Patents
Literature
1575 results about "Delay-locked loop" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
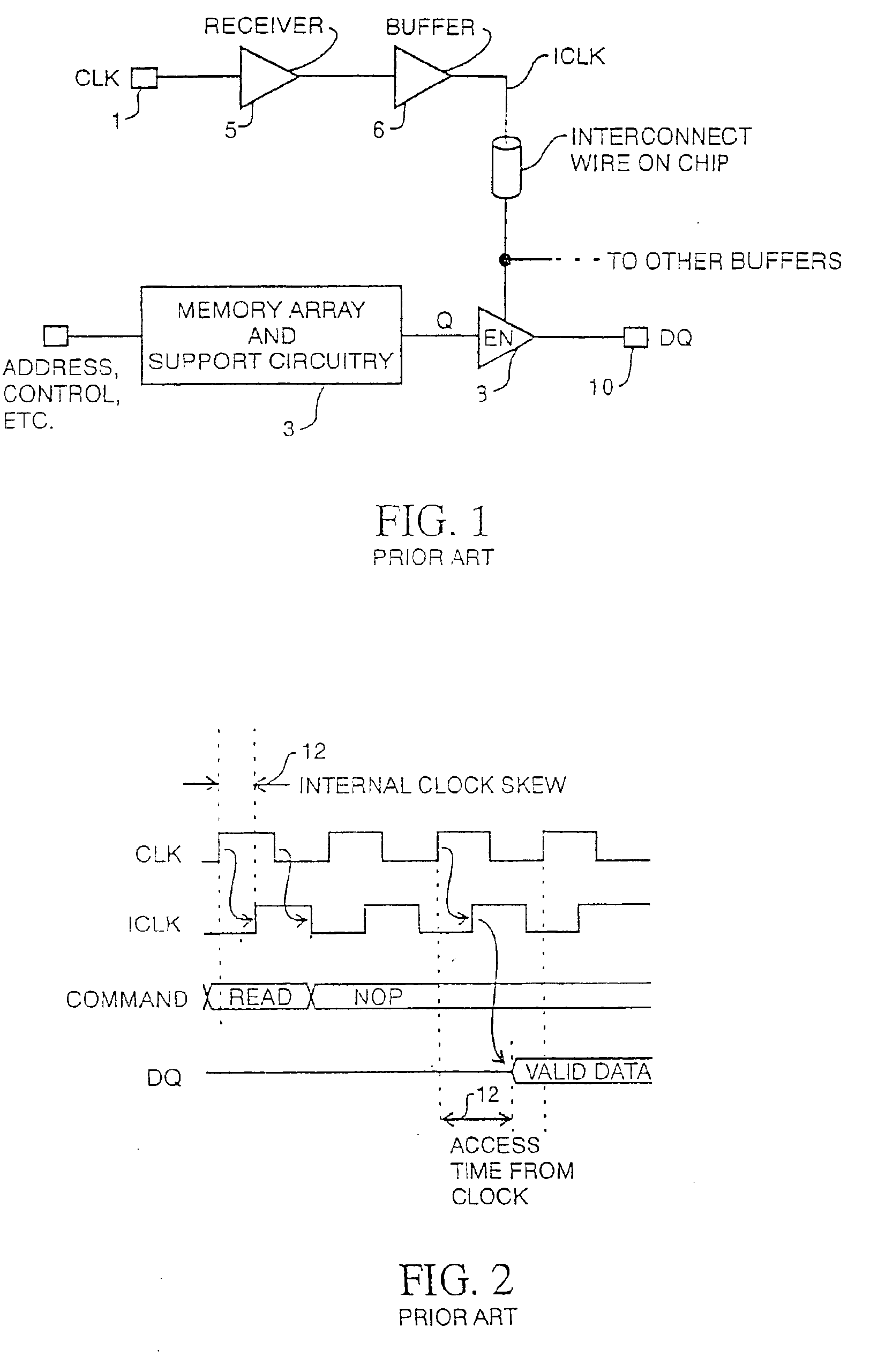
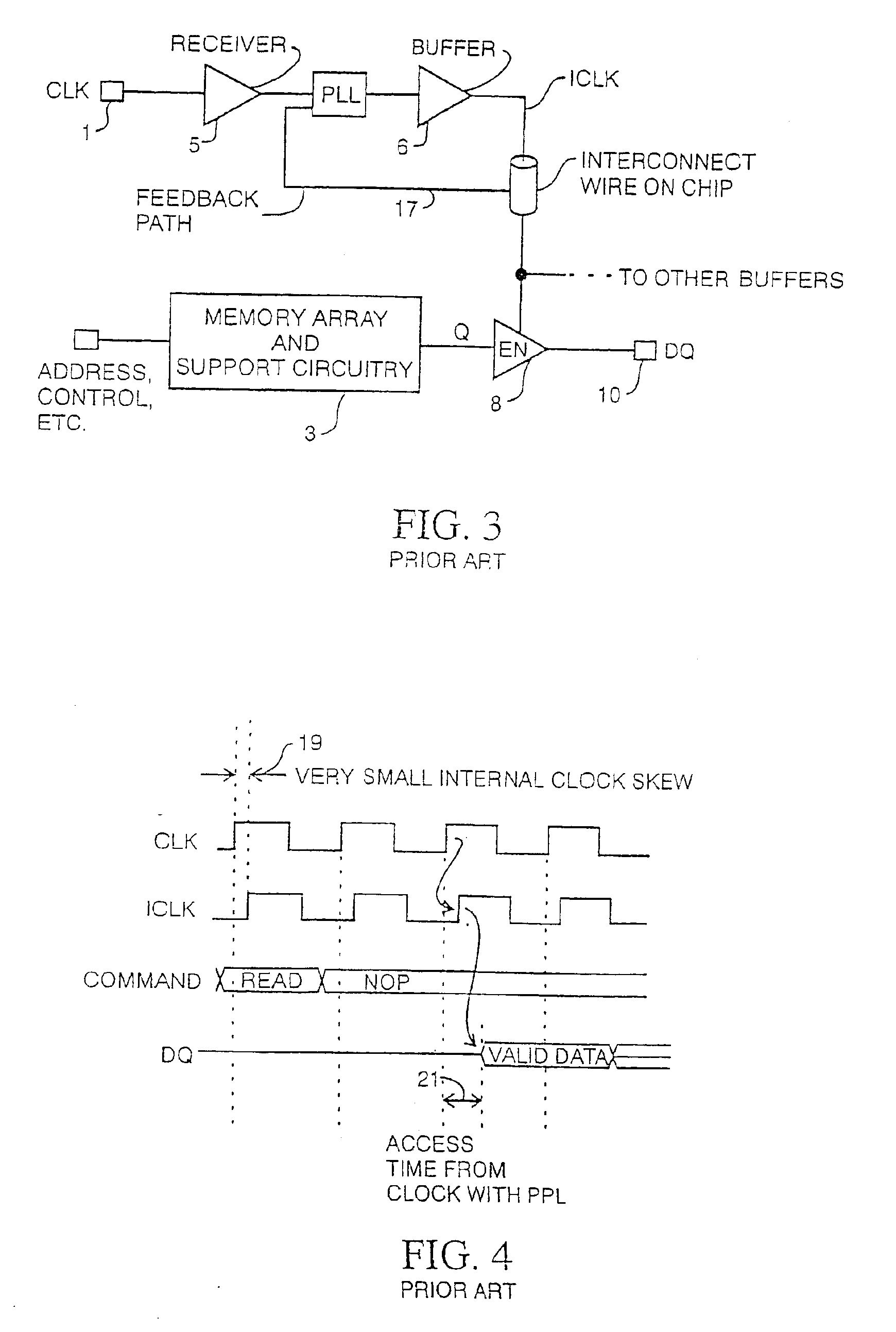
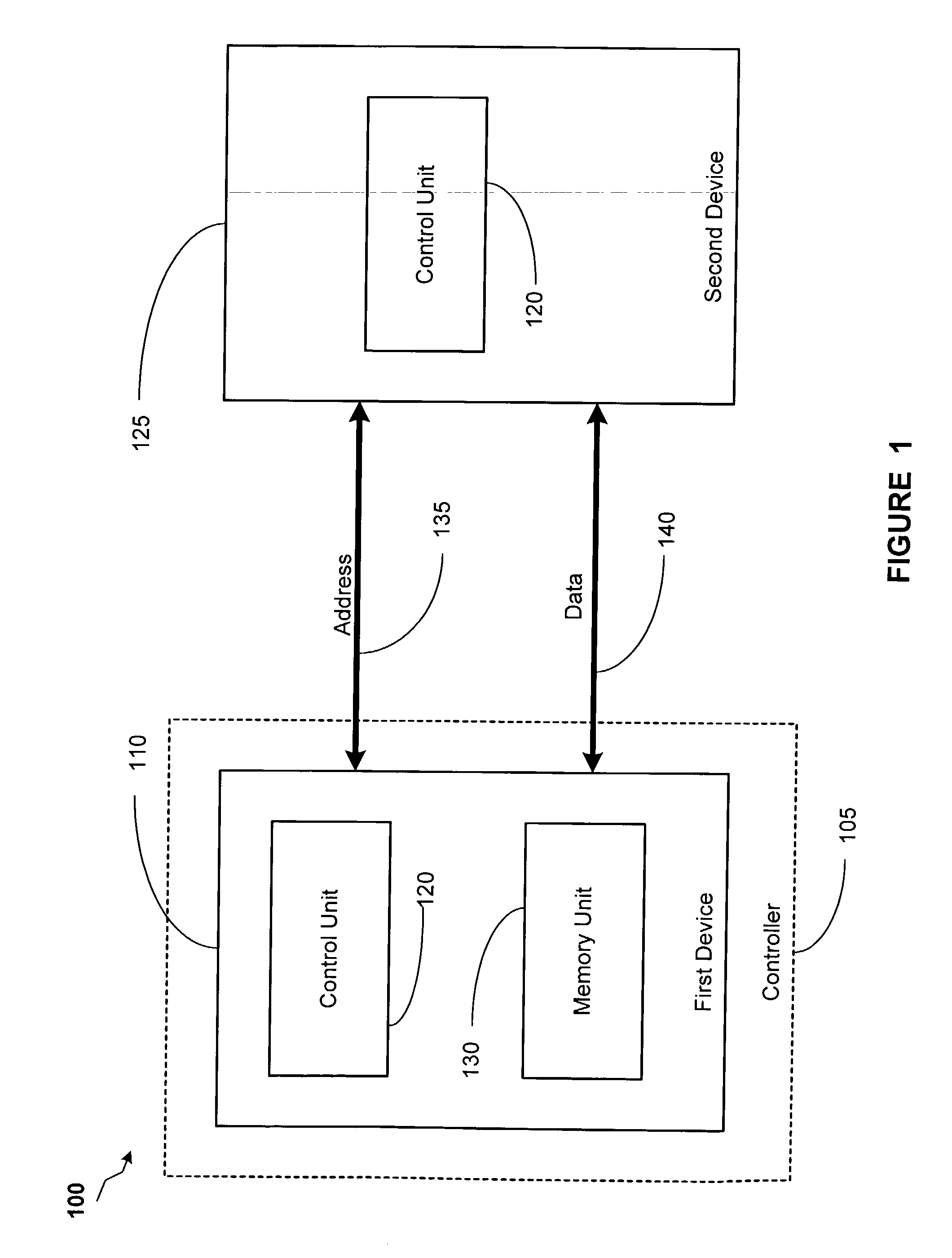
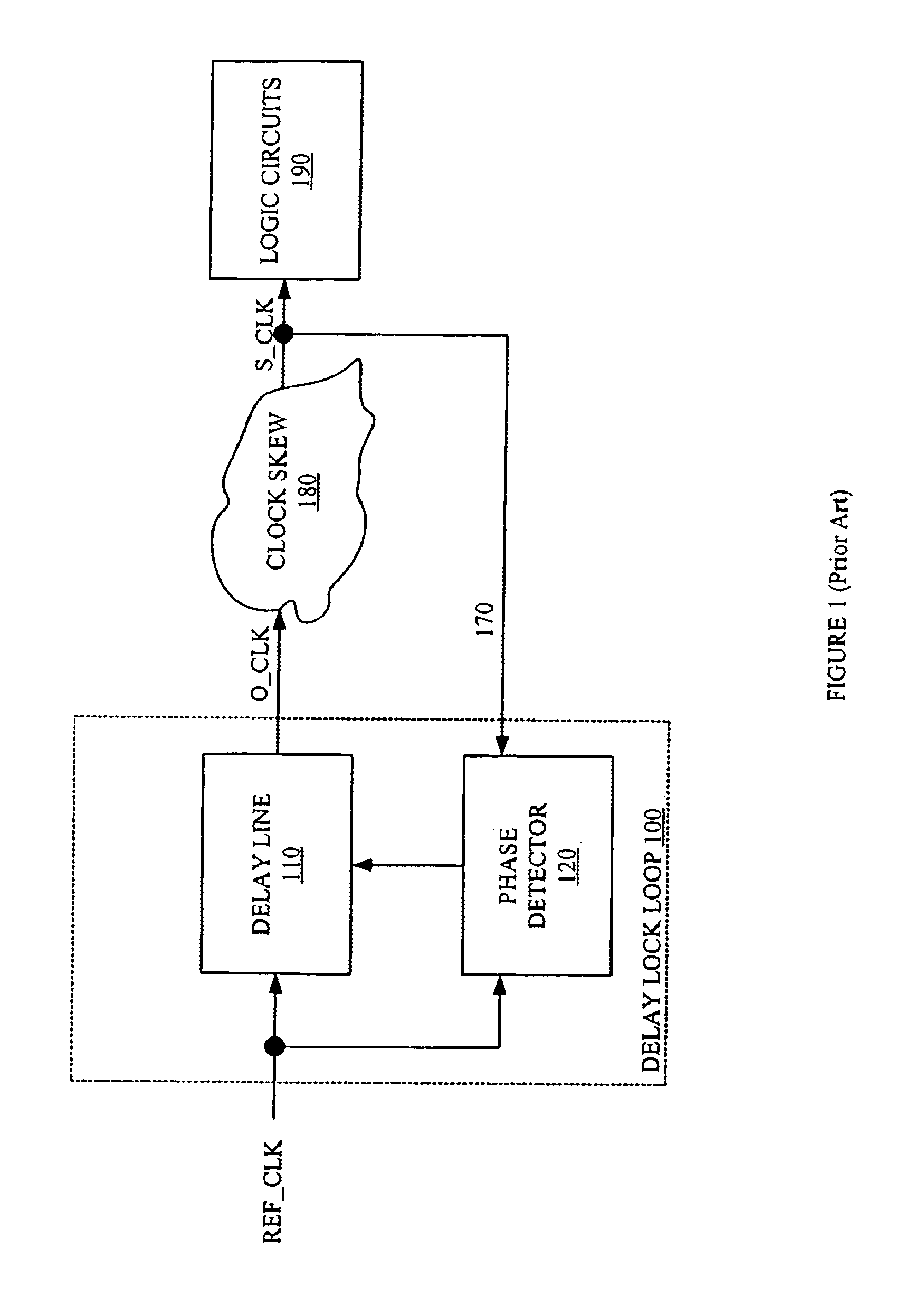
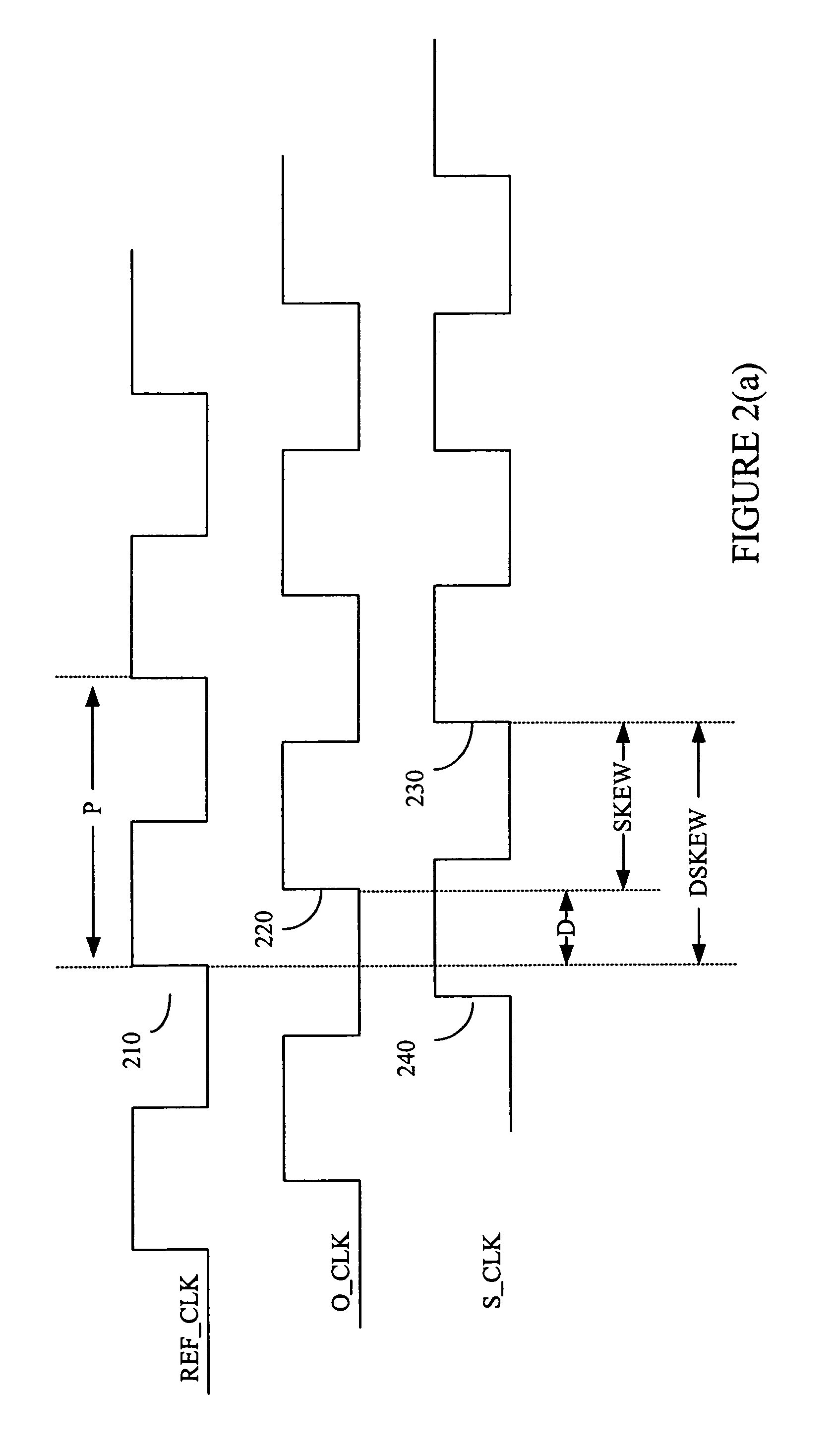
In electronics, a delay-locked loop (DLL) is a digital circuit similar to a phase-locked loop (PLL), with the main difference being the absence of an internal voltage-controlled oscillator, replaced by a delay line.
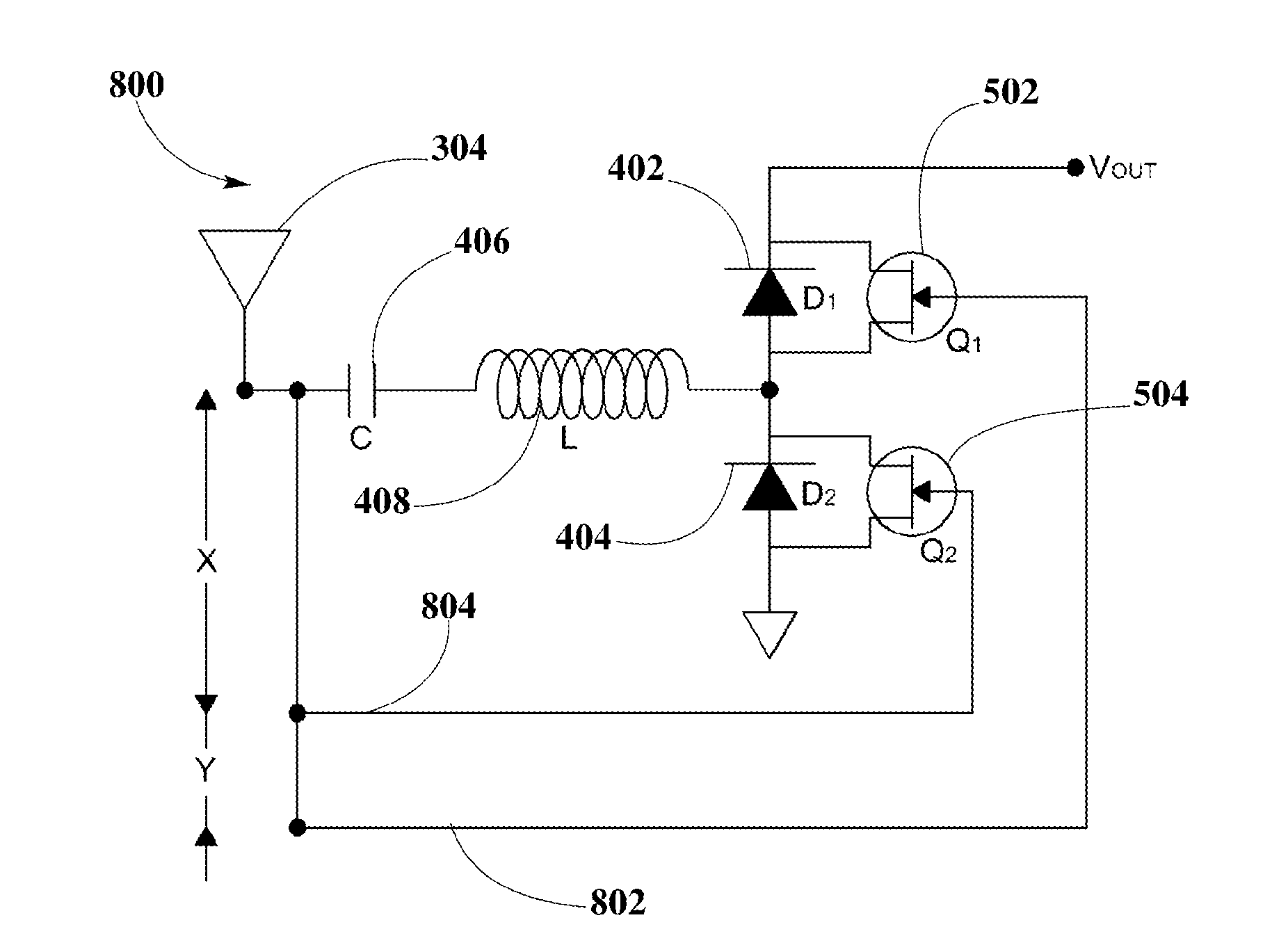
Synchronous Rectifier Design for Wireless Power Receiver
InactiveUS20150326143A1Lower forward voltage dropImprove efficiencyBatteries circuit arrangementsAc-dc conversion without reversalDelay-locked loopSwitching frequency
Synchronous rectifier circuit topologies for a wireless power receiver receiving a supply of power from a wireless transmitter are disclosed. The synchronous rectifier circuit topologies include a half-bridge diode-FET transistor rectifier for rectifying the wireless power into power including a DC waveform, using a control scheme that may be provided by a delay-locked loop clock, or phase shifters, or wavelength links to control conduction of FET transistors in the synchronous rectifier circuit topology, and maintaining a constant switching frequency to have the diodes, coupled to FET transistors, to allow current to flow through each one respectively at the appropriate timing, focusing on high conduction times. The synchronous rectifier circuit topologies may enable power transfer of high-frequency signals at enhanced efficiency due to significant reduction of forward voltage drop and lossless switching.
Owner:ENERGOUS CORPORATION
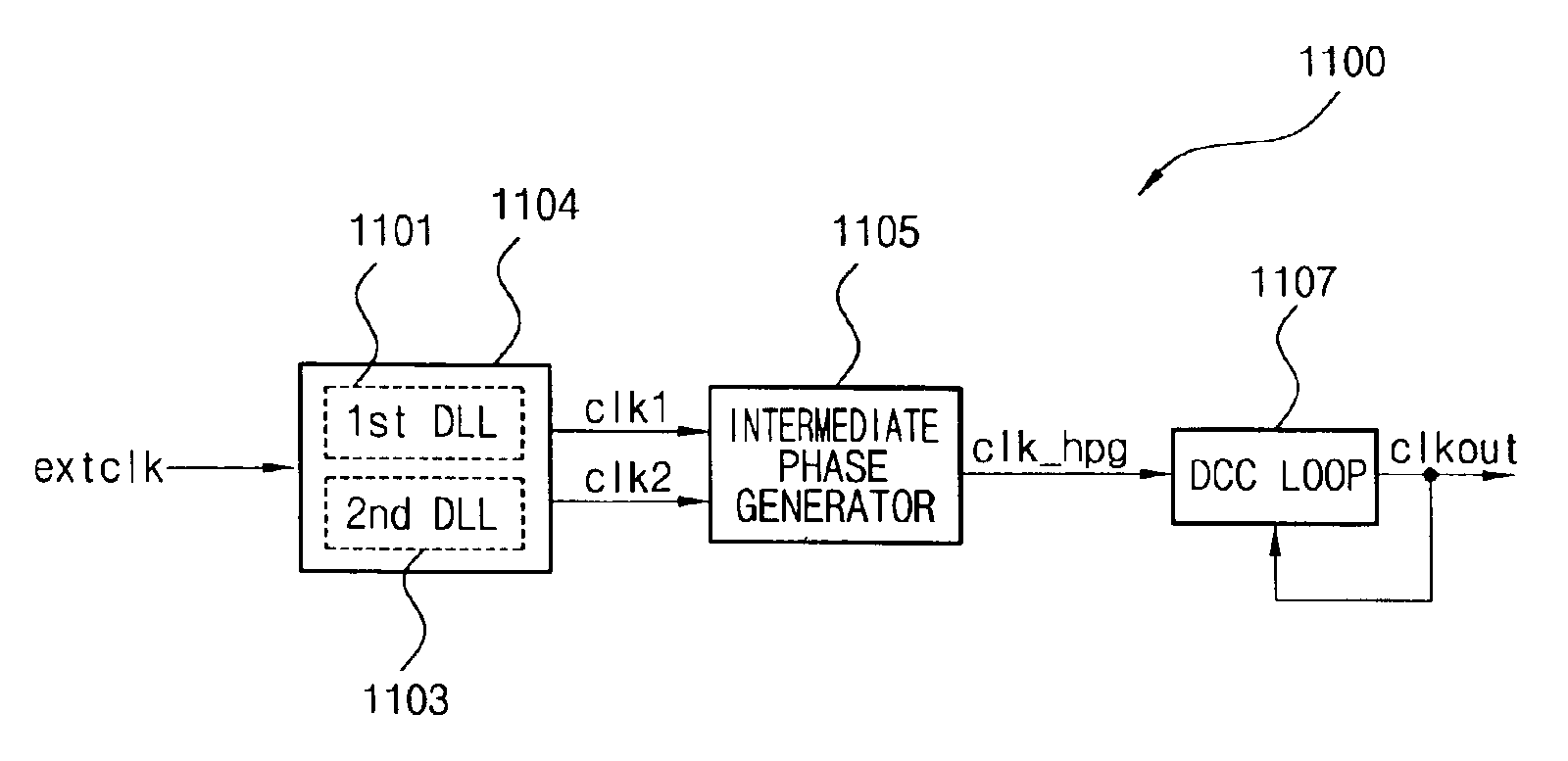
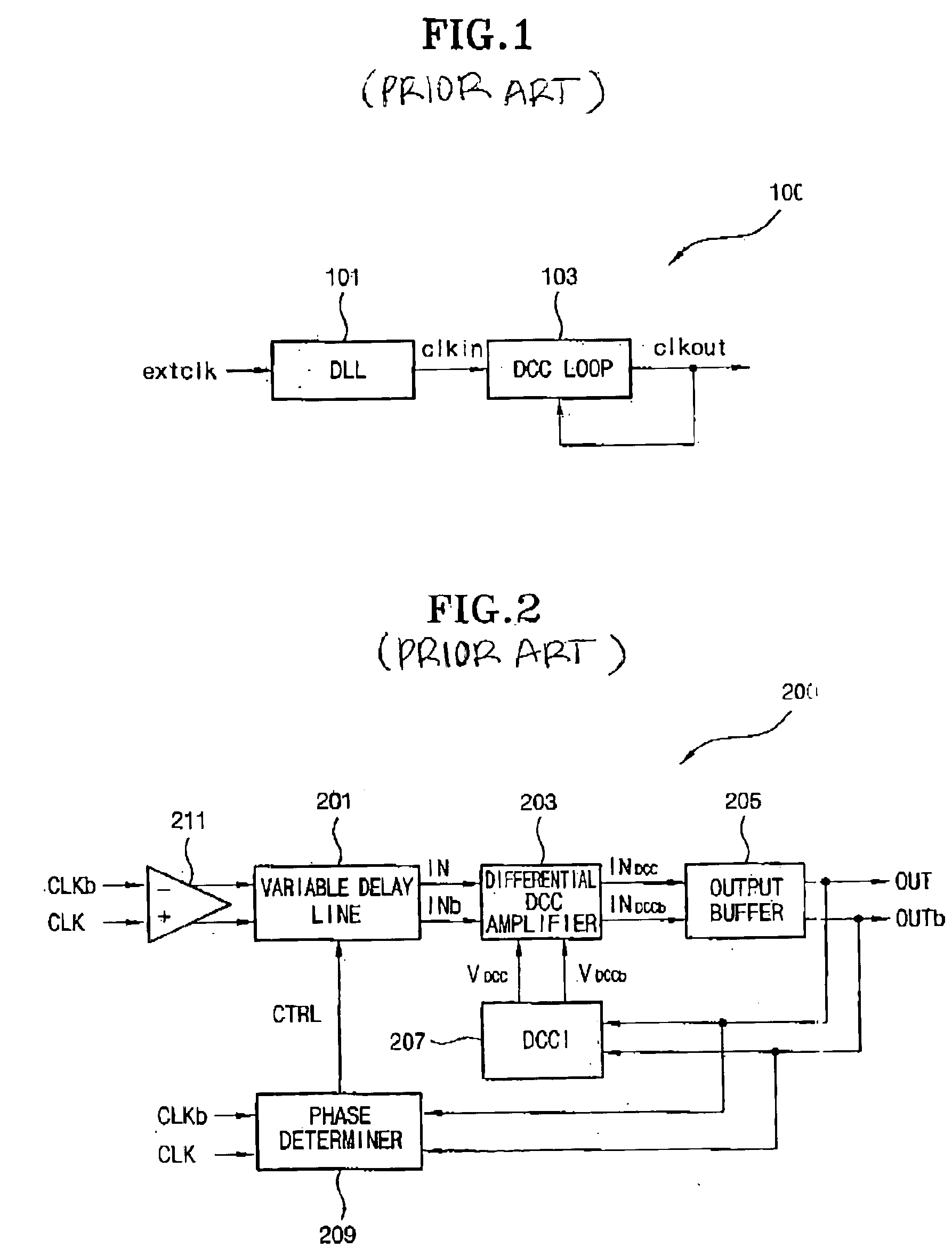
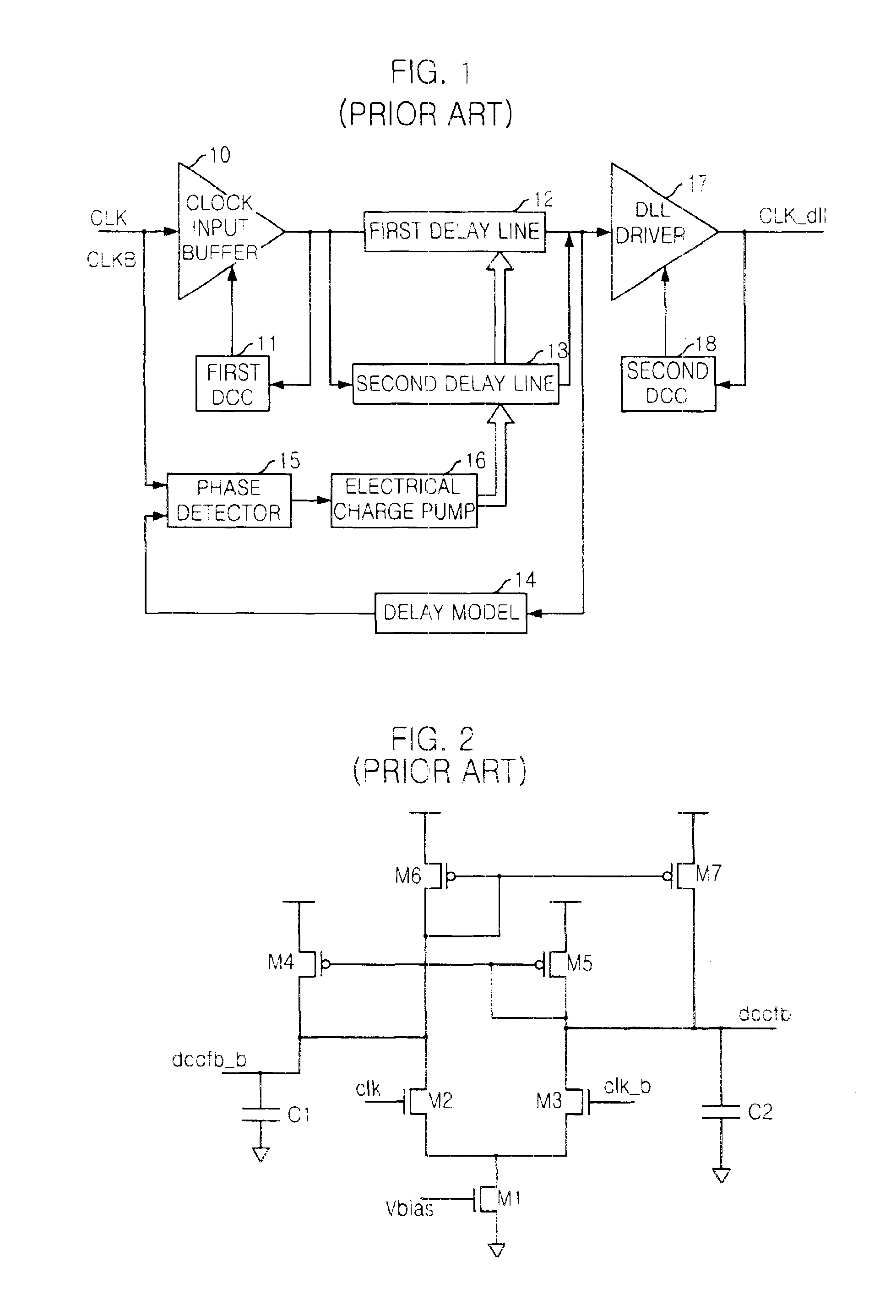
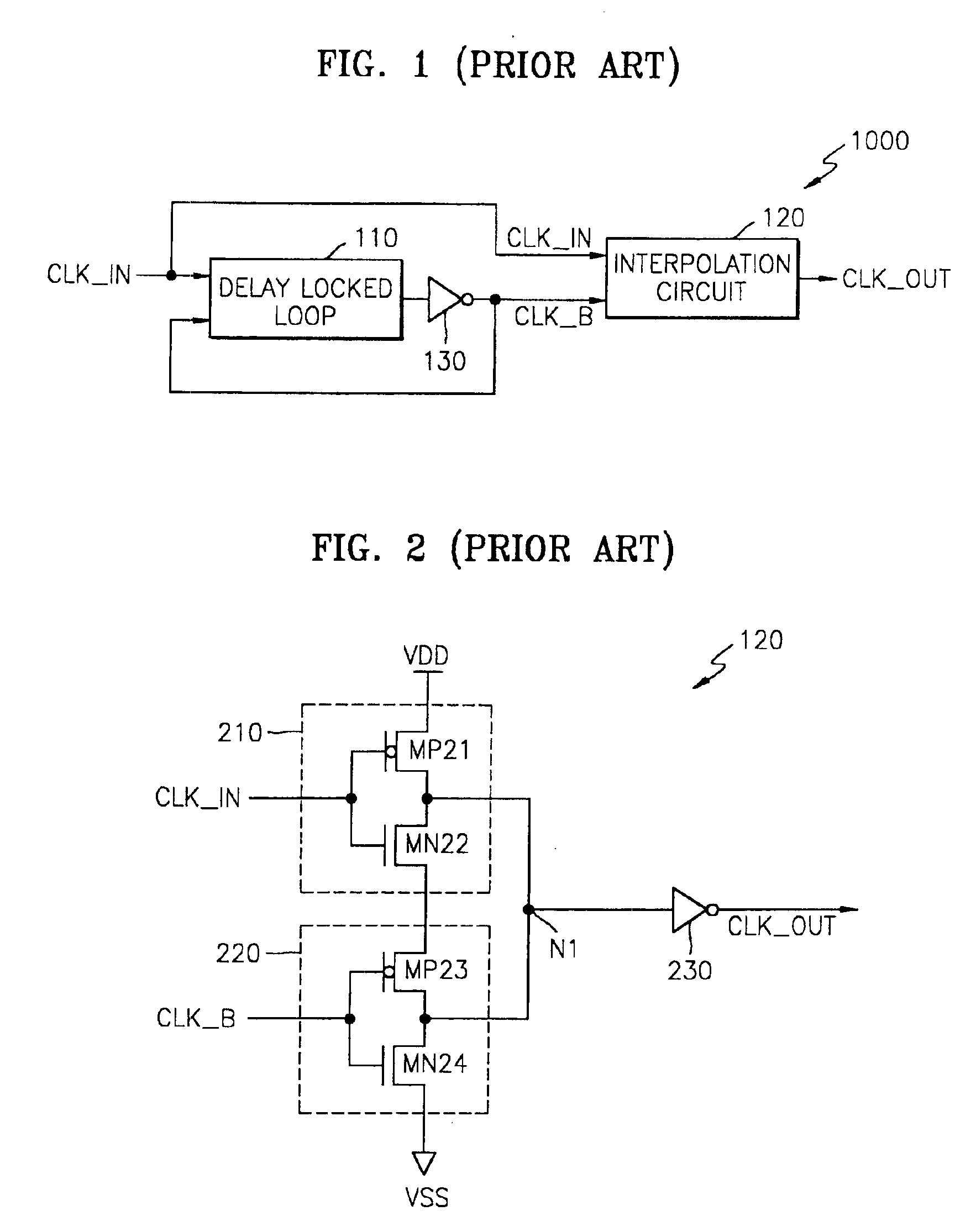
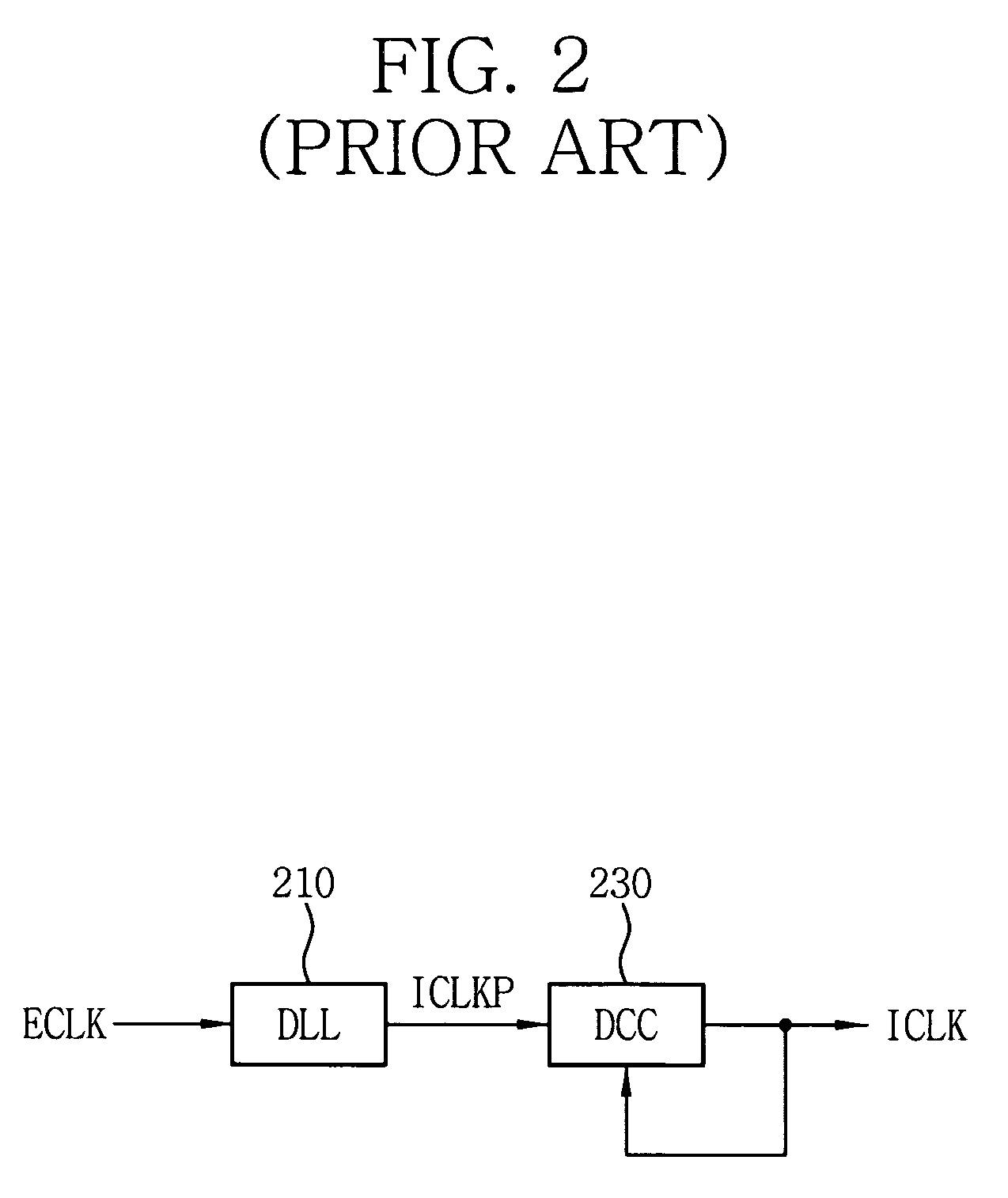
Delay locked loop circuit with duty cycle correction function
InactiveUS6853225B2Improve accuracyShort lock timePulse automatic controlContinuous to patterned pulse manipulationNegative feedbackDelay-locked loop
A delay locked loop (DLL) circuit having a structure in which a method of performing duty cycle correction (DCC) using two DLLs and an intermediate phase composer and a method of performing DCC by forming a closed loop using a negative feedback are combined with each other is provided. The DLL circuit includes a first DLL for receiving an external clock signal and generating a first clock signal and a second DLL for receiving an external clock signal and generating a second clock signal. The first clock signal and the second clock signal are synchronized with an external clock signal. The DLL circuit further includes an intermediate phase generation circuit for receiving the first and second clock signals and generating an intermediate phase clock signal and a DCC loop for receiving the intermediate phase clock signal and generating an output clock signal. The intermediate phase clock signal has an intermediate phase between the phases of the first and second clock signals. The output clock signal is generated through correction of the duty cycle of the intermediate phase clock signal using a value obtained by integrating the output clock signal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
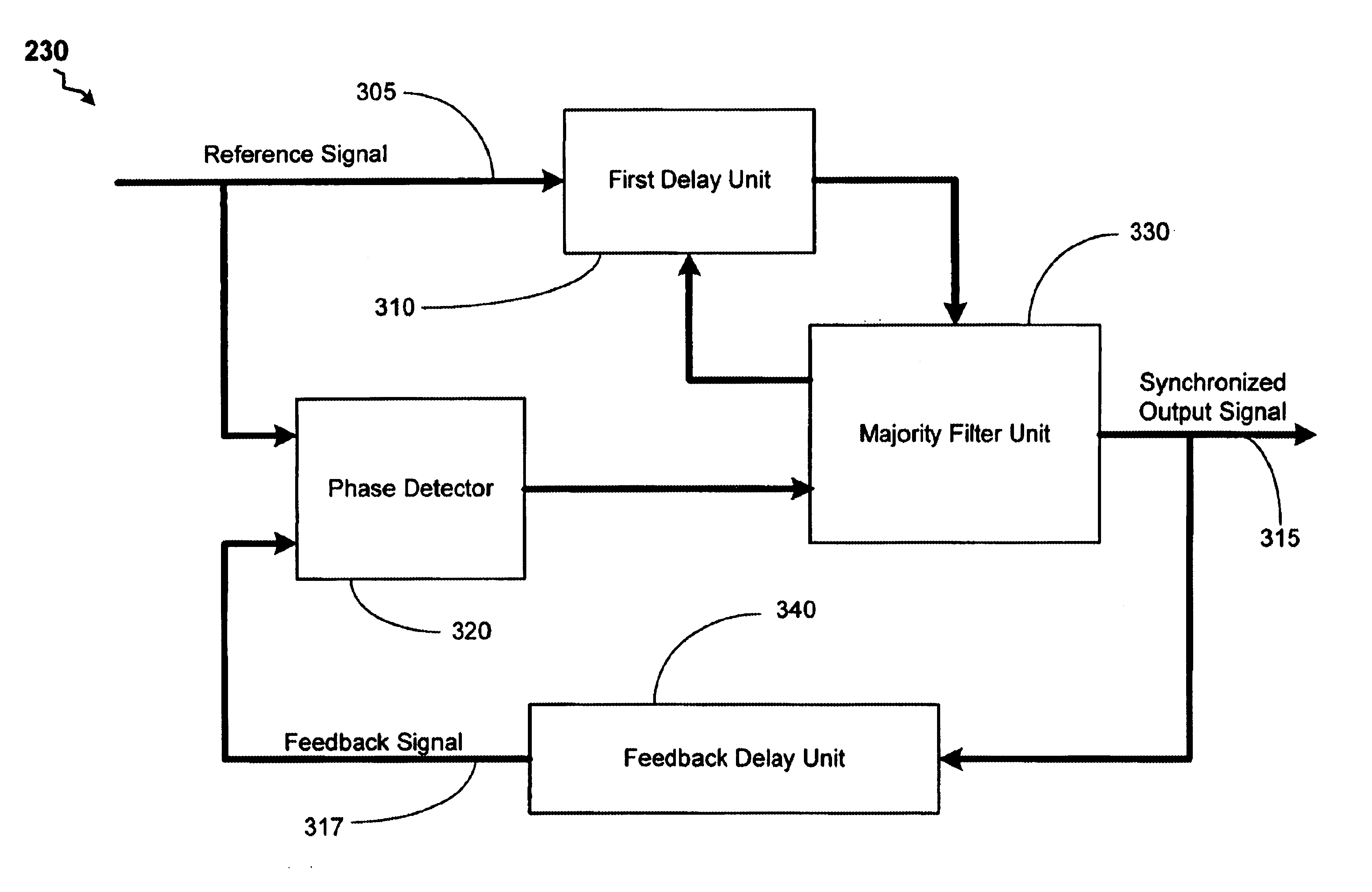
Controlling a delay lock loop circuit
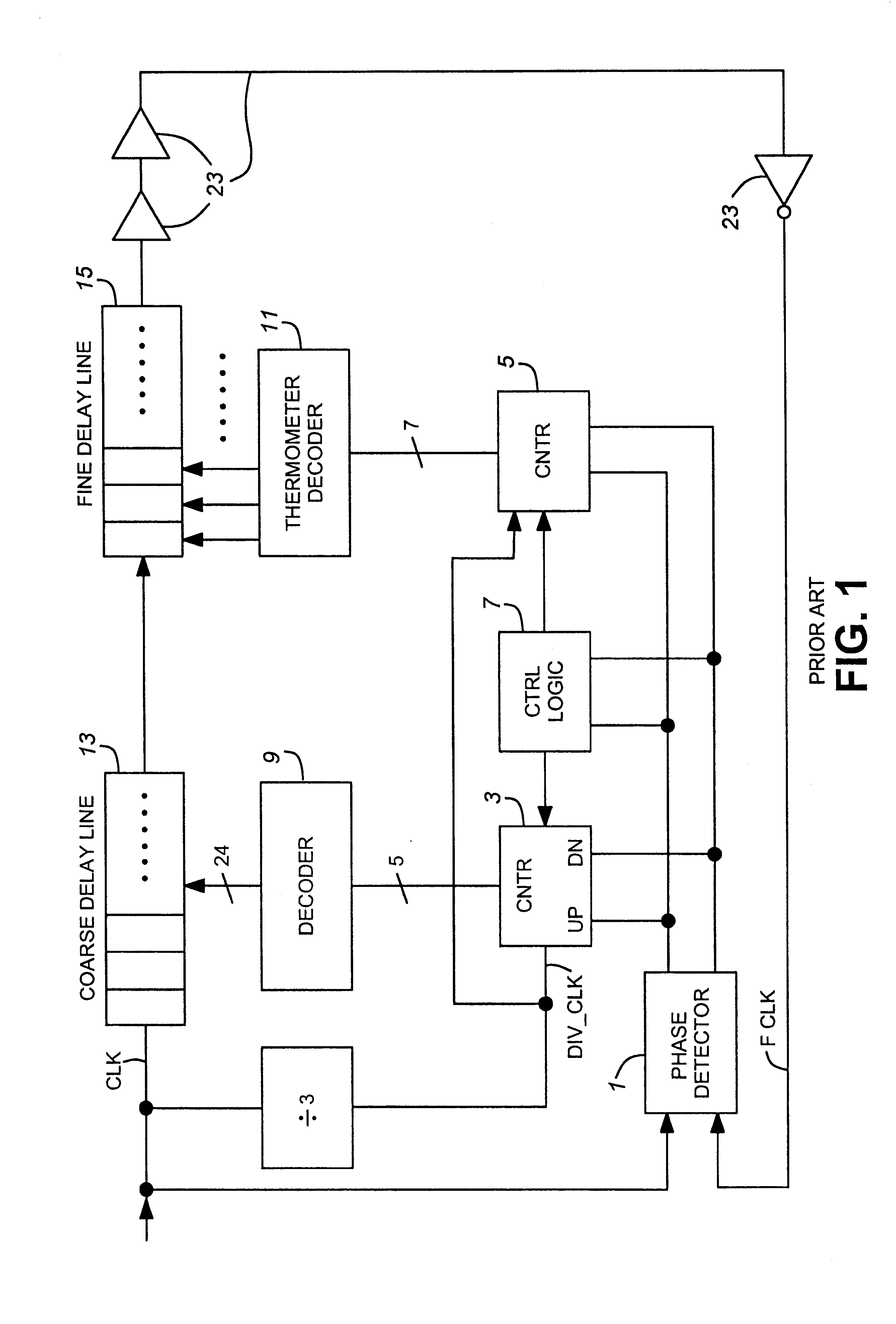
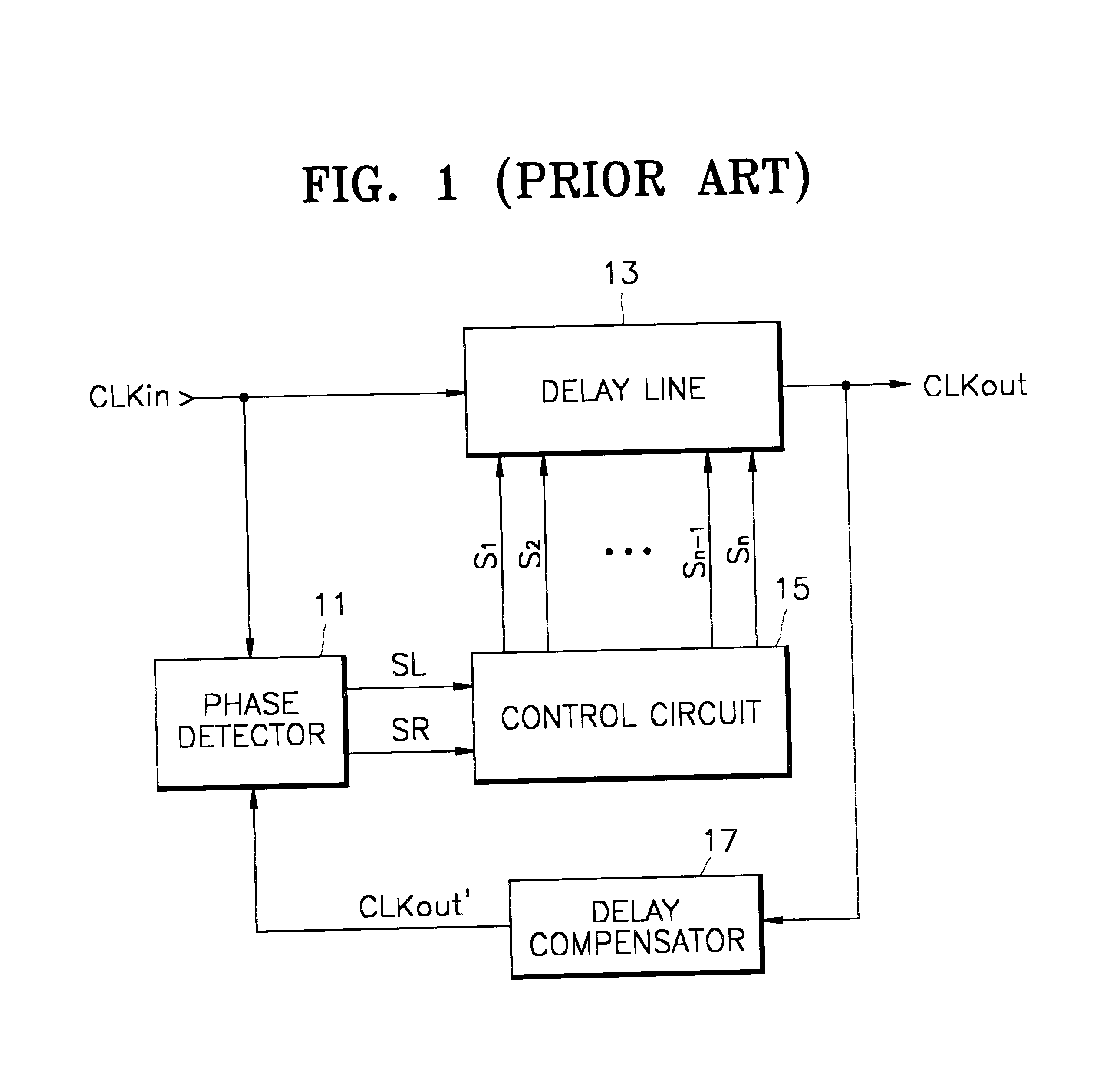
A method and apparatus is provided for performing a filter control of a delay lock loop circuit. A coarse delay and / or a fine delay are implemented upon a reference signal based upon a phase shift between the reference signal and a feedback signal. A synchronized output signal is generated based upon the coarse delay and the fine delay. The apparatus of the present invention includes a delay lock loop to provide an output signal based upon a phase difference between a reference signal and a feedback signal. The delay lock loop comprises a filter to provide a filter response to the phase difference. The filter response is capable of providing a coarse delay and / or a fine delay.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
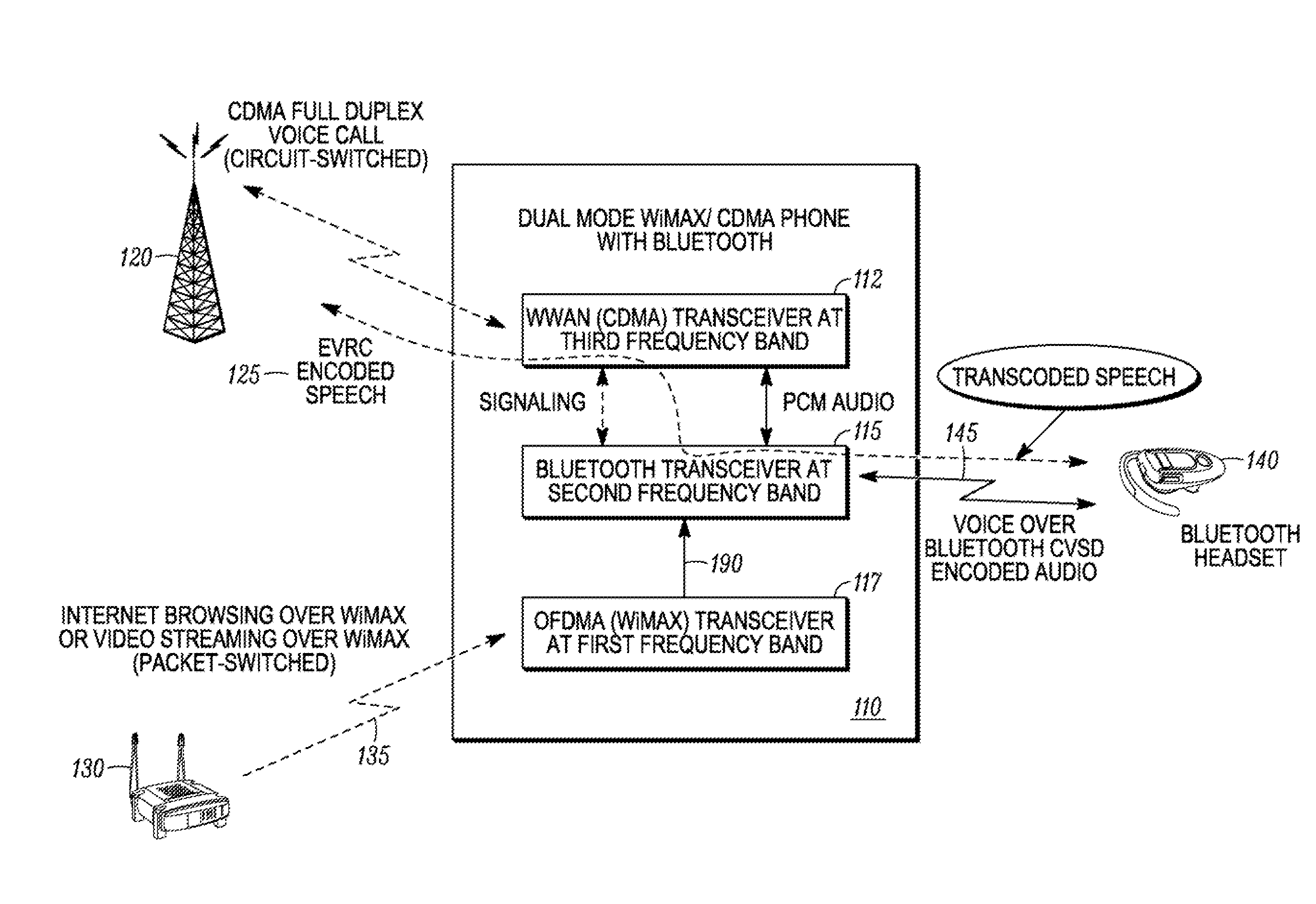
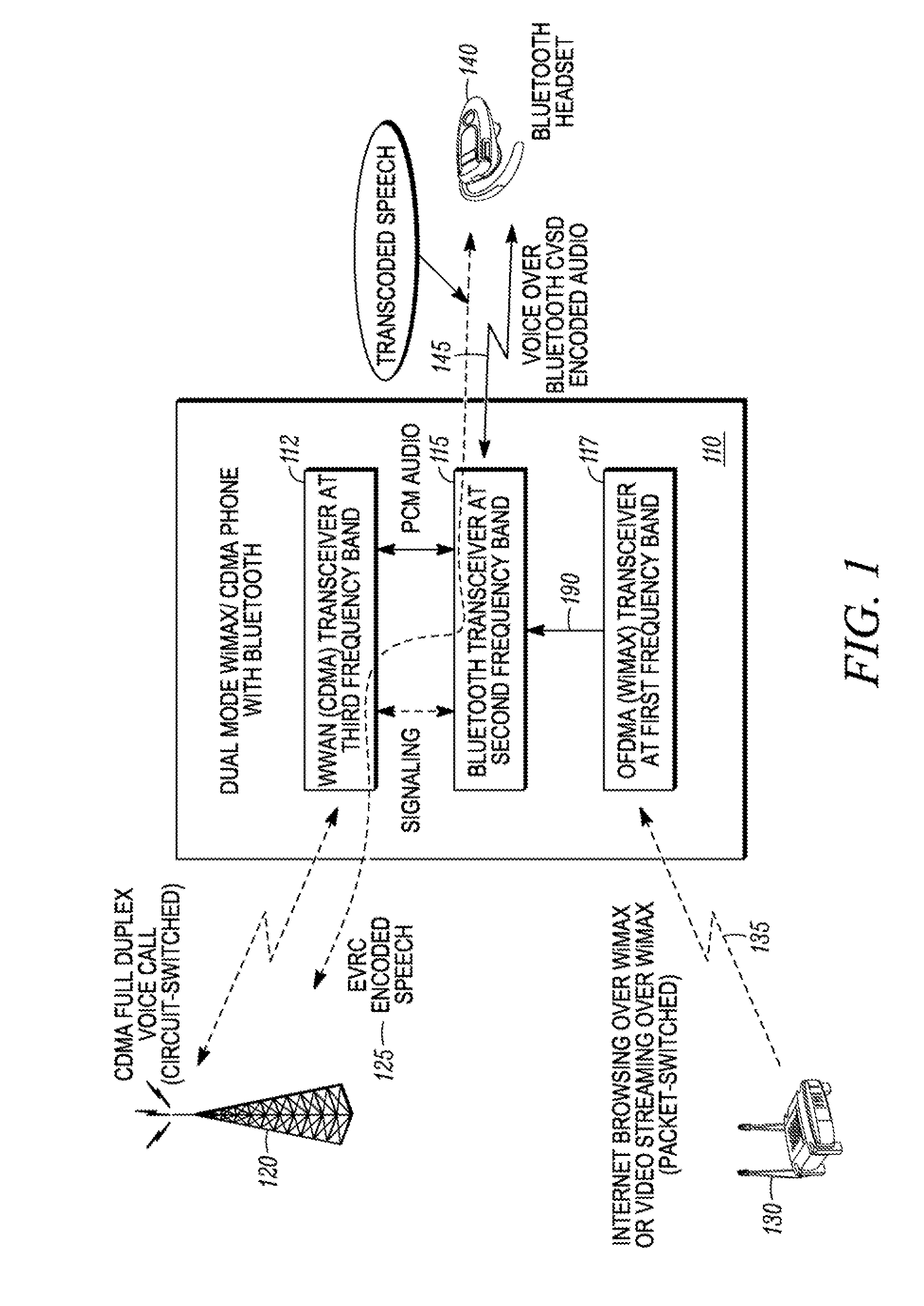
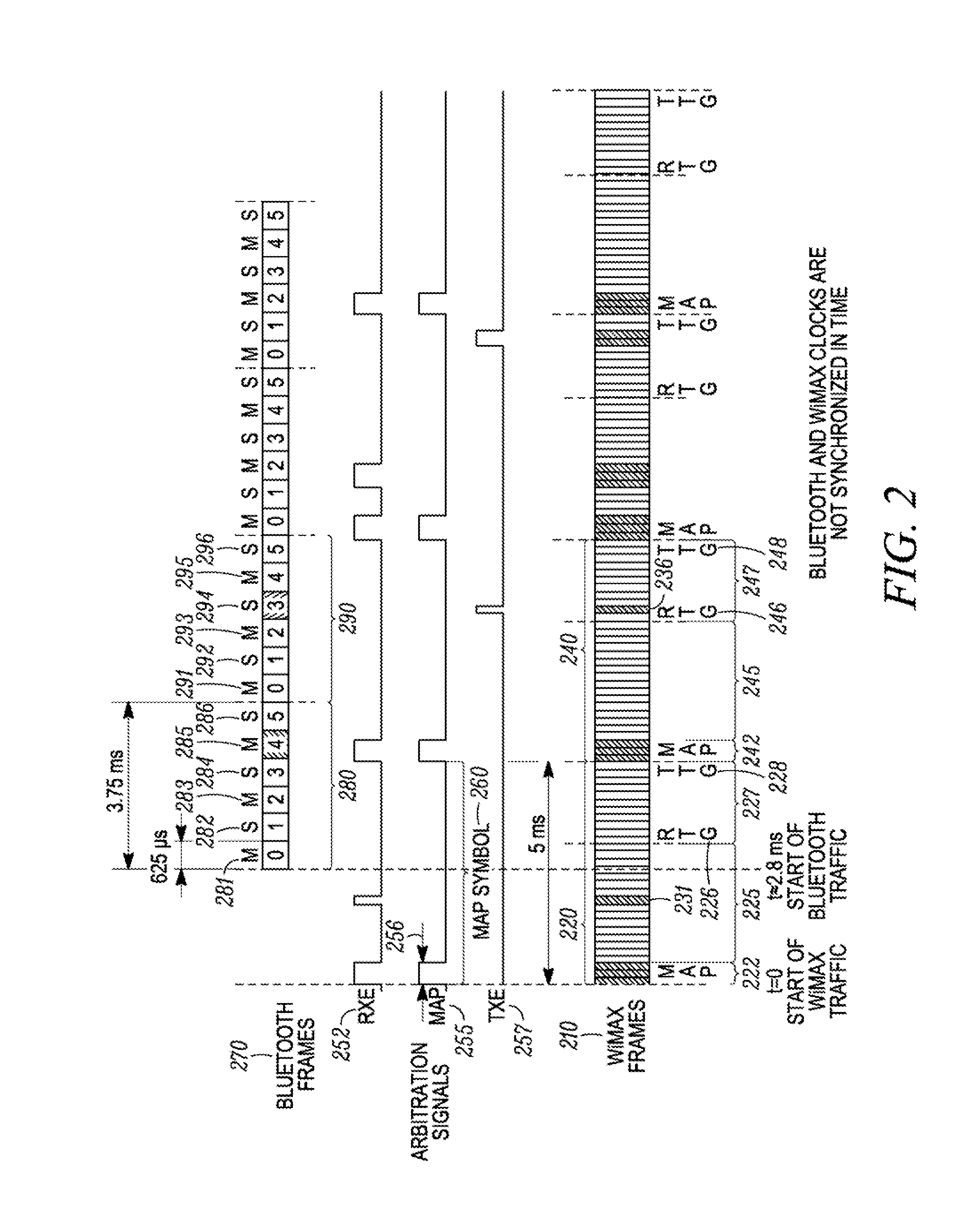
Method and apparatus for coexistence
A method for coexistence of an orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA) receiver (117) such as a WiMAX receiver with a synchronous frame-based transmitter (115) such as a Bluetooth transmitter within a mobile station (110) receives an estimated media access protocol (MAP′) signal indicating when a MAP message is expected to be received by the OFDMA receiver (117) and uses it at a Bluetooth shutdown signal (190) at least when a MAP message is expected to be received. The MAP′ signal can be taken directly from the ODFMA transceiver (117) or it may be produced through analysis of a receiver-enable (RXE) signal that includes not only MAP symbols but also downlink data symbols. The RXE signal can be analyzed using interrupt-and-timer, Fast Fourier Transform, covariance, and / or delay-locked loop techniques to extract historical MAP symbol information and generate expected MAP symbol information. Shutting down a Bluetooth transmitter during expected MAP message receipt permits the OFDMA receiver to maintain synchronicity with an access point while not requiring the Bluetooth transmitter to shut down every time the OFDMA receiver expects to receive an OFDMA symbol.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Time division multiplex data recovery system using close loop phase and delay locked loop
InactiveUS6901126B1Alleviate duty cycle issuesHigh bandwidthPulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionDelay-locked loopClosed loop
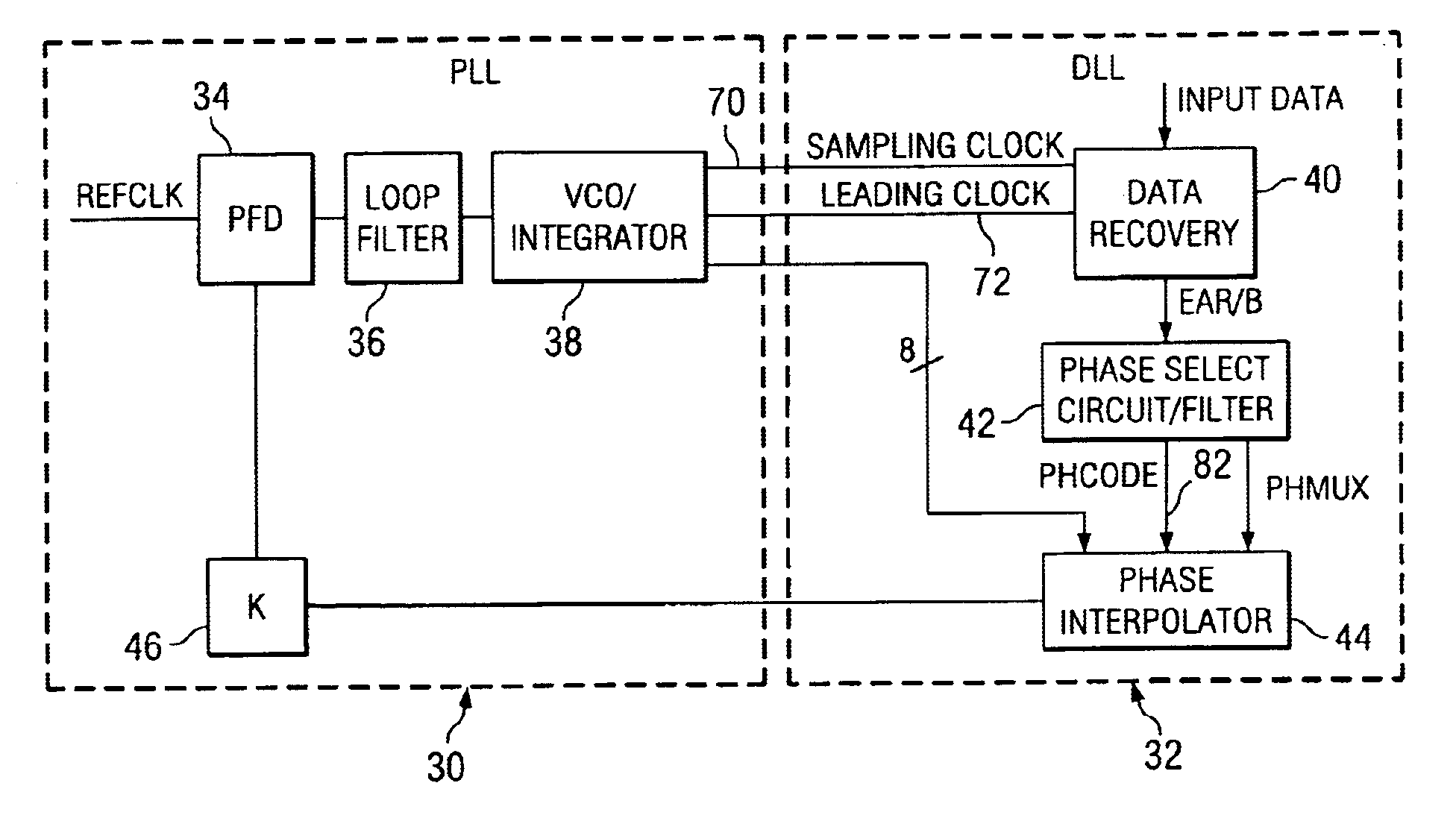
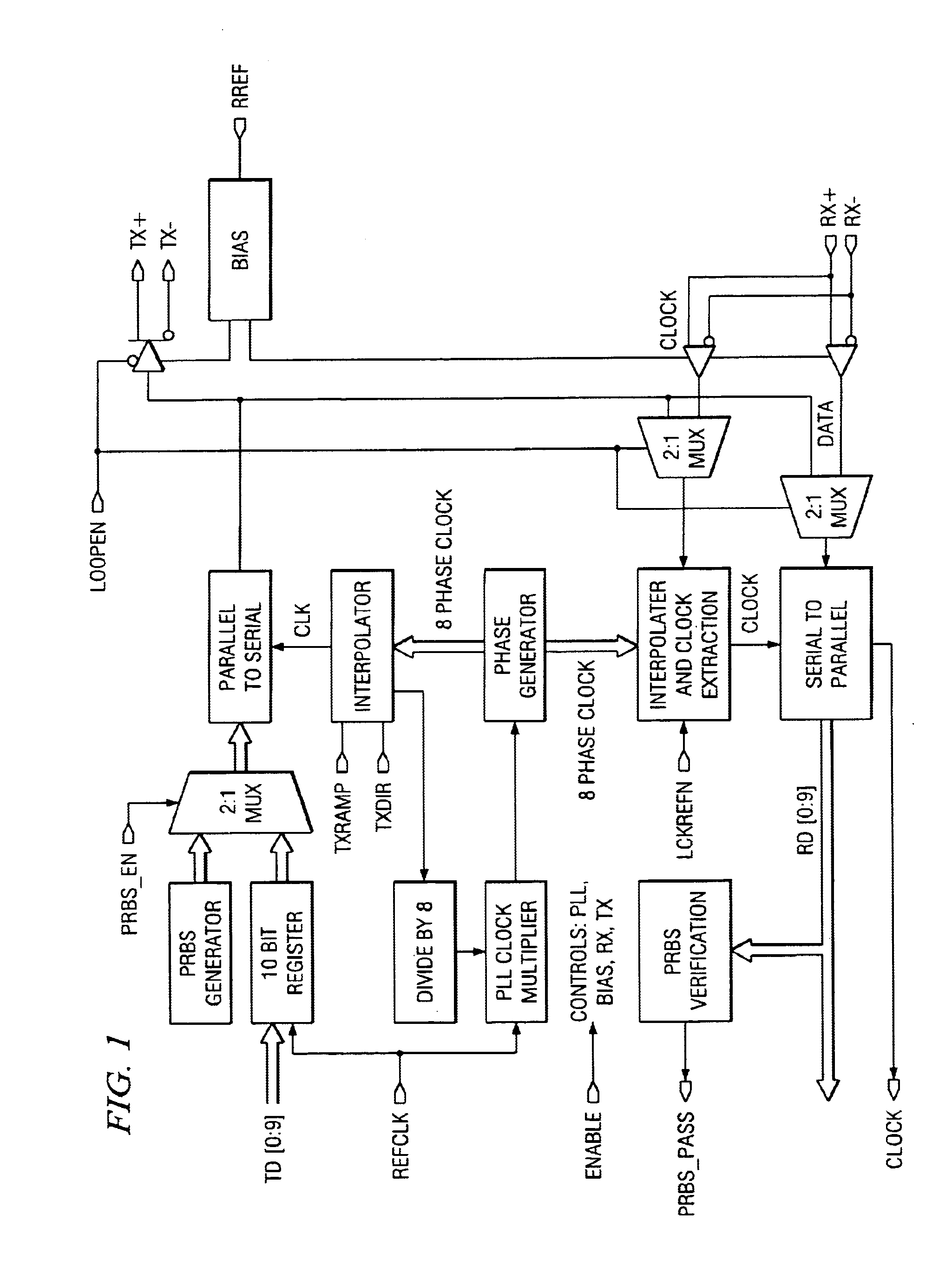
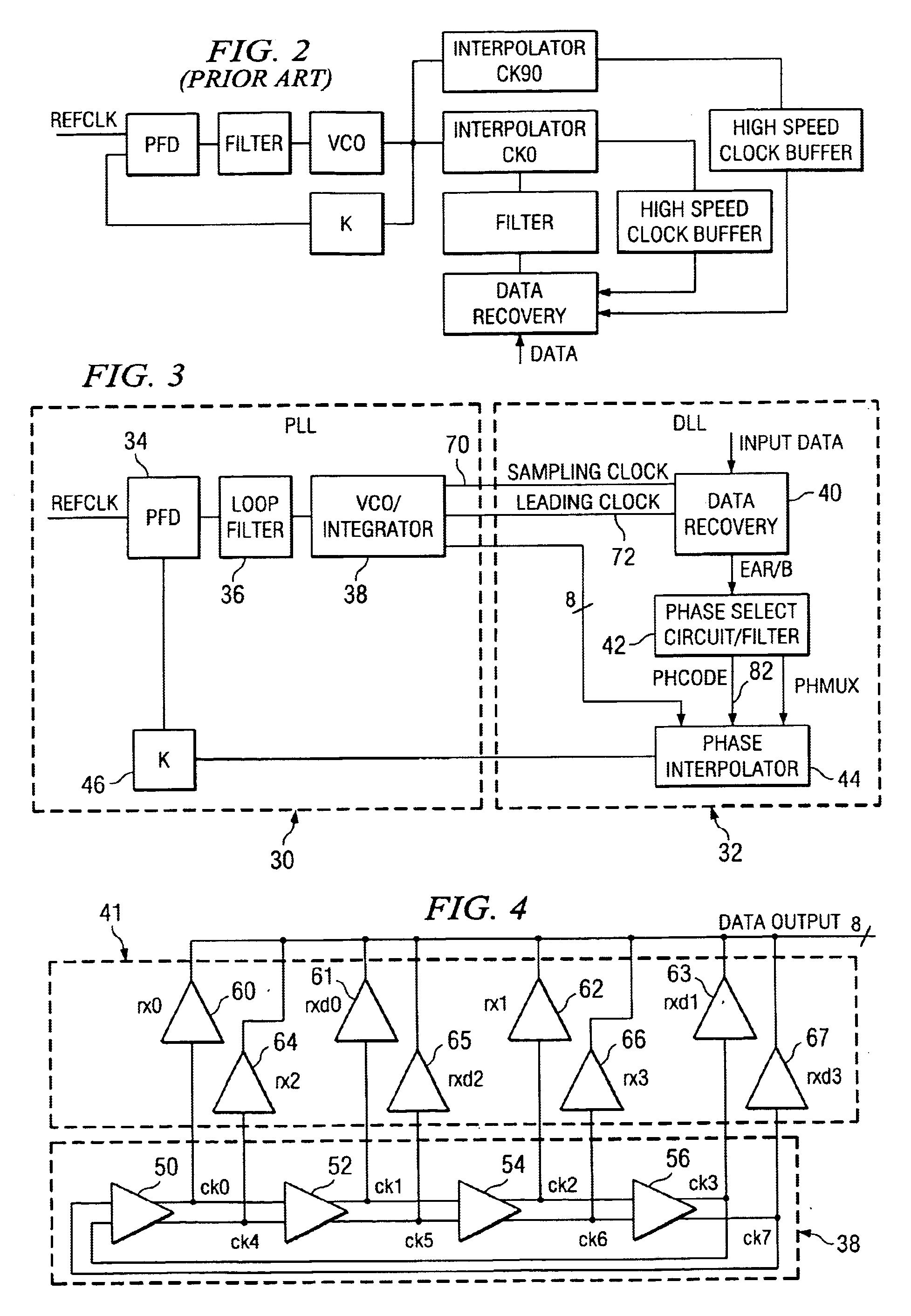
A time division multiplex data recovery system using a closed-loop phase lock loop (PLL) and delay locked loop (DLL) is disclosed. In other words, one closed loop comprises both a phase locked loop (PLL) and a delay locked loop (DLL) in a novel time division multiplex data recovery system. This new architecture comprises a 4 stage Voltage Controlled Oscillator (VCO) used to generate 8 clock signals, 45 degrees phase shifted from one another, for 8 receivers to do the oversampling. An interpolator tracks the received data signal and feeds it back to the Phase / Frequency Detector (PFD). The PFD has a second input of the reference clock which the PFD uses along with the interpolator input to correct the frequency of the PLL. The PLL operates at a high bandwidth. The DLL's bandwidth is several orders lower than the PLL. The DLL activates only a multiplexer and an interpolator continuously, thereby drawing a minimum amount of power.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
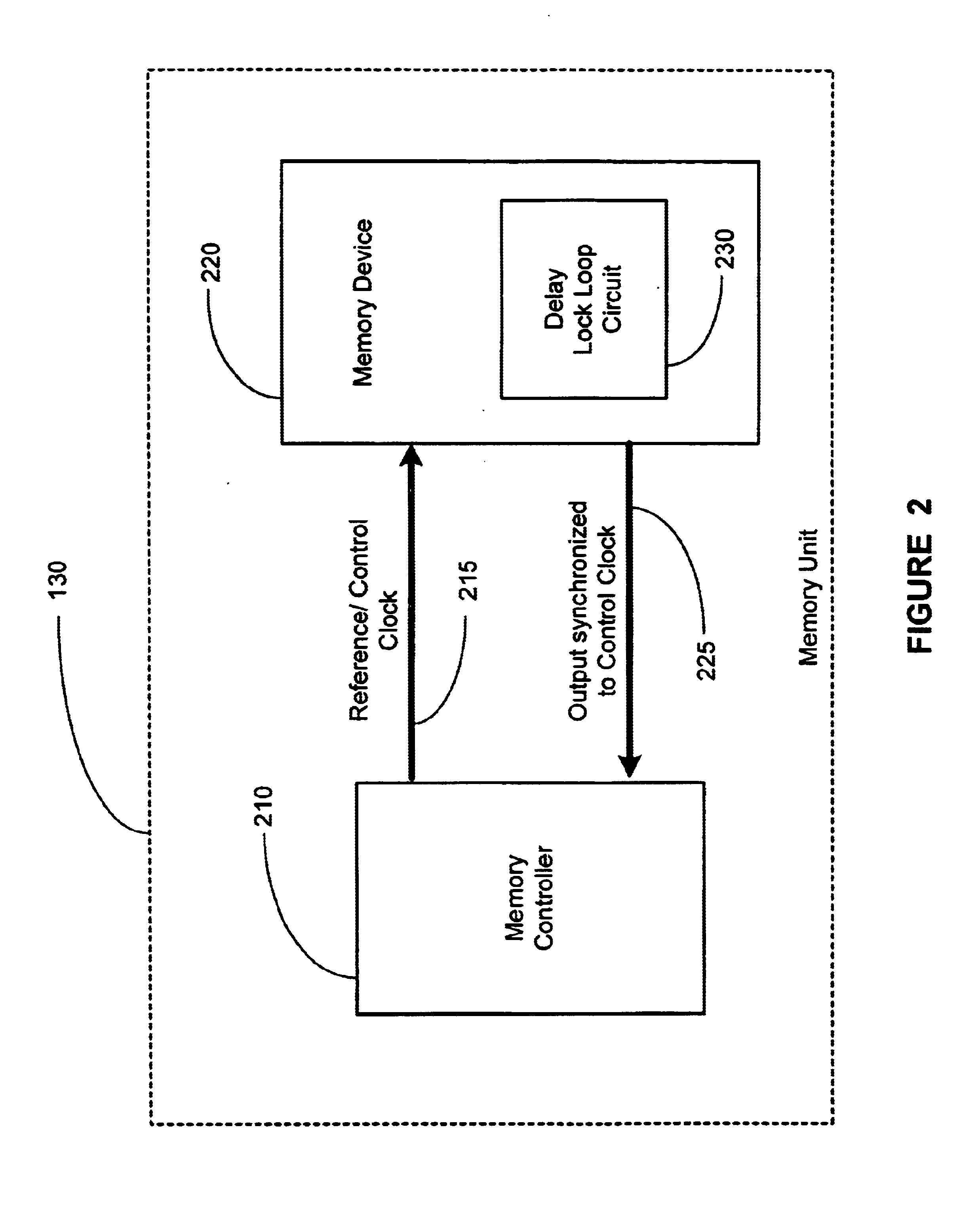
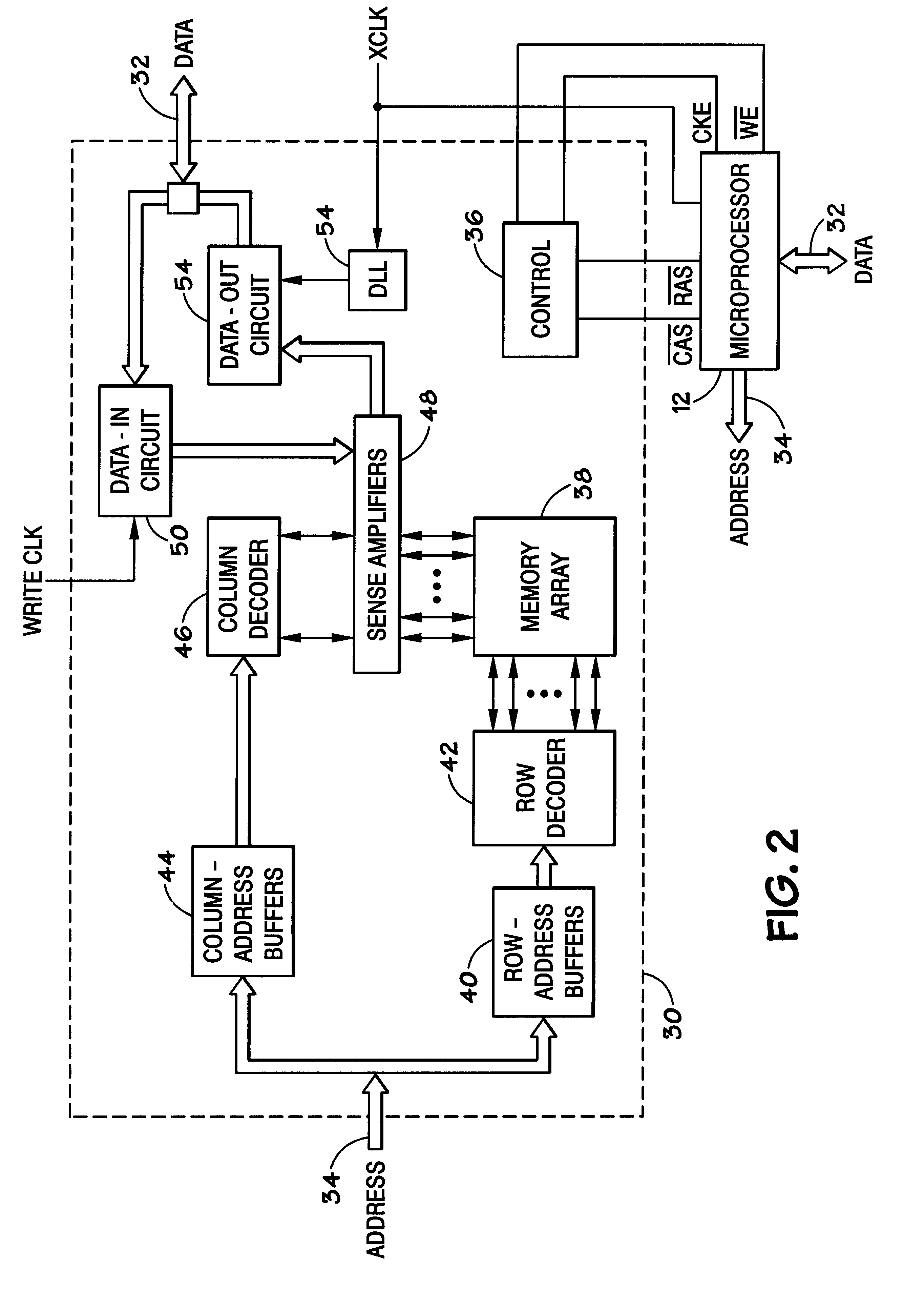
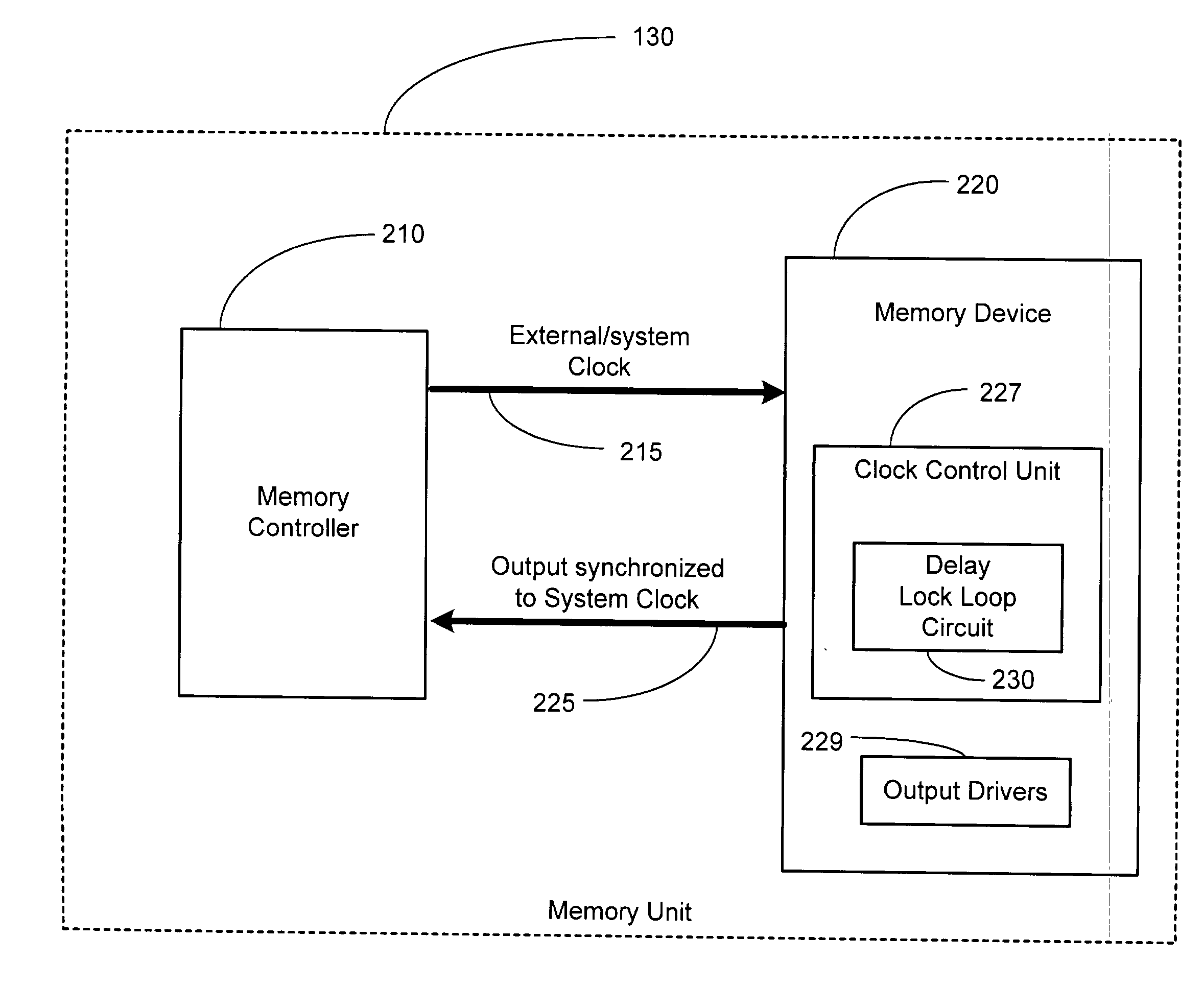
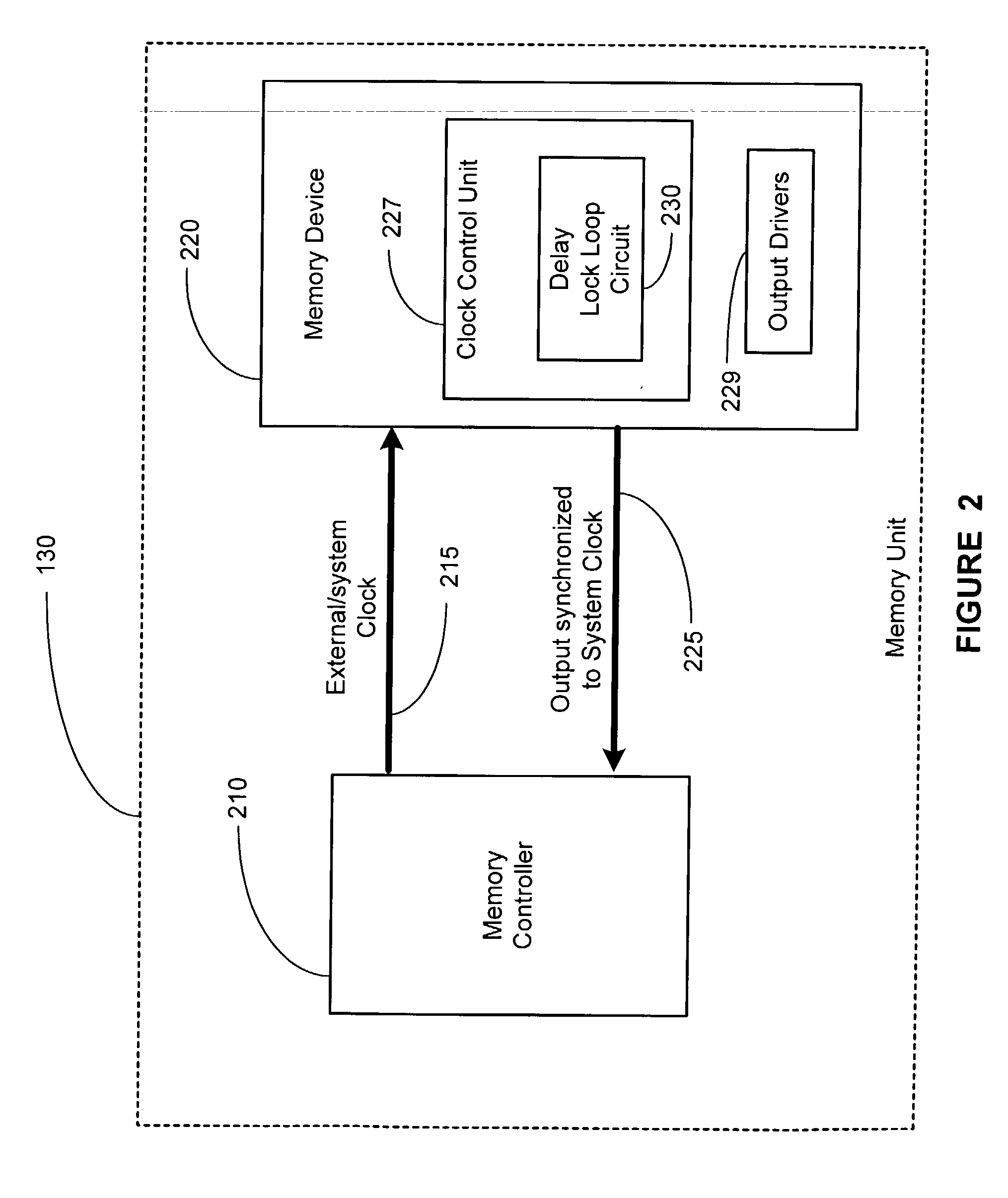
Dual clocked synchronous memory device having a delay time register and method of operating same
InactiveUS6035365AFast readWrite quicklyEnergy efficient ICTMemory adressing/allocation/relocationProcessor registerDelay-locked loop
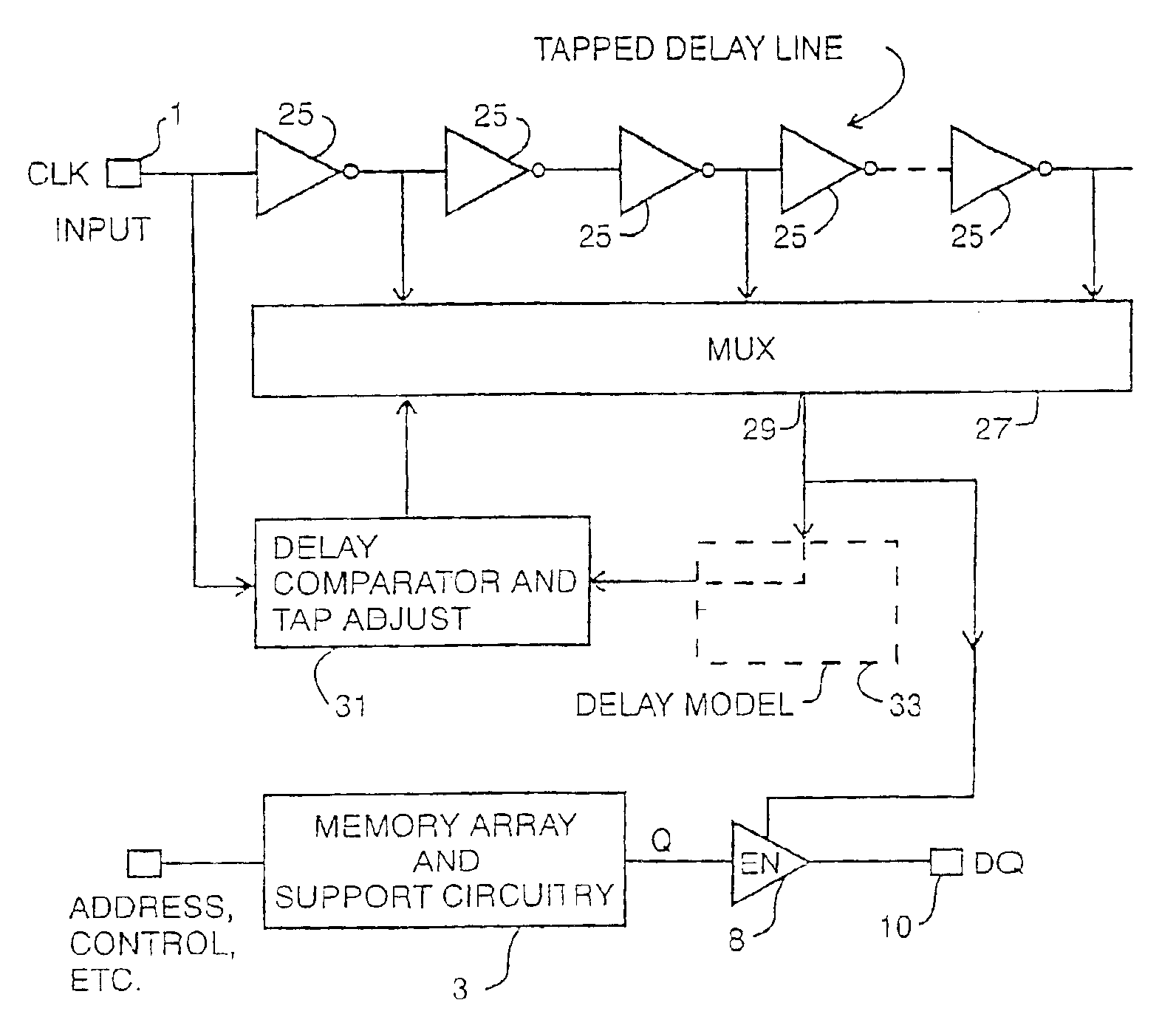
A synchronous memory device having at least one memory section which includes a plurality of memory cells. The memory device comprises a register to store a value which is representative of a delay time after which the memory device responds to a read request and clock receiver circuitry to receive first and second external clock signals. The memory device also includes an output driver(s) to output data on a bus, in response to a read request and in accordance with the delay time, wherein a first portion of the data is output synchronously with respect to the first external clock signal and a second portion of the data is output synchronously with respect to the second external clock signal. The memory device may include a delay locked loop to generate internal clock signal(s) using the external clock signal(s). The output drivers output data on the bus in response to the internal clock signal(s). The memory device may include input receiver circuitry, coupled to the bus, the receive the read request, wherein the read request is sampled from the bus synchronously with respect to the first external clock signal.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
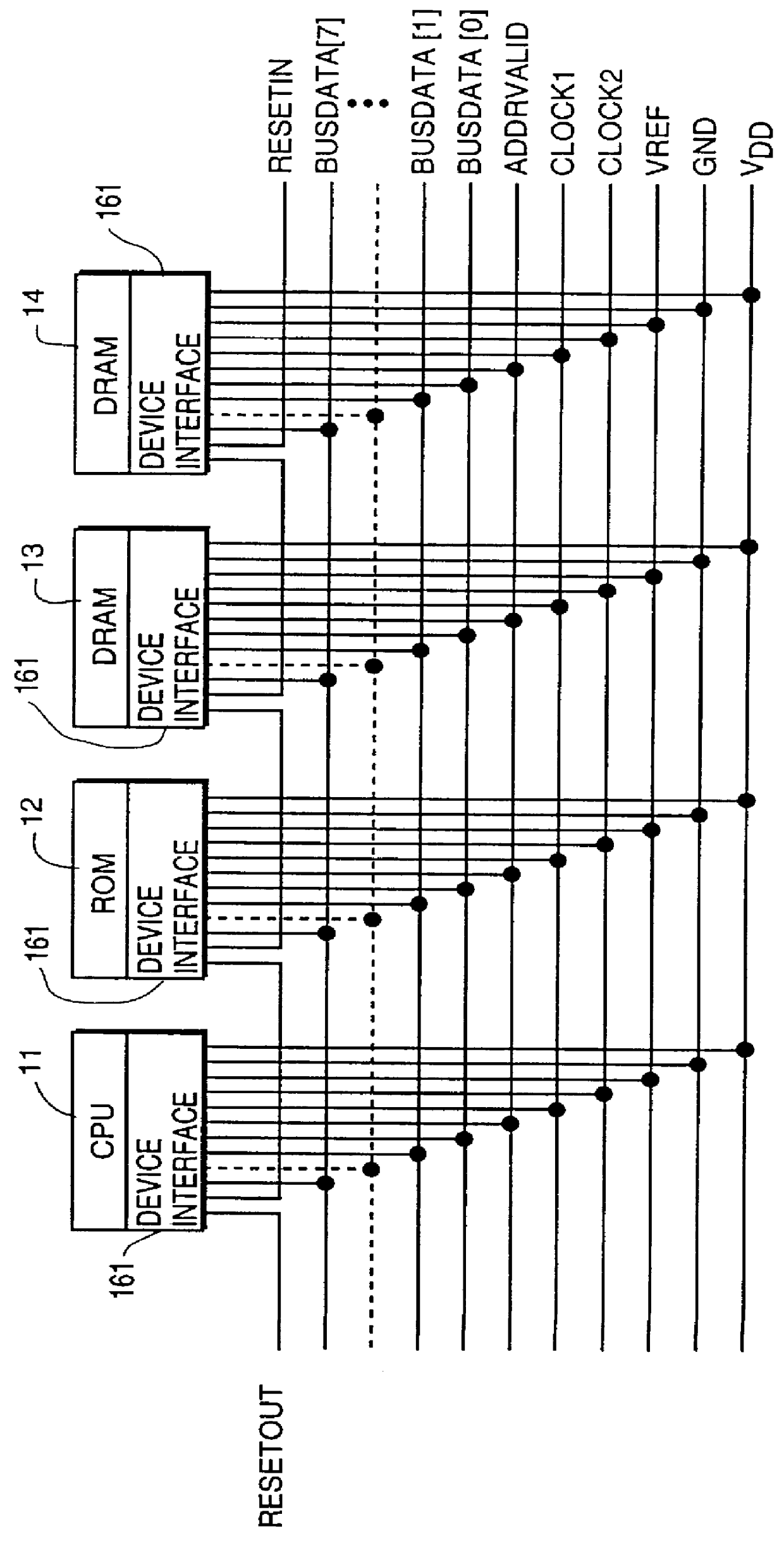
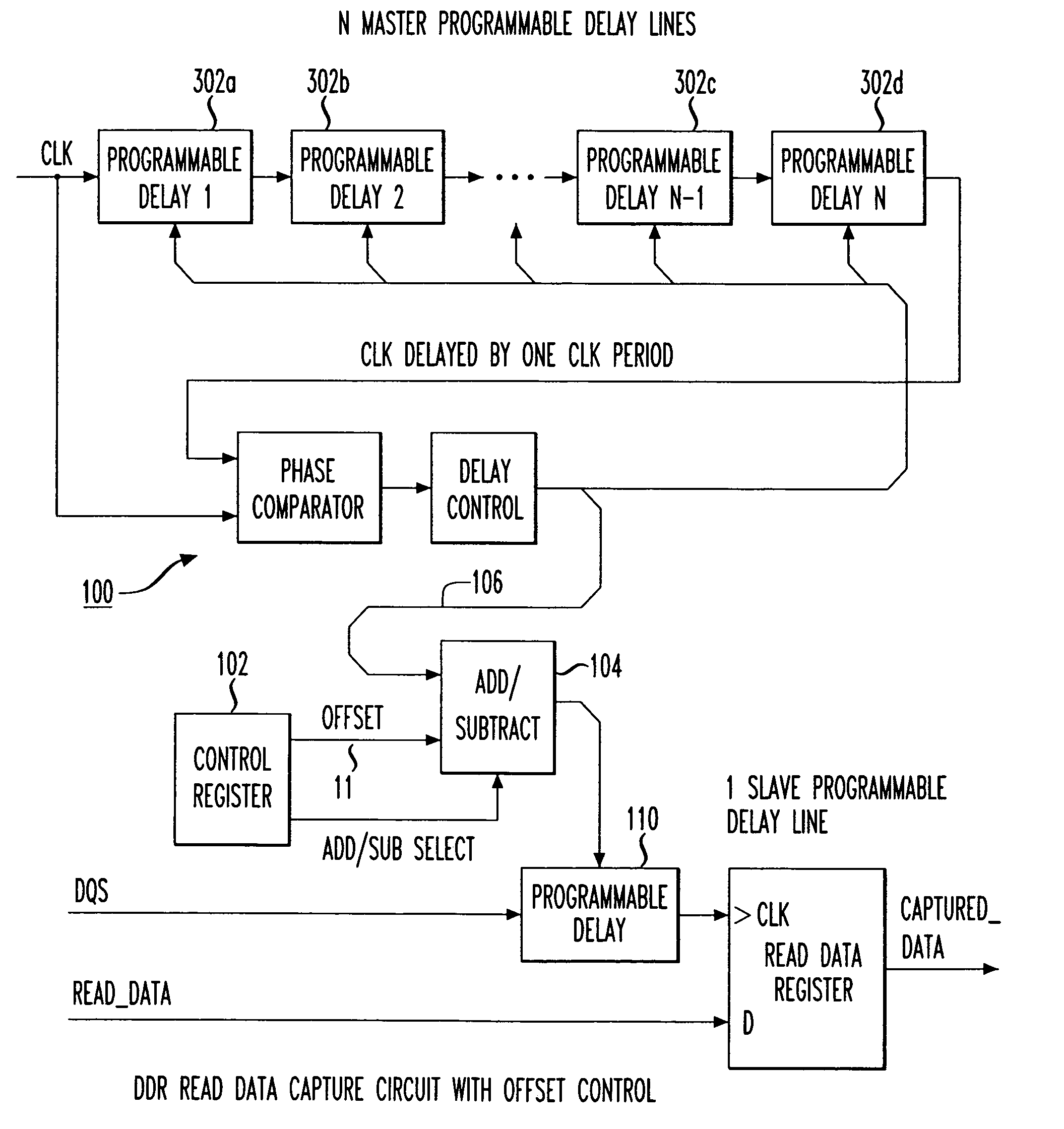
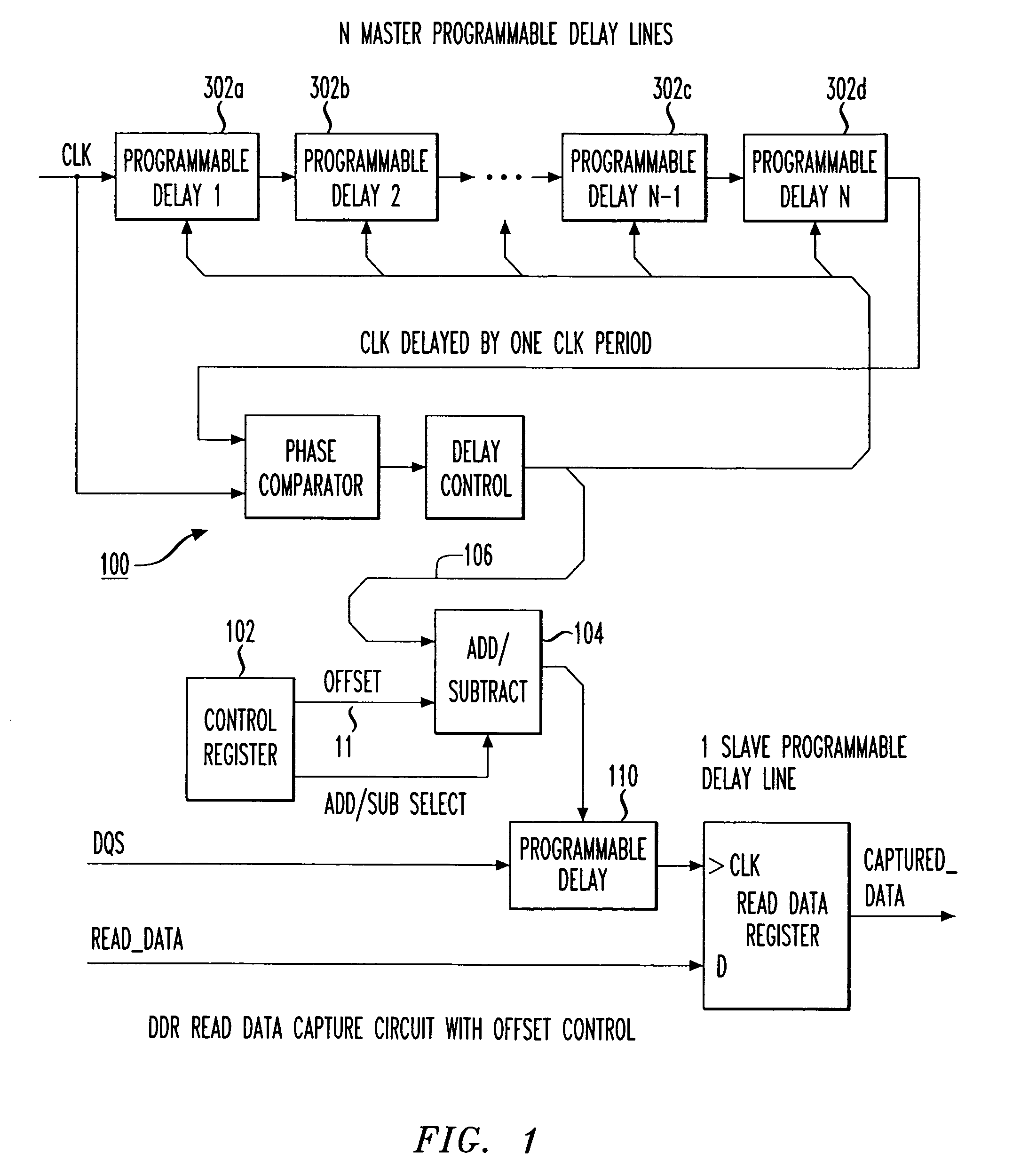
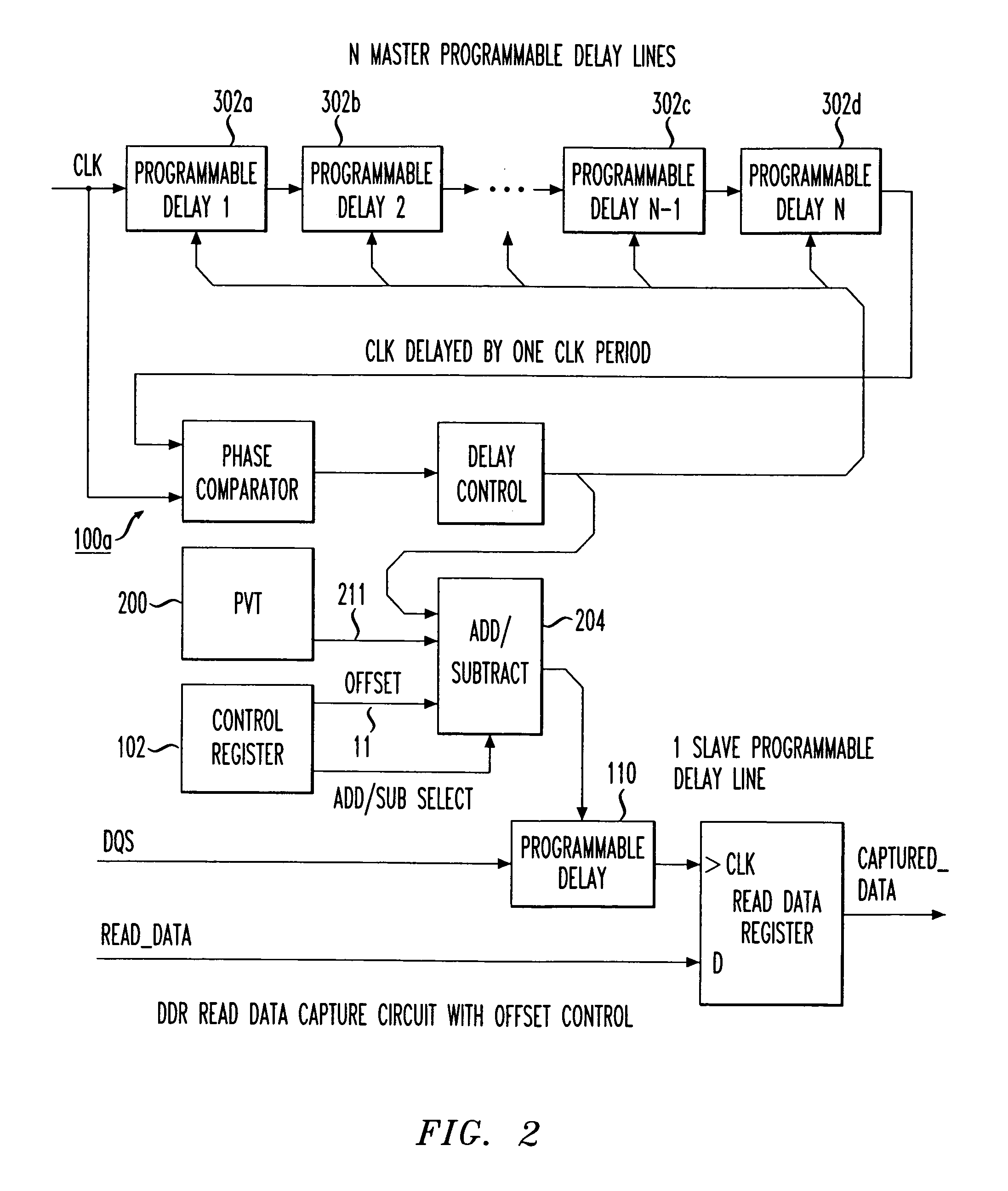
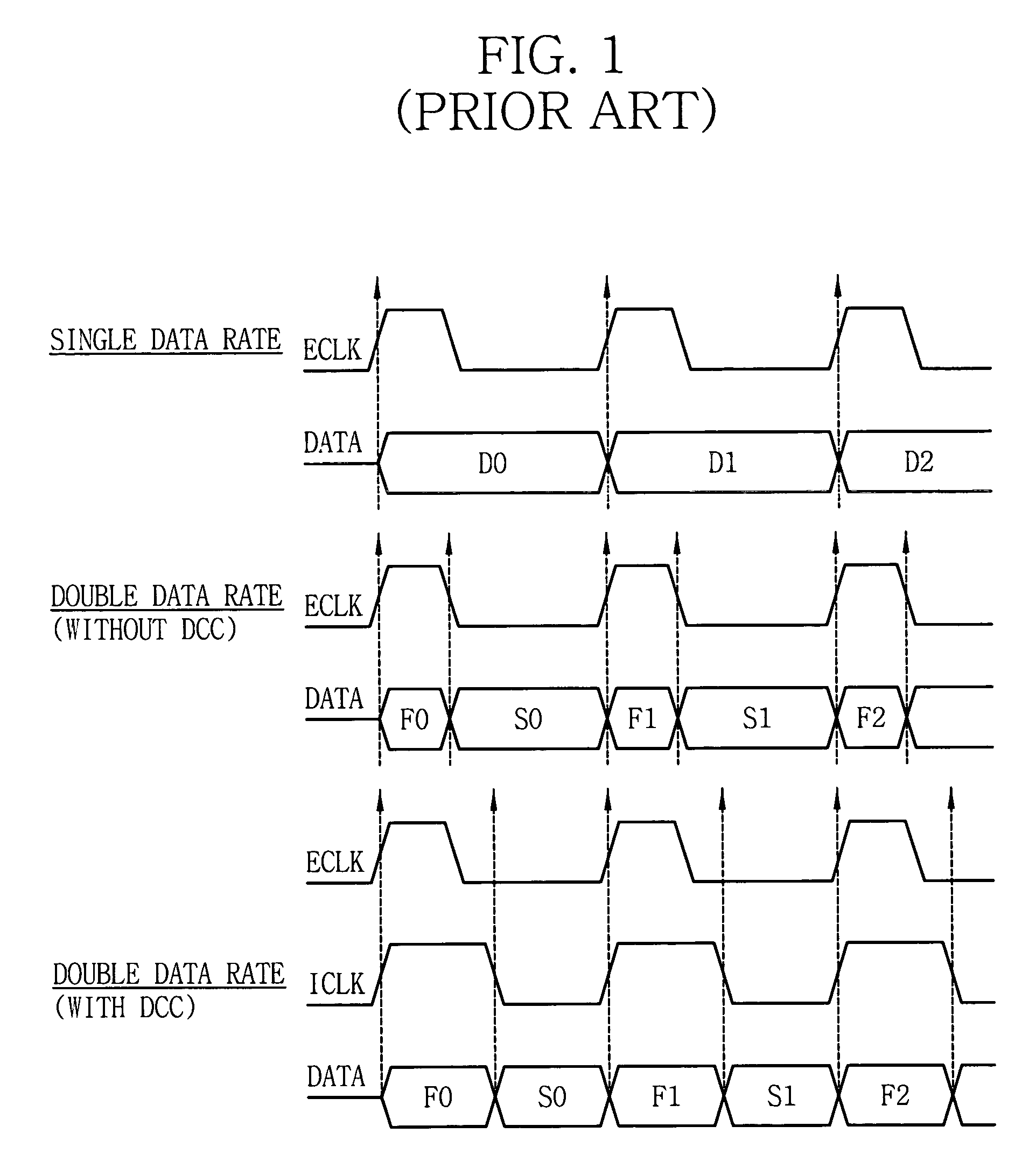
Programmable data strobe offset with DLL for double data rate (DDR) RAM memory
A double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic RAM (SDRAM), or DDR-SDRAM, memory controller employing a delay locked loop (DLL) circuit to delay an SDRAM data strobe (DQS) signal to the center, or ‘eye’ of the read data window. However, in distinction from conventional techniques, the initial delay determined by the DLL is fine tuned with an offset determined by a memory test. Moreover, in an additional embodiment, the delay may be further adjusted during operation to compensate for environmental conditions by a PVT (process, value, temperature) circuit.
Owner:AGERE SYST INC
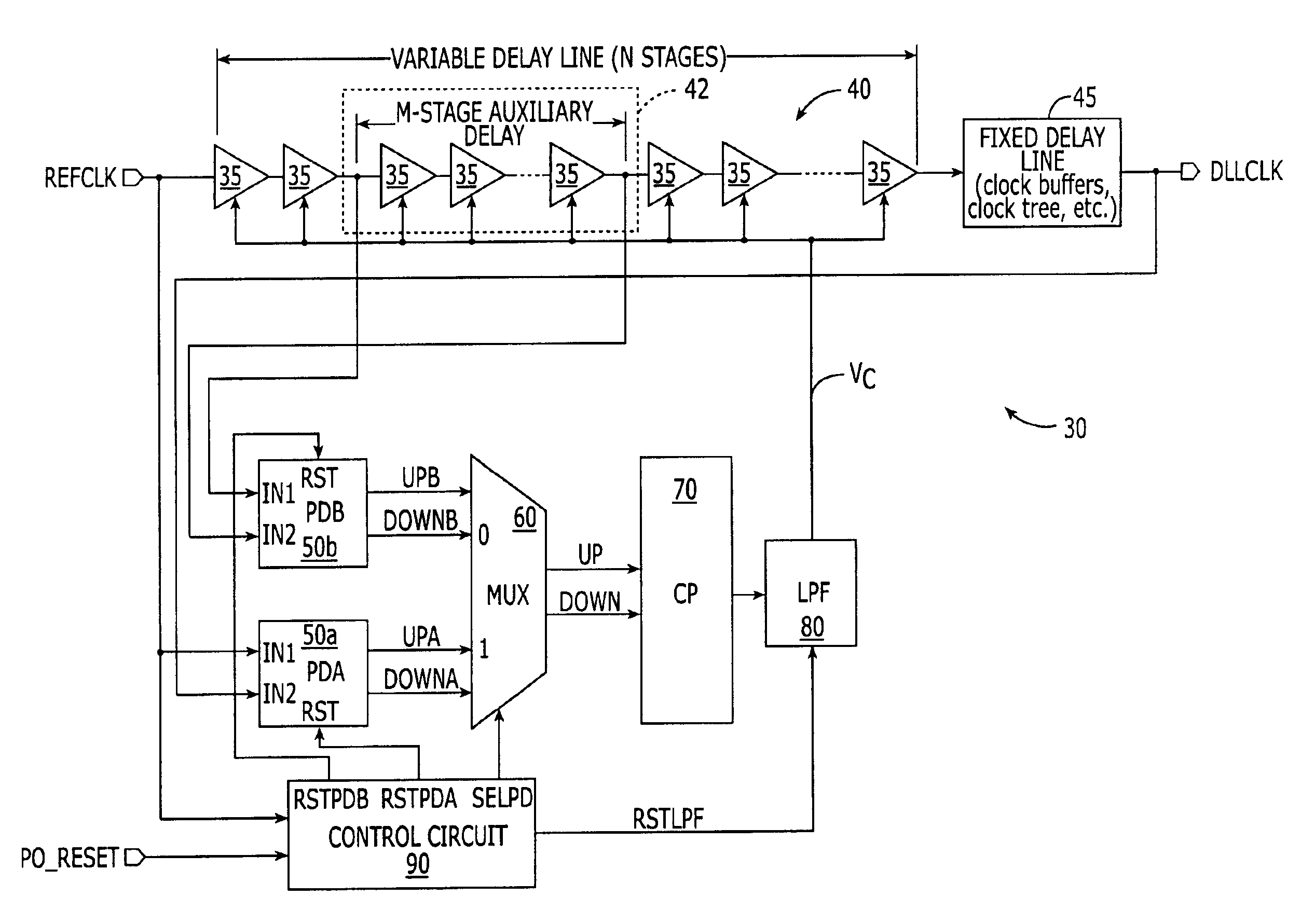
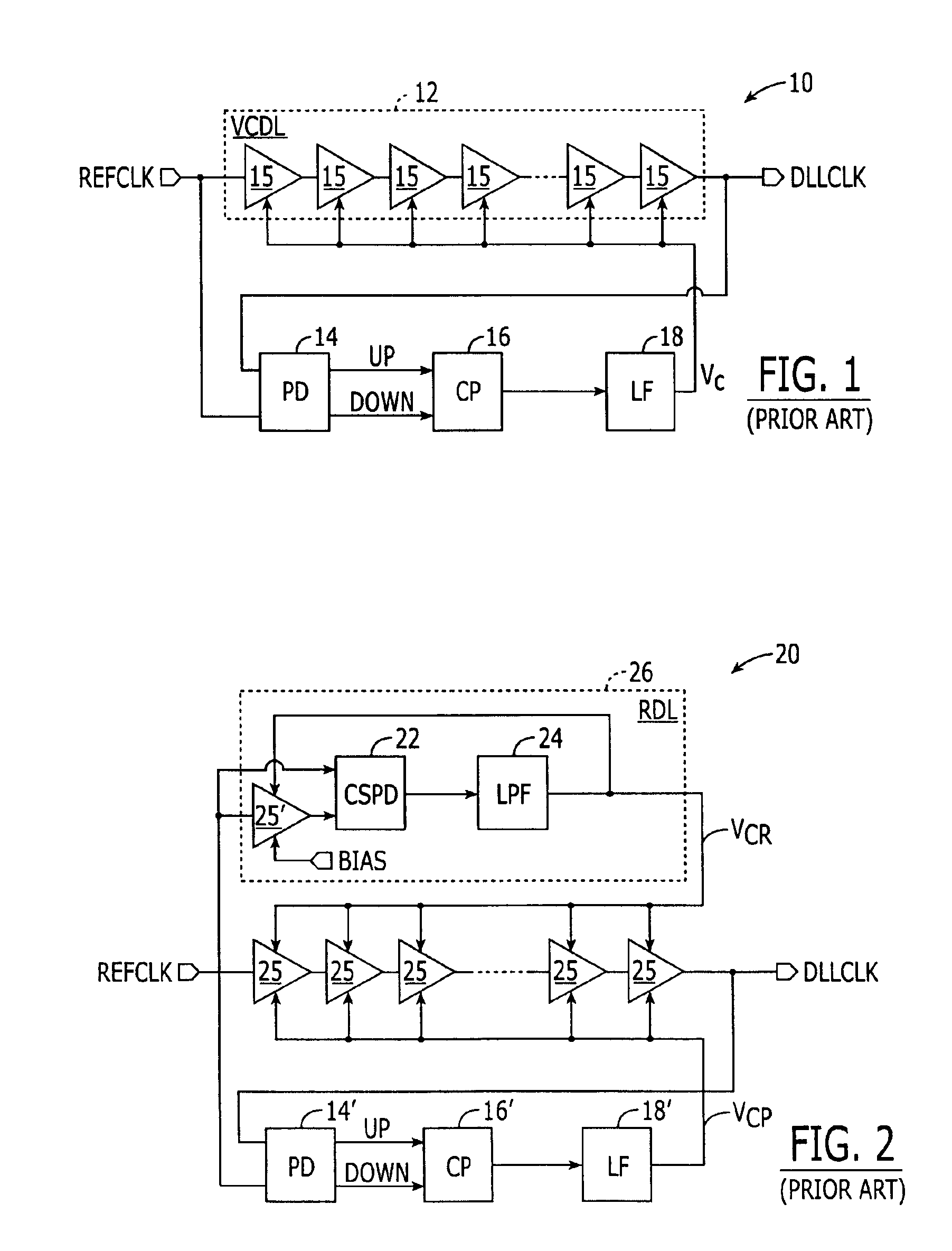
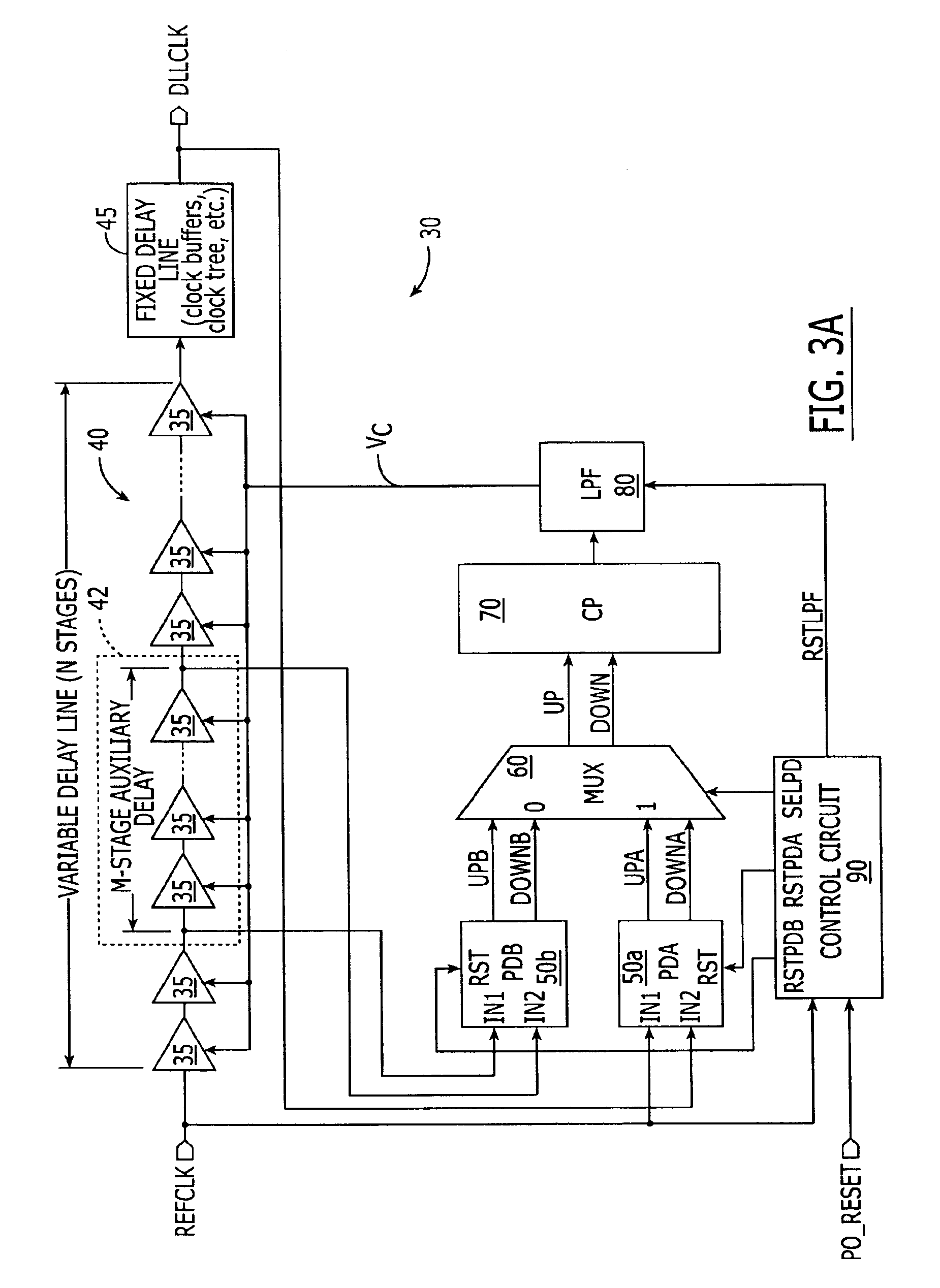
Delay-locked loop (DLL) integrated circuits having high bandwidth and reliable locking characteristics
Delay-locked loops have high bandwidth locking characteristics that are less susceptible process, voltage and temperature (PVT) variations. These DLLs are configured to support transition from a partial feedback loop lock condition to a full feedback loop lock condition during a start-up time interval, in order to insure that a multi-cycle lock condition is established at the time the DLL's clock signal output becomes available. The DLL may include a variable delay line that is responsive to a reference clock signal, an auxiliary phase detector that is electrically coupled to the variable delay line, and a main phase detector that is responsive to the reference clock signal and a feedback clock signal (DLLCLK). The auxiliary phase detector may be an edge-triggered SR-type phase detector and the main phase detector may be a three-state phase frequency detector.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
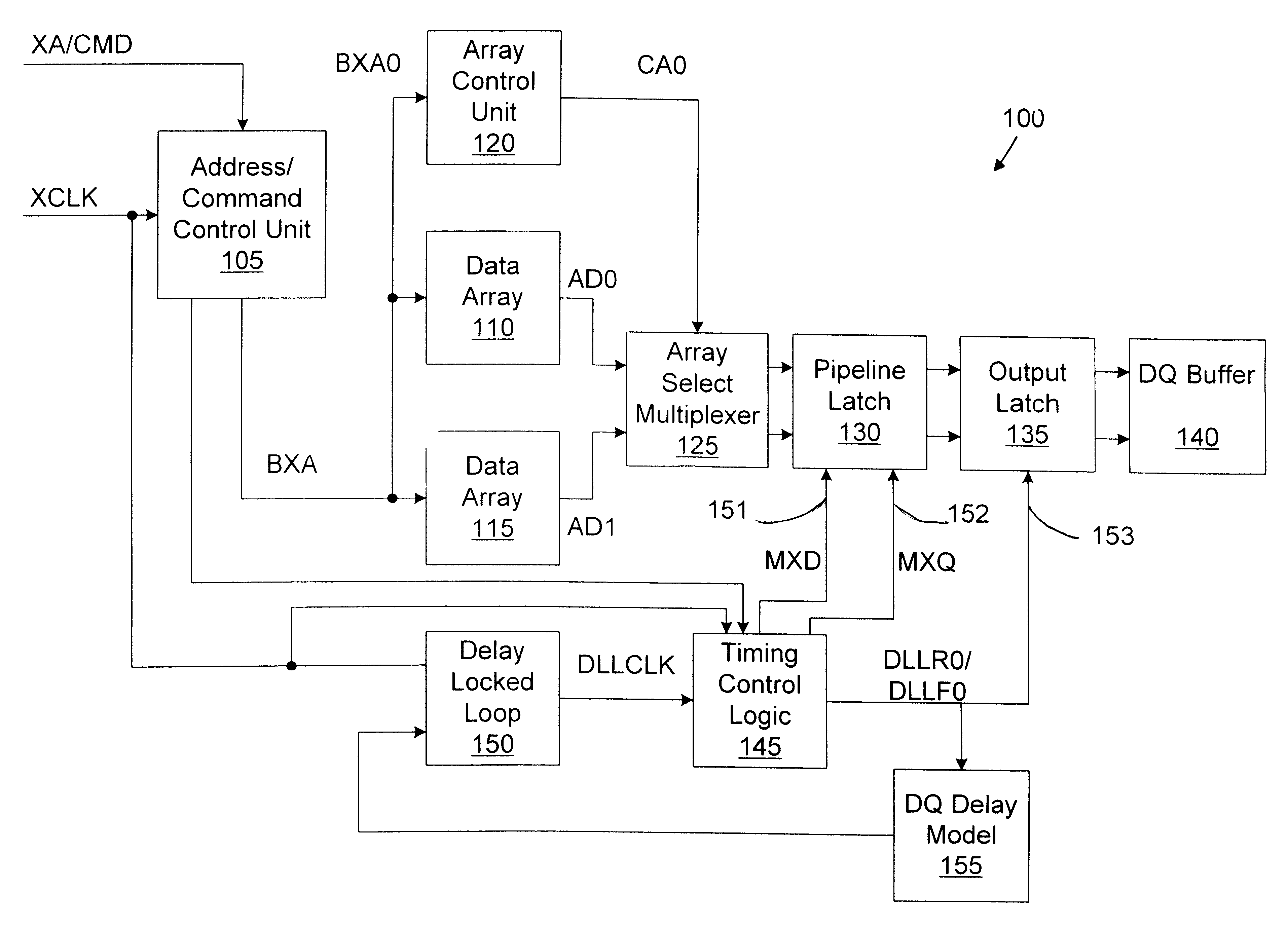
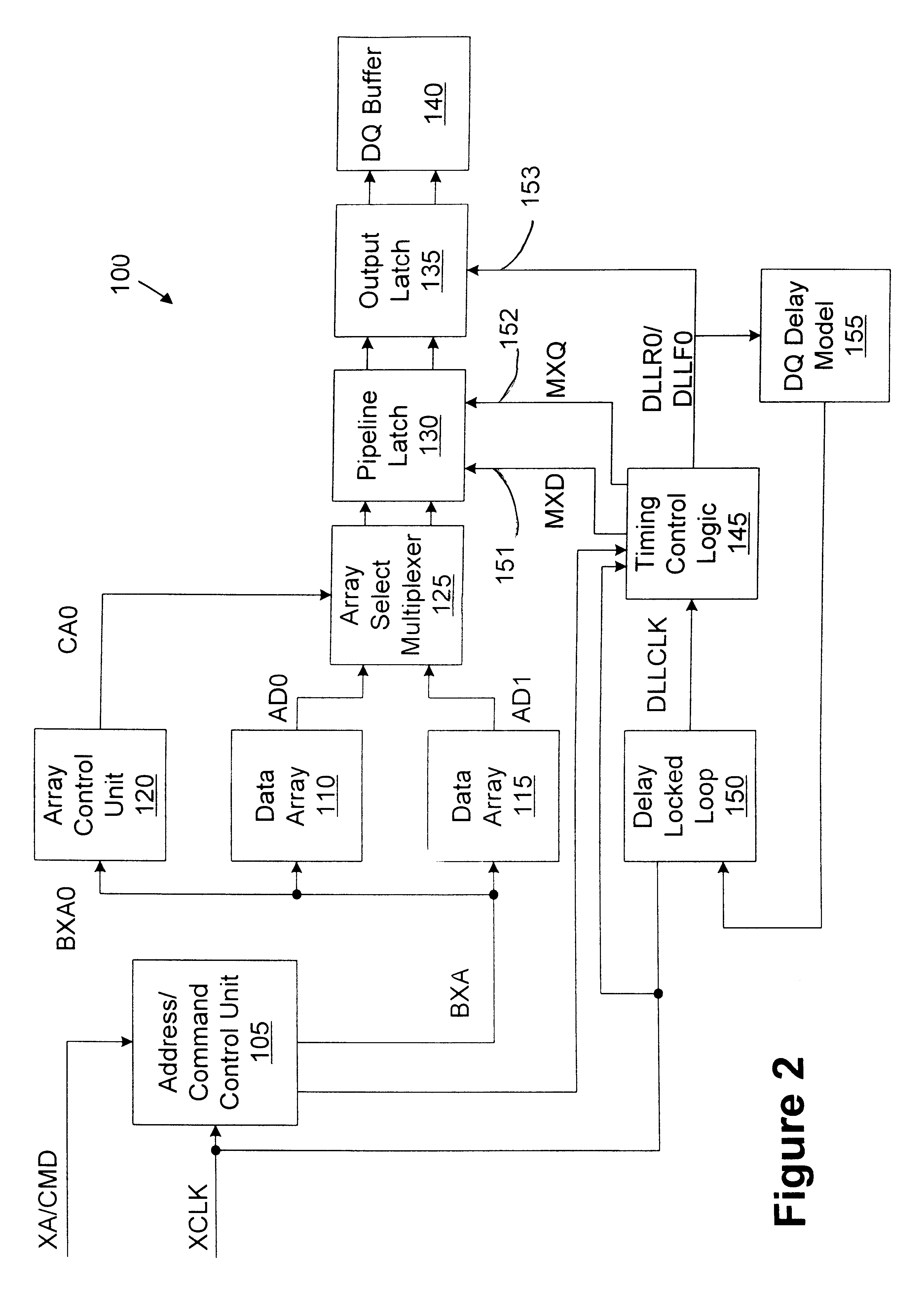
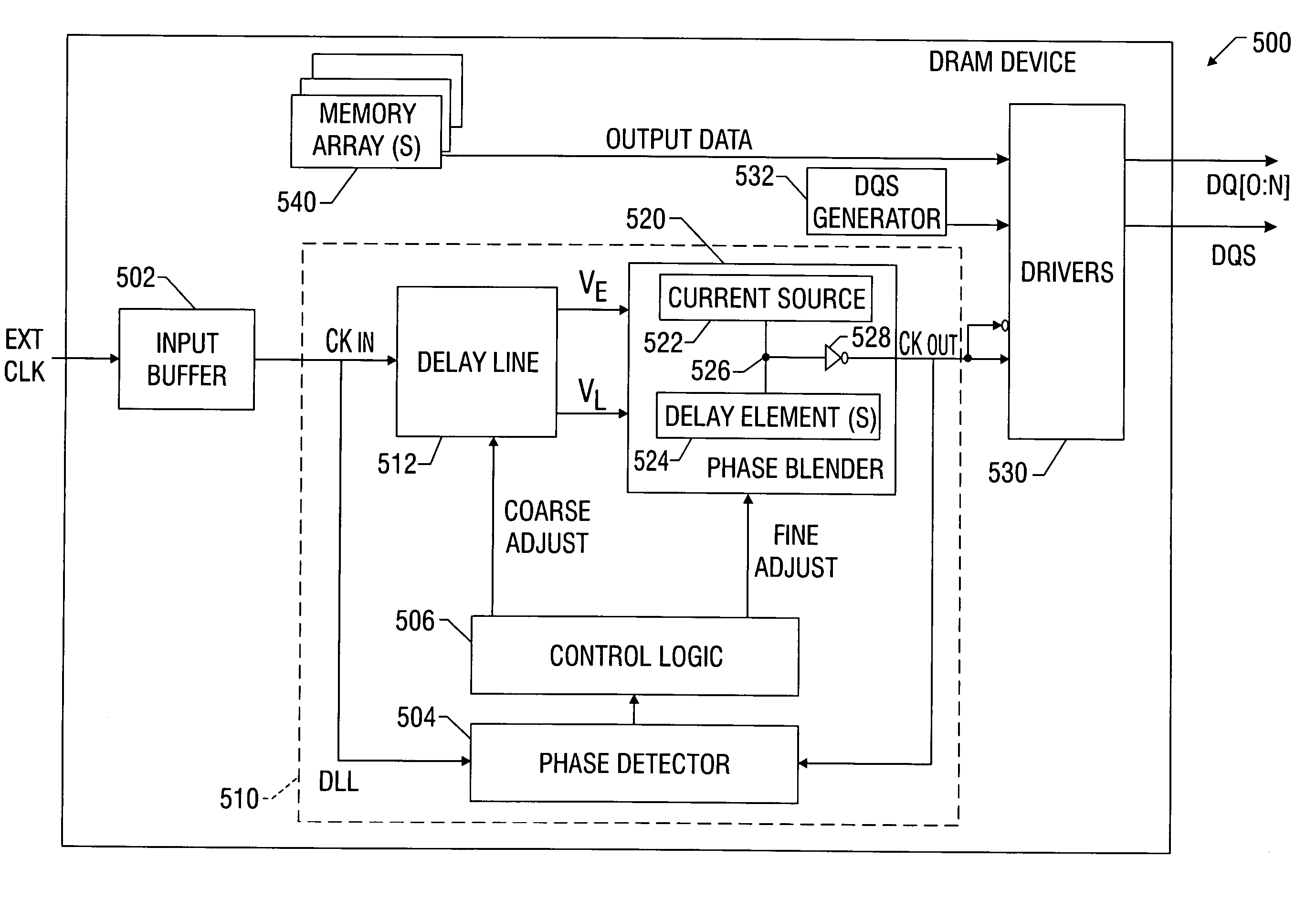
Memory device with synchronized output path
A memory device includes a data array, array control logic, a delay locked loop circuit, timing control logic, and a first storage device. The array control logic is adapted to receive a read command synchronized with an external clock signal and to read at least a first data element from the data array based on the read command. The delay locked loop circuit is adapted to receive the external clock signal and delay the external clock signal by a programmable amount to generate a delay locked loop clock signal. The timing control logic is adapted to generate a first input enable signal based on the external clock signal and a first output enable signal based on the delay locked loop clock signal. The first storage device adapted to receive the first data element. The first storage device has an input terminal enabled in response to the first input enable signal and an output terminal enabled in response to the first output enable signal.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
Process, voltage, temperature independent switched delay compensation scheme
InactiveUS6327318B1Pulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionDelay-locked loopEngineering
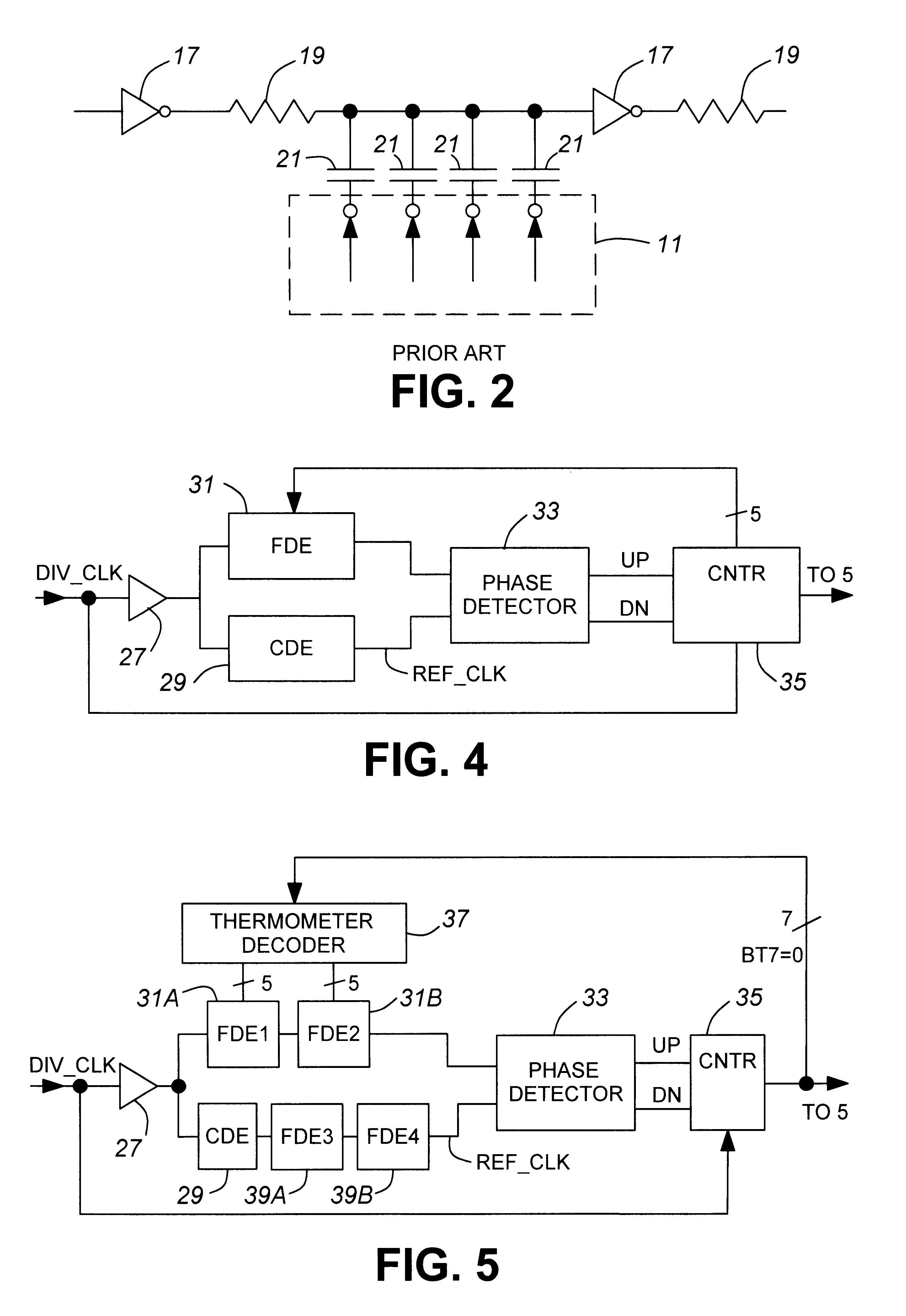
A delay compensation circuit for a delay locked loop which includes a main delay line having a fine delay line comprising fine delay elements and a coarse delay line comprising coarse delay elements, the main delay line being controlled by a controller, the delay compensation circuit comprising: an adjustable fine delay for modeling a coarse delay element, a counter for controlling the adjustable fine delay to a value which is substantially the same as that of a coarse delay element, a circuit for applying a representation of the system clock to the delay compensation circuit, and a circuit for applying the fine delay count from the counter to the controller for adjusting the fine delay line of the main delay line to a value which is substantially the same as that of a coarse delay element of the main delay line.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
Phase-locked loop circuit and delay-locked loop circuit
InactiveUS6954511B2Reduce changesPulse automatic controlTransmissionPhase locked loop circuitLow-pass filter
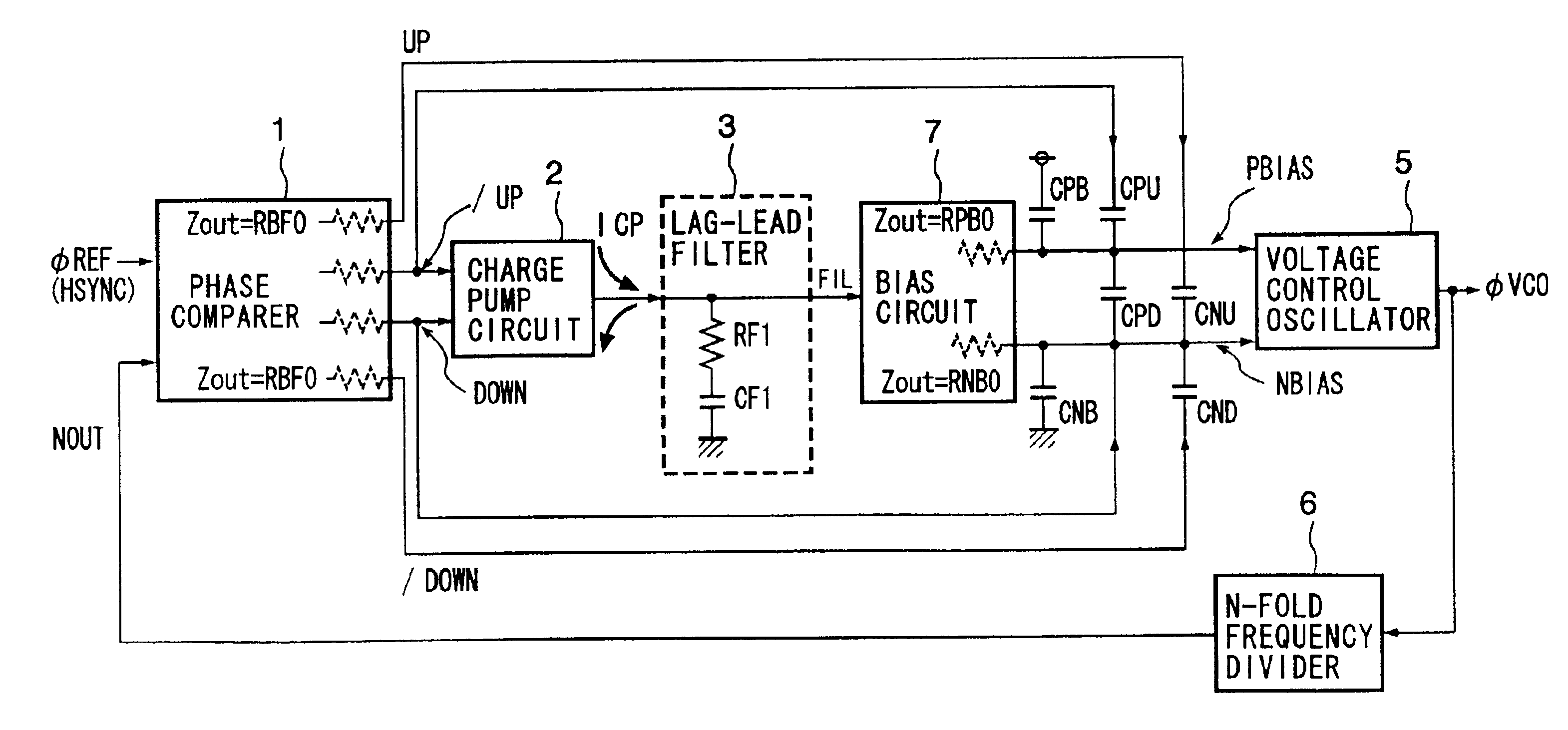
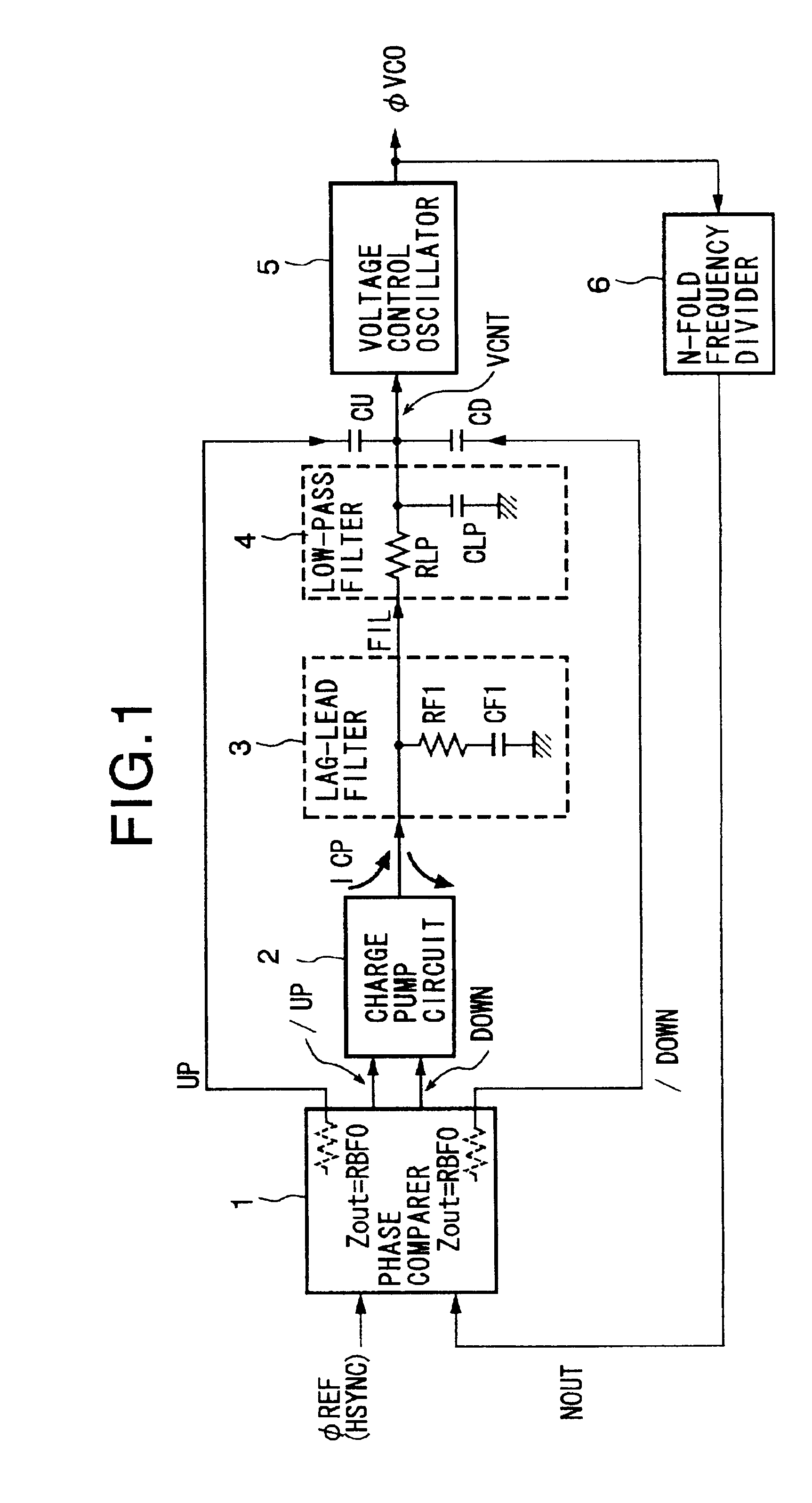
A PLL circuit and a DLL circuit able to stabilize a control voltage within a short time after a phase pull-in operation in each cycle of a reference clock. In a phase comparator, the size of a leading phase or a delayed phase of a feedback signal is detected with respect to a reference clock signa, and pulse signals having pulse widths corresponding to the size are output. A current corresponding to the signals is output from a charge pump circuit to a lag-lead filter, and a control voltage obtained by removing noise of the above output is output from a low-pass filter to a voltage-controlled oscillator. Furthermore, through capacitors, pulse signals are superposed on the control voltage, and a sharp waveform is obtained by correcting blunting of the waveform by the low-pass filter. Due to this, the control voltage is stabilized within a short time after a phase pull-in operation in each cycle of the reference clock signal.
Owner:SONY CORP
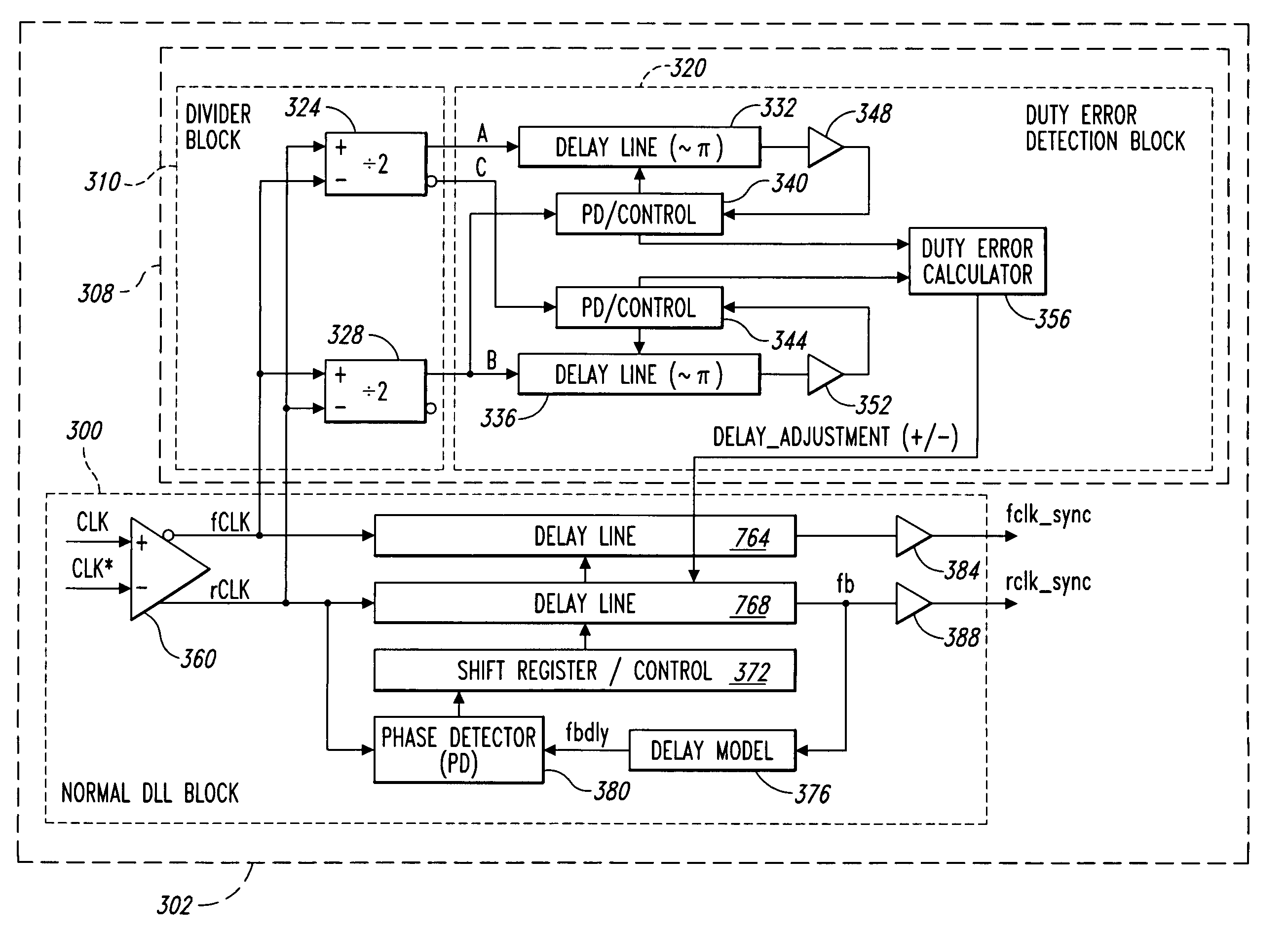
Clock generator having a delay locked loop and duty cycle correction circuit in a parallel configuration
ActiveUS20070086267A1Pulse automatic controlManipulation where pulse delivered at different timesDelay-locked loopClock generator
A clock generator having a delay locked loop and a duty cycle correction circuit. The delay locked loop adjusts a first adjustable delay circuit to generate a first output clock signal that is synchronized with a first input clock signal and adjusts a second adjustable delay circuit to provide a delay that is equal to the first adjustable delay circuit. A duty cycle correction circuit is coupled to the first and second inputs of the delay locked loop and further coupled to the second adjustable delay circuit. The duty cycle correction circuit is configured to determine a duty cycle error of at least one of the first and second input clock signals and adjust the second adjustable delay circuit to provide a corrected delay compensating for the duty cycle error.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Delay locked loop implementation in a synchronous dynamic random access memory
InactiveUS6992950B2High operating requirementsLess standby current and start-up timePulse automatic controlSingle output arrangementsRandom access memoryDelay-locked loop
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
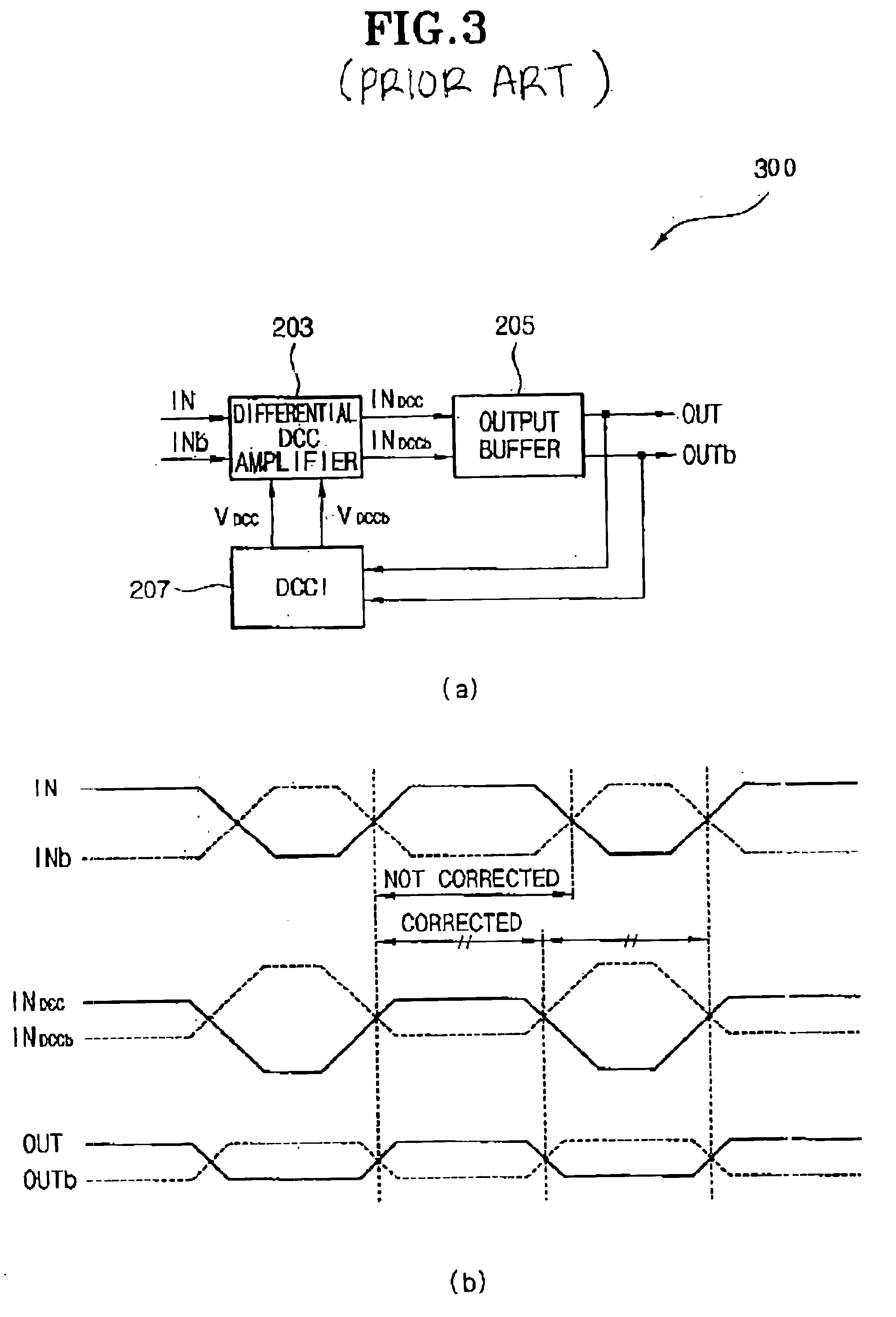
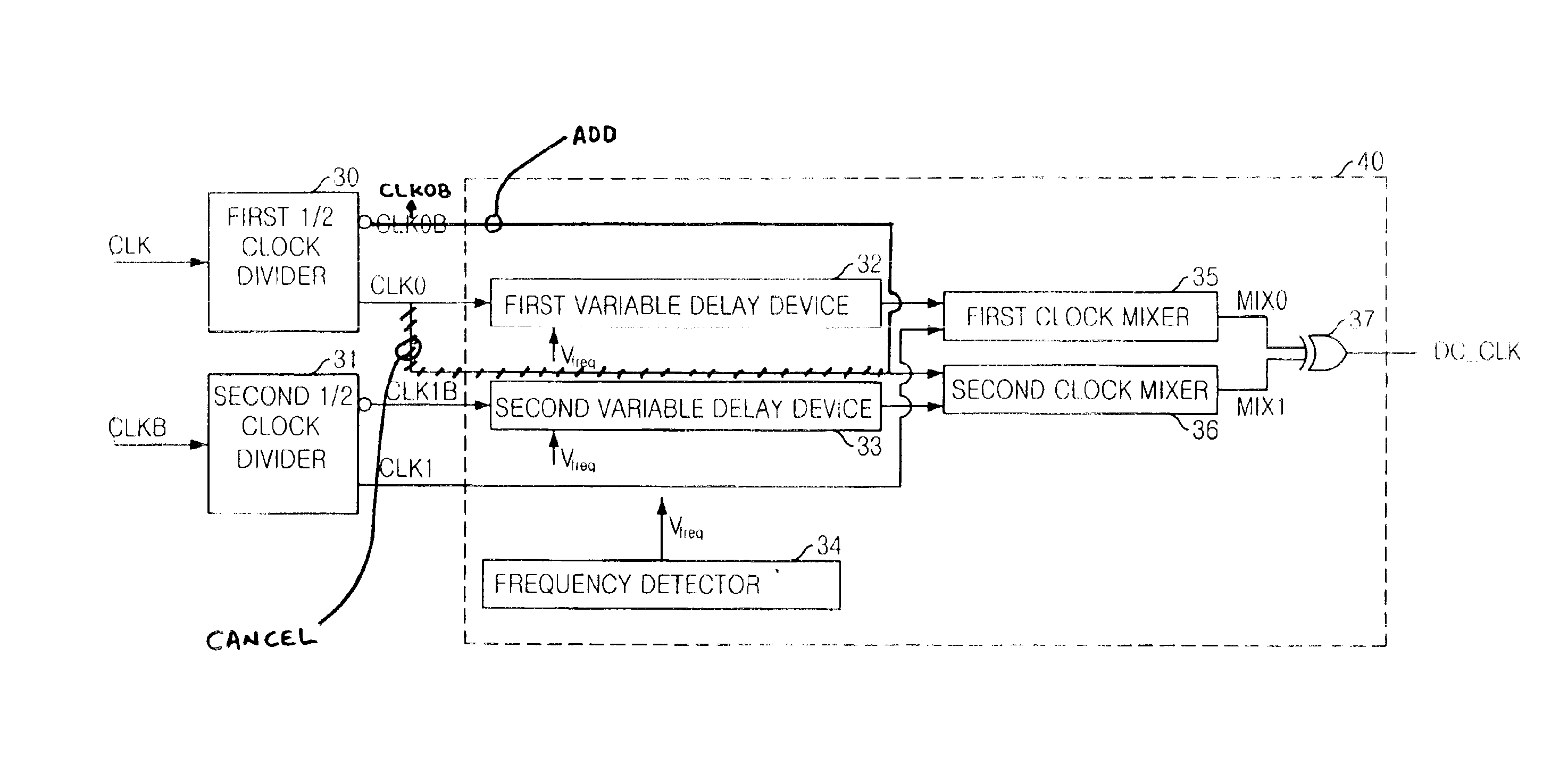
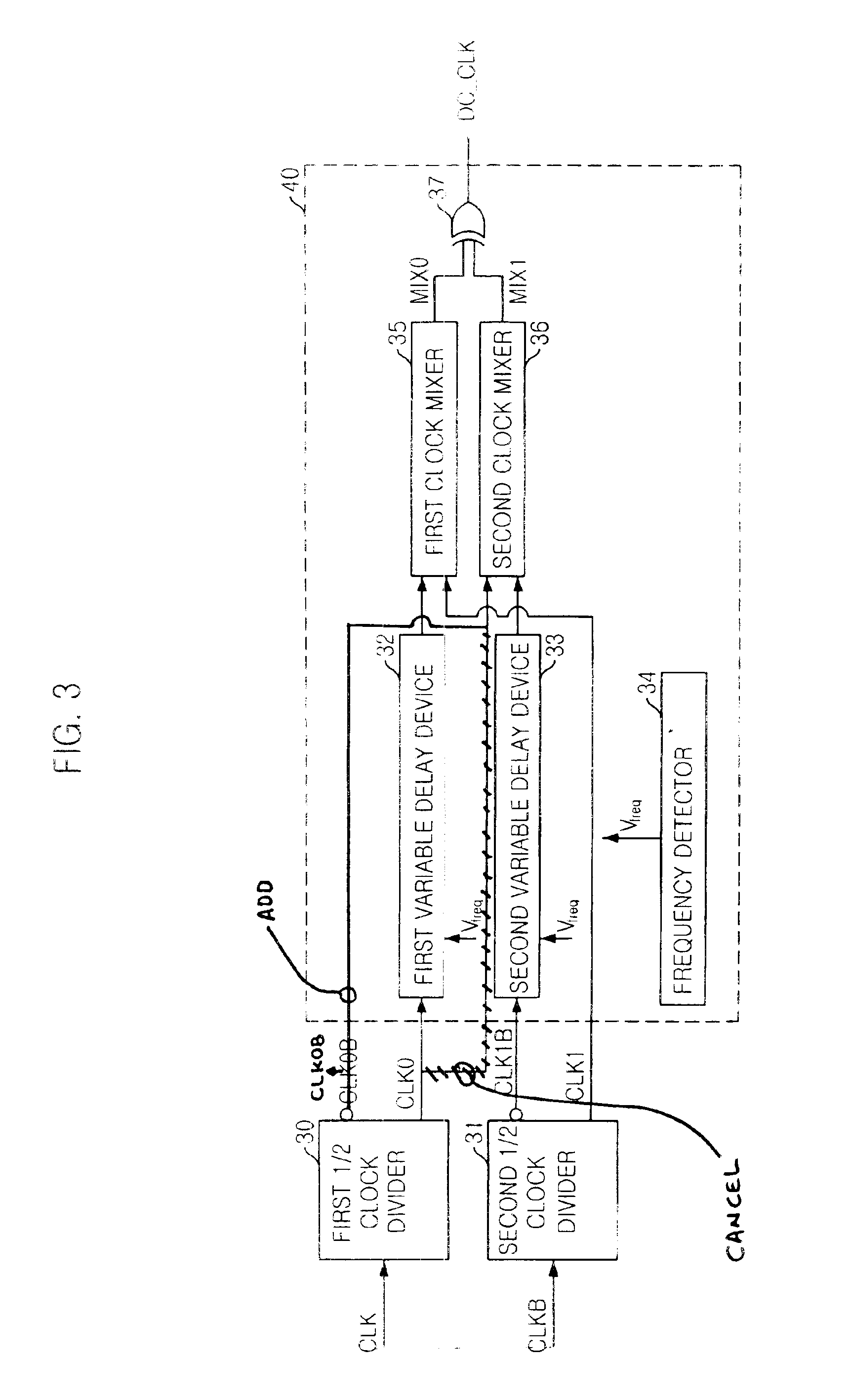
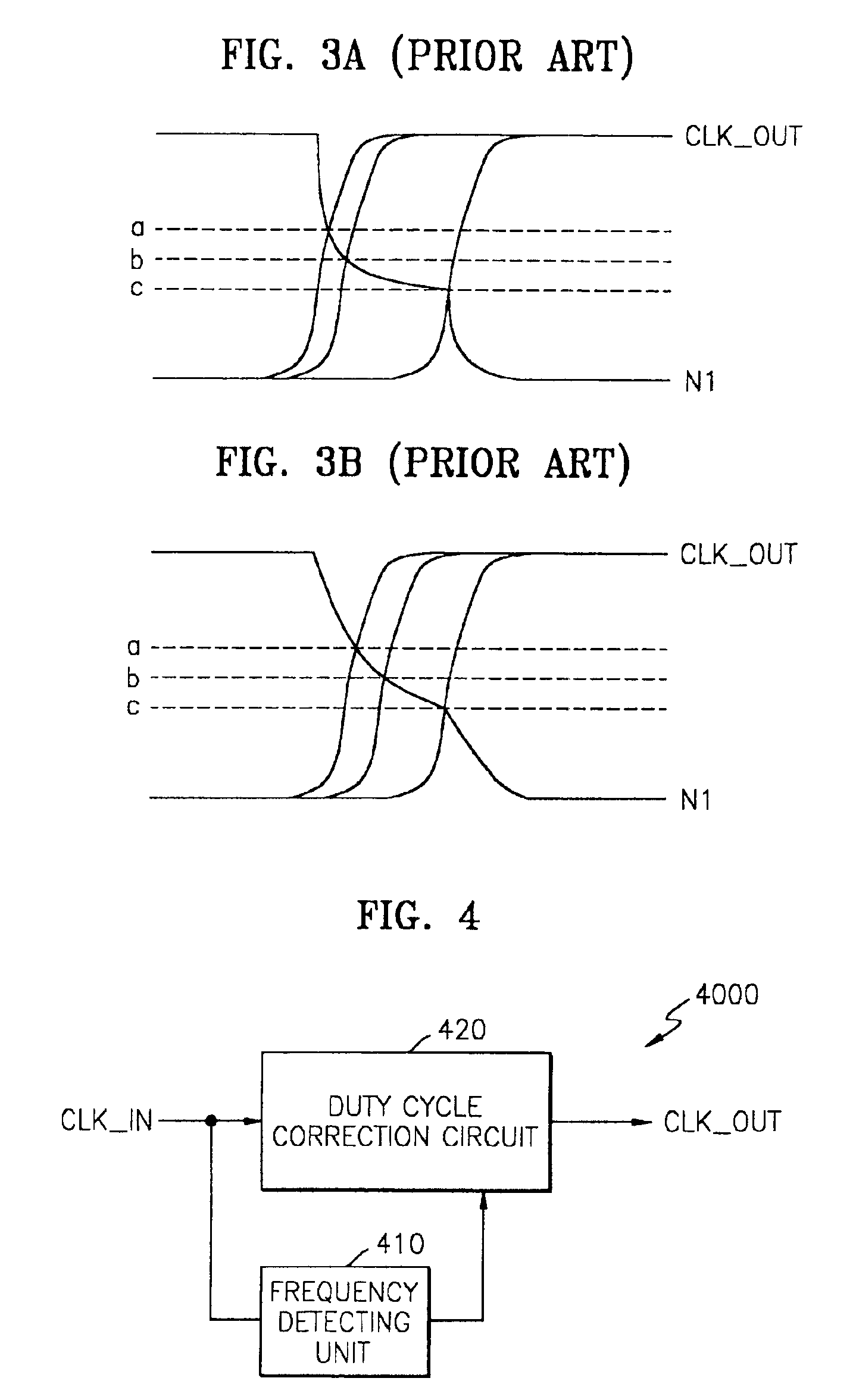
Duty cycle correction circuit and delay locked loop having the same
InactiveUS6859081B2Reduce power consumptionPulse automatic controlContinuous to patterned pulse manipulationClock rateFrequency mixer
A duty cycle correction (DCC) circuit including first and second clock dividers for dividing ordinary and sub-input clocks. Optional first and second variable delay devices delay the divided clocks. First and second mixers mix an optionally delayed ordinary divided clock and sub-ordinary divided clock, or an ordinary divided clock and an optionally delayed sub-ordinary divided clock. A logic combination device is included to produce a clock at the same frequency as the ordinary and sub-input clocks, with a corrected duty cycle.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
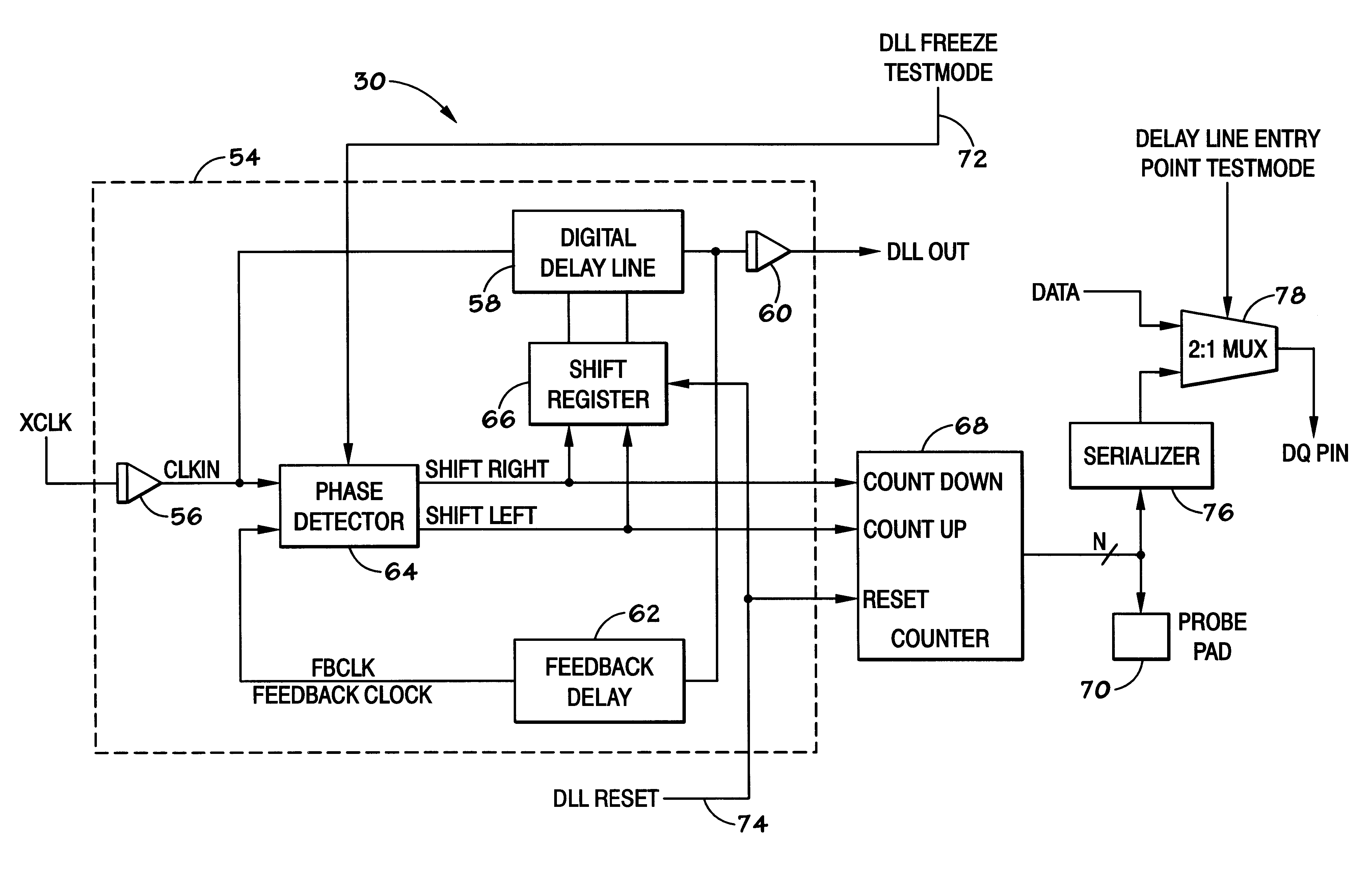
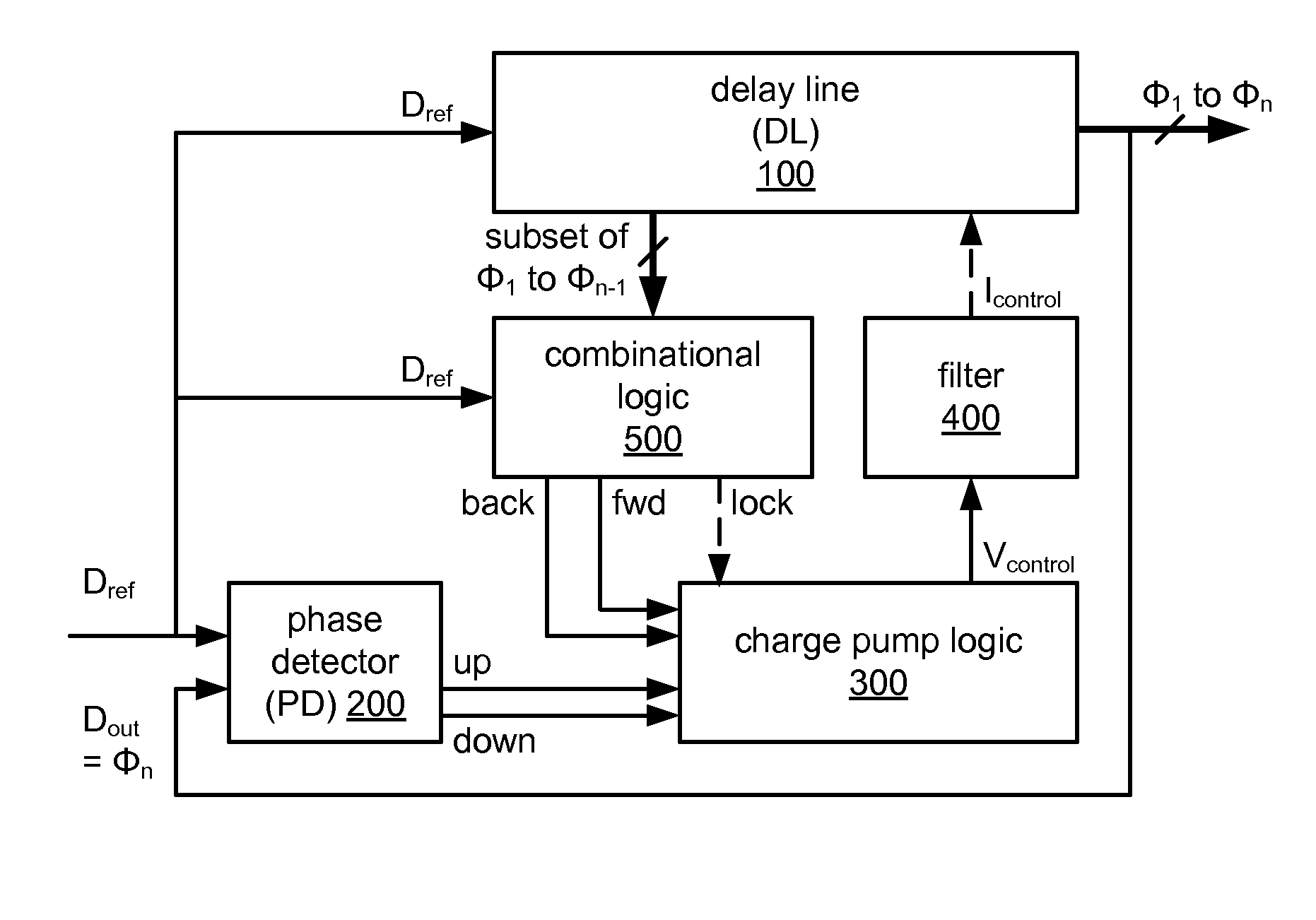
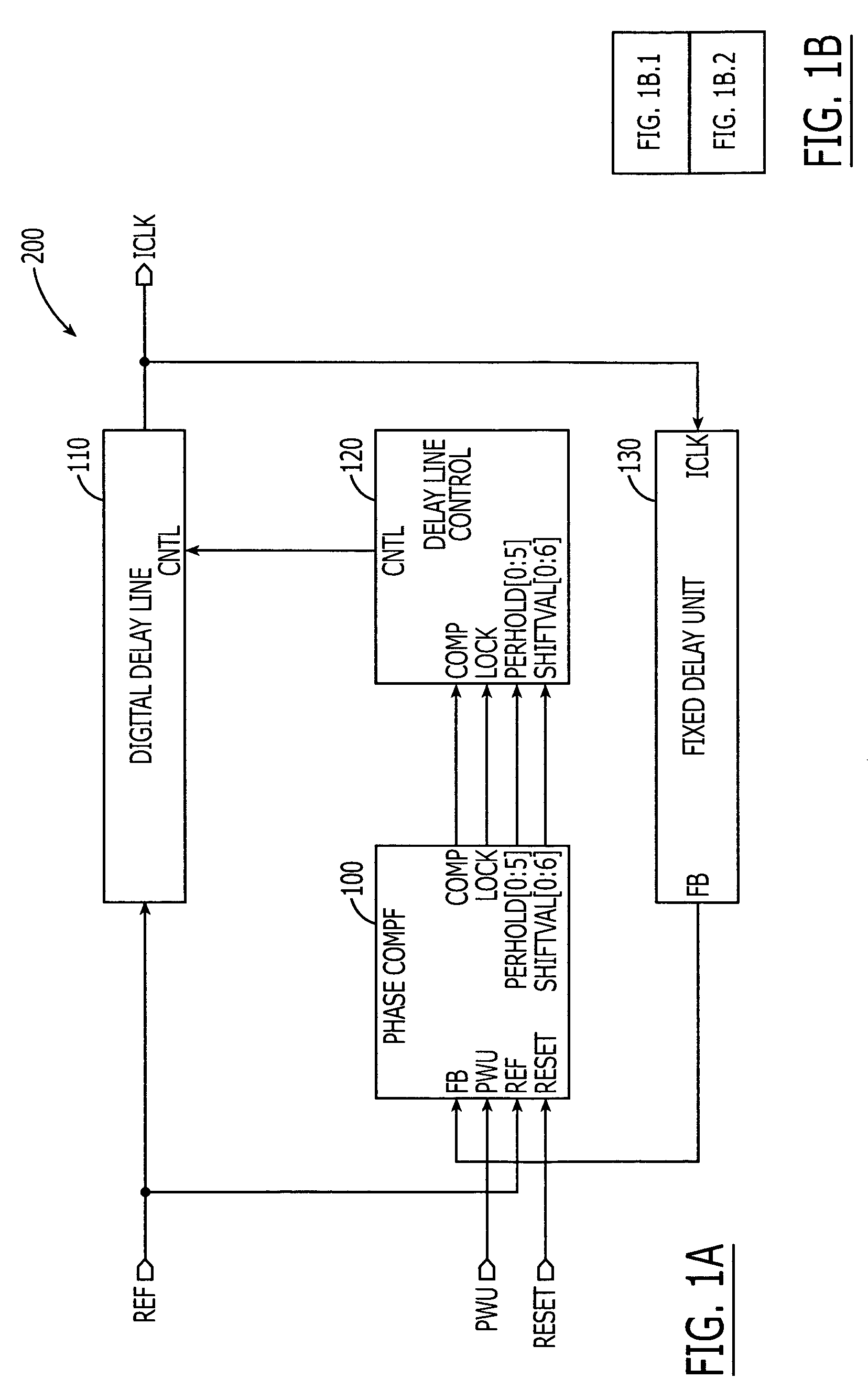
Method and apparatus for determining digital delay line entry point
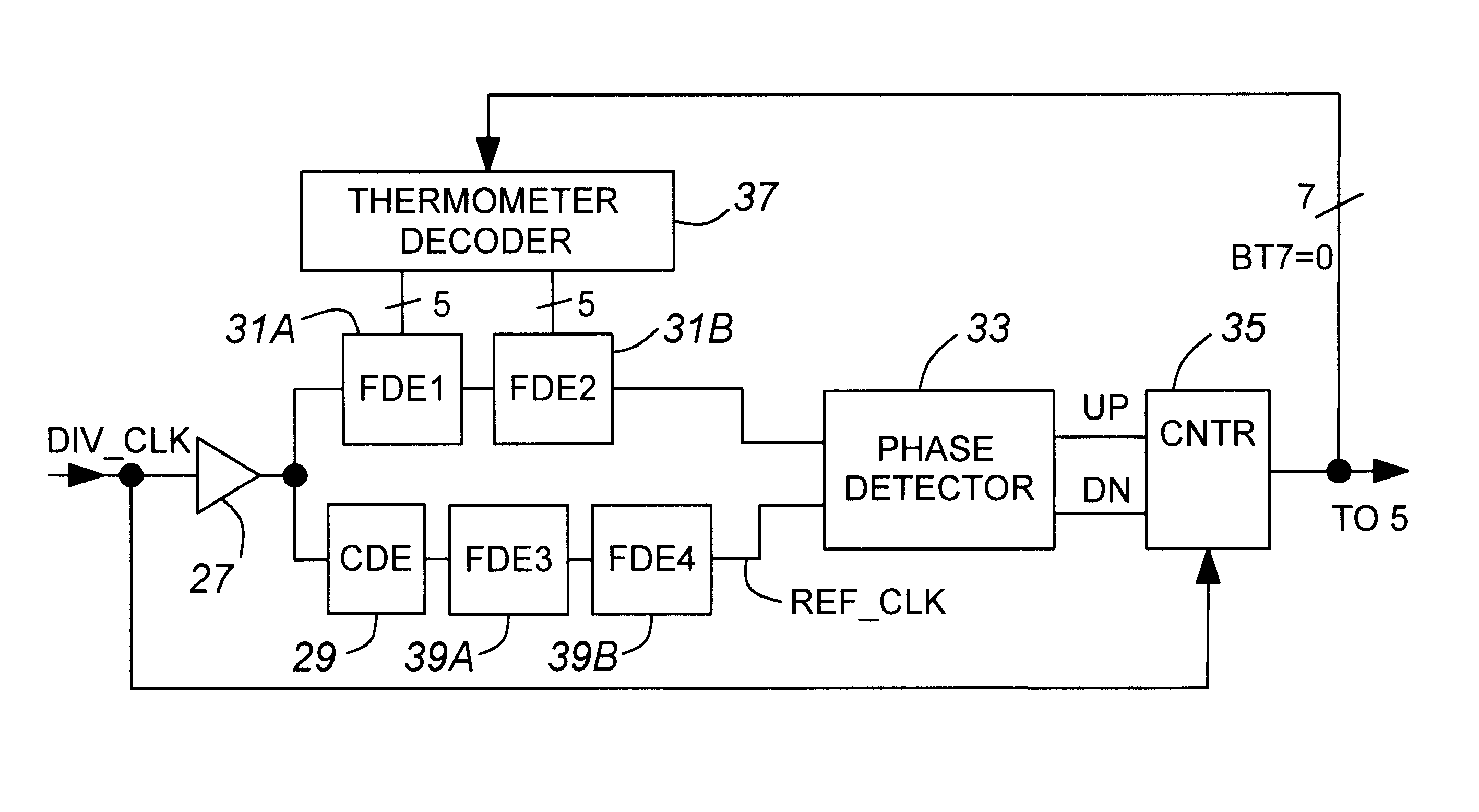
A method and apparatus to characterize a synchronous device after it is packaged. For synchronous devices, such as SDRAMs implementing a Delay Locked Loop (DLL) to synchronize one signal, such as an external clock signal with a second signal, such as a data signal, a counter is coupled to the phase detector of the DLL to track the entry point of the delay line. The entry point information can be taken over a variety of voltages, temperatures, and frequencies to characterize the DLL. The counter may be located on the synchronous device or external to the device.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
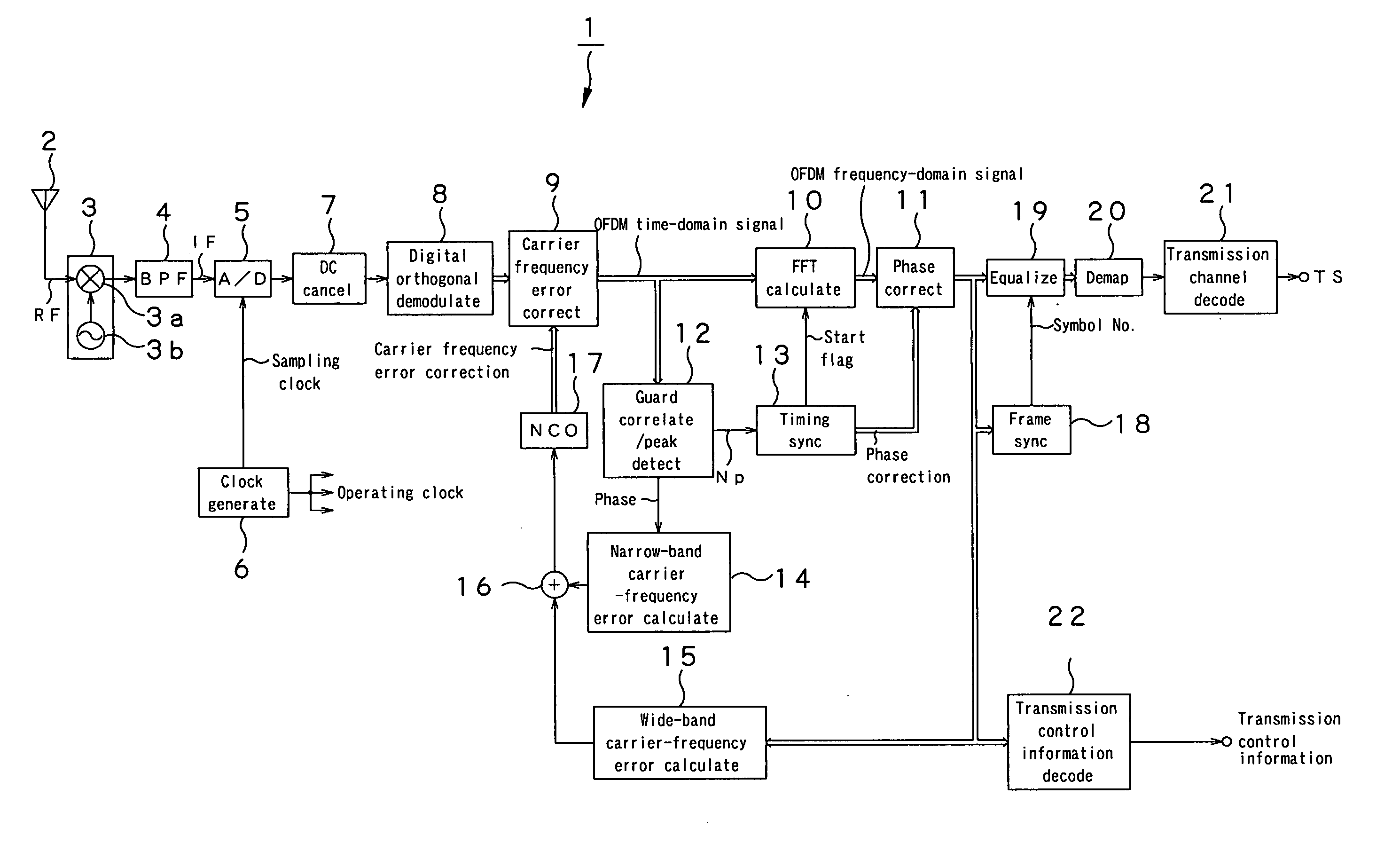
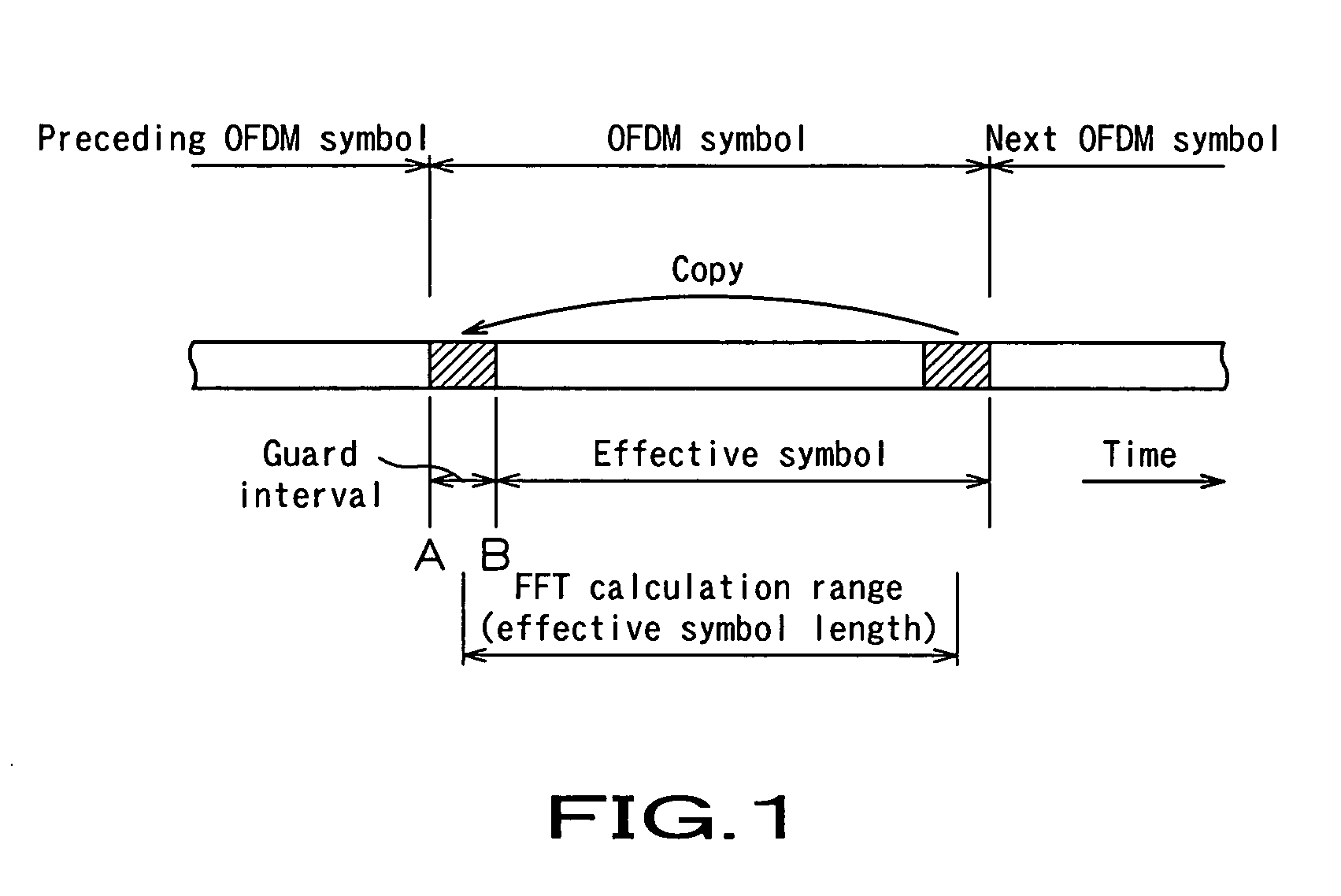
Ofdm demodulation apparatus
InactiveUS20050147186A1Improve accuracySynchronisation signal speed/phase controlFrequency-modulated carrier systemsGuard intervalDelay-locked loop
An OFDM demodulation (1) is provided which includes a guard correlation / peak time detection circuit (12) to generate a peak timing Np of a guard interval correlation value, and a timing synchronization circuit (13) to estimate a symbol-boundary time Nx from the peak timing Np. The timing synchronization circuit (13) calculates the symbol-boundary time Nx by filtering the peak time Np by a DLL (delay locked loop) filter (43). Further, the DLL filter (43) includes a limiter (52) to limit the range of phase-error component and an asymmetric gain circuit (53) to change the magnitude of the gain correspondingly to the polarity of the phase error to prevent the timing from being pulled out due to a fading or multipath.
Owner:SONY CORP
Controlling data strobe output
A method and apparatus is provided for controlling a data strobe. A latency of operation relating to a data operation of a device is determined. A delay lock loop signal is generated for the data operation of the device. The delay lock loop signal is compared to an external clock to determine a phase difference. A determination is made as to whether the delay lock loop signal is early based upon the phase difference. A signal is adjusted in response to the latency of operation is performed based upon the determination that the delay lock loop signal is early.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
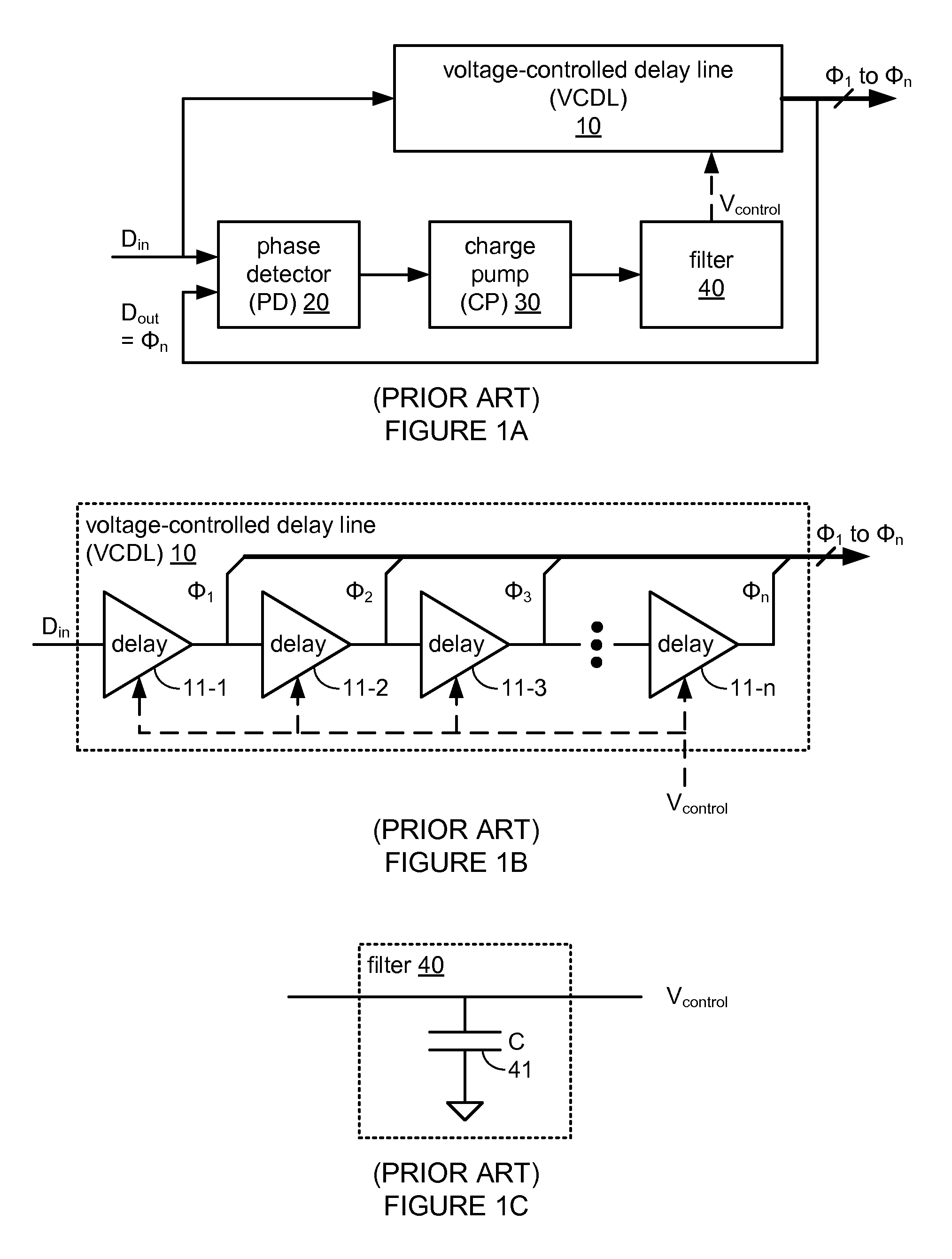
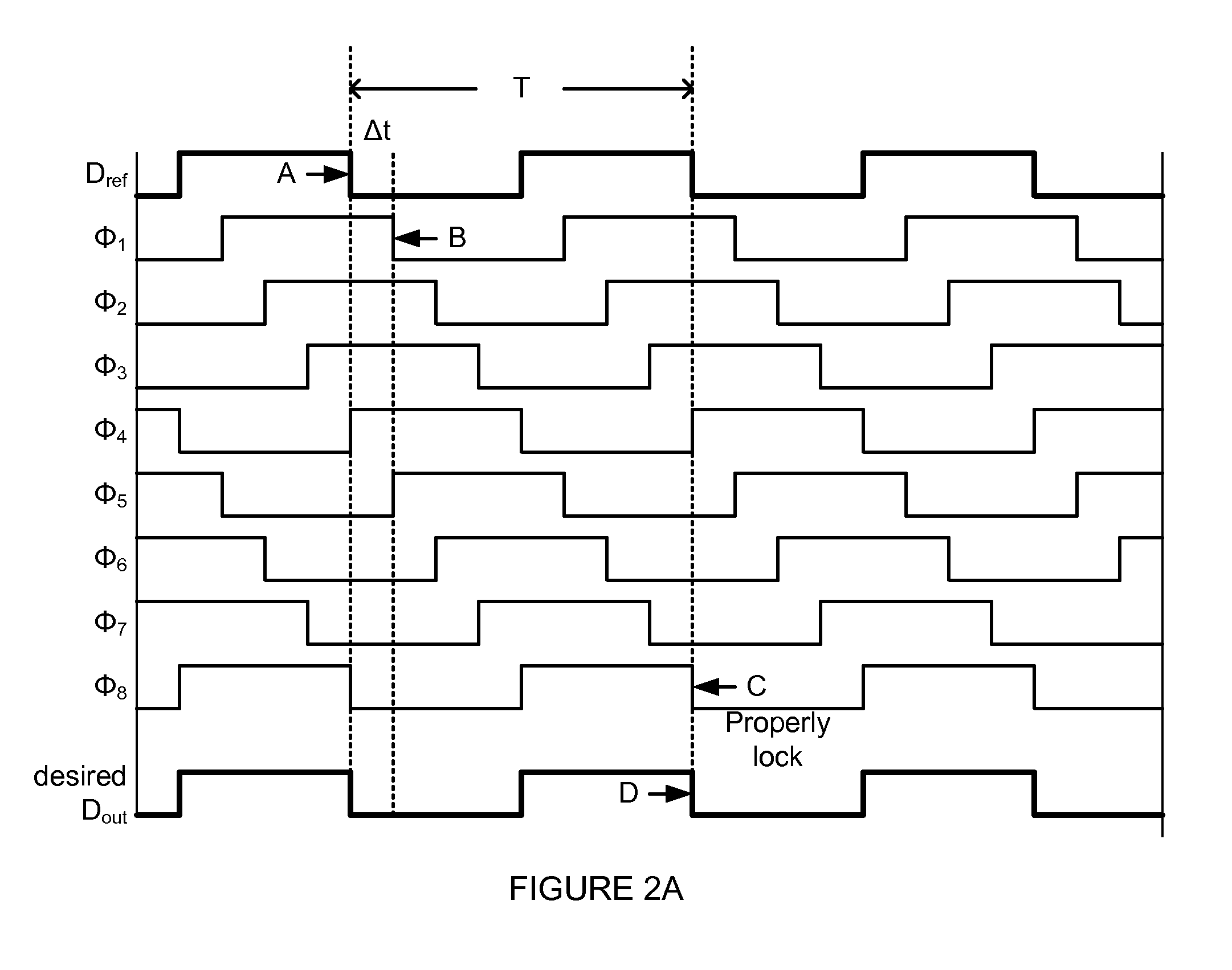
False lock protection in a delay-locked loop (DLL)
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG KANGDE XIN OPTRONICS MATERIAL +1
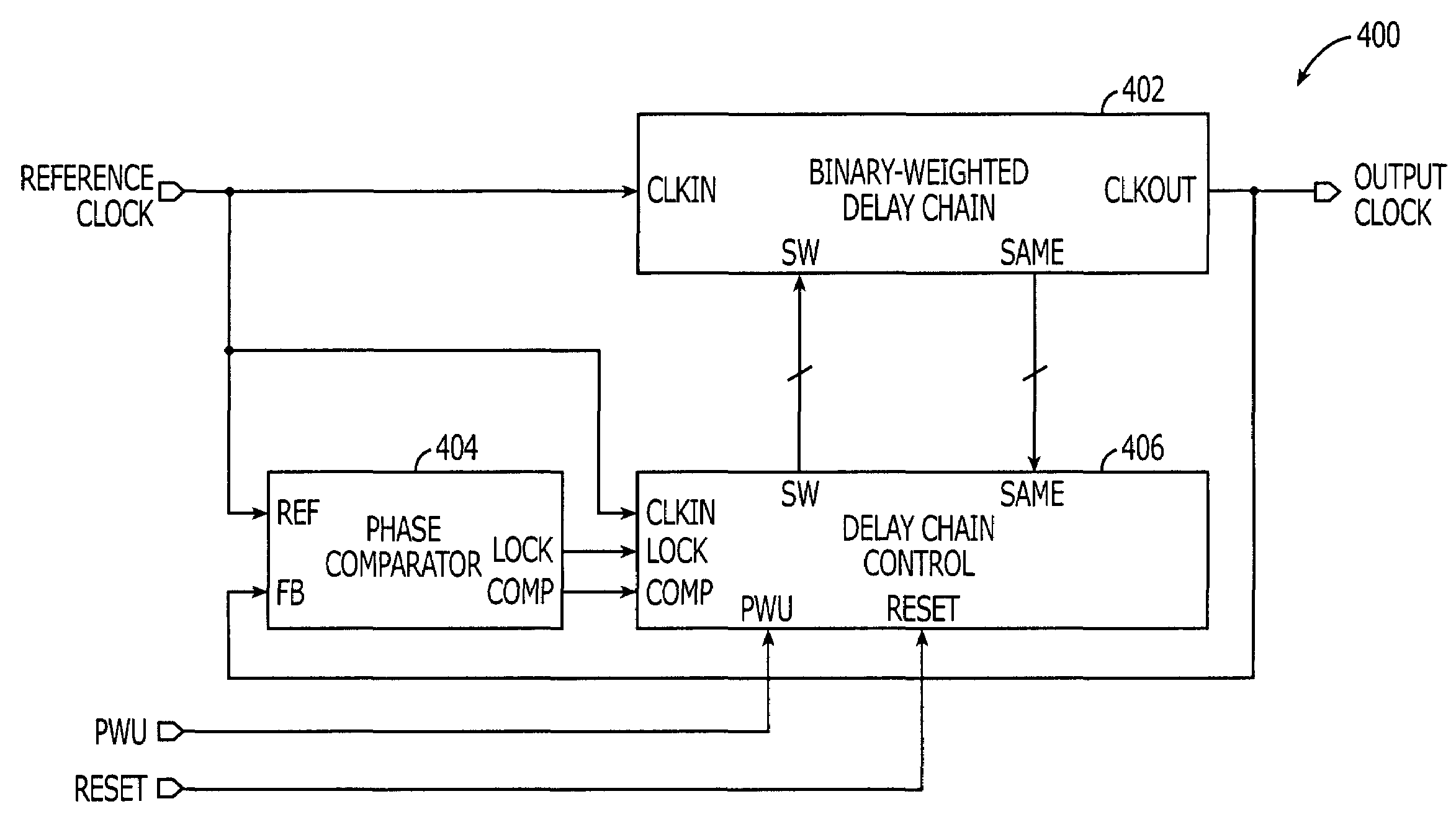
Delay-locked loop (DLL) integrated circuits having binary-weighted delay chain units with built-in phase comparators that support efficient phase locking
ActiveUS7119591B1Facilitates efficient locking of lockedMultiple input and output pulse circuitsPulse automatic controlDelay-locked loopEngineering
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Wide frequency range delay locked loop
ActiveUS7336752B2Improve accuracyImprove stabilityPulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionDelay-locked loopSilicon
A delay locked loop operates over a wide range of frequencies and has high accuracy, small silicon area usage, low power consumption and a short lock time. The DLL combines an analog domain and a digital domain. The digital domain is responsible for initial lock and operational point stability and is frozen after the lock is reached. The analog domain is responsible for normal operation after lock is reached and provides high accuracy using smaller silicon area and low power.
Owner:MOSAID TECH
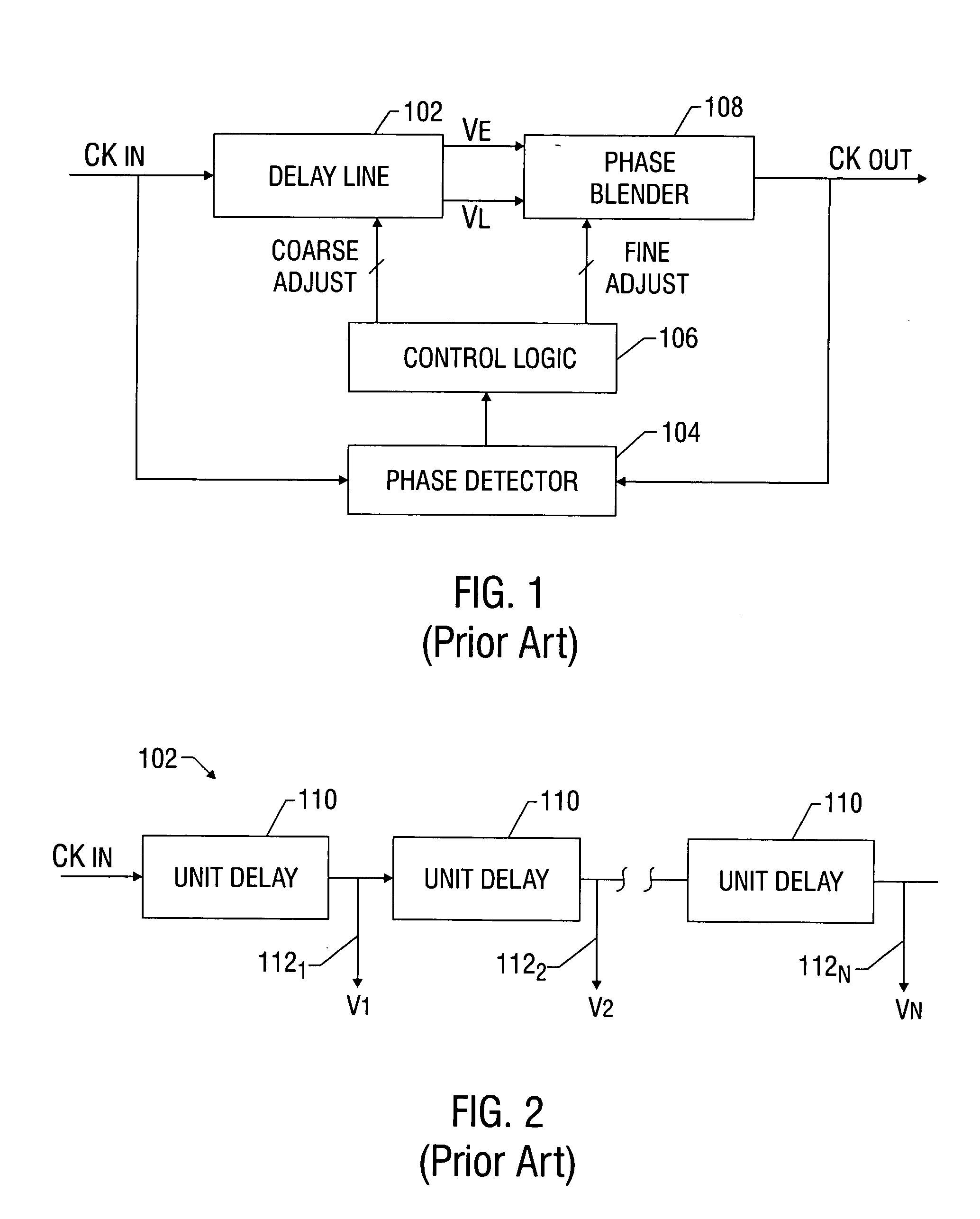
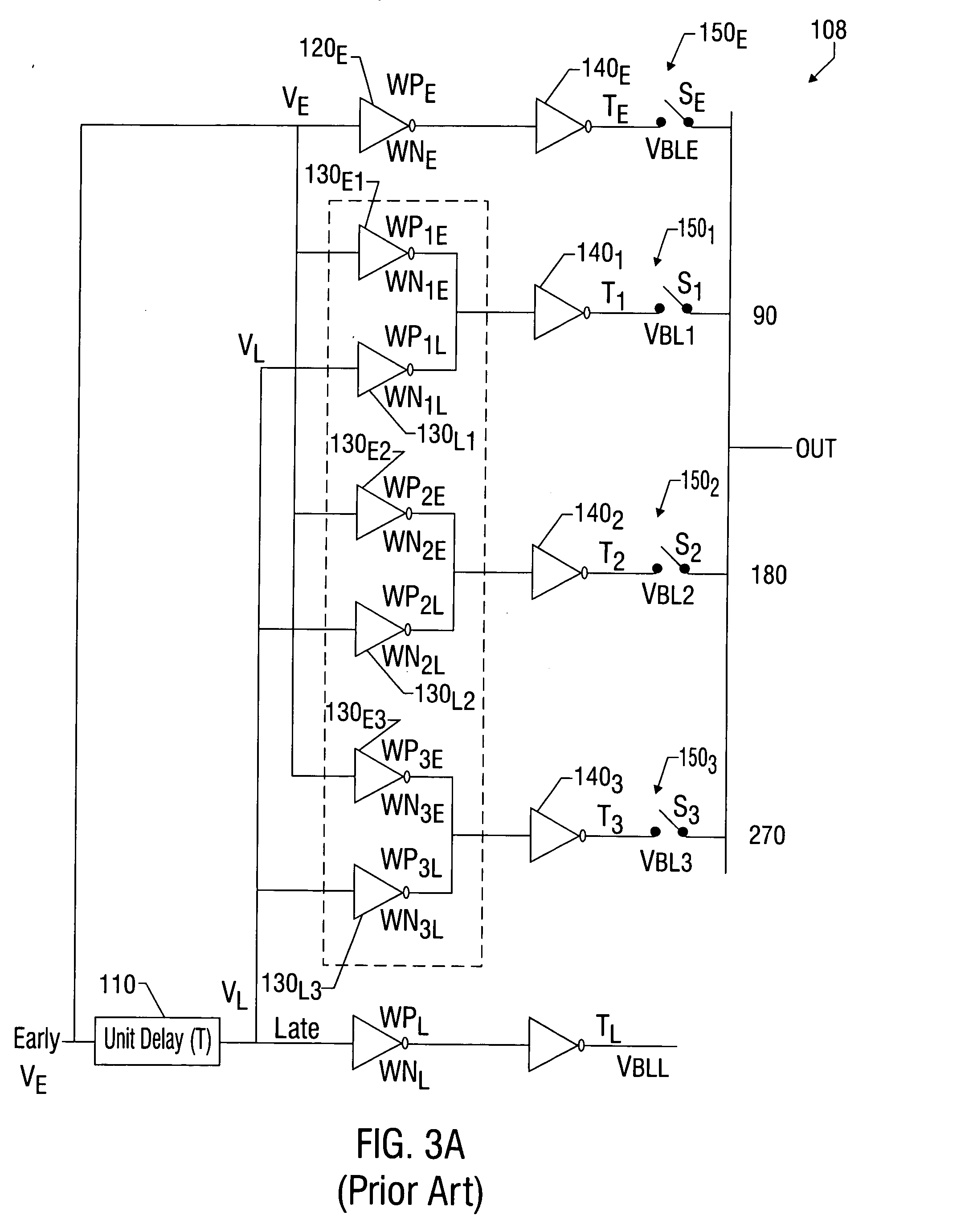
Delay locked loop phase blender circuit
InactiveUS20050093594A1Pulse automatic controlSingle output arrangementsDelay-locked loopEngineering
Techniques and circuit configurations for fine phase adjustments, for example, in a delay-locked loop (DLL) circuit are provided. Multiple phase signals may be generated from a single current source by selectively coupling one or more delay elements to an output node of the current source. The delay elements may vary the timing of a signal generated by switching the current source.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
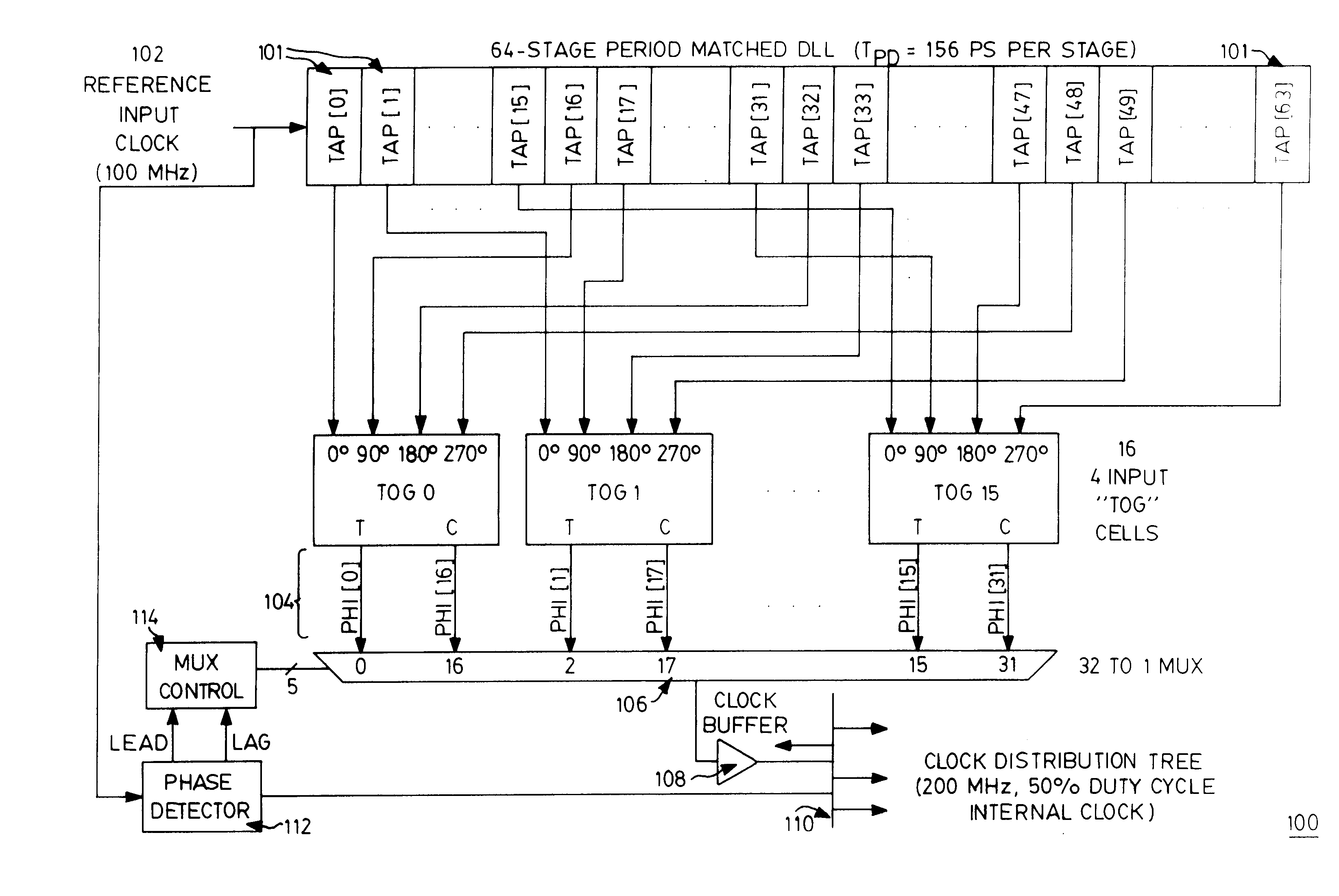
Frequency-doubling delay locked loop
A frequency multiplier circuit comprising a delay line receiving at one end thereof a reference clock for generating clock tap outputs from respective ones of a plurality of period matched delay elements; a clock combining circuit responsive to pairs of tap outputs for generating a rising and falling edge of an output clock pulse from respective ones of the pairs whereby the output clock period is less than the input clock period.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
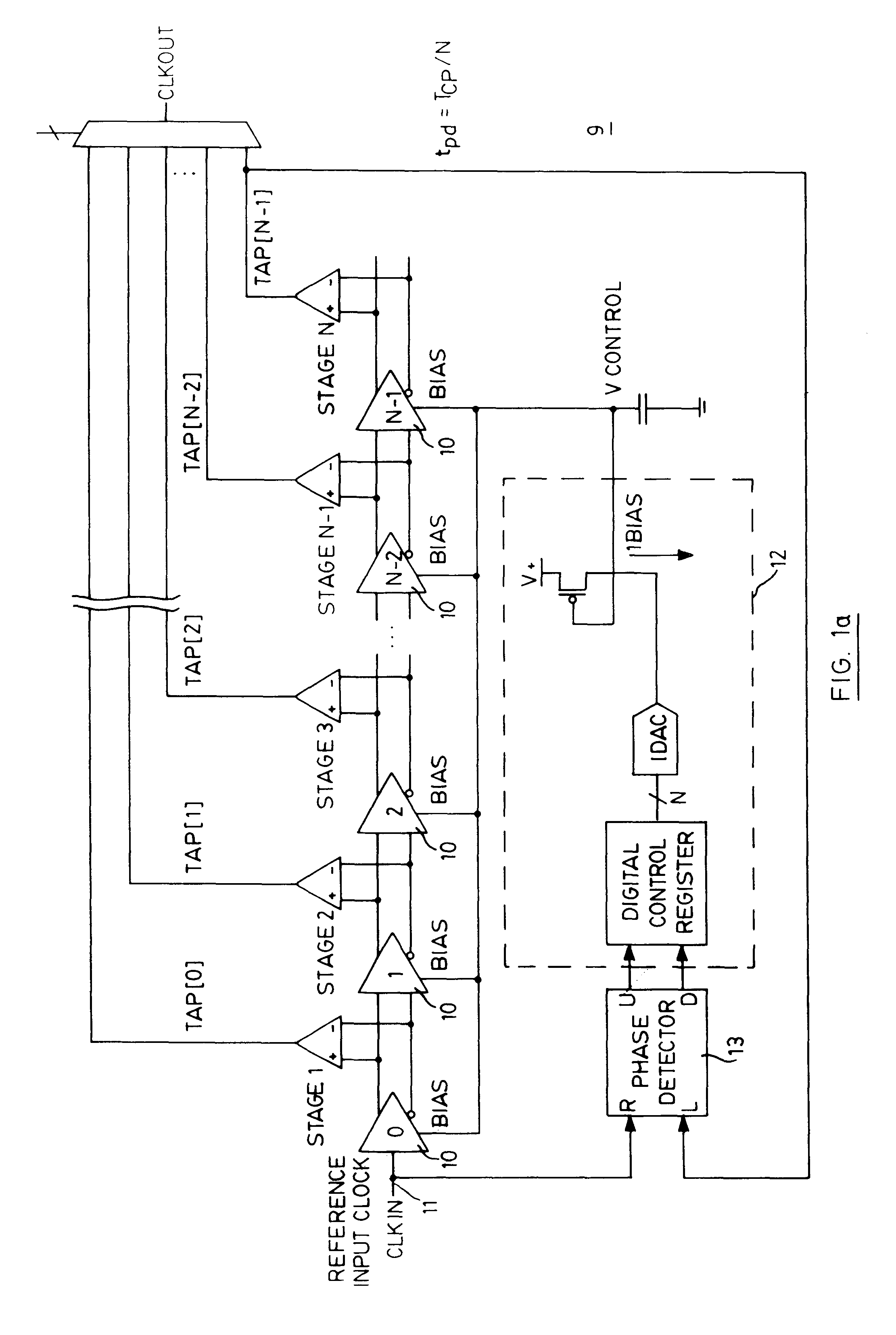
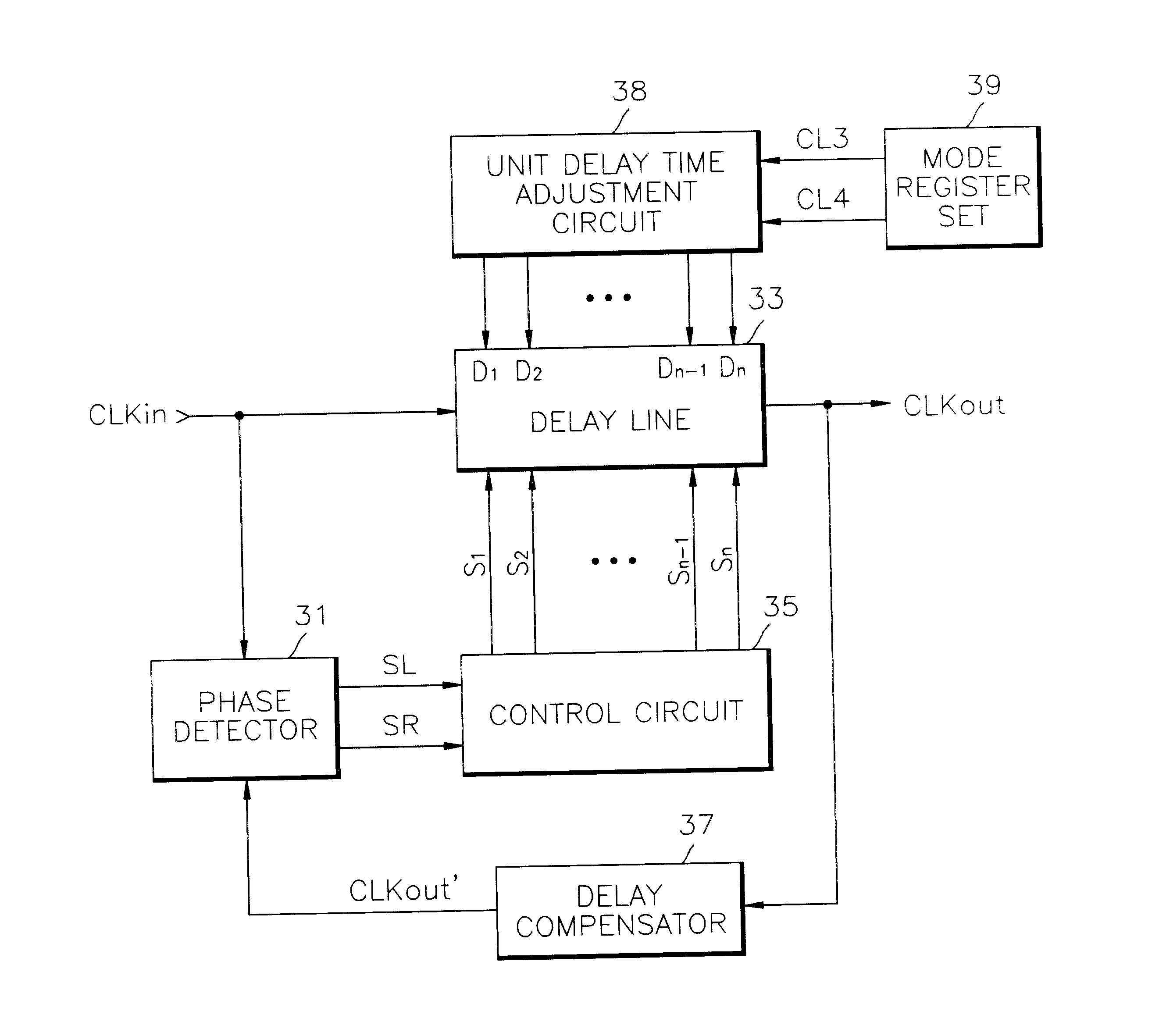
Delay locked loop circuit and method having adjustable locking resolution
A delay line receives an input clock signal and includes a cascaded plurality of unit delay circuits. A mode register set stores a value indicative of a column-address-strobe (CAS) latency of the memory device, and an adjustment circuit varies a delay time of the unit delay circuits according to the CAS latency stored in the mode register set. A phase detector detects a phase difference between the input clock signal and an output clock signal of the delay line, and a control circuit which controls an enabled state of the unit delay circuits according to an output of said phase detector.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Clock generator having a delay locked loop and duty cycle correction circuit in a parallel configuration
ActiveUS7227809B2Pulse automatic controlManipulation where pulse delivered at different timesDelay-locked loopClock generator
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
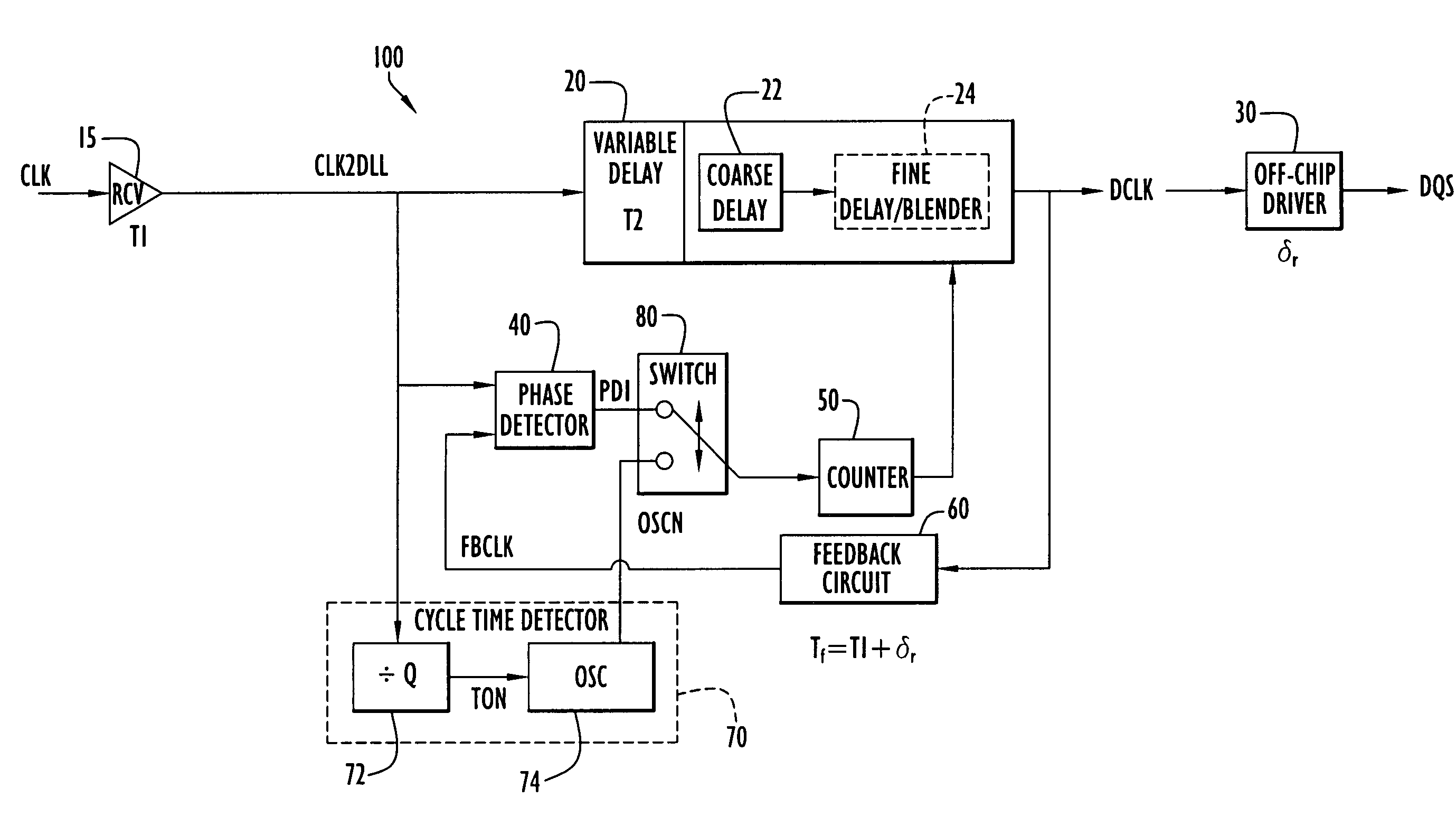
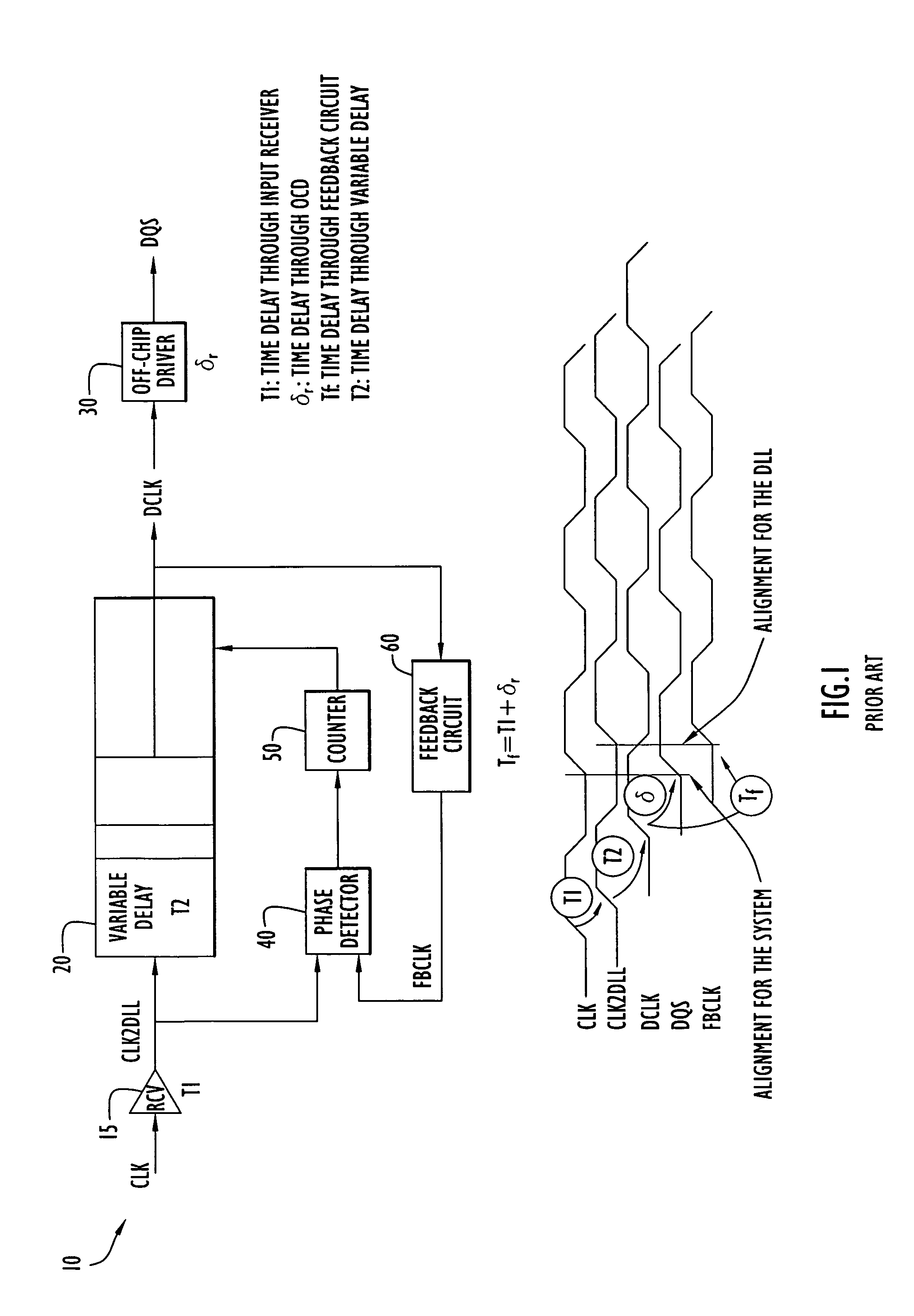
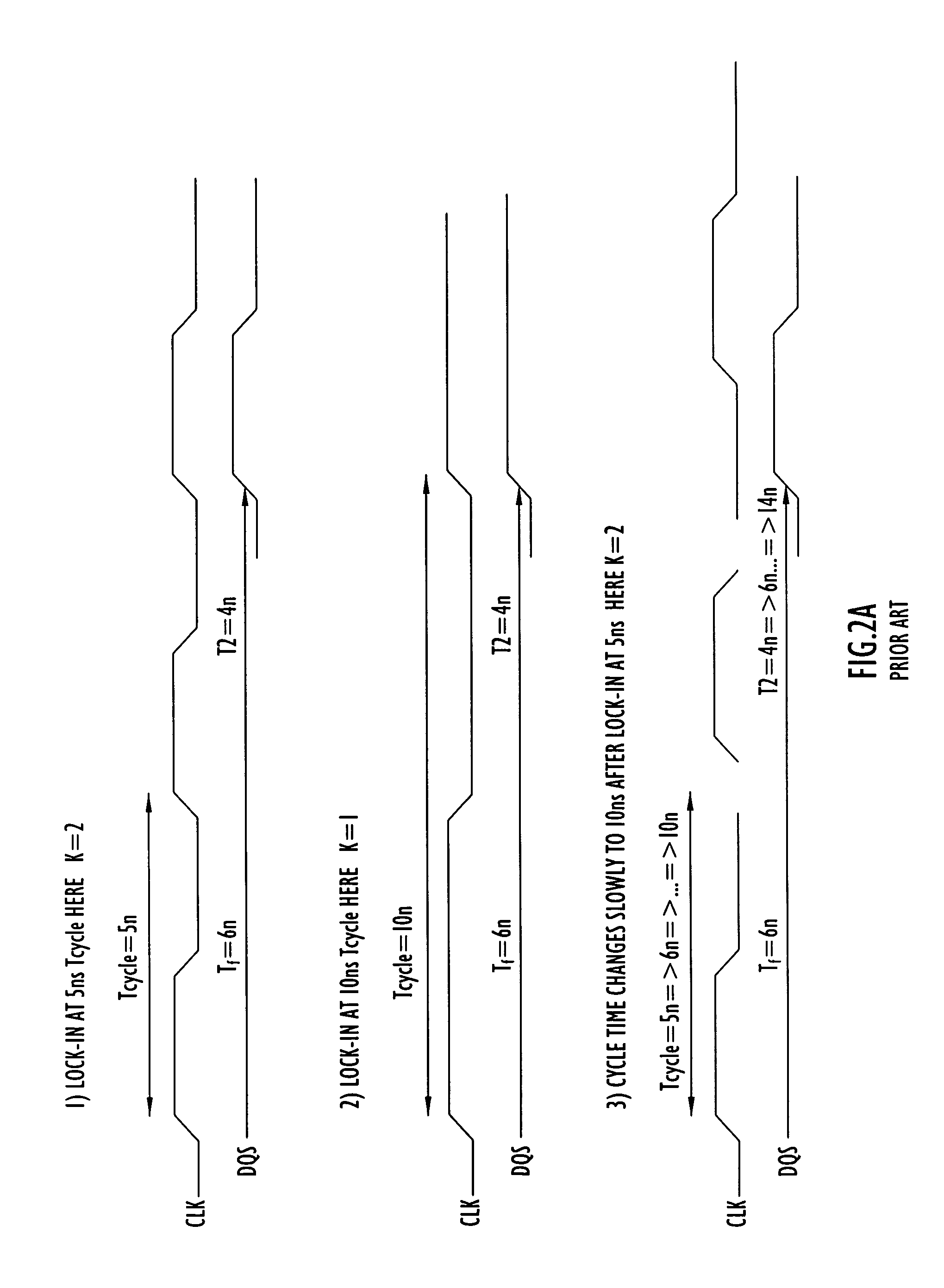
Method and apparatus compensating for frequency drift in a delay locked loop
A delay locked loop (DLL) according to the present invention includes a cycle time detector to determine the quantity of delay elements within a clock cycle and adjust a DLL counter controlling a DLL variable delay line to enable operation or locking in response to DLL overflow and underflow conditions. The cycle time detector includes a ring oscillator having a strong correlation between the oscillator period and the DLL delay elements. The output of the oscillator controls the counter to provide a new locking position for the DLL in the presence of overflow or underflow conditions. The oscillator is driven for an interval corresponding to the product of the external clock period and the quantity of delay elements in the ring oscillator. In effect, the delay of the DLL is adjusted to the preceding or succeeding external clock period to enable locking in response to overflow or underflow conditions.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
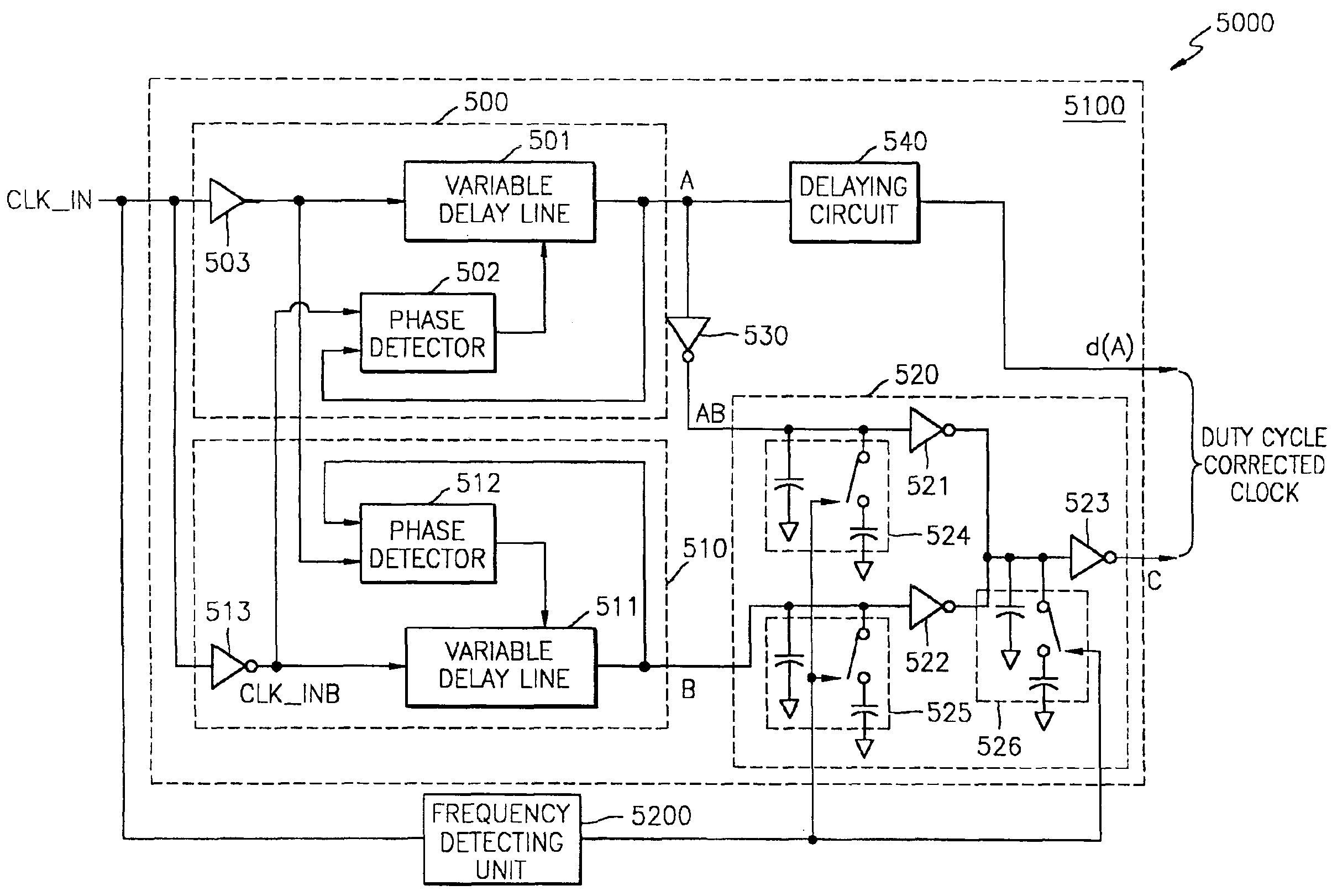
Semiconductor memory device having duty cycle correction circuit and interpolation circuit interpolating clock signal in the semiconductor memory device
ActiveUS6934215B2Small capacitanceLarge capacitanceContinuous to patterned pulse manipulationDigital storageClock rateDelay-locked loop
A semiconductor memory device having a duty cycle correction circuit and an interpolating circuit interpolating a clock signal in the semiconductor memory device are disclosed. The semiconductor memory device comprises a duty cycle correction circuit, which receives an external clock, corrects the duty cycle of the external clock, and outputs the corrected duty cycle. The duty cycle correction circuit comprises a first delay locked loop that receives the external clock, inverts the external clock, synchronizes the external clock with the inverted external clock, and outputs the synchronized clock; a second delay locked loop that receives the inverted external clock, synchronizes the inverted external clock with the external clock and outputs the synchronized clock; an inverting circuit that inverts the output signal of the first delay locked loop; an interpolation circuit that interpolates the output signal of the inverting circuit with the output signal of the second delay locked loop, and outputs the interpolated signal; and a control circuit that controls the interpolation circuit in response to the clock frequency information of the external clock.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
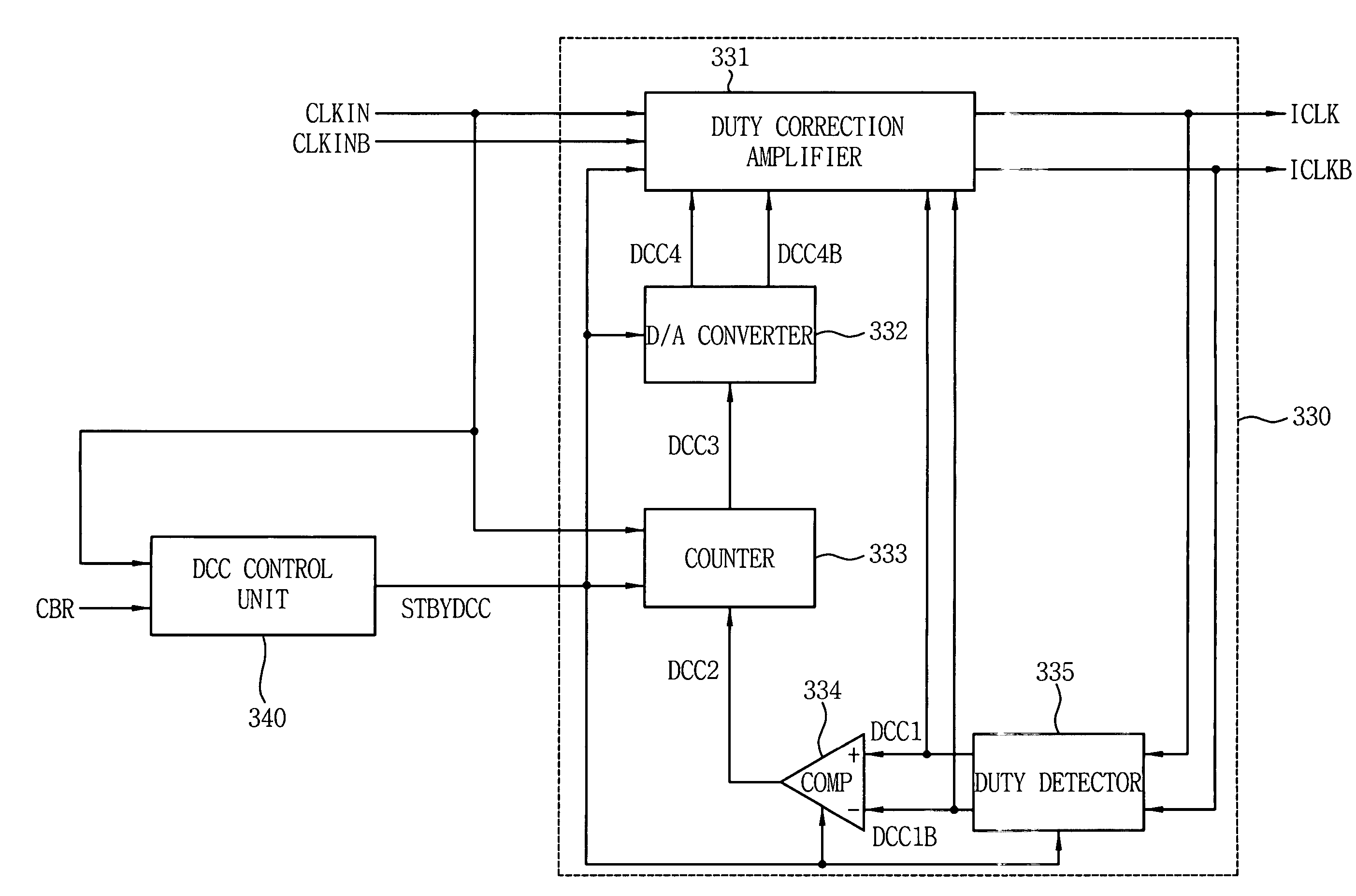
Duty cycle correction circuits suitable for use in delay-locked loops and methods of correcting duty cycles of periodic signals
InactiveUS7199634B2Pulse automatic controlContinuous to patterned pulse manipulationControl signalDelay-locked loop
Delay-locked loop integrated circuits include a duty cycle correction circuit. This duty cycle correction circuit generates at least one output clock signal having a substantially uniform duty cycle in response to at least one input clock signal having a non-uniform duty cycle. The duty cycle correction circuit is also responsive to a standby control signal that synchronizes timing of power-saving duty cycle update operations within the duty cycle correction circuit. These update operations reset the set point of the correction circuit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
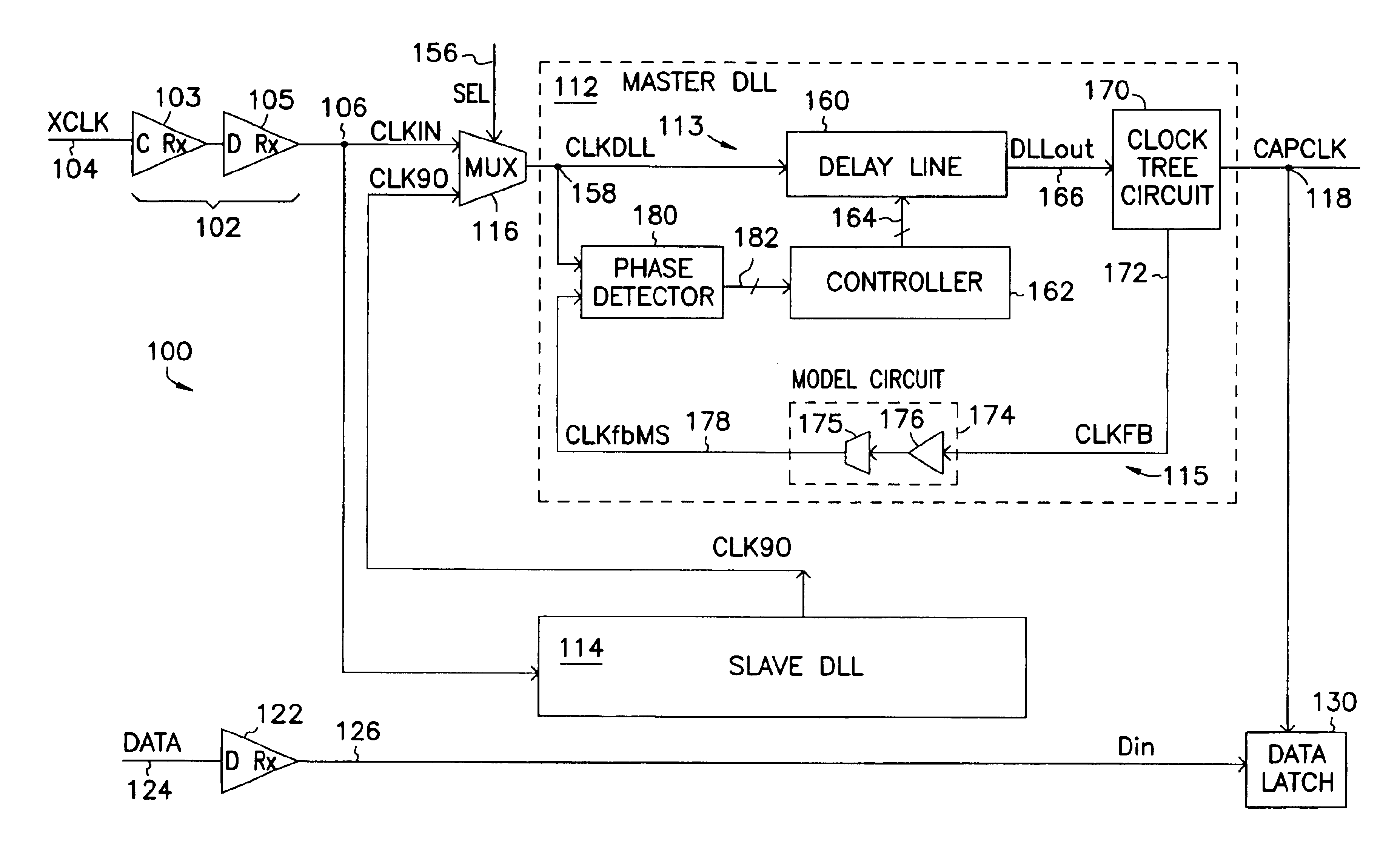
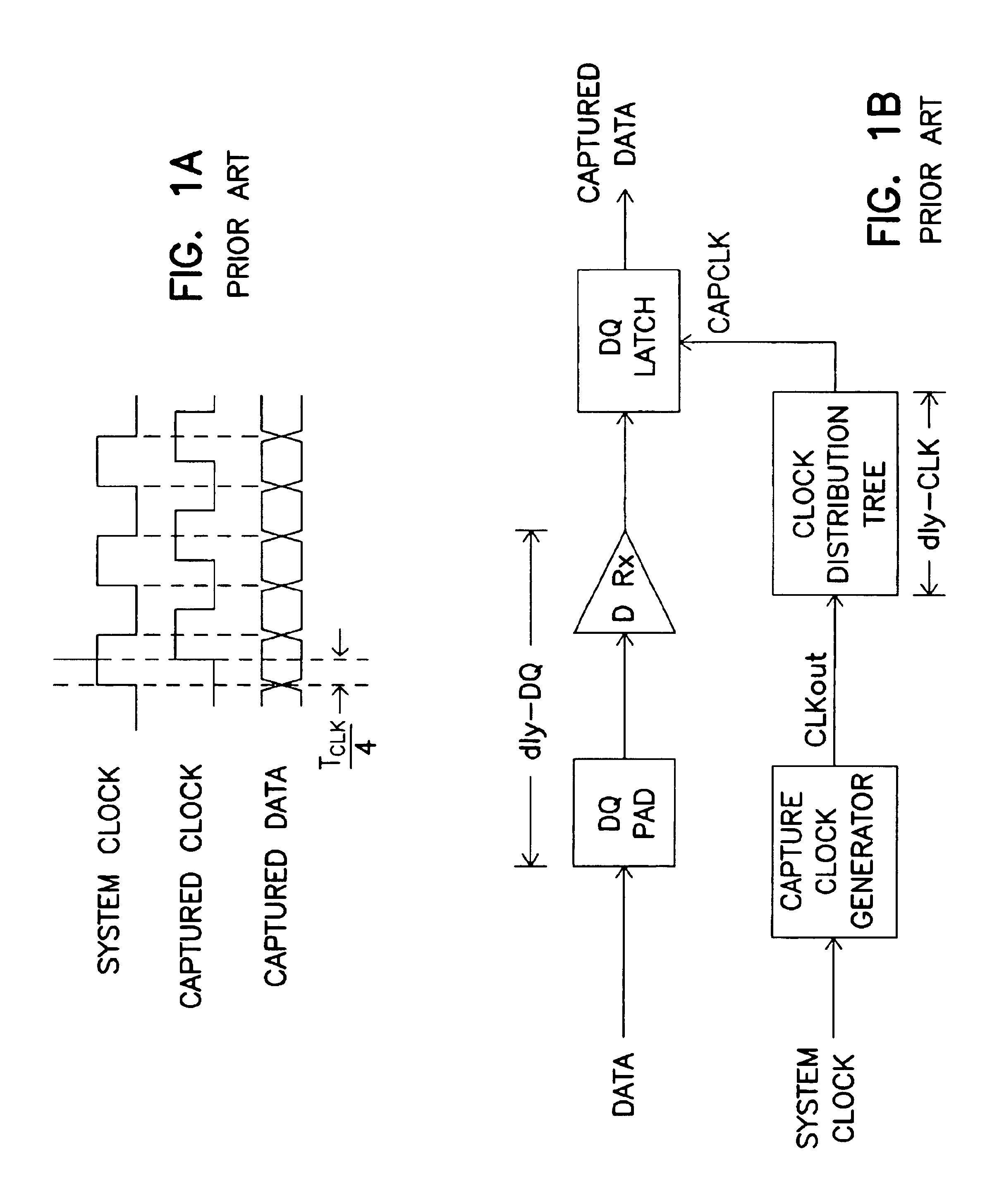
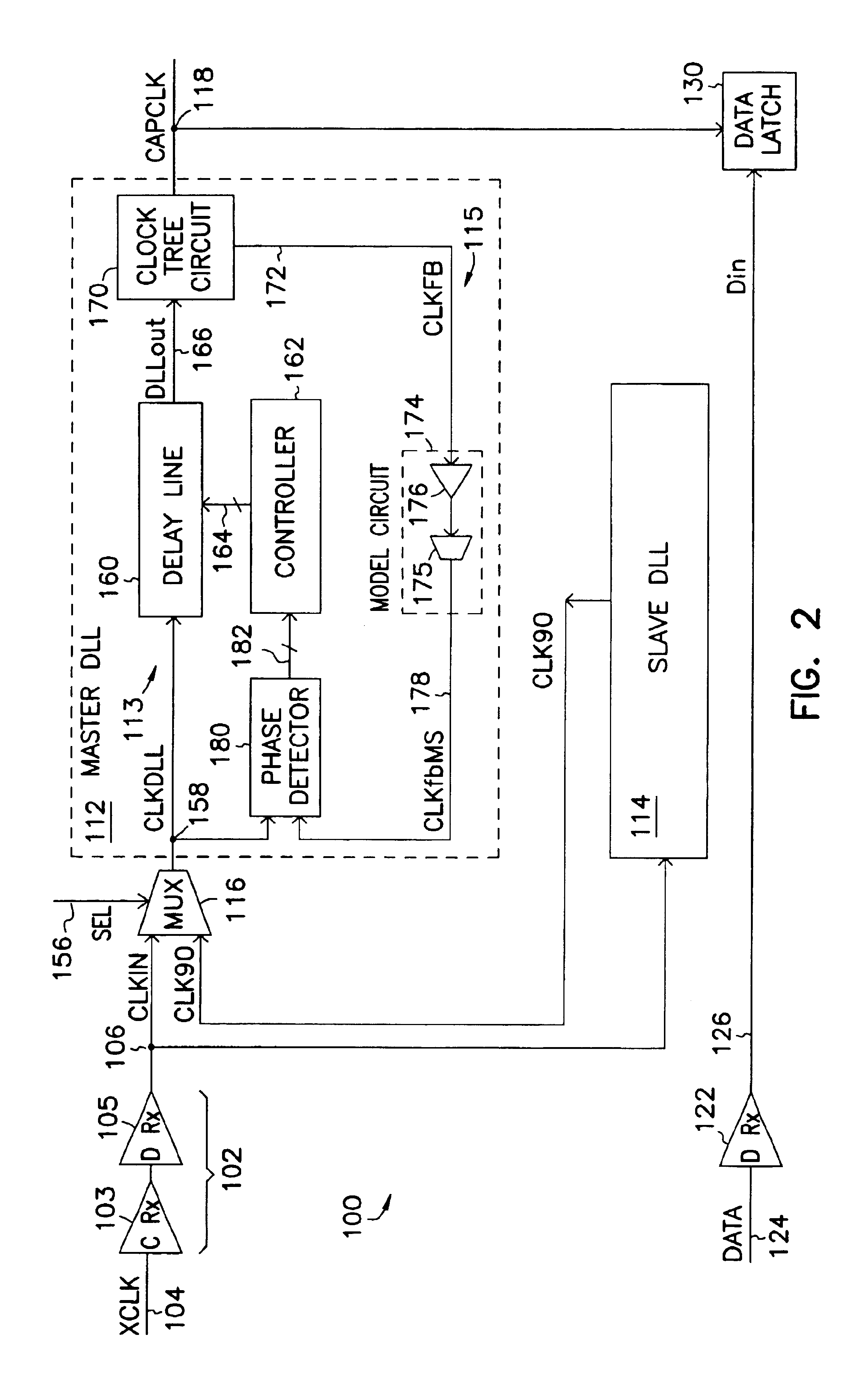
Capture clock generator using master and slave delay locked loops
A clock generator comprising a master delay locked loop (DLL) and a slave DLL to capture a data signal. The slave DLL generates a slave output signal based on a clock signal. The master DLL receives the slave output signal and compensates variations in delays of the data and clock signals to generate a capture clock signal. When the master and slave DLLs are locked, the capture clock signal is center aligned with the data signal.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
Method and apparatus for characterizing a delay locked loop
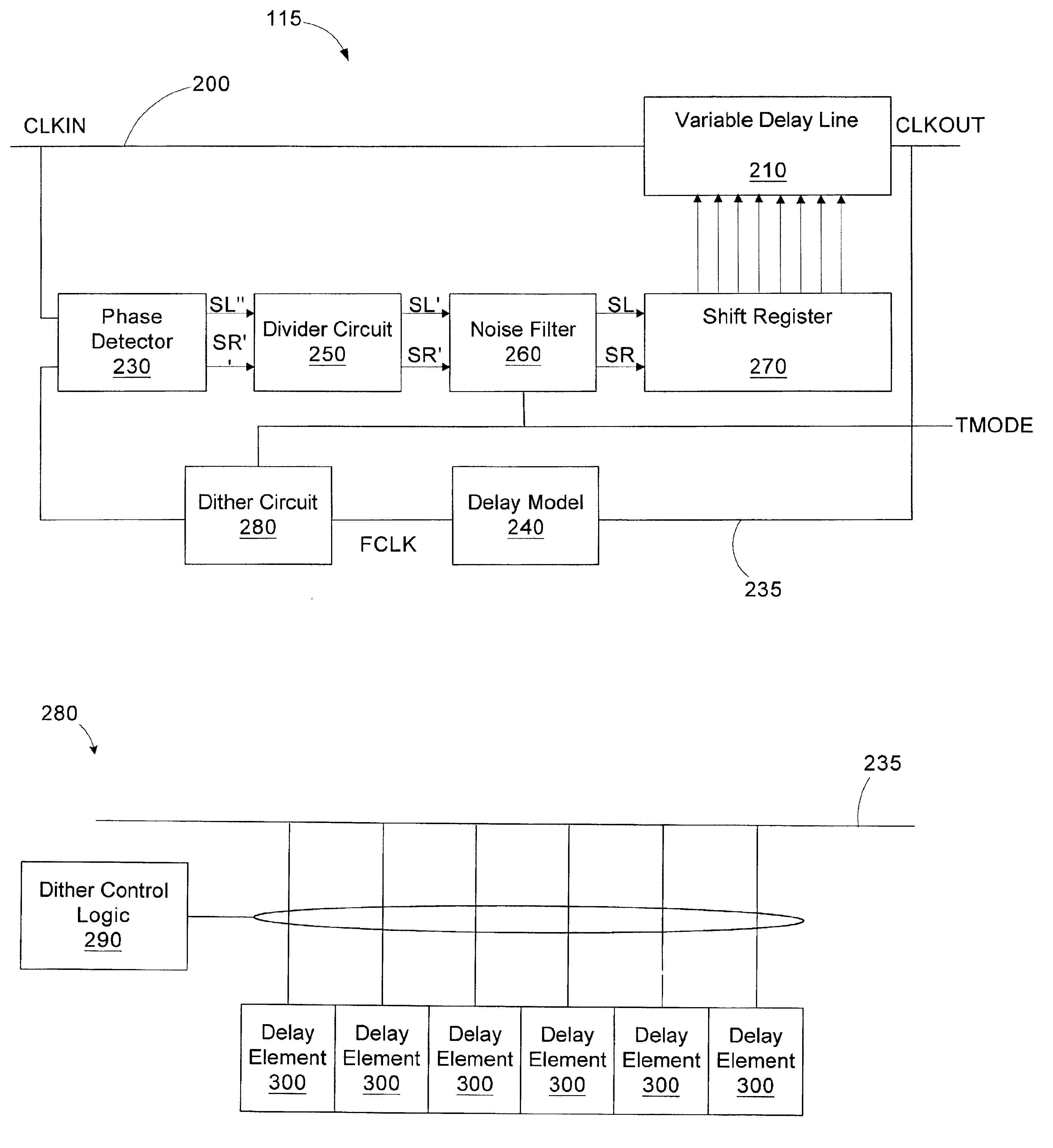
A delay locked loop includes a forward path, a feedback path, a phase detector, logic, and a dither circuit. The forward path includes a delay line configured to receive an input clock signal and delay the input clock signal by a time interval to generate an output clock signal. The feedback path is configured to provide a feedback clock signal based on the output clock signal. The phase detector is configured to compare the input clock signal and the feedback clock signal and generate a shift signal if the output clock signal is not in phase with the input clock signal. The logic is coupled to the delay line and configured to receive the shift signal and control the time interval based on the shift signal. The dither circuit is coupled to the delay line and configured to introduce a delay responsive to an assertion of a test mode enable signal.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
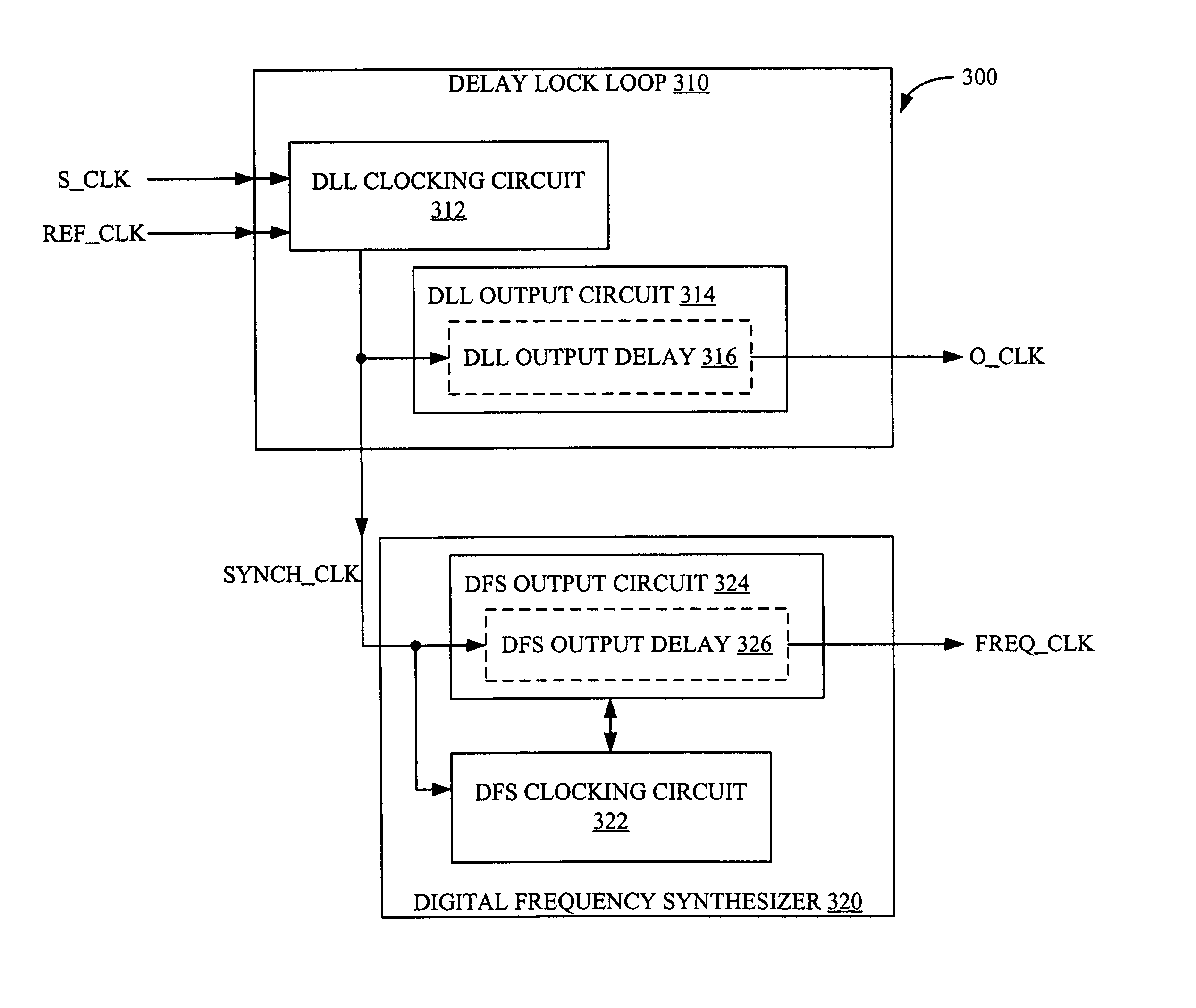
Synchronized multi-output digital clock manager
InactiveUS7187742B1Pulse automatic controlTime-division multiplexDelay-locked loopDigital clock manager
A digital clock manager is provided. The digital clock manager generates an output clock signal that causes a skewed clock signal to be synchronized with a reference clock signal. Furthermore, the digital clock manager generates a frequency adjusted clock signal that is synchronized with the output clock signal during concurrence periods. The digital clock manager includes a delay lock loop and a digital frequency synthesizer. The delay lock loop generates a synchronizing clock signal that is provided to the digital frequency synthesizer. The output clock signal lags the synchronizing clock signal by a DLL output delay. Similarly, the frequency adjusted clock signal lags the synchronizing clock signal by a DFS output delay. By matching the DLL output delay to the DFS output delay, the digital clock manager synchronizes the output clock signal and the frequency adjusted clock signal.
Owner:XILINX INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com