Patents
Literature
1246 results about "Motion transfer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
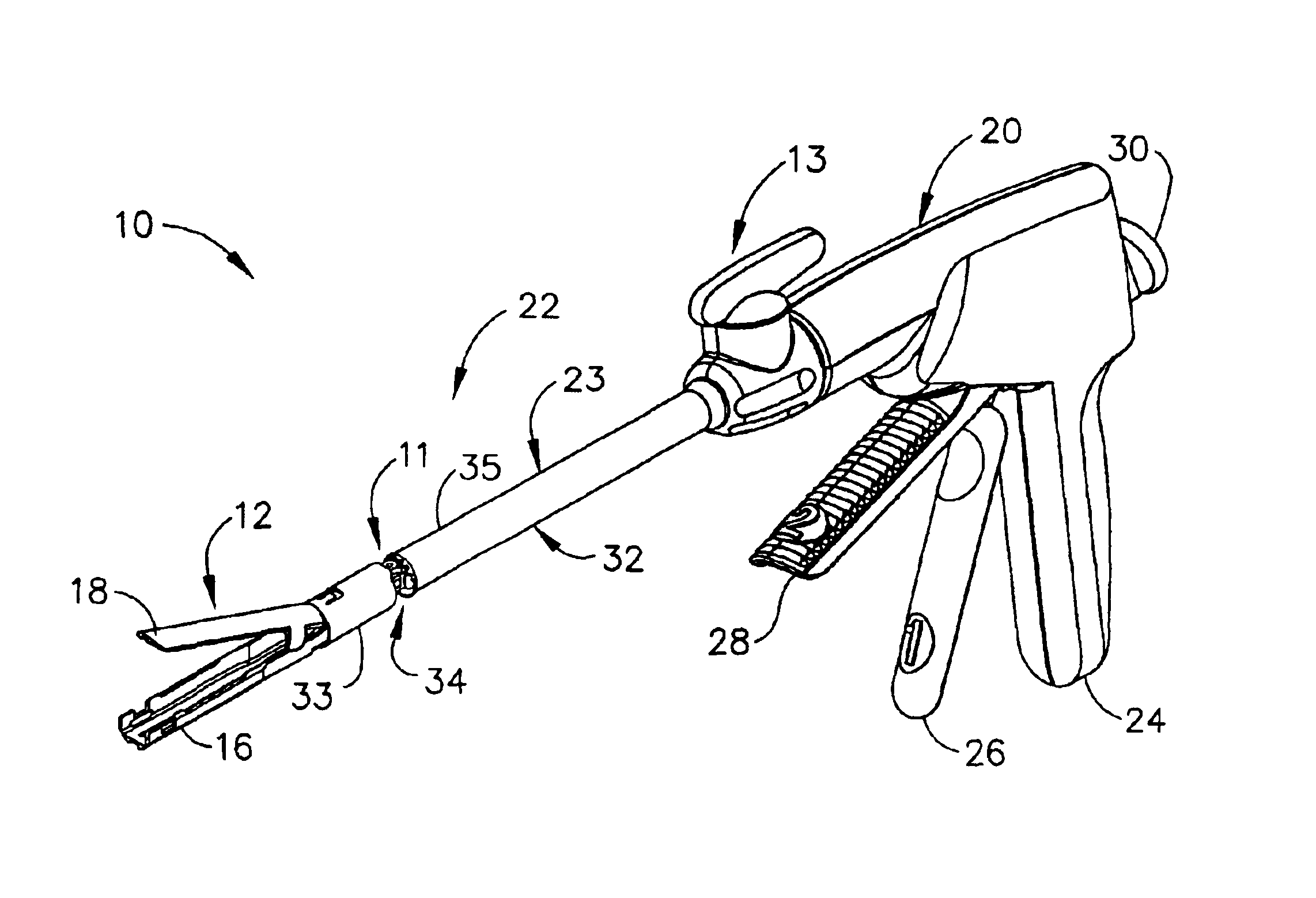
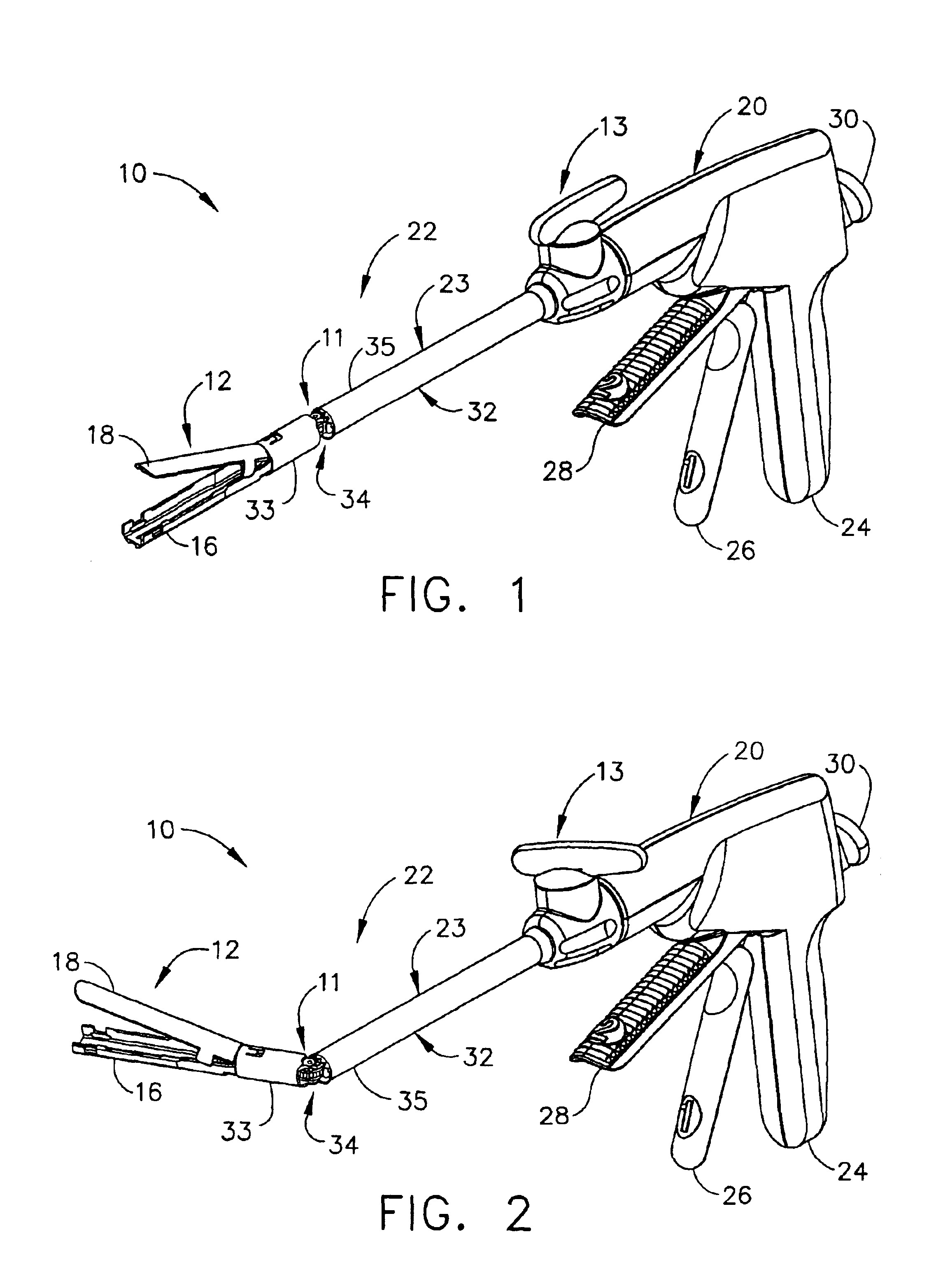
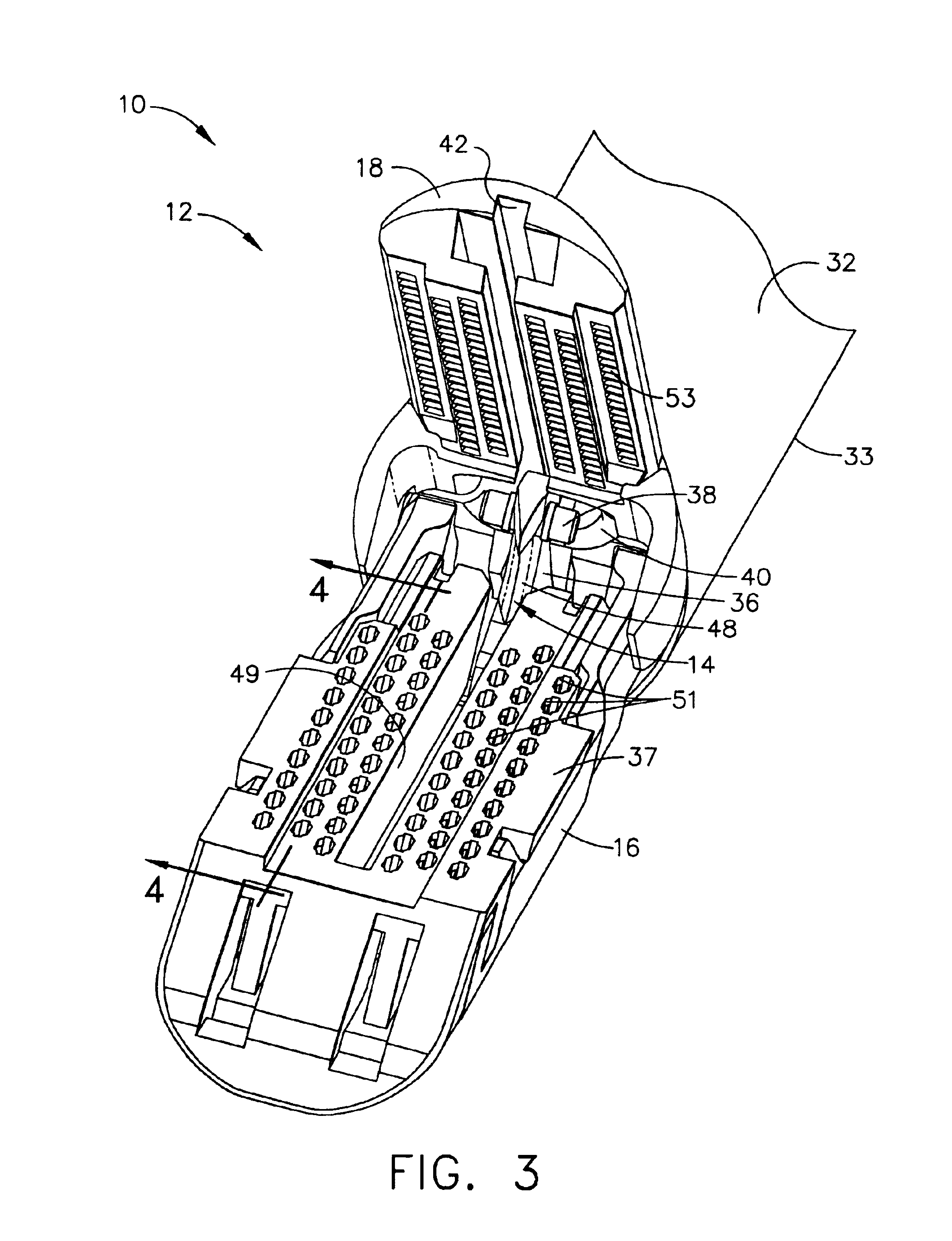
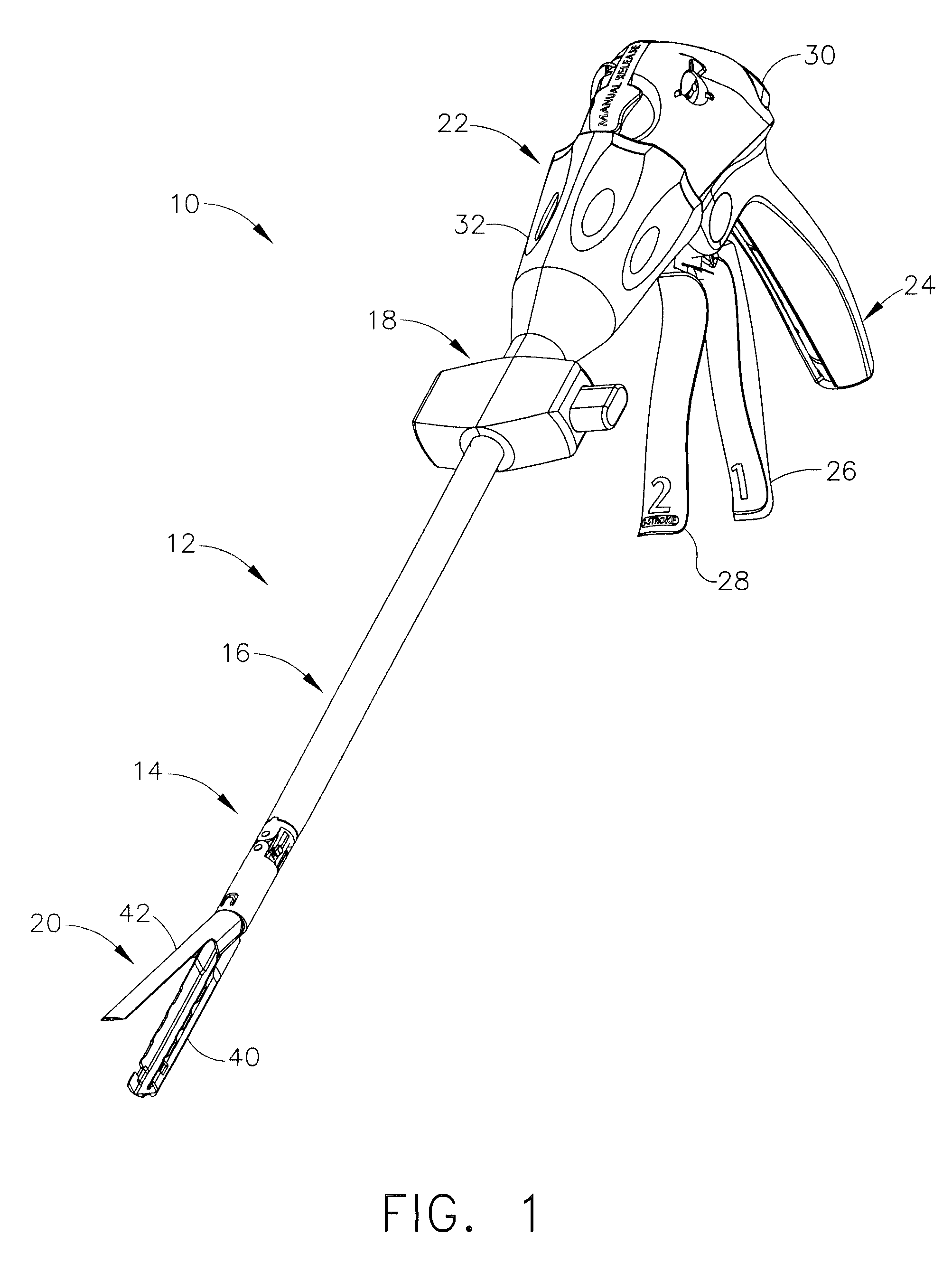
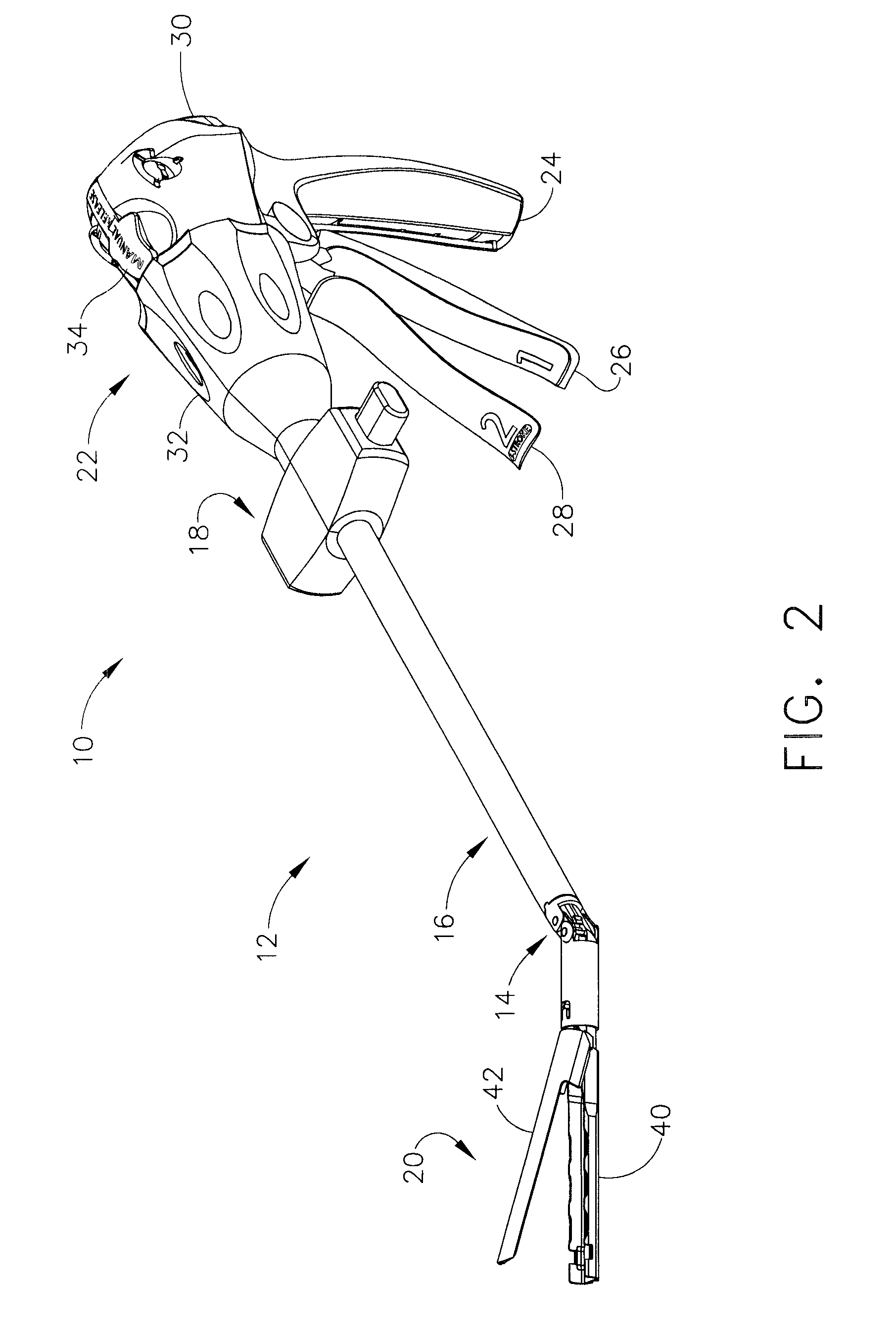
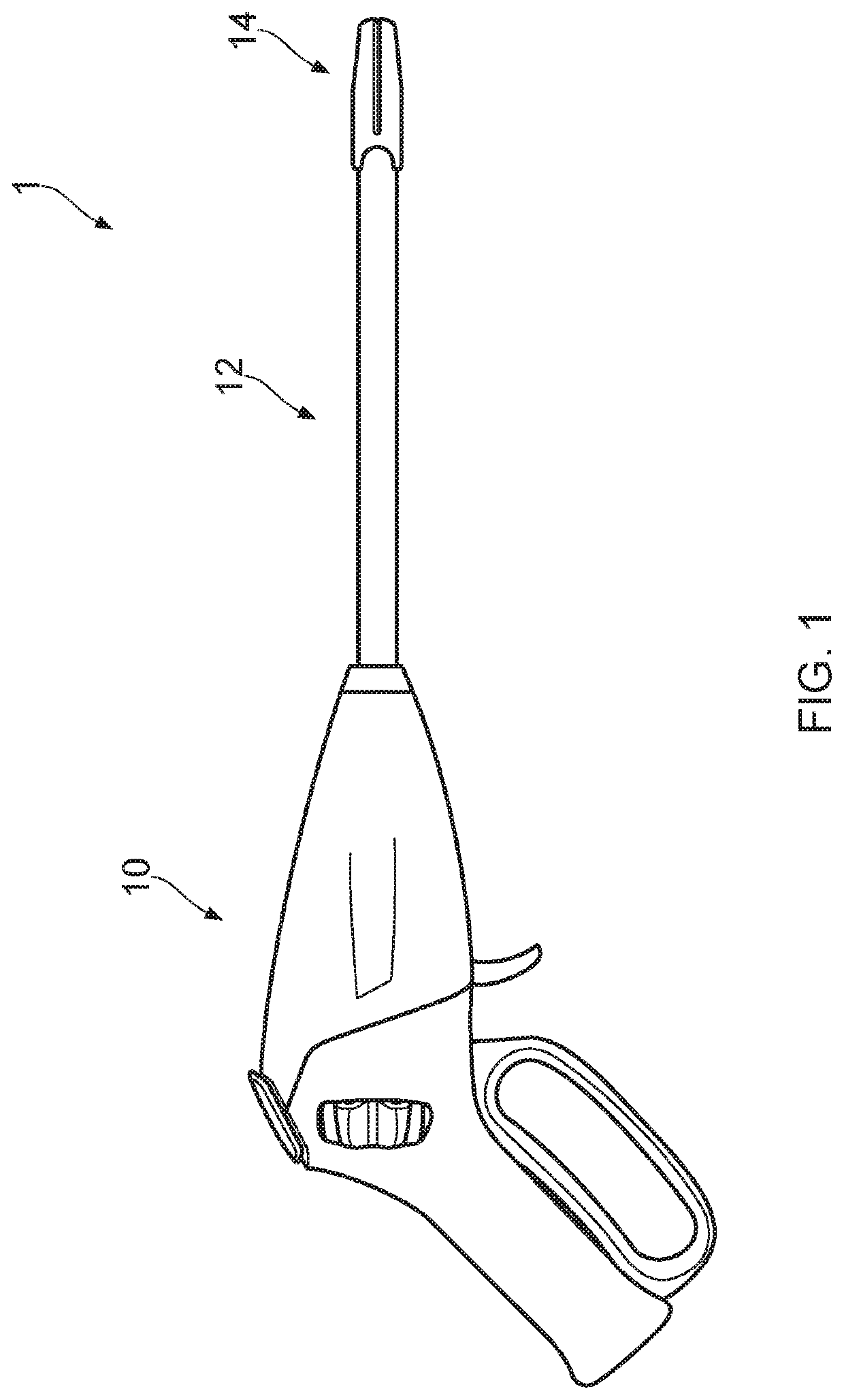
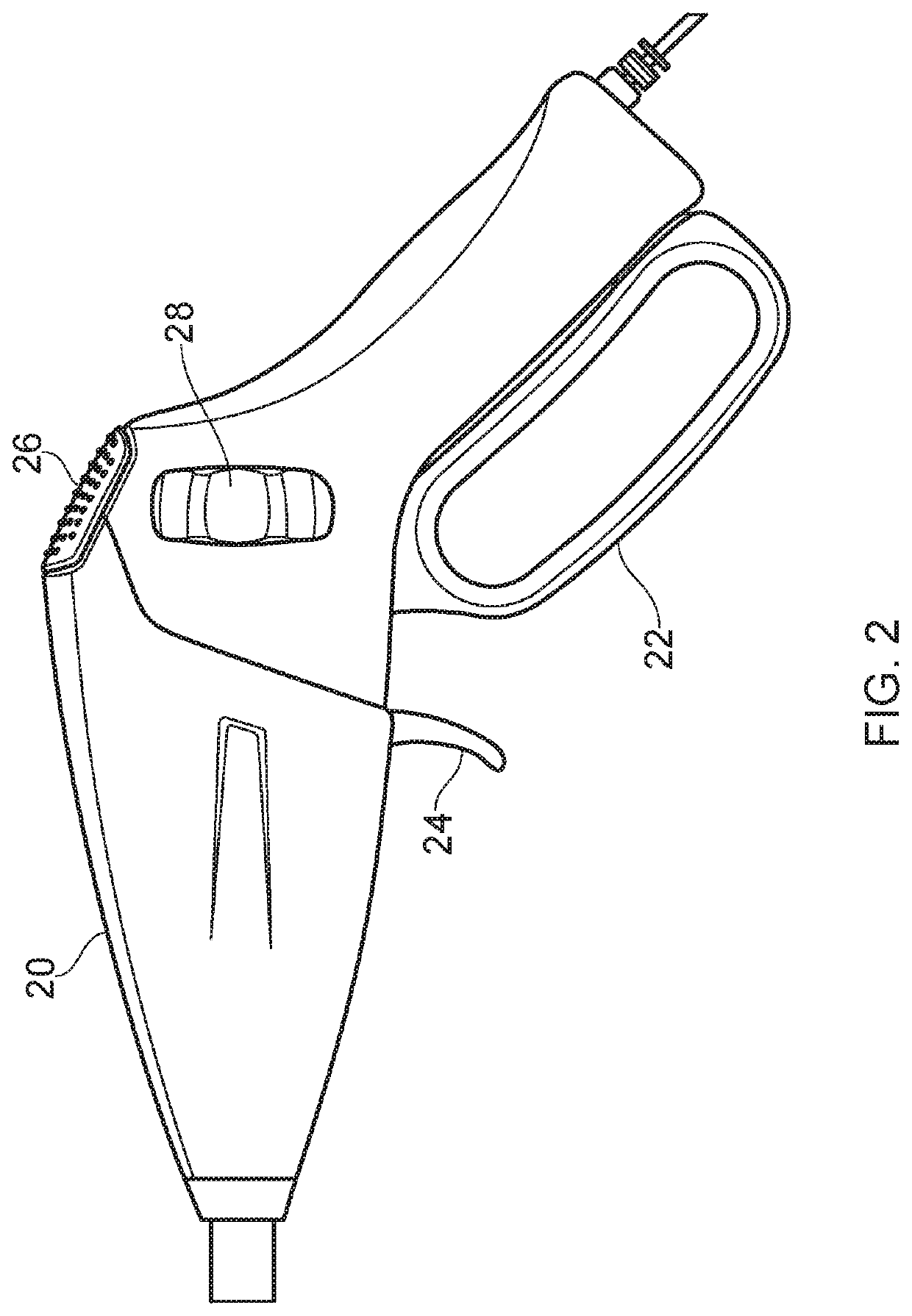
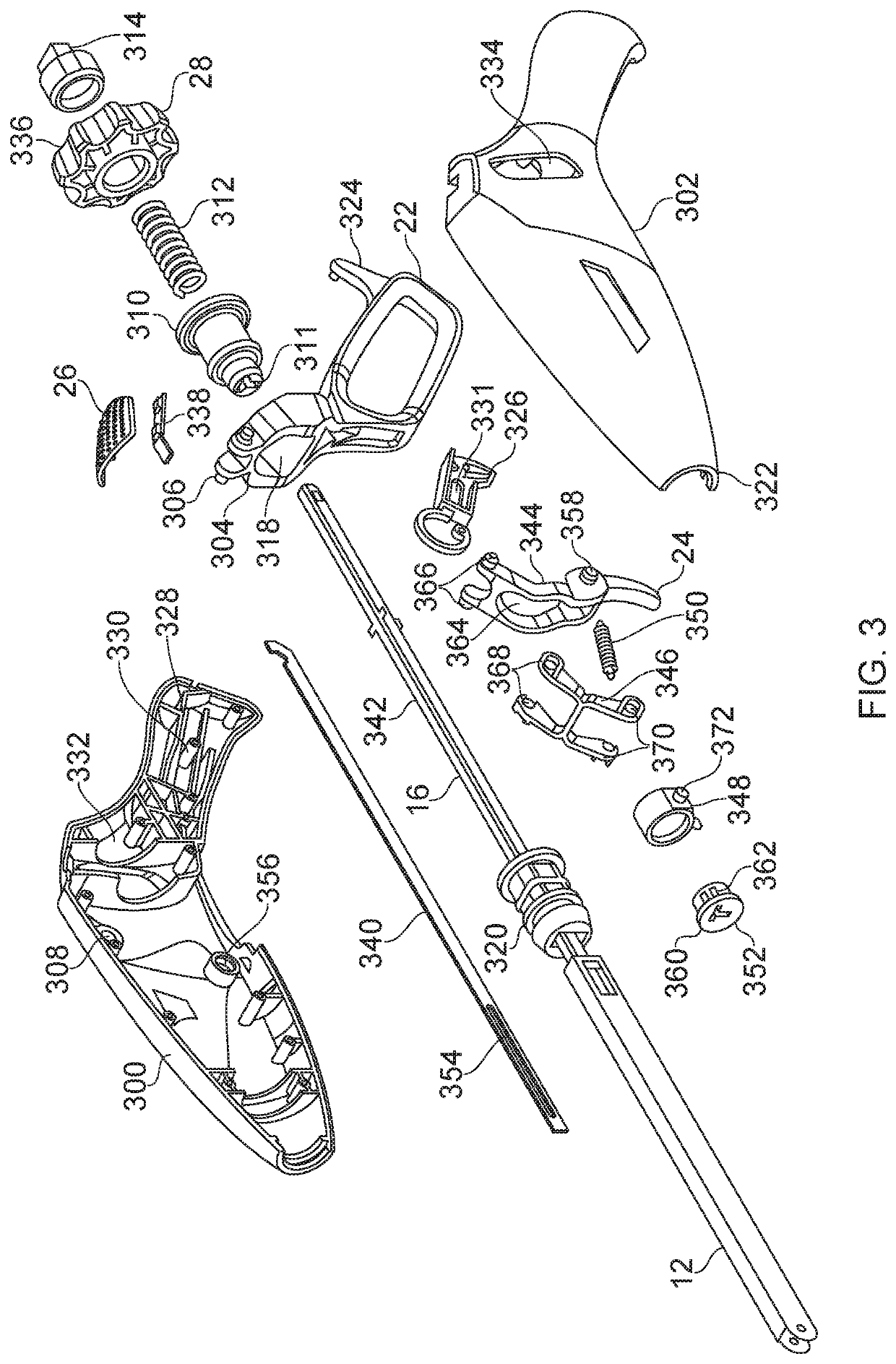
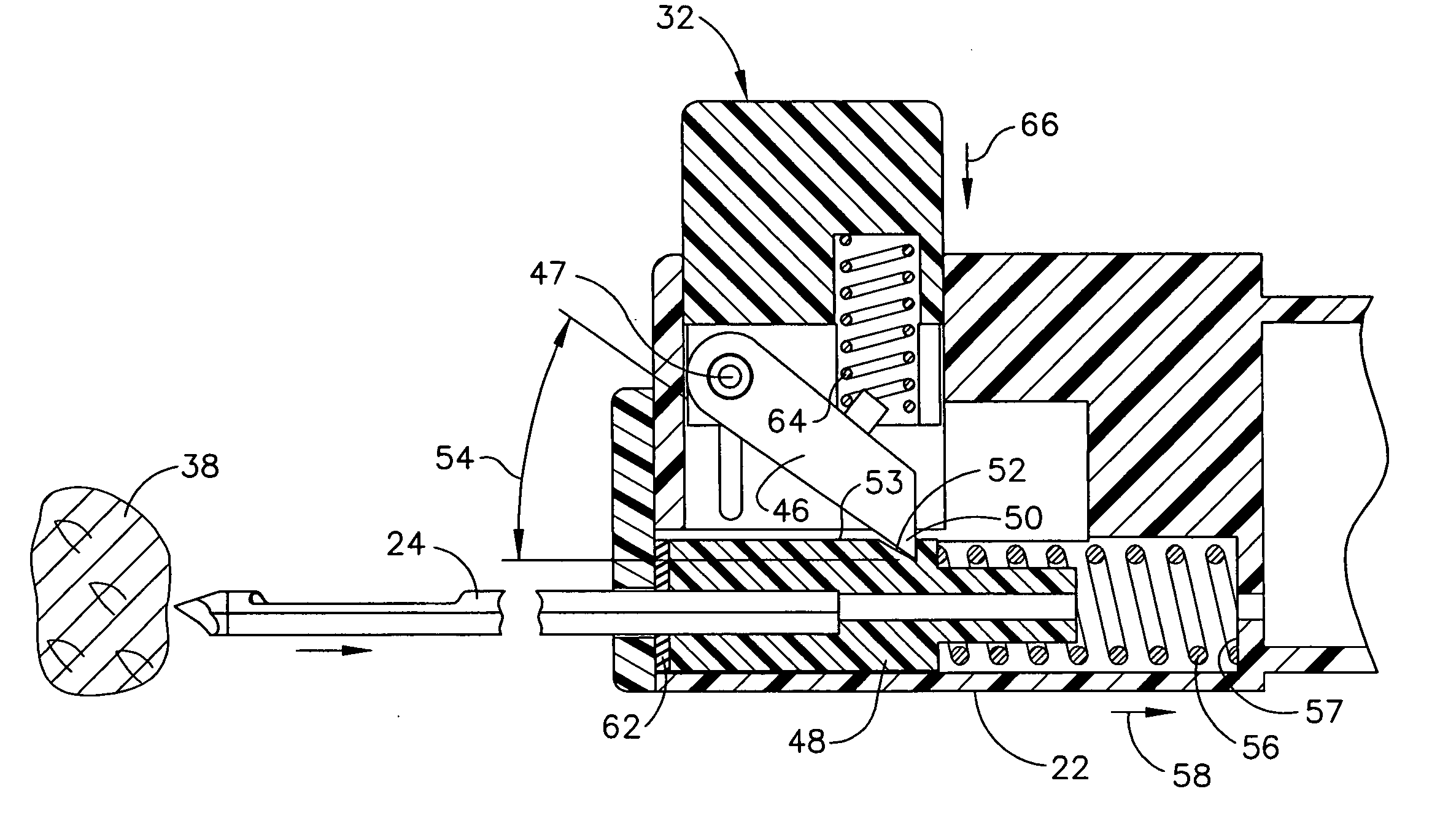
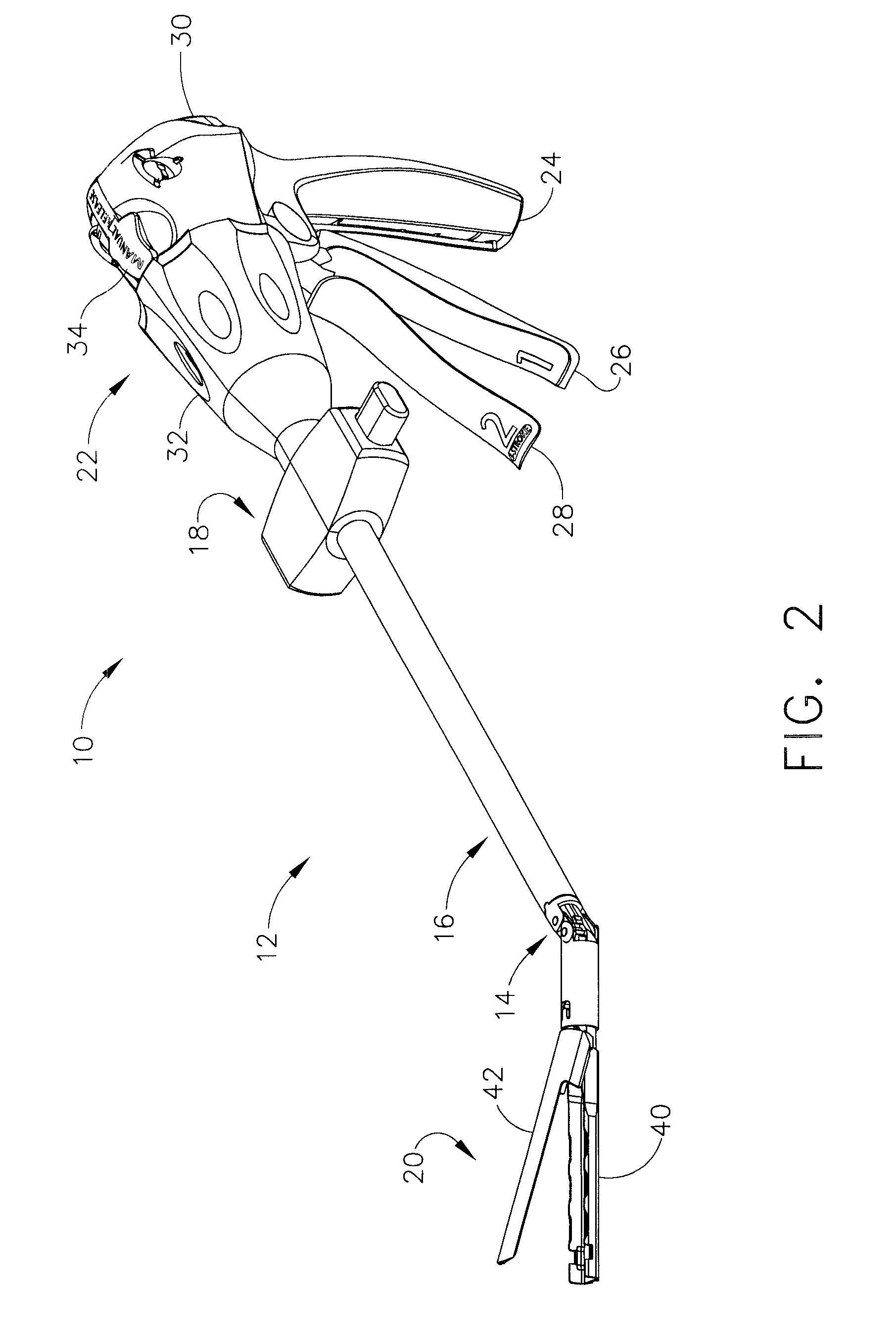
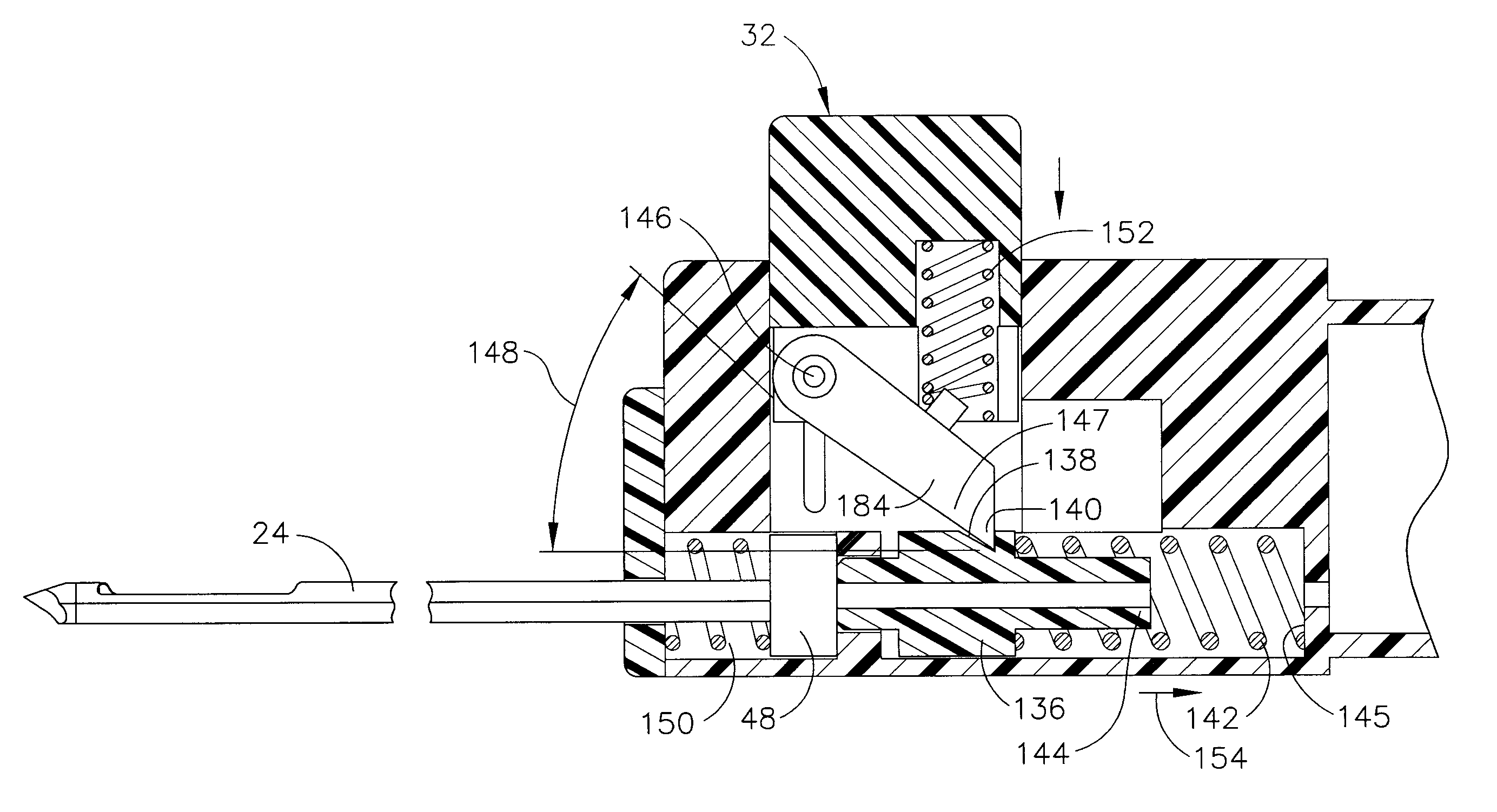
Surgical instrument with a lateral-moving articulation control
InactiveUS6981628B2Complicate amountComplicate directionSuture equipmentsStapling toolsEngineeringTarsal Joint
An articulating surgical instrument suited for endoscopic use includes a lateral articulation control into a handle portion that provides an intuitive visual and tactile indication to the clinician as to the amount and direction of articulation of an end effector at a distal end of a shaft. Lateral movement of a lateral control actuator is converted into a longitudinal motion or a rotational motion transferred by the shaft to an articulation mechanism. A version of a lateral articulation control for a rotationally driven articulation mechanism incorporates an articulation backdrive lockout that prevents forces on the end effector from causing the selected amount of articulation from being changed.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
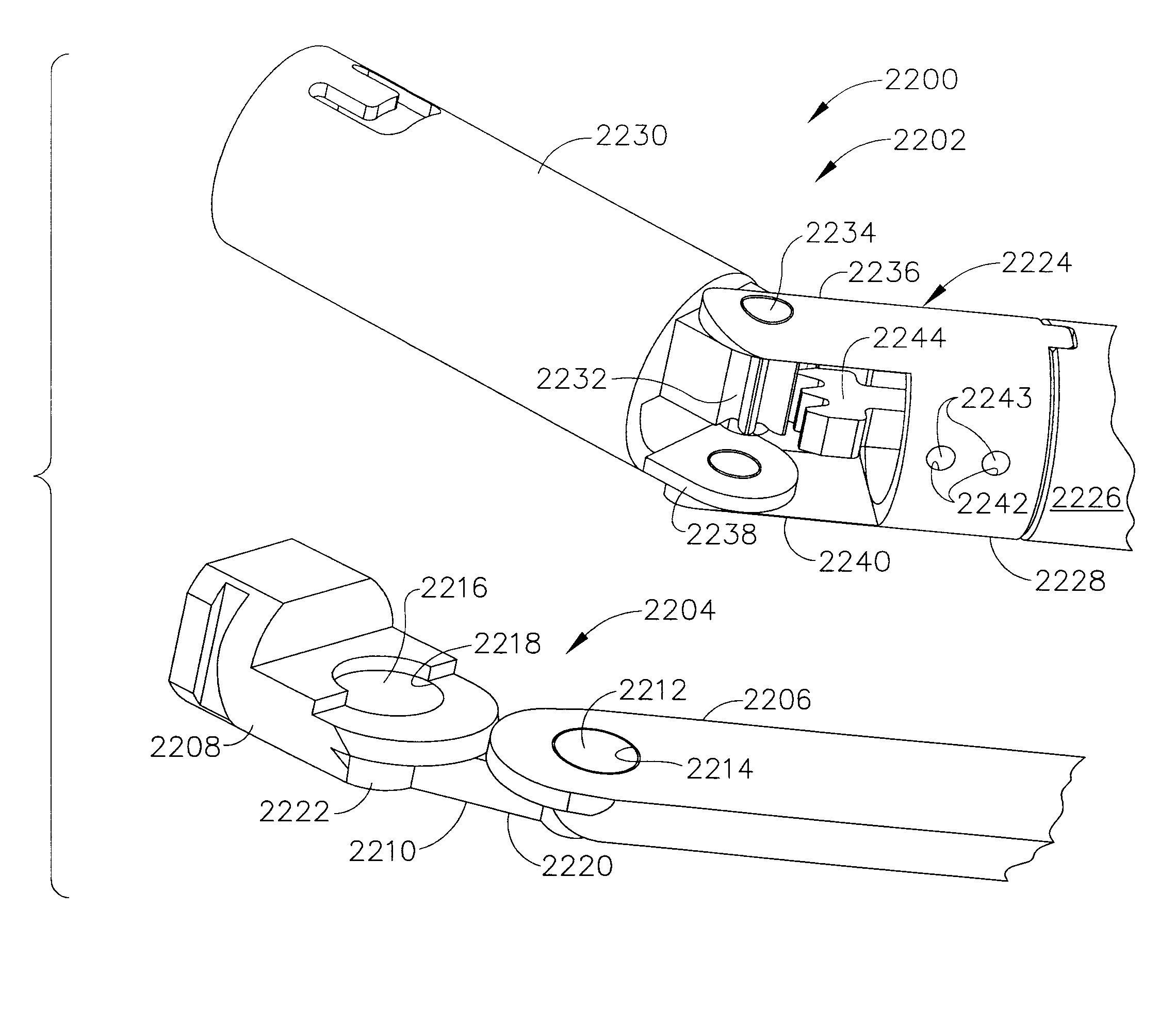
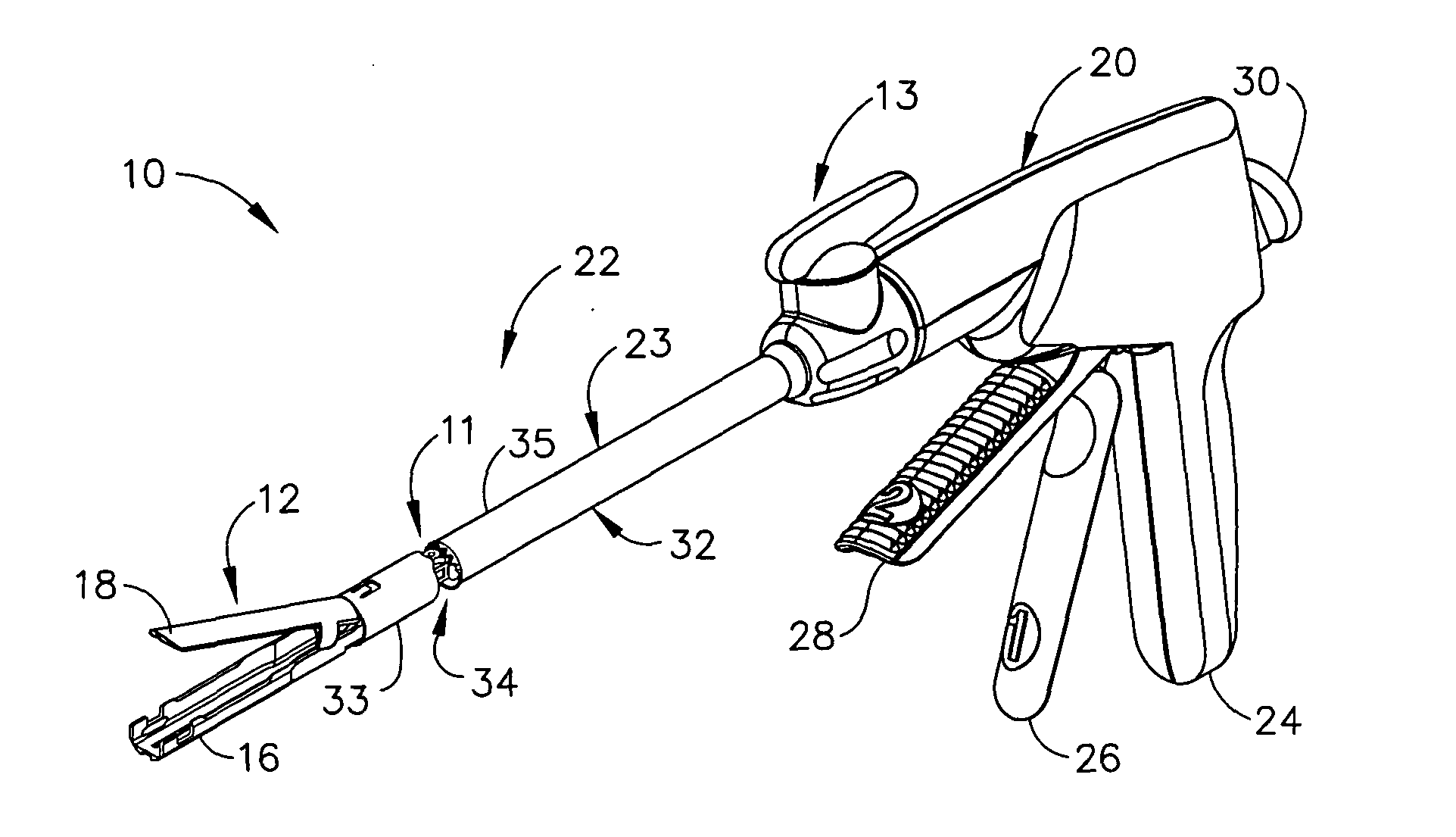
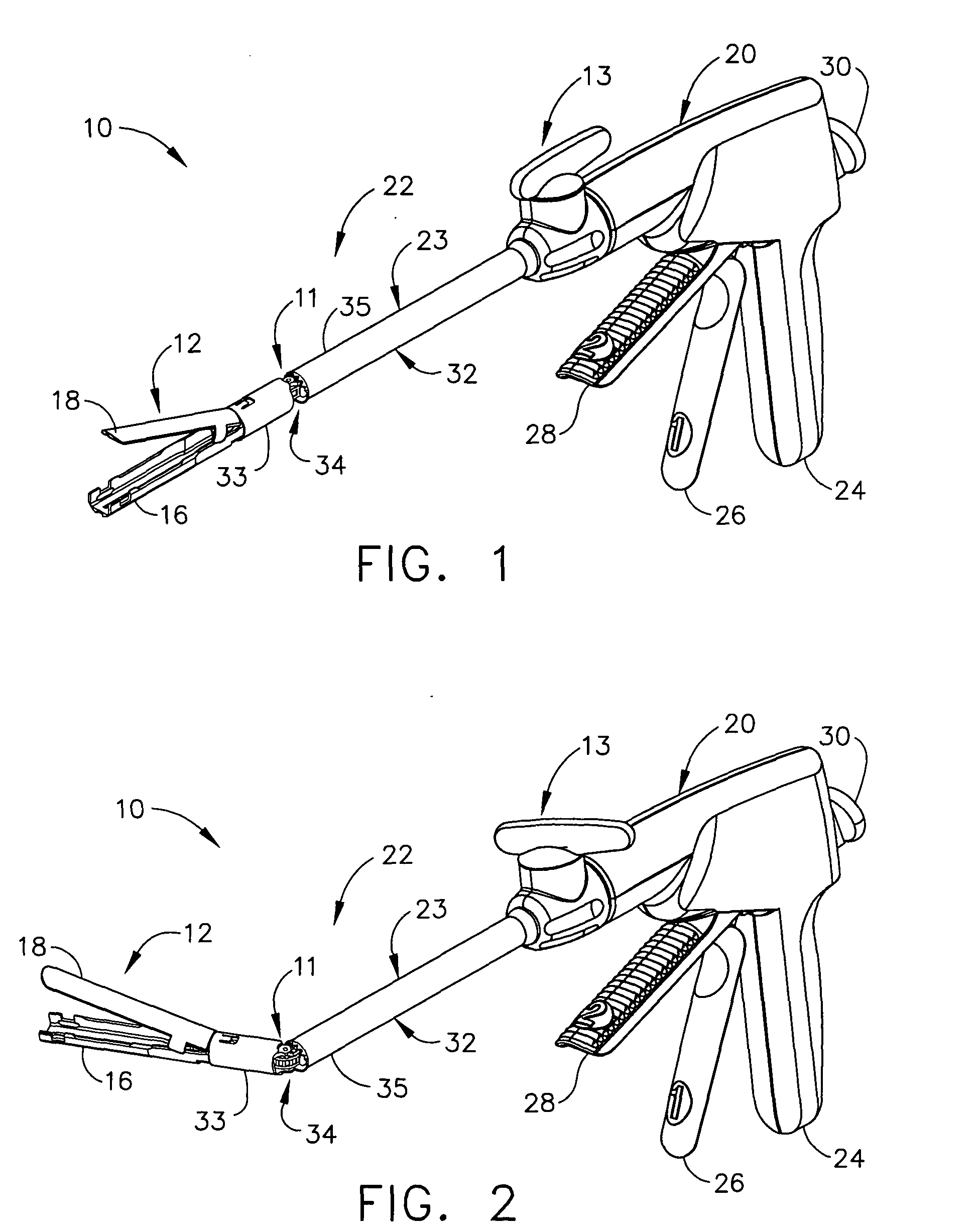
Surgical instrument with articulating shaft with single pivot closure and double pivot frame ground
ActiveUS7784662B2Give flexibilityIncrease flexibilitySuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical siteEngineering
A surgical stapling and severing instrument particularly suited to endoscopic use includes a proximal portion that is manipulated external to a patient to position an attached elongate shaft and end effector to a desired surgical site inside of the patient. An articulation joint pivotally attaches the end effector to the elongate shaft to give further clinical flexibility in reaching tissue at a desired angle. A closure tube assembly includes a single pivoting portion that overrides the articulation joint in order to distally translate to the end effector to close, yet pass over an articulated shaft by having a multiple pivot frame ground encompassed therein to accommodate the longitudinal change in closure sleeve pivot. Thereby, additional clinical flexibility in positioning the end effector is achieved without losing the ability for separate closure and firing motions transferred by the shaft.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Surgical instrument with a lateral-moving articulation control
InactiveUS20050006430A1Complicate amountComplicate directionSuture equipmentsStapling toolsEngineeringSacroiliac joint
An articulating surgical instrument suited for endoscopic use includes a lateral articulation control into a handle portion that provides an intuitive visual and tactile indication to the clinician as to the amount and direction of articulation of an end effector at a distal end of a shaft. Lateral movement of a lateral control actuator is converted into a longitudinal motion or a rotational motion transferred by the shaft to an articulation mechanism. A version of a lateral articulation control for a rotationally driven articulation mechanism incorporates an articulation backdrive lockout that prevents forces on the end effector from causing the selected amount of articulation from being changed.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Apparatus and method for tissue removal
InactiveUS20020029055A1Less energyReduce frictionSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsWood splinterMotion transfer
Percutaneous tissue removal apparatus comprises a flexible drill shaft, a cutting tip mounted on the shaft for placement adjacent a tissue mass for cutting the tissue, means for transmitting motion to the shaft to move the cutting tip against the tissue to cut tissue fragments from the tissue, and means for removing the tissue fragments along the shaft by suction to a location outside the tissue mass while cutting. The apparatus may include means for collecting one or more selected components of the harvested tissue fragments for implantation of the fragments preferably into the body of the patient from whom they were removed. Where the tissue to be cut is bone, a cutting tip is preferably made of a polymeric material which is softer than the cortical portion of the bone, although the cutting tip may be made of a ceramic or a composite material. A second flexible shaft may be provided either within or about the flexible drill shaft. The harvested tissue fragments may be implanted in the donor patient's body.
Owner:BONUTTI SKELETAL INNOVATIONS +2
Electrosurgical device
An improved surgical instrument having an end effector mounted on the end of an elongate shaft extending from a handle. The end-effector has different operations, including grasping, cutting, and sealing and / or coagulating tissue, and one of the operations is controlled by a drive handle mechanism. The drive handle mechanism includes an actuator, a drive shaft and a spring assembly for transferring movement of the actuator to the drive shaft, which in turn controls the end effector. The drive handle mechanism limits the amount of force transferred from the drive handle mechanism to the end effector, preventing damage to the tissue. As the actuator is operated, the spring assembly transfers the movement of the actuator to the drive shaft and the end effector. At the same time, the spring assembly compresses to absorb some of the force applied. Such configuration prevents the tissue being unintentionally damaged by the end effector.
Owner:GYRUS MEDICAL LTD
Biopsy instrument with improved needle penetration
InactiveUS20060155210A1Improve permeabilityPiercing especially dense tissueSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsNeedle penetrationBiopsy instruments
The present invention provides a biopsy instrument with improved needle penetration for piercing dense tissue. The device may comprise a needle slidably retained in a housing. The device may further comprise an actuation member that may be adapted to communicate longitudinal motion to the needle in a first direction. The device may further include a propulsion element that provides the needle with return motion in a second direction. The device may be fired multiple times to create repeating reciprocal motion. In one version, the device may reciprocate several times as a result of a single engagement of the actuation member.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
Surgical instrument with articulating shaft with single pivot closure and double pivot frame ground
ActiveUS20060229665A1Give clinical flexibilityEnhanced clinical flexibilitySuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical siteEngineering
A surgical stapling and severing instrument particularly suited to endoscopic use includes a proximal portion that is manipulated external to a patient to position an attached elongate shaft and end effector to a desired surgical site inside of the patient. An articulation joint pivotally attaches the end effector to the elongate shaft to give further clinical flexibility in reaching tissue at a desired angle. A closure tube assembly includes a single pivoting portion that overrides the articulation joint in order to distally translate to the end effector to close, yet pass over an articulated shaft by having a multiple pivot frame ground encompassed therein to accommodate the longitudinal change in closure sleeve pivot. Thereby, additional clinical flexibility in positioning the end effector is achieved without losing the ability for separate closure and firing motions transferred by the shaft.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Apparatus and method for tissue removal
InactiveUS6174313B1Various locationsReduce frictionSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsWood splinterMotion transfer
Percutaneous tissue removal apparatus comprises a flexible drill shaft, a cutting tip mounted on the shaft for placement adjacent a tissue mass for cutting the tissue, means for transmitting motion to the shaft to move the cutting tip against the tissue to cut tissue fragments from the tissue, and means for removing the tissue fragments along the shaft by suction to a location outside the tissue mass while cutting. The apparatus may include means for collecting one or more selected components of the harvested tissue fragments for implantation of the fragments preferably into the body of the patient from whom they were removed. Where the tissue to be cut is bone, a cutting tip is preferably made of a polymeric material which is softer than the cortical portion of the bone, although the cutting tip may be made of a ceramic or a composite material. A second flexible shaft may be provided either within or about the flexible drill shaft. The harvested tissue fragments may be implanted in the donor patient's body.
Owner:BONUTTI SKELETAL INNOVATIONS +1
Biopsy instrument with improved needle penetration
InactiveUS7470237B2Piercing especially dense tissueSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsNeedle penetrationBiopsy instruments
The present invention provides a biopsy instrument with improved needle penetration for piercing dense tissue. The device may comprise a needle slidably retained in a housing. The device may further comprise an actuation member that may be adapted to communicate longitudinal motion to the needle in a first direction. The device may further include a propulsion element that provides the needle with return motion in a second direction. The device may be fired multiple times to create repeating reciprocal motion. In one version, the device may reciprocate several times as a result of a single engagement of the actuation member.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
Transmission for a remote catheterization system
Owner:CORINDUS
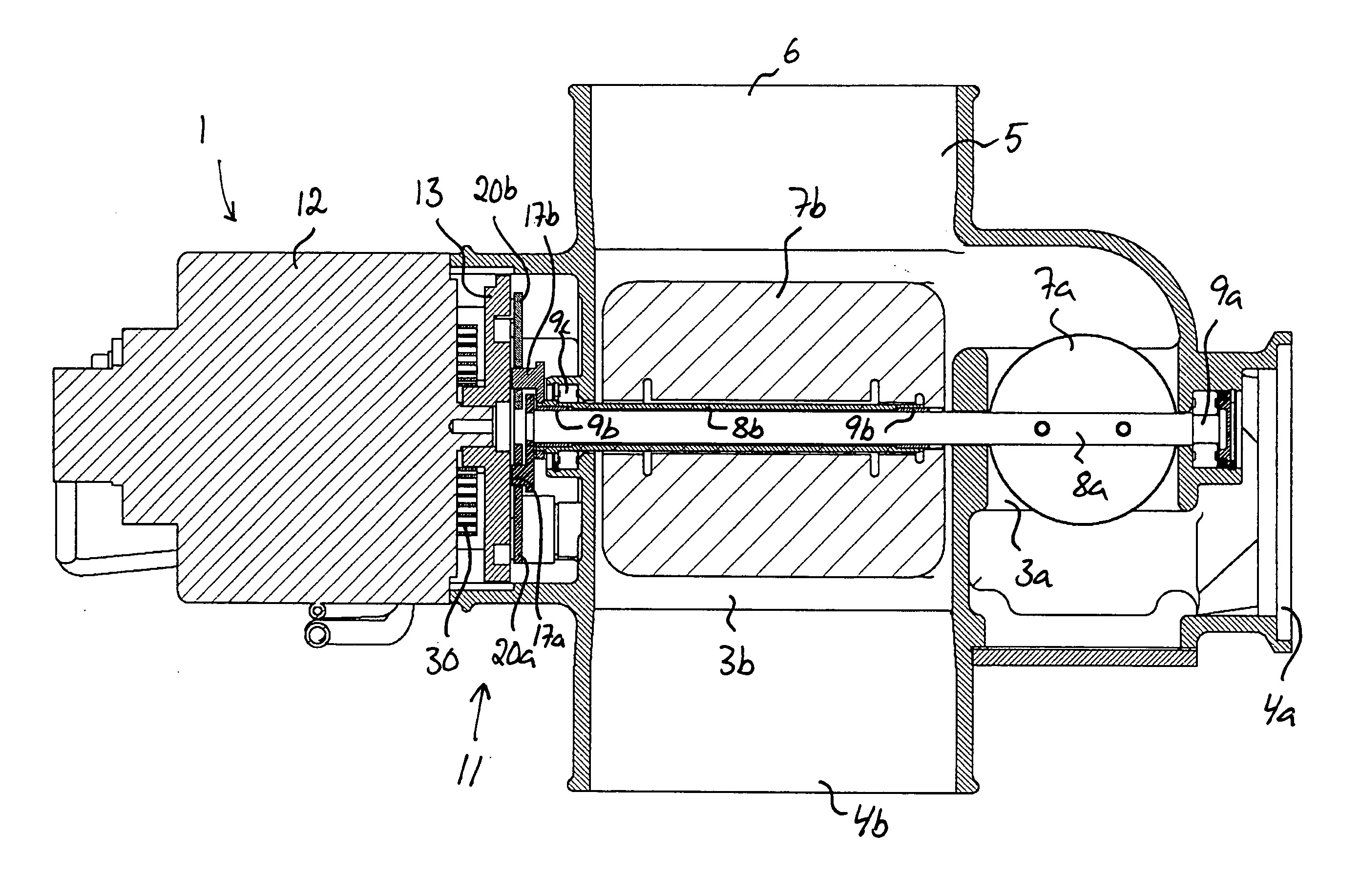
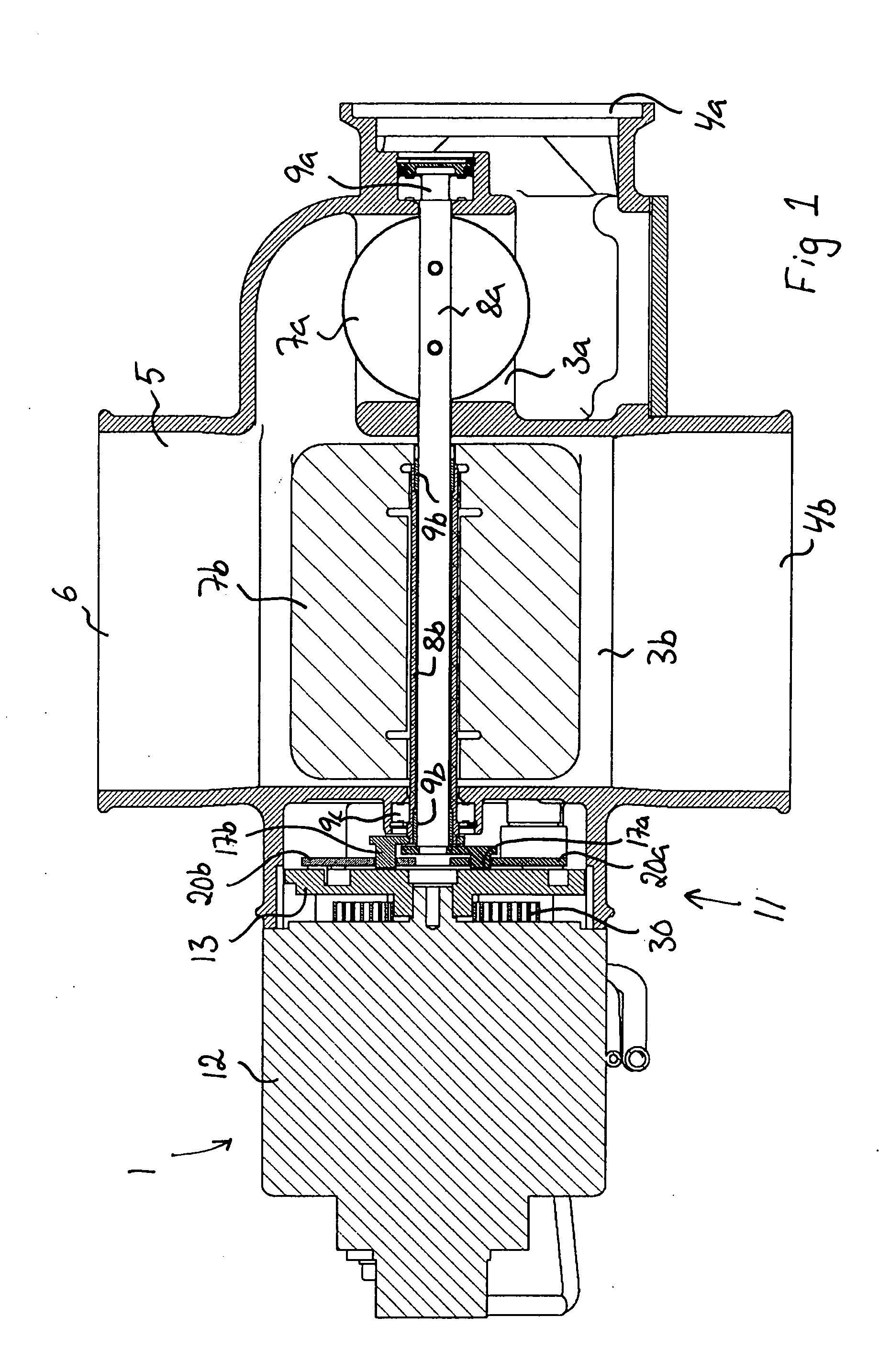
Valve device
InactiveUS20050241702A1Function increaseEasy to adjustInternal combustion piston enginesEngine operationsControl theoryMotion transfer
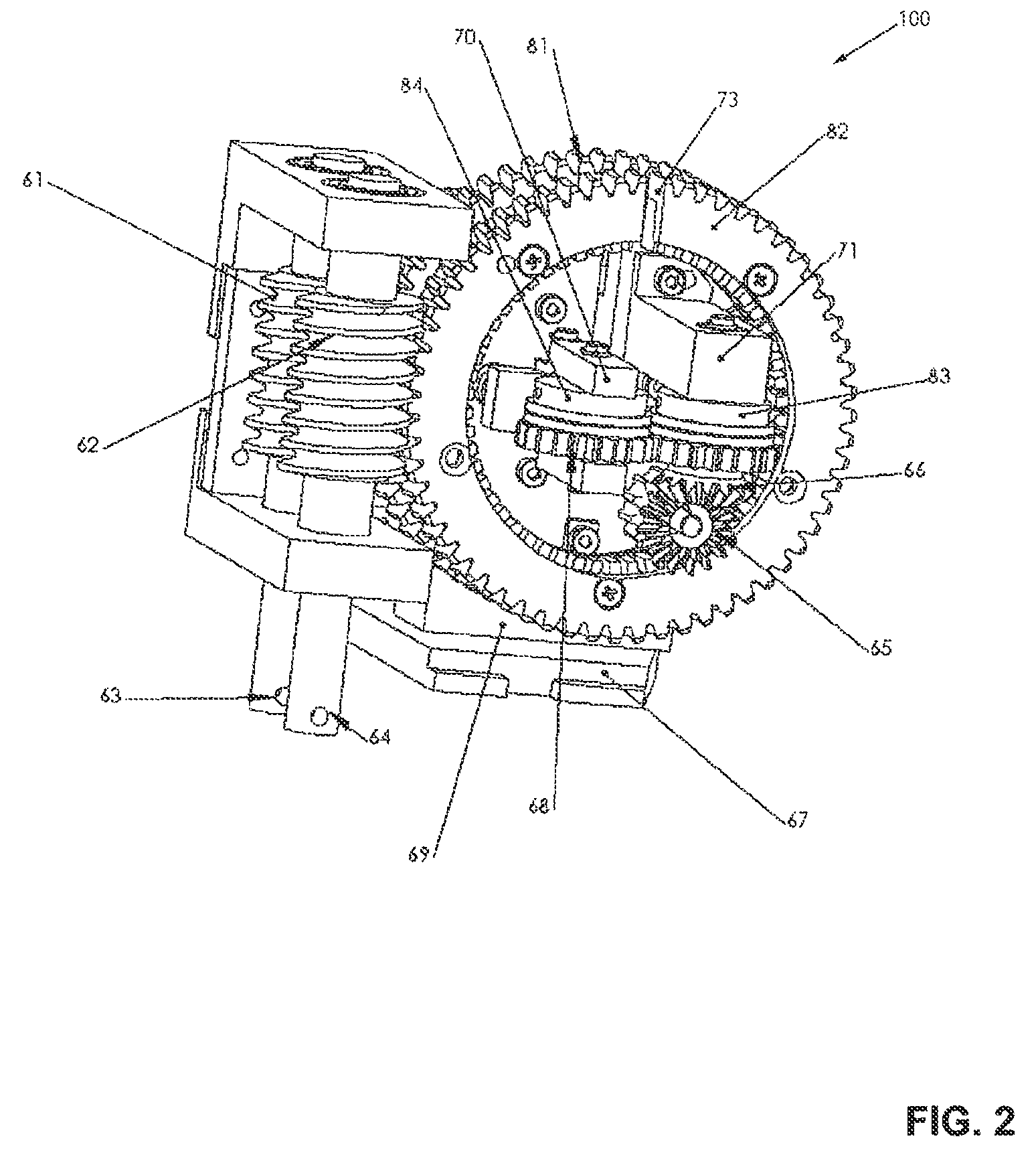
The invention relates to a valve device comprising a valve housing (2) with a first and a second flow channel (3a, 3b), and a first and second damper shaft (8a, 8b), which are rotatable relative to the valve housing (2). A first damper (7a) is arranged in the first flow channel (3a) fixed to the first damper shaft (8a) and a second damper (7b) is arranged in the second flow channel (3b) fixed to the second damper shaft (8b). A rotatable regulating member (13) is arranged to control the rotational position of the damper shafts (8a, 8b) via two motion transfer members (20a, 20b), the respective motion transfer member (20a, 20b) being in engagement with a guiding (21) of the regulating member (13) so that the rotational position of the motion transfer member and thereby the rotational position of the associated damper shaft (8a, 8b) is controlled by the rotational position of the regulating member via this guiding (21).
Owner:STT EMTEC AB
Seated stepper
InactiveUS6932745B1Body workoutLower body workoutMuscle exercising devicesMovement coordination devicesGear wheelReciprocating motion
The seated stepper is provided for exercising the lower body. The stepper includes a frame having opposite sides and a longitudinal axis, and a seat attached to the frame. First and second foot lever arrangements are pivotally coupled together on opposite sides of the frame to move alternately in forward and rearward directions towards forward and rearward positions. The foot lever arrangements have linearly moveable right and left foot receptacles adapted to be engaged by an exerciser's feet. First and second motion transfer arrangements are mounted on opposite sides of the frame and coupled to the foot lever arrangements for enabling reciprocating movement of one foot lever arrangement relative to the other foot lever arrangement. A transmission arrangement is mounted on the frame and is operably connected to the first and second motion transfer arrangements. The transmission arrangement includes upper and lower pulley and gear trains in meshing relationship with one another. A resistance structure is mounted to the frame and is operably connected to the transmission arrangement for resisting pivotal movement of each foot lever arrangement in one of the forward and rearward directions. The transmission arrangement enables either of the foot receptacles to be moved and prevents any inertia from the resistance structure from being transferred back to the foot lever arrangements.
Owner:NORTHLAND INDS
Manually-operated hair clipper
InactiveUS20100083508A1Used directly and easilyImprove gripMetal working apparatusKnife bladesMotion transfer
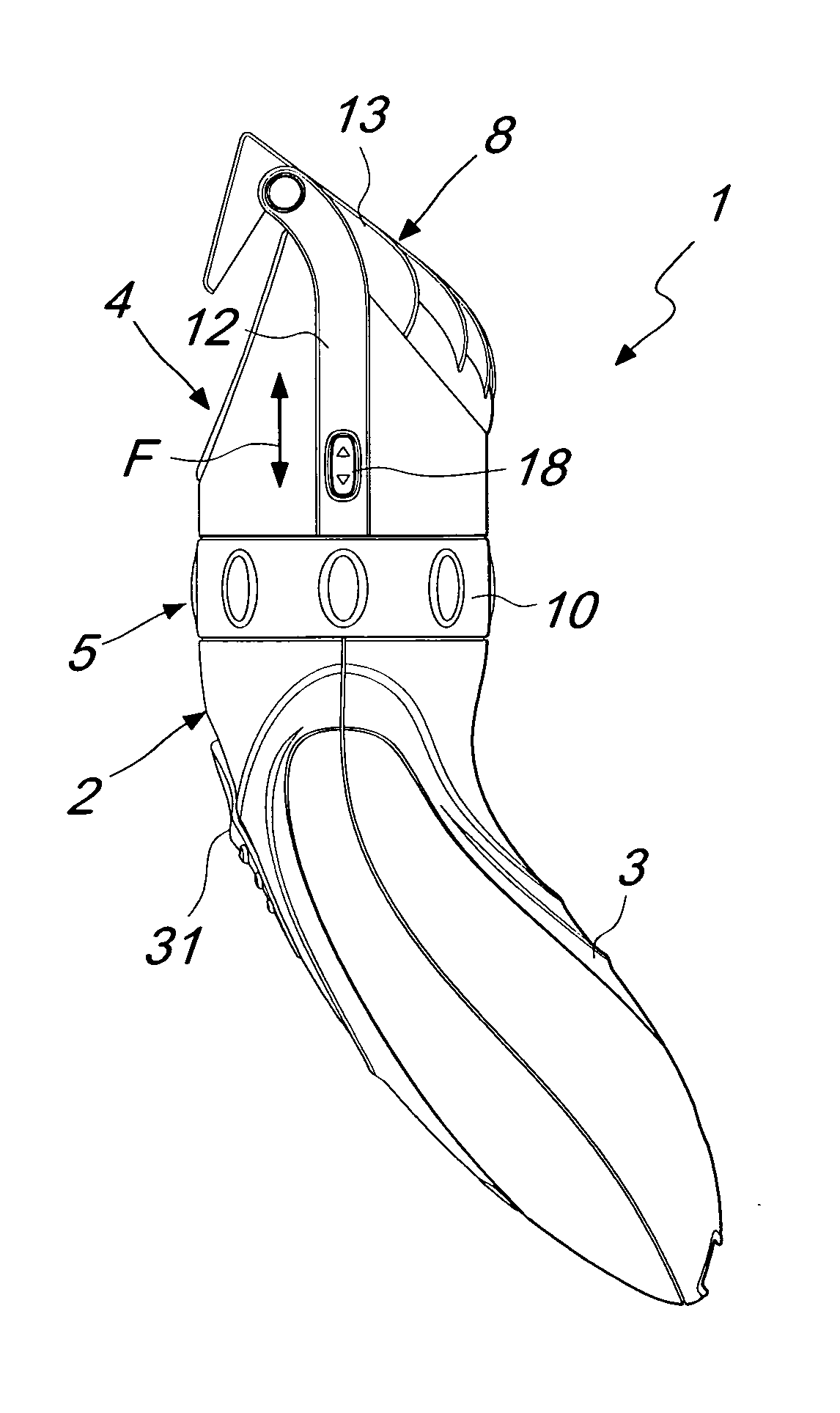
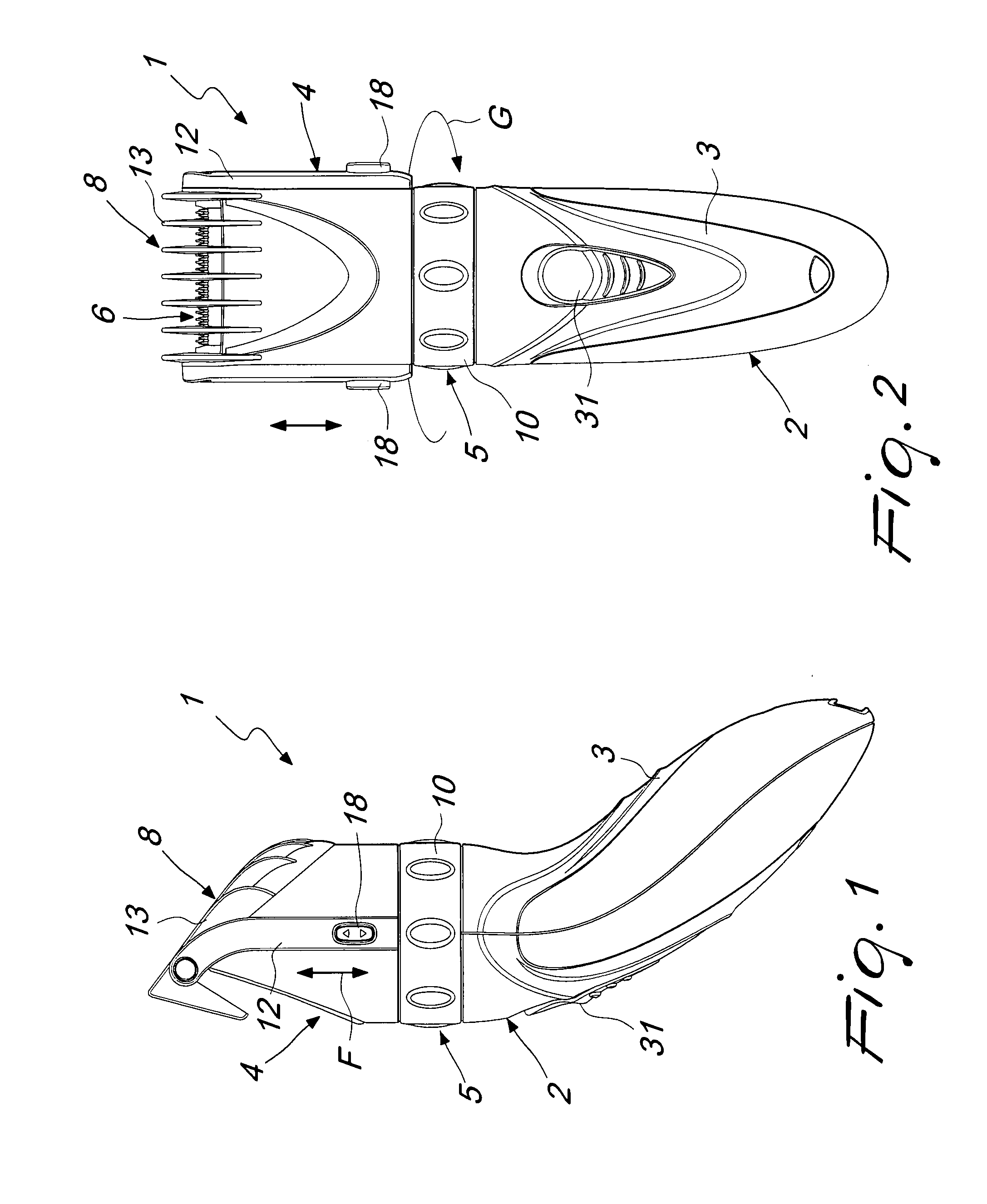
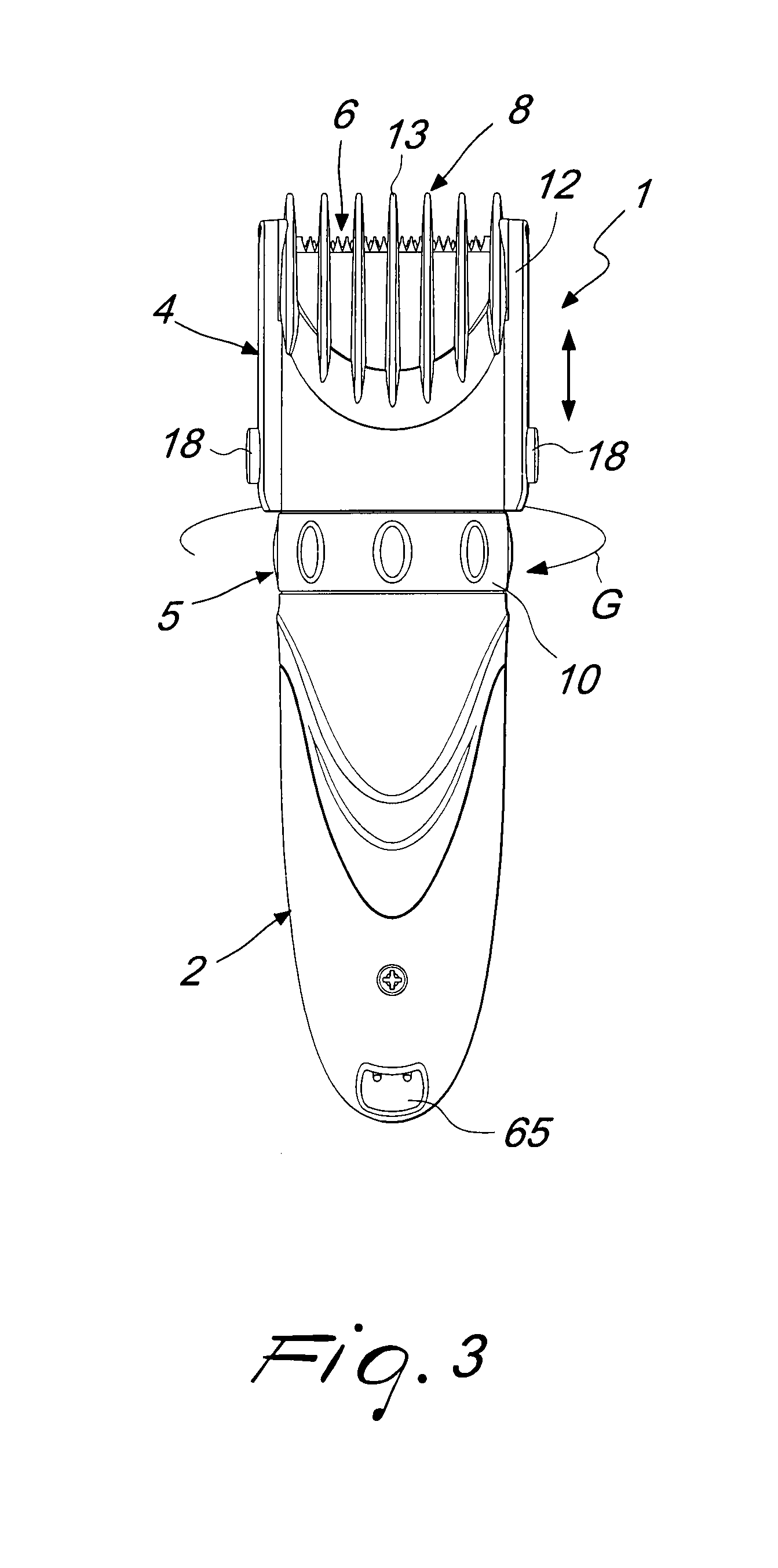
A manually-operated hair clipper, comprising a substantially elongated enclosure, which defines at one end a handle and is provided, at the opposite end, with a working head, which comprises a body for supporting a cutting blade assembly and a motor assembly, elements being provided for transmitting motion from the motor assembly to the cutting blade assembly, at least one comb element, which is associated with the supporting body so that it can slide along a direction for approach and spacing with respect to the cutting blade assembly in order to adjust the cutting length, and at least first teeth for stopping the comb element with respect to the supporting body.
Owner:PERFECT STEAM APPLIANCE
Apparatuses for dispensing materials volumetrically and gravimetrically based on a stored formula and methods of dispensing formulas using the same
InactiveUS20070084520A1Reduce in quantityReduced number of stepLiquid fillingMixer accessoriesAdditive ingredientEngineering
An improved dispensing system and dispensing routine for multiple ingredient formulas is disclosed. The system includes a controller linked to an actuator, a scale and, a means for imparting movement to a plurality of pumps or conveyors and containers for dispensing the plurality of ingredients. After a formula is selected, the controller acts to at least partially load the pump with the first of said ingredients, reads the scale to account for the weight of the receptacle, calculates the motion of the pump required to dispense the target amount of said first ingredient, and either executes a percentage or portion of the motion of the pump required to dispense the target amount of said first ingredient, leaving a remaining amount or a safety factor in the form of a previously determined <maximum overshoot> value. Both techniques avoid an over-dispense which would require the batch to be rejected. The remaining amount may be dispense iteratively using a calibration table or plot and a safety factor or, in an alternative method, the remaining amount may be divided by 2 to generate a “first half” value. The controller may then use a calibration table to calculate a motion of the pump needed to dispense the “first half.” After the first half is dispensed, the actual amount dispensed is measured and compared to the first half value and the difference is doubled and added to the first half value to generate a “second half” value which is dispensed. The cumulative dispensed amount is compared to the target amount and, if within tolerance, the next ingredient is dispensed. The routine is a fast and efficient means for gravimetrically dispensing each ingredient of a multiple ingredient formula and is applicable to liquid and powder ingredients.
Owner:FAST & FLUID MANAGEMENT
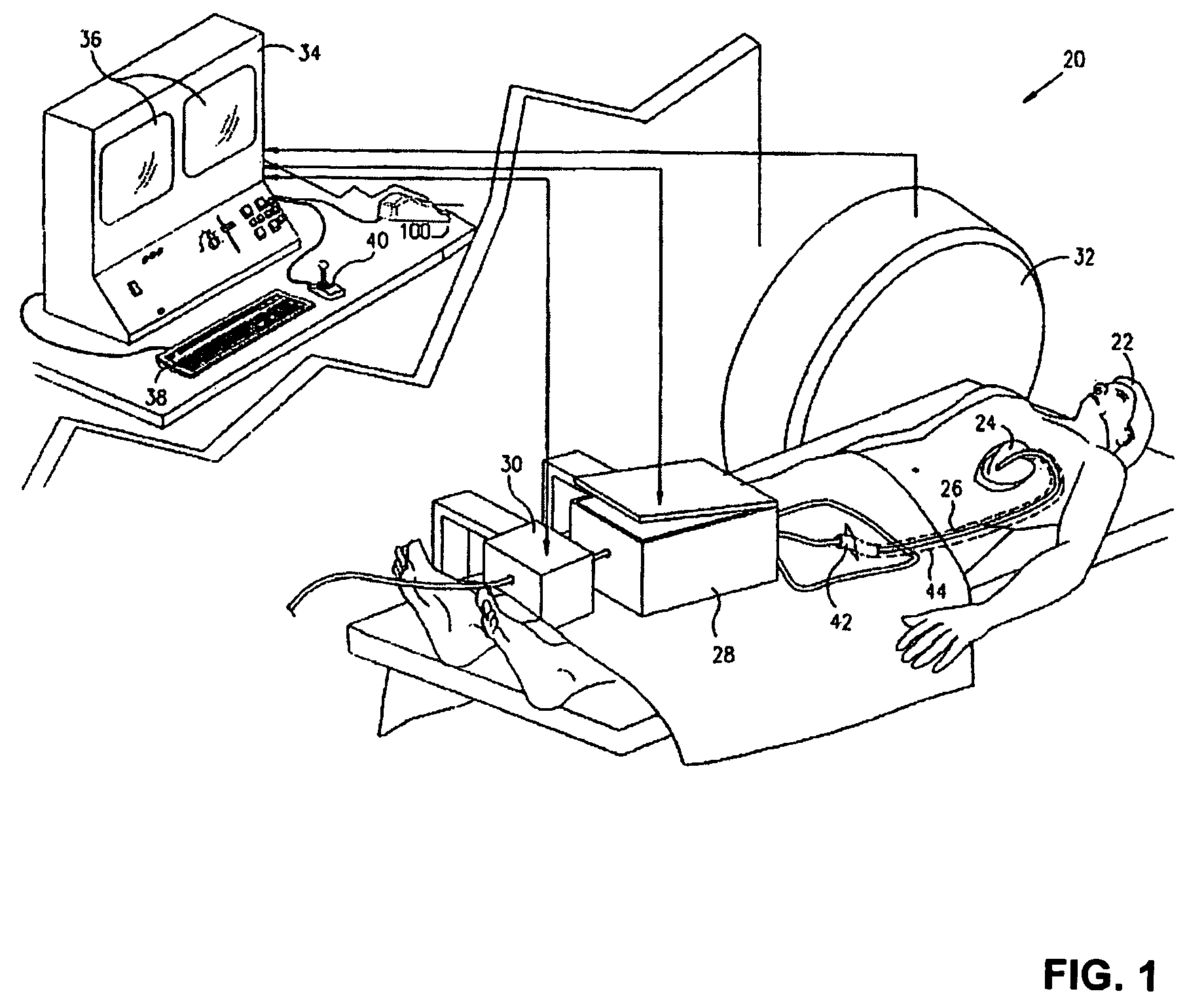
System and Methods for Advancing a Catheter
InactiveUS20080045892A1Reduce repeated x-ray exposureReduce X-ray exposureElectrotherapyDiagnosticsControl systemEngineering
An advancer system is described for moving an elongate medical device within a body. The system includes a drive unit having a motor. The drive unit is configured to translate movement of the motor to the device so as to alternately advance and retract the device relative to the body. The advancer system also includes a user-operable control system configured to control the drive unit. The control system can interface with a magnetic navigation system. The above-described system allows an operating physician to control catheter advancement and retraction while remaining outside an x-ray imaging field. Thus the physician is freed from repeated x-ray exposure.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
Multi-layer multi-material foam mattresses
The multi-layer multi-material foam mattresses of the present disclosure and related inventions provide novel combinations of multiple layer, multiple material foam layers or stacks which provide unexpected and improved support characteristics and pressure relief and distribution. By combining multiple layers of visco-elastic or latex foam as the top structure of a mattress supported by underlying layers of a laminated urethane foam core, the conformance properties of visco-elastic or latex foam are achieved along with structural support from the underlying core. The multi-layer multi-material foam mattresses of the present disclosure and related inventions include in the various embodiments two or three layers of a first type of foam such as visco-elastic foam or latex foam, in combination with a multi-layer foam support core of a second type of foam such as urethane foam. The disclosed multi-layer / multi-material foam combinations provide superior comfort and conformance, pressure relief, orthopedic support and dampen motion transfer. The multiple layers of the first type of foam preferably have differing density and mass and / or thickness to provide relative gradation between layers and a aggregate performance of support and conformance to body contours and resulting pressure distribution, i.e., avoidance of pressure concentrations. The multiple layers of the second type of foam preferably have differing density and mass and / or thickness to provide relative gradation between layers and aggregate performance of softness and support for the overlying layers of the first type of foam.
Owner:SEALY TECH LLC
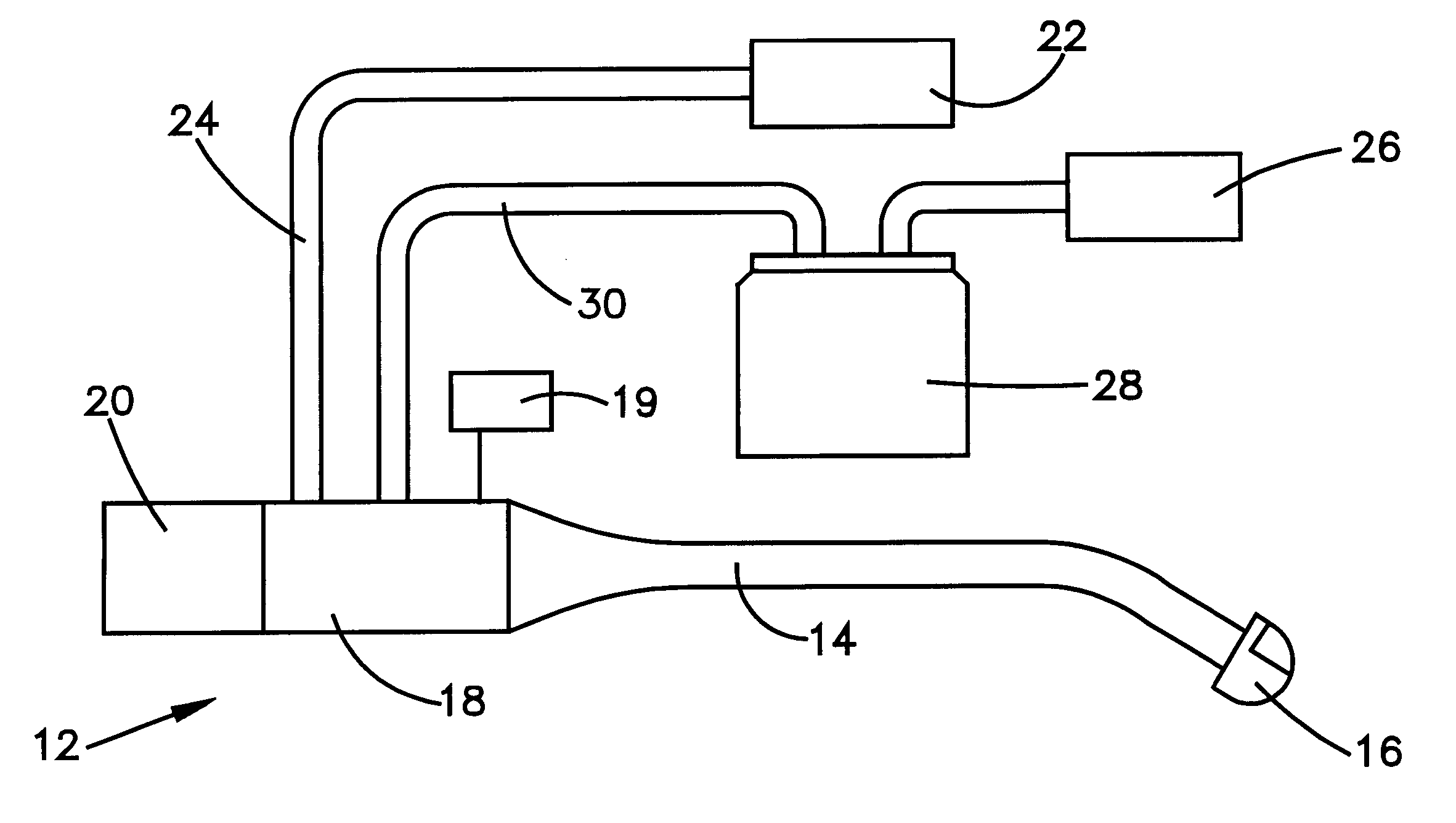
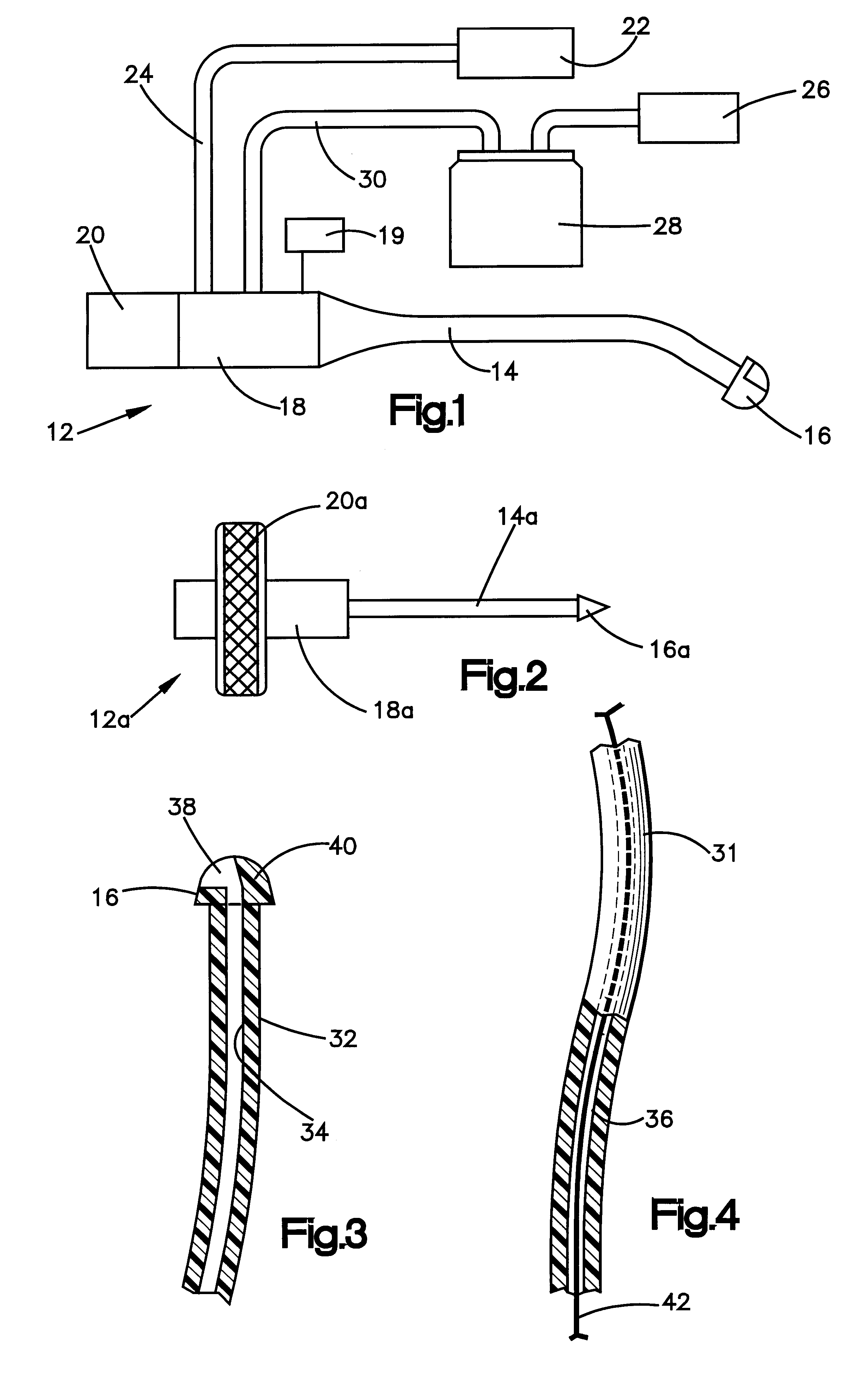
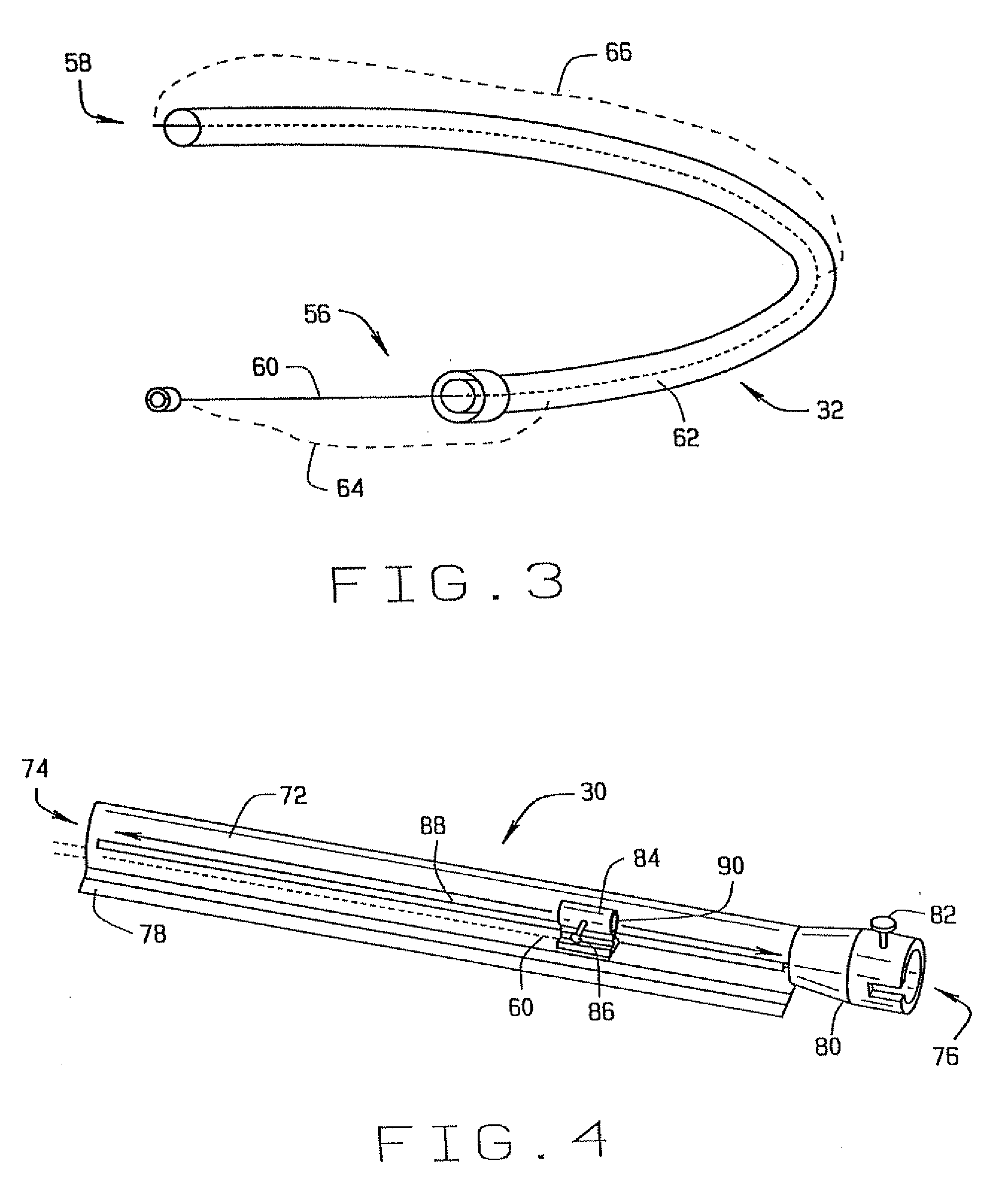
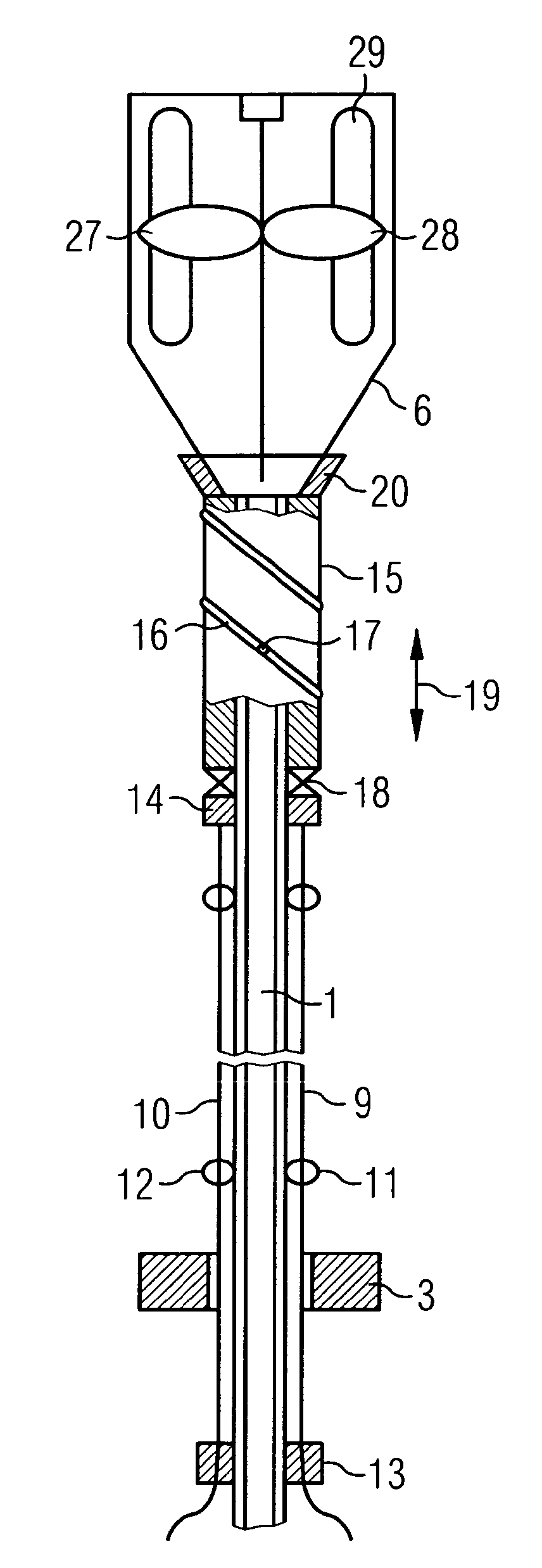
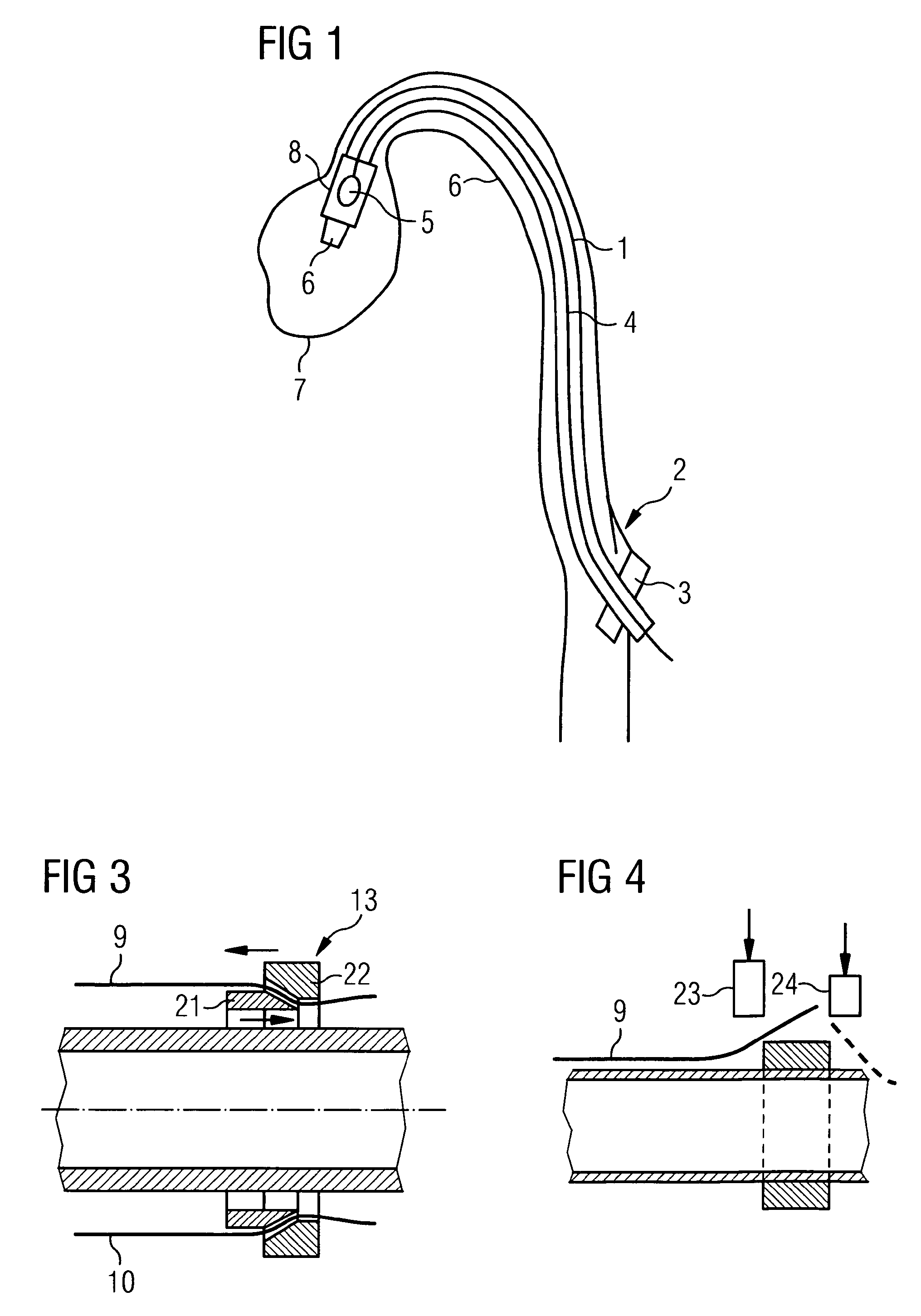
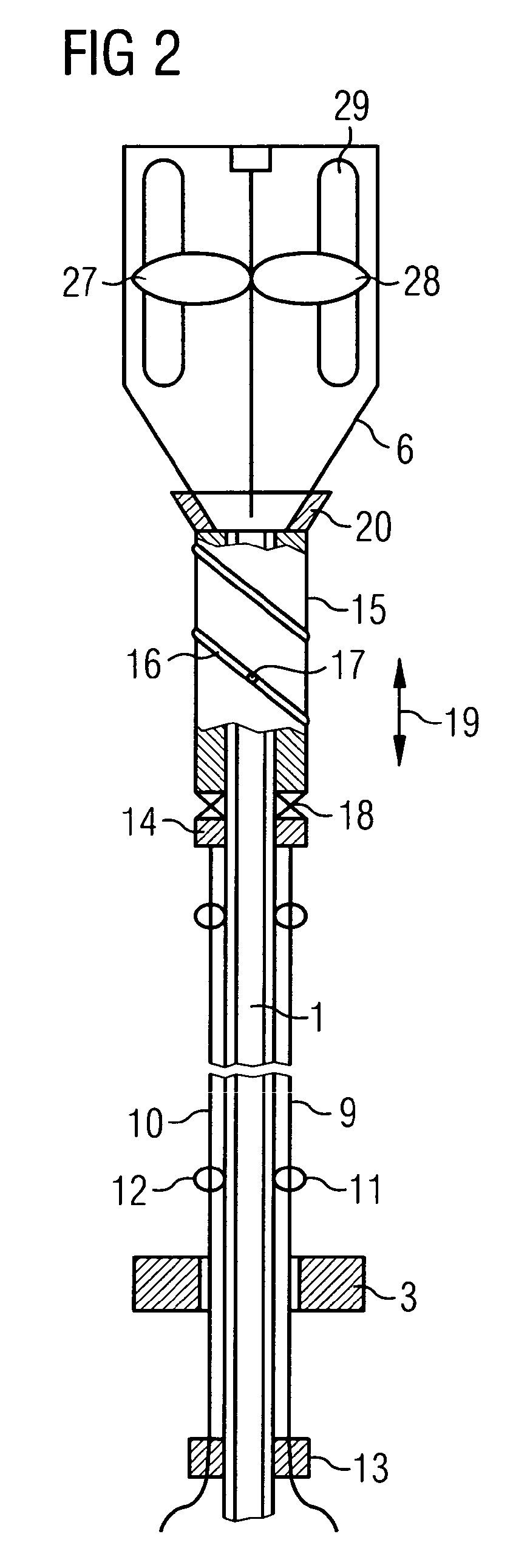
Catheter device having a catheter and an actuation device
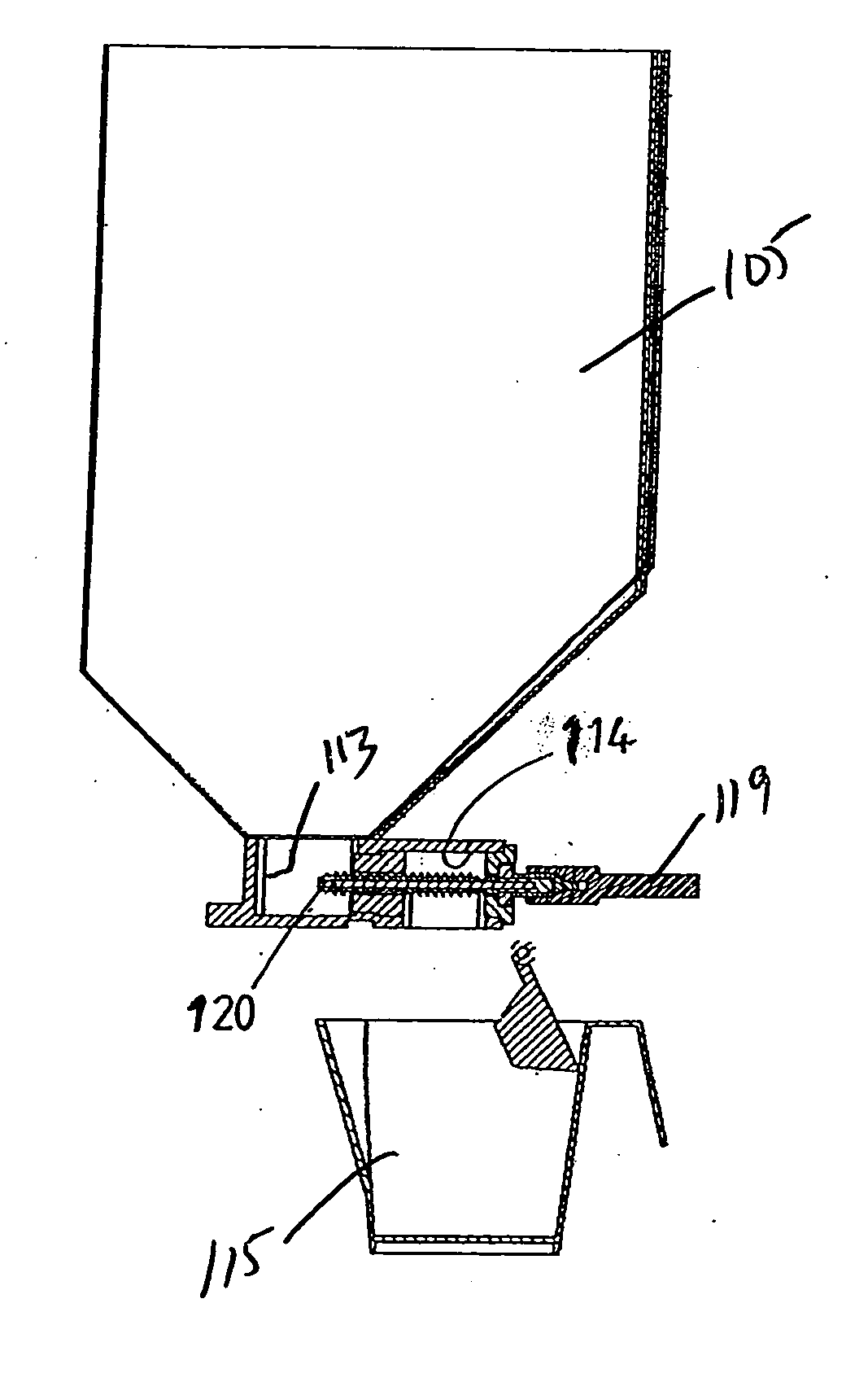
The invention relates to a catheter device, having a catheter (1), an actuation device (8) at a first end of the catheter and also a mechanical transmission element (9, 10) for transmitting a movement along the catheter to the actuation device, the actuation device having a coupling element (14) which is connected to the transmission element (9, 10) and can be actuated by the latter relative to the longitudinal direction of the catheter in a first degree of freedom, and also a conversion element (15) which can be actuated by the coupling element and which converts the actuation movement at least partially into a movement in a second degree of freedom. As a result, a combined movement at the distal end of the catheter can be produced particularly simply for compression and release of a functional element.
Owner:ECP ENTWICKLUNGSGMBH
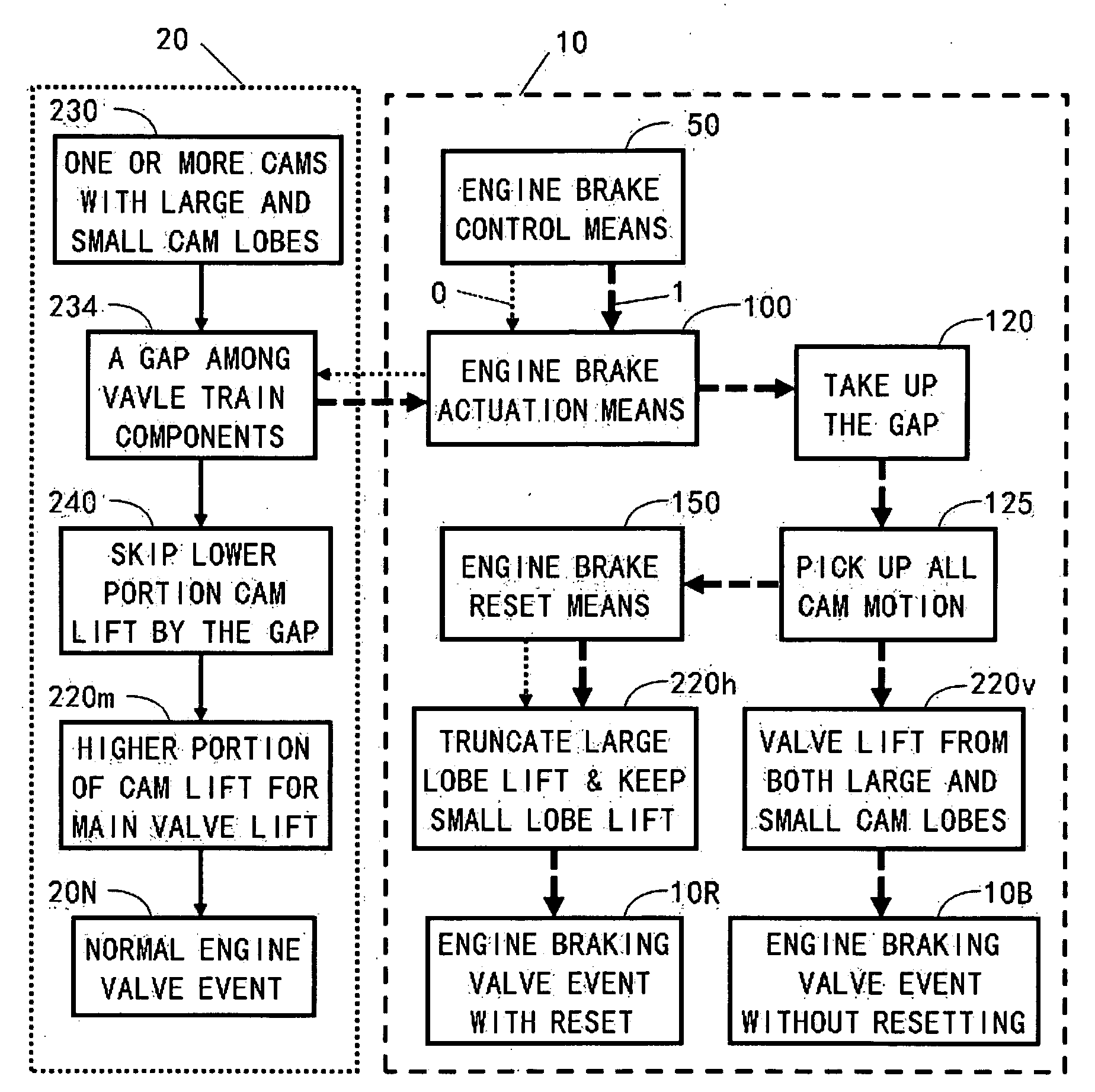
Integrated engine brake with mechanical linkage
ActiveUS20100170472A1Rapid responseImprove performanceValve drivesOutput powerExhaust valveExternal combustion engine
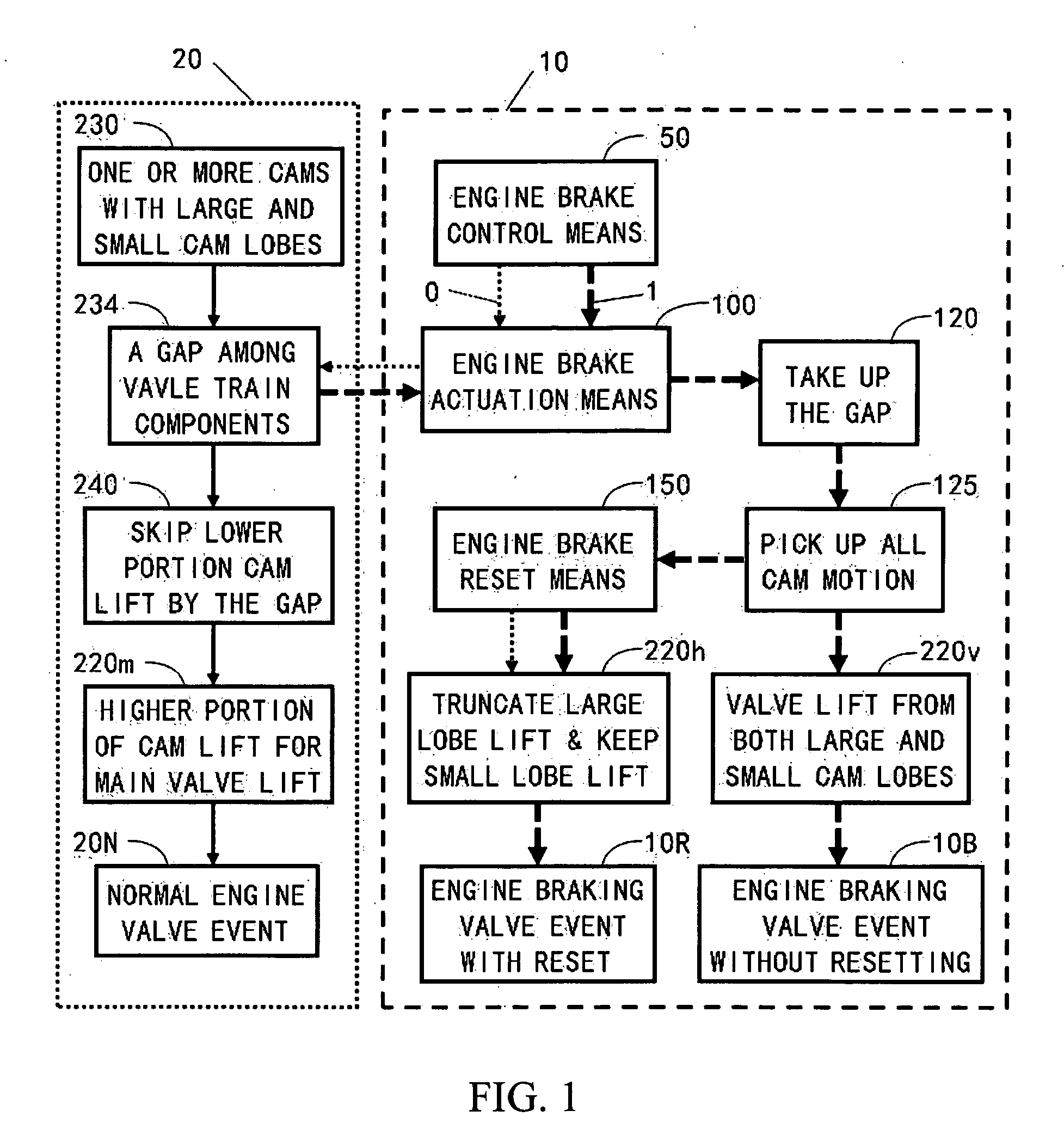
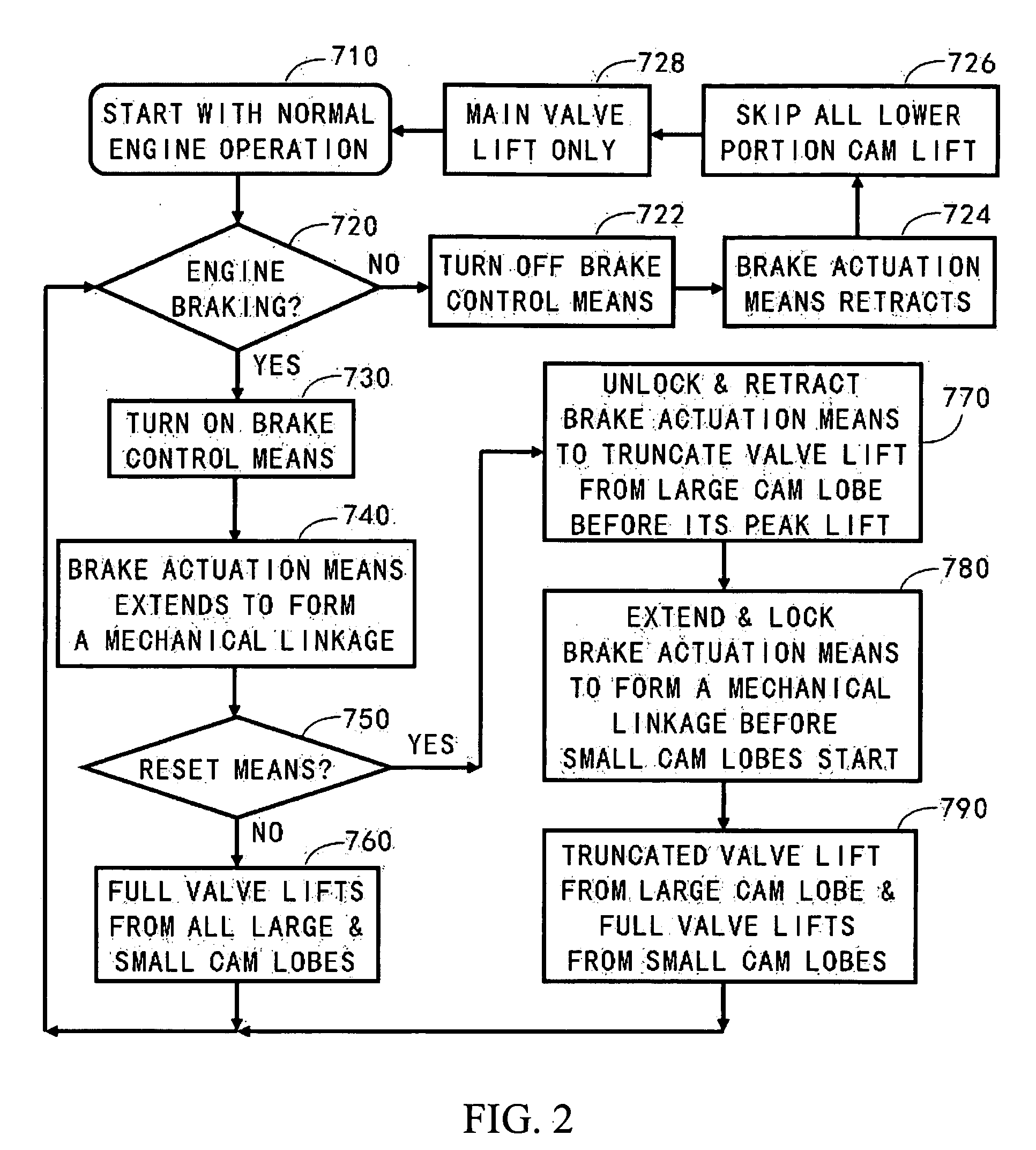
Apparatus and method are disclosed for converting an internal combustion engine from a normal engine operation (20) to an engine braking operation (10). The engine includes exhaust valve train components comprising at least one exhaust valve (300) and at least one cam (230) for cyclically opening and closing the at least one exhaust valve (300). The apparatus comprises actuation means (100) having at least one component integrated into at least one of the exhaust valve train components, such as a rocker arm (210) or a valve bridge (400). The actuation means (100) has an inoperative position and an operative position. In the inoperative position, the actuation means (100) is retracted and the small braking cam lobes (232&233) are skipped to generate a main valve lift profile (220m) for the normal engine operation (20). In the operative position, the actuation means (100) is extended to form a mechanical linkage so that the motion from all the cam lobes (220, 232&233) is transmitted to the at least one exhaust valve (300) for the engine braking operation (10). The apparatus further comprises control means (50) for moving the actuation means (100) between the inoperative position and the operative position to achieve the conversion between the normal engine operation (20) and the engine braking operation (10). The apparatus also includes valve lash adjusting mechanism, oil retraining means (350), and engine brake reset means (150).
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSOON AUTOPARTS CO LTD
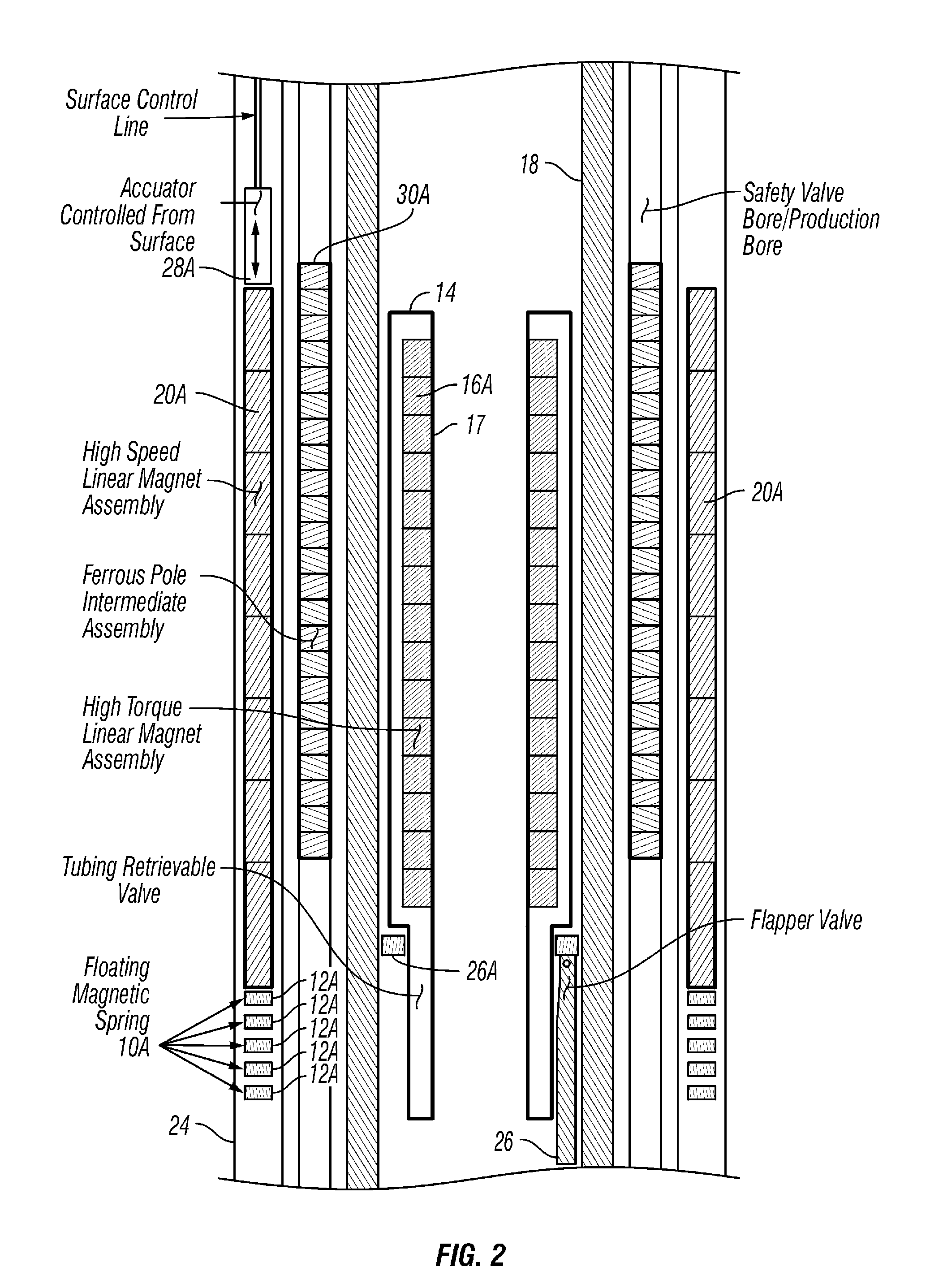
Wellbore Valve Having Linear Magnetically Geared Valve Actuator
InactiveUS20070289734A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesFluid removalValve actuatorMotion transfer
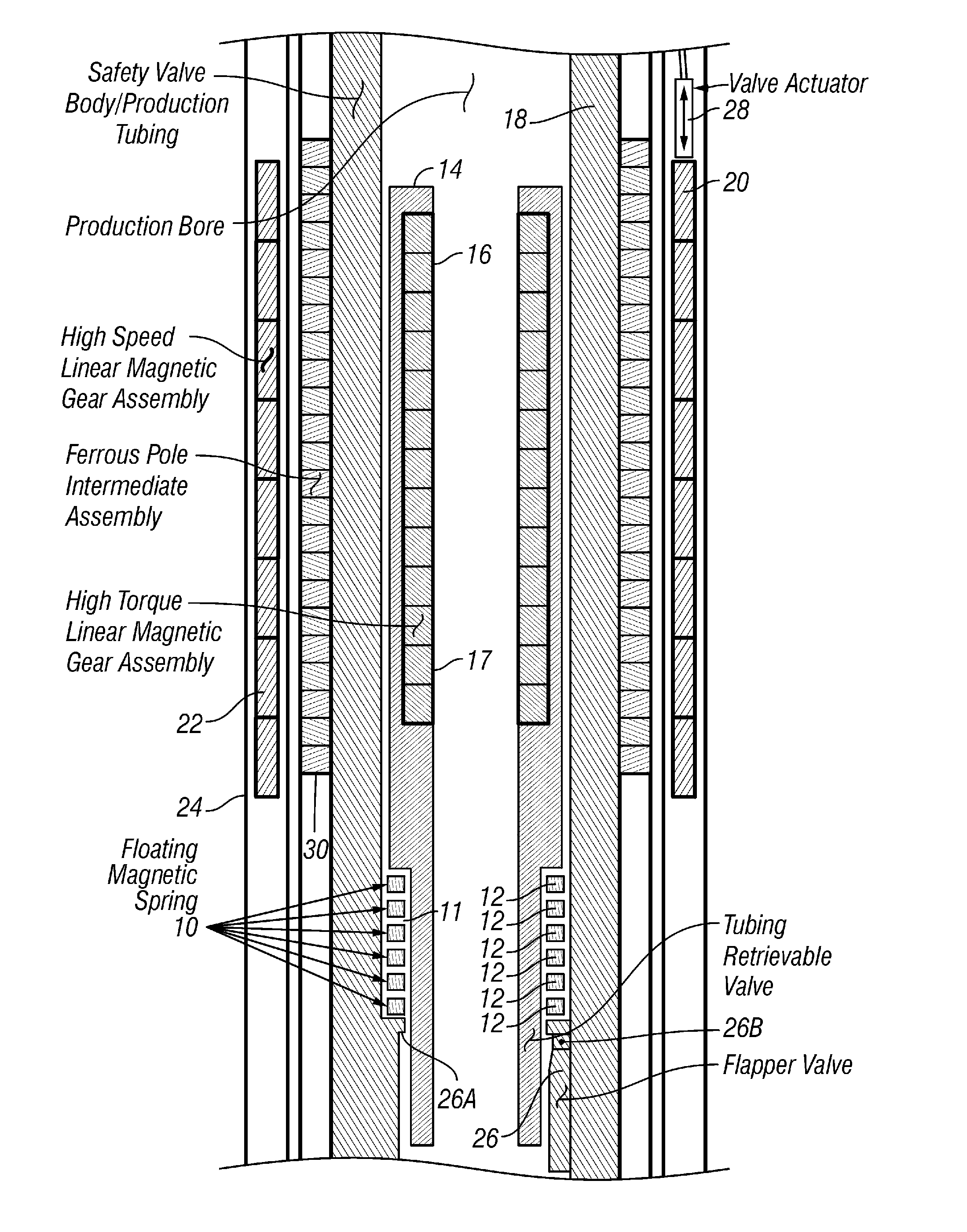
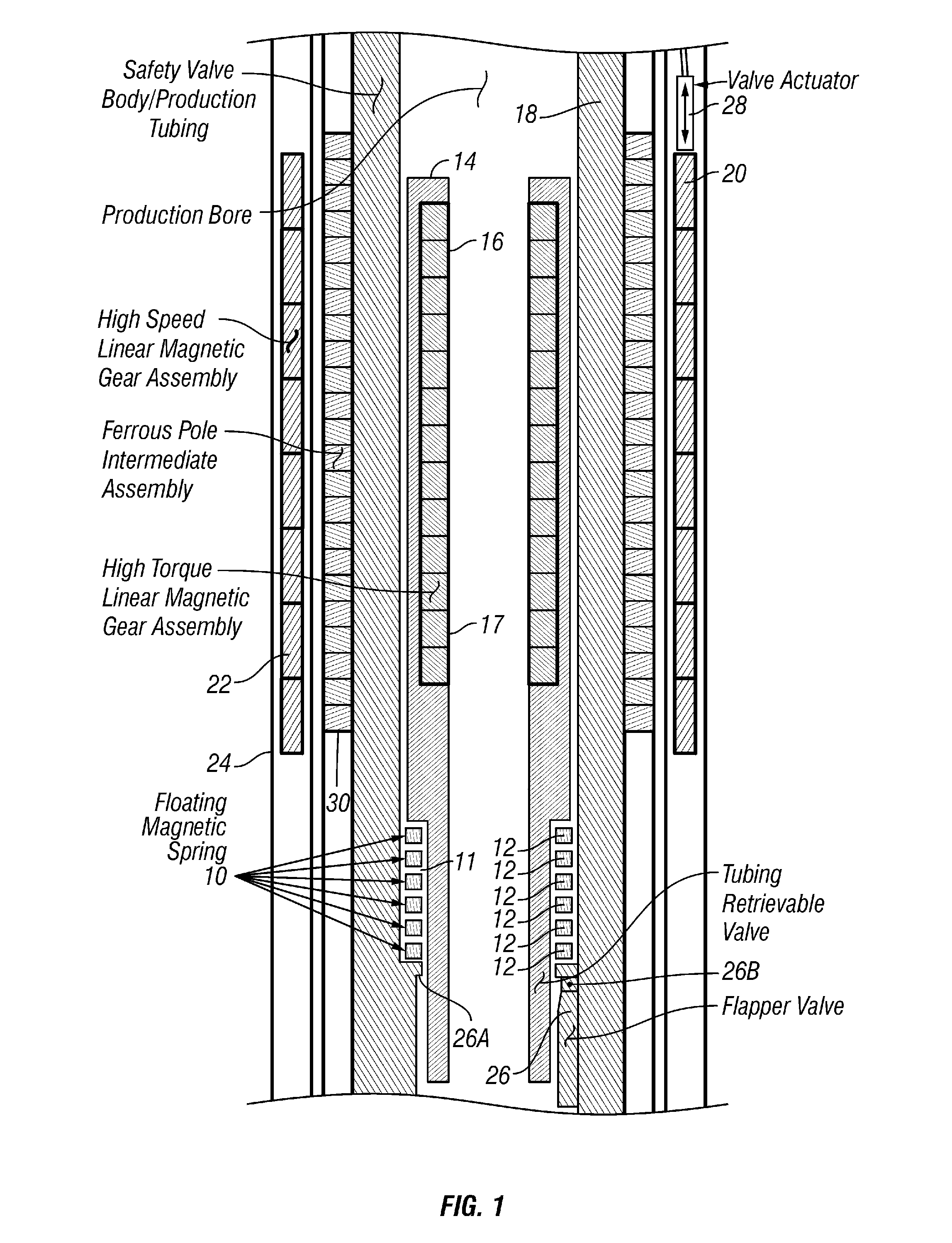
A wellbore valve includes a valve operator arranged to move axially along an interior of the wellbore, the valve operator arranged to operate a valve. A valve actuator is disposed proximate the valve operator. The valve actuator is arranged to move from one longitudinal position to another. A linear magnetic gear is coupled at an input element thereof to the valve actuator. The gear is coupled at an output element thereof to the valve operator such that motion of the valve actuator is transferred to the valve operator.
Owner:MAGNOMATICS LTD
Multiple-tool machine for combined cutting of slabs of hard material
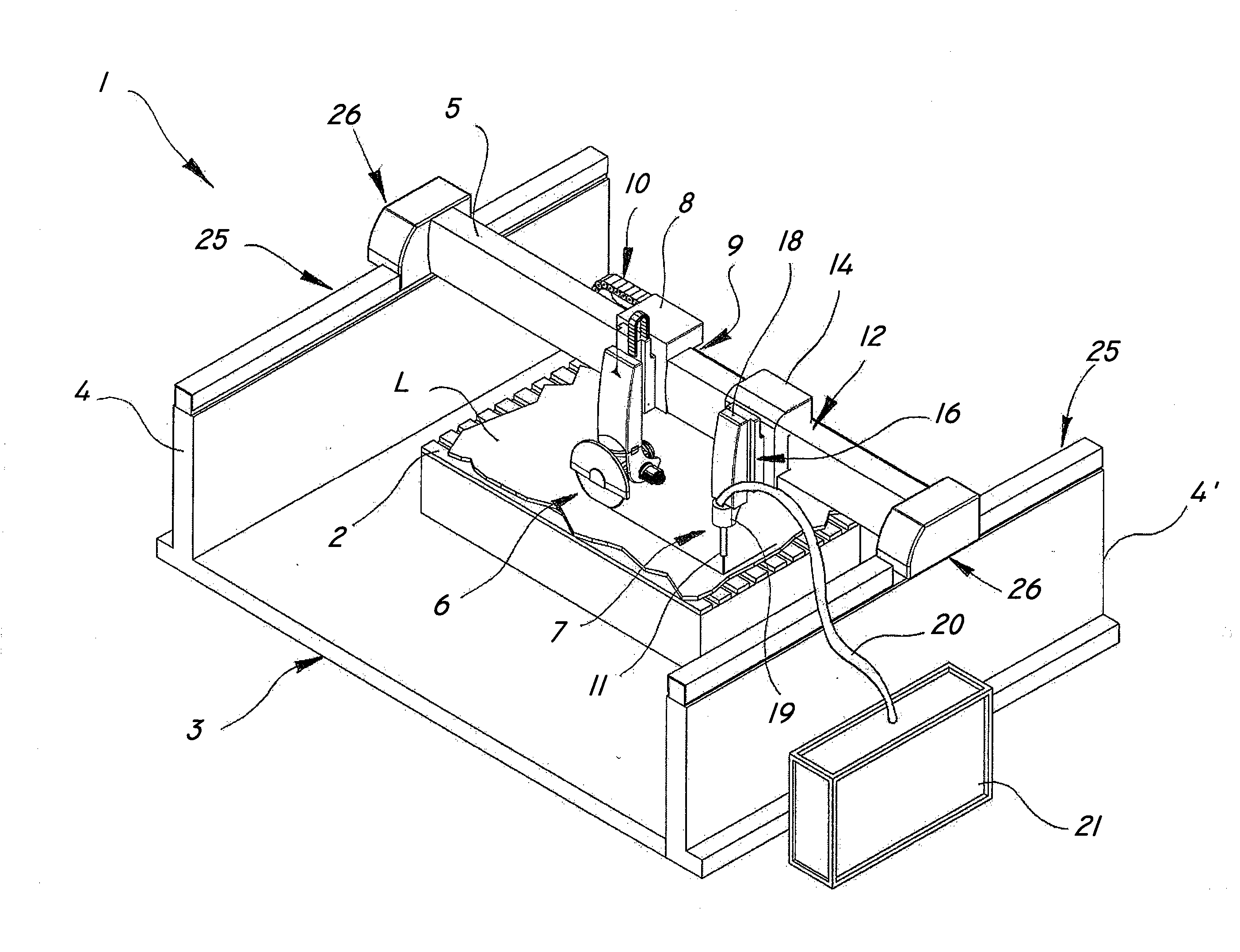
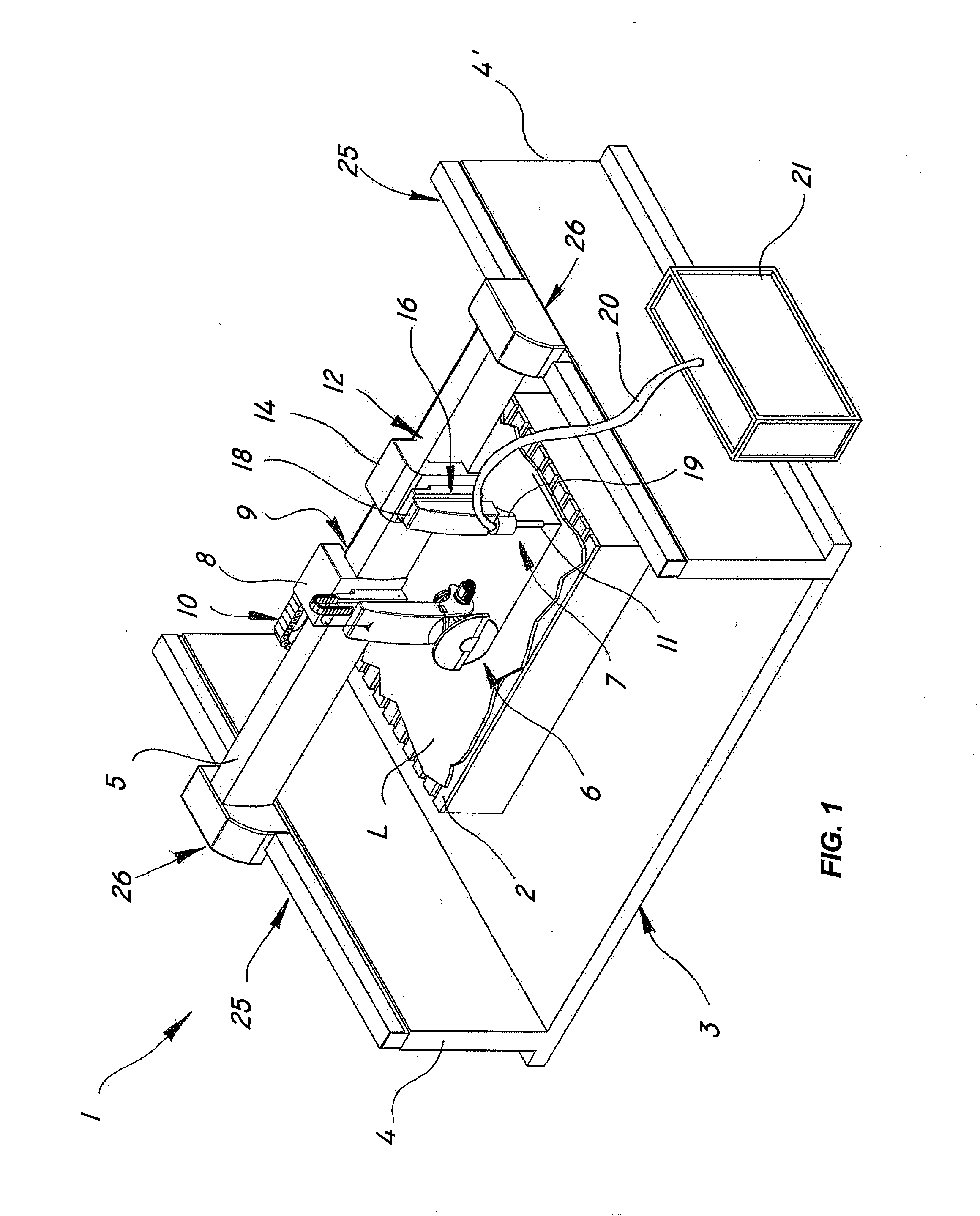
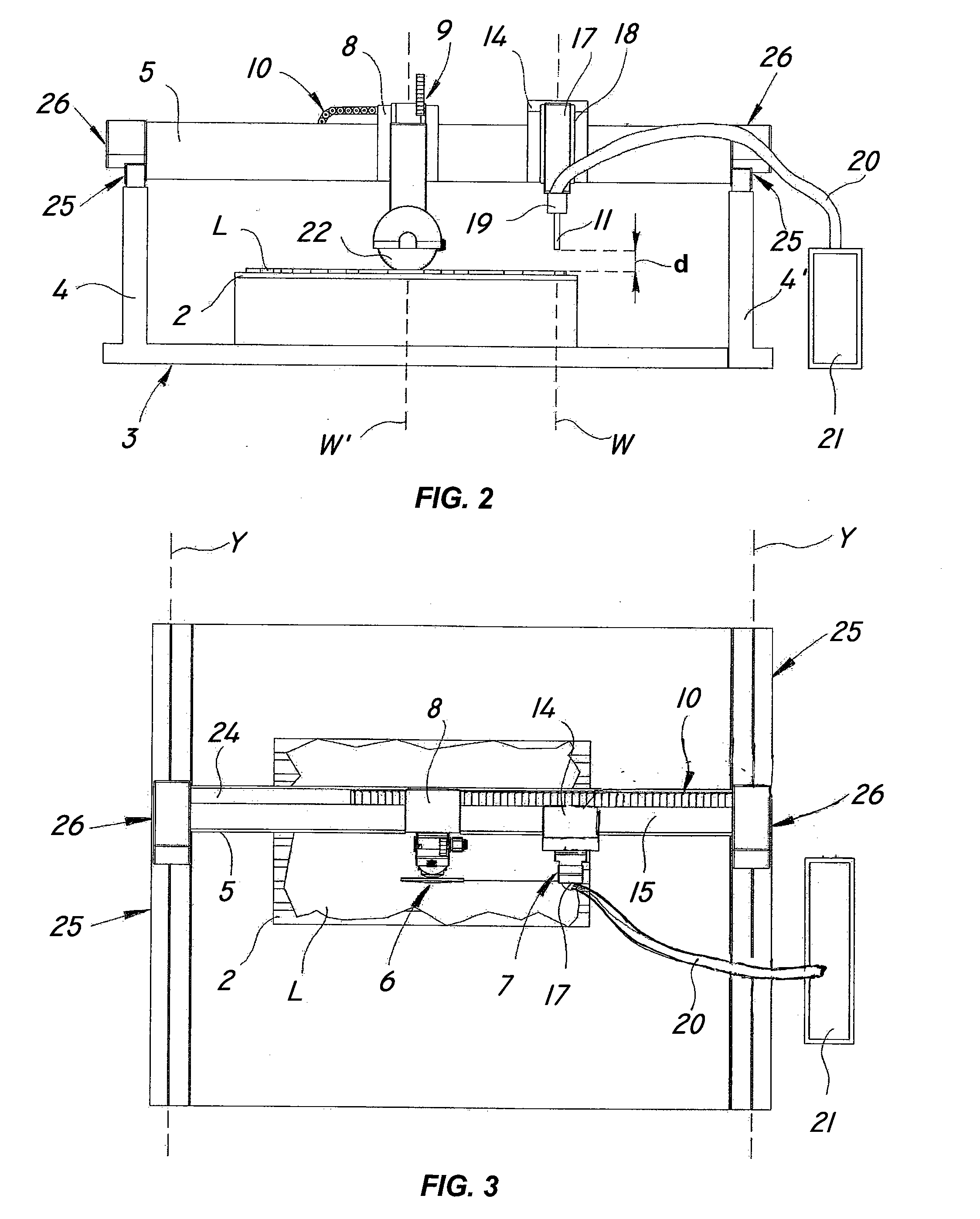
InactiveUS20080110311A1Improve efficiencyCost effectiveMetal sawing devicesGuide fencesClassical mechanicsStringer
The present invention relates to processing of hard materials, and more particularly relates to a multiple-tool machine for the combined cutting of slabs of hard materials such as stone, marble, granite, concrete, wood, metal, glass and the like. One embodiment of the present invention includes a support surface for receiving a slab; a load-bearing frame with a longitudinal beam extending over the support surface; a first disk blade cutting tool mounted on a first slide and movable along a first guide connected to the beam; a first motion imparting device for moving the first slide; a second cutting tool with a nozzle for high-pressure waterjet cutting, which is mounted in sliding relationship to a second guide coupled to the beam; and a second motion imparting device, other than the first motion imparting device, for translating the second cutting tool independently of the first cutting tool.
Owner:SIMEC SPA
Motion transmitting apparatus
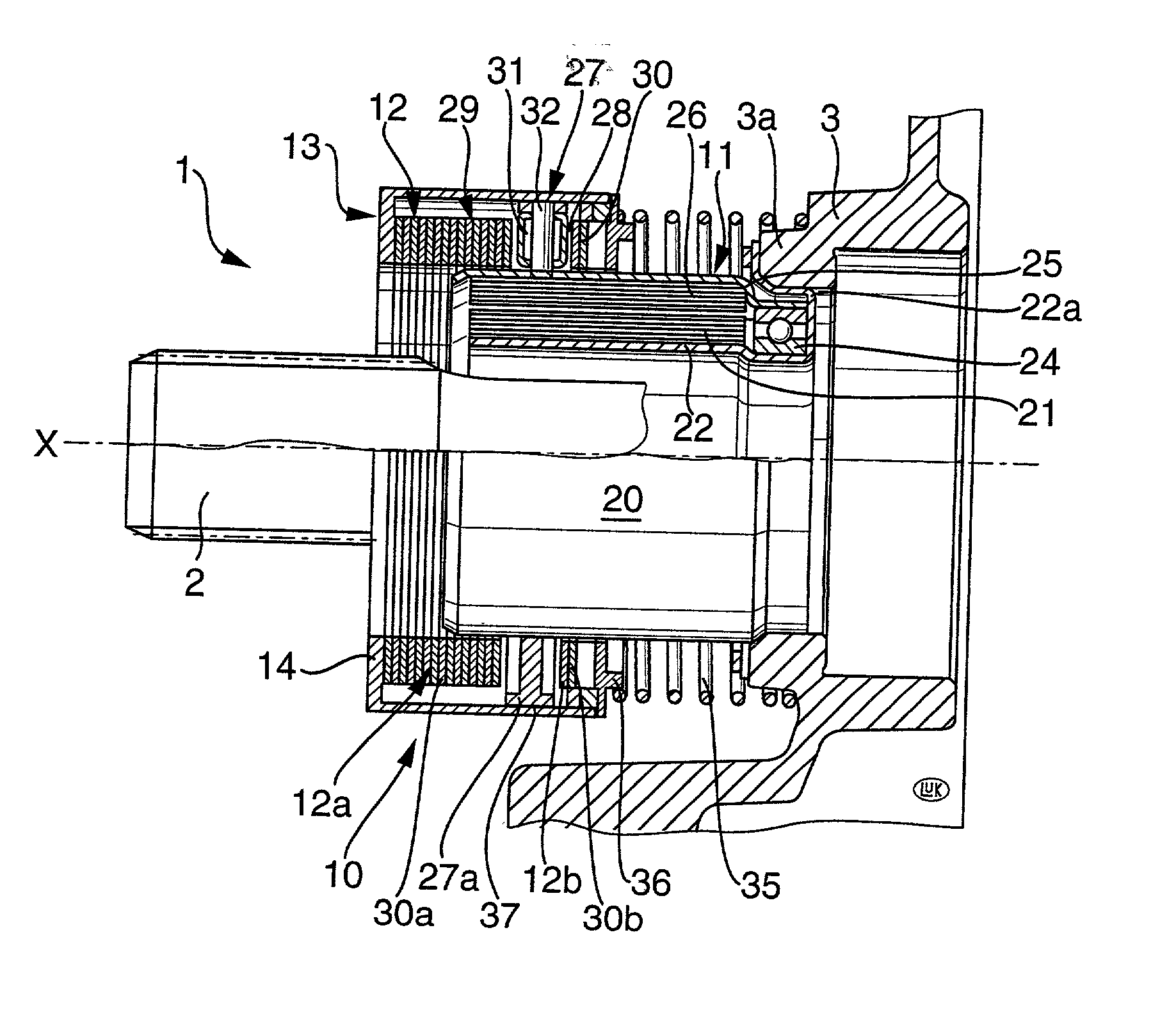
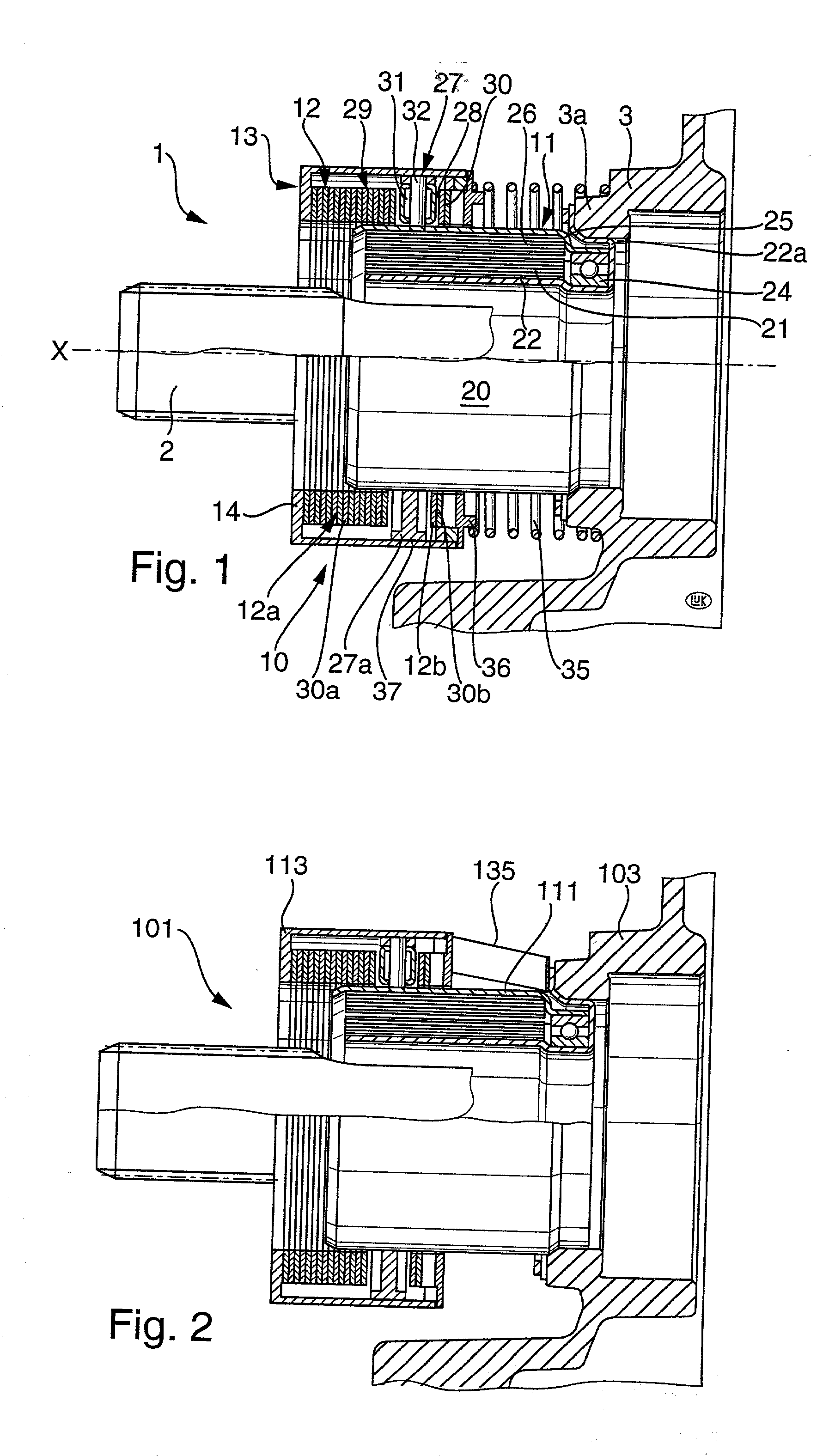
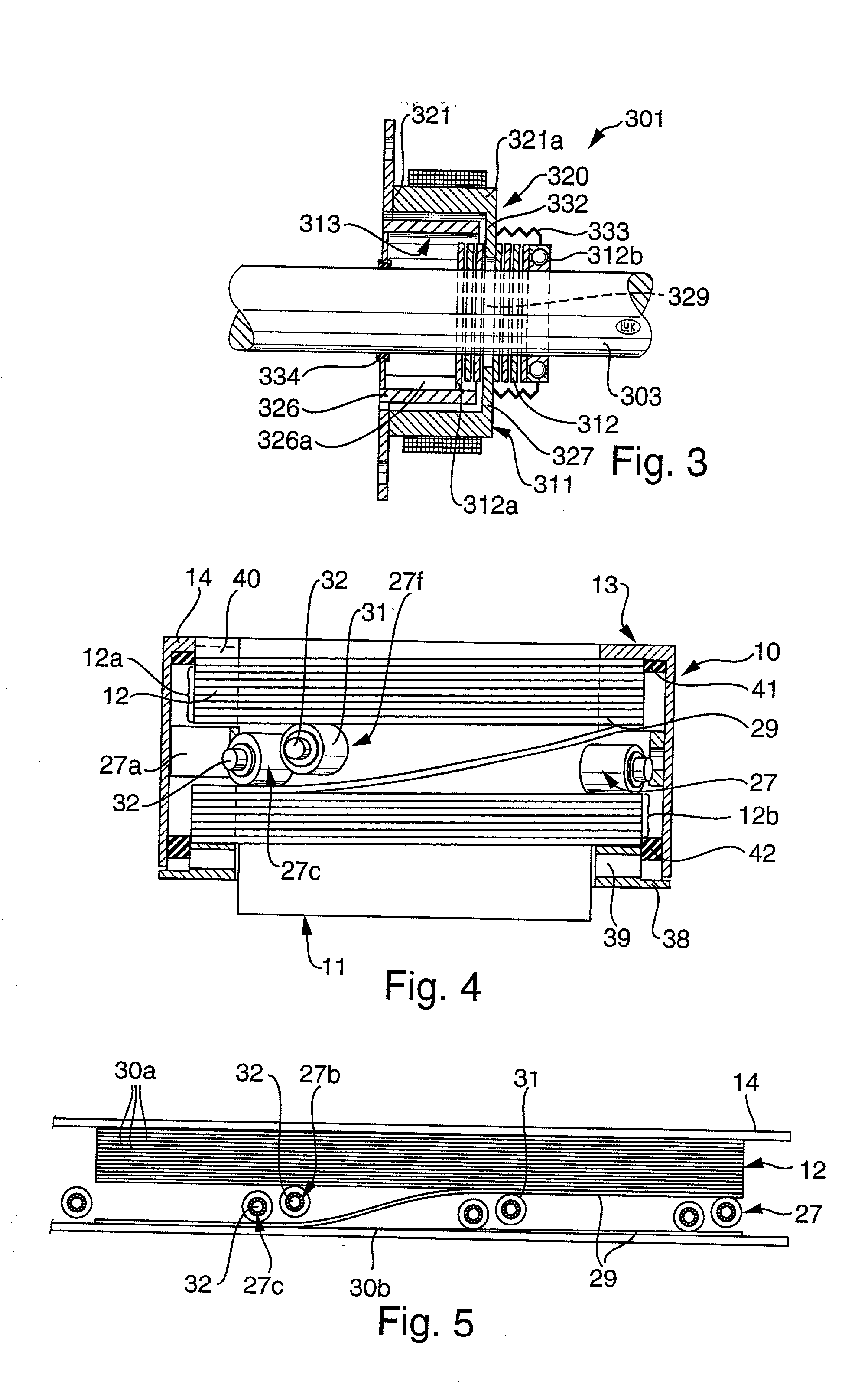
InactiveUS20020065171A1More versatileLess expensiveFluid actuated clutchesMagnetically actuated clutchesMobile vehicleCoil spring
A motion transmitting apparatus wherein an electric motor, an engine or another prime mover rotates an axially fixed first part relative to a coaxial axially movable non-rotatable second part. The structure which serves to move the second part axially in response to clockwise or counterclockwise rotation of the first part includes a follower borne by the first part and a helical spring having end convolutions affixed to the first part. The follower extends between two intermediate convolutions of the helical spring. If the apparatus is utilized in the power train of a motor vehicle, the axially movable part can serve to engage or disengage or change the extent of engagement of the friction clutch between the output element of the engine and the input element of the change-speed transmission.
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
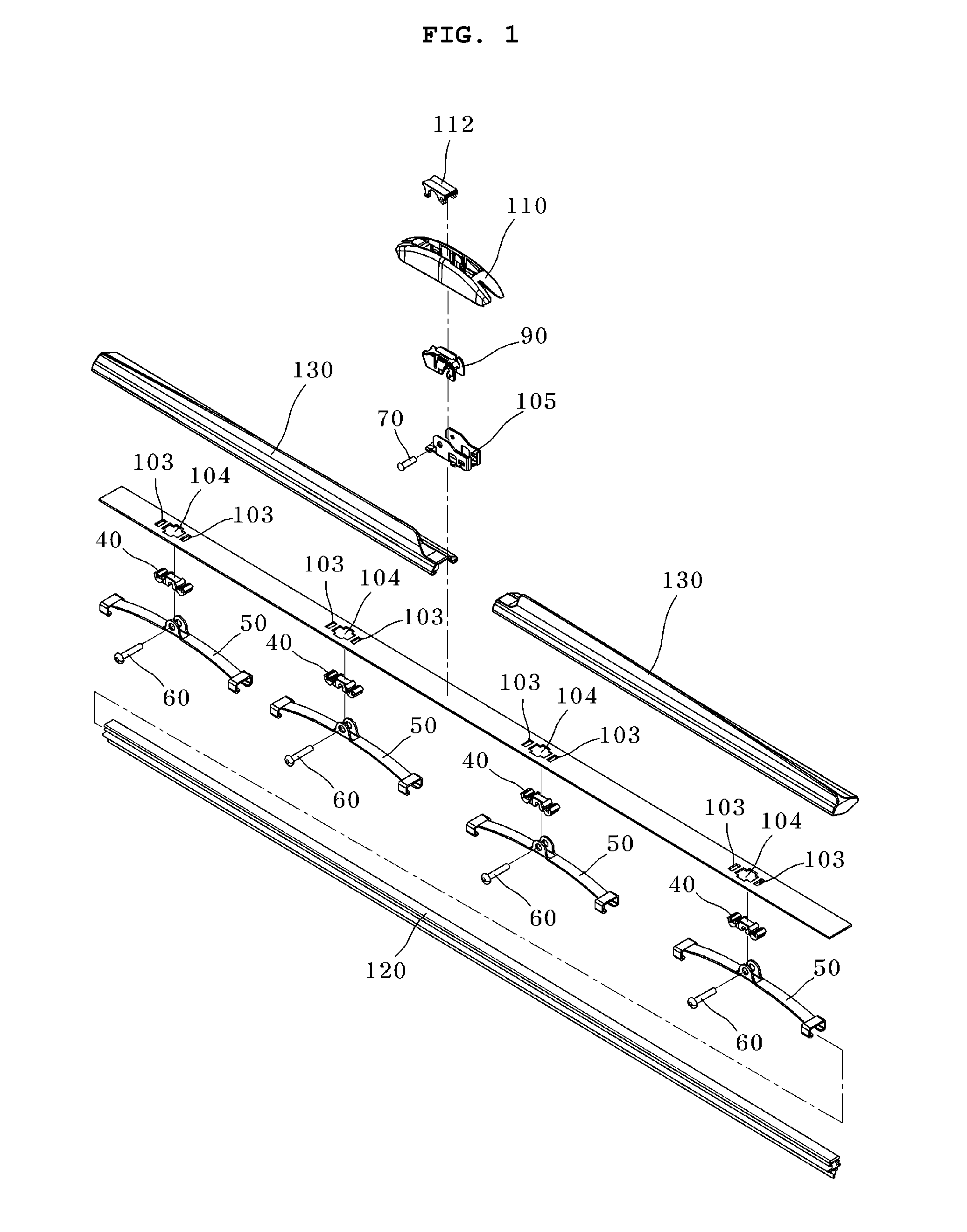
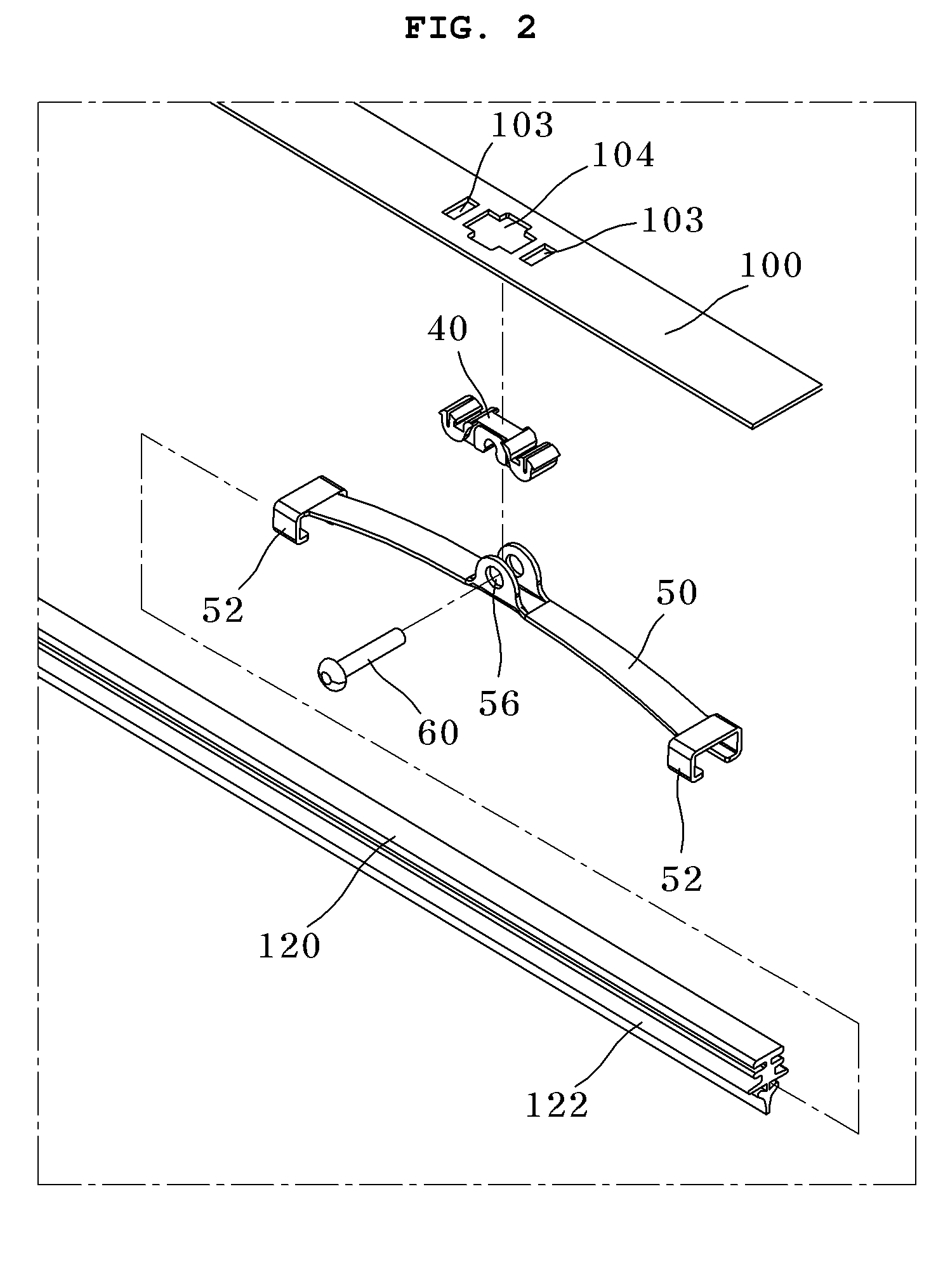
Wiper Blade Assembly Having Rotatable Auxiliary Beam
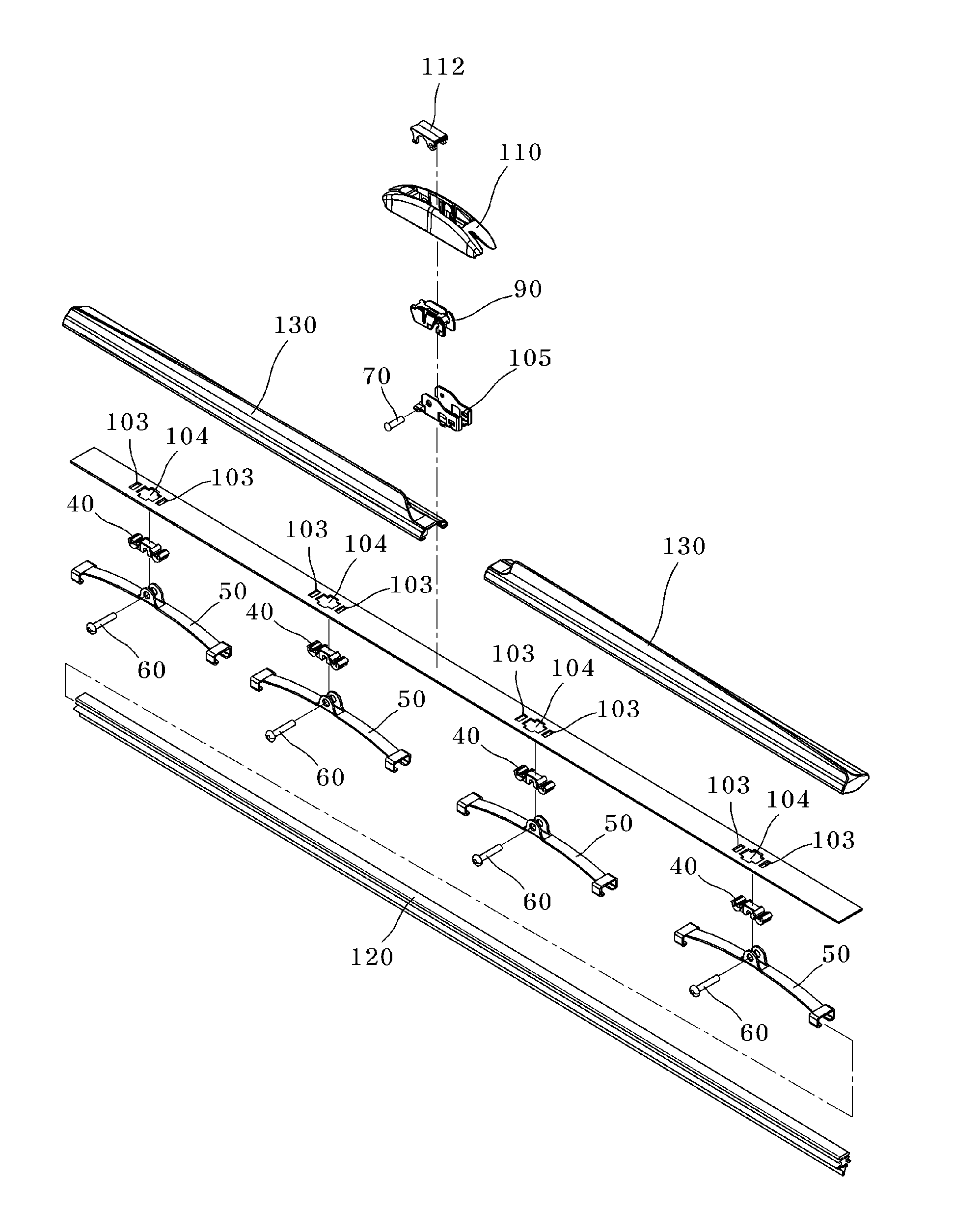
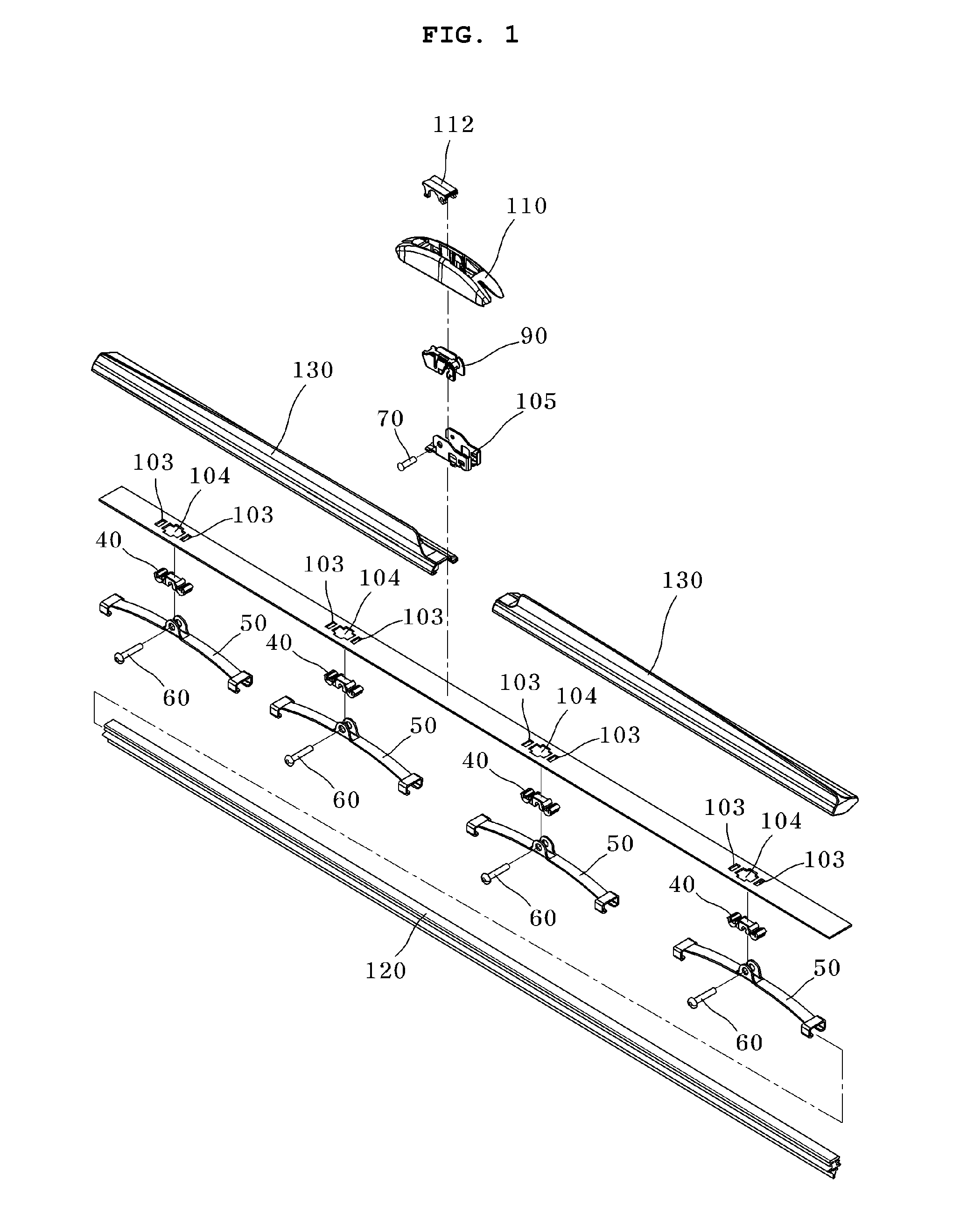
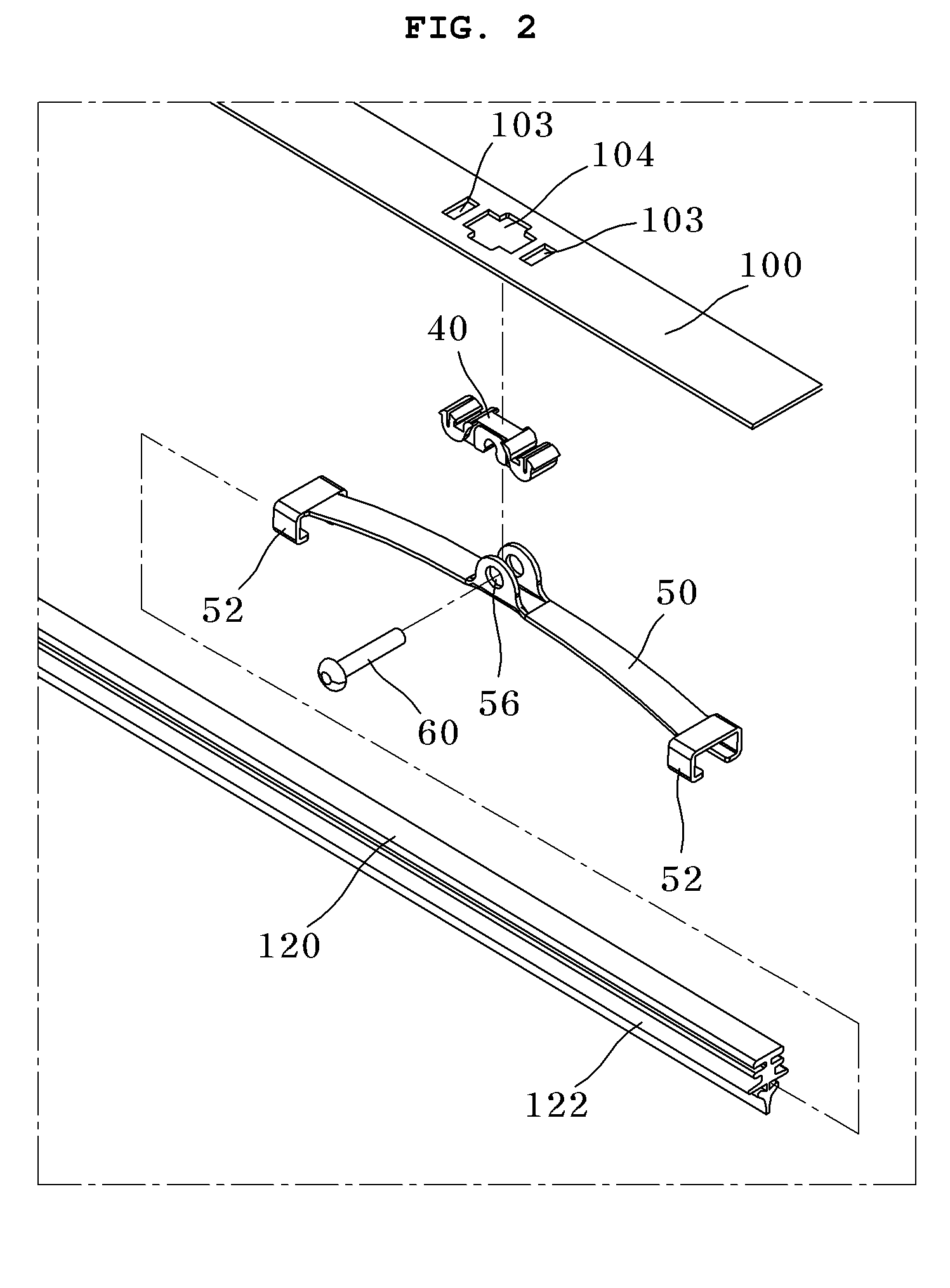
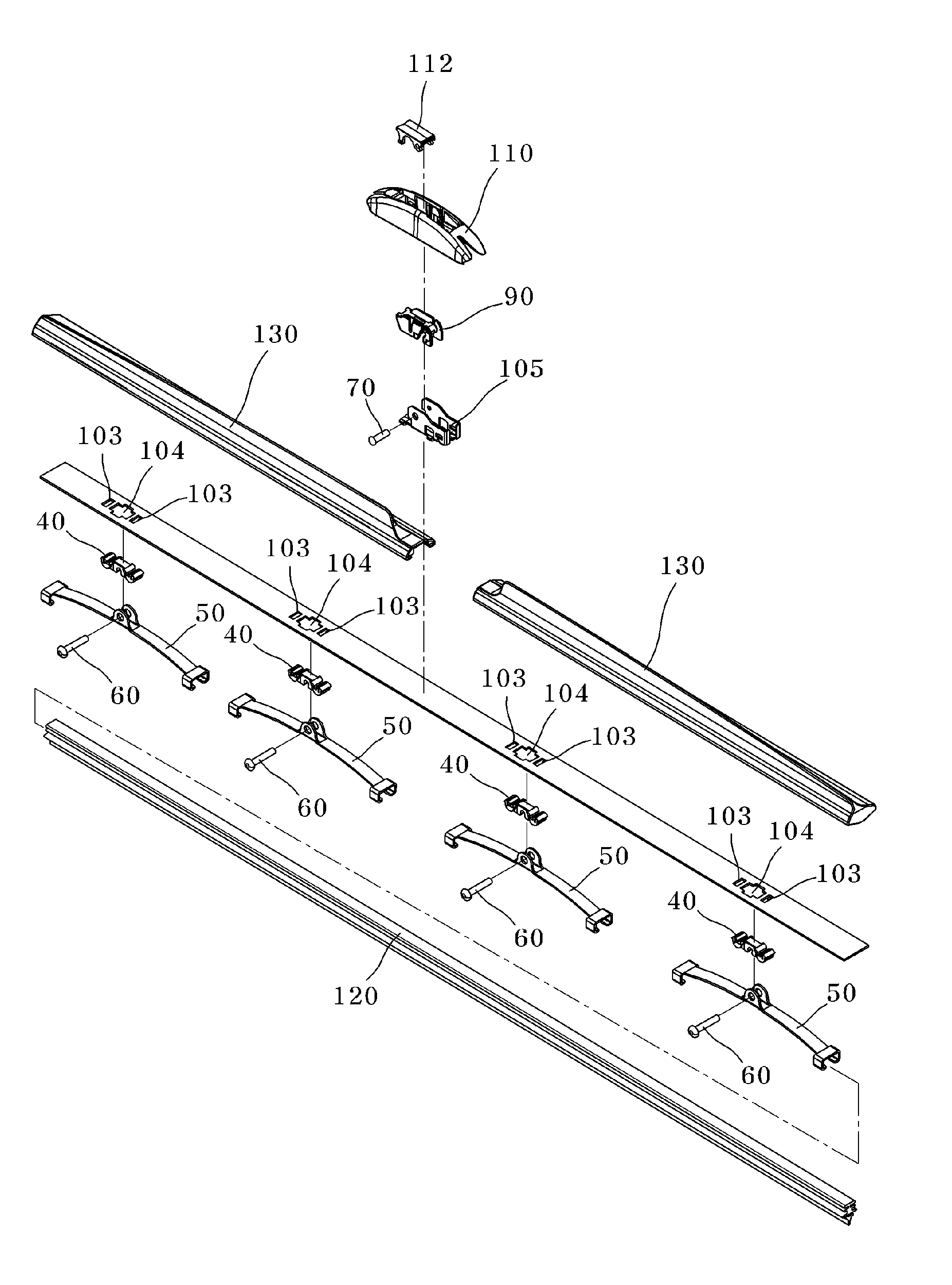
InactiveUS20100281645A1Rotational movement can be restrictedWindow cleanersVehicle cleaningMotion transferWindshield
A wiper blade assembly for wiping a windshield of a vehicle actuated by a wiper arm includes a flexible elongated wiper blade adapted to elastically contact with the windshield of the vehicle, a guide beam adapted to transfer the load and motion applied from the wiper arm to the wiper blade, the guide beam having an initial curvature, a plurality of connection members provided along a longitudinal direction of the guide beam, and a plurality of auxiliary beams rotatably coupled to the connection members, serving to hold the wiper blade.
Owner:KB WIPER SYST CO LTD
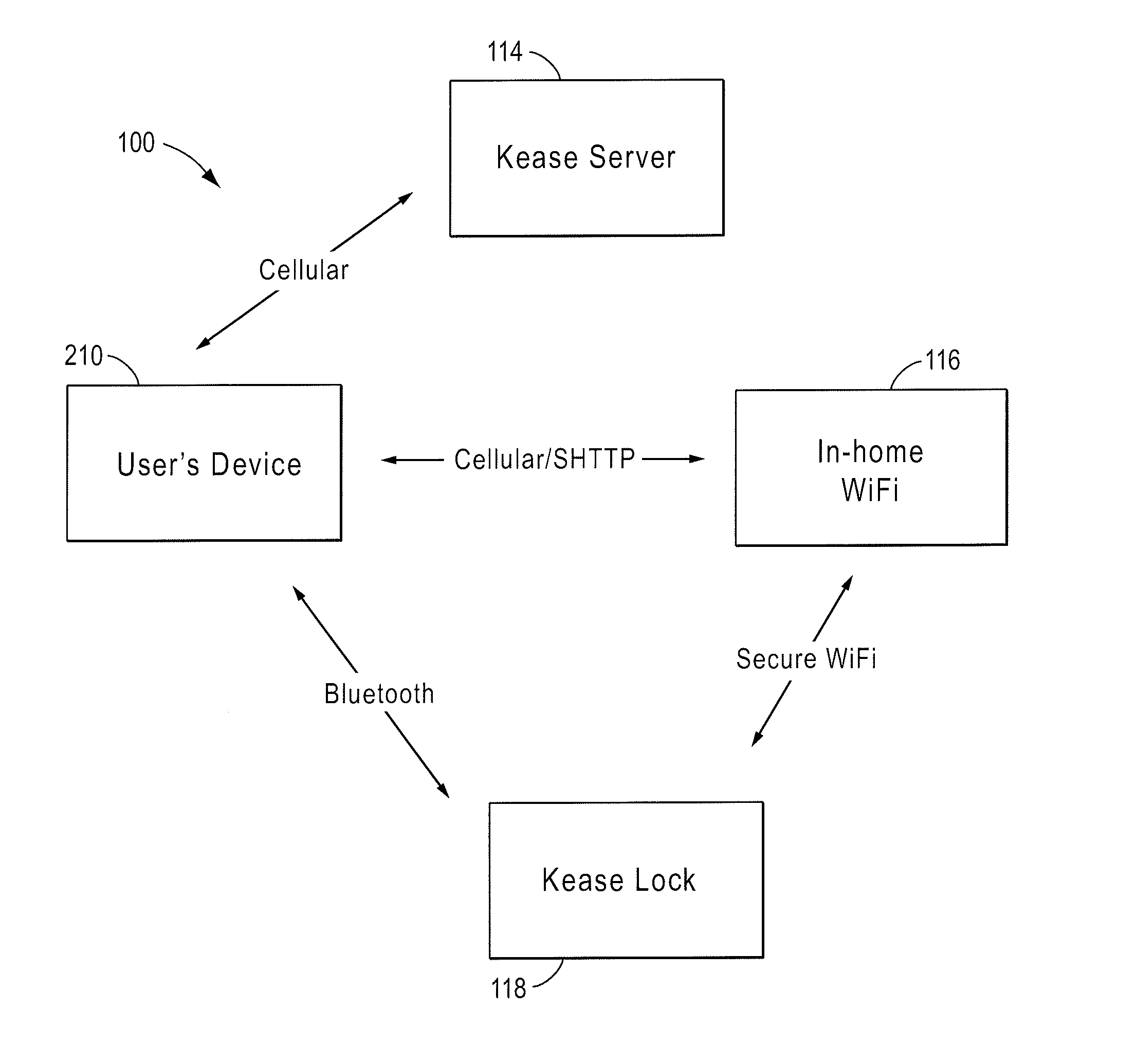
Intelligent door lock system with wireless access control system
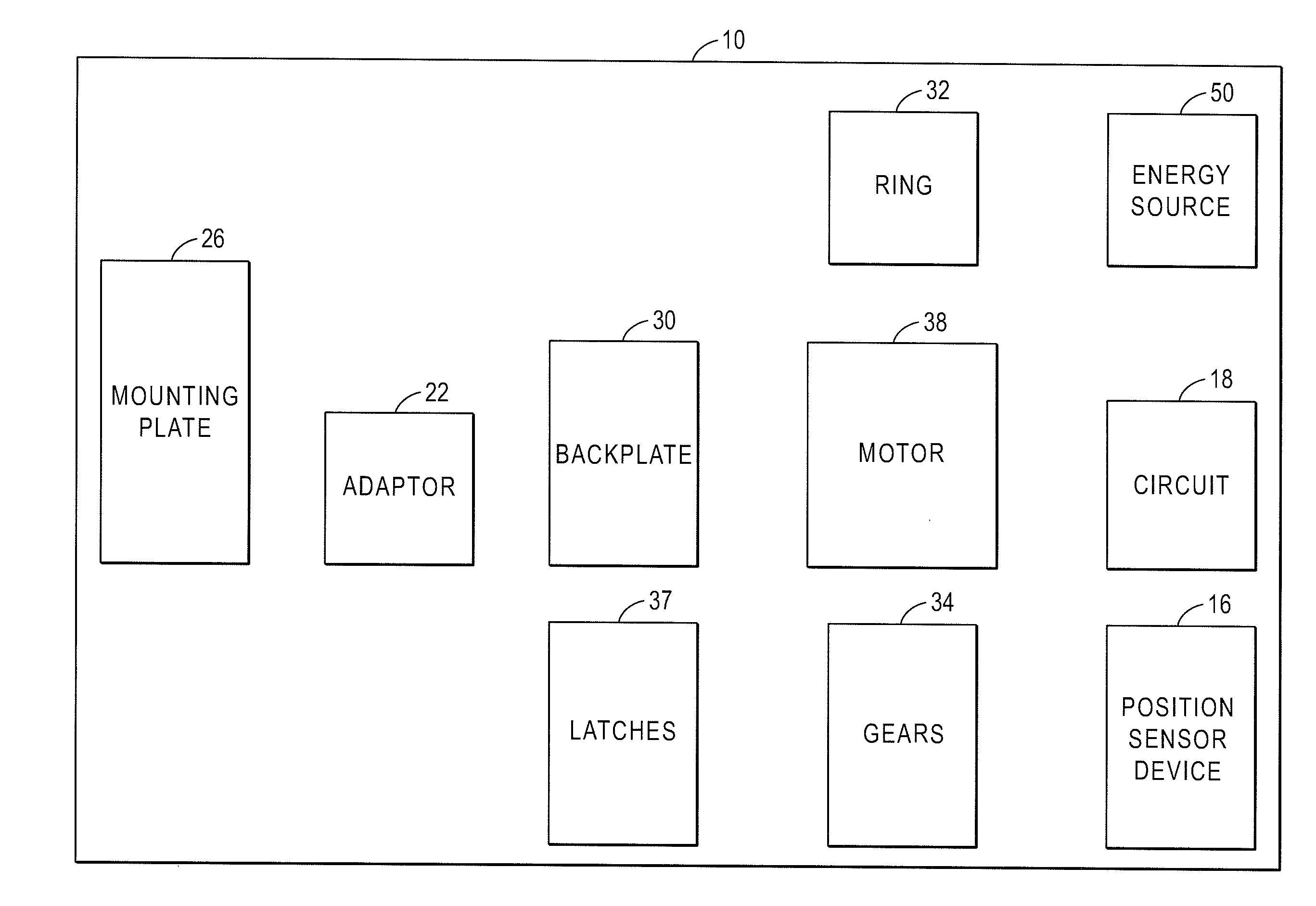
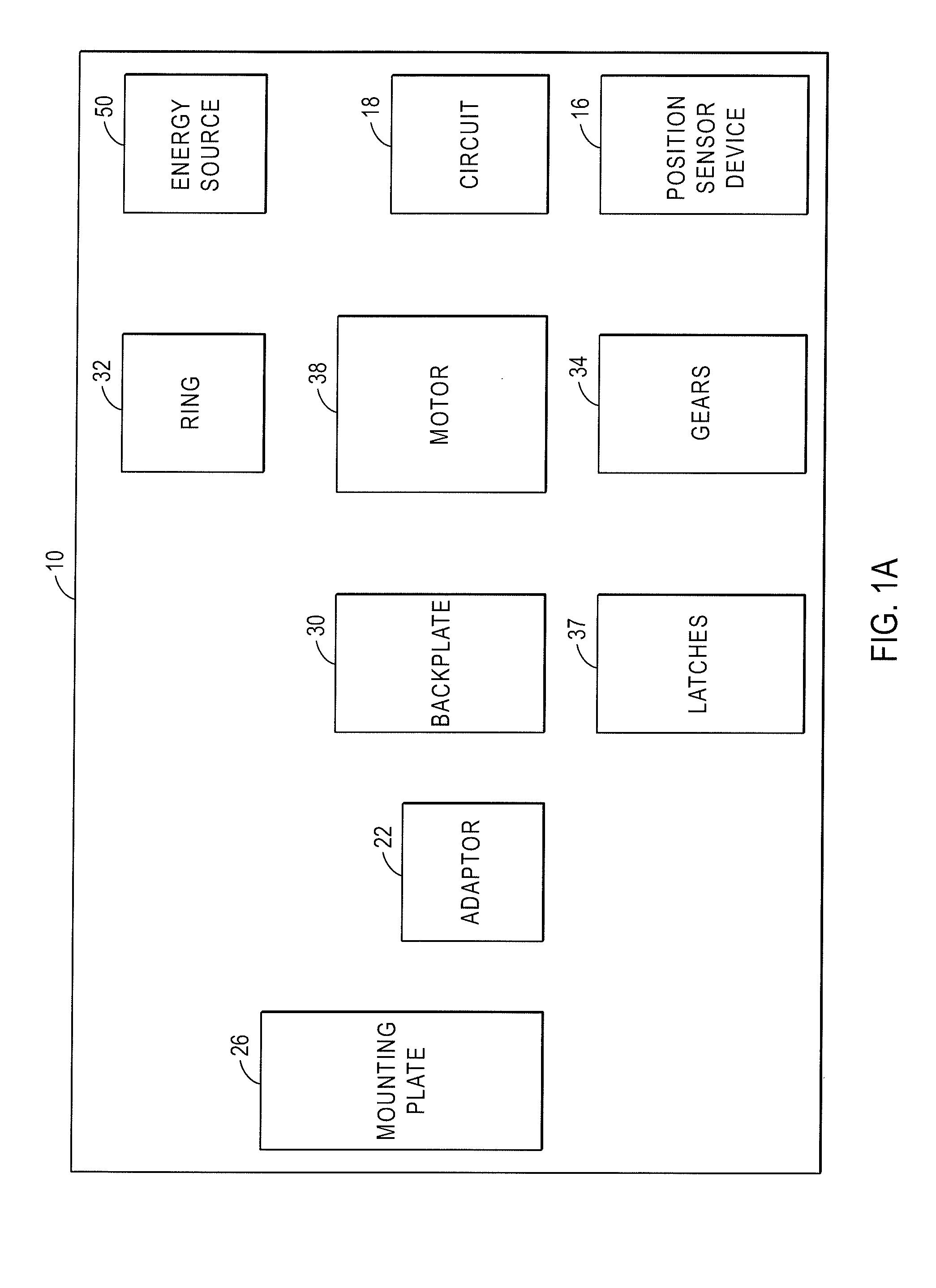
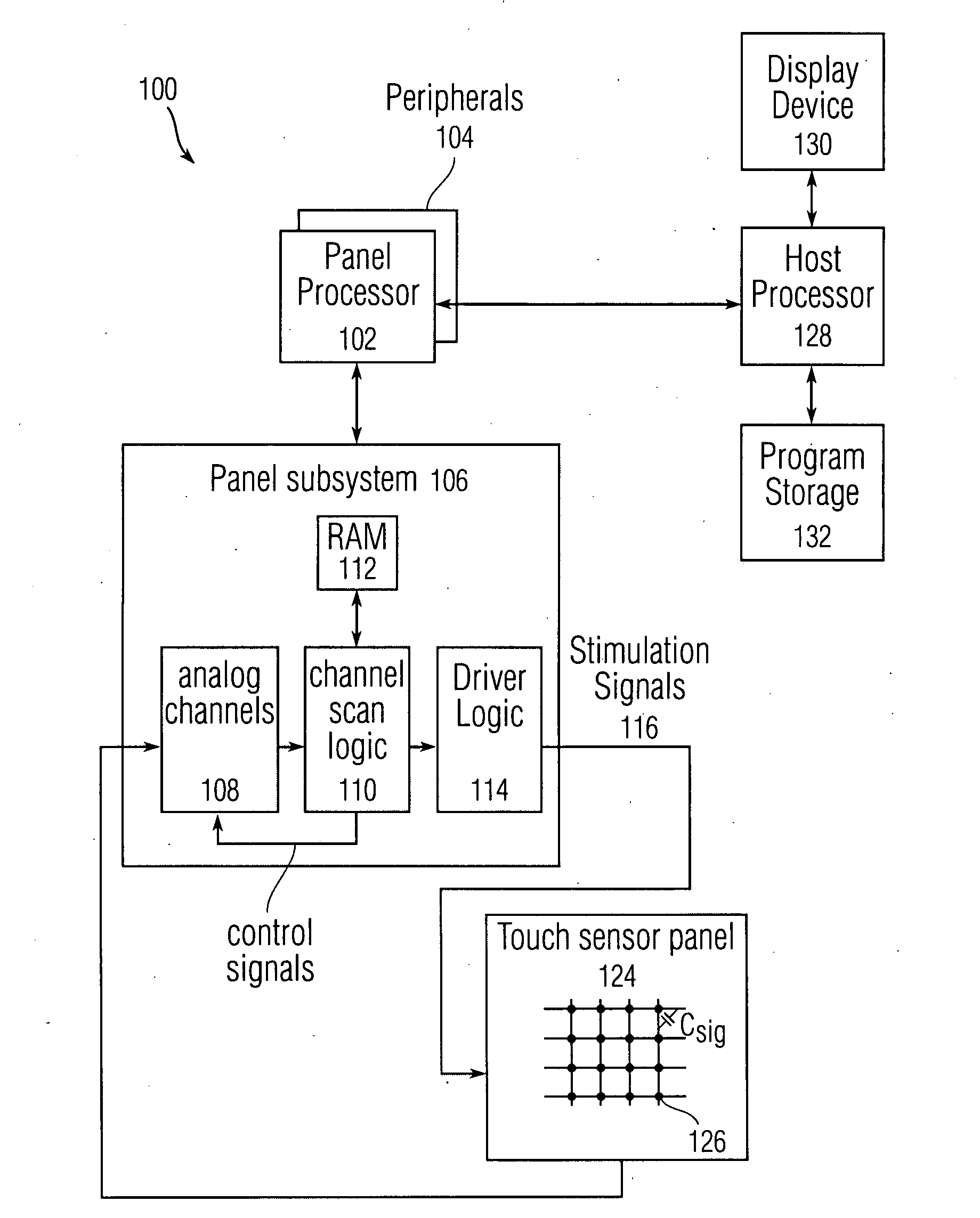
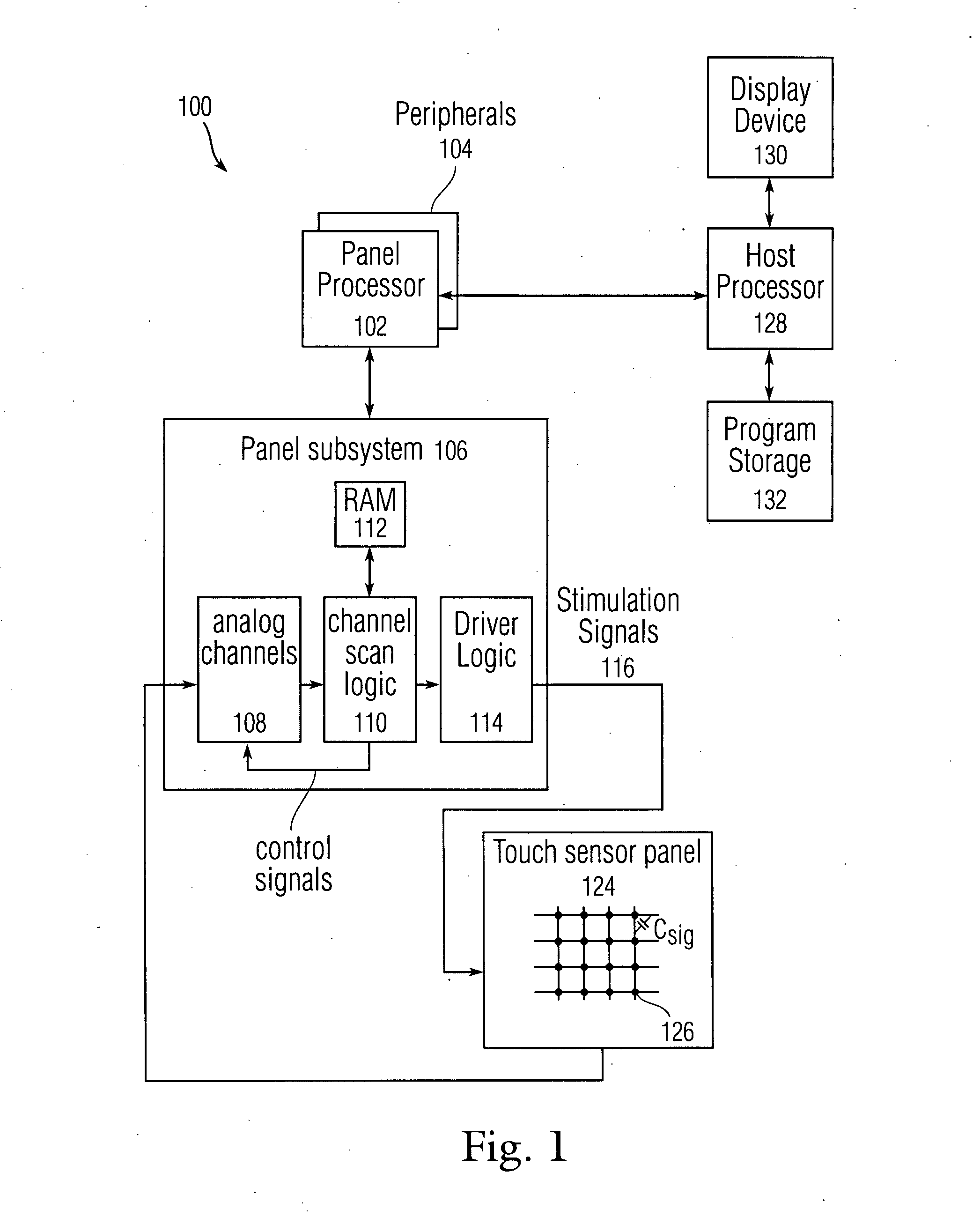
ActiveUS20160049025A1Transmit signalElectric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsAccelerometerControl system
A wireless access control system locks or unlocks a door at a dwelling. A remote access device transmits a signal. A lock system, for locking and unlocking a door in which the lock is located, includes a lock, a processor with a memory, one or more wireless communication devices coupled to a circuit and one or more motion transfer device coupled to a drive shaft. The lock receives the signal and enables the lock to be one of locked or unlocked in response to the signal. The remote access device has a controller for generating the signal, and an accelerometer providing an acceleration signal to the controller when the accelerometer experiences an acceleration. The controller generates the signal in response to the acceleration signal.
Owner:AUGUST HOME
Techniques for reducing jitter for taps
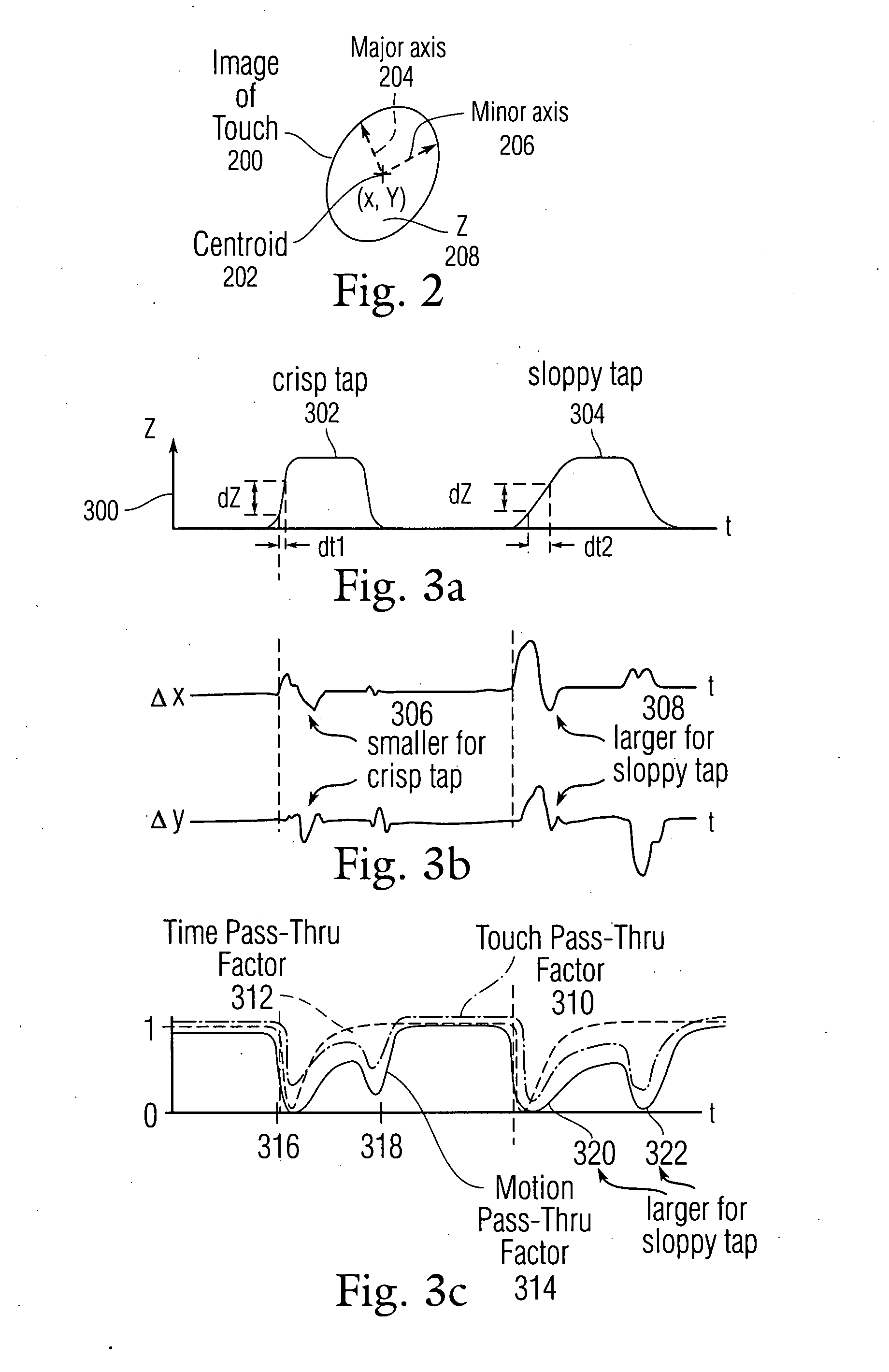
ActiveUS20080309630A1Wireless commuication servicesInput/output processes for data processingTemporal instabilityMotion transfer
Distinguishing sloppy taps from sliding motions is disclosed using an algorithm that can take into account both a time instability factor Tinst and a touch instability factor Zinst. A limited amount of motion per frame can be subtracted off immediately following the detection of a touch event. Small lateral motions indicative of a sloppy tap can be suppressed, while fast finger motions indicative of a quick, long cursor movement can immediately pass through the filter without being suppressed by a significant amount. A motion pass-through suppression factor can be applied subtractively to motion in particular direction as a function of Zinst and Tinst, wherein Zinst can represent a suppression value given as a finger speed for a particular percentage change in touch instability per frame, and Tinst can represent a suppression value given as finger speed for a particular tpress.
Owner:APPLE INC
Calibration structure for circuit breakers having bimetallic trip member
InactiveUS6720856B1Less sensitivityIncreased durabilityElectrothermal relaysThermally actuated switchesContact forceActuator
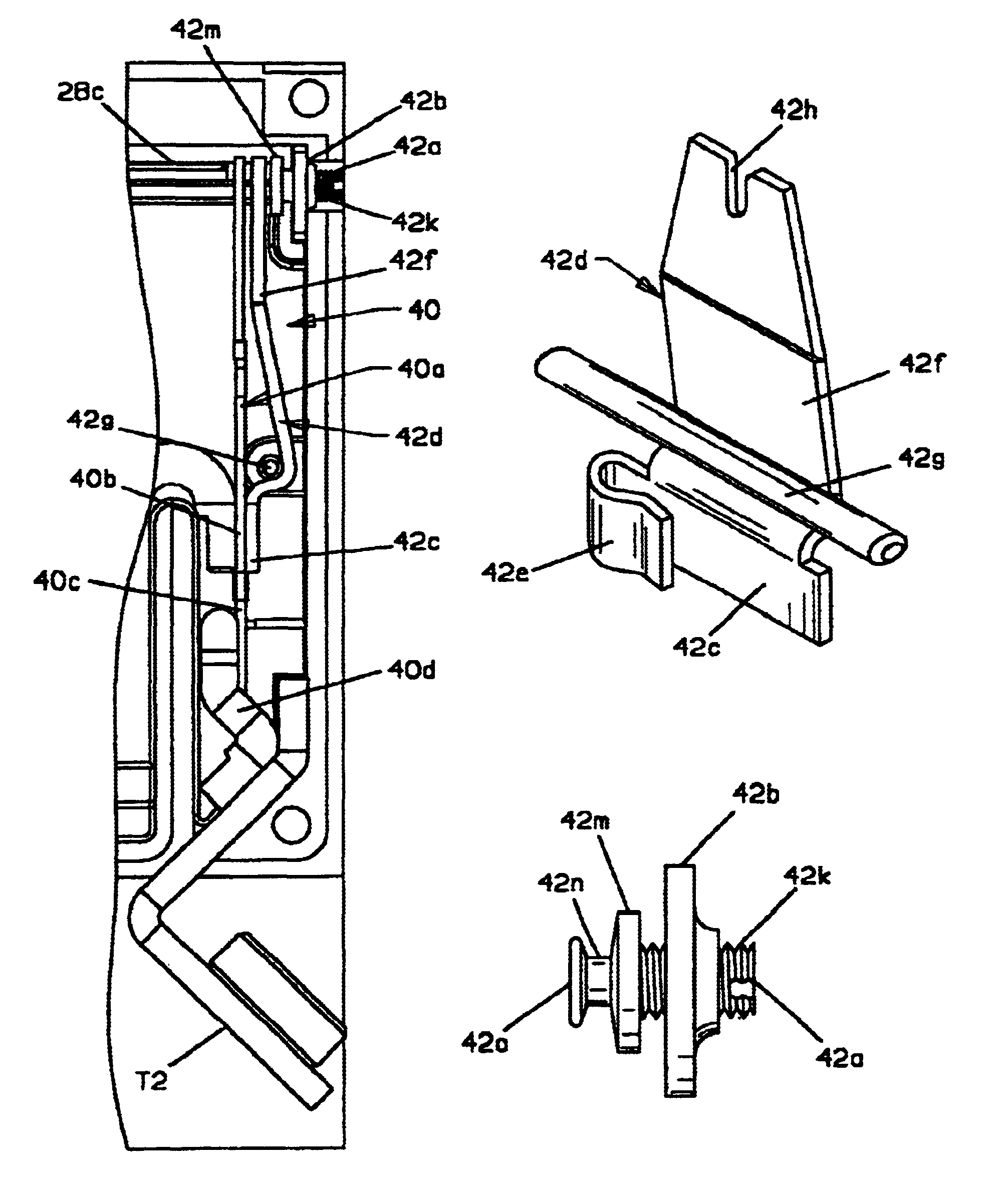
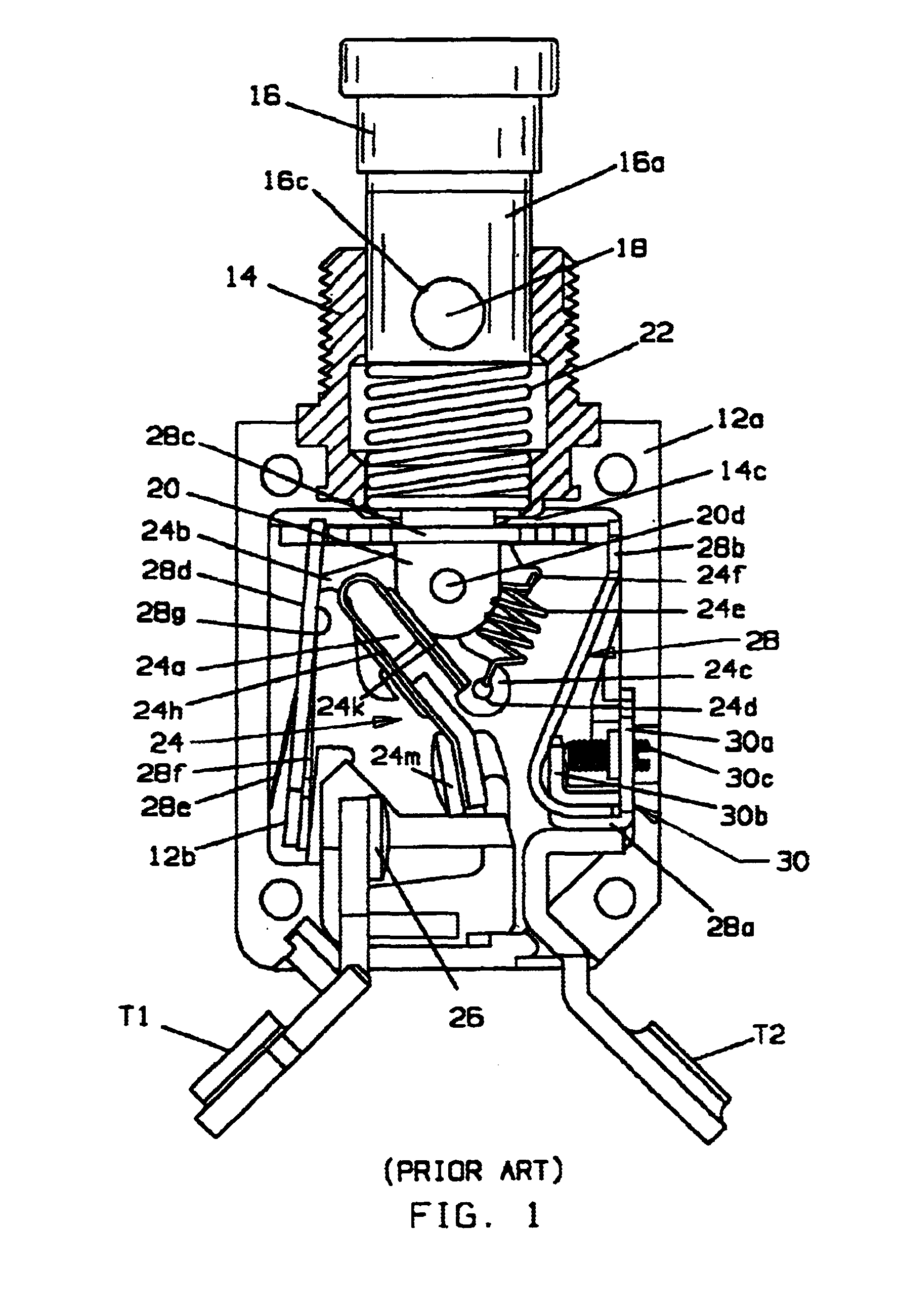
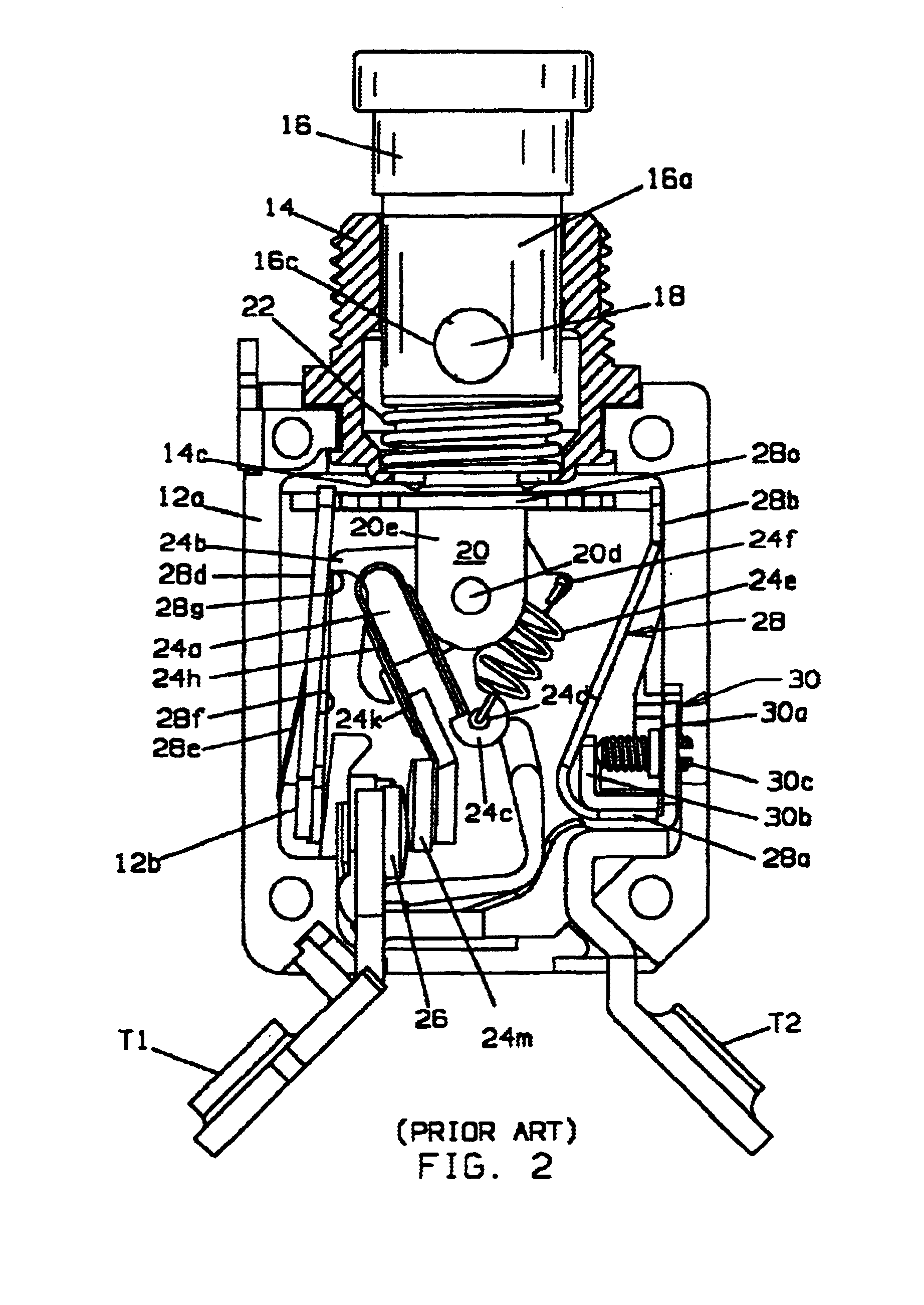
A thermally compensated circuit breaker has a movable contact assembly (24) which mounts a movable electrical contact (24m) for movement between open and closed contacts positions with a stationary electrical contact (26). The contacts are maintained in the closed circuits position by a latching mechanism (24b, 28g) which prevents opening of the contacts through an opening contacts force provided by a spring (24e). A current carrying trip arm (40a, 44a) deflects upon sufficient I.sup.2 R heating to transfer motion to the latch to separate the latch (24b) from the latch receiving catch (28g) to trip the circuit breaker. The trip arm (40a, 44a) is part of a pivotably mounted actuator assembly (40, 44) having a movable end portion spaced from the pivot disposed adjacent a motion transfer member (28c). A calibration screw (42a) is located so that the longitudinal axis is in line with a movable end portion of the actuator assembly and the motion transfer member. In one embodiment the head of the calibration screw is captured in a slot in the free end of a calibration base (42d) attached to the trip arm so that deflection of the trip arm directly transfers motion to the motion transfer member and in another embodiment the calibration screw head is captured in a slot in the free end of the trip arm so that a bowing deflection of the trip arm causes a calibration base (46) to which it is attached at an end thereof to rotate with the calibration base directly transferring motion to the motion transfer member.
Owner:SENSATA TECH MASSACHUSETTS INC
Wireless access control system and methods for intelligent door lock system
ActiveUS20160049026A1Electric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsControl systemDrive shaft
A wireless access control system includes a mobile device for accessing a lock. A mobile device controller generates a signal configured to be transmitted to an intelligent lock system. The intelligent lock system includes a lock, a processor with a memory, one or more wireless communication devices coupled to a circuit and one or more motion transfer device coupled to a drive shaft, the lock receiving the signal, and enabling a change of a state of the lock between locked and unlocked. A geo-positioning system sensor determines a geographic location of the mobile device, the controller determines whether or not the geographic position is within a geo-fence for the lock.
Owner:AUGUST HOME
Surgical cutter with exchangeable cutter blades
InactiveUS20080033466A1Extended service lifeReduce coefficient of frictionIncision instrumentsExcision instrumentsReady to useEngineering
Cutters for disrupting tissue include a cutter body and replaceable cutter blades. The cutter blades may be placed in one of three positions (sheathed for transport, unsheathed for use, and sufficiently exposed for blade exchange) by the relative movement of a cutter sheath with respect to the engagement zone between the cutter blade and the cutter body. The relative movement of the cutter sheath may be limited to an operational range to preclude inadvertent exposure of the cutter blade to prevent unintended disengagement from the cutter body. Various sheath limiters are disclosed that selectively limit movement of the cutter sheath to an operational range or allow extraordinary movement to allow blade exchange. In some instances other intermediate stops may be used to further limit the relative motion. The relative motion could be imparted by the movement of a cutter rod (rather than the movement of the cutter sheath) and thus limited by a rod limiter. Cutter blades with different attributes (such as throw length, cutter blade angle, type and location of blade edges) are adapted to achieve different objectives.
Owner:TRANS1
Airborne wind energy conversion system with fast motion transfer
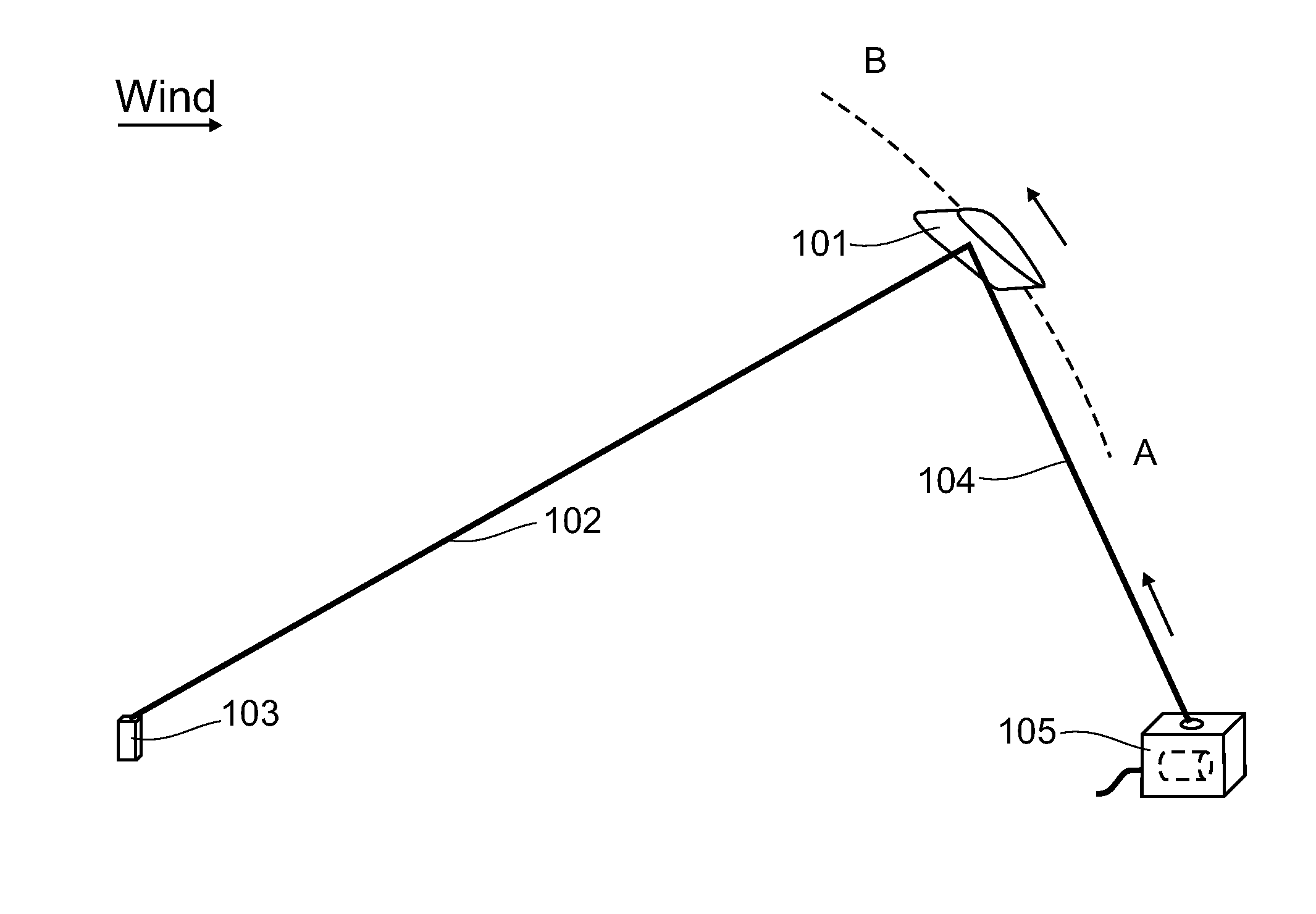
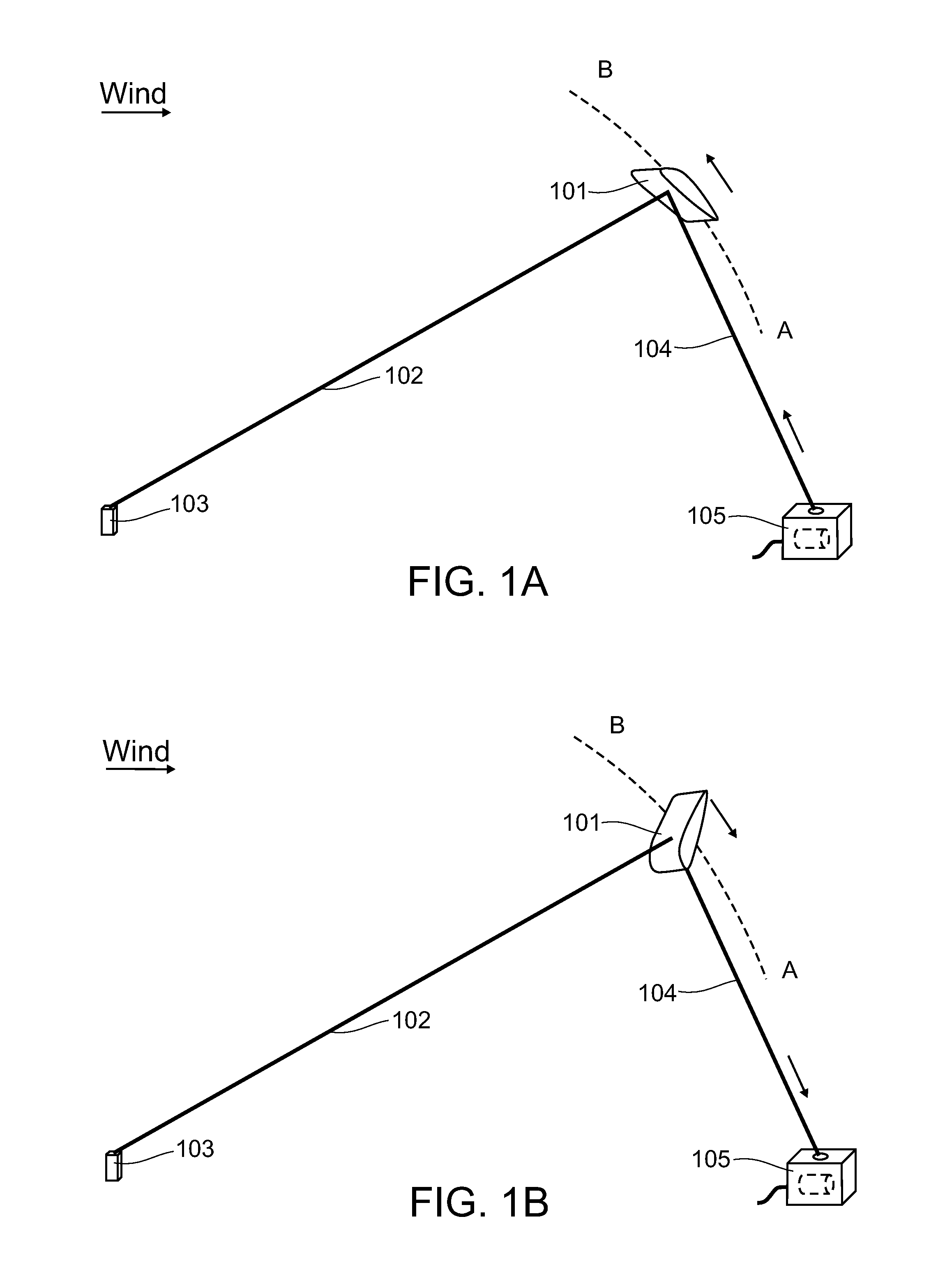
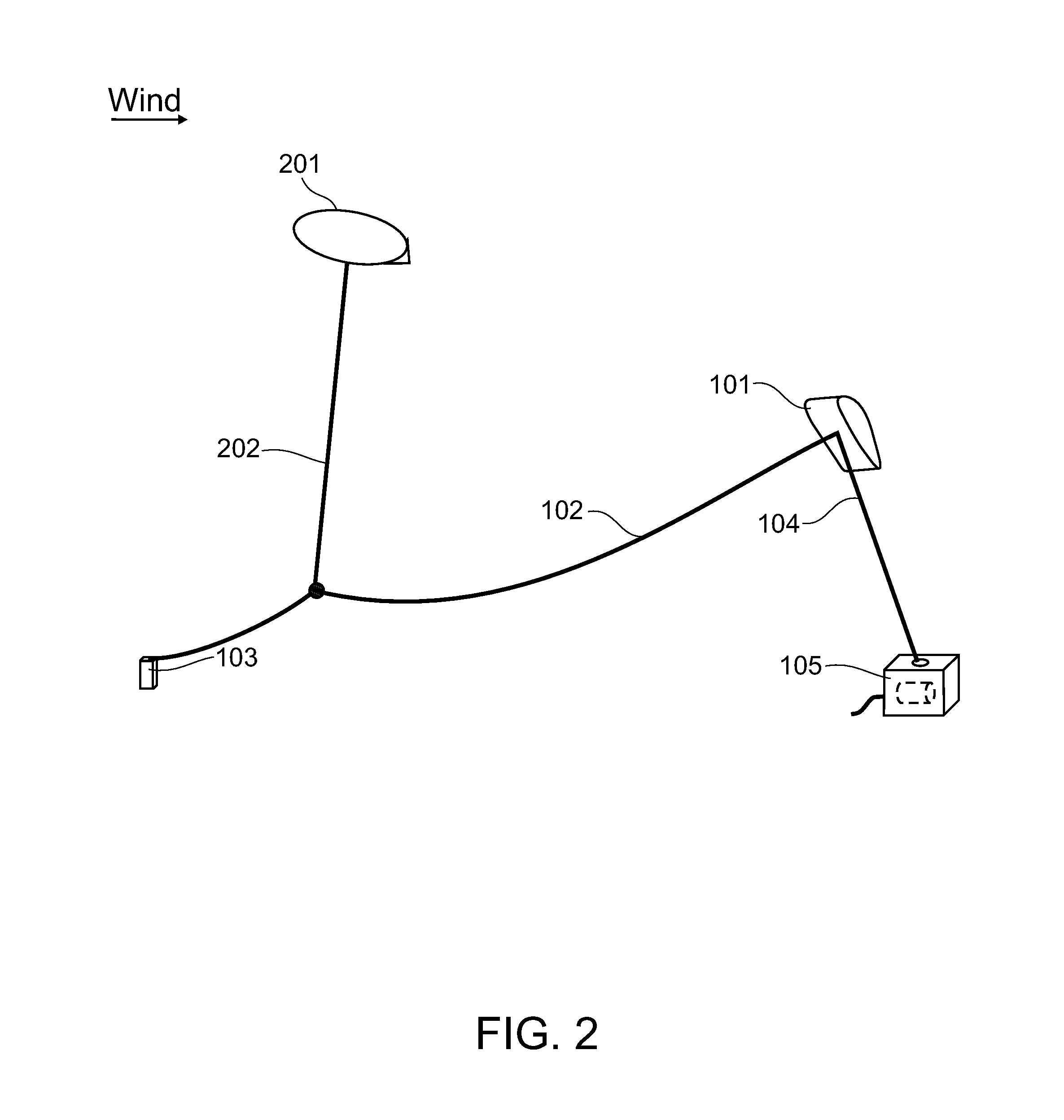
InactiveUS20130134261A1Raise the ratioWing areaMachines/enginesWind motor combinationsEngineeringWind energy conversion
Airborne wind energy conversion system a with flying wing, using a cable or belt to transmit motion to a rotor of a ground based electrical generator with high velocity, achieving high aerodynamic efficiency of the wings and high power for a given torque.
Owner:GOLDSTEIN LEONID
Wiper blade assembly having rotatable auxiliary beam
A wiper blade assembly for wiping a windshield of a vehicle actuated by a wiper arm includes a flexible elongated wiper blade adapted to elastically contact with the windshield of the vehicle, a guide beam adapted to transfer the load and motion applied from the wiper arm to the wiper blade, the guide beam having an initial curvature, a plurality of connection members provided along a longitudinal direction of the guide beam, and a plurality of auxiliary beams rotatably coupled to the connection members, serving to hold the wiper blade.
Owner:KB WIPER SYST CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com