Patents
Literature
1266 results about "Slew rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In electronics, slew rate is defined as the change of voltage or current, or any other electrical quantity, per unit of time. Expressed in SI units, the unit of measurement is volts/second or amperes/second or the unit being discussed, (but is usually expressed in V/μs). Electronic circuits may specify minimum or maximum limits on the slew rates for their inputs or outputs, with these limits only valid under some set of given conditions (e.g. output loading).
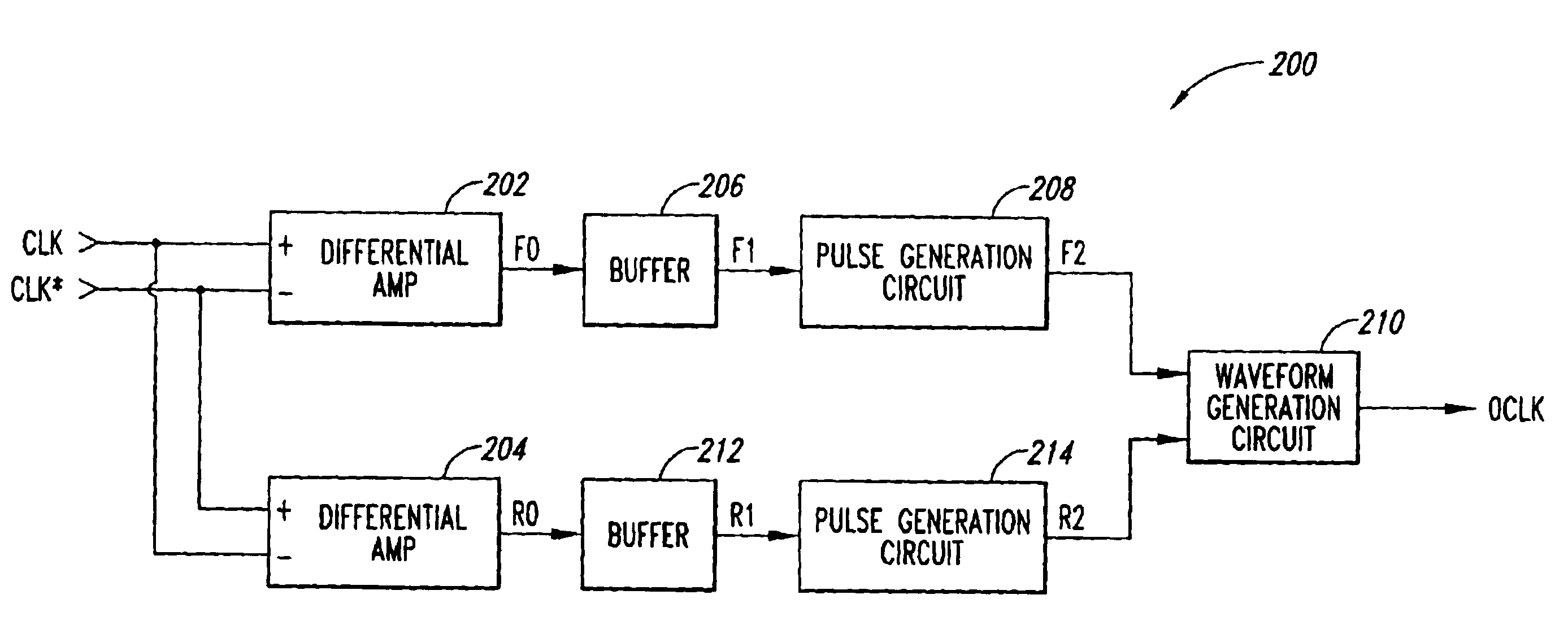
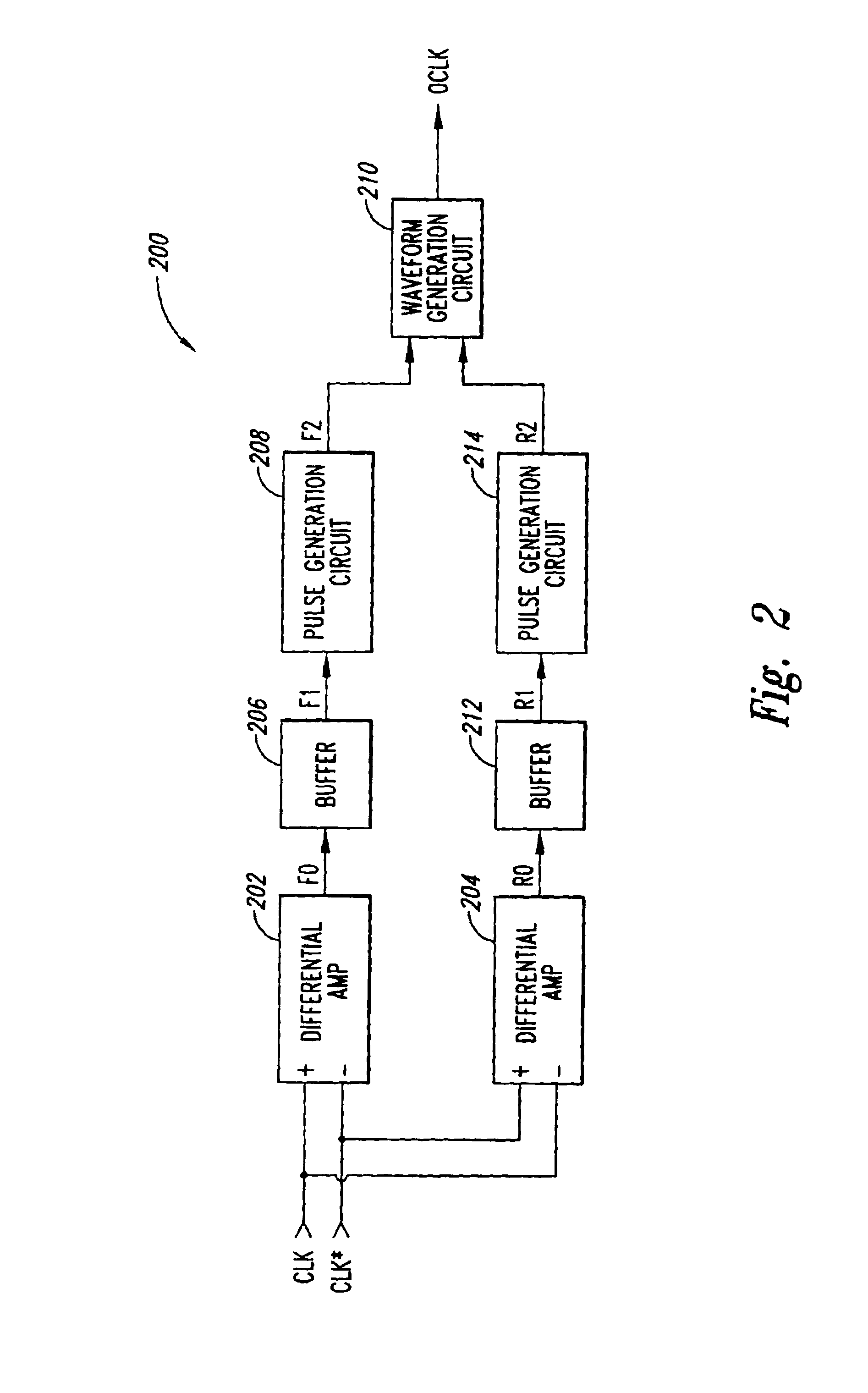
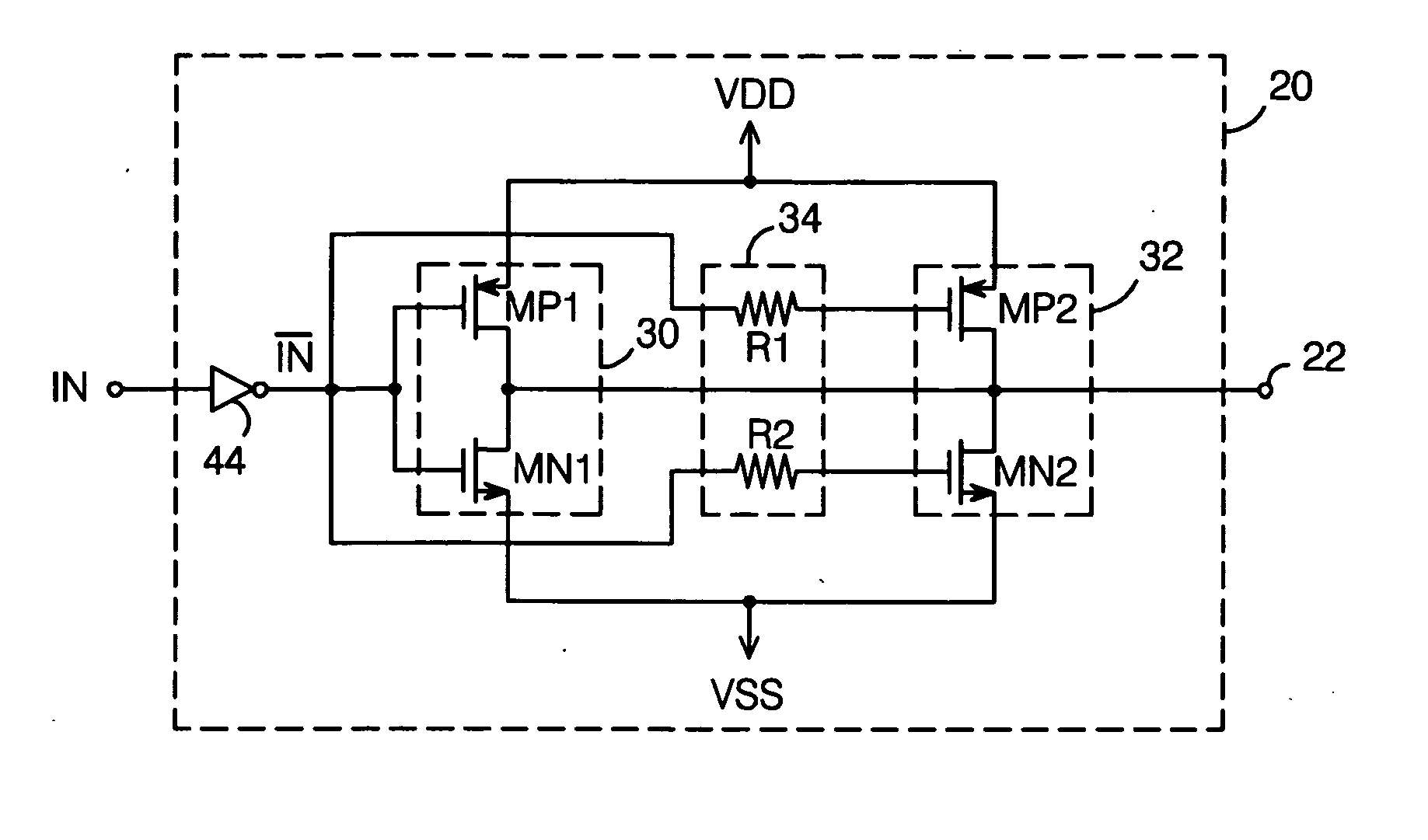
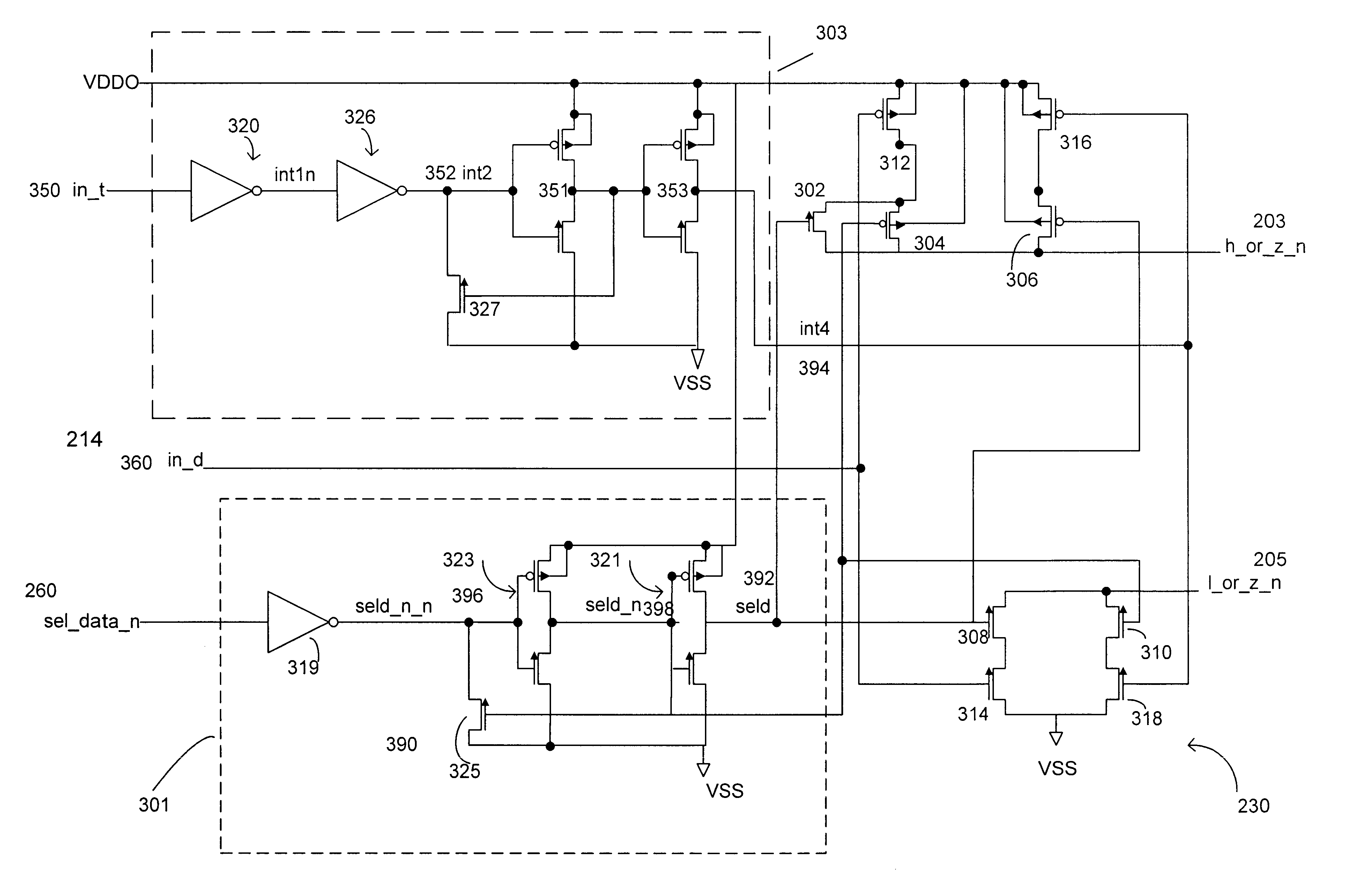
Low skew clock input buffer and method
InactiveUS6847582B2Reliability increasing modificationsDigital storageAudio power amplifierLogic state
An input buffer includes first and second cross-coupled differential amplifiers. Each amplifier drives a buffer signal from a first logic state to a second logic state at a first slew rate when input signal transitions from a first logic state to a second logic state and a complementary input signal transitions from the second logic state to the first logic state, and drives the buffer signal from the second logic state to the first logic state at a second slew rate when the signal transitions are the complement of these previous transitions. An output circuit generates a first edge of an output signal when the buffer signal from the first amplifier transitions from the first logic state to the second logic state and generates a second edged of the output signal when the buffer signal from the second amplifier transitions from the first to the second logic state.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
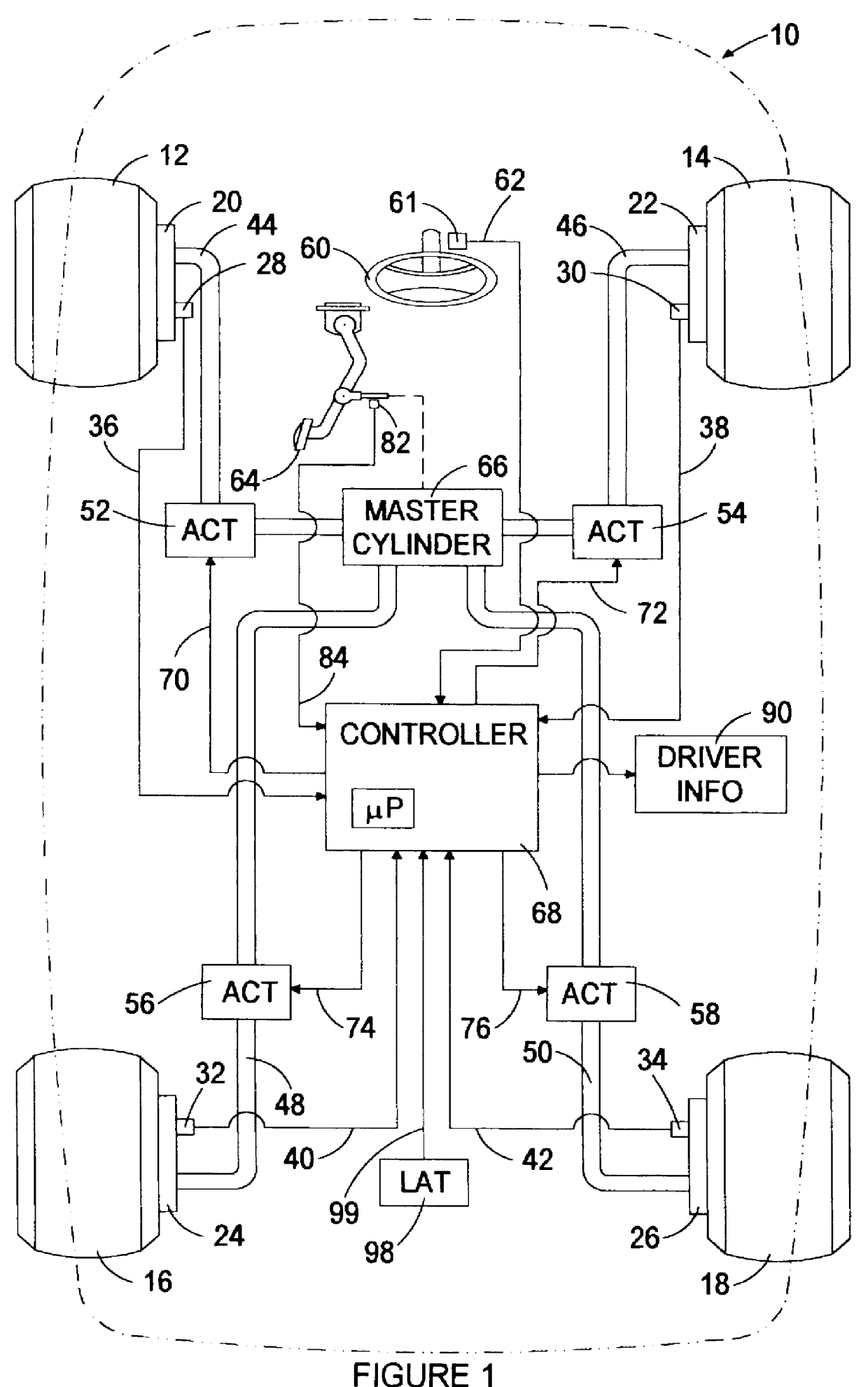
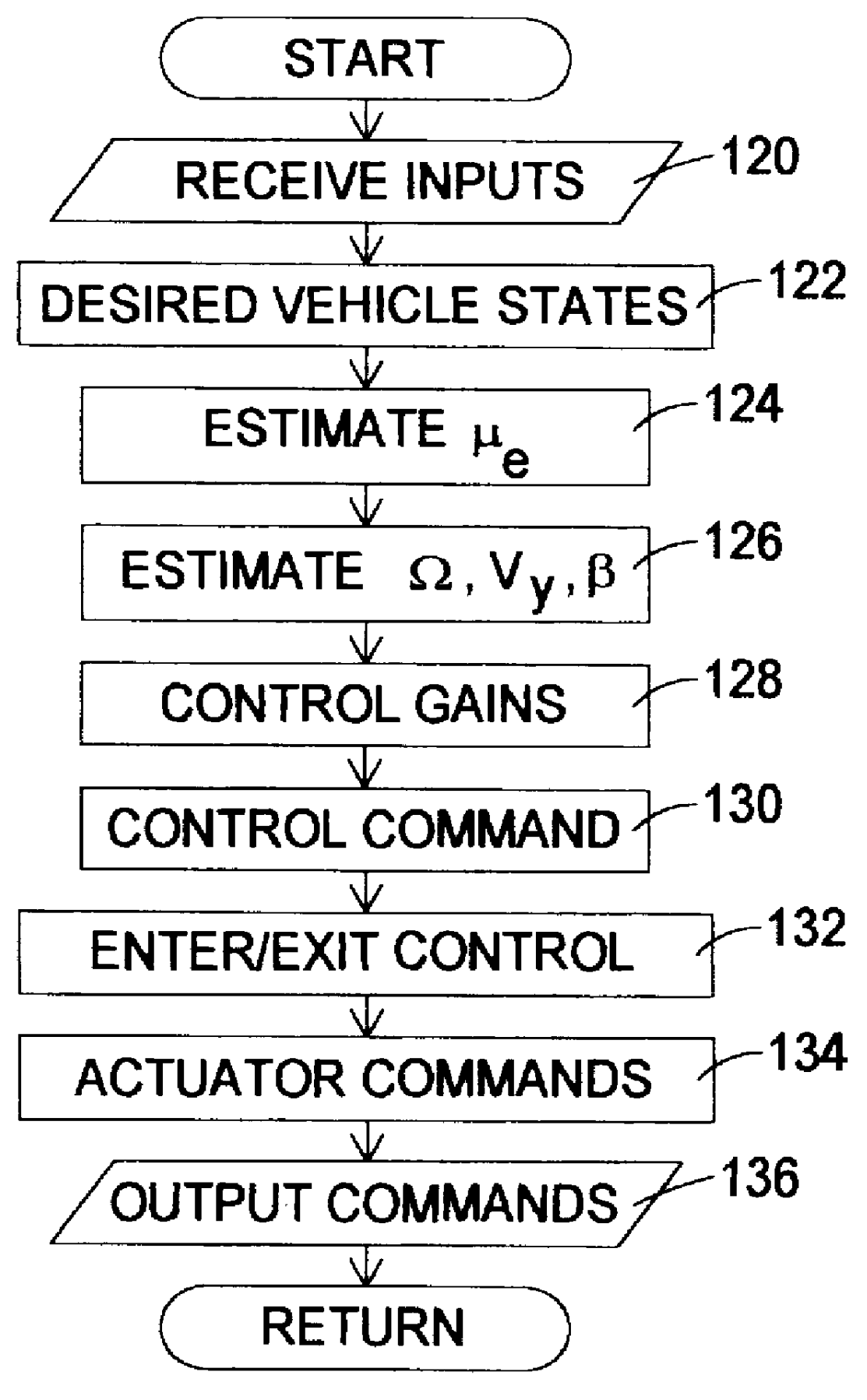
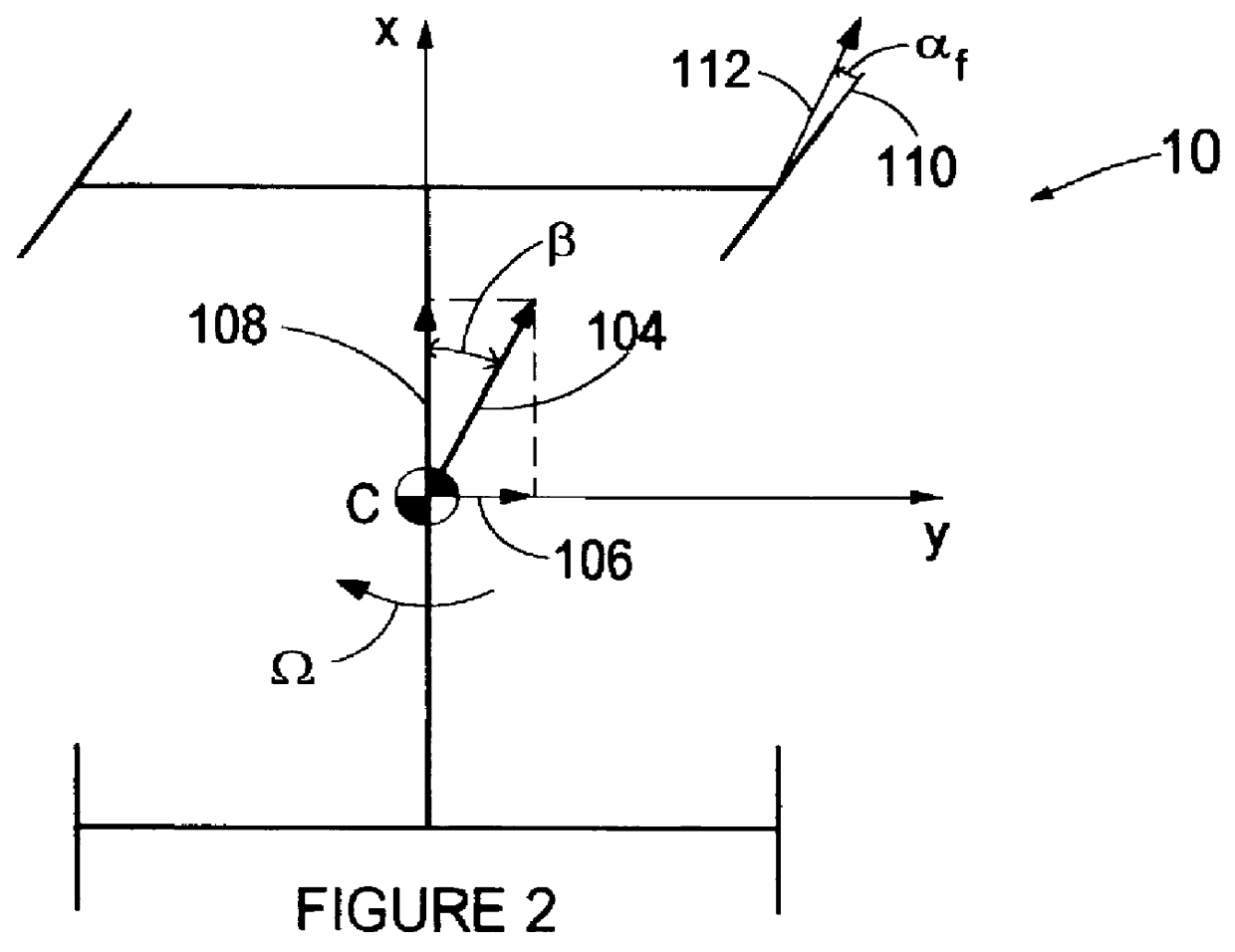
Active brake control including estimation of yaw rate and slip angle
An improved vehicle active brake control based on an estimate of vehicle yaw rate and slip angle, wherein the estimate is based on a weighted average of two yaw rate values developed with two different estimation techniques. In general, the first estimate of yaw rate is based on the relative velocity of the un-driven wheels, and the second estimate is based on a measure of lateral acceleration. Confidence levels in each estimate are determined and used to form a third or preliminary yaw rate estimate based on a weighted average of the first and second estimates, and the third estimate is supplied to a closed-loop nonlinear dynamic observer which develops the final estimate of yaw rate, along with estimates of lateral velocity and side-slip angle.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC +1
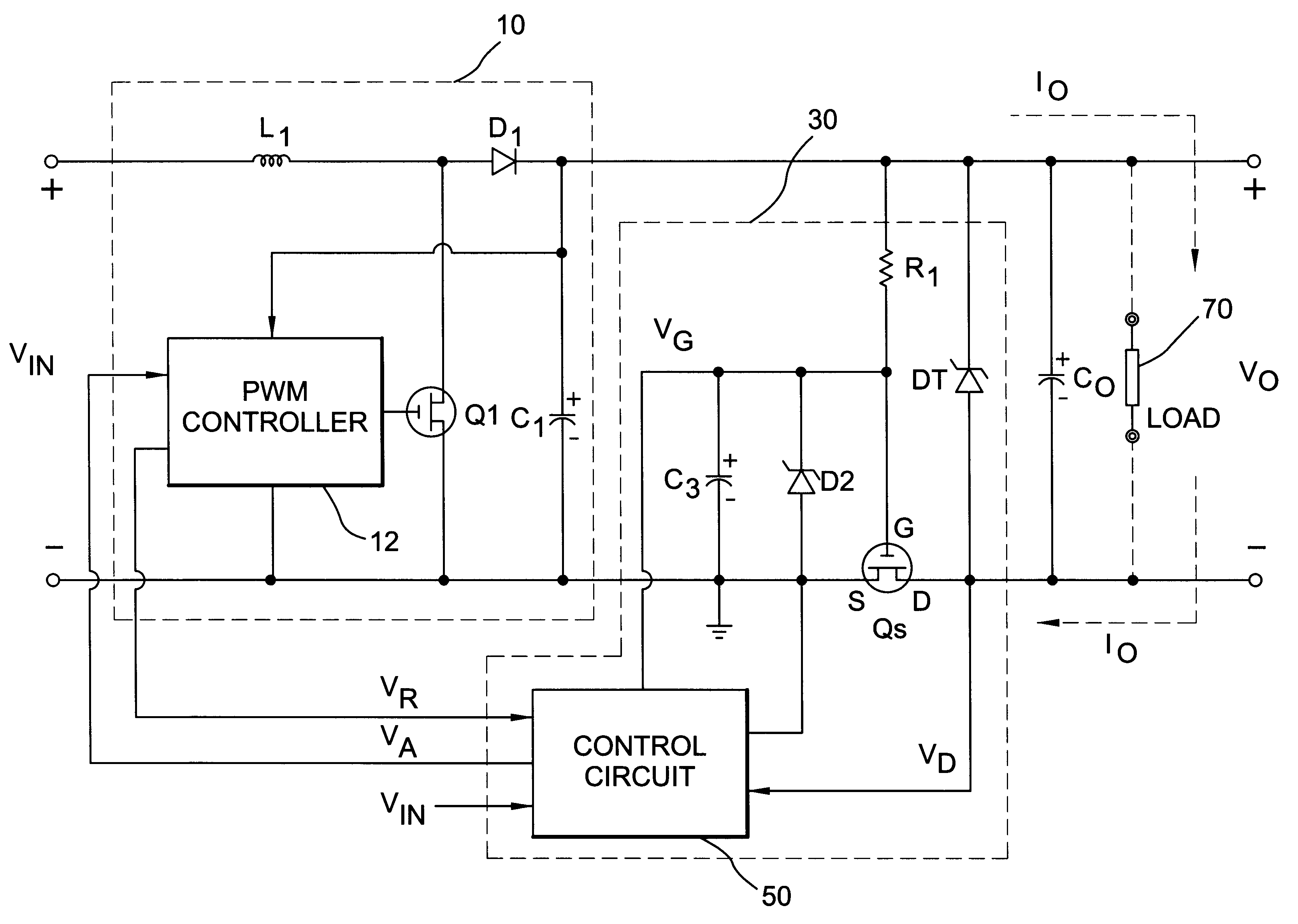
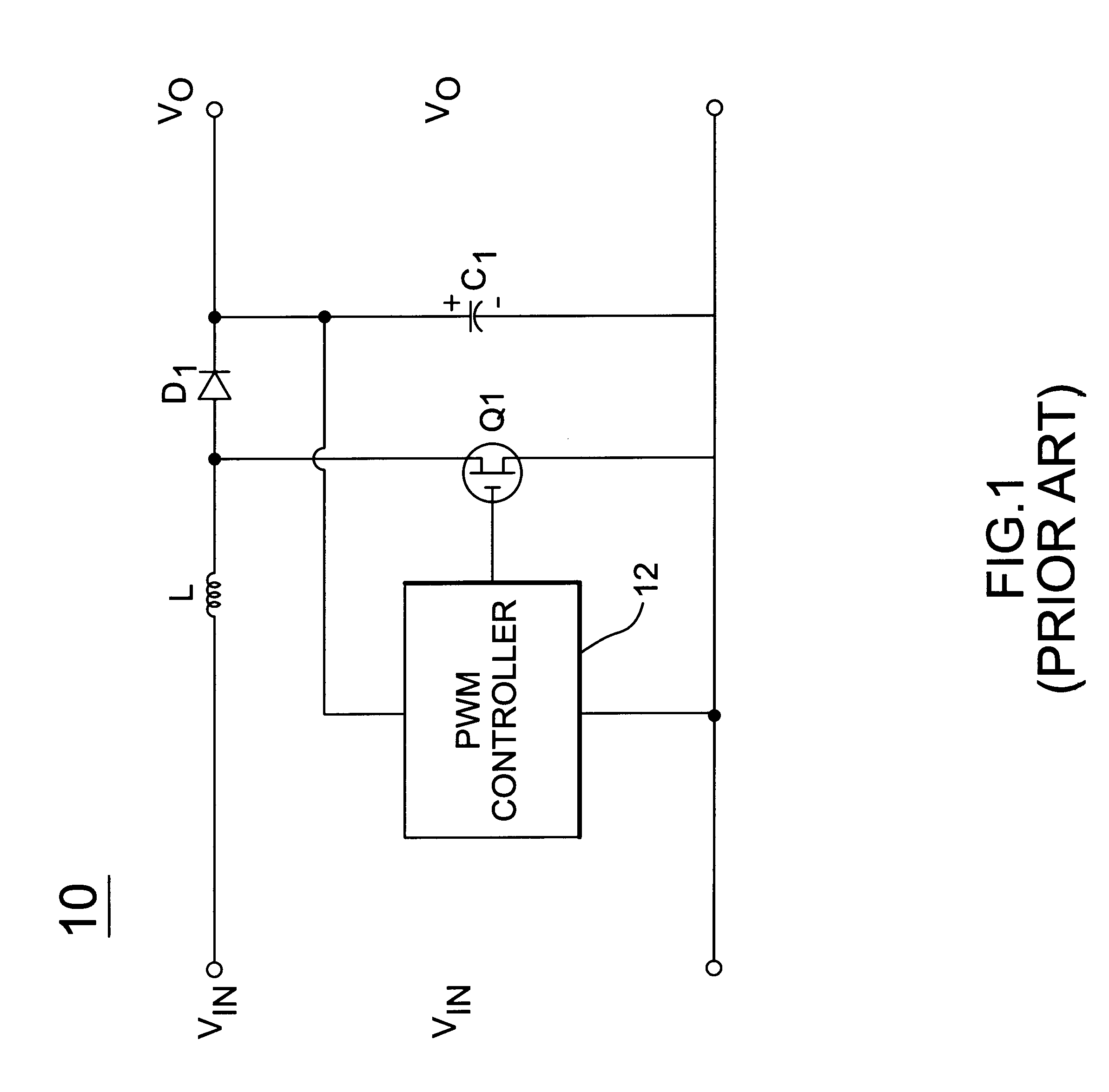
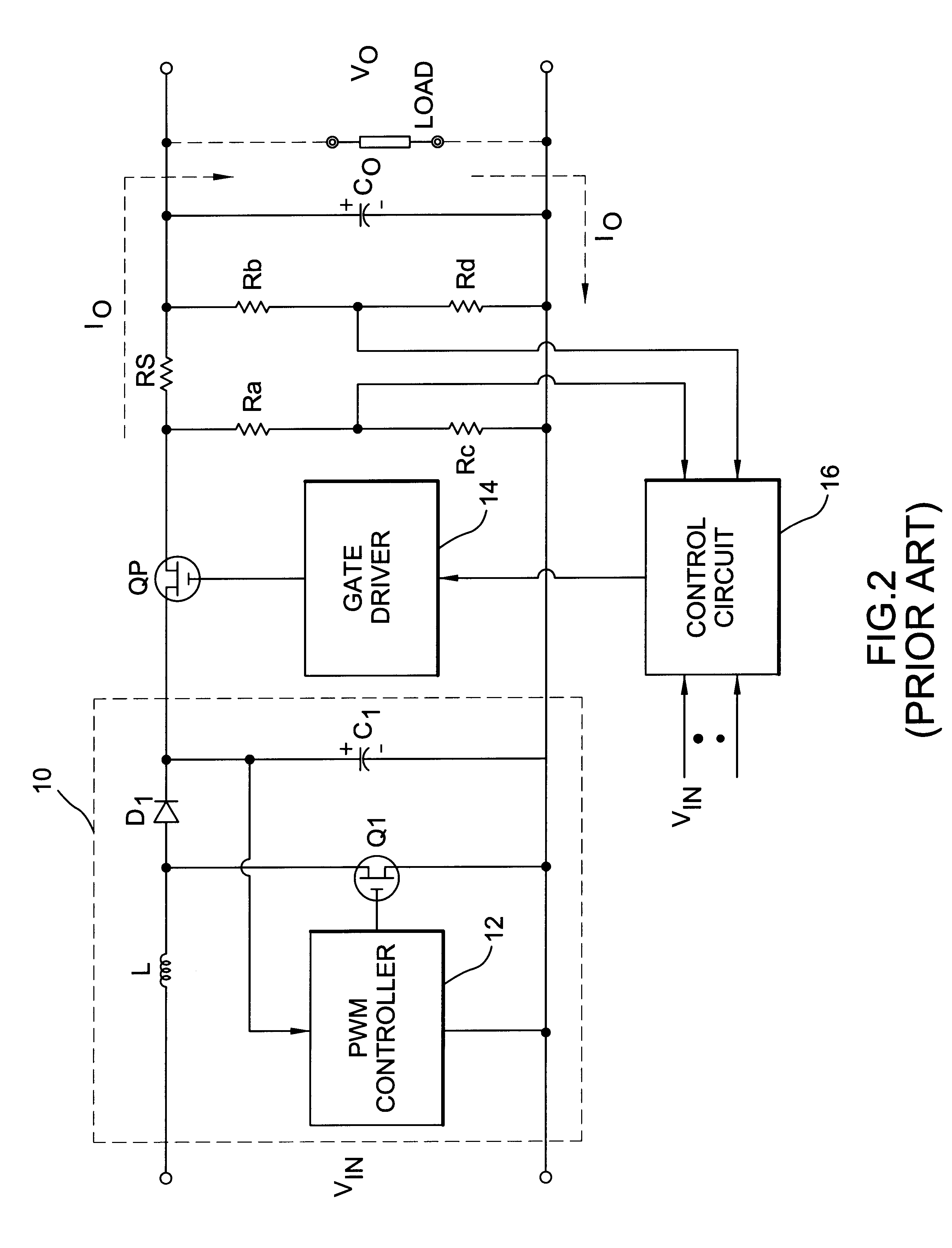
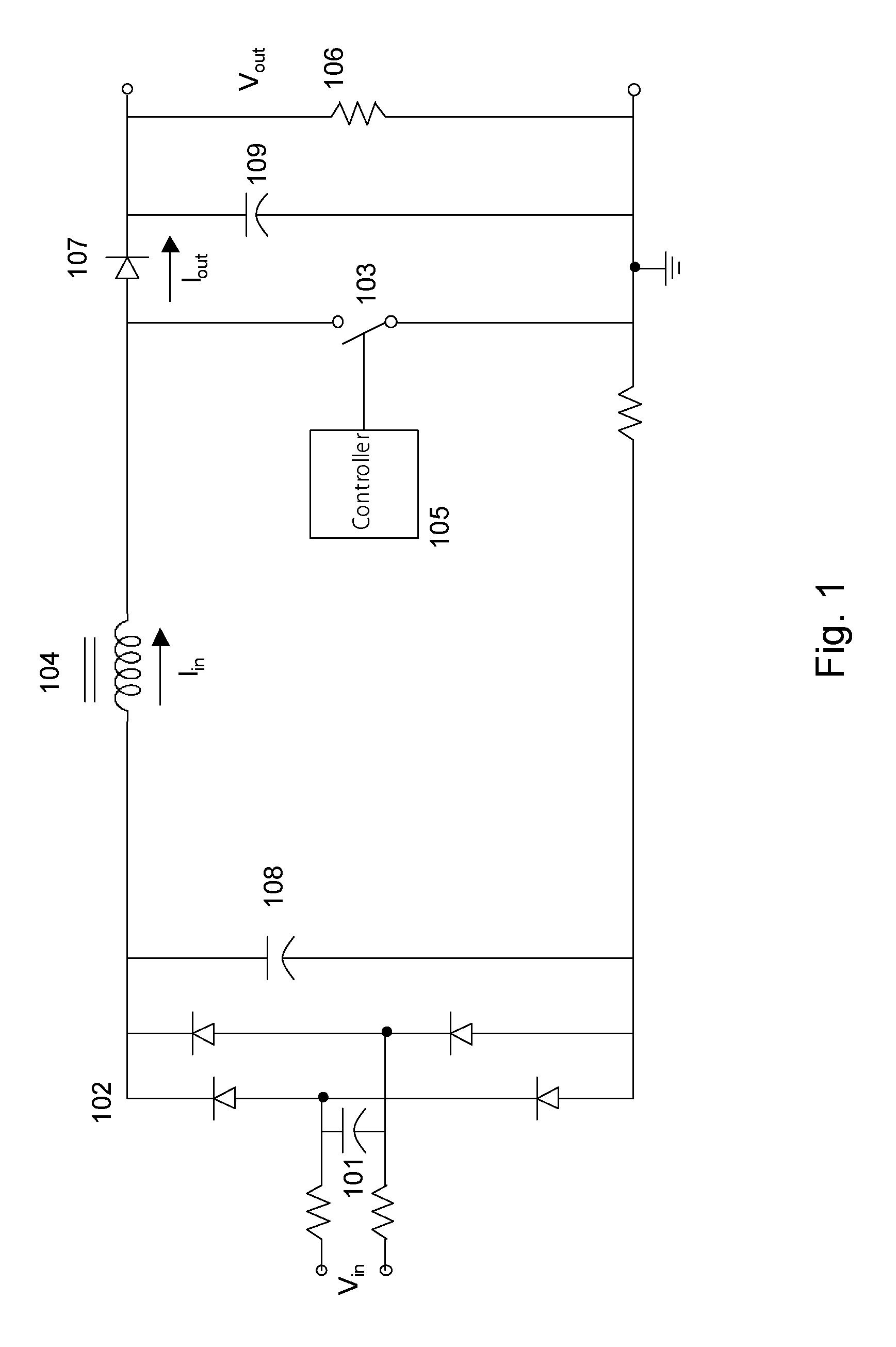
Protection circuit for a boost power converter
InactiveUS6185082B1Apparatus without intermediate ac conversionArrangements responsive to excess currentCurrent limitingTime delays
A protection circuit for a boost power converter provides input under-voltage protection and output over-voltage and over-current protection. The protection circuit includes a control power MOSFET connected in series between the ground of the boost power converter and the ground of the load. The arrangement of the circuit makes it easy to drive the gate of an N-channel power MOSFET and is ideal for current-limiting control, which utilizes the Rds-on of the MOSFET as a current sensing element. Neither a specific gate-driver nor a current sensing resistor is required, and thus high efficiency can be achieved. Furthermore, the slow slew-rate at the gate of the MOSFET provides a soft-start to the load. The protection circuit includes a temperature compensation circuitry to offset the variation of the Rds-on. A time delay circuit prevents the switching elements and protection elements from overload damage.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
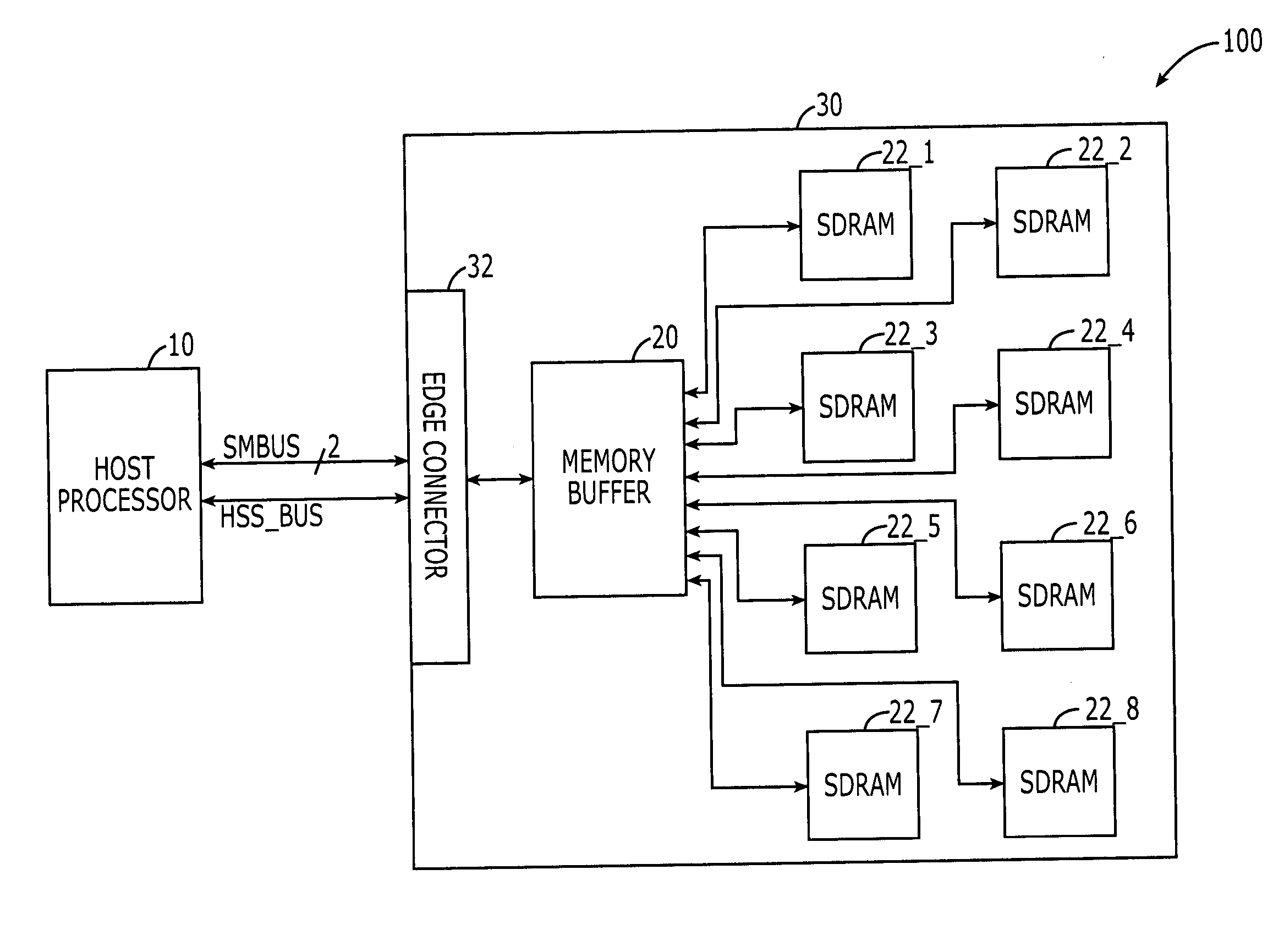
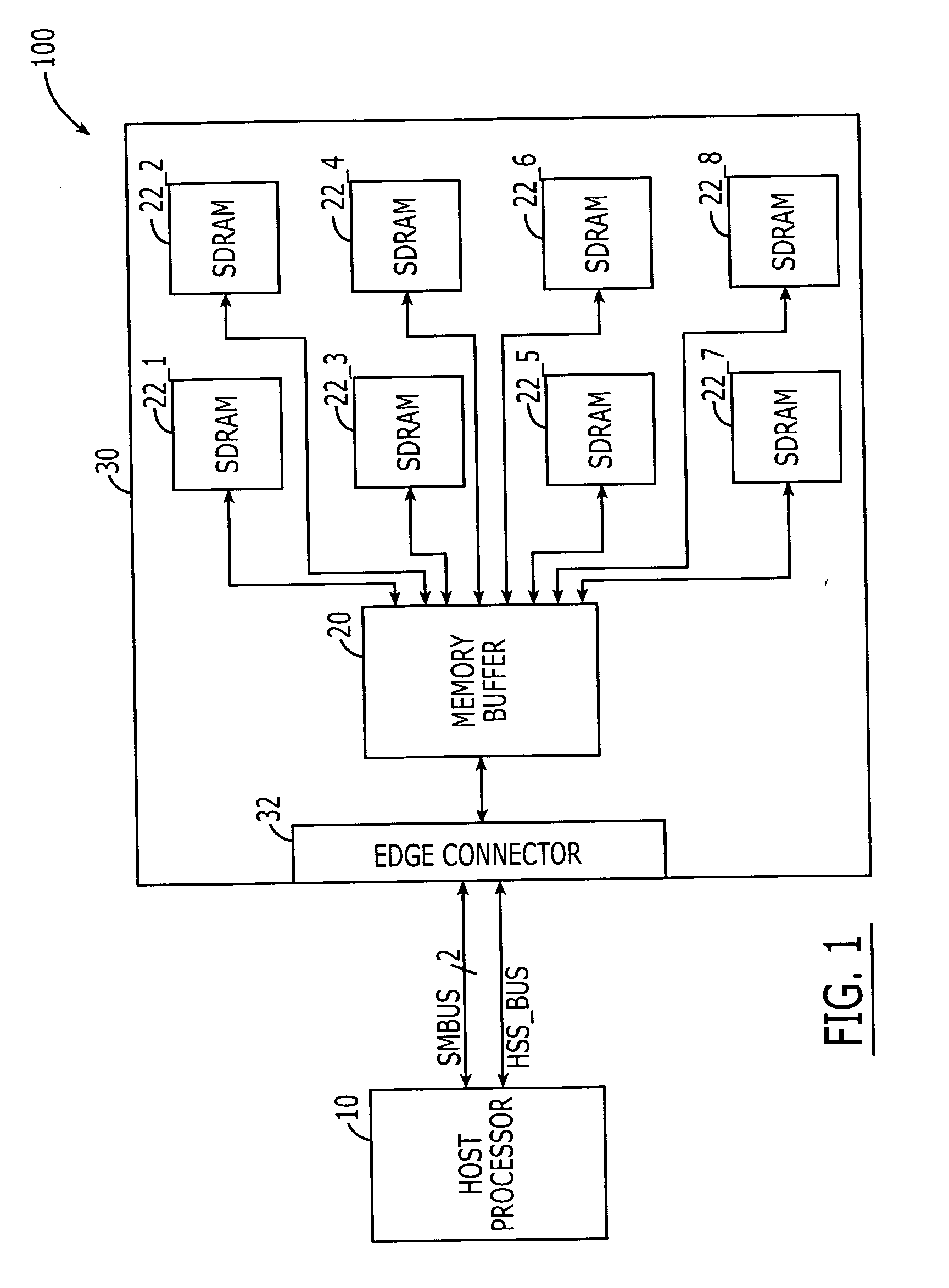
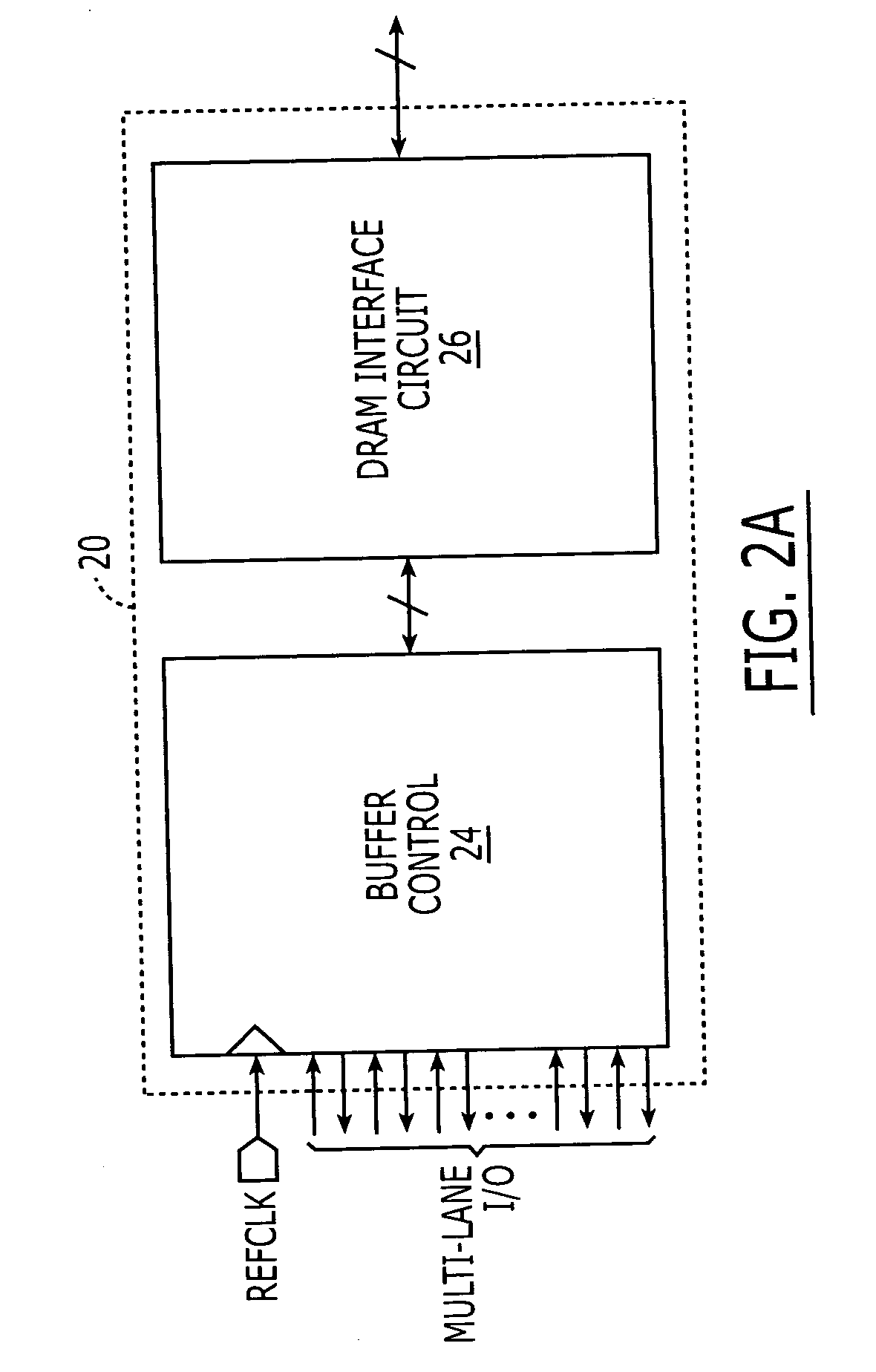
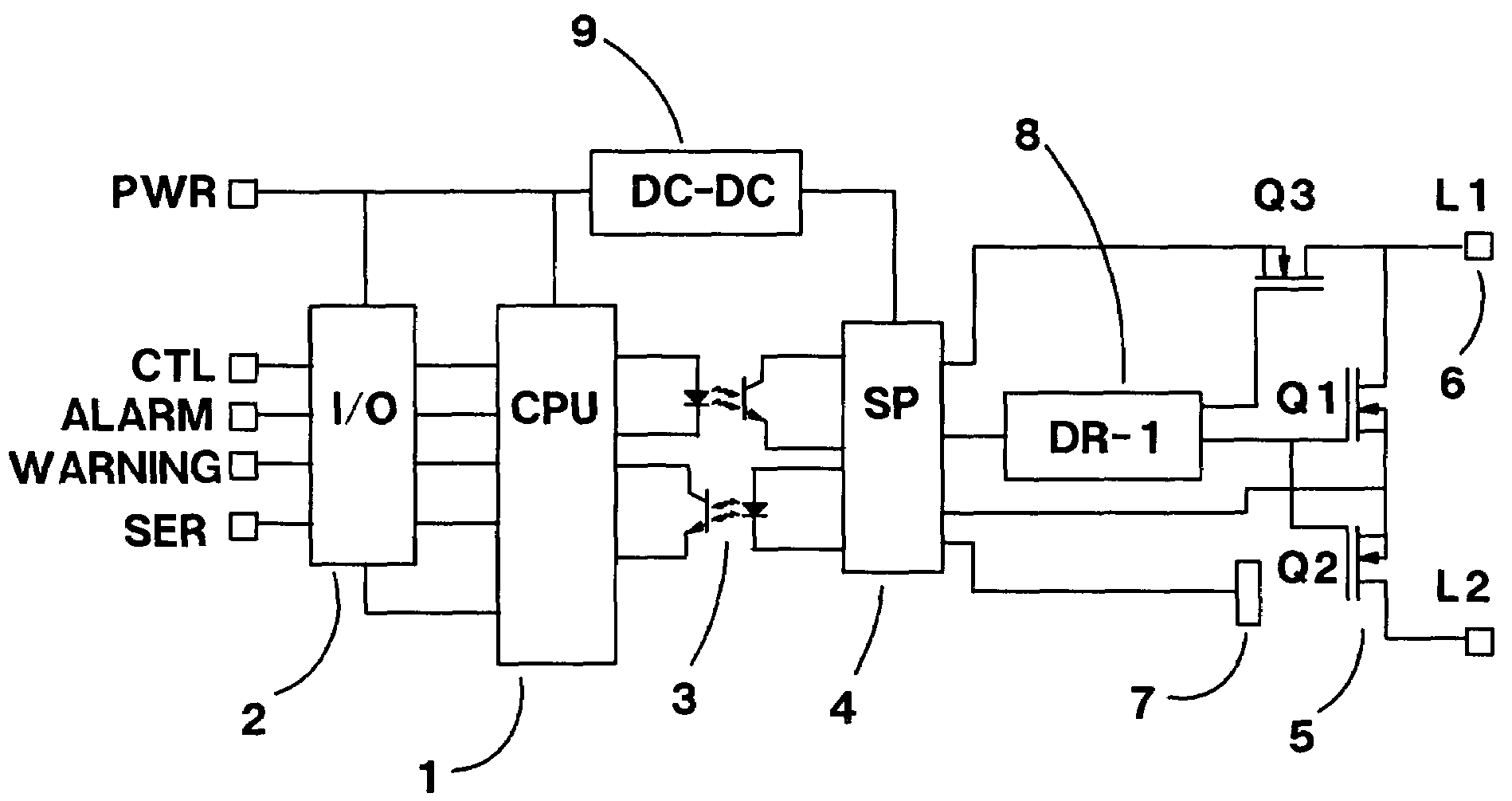
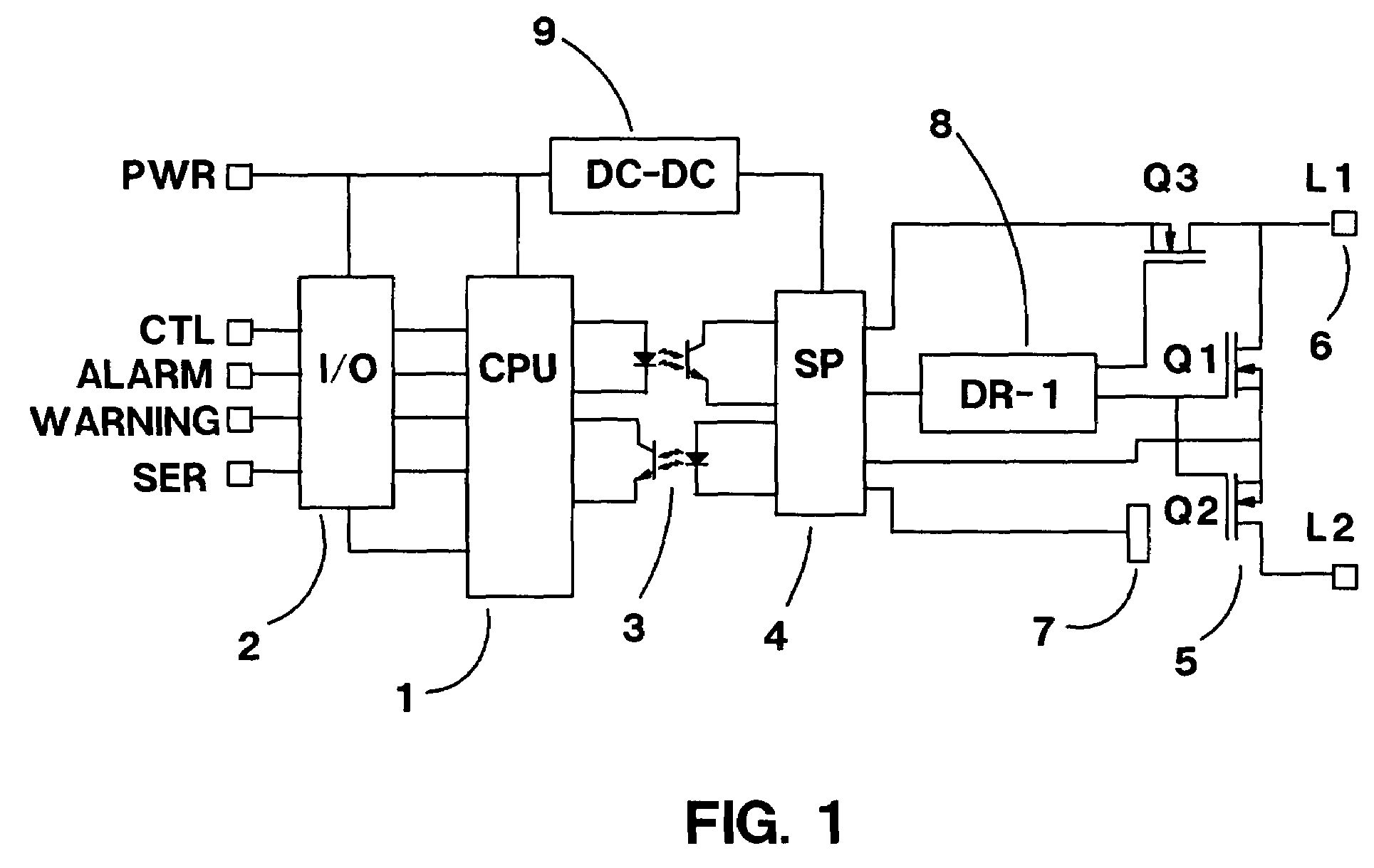
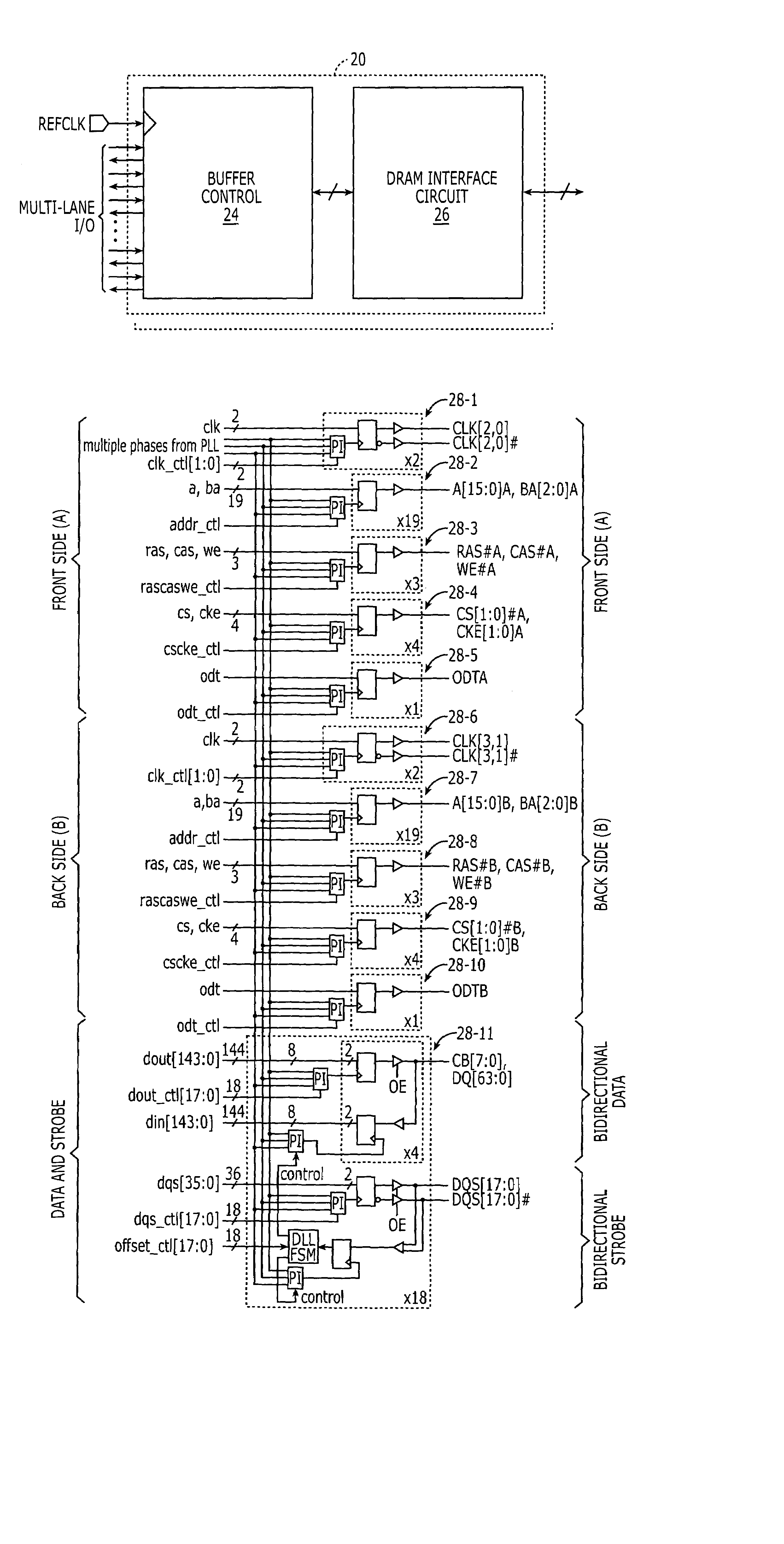
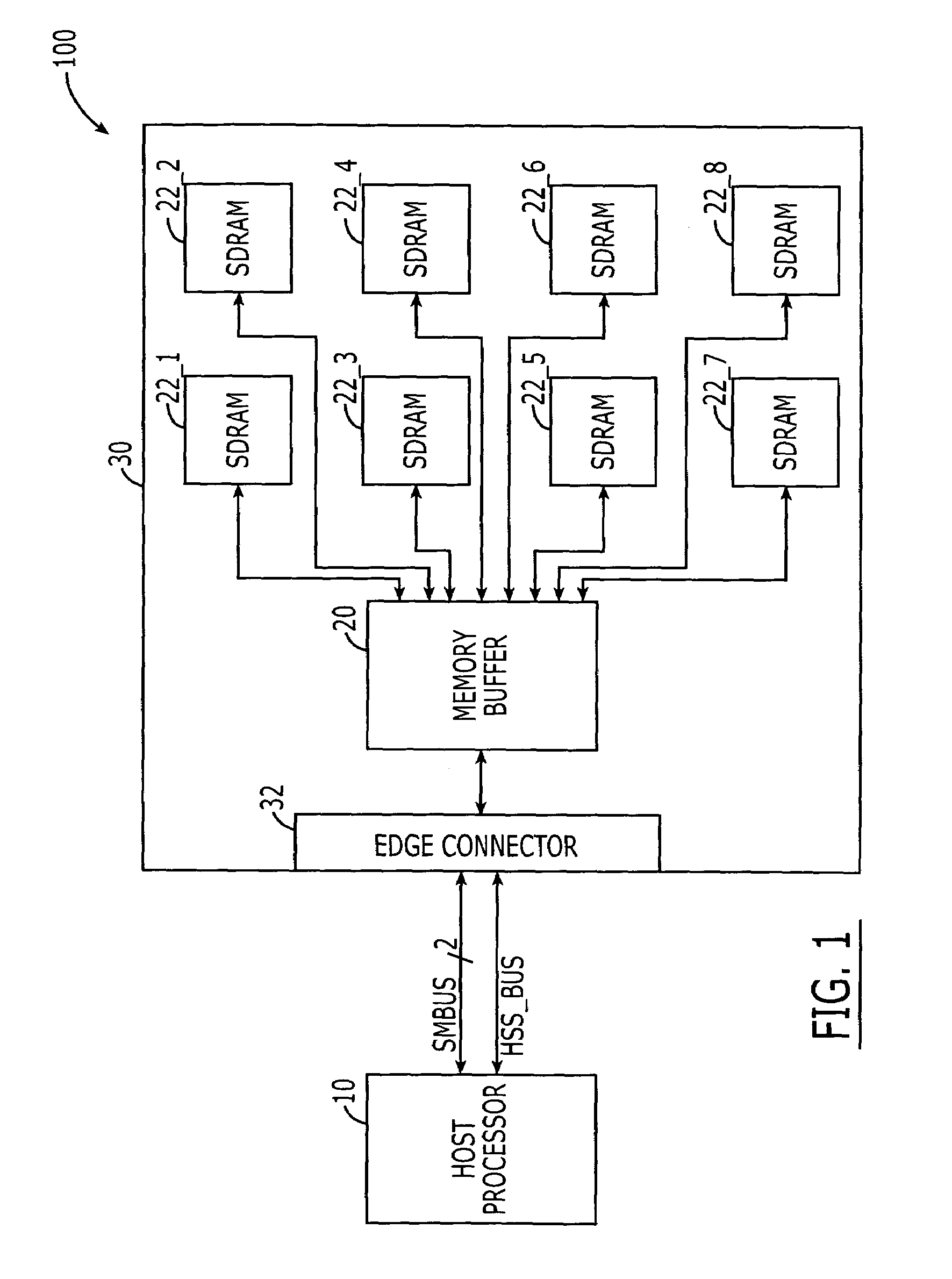
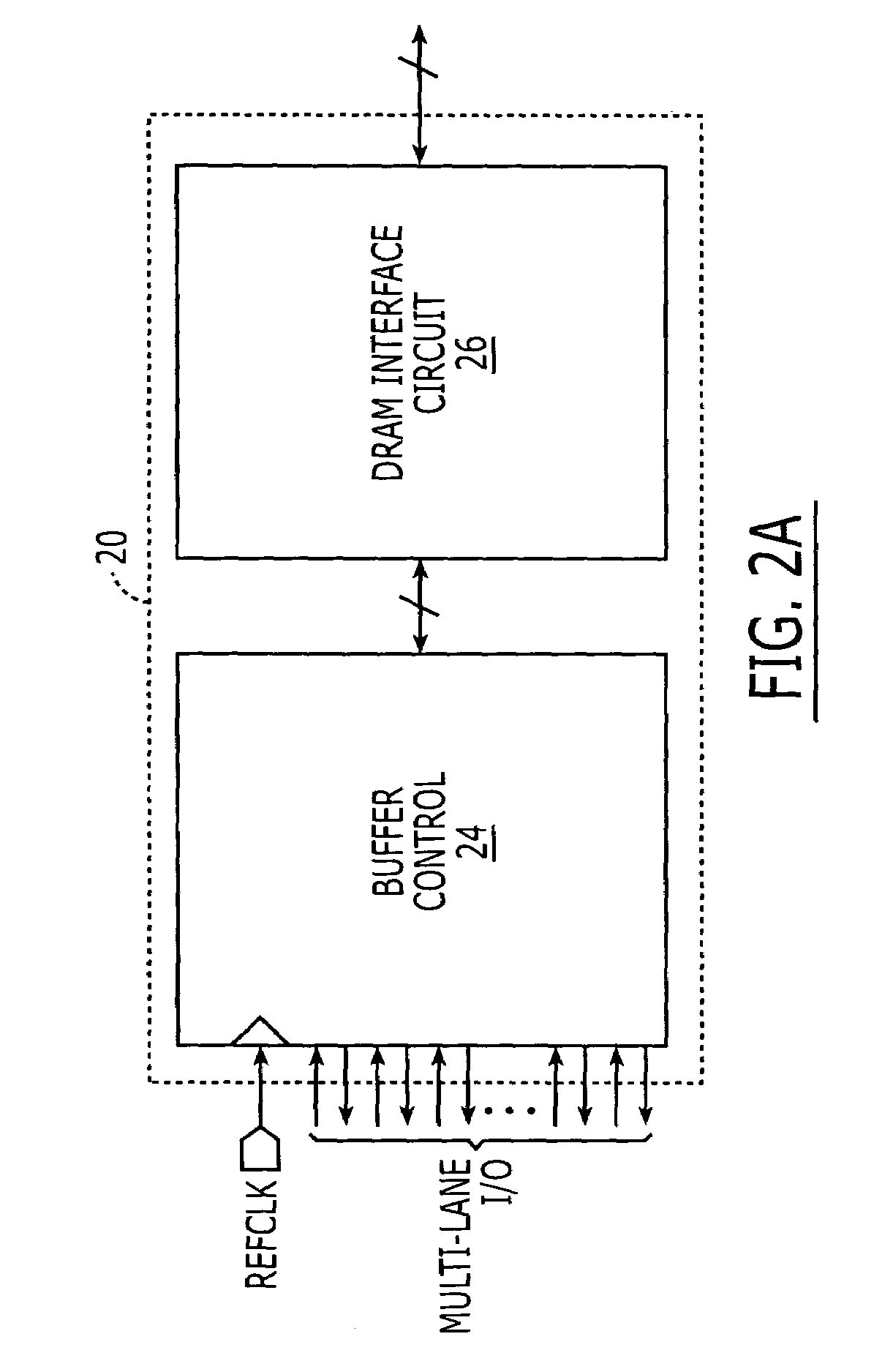
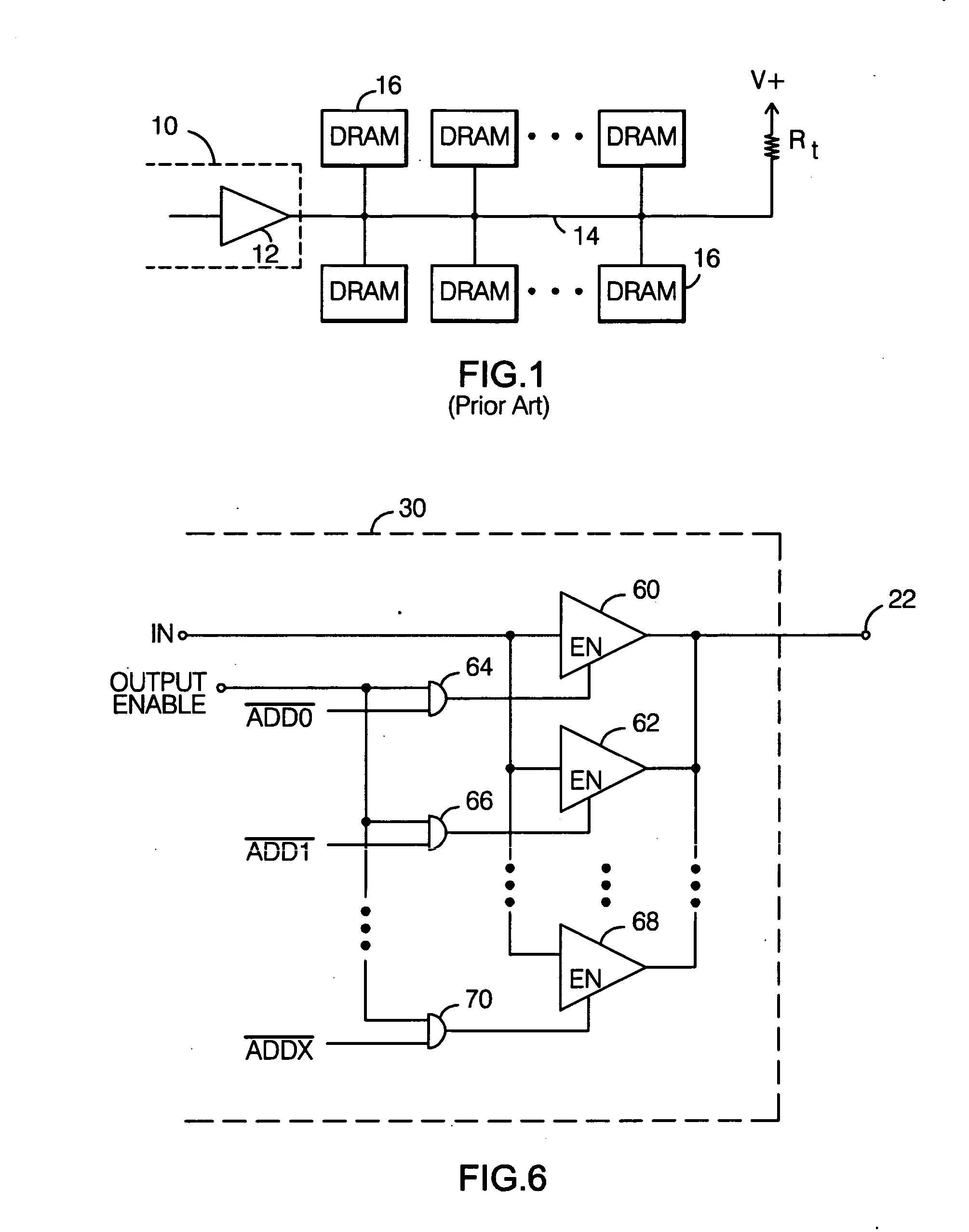
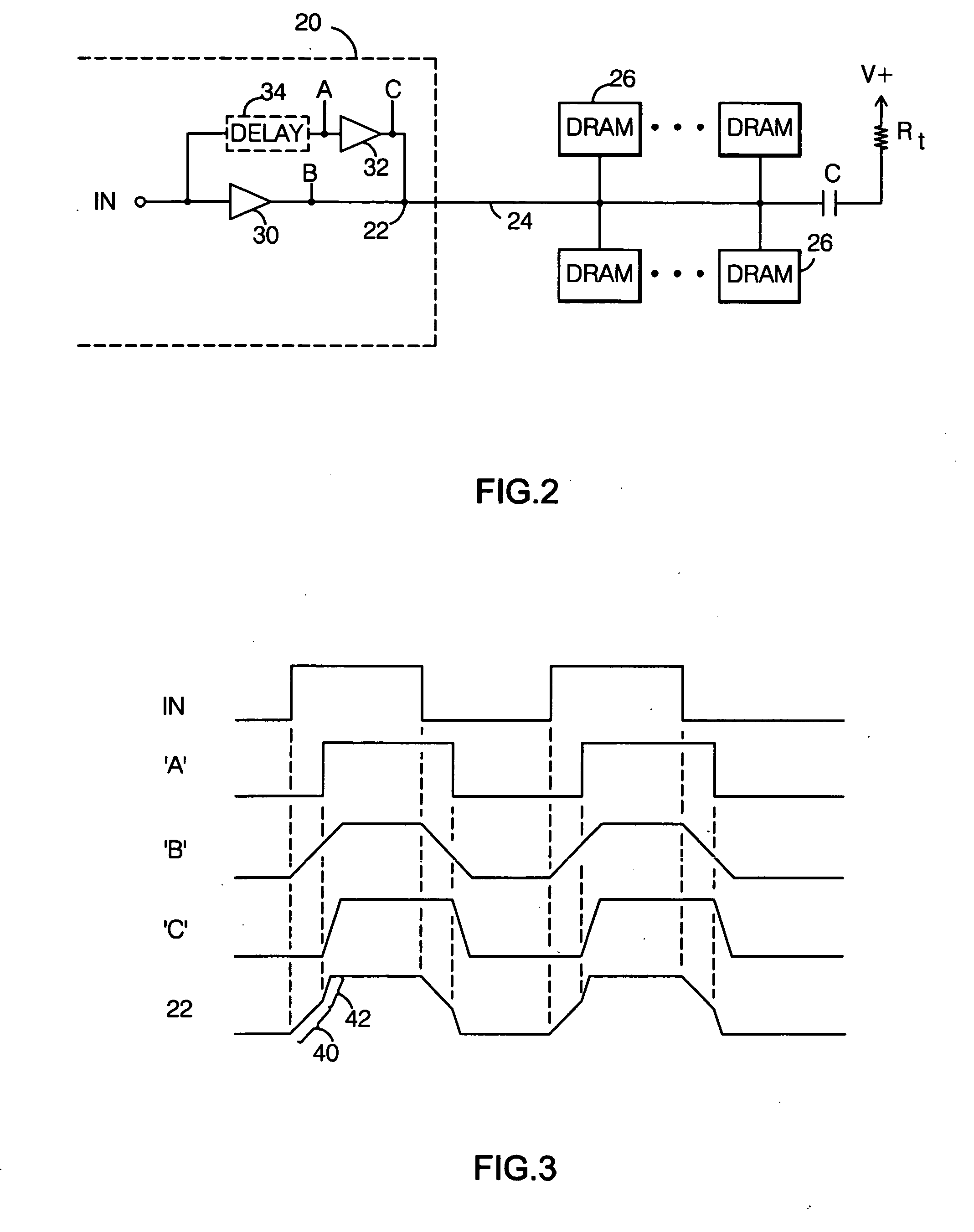
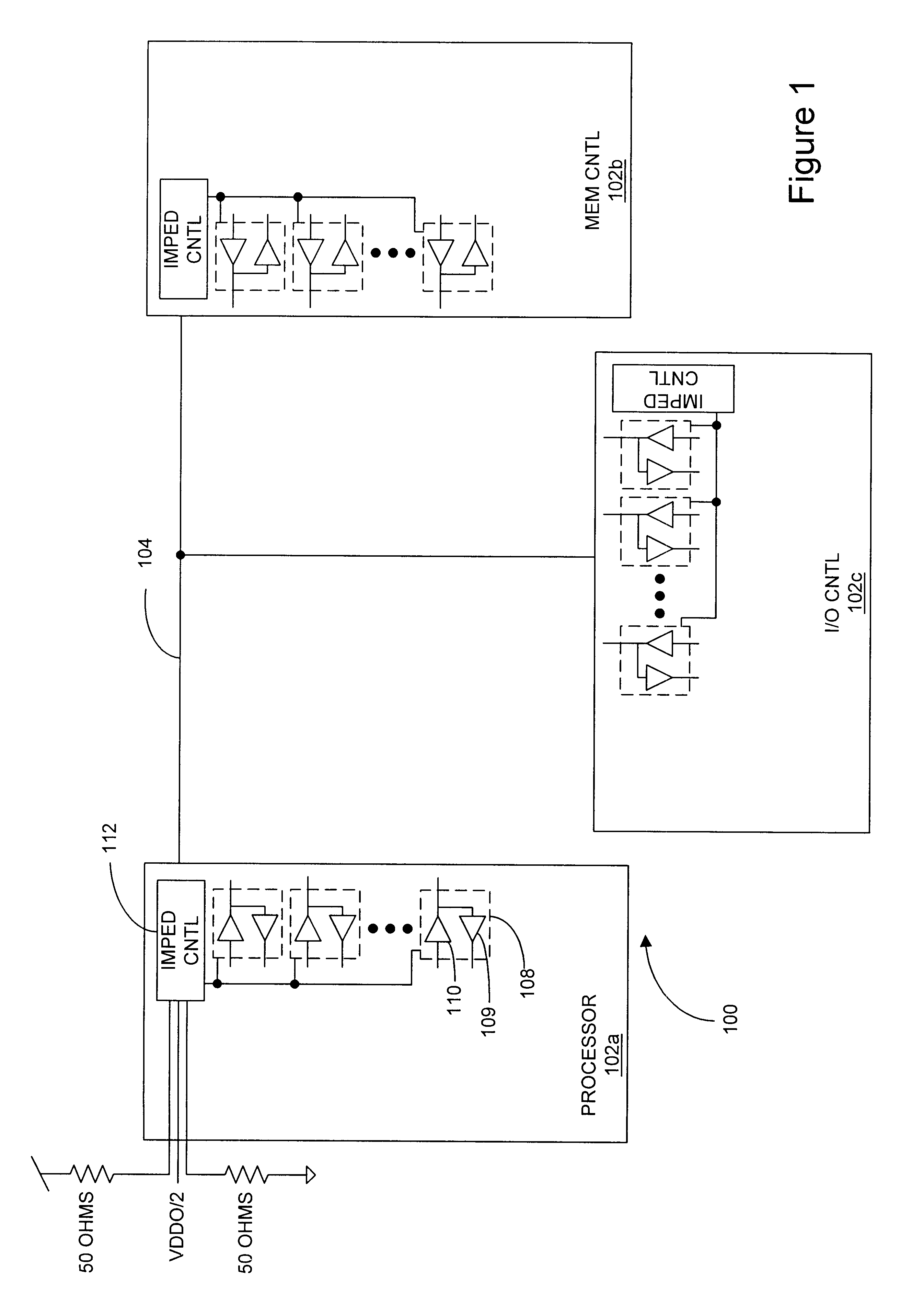
DRAM interface circuits having enhanced skew, slew rate and impedance control
Fully-buffered dual in-line memory modules (FB-DIMM) include advanced memory buffers (AMBs) having enhanced skew, slew rate and output impedance control. The AMB includes user accessible registers that can be programmed to carefully control the edge placement (or phase) of signals generated from the AMB to multiple DRAMs on the module. This control of edge placement, which may be performed independently for each group of signals: clock (CLK, CLK#), command (RAS, CAS, WE), address (including bank address), data (DQ) and data strobe (DQS), provides 360 degrees of control (or one period). This means that any group of signals can be moved independently by one complete period relatively to any other group.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Structure and method for super FET mixer having logic-gate generated FET square-wave switching signal
InactiveUS6144236AModulation transference by semiconductor devices with minimum 2 electrodesModulation transference balanced arrangementsRadio receiverTransformer
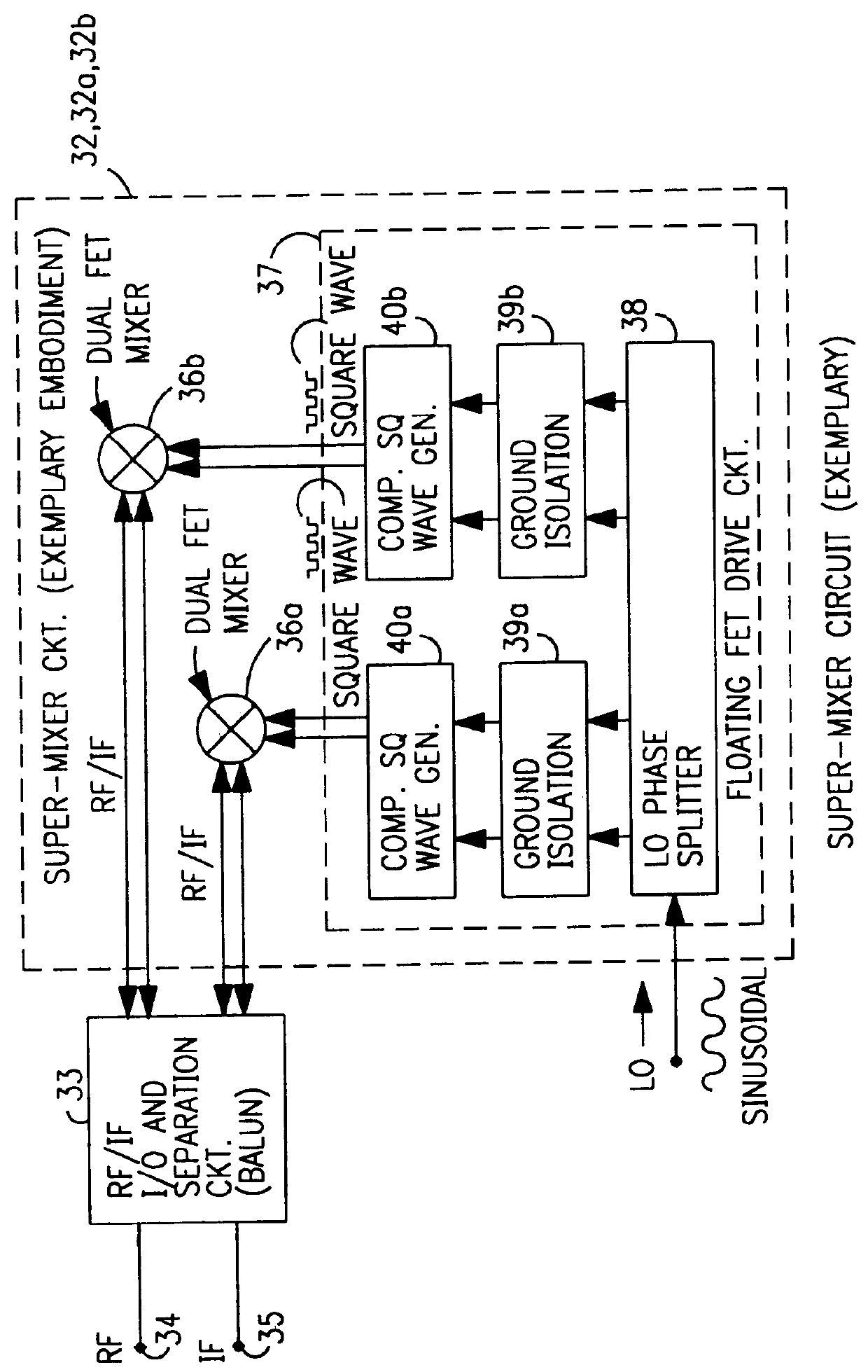
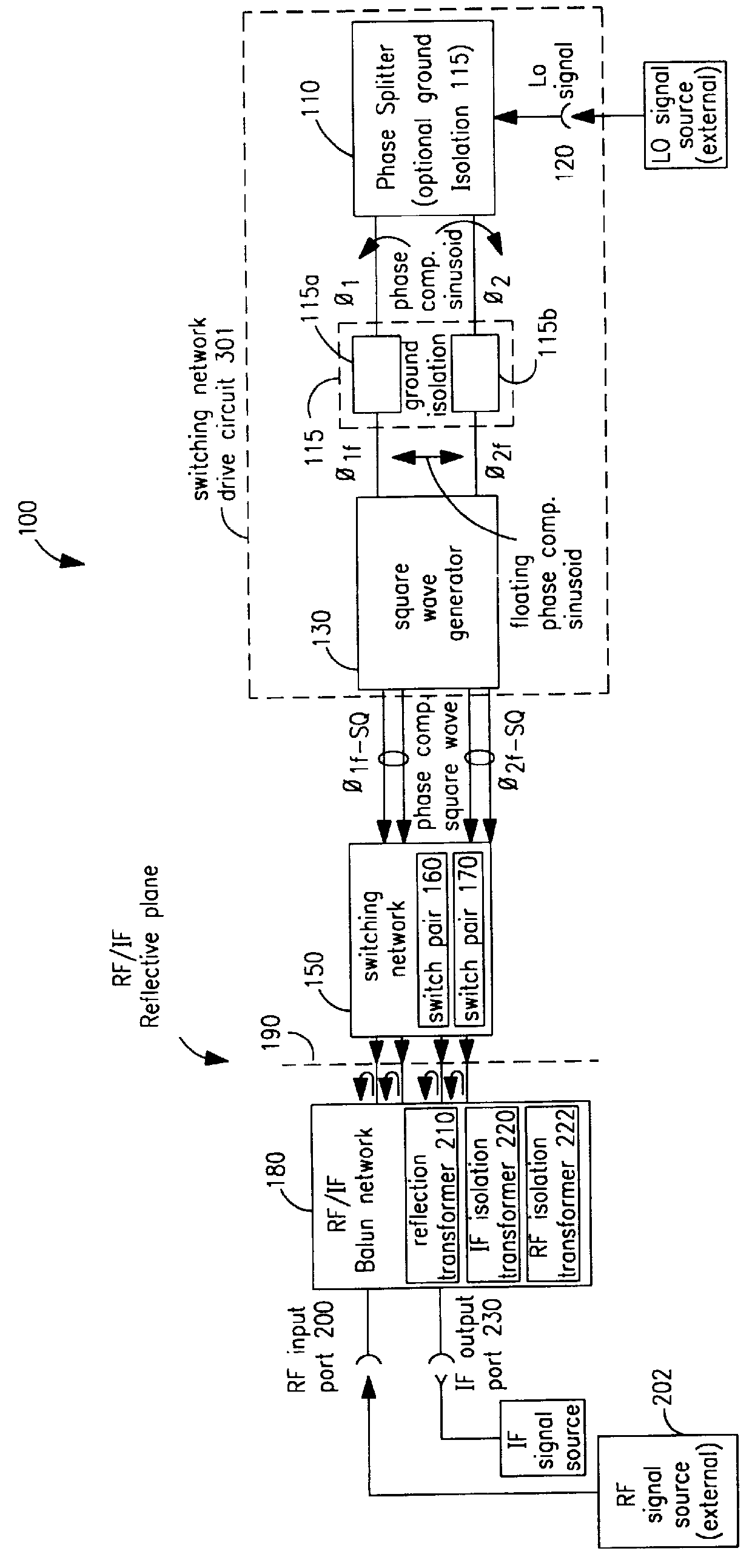
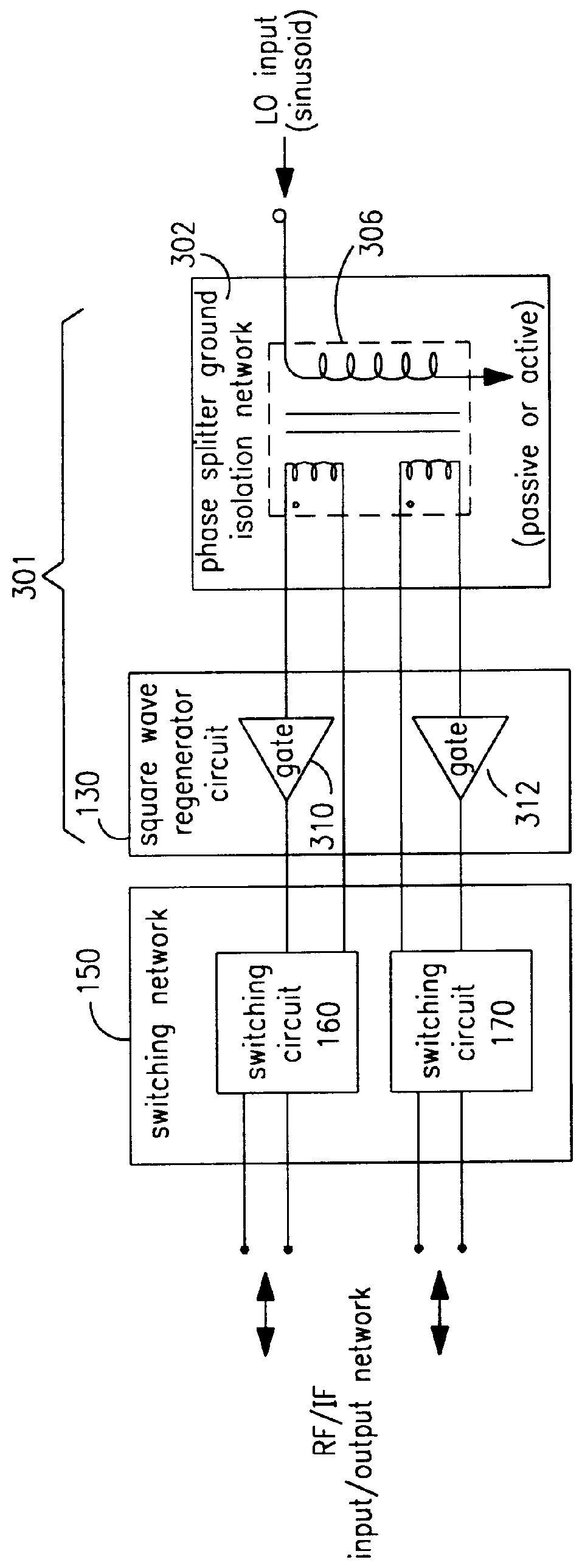
A mixing method and mixer structure provide a circuit topology suitable for use in radio receivers, transmitters, tuners, instrumentation systems, telemetry systems, and other systems and devices performing frequency conversion in either homodyne or heterodyne implementations. The inventive mixer may be used for wireless communication devices including radios, cellular telephones, and telemetry systems whether land, sea, airborne, or space based, and whether fixed or mobile. The mixer provides superior intermodulation and harmonic distortion suppression and features excellent conversion loss, noise figure, port match, and port isolation as a result of its circuit topology. The mixer device circuit combines the advantages of series mixing FETs, a triple balanced design using a balanced passive reflection transformer, a precise local oscillator phase splitter, and square wave gate drive having high slew rate signal characteristics to achieve high levels of performance. It is power conservative and offers the advantage of long battery life in portable devices such as portable radios and cellular telephones as it requires only a modest amount of DC and local oscillator drive power, and is useful for operation over at least a multi-decade bandwidth.
Owner:DRS SIGNAL SOLUTIONS
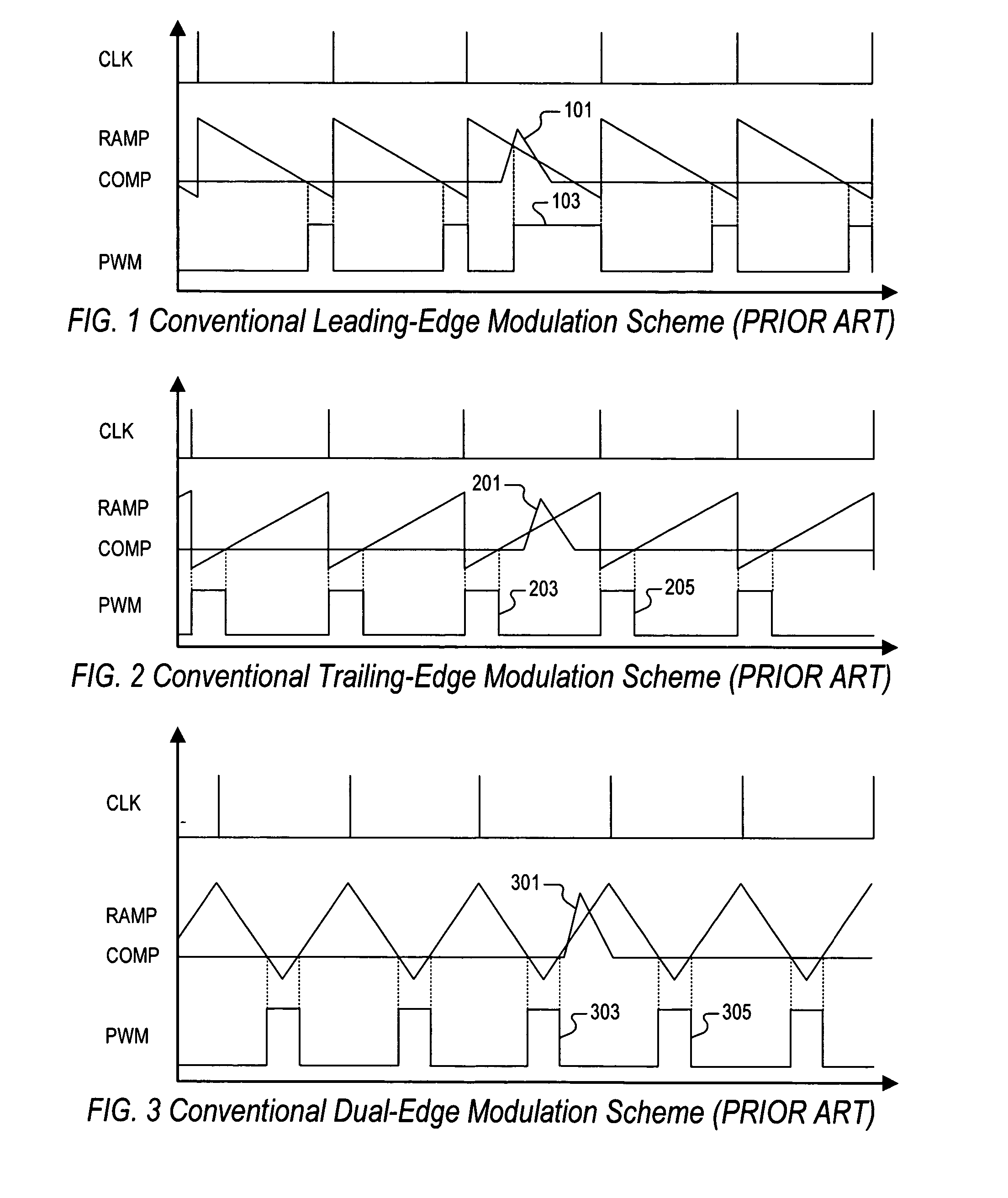
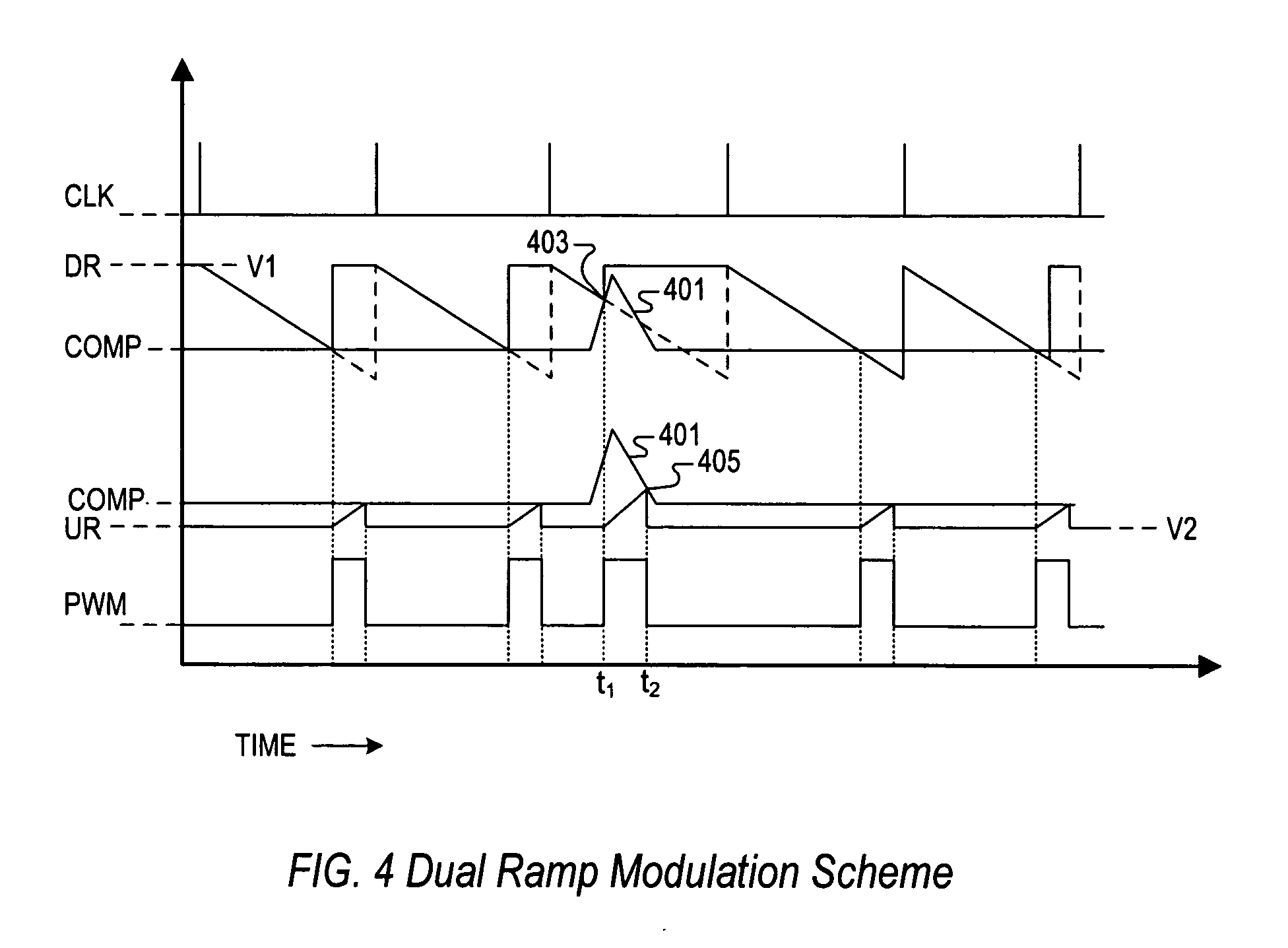
PWM controller with dual-edge modulation using dual ramps
ActiveUS20070013356A1Efficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionLeading edgePulse control
A dual-edge modulation controller including first and second ramp circuits, first and second comparators, an error amplifier and pulse control logic. The first ramp circuit provides a leading-edge ramp synchronous with a clock. The error amplifier compares a feedback signal with a reference and provides a compensation signal. The first comparator compares the leading-edge ramp with the compensation signal and asserts a set signal. The second ramp circuit provides a trailing-edge ramp that begins ramping when the set signal is asserted. The second comparator compares the trailing-edge ramp with the compensation signal and asserts a reset signal. The pulse control logic asserts a PWM signal when the set signal is asserted and de-asserts the PWM signal when the reset signal is asserted. The controller may control multiple phases with current balancing. The slew rate of the ramps may be adjusted based on the number of PWM signal asserted.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Power level transitioning in a surgical instrument
An electrosurgical system and method are disclosed. The system includes an electrosurgical generator adapted to supply electrosurgical energy to tissue. The generator is further adapted to supply an electrosurgical signal at a variable power level. The generator includes sensor circuitry adapted to sense tissue impedance and / or an electrosurgical signal zero crossing. The generator also includes a controller, which may include a microprocessor, that is adapted to receive a tissue impedance signal and / or a waveform zero crossing signal. The controller is configured to monitor tissue impedance, and in response to a threshold value of impedance being reached, to cause a power level of the electrosurgical energy to transition from a first power level to a second power level. The slew rate of the power transition may be in accordance with a transition function, such as a cosine function. The power transition may additionally or alternatively be performed during, or correlated with, an electrosurgical signal zero crossing. The system also includes an electrosurgical instrument including at least one active electrode adapted to apply electrosurgical energy to tissue for treatment.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
Output voltage amplifier and driving device of liquid crystal display using the same
InactiveUS20100231577A1Accurate feedback voltageAvoid heatGated amplifiersCathode-ray tube indicatorsAudio power amplifierLiquid-crystal display
An output voltage amplifier, and a driving device of a liquid crystal display using the same are disclosed. The output voltage amplifier includes: an amplifying unit to generate first and second signals corresponding to a gray voltage input to a first input terminal and a feedback signal input to a second input terminal, and to output a first voltage by using first and second switches driven to be on or off according to the first and second signals; an output unit to apply the first and second data signals to the first and second pixels by using third and fourth switches turned on or off according to the first and second signals; and a feedback circuit unit to selectively supply one of the first voltage and the first and second data signals to the second input terminal. Heating characteristics and a slew rate can be improved.
Owner:MC TECH CO LTD
Intelligent solid state relay/breaker
InactiveUS7304828B1High currentImprove survivabilityArrangements responsive to excess currentEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentHysteresisSlew rate
A solid-state relay / breaker that can replace mechanical units to control any type of AC or DC load. Power MOSFETs or other transistors control a load current. A bypass current sensing path monitors MOSFET current and causes a shutdown through signal processing in the event of an over-current condition. This shutdown resembles that of a slow-blow fuse where the rate of shutdown is proportional to the value of the current. This prevents shutdown on momentary spikes or in-rush. In addition, temperature and internal power supply voltages are monitored to determine additional operational conditions where over-temperature or voltages out of range can also cause shutdown. The MOSFET and current sensing path are turned on and off in staggered timing with different slew rates to provide built-in hysteresis. The device can be manufactured in any type of package to match any type of environment or existing replacement requirement.
Owner:SHVARTSMAN VLADIMIR A
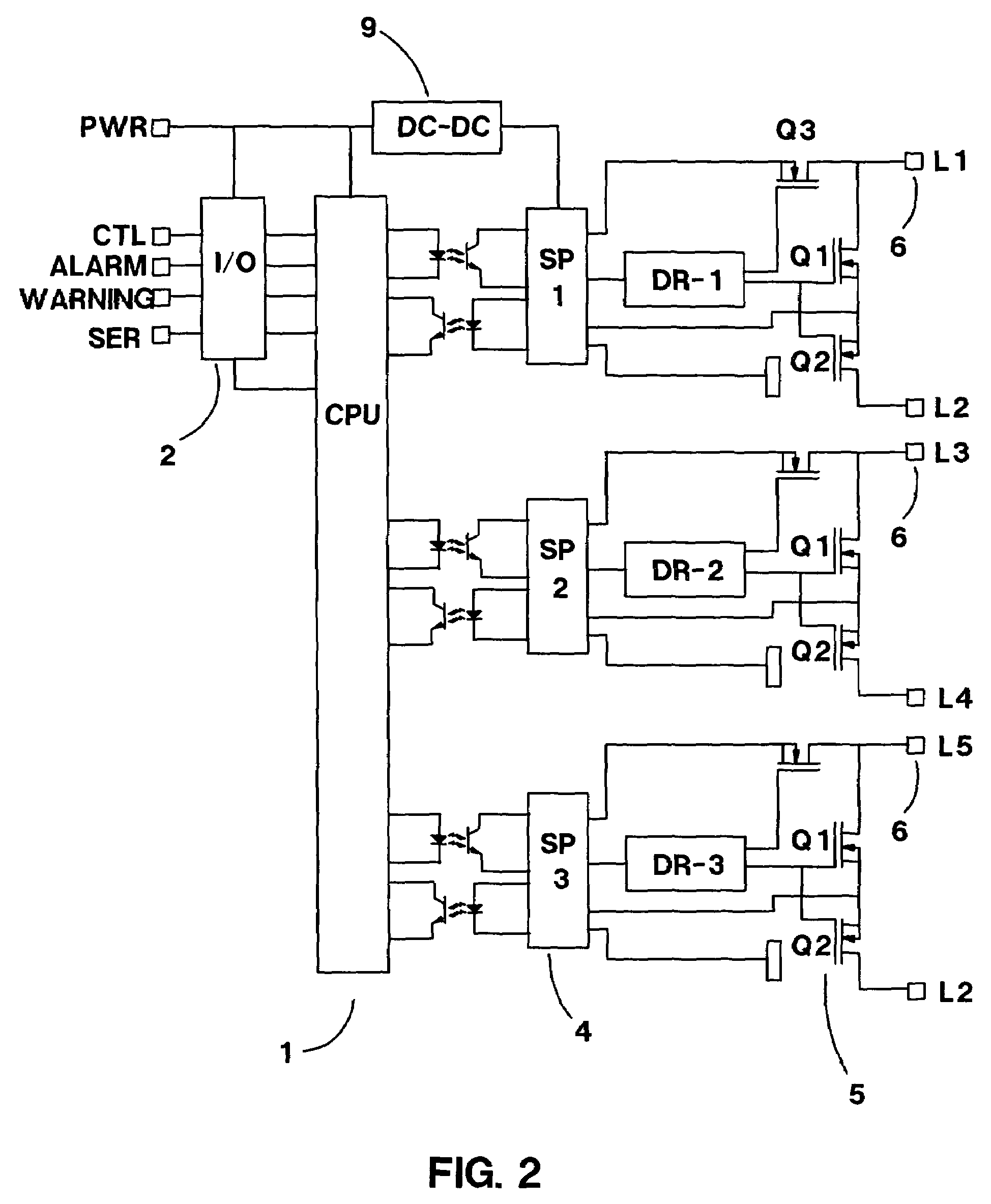
DRAM interface circuits having enhanced skew, slew rate and impedance control
Fully-buffered dual in-line memory modules (FB-DIMM) include advanced memory buffers (AMBs) having enhanced skew, slew rate and output impedance control. The AMB includes user accessible registers that can be programmed to carefully control the edge placement (or phase) of signals generated from the AMB to multiple DRAMs on the module. This control of edge placement, which may be performed independently for each group of signals: clock (CLK, CLK#), command (RAS, CAS, WE), address (including bank address), data (DQ) and data strobe (DQS), provides 360 degrees of control (or one period). This means that any group of signals can be moved independently by one complete period relatively to any other group.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
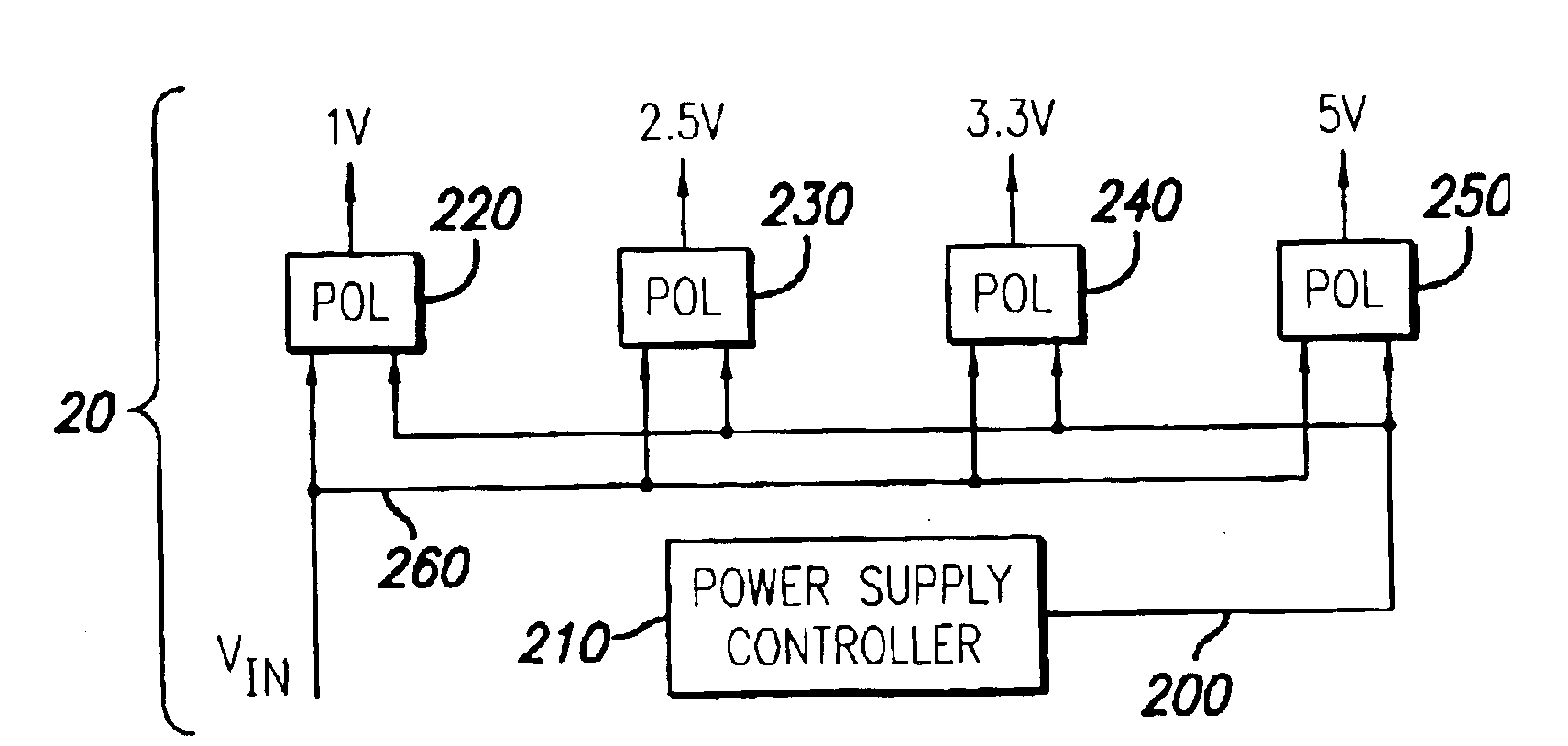
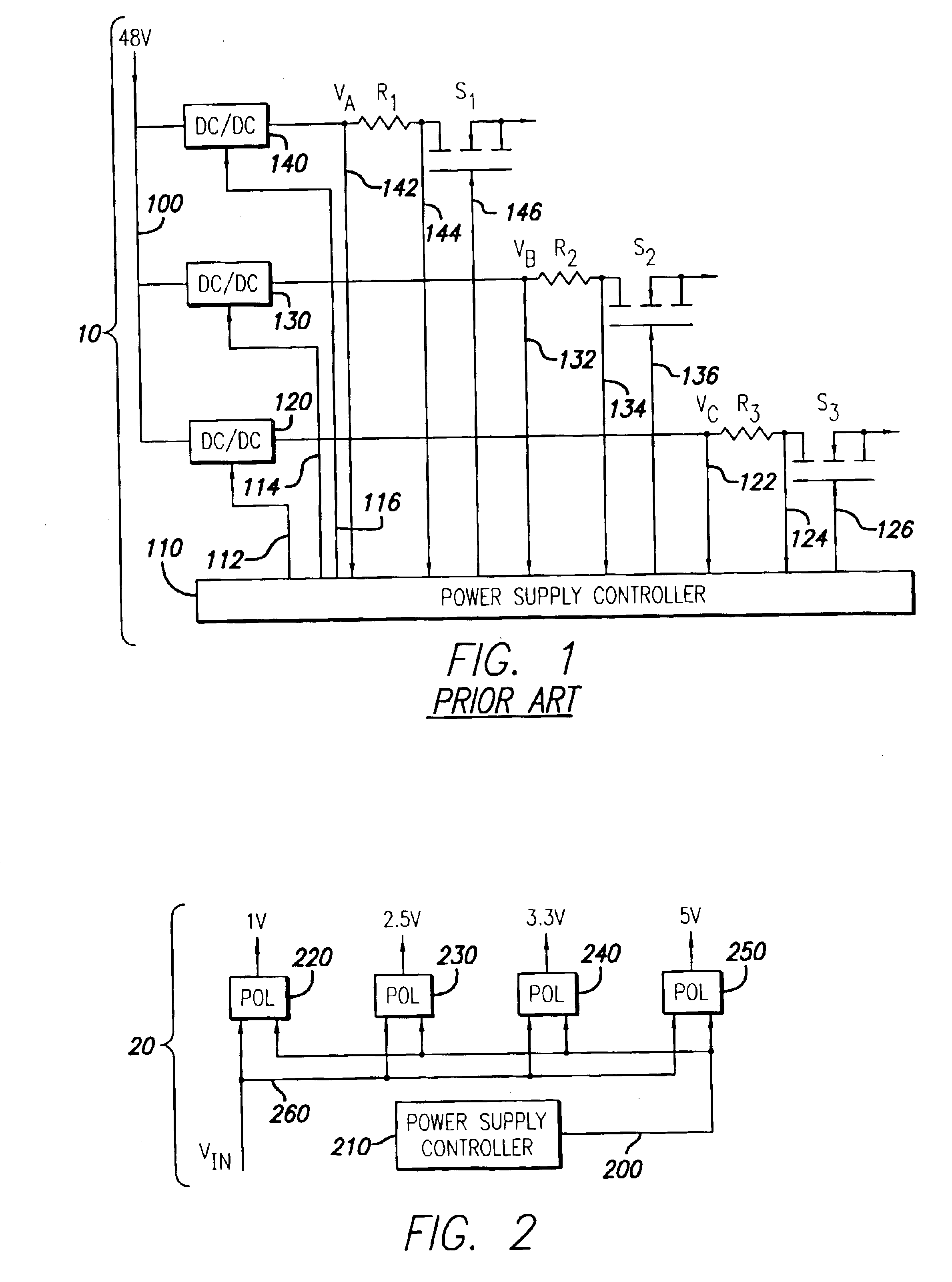
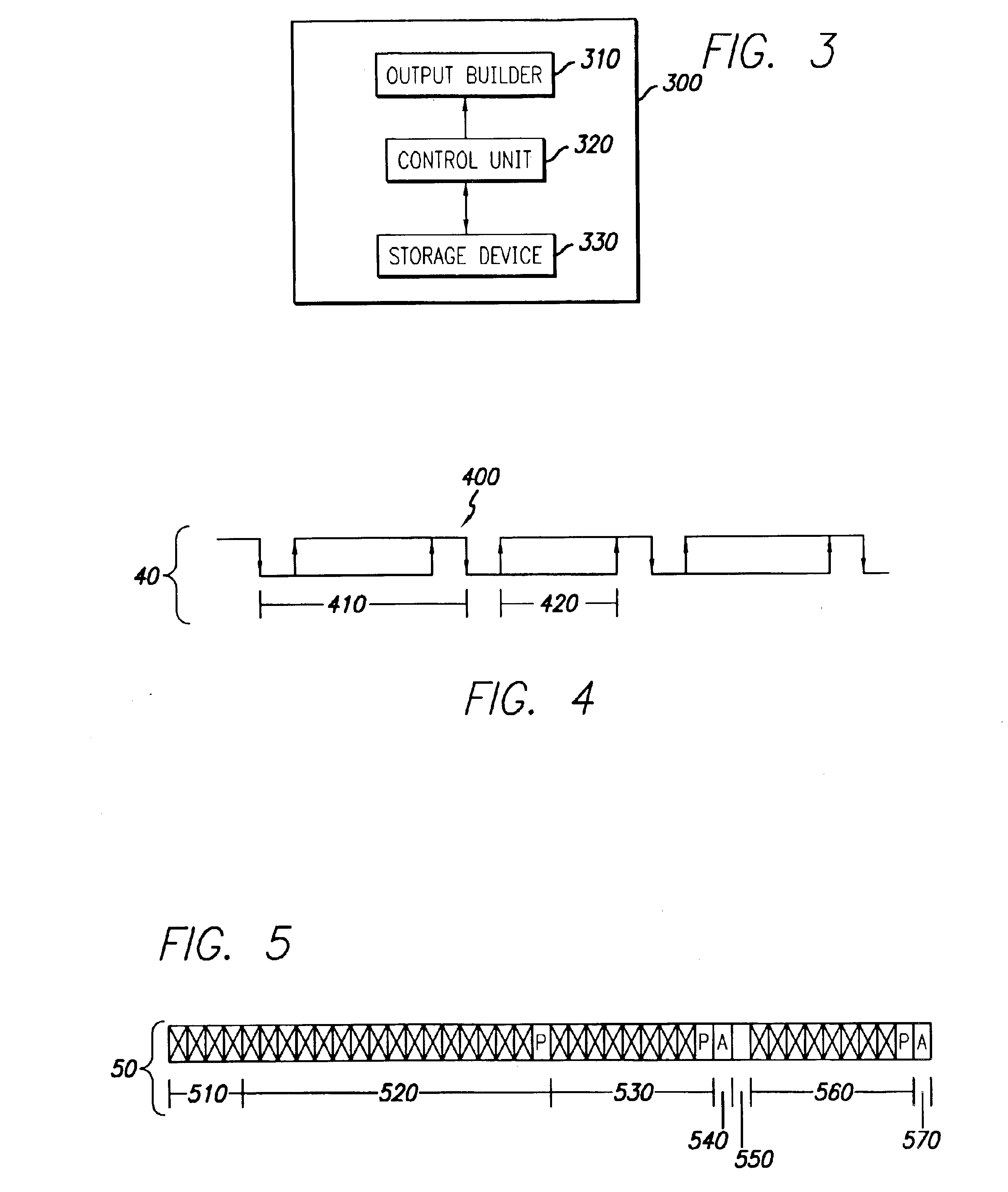
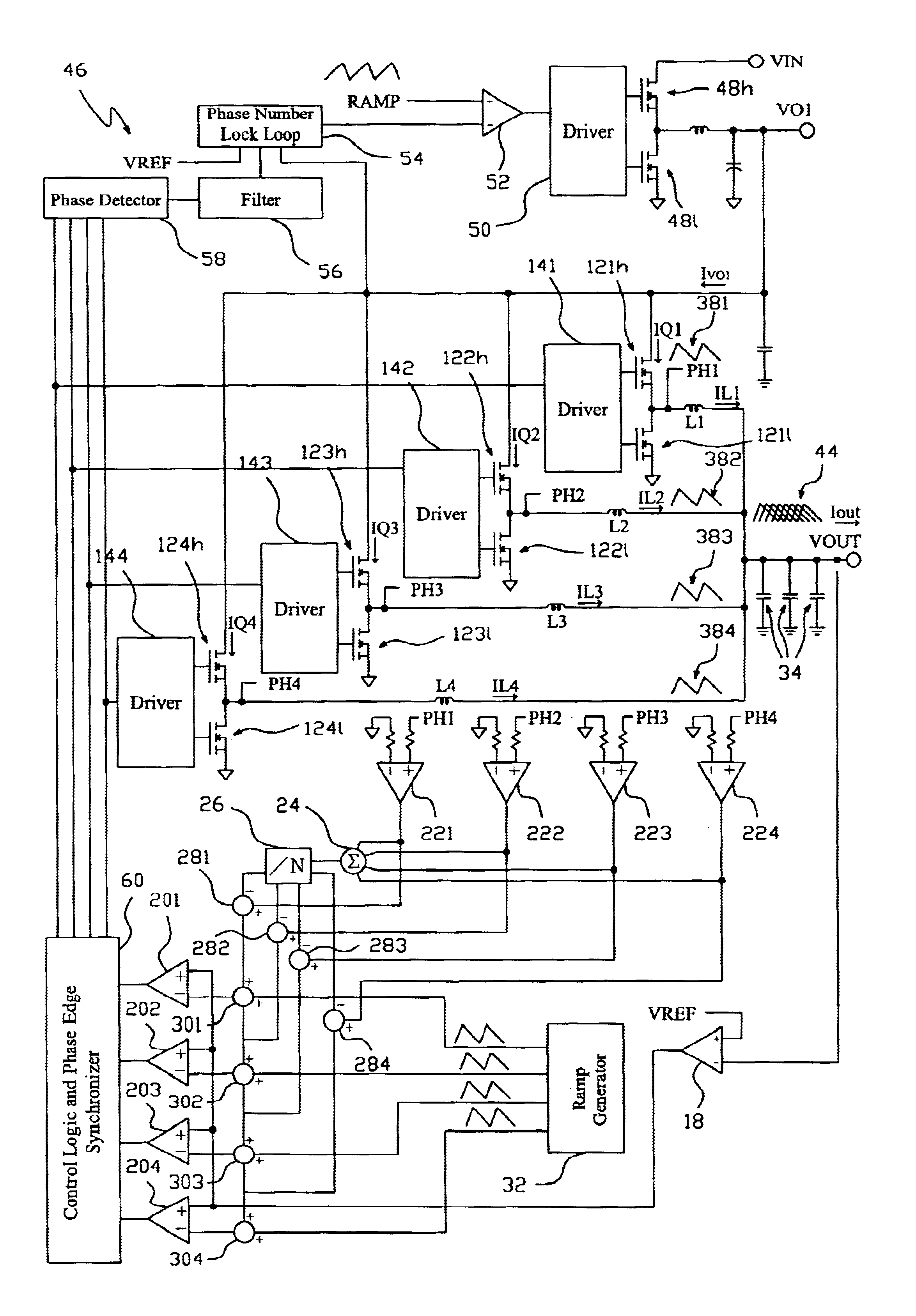
System and method for controlling output-timing parameters of power converters
A system and method is provided for utilizing output-timing data to control at least one output timing parameter of a point-of-load (“POL”) regulator. Specifically, a power supply controller (“controller”) is adapted to transmit output-timing data to at least one POL regulator. In one embodiment of the present invention, each POL regulator includes an output builder, a control unit and a storage device. The control unit is adapted to store the output-timing data in the storage device. The control unit and the output builder are then adapted to produce an output having at least one output timing parameter in accordance with the output-timing data. Examples of output-timing data include sequencing data, turn-on data, turn-off data, termination data, slew-rate data, etc. For example, a POL regulator may be adapted to utilize output-timing data, or a portion thereof (e.g., slew-rate data), to generate an output having a particular slew rate. Similarly, a POL regulator may be adapted to utilize output-timing data, or a portion thereof (e.g., sequencing data, turn-on data, etc.), to determine (or calculate) a period of time to wait (e.g., delay period) before the output is generated. In other words, output-timing data can be used to produce a series of outputs in a particular order, or sequence.
Owner:BEL POWER SOLUTIONS INC
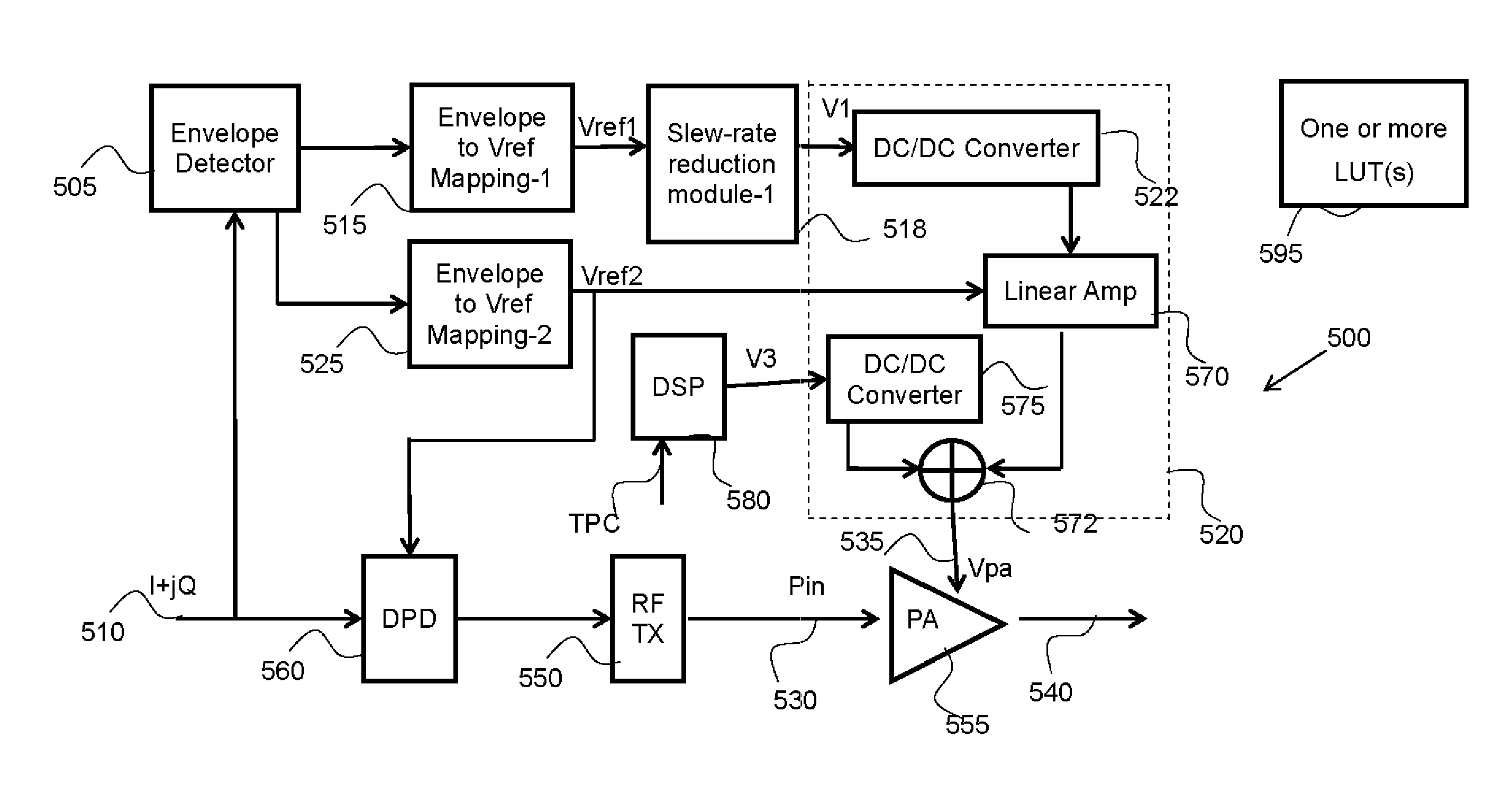
Methods and apparatus for envelope tracking system
ActiveUS9065509B1Mitigate, alleviate or eliminate one orCost effectiveAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionModulated-carrier systemsCommunication unitEnvelope Tracking
A communication unit includes a radio frequency, RF, transmitter having: a power amplifier, PA, module; and an envelope tracking system operably coupled to the PA module and having a supply modulator arranged to variably control a supply voltage for the PA module in response to a number of input samples of an envelope signal; wherein the envelope tracking system further includes at least one slew rate module arranged to re-distribute a maximum slew rate across the number of input samples in a provision of a variable power supply to the PA module.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
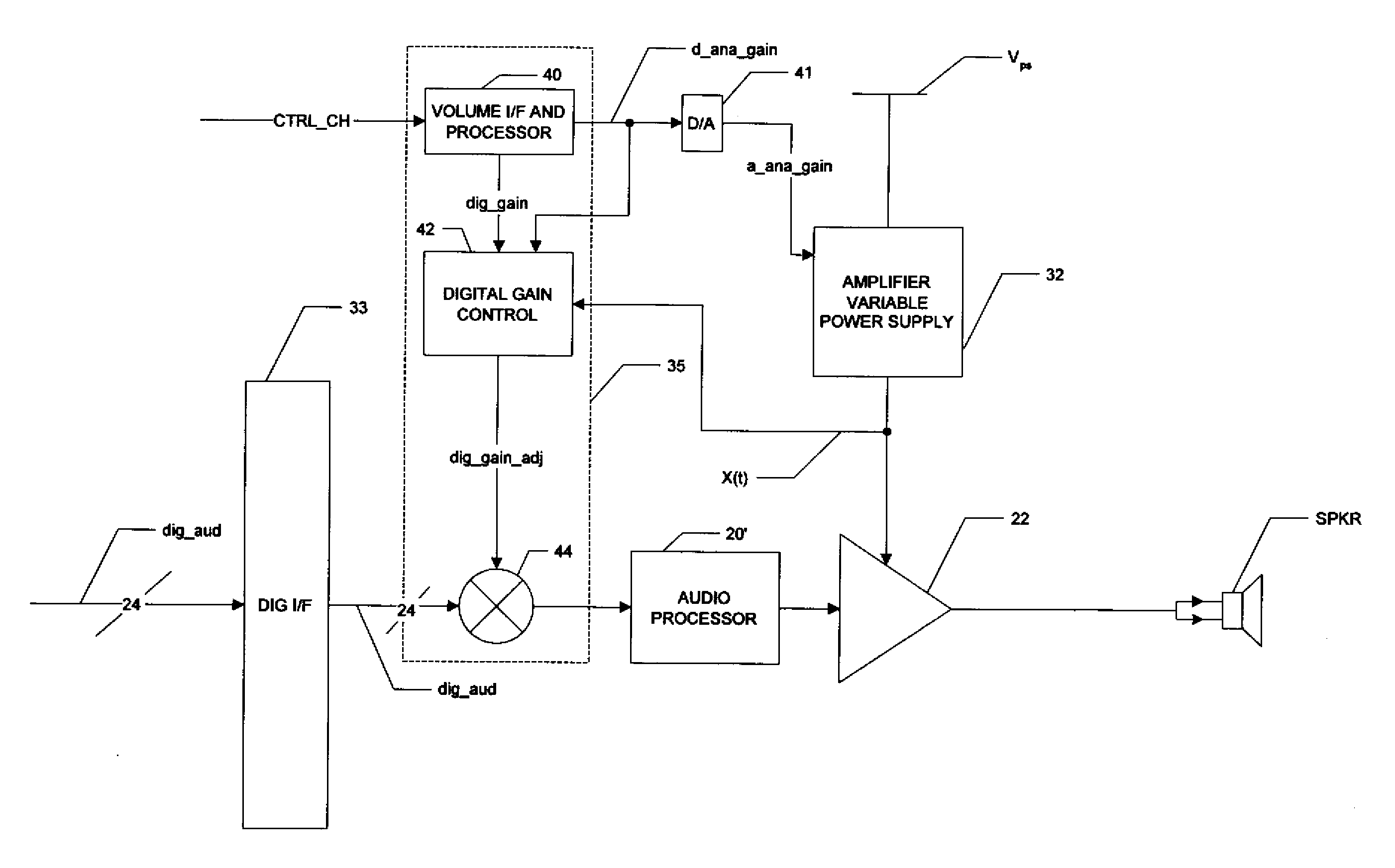
Digital Compensation of Analog Volume Control Gain in a Digital Audio Amplifier
ActiveUS20080123873A1Maintain fidelityEasy to implementSupply voltage varying controlAnalog signal digital controlAudio power amplifierControl signal
A digital audio system including a combination of analog and digital volume control is disclosed. A variable power supply voltage biases a power amplifier for each channel, and applies a bias voltage corresponding to an analog volume control signal. In one disclosed embodiment, digital gain control circuitry compares the bias voltage with the level expected for the analog volume control signal; if the bias voltage has not dropped in response to a reduction in the analog volume control signal, the digital gain control circuitry reduces the digital gain of the input digital audio signal, until the bias voltage responds to the reduced volume. In another disclosed embodiment, modeling or characterization of the audio system is used to derive a digital gain control signal based on the desired volume signal and the amplitude of the digital audio signal itself. In another disclosed embodiment, a slew rate limiter slows the rate of change of the control signal applied to the variable power supply, in which case the slowed control signal is used in the comparison or calculations of the reduced digital gain.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
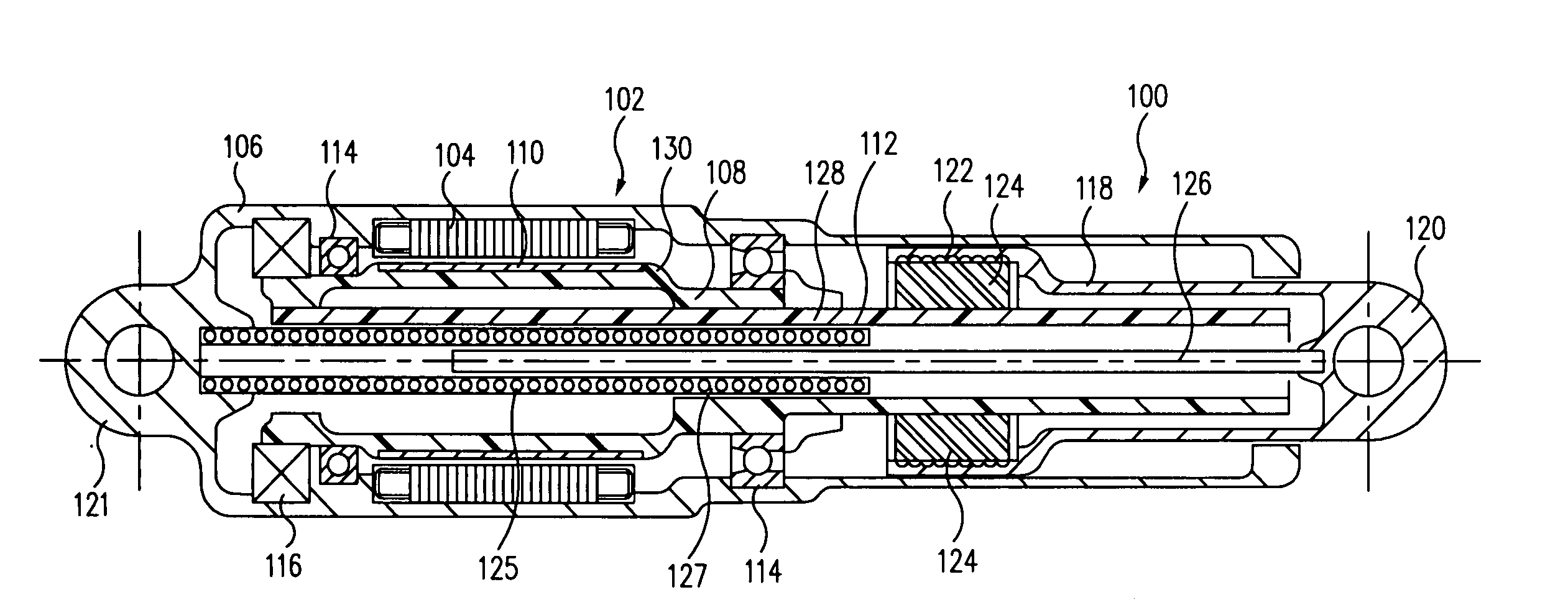
Direct drive electromechanical linear actuators
Direct drive electromechanical rotary-to-linear actuators include one or more electric motors mounted in a housing. Each motor includes a stator and a rotor. The motor drives a planetary drive mechanism that includes an elongated central shaft having one or more helical threads on an external surface coupled to the rotor for conjoint rotation. A planetary nut having helical threads on an internal surface is disposed concentric to the shaft, and a plurality of planetary rollers are disposed concentrically between the shaft and the planetary nut. Each of the rollers has a helical thread on an external surface that is complementary to and in engagement with a thread of the shaft and a thread of the nut. Rotation of the rotor is converted with mechanical advantage into linear movement of the planetary nut. The actuators provide backlash-free operation, higher stiffnesses, slew rates and frequency responses, and better overall efficiency.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Output buffer to drive AC-coupled terminated transmission lines
InactiveUS20070247194A1Reduce power consumptionMaintain integrityLogic circuit coupling/interface arrangementsSnubberSlew rate
An output buffer for driving an AC-coupled resistively terminated transmission line comprises at least first and second drive circuits coupled to an input signal and providing respective drive signals that transition in response to respective transitions of the input signal. The buffer is arranged such that, in response to a given input signal transition, the second drive signal transitions a predetermined amount of time after the first drive signal. The first and second drive signals are summed together to provide the buffer's output signal. The drive circuits are arranged such that the output signal has a first slew rate prior to the transition of the second drive signal, and a second, faster slew rate during the transition of the second drive signal, such that the slew rates reduce ringing that might otherwise occur on the transmission line.
Owner:INPHI
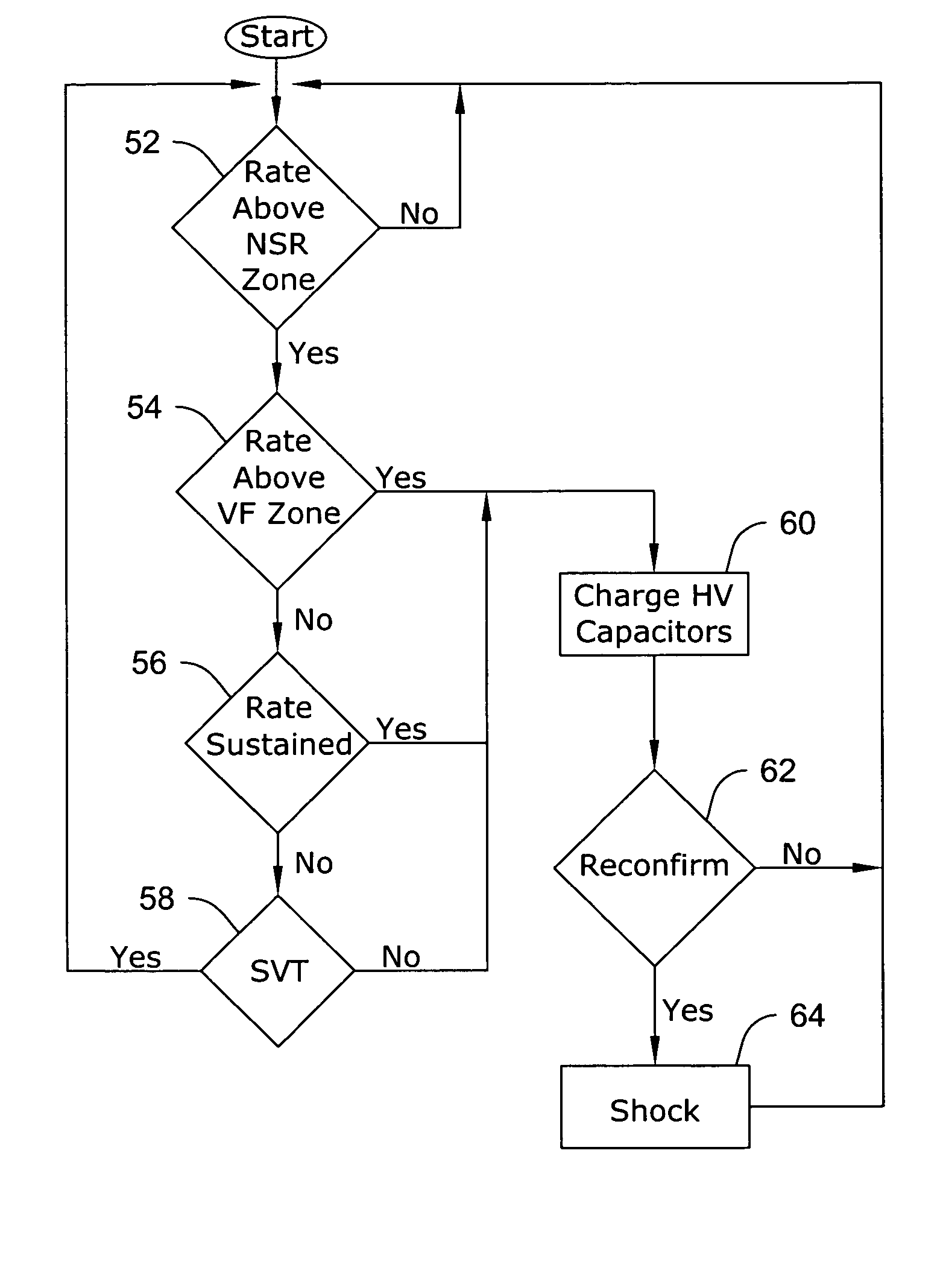
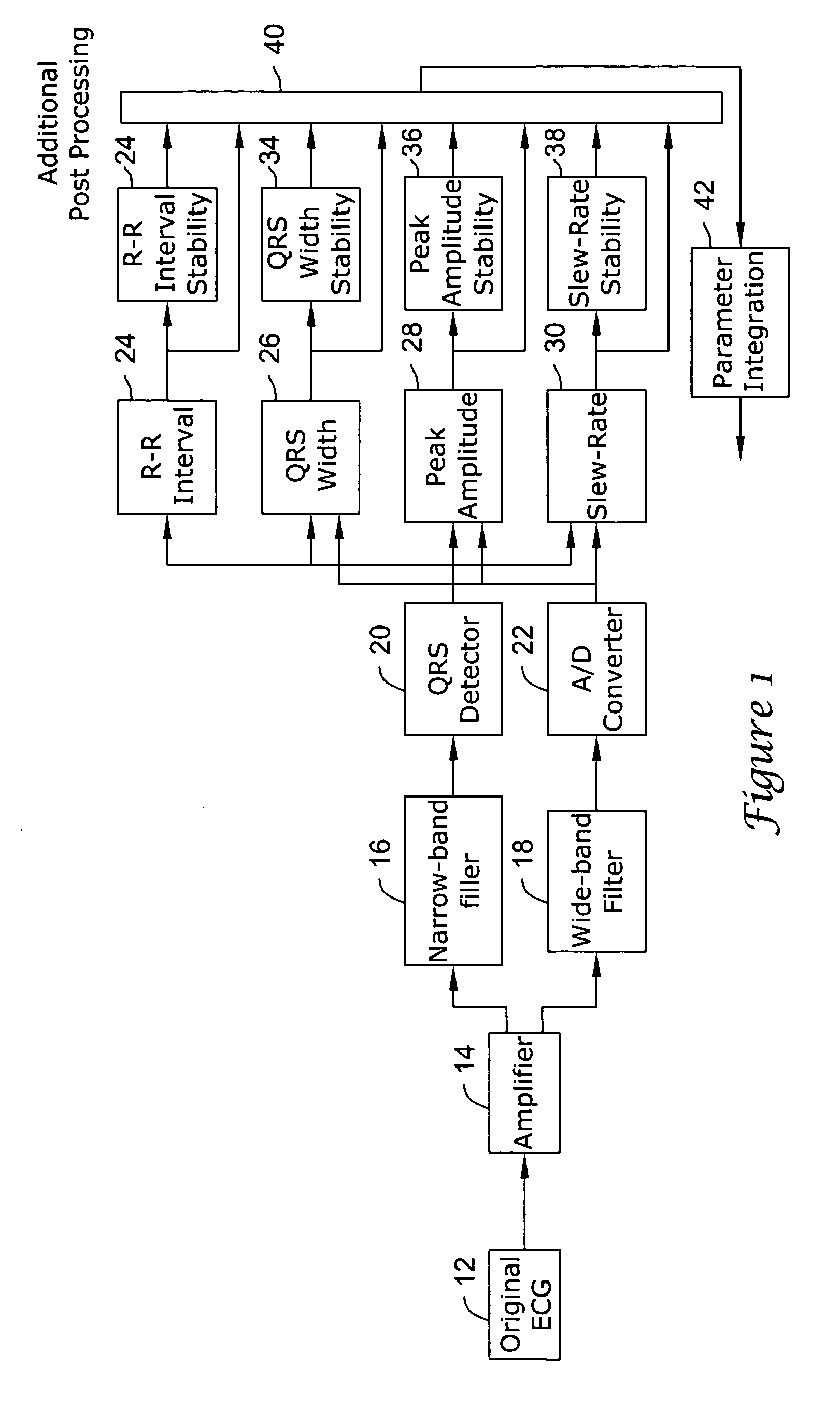
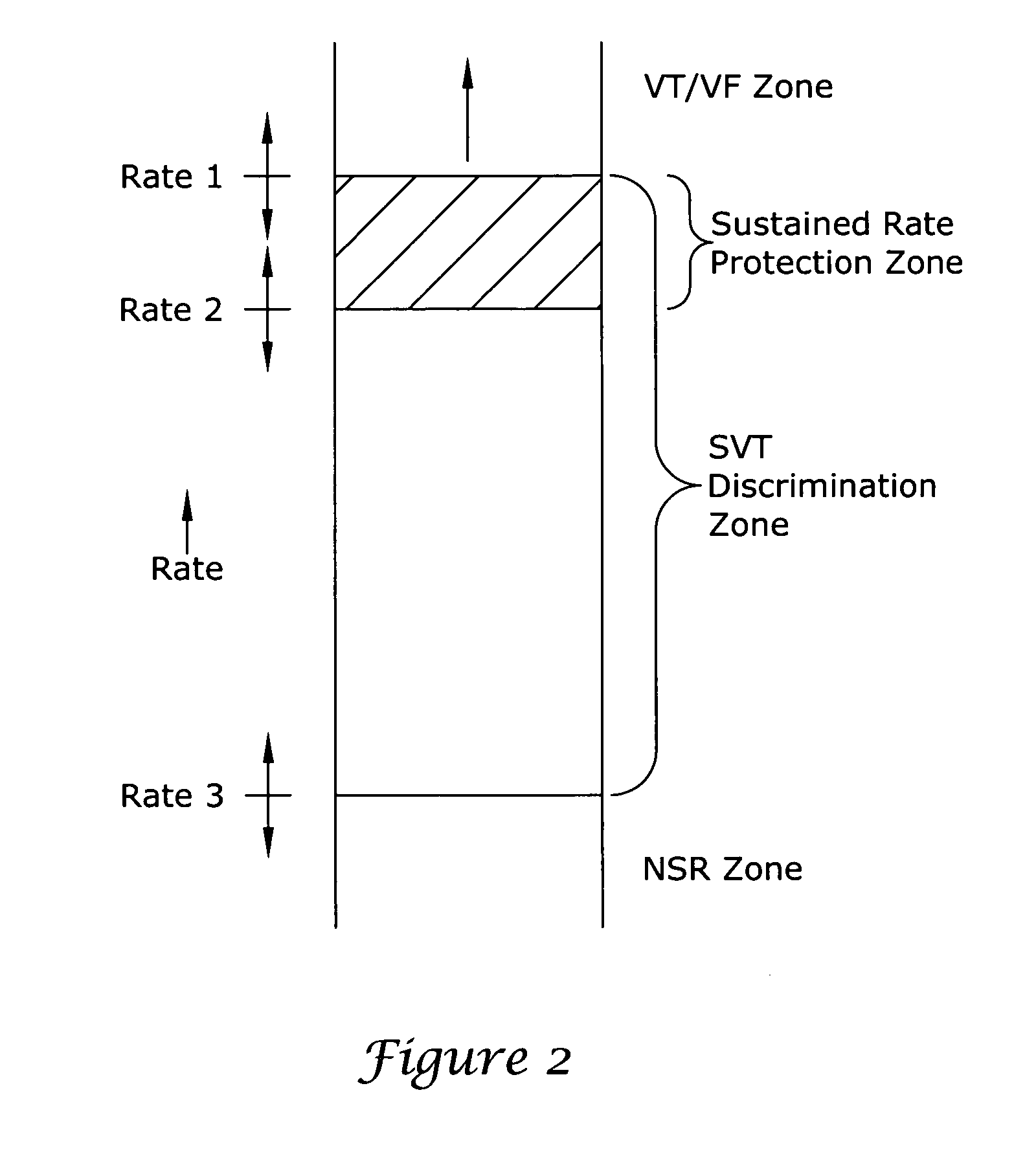
Apparatus and method of arrhythmia detection in a subcutaneous implantable cardioverter/defibrillator
In a subcutaneous implantable cardioverter / defibrillator, cardiac arrhythmias are detected to determine necessary therapeutic action. Cardiac signal information is sensed from far field electrodes implanted in a patient. The sensed cardiac signal information is then amplified and filtered. Parameters such as rate, QRS pulse width, cardiac QRS slew rate, amplitude and stability measures of these parameters from the filtered cardiac signal information are measured, processed and integrated to determine if the cardioverter / defibrillator needs to initiate therapeutic action.
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
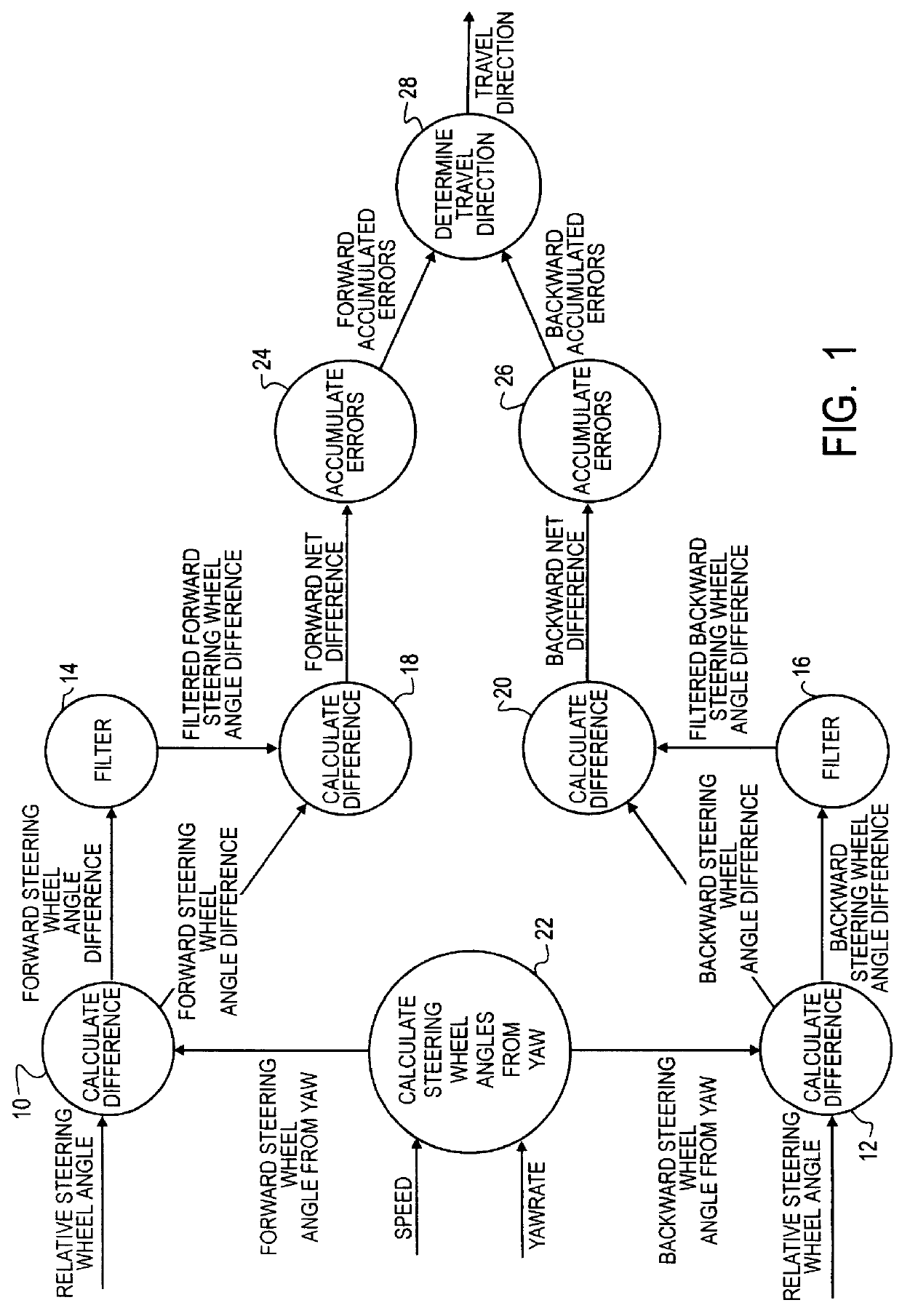
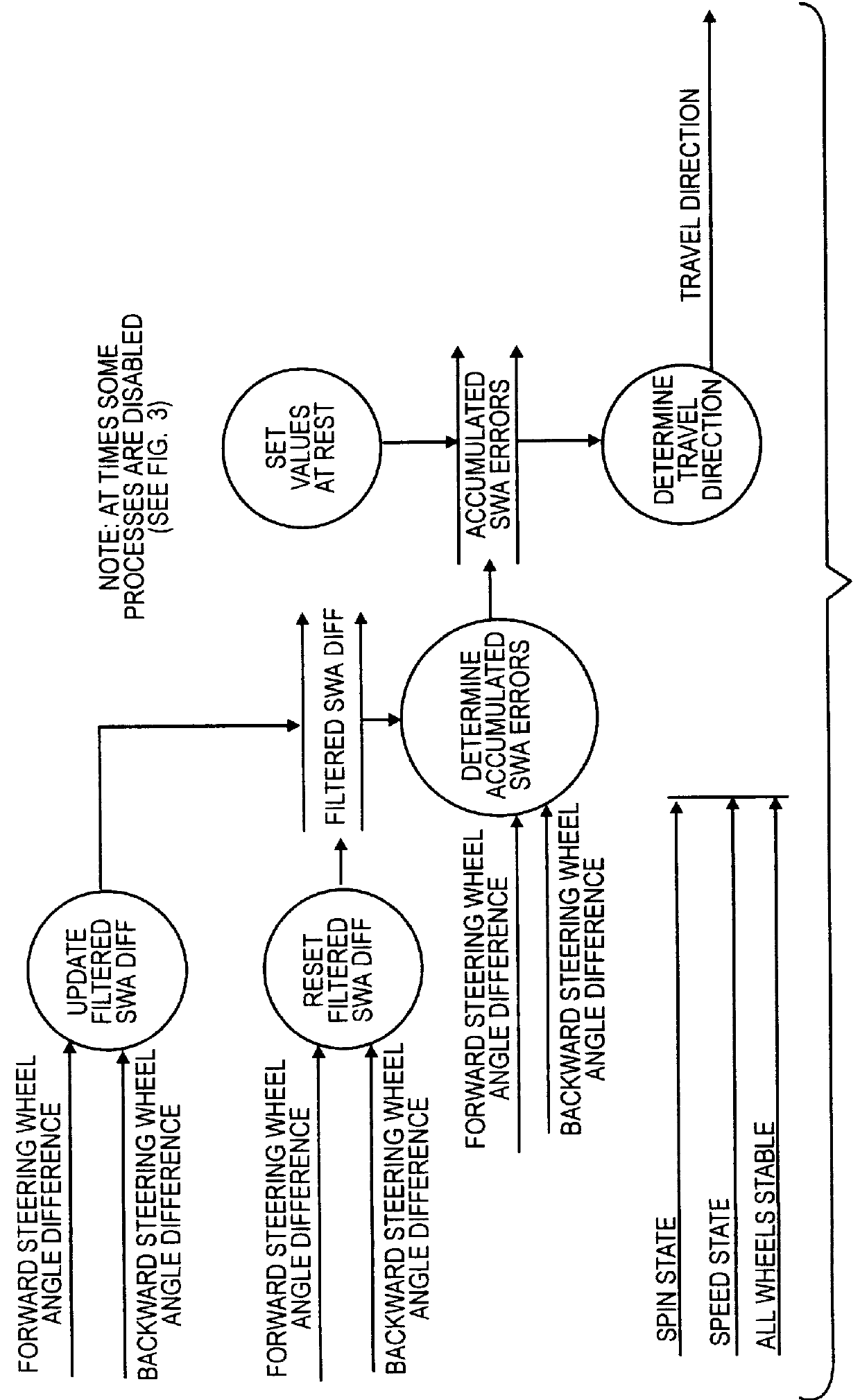
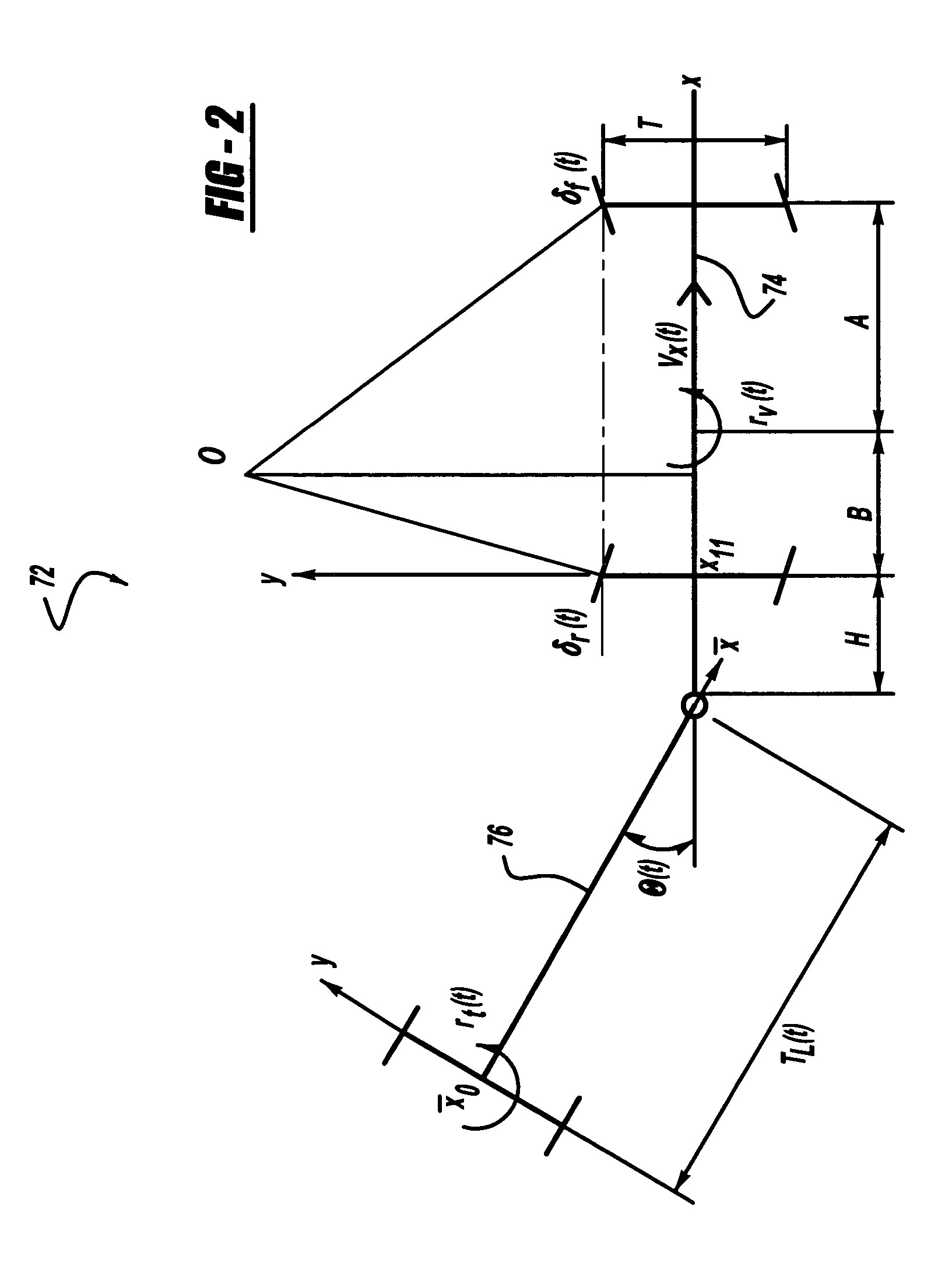
Determining the direction of travel of an automotive vehicle from yaw rate and relative steering wheel angle
A method of using relative steering wheel angle of an automotive vehicle, vehicle yaw rate, and vehicle speed to determine whether the vehicle is traveling forward or backward. Forward and backward steering wheel angles are calculated from vehicle speed and yaw rate (22). A difference between relative steering wheel angle and forward steering wheel angle (10), and a difference between relative steering wheel angle and backward steering wheel angle (12) are calculated. The difference between relative steering wheel angle and forward steering wheel angle is filtered (14), and a difference between the filtered and the unfiltered difference between relative steering wheel angle and forward steering wheel angle is calculated to obtain a forward net difference (18). The difference between relative steering wheel angle and backward steering wheel angle is filtered (16), and a difference between the filtered and the unfiltered difference between relative steering wheel angle and backward steering wheel angle is calculated to obtain a backward net difference (20). While repeatedly performing the foregoing steps, forward net difference values derived from the forward net differences are accumulated (24), and backward net difference values derived from the backward net differences are accumulated (26). The travel direction is determined by comparing the accumulation of forward net difference values and the accumulation of backward net difference values (28). Absolute steering wheel angle and road bank angle can also be calculated.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
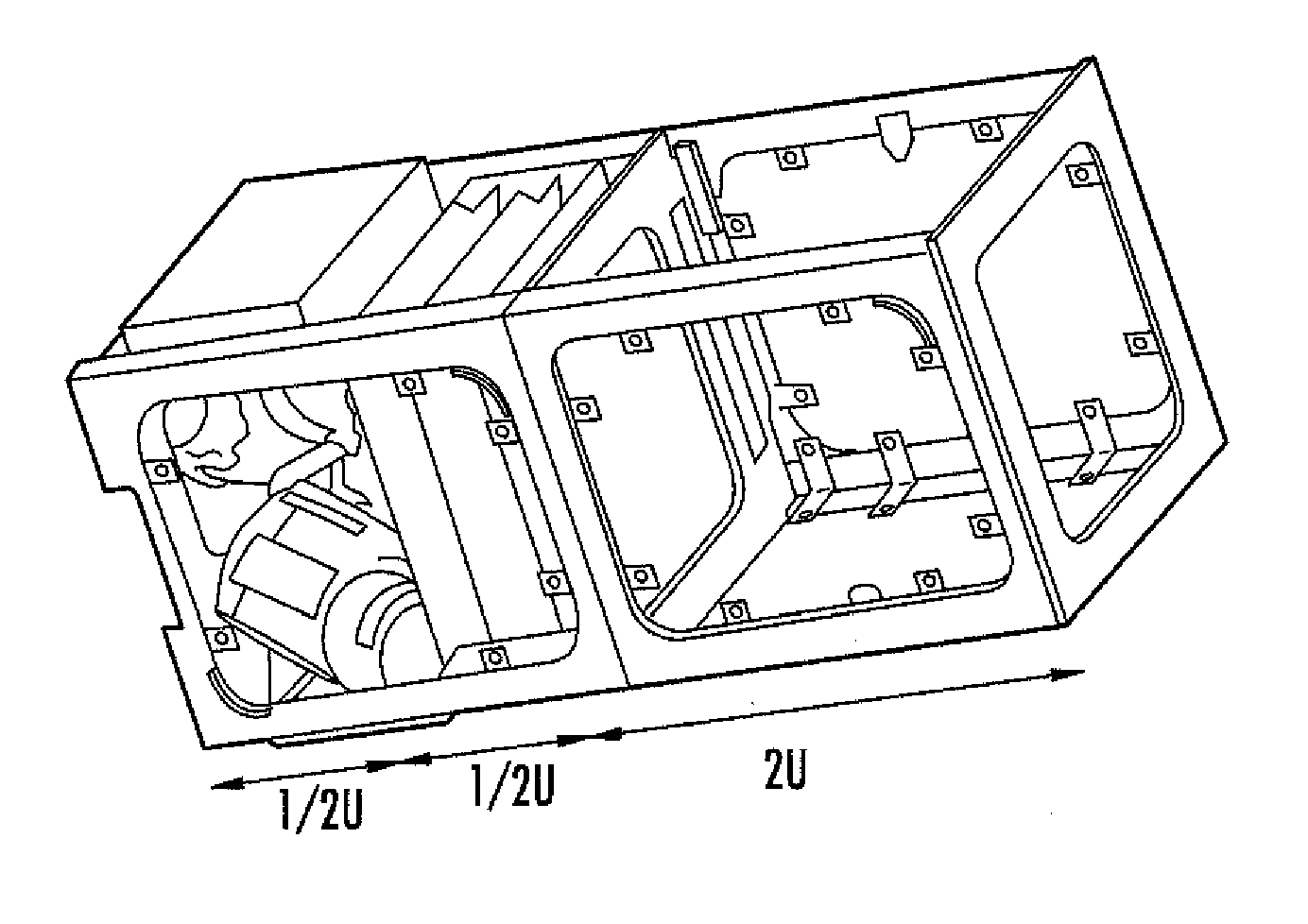
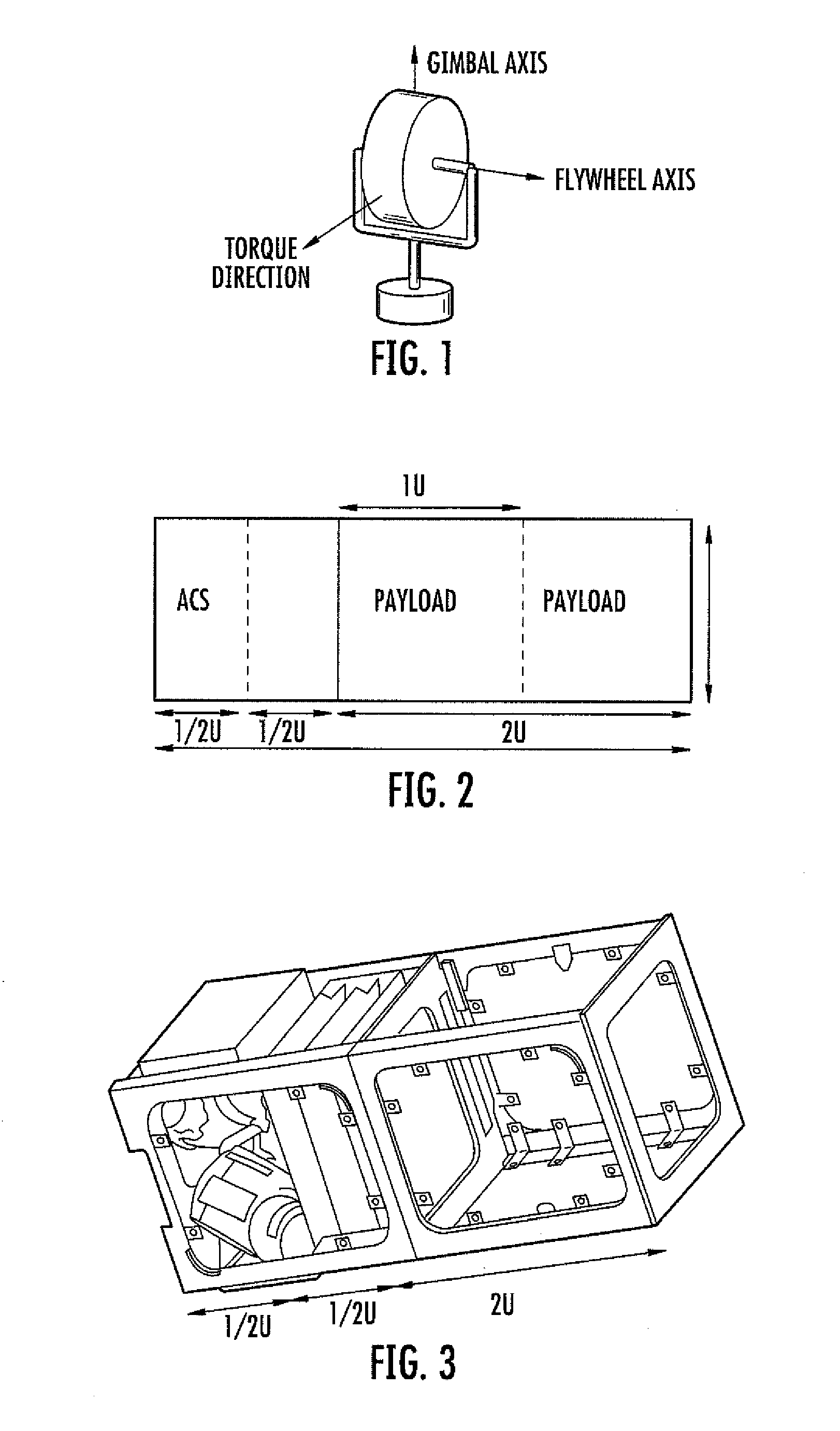
Attitude control system for small satellites
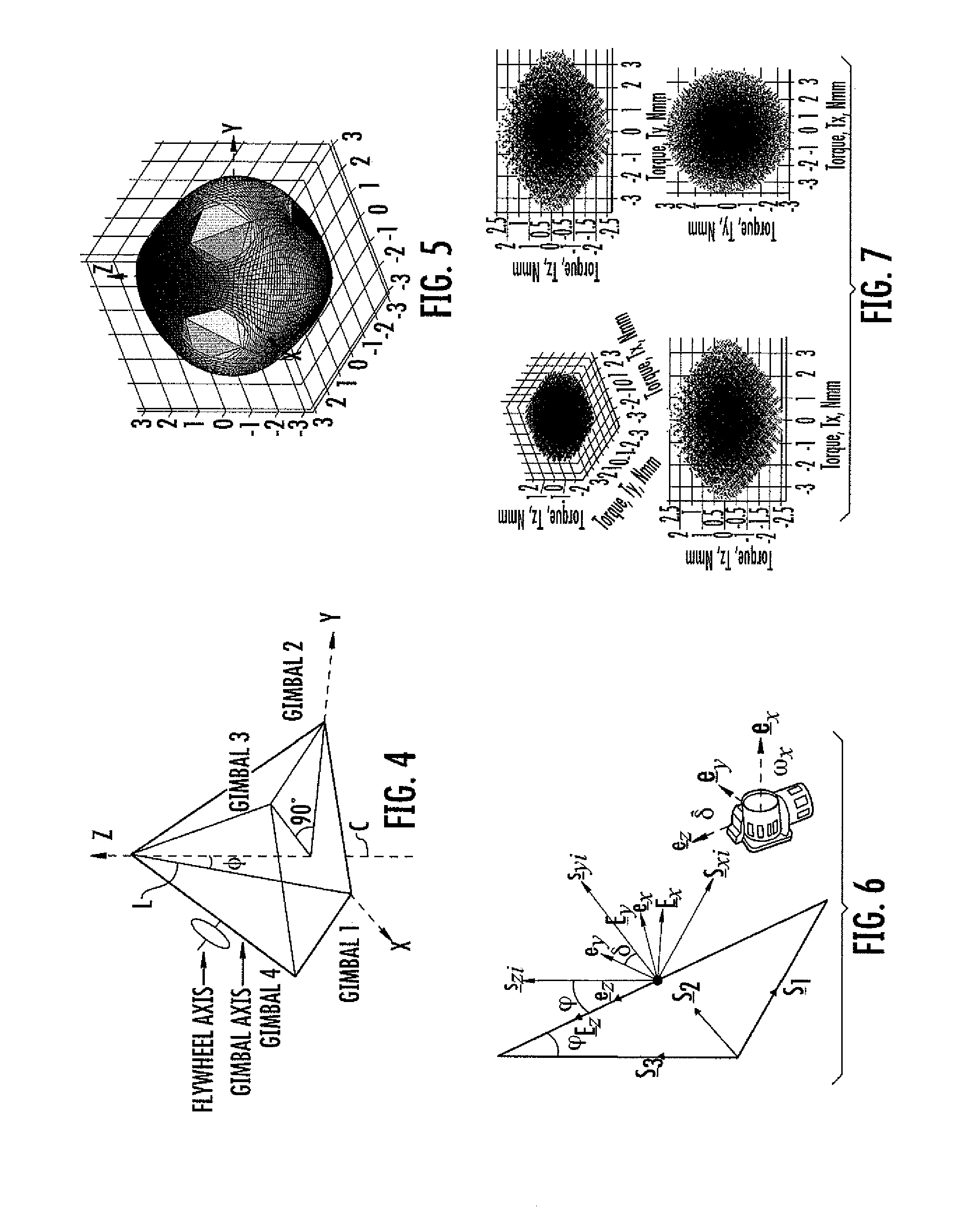
Various embodiments of the present invention include an attitude control system for use with small satellites. According to various embodiments, the system allows rapid retargeting (e.g., high slew rates) and full three-axis attitude control of small satellites using a compact actuation system. In certain embodiments, the compact actuation system includes a plurality of single-gimbaled control moment gyroscopes (SGCMG) arranged in a pyramidal configuration that are disposed within a small satellite.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
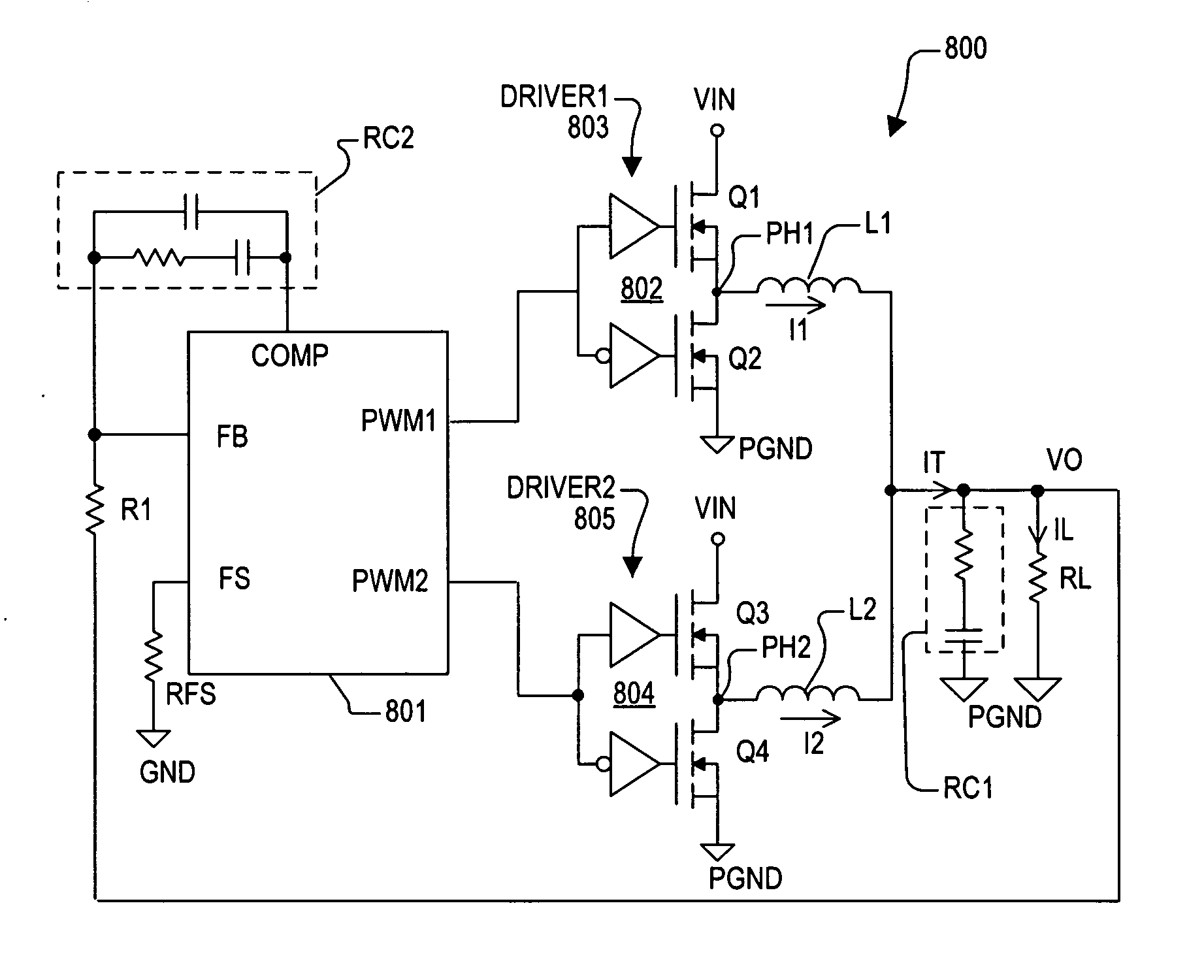
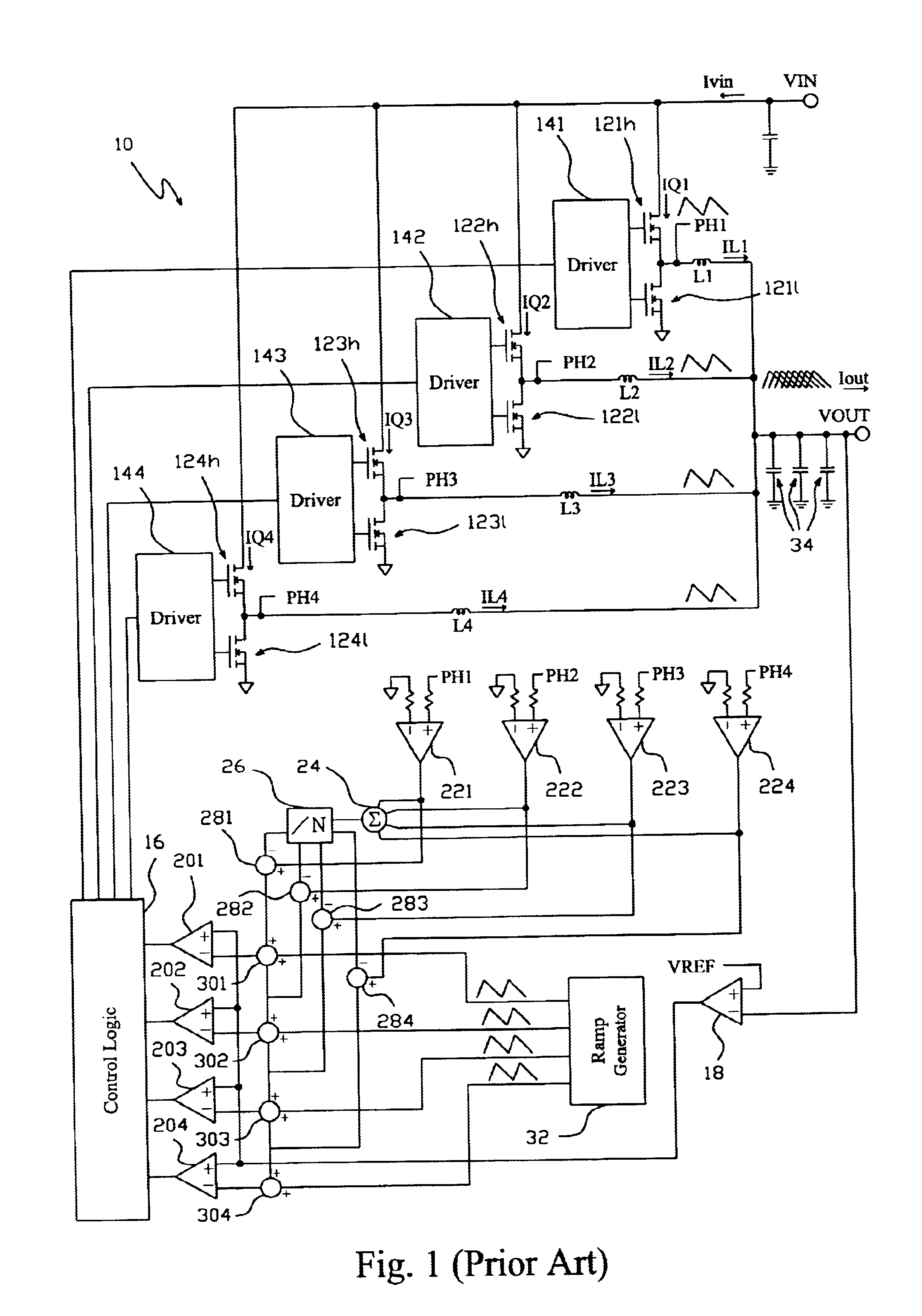
Two-step ripple-free multi-phase buck converter and method thereof
InactiveUS6839252B2Improve conversion efficiencyApparatus without intermediate ac conversionDc source parallel operationMOSFETBuck converter
A two-step ripple-free multi-phase buck converter and method thereof comprises a first-stage voltage regulator to convert an input voltage to an intermediate voltage and a second-stage voltage regulator with a phase number not less than two to further convert the intermediate voltage to an output voltage by a split phase control, in which the ratio of the intermediate voltage to the output voltage is intended to the phase number such that the steady state output current of the converter approaches to be ripple-free, and hence the drivers and MOSFETs for the second-stage voltage regulator are lower cost, the efficiency of the second-stage voltage regulator is improved, and a higher slew rate current is obtained for transient driving capabilities.
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
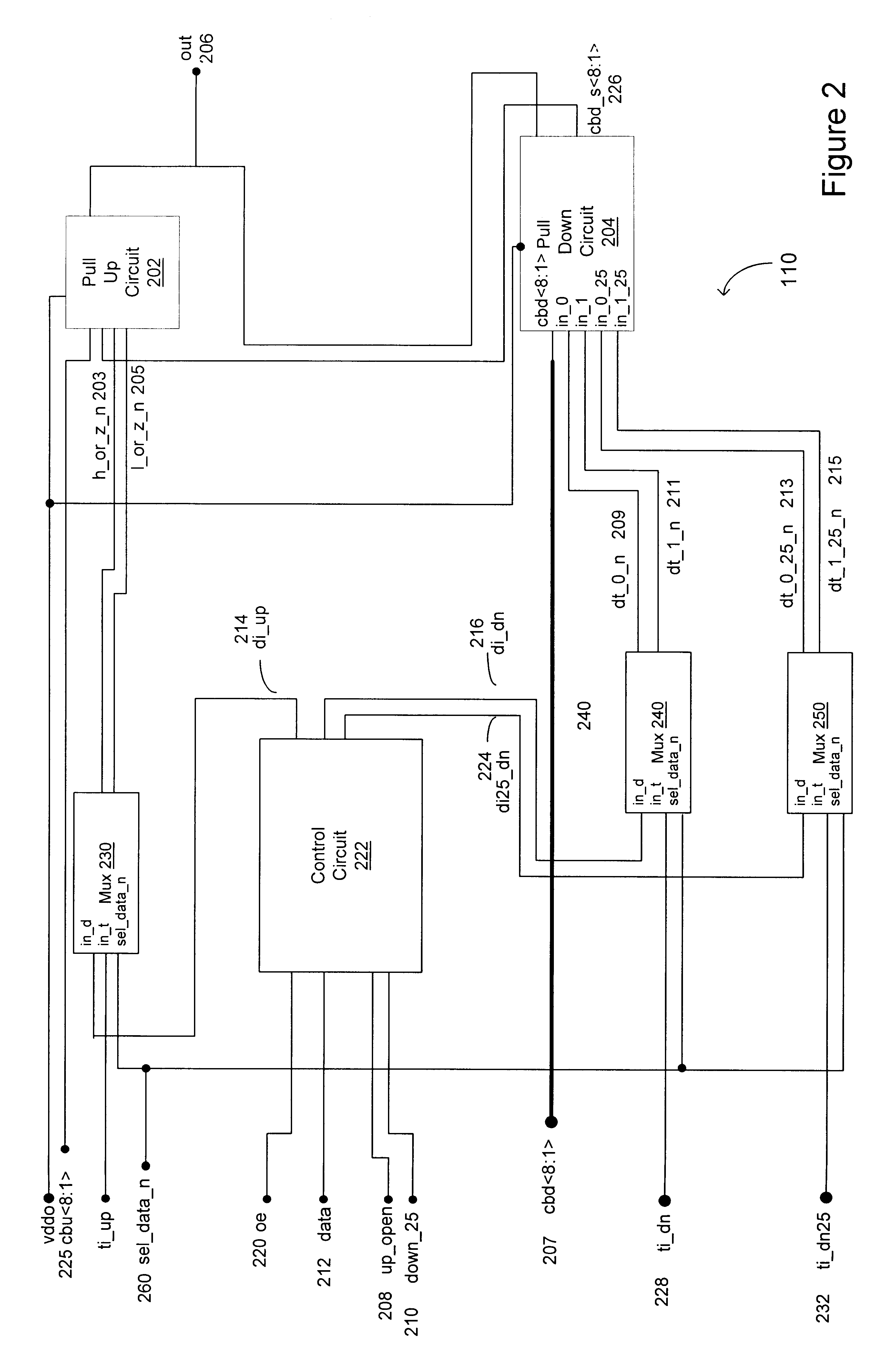
Output buffer with slew rate control and a selection circuit
An output buffer having a controlled output slew rate comprises a first predriver circuit having a first RC circuit and a first output node and a second predriver circuit having a second RC circuit and a second output node. A buffer input node is coupled to the first and second predriver circuits. The output buffer further includes an output circuit having first and second input nodes and a third output node, where the first and second input nodes are coupled, respectively, to the first and second output nodes. The time constants of the RC circuits control a signal slew rate at the third output node of the output circuit, and the value of R may be selected to provide a predetermined, controlled slew rate range at the third output node. A selection circuit aids in the selection of an appropriate value for R.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Circuits and methods for improving slew rate of differential amplifiers
ActiveUS20060091955A1Increase conversion rateReduce power consumptionNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier modifications to reduce detrimental impedenceElectricityFrequency compensation
Circuits and methods are provided for providing high speed operational amplifiers and, in particular, operational amplifiers having frequency compensation circuits that provide improved slew rates with low power dissipation when configured with feedback. Frequency compensation schemes are provided to enable dynamic configuration of frequency compensation circuits implementing miller compensation whereby nodal connections of compensation capacitors are changed during driver setup and driving periods such that compensation capacitors are connected to source voltages to rapidly charge / discharge compensation capacitors using supply source currents during setup period, while providing frequency compensation during the setup and driving periods to maintain circuit stability and prevent oscillation of an output voltage due to the feedback.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Trailer tongue length estimation using a trailer yaw rate sensor
A control system for estimating the tongue length of a trailer being towed by a vehicle in connection with a front wheel steering with or without coordinated rear wheel steering associated with the vehicle. The control system employs an algorithm that calculates an estimated trailer yaw rate based on a corrected tongue length, a front wheel steering angle, a rear wheel steering angle, vehicle speed and a vehicle yaw rate. The estimated trailer yaw rate is compared to a measured trailer yaw rate to generate a yaw rate error that is converted to a tongue length error. The tongue length error is compared to the estimated tongue length to become a corrected estimated tongue length for a next computation period. After a few seconds of processing, the corrected estimated tongue length will be the actual tongue length of the trailer.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
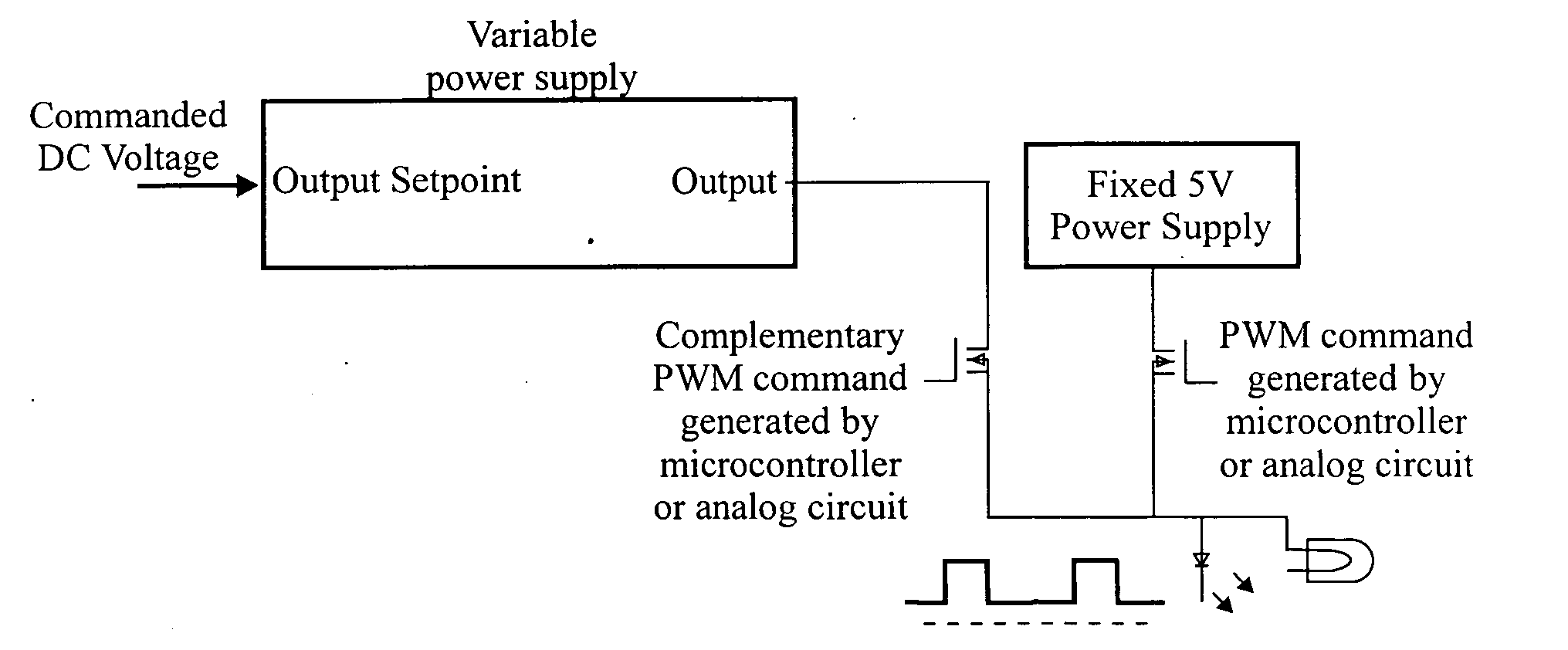
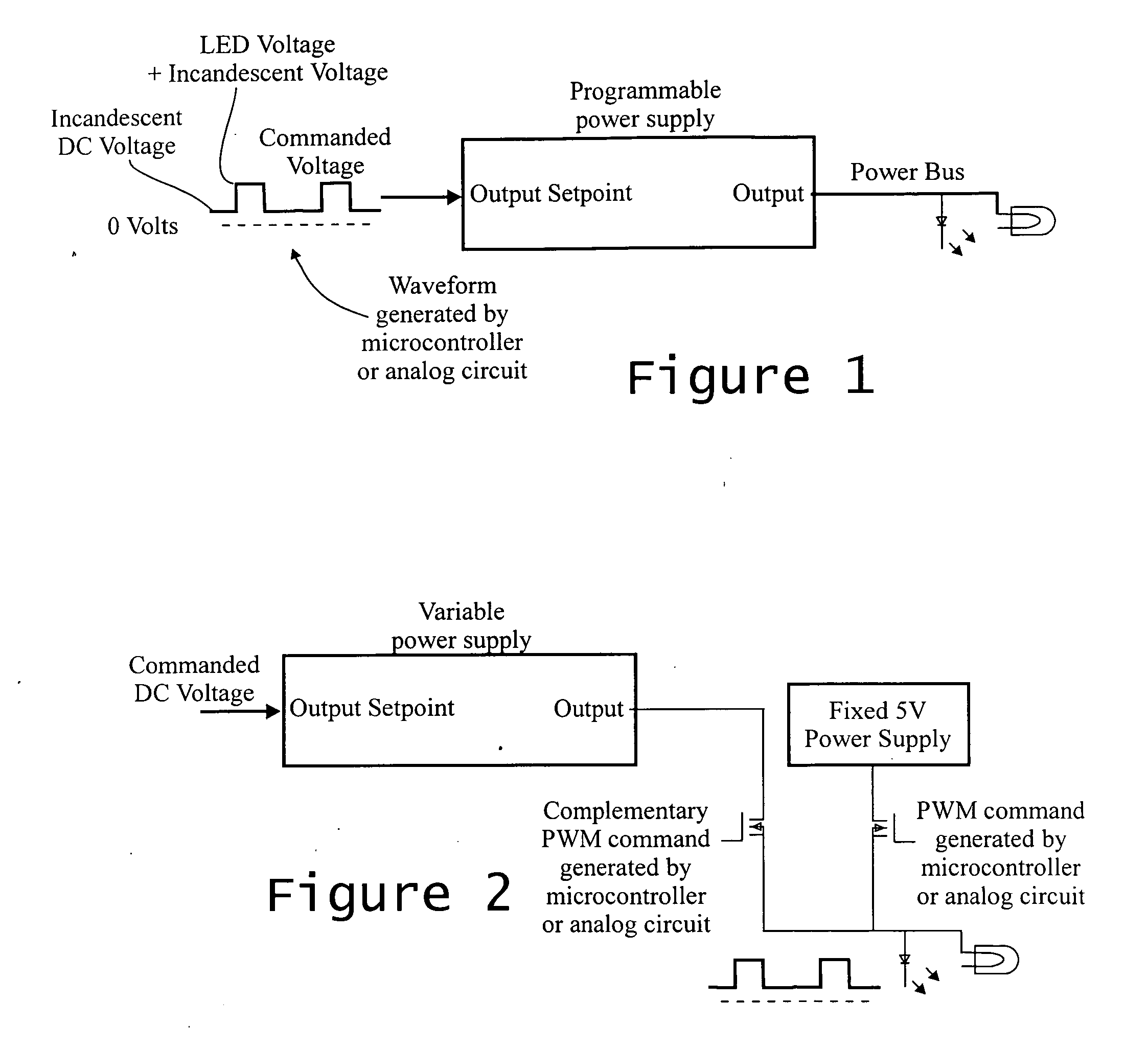
Light dimmer for LED and incandescent lamps
InactiveUS20050168168A1Reduce intensityElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesDimmerSlew rate
The light output intensity of incandescent lamps and LEDs connected to a common lamp power bus are controlled using a composite waveform having two power components: a pulse-width modulated (PWM) component and a direct current DC component. The DC component is maintained below the turn-on voltage for the LEDs. The PWM component controls the light intensity of the LEDs; and the DC component is calculated as a quadrature power series, taking into account that the PWM component contributes to the light intensity of the incandescent lamps. The frequency and slew rate of the PWM component are selected to minimize EMI. A small steady state power component is provided to keep the LEDs slightly turned on to minimize EMI.
Owner:RADIANT POWER
Dynamic termination logic driver with improved impedance control
A driver capable of launching signals into a transmission line and of terminating signals at a receiver end of the transmission line includes within the driver a circuit for controlling the output impedance and a circuit for controlling the output slew rate. Accordingly, a desired output impedance can be advantageously established and maintained over a wide range of variations in operating conditions, manufacturing processes and output voltage levels. Such a driver also advantageously limits any crowbar current, thereby reducing the overall power consumption of the driver with little, if any, degradation of driver performance. The driver includes a pull up circuit coupled to receive at least one of a plurality of control codes. The pull up circuit includes pull up output circuit and an impedance control buffer circuit, a parallel pull up circuit, the parallel pull up circuit and the pull up output circuit being controllable to adjust the impedance of the pull up circuit. The driver also includes a pull down circuit coupled to receive at least one of the plurality of control codes. The pull down circuit includes at least one pull down output circuit and a parallel pull down circuit, the parallel pull down circuit being controllable to adjust the impedance of the pull down circuit. The output impedance of the driver is further controlled during transitional phases of turning on and turning off the pull down circuit and the pull up circuit under a plurality of process, voltage and temperature (PVT) conditions.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
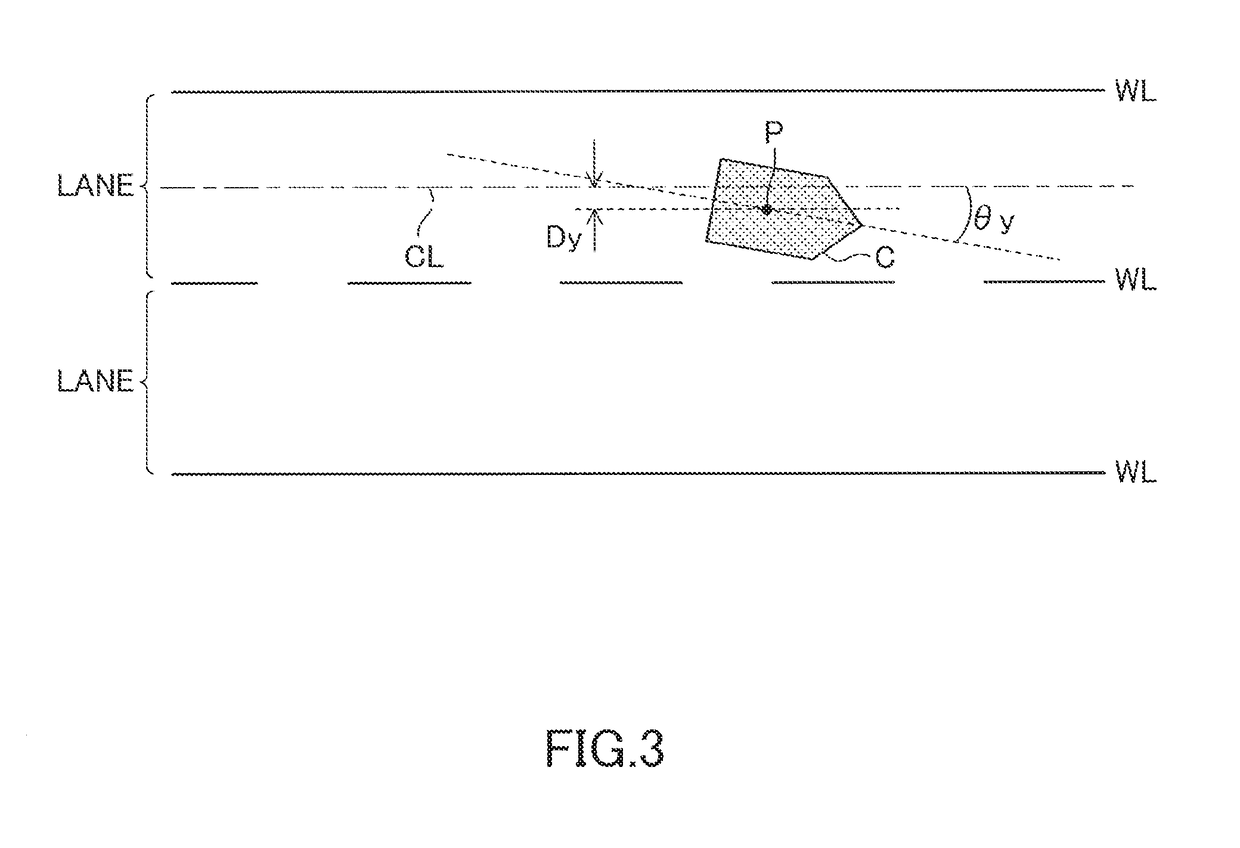
Lane change assist device
A yaw angle return controller is configured to end first yaw angle return control at a predetermined time when a value which is calculated by adding yaw angle detected by a lane recognition device at a predetermined time and an estimated yaw angle change amount is the same as yaw angle at lane change start time under a state where the first yaw angle return control is being executed. The predetermined time comes after the first start time and before the first finish time. The estimated yaw angle change amount is calculated by multiplying the yaw rate detected by a yaw rate sensor at the predetermined time by a predetermined time period for foreseeing.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method and apparatus for encoding and decoding digital communications data
ActiveUS7260155B2Improve robustnessEliminate and minimize and reduce and limit transitionCross-talk reductionAmplitude-modulated pulse demodulationEngineeringSlew rate
In one aspect, the present invention is a system and technique that provides for the systematic development or implementation of codes that increase the robustness of systems employing, for example, PAM-n transmission techniques. The system and technique of this aspect of the invention eliminate, minimize, reduce or limit transitions between extreme signaling levels. As a result, the slew rate employed and / or required by the transmitter may reduce crosstalk and intersymbol interference, and provide for wider “eye” openings from the perspective of the receiver.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Low-voltage-difference voltage-stablizer
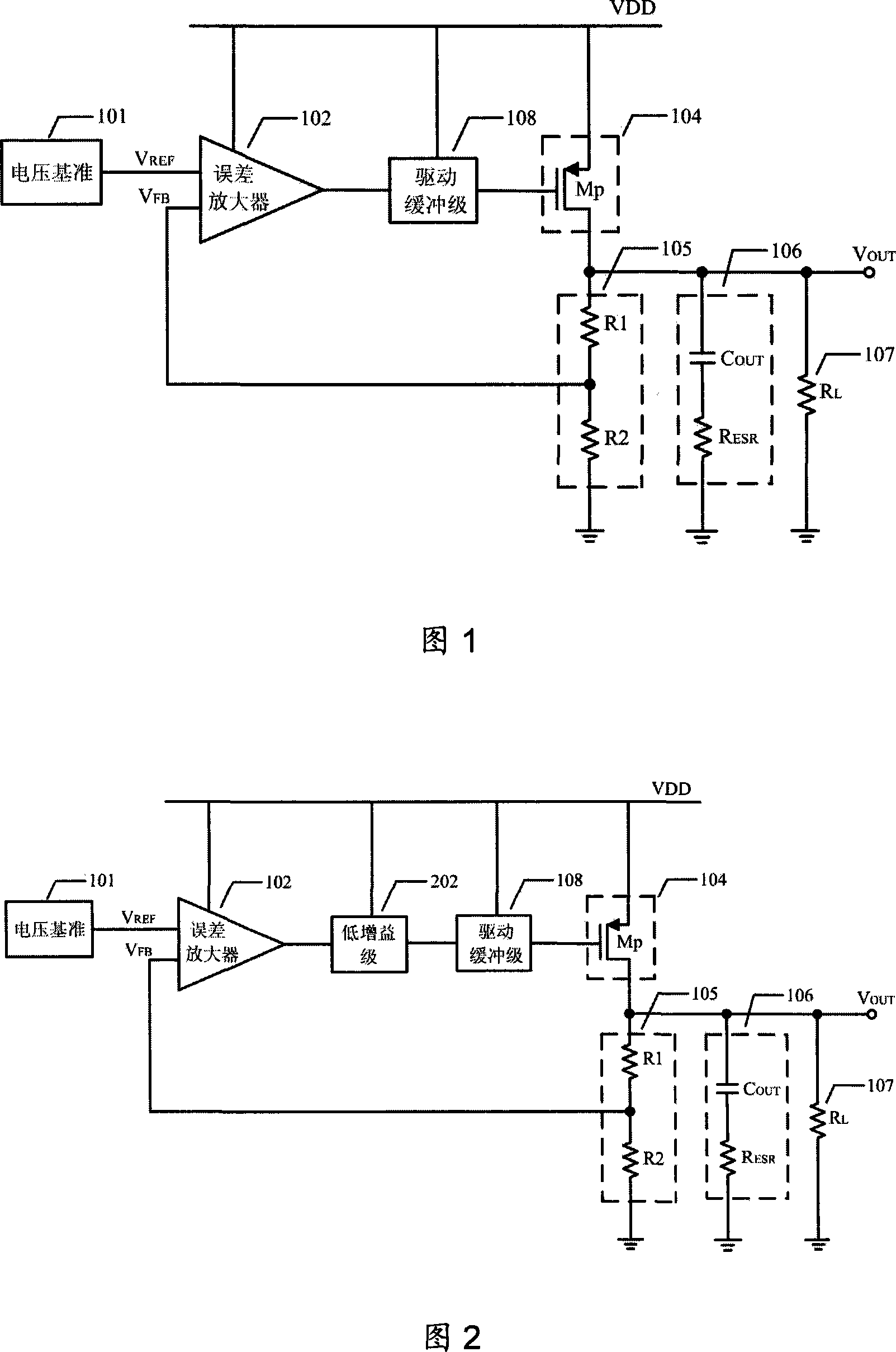
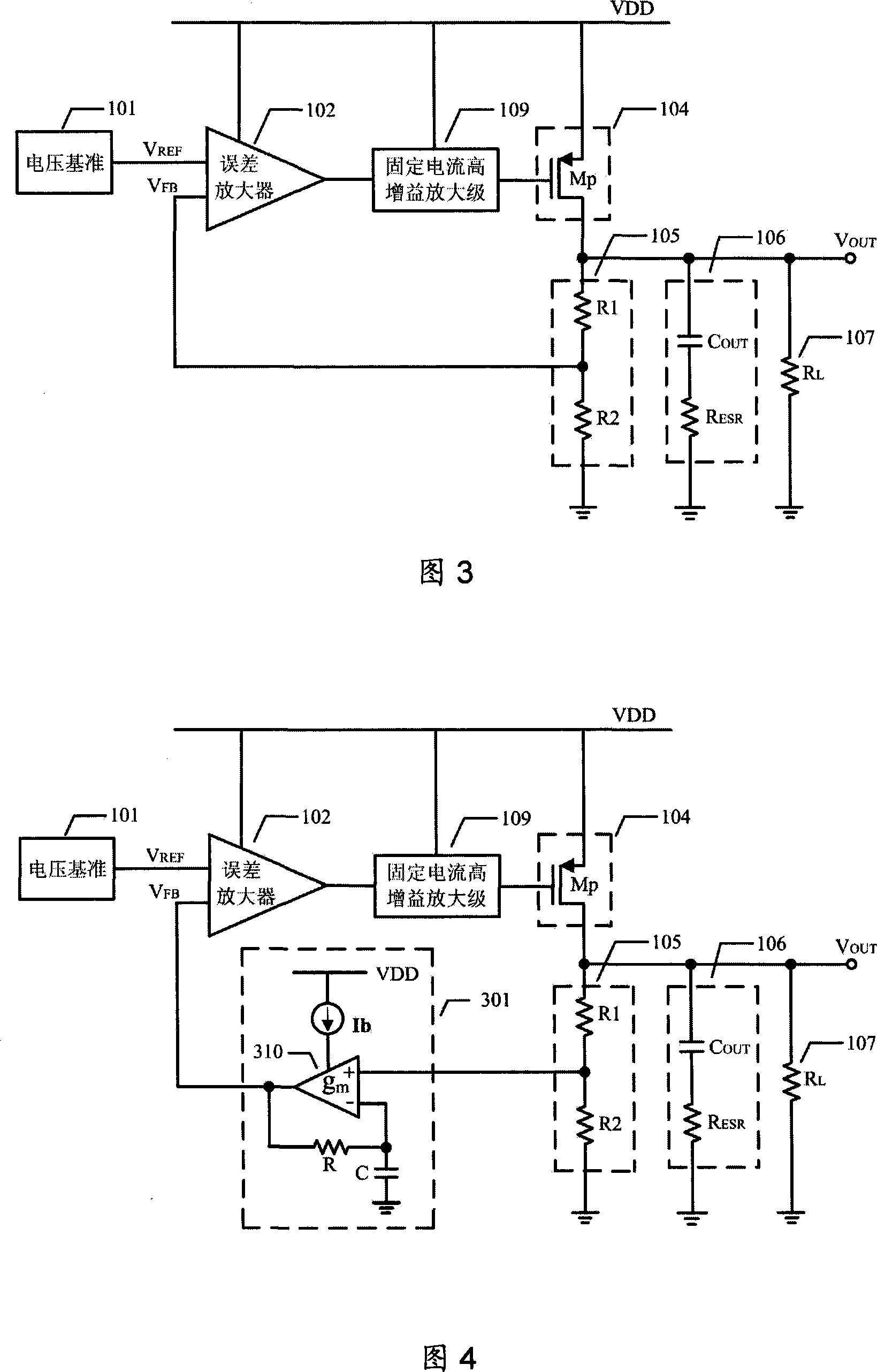
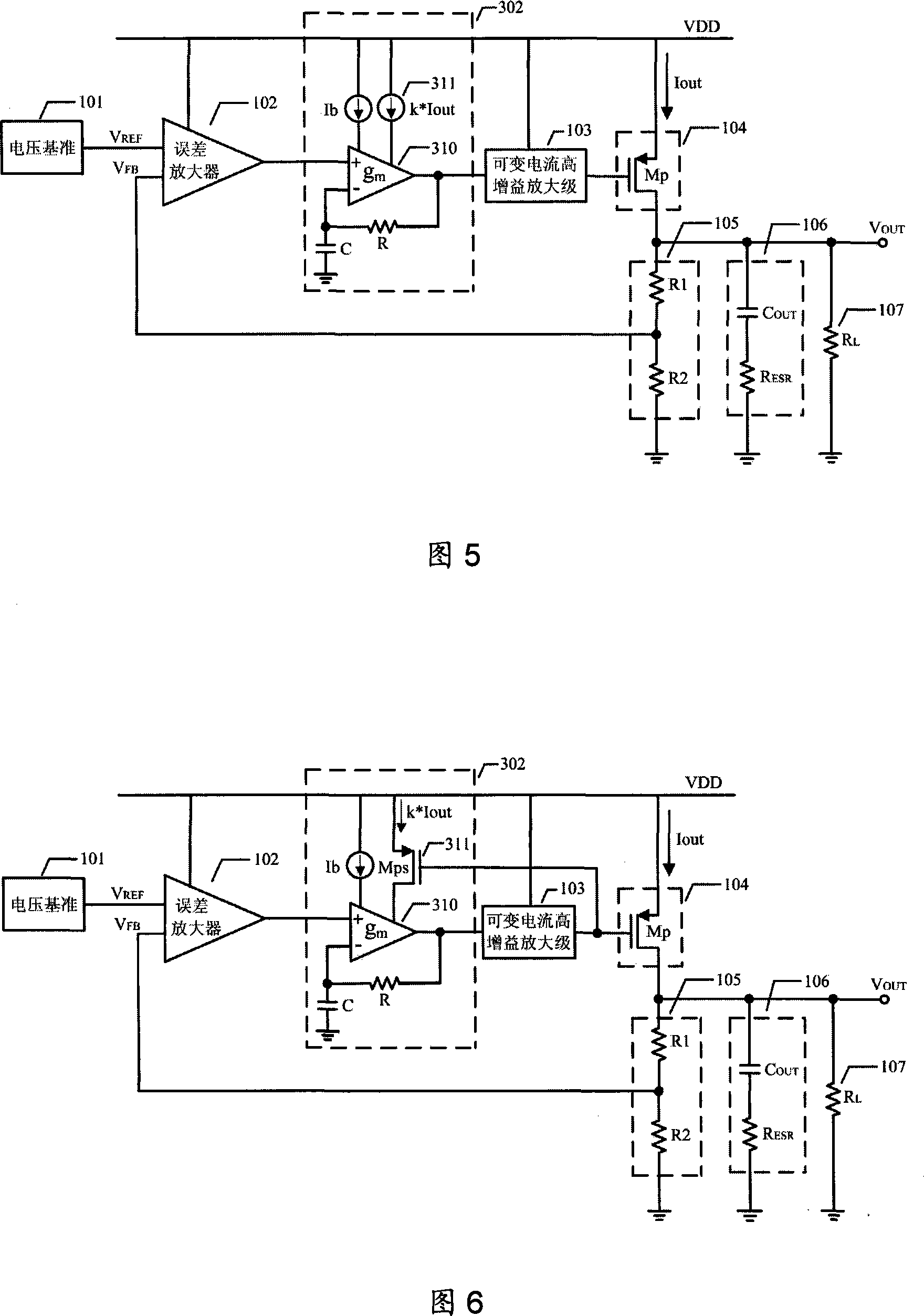
InactiveCN101122804AHigh precisionHigh Voltage Rejection RatioElectric variable regulationLow voltageEngineering
A low voltage difference linear voltage regulator realizes the performance targets such as high output voltage precision, high stability and high supply-voltage rejection ratio by using variable slope gm / C filter circuit module at the output terminal of error amplifier. Variable slope mechanism of the filter circuit module reduces static power consumption of the voltage regulator when the regulator is ideal loaded or light loaded, and produces a parasitic pole whose frequency goes to high when the regulator load voltage increases, accordingly to develop unit gain band width of the voltage regulator and strengthen stability of the heavy loaded or full loaded voltage regulator. Moreover, variable current high-gain amplifier stage used in voltage circuit increases slew rate of voltage regulator internal node and improves interaction capability of the voltage regulator.
Owner:BEIJING MXTRONICS CORP +2
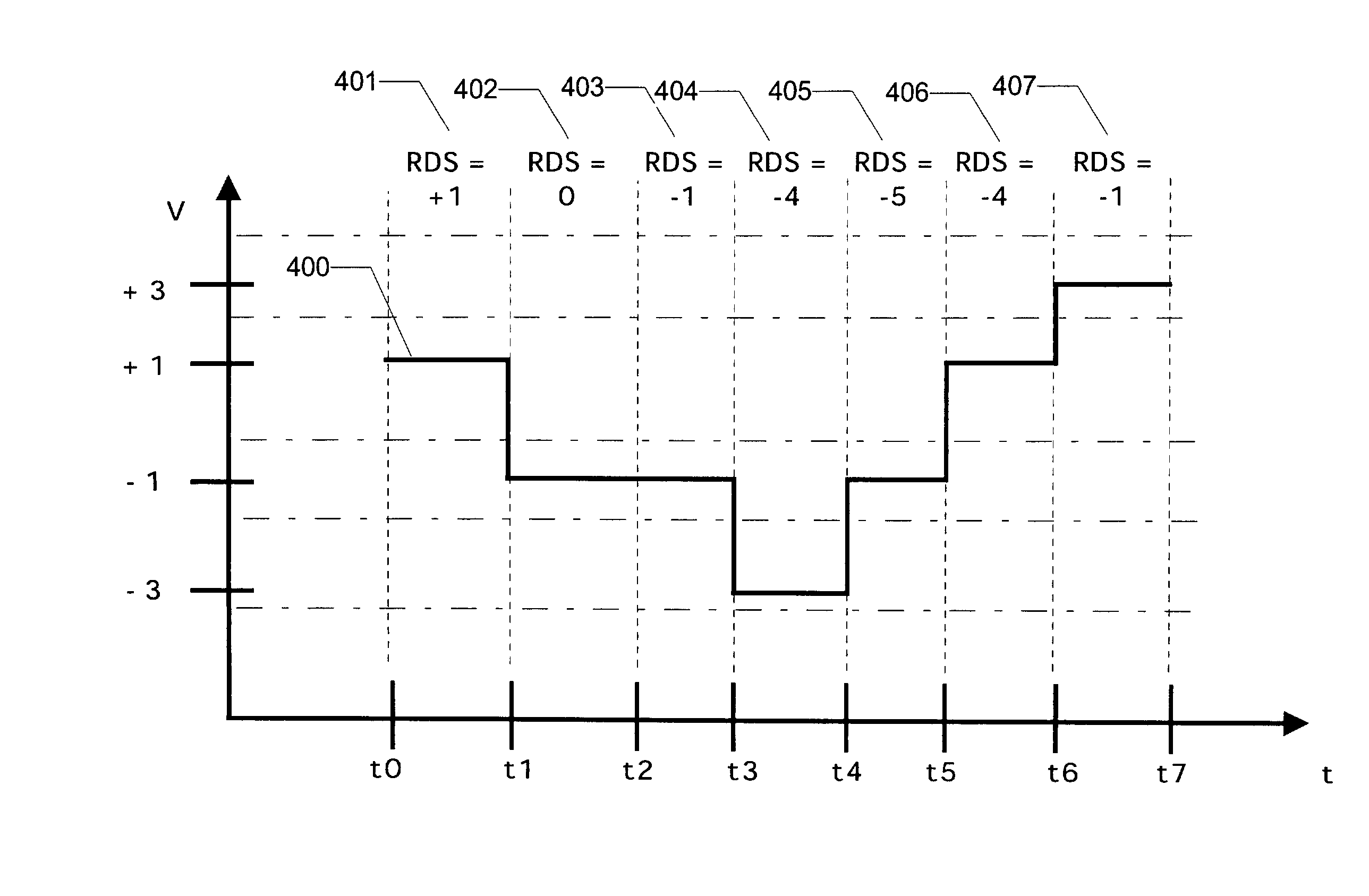
Switching device driving unit and semiconductor apparatus
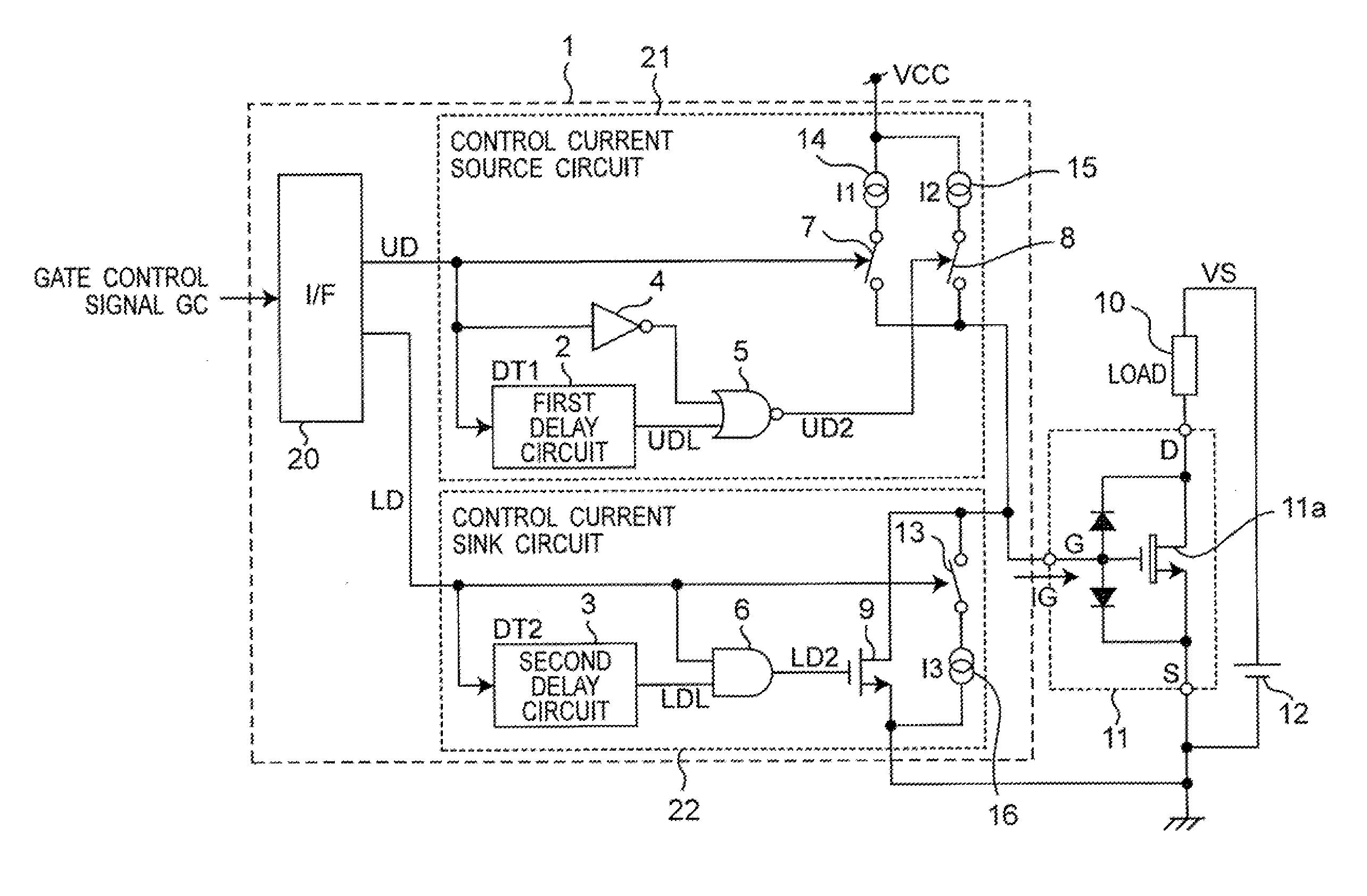
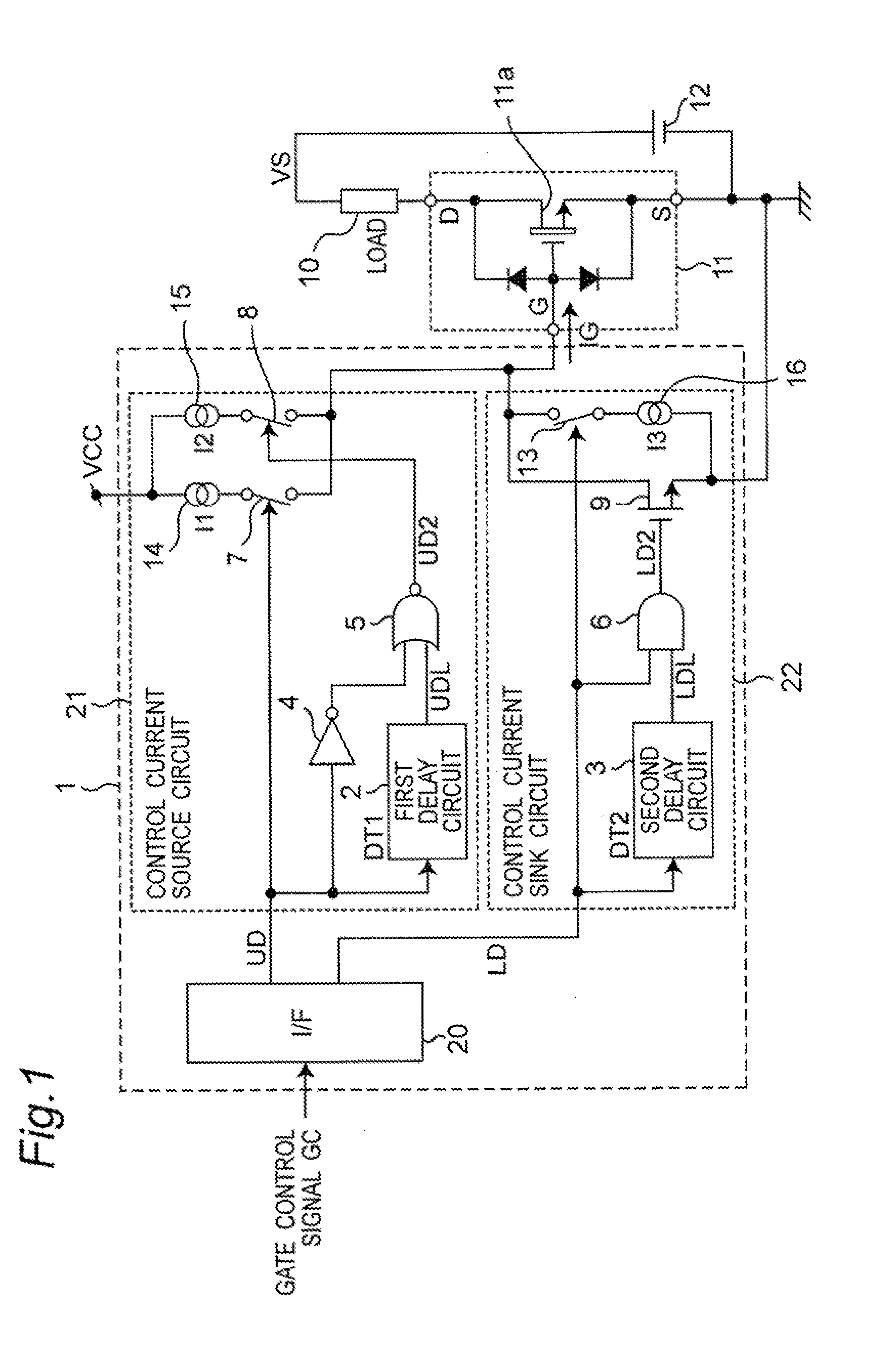
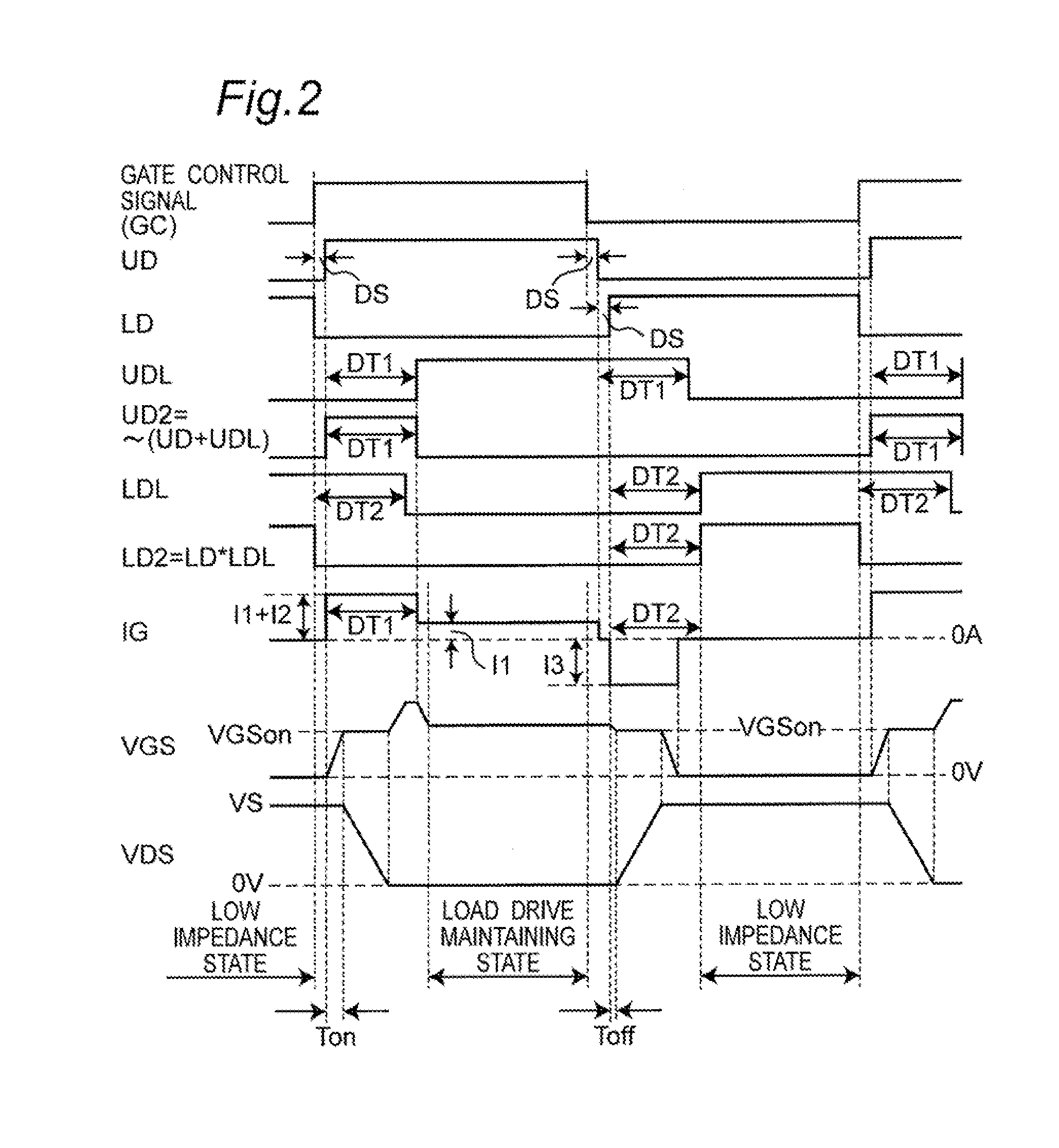
InactiveUS20110241738A1Variation in slew rateAvoid power outagesElectronic switchingElectric pulse generatorDriving currentEngineering
In order to provide a switching device driving unit that, even in a case where a threshold voltage of a switching device is varied, can suppress variations in switching speed, and prevent a power loss caused by an unnecessary gate current in a constant ON operation state of the switching device, so that a desired slew rate can be easily set, a control current source circuit sets to different values based on a first input driving signal, in a driving current to be source-outputted to a gate or a base of the switching device, a current in a stage of an initial ON operation of a switching operation of the switching device and a current in a stage after completion of the switching operation.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method and apparatus for controlling power factor correction
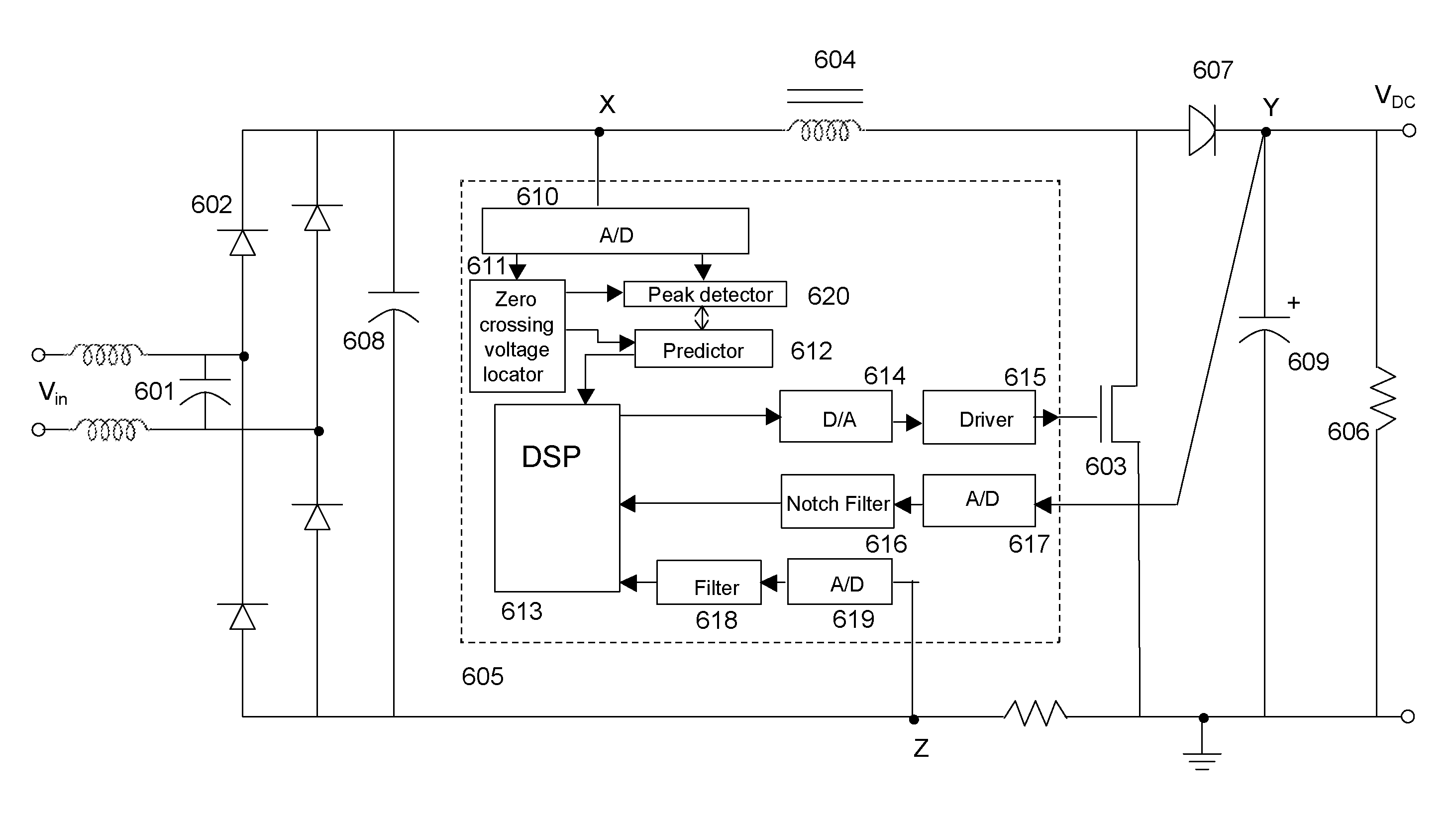
ActiveUS7990740B1Small sizeReduce Harmonic DistortionAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionConstant powerAverage current
In a method and apparatus for controlling power factor correction (PFC) in mixed operation modes, a frequency of the input voltage is obtained by detecting the zero crossing points of the input voltage. A peak of the input voltage is obtained by detecting input voltage with 90 degree phase. Thus, the present invention predicts the input voltage by its frequency and peak and the characteristic of the sine wave. A digital signal processor computes the duty and frequency of a boost switch, switching the operation mode of the boost converter among continuous mode, critical mode and discontinuous mode according to input voltage or the load. According to another aspect, the operation is switched to critical mode from the average current mode when a zero current is detected before the charging and recharging cycle of the boost switch is finished. Overcurrent protection may be achieved by controlling current in response to detected voltage to provide a substantially constant power level. The overcurrent protection may be adaptive in nature. In this aspect, an adaptive driver for a PFC controller reduces the slew rate of signals over the boost switch of the PFC controller. The adaptive driver may have a group of transistors which may be divided into a plurality of branches. The charging current through the boost switch may be increased by turning on an increasing number of branches until the voltage over the switch exceeds a reference voltage, and this may determine the number of branches to drive the boost switch during normal operation.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
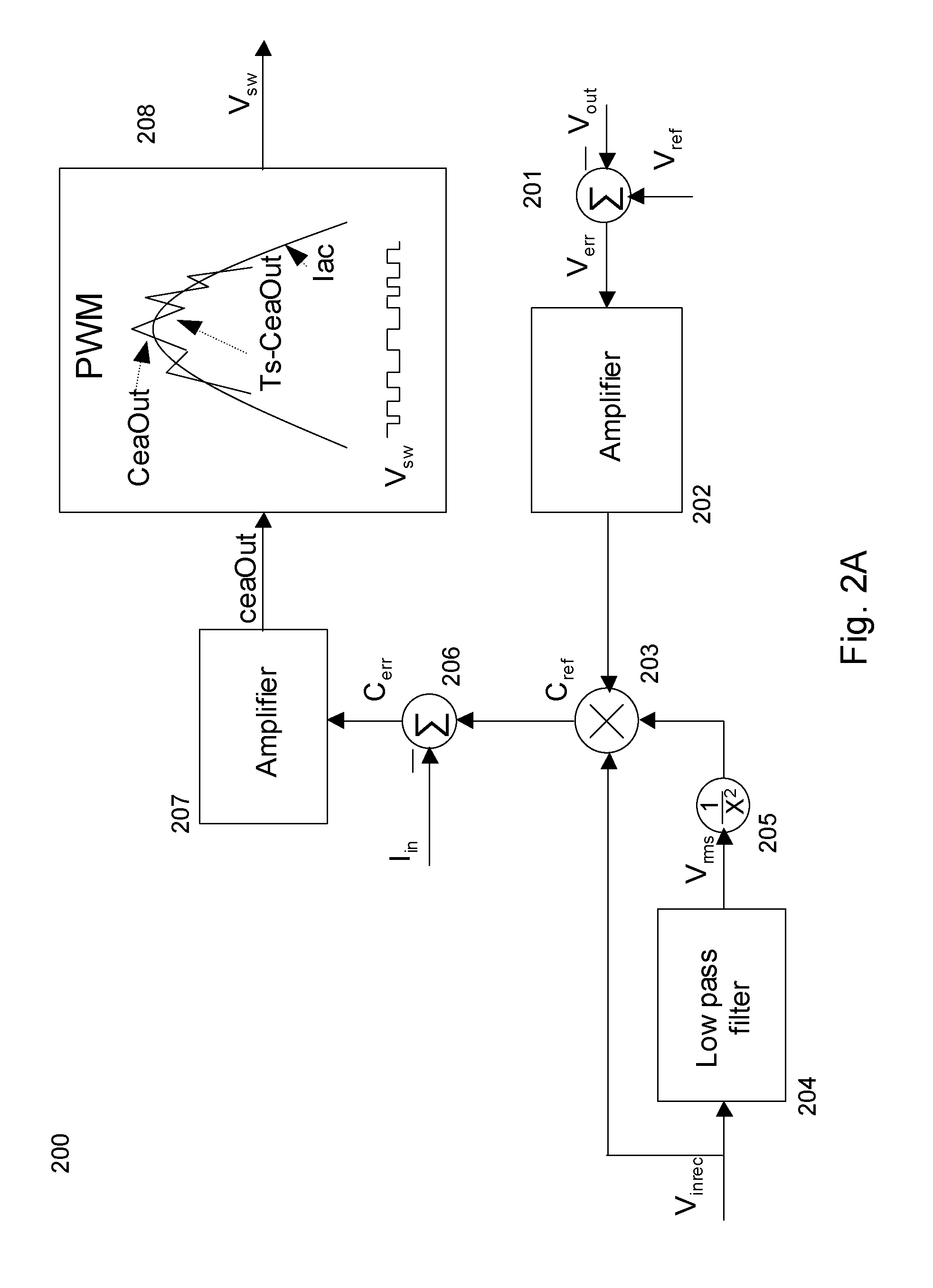
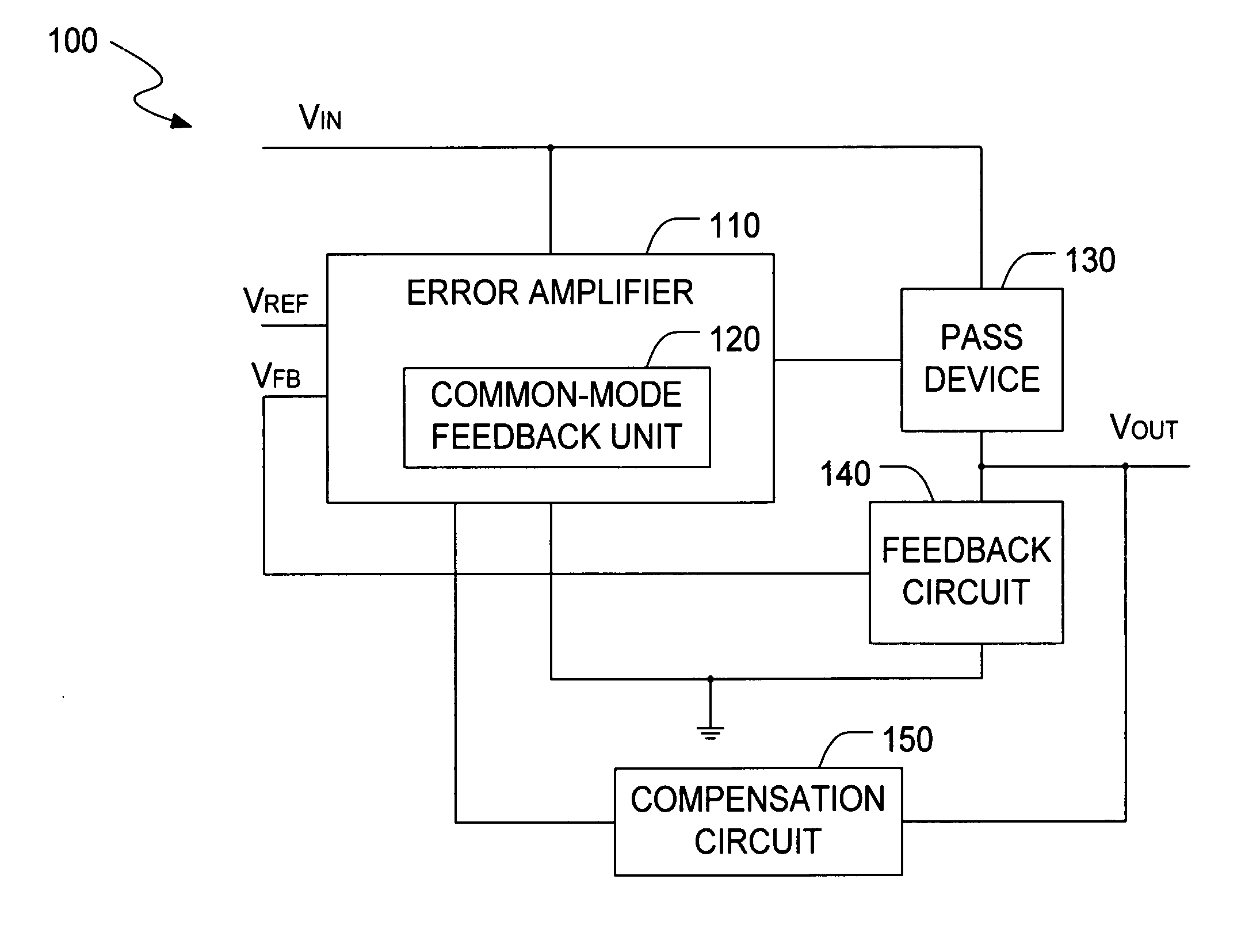
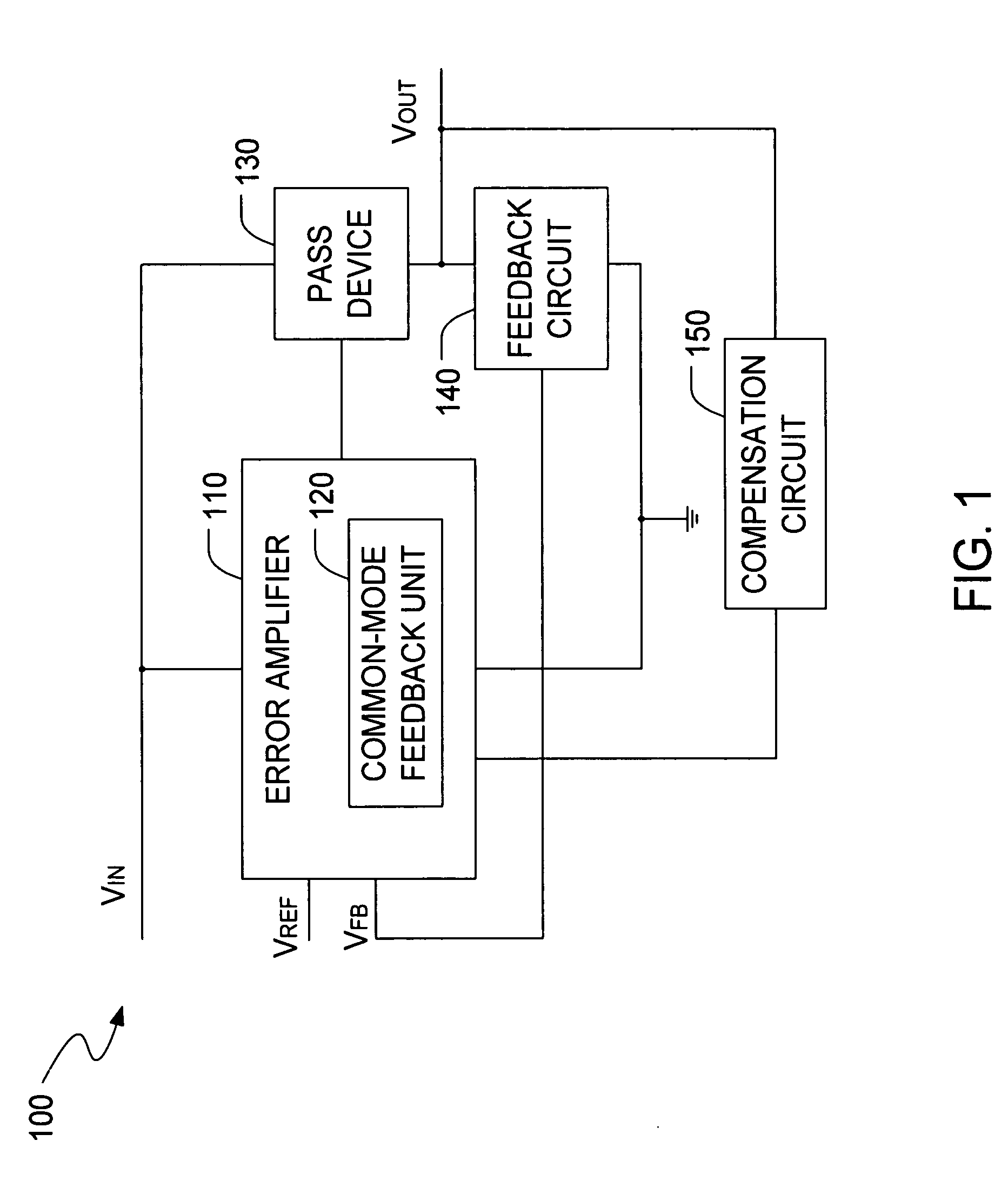
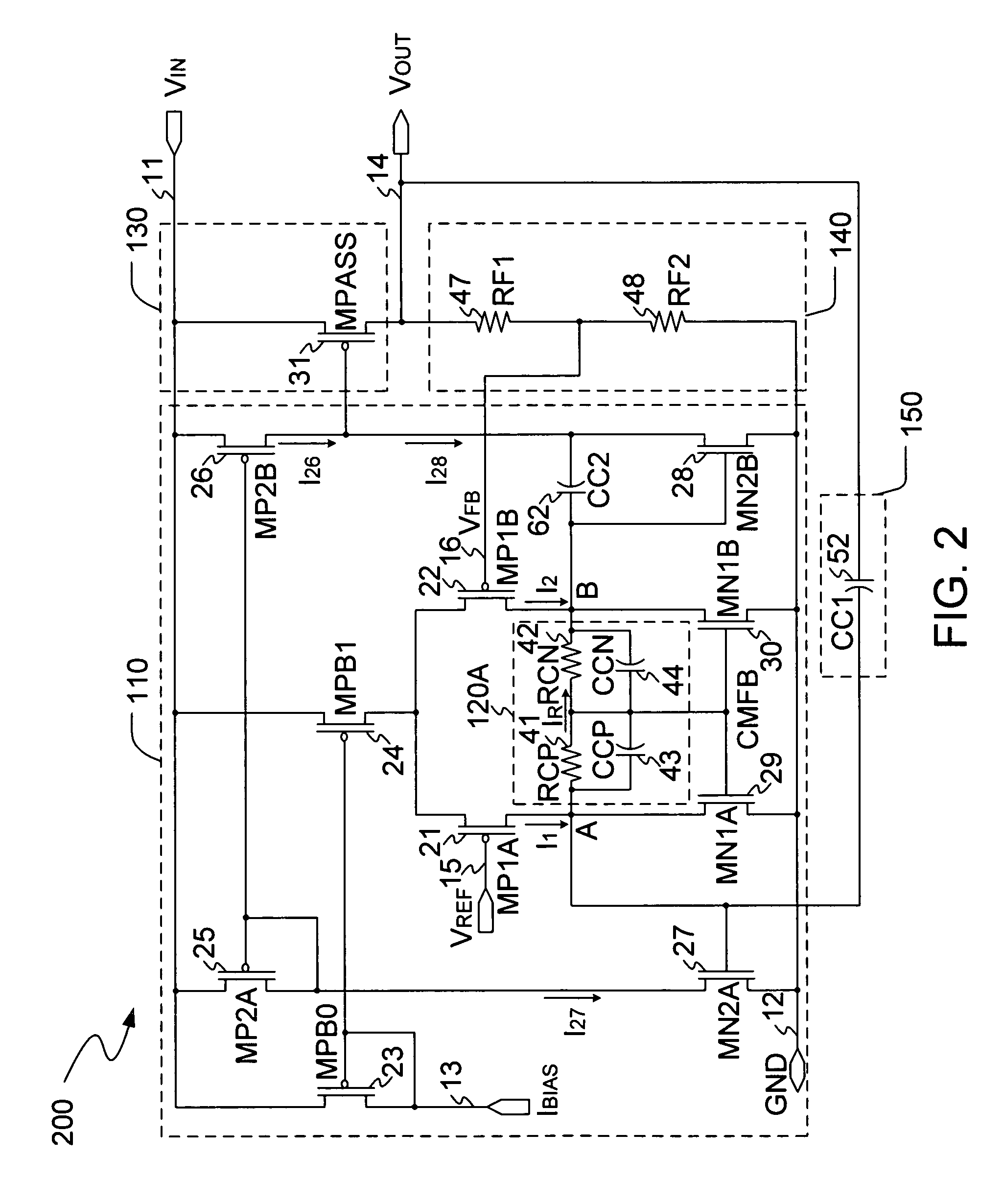
Low drop-out voltage regulator with common-mode feedback
InactiveUS20060197513A1Increase conversion rateStable output voltageAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesElectric variable regulationFrequency compensationAudio power amplifier
The present invention is a LDO voltage regulator circuit with common-mode feedback. The LDO voltage regulator includes an error amplifier with a common-mode feedback unit, a pass device and a compensation circuit. A signal from the pass device acts as an input signal to the error amplifier and is compared with another input signal, producing a differential signal. The differential signal is amplified and then provided to the pass device. A capacitor in the compensation unit provides frequency compensation to the LDO voltage regulator. The common-mode feedback unit incorporated into the error amplifier greatly improves a slew rate of a gate voltage of the pass device.
Owner:O2 MICRO INT LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com