Patents
Literature
475 results about "Angular rotation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
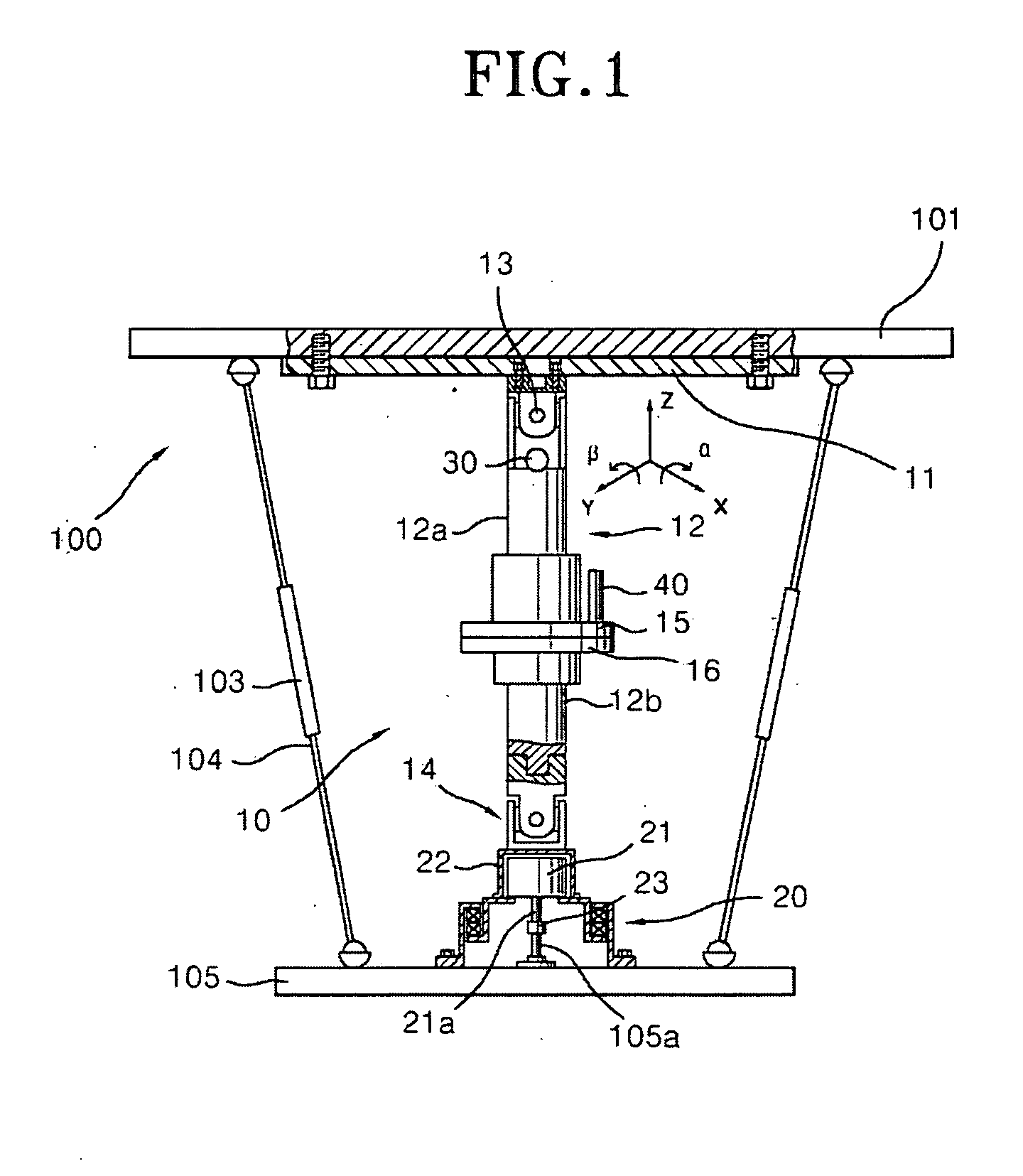
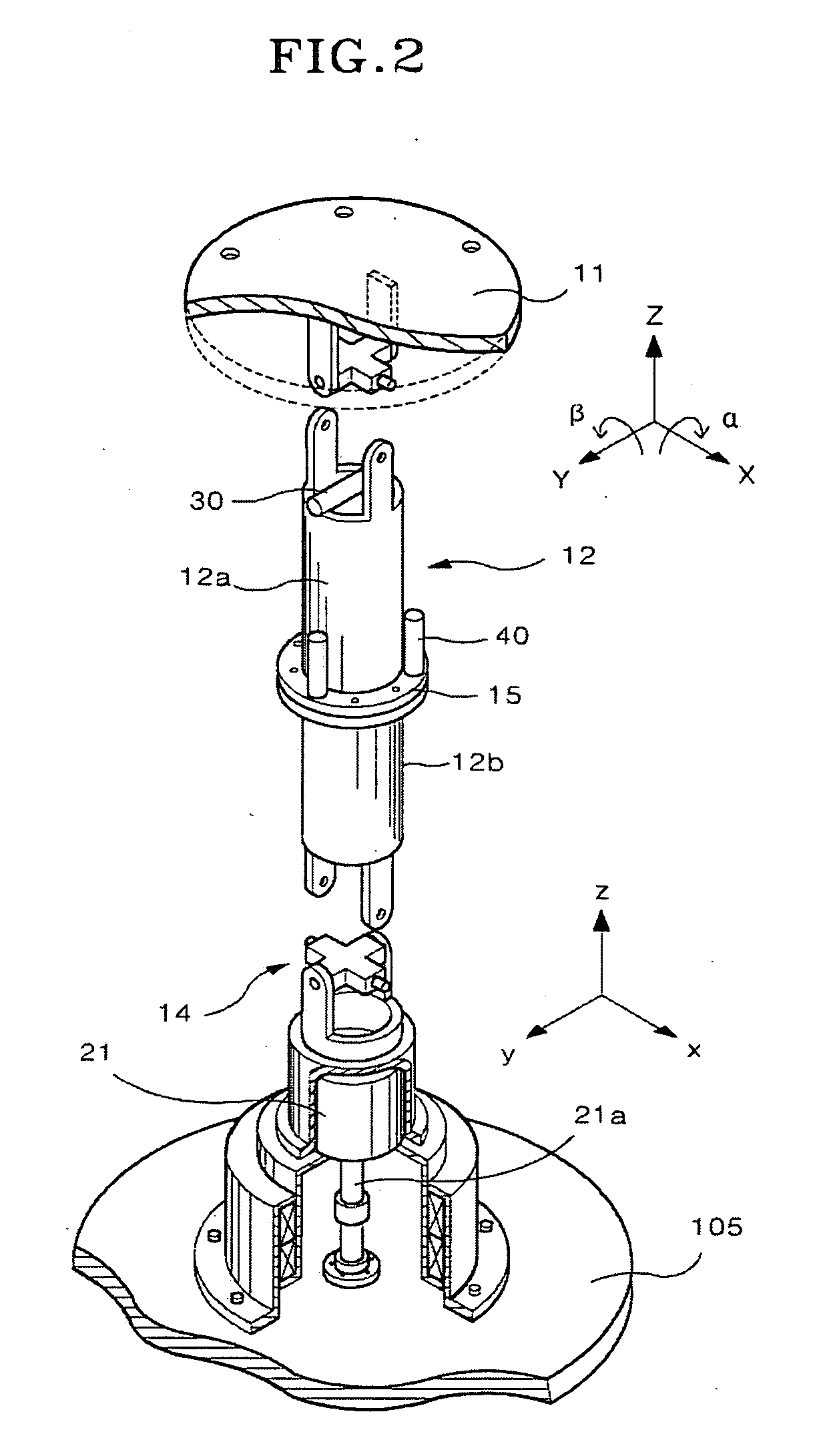
We define angular velocity as the rate of change of an angle. In symbols, this is. where an angular rotation takes place in a time . The greater the rotation angle in a given amount of time, the greater the angular velocity. The units for angular velocity are radians per second (rad/s).
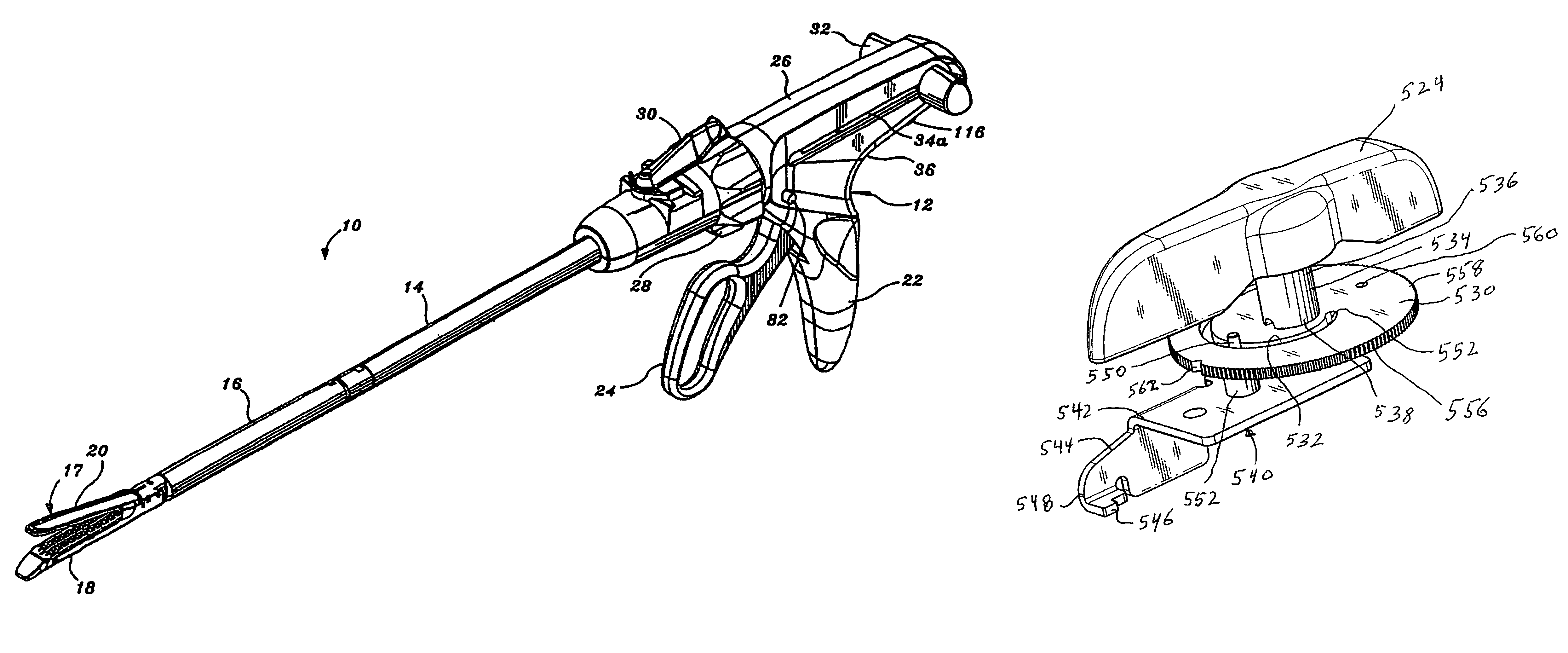
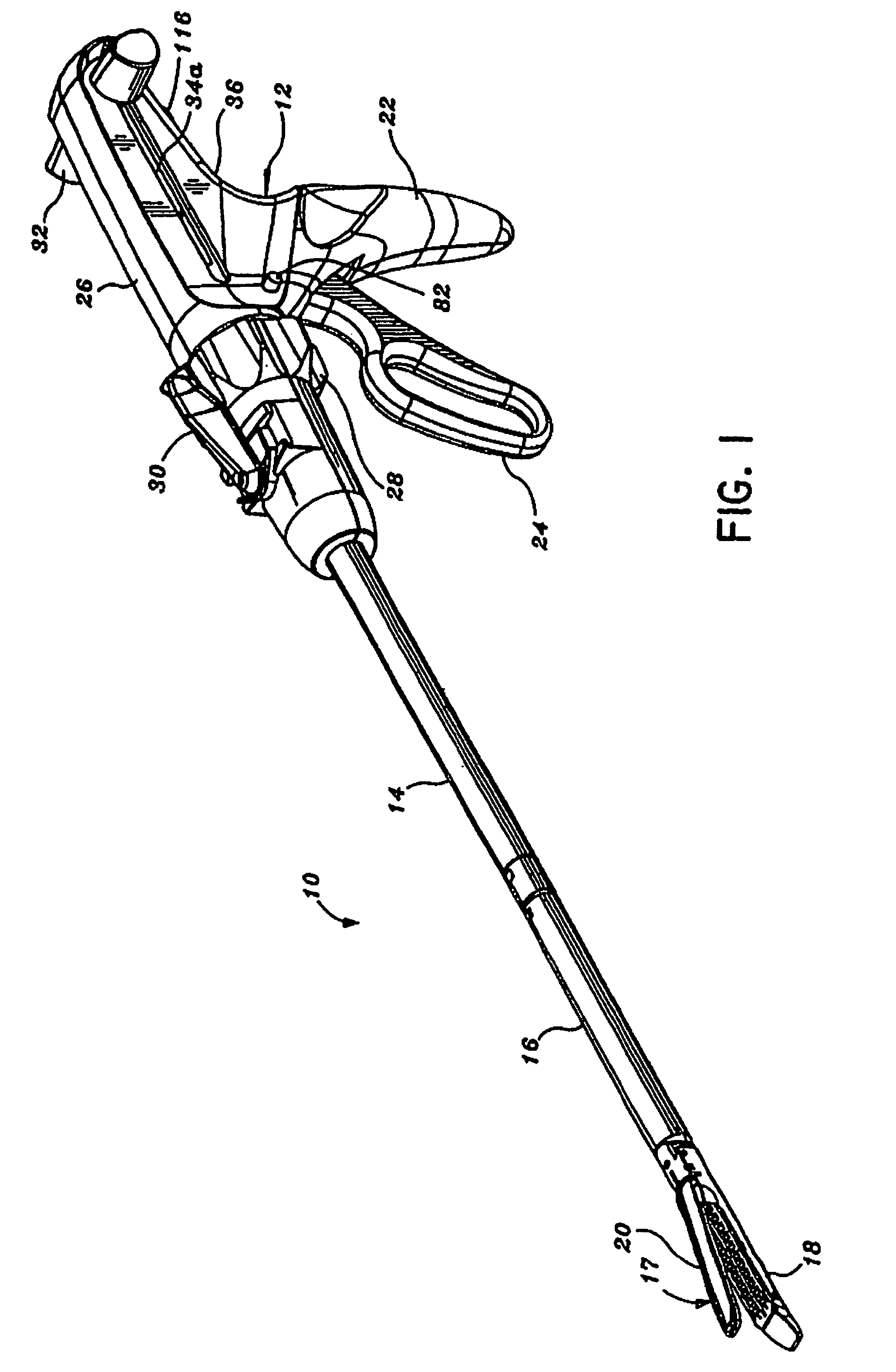
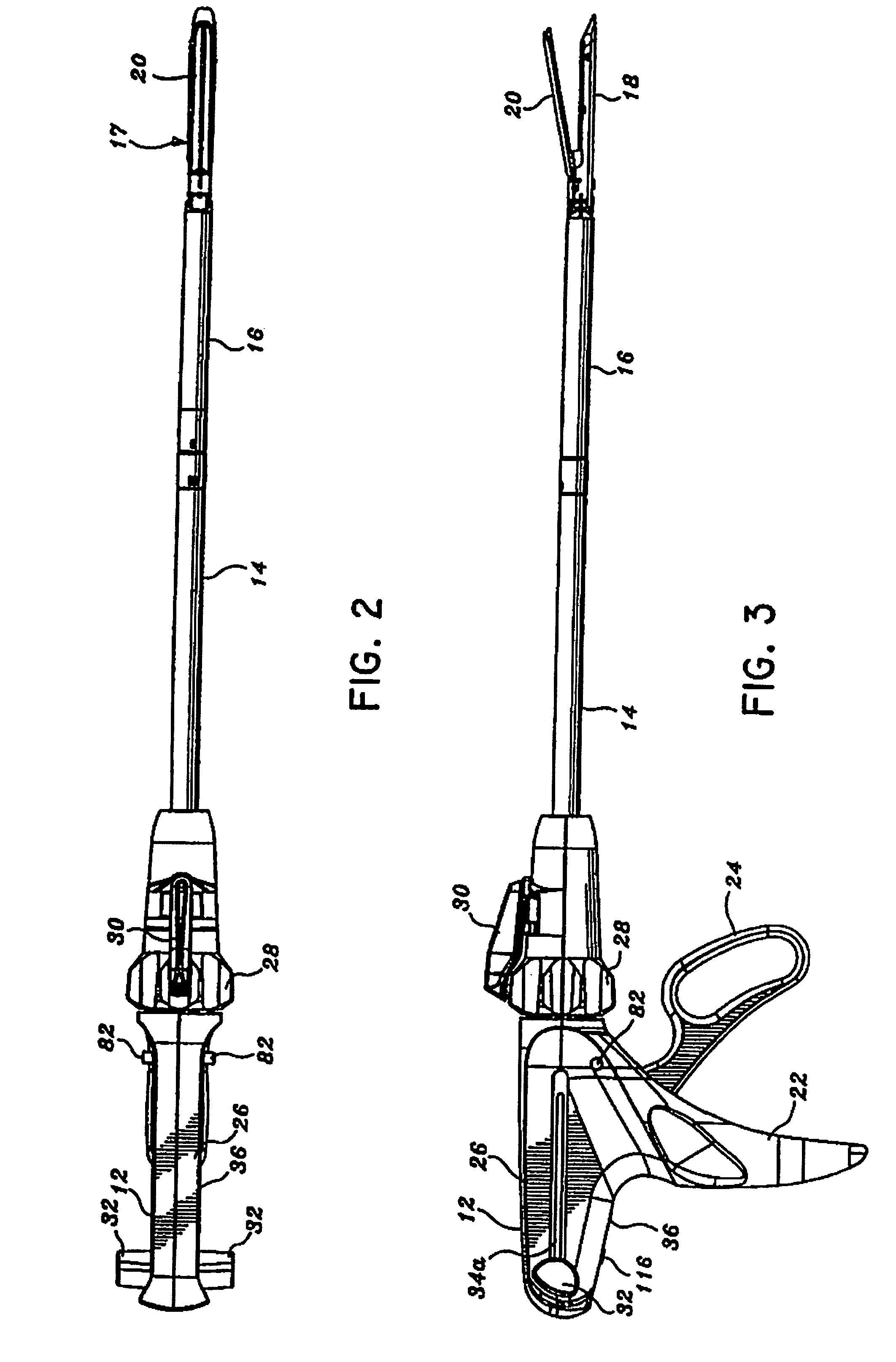
Surgical stapling apparatus having articulation mechanism
An articulation mechanism for use with a surgical apparatus having an articulating tool assembly is described. The articulation mechanism includes a rotatable shaft which is fixedly secured to a disk defining a spiral groove or slot. A linearly movable translation member is provided and includes a pin which is received within the spiral groove such that rotation of the disk effects linear translation of the translation member. The configuration of the spiral groove can be selected to provide any desired ratio of angular rotation of the disk to linear advancement of the translation member. As such, the configuration of the spiral slot can be selected to provide a uniform rate of articulation of the tool assembly of the surgical apparatus or a variable rate of articulation.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
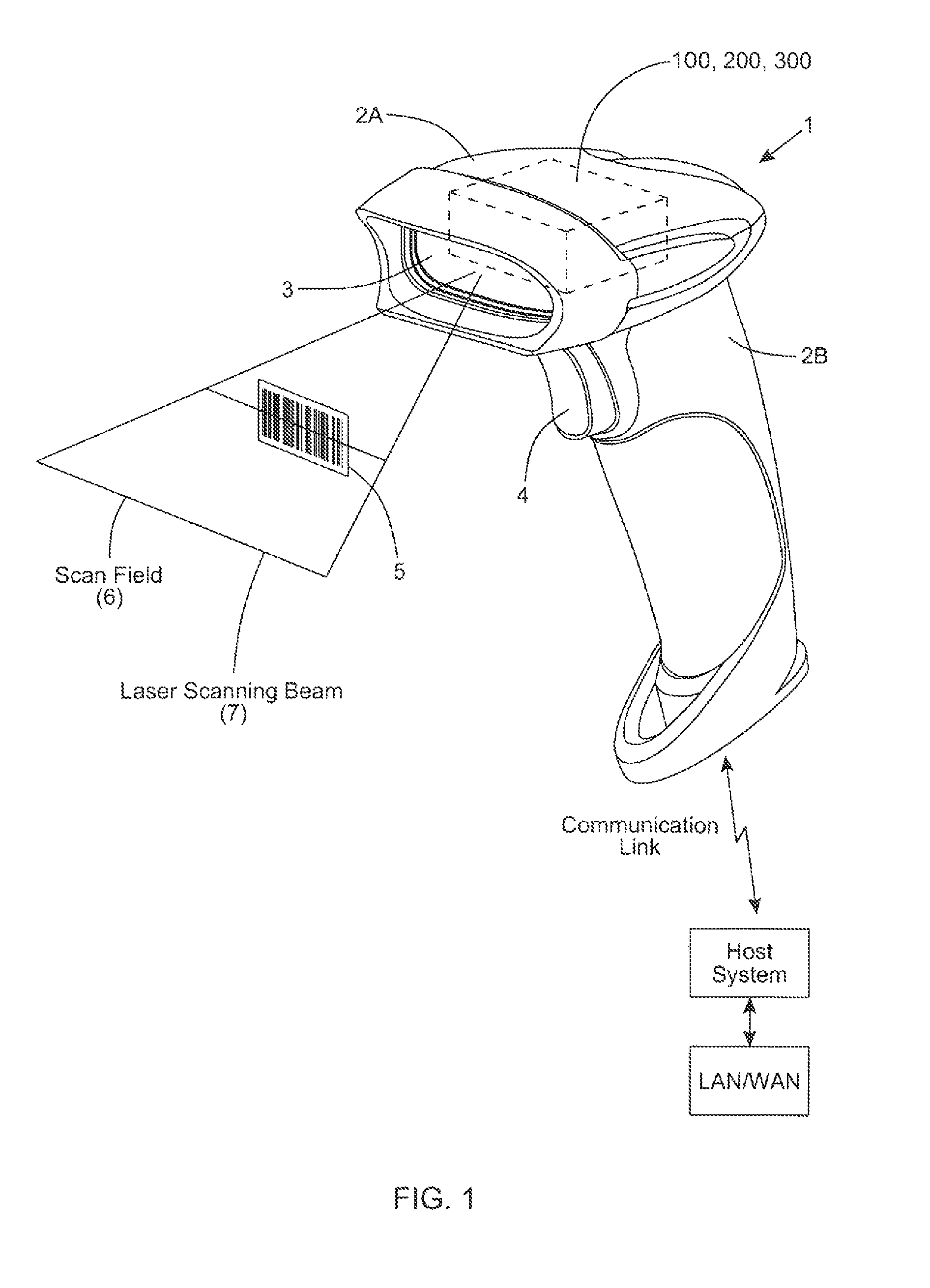
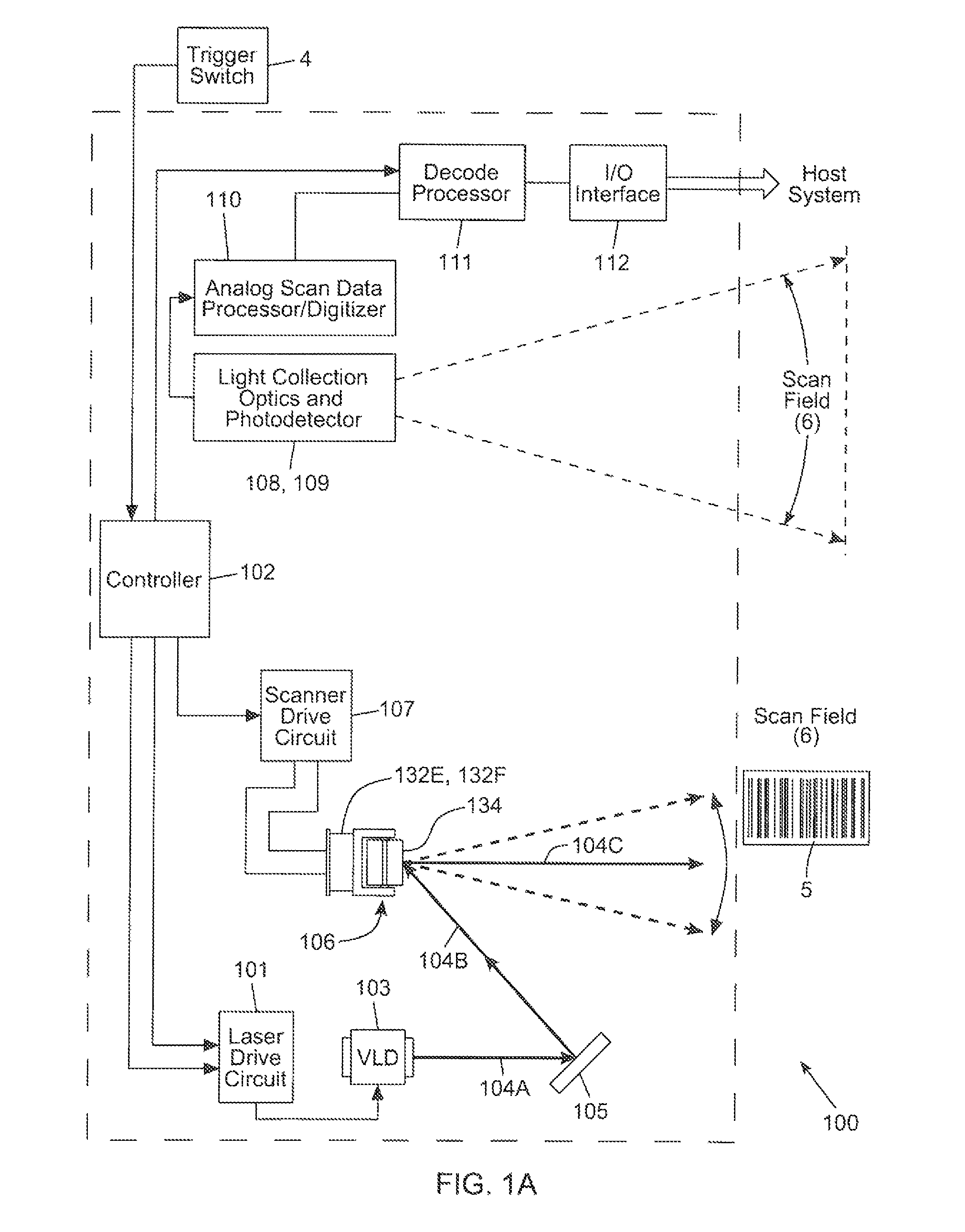
Laser scanning module with rotatably adjustable laser scanning assembly
A laser scanning module employing a laser scanning assembly mounted within a module housing using a mechanism that allows the laser scanning assembly to be rotated to an angular position within the engine housing so that light collection, beam folding and light collection mirrors in the module housing are optically aligned. A PC board is mounted on a side of the housing and has a configuration of elongated apertures of open-ended and / or closed geometry, arranged in a non-parallel manner. An electromagnetic coil structure, associated with the laser scanning assembly, has a linear array of electrically-conductive pins that project through the configuration of elongated holes, at locations along the elongated holes that are determined by the angular rotation of the laser scanning assembly attained during optical alignment conditions during manufacture.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
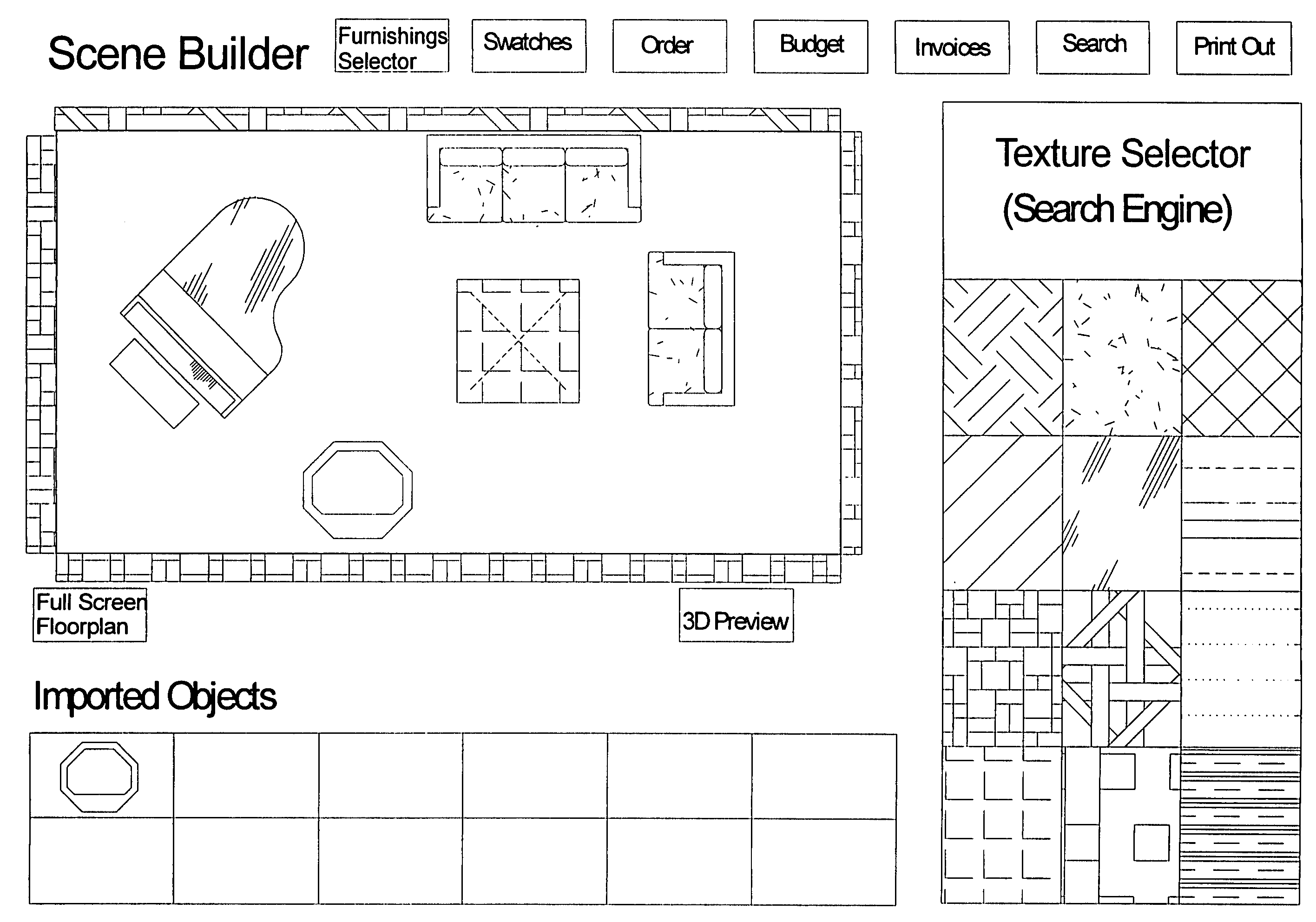
Network-linked interactive three-dimensional composition and display of saleable objects in situ in viewer-selected scenes for purposes of promotion and procurement
InactiveUS7062722B1Sufficiently accurateSufficiently appealingSpecial data processing applicationsMarketingFull custom3d image
A design professional such as an interior designer running a browser program at a client computer (i) optionally causes a digital image of a room, or a room model, or room images to be transmitted across the world wide web to a graphics server computer, and (ii) interactively selects furnishings from this server computer, so as to (iii) receive and display to his or her client a high-fidelity high-quality virtual-reality perspective-view image of furnishings displayed in, most commonly, an actual room of a client's home. Opticians may, for example, (i) upload one or more images of a client's head, and (ii) select eyeglass frames and components, to (iii) display to a prospective customer eyeglasses upon the customer's own head. The realistic images, optionally provided to bona fide design professionals for free, promote the sale to the client of goods which are normally obtained through the graphics service provider, profiting both the service provider and the design professional. Models of existing objects are built as necessary from object views. Full custom objects, including furniture and eyeglasses not yet built, are readily presented in realistic virtual image.Also, a method of interactive advertising permits a prospective customer of a product, such as a vehicle, to view a virtual image of the selected product located within a customer-selected virtual scene, such as the prospective customer's own home driveway. Imaging for all purposes is supported by comprehensive and complete 2D to 3D image translation with precise object placement, scaling, angular rotation, coloration, shading and lighting so as to deliver flattering perspective images that, by selective lighting, arguably look better than actual photographs of real world objects within the real world.
Owner:CARLIN BRUCE +3
Instruments and method for minimally invasive surgery for total hips
InactiveUS7601155B2Precise cuttingHigh cutting precisionSurgical sawsProsthesisLess invasive surgeryRight femoral head
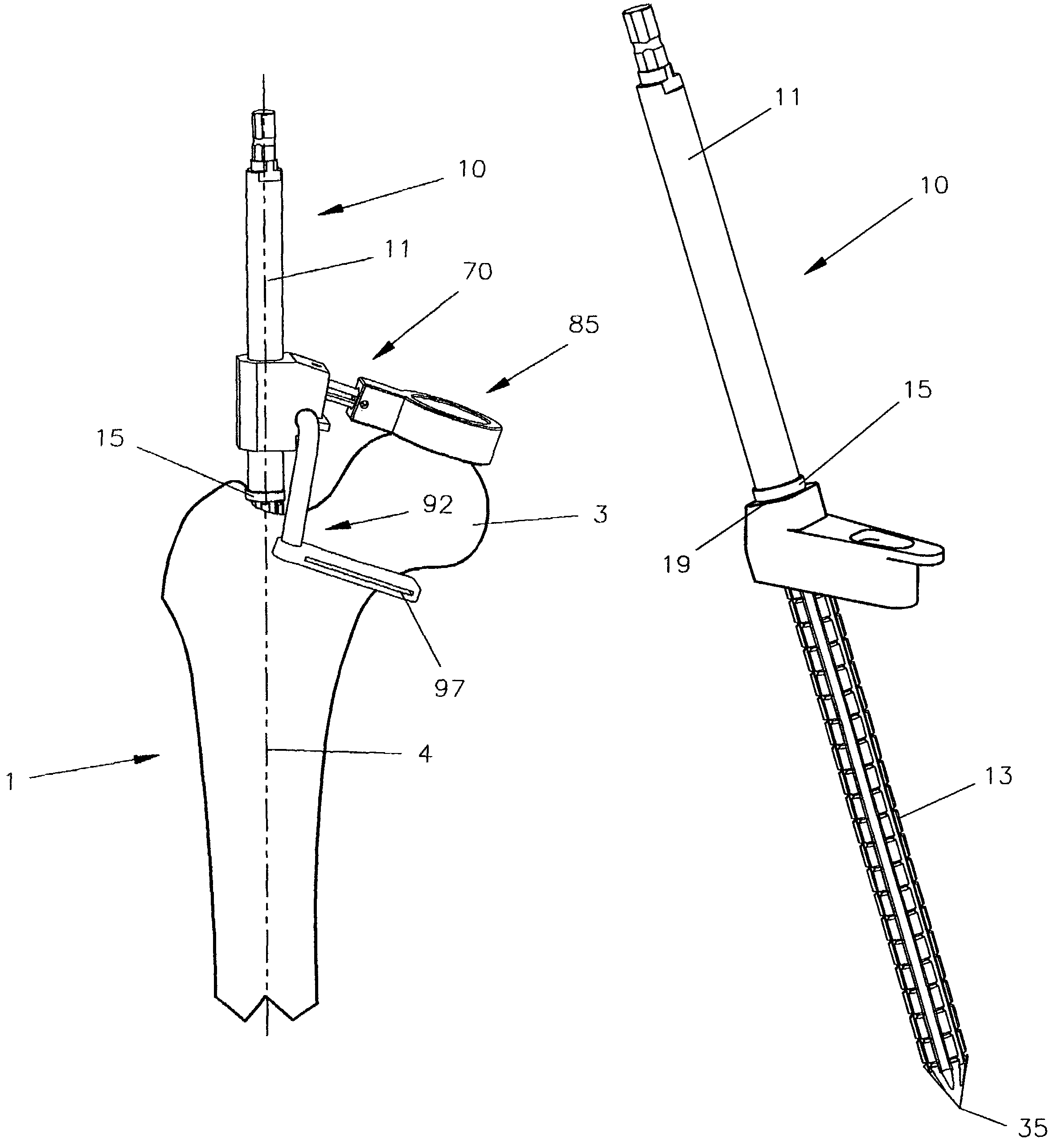
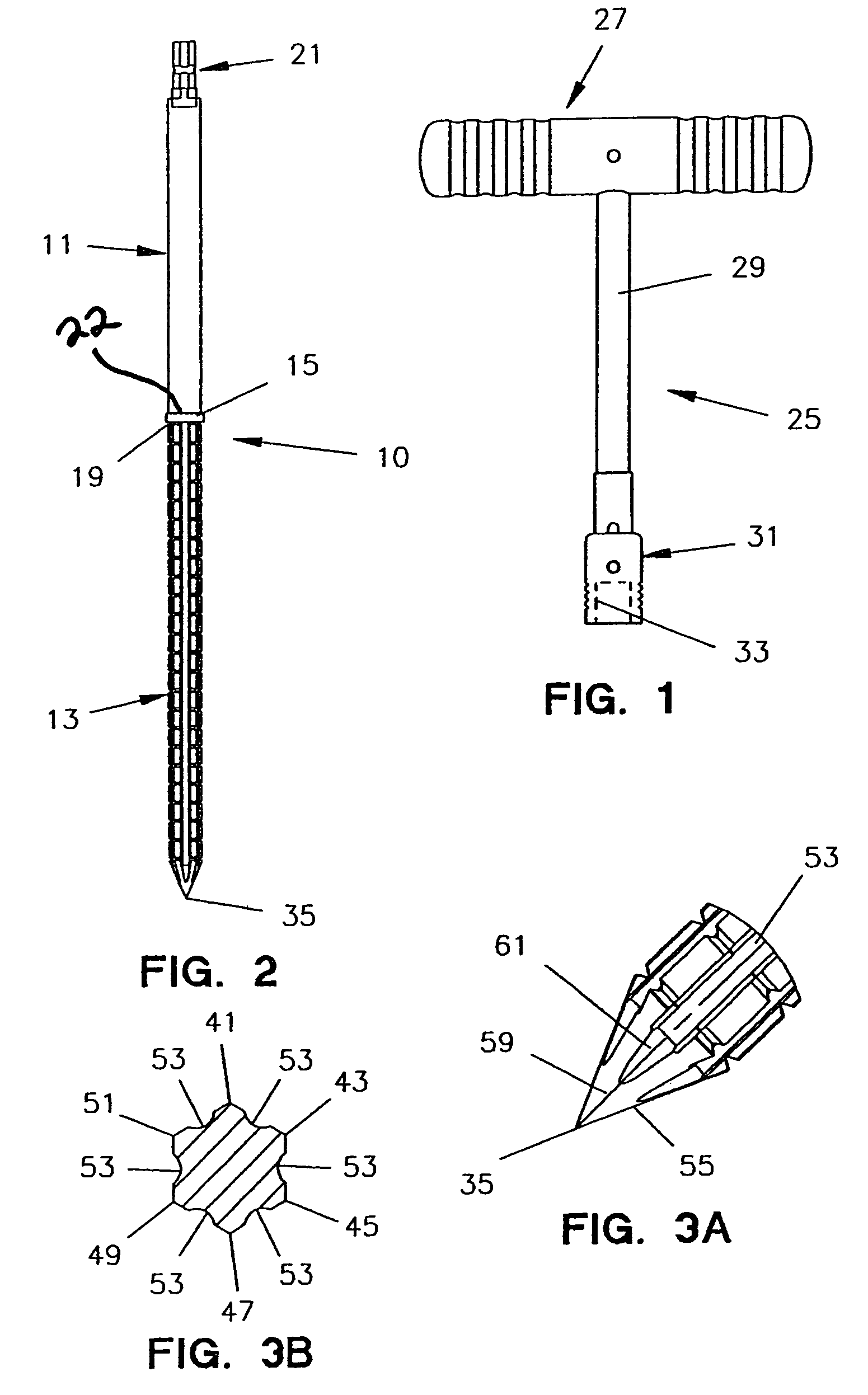
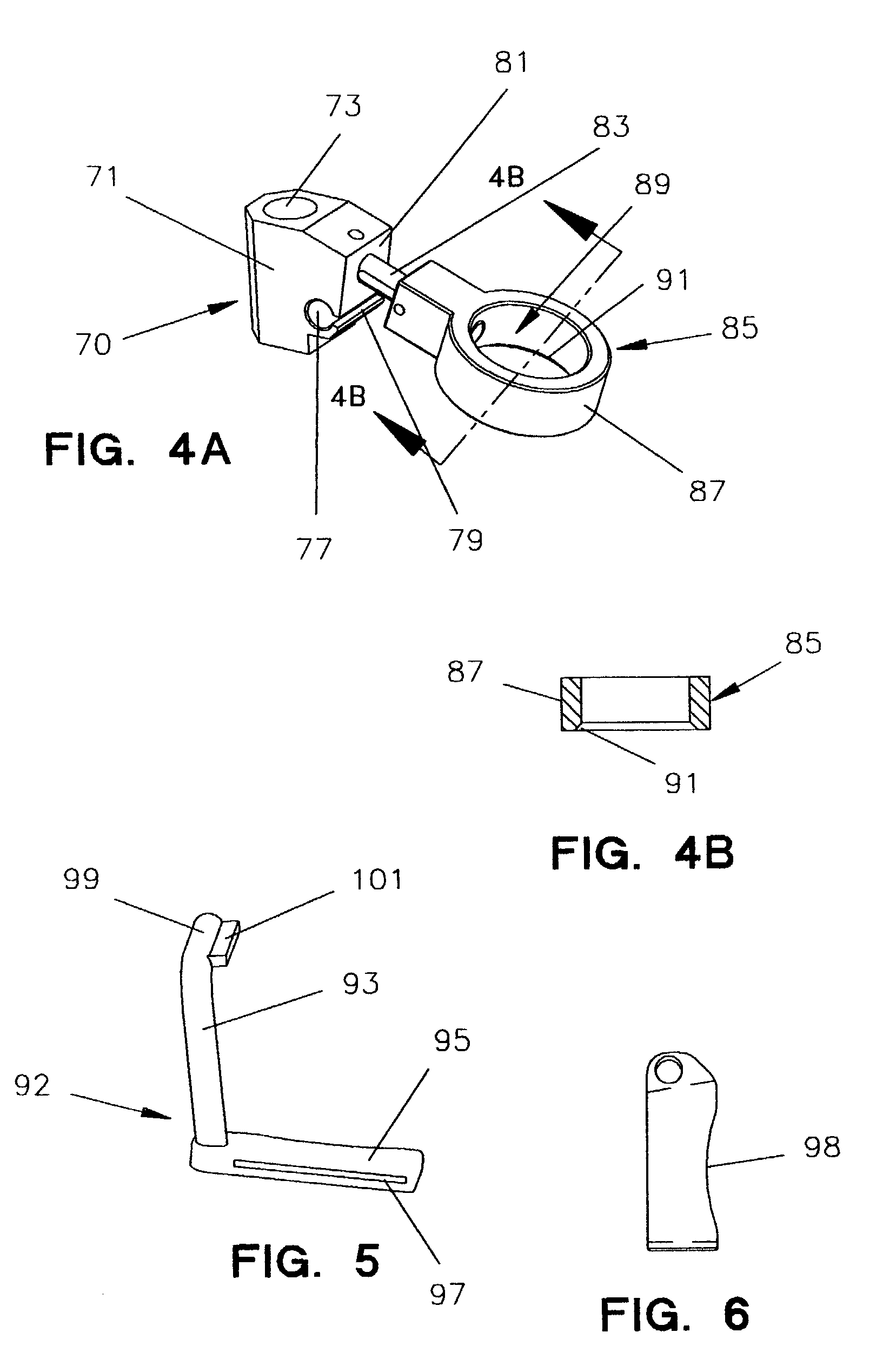
An intramedullary femoral broach aligns two instruments. A femoral neck resector guide slides over the broach and centers on the patient's femoral head to determine the height and angular rotation of resection. A circular ring of the head and cutting arms assure the system will fit any femur. A template is applied to the femoral broach and seats itself against the buttress of the broach locking it into place. The broach is then reinserted into the intramedullary canal. When the template reaches the greater trochanter the sizer is adjusted to the rotational anteversion of the canal. The handle of the femoral broach is struck with a mallet until the template is imbedded into the proximal femoral neck intramedullary bone. A retractor facilitates reaming of the acetabulum through a small anterior incision. A proximal portion digs into the bone of the superior acetabulum to allow for retraction of soft tissues.
Owner:PETERSEN THOMAS D
Optical see-through augmented reality modified-scale display
InactiveUS7002551B2Improve accuracyAccurate currentInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsDisplay device
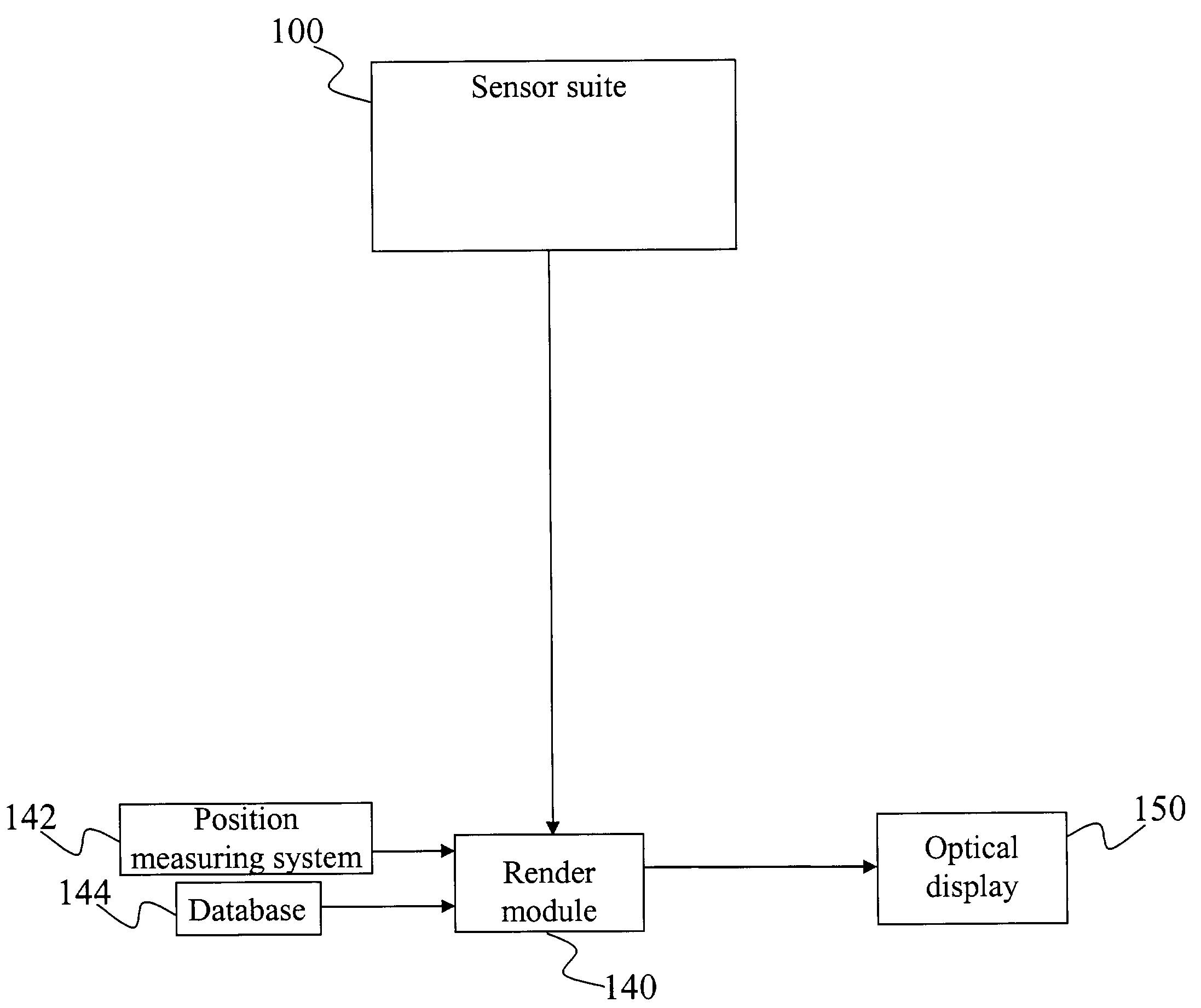
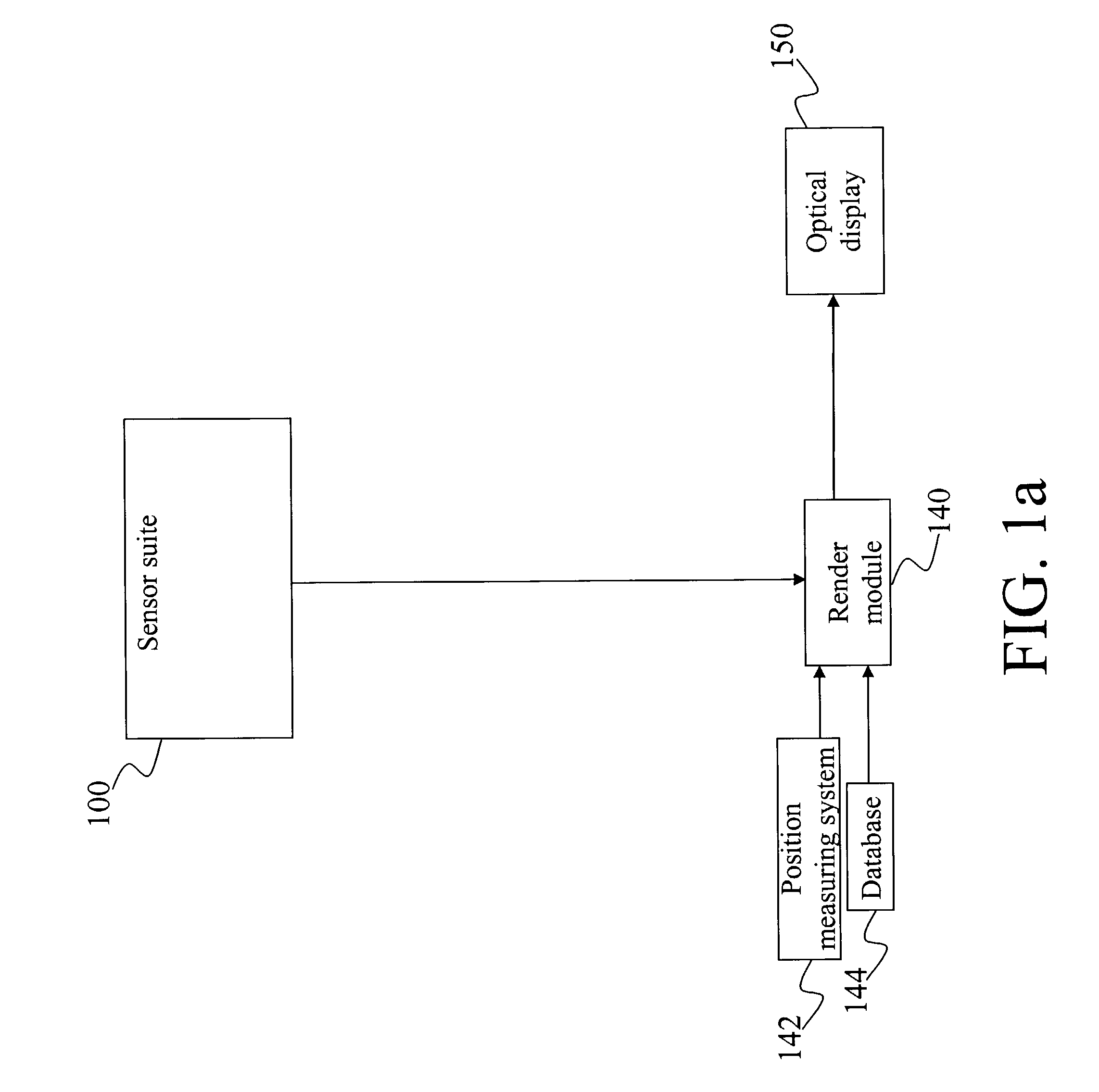
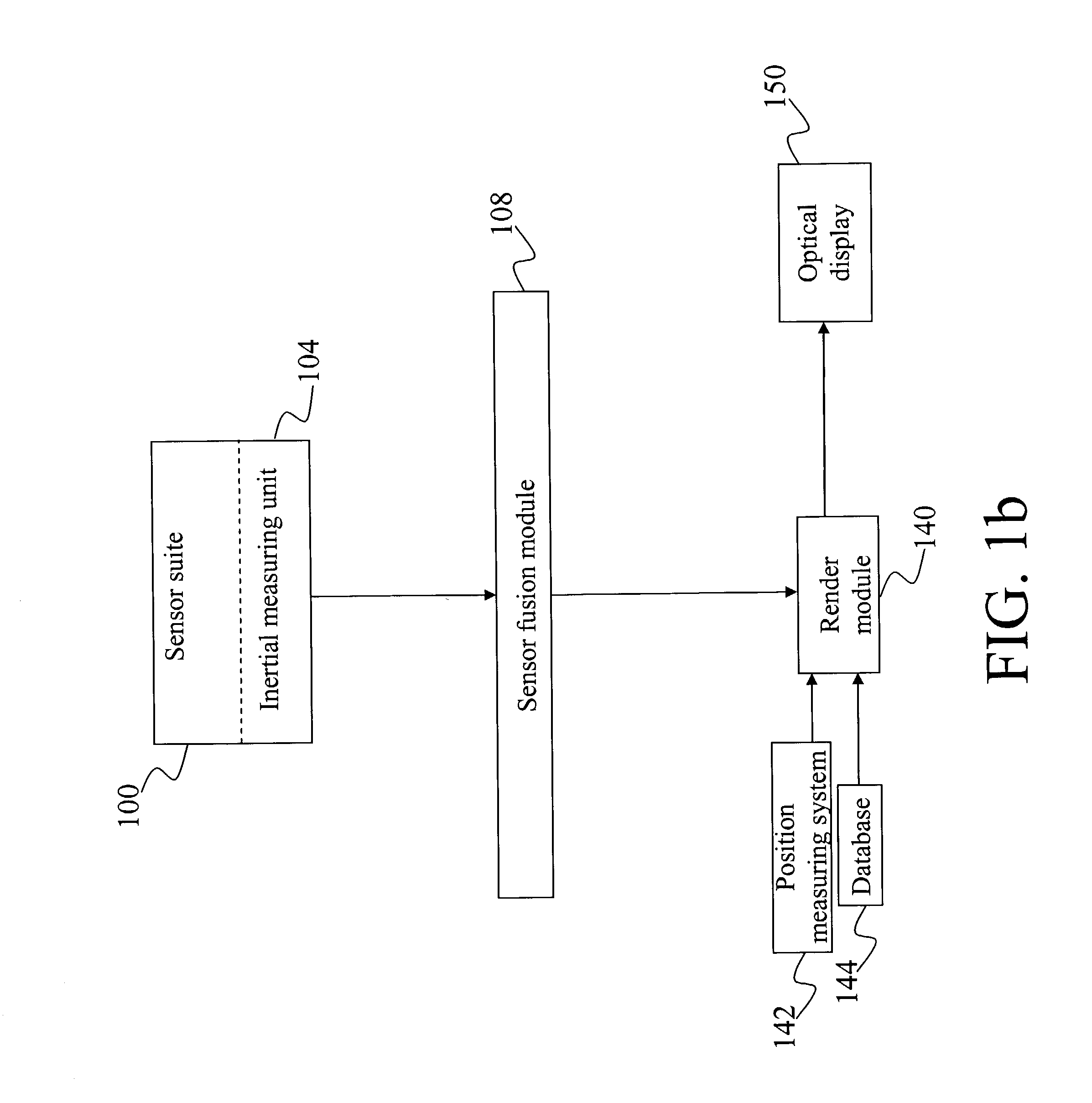
A method and system for providing an optical see-through Augmented Reality modified-scale display. This aspect includes a sensor suite 100 which includes a compass 102, an inertial measuring unit 104, and a video camera 106 for precise measurement of a user's current orientation and angular rotation rate. A sensor fusion module 108 may be included to produce a unified estimate of the user's angular rotation rate and current orientation to be provided to an orientation and rate estimate module 120. The orientation and rate estimate module 120 operates in a static or dynamic (prediction) mode. A render module 140 receives an orientation; and the render module 140 uses the orientation, a position from a position measuring system 142, and data from a database 144 to render graphic images of an object in their correct orientations and positions in an optical display 150.
Owner:HRL LAB
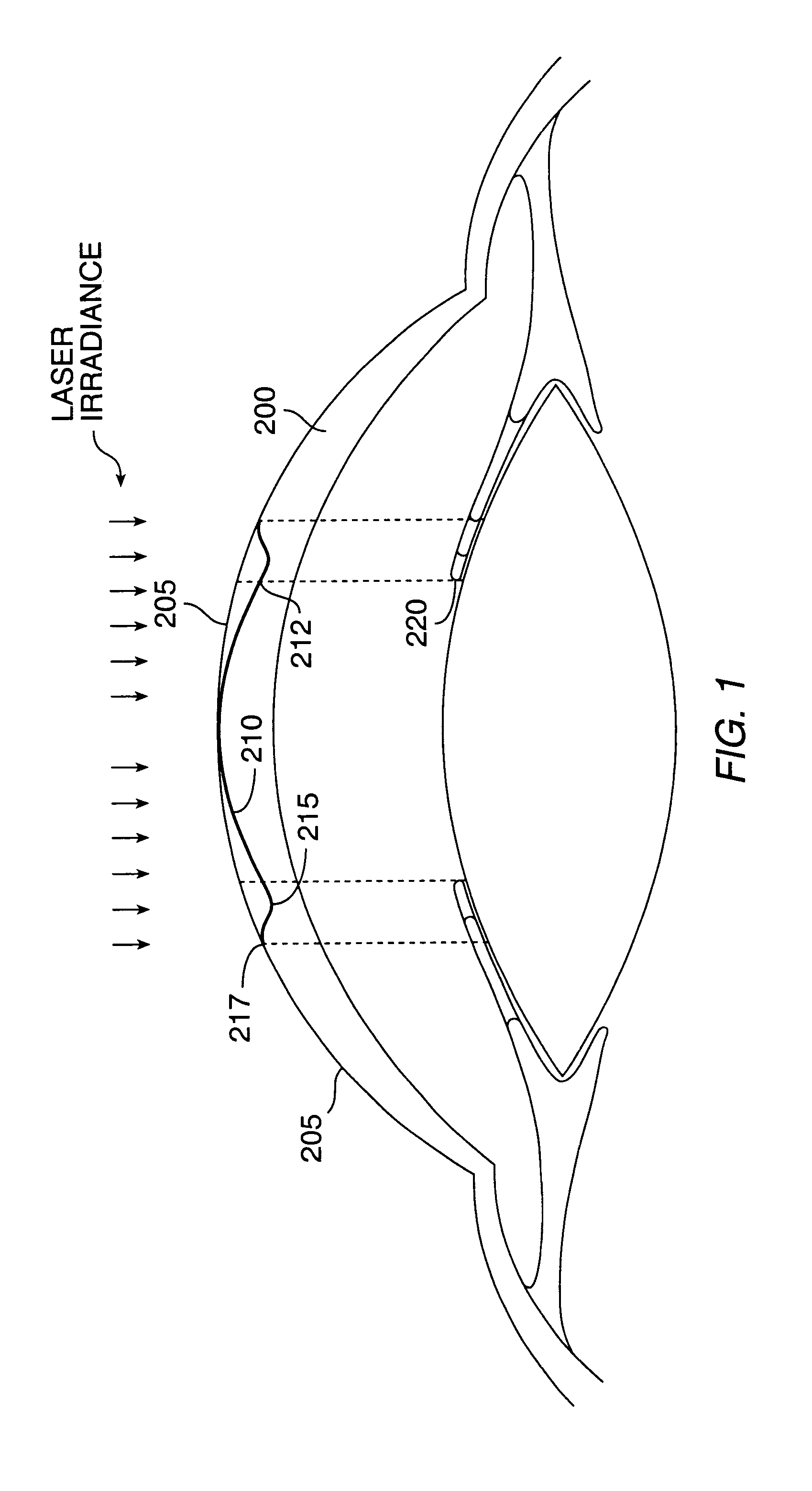
Method and systems for laser treatment of presbyopia using offset imaging
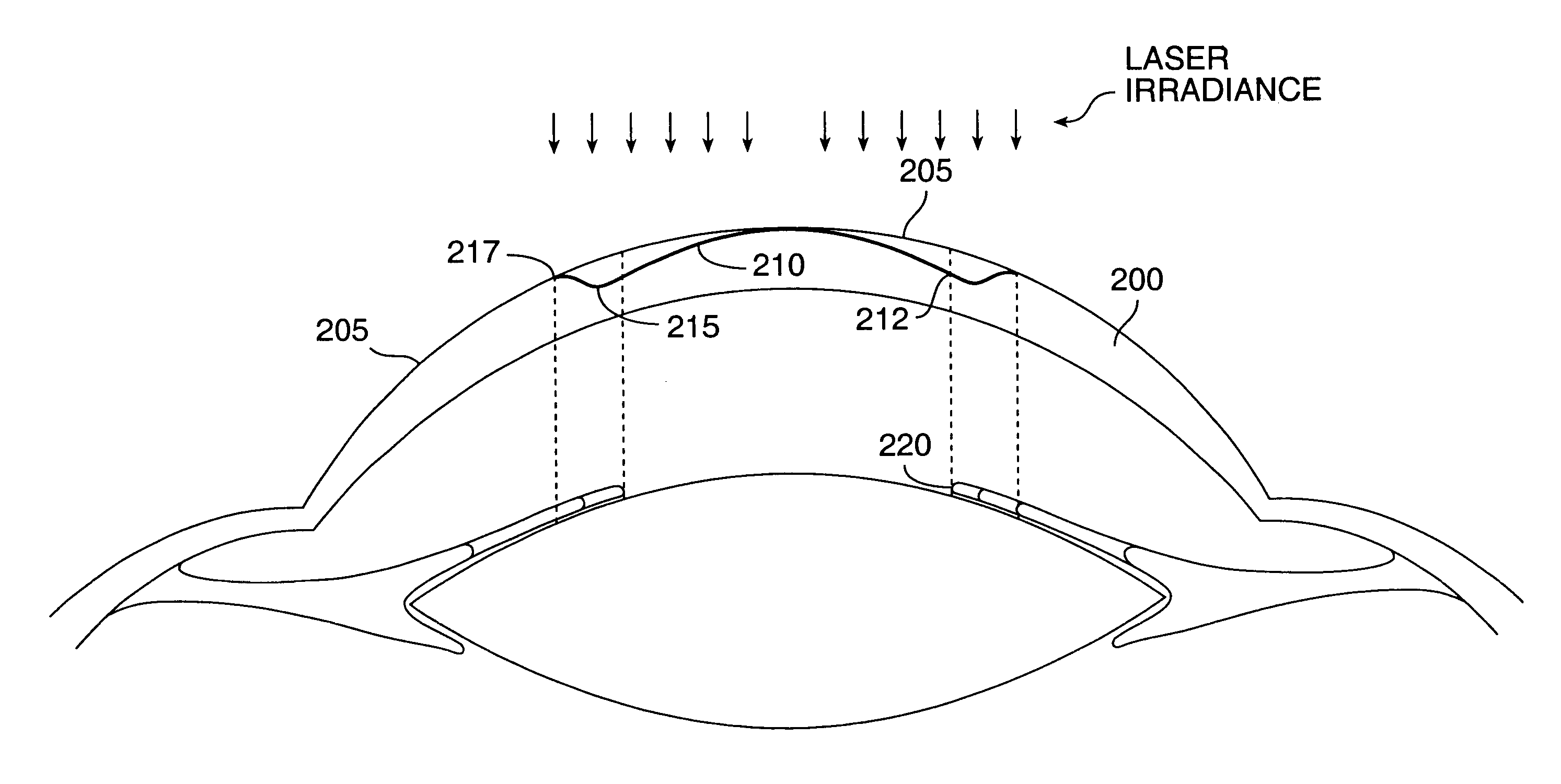
InactiveUS6280435B1Less attractiveReduce discontinuityLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsWide areaHyperopic astigmatism
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
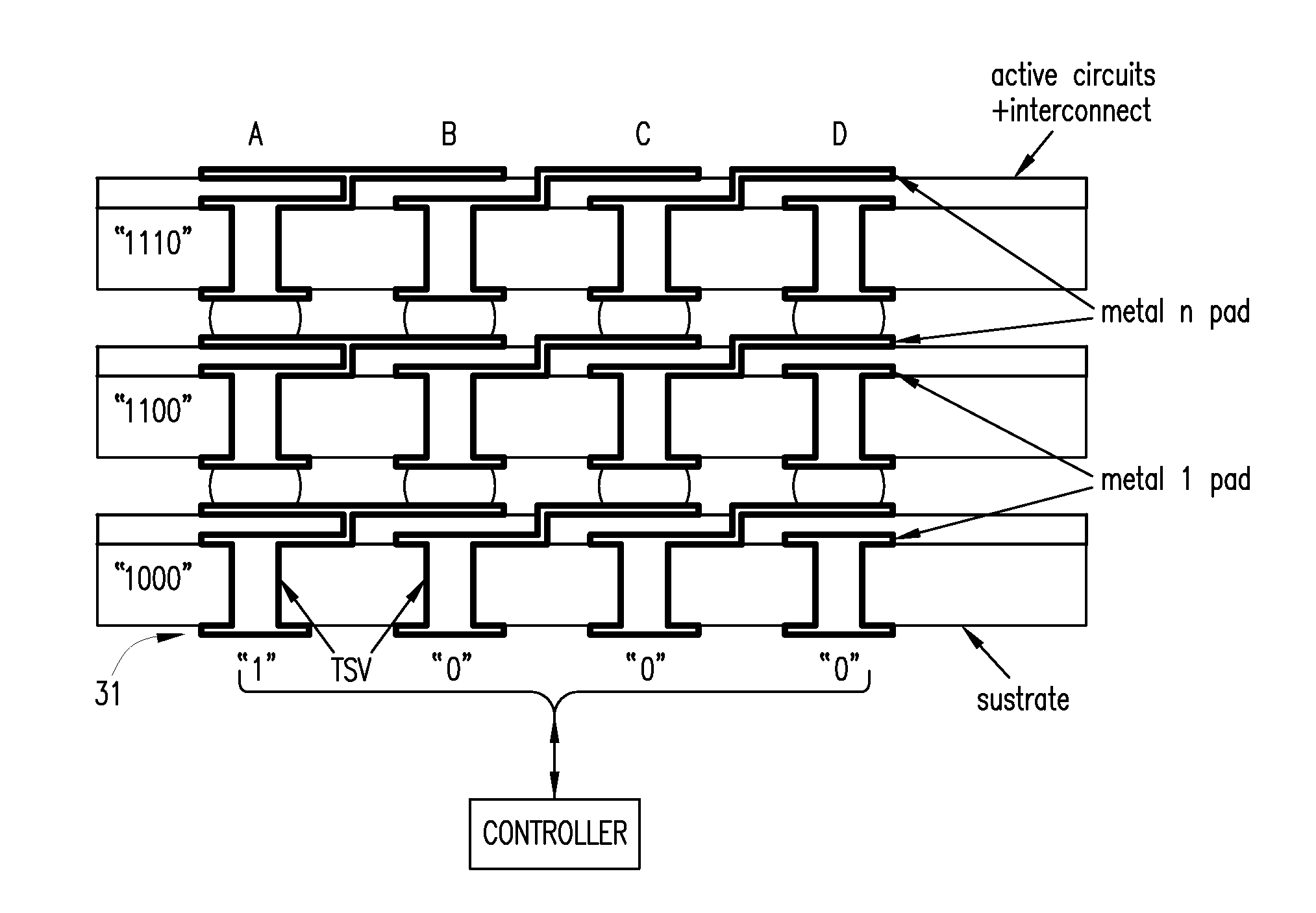
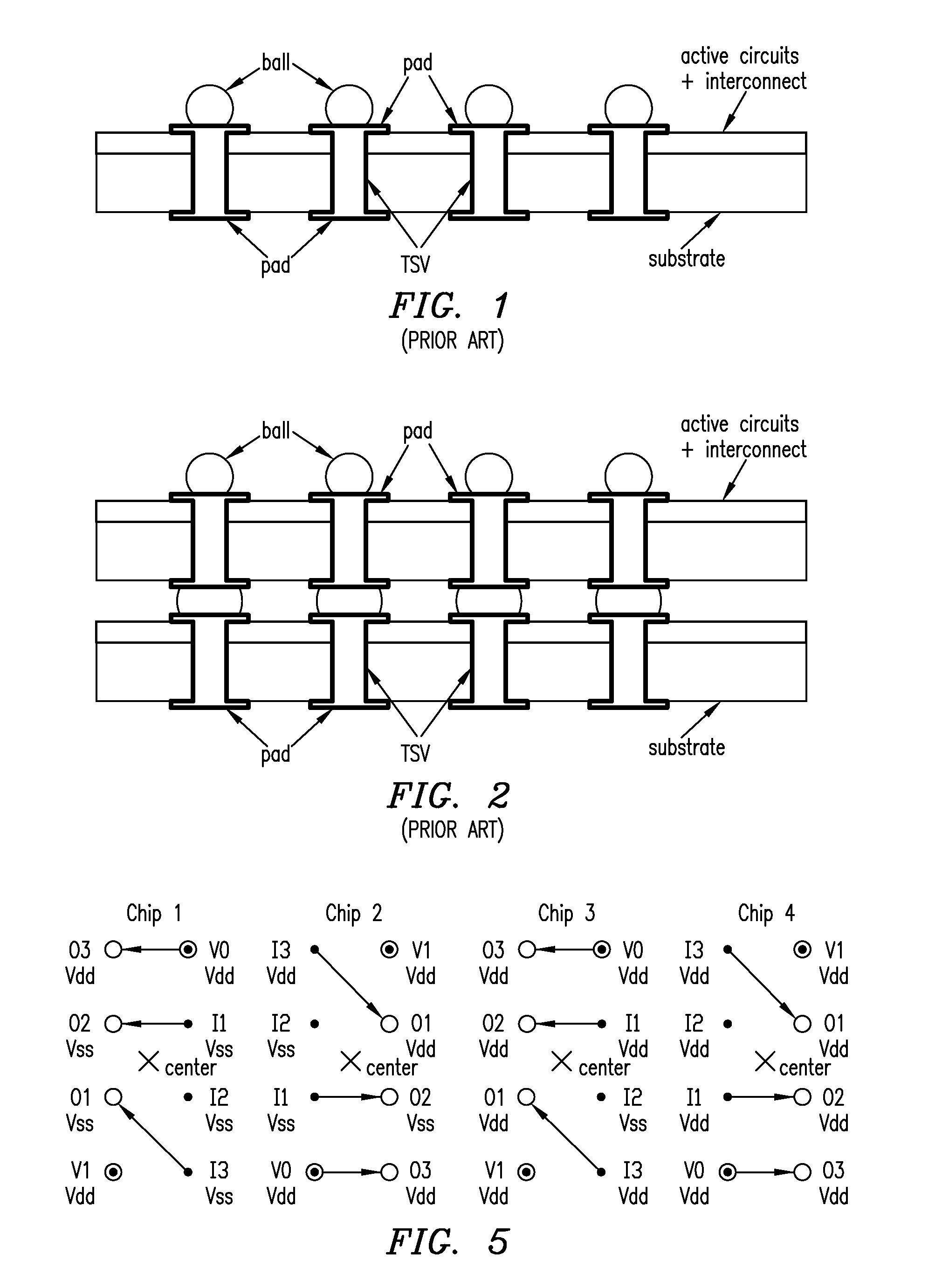
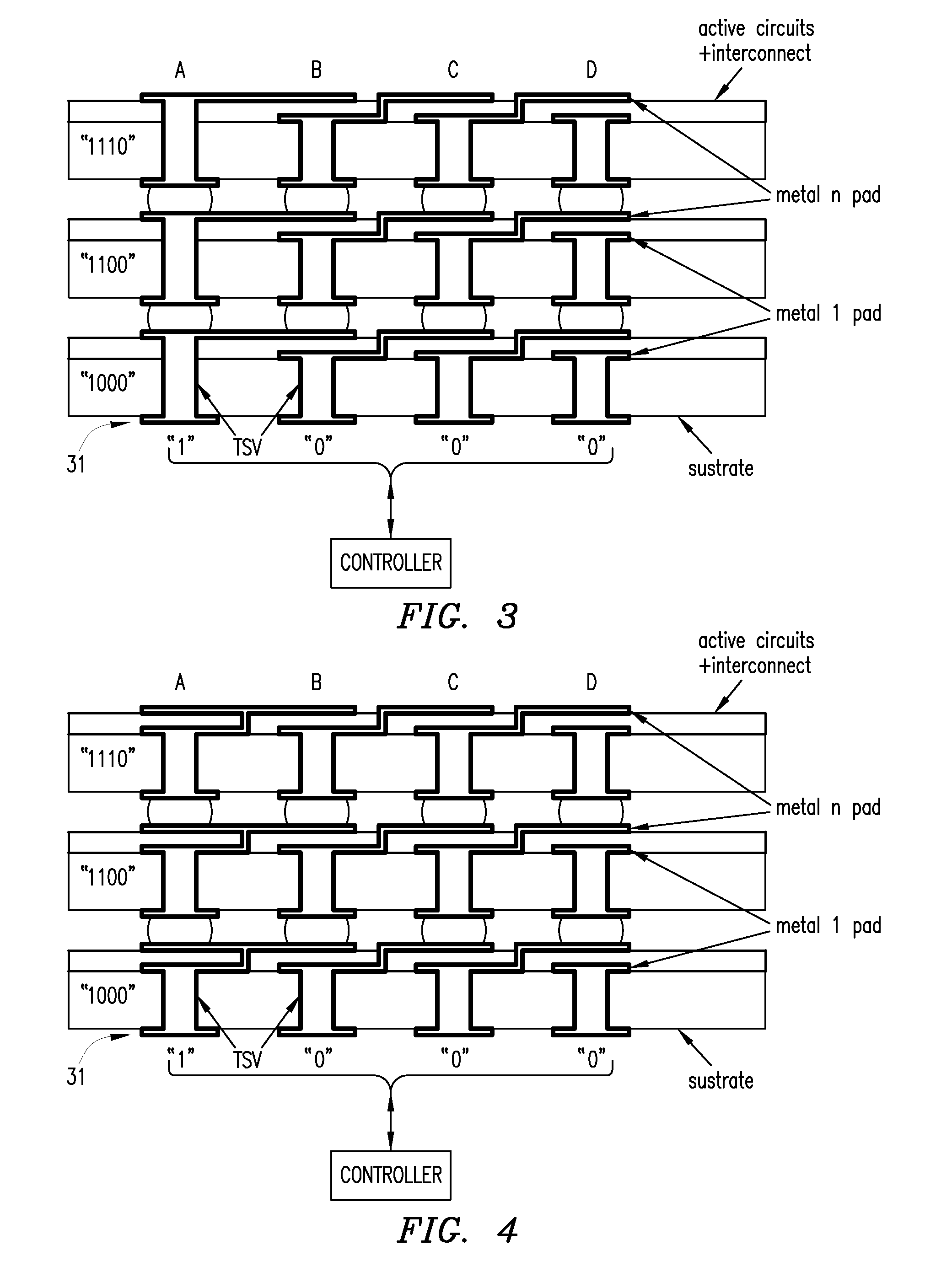
Using interrupted through-silicon-vias in integrated circuits adapted for stacking
In an integrated circuit (IC) adapted for use in a stack of interconnected ICs, interrupted through-silicon-vias (TSVs) are provided in addition to uninterrupted TSVs. The interrupted TSVs provide signal paths other than common parallel paths between the ICs of the stack. This permits IC identification schemes and other functionalities to be implemented using TSVs, without requiring angular rotation of alternate ICs of the stack.
Owner:MOSAID TECH
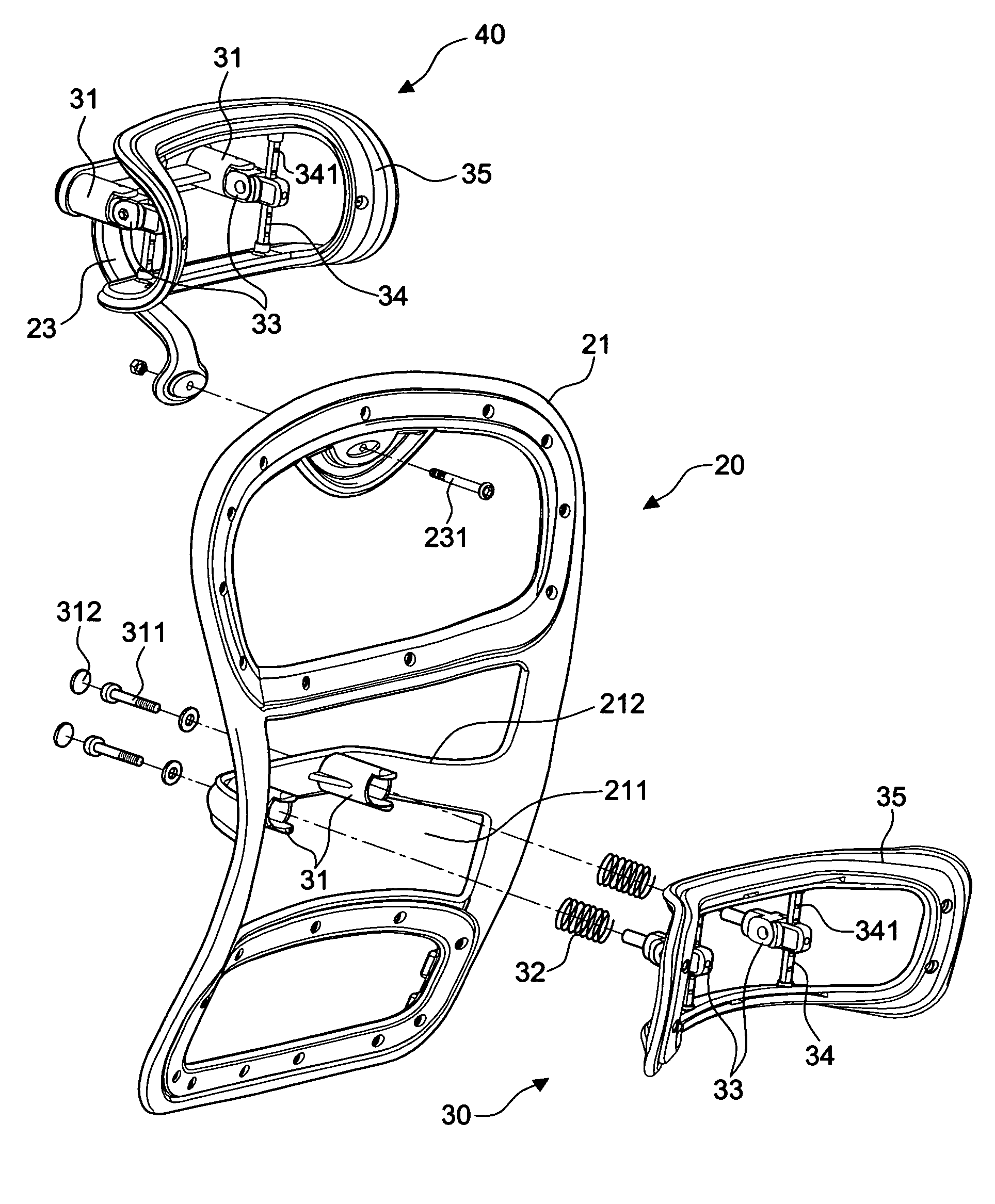
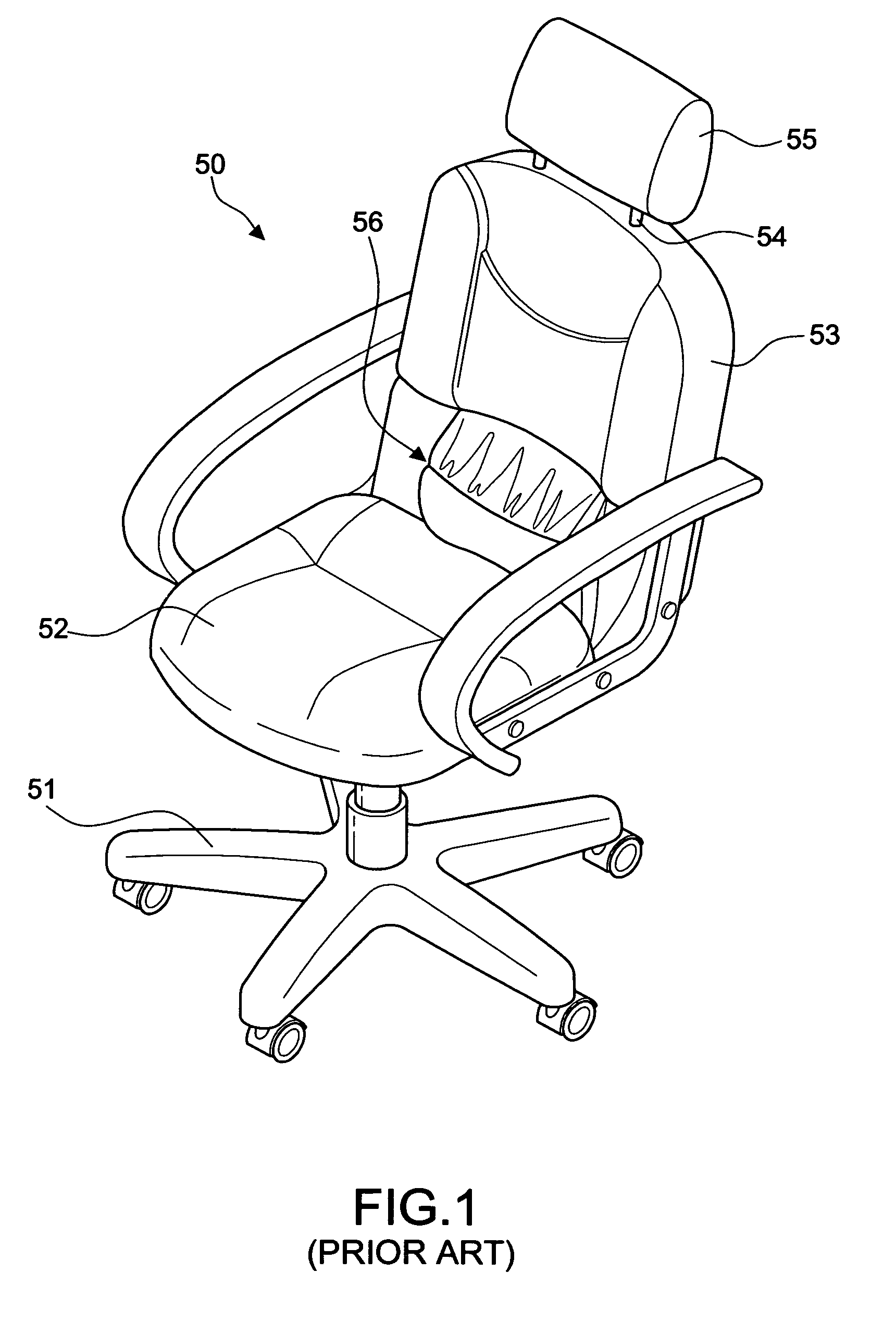
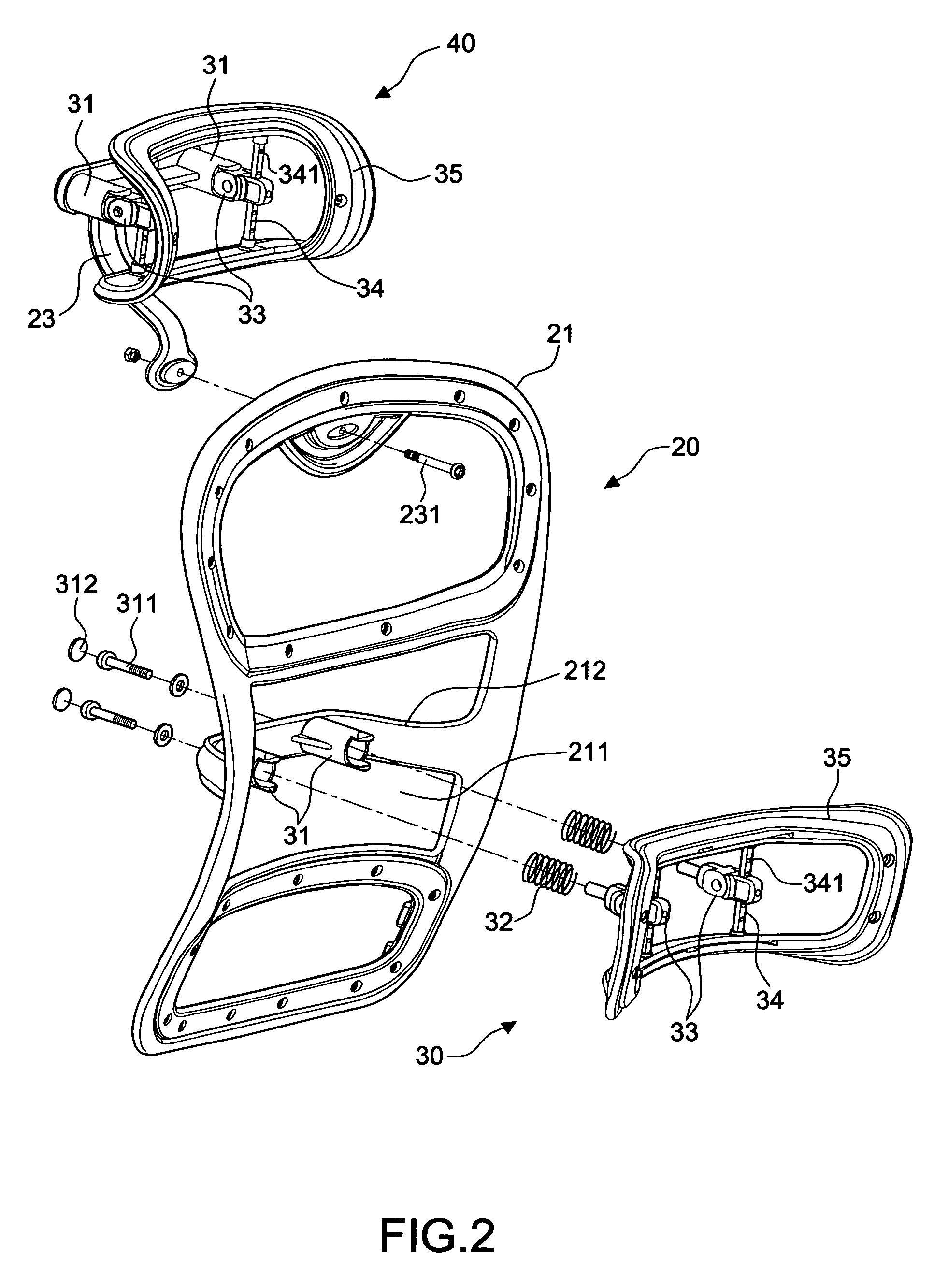
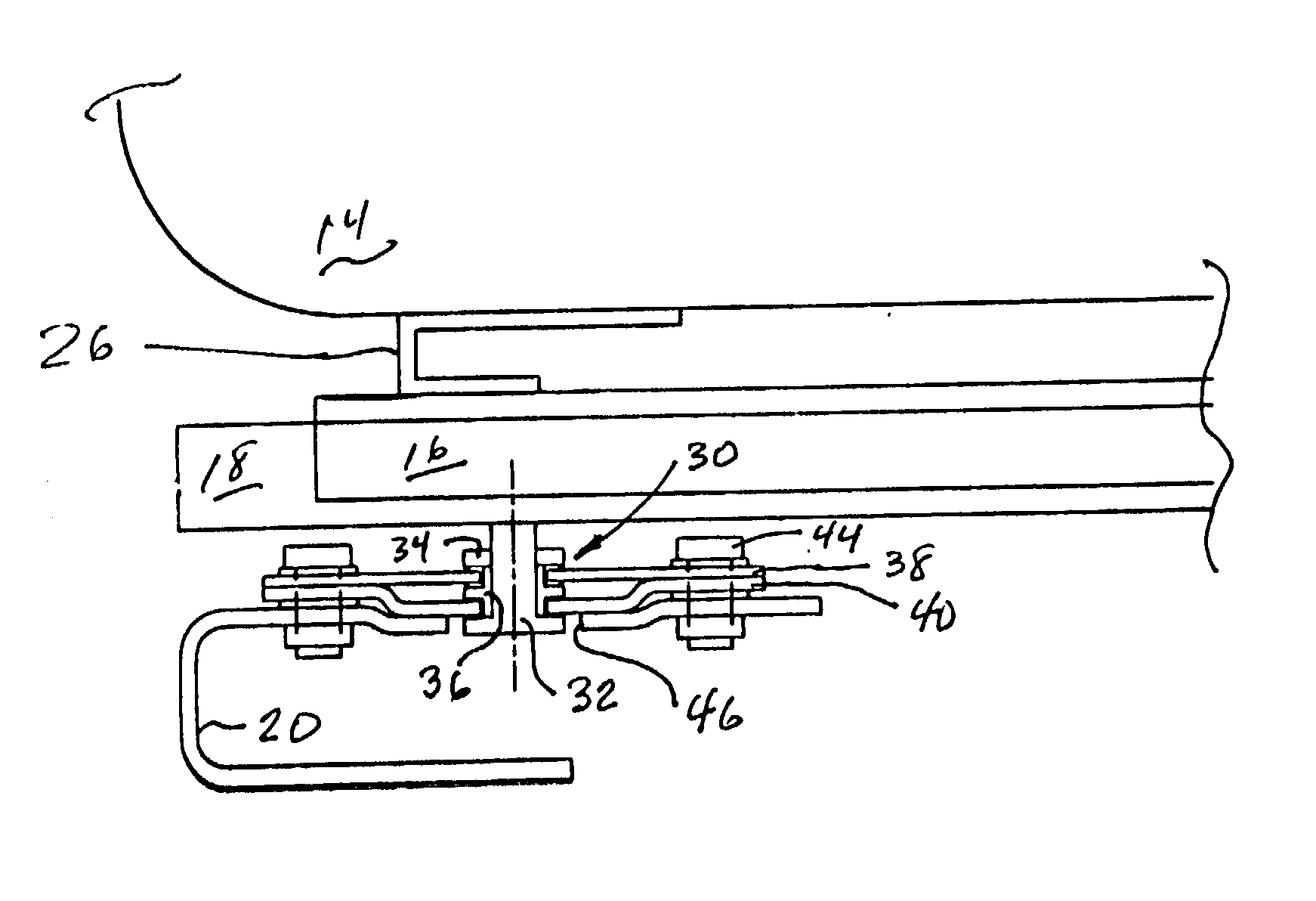
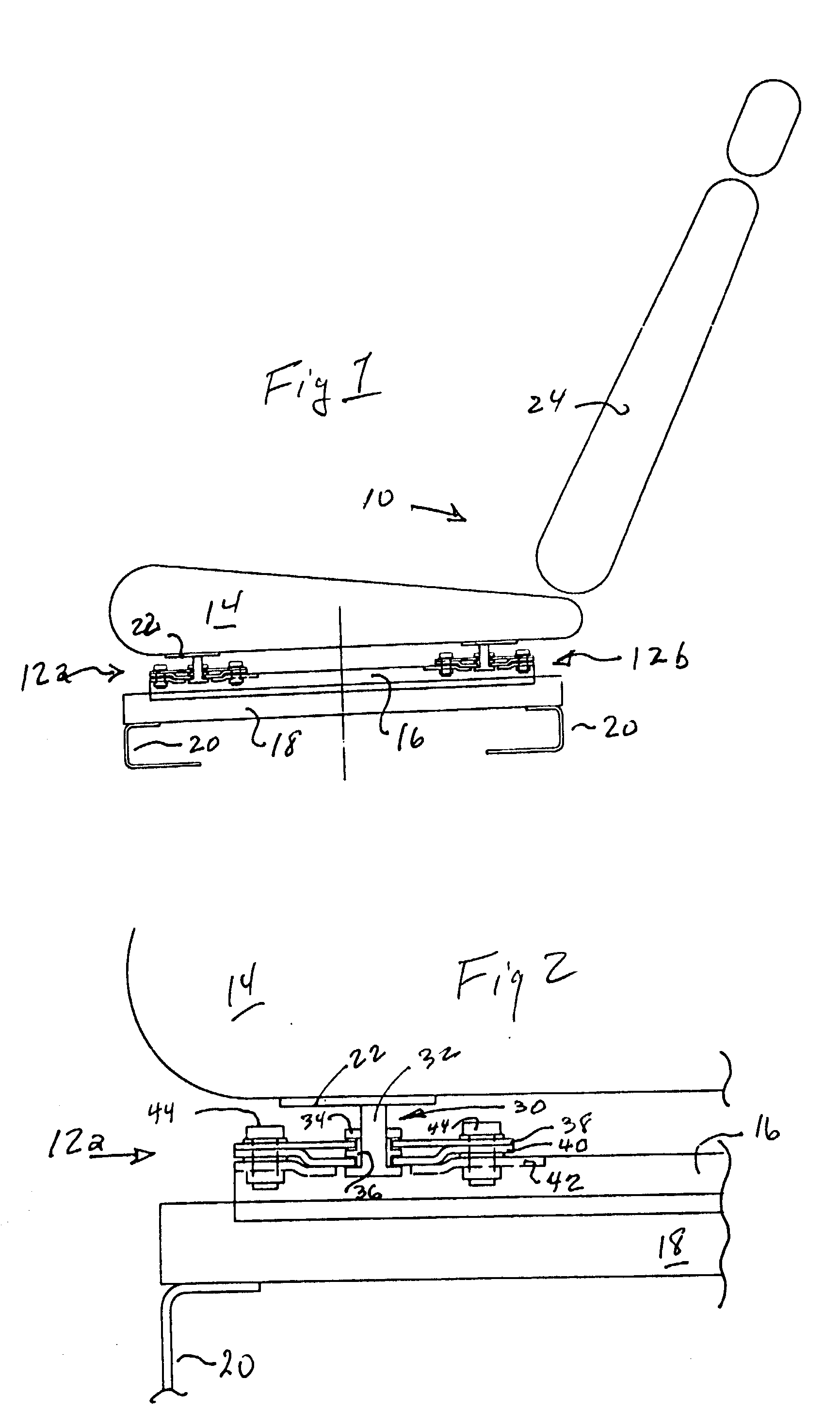
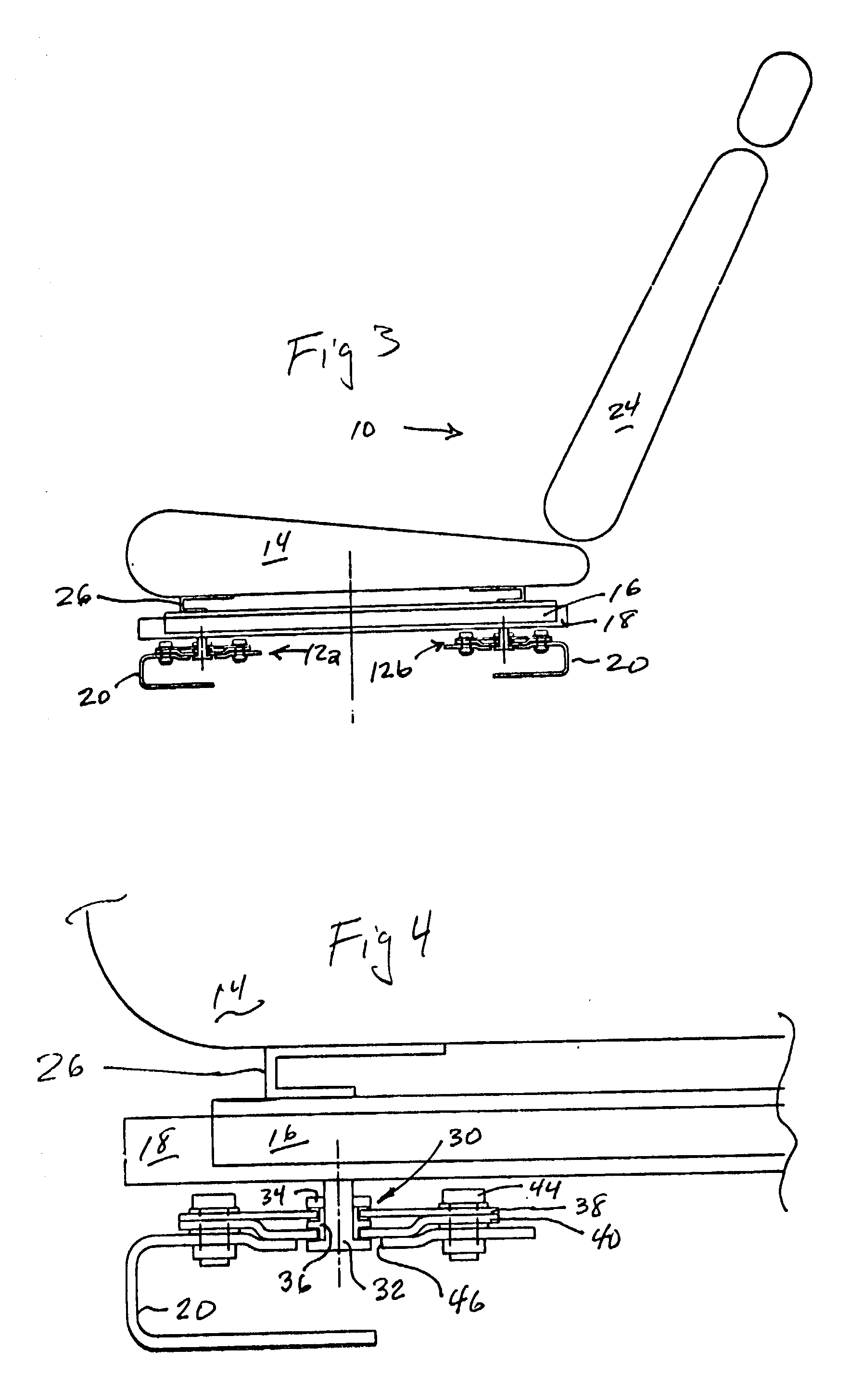
Backrest adjusting device for office chairs
A backrest adjusting device for office chairs comprising: a seat portion having a seat cushion and a stand for supporting the seat cushion; a back having a frame, a back cushion fixed on the surface of the frame, a connecting member for connecting the bottom of the back to a rear side of the seat portion, a hollow containing space formed at the middle section of the back, an n-shaped member being disposed in the containing space and extended backward; and a first attaching device installed on the n-shaped member of the containing space, thereby achieving the adjustment of the three-dimensional space of position, longitudinal buffer and angular rotation. Moreover, the back further includes a support member disposed at the top of the back, and a second attaching device installed on the support member and having a structure identical to the first attaching device. Meanwhile, the first attaching device has an attaching body made in compliance with the shape of a human waist to form a backrest bump. Furthermore, the second attaching device has an attaching body made in compliance with the shape of a human head to form a headrest. In this way, the three-dimensional space such as position, height, longitudinal buffer and angular rotation of a backrest or a headrest is adjustable.
Owner:CHEN YUNG HUA
One-piece fiber optic receptacle having chamfer and alignment ribs
ActiveUS7044650B1Improved alignment sleeve retainer and biasing member supportsEasy alignmentCoupling light guidesFiberEngineering
A one-piece fiber optic receptacle is provided for aligning and optically connecting a plug ferrule with a back-side ferrule of like configuration. The fiber optic receptacle includes a receptacle housing defining an internal cavity opening through an external end and an opposed internal end, an alignment sleeve disposed within the internal cavity and received within the internal end of the receptacle housing, and a sleeve retainer secured to the internal end of the receptacle housing and operable for providing access to the alignment sleeve from the internal end of the receptacle housing. The alignment sleeve includes a chamfer for guiding the back-side ferrule into the alignment sleeve. The sleeve retainer has an opening and a plurality of alignment ribs disposed about the opening for permitting angular rotation of the alignment sleeve relative to the sleeve retainer during insertion of the plug ferrule and the back-side ferrule into the alignment sleeve.
Owner:CORNING CABLE SYST LLC +1
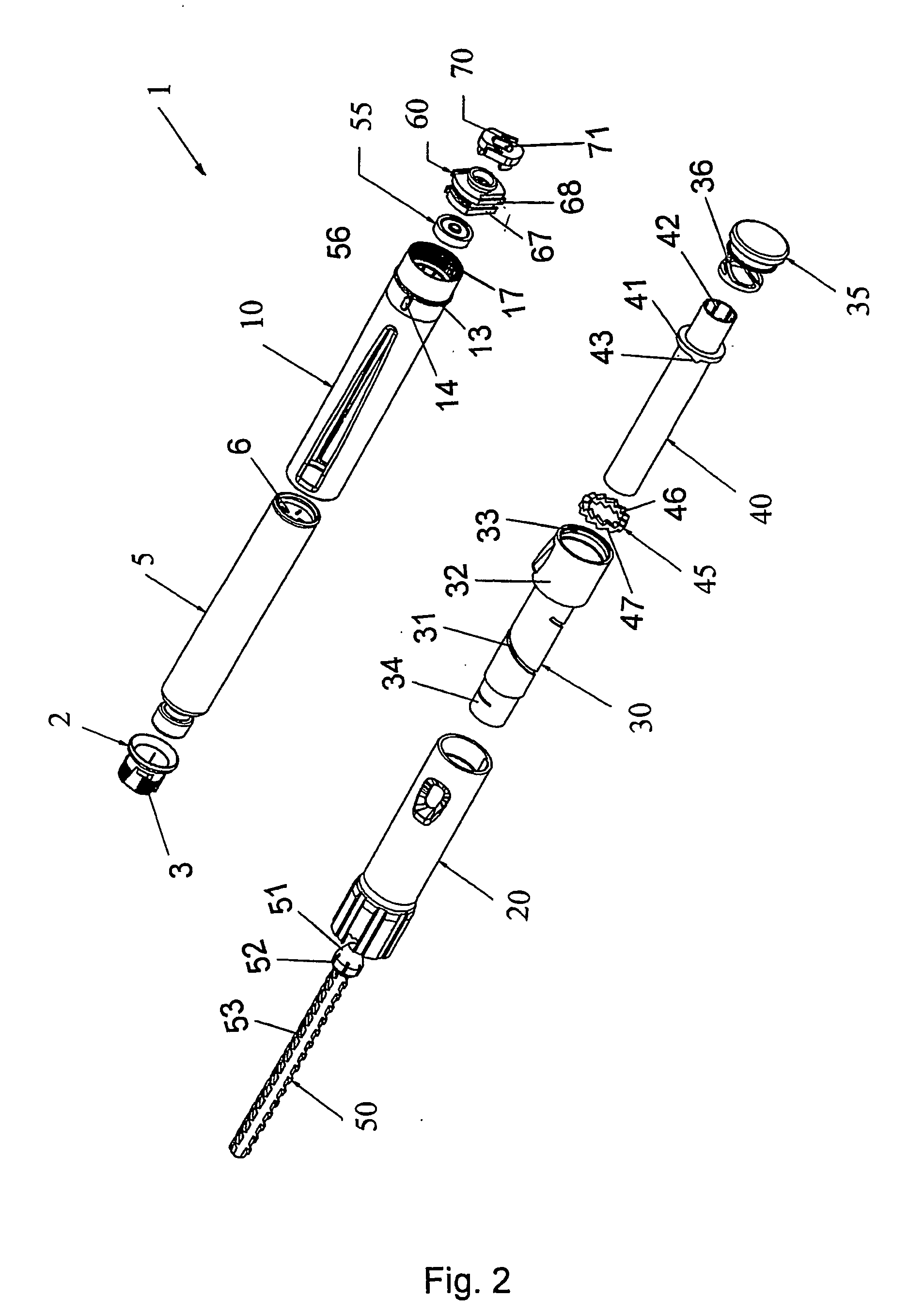
Medical delivery device having air shot means
InactiveUS20070016143A1Prevent rotationAmpoule syringesIntravenous devicesEngineeringAngular rotation
An air shot or priming mechanism for an injection pen. The injection pen comprises a cartridge-holder and a housing. The cartridge-holder interacts with a nut-member capable of driving the piston rod forward when relatively rotated. The cartridge-holder is rotational coupled to the housing such that rotation of the cartridge-holder relatively to the housing causes the nut-member and the piston rod to rotate relatively, thus the relative angular rotation between the cartridge-holder and the housing determines the size of the air shot so performed.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
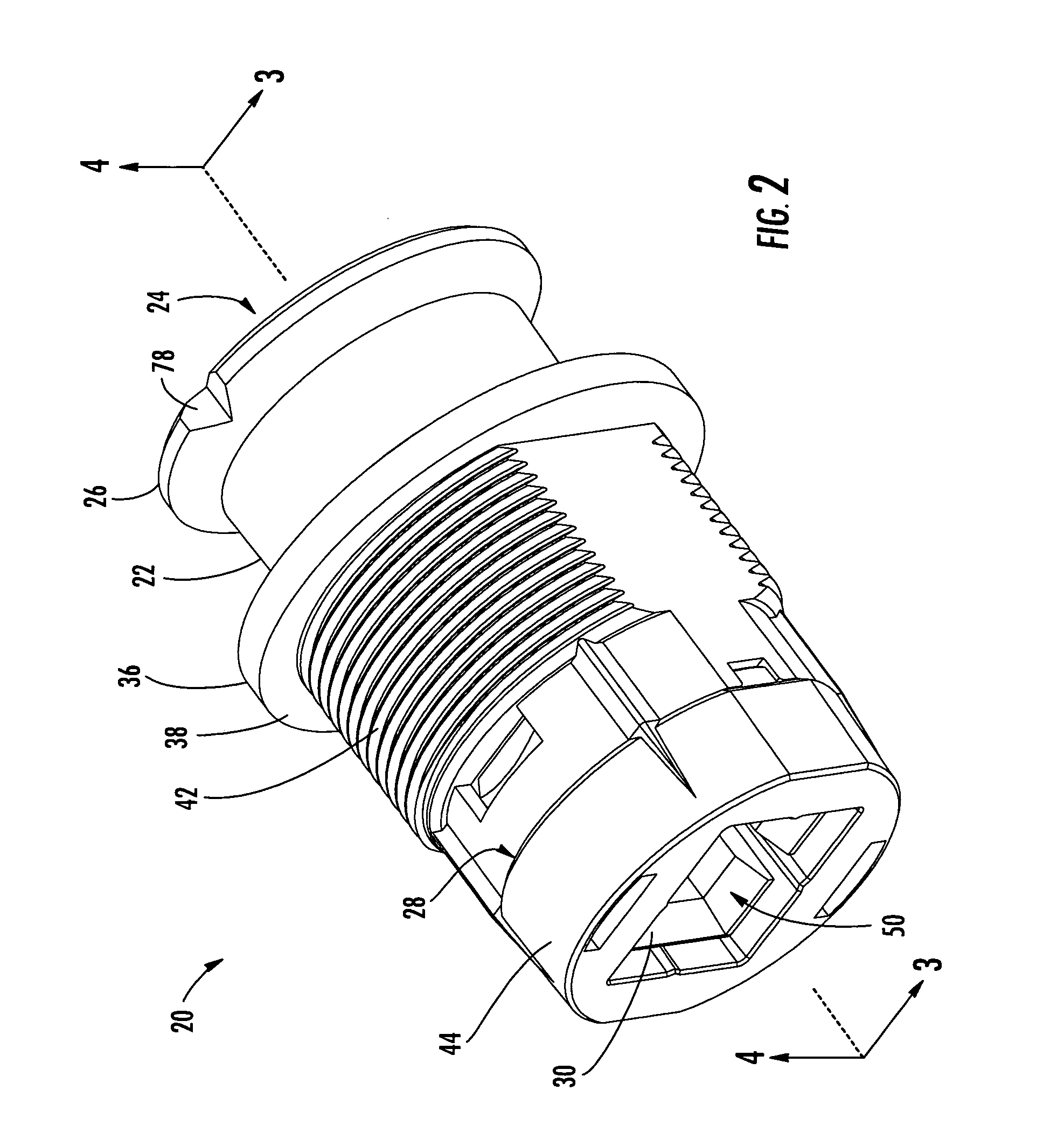
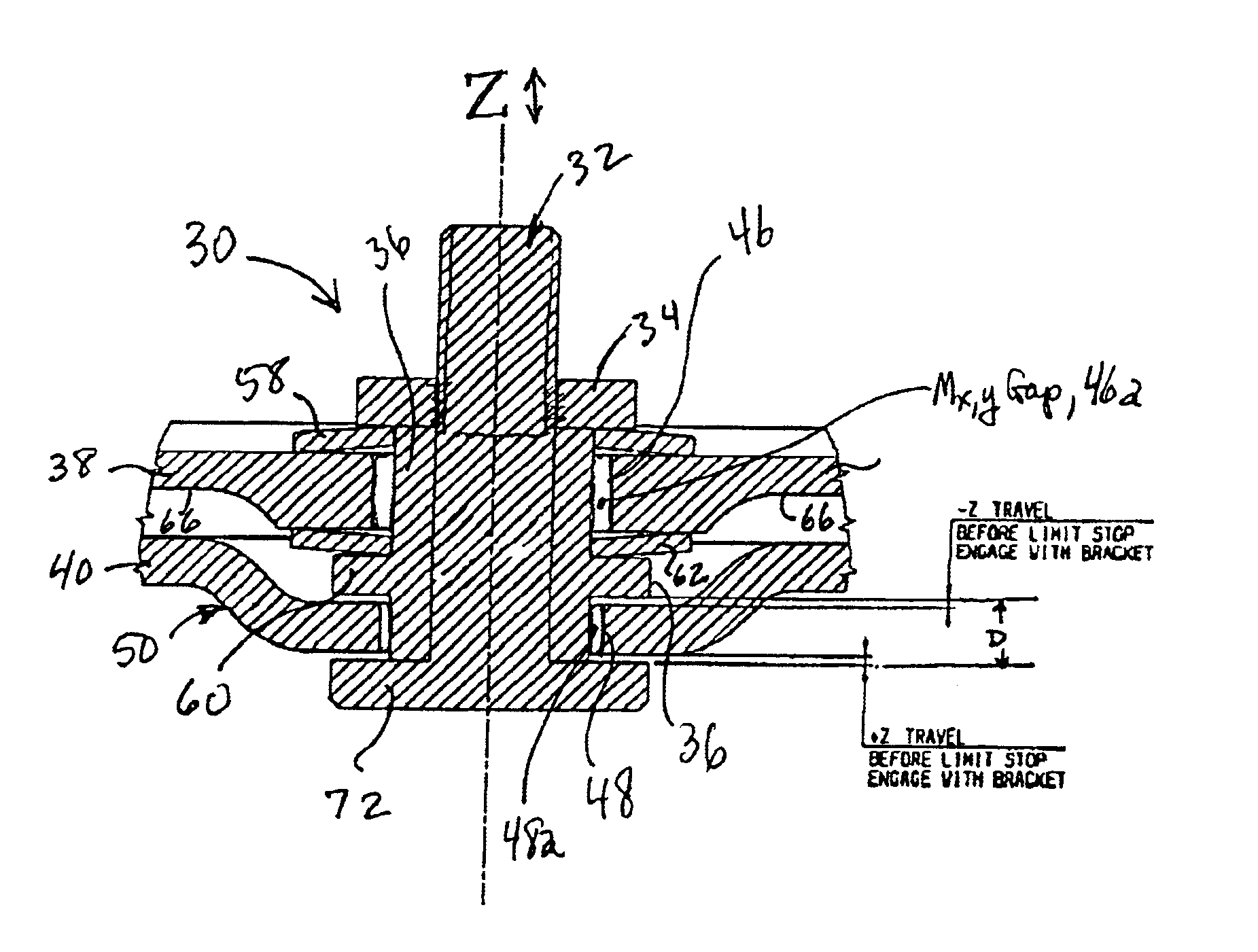
Weight sensors having centralized loose tolerance universal force and Mx/My moments overload stops
InactiveUS20030106723A1Increase angular travel permittedConvenient travelWeighing apparatus using elastically-deformable membersElectric devicesModularityAngular rotation
Automotive load cells having centralized, multi-axis, loose tolerance overload / limit stops provide improved strain gauge response. The modular, integrated stop assemblies magnify sensor substrate deflection by use of opposed concave (Belleville) springs are used in direct contact with the substrate to accommodate ±Z axis deflection and Mx / My moment angular rotation. A flanged guide member on the load stud permits a wide range of geometries. The substrate is thickened around the load stud hole and the outboard support bolt holes. Hollow rivets assist in design modularity. Strain gauges are placed at the yield zones symmetrically with respect to the X axis. The substrate hole Mx / My gap is larger than the stop bracket hole to insure a positive stop for Mx / My moments prior to yield. The inventive multi-axis stop assembly is used in any type load cell, including rectangular, thinned, notched, necked / dogbone, or cantilever substrates with any strain gauge layout configuration.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH CORP
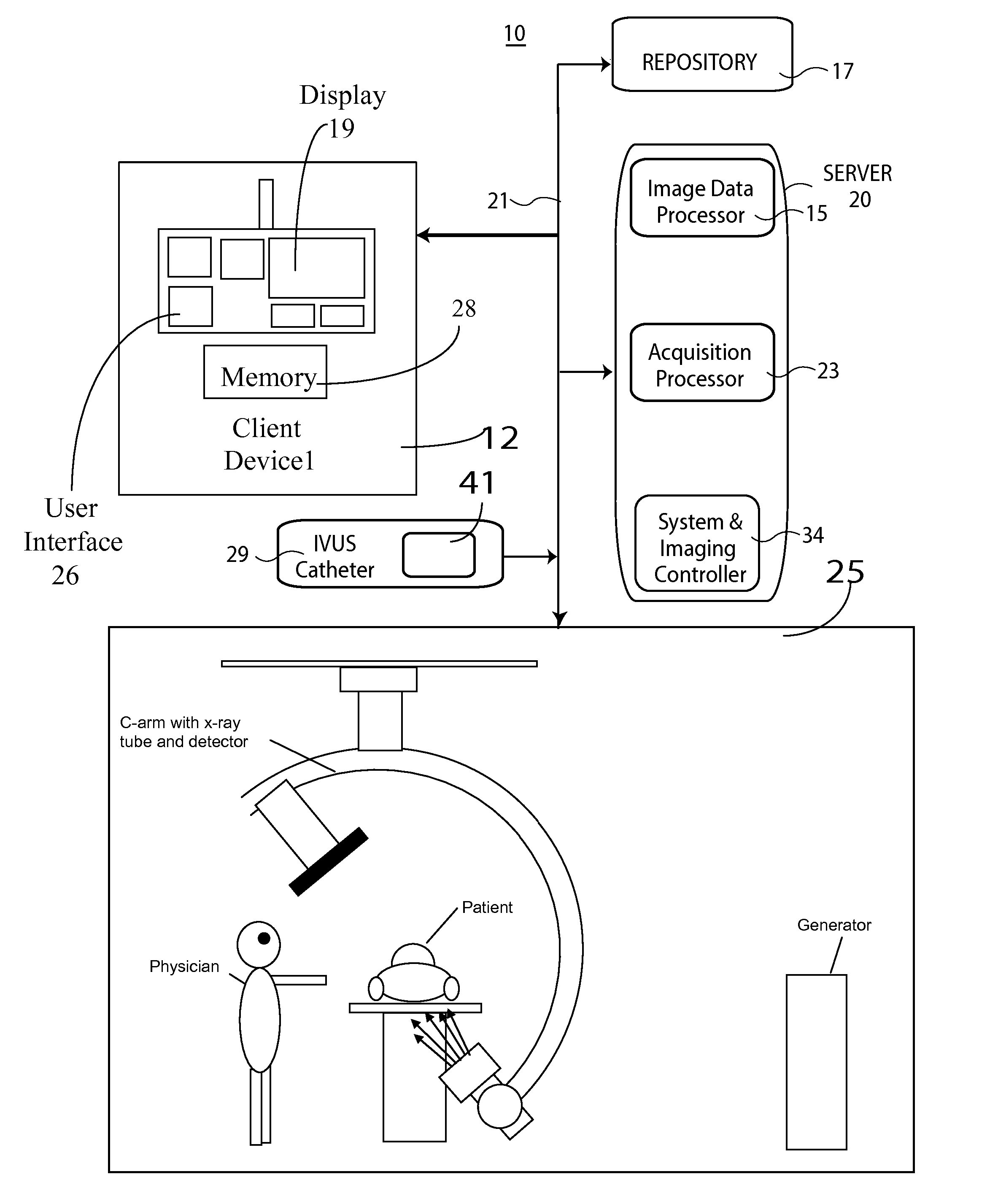
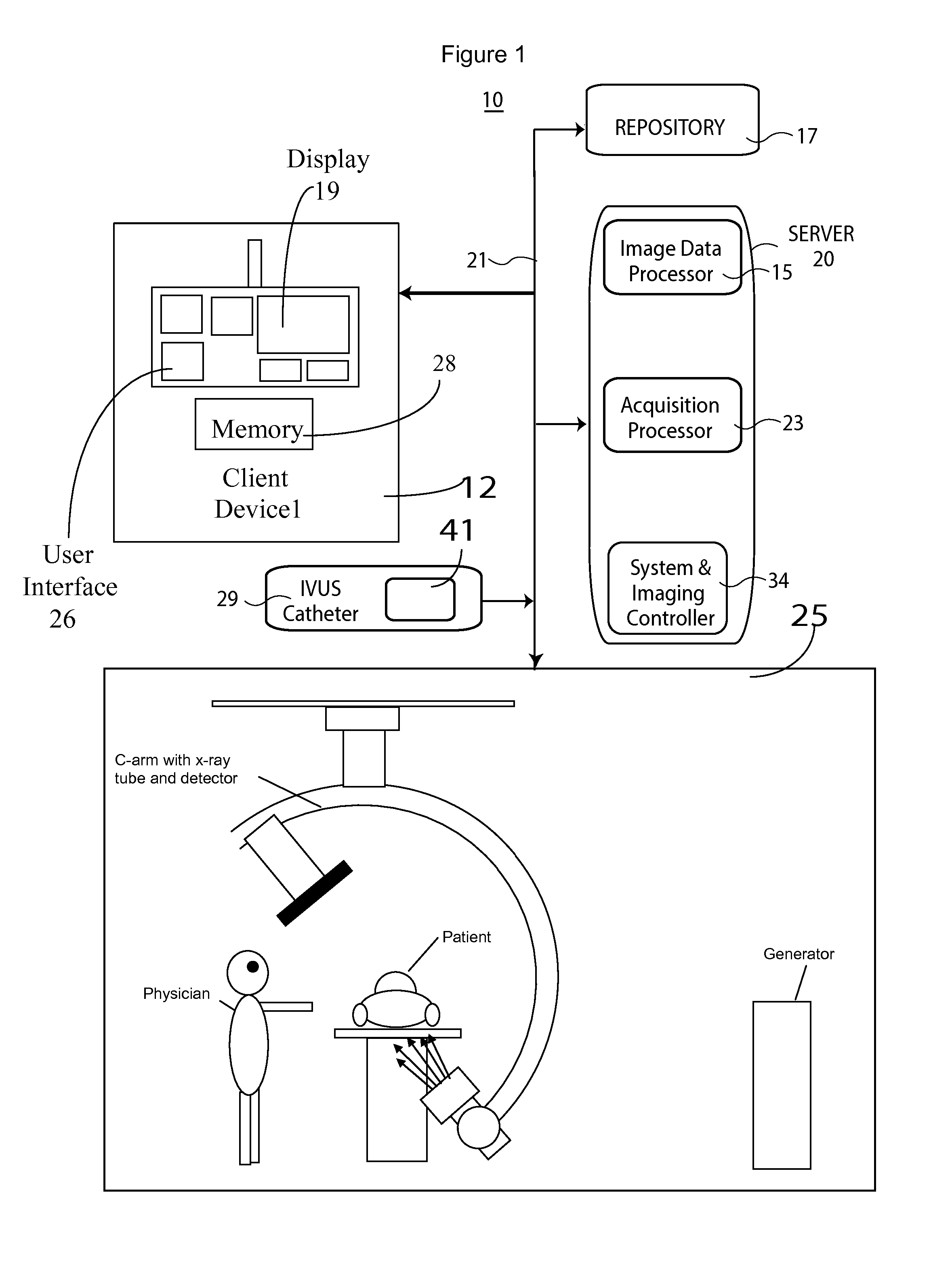
System for Detecting Rotation Angle of a Catheter in an X-ray Image
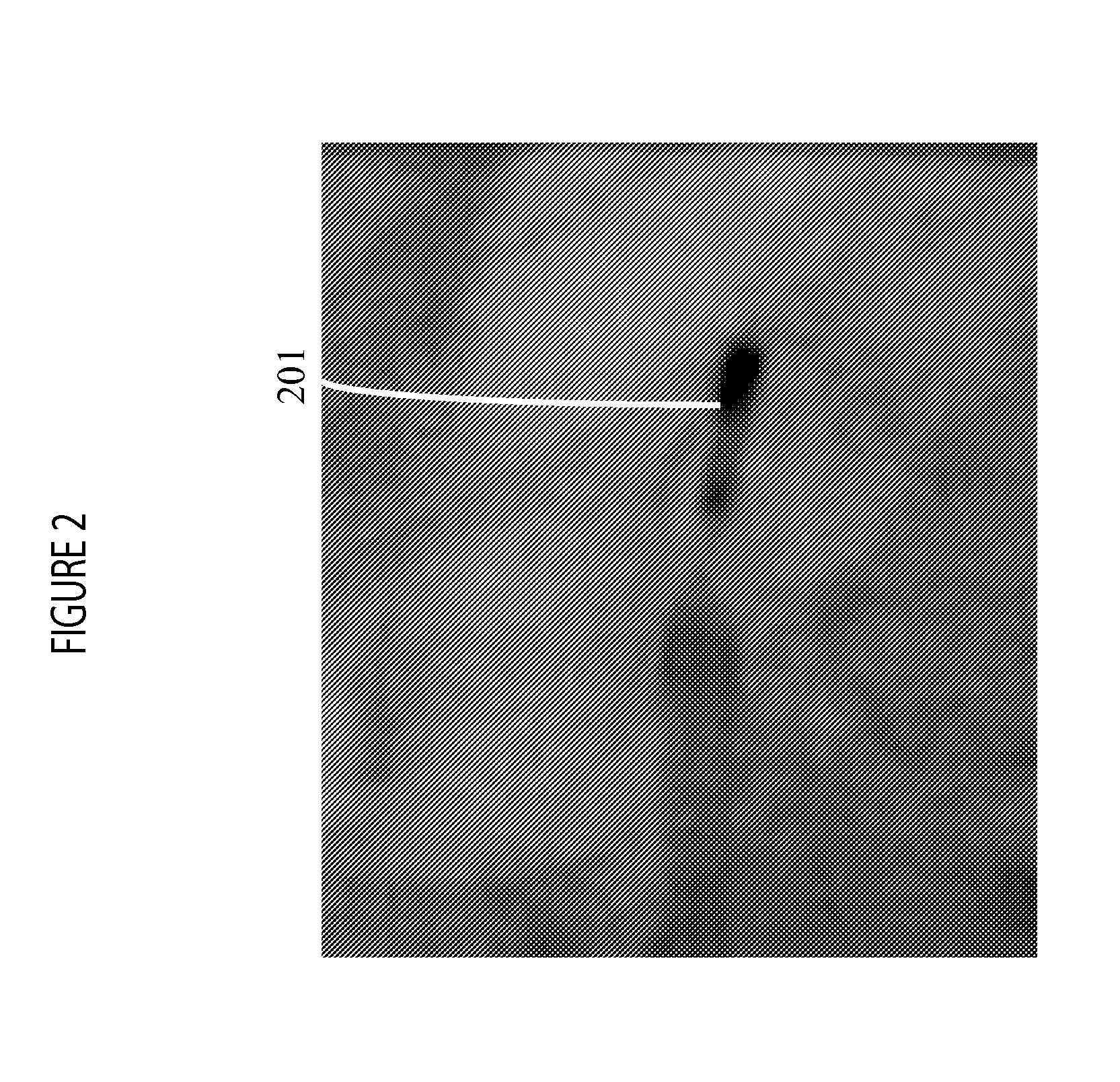
An IVUS catheter is advantageously provided with a particular radio-opaque pattern enabling detection of catheter rotation angle with respect to an X-ray imaging source for co-registering IVUS image data with angiographic X-ray or CT image data, for example. An ultrasound catheter system supports orientation and display of intra-vascular ultrasound imaging data. The system comprises an ultrasound catheter for acquiring ultrasound images comprising a body having a pattern of radio-opaque material on the external surface of the catheter body. The pattern varies with angular rotation of the catheter and indicates an angle of rotation of a predetermined reference orientation of the catheter relative to an X-ray radiation source, so that an X-ray image of the catheter body indicates the pattern and the pattern is analyzable by an image data processor to determine the angle of rotation.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
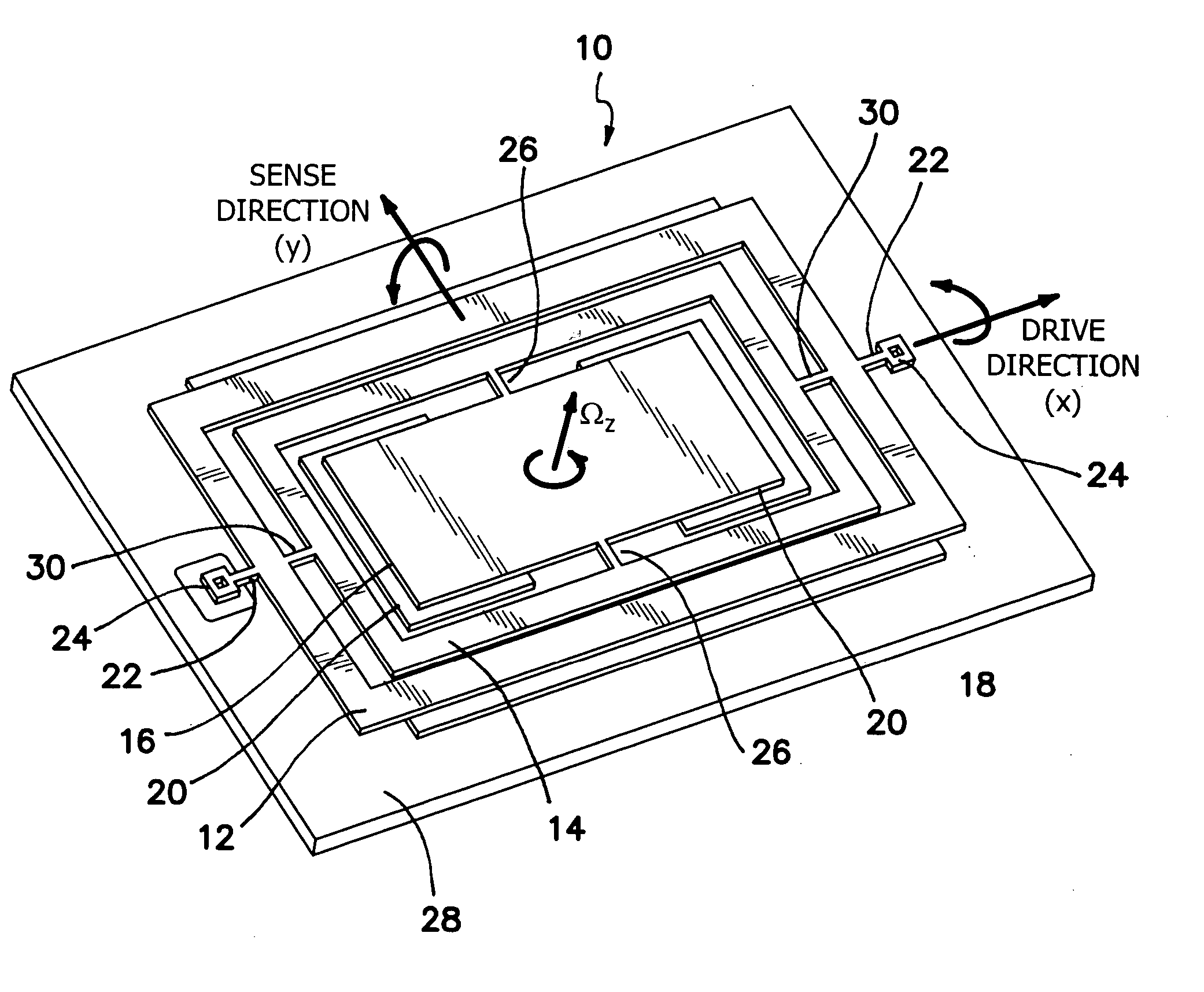
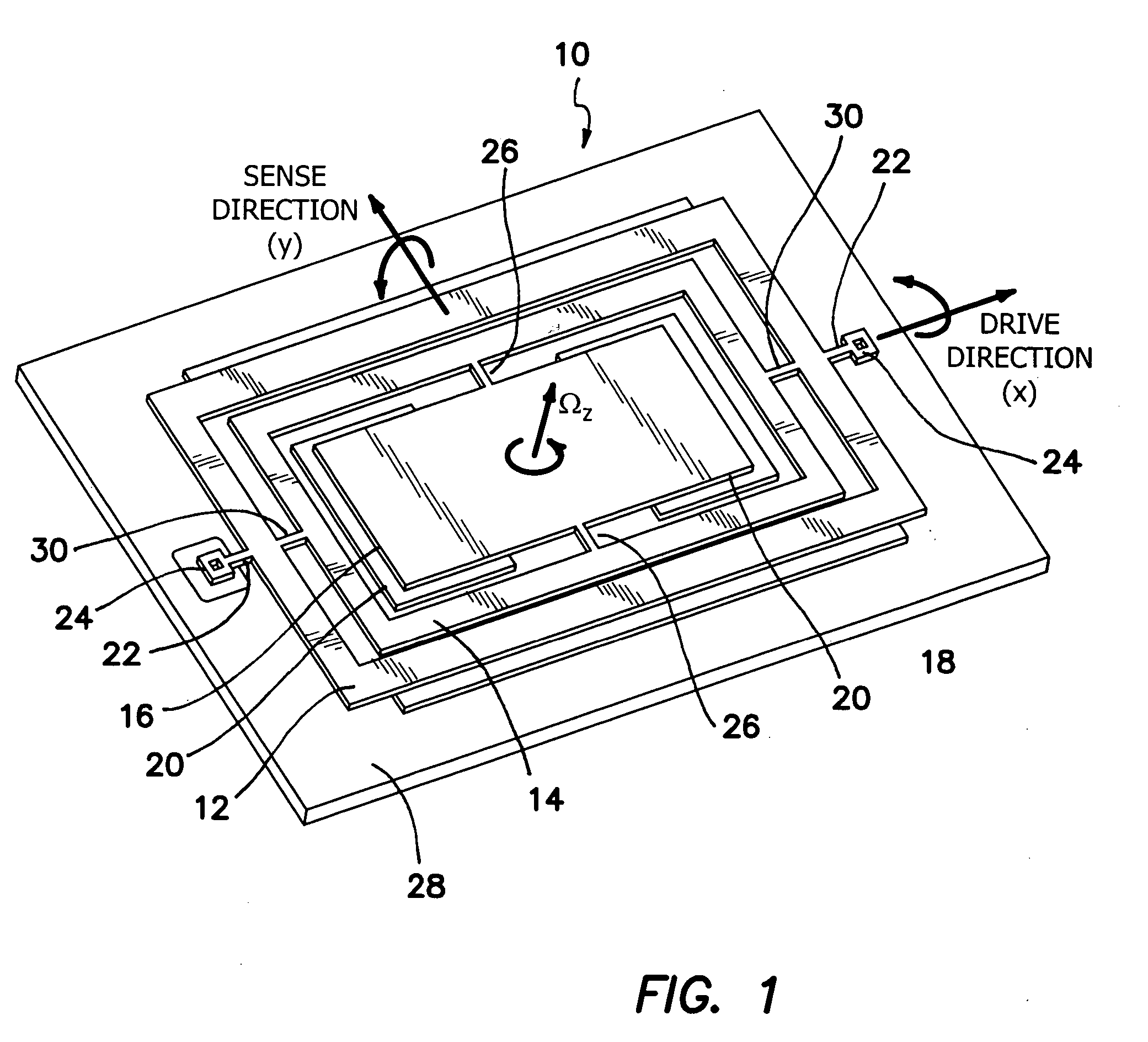
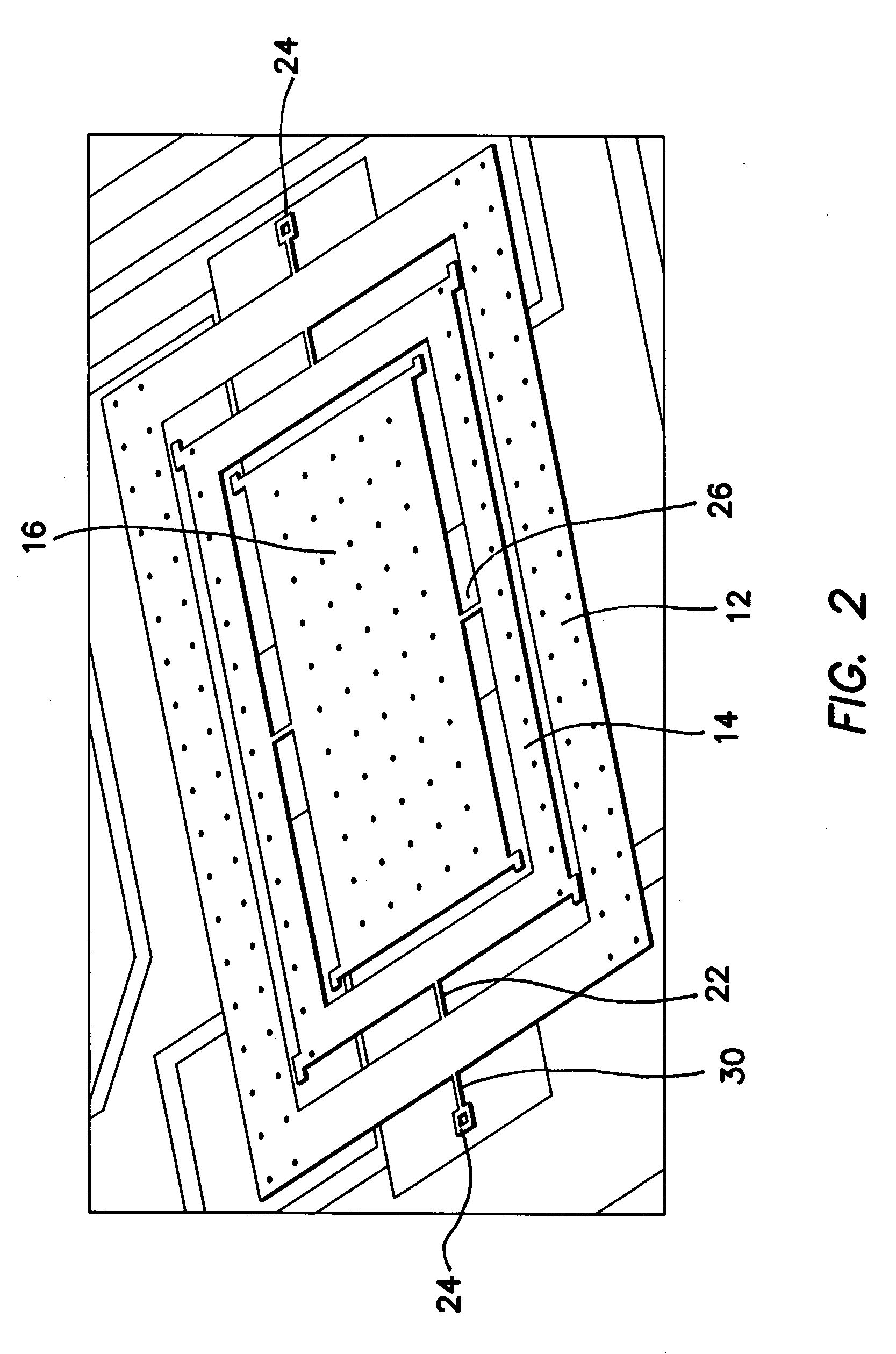
Torsional nonresonant z-axis micromachined gyroscope with non-resonant actuation to measure the angular rotation of an object
InactiveUS20060032308A1Minimizing nonlinear force profileMinimizing instabilityAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsGyroscopeParallel plate
A gimbal-type torsional z-axis micromachined gyroscope with a non-resonant actuation scheme measures angular rate of an object with respect to the axis normal to the substrate plane (the z-axis). A 2 degrees-of-freedom (2-DOF) drive-mode oscillator is comprised of a sensing plate suspended inside two gimbals. By utilizing dynamic amplification of torsional oscillations in the drive-mode instead of resonance, large oscillation amplitudes of the sensing element is achieved with small actuation amplitudes, providing improved linearity and stability despite parallel-plate actuation. The device operates at resonance in the sense direction for improved sensitivity, while the drive direction amplitude is inherently constant within the same frequency band.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
One-piece fiber optic receptacle having chamfer and alignment ribs
ActiveUS20060088247A1Easy alignmentImproved alignment sleeve retainer and biasing member supportsCoupling light guidesFiberAngular rotation
A one-piece fiber optic receptacle is provided for aligning and optically connecting a plug ferrule with a back-side ferrule of like configuration. The fiber optic receptacle includes a receptacle housing defining an internal cavity opening through an external end and an opposed internal end, an alignment sleeve disposed within the internal cavity and received within the internal end of the receptacle housing, and a sleeve retainer secured to the internal end of the receptacle housing and operable for providing access to the alignment sleeve from the internal end of the receptacle housing. The alignment sleeve includes a chamfer for guiding the back-side ferrule into the alignment sleeve. The sleeve retainer has an opening and a plurality of alignment ribs disposed about the opening for permitting angular rotation of the alignment sleeve relative to the sleeve retainer during insertion of the plug ferrule and the back-side ferrule into the alignment sleeve.
Owner:CORNING CABLE SYST LLC +1
Weight sensors having centralized loose tolerance universal force and Mx/My moments overload stops
InactiveUS6916997B2Convenient travelReduce loadWeighing apparatus using elastically-deformable membersElectric devicesModularityAngular rotation
Automotive load cells having centralized, multi-axis, loose tolerance overload / limit stops provide improved strain gauge response. The modular, integrated stop assemblies magnify sensor substrate deflection by use of opposed concave (Belleville) springs are used in direct contact with the substrate to accommodate ±Z axis deflection and Mx / My moment angular rotation. A flanged guide member on the load stud permits a wide range of geometries. The substrate is thickened around the load stud hole and the outboard support bolt holes. Hollow rivets assist in design modularity. Strain gauges are placed at the yield zones symmetrically with respect to the X axis. The substrate hole Mx / My gap is larger than the stop bracket hole to insure a positive stop for Mx / My moments prior to yield. The inventive multi-axis stop assembly is used in any type load cell, including rectangular, thinned, notched, necked / dogbone, or cantilever substrates with any strain gauge layout configuration.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH CORP
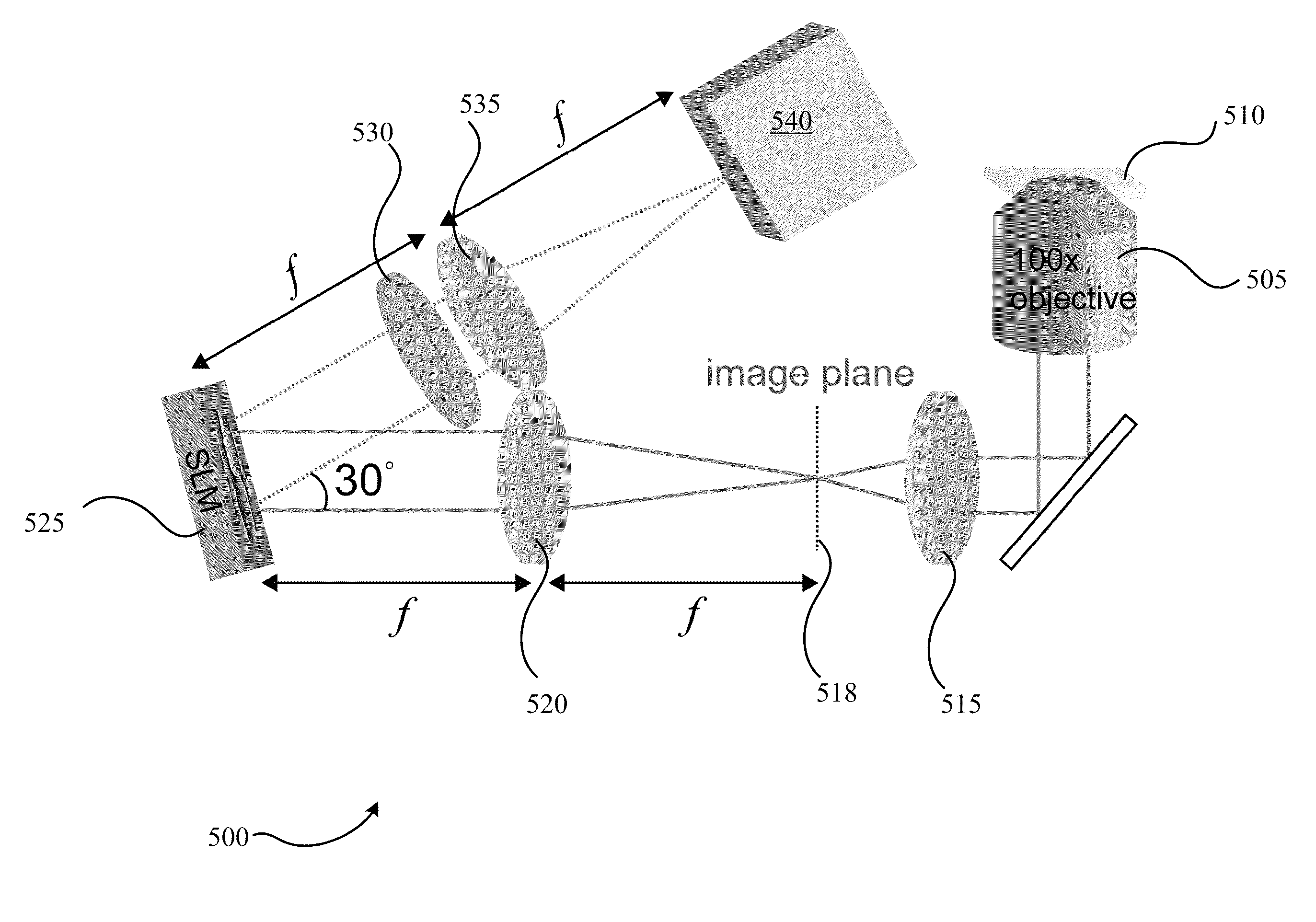
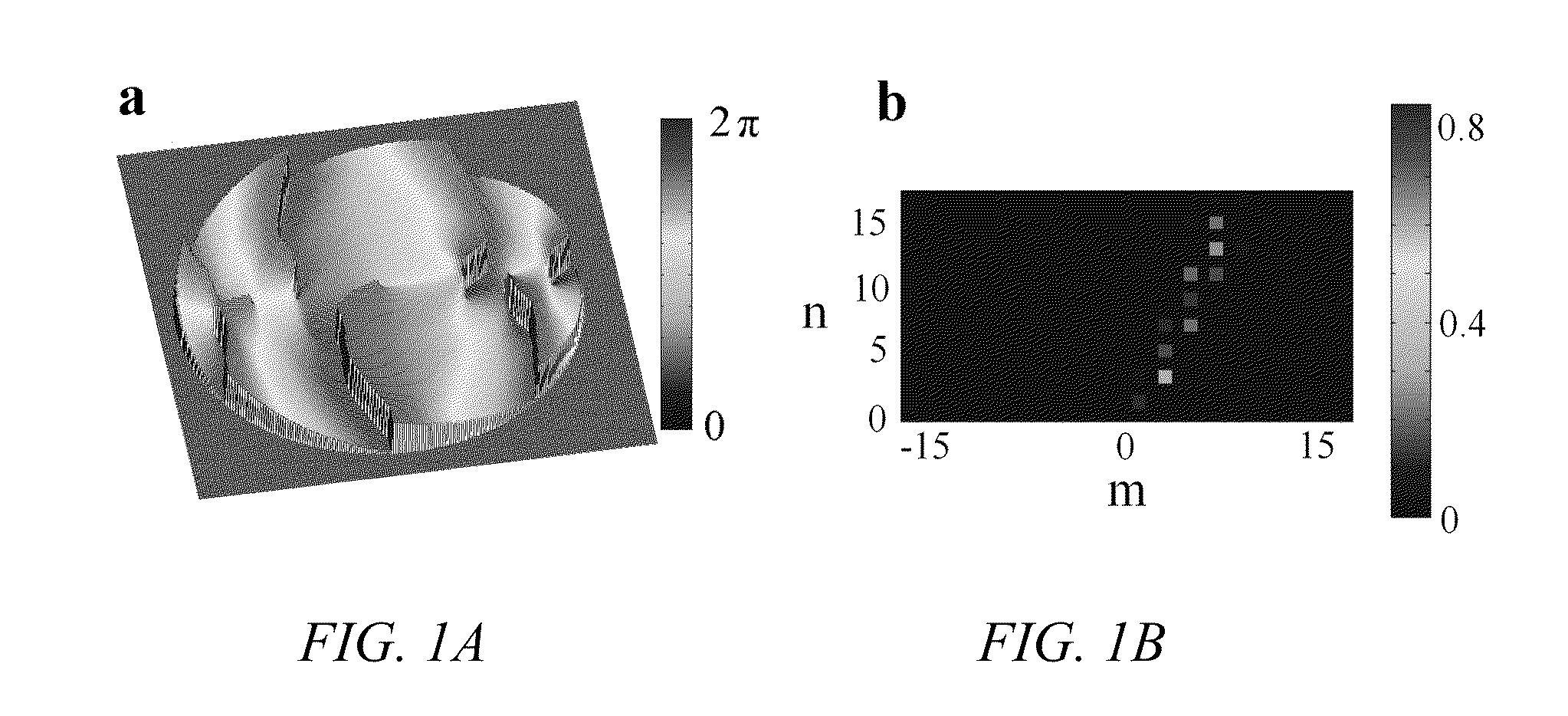
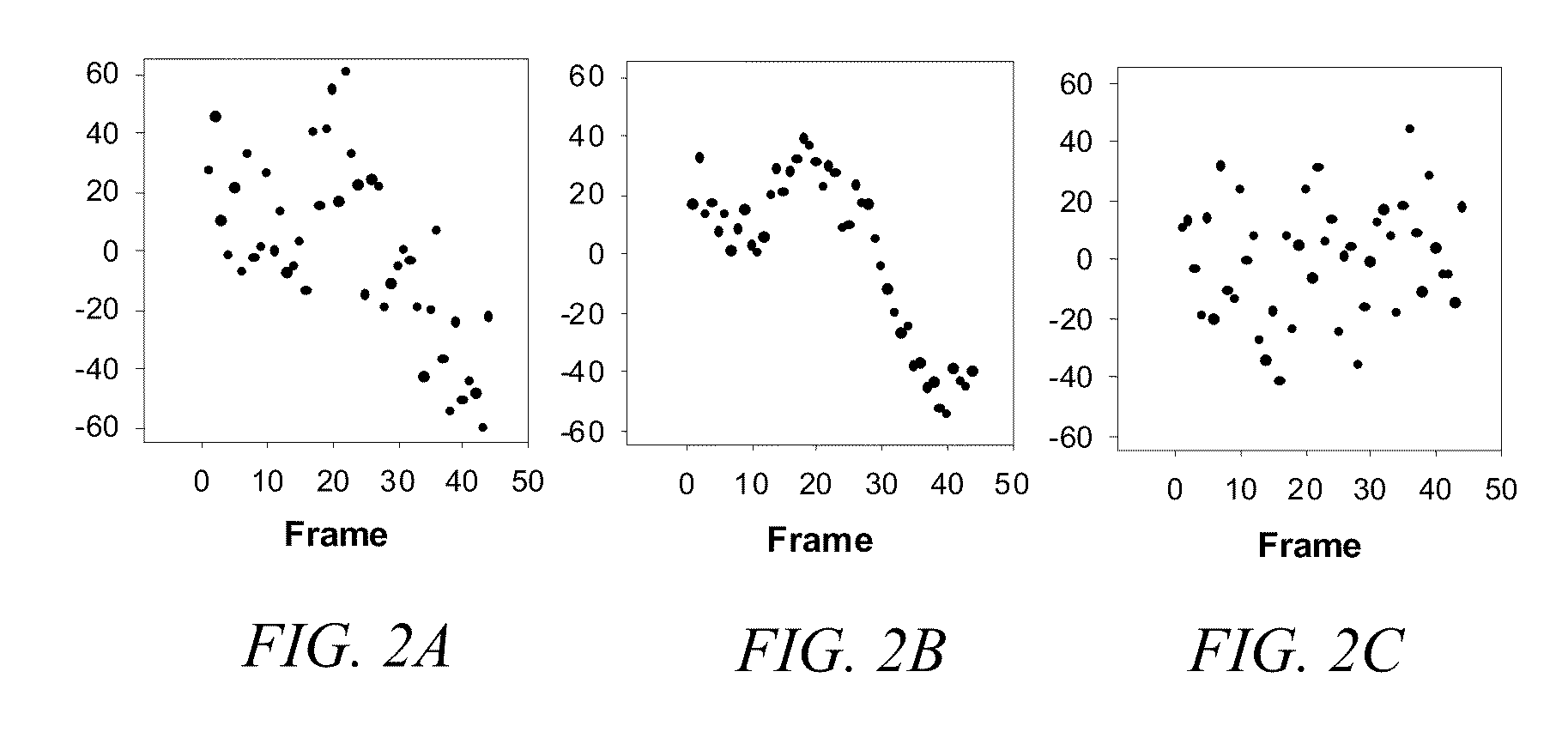
Three-dimensional single-molecule fluorescence imaging beyond the diffraction limit using a double-helix point spread function
Embodiments of the present invention can resolve molecules beyond the optical diffraction limit in three dimensions. A double-helix point spread function can be used to in conjunction with a microscope to provide dual-lobed images of a molecule. Based on the rotation of the dual-lobed image, the axial position of the molecule can be estimated or determined. In some embodiments, the angular rotation of the dual-lobed imaged can be determined using a centroid fit calculation or by finding the midpoints of the centers of the two lobes. Regardless of the technique, the correspondence between the rotation and axial position can be utilized. A double-helix point spread function can also be used to determine the lateral positions of molecules and hence their three-dimensional location.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
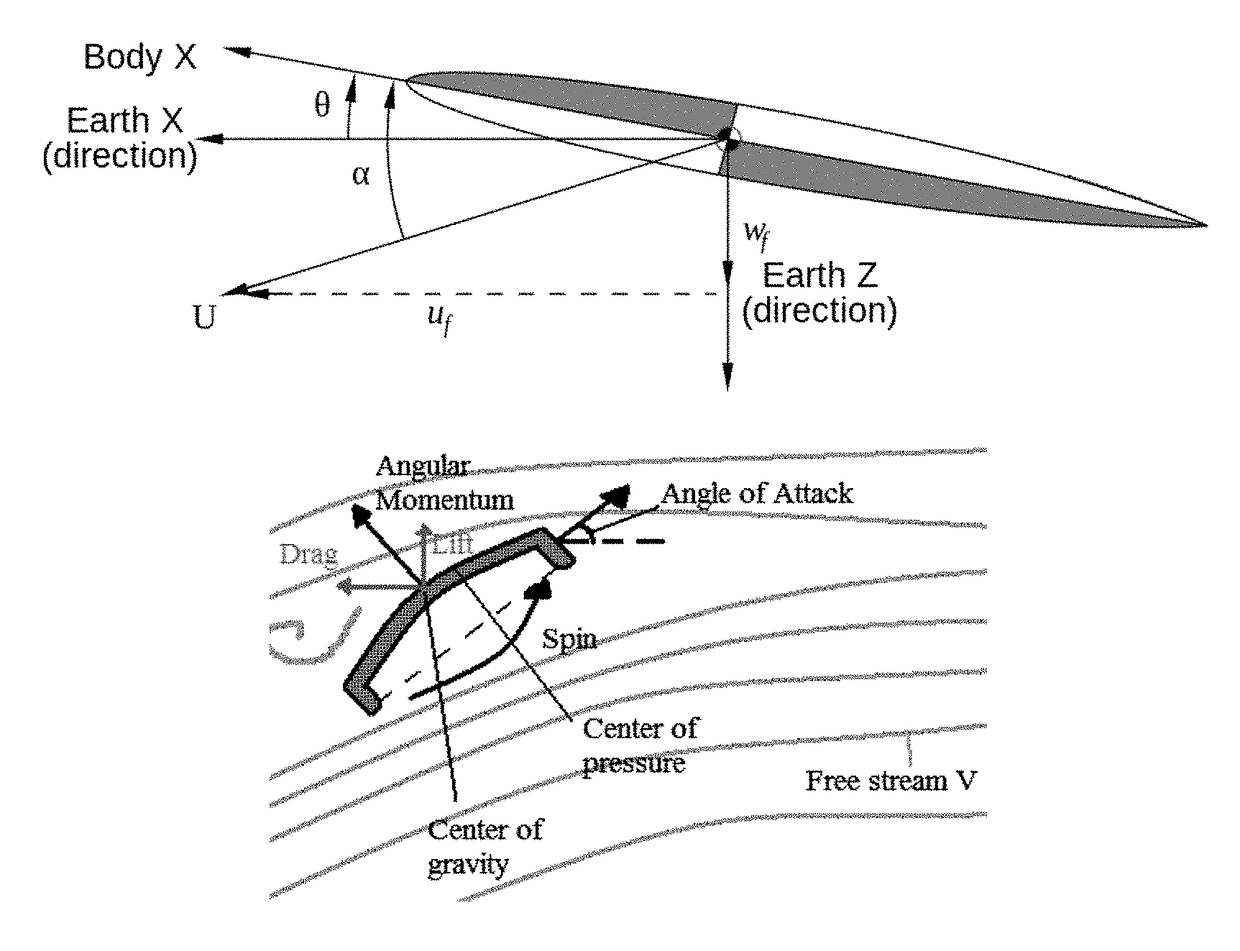
Steerable rotating projectile
A method for controlling a flying projectile which rotates during flight, comprising: determining an angle of rotation of an inertial mass spinning about an axis during flight; and controlling at least one actuator for altering at least a portion of an aerodynamic structure, selectively in dependence on the determined angle of rotation and a control input, to control aerodynamic forces during flight. An aerodynamic surface may rotate and interact with surrounding air during flight, to produce aerodynamic forces. A sensor determines an angular rotation of the spin during flight. A control system, responsive to the sensor, produces a control signal in dependence on the determined angular rotation. An actuator selectively alters an aerodynamic characteristic of the aerodynamic surface in response to the control signal.
Owner:HOFFBERG STEVEN M
Device for distributing gas to a cooking appliance
A gas tap for controlling the flow of a gas to a cooking appliance. In one embodiment, the gas tap includes a body and a rotatable regulation member positioned within the valve body, the valve body having a stationary groove for the inlet of gas from an exterior wall surface to an interior wall surface of the body, the regulation member having a passage opening for the inlet of gas from an exterior surface to an interior cavity of the regulation member, the passage opening moving with an angular rotation of the regulation member. The groove and passage opening are shaped, dimensioned and positioned relative to one another such that the regulation of an intermediate gas flow Qgra (a flow between Qmax and Qmin) is proportional to the angular displacement of the rotatable regulation member.
Owner:COPRECITEC
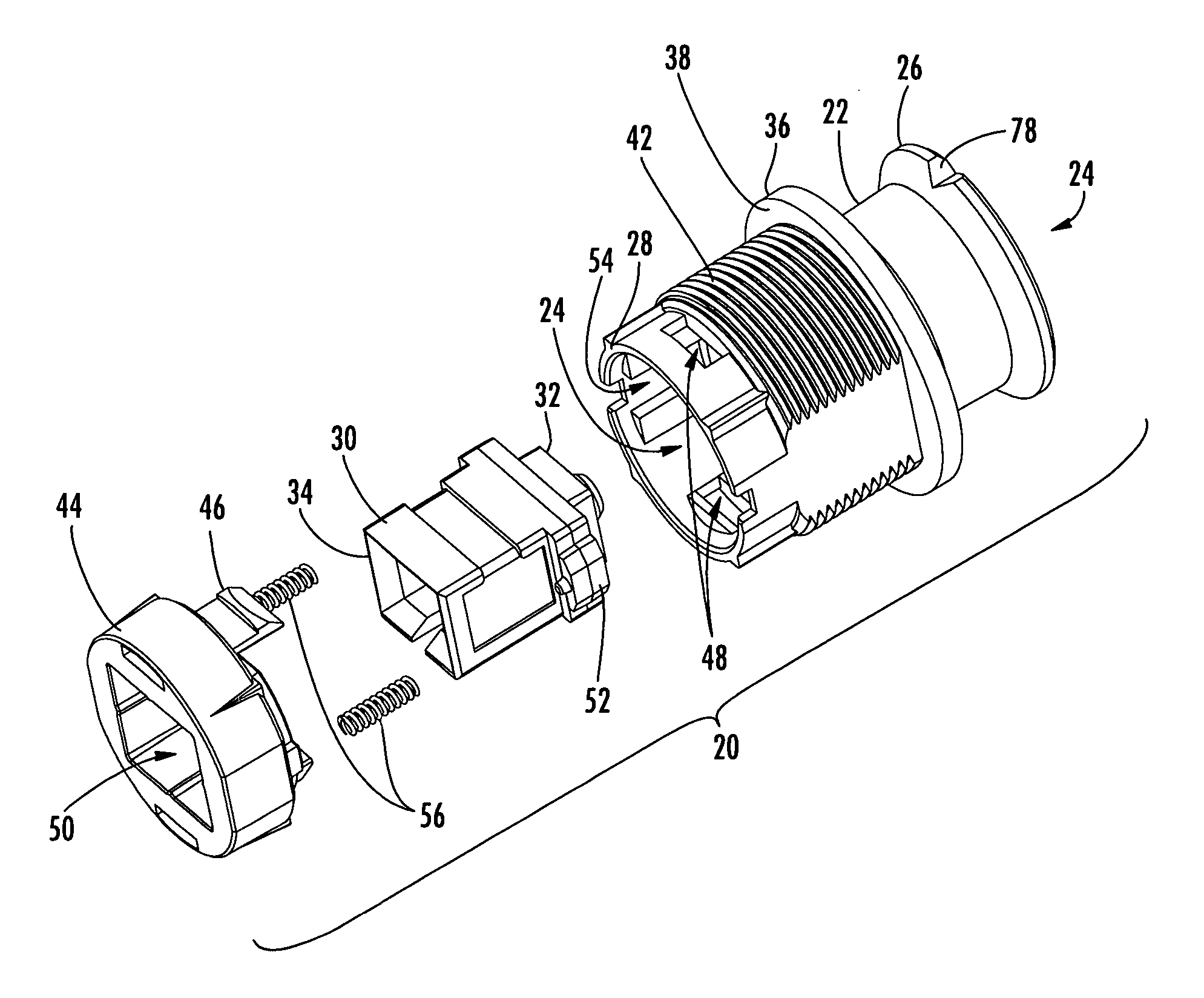
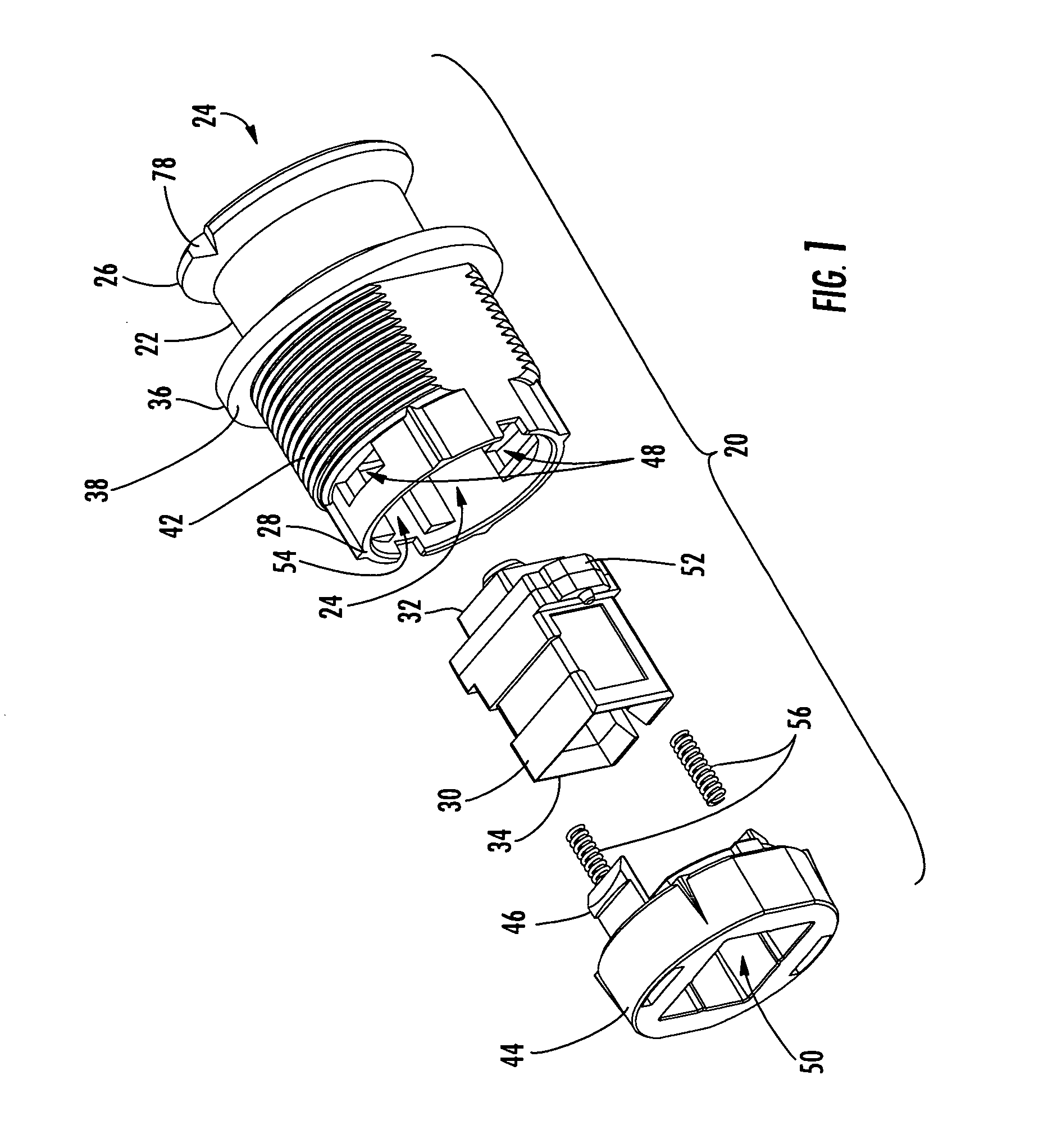
Contactless angular position sensor and method for sensing angular position of a rotatable shaft
InactiveUS7307415B2Improve accuracyRobust constructionSolid-state devicesMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesSignal conditioning circuitsAngular rotation
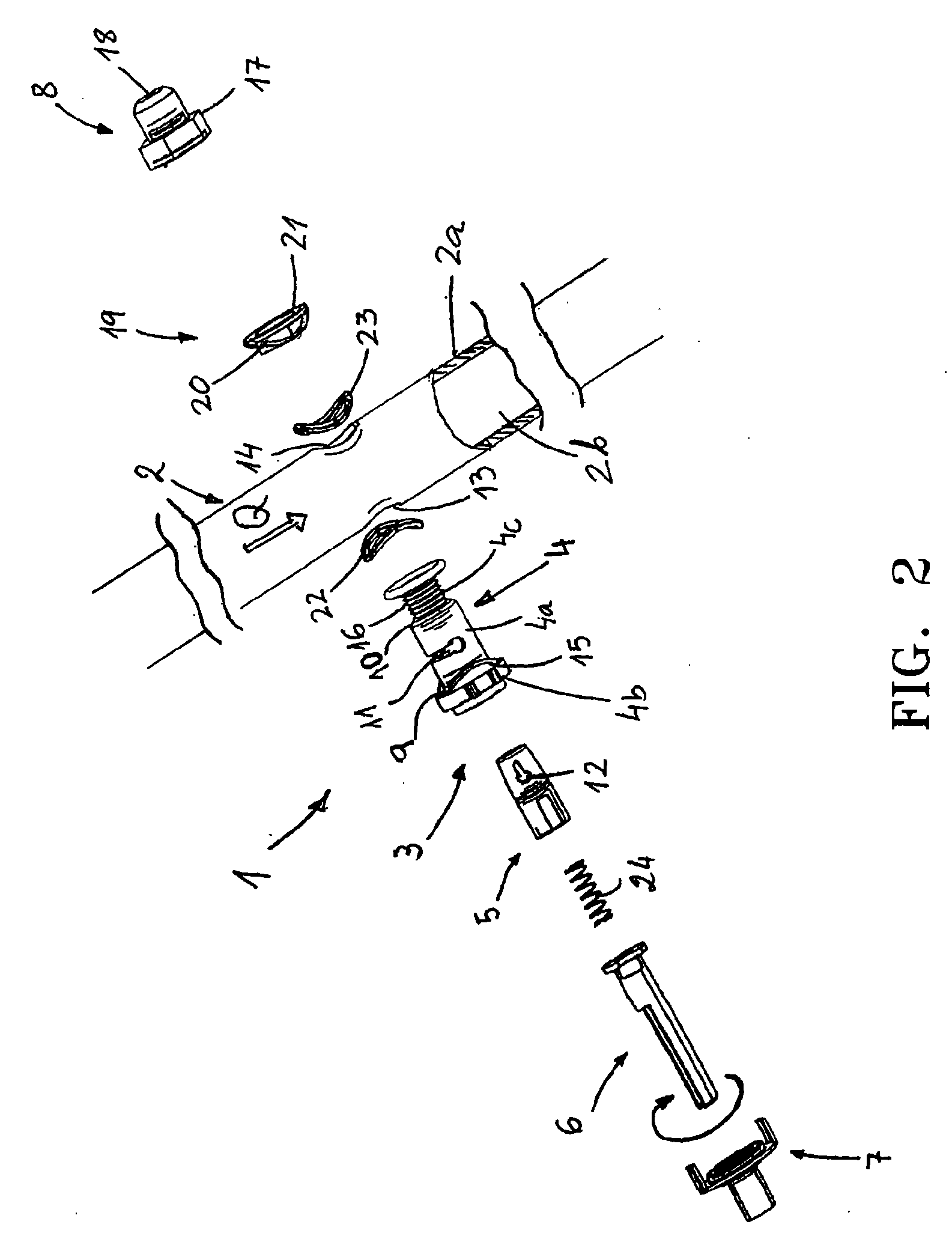
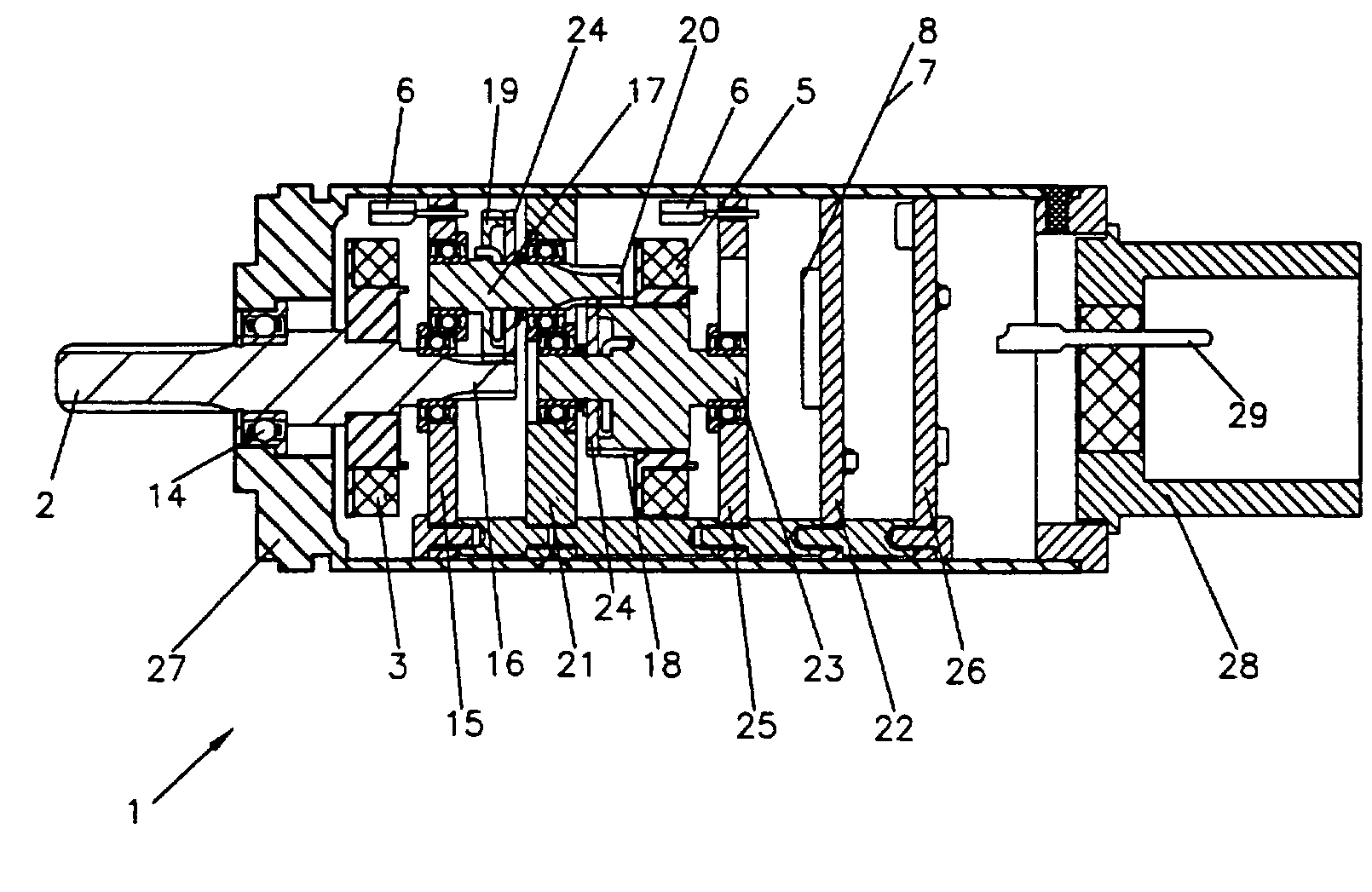
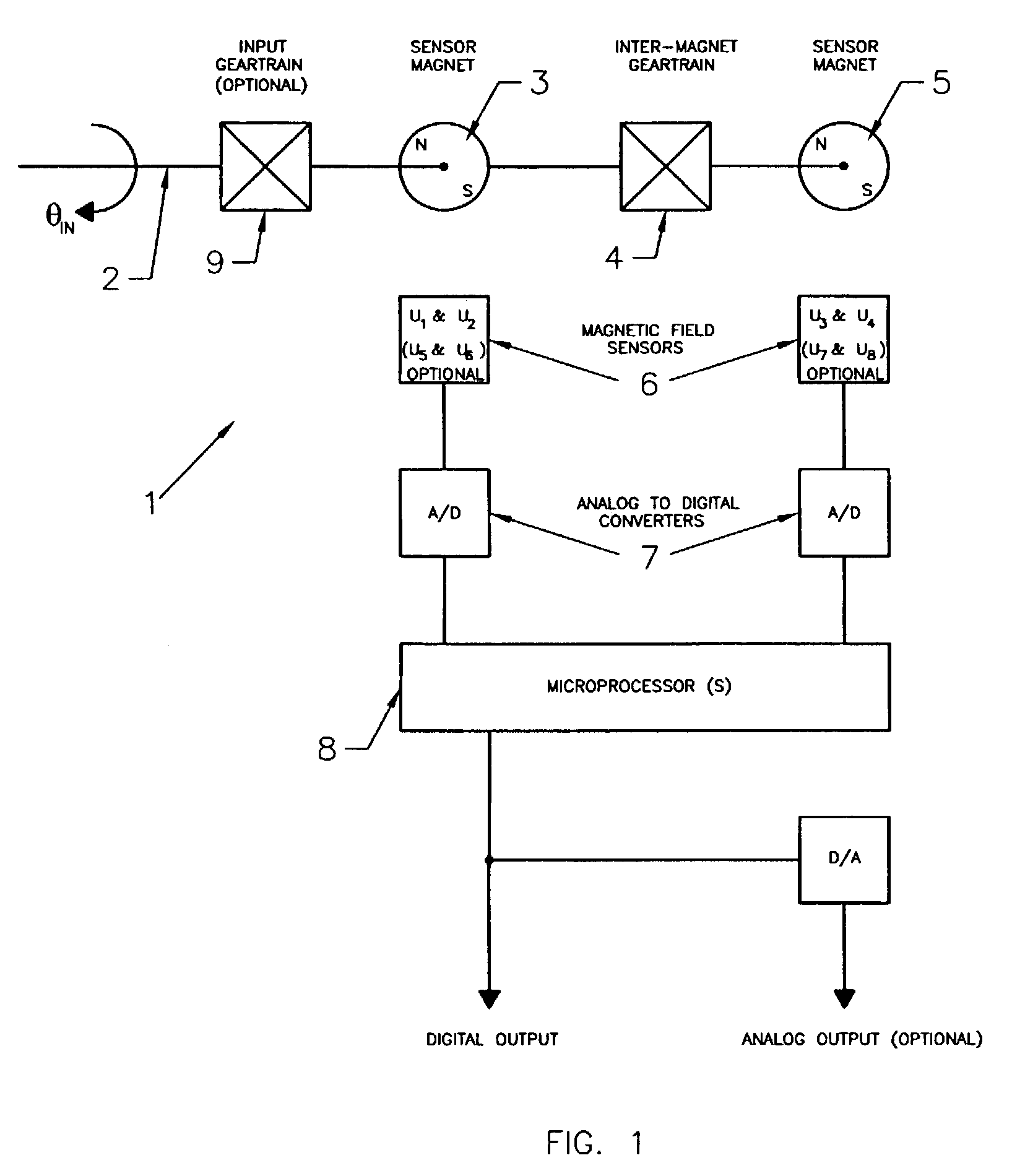
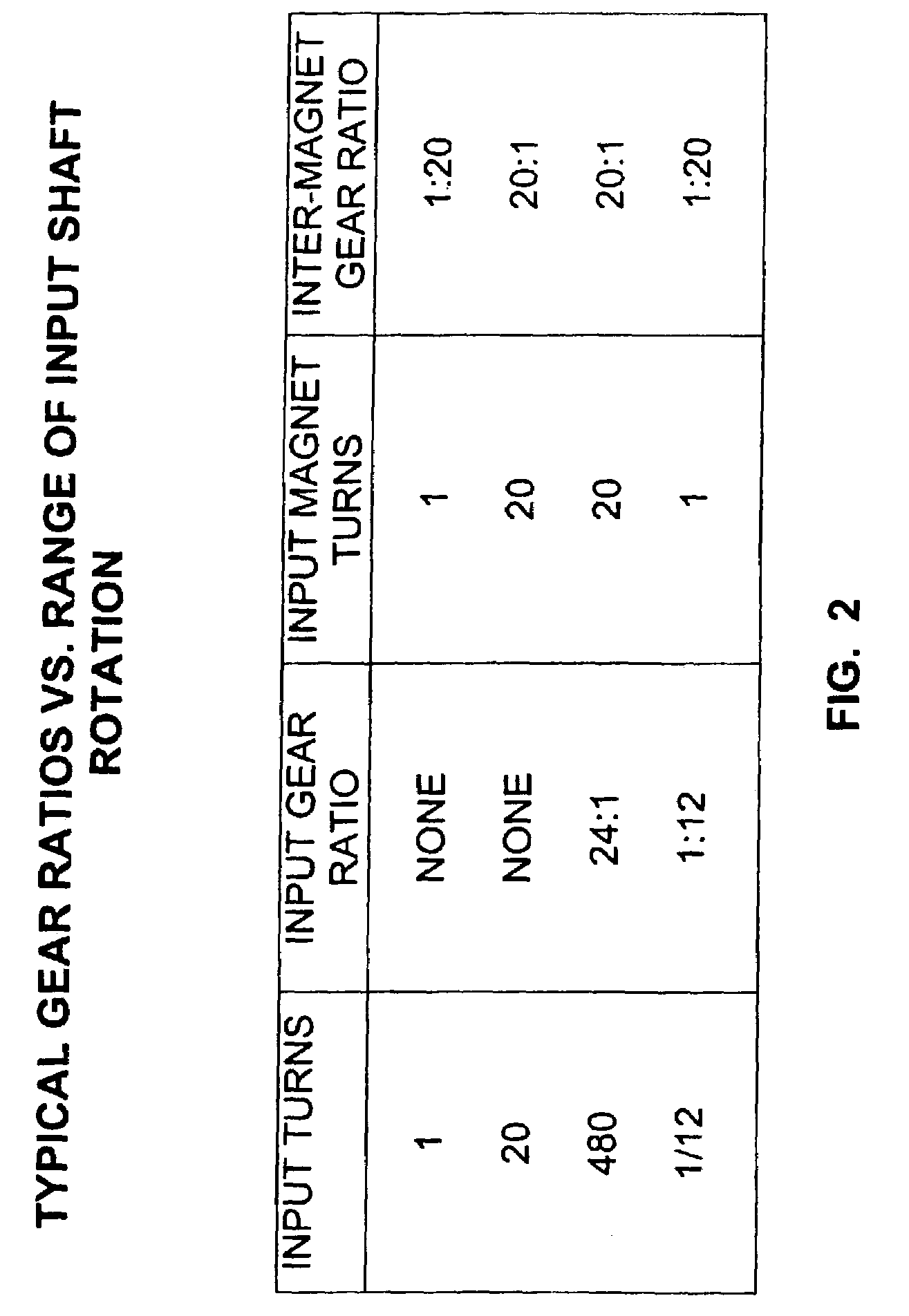
A contactless rotary shaft position sensor provides for precision computation of shaft angle for a wide range of input shaft rotational angles. The sensor includes two annular two-pole magnets which are connected by a precision, motion-transmitting gear train. An optional second gear train between one of the magnets and the input shaft can provide additional angular rotation scaling to accurately measure either fractional or a large number of multiple turns of the input shaft. The gear ratios are selected such that one of the magnets does not rotate more than one revolution. Pairs of ratiometric Hall-effect or magnetoresistive sensors provide differential voltage signals which are used for sensing angular position of each magnet over a full 360 degrees of rotation. The single-turn magnet provides an absolute, coarse indication of input shaft rotation with a typical accuracy of 2%. The gear ratio between the magnets produces several turns of the second magnet for each turn of the single-turn magnet. Since the gear ratio between the magnets is fixed, the angle sensed for the multi-turn magnet can be predicted from the position of the single-turn magnet. This is compared to the multi-turn magnet's actual sensed rotation. The result is an improvement in accuracy directly proportional to the gear ratio between the magnets. Computation of the individual magnet rotation angles and the input shaft angle is performed using a microprocessor and appropriate signal conditioning circuits. Utilizing two magnets, input shaft rotation can be accurately measured to within 0.1% of maximum range.
Owner:BVR TECH
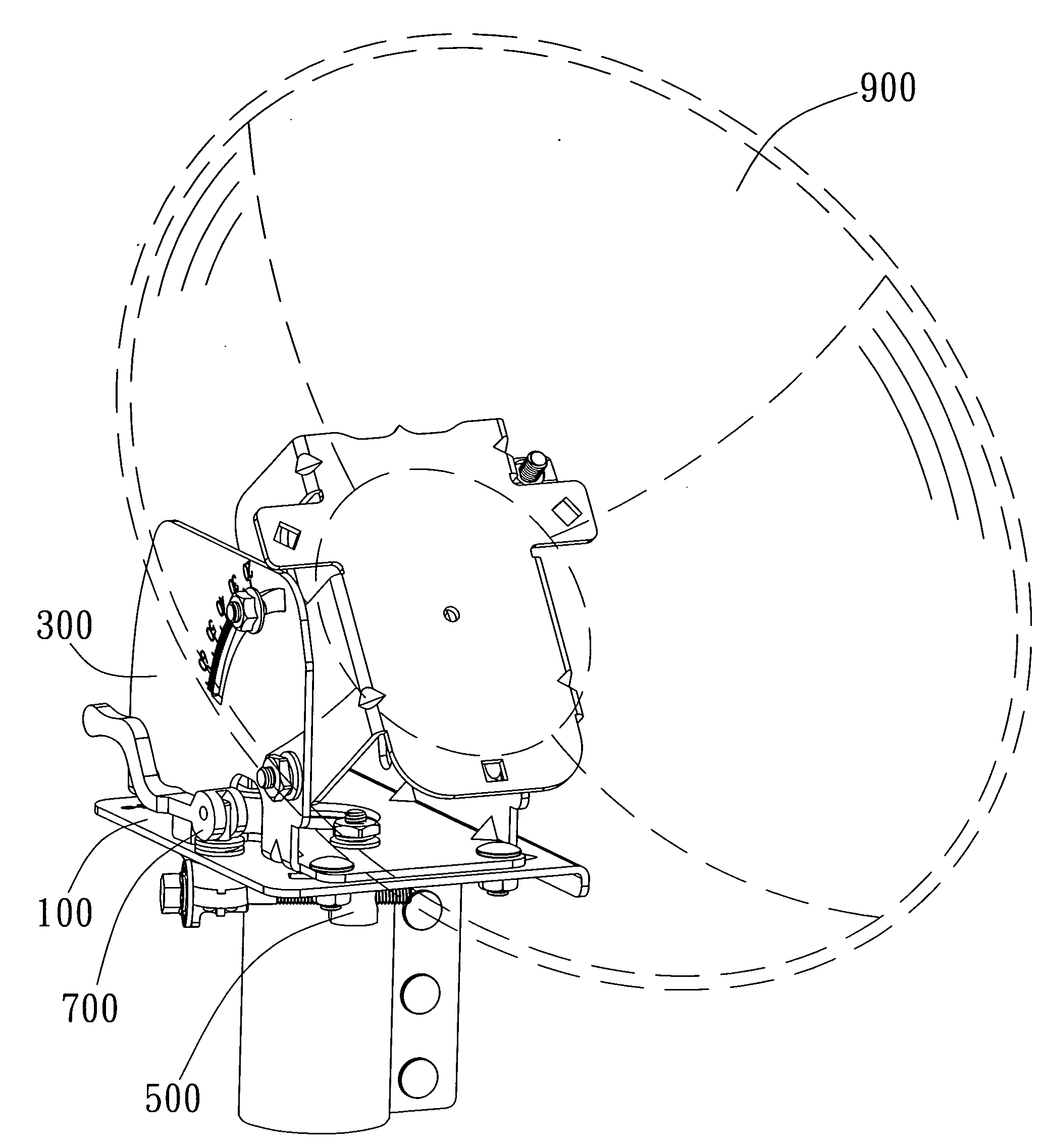
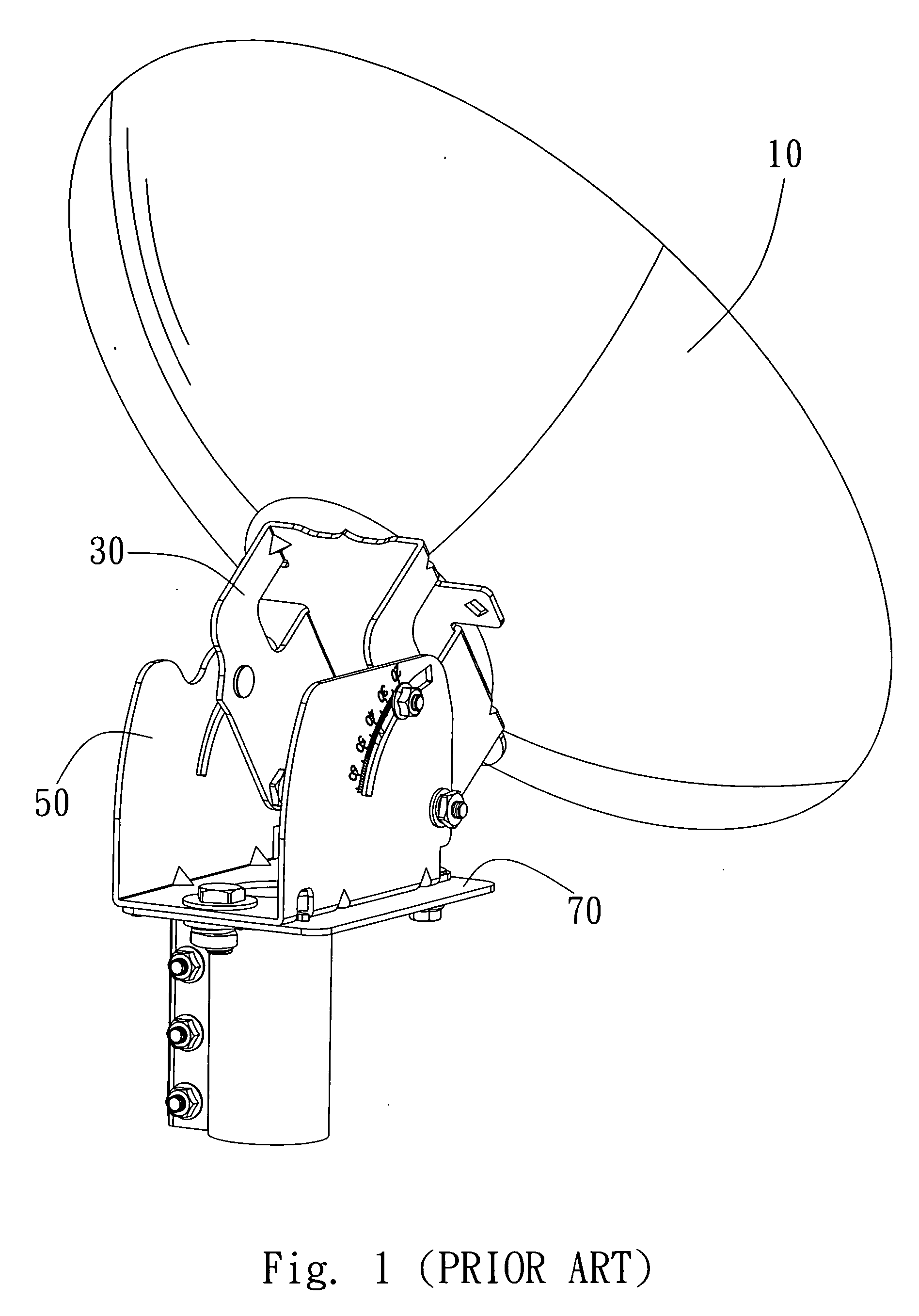
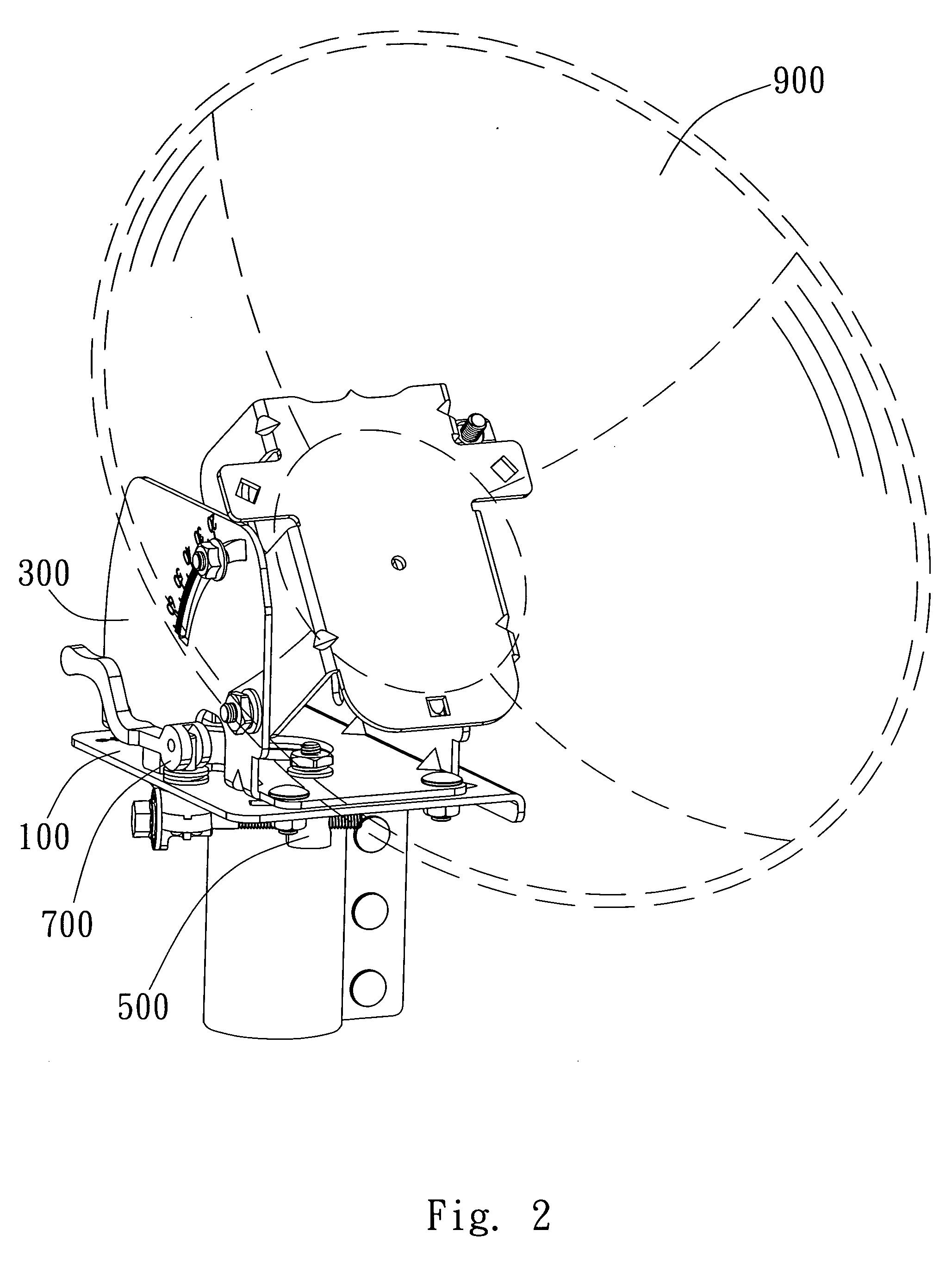
Satellite receiver
ActiveUS20090061761A1Control displacementEasy to adjustPipe supportsAntenna supports/mountingsRelative displacementEngineering
The present invention provides a satellite receiver comprising a base, a rotation stand, an adjusting mechanism, and a positioning device. The base has an axis aperture and a first slot. The rotation stand is rotatably attached to the base through the axis aperture. The adjusting mechanism has a connection end and an adjusting end. The connection end is coupled with the rotation stand and is movable together with the upper stand to generate displacement relative to the base. The positioning device is coupled with the adjusting end and passes through the first slot. When the upper stand rotates relatively to the base, the adjusting mechanism drives the positioning device to move along the first slot. The first slot limits the angular rotation of the rotation stand and the positioning device and selectively constrains the relative displacement between the connecting unit and the base.
Owner:WISTRON NEWEB
Motorized ultrasonic scanhead
ActiveUS20070038110A1Improved EMI protectionImprove eyesightUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterContinuous scanningLaparoscopes
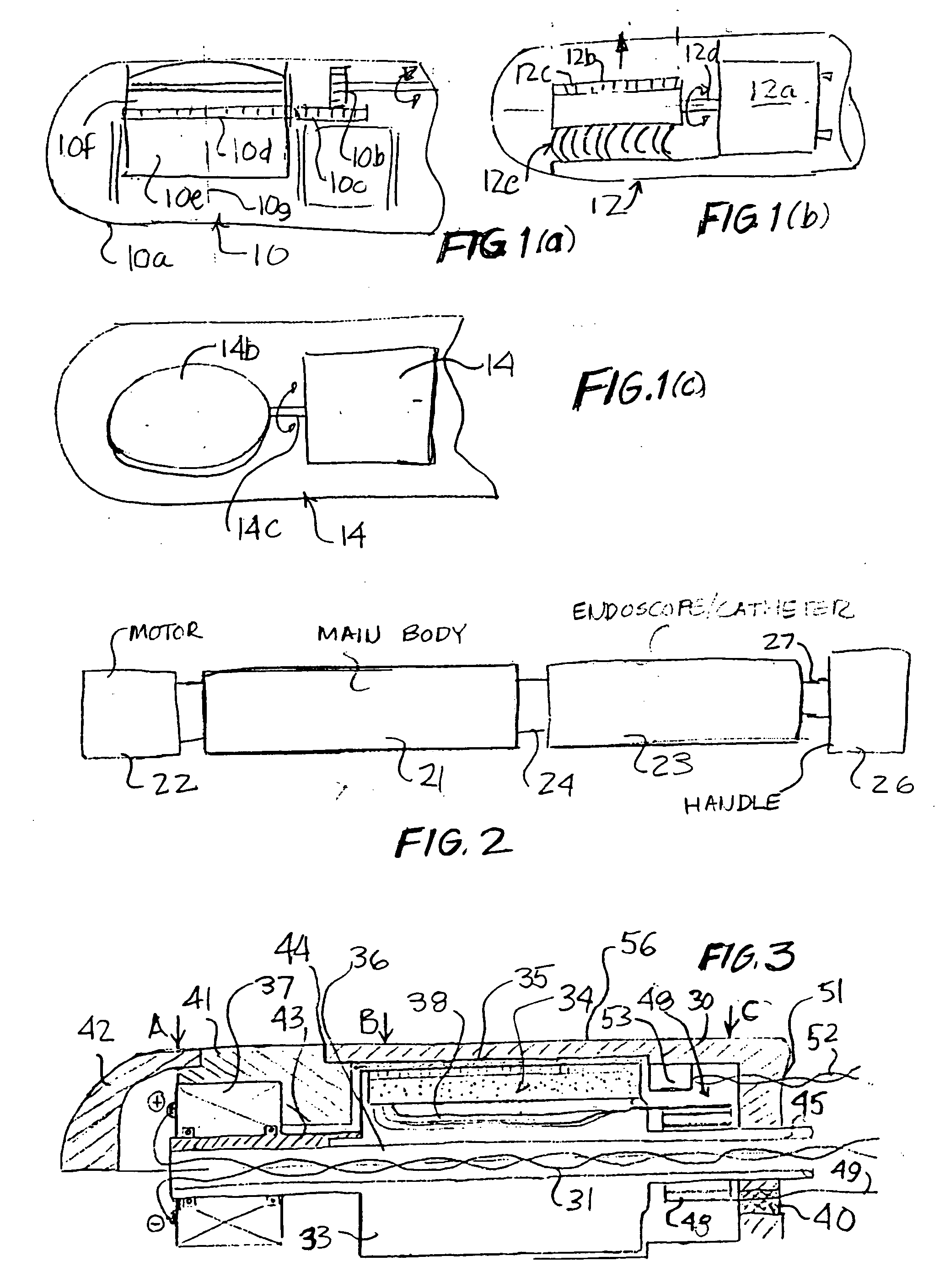
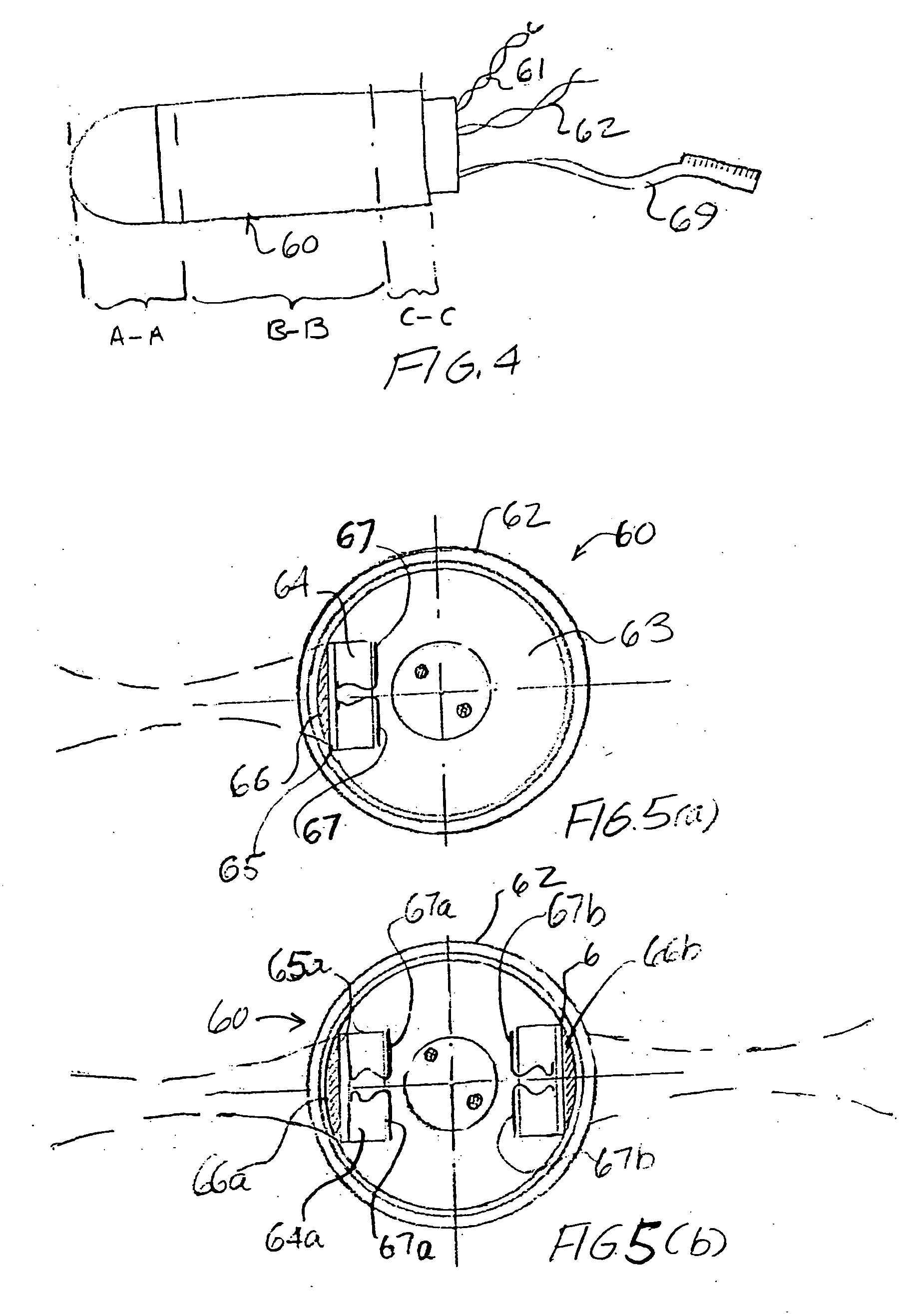
A motorized scanhead device is capable of rotating an array transducer through 360 degrees of angular rotation in a manner such as to provide acquisition of images in successive scanning planes arranged around the principal axis of the device. The device can be incorporated in endoscopes (e.g., transesophageal endoscopes), laparoscopes, endocavity or intracavity probes so as to provide an expanded angle of vision or to render 3D images, without the need for external movement of the device. The motorized scanhead device includes a motor that is isolated from the transducer signal interconnections in order to minimize electrical discharges associated with motor operation and to provide more room between an associated probe housing and the scanhead device.
Owner:VERMON
Surround sound positioning tower system and method
ActiveUS7090047B1Smooth rotationSimple configurationLoudspeaker casing supportsCasings/cabinets/drawers detailsEngineeringAngular rotation
A surround sound system and method involving a surround sound tower; a base plate; and a structure for positioning the surround sound tower on the base plate, the surround sound tower being mounted on, and normal to, the positioning structure for customizing sound direction and constructive interference patterns by interactively positioning the sound tower and / or at least one sound tower and by modular usage of tweeters, economizing floor space, especially in a home theater environment. The positioning structure may have a structure for indicating an angular rotation of the surround sound tower relative to the base plate and a structure for facilitating rotation of the angular rotation indicating structure.
Owner:MONSTER
System and method for using microgyros to measure the orientation of a survey tool within a borehole
A system and method for determining an orientation of the survey tool within a borehole utilizes a survey tool including a plurality of rotation sensors each having a sensing axis and a direction of least acceleration sensitivity. The plurality of rotation sensors are mounted in a housing with their sensing axes generally parallel to one another and with their directions of least acceleration sensitivity generally non-parallel to one another. The survey tool further includes a controller adapted to calculate a weighted average of the detected angular rotation rates from the plurality of rotation sensors. The weighted average includes the detected angular rotation rate of each rotation sensor about its sensing axis weighted by the detected acceleration along its direction of least acceleration sensitivity.
Owner:GYRODATA
Festooned trim clip system and method for attaching festooned clips to a substrate
ActiveUS20080258523A1Optimization rangeEasy to bendSnap fastenersVehicle seatsEngineeringAngular rotation
This invention provides a single or multi-ganged clip that can be grouped into a festooned arrangement. That is, a plurality of clips are arranged together into a discrete assembly along a line of extension so that a human or automated handler can retrieve a grouping, separate one-clip-at-a-time from the grouping, and apply the separated clip to a mold cavity or other assembly structure. Each clip can include a base with opposing ends aligned in the direction of extension and transverse to an elongation direction for a connecting segment (if any) between ganged clip members. In an illustrative embodiment, these base ends include opposing male and female connectors. In this embodiment the male connector is a cylinder with an axis that extends transverse to the direction of elongation and the female connector defines a conforming cylindrical inner diameter, which allows it to nest over the male cylinder. A gap opening is provided at the far edge of the female connector to provide clearance for the base that connects the male cylinder to the clip member base end. This gap can be sized to allow a predetermined range of angular rotation of the male connector within the female connector. Clips can be stored as discrete groupings that are stacked in a container, or paid out in a continuous grouping from a spool.
Owner:HOPE GLOBAL DIV OF NFA
Surgical table
Owner:RELIANCE MEDICAL PRODS
Rotary servovalve and control system
InactiveUS6269838B1Less torqueIncrease frequency bandwidth of responsivenessOperating means/releasing devices for valvesServomotor componentsFluid controlAngular rotation
An improved rotary servovalve system employs a rotary magnetic solenoid having an armature that includes at least one permanent magnet. The armature is rotatable relative to a stator formed as an electromagnet which is energizable to create alternative electromagnetic fields having opposite polarities from each other. When deenergized, the stator allows the armature to return to a neutral, null position from positions of extreme rotation in opposite angular directions due to the magnetic force of the permanent magnet of the armature. The armature is coupled to carry a movable valve element in angular rotation therewith, so that flow through the servovalve of the system can occur in alternative directions. Also, the valve element is biased toward a position in which all of the valve ports are closed when power is removed from the rotary solenoid. The control circuit employed in the rotary servovalve system expands the bandwidth of response of the solenoid actuator by compensating for frequency variations in the input command signal and in the feedback signal. This compensation is achieved utilizing a combined proportional, integral, and differential amplification circuit. Also, imbalance of fluid forces within the servovalve mechanism can be avoided by utilizing a pair of inlet orifices, a pair of outlet orifices, a pair of first fluid control orifices, and a pair of second fluid control orifices. The orifices within each pair are located on opposite sides of the valve housing from each other.
Owner:WOODWORTH RAYMOND DEXTER
System and method for using microgyros to measure the orientation of a survey tool within a borehole
ActiveUS20050224257A1SurveyNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAngular rotationDirection detection
A system and method for determining an orientation of the survey tool within a borehole utilizes a survey tool including a plurality of rotation sensors each having a sensing axis and a direction of least acceleration sensitivity. The plurality of rotation sensors are mounted in a housing with their sensing axes generally parallel to one another and with their directions of least acceleration sensitivity generally non-parallel to one another. The survey tool further includes a controller adapted to calculate a weighted average of the detected angular rotation rates from the plurality of rotation sensors. The weighted average includes the detected angular rotation rate of each rotation sensor about its sensing axis weighted by the detected acceleration along its direction of least acceleration sensitivity.
Owner:GYRODATA
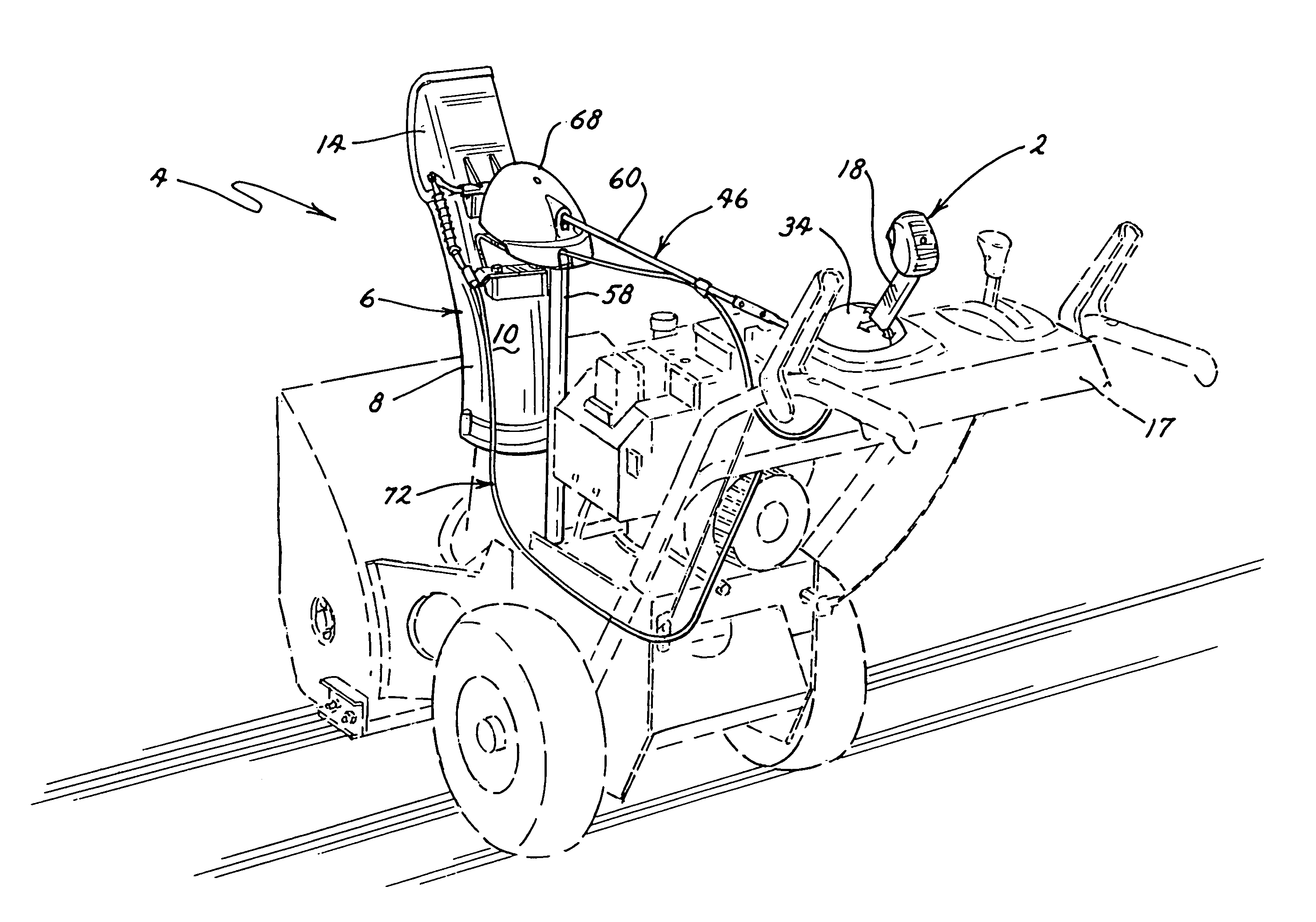
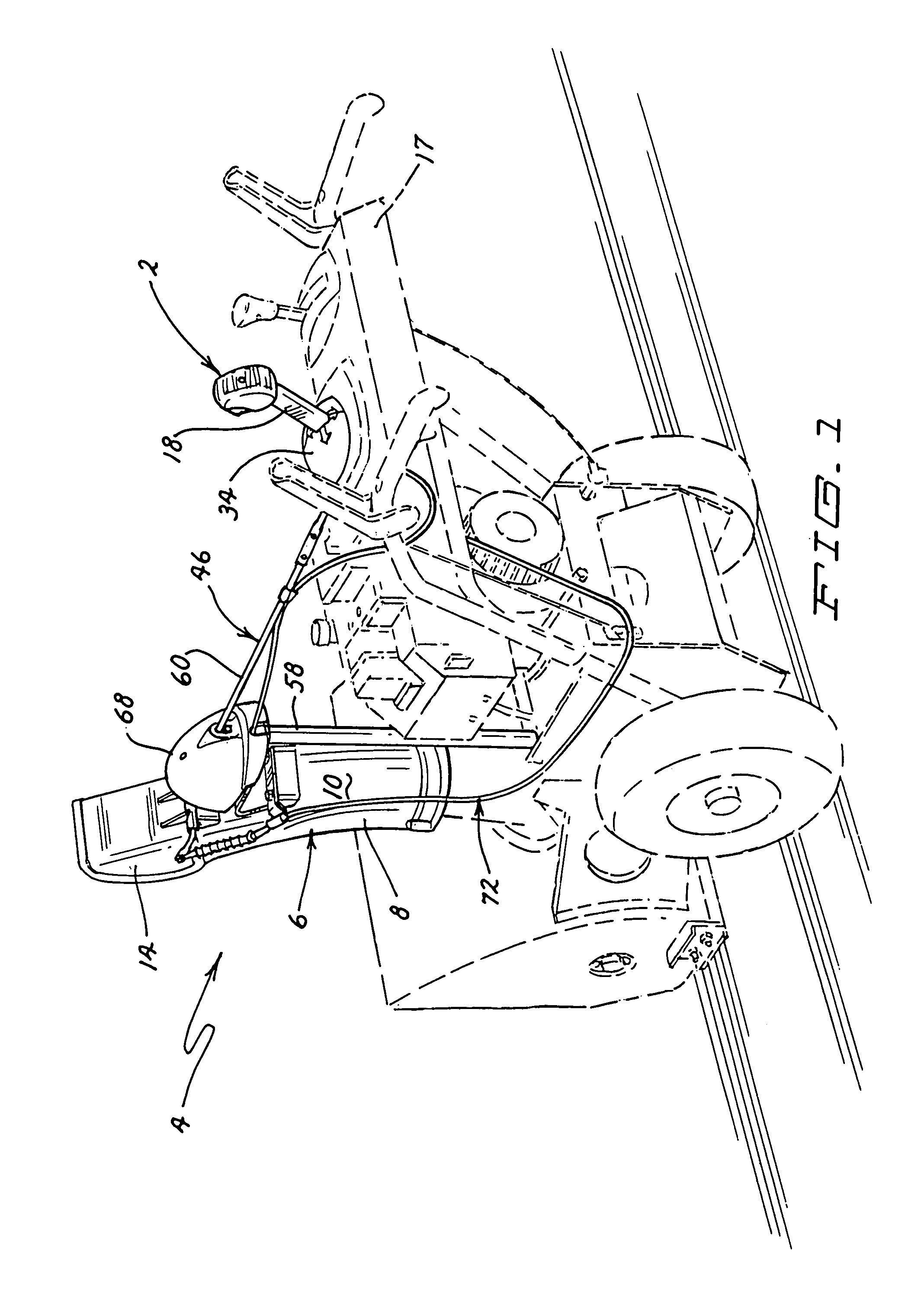
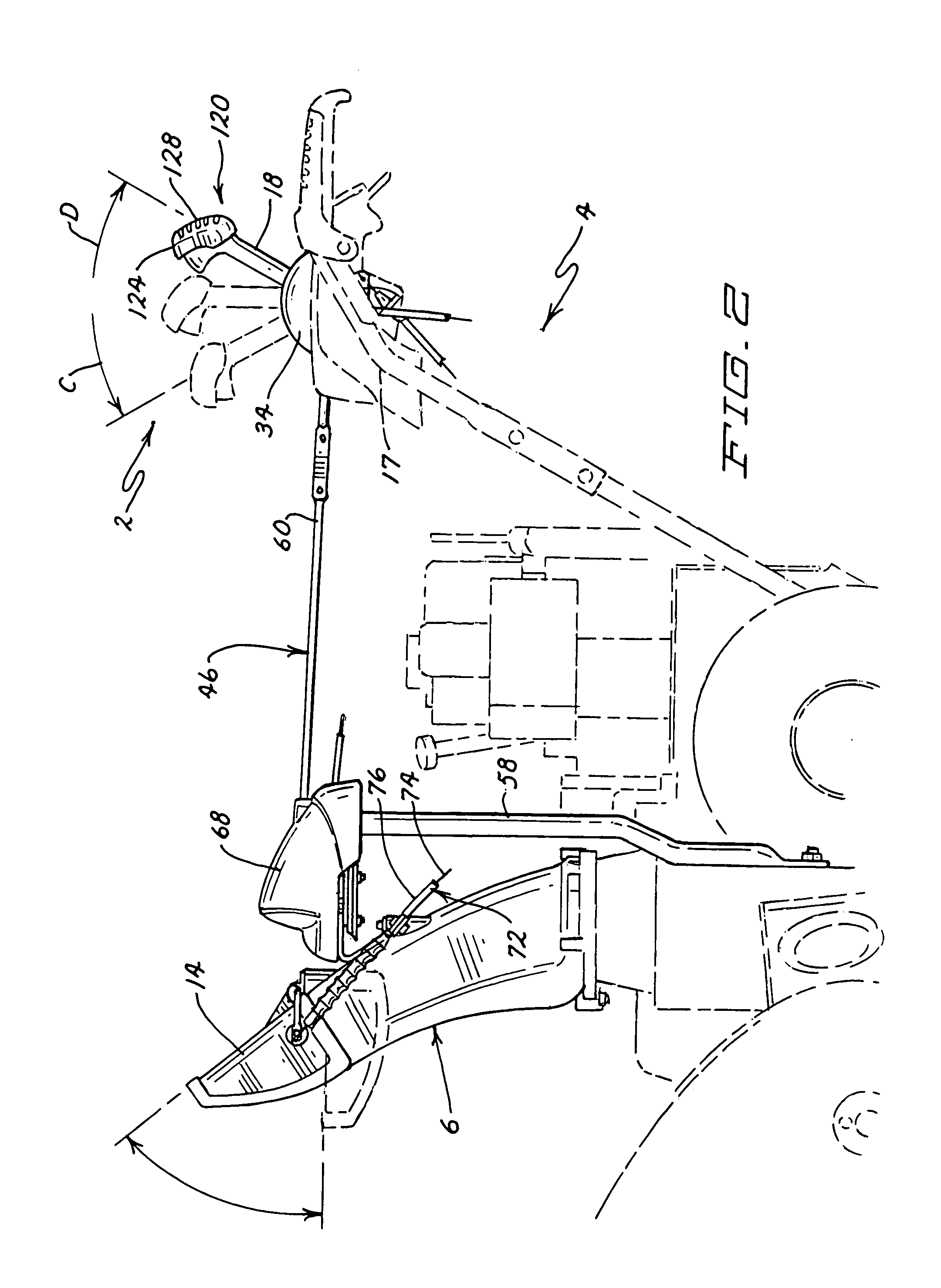
Snowthrower chute and deflector control
A single joystick type control handle controls the chute and deflector of a snowthrower. The control handle can be moved laterally from side to side and a second linkage including a gear connection laterally rotates the chute from side to side in the same direction, i.e. movement of the control handle to the left rotates the chute to the left and vise versa. The gear connection has a mechanical advantage that increases the amount of the angular rotation of the chute, i.e. the chute rotates further than the angular movement of the control handle. The control handle can also be moved longitudinally from fore to aft and a second linkage comprising a flexible cable pivots the deflector up and down on the chute in the same direction, i.e. moving the control handle forward pivots the deflector down and vise versa. A locking mechanism is provided to hold the chute and the deflector in their adjusted positions.
Owner:TORO CO THE
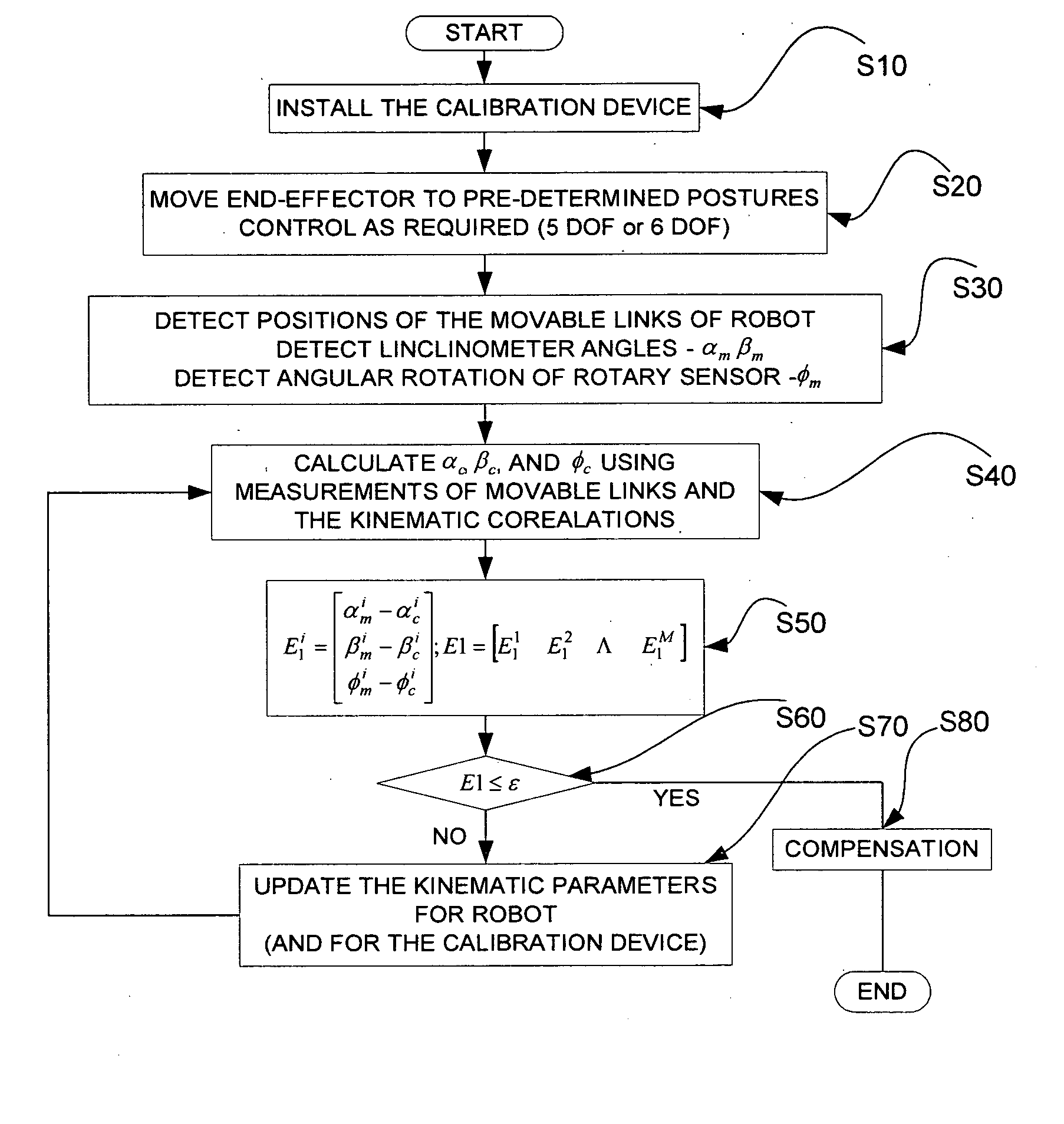
Device and method for kinematic calibration of robots
The present invention provides a device for kinematic calibration of a robot, comprising a supporting member fixed to the base of a robot; a constraint link installed between the supporting member and an end-effector of the robot connected to the base of the robot through a plurality of movable links so as to constrain a distance between the base and the end-effector of the robot; two joints installed at the constraint link; a mean to detect angular rotation for measuring angular rotation of the end-effector when the end-effector of the robot moves to a predetermine posture; a mean to detect inclination of the constrain link installed at the constraint link about two mutually perpendicular axes for measuring inclination of the constraint link about X and Y axes; a mean to detect variation of the length for measuring variation of length of the constraint link.
Owner:GWANGJU INST OF SCI & TECH
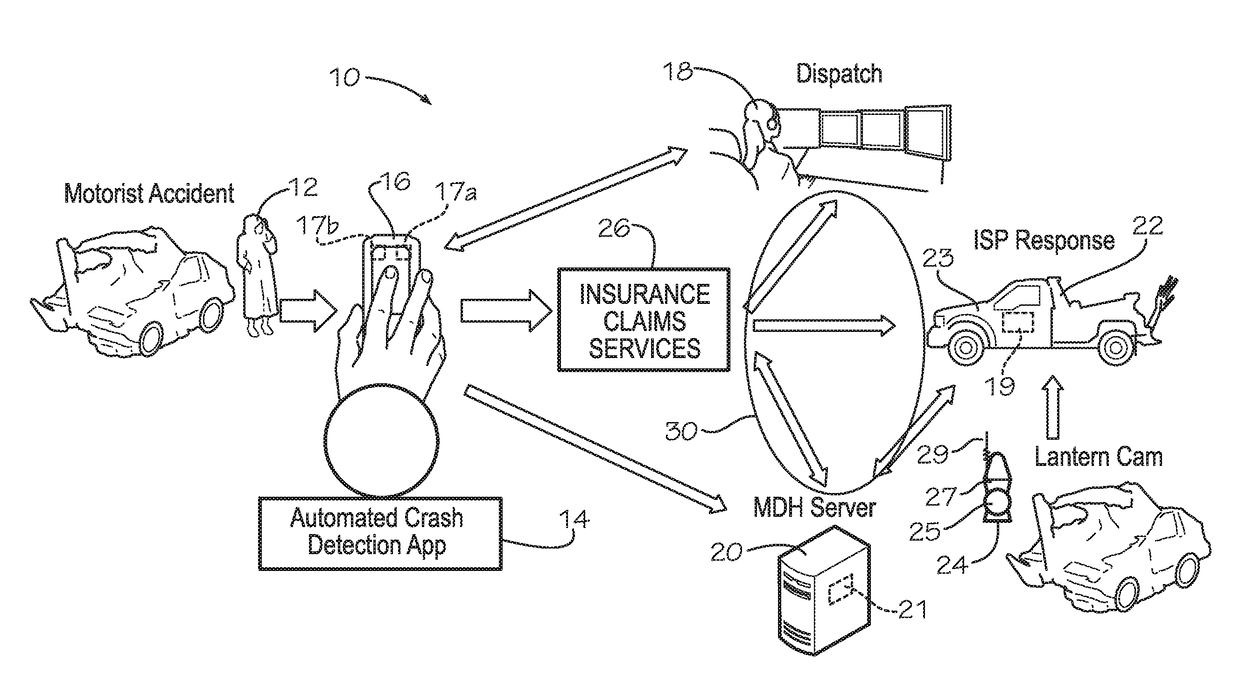
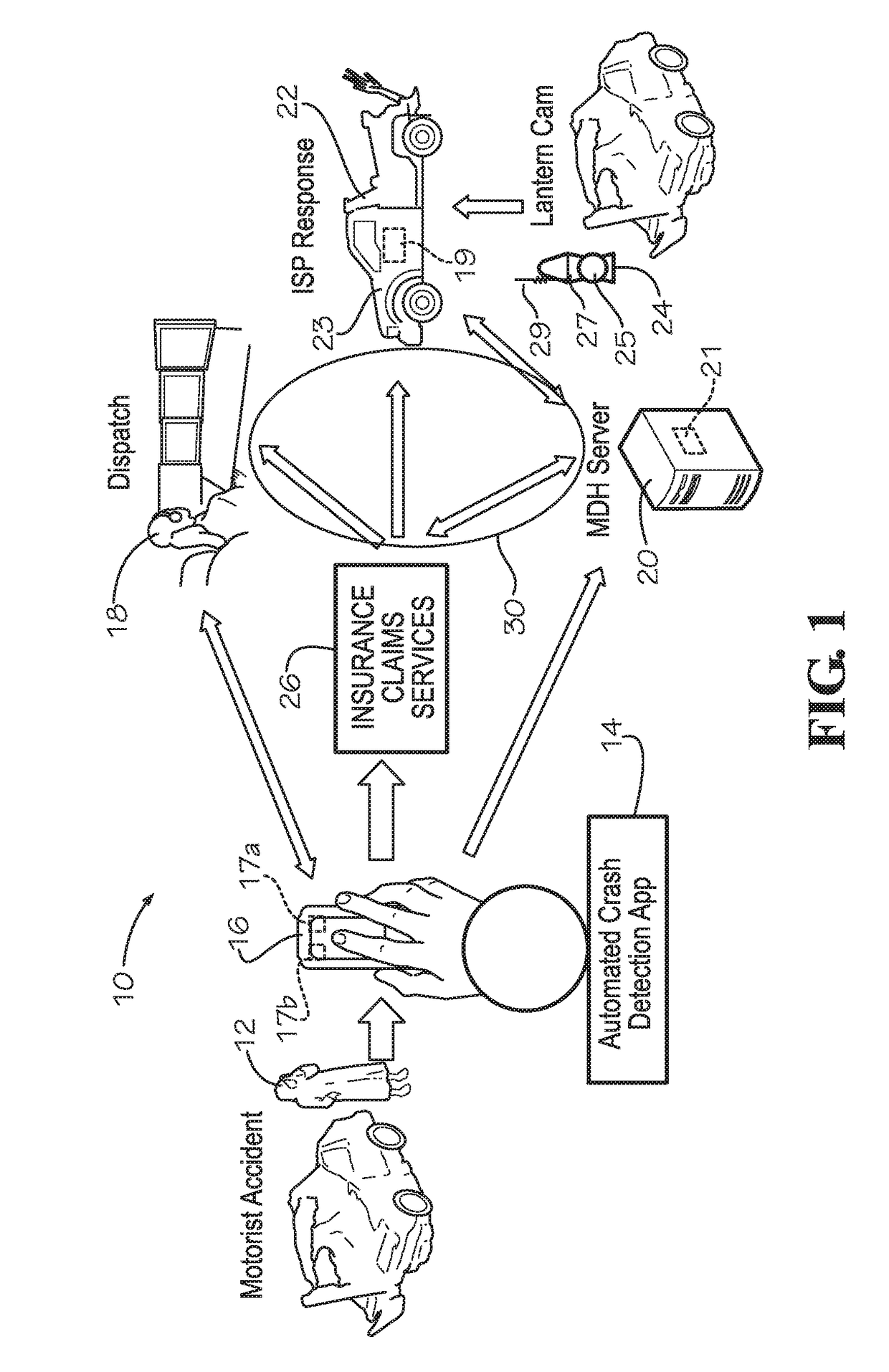
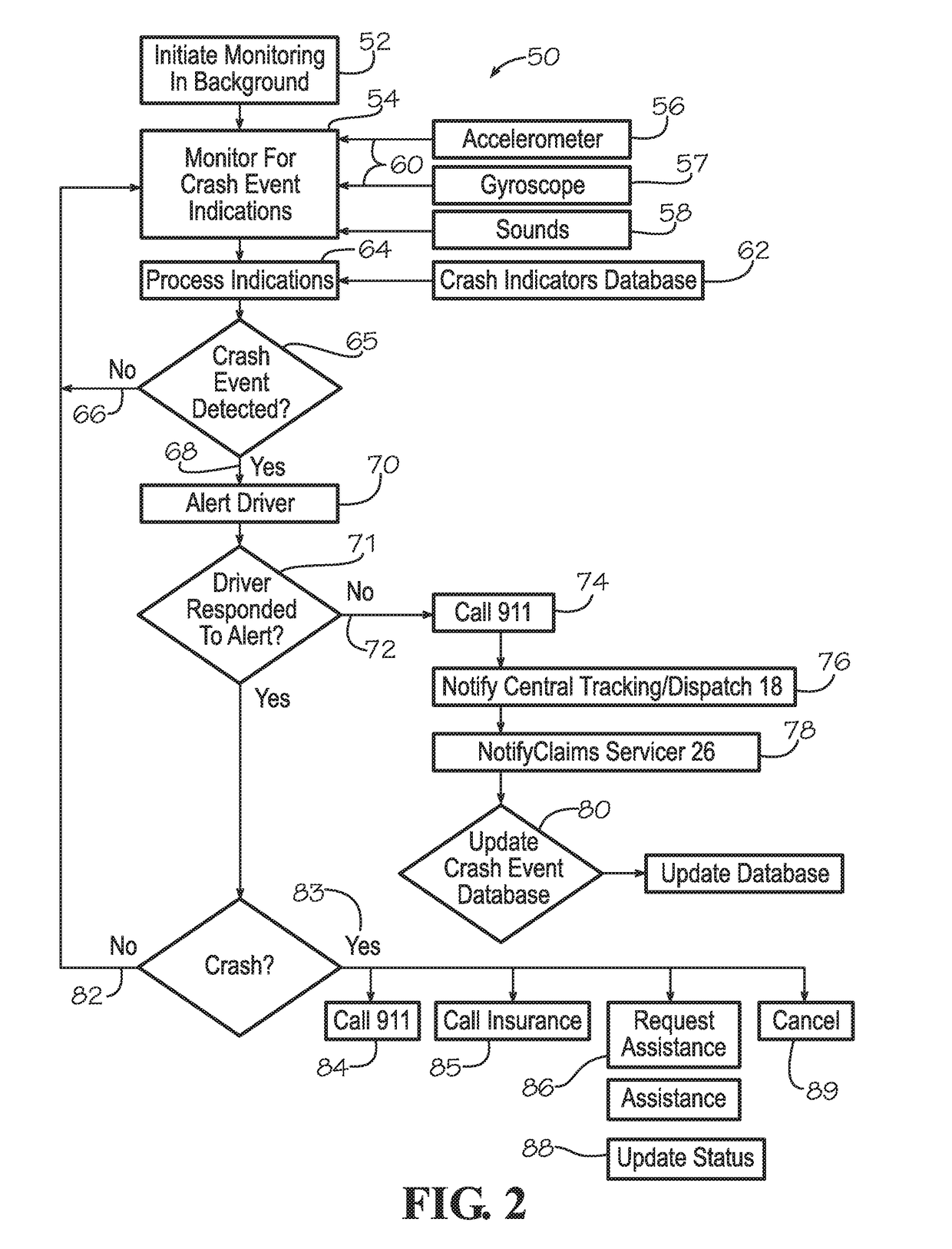
Crash Event Detection, Response and Reporting Apparatus and Method
A crash detection system with a mobile communications device configured for periodically interrogating (a) a motion signal to determine whether a change in motion (acceleration or angular rotation) exceeds a predetermined motion threshold and (b) a sound signal to determine whether a sequence of sensed sound signals within a predetermined period matches crash sound indicators of (i) glass breakage and (ii) metal folding, displaying selectable options upon detection of a crash incident, and upon a failure to select within a predetermined period, communicating an identifier and crash incident information dispatch center for dispatching a response servicer.
Owner:MOBILE VIDEO COMPUTING SOLUTIONS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com