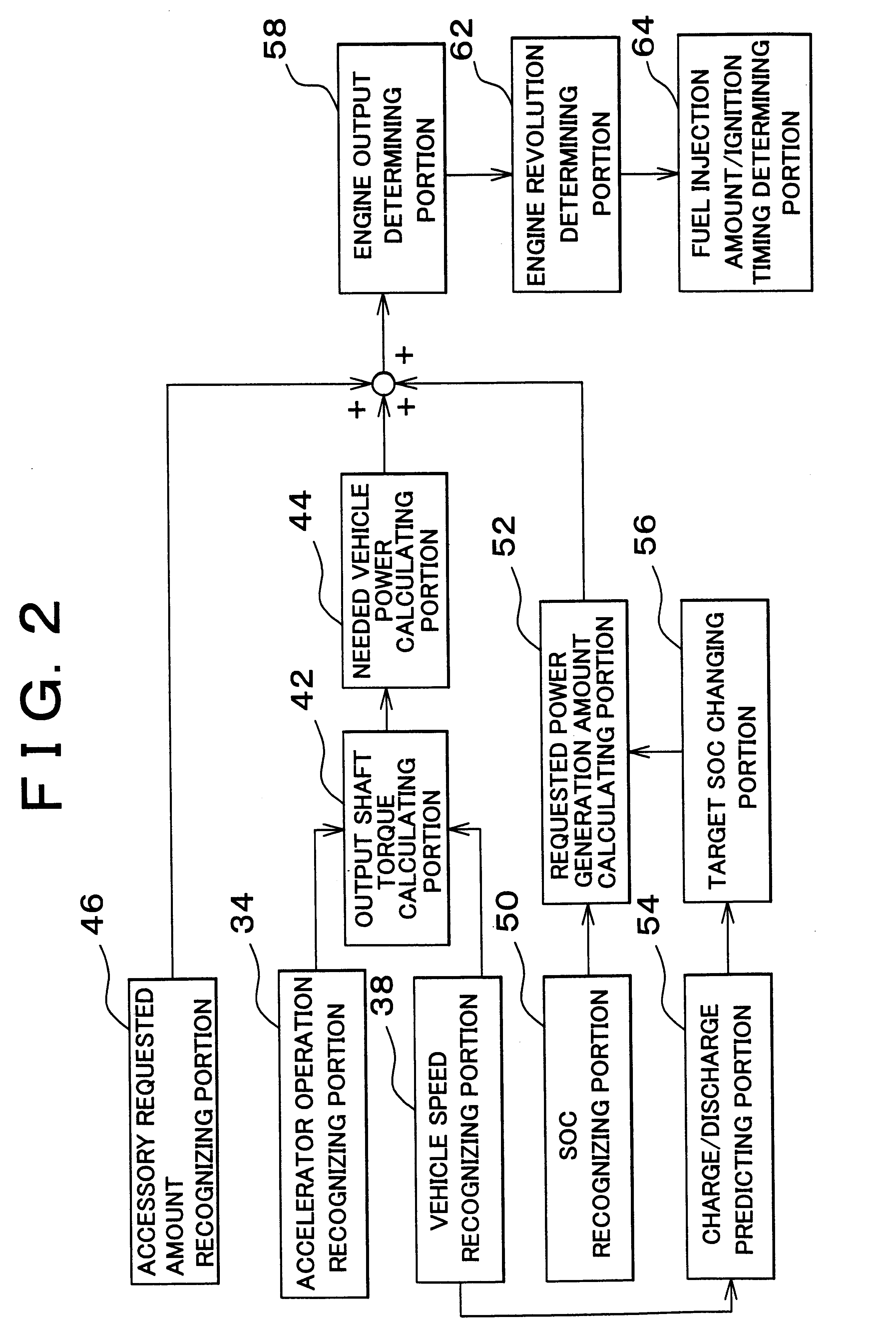
Electric energy charging control apparatus and method for hybrid vehicle
InactiveUS6344732B2Improve charging capacityReduce the amount of solutionHybrid vehiclesBatteries circuit arrangementsState of chargeCharge control
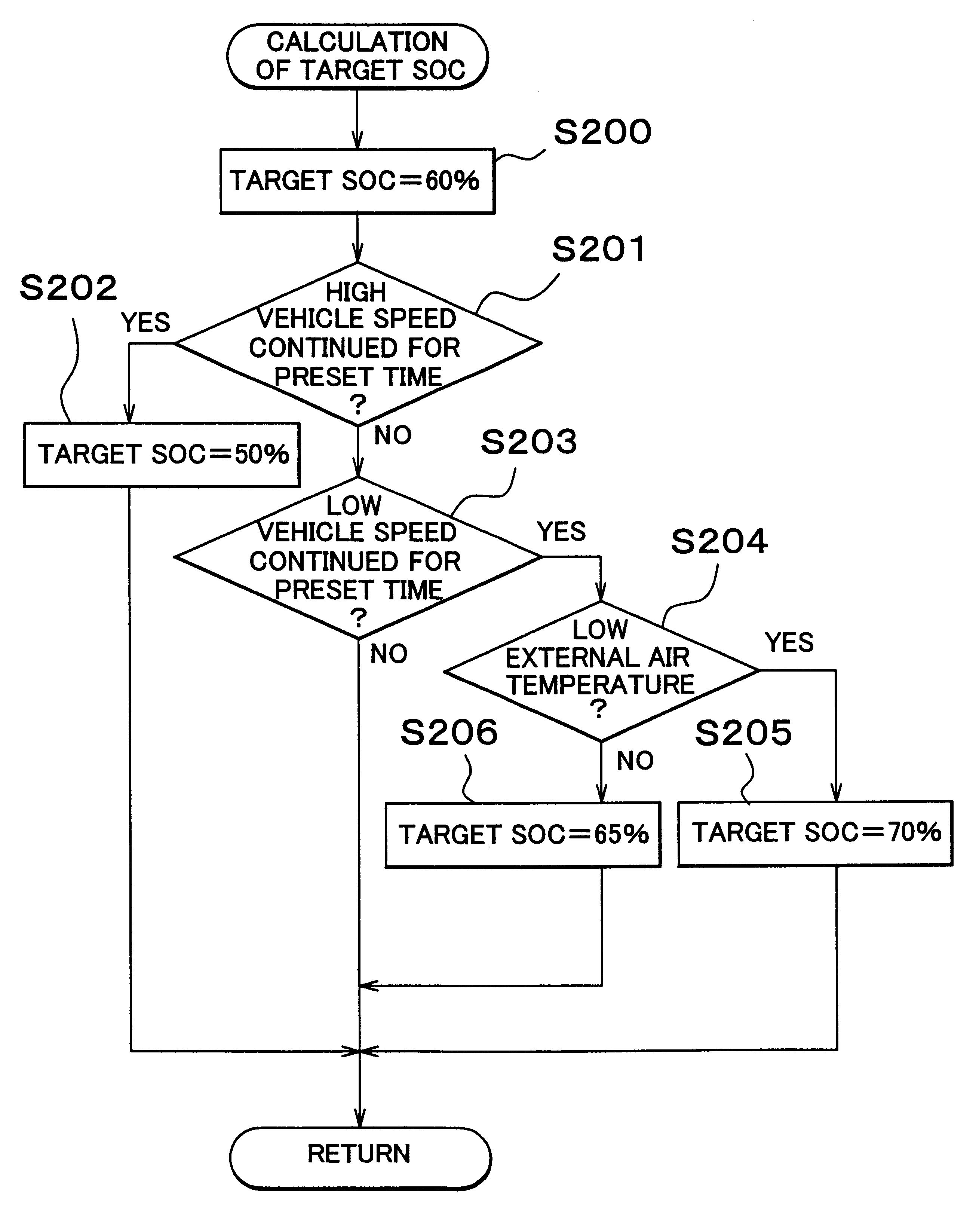
A controller predicts a requested state of charge / discharge corresponding to a future run of a hybrid vehicle. If it is predicted that the hybrid vehicle will be stopped and restarted, or will be greatly accelerated and therefore that a request for a great discharge will be outputted in the future, the controller increases a target SOC of an HV battery to increase the value to which the charge of the HV battery will be converged in preparation for the great discharge. If it is predicted that a great regenerative electric power will be generated by a vehicle deceleration and therefore that a request for charging will be outputted, the target SOC is reduced, and the amount of charge in the HV battery is reduced, so that the regenerative power generated can be efficiency recovered.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
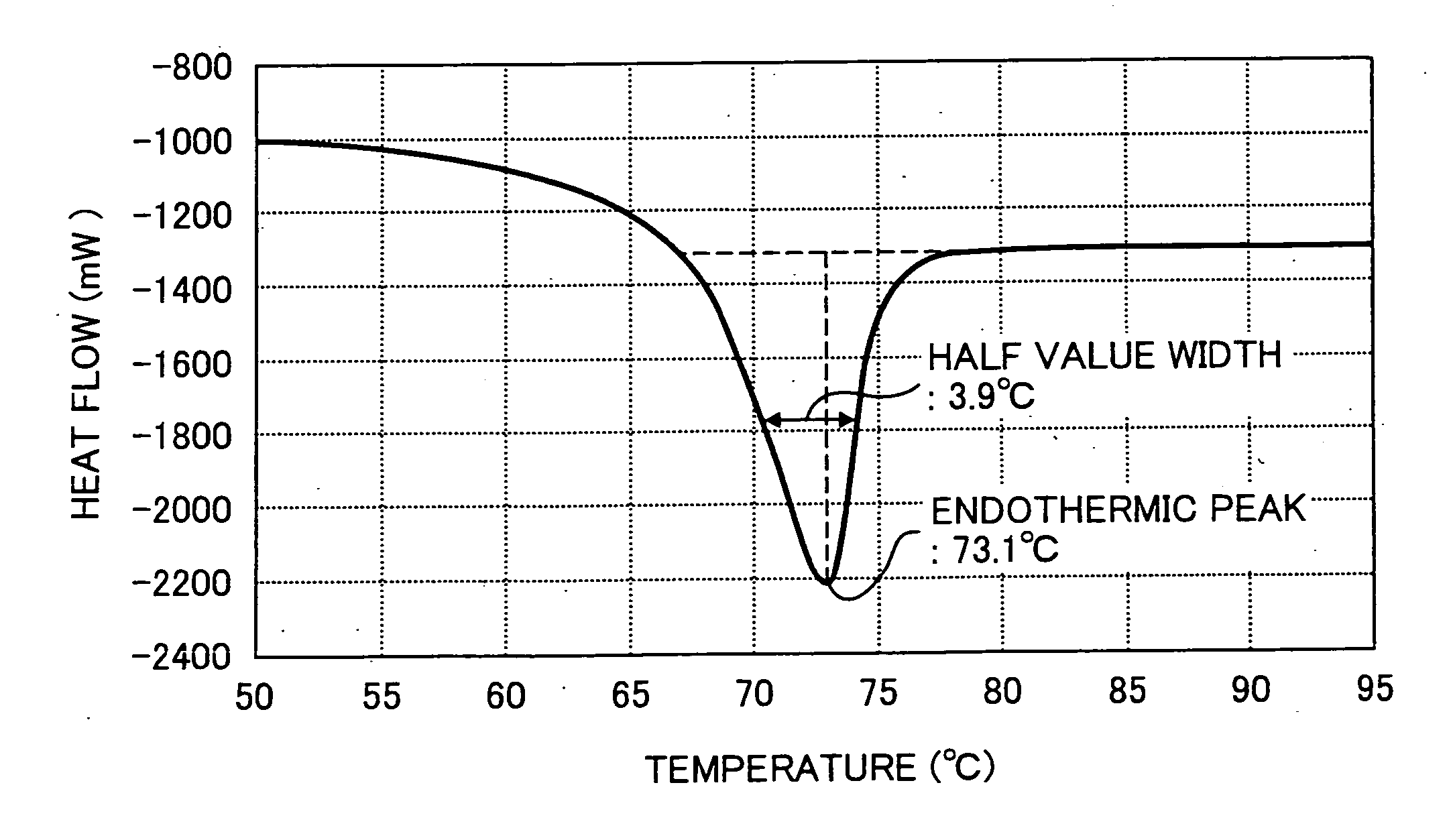
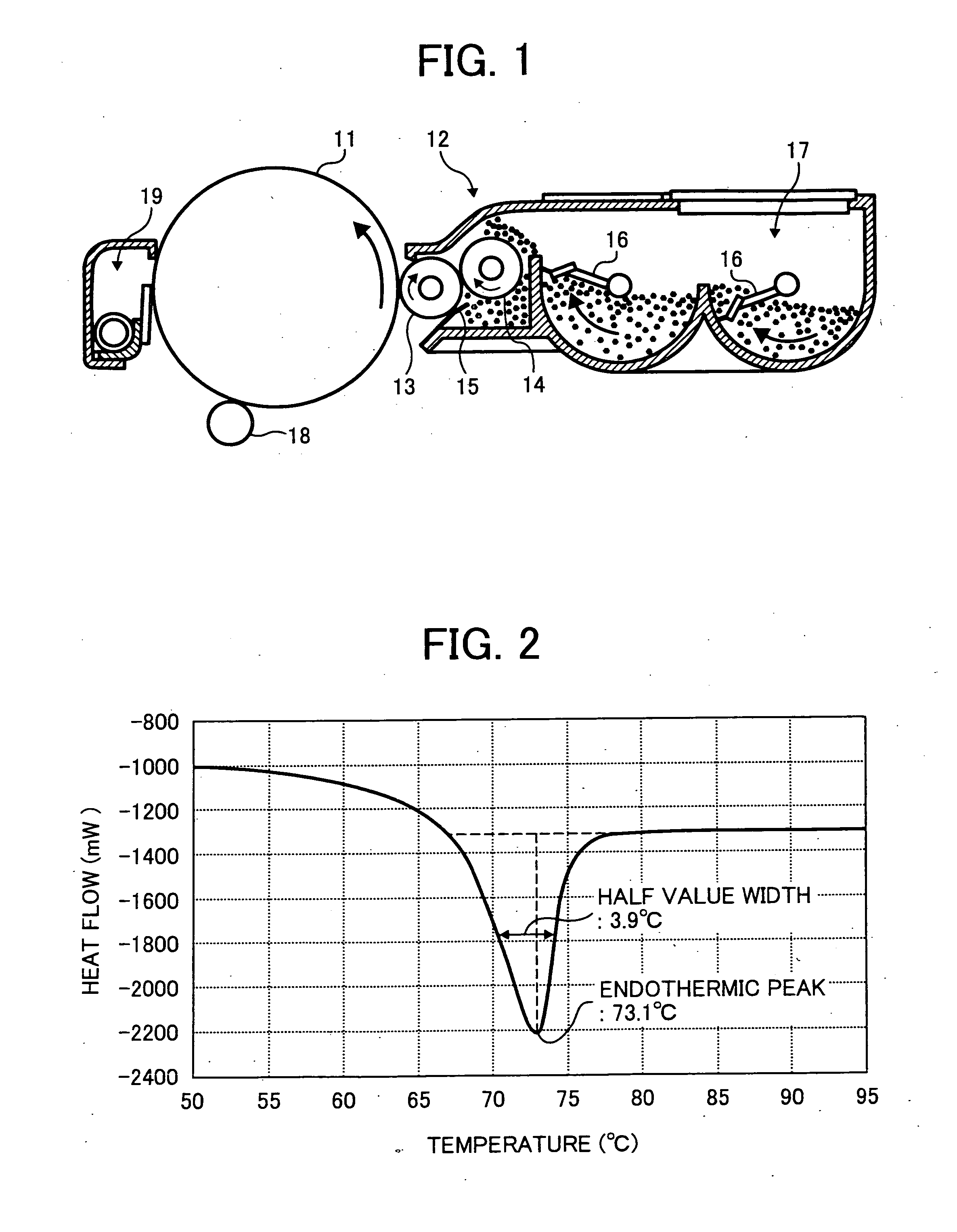
Toner, image forming method and process cartridge
InactiveUS20070026335A1DevelopersElectrographic processes using charge patternChemical structurePolyester
A toner containing a binder resin containing a resin having a polyester skeleton, a wax containing a hydrocarbon based wax, a colorant, and a charge controlling agent represented by the following chemical structure, wherein the toner has at least one endothermic peak in a range of from 60 to 80 ° C. when measured by a differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). In the chemical structure, M represents one of Li, Na and K, R1, R2, R3 and R4 each, independently, represent one of a hydrogen atom, an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, an alkoxy group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, and a halogen atom, and n represents an integer of from 1 to 5, and when n is from 2 to 5, each of R1, R2, R3 and R4 can be different from the other.
Owner:RICOH KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com