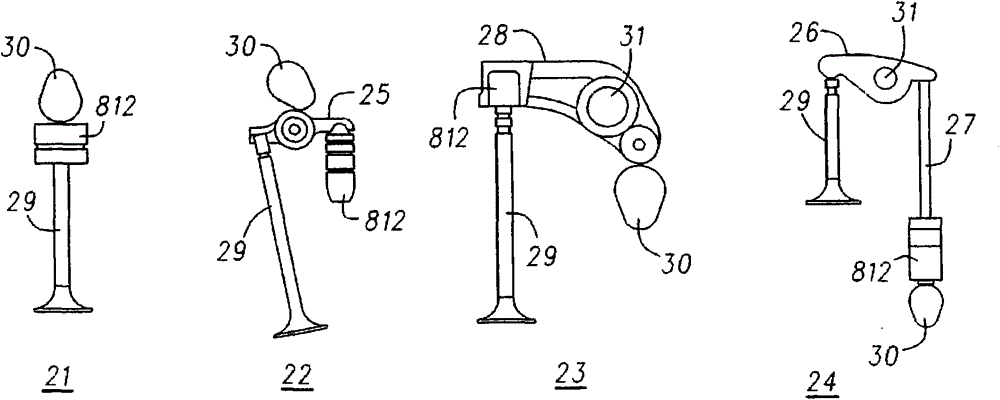
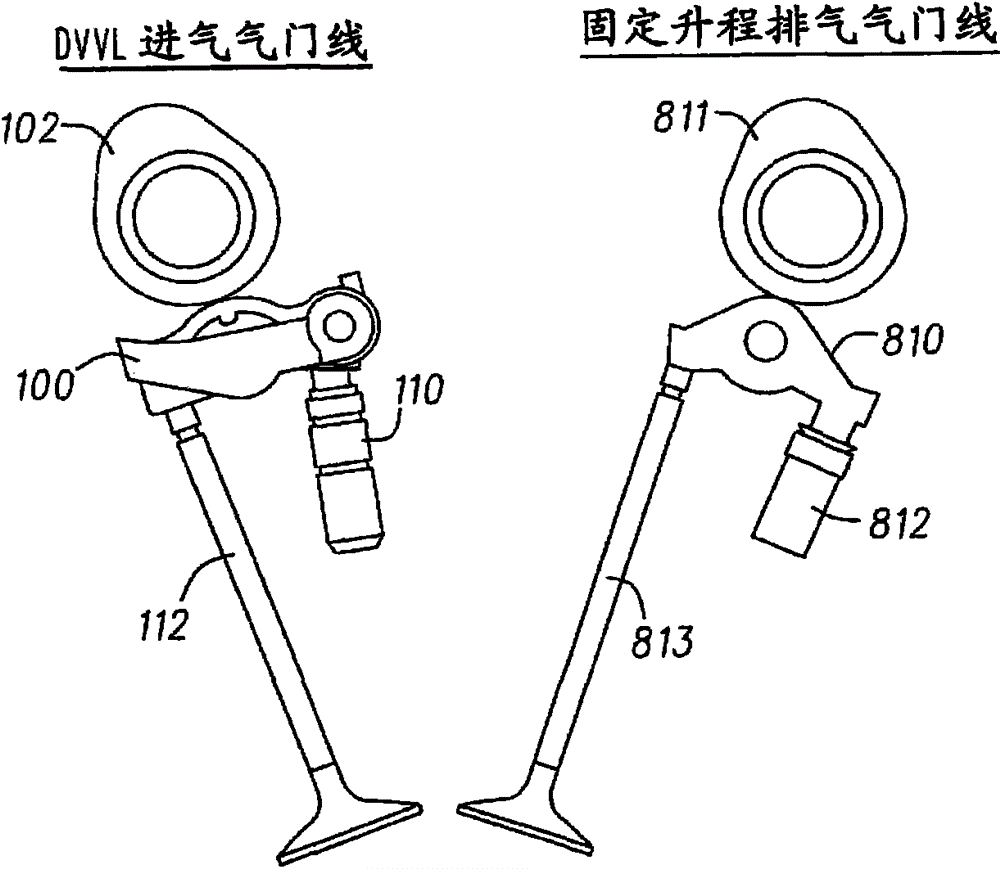
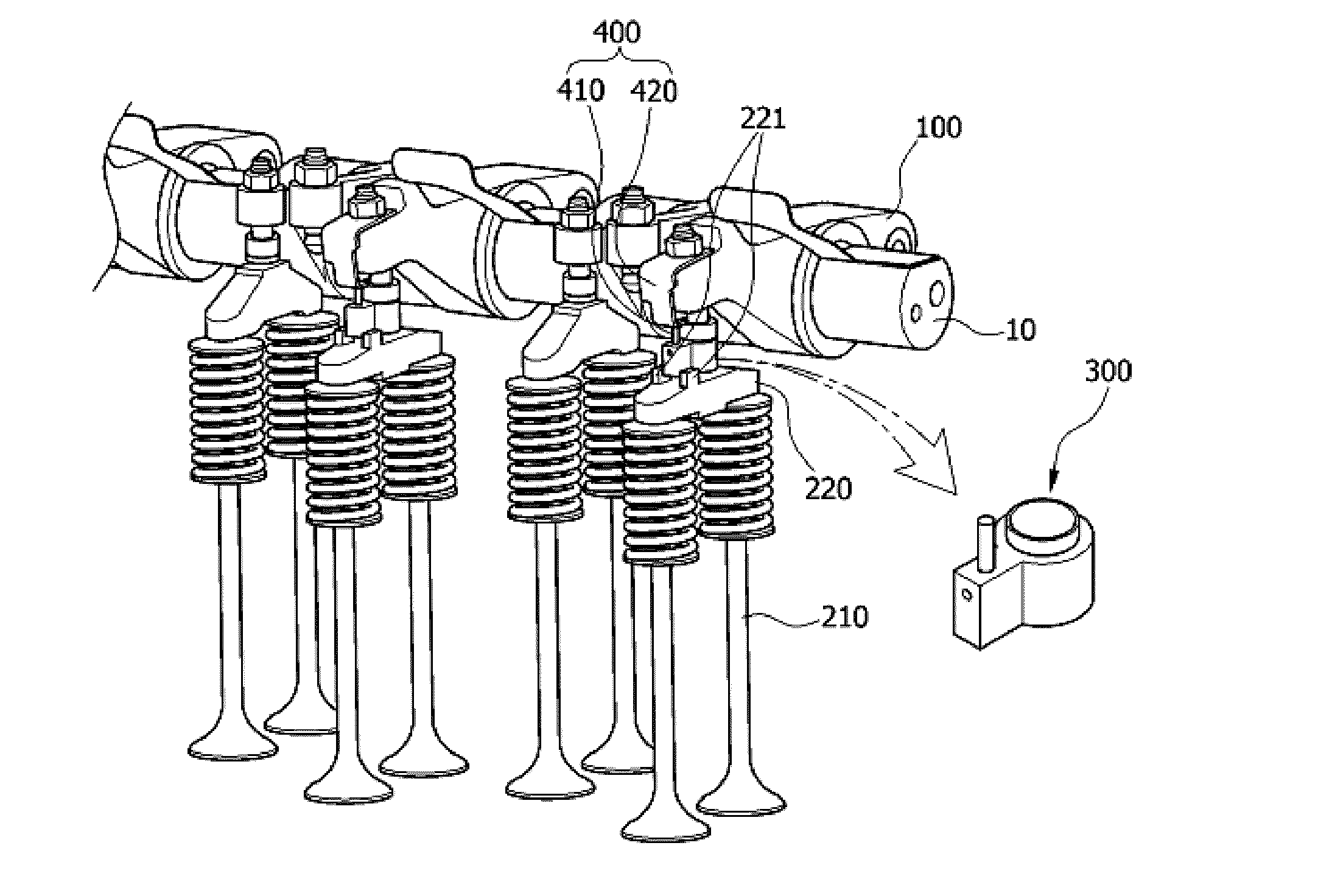
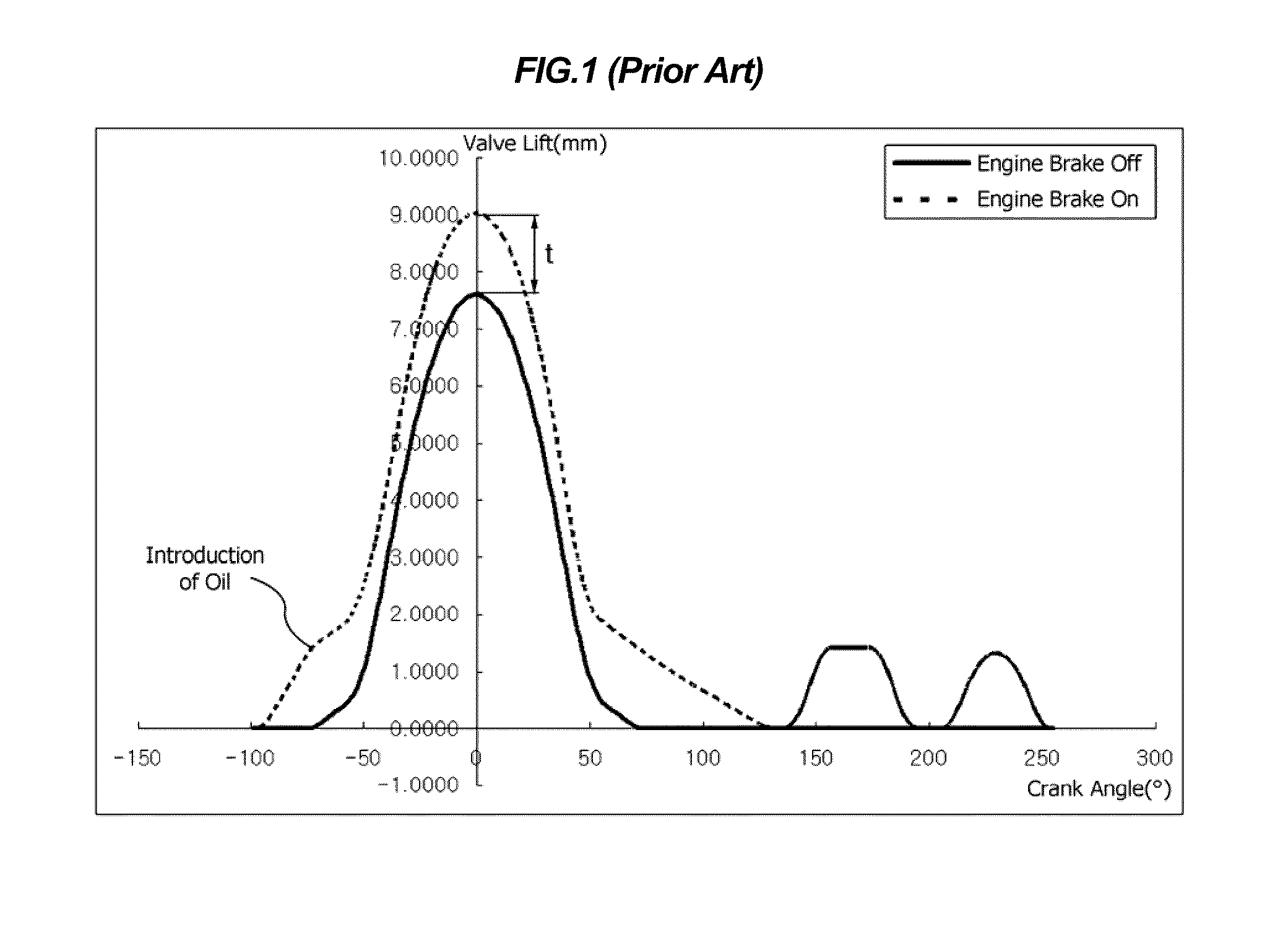
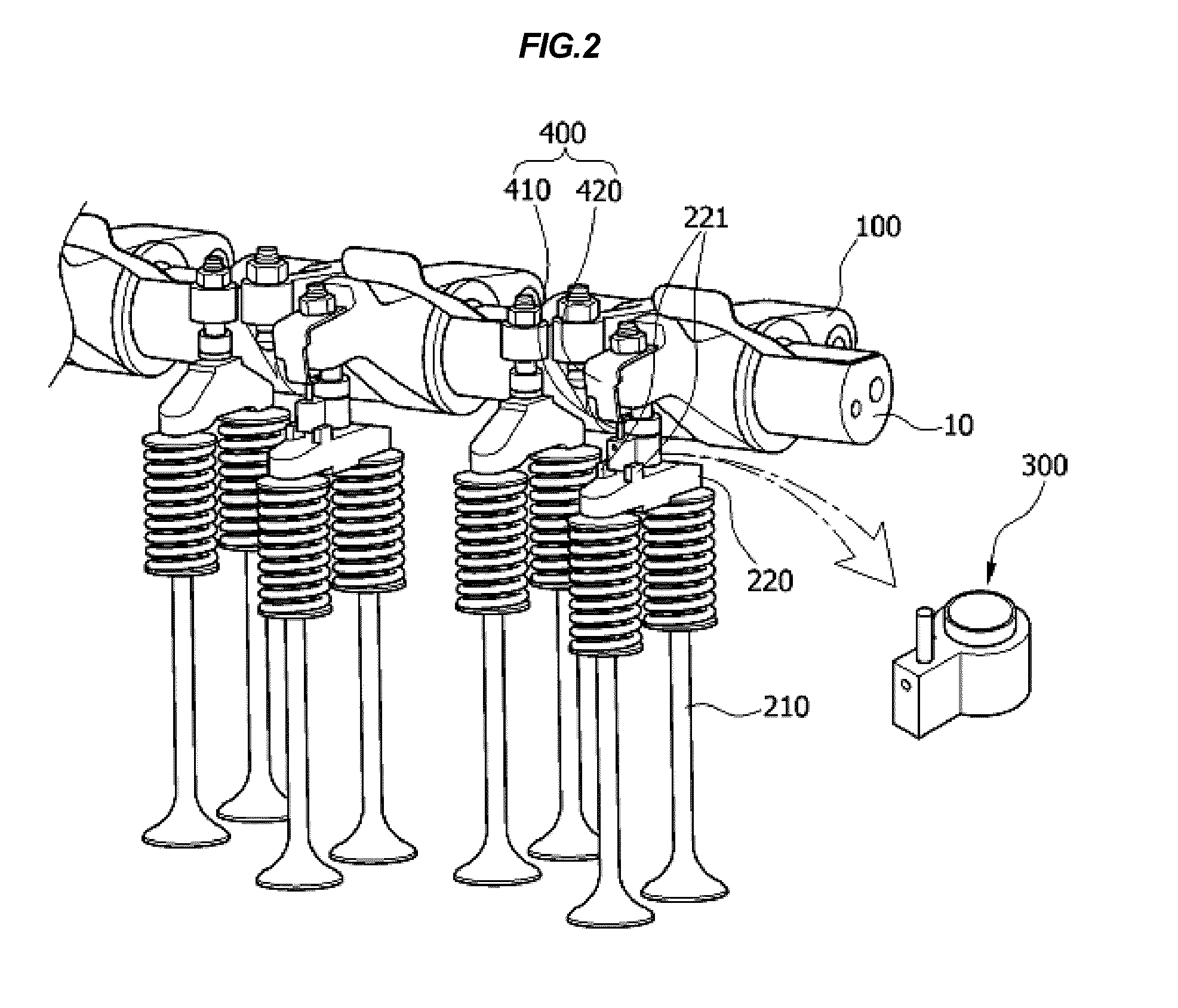
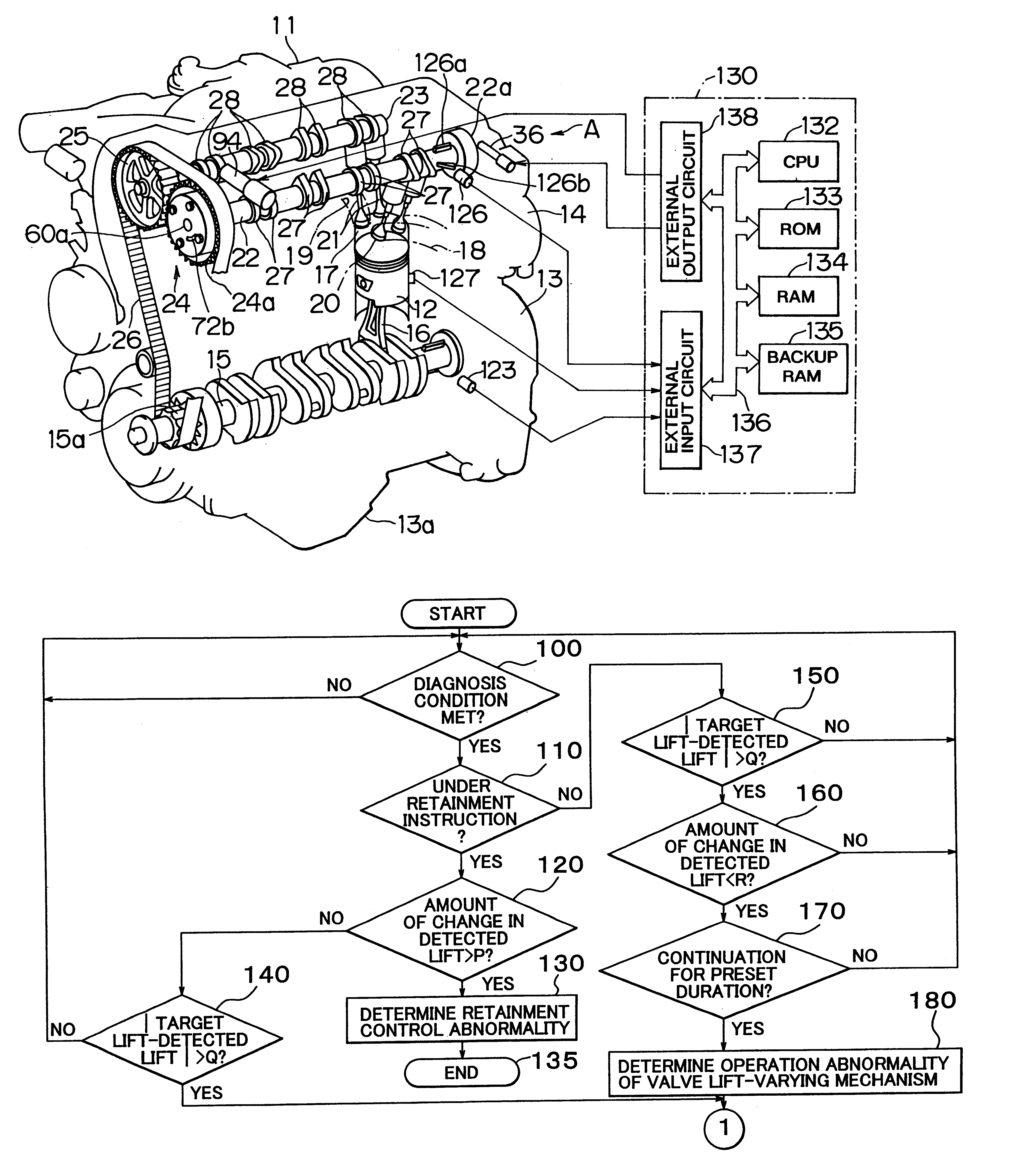
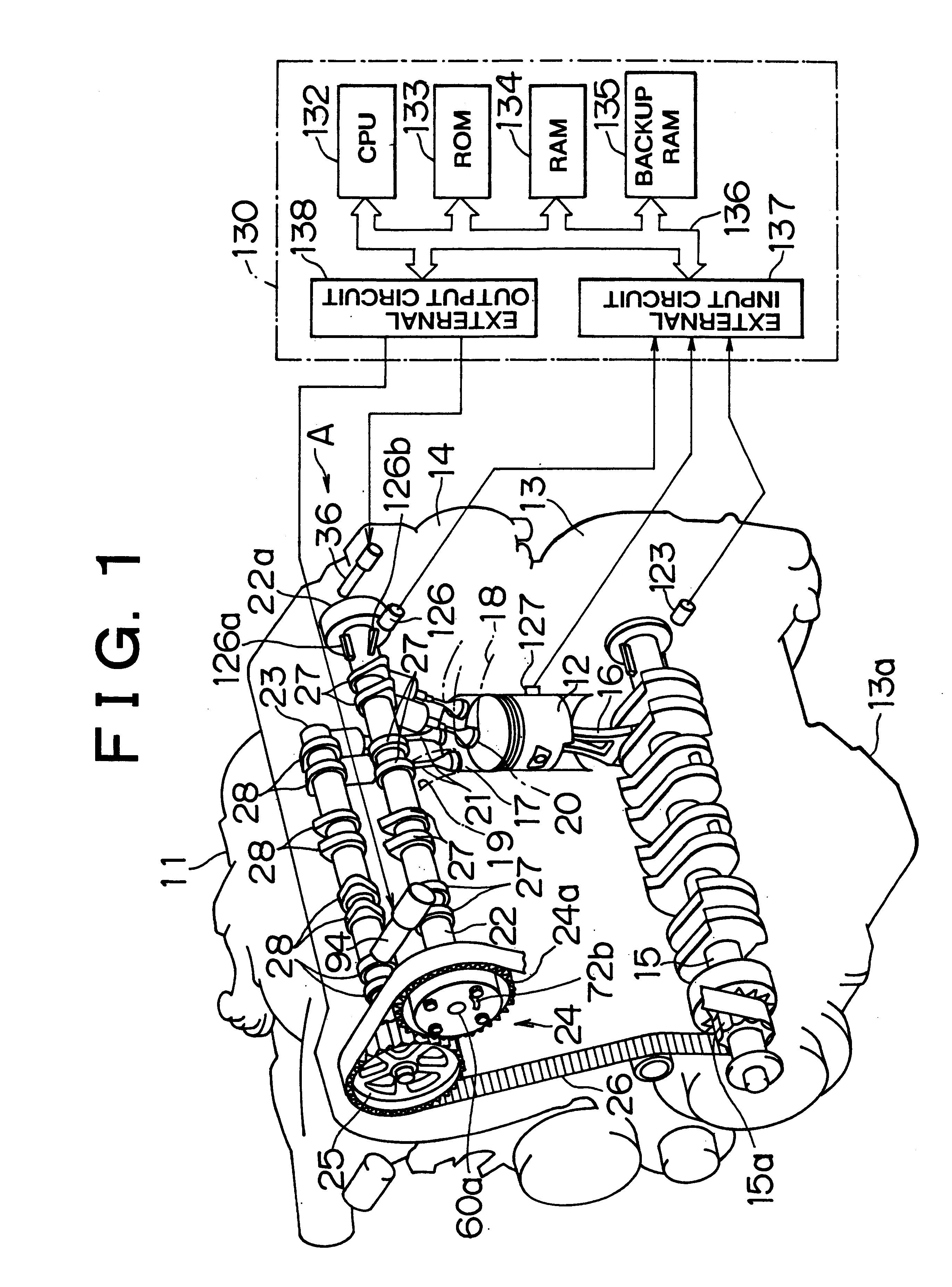
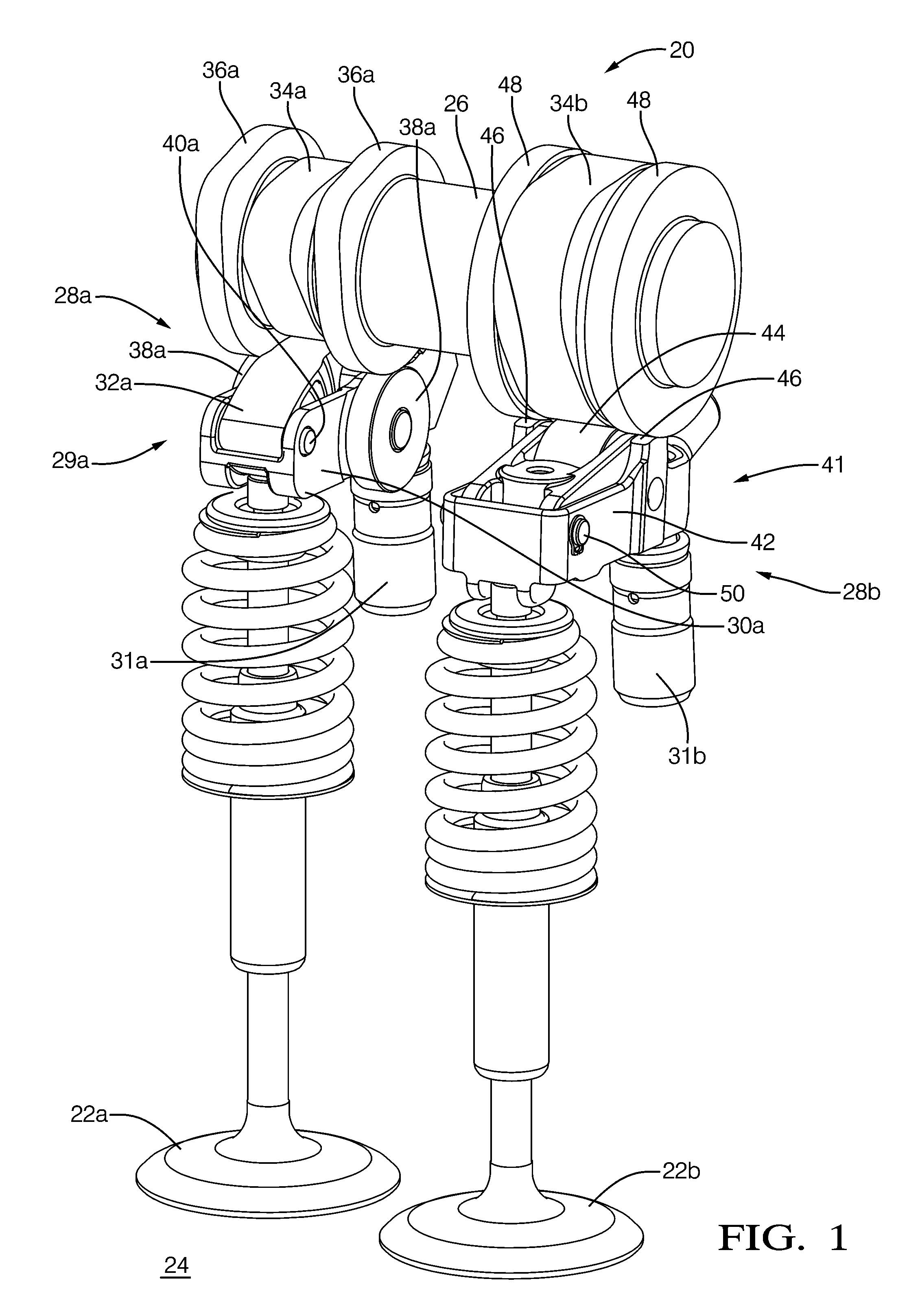
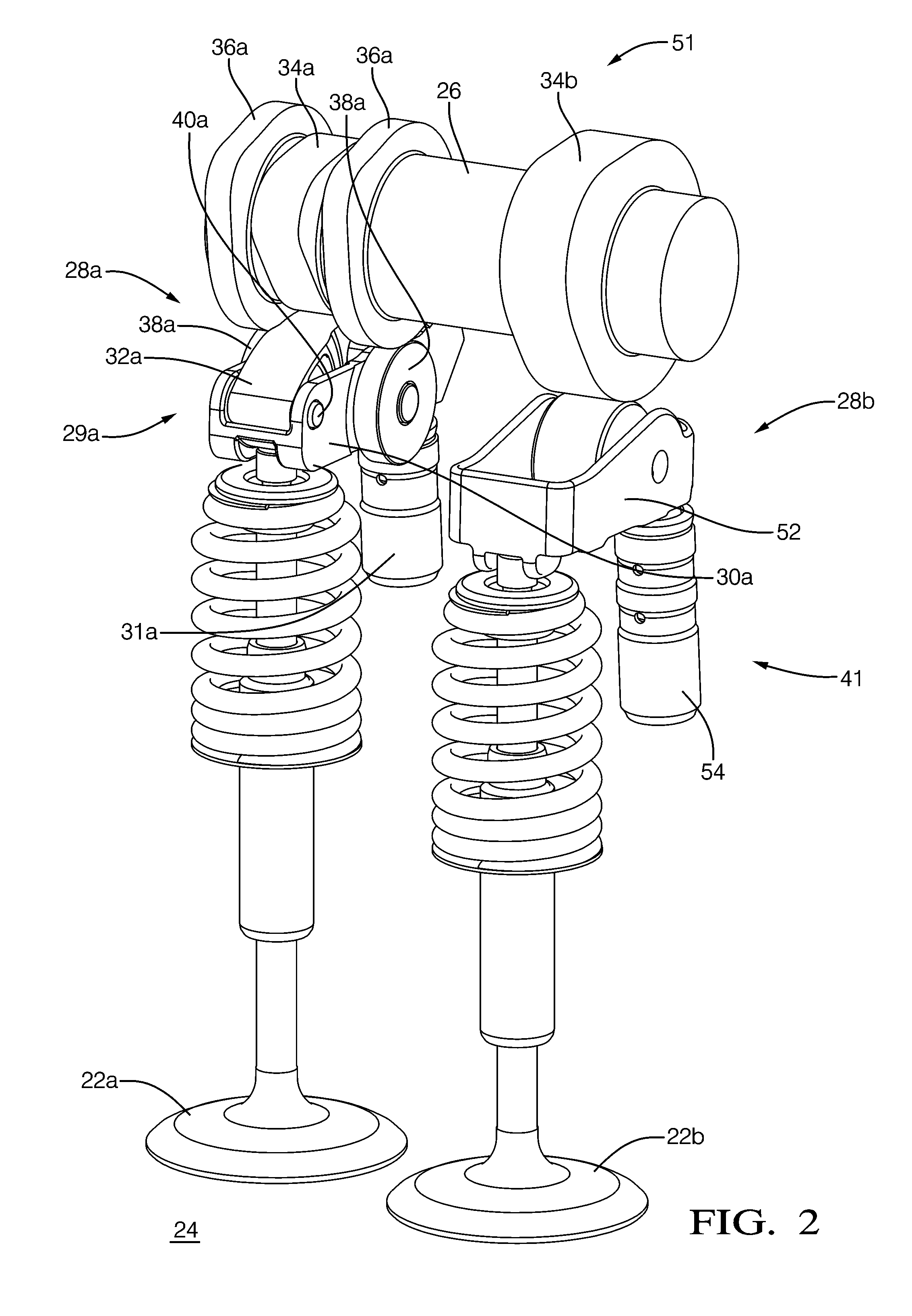
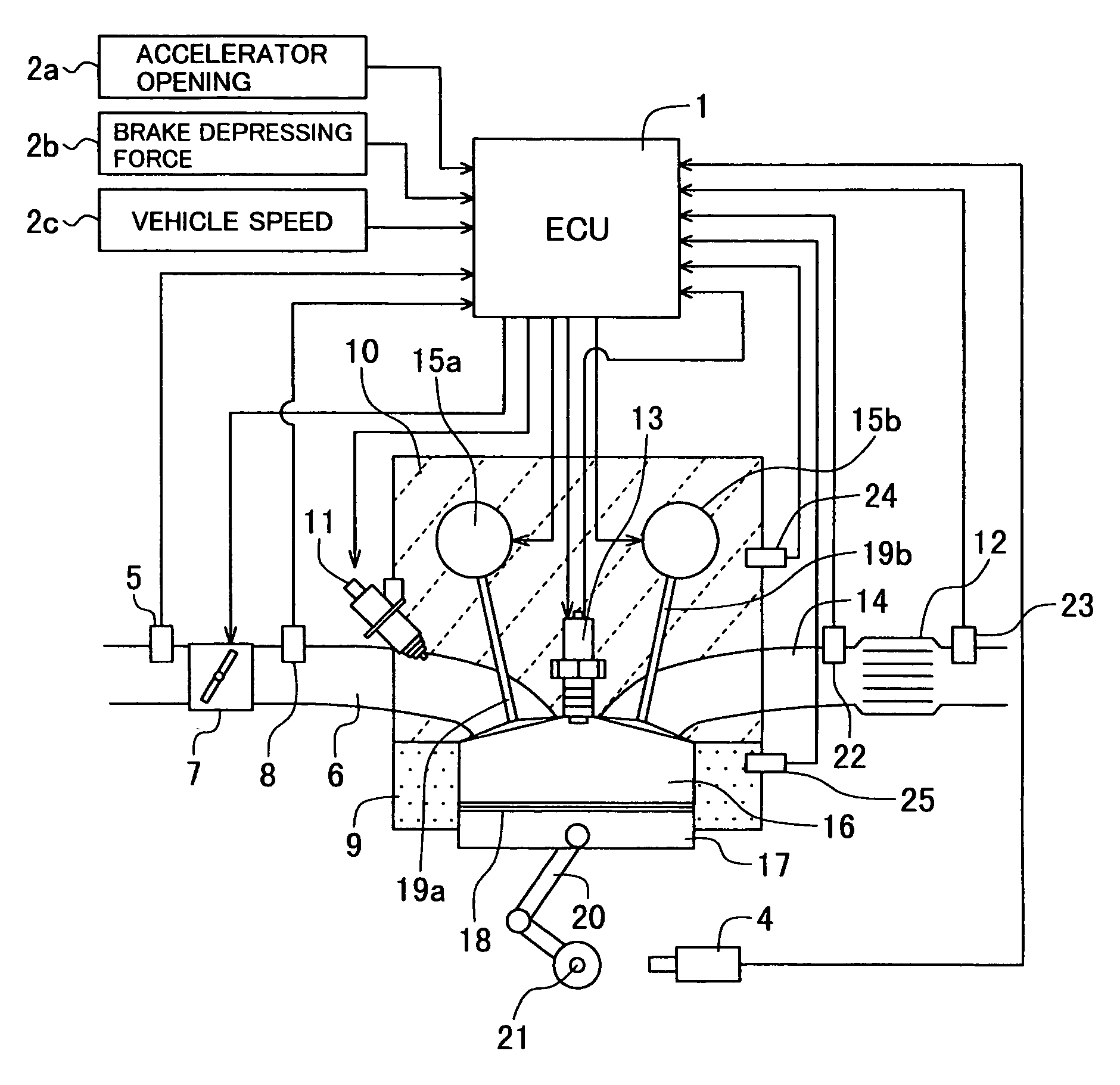
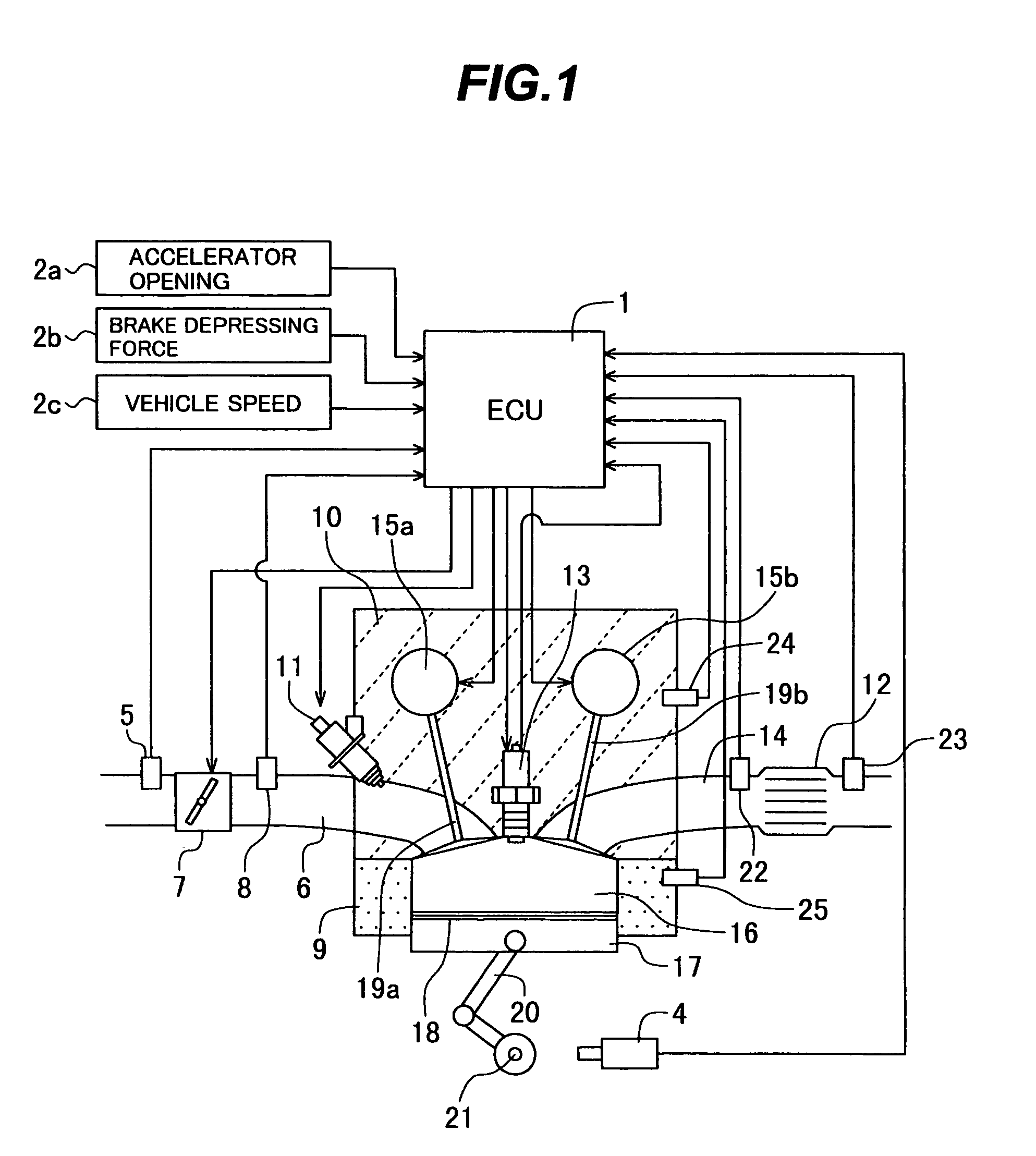
Patents
Literature
1266 results about "Valve lift" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
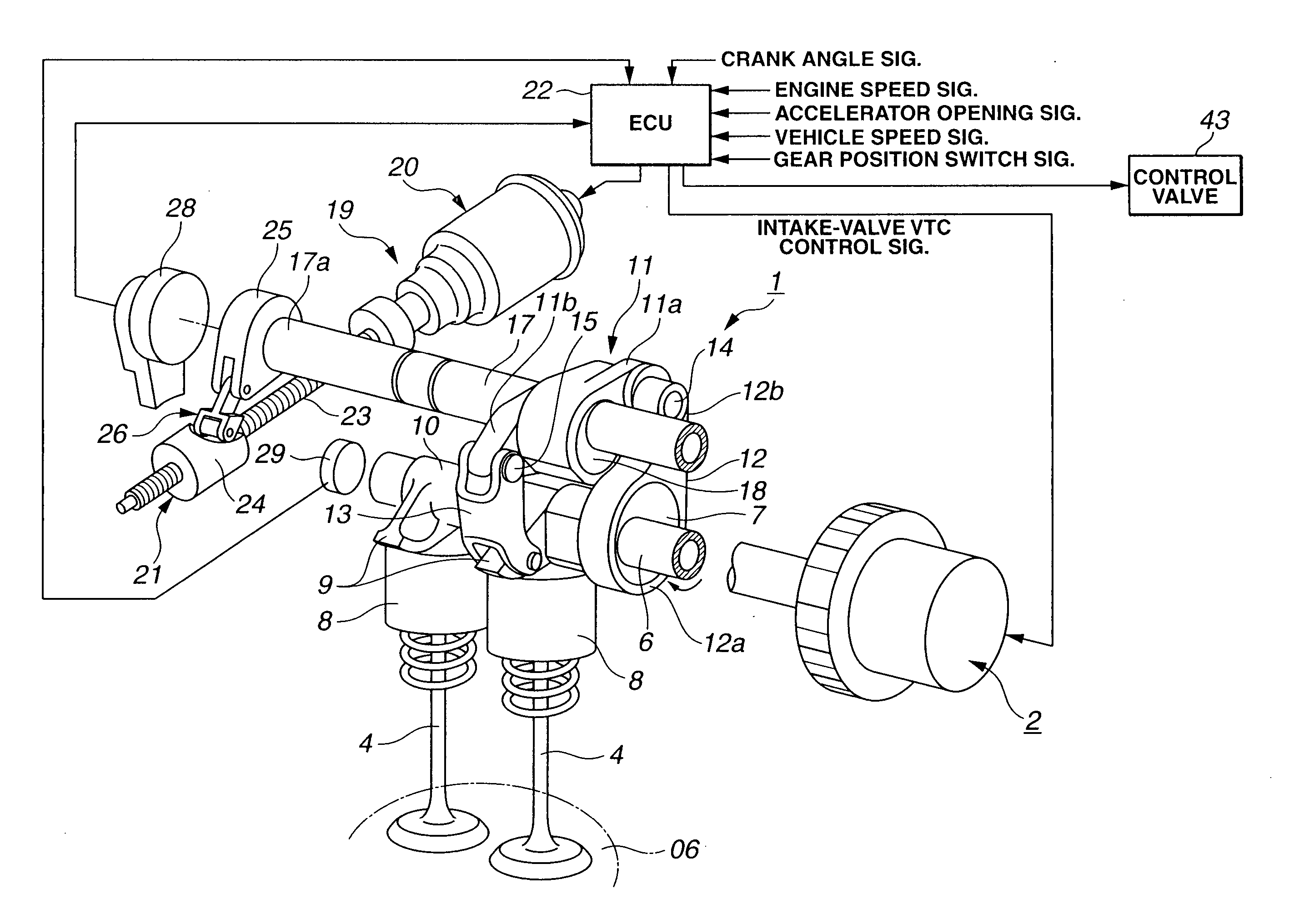
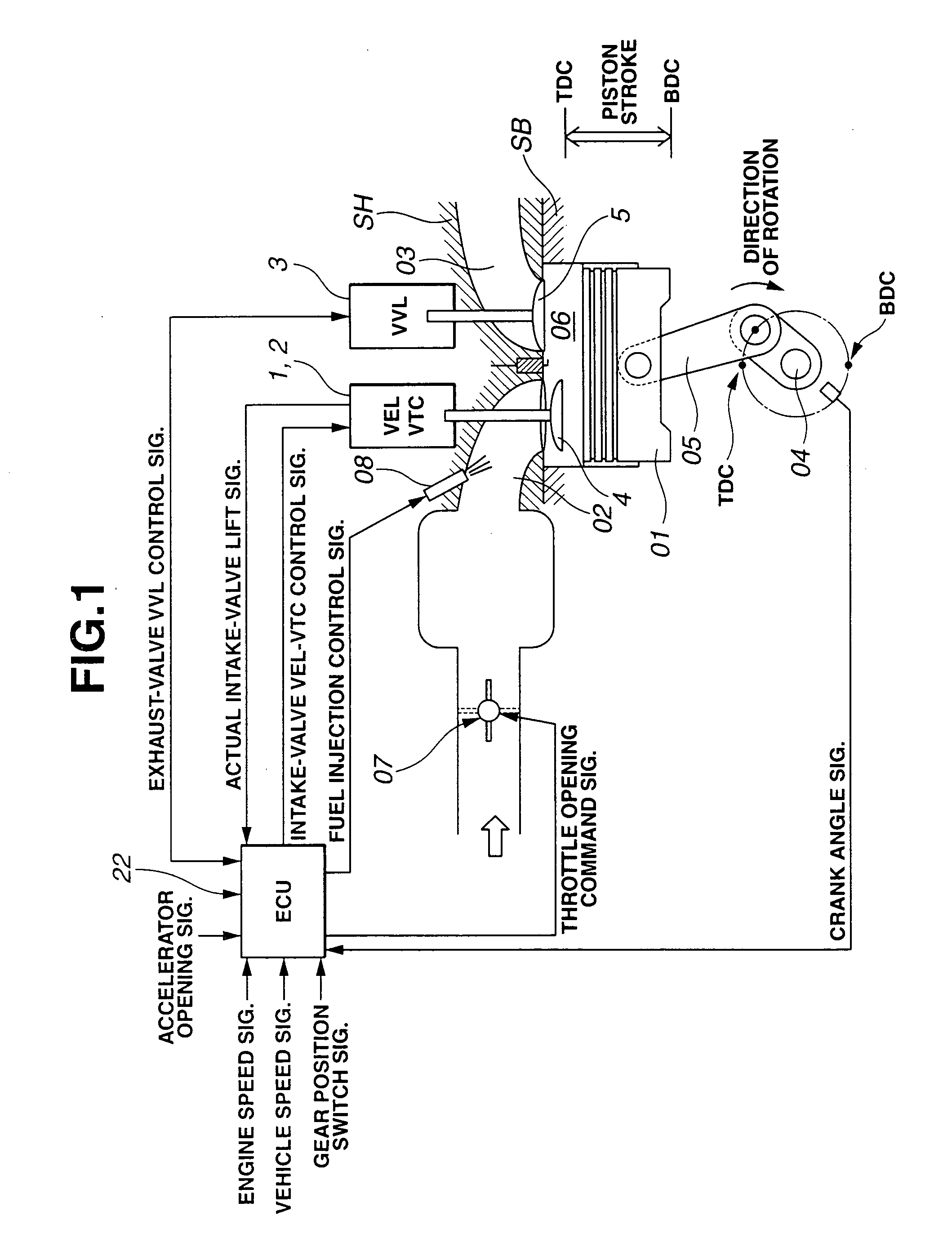
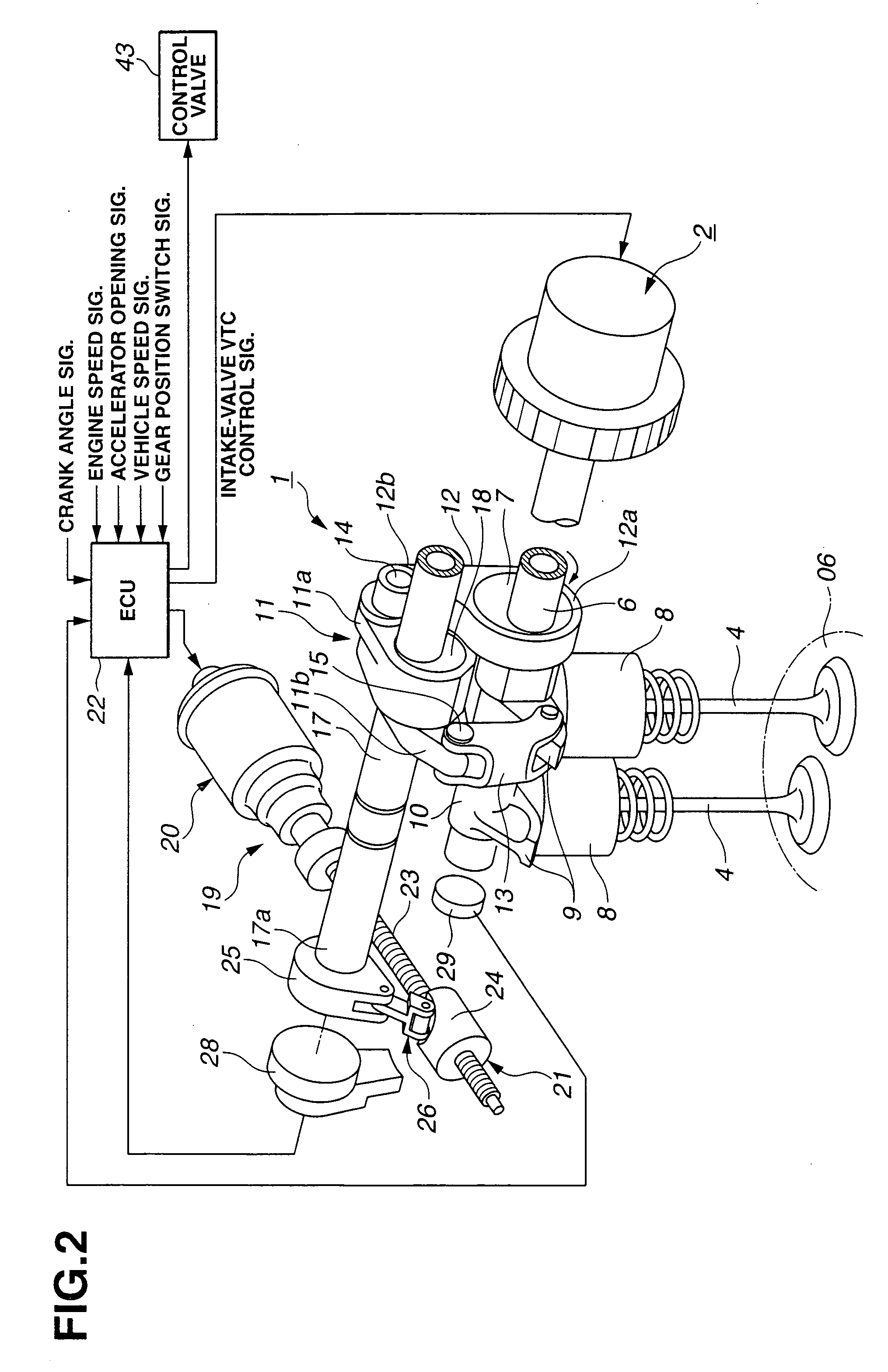
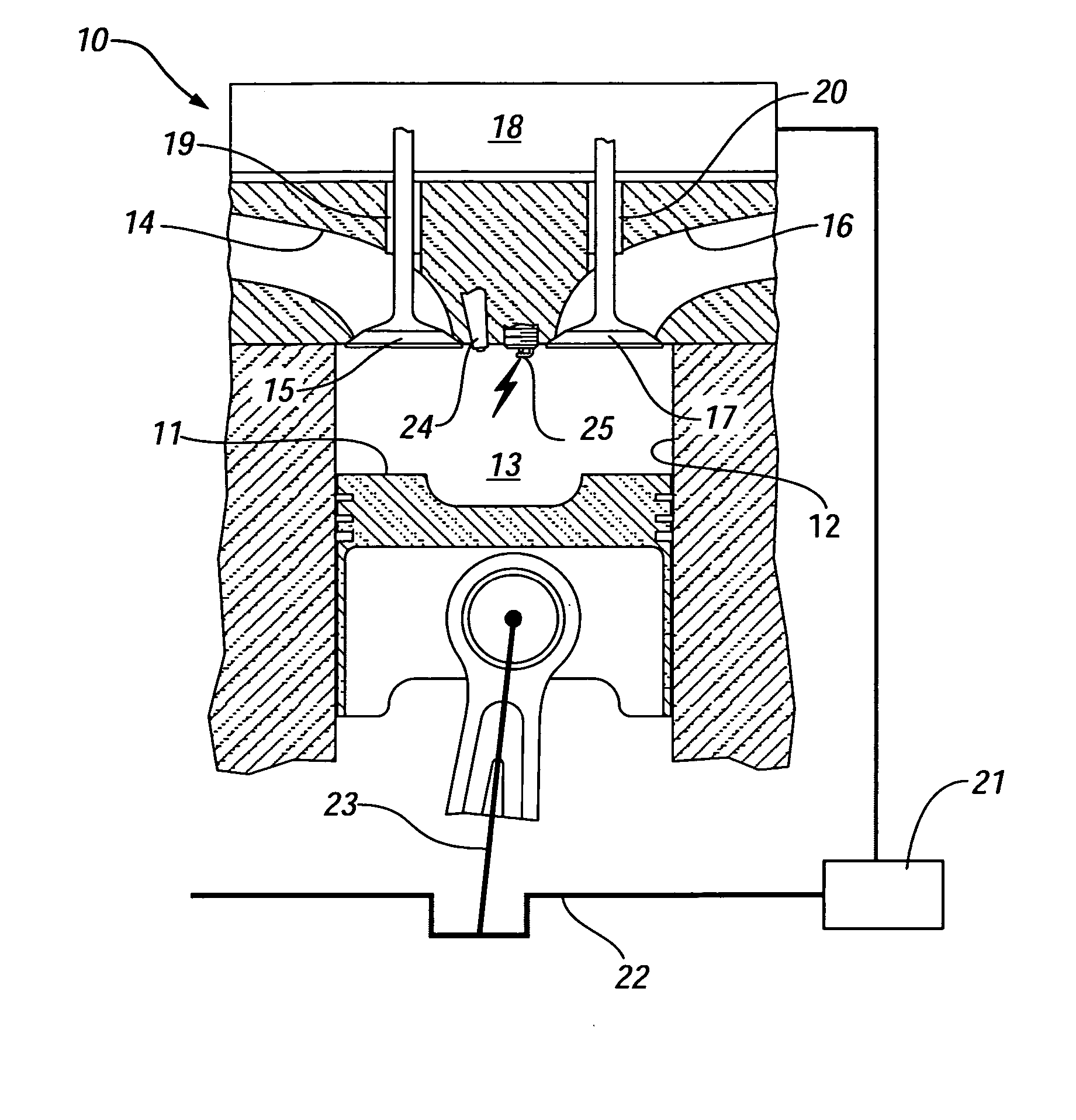
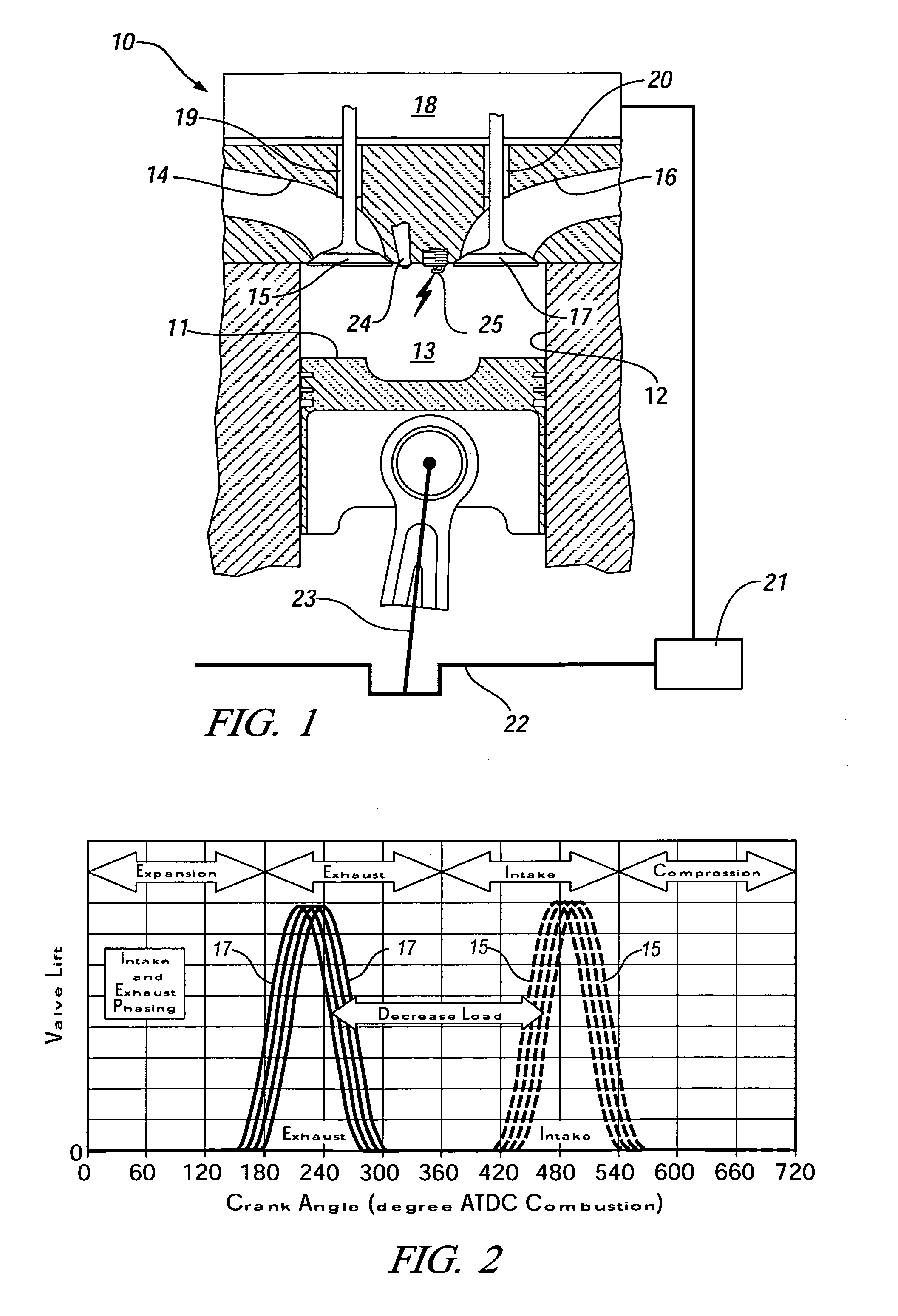
Cylinder cutoff control apparatus of internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20060037578A1Reduced engine braking effectTendency increaseValve arrangementsElectrical controlExhaust valveTop dead center
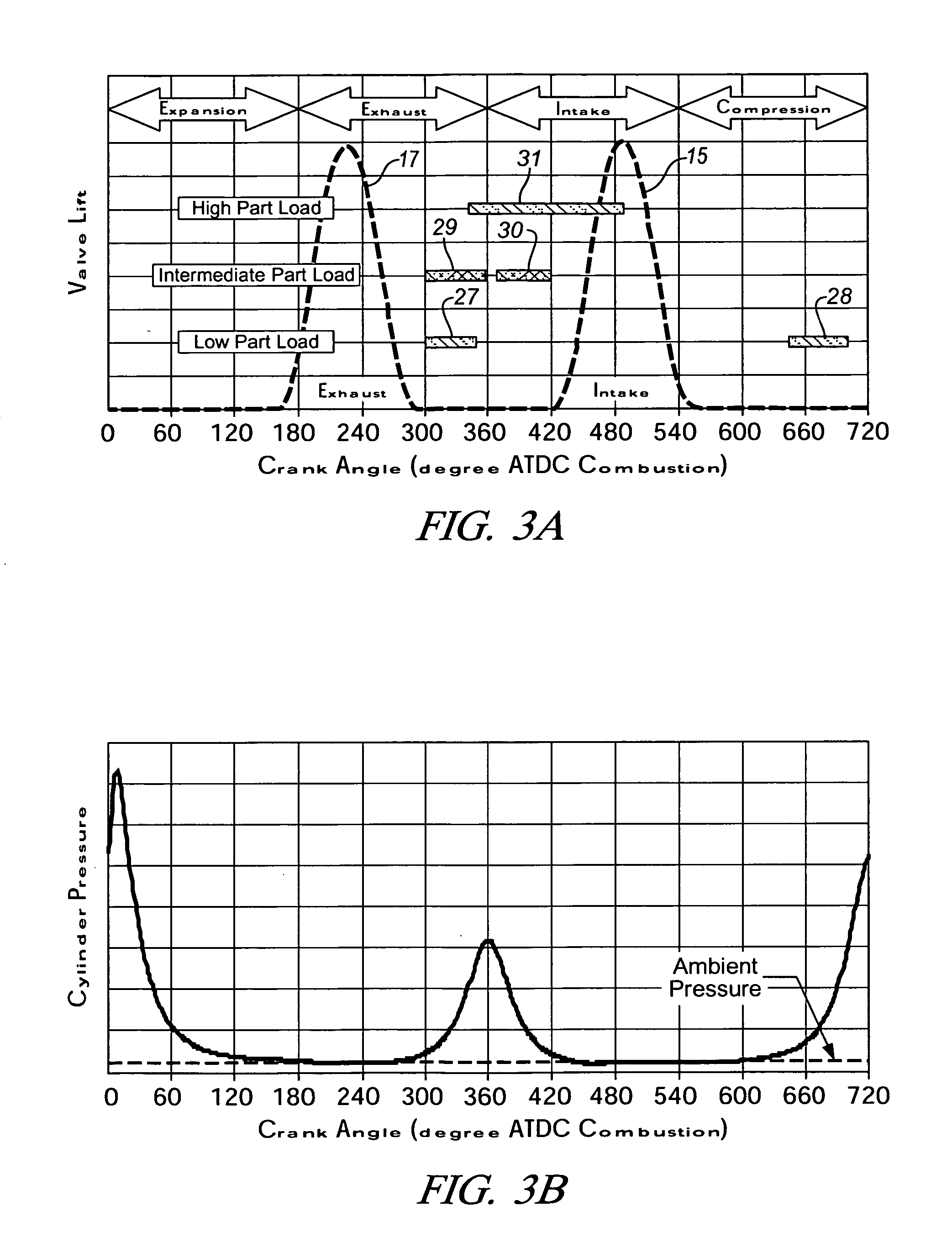
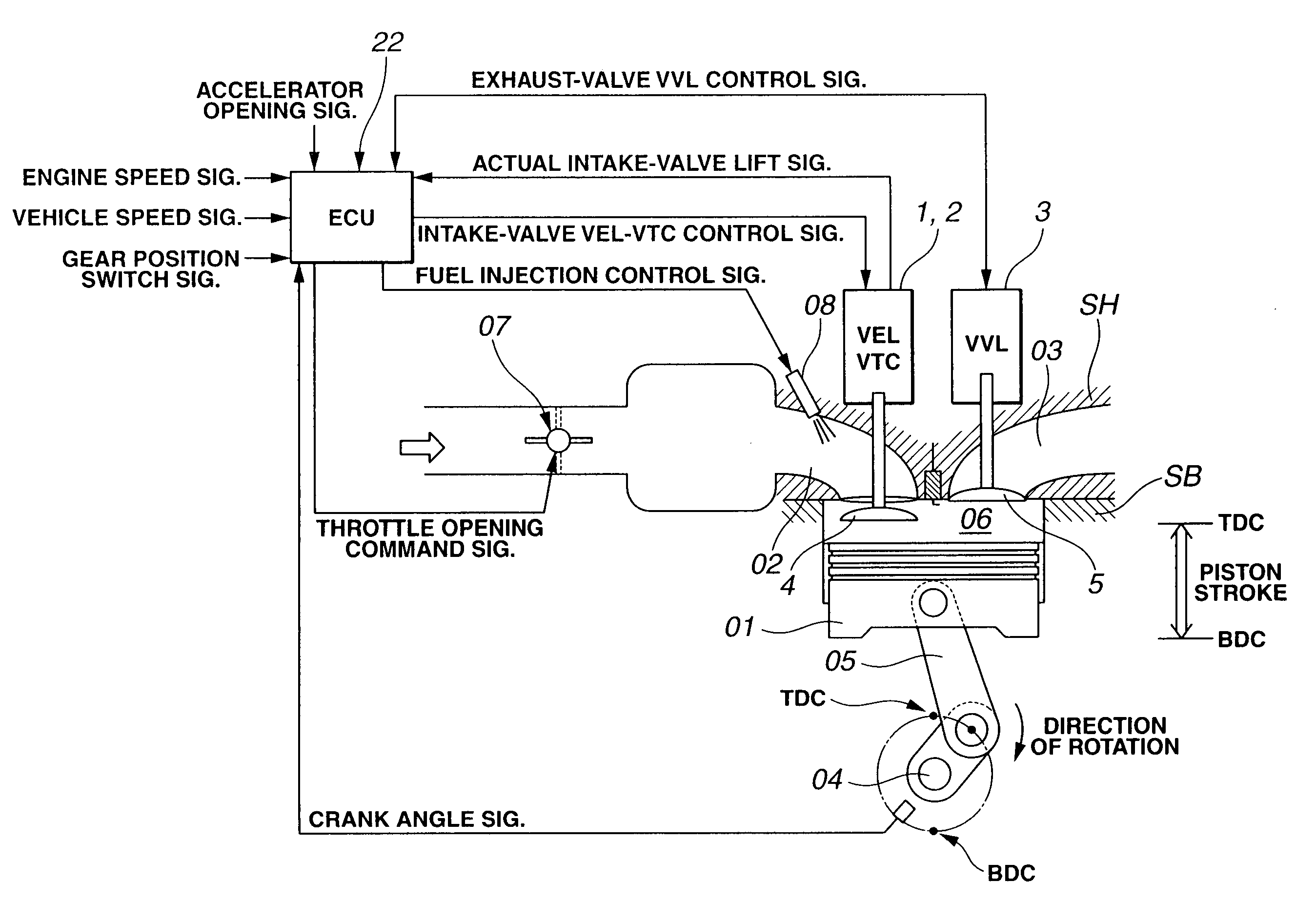
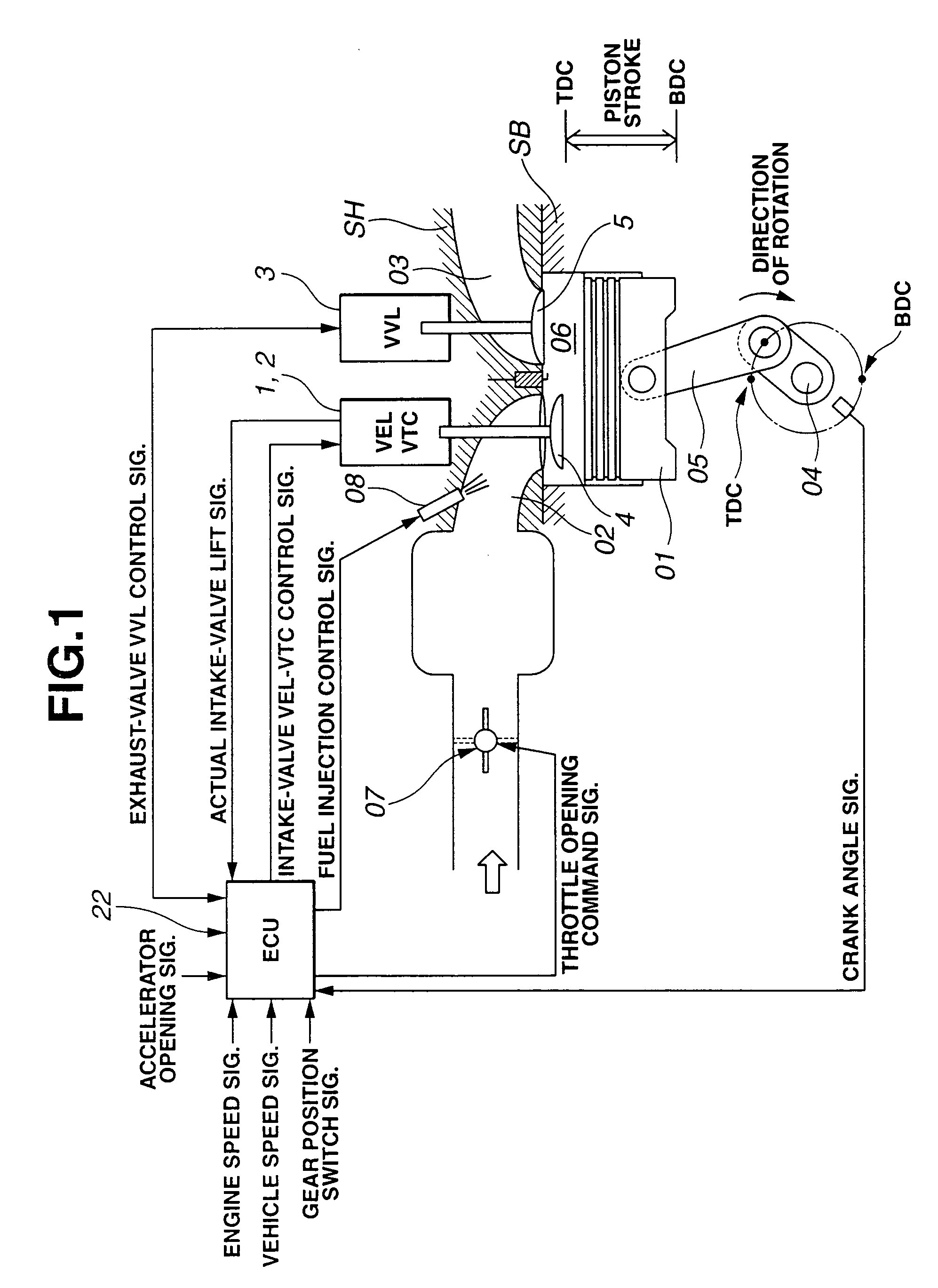
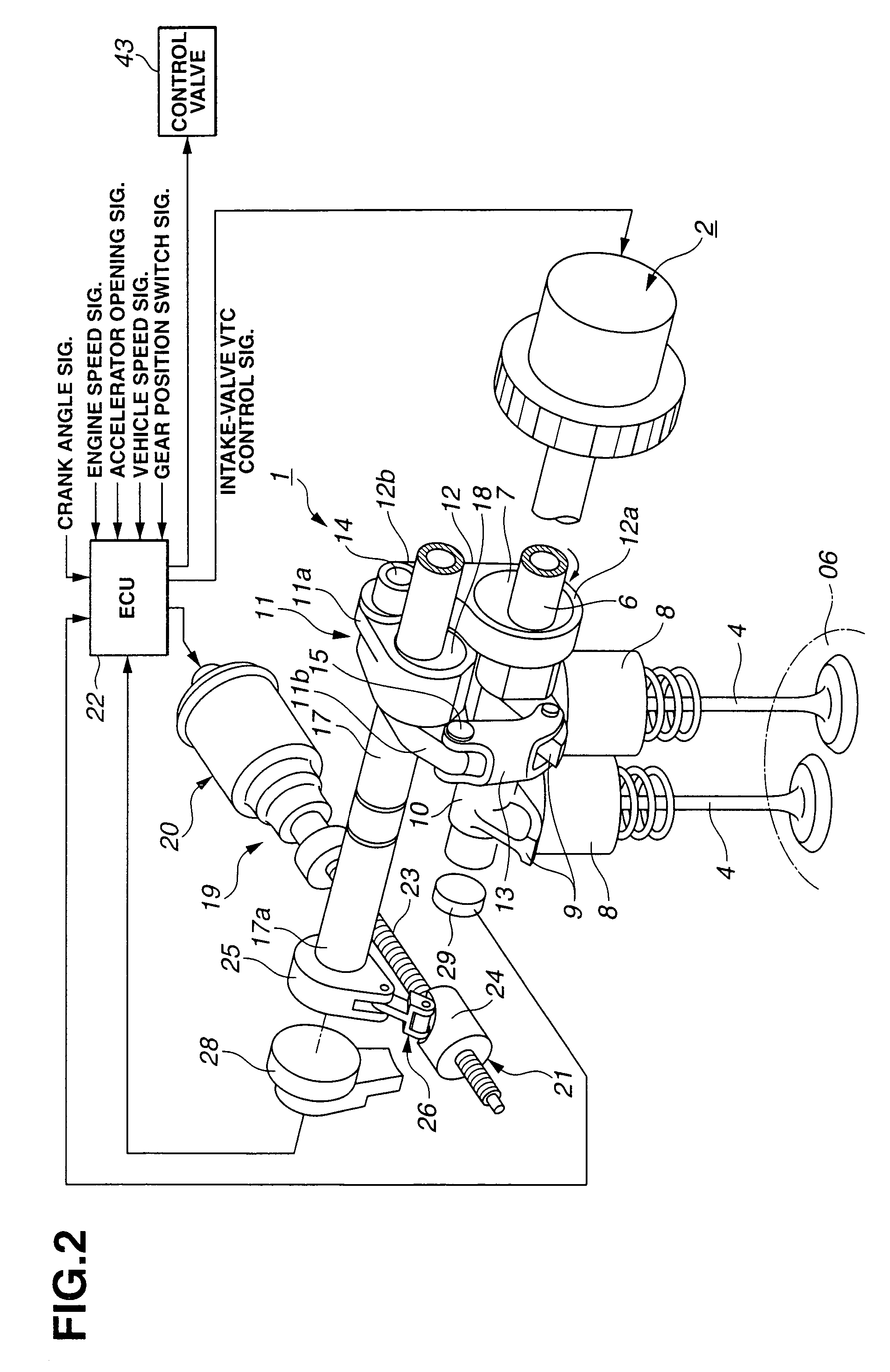
A cylinder cutoff control apparatus of an engine initiates a cylinder cutoff mode only when two conditions, namely a low load condition such as a vehicle cruising condition and an intake valve closure timing controlled to a given timing value before a bottom dead center, are both satisfied. A fuel cutoff mode is executed prior to the cylinder cutoff mode. During a transition to the cylinder cutoff mode, the control apparatus holds an intake valve open timing at a given timing value substantially corresponding to a top dead center, simultaneously with reducing an intake valve lift amount of each intake valve, subjected to cylinder cutoff control, to a zero lift. Immediately when the intake valve lift amount is reduced to below a lift threshold value, an exhaust valve lift amount of each exhaust valve, subjected to the cylinder cutoff control, is controlled to a zero lift.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Hydraulic valve mechanism of variable valve lift
ActiveCN101713308AImprove performanceNo significant change in volumeMachines/enginesNon-mechanical valveGear wheelEngineering
The invention discloses a hydraulic valve mechanism of a variable valve lift. The hydraulic valve mechanism of the variable valve lift comprises a valve spool of a puller cam, a sleeve capable of rotating relative to the valve spool and a seal gland connected with a valve. The top end of the sleeve is adapted to the valve spool; the bottom of the sleeve is adapted to the seal gland and an oil chamber is formed in the middle part of the sleeve. The hydraulic valve mechanism of the variable valve lift is characterized in that a valve spool oil duct is formed in the valve spool; an inlet of the valve spool oil duct is movably adapted to a sleeve oil duct; the outlet of the valve spool oil duct is communicated with the oil chamber; and the inlet of the valve spool oil duct is in shape of a helical notch. Part of gears are arranged outside the sleeve so as to drive the sleeve to rotate by racks or other similar mechanisms. A return spring is further arranged on the valve spool. The problems of complicated structure, high cost and low reliability existing in prior art are solved. The hydraulic valve mechanism of the variable valve lift is a hydraulic valve mechanism which is capable of realizing quick response.
Owner:CHERY AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
Method for transition between controlled auto-ignition and spark ignition modes in direct fuel injection engines
InactiveUS20060196466A1Eliminate misfiringEliminate partial burnValve arrangementsElectrical controlHomogeneous charge compression ignitionExhaust valve
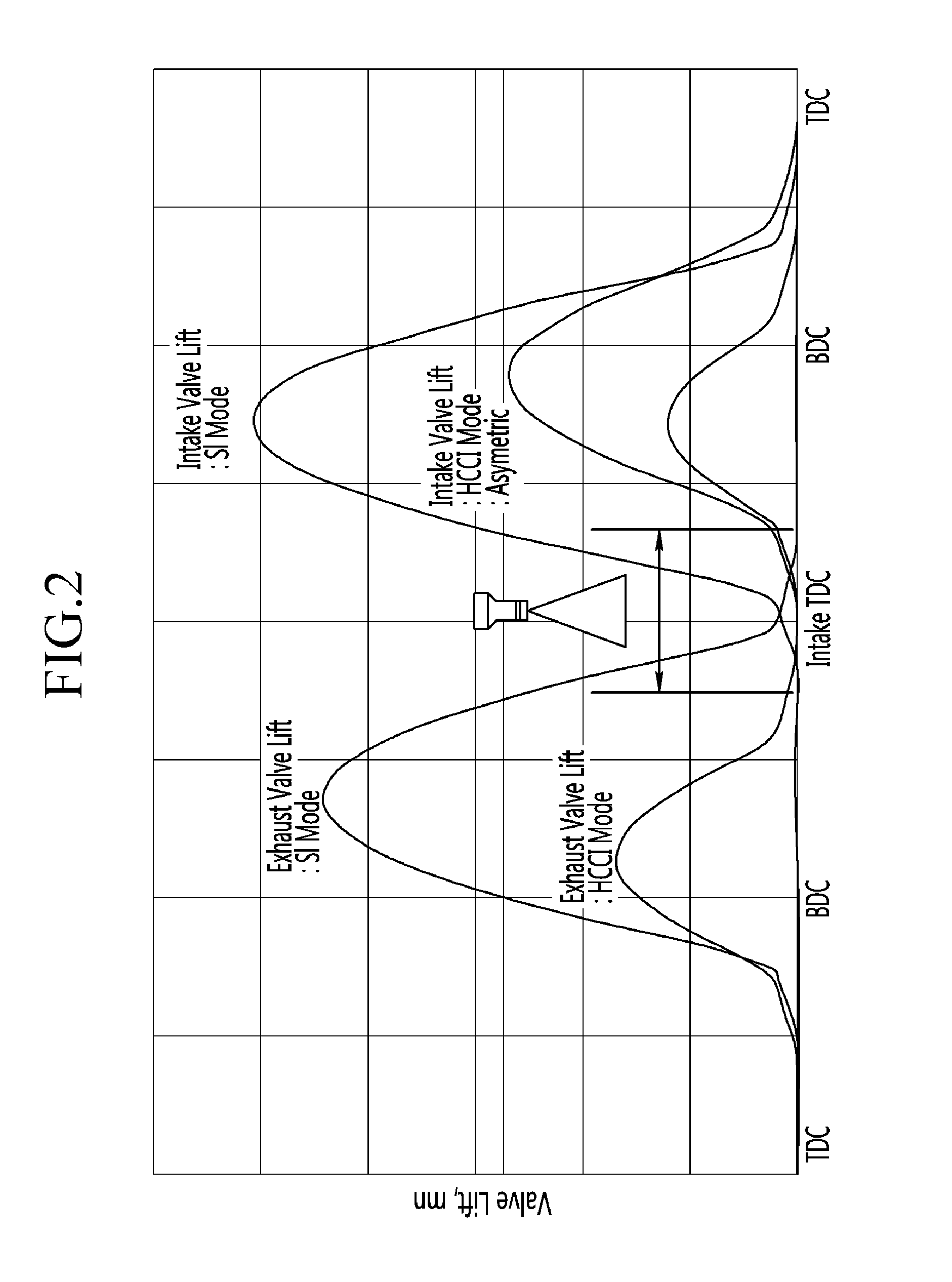
A method is provided for control of transition between combustion modes of a direct-injection engine operable in a homogeneous charge compression ignition (HCCI) mode at lower loads and a spark ignition flame propagation (SI) mode at higher loads. The engine includes a variable valve actuation system including two-step high and low lift valve actuation and separate cam phasing for both intake and exhaust valves. The method includes operating the engine at steady state, with fuel-air-exhaust gas mixtures at predetermined conditions, for each speed and load, and controlling the engine during mode changes between the HCCI mode and the SI mode by switching the exhaust and intake valves between low lift for HCCI operation and high lift for SI operation. High load may be an SI throttled mode with an intermediate unthrottled mode (SI / NTLC} in which transition between HCCI and SI / NTLC modes requires switching only the exhaust valve lift and transition between SI / NTLC and SI throttled modes requires switching only the intake valve lift, with predetermined phase adjustments in the valve timing phasing.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Cylinder cutoff control apparatus of internal combustion engine
A cylinder cutoff control apparatus of an engine initiates a cylinder cutoff mode only when two conditions, namely a low load condition such as a vehicle cruising condition and an intake valve closure timing controlled to a given timing value before a bottom dead center, are both satisfied. A fuel cutoff mode is executed prior to the cylinder cutoff mode. During a transition to the cylinder cutoff mode, the control apparatus holds an intake valve open timing at a given timing value substantially corresponding to a top dead center, simultaneously with reducing an intake valve lift amount of each intake valve, subjected to cylinder cutoff control, to a zero lift. Immediately when the intake valve lift amount is reduced to below a lift threshold value, an exhaust valve lift amount of each exhaust valve, subjected to the cylinder cutoff control, is controlled to a zero lift.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
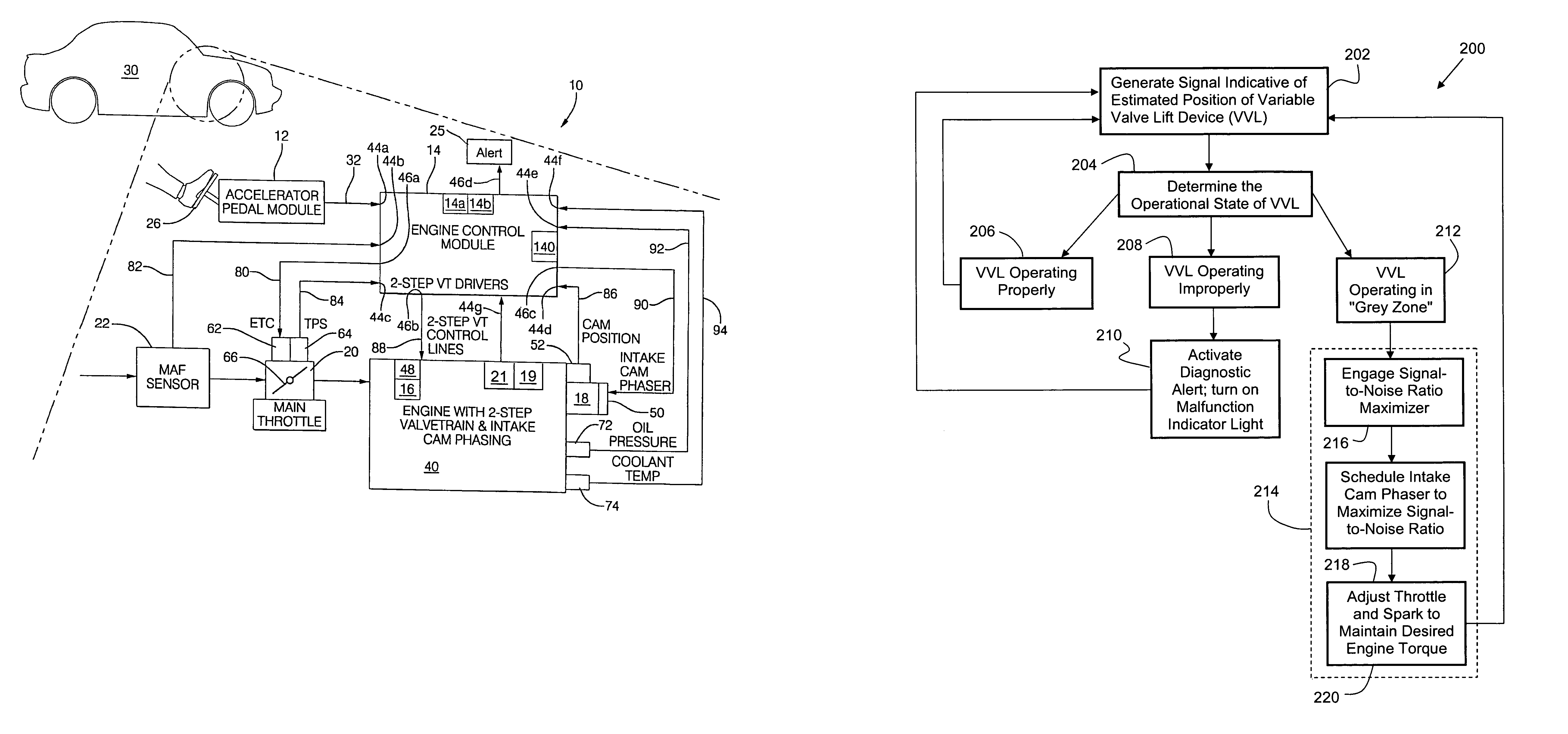
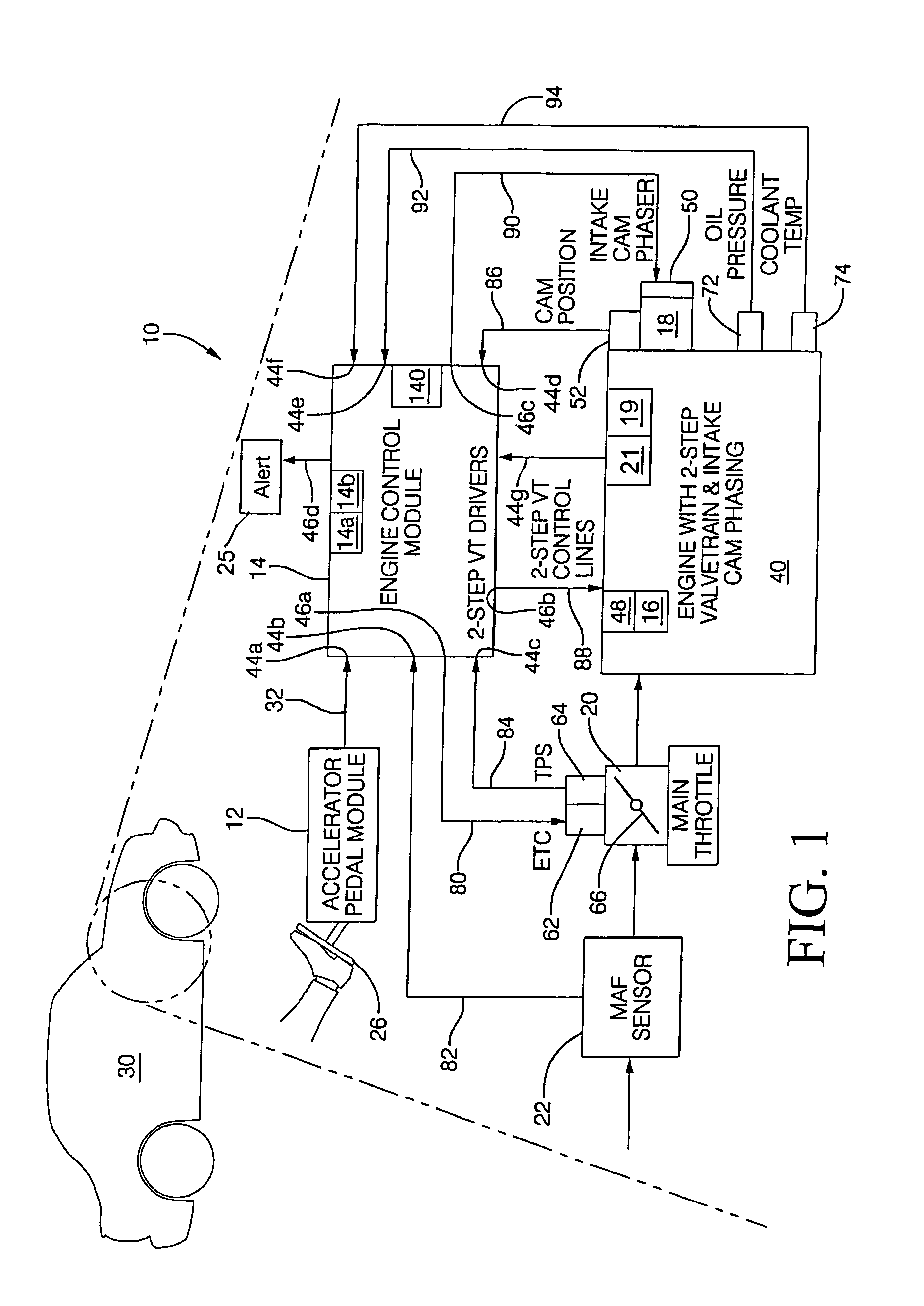
Method for effectively diagnosing the operational state of a variable valve lift device
ActiveUS7063057B1Reliably indicate operational stateHigh degree of certaintyAnalogue computers for vehiclesValve arrangementsEngineeringValve lift
A method for diagnosing the operational state of a variable valve lift device (VVL) is provided. The method includes providing a first signal indicative of an estimated position of the VVL, the first signal having a first signal-to-noise ratio; determining that the first signal represents either a first condition indicating that the VVL is operating in one of two modes of operation, a second condition indicating that the VVL is not operating in the two modes of operation, and a third condition where the first signal is not in the first or second conditions; and adjusting a camshaft phase angle when the first signal is in the third condition so that the first signal has a second signal-to-noise ratio, wherein the second signal-to-noise ratio is greater than the first signal-to-noise ratio, whereby the operational state of the VVL is identified as one of the first and second conditions.
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
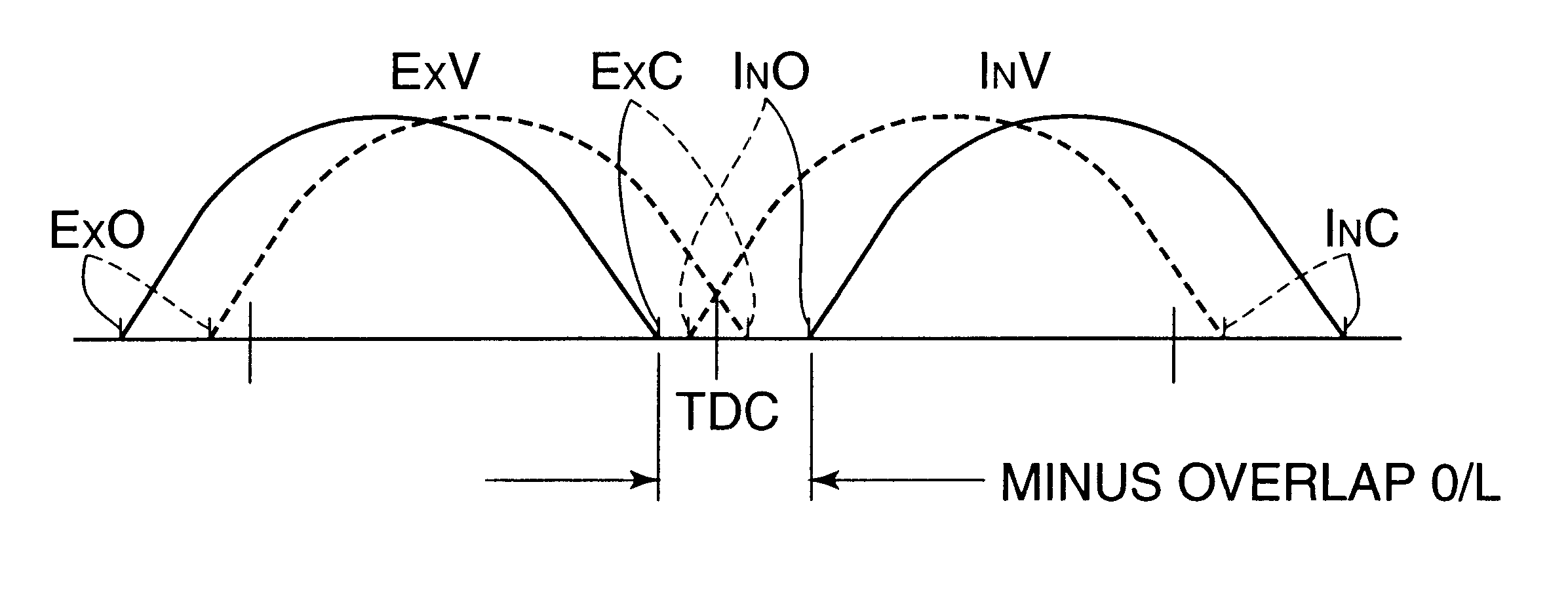
Automotive four-cycle engine
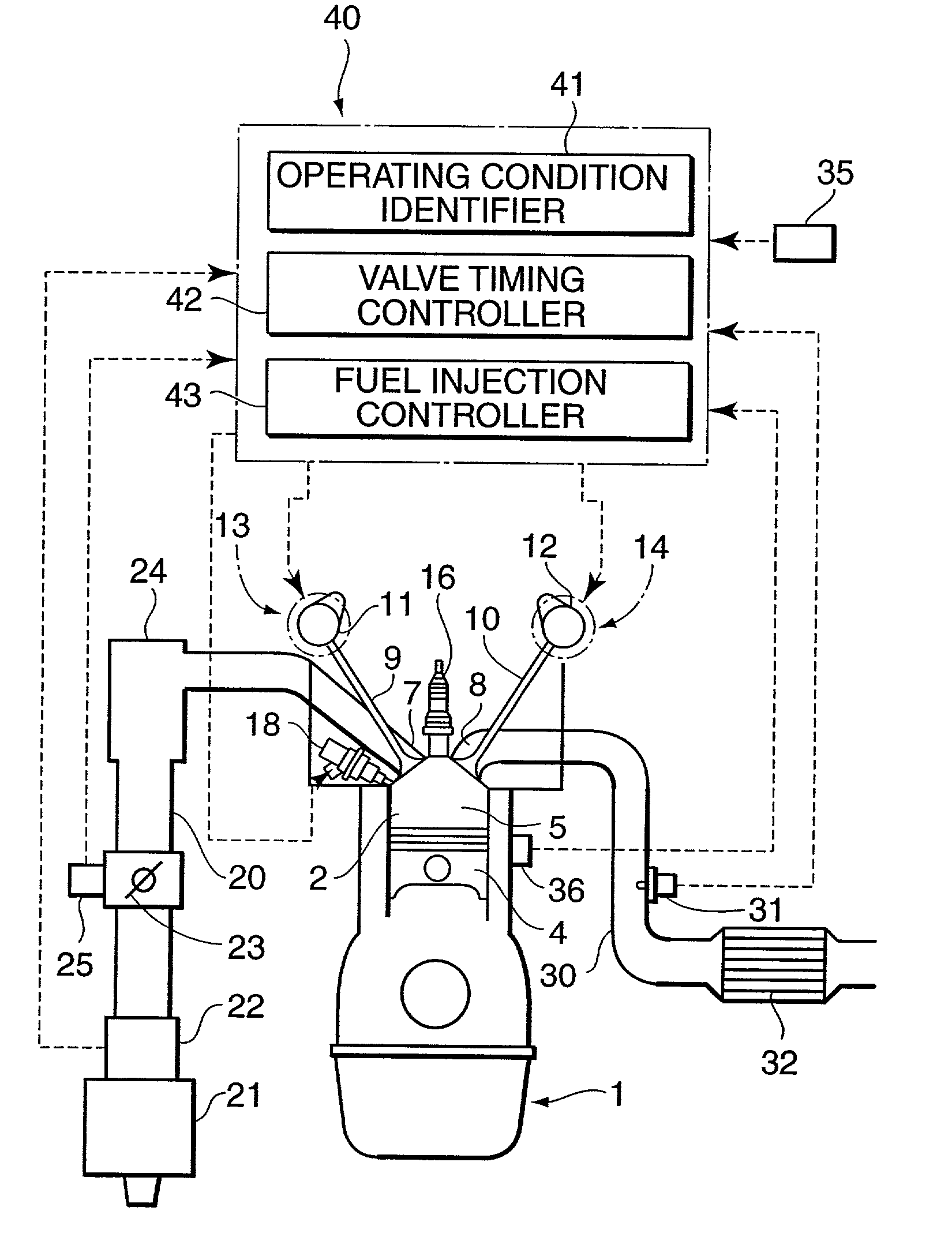
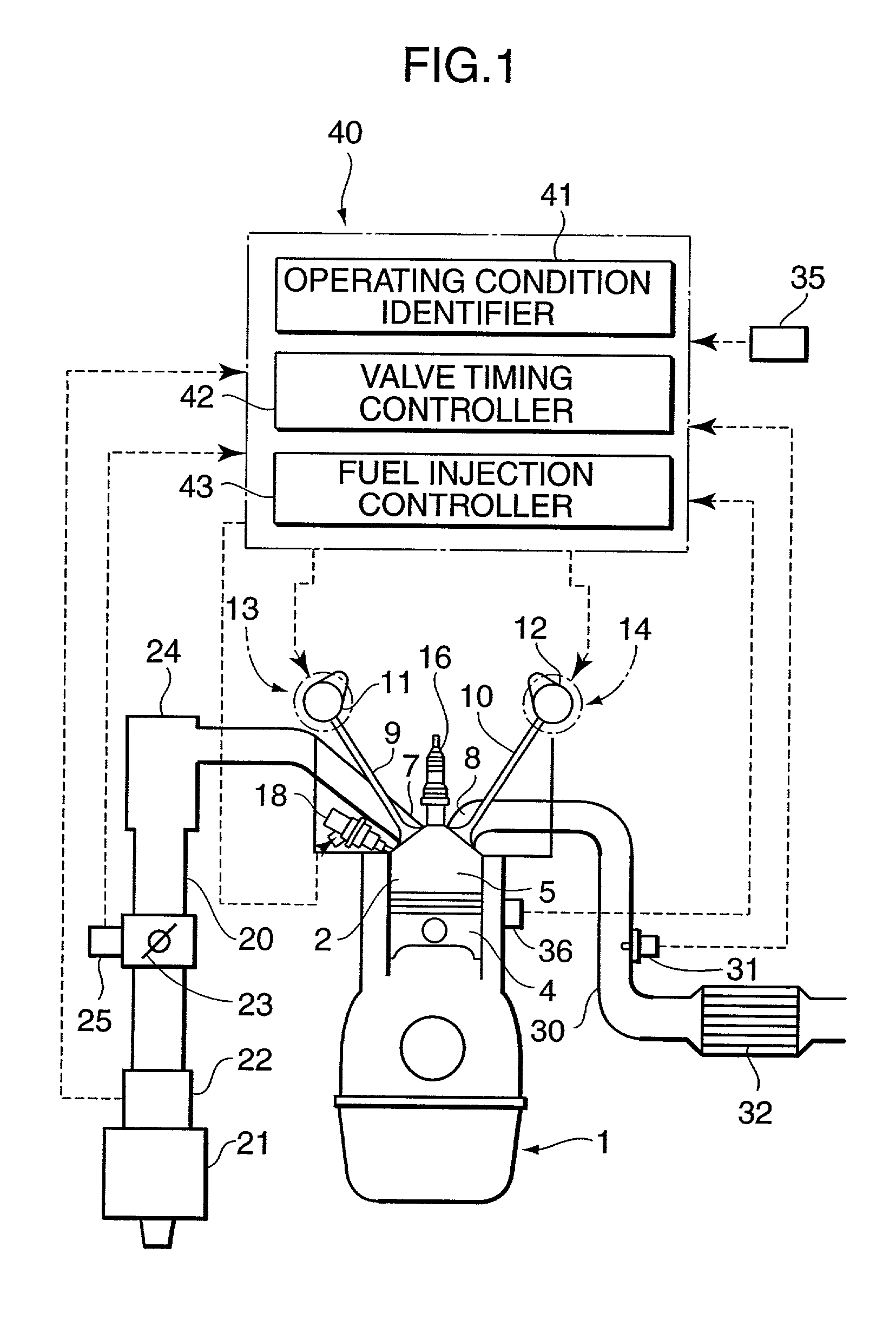
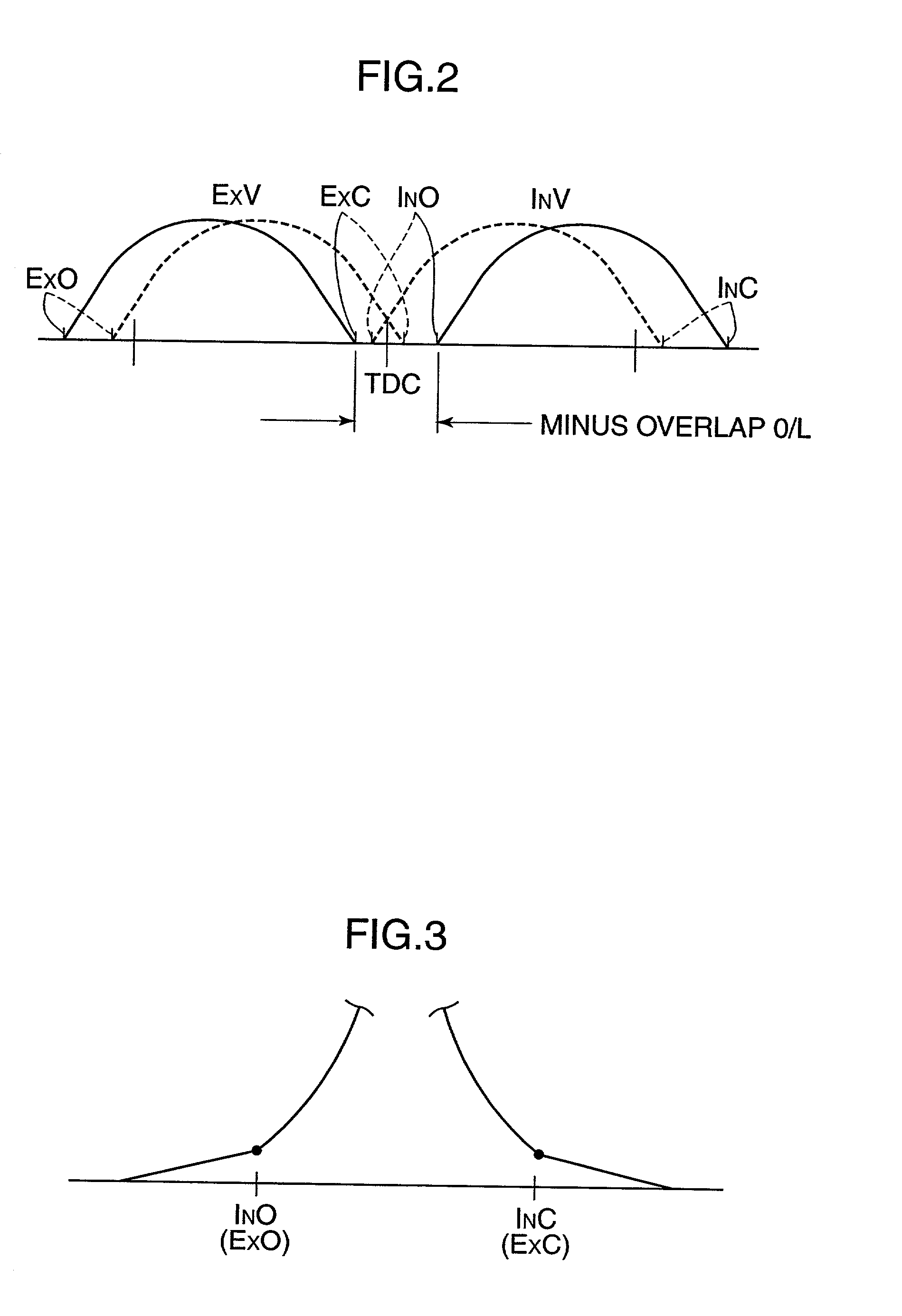
InactiveUS6626164B2Sufficient effectAvoid increase in combustion temperature and exhaust gas temperatureValve arrangementsElectrical controlExhaust valveTop dead center
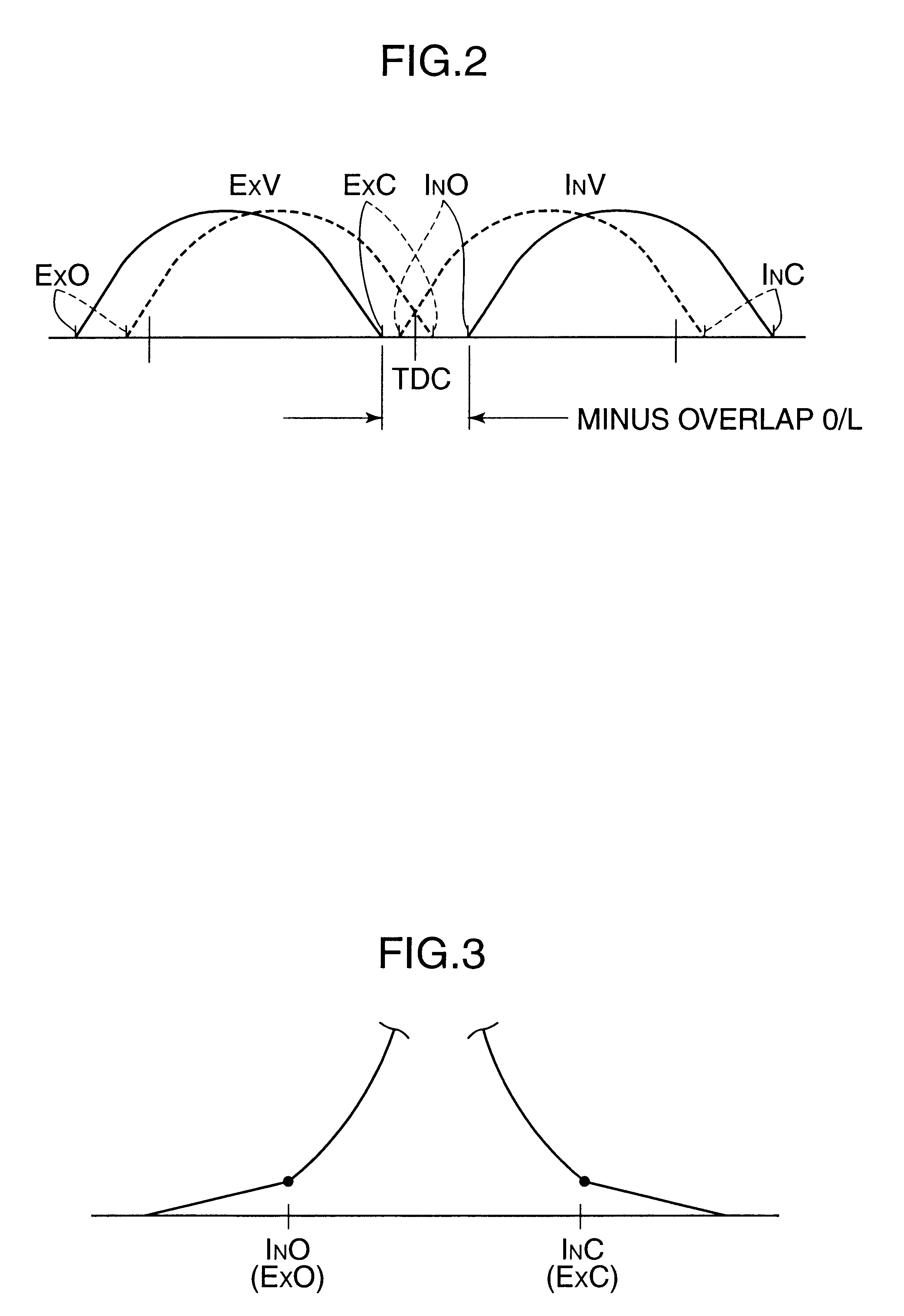
A four-cycle engine is provided with valve timing adjusters for adjusting opening and closing timing an and an exhaust valve. In medium- to high-speed ranges in medium- to high-load regions of the engine, a closing point (ExC) of the exhaust valve defined as a point of transfer from an acceleration portion to a constant speed portion on its valve lift characteristics curve is set to a point a specific period before an intake top dead center, and an opening point (InO) of the intake valve defined as a point of transfer from a constant speed portion to an acceleration portion on its valve lift characteristics curve is set to a point after the intake top dead center. In addition, the period from the closing point (ExC) of the exhaust valve to the opening point (InO) of the intake valve is made longer in the medium-speed range than in the high-speed range in the medium- to high-load regions of the engine.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
Integrated engine brake with mechanical linkage
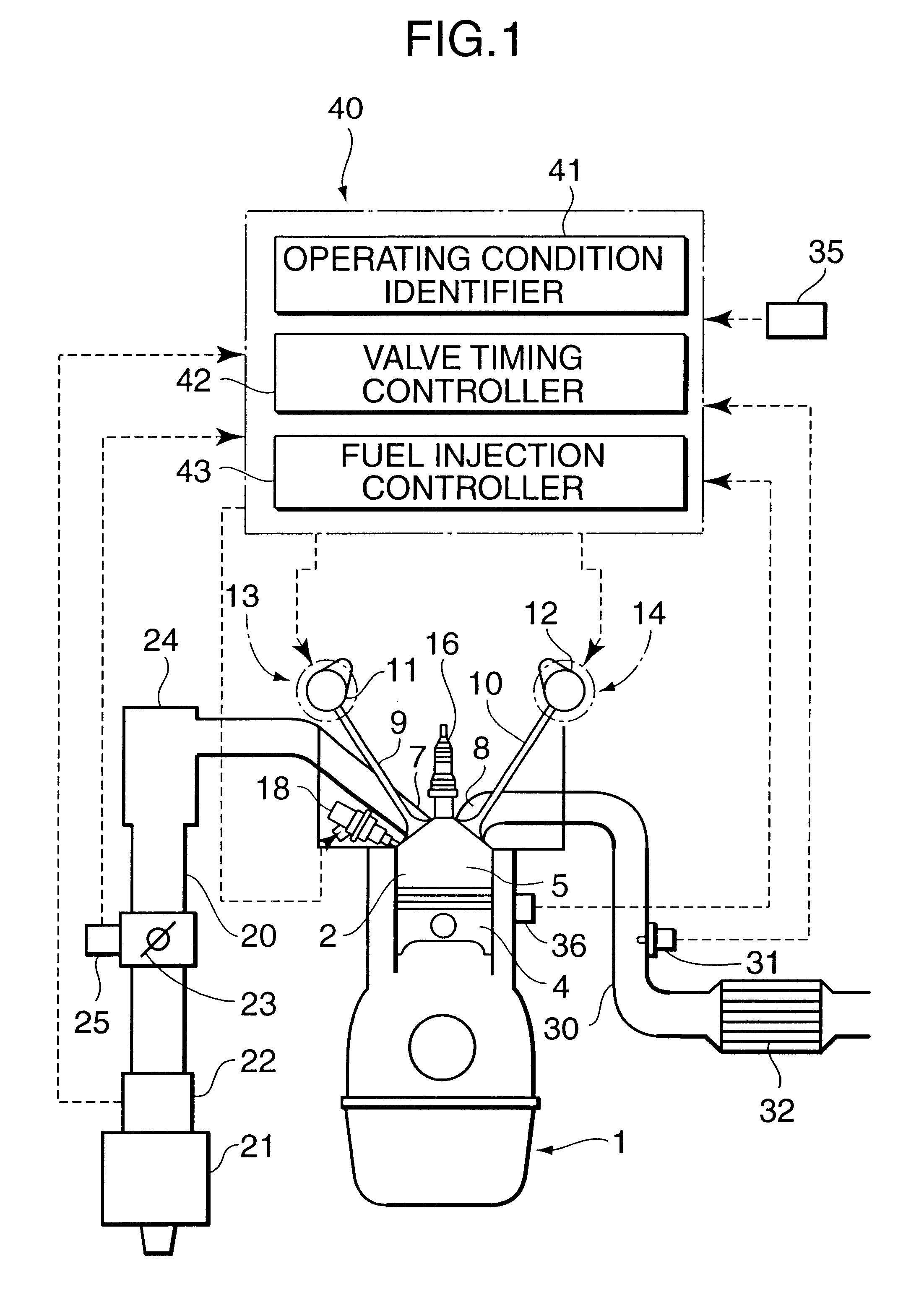
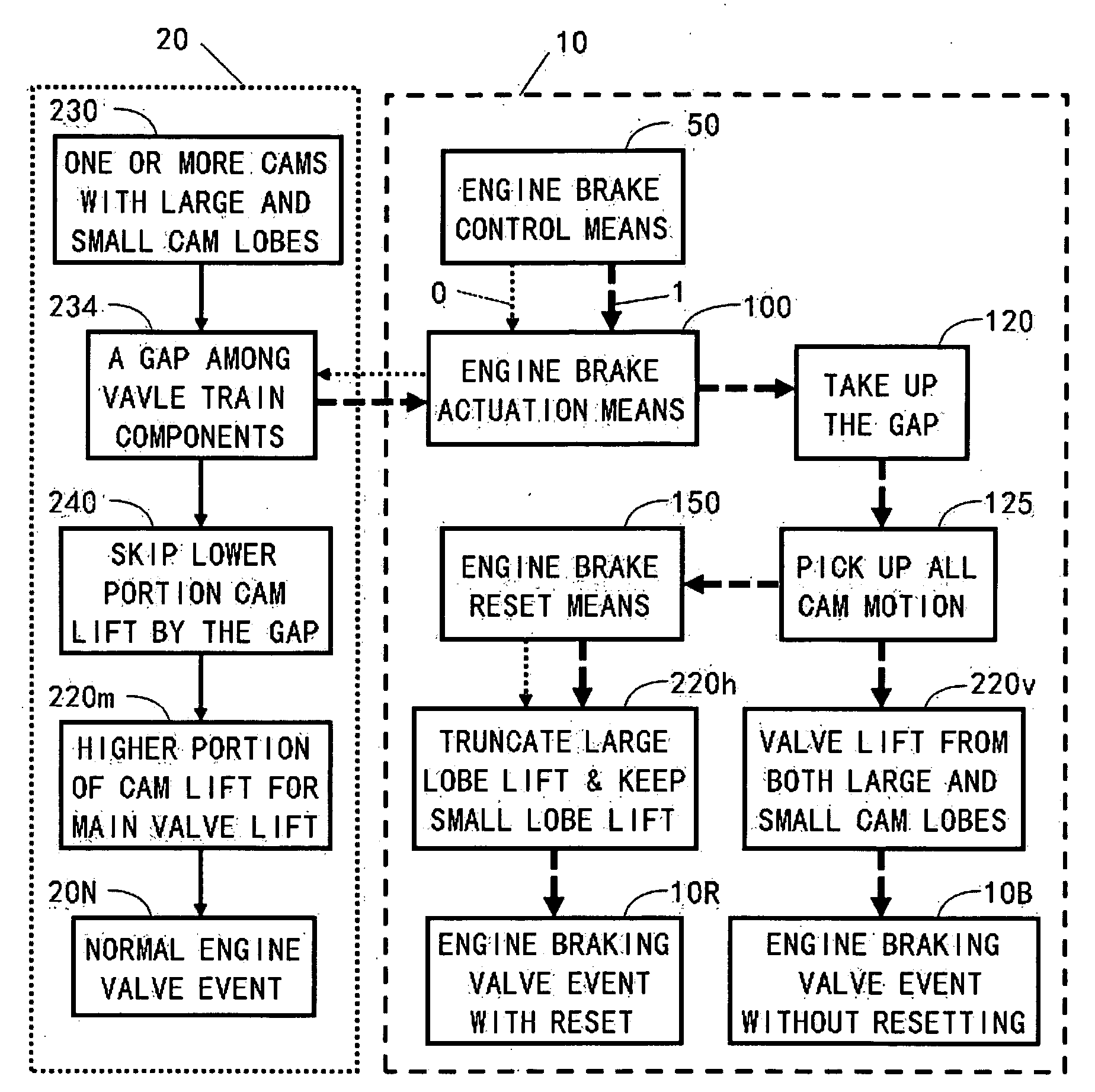
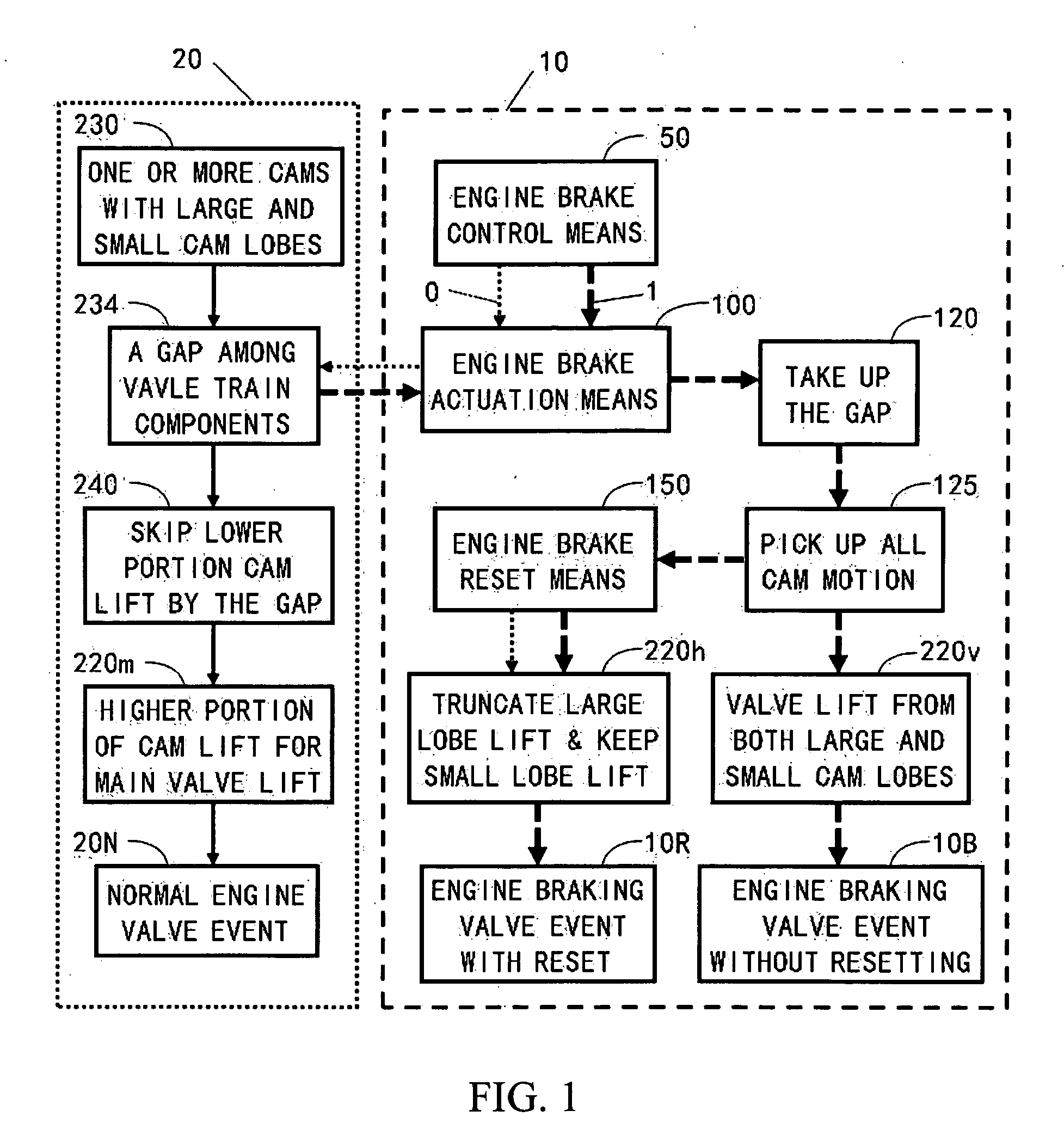
ActiveUS20100170472A1Rapid responseImprove performanceValve drivesOutput powerExhaust valveExternal combustion engine
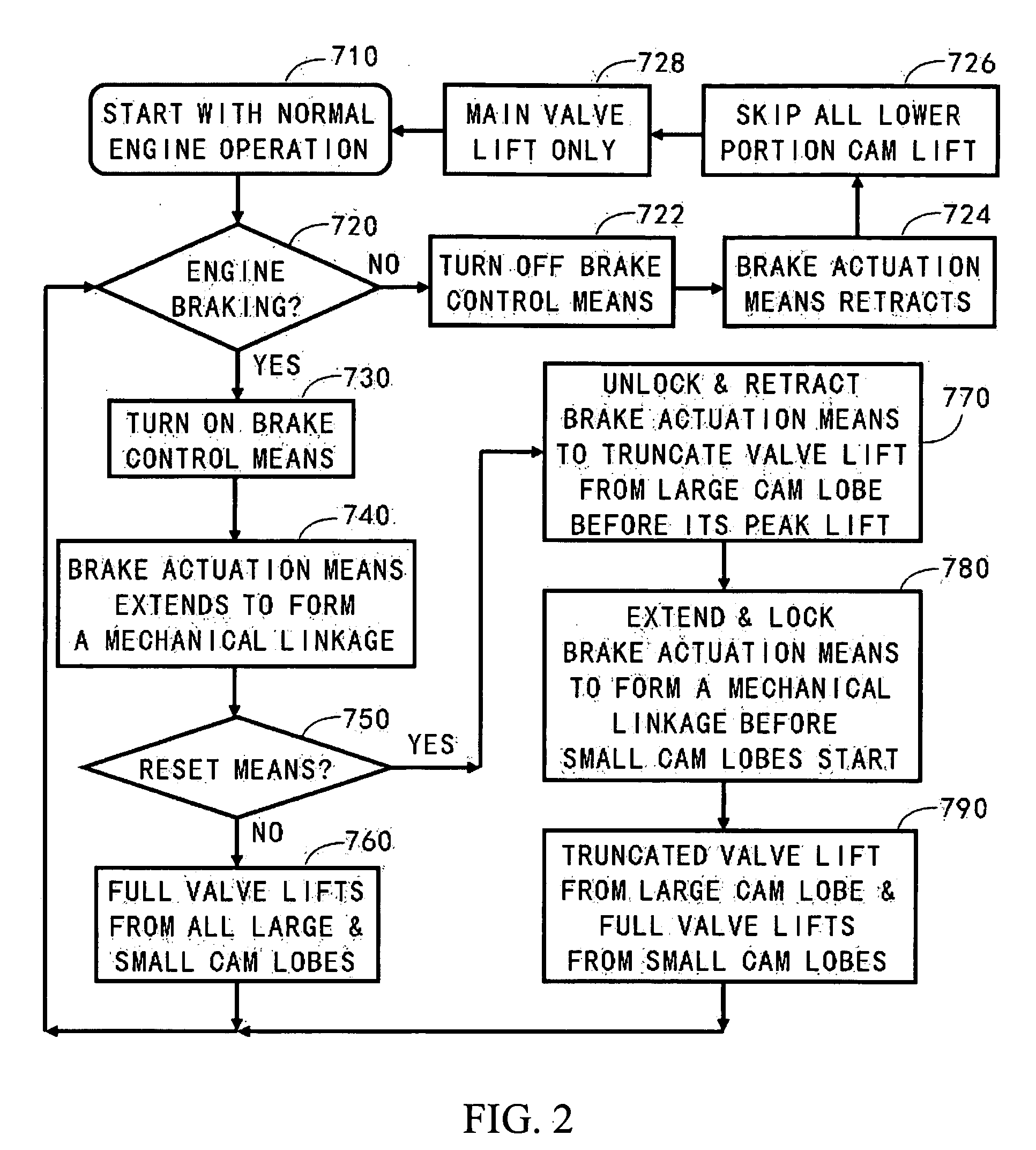
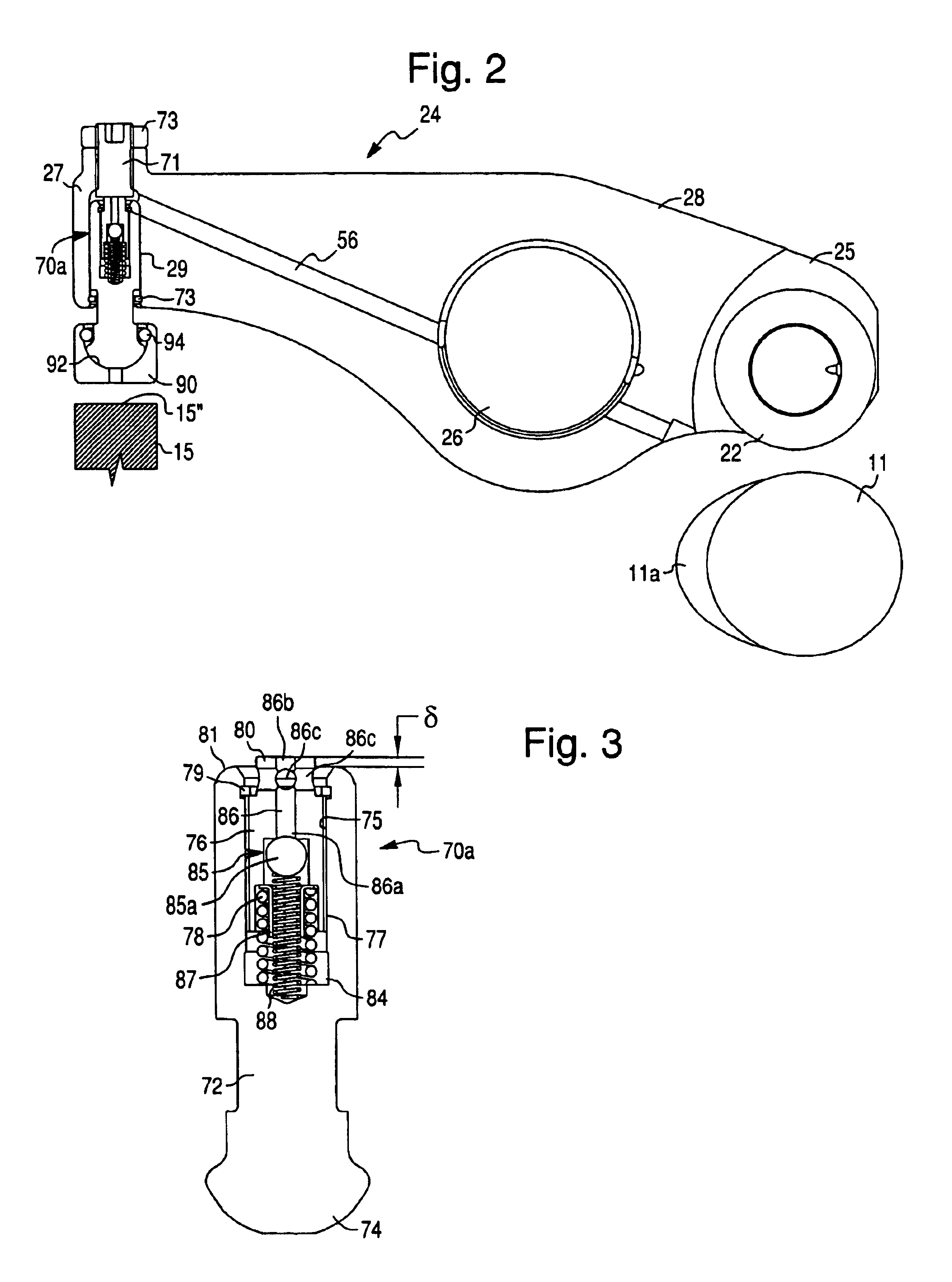
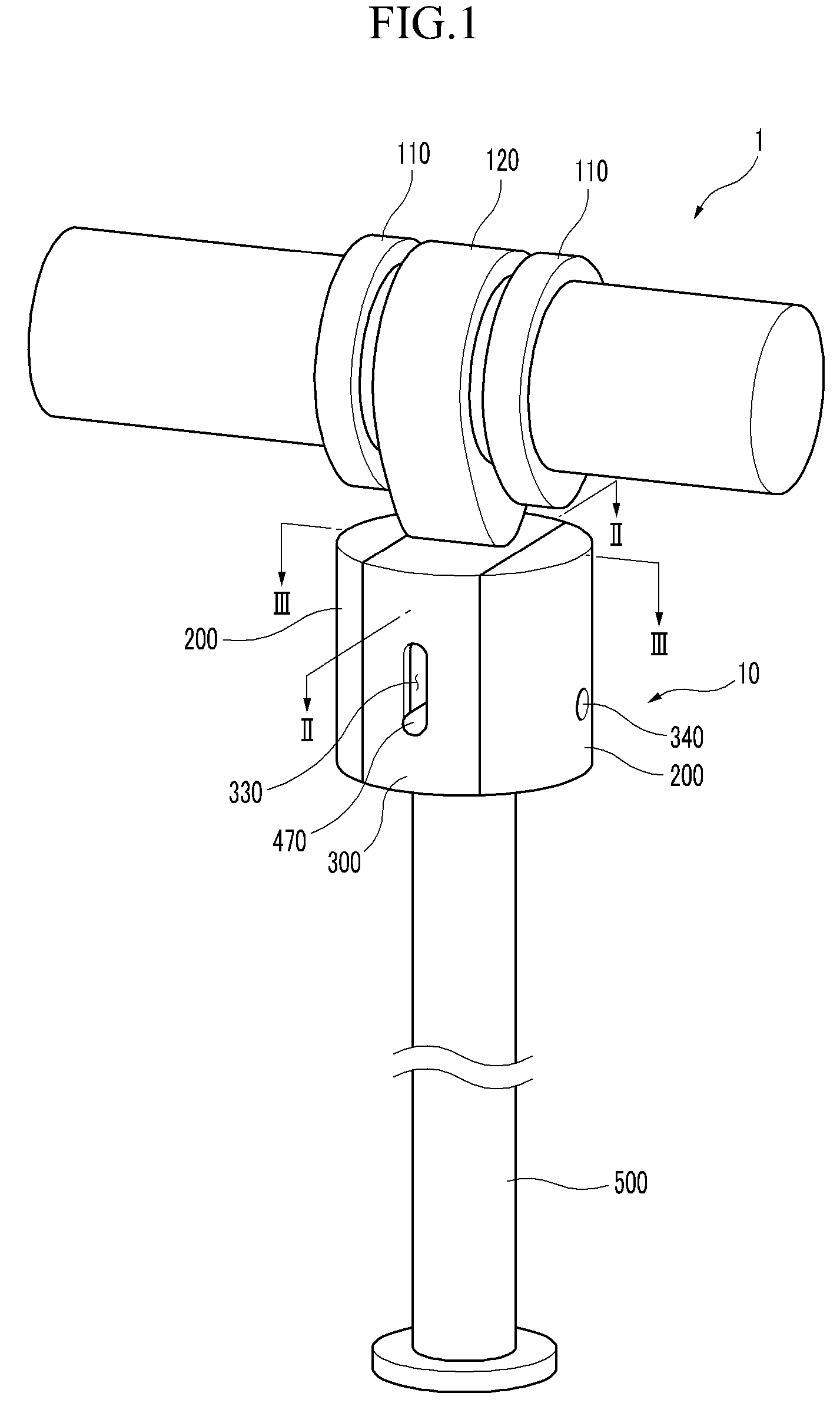
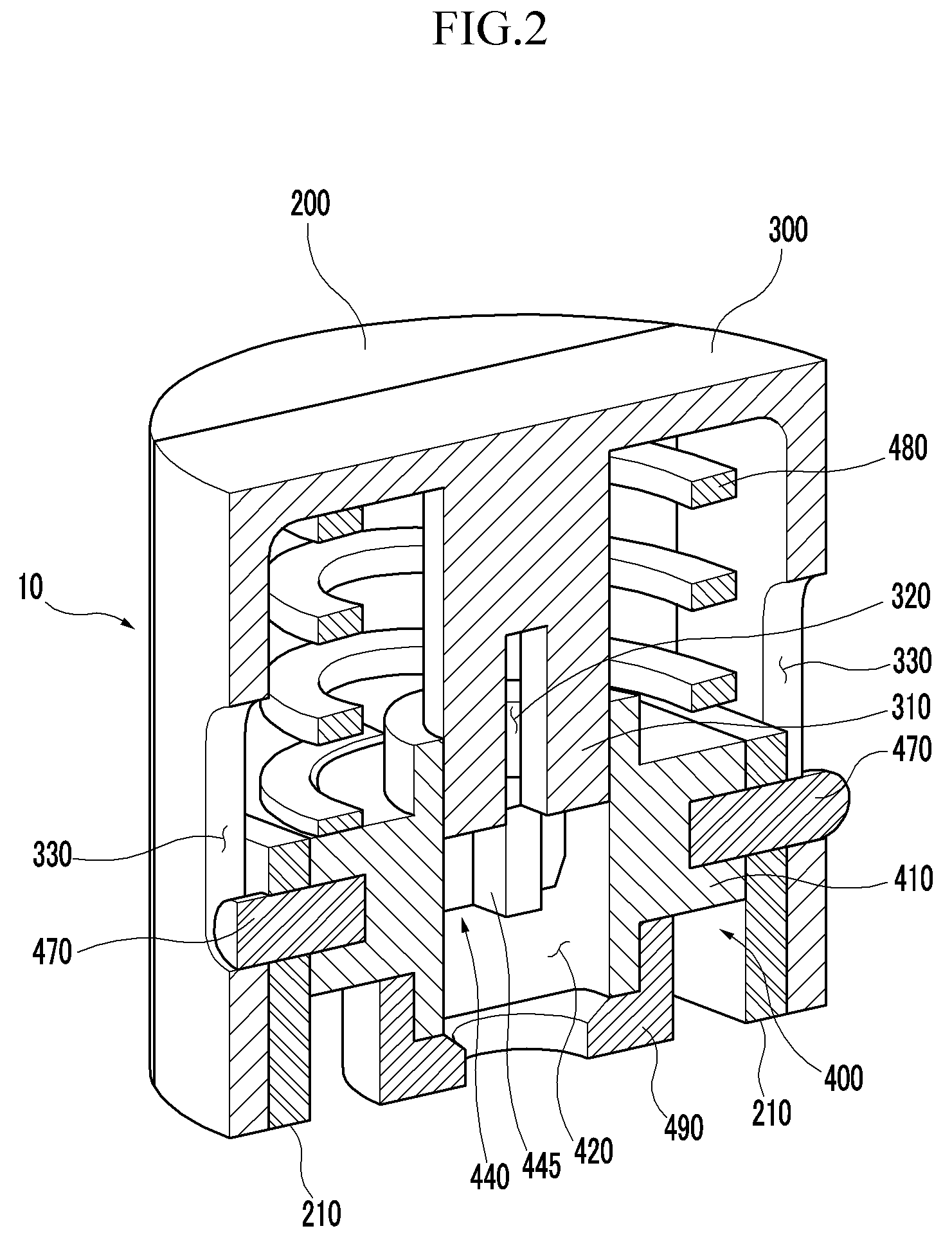
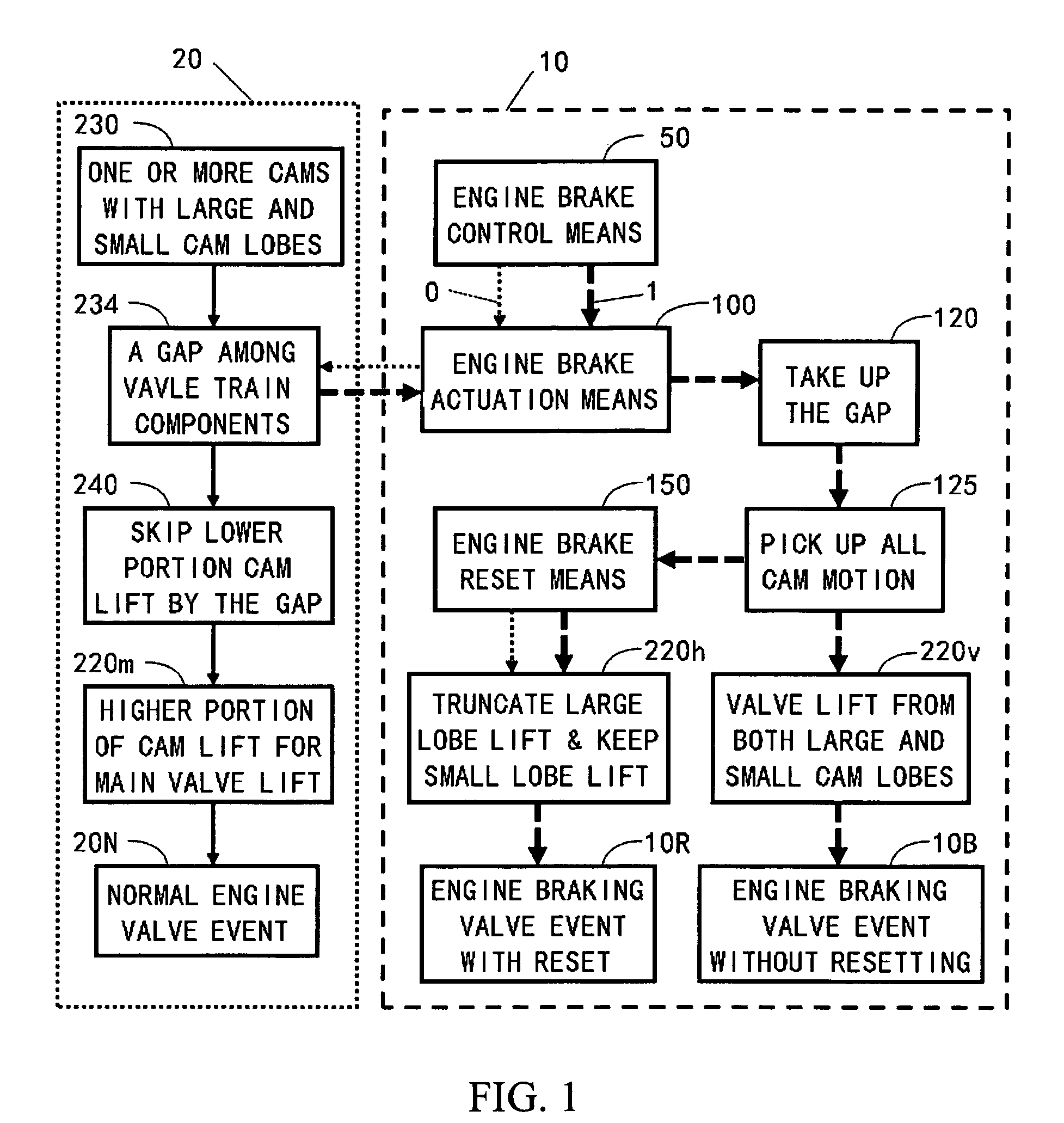
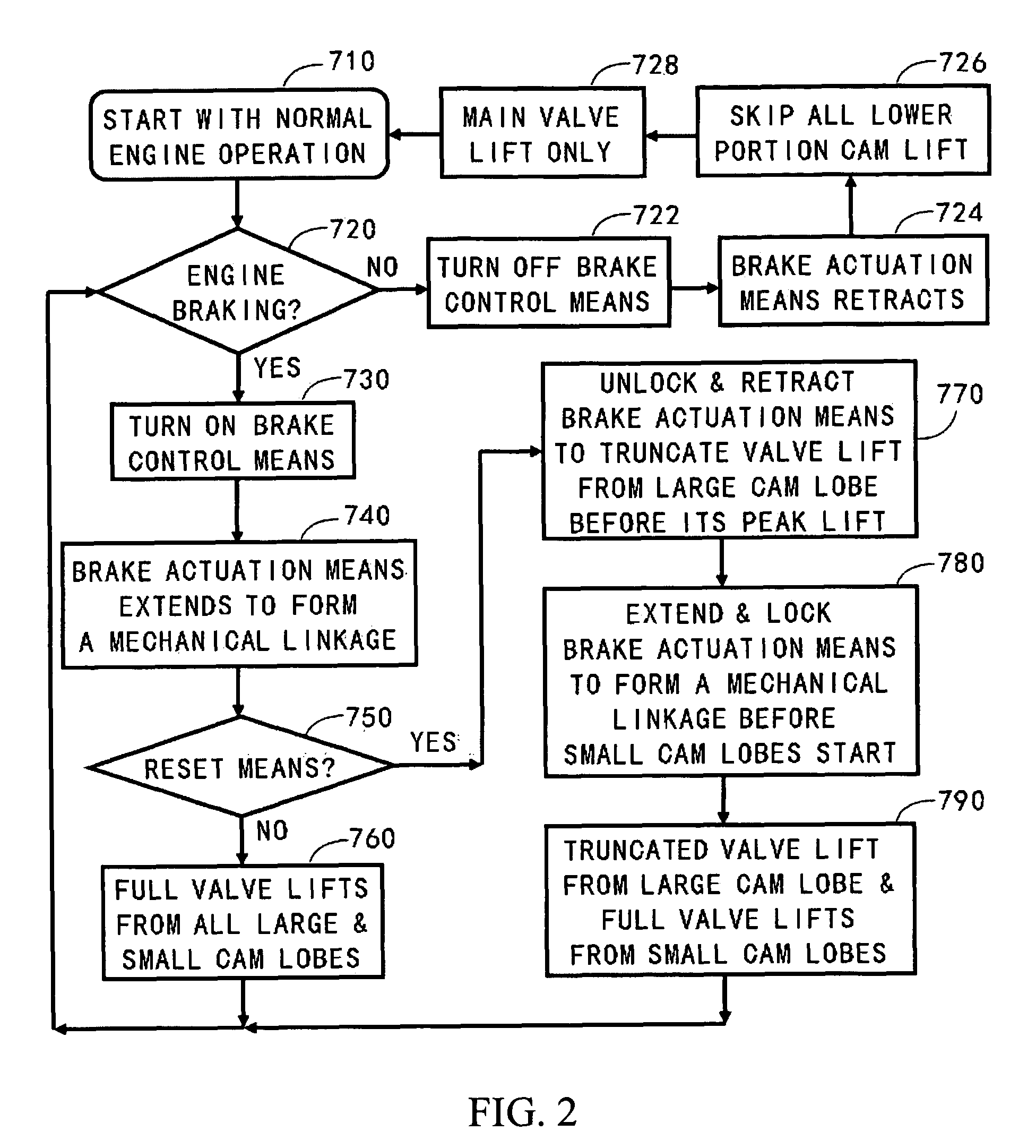
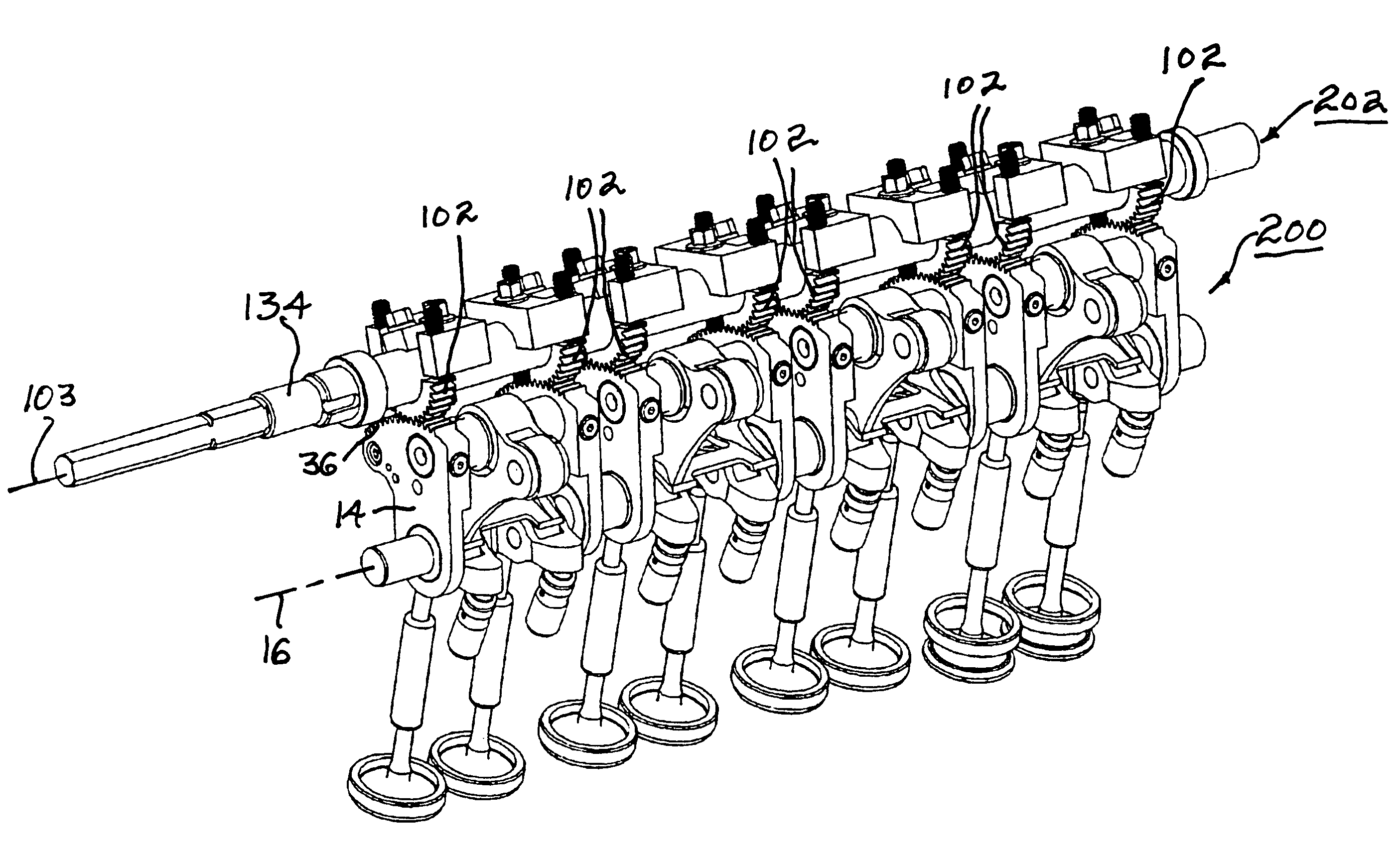
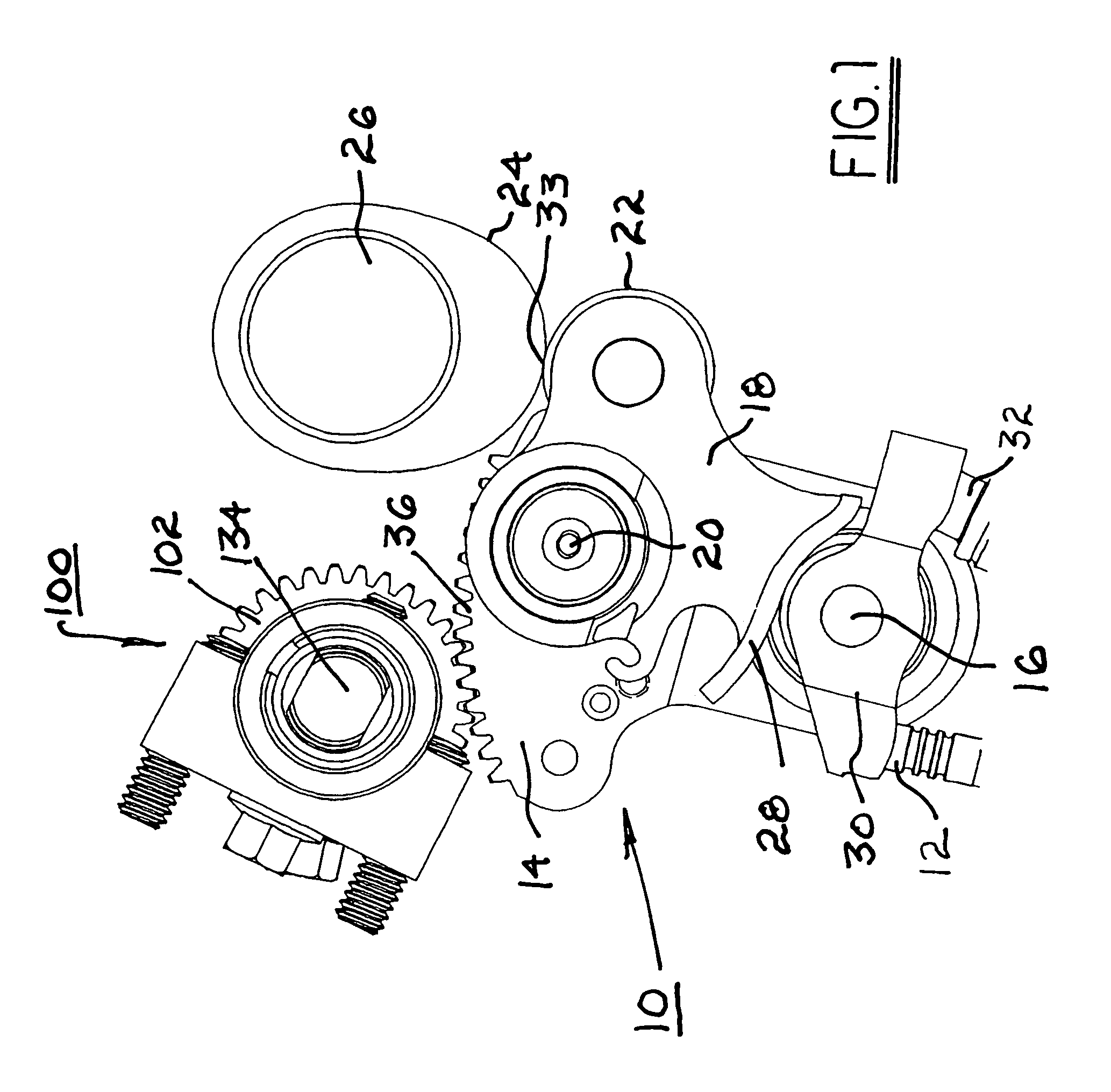
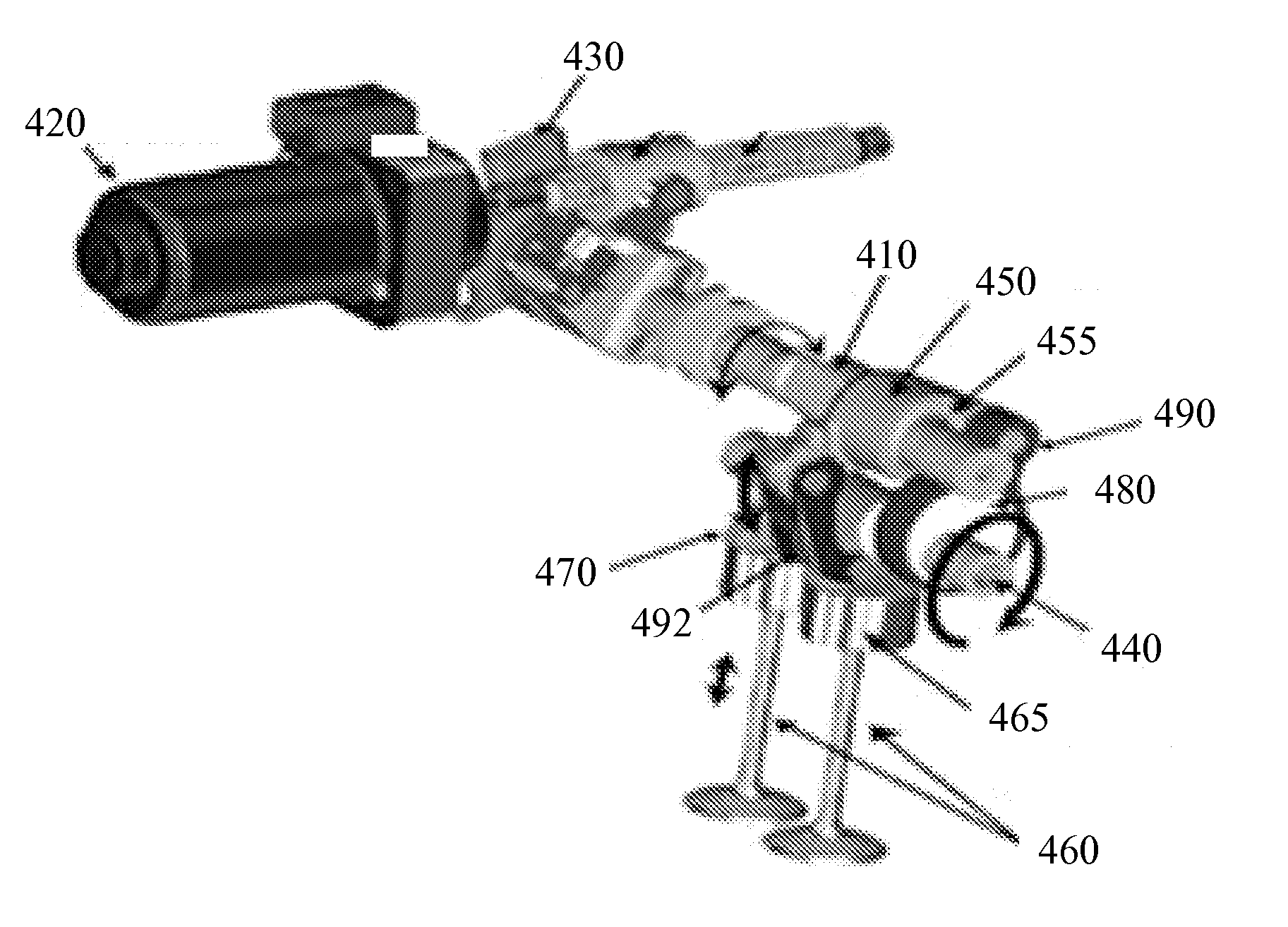
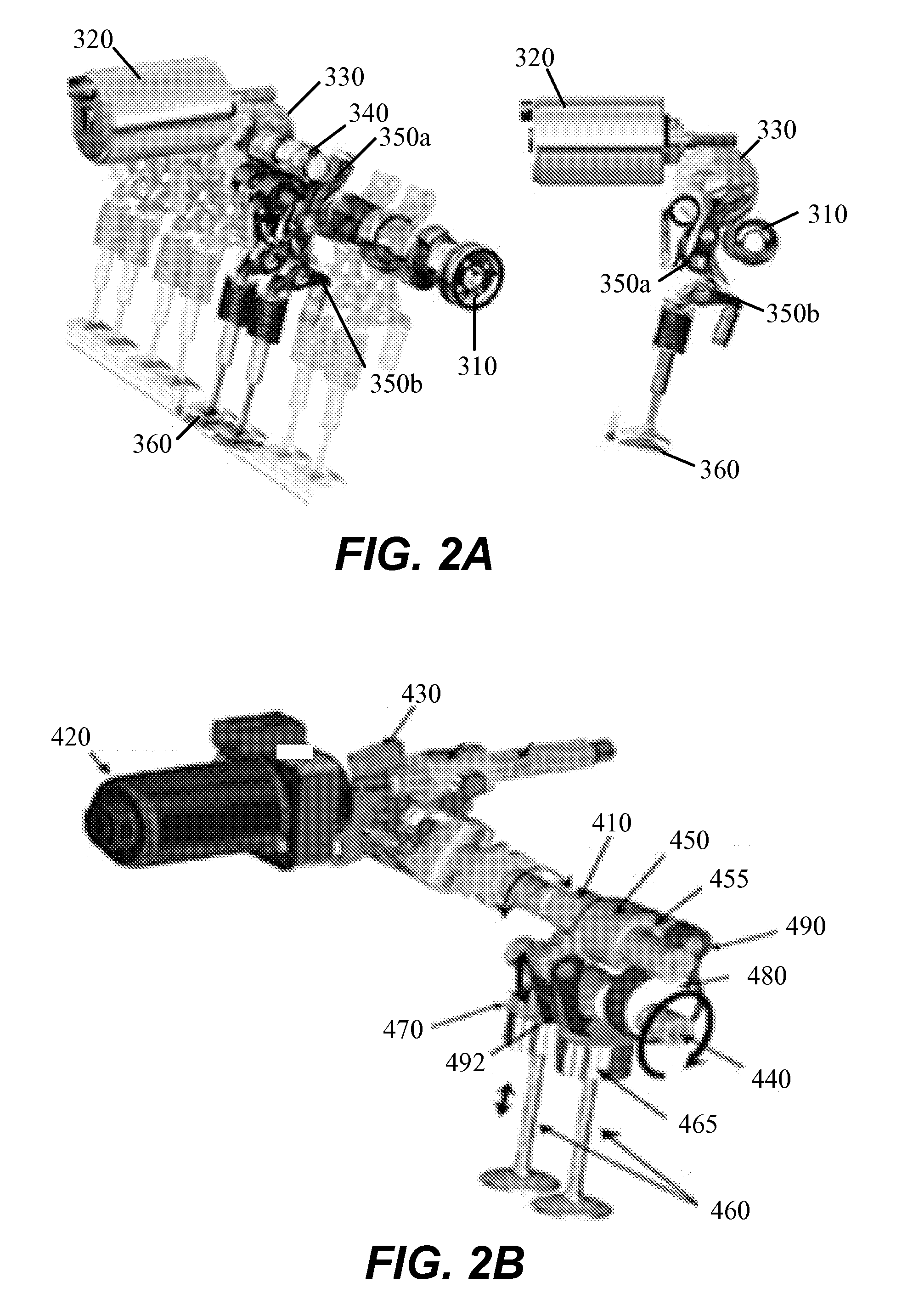
Apparatus and method are disclosed for converting an internal combustion engine from a normal engine operation (20) to an engine braking operation (10). The engine includes exhaust valve train components comprising at least one exhaust valve (300) and at least one cam (230) for cyclically opening and closing the at least one exhaust valve (300). The apparatus comprises actuation means (100) having at least one component integrated into at least one of the exhaust valve train components, such as a rocker arm (210) or a valve bridge (400). The actuation means (100) has an inoperative position and an operative position. In the inoperative position, the actuation means (100) is retracted and the small braking cam lobes (232&233) are skipped to generate a main valve lift profile (220m) for the normal engine operation (20). In the operative position, the actuation means (100) is extended to form a mechanical linkage so that the motion from all the cam lobes (220, 232&233) is transmitted to the at least one exhaust valve (300) for the engine braking operation (10). The apparatus further comprises control means (50) for moving the actuation means (100) between the inoperative position and the operative position to achieve the conversion between the normal engine operation (20) and the engine braking operation (10). The apparatus also includes valve lash adjusting mechanism, oil retraining means (350), and engine brake reset means (150).
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSOON AUTOPARTS CO LTD
Spark-ignition gasoline engine
ActiveUS20070227503A1Improve fuel economyShorten burn timeElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesLow speedTop dead center
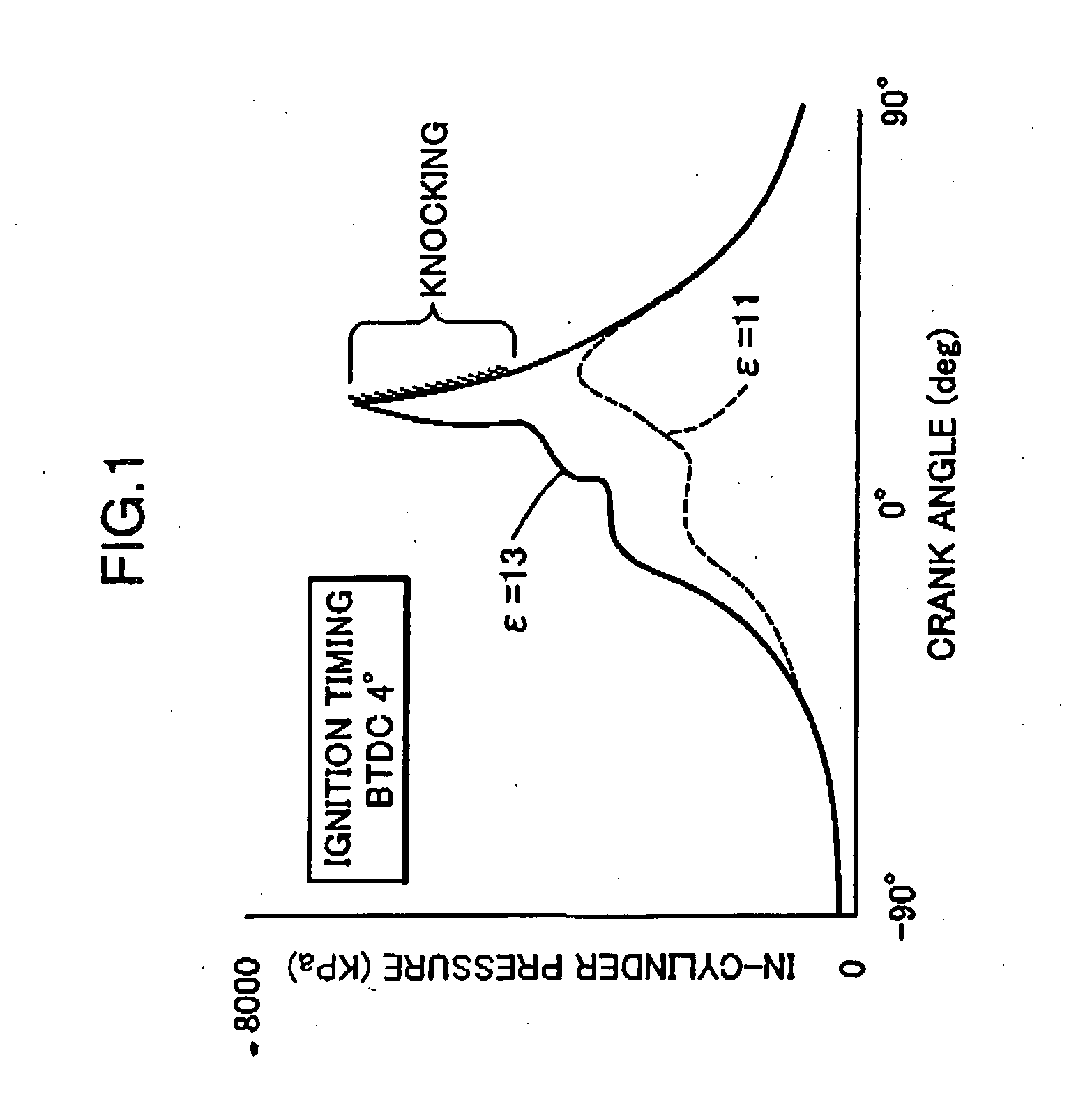
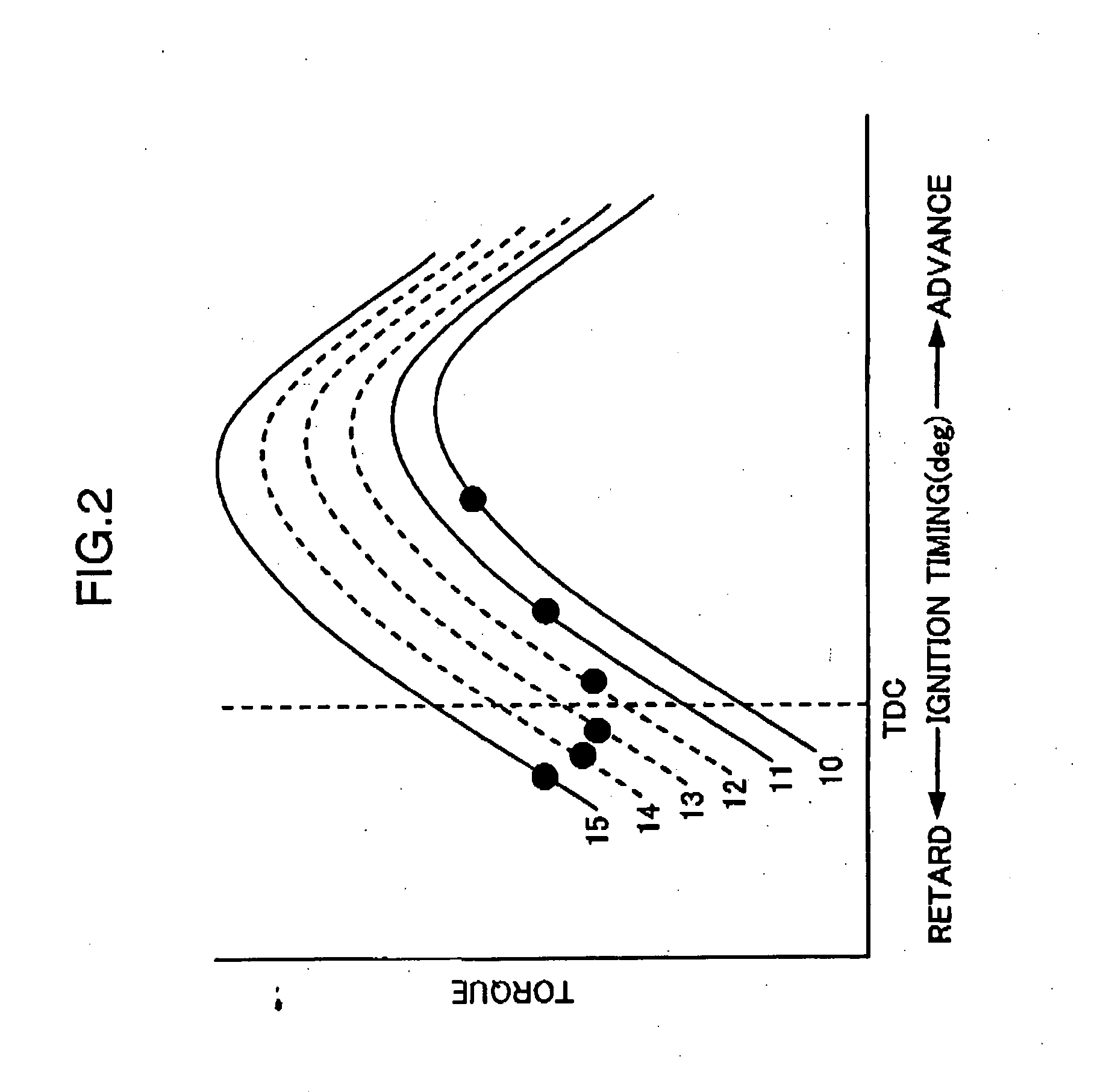
Disclosed is a spark-ignition gasoline engine, which comprises control means operable, when an engine operation zone is a high-load operation zone including a WOT region within at least a low speed range, to adjust a closing timing of an intake valve in such a manner as to maintain an effective compression ratio at 13 or more, and retard an ignition timing to a point within a predetermined stroke range just after a top dead center of a compression stroke, wherein the effective compression ratio is calculated based on an intake-valve closing timing defined by a valve lift amount of 1 mm. The present invention can provide a spark-ignition gasoline engine having both a low-cost performance and a high engine-power performance even in a high-load operation zone (particularly WOT region) in a low speed range.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
Variable valve actuation system of internal combustion engine and control apparatus of internal combustion engine
ActiveUS20090228187A1Improve responsivenessEngine-torque-increase responsivenessAnalogue computers for vehiclesValve arrangementsExhaust valvePhase shifted
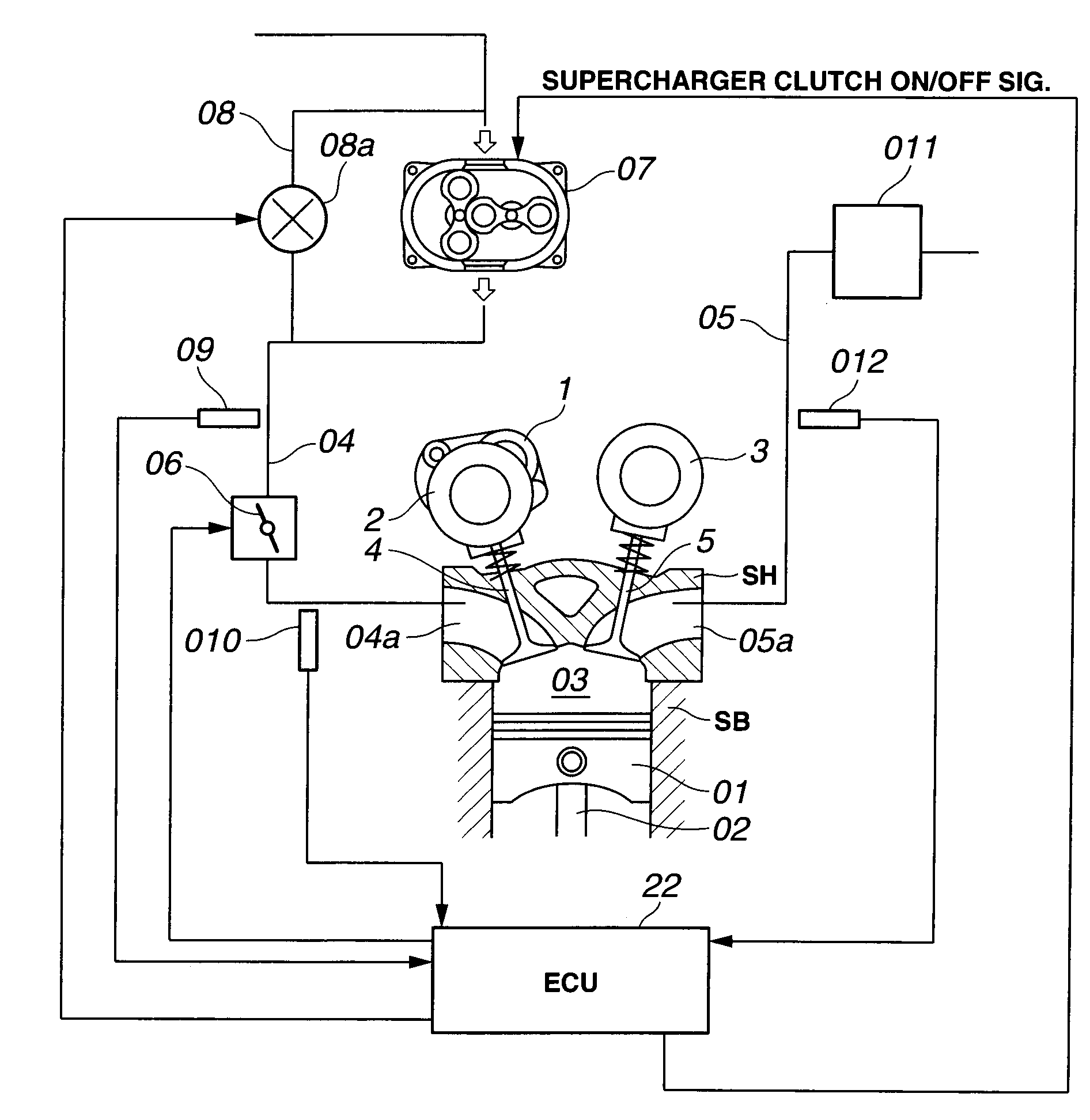
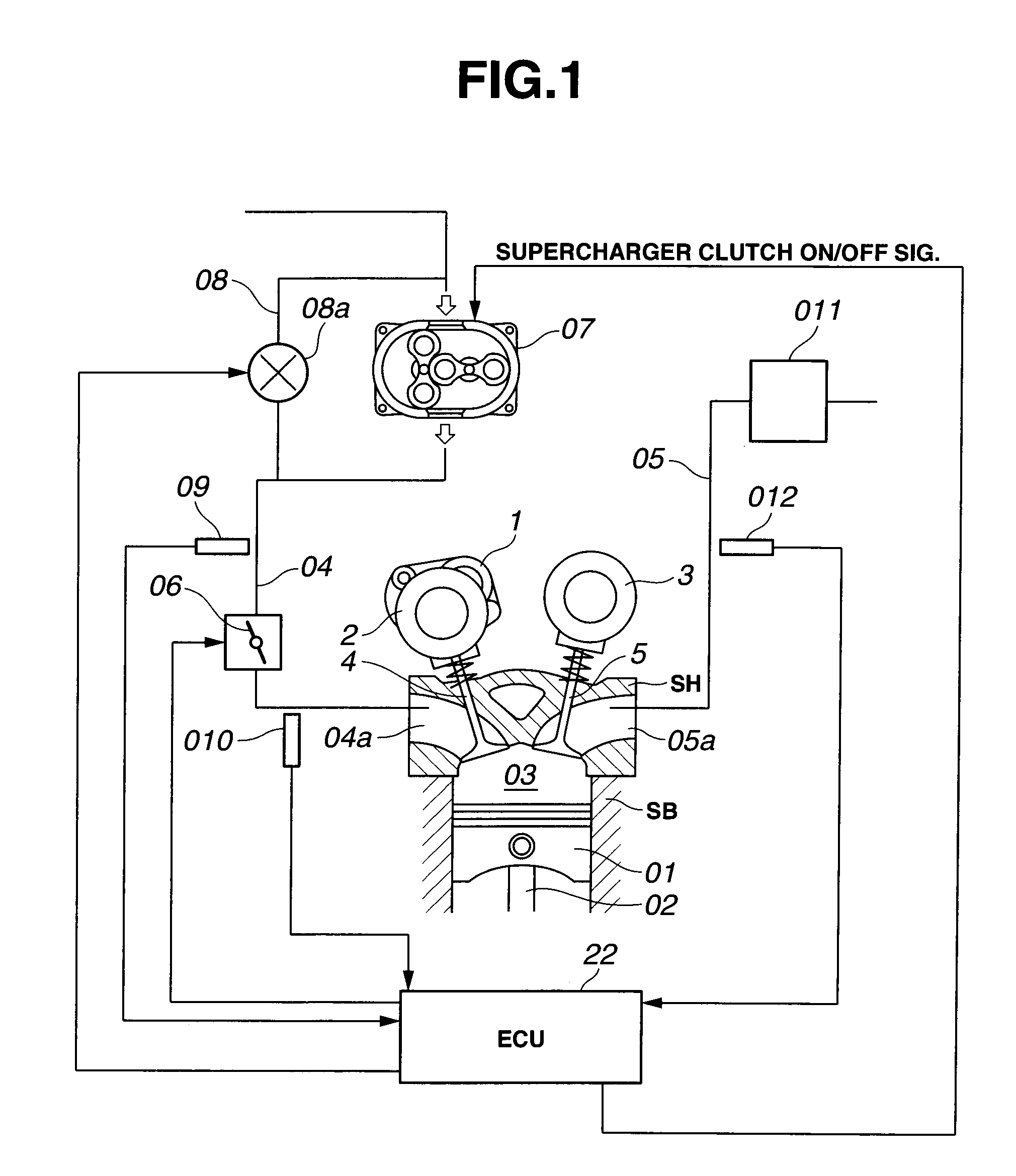
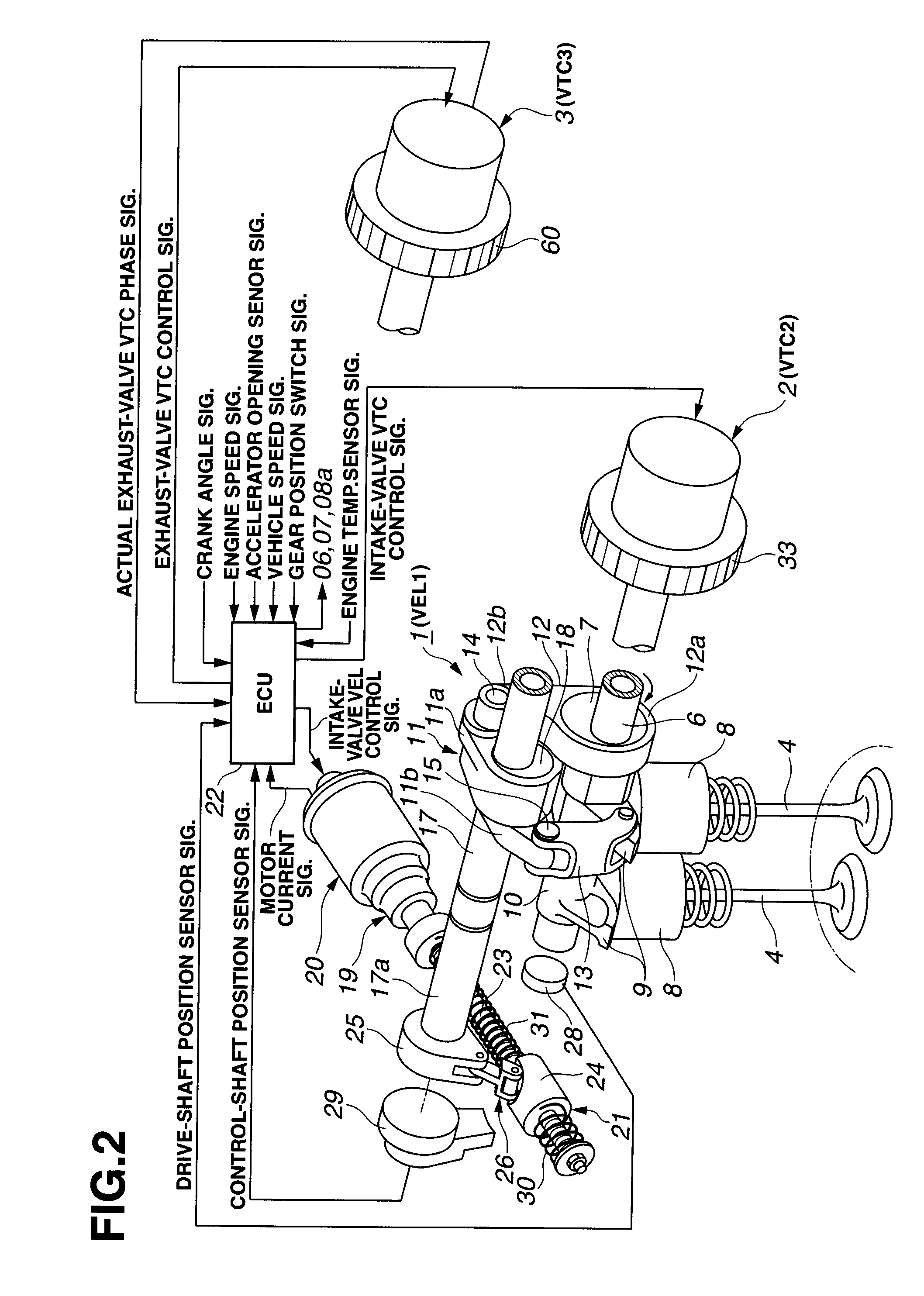
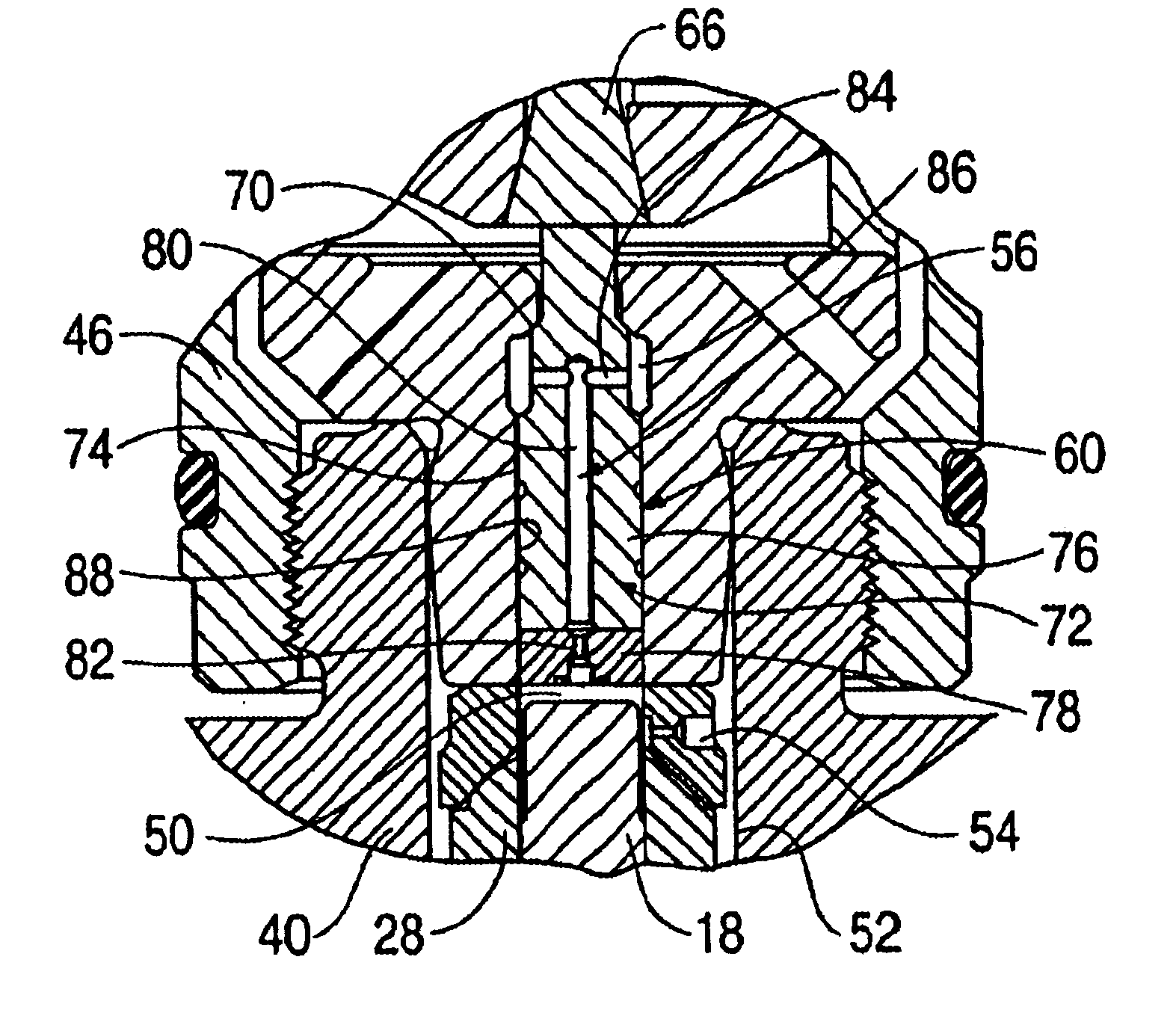
In a control apparatus of a supercharged internal combustion engine, a variable valve actuation system interacts with an engine control system. A controller is configured or programmed to increase an intake-valve lift by a variable valve lift mechanism, which is provided for variably controlling at least the intake-valve lift of engine valves, when starting from a vehicle stand-still state or when accelerating from an idling state or a light load state. The controller is further configured or programmed to increase a valve overlap of intake and exhaust valves by a variable phase control mechanism, which is provided for variably phase-shifting a central phase angle of a valve lift characteristic curve of at least one of the intake and exhaust valves, while increasing a boost pressure of intake air introduced into an engine cylinder by a supercharging device, after the intake-valve lift has been increased.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Fuel injector with feedback control
InactiveUS6837221B2Minimize consumptionMeet the requirementsEngine testingMachines/enginesEngineeringControl valves
An injector is provided which includes a nozzle valve element, a control volume, and an injection control valve including a control valve member for controlling fuel flow from the control volume so as to control nozzle valve movement. Importantly, the injector includes a nozzle valve lift detecting device for detecting nozzle valve lift and providing a nozzle valve element lift feedback signal. Feedback signals are improved and control valve member oscillations are minimized by positioning a valve seat associated with the control valve member a spaced distance from the control volume, positioning a drain orifice such that the nozzle valve element restricts flow through a drain circuit when in an open position and extending the control valve member from the valve seat to the control volume to form an end wall of the control volume.
Owner:CUMMINS INC
Modal variable valve actuation system for internal combustion engine and method for operating the same
ActiveUS6925976B2Improve fuel economyImprove power densityValve drivesOutput powerExhaust brakeInlet valve
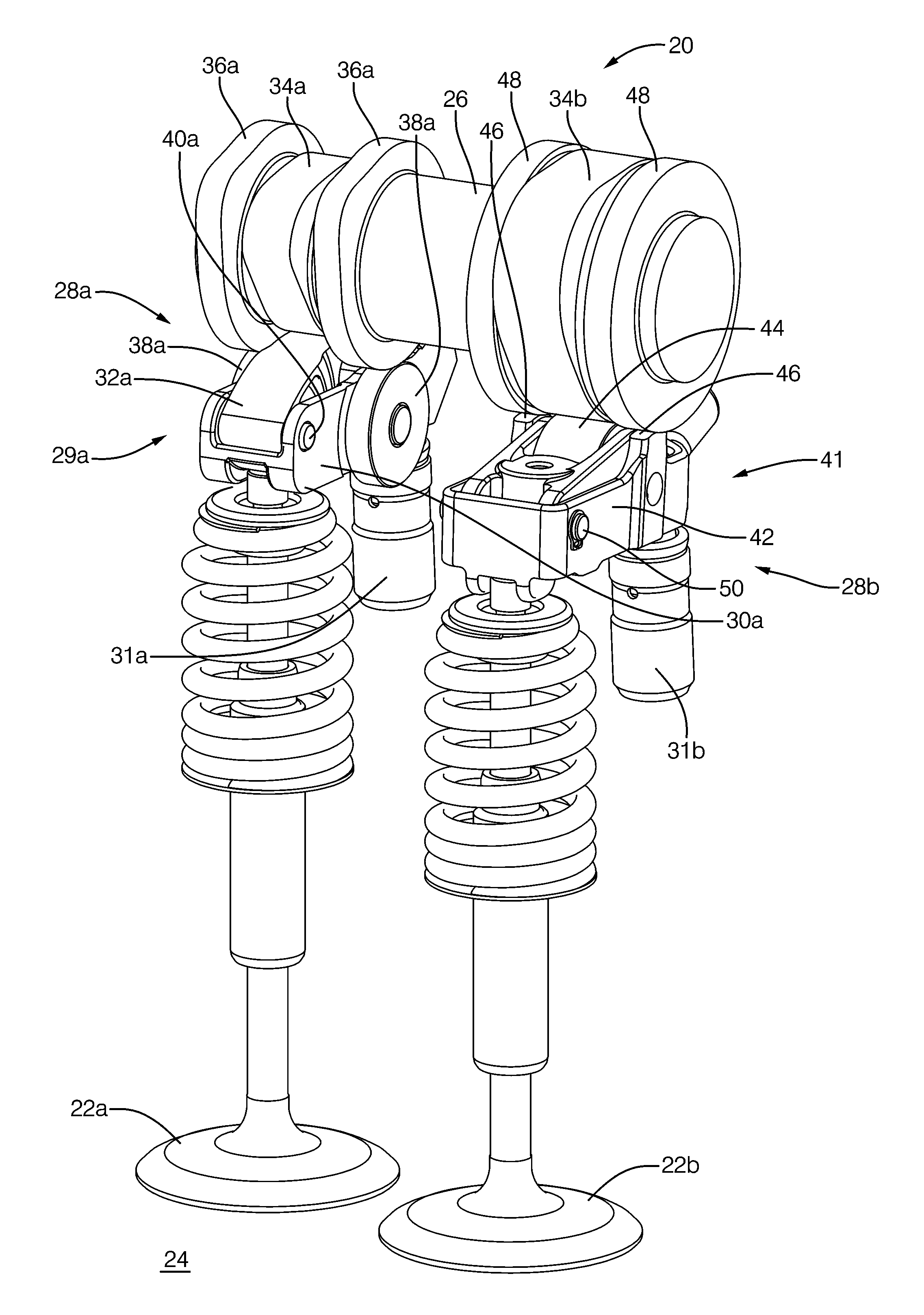
A variable valve actuation system for providing discrete exhaust and intake valve lift profiles for various operating modes of an internal combustion engine. The variable valve actuation system includes exhaust and intake rocker assemblies, exhaust and intake hydraulic extension devices operatively coupling corresponding rocker assemblies with respective engine valves and exhaust and intake control valves for selectively supplying the pressurized hydraulic fluid to the extension devices so as to independently switch them between a pressurized condition and a depressurized condition. The engine further includes an exhaust brake provided to initiate a small lift of the exhaust valve during the engine braking operation while the exhaust extension device maintains the exhaust valve open during a compression stroke for bleeder-compression release braking. The exhaust and intake valves can be adjusted independently to provide combinations of valve lift modes.
Owner:JENARA ENTERPRISES
Method for controlling the adjustment of the valves in a combustion engine with variable valves and a vehicle with such an engine with electronic controlling device for the valve control
InactiveUS20060199699A1Improve responseReduce stepsElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesVariable valve timingGear wheel
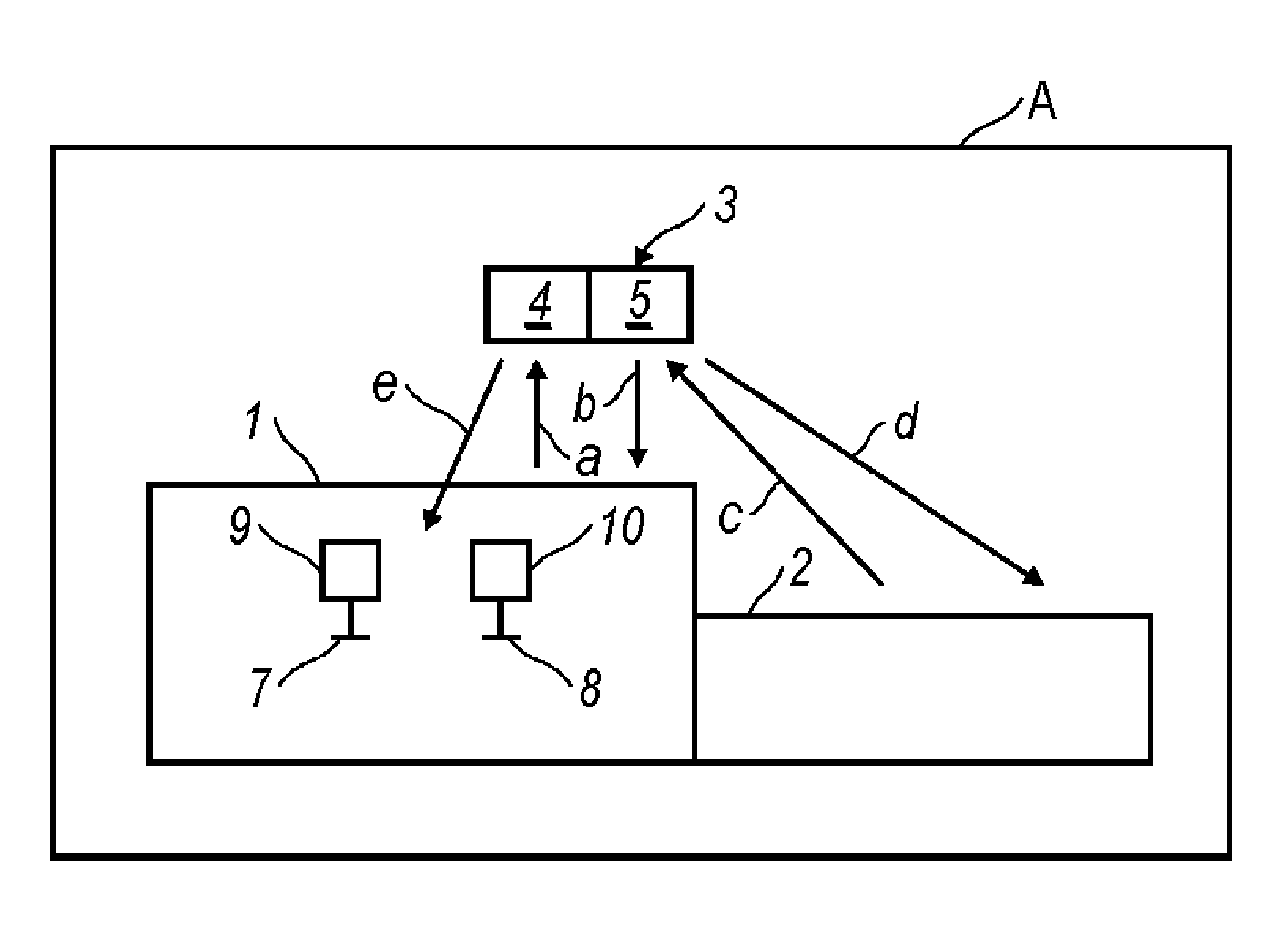
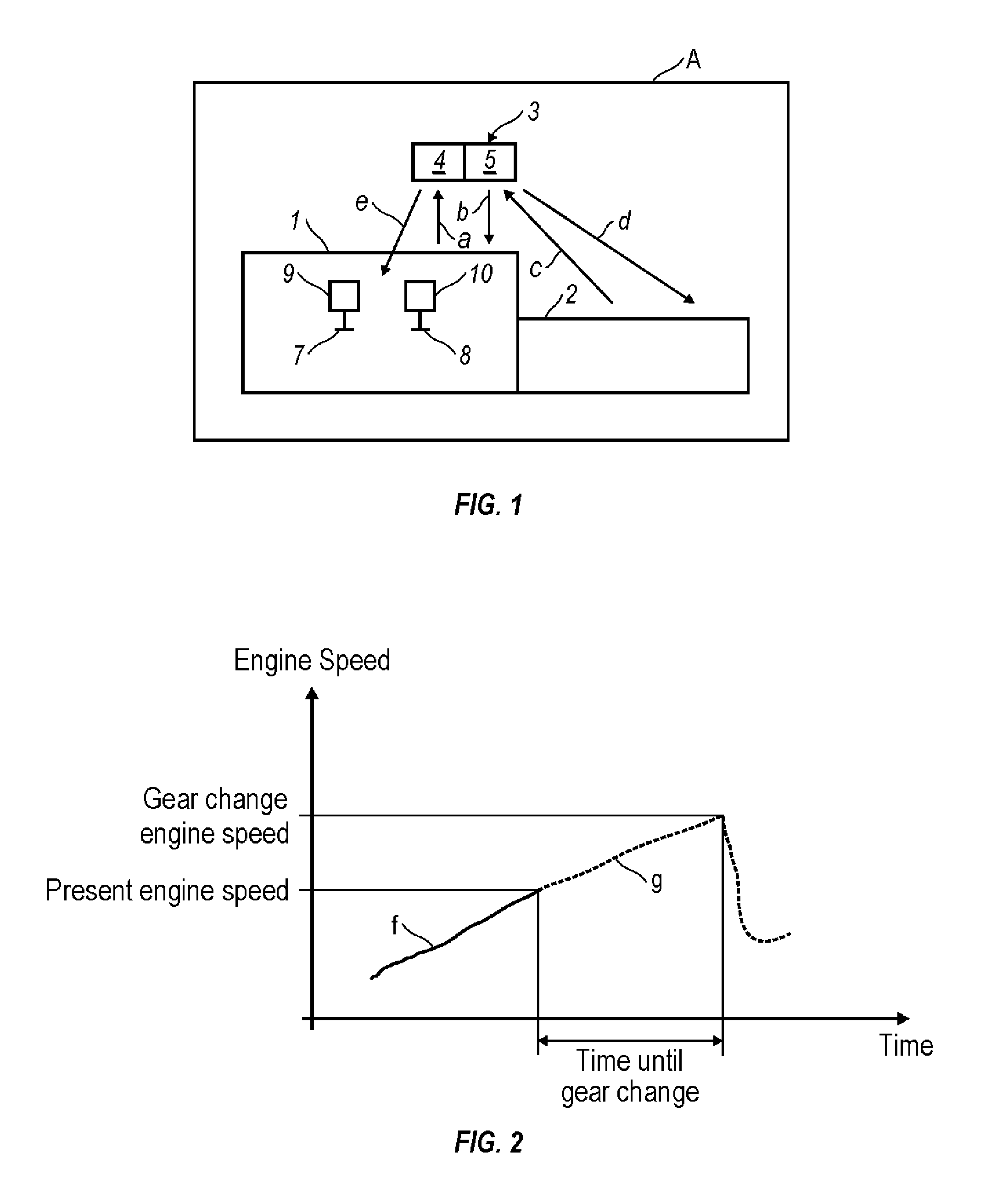
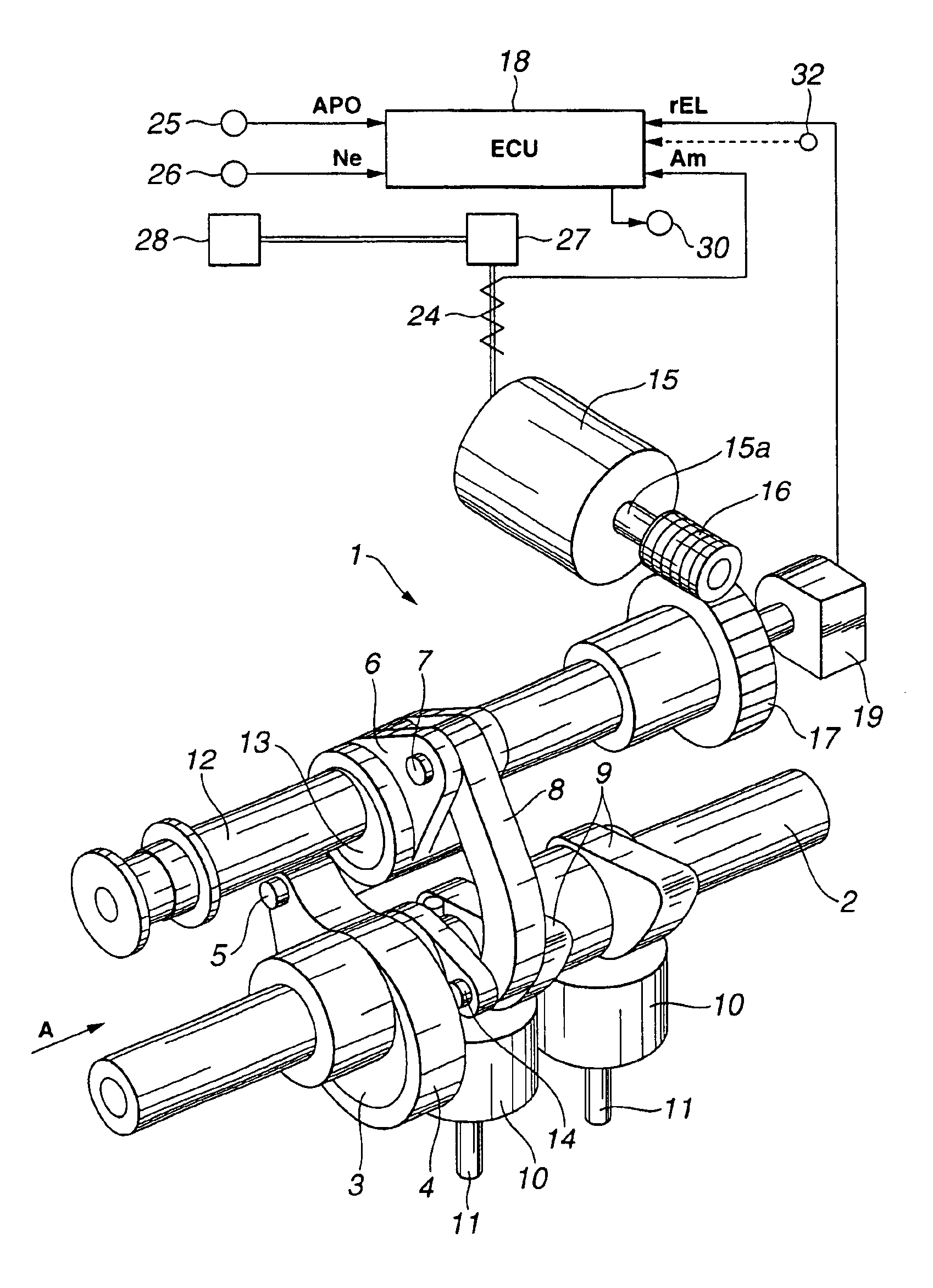
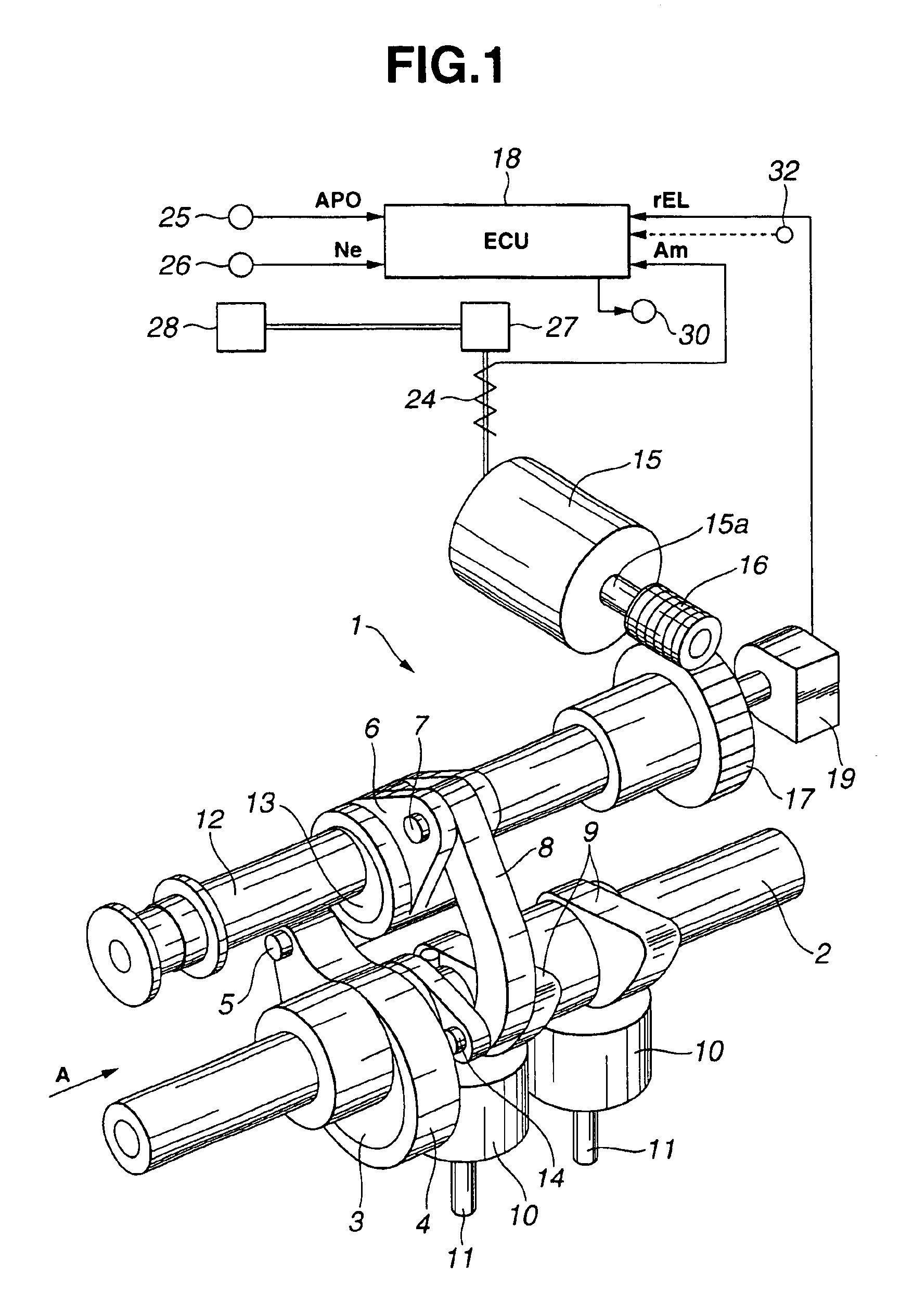
Method and arrangement for providing a vehicle having a combustion engine (1) with valves (7, 8) adapted to have variable valve timing and / or valve lift height. The valves are provided with operating devices (9,10) that are controlled by electronic controlling devices (3), which are arranged, while the vehicle is being driven, with the aid of entered information about at least the gradient of the road and the throttle position, to calculate future resistance to forward motion and the period of time to a future transient in the engine's operating condition, for example in association with a future change of engine operating mode and / or a future gear change in a gearbox (2) connected to the engine. The controlling devices are arranged to control valve timing and / or the valve lift height during the period of time for optimization of the engine's performance, once the transient has arisen.
Owner:VOLVO LASTVAGNAR AB
System for variable valvetrain actuation
InactiveUS20070125329A1Simple taskReduce in quantityValve drivesMachines/enginesCylinder headGasoline
An electromechanical VVA system for controlling the poppet valves in the cylinder head of an internal combustion engine. The system varies valve lift, duration, and phasing in a dependent manner for one or more banks of engine valves. A rocker subassembly for each valve or valve pair is pivotably disposed on a control shaft between the camshaft and the roller finger follower. The control shaft may be displaced about a pivot axis outside the control shaft to change the angular relationship of the rocker subassembly to the camshaft, thus changing the valve opening, closing, and lift. A plurality of control shafts for controlling all valvetrains in an engine bank defines a control shaft assembly. The angular positions of the individual control shafts may be tuned to optimize the valve timing of each cylinder. The system is applicable to the intake and exhaust camshafts of diesel and gasoline engines.
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
Variable valve lift apparatus
InactiveUS7987826B2Reduce manufacturing costSimple structureValve drivesMachines/enginesHigh liftEngineering
A variable valve lift apparatus according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention includes a low lift cam, a high lift cam in parallel with the low lift cam, a low lift tappet body that selectively contacts the low lift cam, a high lift tappet body disposed within the low lift tappet body and constantly contacting the high lift cam, a guide portion that is connected with a valve and selectively connects the low lift tappet body and the high lift tappet body, and a lost motion spring that is disposed between the guide portion and the low lift tappet body and supplies restoring force to the low lift tappet body.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Compression ignition engine
In a compression ignition engine employing a variable valve actuation mechanism variably adjusting an intake valve characteristic including at least one of an intake valve lift and an intake valve closure timing, a control system operates to temporarily lower an effective compression ratio of the engine by controlling the intake valve characteristic during a cranking period of cold starting operation. At a point of time when a predetermined cranking speed threshold value has been reached owing to a cranking speed rise, the effective compression ratio is risen by controlling the intake valve characteristic. After combustion of the engine has been stabilized, the intake valve characteristic is brought closer to a desired value determined based on engine operating conditions by way of closed-loop control.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Vibration-Damping Control Apparatus and Vibration-Damping Control Method for Internal Combustion Engine
InactiveUS20090145381A1Reduce torque variationReduce the amount requiredValve arrangementsElectrical controlCombustionExhaust valve
An apparatus and method of controlling vibration-damping for a vehicular internal combustion engine. The combustion is temporarily stopped in some cylinders among a plurality of cylinders, and the engine is operated by the remaining cylinders. Then, a variable valve mechanism which varies a valve lift amount of at least one of intake and exhaust valves of each cylinder is controlled, to decrease the valve lift amount of at least one of the intake and exhaust valves of each cylinder in which the combustion is temporarily stopped. Further, a rotating electric machine having at least one of functions of an electric motor and a generator is controlled, to apply torque to an output shaft of the engine thereby suppressing torque variation in the output shaft at the time when the combustion is temporarily stopped in some cylinders, so that the torque variation due to uneven explosion intervals is reduced.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Control apparatus for internal combustion engine
InactiveUS6912995B2Effective absorptionSuppress in consumptionElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelExternal combustion engineInlet valve
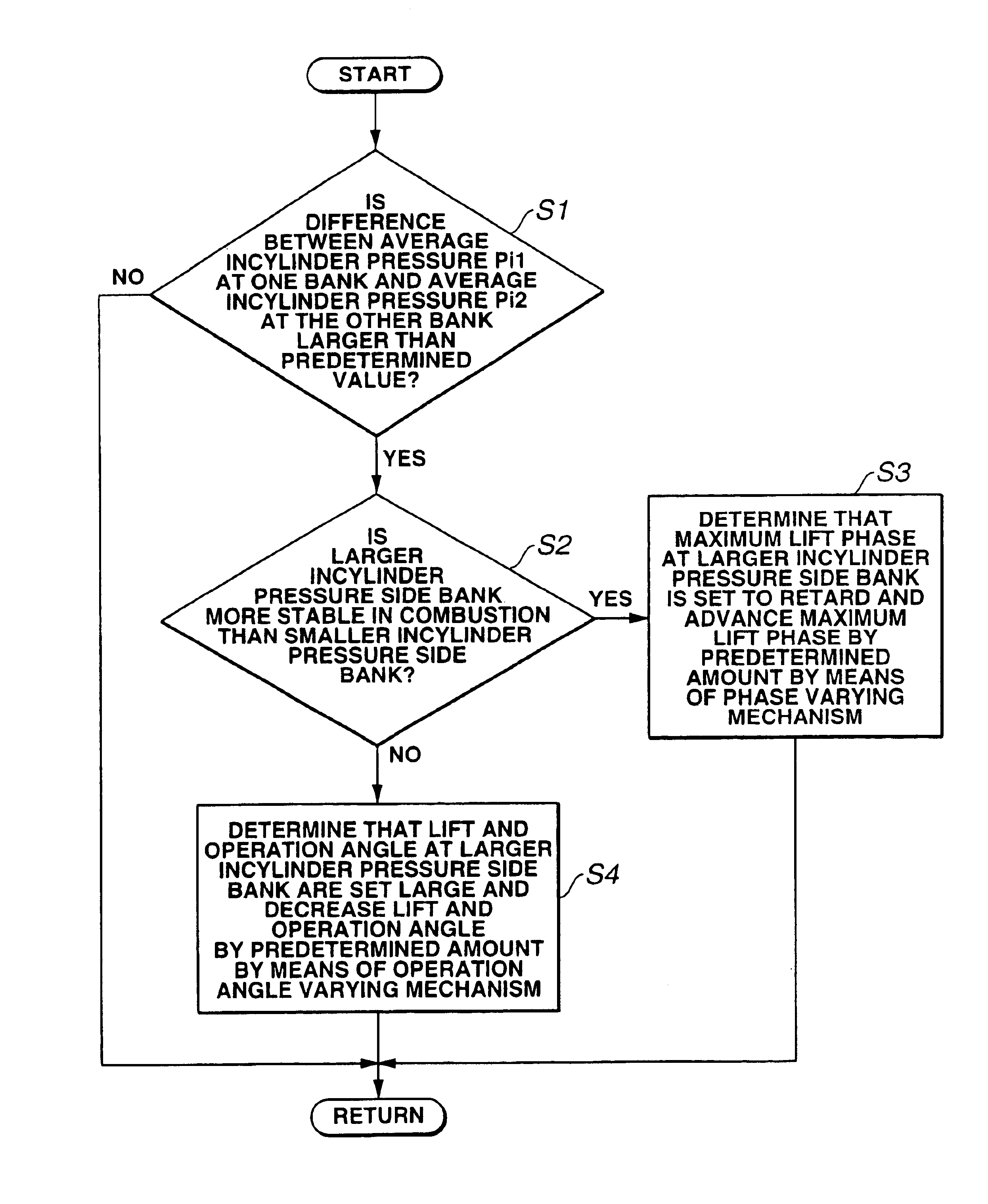
A control apparatus for an internal combustion engine having two cylinder groups and two variable valve control mechanisms provided to the respective cylinder groups, includes a detecting section that detects an incylinder pressure of each cylinder, a comparing section that makes a comparison between the two cylinder groups with respect to a combustion stability and a control section that varies valve lift characteristics of intake valves of one cylinder group which is larger in the average incylinder pressure than the other cylinder group in accordance with a result of comparison by the comparing section so as to make intake air quantities for the respective cylinder groups be equal to each other.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Integrated engine brake with mechanical linkage
ActiveUS8065987B2Fast response (on and off) timeLess componentsValve drivesOutput powerExhaust valveEngineering
Apparatus and method are disclosed for converting an internal combustion engine from a normal engine operation (20) to an engine braking operation (10). The engine includes exhaust valve train components comprising at least one exhaust valve (300) and at least one cam (230) for cyclically opening and closing the at least one exhaust valve (300). The apparatus comprises actuation means (100) having at least one component integrated into at least one of the exhaust valve train components, such as a rocker arm (210) or a valve bridge (400). The actuation means (100) has an inoperative position and an operative position. In the inoperative position, the actuation means (100) is retracted and the small braking cam lobes (232&233) are skipped to generate a main valve lift profile (220m) for the normal engine operation (20). In the operative position, the actuation means (100) is extended to form a mechanical linkage so that the motion from all the cam lobes (220, 232&233) is transmitted to the at least one exhaust valve (300) for the engine braking operation (10). The apparatus further comprises control means (50) for moving the actuation means (100) between the inoperative position and the operative position to achieve the conversion between the normal engine operation (20) and the engine braking operation (10). The apparatus also includes valve lash adjusting mechanism, oil retraining means (350), and engine brake reset means (150).
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSOON AUTOPARTS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for adjusting variable valve lift
An apparatus for adjusting individual valve lift comprising a control arm assembly disposed between the cam lobes and the valve rockers for a multi-valve train. The control arm at each valve includes a driven gear. An actuator shaft includes a mating drive gear at each driven gear for rotating each control arm to vary the overall lift of the valves. In the prior art, the mating drive gears are fixed to the actuator shaft at identical fixed orientations. In accordance with the present invention, each mating drive gear is rotatably adjustable on the actuator shaft to permit changing of the orientation of each gear with respect to the actuator shaft, thereby changing the contact point of the control arm with its respective cam lobe. The lifts of the individual valves may be individually adjusted to provide equal air flow through all the valves in a multi-valve train.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
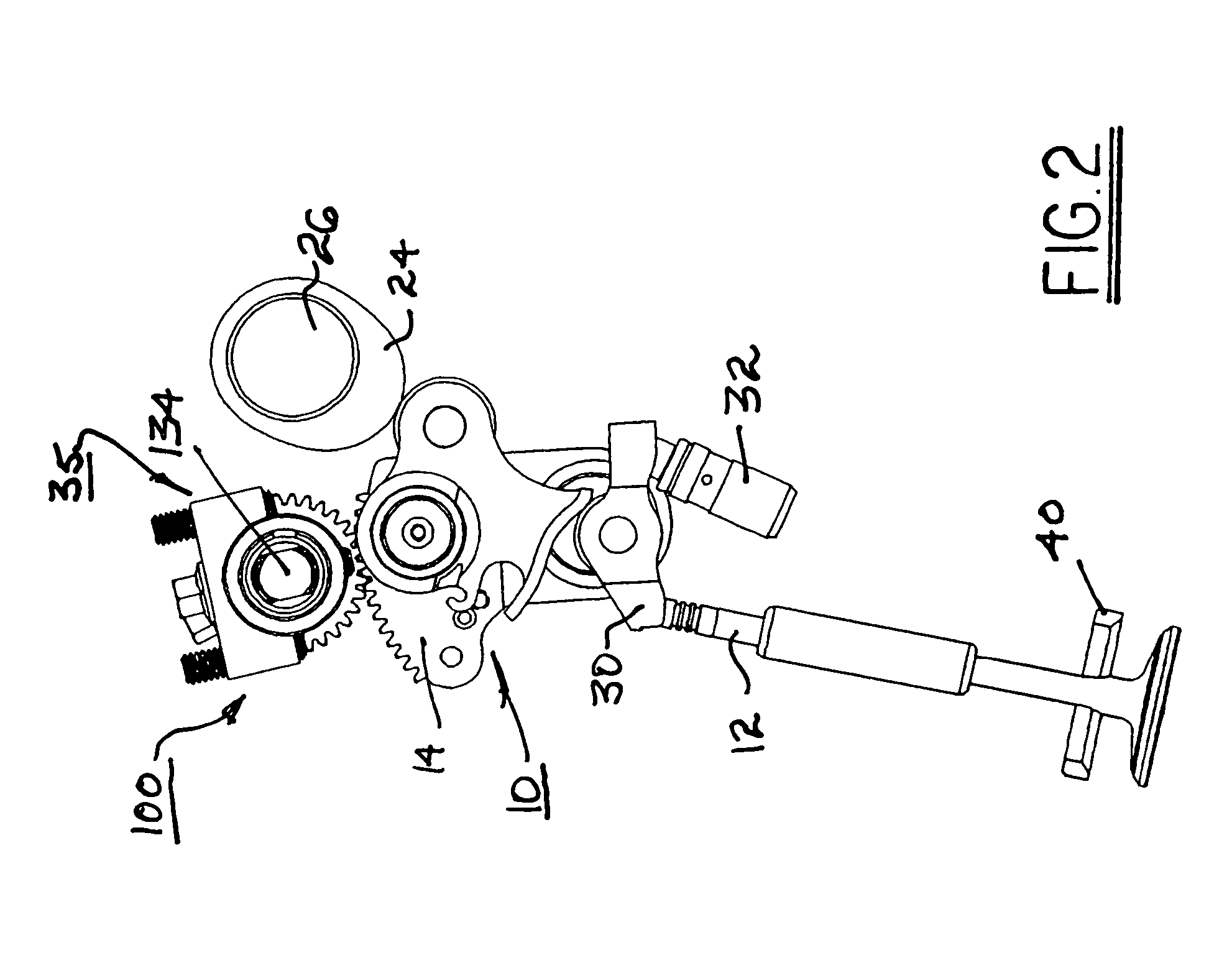
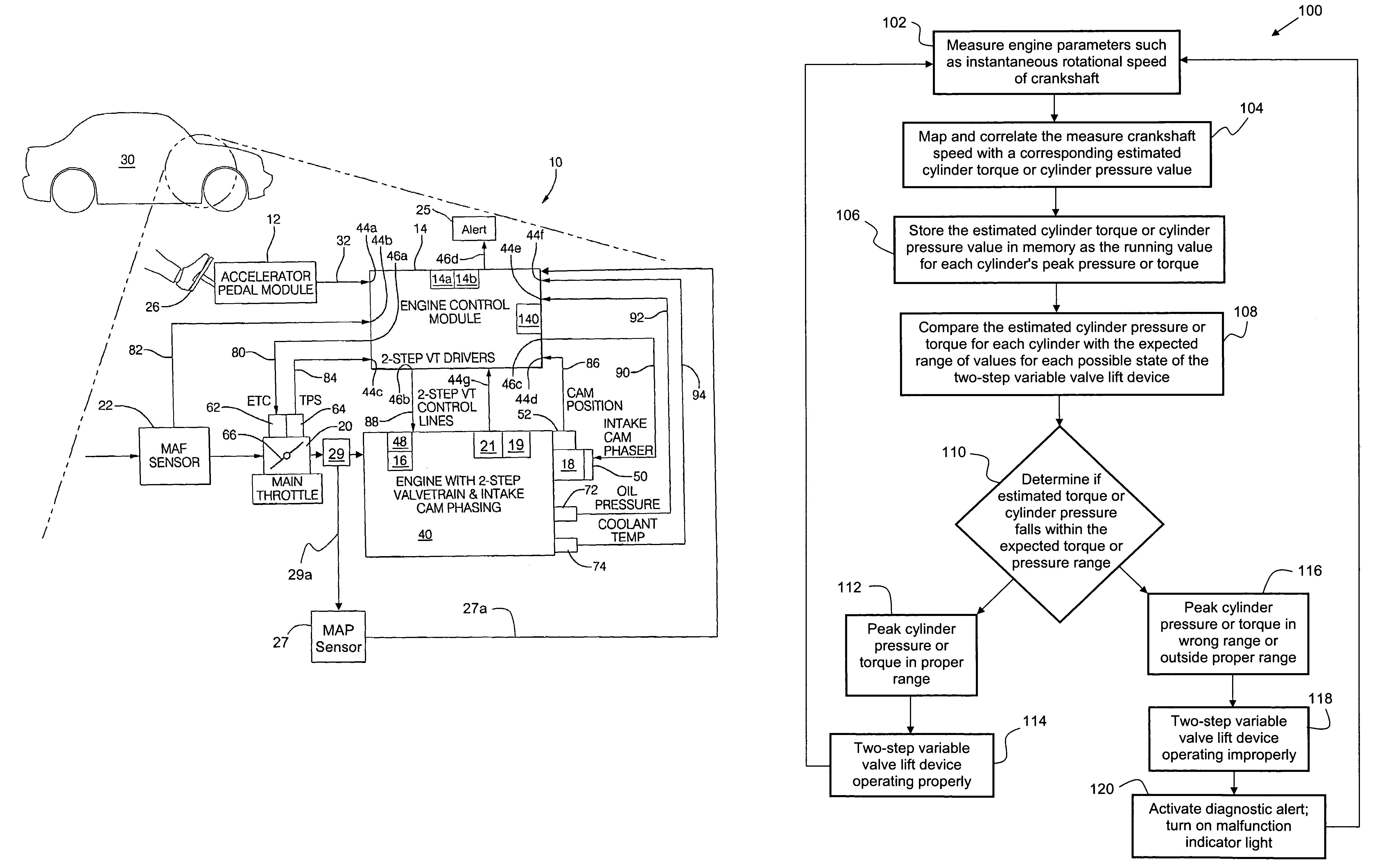
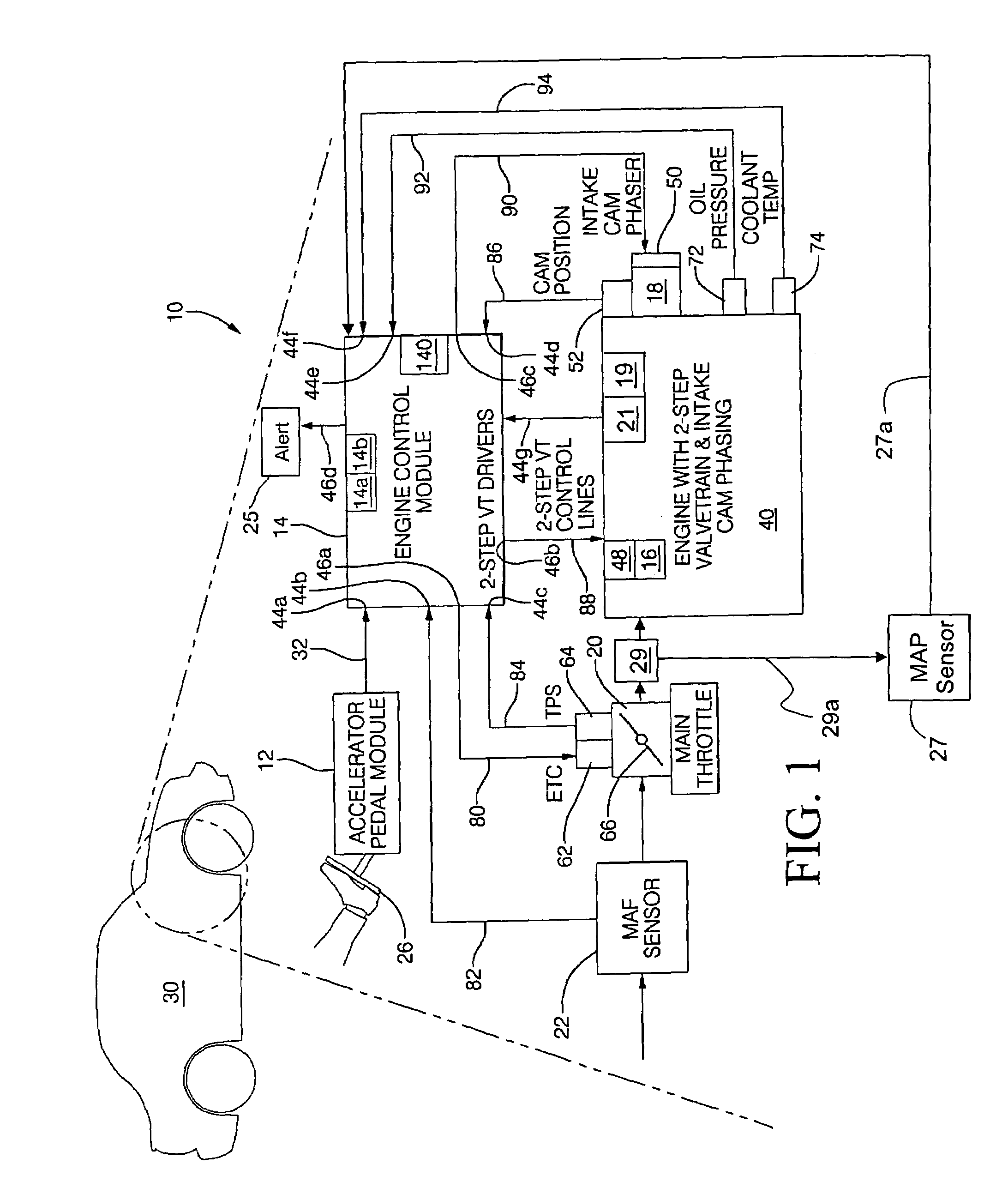
Method for diagnosing the operational state of a two-step variable valve lift device
A method for diagnosing an operational state of a variable valve lift (VVL) device in an engine, wherein the VVL device is capable of operating in two modes of operation. The method includes measuring a rotational speed of an engine crankshaft while the engine is running or cranking, correlating the measured crankshaft speed with an estimated engine cylinder pressure or torque, comparing the estimated engine cylinder pressure or torque with an expected range of engine cylinder pressure or torque values for the two modes of operation for the VVL device, determining if the estimated engine cylinder pressure or torque falls within the expected range of engine cylinder pressure or torque values, and activating an alert if the estimated engine cylinder pressure or torque falls outside the expected range of engine cylinder pressure or torque values to provide notification that the VVL device is operating in an improper mode of operation.
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
Automotive four-cycle engine
InactiveUS20020166536A1Improve engine performanceRaise the combustion temperatureValve arrangementsElectrical controlExhaust valveTop dead center
A four-cycle engine is provided with valve timing adjusters for adjusting opening and closing timing an and an exhaust valve. In medium- to high-speed ranges in medium- to high-load regions of the engine, a closing point (ExC) of the exhaust valve defined as a point of transfer from an acceleration portion to a constant speed portion on its valve lift characteristics curve is set to a point a specific period before an intake top dead center, and an opening point (InO) of the intake valve defined as a point of transfer from a constant speed portion to an acceleration portion on its valve lift characteristics curve is set to a point after the intake top dead center. In addition, the period from the closing point (ExC) of the exhaust valve to the opening point (InO) of the intake valve is made longer in the medium-speed range than in the high-speed range in the medium- to high-load regions of the engine.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
Cylinder head arrangement for variable valve actuation rocker arm assemblies
A novel cylinder head arrangement is described for an in-line four cylinder or eight cylinder engine with each head having two end cylinders and two middle cylinders. A modified arrangement allows additional space for the installation of wider rocker arm assemblies used for variable valve lift (VVL), cylinder deactivation (CDA) and other types of variable valve actuation (VVA) in these existing cylinder head designs. In the first embodiment, cam towers of conventional designs adjacent the end two cylinders are not used. At least one end support is used which may be an outboard bearing on a camshaft for each end. The wider rocker assemblies may then be installed. In an alternative embodiment, the cam towers adjacent the inner two cylinders are eliminated and a single camshaft support piece with a support bearing is installed between the inner cylinders to provide support for the camshafts. The wider rocker assemblies may then be installed on at least one of the middle cylinders. The system also includes a novel oil control valve that operates latches in switching rocker arm assemblies.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD
Compression release engine brake unit
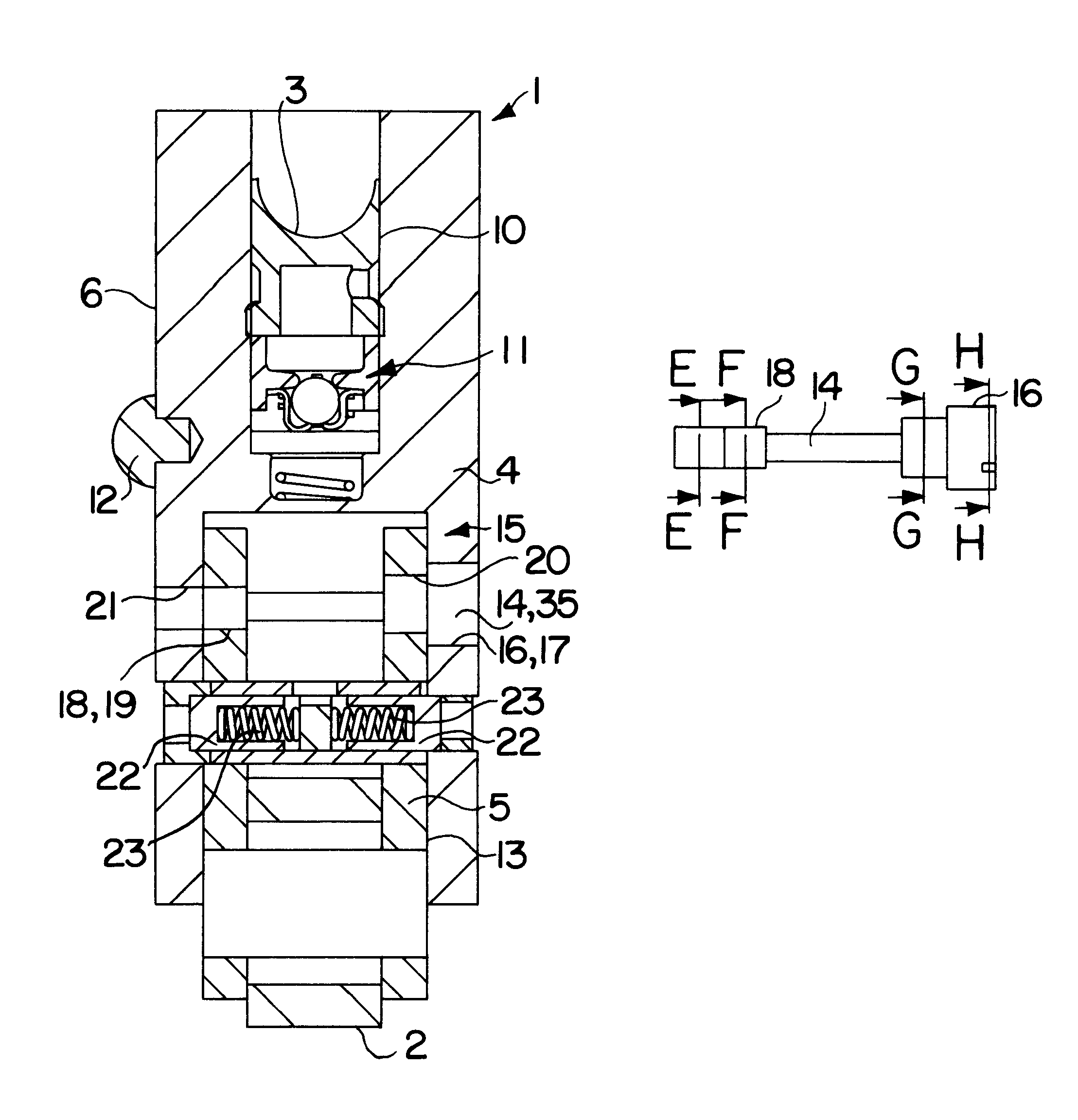
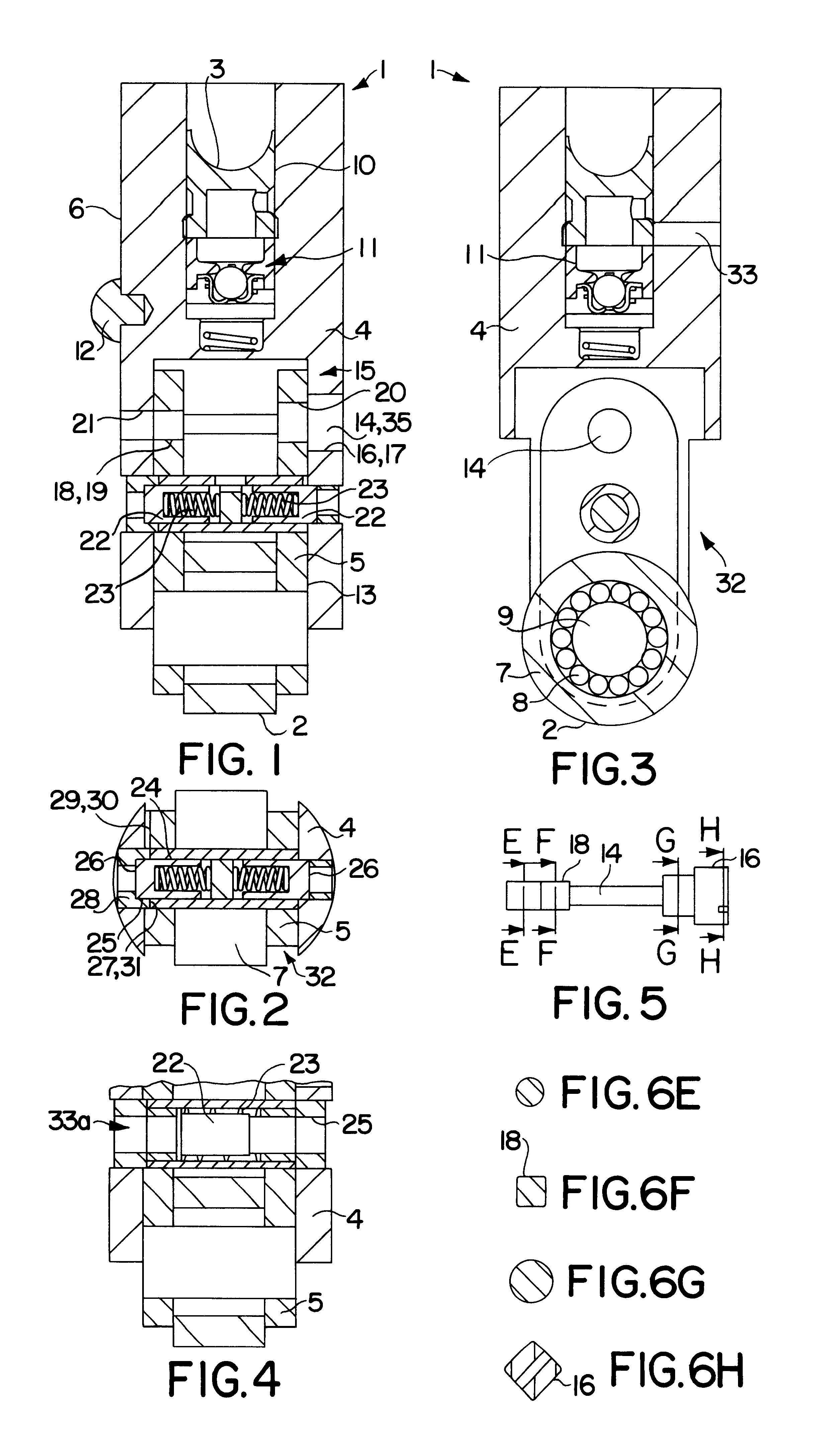
A compression release engine brake unit includes an oil outlet passage formed in a socket brake, which stores engine brake oil, and a reset member opening or closing the outlet passage. The reset member discharges the engine brake oil by opening the oil outlet passage in response to the rotation of a rocker arm during engine braking and, thereby, the engine brake restores the initial state. Since the compression release engine brake can restore the initial state, the return valve lift is the same as when the compression release engine brake is not actuated. Accordingly, the valve does not butt against an engine piston.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
Valve characteristic control apparatus of internal combustion engine and methods of controlling valve characteristics
InactiveUS6405697B2Accurate diagnosisReduce failureValve arrangementsElectrical controlInlet valveCam
A camshaft provided with three-dimensional cams is connected at its one end to a valve lift-varying actuator. By the valve lift-varying actuator or displacing the camshaft in the directions of an axis of the camshaft, the lift characteristic of intake valves set by the three-dimensional cams is variably controlled to a target amount of valve lift. The valve lift characteristic related to this control is detected as a detected amount of valve lift by a reference-purposed detected portion and a cam angle sensor. An apparatus and a method diagnoses abnormalities in the valve lift-varying actuator by, for example, evaluating whether the amount of change in the detected amount of valve lift is at most a predetermined value and the absolute value of a difference between the detected amount of valve lift and the target amount of valve lift is greater than a predetermined value.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Switchable cam follower
A switchable cam follower (1) for a valve train of an internal combustion engine, which valve train can be actuated indirectly by tappet push rods, the cam follower comprises an outer and an inner section (4,5) end for switching-off the cam follower (1) from the cam lift, the inner section (5) is pivotable relative to the outer section (4) during a valve lift phase of the cam.
Owner:INA WALZLAGER SCHAEFFLER KG
Control system and method for an internal combustion engine
InactiveUS6883476B1Avoid performanceAvoid efficiencyValve arrangementsElectrical controlControl systemEngine valve
A control system for an internal combustion engine having a variable valve operating mechanism capable of varying at least one of a valve lift and an operation angle of an engine valve continuously is provided. The control system comprises a detecting device that detects an operating condition of the variable valve operating mechanism and produces a signal representative thereof, and a controller that controls the operating condition of the variable valve operating mechanism in response to the signal from the detecting device. The controller is programmed to determine whether an operation responsiveness of the variable valve operating mechanism is lowered based on the signal from the detecting device and vary operational characteristics of the variable valve operating mechanism when the operation responsiveness of the variable valve operating mechanism is lowered. A control method is also provided.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Compression ignition gasoline engine
ActiveUS20110108001A1Suppress excessive self-ignitionRapid increase of combustion noiseValve arrangementsElectrical controlCombustion chamberExhaust valve
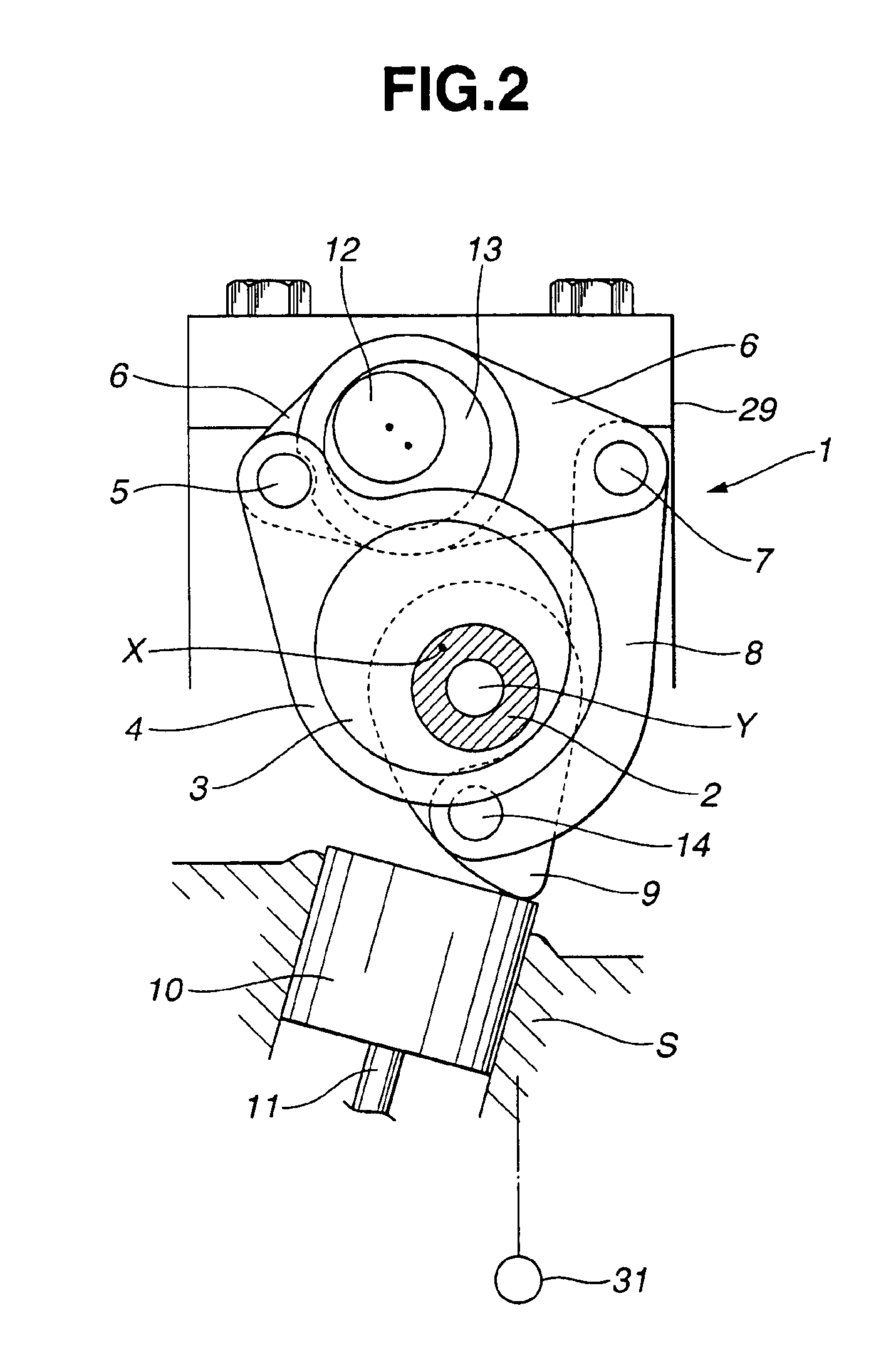
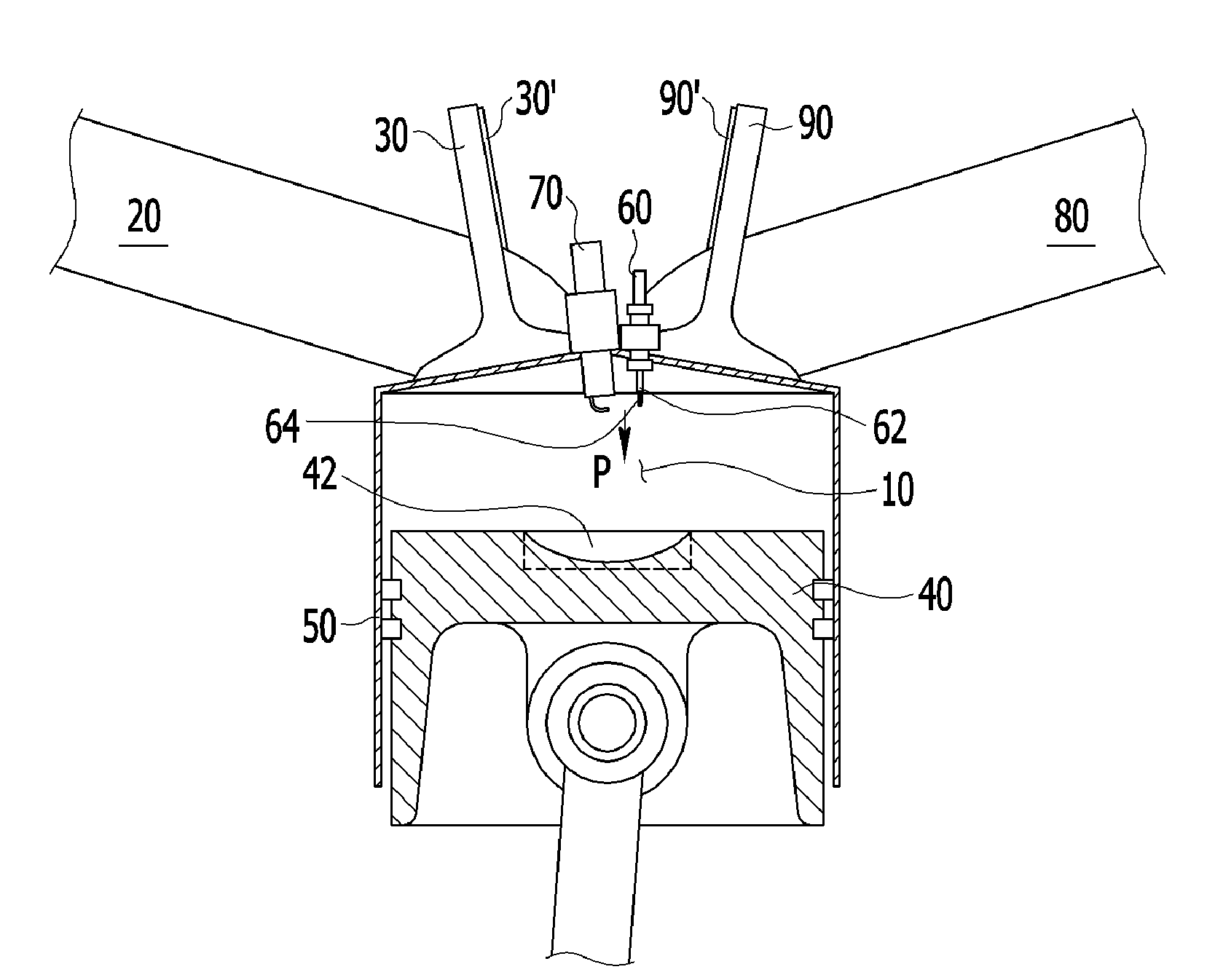
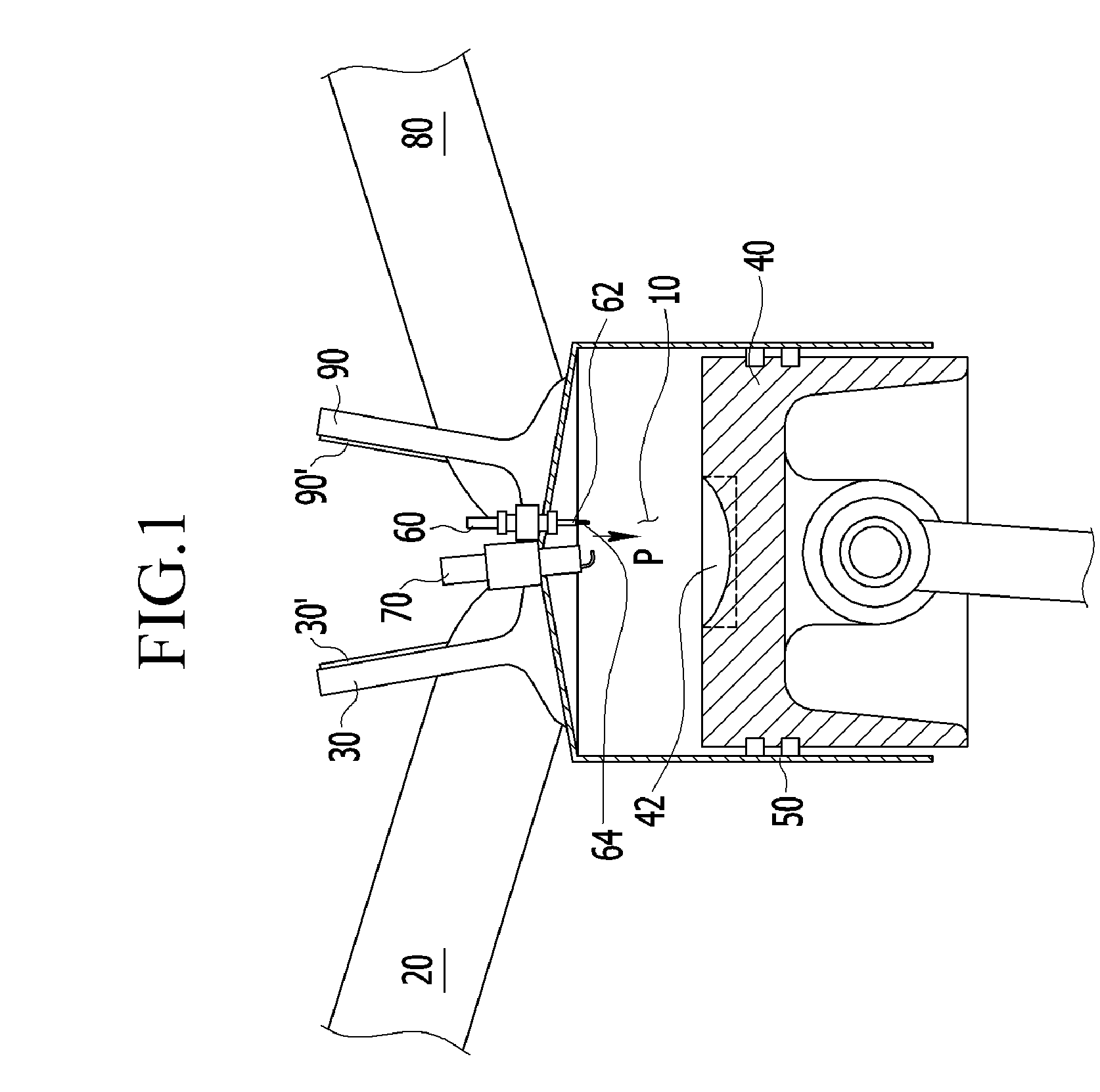
A compression ignition gasoline engine uses low-cetane number fuel, such as gasoline. The engine includes a combustion control device having an injector directly injecting fuel into a combustion chamber, intake and exhaust valves, and a variable valve device changing a valve timing, in which the compression ignition gasoline engine includes: at least two intake valves and two exhaust valves; a spark plug positioned at the center portion of the combustion chamber; and an injector positioned adjacent to the spark plug toward the center portion of the combustion chamber, in which the exhaust valve is a symmetric valve lift in which the lift and the opening section of the tow exhaust valves are the same in low lift, and the intake valve is an asymmetric valve lift in which the lift and the opening of the two intake valves are different in the low lift.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Internal combustion engine using variable valve lift and skip fire control
An internal combustion engine capable of cylinder deactivation or skip fire control in combination with variable valve lift control. One bank of cylinders can be deactivated while the air induction of the other bank of cylinders is regulated using variable valve lift control to increase engine efficiency. An internal combustion engine with two cylinder banks, where control of one cylinder bank using skip fire control can be operating at an appropriate firing fraction in combination with variable valve lift control on the other cylinder bank. A single bank of cylinders can be controlled in a skip fire manner in conjunction with variable valve lift control.
Owner:TULA TECH INC
Dual intake valve system with one deactivation valve and one multi-lift valve for swirl enhancement
ActiveUS8312849B2Increased turbulenceIncrease flow rateValve arrangementsOutput powerInlet valveHigh lift
In a dual intake valve arrangement for an internal combustion engine, a variable valve lift system controls two intake valves for one or more engine cylinders. In each cylinder, one of the intake valves includes an associated two-step actuation device, and the other includes an associated valve deactivation device. To improve in-cylinder air flow turbulence, one valve may be operated in a high-lift or low-lift state while the other valve may be deactivated.
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
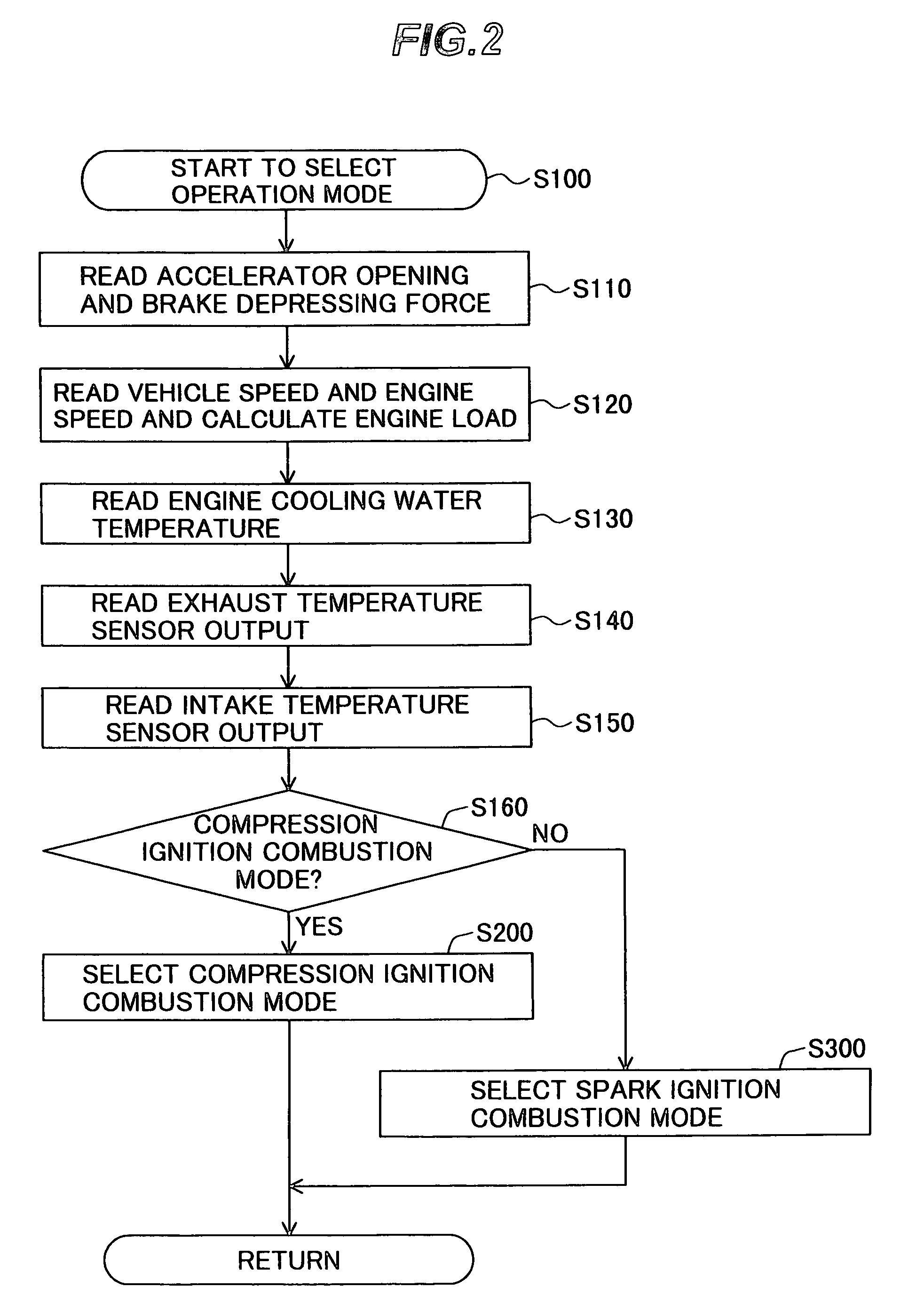
Compression ignition internal combustion engine
InactiveUS7089913B2Increase working areaImproved torque controlValve arrangementsElectrical controlCombustion chamberExhaust valve
A control apparatus operates a compression ignition internal combustion engine by switching between spark ignition combustion using an ignition device and compression ignition combustion which self-ignites a mixture by piston compression. Variable valve mechanisms vary at least one of the valve timings and valve lifts of an intake valve and an exhaust valve. Intake air is regulated to vary the amount of air intake into a combustion chamber on the upstream side of a combustion chamber inlet of the compression ignition internal combustion engine. The variable valve mechanisms and the intake air regulation are controlled during the compression ignition combustion so as to perform the compression ignition combustion.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com