Direct drive electromechanical linear actuators
a linear actuator, direct drive technology, applied in mechanical equipment, gearing, hoisting equipment, etc., can solve problems such as backlash, wear, complexity and cost, and life limitations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first exemplary embodiment
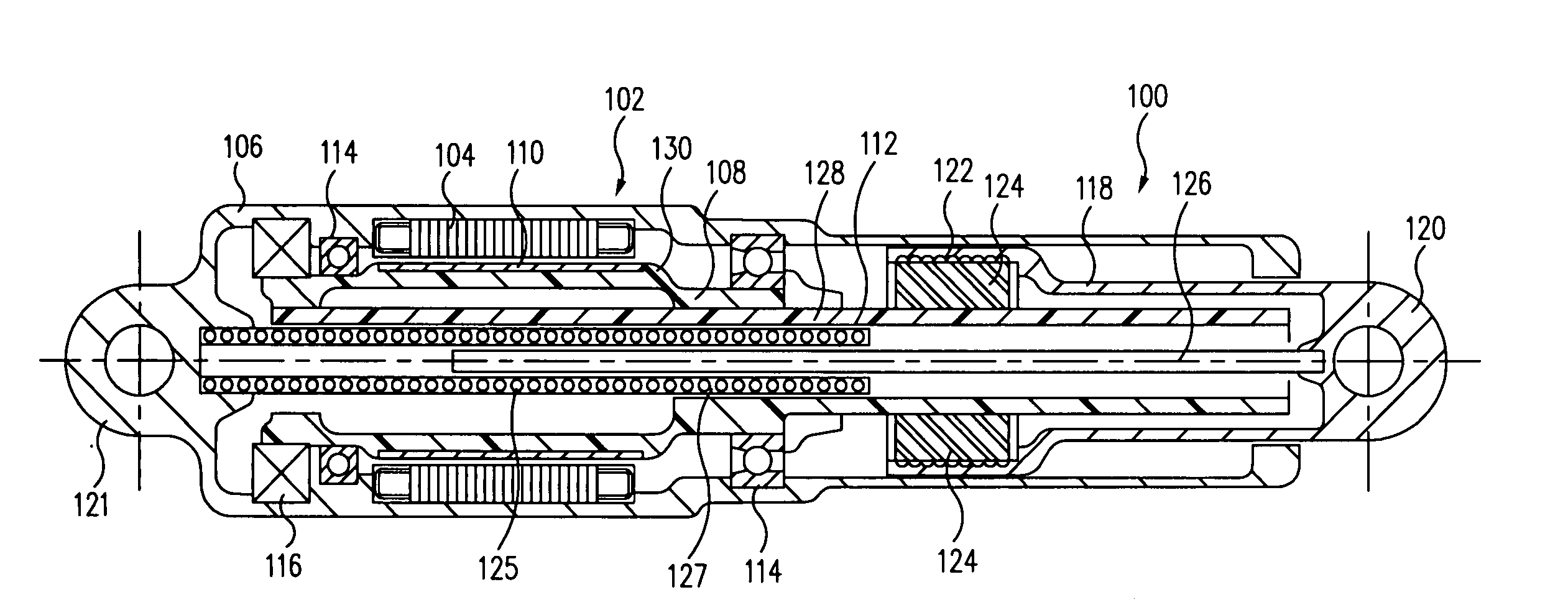
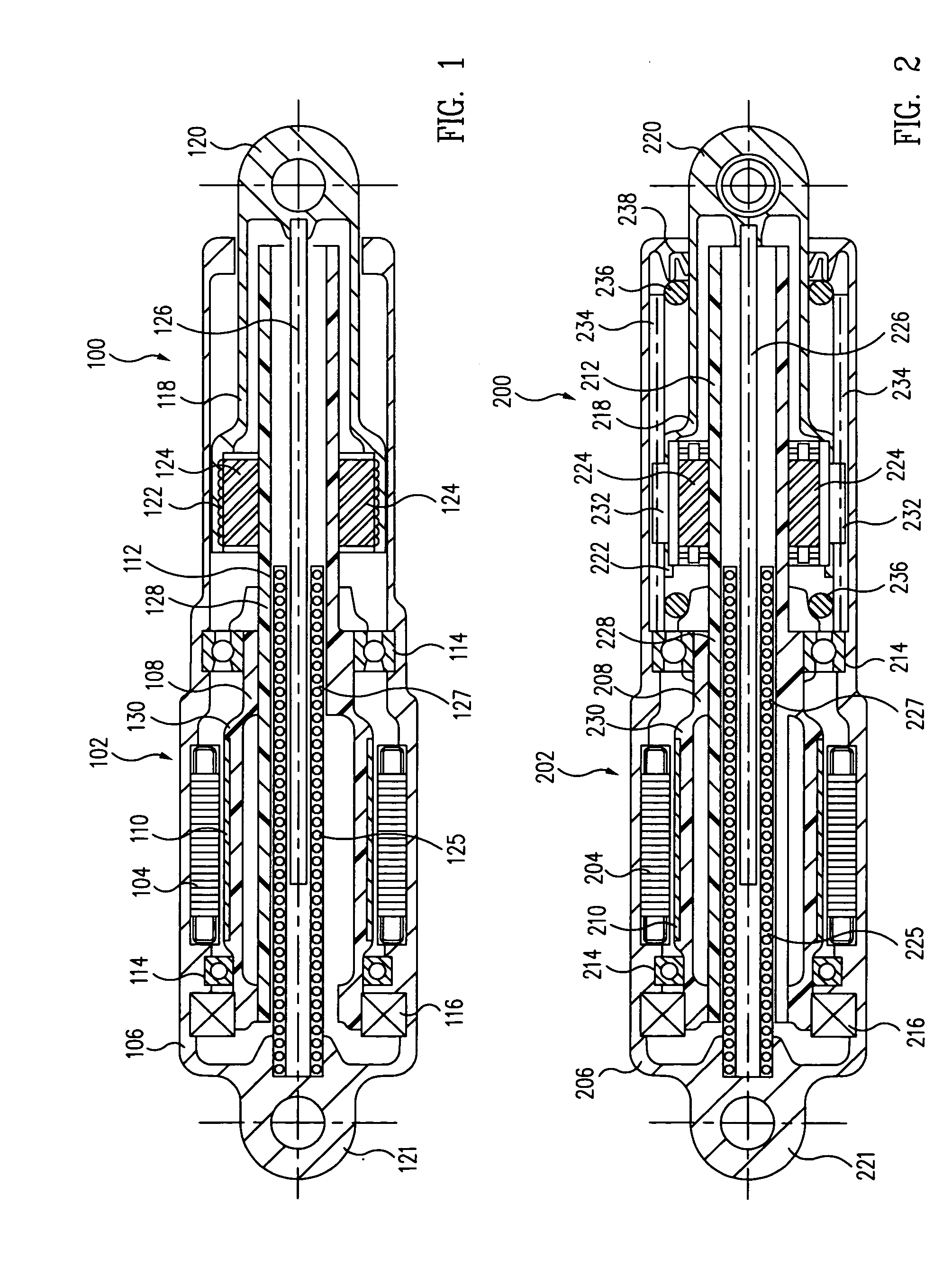
[0030] Turning now to the figures, a first exemplary embodiment of a direct drive electromechanical linear actuator 100 in accordance with the present invention, comprising a single motor, single-ended device, is illustrated in the cross-sectional side elevation view of FIG. 1. The actuator 100 comprises a brushless electric motor 102 having a stator 104 mounted in an elongated housing 106. A rotor 108 incorporating permanent magnets 110 and an elongated, externally threaded central shaft, or lead screw 112, is rotatably supported in the housing by a set of bearings 114. The rotor 108 supports a motor encoder 116 of a known type, which functions as a substitute for a motor commutator, for conjoint rotation with the rotor. A tubular output extension 118 having an output end 120, and containing an internally threaded planetary roller nut 122 located at the opposite end thereof, is disposed coaxially within and guided by the housing for both rotation about and translation along the lon...
second exemplary embodiment
[0033] A second exemplary embodiment of a direct drive electromechanical linear actuator 200 in accordance with the present invention, comprising a single motor, single-ended device with internal torque reaction, is illustrated in the cross-sectional side elevation view of FIG. 2. As may be seen by a comparison of the respective first and second embodiments of FIGS. 1 and 2, the second embodiment of actuator 200 incorporates several of the features of the first embodiment of actuator 100, but with the addition of a nut-and-output-end anti-rotation feature 232 and 234, as illustrated in FIG. 2. In particular, in the second embodiment, low-friction (e.g., Teflon) splines, or sliders 232, are disposed on the planetary nut 222 to slide with a slight interference fit in complementary longitudinal grooves, or tracks 234, disposed in the housing 206. The motor 202, and hence, the torque on the nut 222, is thereby reacted directly back to the housing, in a manner that prevents any rotationa...
third exemplary embodiment
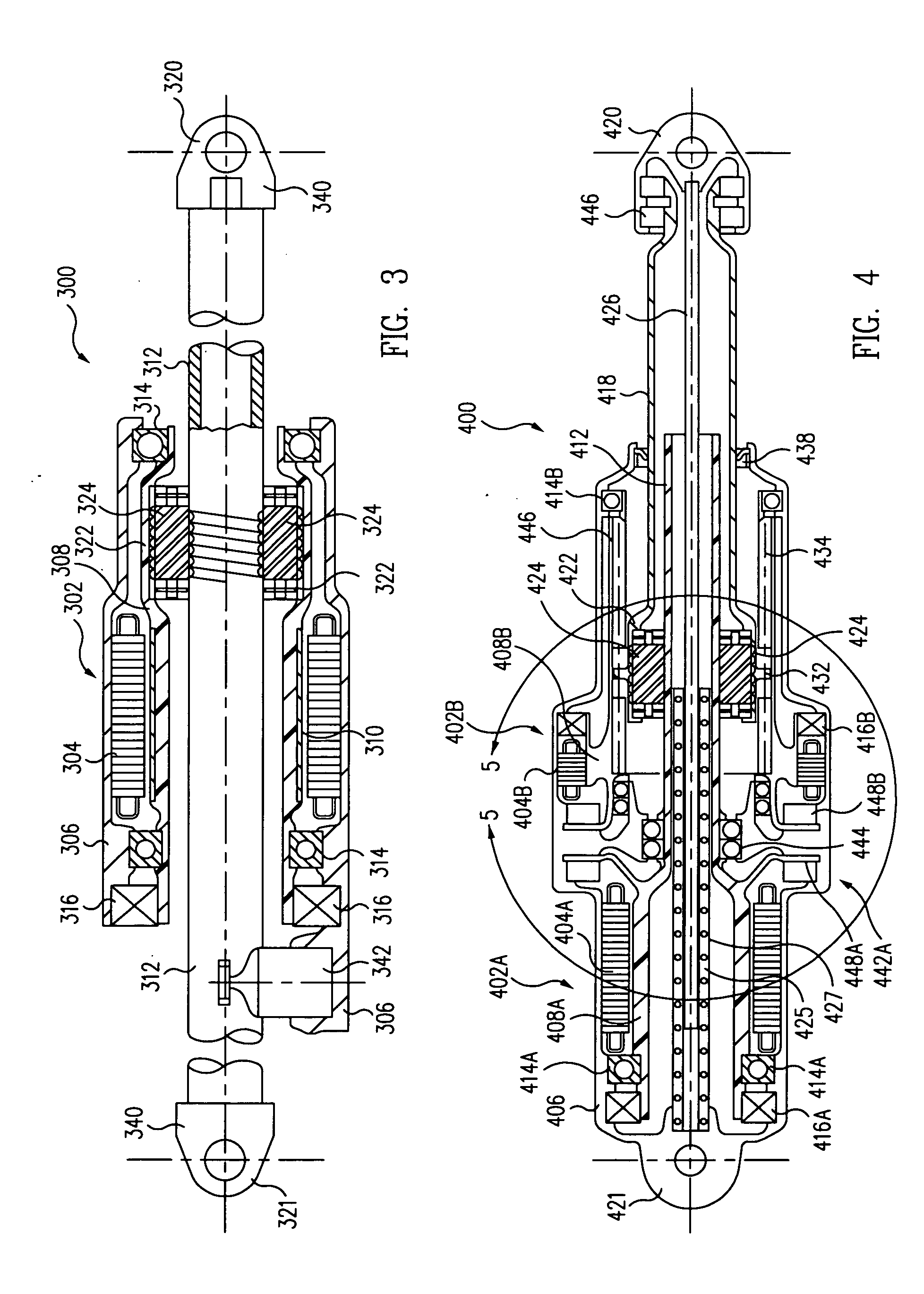
[0036] A third exemplary embodiment of a direct drive electromechanical linear actuator 300 in accordance with the present invention, comprising a single motor, and either a single- or double-ended device with enhanced travel range, is illustrated in the cross-sectional side elevation view of FIG. 3. As in the first and second embodiments above, a brushless electric motor 302 includes a stator portion 304 fixedly mounted in a housing 306. A rotor portion 308 is also rotatably supported in the housing by a set of bearings 314, and the rotor portion may also support a motor encoder 316 for conjoint rotation, as in the embodiments above.
[0037] As illustrated in FIG. 3, the rotor portion 308 of the motor 302 of the third embodiment is made as an elongated annular shaft on which neodymium-iron magnets 310 are mounted, as in the above embodiments, and in which the nut 322 of the planetary roller screw is concentrically mounted. The non-rotating central shaft, or lead screw 312, has a cle...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com