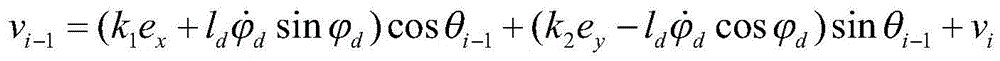Patents
Literature
2412 results about "Robot locomotion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
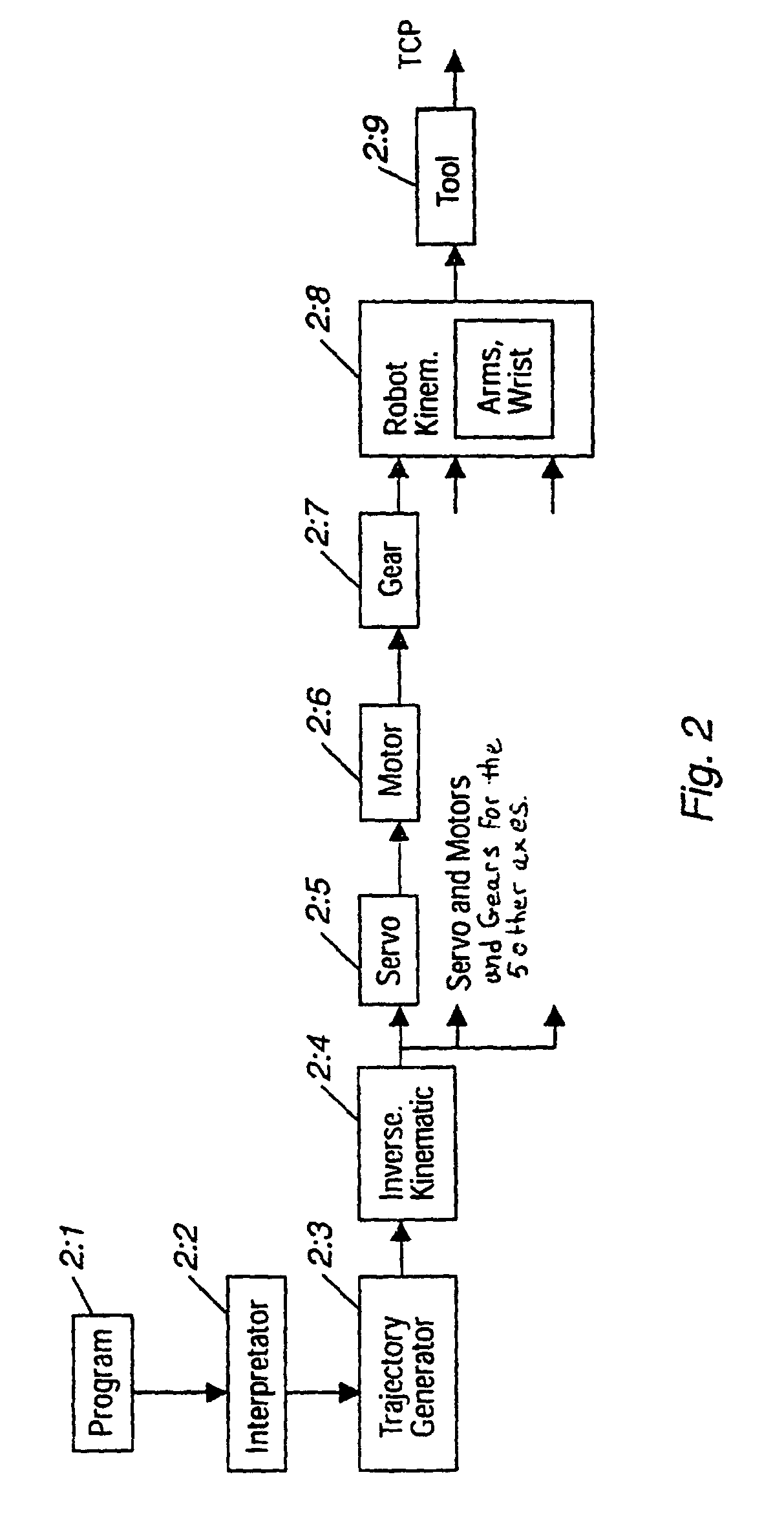
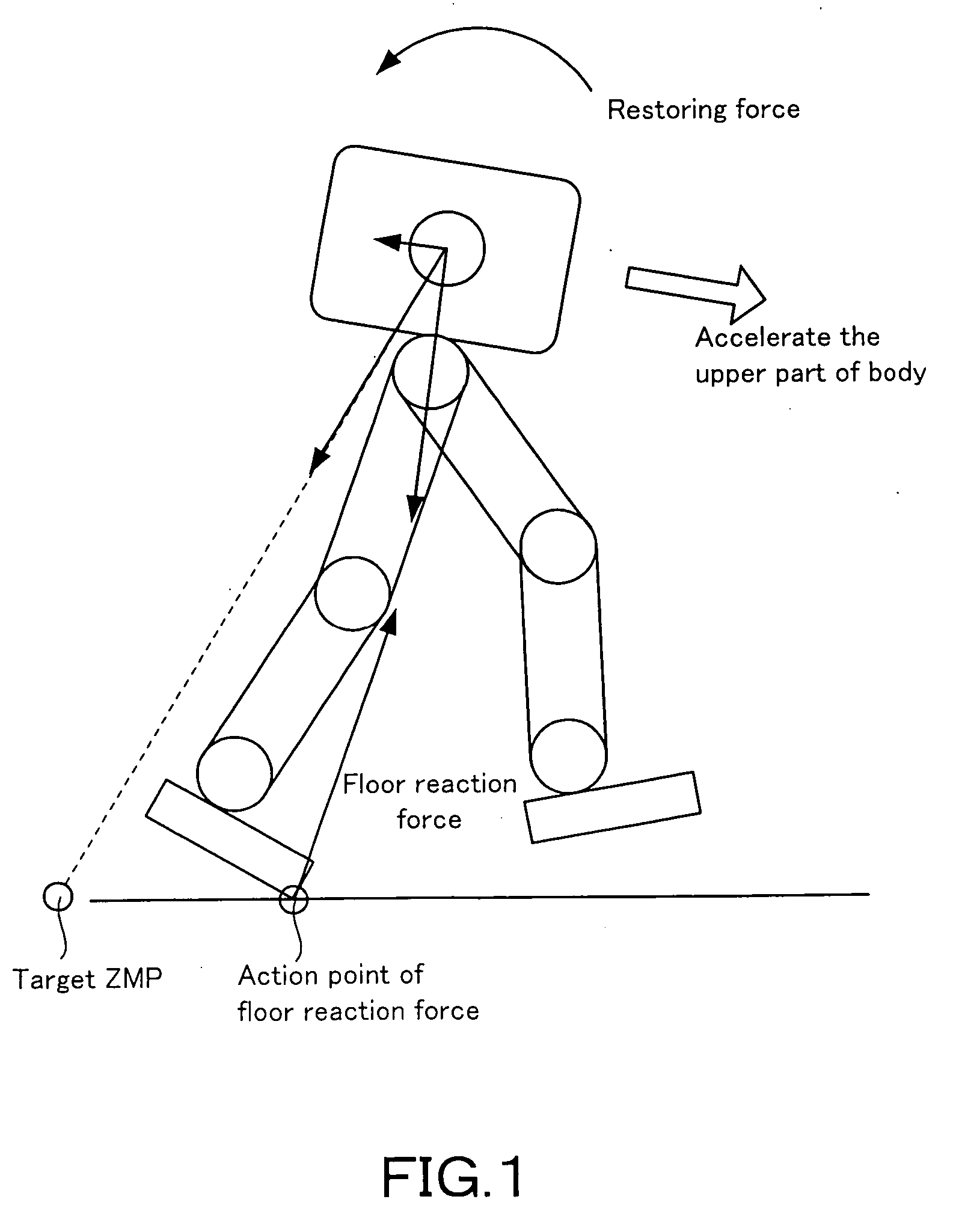
Robot locomotion is the collective name for the various methods that robots use to transport themselves from place to place. Wheeled robots are typically quite energy efficient and simple to control. However, other forms of locomotion may be more appropriate for a number of reasons, for example traversing rough terrain, as well as moving and interacting in human environments. Furthermore, studying bipedal and insect-like robots may beneficially impact on biomechanics.
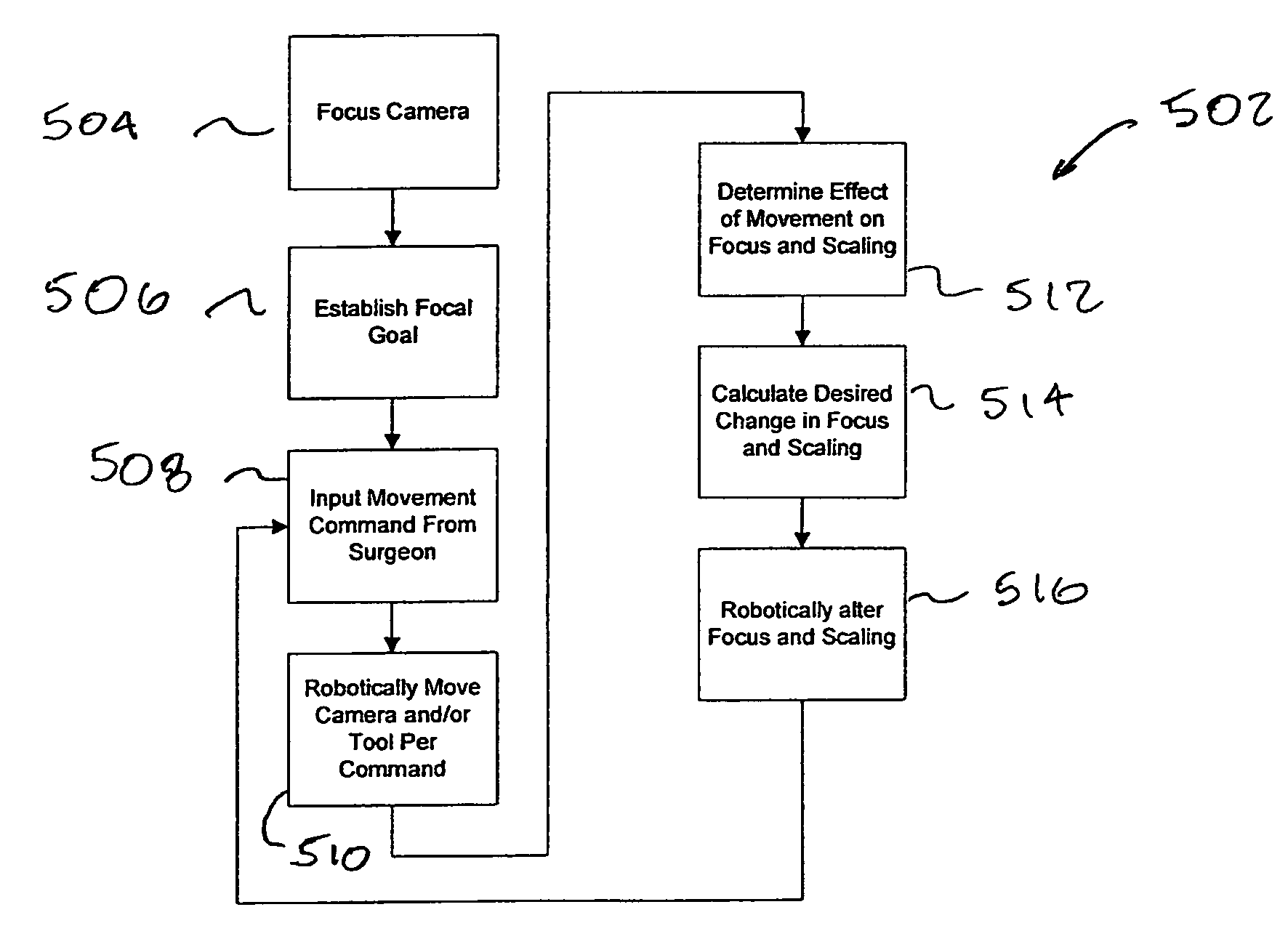
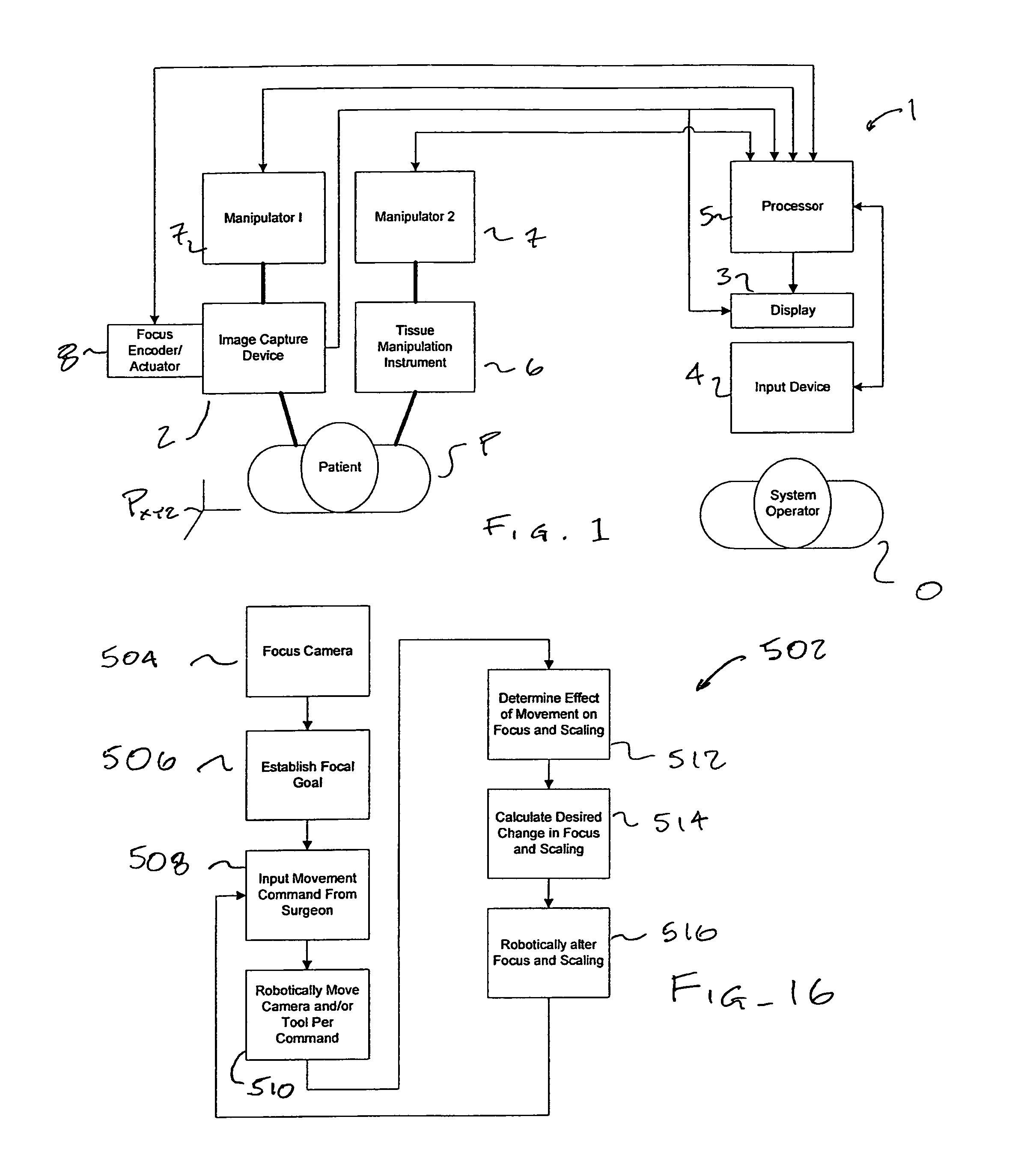
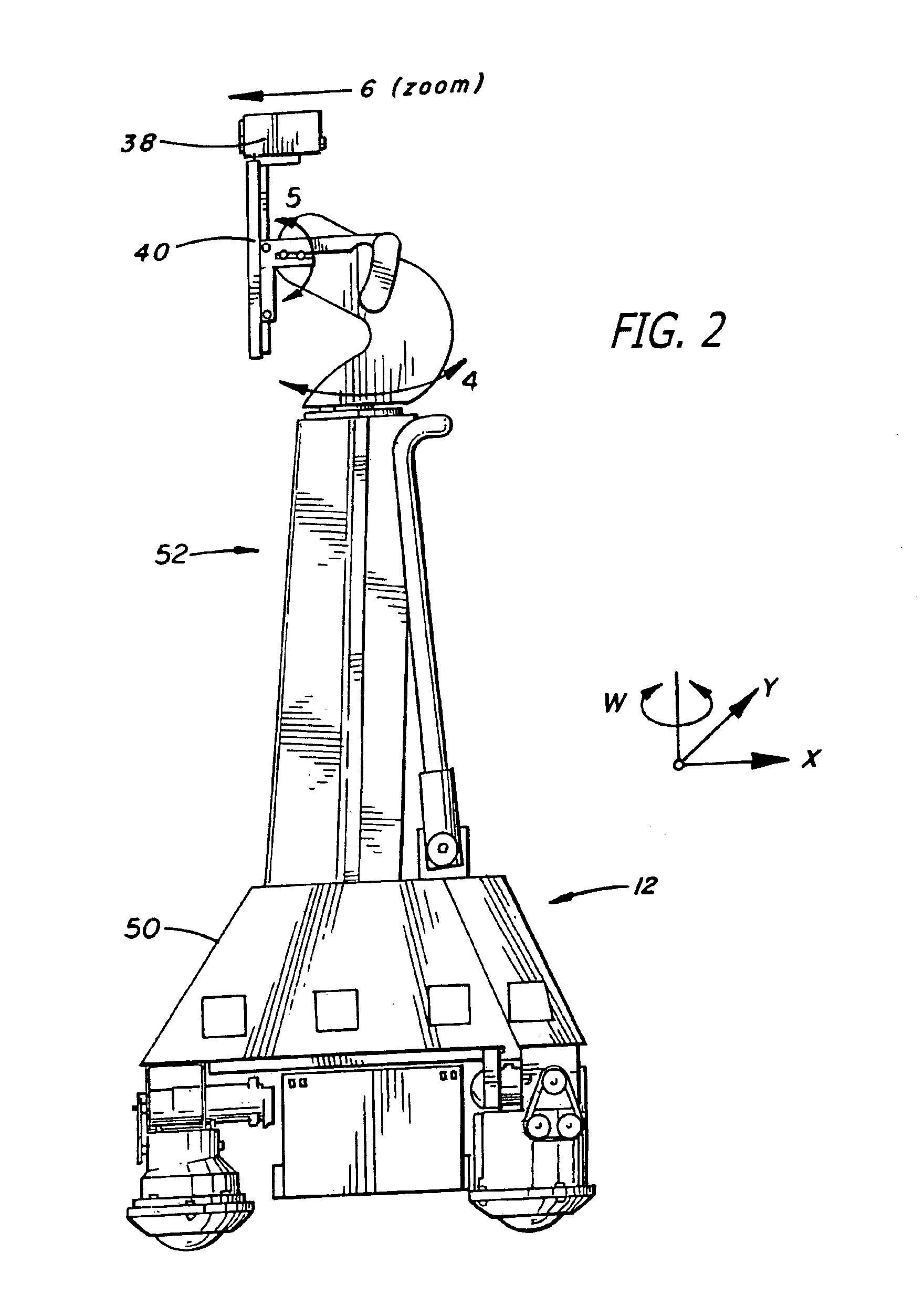
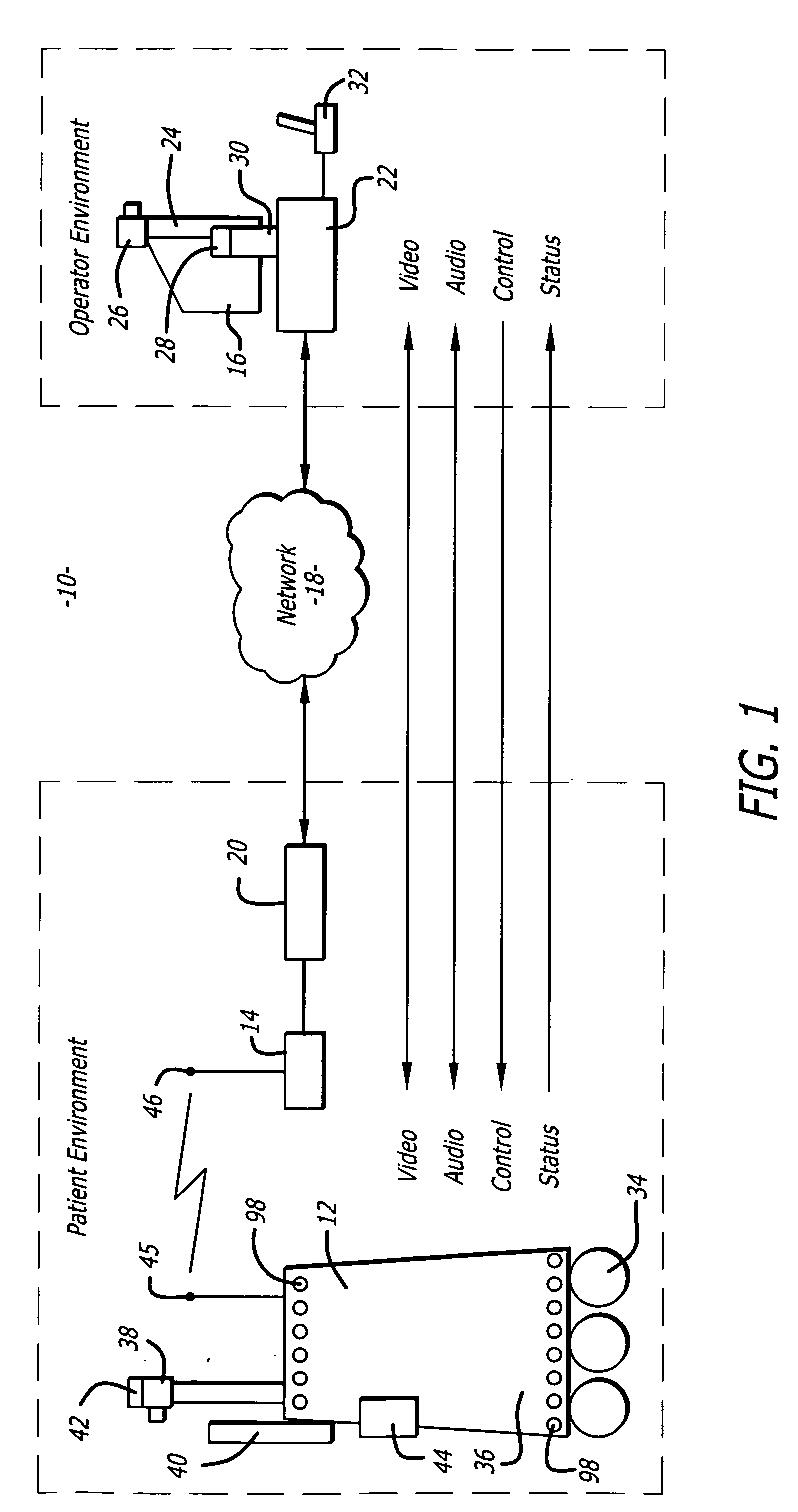
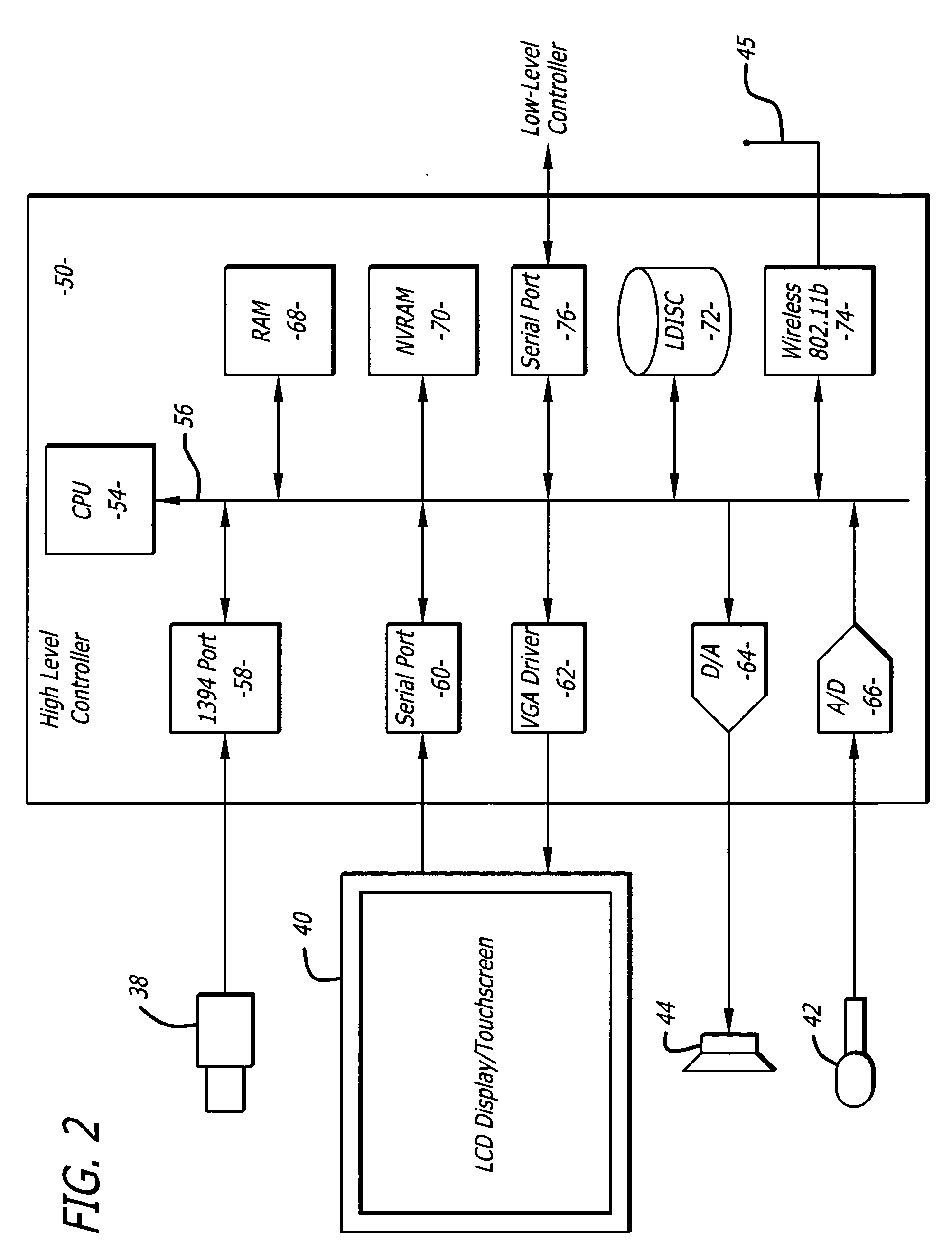
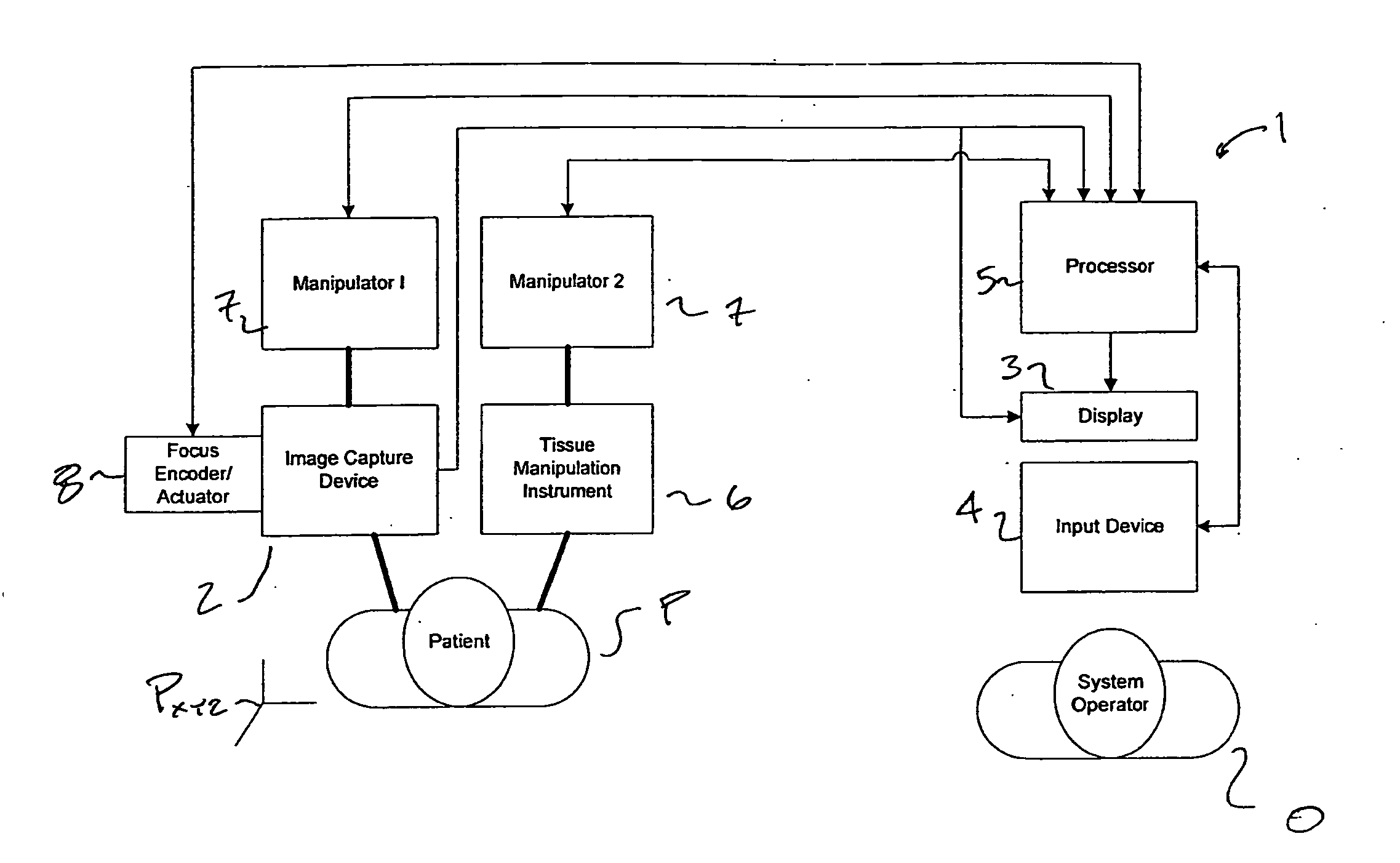
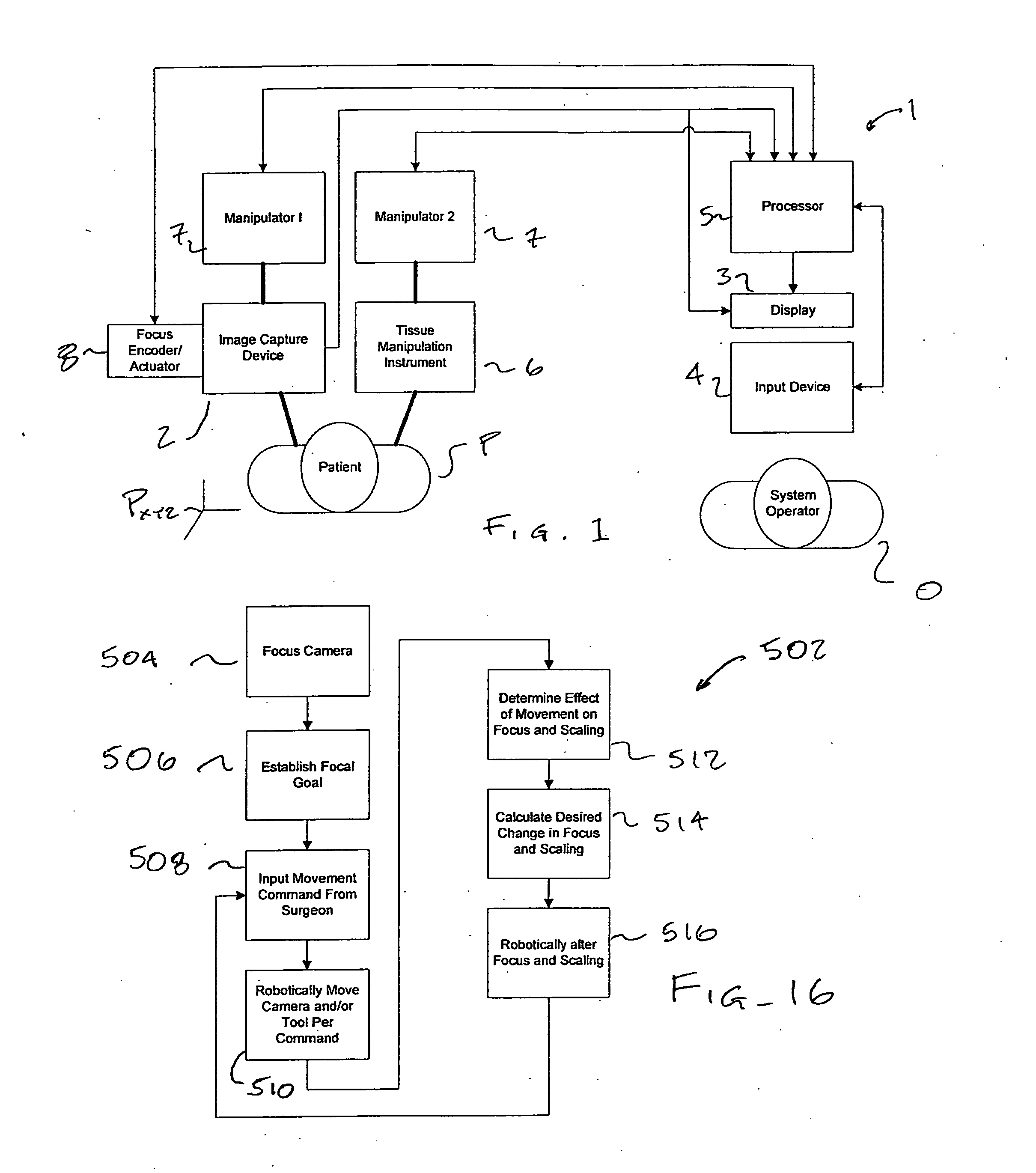
Autofocus and/or autoscaling in telesurgery
ActiveUS8079950B2Enhance perceived correlationComputer controlSimulator controlRemote surgeryComputer graphics (images)
Robotic, telerobotic, and / or telesurgical devices, systems, and methods take advantage of robotic structures and data to calculate changes in the focus of an image capture device in response to movement of the image capture device, a robotic end effector, or the like. As the size of an image of an object shown in the display device varies with changes in a separation distance between that object and the image capture device used to capture the image, a scale factor between a movement command input may be changed in response to moving an input device or a corresponding master / slave robotic movement command of the system. This may enhance the perceived correlation between the input commands and the robotic movements as they appear in the image presented to the system operator.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
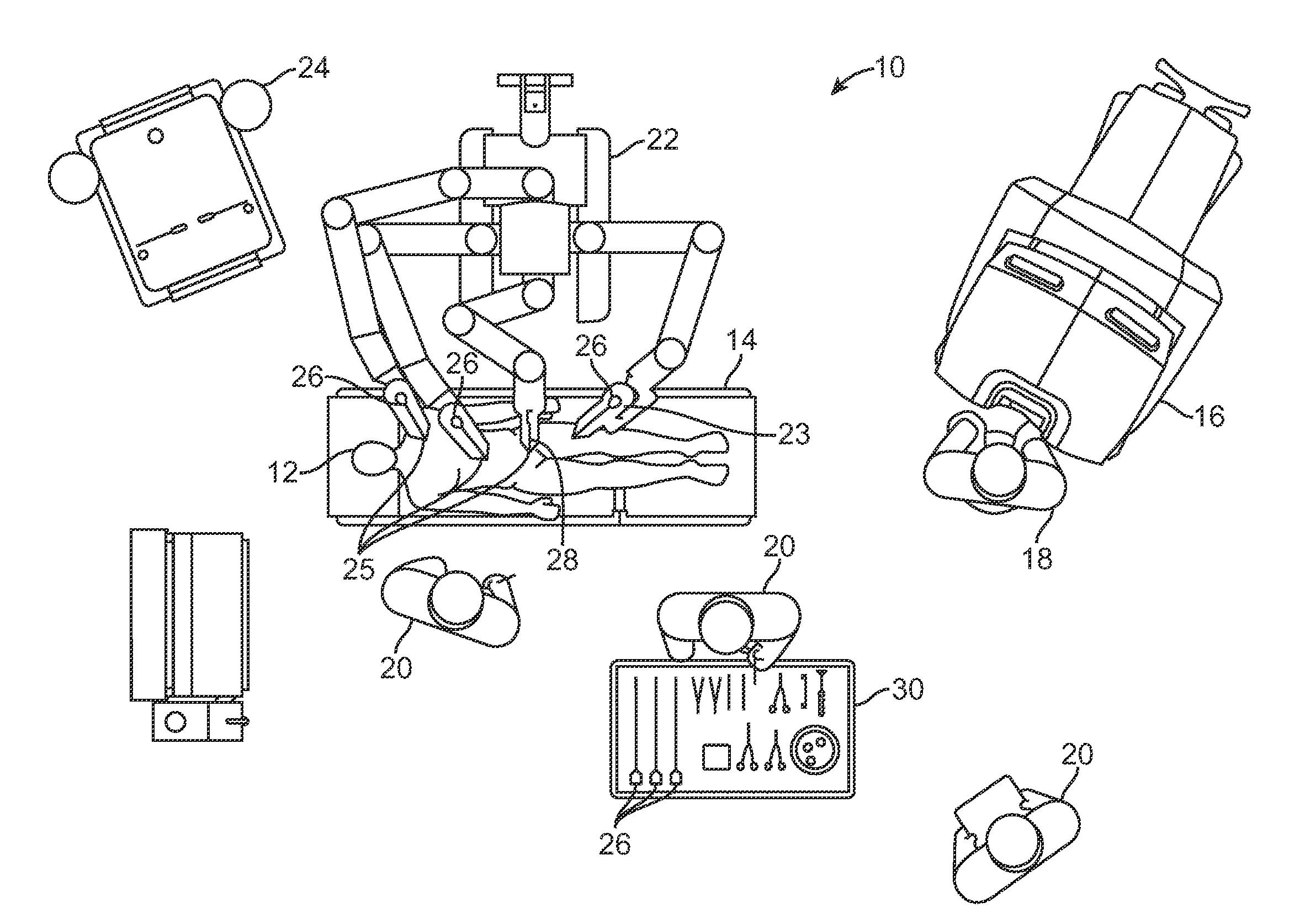
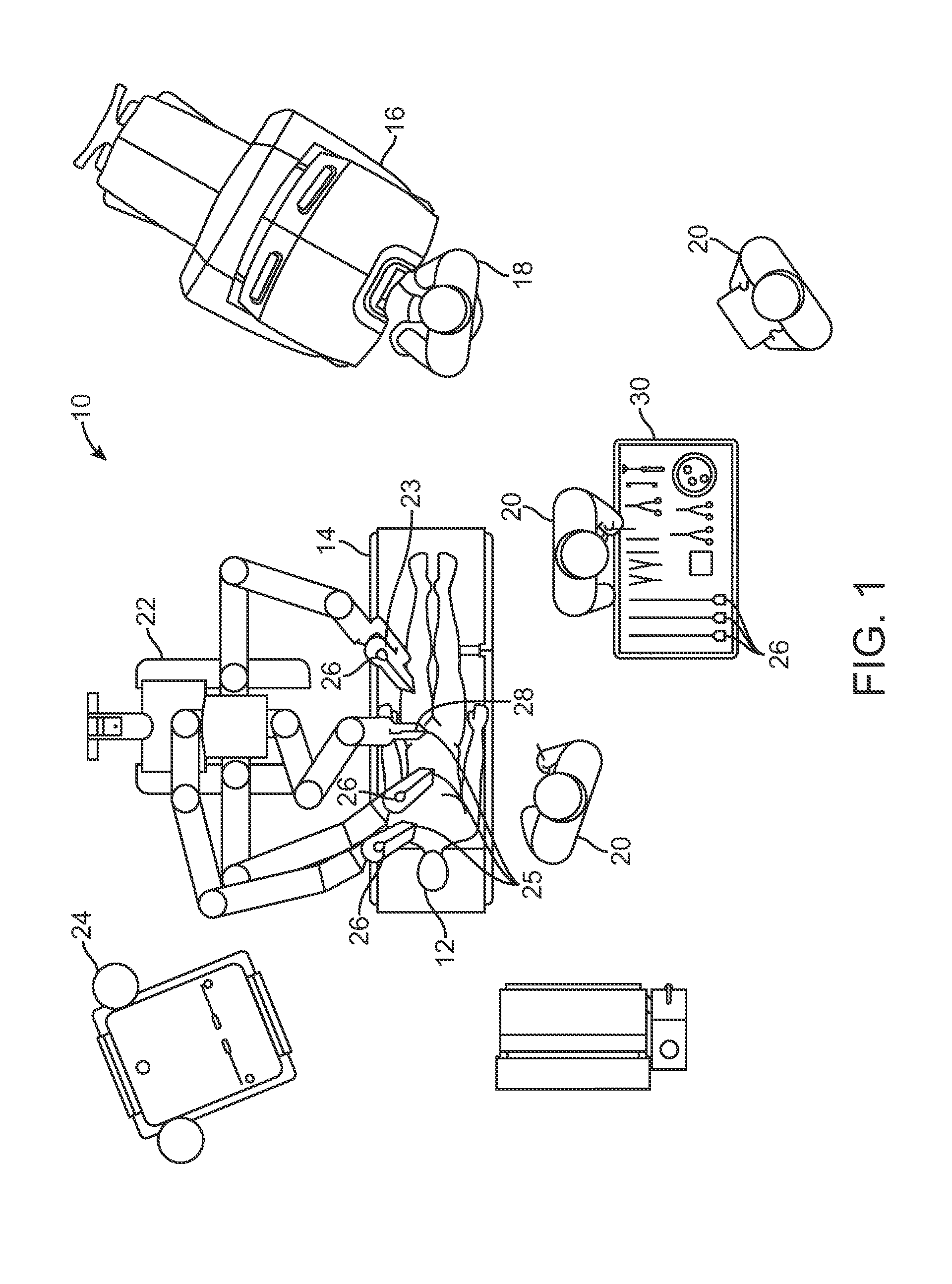
Robotic manipulation methods and systems for executing a domain-specific application in an instrumented environment with electronic minimanipulation libraries
ActiveUS20160059412A1Deal with variationProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlHumanoid robot naoComputer number format
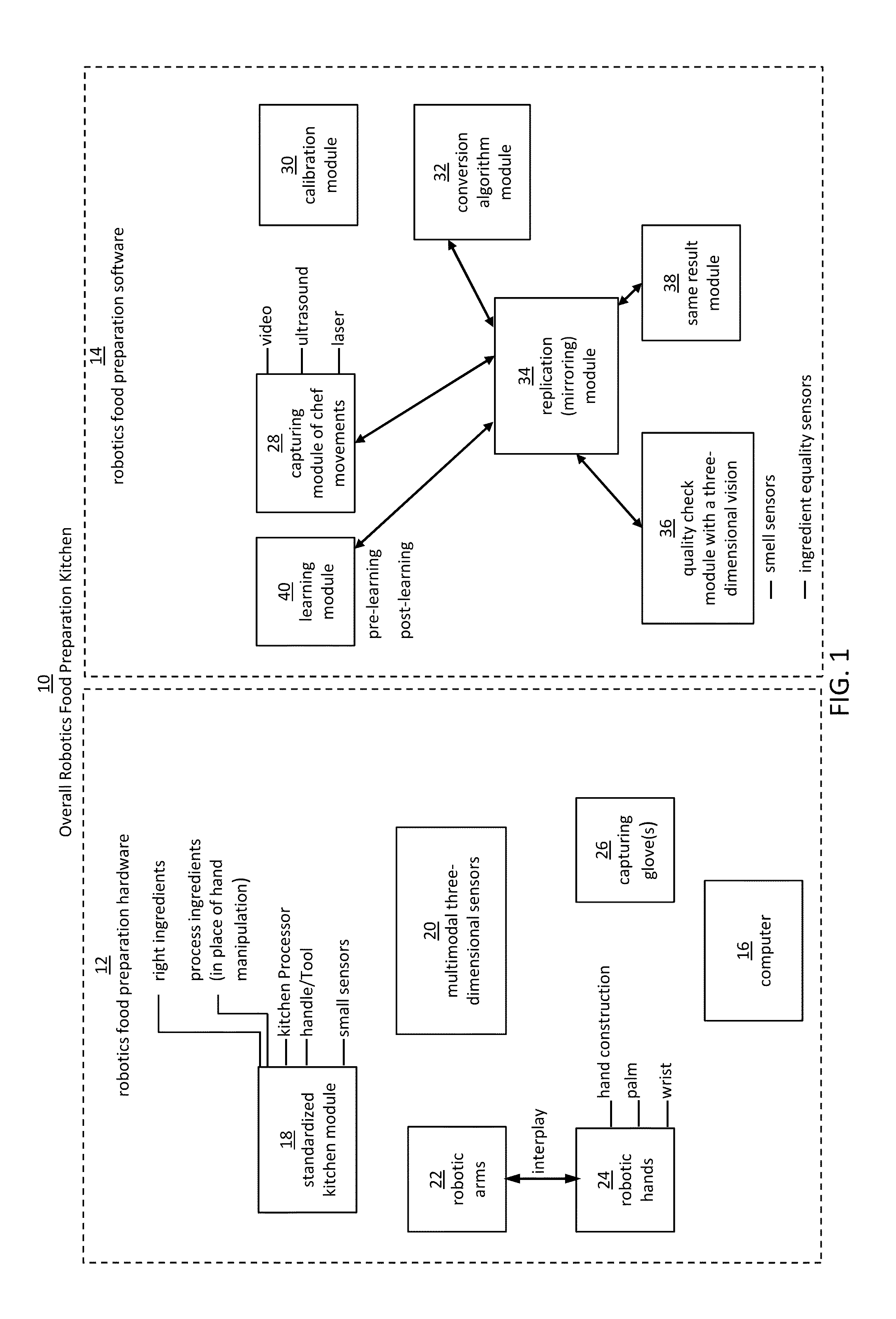
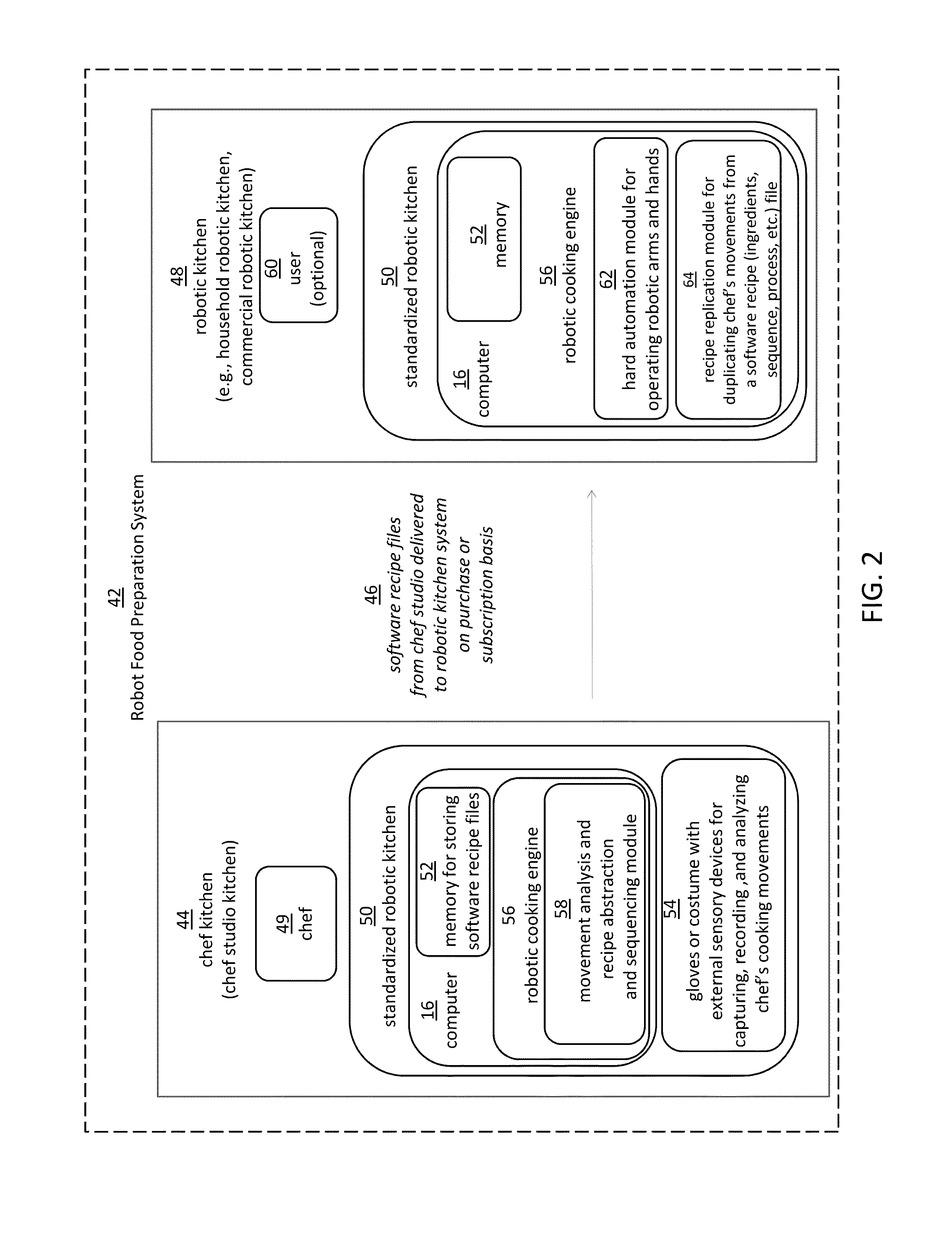
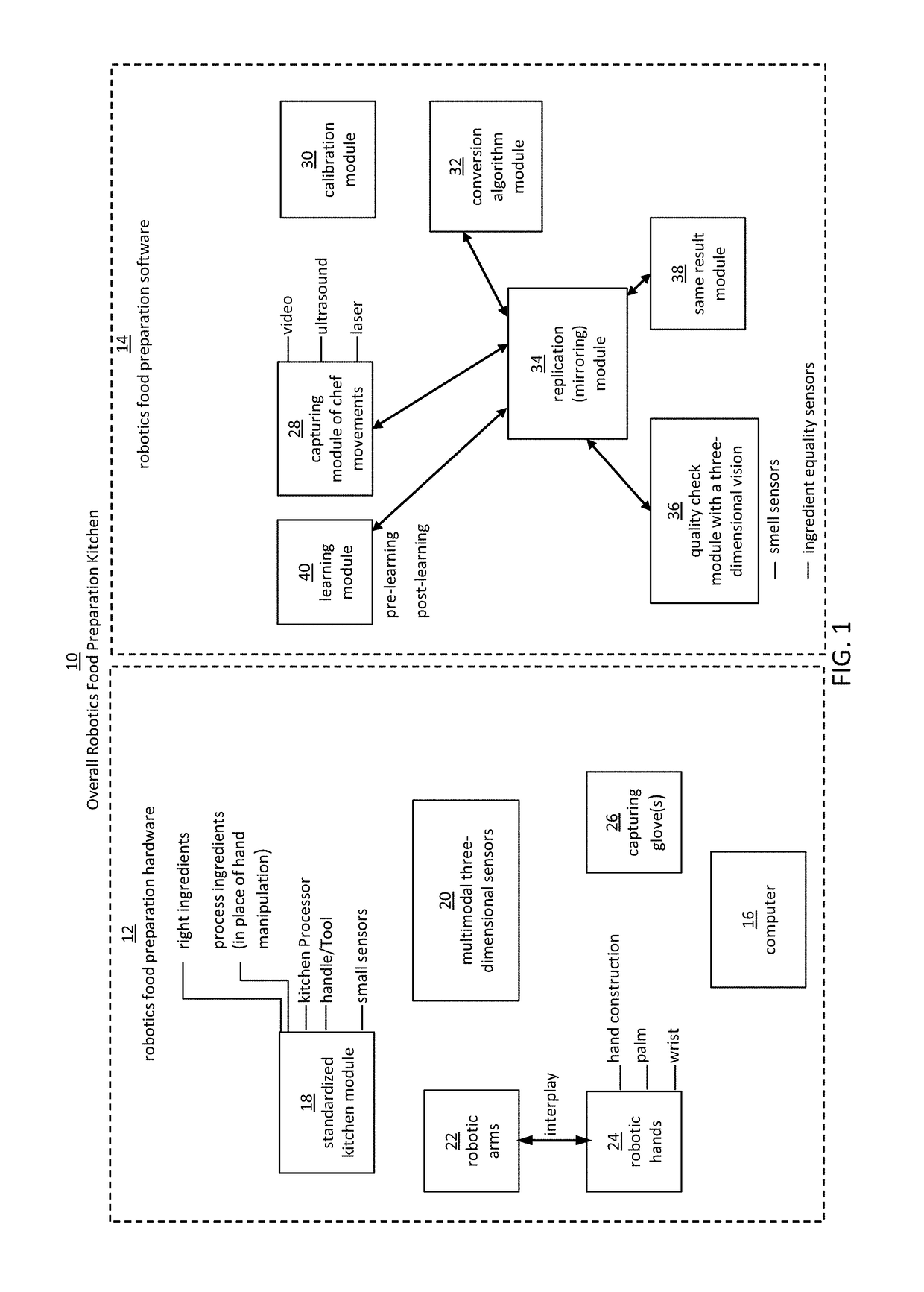
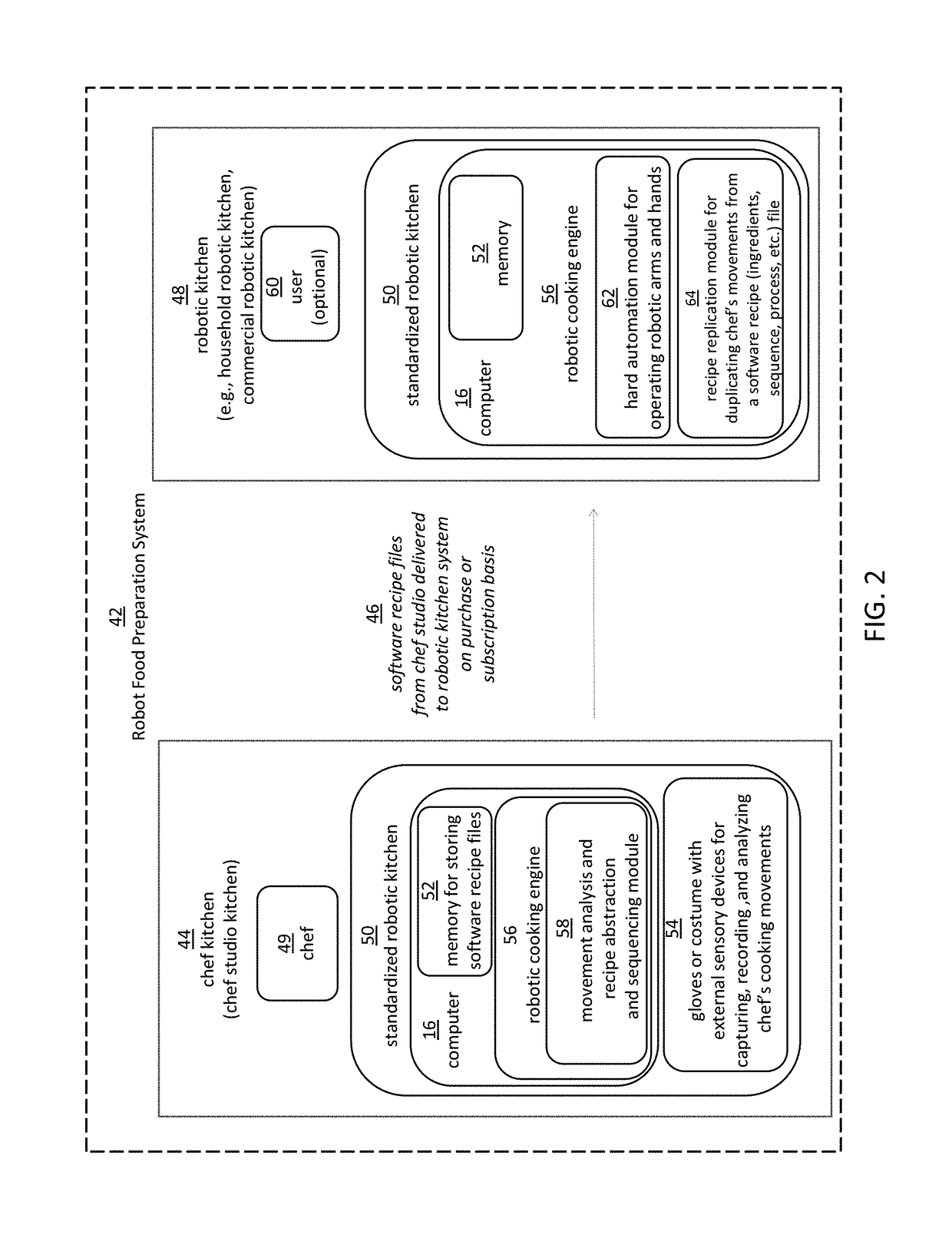
Embodiments of the present disclosure are directed to the technical features relating to the ability of being able to create complex robotic humanoid movements, actions, and interactions with tools and the instrumented environment by automatically building movements for the humanoid; actions and behaviors of the humanoid based on a set of computer-encoded robotic movement and action primitives. The primitives are defined by motions / actions of articulated degrees of freedom that range in complexity from simple to complex, and which can be combined in any form in serial / parallel fashion. These motion-primitives are termed to be minimanipulations and each has a clear time-indexed command input-structure and output behavior / performance profile that is intended to achieve a certain function. Minimanipulations comprise a new way of creating a general programmable-by-example platform for humanoid robots. One or more minimanipulation electronic libraries provide a large suite of higher-level sensing-and-execution sequences that are common building blocks for complex tasks, such as cooking, taking care of the infirm, or other tasks performed by the next generation of humanoid robots.
Owner:MBL LTD
Holonomic platform for a robot
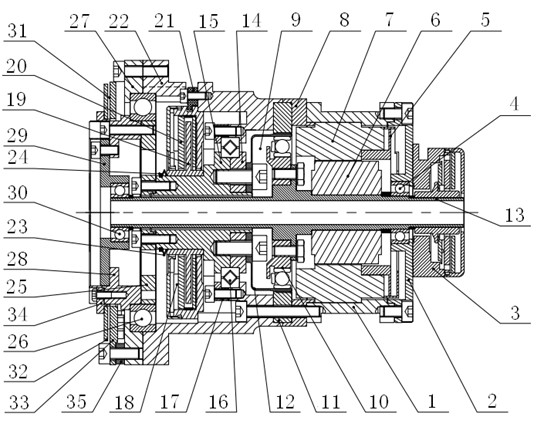
InactiveUS6888333B2Programme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlMechanical engineeringRobot locomotion
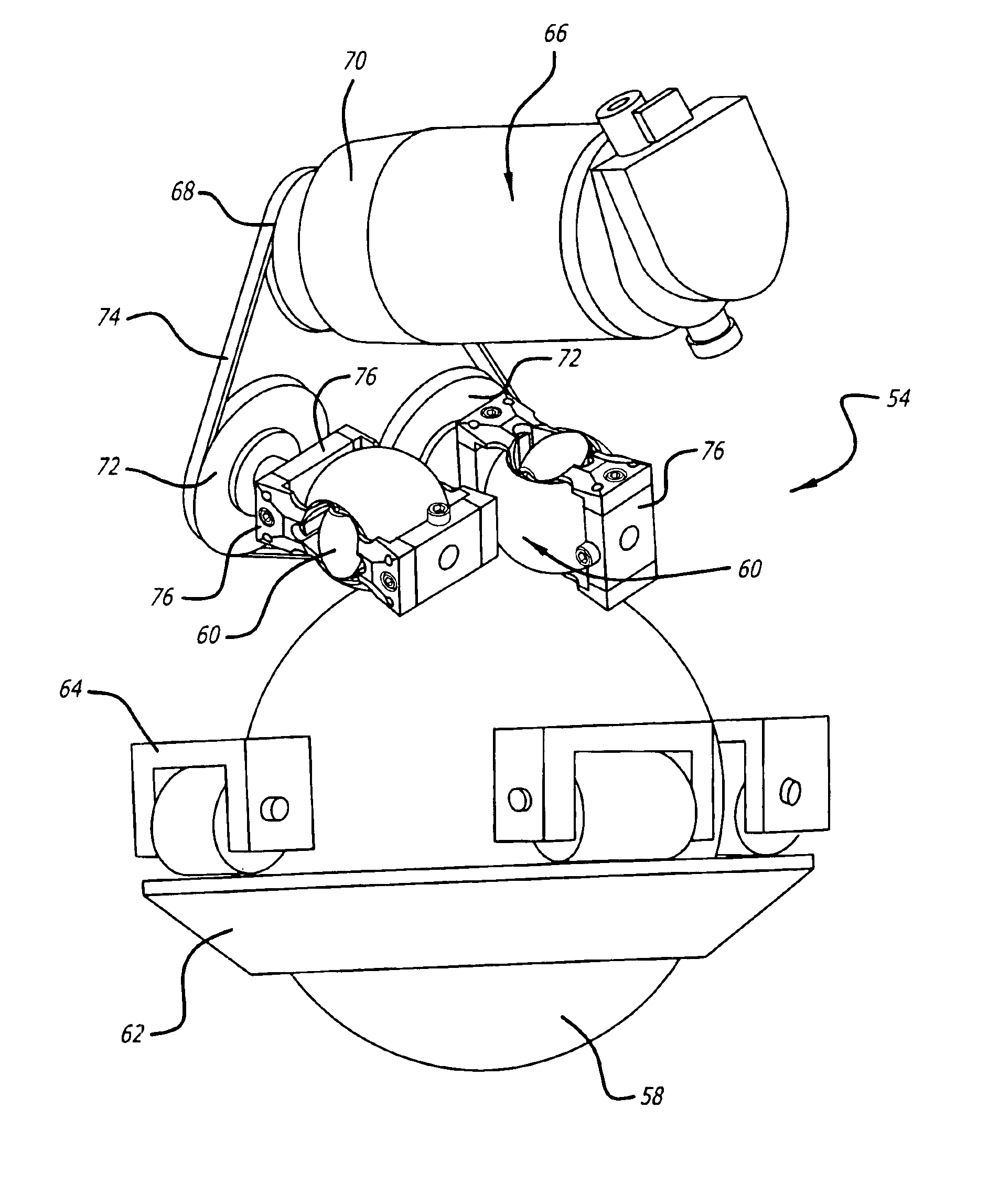
A robot that includes a plurality of roller assemblies. Each roller assembly may include a transmission roller that is spun by a drive mechanism to rotate a drive ball. Rotation of the drive ball propels the robot across a surface. The transmission roller is in continuous contact with the drive ball. Continuous contact between the roller and ball eliminates roller induced wobble in the robot movement, reduces impact forces and resultant stress within the roller assembly and allows for the use of a drive ball that is more complaint than balls in the prior art.
Owner:JONATA SUB TWO INC +1
Efficient Vision and Kinematic Data Fusion For Robotic Surgical Instruments and Other Applications
ActiveUS20100331855A1Easy to adjustSimple and relatively stable adjustment or bias offsetDiagnosticsSurgical robotsRemote surgeryEngineering
Robotic devices, systems, and methods for use in telesurgical therapies through minimally invasive apertures make use of joint-based data throughout much of the robotic kinematic chain, but selectively rely on information from an image capture device to determine location and orientation along the linkage adjacent a pivotal center at which a shaft of the robotic surgical tool enters the patient. A bias offset may be applied to a pose (including both an orientation and a location) at the pivotal center to enhance accuracy. The bias offset may be applied as a simple rigid transformation from the image-based pivotal center pose to a joint-based pivotal center pose.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
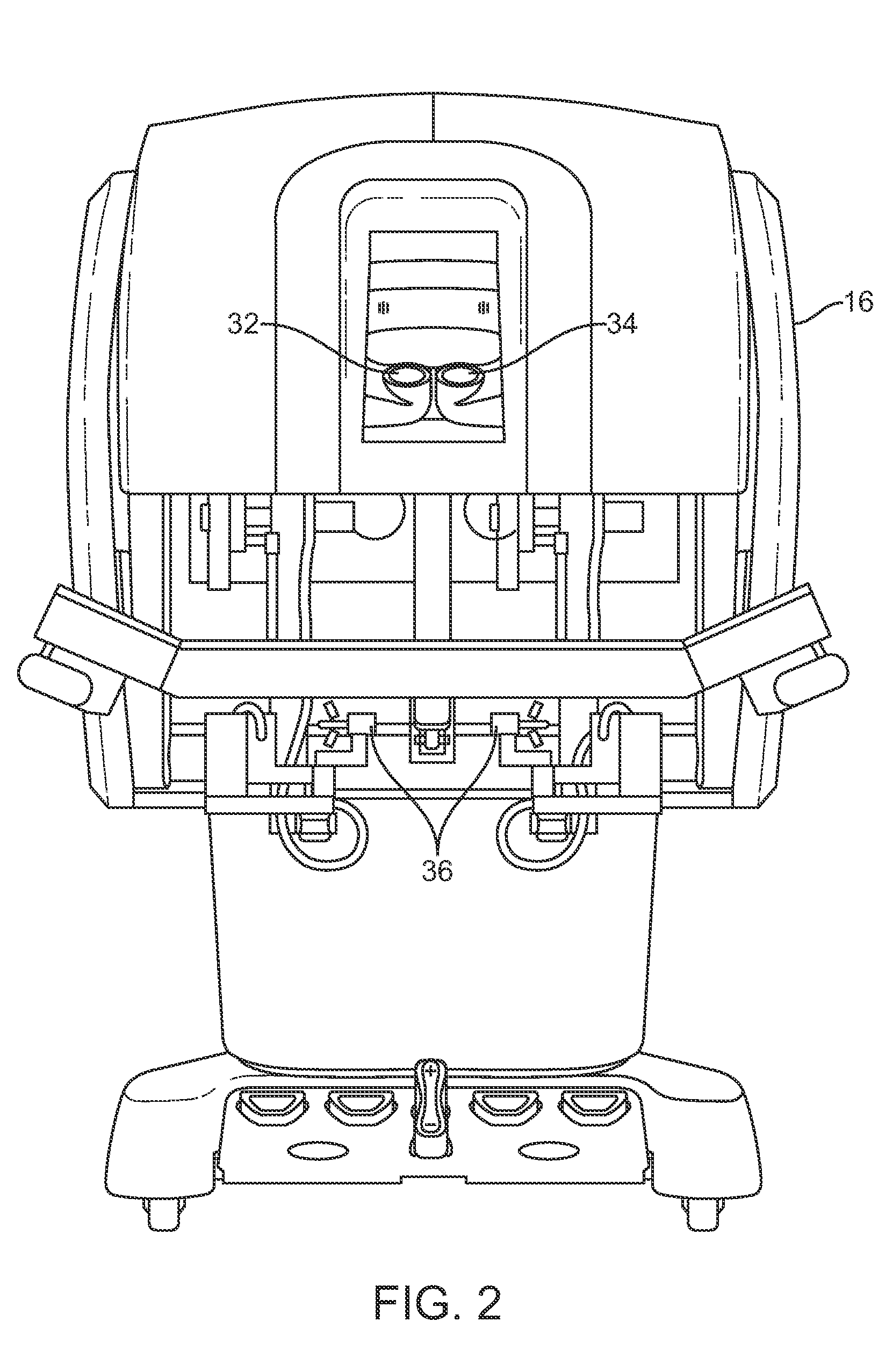
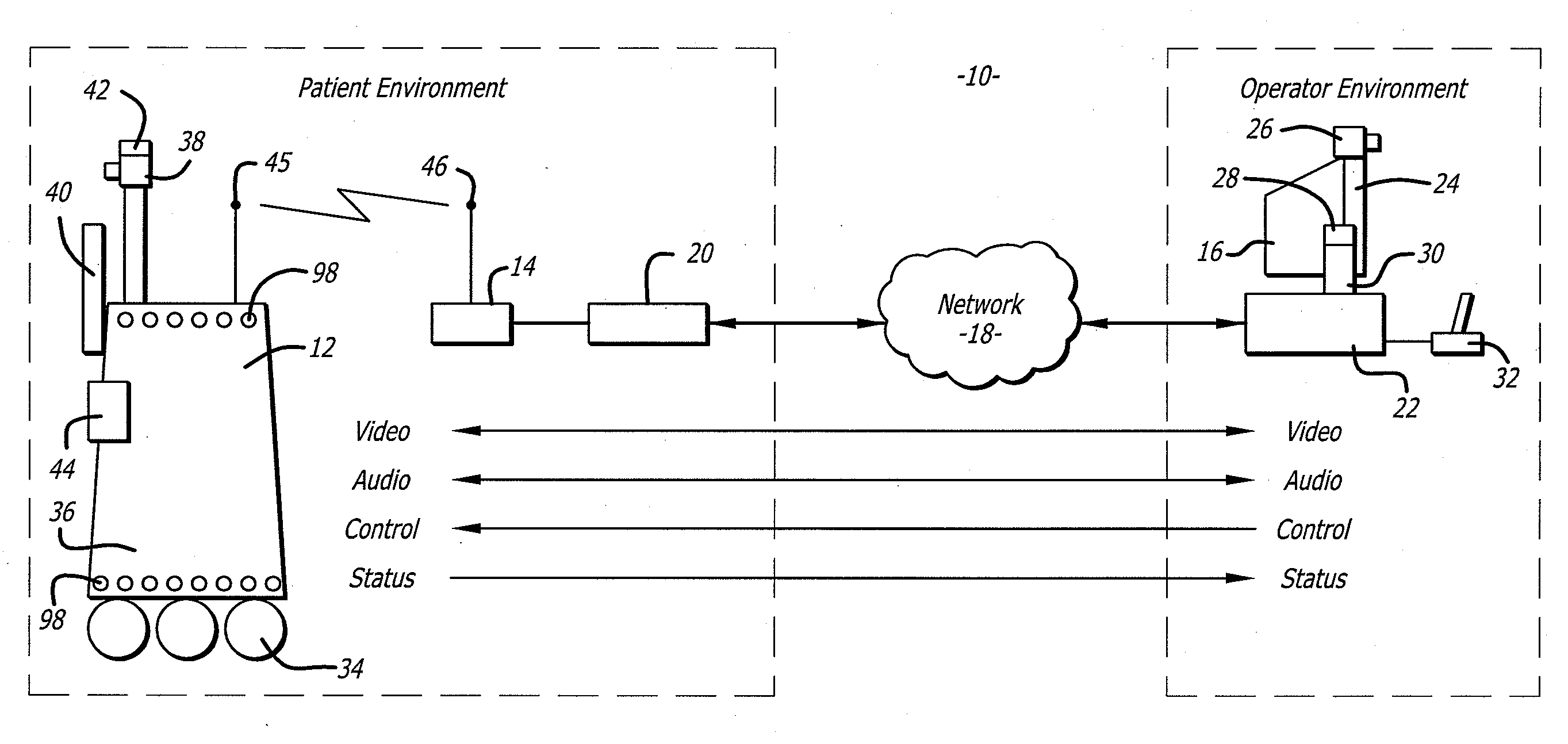
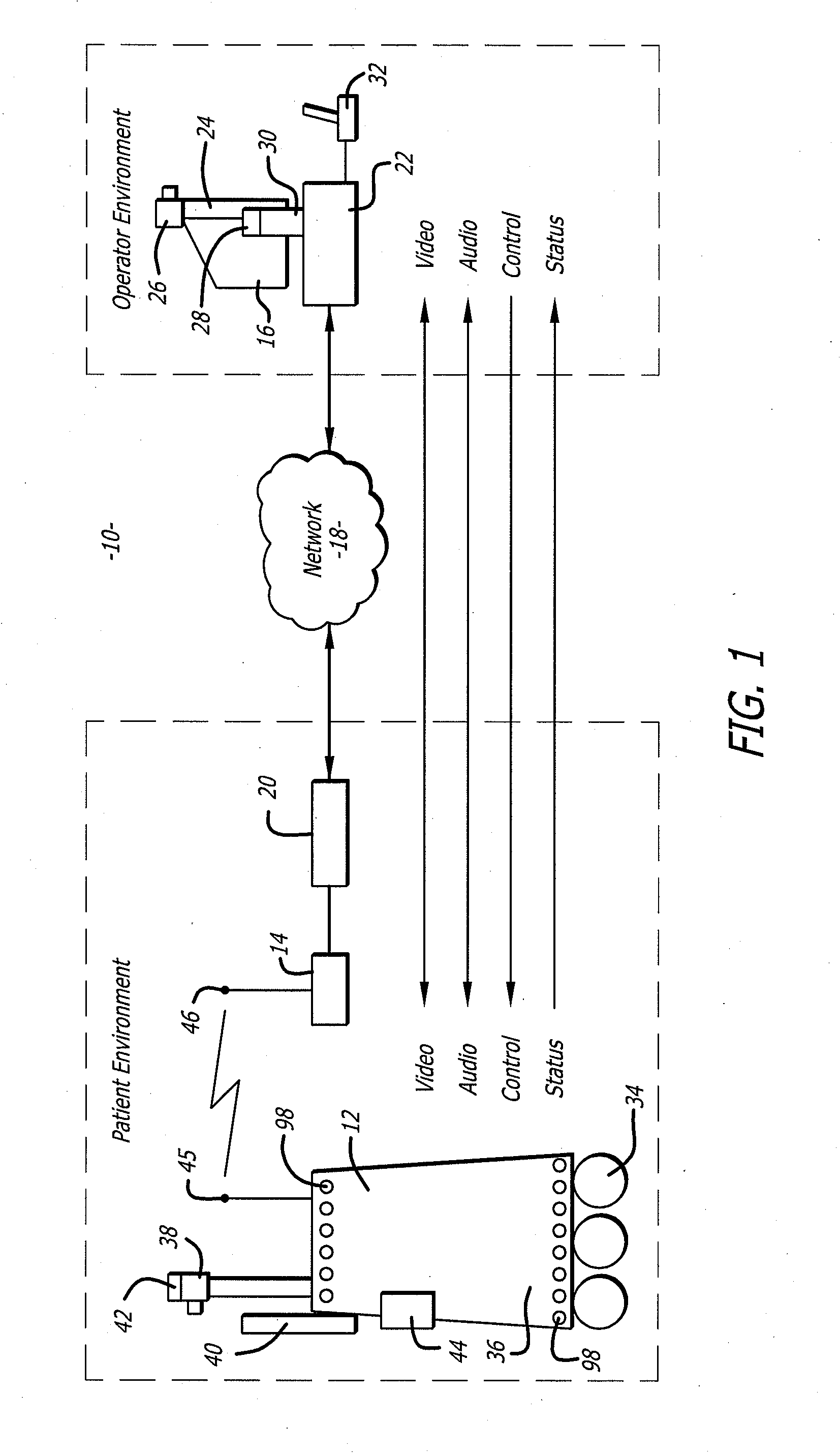
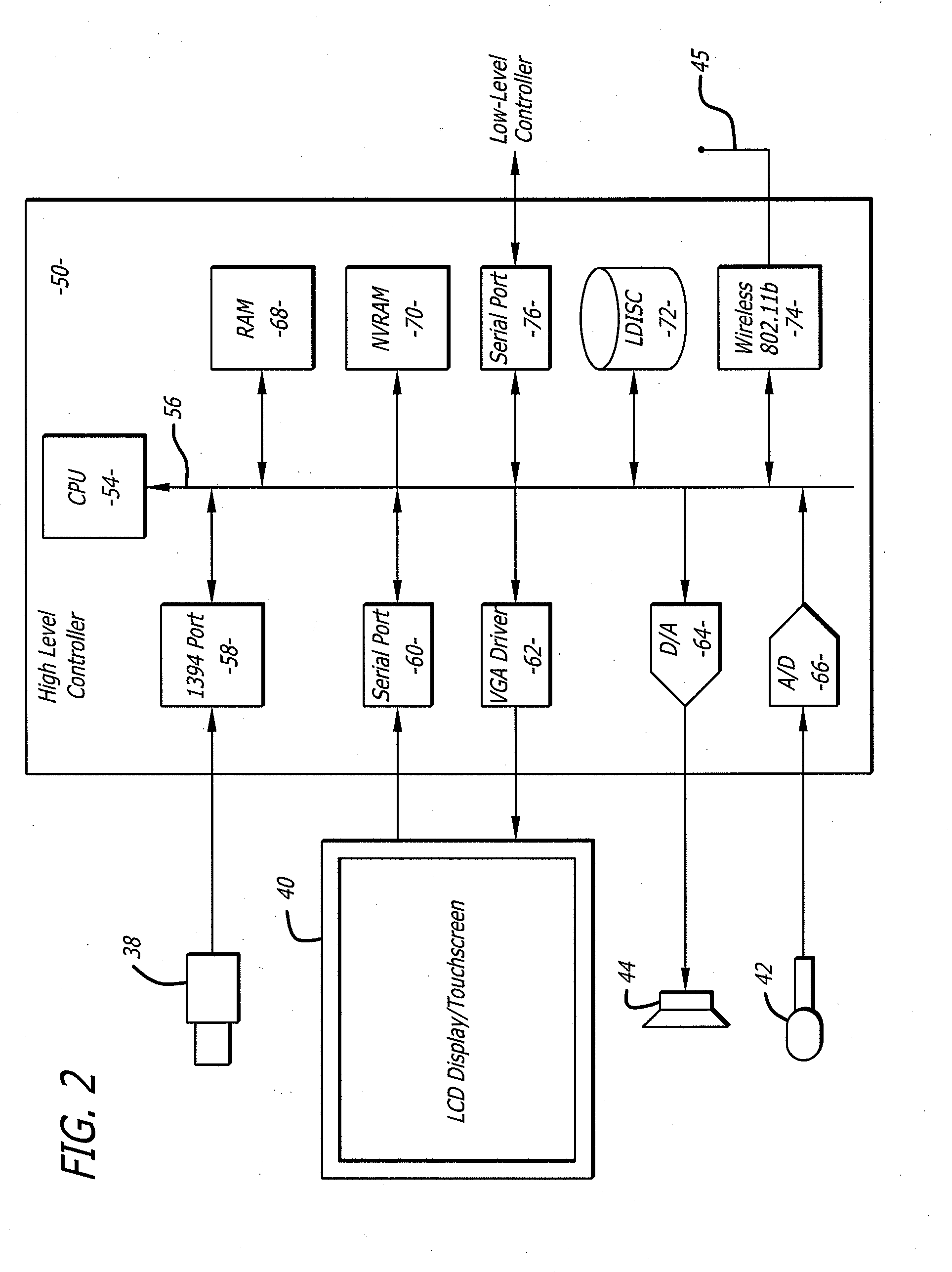
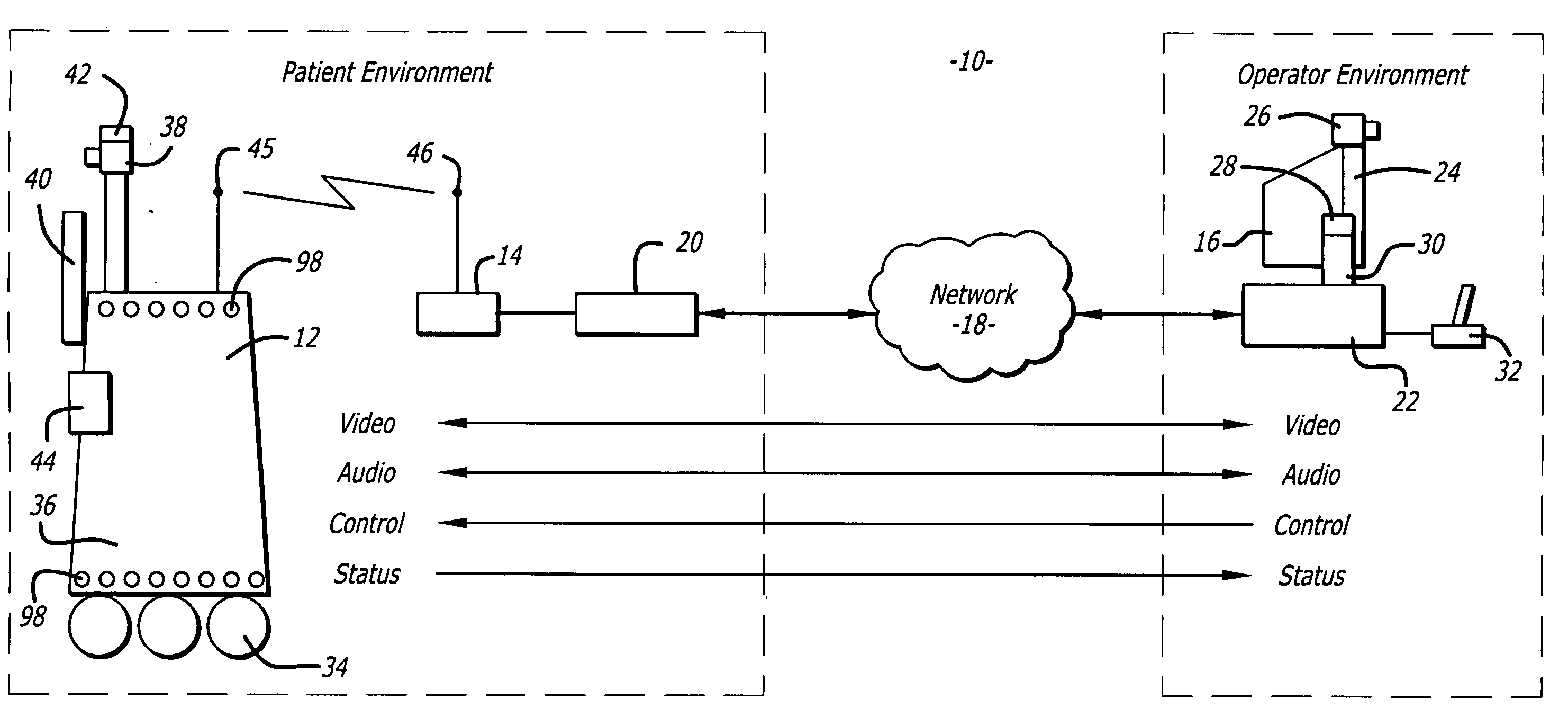
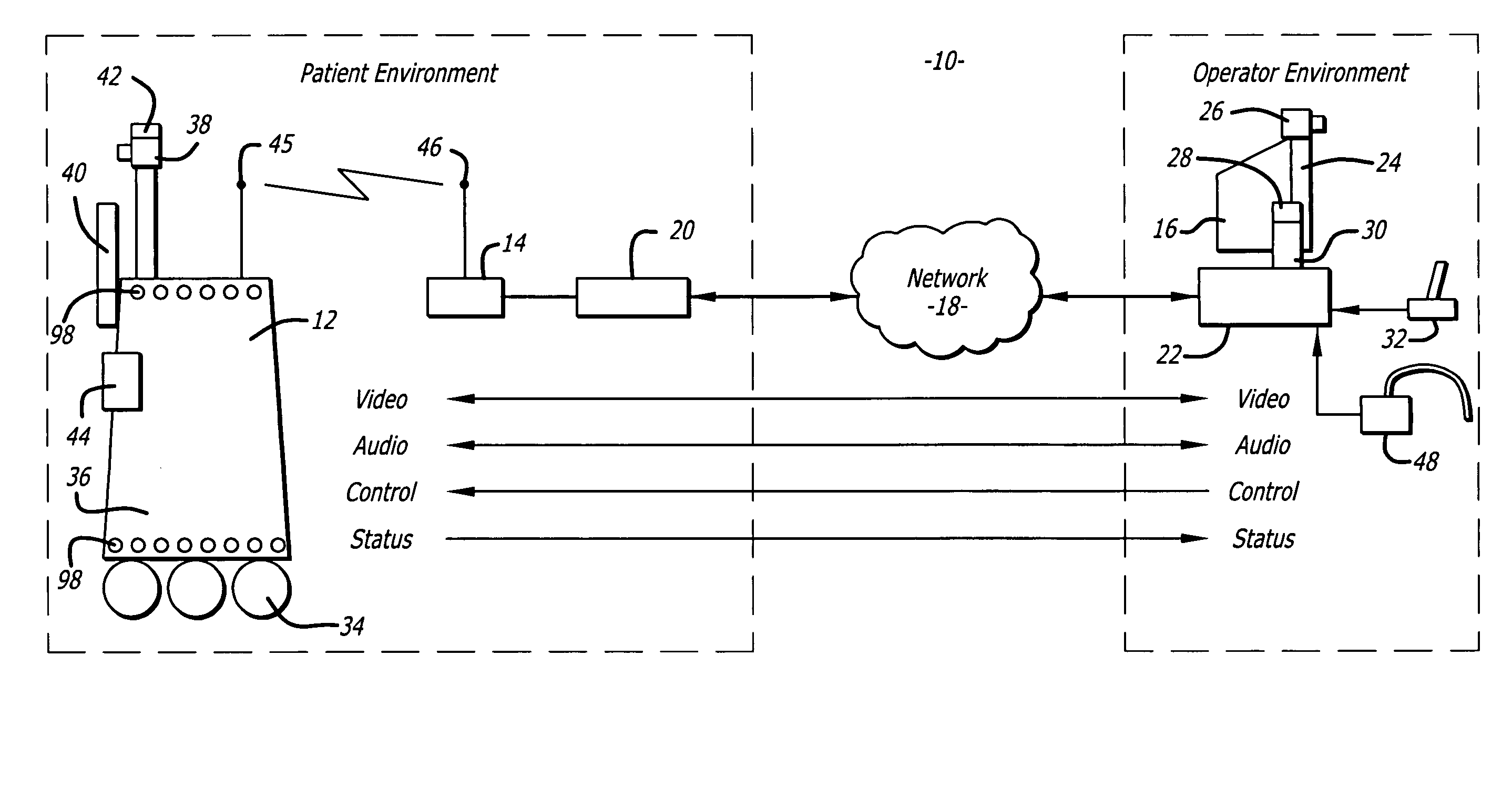
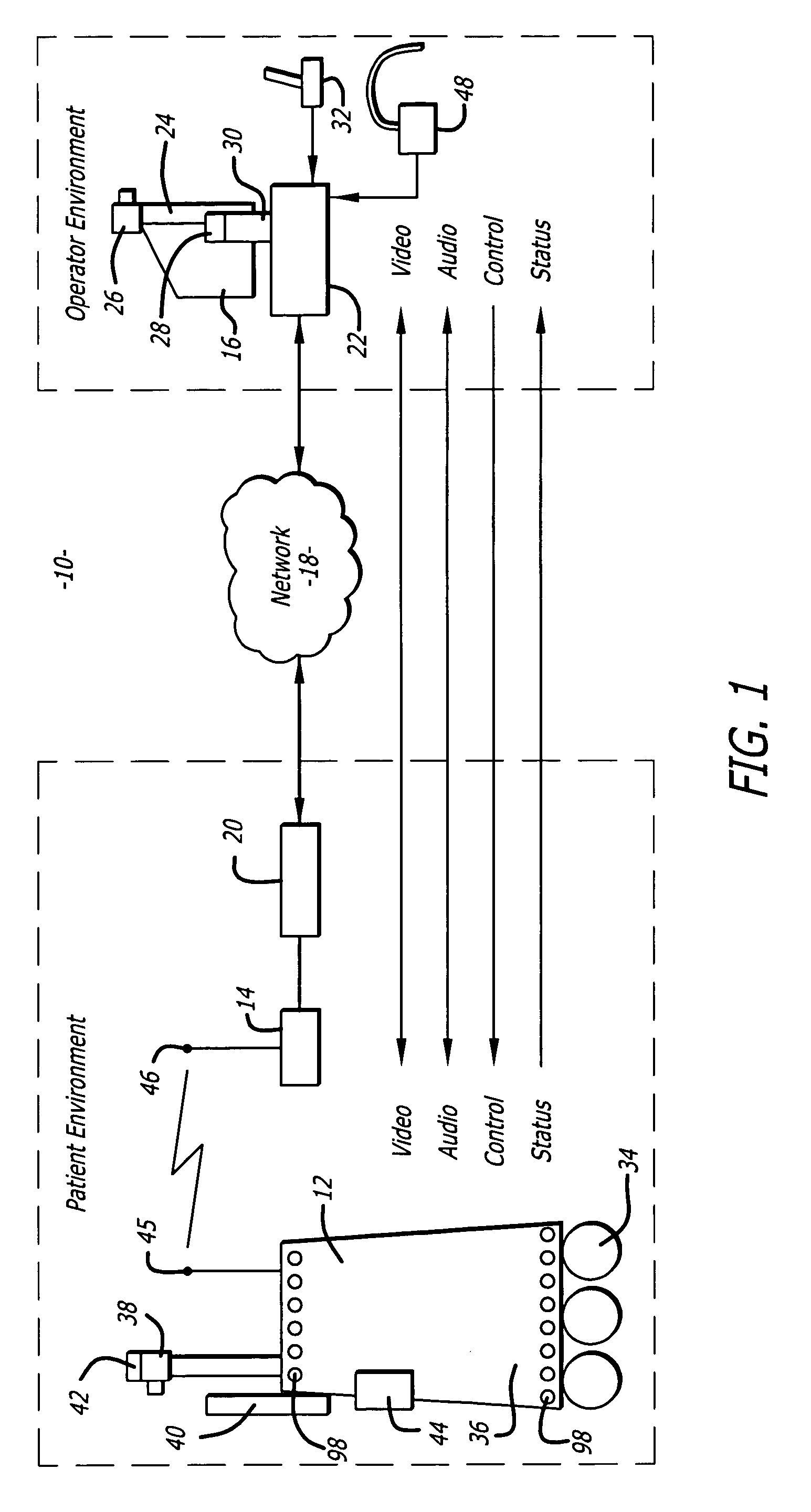
Protocol for a remotely controlled videoconferencing robot
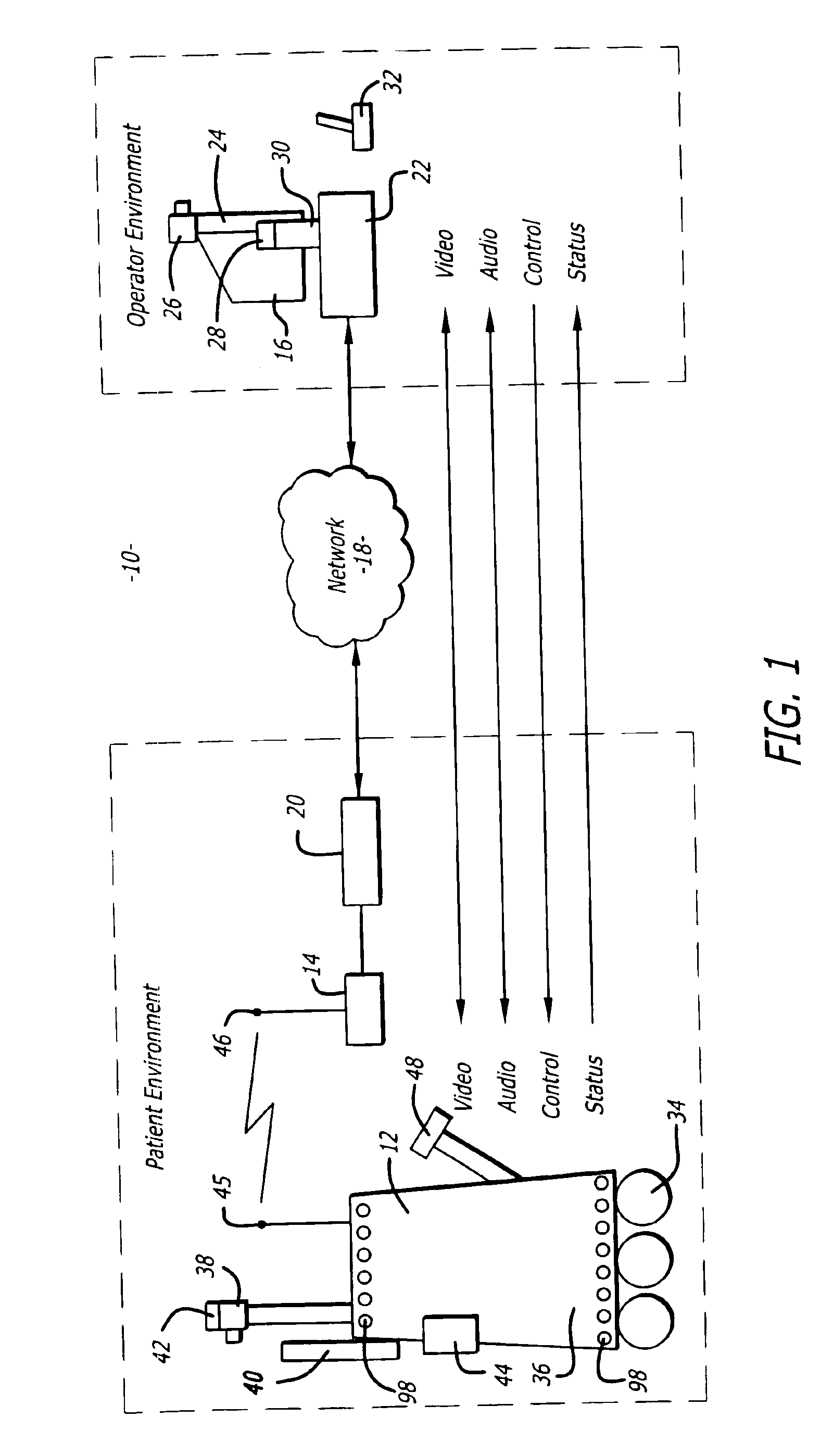
InactiveUS20110071702A1Medical communicationProgramme-controlled manipulatorRobotic systemsEngineering
A robotic system that includes a robot and a remote station. The remote station can generate control commands that are transmitted to the robot through a broadband network. The control commands can be interpreted by the robot to induce action such as robot movement or focusing a robot camera. The robot can generate reporting commands that are transmitted to the remote station through the broadband network. The reporting commands can provide positional feedback or system reports on the robot.
Owner:JONATA SUB TWO INC +1
Protocol for a remotely controlled videoconferencing robot
A robotic system that includes a robot and a remote station. The remote station can generate control commands that are transmitted to the robot through a broadband network. The control commands can be interpreted by the robot to induce action such as robot movement or focusing a robot camera. The robot can generate reporting commands that are transmitted to the remote station through the broadband network. The reporting commands can provide positional feedback or system reports on the robot.
Owner:TELADOC HEALTH INC +1
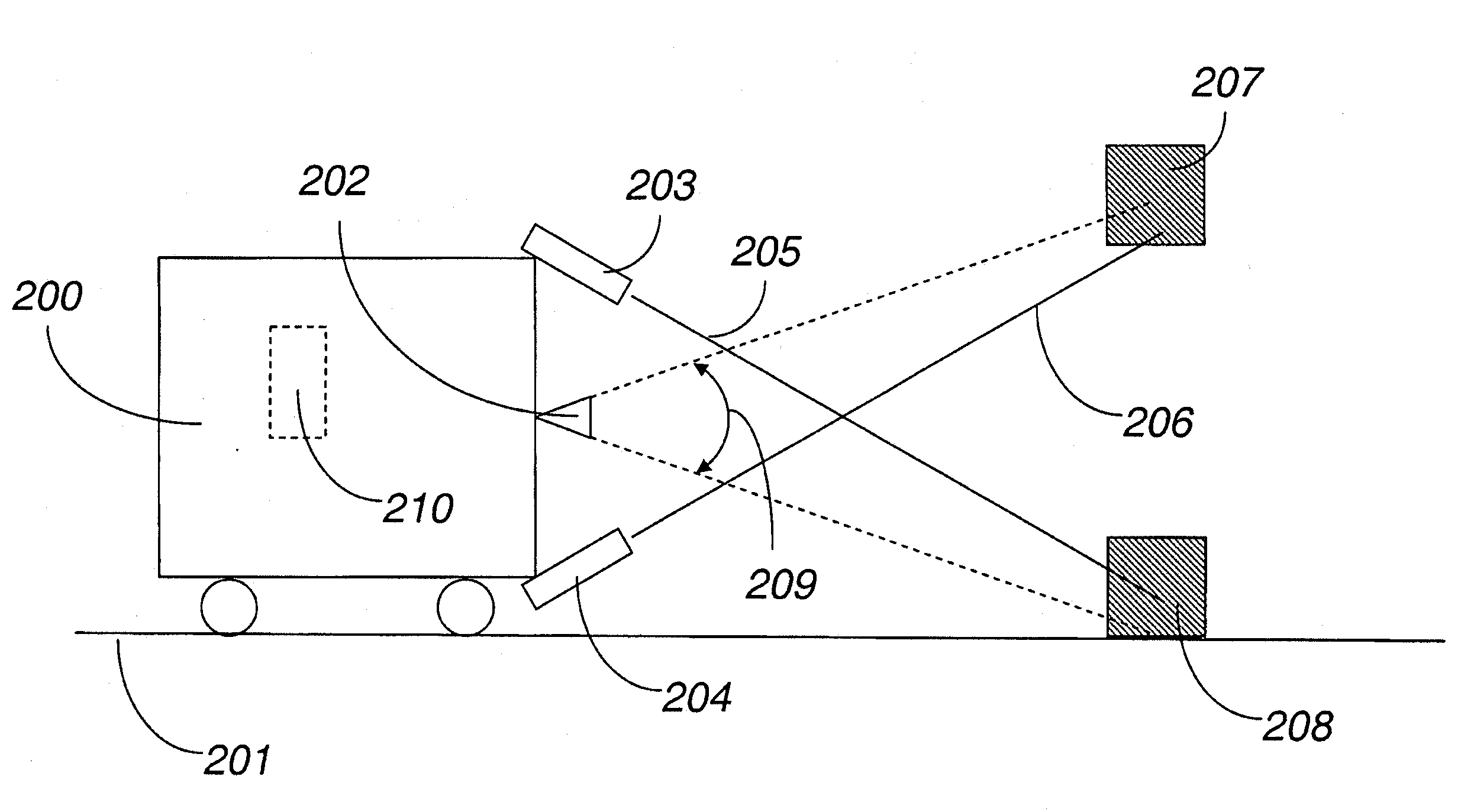
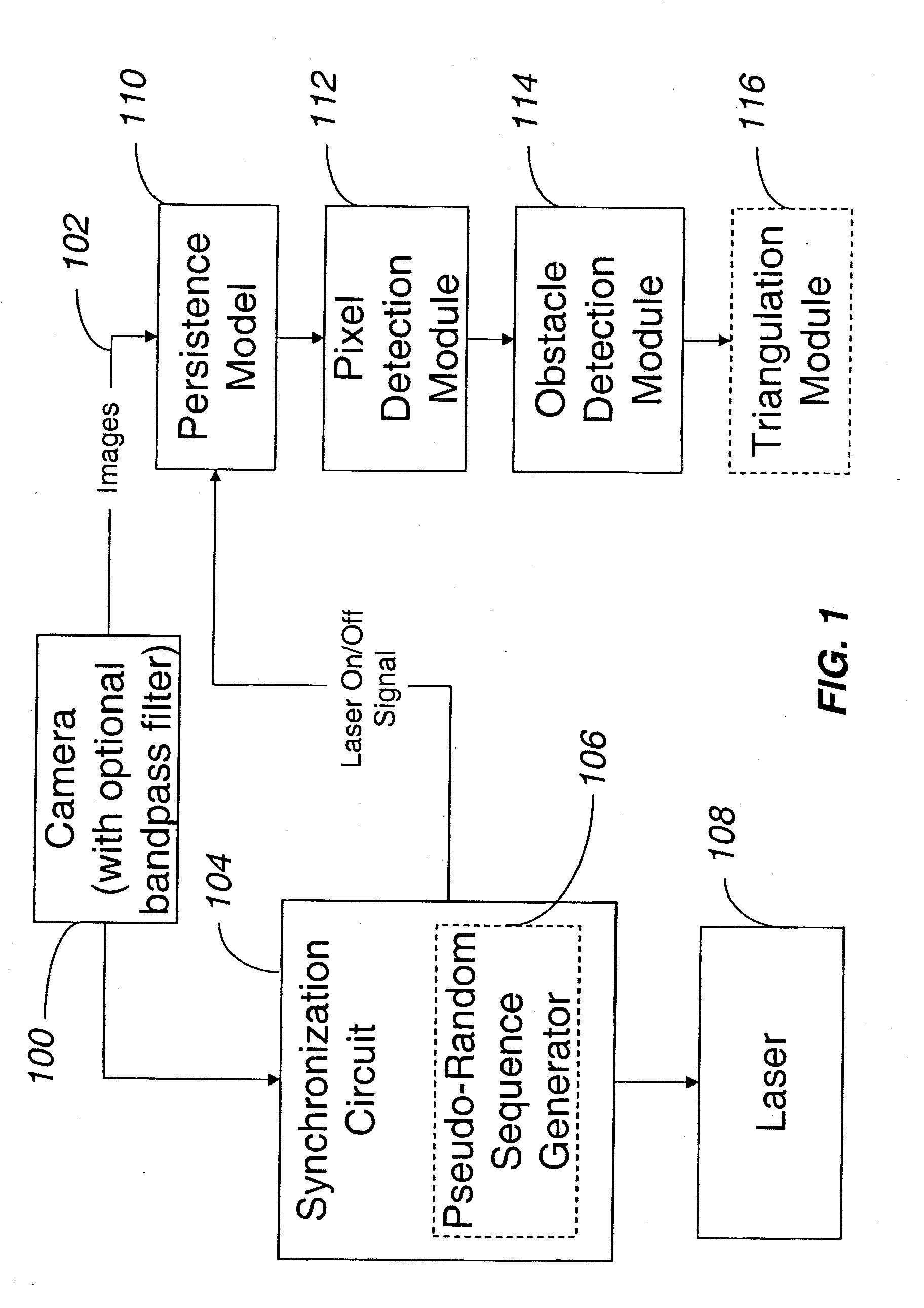
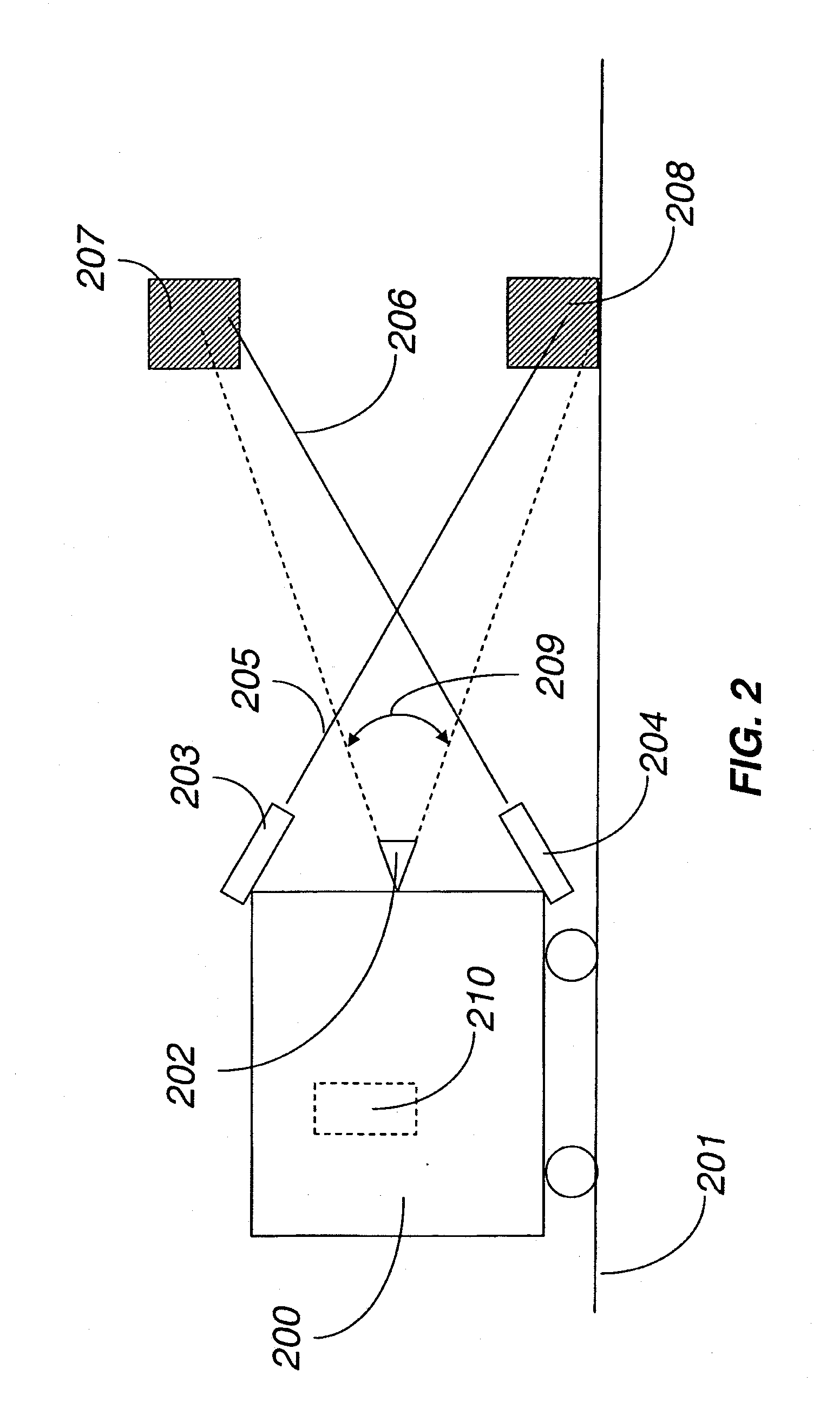
Methods and systems for obstacle detection using structured light
ActiveUS20150168954A1Robust detectionImprove accuracyProgramme controlComputer controlProcessing elementVision sensor
An obstacle detector for a mobile robot while the robot is in motion is disclosed. The detector preferably includes at least one light source configured to project pulsed light in the path of the robot; a visual sensor for capturing a plurality of images of light reflected from the path of the robot; a processing unit configured to extract the reflections from the images; and an obstacle detection unit configured to detect an obstacle in the path of the robot based on the extracted reflections. In the preferred embodiment, the reflections of the projected light are extracted by subtracting pairs of images in which each pair includes a first image captured with the at least one light source on and a second image captured with the at least one light source off, and then combining images of two or more extracted reflections to suppress the background.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
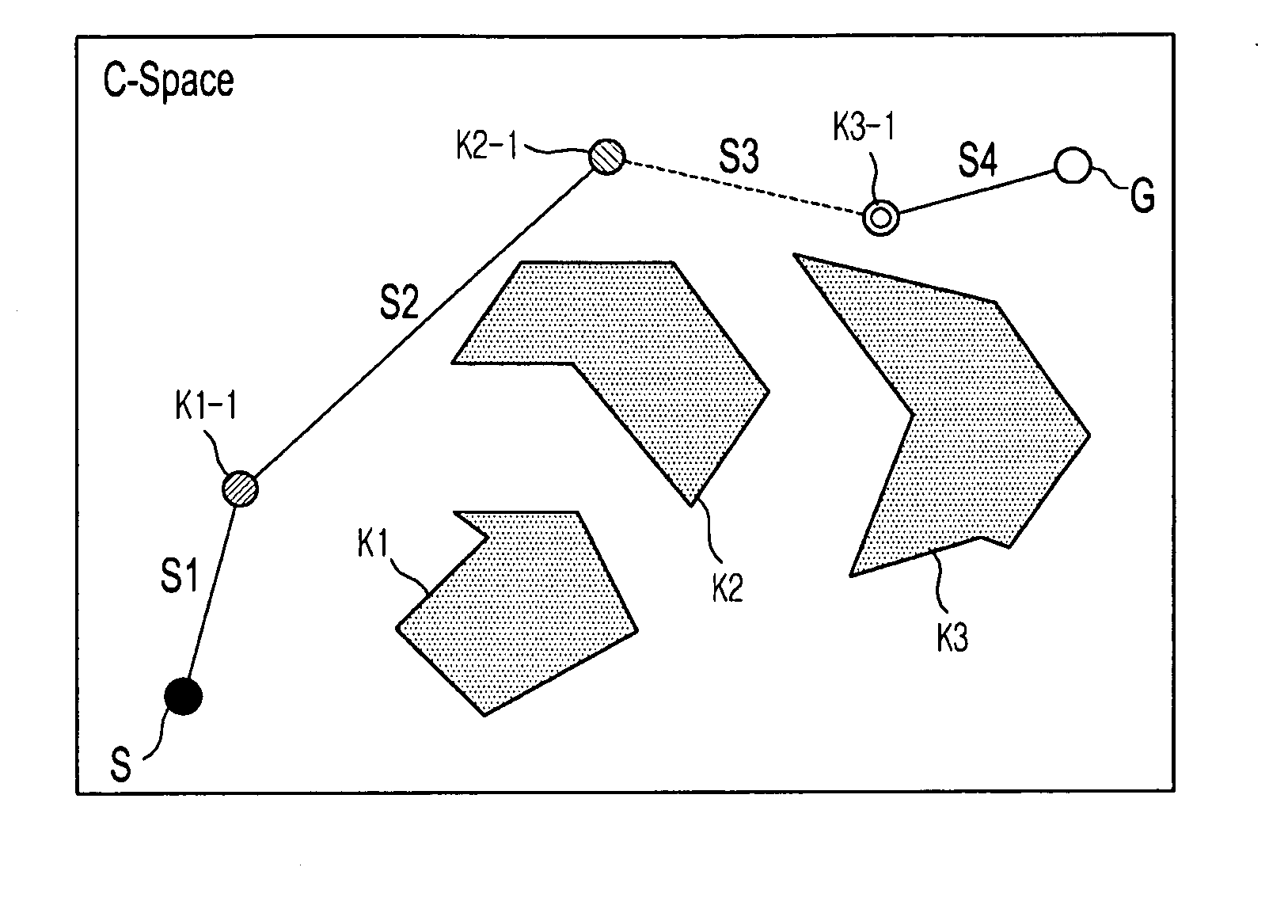
Method and apparatus to plan motion path of robot
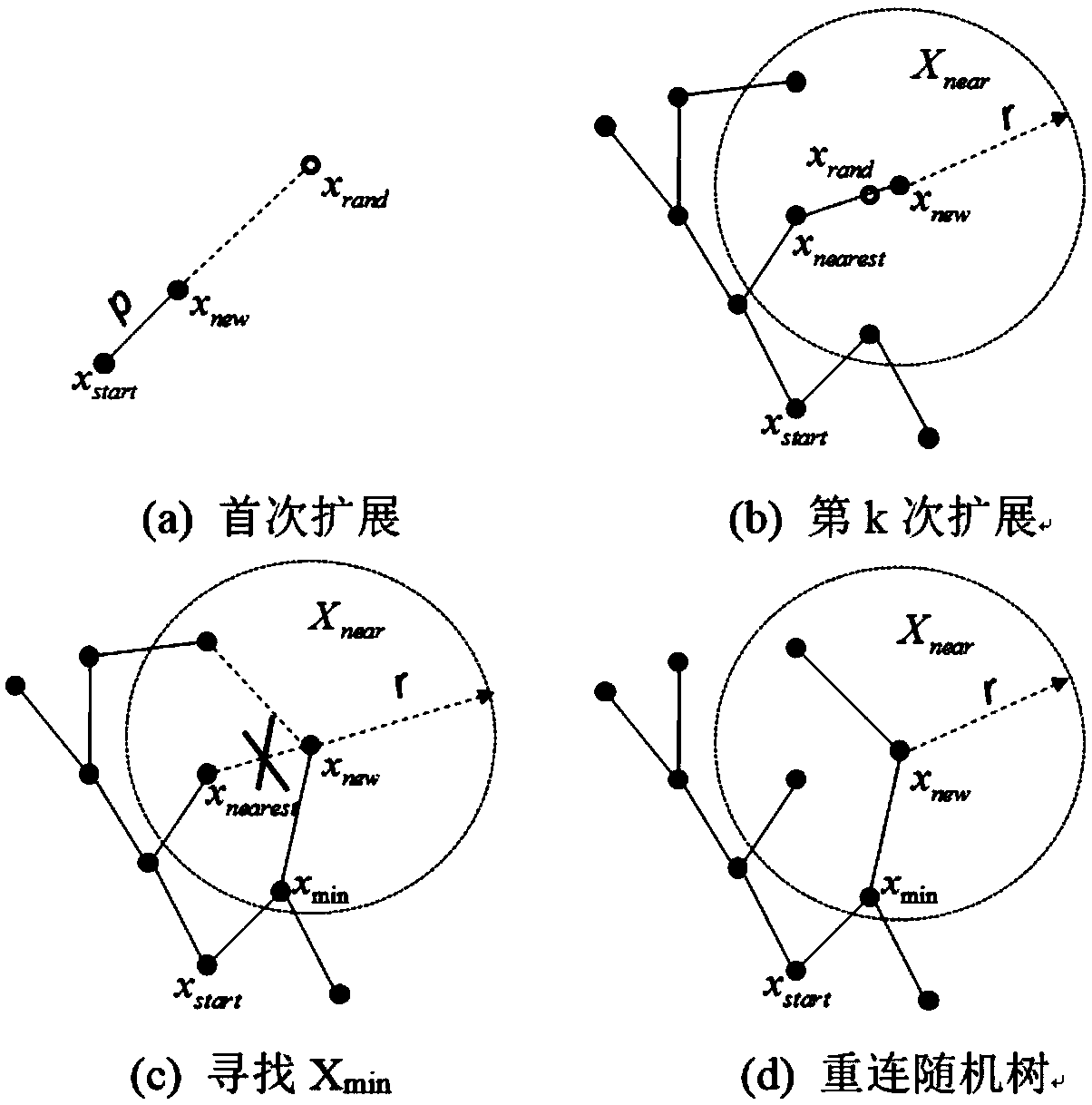
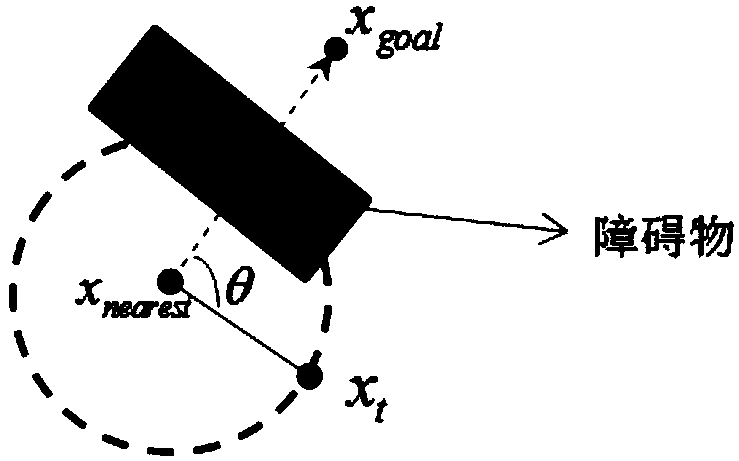
ActiveUS20110035087A1Reduce probabilitySolution can be rapidly obtainedProgramme-controlled manipulatorInstruments for road network navigationAlgorithmRandom tree
A suitable waypoint is selected using a goal score, a section from a start point to a goal point through the waypoint is divided into a plurality of sections based on the waypoint with a solution of inverse kinematics, and trees are simultaneously expanded in the sections using a Best First Search & Rapidly Random Tree (BF-RRT) algorithm so as to generate a path. By this configuration, a probability of local minima occurring is decreased compared with the case where the waypoint is randomly selected. In addition, since the trees are simultaneously expanded in the sections each having the waypoint with a solution of inverse kinematics, the solution may be rapidly obtained. A time consumed to search for an optimal motion path may be shortened and path plan performance may be improved.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
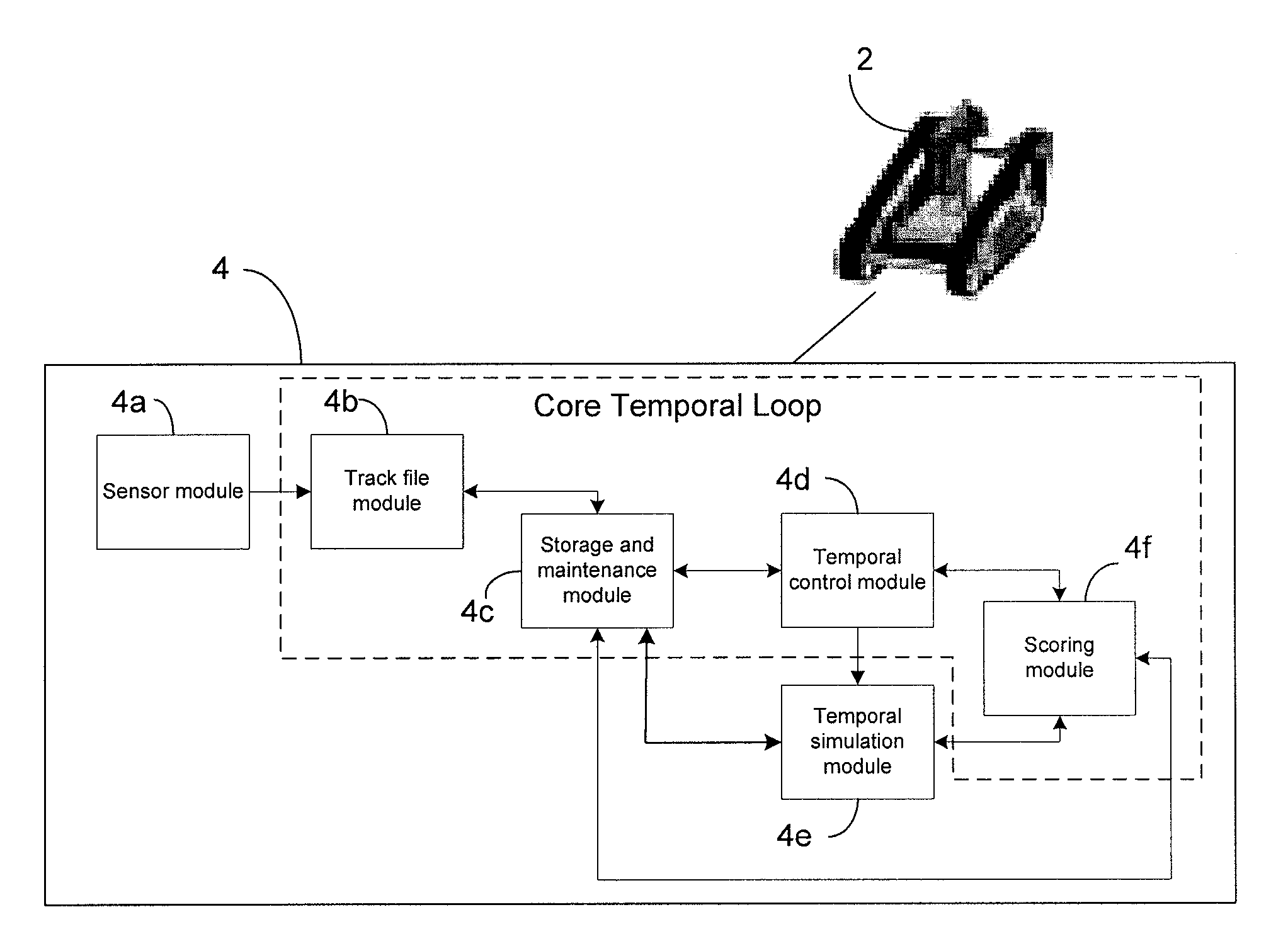
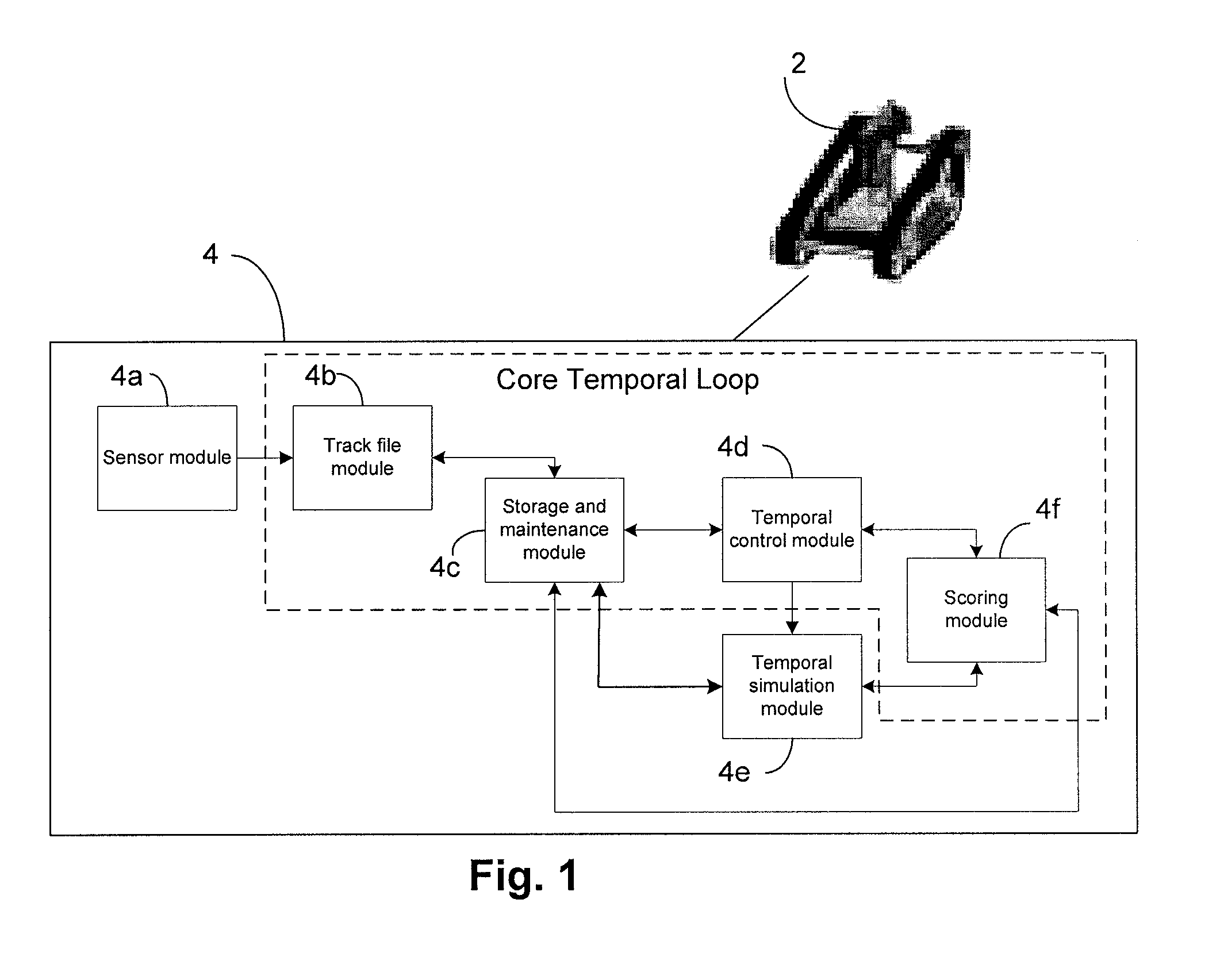
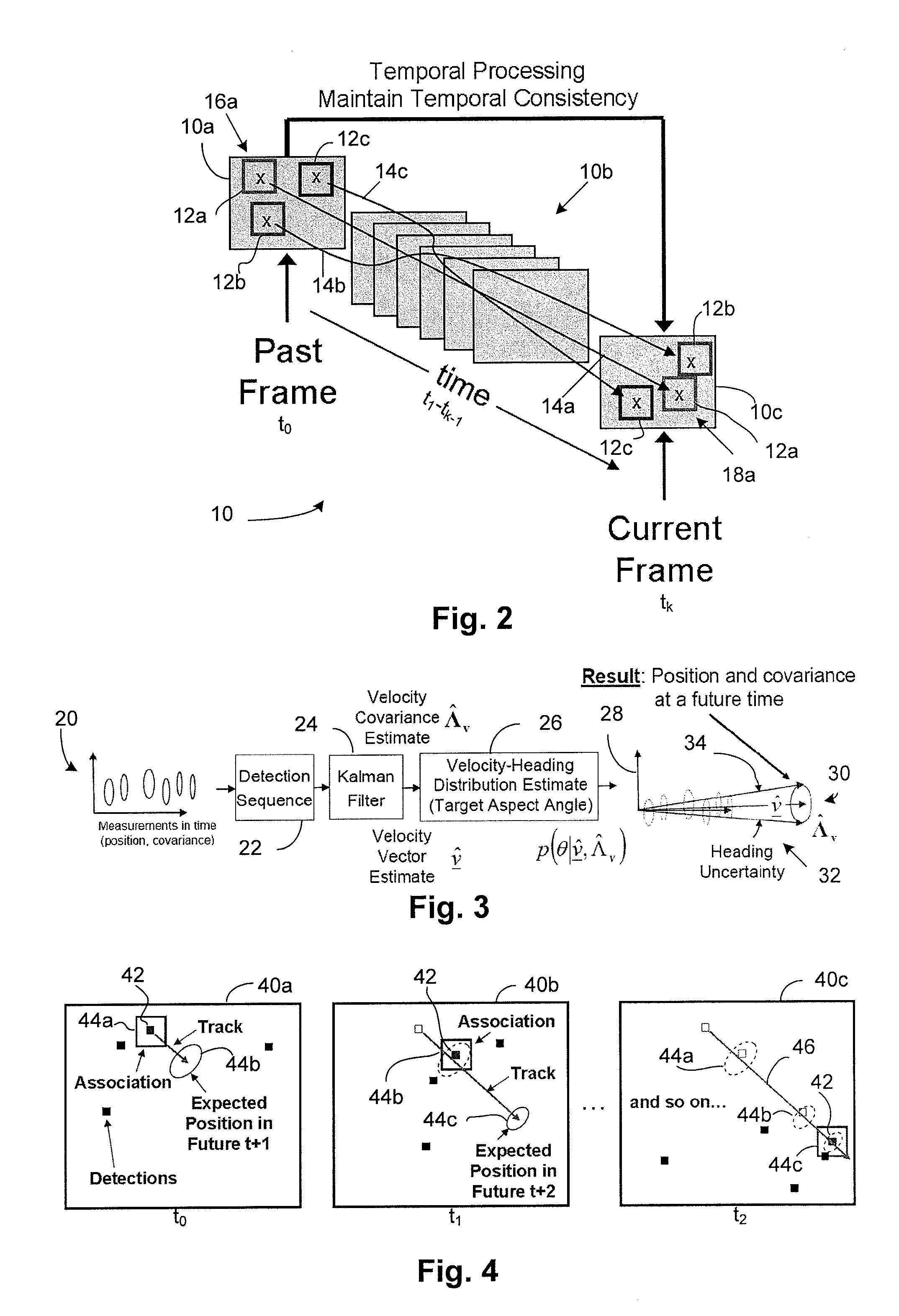
Temporal tracking robot control system
ActiveUS20110231016A1Autonomous decision making processNavigational calculation instrumentsObject basedHypothesis
A temporal controller for mobile robot path planning includes a sensor module for receiving data corresponding to spatial locations of at least one object, and a temporal control module operatively coupled to the sensor module, the temporal control module configured to predict future locations of the at least one object based on data received by the sensor module. The controller further includes a temporal simulation module operatively coupled to the temporal control module, wherein the temporal simulation module configured to use the predicted future locations of the at least one object to simulate multiple robot motion hypothesis for object avoidance and trajectory planning.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Autofocus and/or autoscaling in telesurgery
ActiveUS20070083098A1Enhance perceived correlationProgramme controlComputer controlRemote surgeryDisplay device
Robotic, telerobotic, and / or telesurgical devices, systems, and methods take advantage of robotic structures and data to calculate changes in the focus of an image capture device in response to movement of the image capture device, a robotic end effector, or the like. As the size of an image of an object shown in the display device varies with changes in a separation distance between that object and the image capture device used to capture the image, a scale factor between a movement command input may be changed in response to moving an input device or a corresponding master / slave robotic movement command of the system. This may enhance the perceived correlation between the input commands and the robotic movements as they appear in the image presented to the system operator.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
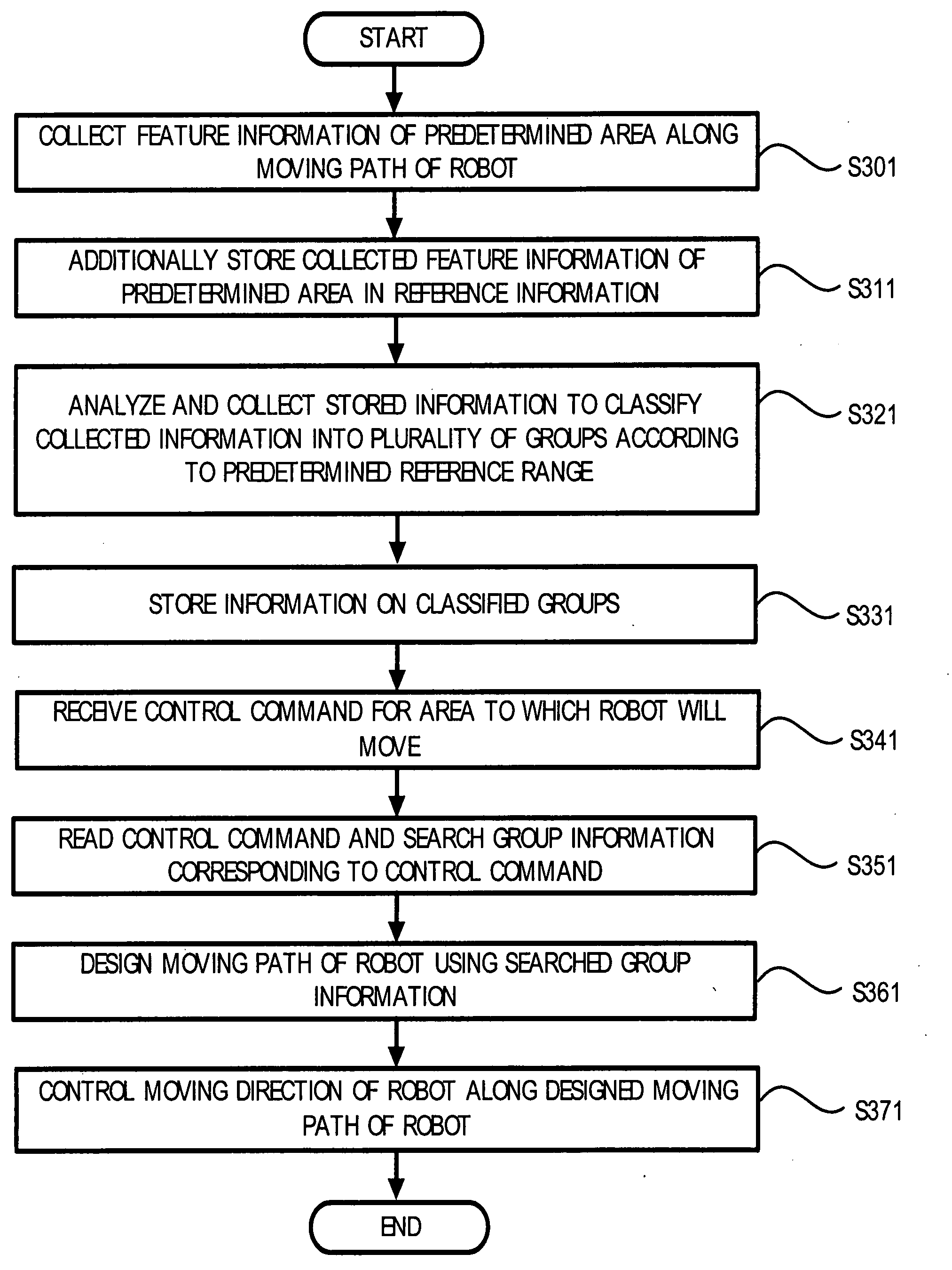
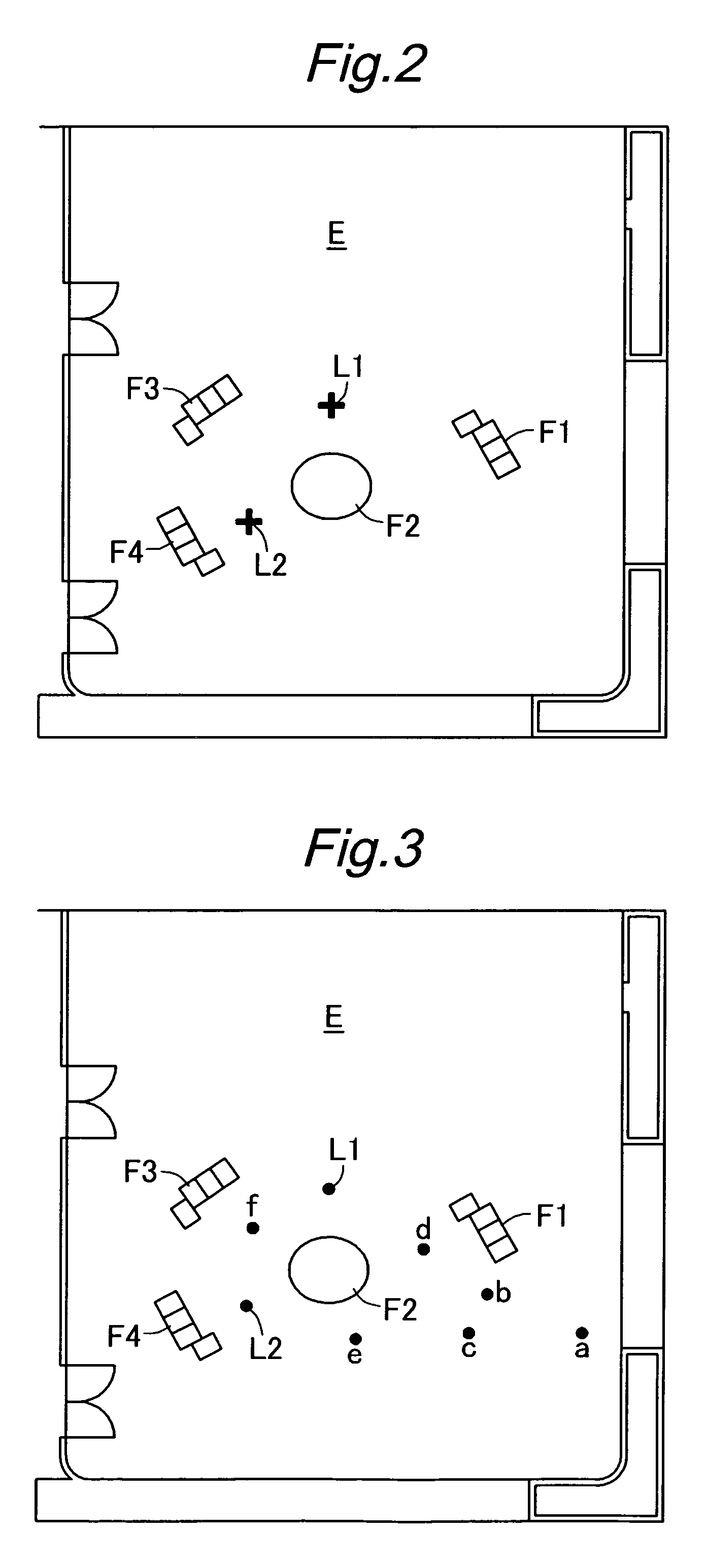
Method, medium and apparatus classifying and collecting area feature information according to a robot's moving path, and a robot controlled by the area features
ActiveUS20070282484A1Programme-controlled manipulatorSpecial data processing applicationsArtificial intelligenceReference range
A method of classifying and collecting feature information of an area according to a robot's moving path, a robot controlled by area features, and a method and apparatus for composing a user interface using the area features are disclosed. The robot includes a plurality of sensor modules to collect feature information of a predetermined area along a moving path of the robot, and an analyzer to analyze the collected feature information of the predetermined area according to a predetermined reference range and to classify the collected feature information into a plurality of groups.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
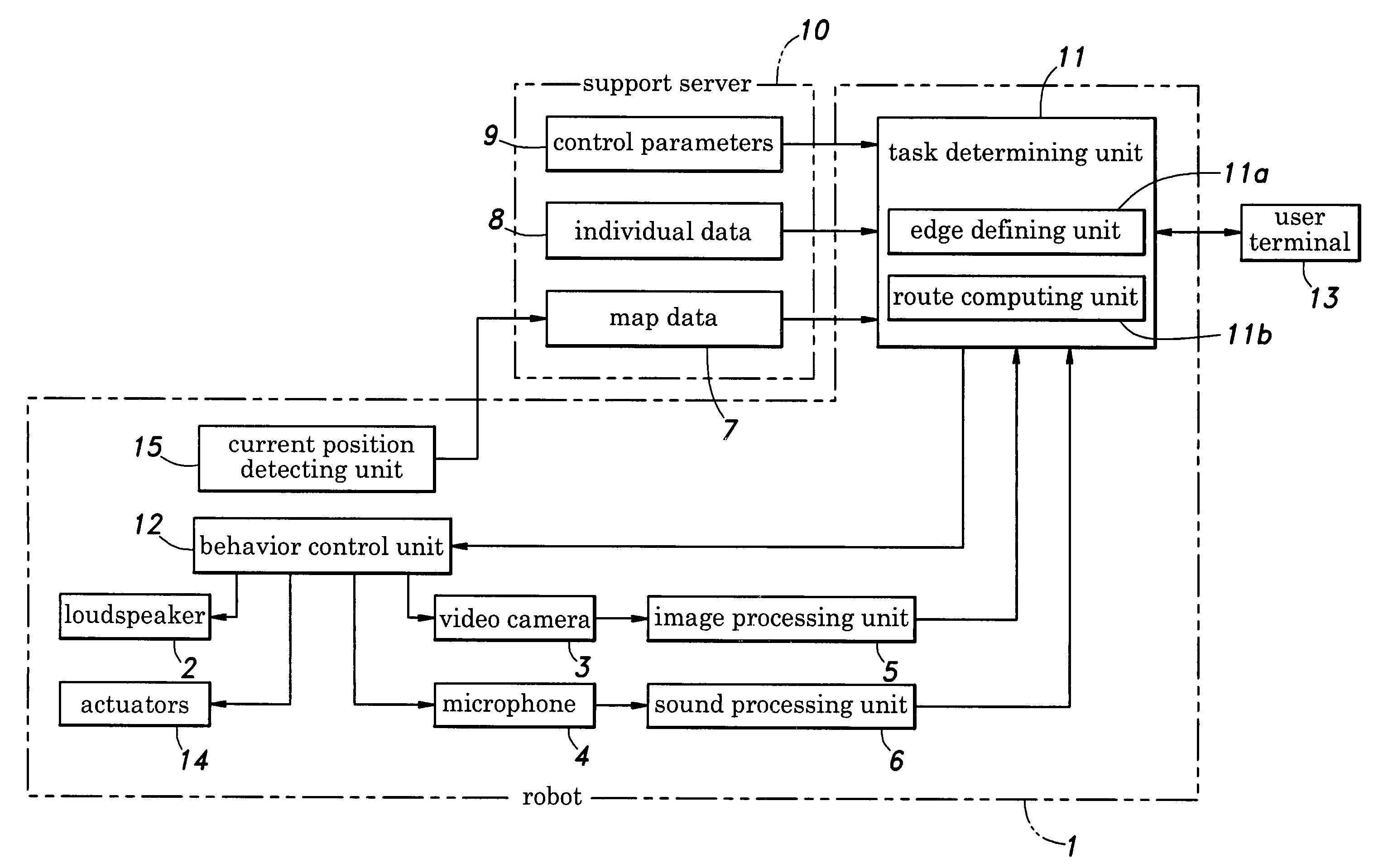
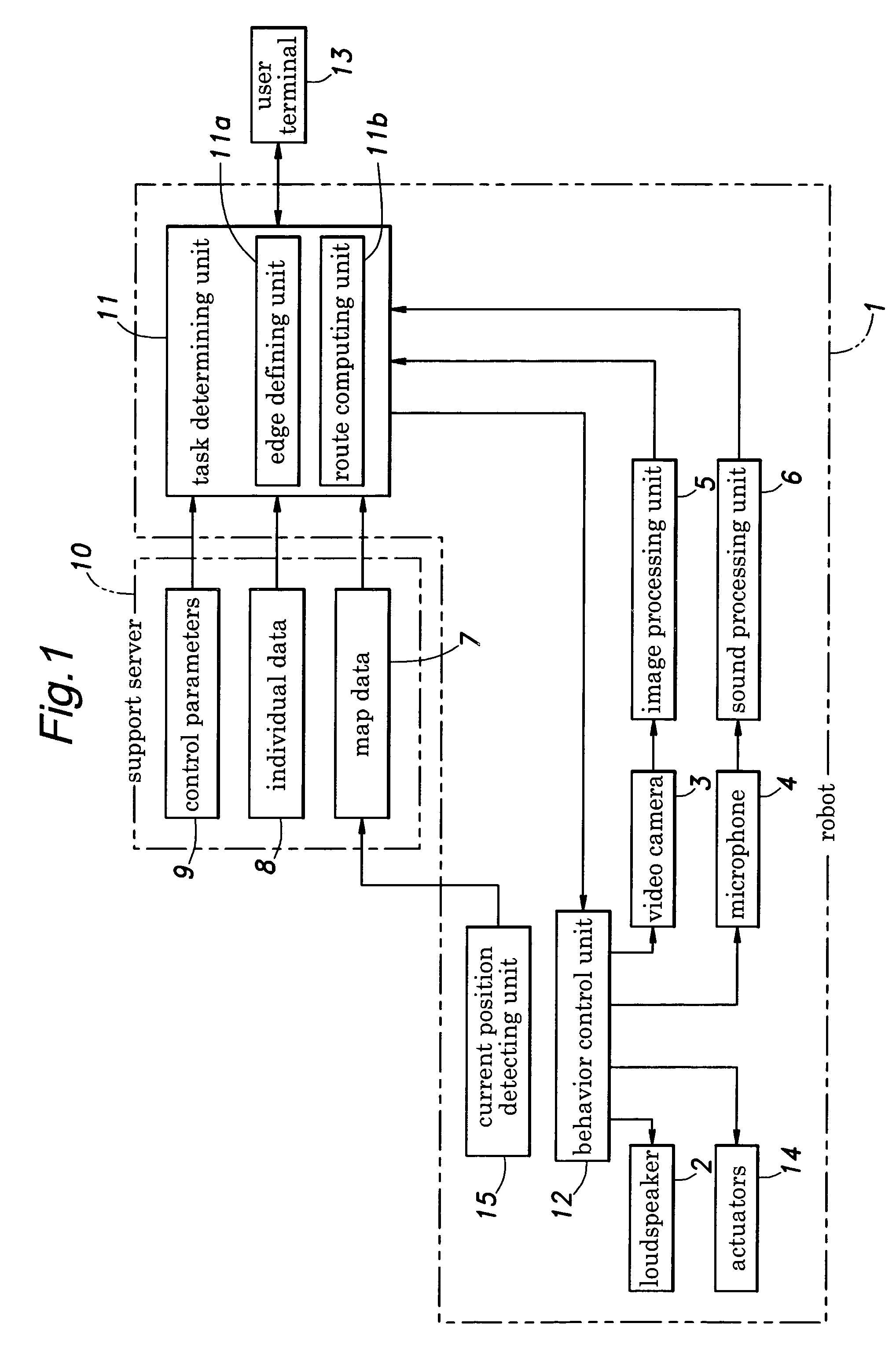
Medical tele-robotic system with a head worn device
ActiveUS7262573B2Input/output for user-computer interactionDiagnosticsVisual field lossRobotic systems
A robot system that includes a robot and a remote station. The remote station includes a head worn device worn on the head of a user. The head worn device senses movement of the user's head and generates corresponding input signals. The input signals are processed into robot movement commands and transmitted to the robot, typically through a broadband network. The robot movement commands move a camera of the robot. The camera movement tracks movement of the user's head so that the user can scan the visual field without having to generate separate input commands for the robot.
Owner:TELADOC HEALTH INC +1
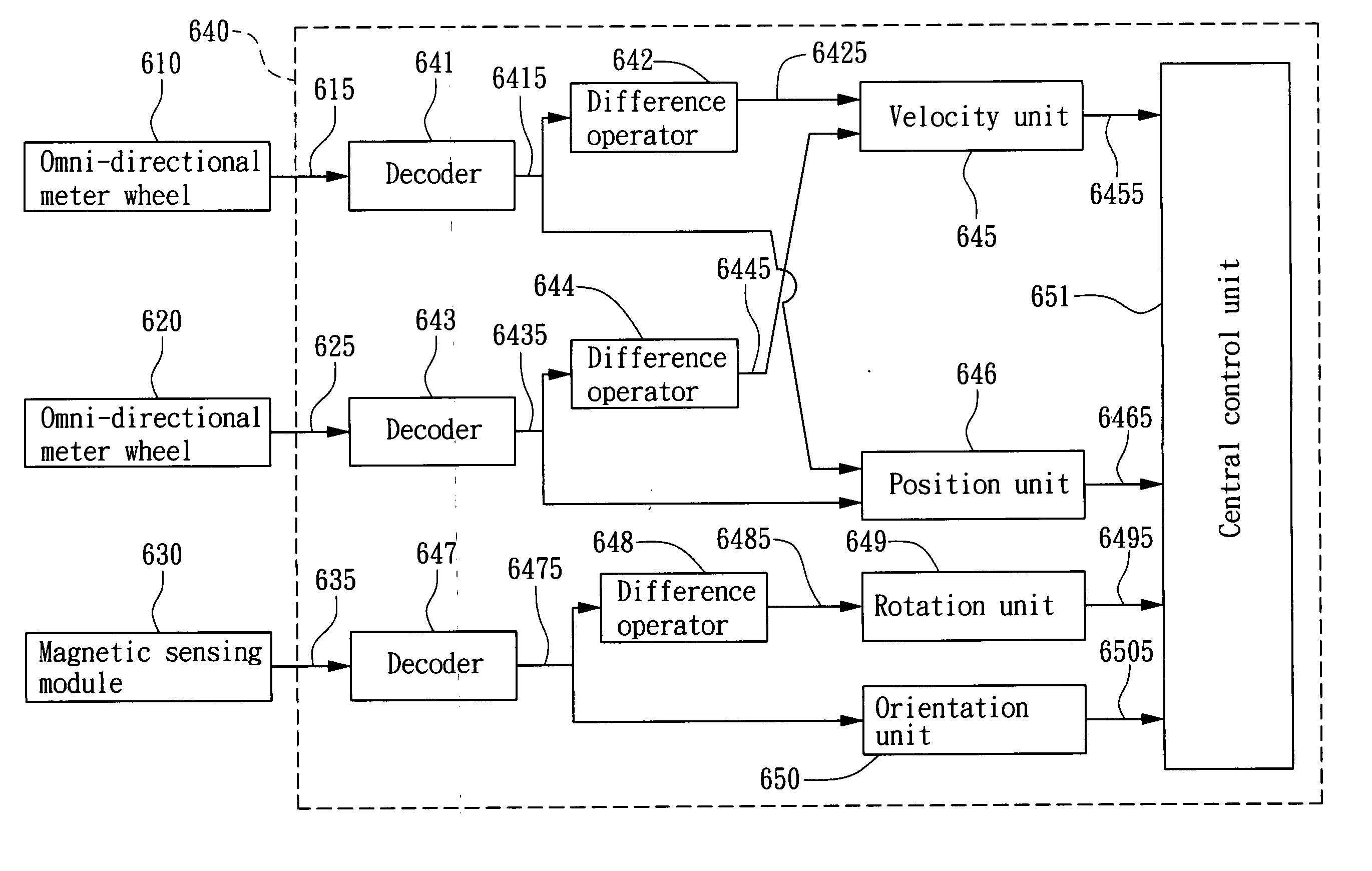
Mobile robot platform and method for sensing movement of the same
A mobile robot platform and a method for sensing movement of the same are disclosed, which utilize two omni-directional meter wheels perpendicular to each other and a magnetic sensing module for detecting a moving condition of the platform moving on a planar surface while transmitting the detected moving condition to a signal processing unit to calculate the position, velocity, angular position and angular velocity of the platform.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
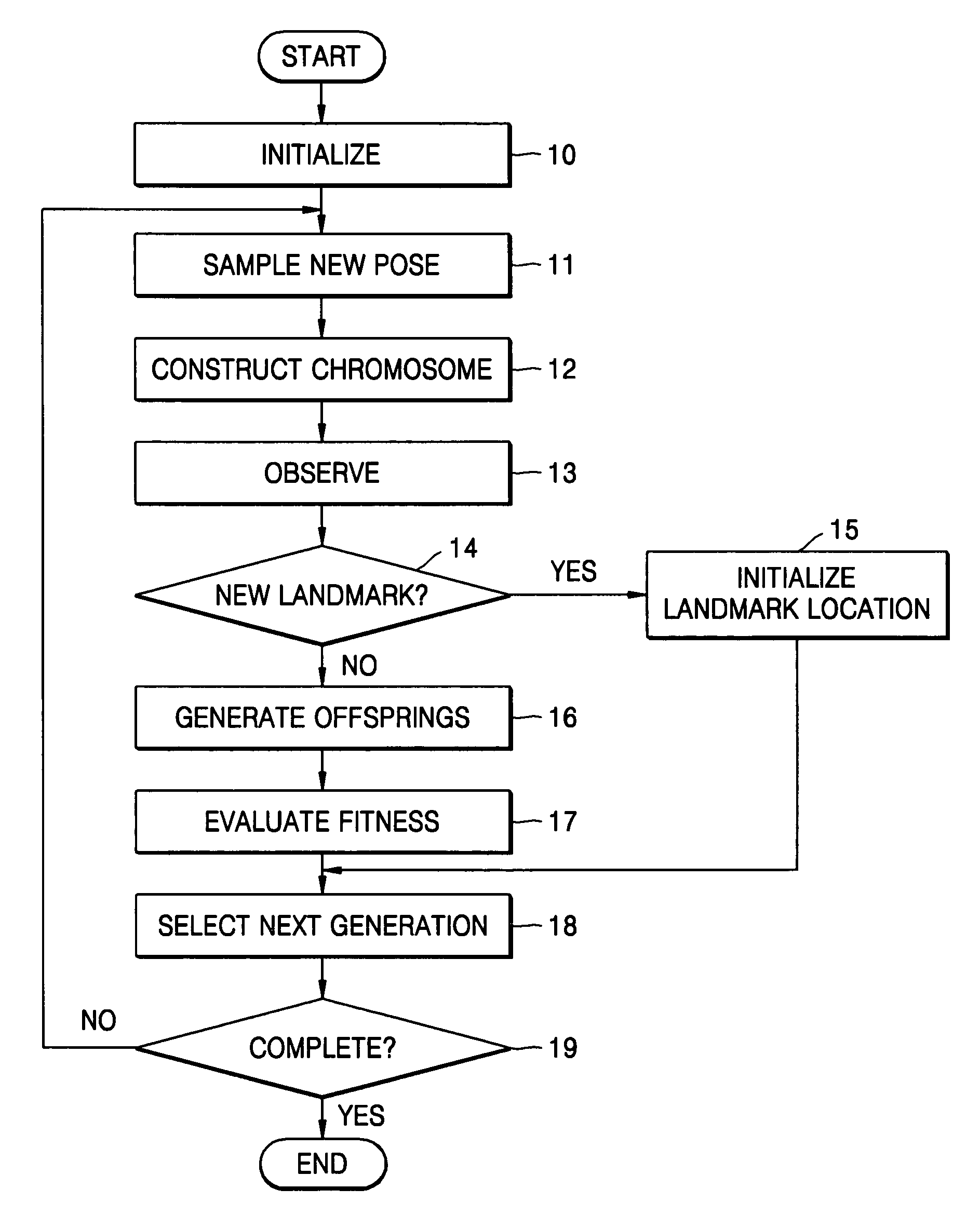
Method used by robot for simultaneous localization and map-building
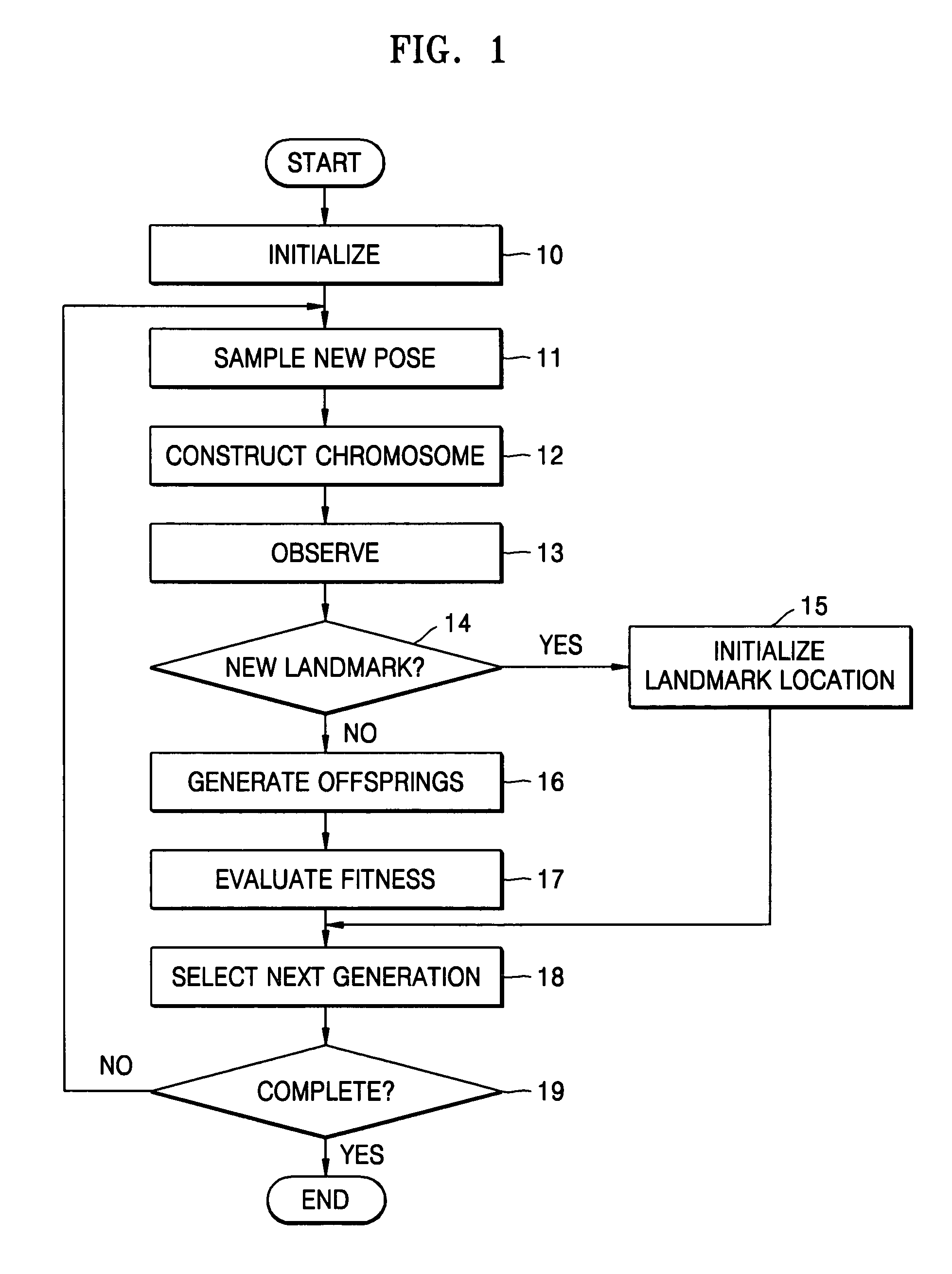
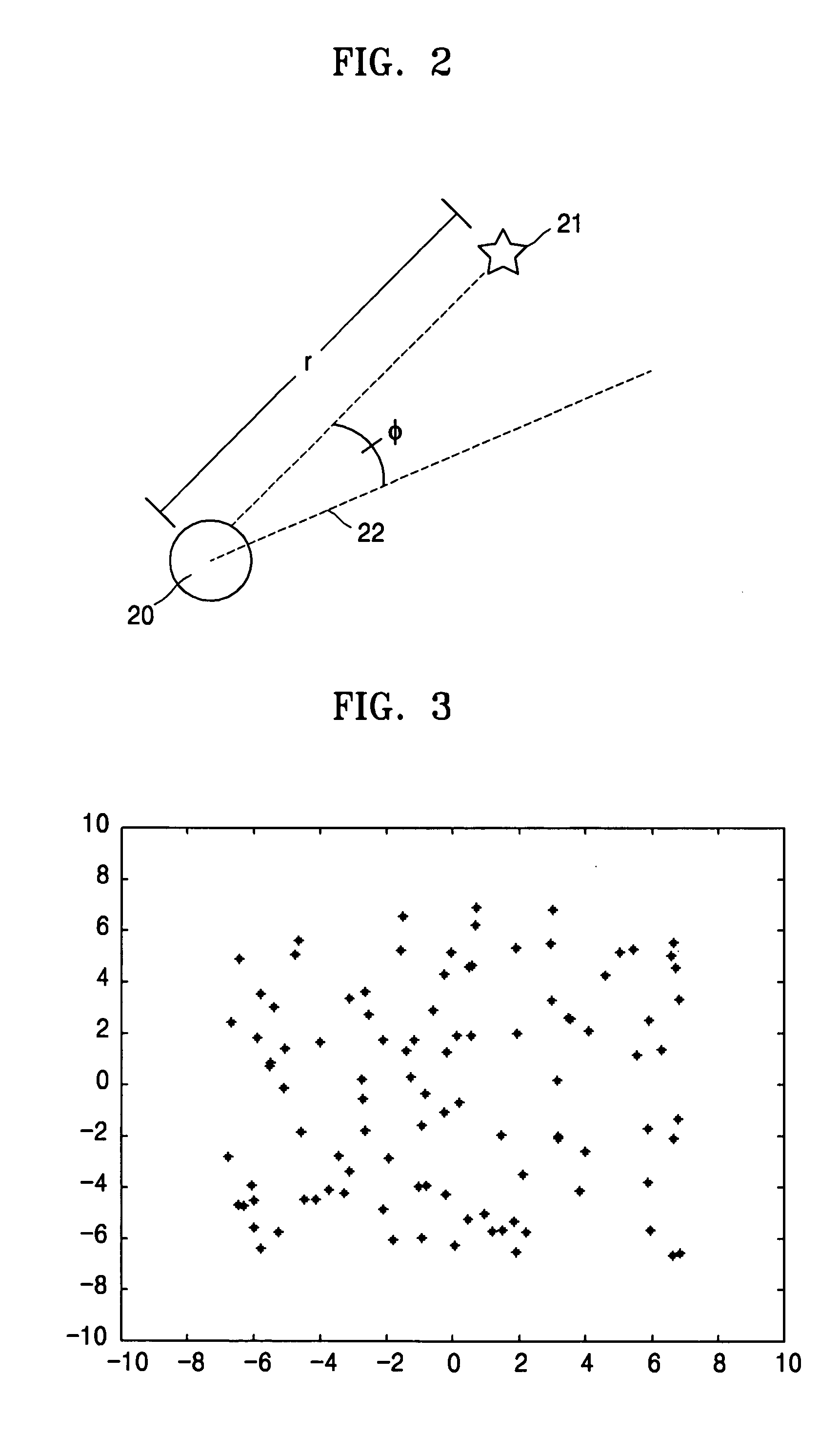
A method used by a robot for simultaneous localization and map-building, including: initializing a pose of the robot and locations of landmarks; sampling a new pose of the robot during motion of the robot, and constructing chromosomes using the locations of the landmarks; observing the landmarks from a present location of the robot; generating offspring from the chromosomes; and selecting next-generation chromosomes from the chromosomes and the offspring using observation values of the landmarks.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Autonomous mobile robot system
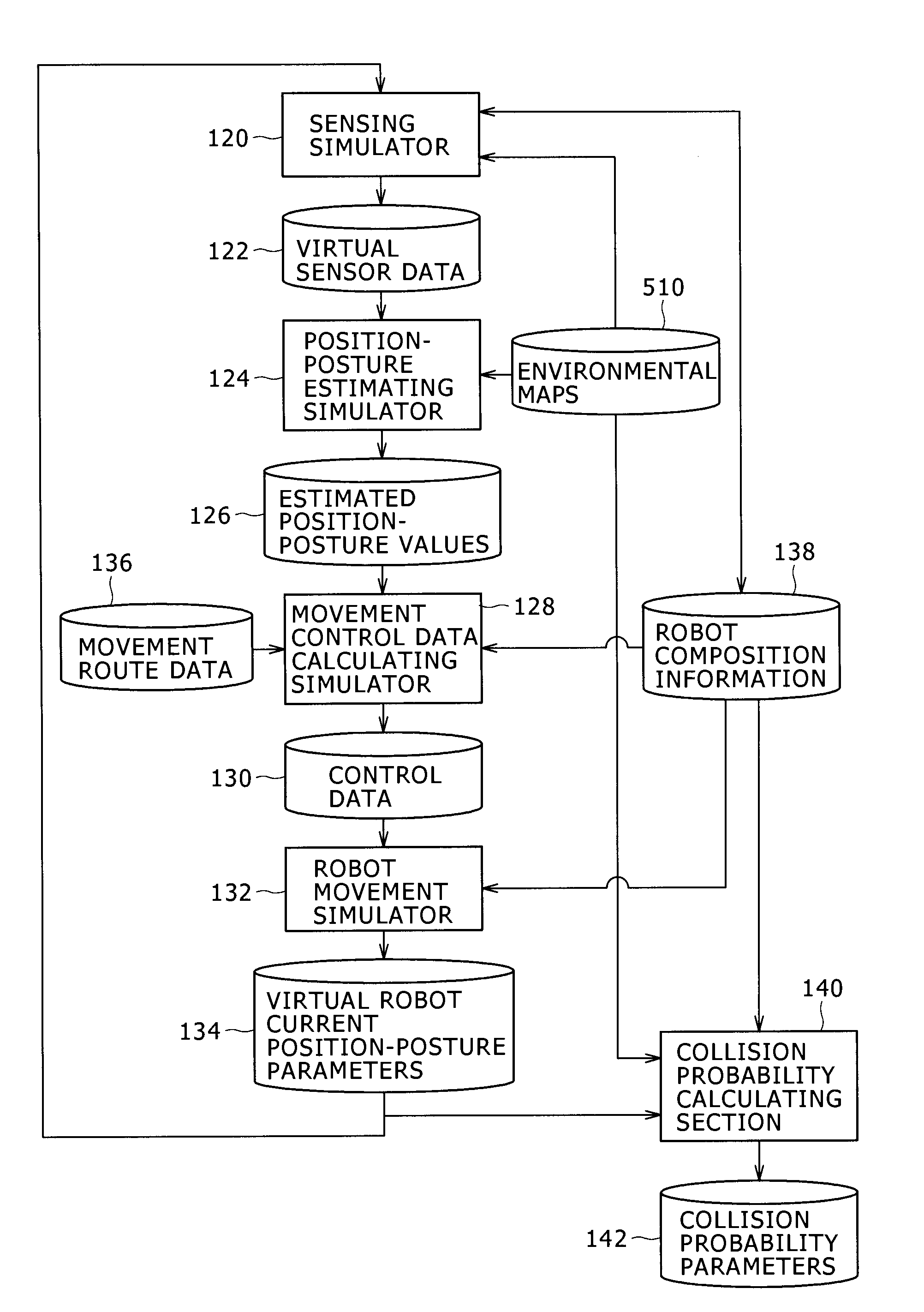
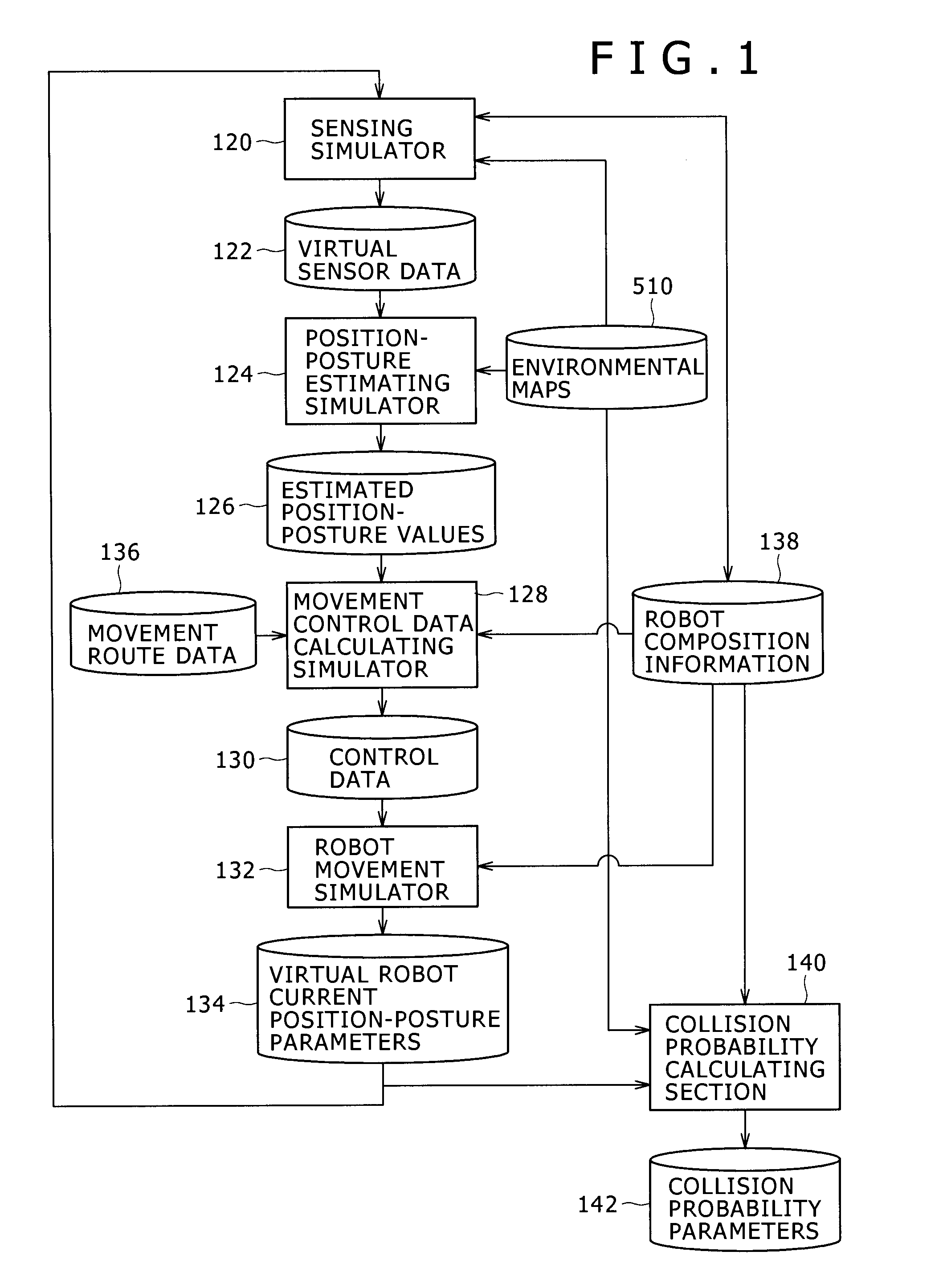
InactiveUS20090326713A1Reduce the likelihood of a collisionReduce the possibilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlSensing dataSimulation
The possibilities of collision of a mobile robot with objects can be reduced significantly in actual robot movements. In an aspect of the present invention, there is provided an autonomous mobile robot system including a mobile robot and a computing system. The mobile robot includes: a sensing section for measuring surrounding conditions of the mobile robot; a position-posture estimating section for estimating position-posture data from sensing data obtained by the sensing section and an environmental map; and a robot moving section for controlling movements of the mobile robot according to movement control data determined from the position-posture data thus estimated and movement route data.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Device and method for making robot track given route at high accuracy
InactiveCN101623867ALow costGuaranteed to workProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorRobotic systemsThree stage
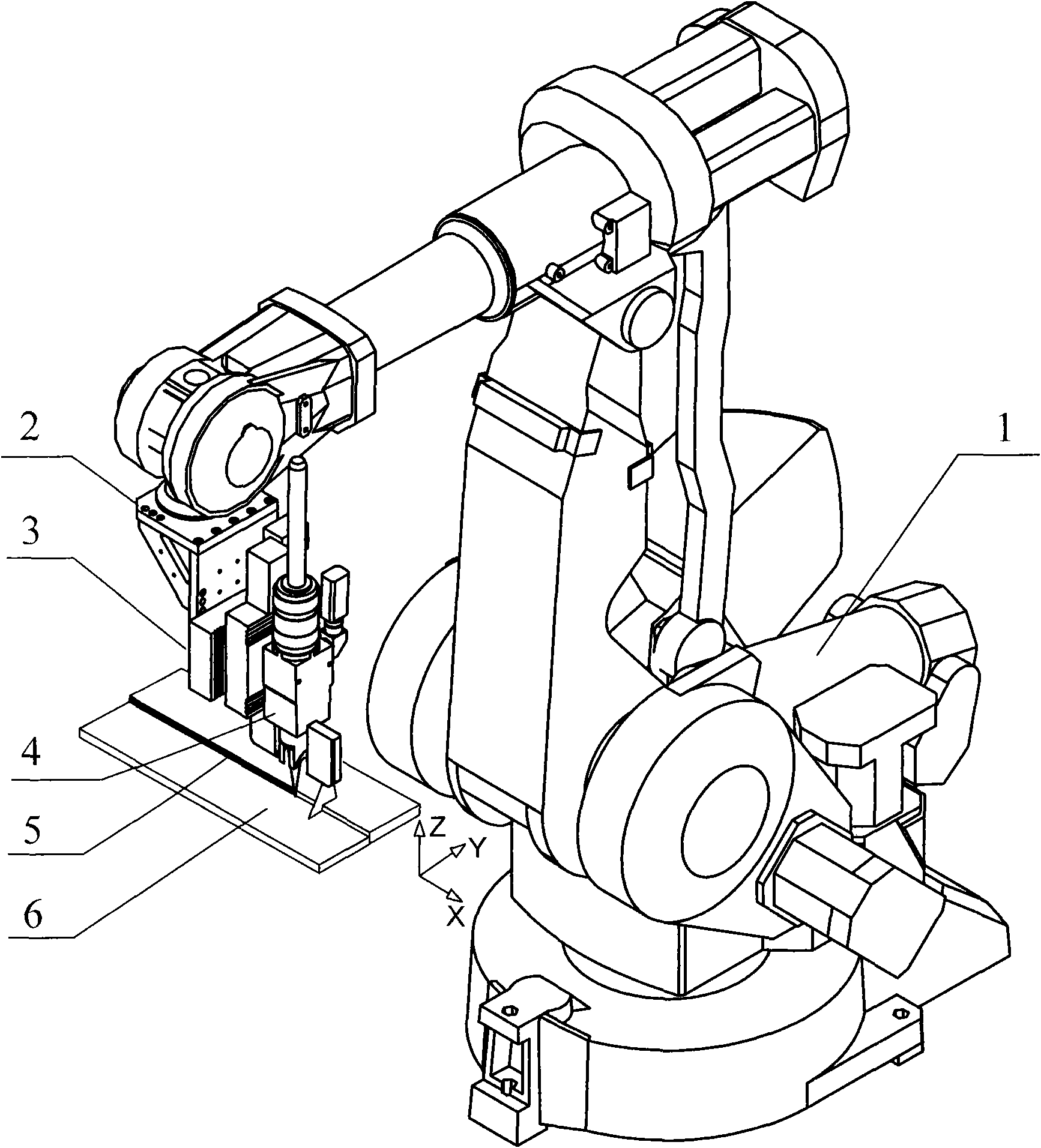
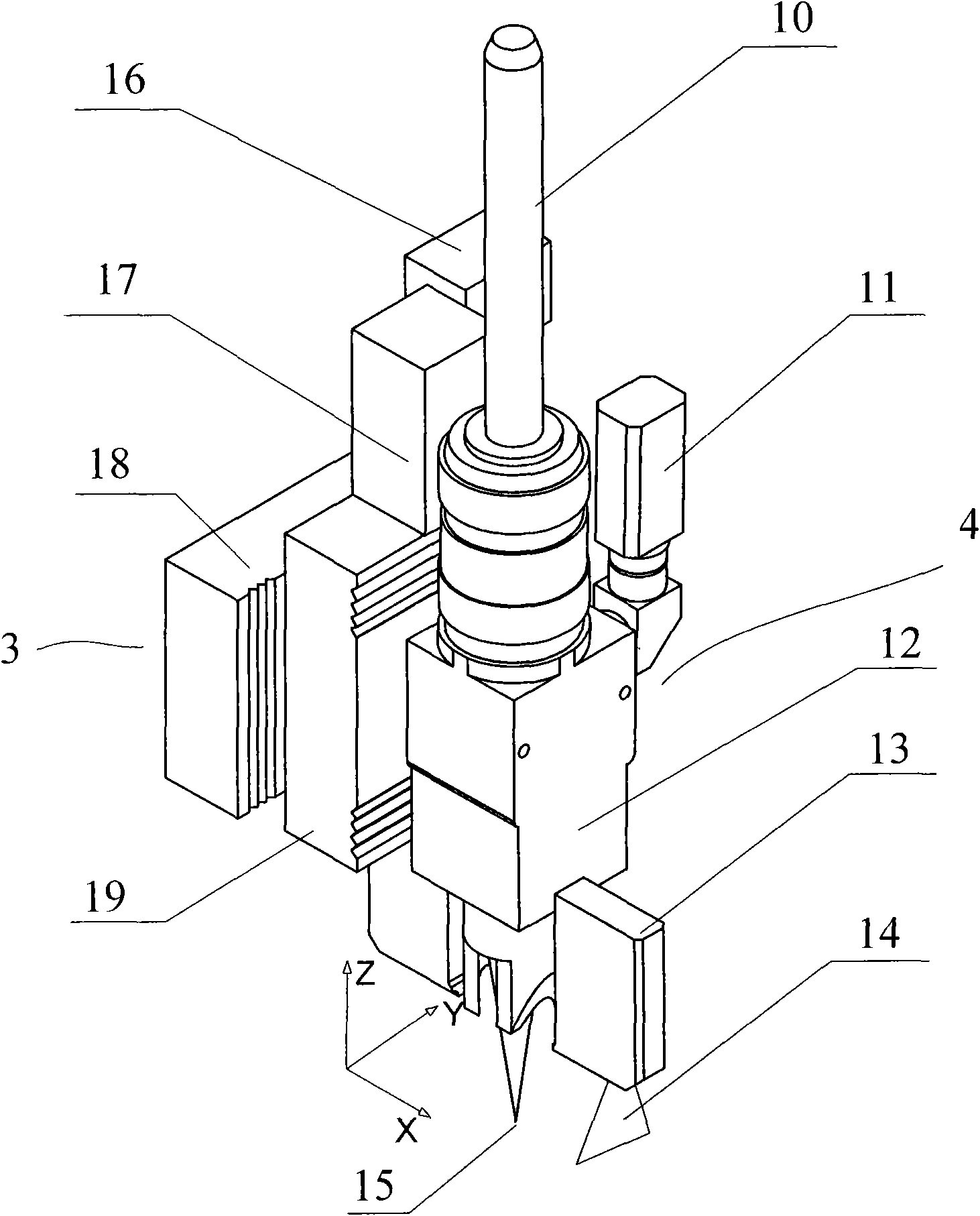
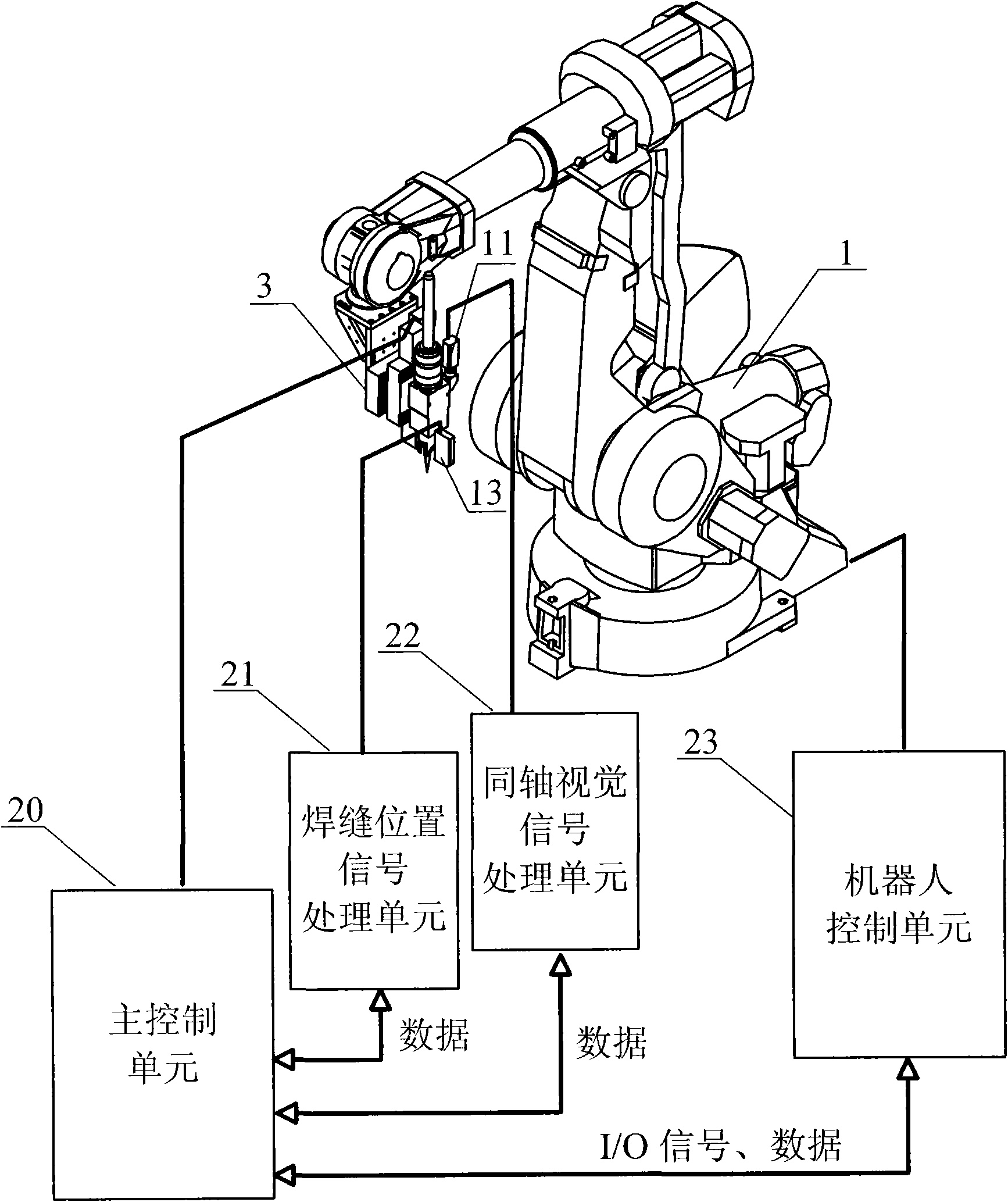
The invention relates to a device and a method for making a robot track a given route at high accuracy, in particular to a robot processing system for performing route tracking and deviation compensation by comprehensively utilizing a coaxial vision sensing system and a welding seam position measurement sensing system, and a route tracking method, which are used for high-accuracy processing of laser welding and the like. The implementation process is divided into three stages; the first two stages comprehensively utilize welding seam position measurement information and coaxial vision measurement information to calculate the deviation between the front welding seam position and the central point of a robot tool and a welding seam so as to obtain the compensation data of the track deviation of the central point of the robot tool and the welding seam position reference data; and the stage of actual welding utilizes the welding seam position measurement information and the welding seam position reference data to perform tracking and compensation control, a position correcting device corrects the motion of a robot system so that the central point of the robot tool moves forwards continuously along the given route, and the deviation of the given route is smaller than the route repeat accuracy of the robot. The device and the method can be widely applied to various occasions required to improve the motion path accuracy of the robot.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cable tunnel routing inspection robot
InactiveCN102562154AAchievement distanceRealize all-round observationRadiation pyrometryMining devicesElectricityElectromagnetic interference
The invention relates to a cable tunnel routing inspection robot which comprises a robot main body, an automatic moving device and a mechanical arm, wherein the automatic moving device is installed on the robot main body, and the automatic moving device is suspended to a track and moves along the track; the mechanical arm is installed on the robot main body, and the tail end of the mechanical arm is provided with a cloud deck; and the robot main body is provided with a control device and a power supply device, and the power supply device is electrically connected with a cable connected with an external power supply cabinet in an inductive way. The cable tunnel routing inspection robot has high waterproof and anti-electromagnetic interference grades, safe power supply way and reliable communication way, the limitations of complex ground environment to the motion ability of the robot can be overcome, all-around image monitoring on equipment in the tunnel can be realized, and the positions of equipment damages and thermal defects and monitoring on the overall environment of the tunnel are detected and positioned.
Owner:SHENYANG SIASUN ROBOT & AUTOMATION
Wearable robotic system for rehabilitation training of the upper limbs
ActiveUS20110251533A1Simple structureLower the volumeDiagnosticsChiropractic devicesRobotic systemsEngineering
The present invention relates to a wearable robot system for rehabilitation training of the upper limbs that has an improved structure to reproduce in detail motion of a human body by selecting a wearing type structure such that robot links move correspondingly to the motion of the upper limbs while decreasing the volume of a rehabilitation and assistance device based on a robot for rehabilitation training of the upper limbs. According the present invention, it is possible to decrease the volume and increase the available space, in addition to creating smooth motion without interfering with the human body by creating a plurality of robot motion paths and selecting the best path from them, because an operation of four degrees of freedom can be achieved by an operation procedure using redundant.
Owner:HANSUNG UNIV IND UNIV COOPERATION FOUND +1
Mobile robot path planning method based on improved RRT* algorithm
InactiveCN108983780AReduce randomnessImprove search efficiencyInstruments for road network navigationPosition/course control in two dimensionsAlgorithmMobile robots path planning
The invention discloses a mobile robot path planning method based on an improved RRT* algorithm. The method introduces a target biasing strategy into a standard RRT* algorithm so as to reduce the randomness of sampling points; provides an avoidance step length extension method in order that a random tree can reasonably stay away from an obstacle area and avoids falling into a local minimum; and smoothes a path obtained by the improved RRT* algorithm by using a reverse sequence connection method smoothing strategy, so as to reduce the direction-changing operations of the robot and achieve the stable movement of the robot. Compared with an original standard RRT* algorithm, the improved RRT* algorithm has a better planned path and takes less time.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
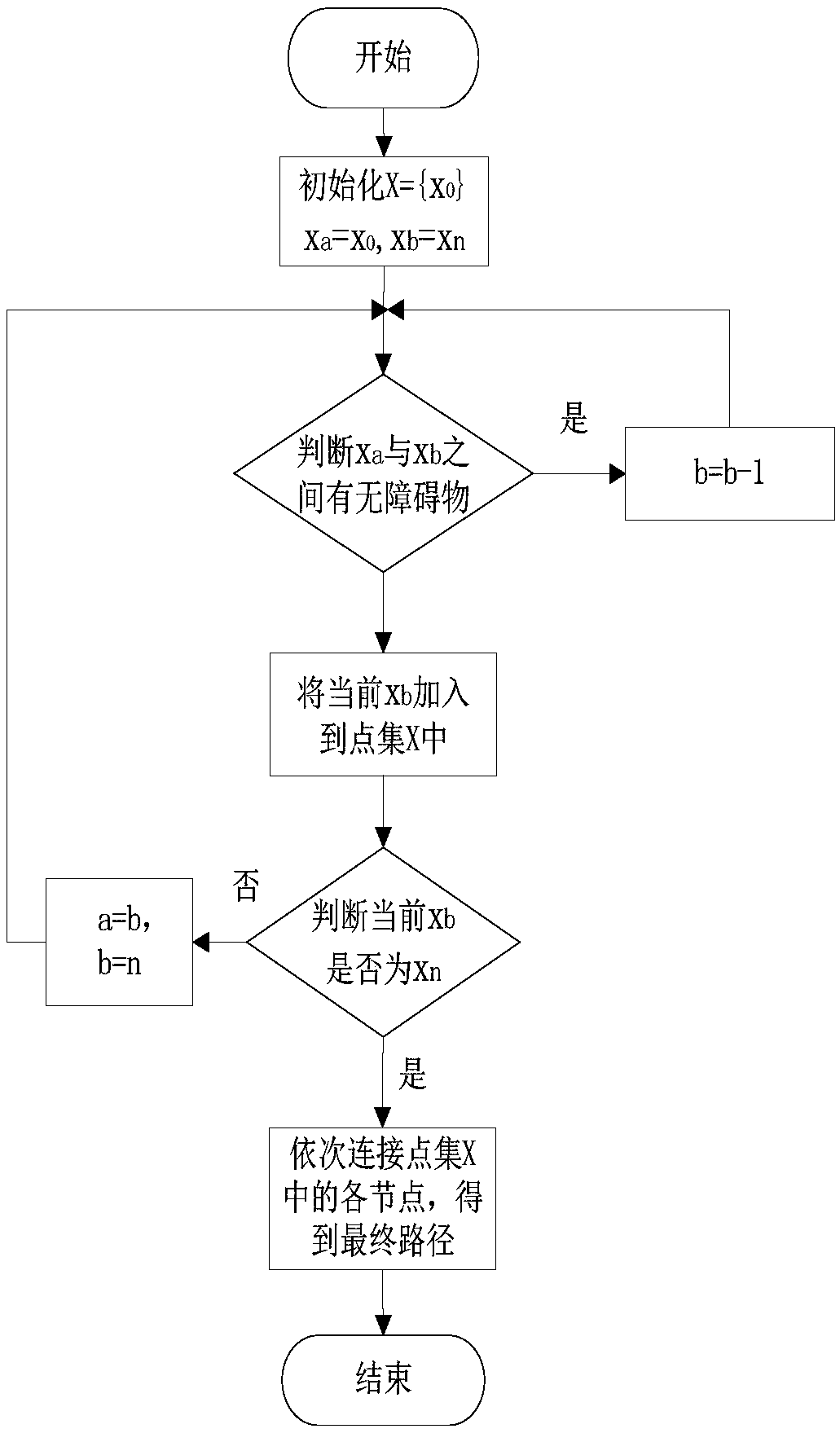
Route generating system for an autonomous mobile robot
ActiveUS7474945B2Easy programmingReduce computing loadAnti-collision systemsComplex mathematical operationsEngineeringRobot locomotion
In a route generating system for an autonomous mobile robot, a plurality of nodes are designated within an area of movement of the robot and an edge is defined between a pair of nodes only if a distance from the one node to the other node is less than a threshold value and there is no obstacle on a line drawn between the one point and the other point. Because the route is generated from a collection of pre-defined edges which are free from obstacles and are selected so as to optimize the generated route, the robot is enabled to travel from the current position to the destination in a safe and optimum fashion. Furthermore, the edges are defined by connecting only those nodes that are relatively close to each other, the candidates of the edges for generating a route can be reduced to a small number and this reduces computational loads. Also, because the route can be selected in a relatively intelligent manner so as to optimize a certain criterion, a clumsy appearance in the movement of the robot can be avoided.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
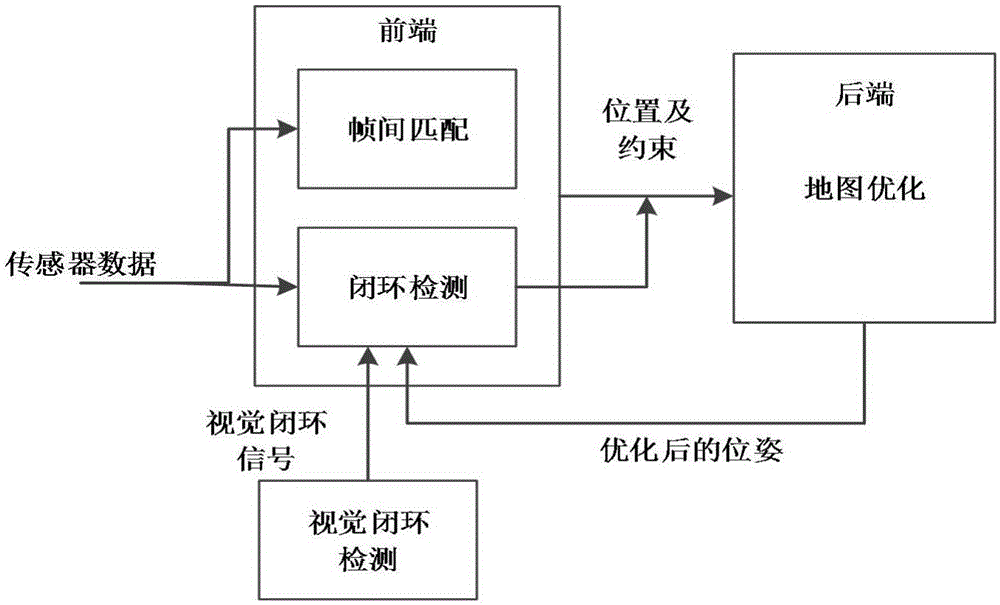
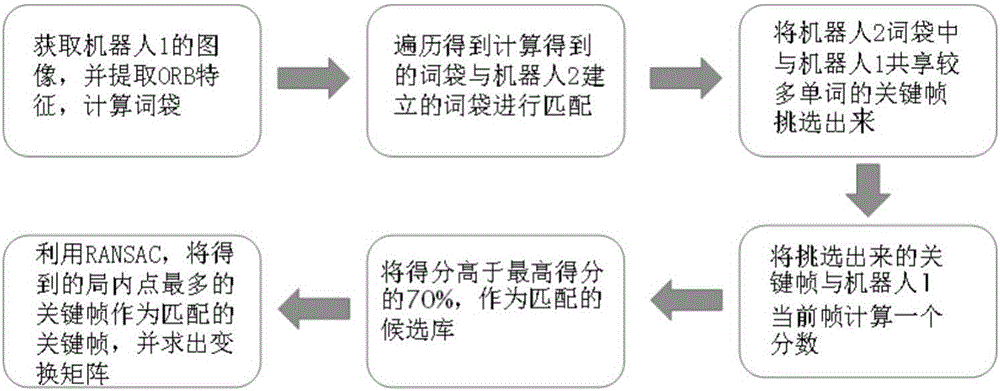
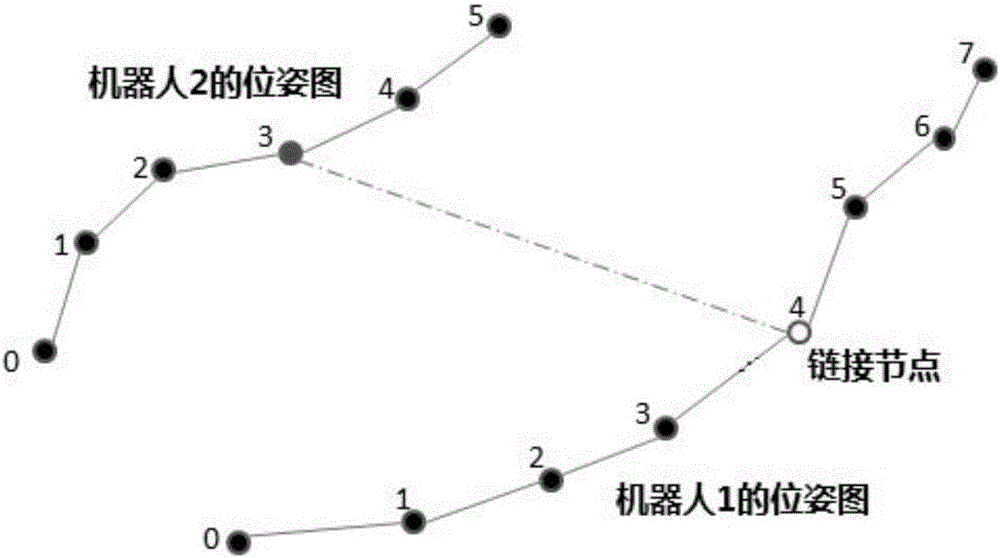
Method for collaborative mapping and locating of multiple robots for large-scale environment
InactiveCN106272423AEliminate Motion Accumulation ErrorsPrecise positioningProgramme-controlled manipulatorAlgorithmMultirobot systems
The invention provides a method for collaborative mapping and locating of multiple robots for a large-scale environment. The method comprises a single-robot laser SLAM algorithm based on a visual detection closed loop, a multi-robot pose constraint estimation algorithm and a multi-robot map fusion algorithm, wherein according to the single-robot laser SLAM algorithm based on the visual detection closed loop, a visual sensor is adopted for assisting a laser sensor in achieving the SLAM algorithm with the more stable roughness. Simultaneous locating and mapping of the multiple robots are achieved through the laser sensor and the visual sensor. The closed loop is detected by obtaining the visual characteristic of the roughness through a camera, and the problem about closed loop detection caused by the robot motion accelerative error is solved effectively; meanwhile through a multi-robot system, simultaneous locating and mapping in the large regional environment are completed efficiently, and the defect that the efficiency is low by means of a single robot is overcome. By the adoption of the method, the precise robot location and map creation of the environment are achieved in the large-scale environment, and the method is also suitable for small-scale environments.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
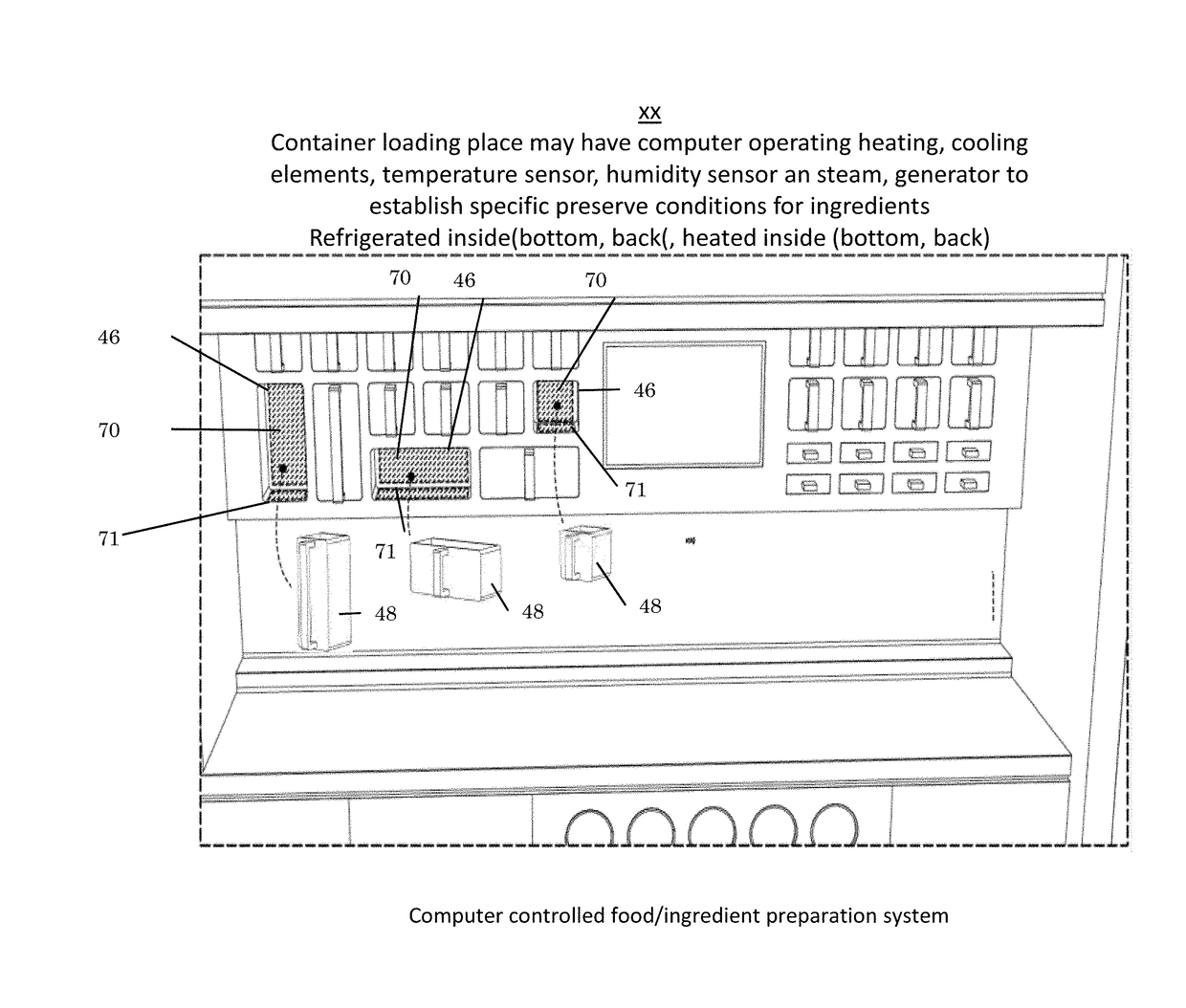
Robotic manipulation methods and systems for executing a domain-specific application in an instrumented environment with containers and electronic minimanipulation libraries
PendingUS20170348854A1Good orientationEasy to moveProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer number formatDegrees of freedom
This disclosure discloses various technical features for creating robotic humanoid movements, actions, and interactions with tools and the instrumented environment by automatically building movements for the humanoid; actions and behaviors of the humanoid based on a set of computer-encoded robotic movement and action primitives. The primitives are defined by motions / actions of articulated degrees of freedom that range in complexity from simple to complex, and which can be combined in any form in serial / parallel fashion. These motion-primitives are termed to be minimanipulations and each has a clear time-indexed command input-structure and output behavior / performance profile that is intended to achieve a certain function. Minimanipulations comprise a new way of creating a programmable-by-example platform for robots. The minimanipulation electronic libraries provide a large suite of higher-level sensing-and-execution sequences that are common building blocks for complex tasks, such as cooking, taking care of the infirm, or other tasks performed by robots.
Owner:MBL LTD
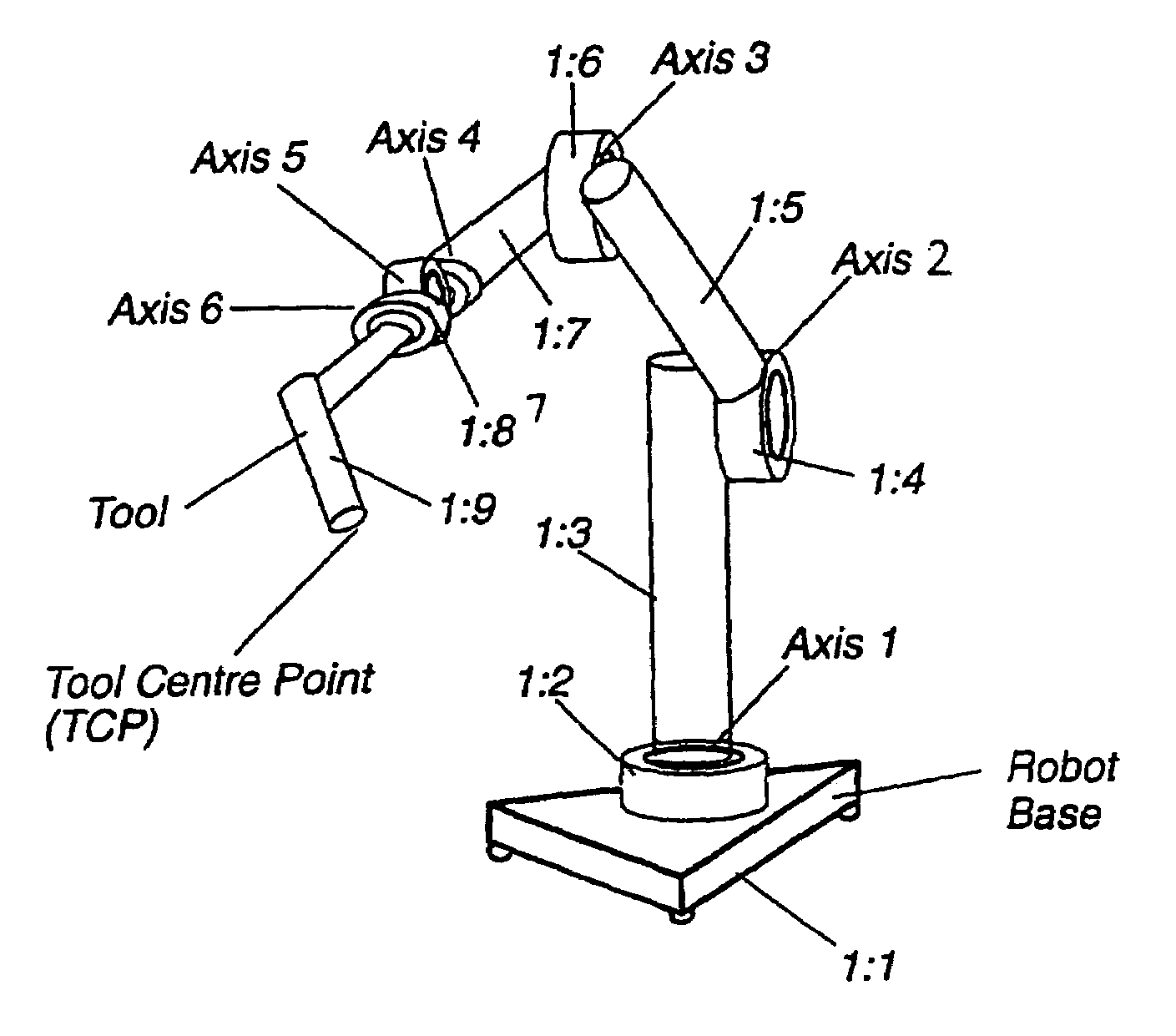
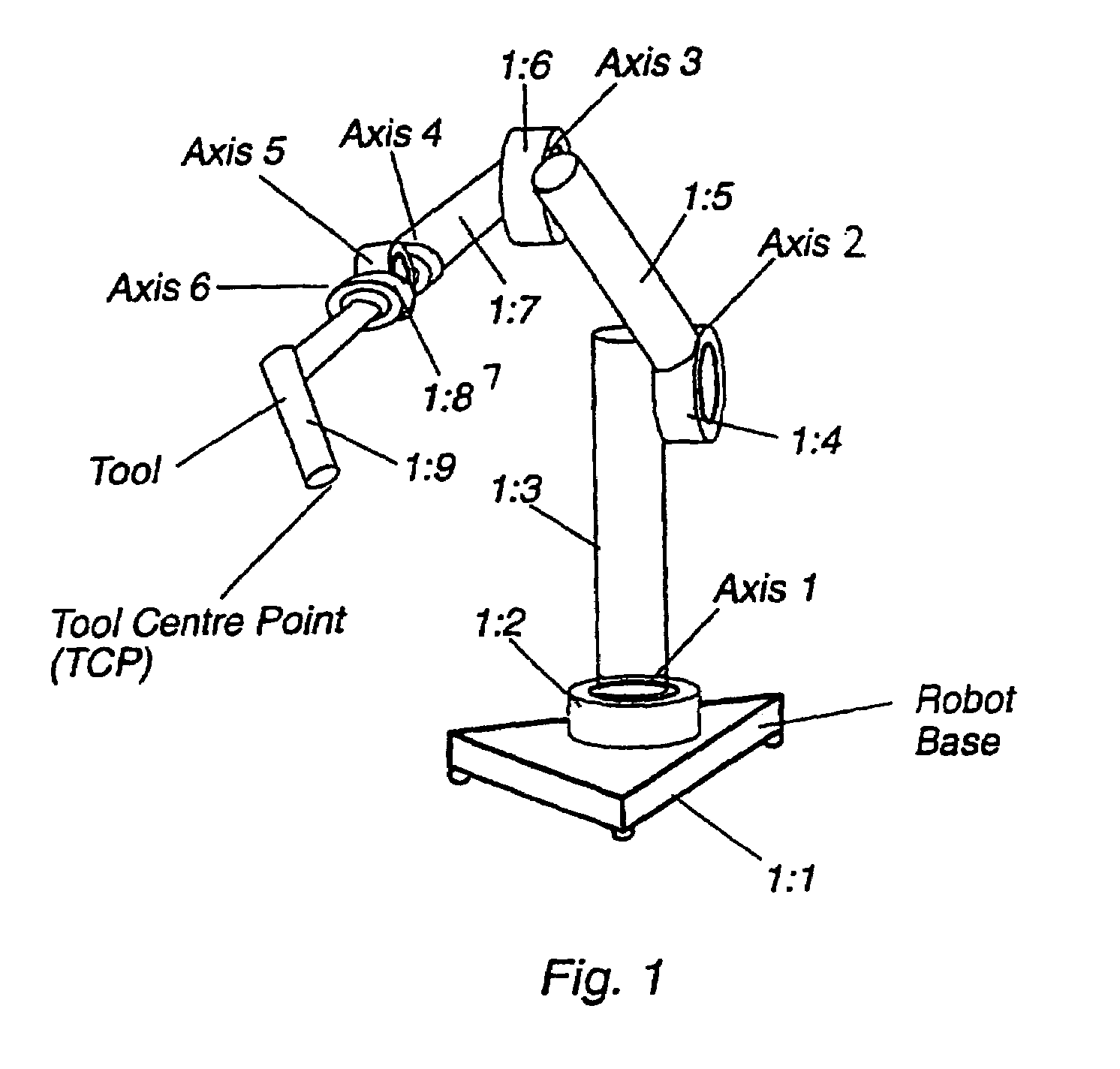
Pathcorrection for an industrial robot
InactiveUS7130718B2Improve accuracyHigh movement precisionProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlControl theoryPath deviation
A method for an industrial robot to increase accuracy in movements of the robot. A first path is formed by bringing a tool supported by the robot to adopt a plurality of generated positions. A plurality of observed positions of the tool moving along the first path are determined. A second path is formed of the determined tool positions. A correction is determined by a path deviation between geometrically determined positions in the first path and the second path.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Robot scheduling method and apparatus
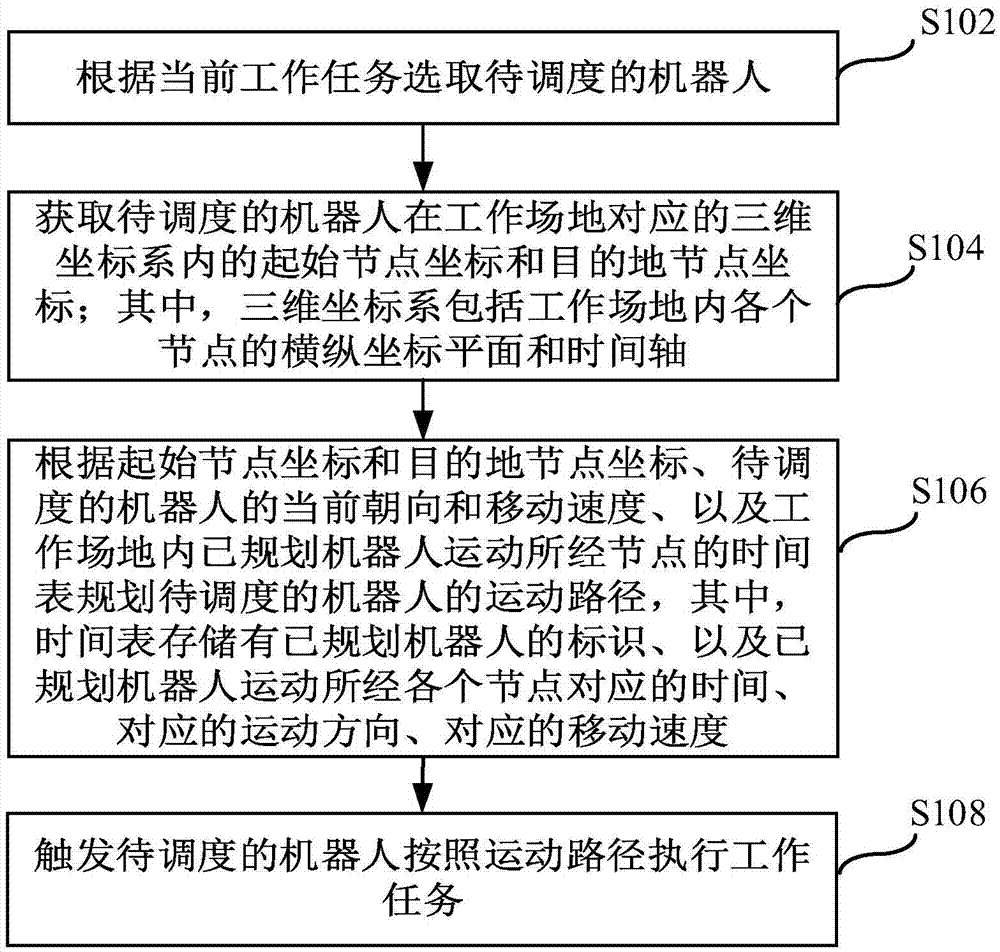
ActiveCN105446343AAvoid colliding with each otherIncrease flexibilityPosition/course control in two dimensionsControl mannerWork task
The invention provides a robot scheduling method and apparatus. The method comprises the following steps: according to a current work task, selecting a robot to be scheduled; obtaining initial node coordinates and destination node coordinates of the robot to be scheduled in a corresponding three-dimensional coordinate system in a work place; according to the initial node coordinates and the destination node coordinates, a moving speed of the robot to be scheduled and a time table about planned nodes which a robot moves past in the work place, planning a movement path of the robot to be scheduled; and triggering the robot to be scheduled to execute a work task according to the movement path. According to the invention, a mode of demonstrating the work place in the form of nodes and the movement path in the form of time through the three-dimensional coordinate system is employed, and according to states of all nodes within preset time between initial nodes and destination nodes of robots, centralized scheduling is performed on the robots in the work place, such that mutual bumps between the robots is avoided, and at the same time, the flexibility of the control mode of the robots is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG LIBIAO ROBOT CO LTD
Robot control algorithm constructing apparatus, robot control algorithm constructing program storage medium, robot controller, robot control program storage medium, and robot
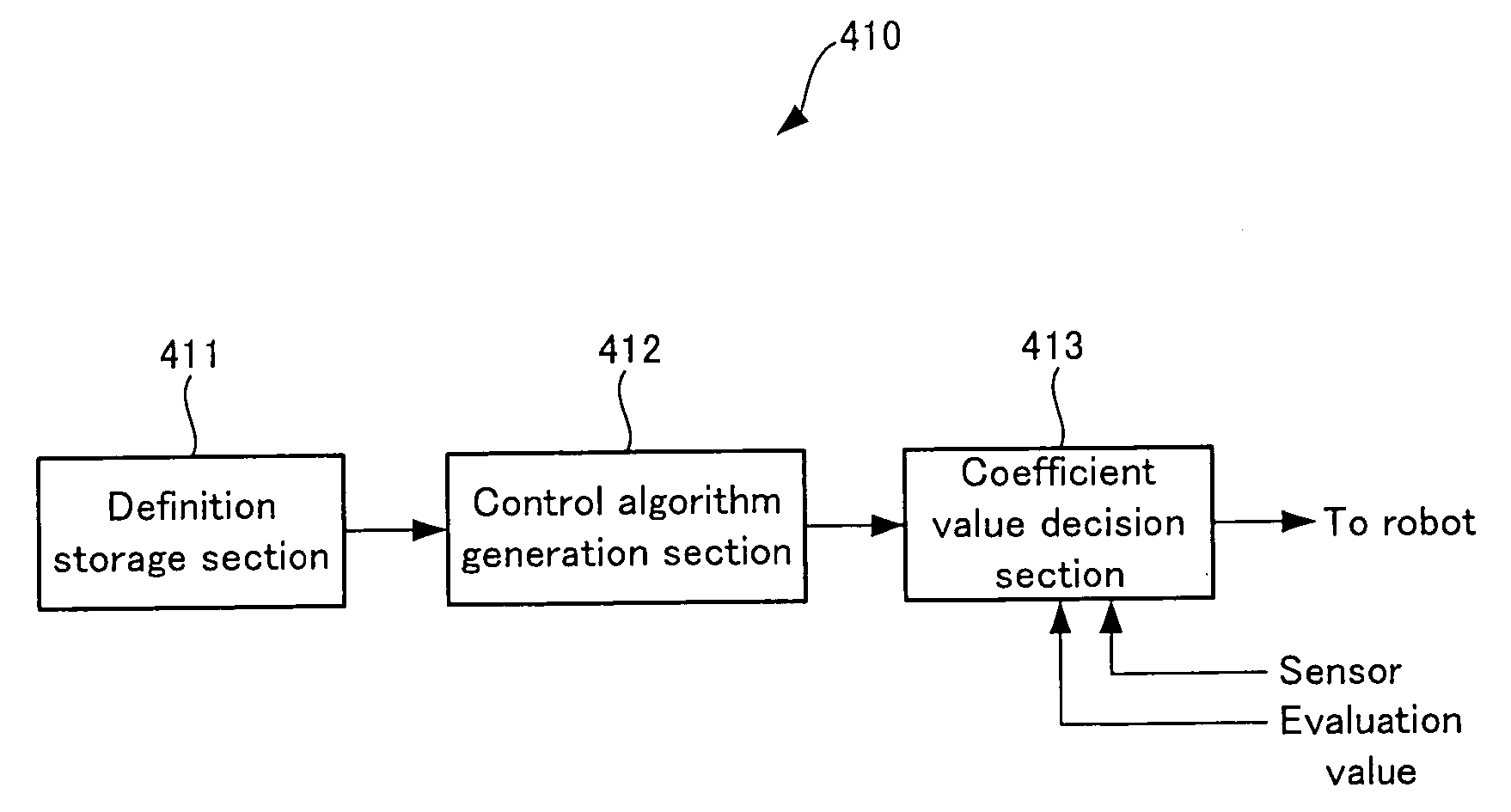
InactiveUS20050119791A1Low costTimely controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlAlgorithmMechanical equation
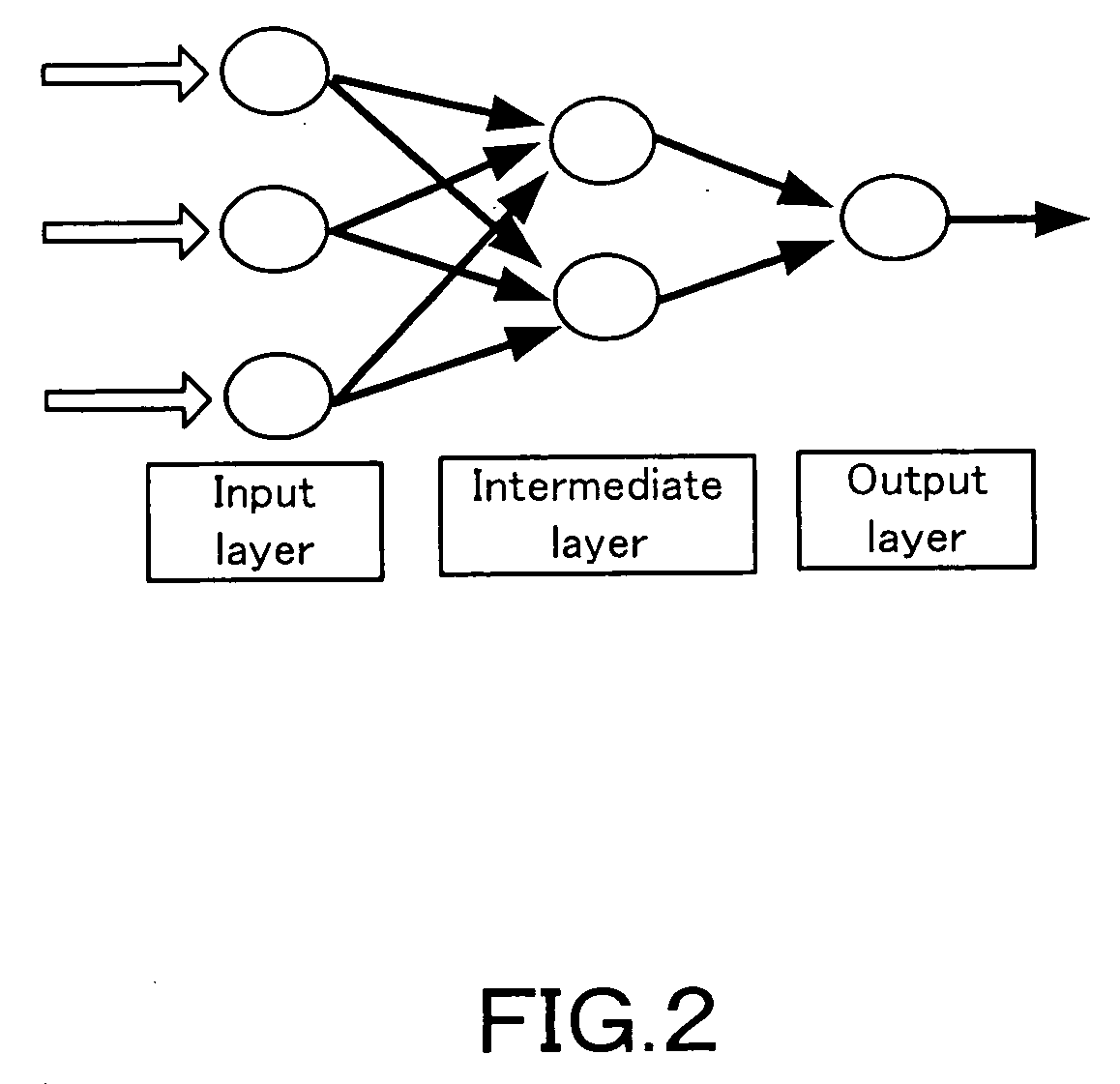
The present invention relates to a control algorithm constructing device that constructs a control algorithm controlling the motion of a robot, and a controller that controls the motion of the robot in accordance with the constructed control algorithm, with the purpose of reducing the cost and time taken to create the control algorithm as compared with the conventional method such as an MZP method to solve a mechanical equation, in which the control algorithm is constructed by a recurrent neural network (RNN) including a neuron generating an output with an analogue lag with respect to an input, the coefficients of the RNN are determined in succession from the term of lower degree to the term of higher degree.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
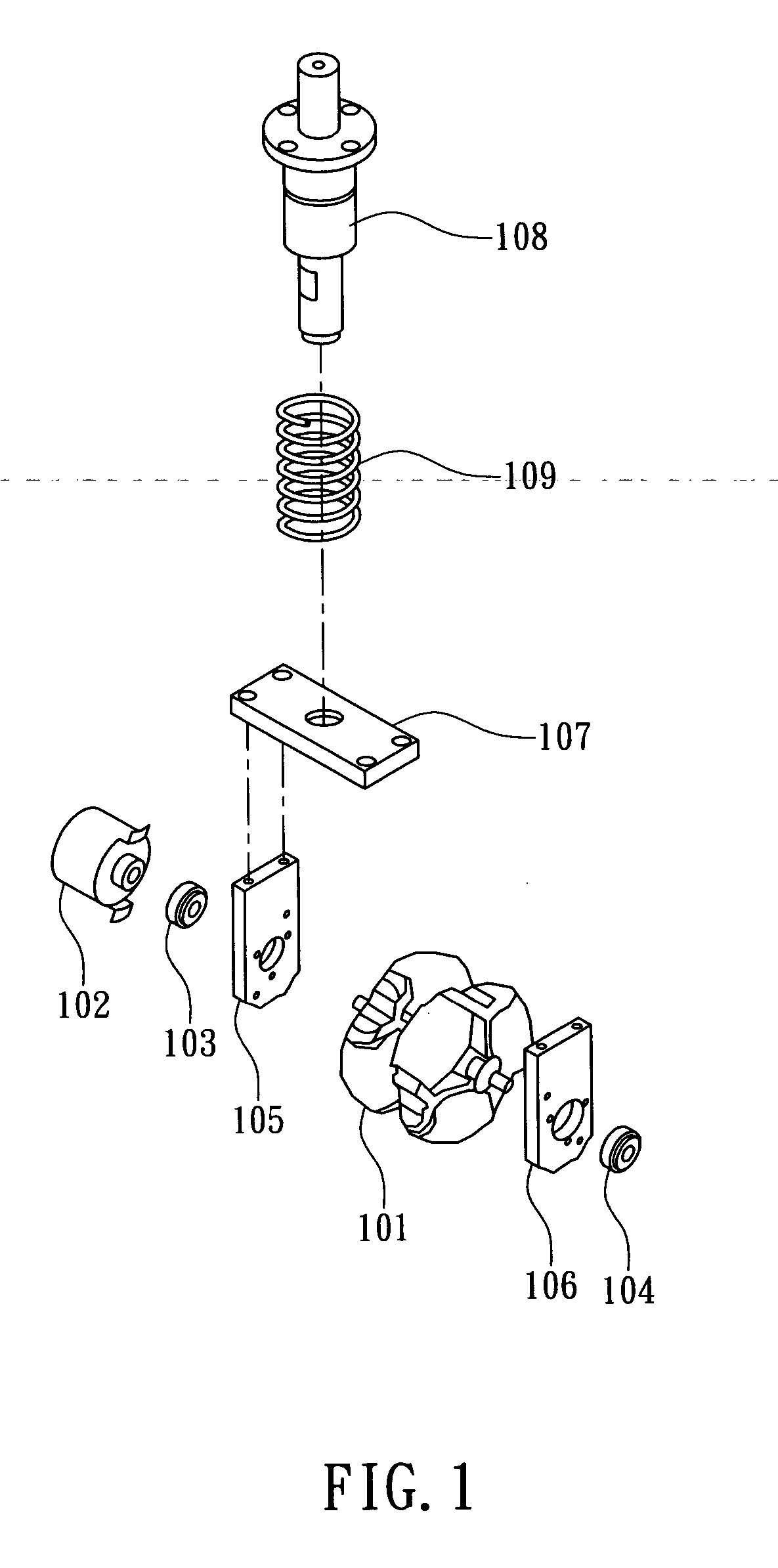
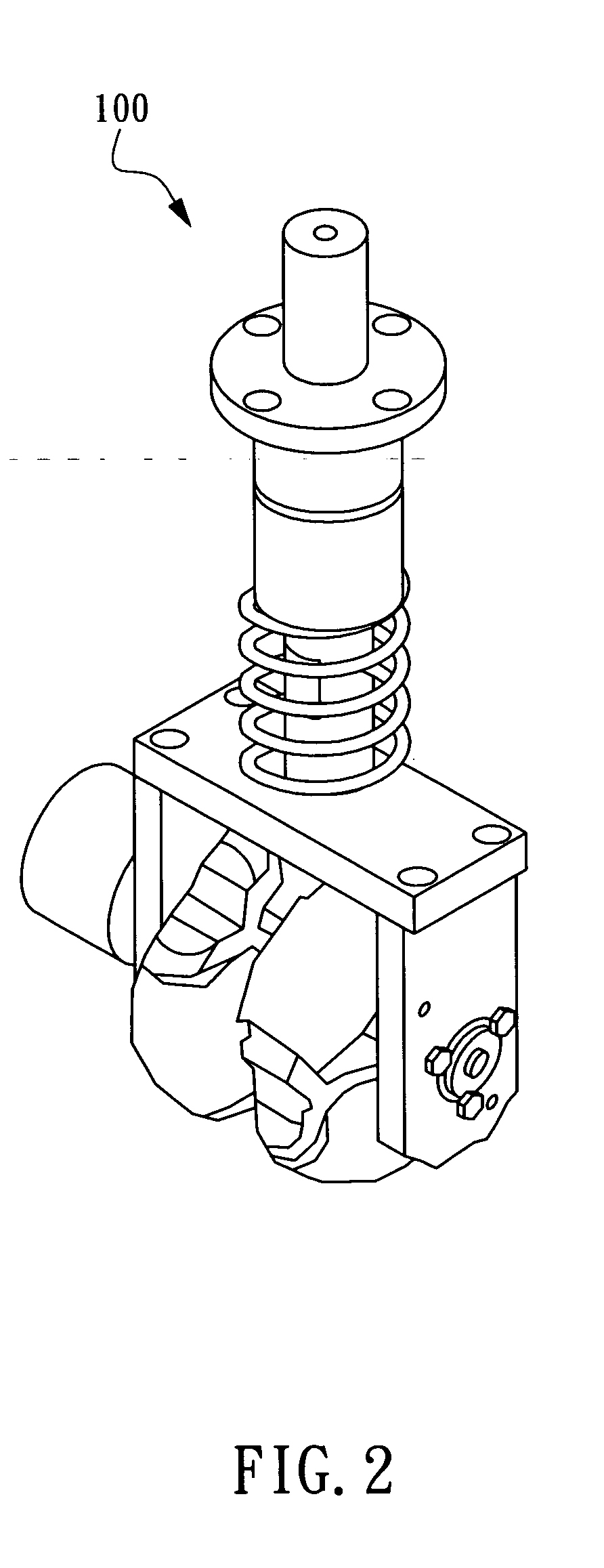
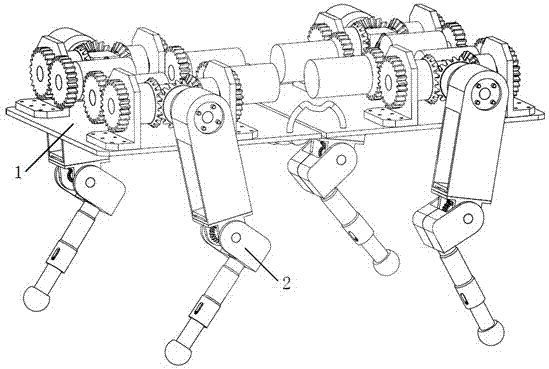
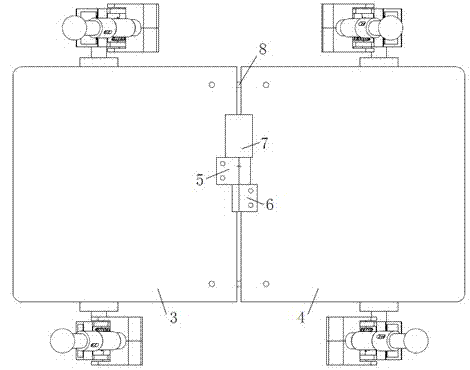
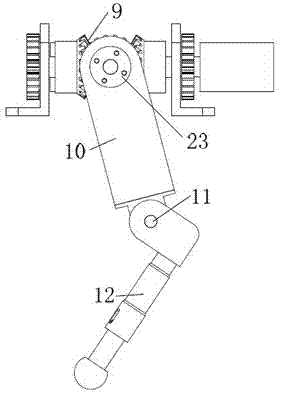
Four-leg robot mechanism based on bionic design
The invention relates to a four-leg robot mechanism based on a bionic design. The four-leg robot mechanism consists of a body frame and four legs. The body frame consists of a front plate and a rear plate, two sides of the body frame are provided with flexible handles, and the robot mechanism is convenient to convey; each leg comprises a hip, a huckle, a knee and a crural part; the hip realizes two freedom degrees by adopting a differential bevel gear; the hip and the huckle are connected by an expansion sleeve to realize fast and convenient assembly and disassembly; the bevel gear drive motion is adopted by the knee; the crural part comprises a large cylinder, a small cylinder, a conical spring and a force sensor; and the large cylinder and the small cylinder are connected through the conical spring, so that the external impact force generated in the walking process of the robot can be buffered, the force sensor on a sole can acquire ground acting force, and the external environment can be conveniently sensed in real time and the robot can be subjected to balanced control conveniently. Through the bionic design idea, a spinal cord and a flexible foot mechanism of the robot are stimulated and designed, the flexibility of the robot movement is improved, the impact of the ground to the robot is reduced, and the robot mechanism has a compact structure and is convenient to install.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
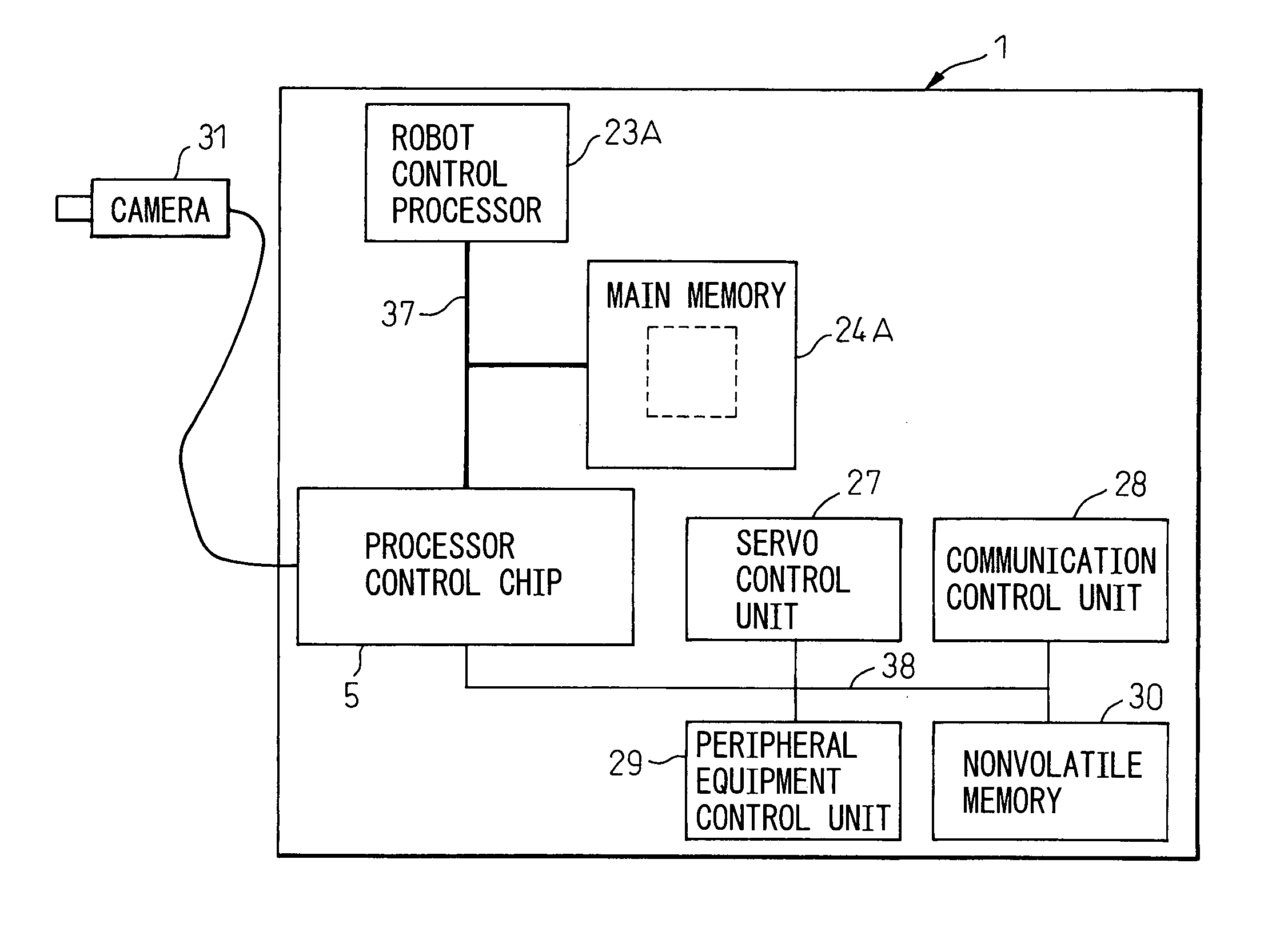
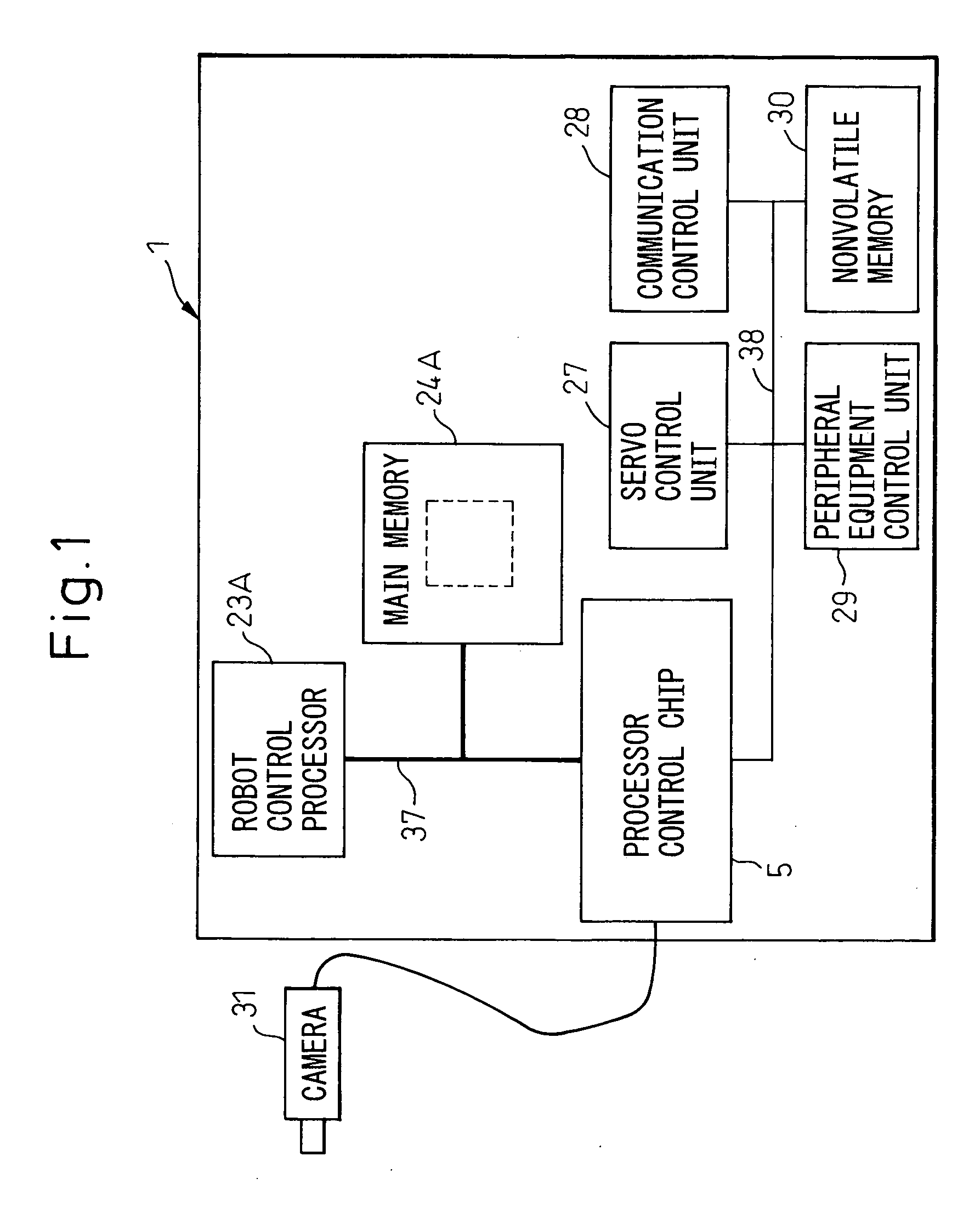
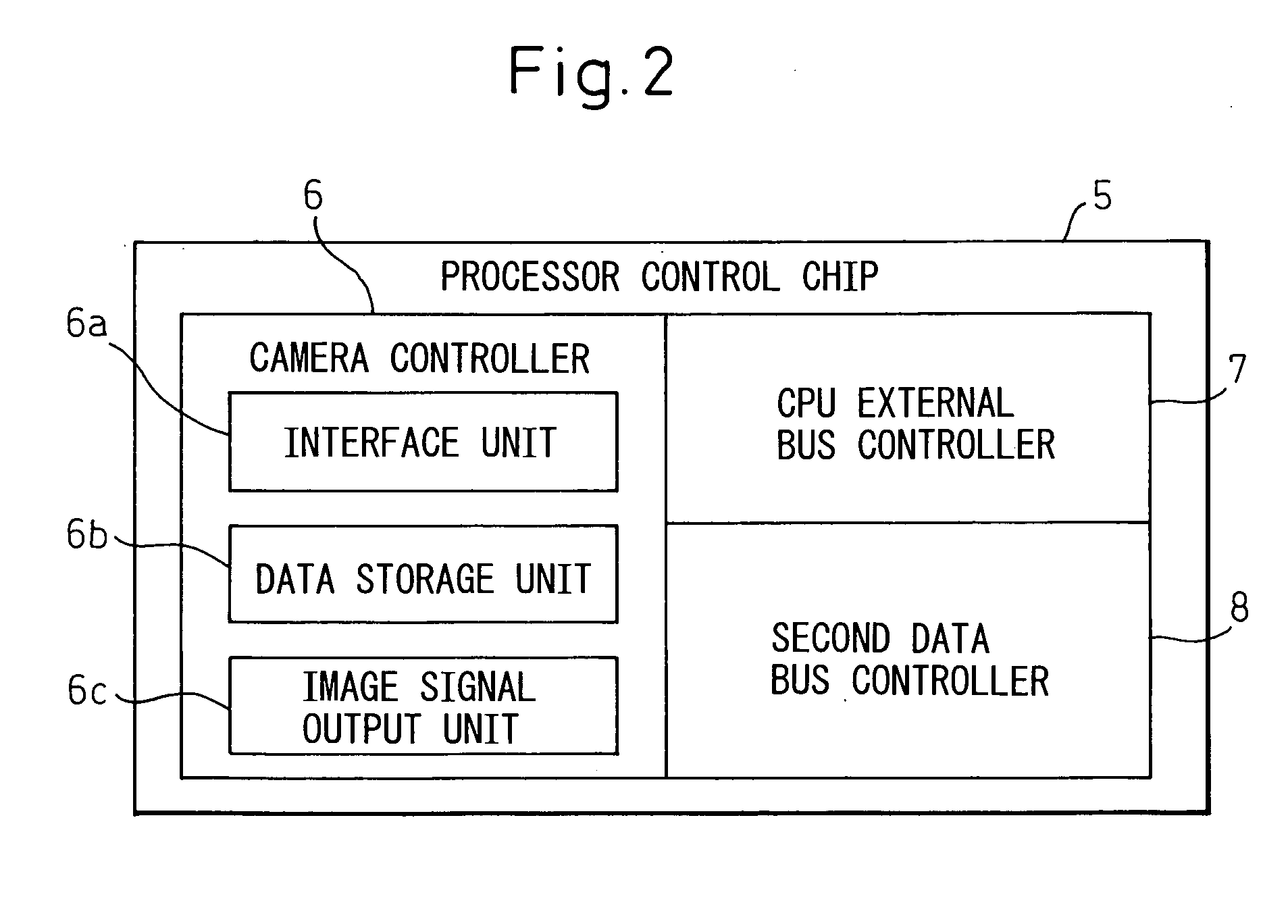
Robot controller
InactiveUS20060279246A1Hindering operationIncrease speedProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorRobot environmentControl data
A robot controller having a function for controlling the motion of a robot, comprising a processor for controlling the robot and for processing the environmental condition data representing the environmental conditions for the robot, a memory accessible by the processor, a writing unit for executing a function of writing the environmental condition into the memory, a first data bus connected to the memory, and a second data bus having a transfer rate lower than that of the first data bus and for transferring the control data used for controlling the robot, wherein the writing unit writes the environmental condition data into the memory through the first data bus, not through the second data bus. The writing unit can be a processor control chip which is connected to the processor through the first data bus.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Elastically-driven modular joint with force feedback control
ActiveCN102632509AIncrease flexibilityImprove compactnessJointsMechanical energy handlingReduction driveRange of motion
The invention discloses an elastically-driven modular joint with force feedback control. comprising assembly components such as a motor stator, a motor rotor, a harmonic speed reducer and the like, so that the design flexibility and compactedness of the joint can be increased; and due to the design of an air routing shaft, the joint is convenient to route, so that the joint is more succinct, the moving range of the joint can be preferably enlarged, and the running reliability of the joint can be improved. Due to the introduction of a first absolute type angle sensor and a second absolute type angle sensor, the angle deviation between an output shaft and an output end cover can be obtained, and the angle deviation is multiplied by the elasticity coefficient of an elastic torsion spring, so that a moment value applicable to the joint can be obtained, for an input feedback value of a joint signal; and a reliable moment feedback signal can be provided for the joint, so that the elastic torsion spring can be deformed, the smoothness can be provided for the joint, and an energy storing mechanism can be further provided for the joint, and the elastically-driven modular joint is applicable to a robot, so that the interaction capability between the robot and the environment can be enhanced, and the running efficiency of the robot can be improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
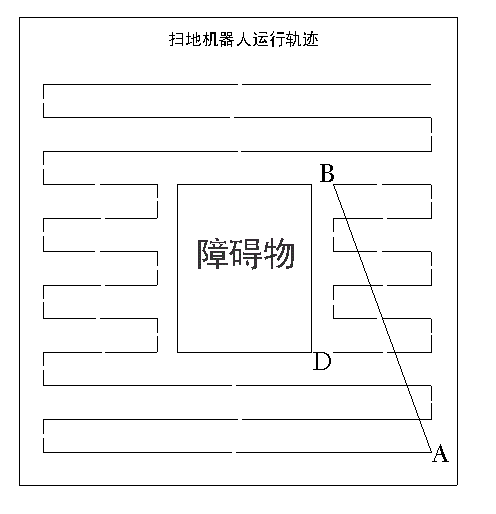
Navigation method for sweeping robot
InactiveCN104536447APrevent crashImprove work efficiencyPosition/course control in two dimensionsComputer graphics (images)Engineering
The invention discloses a navigation method for a sweeping robot. The navigation method comprises the following steps that firstly, an XOY coordinate system is set up for an area to be swept; secondly, the area to be swept is swept by the sweeping robot, the distance from the sweeping robot to front obstacles is measured in real time through an ultrasonic wave by the sweeping robot to decide the locations of the obstacles, meanwhile, the moving trajectory coordinates of the sweeping robot are recorded by the sweeping robot and sent to a PC terminal through an emitter; thirdly, a sweeping robot moving trajectory plan is generated from the moving trajectory coordinates of the sweeping robot by the PC terminal; fourthly, sweeping work is conducted by the sweeping robot according to the sweeping robot moving trajectory plan generated in the third step. The working efficiency of the sweeping robot is improved and the problem of repeated sweeping work conducted by the sweeping robot can not exist through the sweeping robot moving trajectory plan set up in the first time of use.
Owner:重庆广建装饰股份有限公司
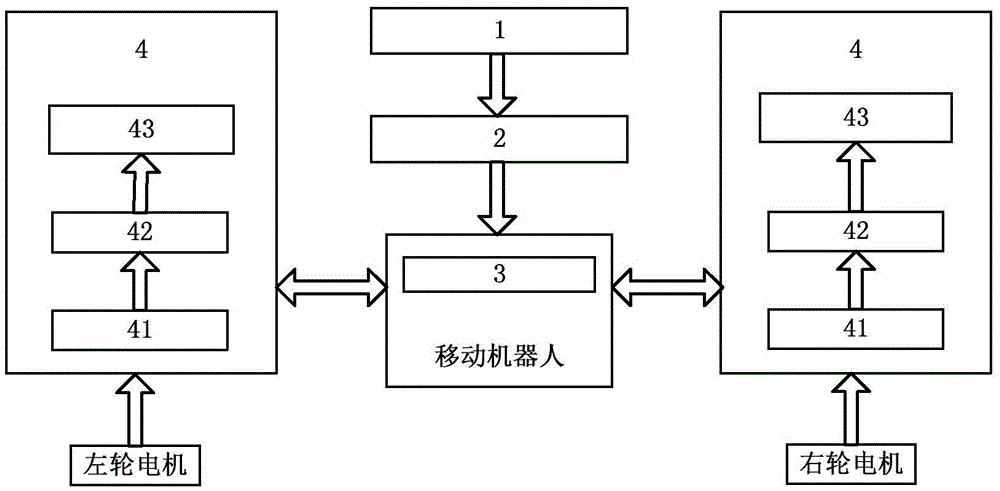
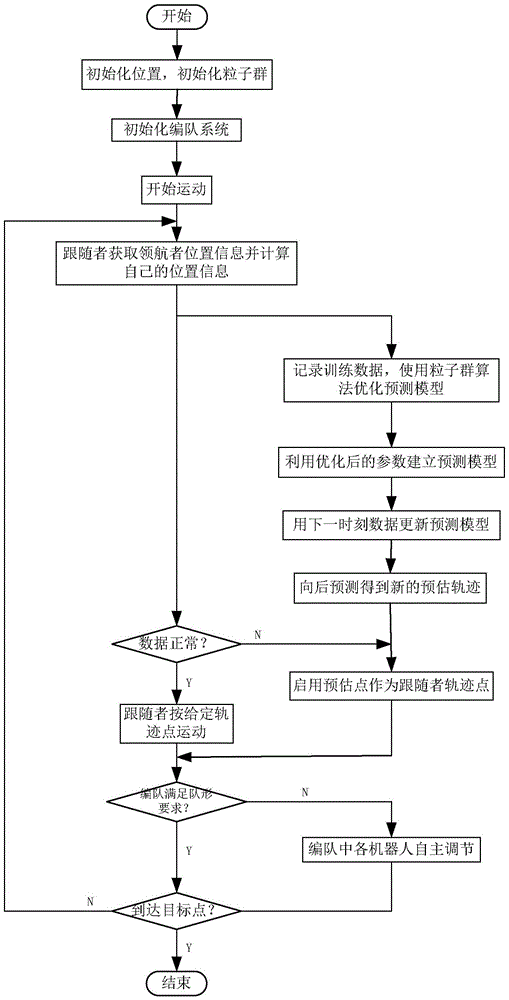
Mobile robot formation control method based on leader-follow
InactiveCN105527960AMake up for the deviationImprove stabilityAutonomous decision making processPosition/direction controlModel parametersNon-linear least squares
The invention provides a mobile robot formation control method based on leader-follow. The method is formed by a global positioning system, a wireless communication system, an algorithm processing system, and a speed control system. The global positioning system obtains the pose information of each robot and sends the pose information to an arithmetic processing system through a wireless communication system, and the formation motion control is finally realized through the information interaction with the speed control system. In a control algorithm, firstly a leader-follow formation motion model is established, a follow robot motion control rate is given, then a follow robot trajectory prediction model is established, a nonlinear least squares method prediction model is employed, a prediction model parameter is optimized by using an improved particle swarm algorithm, a communication data abnormal range is defined, and a prediction point is started to substitute an abnormal point so as to ensure formation motion. According to the method, the prediction model is introduced, the formation order deviation phenomenon caused by temporary communication abnormality, the reliability of follow robot motion is ensured, and the stability of the formation is greatly improved.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com