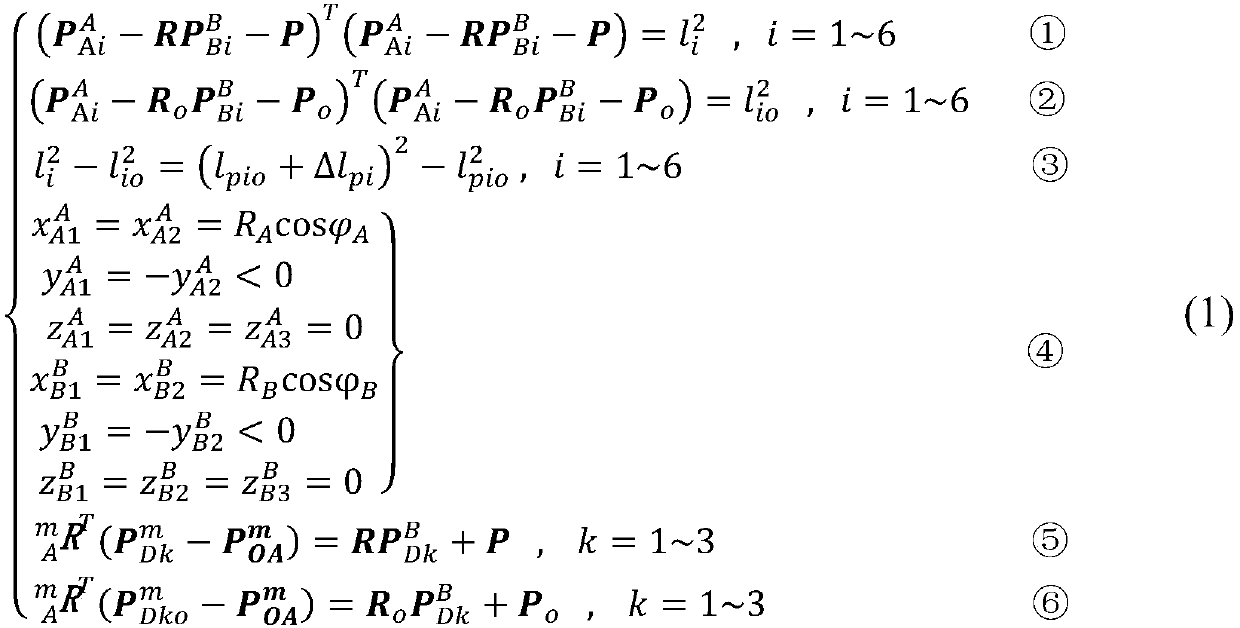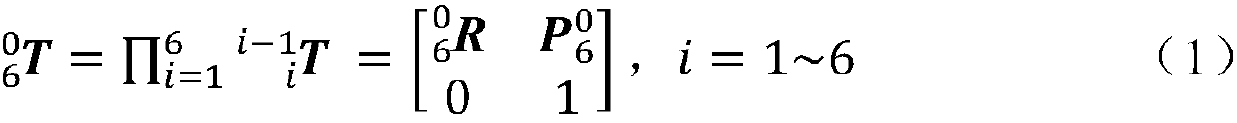Patents
Literature
79 results about "Kinematic calibration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
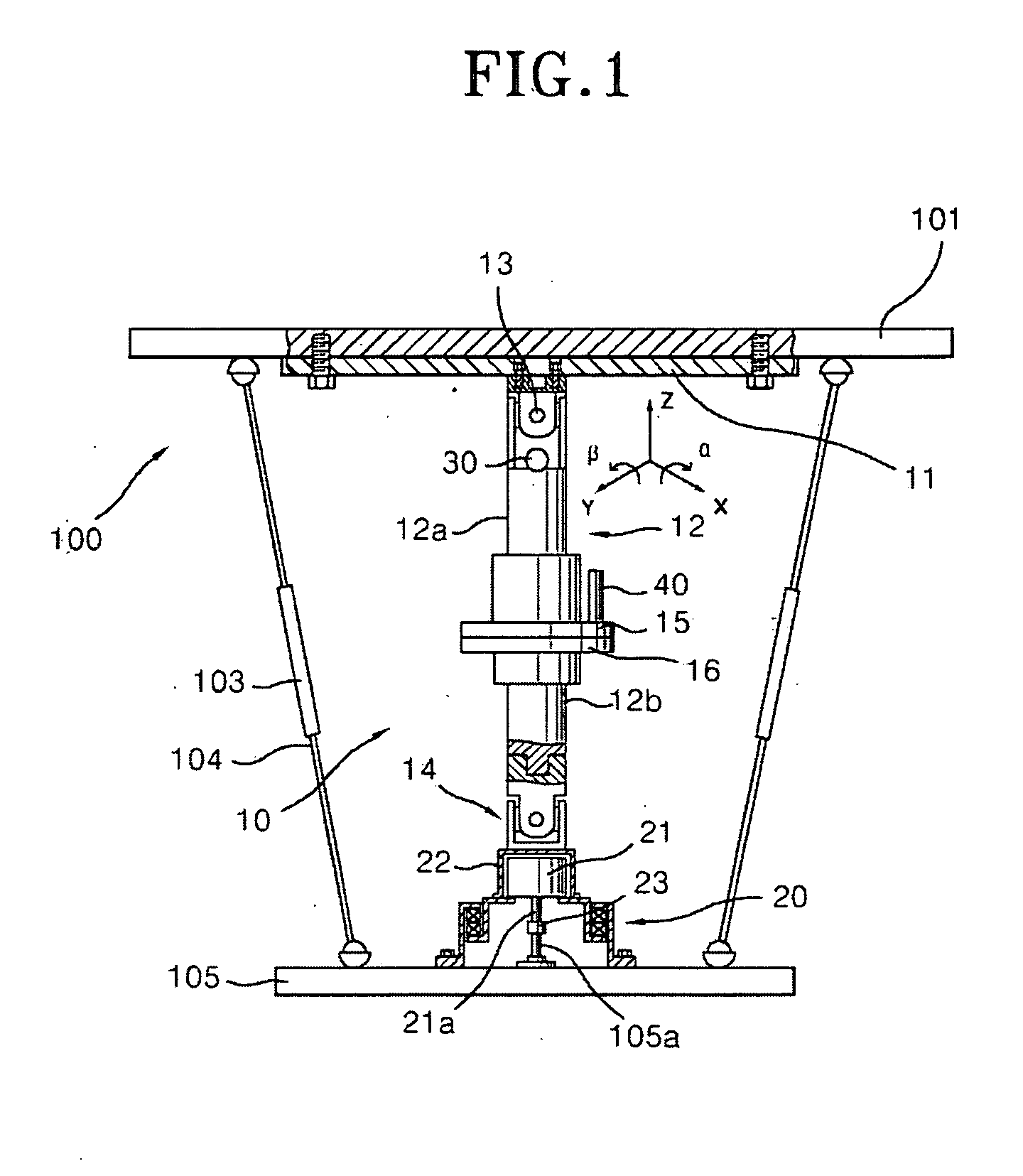
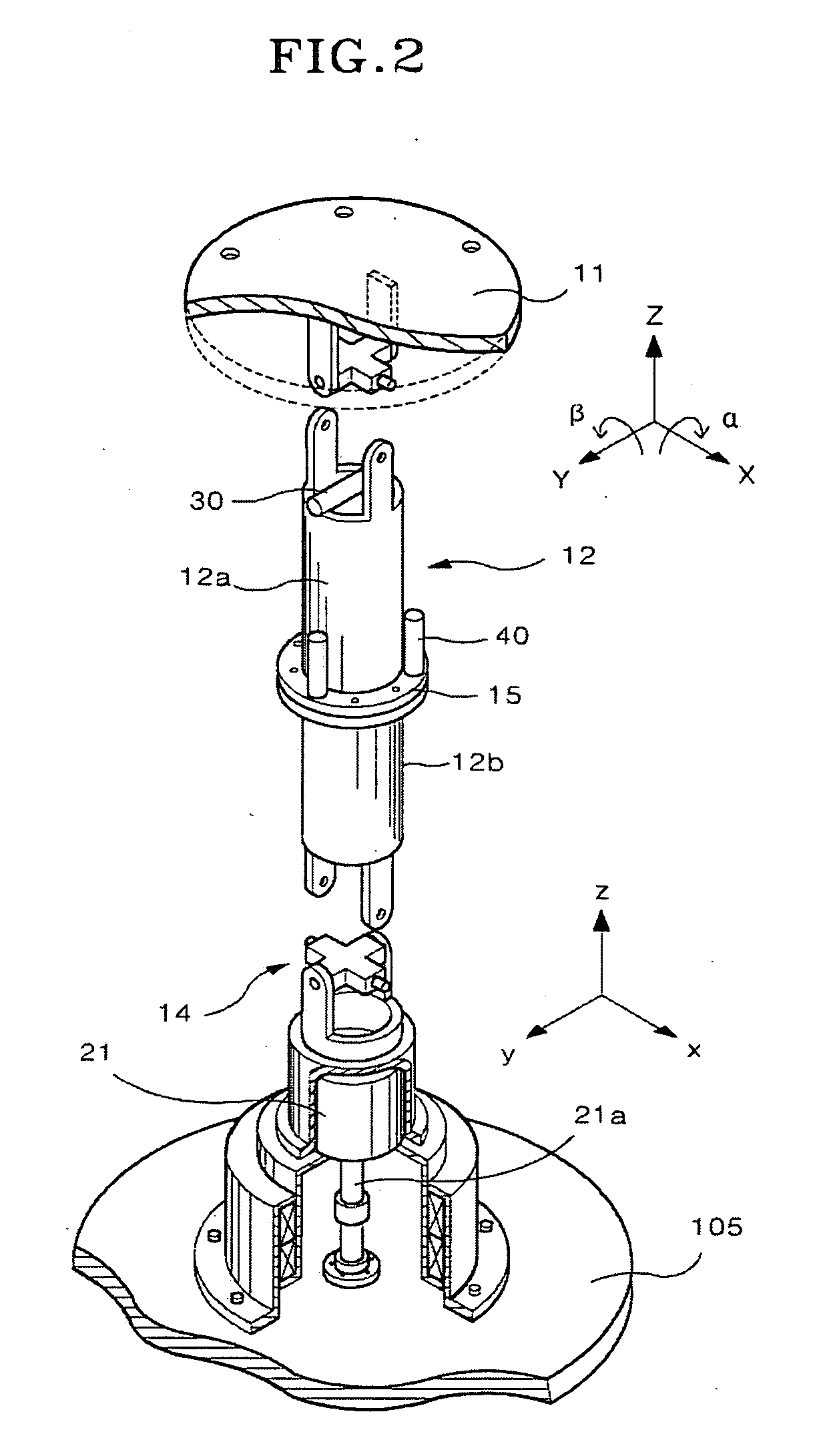
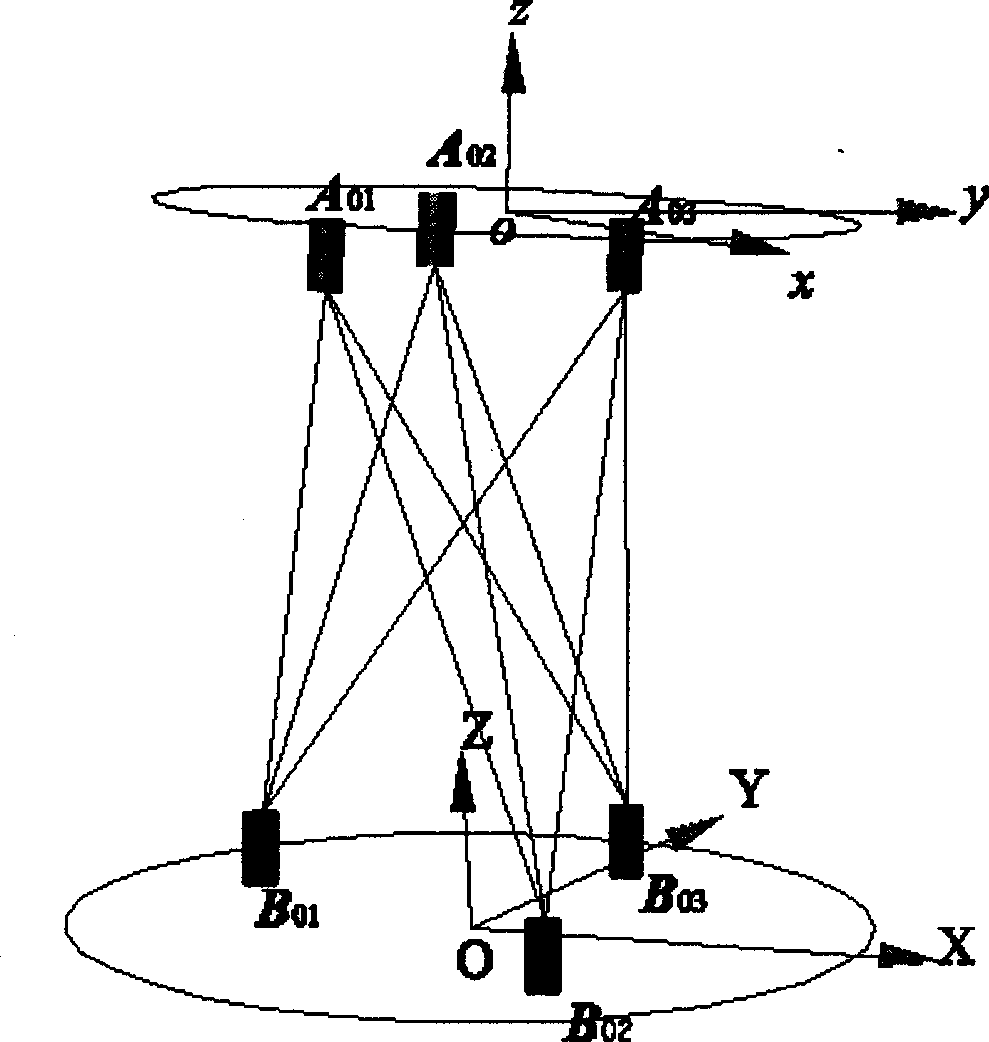
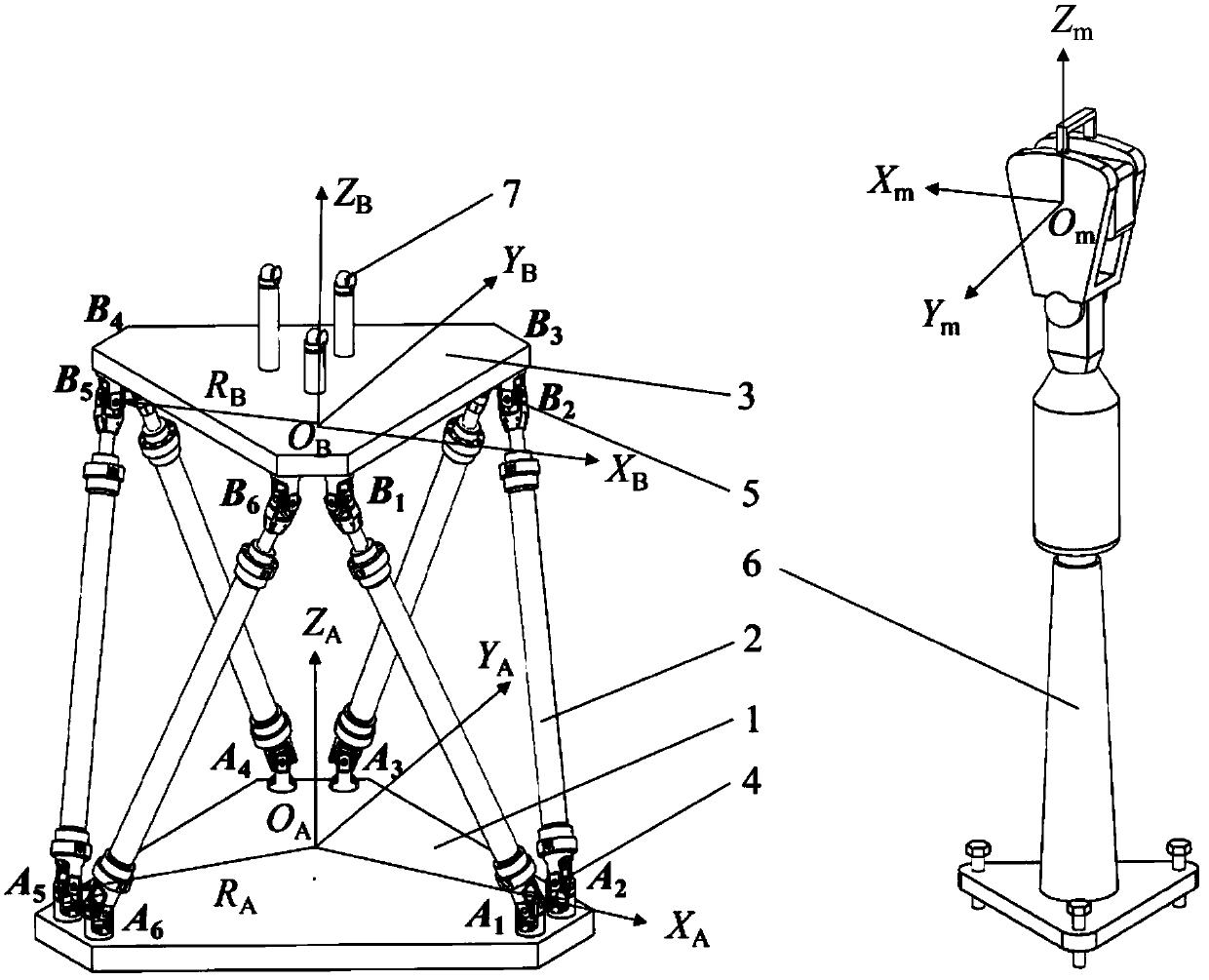
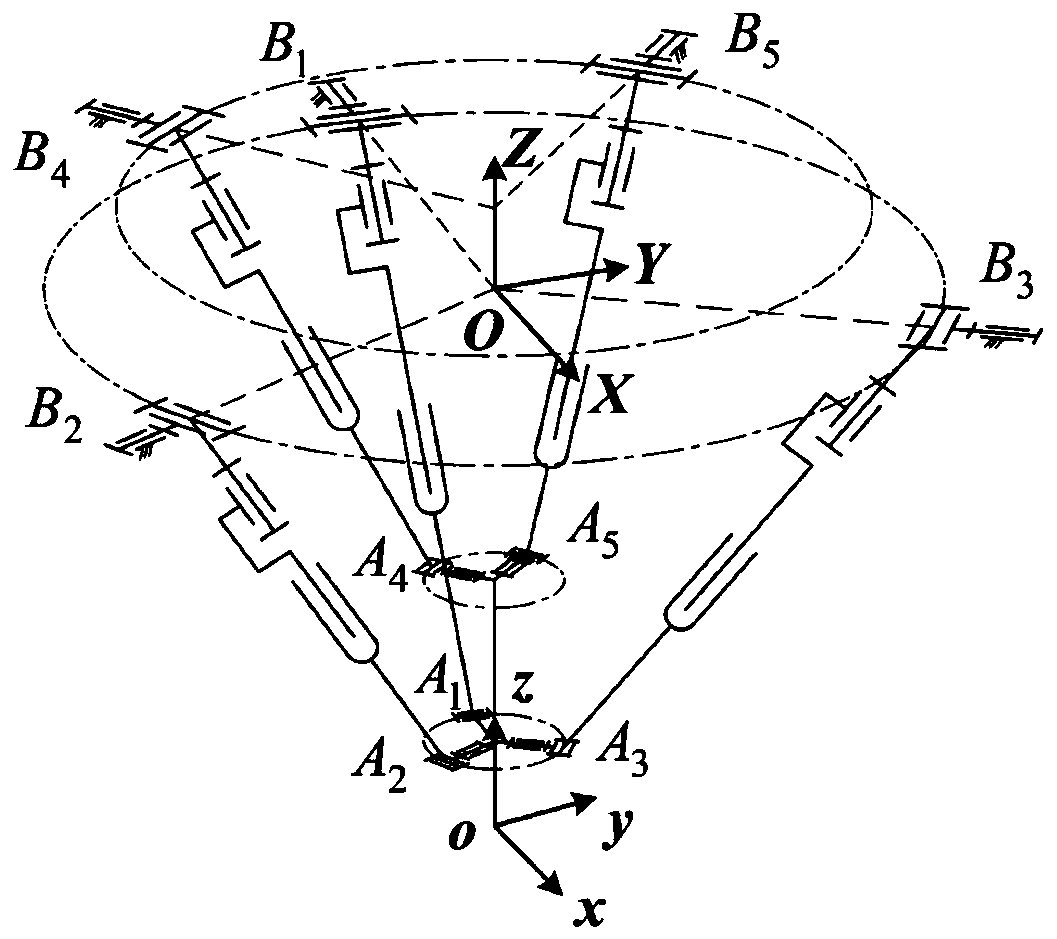
Inclination-angle-constraint-based kinematic calibration method for Stewart parallel robot
InactiveCN102152307AAvoid difficultiesHigh degree of automationProgramme-controlled manipulatorAdaptive controlLeast squaresKinematic calibration
The invention discloses an inclination-angle-constraint-based kinematic calibration method for a Stewart parallel robot. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, theoretically establishing a novel kinematic constraint, which is an inclination angle constant constraint, namely keeping two inclination angles of a motion platform of the Stewart parallel robot relative to a horizontal plane constant group by group; secondly, using a servo regulating way to physically realize the established kinematic constraint in a high-precision way; thirdly, establishing a calibration model on the basis of a principle of least square according to the kinematic constraint; and finally, identifying a model parameter by solving a nonlinear least square optimizing problem and compensating for the model parameter in a robot control software. By making full use of a characteristic that a repeating precision of a measuring instrument is superior to a position measuring precision of the measuring instrument, the method has the advantages of good calibration effect, simple measurement, high automatism in the calibrating process and the like.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
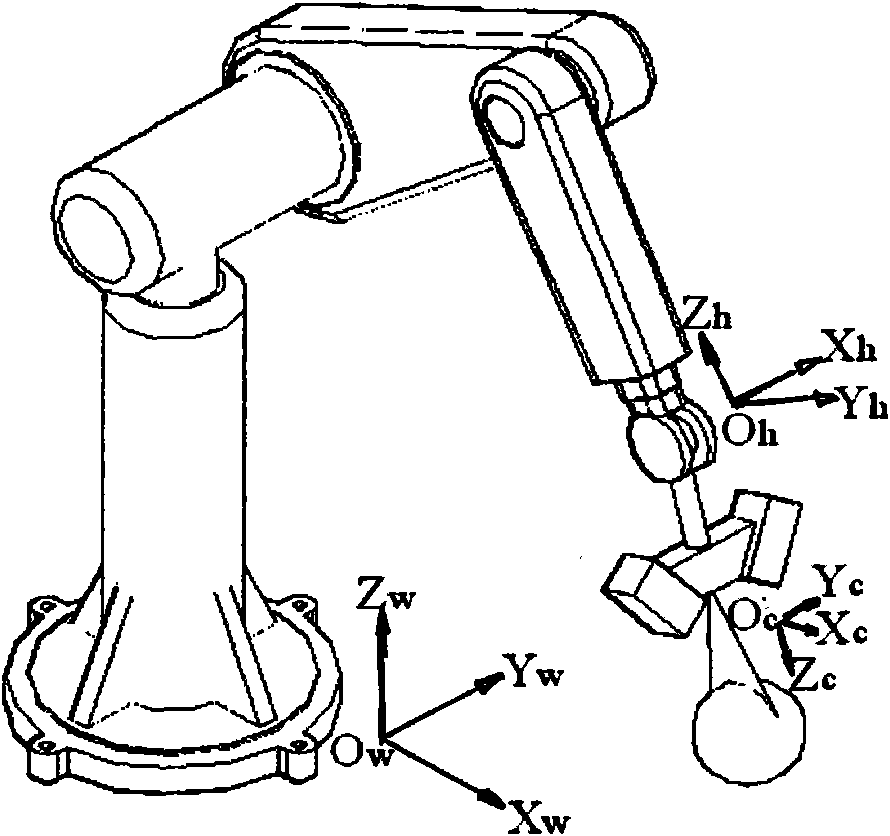
Device and method for kinematic calibration of robots
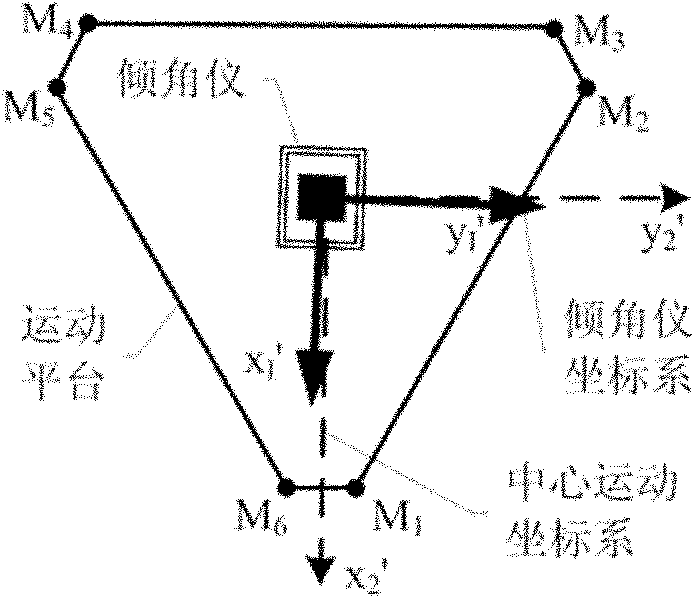
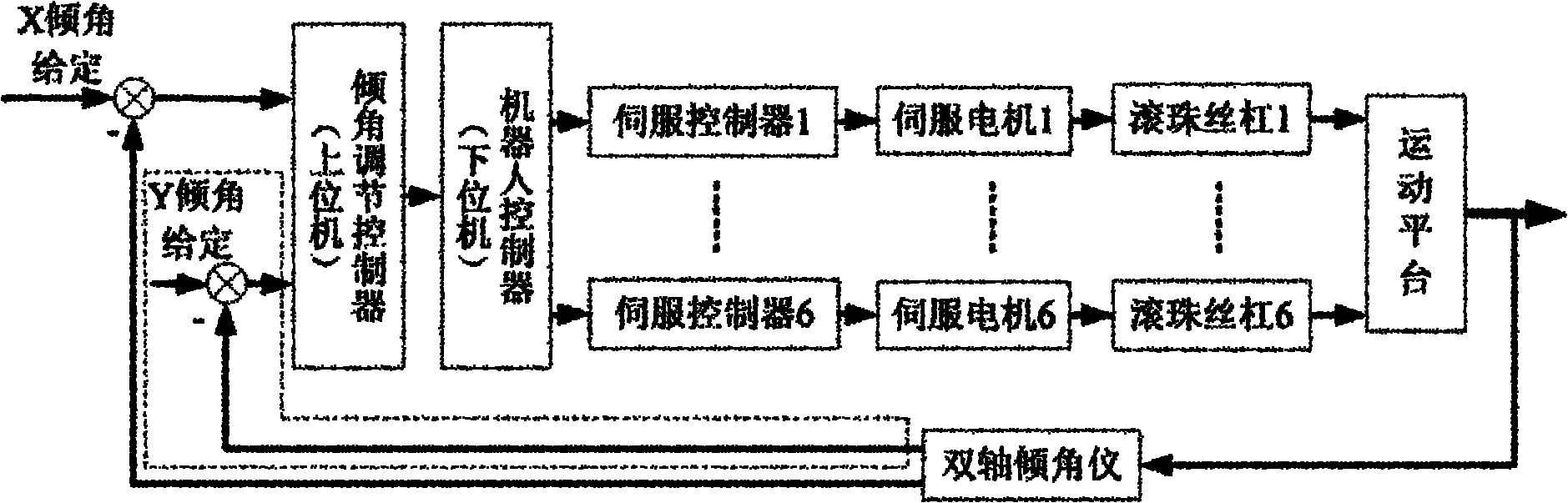
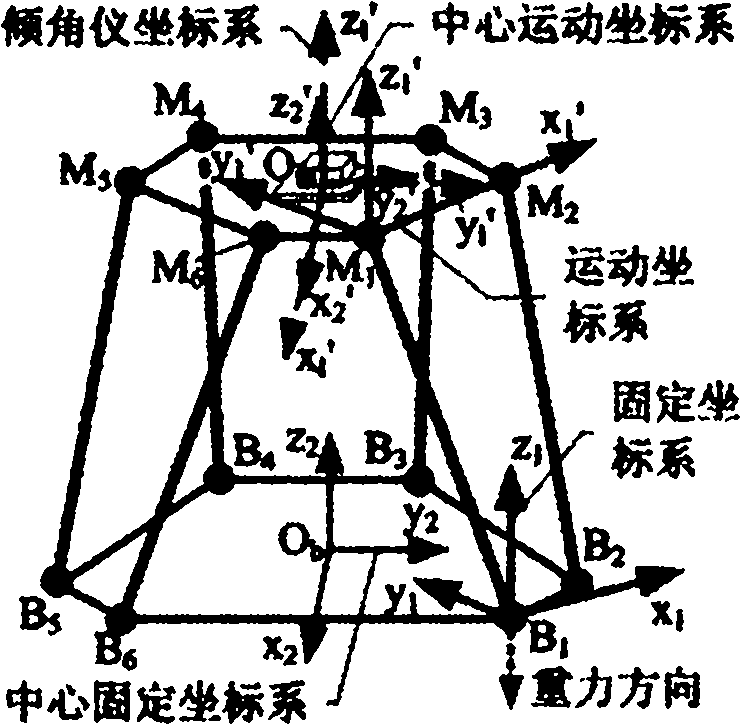
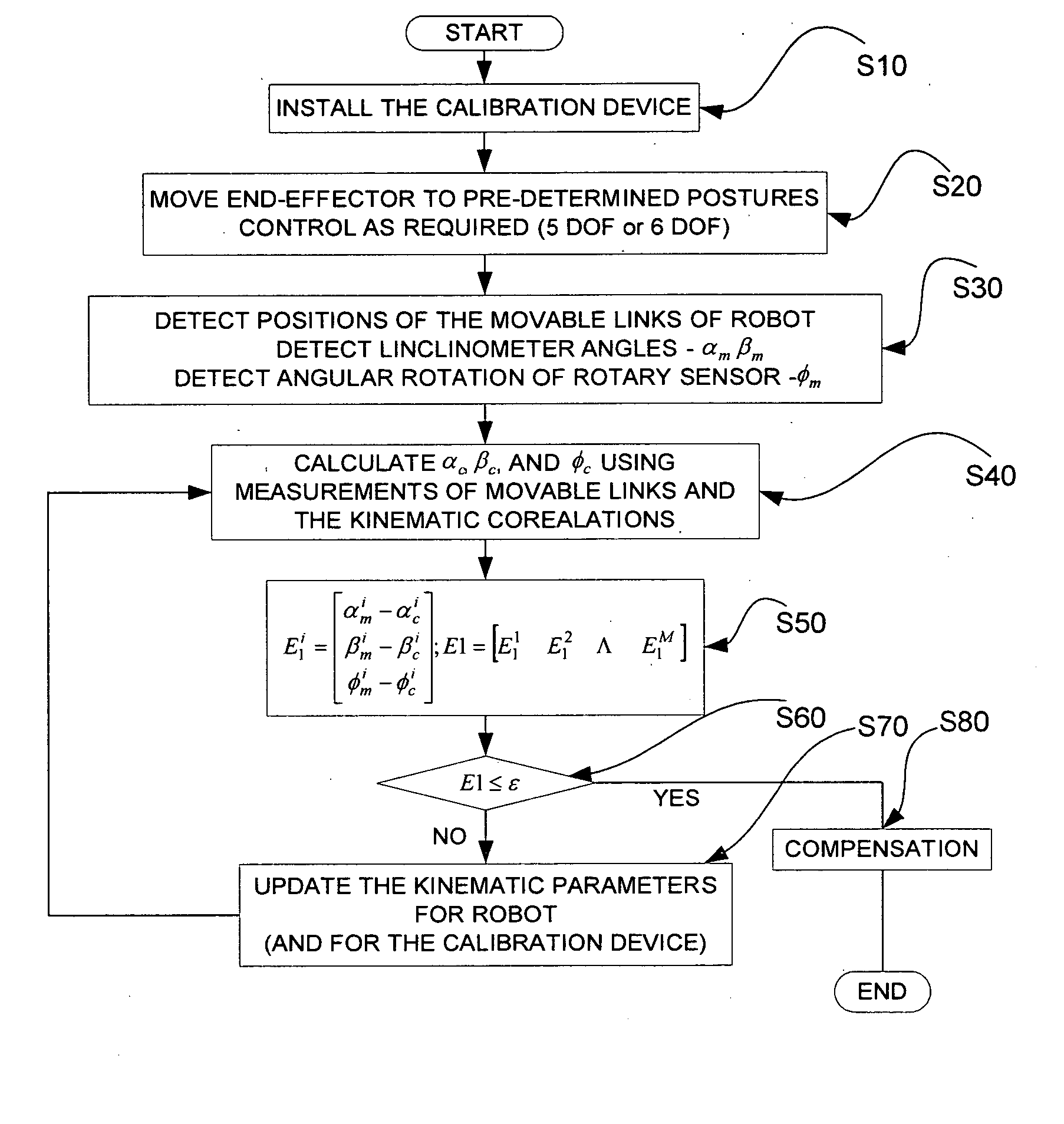
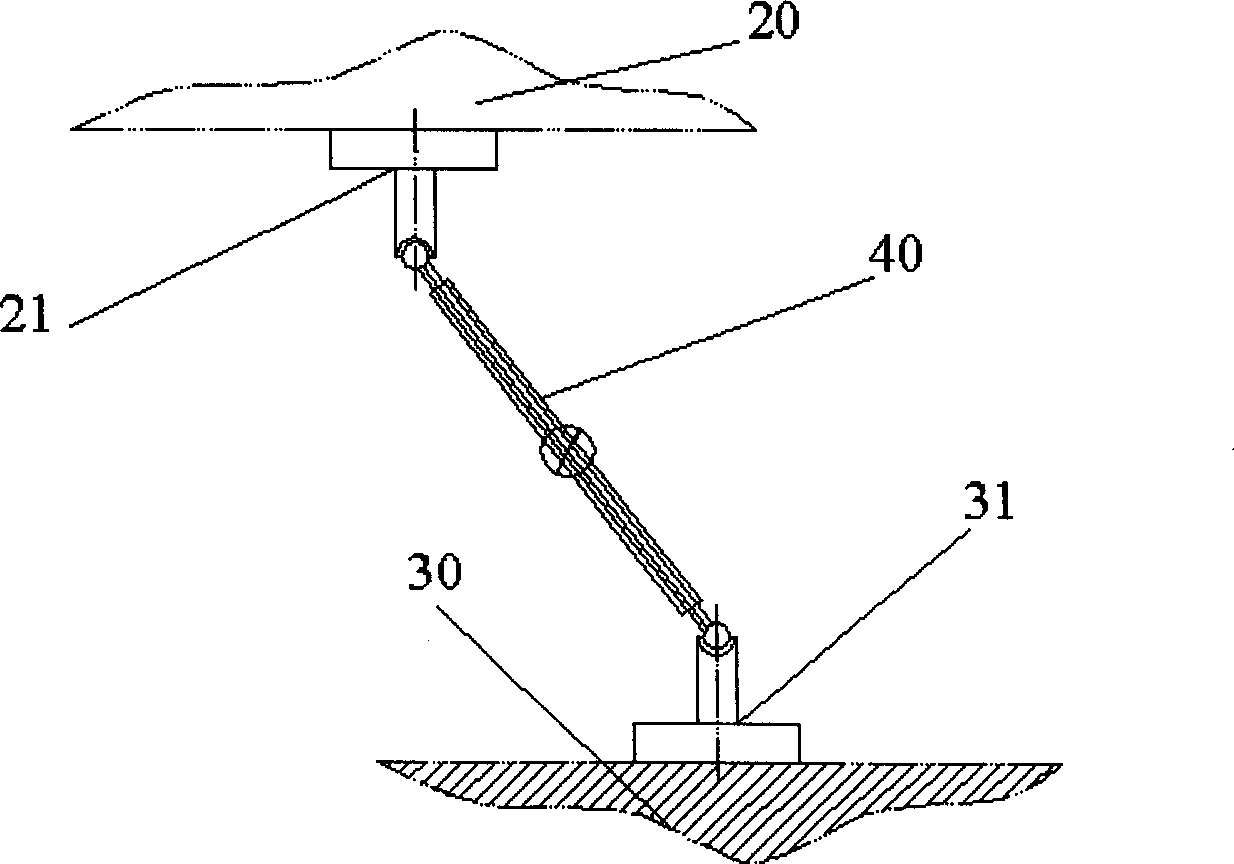
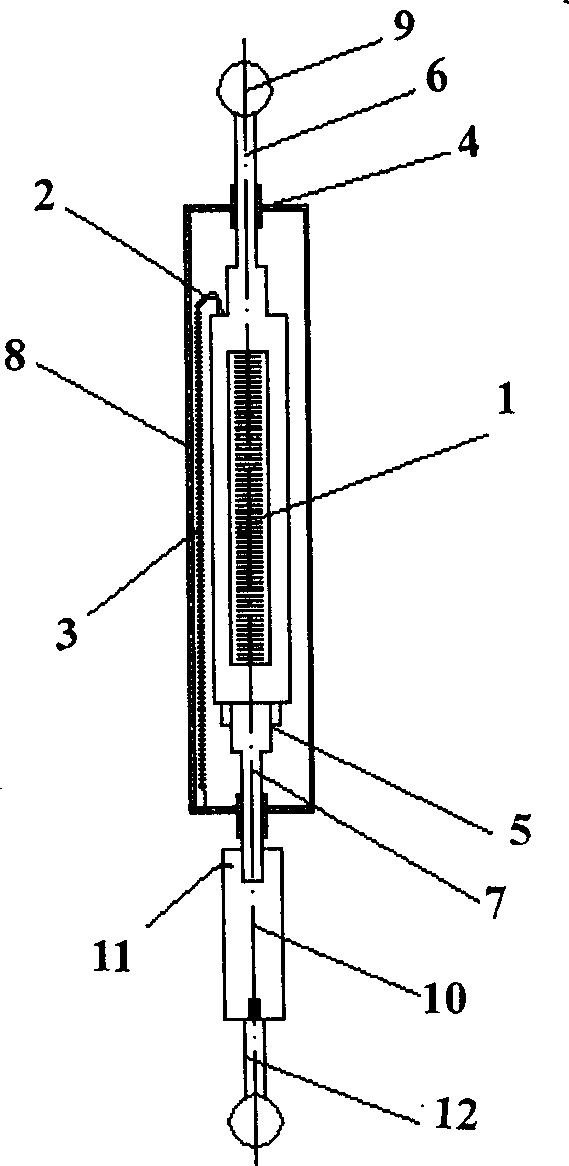
The present invention provides a device for kinematic calibration of a robot, comprising a supporting member fixed to the base of a robot; a constraint link installed between the supporting member and an end-effector of the robot connected to the base of the robot through a plurality of movable links so as to constrain a distance between the base and the end-effector of the robot; two joints installed at the constraint link; a mean to detect angular rotation for measuring angular rotation of the end-effector when the end-effector of the robot moves to a predetermine posture; a mean to detect inclination of the constrain link installed at the constraint link about two mutually perpendicular axes for measuring inclination of the constraint link about X and Y axes; a mean to detect variation of the length for measuring variation of length of the constraint link.
Owner:GWANGJU INST OF SCI & TECH
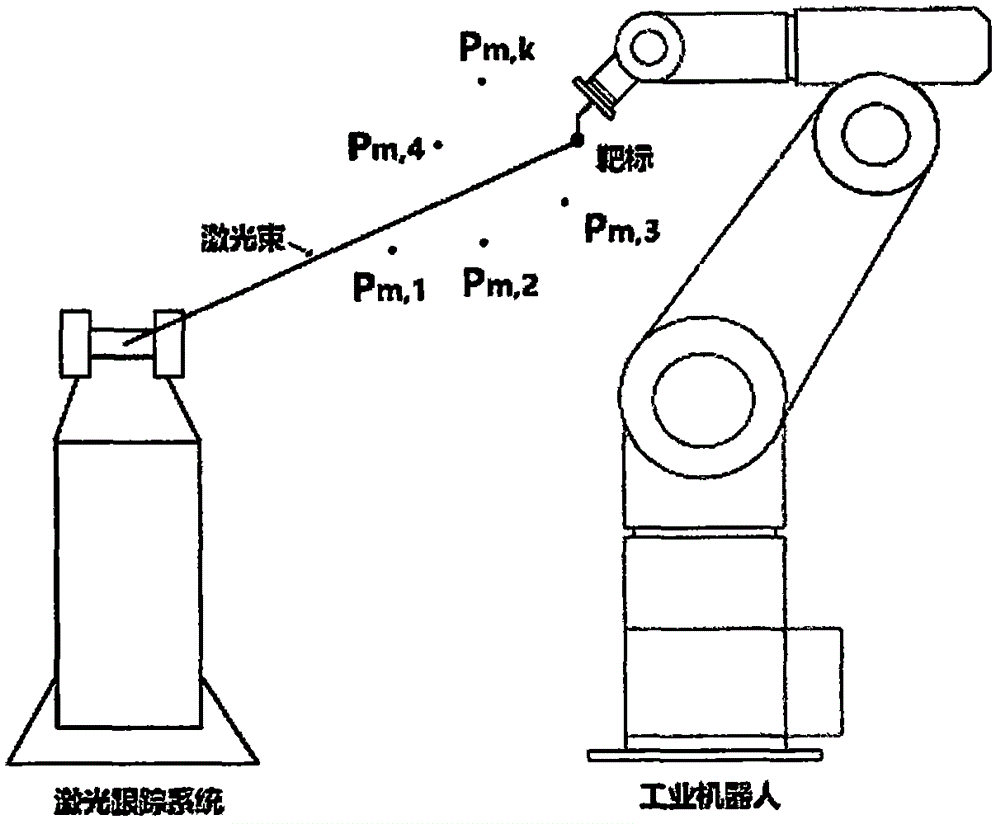
Kinematic calibration system and method for industrial robot
The invention discloses a kinematic calibration system and method for an industrial robot. The kinematic calibration system comprises measurement targets placed in a working area, a robot and an end effector arranged on the robot, as well as a computer, wherein the computer is provided with a first receiving module for reading joint angle data of the robot, a second receiving module for reading detection data of three displacement sensors, a first computation module for computing the nominal coordinate positions of the measurement targets according to data of both the first receiving module and the second receiving module, and a second computation module for computing compensation data of the robot according to the difference between the nominal distance of the measurement targets and the actual distance. The kinematic calibration system can not only correct kinematic parameters of the robot to improve the absolute positioning accuracy of operation but also calibrate the relative position relationship between a workpiece and a base of the robot, is very low in cost and simple and convenient to operate, and can be widely applied to middle and small-sized enterprises.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Industrial robot kinematics calibration system and calibration method
The invention relates to an industrial robot kinematics calibration system. The industrial robot kinematics calibration system comprises a measuring device arranged at the tail end of a robot and further comprises a calibration device and a data processing device which are arranged in the robot work space. According to the device, cost is reduced, carrying and using are convenient, and the devicecan be applied to online rapid calibration of a robot on the work site. A measuring coordinate system is established on the measuring device, and the robot is calibrated; and through a method, calibration of robot body geometric parameter errors, and the conversion relation among a robot coordinate system, the measuring coordinate system and a calibration coordinate system can be achieved at the same time.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
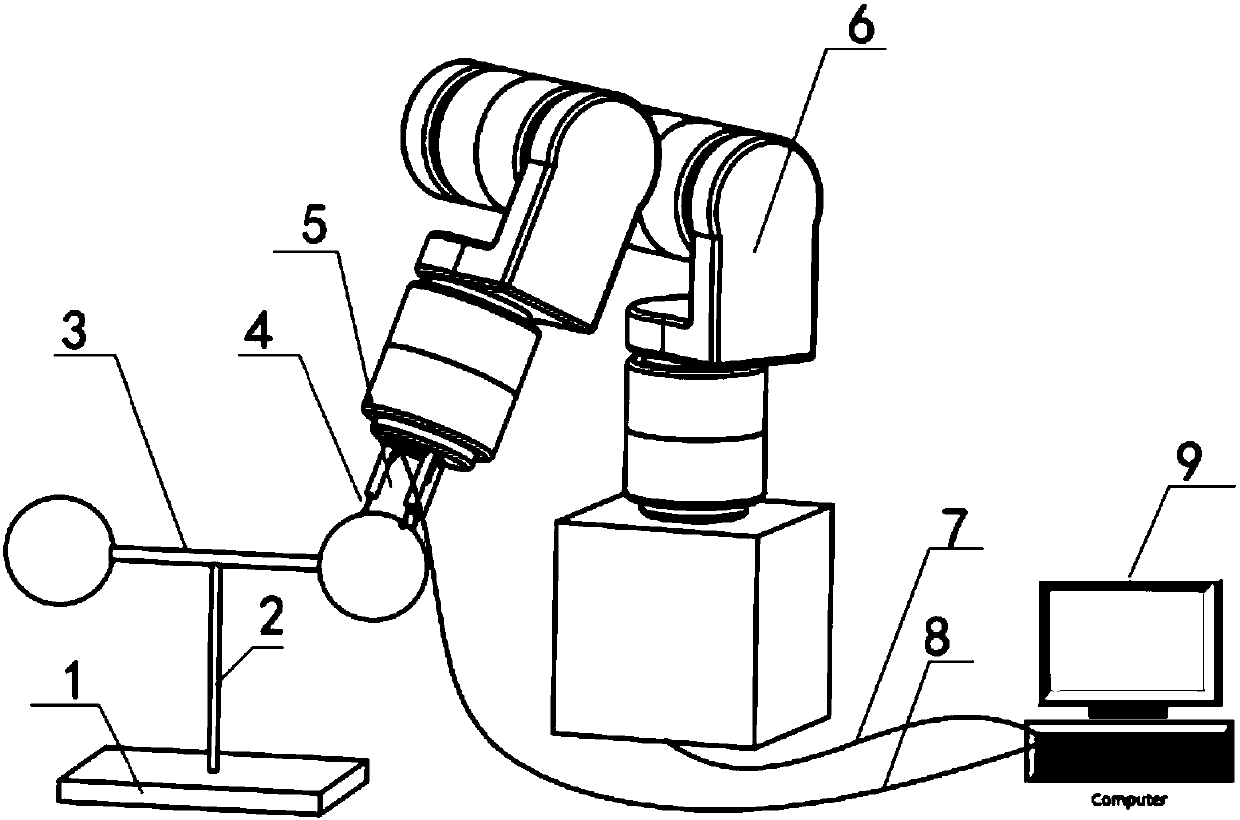
Kinematics calibration method of measurement robot
InactiveCN101660904AEasy to operateHigh precisionUsing optical meansKinematic calibrationEngineering
The invention relates to a kinematics calibration method of a measurement robot; the method mainly aims at computing kinematics parameter error of an industrial robot with a distance-measurement sensor; the method comprises a distance-measurement sensor, an industrial robot and a sphere with known radius, wherein the distance-measurement sensor is arranged at the end of the industrial robot, the sphere with known radius is used as a target and is arranged in a measurable range of a measuring head; the steps of kinematics parameter calibration are: firstly, the robot drives the sensor to measure spherical surface with more than seven poses, measurement data and pose data of the robot are recorded, and then, a centered spherical surface that measurement data is converted to a base coordinatesystem of the robot and spherical radius fixation are taken as a constraint condition, the kinematics parameter error of the robot is computed by nonlinear optimization, so as to realize simultaneouscalibration of a kinematics model and connecting relation of the sensor and the robot.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Method and device for measuring position and attitude in space
InactiveCN1346964ALow priceEasy to realize full digital measurementUsing optical meansFixation pointMeasurement device
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method for calibrating absolute precision of industrial robot based on PMPSD
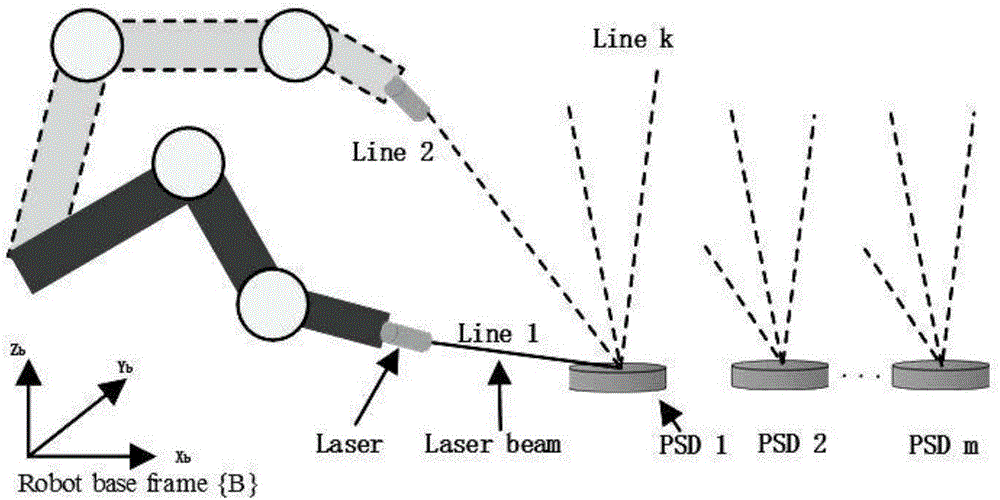
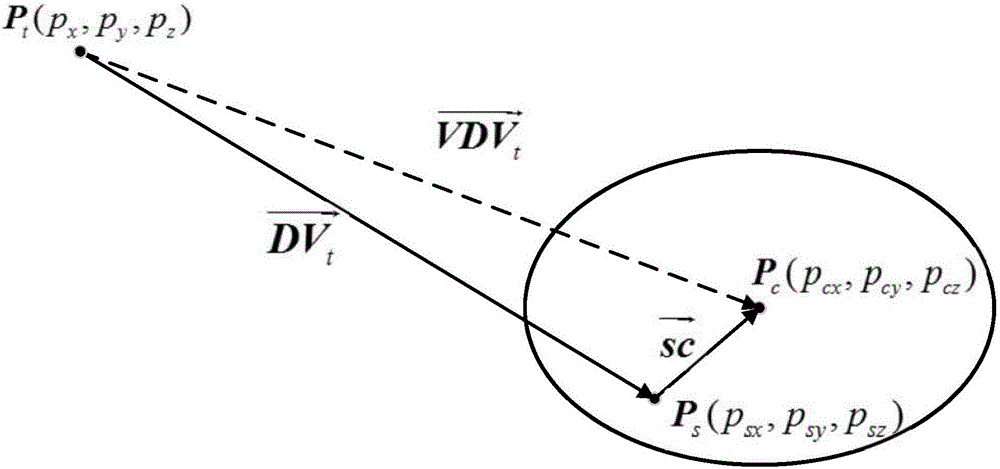
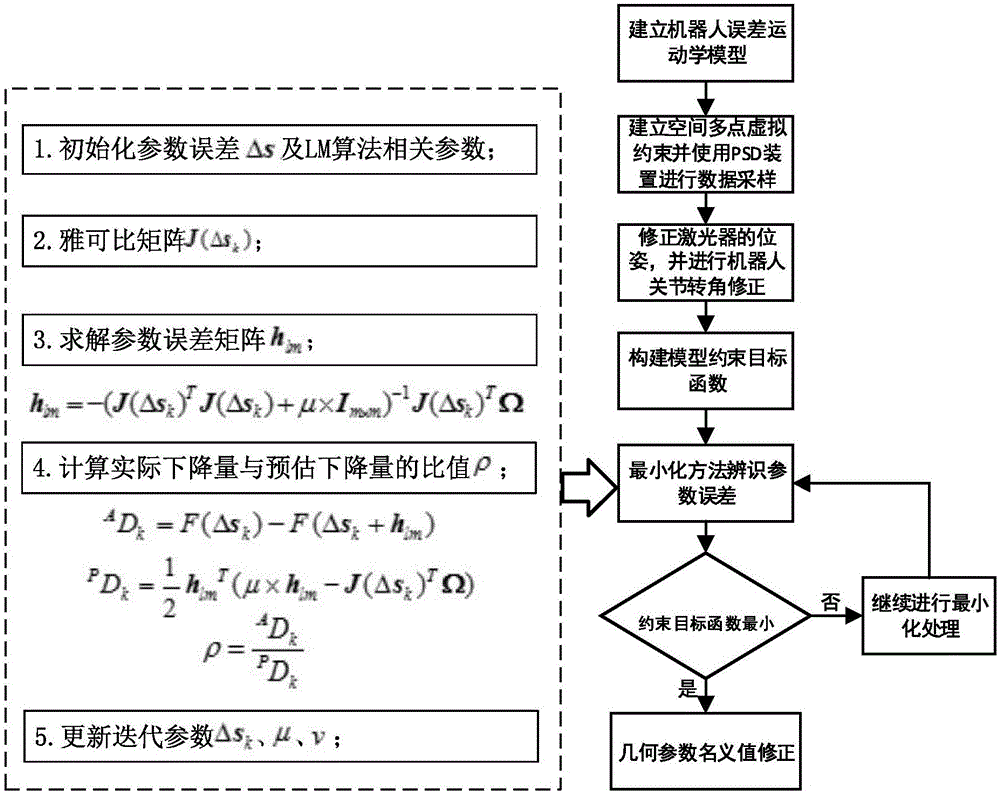
ActiveCN106777656AThe method is general and strongReduce calibration timeGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationKinematic calibrationJoints types
The invention discloses a method for calibrating the absolute precision of an industrial robot based on a PMPSD. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: establishing a robot error kinematic model, constructing a space multipoint virtual constraint, and carrying out data sampling by virtue of a PSD (Position Sensitive Detector); correcting a pose of a terminal laser of the robot by virtue of a space vector relation, correcting a joint corner of the robot by virtue of the corrected pose, and replacing a joint corner obtained from a robot demonstrator and a controller; constructing a model constraint target function, and optimizing the model constraint target function by virtue of a minimizing method, so as to obtain parameter errors of the industrial robot; and finally correcting a geometric parameter nominal value by virtue of the parameter errors, so as to finish the kinematic calibration and absolute precision correction of the industrial robot. By virtue of the method for calibrating the absolute precision of the industrial robot based on the PMPSD, the error problems caused by utilizing a PSD feedback control strategy and coordinate conversion are avoided; and the method is applicable to series-connection joint type robots and plant joint type robots.
Owner:湖州菱创科技有限公司
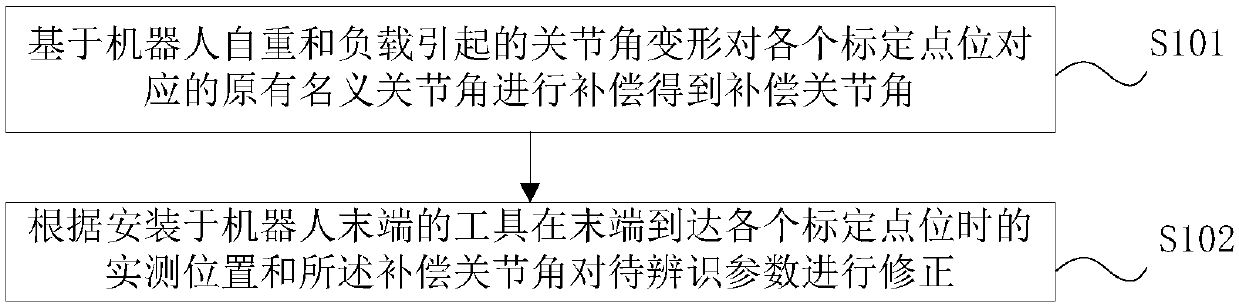
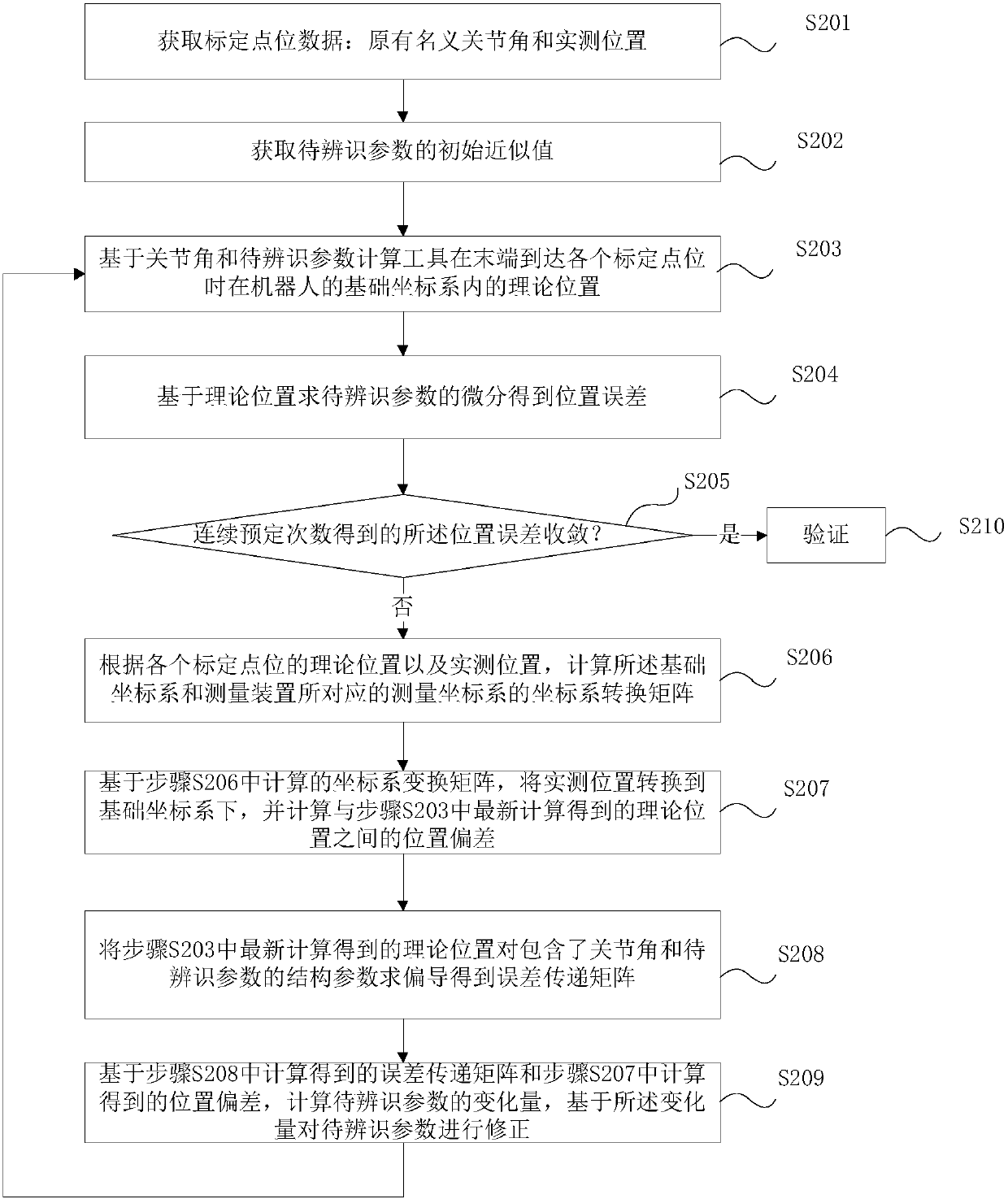
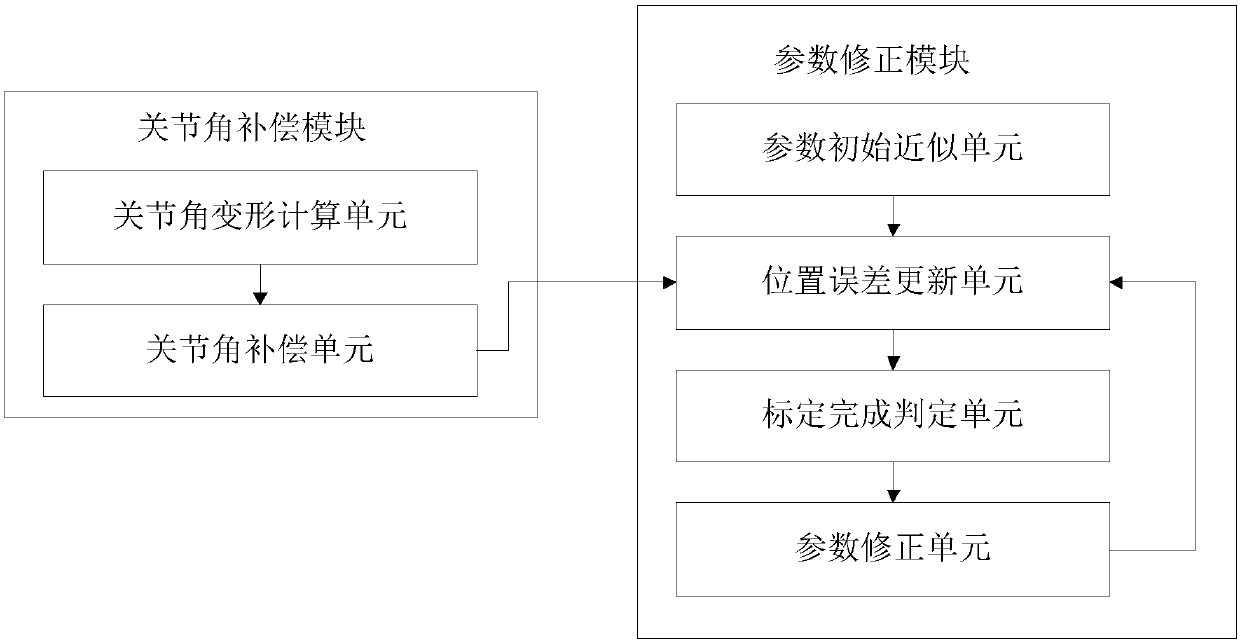
Dead weight and load deformation compensation based robot calibration method and system
ActiveCN108406768AImprove absolute positioning accuracyProgramme-controlled manipulatorKinematicsKinematic calibration
The invention discloses a dead weight and load deformation compensation based robot calibration method and a system. The method comprises the following steps that original nominal joint angles corresponding to each calibration point position are compensated to obtain compensation joint angles on the basis of joint angle deformation caused by the dead weight and load of the robot; according to theactual measured position obtained when a tool installed the tail end of the robot reaches each calibration point position at the tail end and compensation joint angles, to-be-identified parameters arecorrected. According to the method and the system, the original nominal joint angles corresponding to each calibration point position are compensated based on the joint angle deformation caused by the dead weight and load of the robot, the compensation joint angles are adopted instead of the non-original nominal joint angles in the calibration process, so that the calibration process reduces theinfluence on absolute positioning precision caused by the dead weight and load of the robot; and compared with a kinematic calibration algorithm, the absolute positioning precision of the robot can begreatly improved, and the absolute positioning precision of an industrial robot can be greatly improved.
Owner:汇川技术(东莞)有限公司
Kinematic calibration method for Stewart parallel robot
ActiveCN110815206AEasy to operateFriendly interfaceProgramme-controlled manipulatorAlgorithmNonlinear systems of equations
The invention relates to a kinematic calibration method for a Stewart parallel robot. According to the kinematic calibration method for the Stewart parallel robot, model simplification is achieved according to a coordinate system establishment rule to obtain a minimum to-be-identified parameter set, and then a nonlinear kinematic model of the parallel robot is obtained; any fixed measurement equipment and any three fixed target point are adopted, and the posture of a robot fixing platform relative to a measurement coordinate system, the positions of the target points relative to a movable robot platform coordinate system, and the like are used as to-be-identified parameters, so that a simple measurement process is achieved, and operation is easy; the nonlinear kinematic model of the parallel robot is combined with a measurement process model to obtain a nonlinear identification model of a whole calibration system; and the resolution of a nonlinear equation system is converted into theresolution of a nonlinear optimization problem. By the adoption of the kinematic calibration method for the Stewart parallel robot, model establishment is achieved through the complete minimum parameter set, model calibration is easier, and true parameters of the robot are directly resolved on the basis of a nonlinear optimization idea; and the kinematic calibration method has the advantages thatoperation is easy, user interfaces are friendly, and the practicability is high.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
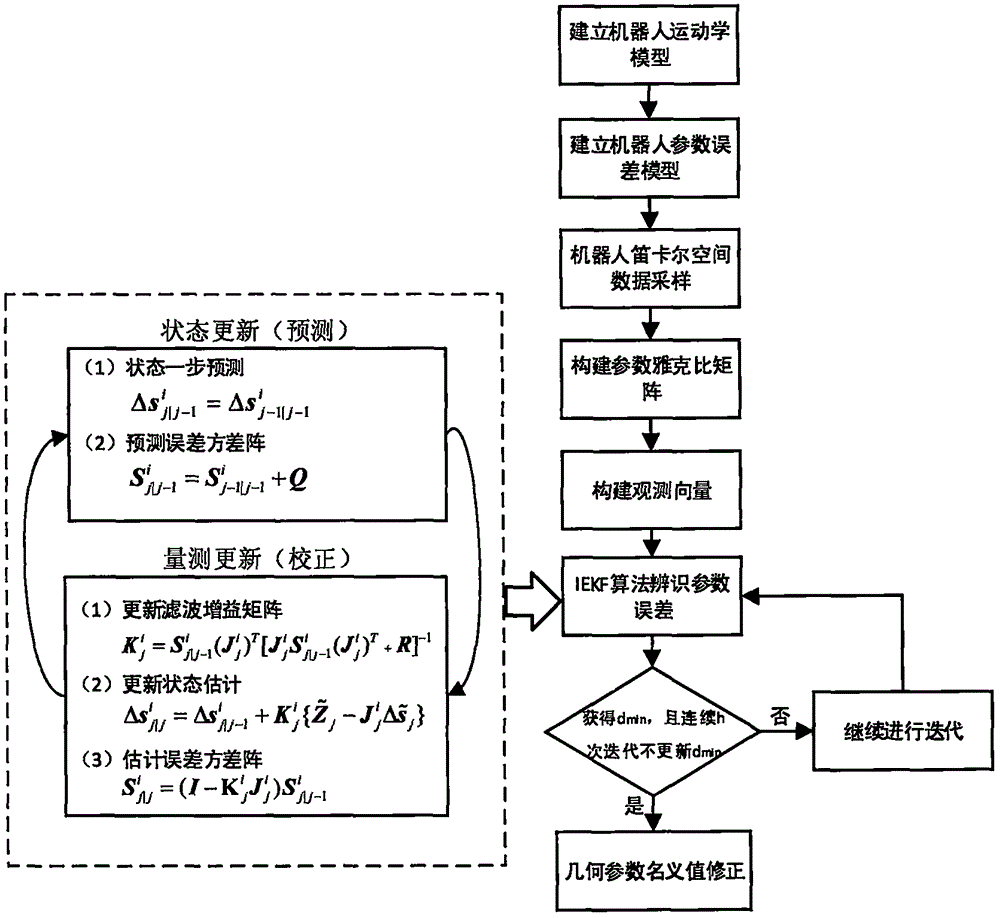
Industrial robot absolute accuracy calibrating method based on IEKF
ActiveCN105773622AThe method is general and strongLess valid dataProgramme-controlled manipulatorAlgorithmKinematic calibration
The invention discloses an industrial robot absolute accuracy calibrating method based on IEKF. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: a parameter error model is built, and a laser tracking system is used for sampling data in a robot terminal position in a Cartesian space to obtain position errors under different coordinates; geometric parameter nominal values are used for building a kinetic model of a robot, and parameter vectors to be identified are built by combining with a vector product method to obtain a parameter Jacobian matrix; and parameter errors in the parameter error model are identified by using an IEKF algorithm, and parameter errors of the robot are obtained through iterative computation. Finally, the parameter errors are used for correcting the geometric parameter nominal values to finish kinematic calibration of the industrial robot so as to realize absolute accuracy calibration of the robot. The robot absolute accuracy calibrating method based on IEKF, provided by the invention, is suitable for any serial joint robot and any plane joint robot.
Owner:湖州菱创科技有限公司
Kinematics calibration method for series-parallel robot
ActiveCN108015808AImprove recognition accuracyImprove stabilityDesign optimisation/simulationManipulatorGeometric errorKinematics
The invention discloses a kinematic calibration method for a series-parallel robot. The kinematic calibration method comprises the following steps that 1, a series-parallel robot geometric error modelis established based on a rotational amount theory; 2, the pose error of the tail end of the series-parallel robot is obtained based on the spatial position detection information of the laser tracker; 3, a geometric error source is identified on the basis of a Liu estimation method; and 4, error compensation is carried out step by step based on a correction controller output method. The kinematiccalibration method has the advantages of being high in precision and efficiency, convenient for industrial field application, and can be implemented on the basis of the robot tail end full-dimensional or few-dimensional pose error detection information; and according to the kinematic calibration method, an error model capable of meeting the completeness, the minimum and the continuity is established, the physical significance of model variables is definite, the ill-posed problem of the identification matrix is effectively solved, the identification precision of the error source and the stability of the identification result are improved, and therefore the compensation precision is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for kinematic calibration of six-degree-of-freedom robot based on monocular vision
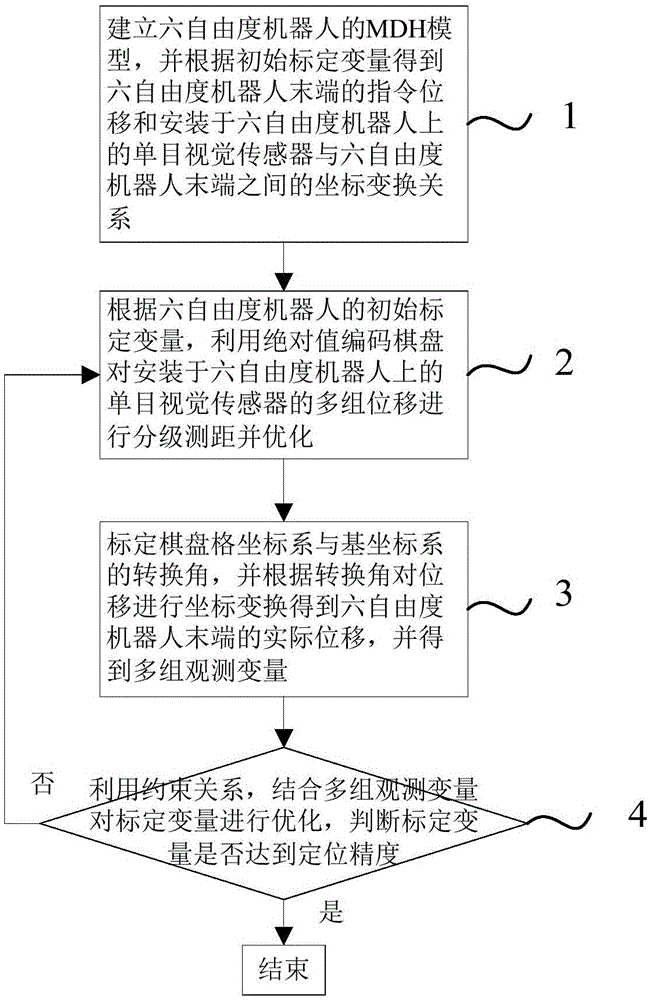
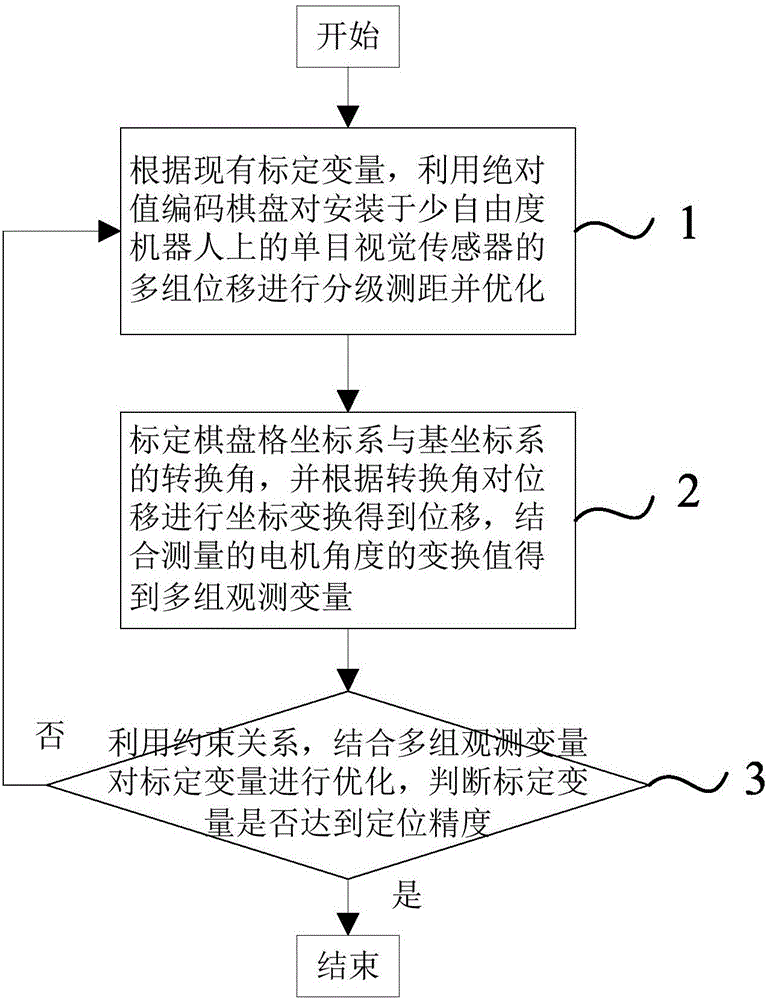
ActiveCN107175660AAccurate modelingImprove accuracyProgramme-controlled manipulatorImage analysisKinematicsKinematic calibration
The invention relates to a method for kinematic calibration of a six-degree-of-freedom robot based on monocular vision. The method comprises the steps that an MDH model of the six-degree-of-freedom robot is built, and instruction displacement of the tail end of the six-degree-of-freedom robot and the coordinate transformation relation (please see the formula in specifications) between a monocular vision sensor installed on the six-degree-of-freedom robot and the tail end of the six-degree-of-freedom robot are obtained according to an initial calibration variable U; according to the initial calibration variable U of the six-degree-of-freedom robot, grading ranging and optimizing are conducted on multiple sets of displacement delta' of the monocular vision sensor installed on the six-degree-of-freedom robot through an absolute value coding checkerboard; actual displacement delta of the tail end of the six-degree-of-freedom robot is obtained, and multiple sets of observed variables Vk are obtained; and the constraint relation is used, the multiple sets of observed variables Vk are combined to optimize the calibration variable U, whether the calibration variable U reaches positioning precision or not is judged, if yes, the kinematic calibration of the six-degree-of-freedom robot is completed, and otherwise, returning is conducted. Compared with the prior art, the method for the kinematic calibration of the six-degree-of-freedom robot based on the monocular vision has the advantages that ranging precision is high, practicability is high, and the cost is saved.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
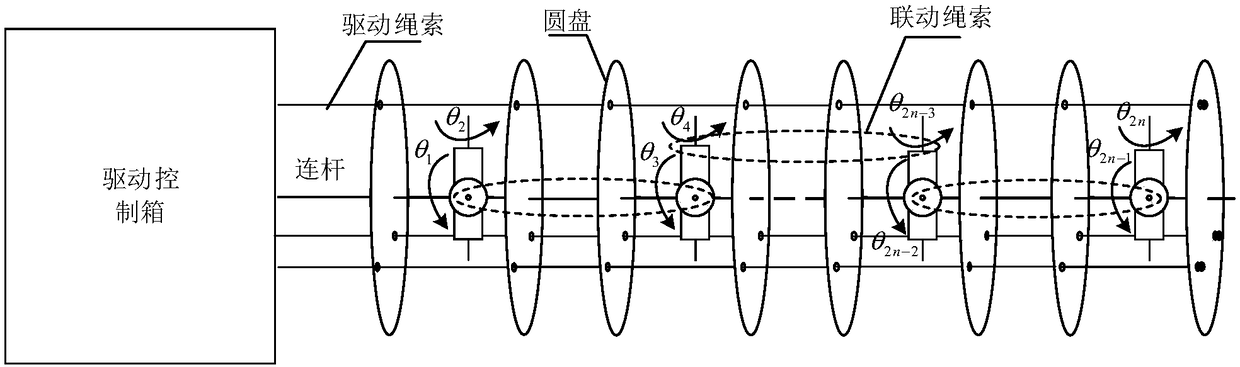
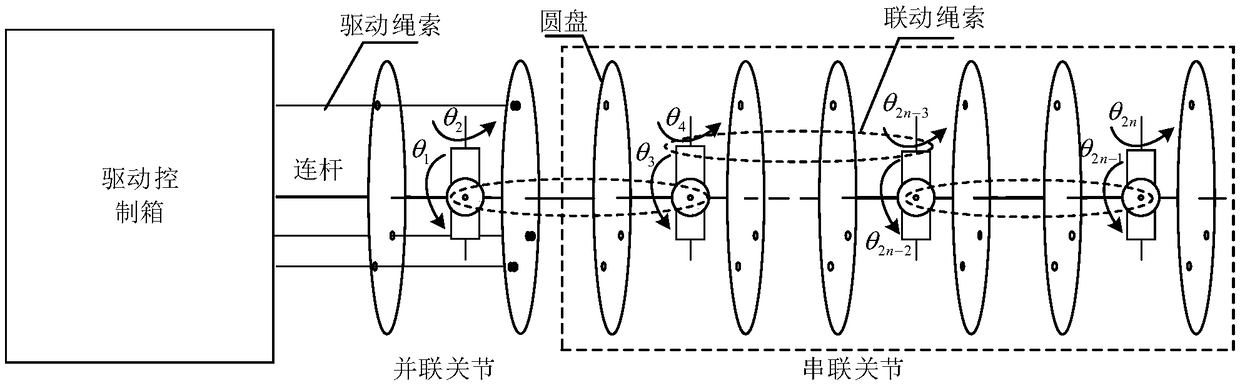
Kinematics calibration method and system for flexible robot
ActiveCN109176488AOvercome the technical problems of strong mutual coupling and low precision of parameter calibrationImprove calibration accuracyProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsKinematicsKinematic calibration
The invention discloses a kinematics calibration method and system for a flexible robot. The method comprises: obtaining the nominal position and posture of a linkage joint segment under zero linkageangle error according to the nominal joint angle of the linkage joint segment; driving the linkage joint segment to reach the nominal rope length of the linkage joint segment by using a parameter decoupling driving structure, obtaining the actual position and posture of the linkage joint segment, finally, obtaining the linkage angle error of the linkage joint segment according to the nominal position and posture of the linkage joint segment and the actual position and posture of the linkage joint segment; and obtaining the linkage angle error of the robot according to the linkage angle errorsof multiple linkage joint segments. The technical problem that the kinematics error parameters of the existing wire drive flexible robot are numerous, strong coupling between the parameters due to theseries-parallel structure, and the parameter calibration precision is low are overcome, and the calibration precision of the robot is improved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
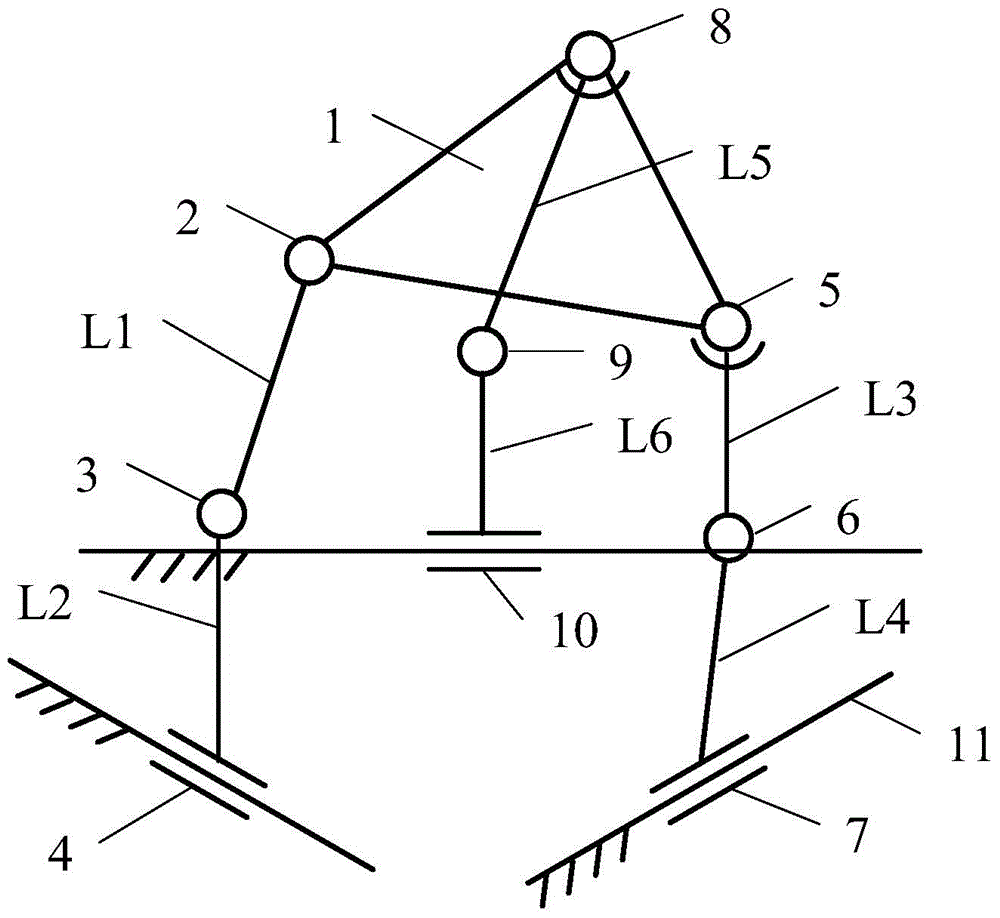
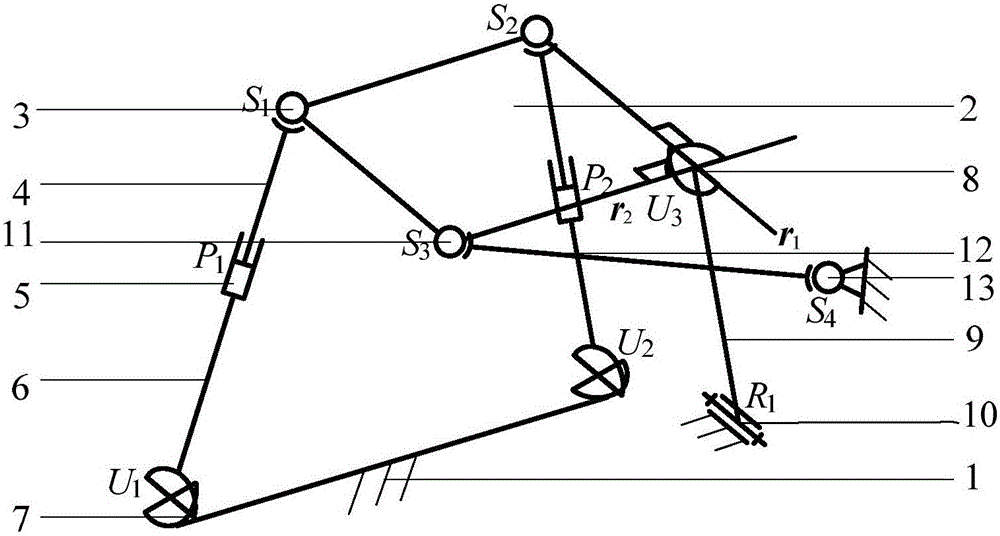
Two-degree-of-freedom rotational parallel mechanism with two continuous rotating axes
ActiveCN105856193AIncrease stiffnessEasy kinematic calibrationProgramme-controlled manipulatorKinematicsSingle degree of freedom
A two-degree-of-freedom rotational parallel mechanism with two continuous rotating axes comprises a fixed platform, a movable platform, and three branch chains which can connect the fixed platform with the movable platform, wherein the first branch chain and the second branch chain are both composed of upper connecting rods and lower connecting rods; the upper connecting rod and the lower connecting rod of the first branch chain are correspondingly connected to the movable platform and the fixed platform through a ball pair and a hook joint; the upper connecting rod and the lower connecting rod of the second branch chain are both connected to the movable platform and the fixed platform through a rotating pair; the upper connecting rods and the lower connecting rods of the two branch chains are connected through moving pairs; two ends of a connecting rod of a third branch chain are correspondingly connected to the movable platform and the fixed platform through the hook joint and the rotating pair; an axis of the rotating pair, connected to the movable platform, of the second branch chain, is overlapped with the axis of the rotating pair, connected to the movable platform through the hook joint, of the third branch chain; the axis of the rotating pair, connected to the fixed platform, of the second branch chain, is parallel to the axis of the rotating pair of the third branch chain. According to the mechanism, the two continuous rotating axes are provided, so that the kinematics calibration and control are easily achieved; in addition, few single-degree-of-freedom moving pairs are provided, so that the rigidity of the whole mechanism is high.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
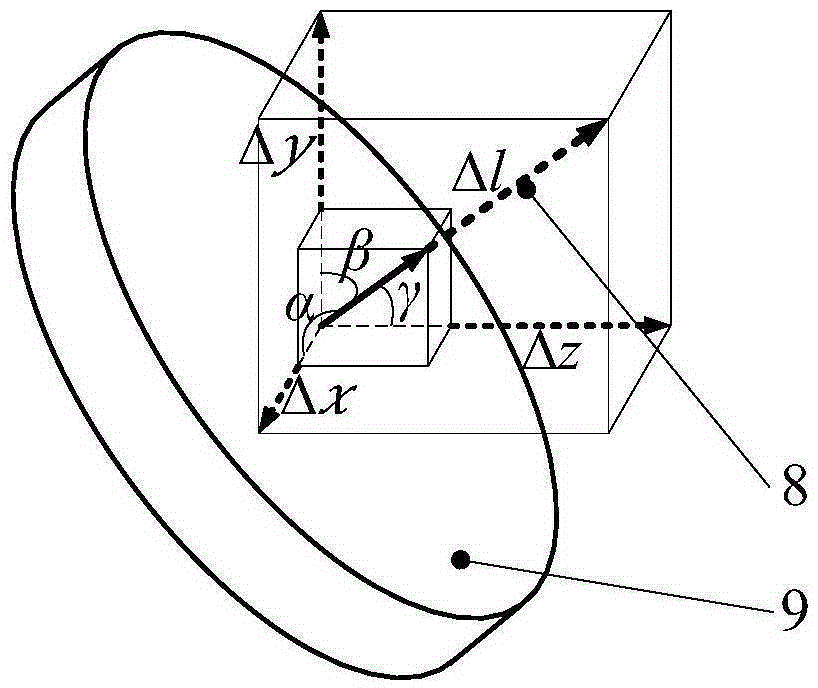
Random attitude measurement method for kinematic calibration of five-shaft hybrid machine tool
ActiveCN105404239AReduce cost of measurementReduced measurement timeProgramme controlComputer controlKinematicsKinematic calibration
The invention relates to a random attitude measurement method for kinematic calibration of a five-shaft hybrid machine tool. The five-shaft hybrid machine tool includes a machine tool work bench and a parallel main shaft head. The parallel main shaft head has two rotation freedom degrees and a translation freedom degree; and relative motion with two translation freedom degrees can be formed by the parallel main shaft and the machine tool work bench. The measurement method is characterized in that a dial indicator is fixed on a moving platform of the parallel main shaft head of the hybrid machine tool along a normal direction; gauge blocks are fixed on the machine tool work bench. The dial indicator extends a delta 1 range by controlling motion of the five-shaft hybrid machine tool, wherein the corresponding displacement of the dial indicator at directions of the three machine tool translation shafts including an X shaft, a Y shaft, and a Z shaft are delta x, delta y, and delta z; inverse cosine functions of ratios of the delta x, delta y, and delta z to a delta 1 are equal to included angles alpha, beta, and gamma between the normal direction of the moving platform and the X shaft, the Y shaft, and the Z shaft respectively, thereby obtaining a moving platform attitude. According to the measurement method, only the dial indicator and the gauge blocks are needed; and the method has characteristics of simple operation, and high economy and practicability. And a random attitude measurement value with high precision can be obtained.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Multi-freedom-degree parallel mechanism
InactiveCN104440879AFew jointsEasy to processProgramme-controlled manipulatorKinematic calibrationEngineering
The invention discloses a multi-freedom-degree parallel mechanism. The multi-freedom-degree parallel mechanism is composed of a motion platform, a fixed platform and three supporting chins connecting the two platforms. The motion platform of the parallel mechanism can achieve motion output of the three supporting chains, the mechanism is simple, machining and manufacturing are easy, a kinematics model is simple, so that kinematics calibration and control become easy. Meanwhile, the number of mechanism joints is small, and the structural rigidity is improved.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHITONG ENERGY SAVING ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Industrial robot step-by-step calibration system and method
PendingCN112847341ALow costLarge measuring rangeProgramme-controlled manipulatorTotal factory controlSimulationKinematic calibration
The invention discloses an industrial robot step-by-step calibration system and method. The calibration system comprises a tail end measuring device arranged on a robot flange, as well as a movable double-ball device, a fixed three-ball-seat device, a counter, a computer and the like which are matched with a robot. The calibration method comprises first-step calibration: calibrating kinematics parameters of the robot by using a wide-area distance error; and second-step calibration: based on the result of the first-step calibration, calibrating the pose of a robot-based coordinate system by using a position error. Furthermore, the calibration method can also comprise the following steps: firstly, calibrating the measurement error of the tail end measurement device; and then carrying out the first-step calibration and the second-step calibration. The calibration system has the advantages of being portable, low in cost and the like; meanwhile, the calibration method improves the precision and reliability of kinematics calibration, calibration of the robot-based coordinate system is achieved, then the absolute positioning precision of the robot is improved, and the application range of the robot in precision manufacturing is widened.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Three-support space mechanism with two same supports
InactiveCN104493811AFew jointsEasy to processProgramme-controlled manipulatorUniversal jointKinematic calibration
The invention discloses a three-support space mechanism with two same supports. The three-support space mechanism comprises a motion platform, a fixed platform and three support chains connecting the two platforms. The first support chain and the second support chain are identical in structure. Each of the first support chain and the second support chain comprises a universal joint pair, a rotation pair, a cylinder pair and connecting rods among the three pairs from the top to bottom. The third support chain comprises a universal pair, a rotation pair, a cylinder pair and connecting rods among the three pairs. The motion platform mechanism of a parallel robot mechanism is simple, kinematic model simpleness is achieved, kinematics calibration and related control are facilitated, and few mechanism joints and easiness in manufacturing are achieved at the same time.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHITONG ENERGY SAVING ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
2PRU (Pseudo-Random Upstream) and CRS (Central Reservation System) spatial parallel robot mechanism
InactiveCN104669251AFew jointsEasy to processProgramme-controlled manipulatorUniversal jointKinematic calibration
The invention relates to a 2PRU (Pseudo-Random Upstream) and CRS (Central Reservation System) spatial parallel robot mechanism. The 2PRU and CRS spatial parallel robot mechanism is formed by a motion platform, a fixed platform and three branch chains, wherein the three branch chains are used for connecting the motion platform and the fixed platform, the first branch chain and the second branch chain in the three branch chains are the same in structure and are respectively formed by a universal joint pair, a rotating pair, a moving pair and connecting rods among the universal joint pair, the rotating pair and the moving pair from top to bottom, and the third branch chain in the three branch chains is formed by a ball pair, a rotating pair, a cylinder pair and connecting rods among the ball pair, the rotating pair and the cylinder pair from top to bottom. According to the 2PRU and CRS spatial parallel robot mechanism disclosed by the invention, three movable motion output can be realized, the mechanism is simple, processing and manufacturing are easy, a kinematic model is simple, kinematic calibration and control can be easier, meanwhile, joints of the mechanism are less, and the structure rigidity is increased.
Owner:柳州市金旭节能科技有限公司
Lower-mobility robot kinematics calibration method based on monocular vision
ActiveCN106671081AImprove ranging accuracyImprove accuracyProgramme-controlled manipulatorKinematicsLow mobility
The invention relates to a lower-mobility robot kinematics calibration method based on monocular vision. The calibration method comprises the steps that according to existing calibration variable U, an absolute value coding chessboard is utilized for carrying out grading distance measuring and optimizing on multiple sets of displacement delta` of a monocular vision sensor installed on a lower-mobility robot; a conversion angle alpha between a checker coordinate system and a base coordinate system is calibrated, coordinate conversion is carried out on the displacement delta` according to the conversion angle alpha, the displacement delta is obtained, and multiple sets of observation variables Vk are obtained in combination with a conversion value of the motor angle theta; the constraint relation is utilized and combined with the multiple sets of observation variables Vk to optimize the calibration variable U to judge whether the variable U reaches location precision or not, if yes, kinematics calibration of the lower-mobility robot is completed, and if not, measurement is carried out again. Compared with the prior art, the method has the beneficial effects of being high in distance measuring precision of the monocular vision sensor and high in practicality and saving cost.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
2PR and PRS spatial parallel robot mechanism
InactiveCN104858857AFew jointsEasy to processProgramme-controlled manipulatorKinematic calibrationEngineering
The invention relates to a 2PR and PRS spatial parallel robot mechanism. The 2PR and PRS spatial parallel robot mechanism comprises a moving platform, a fixed platform and three branch chains for connecting the two platforms; the first branch chain and the second branch chain in the three branch chains are the same in structure, and each of the first branch chain and the second branch chain comprises a revolute pair, a sliding pair and a connecting rod therebetween from the top down; the third branch chain in the three branch chains comprises a ball pair, a revolute pair, a sliding pair and connecting rods among the ball pair, the revolute pair and the sliding pair. According to the 2PR and PRS spatial parallel robot mechanism, three mobile movement output can be realized, the mechanism is simple, the processing and the manufacturing are easy, and the kinematic model is simple and can enable kinematic calibration and control to be easy; meanwhile, the mechanism is less in joint, so that the structural rigidity is improved.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHITONG ENERGY SAVING ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Four-branch-chain and two-degree-of-freedom rotary parallel mechanism with two continuous rotating axes
A four-branch-chain and two-degree-of-freedom rotary parallel mechanism with two continuous rotating axes comprises a fixed platform, a movable platform and four branch chains for connecting the fixed platform with the movable platform, wherein the first branch chain and the second branch chain are of the same structure; one end of each upper connection rod of the first branch chain and the second branch chain is connected with the movable platform through a sphere pair; one end of each lower connection rod of the first branch chain and the second branch chain is connected with the fixed platform through a hook joint; each upper connection rod and the corresponding lower connection rod are connected through a movable pair; the two ends of the third branch chain are connected with the movable platform and the fixed platform through a hook joint and a rotary pair correspondingly, and the axis of the rotary pair is parallel with the axis, close to the fixed platform of the hook joint; and the two ends of a connection rod of the fourth branch chain are connected with the movable platform and the fixed platform through sphere pairs. The axis, close to the fixed platform, of the hook joint of the third branch chain is connected with the center of the sphere pair of the fixed platform through the fourth branch chain, and the axis, connected with the movable platform, of the hook joint is connected with the center of the sphere pair of the movable platform through the fourth branch chain. The mechanism is provided with four supporting branches and can bear large loads, and as the two continuous rotating axes exist, the kinematic calibration and control are easy to implement.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
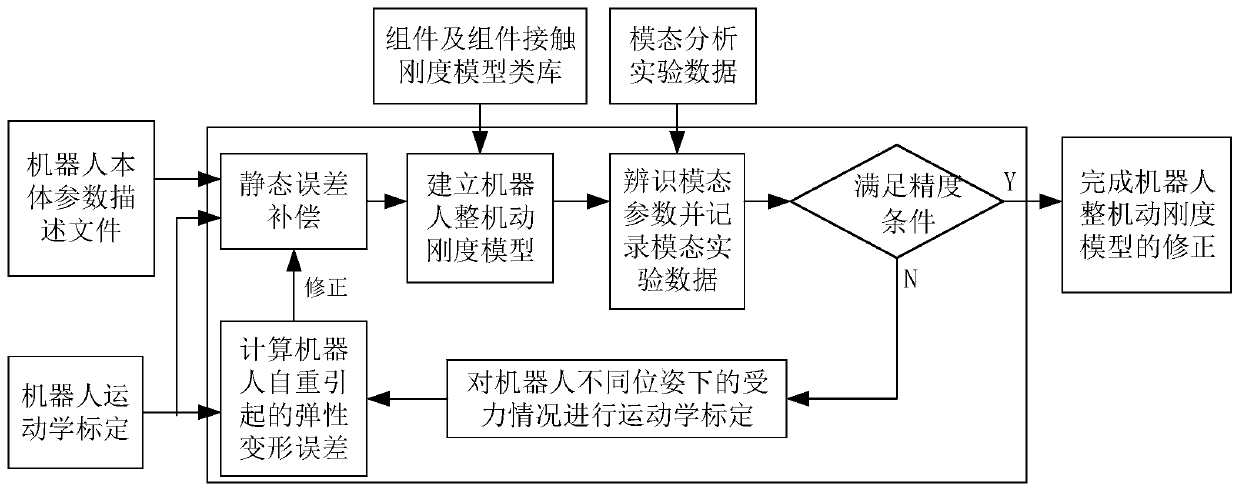
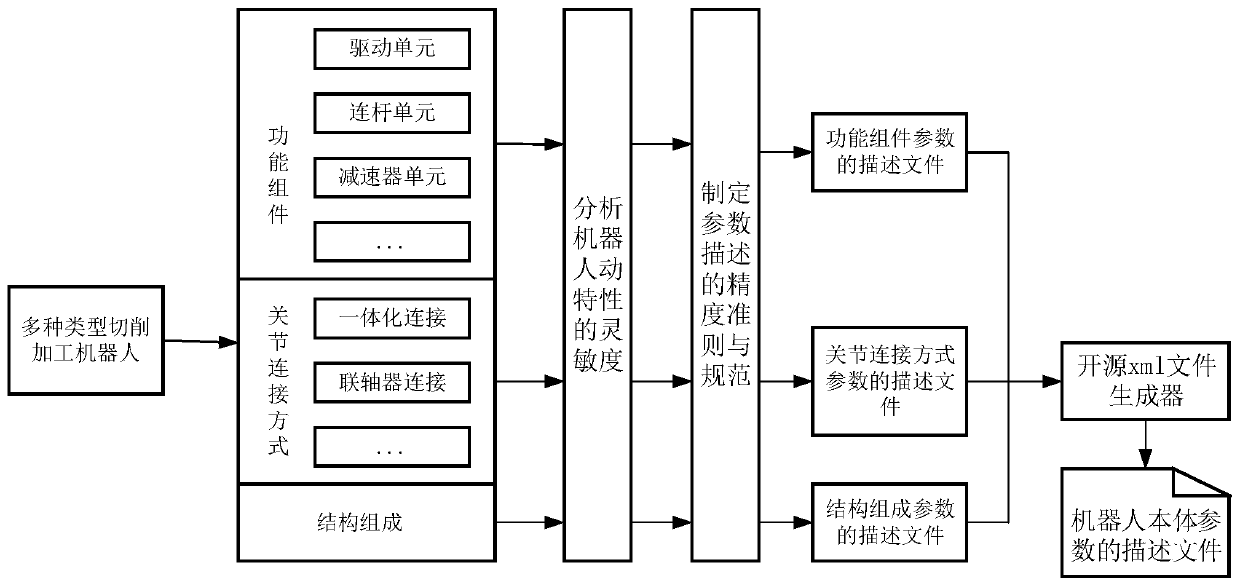
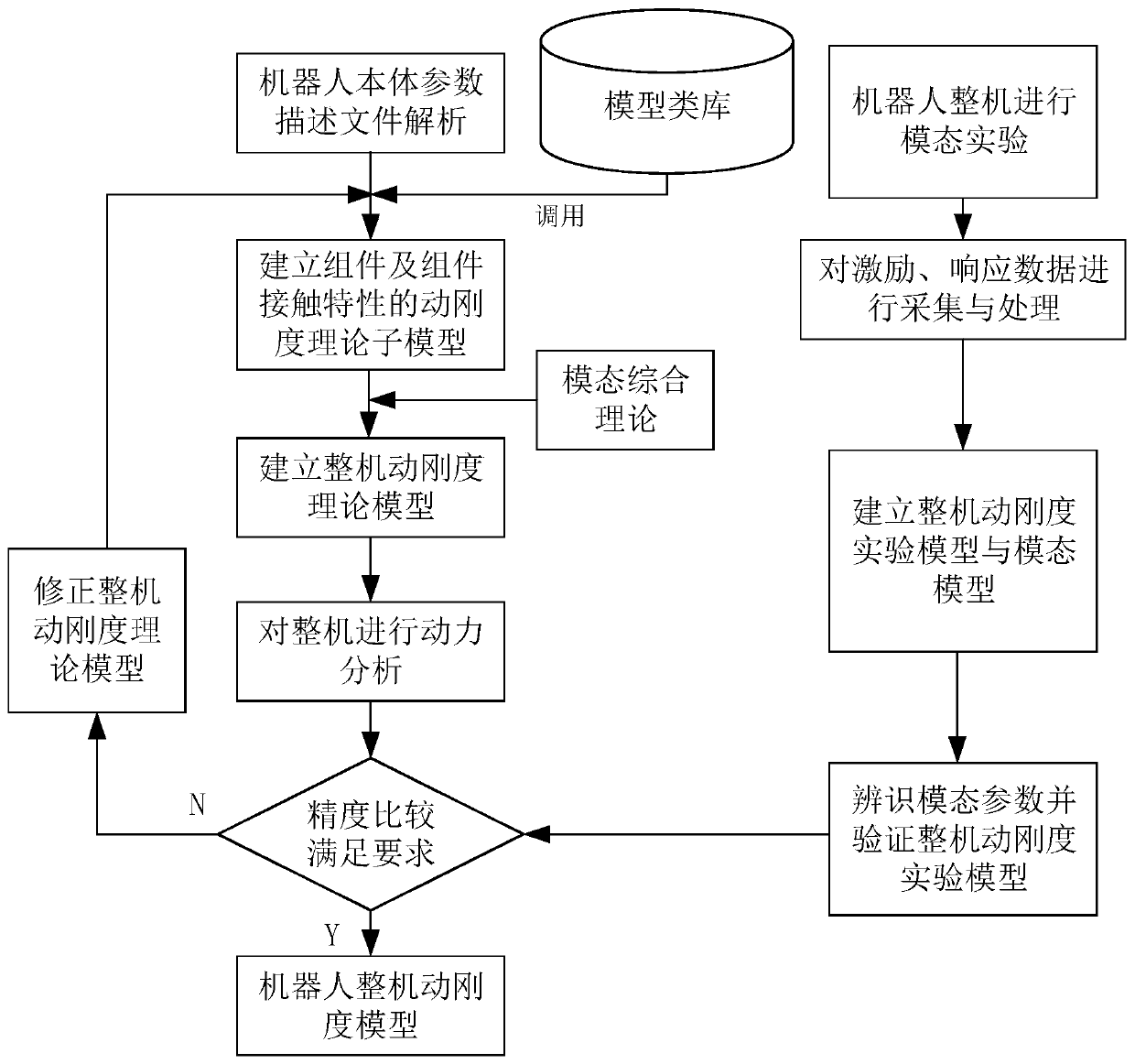
Cutting machining robot static error compensation and dynamic stiffness model correction method
ActiveCN110962124AImprove machining accuracyImplement static error compensationProgramme-controlled manipulatorDynamic stiffnessSimulation
The invention discloses a cutting machining robot static error compensation and dynamic stiffness model correction method and belongs to the robot machining technical field. According to the technicalschemes of the invention, the method comprises the steps that: kinematics calibration is conducted on a robot according to the description file of robot body parameters, robot structure parameters are identified, static error compensation is conducted, and meanwhile, the measurement and calculation data of a calibration process are recorded; a whole robot dynamic stiffness model is established, modal parameters are identified through a modal analysis experiment, and modal experiment data are recorded; whether the pose precision and dynamic stiffness model of the robot meet the tail end positioning precision requirement of the robot or not is detected, if the pose precision and dynamic stiffness model of the robot do not meet the tail end positioning precision requirement, kinematics calibration is performed on the stress conditions of the robot under different poses, elastic deformation error caused by the dead weight of the robot in the calibration process is calculated, and the static error compensation and the whole robot dynamic stiffness model in the calibration process are corrected, and if the pose precision and dynamic stiffness model of the robot meet the tail end positioning precision requirement, the correction of the static error compensation and the dynamic stiffness model of the robot is finished.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
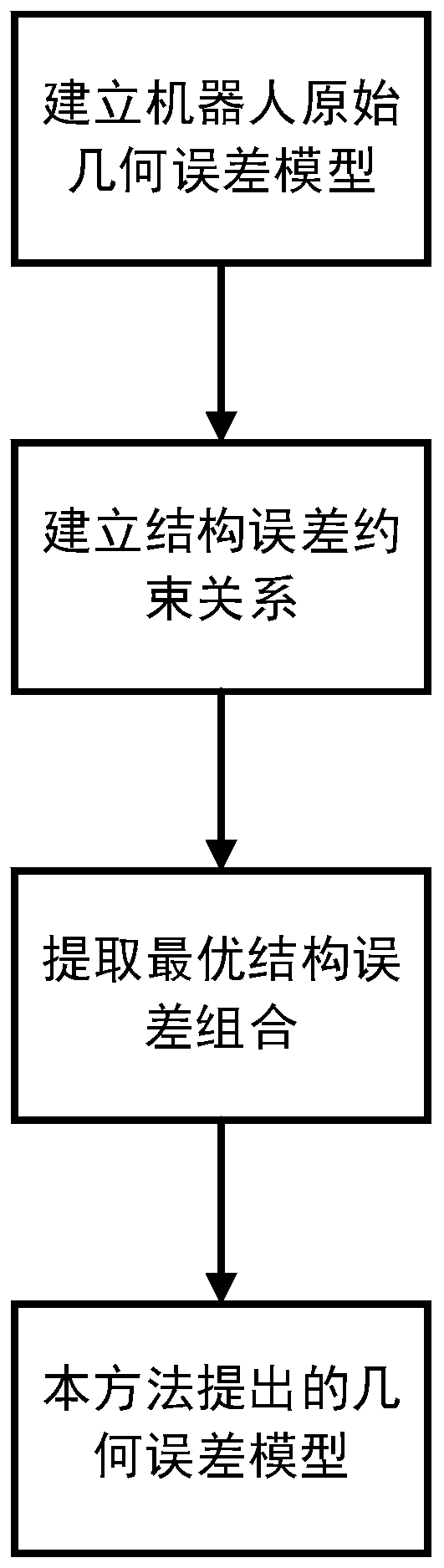
Geometric error modeling method and device of parallel hybrid robot
ActiveCN110977940AAccurately establishedGeneric buildProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsMatrix decompositionAlgorithm
The invention discloses a geometric error modeling method and device of a parallel hybrid robot. The method comprises the following steps that according to a perturbation theory and a D-H matrix method, an original geometric error model of the parallel hybrid robot is derived, and a passive error and a structural error in the parallel hybrid configuration is determined; according to the closed-loop constraint of robot joint chains, a structural error endogenous constraint of the parallel hybrid configuration is determined, and the flow of solving the mathematical expression of the corresponding constraint relation is determined; and according to the transitive relation of the passive error, the structural error, the processes and the terminal end moving platform pose error, the linear independent and the optimal structural error combination conforming to the error endogenous constraint relation is extracted based on a matrix decomposition and simulation method. According to the method,the geometric error modeling problem of the parallel hybrid robot is solved, and therefore the geometric error model of the parallel hybrid robot is built more accurately and universally, so that a priori geometric error model which is more effective and more convenient can be provided for the field of precision research such as kinematic calibration of the parallel hybrid robot, and the method is simple and easy to implement.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Kinematic calibration method of industrial robot
ActiveCN110815204AEasy to operateFriendly interfaceProgramme-controlled manipulatorInternal combustion piston enginesNonlinear systems of equationsControl engineering
The invention relate to a kinematic calibration method of an industrial robot. An intermediate connecting rod coordinate system is established by combination of DH and MDH rules in the establishment process of a kinematic model of the industrial robot, and a minimum parameter set to be identified is obtained. The measurement process is simple and easy to operate by fixing any measuring equipment and any target point, and taking the pose of the robot relative to the measurement coordinate system and the position of the target point relative to the robot end coordinate system as parameters to beidentified. The kinematic model of the industrial robot and the measurement process model are combined, and the nonlinear identification model of the whole calibration system is obtained. The nonlinear equation solving problem is transformed into a nonlinear optimization problem to be solved. The kinematic calibration method of the industrial robot achieves complete minimum parameter set modeling, the calibration model is simpler, and the real parameters of the robot are directly solved based on the nonlinear optimization idea. The method has the advantages of simple operation, friendly userinterface and strong practicability.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multiple support and double platform mechanism
ActiveCN104385264AFew jointsEasy to processProgramme-controlled manipulatorKinematic calibrationEngineering
The invention discloses a multiple support and double platform mechanism. The multiple support and double platform mechanism is composed of a moving platform, a fixing platform and three branched chains connected with the moving platform and the fixing platform, wherein the first branched chain and the second branched chain of the three branched chains are of the same structure, each of the first branched chain and the second branched chain is composed of a ball pair, a rotation pair, a moving pair and connection rods among the ball pair, the rotation pair and the moving pair, which are arranged from top to bottom, and the third branched chain in the three branched chains is composed of another ball pair, another two rotation pairs, a cylindrical pair and connection rods among the another ball pair, the another two rotation pairs and the cylindrical pair. The multiple support and double platform mechanism is of a parallel robot structure, and the moving platform in the parallel robot structure of the multiple support and double platform mechanism can achieve three types of movement output, and therefore the multiple support and double platform mechanism is simple in structure, easy to process and manufacture, and simple in kinematic model, facilitates kinematic calibration and control, and simultaneously comprises a small quantity of mechanism joints, and improves structural rigidity.
Owner:NANTONG HONGFENG NEW ENERGY MACHINERY
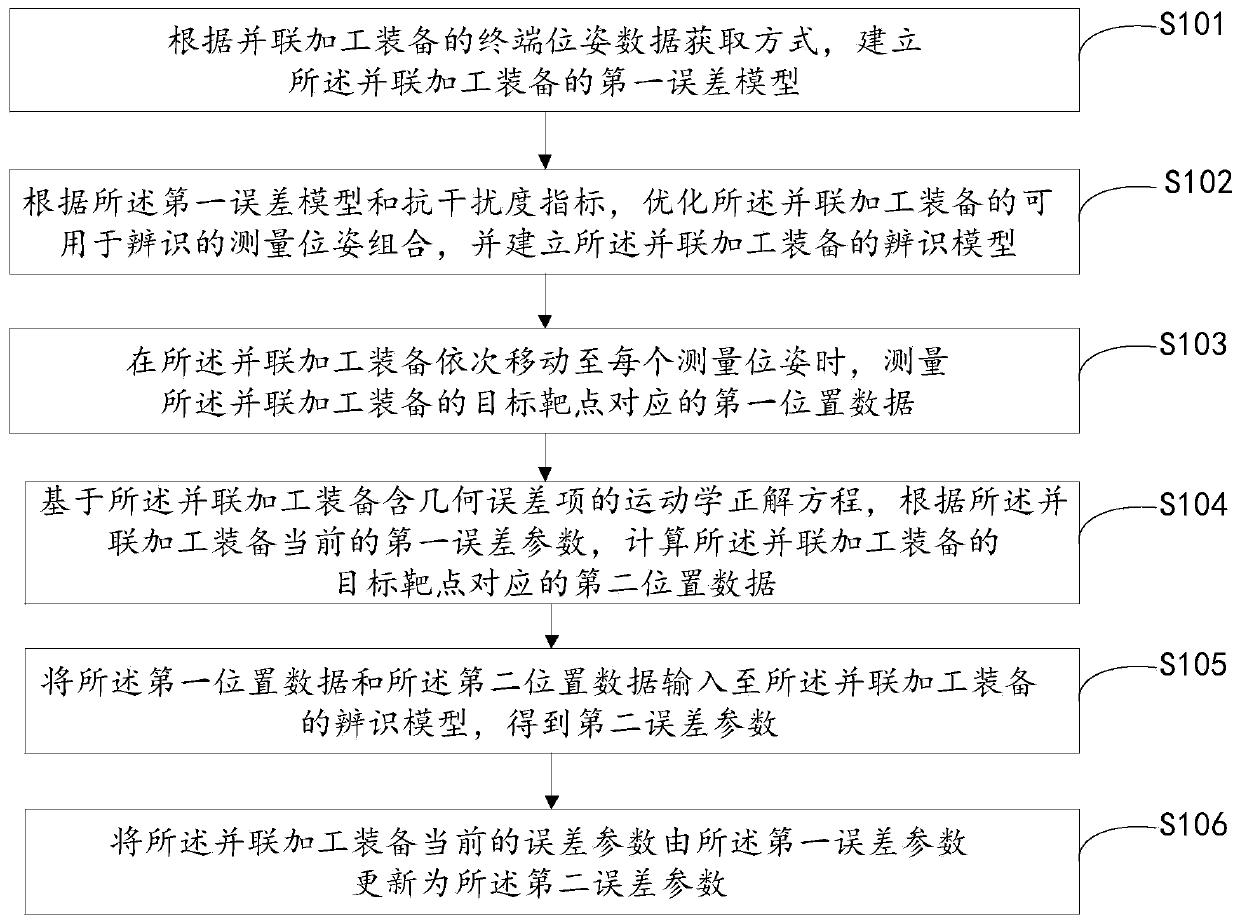
Kinematic calibration method for parallel machining equipment
ActiveCN110871434AImprove recognition accuracyImprove efficiencyProgramme-controlled manipulatorAlgorithmControl engineering
The embodiment of the invention provides a kinematic calibration method for parallel machining equipment, and belongs to the technical field of kinematic calibration. The kinematic calibration methodcomprises the steps that a first error model of the parallel machining equipment is established according to a terminal pose data acquisition mode of the parallel machining equipment; measure pose combination for recognizing of the parallel machining equipment is optimized, first position data corresponding to a target point of the parallel machining equipment are measured, and a recognition modelof the parallel machining equipment is established; according to a current first error parameter of the parallel machining equipment, second position data corresponding to the target point of the parallel machining equipment are measured; the first position data and the second position data are input to the recognition model of the parallel machining equipment to obtain a second error parameter;and a current error parameter of the parallel machining equipment is updated to the second error parameter from the first error parameter. According to the scheme of the kinematic calibration method,the recognition precision and the recognition efficiency of the error parameter of the determined parallel machining equipment are improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Industrial robot kinematic calibration method based on coordinate measuring instrument
ActiveCN109737902AImprove absolute accuracyEliminate redundant parametersMeasurement devicesKinematicsMeasuring instrument
The invention provides an industrial robot kinematic calibration method based on a coordinate measuring instrument. The method comprises a main control module, a power supply module, a display module,a storage module, a bluetooth module and a positioning module. One end of the bluetooth module is connected to the main control module, and the other end of the bluetooth module is wirelessly connected with a bluetooth tag arranged on the body of a worker; the positioning module is connected with the main control module; and the main control module is connected with the display module and the storage module. Through the design of the bluetooth tag, the device is simple in structure, cheap in price, easy to integrate and can be widely used.
Owner:珞石(北京)科技有限公司
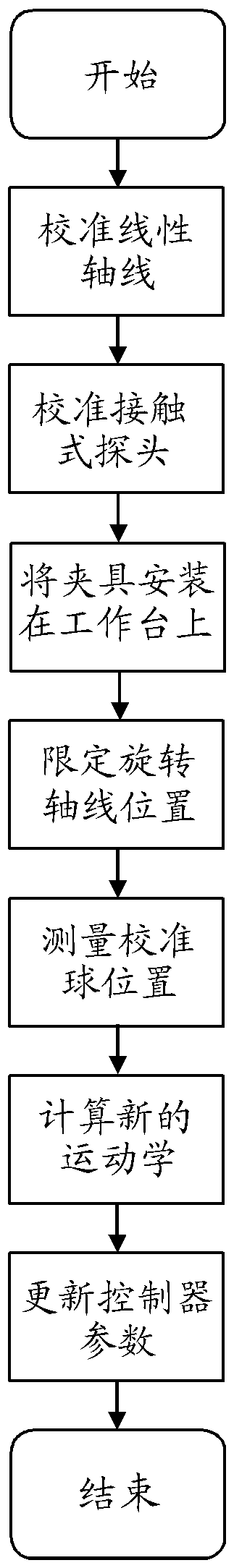
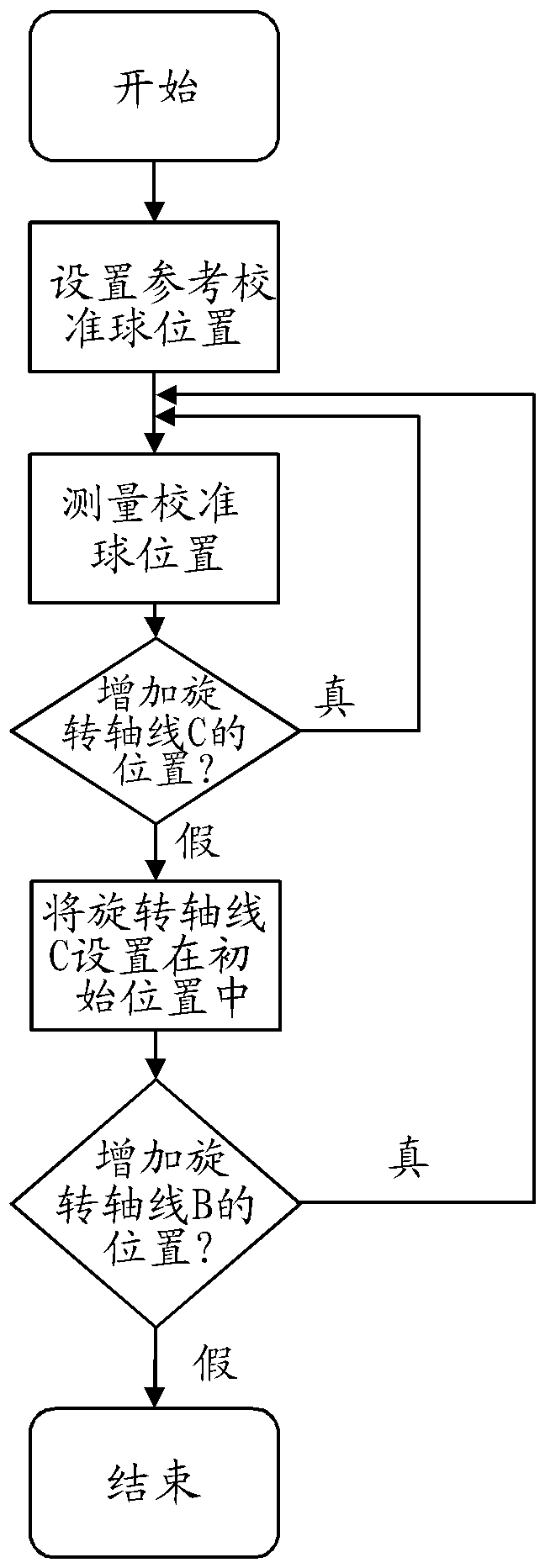
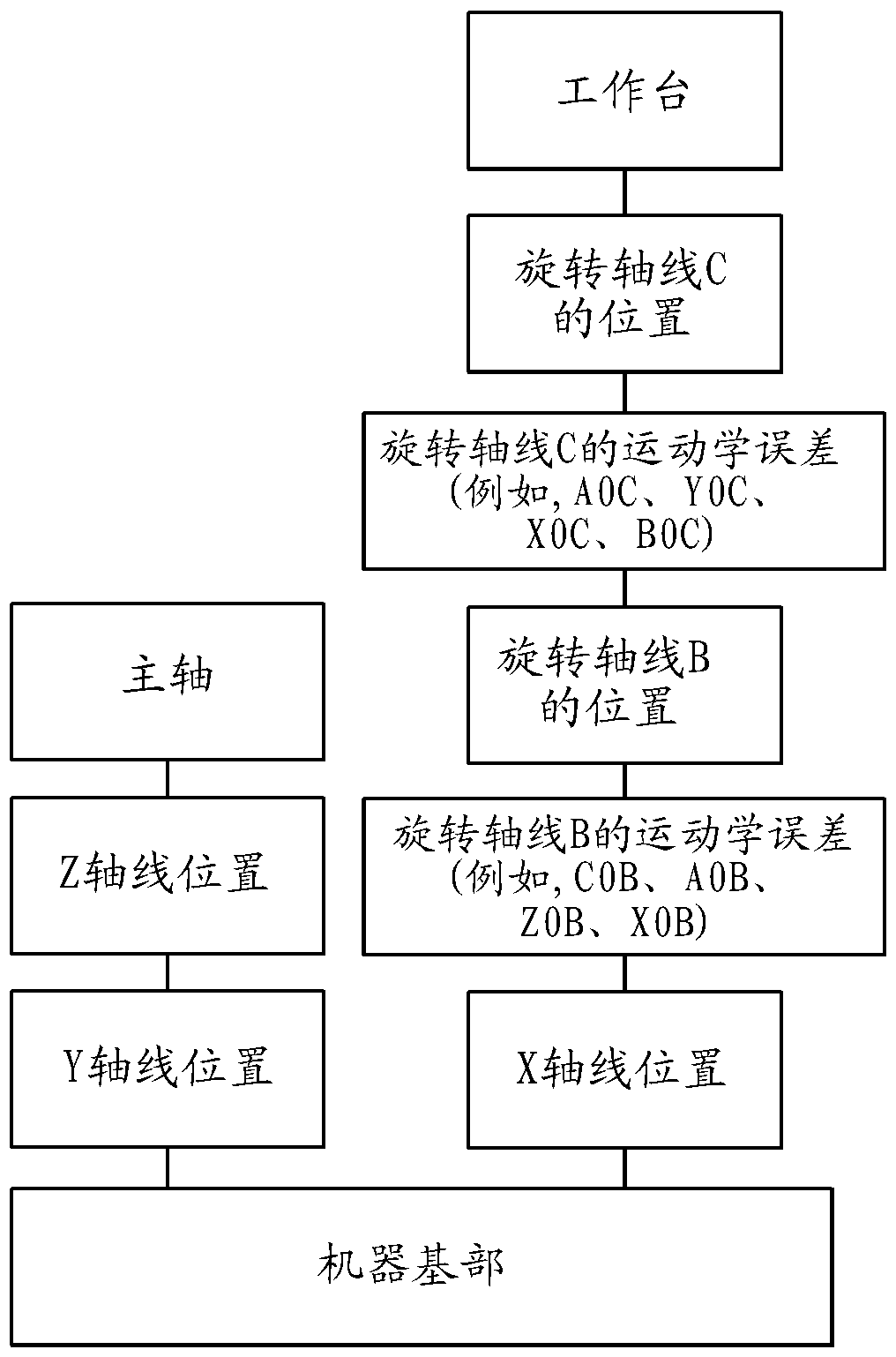
Kinematic calibration
ActiveCN108121294AIdentify Kinematic ErrorsComputer controlSimulator controlNumerical controlRotational axis
The invention relates to kinematic calibration. The present invention relates to a calibration method for numerical controlled machine tools (1), which uses a kinematic model to generate a compensation model for the positioning error occurring with the movement of the linear (X, Y, Z) and rotation axes (B, C, A) of a machine tool (1). The calibration method measures the positions of a calibrationball (6) with a measurement sequence which includes the combined movement of the calibration ball (6) around two rotation axes (C, B or C, A), wherein the measurements around a first rotation axis (C)include at least two rotational position movements around a second axis (B or A).
Owner:GF MACHINING SOLUTIONS AG
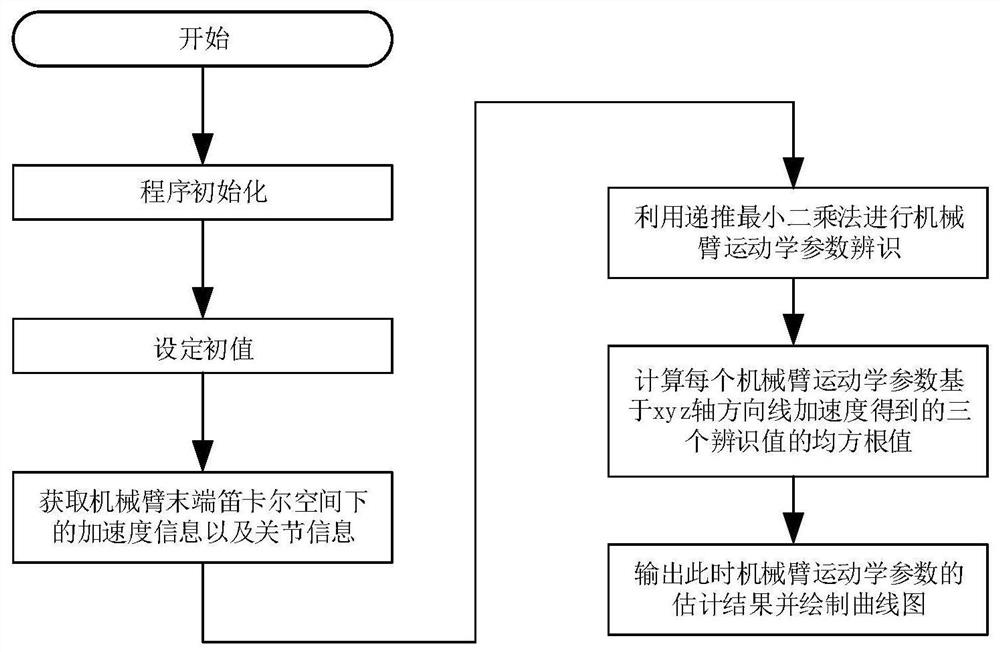
Mechanical arm kinematics parameter calibration method based on inertial measurement unit
ActiveCN111687845AReduce experiment costDoes not take up spaceProgramme-controlled manipulatorClassical mechanicsKinematic calibration
A mechanical arm kinematics parameter calibration method based on an inertial measurement unit comprises the steps that firstly, the relation expression among the linear speed under a mechanical arm tail end Cartesian coordinates, the speed relation under the joint space and the jacobian matrix is constructed, and derivation is conducted; secondly, normalization processing is conducted on the derived relational expression; thirdly, the linear acceleration under the mechanical arm tail end Cartesian space and the angle, the angle speed and the angle acceleration under the mechanical arm joint space are obtained; fourthly, the recursive least-squares method is utilized for conducting mechanical arm parameter identification, and the mechanical arm kinematics parameter calculated value in eachdirection is obtained; and fifthly, the root-mean-square value is obtained from the obtained three values, the mechanical arm kinematics parameter final estimated value at the time is output, and a curve is drawn. By means of the mechanical arm kinematics parameter calibration method, the mechanical arm kinematics calibration cost is reduced. Along with constant improvement of the inertial measurement unit technology, the measuring precision is higher and higher, the precision of the calibration result is higher and higher, and the mechanical arm kinematics parameter calibration method has wider development prospects.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com