Patents
Literature
9050 results about "Surgical instrument" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A surgical instrument is a specially designed tool or device for performing specific actions or carrying out desired effects during a surgery or operation, such as modifying biological tissue, or to provide access for viewing it. Over time, many different kinds of surgical instruments and tools have been invented. Some surgical instruments are designed for general use in surgery, while others are designed for a specific procedure or surgery. Accordingly, the nomenclature of surgical instruments follows certain patterns, such as a description of the action it performs (for example, scalpel, hemostat), the name of its inventor(s) (for example, the Kocher forceps), or a compound scientific name related to the kind of surgery (for example, a tracheotome is a tool used to perform a tracheotomy).
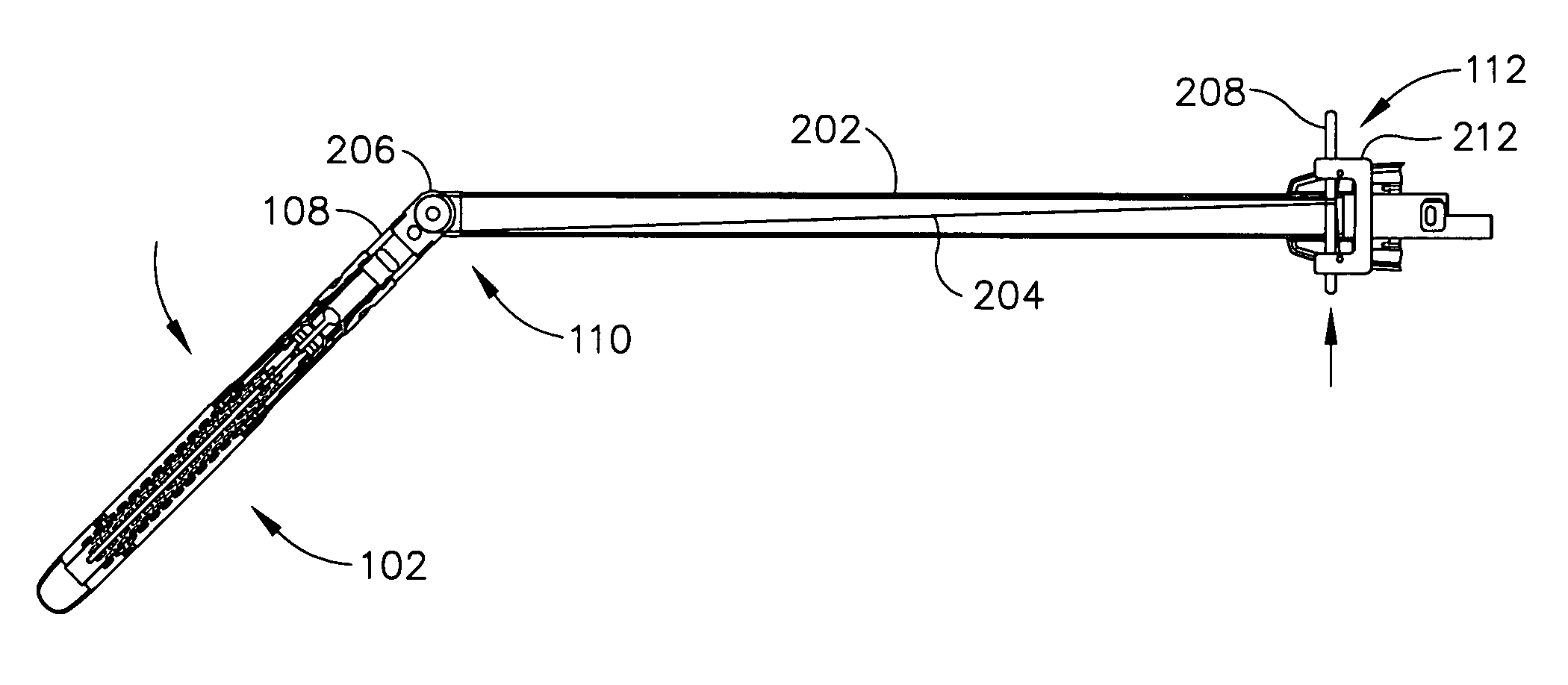
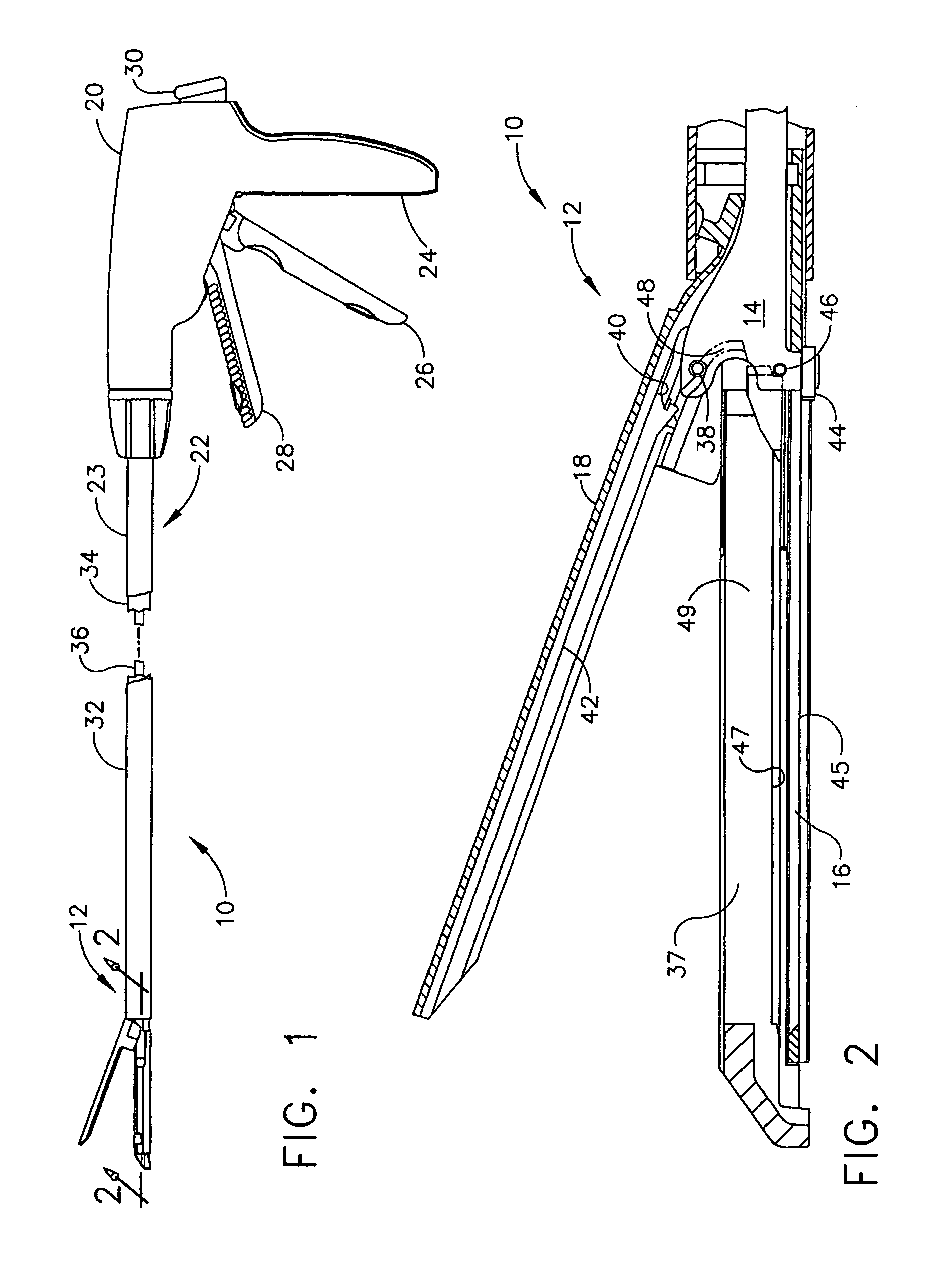
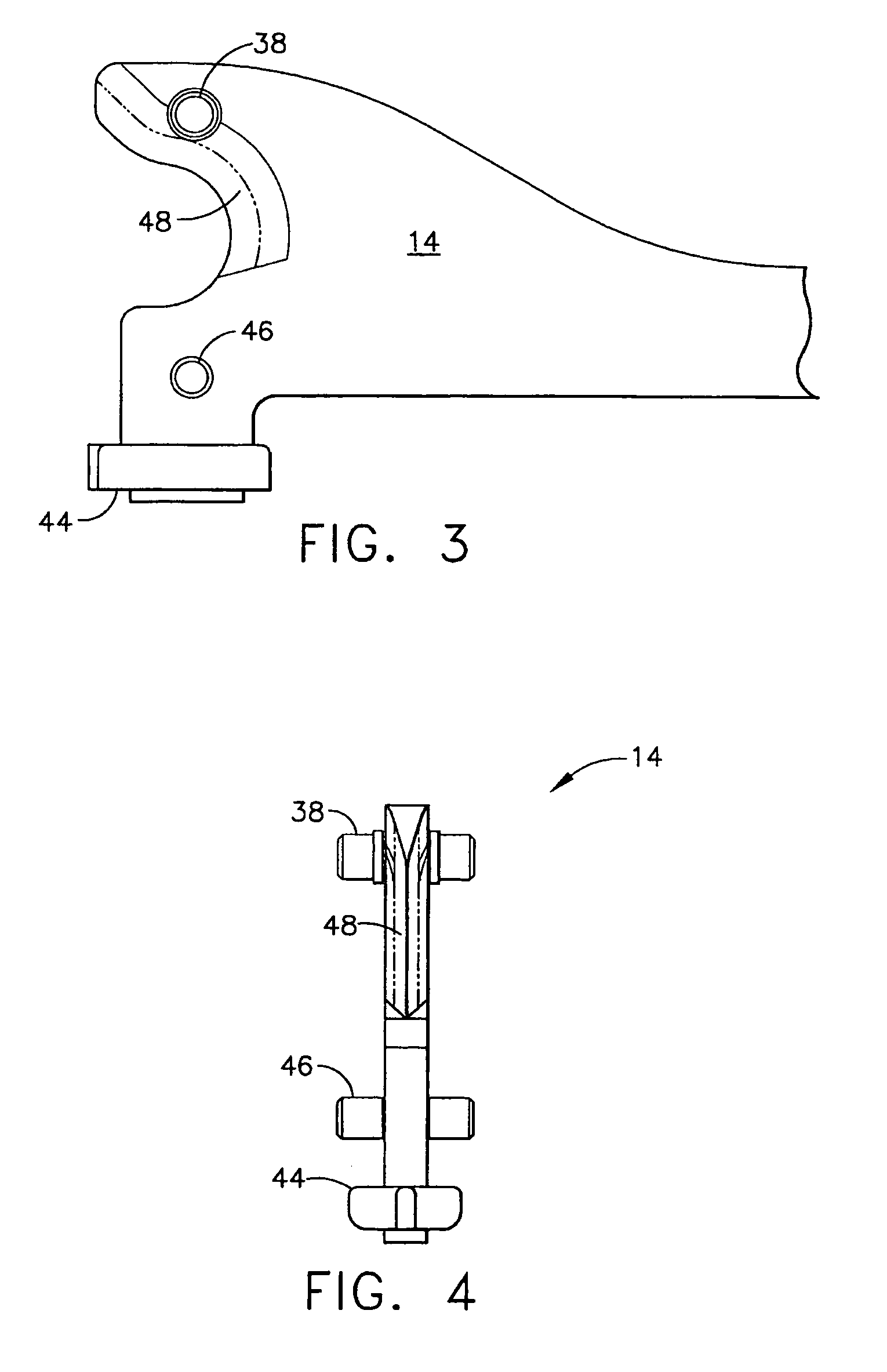
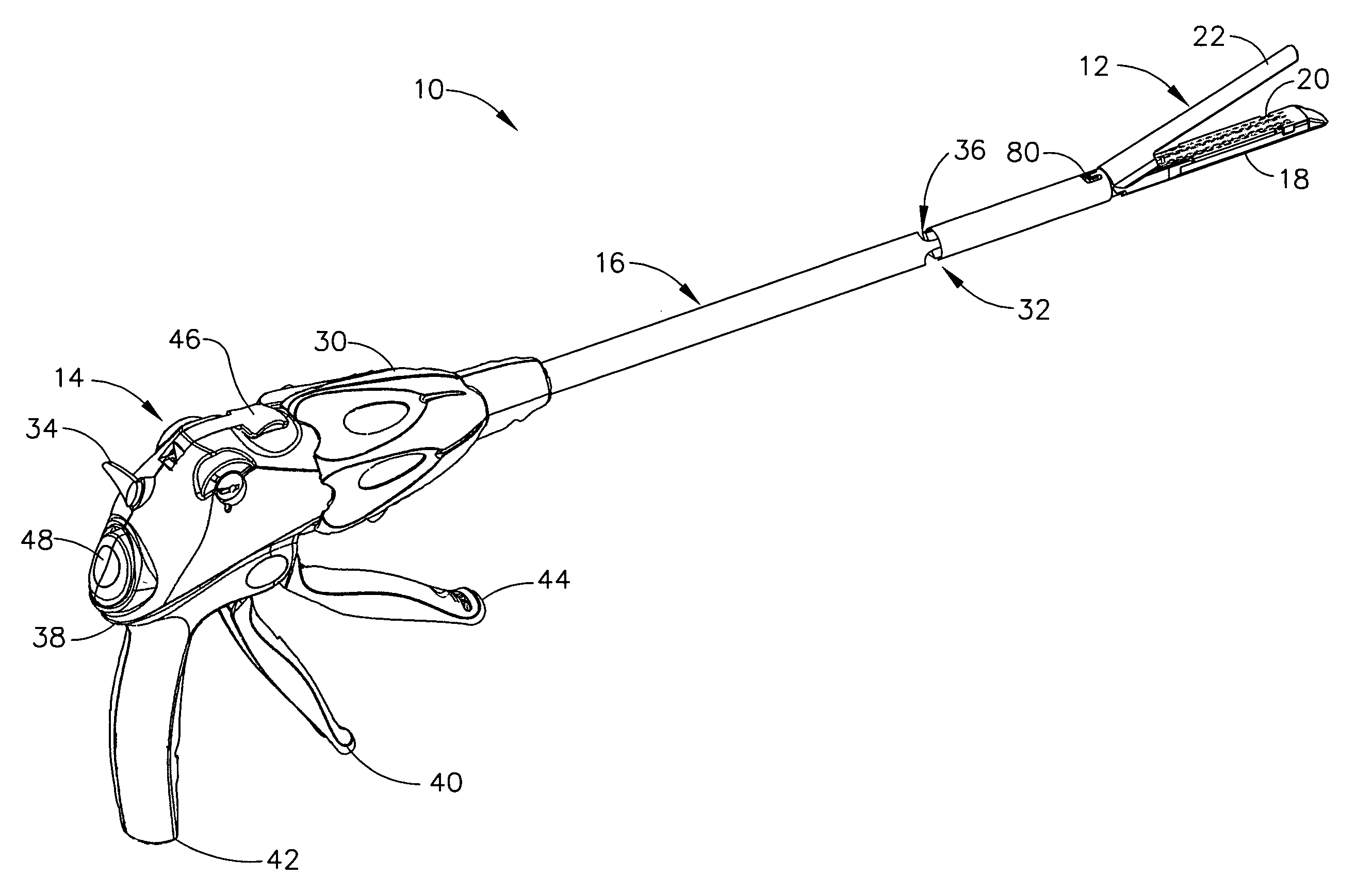
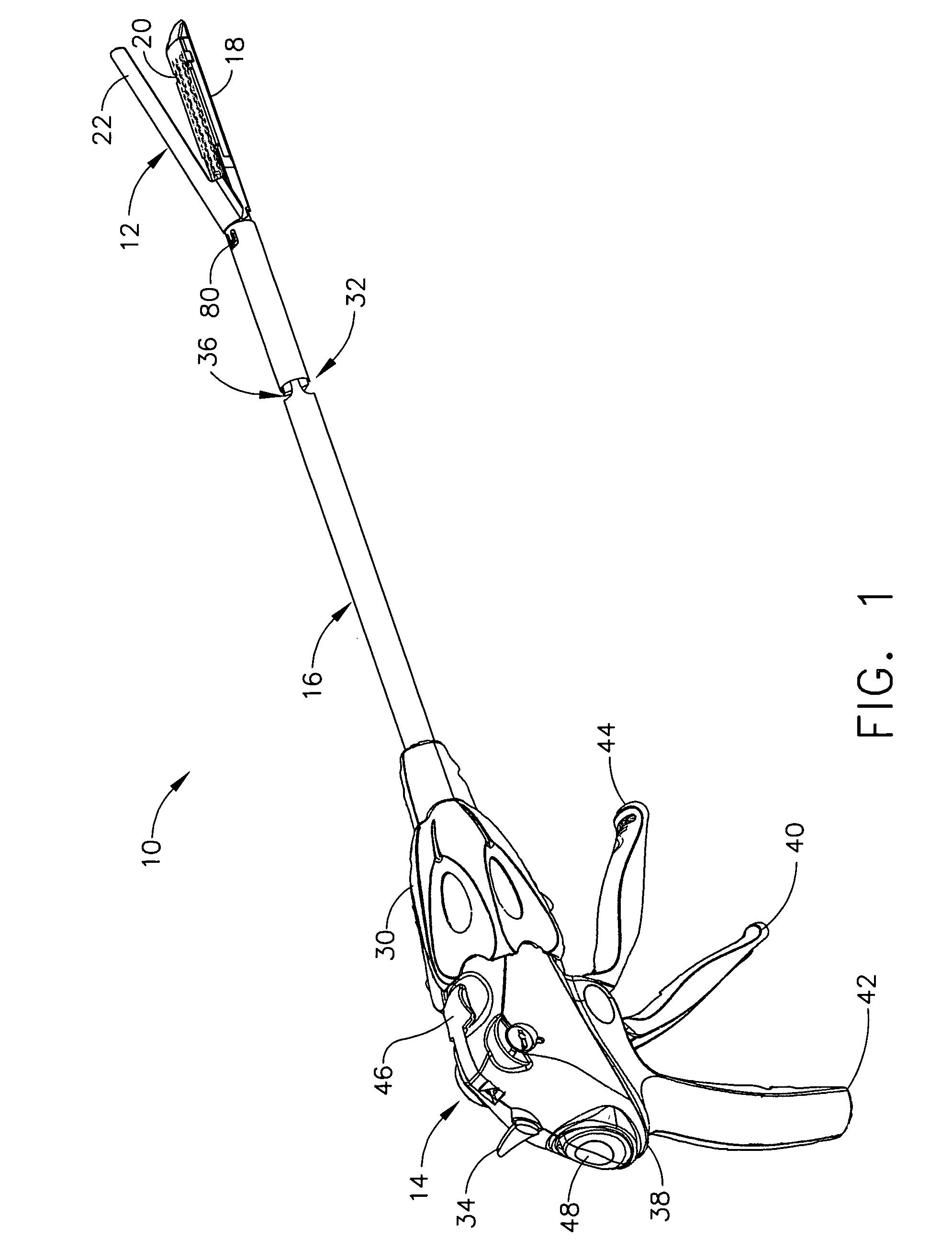
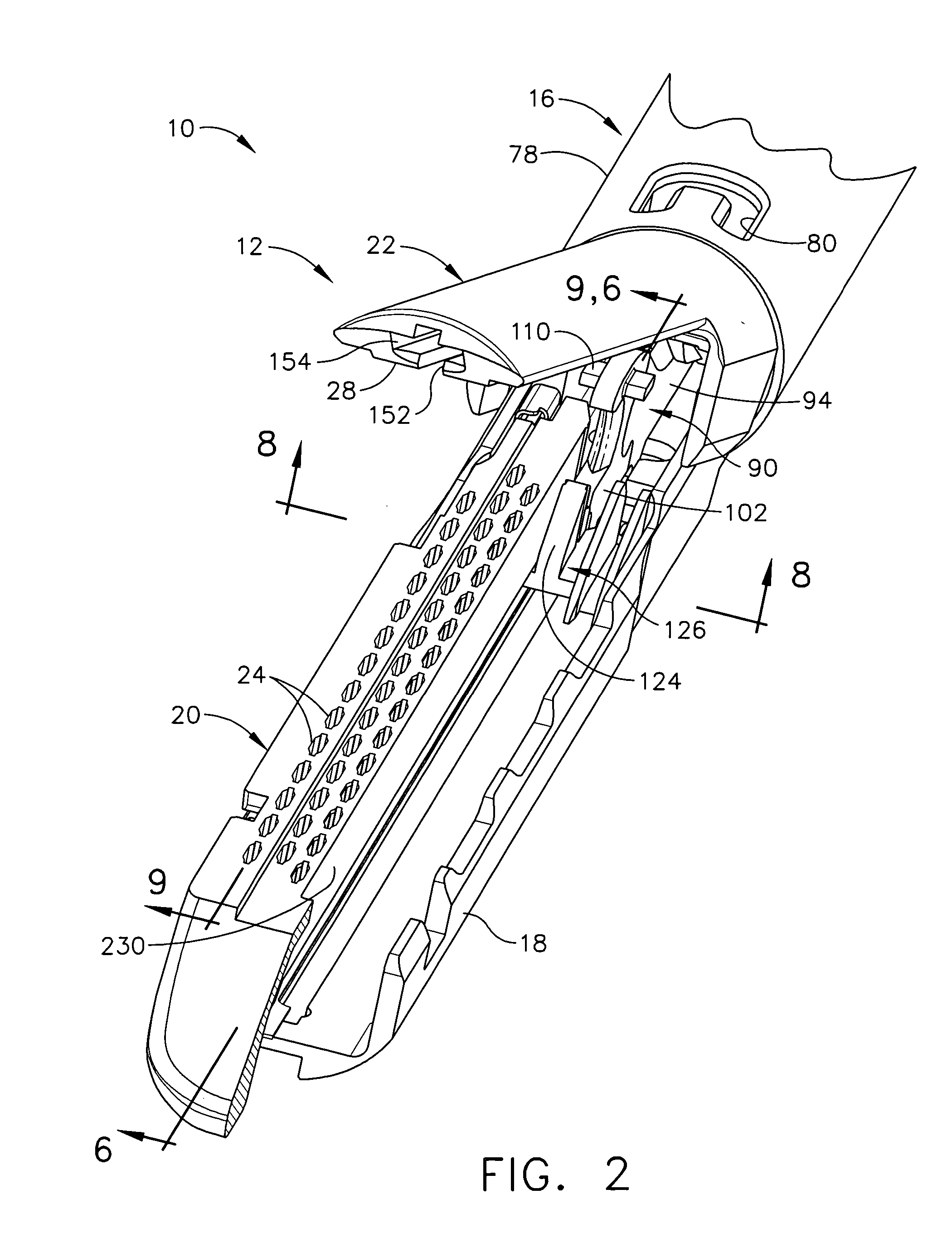
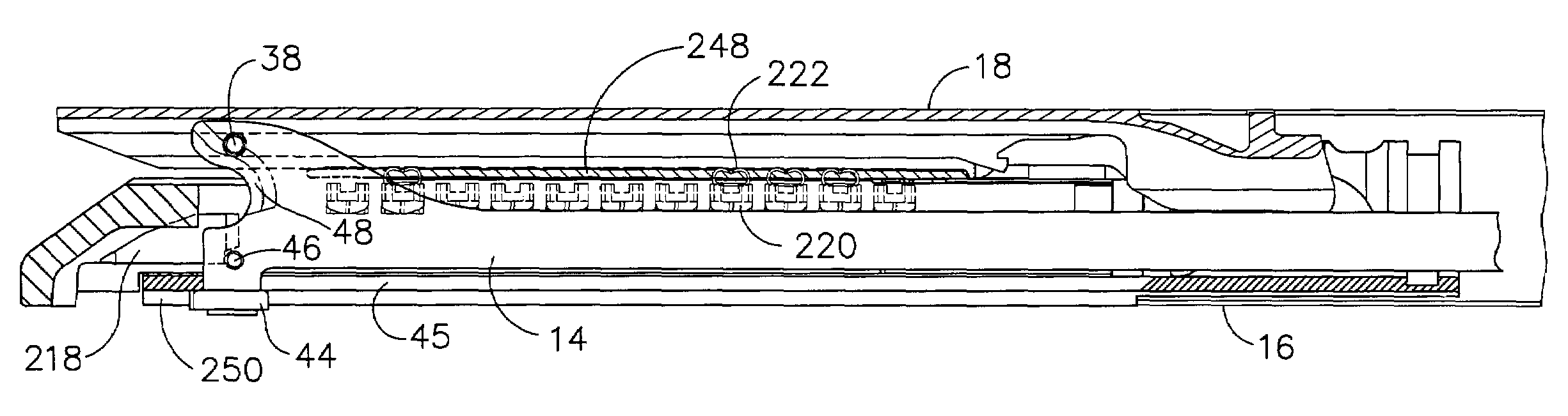
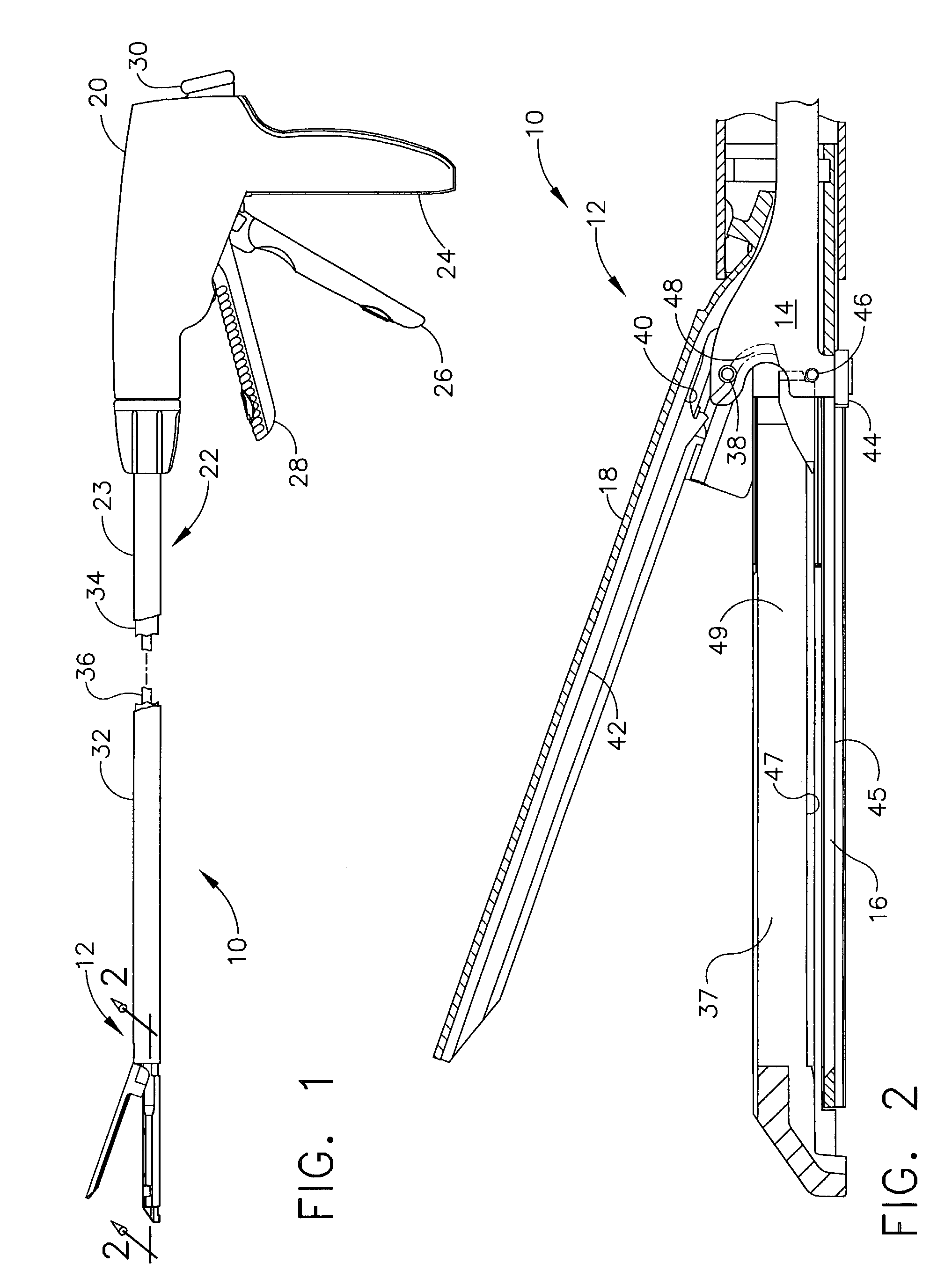
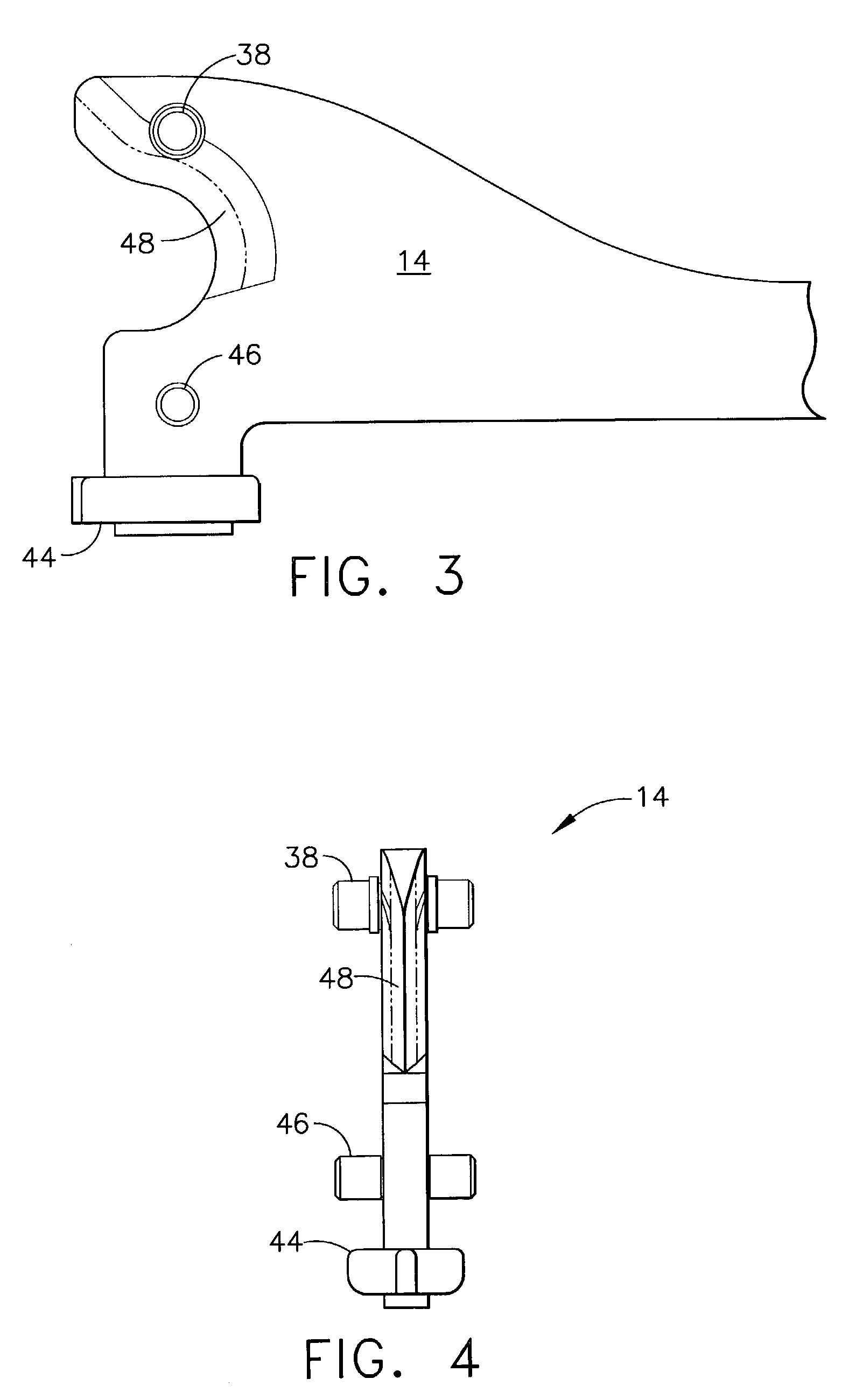
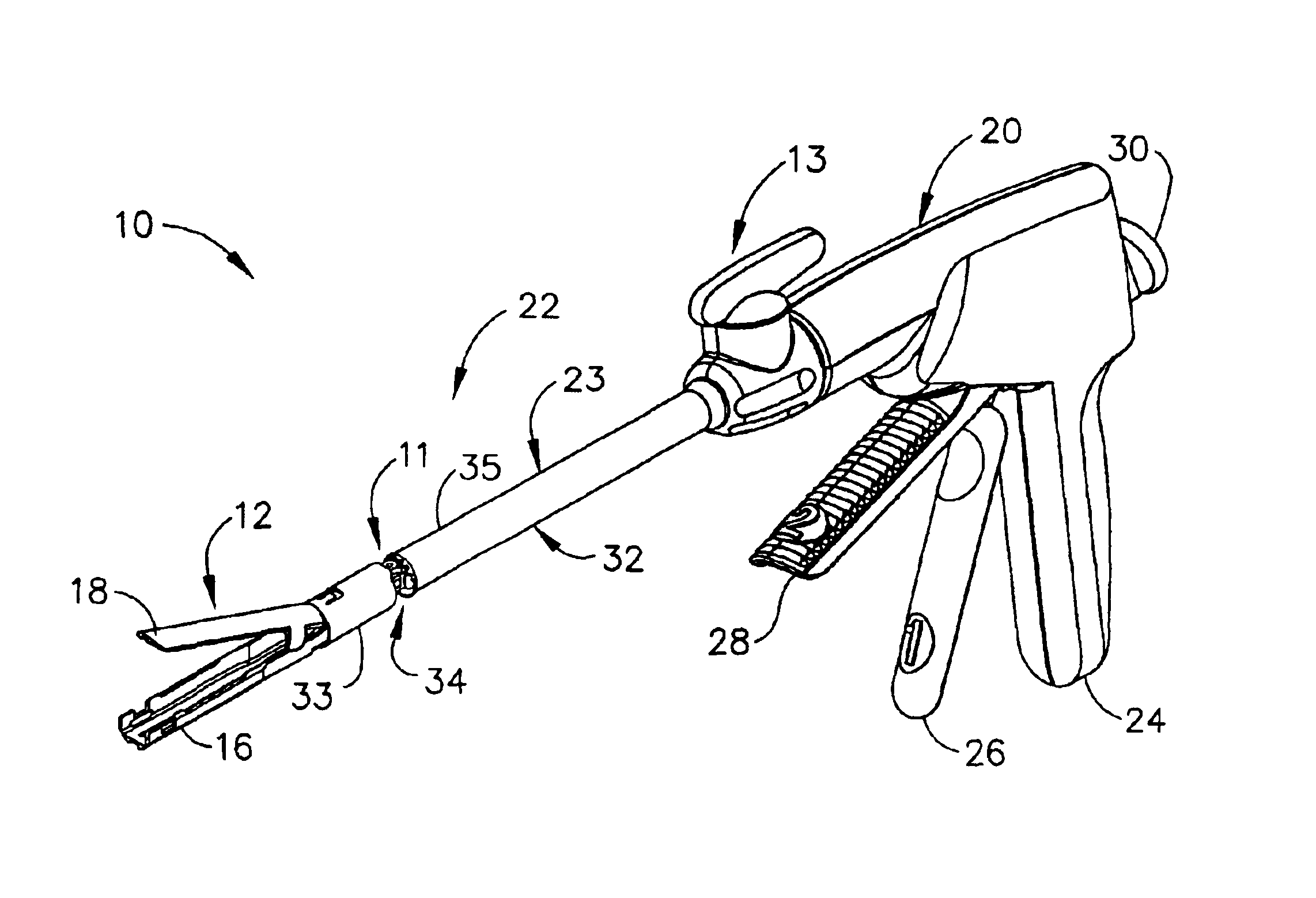
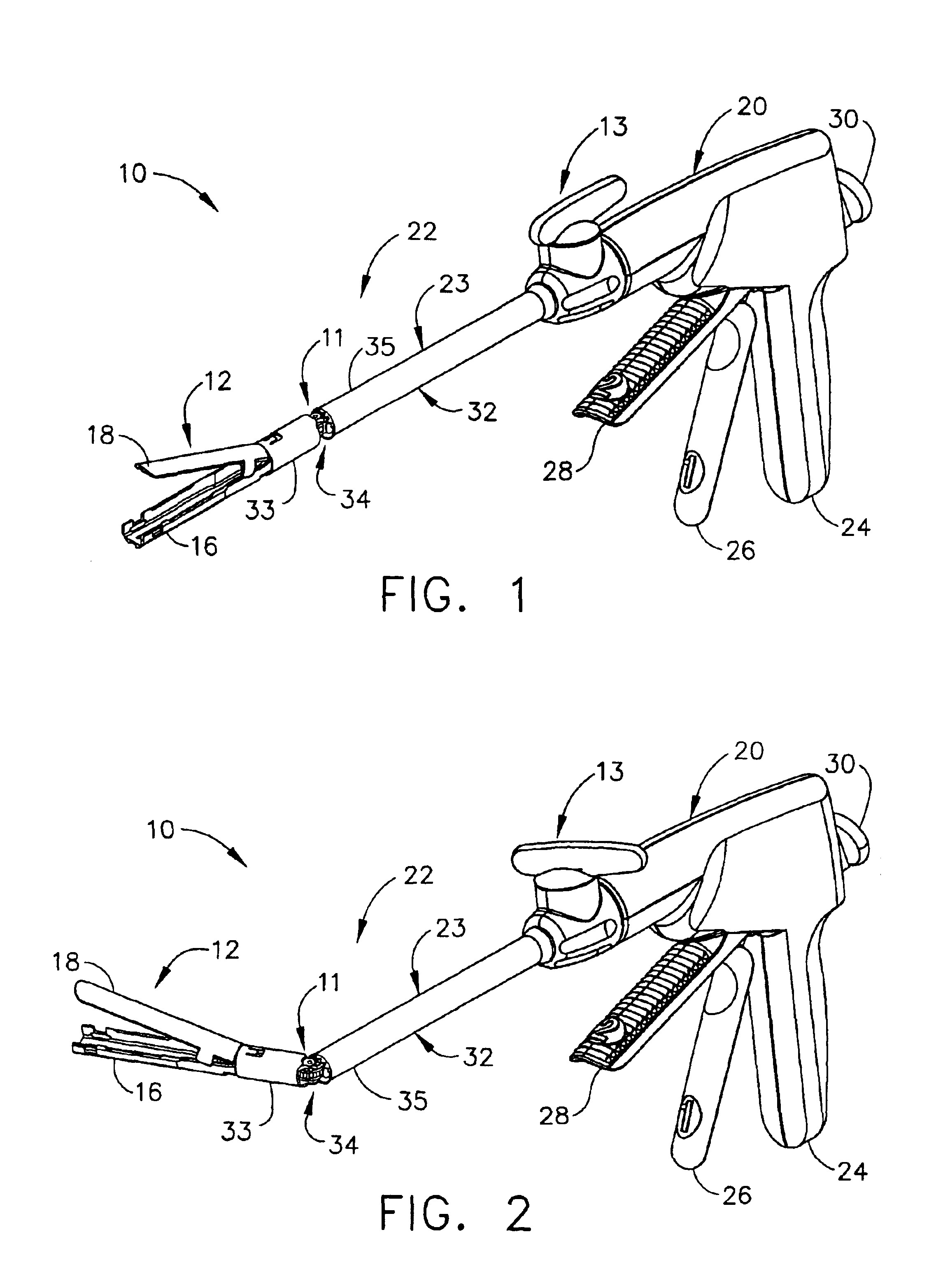
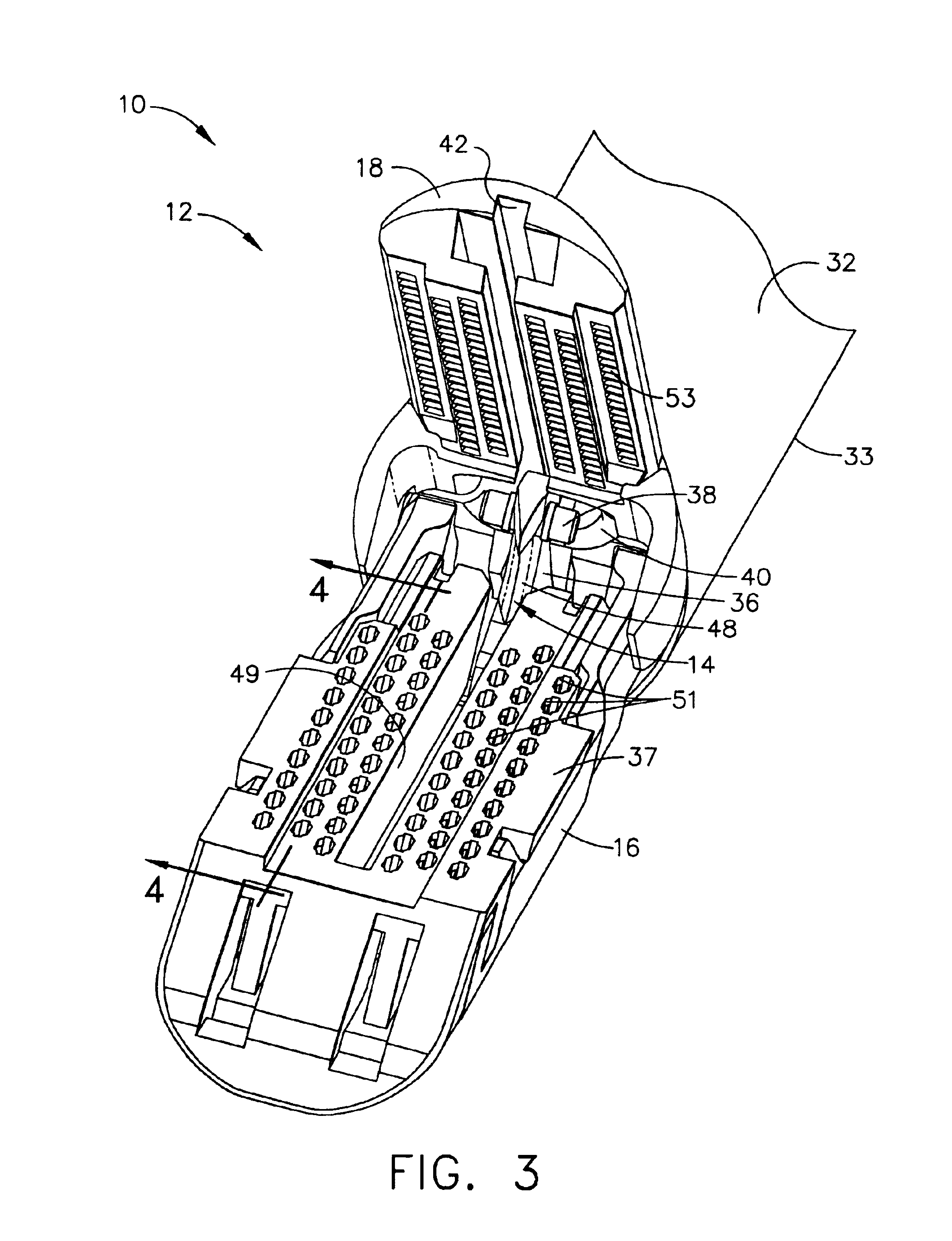
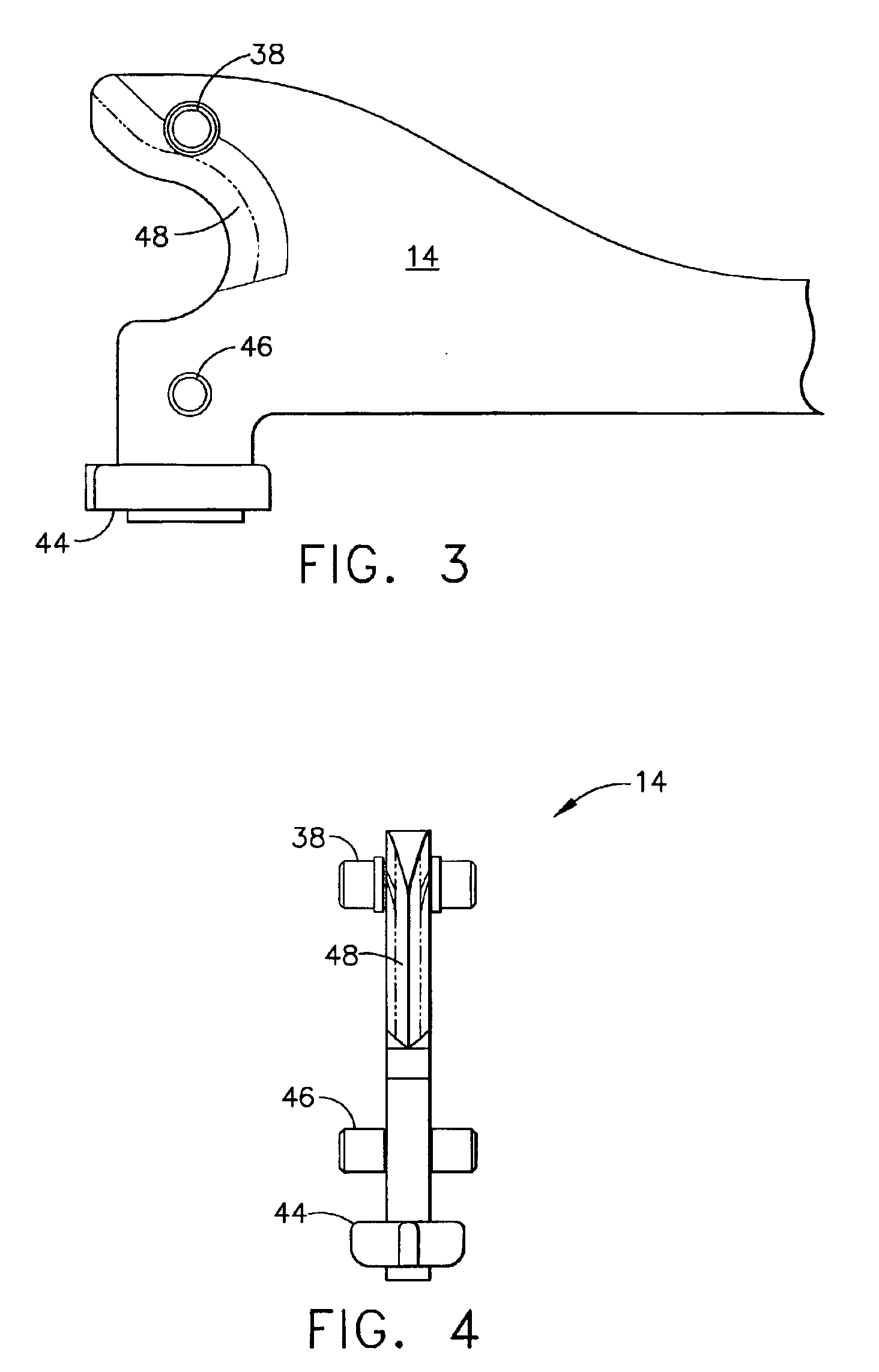
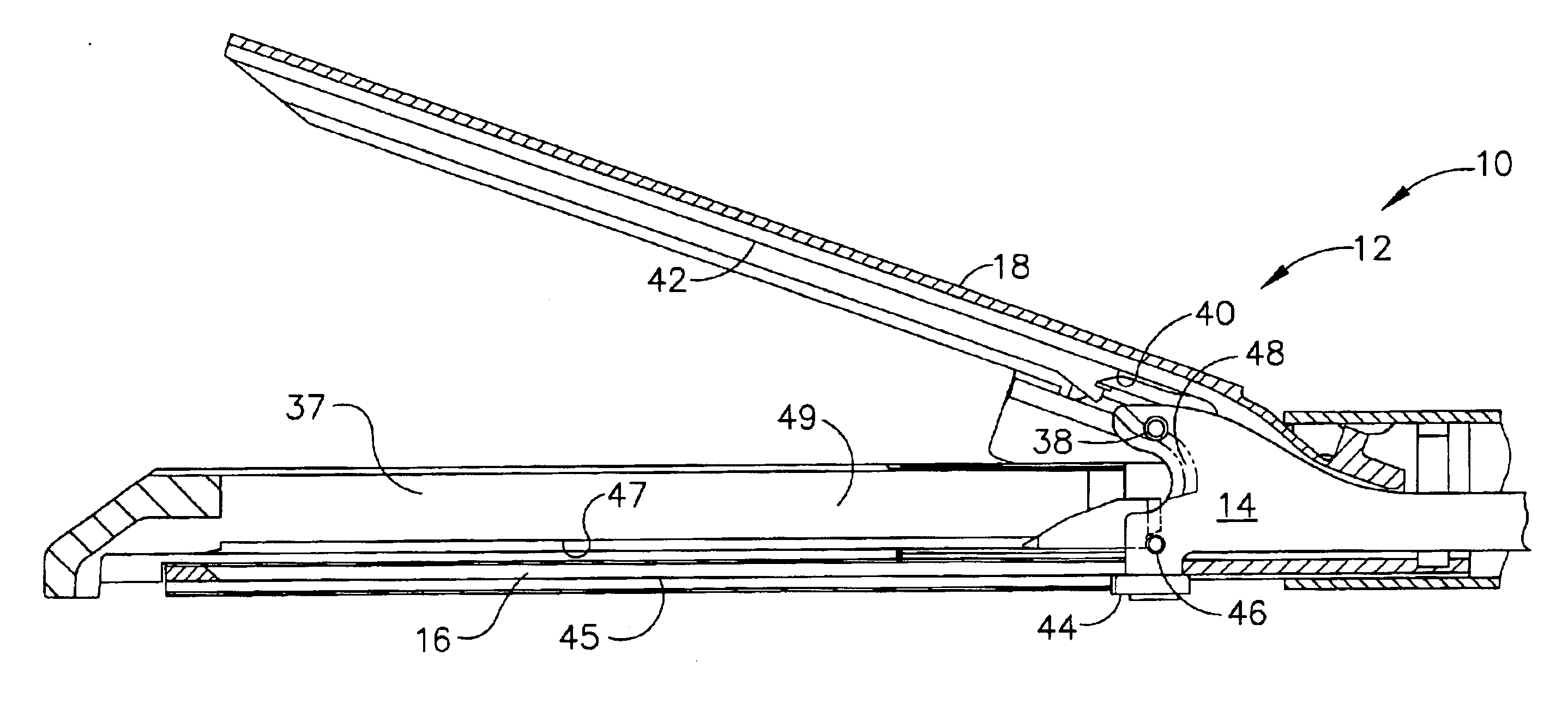
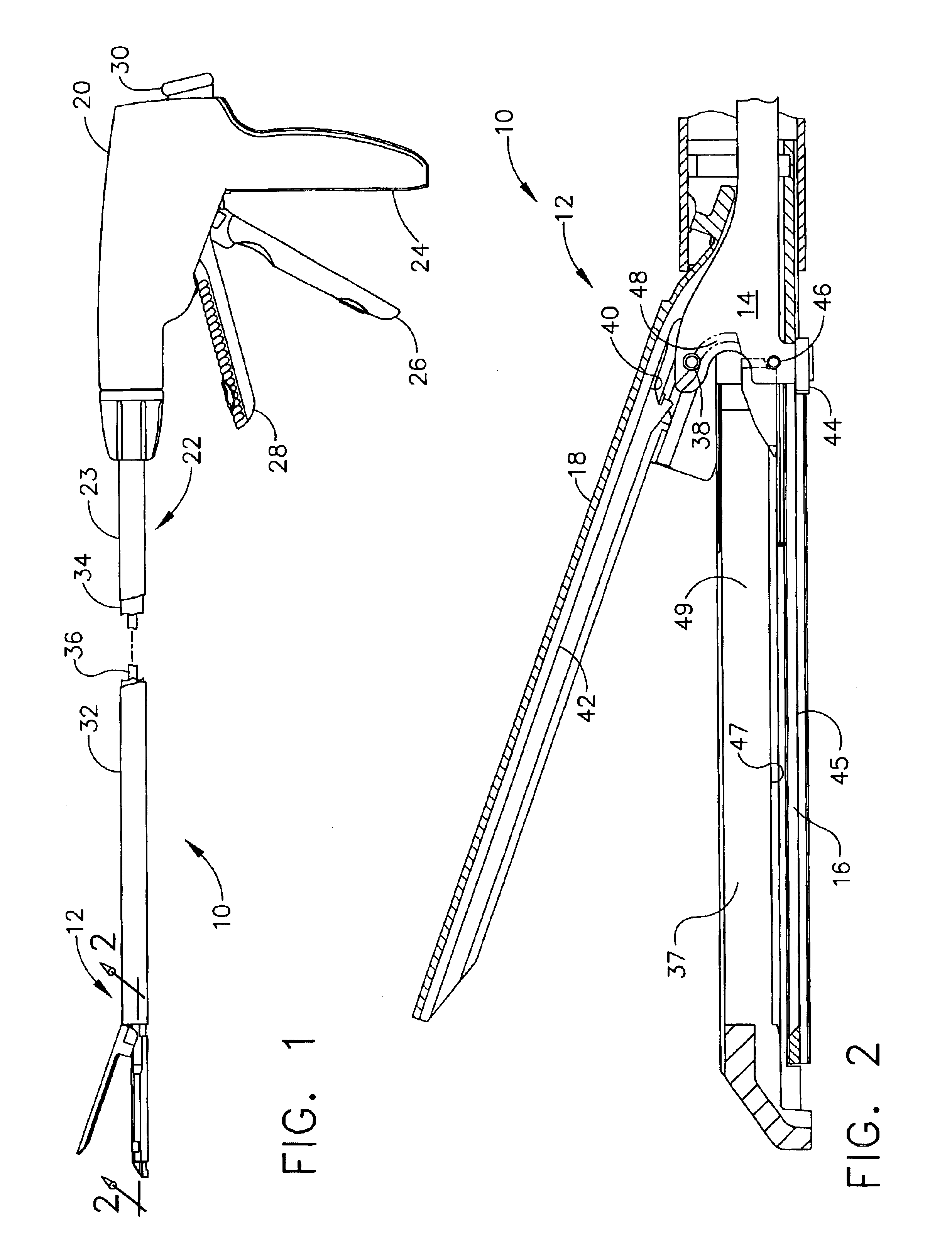
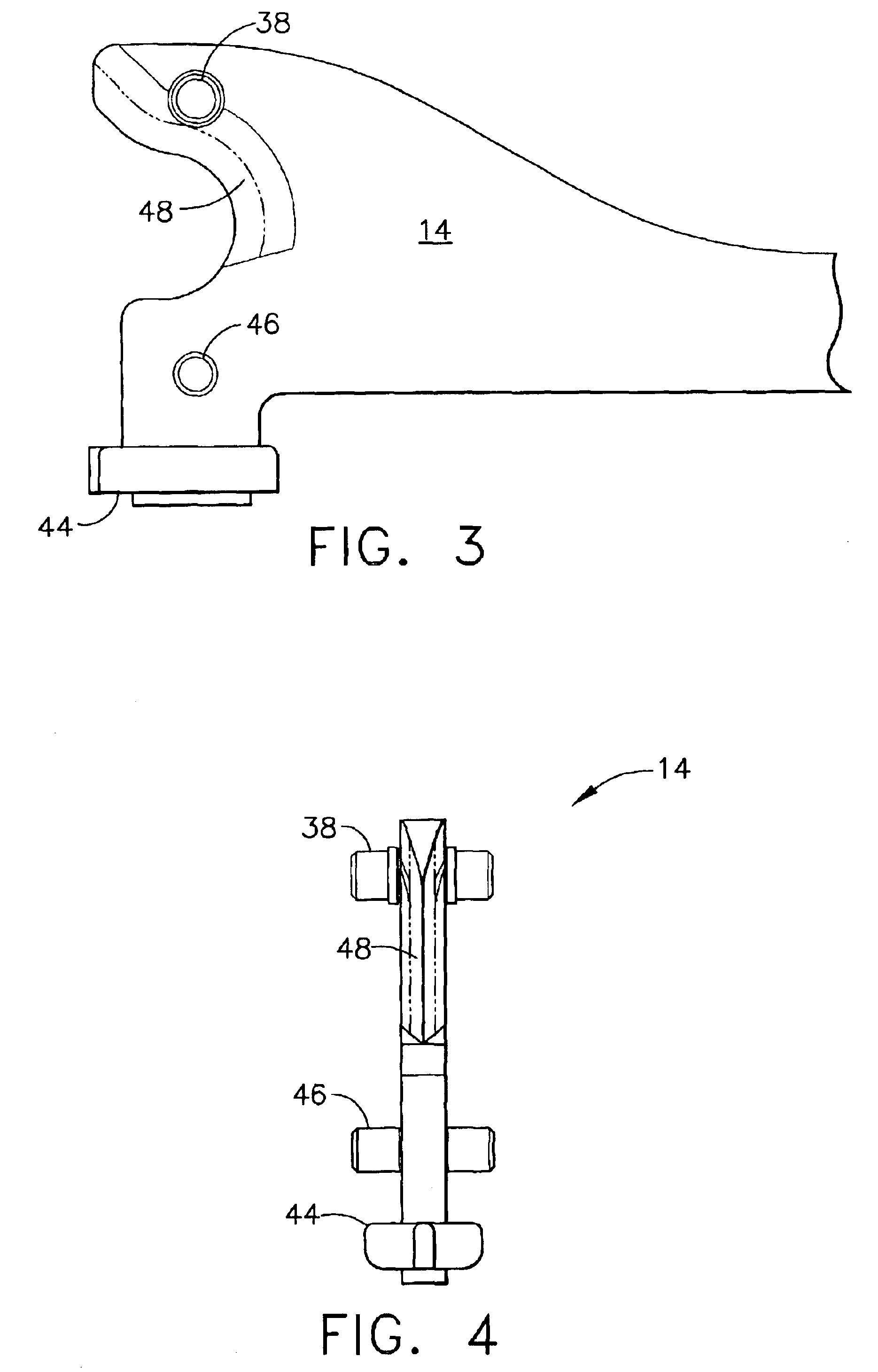
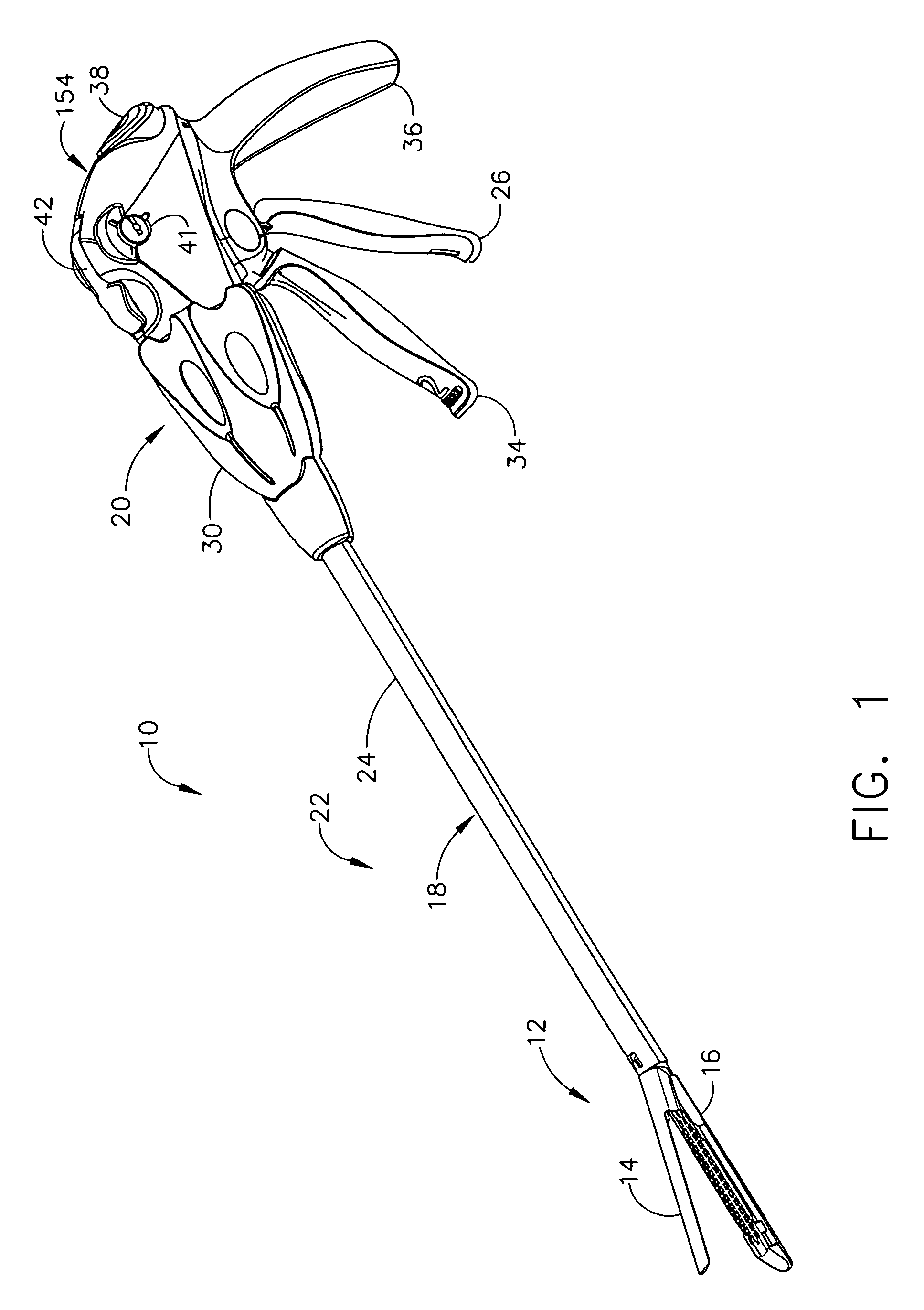
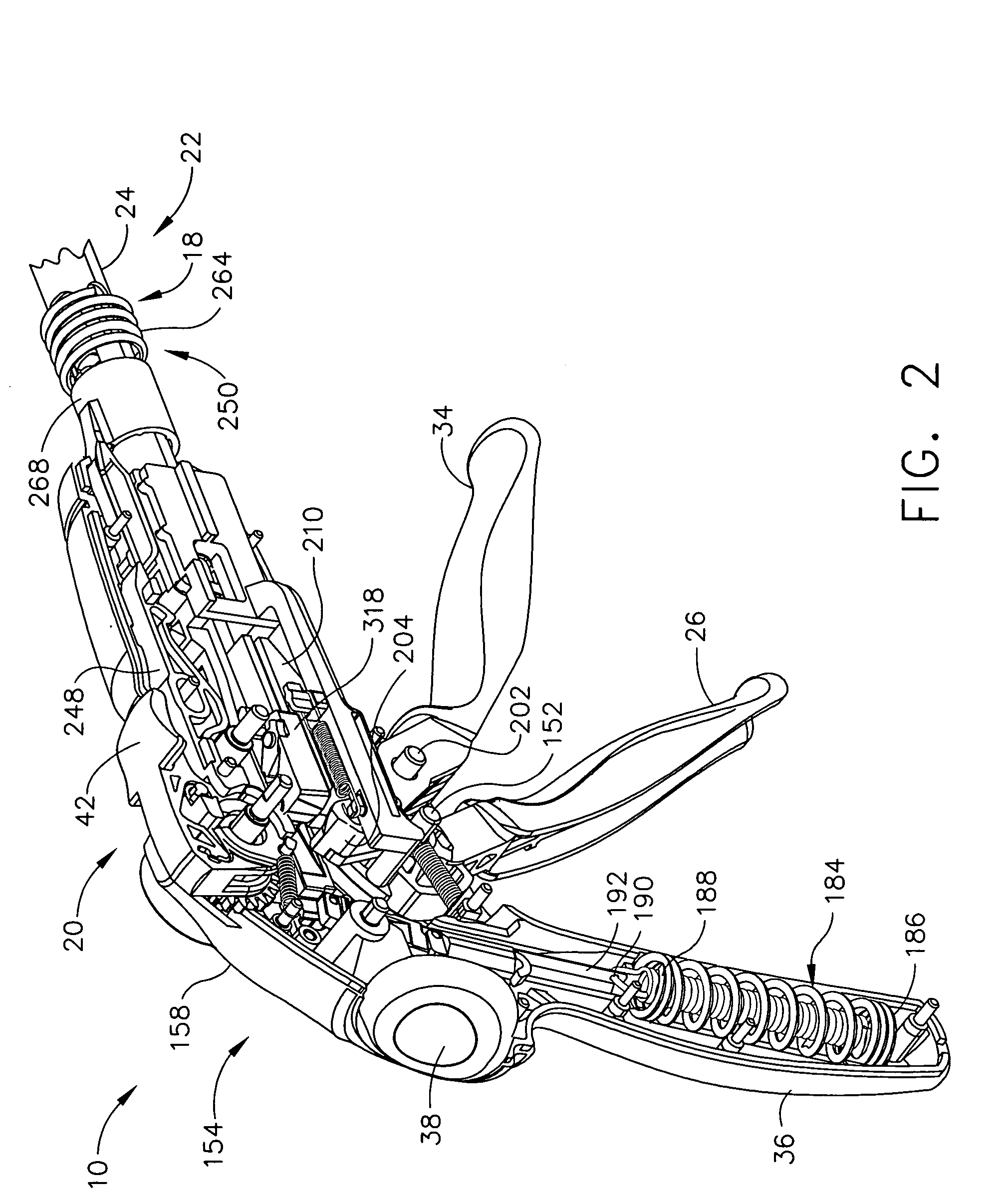
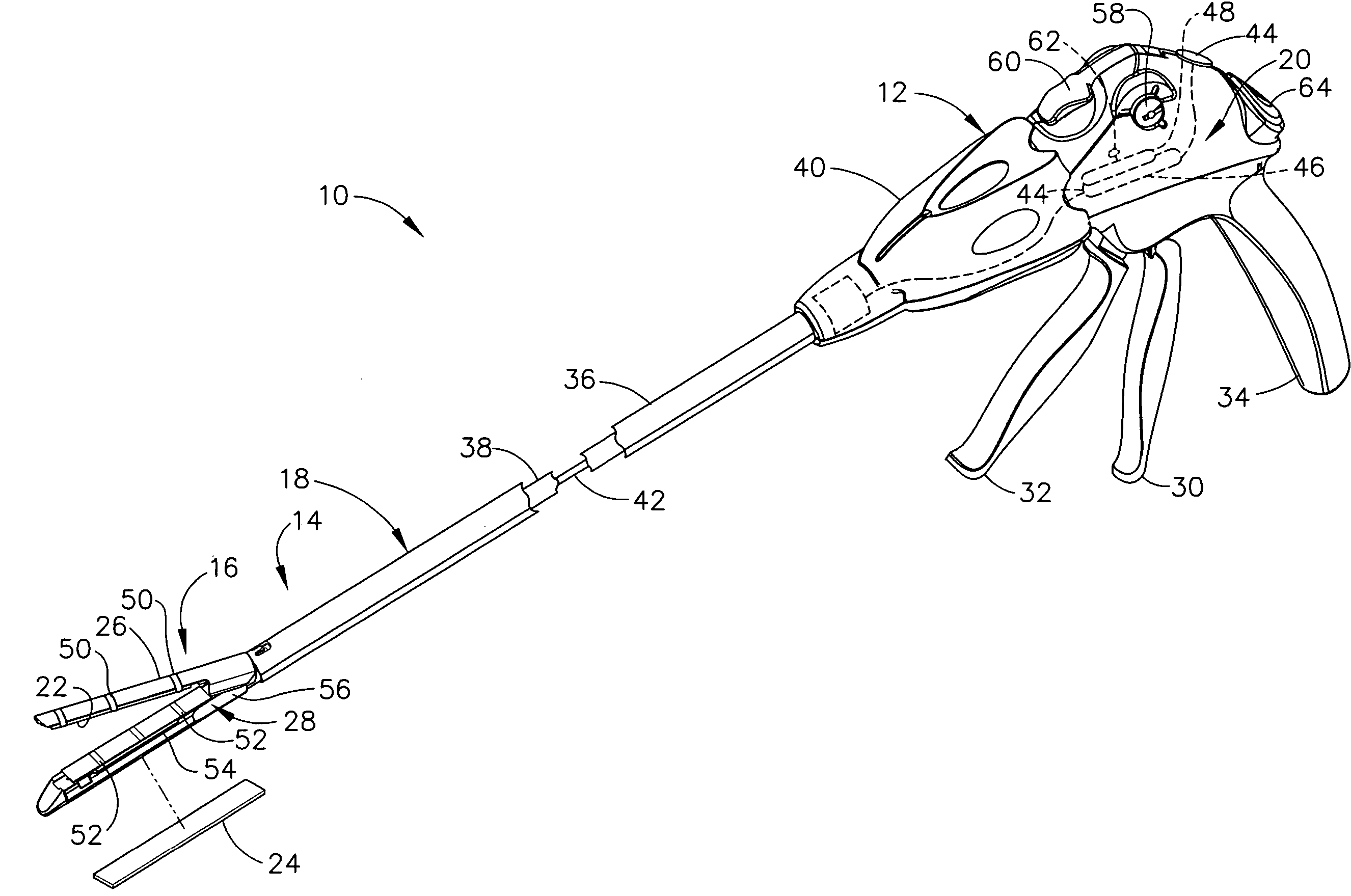
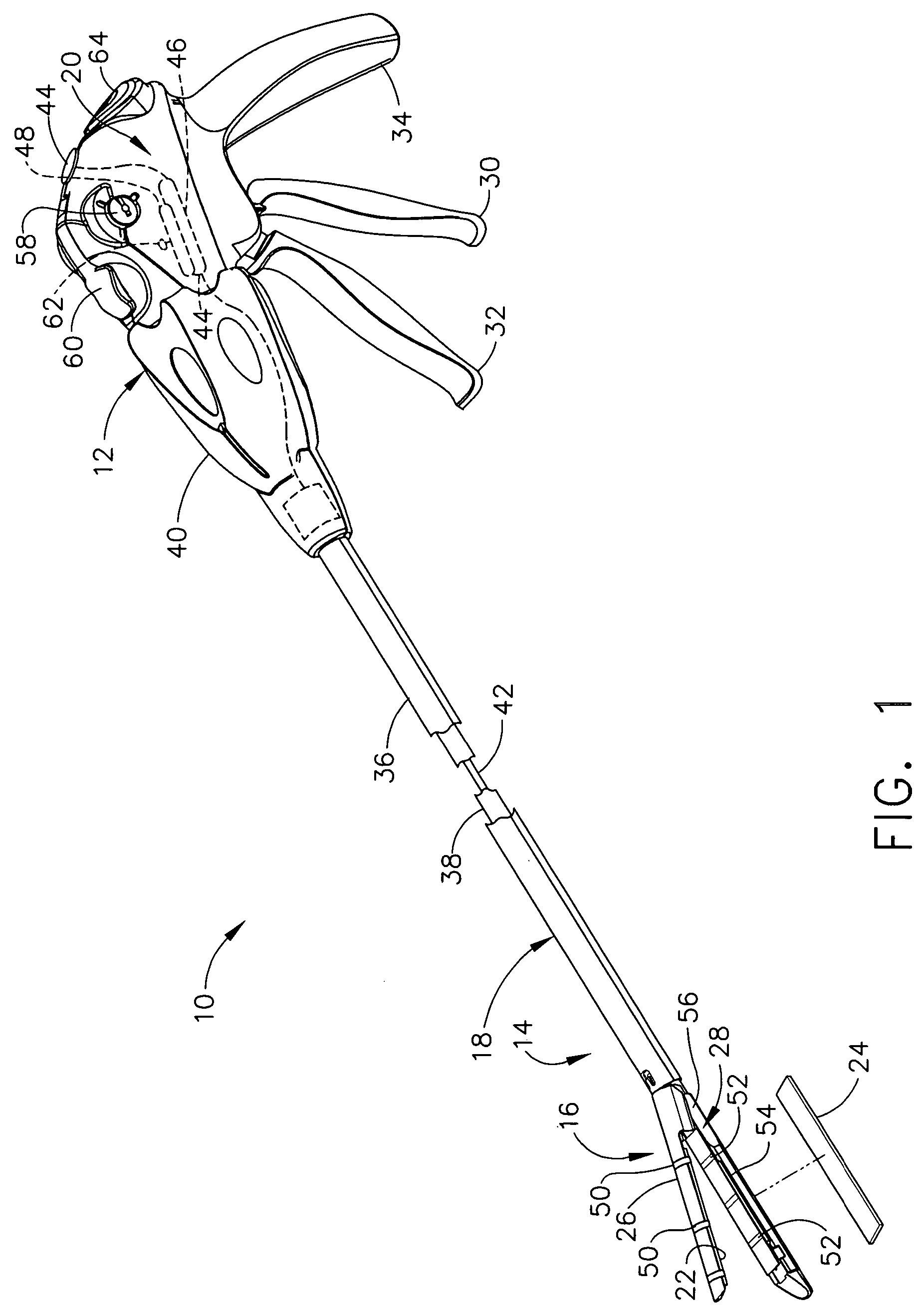
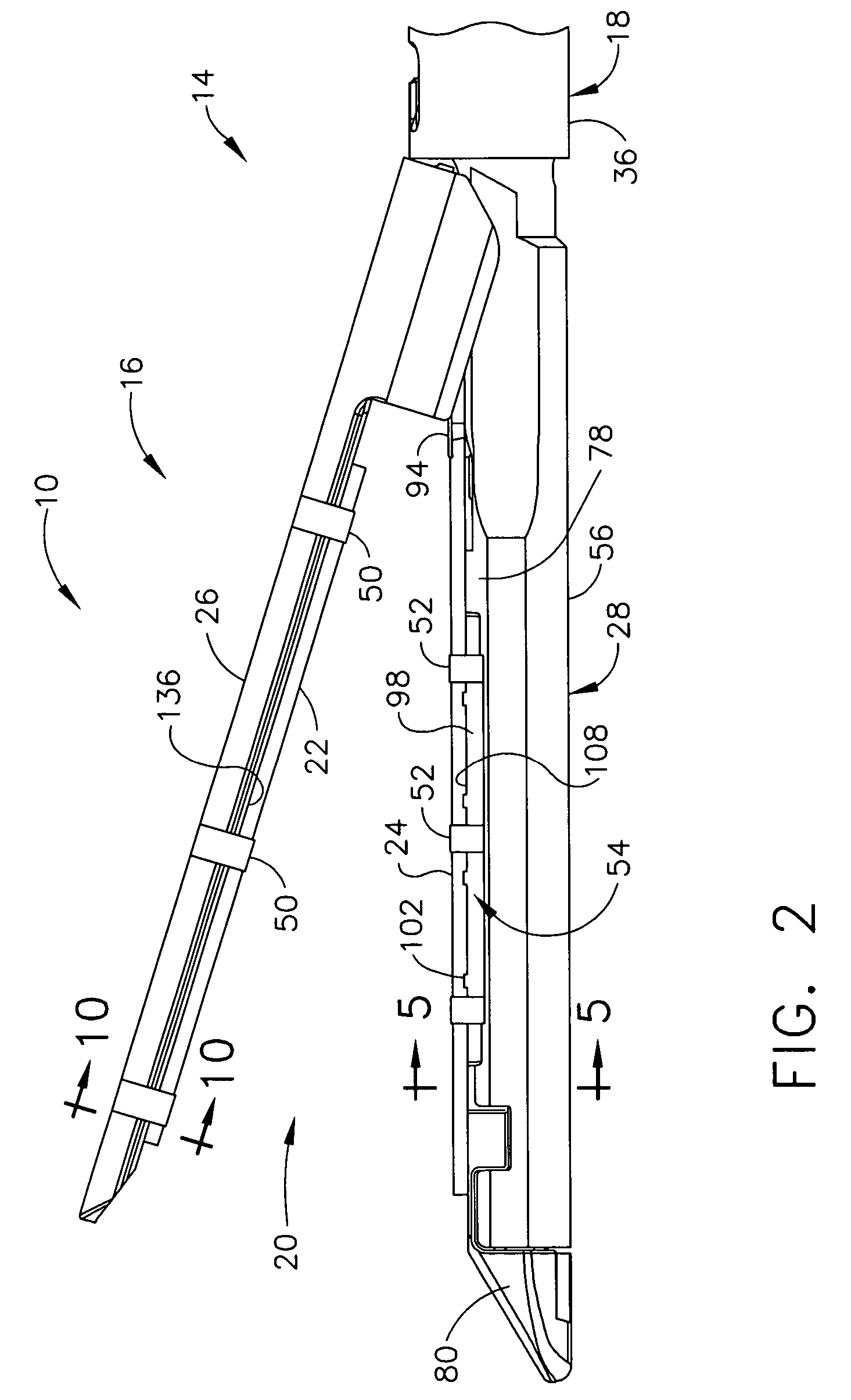
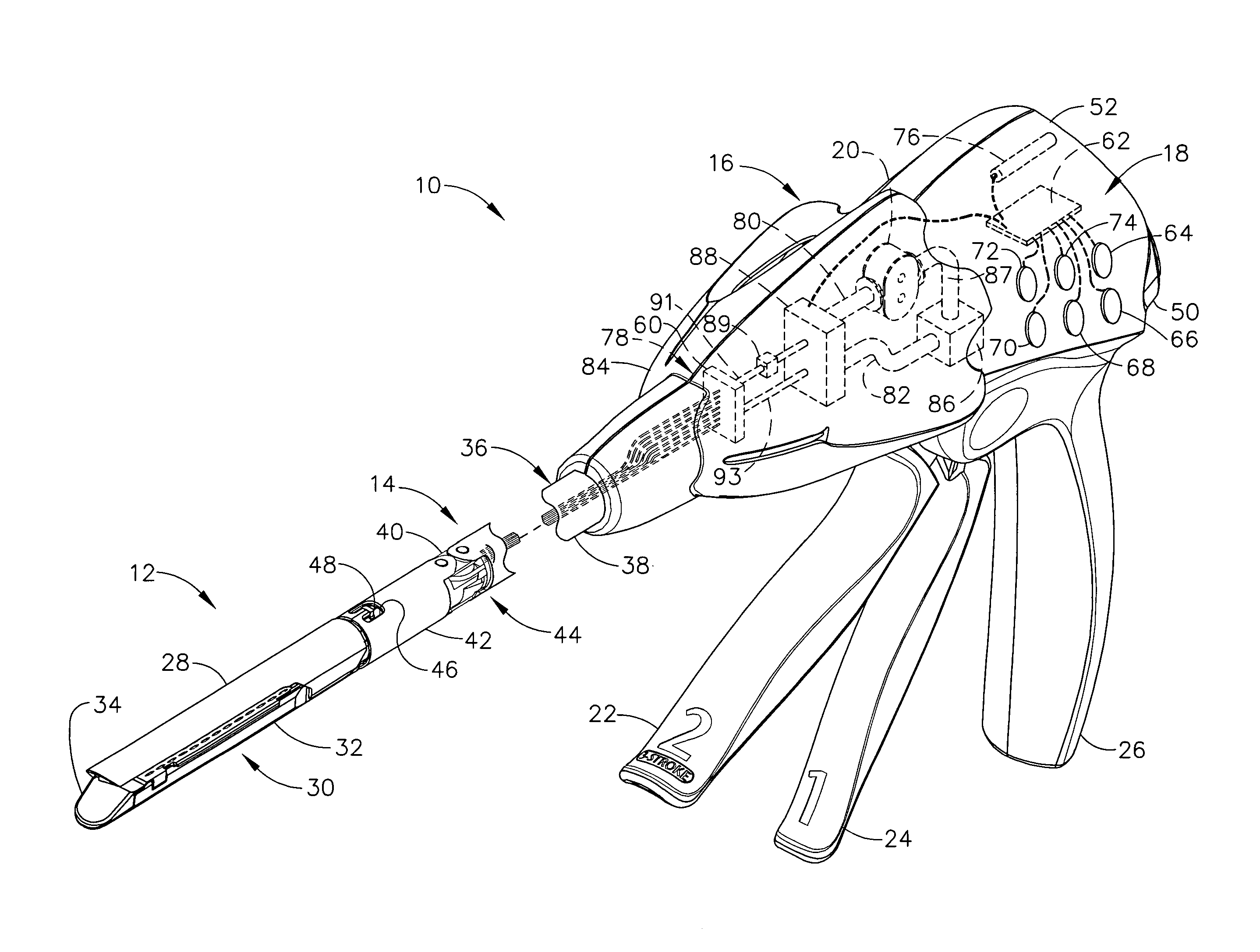
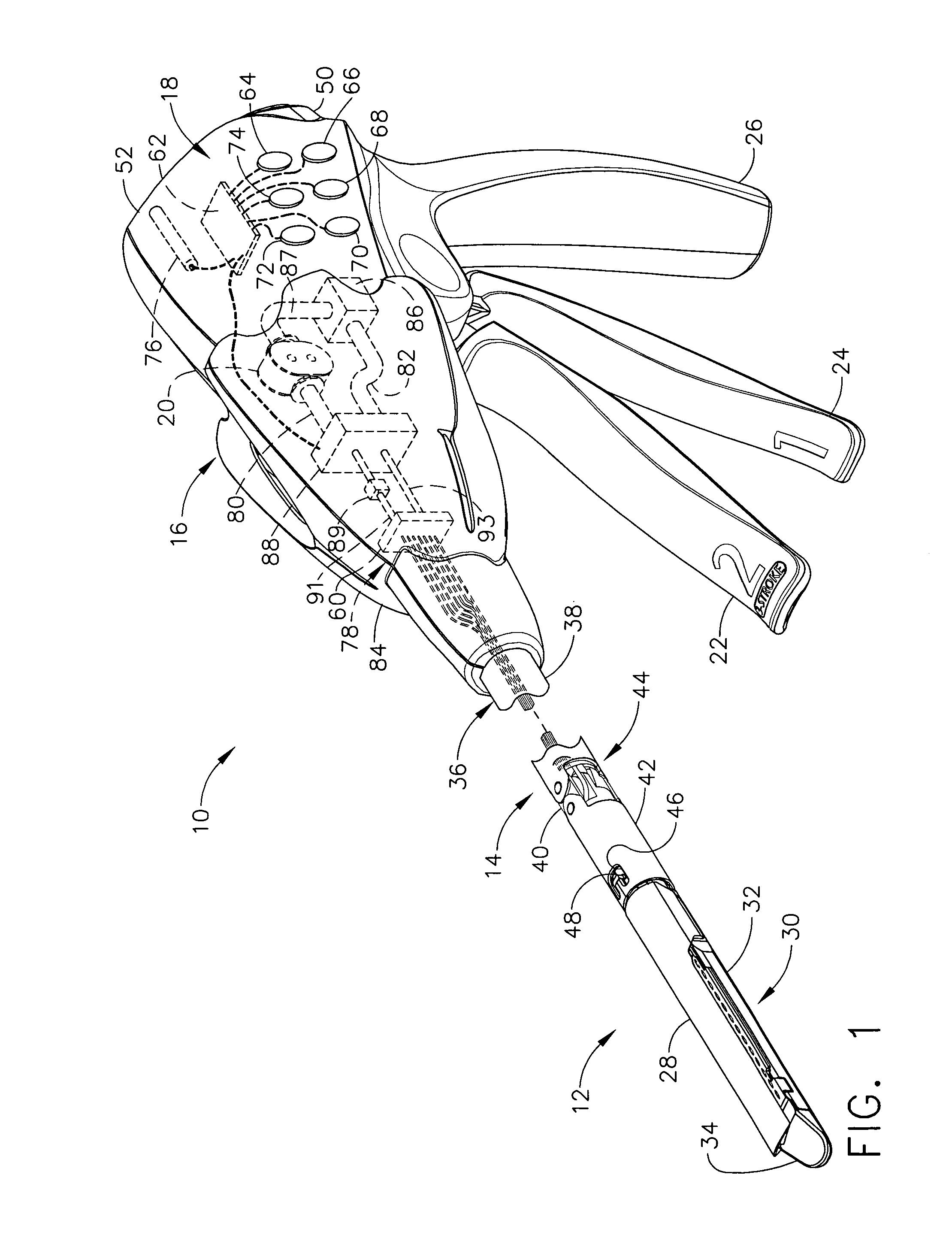
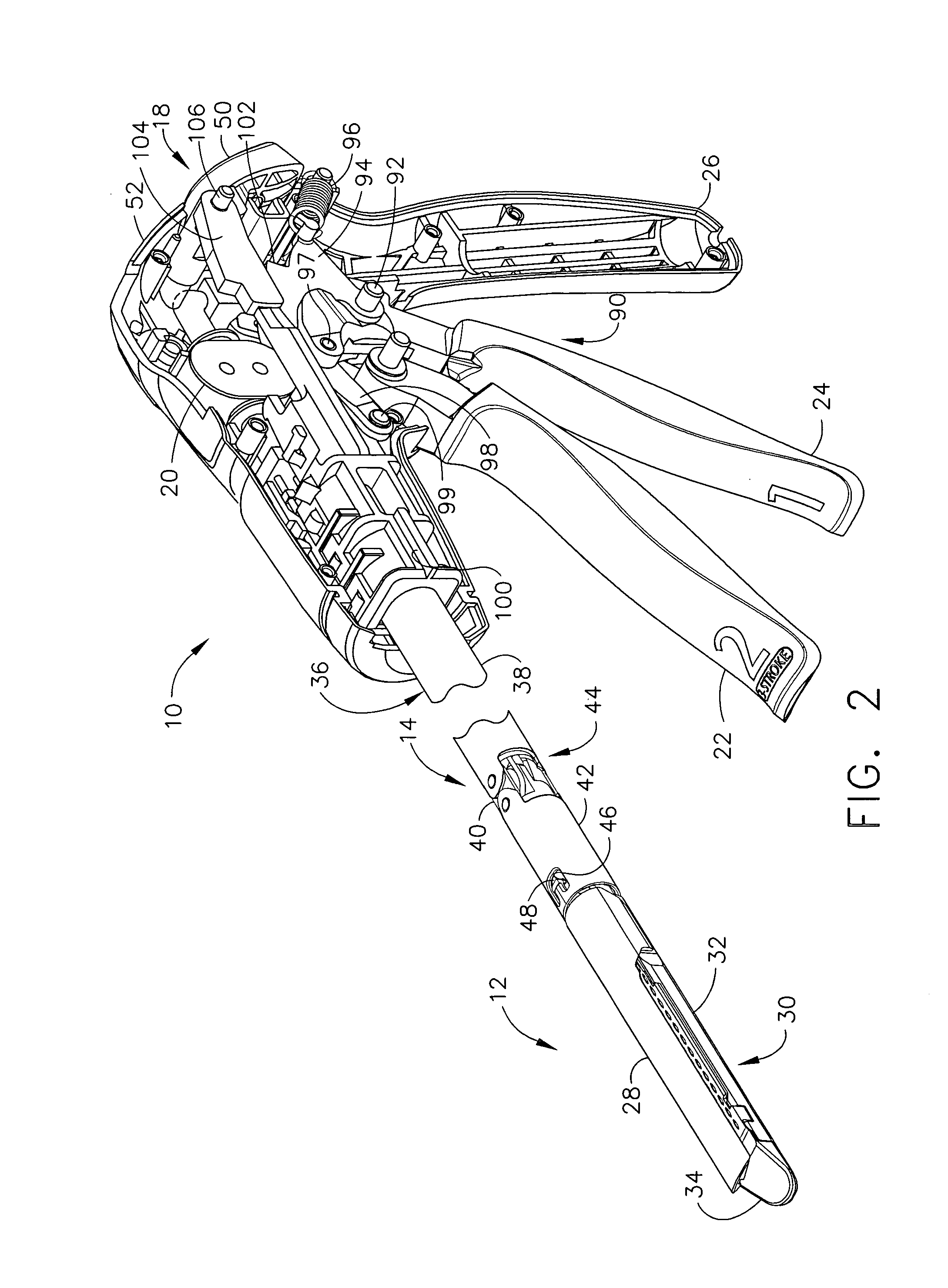
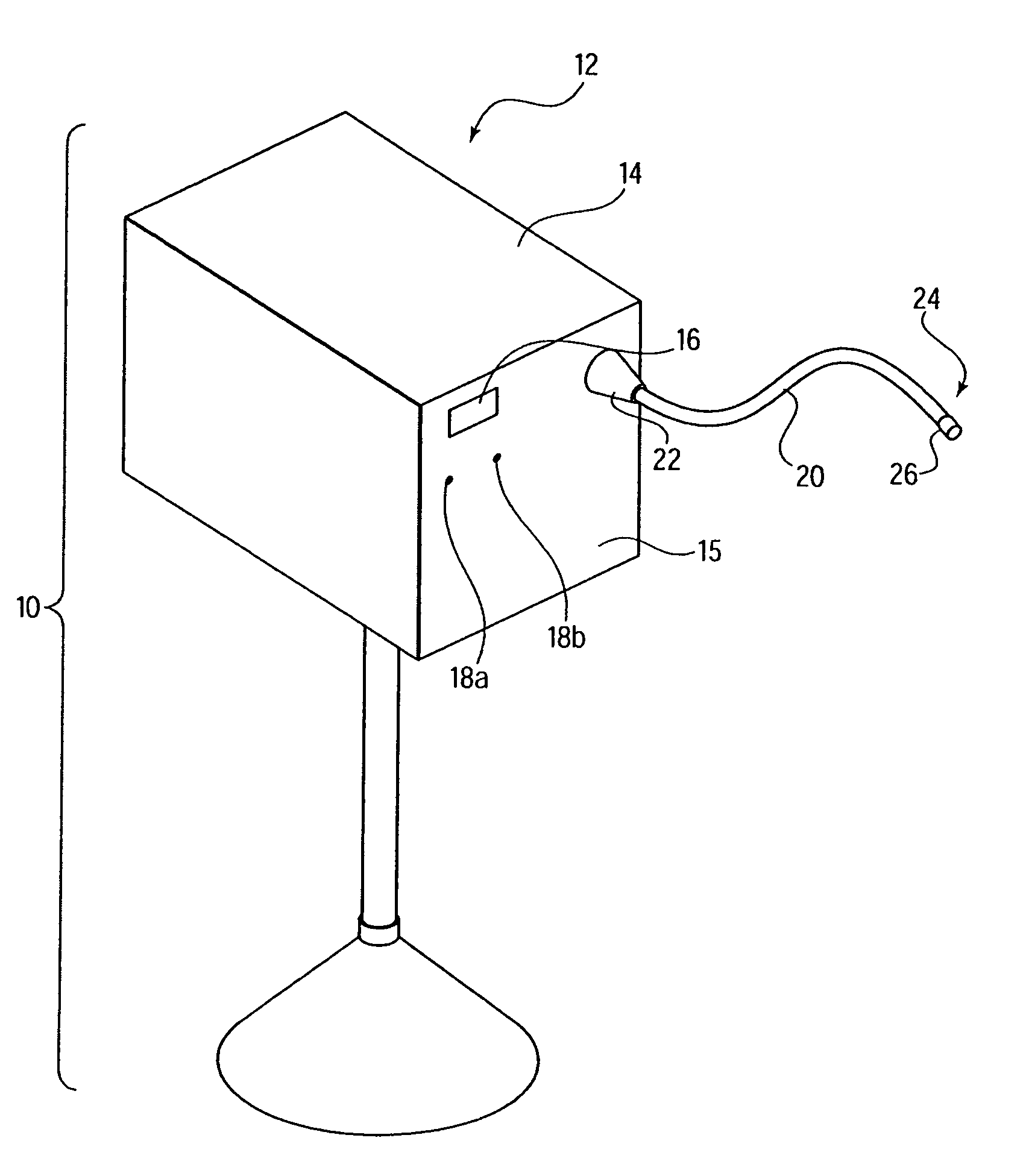
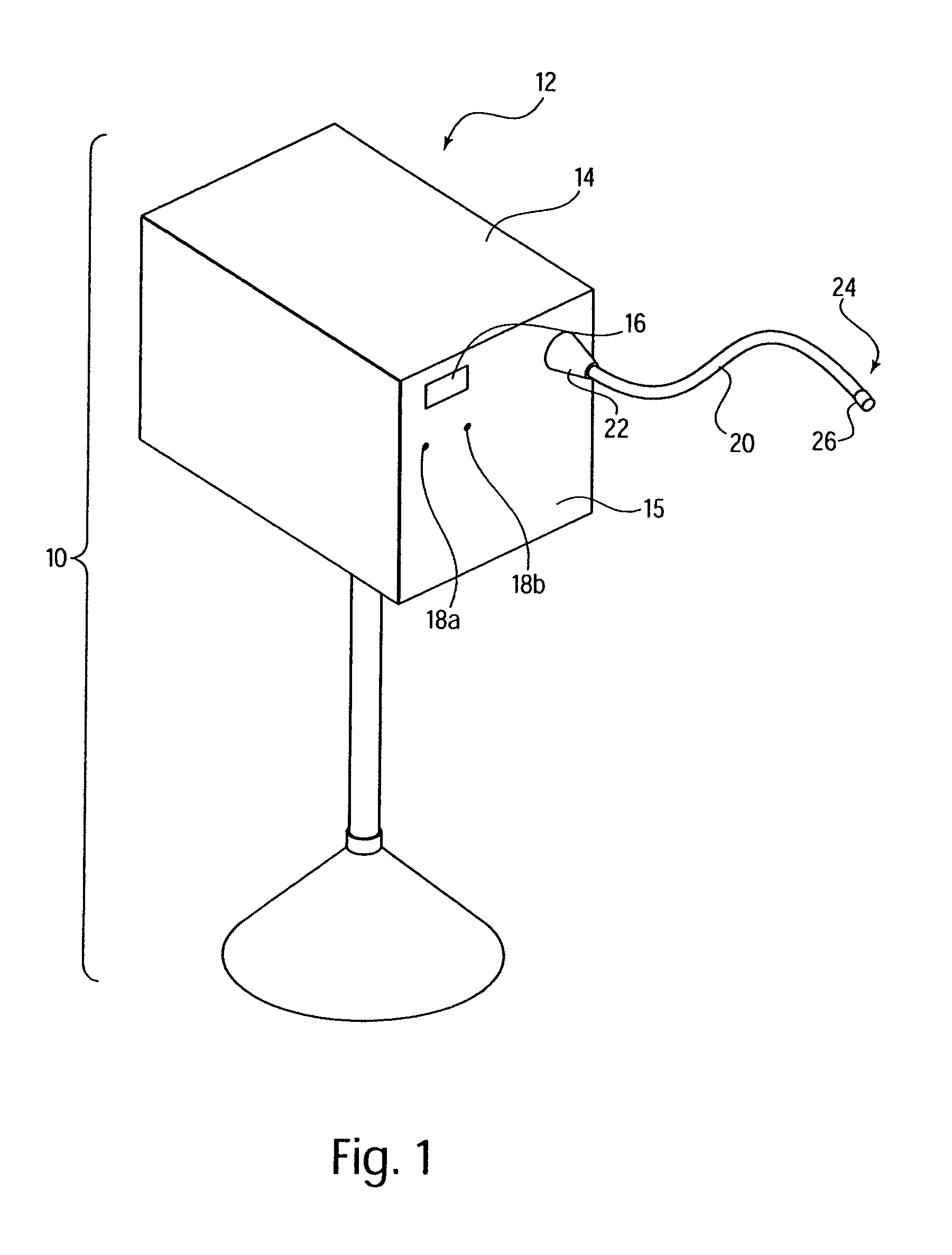
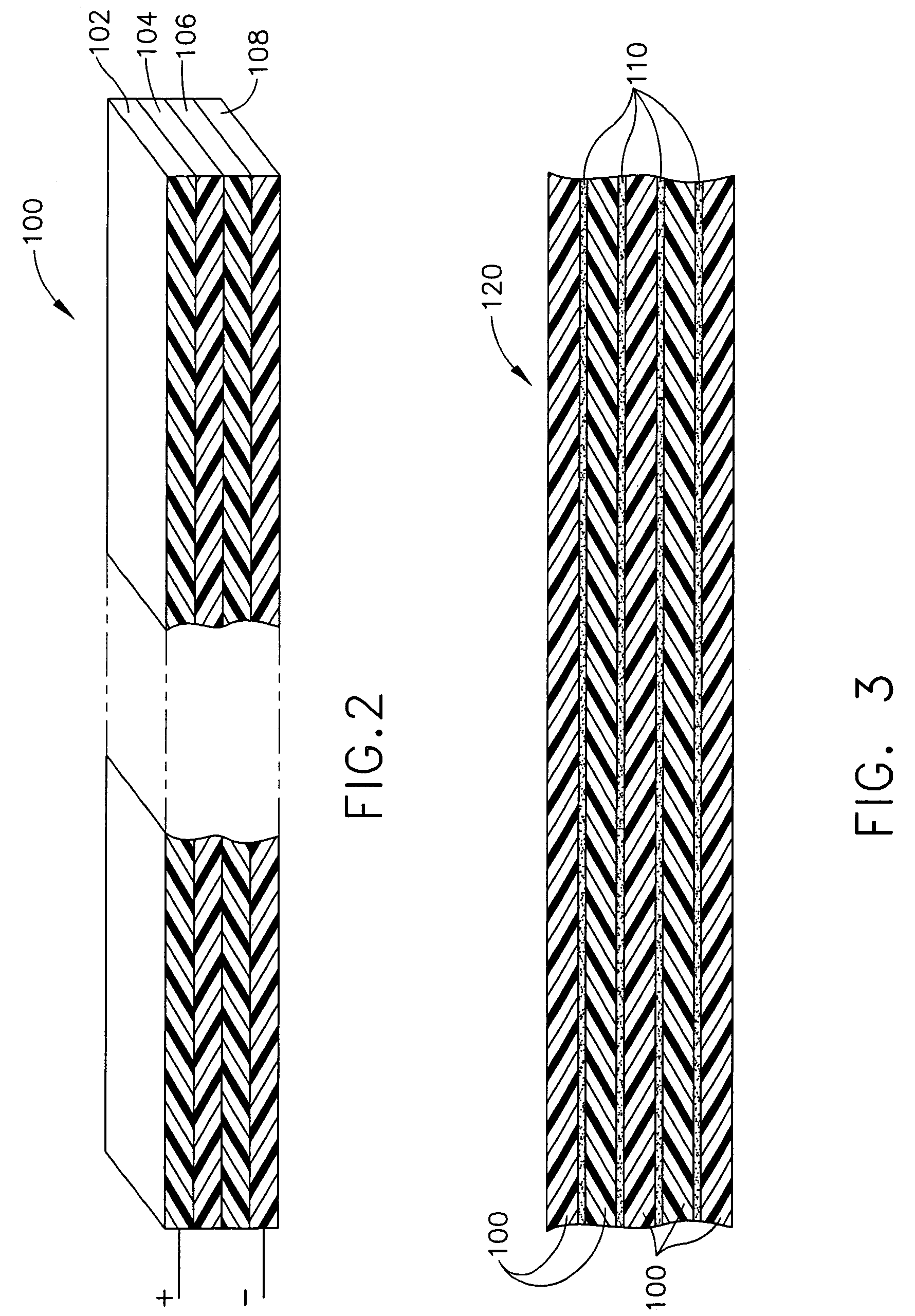
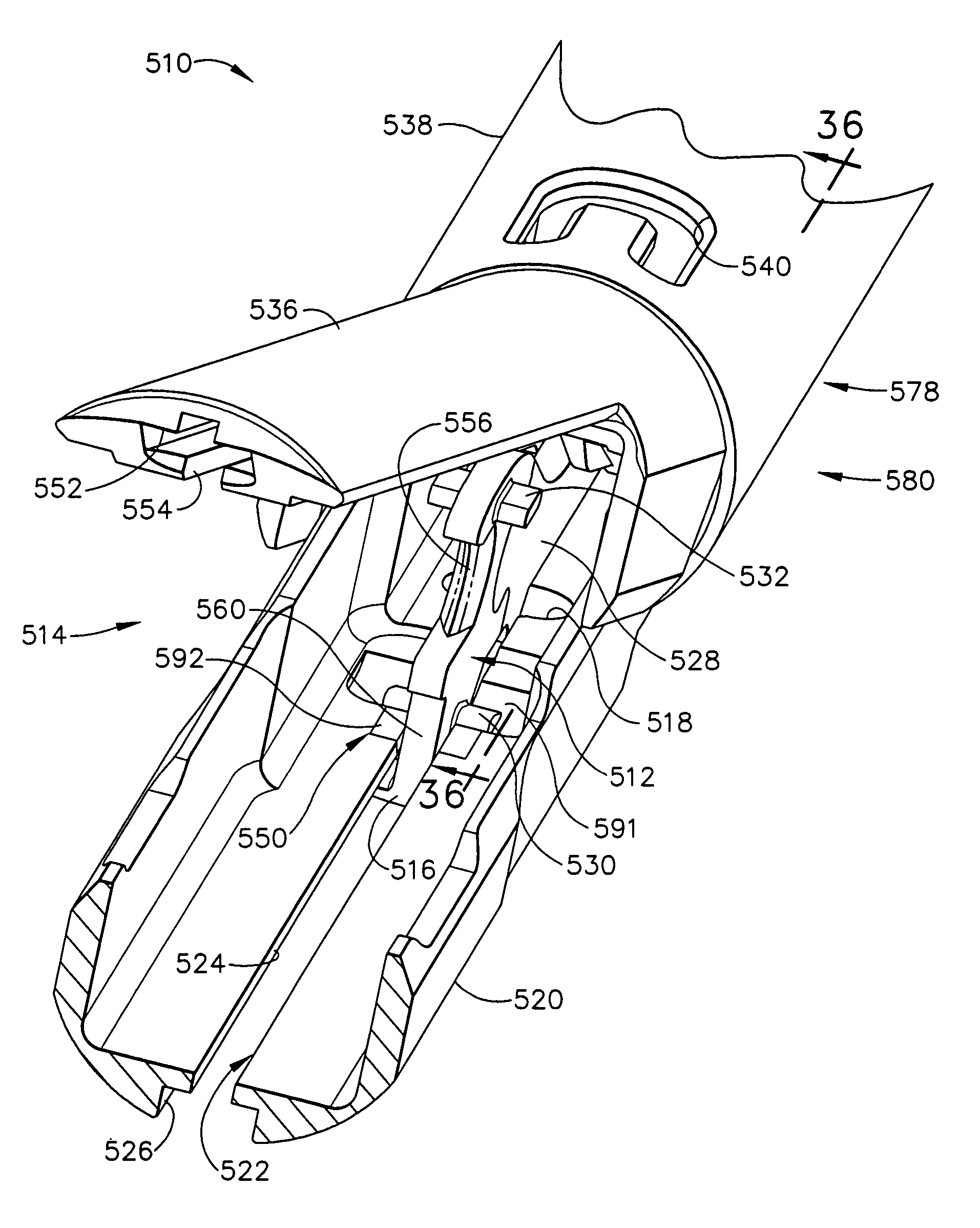
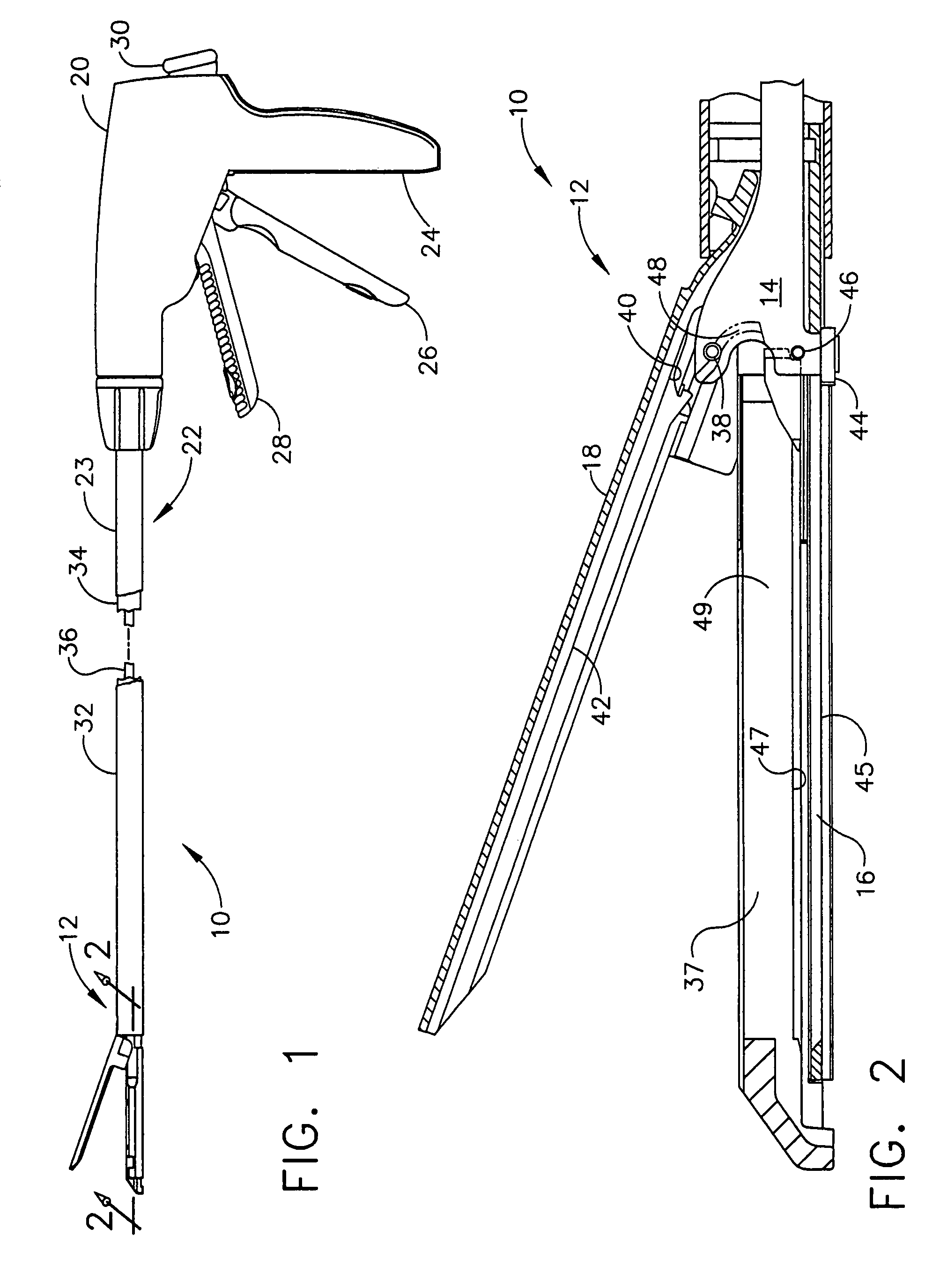
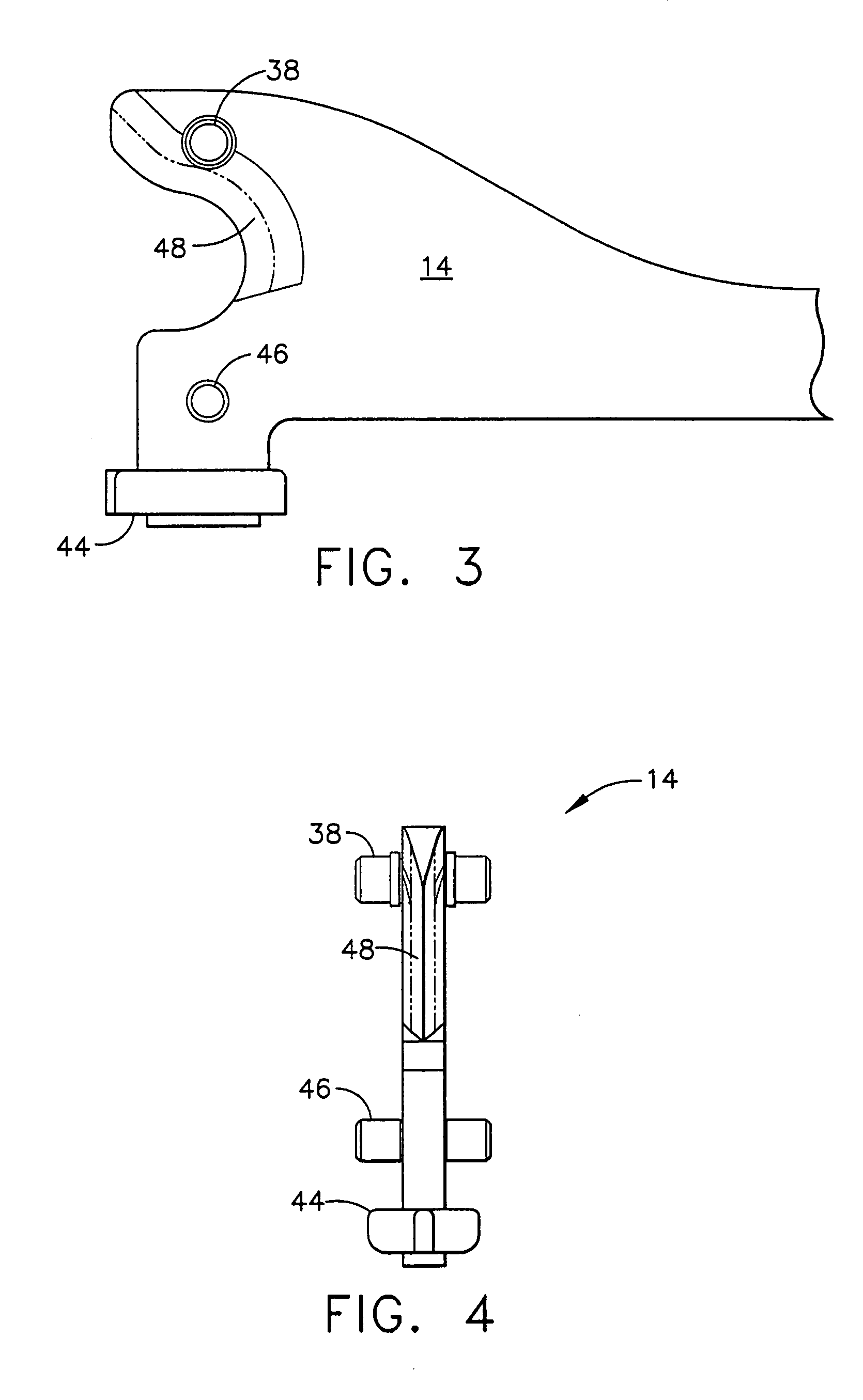
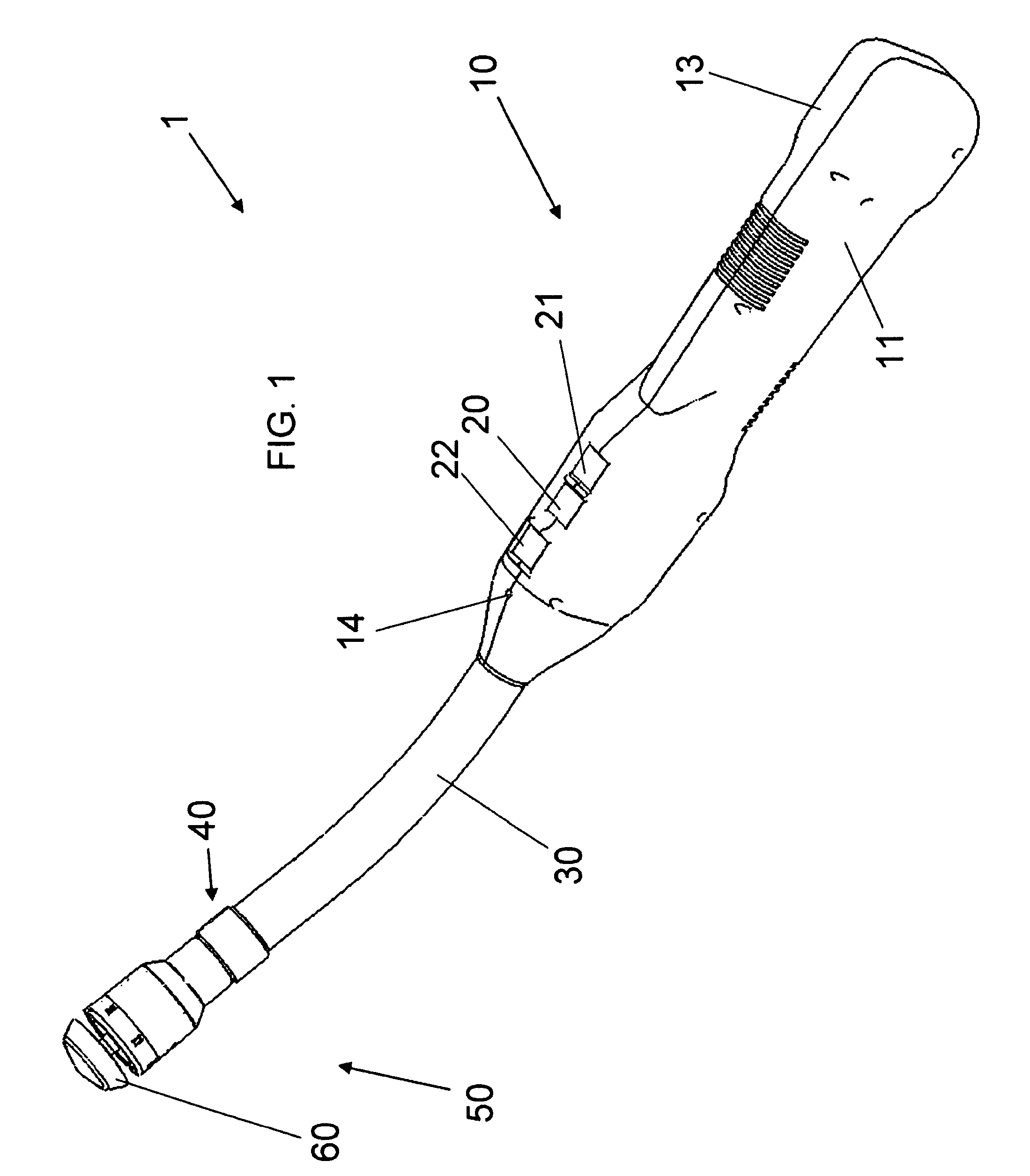
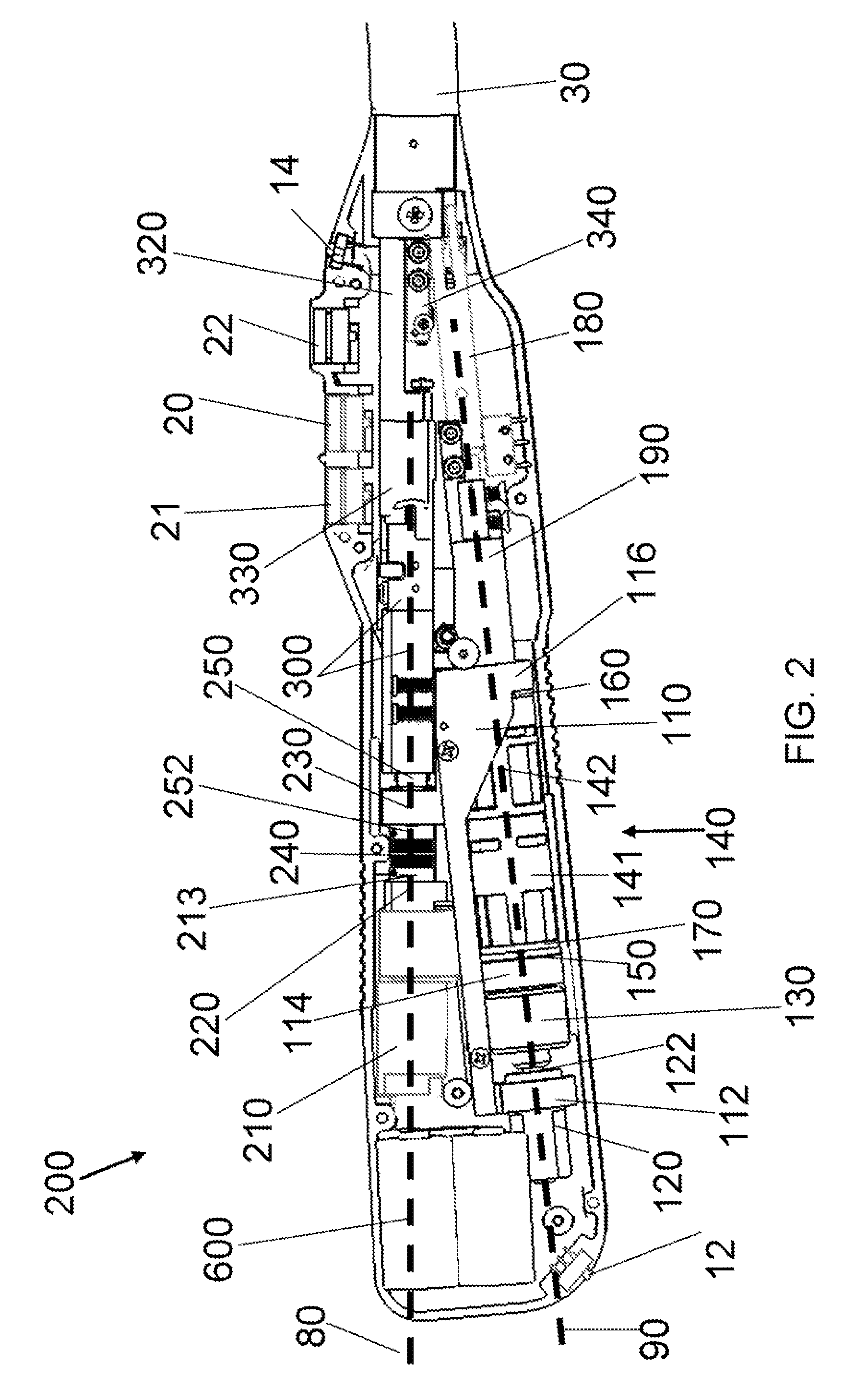
Surgical instrument having an articulating end effector
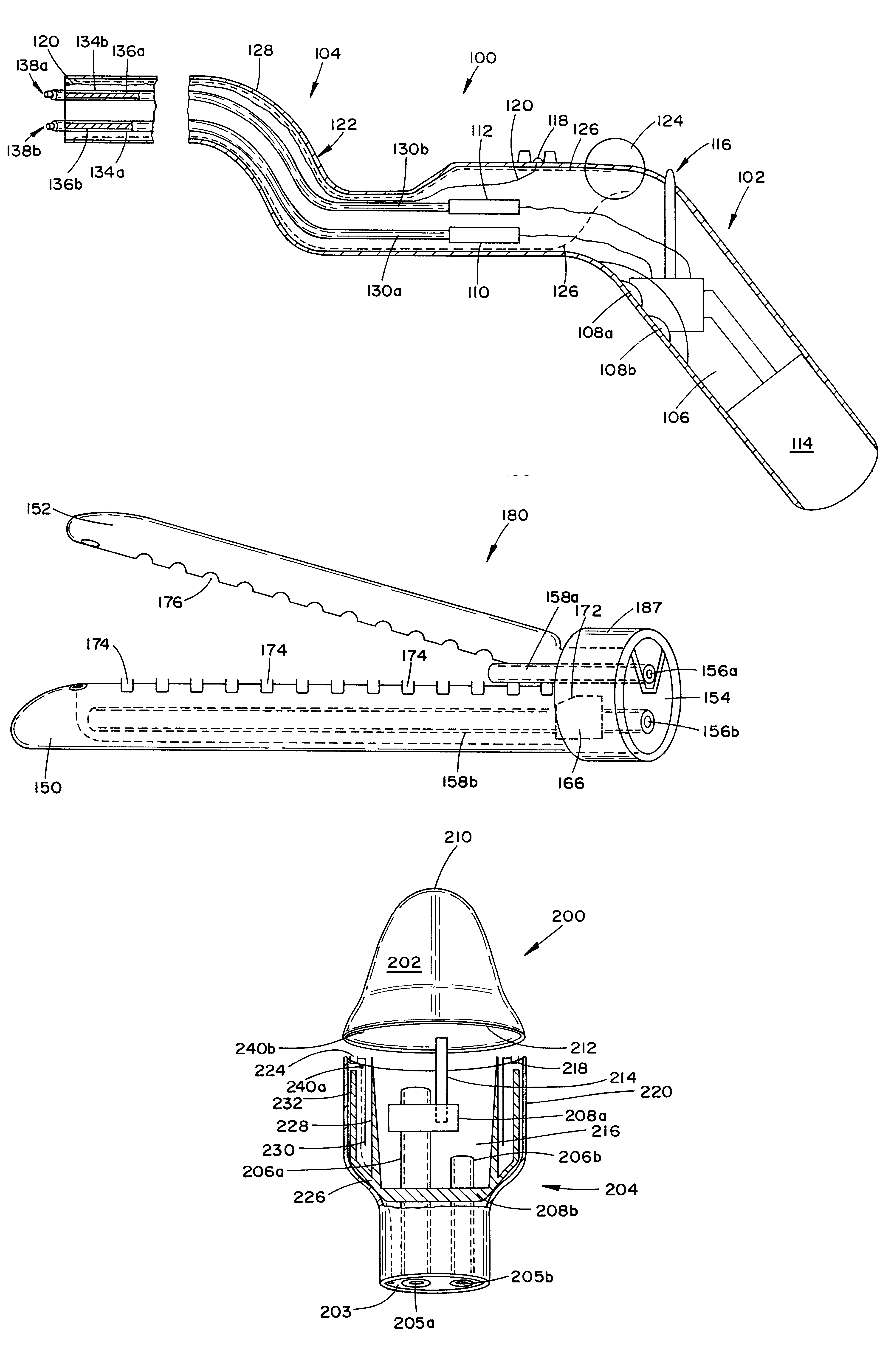
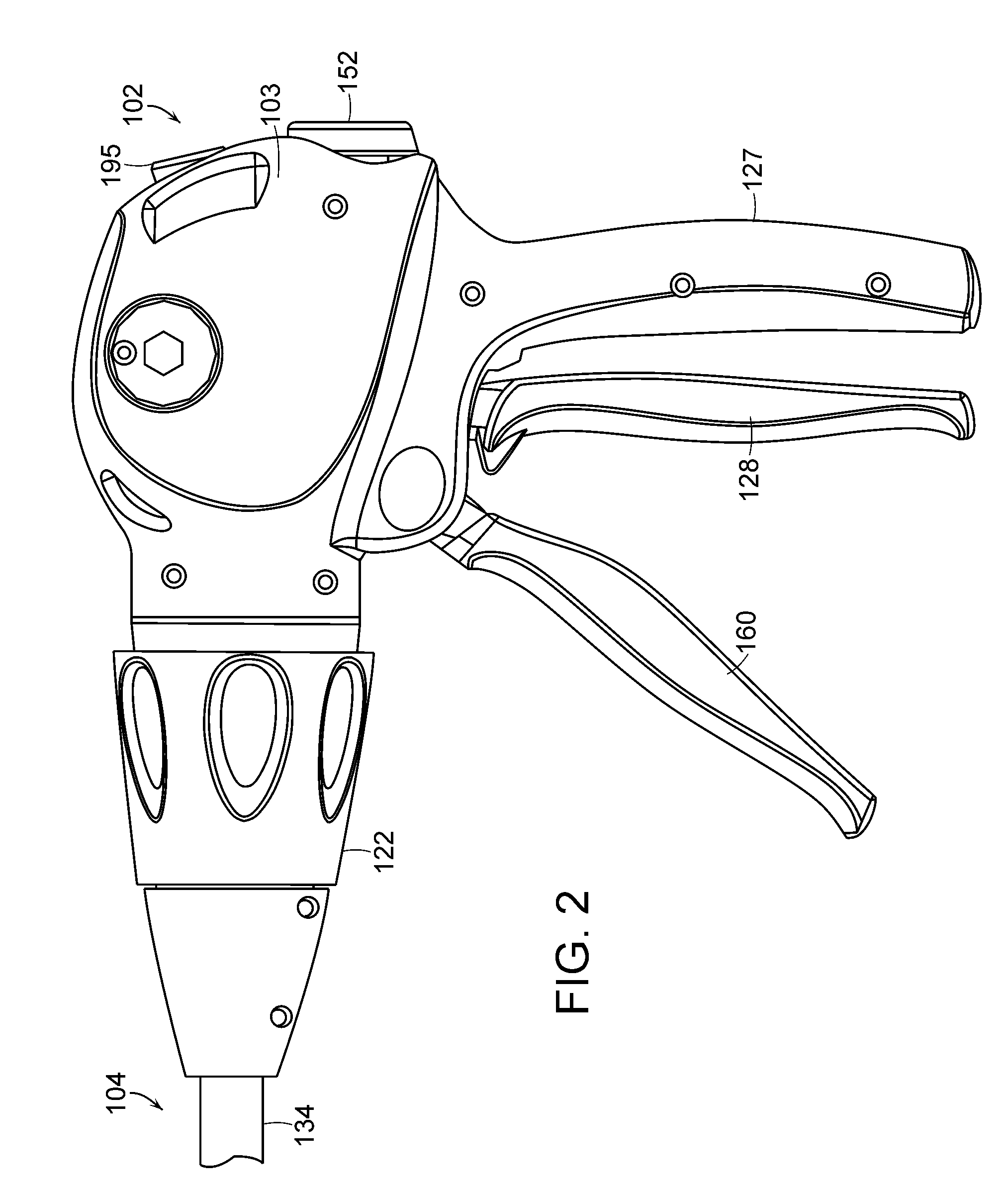
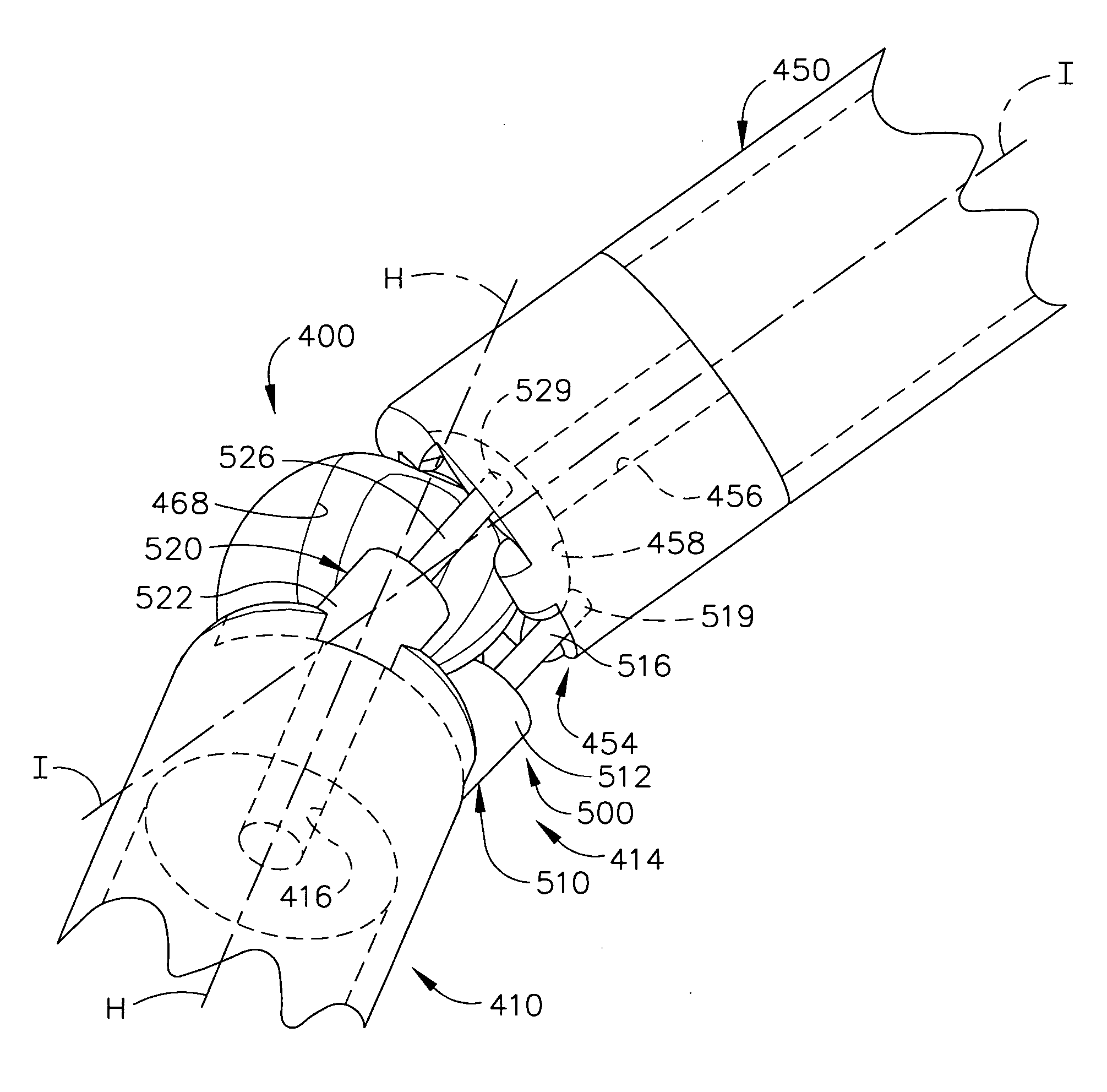
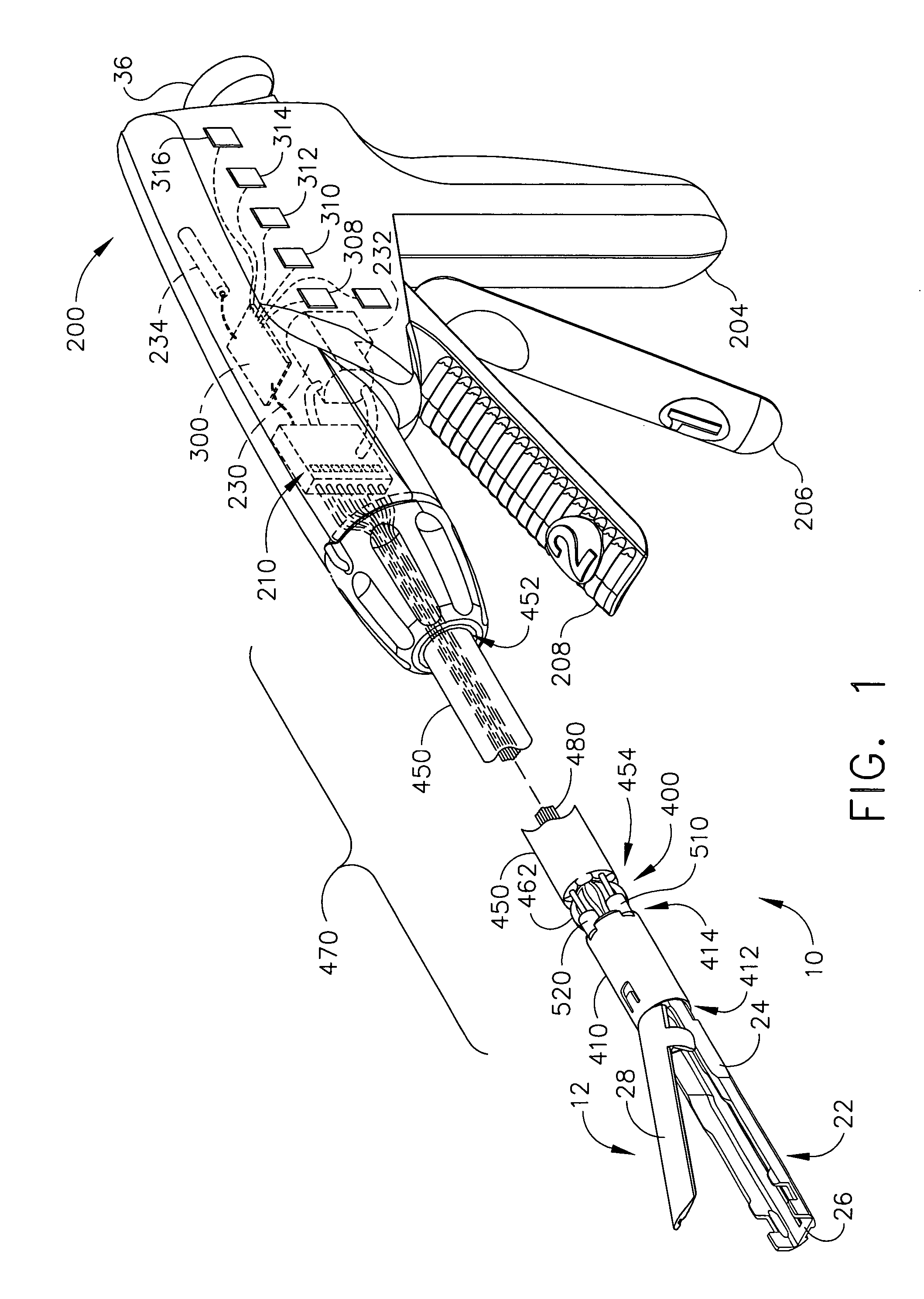
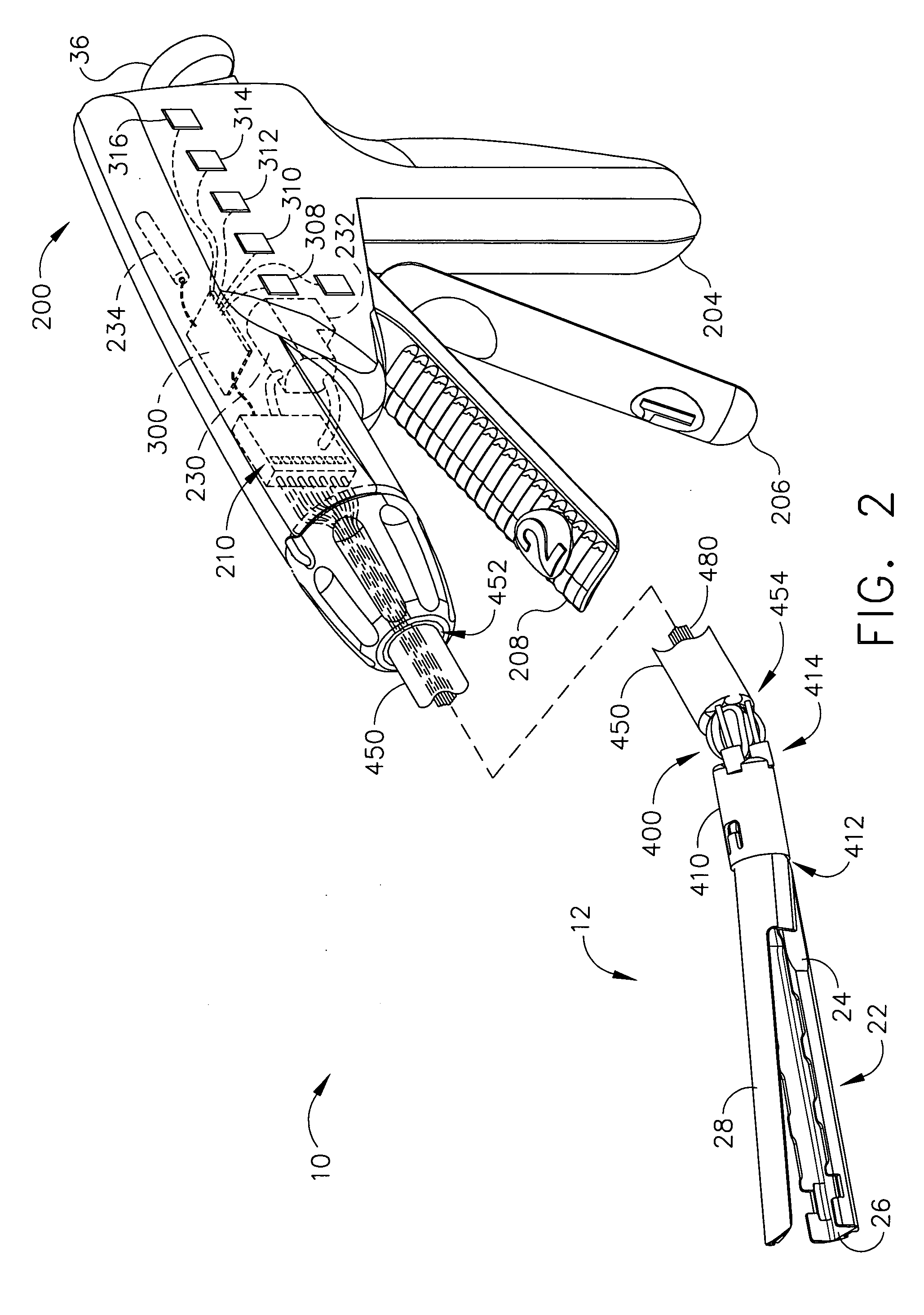
An articulating surgical instrument is shown, which comprises a shaft and an end effector. The shaft has a longitudinal axis, and the end effector is operationally coupled, preferably mechanically coupled, to the shaft at an articulation pivot. The instrument also comprises a first band, and in some embodiments, a second band, each operationally connected to the end effector and extending through at least a portion of the shaft. An articulation control applies a force in a direction substantially transverse to the longitudinal axis, wherein the force, when applied in one direction, is translated through the first band to the end effector to effect rotation of the end effector relative to the shaft about the articulation pivot in a first rotational direction, and when the force is applied in the opposite direction, is translated through the second band to the end effector to effect rotation of the end effector relative to the shaft about the articulation pivot in a second rotational direction.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
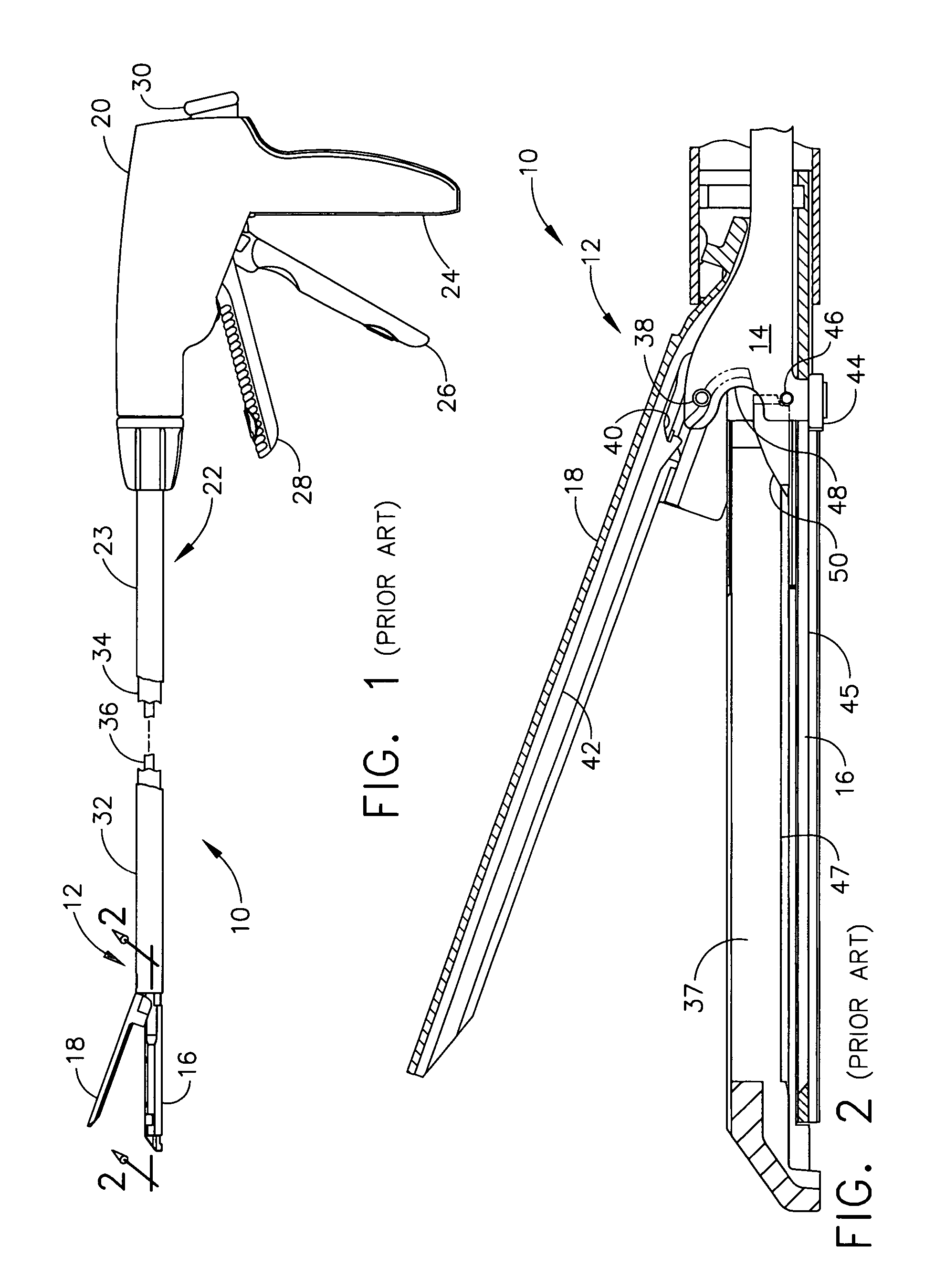
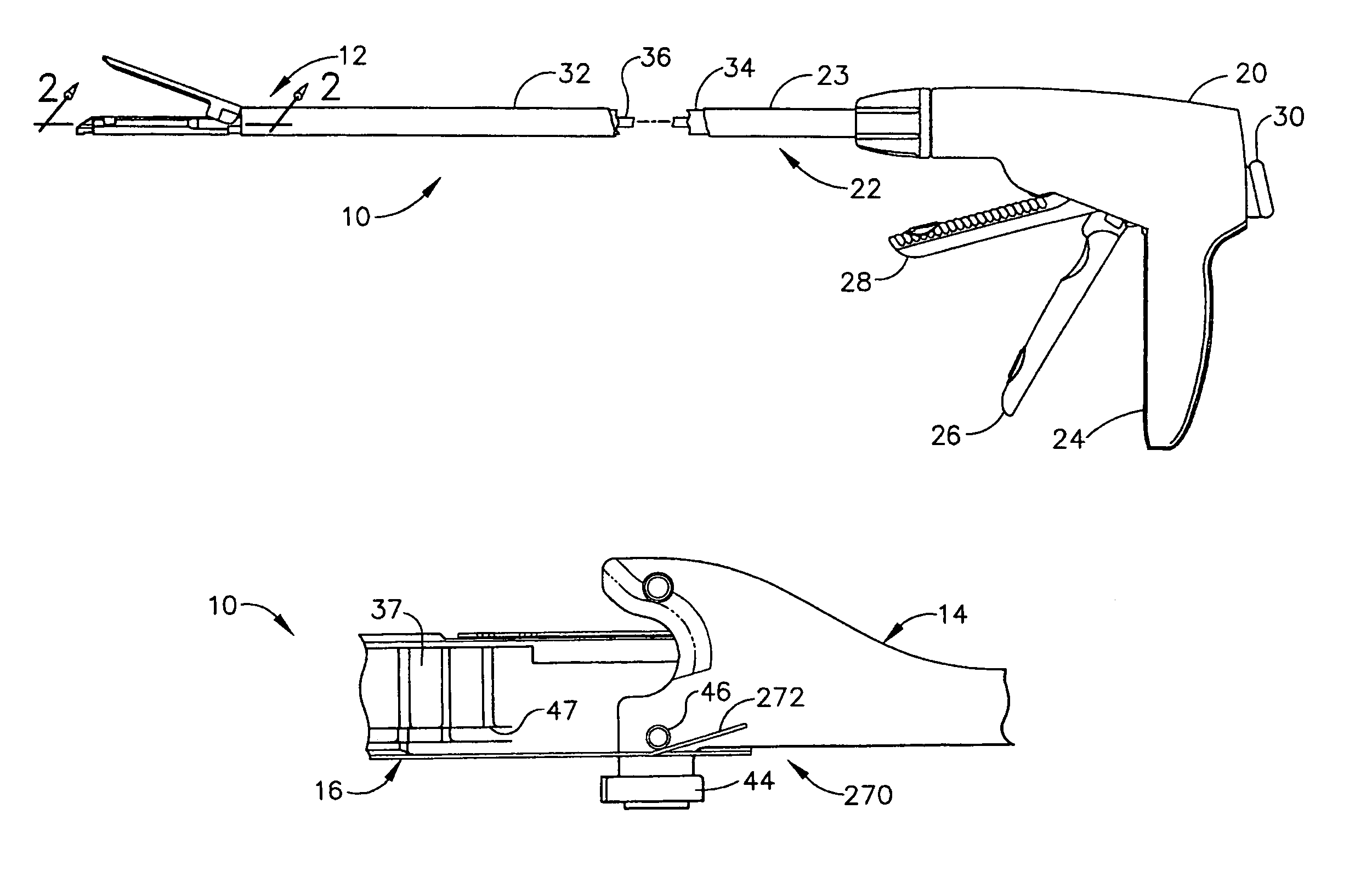
Surgical stapling instrument having a single lockout mechanism for prevention of firing
InactiveUS7380695B2Avoid firePrevent movementSuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical staplePERITONEOSCOPE
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Articulating surgical stapling instrument incorporating a two-piece E-beam firing mechanism
InactiveUS7380696B2Solve the lack of spaceEasy to useSuture equipmentsStapling toolsPERITONEOSCOPEDistal portion
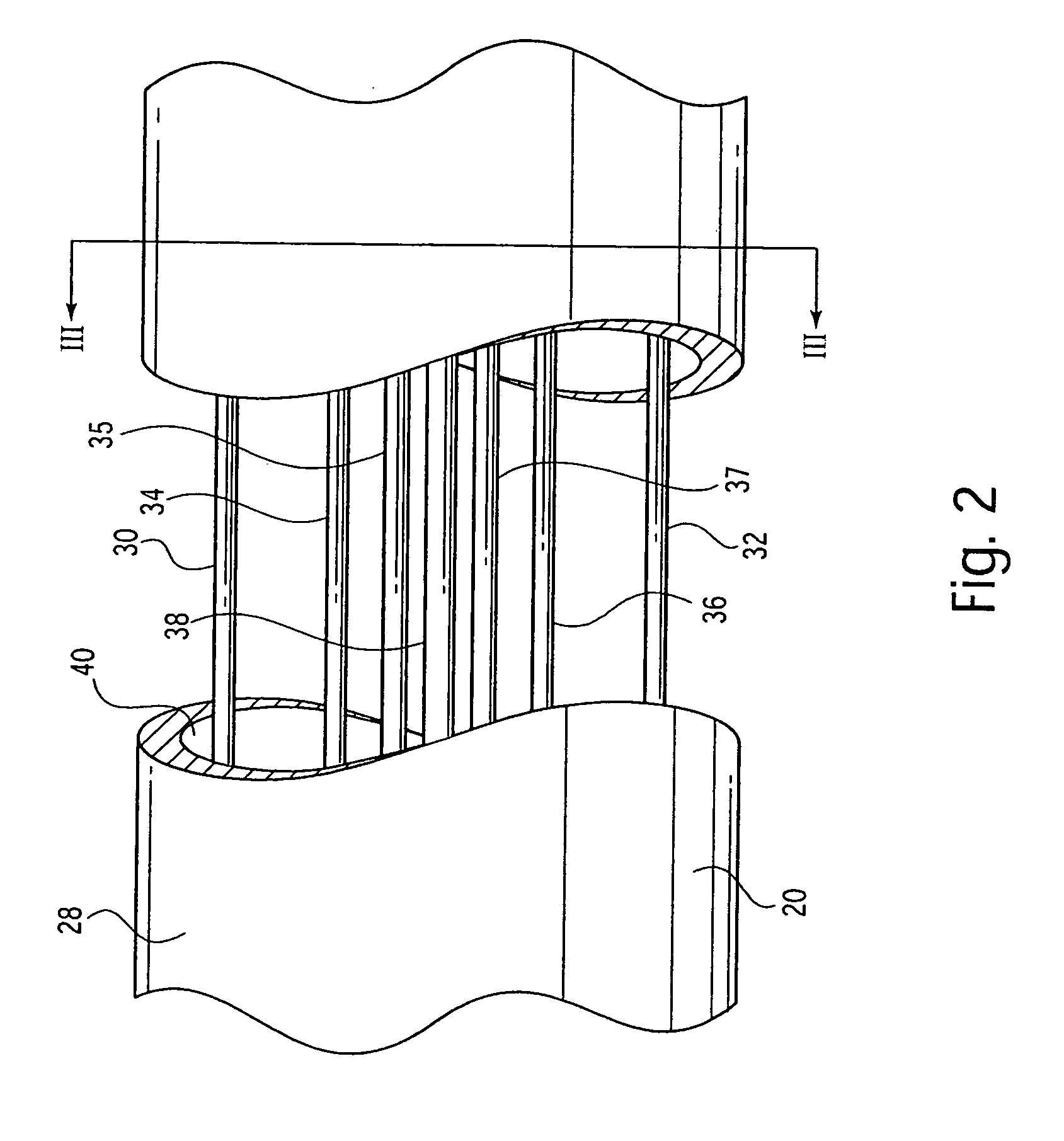
A surgical severing and stapling instrument, suitable for laparoscopic and endoscopic clinical procedures, clamps tissue within an end effector of an elongate channel pivotally opposed by an anvil. An E-beam firing bar moves distally through the clamped end effector to sever tissue and to drive staples on each side of the cut. The E-beam firing bar affirmatively spaces the anvil from the elongate channel to assure properly formed closed staples, especially when an amount of tissue is clamped that is inadequate to space the end effector. In particular, an upper pin of the firing bar longitudinally moves through an anvil slot and a channel slot is captured between a lower cap and a middle pin of the firing bar to assure a minimum spacing. Forming the E-beam from a thickened distal portion and a thinned proximal strip enhances manufacturability and facilitates use in such articulating surgical instruments.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC +1
Surgical stapling instrument with an articulatable end effector
A surgical instrument can comprise a channel configured to support a staple cartridge and, in addition, an anvil pivotable between open and closed positions relative to the channel. The surgical instrument can further comprise a cutting member configured to incise tissue positioned captured between the staple cartridge and the anvil and, in addition, means for stopping the cutting member prior to a distal end datum, wherein the distal end datum can be defined by the distal-most staple cavity in the staple cartridge. In such embodiments, the incision within the tissue may not extend beyond the portion of the tissue that has been stapled.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Surgical stapling instrument having a spent cartridge lockout
InactiveUS6988649B2Avoid firePrevent distal movementSuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical staplePERITONEOSCOPE
A surgical instrument for laparoscopic and endoscopic clinical procedures simultaneously severs and staples tissue clamped in an end effector comprising an elongate channel, which holds a staple cartridge, and a pivotally attached anvil. An E-beam firing bar engages the channel and selectively engages the anvil during distal firing movements, wherein the tissue is severed and stapled driven upward from the staple cartridge to form against the anvil. In particular, a wedge integral to the staple cartridge is driven distally by a middle pin of the firing bar to effect stapling. A lockout mechanism of the staple cartridge responds to the presence of the wedge sled in its unfired position to allow the firing bar to fire. Otherwise, the lockout mechanism prevents firing when the staple cartridge is spent.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INTERNATIONAL
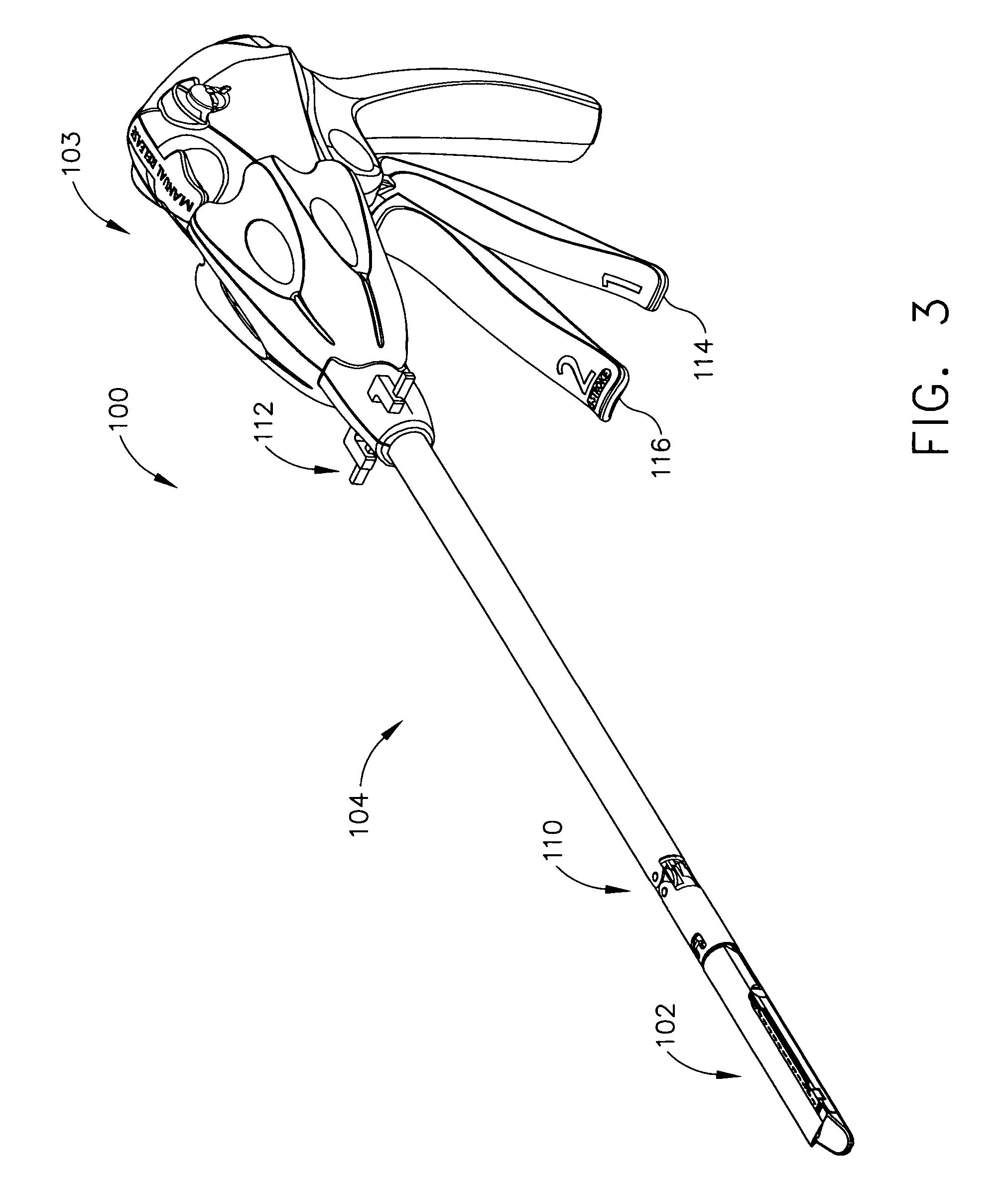
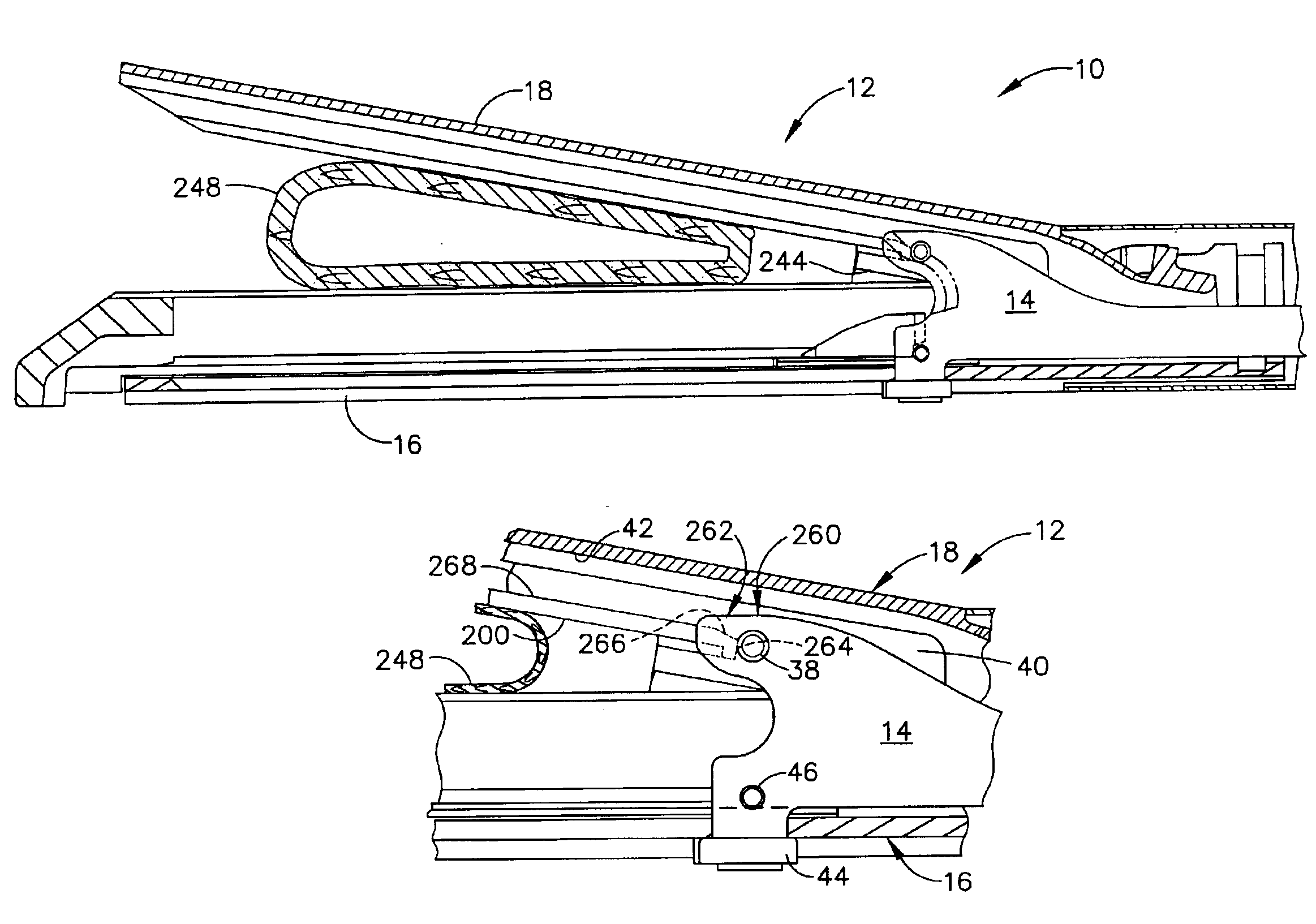
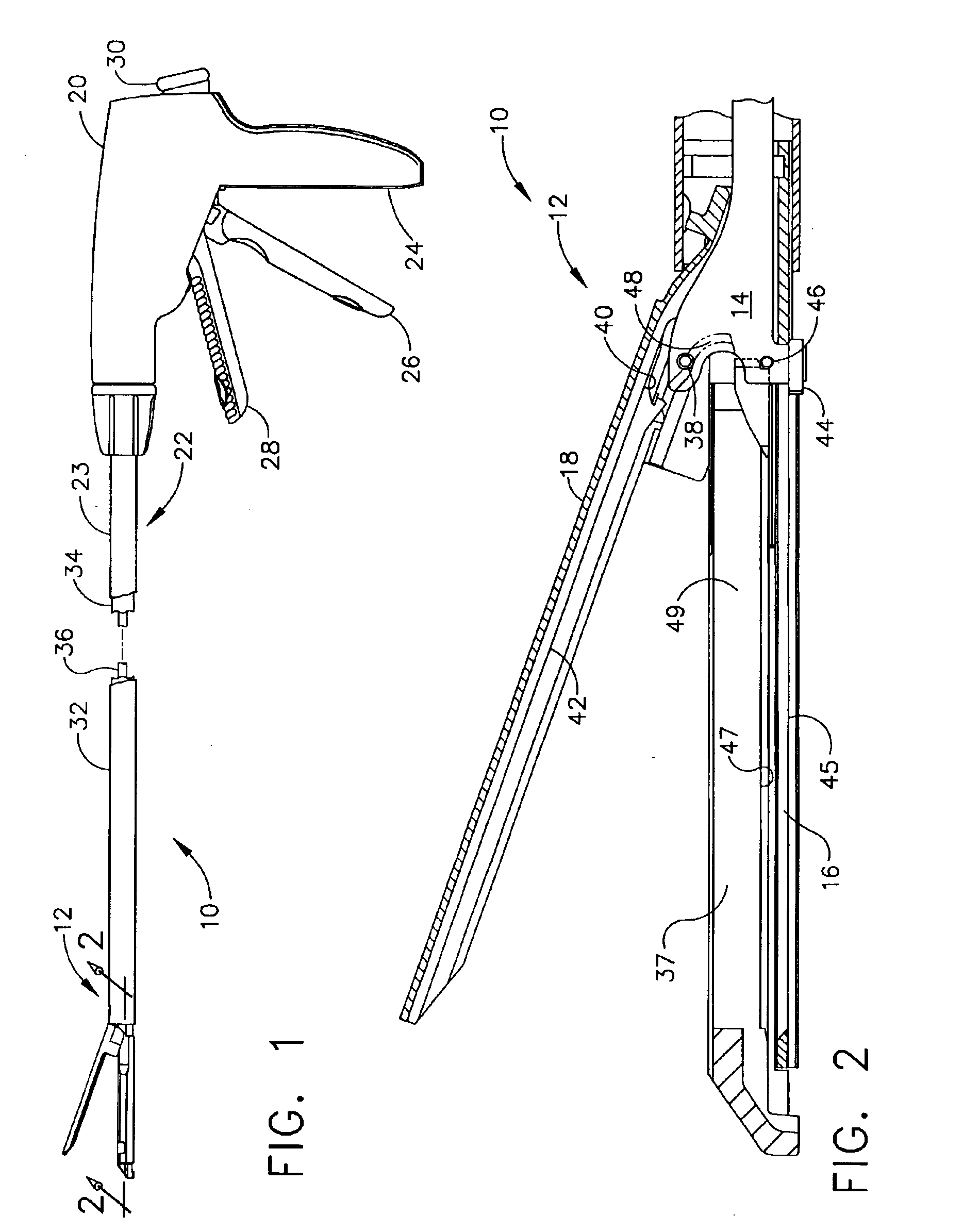
Surgical instrument with a lateral-moving articulation control
InactiveUS6981628B2Complicate amountComplicate directionSuture equipmentsStapling toolsEngineeringTarsal Joint
An articulating surgical instrument suited for endoscopic use includes a lateral articulation control into a handle portion that provides an intuitive visual and tactile indication to the clinician as to the amount and direction of articulation of an end effector at a distal end of a shaft. Lateral movement of a lateral control actuator is converted into a longitudinal motion or a rotational motion transferred by the shaft to an articulation mechanism. A version of a lateral articulation control for a rotationally driven articulation mechanism incorporates an articulation backdrive lockout that prevents forces on the end effector from causing the selected amount of articulation from being changed.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Surgical stapling instrument having a firing lockout for an unclosed anvil
InactiveUS7143923B2Accurate spacingExpand selectionSuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical staplePERITONEOSCOPE
A surgical instrument for laparoscopic and endoscopic clinical procedures simultaneously severs and staples tissue clamped in an end effector comprising an elongate channel, which holds a staple cartridge, and a pivotally attached anvil. An E-beam firing bar engages the channel and selectively engages the anvil during distal firing movements, wherein the tissue is severed and stapled driven upward from the staple cartridge to form against the anvil. In particular an upper pin of the firing bar is disengaged from the anvil before firing. A ramped transition from an anvil to an anvil slot avoids misfiring when the end effector has clamped too much tissue, yet assists in successfully clamping a slightly excess amount of tissue.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Surgical stapling instrument having a single lockout mechanism for prevention of firing
ActiveUS7044352B2Avoid firePrevent distal movementSuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical staplePERITONEOSCOPE
A surgical instrument for laparoscopic and endoscopic clinical procedures simultaneously severs and staples tissue clamped in an end effector comprising an elongate channel, which holds a staple cartridge, and a pivotally attached anvil. An E-beam firing bar engages the channel and selectively engages the anvil during distal firing movements, wherein the tissue is severed and stapled driven upward from the staple cartridge to form against the anvil. In particular, a wedge integral to the staple cartridge is driven distally by a middle pin of the firing bar to effect stapling. A single lockout of the elongate channel responds to the presence of the wedge sled in its unfired position to allow the firing bar to fire. Otherwise, the single lockout prevent firing when the staple cartridge is missing or spent.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Electromechanical driver device for use with anastomosing, stapling, and resecting instruments
An electromechanical driver for use in gastrointestinal tract surgery, including a flexible sheath and a handle, is provided. Also dislosed are a series of surgical attachments which may be utilized in conjunction with the electromechanical driver. The handle of the driver includes at least one motor which is selectively engageable by the actuation of a trigger. The motor is coupled to a flexible drive shaft which extends through the flexible sheath. At a distal end of the flexible sheath, and correspondingly at the end of the drive shaft, the various surgical attachments may be coupled. The turning of the drive shaft provides the necessary power to actuate the surgical instrument.
Owner:DORROS GERALD M D
Surgical instrument incorporating EAP blocking lockout mechanism
ActiveUS7143925B2Preventing closing of the jawsSuture equipmentsStapling toolsEndoscopic surgeryEndoscopic Procedure
A surgical stapling and severing instrument particularly suited to endoscopic procedures incorporates a handle that produces separate closing and firing motions to actuate an end effector. The handle produces multiple firing strokes to reduce the required amount of force required to fire (i.e., staple and sever) the end effector. A linked transmission reduces the required handle longitudinal length, yet achieves a rigid, strong configuration when straightened for firing. One or more electrically activated lockout mechanisms, such as electroactive polymer (EAP) actuators, are biased to prevent firing unless activated. One lockout is a spring-biased side pawl firing mechanism enabled by an EAP block actuator. Another is a firing trigger EAP lock. Yet another is a closure yoke EAP lock. Yet a further one is a manual retraction EAP lock that locks the firing mechanism. Thereby, various sensed or commanded inputs may be incorporated to prevent inadvertent firing.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Surgical stapling instrument having an electroactive polymer actuated buttress deployment mechanism
A surgical instrument for being endoscopically or laparoscopically inserted to a surgical site for simultaneous stapling and severing of tissue includes electrically actuated deployment of buttress pads held on inner surfaces of upper and lower jaws of a staple applying assembly. Thereby, thick or thin layers may be stapled and severed without improper staple formation nor with nonoptimal deployment of the buttress pads. Electroactive polymer (EAP) actuated latches, an EAP channel, or a rigid channel with an EAP pinch lock reliably hold the buttress pad until deployment is desired with a low force to separate the stapled and severed buttress pad / tissue combination with the respective EAP mechanism activated for deployment.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Surgical instrument incorporating an articulation mechanism having rotation about the longitudinal axis
A surgical instrument particularly suited to endoscopic articulates an end effector by including an end effector having a geared articulation mechanism that converts rotational motion from a handle portion. A hollow articulation drive tube transfers the rotation motion in some versions to a spear gear, bevel gear or snaggle tooth gear articulation mechanism. Alternatively, one or more threaded drive rod offset from a longitudinal axis engages a worm gear or flex-neck articulation mechanism.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Rotary hydraulic pump actuated multi-stroke surgical instrument
A surgical instrument (e.g., endocutter, grasper, cutter, staplers, clip applier, access device, drug / gene therapy delivery device, and energy device using ultrasound, RF, laser, etc.) may benefit from having a plurality of hydraulically actuated subsystems (e.g., severing, stapling, articulation, locking / unlocking, lockout enabling / disabling, grasping, etc.) supplied with hydraulic power from a trigger actuated rotary pump (e.g., lobe pump, rotary gear pump, internal rotating gear pump, flexible vane rotor pump, rotary vane pump). Thereby, an available amount of mechanical advantage available at a firing trigger may be optimally distributed to various end effector components, perhaps sequenced by an electroactive polymer or piezoelelectrically actuated function switch block.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Surgical stapling instrument with mechanical mechanism for limiting maximum tissue compression
Various forms of surgical instruments are disclosed. In various embodiments, the instrument includes a cartridge supporting assembly for operably supporting a staple cartridge therein. The cartridge supporting assembly may be responsive to firing and retraction motions applied thereto from a firing assembly. An anvil may be operably coupled to an anvil closure assembly. The anvil closure assembly may be constructed to selectively move the anvil in a proximal direction toward the cartridge supporting assembly to enable a portion of tissue to be clamped between a cartridge supported by the cartridge supporting assembly and the anvil under a predetermined amount of compression. The device may further include a compression limiting assembly that interacts with the anvil closure assembly to prevent further travel of the anvil in the proximal direction toward the cartridge supporting assembly when the predetermined amount of compression has been attained.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Lockout mechanisms and surgical instruments including same
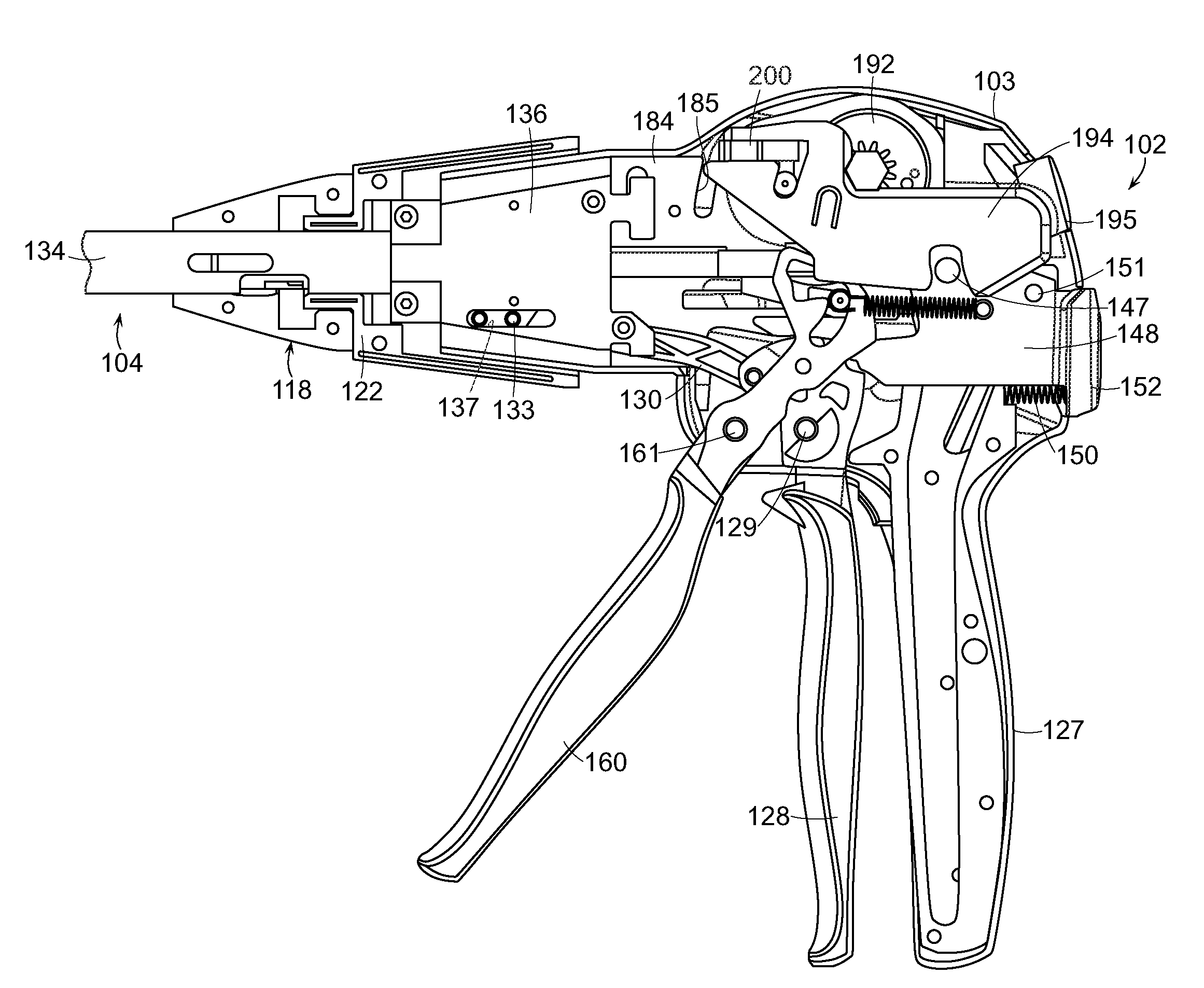
A surgical instrument is disclosed. The surgical instrument includes a handle portion, a channel, an anvil, and staple cartridge, a wedge member, a reciprocating firing device, and a lockout arm. The handle portion is operably configured to produce a firing motion and is coupled to the channel portion. The staple cartridge is engaged by the channel and includes a plurality of staple drivers to cam the staples toward the anvil, which is pivotally attached to the channel. The wedge member is proximal to and longitudinally aligned with the staple drivers, and the reciprocating firing device is responsive to the firing motion to progressively drive the wedge member from an unfired to a fired position. The lockout arm is pivotally attached to the channel and operably configured to pivot between a locked position and an unlocked position with respect to the firing device based upon a position of the wedge member.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
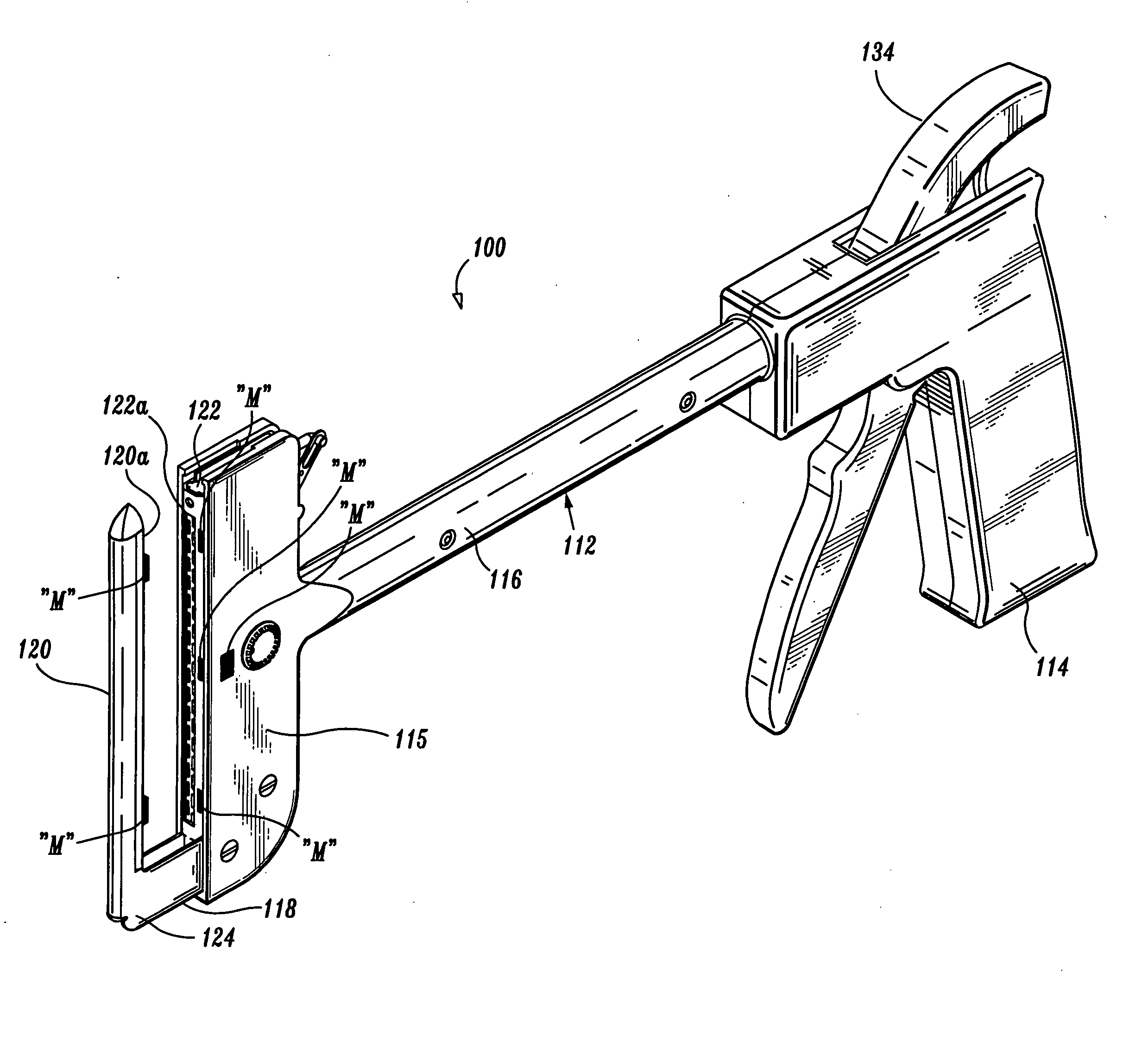
Surgical stapling device
ActiveUS7168604B2Enhanced advantageReduce firing forceSuture equipmentsStapling toolsDilatorSurgical site
A surgical stapling device is disclosed for the treatment of internal hemorrhoids. The surgical stapling device includes a handle portion, an elongated body portion and a head portion including an anvil assembly and a shell assembly. The head portion includes an anvil assembly including a tiltable anvil which will tilt automatically after the device has been fired and unapproximated. The tiltable anvil provides a reduced anvil profile to reduce trauma during removal of the device after the anastomoses procedure has been performed. The anvil assembly of the stapling device may include an approximation mechanism having an anvil retainer including an elongated distal extension dimensioned to be telescopingly received within a longitudinal bore of an anvil center rod of the anvil assembly. The elongated distal extension is of a length to provide telescopic engagement with the anvil center rod without obstructing visualization of the surgical site. A kit including a surgical instrument having a removable anvil assembly and an anvil assembly insertion handle is also disclosed. The kit may also include a speculum, an anal dialator and / or an obturator.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Electro-mechanical surgical device
A surgical device includes a housing and a hollow shaft extending from the housing. The hollow shaft includes one or more drive shafts disposed within the hollow shaft. Each drive shaft is detachably coupled to a surgical instrument and is operable to control moving parts on the surgical instrument. A method for performing a surgical procedure includes the steps of inserting a hollow shaft containing one or more drive shafts into the body via a first orifice; inserting a surgical instrument into the body via a second orifice, the surgical instrument being configured to couple with the hollow shaft to connect the surgical instrument with one or more drive shafts; and coupling the hollow shaft and the surgical instrument after the hollow shaft and surgical instrument are inserted into the body.
Owner:DORROS GERALD M D
Surgical instruments including mems devices
InactiveUS20050131390A1Effective and safer and easy to useReduce the effectSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsSurgical deviceSurgical instrument
Surgical instruments are disclosed that are couplable to or have an end effector or a disposable loading unit with an end effector, and at least one micro-electromechanical system (MEMS) device operatively connected to the surgical instrument for at least one of sensing a condition, measuring a parameter and controlling the condition and / or parameter.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Surgical instrument incorporating an electrically actuated articulation mechanism
A surgical instrument particularly suited to endoscopic use articulates an end effector by including an articulation mechanism in an elongate shaft that incorporates an electrically actuated polymer (EAP) actuator for remotely articulating the end effector.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Surgical instrument with articulating shaft with rigid firing bar supports
A surgical stapling and severing instrument particularly suited to endoscopic use includes a proximal portion that is manipulated external to a patient to position an attached elongate shaft and end effector to a desired surgical site inside of the patient. An articulation joint pivotally attaches the end effector to the elongate shaft to give further clinical flexibility in reaching tissue at a desired angle. A firing bar translates within the elongate shaft and articulates through the articulation joint with a reduced force to fire, supported within a knife slot formed in a link that pivots at both ends, thereby reducing the radius of curvature of the firing bar by half at a particular location. One version includes a link that connects across portions of a closure sleeve assembly and another version includes a link that connects proximal and frame ground portions.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Surgical stapling instrument having an electroactive polymer actuated single lockout mechanism for prevention of firing
InactiveUS7140528B2Avoid firePrevent movementSuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical stapleEngineering
A surgical instrument includes an E-beam firing bar engages the channel and selectively engages the anvil during distal firing movements, wherein the tissue is severed and stapled driven upward from the staple cartridge to form against the anvil. In particular, a wedge integral to the staple cartridge is driven distally by a middle pin of the firing bar to effect stapling. A single lockout of the staple channel responds to the presence of the wedge sled in its unfired position to allow the firing bar to fire. Otherwise, the single lockout prevents firing when the staple cartridge is missing or spent. Further, some versions include an Electroactive Polymer (EAP) actuator that presents an abutting surface, or acts as a trapdoor to a ramped recess in a staple channel to block the firing bar, as an active approach to preventing firing for one or more conditions.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
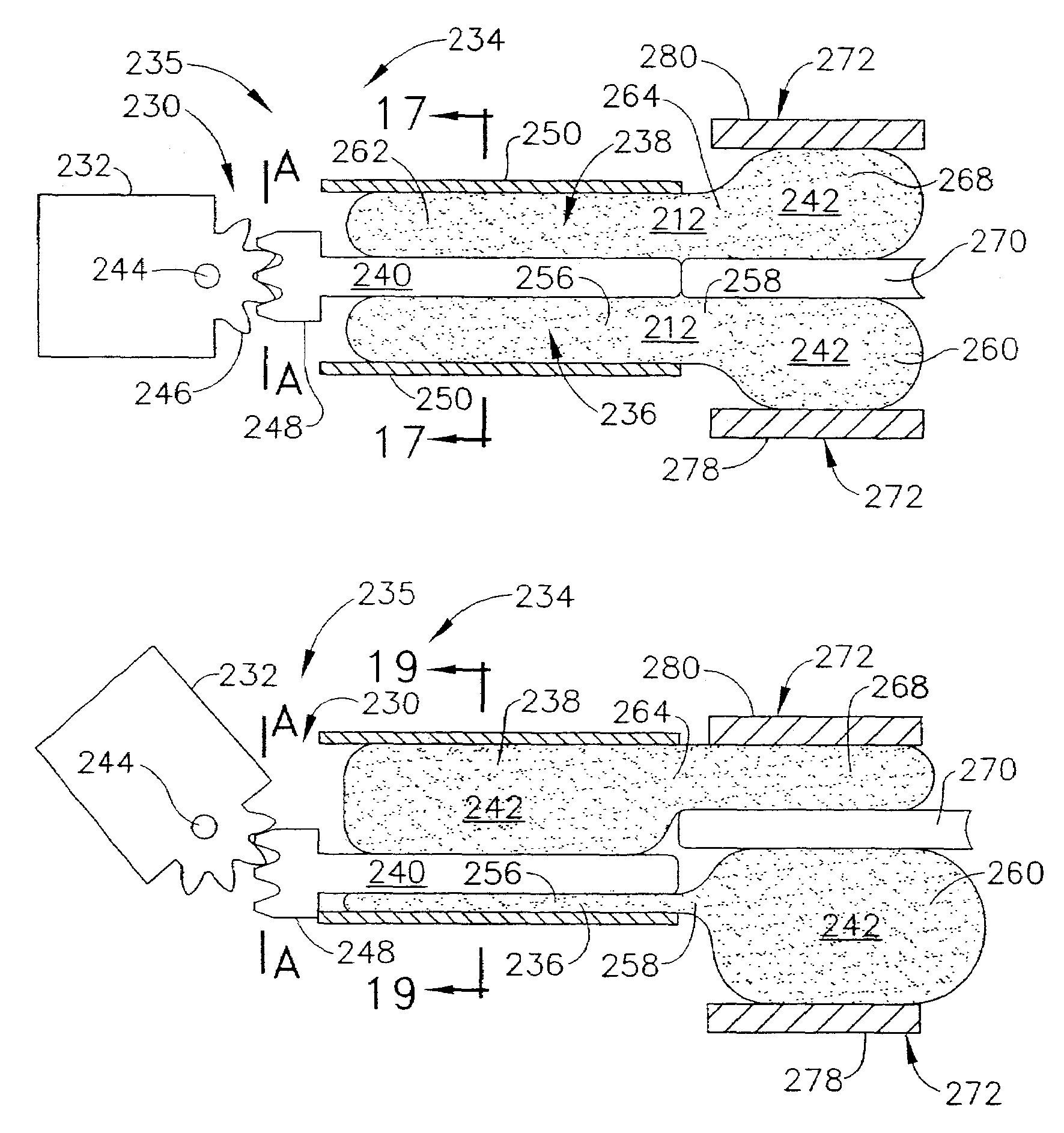
Surgical instrument incorporating a fluid transfer controlled articulation mechanism
ActiveUS7559450B2Give flexibilityOverall design flexibilitySuture equipmentsStapling toolsFluid controlEndoscope
A surgical instrument particularly suited to endoscopic use articulates an end effector by including a fluid transfer articulation mechanism that is proximally controlled. A fluid control, which is attached to a proximal portion, transfers fluid through the elongate shaft through a first fluid passage to a first fluid actuator that responds by articulating an articulation joint. Two opposing fluid actuators may respond to differential fluid transfer to effect articulation. Thereby, design flexibility is achieved by avoiding the design constraints of transferring a mechanical motion through the tight confines of the elongate shaft sufficient to effect articulation.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Surgical stapling instrument with an articulating end effector
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
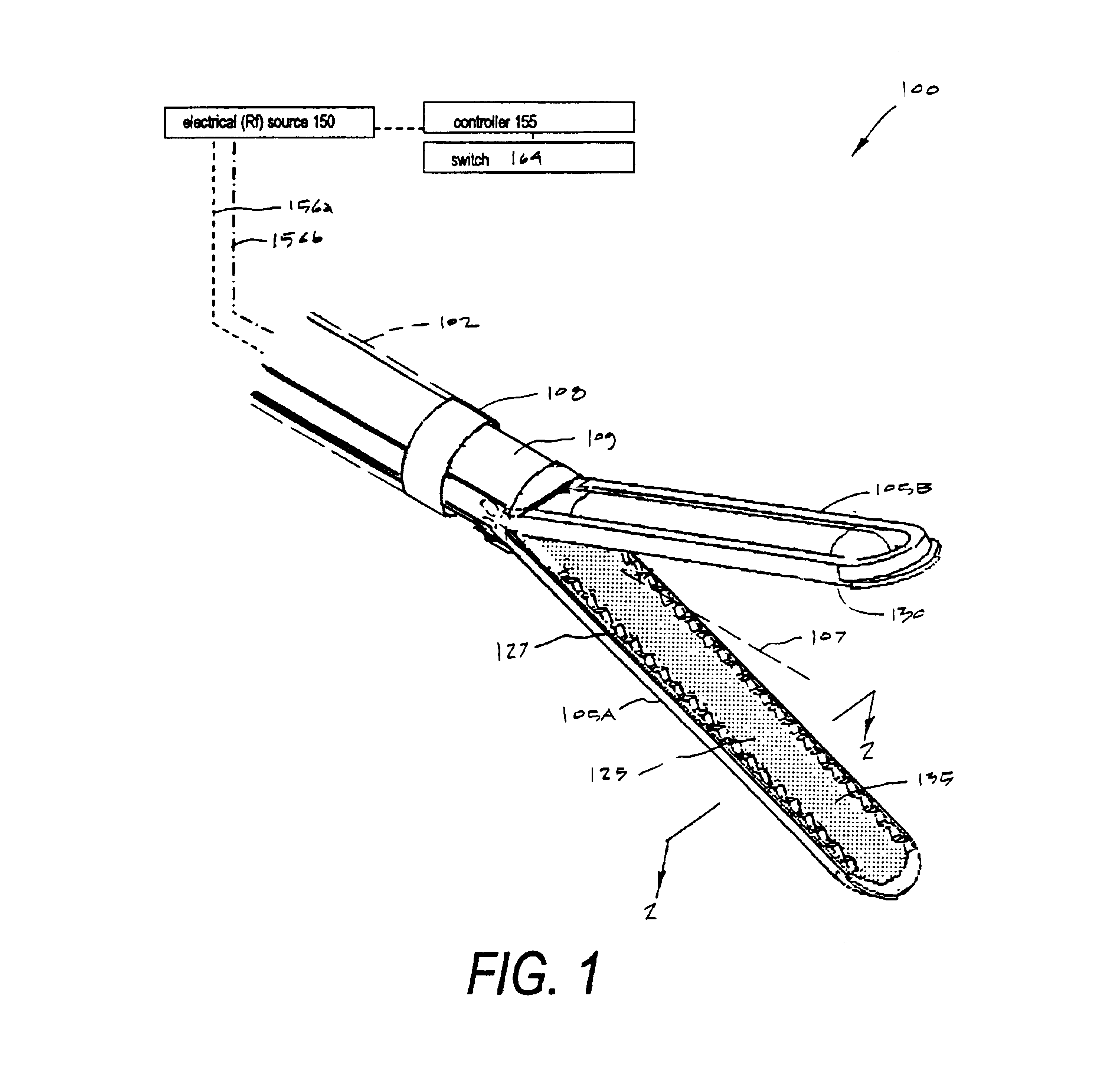
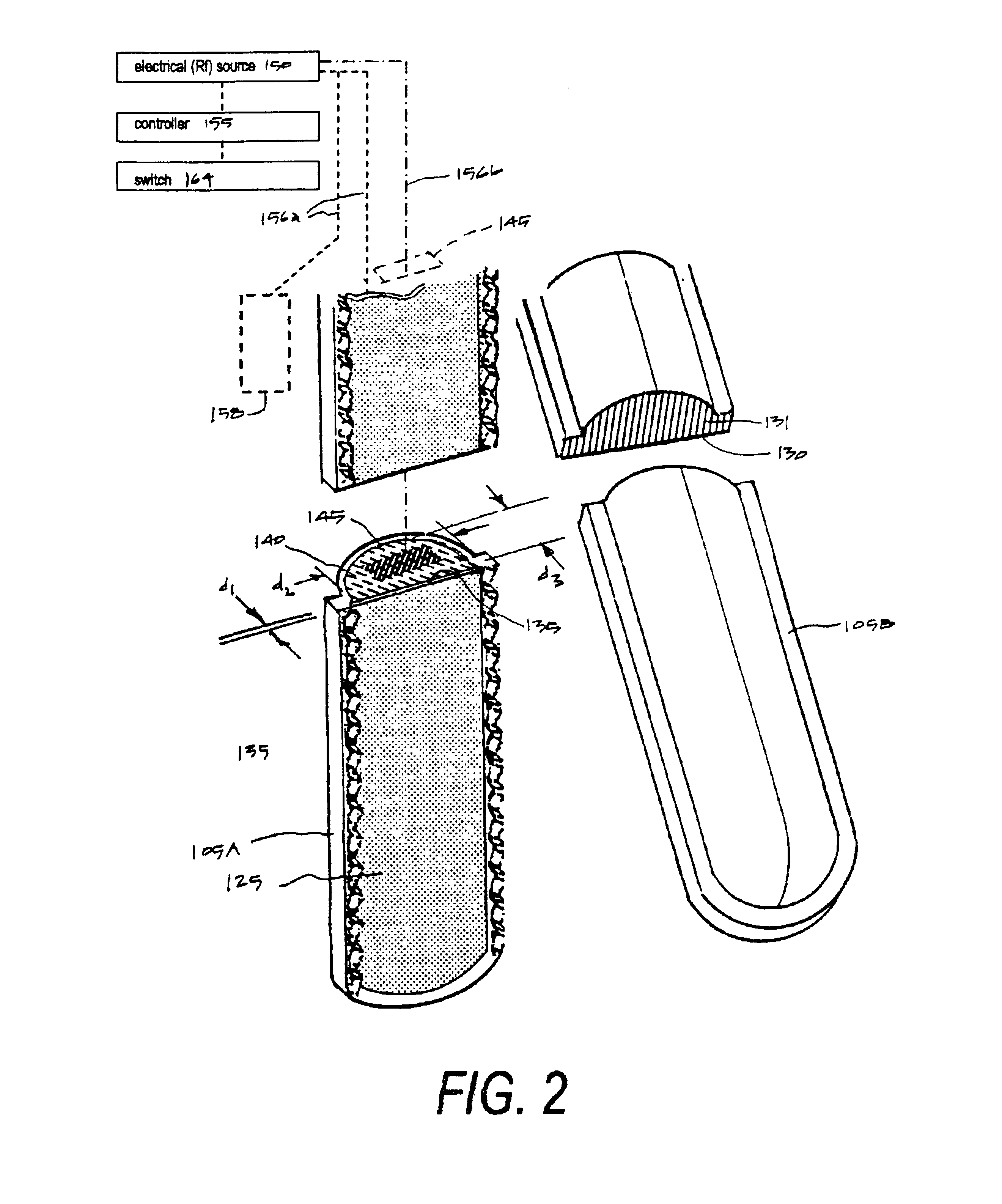
Electrosurgical instrument
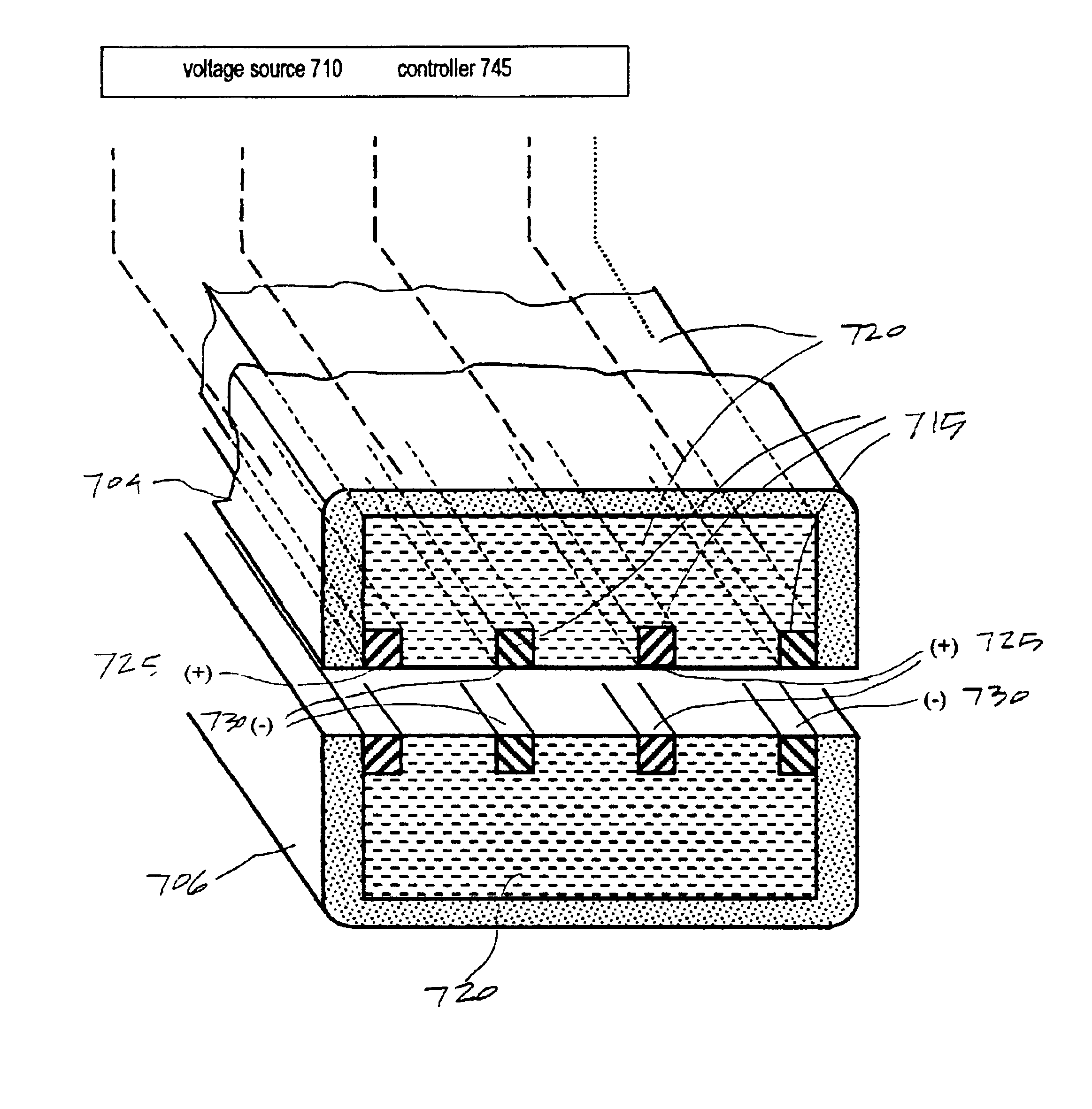
InactiveUS6926716B2Prevent any substantial dehydrationEnergy efficiencySurgical instruments for heatingSurgical forcepsElectrical resistance and conductanceVoltage source
A working end of a surgical instrument that carries first and second jaws for delivering energy to tissue. In a preferred embodiment, at least one jaw of the working end defines a tissue-engagement plane that contacts the targeted tissue. The cross-section of the engagement plane reveals that it defines (i) a first surface conductive portion or a variably resistive matrix of a temperature-sensitive resistive material or a pressure-sensitive resistive material, and (ii) a second surface portion coupled to a fixed resistive material that coupled in series or parallel to a voltage source together with the first portion. In use, the engagement plane will apply active Rf energy to ohmically heat the captured tissue until the point in time that a controller senses an electrical parameter of the tissue such as impedance. Thereafter, the controller switches energy delivery to the second surface portion that is resistively heated to thereby apply energy to tissue by conductive heat transfer.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Hydraulically and electrically actuated articulation joints for surgical instruments
Articulation joints for use in connection with a surgical instrument that has a portion that must be passed through a trocar or similar structure and then articulated relative to another portion of the instrument received within the trocar. Various embodiments of the articulation joint include at least one fluid-actuated cylinder or flexible driven member to articulate the surgical implement relative to the handle assembly of the instrument.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT +1
Surgical stapling instrument with a geared return mechanism
A surgical instrument including a firing drive configured to selectively advance a firing member and / or cutting member relative to an end effector and, in addition, a reversing drive configured to selectively retract the firing member and / or cutting member relative to the end effector. The firing drive can include a pawl which can be selectively engaged with the firing member in order to advance the firing member, wherein the pawl can be disengaged from the firing member when the reversing drive is engaged with the firing member. The reversing drive can include a gear train having a first gear operably engaged with the firing member and, in addition, a second gear operably engaged with the first gear, wherein the second gear can be selectively operable with the trigger such that an actuation of the trigger can retract the firing member and / or cutting element via the first and second gears.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Robotic tool with wristed monopolar electrosurgical end effectors
ActiveUS7824401B2Avoid conductionSmall outer diameterDiagnosticsSurgical instruments for heatingElectrical conductorBlood coagulations
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
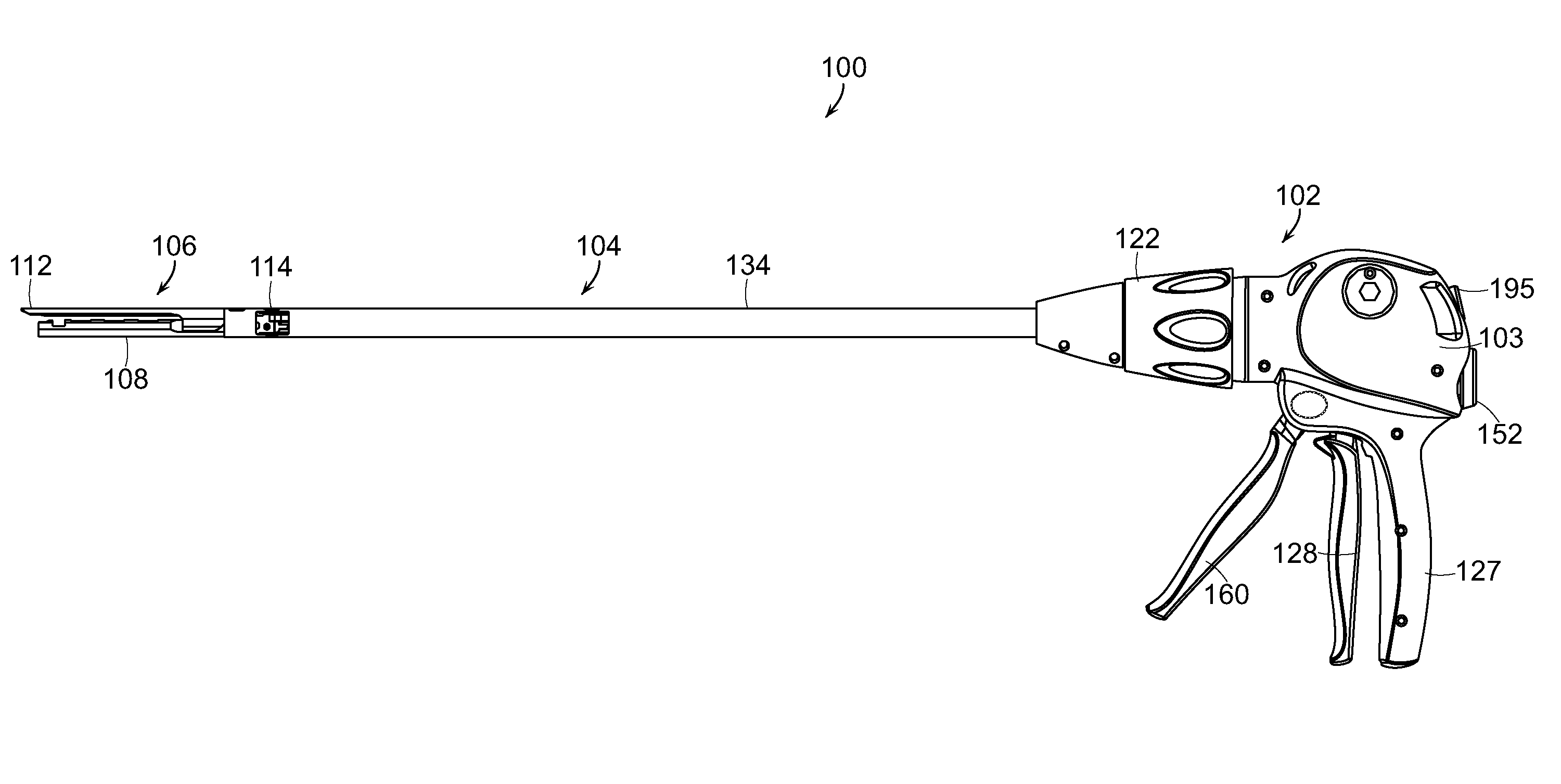
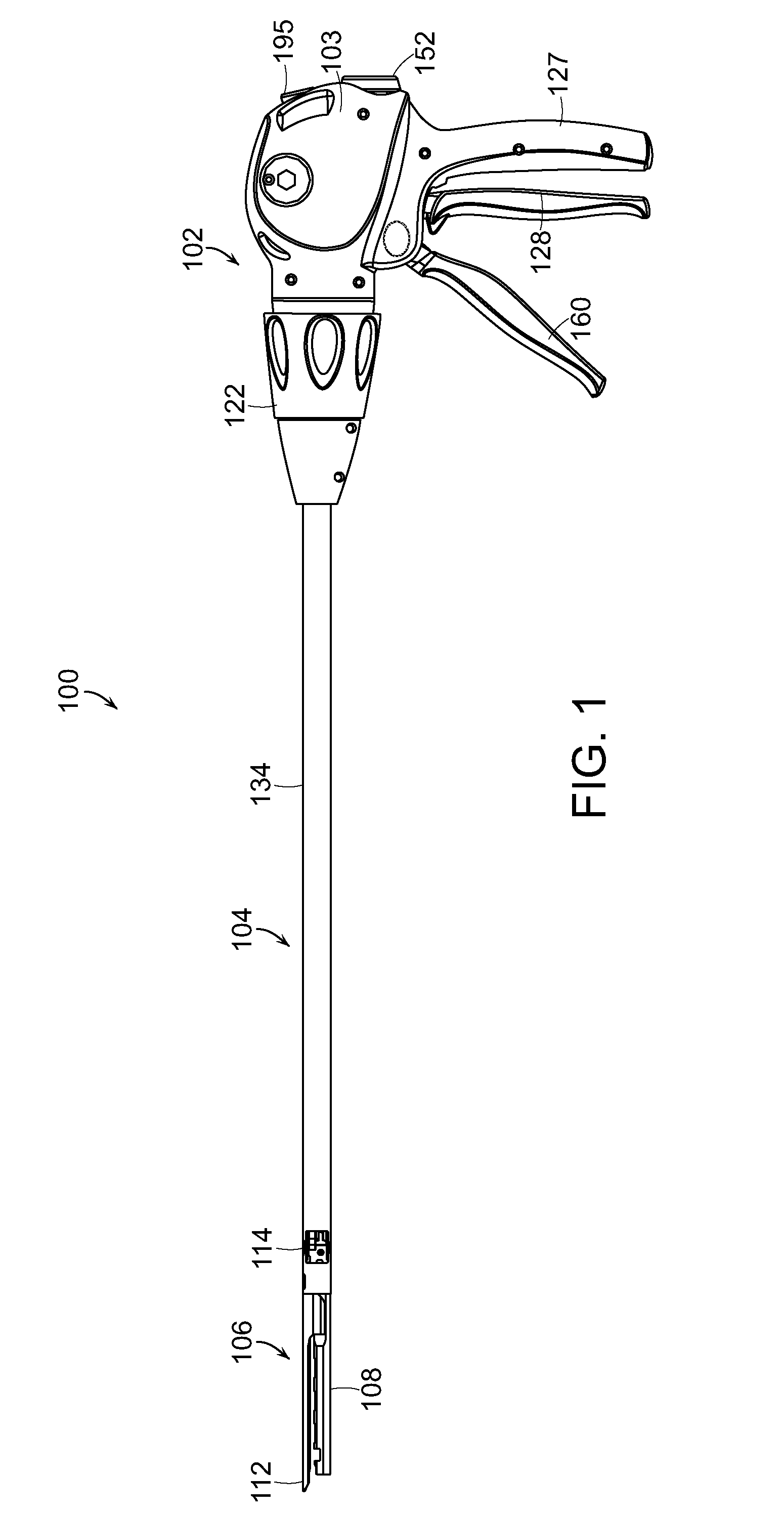
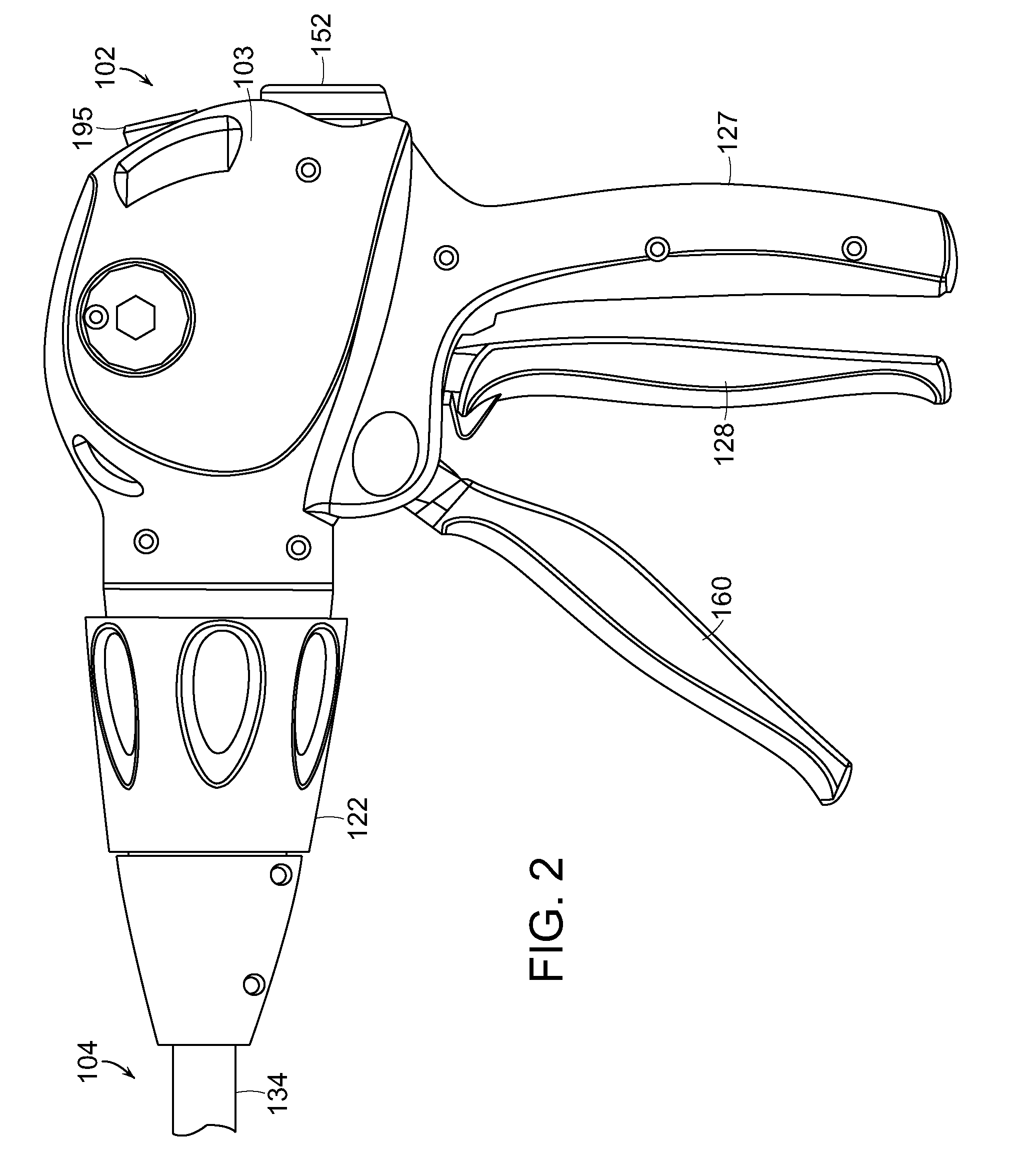
Surgical instrument articulation joint cover
A surgical instrument including a shaft, an end effector, and a joint, wherein the end effector can be moved relative to the shaft about the joint. In various embodiments, the joint can include a cover configured to be positioned intermediate the end effector and the shaft. In at least one embodiment, the cover can be connected to at least one of the end effector and the shaft and can be configured to at least partially surround the joint in order to prevent soft tissue positioned adjacent to the joint from being pulled into and / or pinched by the joint.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Electro-mechanical surgical device
An electro-mechanical surgical device includes: a housing; an elongated shaft extending from the housing, a distal end of the elongated shaft being detachably coupleable to a surgical instrument; at least two axially rotatable drive shafts disposed within the elongated shaft, a distal end of each of the drive shafts being configured to couple with the surgical instrument; a steering cable arrangement, the steering cable arrangement being configured to steer the distal end of the elongated shaft; and a motor system disposed within the housing, the motor system being configured to drive the drive shafts and the steering cable arrangement. A control system may be provided for controlling the motor system. A remote control unit may also be provided for controlling the motor system via the control system. Sensors, such as optical or Hall-effect devices, may be provided for determining the position of the elements of the surgical instrument based on the detected rotation of the drive shafts. A memory unit stores a plurality of operating programs or algorithms, each corresponding to a type of surgical instrument attachable to the electro-mechanical surgical device. The control system reads or selects from the plurality of operating programs or algorithms, the operating program or algorithm corresponding to the type of surgical instrument attached to the electro-mechanical surgical device.
Owner:DORROS GERALD M D
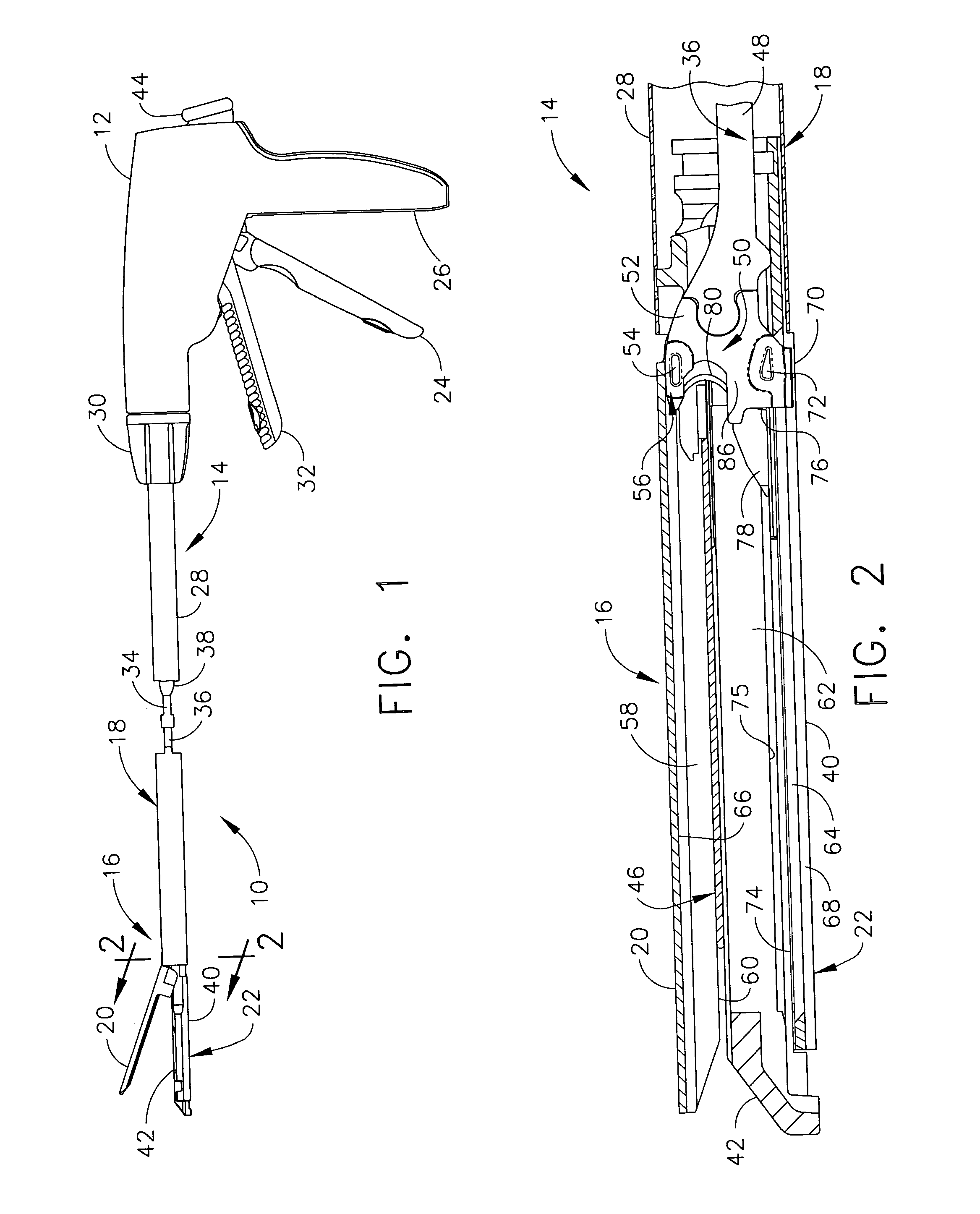
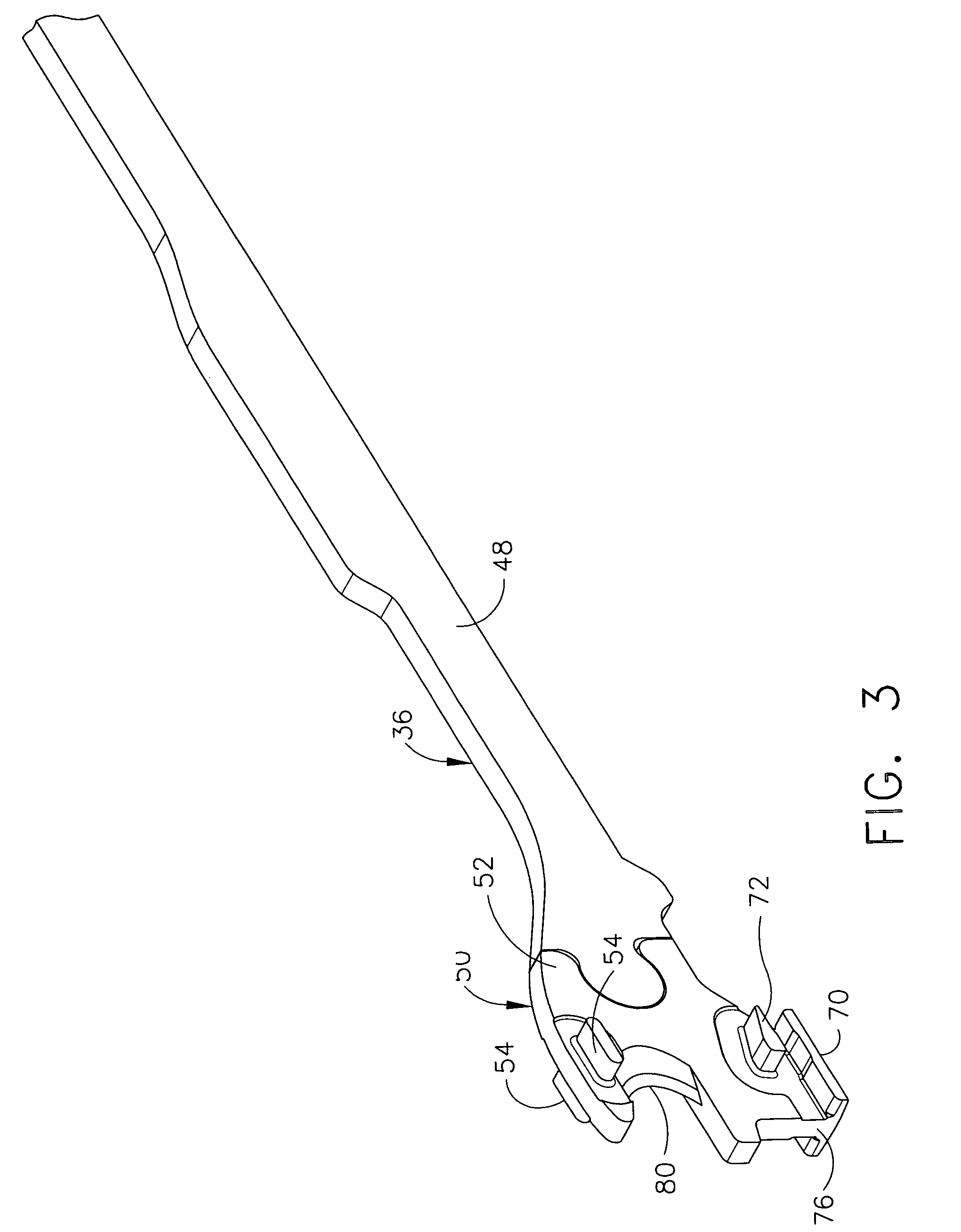
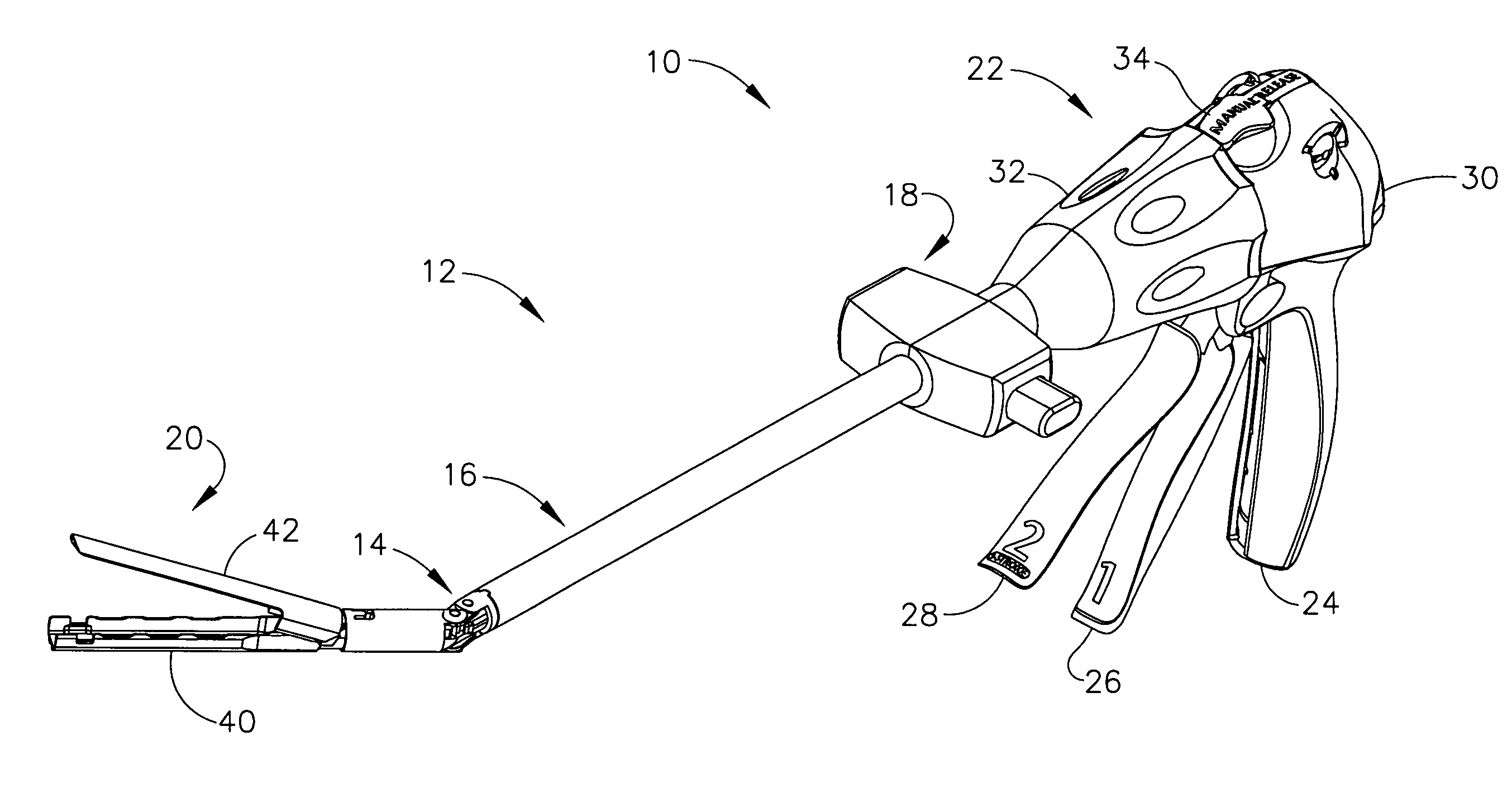
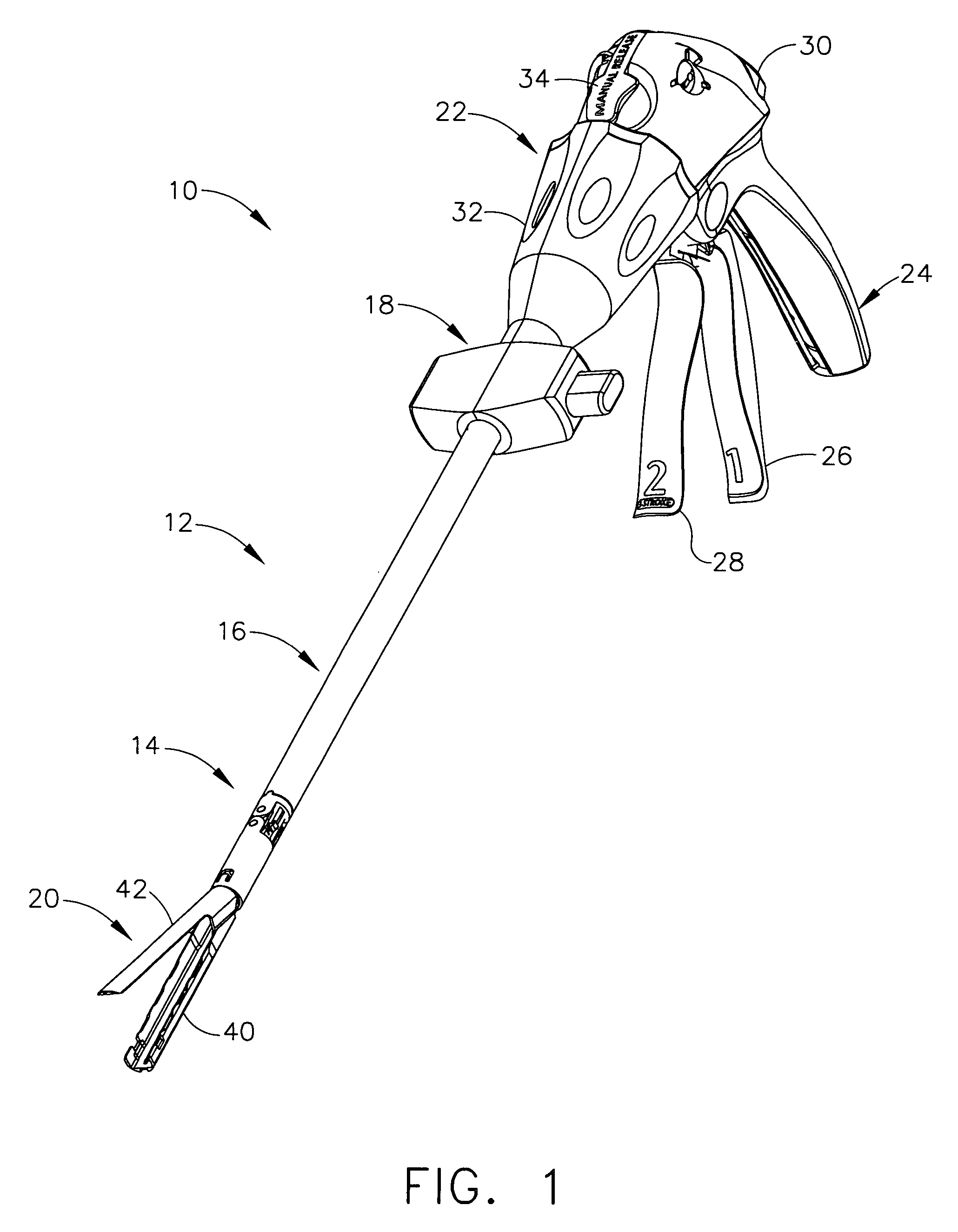
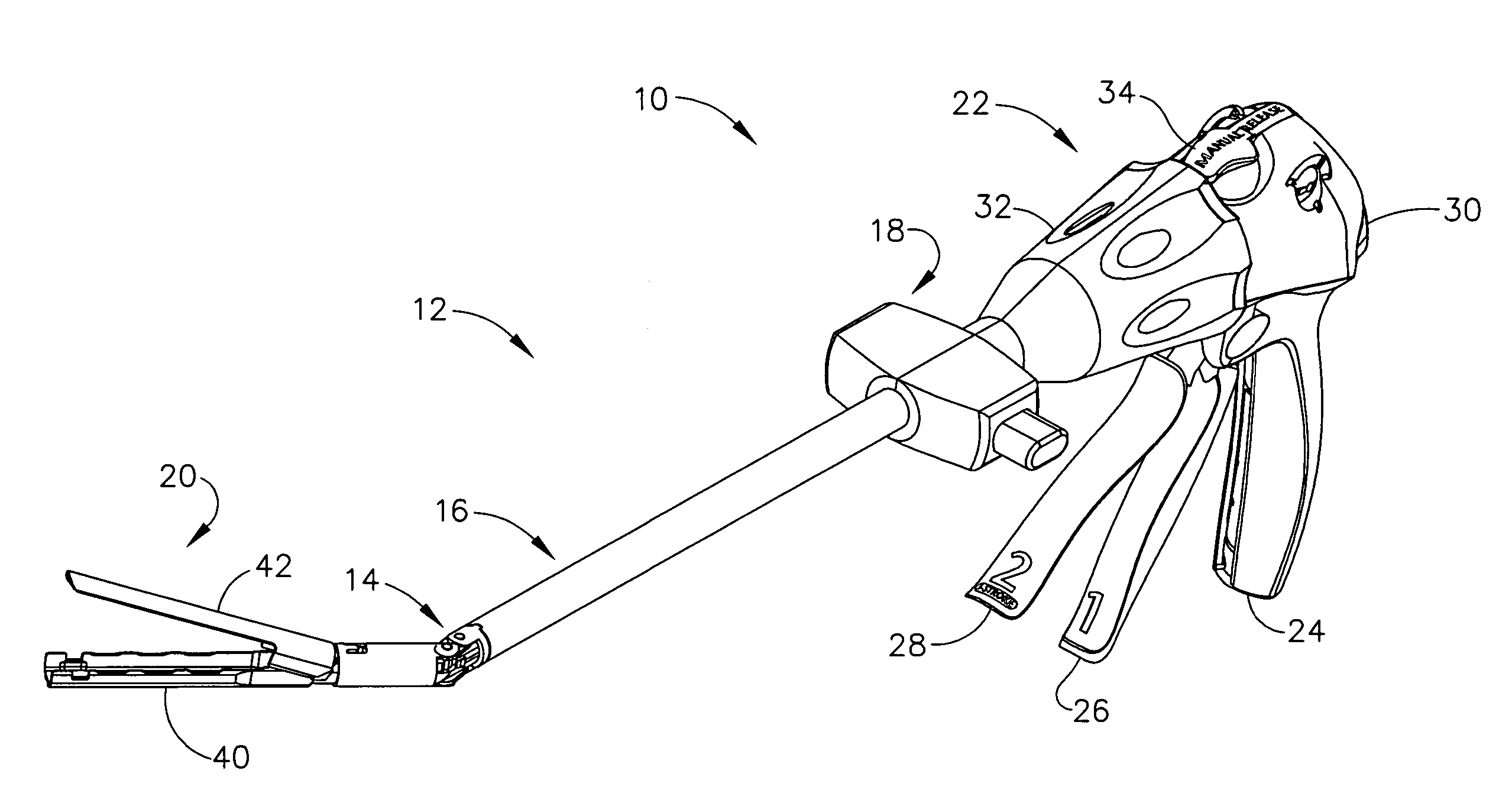
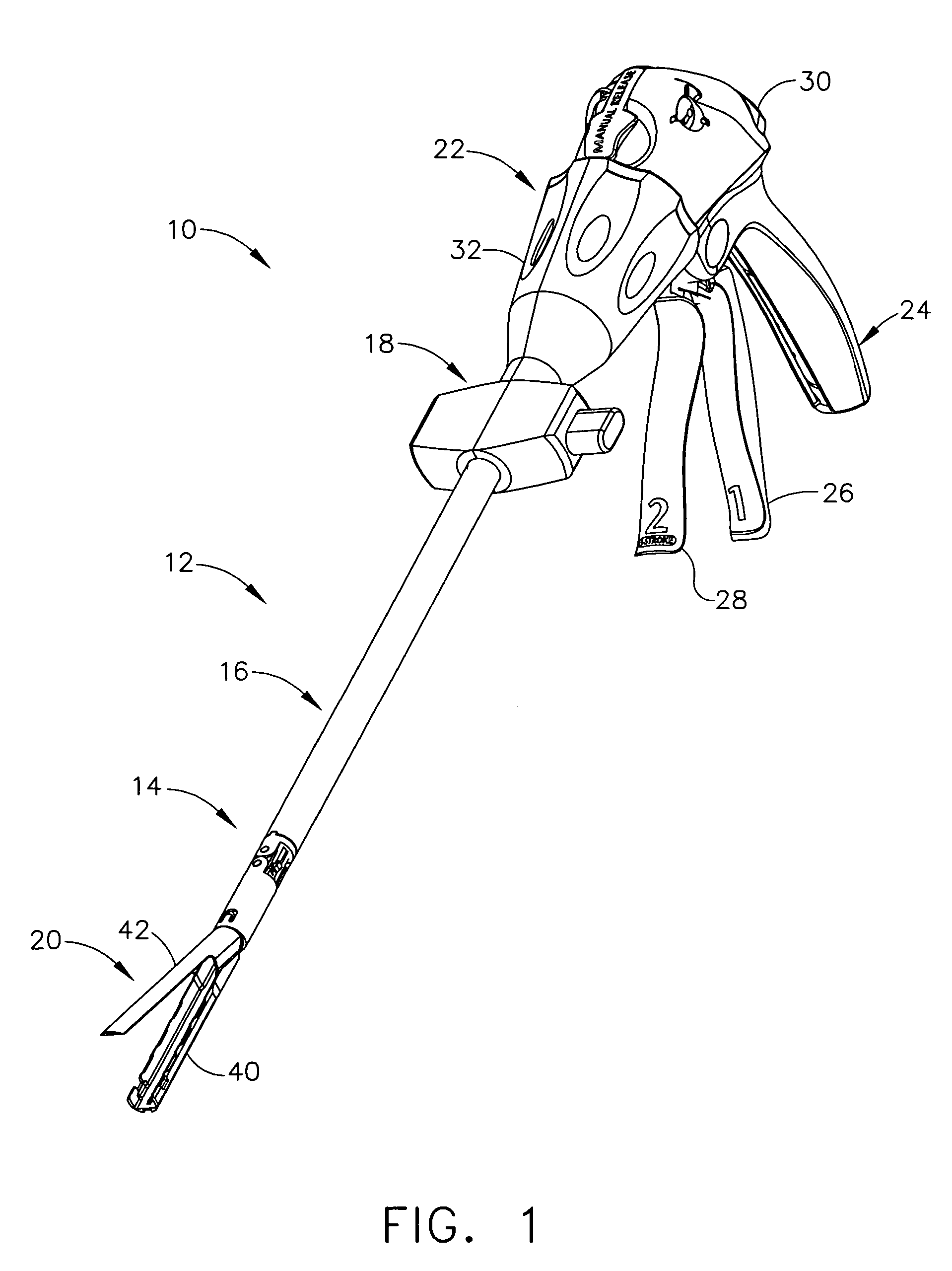
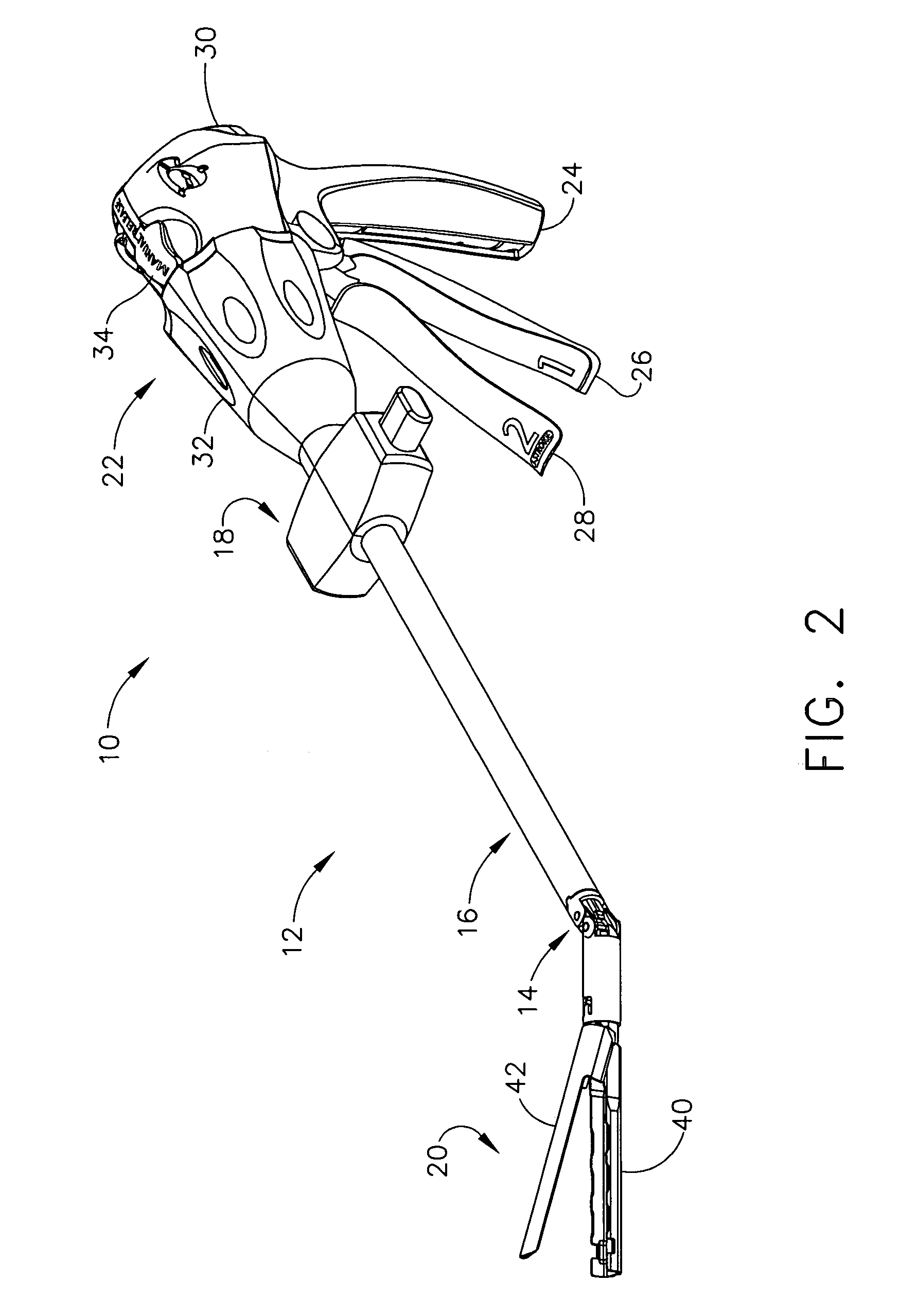
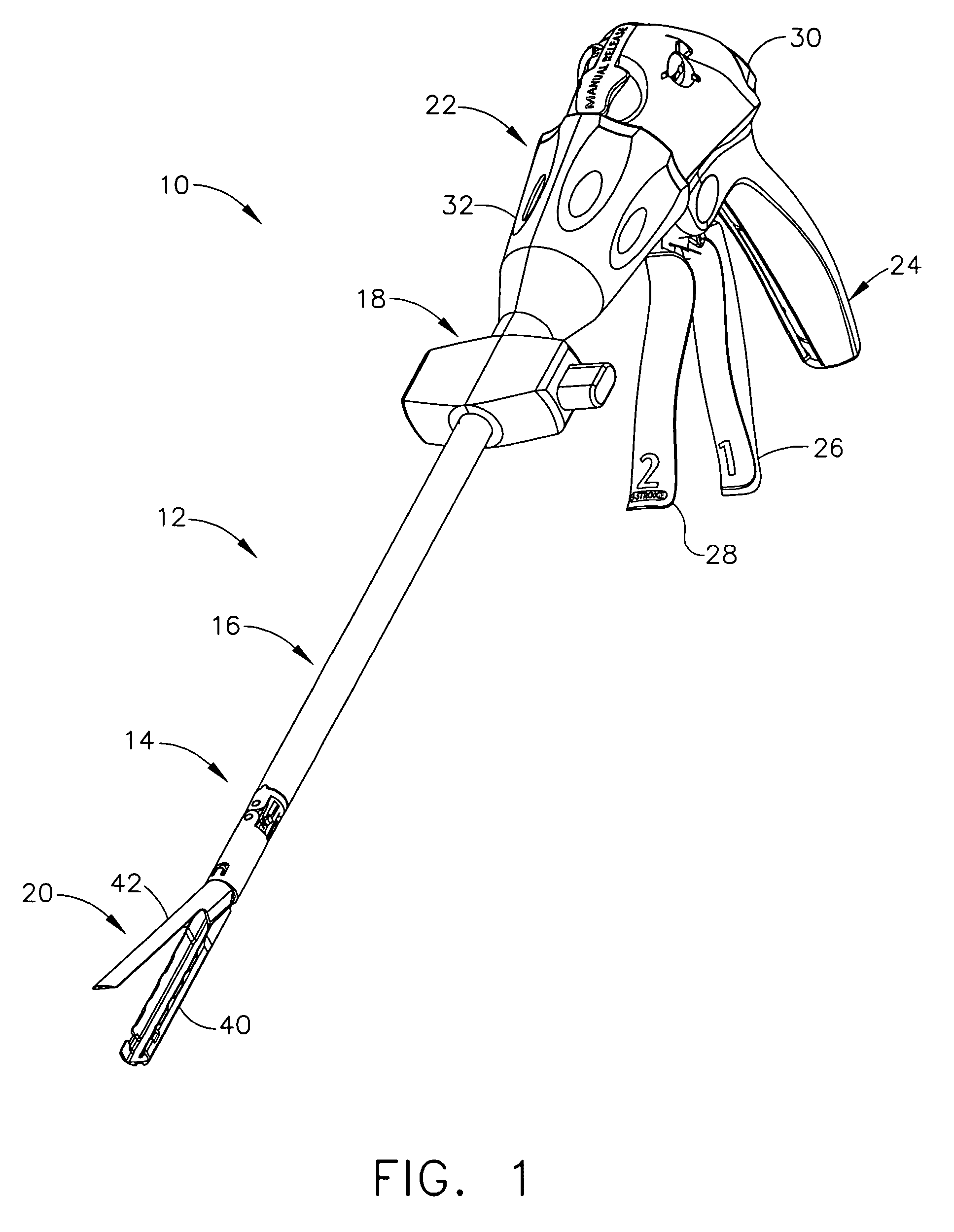
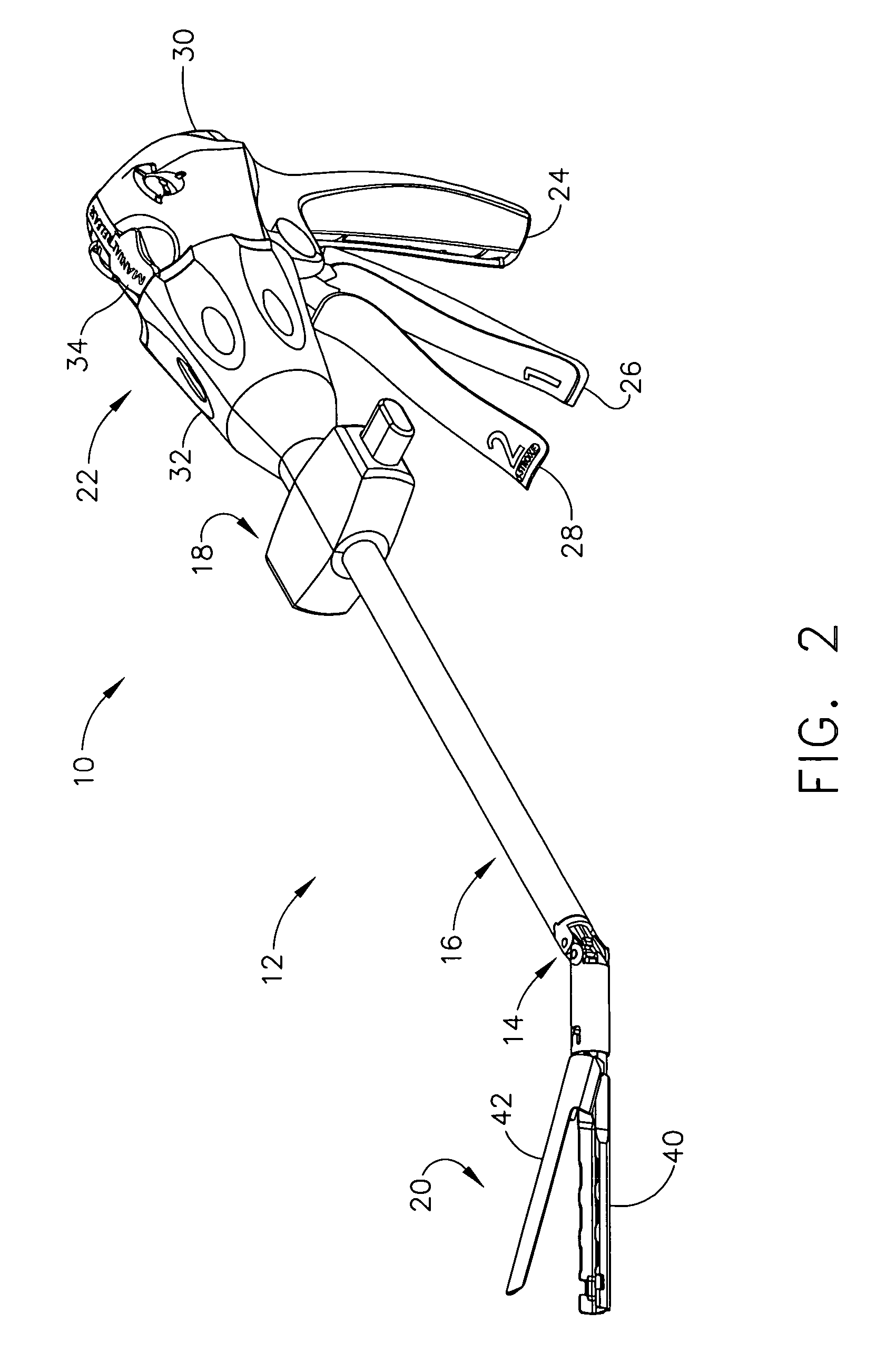
Electrically self-powered surgical instrument with manual release
ActiveUS7959050B2Comfortably fit into a user's handReduce manufacturing difficultySuture equipmentsStapling toolsElectricityEngineering
An electrically operated surgical instrument includes a surgical end effector having an actuation assembly effecting a surgical procedure when actuated and a handle connected to the end effector for actuating the assembly. A part of the assembly moves between start and fully actuated positions. The handle has a self-contained power supply and a drive assembly disposed entirely within the handle. The drive assembly has an electrically powered motor and a controller electrically connected to the power supply and to the motor. The controller selectively operates the motor. A transmission mechanically connects the motor to the moving part and selectively displaces the moving part anywhere between the start and fully extended positions when the motor is operated. A manual release is mechanically coupled to the transmission to selectively interrupt the transmission and, during interruption, displaces the moving part towards the start position independent of motor operation.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com