Patents
Literature
162 results about "Wing root" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The wing root is the part of the wing on a fixed-wing aircraft or winged-spaceship that is closest to the fuselage. On a simple monoplane configuration, this is usually easy to identify. On parasol wing or multiple boom aircraft, the wing may not have a clear root area.
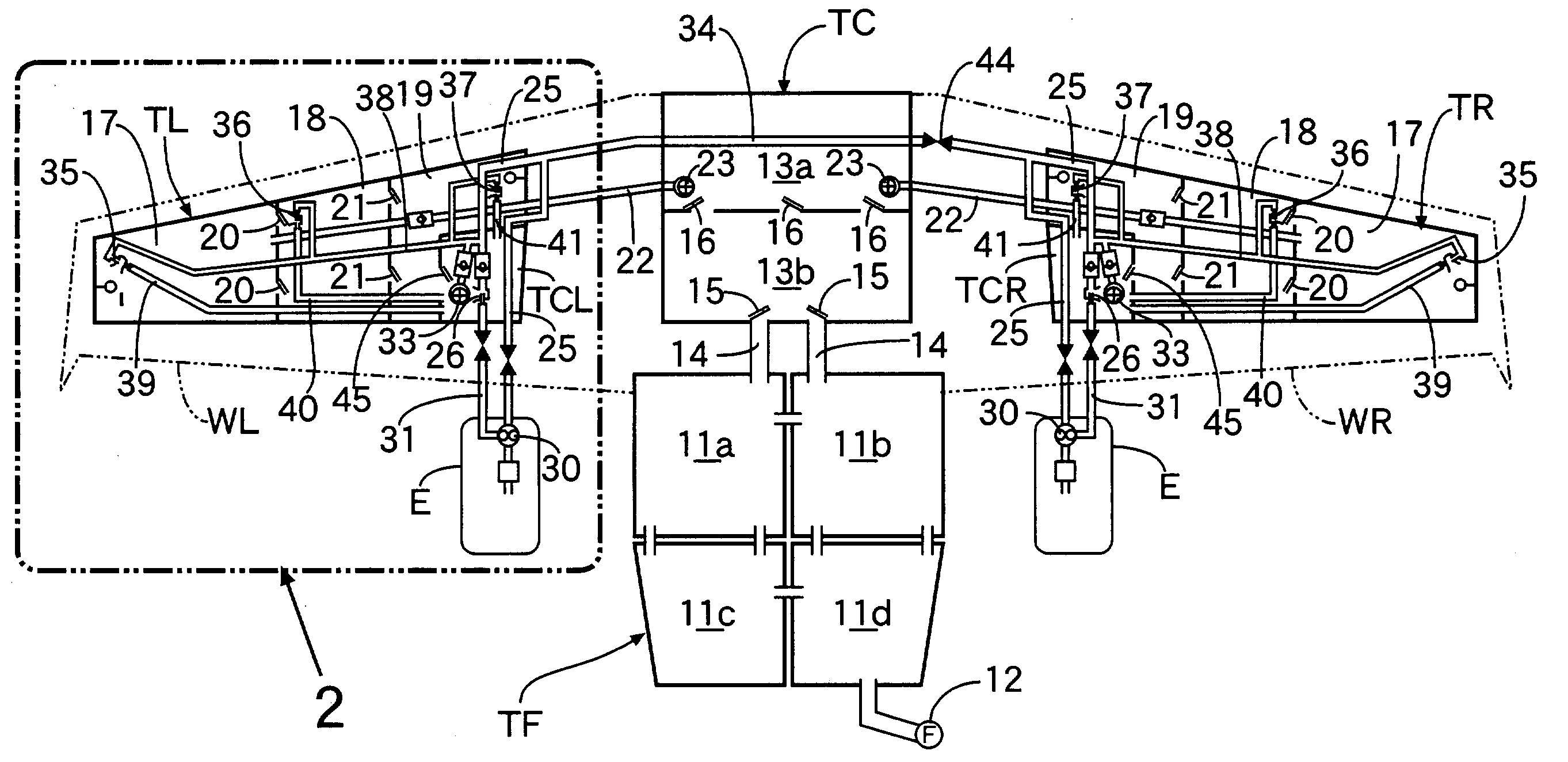
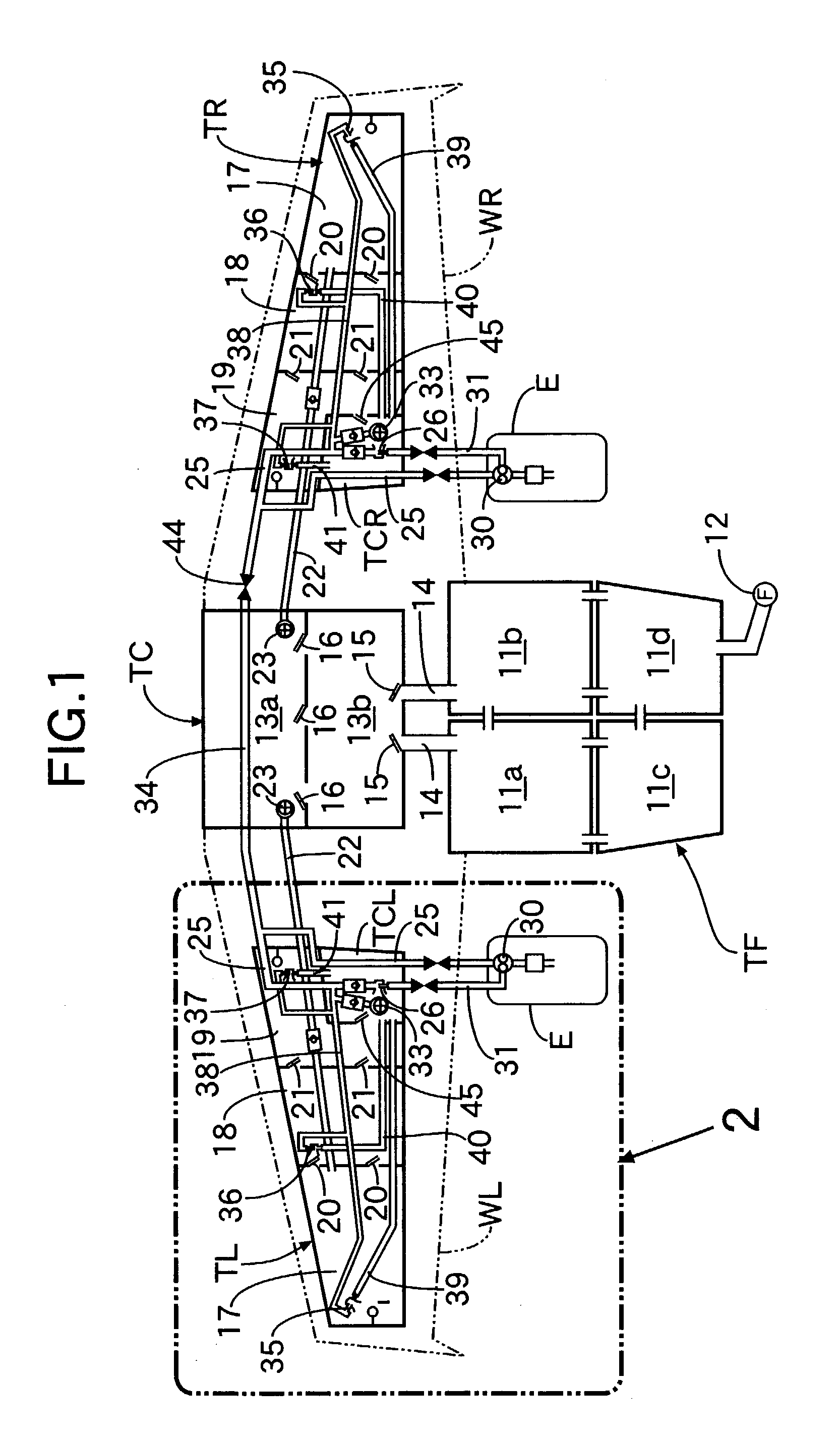
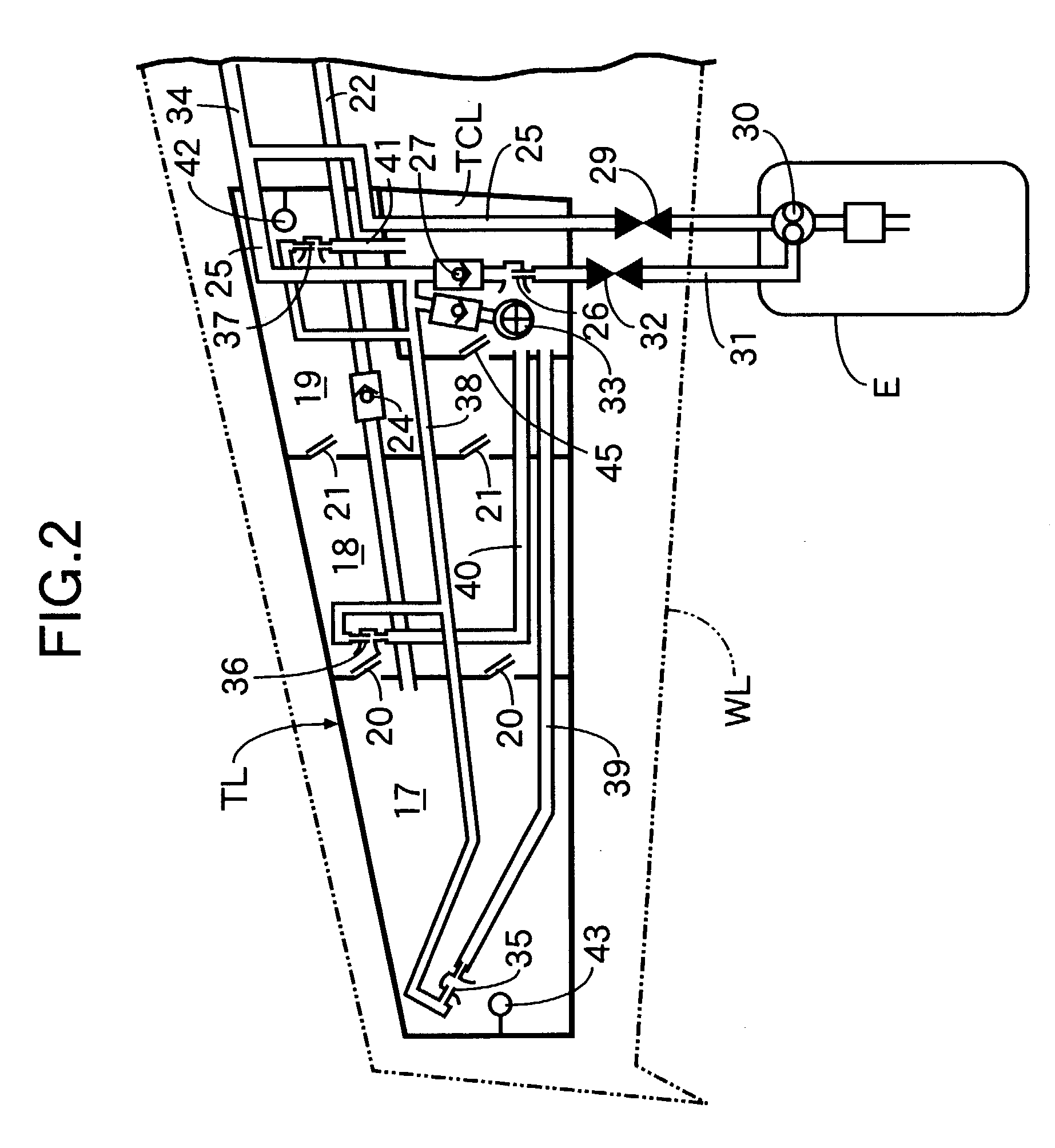
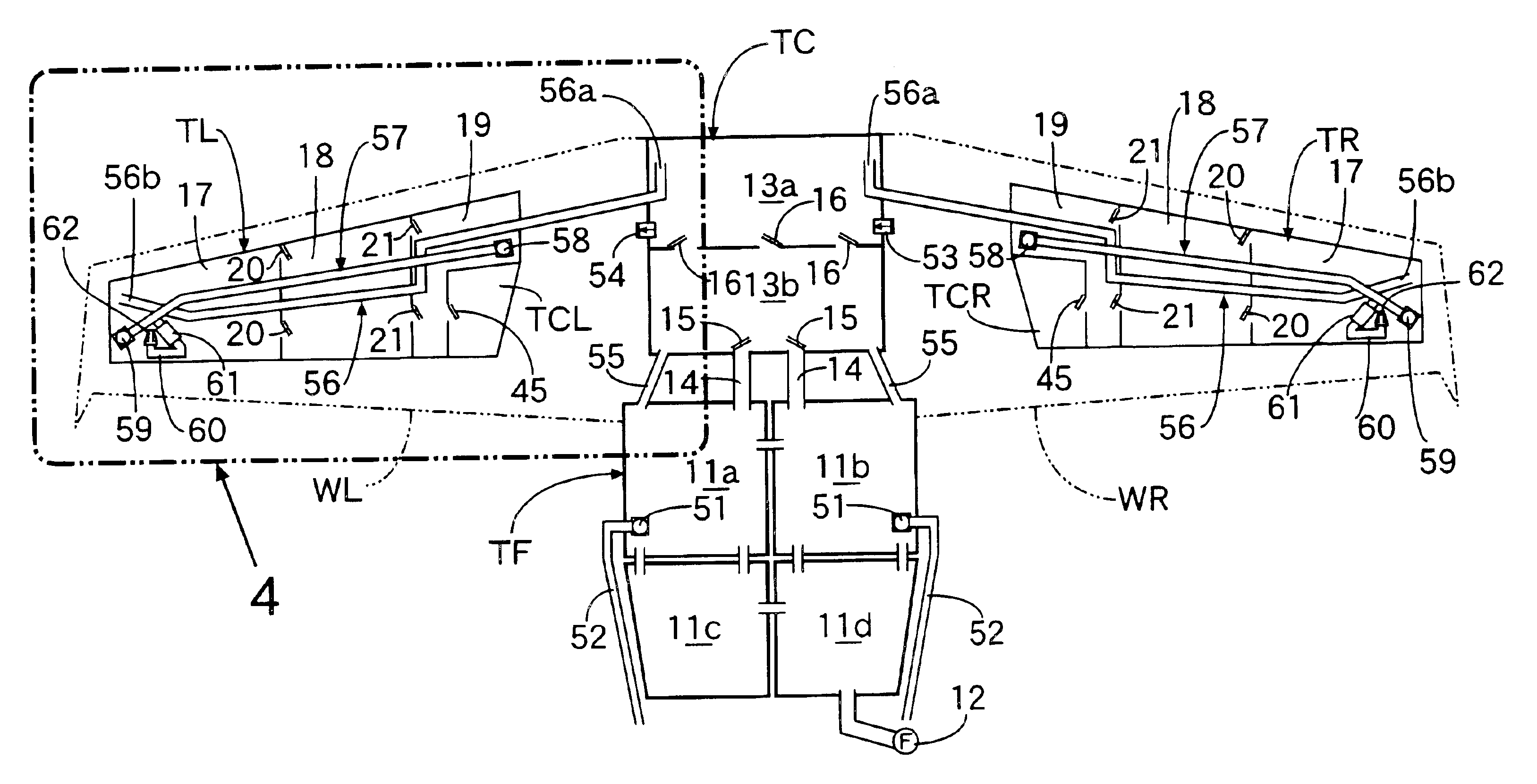
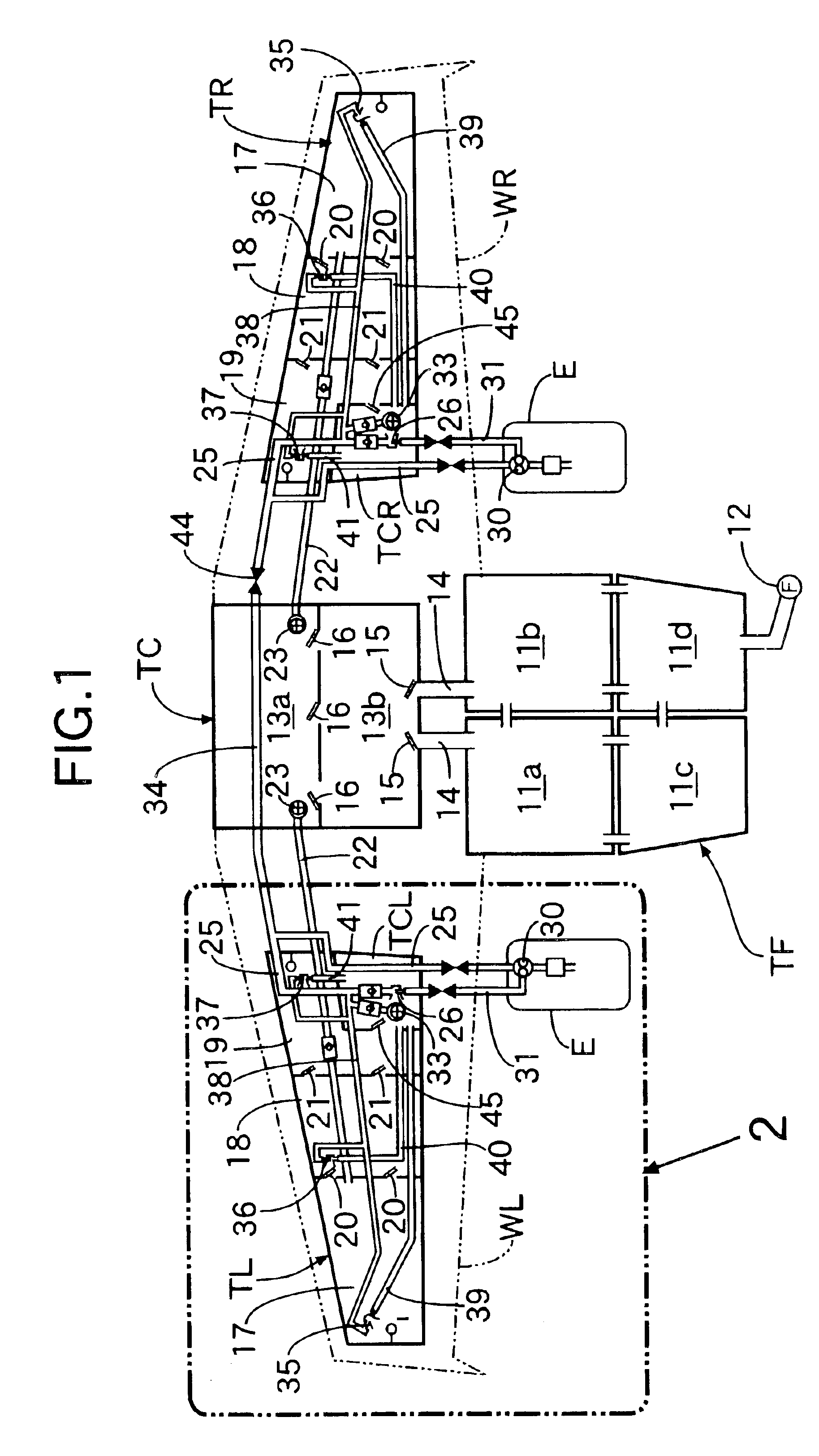
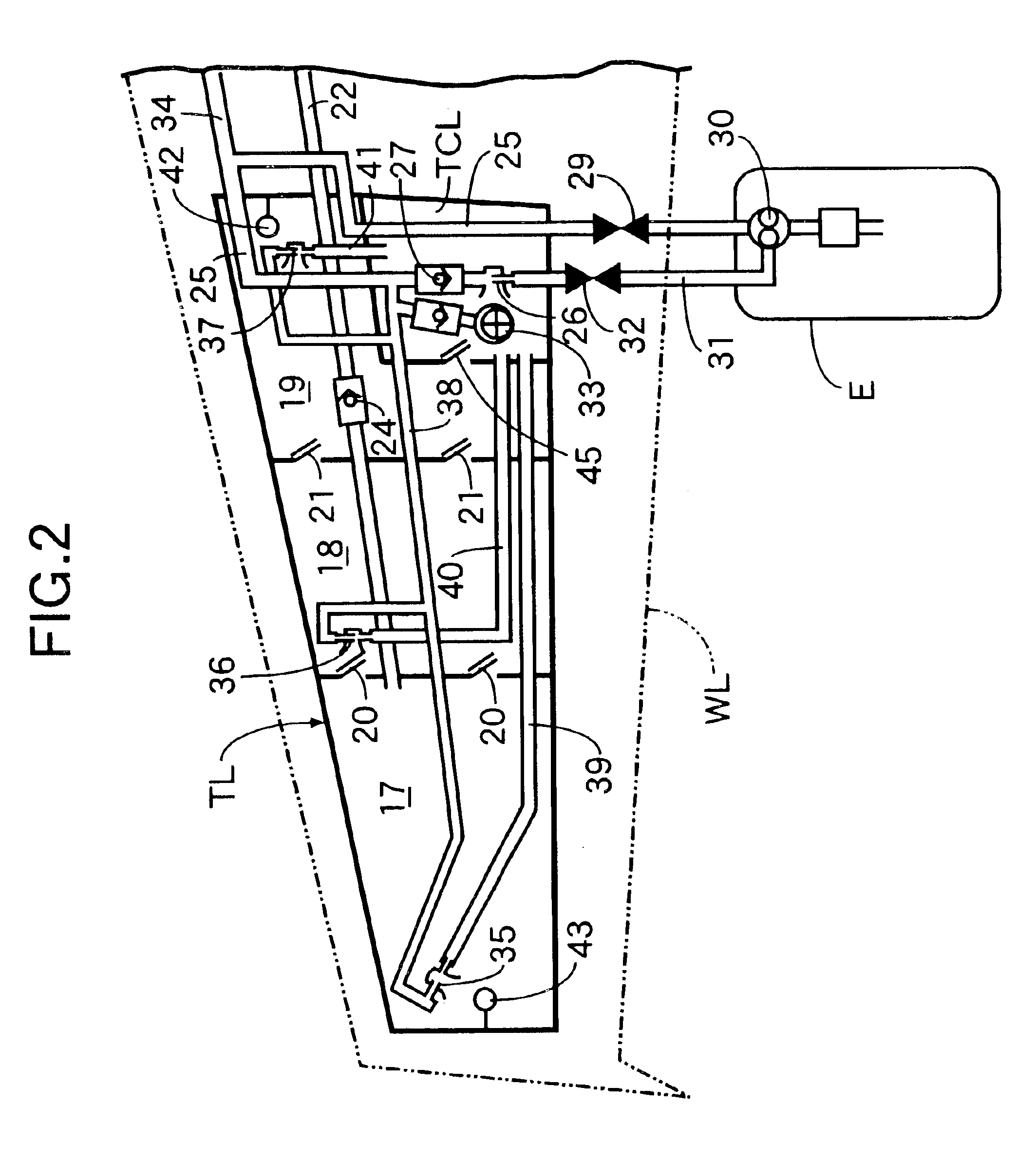
Airplane fuel supply system and airplane wing pipeline assembly method
An airplane fuel supply system includes a wing fuel tank that is formed from a wing tip fuel tank having a wing tip fuel pump; a central fuel tank having a central fuel pump; and a wing root fuel tank having a wing root fuel pump. Fuel movement from the wing tip fuel tank to the central fuel tank is allowed by a flapper valve, and fuel movement from the central fuel tank to the wing root fuel tank is allowed by another flapper valve. When the fuel delivery volume of the wing tip fuel pump is represented by Vt, the fuel delivery volume of the central fuel pump is represented by Vc, the fuel delivery volume of the wing root fuel pump is represented by Vr, and the fuel delivery volume from a collector tank to the engine is represented by Ve, the fuel delivery volumes Vt, Vc, Vr, and Ve are set so as to satisfy the relationships Vr>Ve, Vt+Vc>Ve, and Vc<Ve. This can minimize the size of the fuel pumps for supplying fuel from the airplane wing fuel tank to the engine.
Owner:AMERICAN HONDA MOTOR COMPANY
Airplane fuel supply system and airplane wing pipeline assembly method
An airplane fuel supply system includes a wing fuel tank that is formed from a wing tip fuel tank having a wing tip fuel pump; a central fuel tank having a central fuel pump; and a wing root fuel tank having a wing root fuel pump. Fuel movement from the wing tip fuel tank to the central fuel tank is allowed by a flapper valve, and fuel movement from the central fuel tank to the wing root fuel tank is allowed by another flapper valve. When the fuel delivery volume of the wing tip fuel pump is represented by Vt, the fuel delivery volume of the central fuel pump is represented by Vc, the fuel delivery volume of the wing root fuel pump is represented by Vr, and the fuel delivery volume from a collector tank to the engine is represented by Ve, the fuel delivery volumes Vt, Vc, Vr, and Ve are set so as to satisfy the relationships Vr>Ve, Vt+Vc>Ve, and Vc<Ve. This can minimize the size of the fuel pumps for supplying fuel from the airplane wing fuel tank to the engine.
Owner:AMERICAN HONDA MOTOR COMPANY
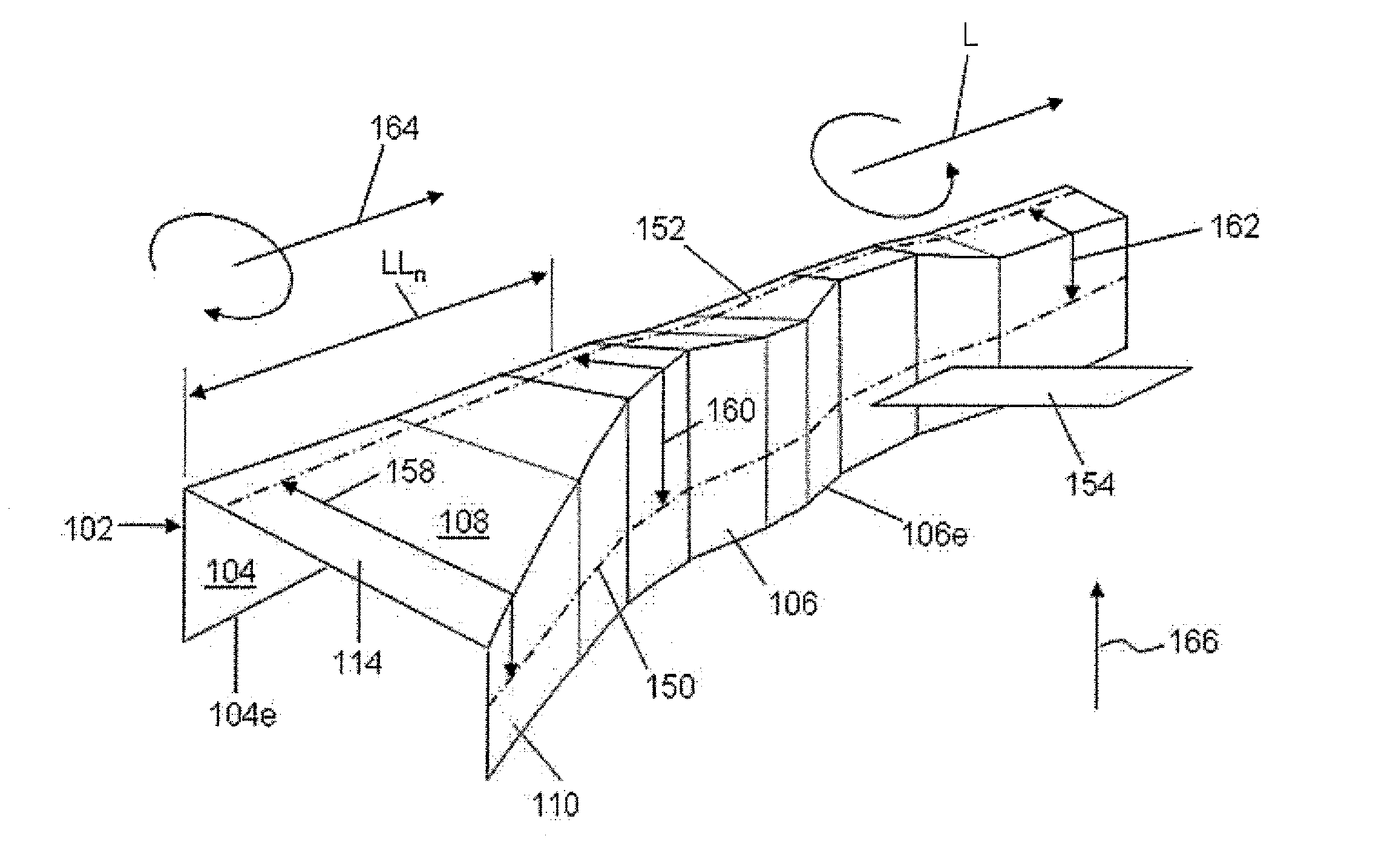
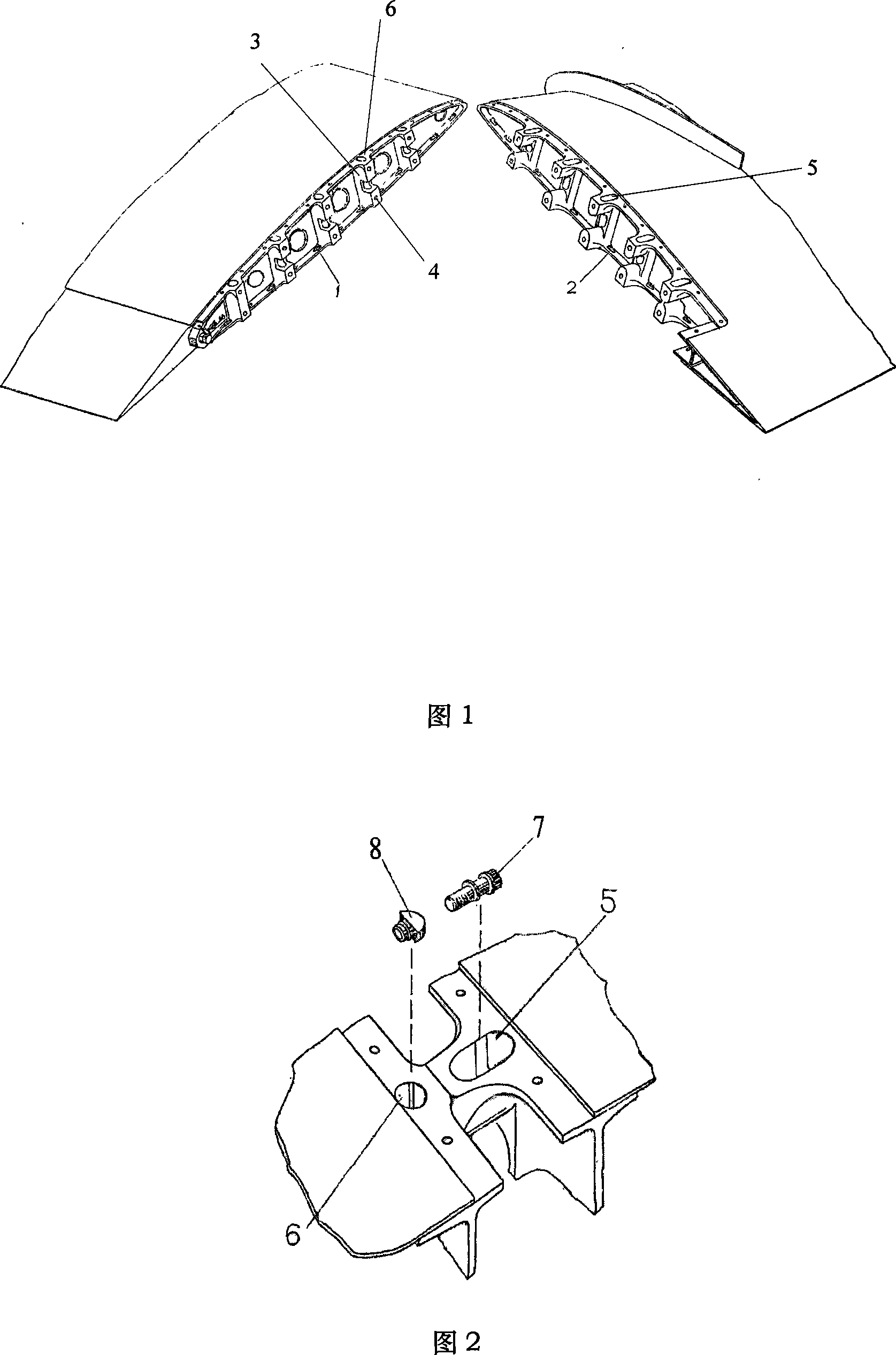
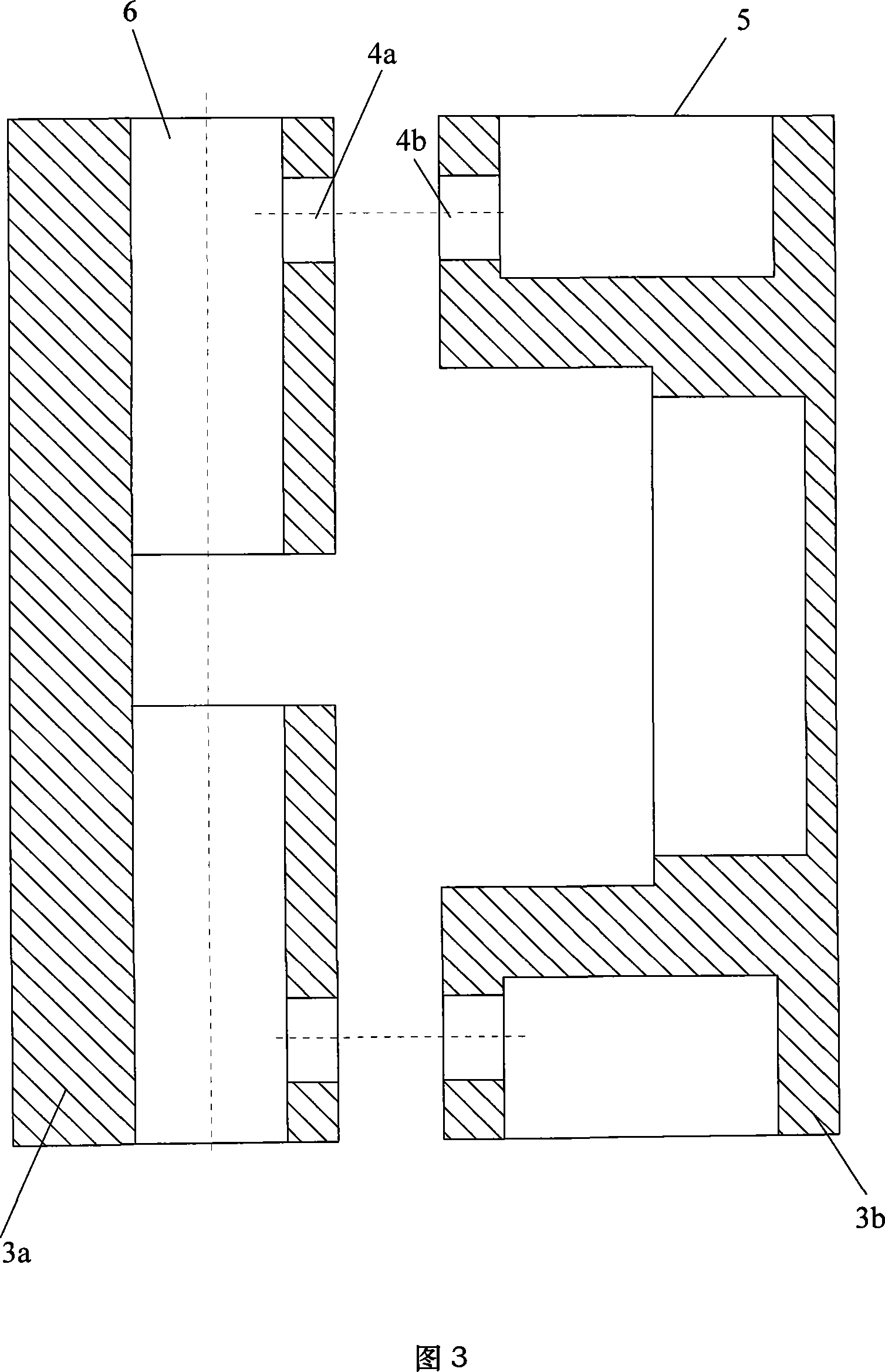
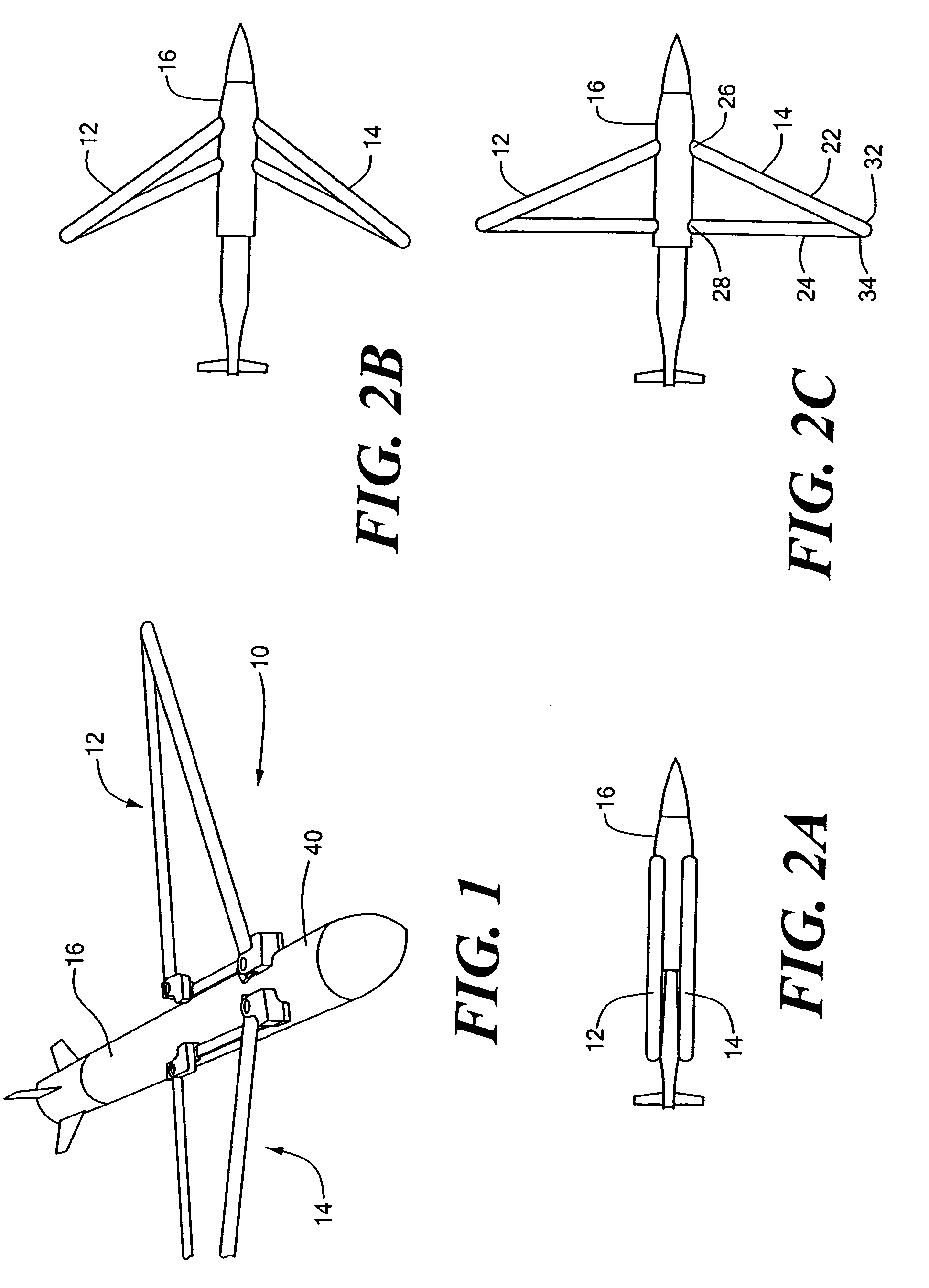
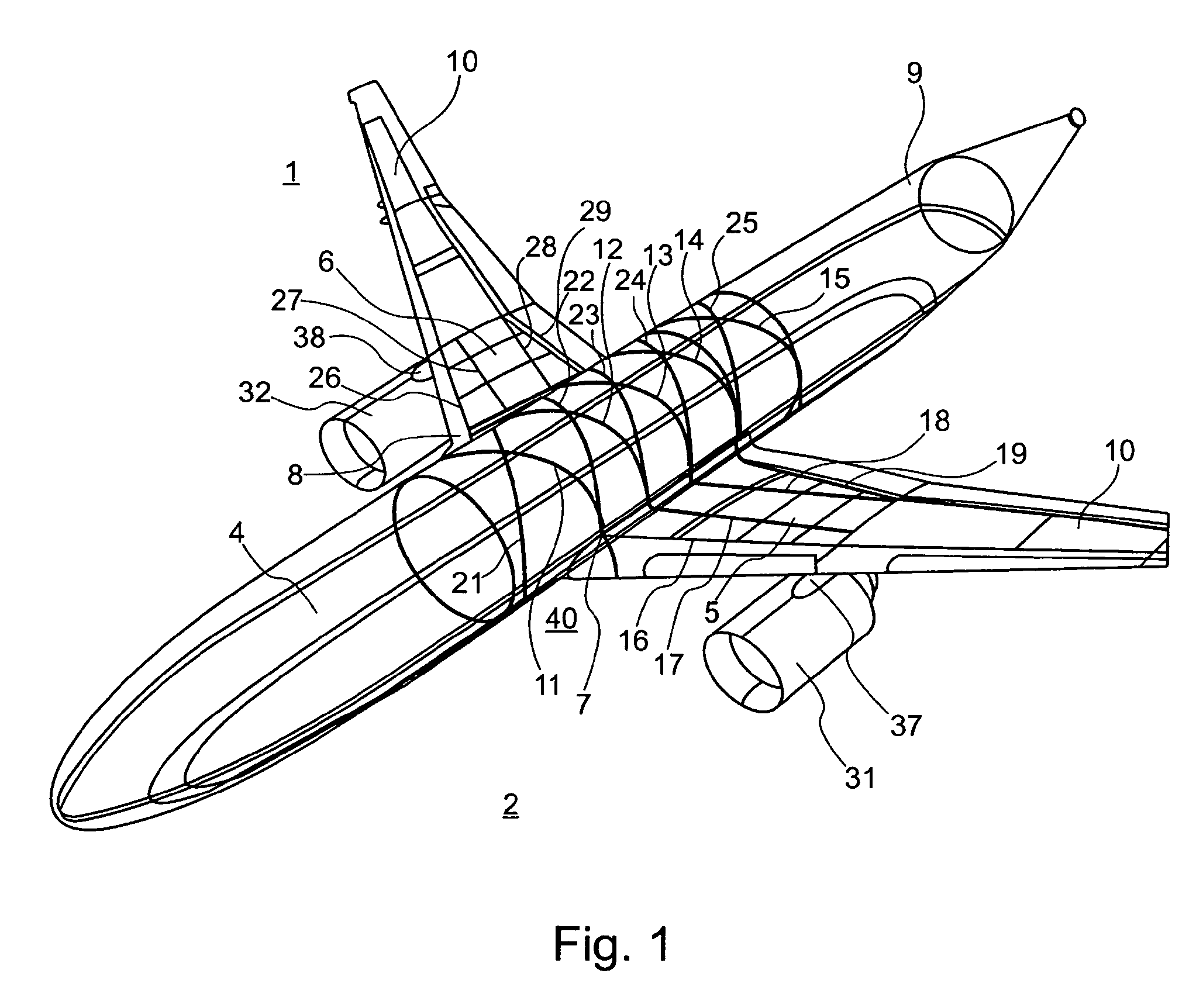
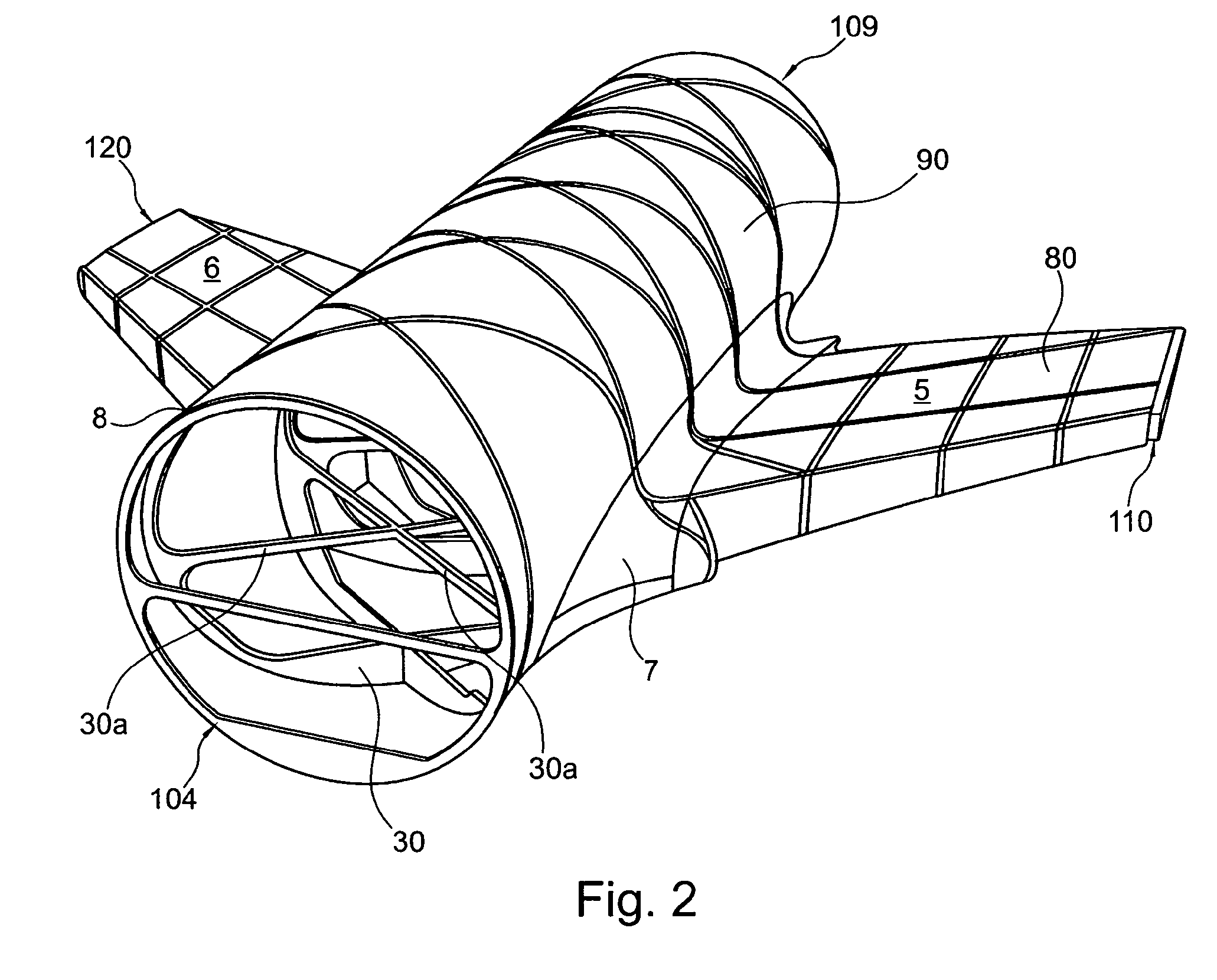
Wing-fuselage section of an aircraft
A wing-fuselage section of an aircraft, which wing-fuselage section comprises a wing root at which the wing of the aircraft is connected to the fuselage, a fuselage region with fuselage frame elements that extent across the longitudinal direction of the aircraft, and a wing region with spars that extend in the direction of the wingspan. According to the invention, the spars of the wing region and the fuselage frame elements of the fuselage region form part of an integral assembly that extends at least over a middle part of the wing and the fuselage region, including the wing roots.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
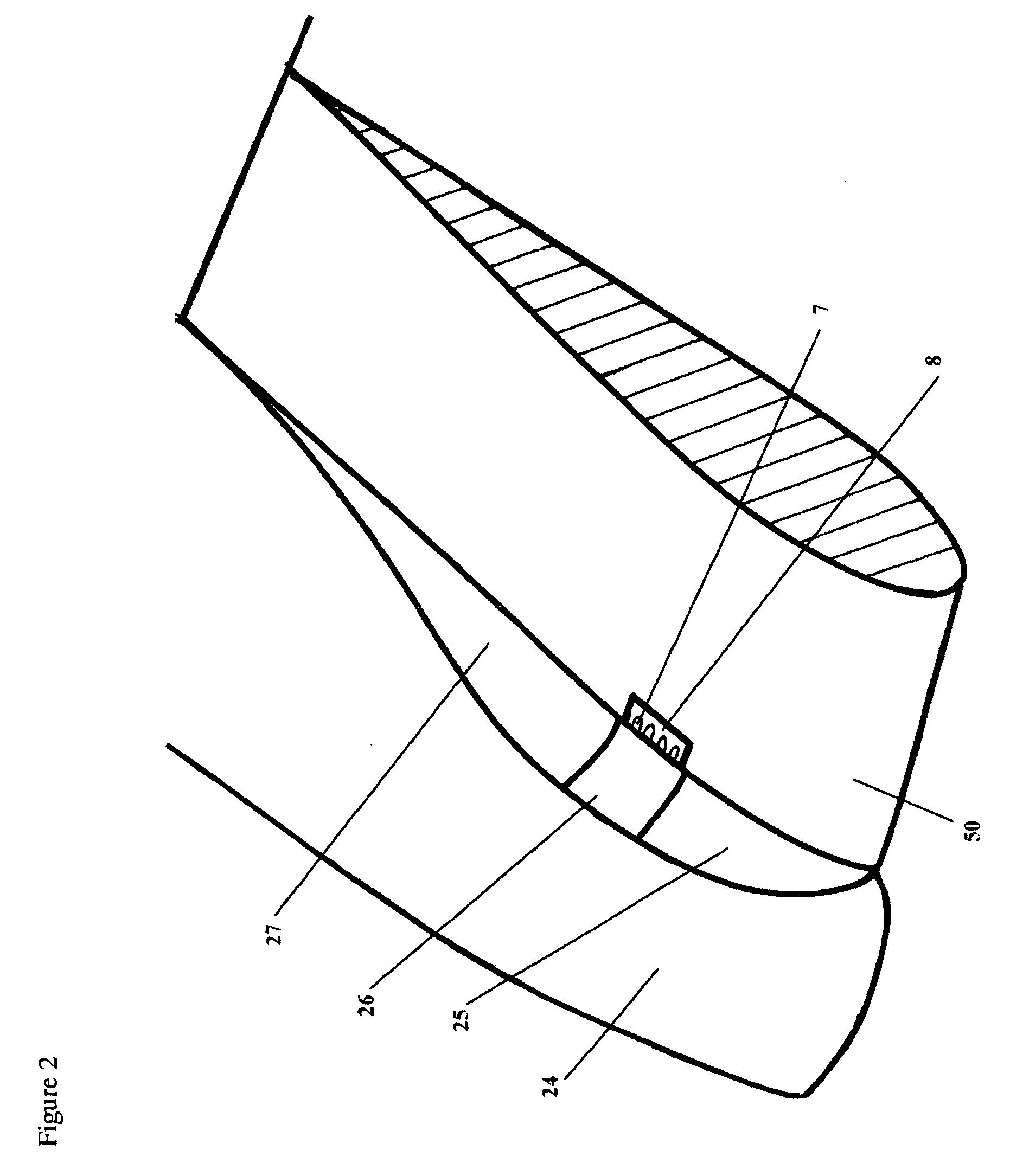
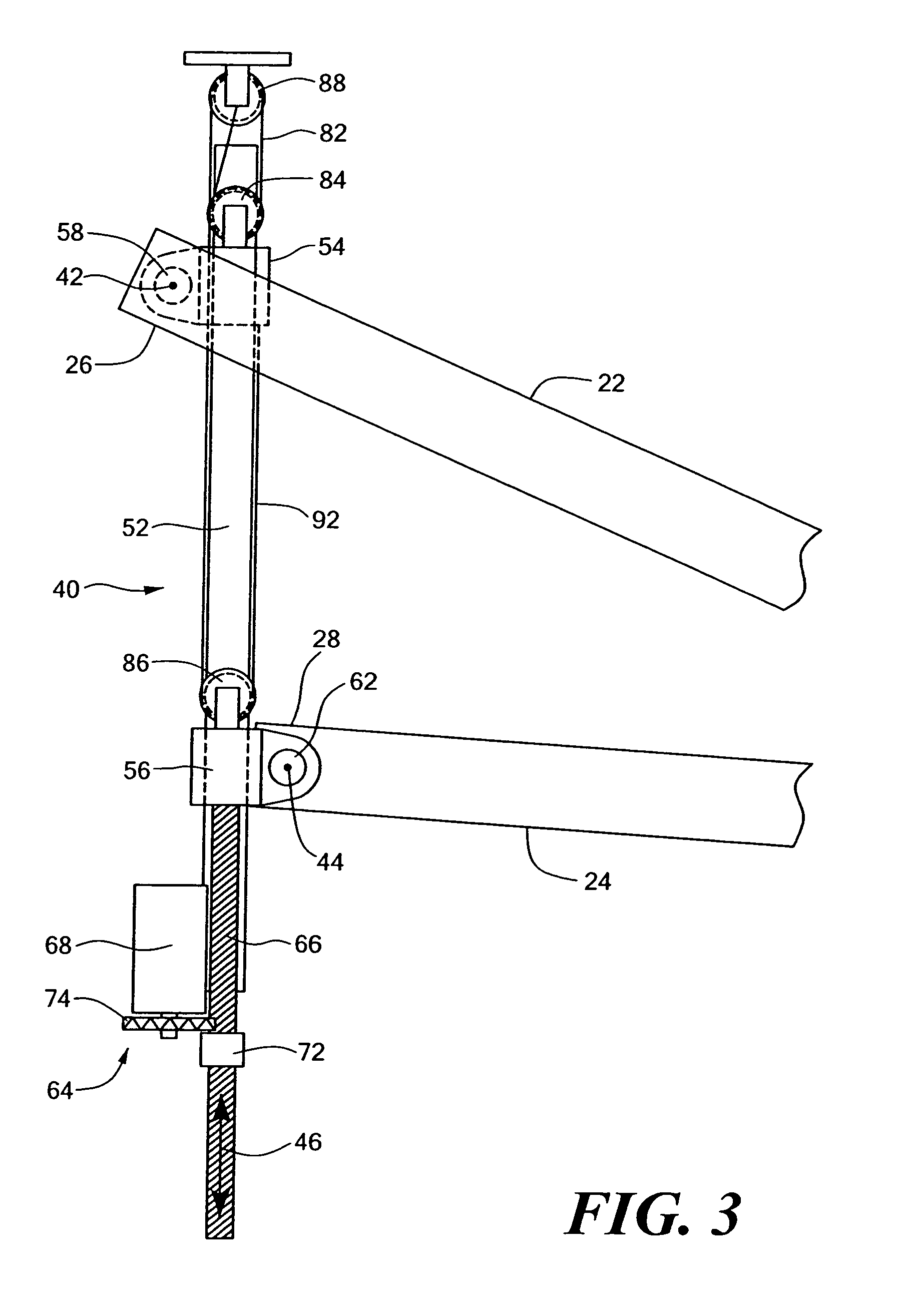
Apparatus for influencing a wing root airflow in an aircraft
An apparatus advantageously influences the wing root airflow along the wing root of an aircraft having a high lift system including leading edge slats provided on the main wings. The apparatus includes a respective vortex generator arranged on the inboard end of each leading edge slat in the area of the wing root, and further includes a respective transition fairing arranged on a separation edge that is let into the leading edge of the wing root and that borders along the inboard edge of the respective slat. The vortex generator is a rigid member fixed to the leading edge slat and may be in the shape of a horn, a disk, or a winglet. The transition fairing may be a rigid member fixed to the wing root along the separation edge, or may be a flexible elastic member that can be inflated to have a variable outer contour. The present system avoids the need of additional independently movable auxiliary flaps, and thus achieves a reduced weight, complexity, and maintenance requirement.
Owner:DAIMLER CHRYSLER AEROSPACE AIRBUS
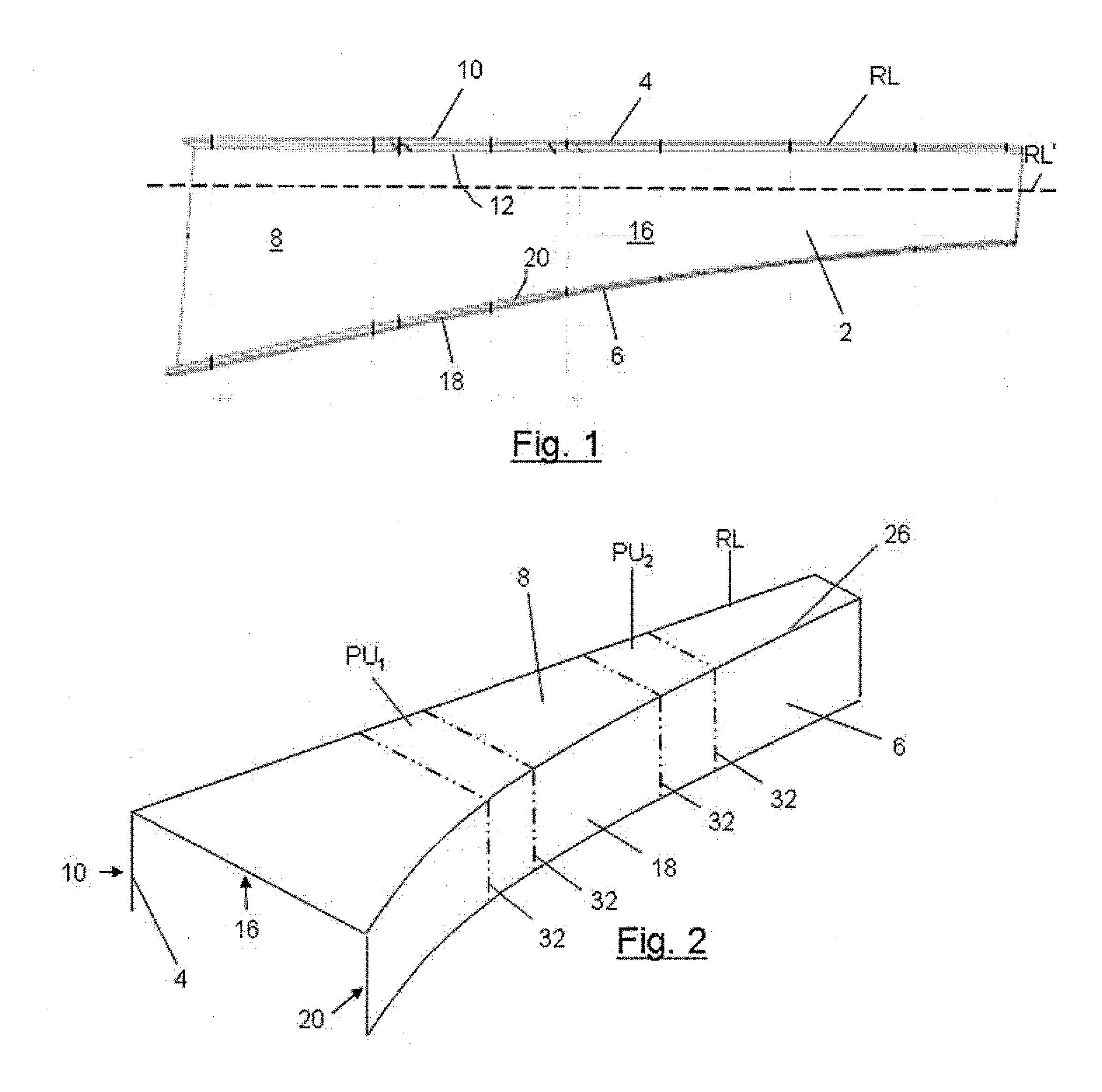
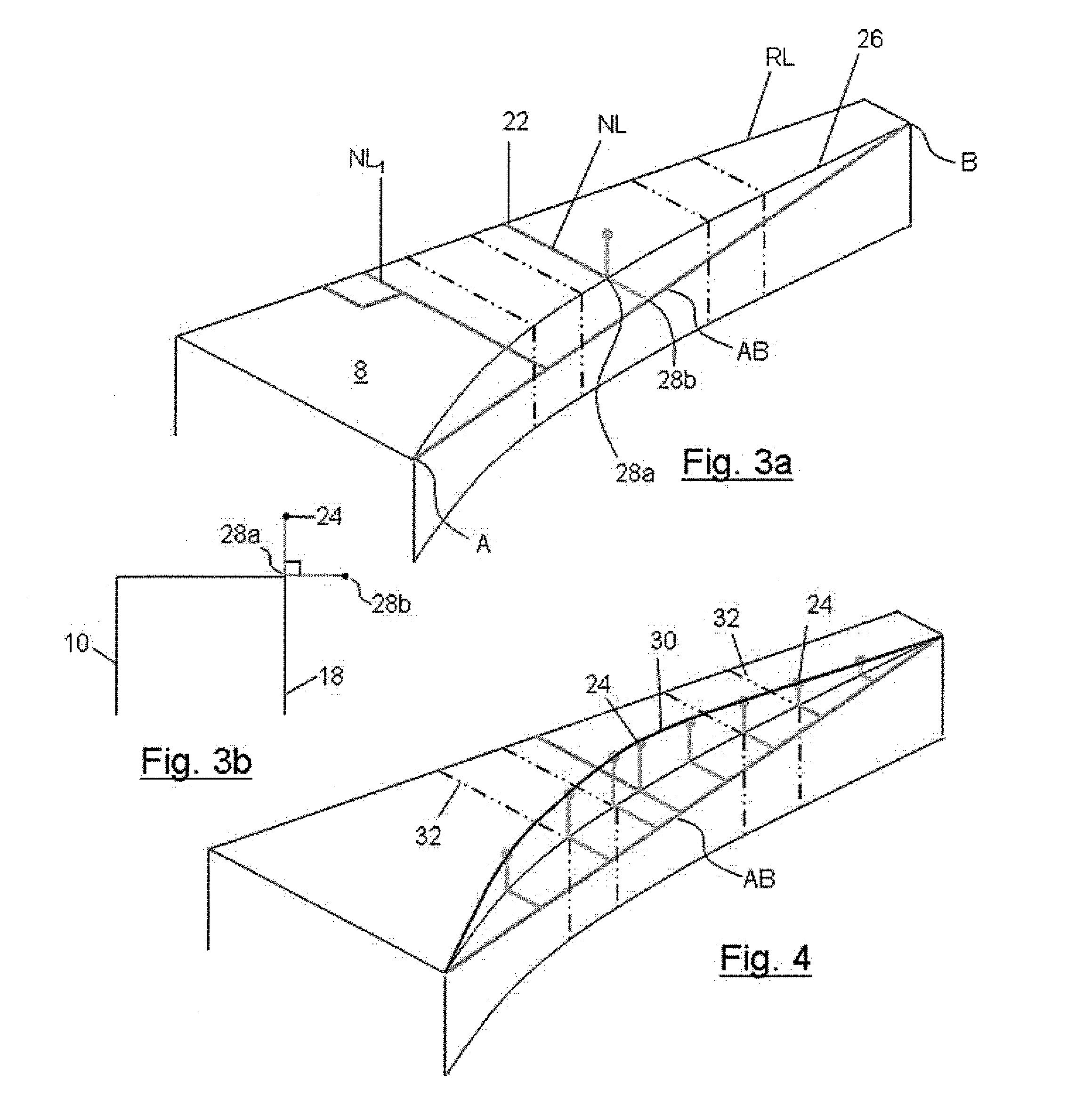
Elongate composite structural members and improvements therein
InactiveUS20100170989A1Reduce riskReduce biasGeometric CADFuselage framesComposite constructionEngineering
A composite material elongate structural member, such as a spar, for use in an aerospace structure, comprises a web disposed between upper and lower flanges. The web may include a clockwise twist about an axis parallel to the length L at a first portion towards the wing-root-end of the spar and a counter-twist in the anticlockwise direction at a second portion towards the wing-tip-end of the spar. The geometry of the spar may vary non-linearly along its length (L) so that the developed width of the spar as measured from a distal edge of the upper flange via the web to a distal edge of the lower flange varies linearly with increasing distance along the length (L). The risk of causing, during fabrication of the spar, undesirable creasing, stressing or stretching of composite material layers in a region in which the geometry of the member varies non-linearly may be reduced by means of such an arrangement.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD
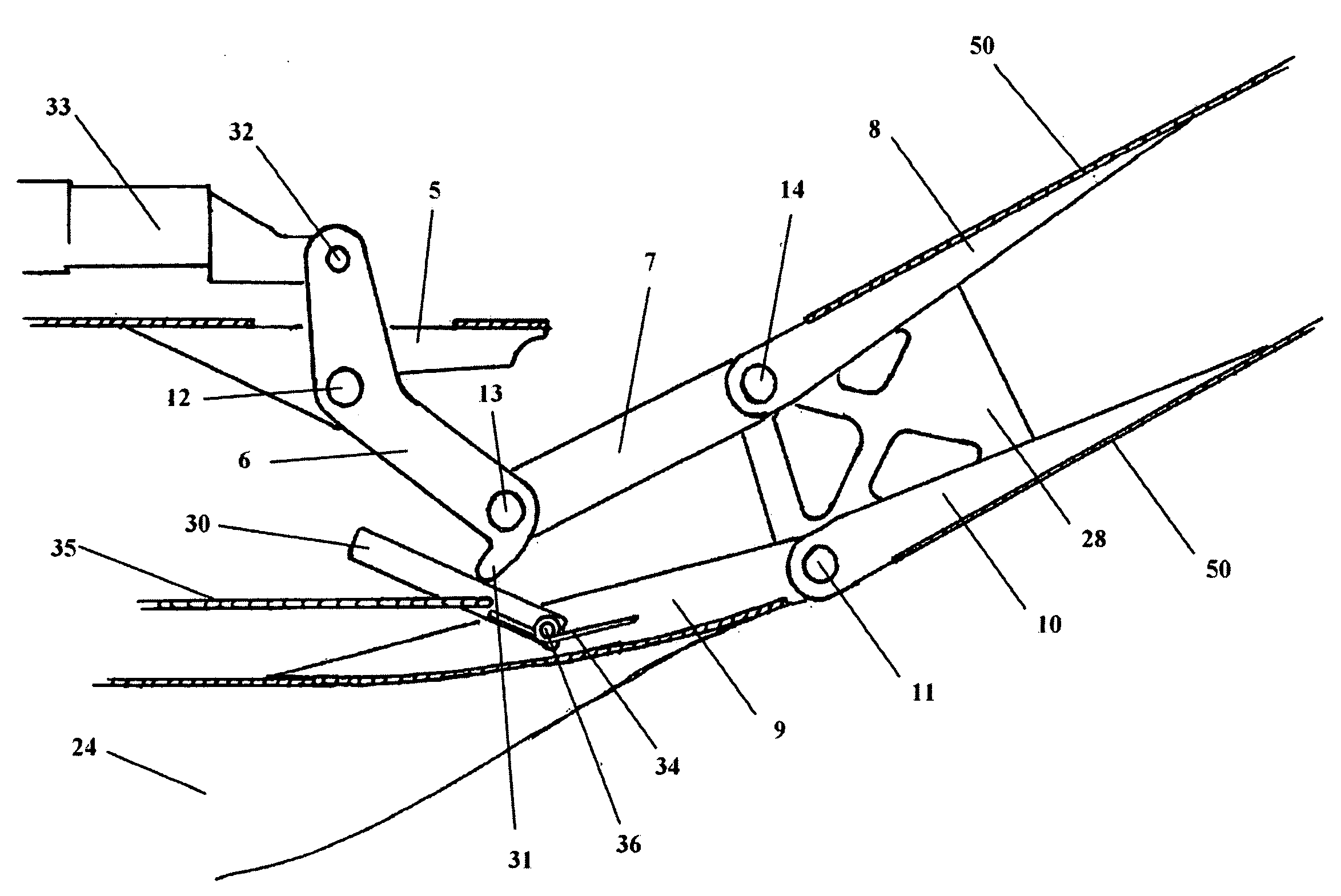
Folding Wing Root Mechanism
ActiveUS20100019080A1Improve protectionImprove trustAircraft stabilisationWing adjustmentsLocking mechanismWing root
Improvements to the hinge of a folding aircraft wing including a load bearing hinge mechanism with multiple locking mechanisms. The mechanism includes rigid panels that cover the hinge area when the wing is deployed, and the wing itself covers the hinge area when the wing is retracted. A control lever is used to actuate the wing and incorporates safety features to prevent unwanted actuation.
Owner:TERRAFUGIA
Folding wing root mechanism
ActiveUS8210473B2Improve protectionImprove trustAircraft stabilisationWing adjustmentsLocking mechanismWing root
Improvements to the hinge of a folding aircraft wing including a load bearing hinge mechanism with multiple locking mechanisms. The mechanism includes rigid panels that cover the hinge area when the wing is deployed, and the wing itself covers the hinge area when the wing is retracted. A control lever is used to actuate the wing and incorporates safety features to prevent unwanted actuation.
Owner:TERRAFUGIA
Connecting structure for middle and outside wings of unmanned aerial vehicle
InactiveCN101214853AReduce complexityReduce manufacturing errorsWingsToy aircraftsButt jointHigh intensity
The present invention discloses a mid-wing and external-wing connection structure of an unmanned aerial vehicle. A mid-wing end rib and an external-wing root rib are the aluminium alloy reinforced ribs with comb-shaped joints. At the butt joint of the two reinforced ribs, the mid-wing and the external-wing are jointed by butt joint bolts made from high-intensified aluminium alloy material. After the mid-wing and the external-wing are butted, a joint seam is covered by a cowling made from composite material that is two rows of bolts are used fix the cowling at the reinforced ribs along the edge of the cowling. The mid-wing end rib and the external-wing root rib are considered as the butt joint of the mid-wing and the external-wing to integrate the joint and the structure as a whole, which reduces the complexity of the coordination relation and the connection relation and the manufacture error and assembly error by single joint, and the joint point and the grinder and the supporting structure of the external-wing are in one axial line, which ensures that the transmission force is continuous. The present invention has simple connection manner, which is convenient for disassembling and assembling and for checking the damage condition of a connection piece.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
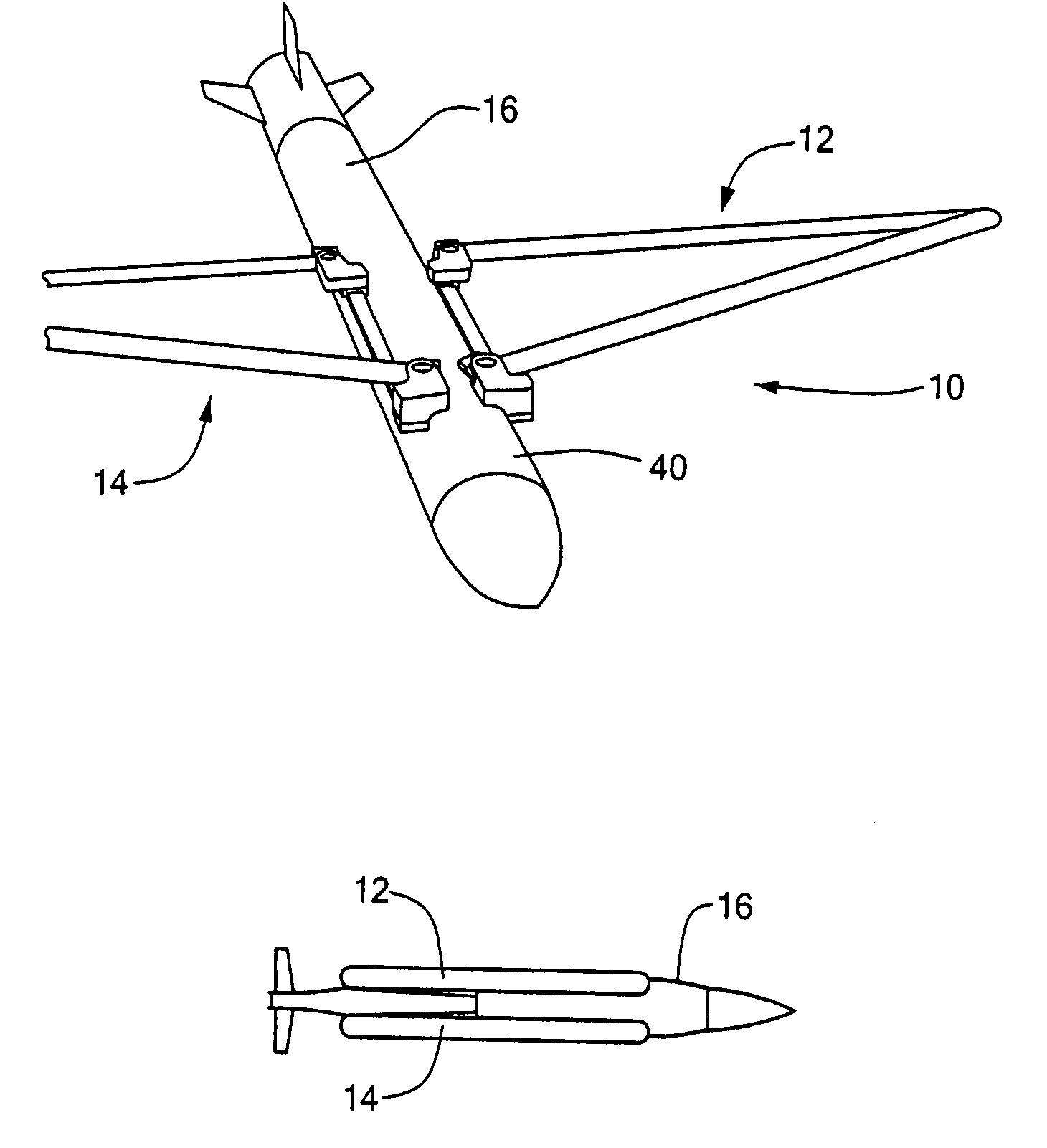
Extendable joined wing system for a fluid-born body
InactiveUS6986481B2Long wingspanHigh aspect ratioEfficient propulsion technologiesWing adjustmentsNoseActuator
An extendable wing system for a fluid-born body has a forward wing and an aft wing pivotably coupled together at a location outward of their wing roots. A linkage mechanism mounted on the body provides both pivoting of the wing roots about a pivot point and translation of the wing roots and their pivot points to extend the joined wings from a stowed position to a deployed position. Translation of the forward wing root pivot point allows the stowed wing system to occupy additional space toward the nose of the body, thereby allowing use of wings having a longer wingspan and greater aspect ratio. The linkage mechanism can also be used to incorporate flight control, such as roll and pitch control, directly into the wing system. In another embodiment, the wings can incorporate actuator elements on or within the wings to effect flight control by deformation of the wing structure.
Owner:KAZAK COMPOSITES
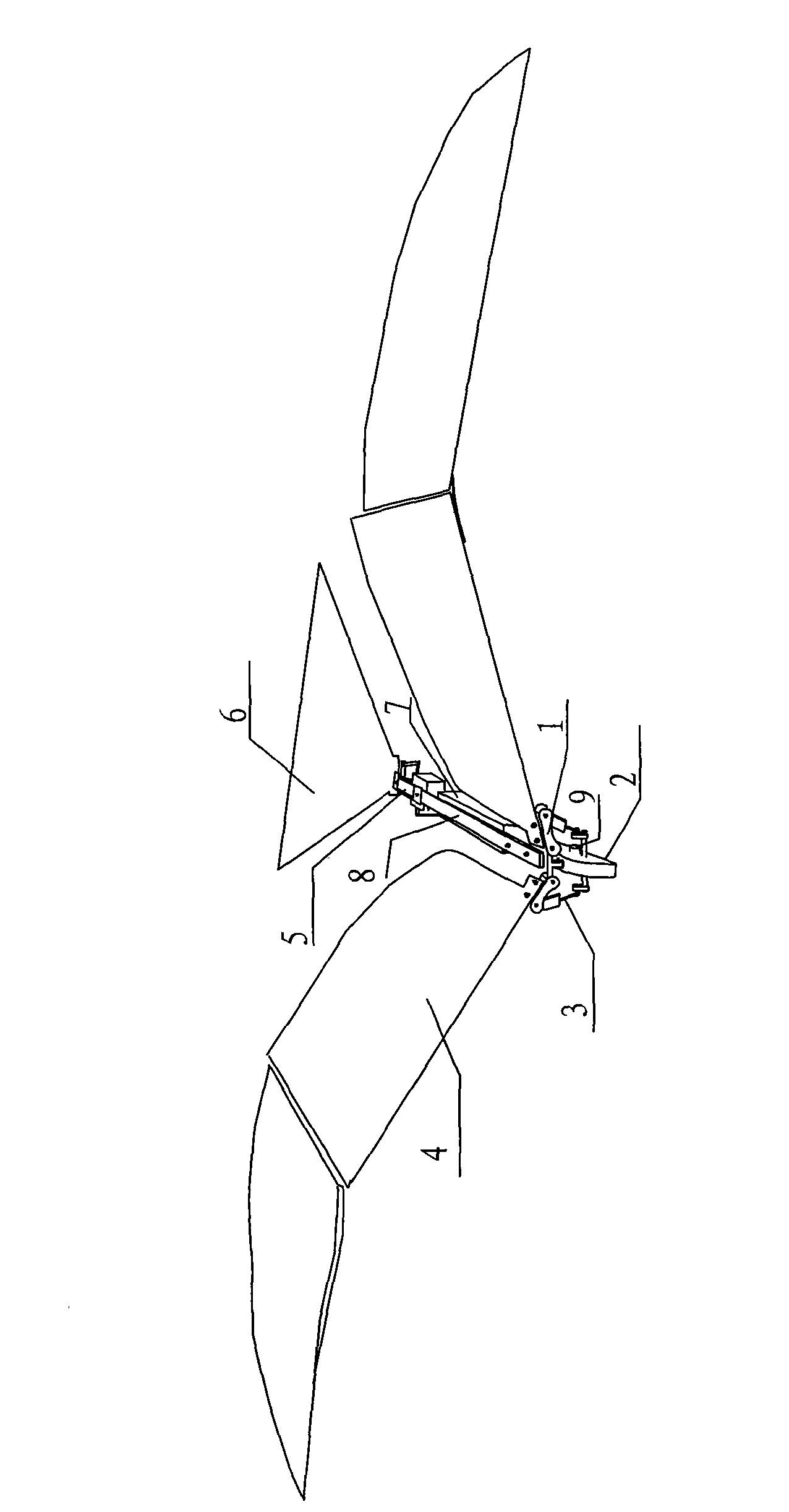
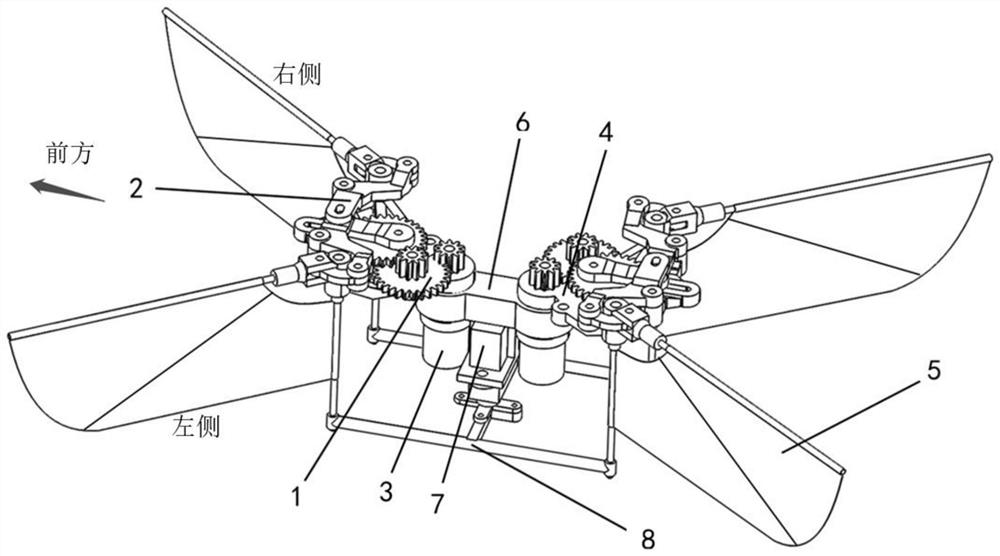
Bidirectional synchronous automatic turning flapping-wing aircraft
A bidirectional synchronous automatic turning flapping-wing aircraft belongs to the field of astronautic bionic aircraft device, comprising an airframe (8), a wing flapping mechanism (1), a bidirectional synchronous output deceleration mechanism (2), a connecting rod (3), an airfoil (4), an empennage control mechanism (5) and an empennage (6); the bidirectional synchronous automatic turning flapping-wing aircraft is characterized in that the wing flapping mechanism (1) comprises a crossed frame (10) and two wing roots (11); the crossed frame (10) is installed on the front end of the airframe (8) through a bearing; two wing roots (11) are respectively installed on two sides of the crossed frame (10); the airfoil (4) is connected with the wing root (11) through a wing bone; the bidirectional synchronous output deceleration mechanism (2) is connected with the wing root (11) through the connecting rod (3); the empennage control mechanism (5) is installed on the rear end of the airframe (8); the empennage (6) is connected with the empennage control mechanism (5). The airfoil is in spot connection with the airframe and performs the bidirectional synchronous automatic turning with high flying efficiency.
Owner:杨绍河
Micro unmanned aerial vehicle carbon fiber rotor wing and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a micro unmanned aerial vehicle carbon fiber rotor wing and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of composite material structures. The rotor wing sequentially comprises a wing tip, a wing body and a wing root from two ends to middle; the wing tip sequentially comprises an upper surface layer and a lower surface layer from top to bottom; the wing body sequentially comprises an upper surface layer, a reinforcing rib, a middle layer and a lower surface layer from top to bottom; the wing root sequentially comprises an upper surface layer, a reinforcing rib, a reinforcing layer, a middle layer and a lower surface layer from top to bottom; and each reinforcing rib extends from the wing root to the critical part of the wing body and the wing tip and is narrowed gradually. Compared with a domestic plastic rotor wing with the same specification, the weight of the rotor wing provided by the invention is reduced by 65%; under unit mass, the output power of the rotor wing provided by the invention is 3.4 times that of the plastic rotor wing; under unit power consumption, the output power of the rotor wing provided by the invention is 1.3 times that of the plastic rotor wing; and under the condition of generating the same lifting power, the power consumption of the rotor wing provided by the invention is reduced by 40%, and the rotation speed is reduced by 30%. The rotor wing provided by the invention can improve the lift efficiency of an unmanned aerial vehicle under the conditions of low rotation speed and low power consumption.
Owner:BEIJING SATELLITE MFG FACTORY
Vertical take-off and landing aircraft with layouts of tilting ducts and connecting wings
InactiveCN108082466AImprove handlingImprove securityVertical landing/take-off aircraftsRotocraftFlight vehicleHeight difference
The invention discloses a vertical take-off and landing aircraft with layouts of tilting ducts and connecting wings. The vertical take-off and landing aircraft comprises a fuselage, tilting duct fans,the connecting wings, undercarriages and an empennage trim fan. The connecting wings are divided into the front wings and the rear wings; the tilting duct fans are arranged in a bilateral symmetry mode and connected with the middle of the fuselage through tilting structures, and an engine arranged inside the fuselage drives the tilting duct fans through transmission mechanisms arranged in the tilting structures so that upward lift force or forward thrust can be provided for the aircraft; the front wing faces and the rear wing faces of the connecting wing structures have the height difference,wing roots of the rear rings are connected to a vertical empennage, wing tips of the rear wings are connected to the middle sections of the front wings, and full-aircraft lift force is provided at the flat flight stage; and the layout of the tilting duct fans and the layout of the connecting wings are combined, and the wing structures are complete. The vertical take-off and landing aircraft can take off and land vertically and hover in the air and can also take off and land in a sliding mode and cruise at a high speed like a fixed wing aircraft; the duct fan propelling mode is quiet and efficient, and the engine is mounted inside the fuselage; and the aircraft overall layout is compact and reasonable, a transmission device is precise and simple, safety and reliability are achieved, and thus high application value is achieved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Wing-fuselage section of an aircraft
A wing-fuselage section of an aircraft, which wing-fuselage section comprises a wing root at which the wing of the aircraft is connected to the fuselage, a fuselage region with fuselage frame elements that extent across the longitudinal direction of the aircraft, and a wing region with spars that extend in the direction of the wingspan. According to the invention, the spars of the wing region and the fuselage frame elements of the fuselage region form part of an integral assembly that extends at least over a middle part of the wing and the fuselage region, including the wing roots.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
Miniature double-flapping-wing air vehicle
ActiveCN112009683AReduce weightSave resourcesOrnithoptersAttitude controlFlapping wingFlight vehicle
The invention discloses a miniature double-flapping-wing air vehicle which comprises a middle connecting structure, an attitude control steering engine, a wing root position control mechanism, a frontflapping wing system and a rear flapping wing system, wherein the front flapping wing system and the rear flapping wing system are identical. According to the miniature double-flapping-wing aircraft,the lift force generation is further enhanced by virtue of a double-wing opening-closing mechanism; the flapping frequencies of the front and rear pairs of wings are influenced by changing the rotating speed of the motor so that the two pairs of wings generate front and rear asymmetric lift force to generate pitching control moment; a wing root position control mechanism is controlled by an attitude control steering engine to change the positions of two groups of wing root rods, and the tensioning degree of a flapping wing membrane is changed so that a left wing and a right wing generate different lifting forces to generate rolling control torque. The two sets of wing roots are controlled through one steering engine, the control mechanism is simplified, the control difficulty is reduced,weight reduction is achieved, resources are saved, and besides, pneumatic lift augmentation is achieved through an opening-closing high lift mechanism.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Electric powered flying wing toy
InactiveUS7377832B2Less thrustImprove efficiencyActuated automaticallyToy aircraftsPropellerTrailing edge
A radio-controlled electrically-powered model flying wing aircraft having a pusher propeller at the rear wing root powered by an electric motor mounted in a streamlined electric motor housing that extends into the wing and blends smoothly into the wing surface at the center wing chord. The motor housing, motor and propeller extend beyond the wing trailing edges to ensure efficient propeller operation and to reduce propeller-induced noise. A battery is secured in a resilient pouch and protected completely inside the wing root, serviceable from the bottom wing surface by removing a quick release flap. Major structural elements are composed of impact resistant, flexible, and resilient materials.
Owner:CHAMBERLAIN MARK SPENCER
Air vehicle aerodynamic configuration with trailing edge supporting wing
ActiveCN105905277AImprove effectivenessHigh structural efficiencyAircraft stabilisationHeat reducing structuresVertical planeFlight vehicle
The invention discloses an air vehicle aerodynamic configuration with two trailing edge supporting wings. The supporting wings are installed below trailing edges of main wings at the two sides of a fuselage of an air vehicle. Wingtips of the supporting wings are connected to the middle parts of the trailing edges of the wings through connection sections. Wing roots of the supporting wings are connected to the fuselage through connection sections. The relative positions of the supporting wings and the main wings are reasonably designed. In a main wing cross section and a supporting wing cross section which are truncated by air flowing to a vertical plane in wingspans of the support wings upwardly during the flying process, the vertical distance between the centroids is a% of the chord length of the cross section of the main wing, wherein a is a constant value from 10 to 40; and meanwhile, the overlapping length of projections of the chord lines of the main wing cross section and the supporting wing cross section on a horizontal plane is b% of the chord length of the cross section of the main wing, wherein b is a constant value from 0 to 15. The aerodynamic configuration increases the total lift-drag ratio and achieves better aerodynamic performances, and also improves the rigidity of large-span-chord ratio wings and improves the total structural efficiency of the air vehicle.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
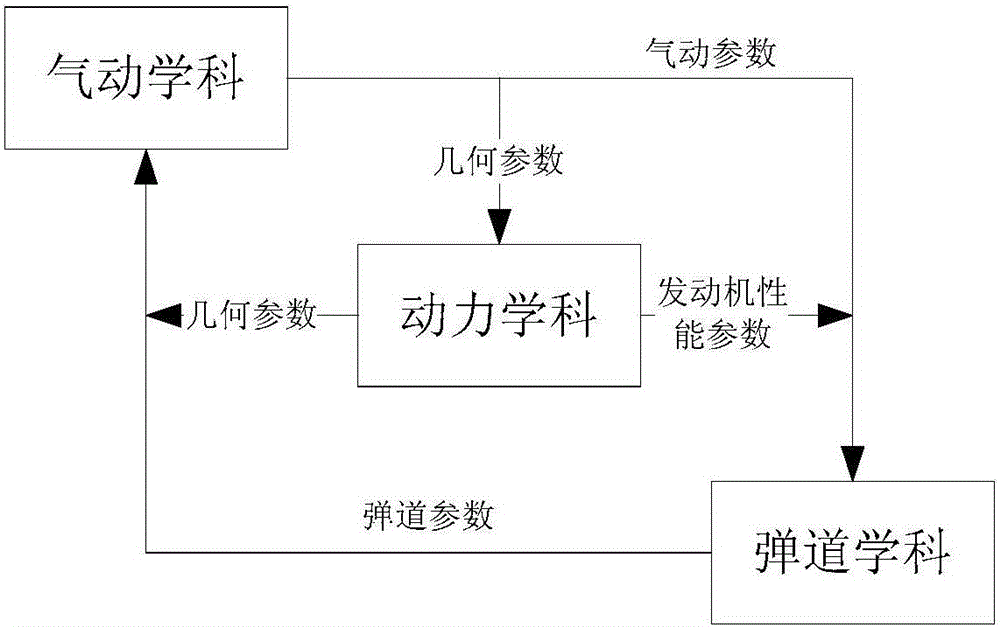
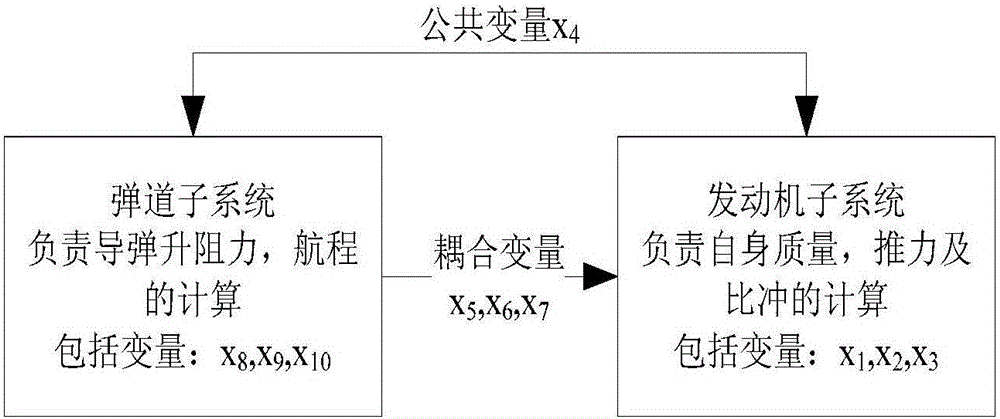
Genetic particle swarm multi-disciplinary design optimization algorithm-based guided missile parameter design method
ActiveCN105975651AAvoid local optimaImprove Design PerformanceGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsParticle swarm algorithmWing root
The invention discloses a genetic particle swarm multi-disciplinary design optimization algorithm-based guided missile parameter design method, relates to a guided missile parameter design method, and aims at solving the problem that the conventional intelligent optimization algorithm-based guided missile parameter design method is not suitable for the conditions of more multi-disciplinary design parameters and variable coupling phenomenon. The method comprises the following steps: selecting an engine throat diameter, an engine combustion surface area, an engine charge thickness, a guided missile outer diameter, an engine specific impulse, engine mass, fuel mass, a missile wing root chord length, an empennage root tip length and an empennage tip chord length as design parameters; and optimizing three control parameters w, c1 and c2 and design parameters in a standard particle swarm algorithm by utilizing a genetic algorithm, and introducing a genetic thought into a particle swarm position updating process when optimizing the particle swarm algorithm in the optimization process. The method disclosed in the invention is suitable for the field of guided missile parameter design.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Wing structure
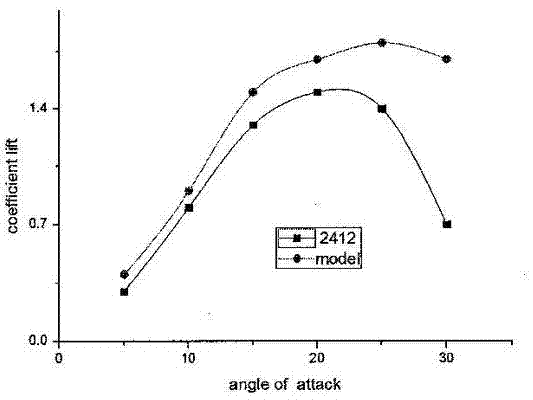
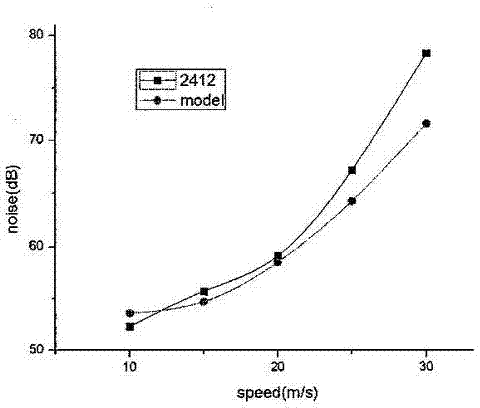
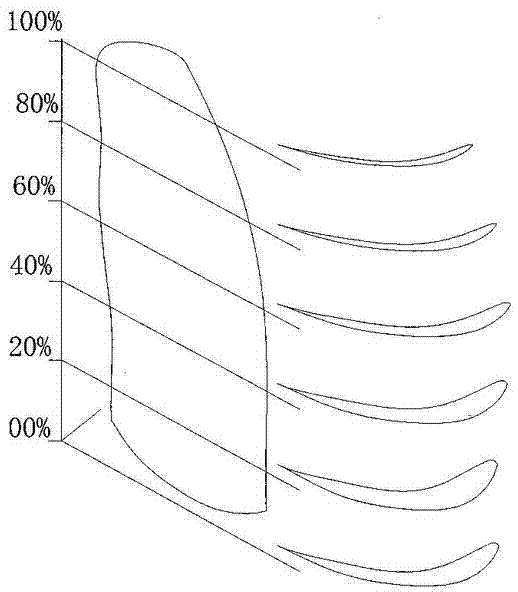
InactiveCN103693187AHigh lift coefficient at low speedLarge stall angleWing shapesLeading edgeClassical mechanics
The invention discloses a wing structure. The wing structure consists of continuous wing profiles, wherein the spans of the wing profiles away from the root of a wing are 0 percent, 20 percent, 40 percent, 60 percent, 80 percent and 100 percent respectively; the ratio of wingspan to chord length is 5.50-7.24; the leading edge of the wing is a high-order curved line of an approximately parabolic shape; the maximum relative curvature of each wing profile is 7.5 percent and is positioned at a position at 17-33 percent of the chord length; the maximum relative thickness of each wing profile is 13.1 percent and is positioned at a position at 11-24 percent of the chord length; the curvature and the thickness of each wing profile tend to be increased and then decreased along the corresponding span. Compared with a parametrically-similar NACA (national advisory committee for aeronautics) 4-digit wing profile, the wing structure has the advantages that a low-speed lift coefficient is large, a resistance coefficient is small, and a large angle of stall is formed; under the condition of same flight parameters, according to the wing structure, the flight noise is low, and the lift coefficient is relatively large when an angle of attack is 25 degrees, and slowly declines when the angle of attack is greater than 25 degrees.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Flight control method and system of flapping wing air vehicle
InactiveCN107203220AReduce torqueReduce weightOrnithoptersPosition/course control in three dimensionsFlapping wingFlight vehicle
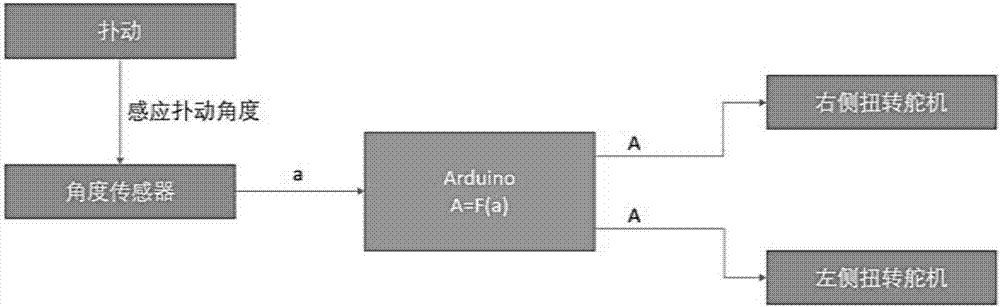
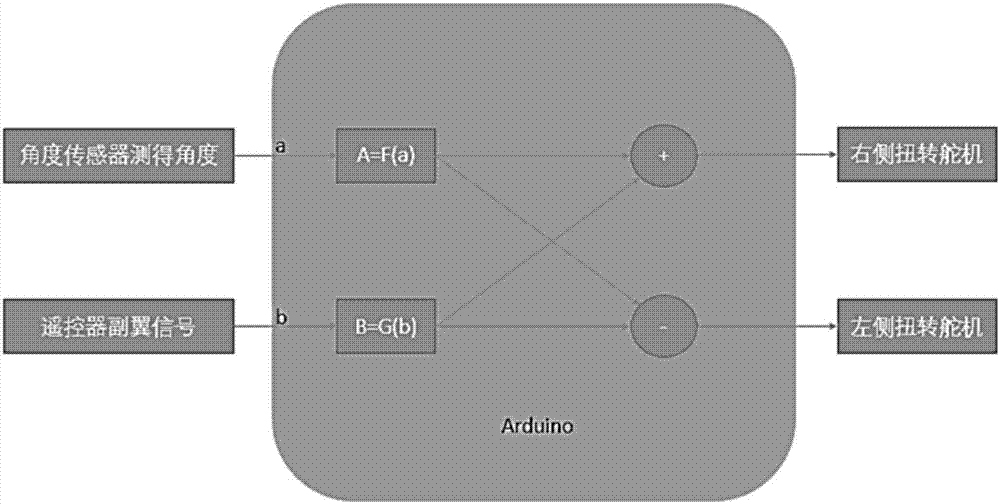
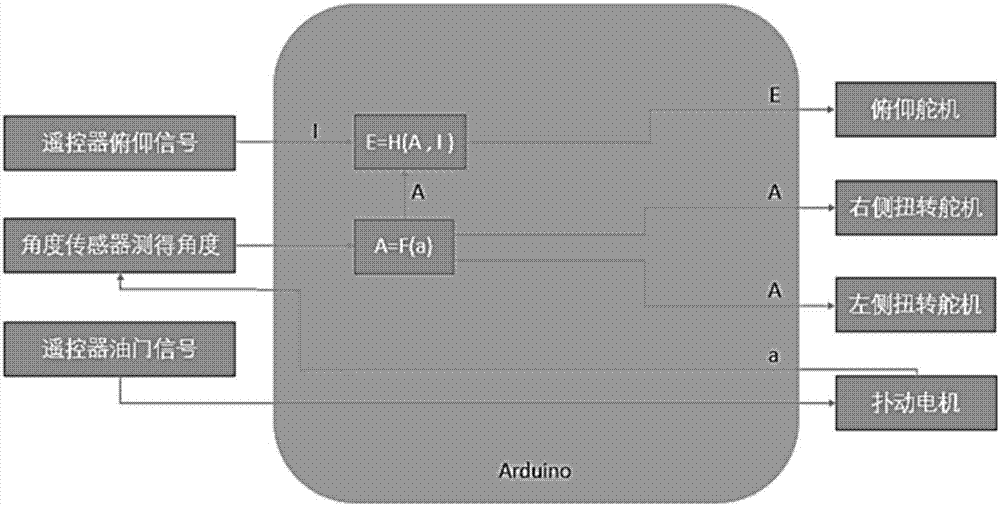
The invention discloses a flight control method of a flapping wing air vehicle. The wing tip torsion angle and the pithing adjusting angle under corresponding flapping angel of a bird are calculated by detecting the flapping angle of a flapping wing of a bionic air vehicle in real time, namely, the relative angle of a wing root connecting rod relative to the horizontal datum of a vehicle body, and a steering engine is set through a torsion angle of a wing tip for torsion of the wing top of the bionic air vehicle and adjustment of pitch attitude, so that the flight efficiency is improved. High stability and maneuverability can be realized; compared with flapping wing air vehicles without wing tip torsion, the flapping wing air vehicle has greatly improved lift force and flight efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Automatic control wind sail type swing wing vertical shaft wind motor
InactiveCN1699744AImprove efficiencyLow costWind motor controlFinal product manufactureLow speedAutomatic control
The invention relates to an automatic control sailing wind generator which comprises: wing foil (1), cross bar (3), wing crank (2), driving vertical axis (7), tower (6), generator (8), overriding clutch (9), centrifugal clutch (10), speed increasing gear (11). It is characterized in that the wing foil (1) comprises wing tip (14), wing panel (17), wing segment (16) and wing root (18). In the wing panel installed a feathering mechanism, in the wing root installed a feathering mechanism and swing mechanism; in the wing crank installed a control device and an over speed feathering sensor. The feathering mechanism can ensure the simultaneous feathering and unloading of each wing foil, in the case of over speed or typhoon, the swing mechanism can ensure to start at low speed and smooth speed automatically. The invention also adopts the sloping drawing wire (5) to draw the wing foil (1) and the cross bar (3), the sloping drawing wire (12) and (13) take each cross bar and the steel cable (4) draws the power (6) to the ground to make the system stable.
Owner:郑衍杲
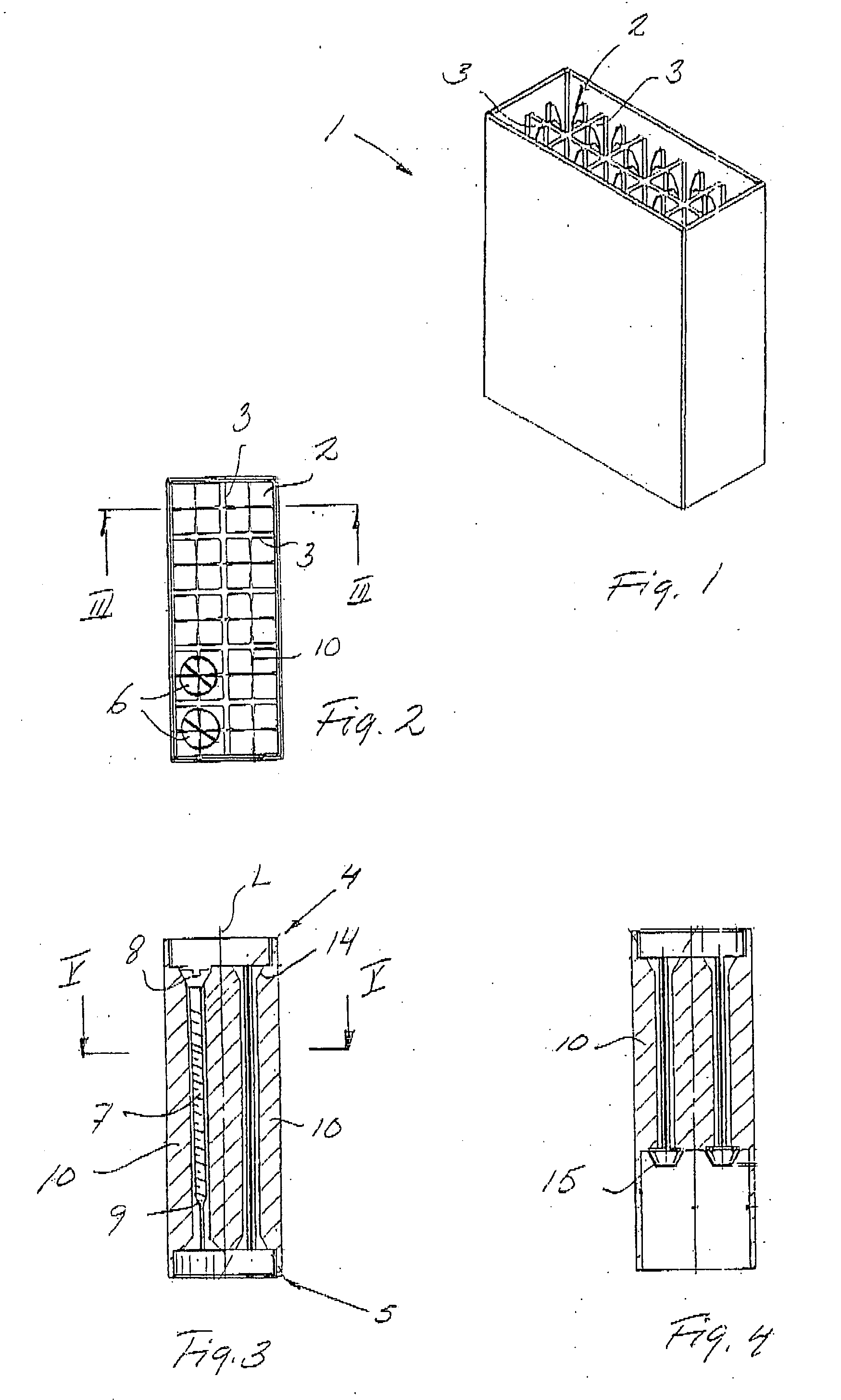
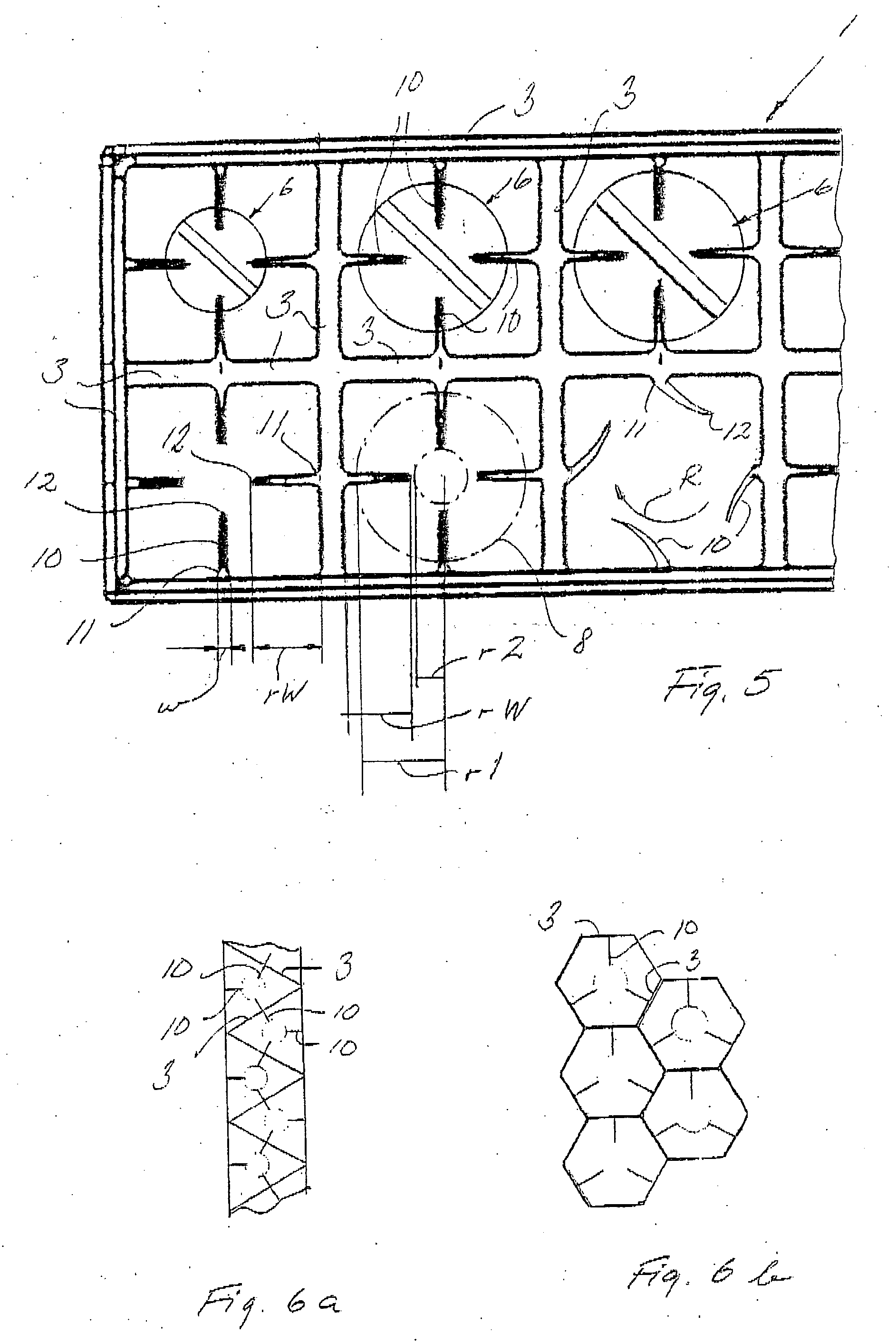
Magazine for housing screws
A magazine for screws includes seats defined by walls connecting longitudinally an insert end with an exit end of the seats, wherein in at least one seat a screw having a shank connecting a screw-head directed towards the insert end to a screw-tip directed towards the exit end, the screw-head having a first radius and the shank a second radius smaller, is housed, than the first radius, the at least one seat being formed internally with at least one wing-member running longitudinally from near the insert end towards the exit end, the at least one wing extending from a wing-root connected to the seat wall to a wing-tip projecting into the seat. In any arbitrary plane intersecting the wing and seat transversally to the longitudinal, the extension of the at least one wing from wing-root to wing-tip radially overlaps the radius of the screw-head, and the at least one wing is flexible from the wing-root towards the wing-tip.
Owner:SUNDSTROM FRED
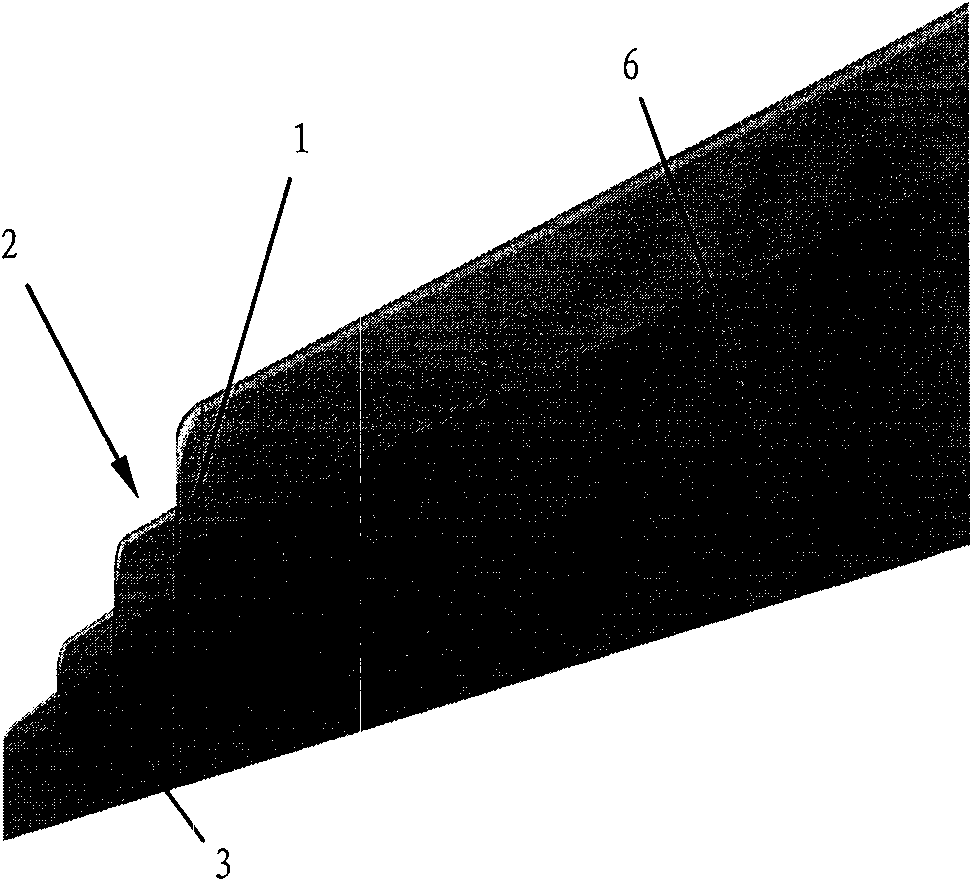
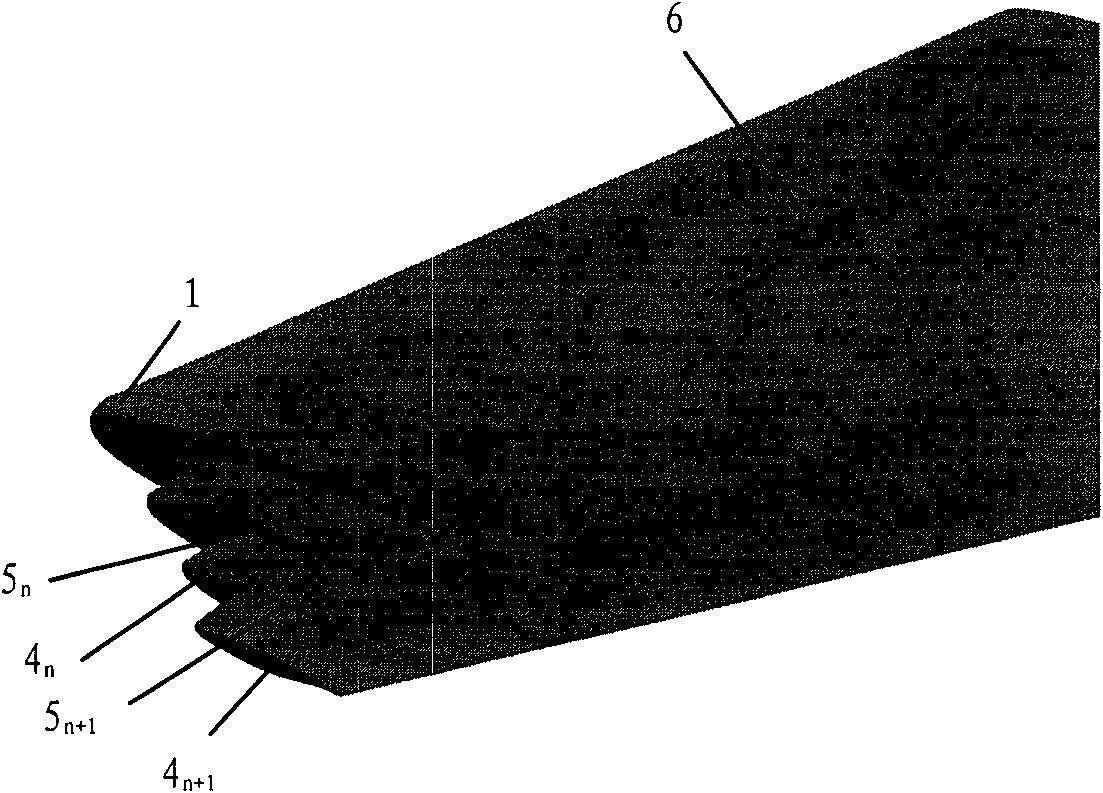
Airplane wingtip device with aligned front edge
ActiveCN102167152ASmall bending moment incrementReduce structural weightWing shapesDrag reductionWingtip deviceFront edge
The invention provides an airplane wingtip device with an aligned front edge, which comprises a transition part and a wingtip part, wherein the inside end of the transition part is connected with the far end of an airplane wing, the outside end of the transition part is connected with the wingtip part, the wingtip part comprises a plurality of wingtip segments, each wingtip segment comprises a wingtip and a wing root, the wing root of the first wingtip segment is connected with the outside end of the transition part and is aligned with the front edge at the outside end of the transition part, the wing root of the (n+1)th wingtip segment is arranged on the wingtip of the nth wingtip segment, and the wing root chord length of the (n+1)th wingtip segment is less than or equal to the wingtip chord length of the nth wingtip segment, wherein n is more than 0. The wingtip device is step-shaped, so that each wingtip is additionally provided with at least one of discontinuity surfaces, the wingtip vortexes induced by the wingtips are restrained with one another, and the vortex intensity is reduced, therefore the airplane wingtip device achieves a damping effect; and the bending moment incremental quantity of each wing root is less, so that the structural weight of the airplane is reduced, and the influence on the buffeting characteristic is less.
Owner:COMAC +1
Aircraft
ActiveUS8322650B2Reduce the total massHigh speedInfluencers by generating vorticesUnmanned aerial vehiclesLow speedCruise control
An aircraft, particularly a solar powered, high altitude, long endurance, unmanned aerial vehicle, is equipped with a combination of canted down, raked back wing tips and trailing “tip tails” carried on booms from the tip regions of the mainplane. Each tip tail is positioned to be subject to the upwash field of the respective wing tip vortex, at least in the cruise condition of the aircraft. The wing tip form can achieve a reduction in induced drag and help to relieve wing root bending moment while the tip tails can act through their connections to the mainplane to provide torsional relief to the latter, particularly under lower incidence / higher speed conditions. In the higher incidence / lower speed cruise condition, however, the presence of the tip tails in the upwash fields of the wing tip vortices means that they can generate lift with a component in the forward direction of flight and hence contribute to the thrust requirements of the aircraft.
Owner:AALTO HAPS LTD
Scheme for improving flapping intensity of flapping-wing aircrafts
The invention relates to an aircraft in fluid media (air or water), particularly to a scheme for improving the flapping intensity of flapping-wing aircrafts. The breakthrough on miniature flapping-wing aircrafts is realized, and however, except miniature flapping-wing aircrafts, high-efficient manned flight cannot be realized so far due to the rigorous requirements for materials. In order to improve the flapping intensity of flapping-wing aircrafts, the invention provides the scheme for improving the flapping intensity of flapping-wing aircrafts. The flapping-wing aircraft comprises an aircraft body, flapping wings, and a flapping mechanism, wherein each flapping wing consists of a wing bar and a wing membrane, and each wing membrane is attached to the corresponding wing bar; the flapping mechanism consists of double-crank hinge mechanisms, usually, the flapping wings of a flapping-wing aircraft or an insect are connected with bodies through one position (usually called wing root), and due to the low intensity of materials, artificial flapping-wing aircrafts cannot realize manned flight. The scheme provided by the invention has the benefits that at least two positions of each flapping wing are connected with the aircraft bodies through the double-crank mechanisms, so that the requirements for the intensity of the materials of the flapping wings are substantially reduced; motors mounted on the aircraft bodies enable the flapping wings to vibrate through the double-crank mechanisms, so that the high-efficient flight of the flapping-wing aircraft is realized.
Owner:李维农
Flying car
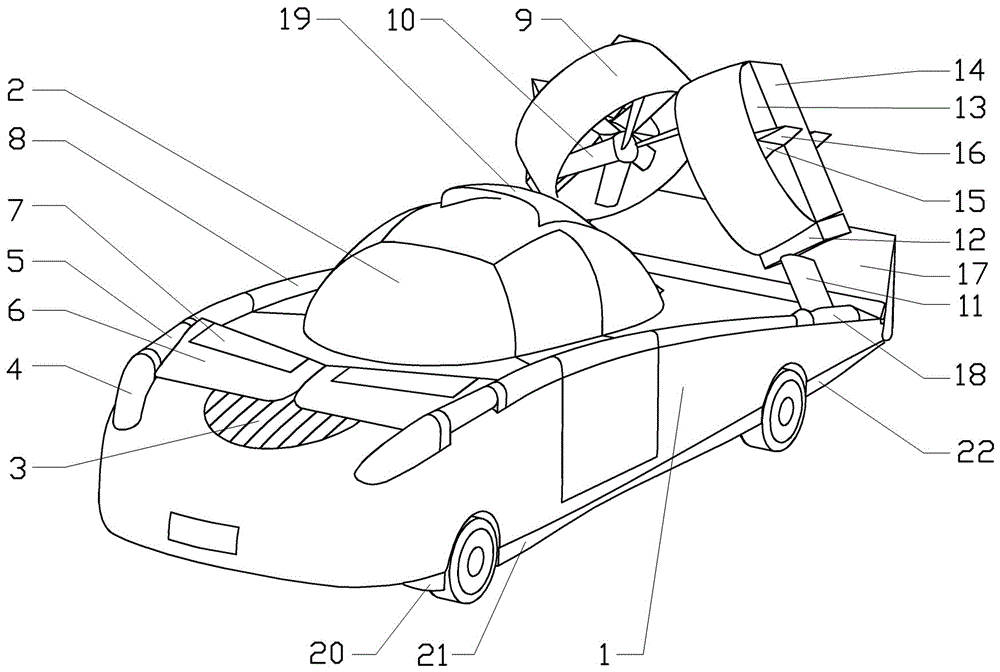
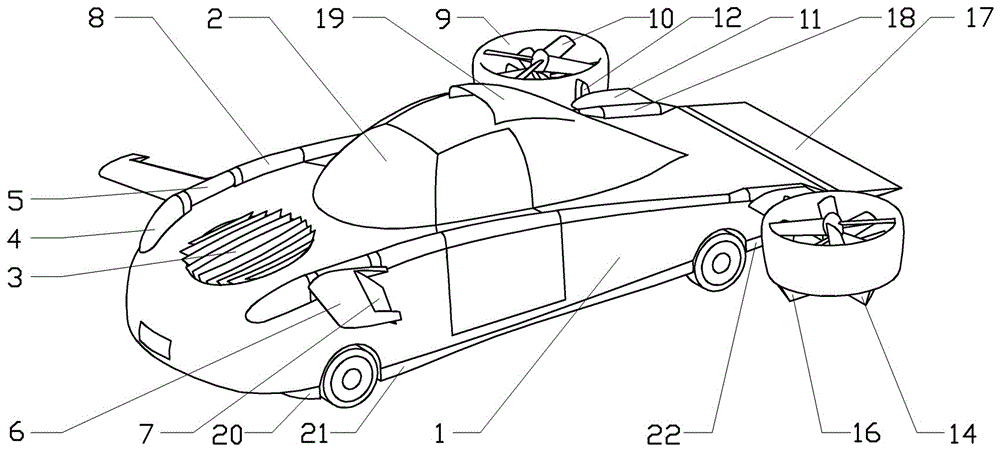
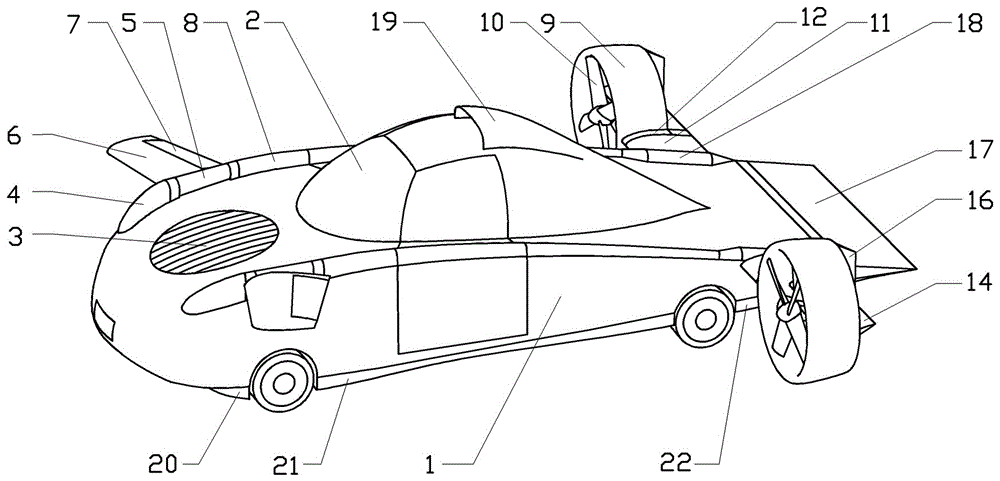
InactiveCN106427434AReduce widthHigh-speed long-distance flightConvertible vehiclesWindow shutterWing root
A flying car comprises a car body in the shape of a lifting body and a water-drop-shaped driving cabin positioned in the middle of the car body. A lifting fan is arranged on the front portion of the car body, an air inlet of the lifting fan is provided with shutters in vertical arrangement, an air outlet is provided with shutters in transverse arrangement, plump car lamps are arranged on two sides of the head of the car body, the rear portion of each car lamp naturally extends to be provided with a duck wing rotating shaft, a wing root of a duck wing composed of a duck wing stabilizing plane and a control plane is connected onto each duck wing rotating shaft, and a propelling pneumatic integrated system is arranged on each of two sides of the rear portion of the car body and can be folded and unfolded through a foldable wing section. Through forward-backward inclination rotating of the propelling pneumatic integrated system and combining with the lifting fan, the duck wings and the car body in the shape of the lifting body, the flying car can vertically take off and land, can fly at high speed and is wide in flying range and low in energy consumption.
Owner:龙川
Flying car
The invention discloses a flying car. The flying car comprises a car body, a wing, an empennage and a propeller, wherein the car body comprises a car body structure, front car doors, rear car doors and a trunk lid; the front car doors, the rear car doors and the trunk lid are hinged to the car body structure respectively; the wing comprises an upper wing and a lower wing and variant mechanisms thereof; the upper wing and the lower wing are hinged to the car body structure respectively; the empennage comprises a horizontal tail, vertical tails and telescopic empennage shafts; one end of each telescopic empennage shaft is fixedly connected with the car body structure, and the other ends of the telescopic empennage shafts are fixedly connected with the wing tips of the horizontal tail and the wing roots of the vertical tails respectively; the propeller comprises propeller blades, a propeller hub and a telescopic propeller shaft; one end of the telescopic propeller shaft is fixedly connected with the car body structure, and the other end of the telescopic propeller shaft is fixedly connected with the propeller hub; the three propeller blades are hinged to the propeller hub respectively. The wing of the flying car adopts a double-wing layout, and under the premise that the total lifting force is ensured, the wingspan length is greatly reduced, so that the wing can be conveniently folded into the car body.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Wing-deformation-based control mechanism of hummingbird-imitation flapping-wing unmanned aerial vehicle
PendingCN110641696ARealize full attitude controlLarge control angleAircraft controlOrnithoptersNylon materialAttitude control
The invention discloses a wing-deformation-based control mechanism of a hummingbird-imitation flapping-wing unmanned aerial vehicle. The control mechanism comprises linear steering engines, a rotary steering engine, a linear steering engine base, a rotary steering engine base, wing joints, steering engine pull rods, semi-cylindrical fasteners, rotary steering engine rocker arms, wing root carbon rods, a wing joint main shaft carbon rod, a rotary steering engine control carbon rod and other parts, wherein the main body parts are obtained through a 3D printing processing mode by using resin or nylon materials, and the mass is very light; the two linear steering engines and the one rotary steering engine are utilized, so that the full-attitude control of the 3 degrees of freedom of pitch, roll and yaw is achieved; and on the basis of realizing full-attitude control, the large pitch, roll and yaw control angle is generated through the structural optimization design, so that the very important significance for controlling the attitude of a prototype in the hovering flight state is achieved, and a foundation for the subsequent design of a lightweight and compact flapping-wing prototype is provided.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Wing mechanism, emitter and method for shortening axial length thereof
PendingCN109625242AShorten the lengthImprove convenienceWing adjustmentsProjectilesSlide plateWing root
The invention discloses a wing mechanism, an emitter and a method for shortening the axial length of the wing mechanism, the wing mechanism comprise a supporting assembly, a right plate and a left plate, one sides of the right plate and left plate, away from the corresponding wing roots are both rotatably connected with the upper surface of the supporting assembly, a sliding plate is slidably arranged at the bottom of the supporting assembly, a chute is arranged on the sliding plate, and the chute comprises a positioning section, a steering section, an inclined pushing section and a limiting section; two chutes are symmetrical along the sliding direction of the supporting assembly; one sides of the lower surfaces of the right plate and left plate, close to the corresponding wing roots, arerespectively provided with a guide shaft, and the bottom ends of the guide shafts are respectively inserted into a chute; when the right wing and the left wing are unfolded, the bottom ends of the guide shafts are positioned in a positioning section and is tangent to a groove wall on the positioning section, close to the tail, and two groove walls parallel to the moving direction of the supporting assembly. According to the invention, the whole length of the wing mechanism is shortened, so that a shorter launching barrel can be adopted, and the convenience for a user to use the wing mechanismis improved.
Owner:成都云鼎智控科技有限公司
Monocular video high precision measuring method for wing wind tunnel test model elastic deformation
ActiveCN106323587AGuaranteed accuracyReduce hardware costsAerodynamic testingObservational errorMeasurement device
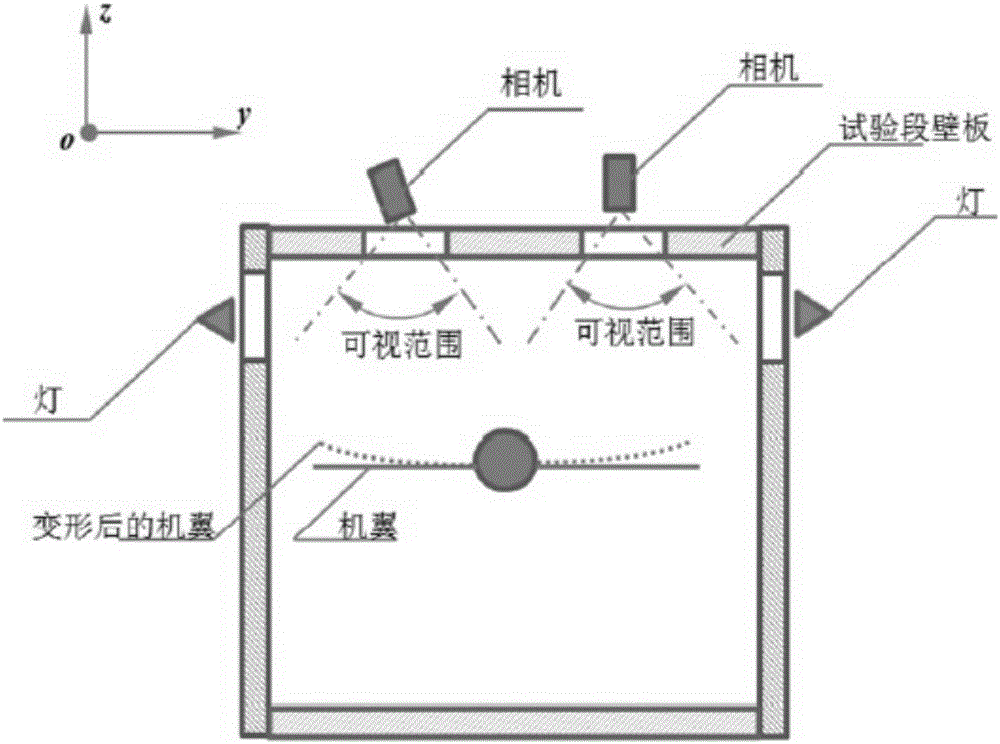
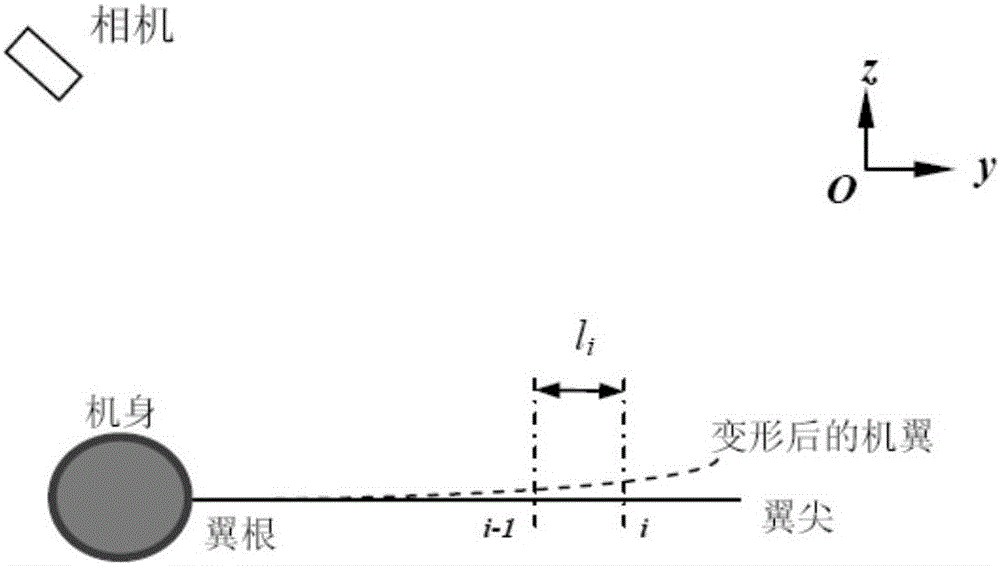
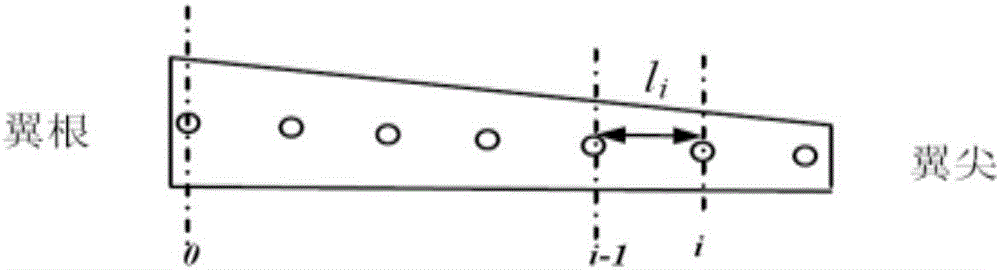
The invention discloses a monocular video high precision measuring method for wing wind tunnel test model elastic deformation. Based on a fact that relative deformation of two adjacent cross sections of a wing wind tunnel test model is small linear elasticity deformation, coordinate figures of corners and deformation mark points Y of all cross sections are orderly calculated from a wing root according to a superposition principle; a conventional monocular video measuring method is adopted, the coordinate figures of the deformation mark points Y are brought in a collinearity equation, and deformation data of the mark points on all the cross sections can be orderly obtained. Via the monocular video high precision measuring method, monocular video measurement errors of wing wind tunnel test model elastic deformation can be greatly reduced, only one camera needs to be used, multi-view video measurement precision can be obtained, hardware cost of a measurement device can be lowered, tedious homonymous point matching work of multi-view video measurement can be prevented, the monocular video high precision measuring method is particularly suitable for an environment where camera installation positions are limited, and the monocular video high precision measuring method has great engineering application prospects.
Owner:INST OF HIGH SPEED AERODYNAMICS OF CHINA AERODYNAMICS RES & DEV CENT
Folding wing unfolding rotating shaft mechanism
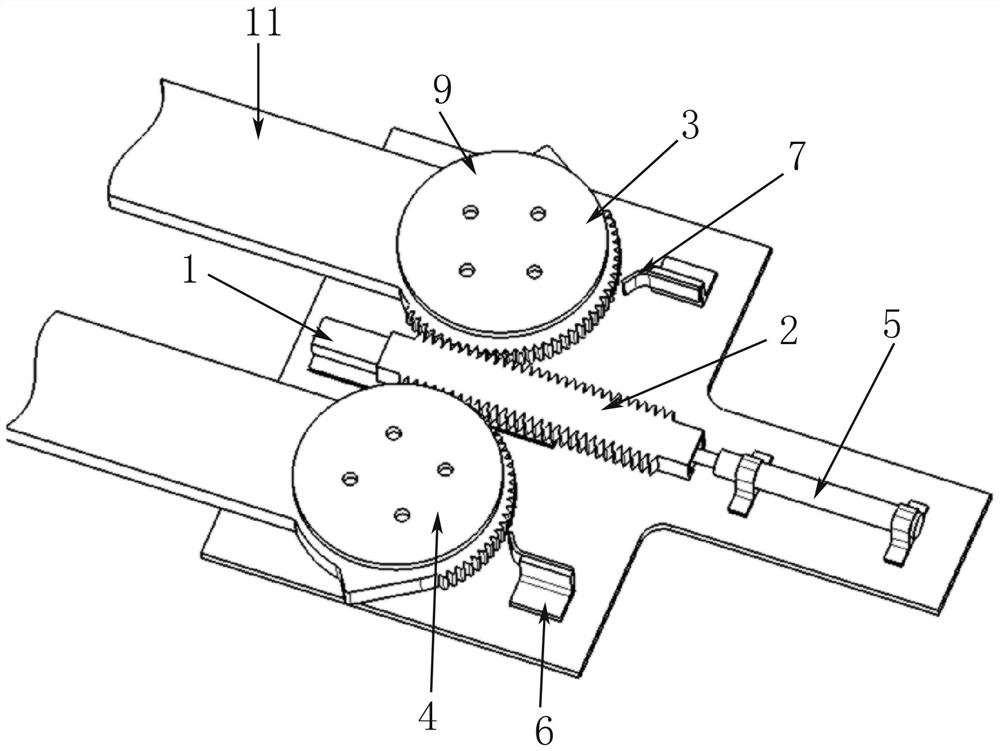
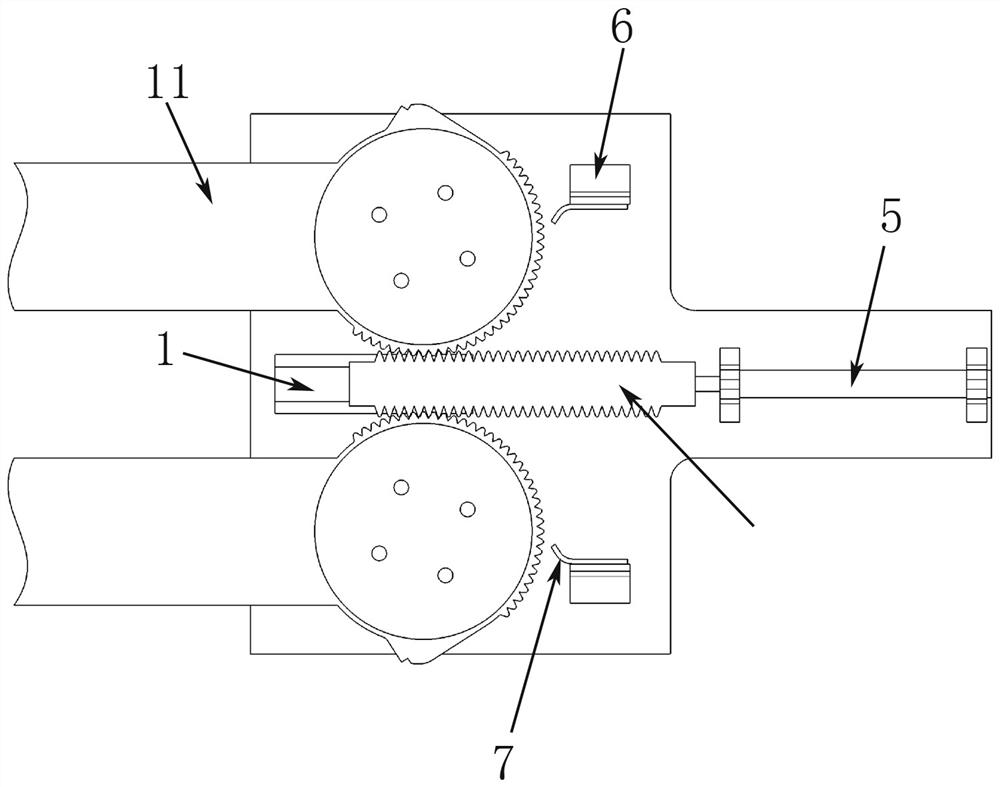
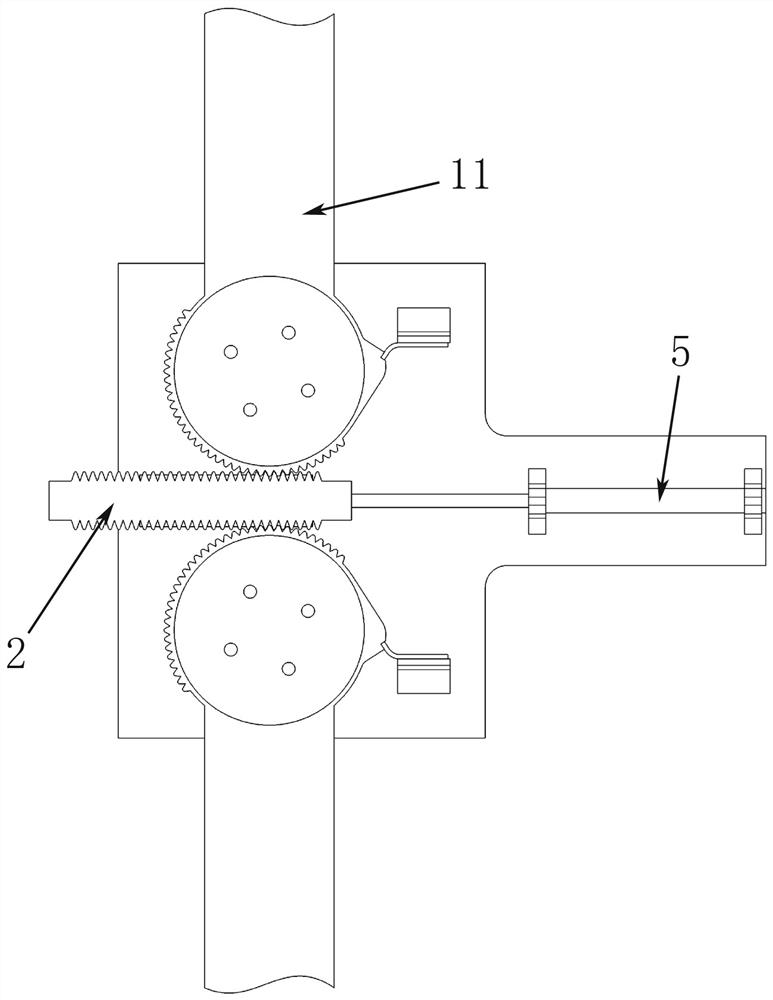
The invention belongs to the technical field of aviation, particularly relates to the technical field of unmanned aerial vehicle wing rotation, and particularly relates to a folding wing unfolding rotating shaft mechanism. The folding wing unfolding rotating shaft mechanism comprises wings and a connecting base fixed to an unmanned aerial vehicle, and two connecting bosses are fixedly arranged onthe connecting base. The two connecting bosses are rotationally connected with the wing root of one wing separately. A sliding rail is fixedly arranged in the connecting base between the connecting bosses. Driving force is provided through a gunpowder actuator cylinder, a rack is pushed to move, a first gear and a second gear are driven to rotate synchronously, and the left wing and the right wingrotate at the same time to be unfolded quickly. The left wing and the right wing adopt independent rotating shafts, and compared with a coaxial unfolding mechanism, the connecting mode is simple, andreliable wing root connection is easily ensured. Compared with multi-connecting-rod force transmission, the transmission of the folding wing unfolding rotating shaft mechanism is achieved in a gear and rack meshing mode, so that the structure is compact, and rotation is more stable.
Owner:XIAN LINGKONG ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com