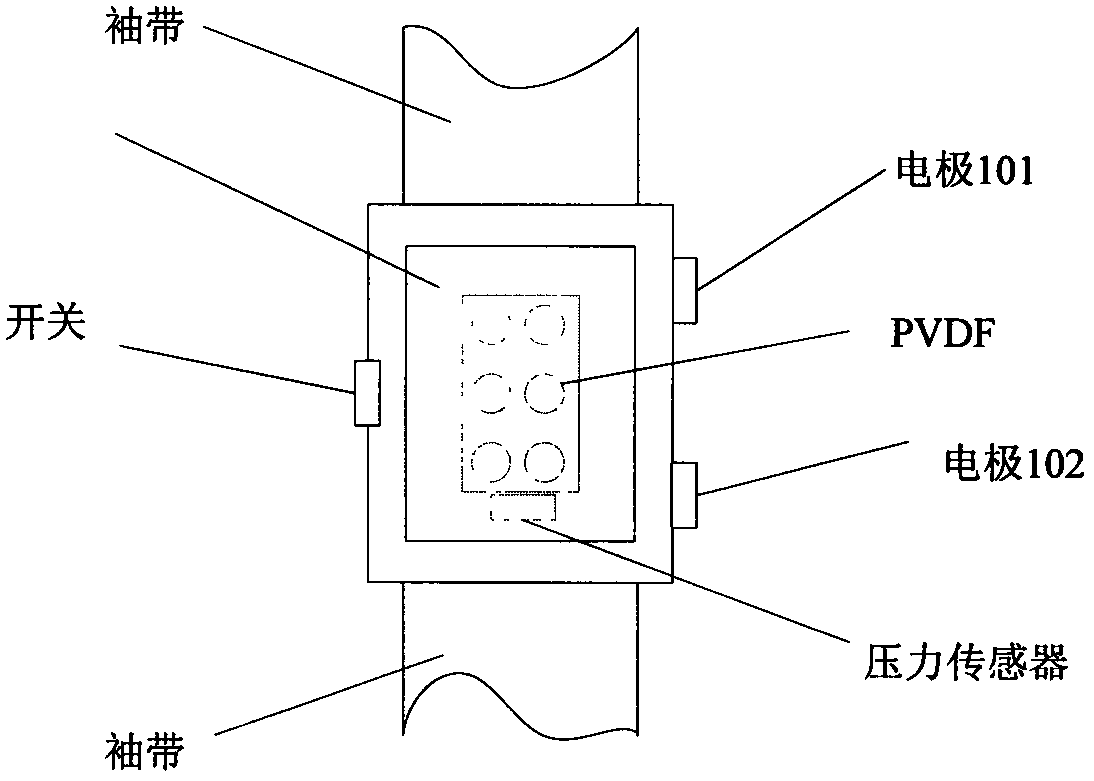
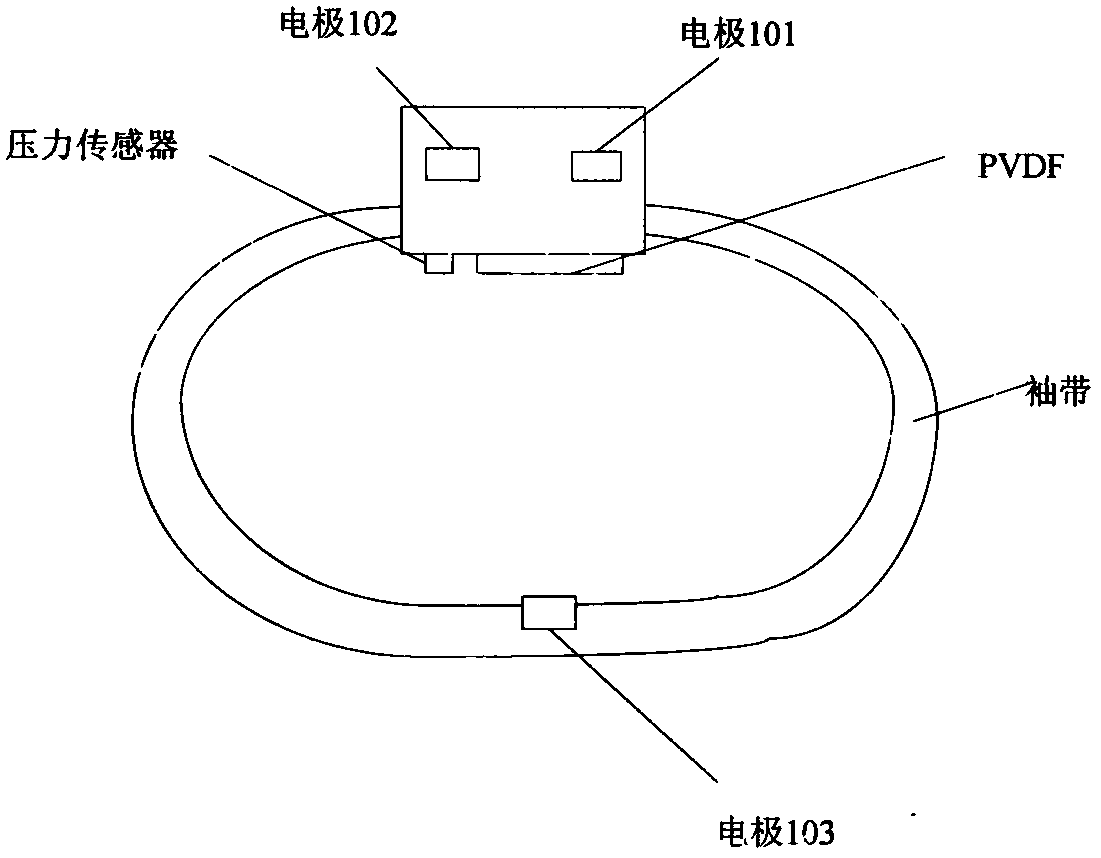
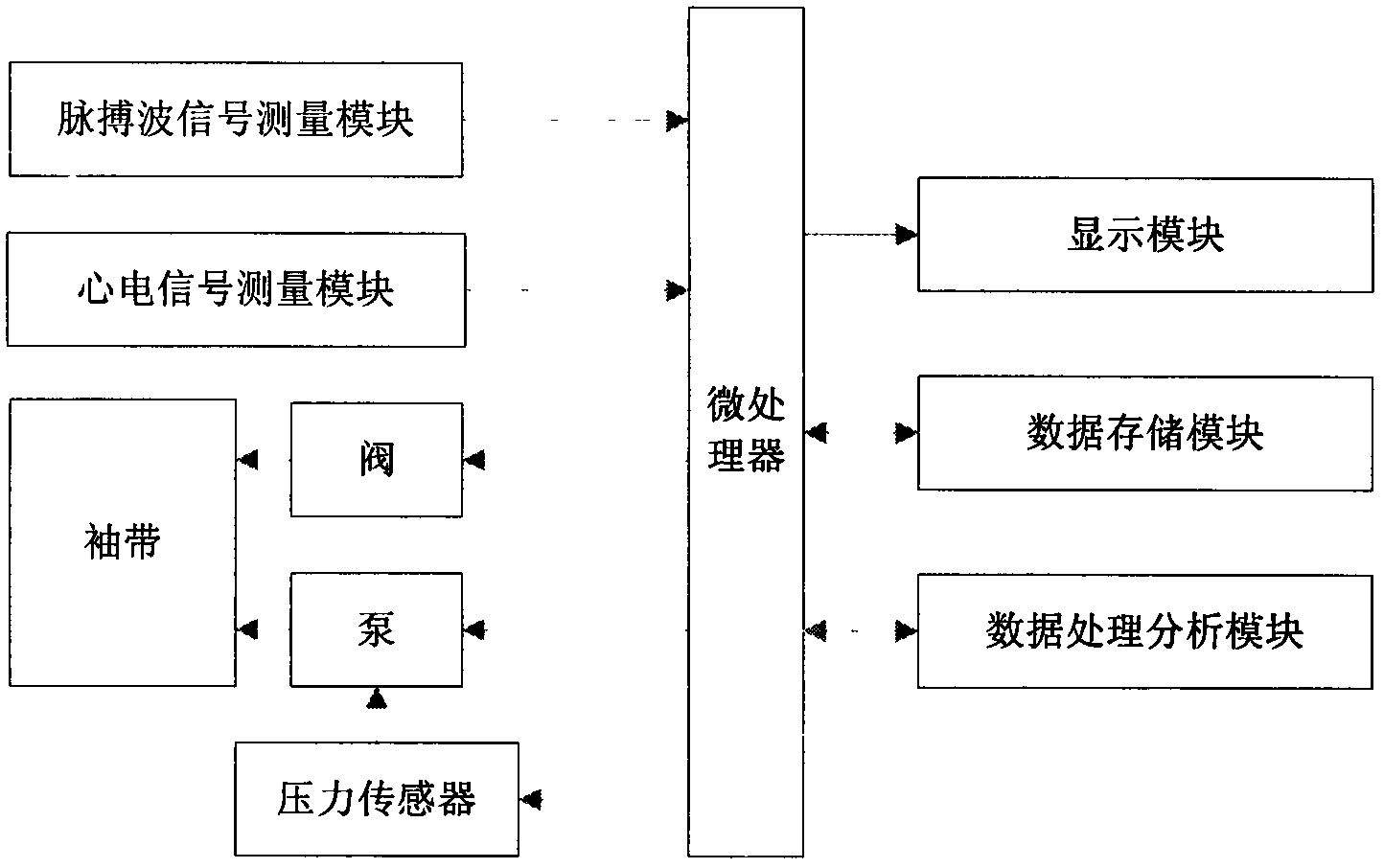
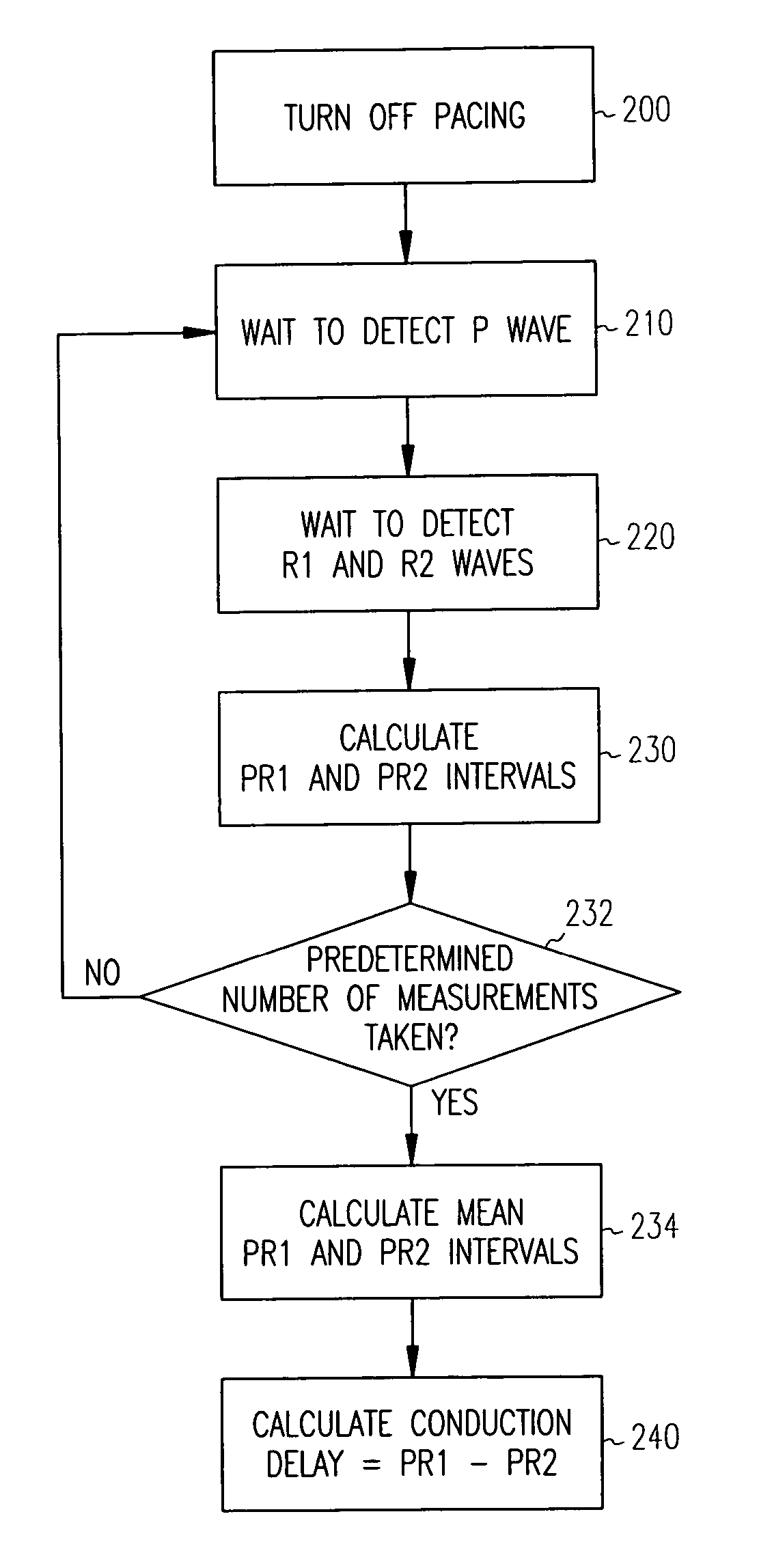
Patents
Literature
829 results about "Conduction time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
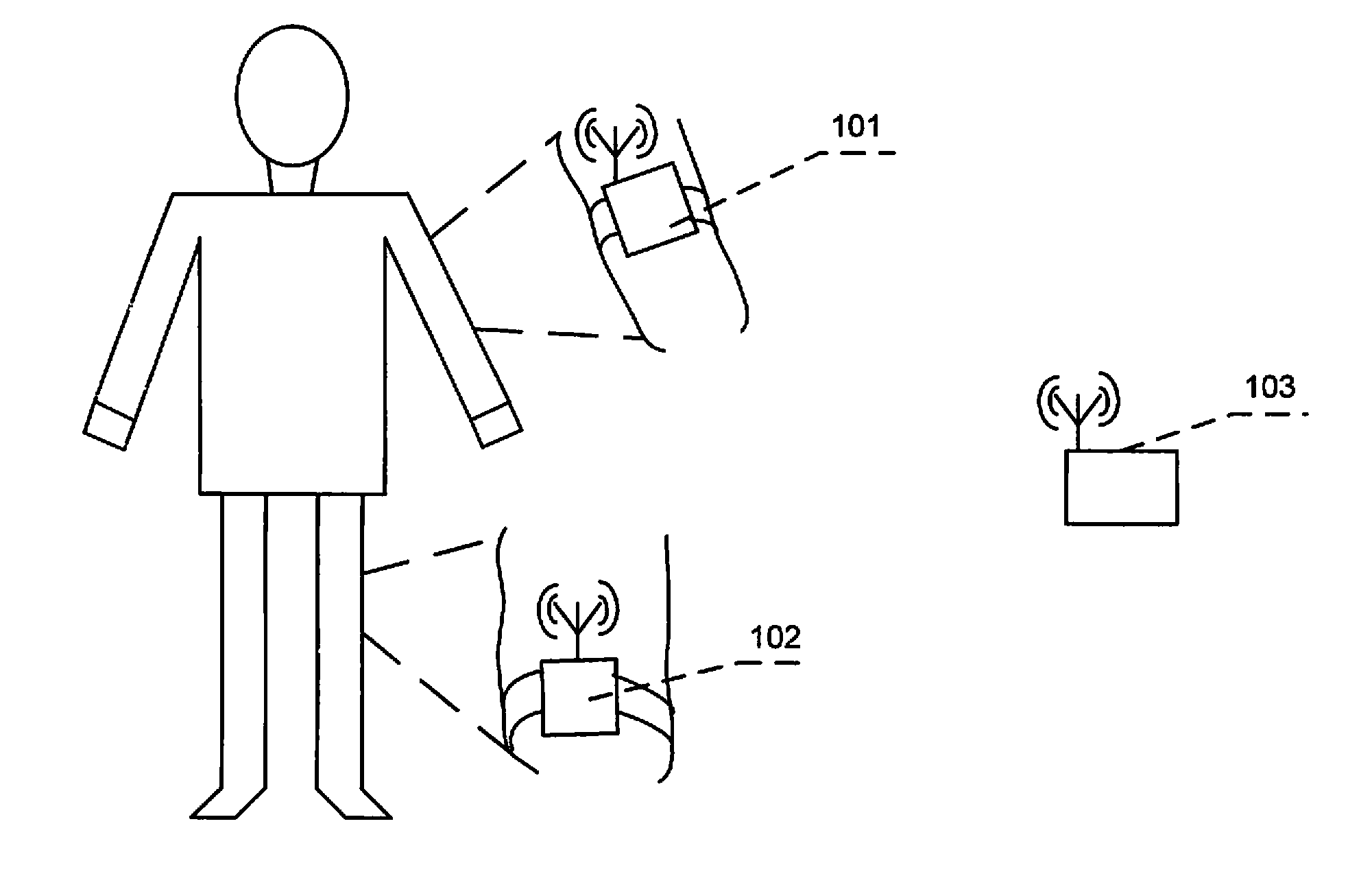
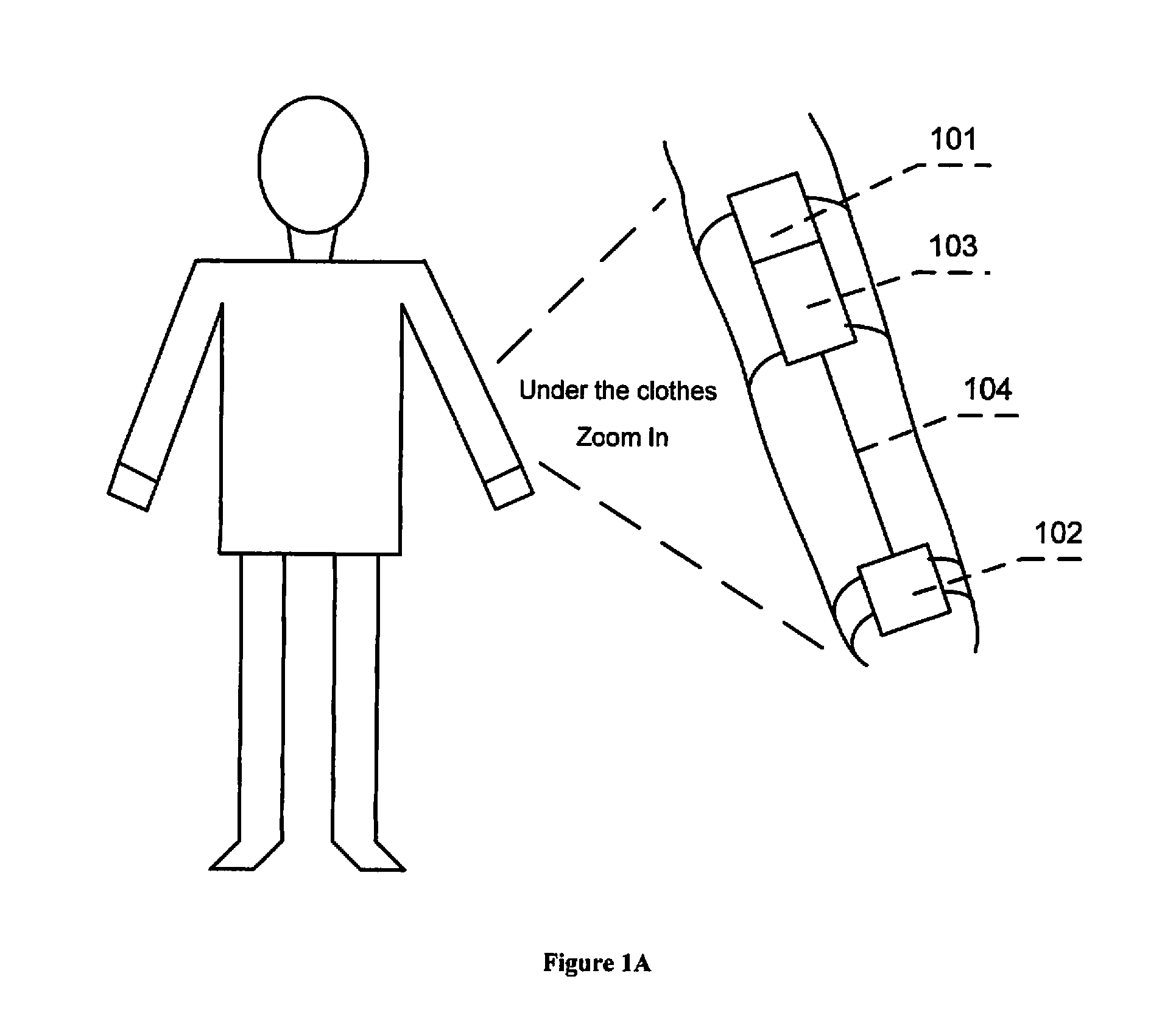
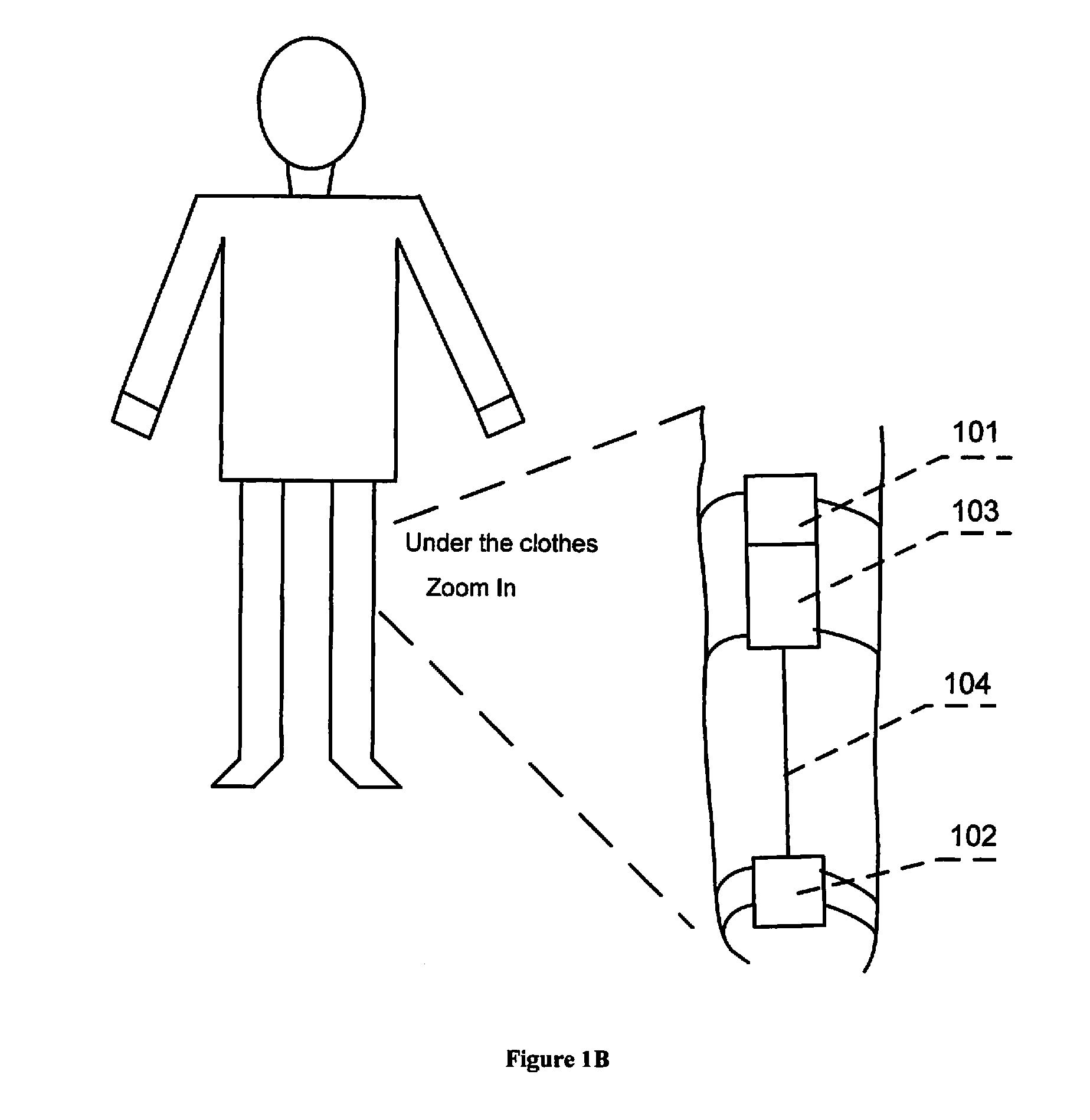
Intraatrial conduction time. in·tra·a·tri·al con·duc·tion time. 1. the total duration of electrical activity of the atria in one cardiac cycle; 2. the time between right atrial and left atrial activation.
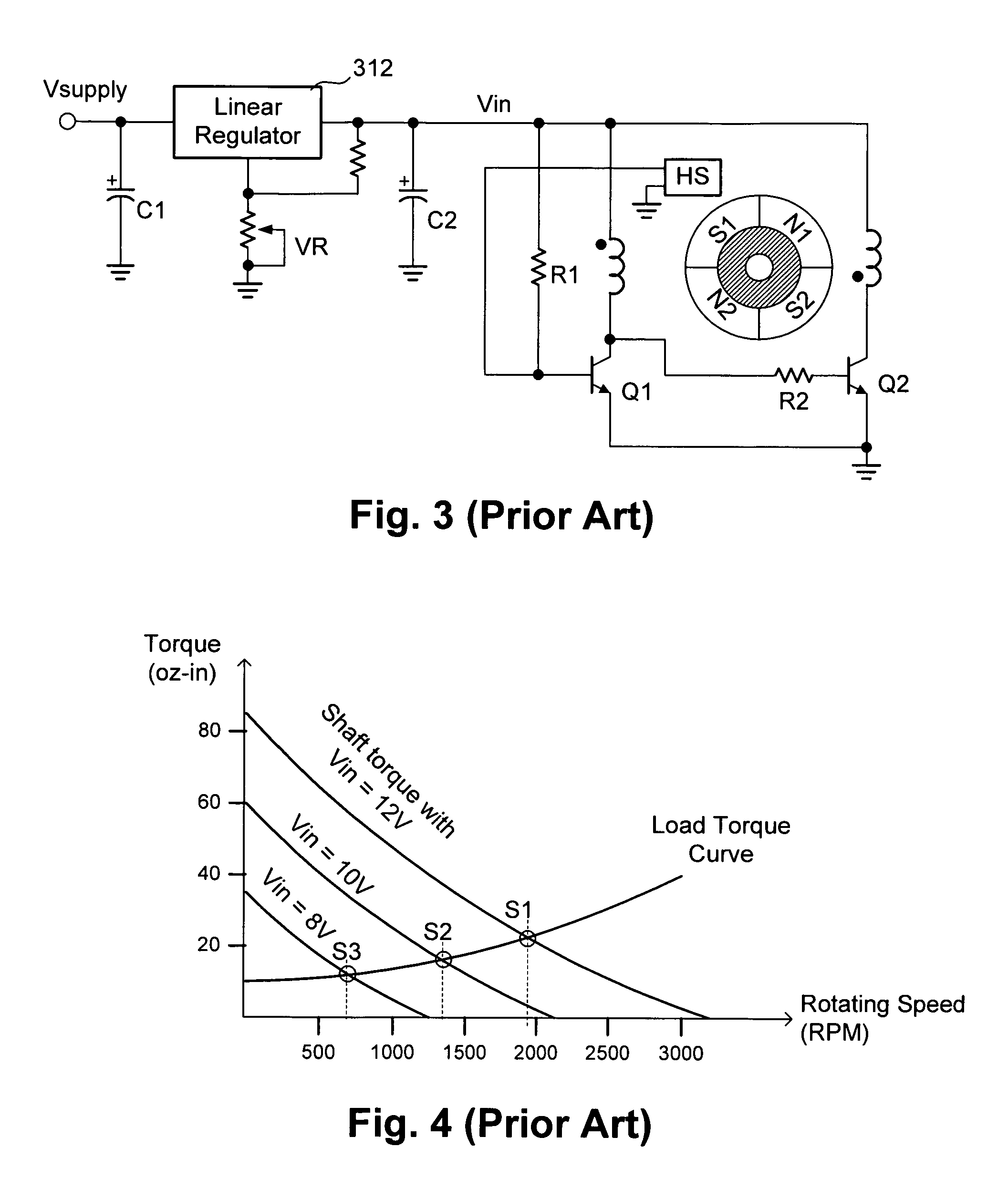
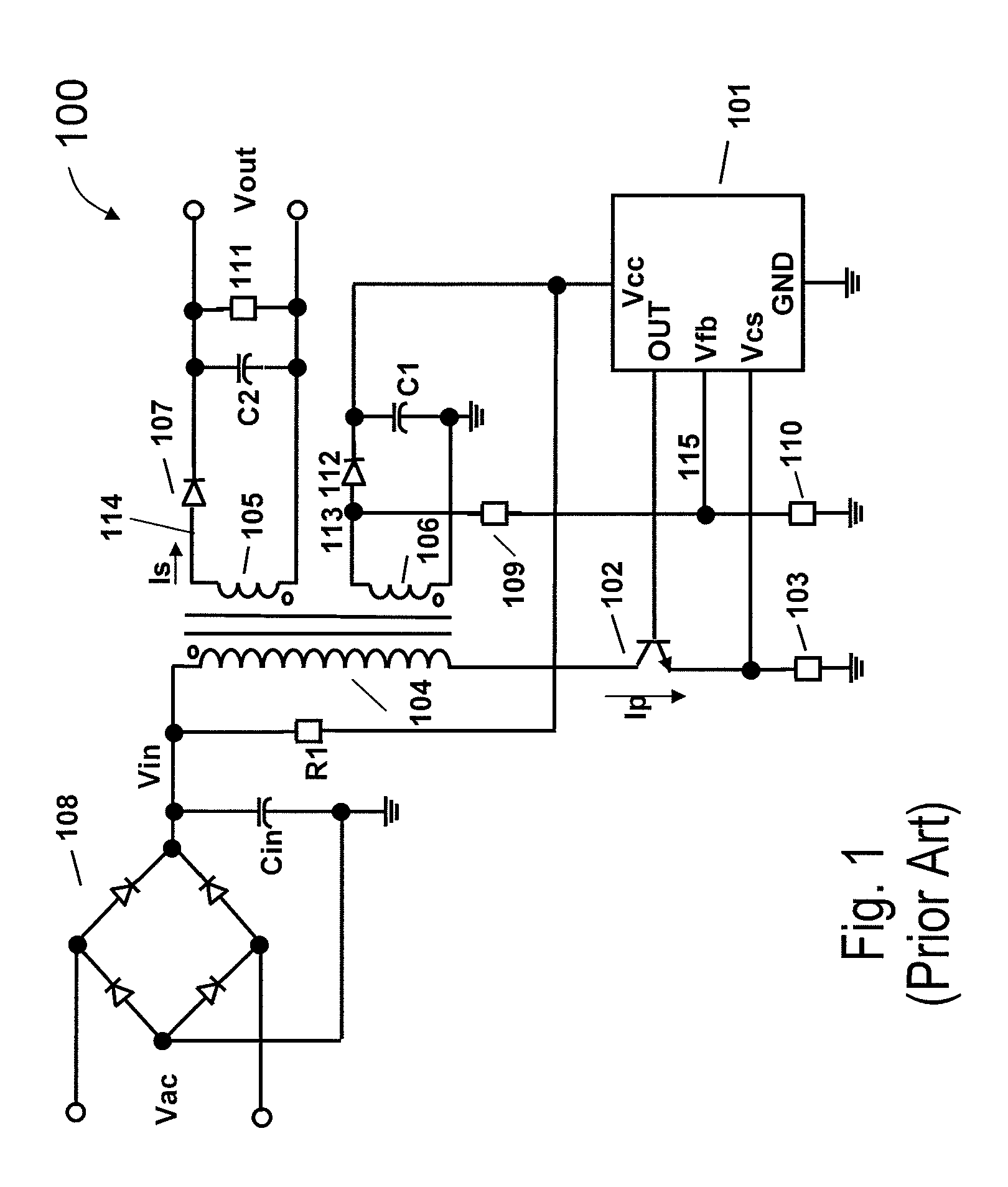
Method and apparatus for quiet variable motor speed control
ActiveUS7330004B2Single-phase induction motor startersMotor/generator/converter stoppersMotor speedEngineering
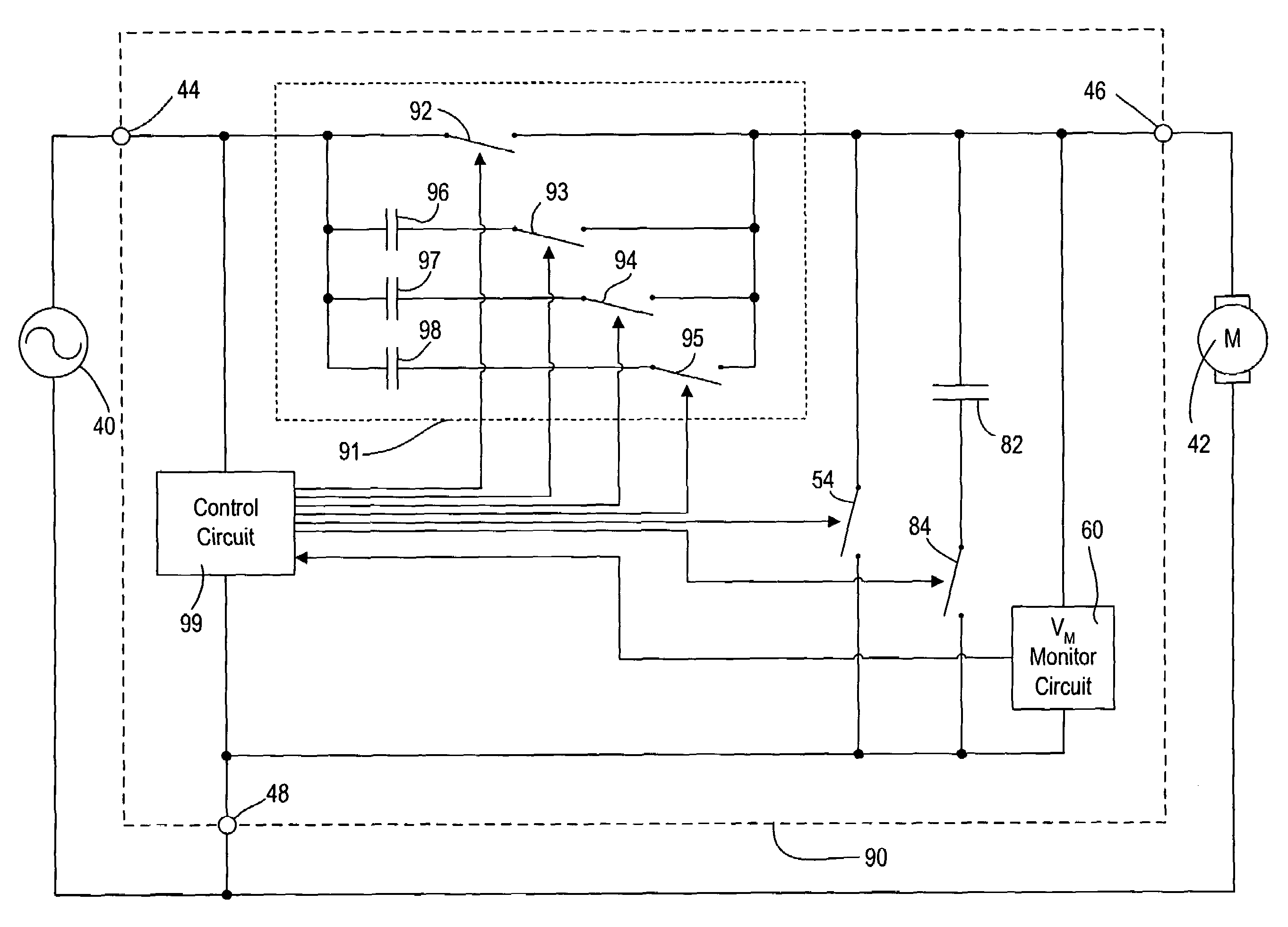
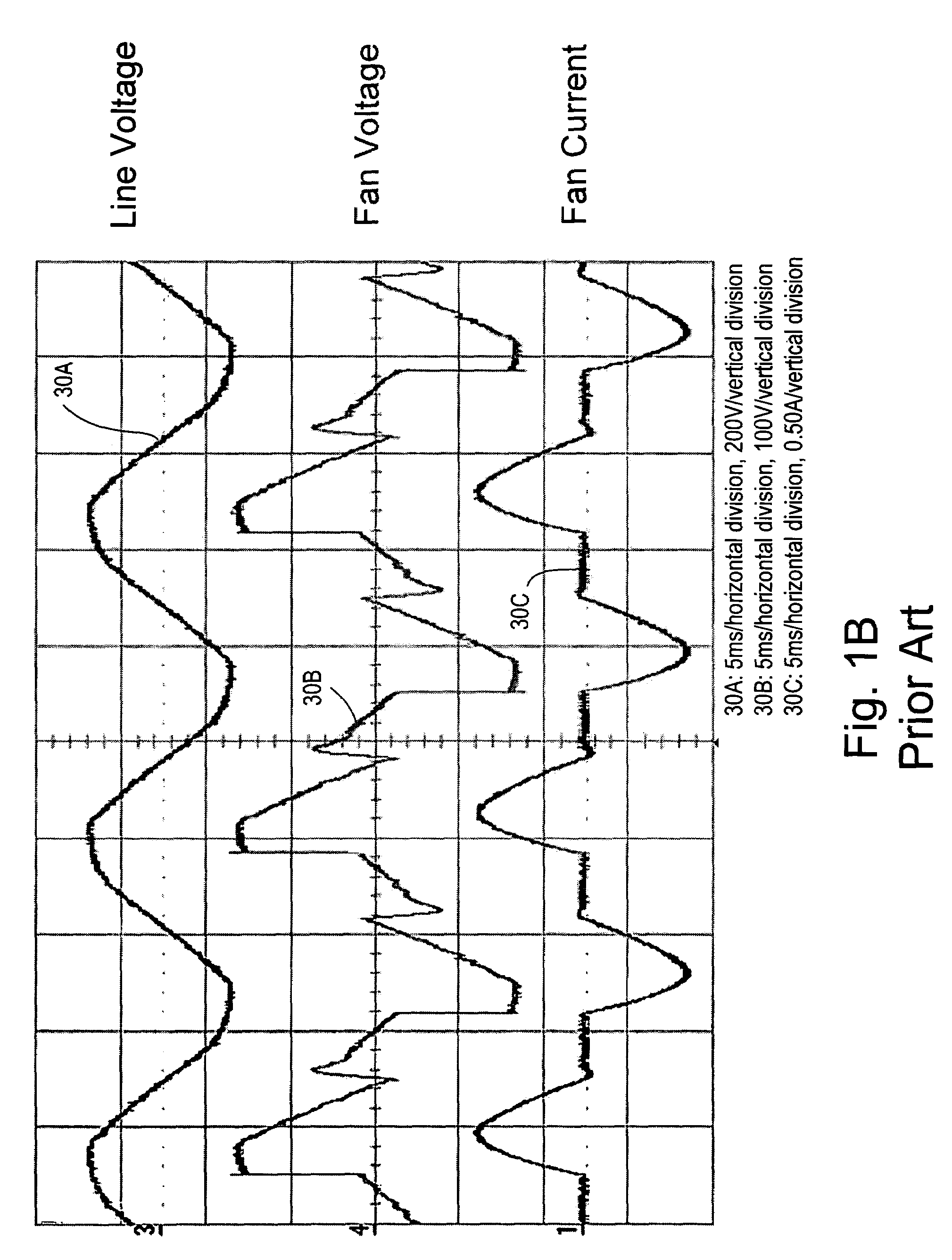
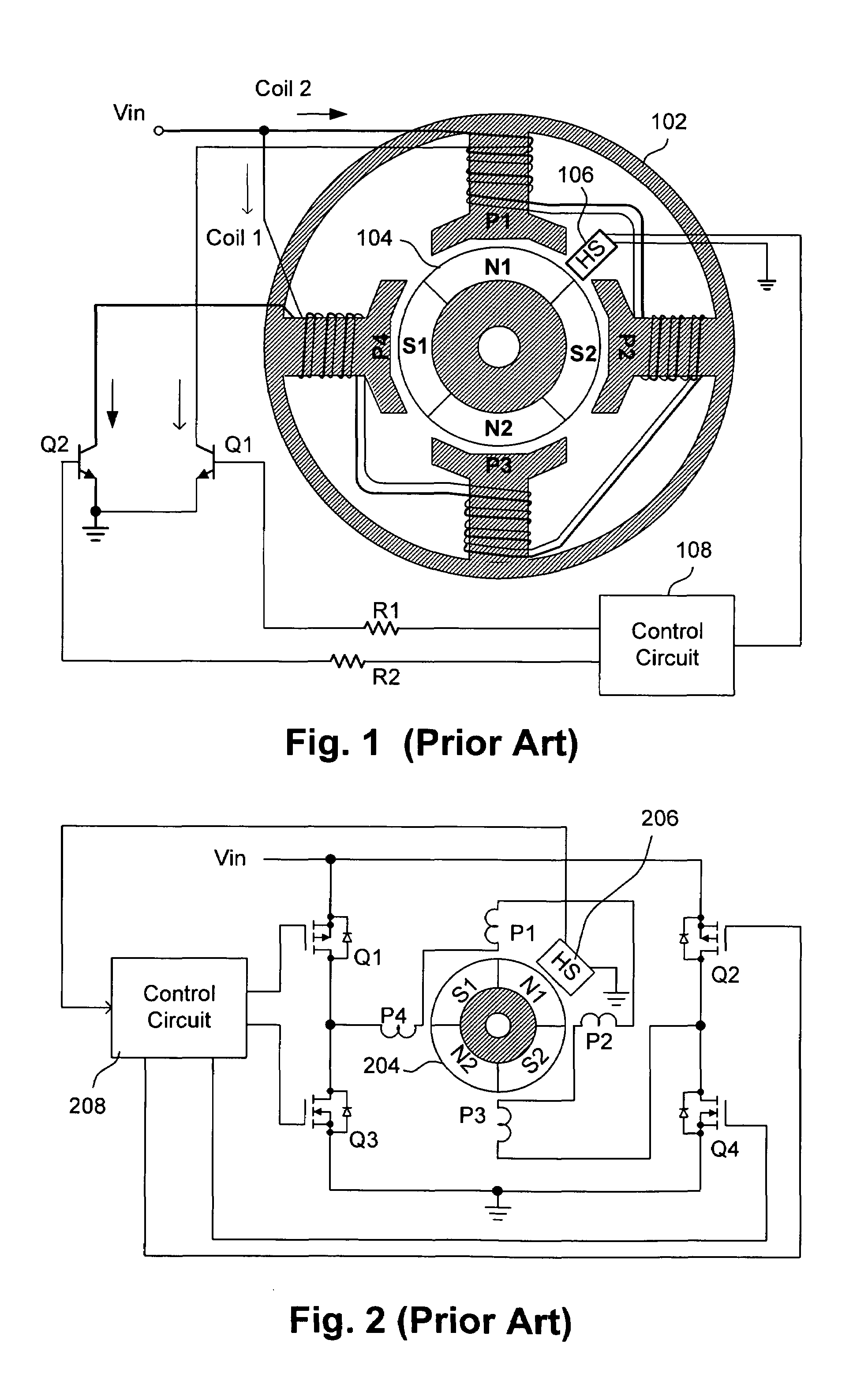
An apparatus for controlling the speed of an AC motor comprising a switch adapted to be coupled in parallel with power terminals for the AC motor; a capacitor coupled in series with the parallel combination of the switch and the motor; the capacitor adapted to provide an AC supply voltage from an AC source to the parallel circuit comprising the motor and the switch; and a control circuit for controlling the conduction time of the switch in order to vary the speed of the motor. The switch is preferably pulse-width modulated at a frequency twice the line frequency of the AC supply voltage, and the switch is turned on when the voltage across the AC motor is zero volts. The apparatus is operable to provide for continuously variable control of the motor speed while minimizing acoustic noise in the motor.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
Synchronous Rectifier Design for Wireless Power Receiver
InactiveUS20150326143A1Lower forward voltage dropImprove efficiencyBatteries circuit arrangementsAc-dc conversion without reversalDelay-locked loopSwitching frequency
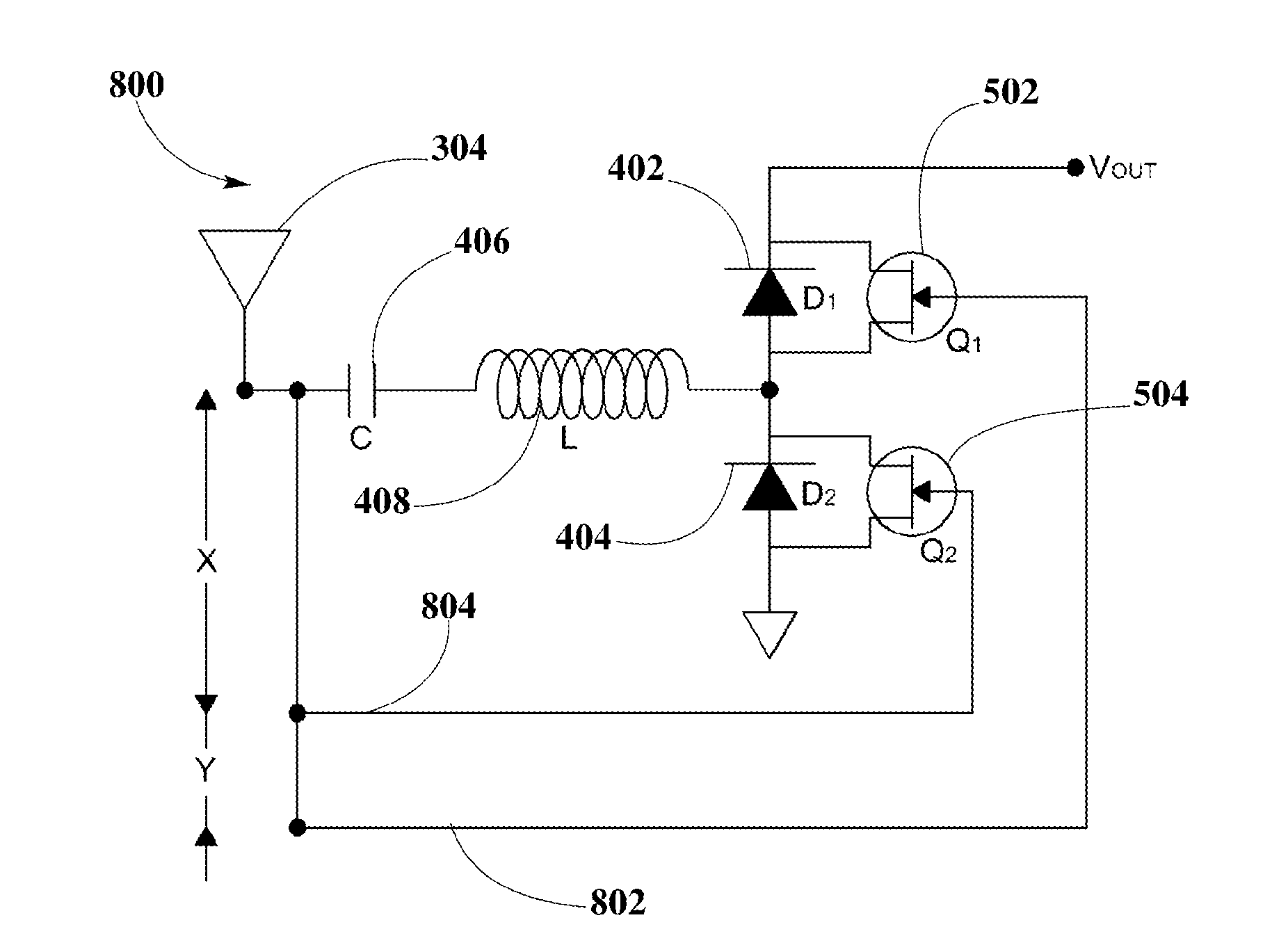
Synchronous rectifier circuit topologies for a wireless power receiver receiving a supply of power from a wireless transmitter are disclosed. The synchronous rectifier circuit topologies include a half-bridge diode-FET transistor rectifier for rectifying the wireless power into power including a DC waveform, using a control scheme that may be provided by a delay-locked loop clock, or phase shifters, or wavelength links to control conduction of FET transistors in the synchronous rectifier circuit topology, and maintaining a constant switching frequency to have the diodes, coupled to FET transistors, to allow current to flow through each one respectively at the appropriate timing, focusing on high conduction times. The synchronous rectifier circuit topologies may enable power transfer of high-frequency signals at enhanced efficiency due to significant reduction of forward voltage drop and lossless switching.
Owner:ENERGOUS CORPORATION
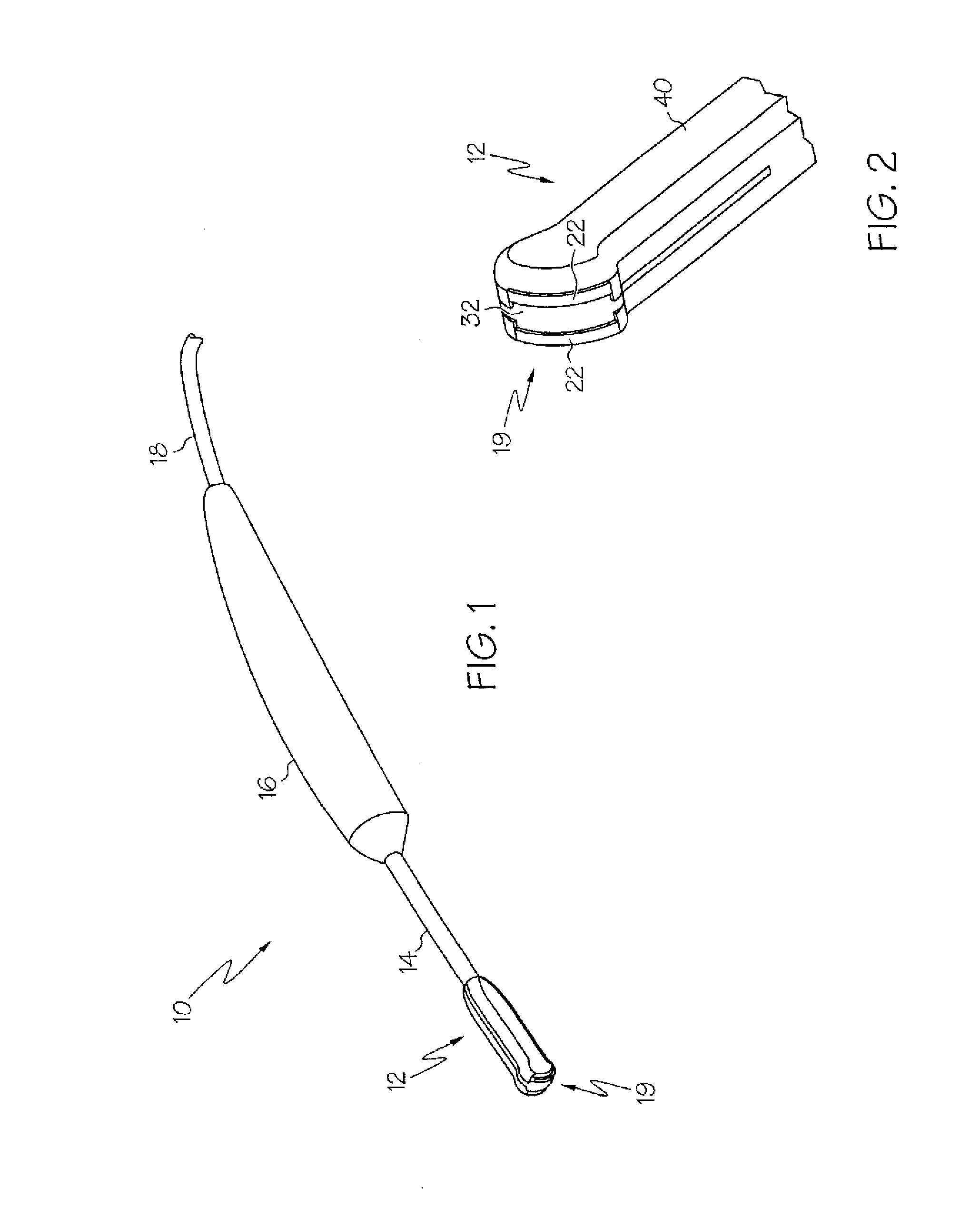
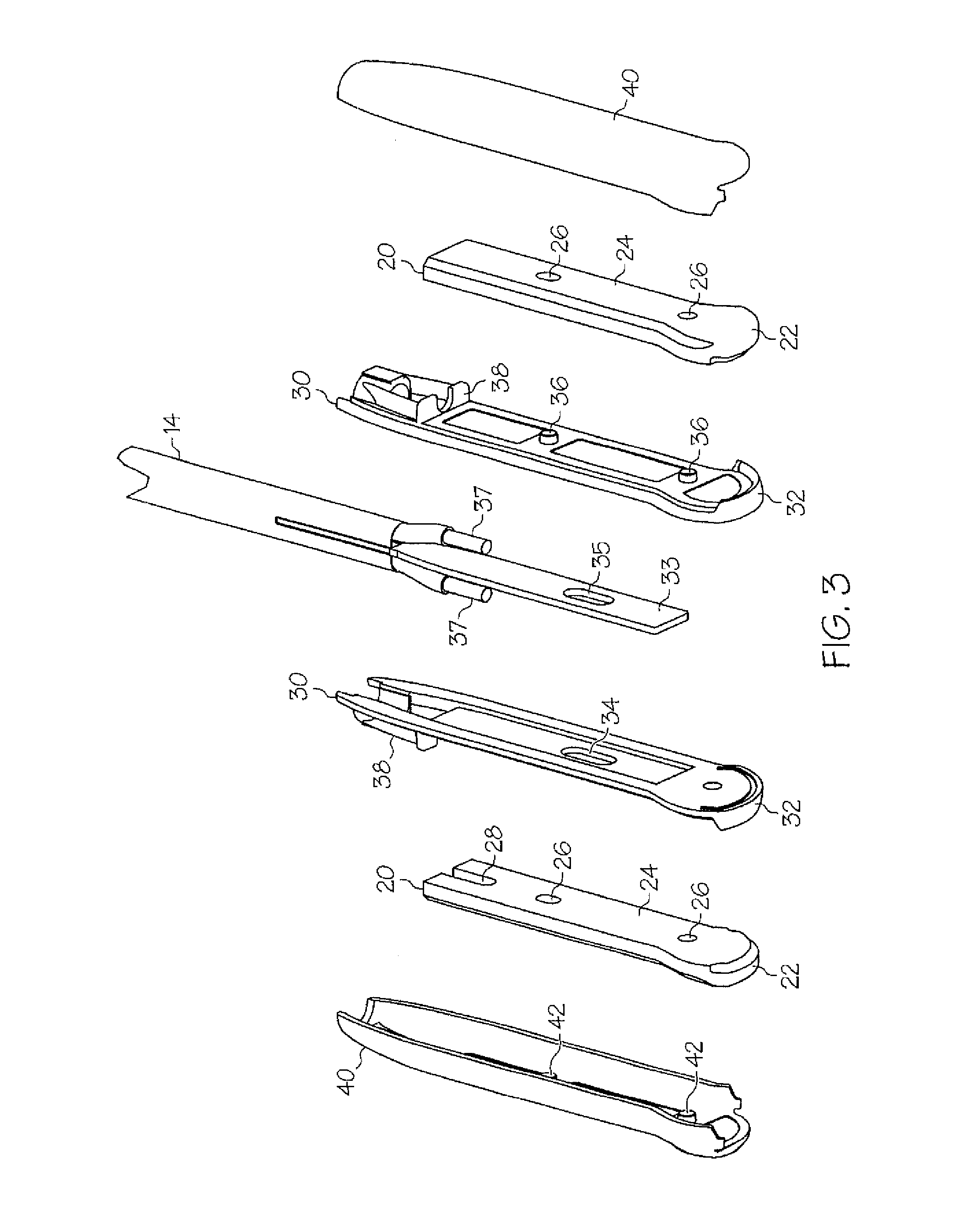
Apparatus and method for assessing transmurality of a tissue ablation
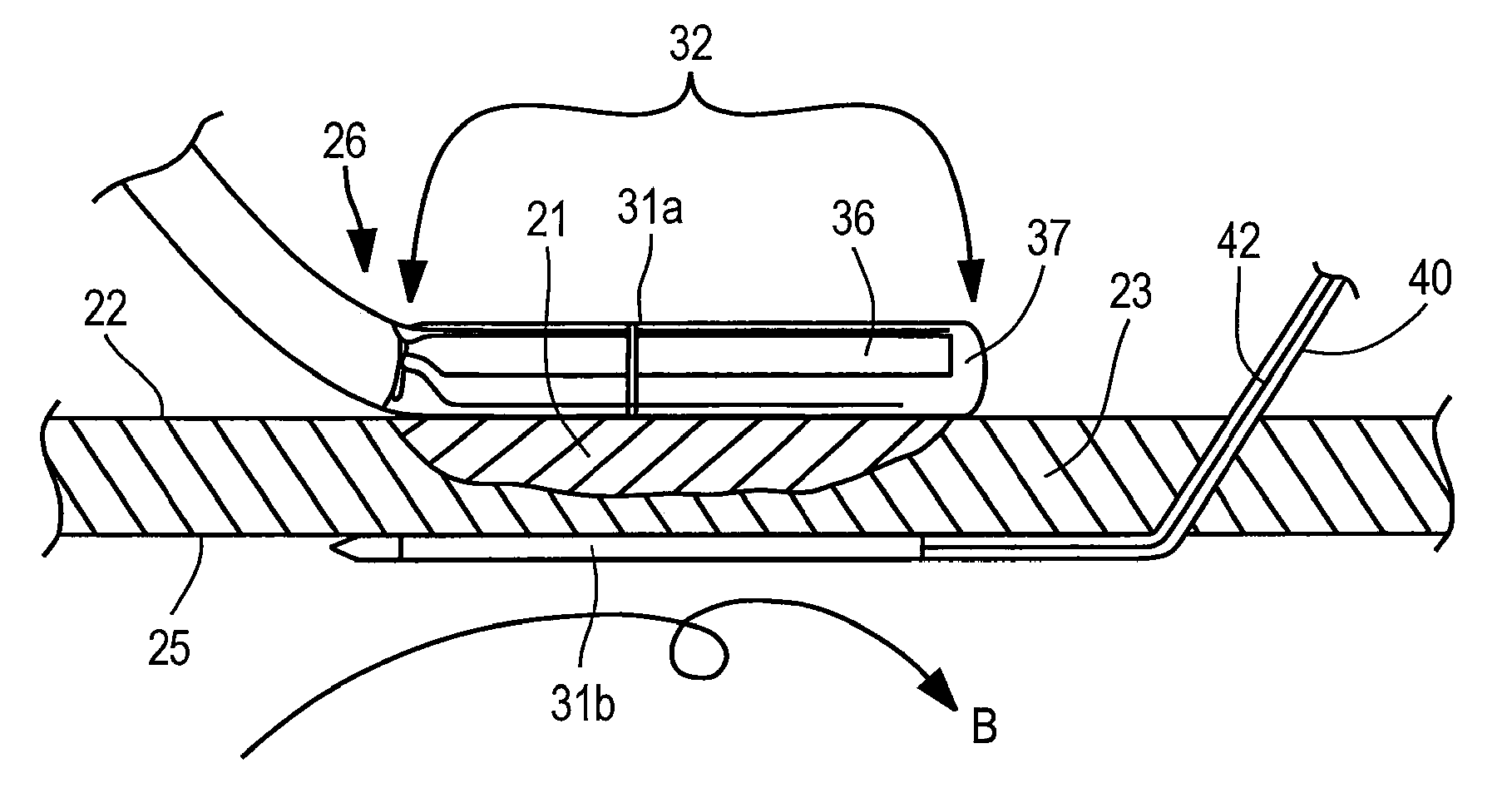
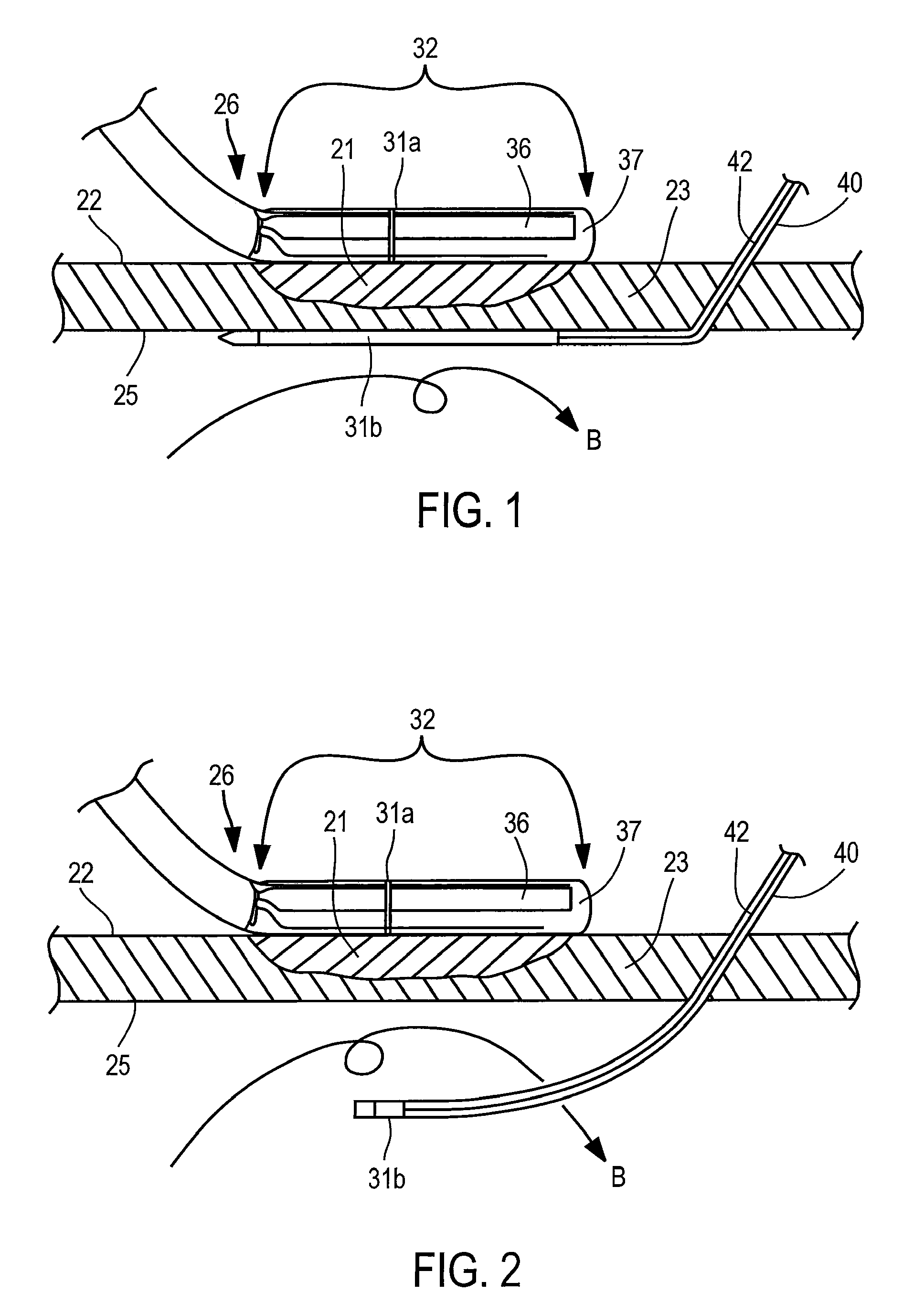
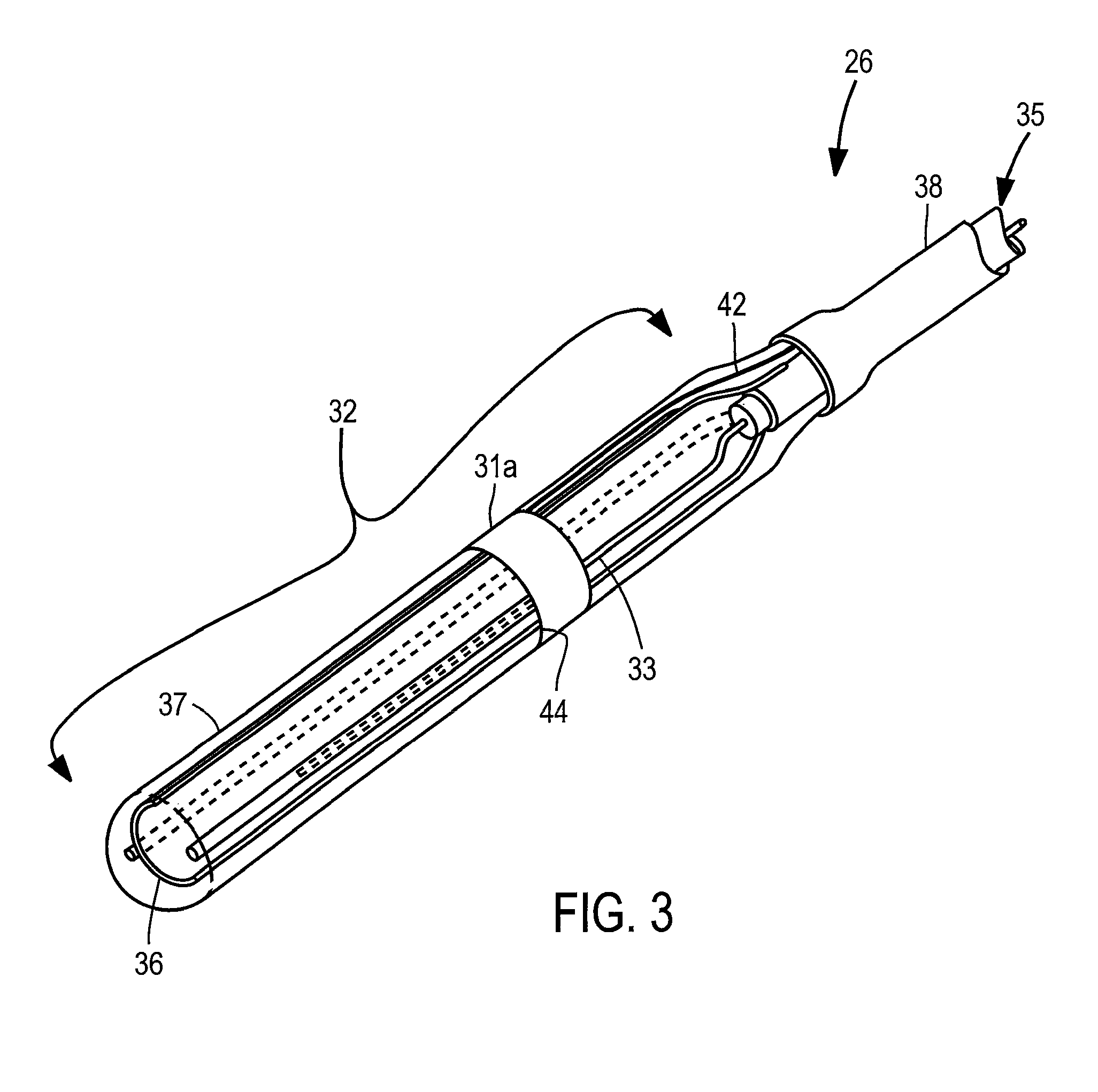
InactiveUS7192427B2Good transmuralityGood signalDiagnostic recording/measuringSurgical instruments for heatingConduction timeTissue ablation
An instrument is provided to assess the transmurality of an ablation lesion from a first surface of a targeted biological tissue to an opposed second surface thereof. The instrument includes at least a first electrode operably attached to an ablation instrument adapted to engage a tissue first surface, and at least a second electrode adapted to engage a tissue second surface, the at least second electrode positioned generally opposed to the at least first electrode. Alternatively, the at least second electrode may be adapted to be placed within a chamber of an organ. These electrodes each measure at least one of conduction time, conduction velocity, phase angle, and impedance through at least a portion of the targeted tissue to determine the transmurality of the ablation lesion.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
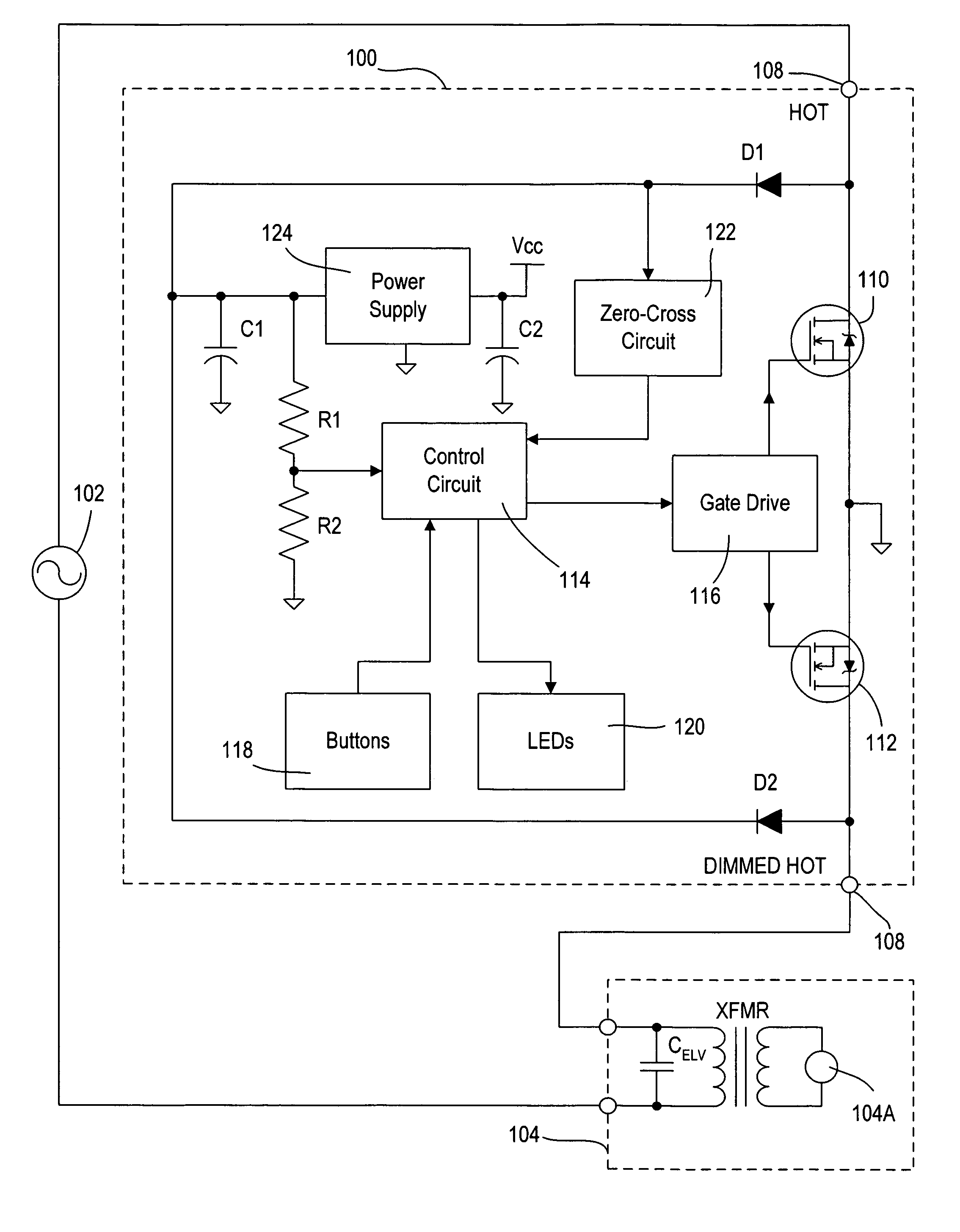
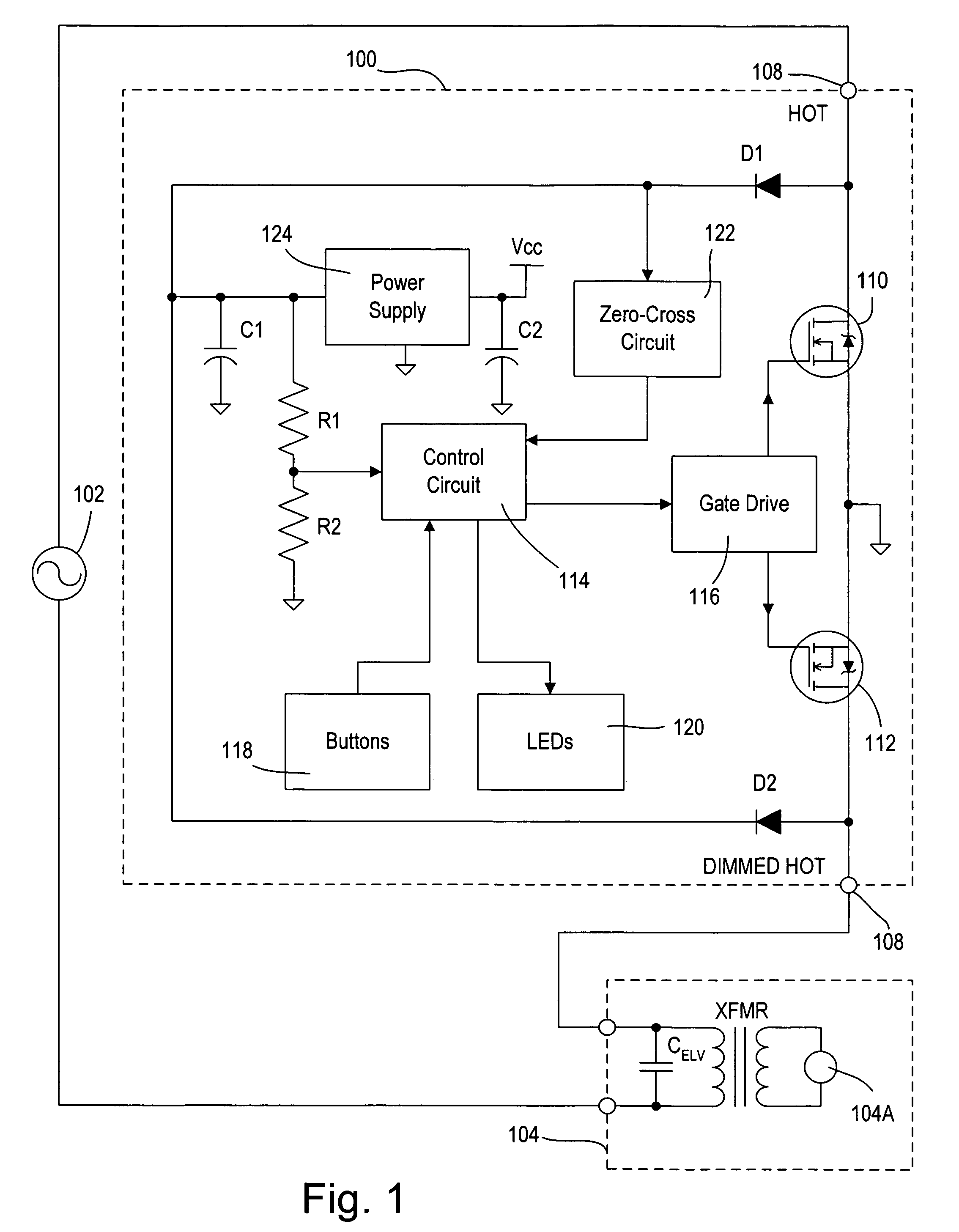
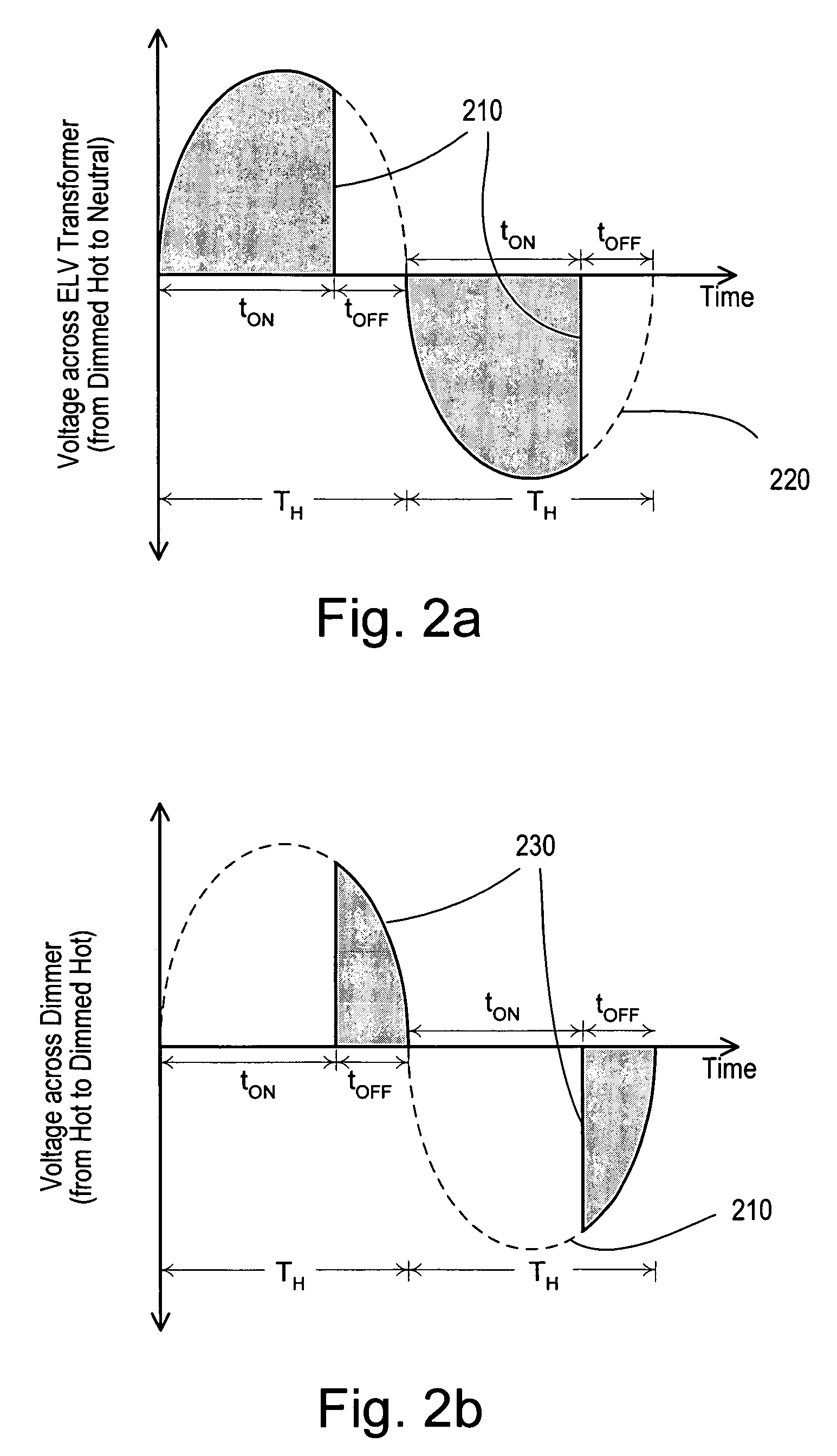
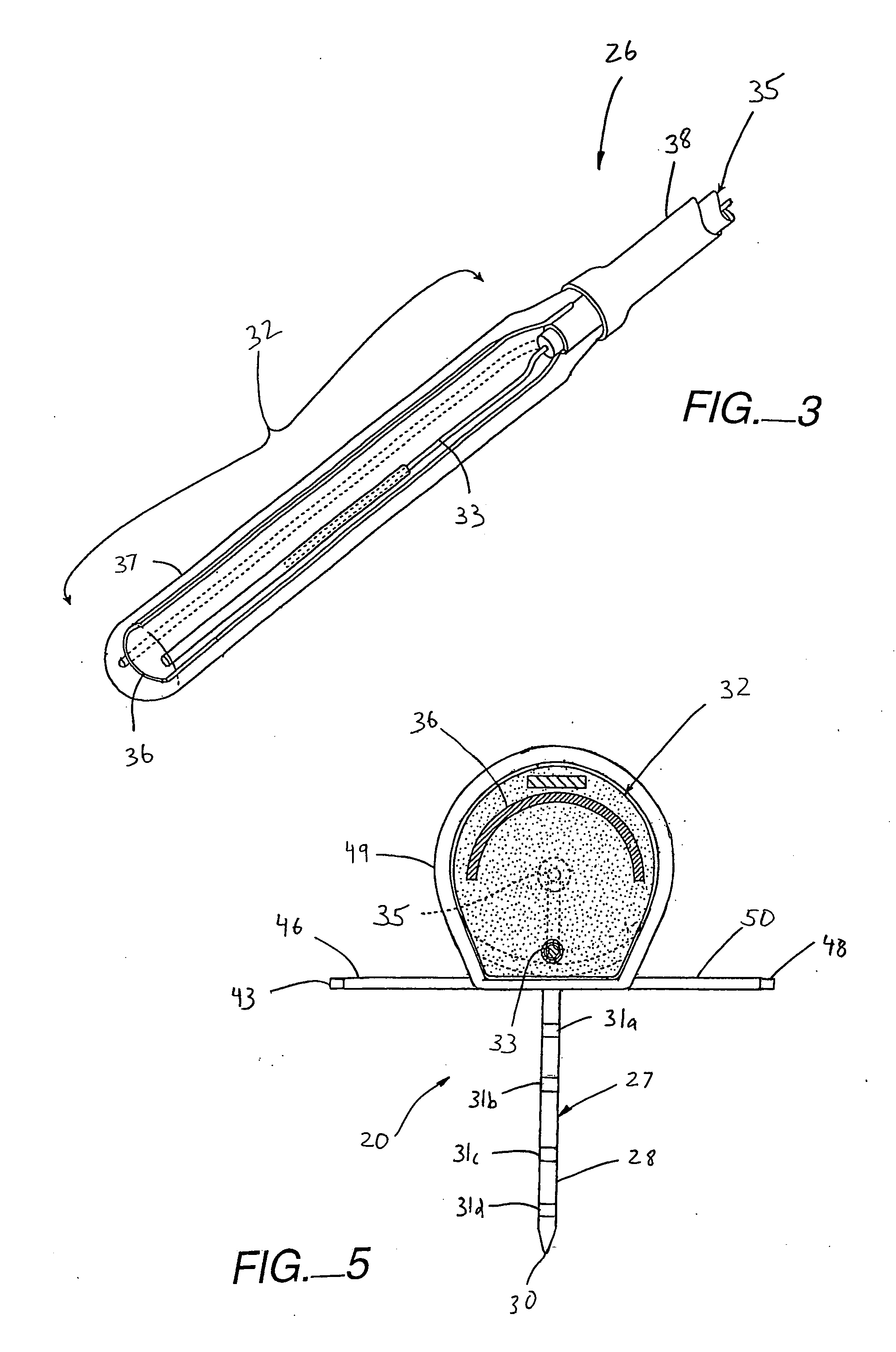
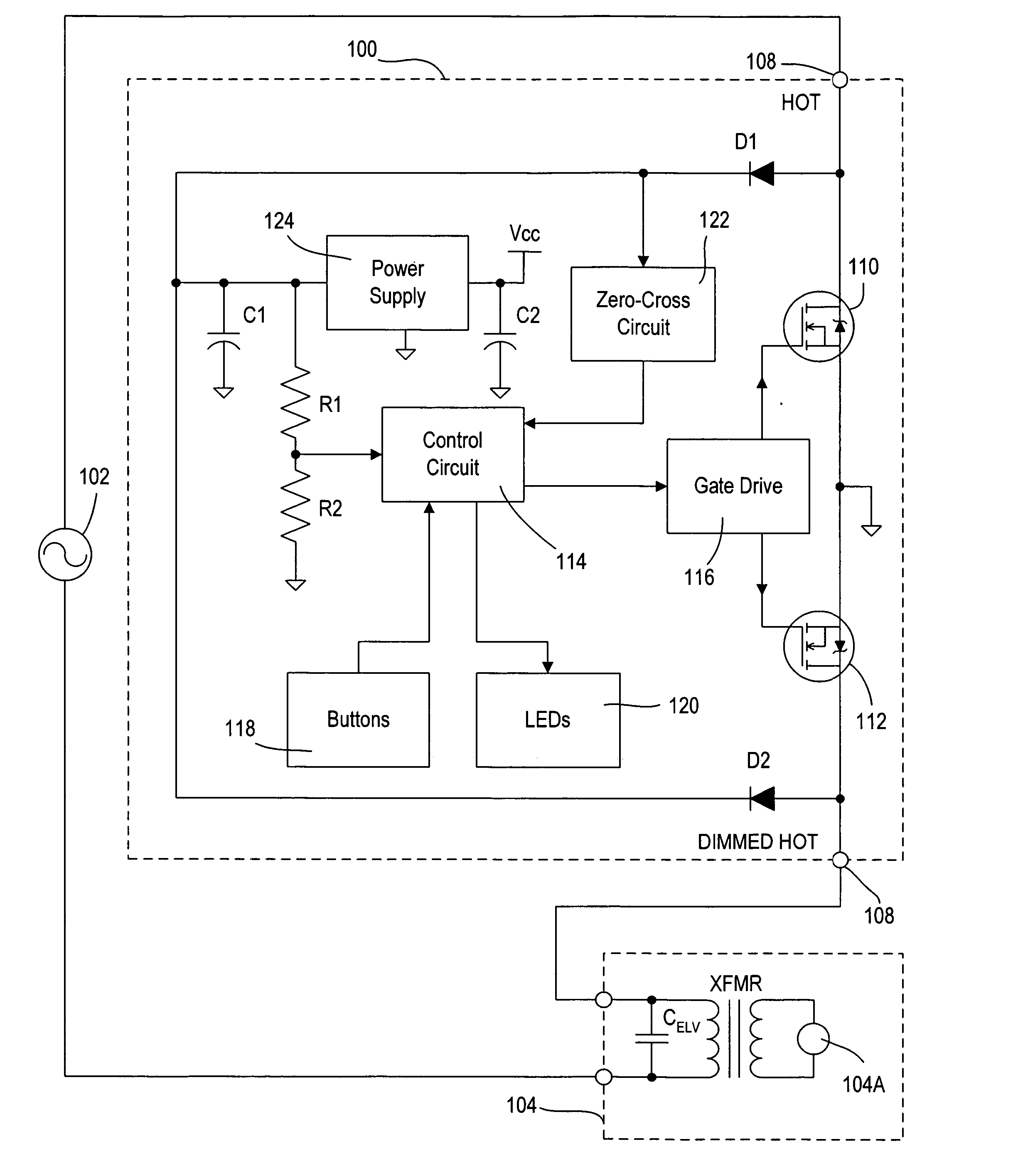
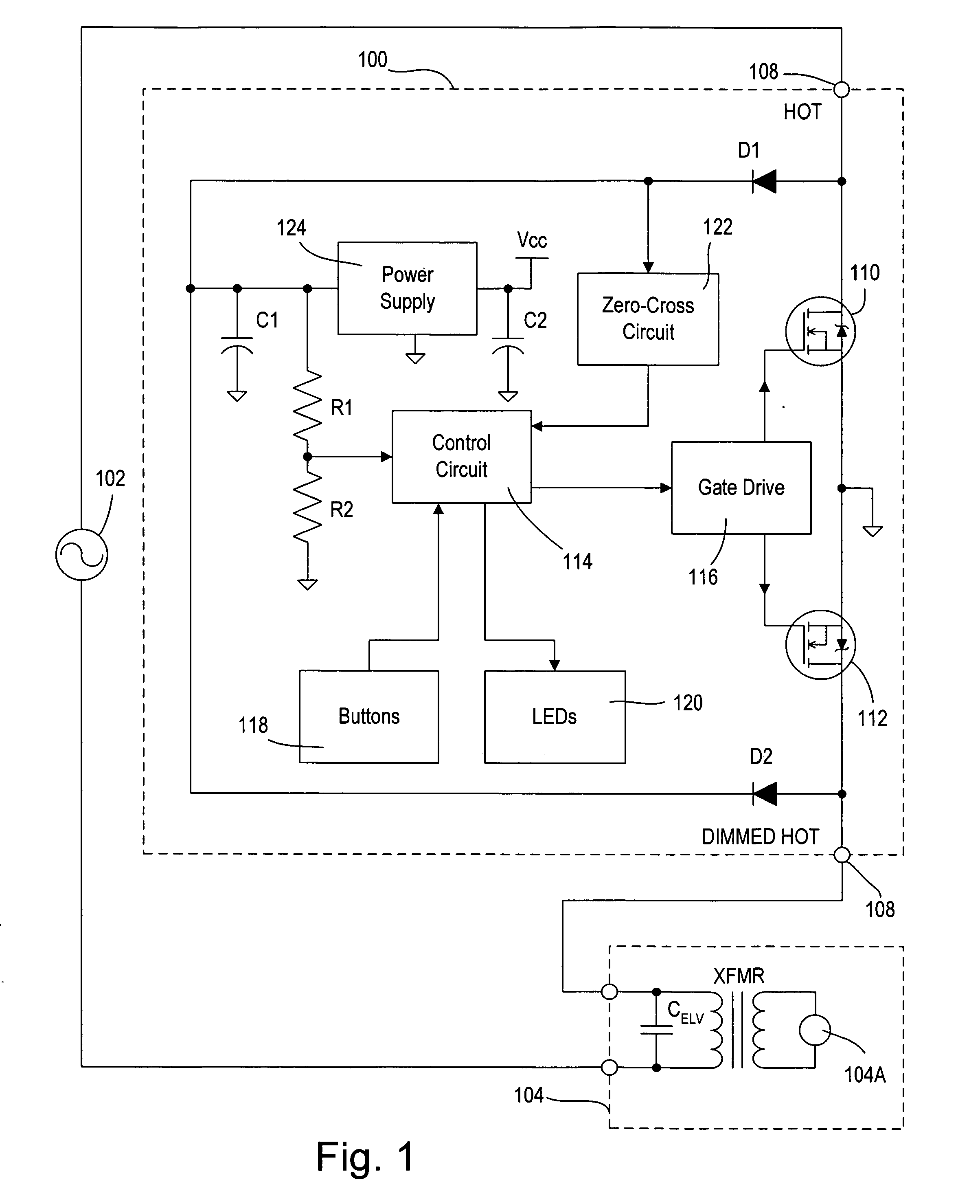
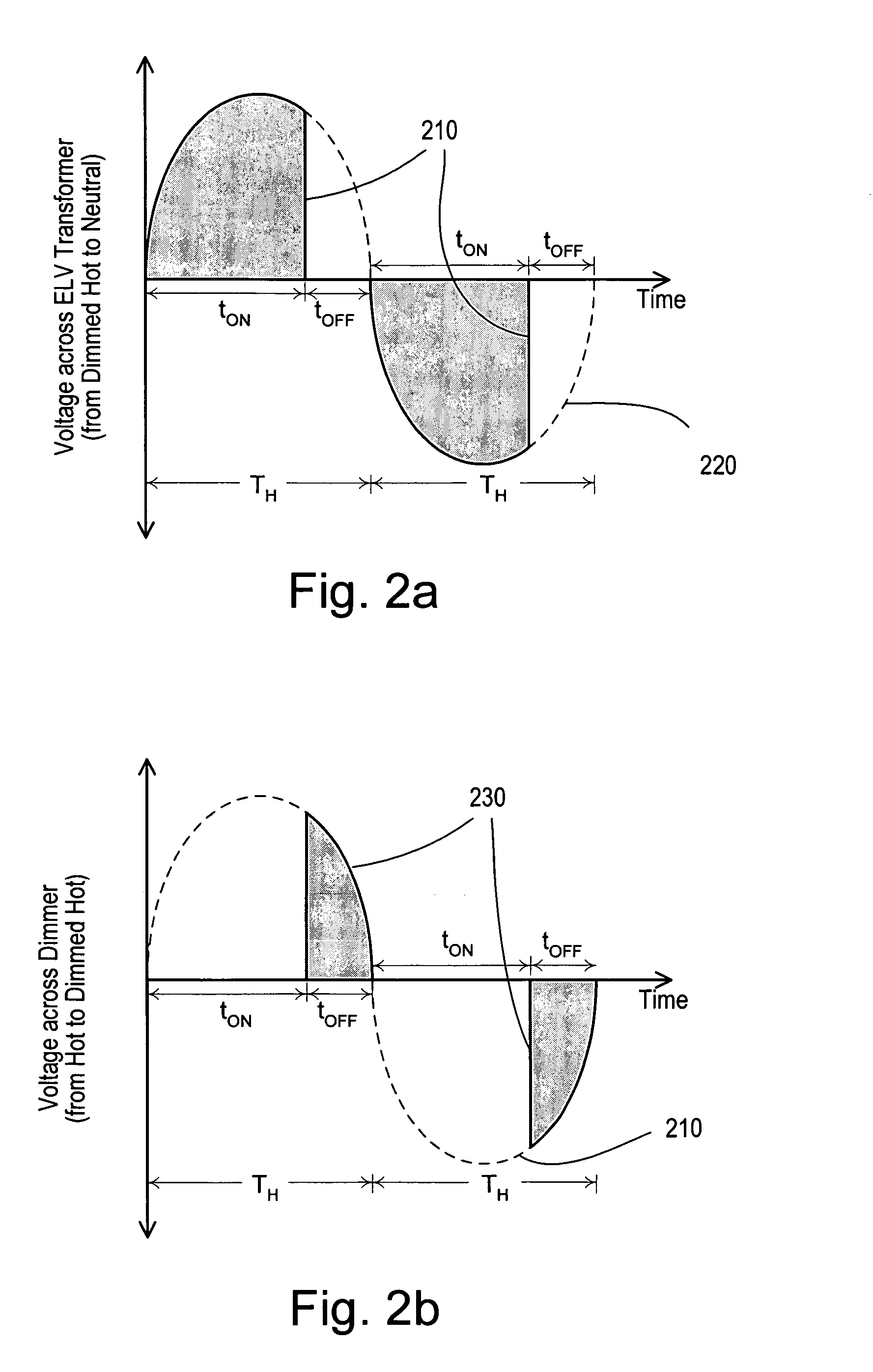
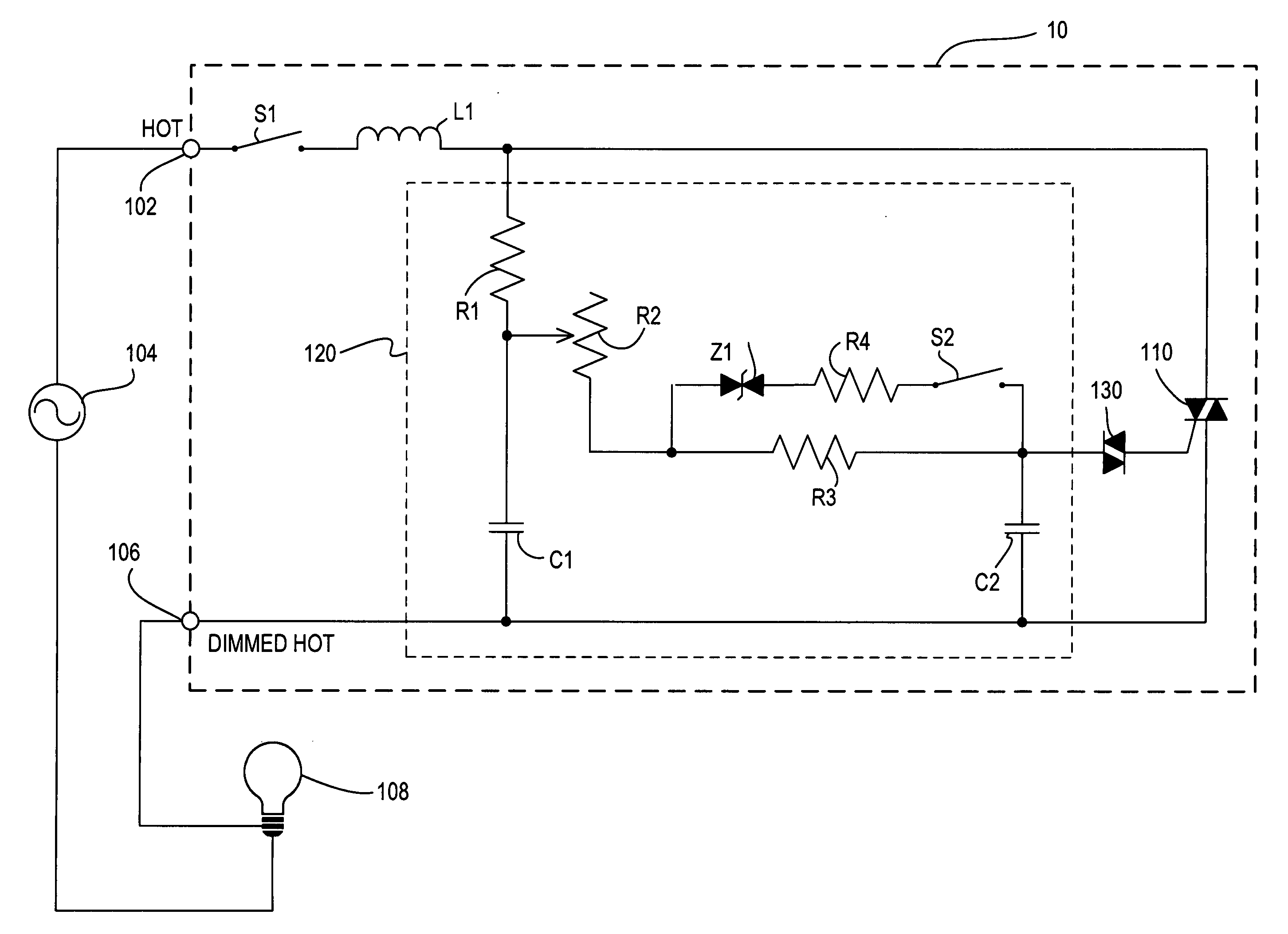
Dimmer having a power supply monitoring circuit
ActiveUS7242150B2Decrease on-timeExtended on-timeElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementDimmerEngineering
A two-wire dimmer for control of a lighting load from an alternating-current (AC) power source includes a semiconductor switch, a power supply, and a control circuit. The power supply includes an energy storage input capacitor that is able to charge only when the semiconductor switch is non-conductive. The control circuit continuously monitors the voltage on the input capacitor and automatically decreases the maximum allowable conduction time of the semiconductor switch when the voltage falls to a level that will not guarantee proper operation of the power supply. The dimmer of the present invention is able to provide the maximum possible conduction time of the semiconductor switch at high end (i.e., maximum light intensity) while simultaneously ensuring sufficient charging time for proper operation of the power supply, and hence, the dimmer.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
Apparatus and method for assessing transmurality of a tissue ablation
InactiveUS7497858B2Good signalGood transmuralityDiagnostic recording/measuringSurgical instruments for heatingTarget tissueTissue ablation
An instrument assesses the transmurality of an ablation lesion from a first surface of a targeted biological tissue to an opposed second surface thereof. The instrument includes at least a first electrode operably attached to an ablation instrument adapted to engage a tissue first surface, and at least a second electrode adapted to engage a tissue second surface, the at least second electrode positioned generally opposed to the at least first electrode. Alternatively, the at least second electrode may be adapted to be placed within a chamber of an organ. These electrodes facilitate measuring at least one of conduction time, conduction velocity, phase angle, and impedance through at least a portion of the targeted tissue to determine the transmurality of the ablation lesion.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
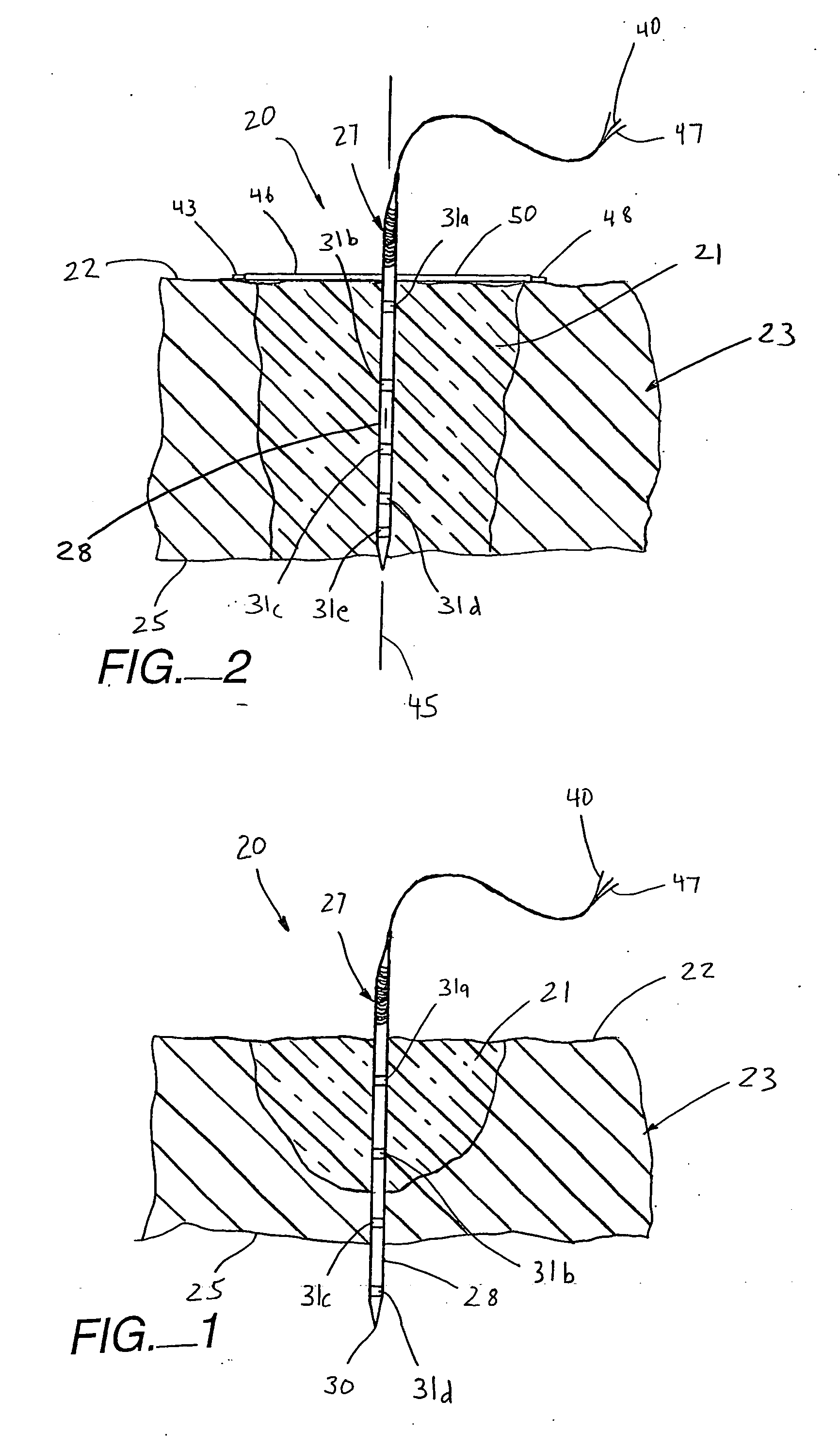
Ablation Device with Sensor
InactiveUS20140194864A1ElectrocardiographySurgical instruments for heatingElectricityConduction time
An electrosurgical device having a distal tip for creating a lesion on tissue includes a first electrode and a second electrode that are parallel for the delivery of RF energy to tissue. A sensor electrode is provided parallel to and spaced away from the first electrode a different distance than the second electrode. When the sensor electrode and at least one of the first and second electrodes are in contact with tissue. The electrosurgical device can perform at least one of the following: ablating tissue, and sensing at least one selected from the group of voltage, tissue impedance, electrical conduction, conduction time, conduction velocity, and signal phase angle.
Owner:ATRICURE
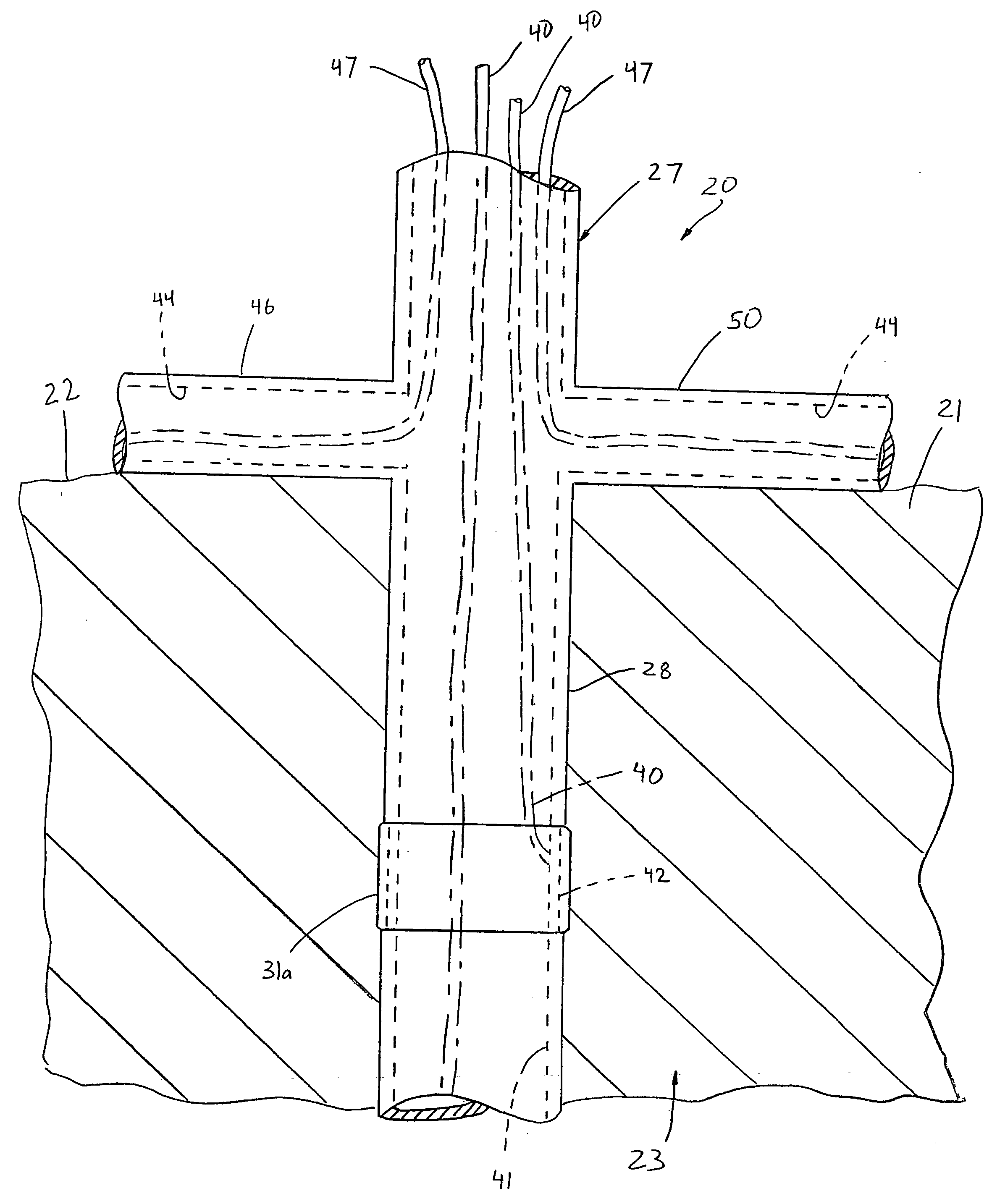
Apparatus and method for assessing tissue ablation transmurality
InactiveUS20050075629A1Prevent reentry circuitSurgical needlesDiagnostic recording/measuringTarget tissueTissue ablation
An instrument is provided to assess the transmurality of an ablation lesion from a first surface of a targeted biological tissue to an opposed second surface thereof. The instrument includes a needle member having an elongated shaft and a distal tip portion adapted to pierce the tissue first surface and into the ablation lesion of the biological tissue. A plurality of needle electrodes are spaced-apart along the elongated shaft. When the needle member pierces the tissue first surface, each the electrode being positioned at different respective depths of the biological tissue from the tissue first surface to the tissue second surface. These electrodes each measure at least one of conduction time, conduction velocity, phase angle, and impedance through at least a portion of the targeted tissue and at the respective depth to determine the transmurality of the ablation lesion.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC +1
Dimmer having a power supply monitoring circuit
ActiveUS20060255745A1Decrease on-timeExtended on-timeElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementCapacitanceEffect light
A two-wire dimmer for control of a lighting load from an alternating-current (AC) power source includes a semiconductor switch, a power supply, and a control circuit. The power supply includes an energy storage input capacitor that is able to charge only when the semiconductor switch is non-conductive. The control circuit continuously monitors the voltage on the input capacitor and automatically decreases the maximum allowable conduction time of the semiconductor switch when the voltage falls to a level that will not guarantee proper operation of the power supply. The dimmer of the present invention is able to provide the maximum possible conduction time of the semiconductor switch at high end (i.e., maximum light intensity) while simultaneously ensuring sufficient charging time for proper operation of the power supply, and hence, the dimmer.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
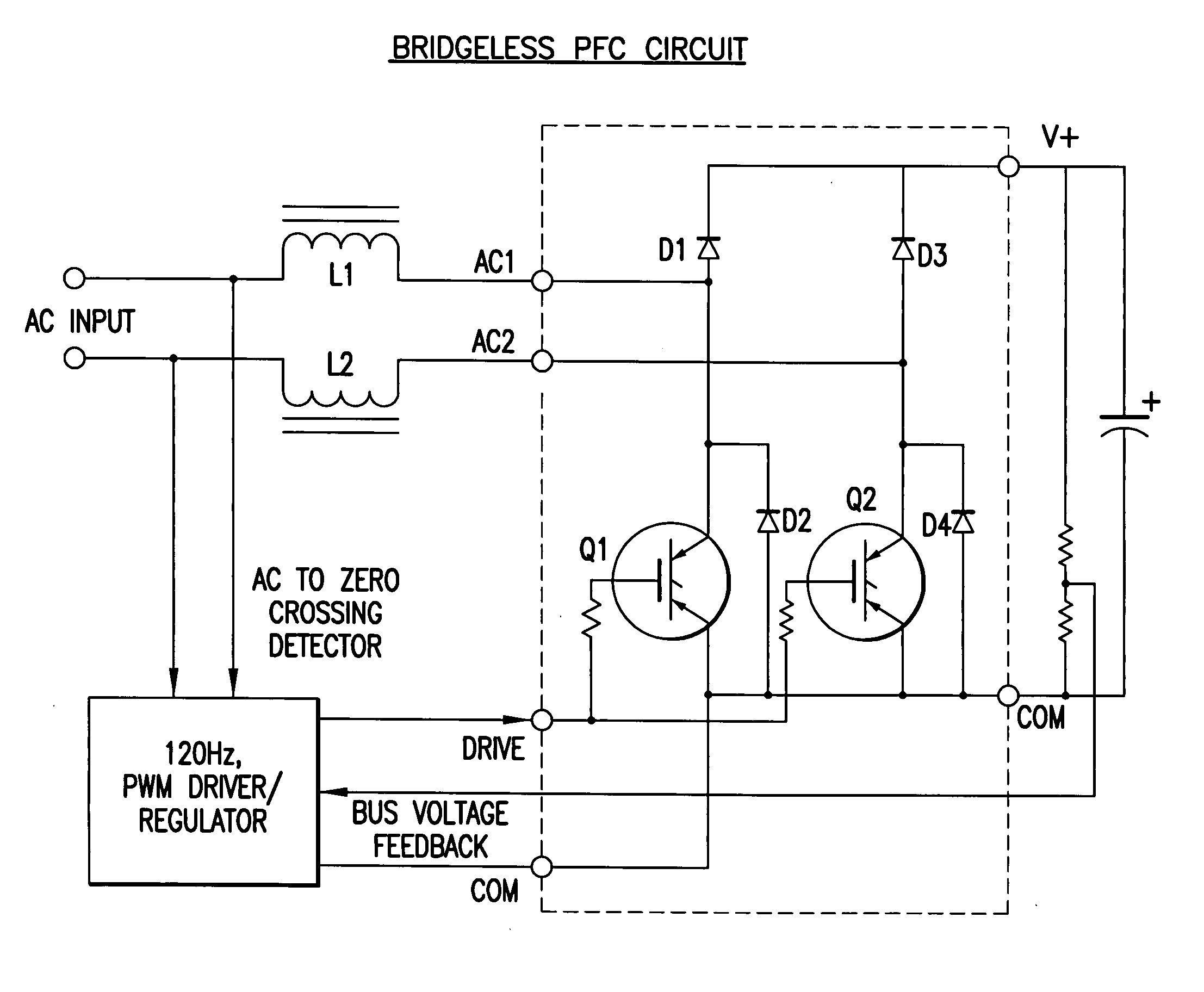
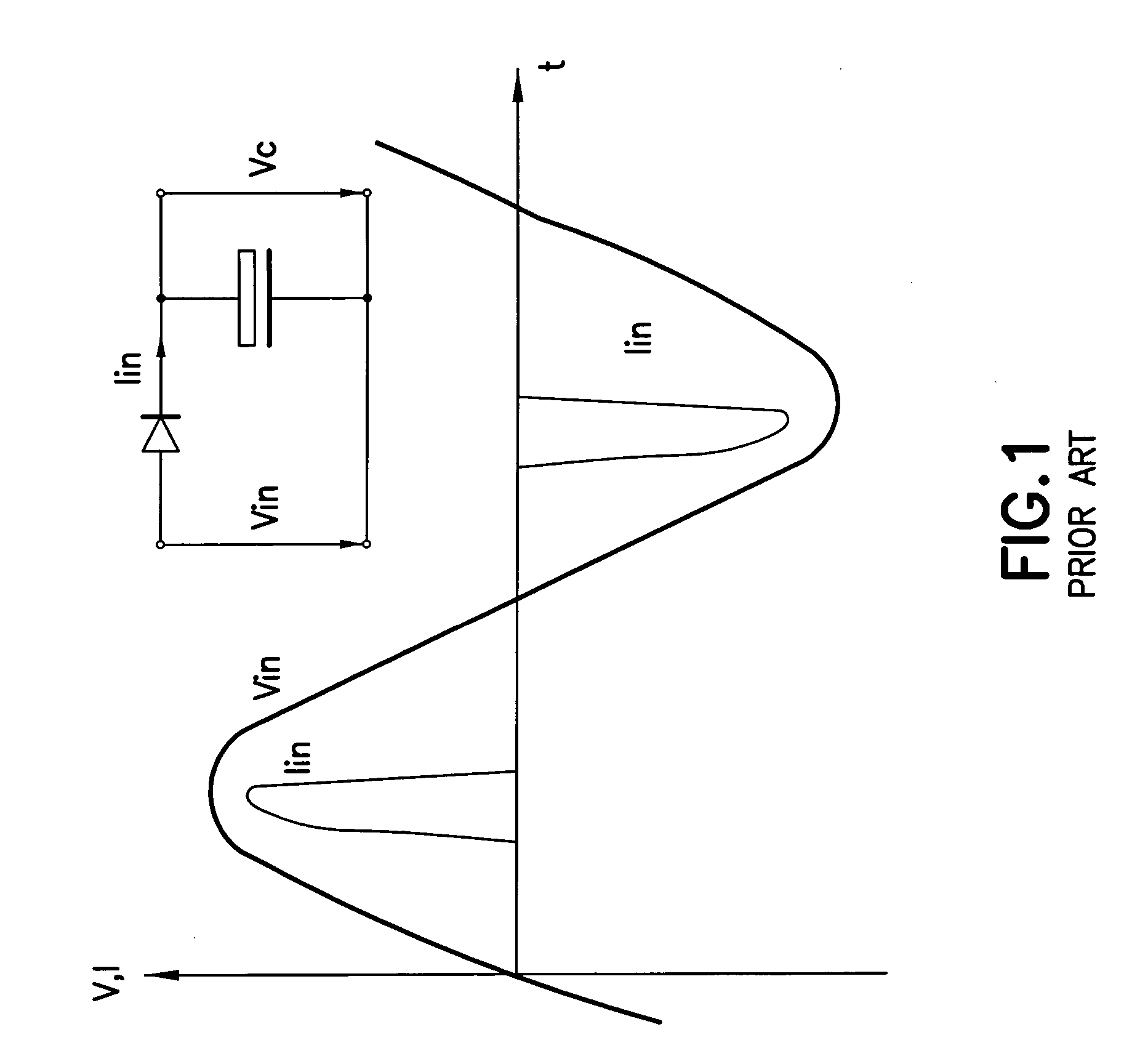
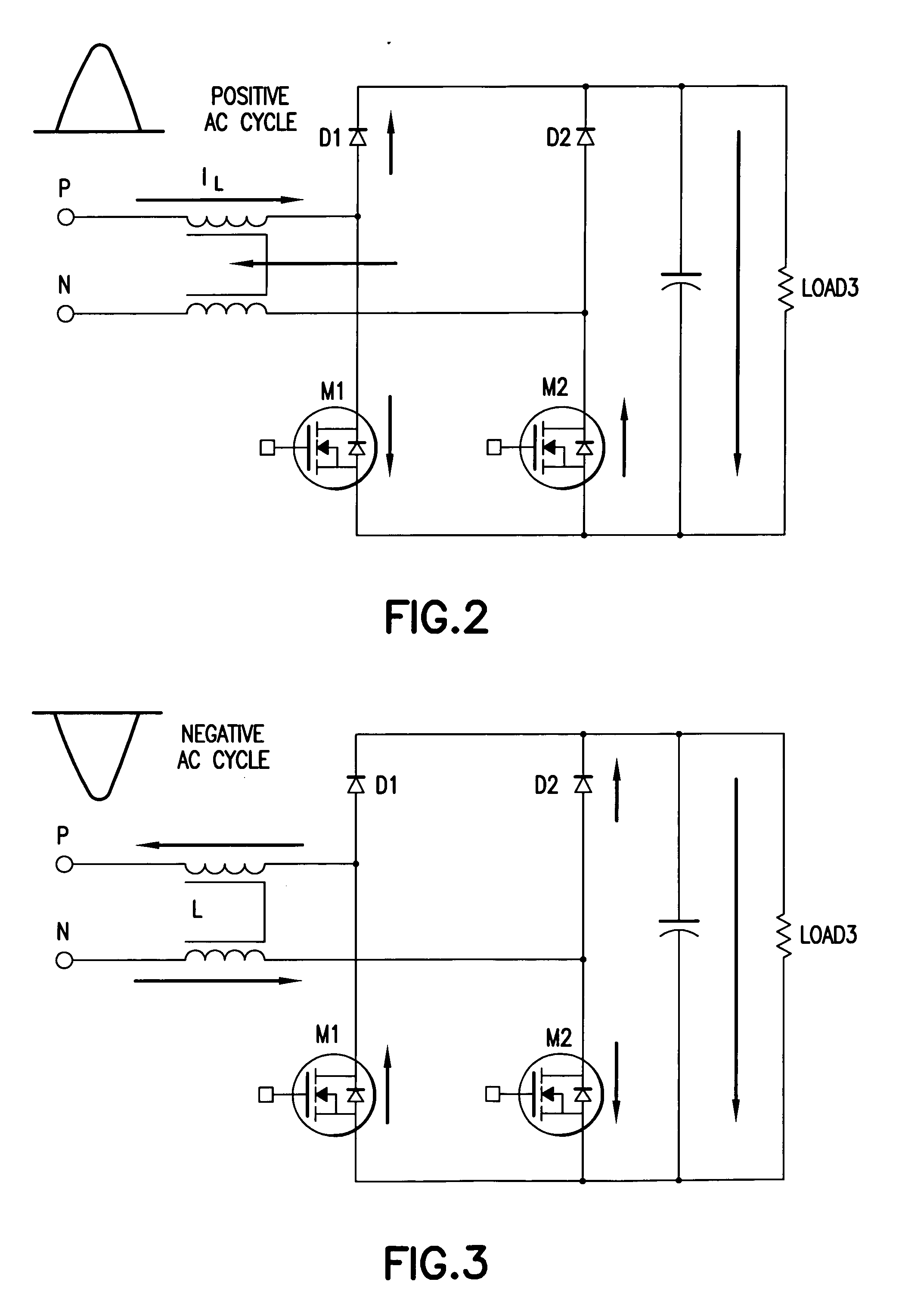
Bridgeless boost converter with PFC circuit
InactiveUS20060198172A1Improve efficiencyLow costAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionControl signalEngineering
A boost type power supply circuit for providing a DC output voltage comprising first and second semiconductor switches coupled between respective input lines and a common connection; an AC input voltage from an AC source being supplied across the input lines; first and second diodes coupled in series with respective ones of the switches; third and fourth diodes coupled across respective ones of the switches in a free-wheeling relationship with the switches; an inductance coupled in at least one of the input lines; a controller for controlling the conduction times of the switches by providing a pulse width control signal to each of the switches; wherein the controller turns on at least one of the switches during a positive half cycle of the AC voltage to allow energy storage in the inductance and turns off the at least one switch to allow the energy stored in the inductance to be supplied to an attached load through one of the first and second diodes and one of the third or fourth diodes; and the controller turns on at least one of the switches during a negative half cycle of the AC voltage to allow energy storage in the inductance and turns off at least one switch to allow the energy stored in the inductance to be supplied to the attached load through one of the first and second diodes and one of the third and fourth diodes. The controller determines an on-time and an off-time of a pulse of the pulse width modulated control signal during each half cycle of the AC voltage, the on-time and off-time of the pulse being controlled to regulate said output voltage and to provide power factor correction of said AC input voltage, based on either voltage sensing or current sensing.
Owner:INTERNATIONAL RECTIFIER COEP
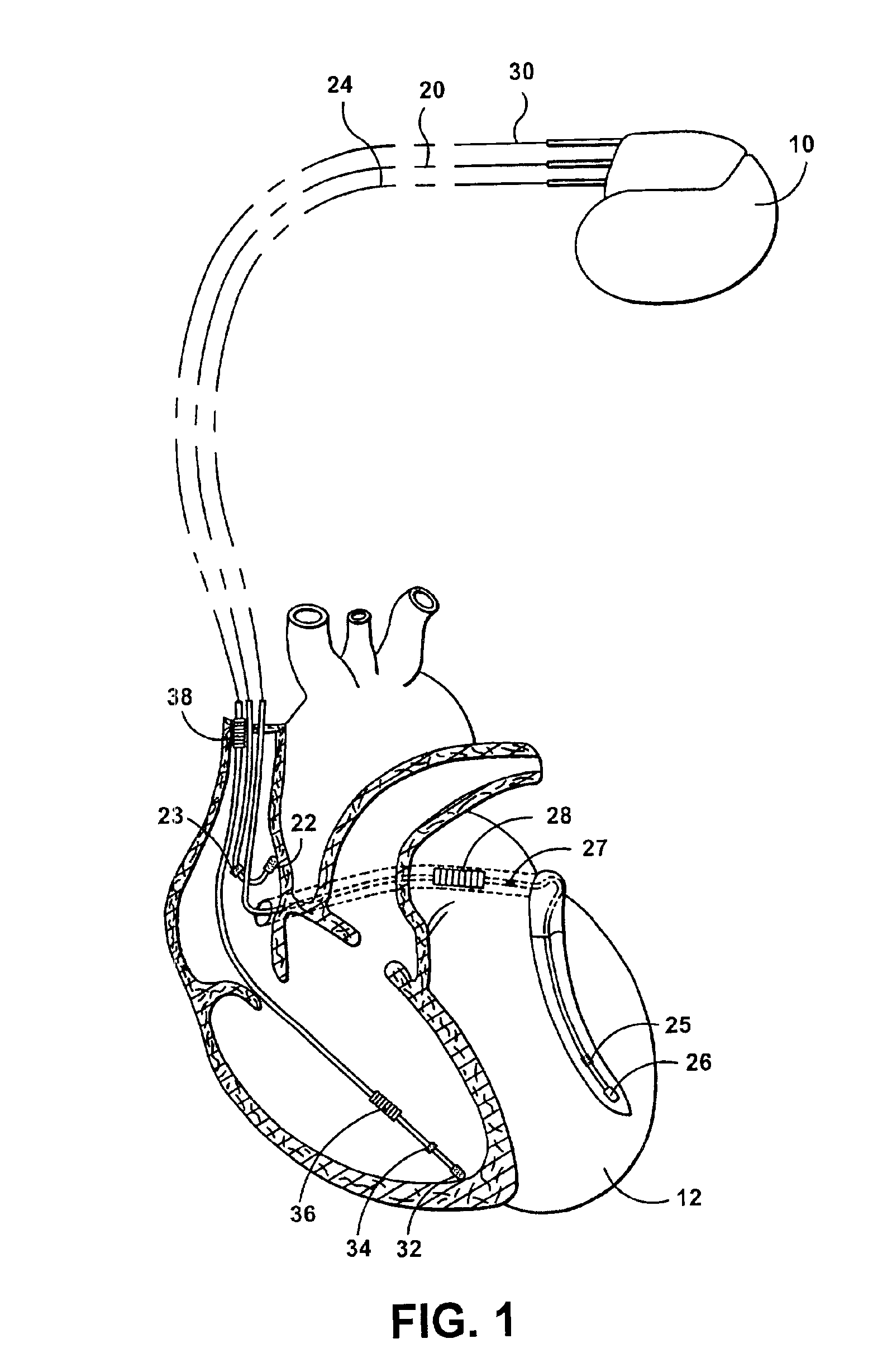
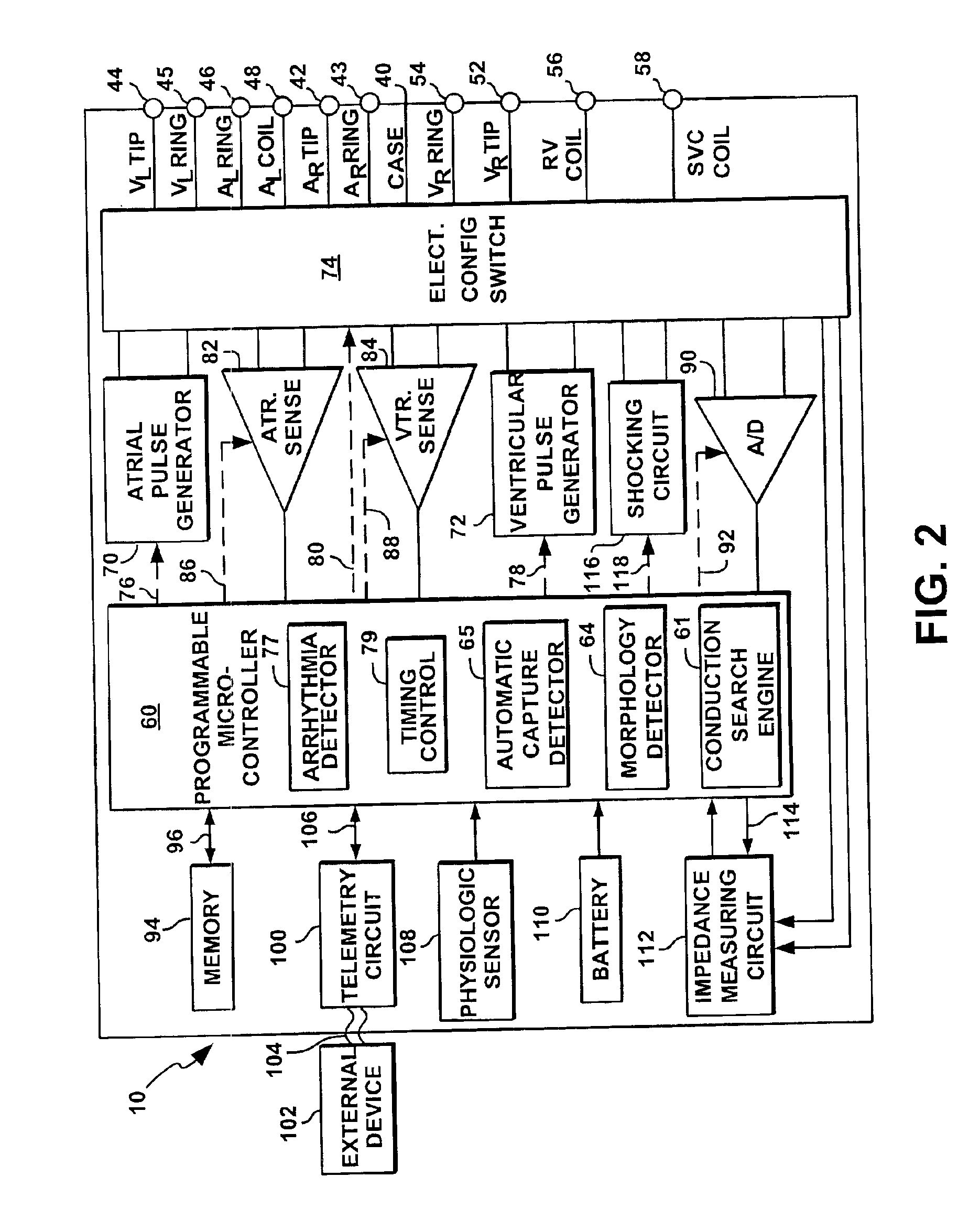
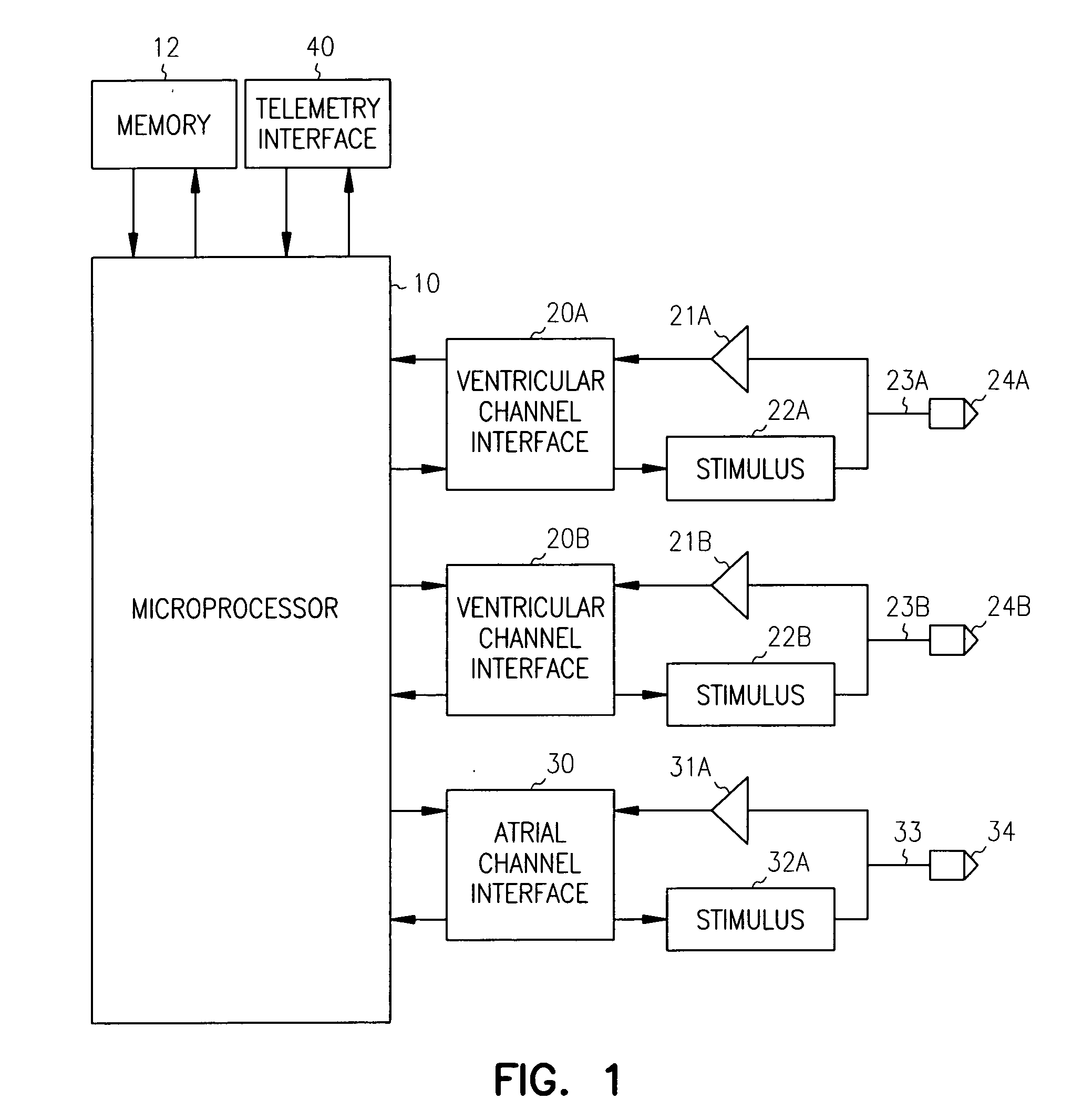
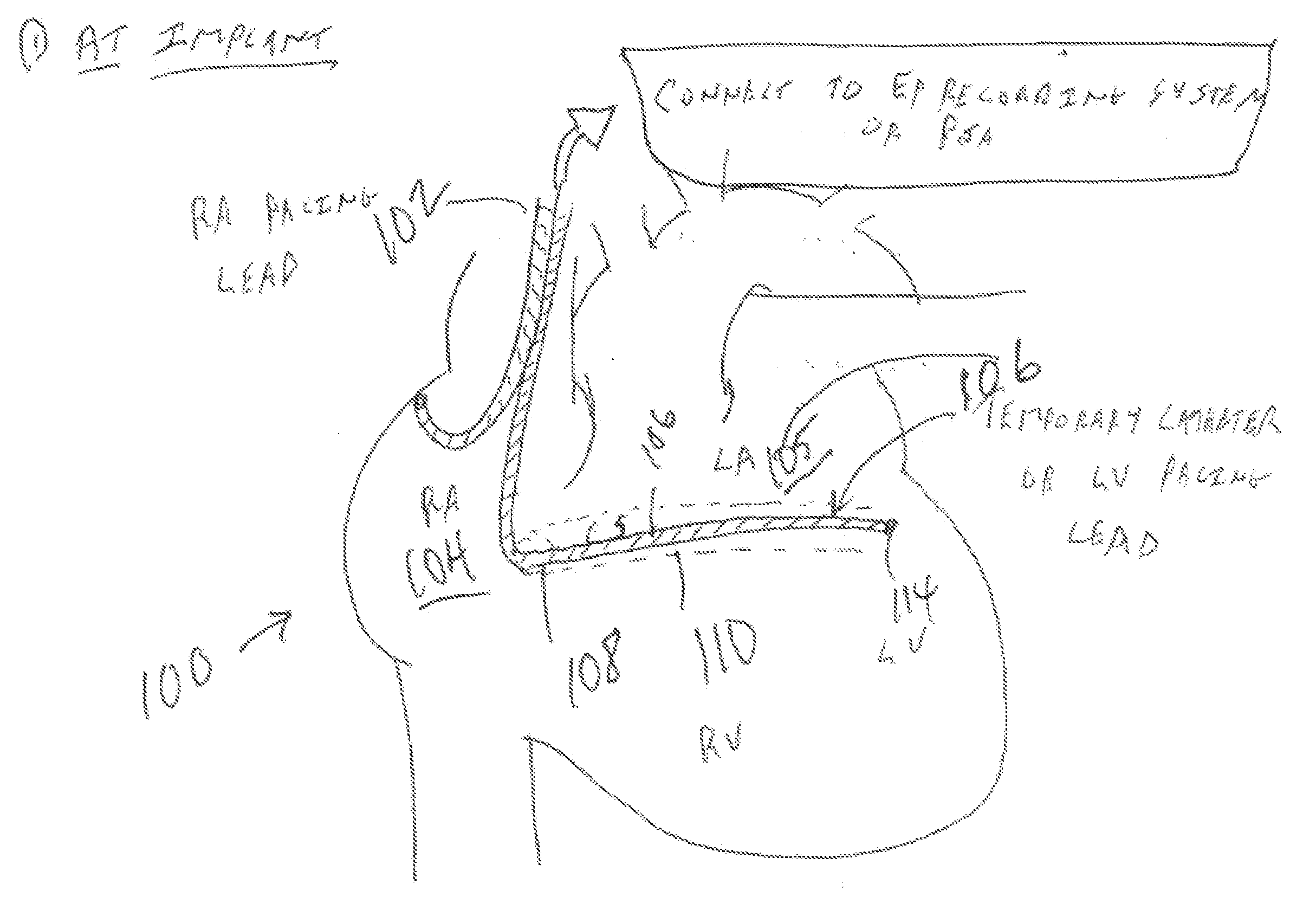
Implantable stimulation device and method for performing inter-chamber conduction search and conduction time measurement
InactiveUS6885893B1Improves cardiac stimulation device performanceAvoid negative effectsHeart stimulatorsConduction timeAtrial conduction
An implantable cardiac stimulation device and associated method set an atrial capture detection window by verifying that inter-atrial conduction is intact, and then measuring the inter-atrial conduction time. The measured inter-atrial conduction time may then be used for setting the atrial capture detection window. Capture verification of a stimulated atrial site is then implemented by detecting a conducted depolarization at another atrial site or in the opposite atrial chamber. A signal received during an atrial capture detection window is compared to a depolarization signal threshold or to a depolarization signal template in order to verify detection of a conducted depolarization signal as evidence of capture at the stimulated site. By sensing depolarization signal away from the stimulated site, the negative effects of lead polarization normally encountered when detecting an evoked response are avoided.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
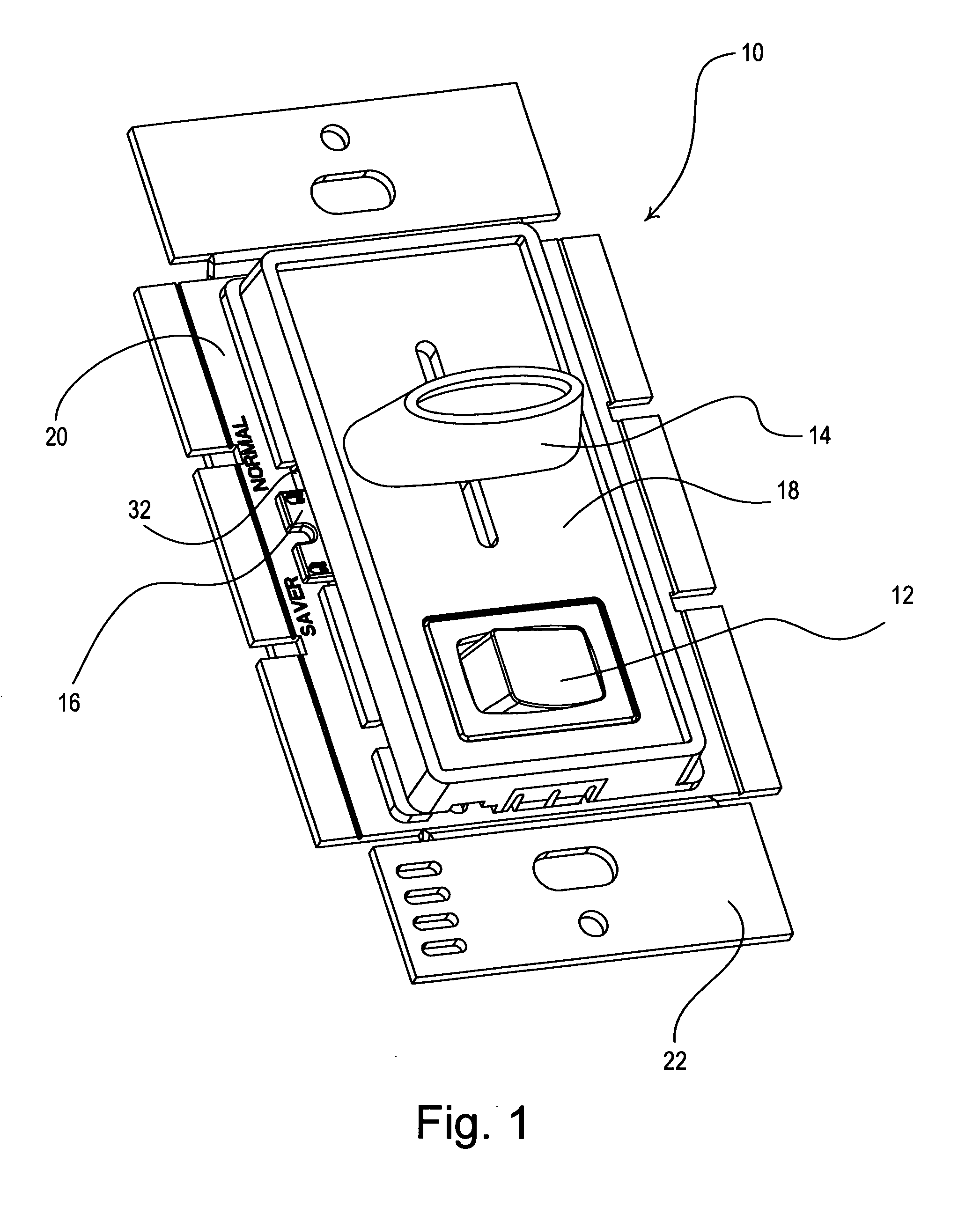
Dimmer switch with adjustable high-end trim
InactiveUS20070285027A1Reducing high-end trimReducing having substantially no affectElectric ignition installationSwitch power arrangementsMinimum timeTRIAC
A dimmer switch has a user adjustable high-end trim. The dimmer switch includes a bidirectional semiconductor switch, such as a triac, for controlling the amount of power delivered from a source of alternating current power to a lighting load, such as an electric lamp. A user-adjustable timing circuit controls the conduction time of the triac from a minimum time to a maximum time. The maximum possible conduction time of the triac is the high-end trim. The minimum possible conduction time of the triac is the low-end trim. The timing circuit includes a user-accessible switch that allows a user to reduce the high-end trim from a first nominal level to a second reduced level, lower than the first level, without substantially affecting the low-end trim. The switch allows a user to switch a transient voltage suppressor into and out of parallel connection with a resistor that is part of an RC timing circuit for the triac. The dimmer switch advantageously uses less energy and the lifetime of the lamp is extended when the second reduced level of the high-end trim is selected.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
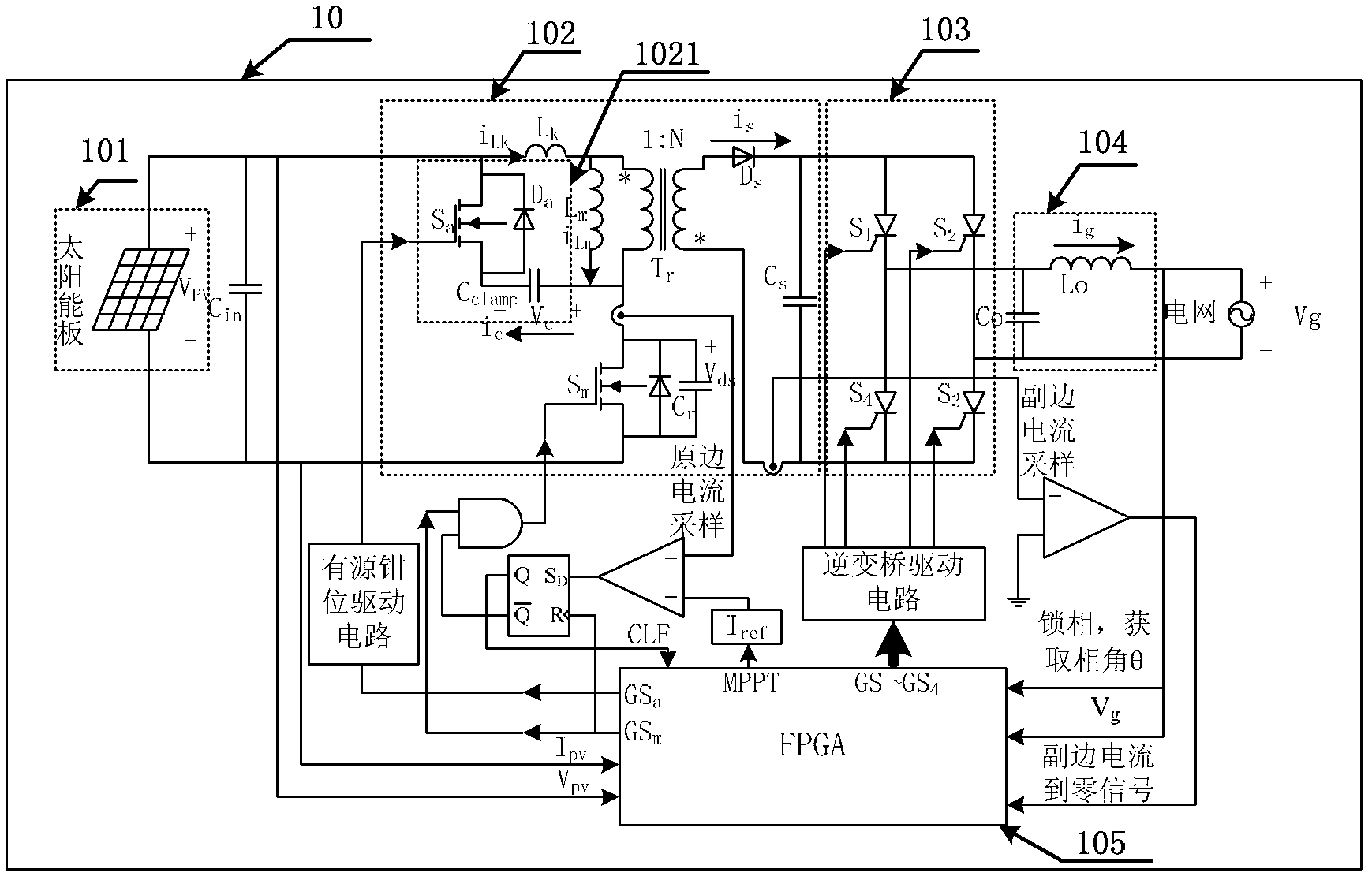
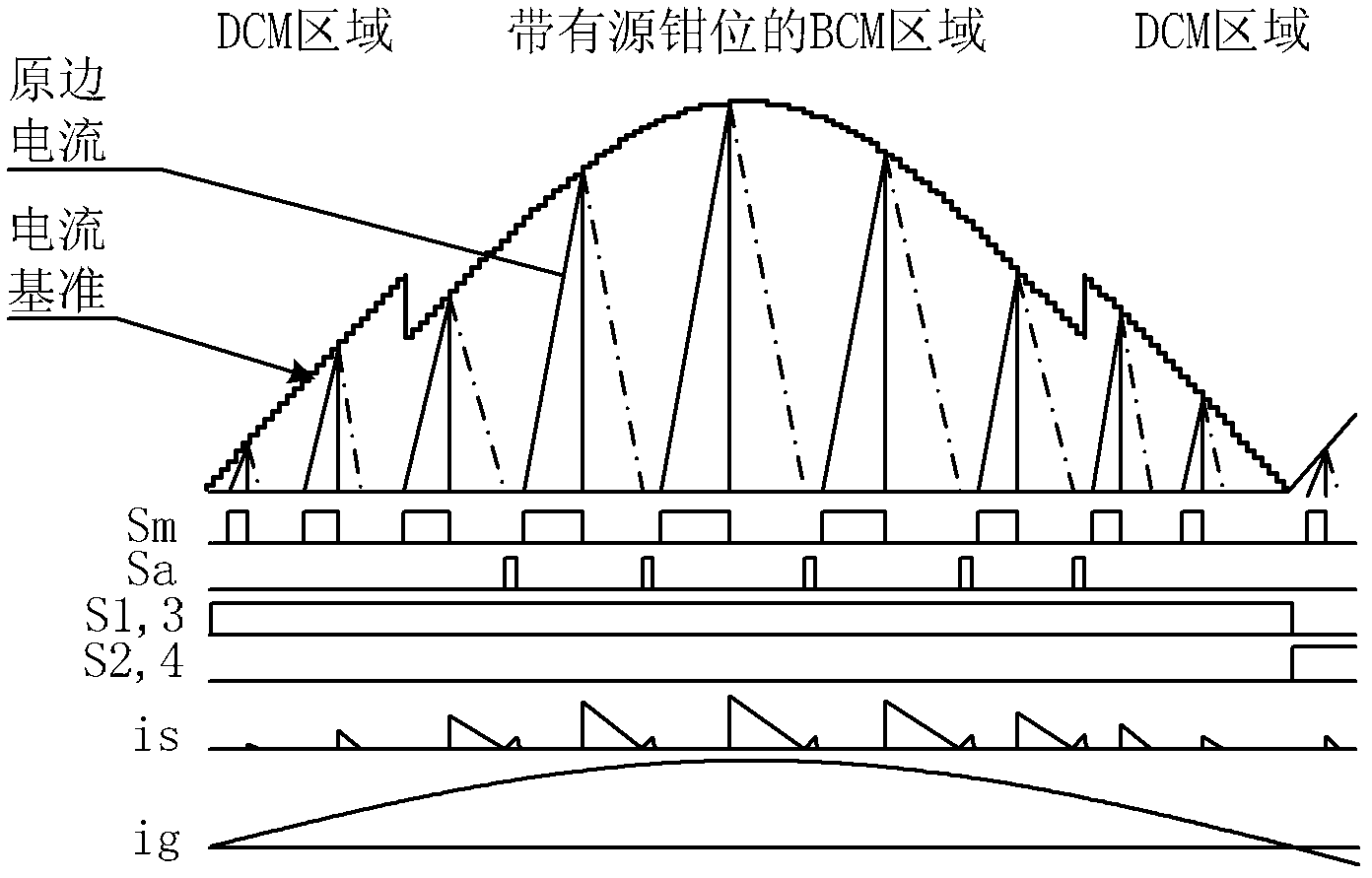
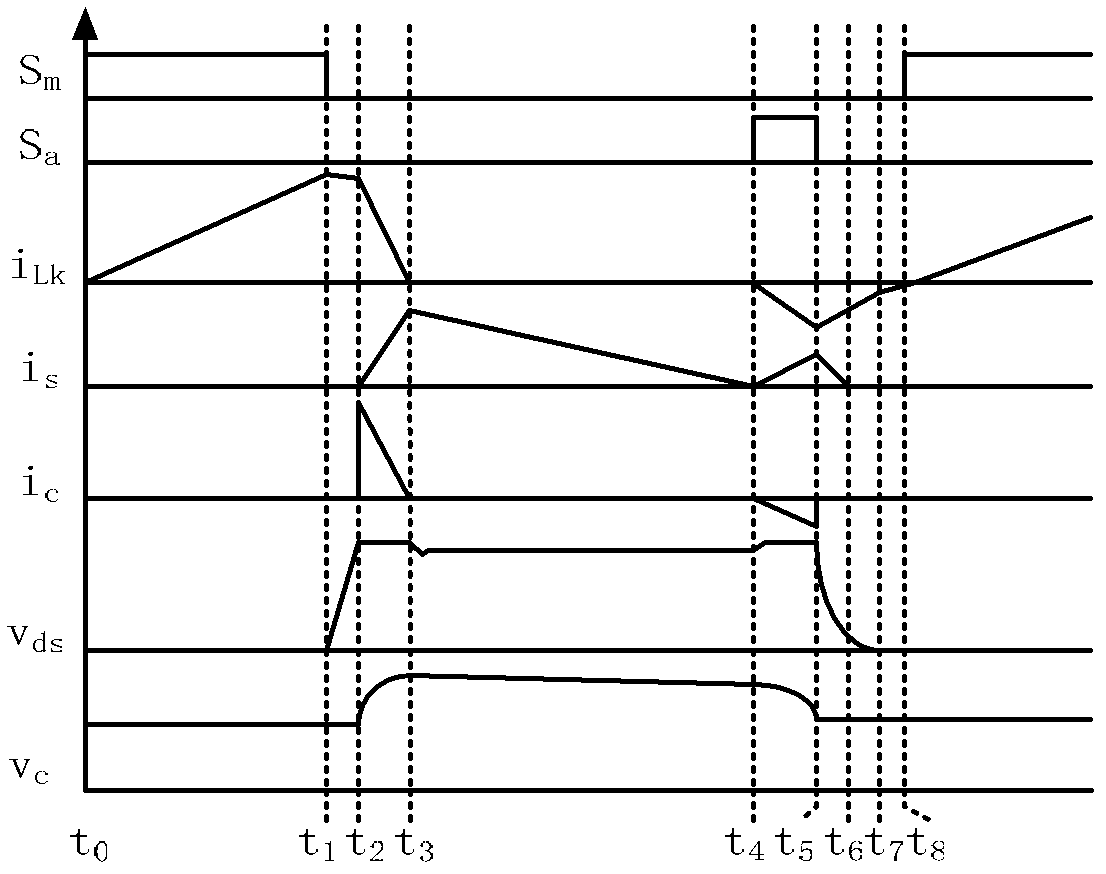
Control method applied to active-clamp flyback miniature photovoltaic grid-connected inverter device
ActiveCN102307017AImprove EMI characteristicsImprove efficiencyDc-dc conversionPhotovoltaic energy generationConstant frequencyPeak value
The invention relates to a control method which can be applied to an active-clamp flyback miniature photovoltaic grid-connected inverter device. The active-clamp flyback miniature photovoltaic grid-connected inverter device comprises a flyback converter and a power frequency polarity conversion circuit. In the device, a current reference is used for controlling a flyback primary-side current peak value so that the device can output a half-wave sinusoidal current, and the output voltage is clamped by a grid voltage. When the instantaneous power is lower, a constant frequency current discontinuous mode in combined with a variable frequency current critical continuous mode is adopted in the flyback control method. When the flyback converter works in a variable frequency current critical discontinuous mode, an auxiliary switching tube can be conducted for a period of time when the secondary-side current of the flyback converter reaches zero, the conduction time can be accurately controlled by a digital chip, thus realizing the leakage inductance energy feedback and the soft switch of a master switching tube under the condition of wide-range output voltages and different instantaneous powers and greatly improving the efficiency under the condition of full loads.
Owner:ALTENERGY POWER SYST
Switching power supply controller for constant current driving of LED by primary side control and method for constant current driving of LED
ActiveCN102364990AImprove securityLow costDc-dc conversionElectric light circuit arrangementPower factorTransformer
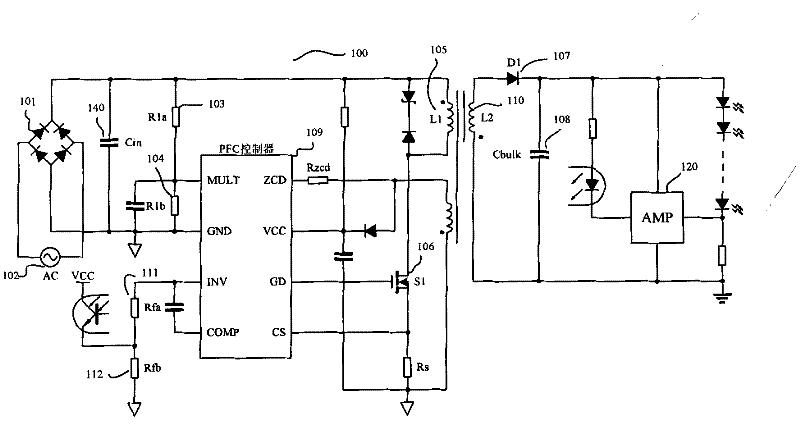
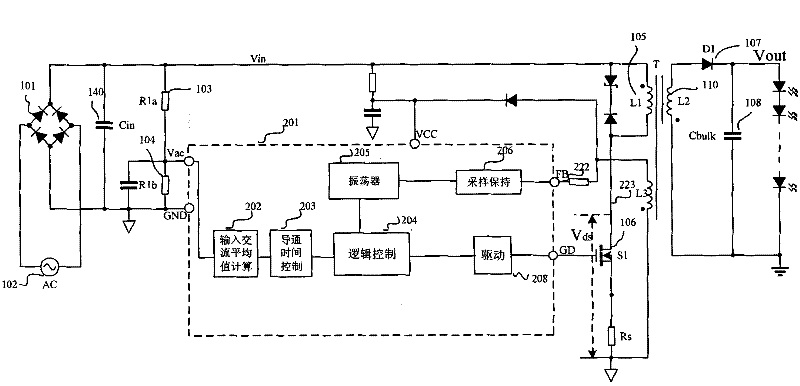
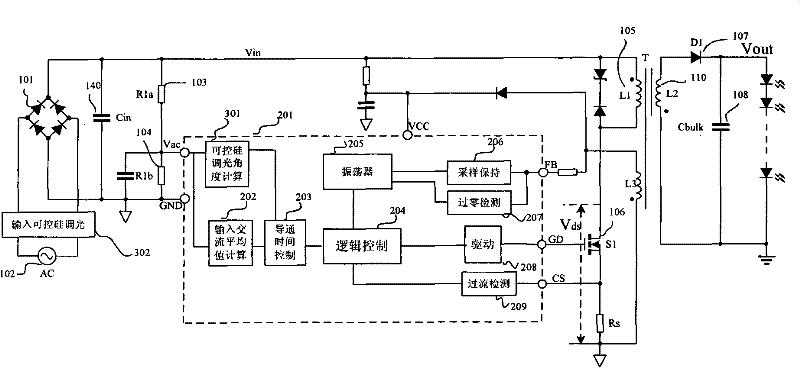
The invention discloses a switching power supply controller for constant current driving of an LED by primary side control, a method for the constant current driving of the LED and a switching power supply formed by using the switching power supply controller. The switching power supply controller comprises an oscillator circuit, an input alternating current average value calculating circuit, a conduction time control circuit, a logic control circuit and a driving circuit. The controller controls the constant current driving of the LED by using a primary side control method to realize same output current and high power factor under the condition with controlled silicon dimming and high-low voltage input; and transformer isolation is directly used, so that the safety performance of the circuits is improved, a peripheral circuit is simple, the circuit cost is reduced, and the PCB (printed circuit board) distribution space is very small in favor of product miniaturization.
Owner:HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS
Synchronous rectifier control circuit and switch power supply employing same
ActiveCN102723856AImprove conversion efficiencyEliminate secondary negative currentEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionControl circuitSecondary side
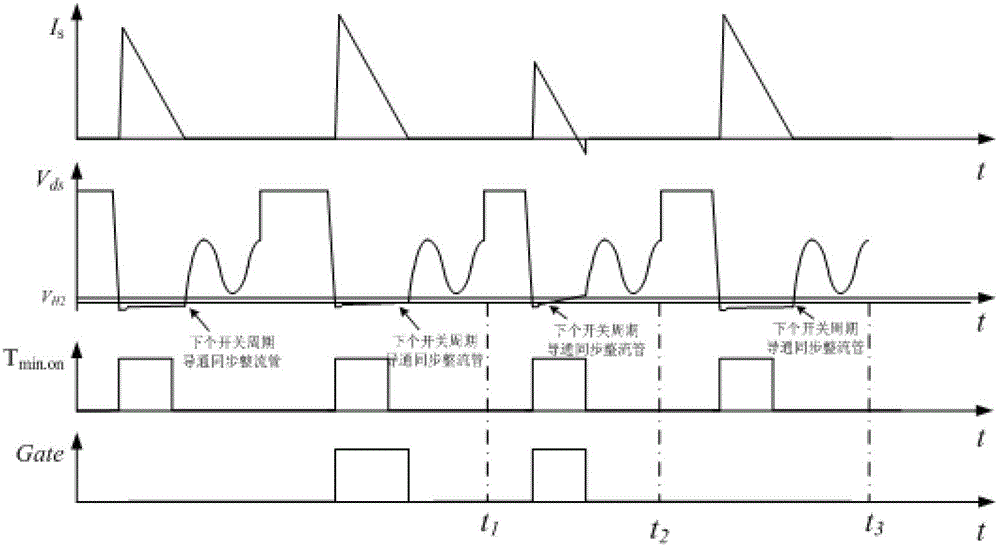
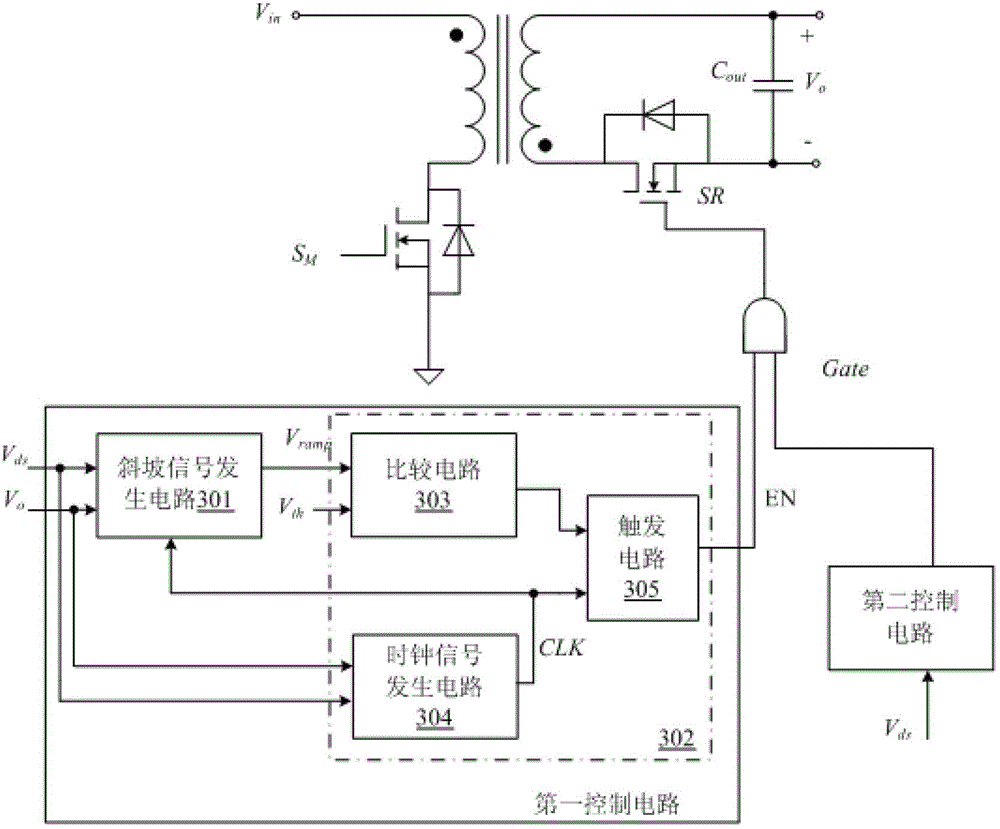
The invention discloses a synchronous rectifier control circuit and a switch power supply employing the same. Whether the conduction time of a synchronous rectifier switch tube meets the requirement of the minimum conduction time in the same switch period and in the conduction interval of a primary side power switch tube can be judged, and the conduction of synchronous rectifier switch tube in the switch period is controlled according to the judgment result, so that secondary side current is completely avoided, electric energy is saved, and the conversion efficiency of the whole power supply circuit is greatly improved.
Owner:SILERGY SEMICON TECH (HANGZHOU) CO LTD
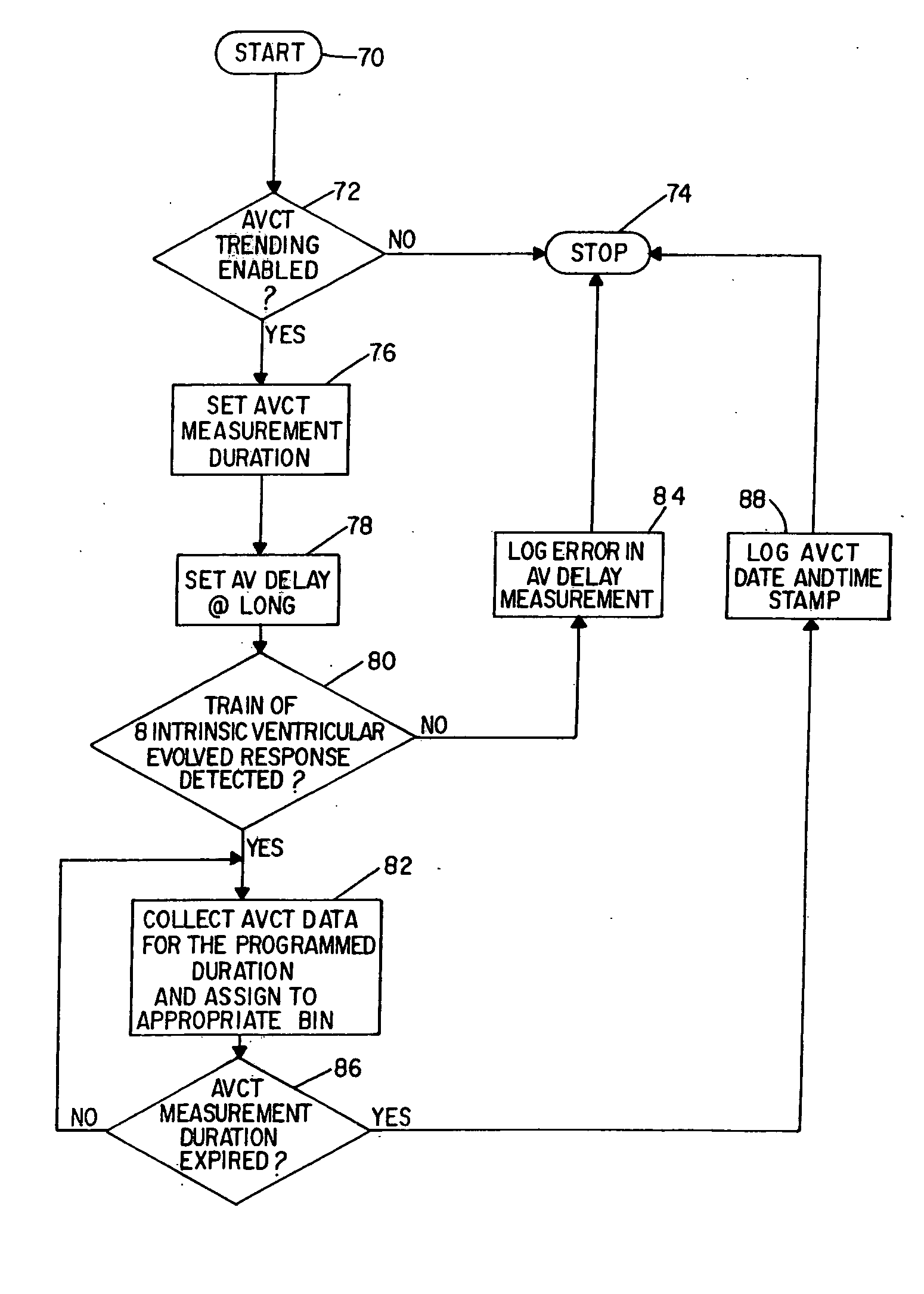
Trending of conduction time for optimization of cardiac resynchronization therapy in cardiac rhythm management system
A method of optimizing cardiac resynchronization therapy delay over a patient's full range of activity for use in operating an implantable cardiac pacing device and such a device are disclosed. The method includes measuring selected conduction time between selected sites in the heart for a plurality of beats and logging the values on a periodic repeating programmable basis to produce cumulative data and constructing a current template of conduction time in relation to one or more other sensed parameters of interest over a desired range of patient activity levels. The current template is used to derive suggested optimum pacing timing.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
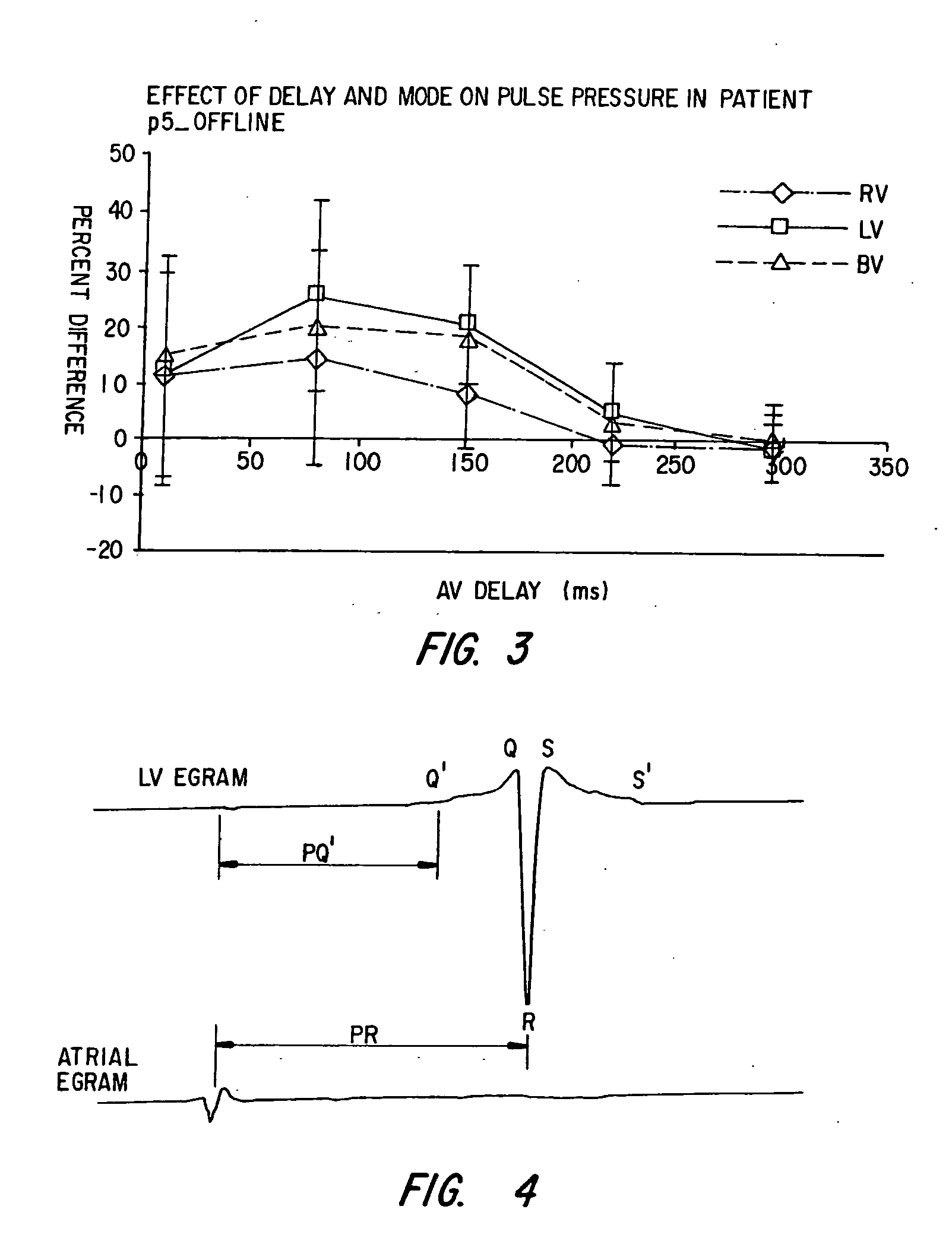
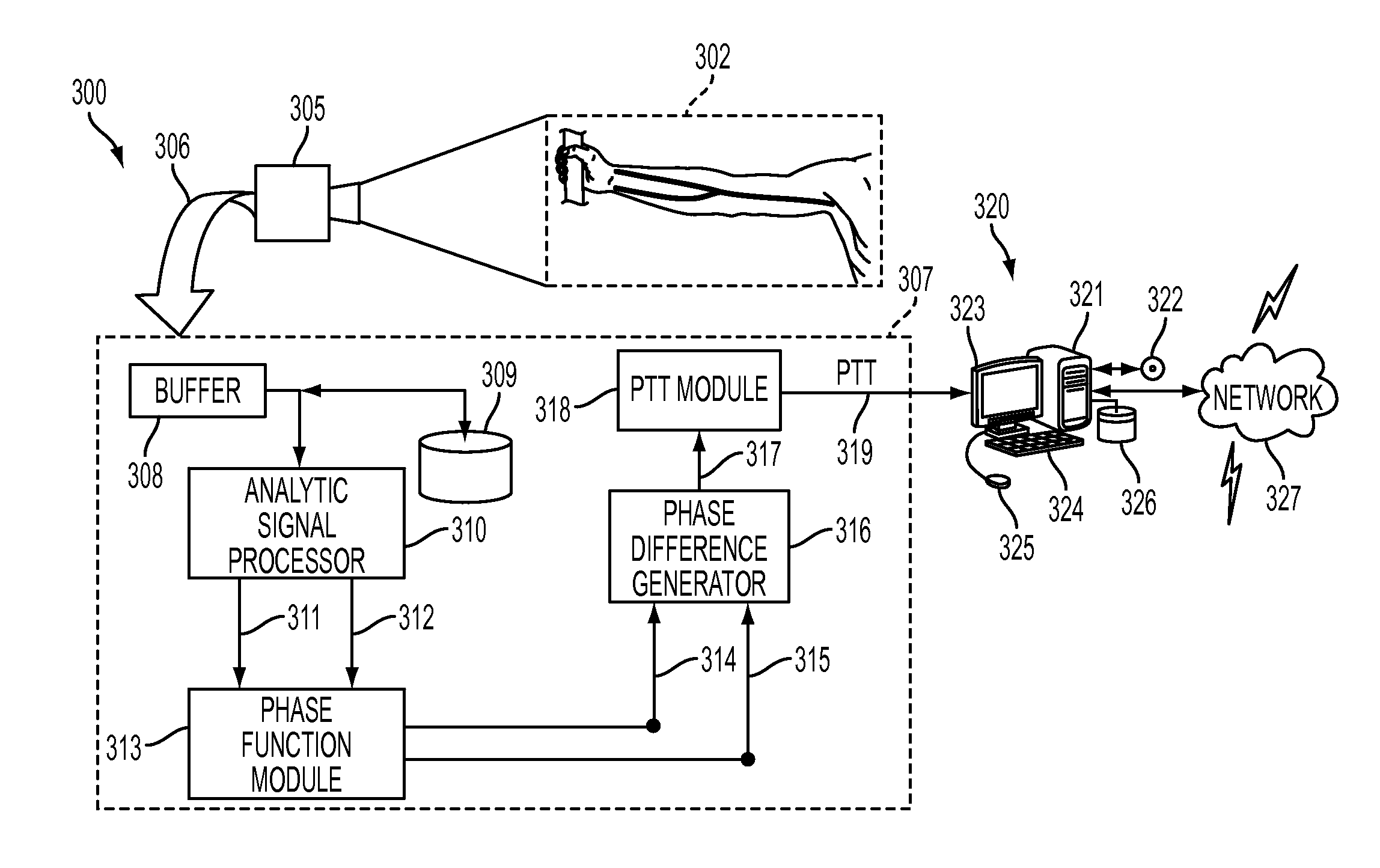
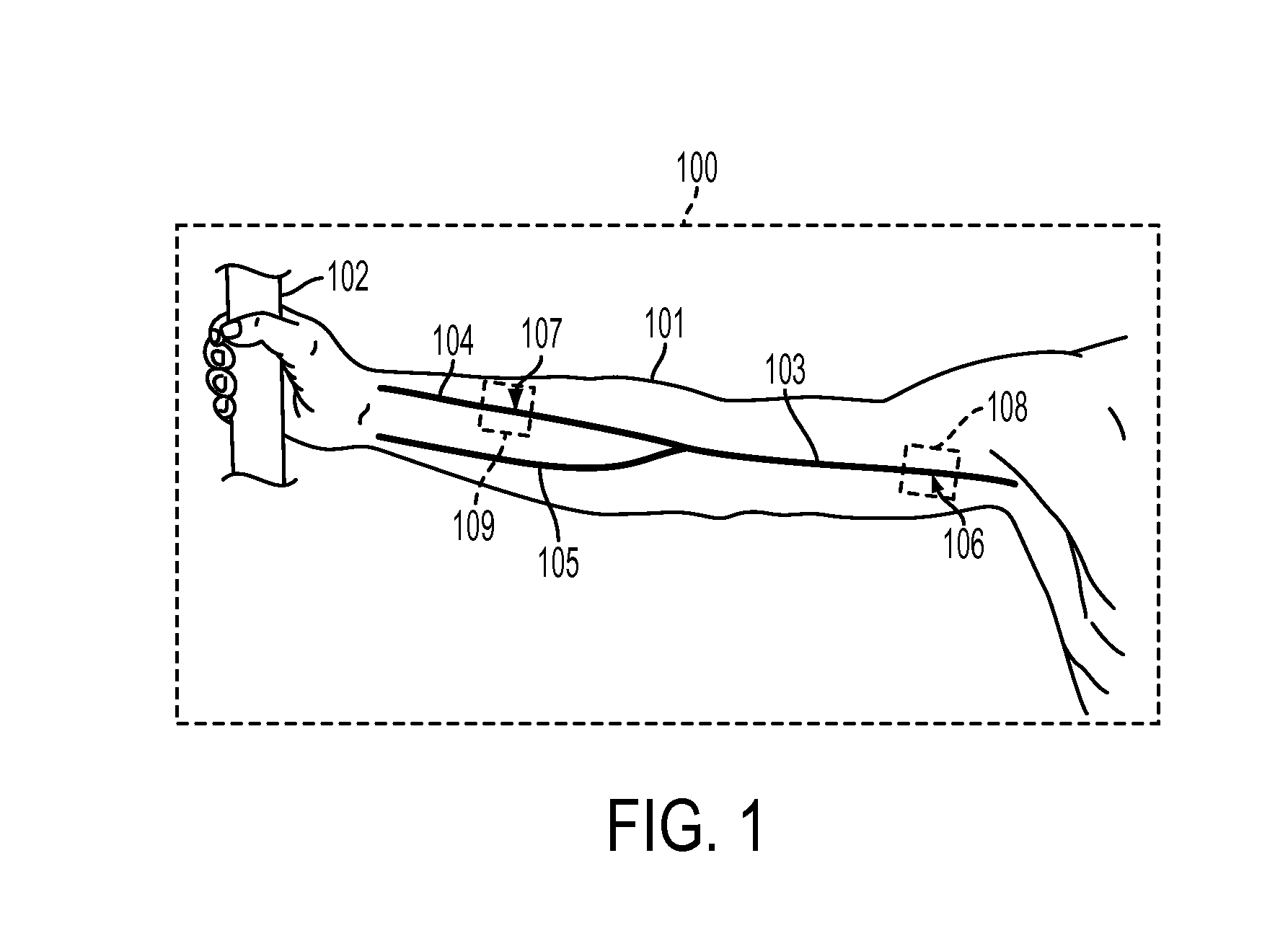
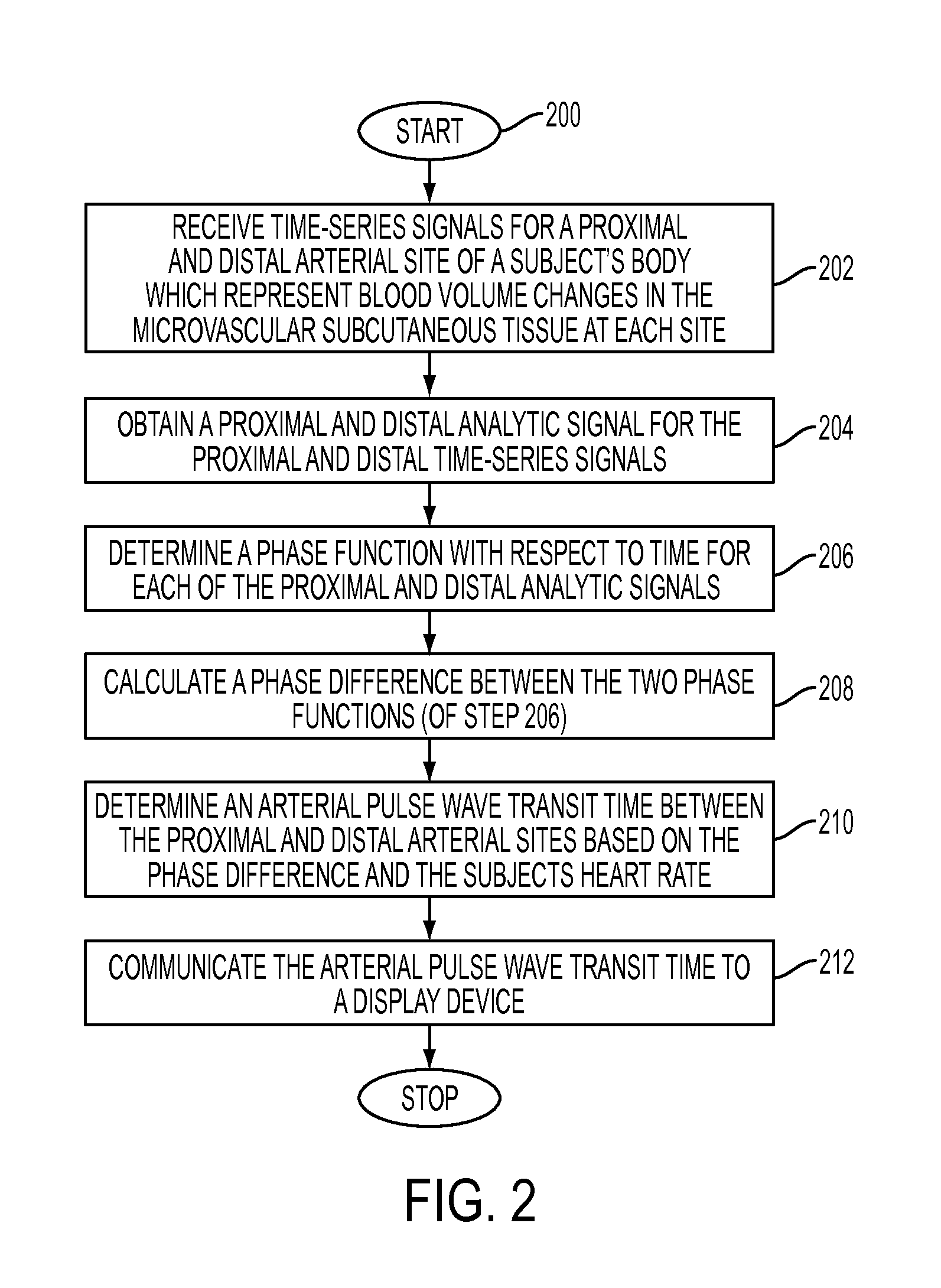
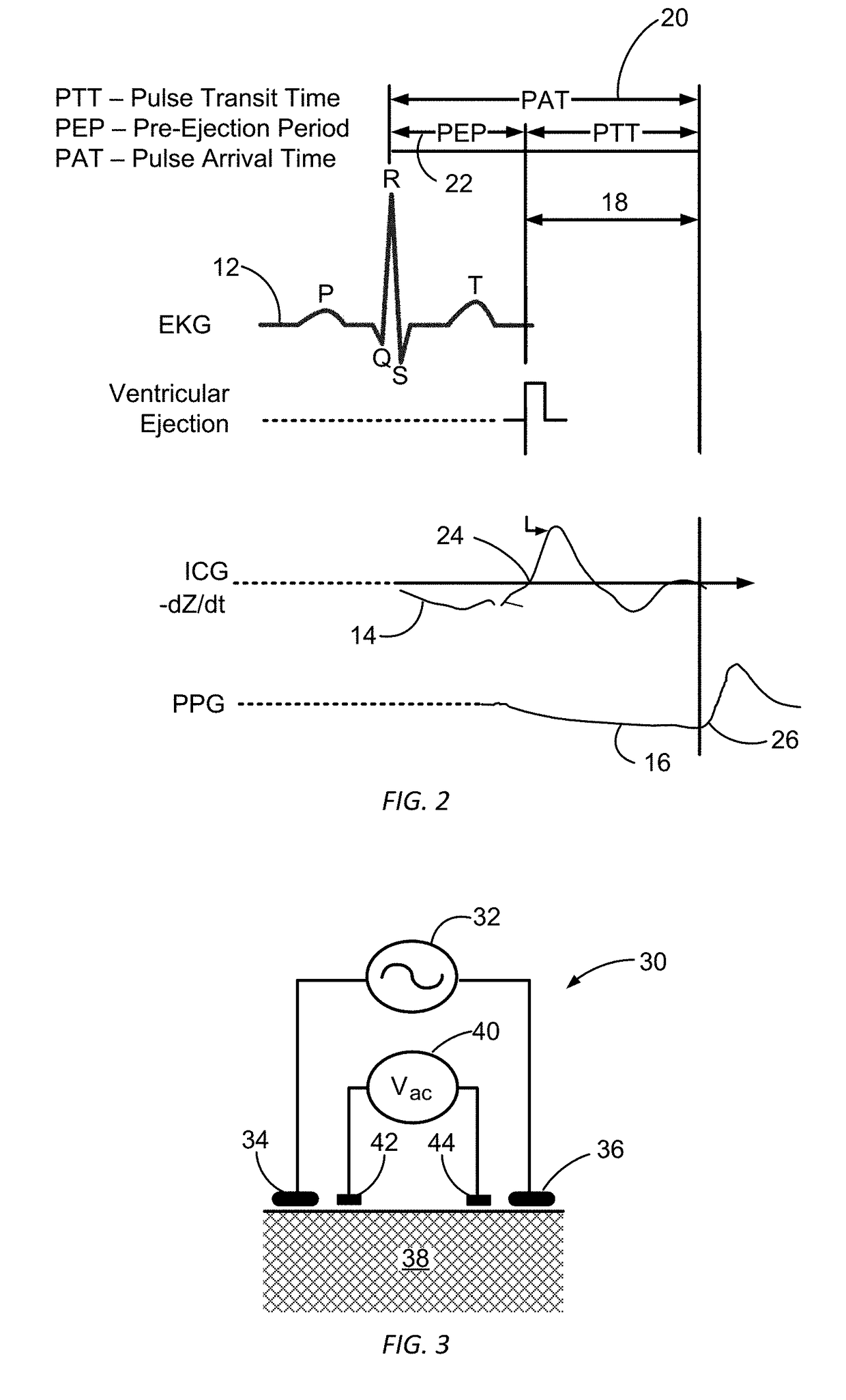
Determining arterial pulse transit time from time-series signals obtained at proximal and distal arterial sites
What is disclosed is a system and method for determining arterial pulse transit time (PTT) for a subject. In one embodiment, time-series signals are received for each of a proximal and distal arterial site of a subject's body which represent blood volume changes in the microvascular tissue at each site. A proximal and distal analytic signal is obtained which has a first component being a waveform of the respective time-series signal and a second component being a transform of the respective waveform. A phase function is determined for the first and second components of each analytic signal. The phase function obtained for the proximal waveform is then subtracted from the phase function obtained for the distal waveform to get a phase difference. The phase difference is analyzed with the subject's heart rate to determine an arterial pulse wave transit time between the two proximal and distal sites.
Owner:XEROX CORP
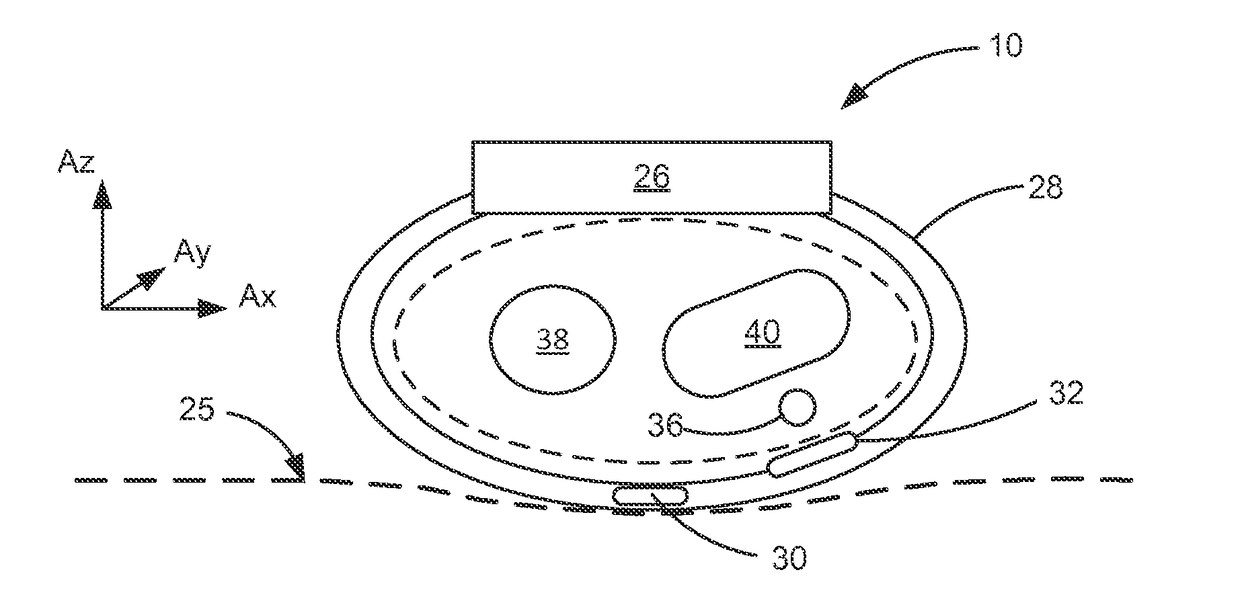
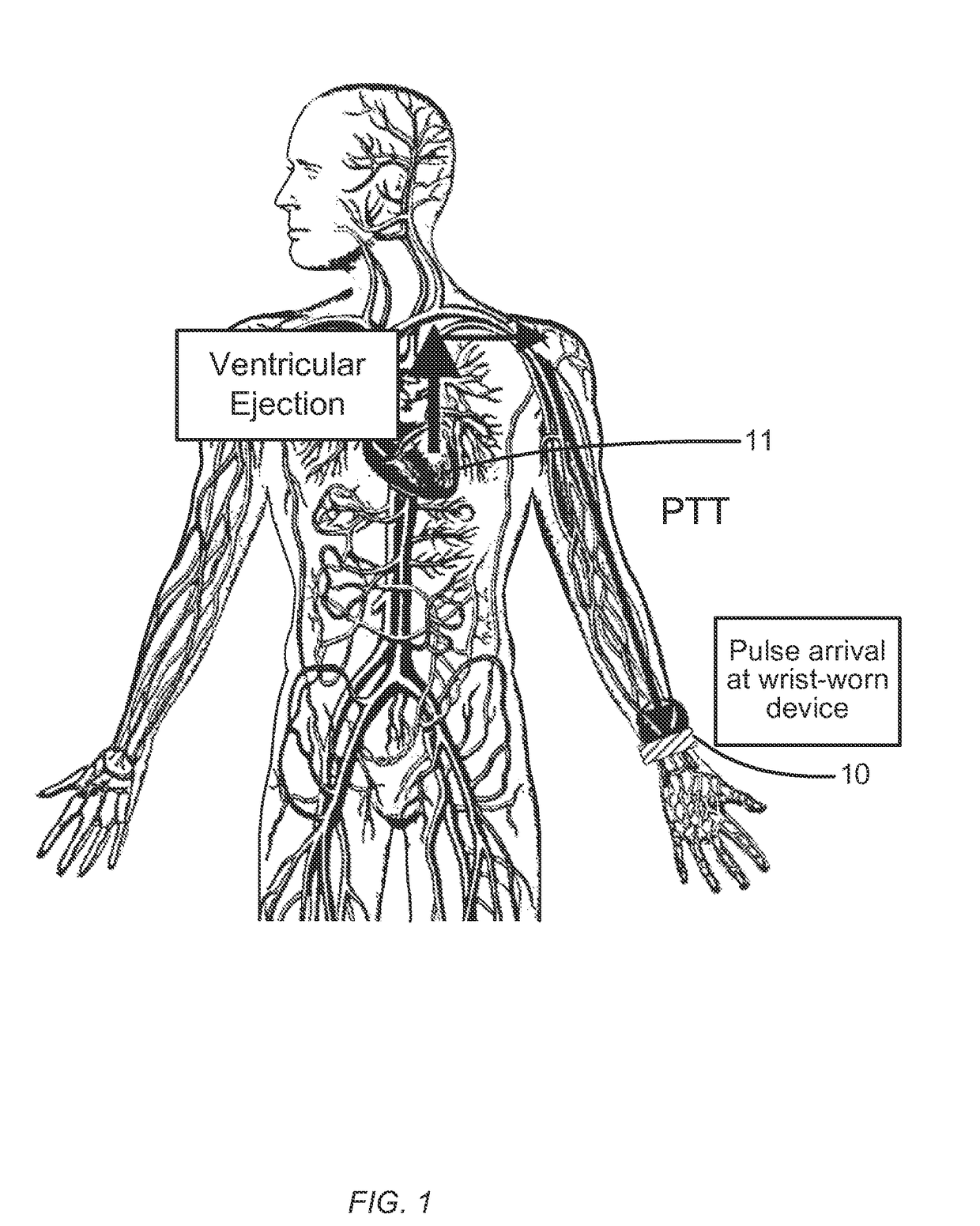
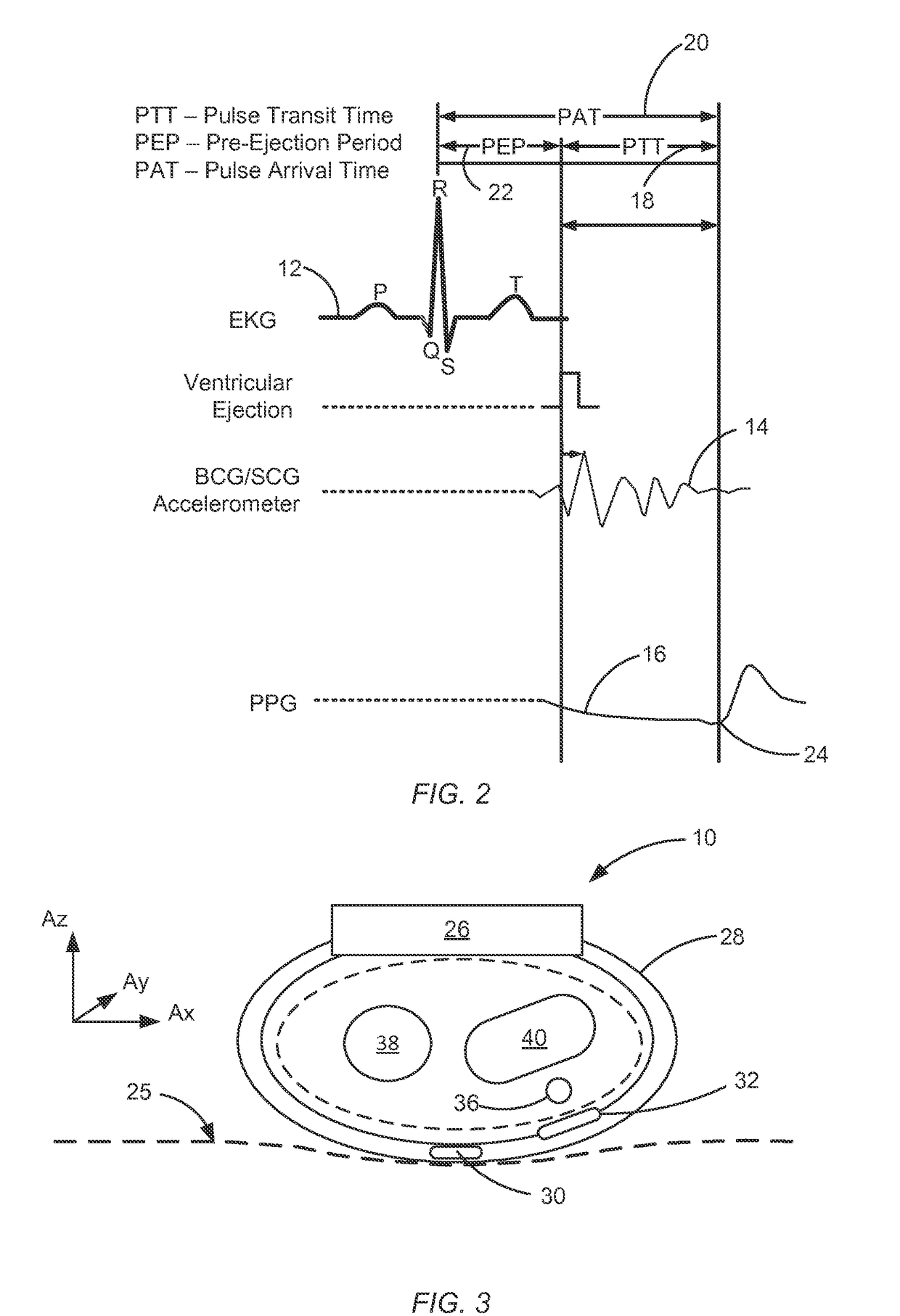
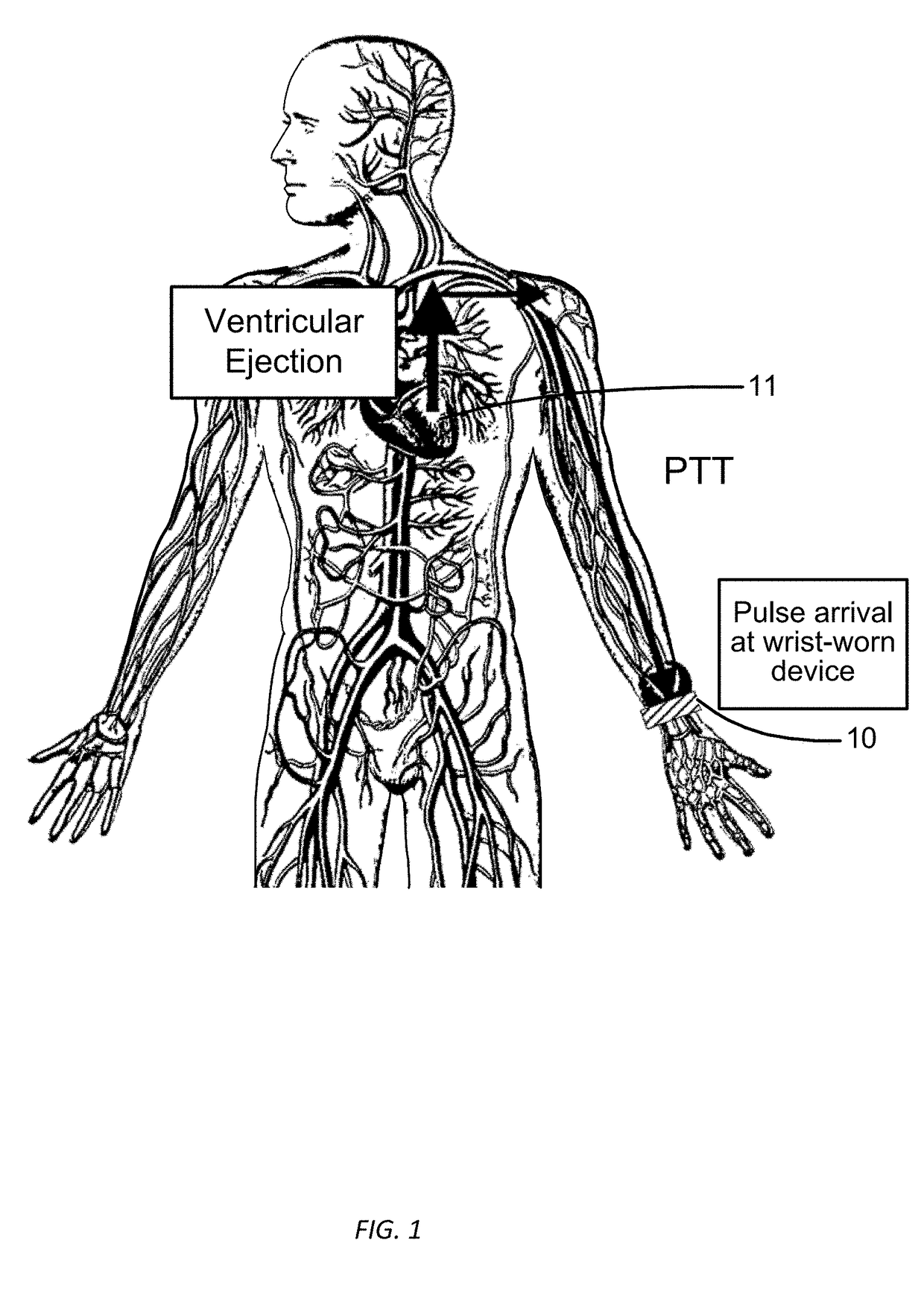
Wrist worn accelerometer for pulse transit time (PTT) measurements of blood pressure
ActiveUS20170281024A1Cancel noiseEasy to detectEvaluation of blood vesselsSensorsAccelerometerPulse pressure
Wrist-worn devices and related methods measure a pulse transit time non-invasively and calculate a blood pressure value using the pulse transit time. A wrist-worn device includes an accelerometer, a photo-plethysmogram (PPG) or a pulse pressure sensor, and a controller. The PPG or the pulse pressure sensor coupled to the wrist-worn device for detecting an arrival of a blood pressure pulse at the user's wrist. The controller is configured to process output signals from the accelerometer to detect when the blood pressure pulse is propagated from the left ventricle of the user's heart, process a signal from the PPG or the pulse pressure sensor to detect when the blood pressure pulse arrives at the wrist, calculate a pulse transit time (PTT) for propagation of the blood pressure pulse from the left ventricle to the wrist, and generate one or more blood pressure values for the user based on the PTT.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method and apparatus for continuously measuring blood pressure
InactiveCN1849998AExclude positiveEliminate distractionsEvaluation of blood vesselsSensorsPersonalizationCardiac cycle
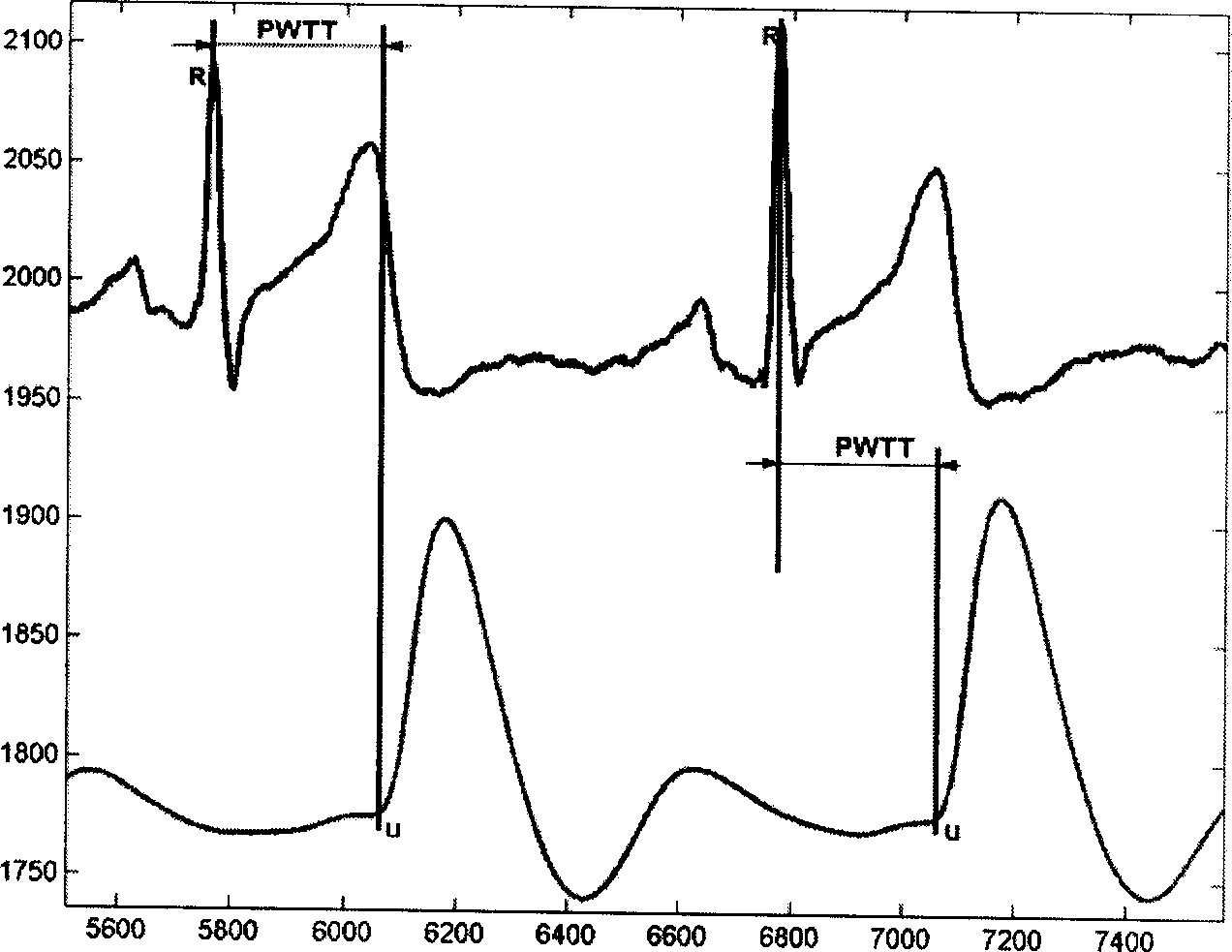
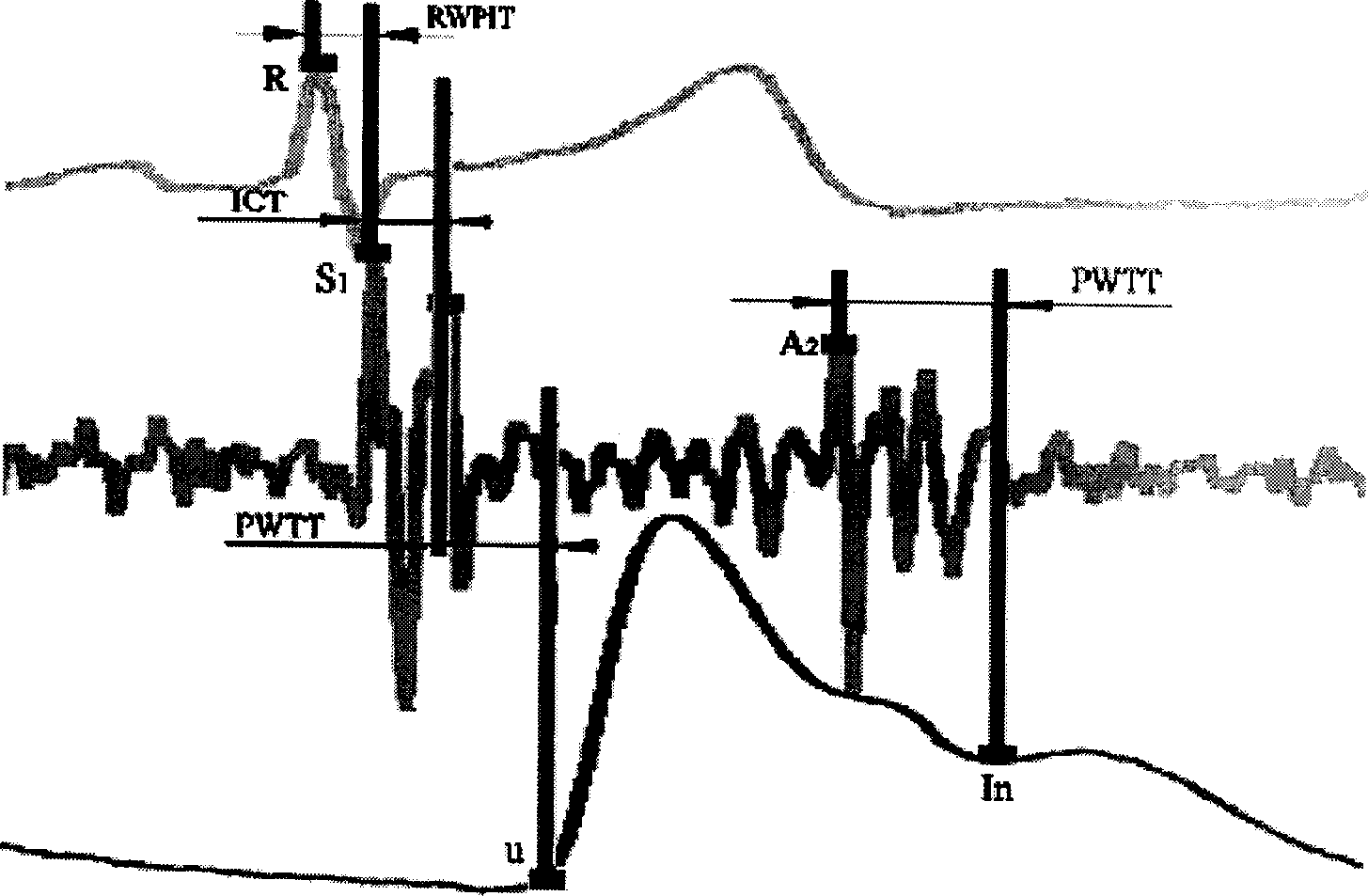
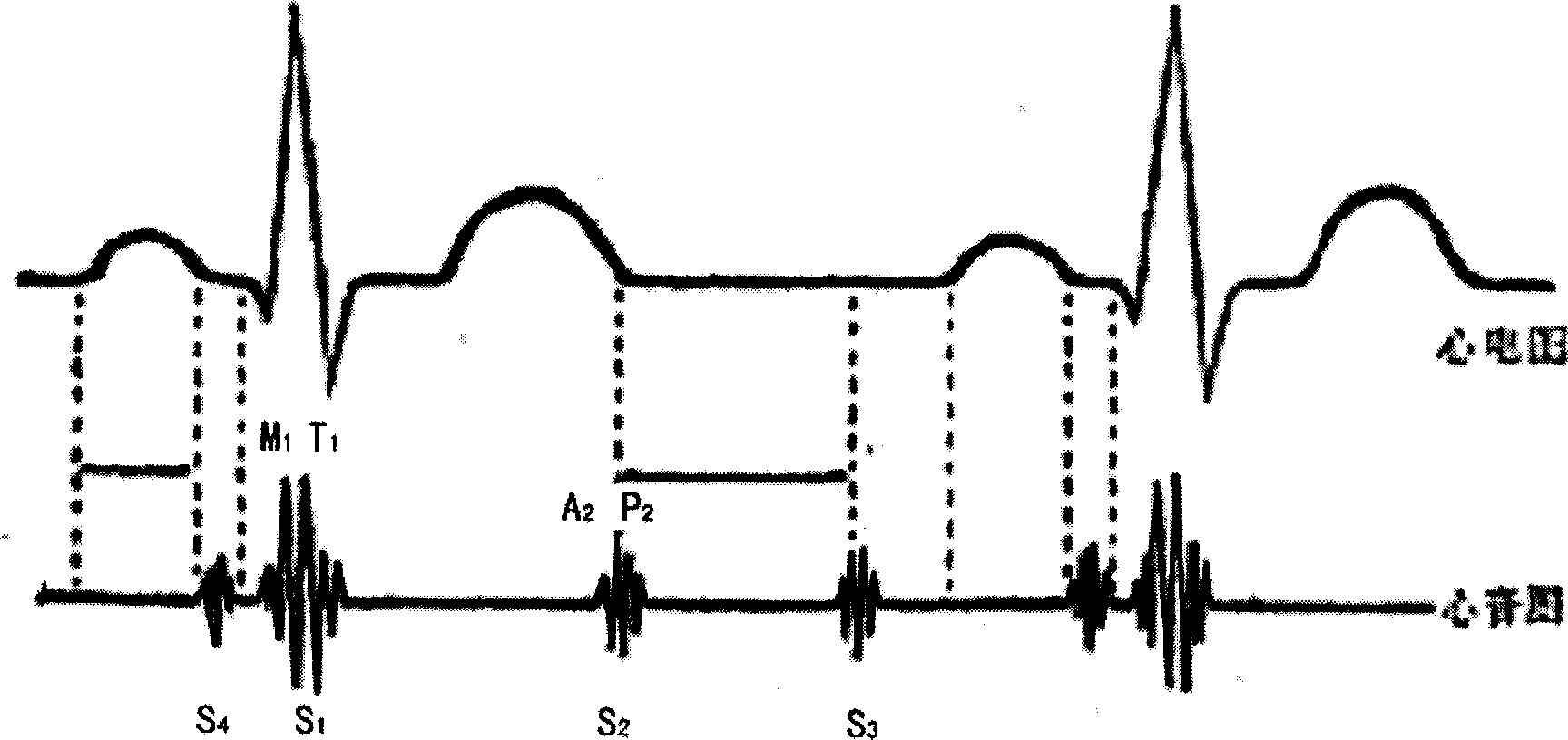
The present invention relates to a method for continuously measuring blood pressure and its equipment. Said method is characterized by that it creates a regression equation between pulse wave conduction time and arterial pressure: BP=a+b*PWTT for measurand person; and utilizes personalization correction technique to define intercept and regression coefficient b of measurand person. Besides, said invention also provides a method for continuously obtaining pulse wave conduction time PWTT by using pulse wave of human body, electrocardiogram signal and phonocardiogram signal and its concrete steps. Said method can raise accuracy for continuously measuring blood pressure, and can be used for measuring head blood pressure.
Owner:AVIATION MEDICINE INST AIR FORCE PLA +1
Speed control of brushless DC motors
InactiveUS7259531B1Convenient speed adjustmentEliminate degradationAC motor controlSynchronous motors startersEngineeringControl circuit
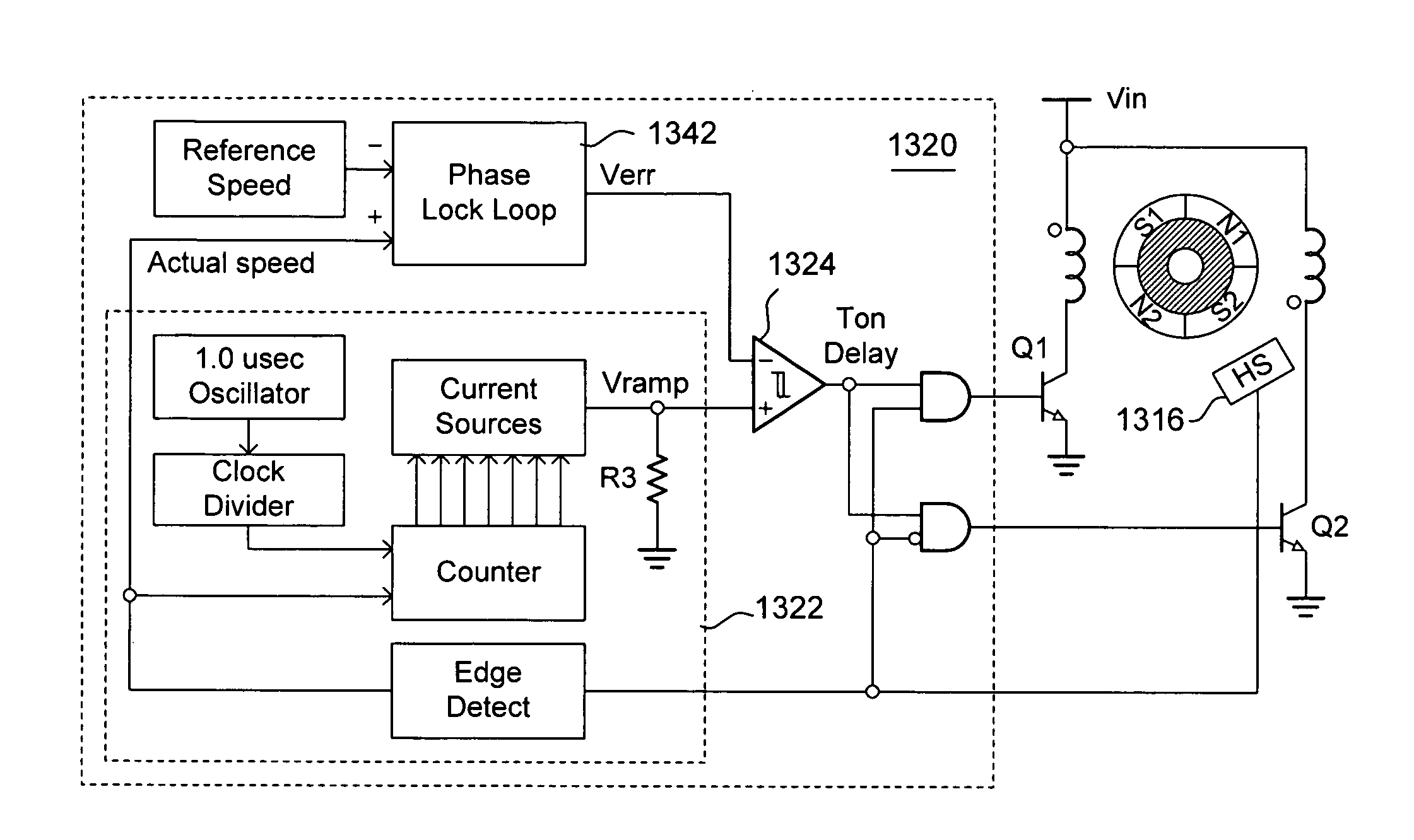
The speed control apparatus comprises a plurality of Hall sensors, a plurality of switches, a turn-on control circuit, and a gate drive logic. The Hall sensors are configured to detect magnetic rotor sections of a poly-phase brushless DC motor at different positions. The switches apply voltages on a plurality of windings to respectively produce magnetic north or south on stator poles of the poly-phase BLDC motor. The turn-on control circuit generates a conduction time reduction after each output transition of the Hall sensors. The gate drive logic separately turns on or turns off the switches according to different output transitions of the Hall sensors to respectively apply voltages on the windings with the conduction time reduction.
Owner:GREEN MARK TECH
Electrical coupling of pulse transit time (PTT) measurement system to heart for blood pressure measurment
ActiveUS20170340219A1Reduce usageElectrocardiographyEvaluation of blood vesselsCouplingMean transit time
Wrist-worn devices and related methods measure a pulse transit time non-invasively and calculate a blood pressure value using the pulse transit time. A wrist-worn device include a wrist-worn elongate band, at least four EKG or ICG electrodes coupled to the wrist-worn device for detecting a ventricular ejection of a heart, a photo-plethysmogram (PPG) sensor coupled to the wrist-worn device for detecting arrival of a blood pressure pulse at the user's wrist, and a controller configured to calculate a pulse transit time (PTT) for the blood pressure pulse. The controller calculates one or more blood pressure values for the user based on the PTT.
Owner:APPLE INC
Research of dynamic blood pressure detection and calibration method of radial artery
InactiveCN104257371AImprove comfortSmall changes in body positionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsOscillometryEcg signal
The invention relates to a dynamic blood pressure detection and calibration method of a radial artery. The method comprises the following steps: measuring a blood pressure value BP1 to perform first calibration by using oscillography; measuring a blood pressure value BP2 to perform second calibration by using correlation of an electrocardiosignal, a pulse wave signal and human arterial pressure; finally performing continuous monitoring of blood pressure by using the linear relation between pulse wave transmission time difference PWT of two different parts on a wrist and the human arterial blood pressure which are measured at the same time.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
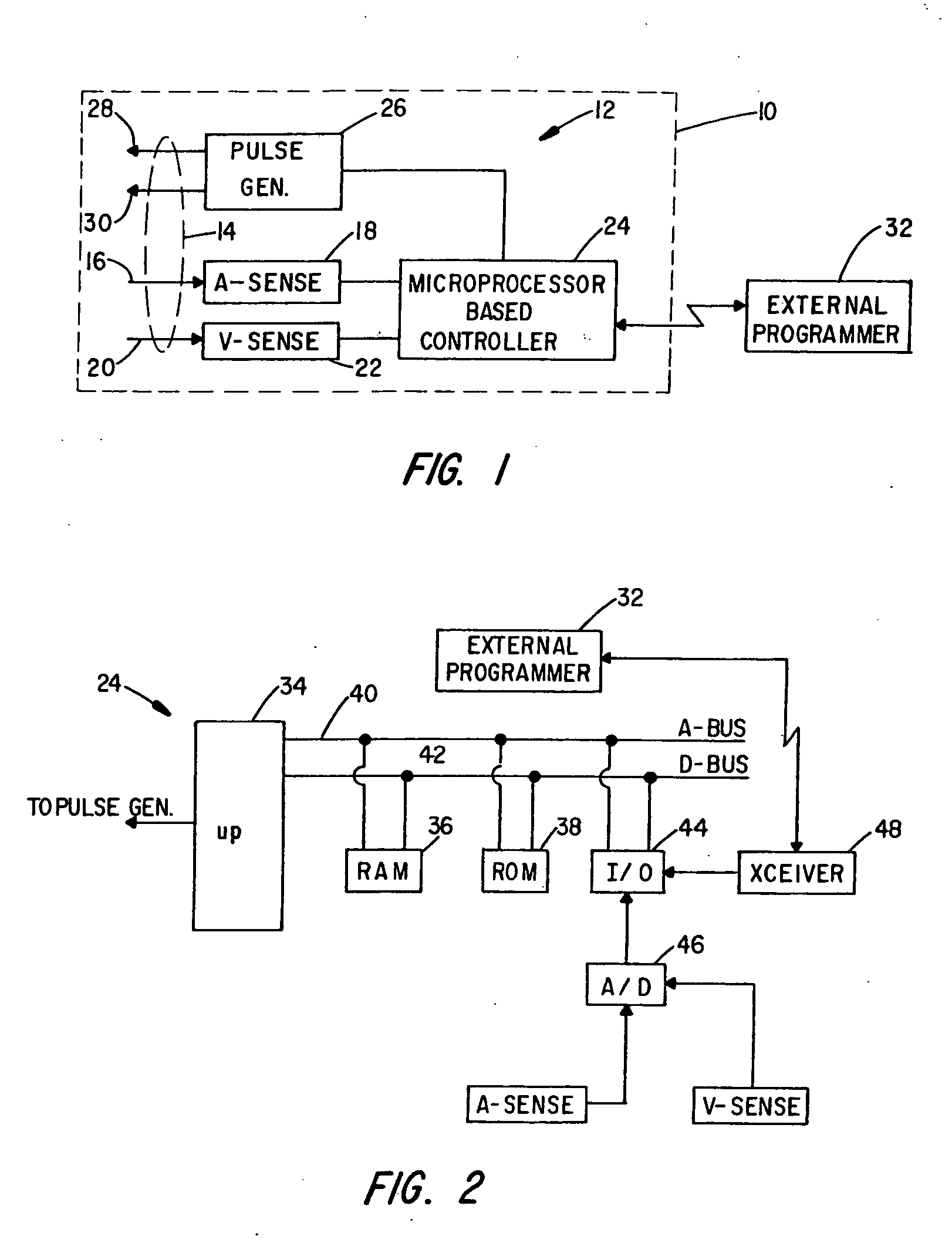
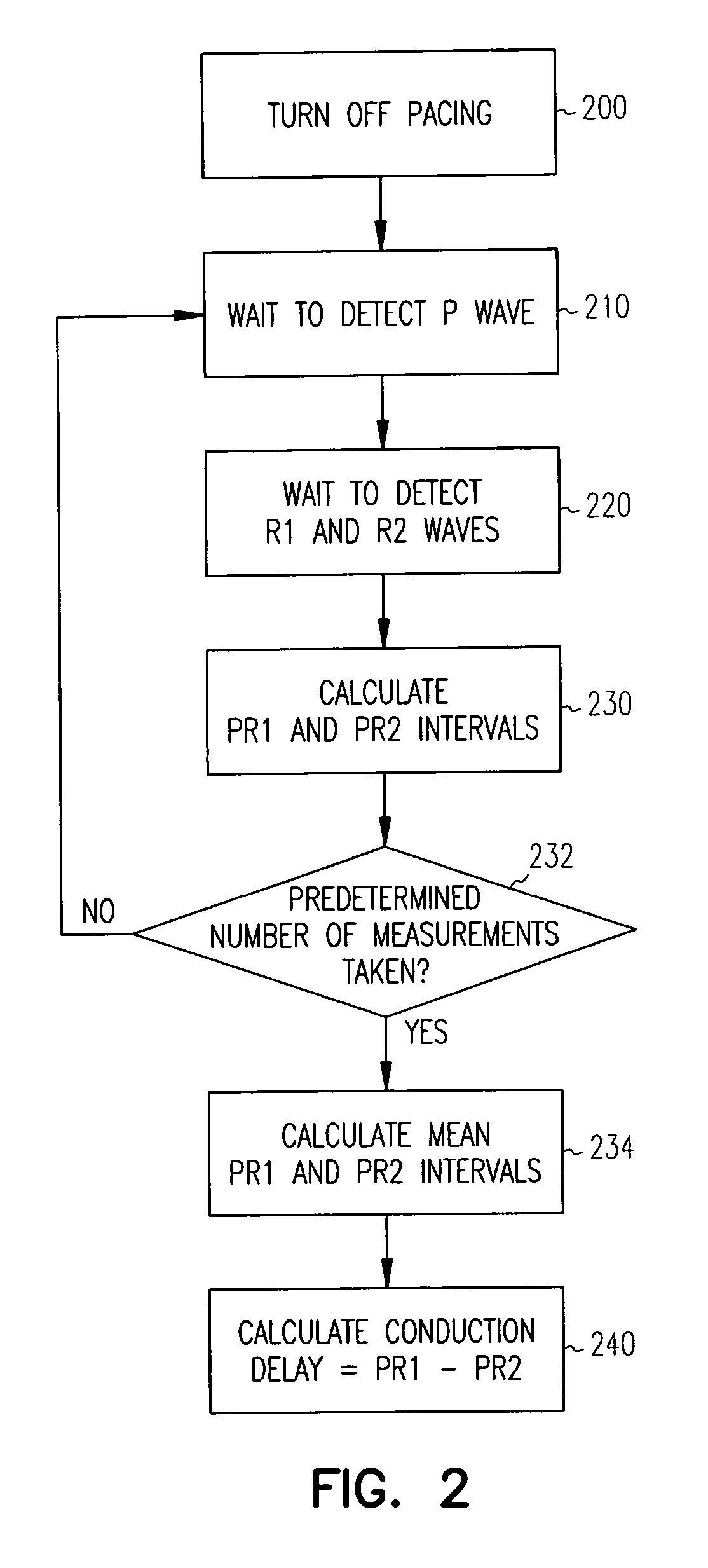
Ventricular conduction delay trending system and method
A method and system for ascertaining the condition of the heart's conduction system in a patient treated for congestive heart failure with pacing therapy. In accordance with the invention, changes in ventricular activation patterns are monitored over time in order to detect changes in the heart's conduction system that may occur due to physiological regeneration of conduction pathways. The activation patterns are reflected by electrogram signals detected from different ventricular locations. By measuring the difference in conduction times of an excitation impulse traveling from the AV node to the different ventricular locations, a parameter representative of the heart's conduction system is obtained that may be used to adjust the pacing therapy in accordance therewith.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
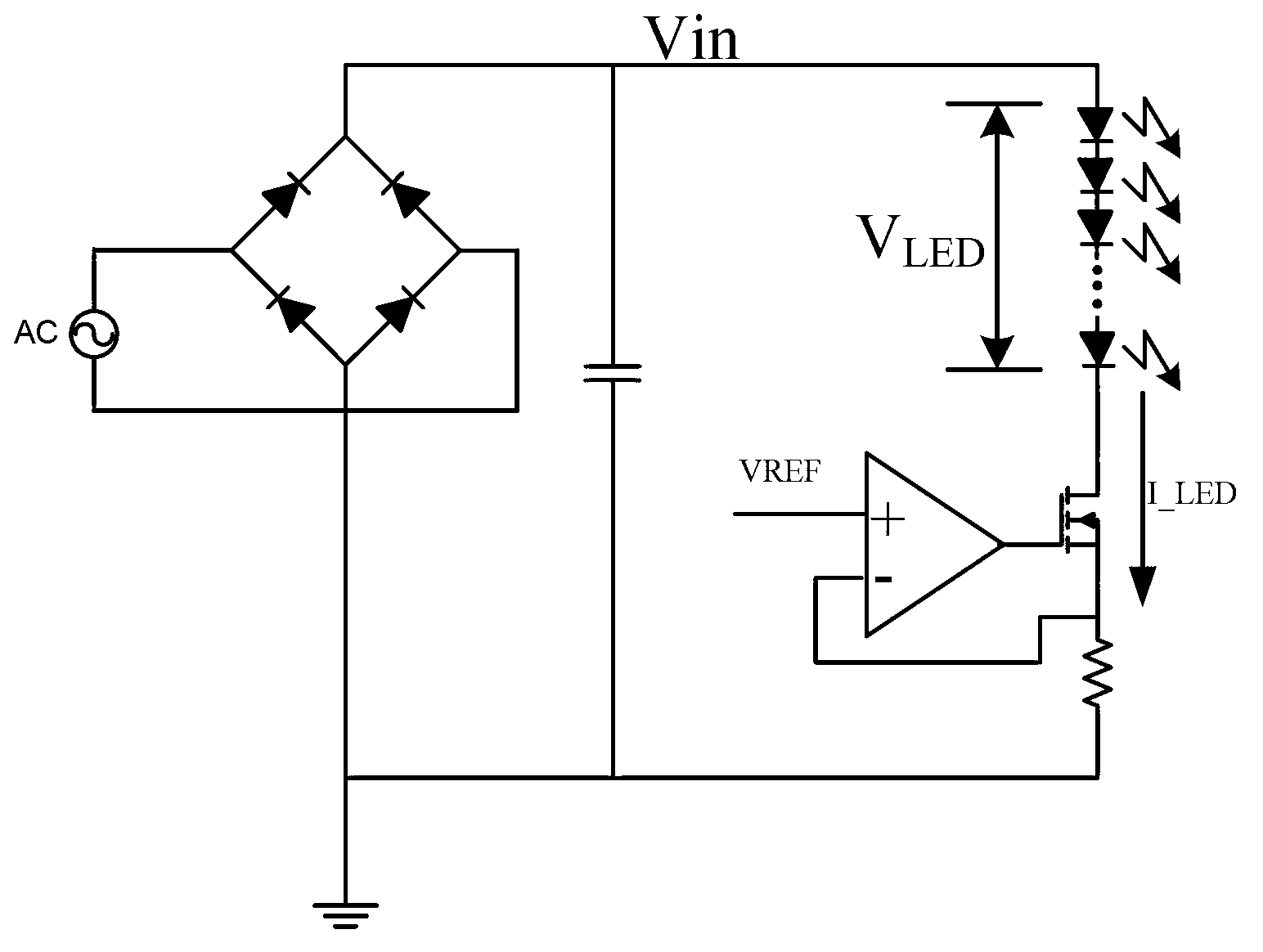
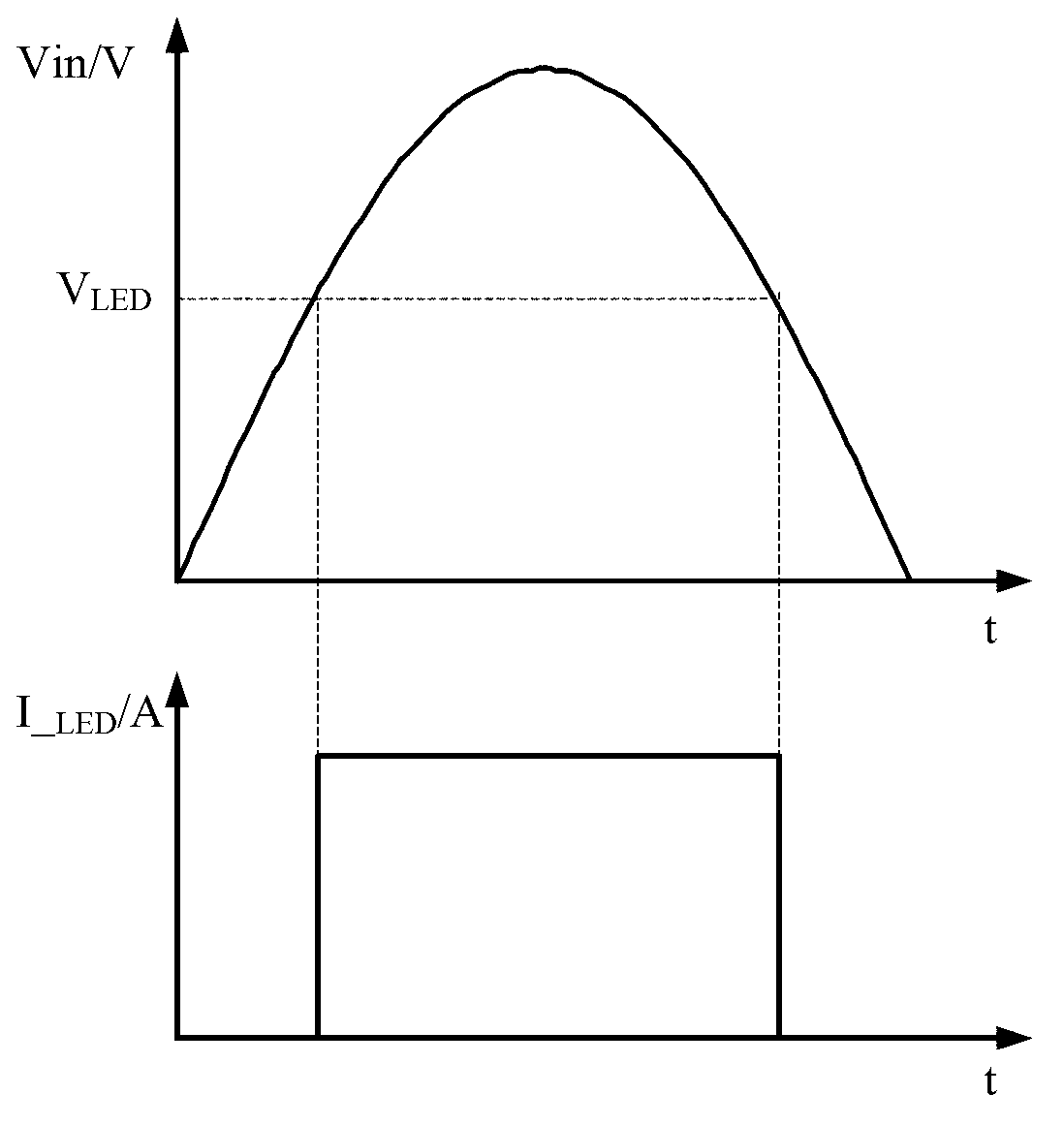
LED driver with adjustable conduction time
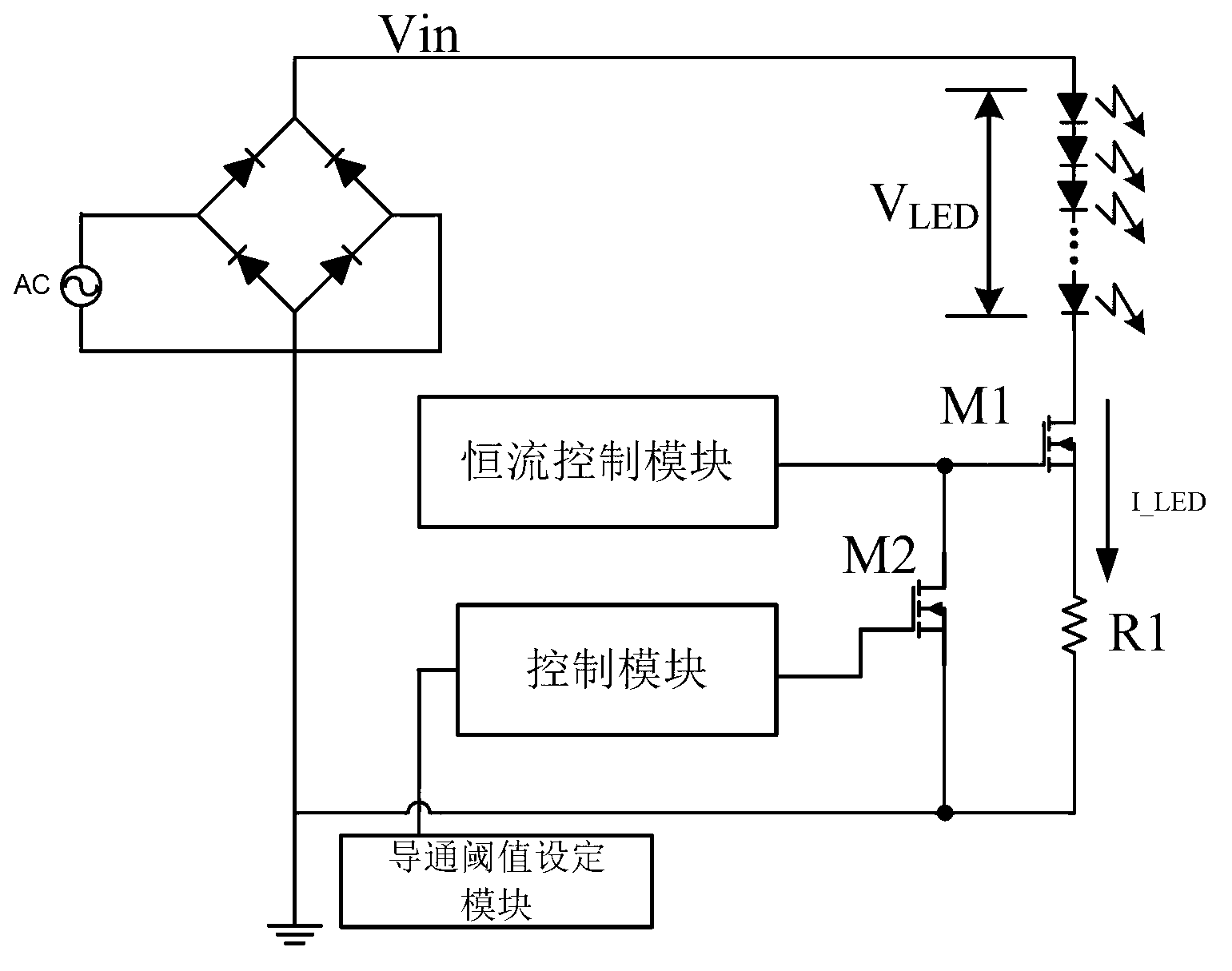
ActiveCN103260302AAvoid large pressure differenceImprove efficiencyElectric light circuit arrangementEnergy saving control techniquesLinear controlValue set
The invention relates to an LED driver with an adjustable conduction time. The LED driver with the adjustable conduction time comprises one way or multiple ways of LEDs, a conductive threshold value setting module and a controlling module, wherein the LEDs are conducted when power supply voltage rises to LED conduction voltage, the conductive threshold value setting module is used for setting the LED conductive time, and the controlling module is used for disconnecting the one way or the multiple ways of LEDs when the power supply voltage rises to exceed an LED conduction voltage setting threshold value, and connecting the one way or the multiple ways of LEDs when the power supply voltage reduces to exceed the LED conduction voltage setting threshold value according to the conduction time of the LEDs, wherein the setting threshold value is related to the LED conduction threshold value. Due to comparison of an input voltage and an LED voltage drop, conduction time of the LEDs is controlled, the problem that voltage differences of the input voltage and the LED voltage are too large is solved, efficiency of a linear LED driving circuit is improved, circuit heating value is reduced, and application reliability is enhanced. In addition, the LED driver with the adjustable conduction time flexibly achieves the compromising design of high efficiency of the linear controlling scheme and a PF value through controlling the LED conduction time.
Owner:MAXIC TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION
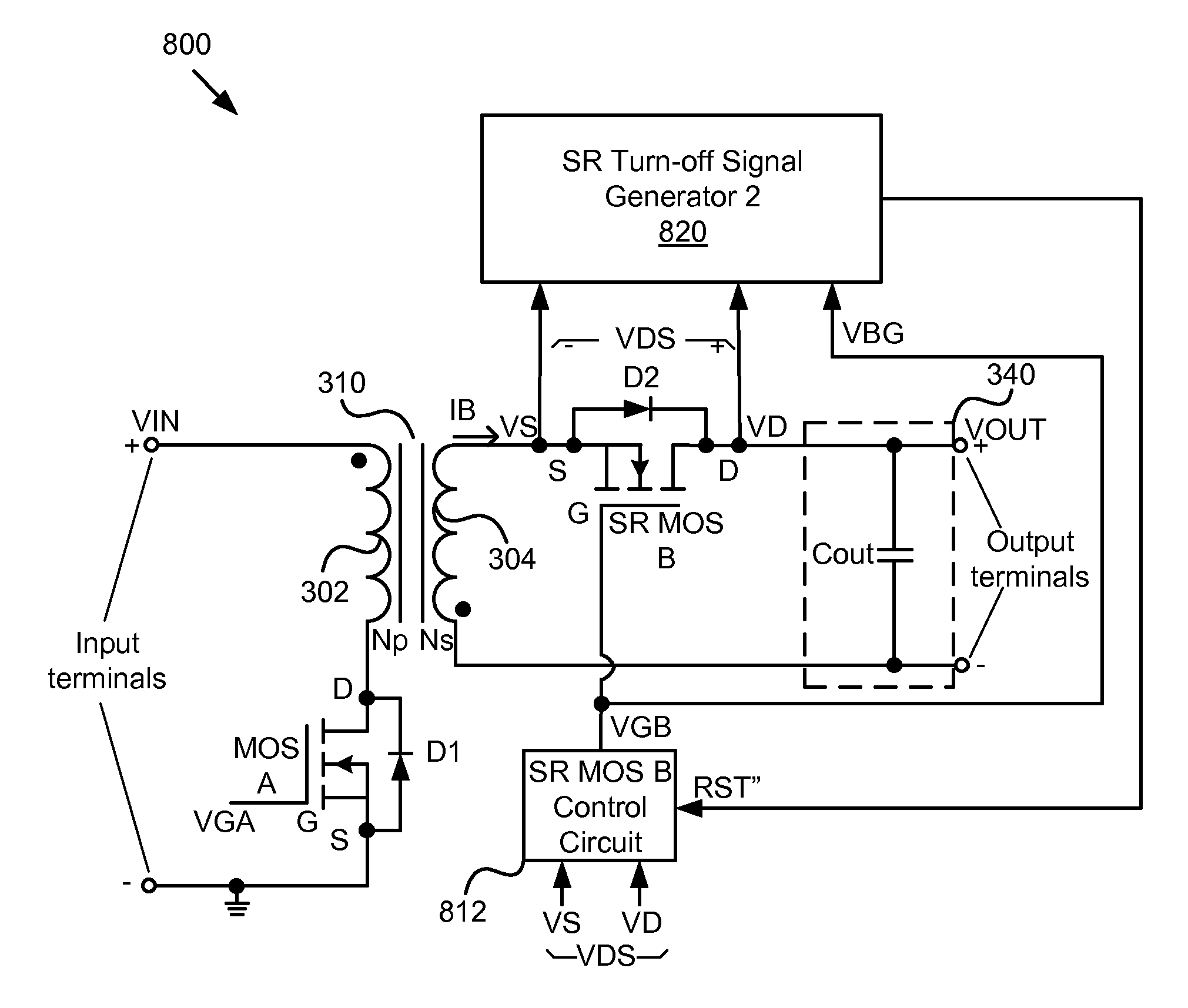
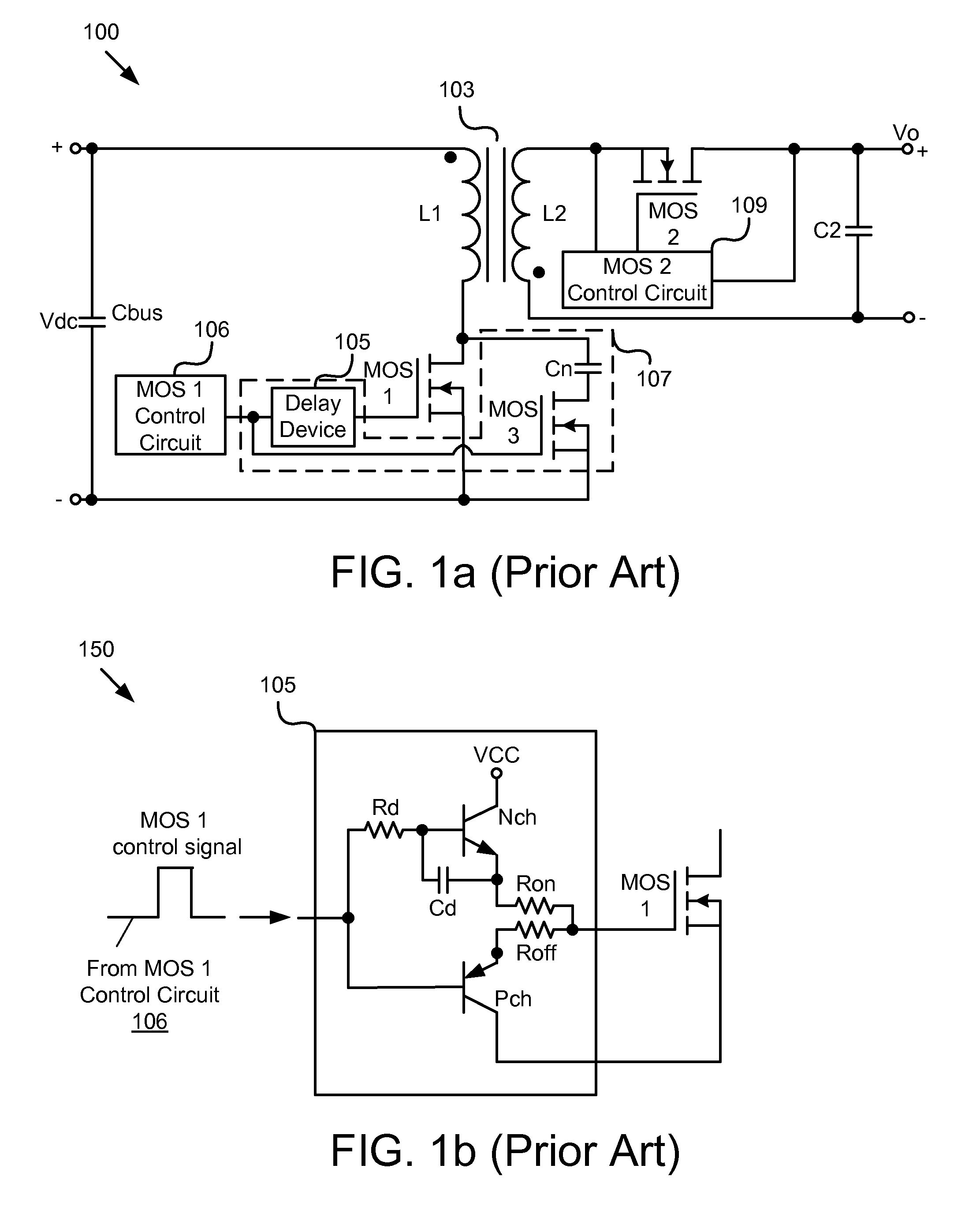
Body diode conduction optimization in mosfet synchronous rectifier
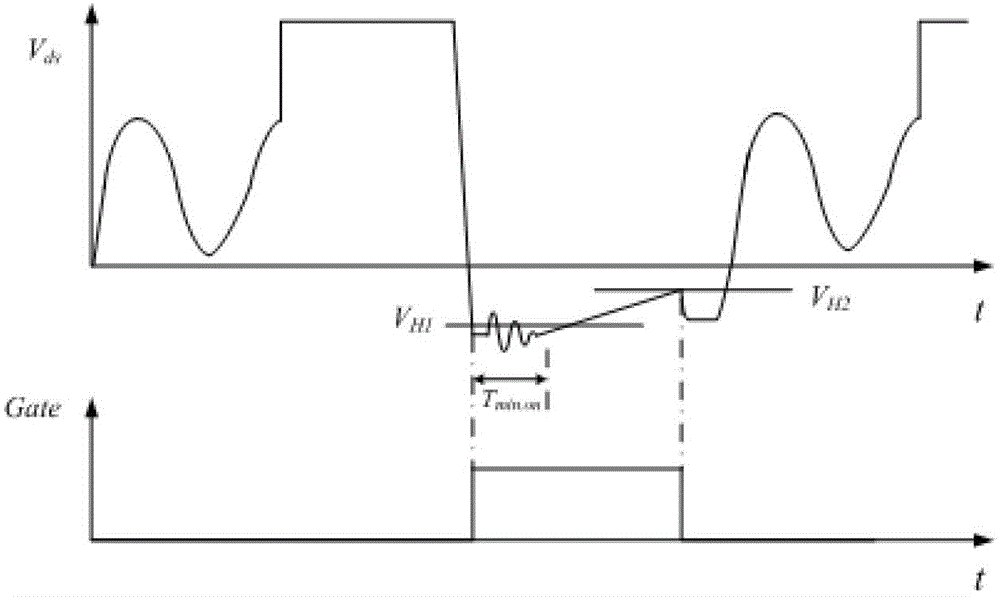
To maximize power efficiency, dead time between “on” times of a synchronous rectifier (“SR”) MOSFET switch and a main switch for CCM operation in particular in isolated and non-isolated self-driven synchronous DC-DC converters needs to be optimized. To accomplish that objective, the latest conduction time t of a body diode of the SR MOSFET following conduction thereof is determined, compared with a selected fixed optimum period T1, and incrementally or decrementally adjusted in a subsequent switching cycle while t is unequal to T1, depending on whether t is shorter or longer than T1, so that t eventually is made substantially equal to T1 in length. This process is to be repeated continuously.
Owner:JOULWATT TECH INC LTD
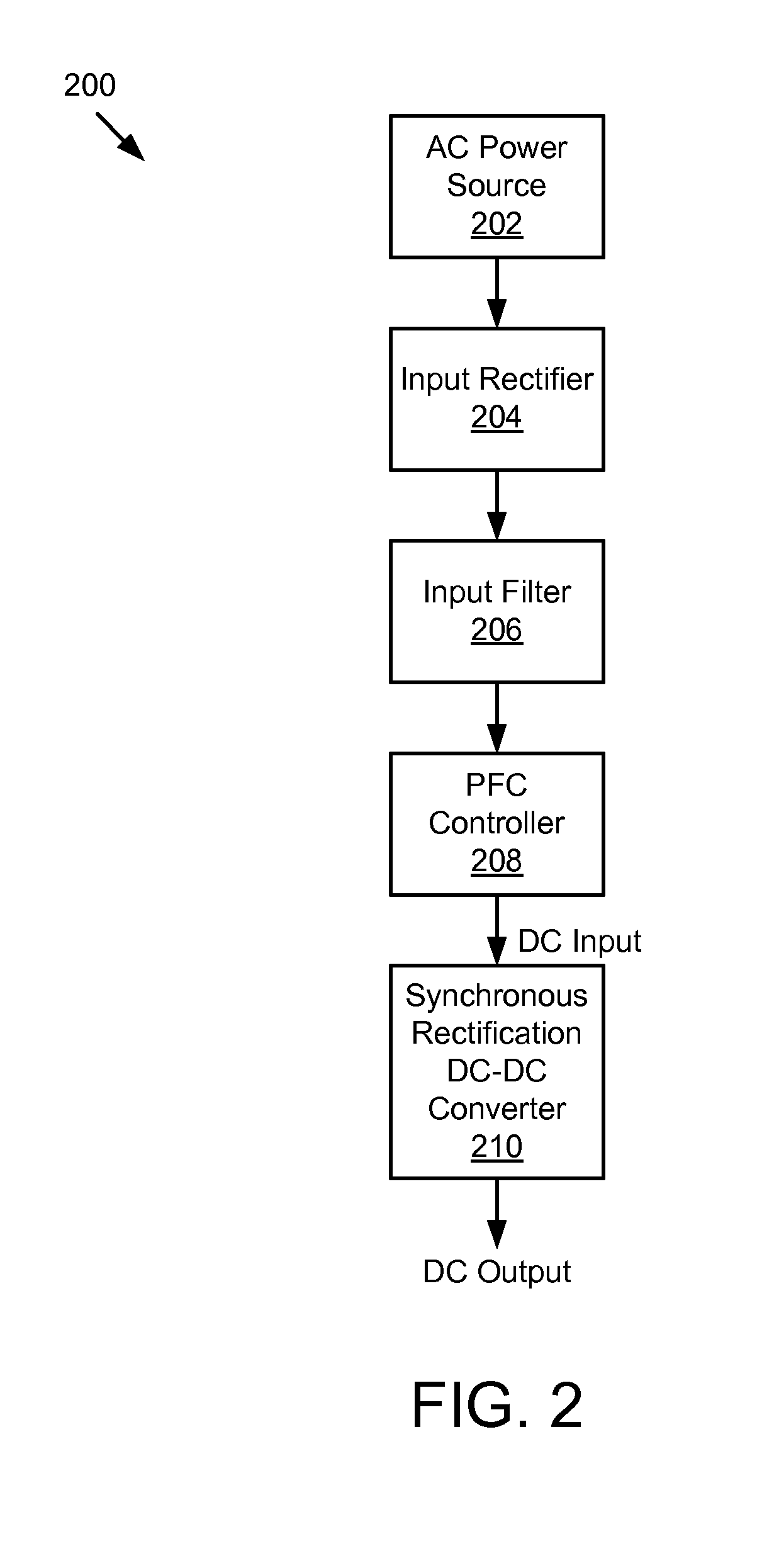
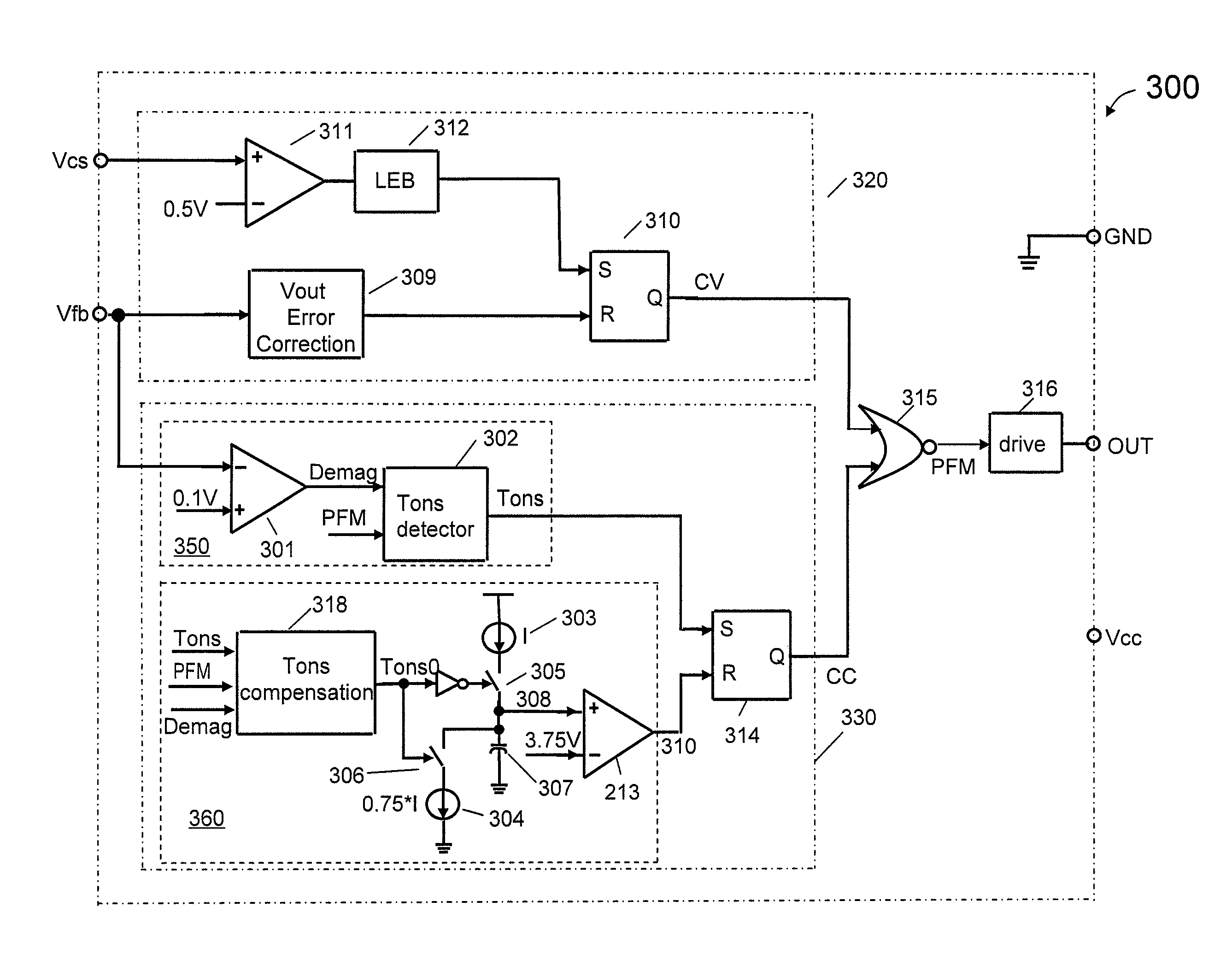
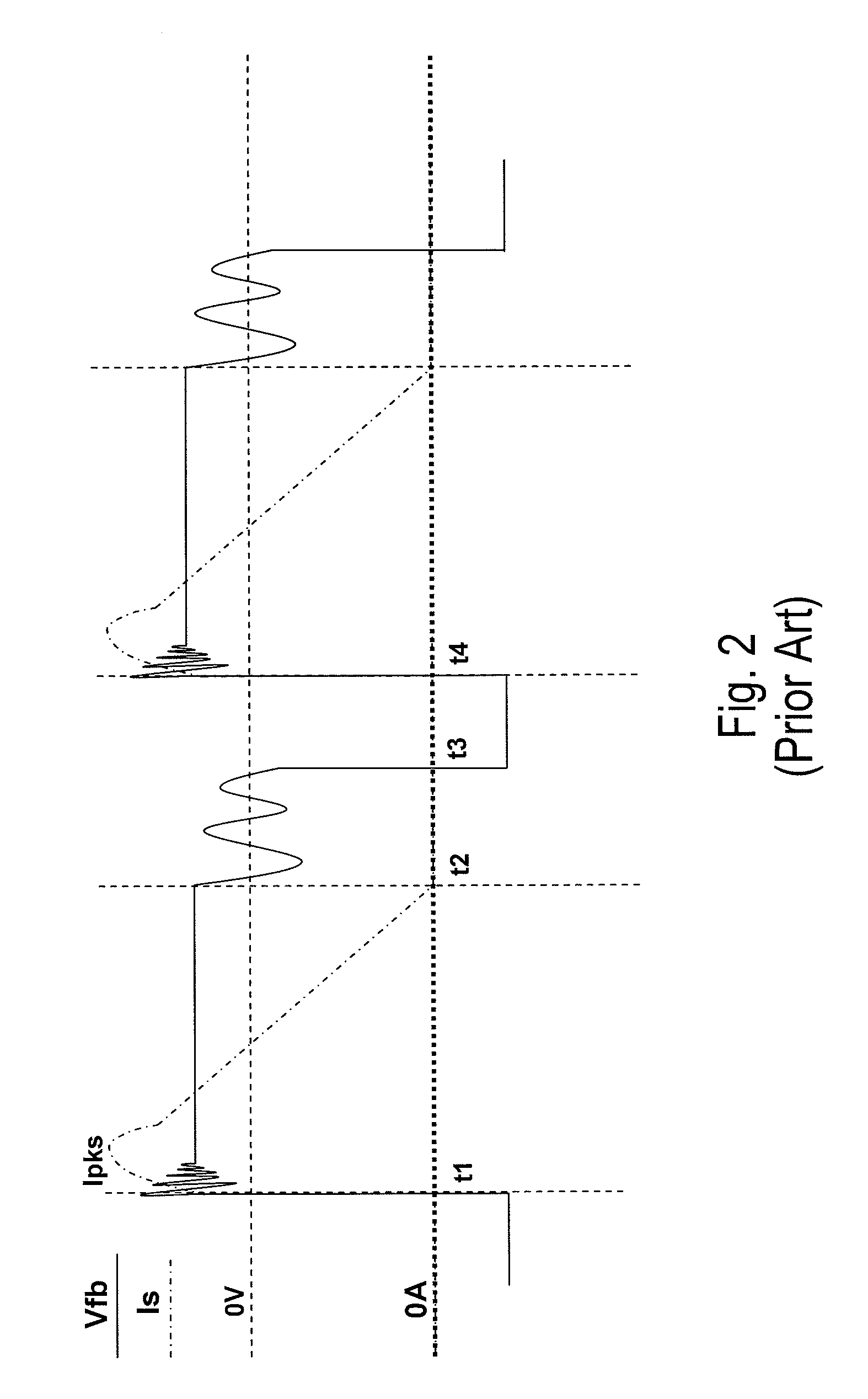
Method and apparatus for controlling a constant current output in a switching mode power supply
ActiveUS8213203B2Reduces and eliminates errorAc-dc conversionDc-dc conversionControl signalEngineering
A controller for providing a constant output current control signal in a switched mode power supply (SMPS) includes a conduction time compensation circuit that is configured to produce a compensated conduction time interval signal that includes compensation for a ringing waveform of a feedback signal. The compensated signal reflects more accurately the actual conductive time of a rectifying diode in a secondary winding of the switched mode power supply. In one embodiment, the compensated conduction time interval signal is used to generate a fixed ratio between the conduction time and the non-conduction time of the rectifying diode. In another embodiment, the controller also provides a constant voltage control signal.
Owner:BCD SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
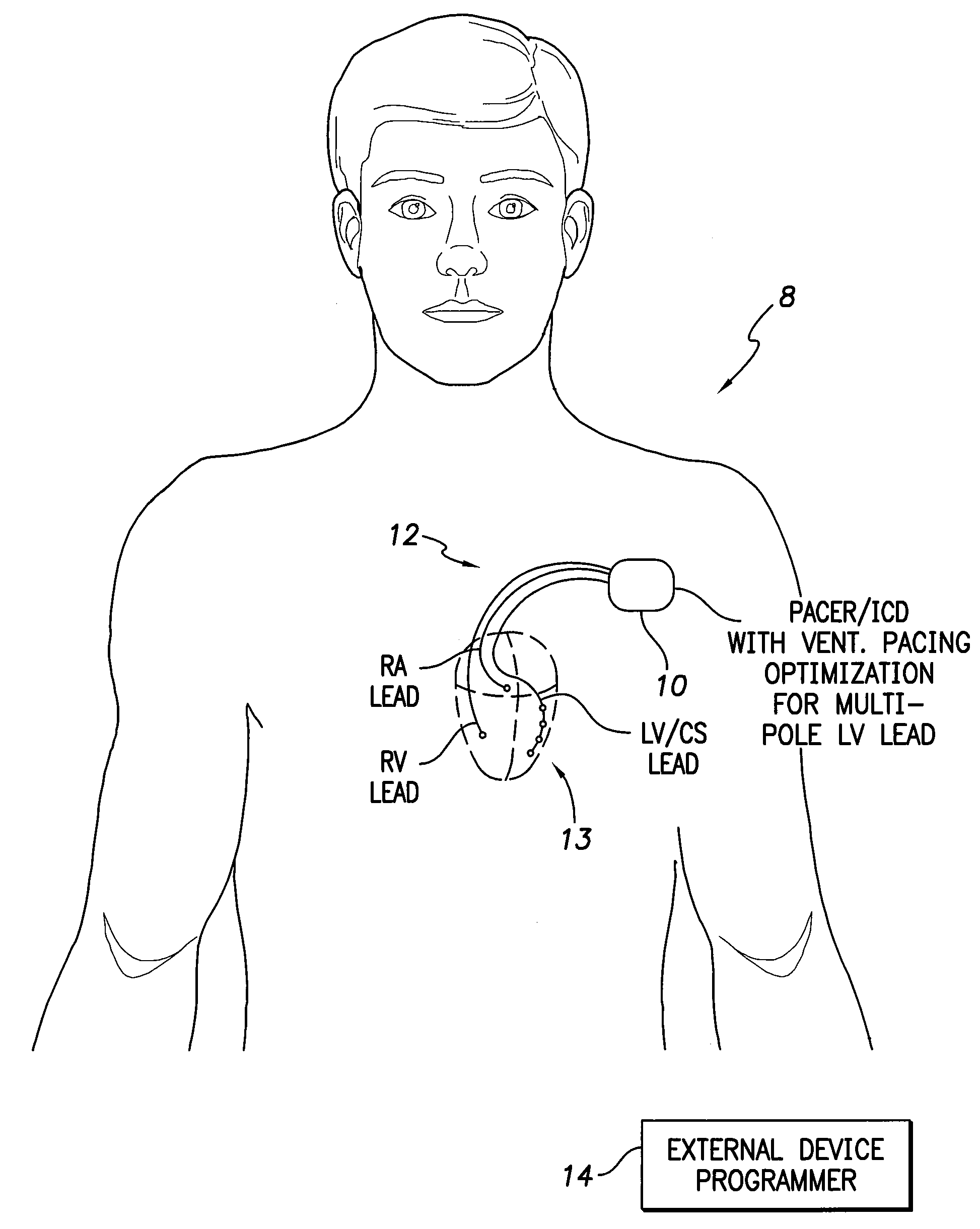
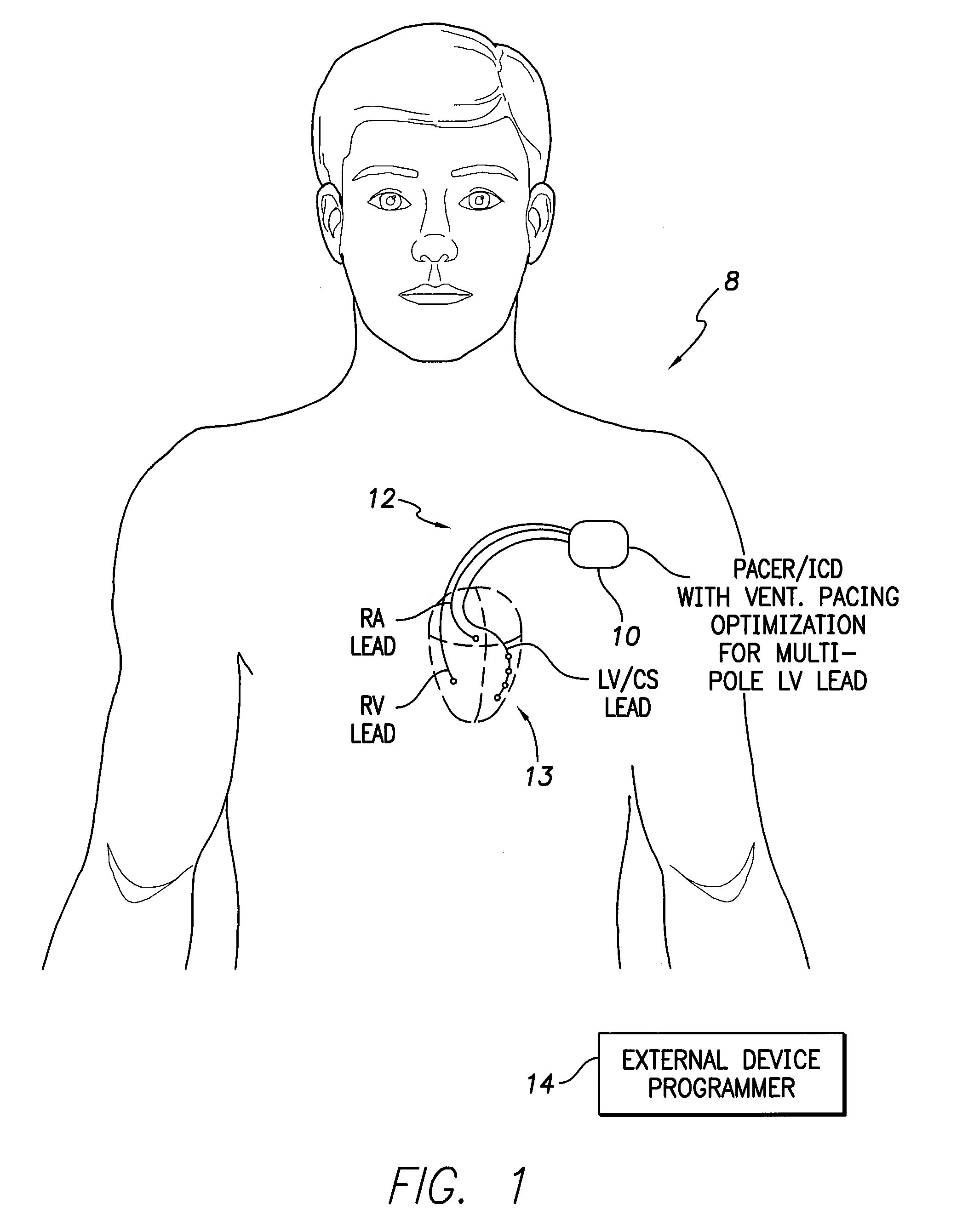
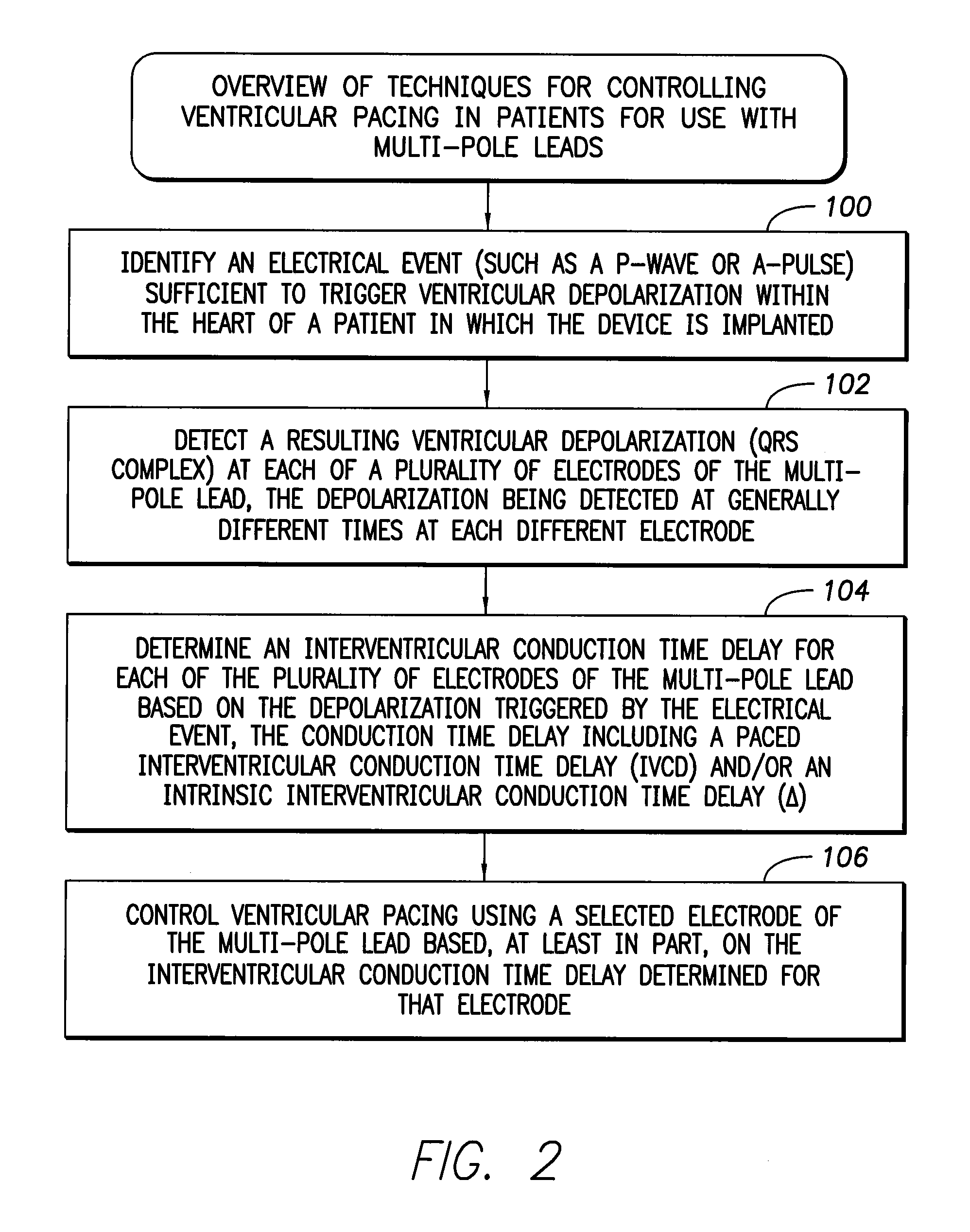
Systems and methods for optimizing ventricular pacing delays for use with multi-pole leads
ActiveUS20110022110A1Quick judgmentShorten test timeHeart stimulatorsLeft ventricular sizeTested time
Techniques are provided for use by implantable medical devices for controlling ventricular pacing using a multi-pole left ventricular (LV) lead. In one example, a single “V sense” test is performed to determine intrinsic interventricular conduction time delays (Δn) between the RV electrode and each of the LV electrodes of the multi-pole lead. Likewise, a single “RV pace” test is performed to determine paced interventricular conduction time delays (IVCD_RLn) between the RV electrode and each of the LV electrodes. A set of “LV pace” tests is then performed to determine paced interventricular conduction time delays (IVCD_LRn) between individual LV electrodes and the RV electrode. Optimal or preferred interventricular pacing delays are determined using the intrinsic interventricular conduction delay (Δn) values and a set of interventricular correction terms (εn) determined from the results of the RV pace test and the set of LV pace tests. With these techniques, overall test time can be reduced.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
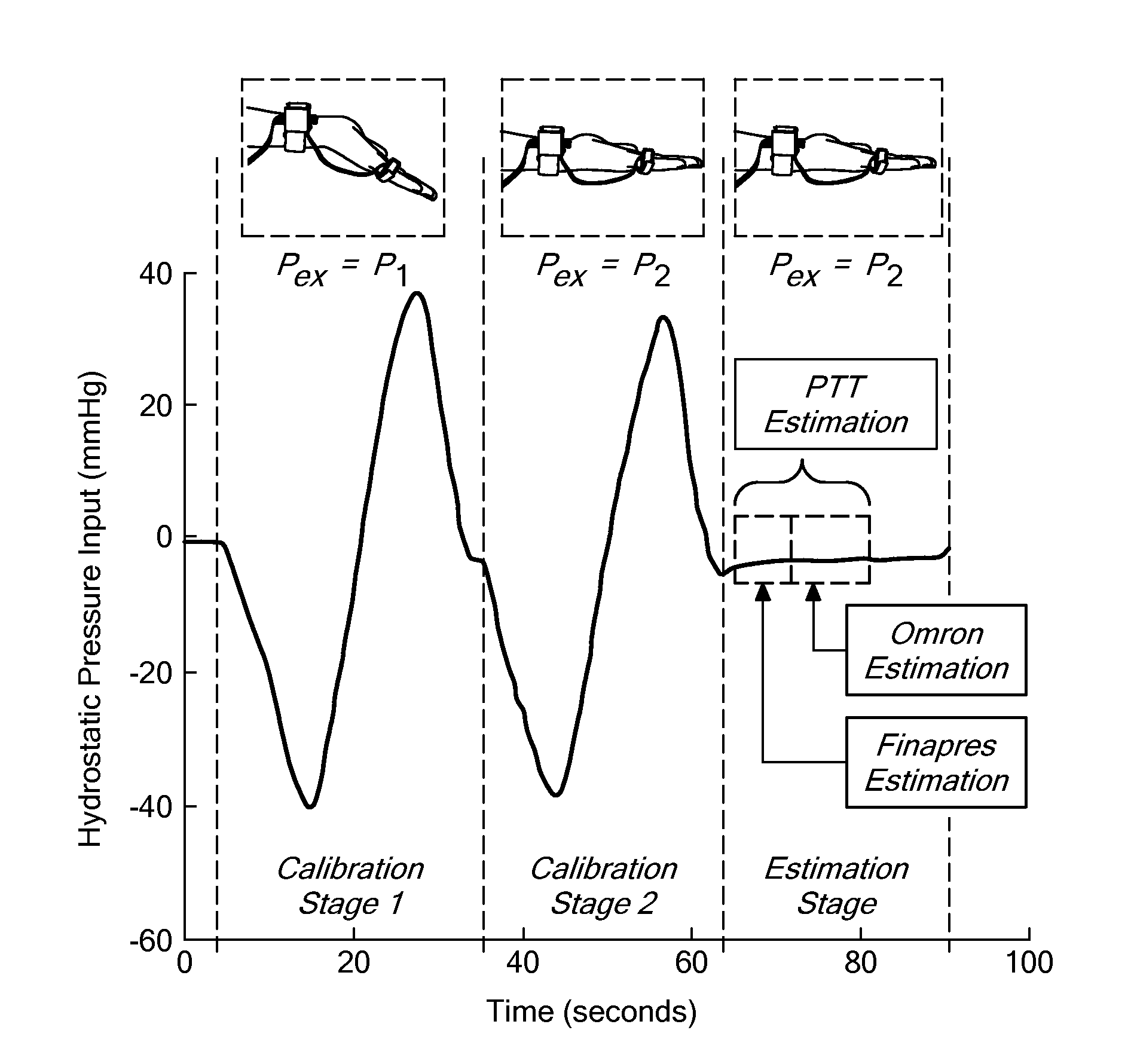
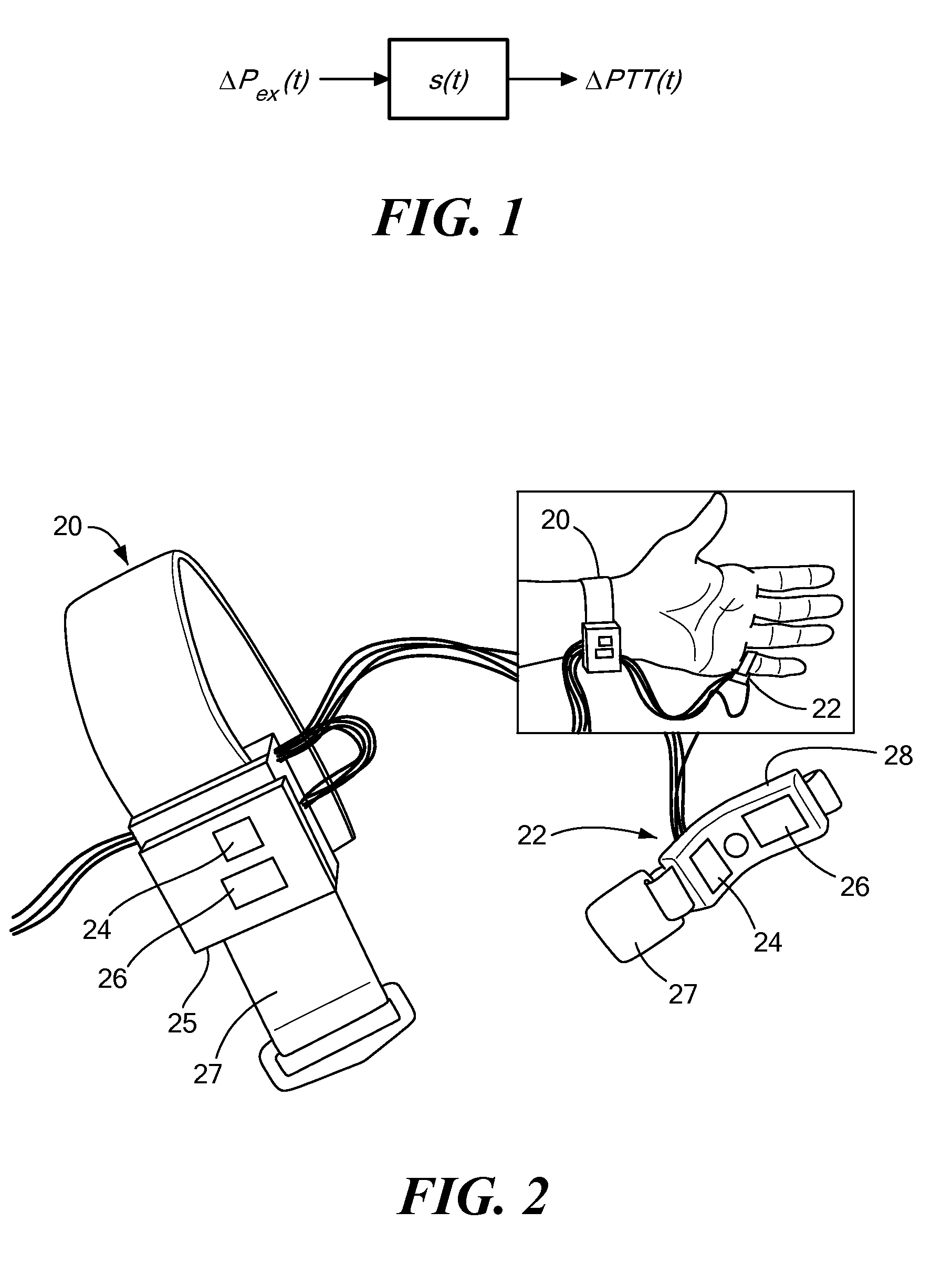
Calibration of pulse transit time measurements to arterial blood pressure using external arterial pressure applied along the pulse transit path
An apparatus and methods for adaptive and autonomous calibration of pulse transit time measurements to obtain arterial blood pressure using arterial pressure variation. The apparatus and methods give pulse transit time (PTT) devices an ability to self-calibrate. The methods apply a distributed model with lumped parameters, and may be implemented, for example, using pulse transit time measurements derived from a wearable photoplethysmograph (PPG) sensor architecture with an intervening pressurizing mechanism.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Dc-dc converters
ActiveUS20110050185A1Easy to controlTransistorEfficient power electronics conversionCurrent loadCurrent loop control
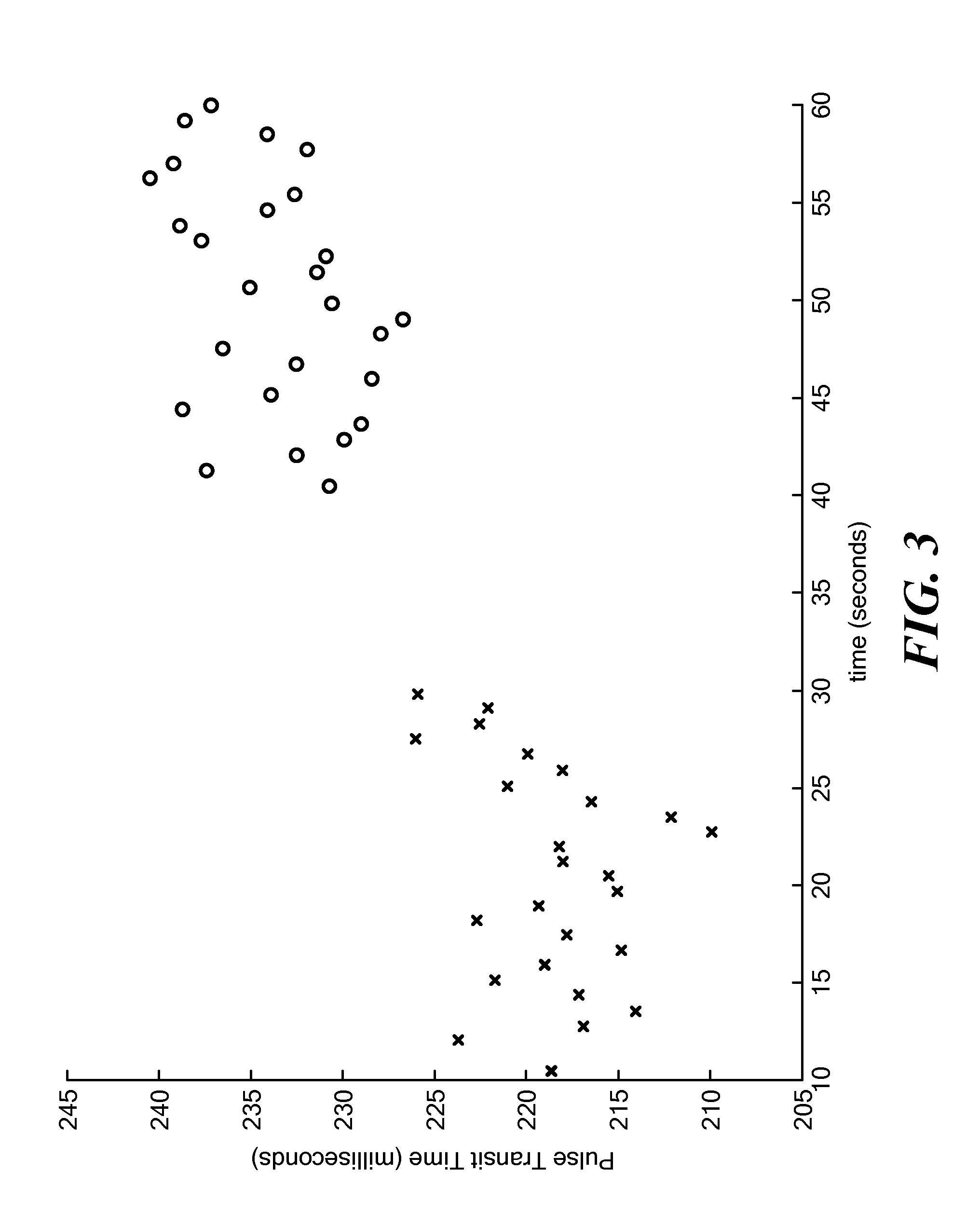
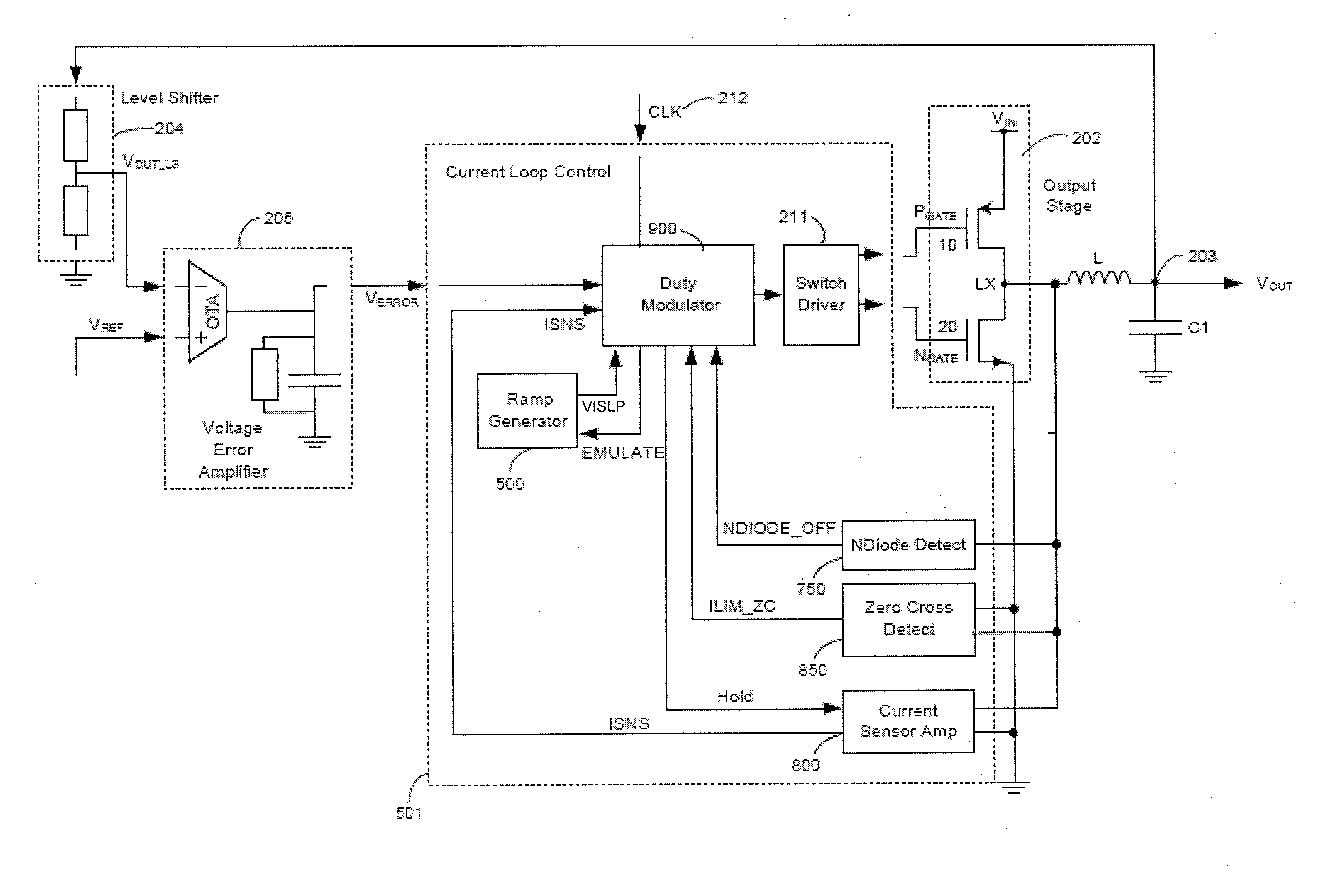
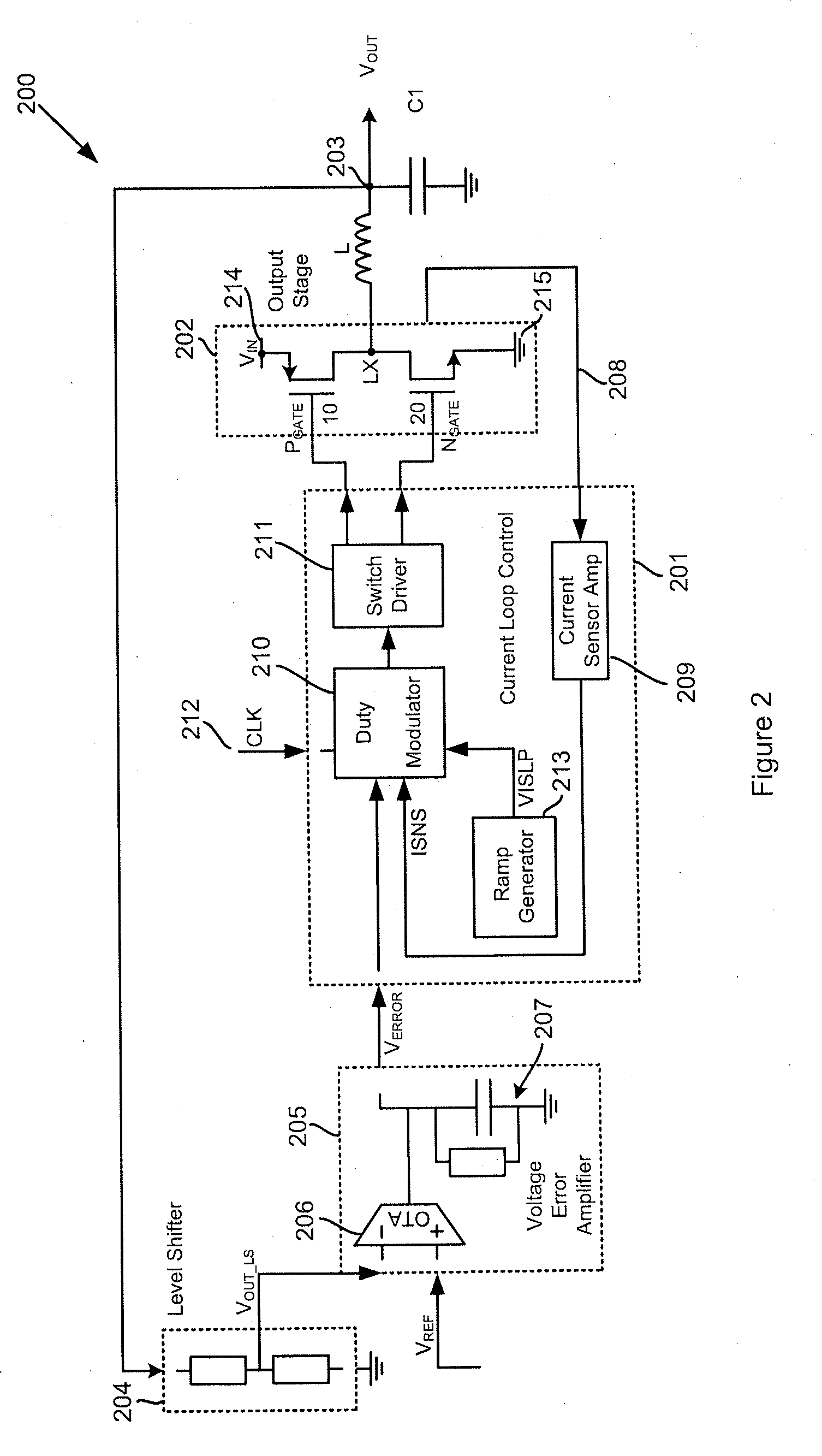
Methods and apparatus for control of DC-DC converters, especially in valley current mode. The DC-DC converter is operable so that a low side supply switch may be turned off, before the high side supply switch is turned on. During the period when both switches are off the current loop control remains active and the change in inductor (L) current is emulated. One embodiment uses a current sensor for lossless current sensing and emulates the change in inductor current by holding the value of the output of the current sensor (ISNS) at the time that the low side switch turns off and adding an emulated ramp signal (VISLP) until the inductor current reaches zero. Embodiment employing a pulse-skip mode of operation based on a minimum conduction time are also disclosed. The invention enables a seamless transition from Continuous Conduction Mode the Discontinuous Conduction Mode and Pulse Skipping and provide converters that are efficient at low current loads.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Metod and continuously wearable noninvasive apparatus for automatically detecting a stroke and other abnormal health conditions
ActiveUS20140276123A1Easy to operateImprove accuracyInertial sensorsCatheterRisk strokeConduction time
Method and continuously wearable noninvasive apparatus for automatically detecting a stroke's onset are invented. The method comprises measuring pulse transit time or a related hemodynamic parameter and using adaptive pattern learning and stroke identification algorithms to identify the start of a stroke attack. The algorithms are run on an embedded processor and electronics in the apparatus. The result of the identification and detection is used to generate an alarm to alert the patient, caregiver or medical professional to immediately seek further medical treatment. The method can also be applied to identify and detect other abnormal health conditions.
Owner:YANG YINGCHANG
Predicting chronic optimal a-v intervals for biventricular pacing via observed inter-atrial delay
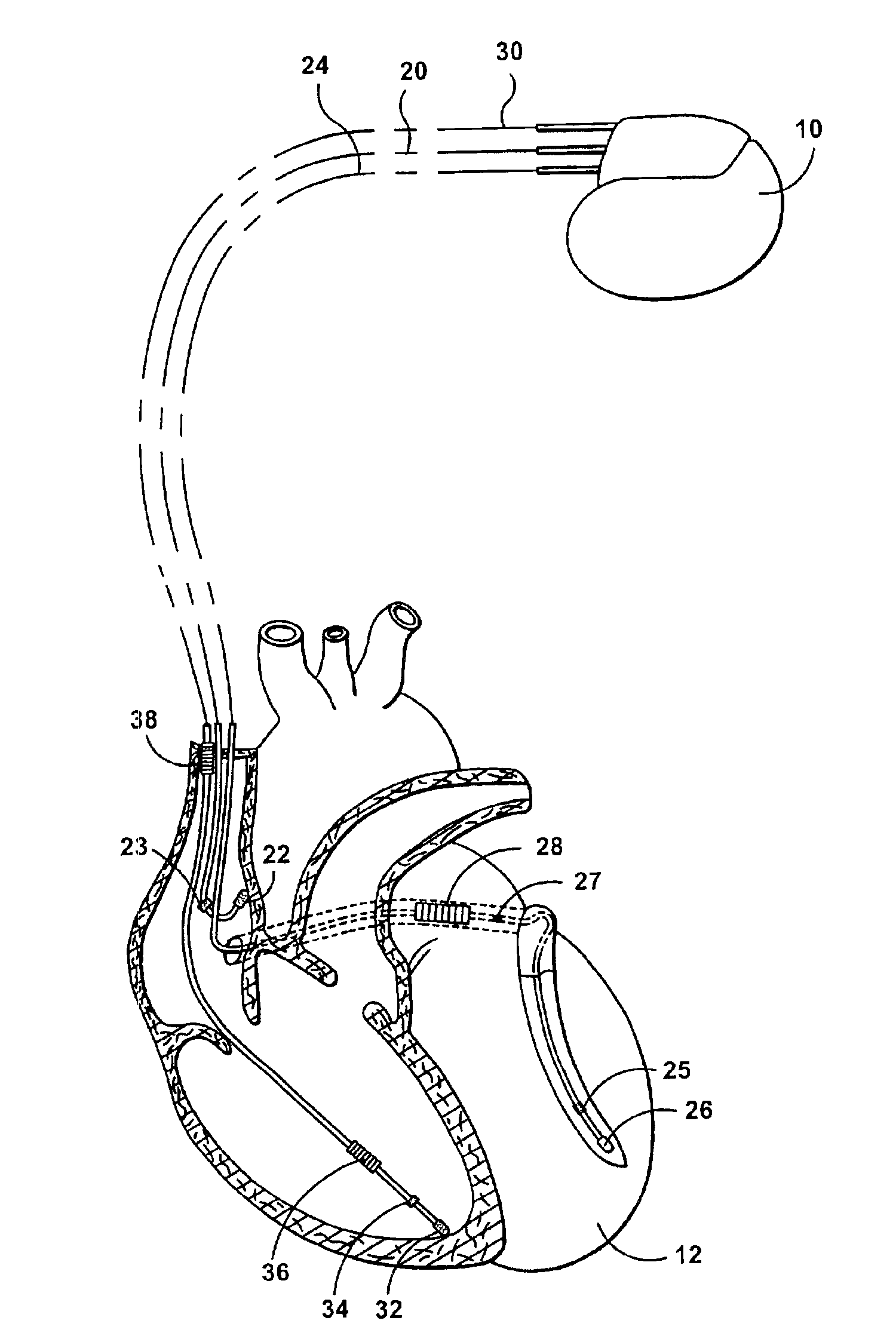
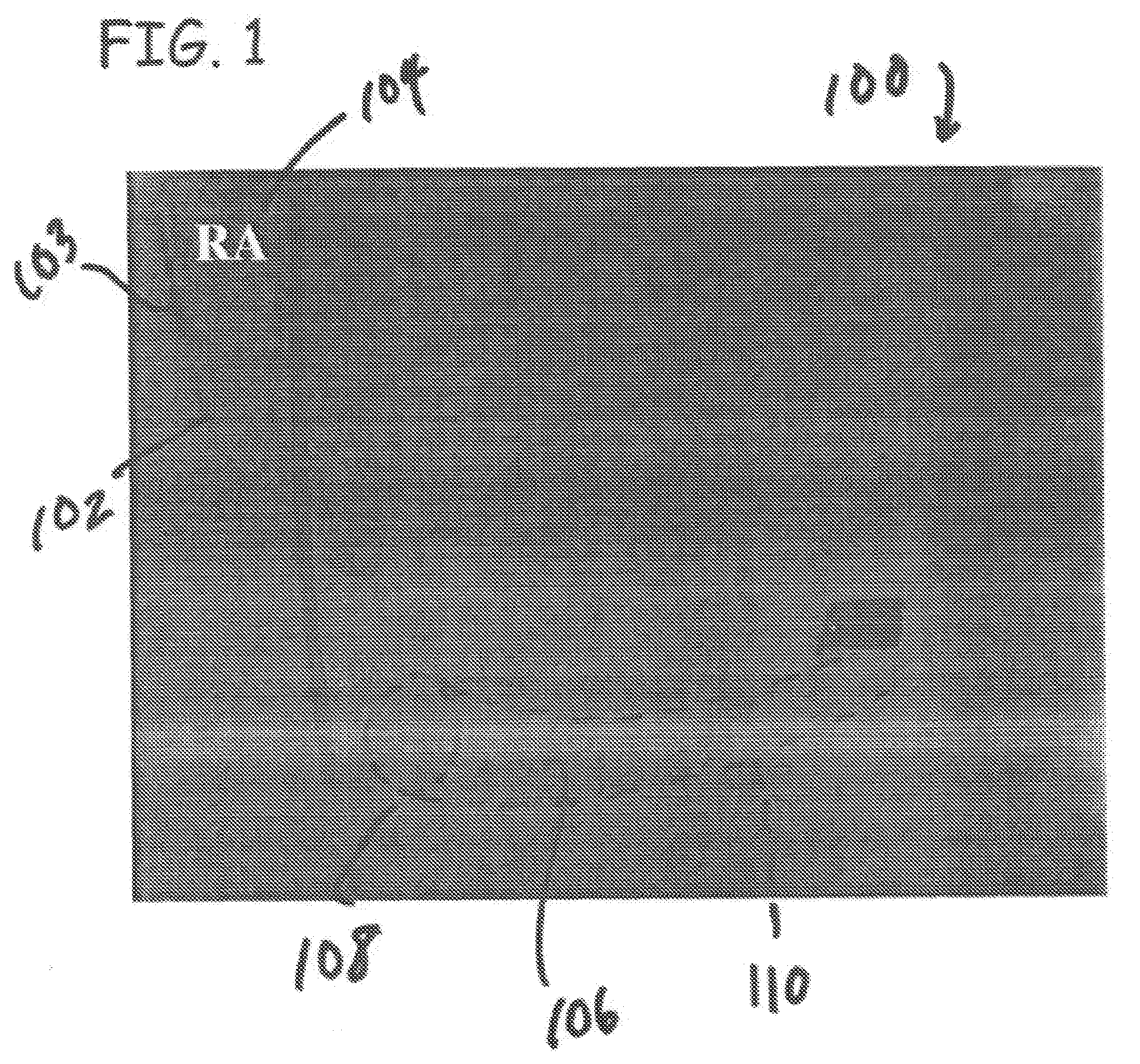
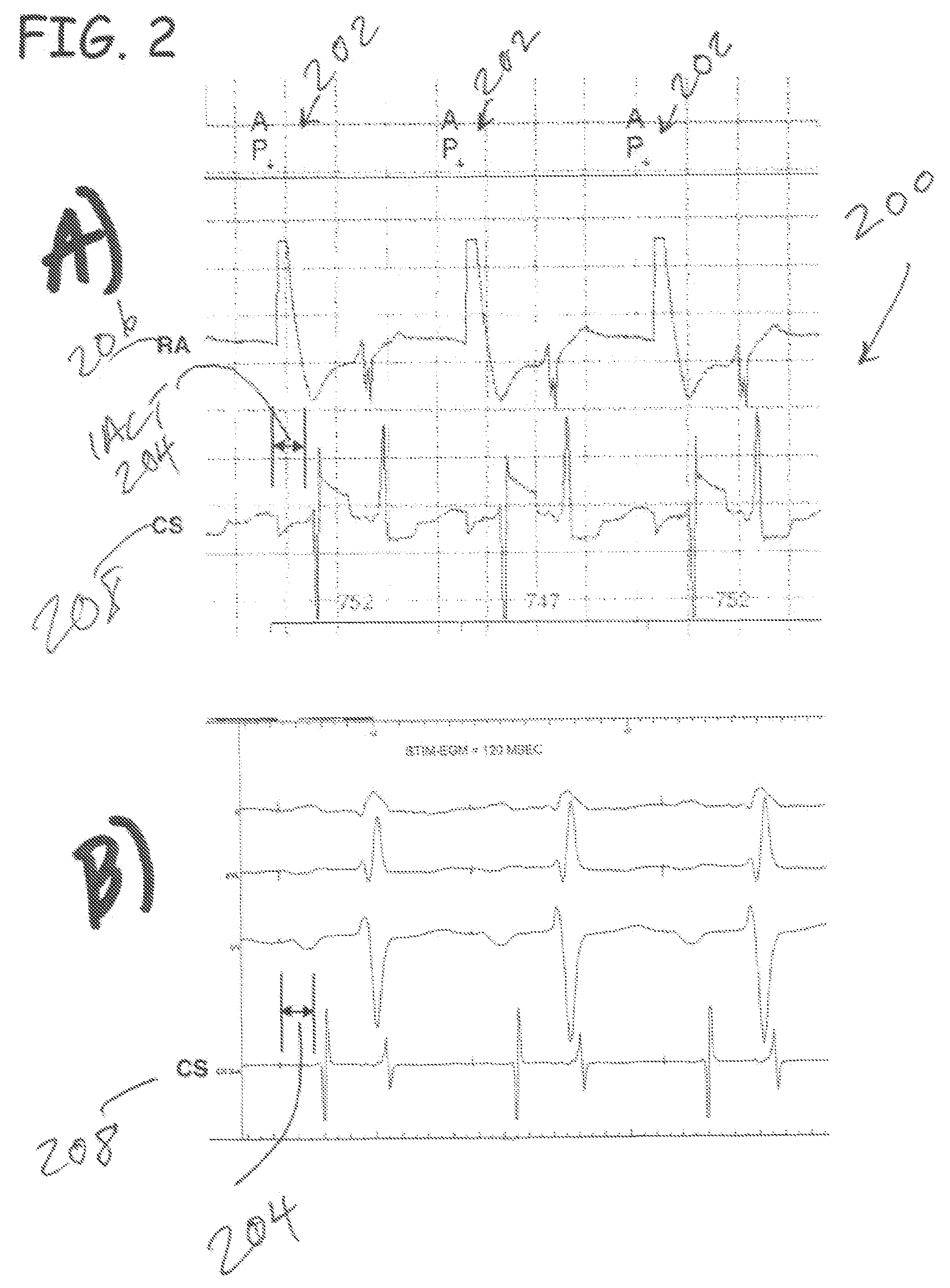
ActiveUS20080027488A1Maximize fillEasy to shrinkElectrocardiographyTransvascular endocardial electrodesAtrial cavityLeft ventricular size
Herein provided are methods for optimizing the atrio-ventricular (A-V) delay for efficacious delivery of cardiac resynchronization therapy. The A-V delay is set such that pacing-induced left ventricular contraction occurs following completion of left atrial (LA) contraction. This maximizes left ventricular filling (preload) which theoretically results in optimal LV contraction via the Frank-Starling mechanism. In CRT devices, the programmed A-V delay starts with detection of electrical activity in the right atrium (RA). Thus, a major component of the A-V delay is the time required for inter-atrial conduction time (IACT) from the RA to the LA. This IACT can be measured during implantation as the time from the atrial lead stimulation artifact to local electrograms in a coronary sinus (CS) catheter. Assuming that the beginning of LA contraction closely corresponds with the beginning of LA electrical activity, the optimal AV delay should be related to the time between the start of RA electrical activity and the start of LA electrical activity plus the duration of LA atrial contraction. Thus the inventors hypothesized that during atrial pacing the IACT measured at implantation correlated with the echocardiographically defined optimal paced AV delay (PAV).
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com