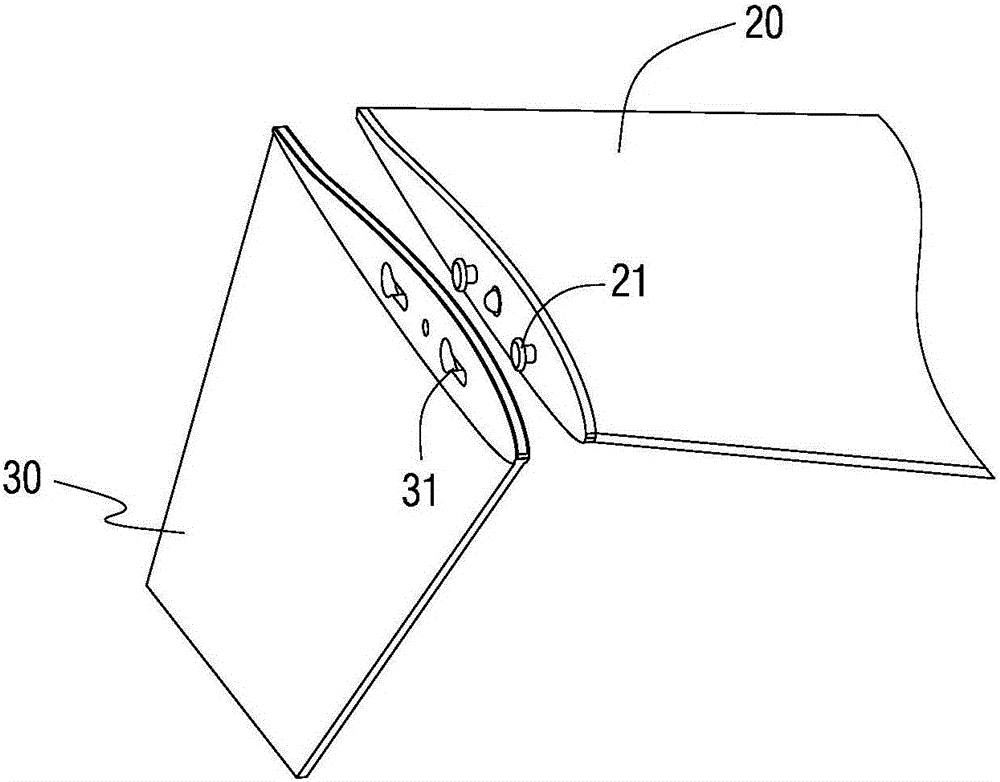
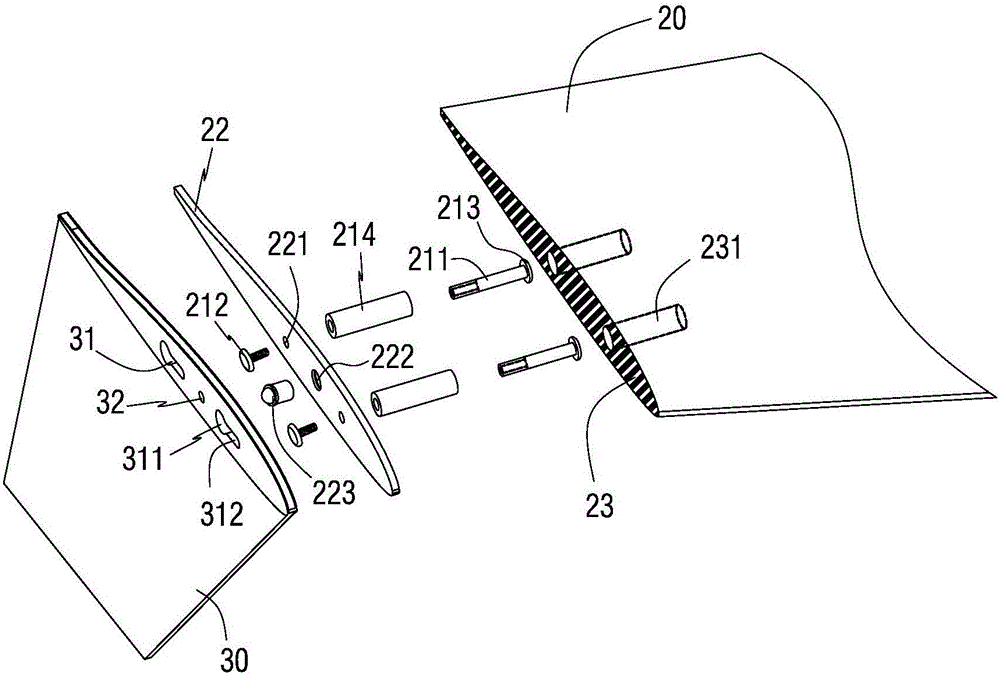
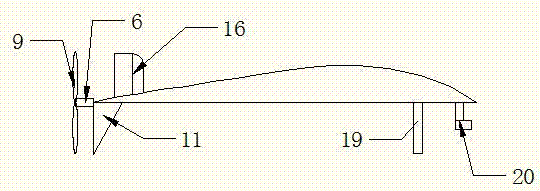Patents
Literature
87 results about "Wingtip device" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
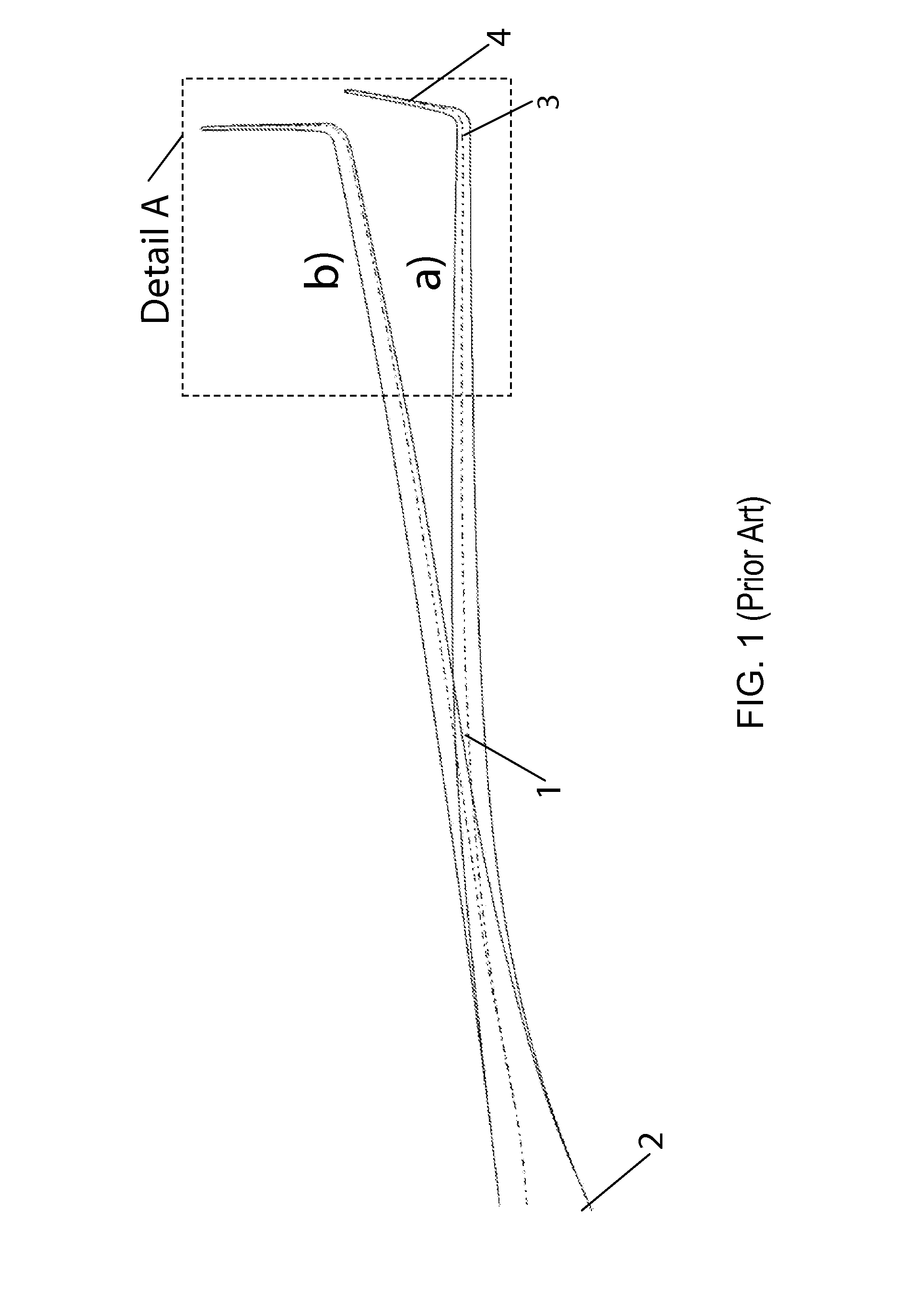
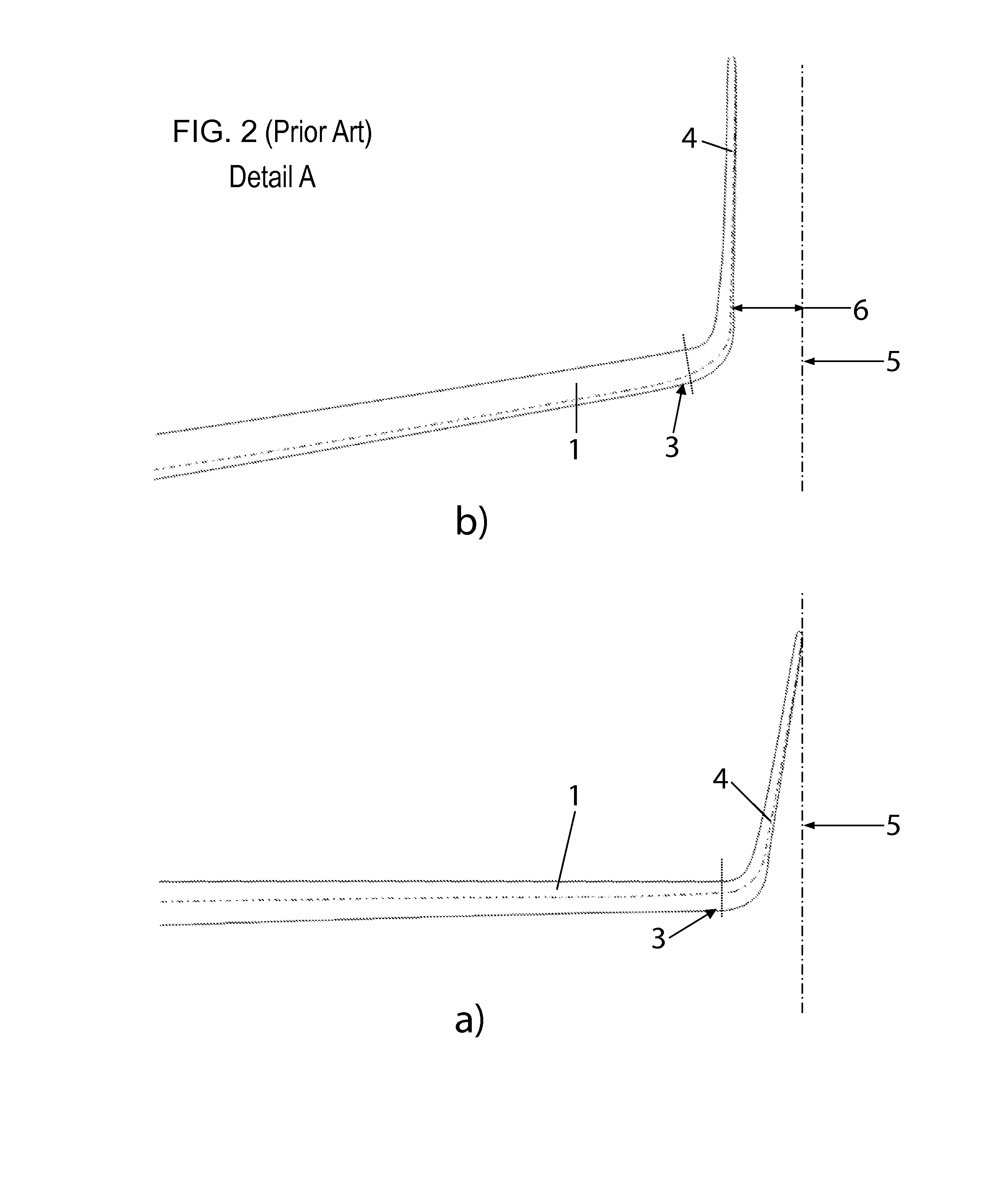
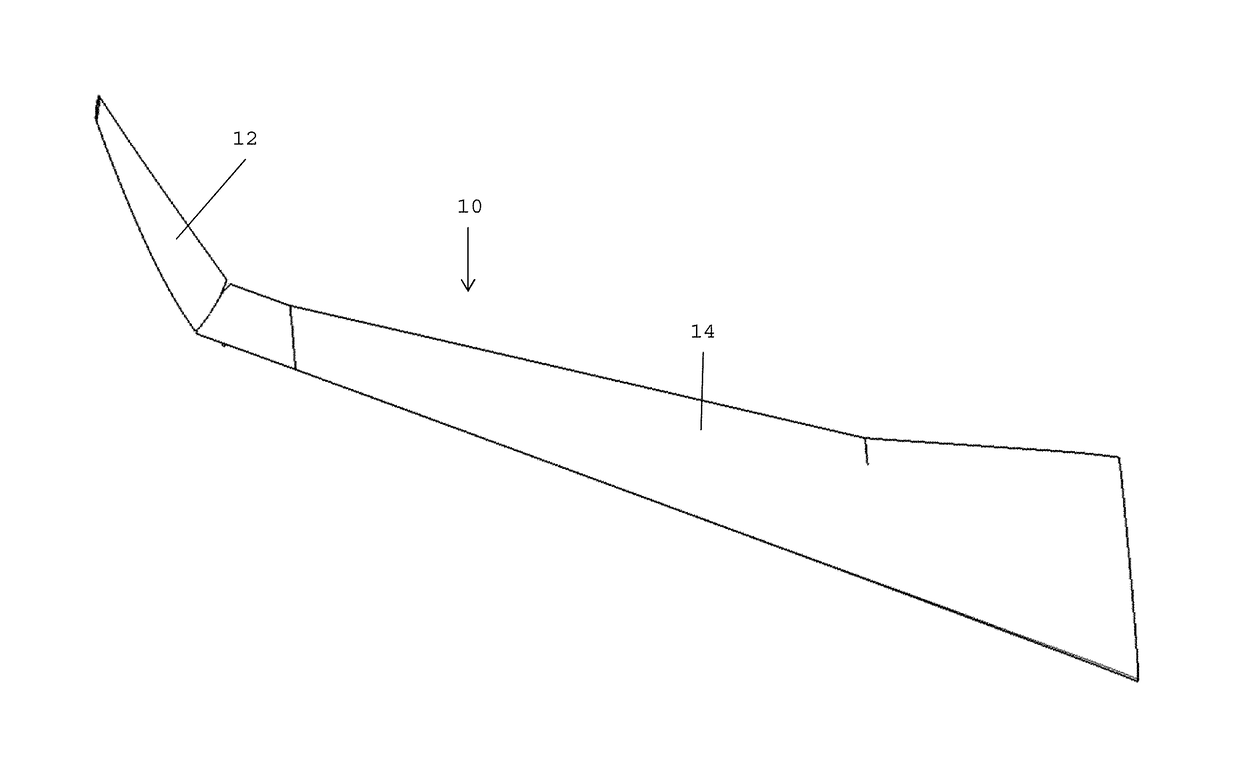
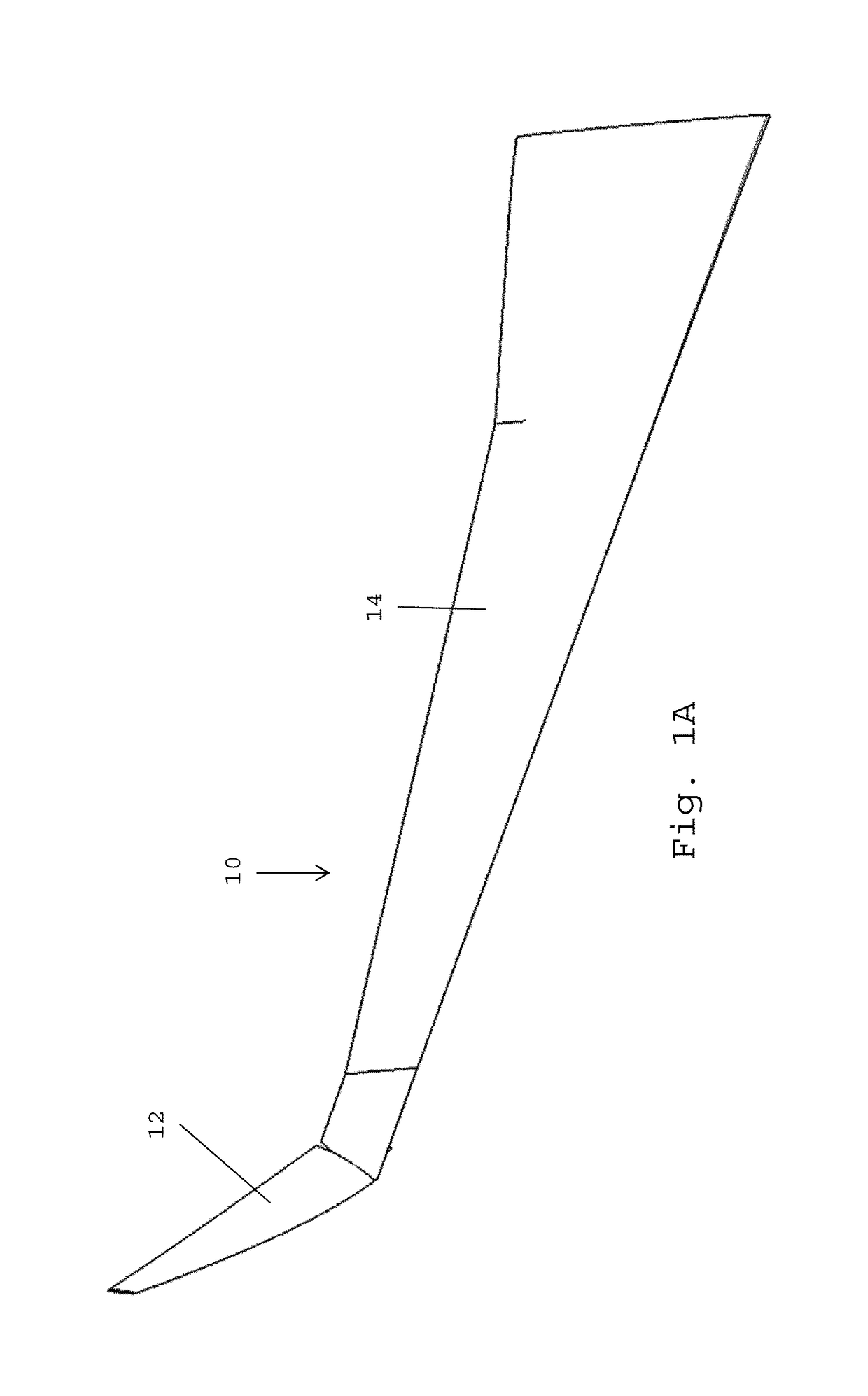
Wingtip devices are intended to improve the efficiency of fixed-wing aircraft by reducing drag. Although there are several types of wing tip devices which function in different manners, their intended effect is always to reduce an aircraft's drag by partial recovery of the tip vortex energy. Wingtip devices can also improve aircraft handling characteristics and enhance safety for following aircraft. Such devices increase the effective aspect ratio of a wing without greatly increasing the wingspan. Extending the span would lower lift-induced drag, but would increase parasitic drag and would require boosting the strength and weight of the wing. At some point, there is no net benefit from further increased span. There may also be operational considerations that limit the allowable wingspan (e.g., available width at airport gates).
Wing tip device
ActiveUS20050133672A1Reduce the impactUndesirable oscillationInfluencers by generating vorticesWingsFlight vehicleWingtip device
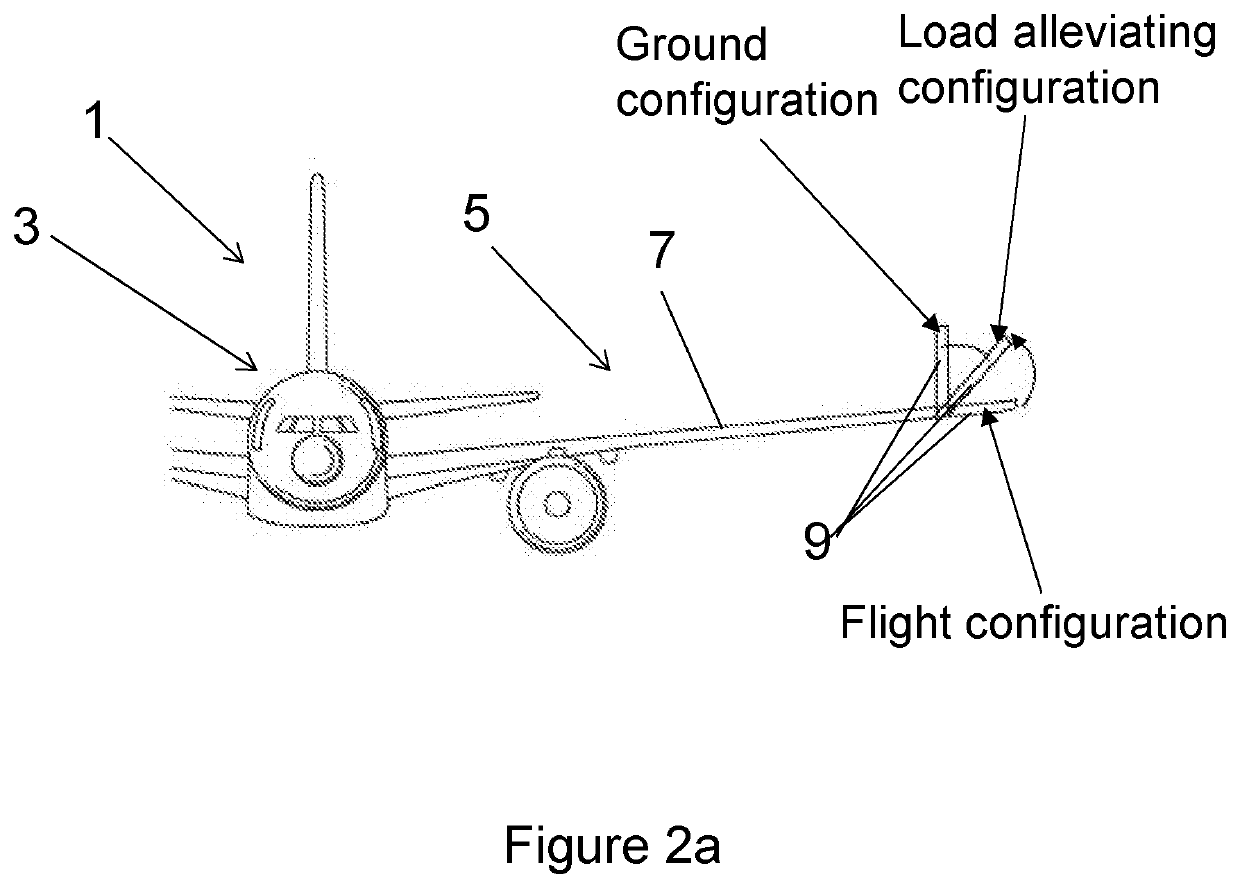
An aircraft comprises a wing tip device, for example a winglet, a raked-tip device, a wing tip fence or a planar wing extension, mounted in the region of the tip of a wing on the aircraft. The wing tip device is rotatably moveable between a first position and a second position, in which the upward lift produced by the wing or the wing tip device is reduced. During flight, the bending moment at the root of the aircraft wing therefore changes in dependence on the position of the wing tip device. The maximum bending moment in the aircraft wing sustained during high-load conditions is thereby reduced, allowing the structural mass of the aircraft to be reduced.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD
Wing tip device
ActiveUS20130092797A1Reduce interference drag effectWell mixedInfluencers by generating vorticesAircraft stabilisationTrailing edgeLower wing
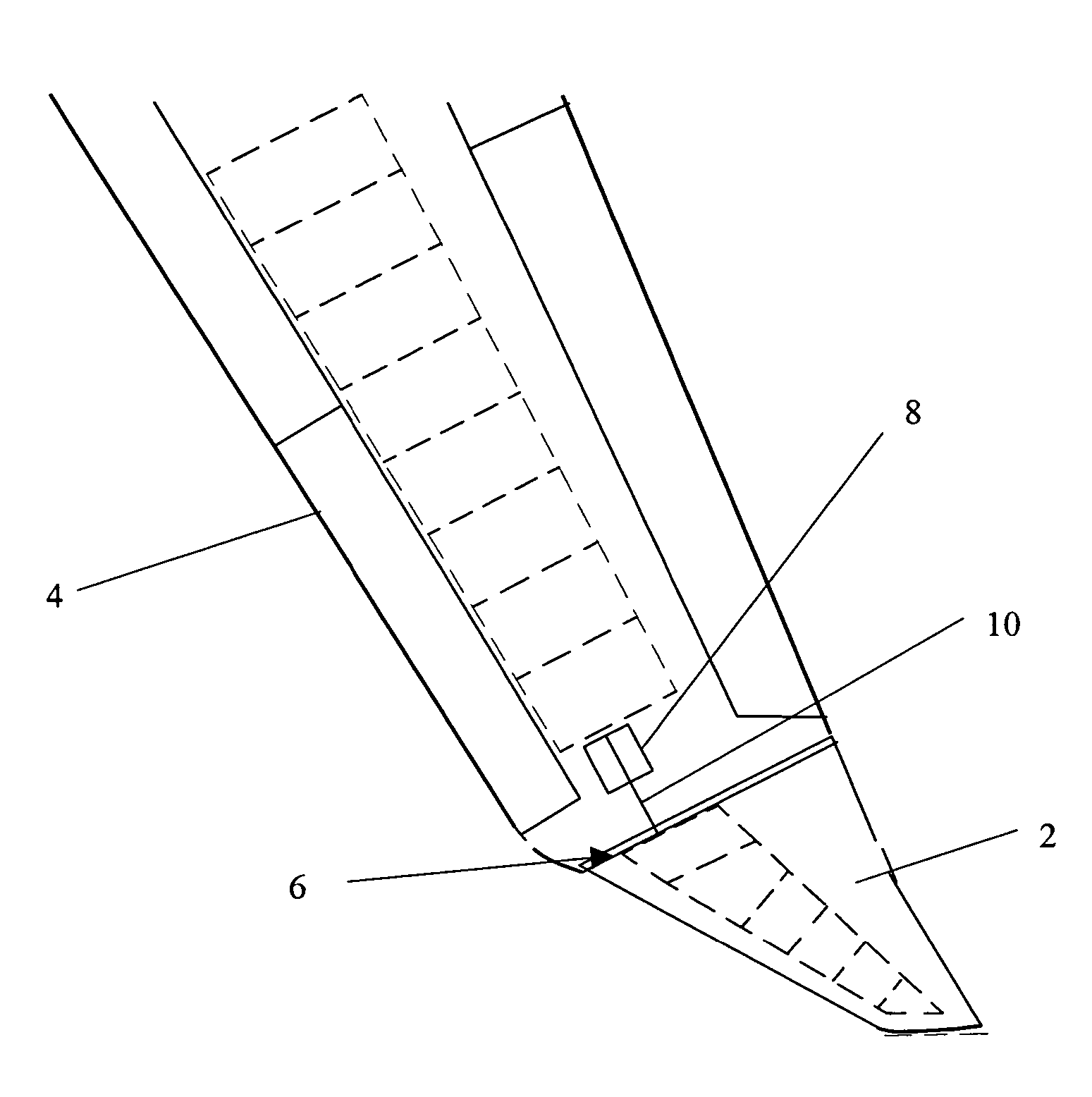
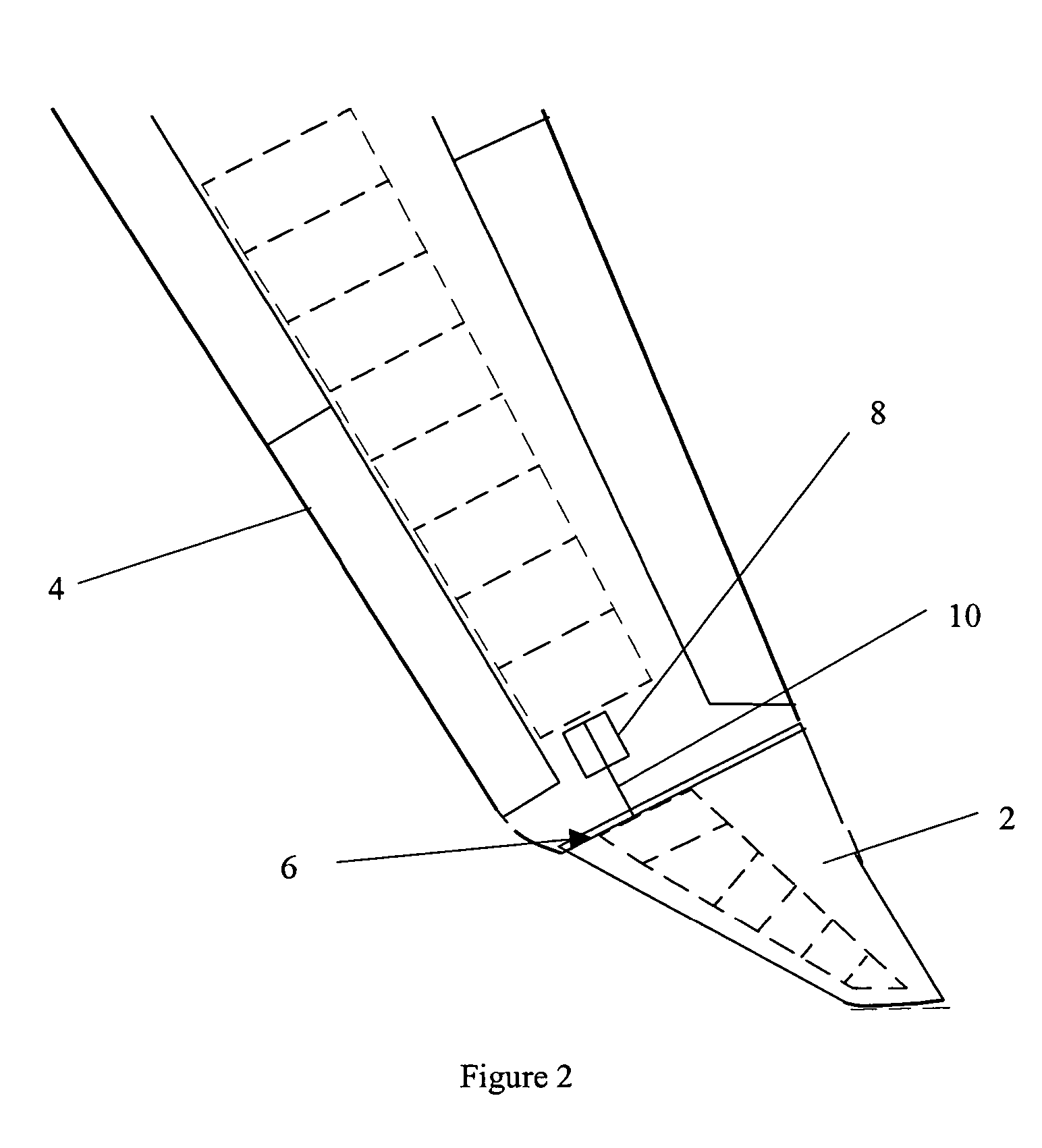
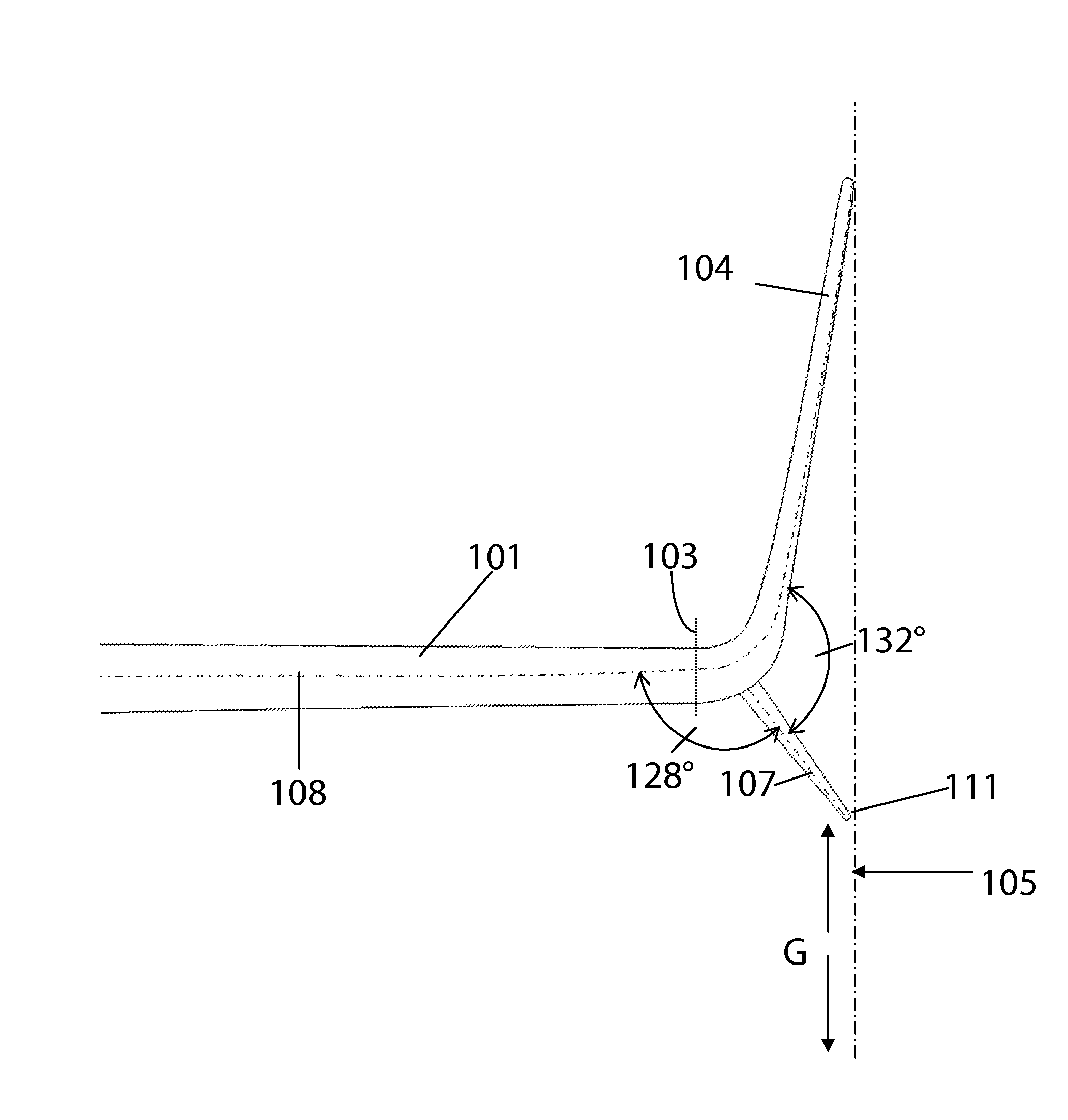
A wing tip device for fixing to the outboard end of a wing, the wing defining a wing plane, includes: an upper wing-like element projecting upwardly with respect to the wing plane and having a trailing edge; and a lower wing-like element fixed with respect to the upper wing-like element and having a root chord and a trailing edge, the lower wing-like element root chord intersecting with the upper wing-like element, and the lower wing-like element projecting downwardly from the intersection. The upper wing-like element is larger than the lower wing-like element and the trailing edge of the lower wing-like element is adjacent the trailing edge of the upper wing-like element at the intersection. An included angle between the upper and lower wing-like elements at the intersection is less than, or equal to, 160 degrees.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD +1
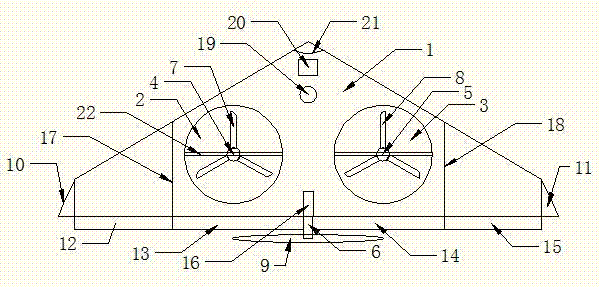
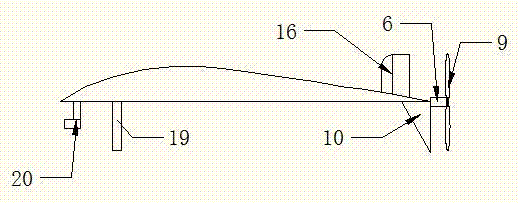
Flying wing type double-duct vertical taking-off and landing aircraft
InactiveCN107089316AImprove flight efficiencyImprove stealth performanceFuselagesVertical landing/take-off aircraftsFlight vehicleWingtip device
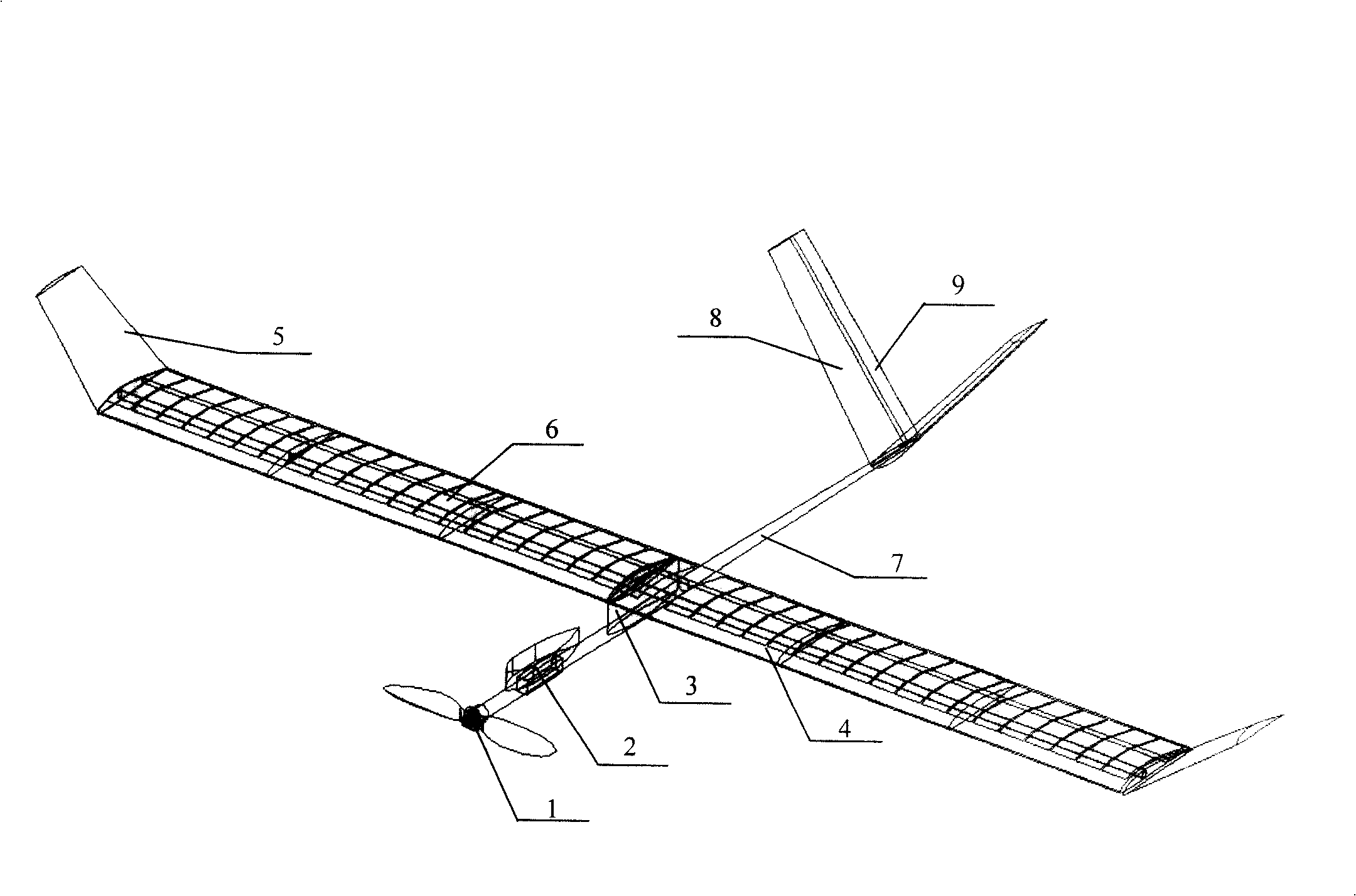
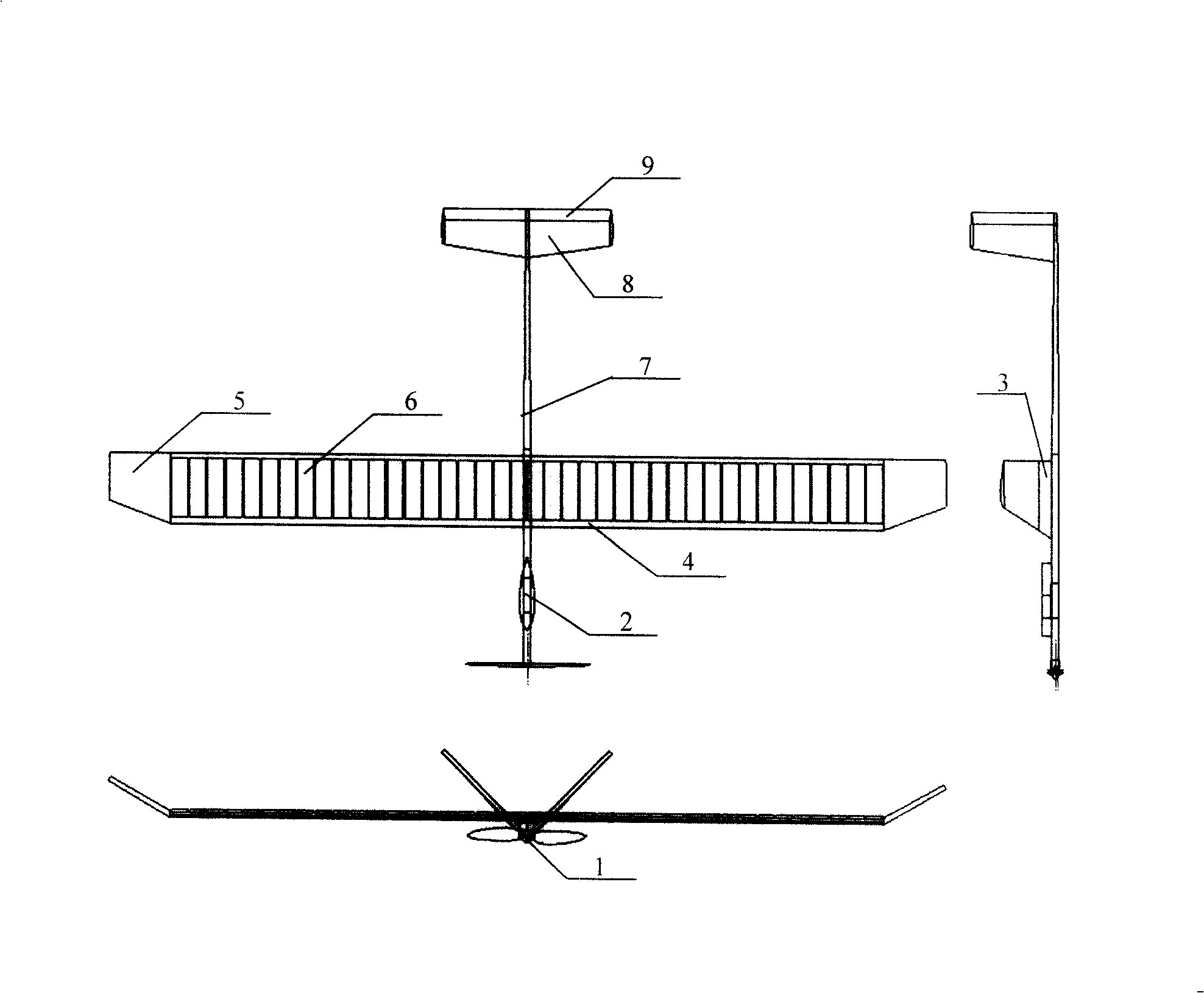
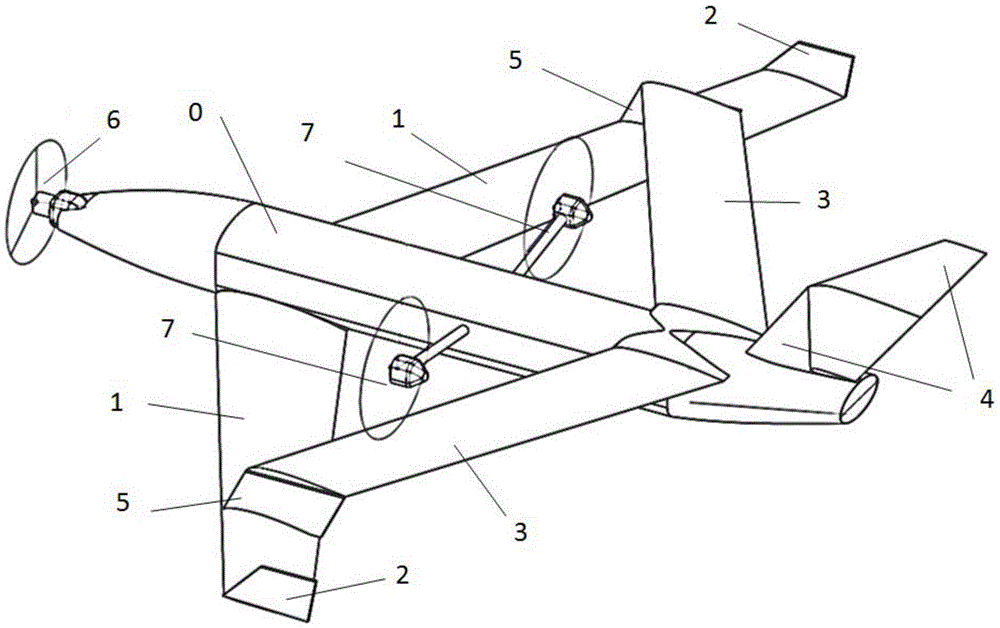
A flying-wing double-ducted vertical take-off and landing aircraft. It mainly consists of five parts. The first part is the fuselage 1, the second part is the No. 1 ducted engine 4, the No. 2 ducted engine 5 and the rear engine 6, the third part is the vertical tail 16, the No. 1 horizontal tail 12, the No. 2 horizontal tail 13, No. 3 horizontal stabilizer 14, No. 4 horizontal stabilizer 15, No. 1 winglet 10, No. 2 winglet 11. The fourth part is the support rod 19 , and the fifth part is the externally mounted pan / tilt head and the camera or photoelectric sensor 20 . The fuselage 1 is a flying wing type, the fuselage 1 can be folded, and the fold line 17 and the fold line 2 18 are the folding points of the fuselage. There are No. 1 duct 2 and No. 2 duct 3 distributed on the fuselage 1. No. 1 ducted engine 4 and No. 2 ducted engine 5 are located in the center of No. 1 duct 2 and No. 2 duct 3, respectively, and are connected by connecting The rod 22 is fixed. The No. 1 ducted engine 4 and the No. 2 ducted engine 5 are respectively equipped with a No. 1 propeller 7 and a No. 2 propeller 8 . The rear engine 6 is located in the center of the tail of the fuselage 1 , and a rear propeller 9 is installed on the rear engine 6 . The No. 1 horizontal stabilizer 12 , the No. 2 horizontal stabilizer 13 , the No. 3 horizontal stabilizer 14 , and the No. 4 horizontal stabilizer 15 of the aircraft are respectively located at the rear of the fuselage 1 . The No. 1 winglet 10 and the No. 2 winglet 11 of the aircraft are located on the left and right sides of the fuselage 1 respectively, and are bent downward. The vertical tail 16 of the aircraft is located in the middle of the tail of the fuselage 1 , on the upper part of the fuselage 1 . The support rod 19 is located in the middle of the front part of the fuselage 1 , and is located in the lower part of the fuselage 1 . The camera or photoelectric sensor is located in the middle of the front of the body 1 and is installed under the body 1 . The sweep angle 21 is the sweep angle of the flying wing fuselage 1 .
Owner:张飞
Solar pilotless plane
InactiveCN101254753AImprove the lift-to-drag ratioImprove hovering performanceToy aircraftsVehicular energy storageVertical stabilityHigh energy
The invention relates to a solar unmanned aircraft. In order to overcome the problems of difficult flight control and bad stability of the flying wing solar unmanned aircrafts, the invention adopts the configuration of tip winglets(5) arranged at the outer segments of a large aspect-ratio high wing, a V shaped empennage and a wing(4); the wing(4) is connected with and a fuselage(7) through a bridge wing(3) and a controlling rudder(9) is arranged on the V shaped empennage(8) to realize the pitching and yawing control of the aircraft. Combining the characteristic of the high energy conversion efficiency of a flexible thin film solar battery, the invention lays the flexible thin film solar battery(6) on the wing(4). An engine and propeller propulsion system (1) adopts a haul-in-type, and an equipment cabin (2) is arranged at the front part of the fuselage(7). The solar unmanned aircraft improves the lift-drag ratio of the aerial vehicle, prolongs the operation time and effectively improves the horizontal and the vertical stabilities and maneuverability of the aircraft, thus relieving the problems of bad stability and bad maneuverability of the flying wing configuration.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Rakelet
InactiveUS8382041B1Improve enduranceIncrease rangeAdditive manufacturing apparatusInfluencers by generating vorticesWingtip deviceAirplane
A rakelet comprises a raked portion and a winglet portion that selectively integrate features of raked wingtips and winglets into a wingtip device that improves aircraft endurance and range over standard wings and over other wingtip devices such as raked wings, winglets, and the like. The features of the rakelet can be configured to improve and maximize the range and endurance for any particular aircraft.
Owner:AIR FORCE US SEC THE THE
Rotational joint for an aircraft folding wing
ActiveUS20170355438A1Reducing and eliminating undesirable forceReduce spanWing adjustmentsDrag reductionRotational axisCoupling
An aircraft (2) including a wing (1), the wing (1) comprising a fixed wing (3) and a wing tip device (4) that is rotatable between a flight configuration and a ground configuration, the wing having a rotational joint (101) that rotatably couples the wing tip device (4) to the fixed wing (3), the rotational joint having an outer race (8) and an inner race (9), one of which is rotationally fixed relative to the wing tip device (4), to rotate about a rotational axis (B), and the other of which is rotationally fixed relative to the fixed wing (3), a rotational drive member (70) and the race that is rotationally fixed relative to the wing tip device (4) each being provided with a coupling section (110, 111, 114), the coupling sections being coupled to each other by a coupling member (119), that is received in a bore (112, 113) in one of the coupling sections, such that rotation of the drive member (70) rotates the race that is rotationally fixed relative to the wing tip device, to rotate the wing tip device (4) from one configuration to the other, wherein the coupling member (119) is mounted in the bore such that it is movable radially within the bore.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
Unmanned aerial vehicle
InactiveUS20120091284A1Protection from damageStabilizing and controlling movementUnmanned aerial vehiclesDigital data processing detailsJet aeroplaneWingtip device
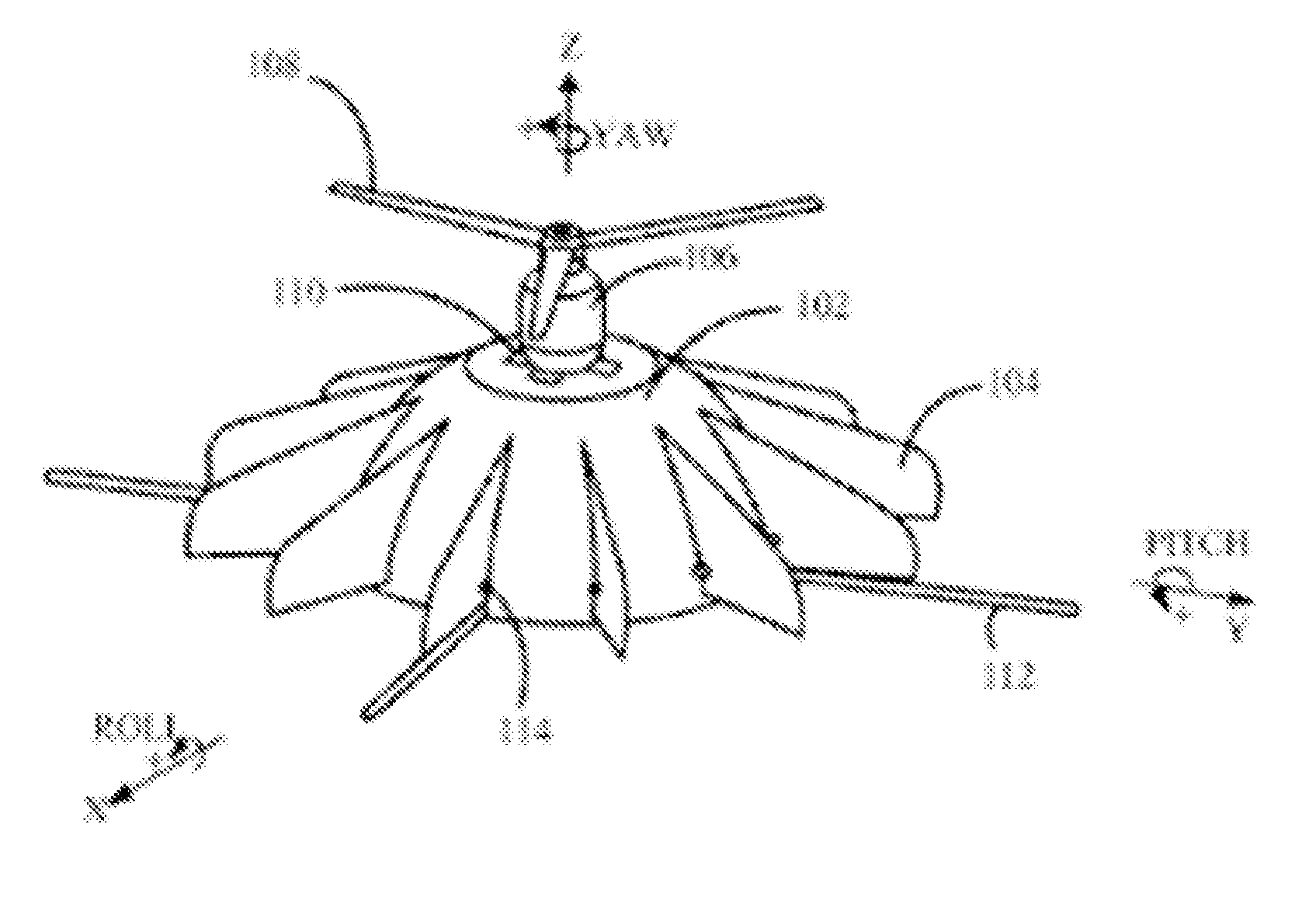
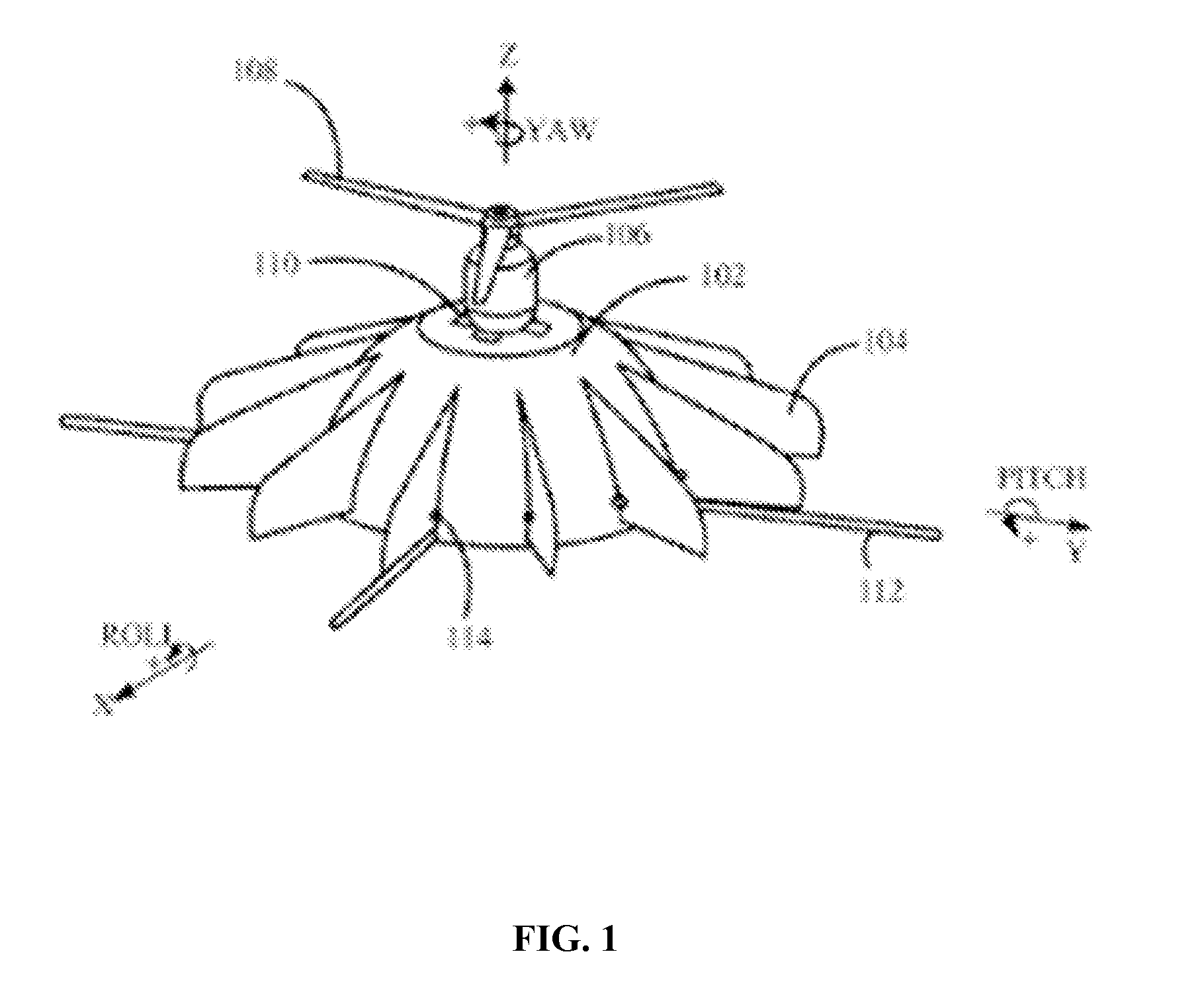
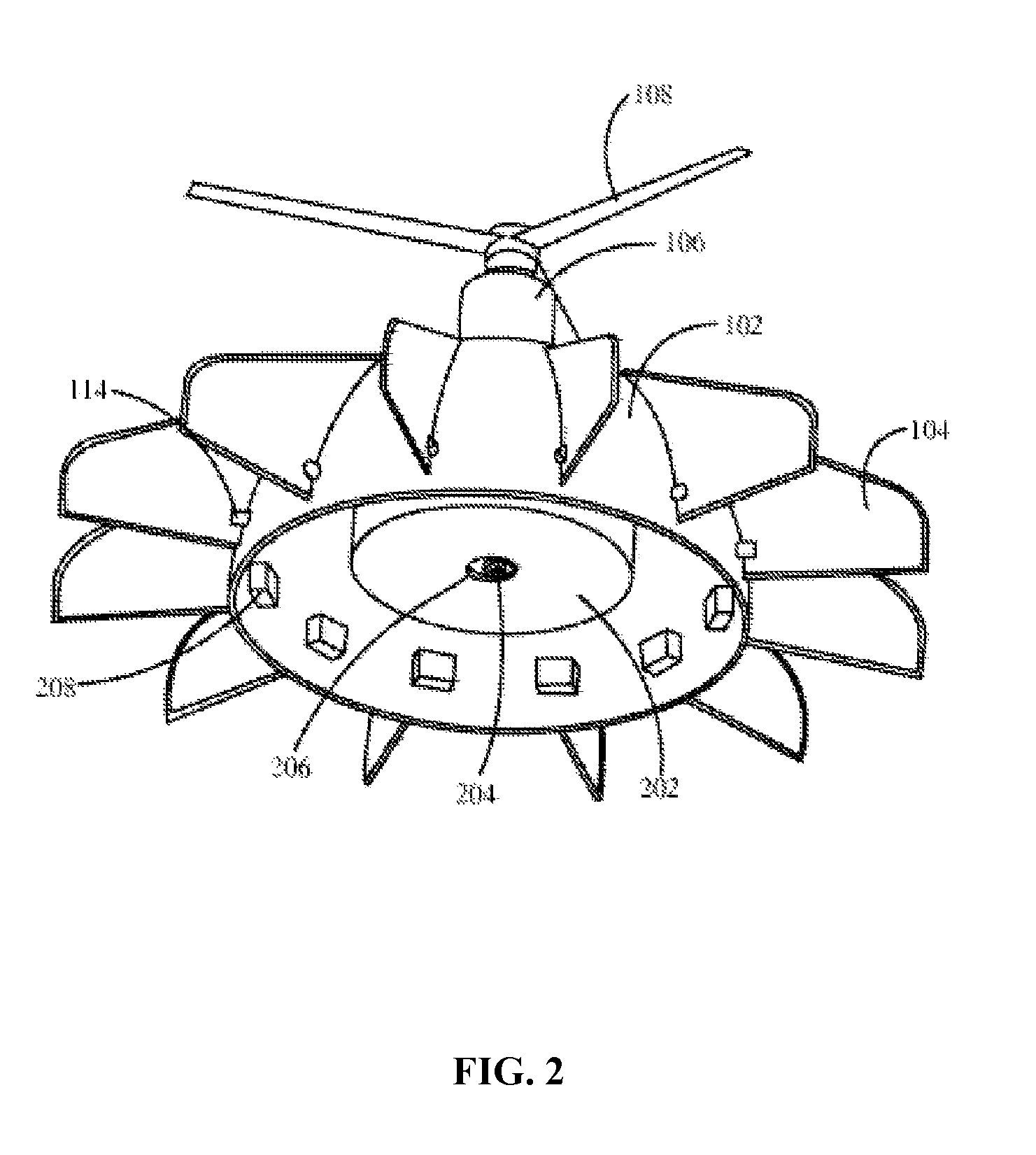
The various embodiments of the present invention provide an unmanned aerial vehicle comprising a hemispherical body, a brushless type electrical, a propeller, a plurality of wingtip devices, a plurality of servomotors and each of the plurality of the servomotors is connected to each of the plurality of the wingtip devices respectively, a plurality of carbon rods, and a casing. The brushless type electrical motor provides a lifting force for a Vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) and the plurality of wing tip devices are classified into three types of wing tip devices and the three types of wing tip devices are controlled by the respective servomotors to control yaw, pitch and roll movements thereby stabilizing and controlling the movement of an aircraft.
Owner:GOODARZI HOSEIN
Pneumatic layout of dual flying wings of UAV (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle)
The invention relates to a pneumatic layout of dual flying wings of a UAV (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle). The pneumatic layout is characterized by comprising a pneumatic layout of a blended wing body flying wing, a layout of installing a turbofan engine above the rear section of the blended wing body flying wing and a pneumatic layout of installing a stabilator at two sides of a nacelle on the outer wall of the turbofan engine, wherein the blended wing body flying wing with a high lift-to-drag ratio is formed by a fuselage, wings, wingtip winglets and direction ailerons together; the stabilator which is used for providing a positive lifting force during flight trimming of the UAV is formed by horizontal tails and horizontal tail winglets, and the dual flying wings are formed by the blended wing body flying wing and the stabilator together. According to the pneumatic layout of the dual flying wings of the UAV, disclosed by the invention, the UAV has high lift-to-drag ratio, good operability and high stability, and the pneumatic layout has the advantage of good stealth performance.
Owner:NAVAL AERONAUTICAL & ASTRONAUTICAL UNIV PLA
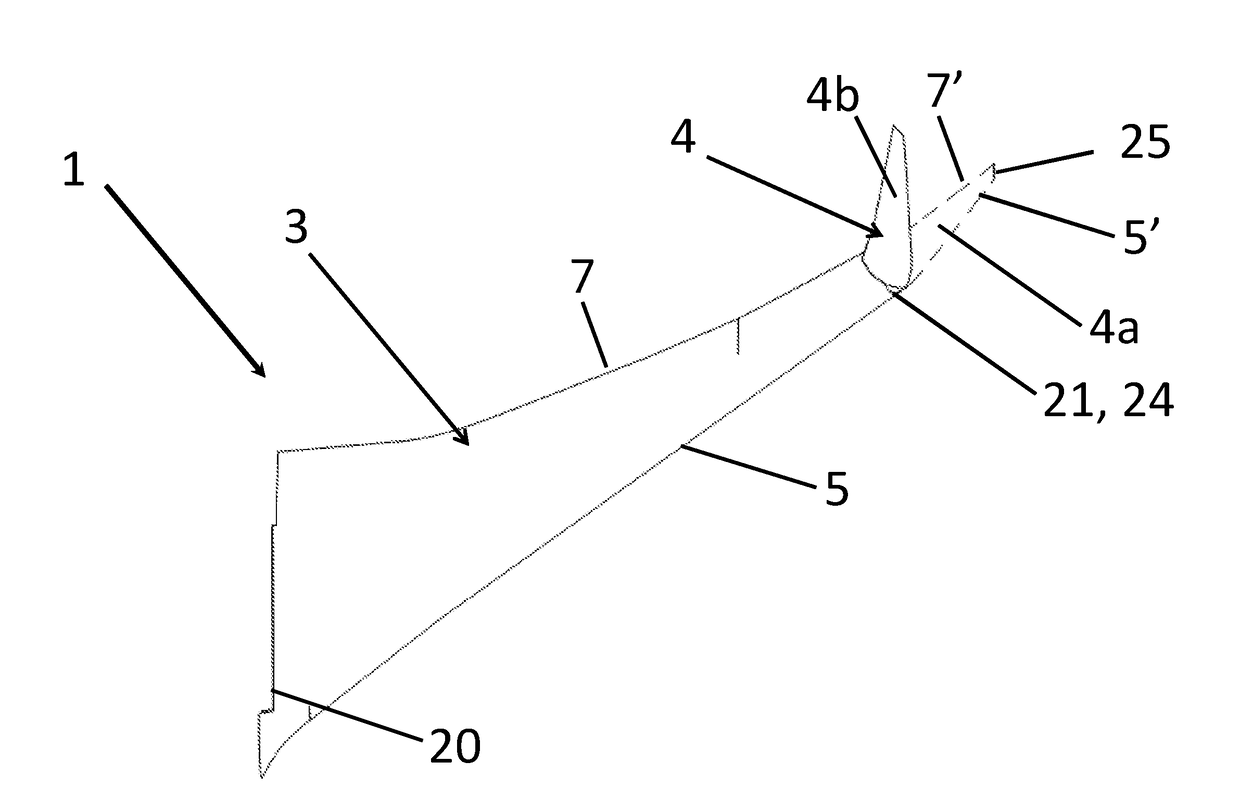
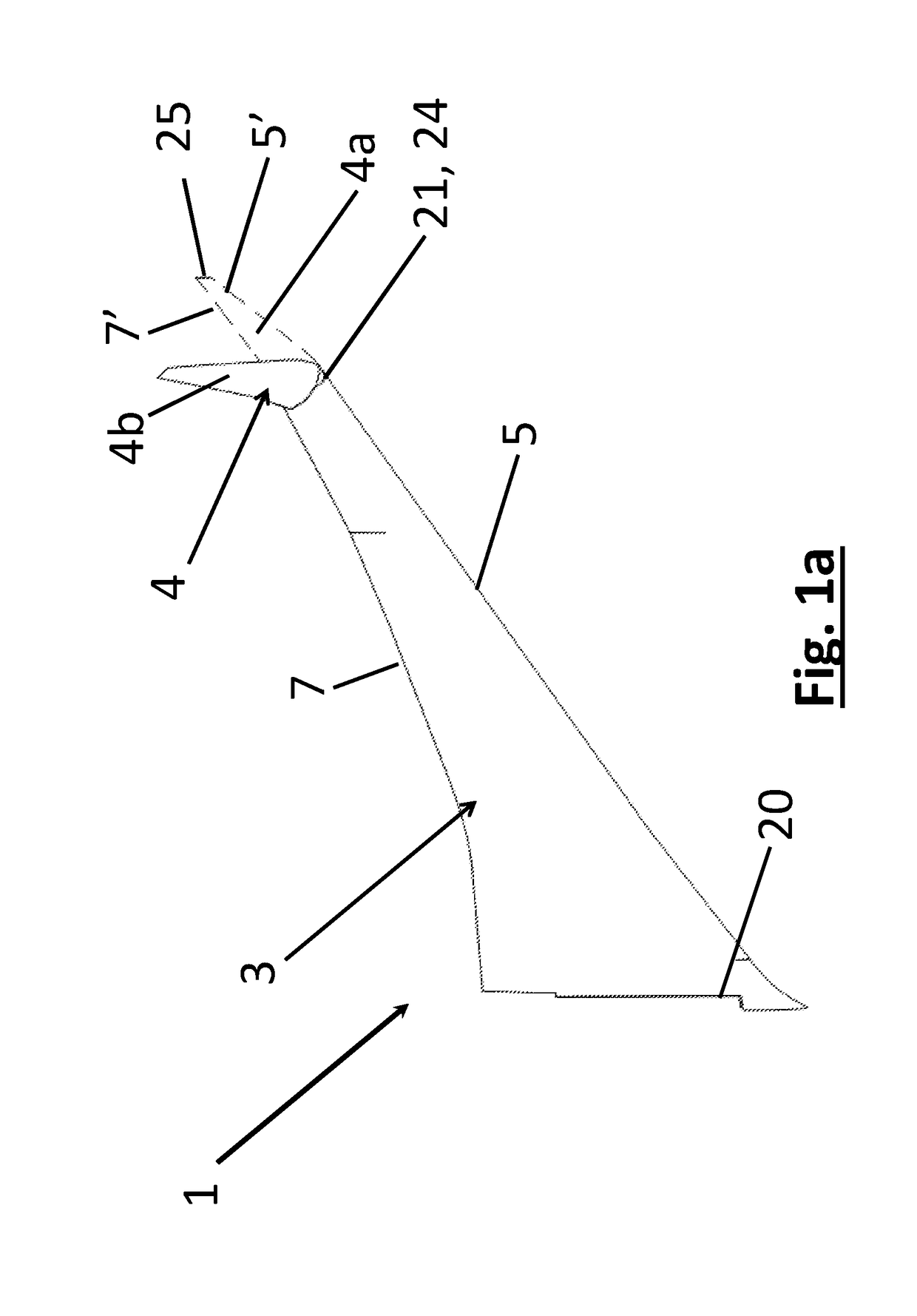
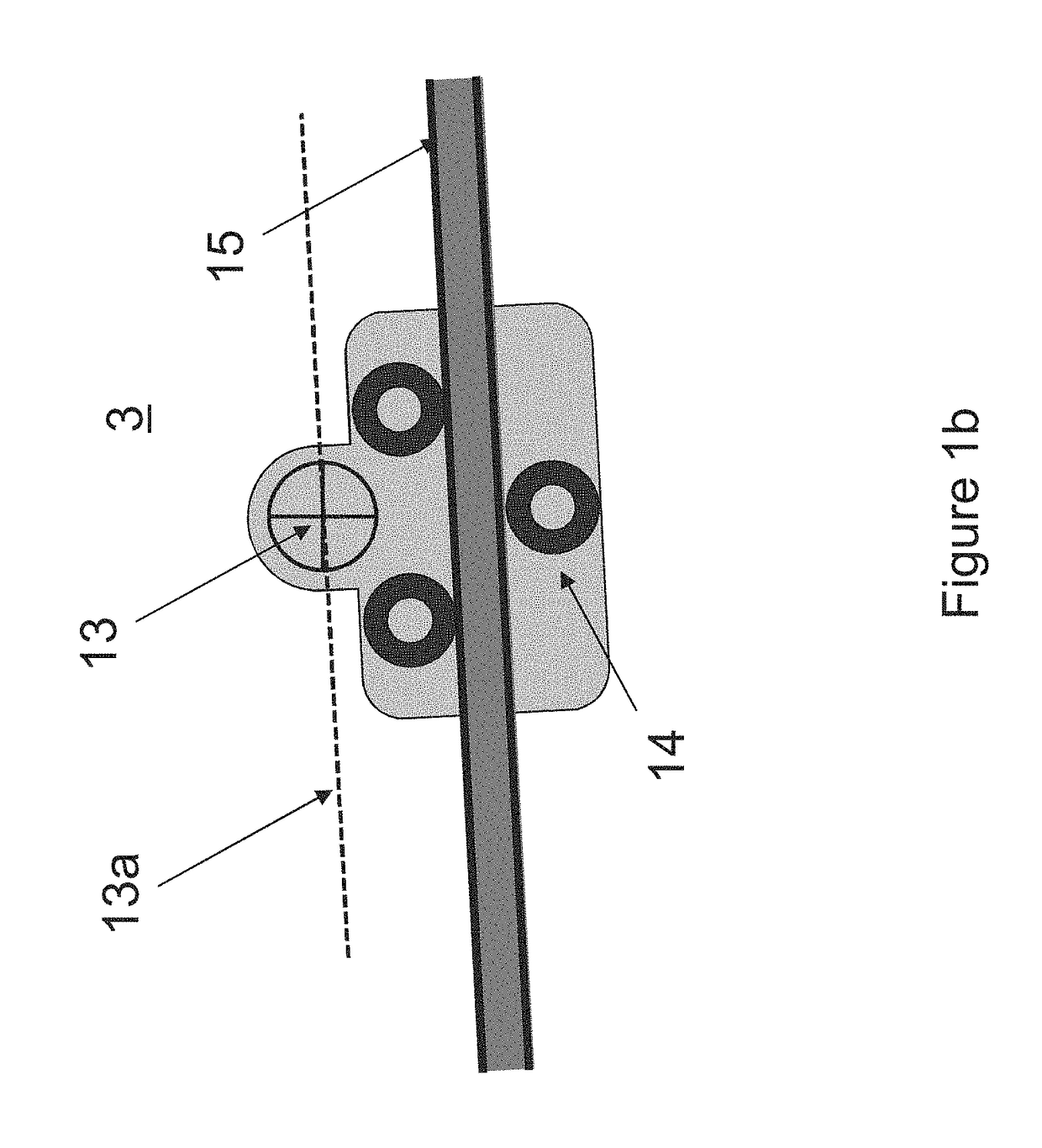
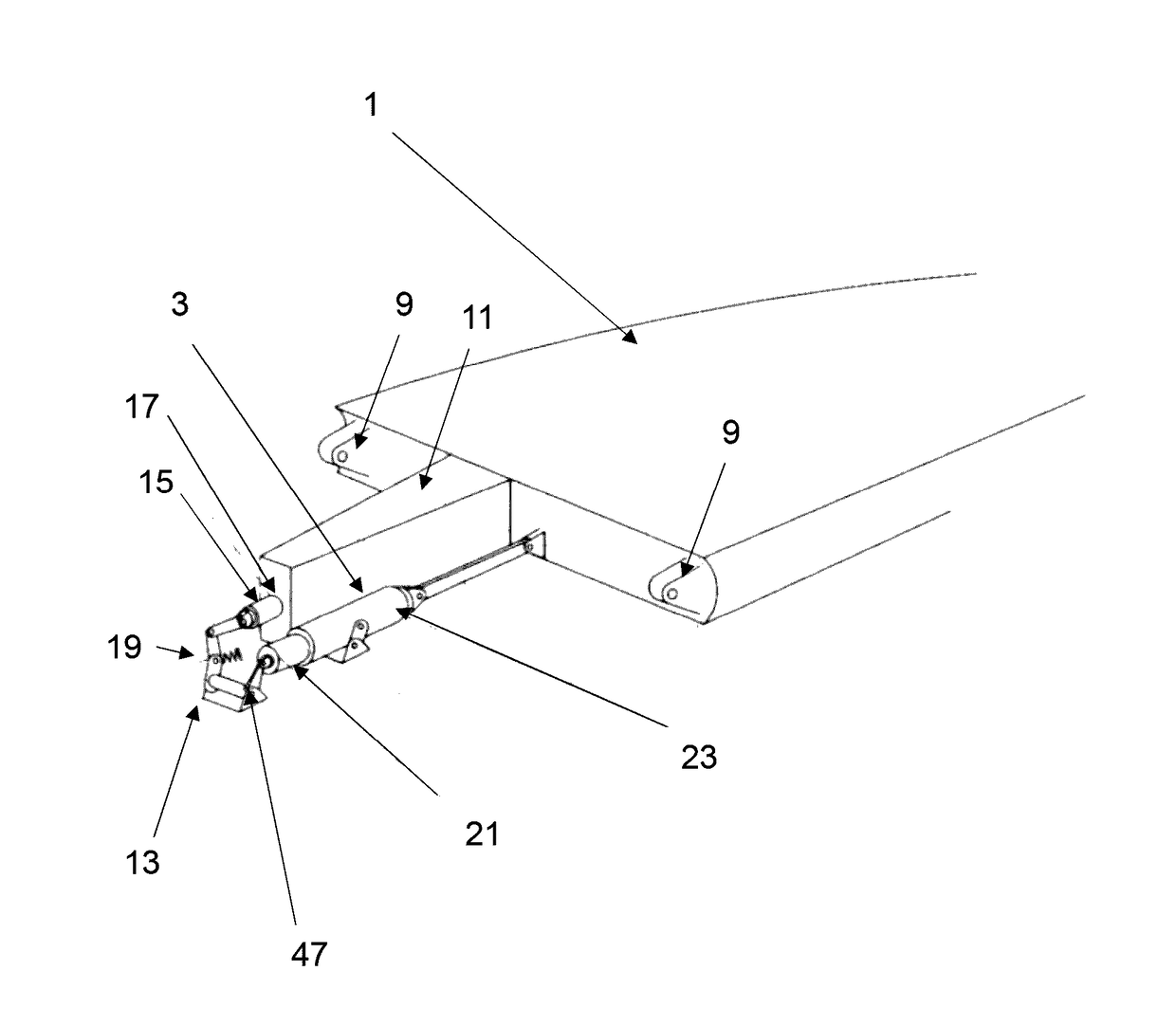
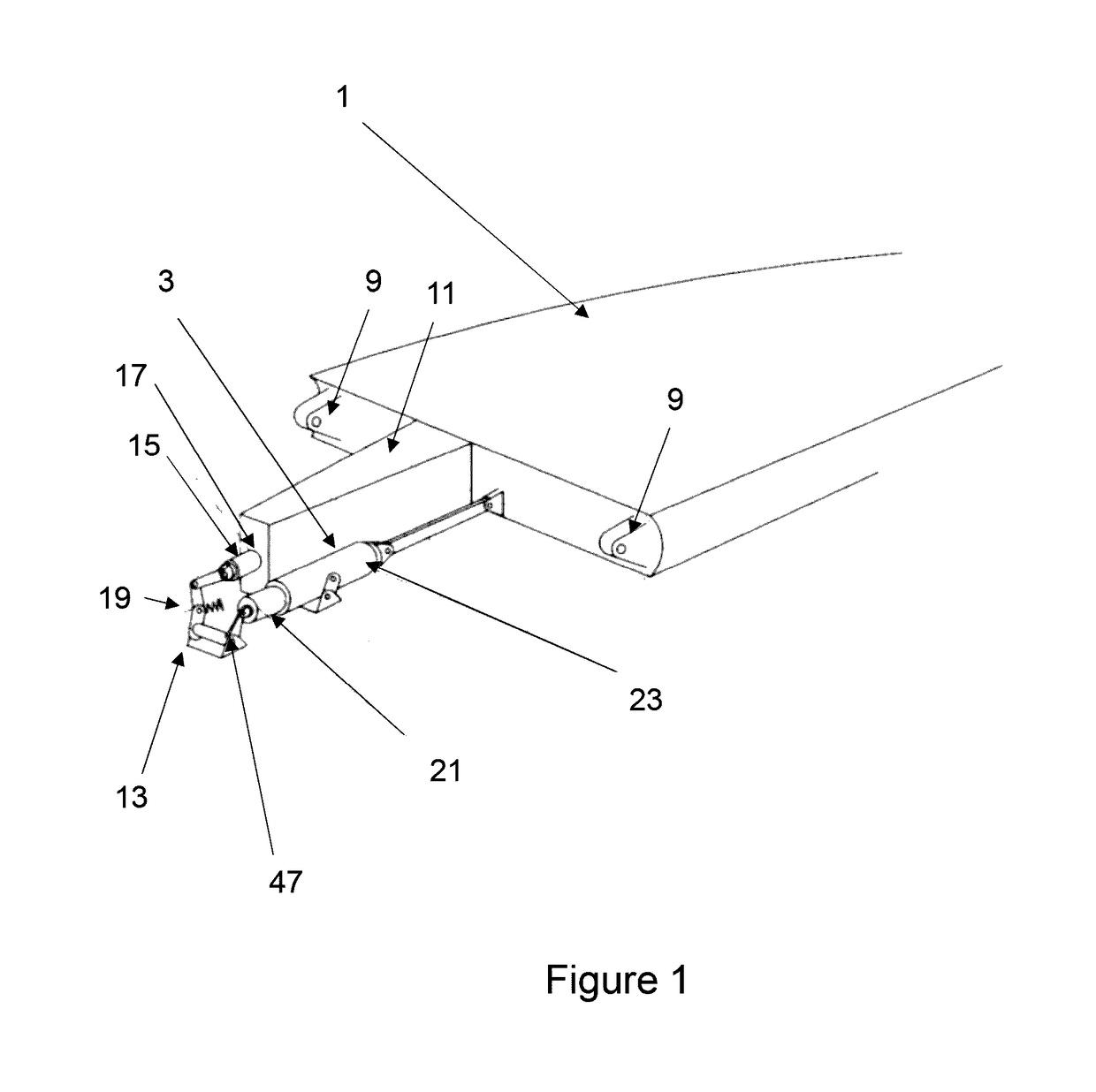
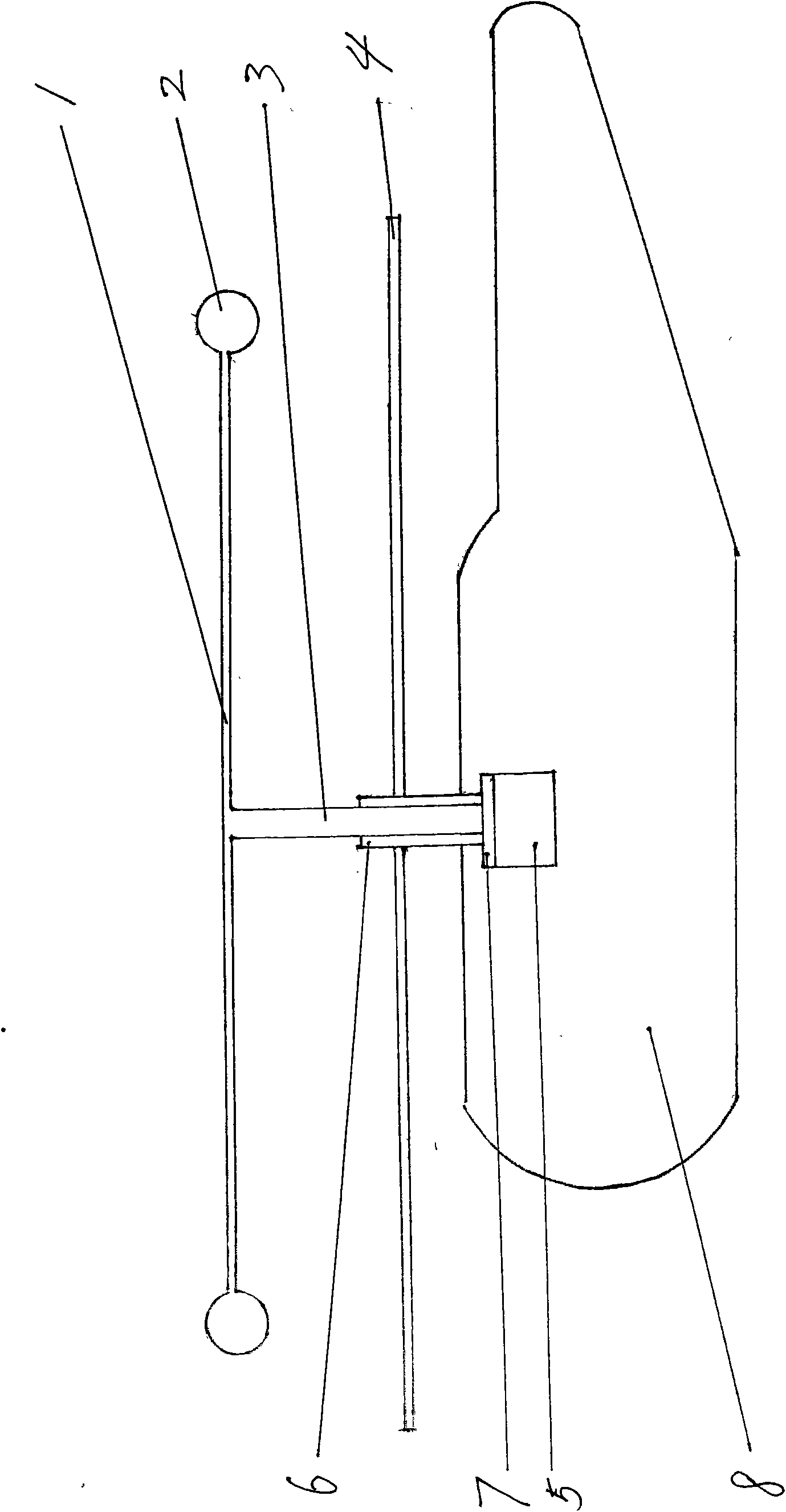
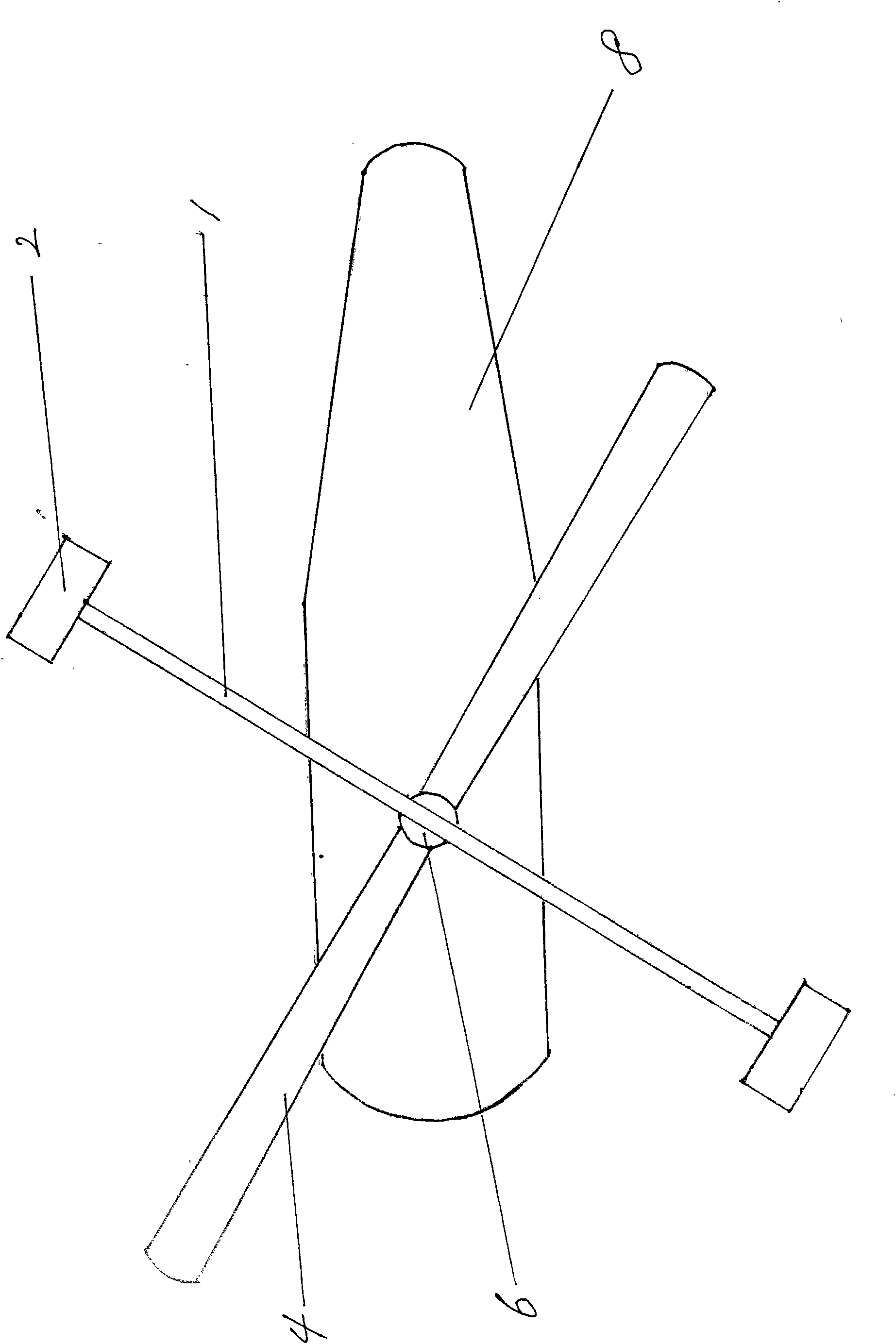
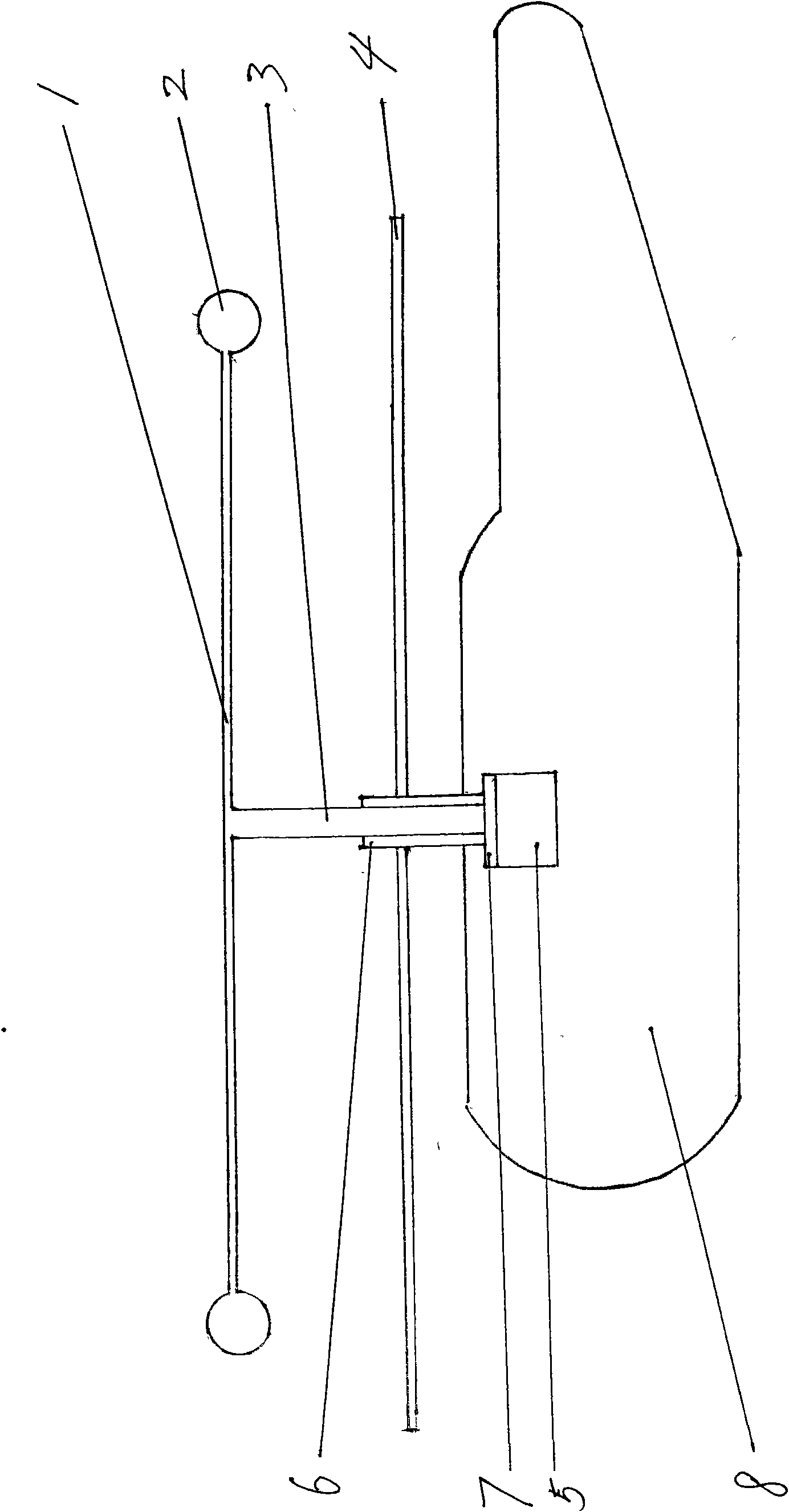
A passenger aircraft with a downwardly foldable wing tip device
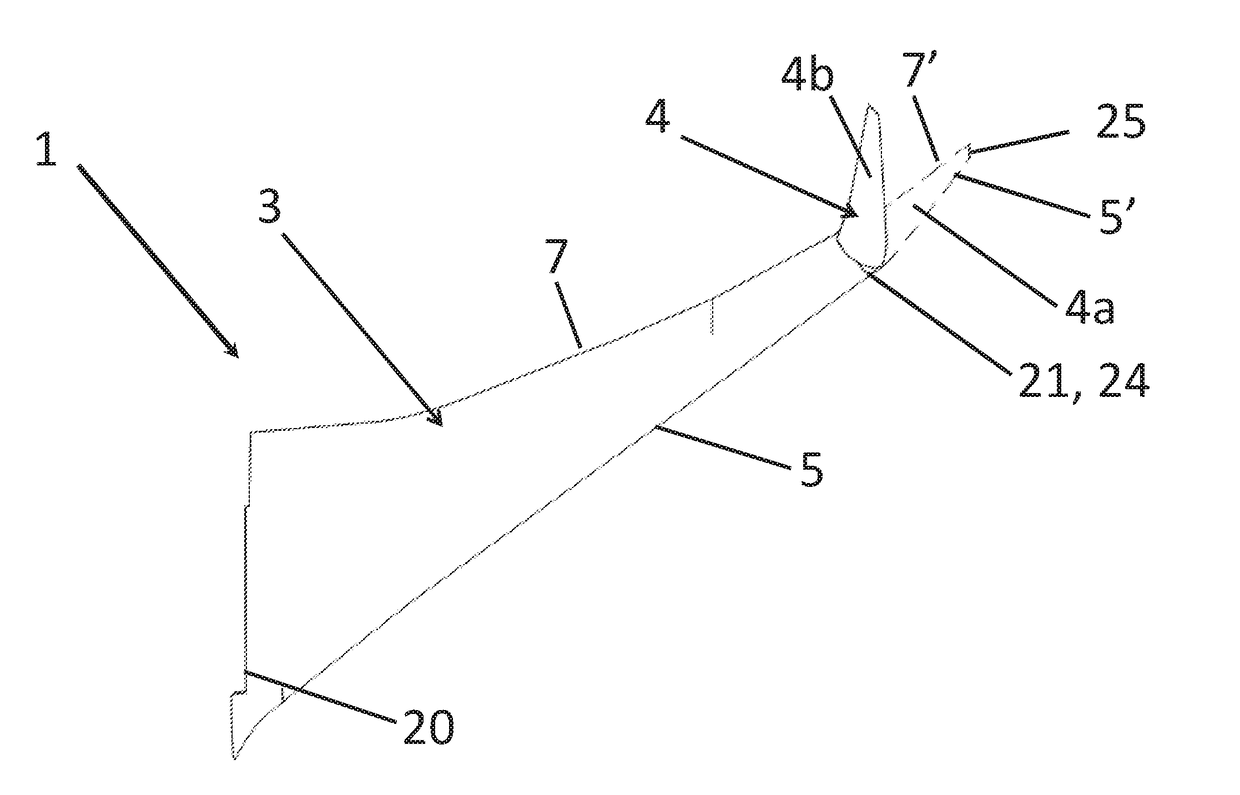
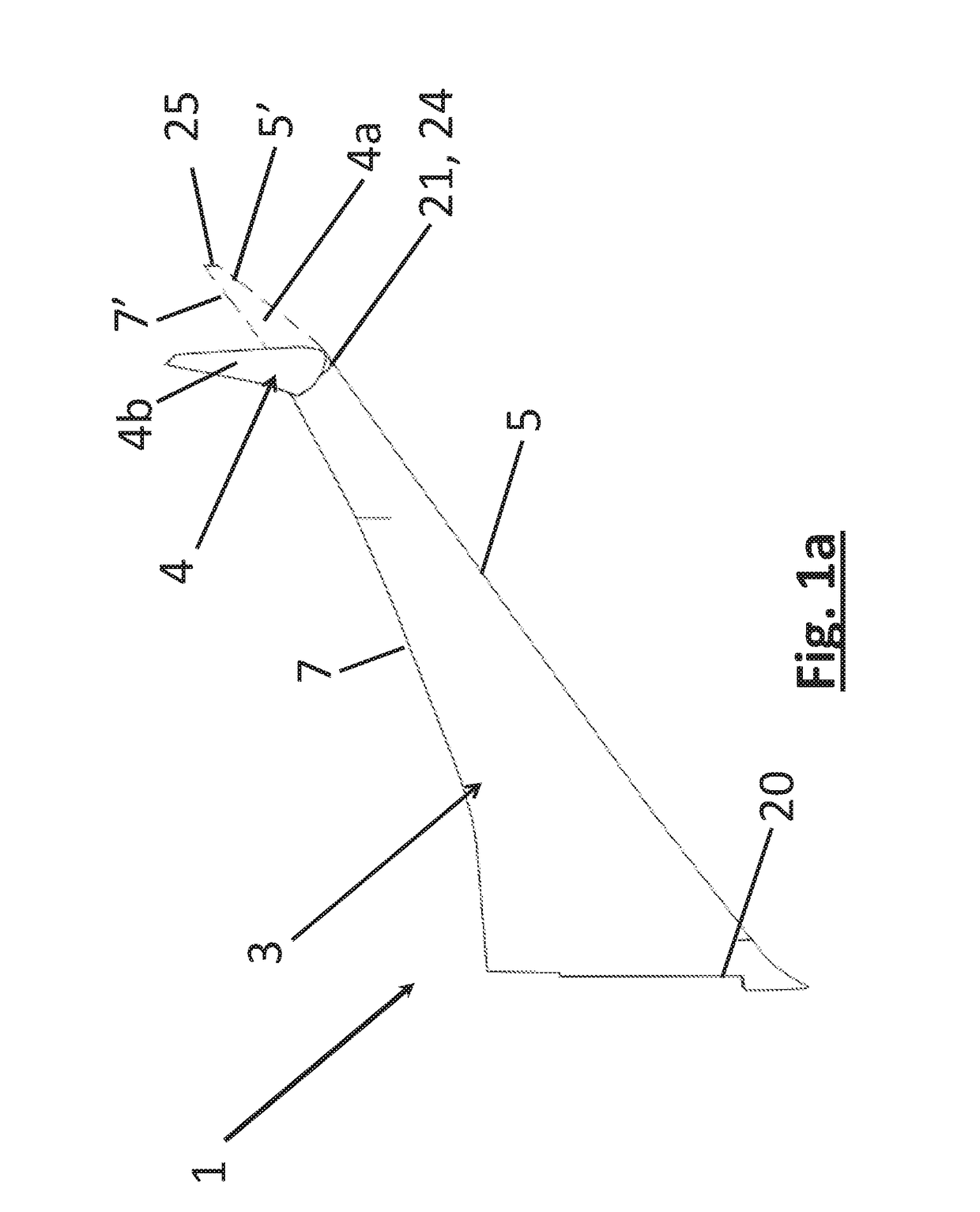
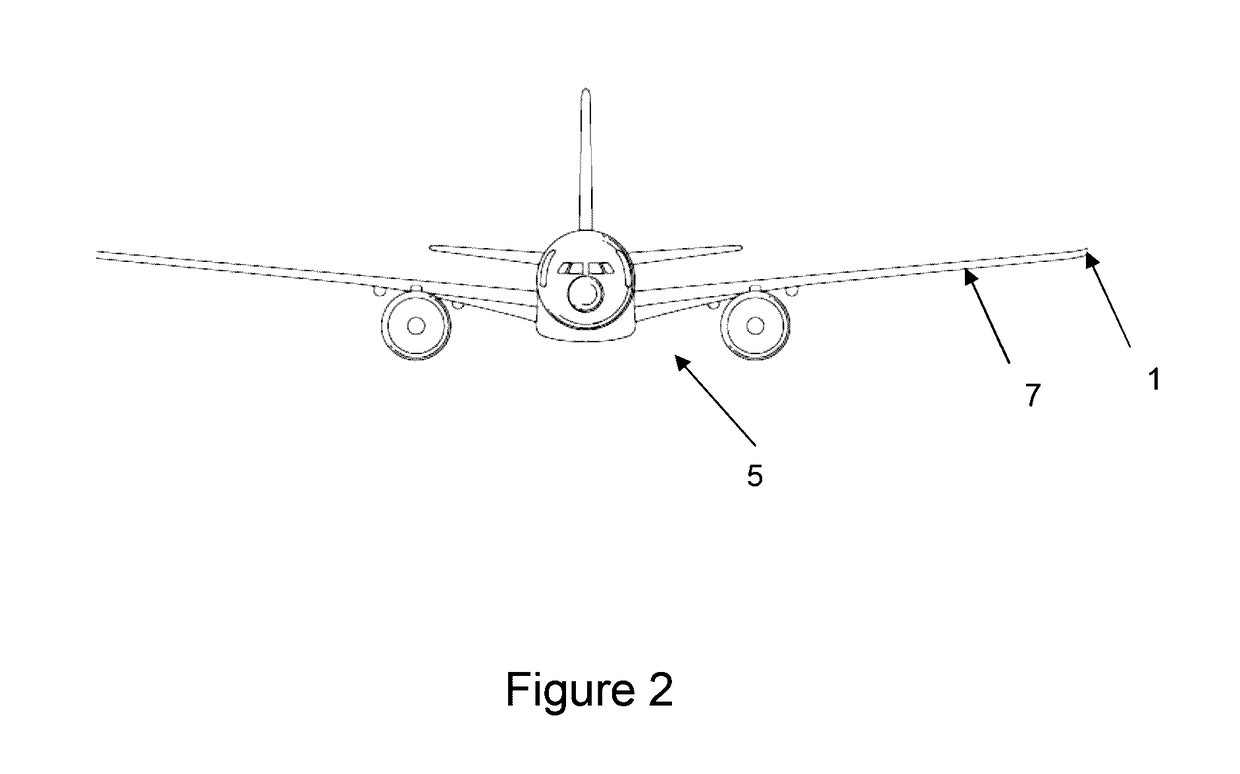
ActiveUS20170113780A1Reduce capacityReduce needWing adjustmentsDrag reductionFlight directionWing configuration
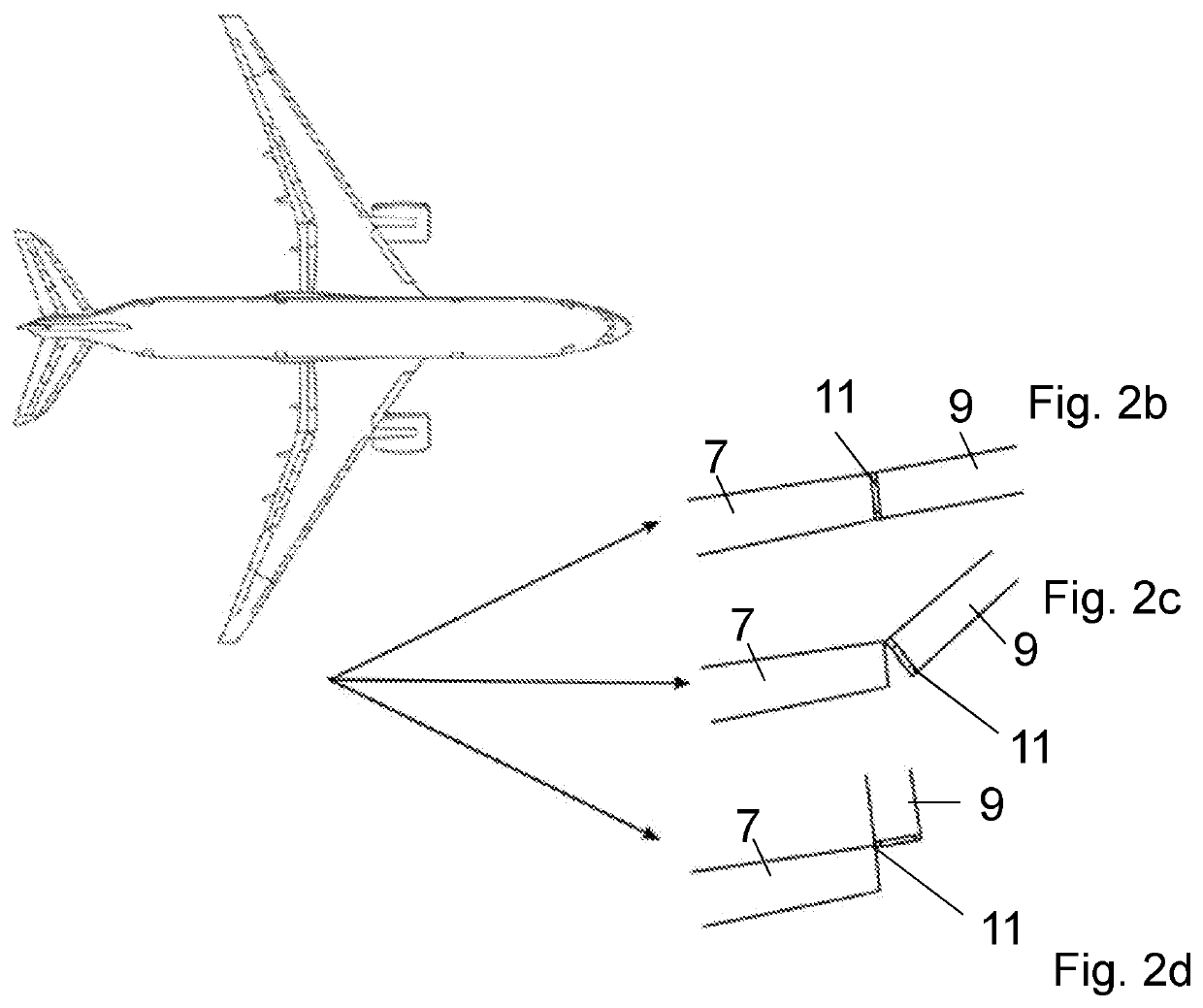
A passenger aircraft including a wing (1) and a wing tip device (3). The wing tip device (3) is moveable between a flight configuration for use during flight and a ground configuration for use during ground-based operations. In the ground configuration the wing tip device is folded downwardly from the flight configuration such that the span of the aircraft is reduced. The wing tip device (3) is connected to the wing along a hinge (9) defining a hinge line (11). The hinge (9) may be arranged to prevent the wing tip device (3) rotating upwardly beyond the flight configuration. The hinge line (11) may be orientated at an angle to the flight direction such that the wing tip device (3) presents a larger frontal area when it is in the ground configuration than when it is in the flight configuration, such that aerodynamic forces urge it to rotate about the hinge line (11) away from the ground configuration and towards the flight configuration.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD
Novel rotor aerodynamic structure for unmanned aerial vehicle
The invention discloses a novel rotor aerodynamic structure for an unmanned aerial vehicle. The novel rotor aerodynamic structure comprises a rotor shaft and blades connected with the rotor shaft. The front edge of each blade is in a sine wave structure, the tail edge of each blade is in an isosceles right triangle shaped sawtooth structure, and the tail end of each blade is provided with a winglet which is perpendicularly mounted at the tail end of the corresponding blade. By the winglets mounted at tips of the blades respectively, streaming around of air on upper and lower surfaces can be inhibited, induced drag caused by wingtip vortexes is reduced, lift force damages caused by streaming around are reduced, lift-drag ratio is increased, and accordingly lift force is increased; in addition, due to adoption of the sine wave structured front edges and the sawtoothed rear edges according to a bionic design, low air resistance and low noise are realized. The novel rotor aerodynamic structure for the unmanned aerial vehicle has advantages of high lift force of the blades, high cruising power and low air resistance and noise in operation.
Owner:成都翼高九天科技有限公司
Unmanned aerial vehicle
InactiveUS8561937B2Protection from damageStabilizing and controlling movementUnmanned aerial vehiclesDigital data processing detailsJet aeroplaneWingtip device
Owner:GOODARZI HOSEIN
Rib arrangement in a wing tip device
ActiveUS20180237127A1Increase stiffnessLight weightInfluencers by generating vorticesSpars/stringersTransonicAirplane
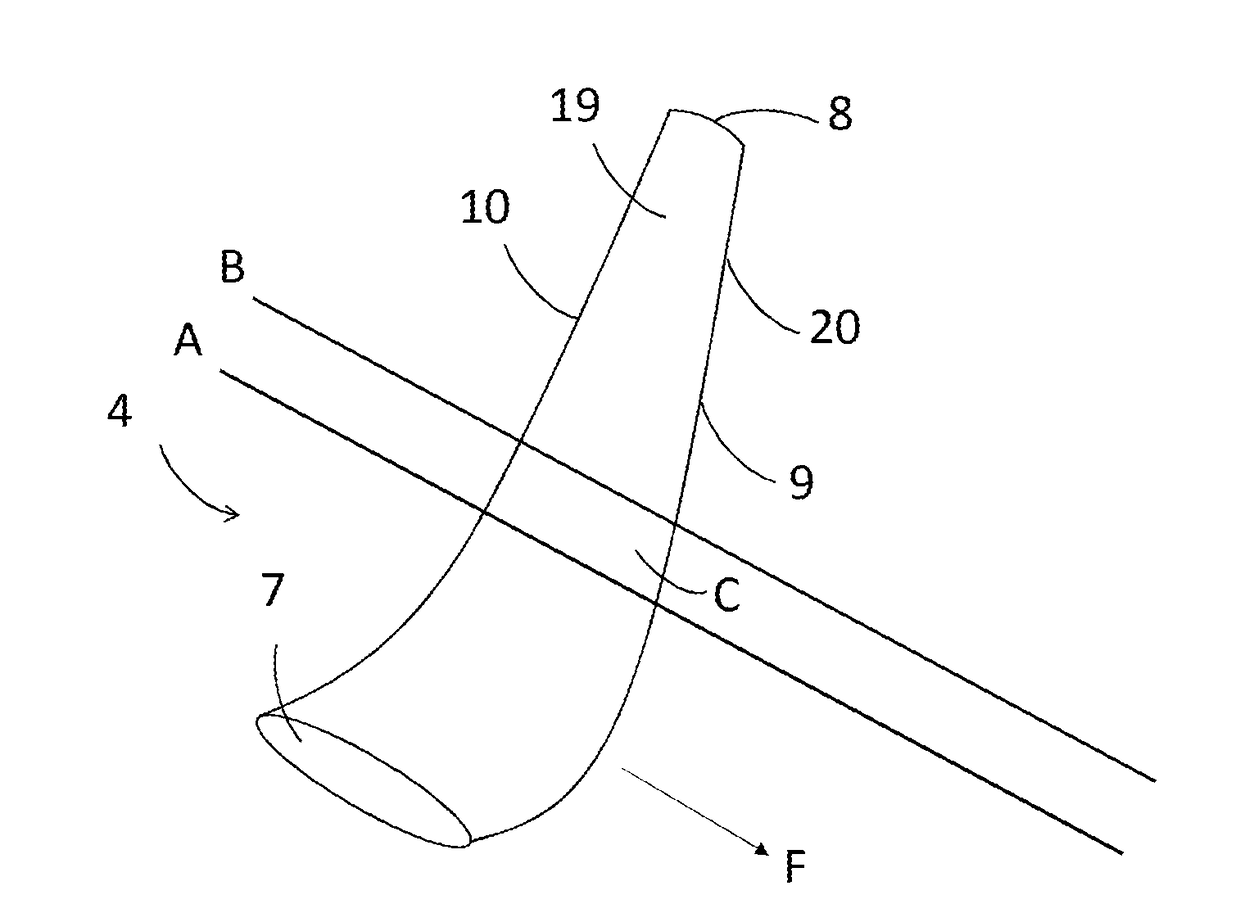
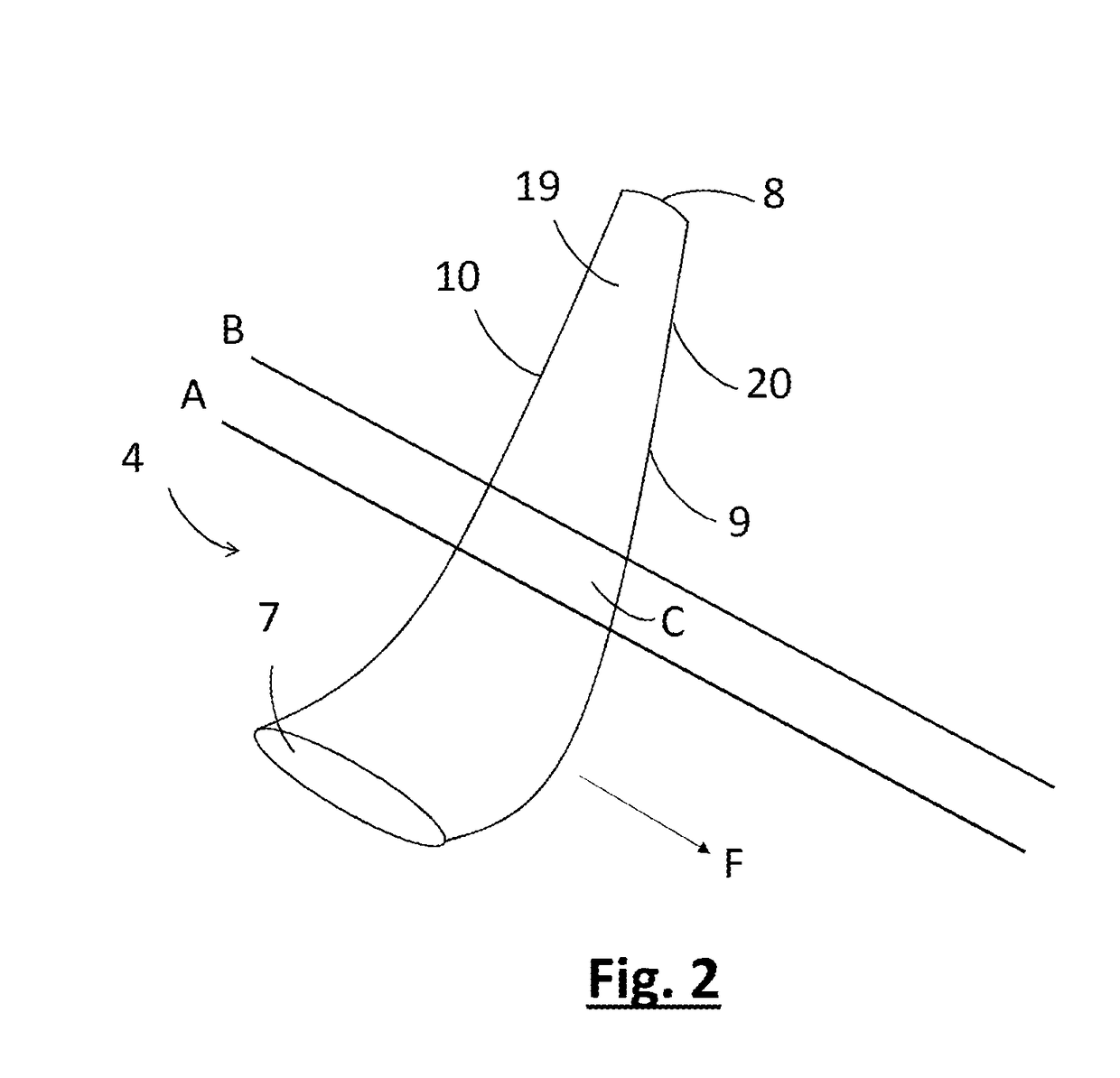
An aircraft (1) having a wing (3) and a wing tip device (4) at the tip of the wing (3), wherein the wing tip device (4) includes a rib (16) positioned in a span wise region (C) of the wing tip device (4) in which transonic flow occurs when the aircraft (1) is in flight. A method of designing an aircraft (1) including predicting where transonic flow occurs on the wing tip device (4) when the aircraft (1) is in flight, and designing the wing tip device (4) with a rib (16) positioned in the span wise region (C) of the wing tip device (4) in which the predicted transonic flow occurs.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD
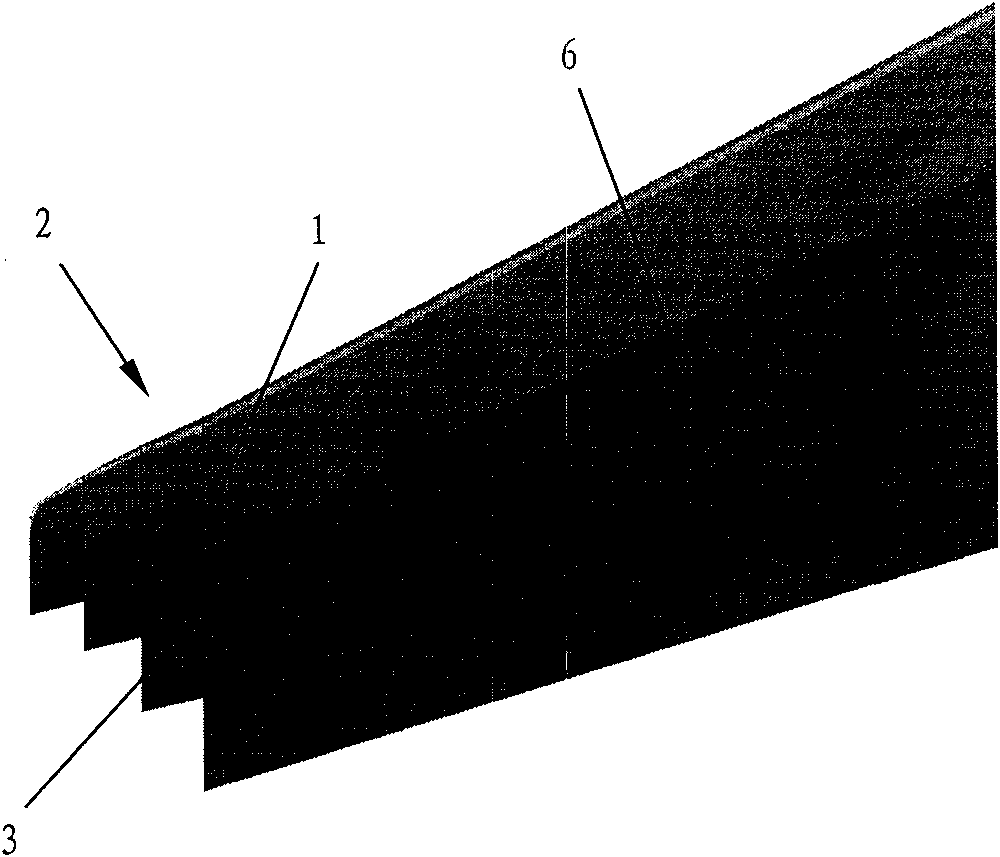
Airplane wingtip device with aligned front edge
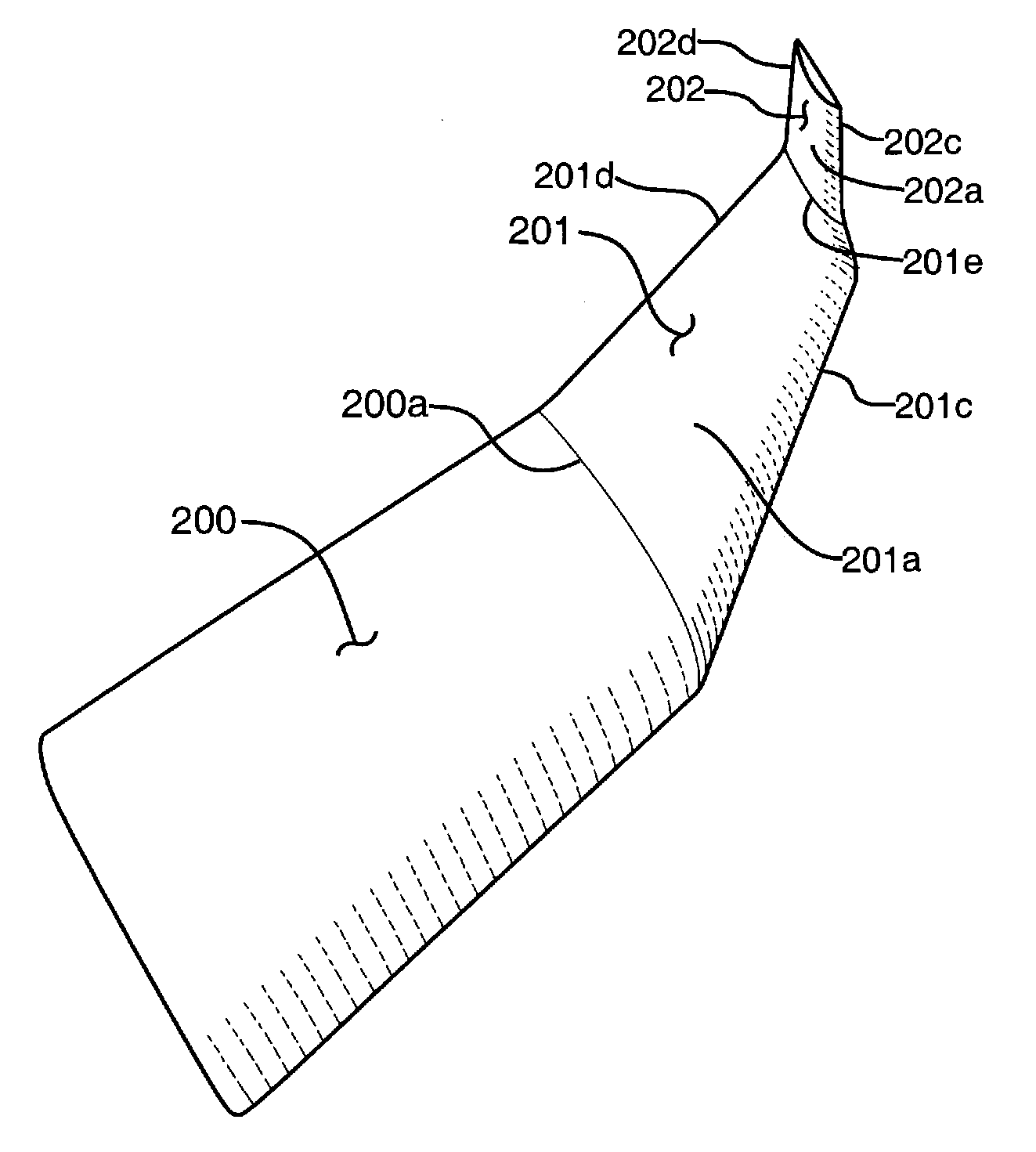
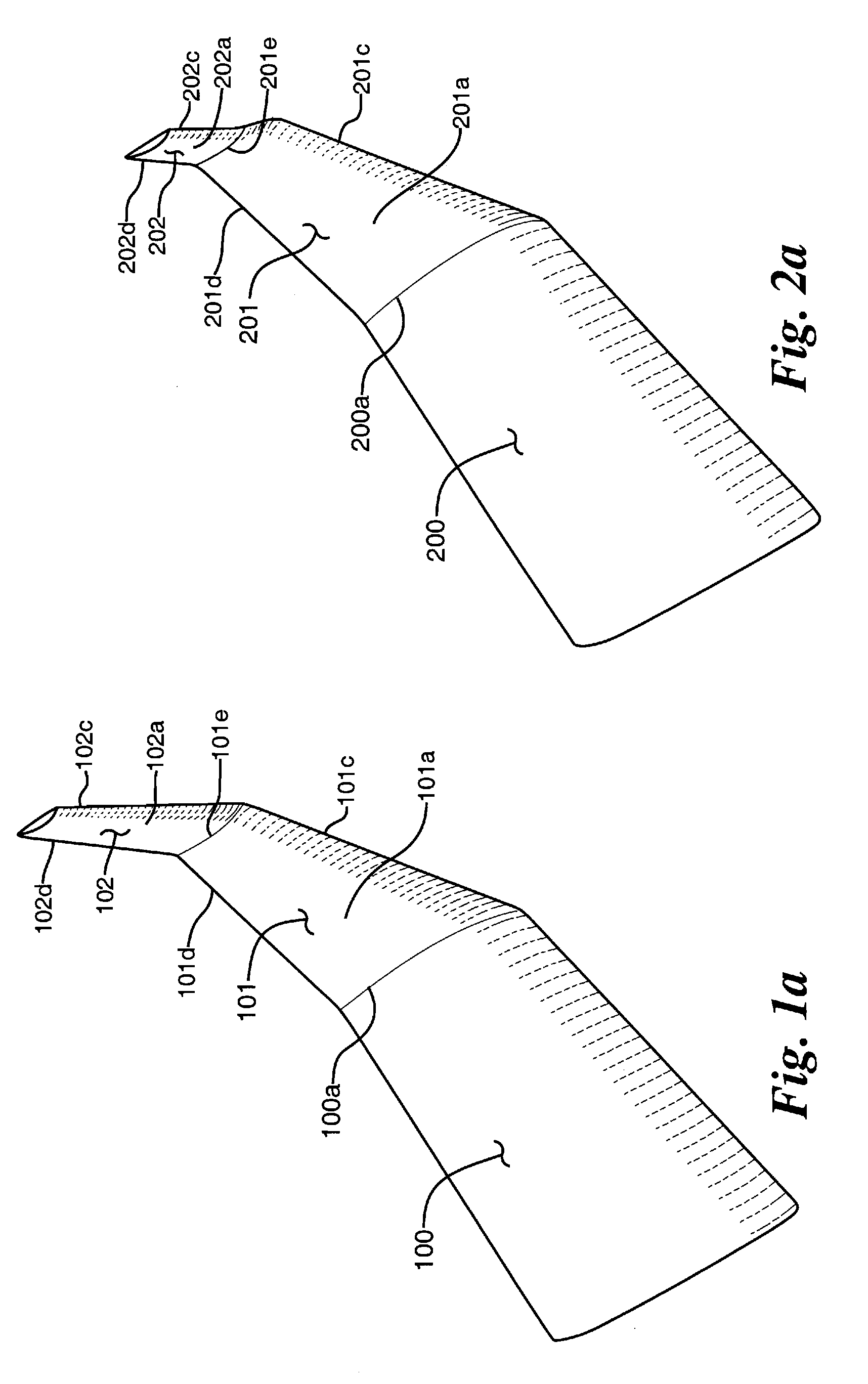
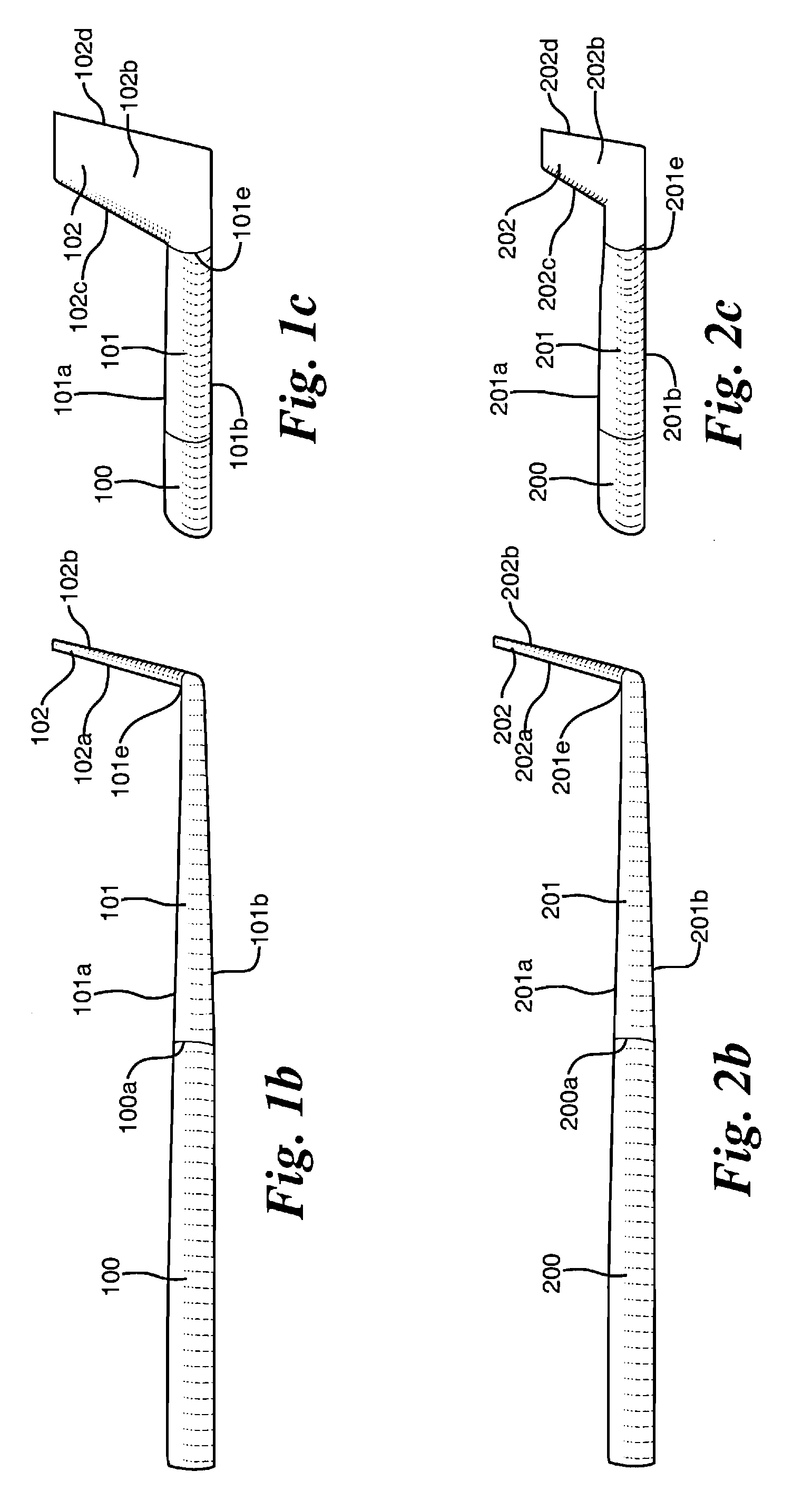
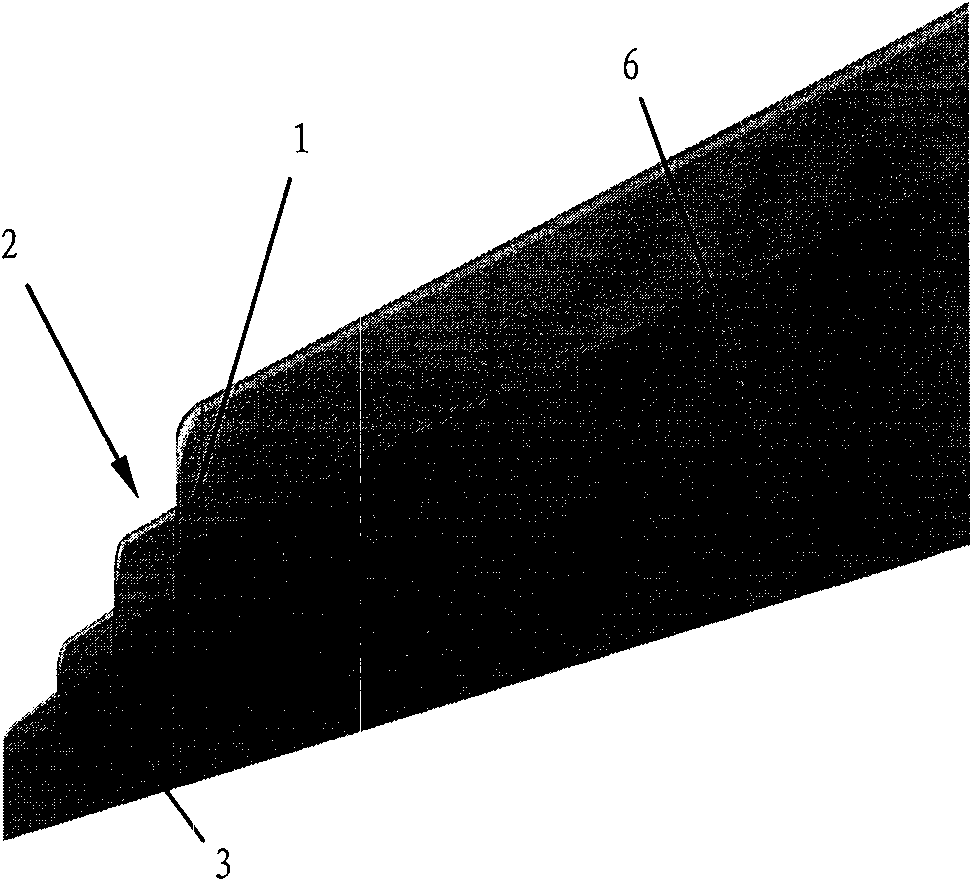
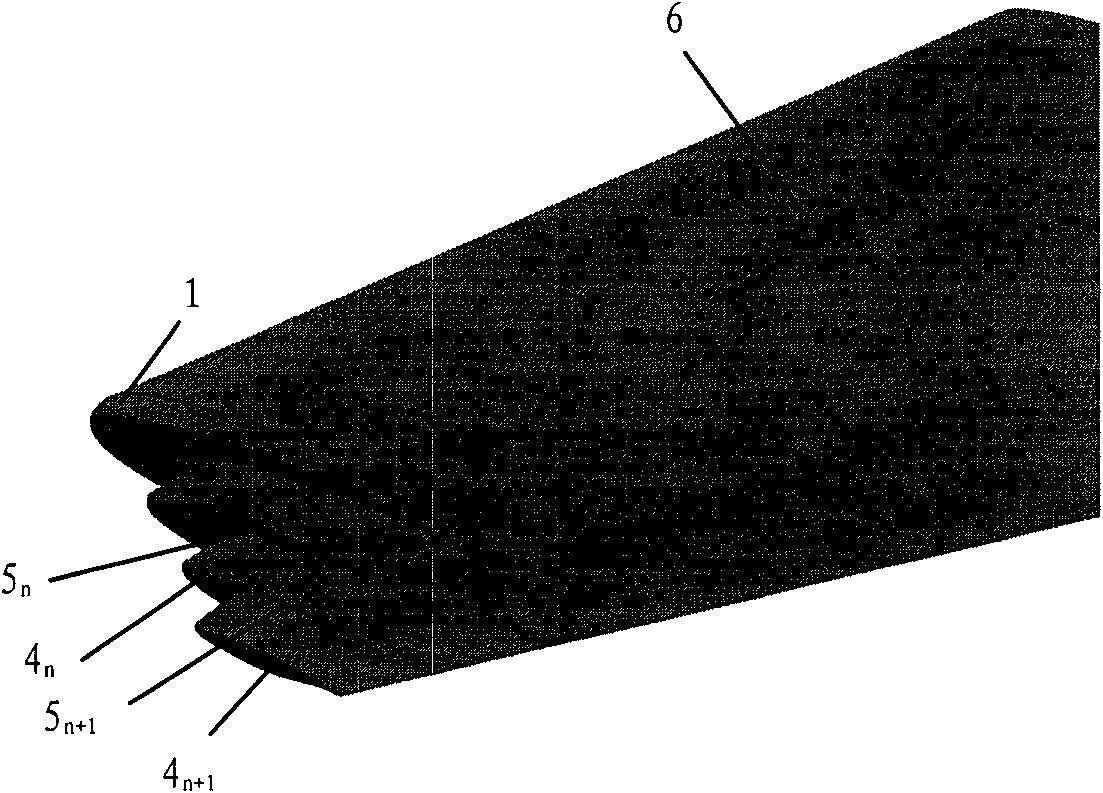
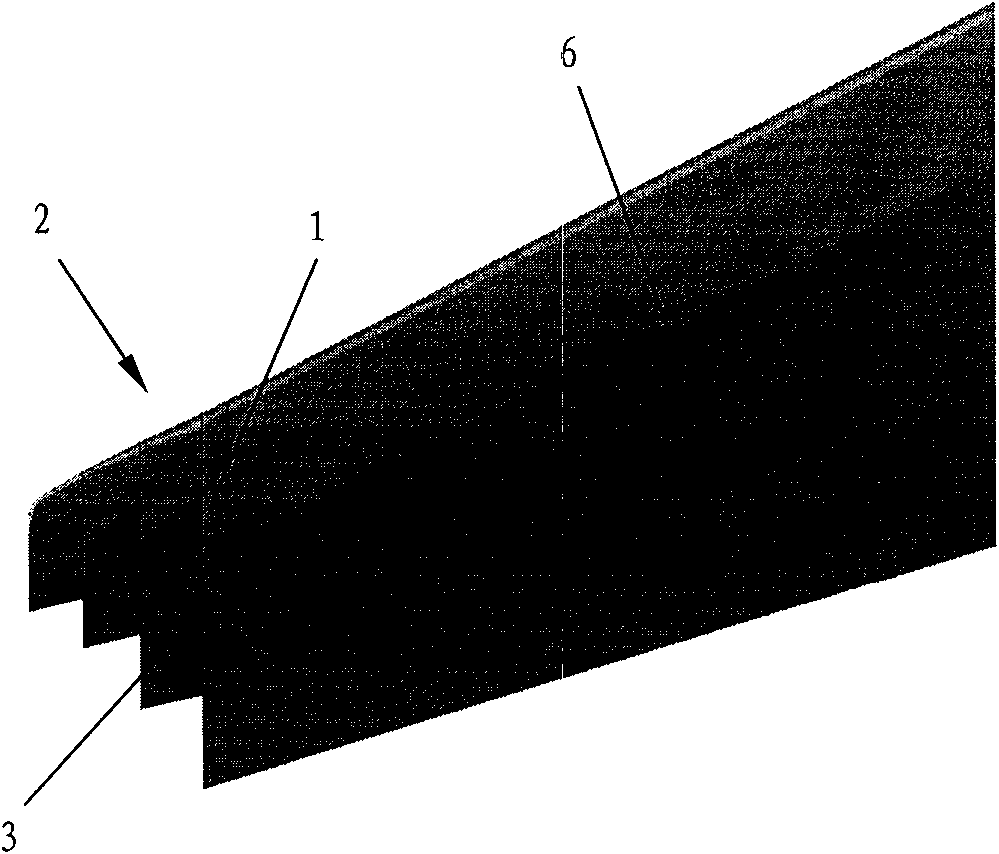
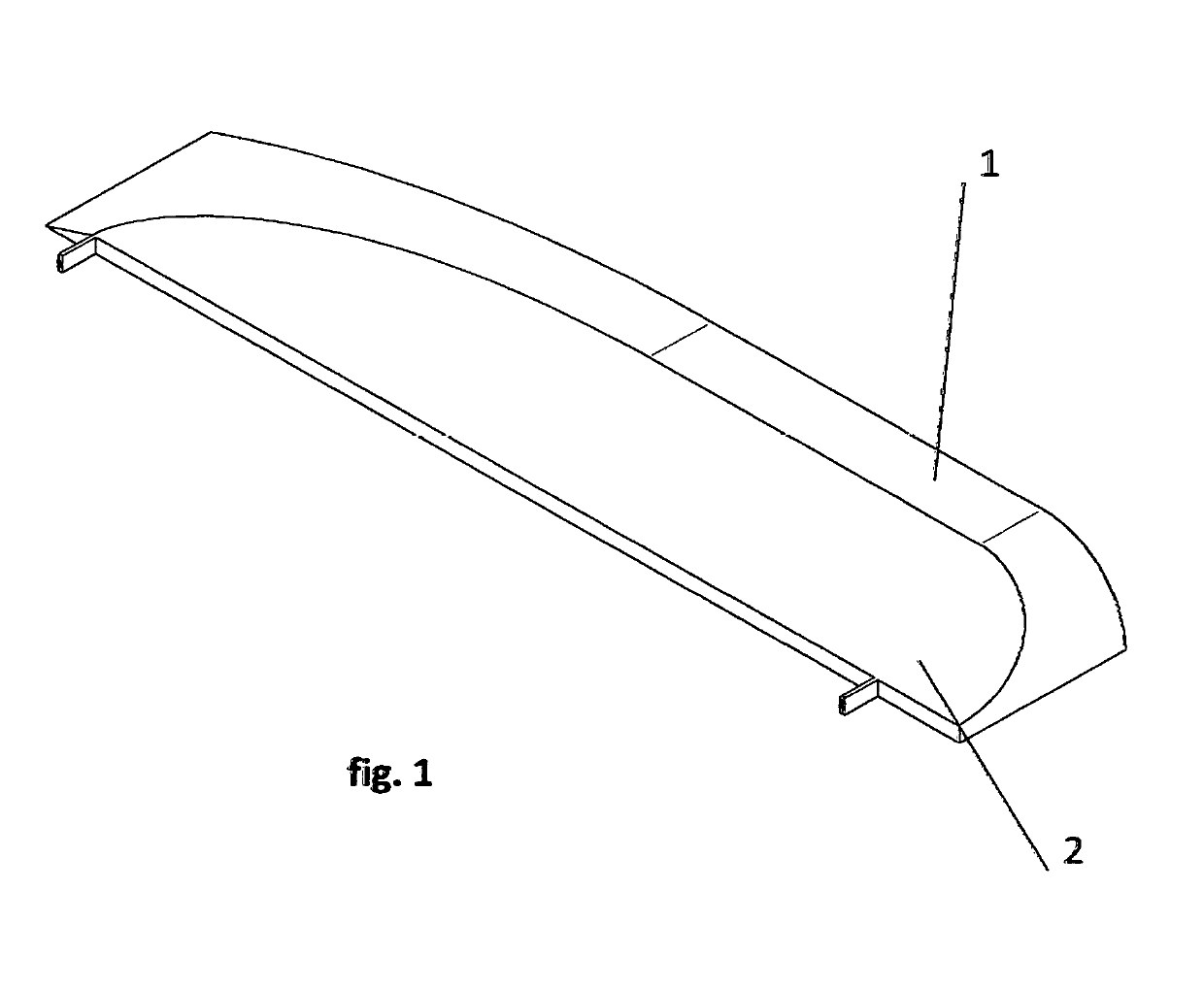
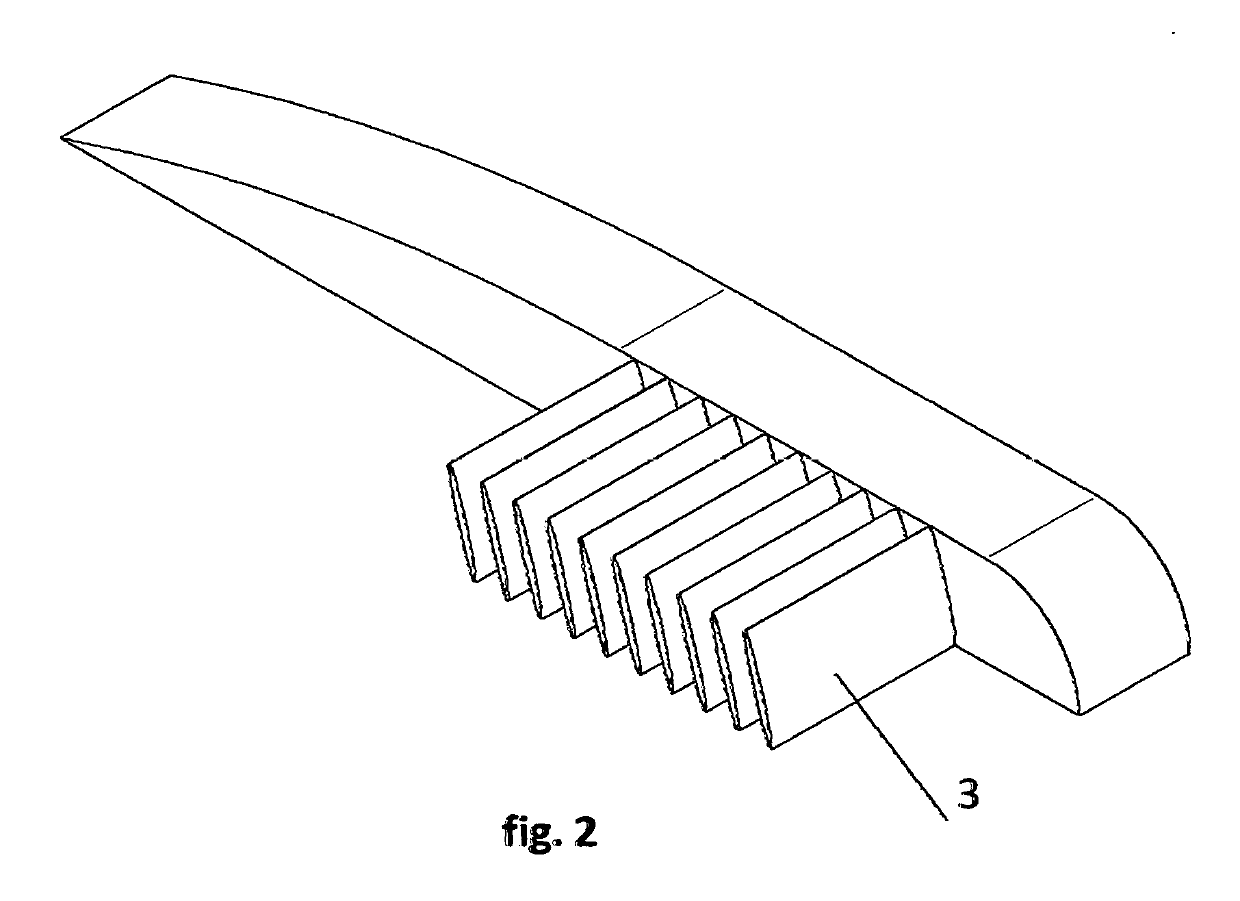
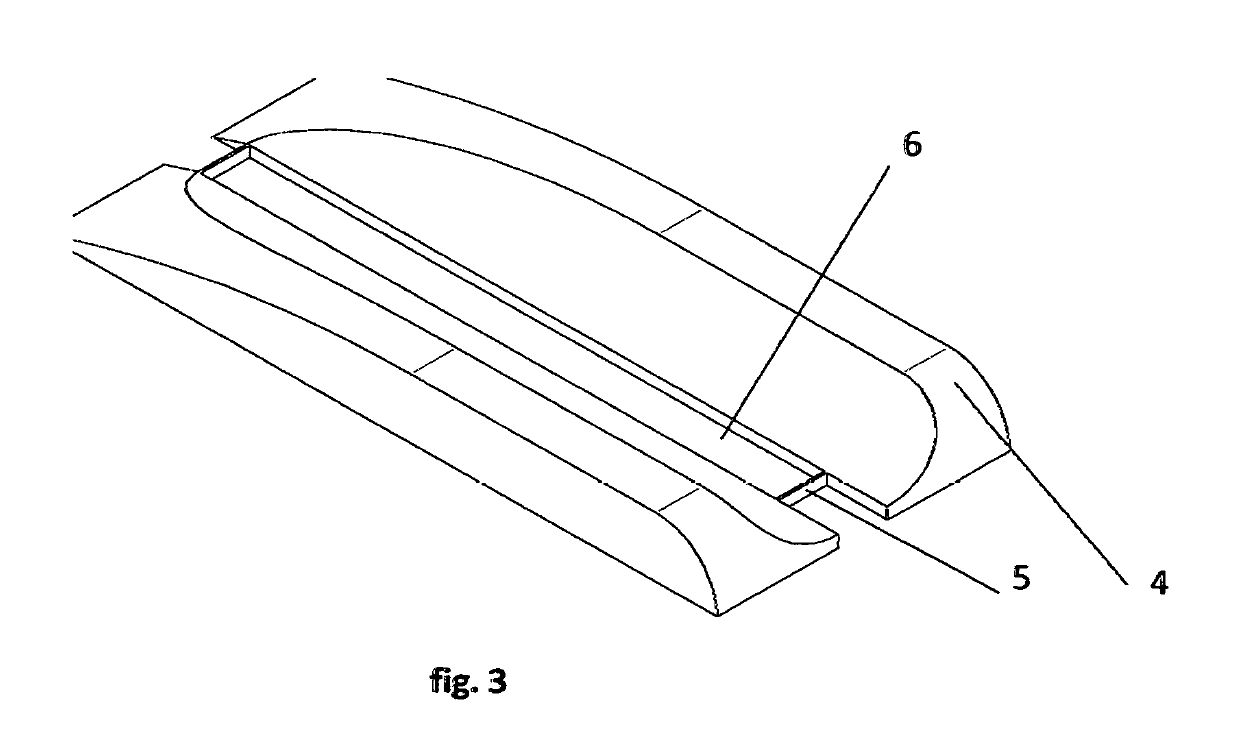
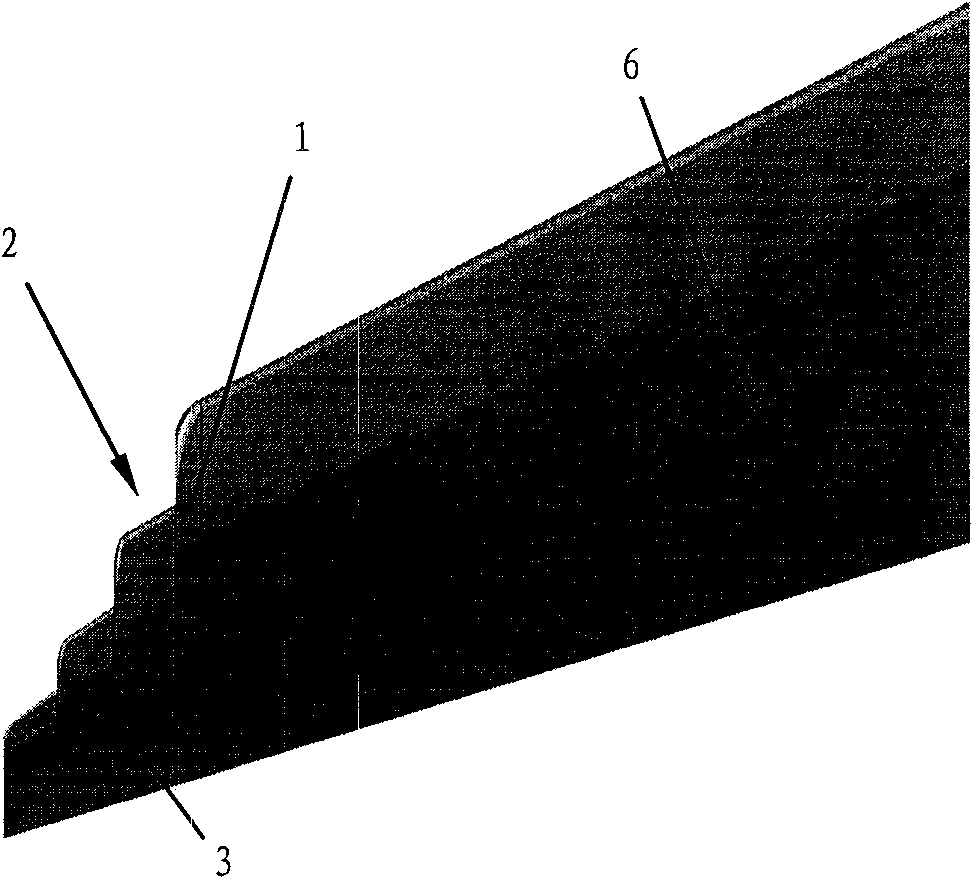
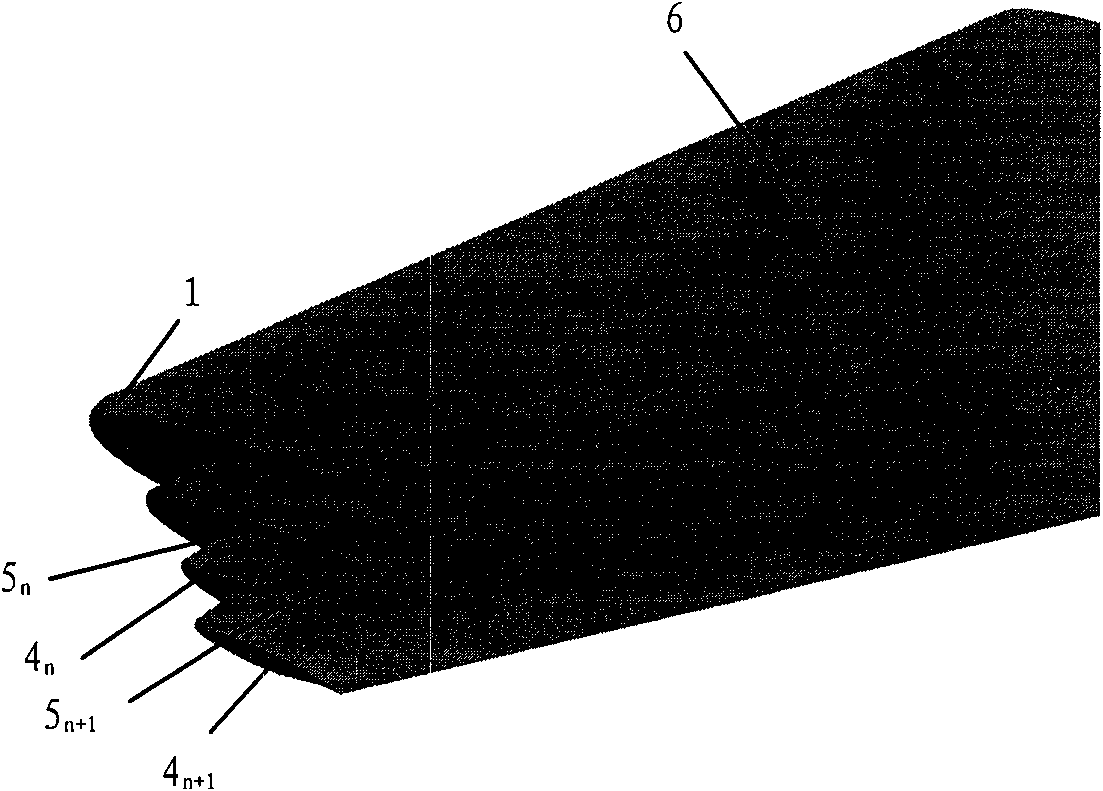
ActiveCN102167152ASmall bending moment incrementReduce structural weightWing shapesDrag reductionWingtip deviceFront edge
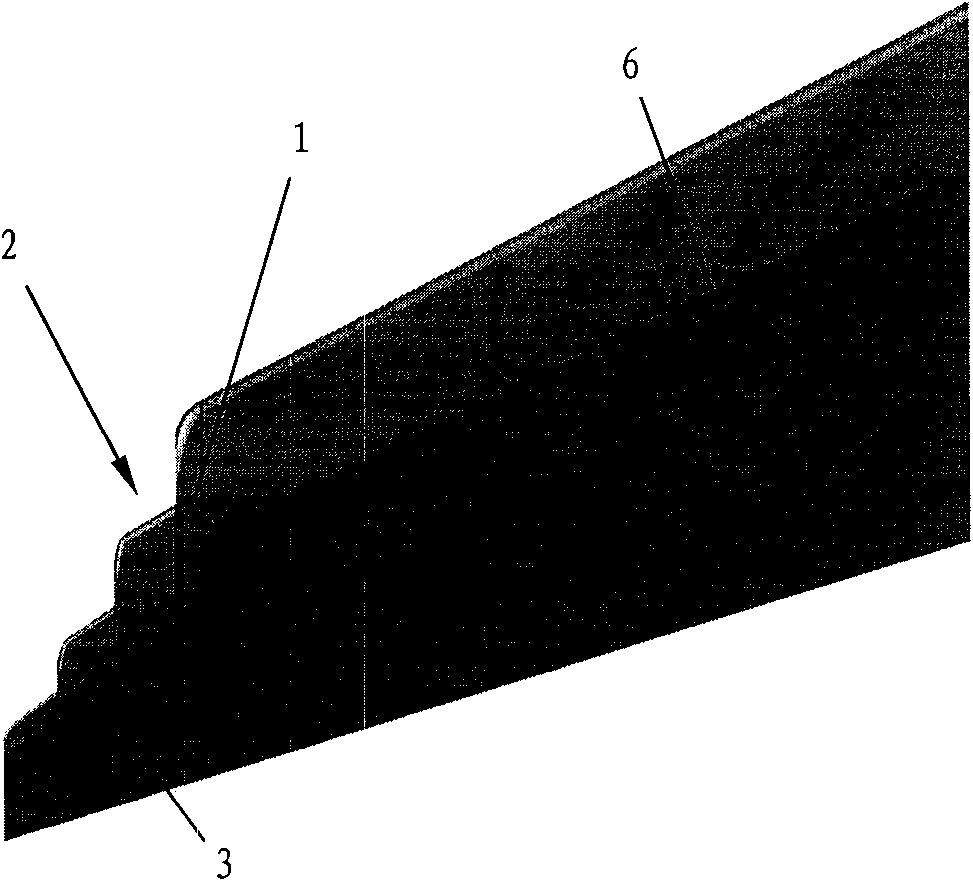
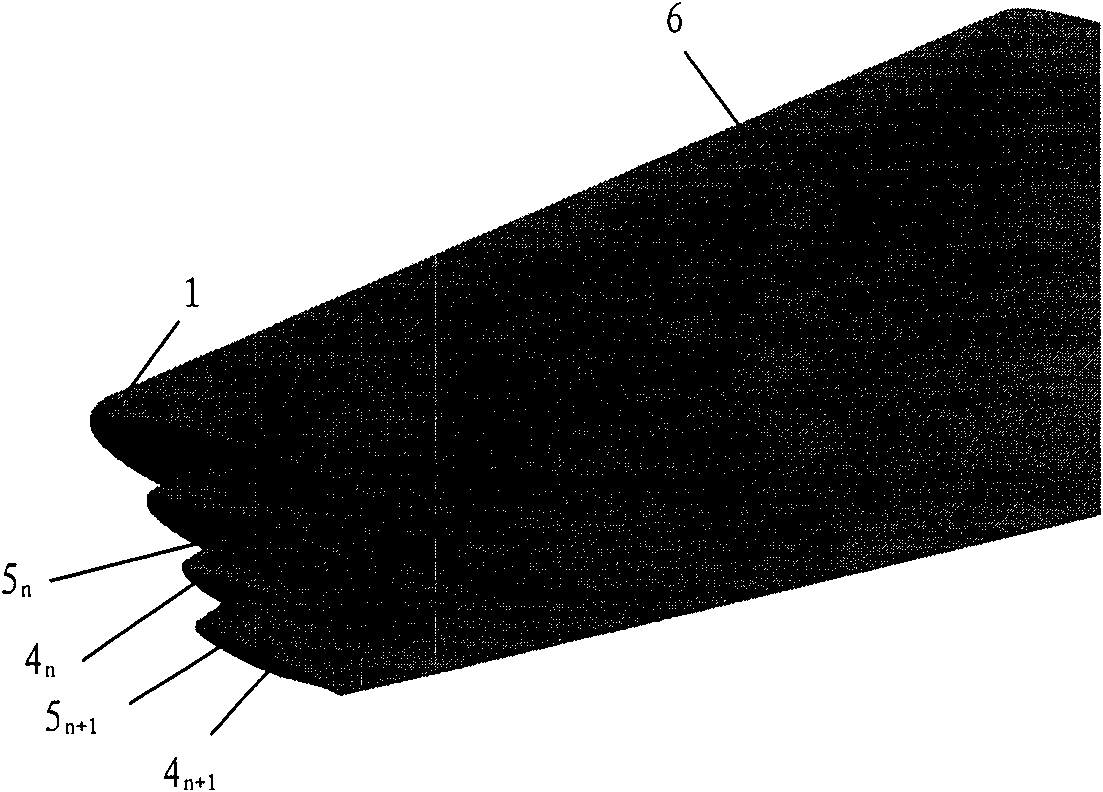
The invention provides an airplane wingtip device with an aligned front edge, which comprises a transition part and a wingtip part, wherein the inside end of the transition part is connected with the far end of an airplane wing, the outside end of the transition part is connected with the wingtip part, the wingtip part comprises a plurality of wingtip segments, each wingtip segment comprises a wingtip and a wing root, the wing root of the first wingtip segment is connected with the outside end of the transition part and is aligned with the front edge at the outside end of the transition part, the wing root of the (n+1)th wingtip segment is arranged on the wingtip of the nth wingtip segment, and the wing root chord length of the (n+1)th wingtip segment is less than or equal to the wingtip chord length of the nth wingtip segment, wherein n is more than 0. The wingtip device is step-shaped, so that each wingtip is additionally provided with at least one of discontinuity surfaces, the wingtip vortexes induced by the wingtips are restrained with one another, and the vortex intensity is reduced, therefore the airplane wingtip device achieves a damping effect; and the bending moment incremental quantity of each wing root is less, so that the structural weight of the airplane is reduced, and the influence on the buffeting characteristic is less.
Owner:COMAC +1
Vertical take-off and landing unmanned aerial vehicle with vectored thrust duct engines
ActiveCN107985589AFlying fastFlexible postureRemote controlled aircraftAlighting gearWingtip deviceFixed wing
The invention discloses a vertical take-off and landing unmanned aerial vehicle with vectored thrust duct engines. The unmanned aerial vehicle includes a vehicle body, wings and a vertical tail are separately fixedly installed at the middle and the tail of the vehicle body, the tail ends of the wings are provided with wingtips, vectored thrust duct engines are installed below the wings, and the vertical tail and the wingtips are provided with take-off and landing buffering mechanism. The vertical take-off and landing unmanned aerial vehicle with the vectored thrust duct engines uses the take-off and landing buffering mechanism to vertically take off and land, the flight speed of fixed wing unmanned aerial vehicle is possessed on the one hand, the vertical take-off and landing unmanned aerial vehicle with the vectored thrust duct engines can vertically take off and land and hang in the air like a rotor unmanned aerial vehicle, and the dependency of the unmanned aerial vehicle for sitesand runways is greatly reduced.
Owner:SHENYANG AEROSPACE UNIVERSITY
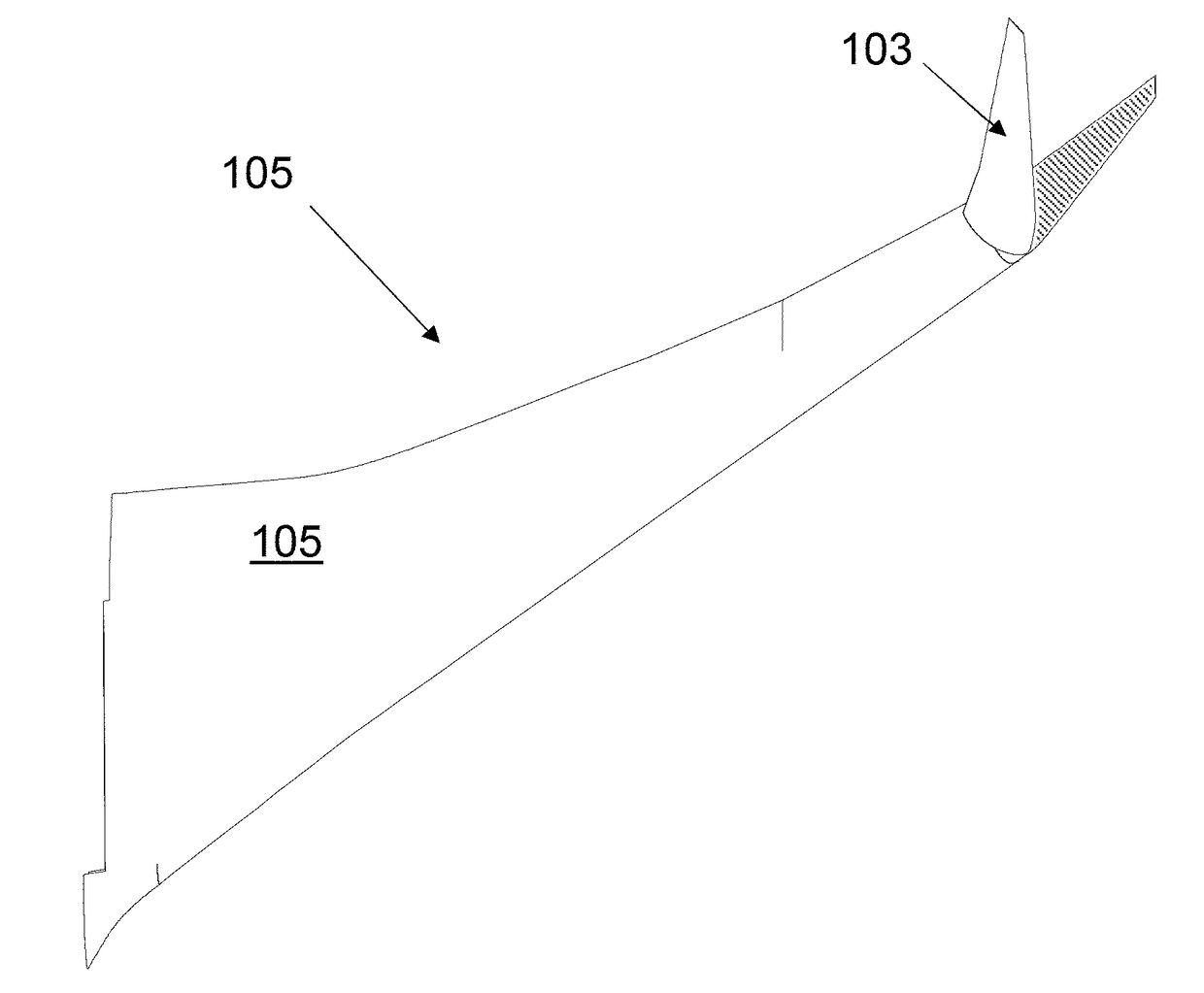
Arrangement of ribs at an interface between an outer end of a wing and a moveable wing tip device
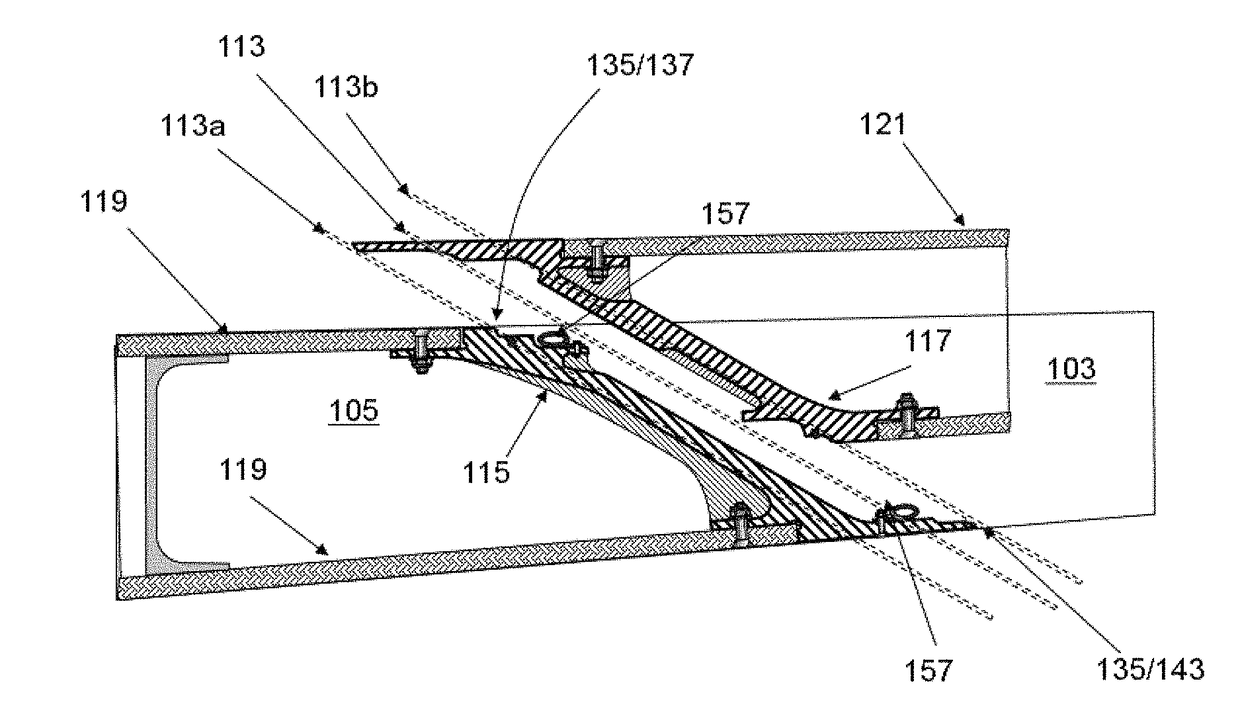
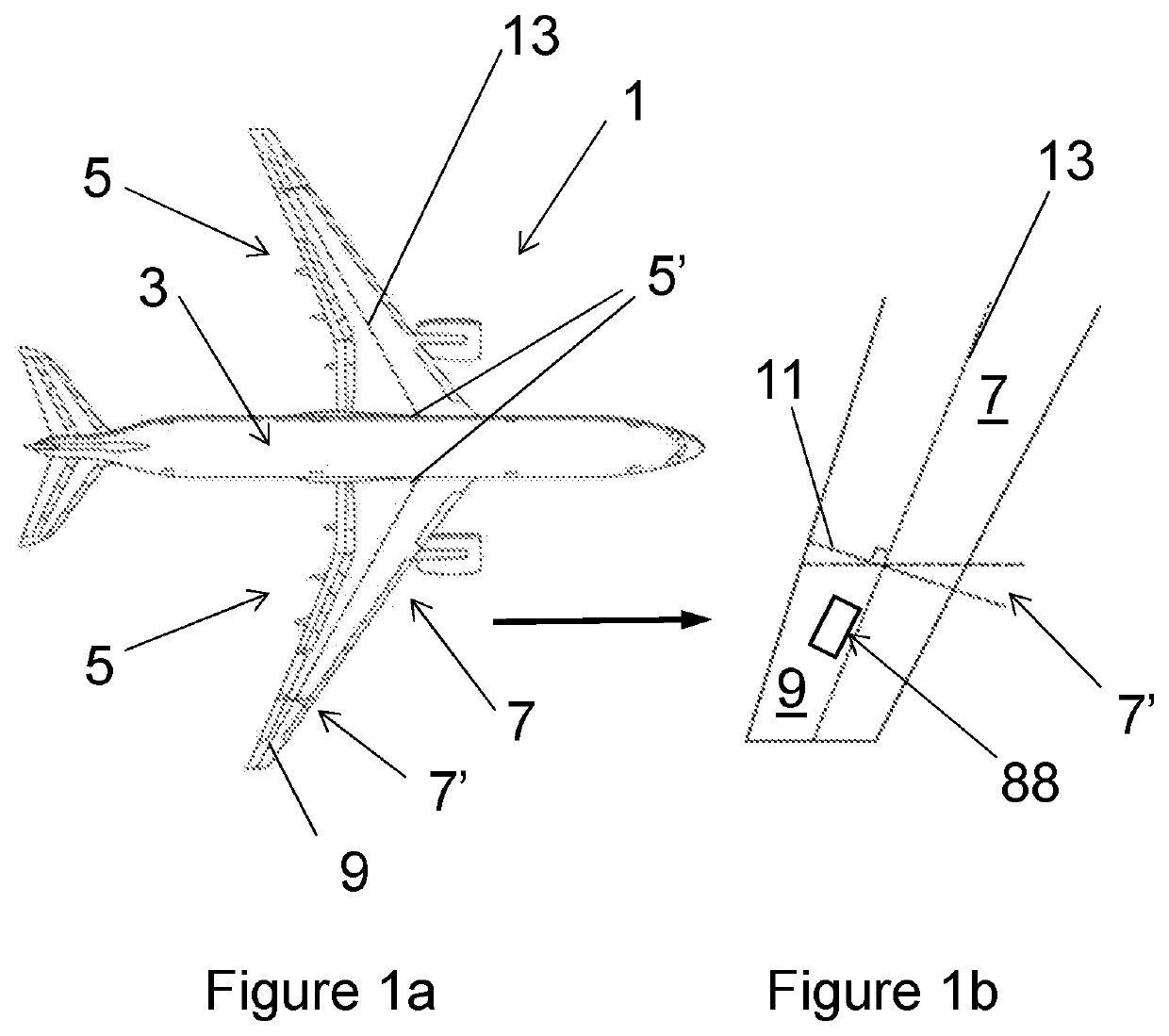
An aircraft (102) having a wing assembly (101) including a fixed wing (105) with a wing tip device (103). The wing tip device (103) is moveable between: a flight configuration; and a ground configuration. The outer end of the fixed wing (105) terminates at an outer rib (115), and the inner end of the wing tip device (103) terminates at an inner rib (117). The outer and inner ribs (115, 117) are located on opposing sides of an interface between the fixed wing (105) and the wing tip device (103). The fixed wing-skin (119) terminates inwardly of the interface, but the outer rib (115) has a surface-forming portion (127) forming an extension of the fixed wing-skin towards the interface. The wing tip device-skin (121) terminates outwardly of the interface, but the inner rib has a surface-forming portion (129) forming an extension of the wing tip device-skin towards the interface.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD
Rotational joint for an aircraft folding wing
ActiveUS20180222569A1Reduce concentrated loadPrecise alignmentWing adjustmentsDrag reductionLocking mechanismWingtip device
An aircraft (2) including a wing (1), the wing (1) having a fixed wing (3) and a wing tip device (4) at the tip of the fixed wing (3), the wing tip device (4) being rotatable relative to the fixed wing (3) between flight and ground configurations, the aircraft including a rotational joint (10) with a rotation mechanism (11) that rotatably couples the wing tip device (4) to the fixed wing (3) and a locking mechanism including a locking bore (53, 54) and a locking pin (51) that is receivable in the locking bore to lock the wing tip device (4) in one of the flight or ground configurations, wherein the rotational joint includes an alignment mechanism including an alignment pin (61) and an alignment bore (62, 63) and at least one of the alignment pin and alignment bore is tapered such that engagement of the alignment pin (61) in the alignment bore acts to guide the locking bore and locking pin into alignment.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD
Arrangement for effecting movement of a wing tip device between a flight configuration and a ground configuration
ActiveUS10137977B2Simple and reliable actuationLocking/braking the actuator is reducedInfluencers by generating vorticesWing adjustmentsWing configurationActuator
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD
Dual-purpose locking and folding arrangement for an aircraft wing tip device
ActiveUS20170152015A1Easy to unlockRelieve the static bending momentWith power amplificationServomotorsClassical mechanicsWingtip device
An aircraft (5) including a wing (7) having a wing tip device (1) configurable between: a flight configuration and a ground configuration in which the span of the wing (7) is reduced. The aircraft (5) further includes a lock (13) for locking the wing tip device (1) in the flight configuration, and an actuator (3) for unlocking the lock (13) and for subsequently actuating the wing tip device (1) to the ground configuration. The actuator (3) is a two-stage hydraulic actuator, including a first hydraulic actuator stage (21) arranged to unlock the lock and a second hydraulic actuator stage (23) arranged to actuate the wing tip device (1) to the ground configuration. The first and second hydraulic actuator stages (21, 23) are arranged in series such that the second actuator stage (23) is unable to receive a hydraulic input feed until the first actuator stage (21) unlocks the lock (13).
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD
Interface between an outer end of a wing and a moveable wing tip device
ActiveUS20170355439A1Increase the areaEasy to separateEngine sealsWing adjustmentsFixed wingAirplane
An aircraft (102) including a wing (101), having a fixed wing (105) with a wing tip device (103) moveably mounted at the outer end thereof. The wing tip device (103) is moveable between: a flight configuration; and a ground configuration. The wing tip device (103) and the fixed wing (105) are separated along an oblique primary cut plane (113). The wing tip device (103) and the fixed wing (105) meet along an interfacing cut line (135). The interfacing cut line (135) comprises a first length (137) offset from the primary cut plane (113) in a first direction; a second length (141) offset from the primary cut plane (113) in a second direction, opposite to the first direction; and a transition section (139) over which the interfacing cut line (135) transitions from the first length to the second length.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD
Overall design of tilt-rotor aircraft
The invention provides overall design of a tilt-rotor aircraft. According to the technical scheme, a wing arrangement structure and power distribution of the aircraft are provided. The aircraft comprises a fuselage, front wings, T-shaped emages, winglets and a rear wing. The ends of the front wings are provided with the winglets. The rear wing is connected with the main wings through a connecting plate and connected with the fuselage. The T-shaped emages are arranged on the rear portion of the whole aircraft. Three engines are further mounted and independently move. The included angles between the axial directions of the engines and the horizontal plane during vertical take-off and landing of the aircraft are 80-100 degrees. The rotating speeds and the angles of the engines are adjusted through a flight control system. The engines assist to control the posture of the aircraft. When the aircraft tilts, the engines forward rotate till the included angles between the axial directions of the engines and the horizontal plane are zero degree.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
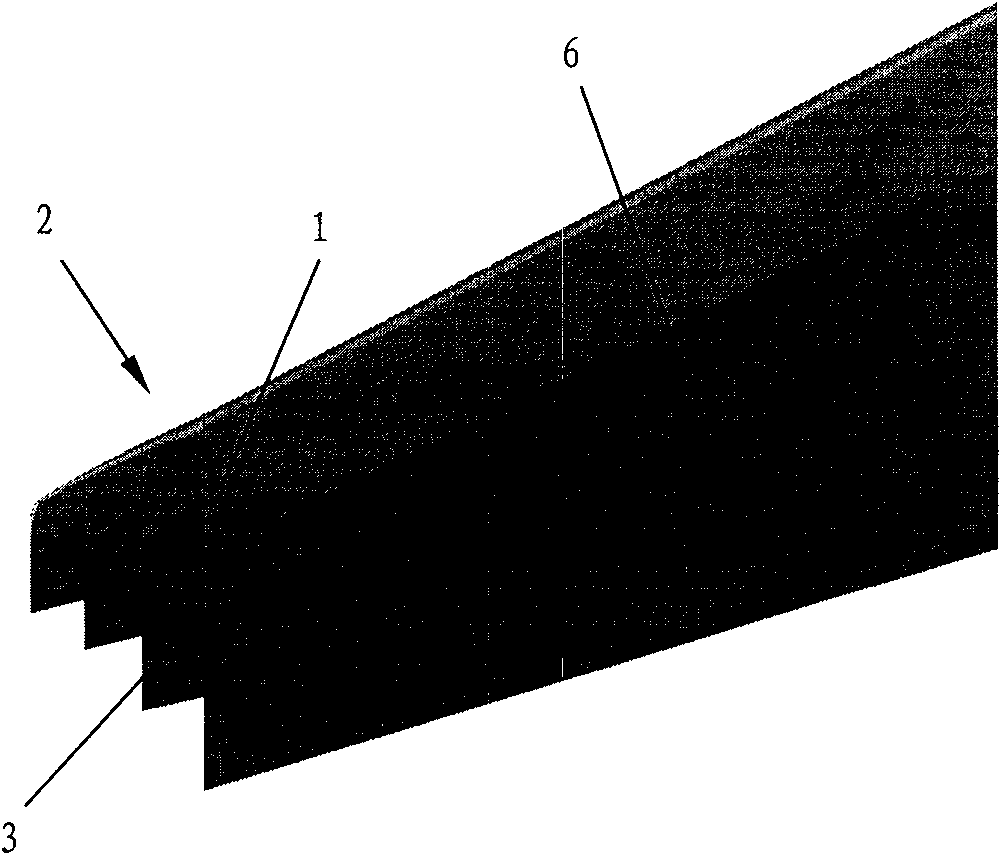
Airplane wingtip device with aligned back edges
ActiveCN102167153ASmall bending moment incrementReduce structural weightWing shapesHeat reducing structuresJet aeroplaneWingtip device
The invention discloses an airplane wingtip device, which comprises a transition part and a wingtip part, wherein the end part of the inner side of the transition part is connected with the far end of an airplane wing; the end part of the outer side of the transition part is connected with the wingtip part; the wingtip part comprises a plurality of wingtip sections; each wingtip section comprises a wingtip and a wing root respectively; the wing root of the first wingtip section is connected with the end part of the outer side of the transition part, and is aligned with the back edge of the end part of the outer side of the transition part; the wing root of the (n+1)th wingtip section is positioned on the wingtip of the nth wingtip section; the chord length of the wing root of the (n+1)th wingtip section is smaller than or equal to that of the wingtip of the nth wingtip section; and n is more than 0. The wingtip device disclosed by the invention is arranged in a step form, and each wingtip is provided with more than one discontinuity surface, so that wingtip vortexes induced from the wingtips suppress one another, the vortex intensity is weakened, and the resistance reducing effect is achieved; moreover, the bending moment increment of the wing roots is smaller, so that the structural weight of the airplane is lightened, and the influence on flutter characteristic is smaller.
Owner:COMAC +1
Helicopter with separated tip jet device and main rotor wing
The invention discloses a helicopter with a separated tip jet device and a main rotor wing. The tip jet device is arranged at the front end of a power wing, an output shaft of the power wing is connected with the main rotor wing through a decelerator system so that the rotating speed of the main rotor wing is lower than that of the power wing; and the output shaft of the power wing, a deceleratorand an output shaft of the decelerator are hinged with a helicopter body. The helicopter solves the problem that the tip jet device of the known tip jet type helicopter has high efficiency at supersonic speed while the propulsive efficiency of the main rotor wing declines when the wing tip linear speed is at the supersonic speed; and the working efficiency of the tip jet device and the propulsiveefficiency of the main rotor wing achieve best states.
Owner:余志刚
Folding wing tip and rotating locking member
ActiveUS20170334543A1Prevent rotationReduce and prevent locking pin hoggingWing adjustmentsDrag reductionEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD
Unmanned aerial vehicle
Owner:尹鸿俊
Four-duct flying-wing type unmanned aerial vehicle
InactiveCN106628115AEnhanced heading stabilityConvenient ArrangementAircraft navigation controlHeat reducing structuresLow noiseAttitude control
The invention discloses a four-duct flying-wing type unmanned aerial vehicle which comprises ducts, fans, winglets and a flying-wing type wing, wherein symmetric winglets are mounted on the tip of the flying-wing type wing; four duct fan power systems are mounted on the winglets respectively; and the fans are arranged in the ducts. The invention has the following effects: (1) the four-duct flying-wing type unmanned aerial vehicle has the advantages of fast cruise, vertical take-off and landing, hovering, low noise, autonomous flight and easiness in control; and (2) control of multiple attitudes can be realized, the control method is simpler with high flexibility and is more helpful to implementing specific tasks in complicated special conditions.
Owner:YANTAI NANSHAN UNIV
Actuation assembly with a track and follower for use in moving a wing tip device on an aircraft wing
ActiveUS10464658B2Span of the aircraft wing is reducedReduce spanWing adjustmentsDrag reductionWingtip deviceFixed wing
An aircraft wing having a wing tip device at the tip thereof is disclosed. The wing tip device is configurable between: a flight configuration for use during flight and a ground configuration for use during ground-based operations to reduce span. In the flight configuration, flight loads may be transferred via a load transfer arrangement from the wing tip device into the fixed wing, but during movement of the wing tip device towards the ground configuration, the load transfer arrangement is disengaged. The wing includes an actuation assembly having a sliding chassis coupled to the wing tip device, via a track and follower arrangement. The track includes a wide portion and a narrow portion.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD
Wing or blade design for wingtip device, rotor, propeller, turbine, and compressor blades with energy regeneration
InactiveUS20190101128A1Reduce wingtip vortexEasy to liftPropellersInfluencers by generating vorticesEnergy regenerationWingtip device
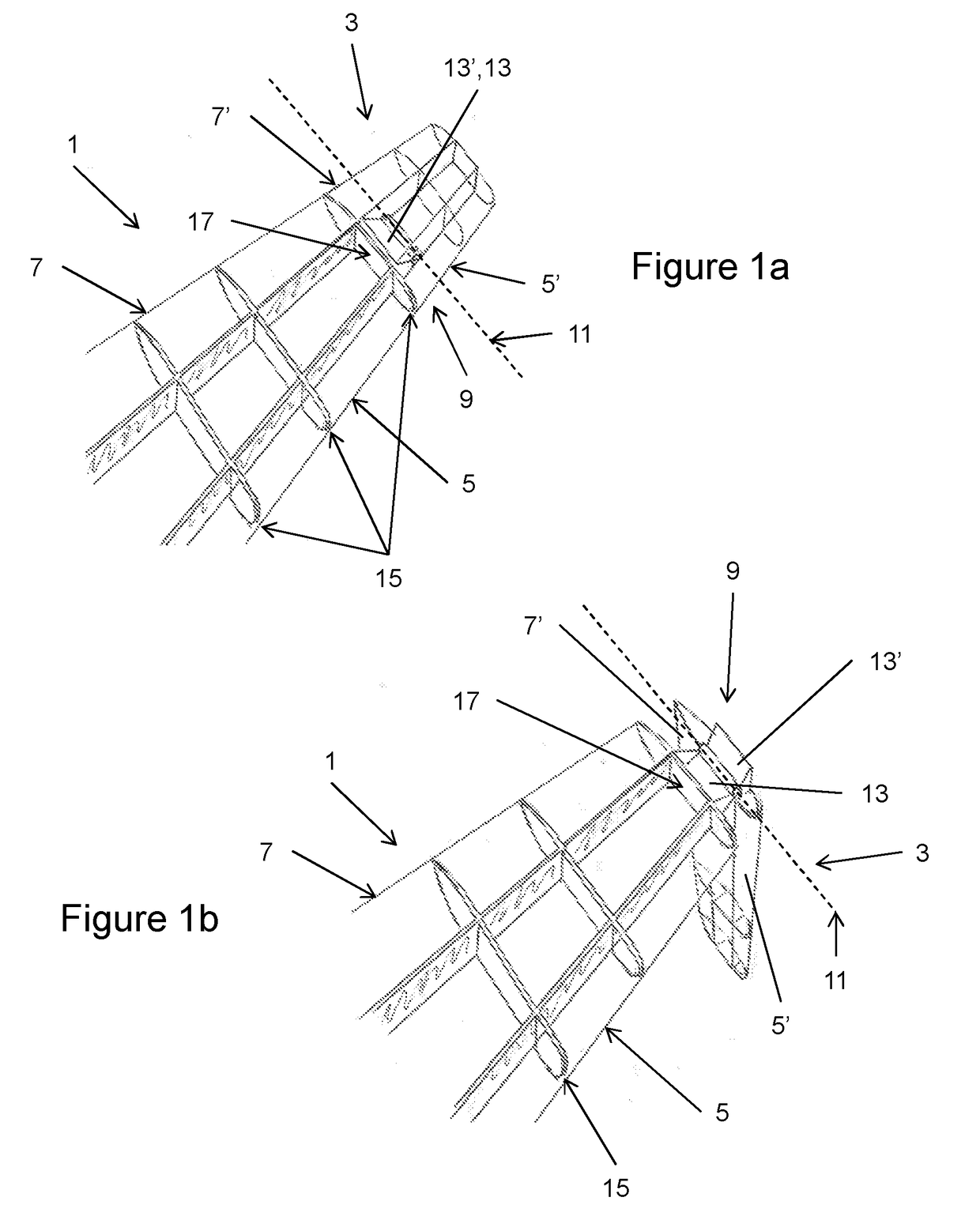
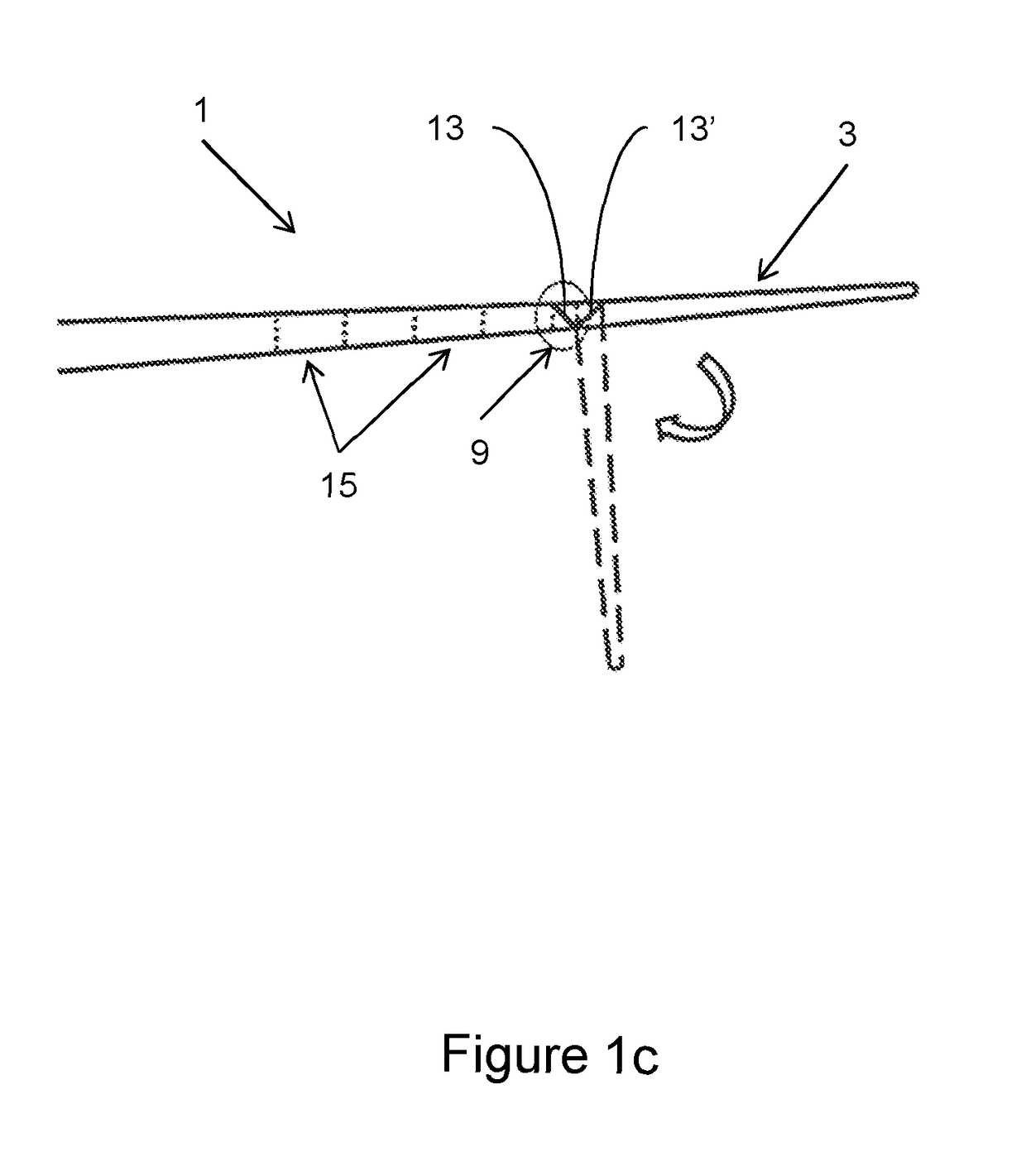
The new wing or blade design for wingtip device, rotor, propeller, turbine, and compressor blades with energy regeneration can be used to generate lift, propel vehicles more efficiently, compress fluids more efficiently, harness energy more efficiently. This system can be used as a wing, as a wingtip device, as a propeller for aircraft or boats or any vehicle moving through a fluid, in a compressor, as a rotor for wind turbine or helicopter, in a gas turbine. The new wing or blade design for wingtip device, rotor, propeller, turbine, and compressor blades with energy regeneration is a series of low aspect ratio wings placed in parallel with gaps between them connected by smaller wings that are placed in the gaps to harness the energy and produce forces; the gaps are shaped to decelerate the fluid and / or accelerate the fluid by varying the cross-sectional area of the gaps. Even if the small aspect ratio makes those wings inefficient, the strength of the vortices is smaller in the gaps.
Owner:MBODJ PAPA ABDOULAYE
Airplane wingtip device
ActiveCN102167154ASmall bending moment incrementReduce structural weightWing shapesHeat reducing structuresJet aeroplaneWingtip device
The invention provides an airplane wingtip device which comprises a transition part and a wingtip part. The inner end part of the transition part is connected with the far end of an airplane wing, and the outer end part of the transition part is connected with the wingtip part; the wingtip part comprises a plurality of wingtip sections; and each wingtip section comprises a wingtip and a wing root respectively, the wing root of the first wingtip section is connected with the outer end part of the transition part, and arranged between the first edge and rear edge of the outer end part of the transition part, the wing root of the (n+1)th wingtip section is placed on the wingtip of the nth wingtip section, and the wing root chord length of the (n+1)th wingtip section is smaller than the wingtip chord length of the nth wingtip section, wherein n is larger than 0. The wingtip device provided by the invention is arranged in a step shape, so that more than one discontinuity surface is added on each wingtip of the wingtip device, wingtip vortexes induced by the wingtips are mutually inhibited, the vortex intensity is weakened, and the effect of reducing resistance is achieved. In addition, the wing root bending moment increment is smaller, the structural weight of an airplane is reduced, and the influence on the flutter characteristic is smaller as well.
Owner:COMAC +1
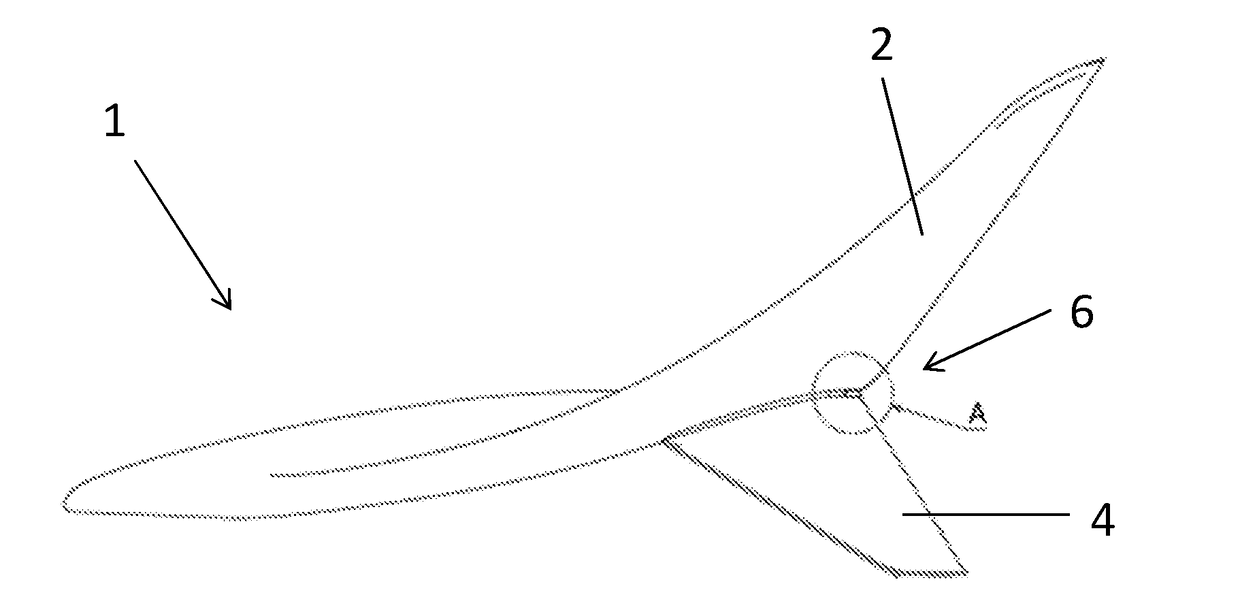
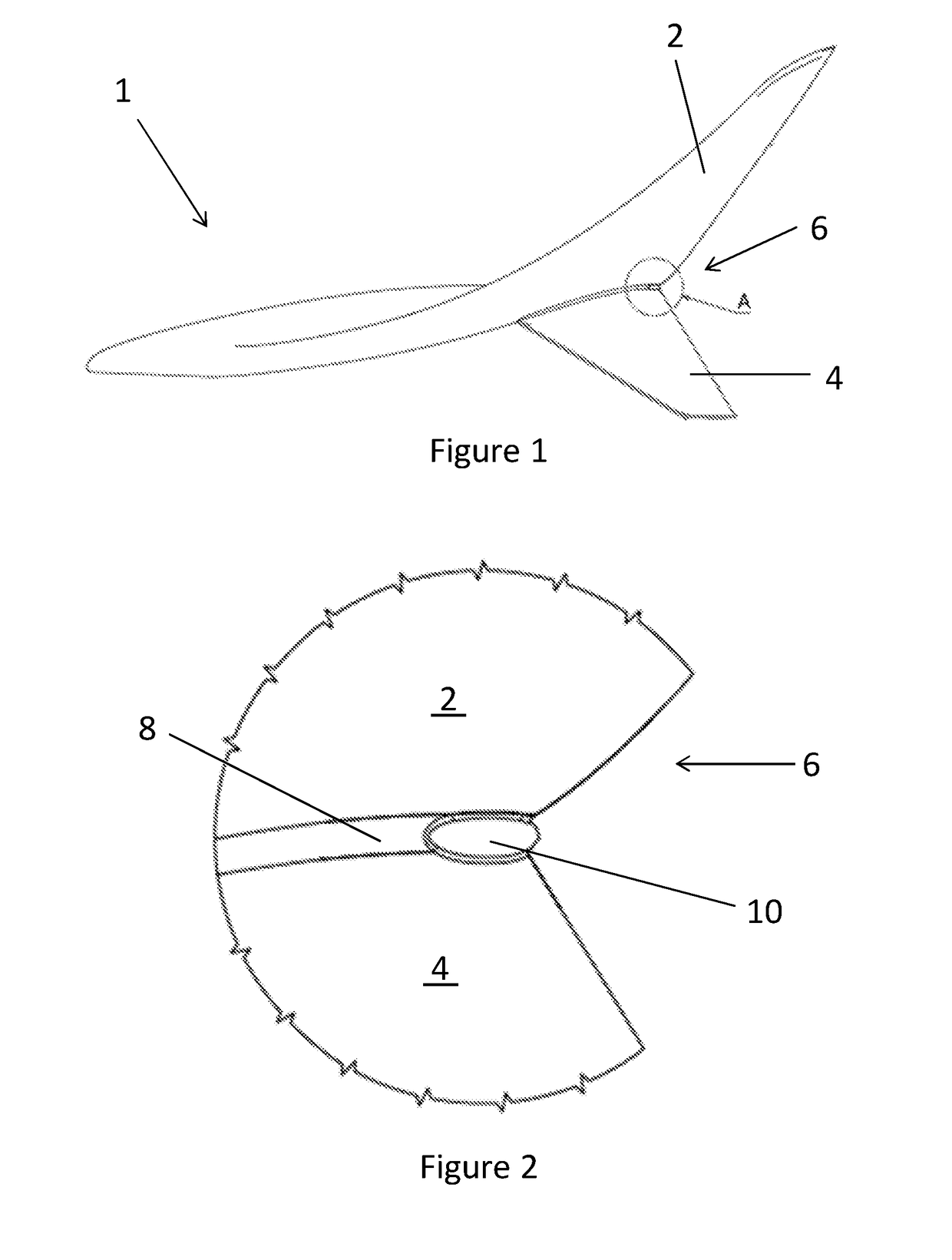
Aircraft light
InactiveUS20180009548A1Facilitate of lightReduce resistanceInfluencers by generating vorticesAircraft lightsWingtip deviceAirplane
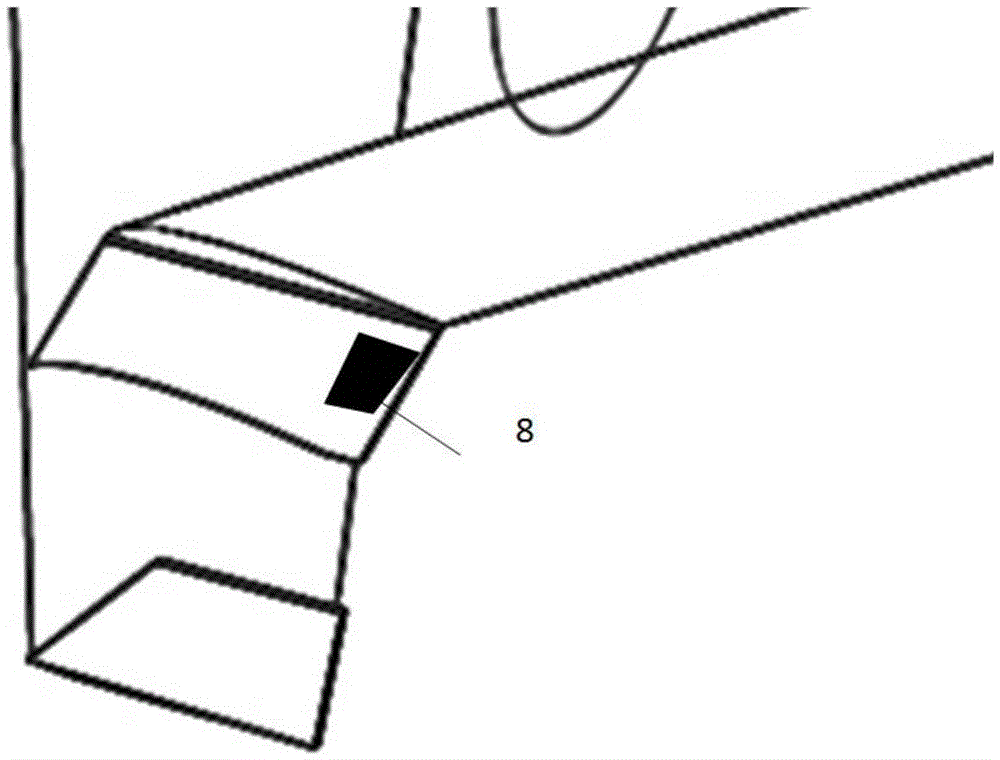
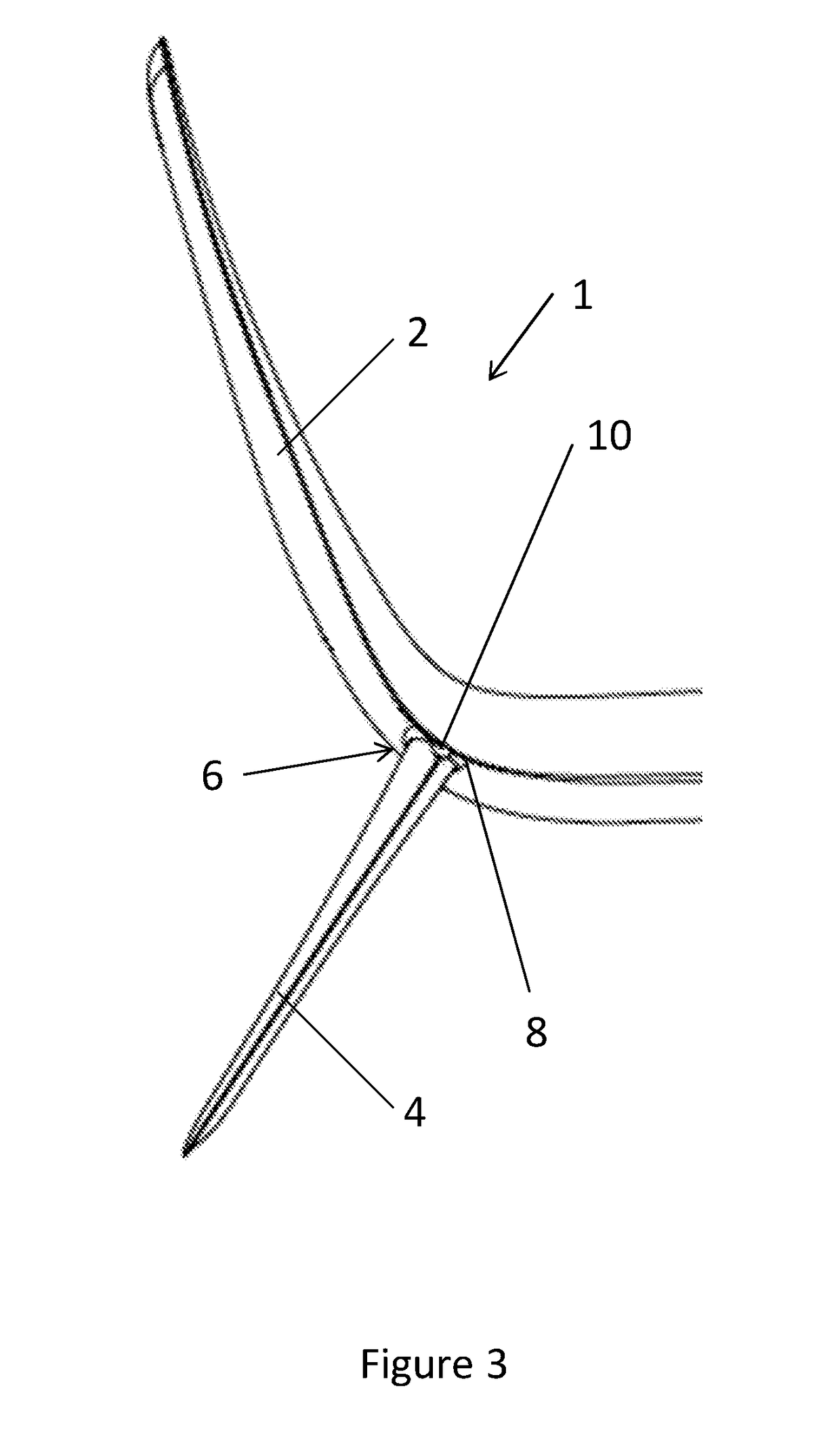
A wingtip device 1 including an upwardly extending winglet 2 and a downwardly extending winglet 4. The downwardly extending winglet 4 is connected to the upwardly extending winglet 2 at a join 6. An aircraft light 10 is located at the join 6 between the upwardly extending winglet 2 and the downwardly extending winglet 4.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD
Apparatus, aircraft and method for moving a wing tip device away from a load-alleviating configuration
ActiveUS20200130816A1Reduce load capacityBig spaceInfluencers by generating vorticesAircraft stabilisationAerodynamic loadFlight vehicle
An aircraft (1) including a fixed wing (7) and a wing tip device (9) moveably mounted thereon. The wing tip device (9) is movable from a load-alleviating configuration to a flight configuration. The wing tip device includes an airflow channel (88) extending between respective apertures (83, 84) on the upper surface and lower surface of the wing tip device. The channel (88) is configurable between an open state in which air can flow through the channel and a closed state in which the airflow through the channel (88), via the apertures (83, 84), is blocked. The channel (88) is configured such that when the wing tip device (9) is in the load-alleviating configuration and the channel (88) is in the open state, the aerodynamic loading on the wing tip device in flight urges the wing tip device towards the flight configuration.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com