Patents
Literature
996 results about "High lift" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
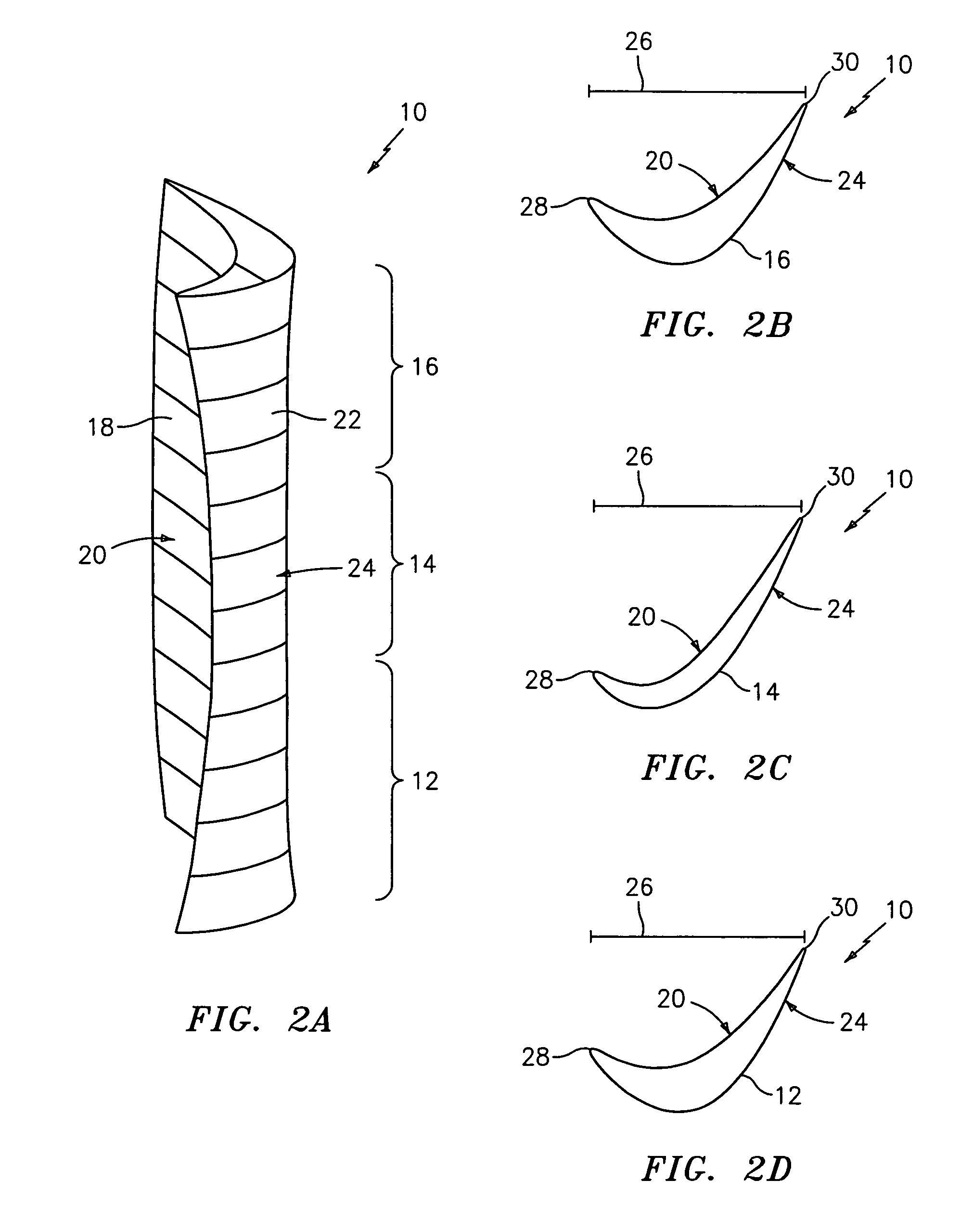
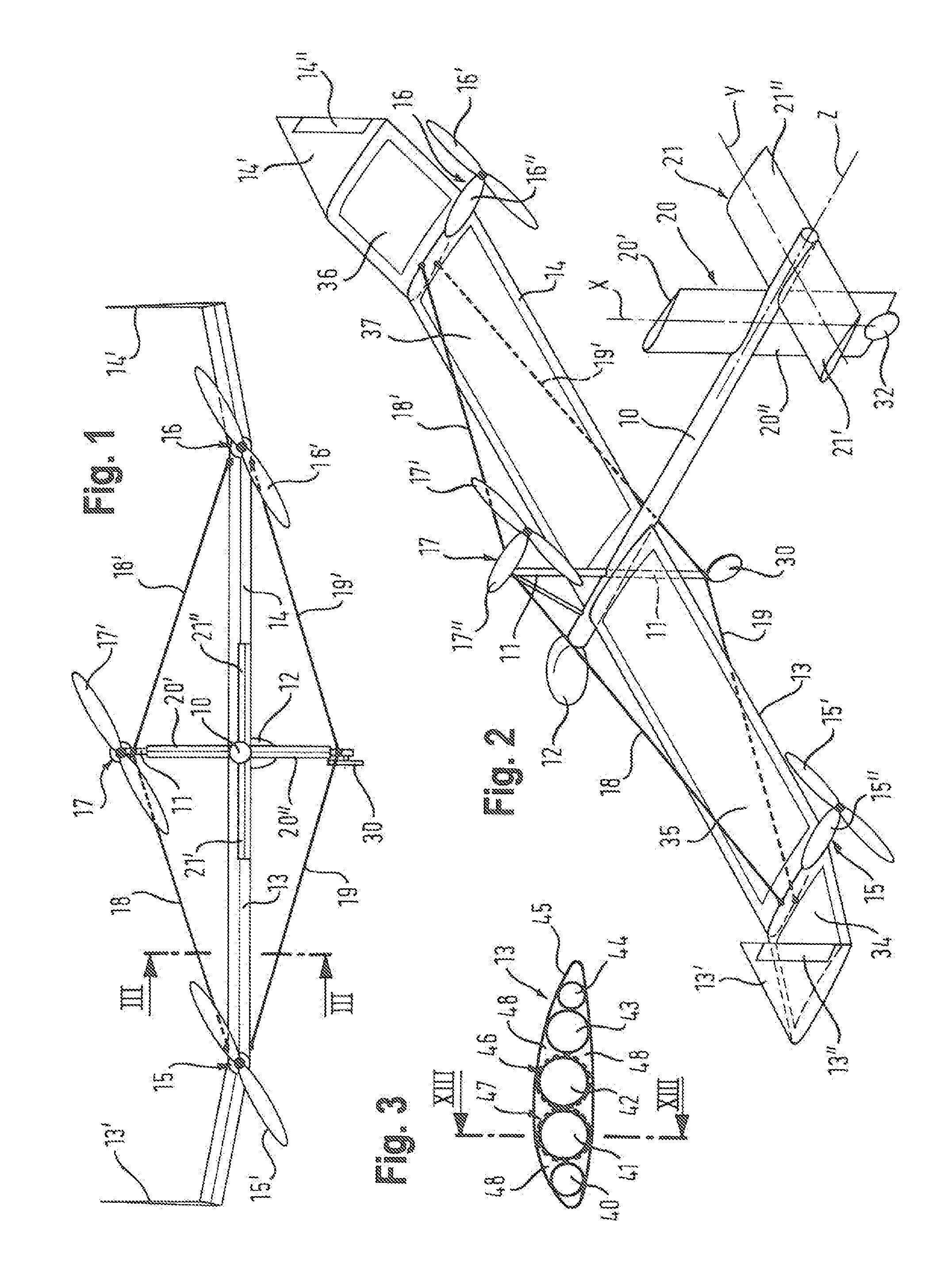
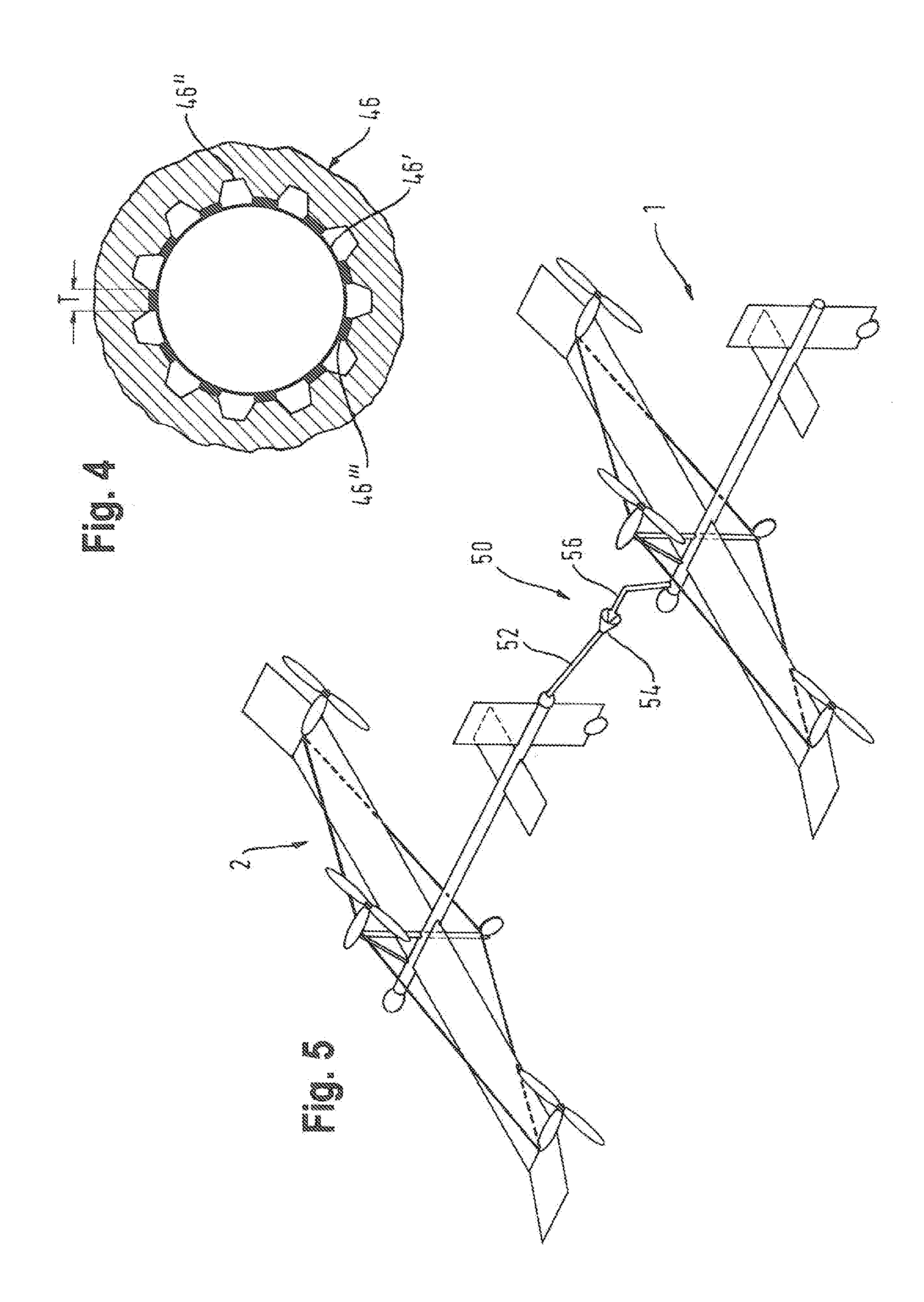
Apparatus and methods for variable sweep body conformal wing with application to projectiles, missiles, and unmanned air vehicles
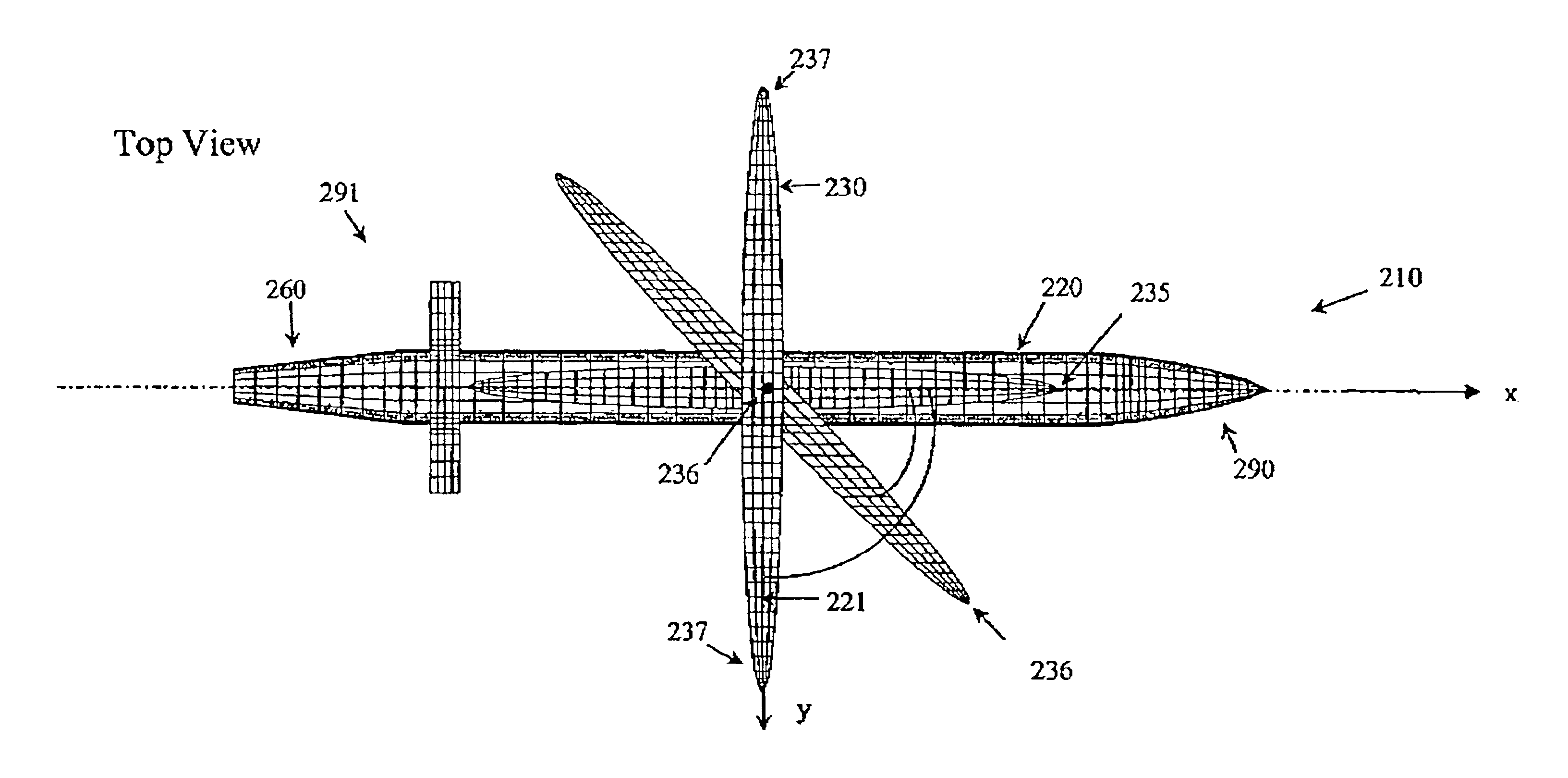
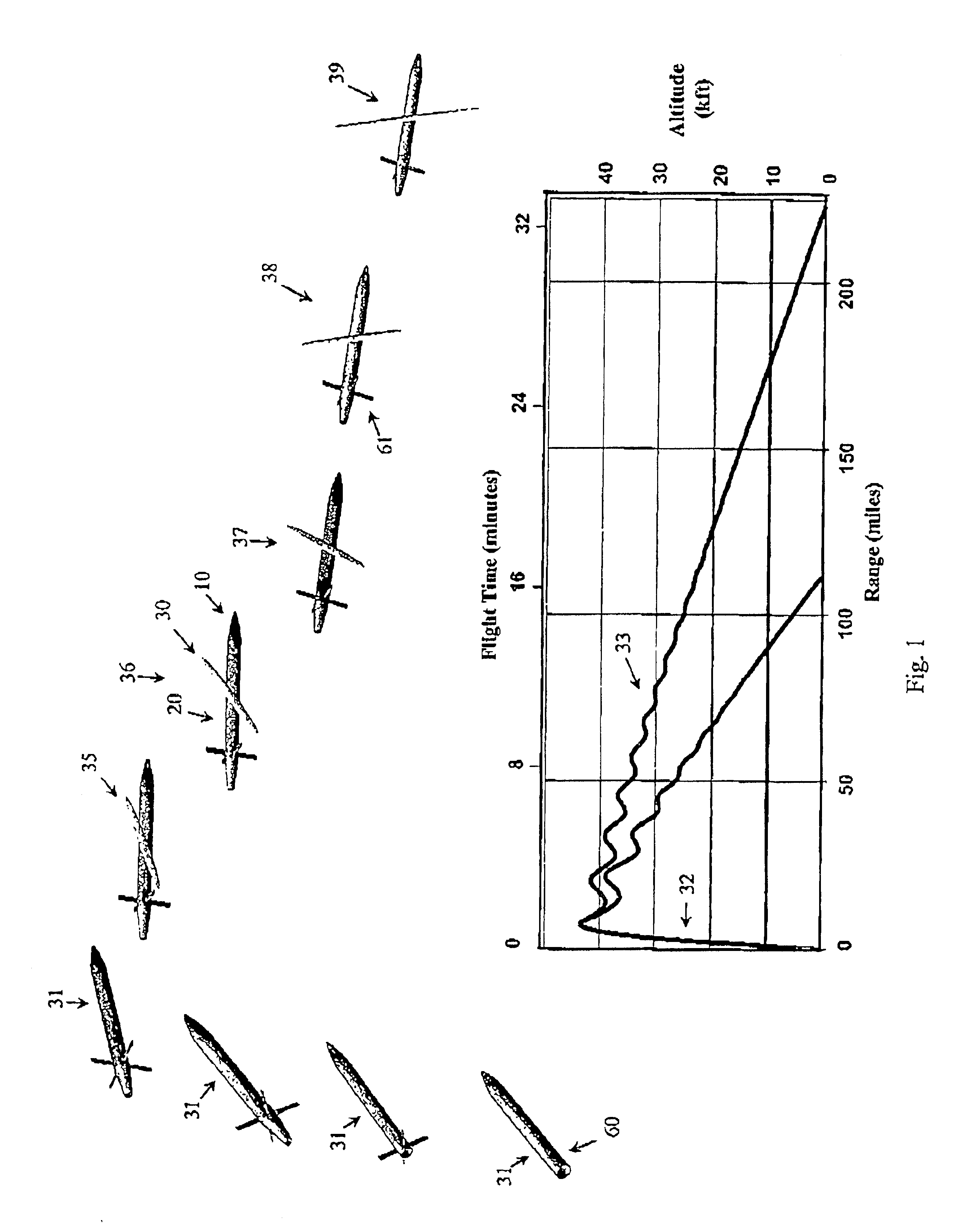
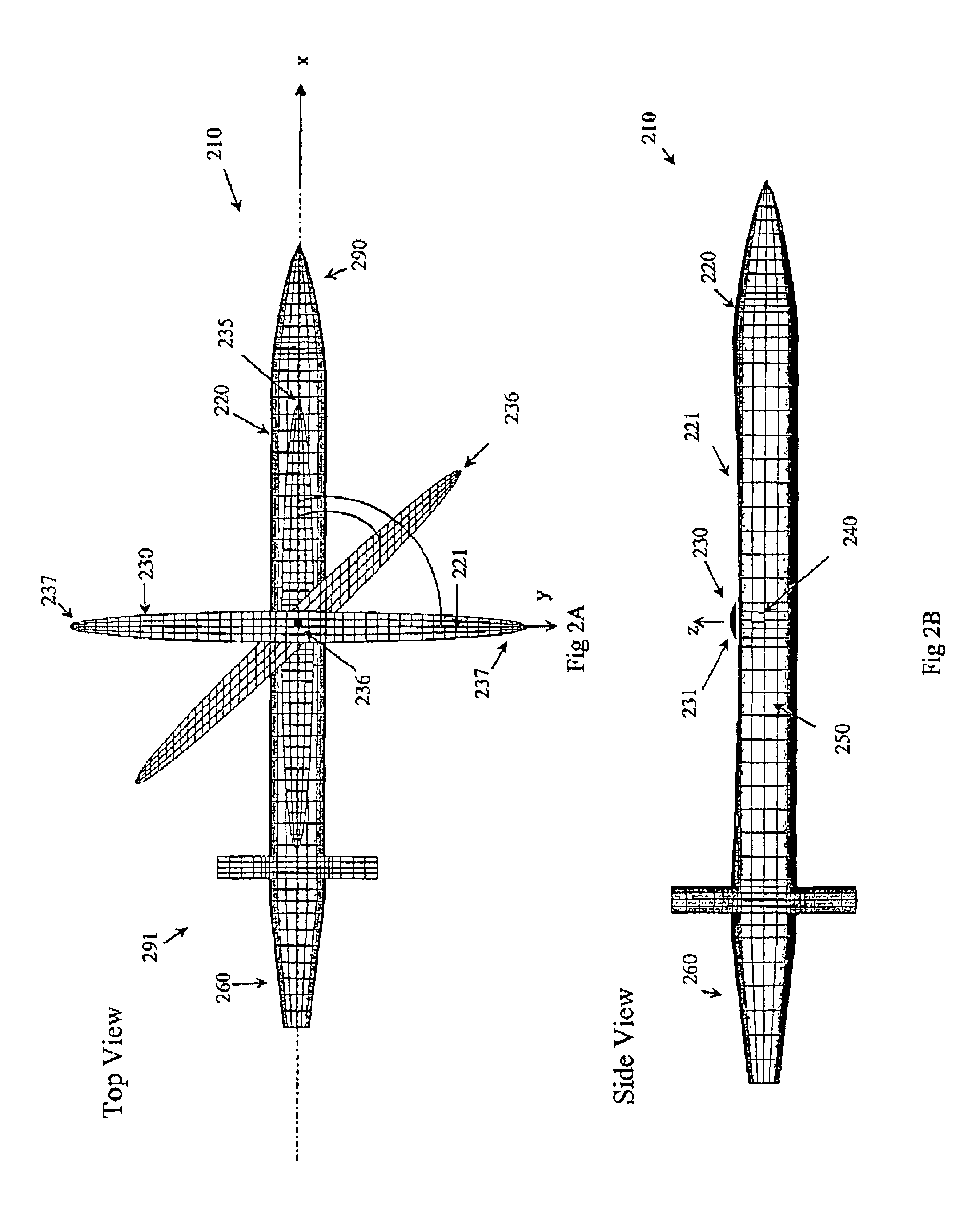
InactiveUS6923404B1Improve aerodynamic efficiencyImprove aerodynamic performanceAircraft stabilisationUnmanned aerial vehiclesBody axisUncrewed vehicle
An unmanned air vehicle (“UAV”) apparatus is configured to have a body and a body-conformal wing. The body-conformal wing is configured to variably sweep from a closed position to a fully deployed position. In the closed position, the body-conformal wing span is aligned with the body axis and in the fully deployed position the body-conformal wing span is perpendicular to the axial direction of the body. Delivery of the UAV comprises the steps of: positioning the span of a body conformal wing in alignment with the axis of the body of the UAV; initiating the flight of the UAV; and adjusting the sweep angle of the body-conformal wing as a function of the current speed, altitude, or attack angle of the UAV, with the adjustment starting at a 0 degree position and varying between a closed position and a fully deployed position. The UAV also has a control mechanism configured to variably adjust the sweep of the body-conformal wing to achieve a high lift over drag ratio through out the flight path of the UAV.
Owner:ZONA TECH
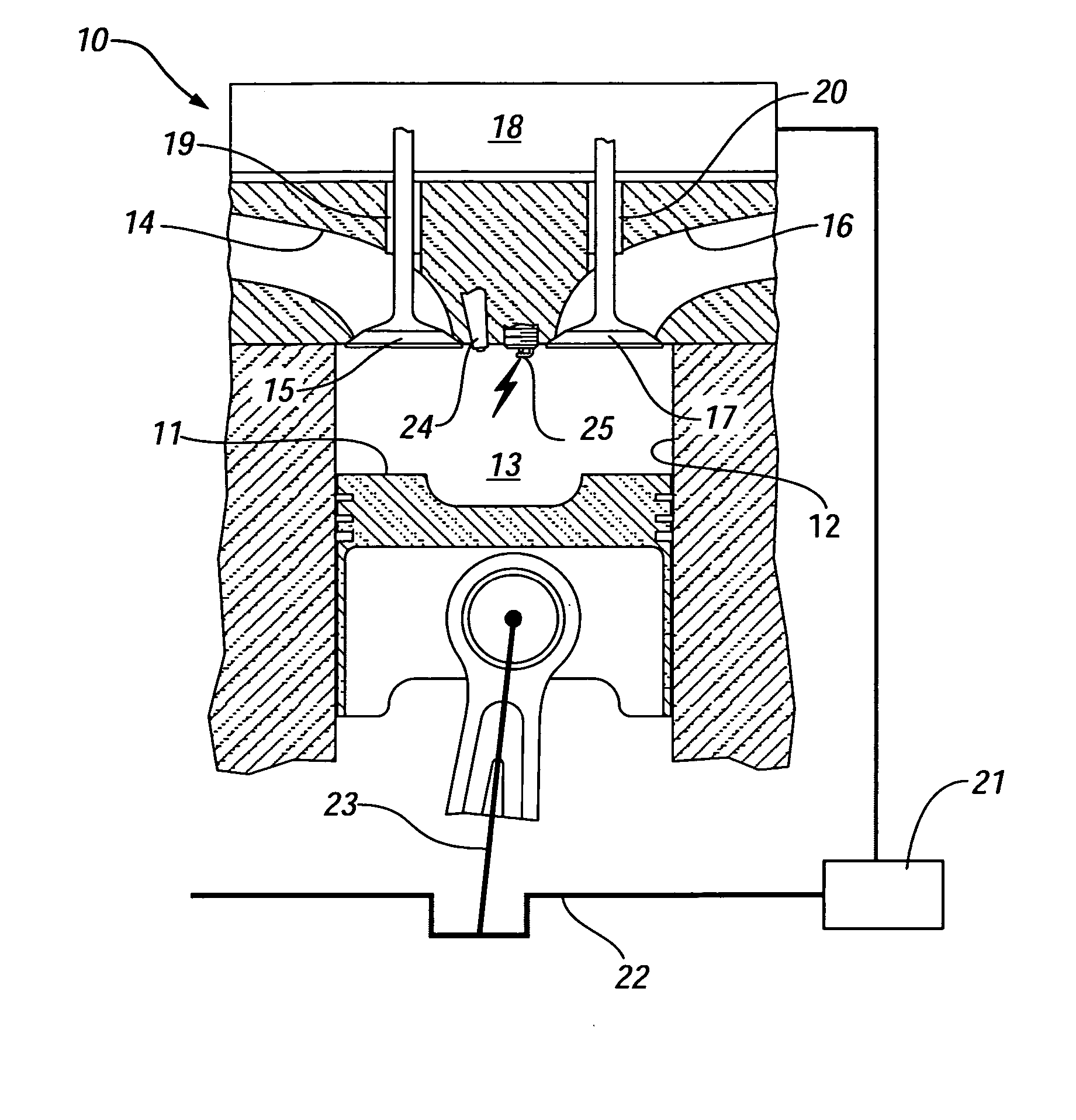
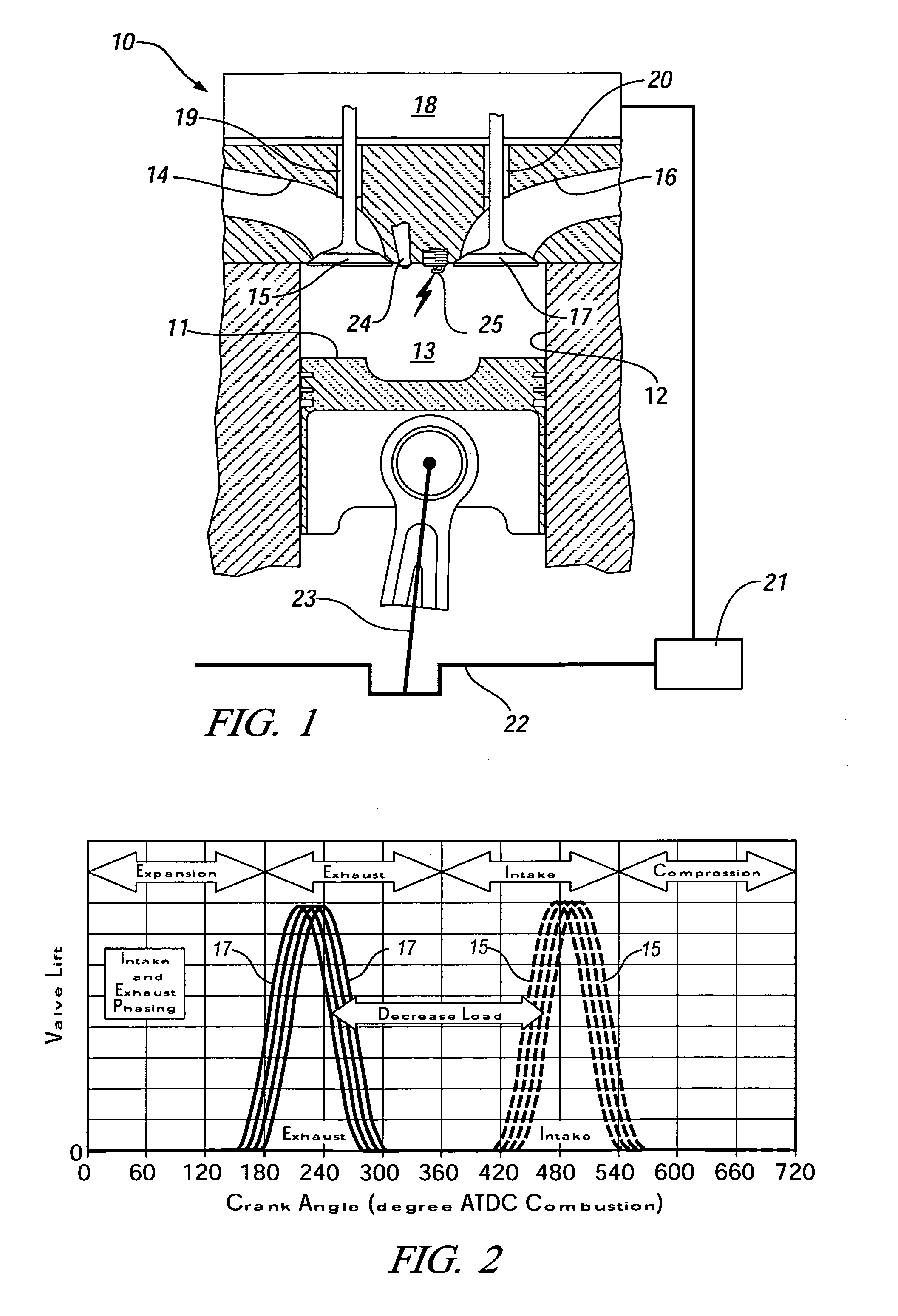
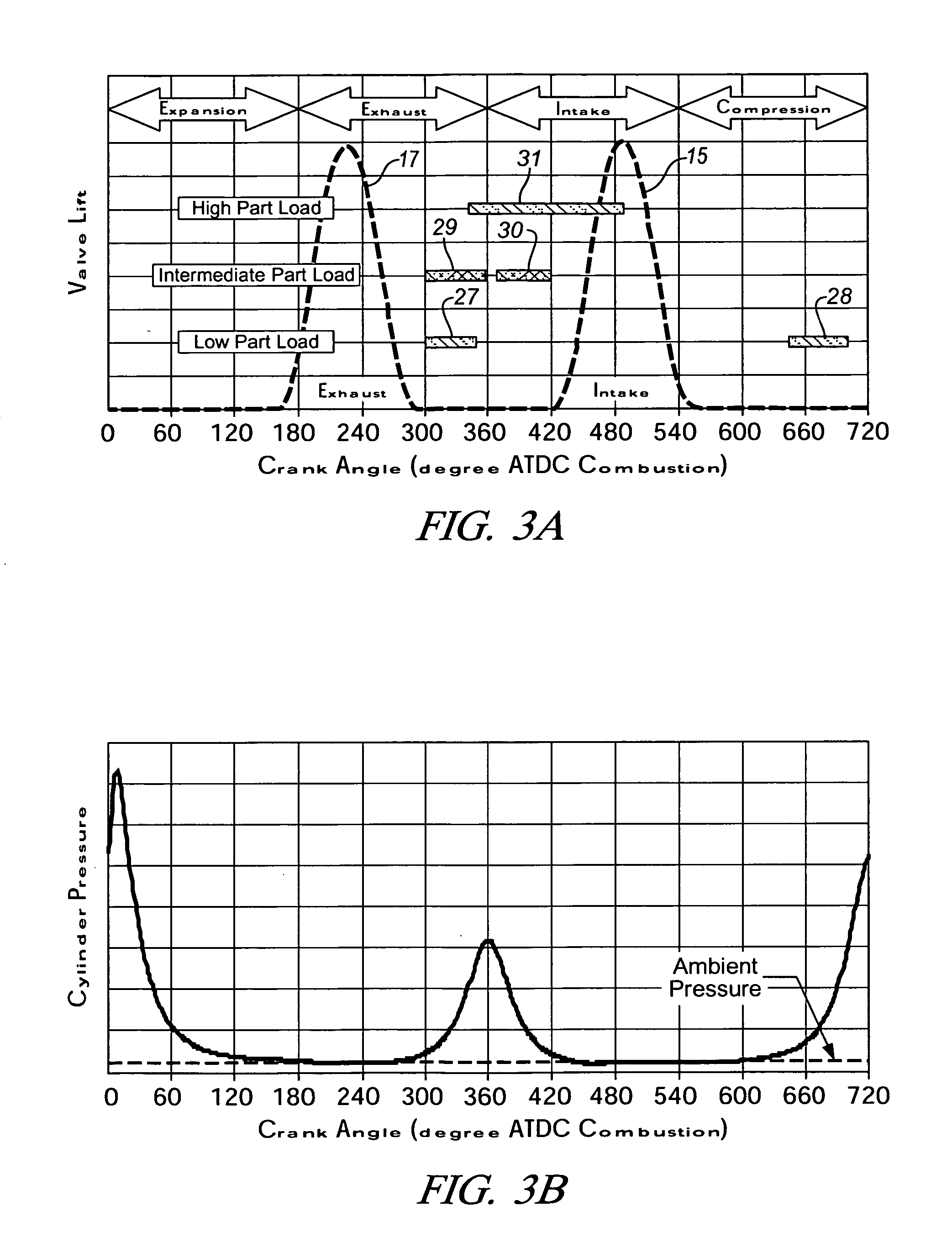
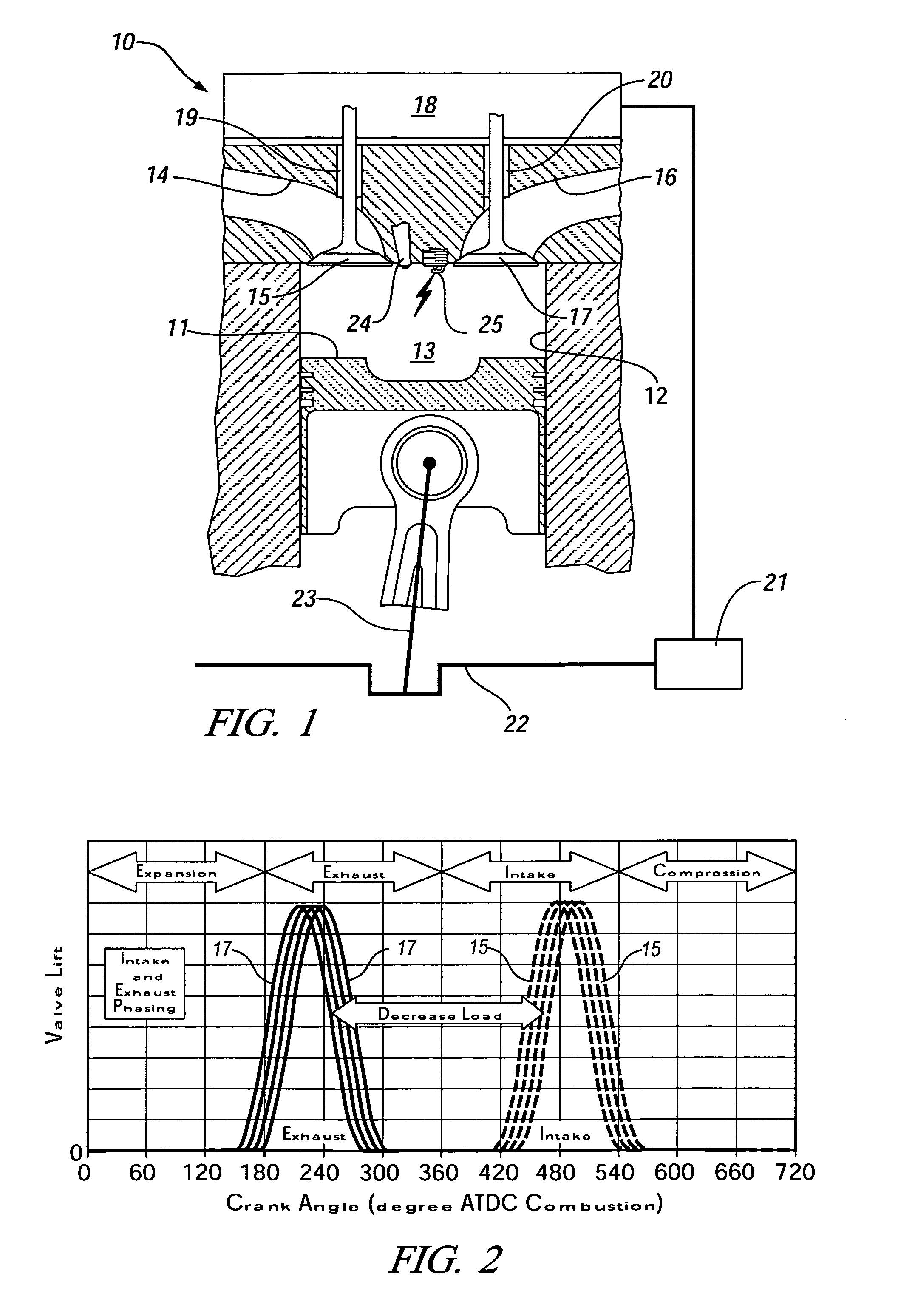
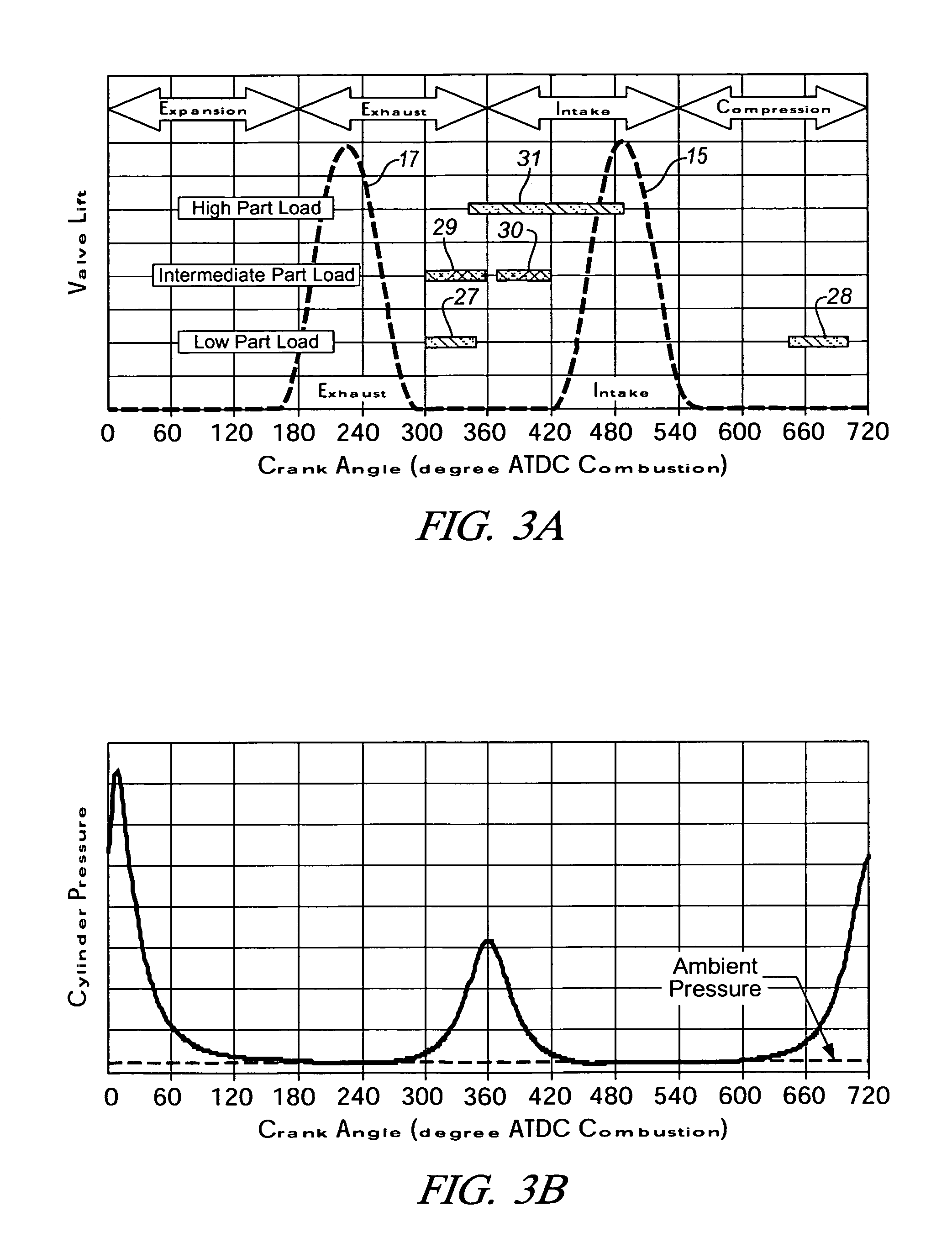
Method for transition between controlled auto-ignition and spark ignition modes in direct fuel injection engines
InactiveUS20060196466A1Eliminate misfiringEliminate partial burnValve arrangementsElectrical controlHomogeneous charge compression ignitionExhaust valve
A method is provided for control of transition between combustion modes of a direct-injection engine operable in a homogeneous charge compression ignition (HCCI) mode at lower loads and a spark ignition flame propagation (SI) mode at higher loads. The engine includes a variable valve actuation system including two-step high and low lift valve actuation and separate cam phasing for both intake and exhaust valves. The method includes operating the engine at steady state, with fuel-air-exhaust gas mixtures at predetermined conditions, for each speed and load, and controlling the engine during mode changes between the HCCI mode and the SI mode by switching the exhaust and intake valves between low lift for HCCI operation and high lift for SI operation. High load may be an SI throttled mode with an intermediate unthrottled mode (SI / NTLC} in which transition between HCCI and SI / NTLC modes requires switching only the exhaust valve lift and transition between SI / NTLC and SI throttled modes requires switching only the intake valve lift, with predetermined phase adjustments in the valve timing phasing.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Noise reducing vortex generators on aircraft wing control surfaces
InactiveUS6491260B2Eliminate the effects ofReduced strengthInfluencers by generating vorticesWingsBristleHigh lift
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
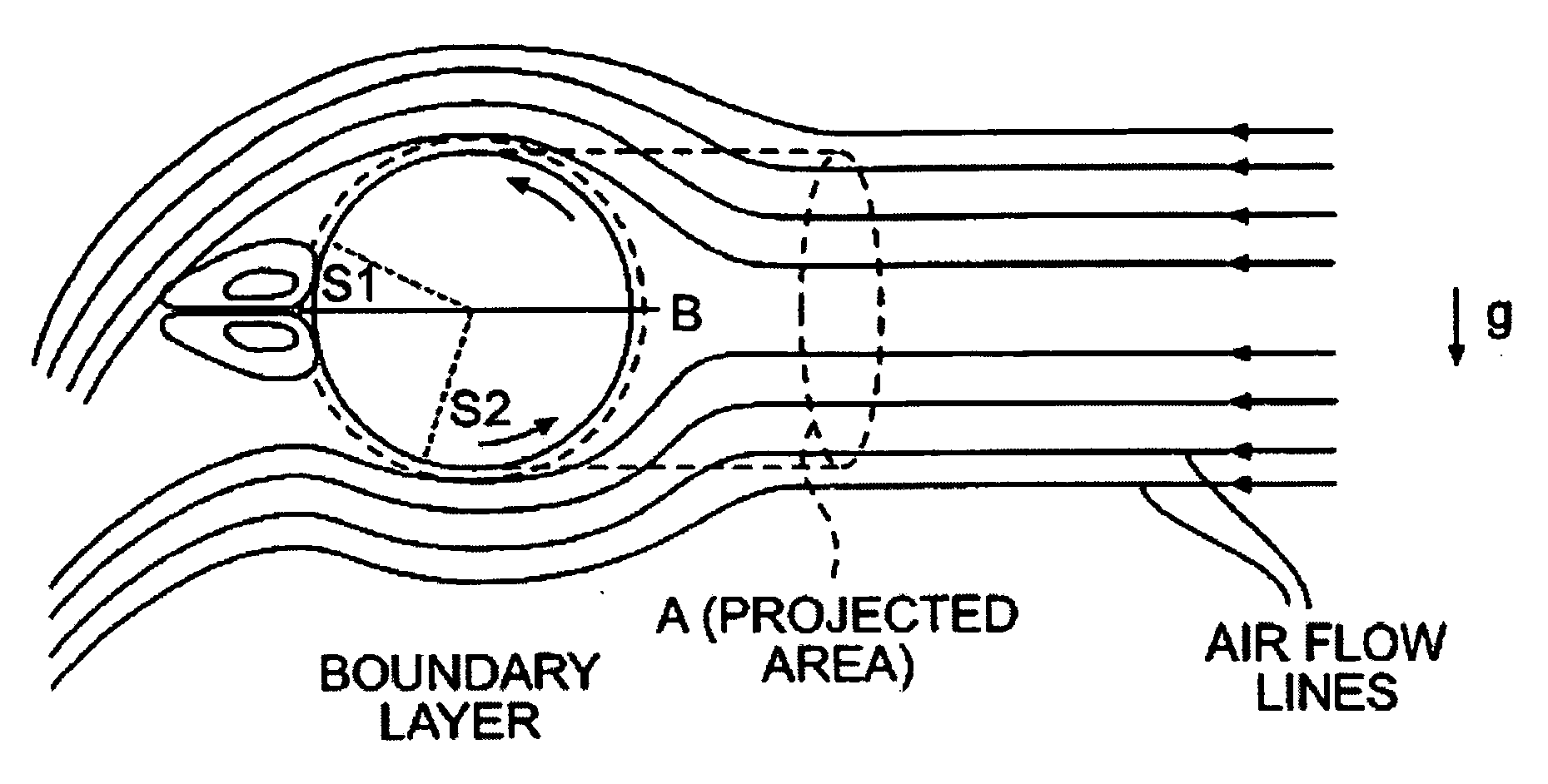
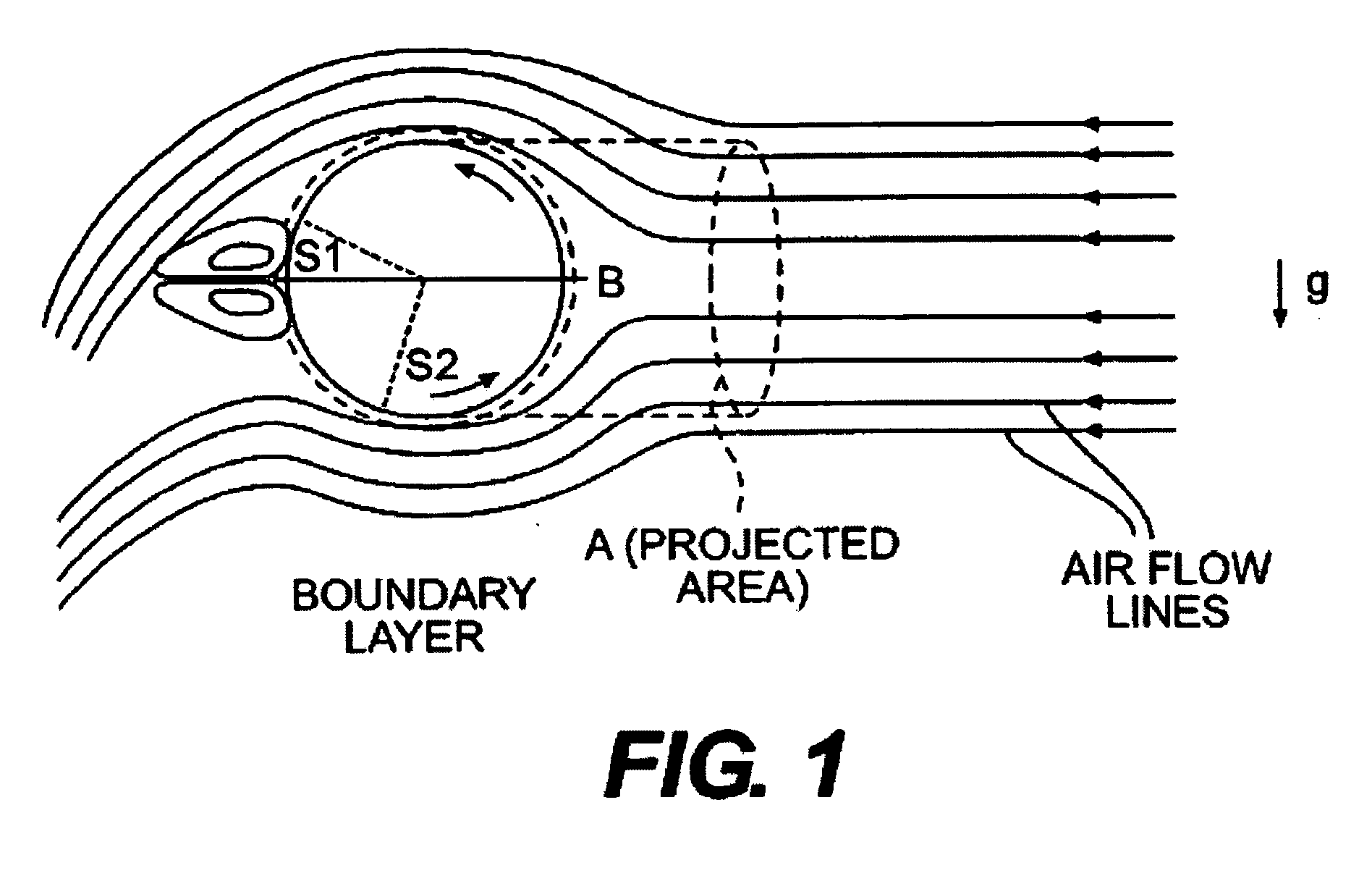
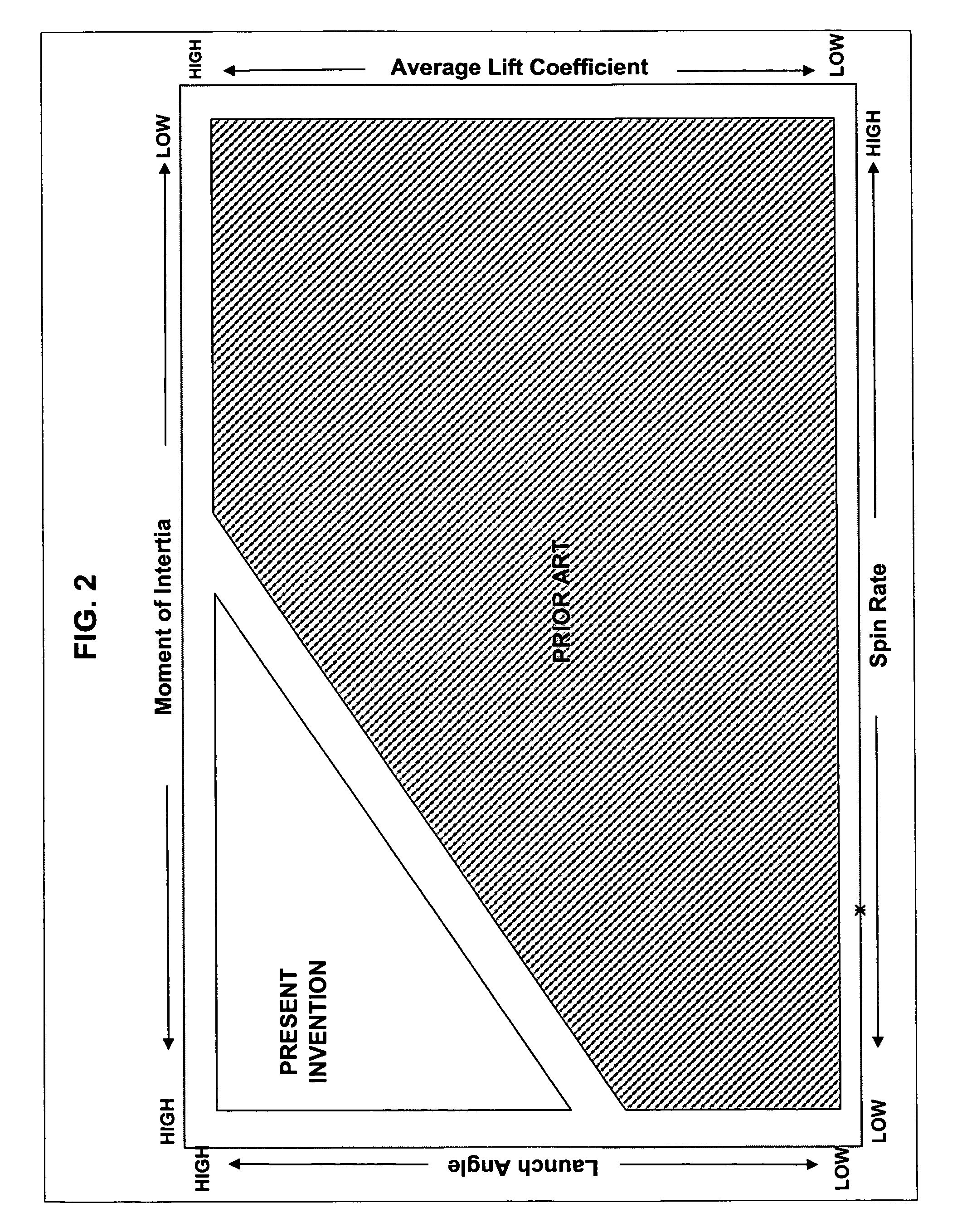
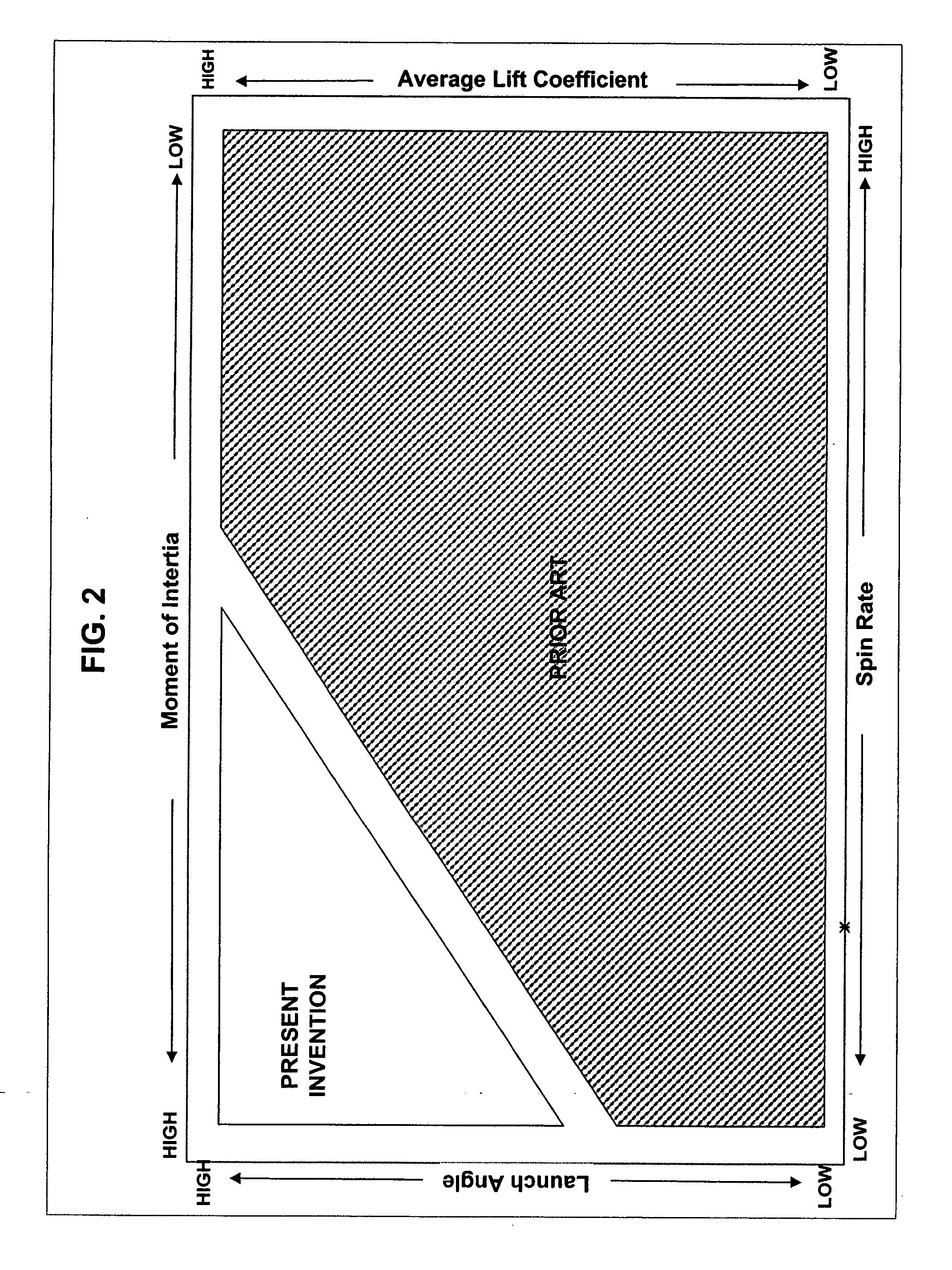
Golf ball having specific spin, moment of inertia, lift, and drag relationship
Golf ball with a novel combination of spin rate, lift coefficient, drag coefficients, and optionally moment of intertia: a golf ball with a low spin rate, a high lift coefficient, a low drag coefficient, and optionally a high moment of inertia; and a golf ball with a high spin rate, a low lift coefficient, a low drag coefficient, and optionally a low moment of inertia.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
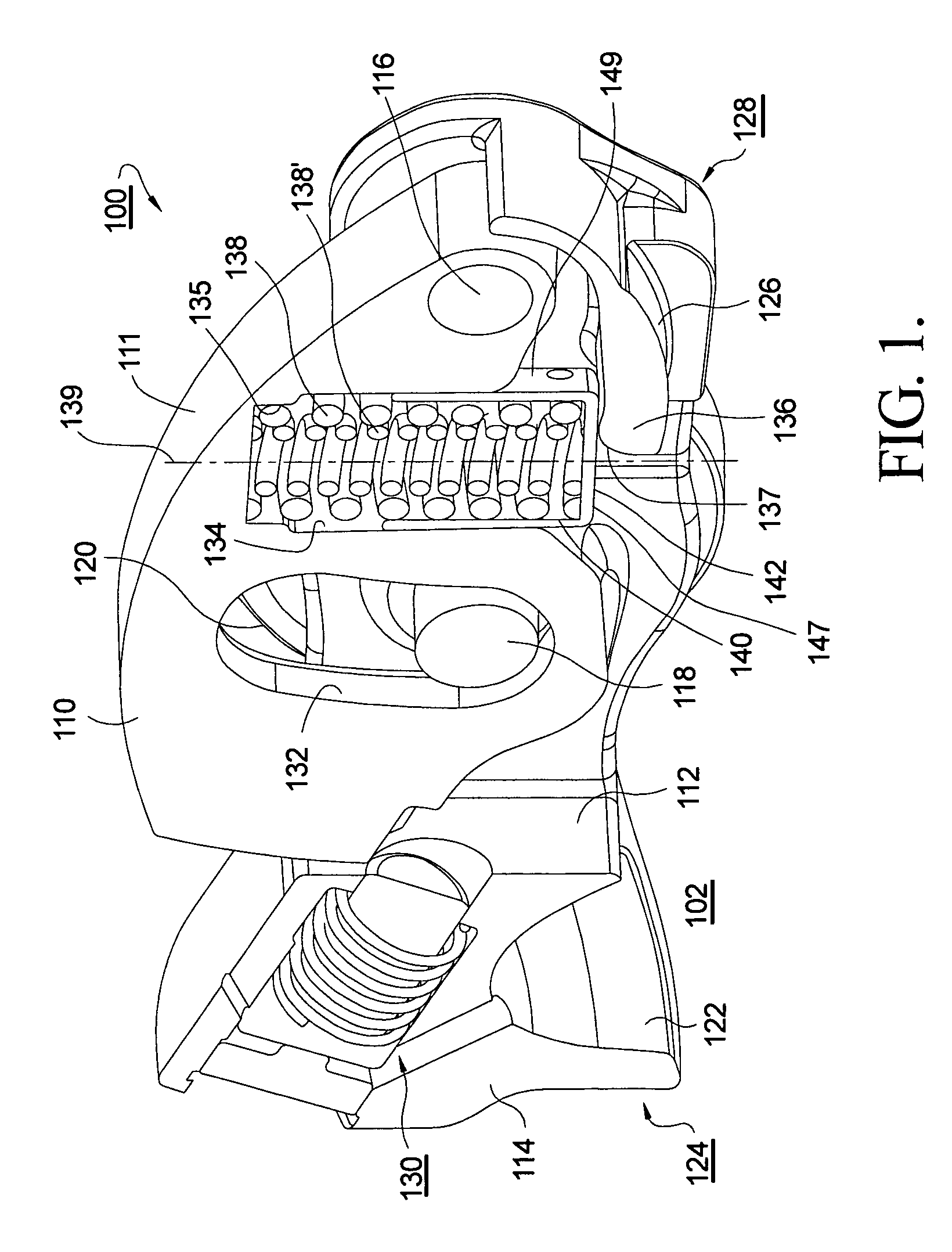
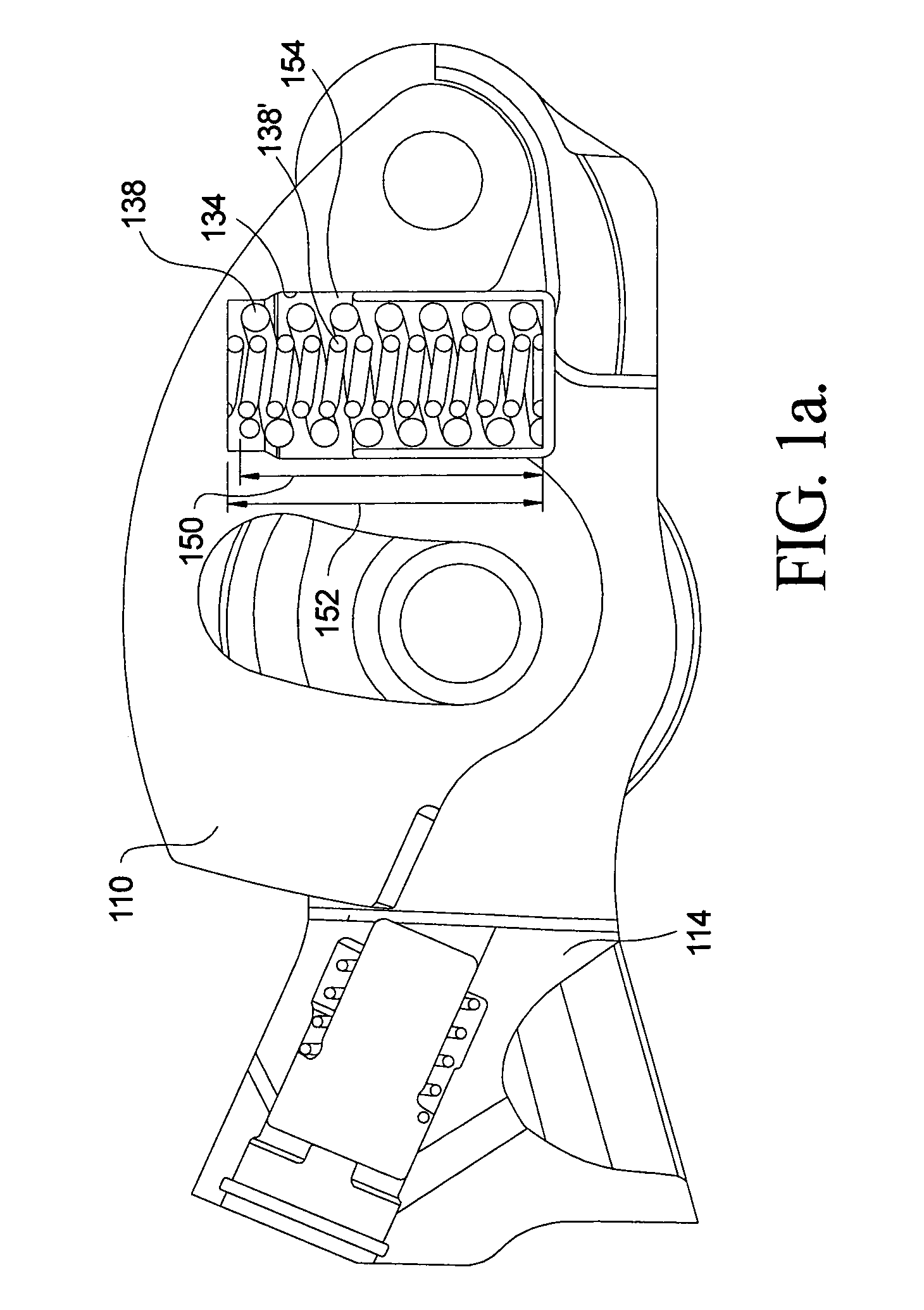
Two-step roller finger follower
A two-step roller finger follower having a high-lift follower portion that rotates relative to a low-lift follower portion about a pivot shaft, including a lost-motion compression spring disposed in a linear bore formed in the high-lift portion to exert force against an curved pad on the back side of the valve pallet of the low-lift portion. The spring is retained and guided in its bore by a spring retainer having a planar bottom for engaging the curved pad. Preferably the retainer is a cup positioned in the spring bore such that the stroke of the cup is limited, to prevent leak-down of the associated hydraulic lash adjuster. Driving the spring by a linear-acting retainer in a linear bore causes the spring to be compressed linearly, resulting in a highly stable and predictable spring rate.
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
Golf ball having specific spin, moment of inertia, lift, and drag relationship
Golf ball with a novel combination of spin rate, lift coefficient, drag coefficients, and optionally moment of intertia: a golf ball with a low spin rate, a high lift coefficient, a low drag coefficient, and optionally a high moment of inertia; and a golf ball with a high spin rate, a low lift coefficient, a low drag coefficient, and optionally a low moment of inertia.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
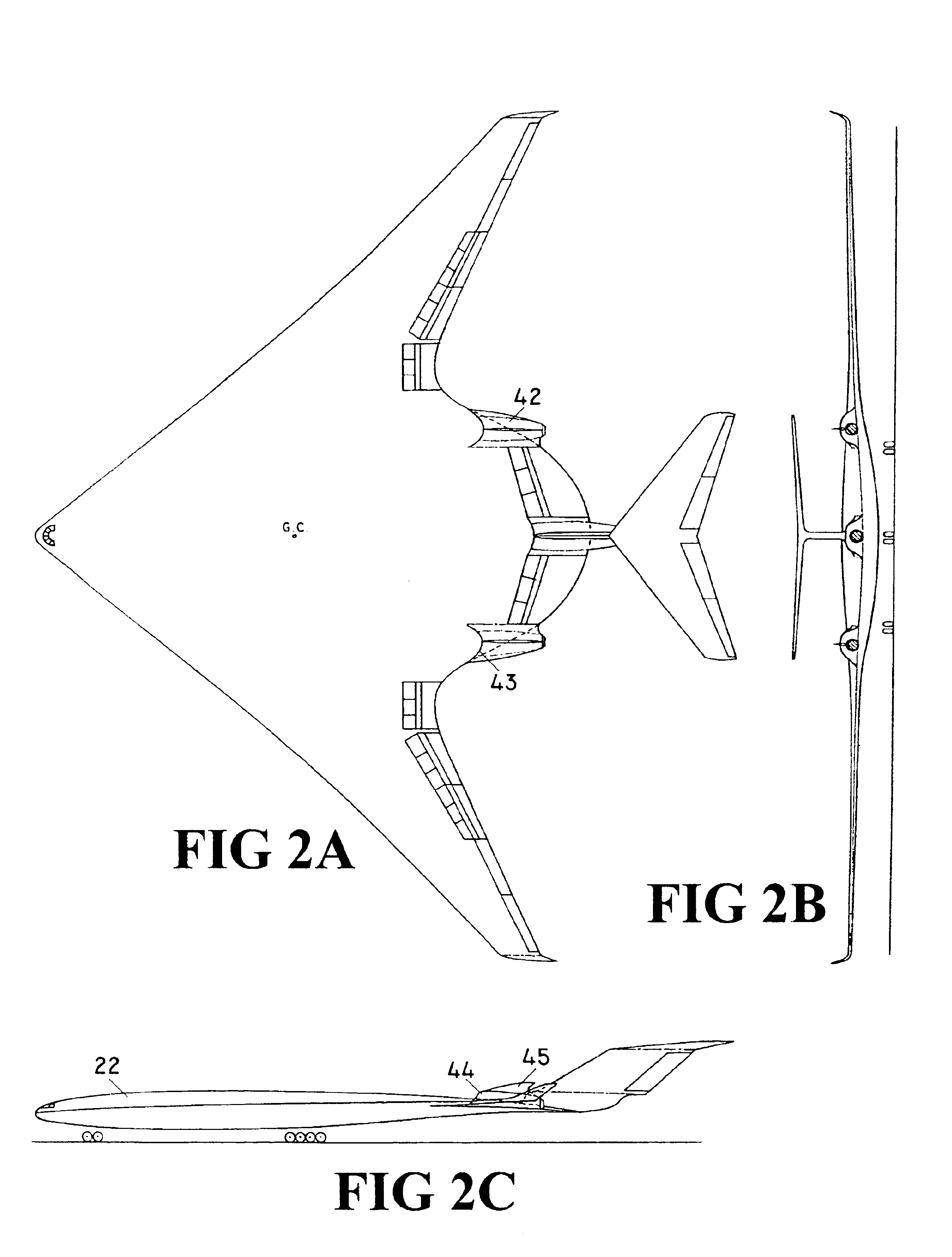
Deltoid main wing aerodynamic configurations
InactiveUS20100163670A1Improve lifting performanceReduce reflectivityAircraft stabilisationWing shapesHigh liftSupersonic speed
Deltoid Main Wing idea provides for several innovative aerodynamic configurations for large subsonic and supersonic civil and military aircraft including “T-tailed Deltoid Main Wing” configuration that allows for design of high-subsonic jumbo jet passenger aircraft with a capacity between 200 and 700 passengers whose outer dimensions fit within 80 m box on class VI airports while having more than twice lower fuel consumption per unit of payload when compared to the present classical-concept aircraft with the same passenger capacity, while further allowing for design of all-size and all-purpose, high-lift-capacity, and long-range unmanned aircraft.
Owner:DIZDAREVIC FARUK +1
Latch timing mechanism for a two-step roller finger cam follower
In a two-step roller finger cam follower, a slider arm for engaging a high-lift cam lobe is pivotally mounted to the body and can variably engage a latch pin slidably disposed in a latch pin channel. A second channel in the body opens onto the slider arm and contains a timing pin that rides on an eccentric surface of the slider arm to extend or retract the timing pin. A bore between the latch pin channel and the timing pin channel contains a ball controlled by the timing pin to lock the latch pin into an engaged or disengaged position. The cam lobe has an undercut region such that the latch pin is allowed to move between engaged and disengaged position only when the slider arm is in the undercut region of the cam lobe. The latch pin can move only when the timing pin permits.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
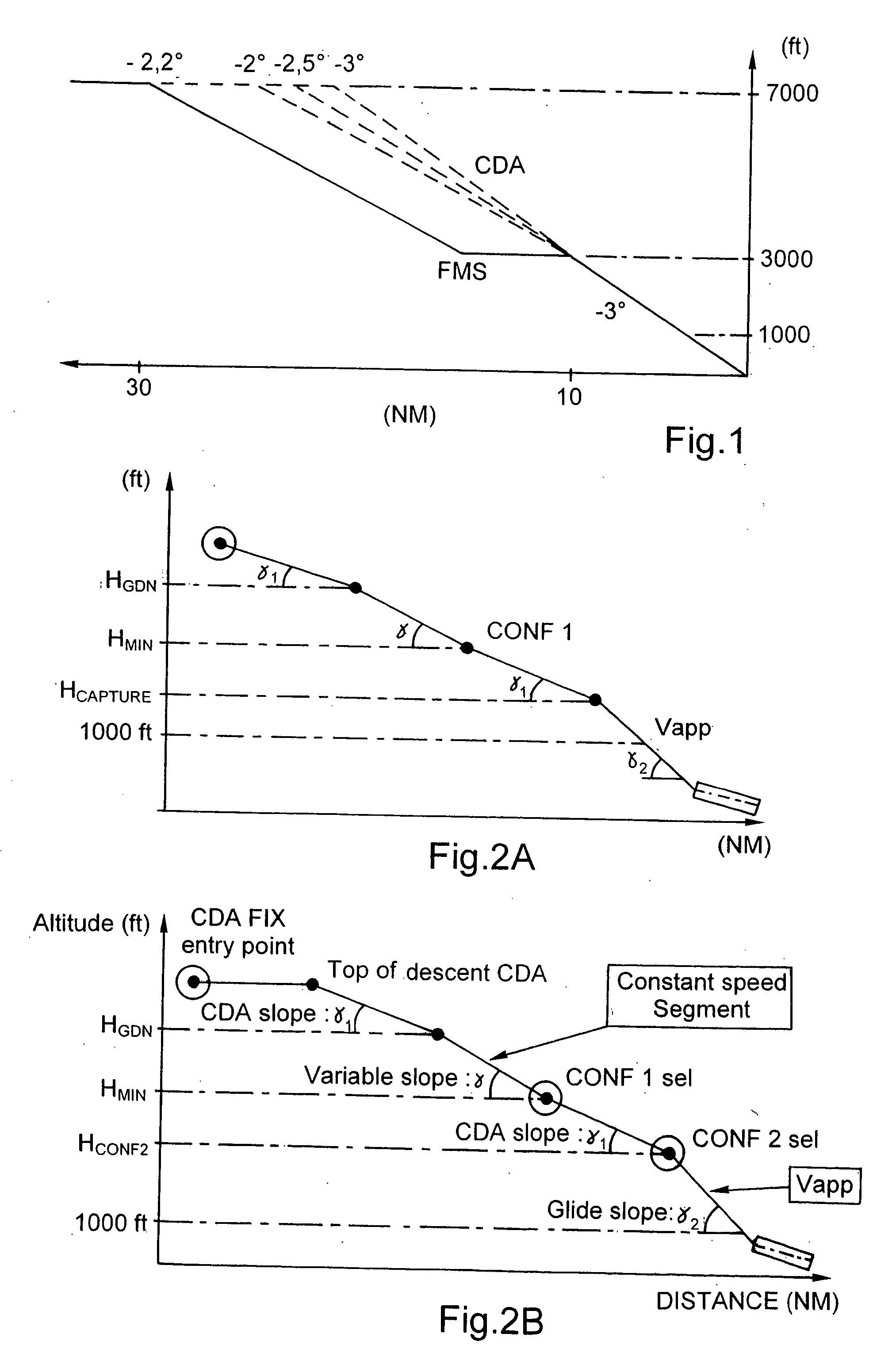
Navigation system for an aircraft and associated command process
ActiveUS20060265110A1Sure easyReduce needAnalogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficHigh liftNavigation system
A navigation system for an aircraft, including a calculator of an estimated flight path for the aircraft; a device for determining an estimated value of a flight parameter that corresponds to an estimated speed for the extension of at least a portion of the high-lift devices of the aircraft; and a display of an indication for such estimated value. A command process for such a system and an aircraft equipped with such a system are also disclosed.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
Airfoil embodying mixed loading conventions
A high-lift airfoil embodying a combination of loading conventions in a single design specifically to reduce and control total pressure losses that occur in the flow channels between airfoils employed in turbomachinery applications is disclosed herein. The mixed-loading high-lift airfoil designs embody and exhibit the best total profile and secondary loss characteristics possessed by both aft-loaded airfoil and front-loaded airfoil conventions through controlling the development and interaction of boundary layers forming along the surfaces of the airfoils and the endwalls in such applications. The mixed-loading high-lift airfoil may be utilized in both rotating and non-rotating turbomachinery applications.
Owner:RAYTHEON TECH CORP
Aerodynamic performance enhancements using discharge plasma actuators
ActiveUS20100329838A1Easy maintenanceImprove performanceWind motor controlPump componentsPerformance enhancementPlasma actuator
The current invention provides significant performance improvements or significant energy savings for fans used in these applications: personal, industrial and automotive cooling, ventilation, vacuuming and dust removal, inflating, computer component cooling, propulsors for unmanned and manned air vehicles, propulsors for airboats, air-cushion vehicles, airships and model aircraft. Additionally, the invention provides higher performance such as higher lift and higher lift efficiency to small air vehicles. These advantages are achieved by using plasma actuators to provide active flow control effectors into thin fan blades and wing.
Owner:GREENBLATT DAVID
Systems and methods for aerial dispersion of materials
InactiveUS20050072880A1Improve lifting performanceQuick assemblyFire rescueFreight handlingFlight vehicleFirefighting
Aerial dispersion systems that may be employed to allow rapid and temporary conversion of aircraft for aerial dispersion purposes, such as aerial fire-fighting. The aerial dispersion systems may be implemented using modular components that may be configured for compatibility with conventional cargo loading and unloading systems of modern aircraft, including side-loading cargo systems of wide body passenger and cargo aircraft having high lift capacities. The aerial dispersion systems may be rapidly installed in a large fleet of high capacity aircraft in response to a wildfire or other rapidly-developing emergency such as an oil spill, chemical or biological contamination incident, building or refinery fire, etc. After use, the aircraft of the fleet may be rapidly de-modified and returned to original condition. The aerial dispersion systems may be operated with a fleet of aircraft in a coordinated manner, for example, as part of an aerial firefighting formation having multiple aircraft sharing information and / or common control.
Owner:L 3 INTEGRATED SYST +1
High Altitude Aircraft, Aircraft Unit and Method for Operating an Aircraft Unit
InactiveUS20140252156A1Unlimited flying timePower installationsAircraft controlFlight vehiclePropeller
A high-altitude unmanned stratosphere aerial vehicle includes a fuselage, wings, control surfaces, and a propulsion system including an engine and a propeller. Each wing has a plurality of hoses and wing spars extending in a direction perpendicularly to the longitudinal fuselage axis and are surrounded by a skin forming a wing covering that determines the cross-sectional contour of the wing, the cross-sectional contour forming a laminar flow airfoil that generates high lift when there is low flow resistance. At the free end facing away from the fuselage, each wing has a winglet extending transversely to the longitudinal wing axis. The winglet has a movable control surface, which allows an aerodynamic side force to be generated so as to bring the aerial vehicle to a banked position.
Owner:AIRBUS DEFENCE & SPACE
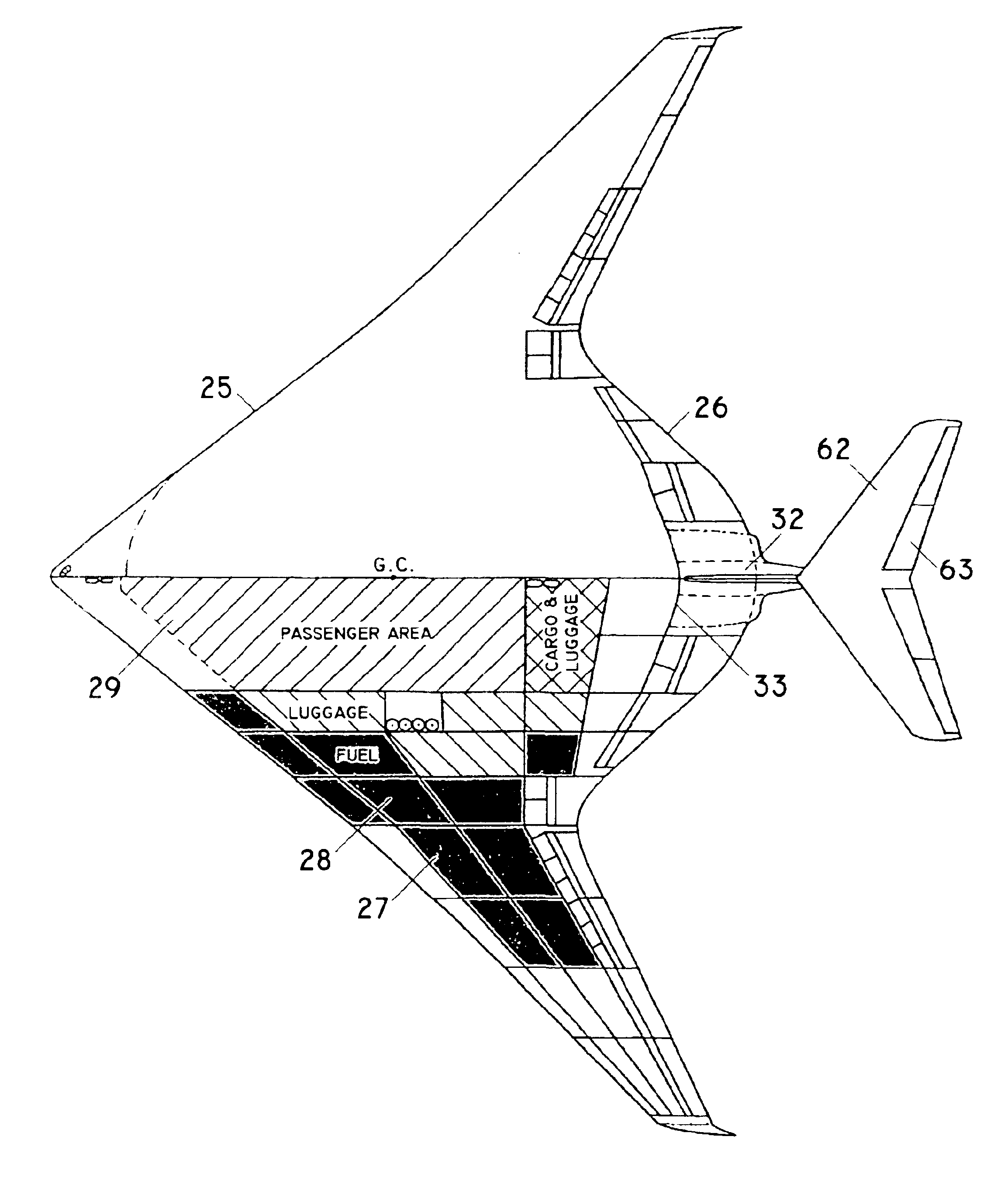
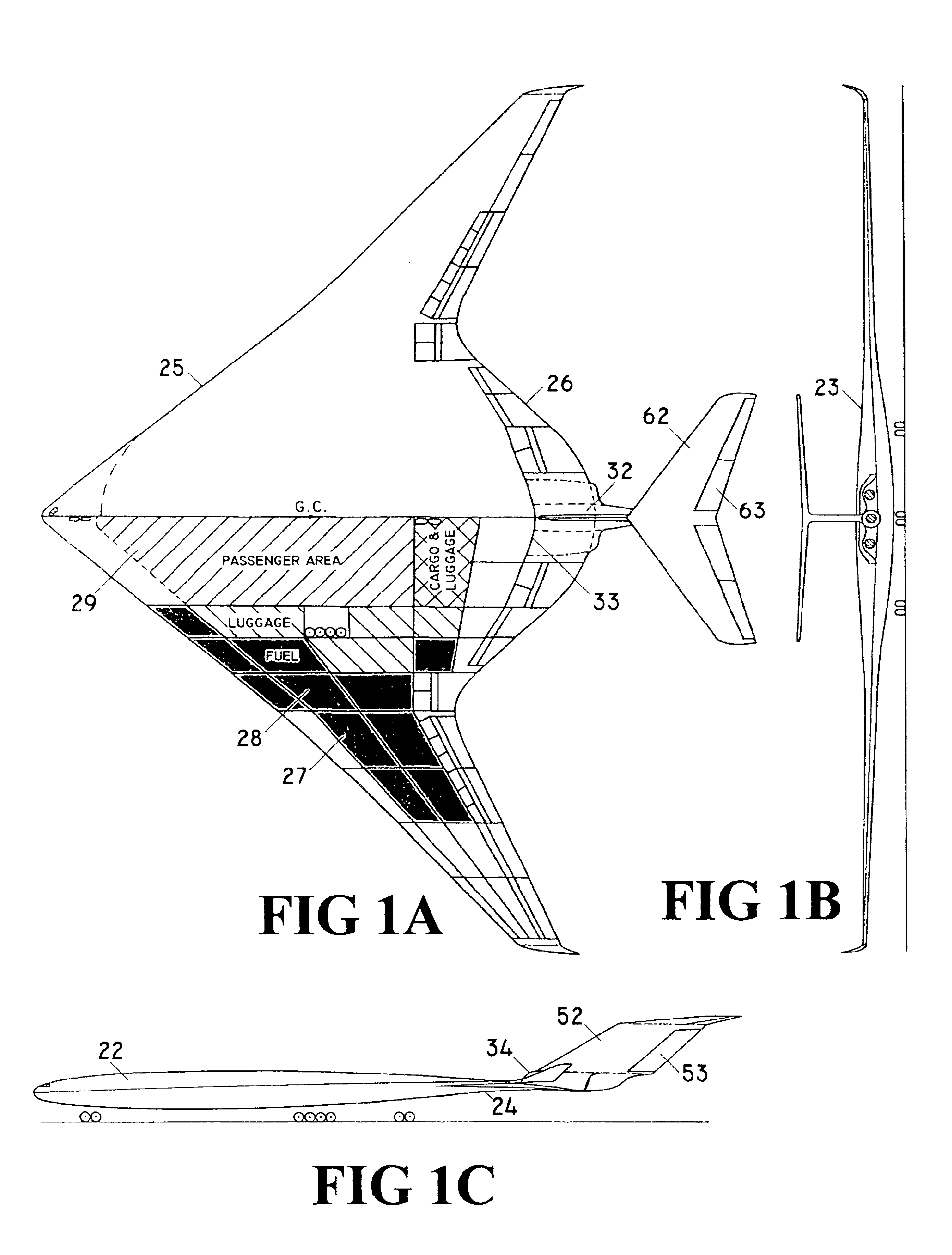
Tailed flying wing aircraft
InactiveUS6923403B1Reduce fuel consumptionIncrease capacityAircraft stabilisationWing shapesLifting capacityHigh lift
The “Tailed Flying Wing Aircraft” idea represents new aerodynamic concepts for large high subsonic aircraft. Large high subsonic aircraft based on these new aerodynamic concepts are having a significantly higher lift capacity and longer range, as well as a significantly lower fuel consumption of at least two times less than the aircraft based on classical fuselage concept with the same external dimensions. In addition, the aircraft based on the new concepts are having a significantly better longitudinal stability and maneuverability, as well as aerodynamic efficiency at high subsonic speed than aircraft based on “Tailless Flying Wing” concepts. The aircraft based on the “Tailed Flying Wing Aircraft” idea satisfy all safety requirements for civil aircraft. They also have simple shapes for manufacturing, hence this idea provides for new realistic advanced aerodynamic concepts for the next generations of large subsonic aircraft.
Owner:DIZDAREVIC FARUK +1
Airfoil for a helicoptor rotor blade
An airfoil family for a helicopter rotor blade, designated SC362XX. SC362XX essentially removes the large lower surface suction peak associated with ‘drag creep’ at moderate lift coefficients while reducing the peak Mach number and shock strength at high lift / Mach number conditions. Another optional airfoil family for use at inboard regions of the helicopter rotor, which is designated SC3252XX airfoil family, is a relatively thicker airfoil section that includes a significant increase in thickness forward of the 30% x / c location to provide a relatively thick and rigid inboard section. The lift coefficient at which the drag divergence Mach number was optimized is the same in both families thereby readily providing application to a single rotor blade.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
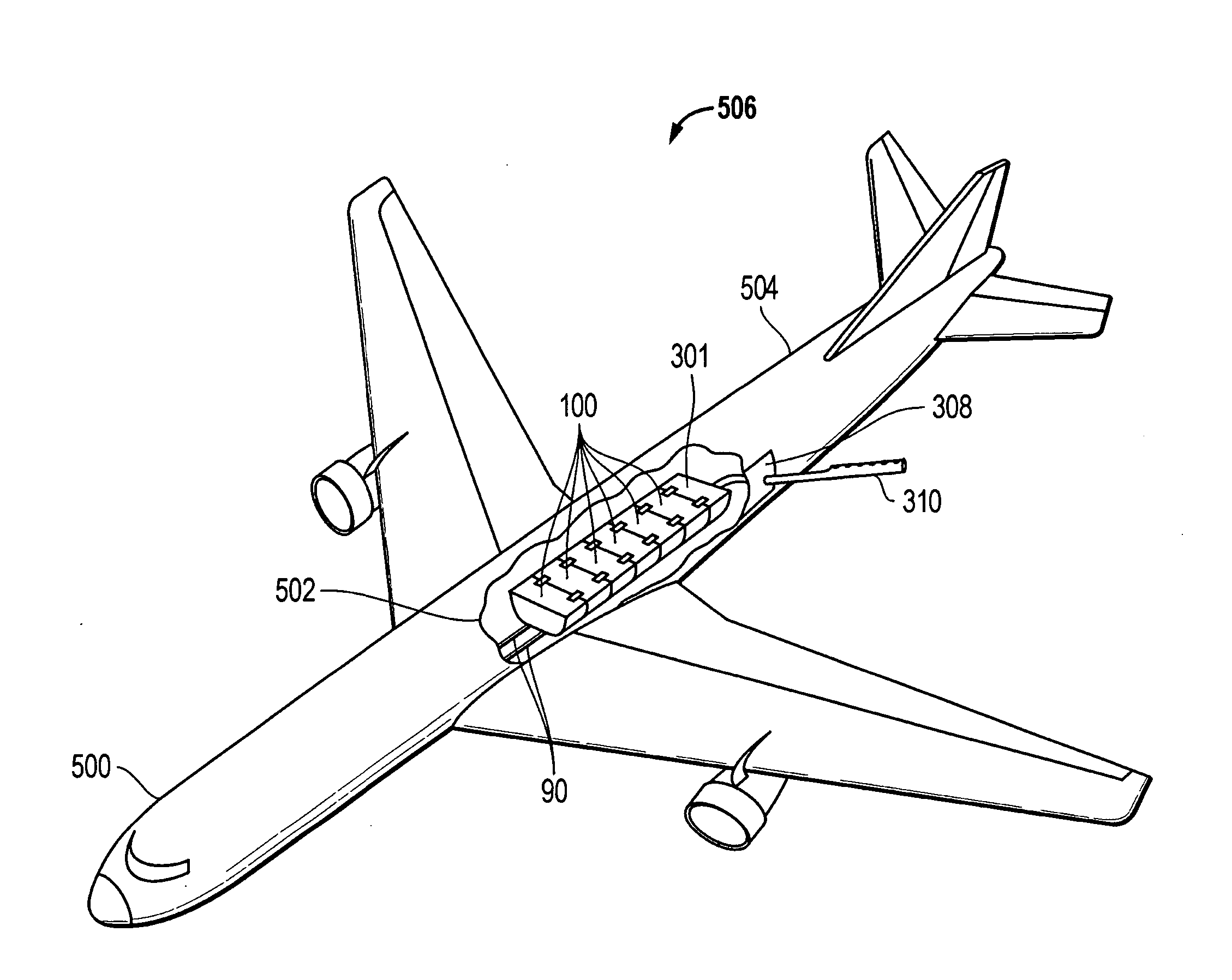
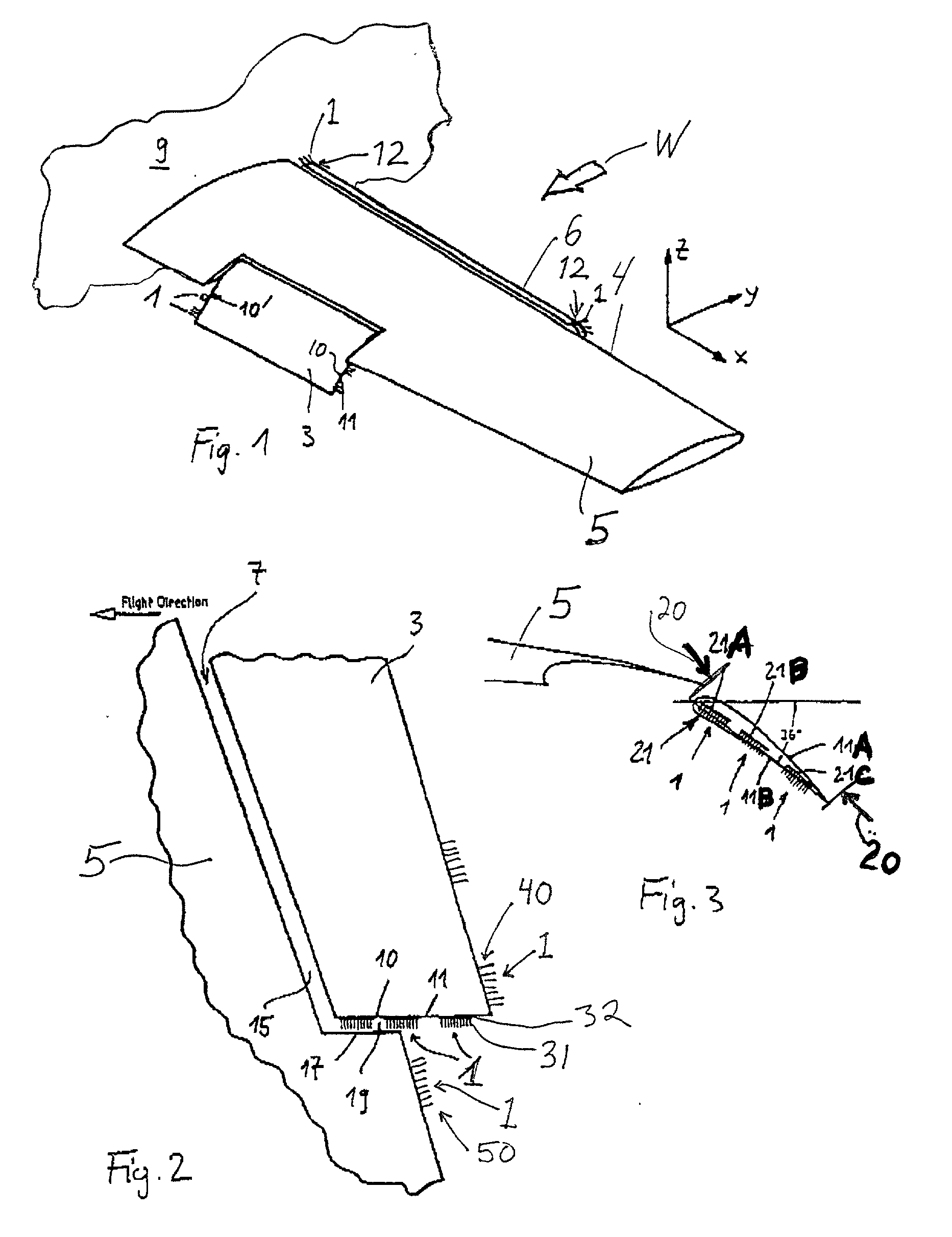
Aircraft wing leading edge high lift device with suction
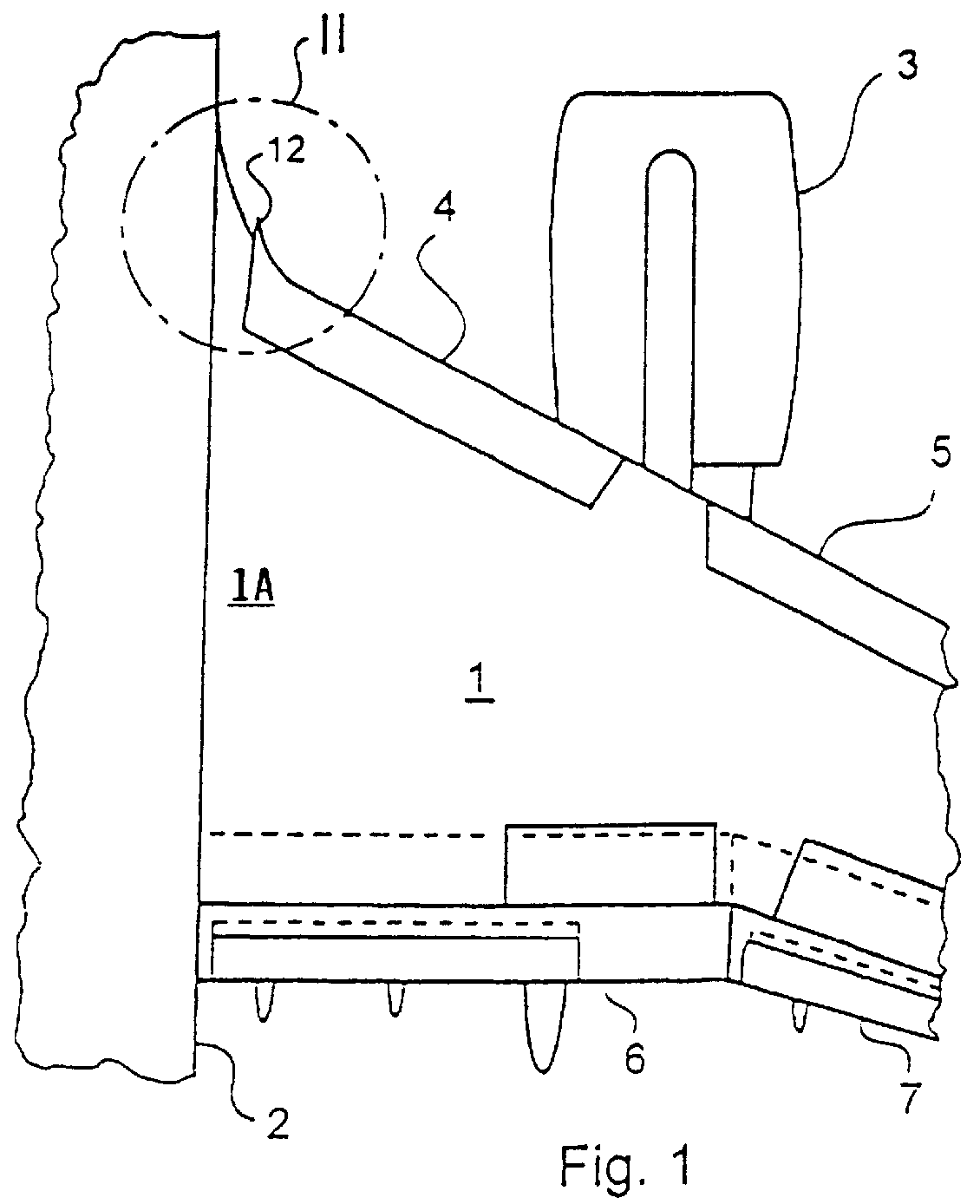
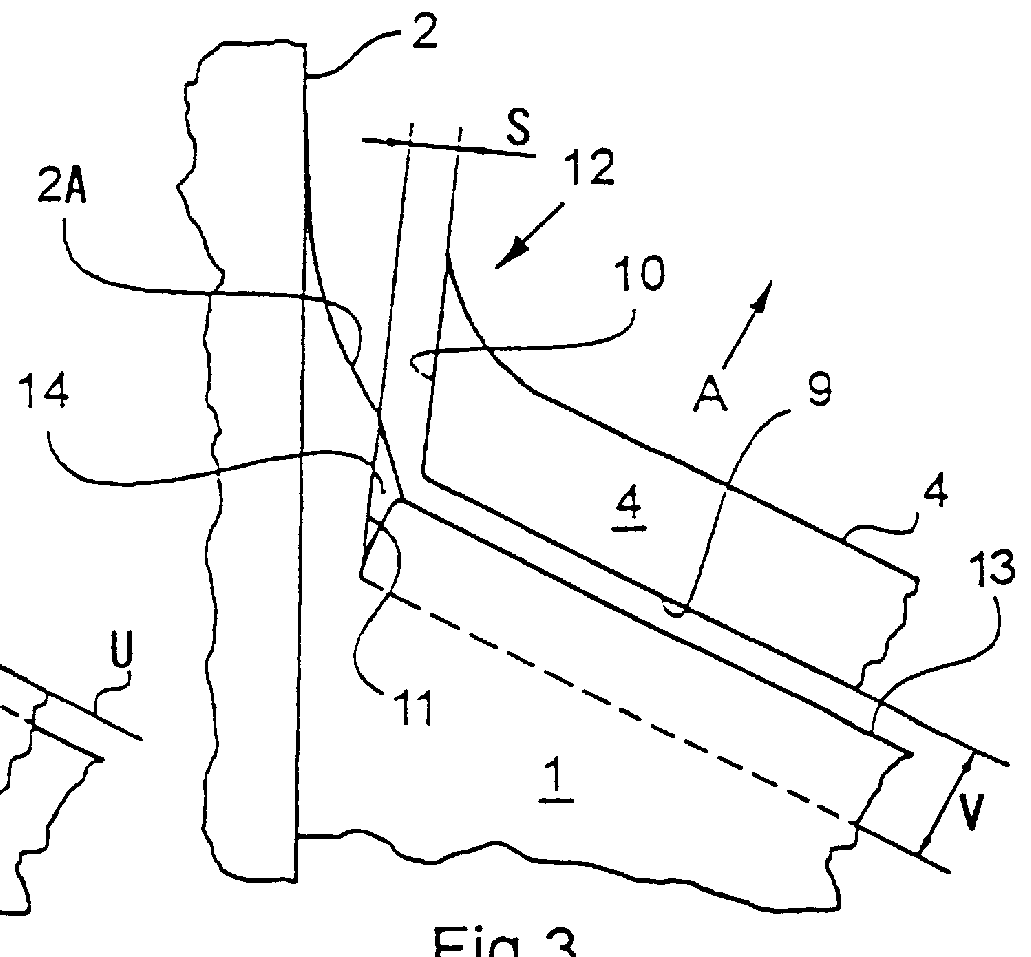
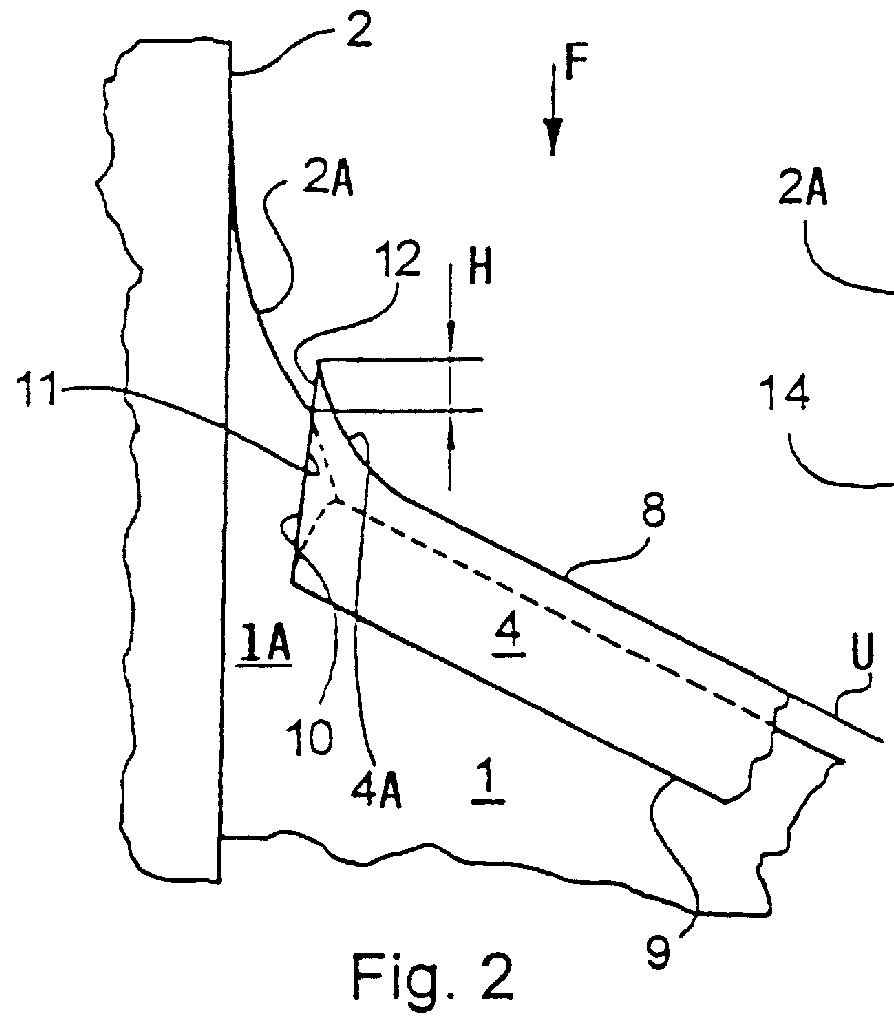
InactiveUS6135395AReduce resistanceReduce layeringBoundary layer controlsFluid dynamicsLeading edgeAircraft landing
An aircraft wing, wing assembly and method of reducing drag are provided. The wing asembly includes a main wing portion (10) and a leading edge high lift portion (12). The high lift portion is movable between a retracted position in which it generally merges with the main wing portion and a deployed position forwardly thereof. At least a substantial part of an upper surface (22) of the high lift portion is air permeable or perforated and in flow communication with a suction passage (30) in it. In flight, suction may be applied to the suction passage to reduce the chordwise extent of the turbulent boundary layer over the upper or lower wing surface.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD
Method for transition between controlled auto-ignition and spark ignition modes in direct fuel injection engines
InactiveUS7370616B2Eliminate misfiring and partial burnsValve arrangementsElectrical controlHomogeneous charge compression ignitionExhaust valve
A method is provided for control of transition between combustion modes of a direct-injection engine operable in a homogeneous charge compression ignition (HCCI) mode at lower loads and a spark ignition flame propagation (SI) mode at higher loads. The engine includes a variable valve actuation system including two-step high and low lift valve actuation and separate cam phasing for both intake and exhaust valves. The method includes operating the engine at steady state, with fuel-air-exhaust gas mixtures at predetermined conditions, for each speed and load, and controlling the engine during mode changes between the HCCI mode and the SI mode by switching the exhaust and intake valves between low lift for HCCI operation and high lift for SI operation. High load may be an SI throttled mode with an intermediate unthrottled mode (SI / NTLC} in which transition between HCCI and SI / NTLC modes requires switching only the exhaust valve lift and transition between SI / NTLC and SI throttled modes requires switching only the intake valve lift, with predetermined phase adjustments in the valve timing phasing.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
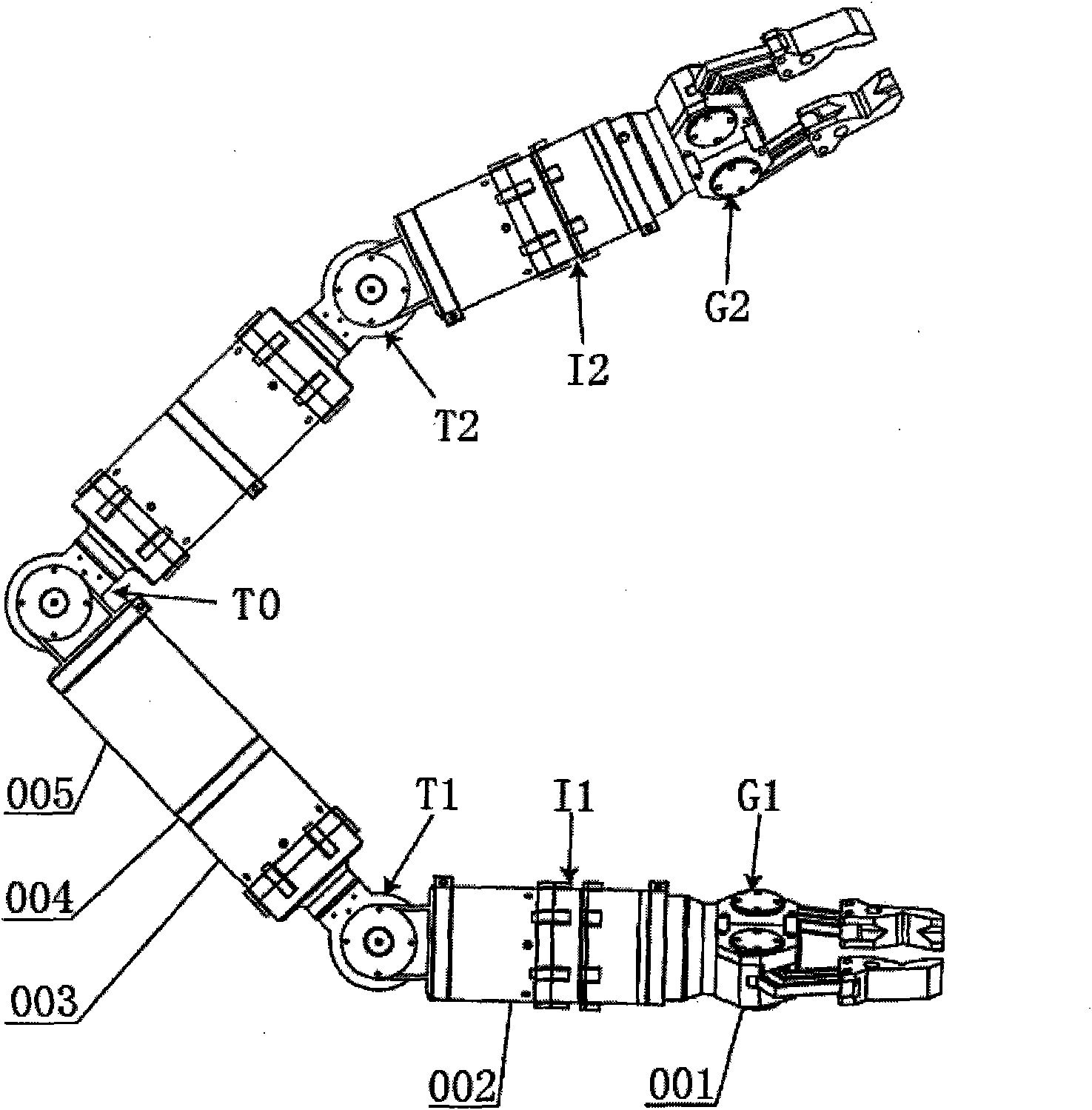
Modularized biomimetic climbing robot
InactiveCN101664927AImprove climbing abilityImprove adaptabilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorRotational freedomModularity
The invention discloses a biomimetic climbing robot which consists of five joint modules and two clamp holder modules. Each joint module has a rotational freedom and is driven by a direct current servo motor. The joint module has such two kinds as I type and T type, and joint rotating shafts are parallel to and perpendicular to the axial line of a joint connecting rod respectively. All modules areconnected successively by snap rings in a series mode, with the sequence as follows: clamp holder, I type joint, T type joint, T type joint, T type joint, I type joint, clamp holder. The rotating shafts of three T type joint modules are parallel to each other and are mutually perpendicular to the rotating shafts of the I type joint modules at both ends. The robot can climb on a rod and a tree andin a truss with equal steps in modes of inchworm, torsion and reversal and has operating function. The robot is characterized by small freedom, easy construction, simple structure and control, strongclimbing capability, good applicability to climbing objects and the like, thus being capable of being applied to high-lift operation in such fields as the agriculture, forestry and building industries.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
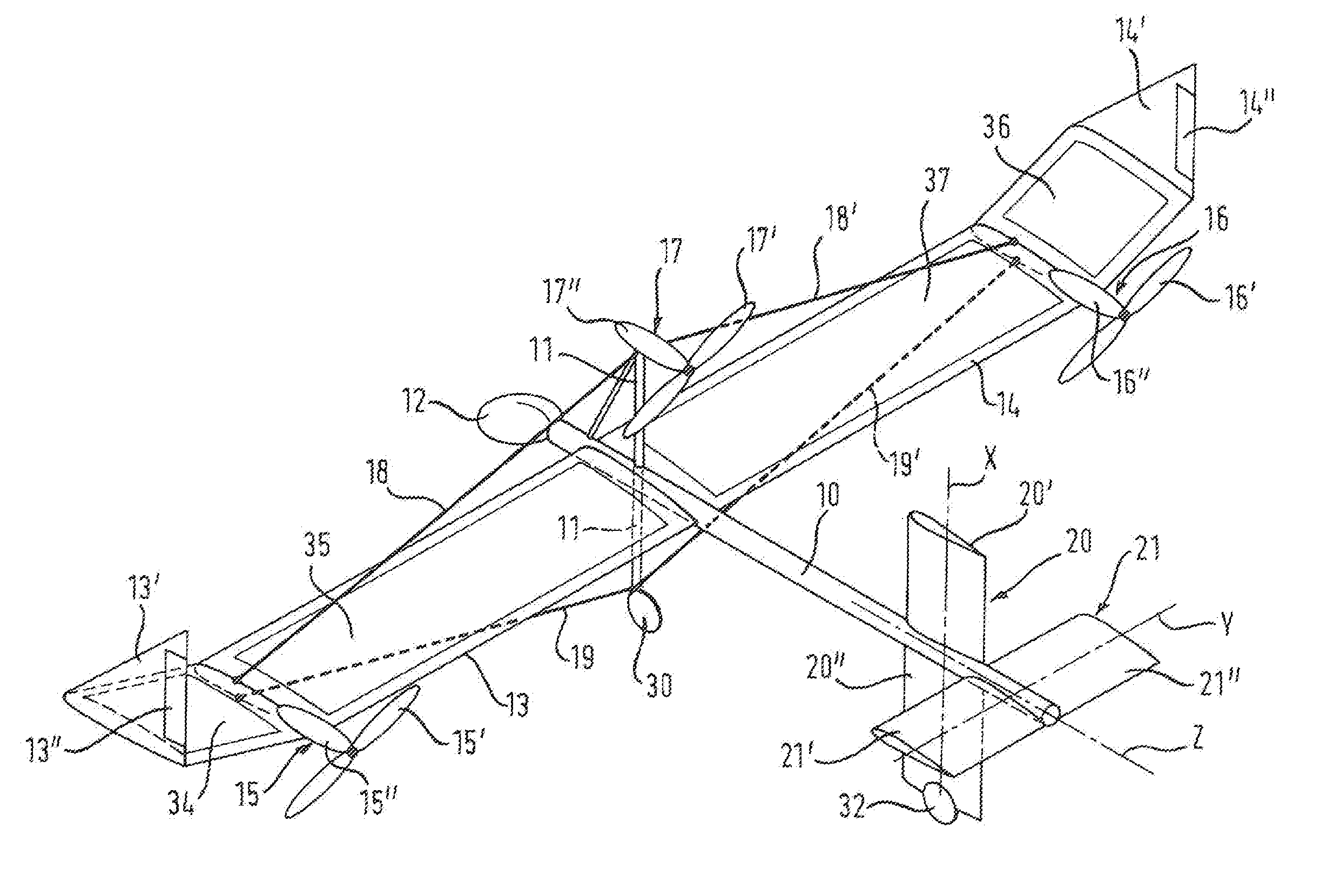
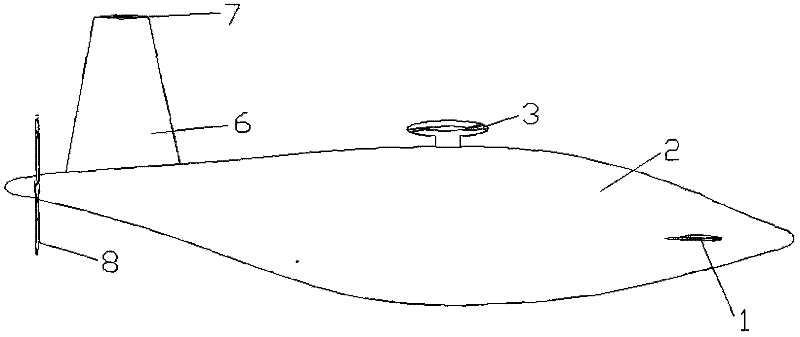
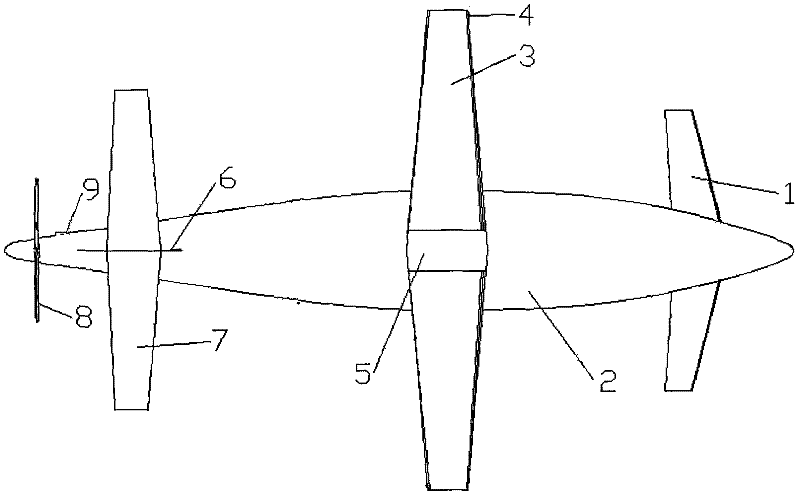
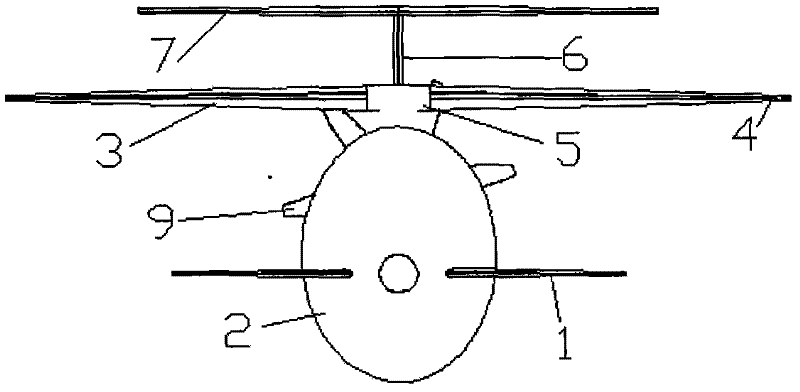
Rotor blade airplane with variable flight mode
The invention provides a rotor blade airplane with a variable flight mode, comprising an airplane body, a plurality of canards, a rotor blade, an empennage and a power system. The rotor blade airplane is characterized in that the canards are symmetrically arranged at two sides of the head of the airplane body; the empennage comprises a perpendicular empennage and a horizontal empennage, the perpendicular empennage is arranged at the back of the airplane body, and the horizontal empennage is arranged at the top end of the perpendicular empennage to form into the 'T'-shaped empennage; the canards, the rotor blade and the horizontal empennage are distributed with one another in the manner of a step from low to high along with the Z direction of the airplane; and a plurality of high lift devices are arranged on the canards and the horizontal empennage, and the lift force requirement for the controllable flight of the airplane can be met by a lift force generated on the canards and the horizontal empennage during transition flight. The rotor blade airplane can prevent the empennage from being directly impacted by the downwash of the rotor blade under a rotor blade flight mode, the distraction to a horizontal tail caused by the downwash of the rotor blade can be reduced, and the airplane can be controlled under the rotor blade flight mode during the transition flight.
Owner:南京优翼航空科技有限公司
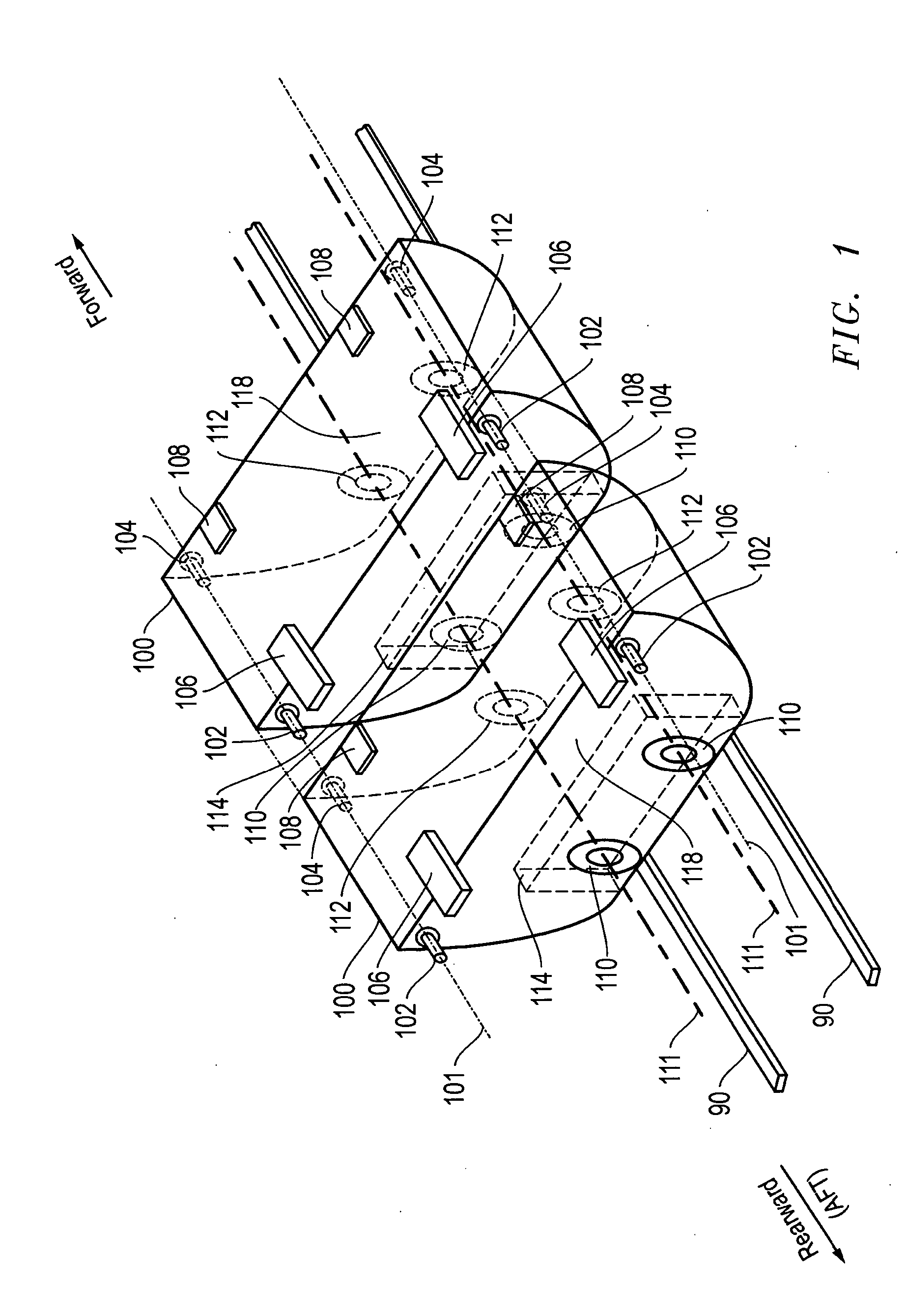
Microfabricated translational stages for control of aerodynamic loading
Micro-electro-mechanical (MEM) translational tabs are introduced for enhancing and controlling aerodynamic loading of lifting surfaces. These microtabs are mounted at or near the trailing edge of lifting surfaces, deploy approximately normal to the surface, and have a maximum deployment height on the order of the boundary layer thickness. Deployment of this type of device effectively changes the camber, thereby affecting the lift generated by the surface. The effect of these microtabs on lift is as powerful as conventional control surfaces such as ailerons. Application of this simple yet innovative lift enhancement and control device will permit the elimination of some of the bulky conventional high-lift and control systems and result in an overall reduction in system weight, complexity and cost.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Two-step roller finger cam follower having angled lock pin
ActiveUS6925978B1Eliminating any bending moment in the latch pinReduce the overall diameterValve arrangementsMachines/enginesHigh liftCam
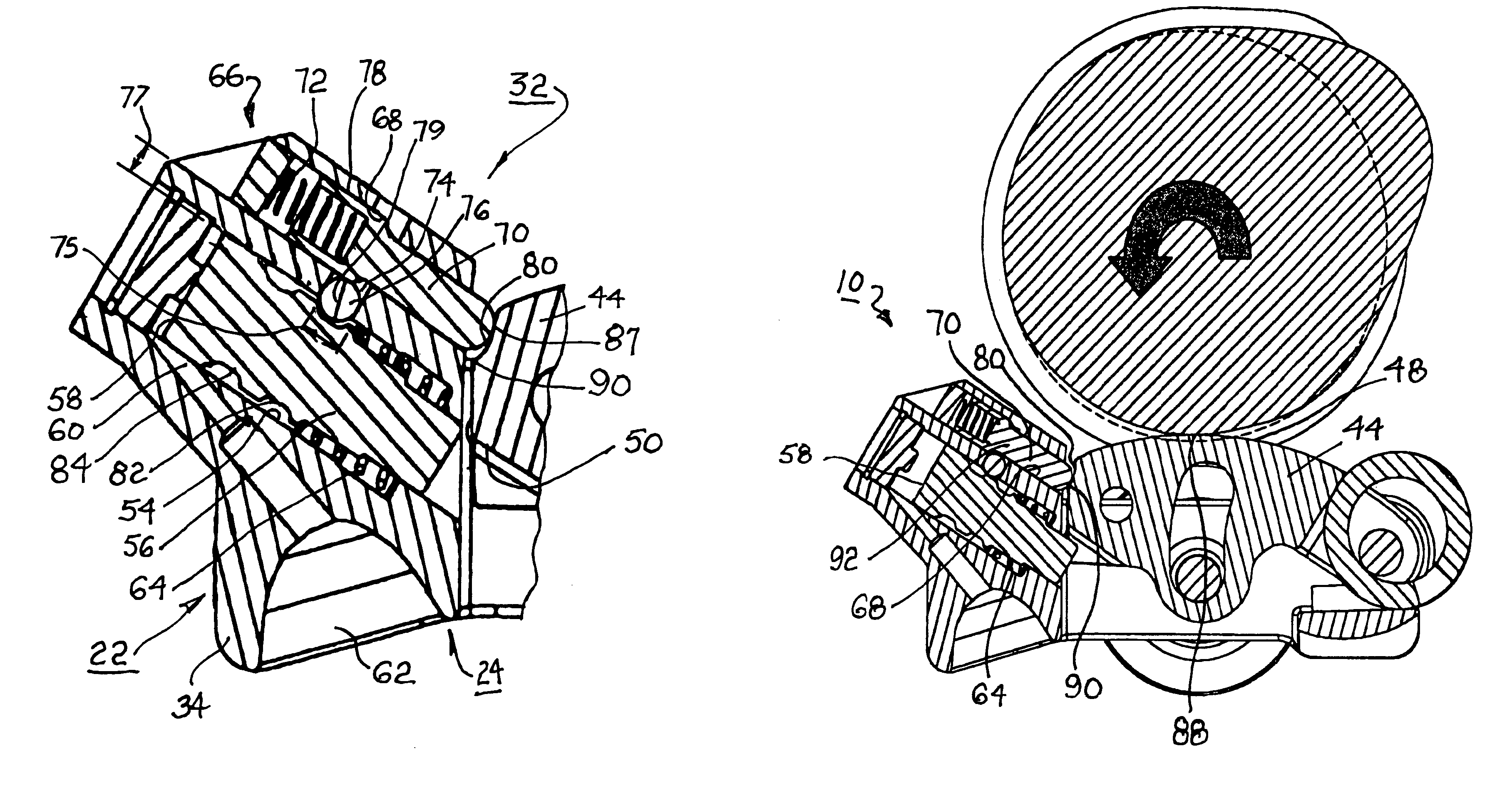
A two-step roller finger follower for shifting between high-lift and low-lift valve modes includes a body having side members defining coaxially disposed shaft orifices, a pallet end, a socket end, a slider arm aperture, and a latch pin channel. The socket end is mountable to a lash adjuster, and the pallet end is matable with a valve stem. A slider arm for engaging a high-lift cam lobe is disposed in the aperture, is pivotably mounted to the body, and includes a slider tip for engaging a latch pin having a nose section. A spool-shaped roller is adapted to follow the surface motion of low-lift cam lobes. The axis of the latch pin intersects a radius extension of the slider arm at an angle of less than 180° such that the latch pin is prevented from accidentally locking the slider arm in its lost-motion position.
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
Dual-use radial turbomachine
The impeller is preferably modified to use back swept, radial or forward swept blades to accommodate relatively low, medium and high lift, respectively applications for both centrifugal compressor and turbine rotor use.
Owner:RTX CORP
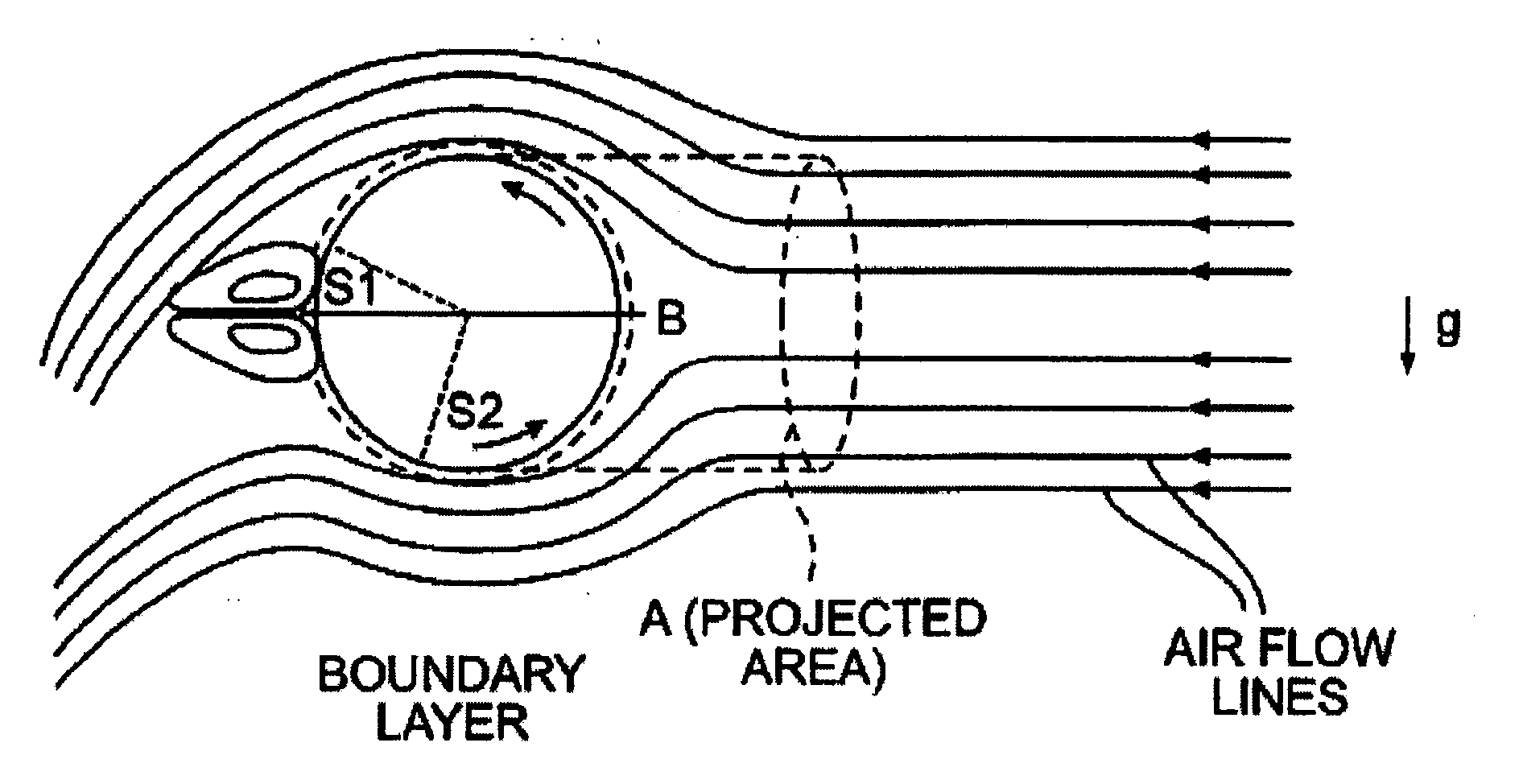
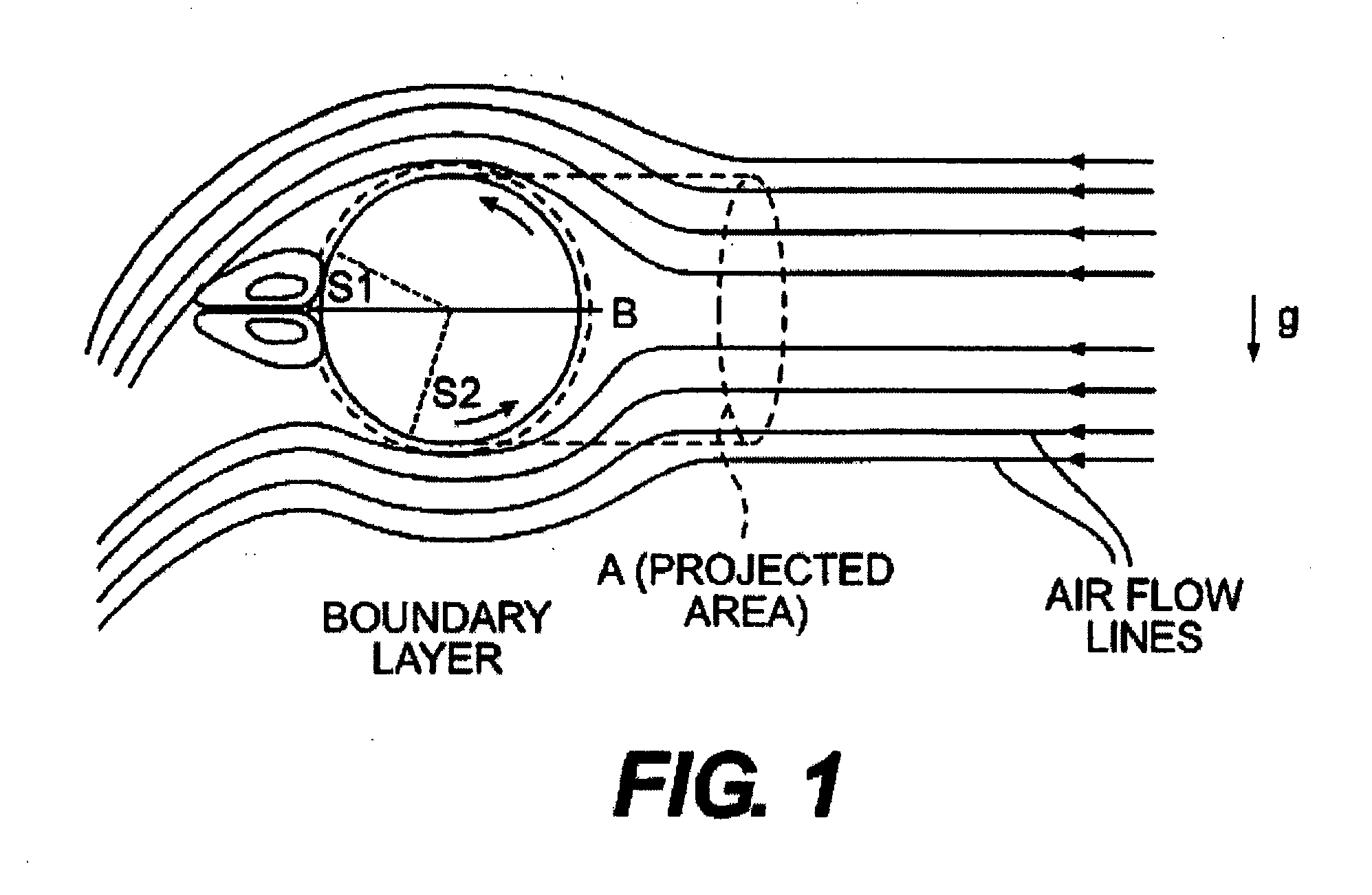
Apparatus for influencing a wing root airflow in an aircraft
An apparatus advantageously influences the wing root airflow along the wing root of an aircraft having a high lift system including leading edge slats provided on the main wings. The apparatus includes a respective vortex generator arranged on the inboard end of each leading edge slat in the area of the wing root, and further includes a respective transition fairing arranged on a separation edge that is let into the leading edge of the wing root and that borders along the inboard edge of the respective slat. The vortex generator is a rigid member fixed to the leading edge slat and may be in the shape of a horn, a disk, or a winglet. The transition fairing may be a rigid member fixed to the wing root along the separation edge, or may be a flexible elastic member that can be inflated to have a variable outer contour. The present system avoids the need of additional independently movable auxiliary flaps, and thus achieves a reduced weight, complexity, and maintenance requirement.
Owner:DAIMLER CHRYSLER AEROSPACE AIRBUS
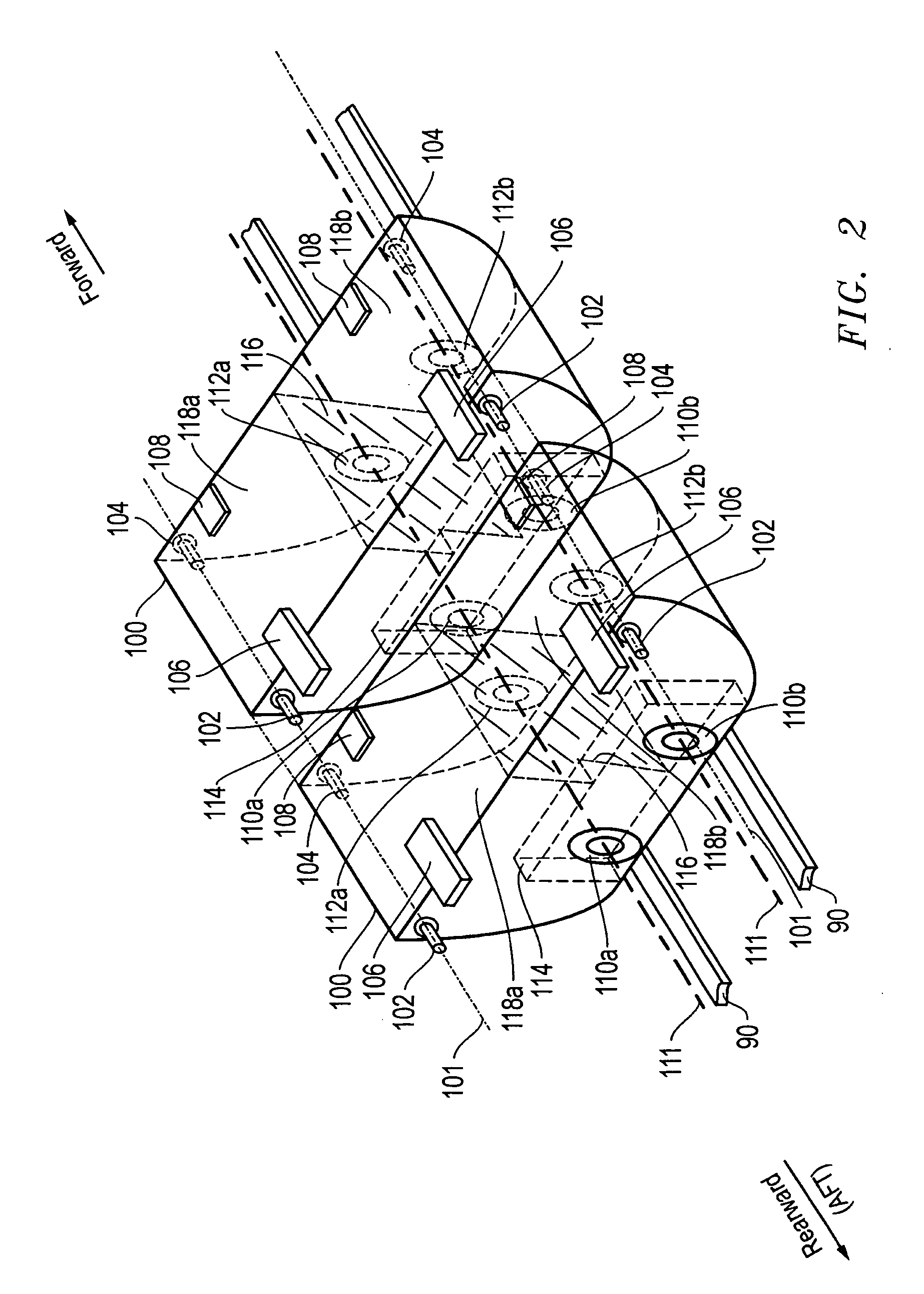
Microfabricated translational stages for control of aerodynamic loading
Micro-electro-mechanical (MEM) translational tabs are introduced for enhancing and controlling aerodynamic loading of lifting surfaces. These microtabs are mounted at or near the trailing edge of lifting surfaces, deploy approximately normal to the surface, and have a maximum deployment height on the order of the boundary layer thickness. Deployment of this type of device effectively changes the camber, thereby affecting the lift generated by the surface. The effect of these microtabs on lift is as powerful as conventional control surfaces such as ailerons. Application of this simple yet innovative lift enhancement and control device will permit the elimination of some of the bulky conventional high-lift and control systems and result in an overall reduction in system weight, complexity and cost.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Variable valve lift apparatus
InactiveUS7987826B2Reduce manufacturing costSimple structureValve drivesMachines/enginesHigh liftEngineering
A variable valve lift apparatus according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention includes a low lift cam, a high lift cam in parallel with the low lift cam, a low lift tappet body that selectively contacts the low lift cam, a high lift tappet body disposed within the low lift tappet body and constantly contacting the high lift cam, a guide portion that is connected with a valve and selectively connects the low lift tappet body and the high lift tappet body, and a lost motion spring that is disposed between the guide portion and the low lift tappet body and supplies restoring force to the low lift tappet body.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
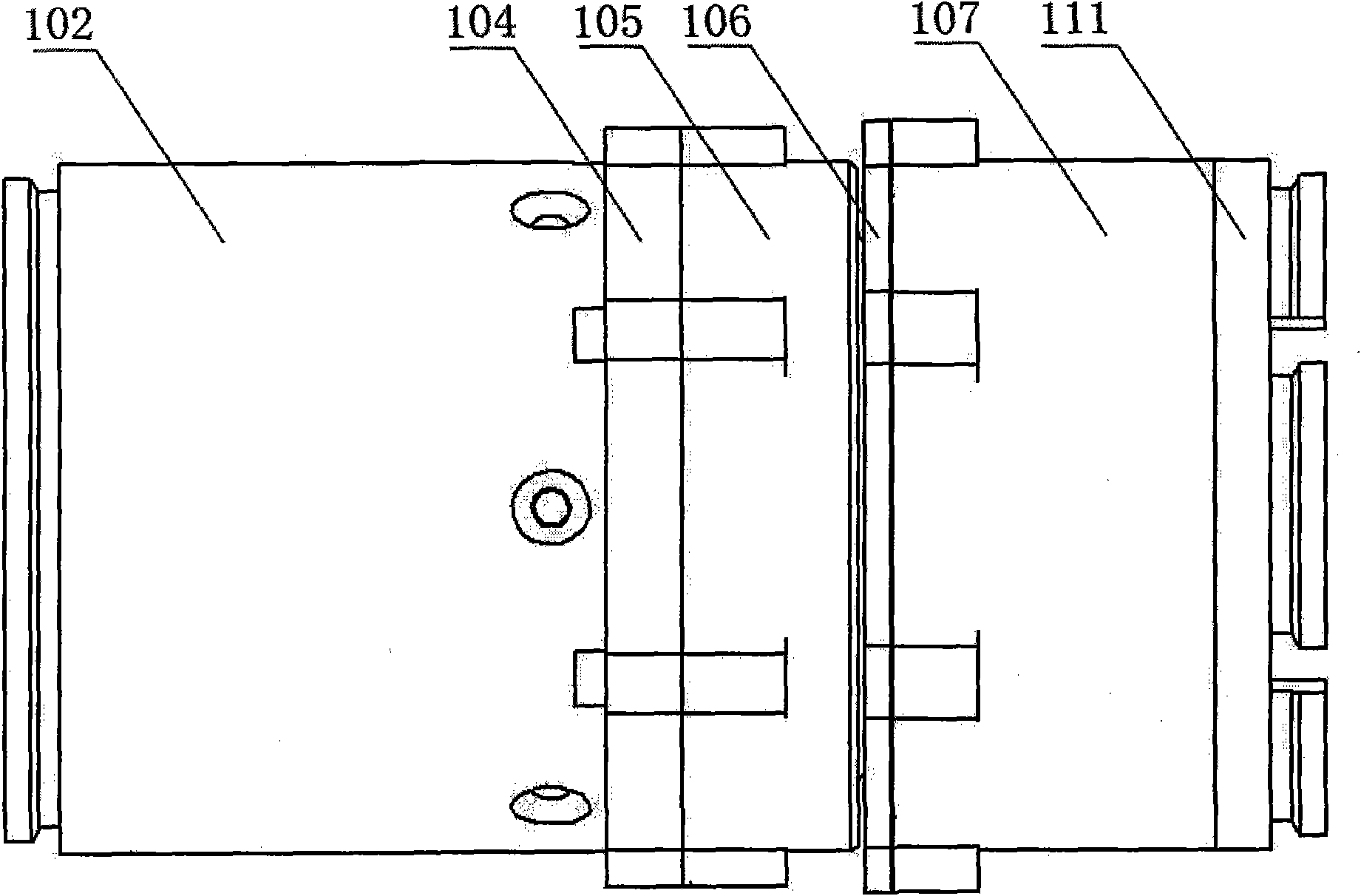
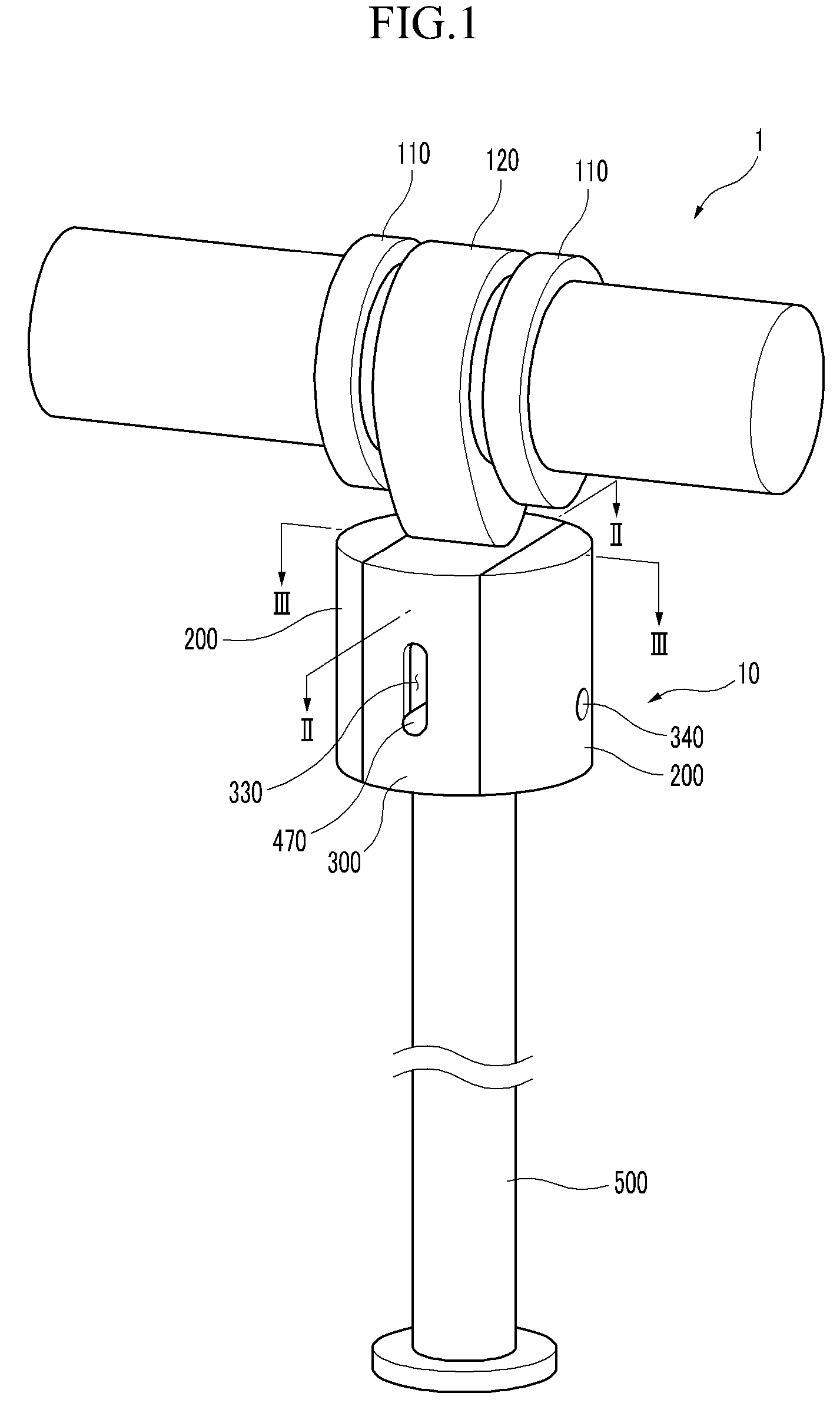
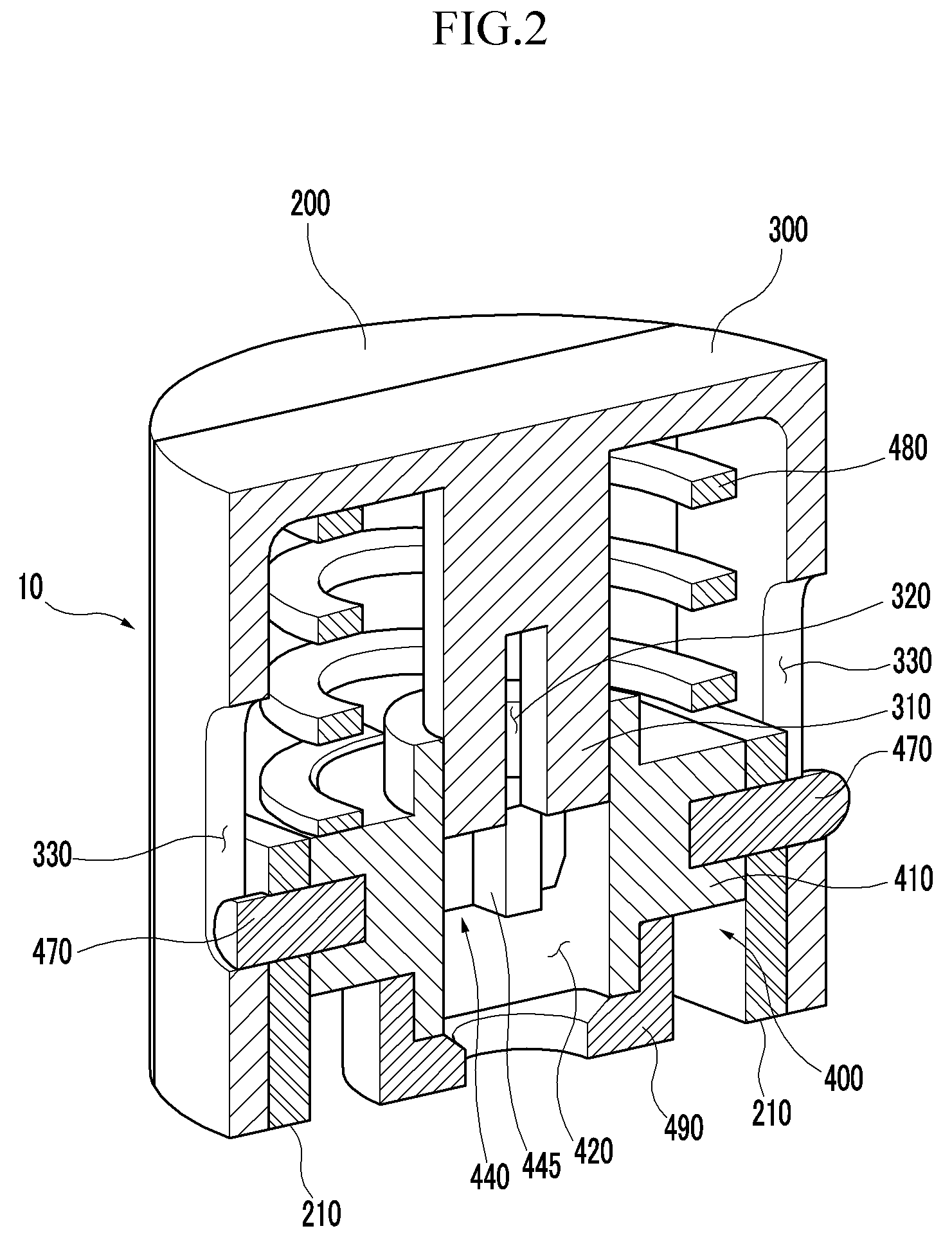
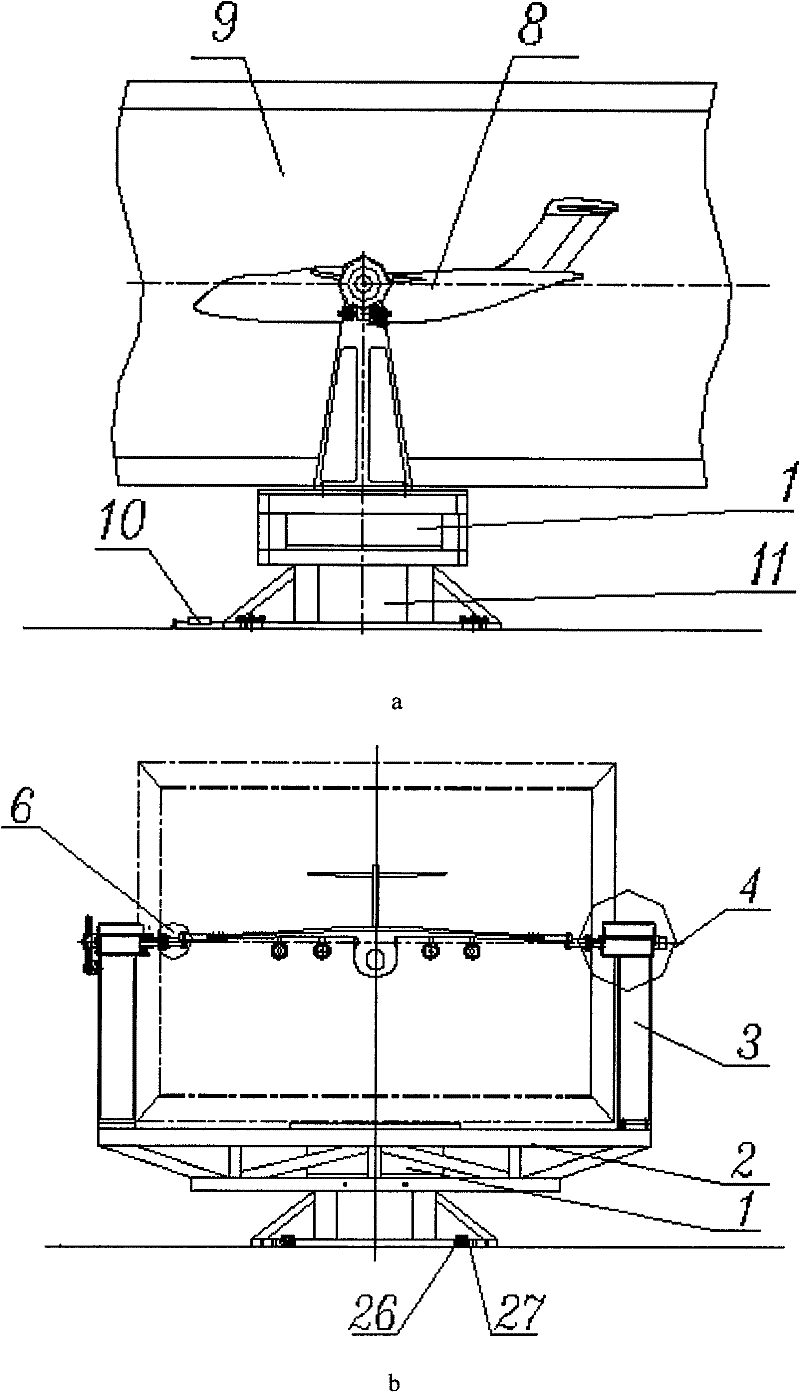
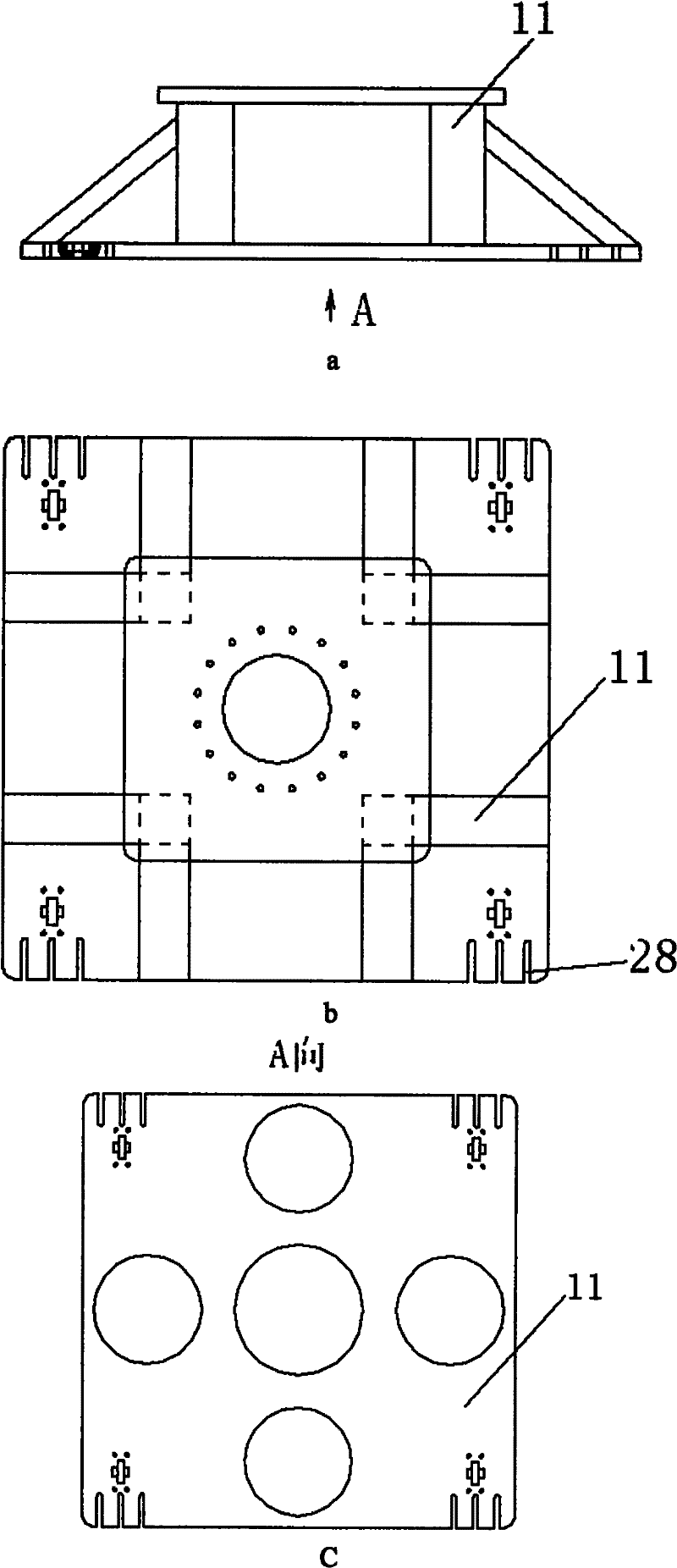
A wingtip support device for wind tunnel test
The invention relates to a wing tip support device for wind tunnel test. The upper connecting surface and the lower connecting surface of a force measuring balance are respectively connected with a support beam top plate and a force platform, two variable attack angle mechanisms are respectively arranged at the top end of a support upright post positioned at the outer sides of two side walls of the middle part of the wind tunnel test section, passing holes of a flange spline shaft are symmetrically arranged on the wind tunnel side wall of the equal height part of the center line of the flangespline shaft of the variable attack angle mechanism, one end of the flange spline shaft passes through the passing hole arranged on the wind tunnel side wall and is positioned in a wind tunnel, the other end of the flange spline shaft is connected with the variable attack angle mechanism arranged outside the wind tunnel, two variable side slide angle mechanisms are positioned in the wind tunnel and are fixed on a flange plate arranged at the end surface of the flange spline shaft positioned in the wind tunnel through a slide plate, and slide flanges of the two variable side slide angle mechanisms are connected with the wing tip of an airplane model through a model connecting element. The wing tip support device is applicable to airplane airdrop and airborne wind tunnel test, and airplane fuselages, high lift devices and afterbody drag wind tunnel tests, and has the characteristics that the structure is simple, the use is convenient, and the test data is reliable.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Navigation system for an aircraft and associated command process
ActiveUS8027758B2Reduce needGood anticipationAnalogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficHigh liftNavigation system
A navigation system for an aircraft, including a calculator of an estimated flight path for the aircraft; a device for determining an estimated value of a flight parameter that corresponds to an estimated speed for the extension of at least a portion of the high-lift devices of the aircraft; and a display of an indication for such estimated value. A command process for such a system and an aircraft equipped with such a system are also disclosed.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
Noise reducing vortex generators on aircraft wing control surfaces
InactiveUS20010032907A1Eliminate the effects ofReduced strengthInfluencers by generating vorticesAircraft stabilisationBristleHigh lift
Vortex generators are arranged on the edges of aircraft wing control surfaces to generate smaller vortices that weaken the main vortex that would otherwise be generated at these areas, and thereby reduce the aerodynamic generation of noise. Each vortex generator includes plural elongated elements in the form of rigid rods or flexible bristles protruding laterally outwardly from the respective edge of the control surface. The vortex generators are preferably arranged on the inboard and outboard edges of high lift flaps and slats.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
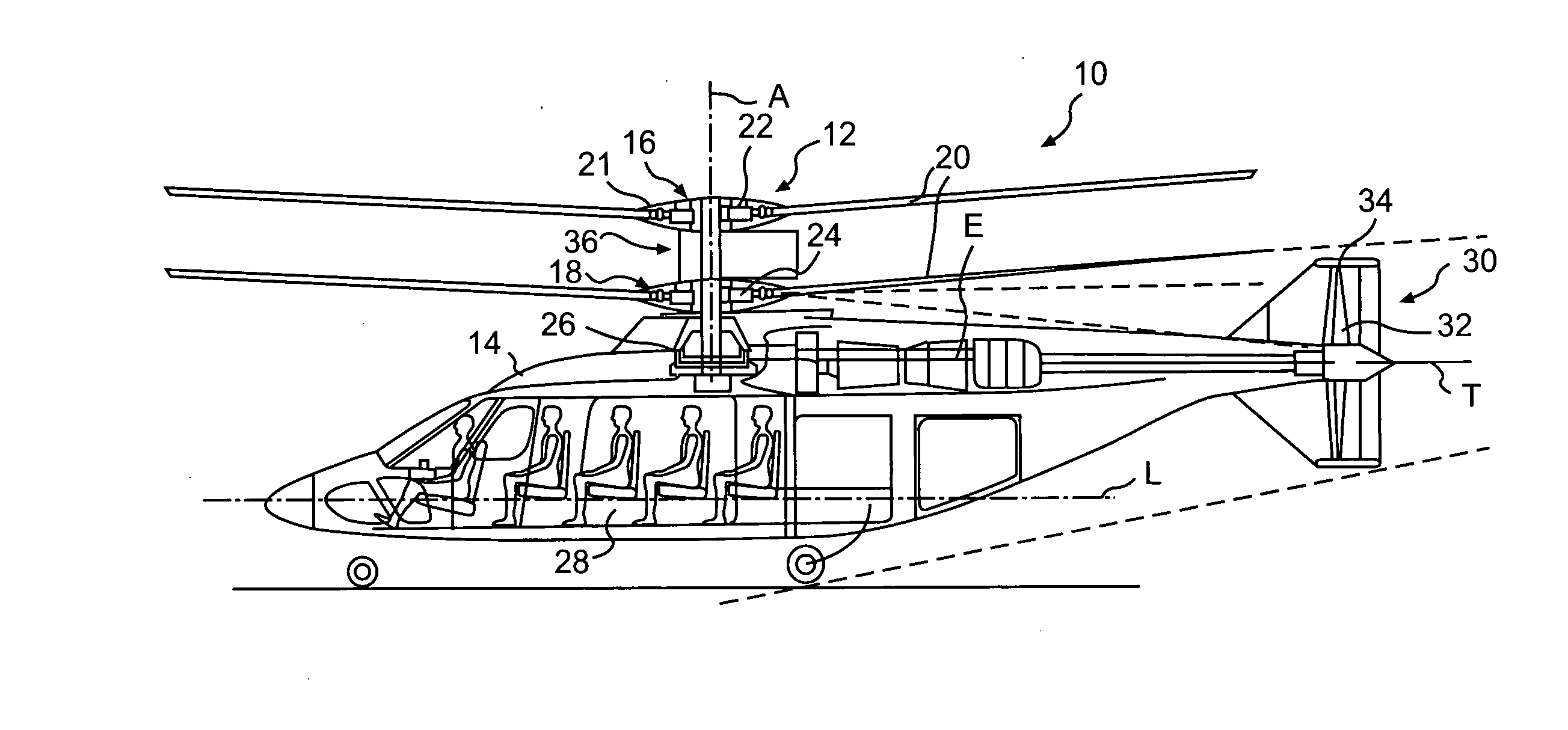
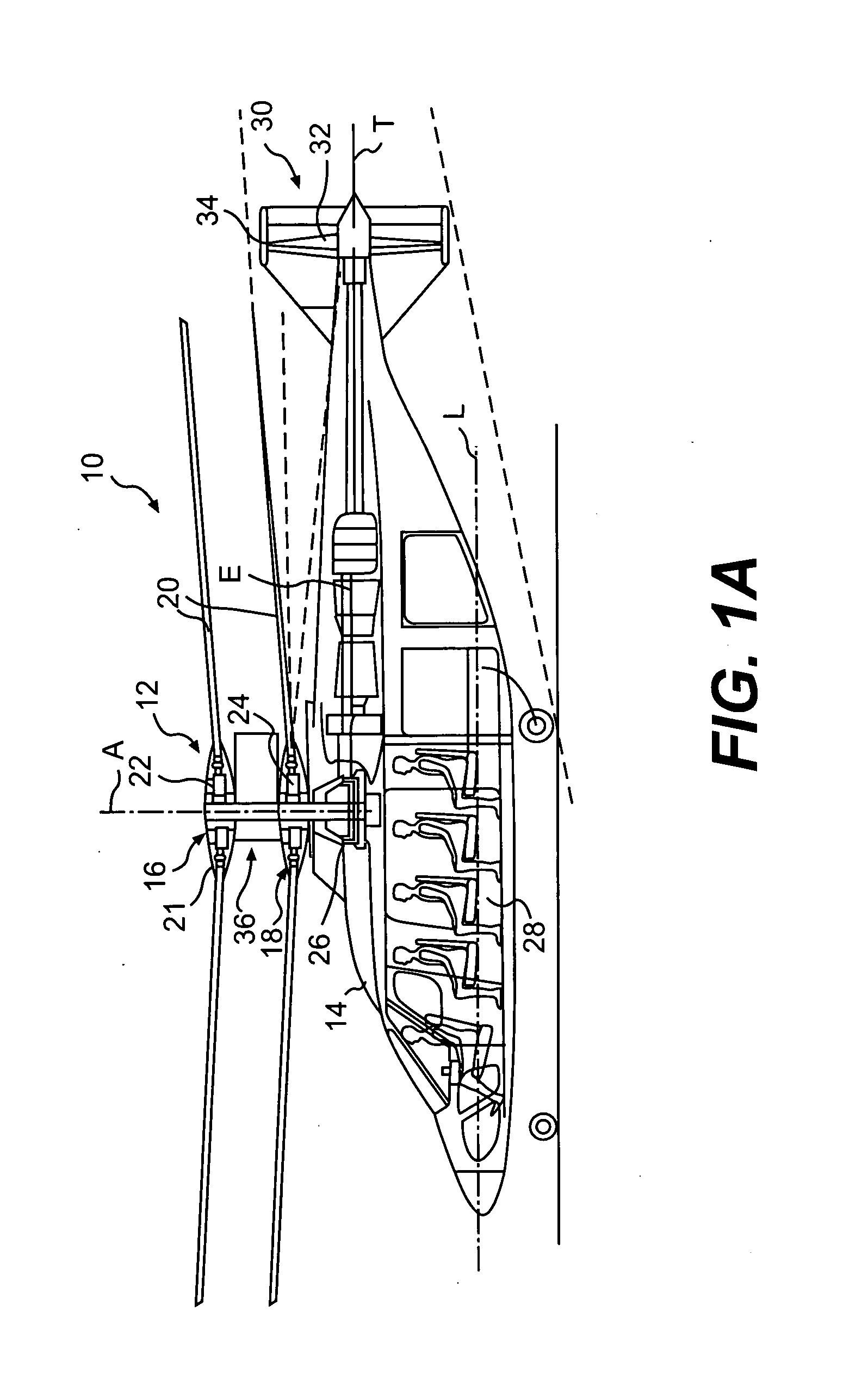
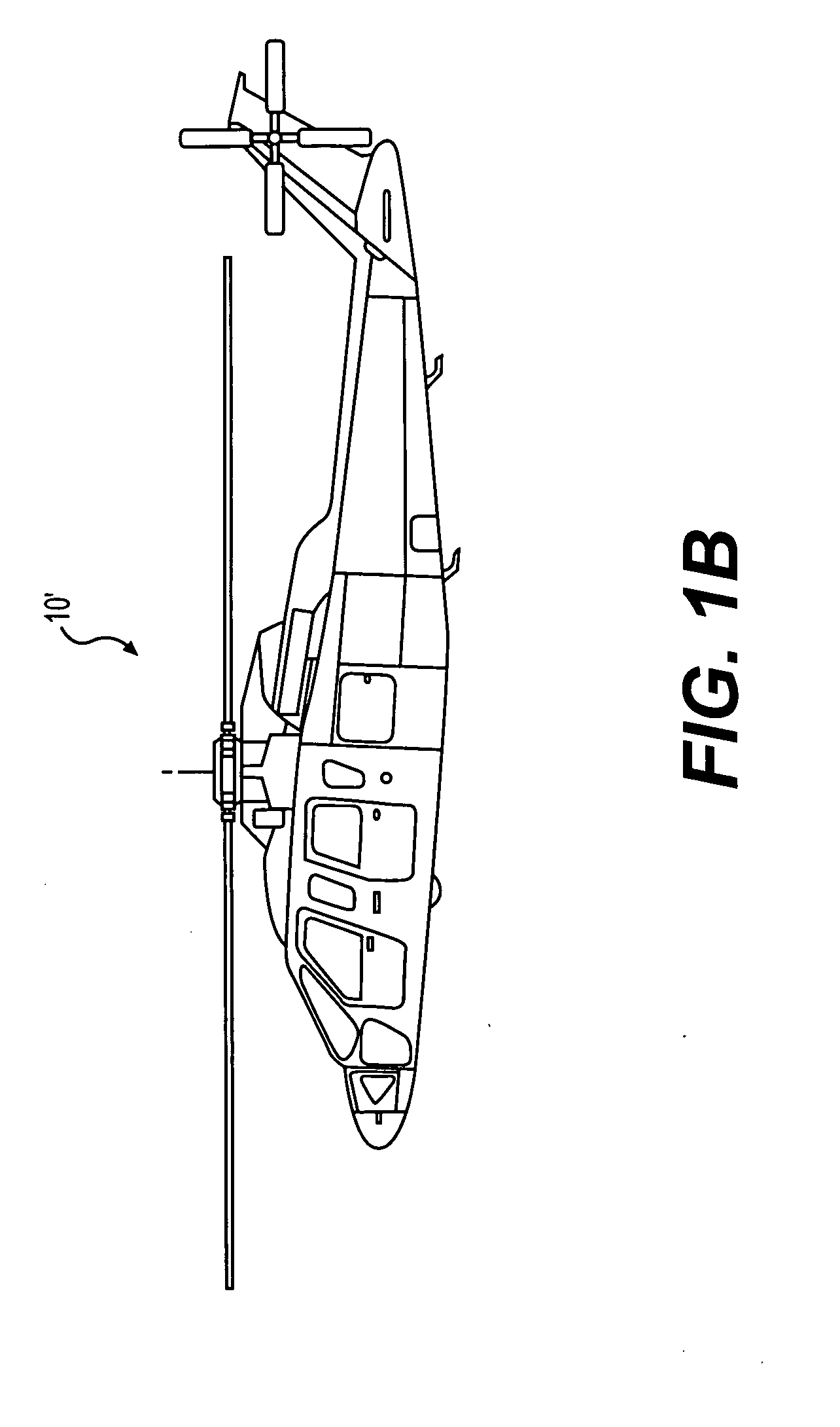
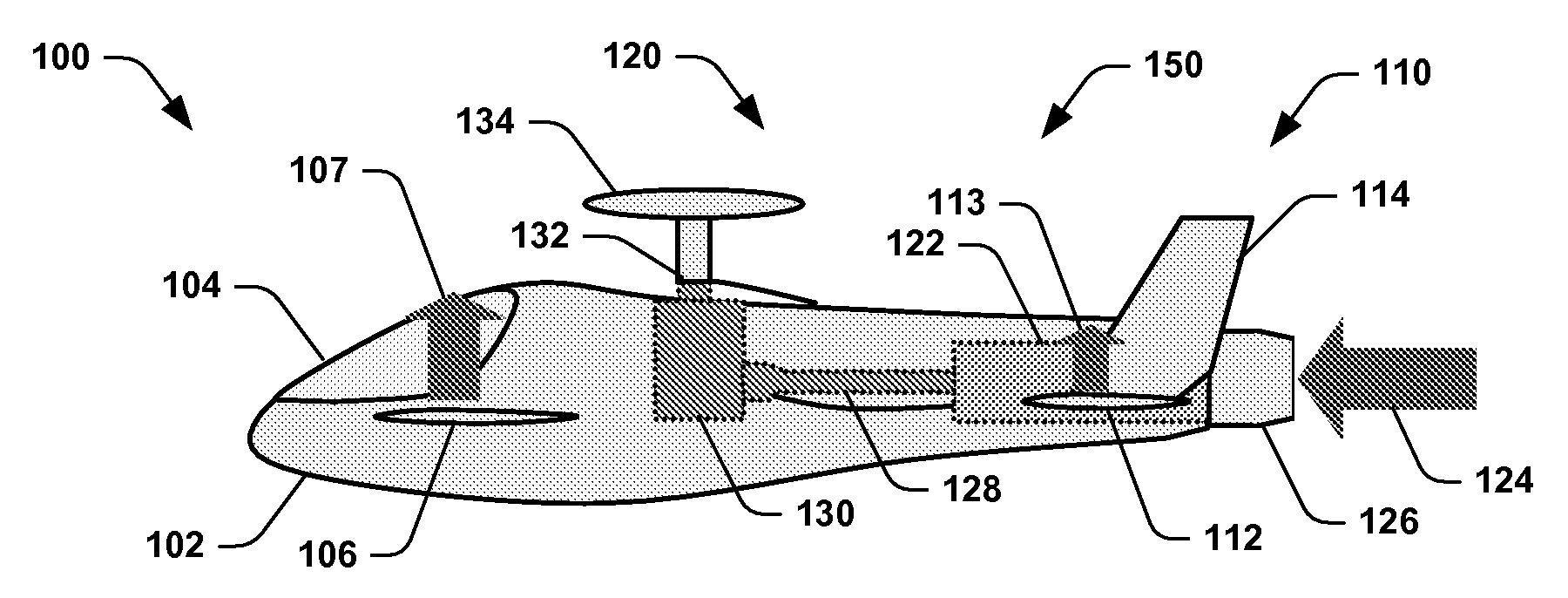
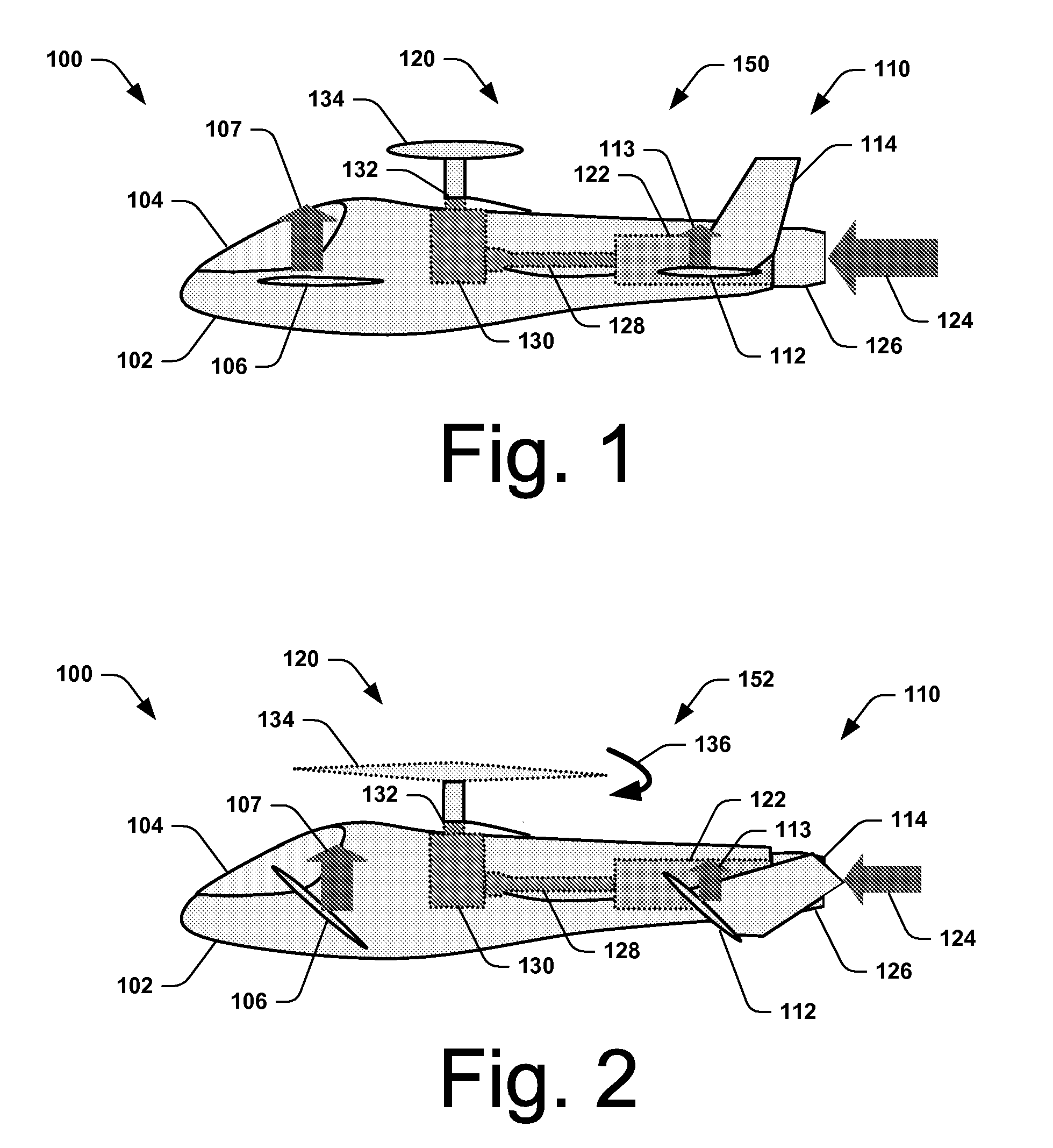
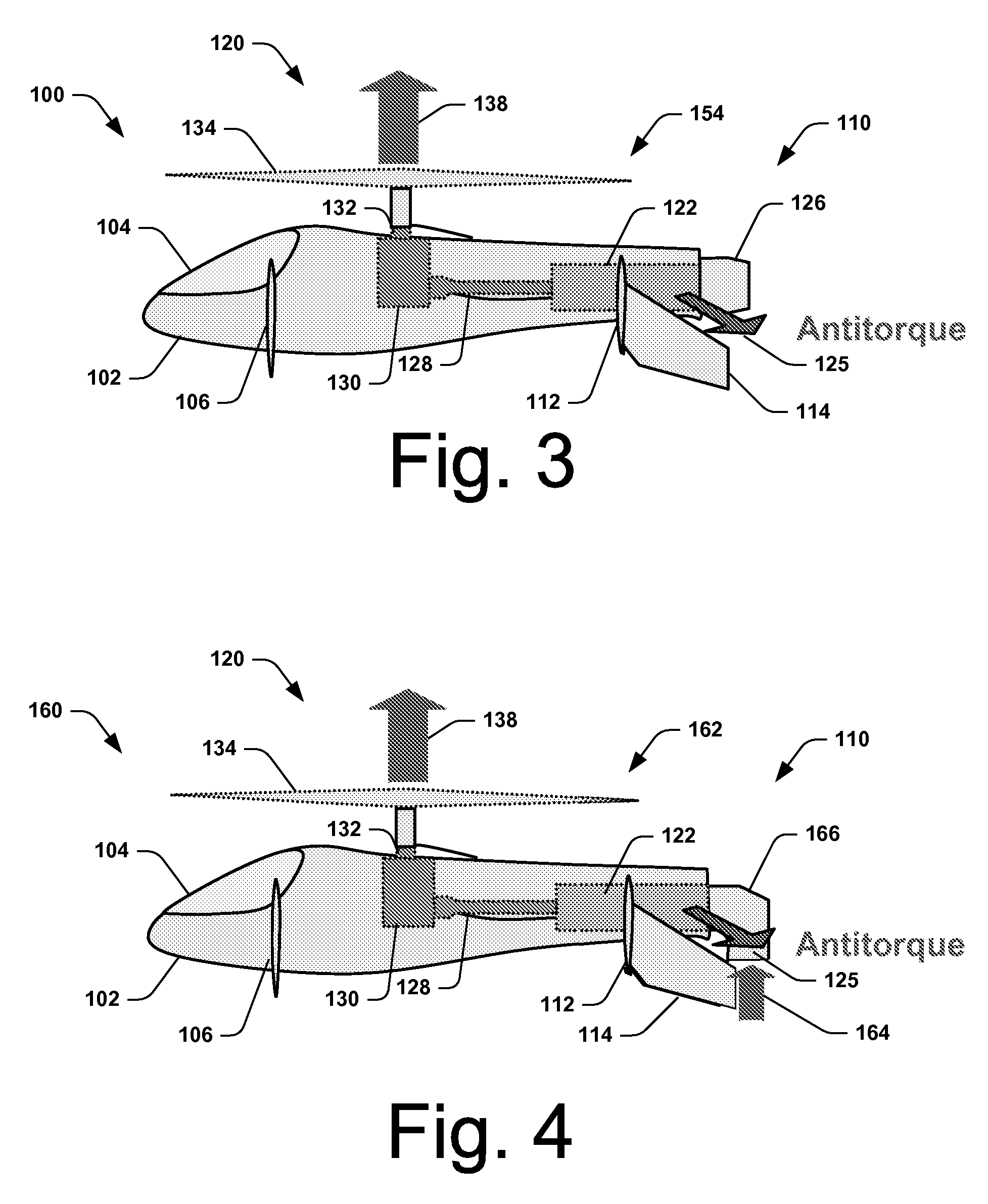
Systems and Methods for Rotor/Wing Aircraft
InactiveUS20090045294A1Smooth transitionAircraft navigation controlEfficient propulsion technologiesFlight vehicleHigh lift
Systems and methods for rotor / wing aircraft are disclosed. In one embodiment, an aircraft includes an airframe, a high-lift canard and tail, a rotor / wing, a propulsion system, and a drive assembly. The drive assembly, which may include a radial inflow turbine, is configured to extract work from the propulsion system to selectively rotate the rotor / wing assembly thus enabling the aircraft to conduct rotary-wing flight, fixed wing flight as well as smoothly transition between the two modes of flight.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
High-lift-to-drag-ratio hypersonic stable gliding reentry guidance method based on drag profile
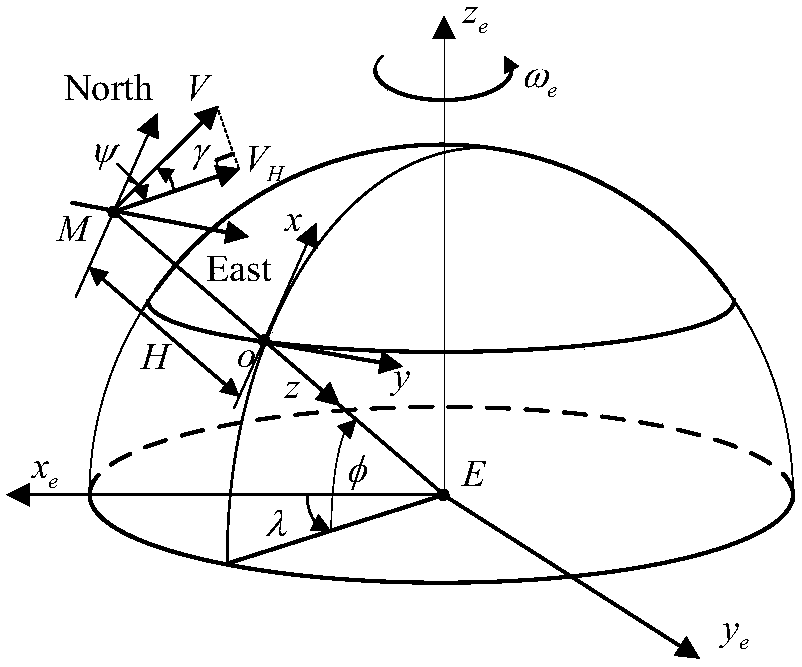
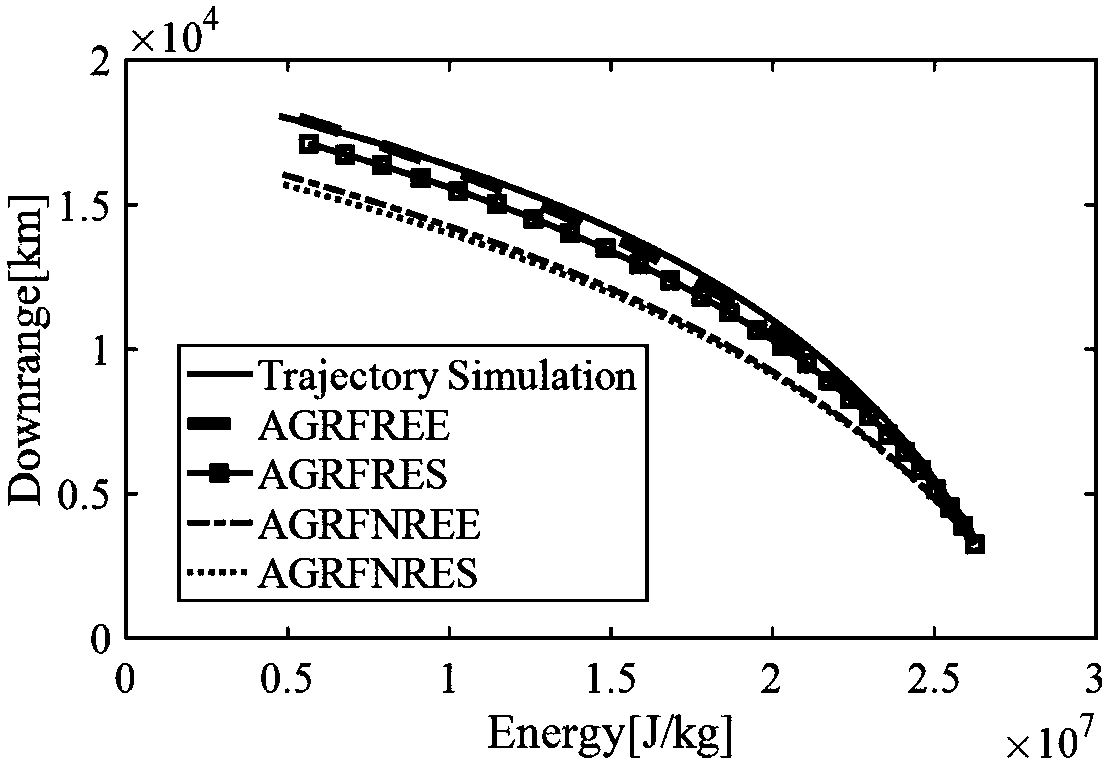
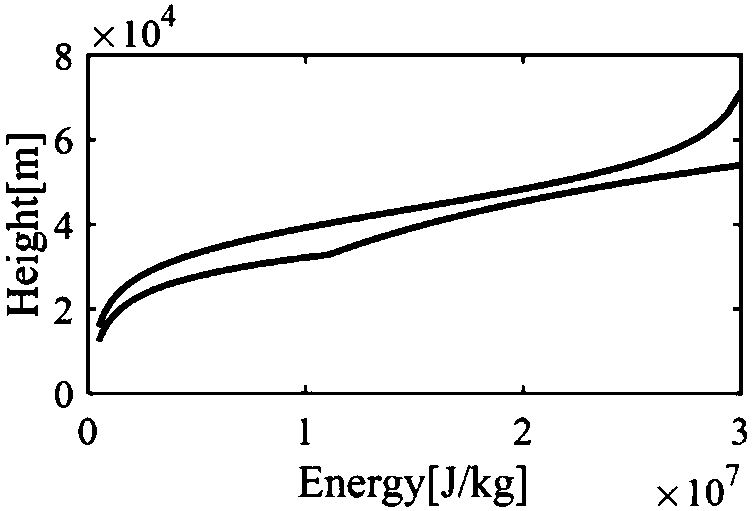
ActiveCN107941087AHigh precisionWell formedGeometric CADCosmonautic vehiclesEarth's rotationFlight vehicle
The invention relates to a high-lift-to-drag-ratio hypersonic stable gliding reentry guidance method based on a drag profile. The method comprises the following steps that the first step, modeling ofa hypersonic flight vehicle is conducted; the second step, gliding distance analytic solution derivation is conducted; the third step, reentry track planning and tracking guidance are conducted; and the fourth step, a stable gliding trajectory tilt angle based on an earth rotation model is derived. The high-lift-to-drag-ratio hypersonic stable gliding reentry guidance method based on the drag profile has the advantages that a gliding distance analytic solution which is higher in accuracy and is based on energy is obtained, the form is simple, and application is convenient; the drag profile isplanned by using the energy as an independent variable, the drag profile is converted into the longitudinal lift-to-drag ratio under the rotating earth background, then a heeling angle is adjusted, tracking is conducted under the condition of the maximum lift-to-drag ratio, and transverse movement is controlled by a course error threshold; and in order to solve the reentry trajectory oscillation problem, the stable gliding trajectory tilt angle based on the earth rotation model is derived, and a trajectory damping technology using the stable gliding trajectory tilt angle as the feedback item is adopted to restrain oscillation.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com