Patents
Literature
14983results about "Suture equipments" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
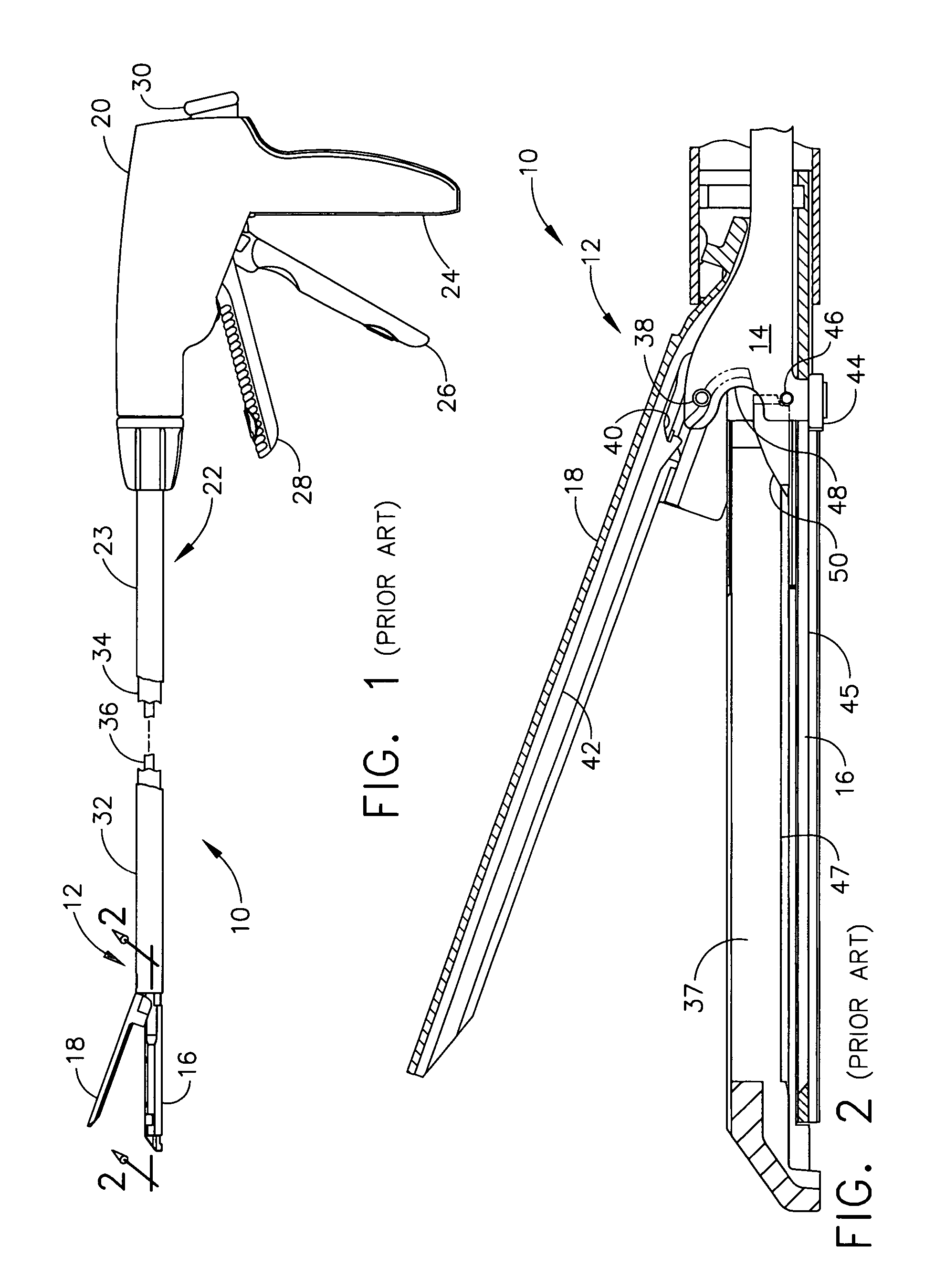
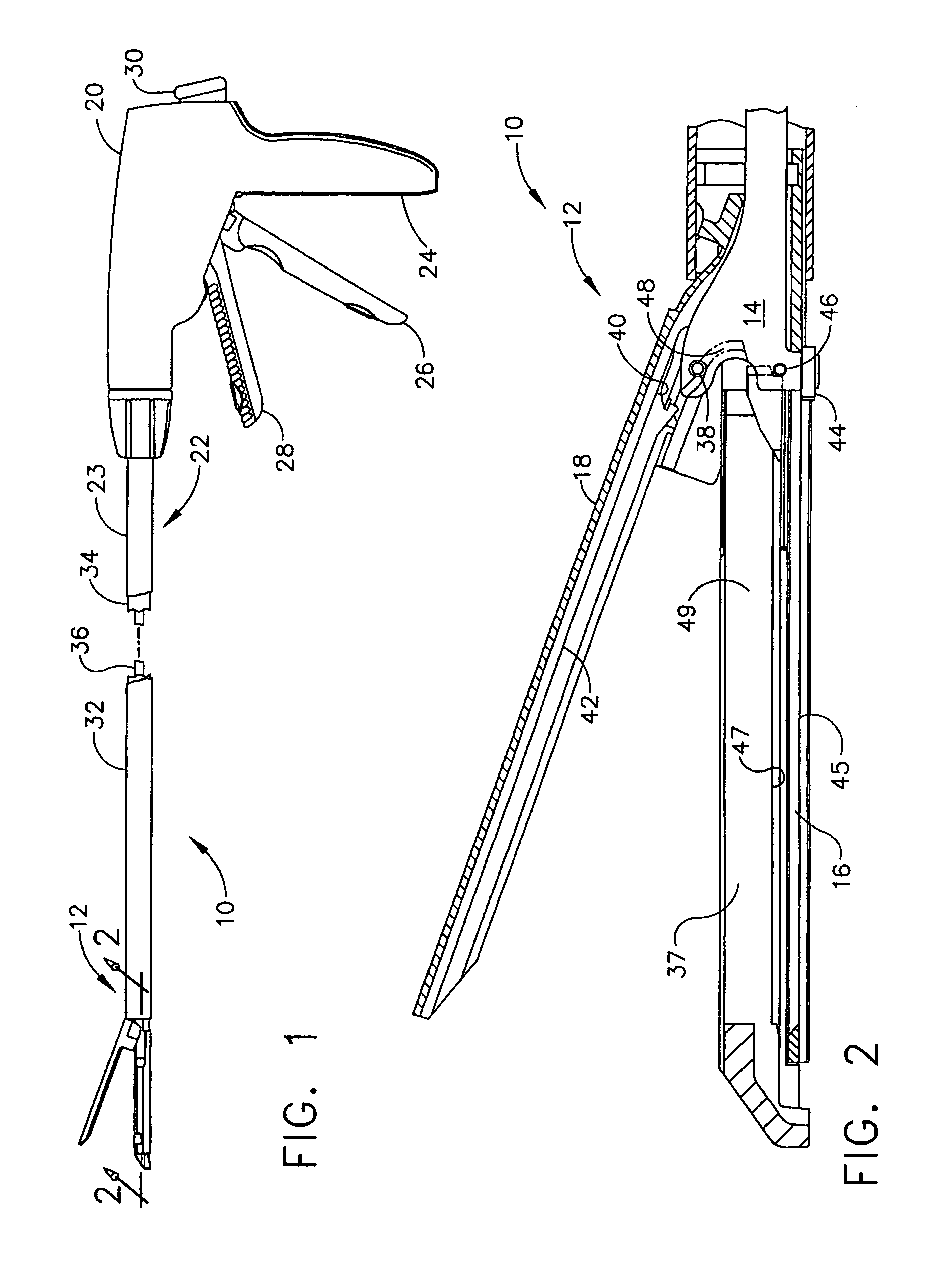
Surgical stapling instrument having separate distinct closing and firing systems
InactiveUS7000818B2Severing and stapling tissueEfficiently formedSuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical stapleEngineering
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
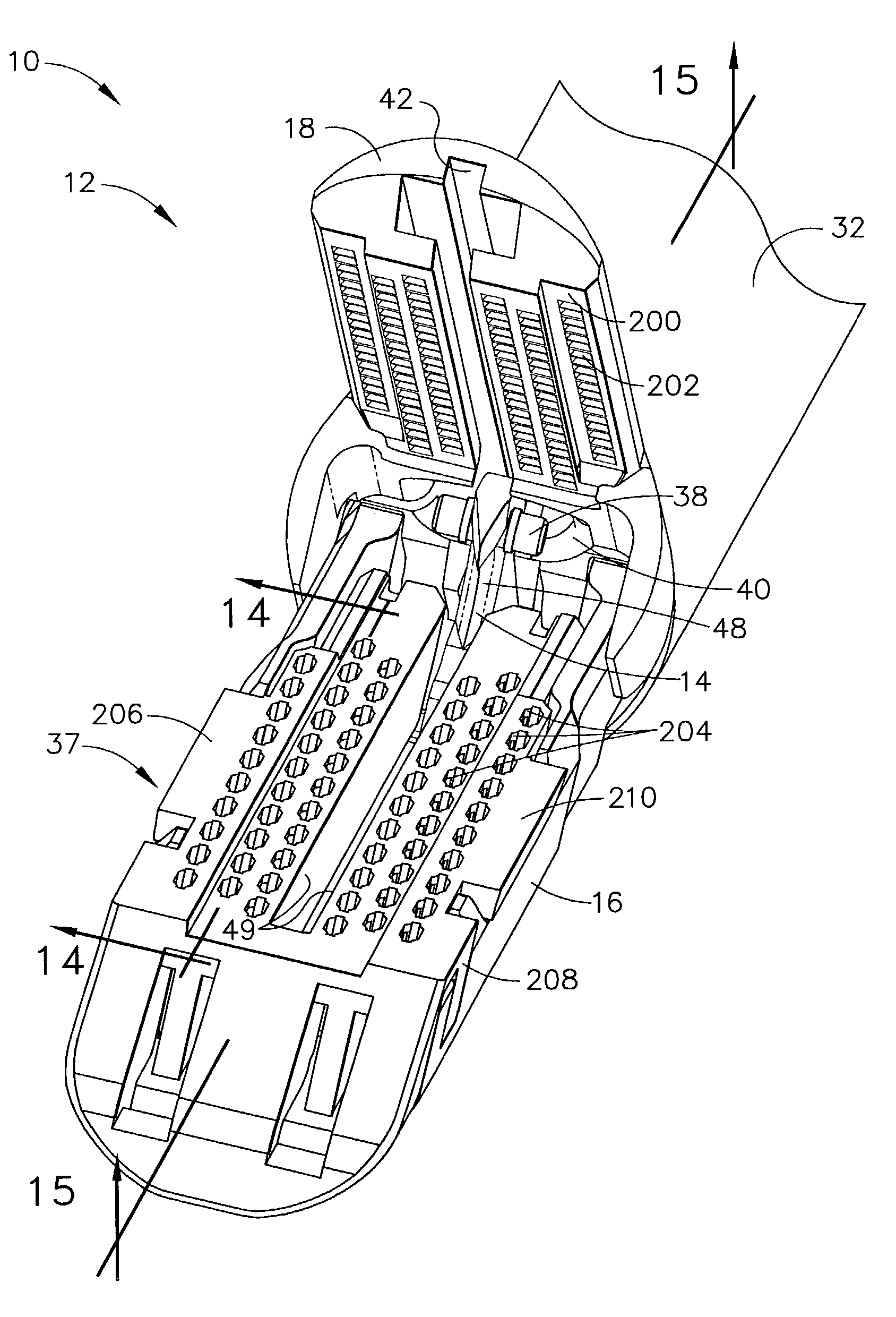
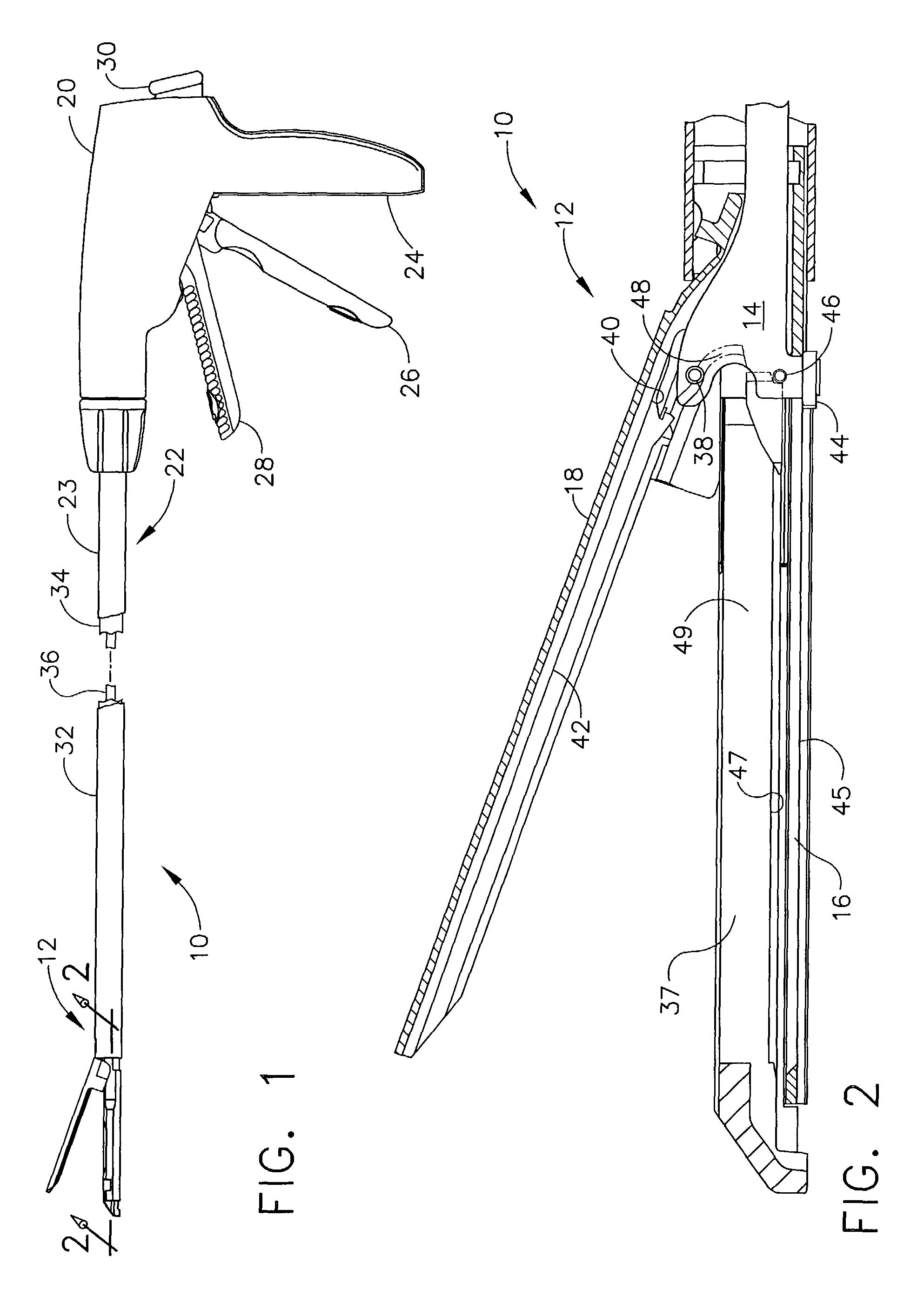
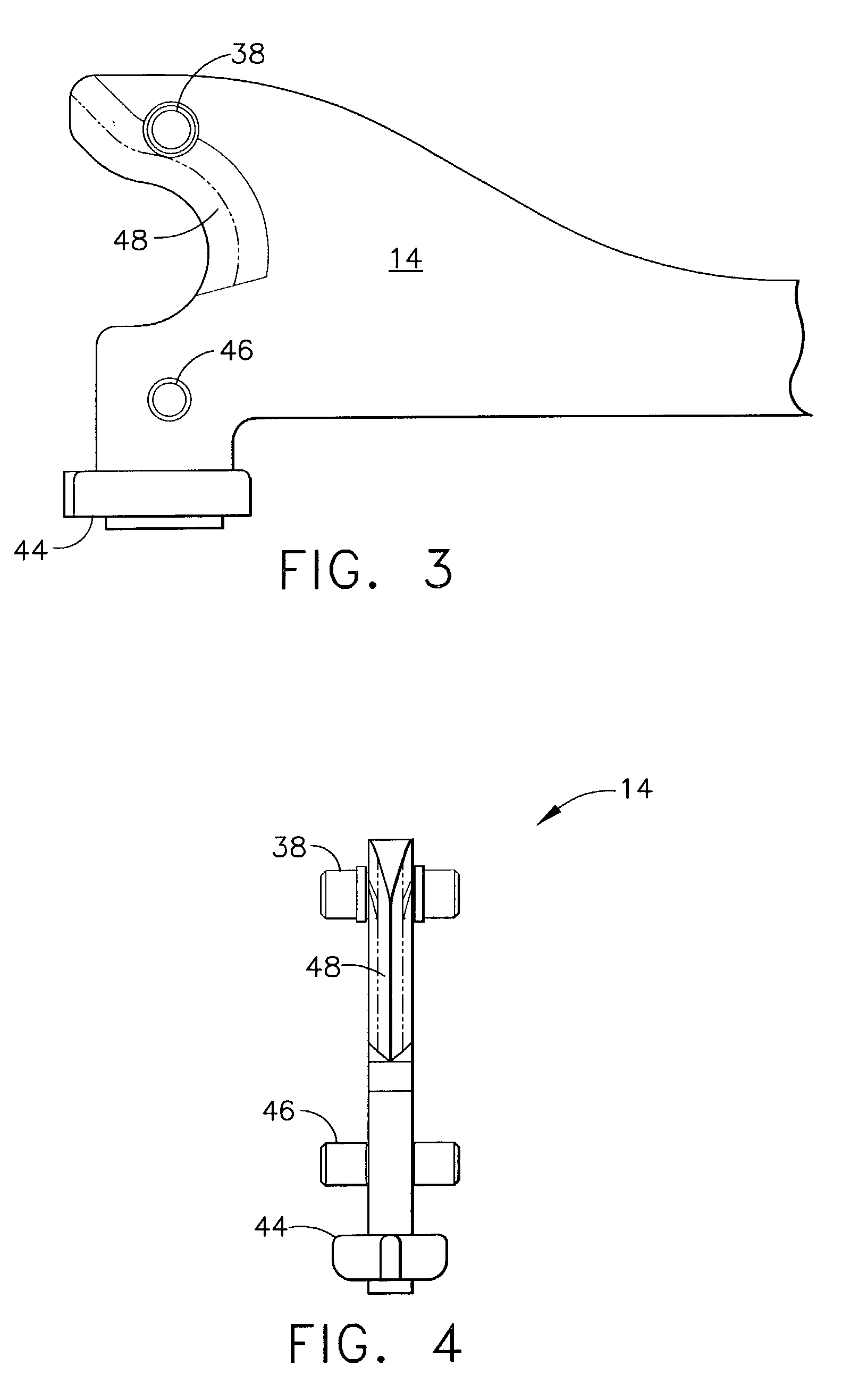
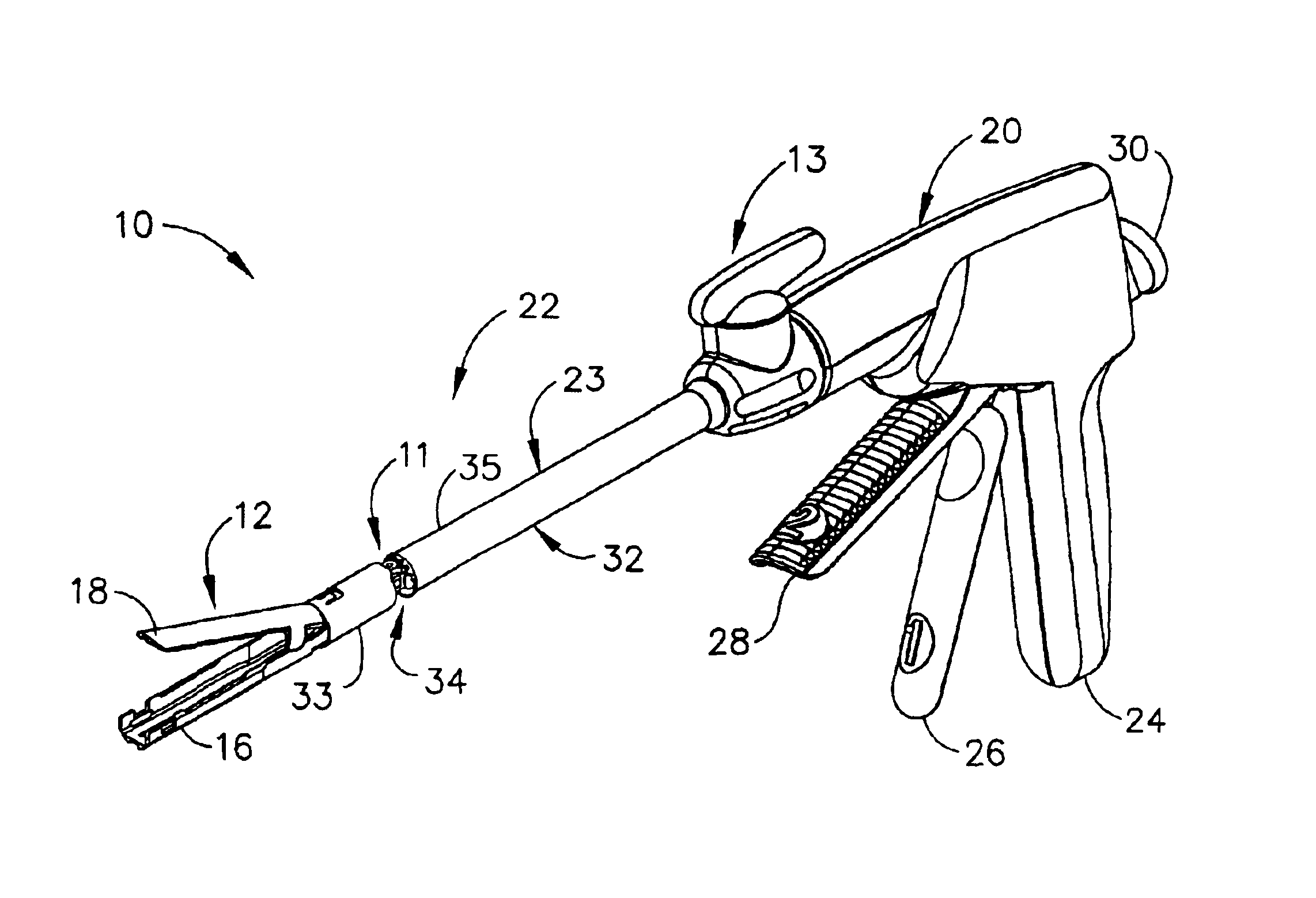
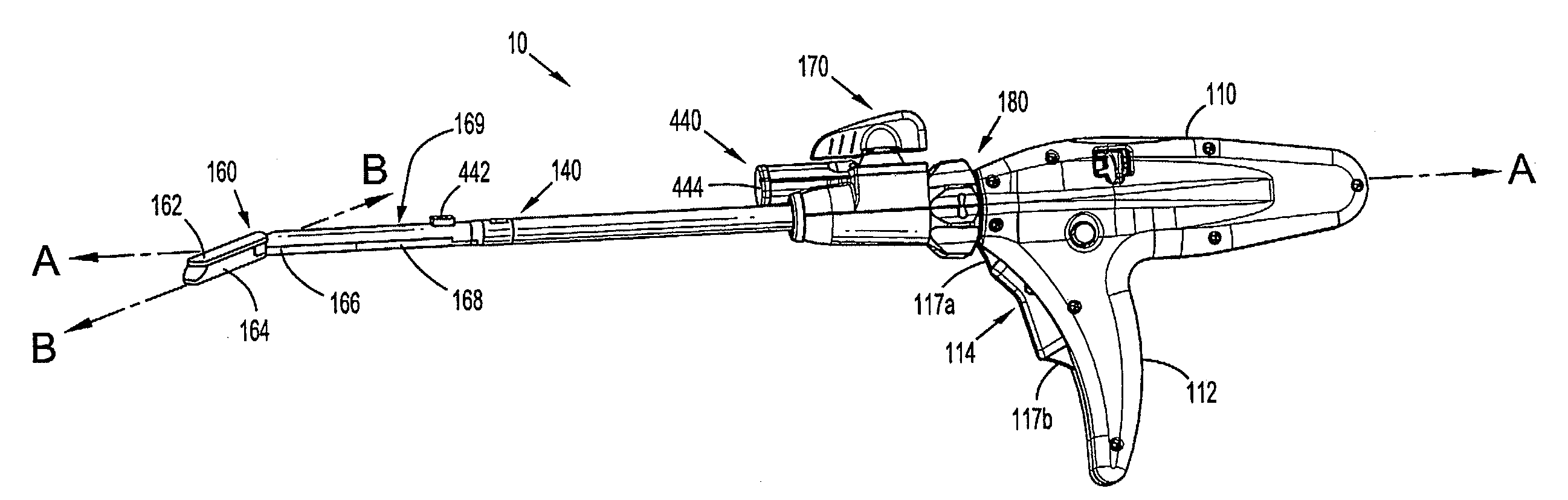
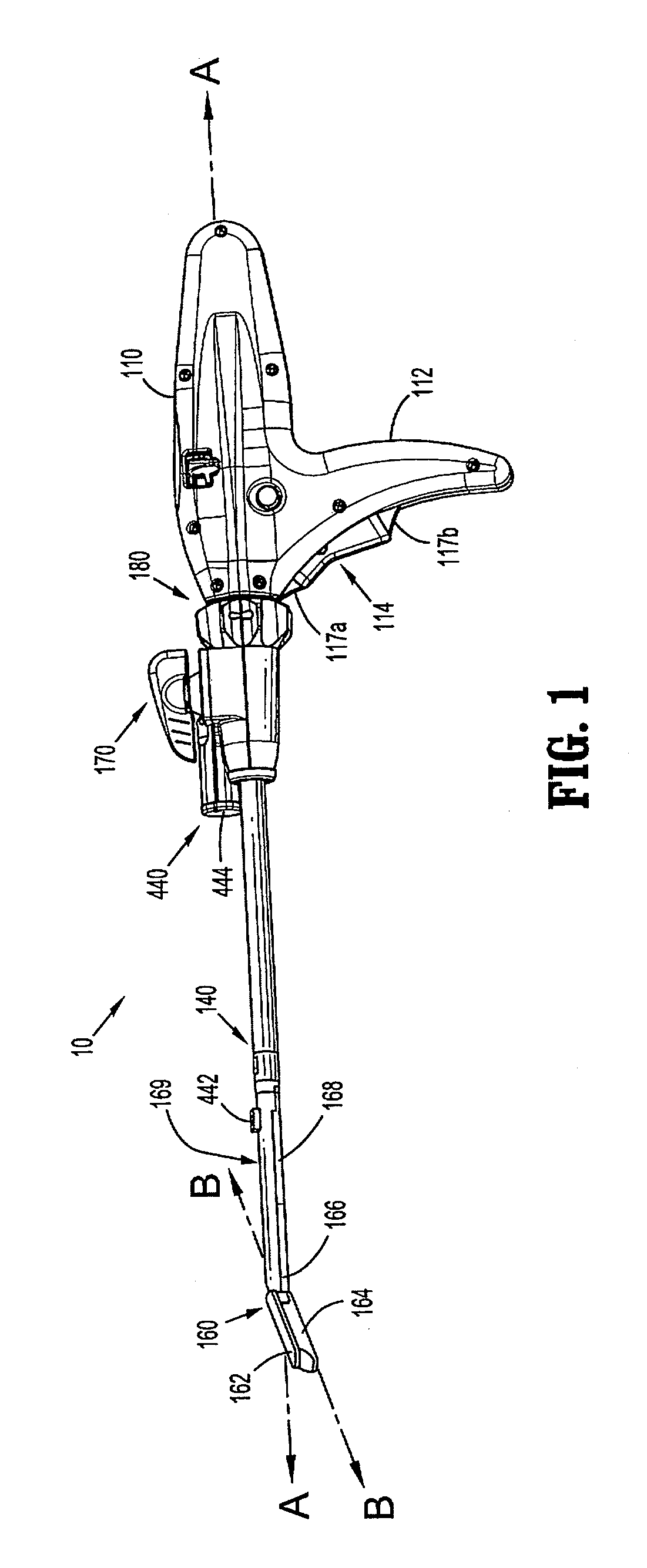
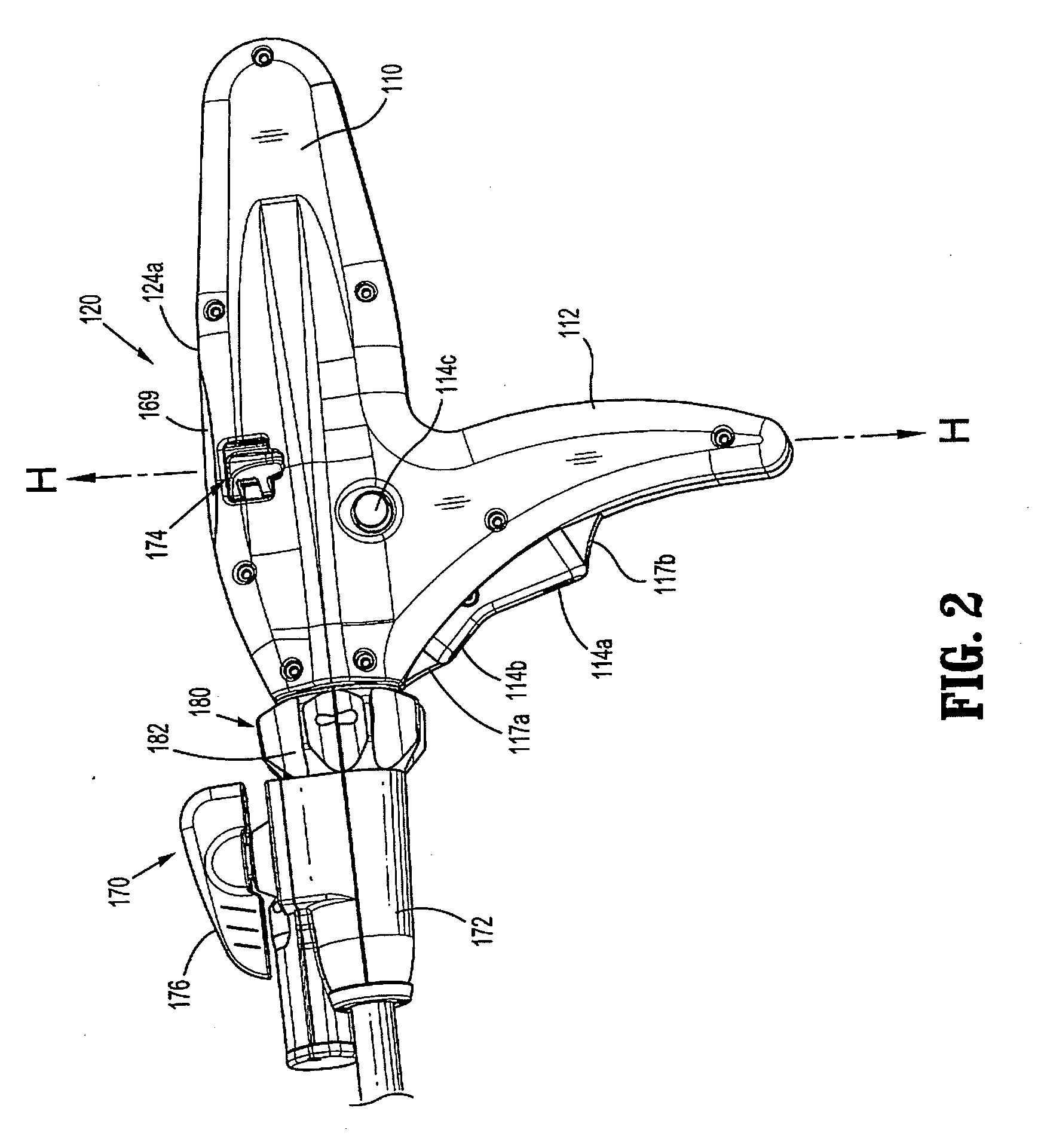
Surgical instrument having an articulating end effector
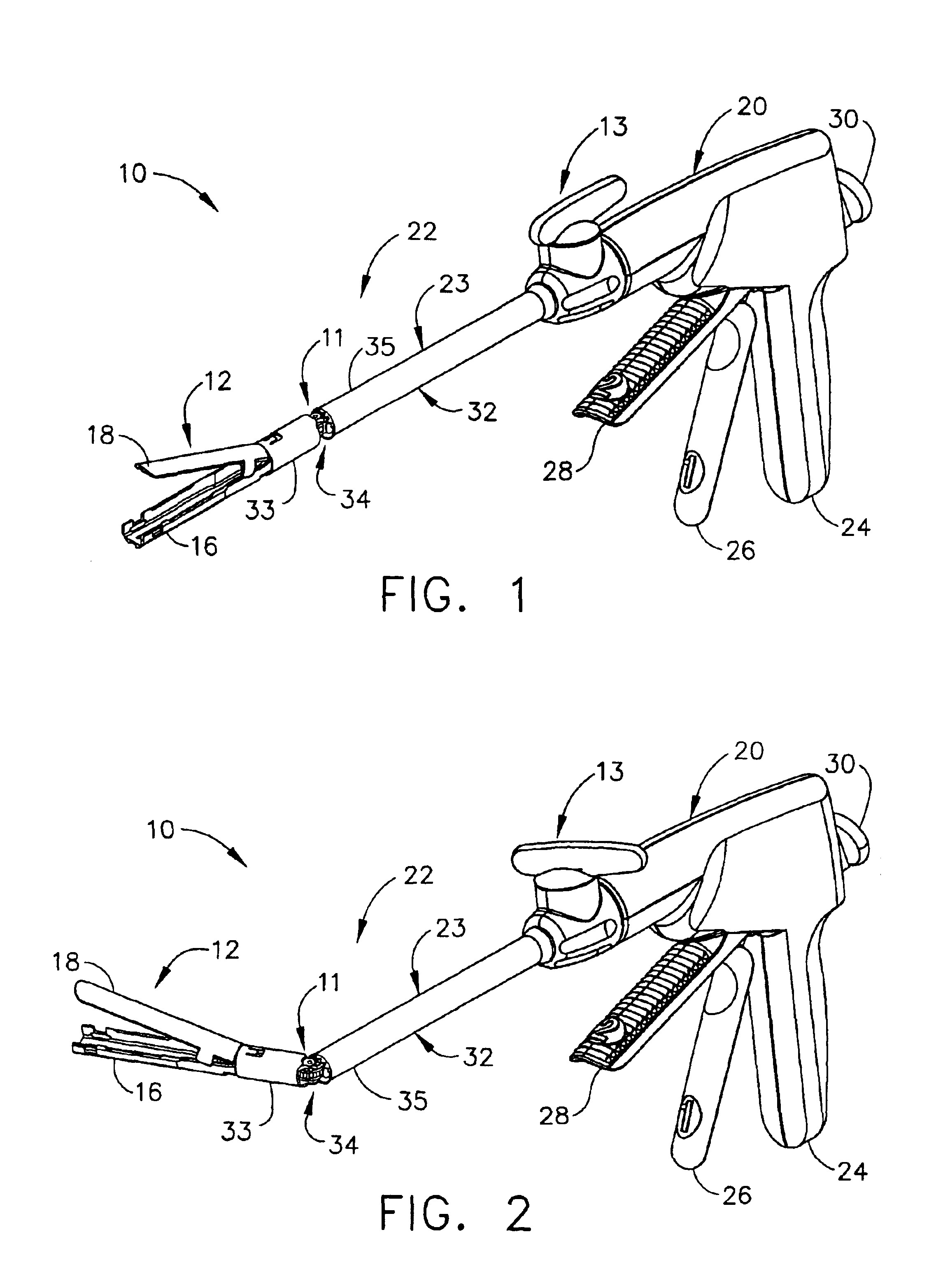
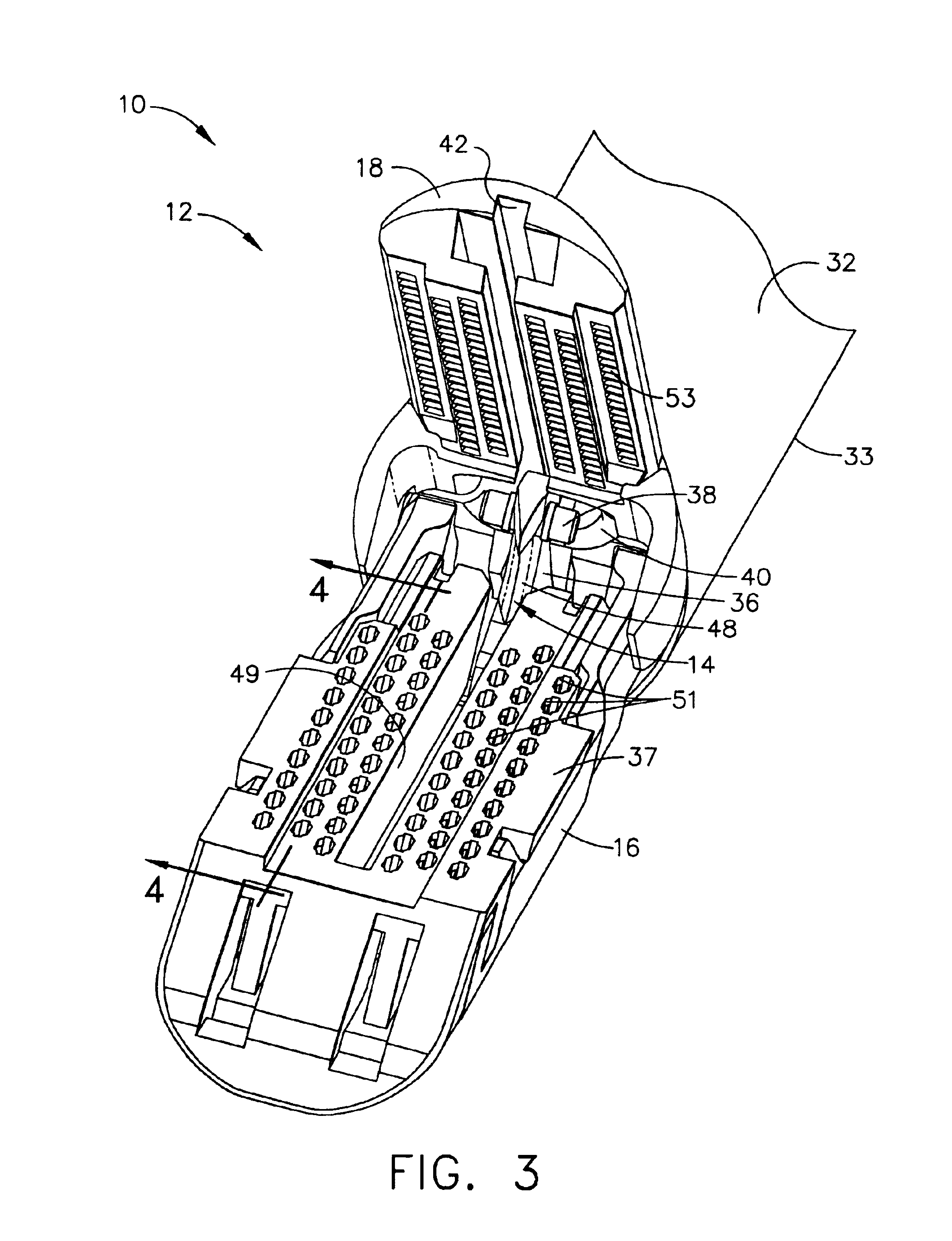
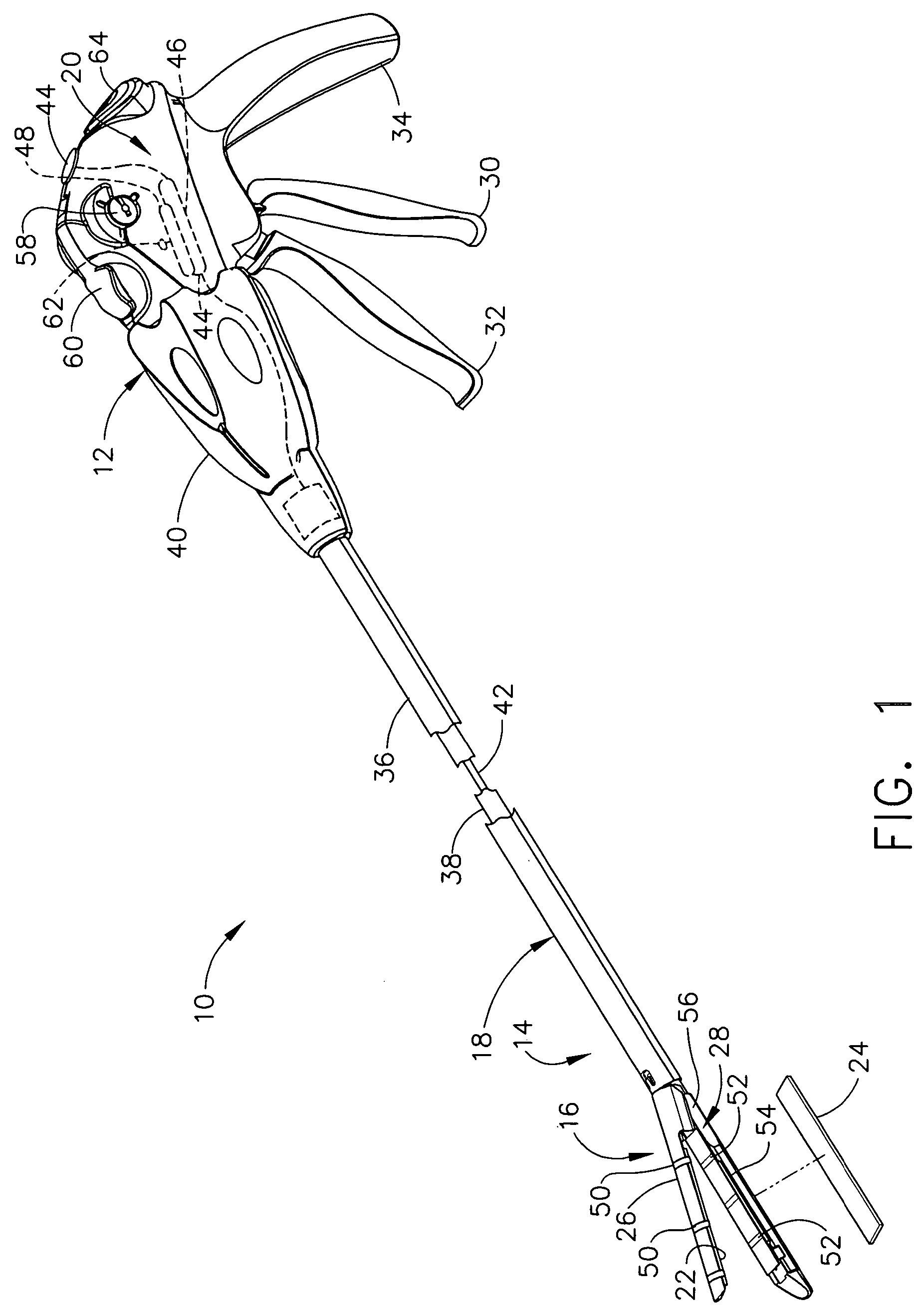
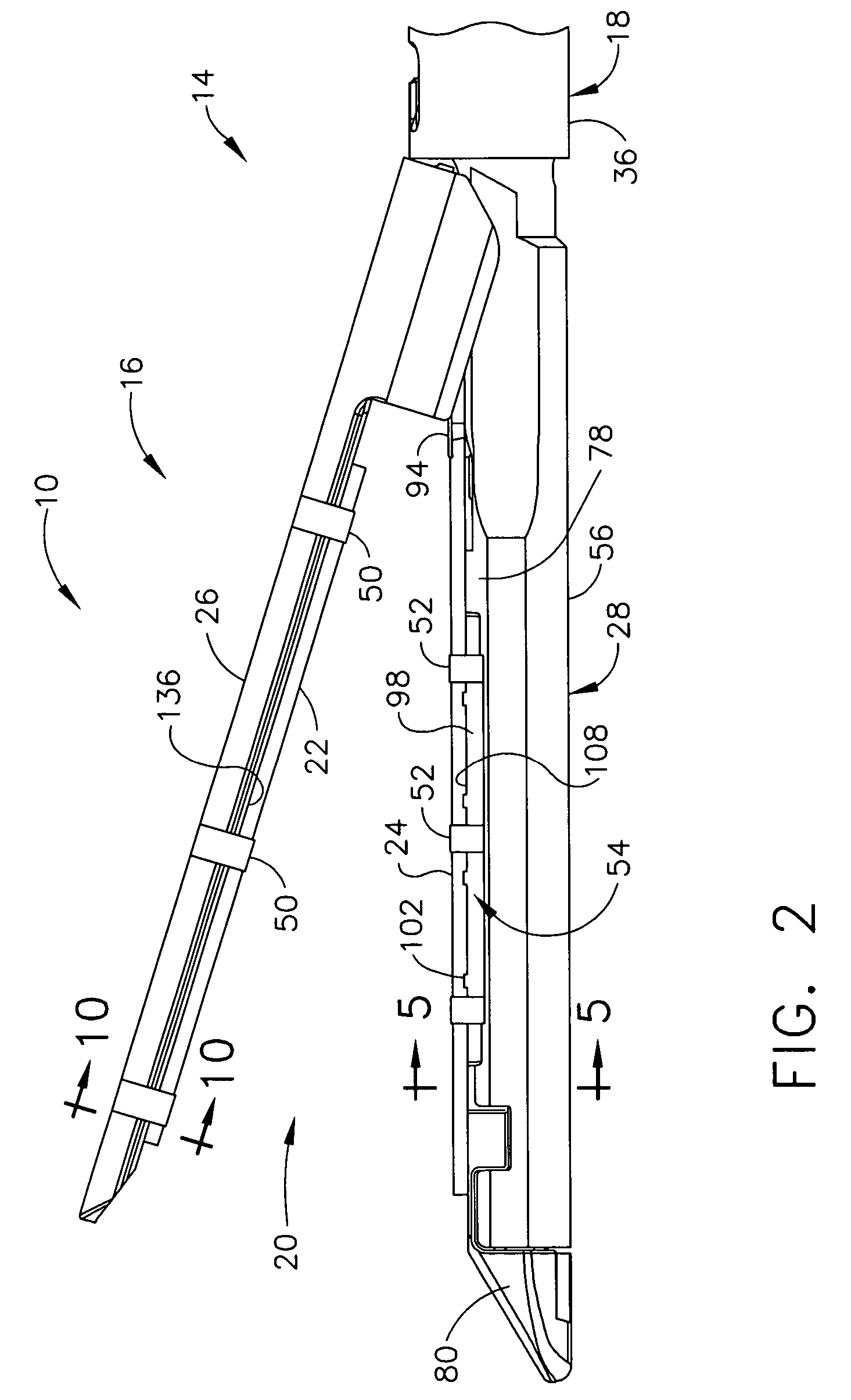
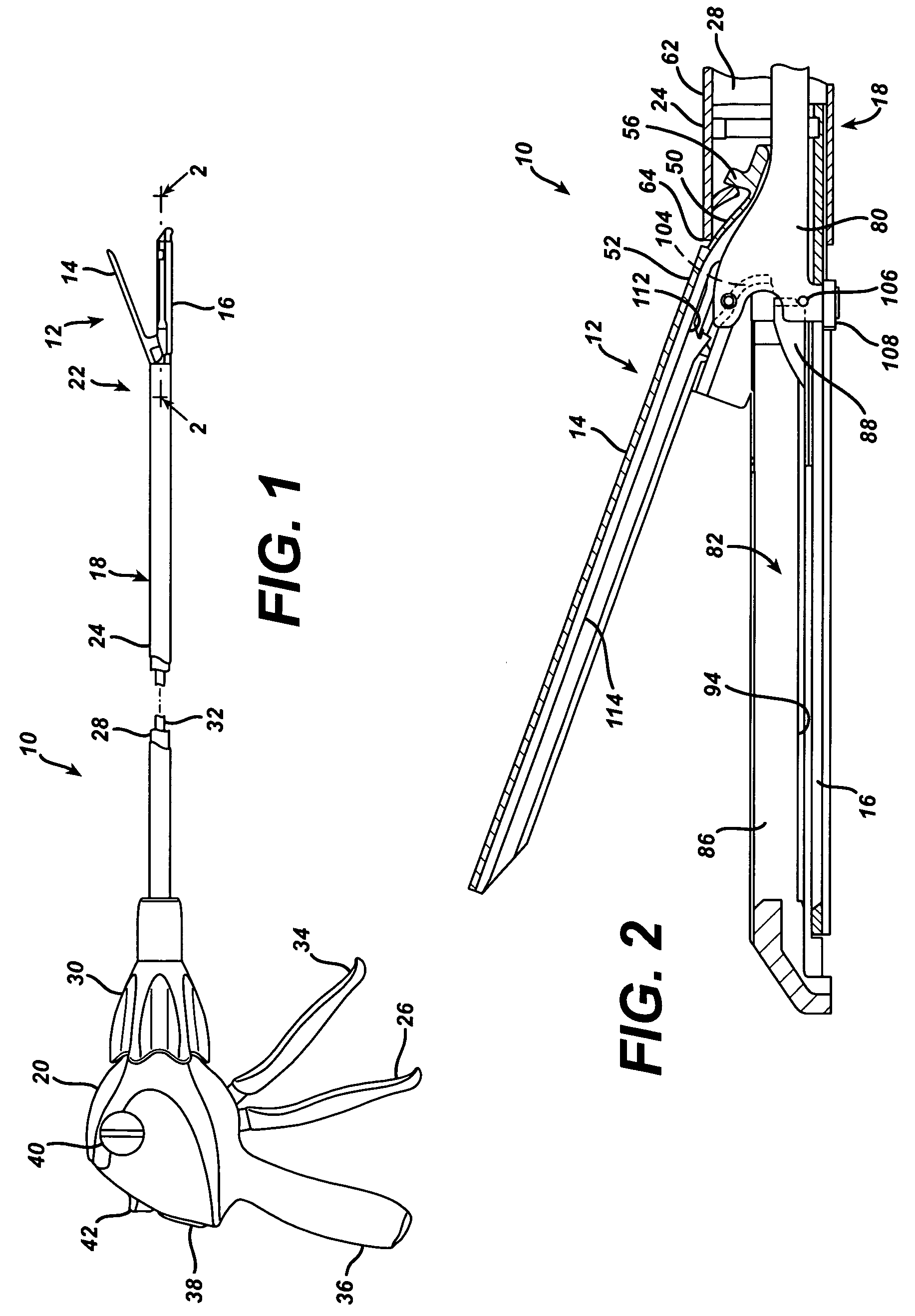
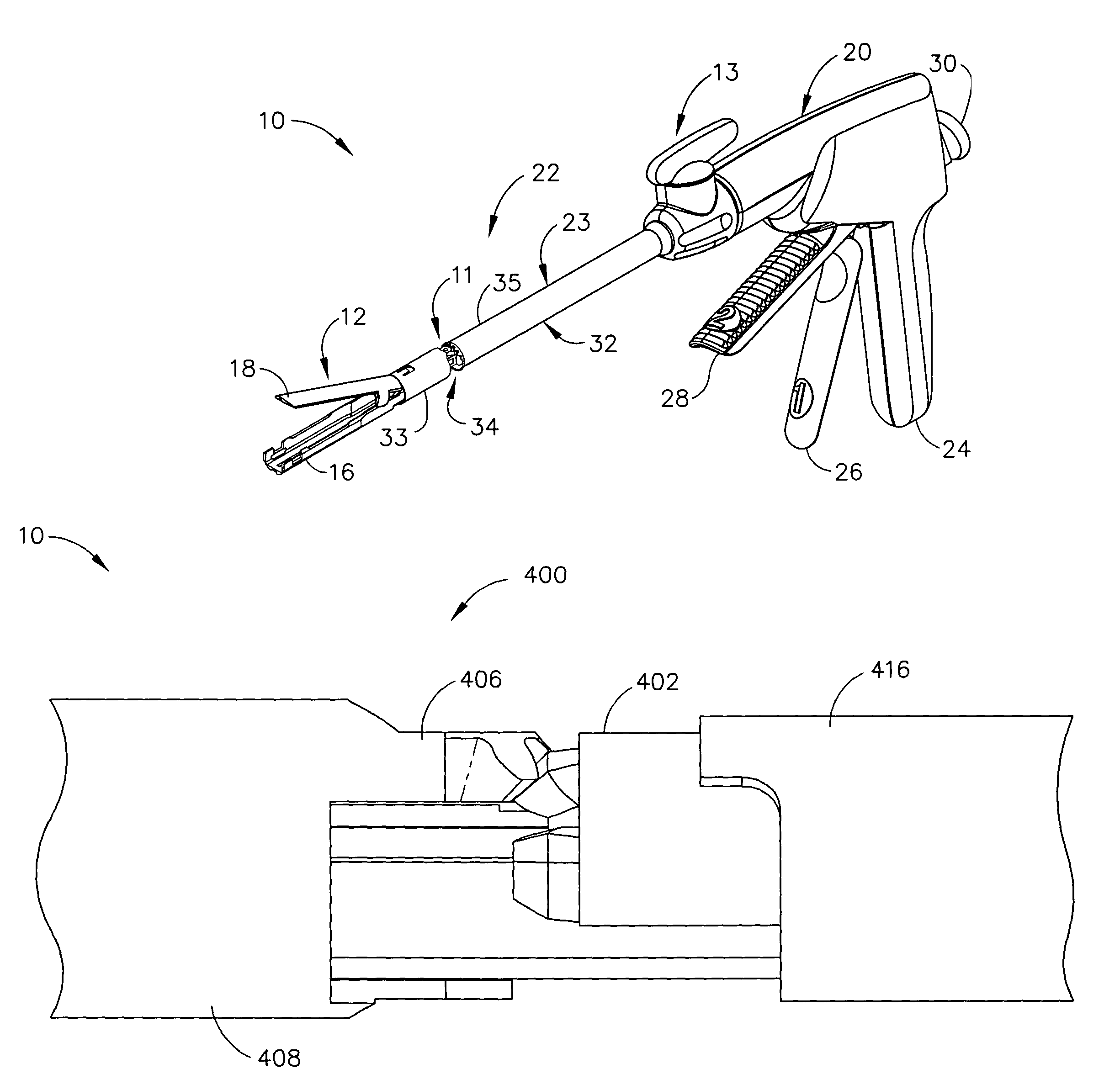
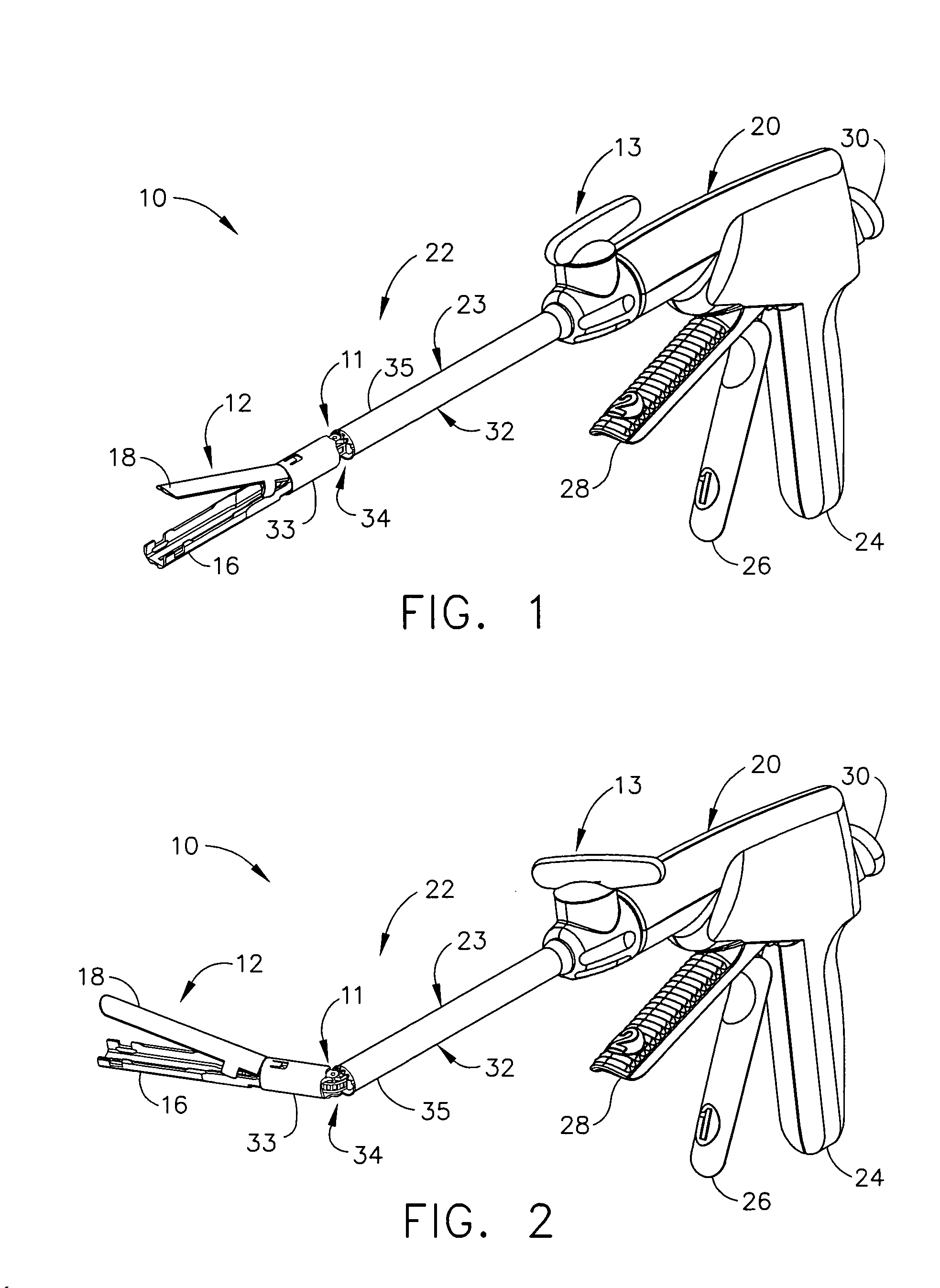
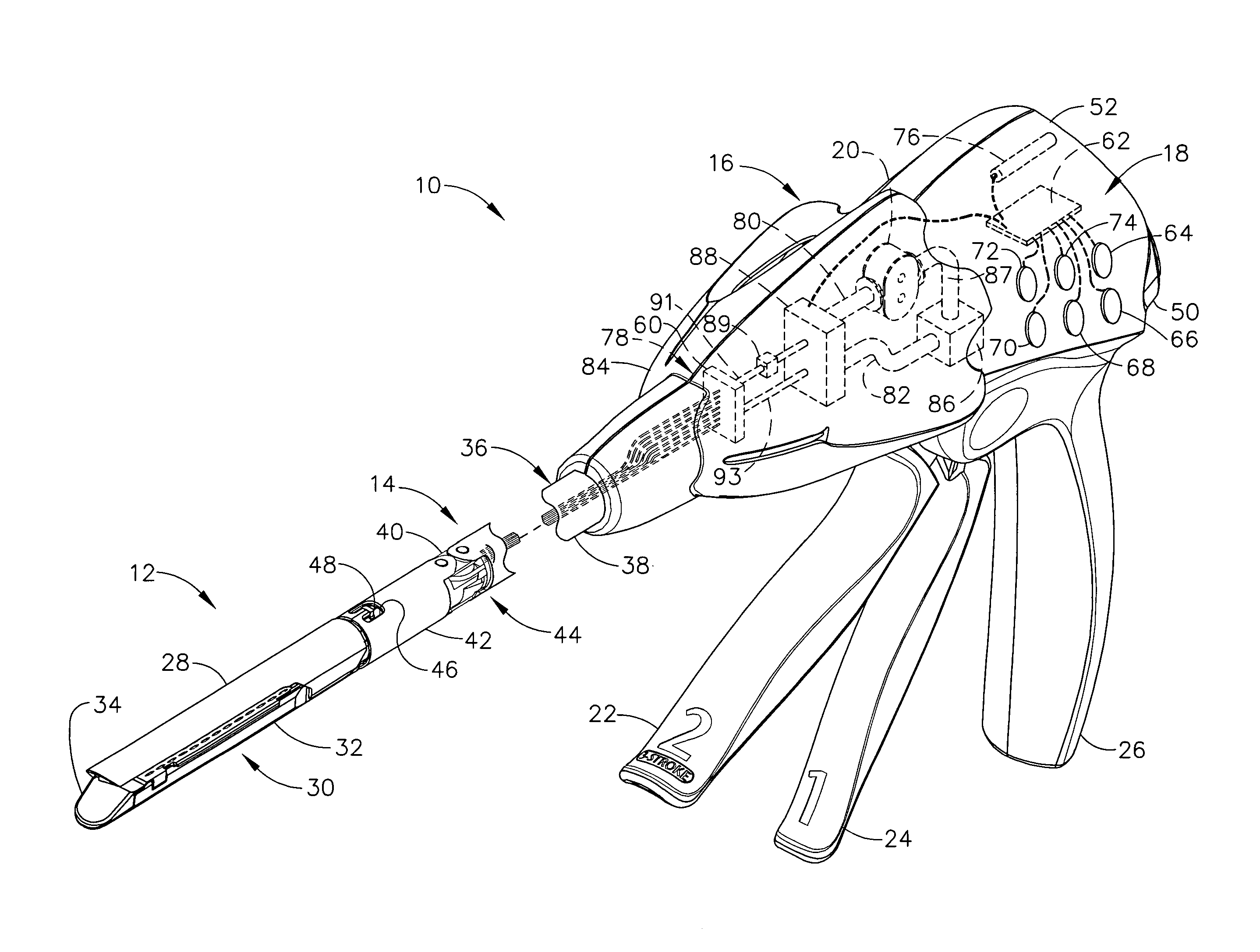
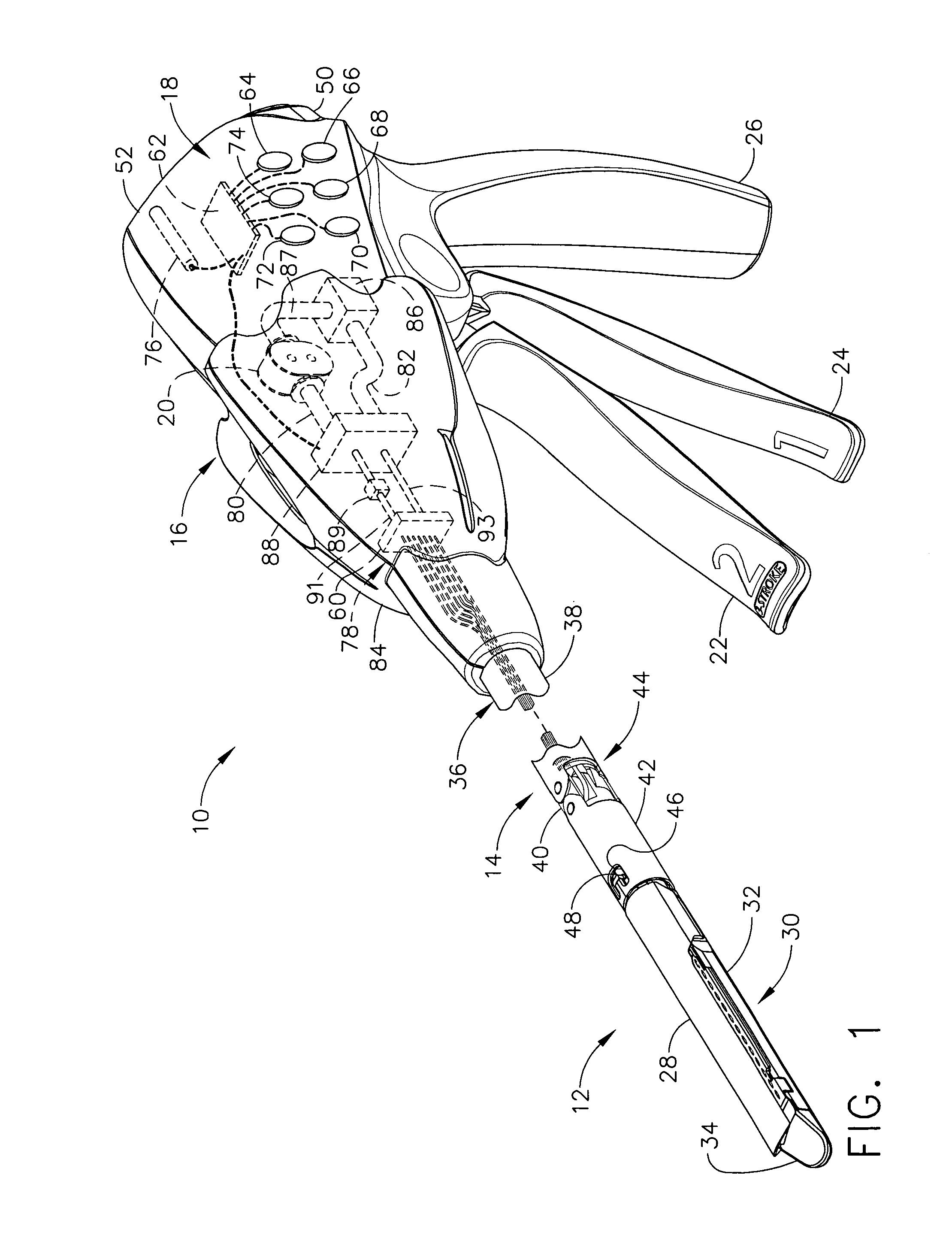
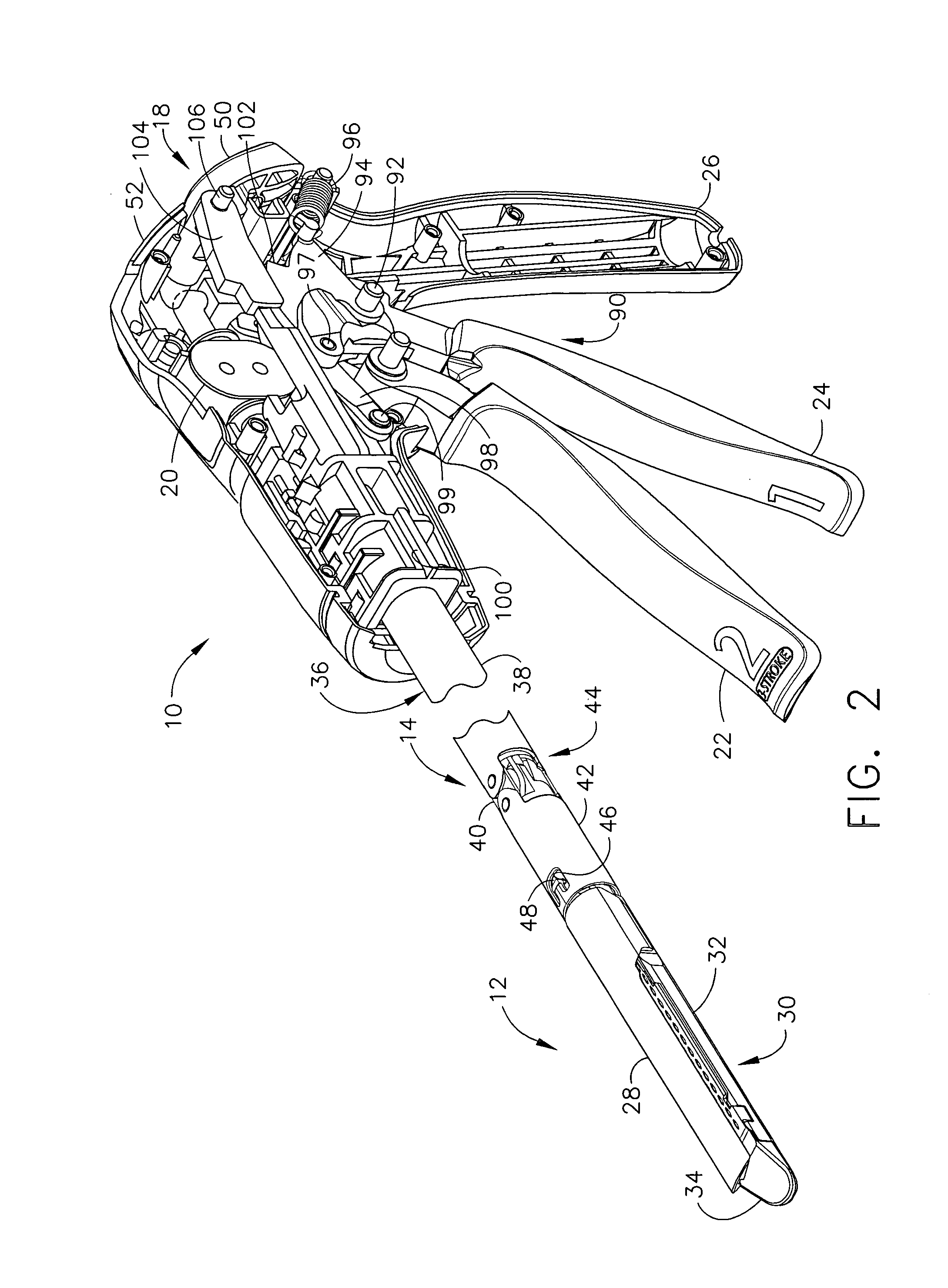
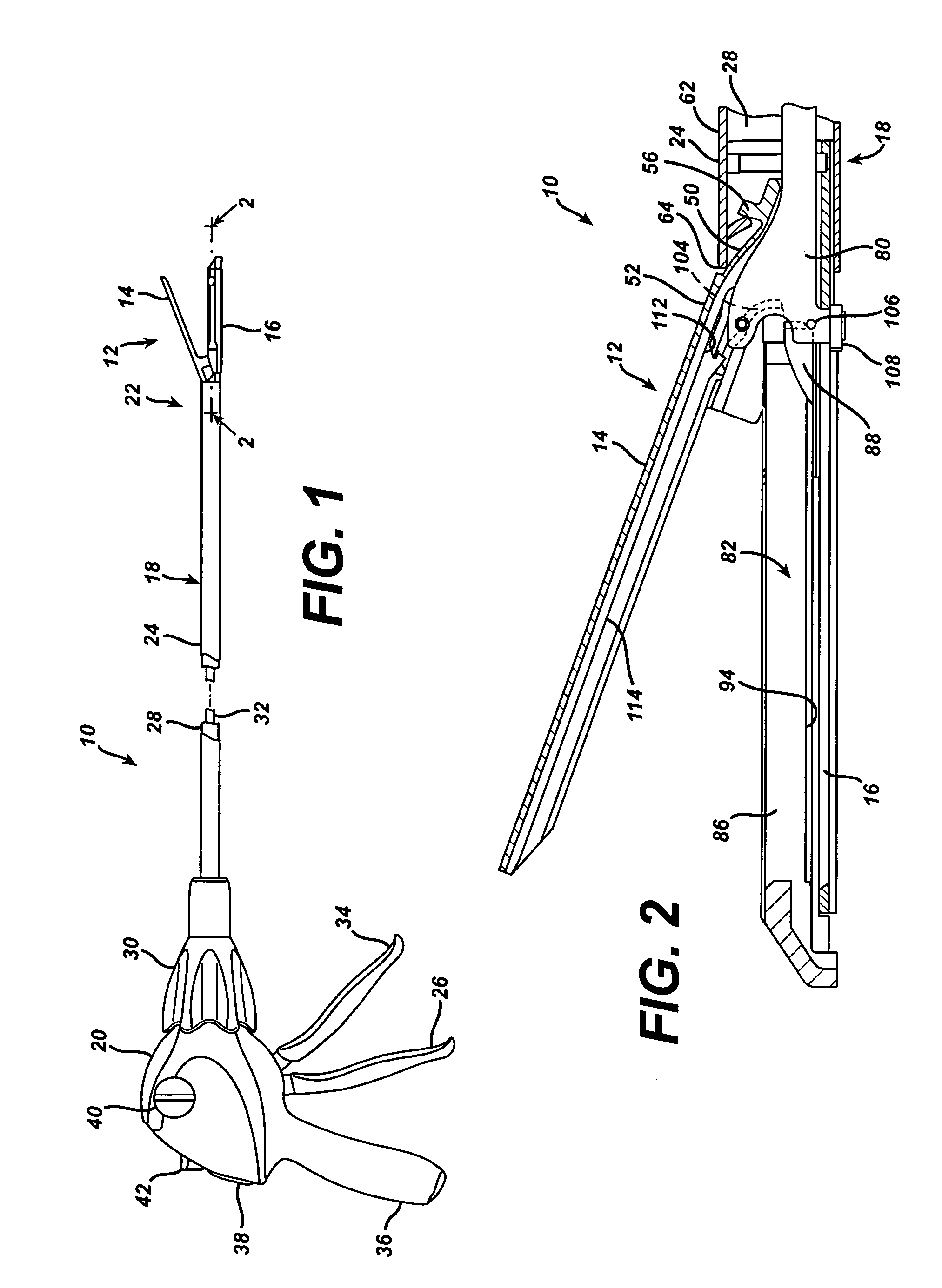
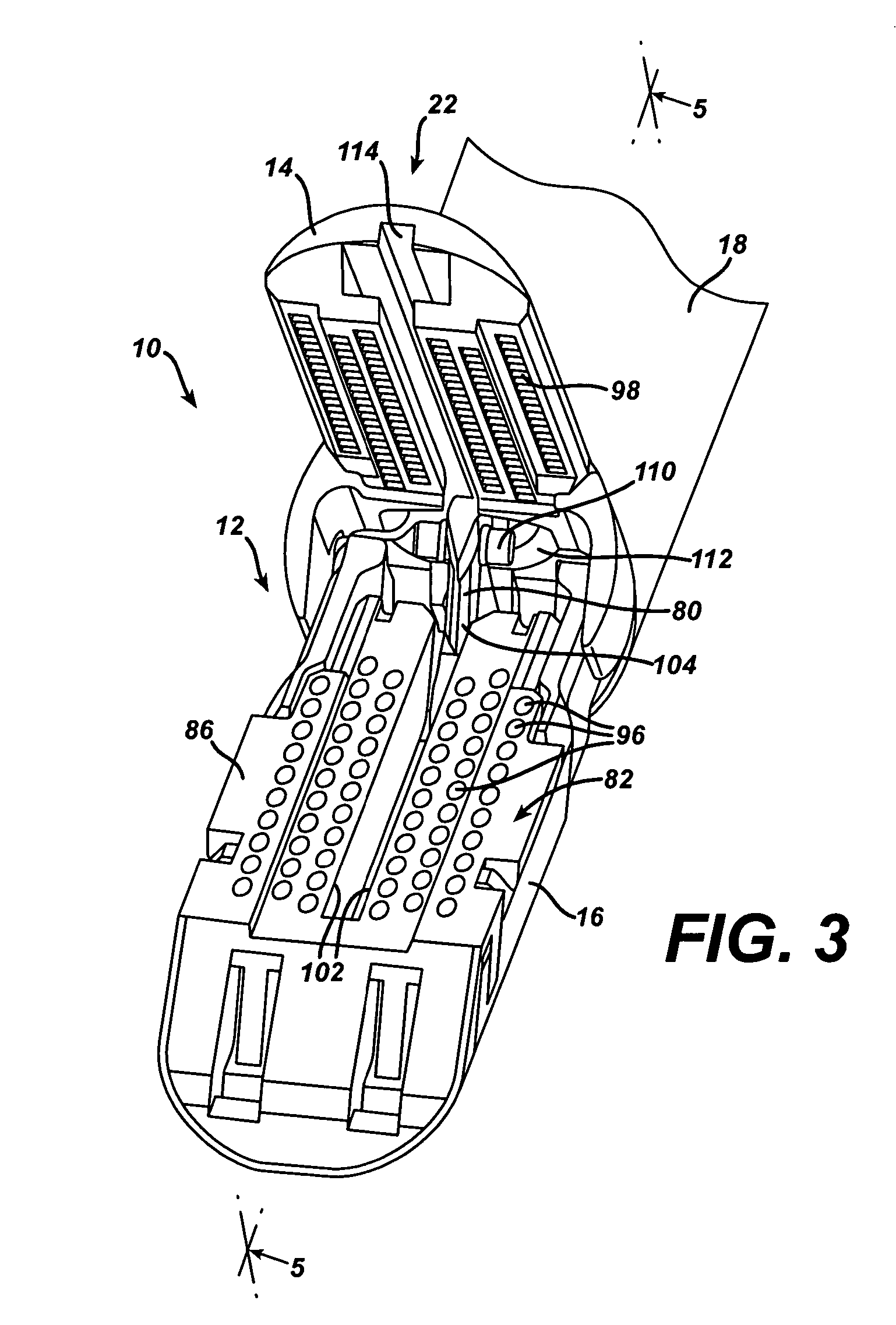
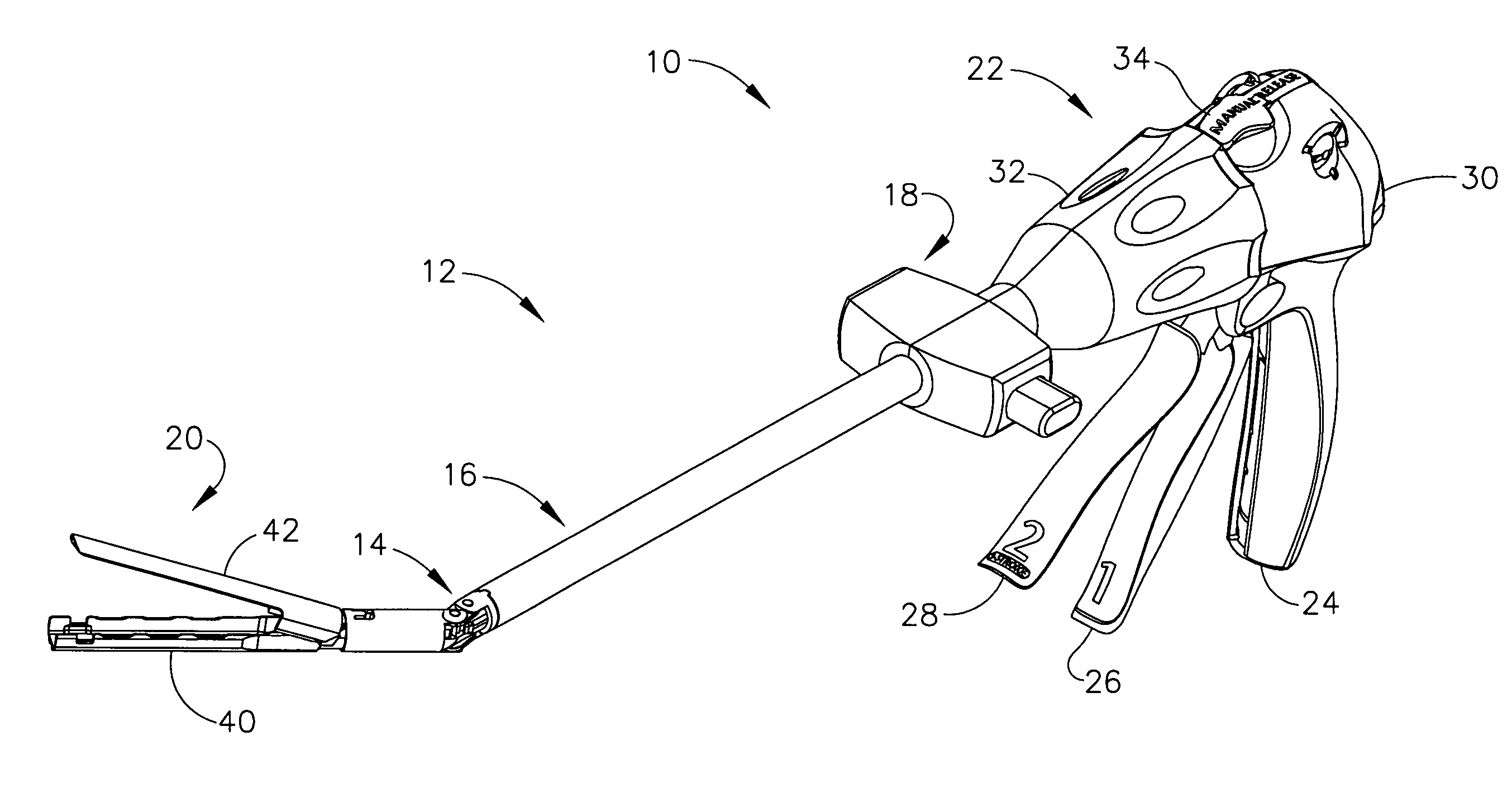
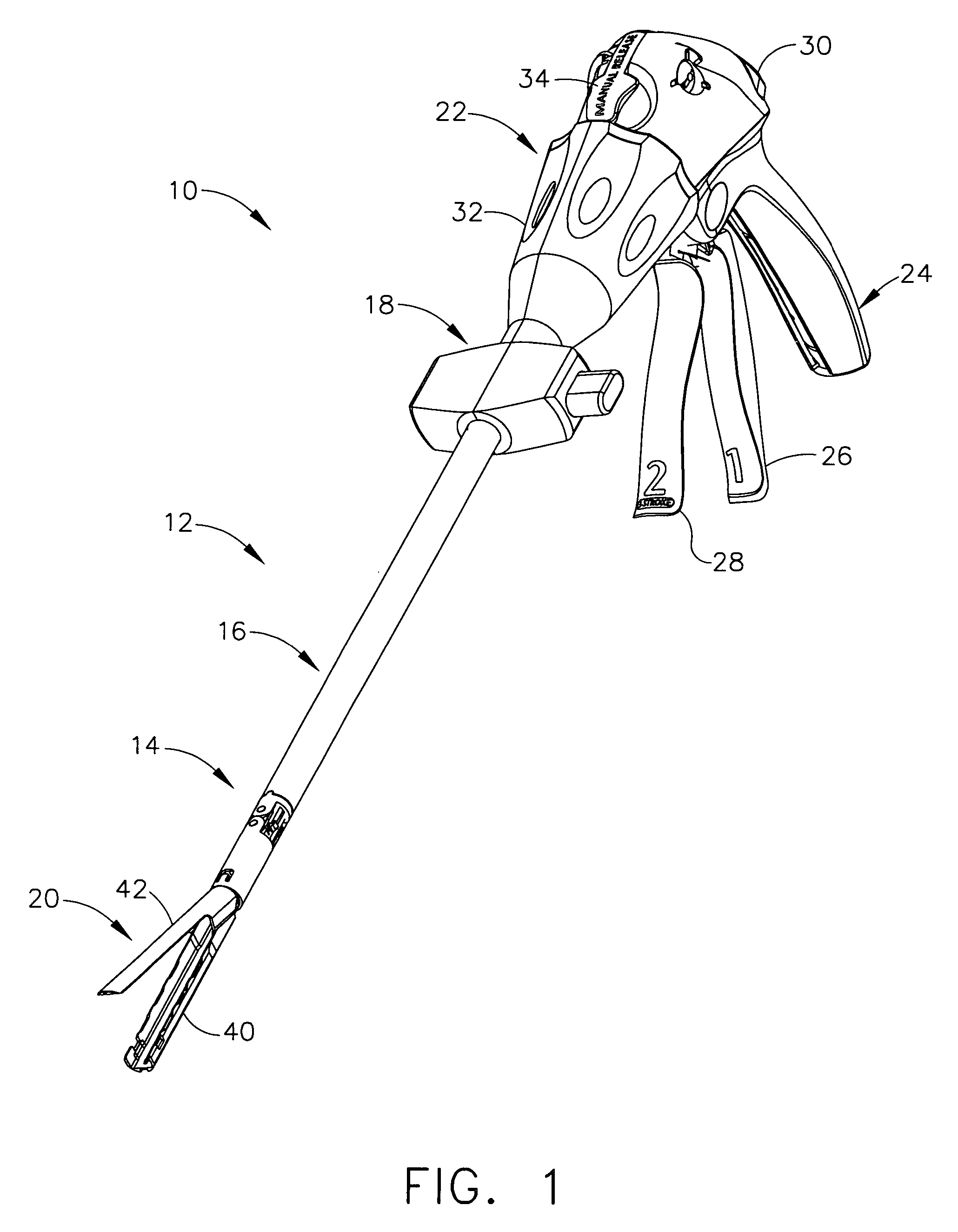
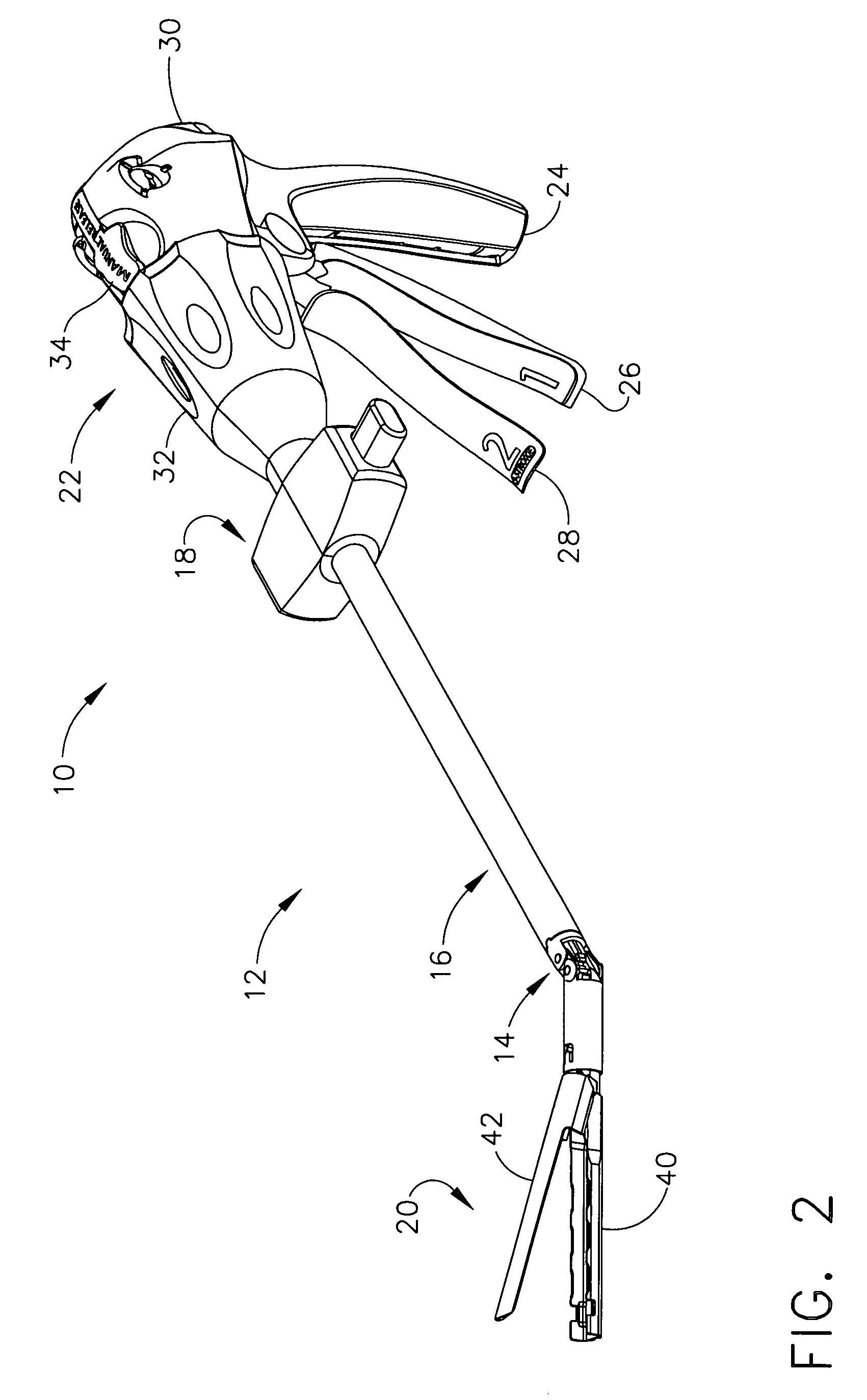
An articulating surgical instrument is shown, which comprises a shaft and an end effector. The shaft has a longitudinal axis, and the end effector is operationally coupled, preferably mechanically coupled, to the shaft at an articulation pivot. The instrument also comprises a first band, and in some embodiments, a second band, each operationally connected to the end effector and extending through at least a portion of the shaft. An articulation control applies a force in a direction substantially transverse to the longitudinal axis, wherein the force, when applied in one direction, is translated through the first band to the end effector to effect rotation of the end effector relative to the shaft about the articulation pivot in a first rotational direction, and when the force is applied in the opposite direction, is translated through the second band to the end effector to effect rotation of the end effector relative to the shaft about the articulation pivot in a second rotational direction.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Surgical stapling instrument having a single lockout mechanism for prevention of firing
InactiveUS7380695B2Avoid firePrevent movementSuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical staplePERITONEOSCOPE
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
End effectors for a surgical cutting and stapling instrument
ActiveUS7980443B2Affected deploymentImprove the forceSuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical stapleEngineering
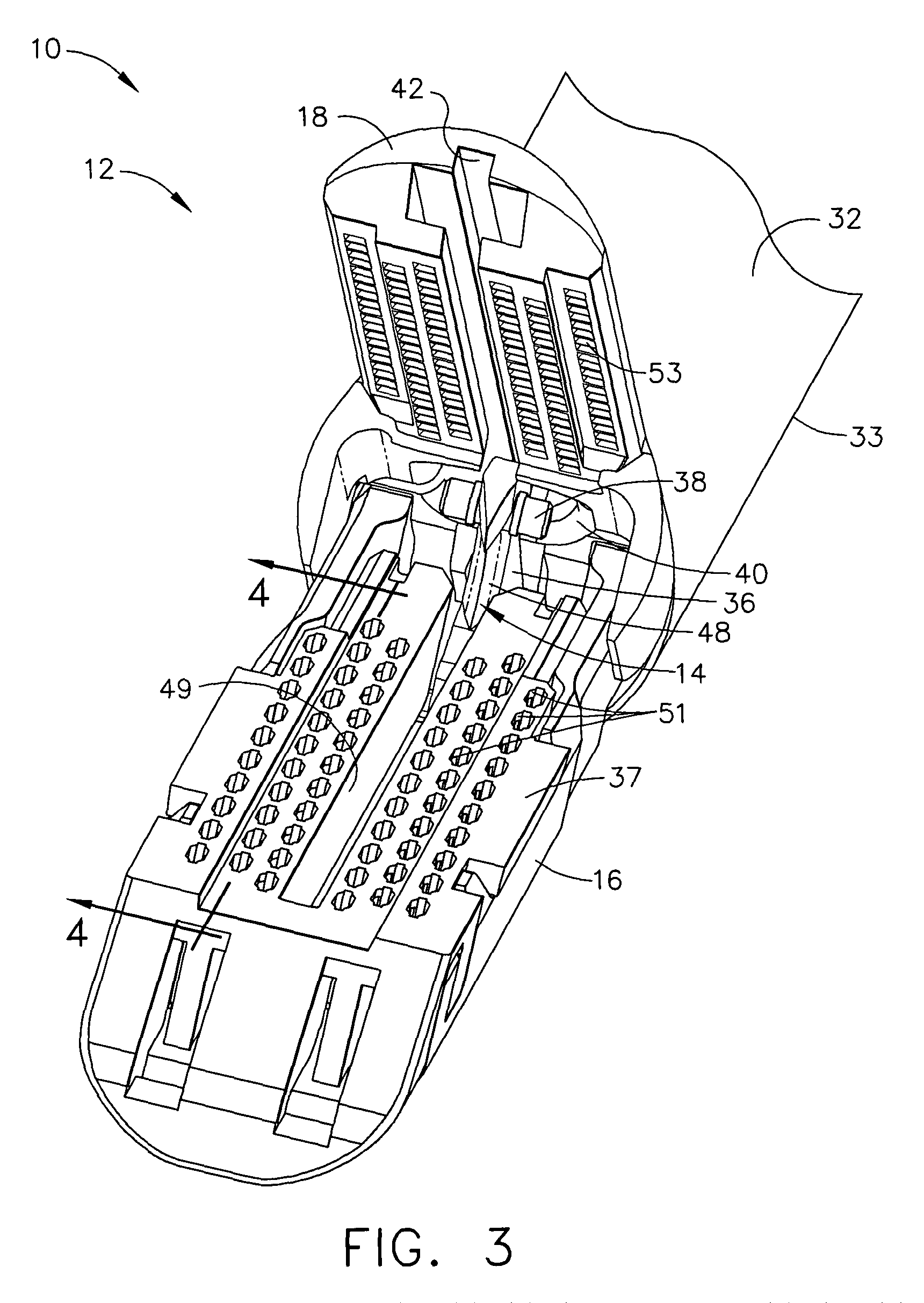
In various embodiments, an anvil of a disposable loading unit including a first member having staple pockets for deforming staples, a first cover plate secured to the first member, and a second cover plate secured to at least one of the first member and the first cover plate, wherein the first and second cover plates can be configured to support the first member. In at least one embodiment, an anvil can include a first member inserted into a second member, where at least one of the first and second members can be deformed to retain one to the other. In various embodiments, a surgical stapling instrument can include a disposable loading unit comprising a staple cartridge, an anvil, and a sleeve, wherein the sleeve can be configured to be slid relative to the staple cartridge and the anvil to hold the anvil in a closed position.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Surgical stapling instrument incorporating an E-beam firing mechanism
InactiveUS6978921B2Solve the lack of spaceSuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical staplePERITONEOSCOPE
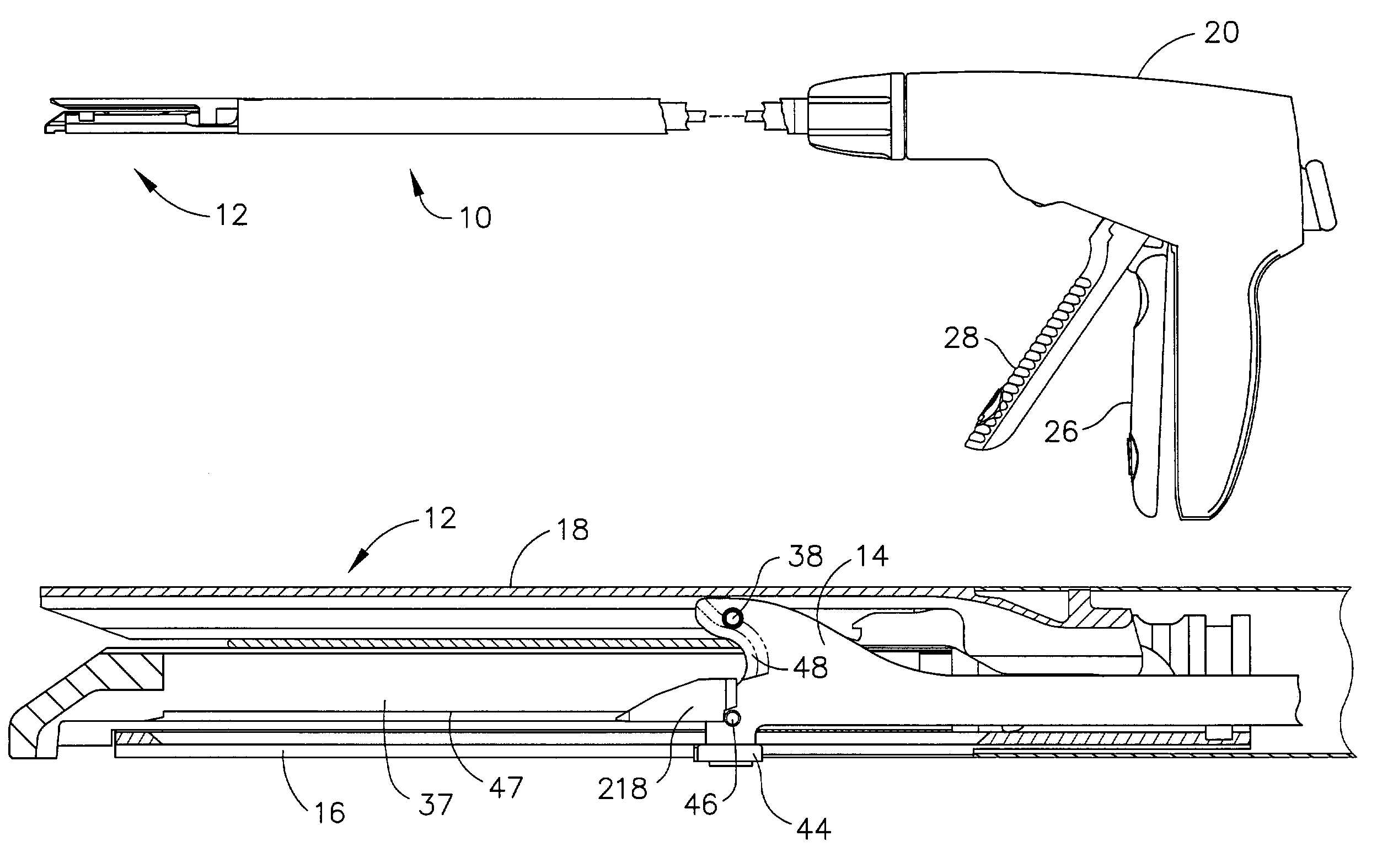
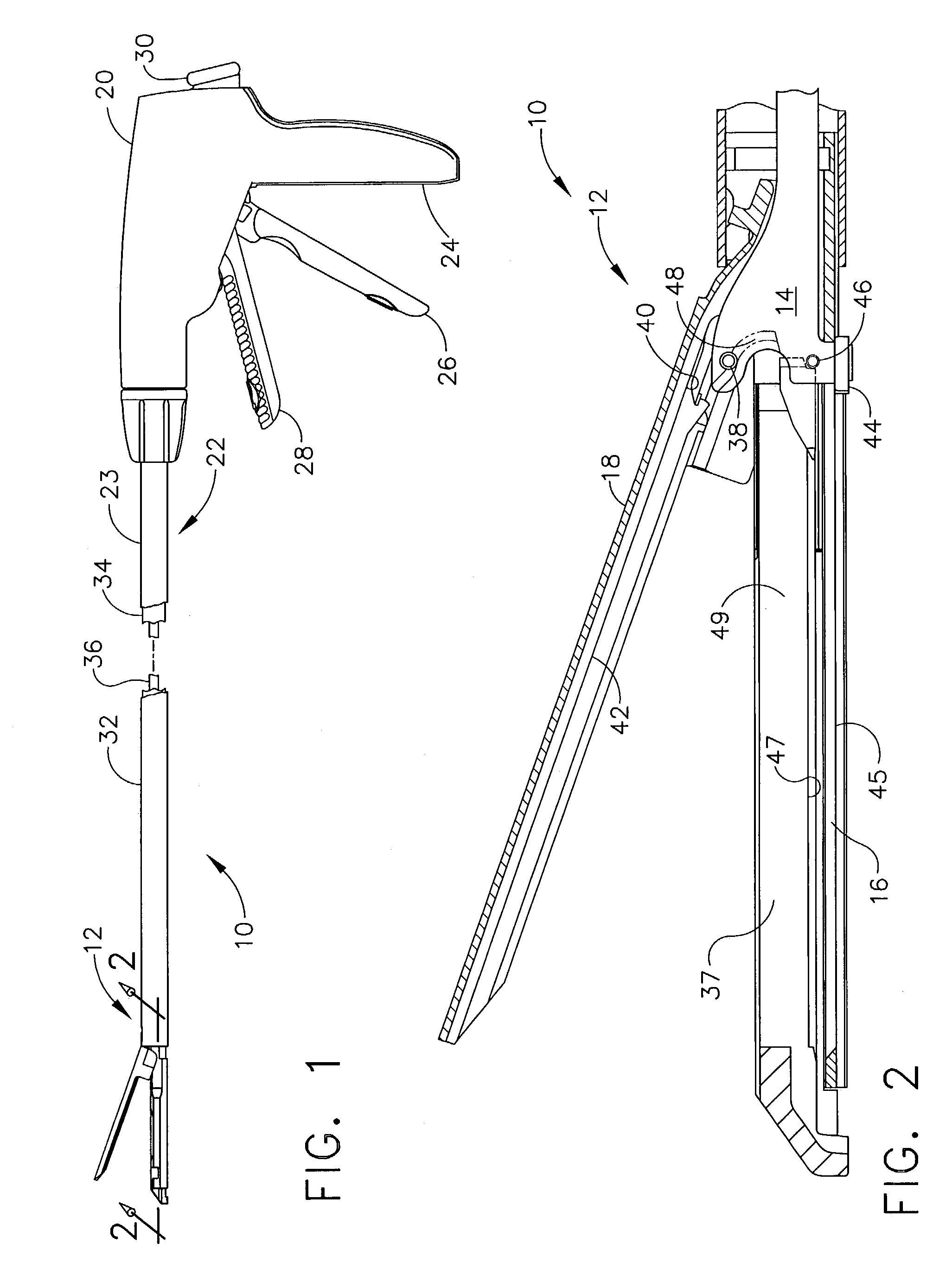
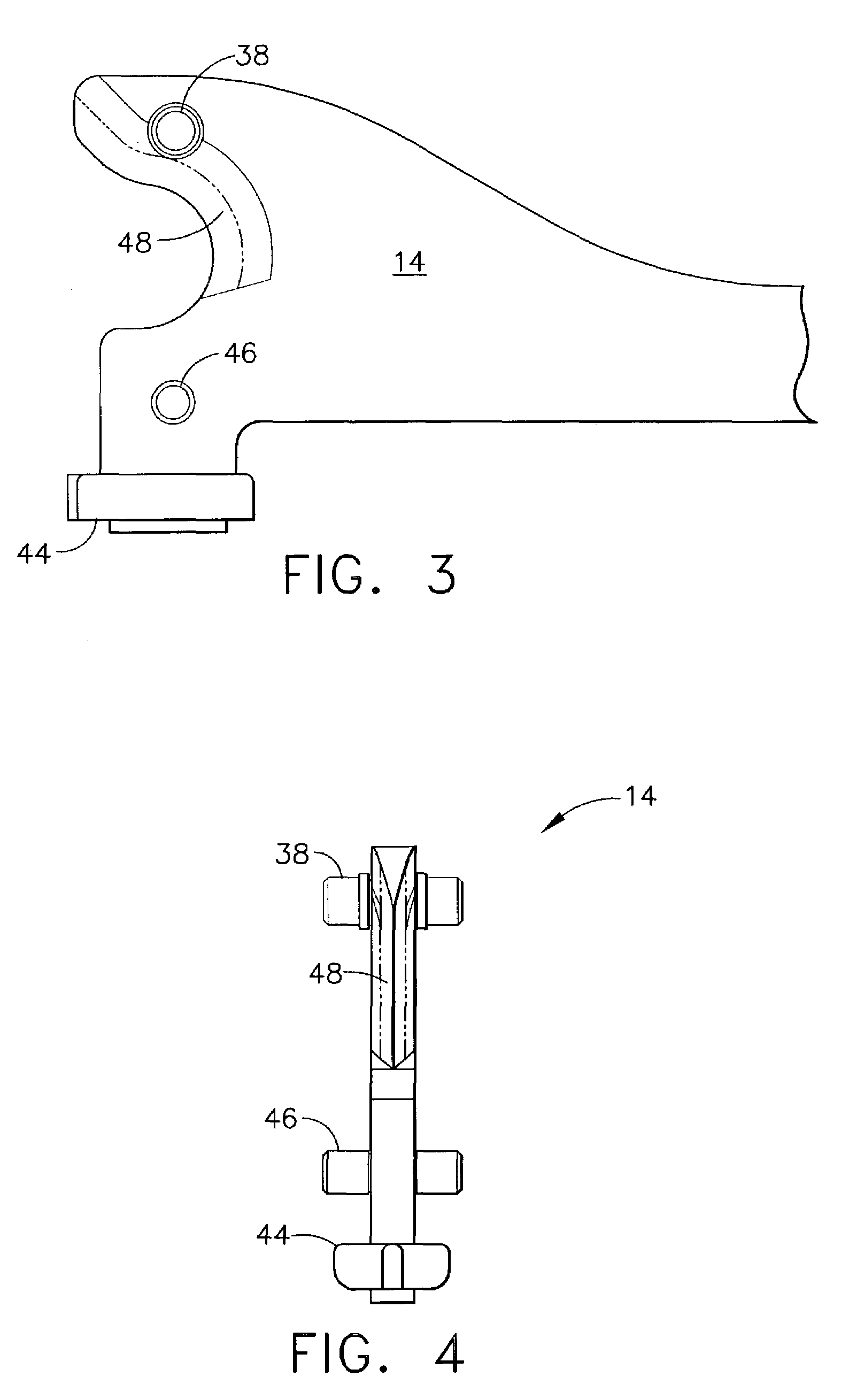
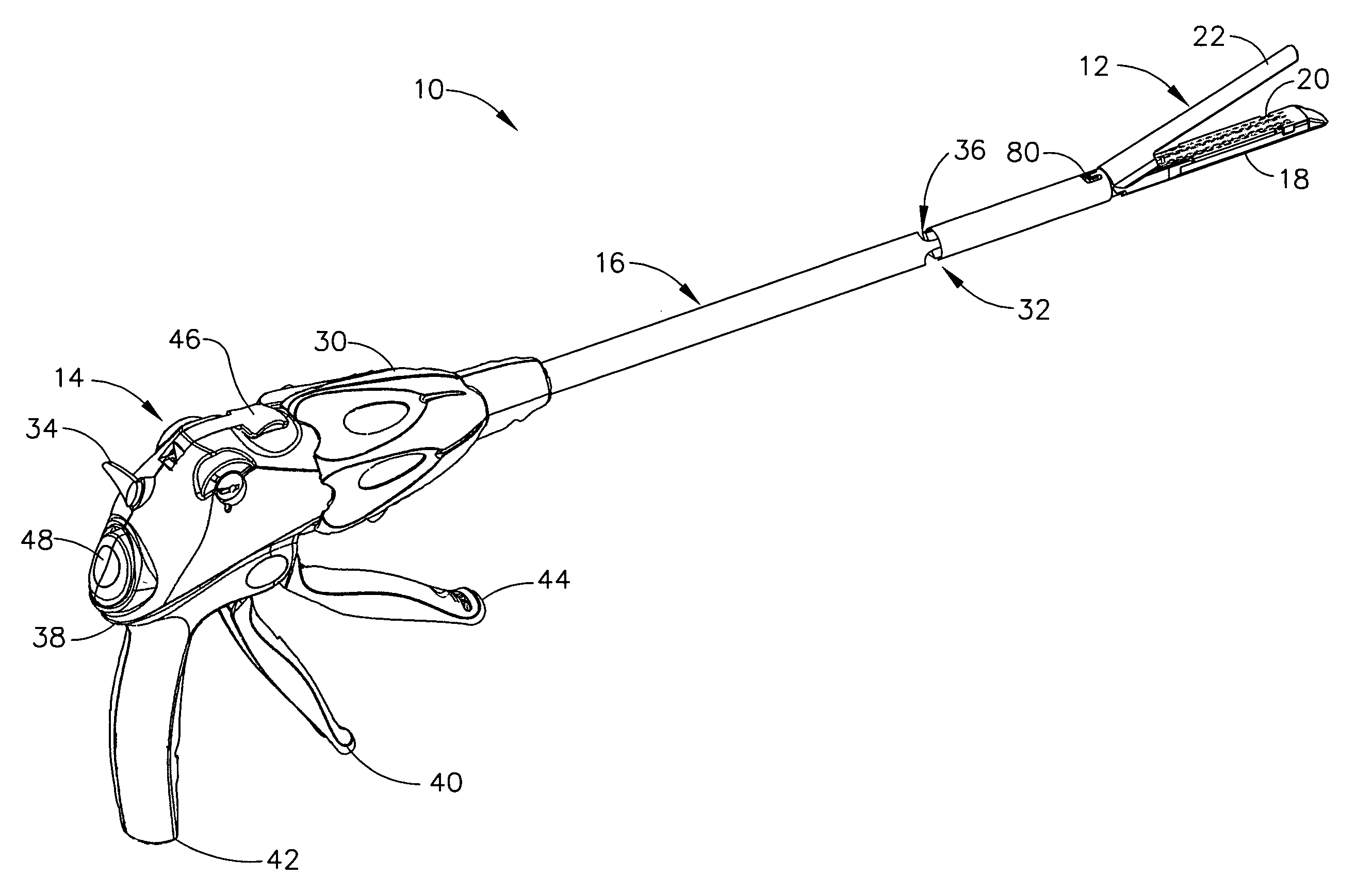
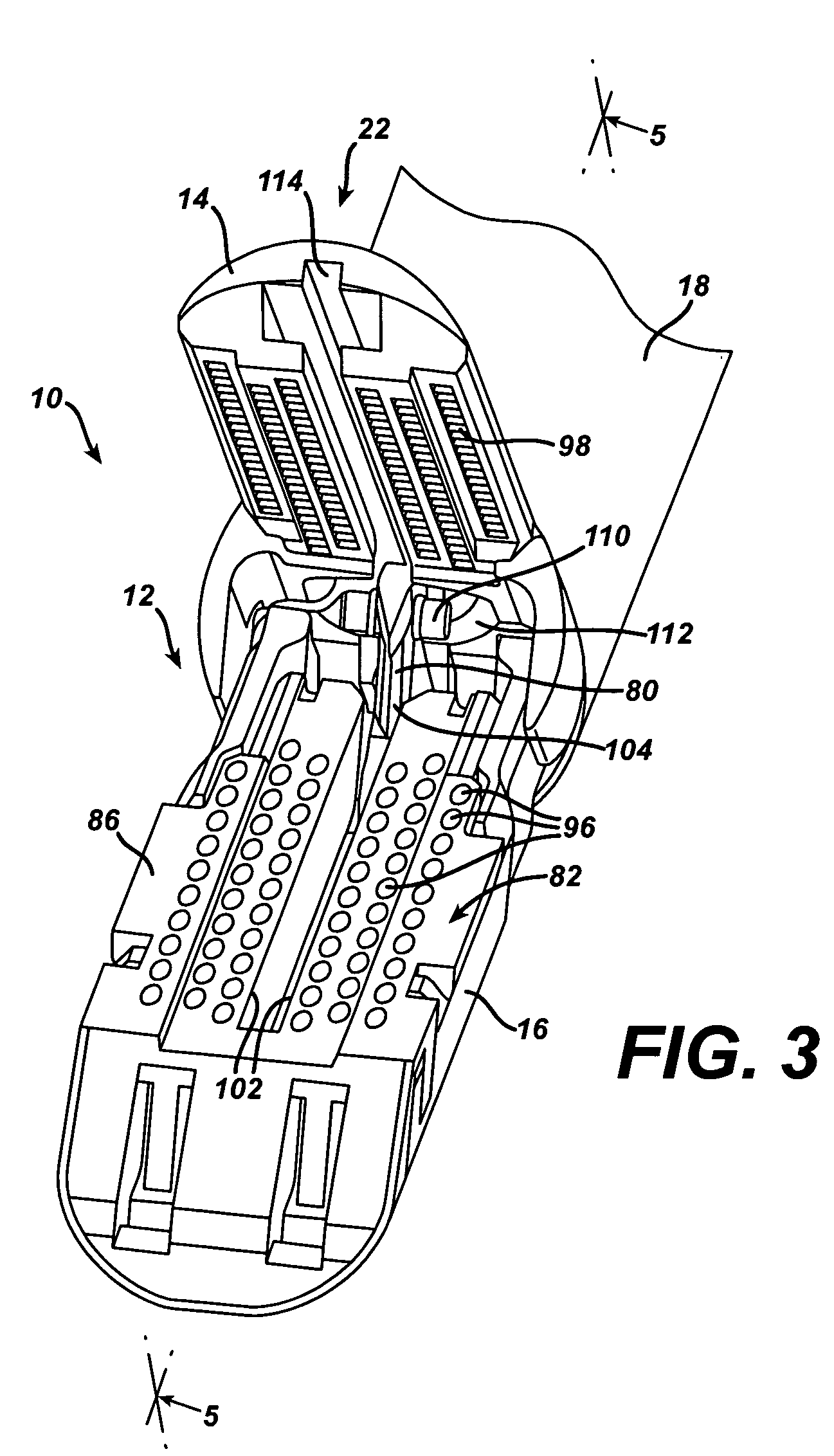
A surgical severing and stapling instrument clamps, suitable for laparoscopic and endoscopic clinical procedures, clamps tissue within an end effector of an elongate channel pivotally opposed by an anvil. An E-beam firing bar moves distally through the clamped end effector to sever tissue and to drive staples on each side of the cut. The E-beam firing bar affirmatively spaces the spaces the anvil from the elongate channel to assure properly formed closed staples, especially when an amount of tissue is clamped that is inadequate to space the end effector. In particular, an upper pin of the firing bar longitudinally moves through an anvil slot and a channel clot is captured between a lower cap and a middle pin of the firing bar to assure a minimum spacing.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Articulating surgical stapling instrument incorporating a two-piece E-beam firing mechanism
InactiveUS7380696B2Solve the lack of spaceEasy to useSuture equipmentsStapling toolsPERITONEOSCOPEDistal portion
A surgical severing and stapling instrument, suitable for laparoscopic and endoscopic clinical procedures, clamps tissue within an end effector of an elongate channel pivotally opposed by an anvil. An E-beam firing bar moves distally through the clamped end effector to sever tissue and to drive staples on each side of the cut. The E-beam firing bar affirmatively spaces the anvil from the elongate channel to assure properly formed closed staples, especially when an amount of tissue is clamped that is inadequate to space the end effector. In particular, an upper pin of the firing bar longitudinally moves through an anvil slot and a channel slot is captured between a lower cap and a middle pin of the firing bar to assure a minimum spacing. Forming the E-beam from a thickened distal portion and a thinned proximal strip enhances manufacturability and facilitates use in such articulating surgical instruments.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC +1
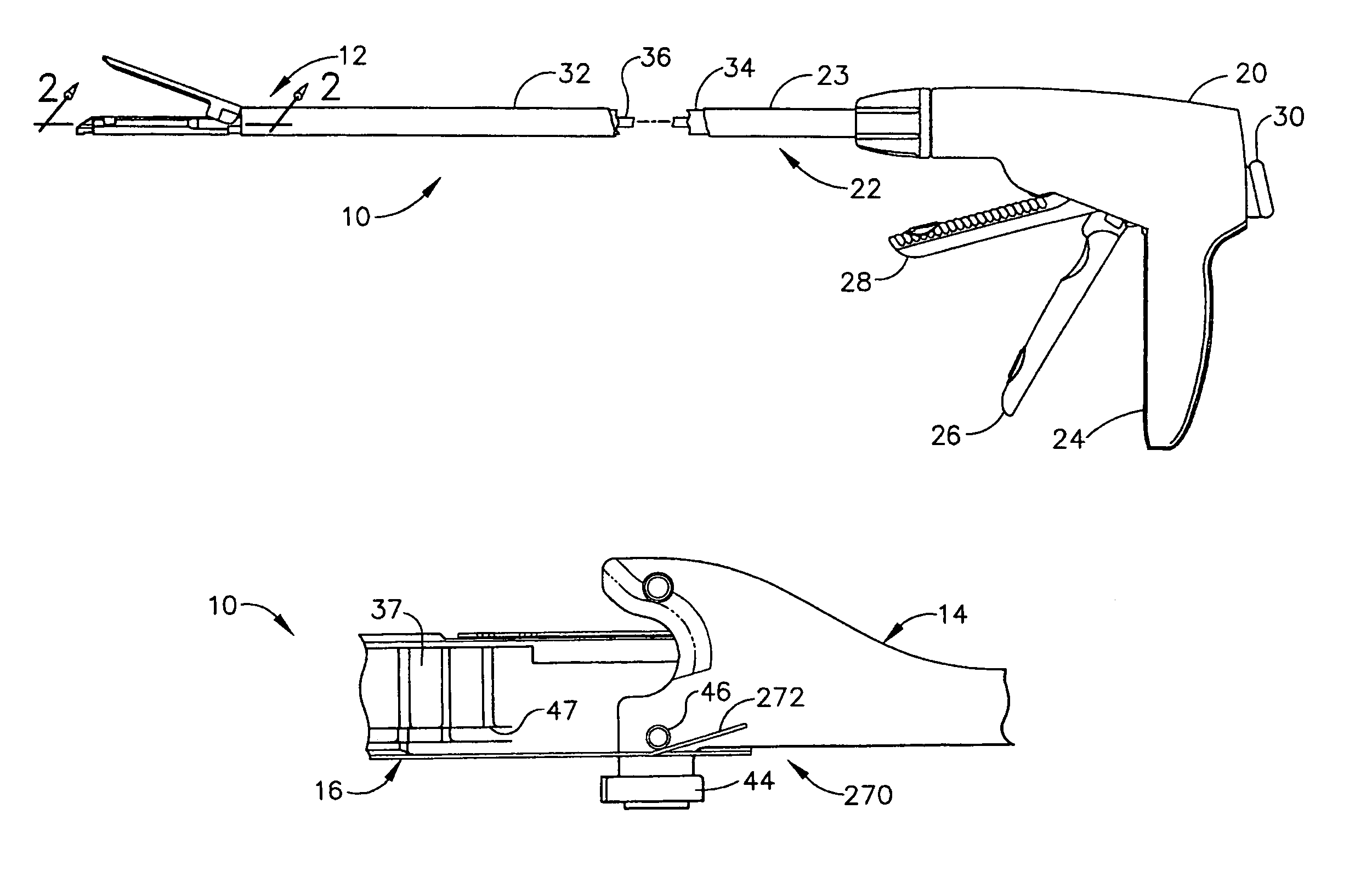
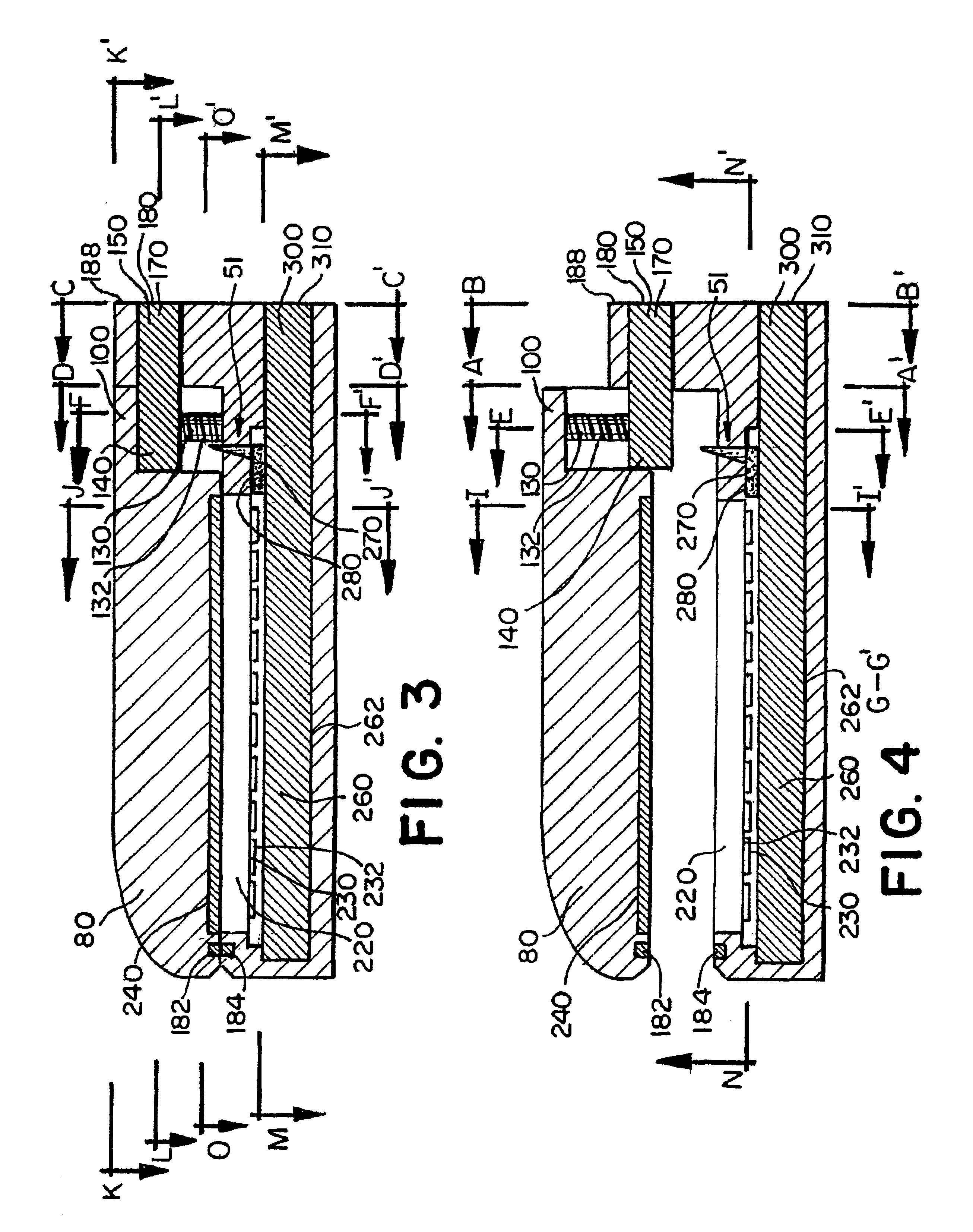
Surgical stapling instrument with an articulatable end effector
A surgical instrument can comprise a channel configured to support a staple cartridge and, in addition, an anvil pivotable between open and closed positions relative to the channel. The surgical instrument can further comprise a cutting member configured to incise tissue positioned captured between the staple cartridge and the anvil and, in addition, means for stopping the cutting member prior to a distal end datum, wherein the distal end datum can be defined by the distal-most staple cavity in the staple cartridge. In such embodiments, the incision within the tissue may not extend beyond the portion of the tissue that has been stapled.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
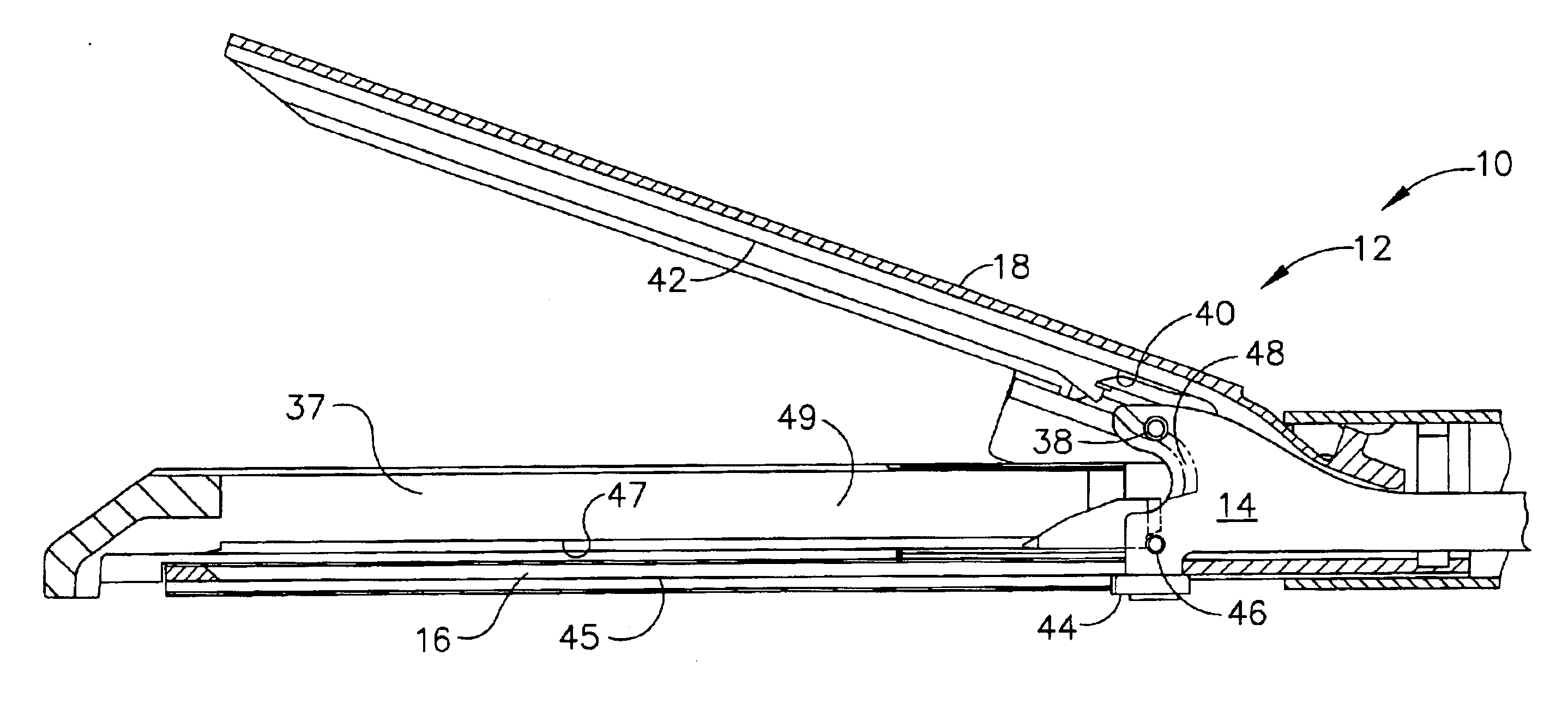
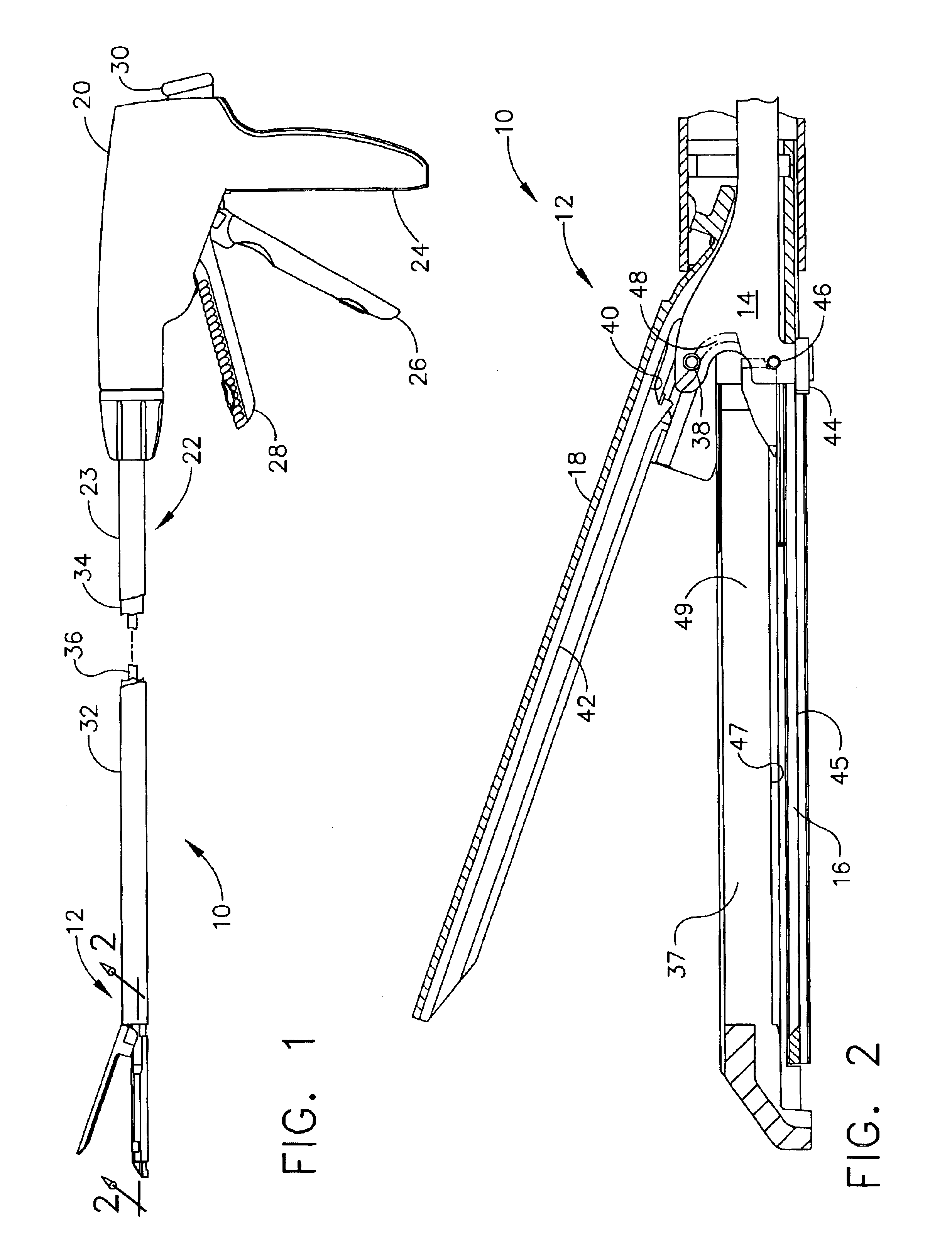
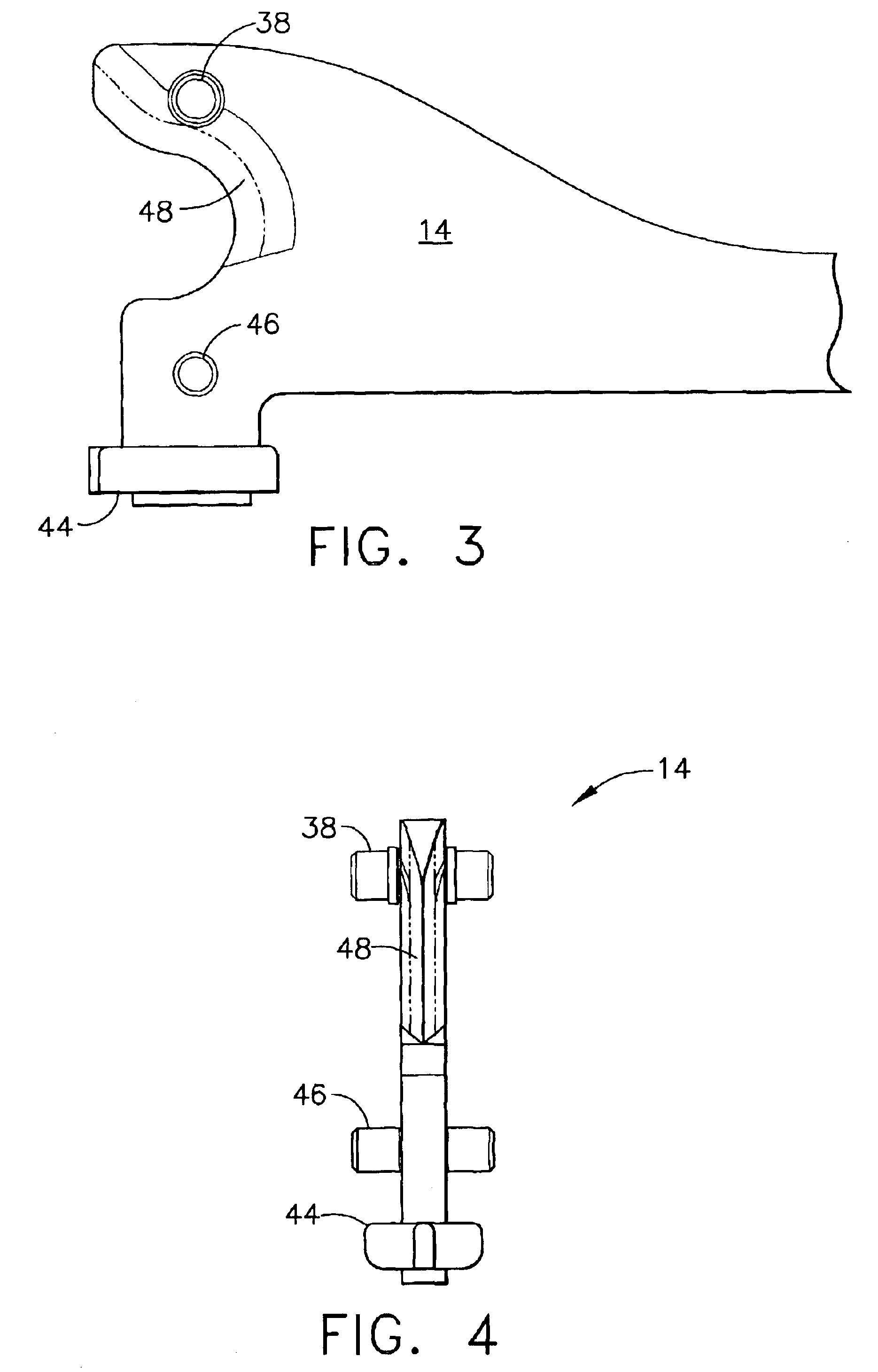
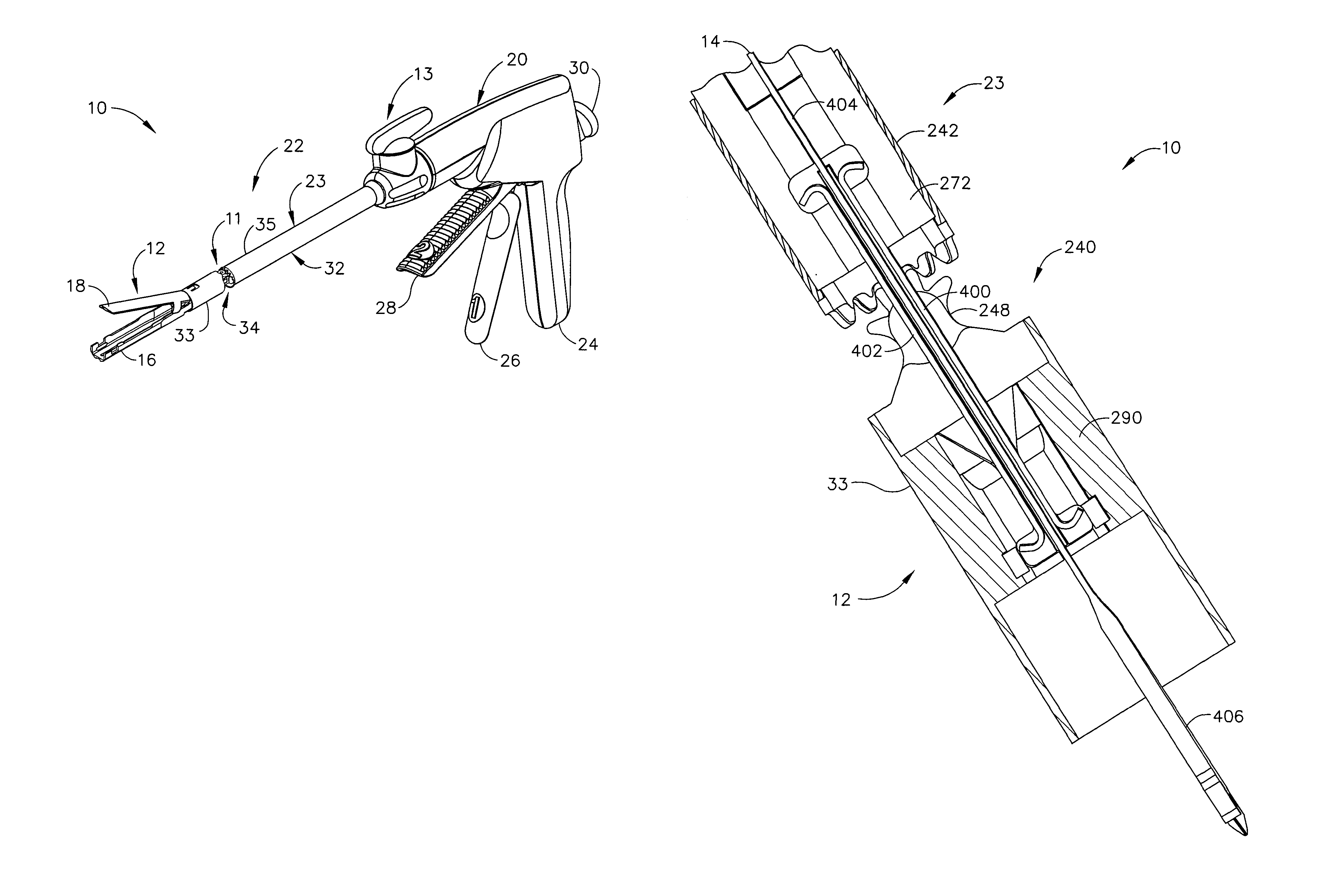
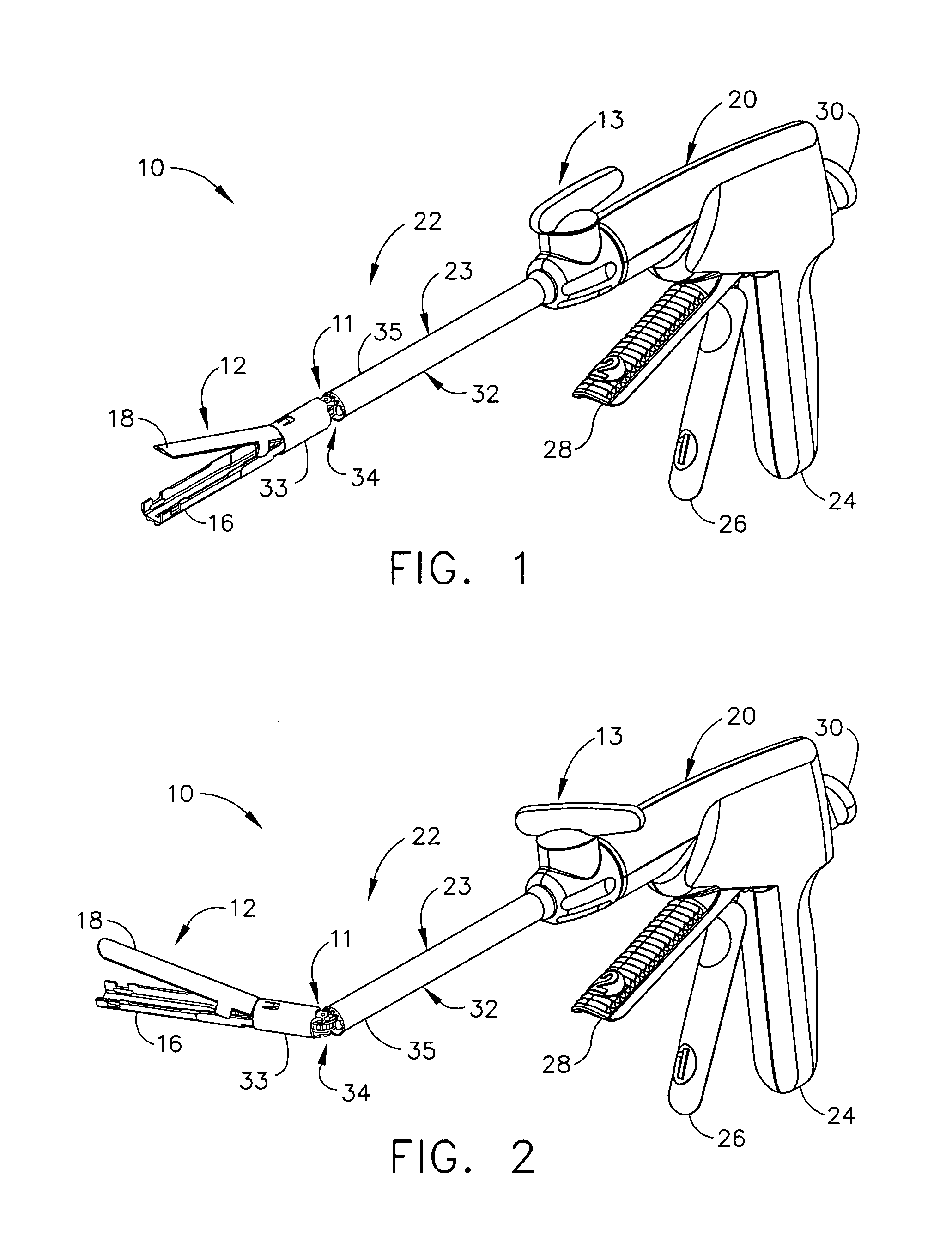
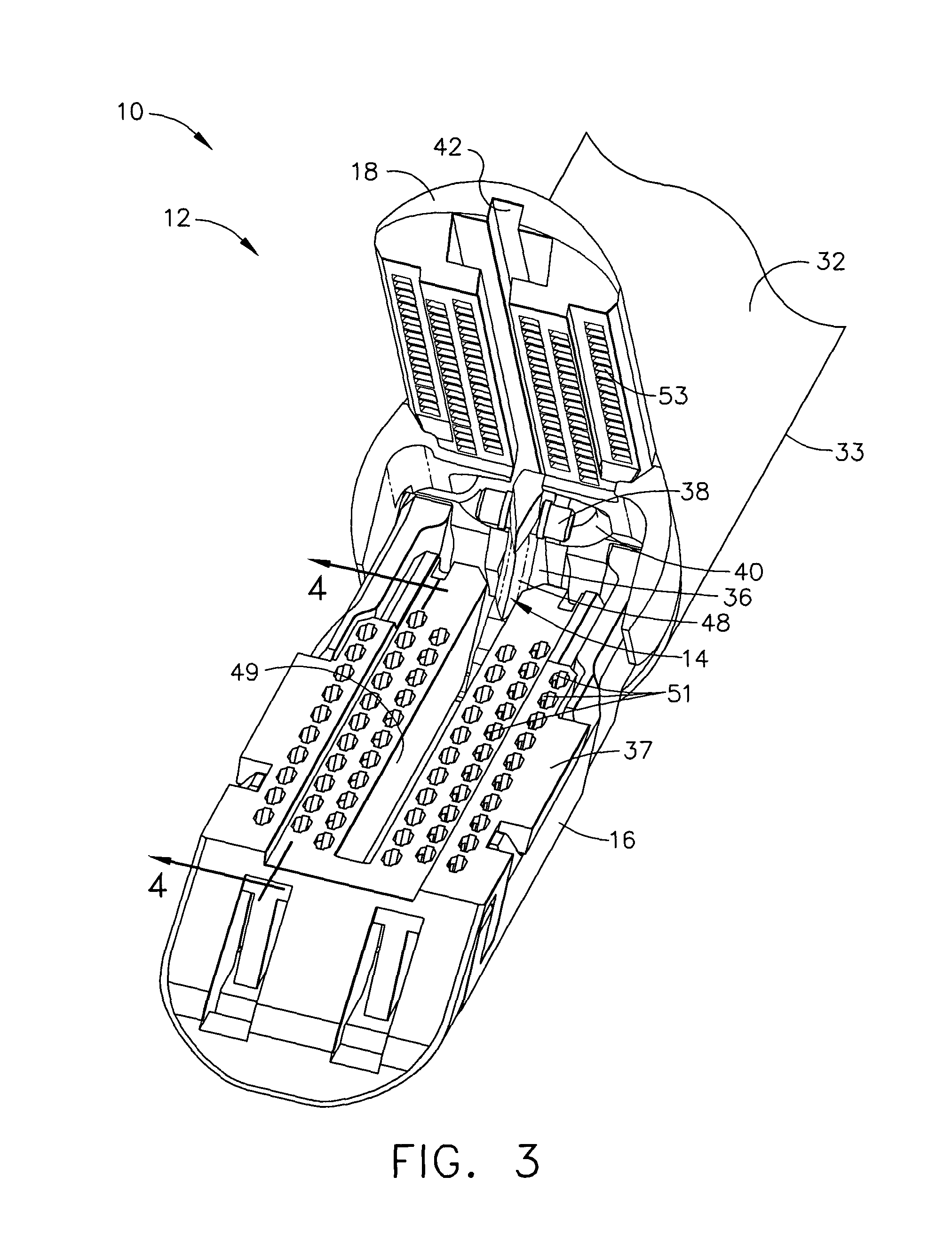
Surgical stapling instrument
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Surgical stapling instrument having a spent cartridge lockout
InactiveUS6988649B2Avoid firePrevent distal movementSuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical staplePERITONEOSCOPE
A surgical instrument for laparoscopic and endoscopic clinical procedures simultaneously severs and staples tissue clamped in an end effector comprising an elongate channel, which holds a staple cartridge, and a pivotally attached anvil. An E-beam firing bar engages the channel and selectively engages the anvil during distal firing movements, wherein the tissue is severed and stapled driven upward from the staple cartridge to form against the anvil. In particular, a wedge integral to the staple cartridge is driven distally by a middle pin of the firing bar to effect stapling. A lockout mechanism of the staple cartridge responds to the presence of the wedge sled in its unfired position to allow the firing bar to fire. Otherwise, the lockout mechanism prevents firing when the staple cartridge is spent.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INTERNATIONAL
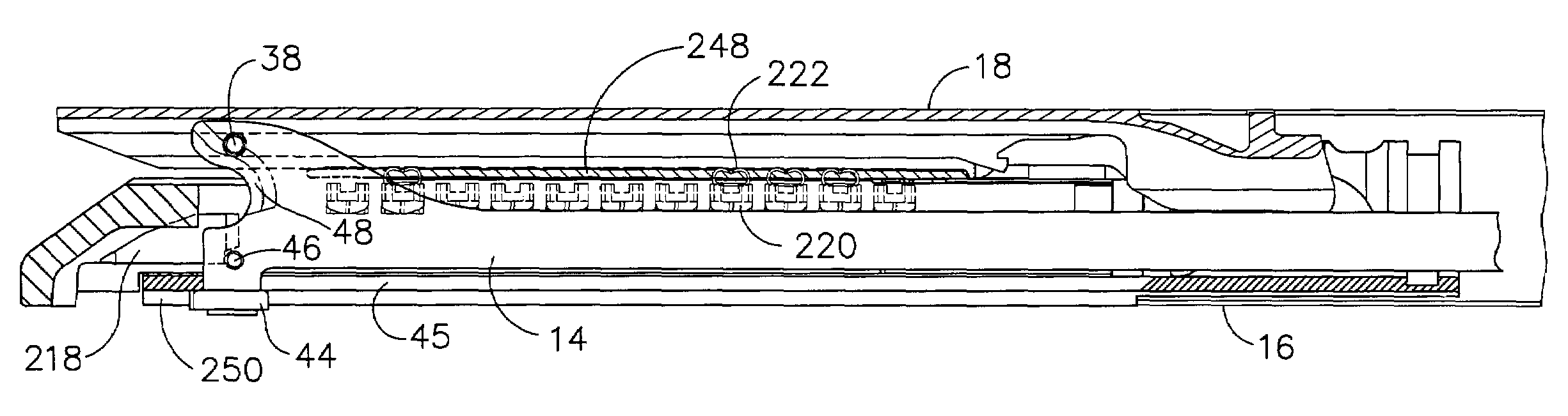
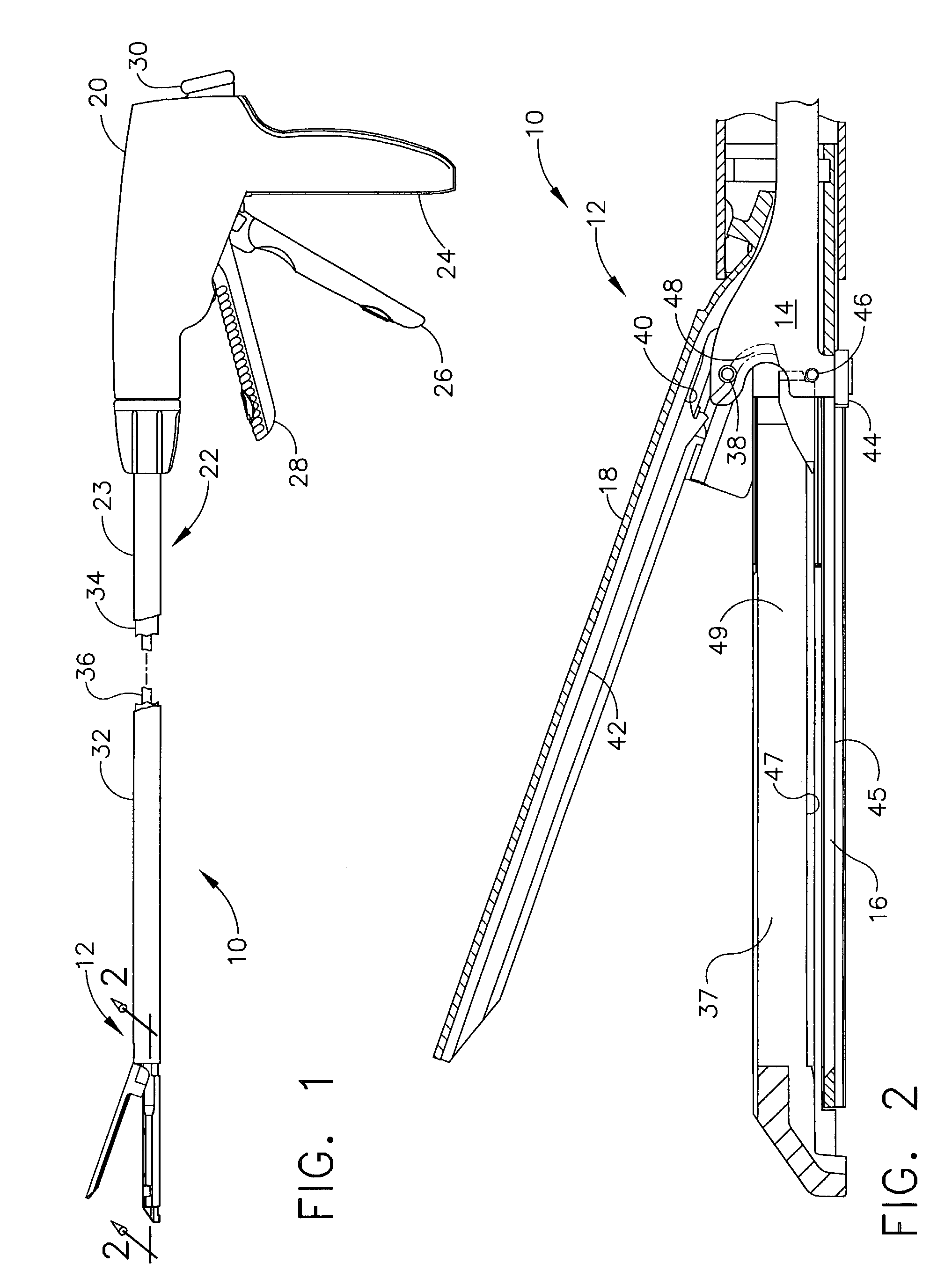
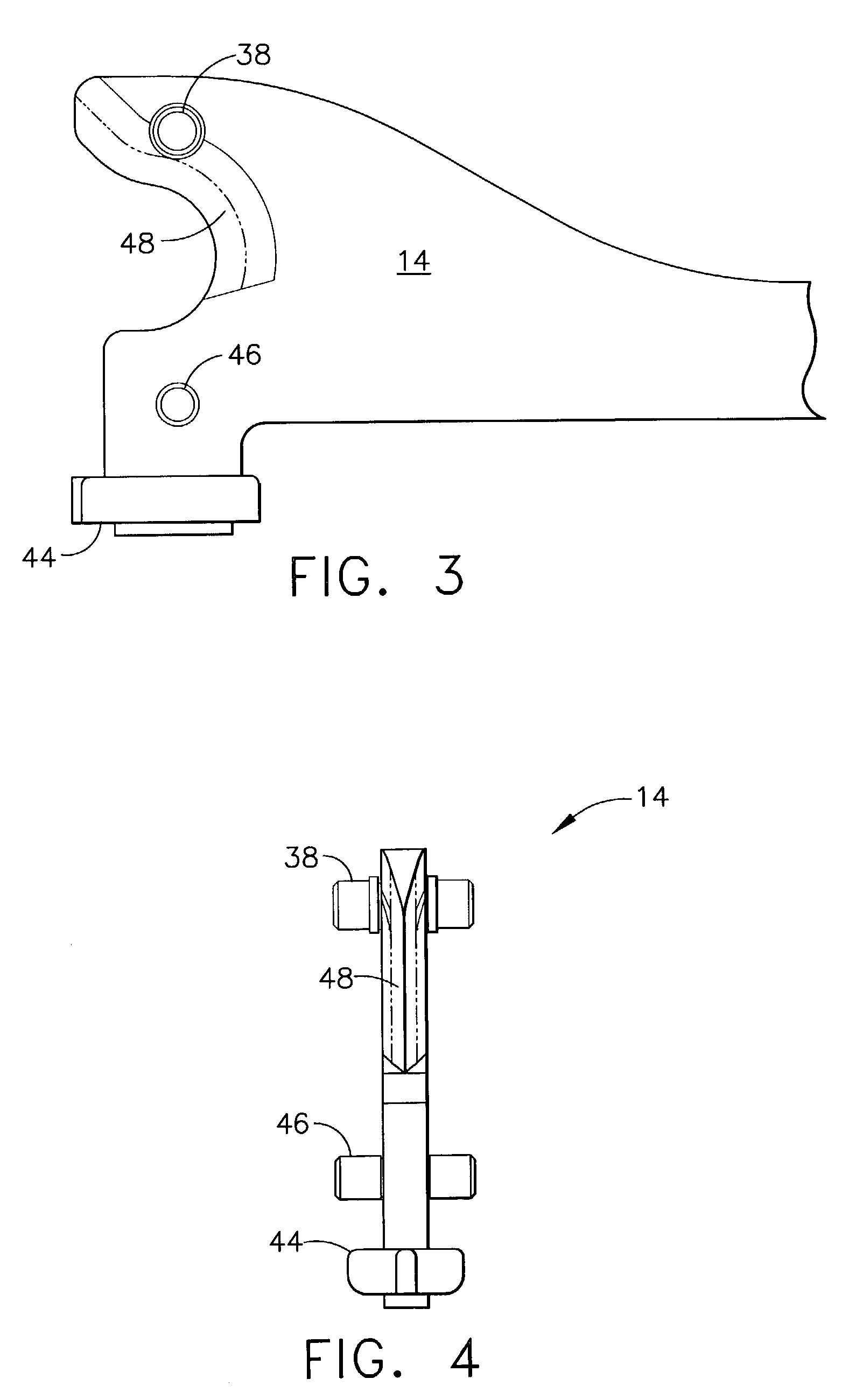
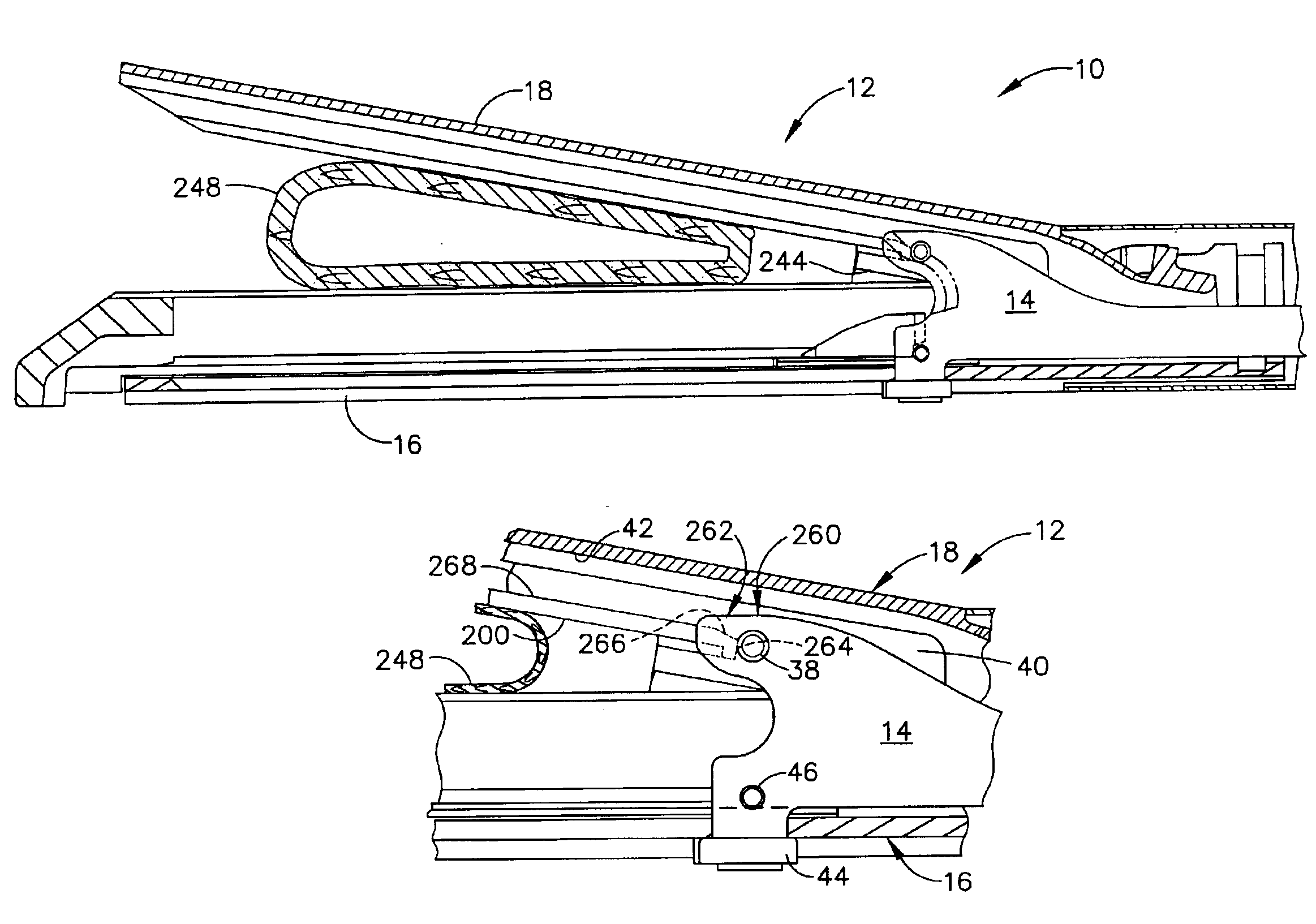
Surgical instrument with a lateral-moving articulation control
InactiveUS6981628B2Complicate amountComplicate directionSuture equipmentsStapling toolsEngineeringTarsal Joint
An articulating surgical instrument suited for endoscopic use includes a lateral articulation control into a handle portion that provides an intuitive visual and tactile indication to the clinician as to the amount and direction of articulation of an end effector at a distal end of a shaft. Lateral movement of a lateral control actuator is converted into a longitudinal motion or a rotational motion transferred by the shaft to an articulation mechanism. A version of a lateral articulation control for a rotationally driven articulation mechanism incorporates an articulation backdrive lockout that prevents forces on the end effector from causing the selected amount of articulation from being changed.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Surgical stapling instrument having a firing lockout for an unclosed anvil
InactiveUS7143923B2Accurate spacingExpand selectionSuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical staplePERITONEOSCOPE
A surgical instrument for laparoscopic and endoscopic clinical procedures simultaneously severs and staples tissue clamped in an end effector comprising an elongate channel, which holds a staple cartridge, and a pivotally attached anvil. An E-beam firing bar engages the channel and selectively engages the anvil during distal firing movements, wherein the tissue is severed and stapled driven upward from the staple cartridge to form against the anvil. In particular an upper pin of the firing bar is disengaged from the anvil before firing. A ramped transition from an anvil to an anvil slot avoids misfiring when the end effector has clamped too much tissue, yet assists in successfully clamping a slightly excess amount of tissue.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
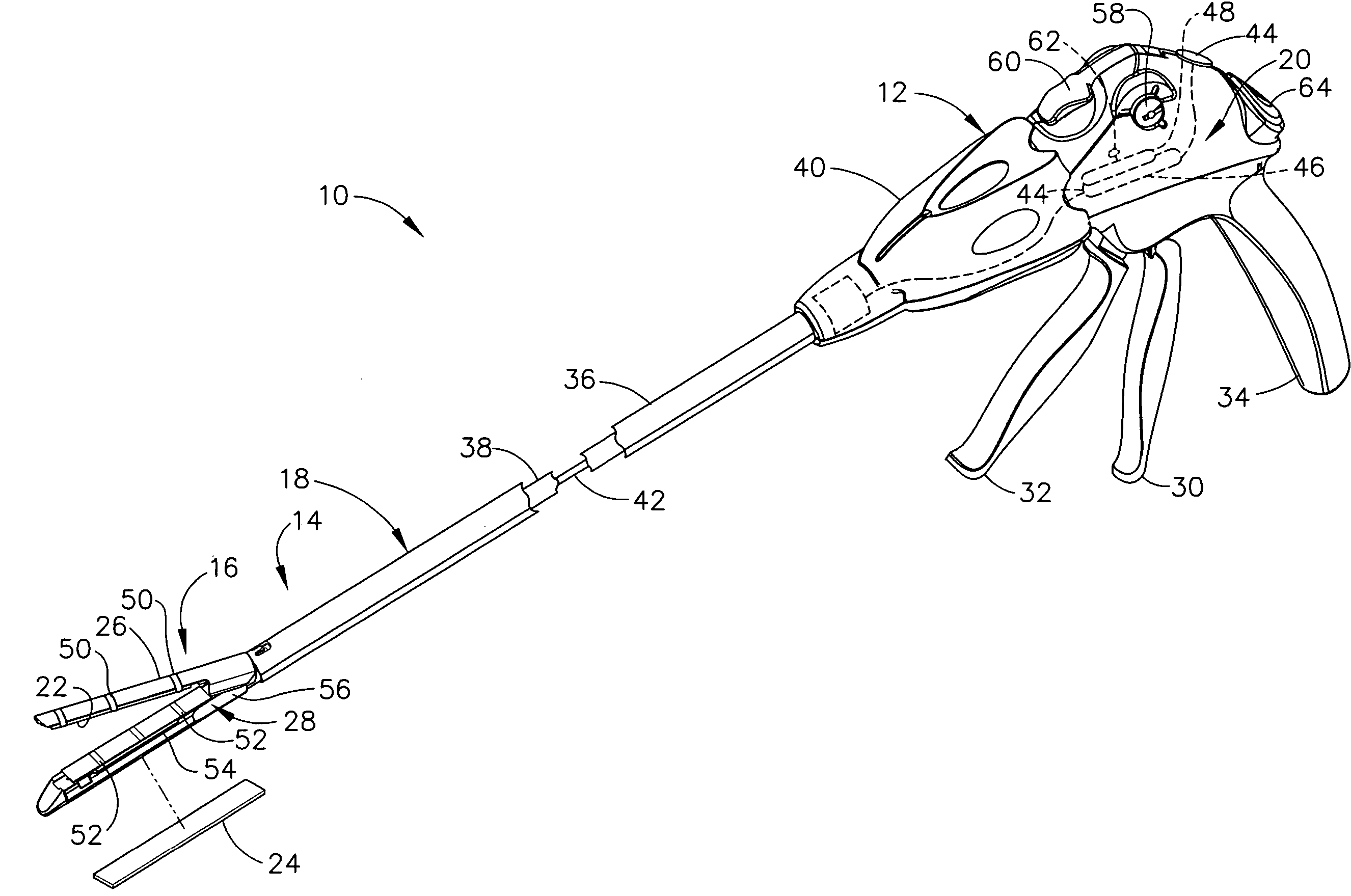
Surgical stapler
InactiveUS6032849AFacilitates convenient removalEasy to engageSuture equipmentsStapling toolsPERITONEOSCOPEEngineering
A surgical device is described herein that can be used to fire different types and sizes of disposable loading units. In a preferred embodiment, the device applies parallel rows of surgical fasteners to body tissue and concomitantly forms an incision between the rows of staples during an endoscopic or laparoscopic surgical procedure. The device can be utilized with disposable loading units configured to apply linear rows of staples measuring from about 15 mm in length to about 60 mm in length and can be used to fire disposable loading units containing surgical clips and individual staples.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Surgical stapling instrument having a single lockout mechanism for prevention of firing
ActiveUS7044352B2Avoid firePrevent distal movementSuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical staplePERITONEOSCOPE
A surgical instrument for laparoscopic and endoscopic clinical procedures simultaneously severs and staples tissue clamped in an end effector comprising an elongate channel, which holds a staple cartridge, and a pivotally attached anvil. An E-beam firing bar engages the channel and selectively engages the anvil during distal firing movements, wherein the tissue is severed and stapled driven upward from the staple cartridge to form against the anvil. In particular, a wedge integral to the staple cartridge is driven distally by a middle pin of the firing bar to effect stapling. A single lockout of the elongate channel responds to the presence of the wedge sled in its unfired position to allow the firing bar to fire. Otherwise, the single lockout prevent firing when the staple cartridge is missing or spent.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
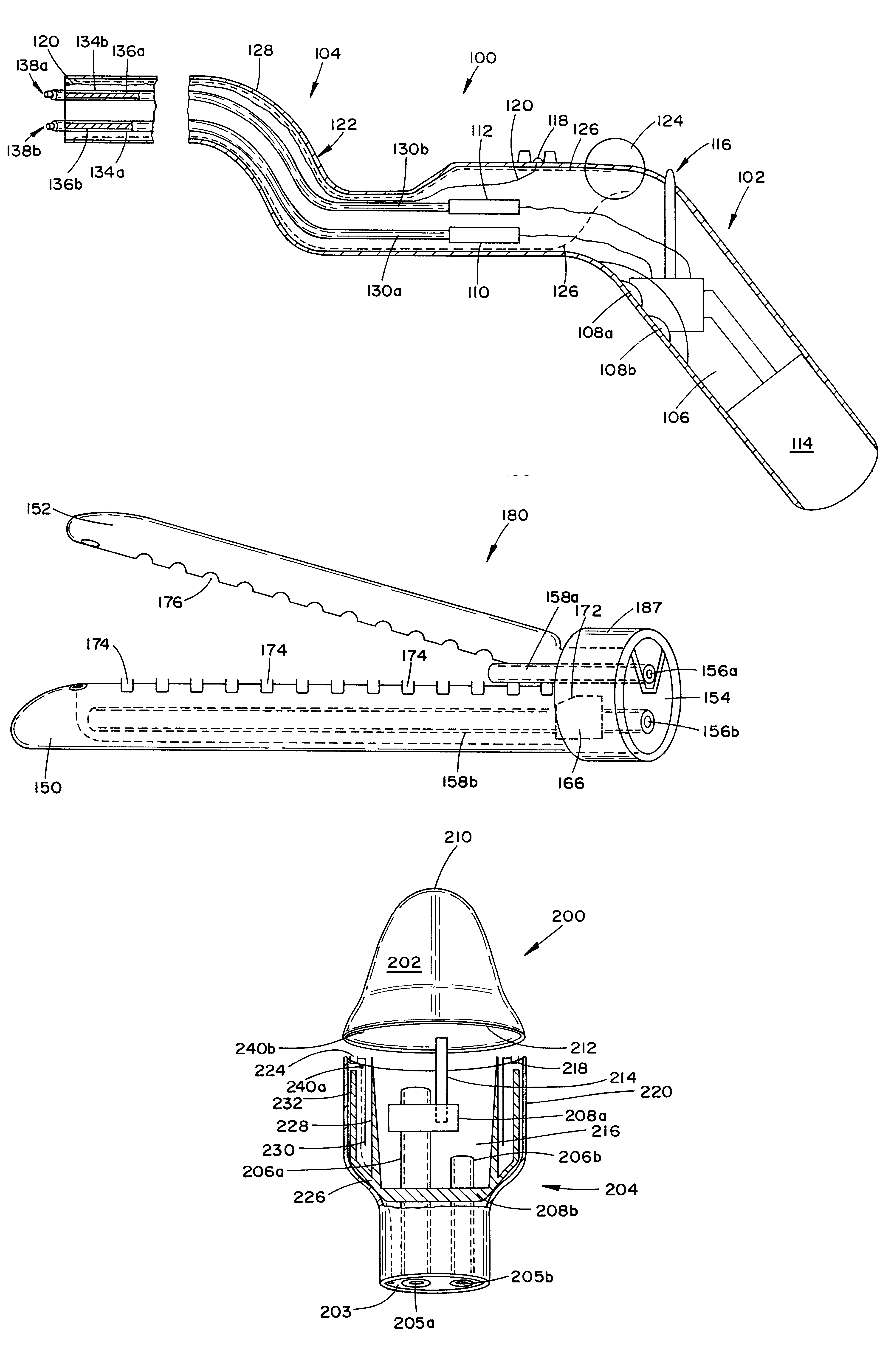
Electromechanical driver device for use with anastomosing, stapling, and resecting instruments
An electromechanical driver for use in gastrointestinal tract surgery, including a flexible sheath and a handle, is provided. Also dislosed are a series of surgical attachments which may be utilized in conjunction with the electromechanical driver. The handle of the driver includes at least one motor which is selectively engageable by the actuation of a trigger. The motor is coupled to a flexible drive shaft which extends through the flexible sheath. At a distal end of the flexible sheath, and correspondingly at the end of the drive shaft, the various surgical attachments may be coupled. The turning of the drive shaft provides the necessary power to actuate the surgical instrument.
Owner:DORROS GERALD M D
Surgical stapling instrument incorporating a firing mechanism having a linked rack transmission
InactiveUS6905057B2Small sizeReduce vertical sizeSuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical stapleEndoscopic surgery
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Surgical instrument incorporating EAP blocking lockout mechanism
ActiveUS7143925B2Preventing closing of the jawsSuture equipmentsStapling toolsEndoscopic surgeryEndoscopic Procedure
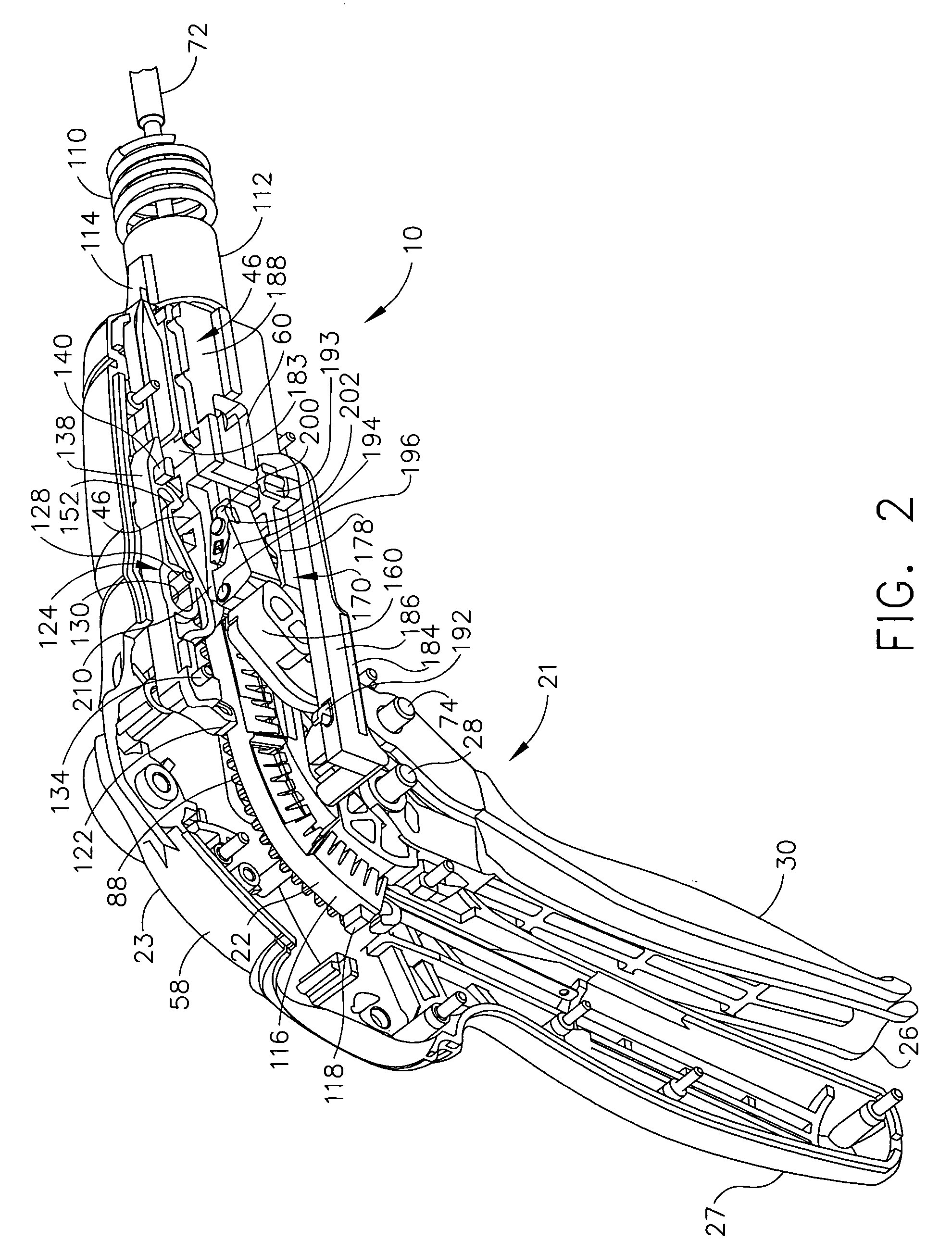
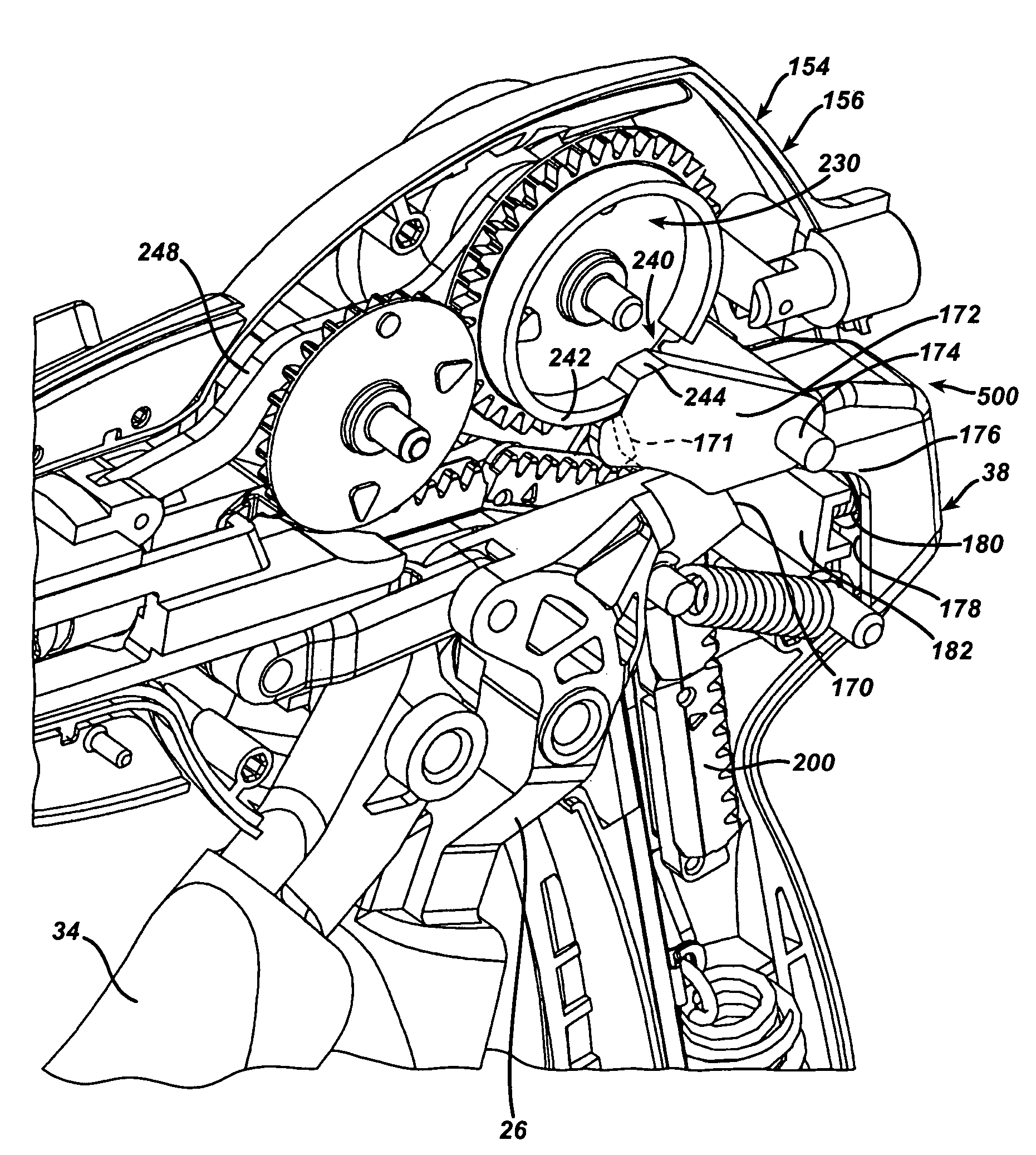
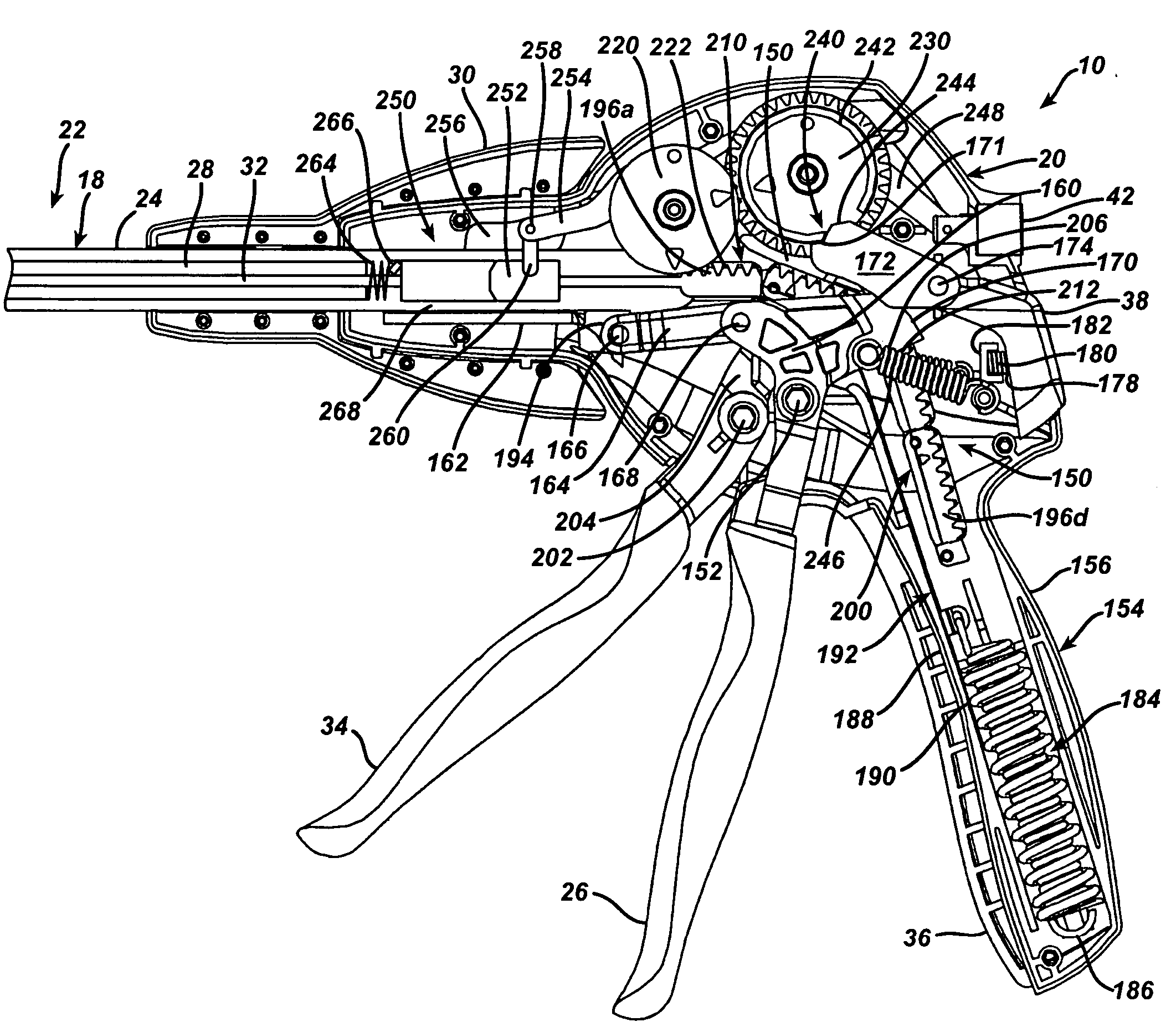
A surgical stapling and severing instrument particularly suited to endoscopic procedures incorporates a handle that produces separate closing and firing motions to actuate an end effector. The handle produces multiple firing strokes to reduce the required amount of force required to fire (i.e., staple and sever) the end effector. A linked transmission reduces the required handle longitudinal length, yet achieves a rigid, strong configuration when straightened for firing. One or more electrically activated lockout mechanisms, such as electroactive polymer (EAP) actuators, are biased to prevent firing unless activated. One lockout is a spring-biased side pawl firing mechanism enabled by an EAP block actuator. Another is a firing trigger EAP lock. Yet another is a closure yoke EAP lock. Yet a further one is a manual retraction EAP lock that locks the firing mechanism. Thereby, various sensed or commanded inputs may be incorporated to prevent inadvertent firing.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Powered surgical stapling device
A powered surgical stapler is disclosed. The stapler includes a housing, an endoscopic portion extending distally from the housing and defining a first longitudinal axis, a drive motor disposed at least partially within a housing and a firing rod disposed in mechanical cooperation with the drive motor. The firing rod is rotatable by the motor about the first longitudinal axis extending therethrough. The stapler also includes an end effector disposed adjacent a distal portion of the endoscopic portion. The end effector is in mechanical cooperation with the firing rod so that the firing rod drives a surgical function of the end effector. The stapler further includes a control system having a plurality of sensors coupled to the drive motor, the firing rod, the loading unit and the end effector, the plurality of sensors configured to detect operating parameters thereof. The control system also includes a microcontroller coupled to the plurality of sensors and being configured to determine operating status of the powered surgical stapler as a function of the detected operating parameters.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Surgical stapling instrument having an electroactive polymer actuated buttress deployment mechanism
A surgical instrument for being endoscopically or laparoscopically inserted to a surgical site for simultaneous stapling and severing of tissue includes electrically actuated deployment of buttress pads held on inner surfaces of upper and lower jaws of a staple applying assembly. Thereby, thick or thin layers may be stapled and severed without improper staple formation nor with nonoptimal deployment of the buttress pads. Electroactive polymer (EAP) actuated latches, an EAP channel, or a rigid channel with an EAP pinch lock reliably hold the buttress pad until deployment is desired with a low force to separate the stapled and severed buttress pad / tissue combination with the respective EAP mechanism activated for deployment.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
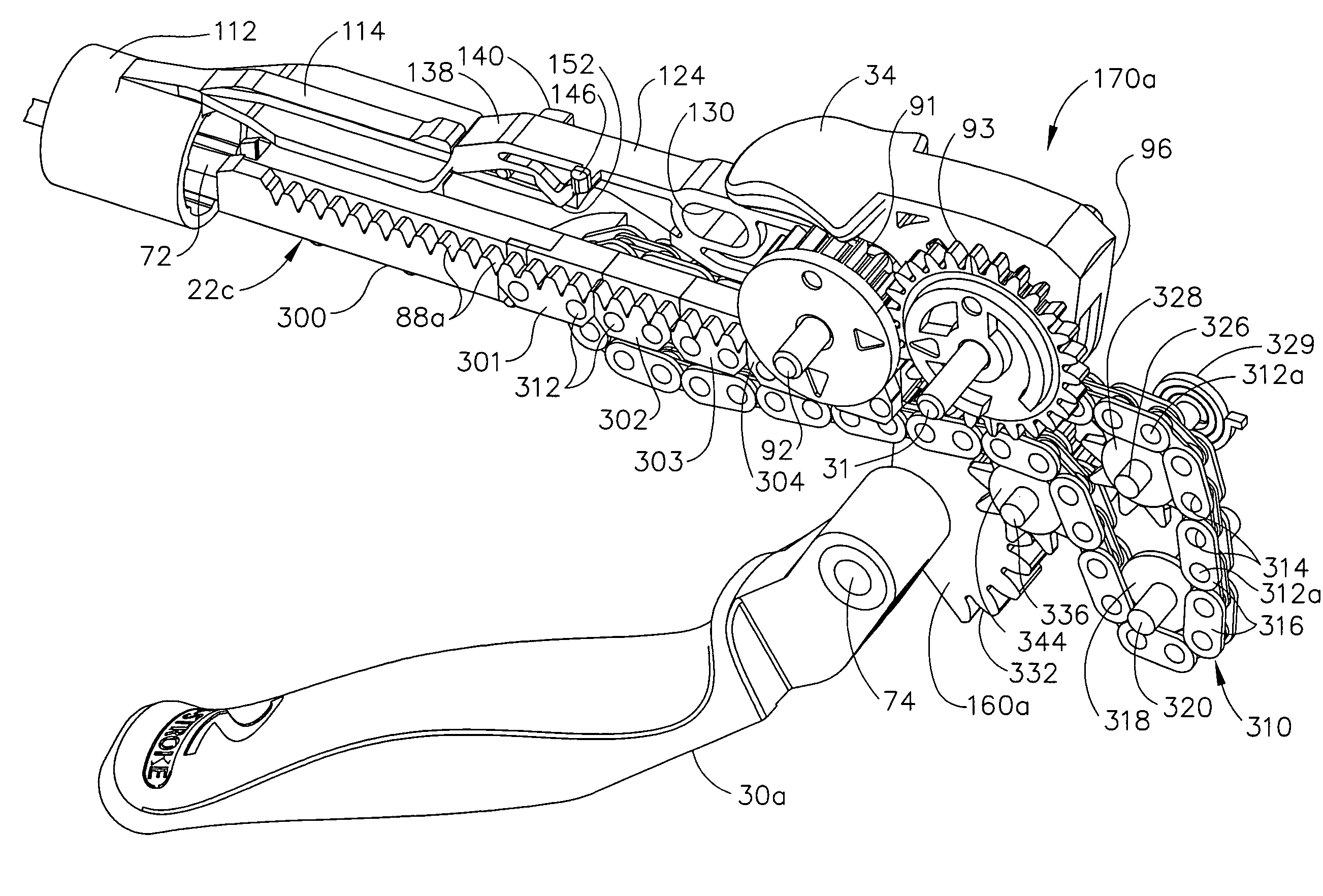
Surgical stapling instrument incorporating a multi-stroke firing mechanism with a flexible rack
InactiveUS7303108B2Shorten the lengthSuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical stapleReciprocating motion
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Surgical stapling instrument having multistroke firing with opening lockout
A surgical stapling and severing instrument particularly suited to endoscopic procedures incorporates a handle that produces separate closing and firing motions to actuate an end effector. In particular, the handle produces multiple firing strokes in order to reduce the required amount of force required to fire (i.e., staple and sever) the end effector. A linked transmission reduces the required handle longitudinal length, yet achieves a rigid, strong configuration when straightened for firing. A traction biased firing mechanism avoids binding in driving this straightened linked rack in cooperation with an anti-backup mechanism, with a lockout mechanism that prevents releasing the closure trigger during firing. Furthermore, an external indicator gives feedback to the surgeon as to how far firing has progressed, as well as providing a manual retraction capability.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Methods and apparatus for performing transluminal and other procedures
InactiveUS20070135803A1Prevent overflowPrevent leakageSuture equipmentsEar treatmentSurgeryInstrumentation
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Surgical apparatus and method
InactiveUS6264086B1Minimizing chanceGood removal effectSuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical stapleSurgical incision
Owner:MCGUCKIN JR JAMES F
Surgical clamping, cutting and stapling device
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Surgical stapling instrument incorporating a tapered firing bar for increased flexibility around the articulation joint
A surgical stapling and severing instrument particularly suited to endoscopic articulates an end effector by having a geared articulation mechanism that converts rotational motion from a handle portion. A firing bar longitudinally translates between the handle portion and the end effector. The firing bar head is thickened in order to present an undistorted cutting edge and engagement features to the opposing jaws of the end effector. The firing bar also advantageously includes a thinned or tapered proximal portion in the form of a strip or band that negotiates the articulation mechanism.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Surgical instrument incorporating an articulation mechanism having rotation about the longitudinal axis
A surgical instrument particularly suited to endoscopic articulates an end effector by including an end effector having a geared articulation mechanism that converts rotational motion from a handle portion. A hollow articulation drive tube transfers the rotation motion in some versions to a spear gear, bevel gear or snaggle tooth gear articulation mechanism. Alternatively, one or more threaded drive rod offset from a longitudinal axis engages a worm gear or flex-neck articulation mechanism.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Rotary hydraulic pump actuated multi-stroke surgical instrument
A surgical instrument (e.g., endocutter, grasper, cutter, staplers, clip applier, access device, drug / gene therapy delivery device, and energy device using ultrasound, RF, laser, etc.) may benefit from having a plurality of hydraulically actuated subsystems (e.g., severing, stapling, articulation, locking / unlocking, lockout enabling / disabling, grasping, etc.) supplied with hydraulic power from a trigger actuated rotary pump (e.g., lobe pump, rotary gear pump, internal rotating gear pump, flexible vane rotor pump, rotary vane pump). Thereby, an available amount of mechanical advantage available at a firing trigger may be optimally distributed to various end effector components, perhaps sequenced by an electroactive polymer or piezoelelectrically actuated function switch block.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Surgical stapling device
ActiveUS7159750B2Easy to operatePositioning is simple and fastSuture equipmentsStapling toolsEngineeringActuator
A surgical device is disclosed which includes a handle portion, a central body portion and a Simple Use Loading Unit (“SULU”) [SULU]. The SULU includes a proximal body portion, an intermediate pivot member and a tool assembly. The intermediate pivot member is pivotally secured to the proximal body portion about a first pivot axis and the tool assembly is pivotally secured to the intermediate pivot member about a second pivot axis which is orthogonal to the first pivot axis. The SULU includes a plurality of articulation links which are operably connected to the tool assembly by non-rigid links. The articulation links are adapted to releasably engage articulation links positioned in the central body portion. The body portion articulation links are connected to an articulation actuator which is supported for omni-directional movement to effect articulation of the tool assembly about the first and second axes. The handle portion includes a spindle and barrel assembly drive mechanism for advancing and retracting a drive member positioned in the tool assembly. In one embodiment, the tool assembly includes a cartridge assembly having a plurality of staples and an anvil assembly.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Surgical stapling instrument with mechanical mechanism for limiting maximum tissue compression
Various forms of surgical instruments are disclosed. In various embodiments, the instrument includes a cartridge supporting assembly for operably supporting a staple cartridge therein. The cartridge supporting assembly may be responsive to firing and retraction motions applied thereto from a firing assembly. An anvil may be operably coupled to an anvil closure assembly. The anvil closure assembly may be constructed to selectively move the anvil in a proximal direction toward the cartridge supporting assembly to enable a portion of tissue to be clamped between a cartridge supported by the cartridge supporting assembly and the anvil under a predetermined amount of compression. The device may further include a compression limiting assembly that interacts with the anvil closure assembly to prevent further travel of the anvil in the proximal direction toward the cartridge supporting assembly when the predetermined amount of compression has been attained.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Surgical stapling instrument with multistroke firing incorporating an anti-backup mechanism
ActiveUS6959852B2Prevent returnAvoid resistanceSuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical stapleEndoscopic surgery
A surgical stapling and severing instrument particularly suited to endoscopic procedures incorporates a handle that produces separate closing and firing motions to actuate an end effector. In particular, the handle produces multiple firing strokes in order to reduce the required amount of force required to fire (i.e., staple and sever) the end effector. A linked transmission reduces the required handle longitudinal length, yet achieves a rigid, strong configuration when straightened for firing. A traction biased firing mechanism avoids binding in driving this straightened linked rack in cooperation with an anti-backup mechanism, with a lockout mechanism that prevents releasing the closure trigger during firing. Furthermore, an external indicator gives feedback to the surgeon as to how far firing has progressed, as well as providing a manual retraction capability.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
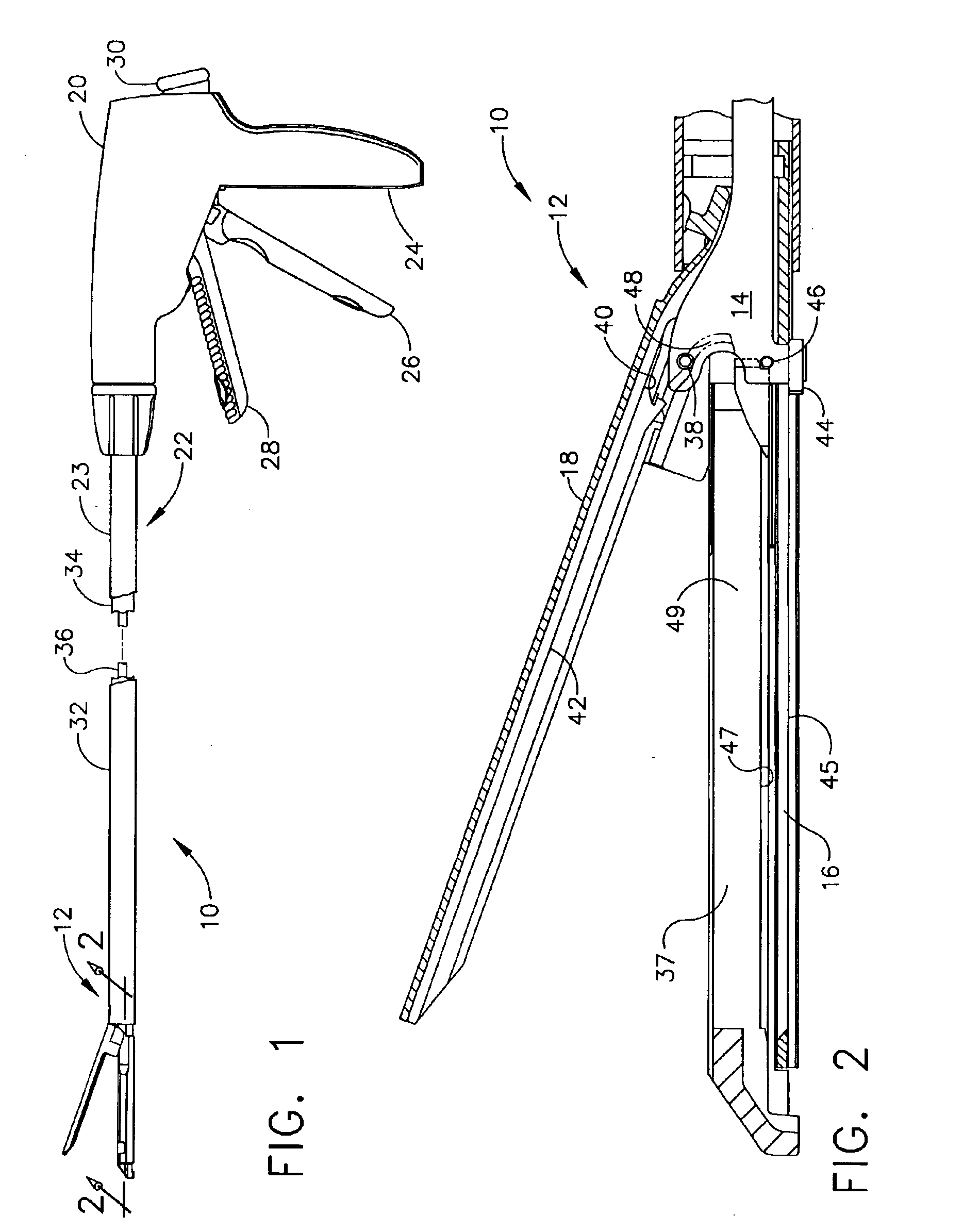
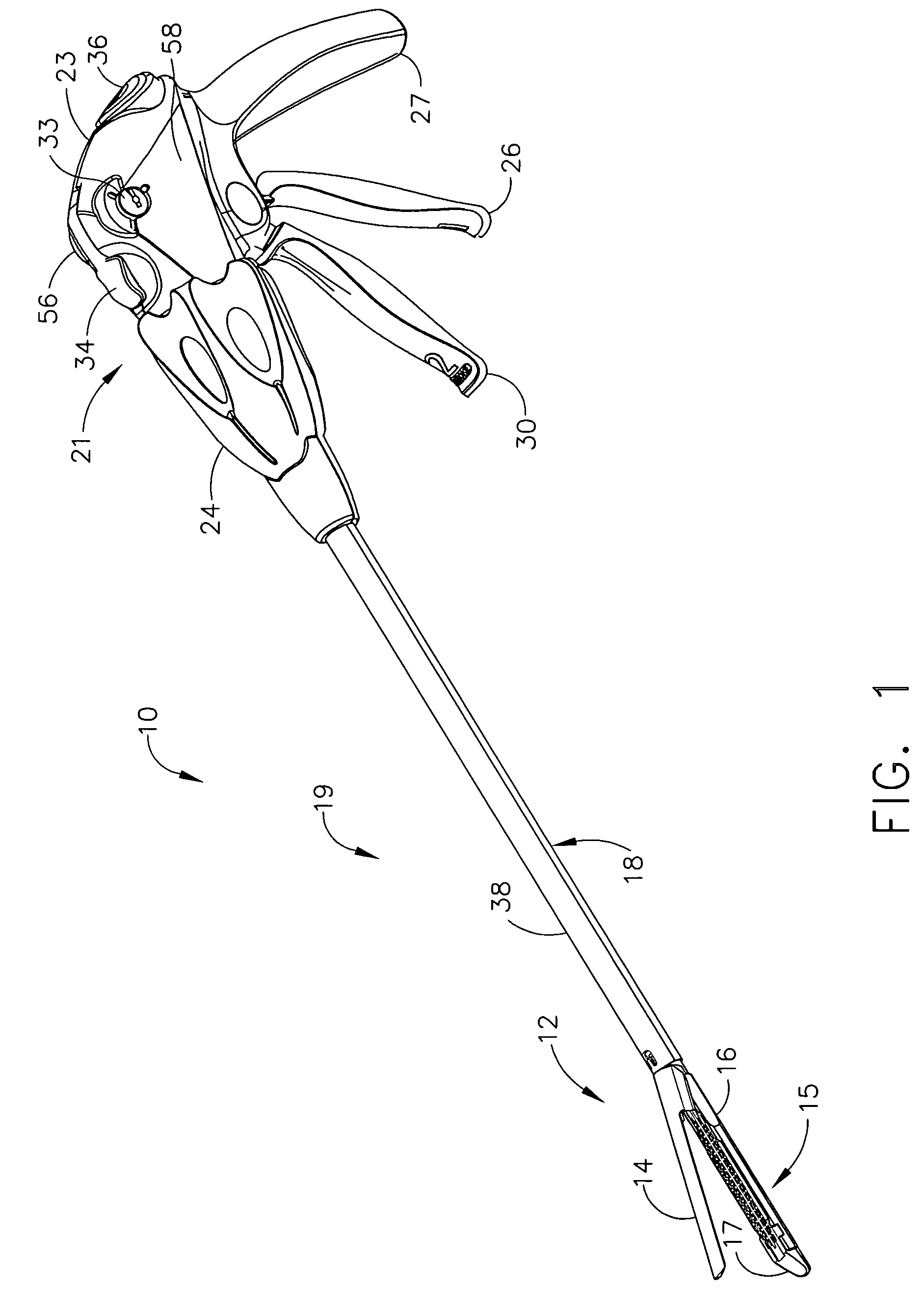
Lockout mechanisms and surgical instruments including same
A surgical instrument is disclosed. The surgical instrument includes a handle portion, a channel, an anvil, and staple cartridge, a wedge member, a reciprocating firing device, and a lockout arm. The handle portion is operably configured to produce a firing motion and is coupled to the channel portion. The staple cartridge is engaged by the channel and includes a plurality of staple drivers to cam the staples toward the anvil, which is pivotally attached to the channel. The wedge member is proximal to and longitudinally aligned with the staple drivers, and the reciprocating firing device is responsive to the firing motion to progressively drive the wedge member from an unfired to a fired position. The lockout arm is pivotally attached to the channel and operably configured to pivot between a locked position and an unlocked position with respect to the firing device based upon a position of the wedge member.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com