Patents
Literature
135 results about "CAS latency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
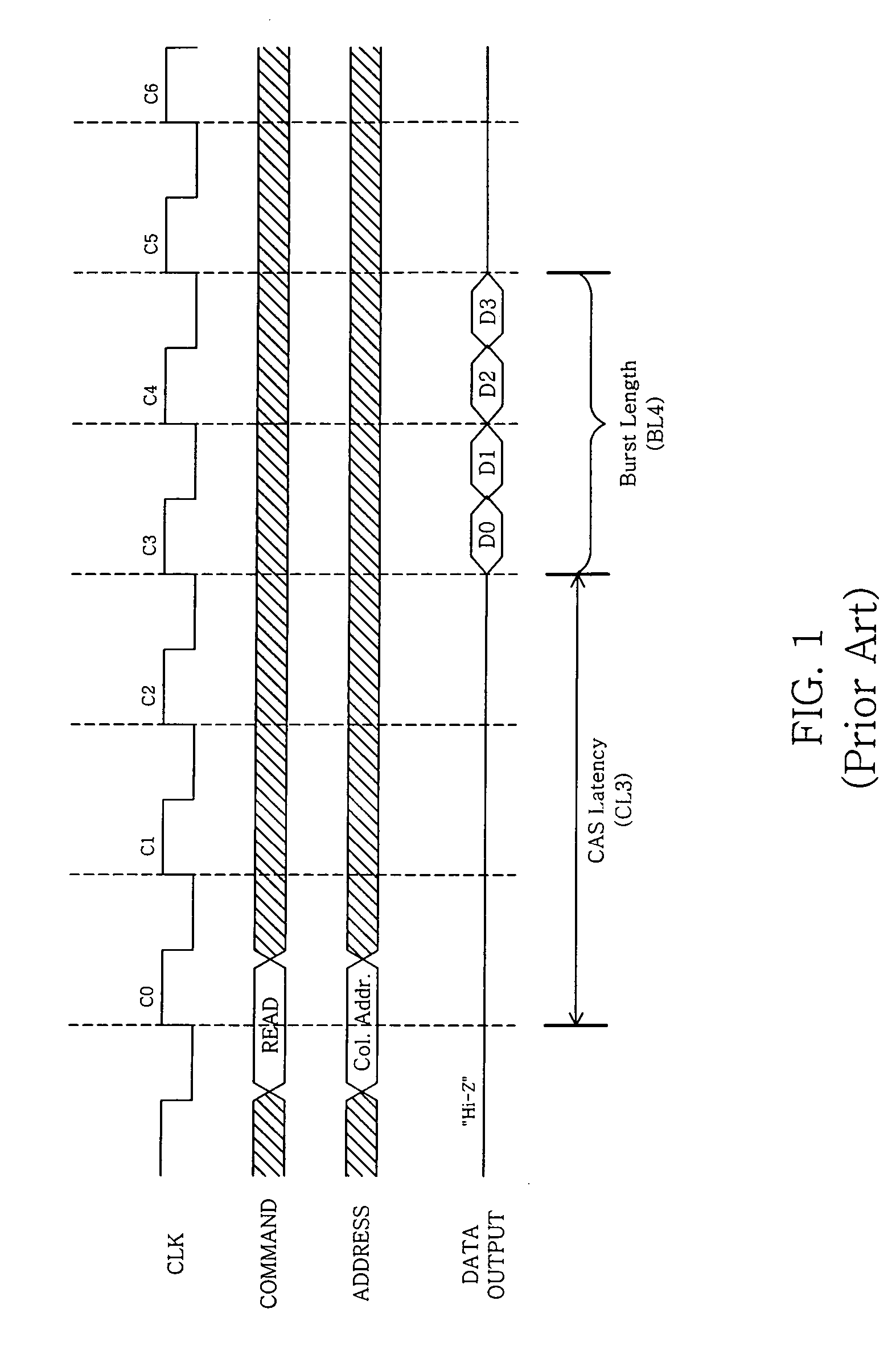
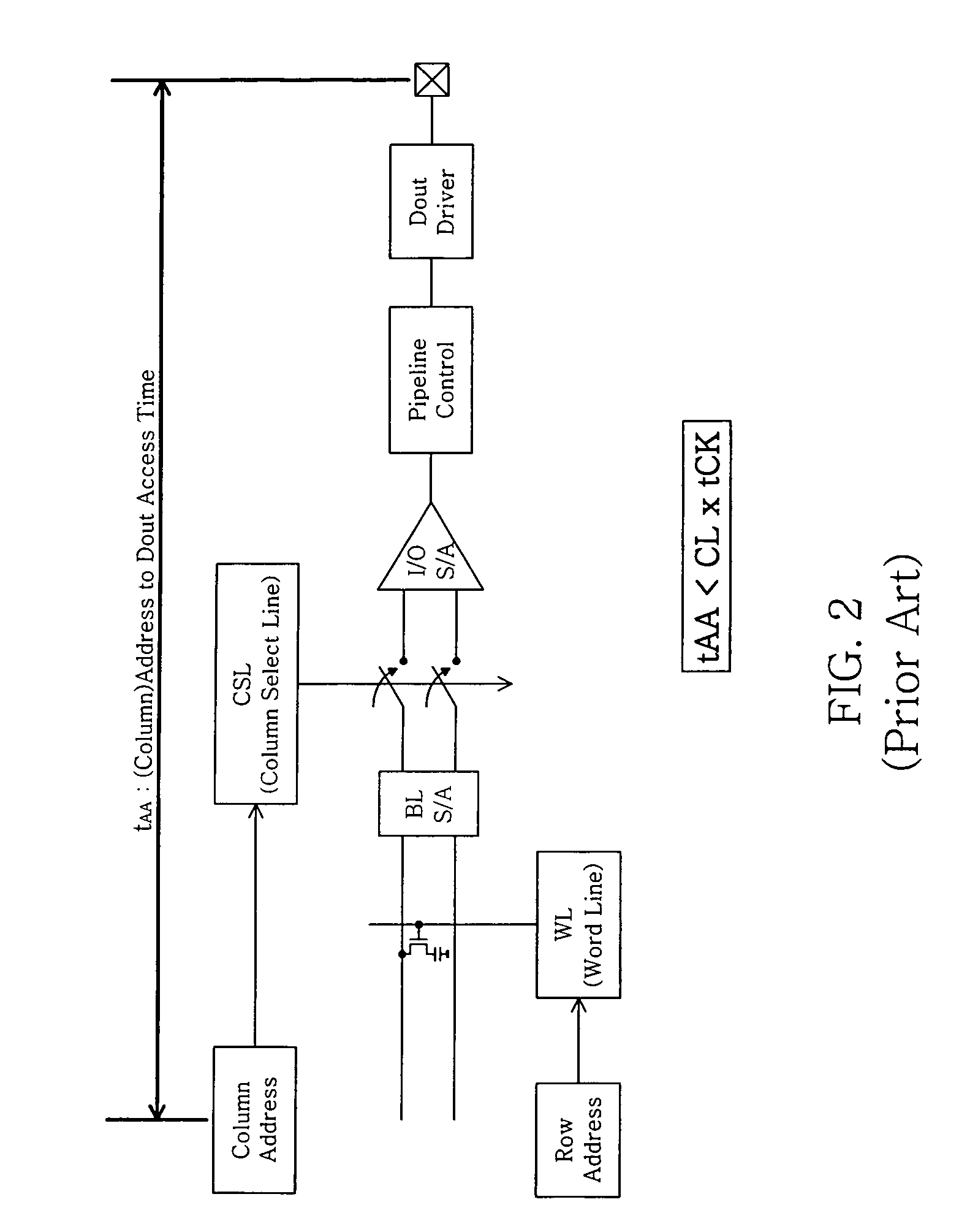
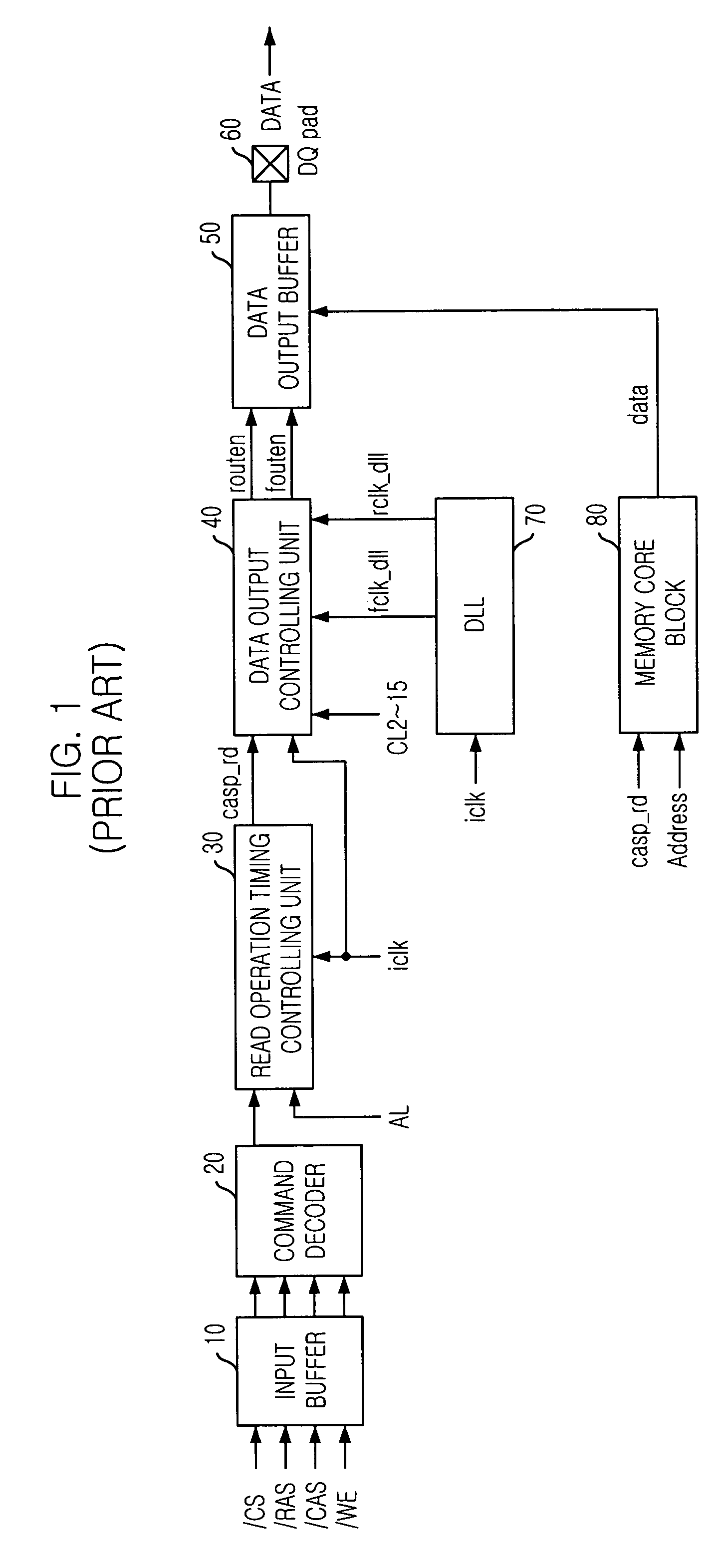
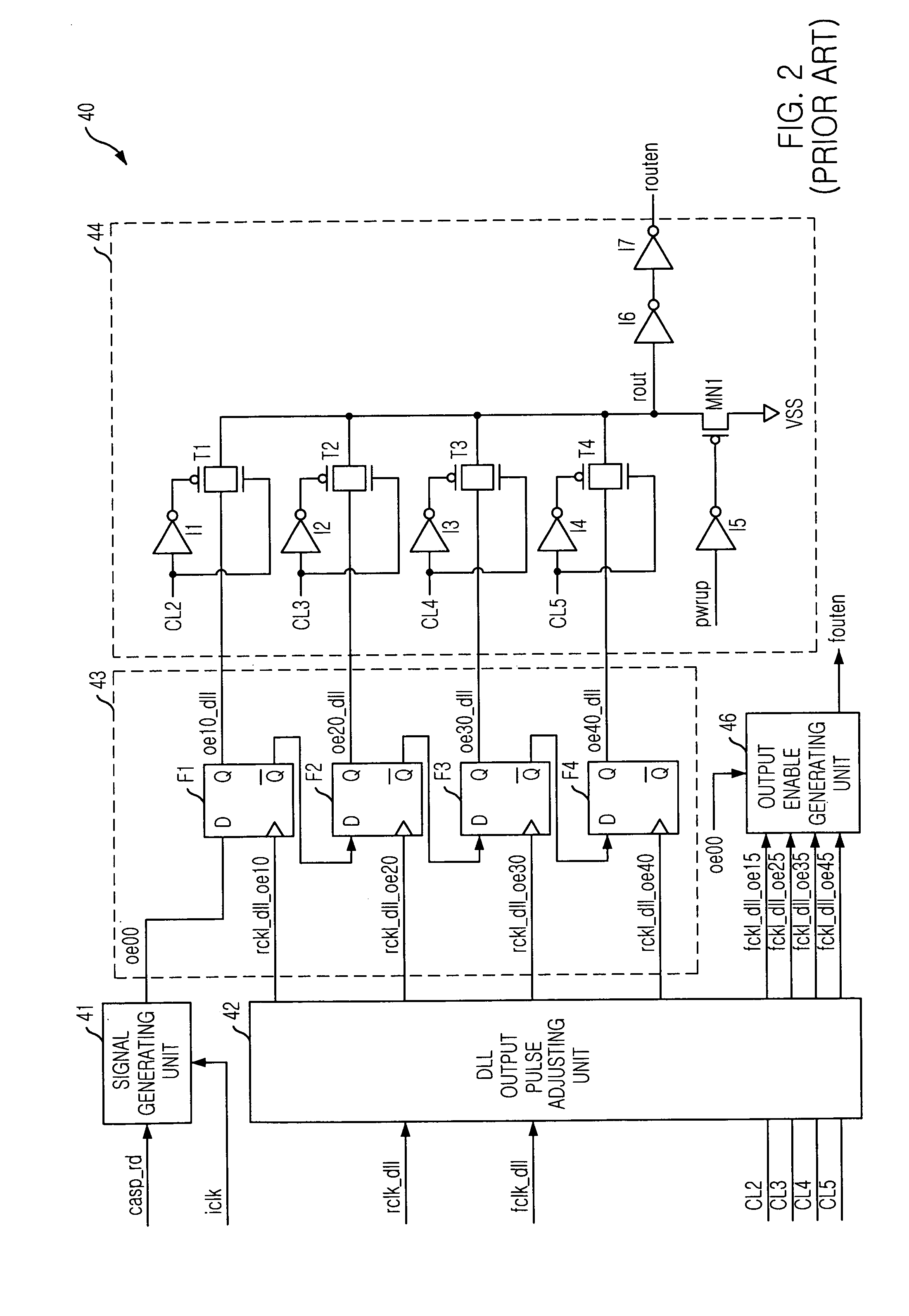
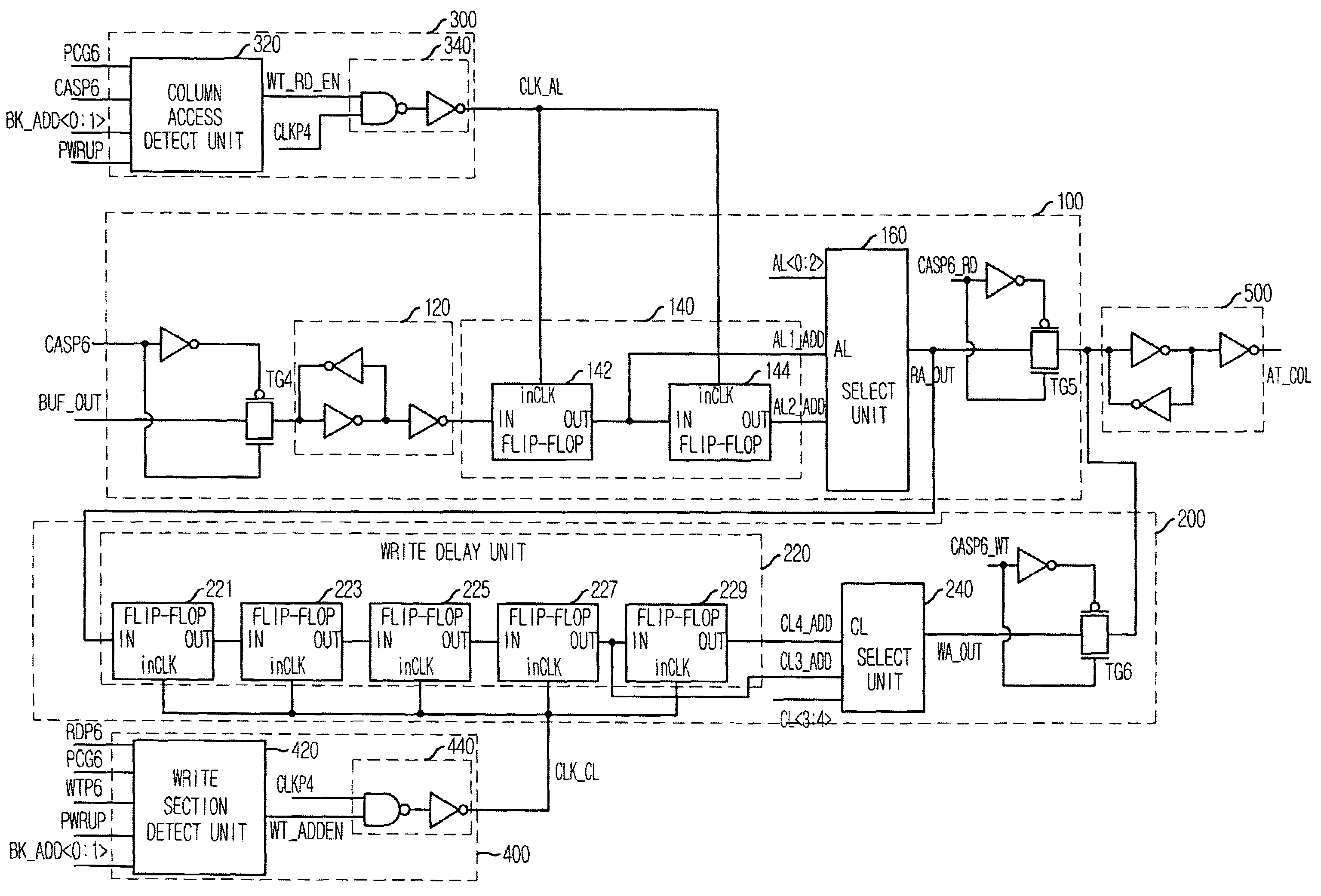
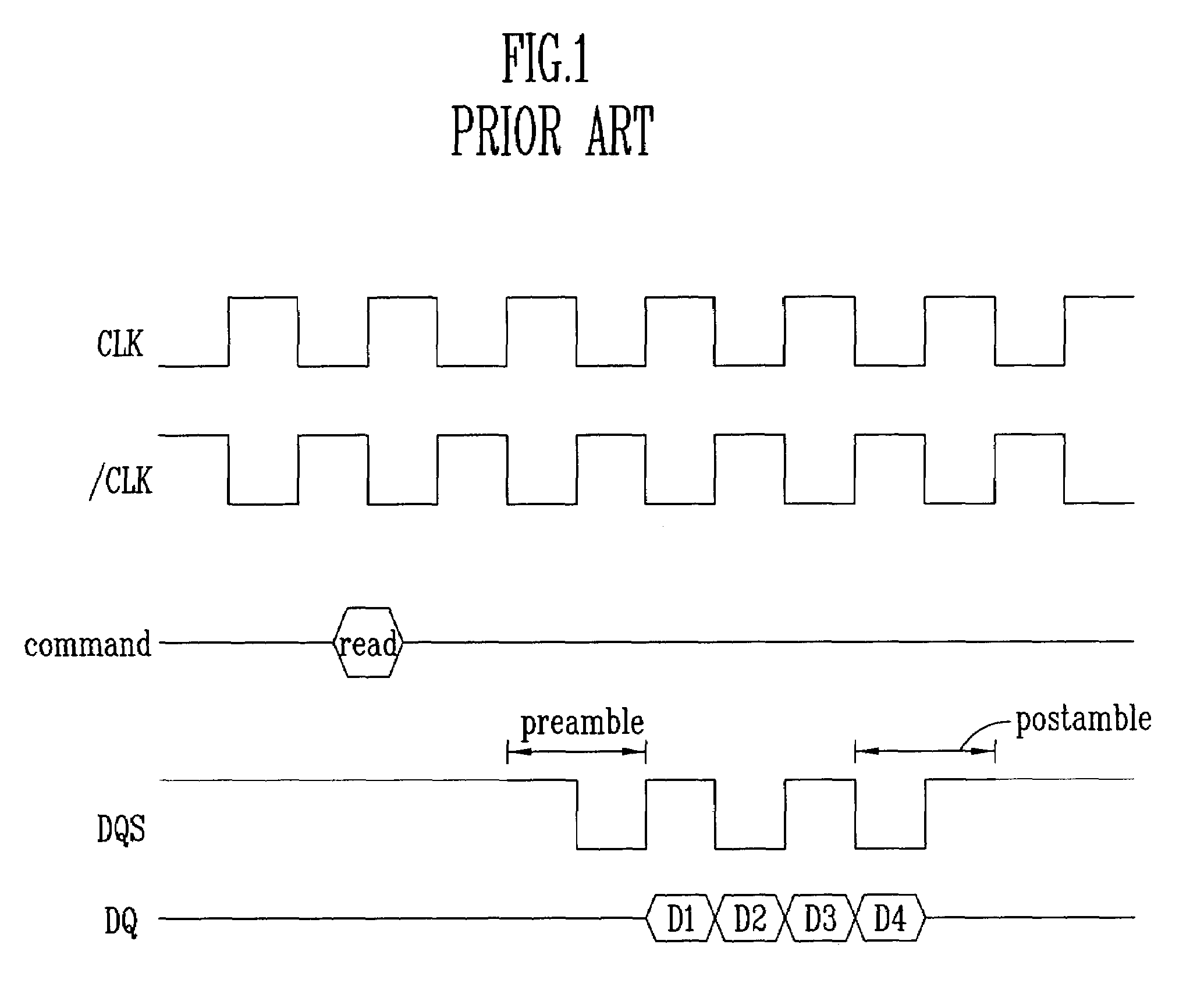
Column Access Strobe (CAS) latency, or CL, is the delay time between the READ command and the moment data is available. In asynchronous DRAM, the interval is specified in nanoseconds (absolute time). In synchronous DRAM, the interval is specified in clock cycles. Because the latency is dependent upon a number of clock ticks instead of absolute time, the actual time for an SDRAM module to respond to a CAS event might vary between uses of the same module if the clock rate differs.
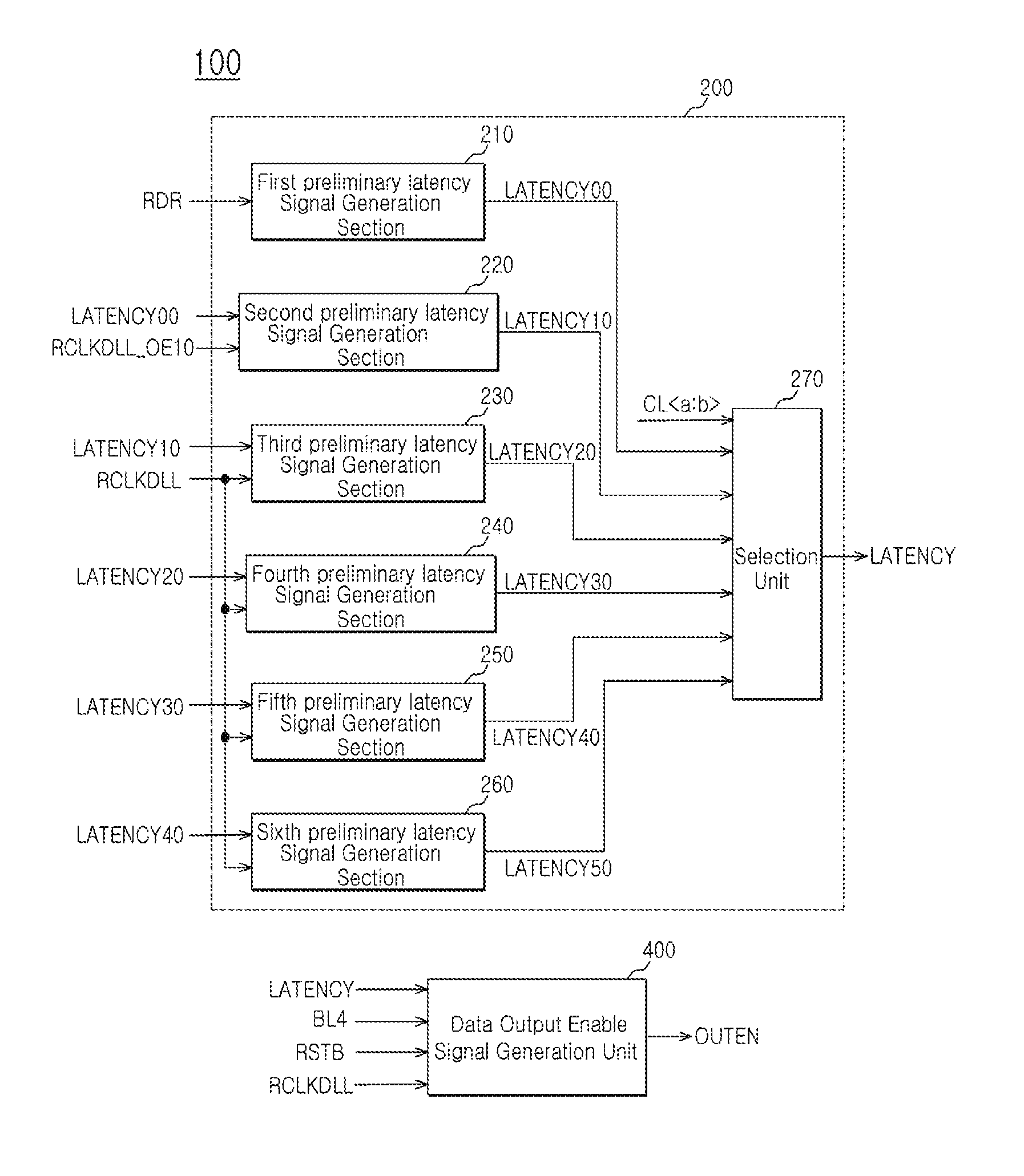
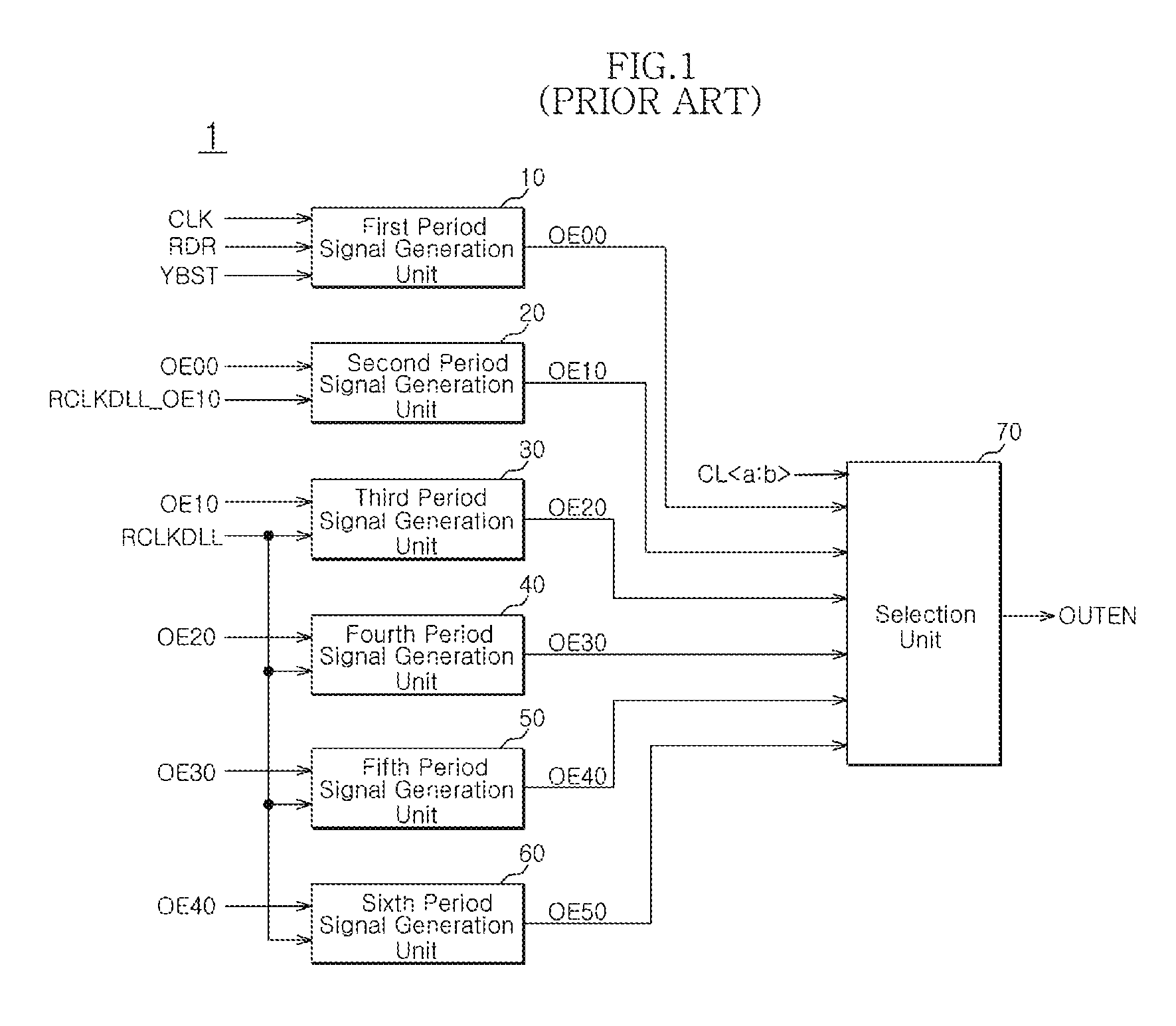
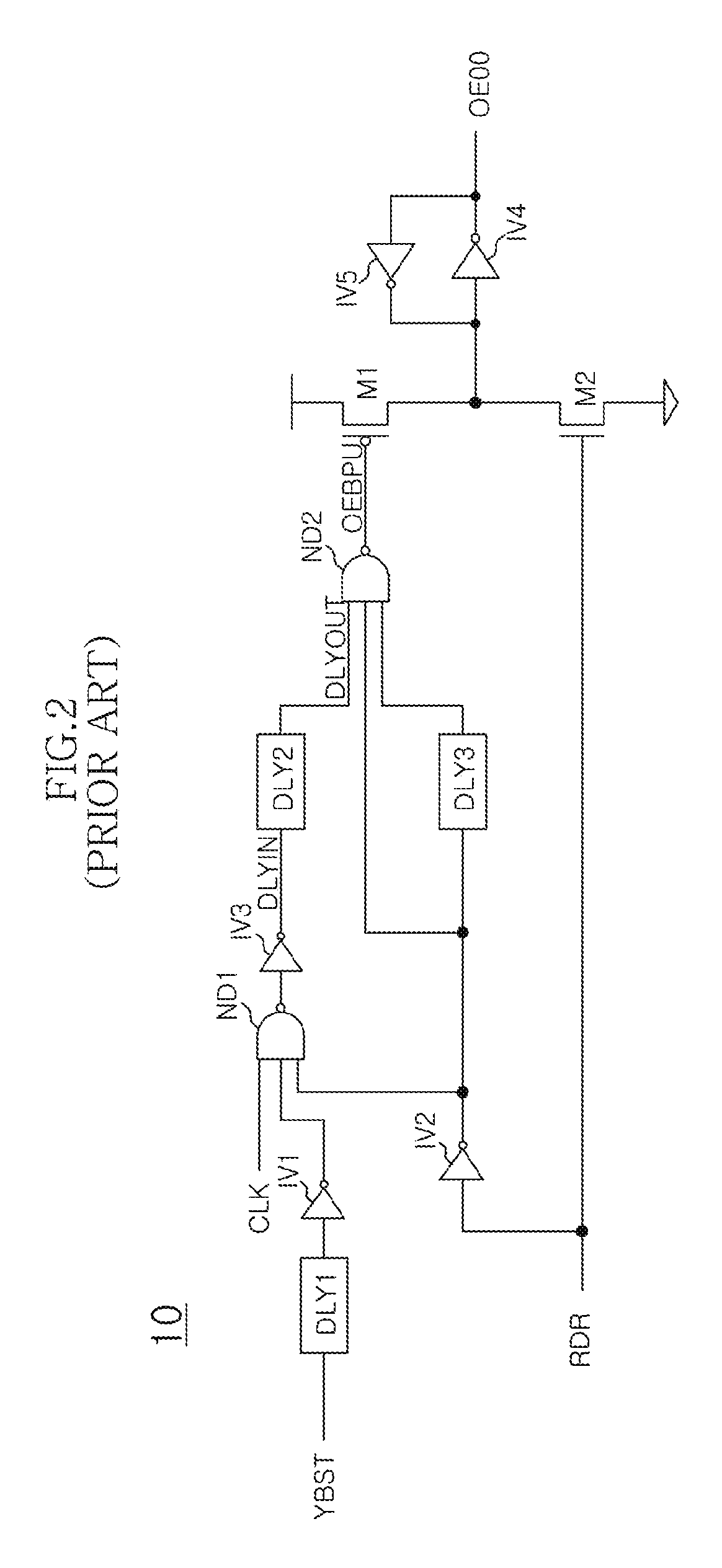
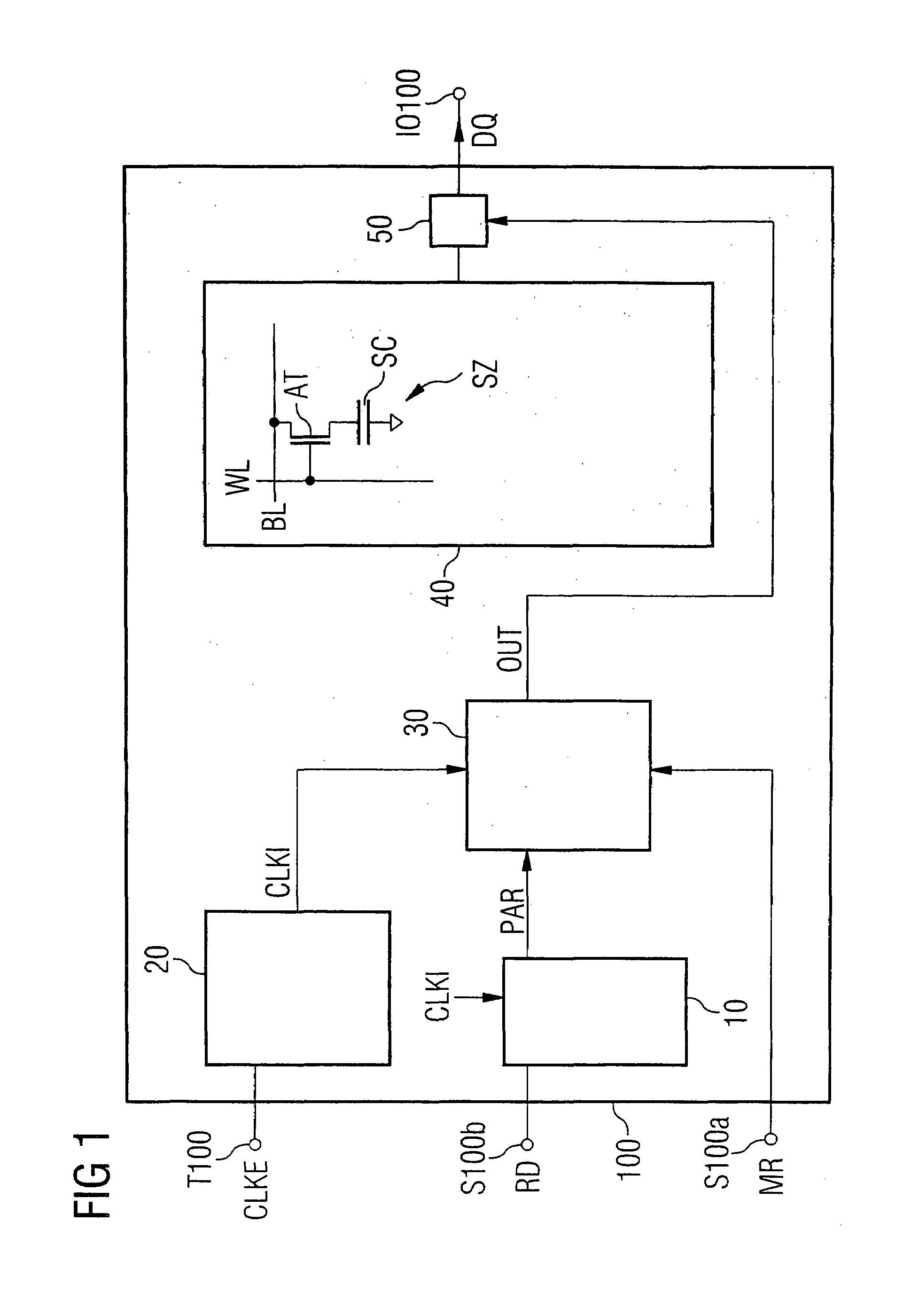
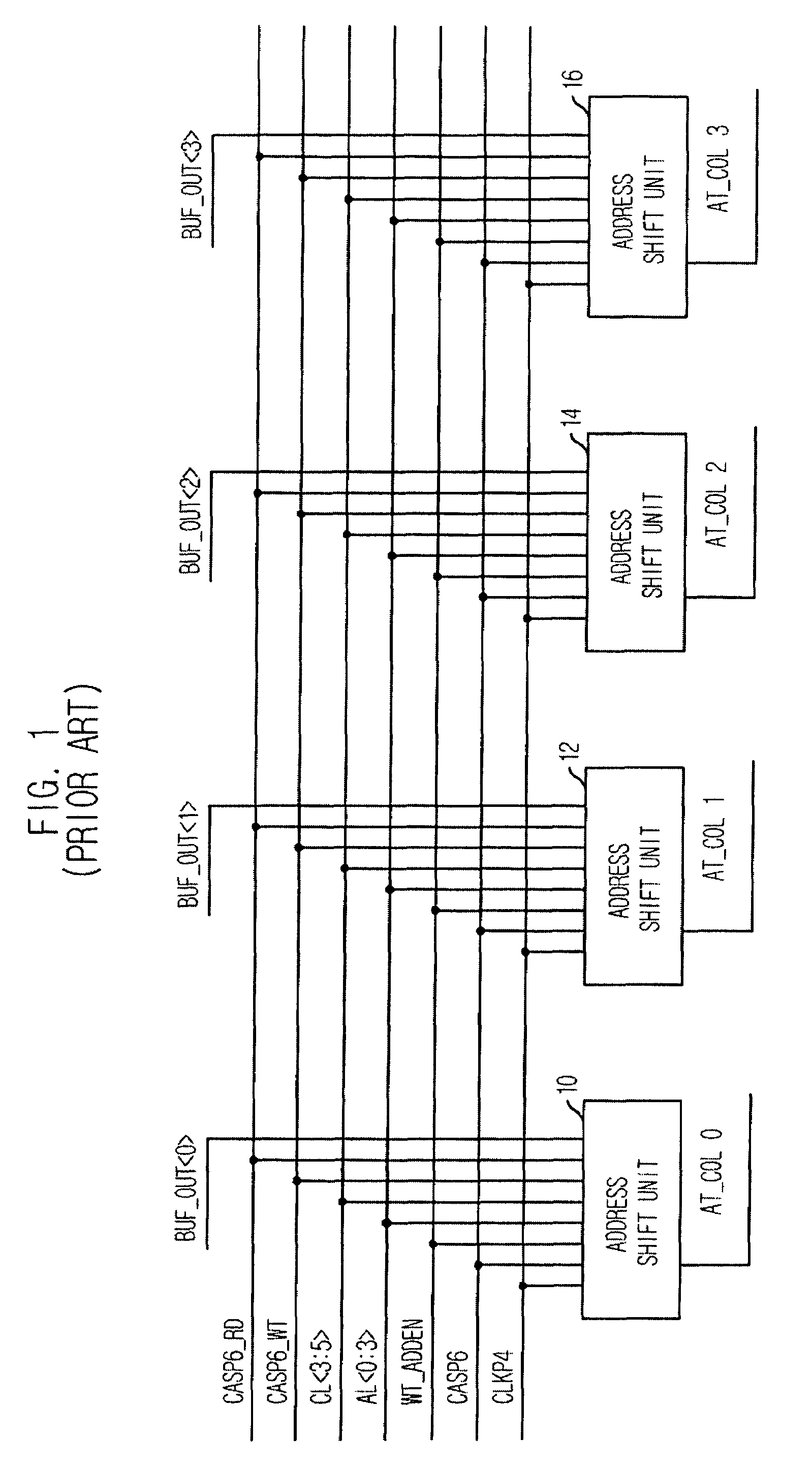
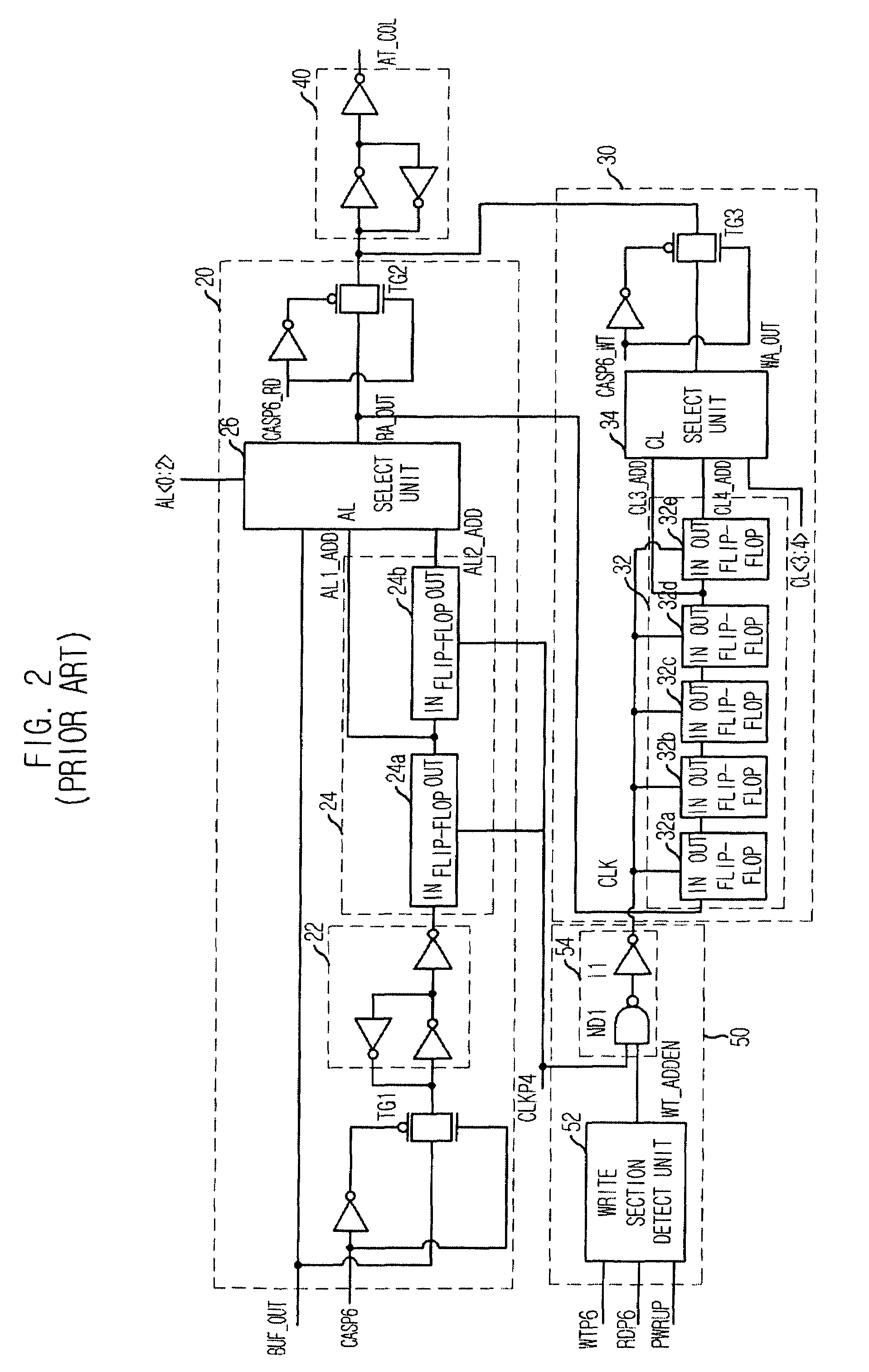
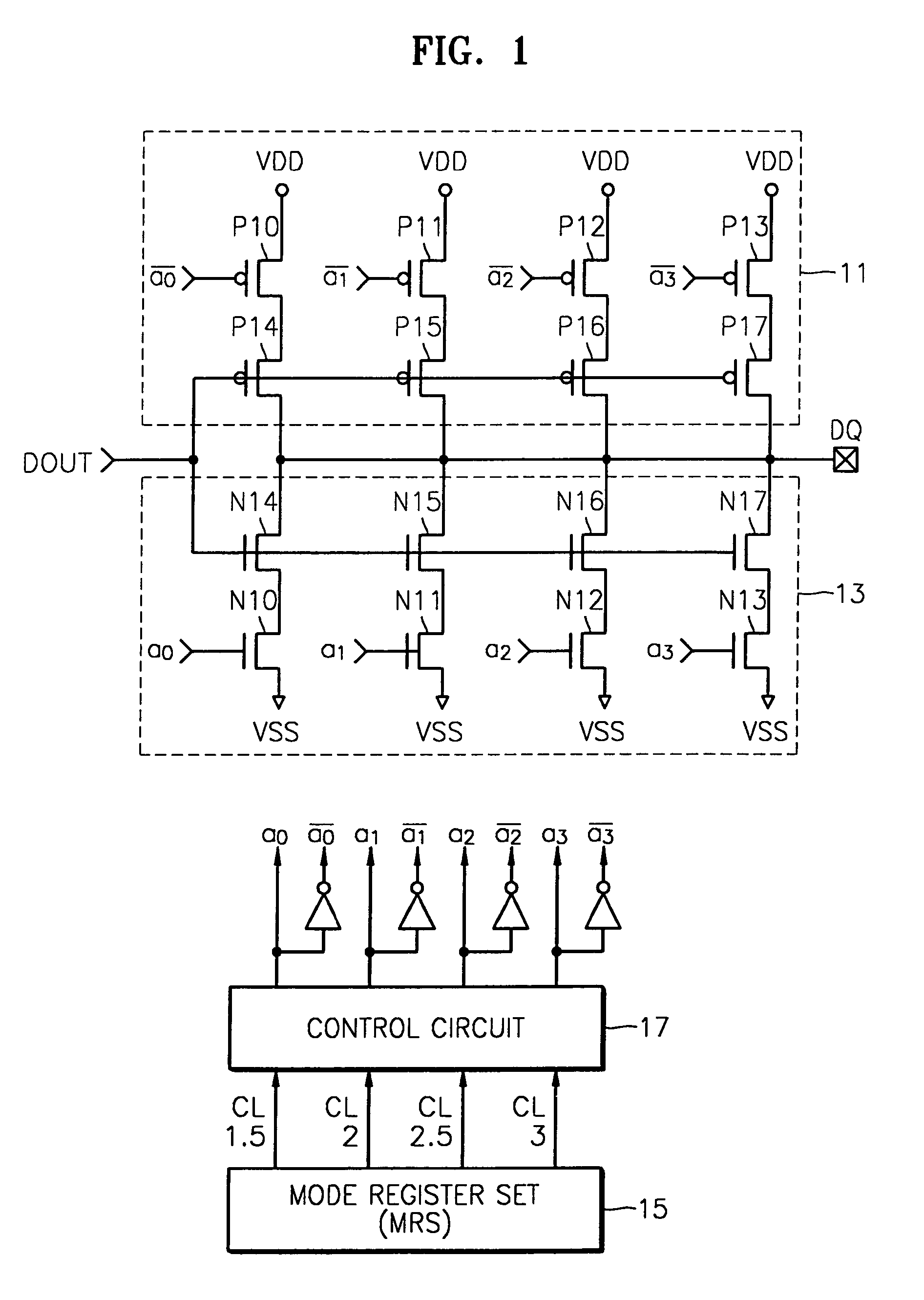
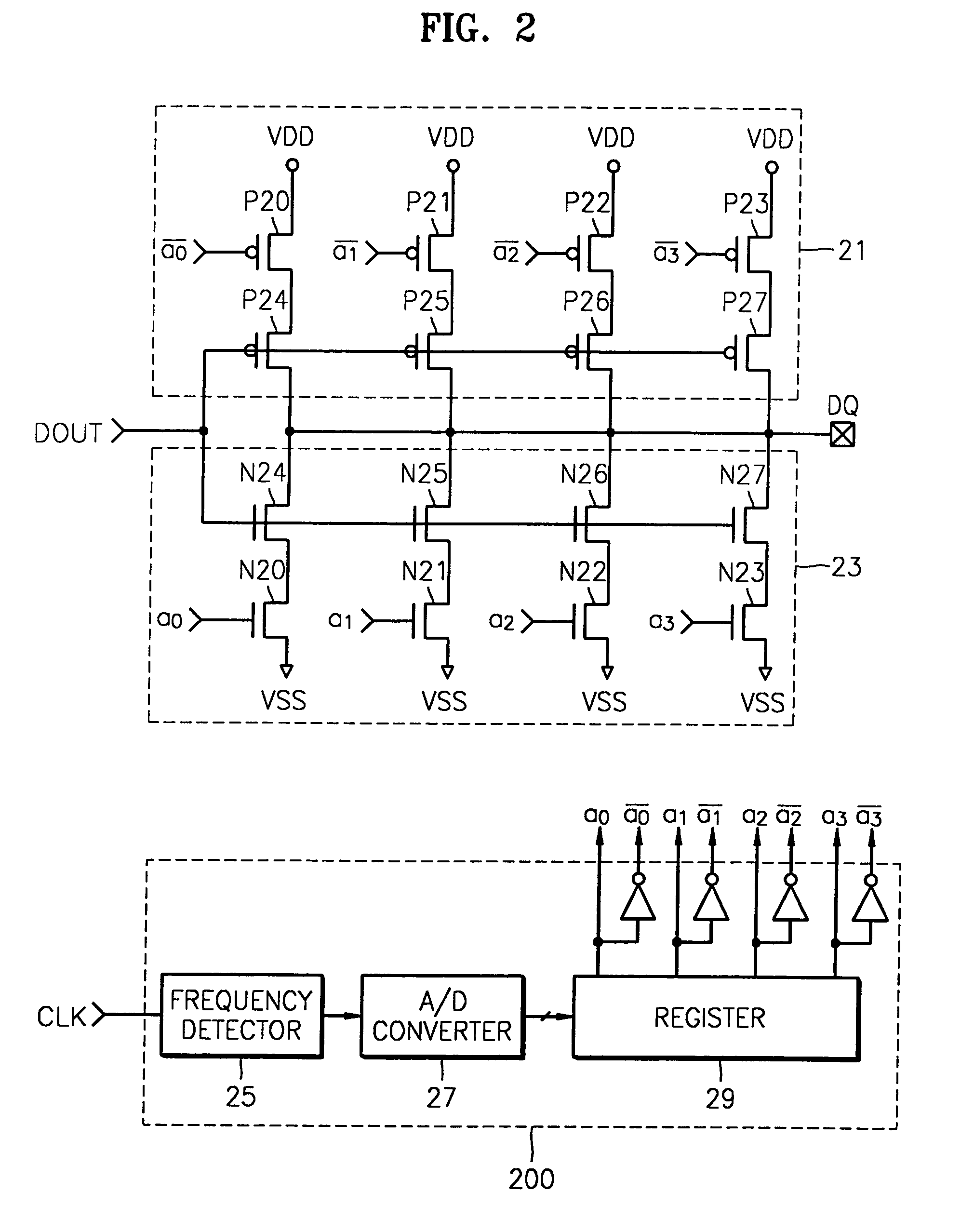
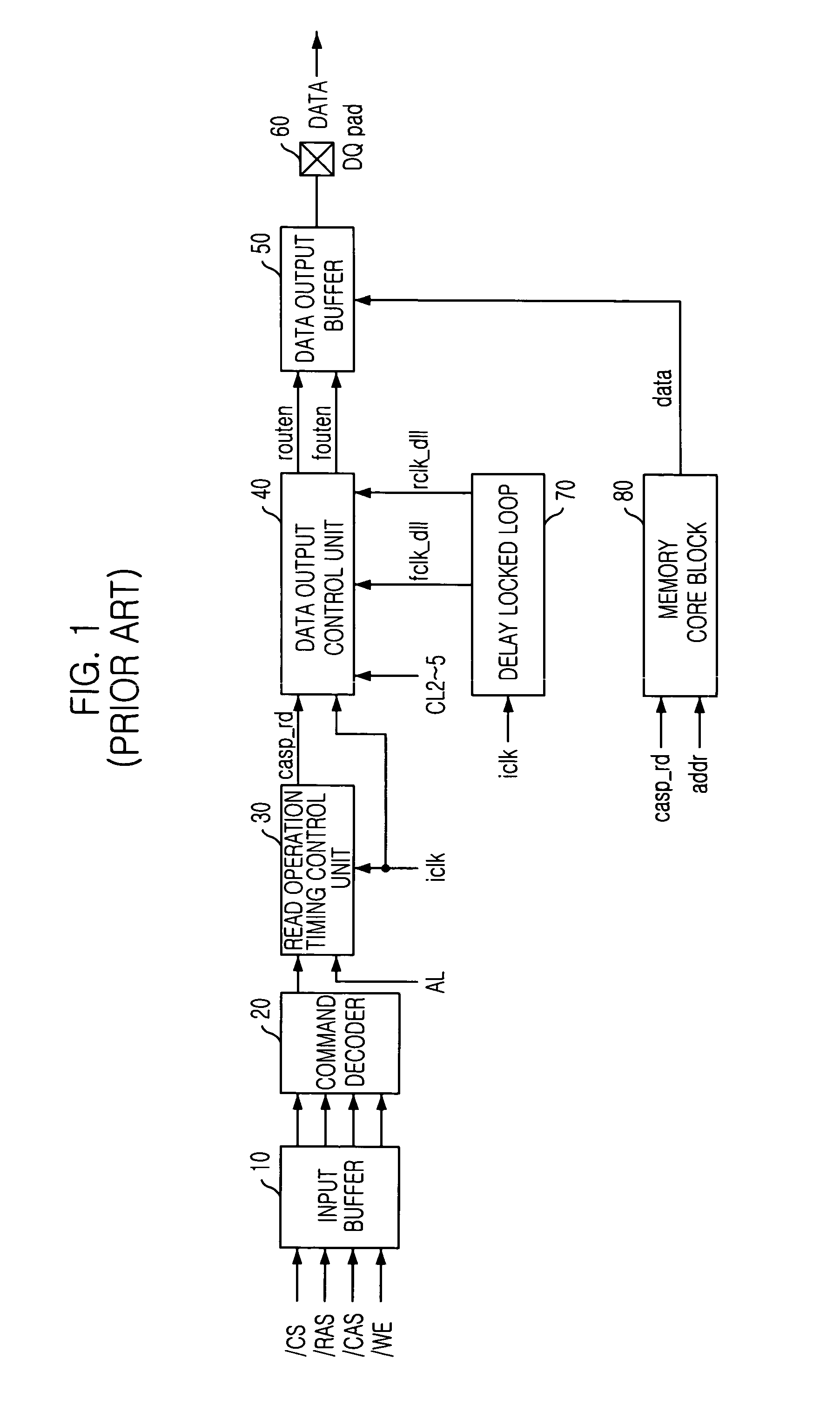
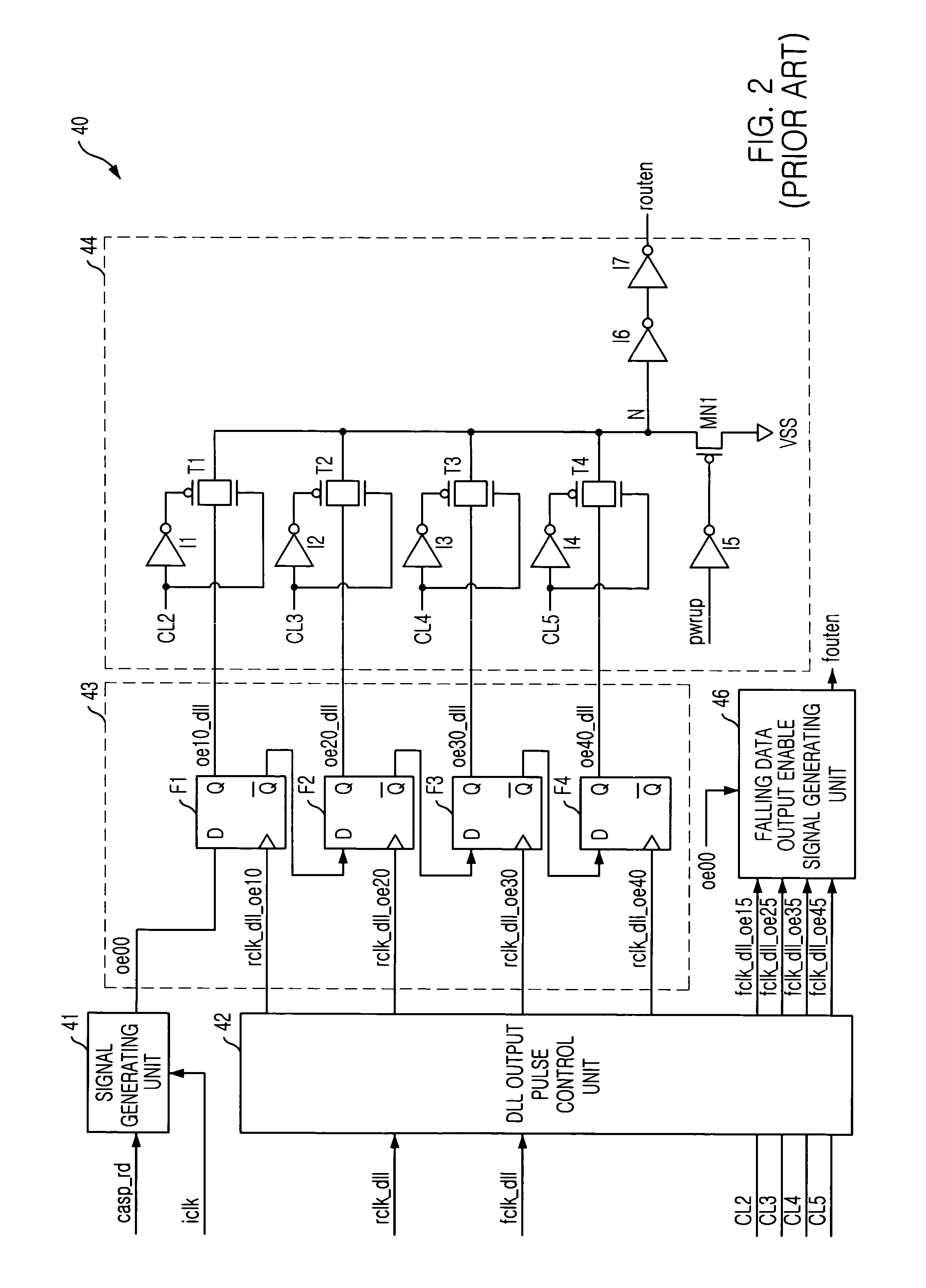
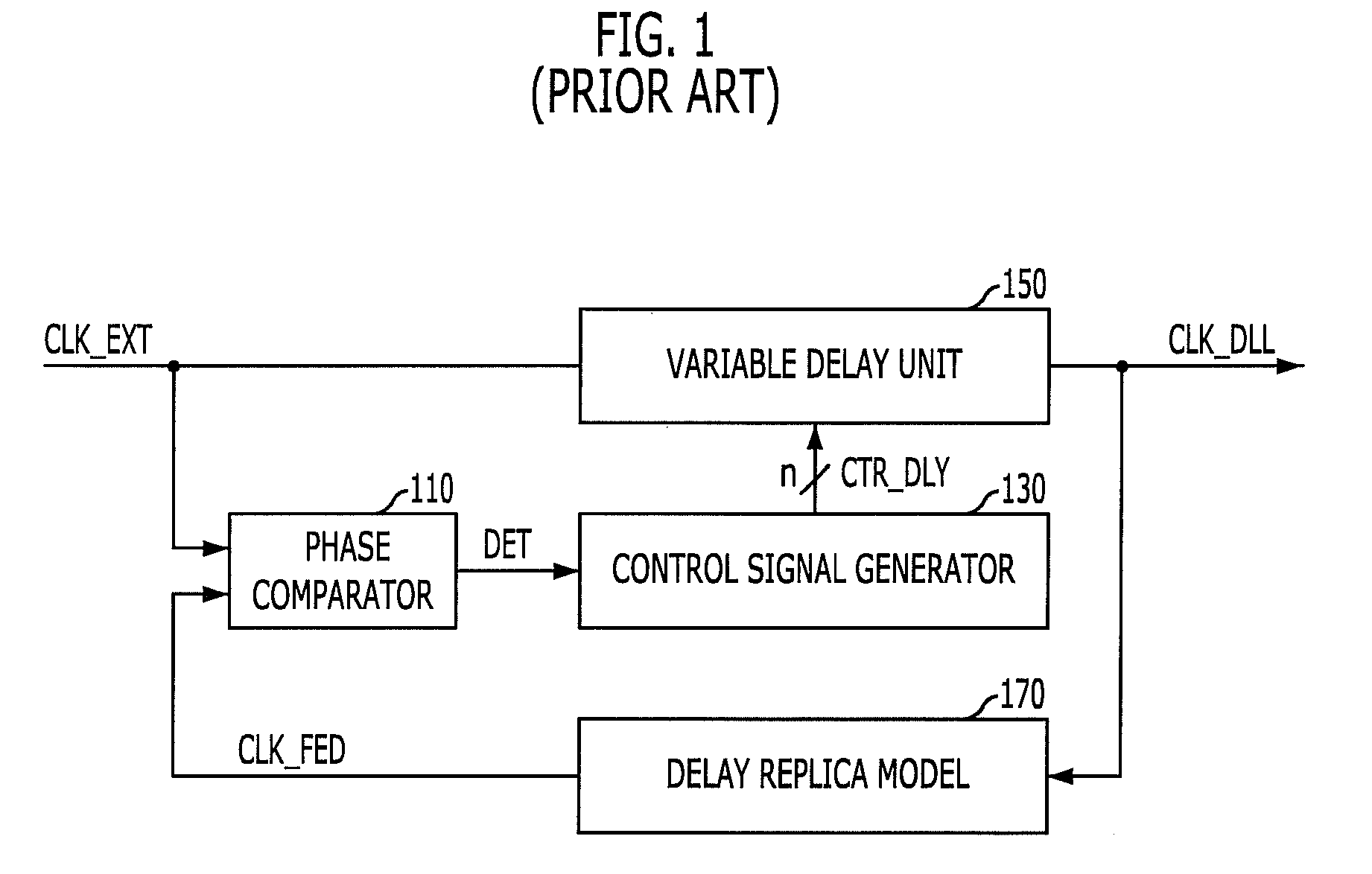
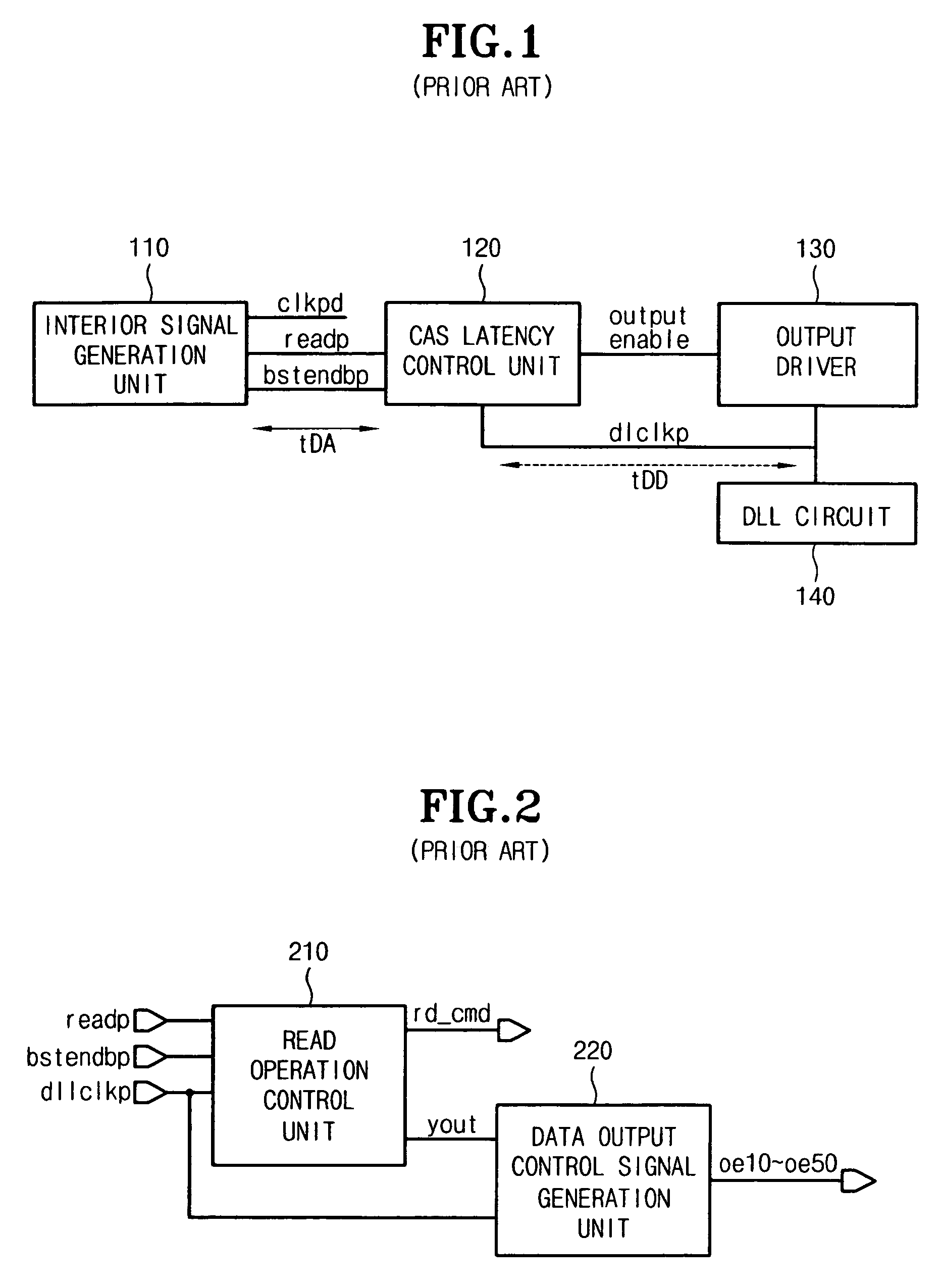
Output enable signal generation circuit of semiconductor memory
An output enable signal generation circuit of a semiconductor memory includes: a latency signal generation unit configured to generate a latency signal for designating activation timing of a data output enable signal in response to a read signal and a CAS latency signal; and a data output enable signal generation unit configured to control the activation timing and deactivation timing of the data output enable signal in response to the latency signal and a signal generated by shifting the latency signal based on a burst length (BL).
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
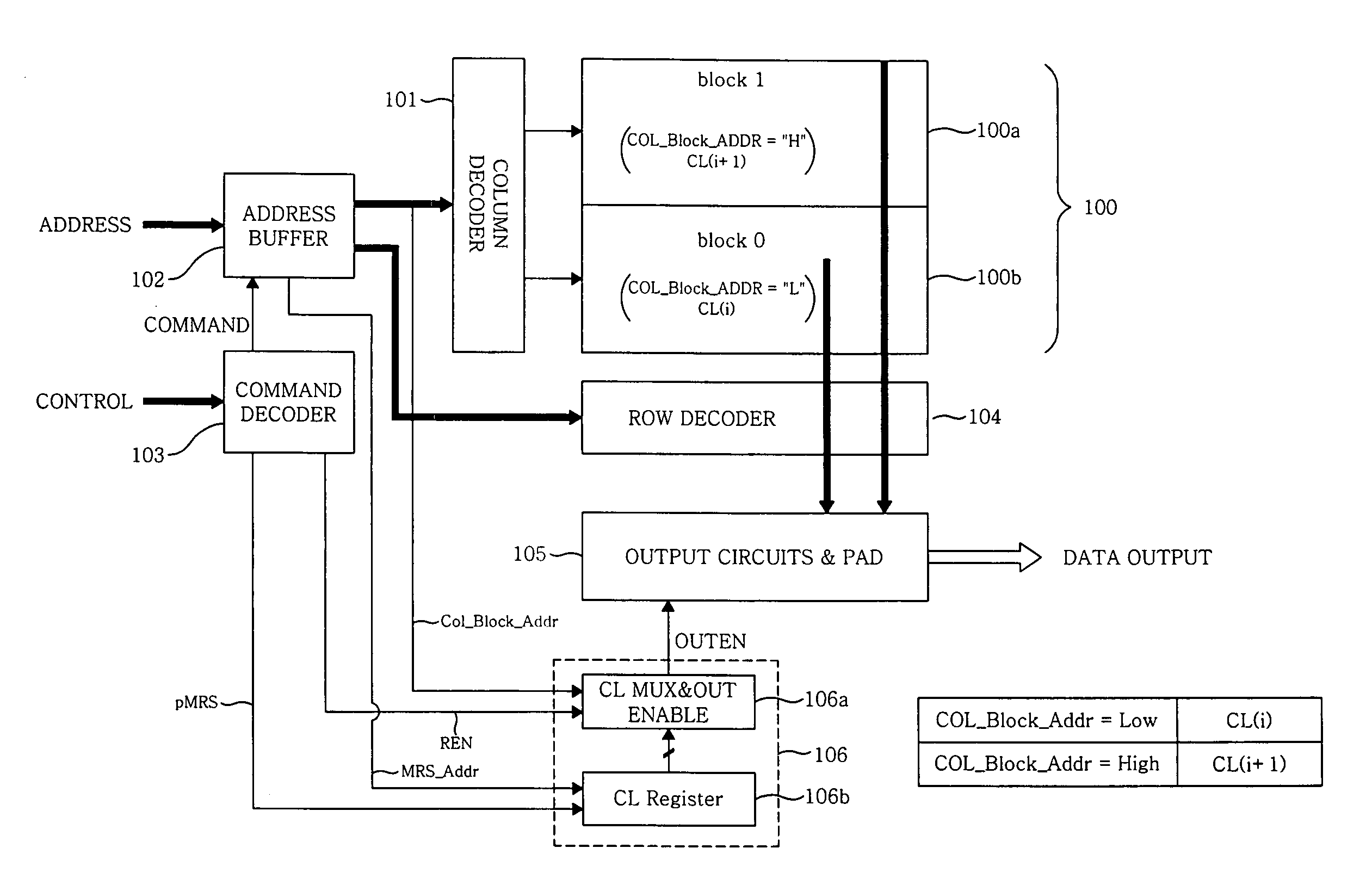
Semiconductor memories with block-dedicated programmable latency register
An apparatus and method to delay output of data from different regions of a memory device in response to a read enable signal, the delaying of the output of data is based on the location of the regions of the memory device with respect to an output circuit that receives the data, wherein the different regions of the memory device have different CAS latency values dedicated to each region to set the delay time of each region of the memory device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
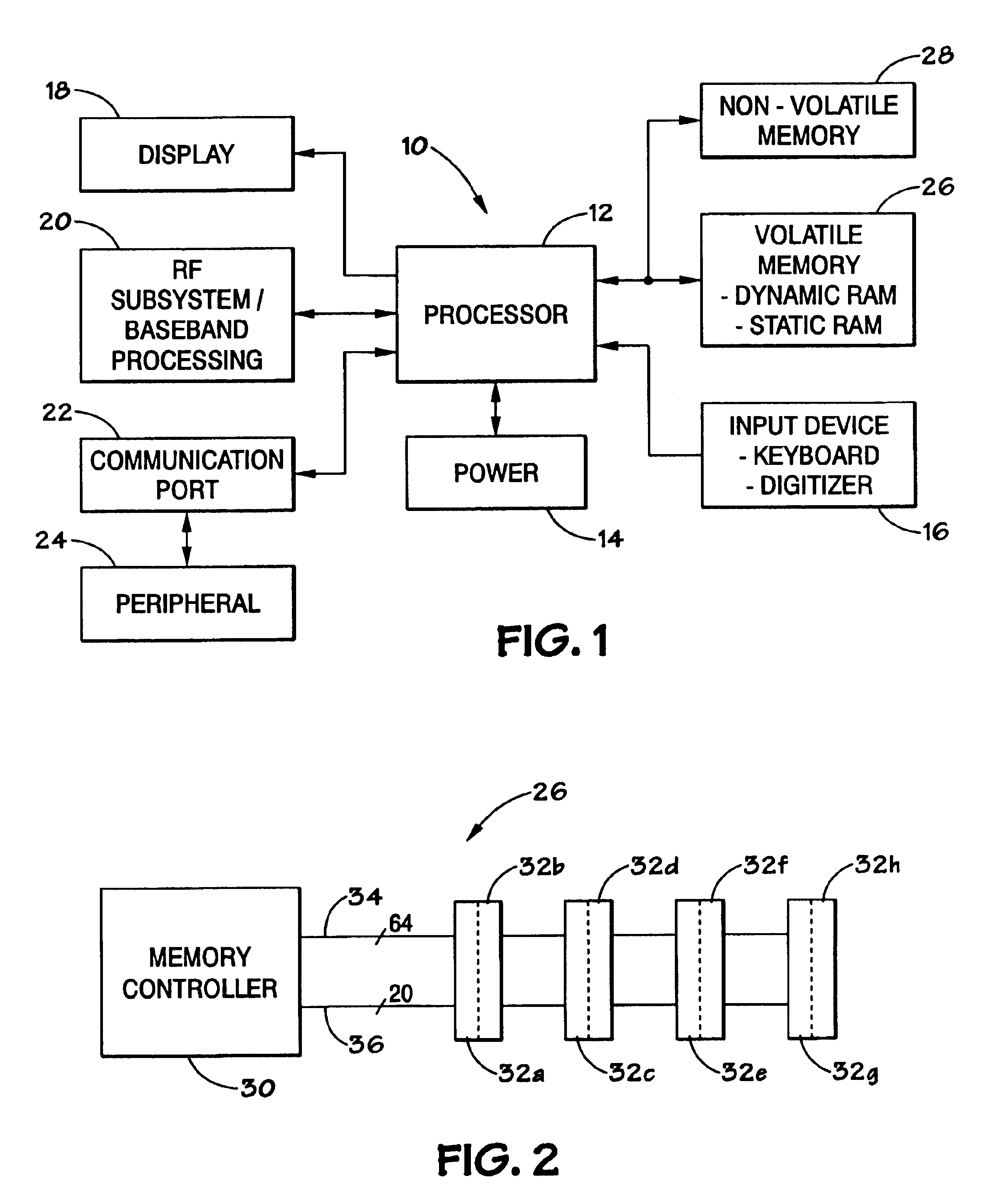
Method and system for resolving interoperability of multiple types of dual in-line memory modules
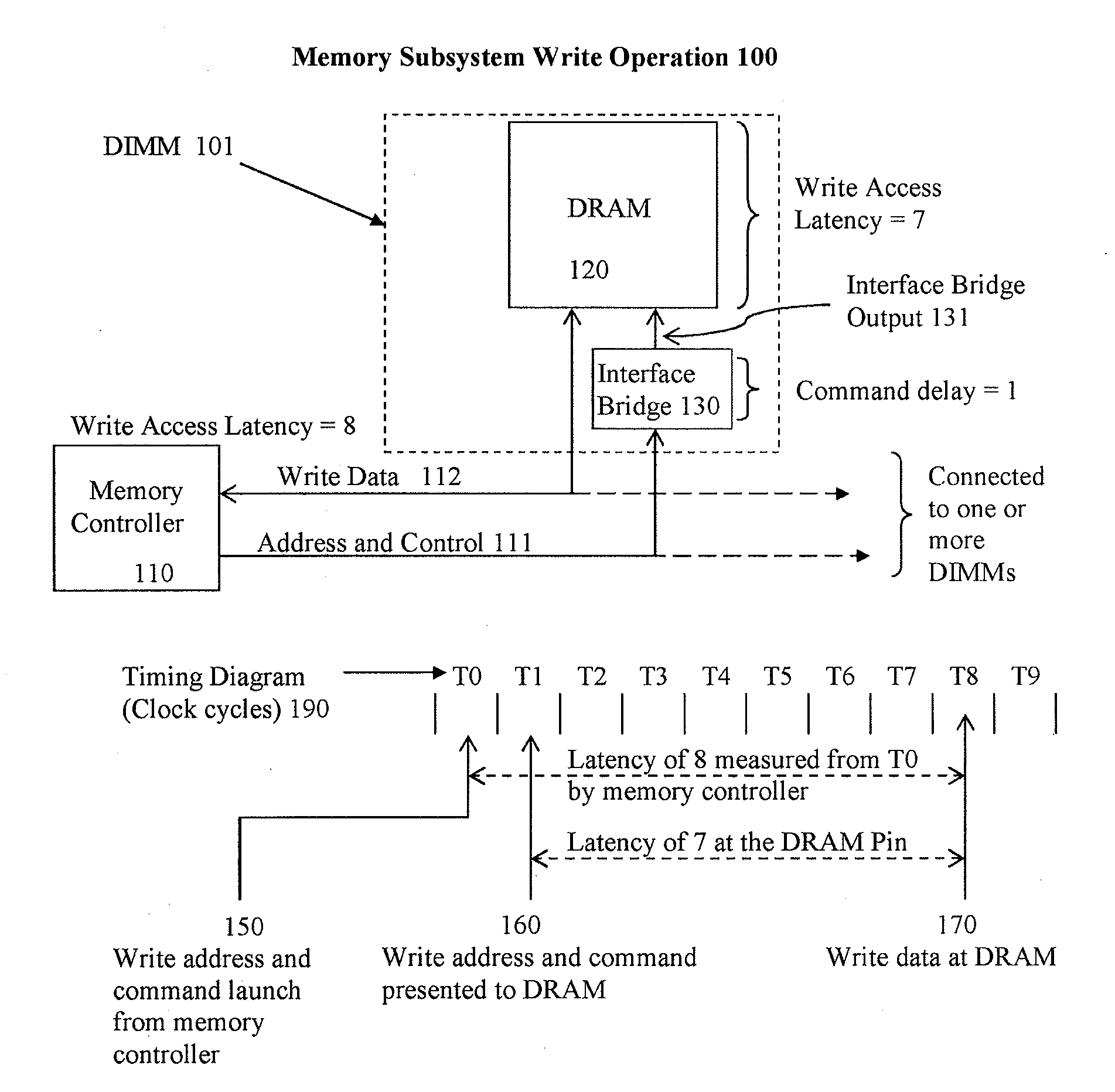
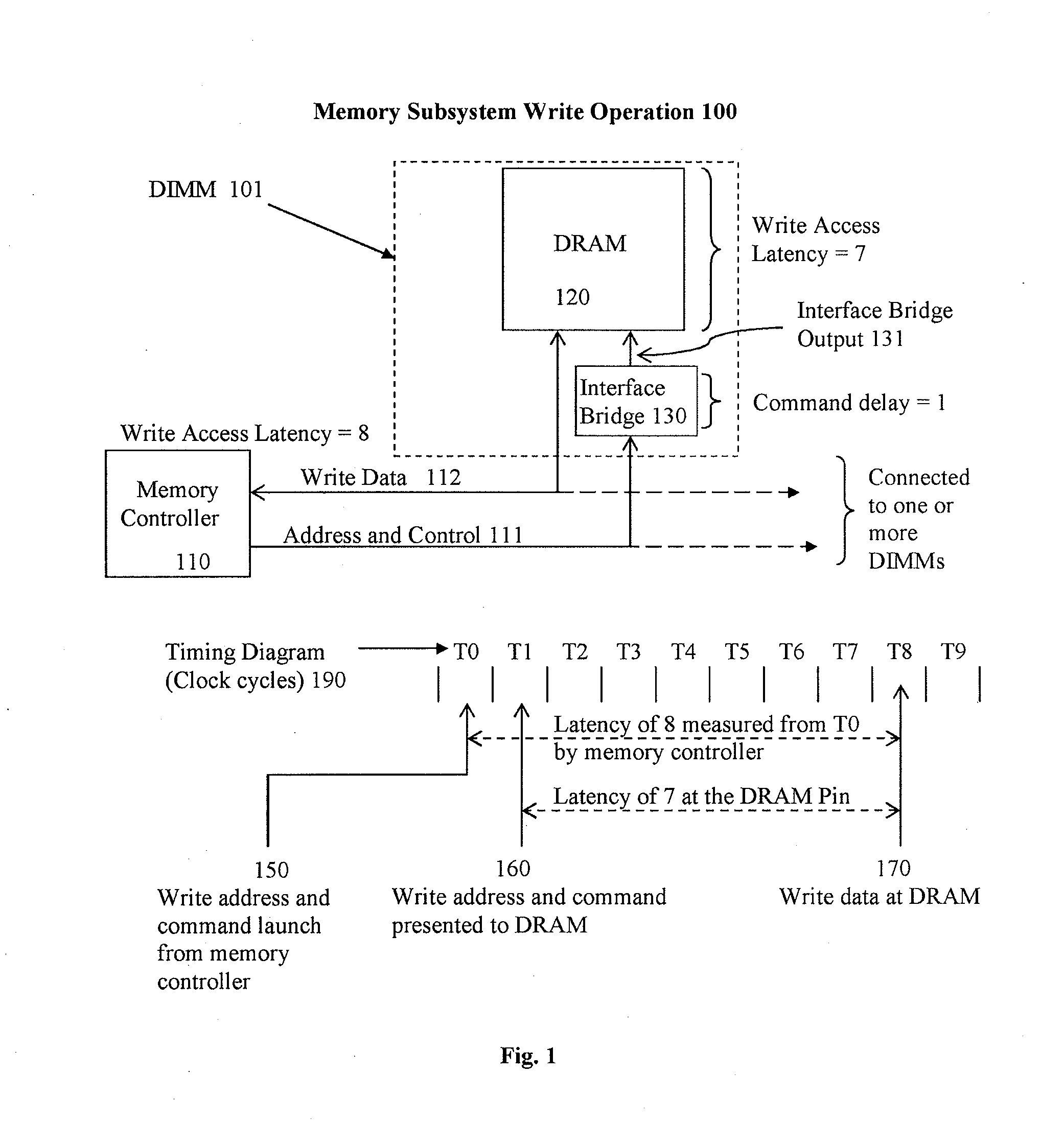
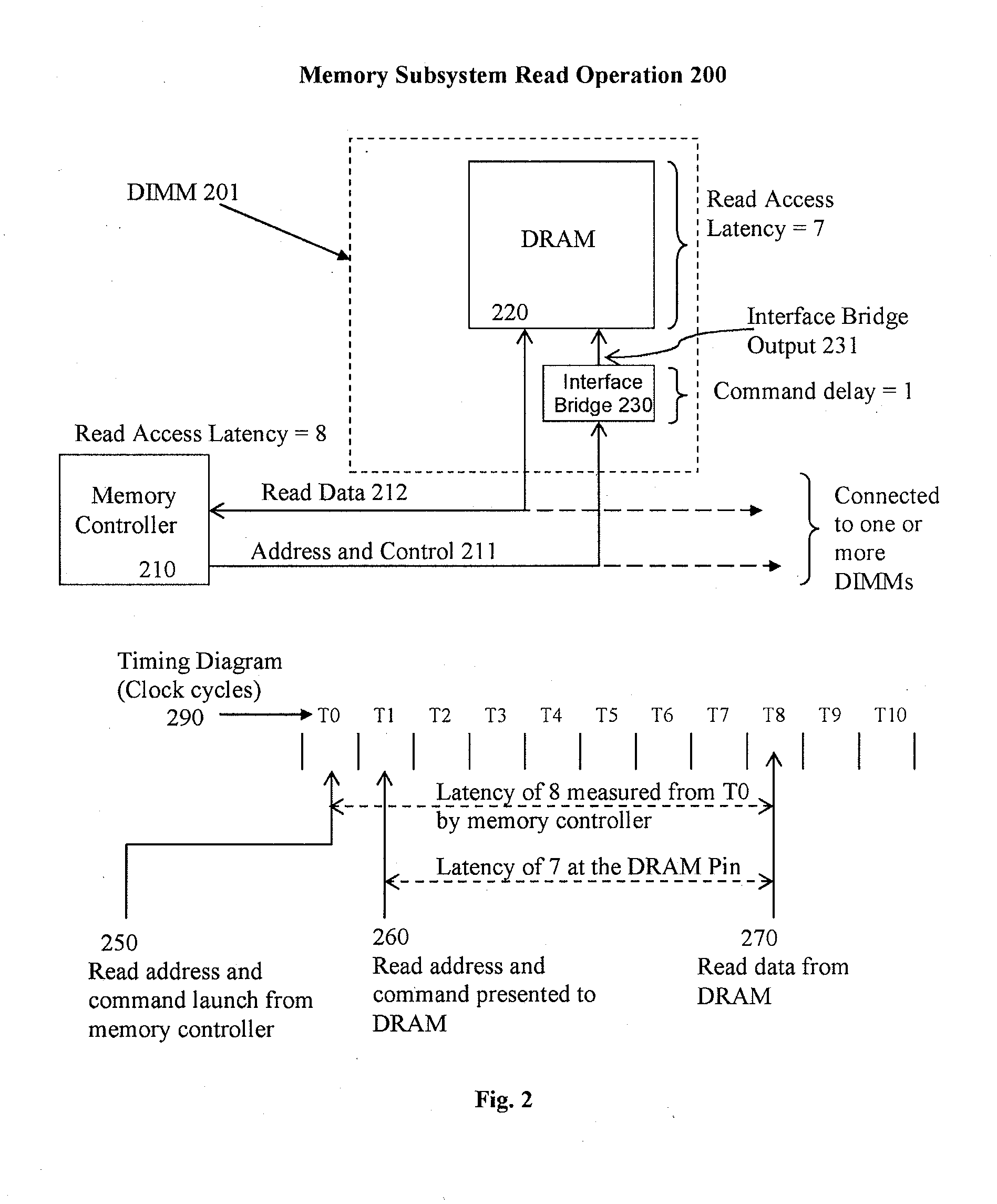
Systems and methods are described for resolving certain interoperability issues among multiple types of memory modules in the same memory subsystem. The system provides a single data load DIMM for constructing a high density and high speed memory subsystem that supports the standard JEDEC RDIMM interface while presenting a single load to the memory controller. At least one memory module includes one or more DRAM, a bi-directional data buffer and an interface bridge with a conflict resolution block. The interface bridge translates the CAS latency (CL) programming value that a memory controller sends to program the DRAMs, modifies the latency value, and is used for resolving command conflicts between the DRAMs and the memory controller to insure proper operation of the memory subsystem.
Owner:NETLIST INC
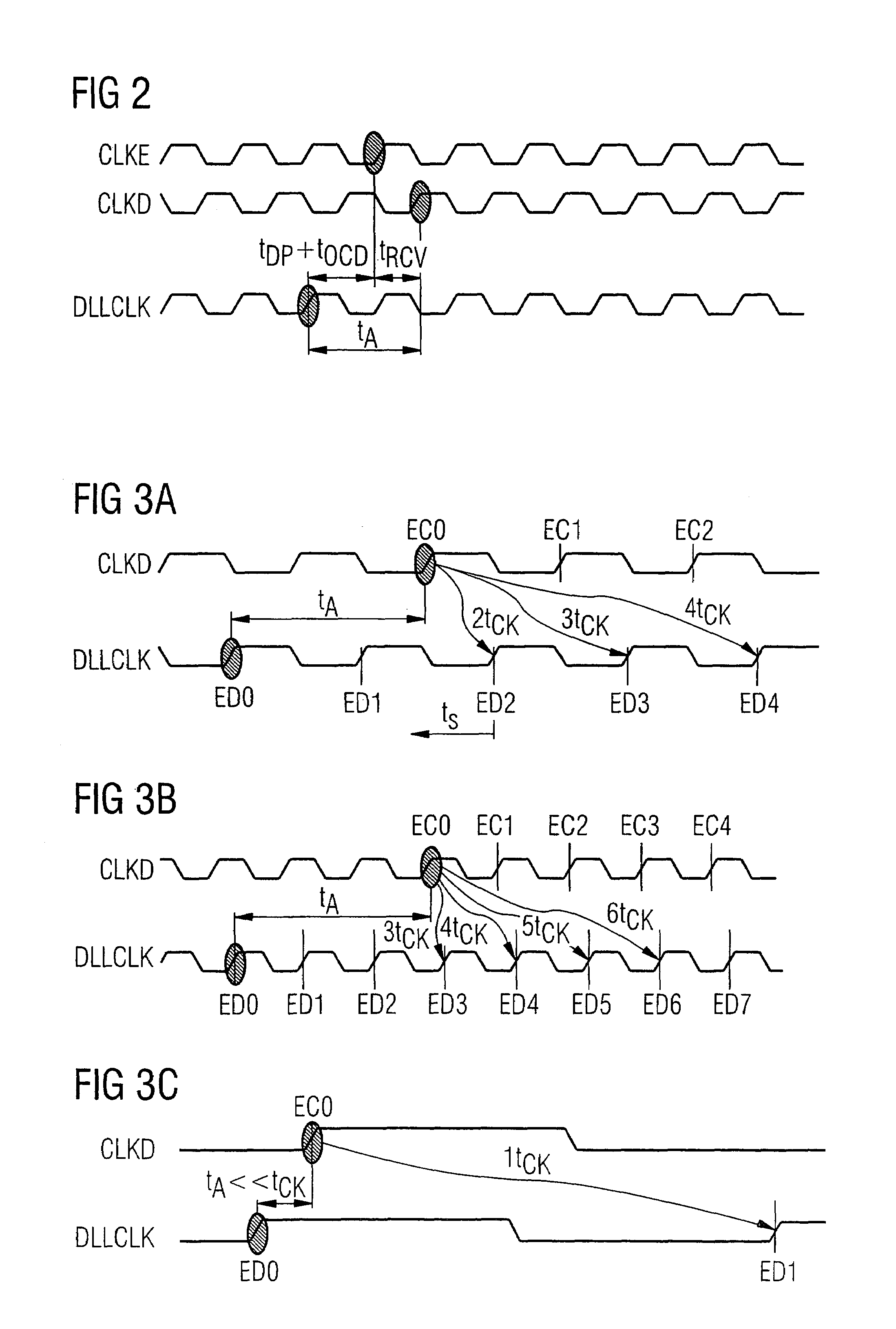
Latency reduction using negative clock edge and read flags
InactiveUS20040034755A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationGenerating/distributing signalsCombined useCAS latency
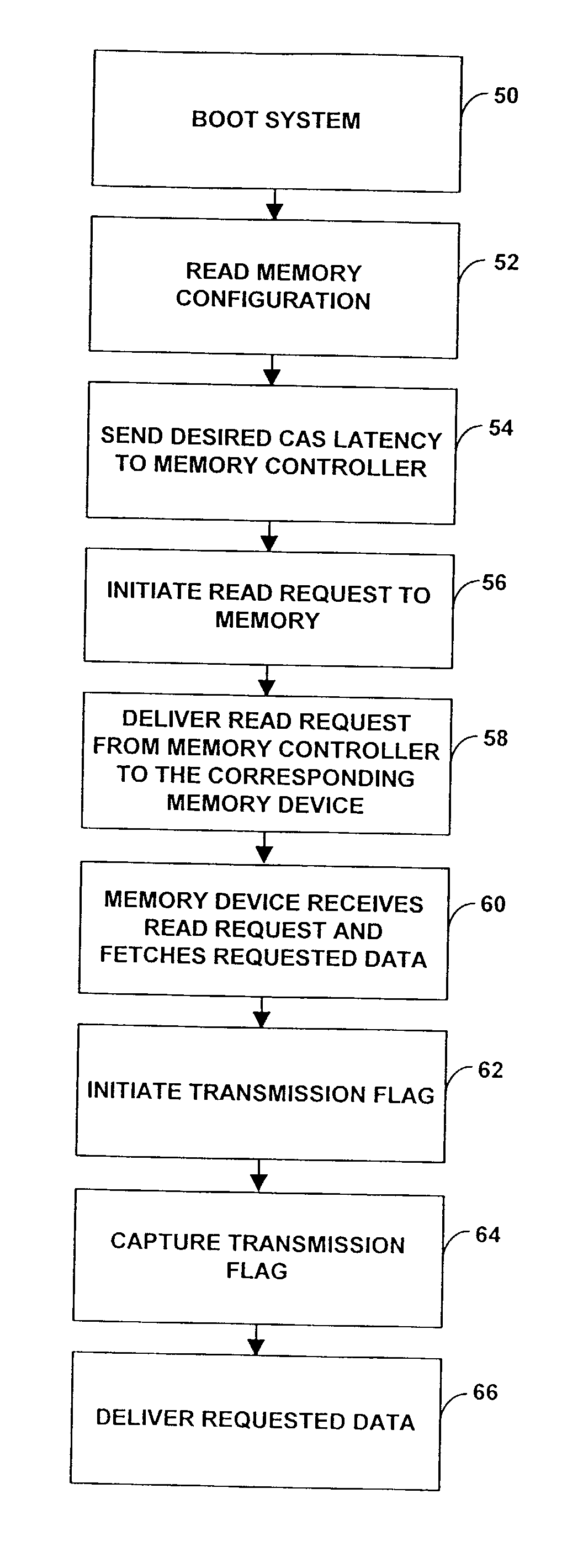
A method of selecting CAS latencies in a system. Specifically, a system which includes a plurality of memory devices and a memory controller is provided. Because different memory devices may have different CAS latencies, a system CAS latency is selected wherein the system CAS latency is the fastest common CAS latency of each of the plurality of memory devices. After a read request is delivered to a memory device, the memory controller initiates a transmission flag to the memory device at a time equal to the system CAS latency, indicating that it is safe to transmit the requested data from the memory device to the memory controller. The transmission flags may be used in conjunction with mode registers such that one or both of the transmission flag and the data may be received by or delivered by a corresponding memory device.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
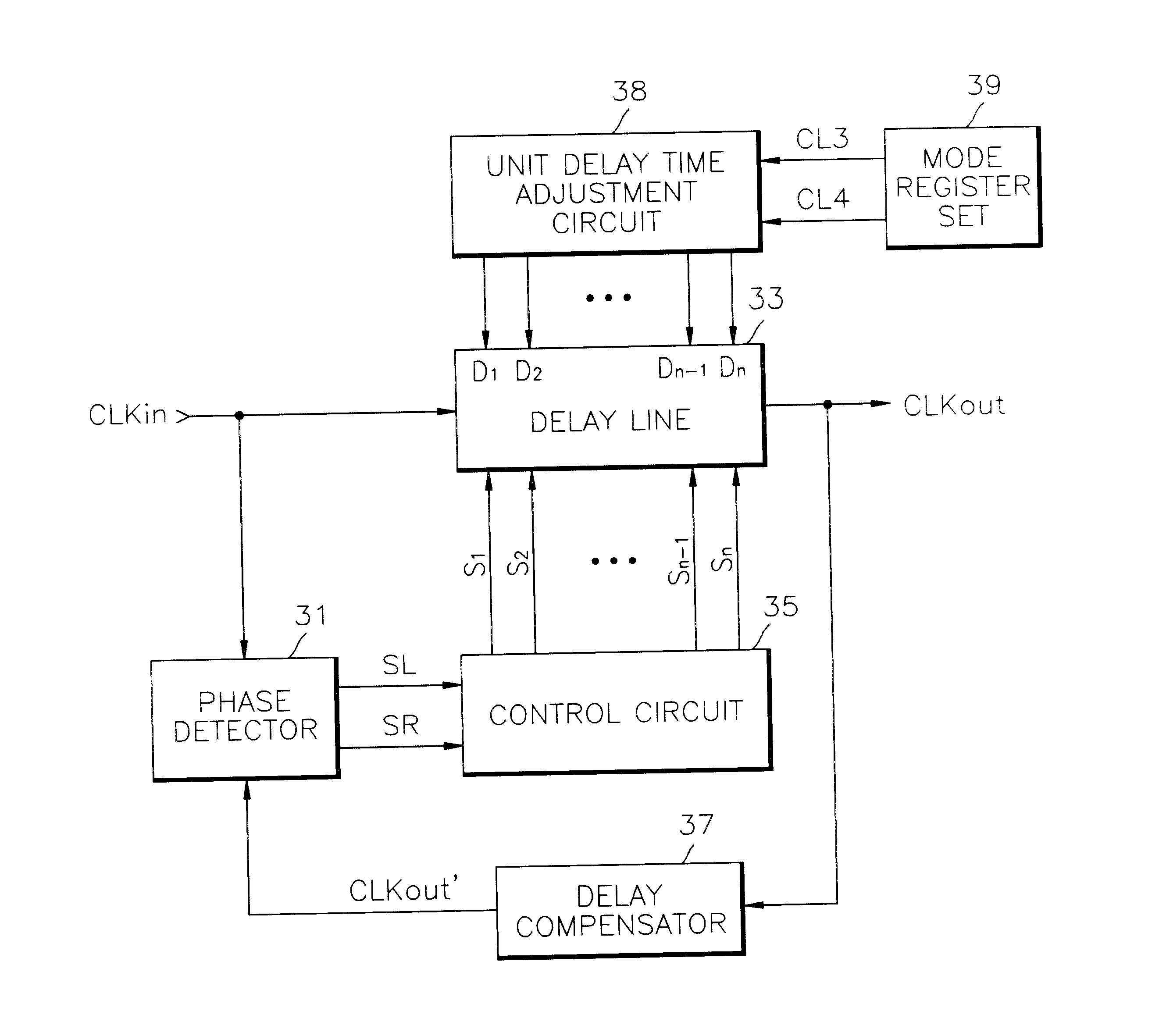
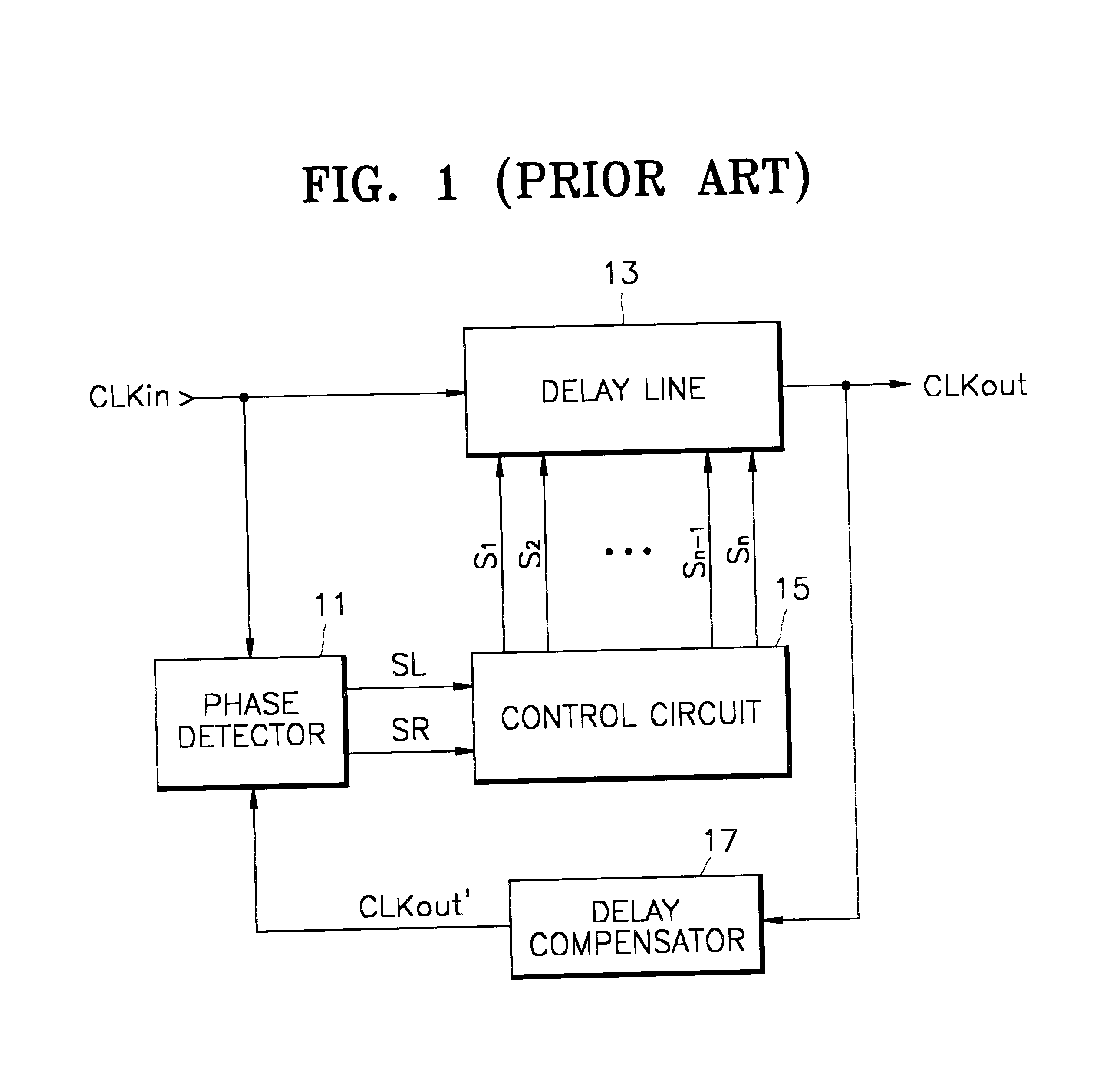
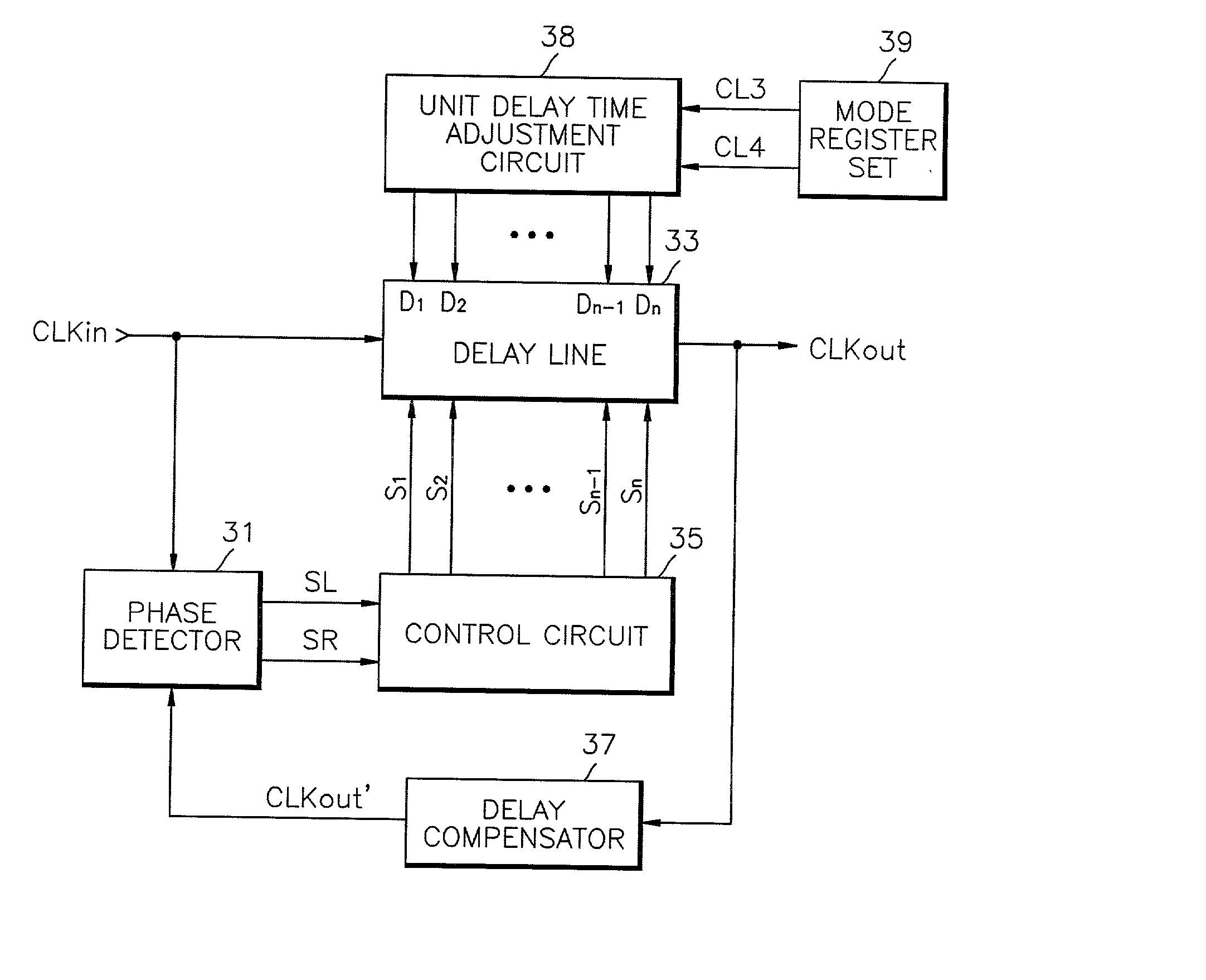
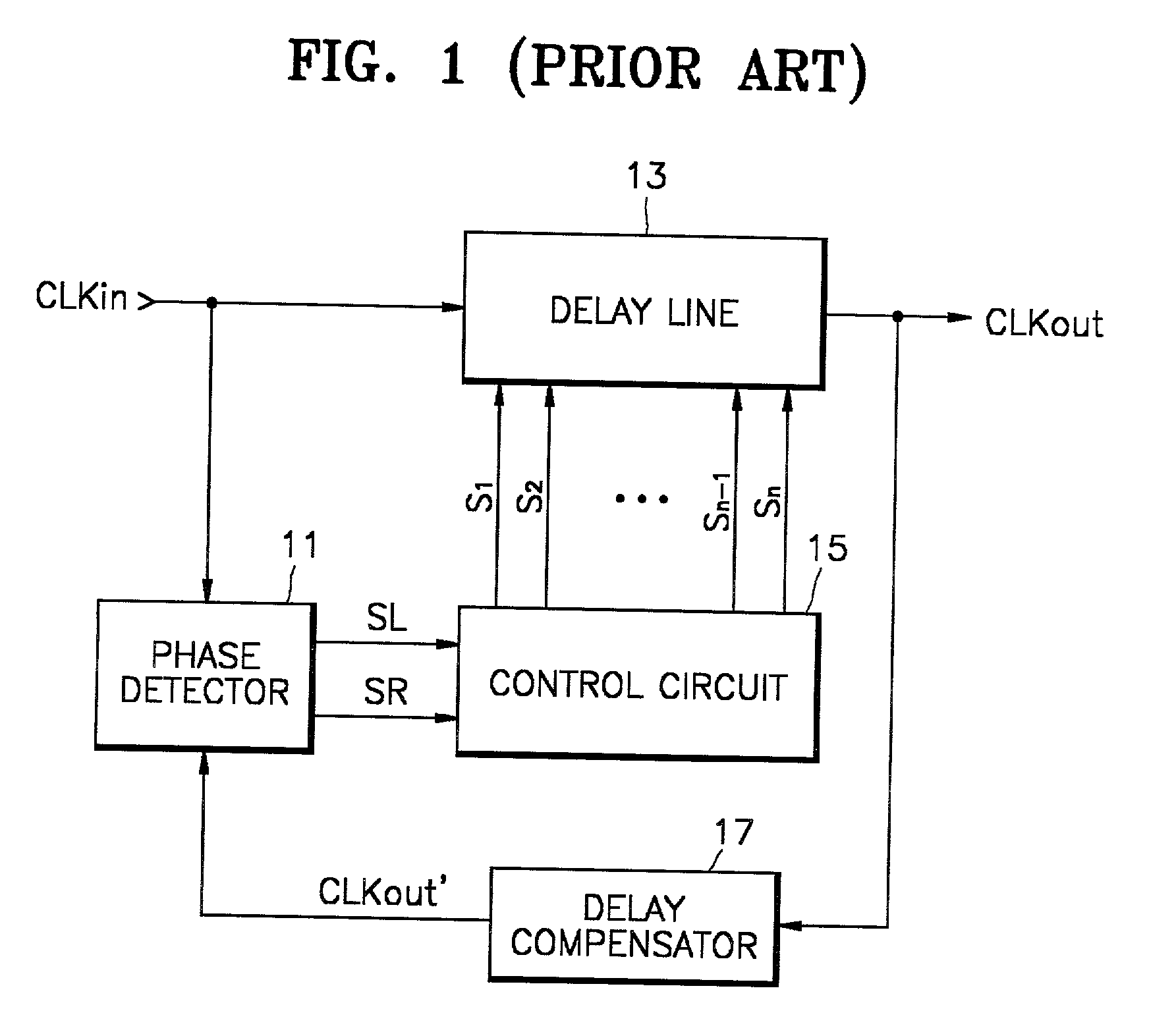
Delay locked loop circuit and method having adjustable locking resolution
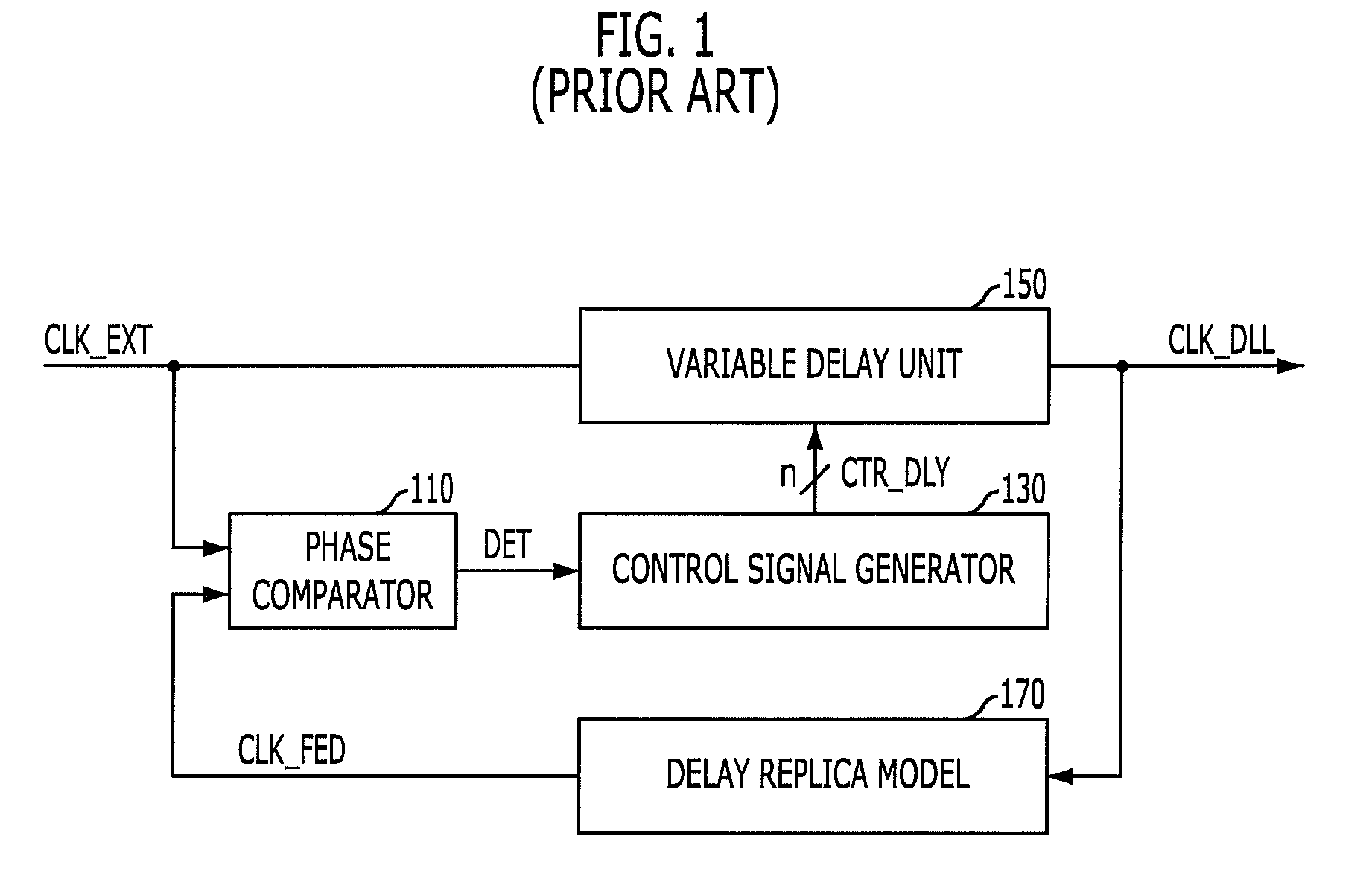
A delay line receives an input clock signal and includes a cascaded plurality of unit delay circuits. A mode register set stores a value indicative of a column-address-strobe (CAS) latency of the memory device, and an adjustment circuit varies a delay time of the unit delay circuits according to the CAS latency stored in the mode register set. A phase detector detects a phase difference between the input clock signal and an output clock signal of the delay line, and a control circuit which controls an enabled state of the unit delay circuits according to an output of said phase detector.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
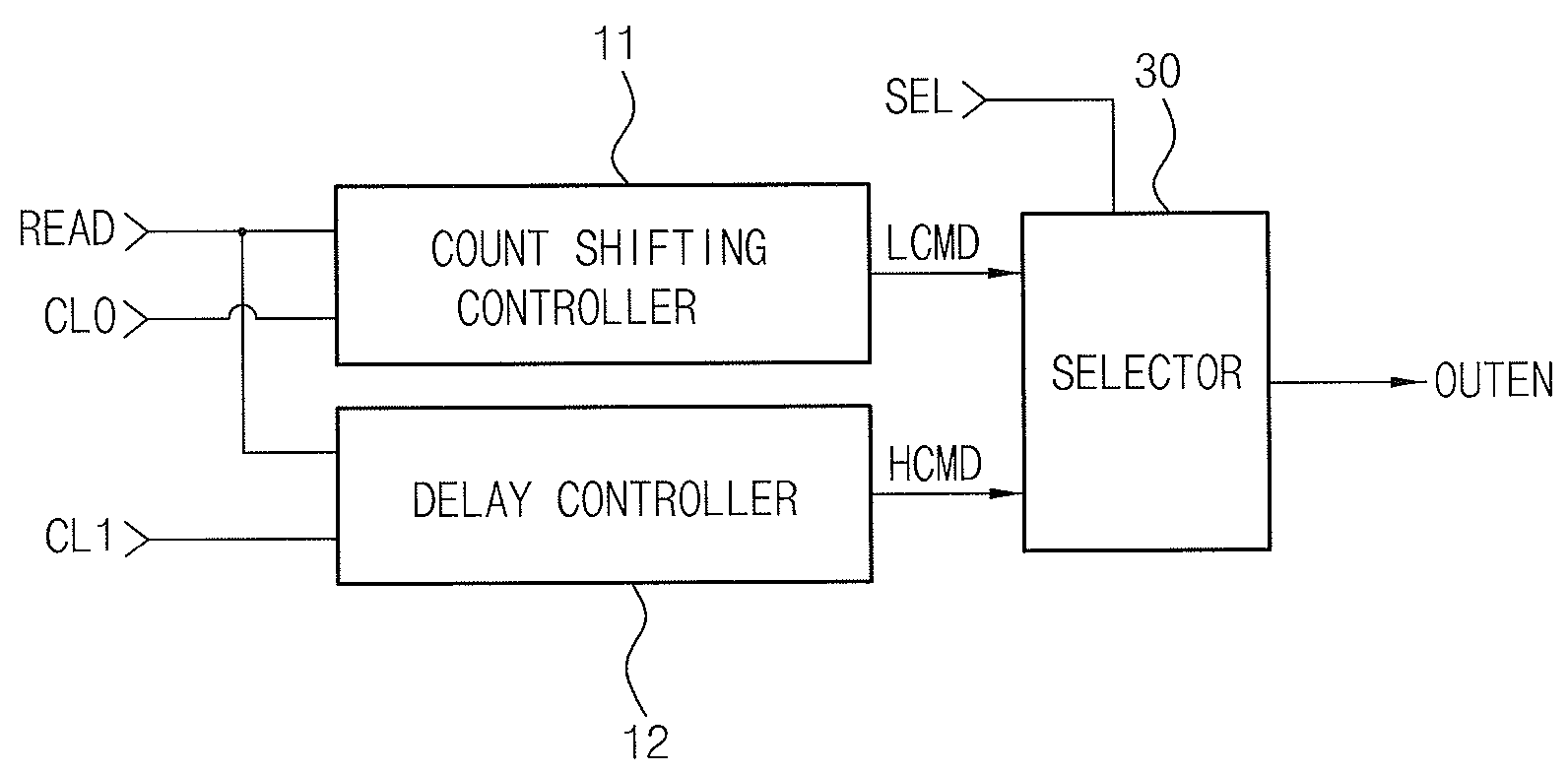
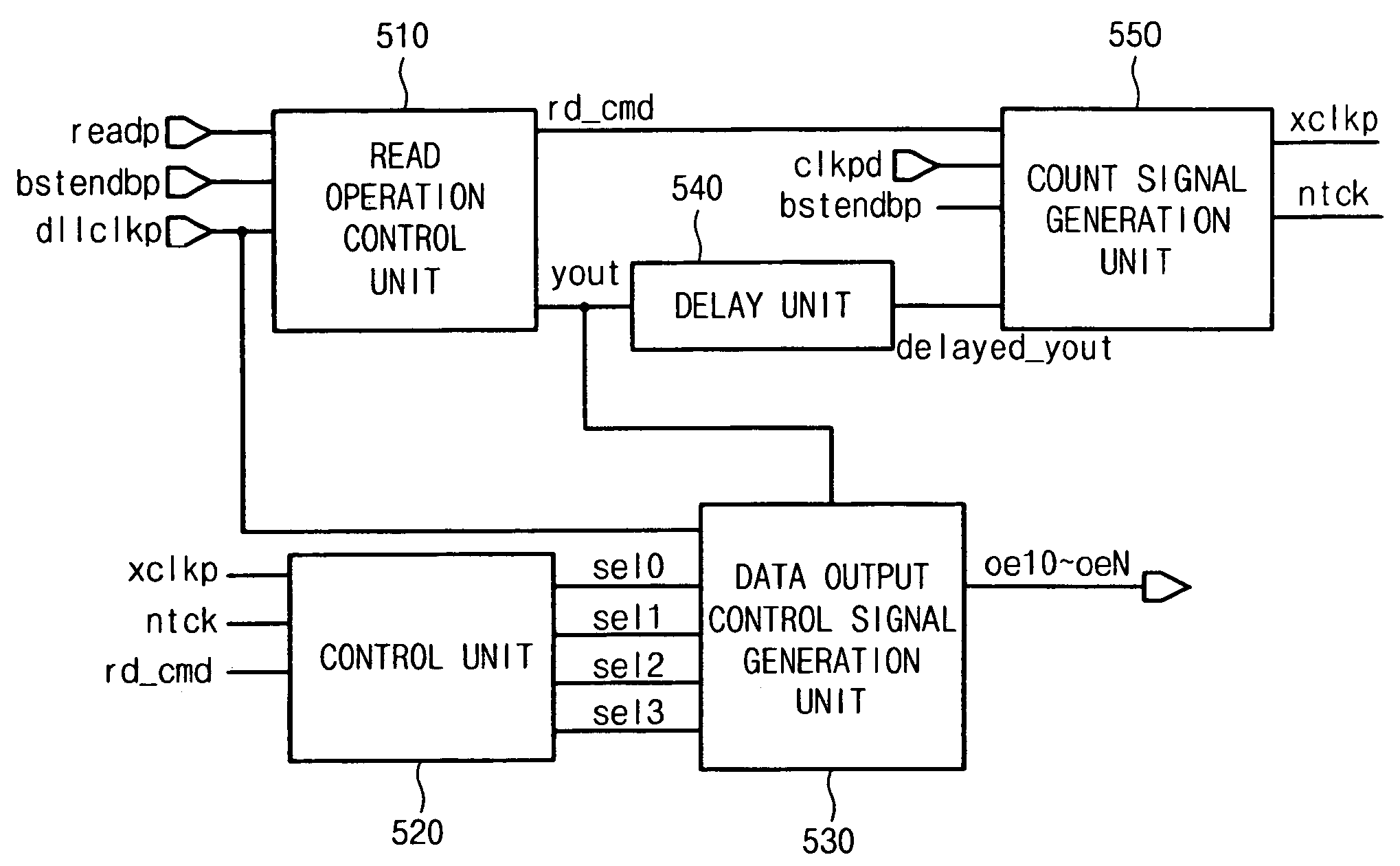
Data output control circuit and data output control method
A data output control circuit controls a data output in a read operation. A data output control method includes a count shifting mode and a delay mode and can be used in low and high frequency operations, so that a data output can be stably controlled in a broad frequency range. The data output control circuit includes: a low frequency mode controller a high frequency mode controller and a selector selecting any one of first and second command signals through CAS latency information to be output as a data output control signal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Semiconductor device for domain crossing
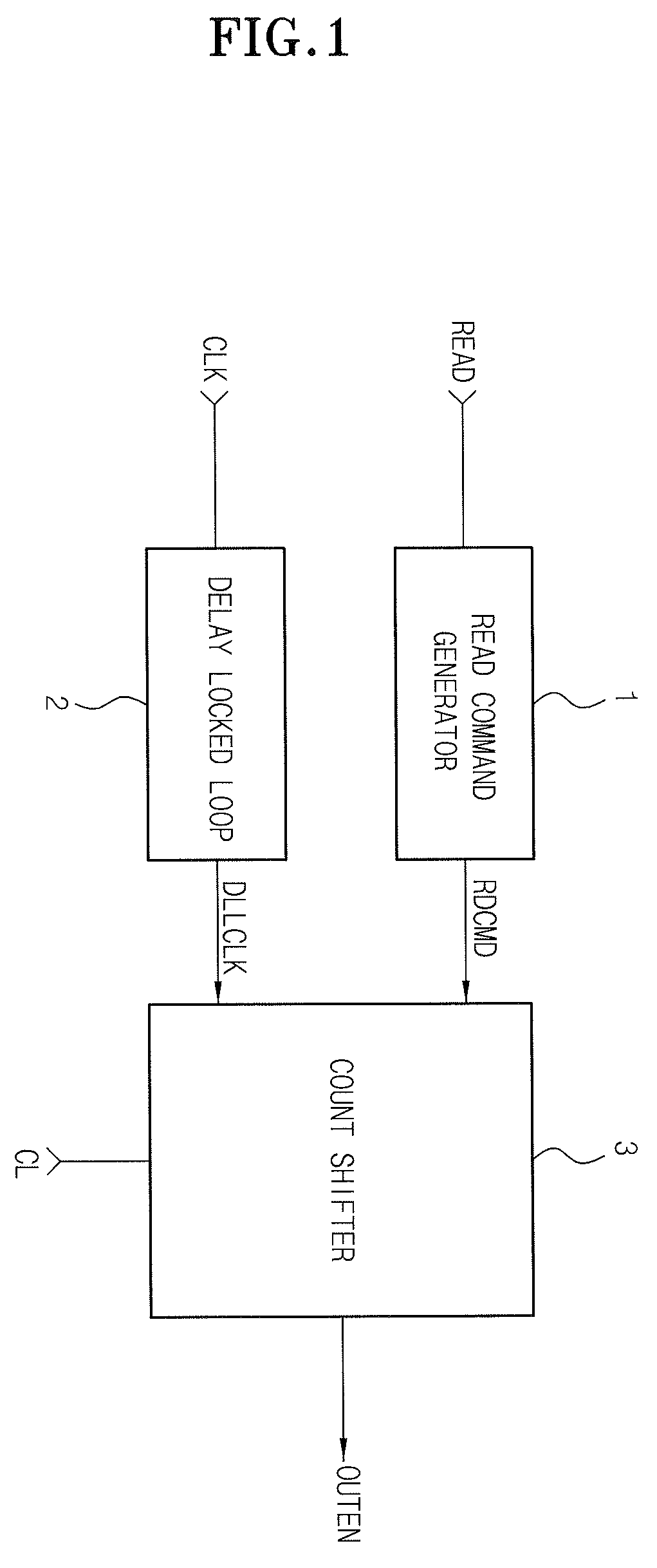
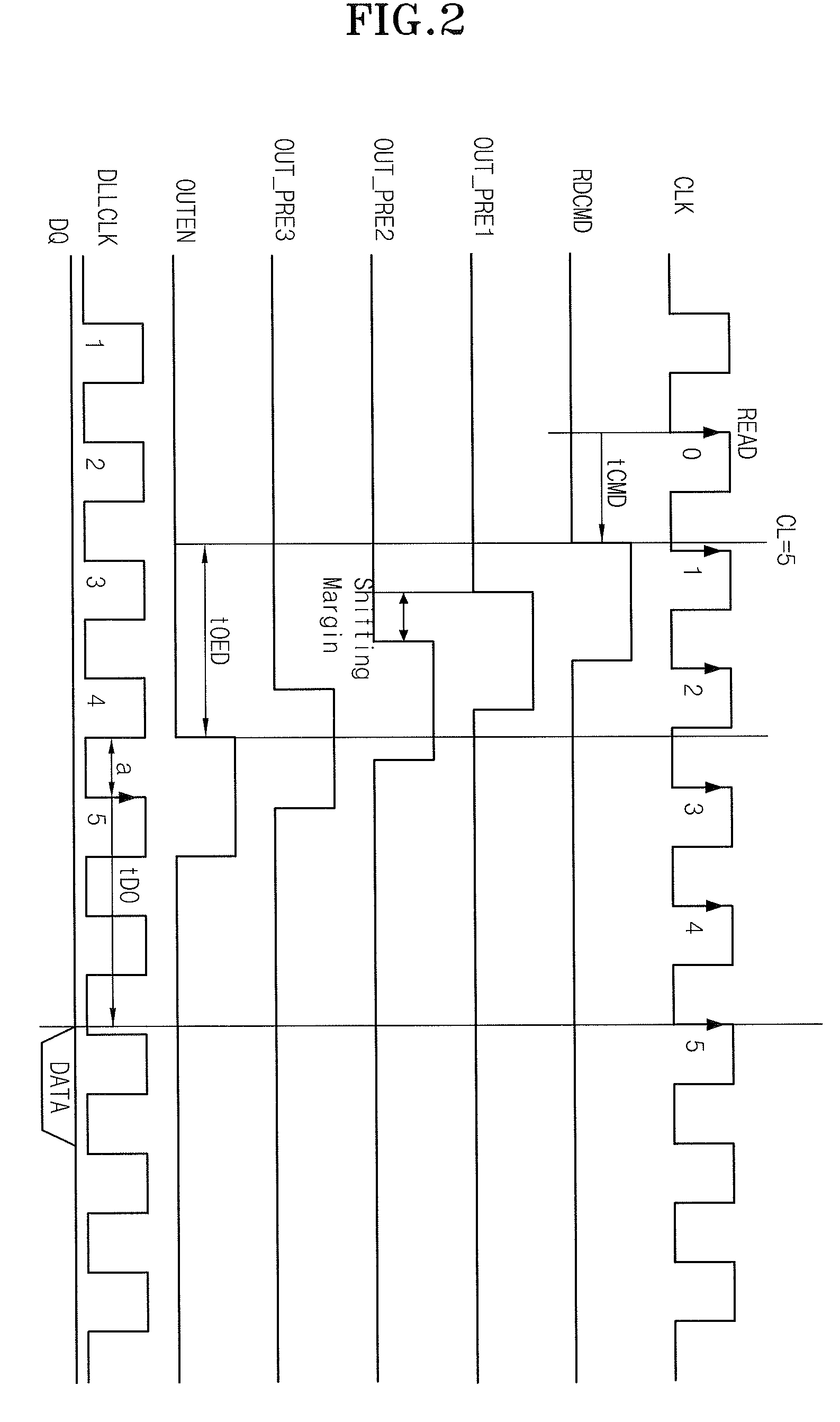
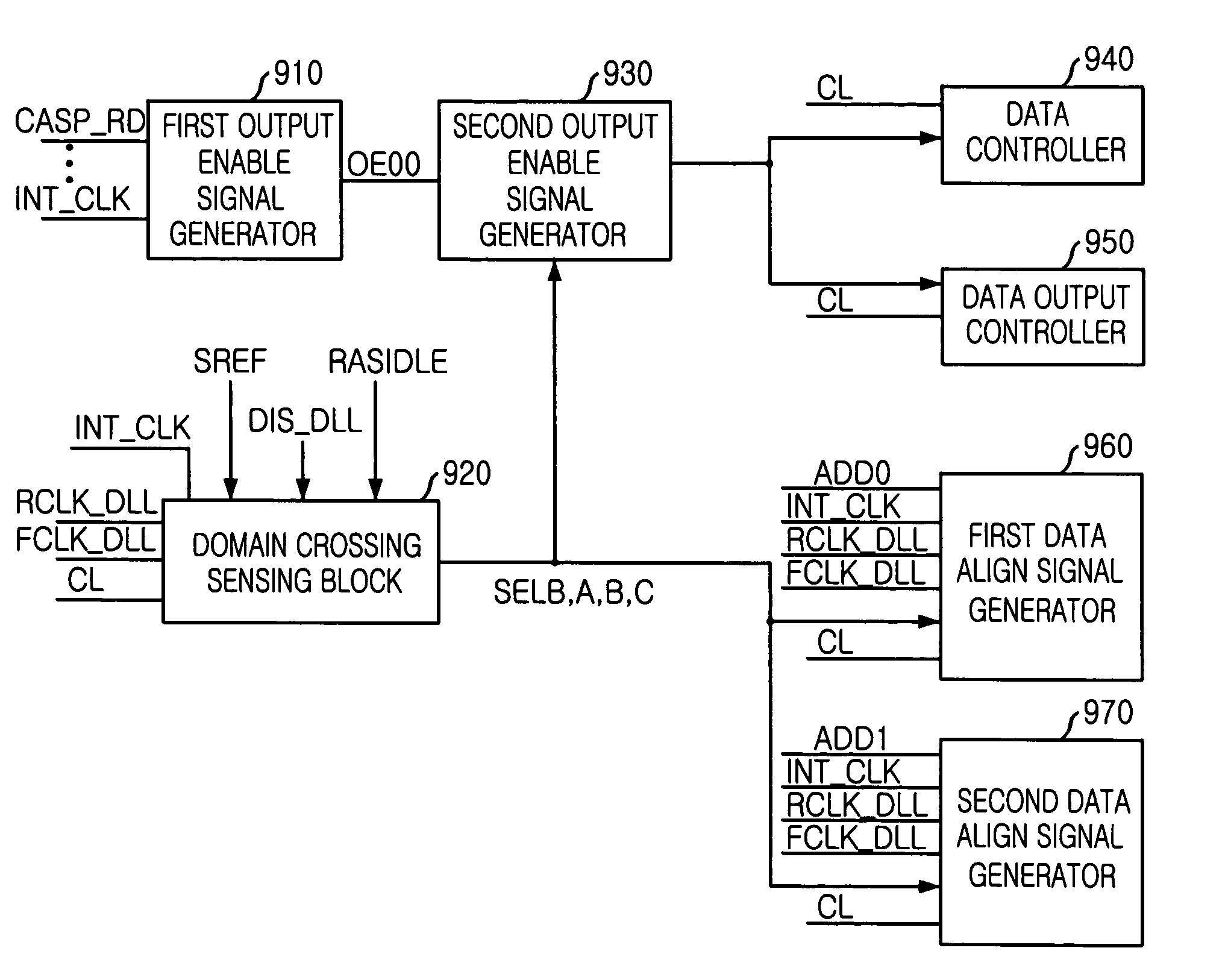
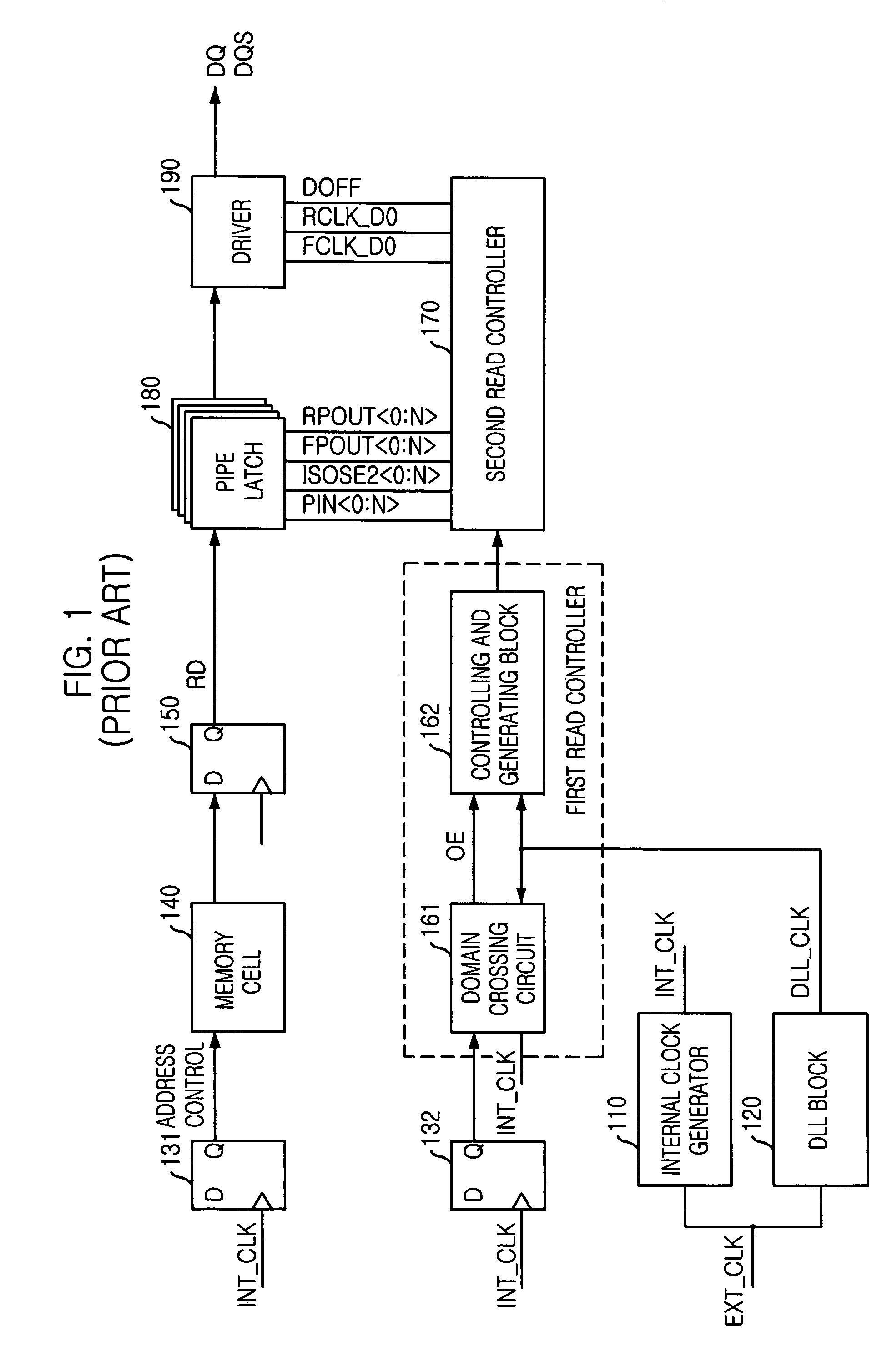
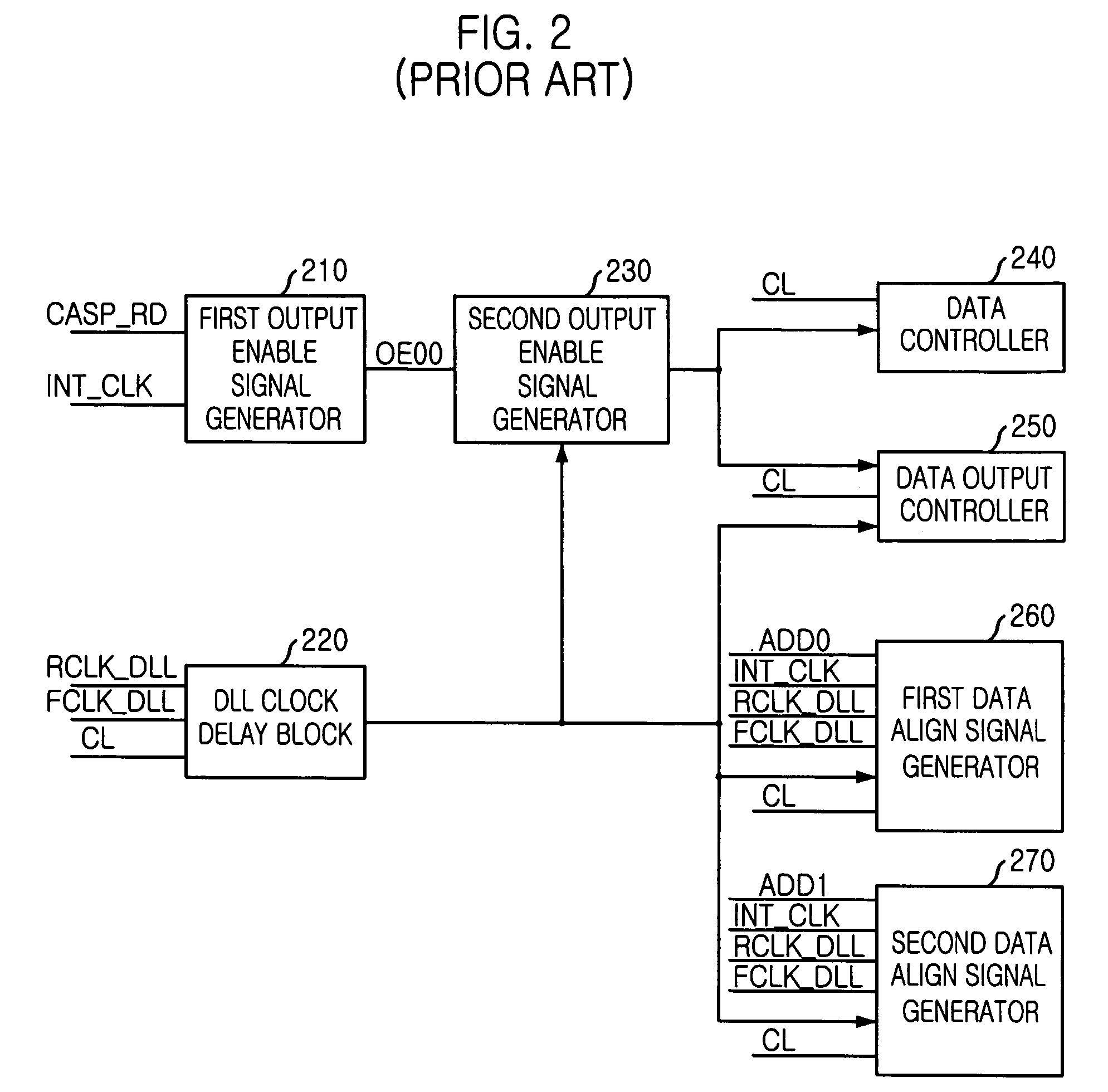
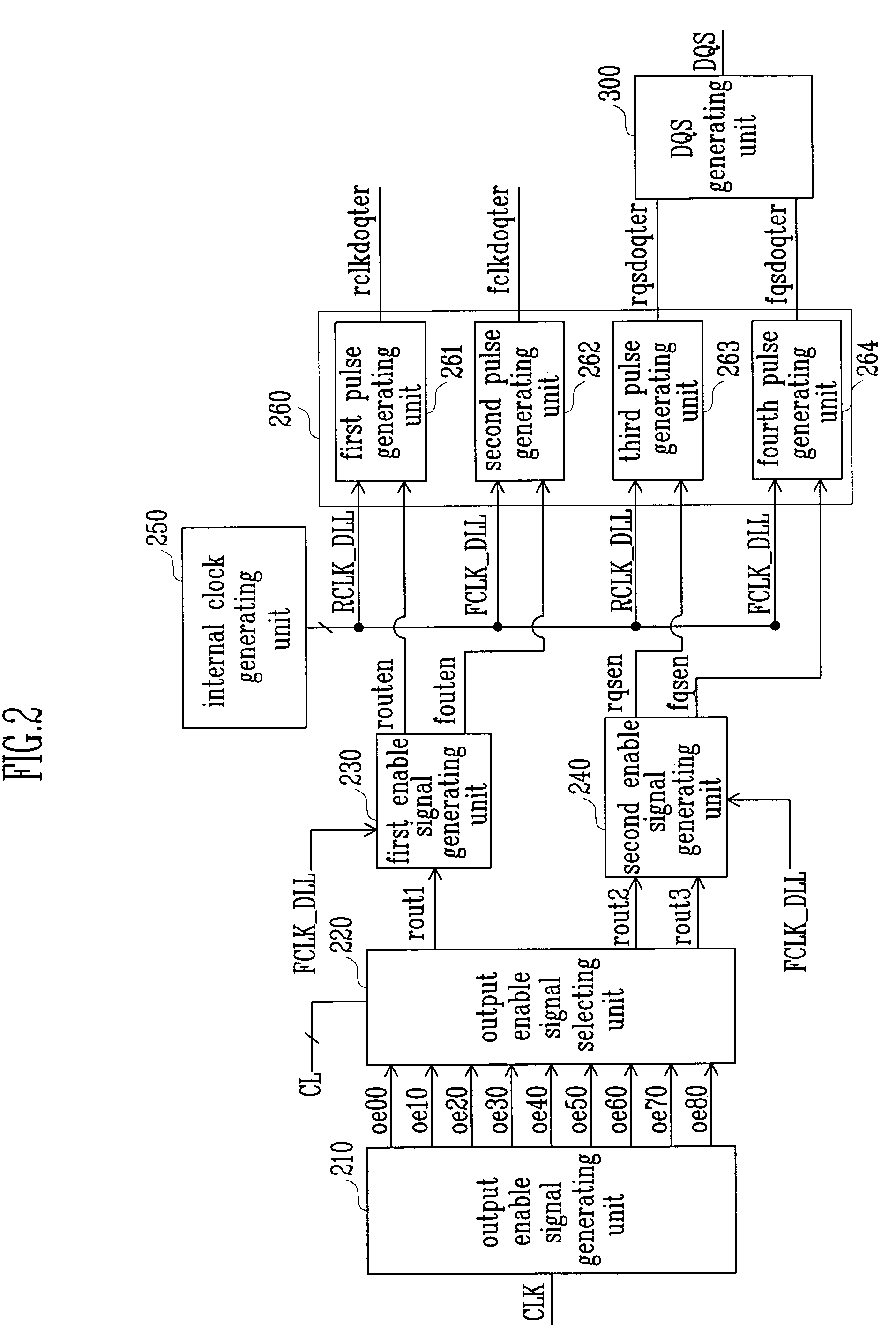
An apparatus, for use in a semiconductor device, for providing a domain crossing operation. The apparatus includes a domain crossing sensing block, in response to an operation mode signal, first and second delay locked loop (DLL) clock signals and a CAS latency, generates a plurality of selection signals. An output enable signal generator, in response to the plurality of selection signals, generates a plurality of output enable signals. A data control block, in response to the output enable signals and the CAS latency, controls a data output operation in the semiconductor device. Each of a plurality of data align block, in response to the selection signals, the first and second DLL clock signals and an address signal, aligns data corresponding to the address signal in the data output operation.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
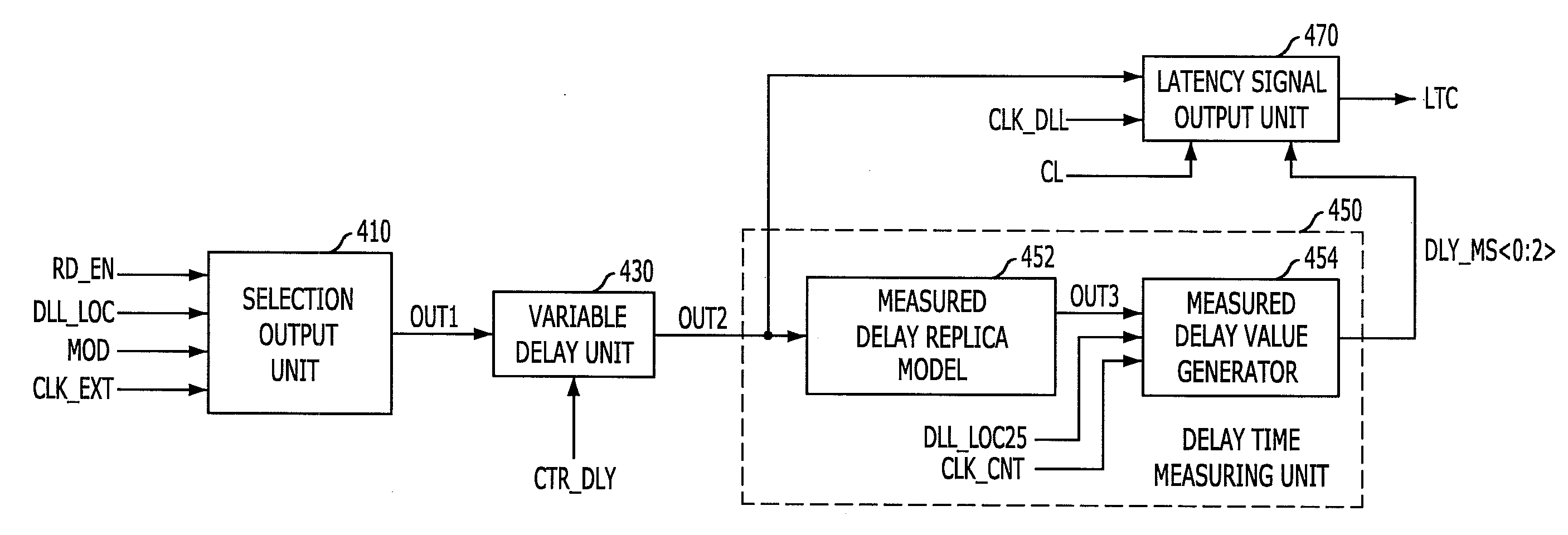
Latency signal generating circuit and semconductor device having the same
InactiveUS8030981B2Guaranteed high speed operationReduce power consumptionPulse automatic controlDigital storageDelay-locked loopInput control
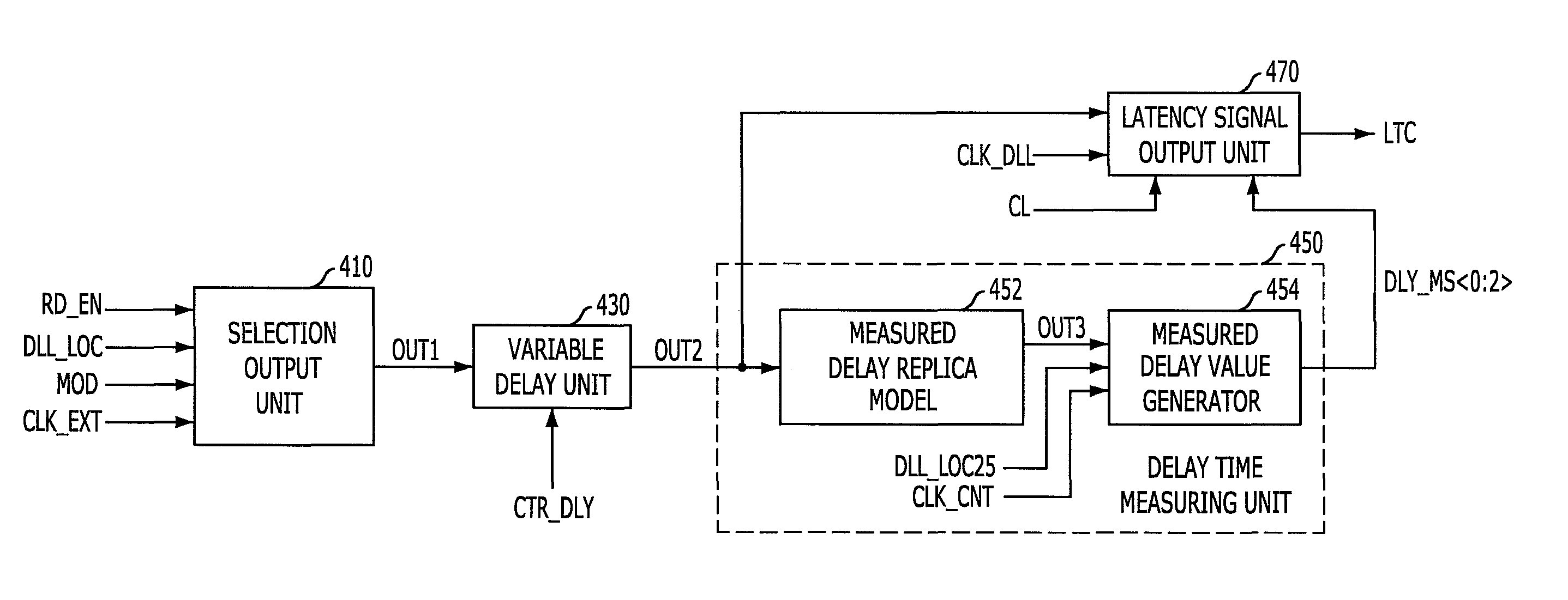
A semiconductor device includes a latency signal generating circuit for generating a latency signal corresponding CAS latency by measuring a delay amount reflected at a delay locked loop and reflecting the measured delay amount at a read command signal, and a delay locked loop for controlling an internal clock signal applied to the latency signal generating circuit corresponding to the read command and the latency signal. The semiconductor device includes an internal clock signal generating block configured to generate an internal clock signal, a latency generating block configured to generate a latency signal by synchronizing a read command signal with the internal clock signal at a time corresponding to a CAS latency value and a measured delay value, and an input controlling block configured to activate the reference clock signal using an external clock signal in response to the read command signal and the latency signal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
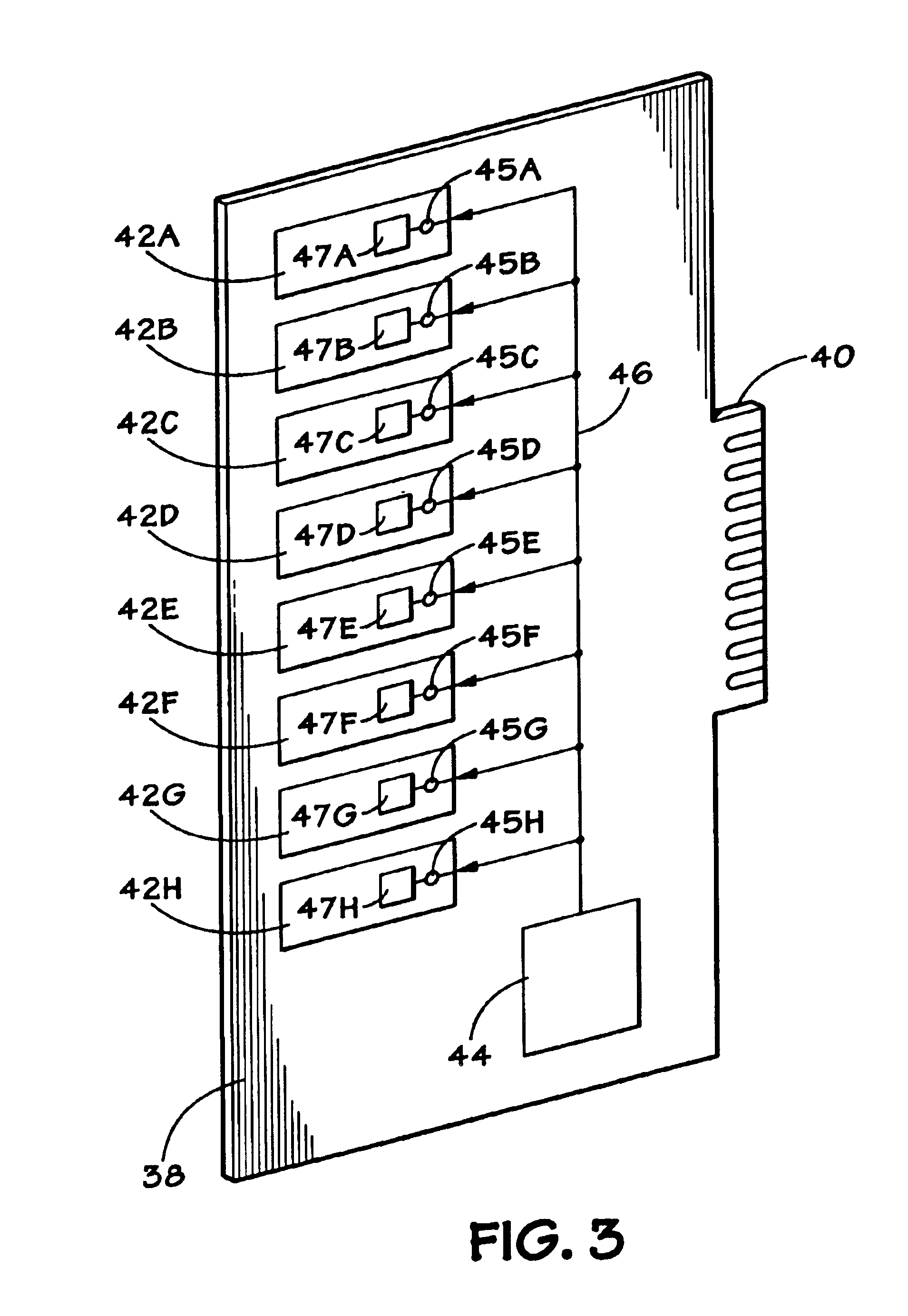
Memory device with improved output operation margin
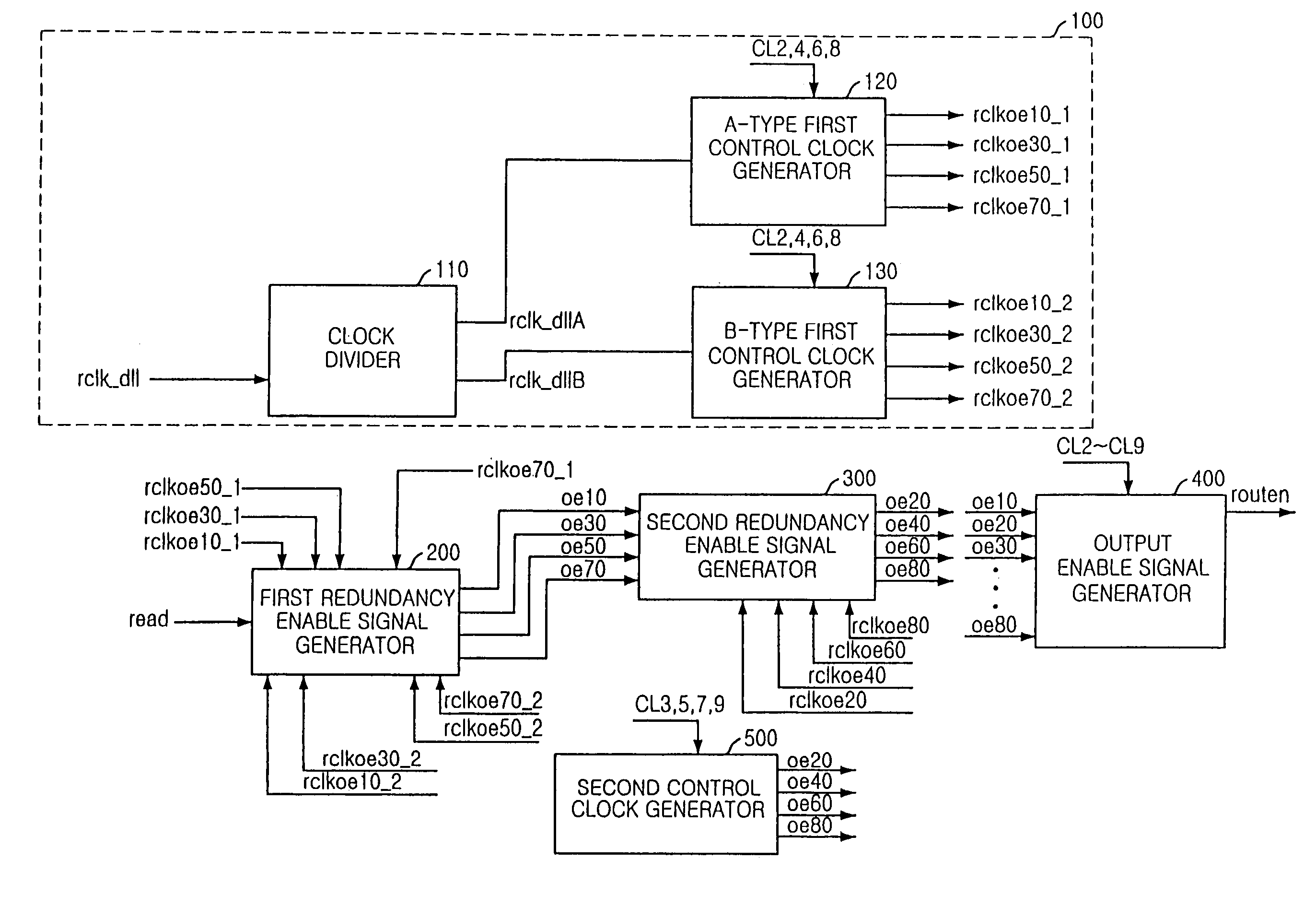
InactiveUS6987705B2Wide-ranging CAS latency modeGuaranteed uptimeDigital storageSignal generatorClock generator
A synchronous memory device which generates a data output enable signal corresponding to a set CAS latency mode including: a control clock generator for generating an A-type first control clock and a B-type first control clock; a first redundancy enable signal generator for shifting an internal read signal by a predetermined interval in synchronization with one of the A-type first control clock and the B-type first control clock and generating a plurality of first redundancy enable signals; a second redundancy enable signal generator for synchronizing the plurality of first redundancy enable signals with a DLL clock and generating a plurality of second redundancy enable signals; and an output enable signal generator for selecting one redundancy enable signal corresponding to the set CAS latency mode among the first redundancy enable signals and the second redundancy enable signals and generating the selected redundancy enable signal as the data output enable signal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Integrated semiconductor memory device for synchronizing a signal with a clock signal
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
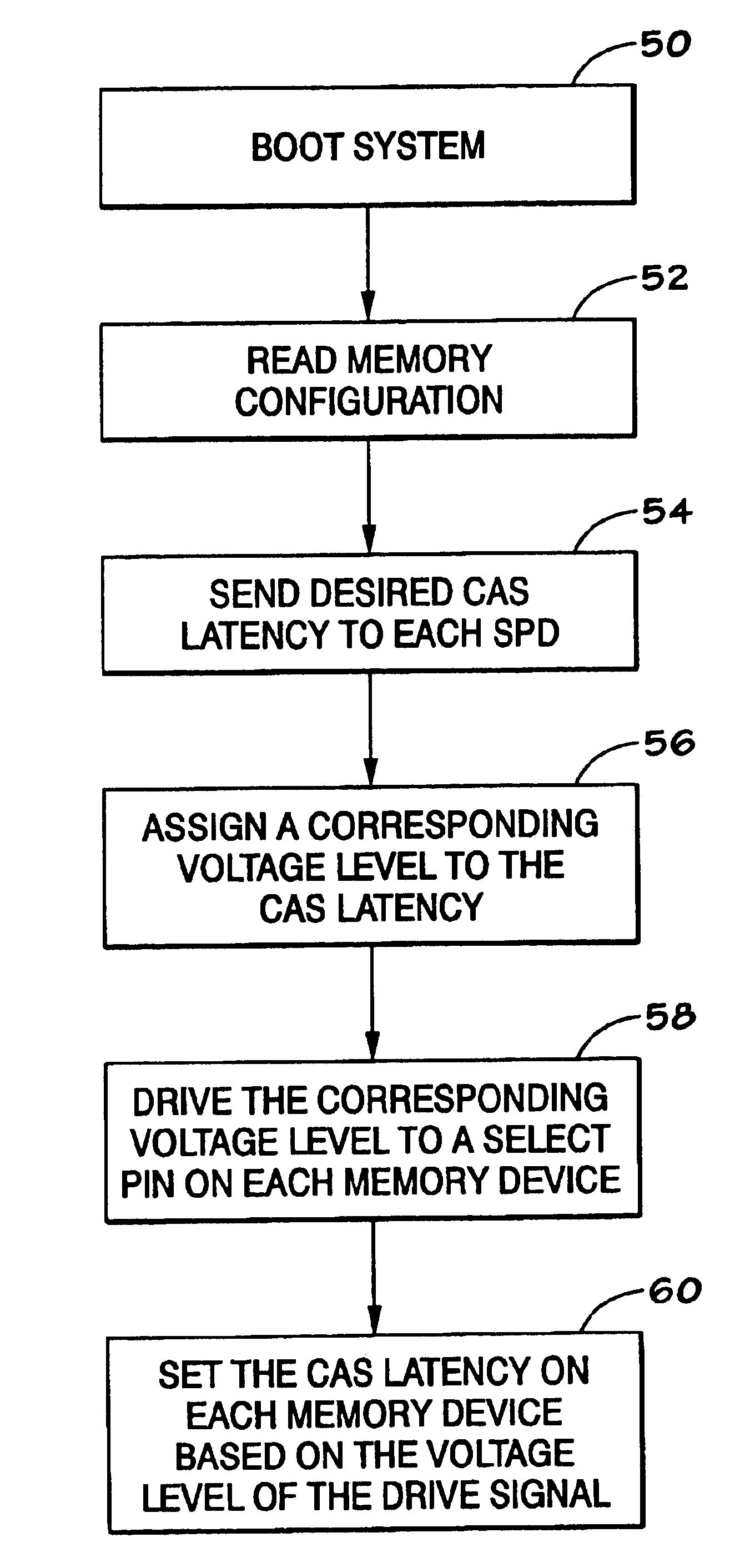
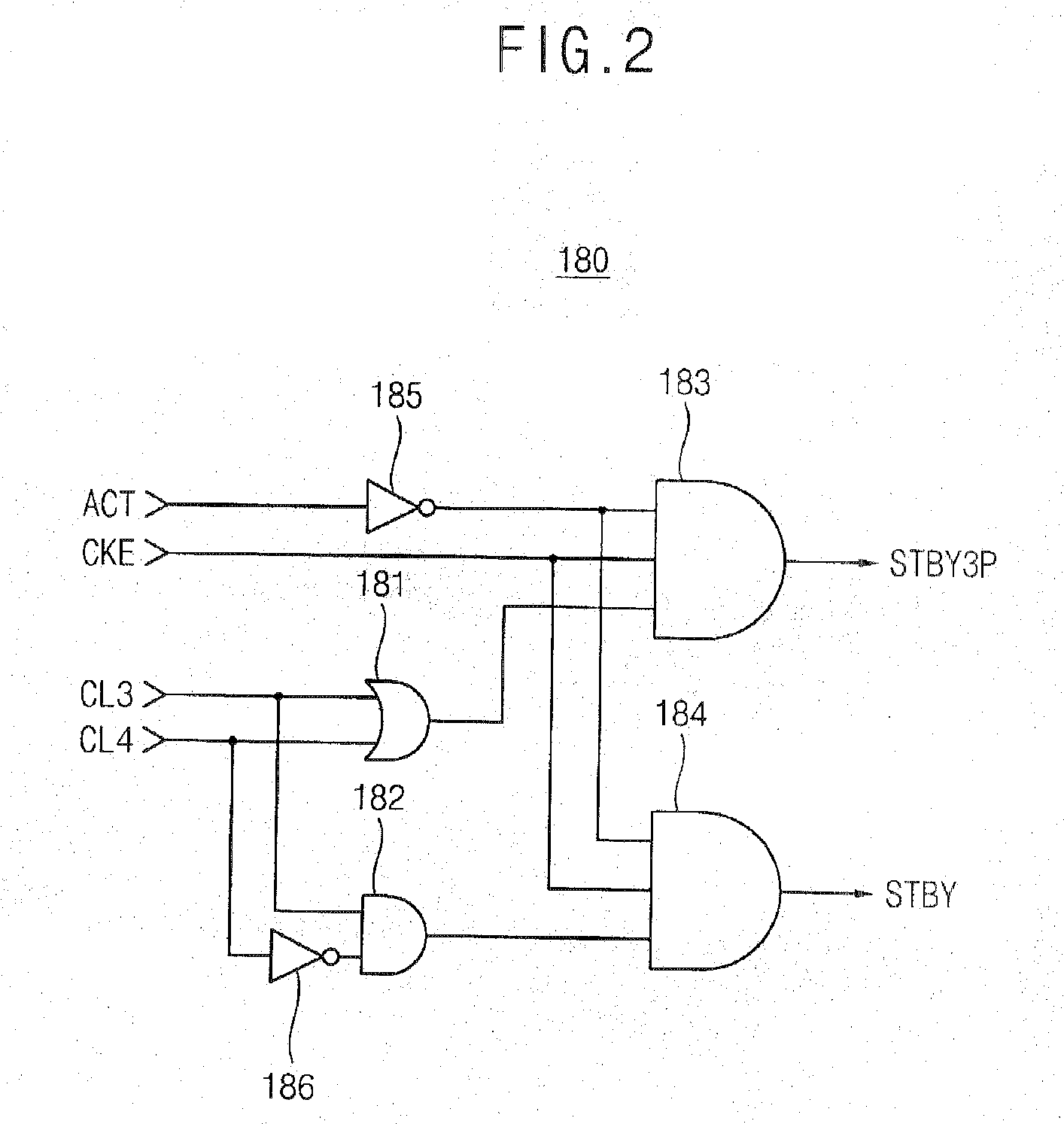
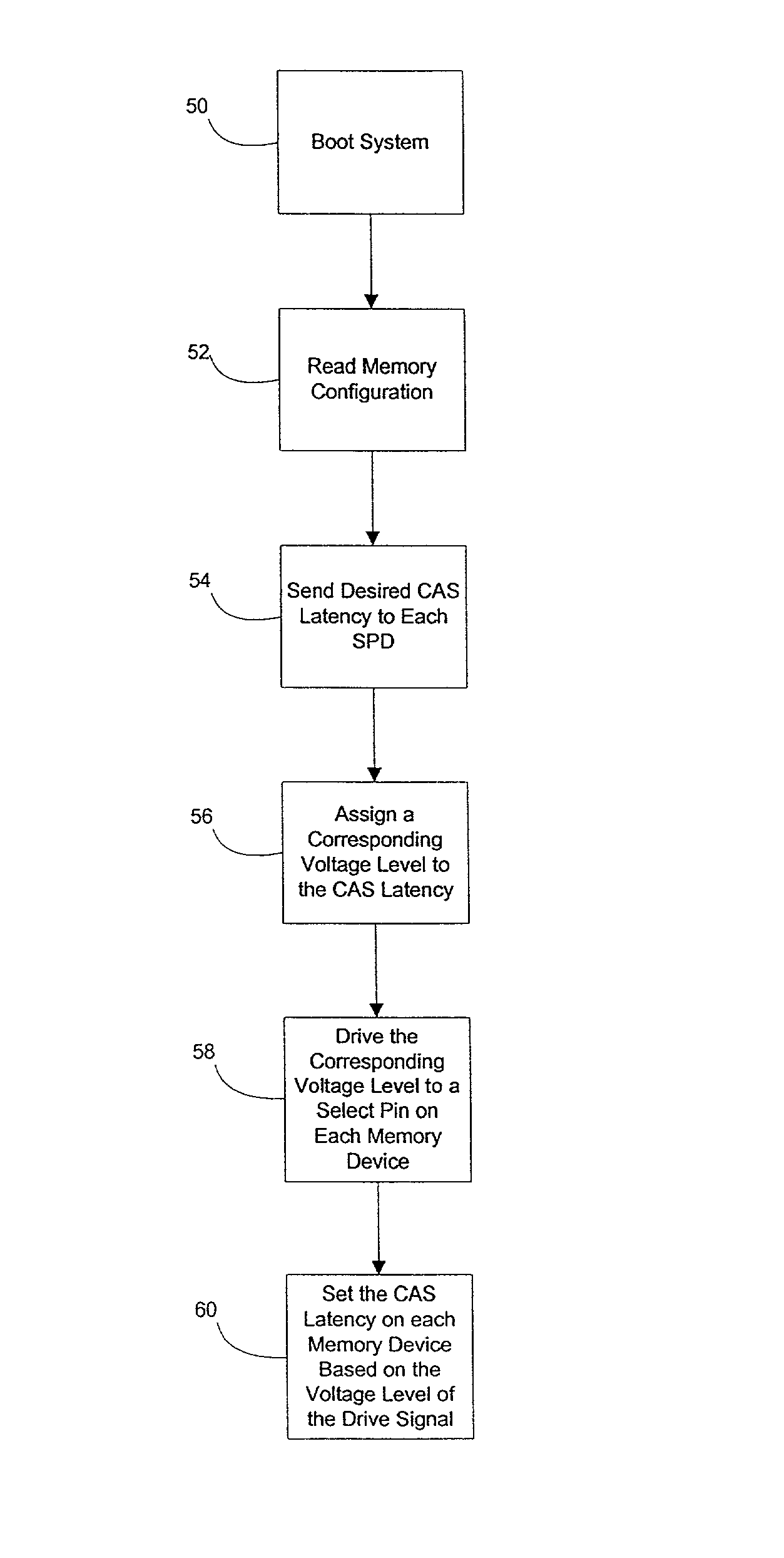
Cas latency select utilizing multilevel signaling
A method of selecting CAS latencies in a system. Specifically, a system which includes a plurality of memory modules is provided. Because different memory modules may have different CAS latencies, multilevel signaling is used to standardize the CAS latencies throughout the system. A static pin is provided on each memory device such that a drive signal can be received. The voltage level of the drive signal corresponds to a selected CAS latency for the system.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
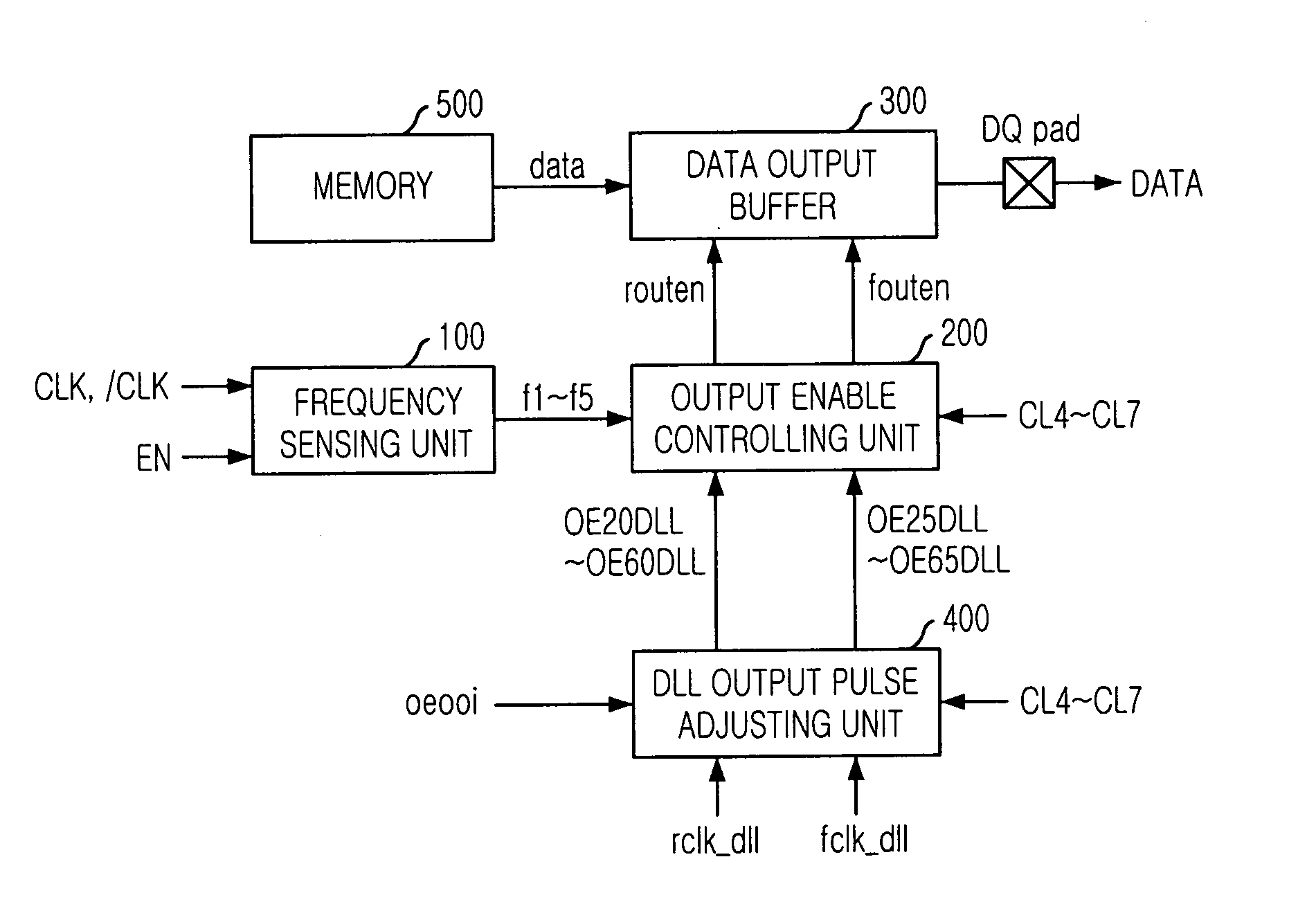
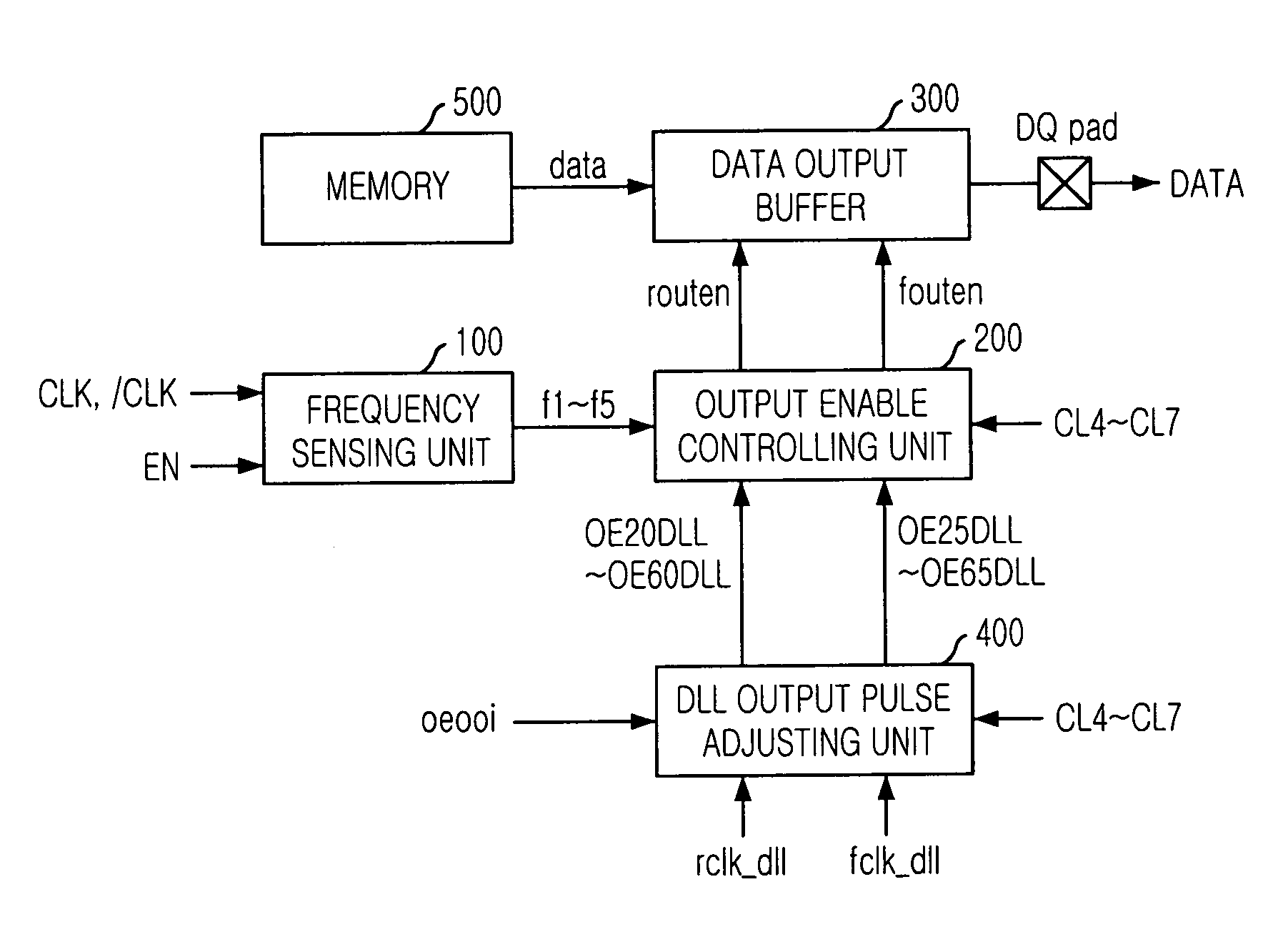
Semiconductor memory device for controlling output timing of data depending on frequency variation
InactiveUS20050248997A1Pulse automatic controlPulse train pattern monitoringDelay-locked loopEngineering
A semiconductor memory device is capable of controlling the data output timing depending on the operating frequency so as to output data with optimized for the operating frequency. Further, in the high frequency operation, the memory device can output data reliably so as to facilitate development of high frequency memory device. The semiconductor memory device comprises a frequency sensing unit for sensing an operating frequency by sensing an amount of lead of a delay locked clock in a delay locked loop compared to an external clock signal, an output enable controlling unit for outputting an output enable signal in response to a CAS latency with controlling the output timing of the output enable signal based on the frequency that is sensed by the frequency sensing unit, and a data output buffer for outputting data that is transferred from a memory core region in response to the output enable signal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Semiconductor memory device for controlling output timing of data depending on frequency variation
InactiveUS7027336B2Pulse automatic controlPulse train pattern monitoringDelay-locked loopEngineering
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
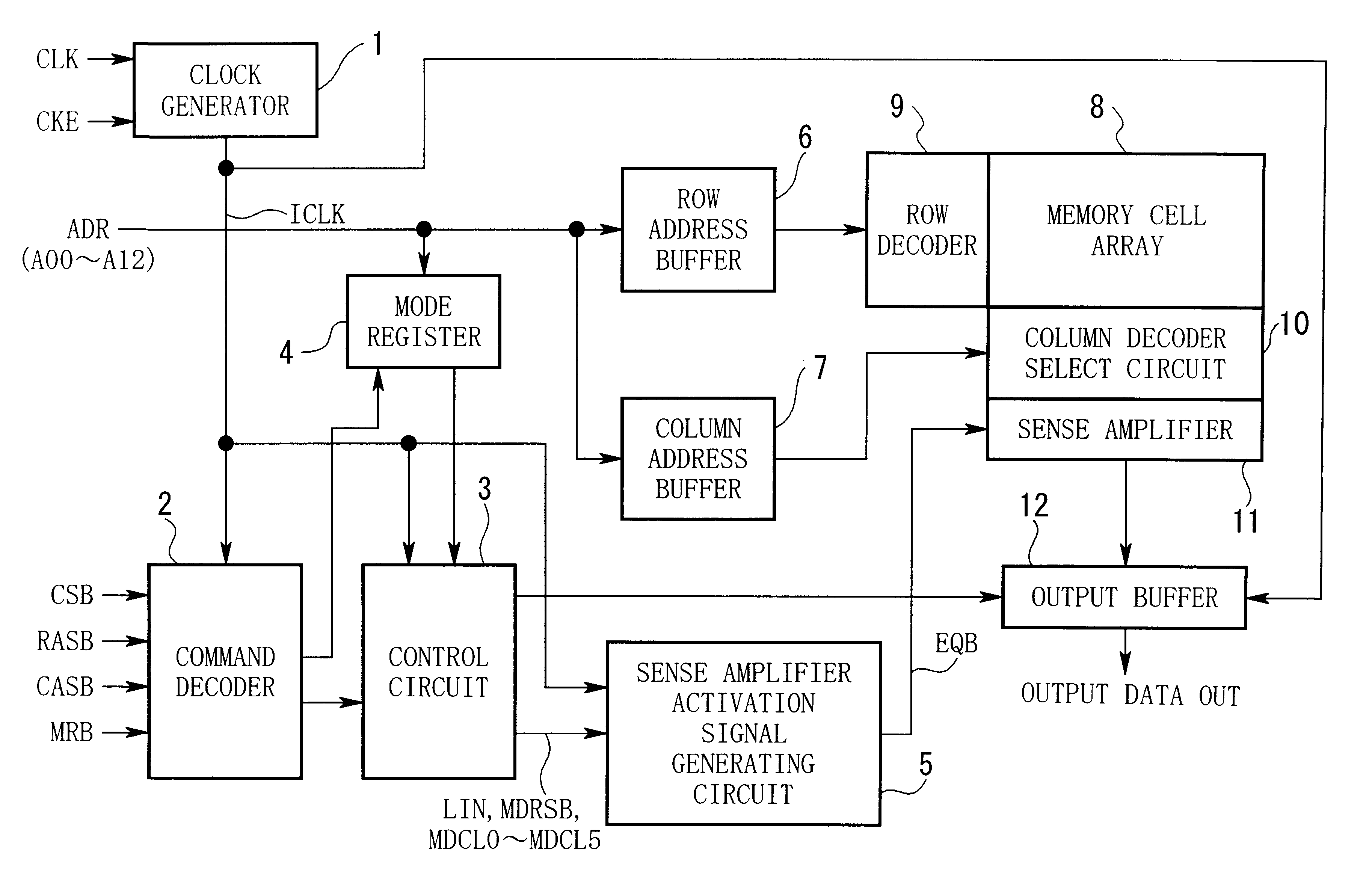
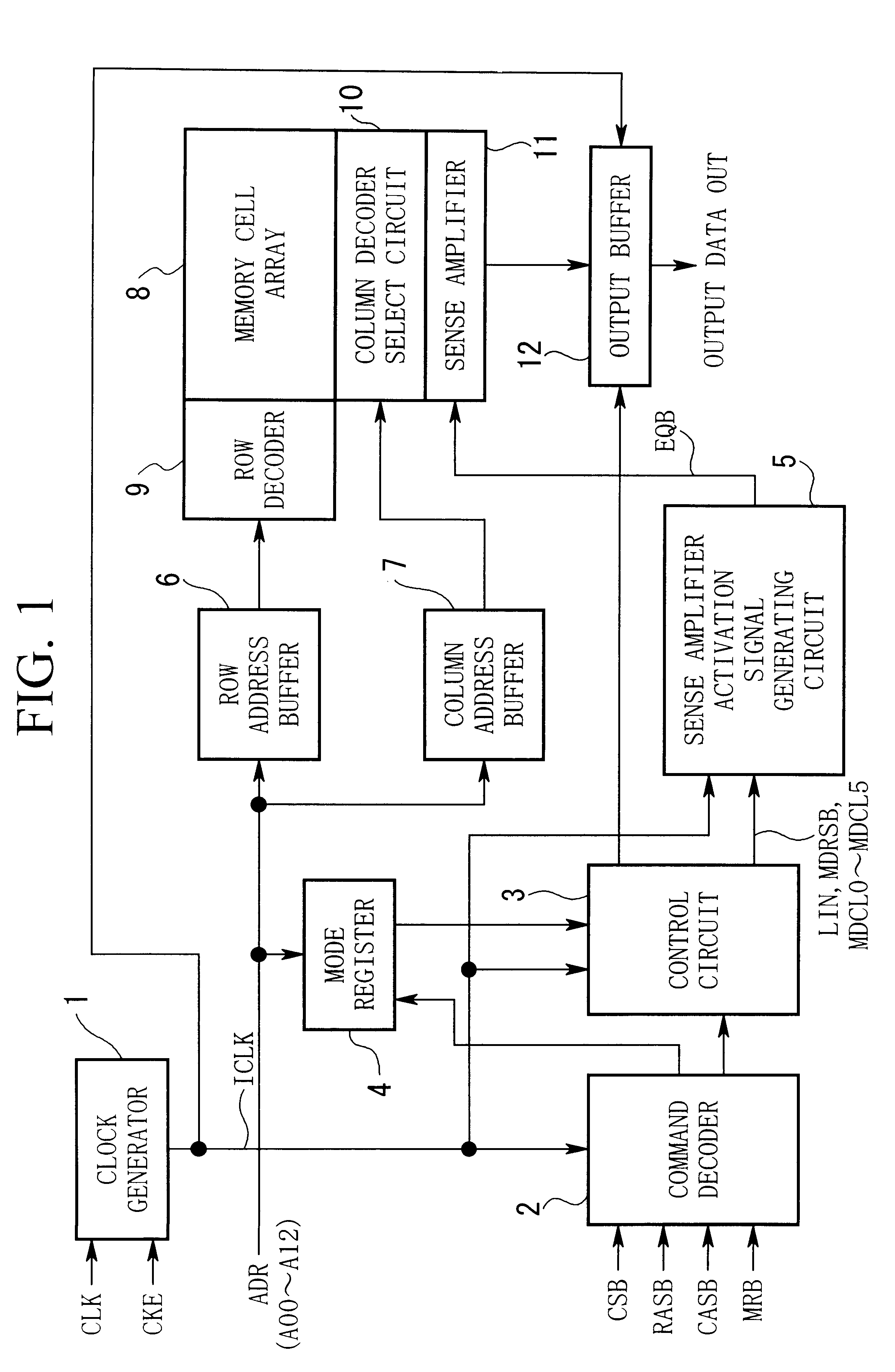
Semiconductor memory device
ActiveUS7280430B2Total current dropDigital storageSubstation equipmentCurrent consumptionActive state
Disclosed herein is a semiconductor memory device for reducing an unnecessary current consumption occurred in an idle state or an active state. The semiconductor memory device includes a driving clock supply unit for supplying a driving clock during a read or a write operation of each bank; a delay unit for generating a read address or a write address in synchronization with the driving clock by delaying an address by a predetermined time based on one of an additive latency, a CAS latency and a combination thereof; and an output unit for latching the read address or the write address to output the latched signal as an internal column address.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Delay locked loop circuit and method having adjustable locking resolution
A delay line receives an input clock signal and includes a cascaded plurality of unit delay circuits. A mode register set stores a value indicative of a column-address-strobe (CAS) latency of the memory device, and an adjustment circuit varies a delay time of the unit delay circuits according to the CAS latency stored in the mode register set. A phase detector detects a phase difference between the input clock signal and an output clock signal of the delay line, and a control circuit which controls an enabled state of the unit delay circuits according to an output of said phase detector.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Data output control circuit
A data output control circuit for use in a synchronous semiconductor memory device including: a first data output enable signal generation unit for receiving an internal signal and generating a rising data output enable signal synchronizing with a rising edge of a DLL clock signal according to a CAS latency; and a second data output enable signal generation unit for receiving the rising data output enable signal and generating a falling data output enable signal synchronizing with a falling edge of the DLL clock signal.
Owner:MOSAID TECH
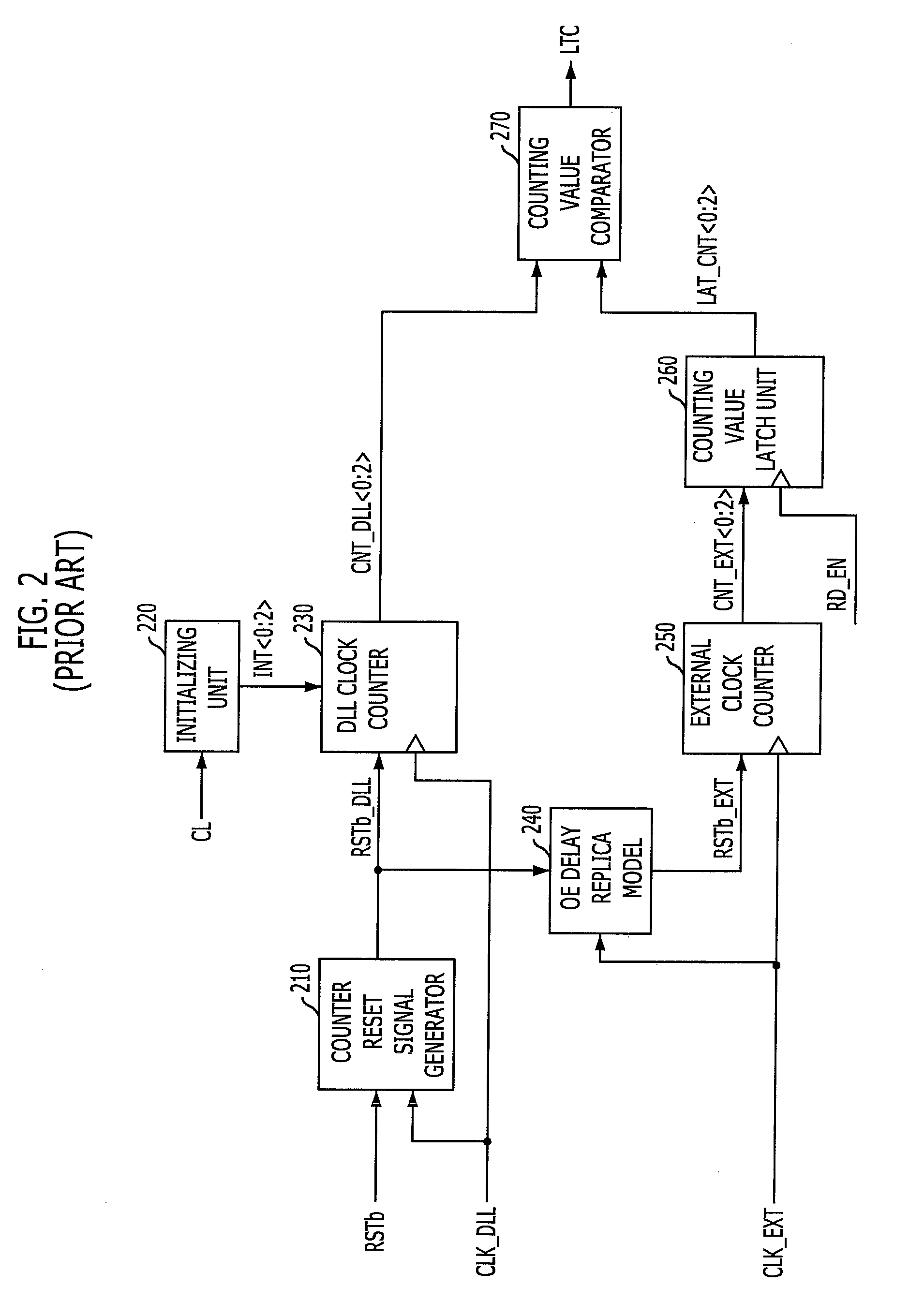
Integrated semiconductor memory device for synchronizing a signal with a clock signal
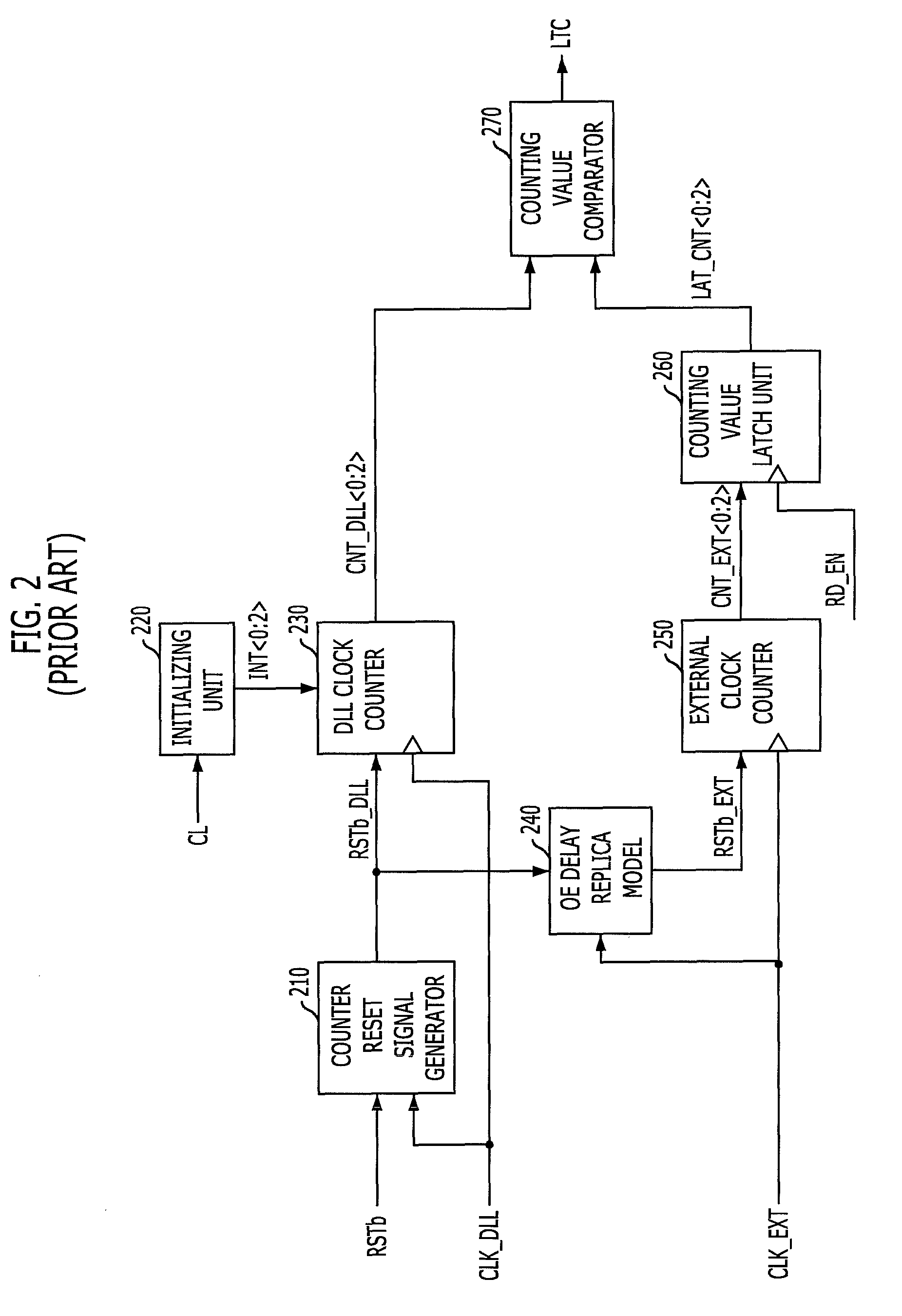
A semiconductor memory includes a control circuit for generating an internal read command signal depending on an externally applied read command signal. A clock generating circuit generates a system clock signal and a time shifted clock signal generated by a DLL circuit. A latency counter circuit comprises a first control circuit for generating a first control signal and a second control circuit for generating a second control signal. The first control signal is used to latch the internal read command signal in one of FIFO-latching cells. The latching is carried out in a system clock domain. The second control signal is used to release a time shifted internal read command signal from one of the FIFO-latching cells in a DLL clock domain. The relationship between first and second control signals determines a CAS latency by which data items appear at a data terminal synchronous with an externally applied clock signal.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS
Output driver capable of controlling slew rate of output signal according to operating frequency information or CAS latency information
InactiveUS7035148B2Effectively slew rateElectronic switchingDigital storageSlew rateFrequency detection
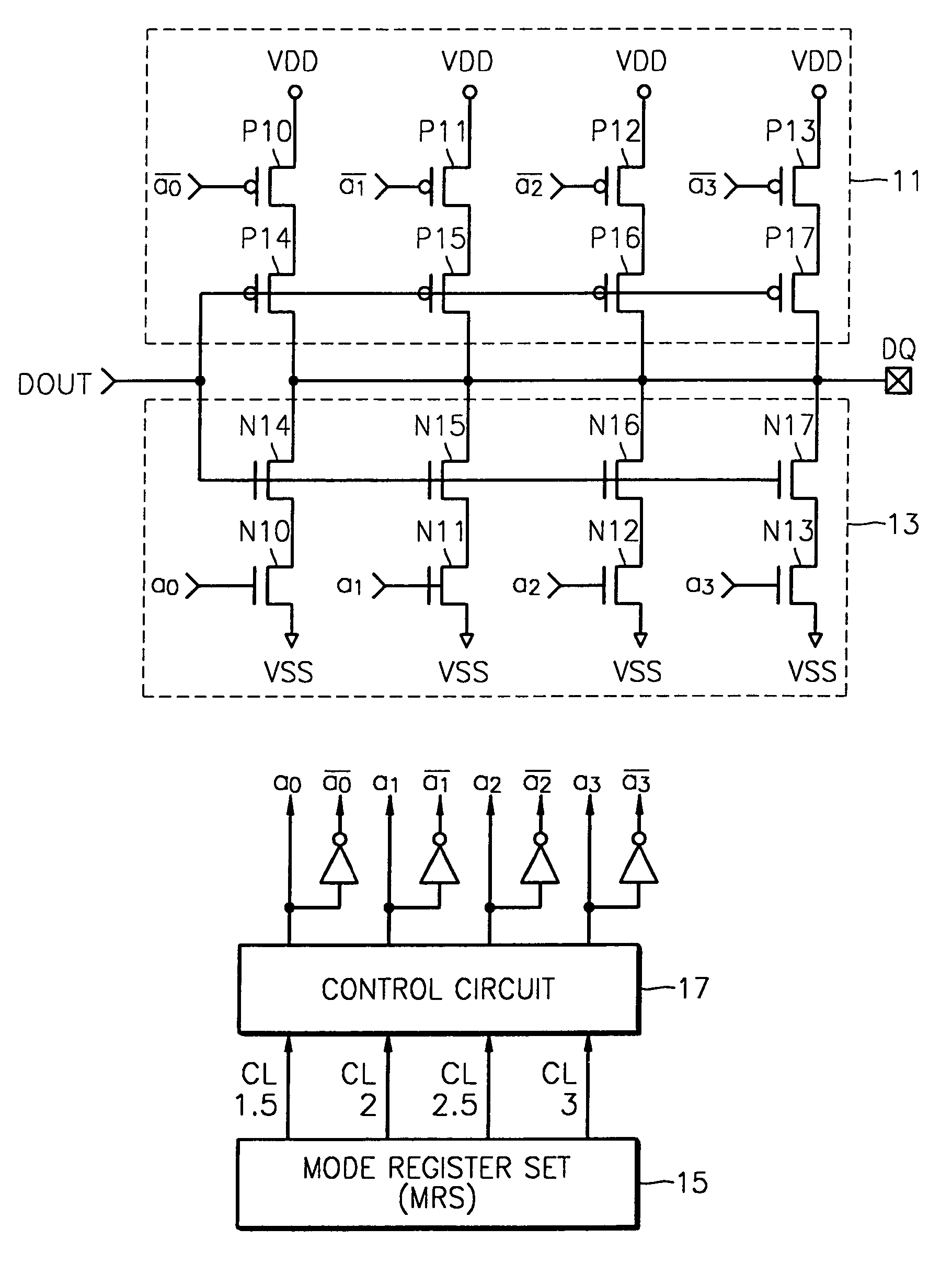
An output driver effectively controls the slew rate of an output signal according to CAS latency information including frequency information of an operating clock signal or according to frequency information obtained by detecting the frequency of the operating clock signal. The output driver includes an output terminal, a pull-up driver which pulls-up the output terminal, and a pull-down driver which pulls-down the output terminal. Also, the output driver further includes a mode register set (MRS) which stores CAS latency information of the semiconductor memory device. Driving capabilities of the pull-up driver and the pull-down driver are varied in response to the CAS latency information. The output driver may include a frequency detector which detects and stores the operating frequency of the semiconductor memory device. In this case, the driving capabilities of the pull-up driver and the pull-down driver are varied in response to output signals output from the frequency detector.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
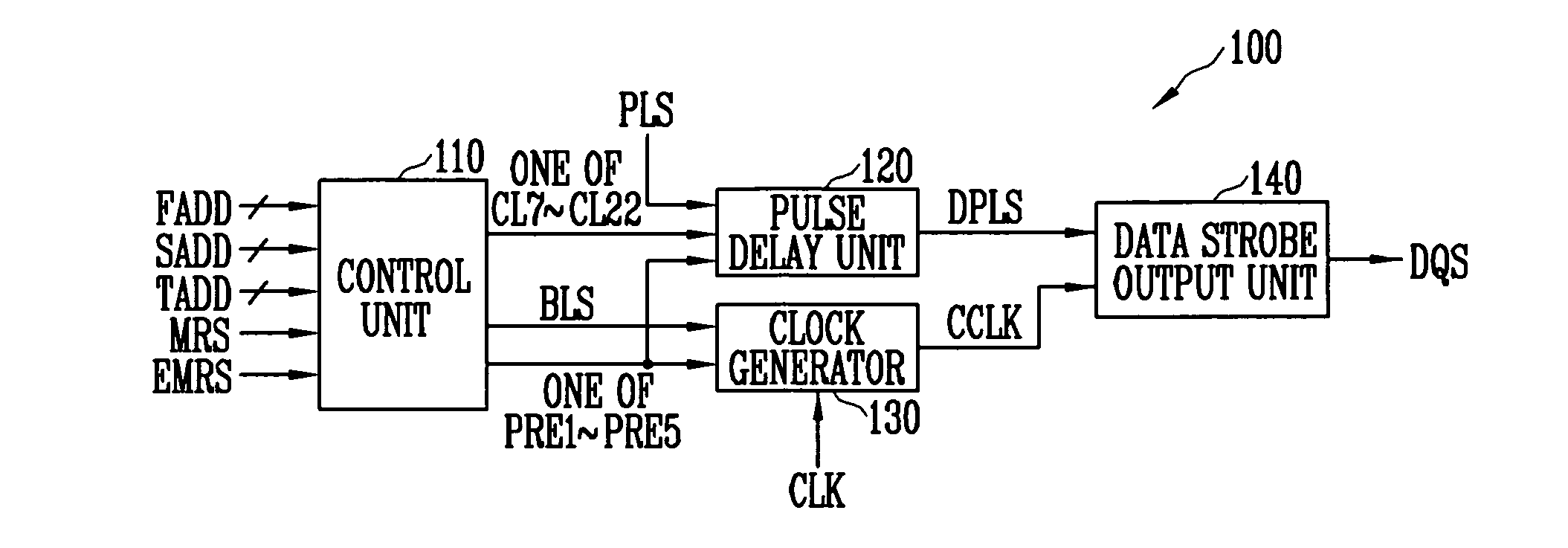
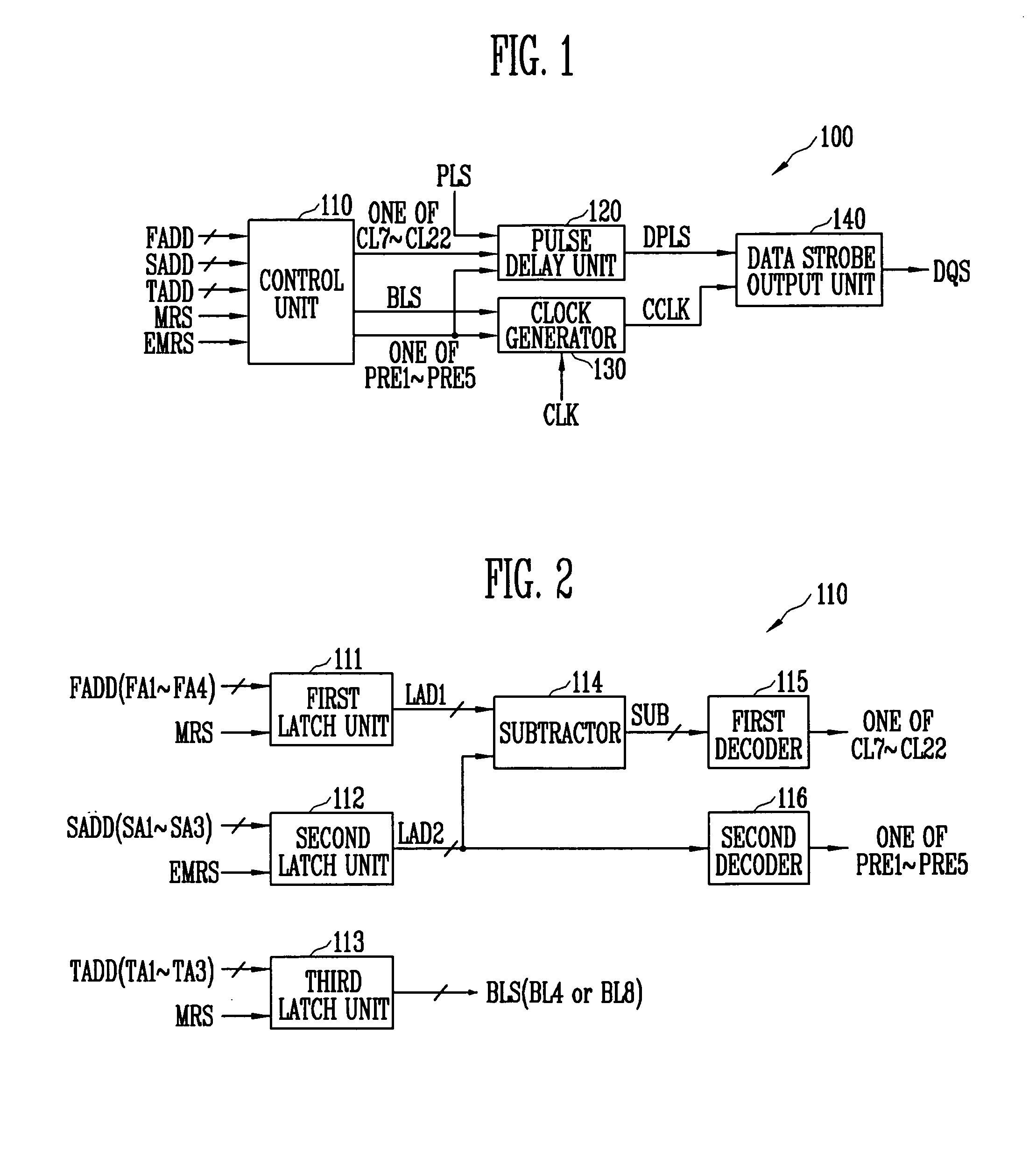
Data strobe signal generator for generating data strobe signal based on adjustable preamble value and semiconductor memory device with the same
InactiveUS20070291558A1Stabilized data output operationIncrease speedDigital storageHigh speed memoryControl signal
A data strobe signal generator according to the present invention includes a control unit, a pulse delay unit, a clock generator, and a data strobe output unit. The control unit generates a CAS latency signal and a preamble signal. The pulse delay unit delays a pulse signal for predetermined time and outputs a delayed pulse signal. The clock generator outputs a control clock signal. The data strobe output unit outputs a data strobe signal. The data strobe signal generator and the semiconductor memory device having the same according to the present invention generate a data strobe signal based on an adjustable preamble value, thereby ensuring the stabilized data output operation of a high-speed memory device.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
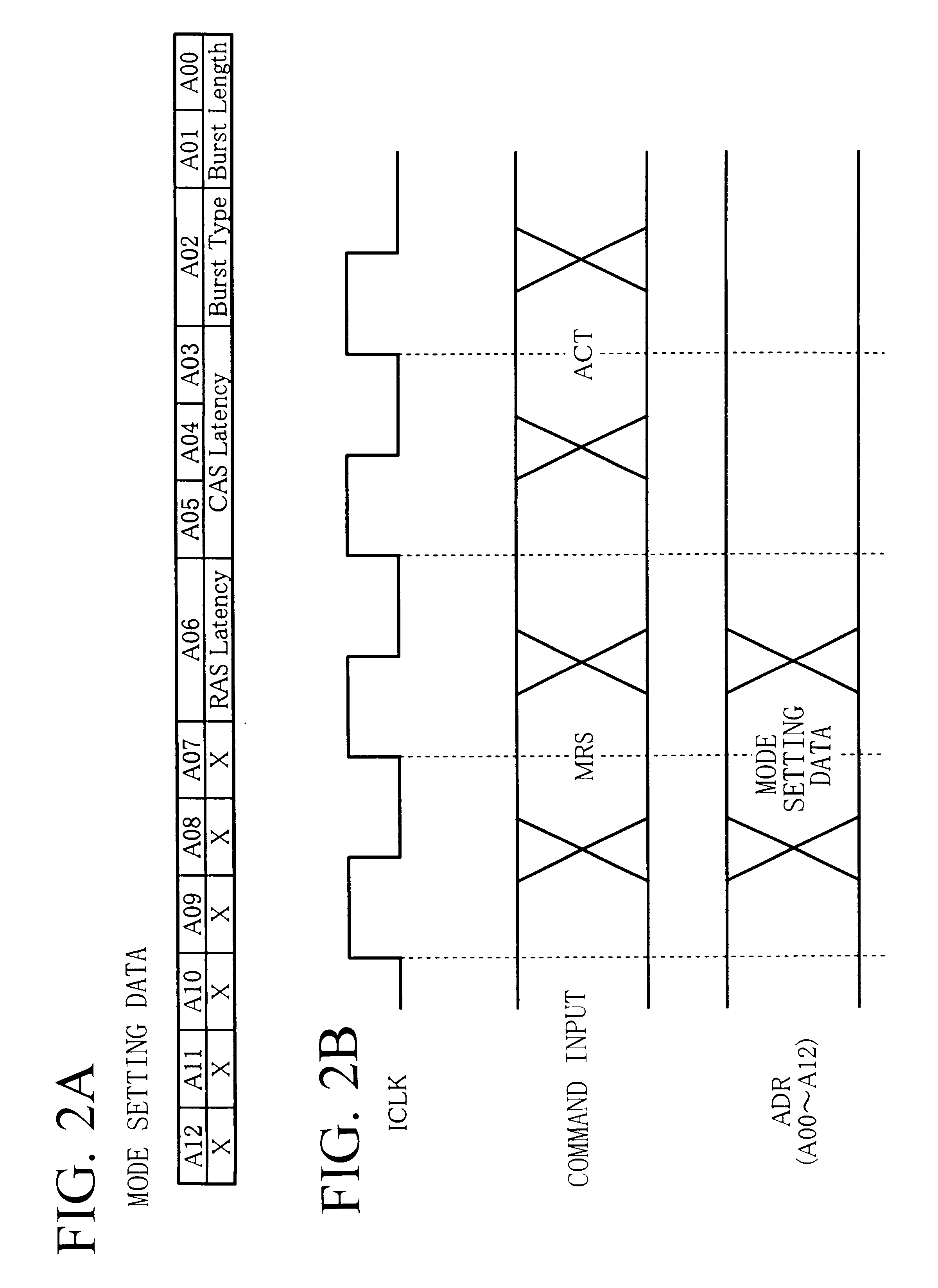
Semiconductor memory device
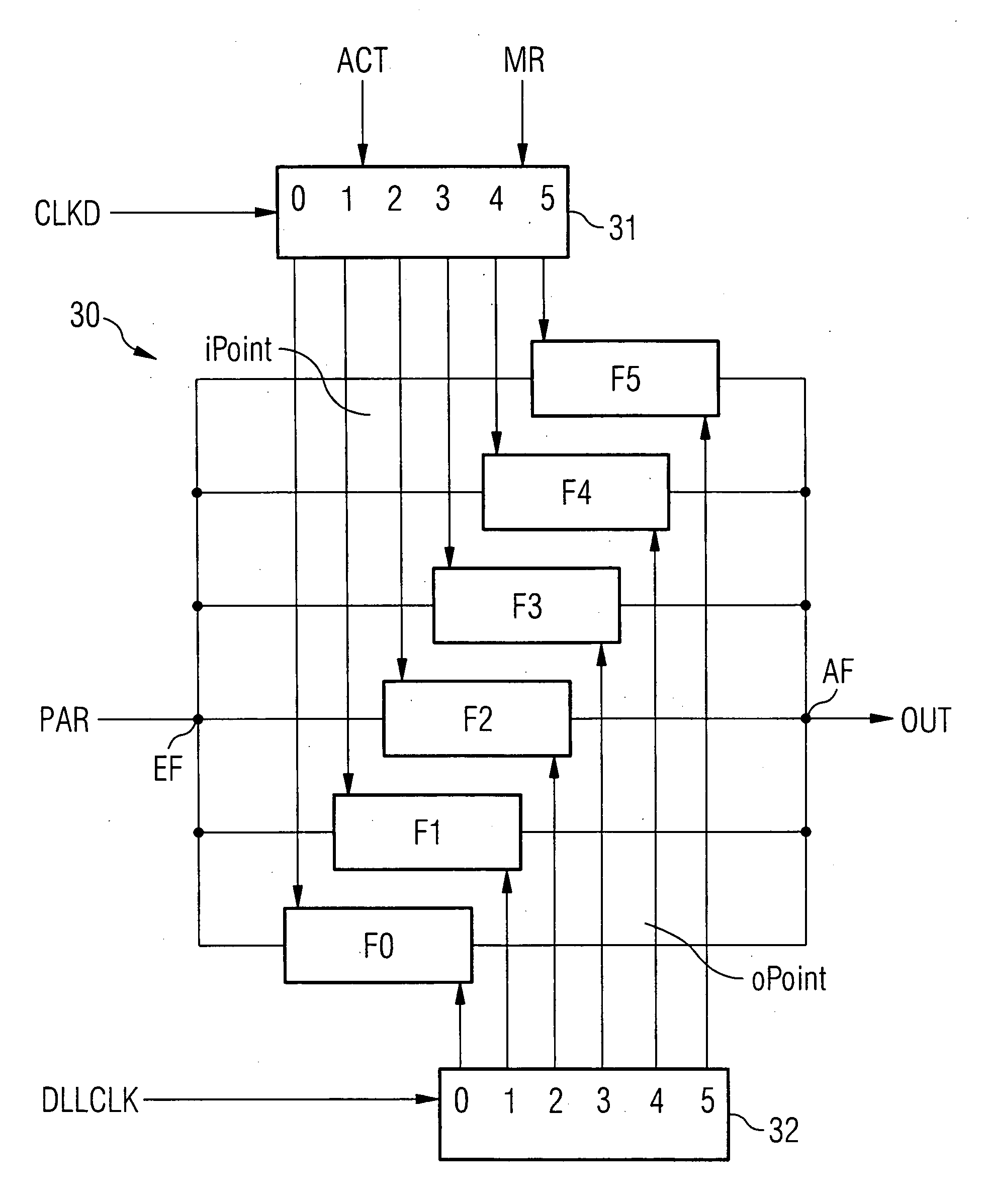
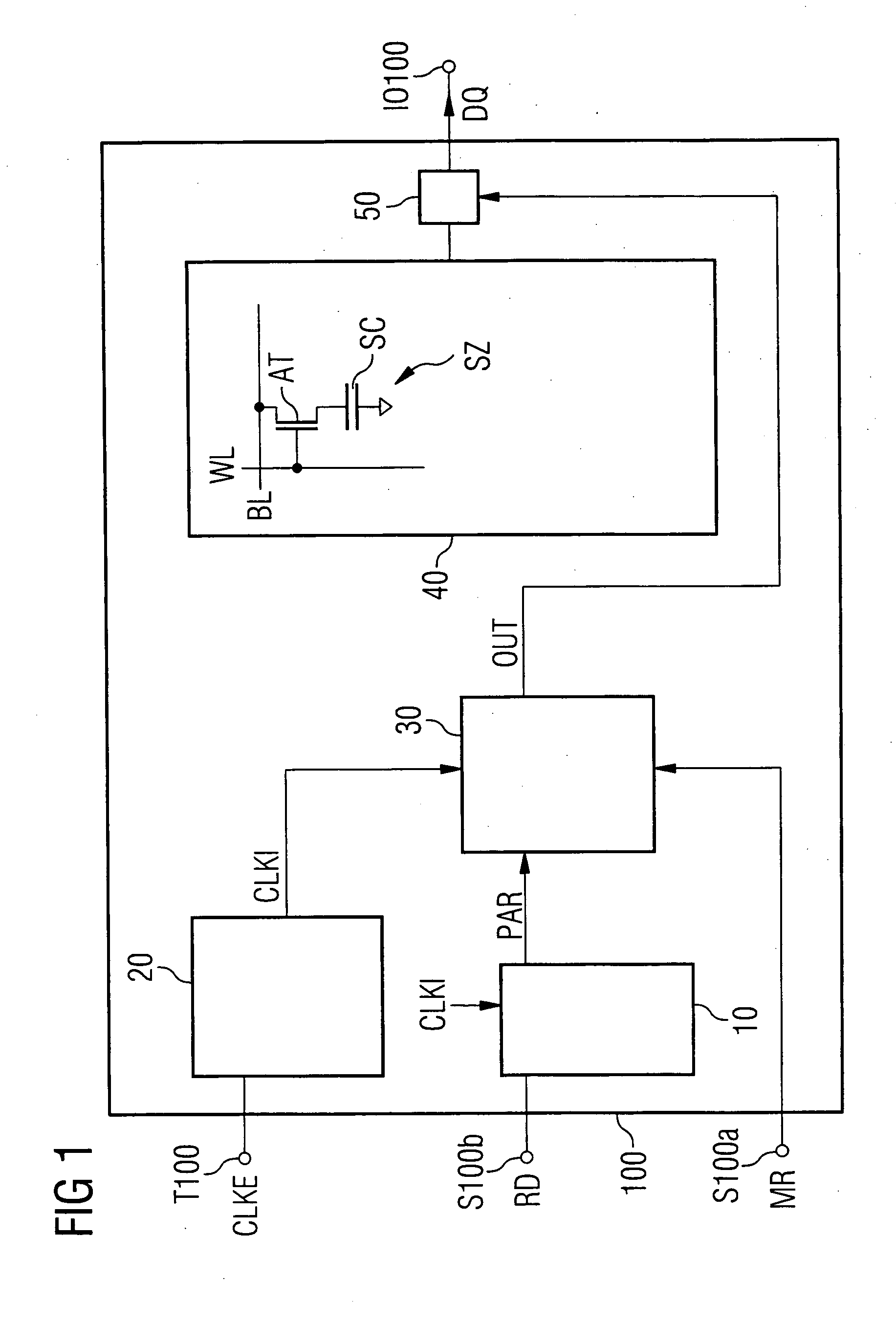
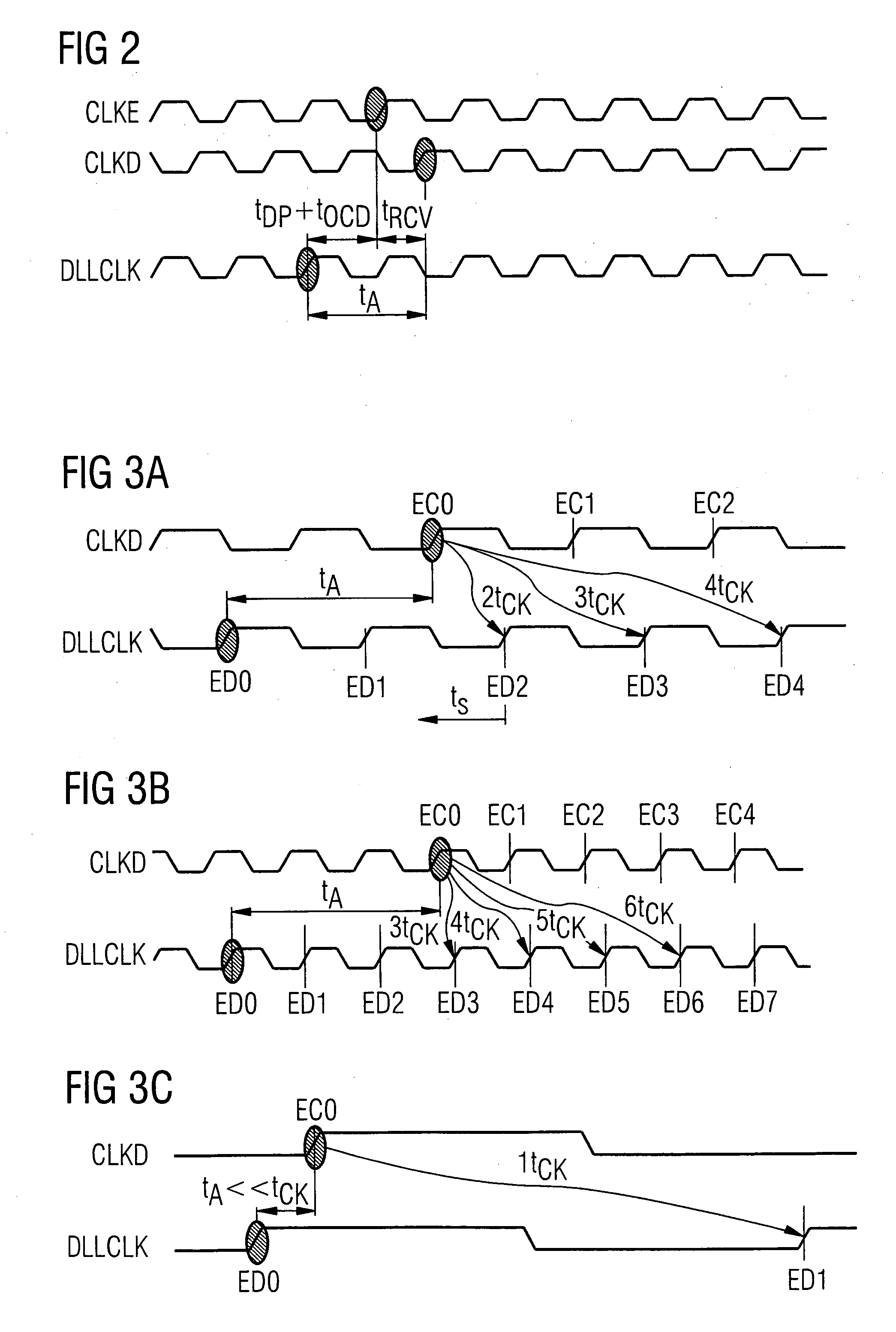
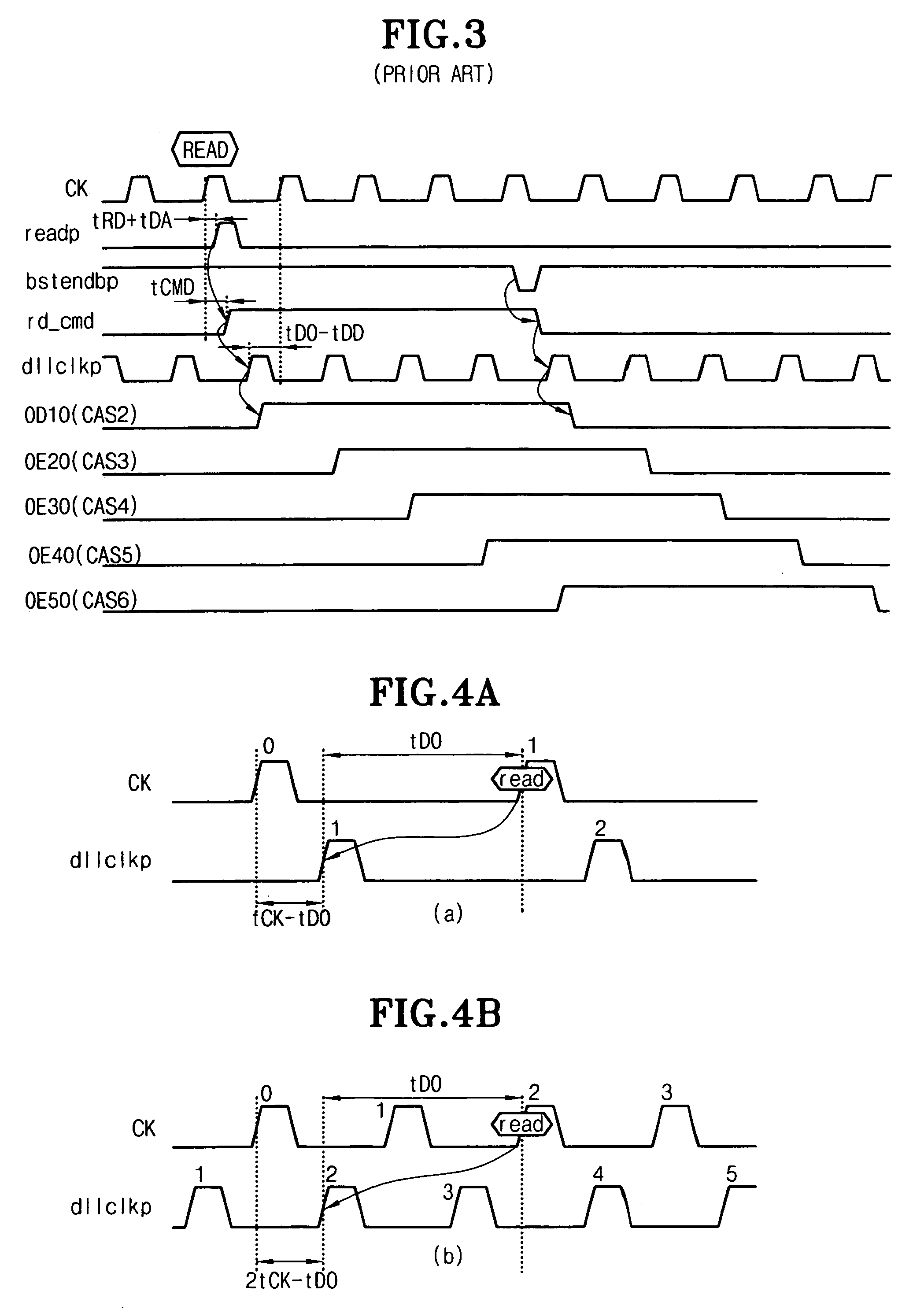
To provide a semiconductor memory device that can ensure adequate read margin by effectively utilizing a period for assigned CAS latency. CAS latency is preset before reading. An ACT command is input to activate a word line corresponding to a row address. A READ command is input at a zeroth clock pulse of an internal clock and a digit line corresponding to a column address is connected to a sense amplifier. A sense amplifier activation signal is activated independently of CAS latency to start an equalizing and sense operation. Afterwards, a sense amplifier activation signal is deactivated after two through 5 cycles depending on CAS latency, and the equalizing and sense operation are terminated. Subsequently, an output operation for transferring the sensed result from the sense amplifier to an output pin is performed, and first data is available from a fifth through the eighth clock pulse depending on CAS latency.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
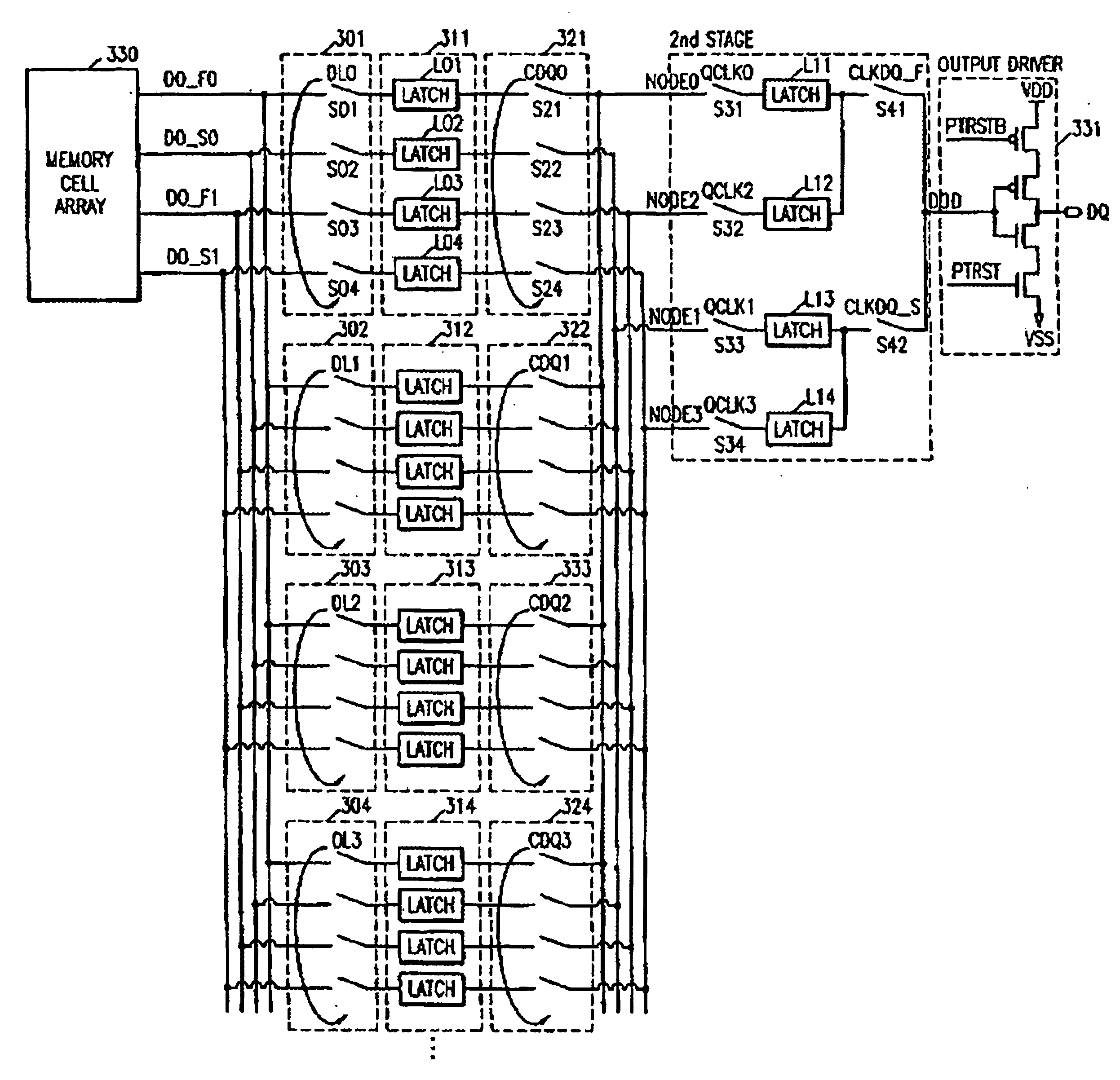
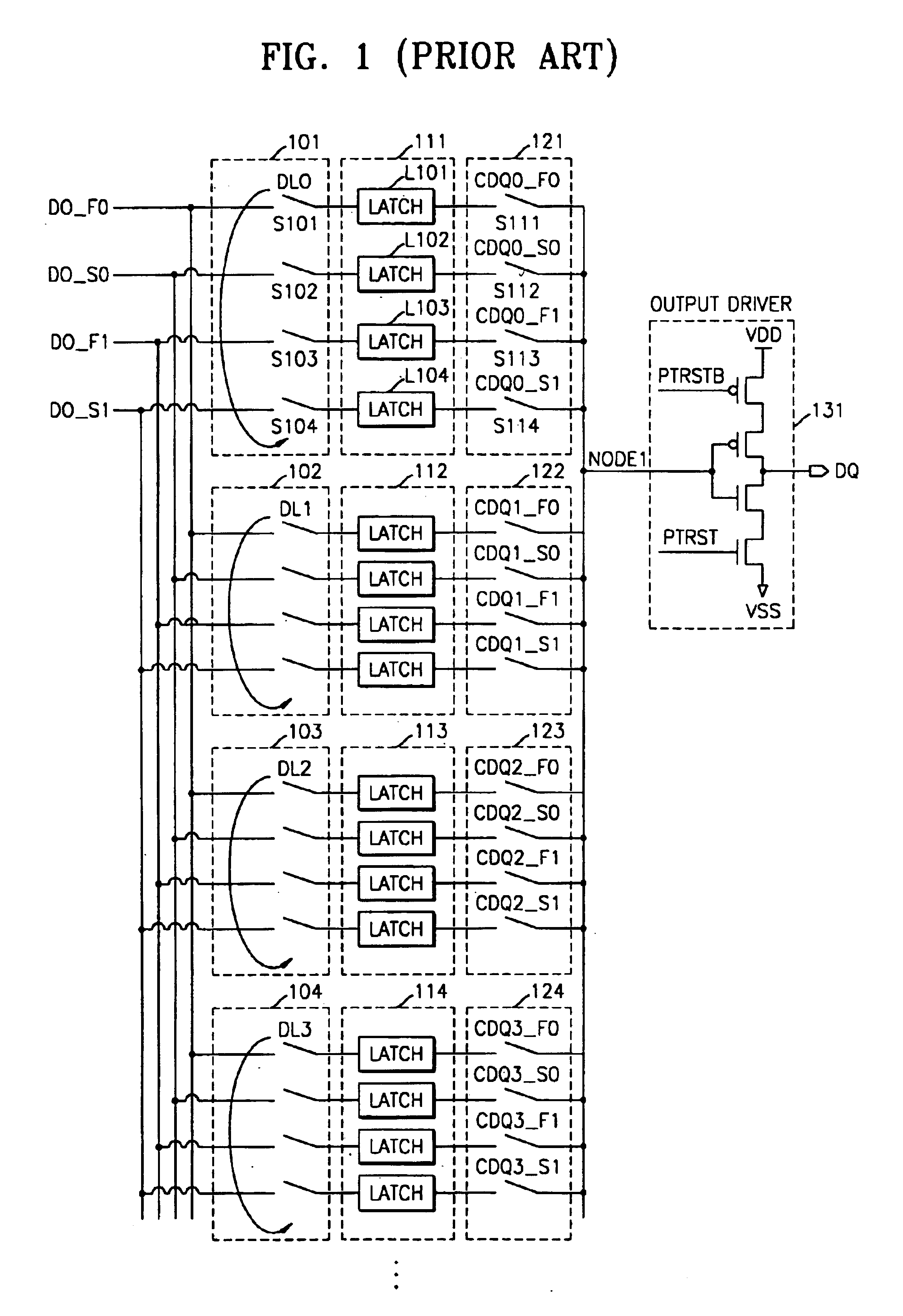
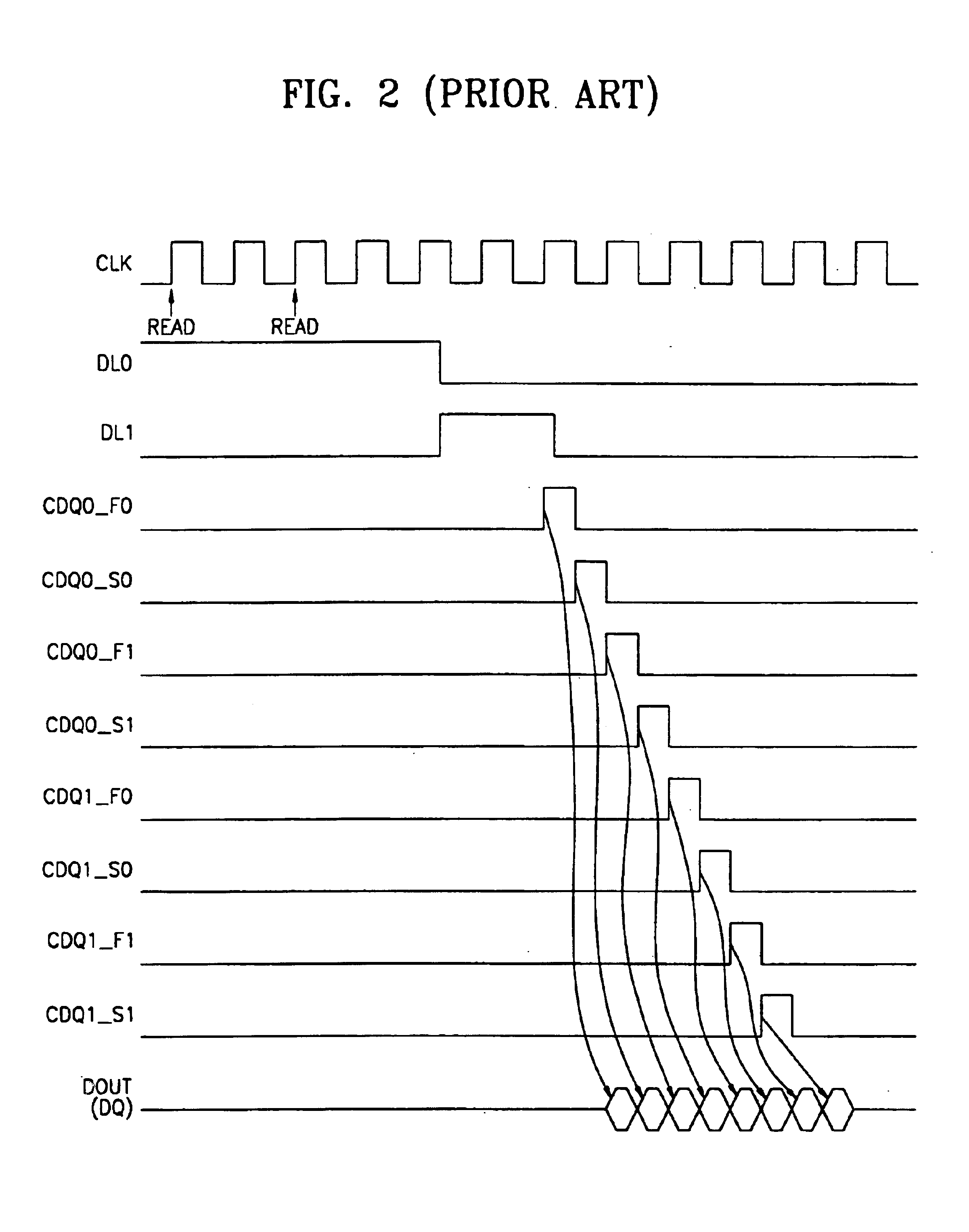
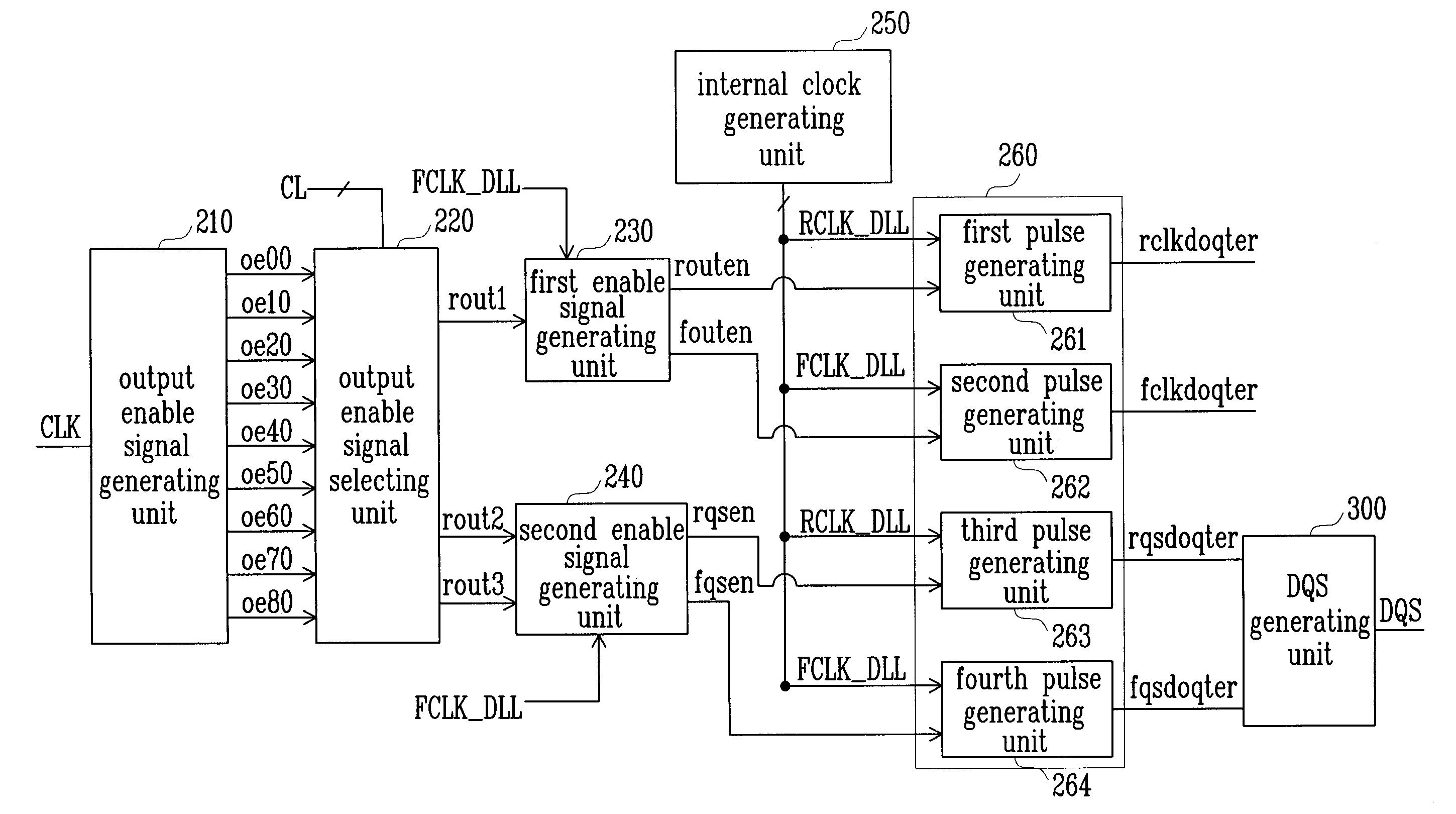
Multi-stage output multiplexing circuits and methods for double data rate synchronous memory devices
An output multiplexing circuit for a Double Data Rate (DDR) synchronous memory device includes n first latches, n first switches, n second switches, n second latches, and two third switches. The n first latches simultaneously prefetch n-bit data transmitted from a memory cell array via a data path. The n first switches simultaneously transfer the n-bit data prefetched into the first latches to n nodes in response to a CAS latency information signal. The n second switches simultaneously transfer data on the nodes in response to n signals that are synchronized with a clock signal and sequentially generated at a predetermined interval. The n second latches store the data transferred via the second switches. The two third switches sequentially transfer the data stored in the n second latches to an input terminal of an output driver of the memory device at a rising edge and a falling edge of a delay signal of the clock signal. Analogous methods also are described.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Data output control circuit
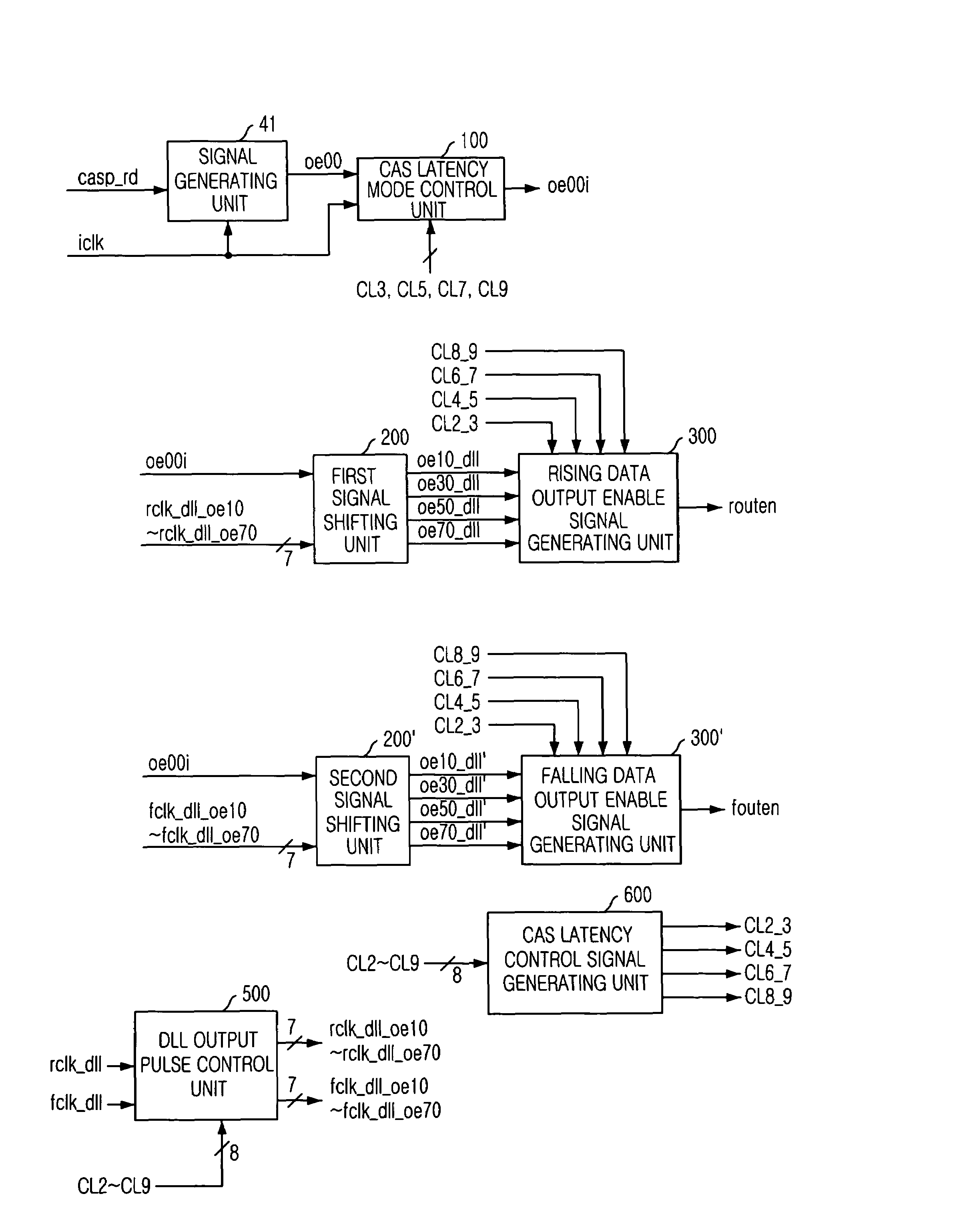
A data output control circuit for use in a synchronous semiconductor memory device, which has a plurality of CAS latency modes, includes a signal generating unit for generating an internal signal corresponding to an input command; a CAS latency mode control unit for outputting the internal signal as a controlled internal signal; a signal shifting unit for generating a plurality of shifted signals by synchronizing the controlled internal signal with a DLL clock signal; and a data output enable signal generating unit for outputting one of the plurality of shifted signals as a data output enable signal depending on a plurality of control signals, wherein each of the plurality of control signals corresponds to two or more continuous CAS latency modes.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
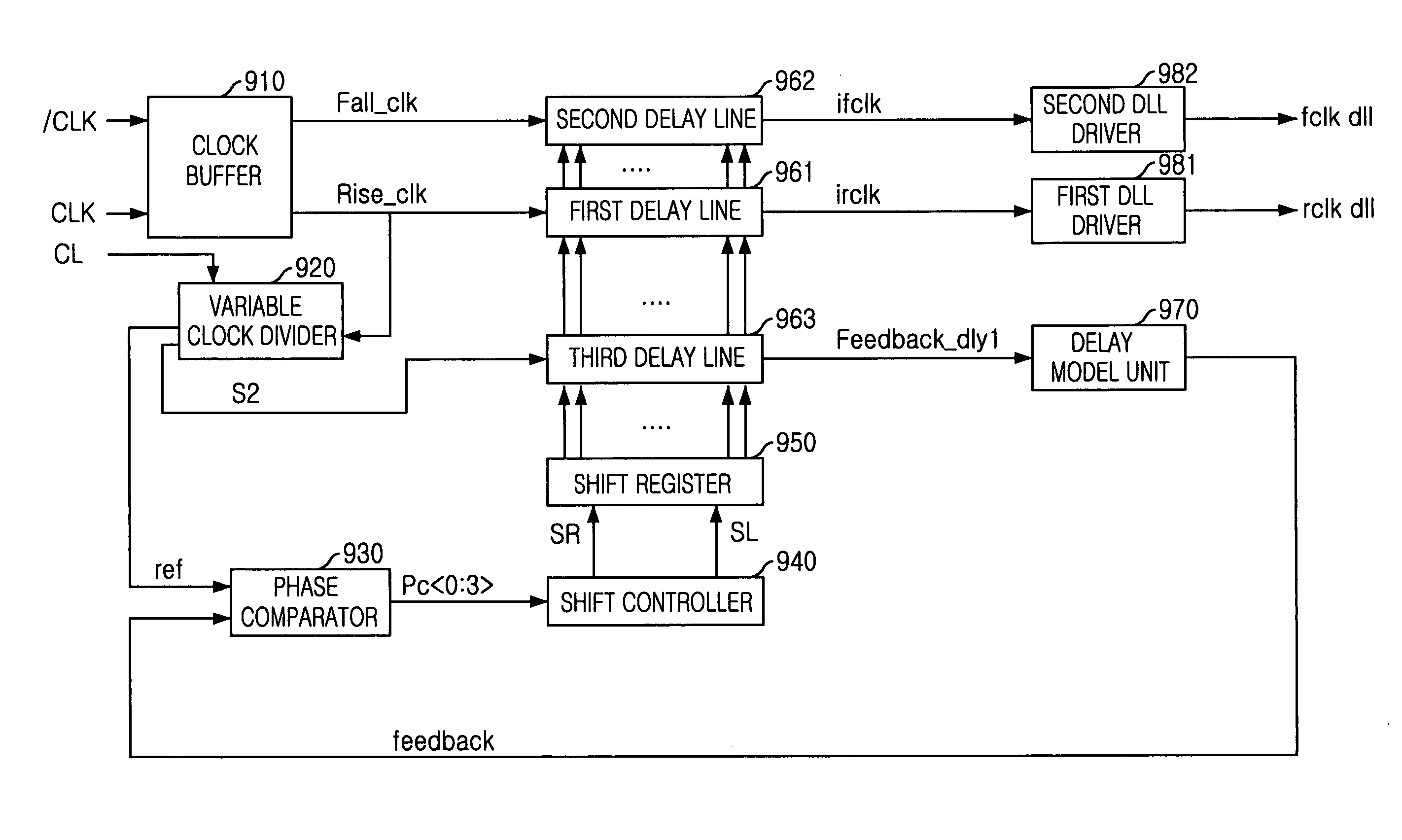
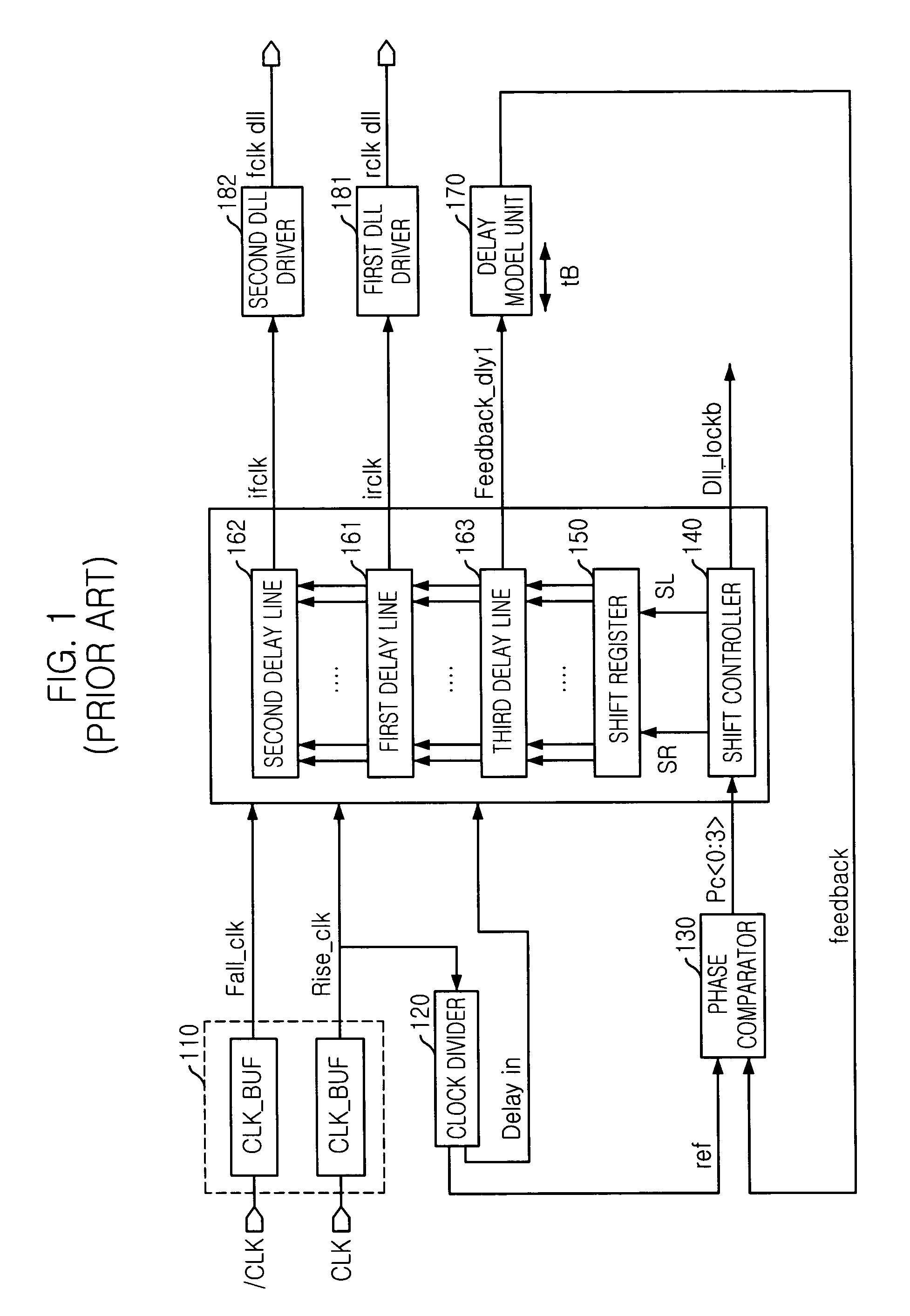
Delay locked loop (DLL) in semiconductor device
A delay locked loop (DLL) in a semiconductor device, includes an clock buffer receiving an external clock signal and an inverted clock signal and outputting first and second internal clock signals to be used in the DLL circuit; and a variable clock divider receiving the second internal signal from the clock buffer and variably dividing the second internal clock signal to have a predetermined pulse width according to a control signal based on a column address strobe (CAS) latency, which is set according to a frequency of the external clock signal, wherein the control signal is initially set to have a first logic level and is enabled to a second logic level when the CAS latency corresponds to a high frequency.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Methods for generating output control signals in synchronous semiconductor memory devices and related semiconductor memory devices
A synchronous semiconductor memory device includes an output control signal generating circuit that generates a data output control signal in response to an internal clock signal, an output control clock signal and a CAS latency signal. The output control signal generating circuit successively shifts read information signals in response to the internal clock signal and the output control clock signal, both source clocks of which are identical, and generates one of the shifted read information signals as an output control signal for indicating a data output period in response to the CAS latency signal. The synchronous semiconductor memory device can synchronize the source clocks of the clock signals used in the output control signal generating circuit thereby reducing the influence of clock jitter.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
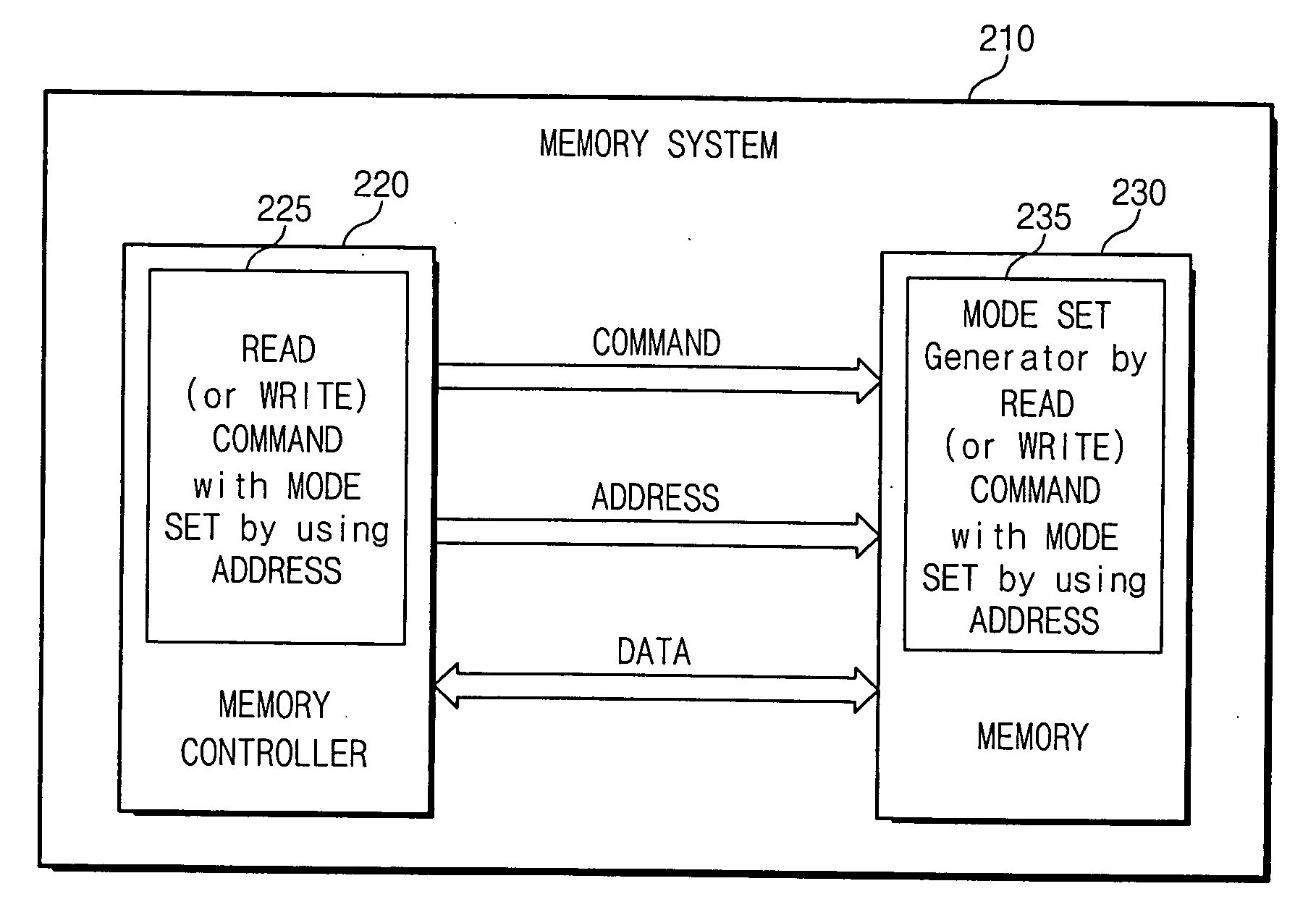
Method and memory system in which operating mode is set using address signal
A memory system, memory device, and method for setting an operating mode of a memory device include a memory cell array; row and column decoders which select a row and a column of the memory cell array, respectively, according to a multi-bit address signal; and a mode control circuit which receives at least one bit from the multi-bit address signal used in the selection of the row or the column, and which sets an operating mode of the memory device according to the at least one bit, wherein the operating mode is one of a burst length mode, a DLL reset mode, a test mode, a CAS latency mode, and a burst type mode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20100164572A1Guaranteed high speed operationReduce power consumptionPulse automatic controlDigital storageDelay-locked loopInput control
A semiconductor device includes a latency signal generating circuit for generating a latency signal corresponding CAS latency by measuring a delay amount reflected at a delay locked loop and reflecting the measured delay amount at a read command signal, and a delay locked loop for controlling an internal clock signal applied to the latency signal generating circuit corresponding to the read command and the latency signal. The semiconductor device includes an internal clock signal generating block configured to generate an internal clock signal, a latency generating block configured to generate a latency signal by synchronizing a read command signal with the internal clock signal at a time corresponding to a CAS latency value and a measured delay value, and an input controlling block configured to activate the reference clock signal using an external clock signal in response to the read command signal and the latency signal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
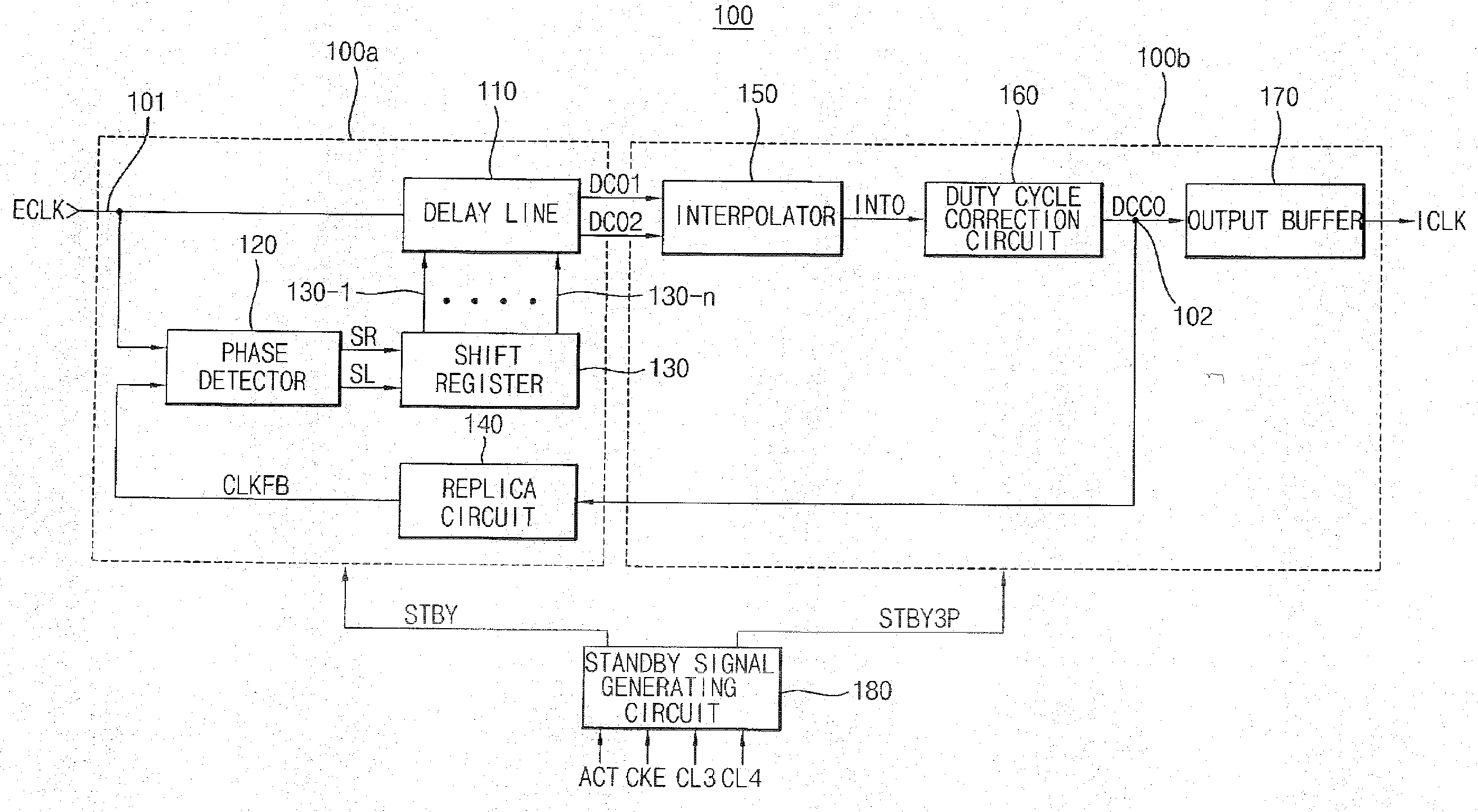
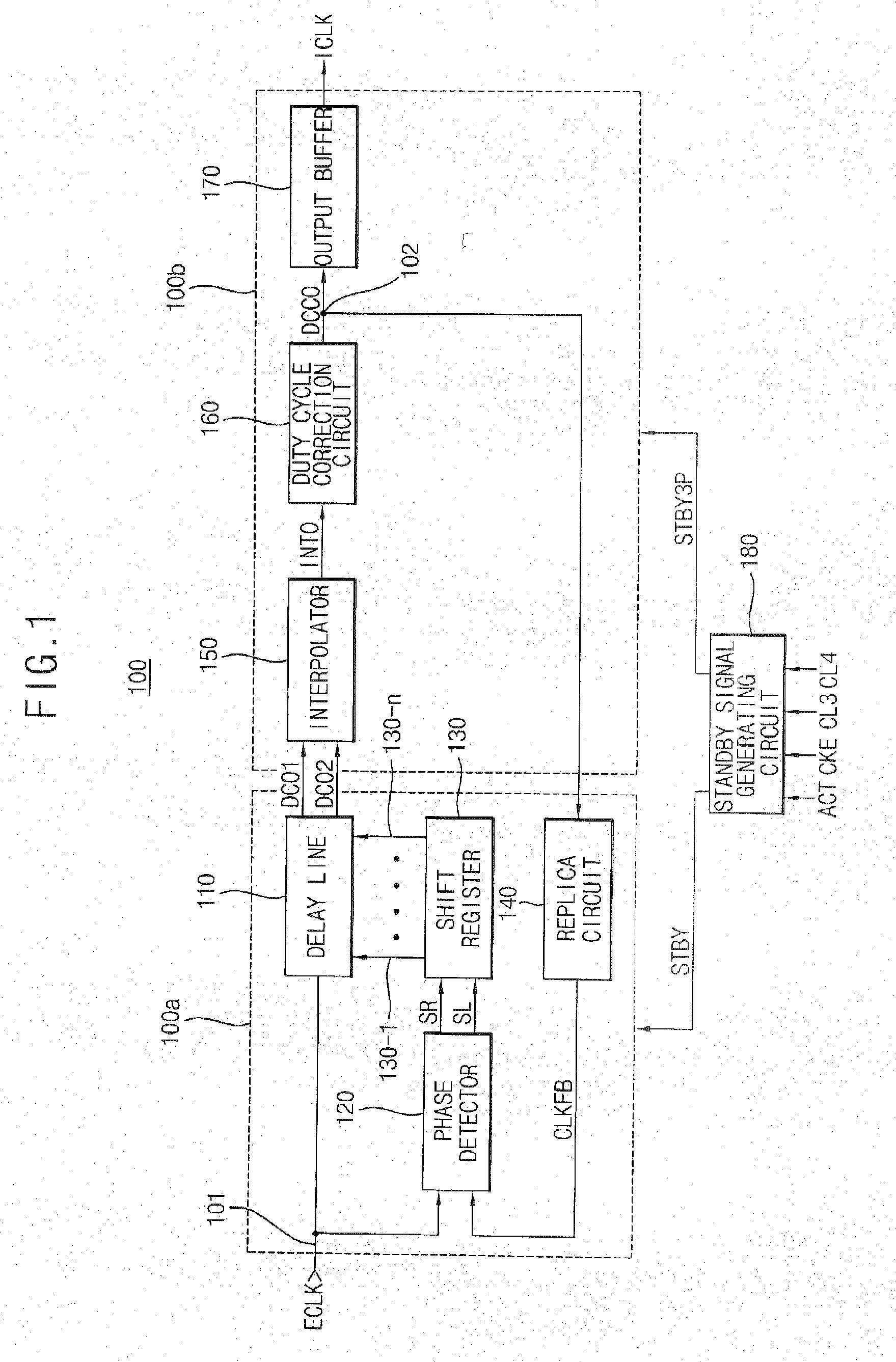
Delay-locked loop circuit of a semiconductor device and method of controlling the same
A delay-locked loop (DLL) circuit includes a standby signal generating circuit, a front stage circuit, and a back stage circuit. The standby signal generating circuit generates a first standby signal and a second standby signal in response to an active signal, a crock enable signal, a first column address strobe (CAS) latency signal, and a second CAS latency signal. The front stage circuit compares the phase of an external clock signal and the phase of a feedback signal and delays the external clock signal based on the phase difference between the external clock signal and the feedback signal to generate a first clock signal. The back stage circuit executes interpolation and duty-cycle correction on the first clock signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Cas latency select utilizing multilevel signaling
A method of selecting CAS latencies in a system. Specifically, a system which includes a plurality of memory modules is provided. Because different memory modules may have different CAS latencies, multilevel signaling is used to standardize the CAS latencies throughout the system. A static pin is provided on each memory device such that a drive signal can be received. The voltage level of the drive signal corresponds to a selected CAS latency for the system.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Method for controlling data output timing of memory device and device therefor
Disclosed is a device for controlling data output of a memory device using a DLL clock signal, the device comprising: an output driver for outputting data; and a CAS latency control unit for generating a signal adjusting an operation timing of the output driver depending on CAS latency, wherein the CAS latency control unit generates a signal for controlling the output driver by using time difference between the DLL clock signal and an external clock applied to the memory device from an exterior.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Features
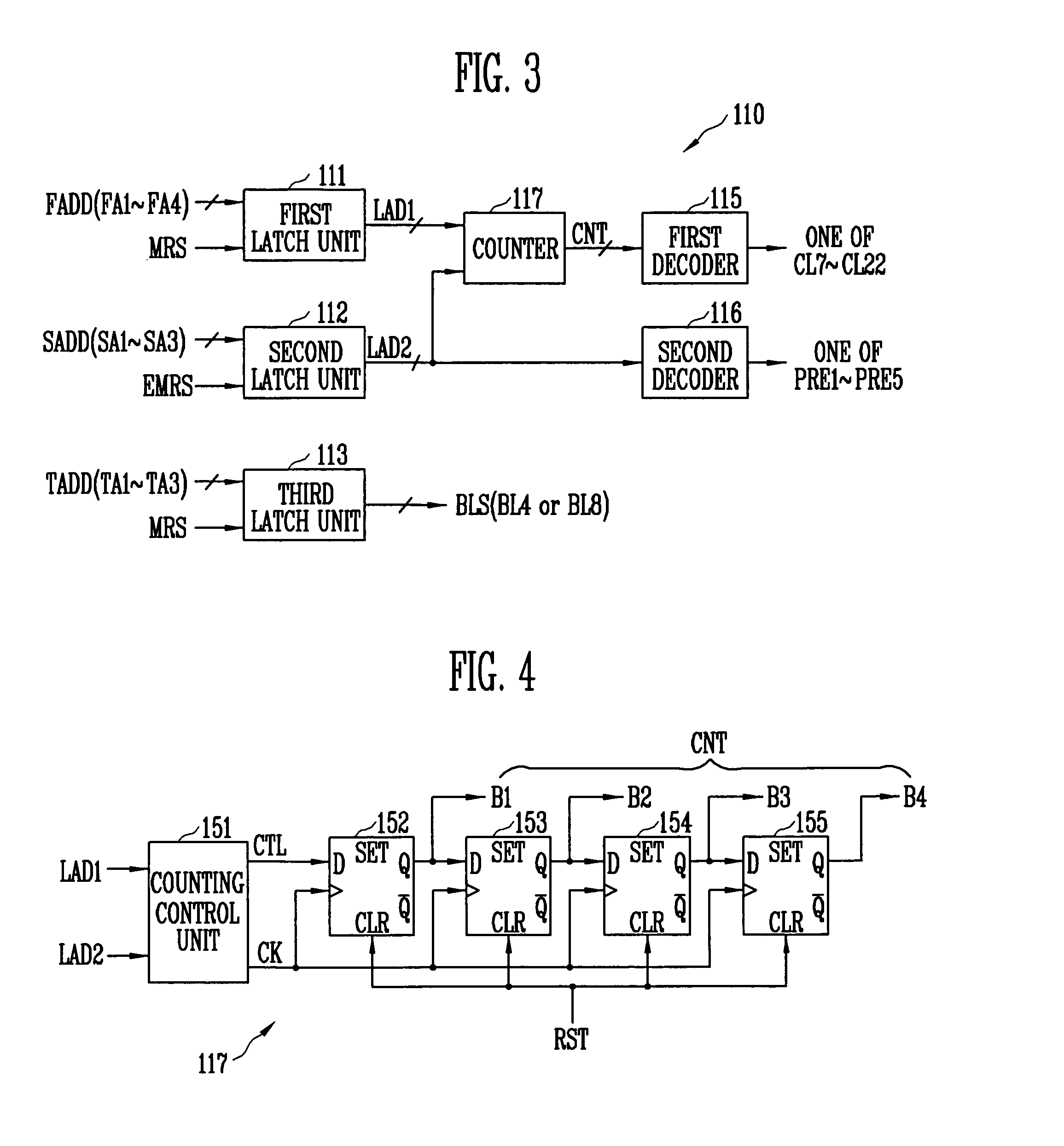
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com