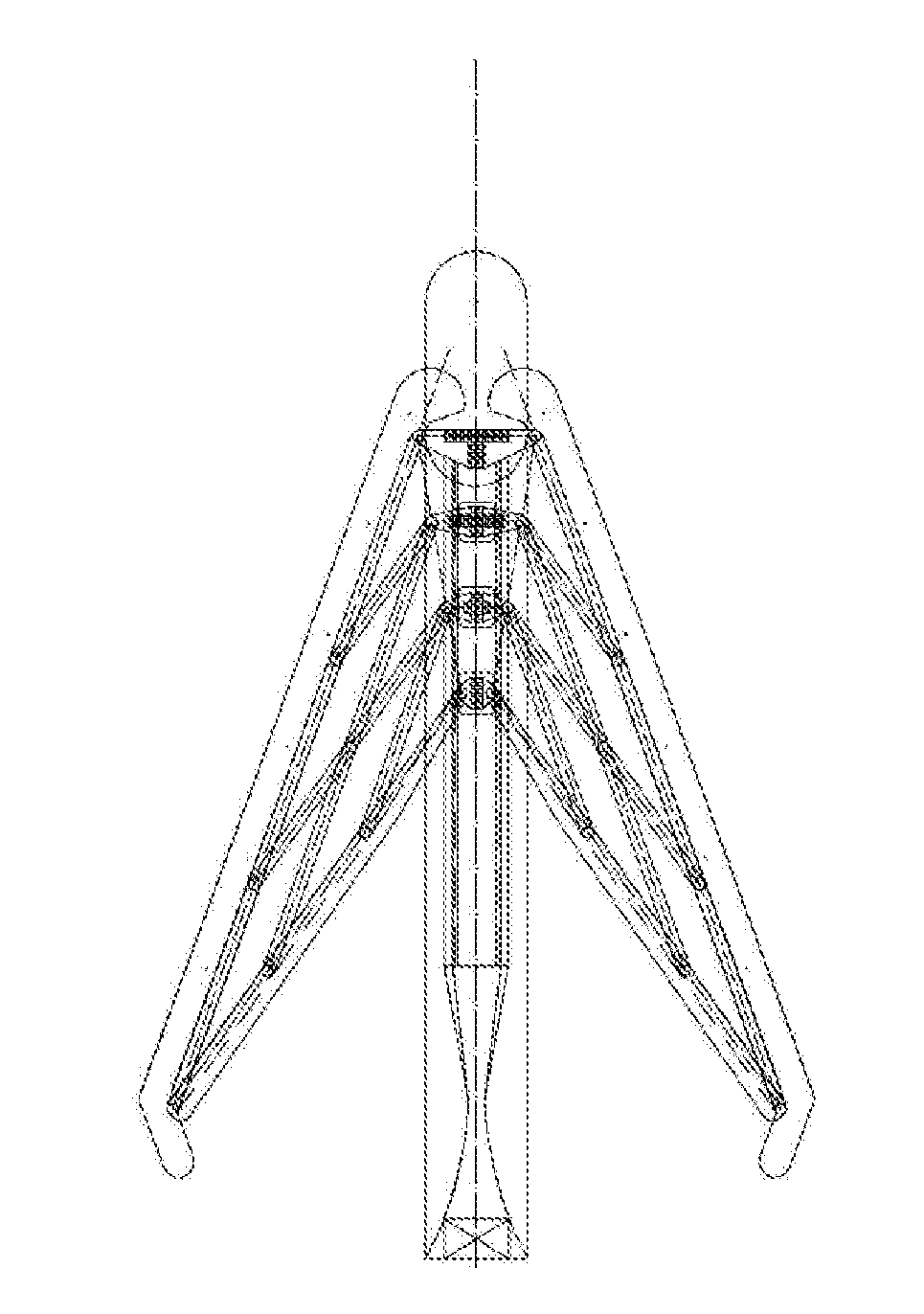
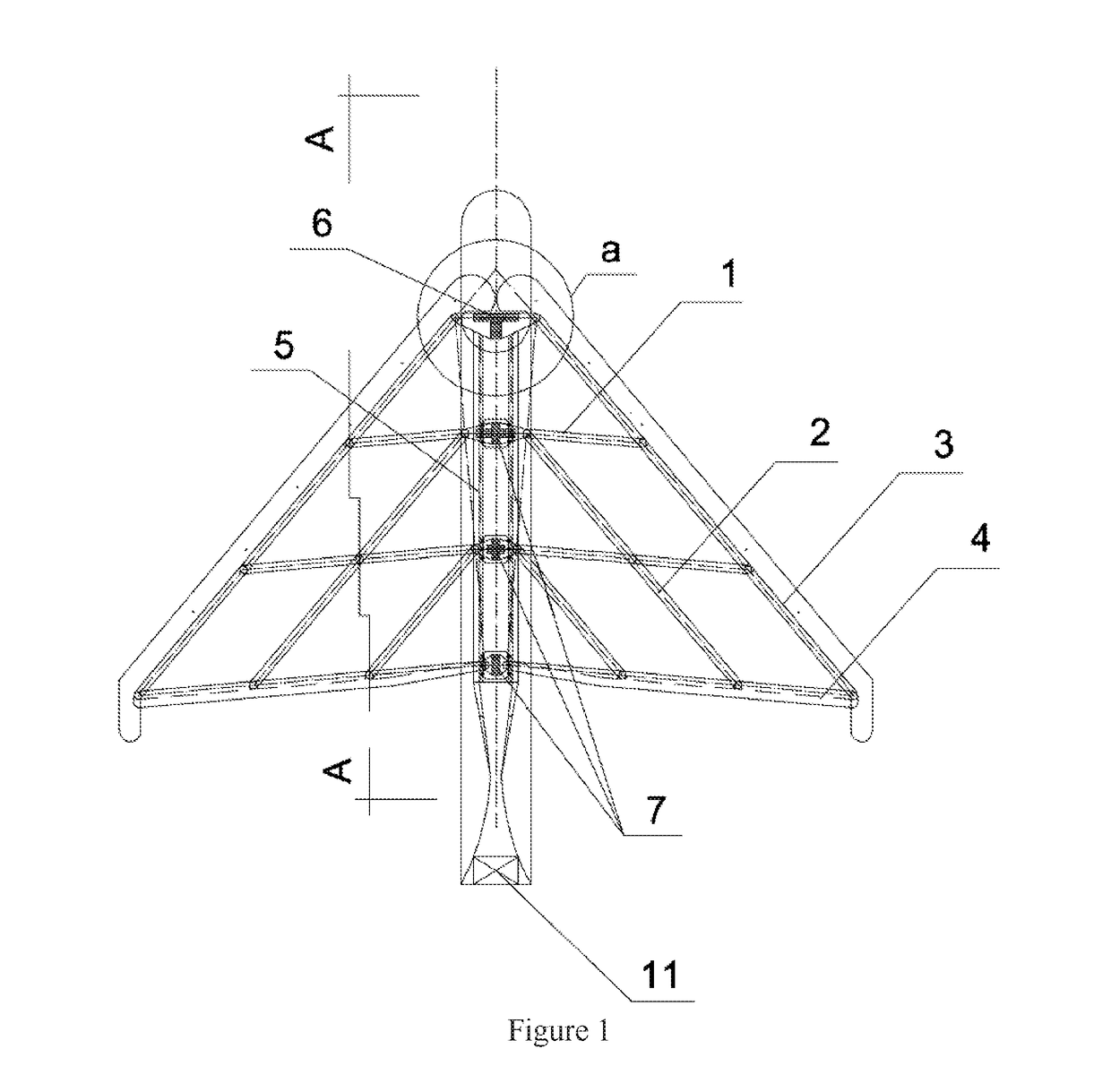
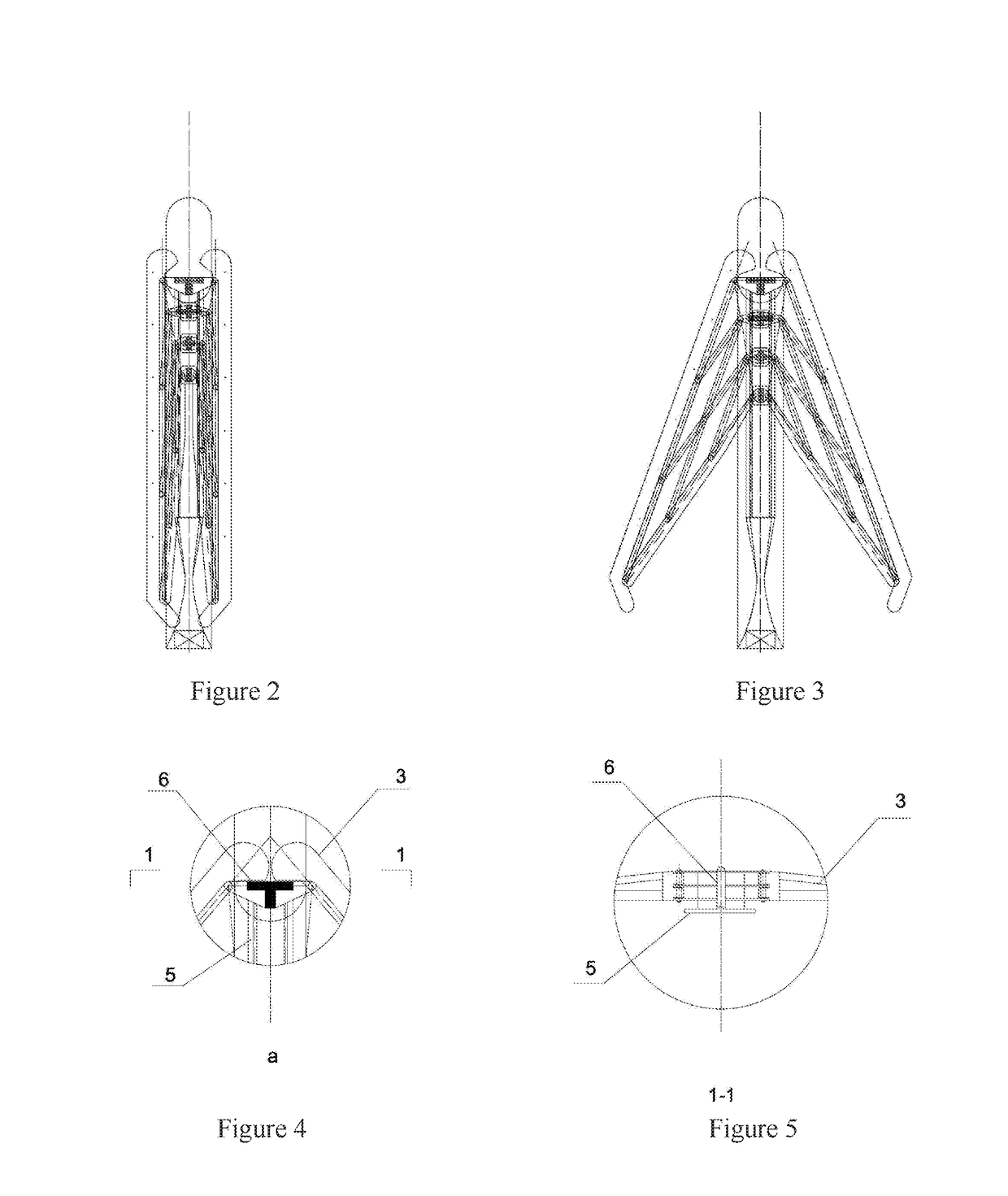
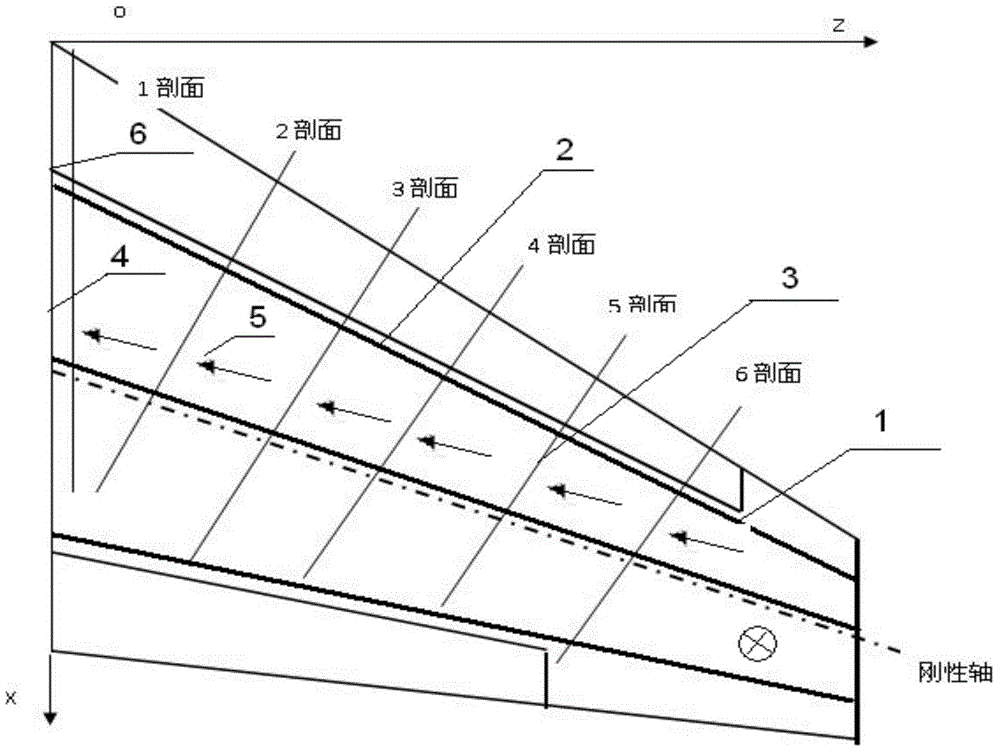
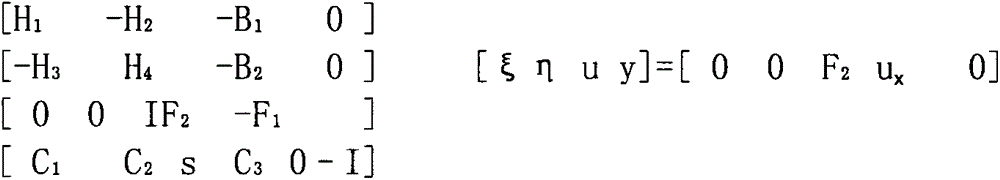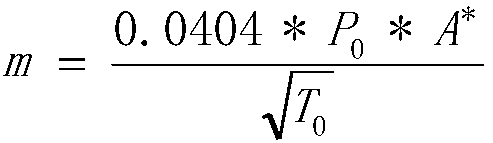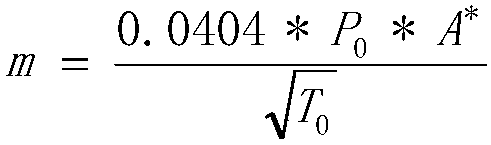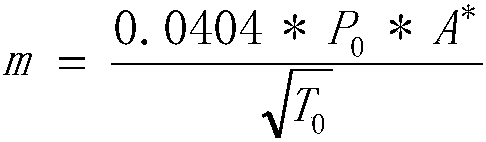Patents
Literature
364 results about "Aerodynamic load" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In aerodynamics, load factor is the ratio of the maximum load an aircraft can sustain to the gross weight of the aircraft.
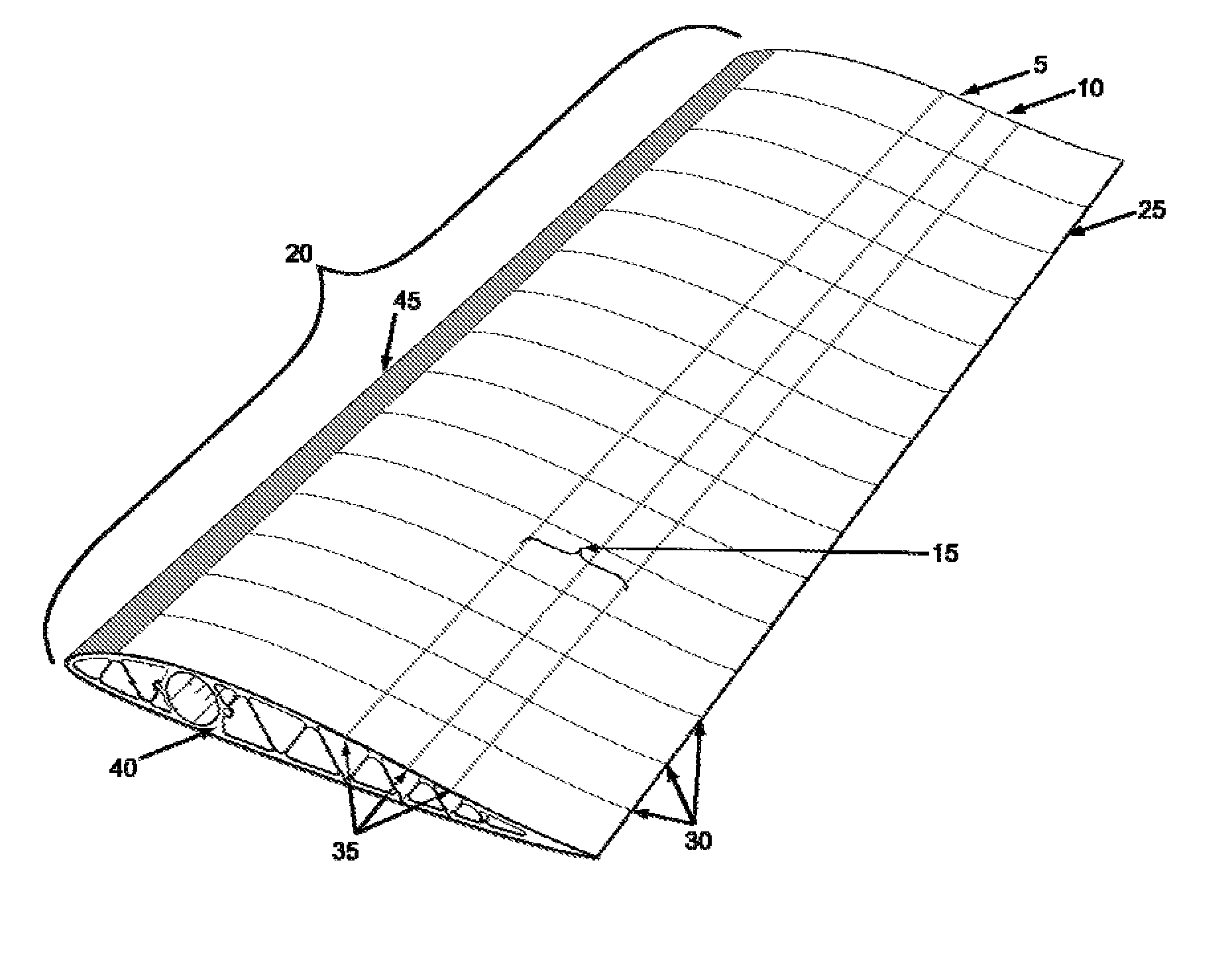
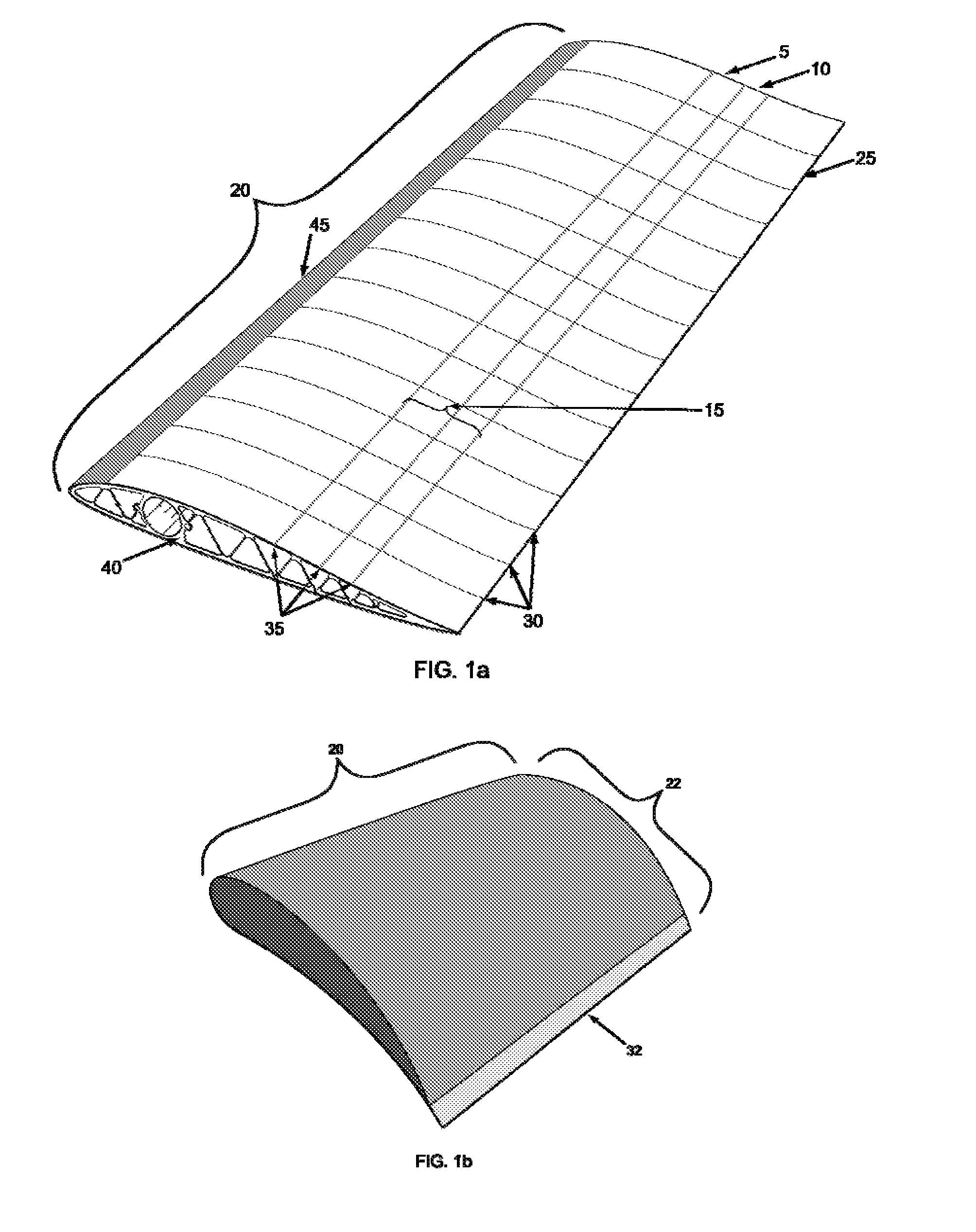
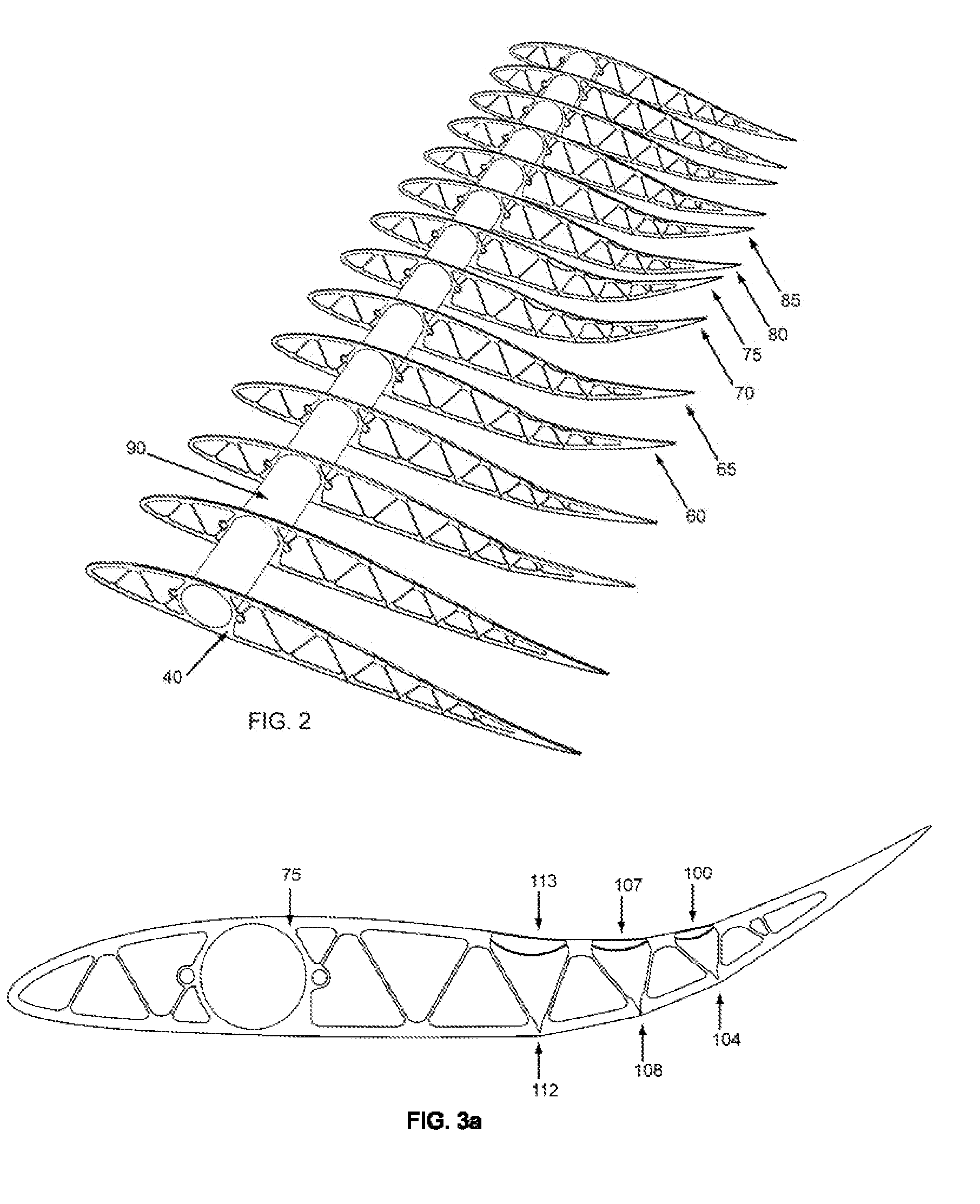
Passive adaptive structures
ActiveUS20110084174A1Reduce quality problemsMinimizing weight penaltyPropellersRotary propellersMorphingAerodynamic drag
Morphing an aerodynamic body's geometry in situ can optimize its aerodynamic properties, increasing range, reducing fuel consumption, and improving many performance parameters. The aerodynamic load exerted on the body by the flow is one such parameter, typically characterized as lift or drag. It is the aim of the present disclosure to teach the use of passive adaptive morphing structures to manage these aerodynamic loads.
Owner:CORNERSTONE RES GROUP
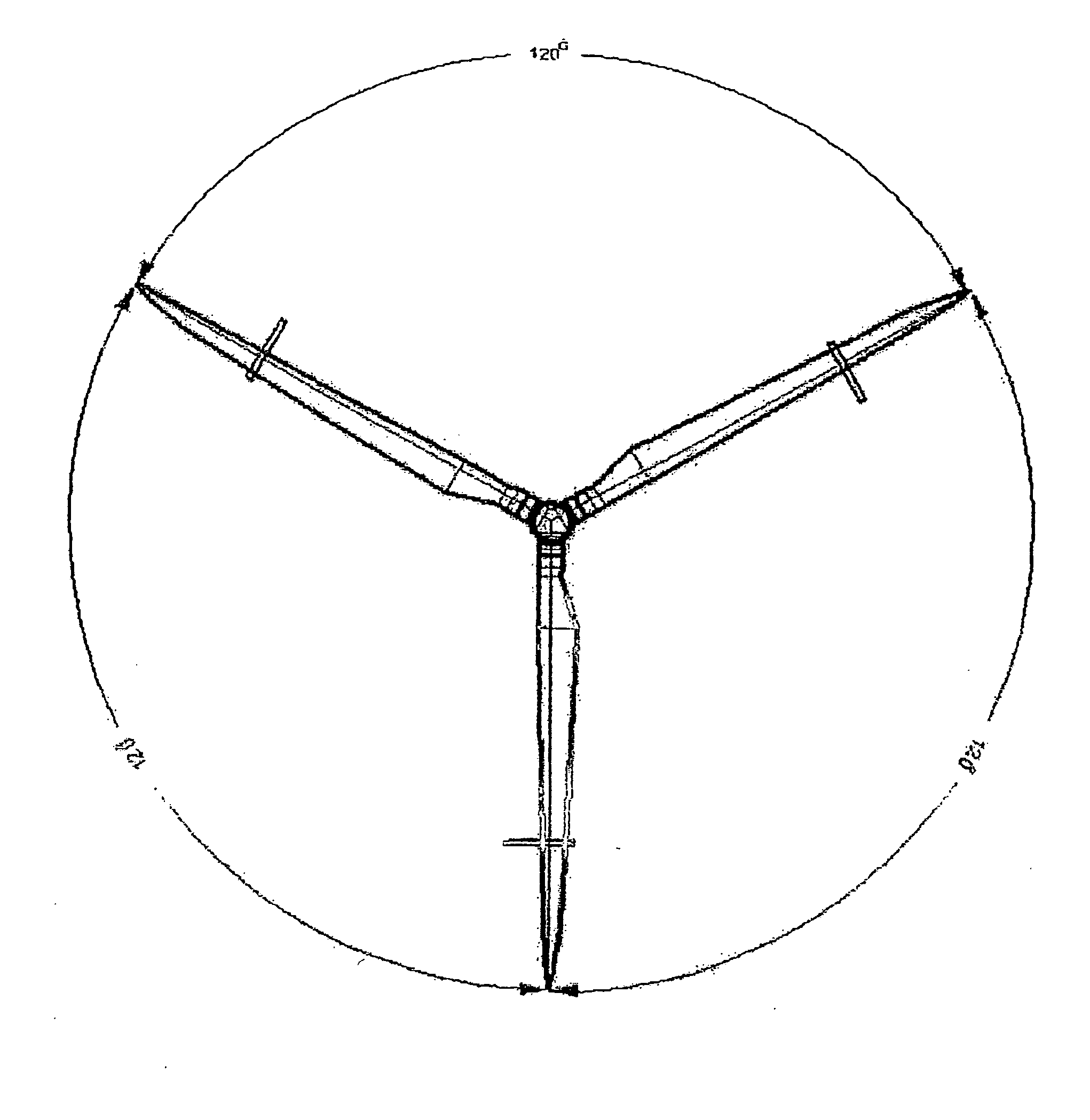
Method of controlling aerodynamic load of a wind turbine based on local blade flow measurement
The present invention relates to a method of controlling the aerodynamic load of a wind turbine's blades individually in such a way that the dynamic aerodynamic loads on the turbine are reduced and power production is optimised. In general the present invention will improve the overall stability of the turbine leading to reduce fatigue loads, reduced extreme loads during operation and reduced risk of blade-tower interaction. In particular preferred embodiment of the invention, flow properties are measured locally on the different blades or in front of the blades and from these measurements the pitch angle settings are changed, in other ways changing the aerodynamic properties, for the blades through a control unit.
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
Passive adaptive structures
ActiveUS20110042524A1Reduce quality problemsMinimizing weight penaltyPropellersControl initiation meansMorphingAerodynamic drag
Morphing an aerodynamic body's geometry in situ can optimize its aerodynamic properties, increasing range, reducing fuel consumption, and improving many performance parameters. The aerodynamic load exerted on the body by the flow is one such parameter, typically characterized as lift or drag. It is the aim of the present disclosure to teach the use of passive adaptive morphing structures to manage these aerodynamic loads.
Owner:CORNERSTONE RES GROUP
Application and design for embedding bionic honeycomb-shaped active safety escape capsule into aircraft
The invention provides the application and design for embedding a bionic honeycomb-shaped active safety escape capsule into an aircraft. The application and design comprise the following related technologies including redesign of a main machine body of the aircraft for the embedded type bionic honeycomb-shaped active safety escape capsule, internal space layout design of the main machine body of the aircraft for the embedded type bionic honeycomb-shaped active safety escape capsule, design of an escape capsule embedded type shell and the shape, analysis of influences of the embedded escape capsule on the overall load of the aircraft, integral analysis and determination of flight aerodynamic load data, selection of an escape capsule material, escape capsule ejection mode analysis and ejection device design, logic design of launch motion of the escape capsule, internal space structure analysis of the escape capsule; active safety design of space landing of the escape capsule, description of flight dynamics influences of the escape capsule on the aircraft during and after separation, and design of an active help seeking system of the escape capsule. In this way, the application and design for researching and manufacturing the bionic honeycomb-shaped active safety escape capsule embedded into the aircraft are achieved.
Owner:王晨
Method of controlling aerodynamic load of a wind turbine based on local blade flow measurement
The present invention relates to a method of controlling the aerodynamic load of a wind turbine's blades individually in such a way that the dynamic aerodynamic loads on the turbine are reduced and power production is optimised. In general the present invention will improve the overall stability of the turbine leading to reduce fatigue loads, reduced extreme loads during operation and reduced risk of blade-tower interaction. In particular preferred embodiment of the invention, flow properties are measured locally on the different blades or in front of the blades and from these measurements the pitch angle settings are changed, in other ways changing the aerodynamic properties, for the blades through a control unit.
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
Vortex dynamics turbine
InactiveUS20110229321A1Improved aerodynamicsSuppressing adverse pressure gradientPropellersHydro energy generationAerodynamic loadTurbine blade
The invention relates to the use of Air and Hydro Turbines for power generation. It seeks to enhance the energy-capturing potential of air / water turbines, and hence expand the geography where they can be used. It is mainly represented by a device consisting of a vortex generator and a vortex accelerator. This vorticity device operates in a combination of 2 modes: (1) Control airfoil circulation at the blade tips and hence control or alleviate the aerodynamic loading on the turbine blades. (2) Induce suction that can be used to transfer momentum to the flow close to the surface of the blade. Specifically, the generated suction drives secondary fluid flow, which is used to enhance the aerodynamic characteristics of the turbine blades / wings, by doing the following: (1) Suppressing adverse pressure gradients, (2) Suppressing the stall or separation bubble, (3) Laminarize the flow over the blade or wing.
Owner:AEROVORTEX MILLS
Bending combined two-dimension time-varying load loading unit
InactiveCN101441477AImplement collaborative loadingReproduce the working stateAerodynamic testingHydrodynamic testingAerodynamic loadEngineering
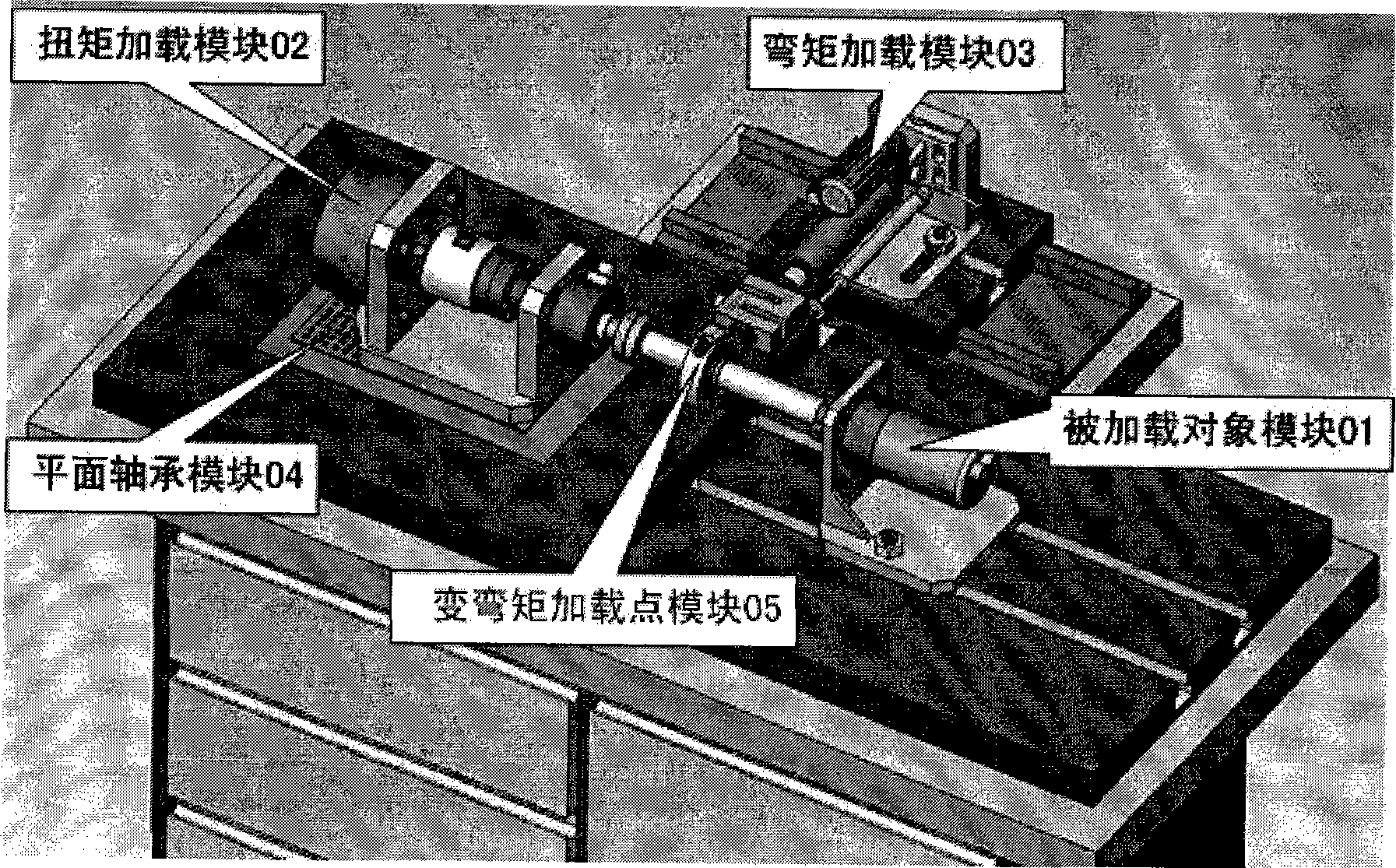
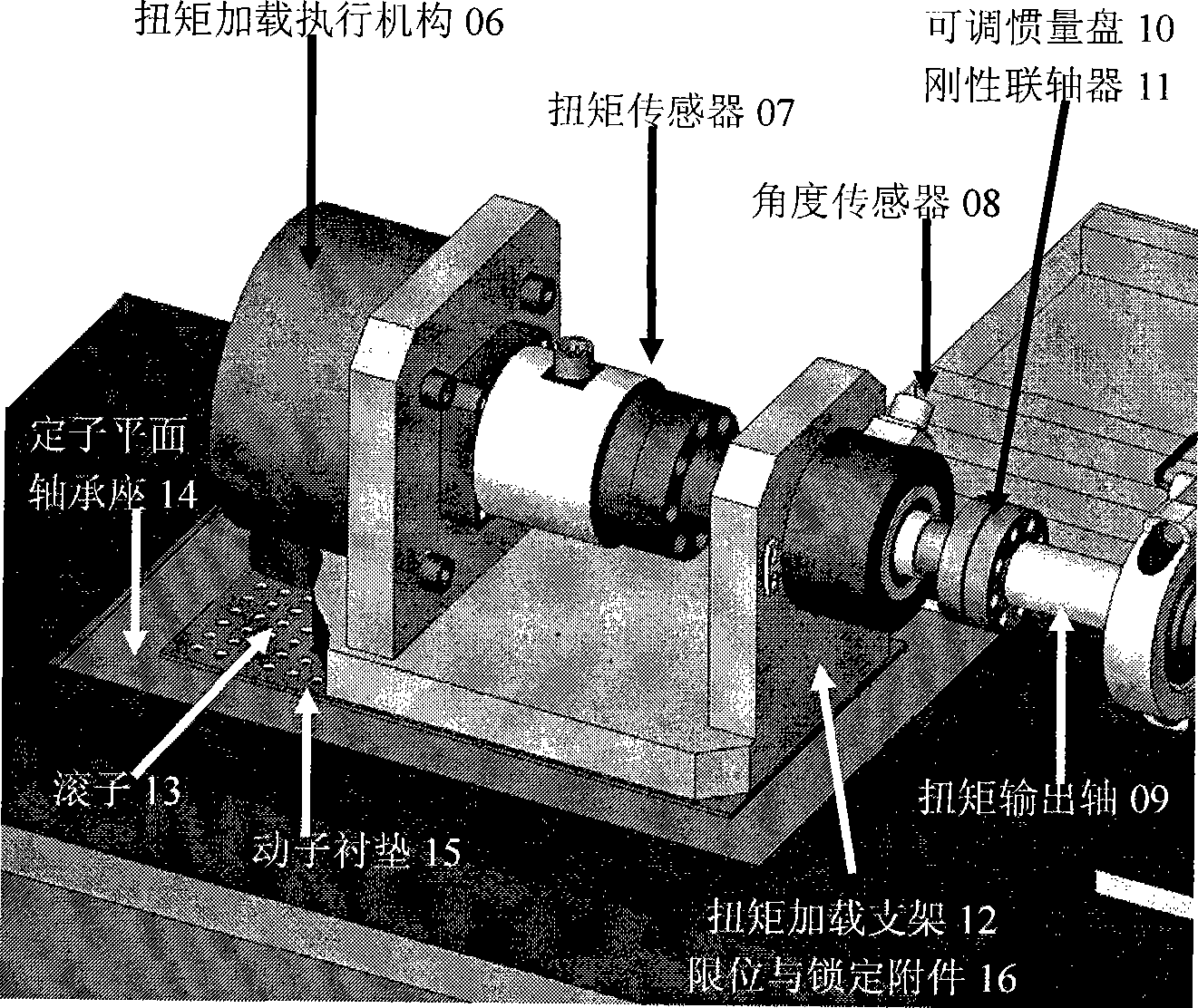
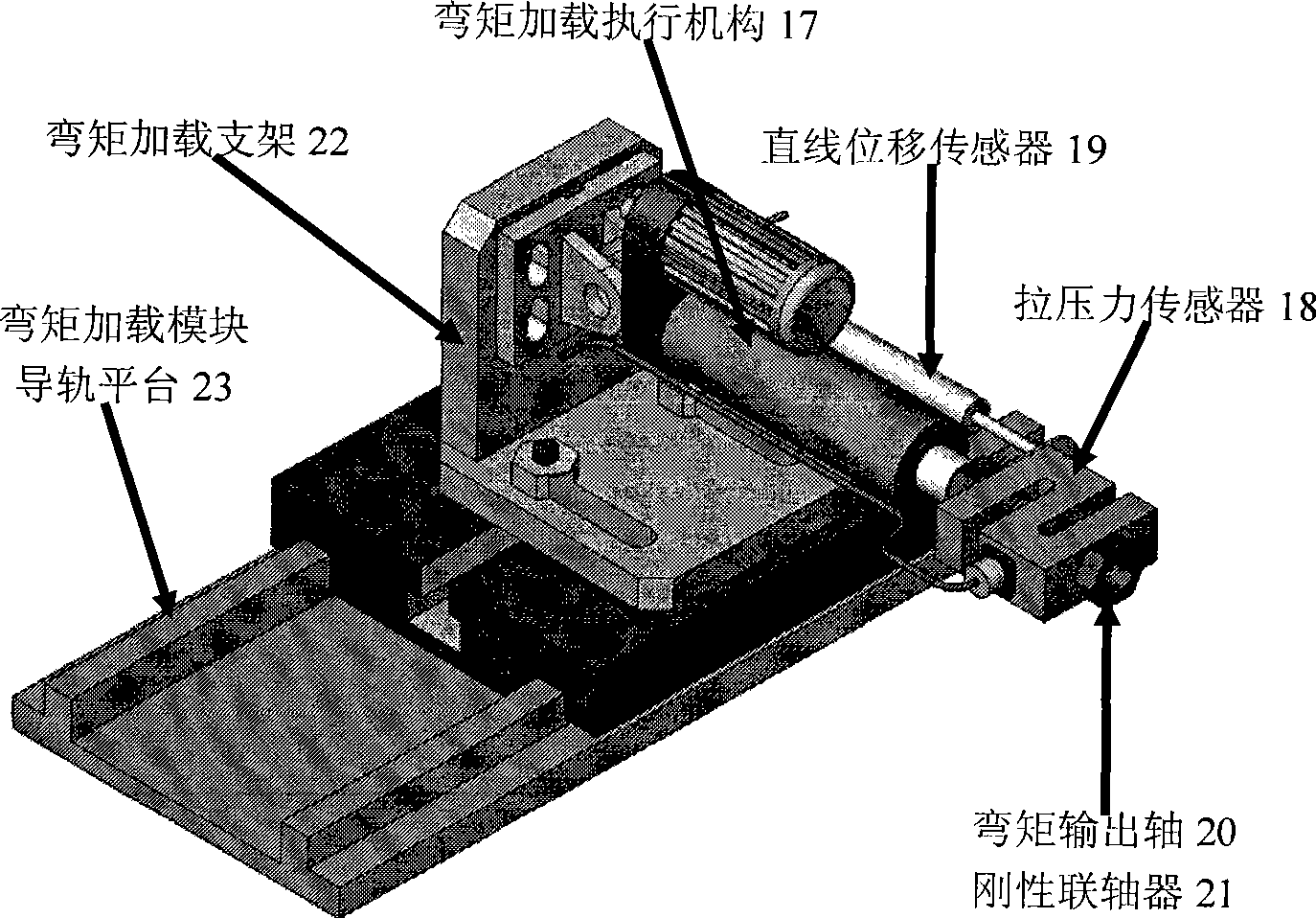
The invention relates to the technical field of electro-mechanical servo control and implements a bending-torsion combination two-dimensional time-varying load loading device and relates to two-dimensional combination load applying device taking torque loading and bending moment loading as the core. The actuating mechanism of the bending-torsion combination two-dimensional time-varying load loading device mainly comprises: a to-be-loaded object module 01, a torque loading module 02, a bending moment loading module 03, a plane bearing module 04 and a variable bending moment loading point module 05. The device is used for applying time-varying load to a tested actuating mechanism physically in real time. The device is mainly used for aerospace rudder-face actuator aerodynamic load simulation, ship rudder-face and fin stabilizer actuator loading and vehicle motor and transmission load simulation. The most remarkable characteristic of the device is synchronous application of bending-torsion two-dimensional time-varying loads. The device can realize the prior time-varying torque loading and synchronously apply time-varying bending moment load to a shaft of an object to be loaded; and an action spot of the bending moment is variable in real time.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Modified wind turbine airfoil
InactiveUS6705838B1Increased complexityRaise the possibilityPropellersRotary propellersLeading edgeTurbine blade
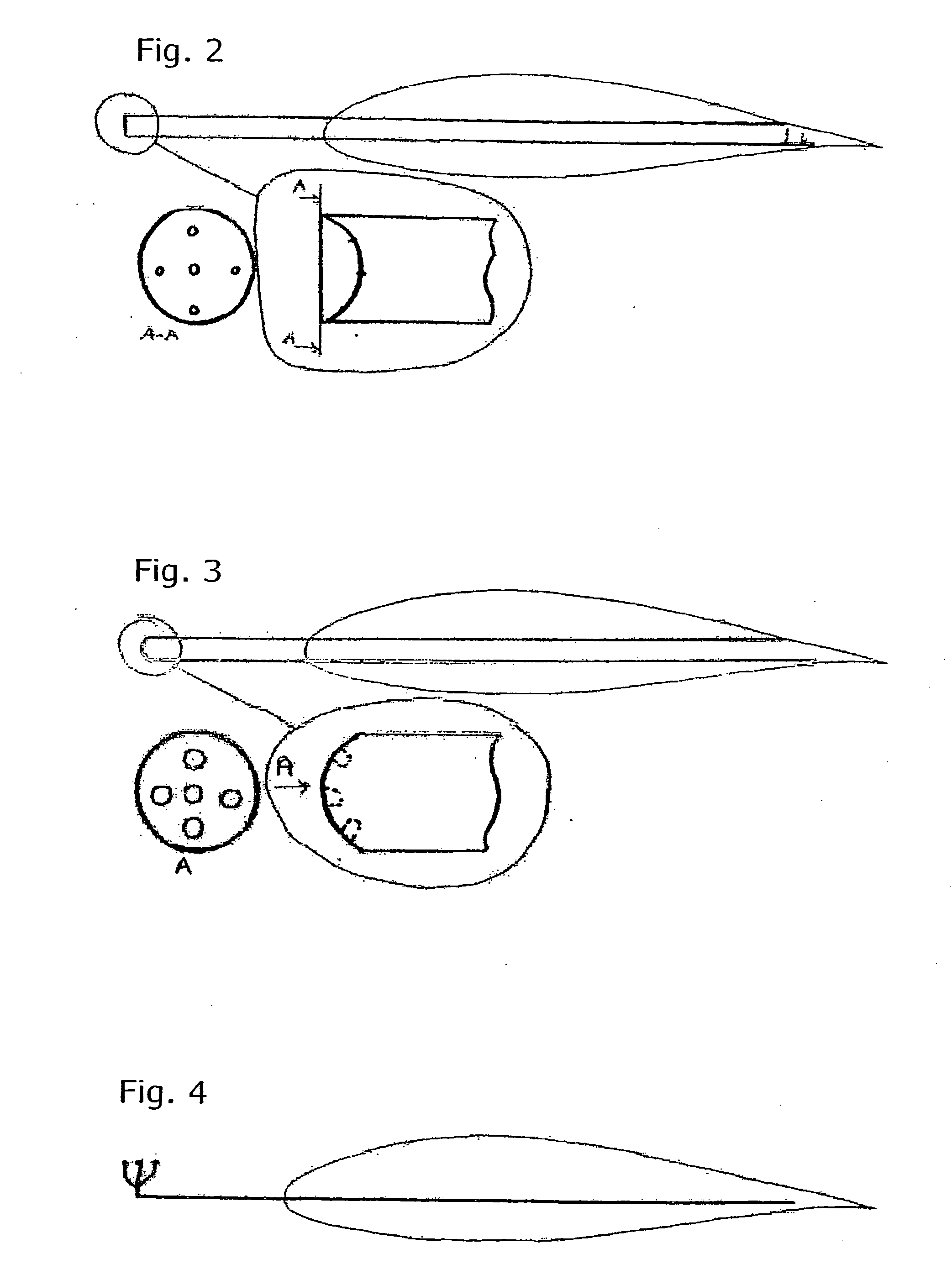
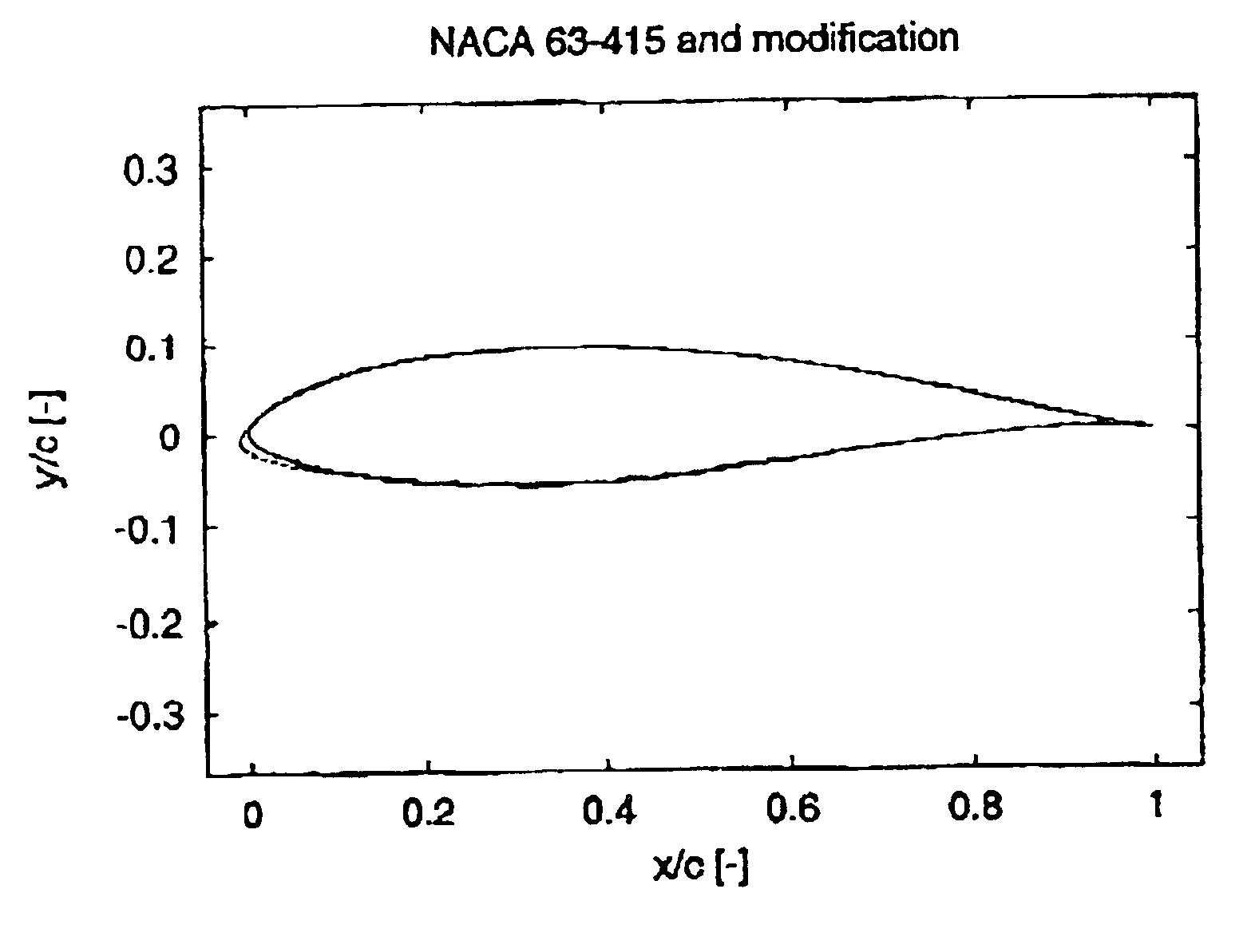
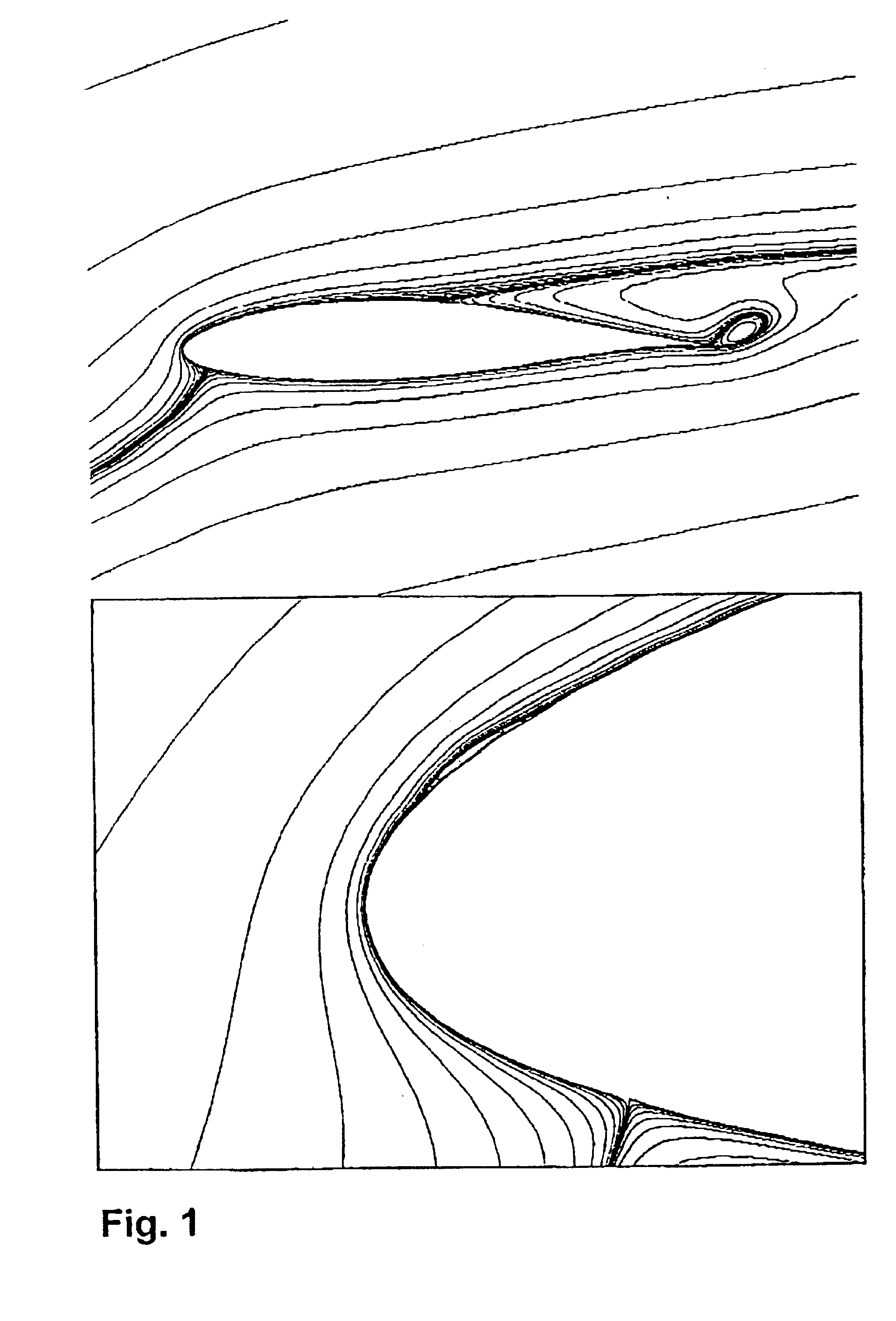
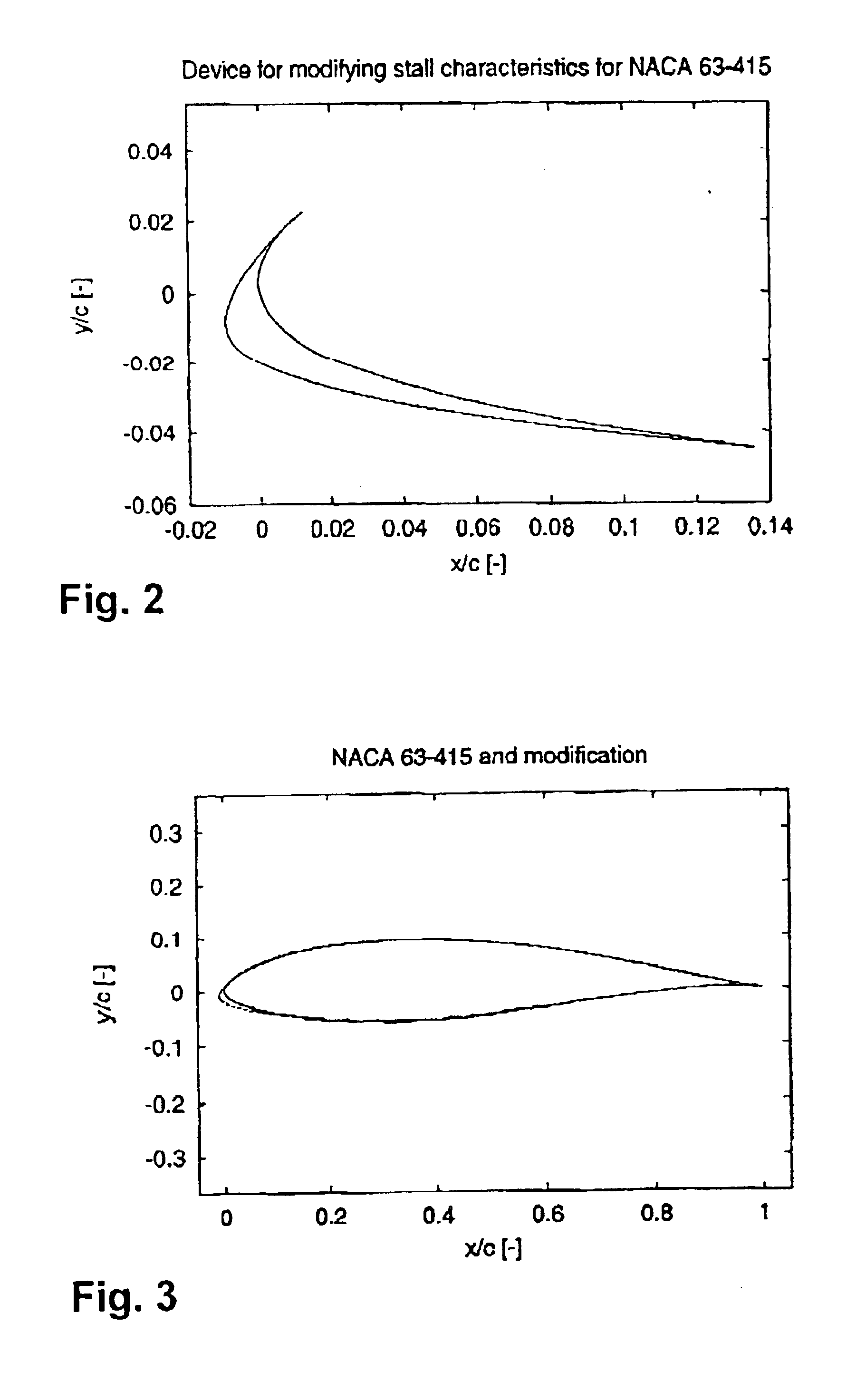
The present invention relates in a broad aspect to a method for design and modification of airfoils useful for wind turbine applications, which airfoils possess smooth and stable characteristics in stall. These characteristics comprise: (1) No or very little tendency to double stall, (2) Insensitivity or little sensitivity of maximum lift to leading edge roughness, (3) High lift-drag ratio just before maximum lift, (4) Small variations of the aerodynamic loads in stall and (5) Sufficient aerodynamic damping to suppress blade vibrations in stall. The invention further relates to blades and / or airfoil sections in general which posses smooth and stabile characteristics in stall. Also, it relates to a method of implementing the desired shape on an airfoil or a wind turbine blade.
Owner:FORSKNINGSCENTER RISO ROSKILDE
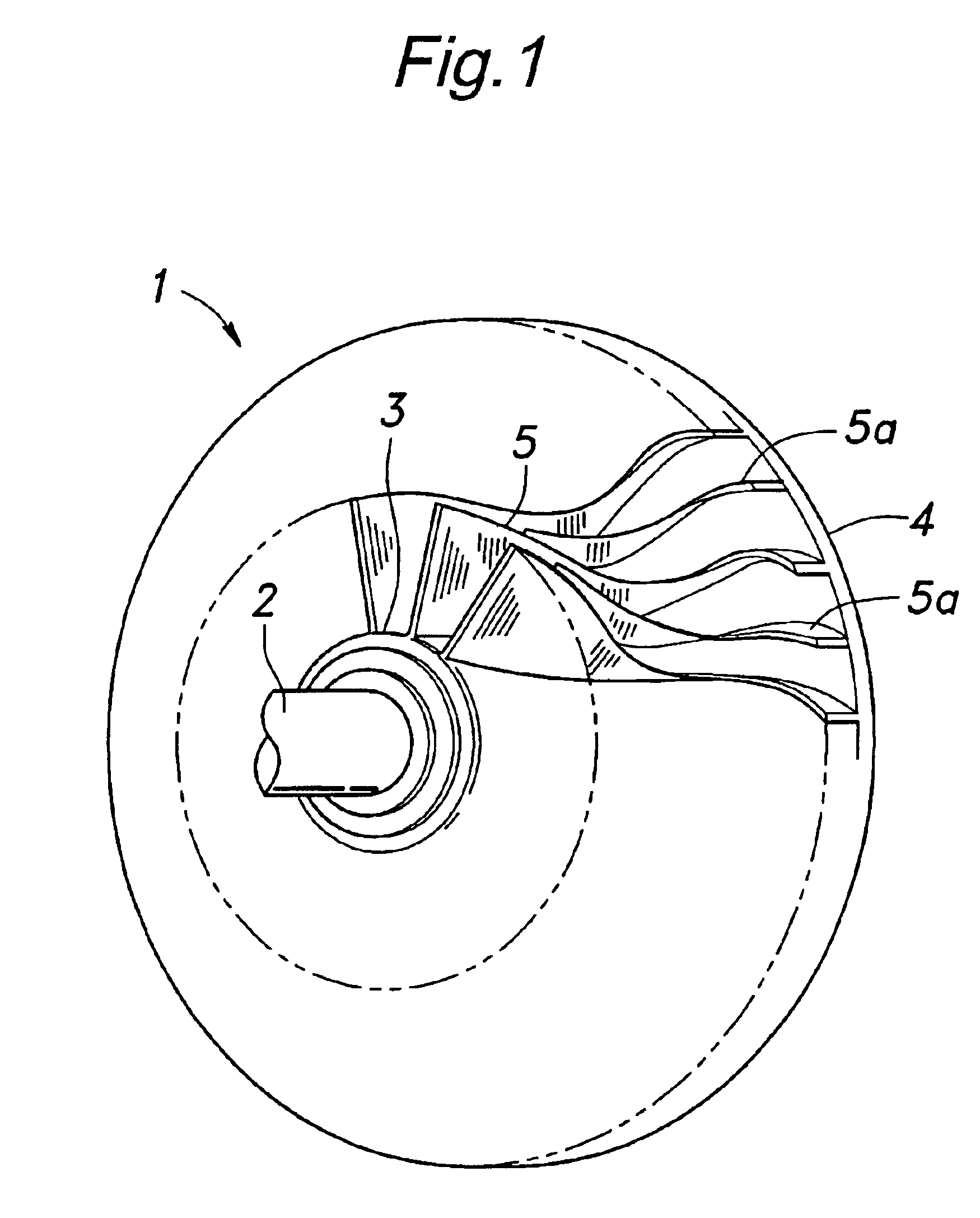
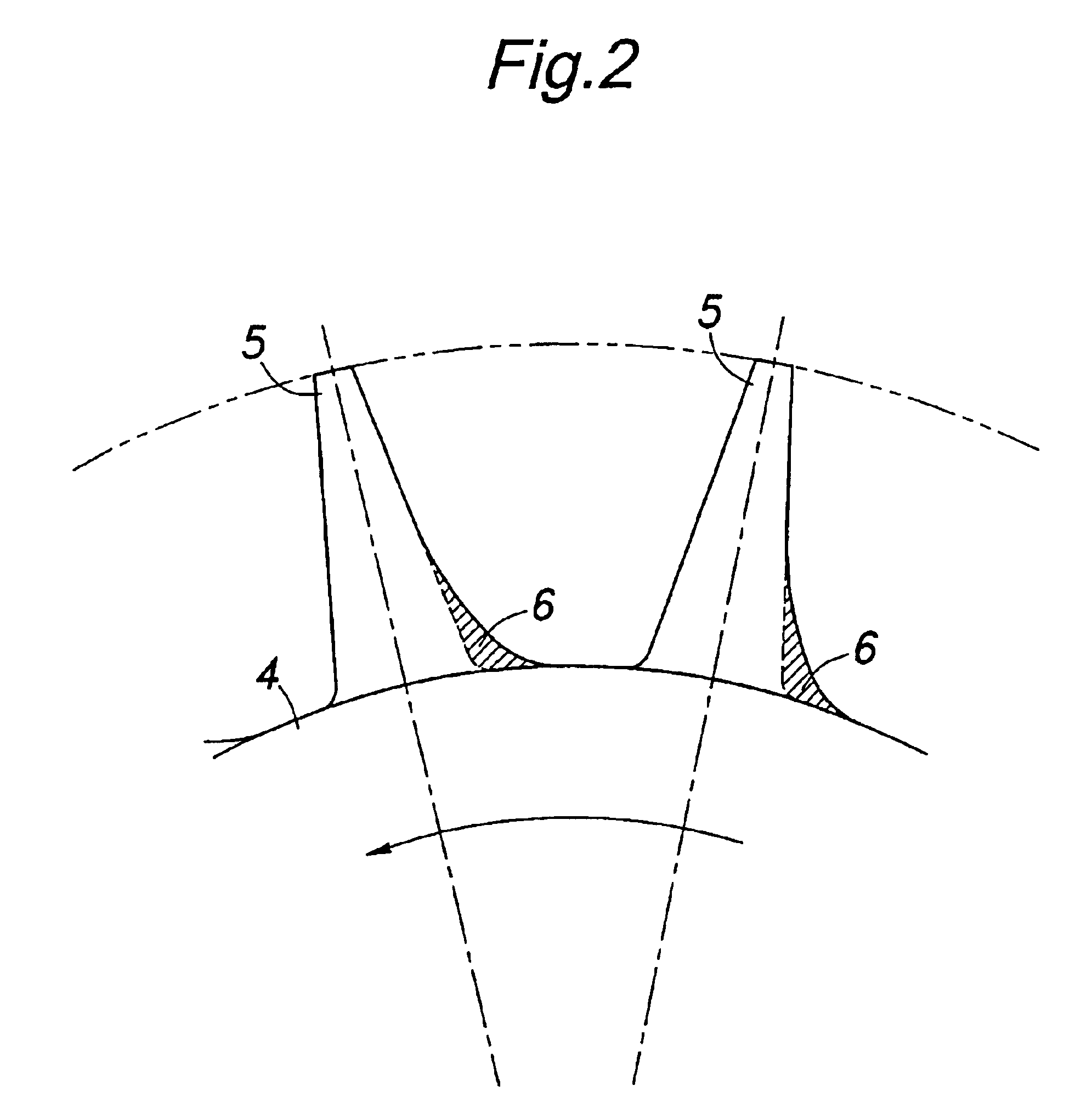
Impeller for centrifugal compressors
InactiveUS6905310B2Interference minimizationMinimizes separationPropellersRotary propellersSuction stressAerodynamic load
In an impeller for centrifugal compressors comprising a plurality of blades each having a base end attached to a central hub, each of the blades is given with a thickness which increases progressively toward a hub end thereof, and a suction surface side of the blade is given with a greater thickness increase rate with respect to a neutral plane than a pressure surface side of the blade. Thereby, the inter-blade channel is narrowed locally in the region near the hub end of the suction surface of each blade, and this locally reduces the aerodynamic loading on the blade. In particular, the surge property is improved, and the generation of radially outwardly directed secondary flows can be minimized. This allows the distribution of aerodynamic loading in the radial direction or from the tip end to the hub end of each blade to be controlled at will, and enables the optimum design of the impeller.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
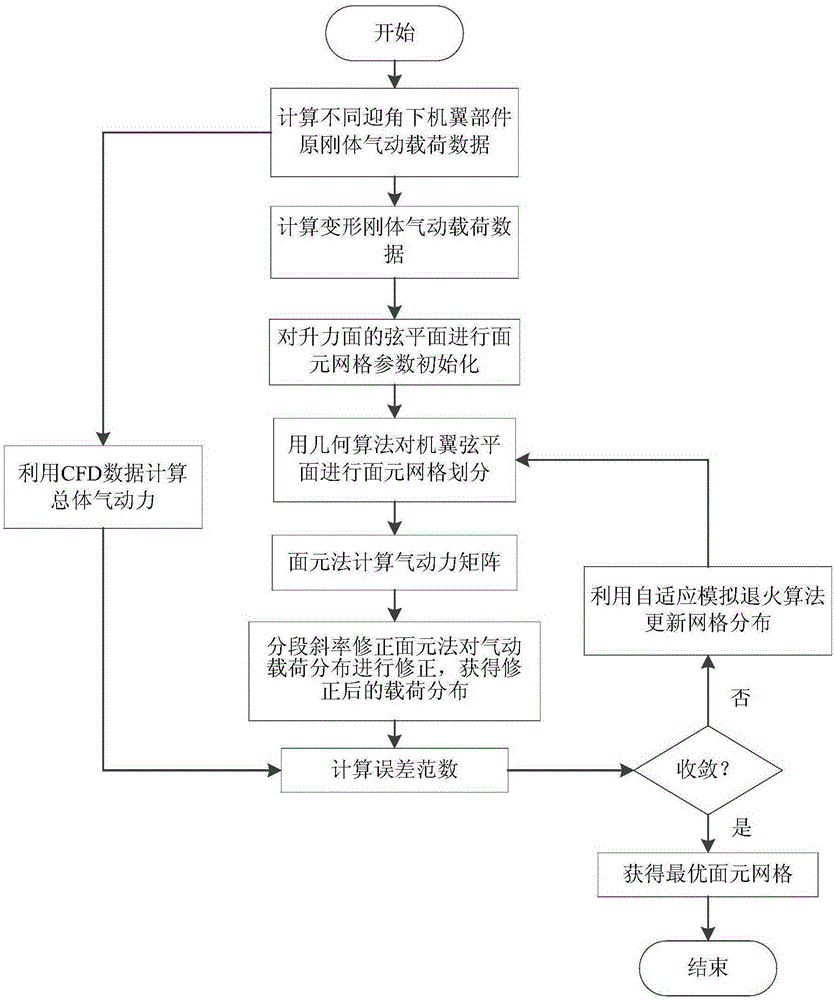
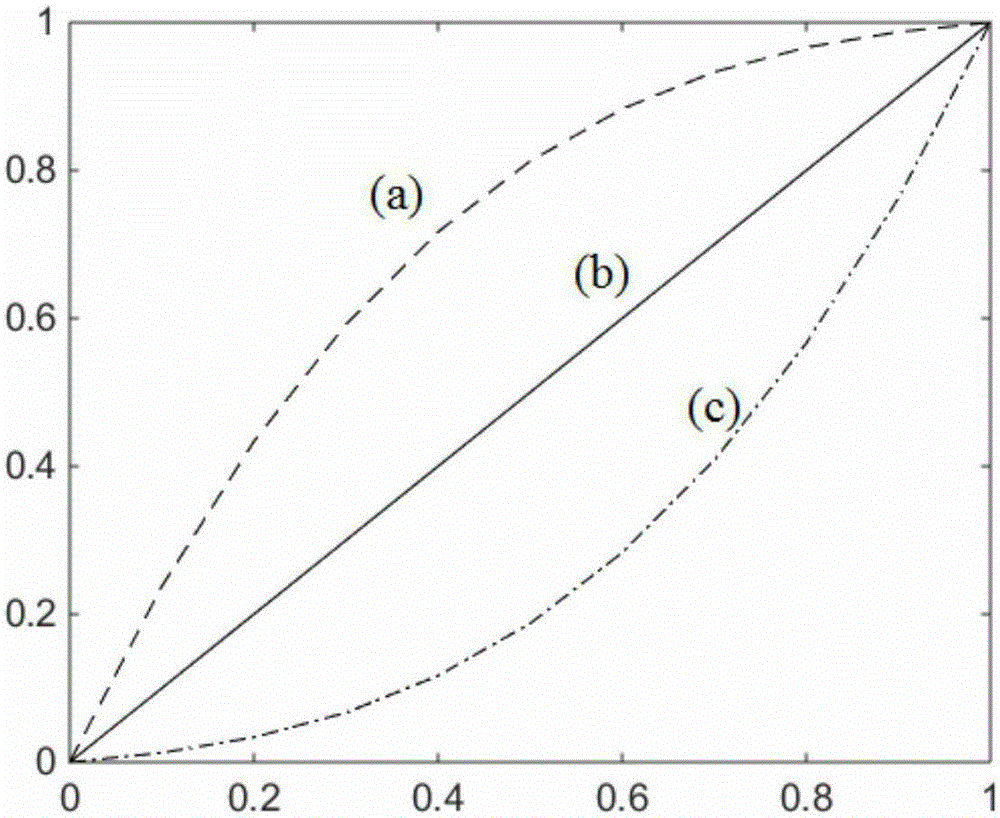
Surface element correction and grid beforehand self-adaption calculation method
ActiveCN105183996AImprove computing efficiencyHigh precisionSpecial data processing applications3D modellingAdaptive simulated annealingCorrection method
The invention relates to a surface element correction and grid beforehand self-adaption calculation method. According to the method, segmented linearizing correction is carried out on a low-order surface element method with multiple groups of CFD aerodynamic force load data under different attack angles, and distribution of surface element calculation grids is optimized by adopting a self-adaption simulated annealing algorithm. By means of self-adaption optimization of the surface element grids, the accuracy of the surface element correction method is improved, and the defect that a traditional surface element correction method depends on grid distribution is overcome. When the optimized grids are applied to the surface element correction method, the advantage of high calculation efficiency of the surface element method is kept, the accuracy of overall wing stress close to the CFD data can be ensured, and the accuracy and efficiency in the aeroelasticity optimal iteration design process are effectively improved. The accuracy error between the obtained aerodynamic load data and CFD calculation results is within 2% and effectively extends to the non-linear segment in which aerodynamic loads change along with the attack angle, and the aerodynamic load calculation efficiency in the changing process of structural rigidity parameters is improved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Skin for morphing wings
InactiveCN102060101AGuaranteed to be smoothRealize health monitoringWingsIsosceles trapezoidVibration control
The invention discloses a skin for morphing wings, belonging to the technical field of design of morphing aircrafts. The skin for the morphing wings is made from fibre reinforced composites, and the cross section of the skin is in an isosceles trapezoid ripple structure. The invention also carries out analysis aiming at the chordwise and spanwise equivalent elastic modulus and flexural modulus ofthe skin structure with isosceles trapezoid ripples, provides a corresponding mathematical model and can further optimize the skin structure according to the mathematical model. The invention meets the requirements of the skin of the morphing wings of the morphing aircrafts for large deformation aerodynamic load bearing, can realize the design optimization of the skin structure under different load operating conditions according to the mathematical analysis model of the equivalent elastic modulus and the flexural modulus in two different directions of the skin structure, also has structure health monitoring and self-adapting deformation capability and can realize optimal aerodynamic characteristics by controlling the shape and the vibration of the skin.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
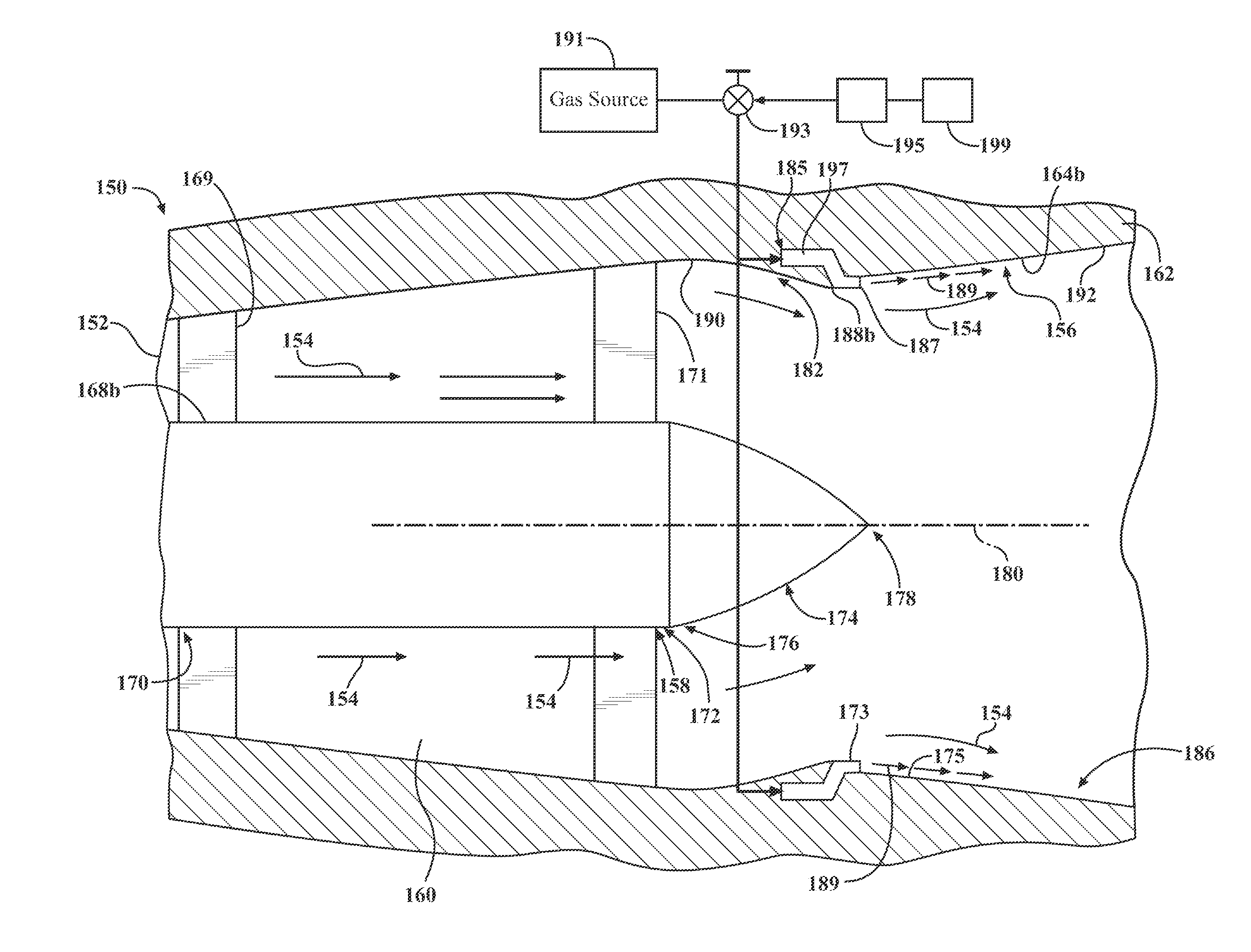
Turbine exhaust diffuser with region of reduced flow area and outer boundary gas flow
An exhaust diffuser system and method for a turbine engine. The outer boundary may include a region in which the outer boundary extends radially inwardly toward the hub structure and may direct at least a portion of an exhaust flow in the diffuser toward the hub structure. At least one gas jet is provided including a jet exit located on the outer boundary. The jet exit may discharge a flow of gas downstream substantially parallel to an inner surface of the outer boundary to direct a portion of the exhaust flow in the diffuser toward the outer boundary to effect a radially outward flow of at least a portion of the exhaust gas flow toward the outer boundary to balance an aerodynamic load between the outer and inner boundaries.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Horizontal testing device for reliability test of aircraft landing gear door uplock
ActiveCN103983443AImplement job triggersRealize arc motionMachine part testingVibration testingAerodynamic loadSimulation
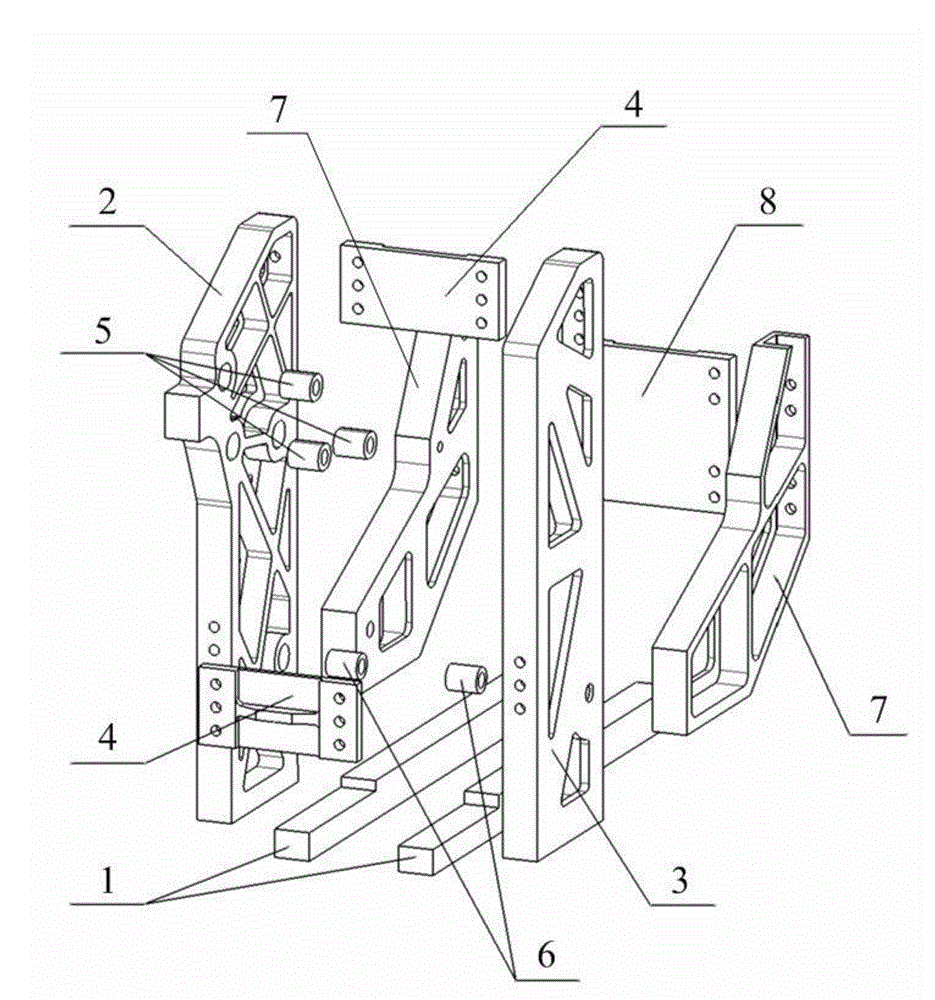
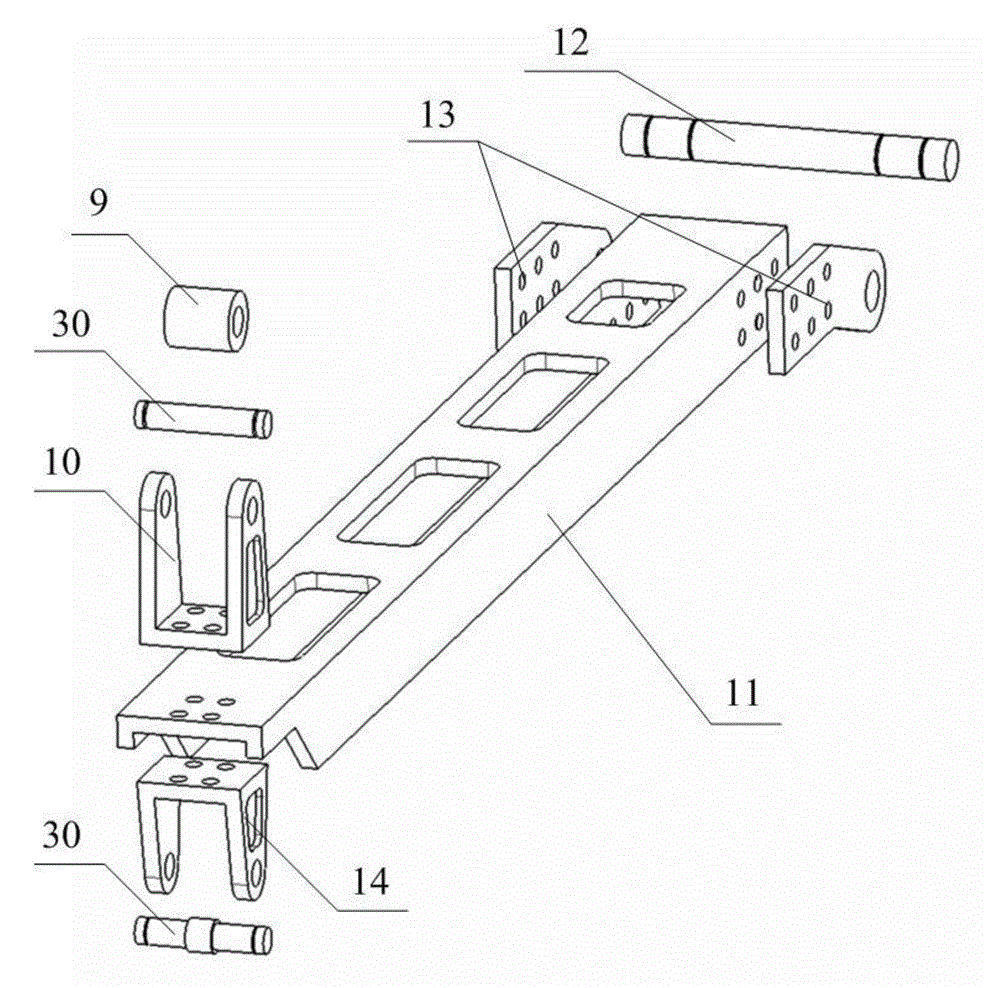
The invention discloses a horizontal testing device for a reliability test of an aircraft landing gear door uplock. The horizontal testing device is composed of a connecting and supporting structure, a simulated door structure and a driving and loading structure, wherein the door uplock to be tested, the simulated door structure and the driving and loading structure are all installed on the connecting and supporting structure, the simulated door structure comprises a lock ring, a lock ring support, a rotary cross beam and a bearing support, and the driving and loading structure comprises a composite rocker arm, a transmission connecting rod, a main bearing shaft, a hydraulic actuator cylinder, an actuator cylinder transmission connecting rod, a loading assembly and a loading transmission connecting rod. The horizontal testing device can be matched with a vibration table to achieve vibration stress loading, can be matched with a comprehensive environment testing box to achieve the change of working temperature, can be matched with a hydraulic system to achieve the work triggering of the door uplock to be tested, and can simulate the loading of aerodynamic loads through a loading structure. According to the horizontal testing device, the loading structure is compact, the degree of freedom of work is high, additional resistance is small, circular motion of the lock ring can be achieved, and load control is accurate.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
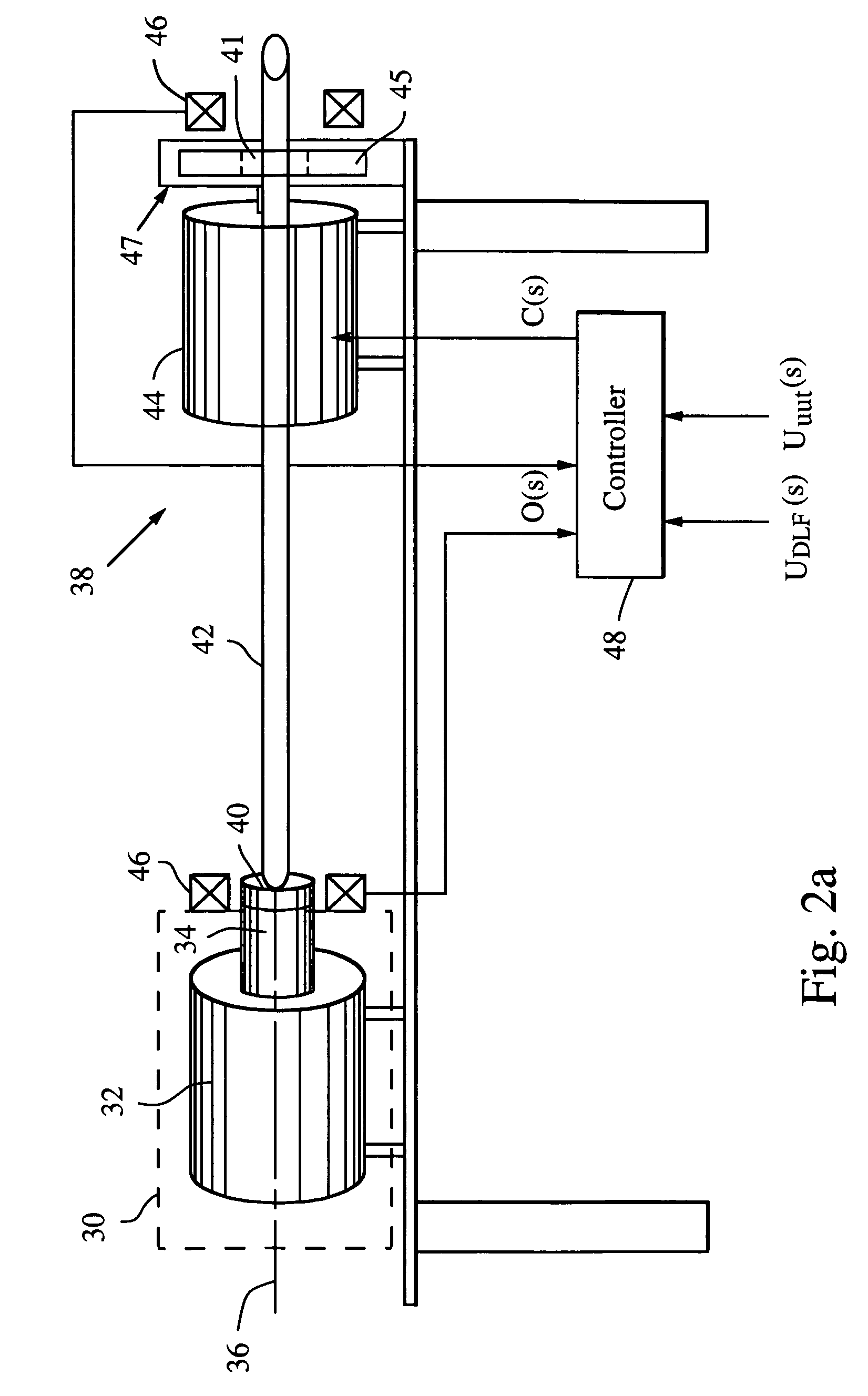
Dynamic load fixture for application of torsion loads for rotary mechanical systems
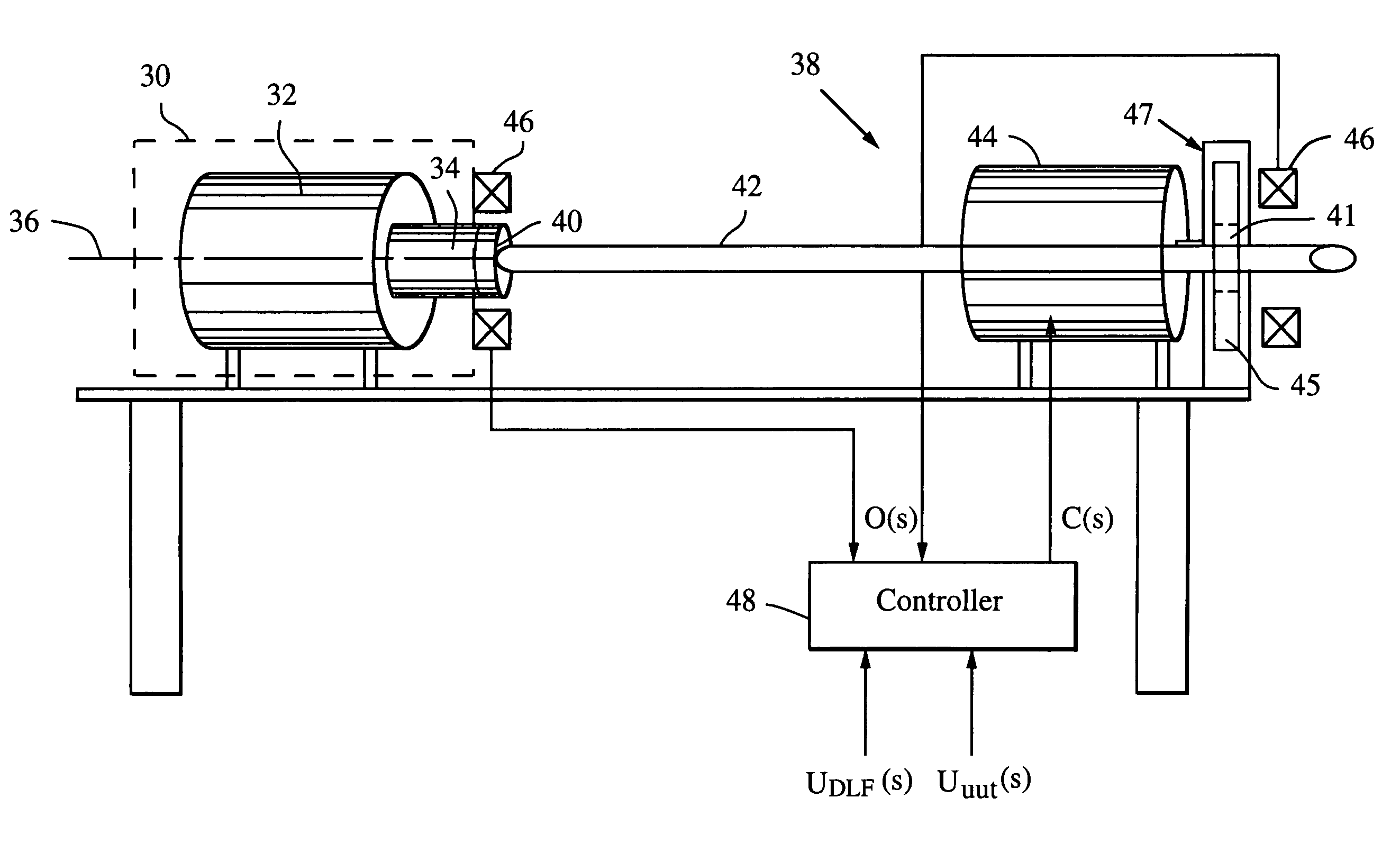
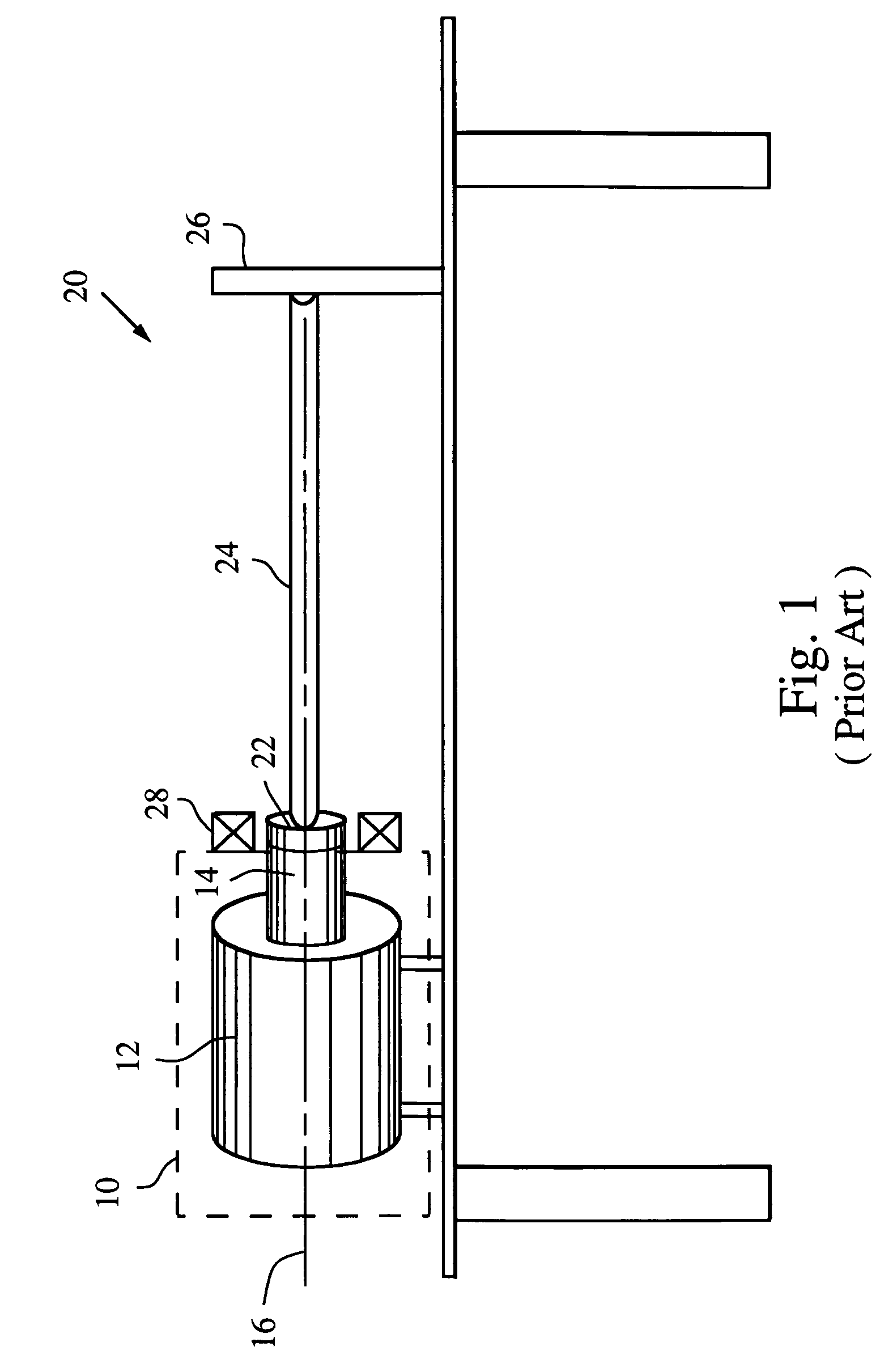
ActiveUS7165465B2Efficient reproductionImprove response bandwidthMachine part testingWork measurementNegative feedbackAerodynamic load
A dynamic load fixture (DLF) applies a torsion load to a unit under test (UUT) to achieve the demanding aerodynamic load exposures encountered by a control actuation system (CAS) in flight. Instead of fixing the end of the torsion bar, the DLF controls the application of torque to the torsion bar, hence the UUT via a DLF motor. The dynamic load can be independent of the angular rotation of the UUT, which allows the DLF to more effectively reproduce desired acceptance tests such as torque-at-rate and nonlinear loads. Furthermore, application of the loads through a torsion bar allows the system the compliance needed to generate precise loads while allowing for the flexibility of changing torsion bars to test a wide variety of UUT on one test platform. To achieve the demanding aerodynamic load exposures encountered by a CAS in flight, the controller must be able to respond both very fast and very precisely. Control is enhanced by the thorough characterization of the DLF and application of either “classic” negative feedback control or “modern” state-space control methods of linear observers and quadratic optimum control.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Secondary splitter blade type centrifugal impeller
InactiveCN101598138AImprove mobilityImprove flow efficiencyPump componentsPumpsImpellerAerodynamic load
The invention discloses a secondary splitter blade type centrifugal impeller, comprising a long blade extending from impeller inlet to impeller outlet. The suction surface of the long blade and the pressure surface of an adjacent long blade form a complete air flow passage; wherein a middle blade is arranged between the two long blades to form a primary splitter blade; the two sides of the middle blade are respectively provided with a short blade to form a secondary splitter blade; the inlet of the middle blade deflects toward the suction surface in the air flow passage; the inlet at the wheel disc side of the short blade deflects towards the suction surface in the air flow passage, and the inlet at the wheel cap of the short blade deflects towards one side of the pressure surface in the air flow passage; the number ratio of the long, middle and short blades is 1:1:2; and the long, middle and short blades are evenly distributed at the periphery of the outlet of the impeller. The centrifugal impeller of the invention gradually increases splitter blades, and can effectively allocate blade passage gas flow and blade aerodynamic load, improve flow uniformity at the impeller outlet and improve pressurizing capacity and steady operation range of the centrifugal impeller.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Control surface of aircraft
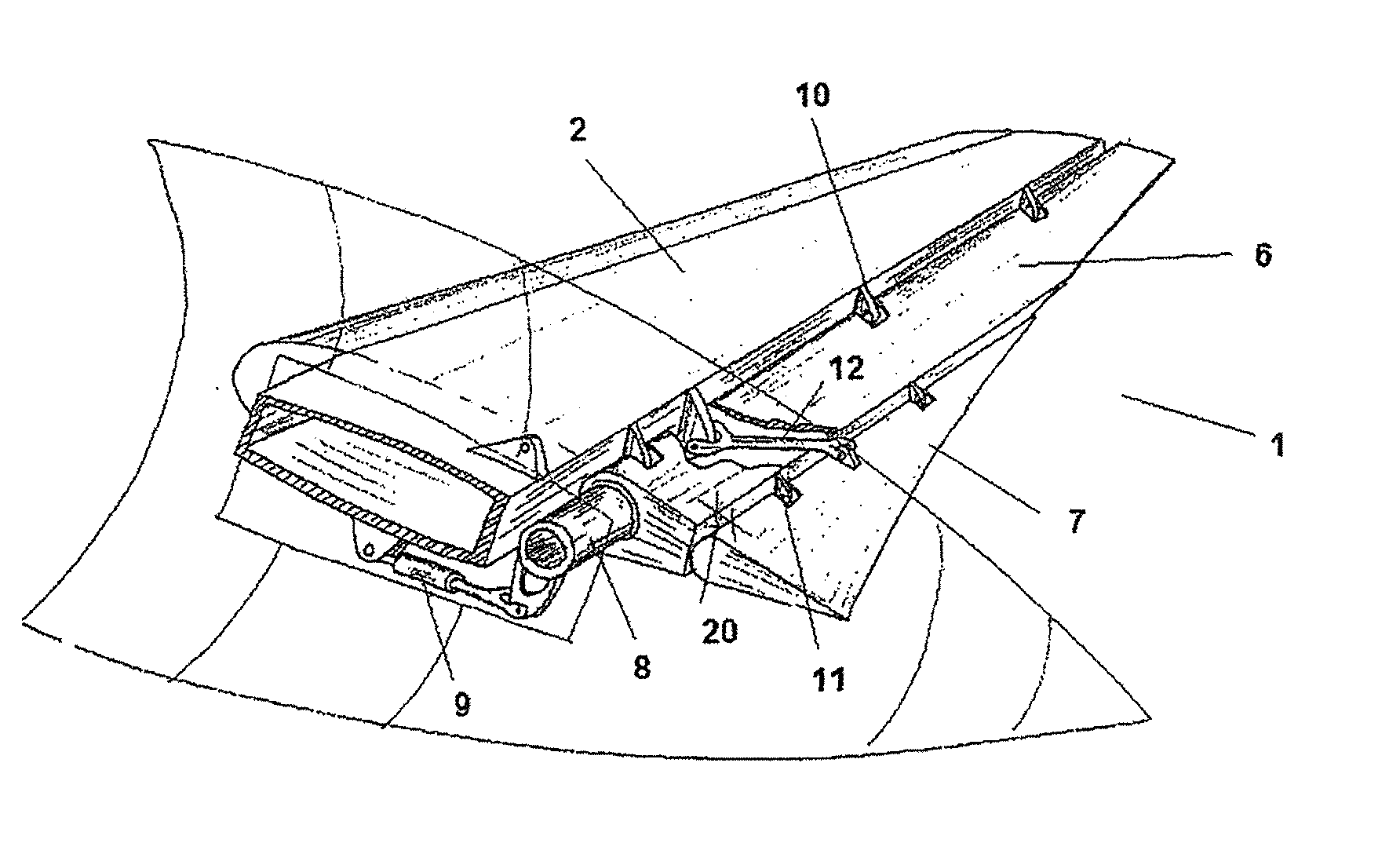
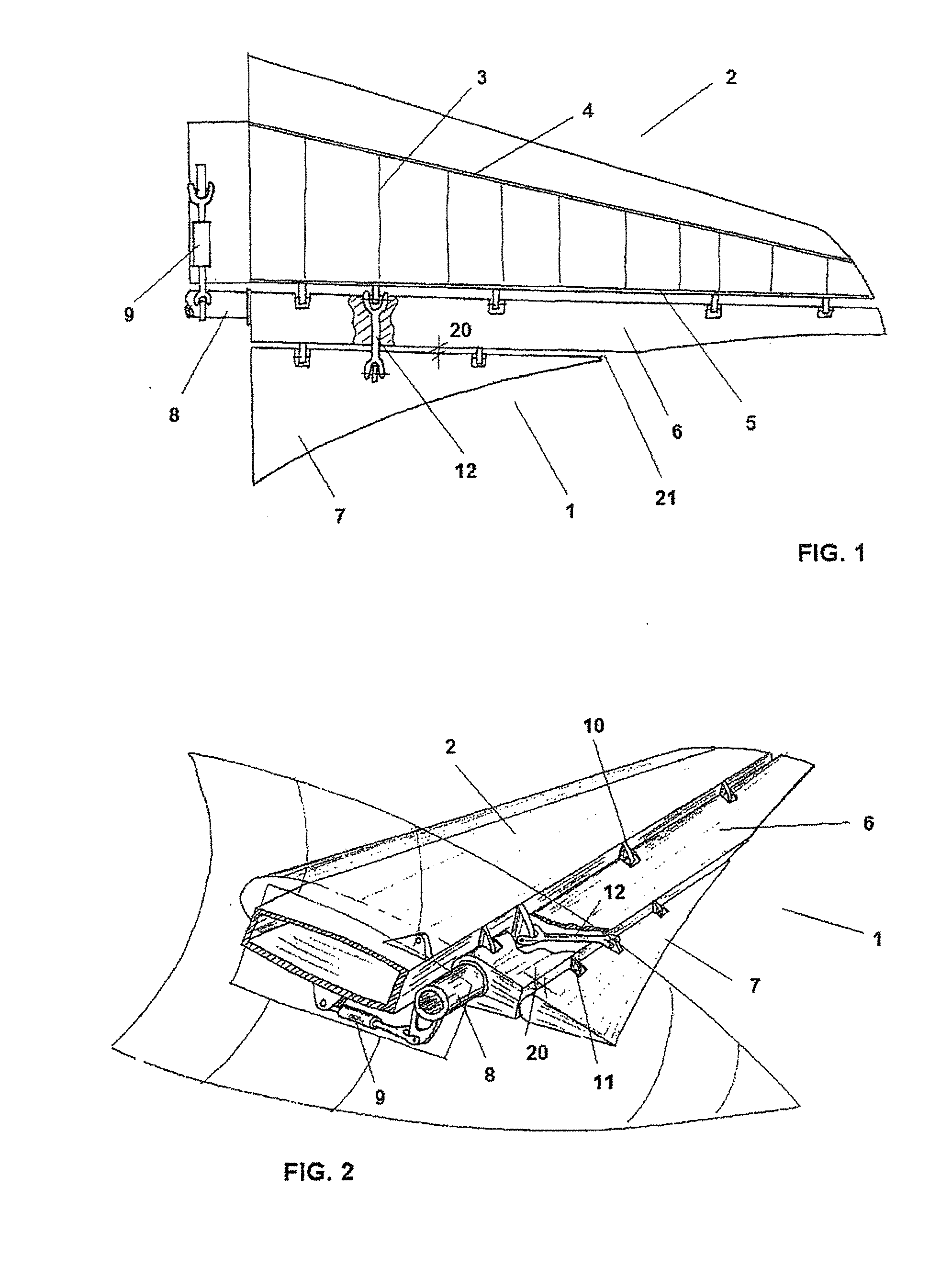
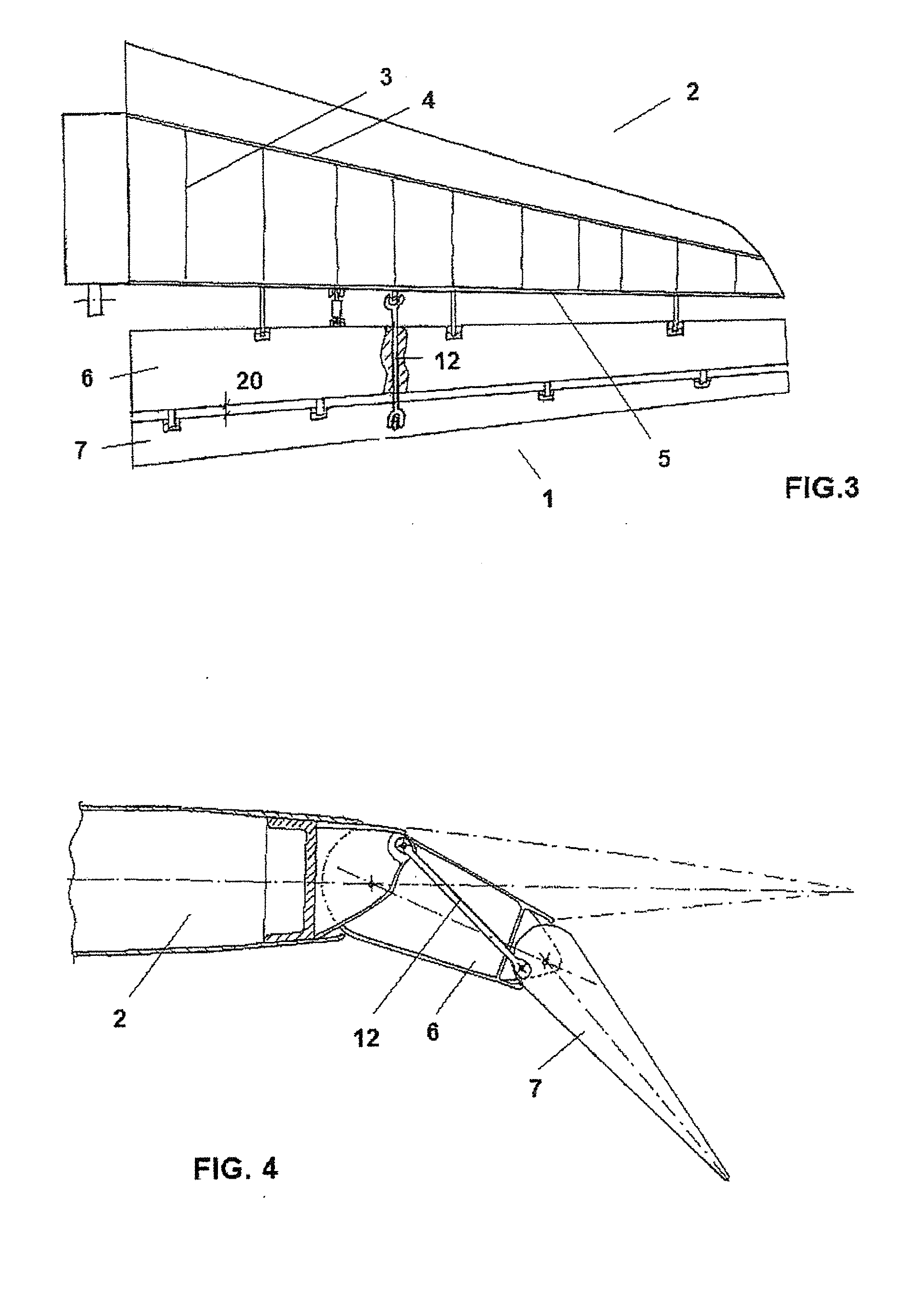
InactiveUS20100019083A1Greater effective curvatureAircraft stabilisationWing adjustmentsAerodynamic loadEngineering
Aircraft control surface (1), in particular for an aircraft lifting surface (2), that comprises a primary control surface (6) that comprises a hinge axis (10), and a secondary control surface (7) that comprises a hinge axis (11), with the secondary control surface (7) rotating by means of its hinge axis (11) relative to the primary control surface (6), said secondary control surface (7) only partially occupying the span of the primary control surface (6), the length of the secondary control surface (7) along its hinge axis (11) being significantly less than the length of the primary control surface (6) along its hinge axis (10), and moreover the width or chord of said secondary control surface (7) along the direction of its hinge axis (11) narrows significantly towards the tip of the lifting surface (2) according to a law of narrowing designed expressly for adapting the distribution of torsional stiffness along the span of the lifting surface (2) to the distribution of aerodynamic load thereon, whereas the distribution of effective curvature due to the deflection of said control surface (1) is such that it increases the stalling angle of the lifting surface (2).
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS SL
Deformable aerofoil cover with changeable rigidity
InactiveCN101513932AImprove the shortcomings of low carrying capacityReduced carrying capacitySynthetic resin layered productsWingsRubber materialAerodynamic load
A deformable aerofoil cover with changeable rigidity relates to a deformable aerofoil cover. The invention solves the problem that the cover of the existing rubber material has poor capacity of bearing aerodynamic load and the problem of low entire bearing capacity of the aerofoil. In the invention, a plurality of reinforced pipes with changeable rigidity (2) are embedded into a silastic cover matrix (1) in parallel; each control valve (3) is arranged on the outer surface of the silastic cover matrix (1) and is communicated with the corresponding reinforced pipes with changeable rigidity (2); the two ends of each reinforced pipe with changeable rigidity (2) are all closed; each reinforced pipe with changeable rigidity (2) consists of a composite material outer layer (4), an inner liner pipe (5) and working liquid (6); the composite material outer layer (4) is coated on the outer surface of the inner liner pipe (5); and the working liquid (6) is filled in the inner liner pipe (5). The cover of the invention has strong capacity of bearing the aerodynamic load, and the entire loading capacity of the aerofoil is high, thus meeting the requirement of large-deformation of the deformable cover.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Rack and pinion hydraulic pressure horizontal loading retraction and extending test table mechanism
ActiveCN102095592AIncrease the itineraryHigh speedStructural/machines measurementGear wheelAerodynamic load
The invention discloses a rack and pinion hydraulic pressure horizontal loading retraction and extending test table mechanism and belongs to the technical field of undercarriage test. The rack and pinion hydraulic pressure horizontal loading retraction and extending test table mechanism mainly comprises a loading supporting mechanism, a hydraulic pressure loading and retarding mechanism, and a simulation horizontal force loading mechanism; wherein the loading supporting mechanism consists of a vertical shaft frame, an upper connection seat (8), a lower connection seat (23), and a lifting plate (9); and the hydraulic pressure loading and retarding mechanism consists of a linkage turntable (27), a reduction gear (26), a rack (25) and a loading actuator cylinder (24); and the simulation horizontal force loading mechanism consists of an arc guide rail (18), a first movable pulley (17), a second movable pulley (19), a fixed pulley (21) and a wire rope (20). During test, the rack and pinionhydraulic pressure horizontal loading retraction and extending test table mechanism loads an undercarriage by simulating aerodynamic load and solves the problems of insufficient travel of the loadingactuator cylinder and loading speed, guarantees that the lateral force is always in a horizontal direction, and is more close to an actual stress model.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
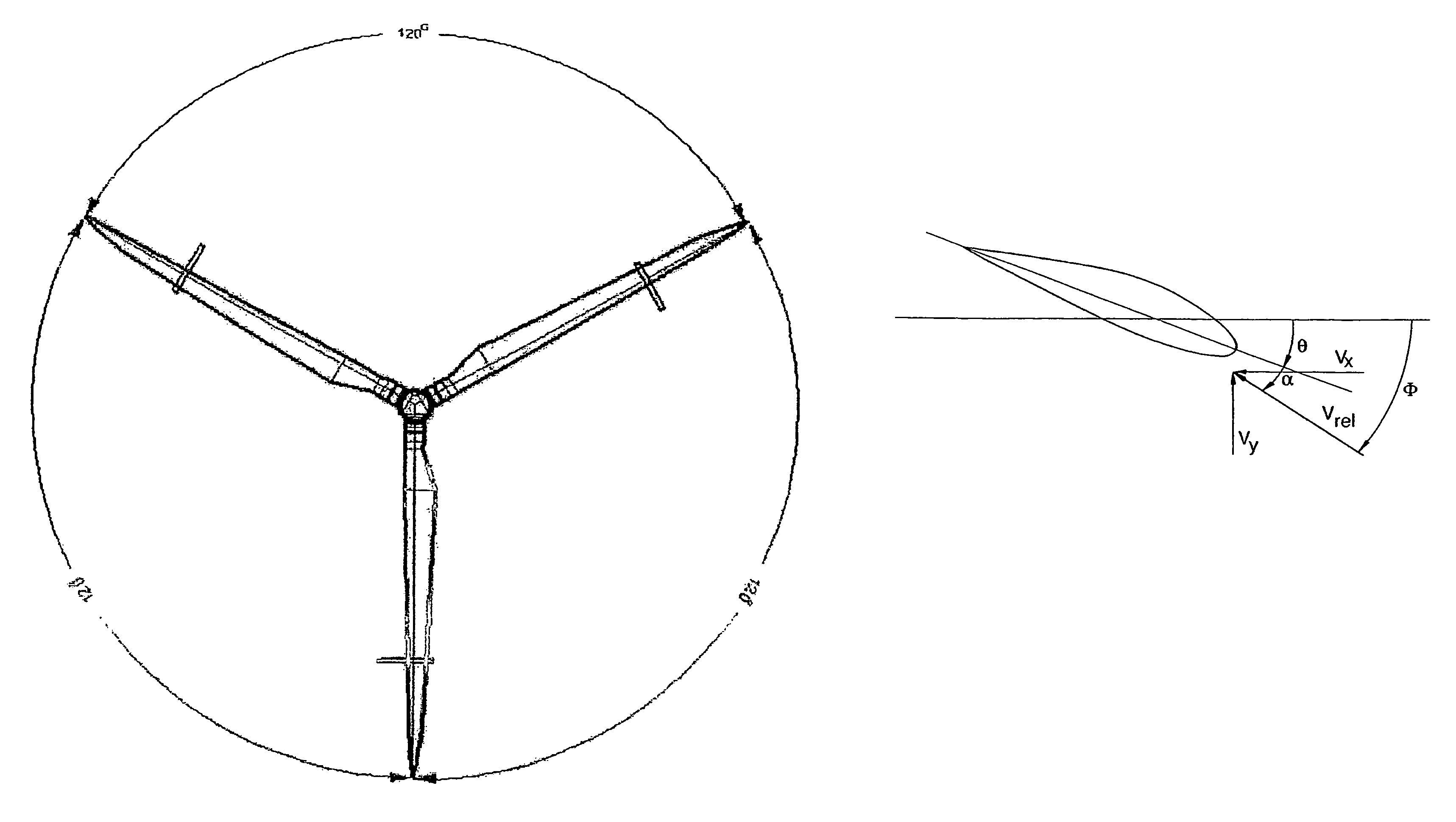
Variable tip speed ratio tracking control for wind turbines
ActiveUS20090220340A1Increase energy capture power coefficientPropellersComparison table algorithmsTurbine bladeAerodynamic load
The present invention relates to a method of controlling the aerodynamic load of a wind turbine blade by controlling the tip speed ratio (TSR) and / or blade pitch setting of the wind turbine blade so as to optimize power production. A wind turbine blade undergoes an aero-elastic response including deflection and twist that is a function of the blade loading. The blade loading is dependent on the wind speed, TSR, and pitch setting. The aero-elastic response requires a different TSR and / or pitch to be selected throughout the power curve in order to maintain the optimum power production and to improve energy capture.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Foldable wing and rotocraft and glider using the same
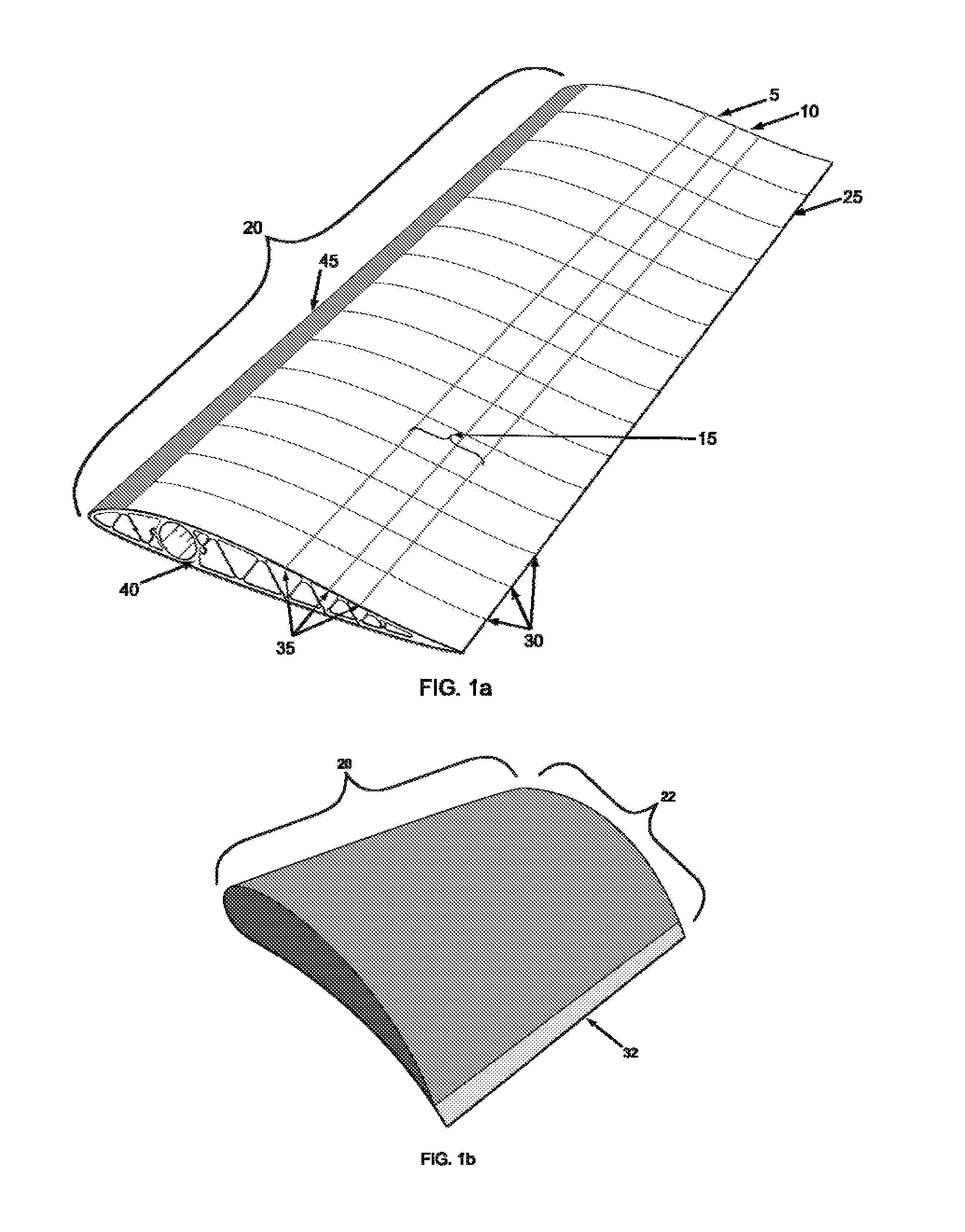
The present invention provides a foldable wing which comprises a wing supporting skeleton, a sliding rail, a skin supporting rib, a skin and a wing movement unit. The wing supporting skeleton comprises a horizontal beam, a longitudinal beam, a wing front edge beam, a wing trailing edge beam, a fixture connector and a sliding block, The wing supporting skeleton is a triangular girder for maintaining planar and sectional shapes of the foldable wing, supporting the skin supporting rib and the skin, and sustaining an aerodynamic load from the skin and a load of a fuselage. After the triangular girder is subjected to a force of the wing movement unit, a shape and an area of the triangular girder are changed so as to achieve folding and unfolding of the foldable wing. A rotocraft and a glider using the foldable wing are also provided.
Owner:JI LANPING +1
Method for actually measuring wing torque loads of high-manoeuvrability aircraft
InactiveCN103979119AFix implementation issuesGuaranteed accuracyAircraft components testingFlight testMeasurement test
The invention belongs to the field of aircraft flight load actual measurement and relates to a method for actually measuring wing torque loads of a high-manoeuvrability aircraft. The method comprises the following steps: 1, determining a structure or a part sensitive to influences of wing aerodynamic loads on wing torque loads by virtue of wing finite element computation and analysis; 2, realizing a torque load test system for each section of wings by virtue of adopting a sensitive torque bridge piece distribution scheme and a torque bridge combination technology; 3, performing a ground calibration test on the torque loads according to the structure or part sensitive to the influences of the aerodynamic loads on the wing torque loads, thereby obtaining conversion relation between external loads and bridge strain gauge signals by virtue of the ground calibration test; 4, performing a flight load actual measurement flight test, thereby obtaining the torque loads of each section of the wings according to the bridge strain gauge signals during flight. The method has the advantages that by virtue of aiming at the implementation difficulty in aircraft wing torque load actual measurement, the implementation problem of a torque load flight actual measurement test is solved, and the accuracy and high precision of the wing torque load test are ensured.
Owner:SHENYANG AIRCRAFT DESIGN INST AVIATION IND CORP OF CHINA
Car having an enhanced front aerodynamic load
ActiveUS20190233022A1Reduce air resistanceHigher front downforceVehicle body stabilisationSuperstructure subunitsAerodynamic loadWindshield
A car comprising a pair of front wheels, a pair of rear wheels, an outer body having a front hood and a front bumper, and a passenger compartment formed inside the outer body between the front and the rear wheels and frontally delimited by a windscreen connected with the front hood; the car being also provided with: an aerodynamic duct extending between an inlet opening formed through the front bumper and an outlet opening formed through the front hood to allow an ascending air flow during the travel of the car; and a wing-shaped profile positioned at the inlet opening and configured to increase the air suction effect by means of the duct during the travel of the car and to increase the front aerodynamic load on the car by acting as a spoiler.
Owner:SPAN FERRARI SPA
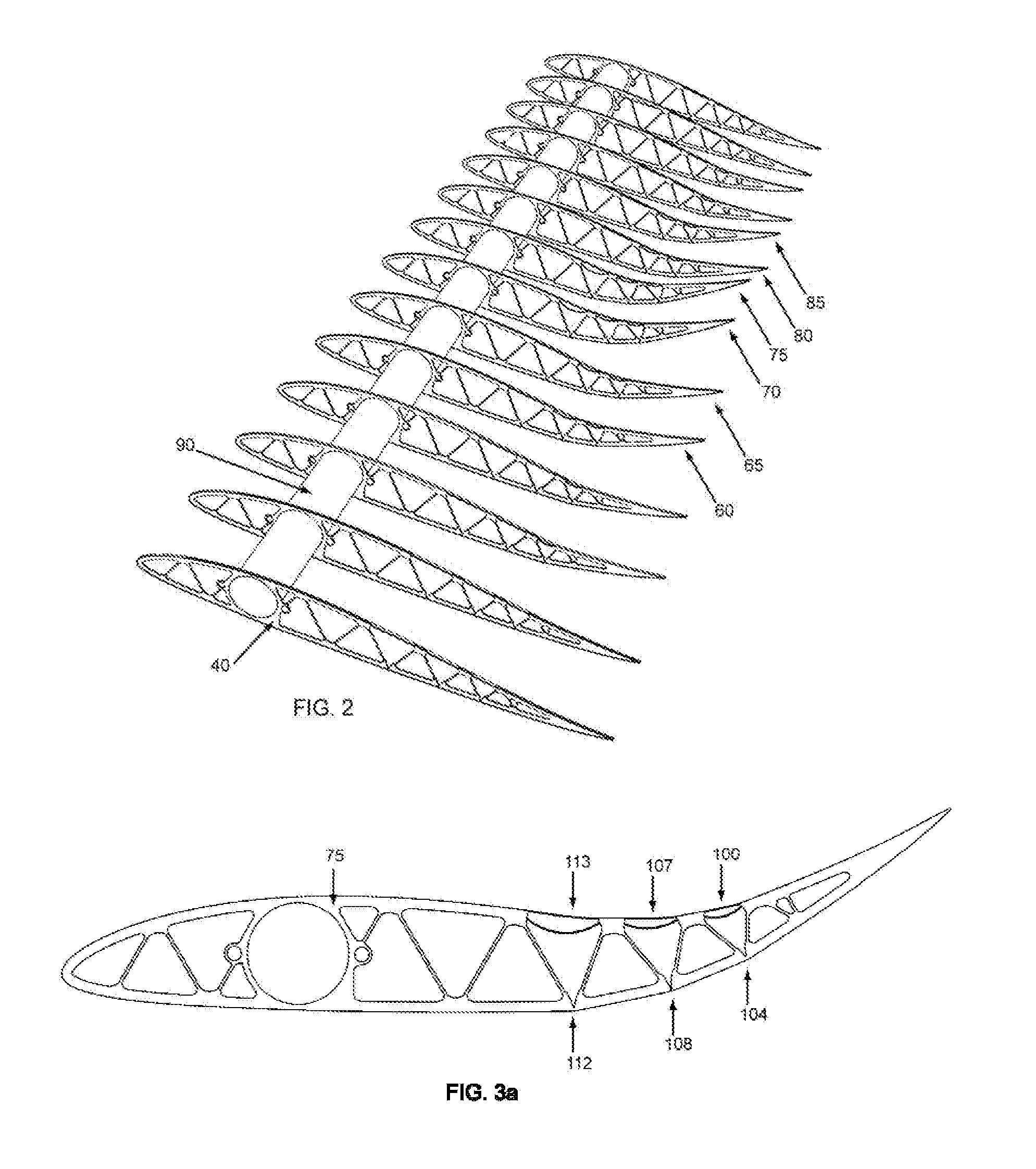
Rotor blade extension portion having a skin located over a framework
ActiveUS20100028162A1Prevent bucklingGuaranteed normal transmissionPropellersEngine manufactureAerodynamic loadEngineering
A wind turbine rotor blade extension portion having a permanent framework with one or more chord-wise members and a substantially span-wise member. A membrane is located over the framework to thereby generate a streamlined surface. The extension portion is configured to transmit aerodynamic loads from the membrane, along the chord-wise members to a rotor blade to which the extension portion is connected, in use.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
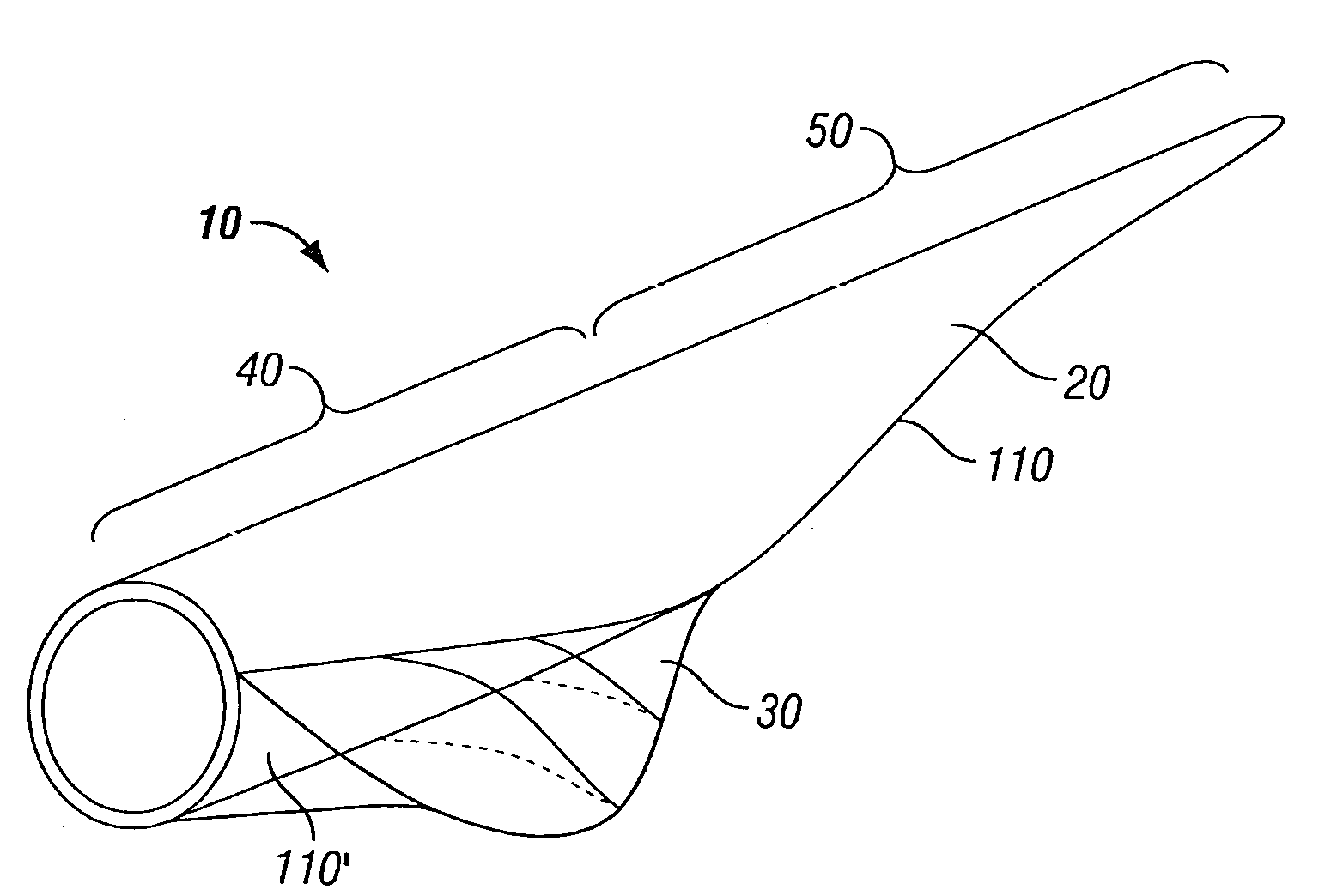
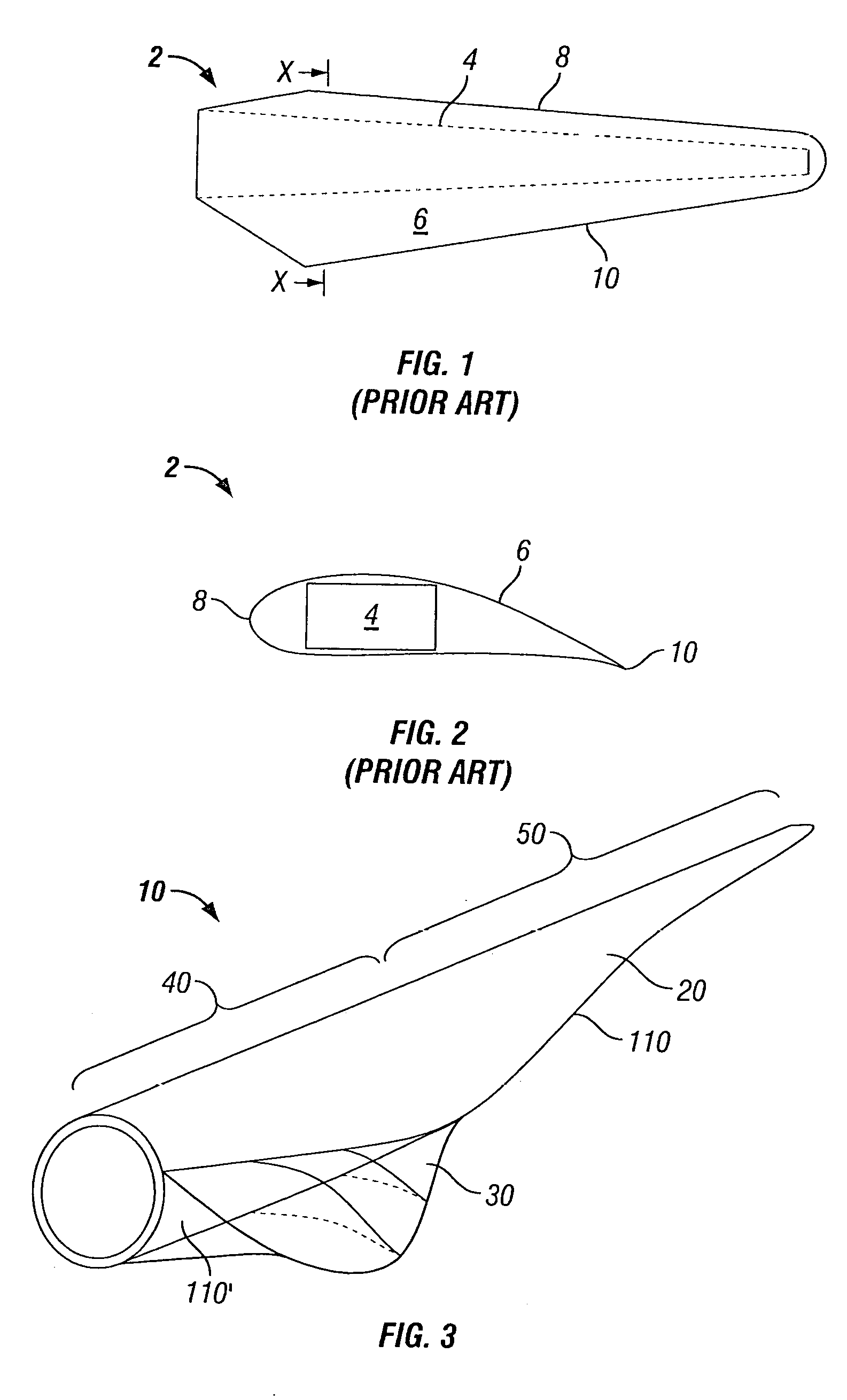
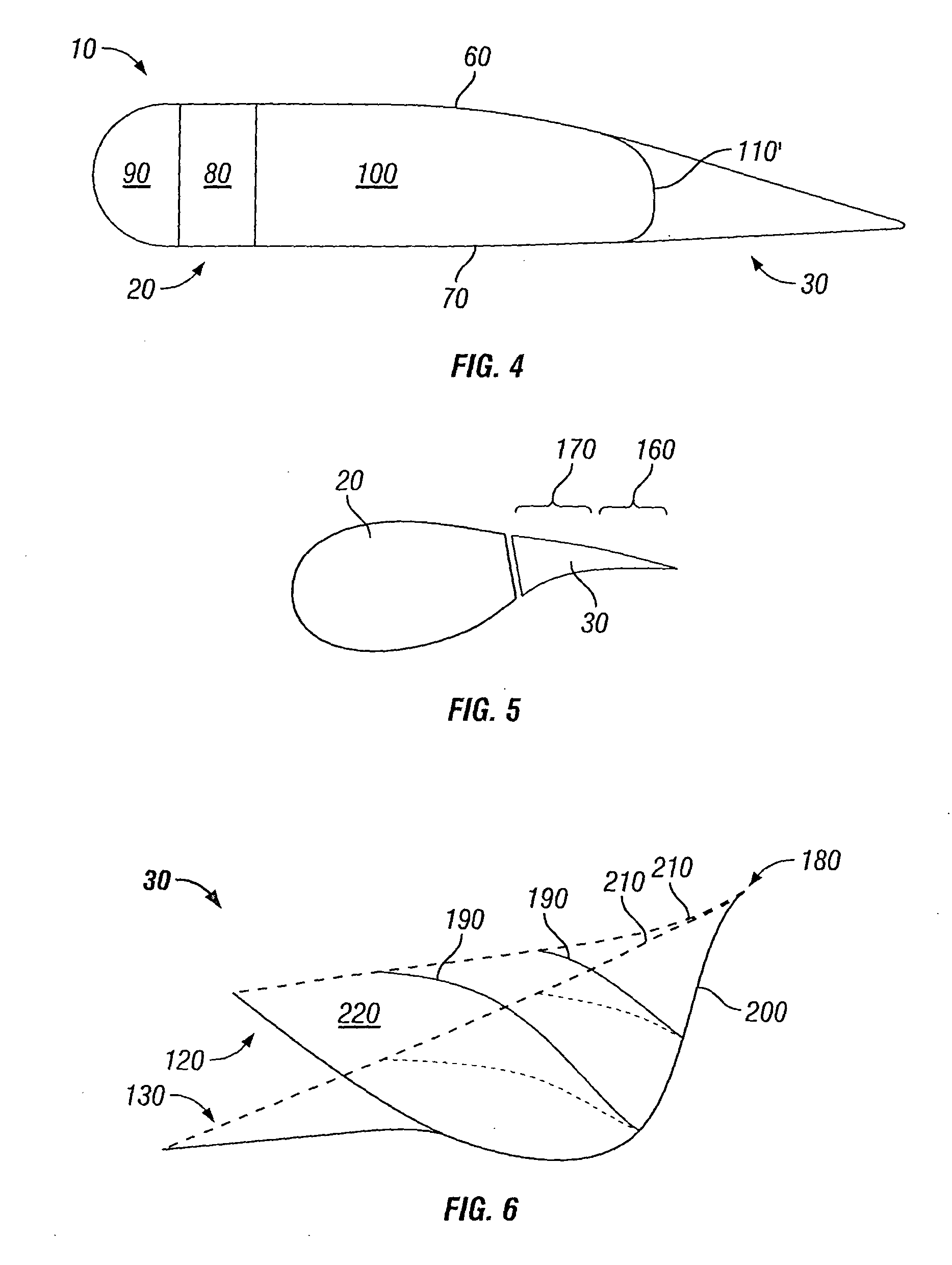
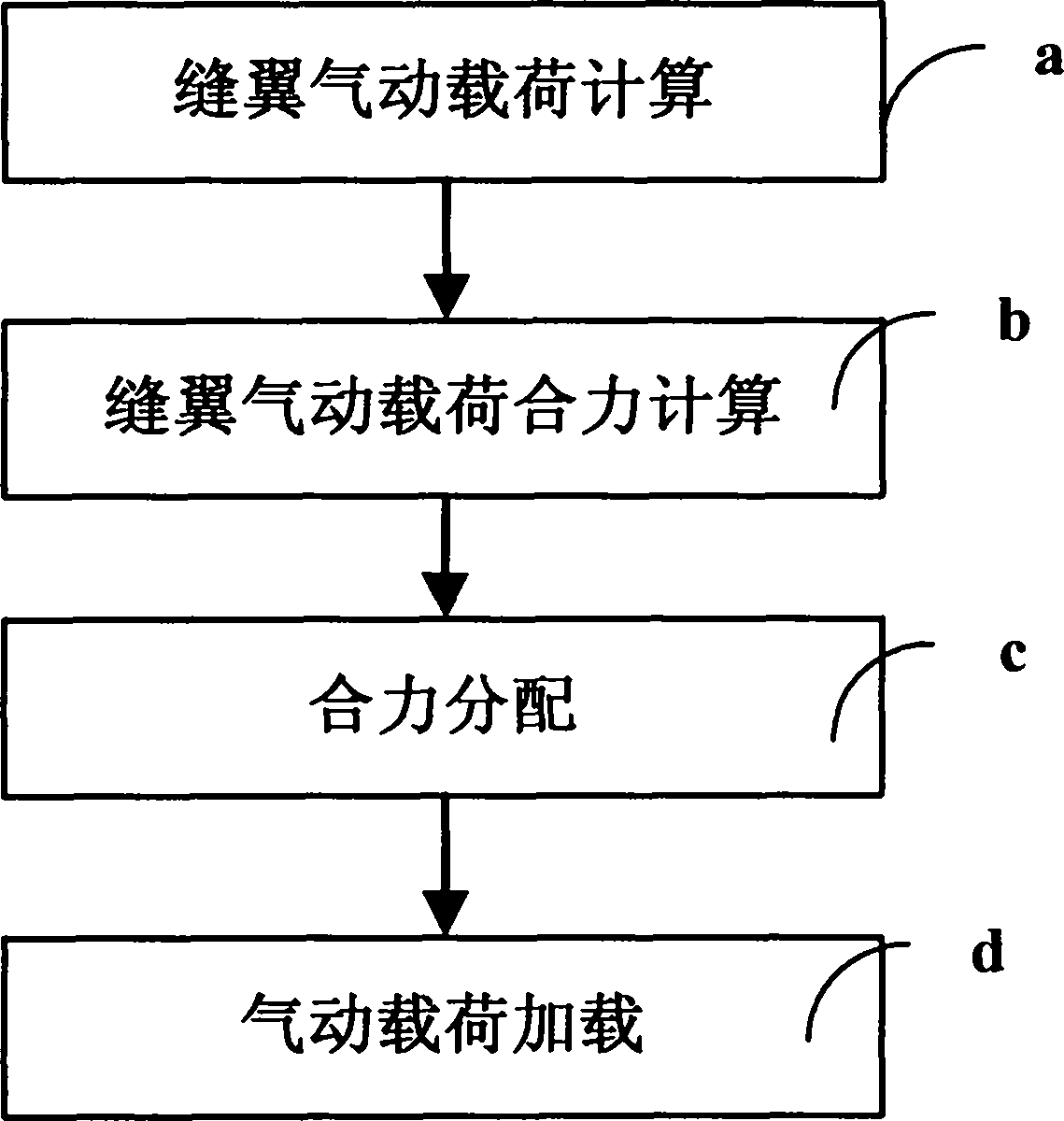
Aerodynamic load loading method used for reliability tests on aircraft flap and slat system
The invention relates to an aerodynamic load loading method used for reliability tests on an aircraft flap and slat system. The method includes the concrete steps that first, aerodynamic loads of each slat in various flight states are obtained through wind tunnel tests or simulating calculation; second, according to the aerodynamic loads of each aircraft slat in various flight states, the resultant force of the aerodynamic loads on the face of each slat in various flight states is calculated; third, the resultant force of the aerodynamic loads on the face of each aircraft slat in various flight states is decomposed into a plurality of component forces, and the magnitudes and the directions of the component forces are obtained; fourth, the component forces in the third step are evenly distributed and loaded to the face of each slat through adhesive tape and a lever system. According to the aerodynamic load loading method, the aerodynamic loads of each slat in various states during a flight period are considered; the aerodynamic loads obtained through tests or simulation can be effectively converted in the loading modes achieved in the tests, and real aerodynamic loads are guaranteed.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Aerodynamic loading system and loading method for undercarriage self-control spring-damping system
ActiveCN102717897AGood load simulation continuitySmall footprintAircraft components testingAerodynamic loadActuator
The invention discloses an aerodynamic loading system and a loading method for aero-undercarriage self-control spring-damping system and belongs to aero-undercarriage control test systems. The aerodynamic loading system comprises a test rack (1), an aero-undercarriage (2), a strutting actuator (3) and a support frame (4), wherein the strutting actuator (3) and the support frame (4) are connected on the aero-undercarriage (2), an aerodynamic loading direction control mechanism controls the direction of aerodynamic load during undercarriage control, and an aerodynamic loading size simulation mechanism controls the size of the aerodynamic load during the undercarriage control. The aerodynamic loading system and the loading method for the self-control spring-damping system is high in loading accuracy, good in loading simulation continuity, concise in structure and applicable to tests of undercarriage control of various planes and can provide corresponding accurate parameters for design and development of aero-undercarriages.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Deformable skin structure with designable poisson ratio
The invention relates to a wing skin structure, in particular to a deformable skin structure with a designable poisson ratio, aiming at solving the problem that the existing skin structure cannot meet the requirements of lower deformation rigidity along the deformation direction and higher structural rigidity along other non-deformation directions, thus being not capable of bearing aerodynamic load and inertia load. The deformable skin structure comprises a honeycomb structure base body, a flexible elastomer and a plurality of pneumatic artificial muscles, wherein the honeycomb structure base body is a honeycomb structure body formed by arranging positive poisson ratio honeycomb unit bodies and negative poisson ratio honeycomb unit bodies in a mixed way; the flexible elastomer is poured onto the honeycomb structure base body and the plurality of pneumatic artificial muscles so as to form a flexible panel. The deformable skin structure with the designable poisson ratio is used for manufacturing aircraft wing skin.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Calibration method of balance with air bridge of wind tunnel strain considering pressure influence
ActiveCN108507752AShorten the calibration cycleImprove R&D efficiencyAerodynamic testingAir bridgeAerodynamic load
The present invention provides a calibration method of a wind tunnel strain balance with an air bridge considering pressure influence. Working formulas, with a limited quantity, of a balance with an air bridge in different pressure states are employed to perform fitting and generate a general balance working formula suitable for a pressure range required by a test, and the general balance workingformula comprises pressure parameters. The pressure parameters are added into the general balance working formula of the balance with the air bridge, and when wind tunnel test is performed, an actually measurement pressure value and electrical signal increment value of each component of the balance are substituted into the general balance working formula to calculate and obtain accurate aerodynamic loading. Compared to the calculation result of a traditional balance formula, the general balance working formula can obtain more accurate aerodynamic loading so as to facilitate improvement of accuracy of the type of the wind tunnel test.
Owner:INST OF HIGH SPEED AERODYNAMICS OF CHINA AERODYNAMICS RES & DEV CENT
Six-component optical fiber aerodynamic force measuring balance and outputting signal combining method
ActiveCN108195554AMeet the six-component aerodynamic load measurement requirementsSolve the difficult problem of layingAerodynamic testingFluid pressure measurement by optical meansAerodynamic loadRolling moment
The invention discloses a six-component optical fiber aerodynamic force measuring balance and an outputting signal combining method. The six-component optical fiber aerodynamic force measuring balancecomprises a model connecting end, a normal force / pitch moment / lateral force / yawing moment / rolling moment combined measuring element, an axial force measuring element, a strut and a support connectingend. Holes and grooves which are used for laying of optical fibers guided out by optical fiber strain gauges on the various measuring elements are formed in a structural body of the optical fiber aerodynamic force measuring balance, the problem that laying of lead-out lines of optical fiber strain gauges, particularly laying of lead-out lines of optical fiber strain gauges of axial force elements, is difficult can be solved effectively, requirements of six-component aerodynamic load measurement of an aerodynamic force test of a wind tunnel model of an aerospace craft are met, reasonable combination of output signals of the optical fiber strain gauges is adopted, interference among the various components of the optical fiber aerodynamic force measuring balance can be relieved or eliminatedeffectively, and six components of the optical fiber aerodynamic force measuring balance are measured independently.
Owner:中国空气动力研究与发展中心超高速空气动力研究所
A wind tunnel test facility for the separation simulation of the cowling of an aspirated hypersonic vehicle
PendingCN109250149ABreach of integrityDoes not affect ventilationAircraft components testingAerodynamic loadFlight vehicle
The invention discloses a wind tunnel test facility for the separation simulation of the cowling of an aspirated hypersonic vehicle, comprising a model apparatus and a jet apparatus. Based on the ideaof integrative design, the requirements of model support, jet air supply, separation distance adjustment and securing the similarity of inter-stage area are comprehensively considered in the device;the designed modified aircraft precursor has the functions of model support, jet air supply and separation distance adjustment, and ensures the similarity of the shape of the inter-stage area. The designed gas supply adapter bar has the functions of model support and jet gas supply, and the whole test device is easy to assemble and disassemble, and is convenient to use. The wind tunnel test deviceof the invention solves the key technical problems such as model support, separation distance adjustment and reverse thrust jet simulation faced by the current experiment. The similarity of the fairing is ensured, and no additional hard-to-correct interference is introduced, and the reliable fairing aerodynamic load data is obtained under the interaction between the reverse jet and the incoming flow.
Owner:中国空气动力研究与发展中心超高速空气动力研究所
Test method by loading alternating aerodynamic load outside train body of high-speed train
ActiveCN101982752AMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesFluid-tightness measurement using fluid/vacuumElectricityAerodynamic load
The invention relates to a test method by loading an alternating aerodynamic load outside train body of a high-speed train. The method adopts a load loading device to perform loading and unloading to the train body to be tested, wherein a detection sensor is arranged on the train body to be tested; the detection sensor and the control system of the load loading device are electrically connected with a computer system; the load loading device is controlled by the computer system to perform automatic loading and unloading to the train body to be tested repeatedly according to the preset working conditions and cycle number; the computer system collects test data instantly through the detection sensor and stores the test data; and after the detection sensor is installed on the train body to be tested, the train body to be tested performs sealing treatment; when the demand of the sealing detection is met, the train body to be tested is placed in the sealing container of the load loading device; the pressure in the train body to be tested is equal to one atmospheric pressure before the test; and the alternating aerodynamic load generated by the load loading device is directly loaded on the outer surface of the train body to be tested. A gap through which a worker enters to detect during the test is left between the cavity of the sealing container of the load loading device and the outer wall of the train body to be tested.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com