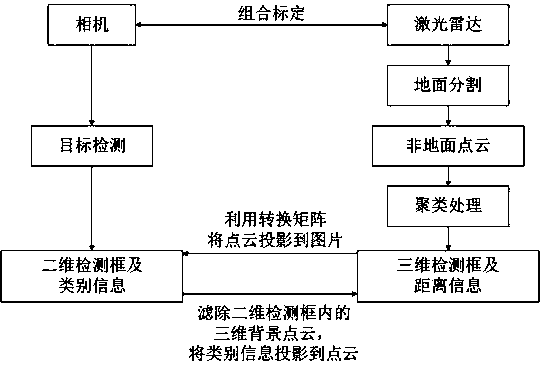
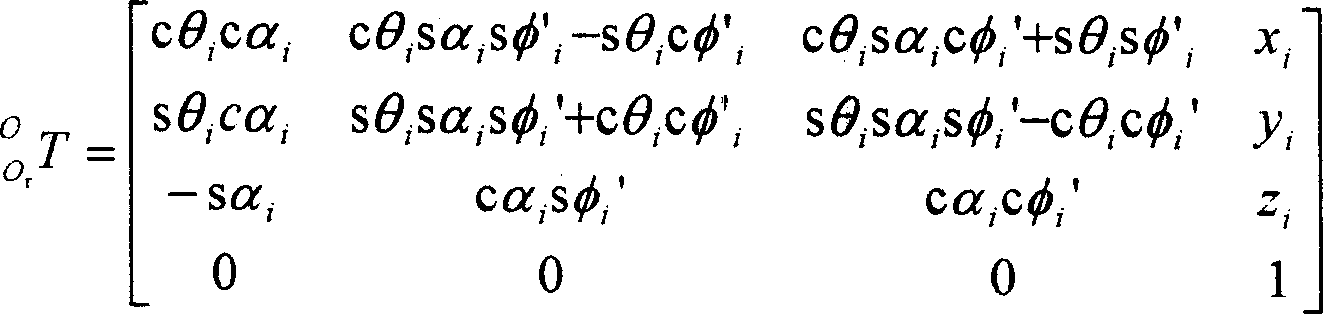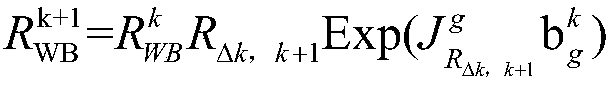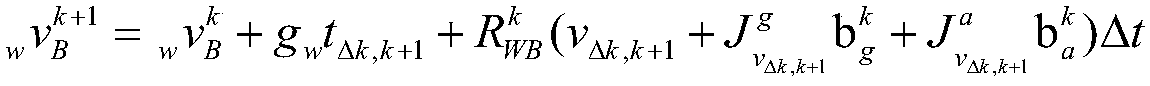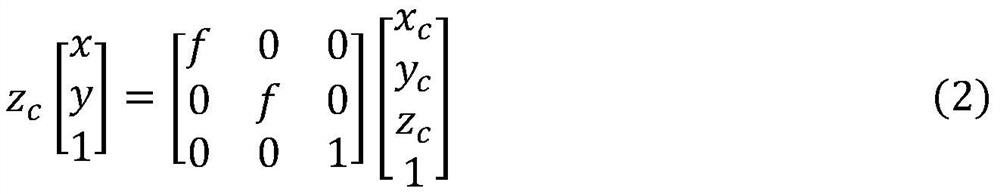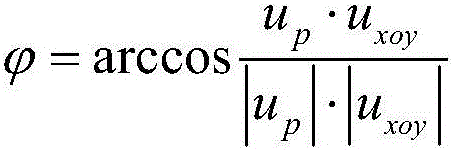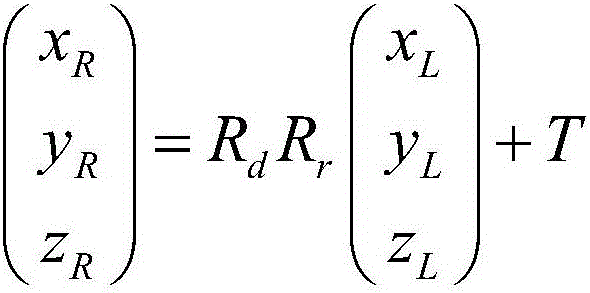Patents
Literature
151 results about "Robot environment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
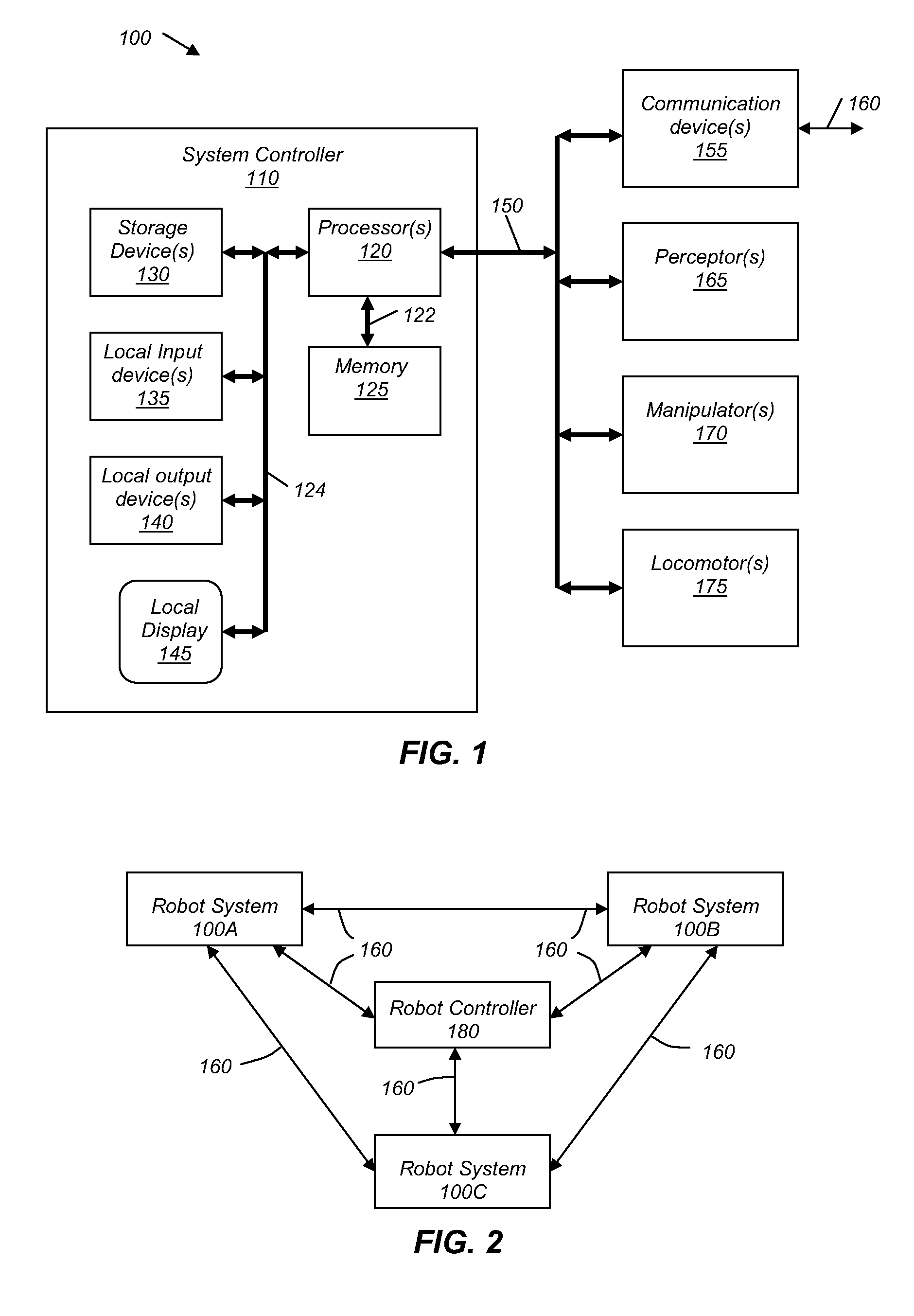
Method and system for remote control of mobile robot
InactiveUS6845297B2Easy to navigateSimplified user interfaceProgramme-controlled manipulatorBronchoscopesRobot environmentTele operation
A system for tele-operating a robot in an environment includes a user interface for controlling the tele-operation of the robot, an imaging device associated with the robot for providing image information representative of the environment around the robot, means for transmitting the image information to the user interface, means for converting the image information to a user-perceptible image at the user interface, means for designating one or more waypoints located anywhere in the user-perceptible image towards which the robot will move, the waypoint in the user-perceptible image towards which the robot will first move being designated as the active waypoint using an icon, means for automatically converting the location of the active waypoint in the user-perceptible image into a target location having x, y, and z coordinates in the environment of the robot, means for providing real-time instructions to the robot from the user interface to move the robot from the robot's current location in the environment to the x, y, and z coordinates of the target location in the environment, and means for moving the icon representing the active waypoint in the user-perceptible image to a new location in the user-perceptible image while the robot is executing the real-time instruction, wherein the location-converting means automatically converts the new location of the icon representing the active waypoint into a new target location having x, y, and z coordinates in the environment of the robot towards which the robot will move.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
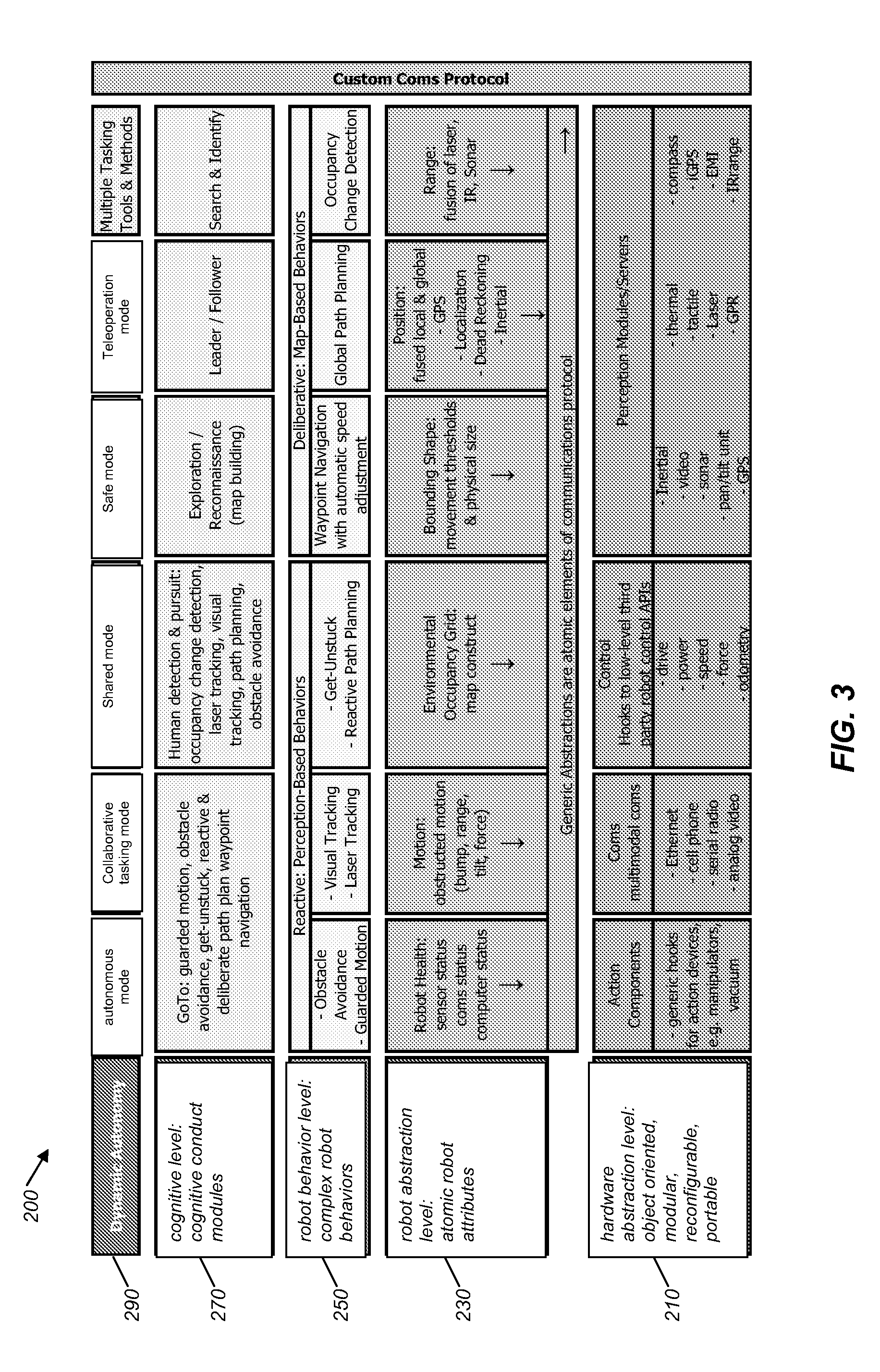
System and method for seamless task-directed autonomy for robots
ActiveUS20090234499A1Programme-controlled manipulatorAutonomous decision making processRobot planningProgram planning
Systems, methods, and user interfaces are used for controlling a robot. An environment map and a robot designator are presented to a user. The user may place, move, and modify task designators on the environment map. The task designators indicate a position in the environment map and indicate a task for the robot to achieve. A control intermediary links task designators with robot instructions issued to the robot. The control intermediary analyzes a relative position between the task designators and the robot. The control intermediary uses the analysis to determine a task-oriented autonomy level for the robot and communicates target achievement information to the robot. The target achievement information may include instructions for directly guiding the robot if the autonomy level indicates low robot initiative and may include instructions for directing the robot to determine a robot plan for achieving the task if the autonomy level indicates high robot initiative.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC +1
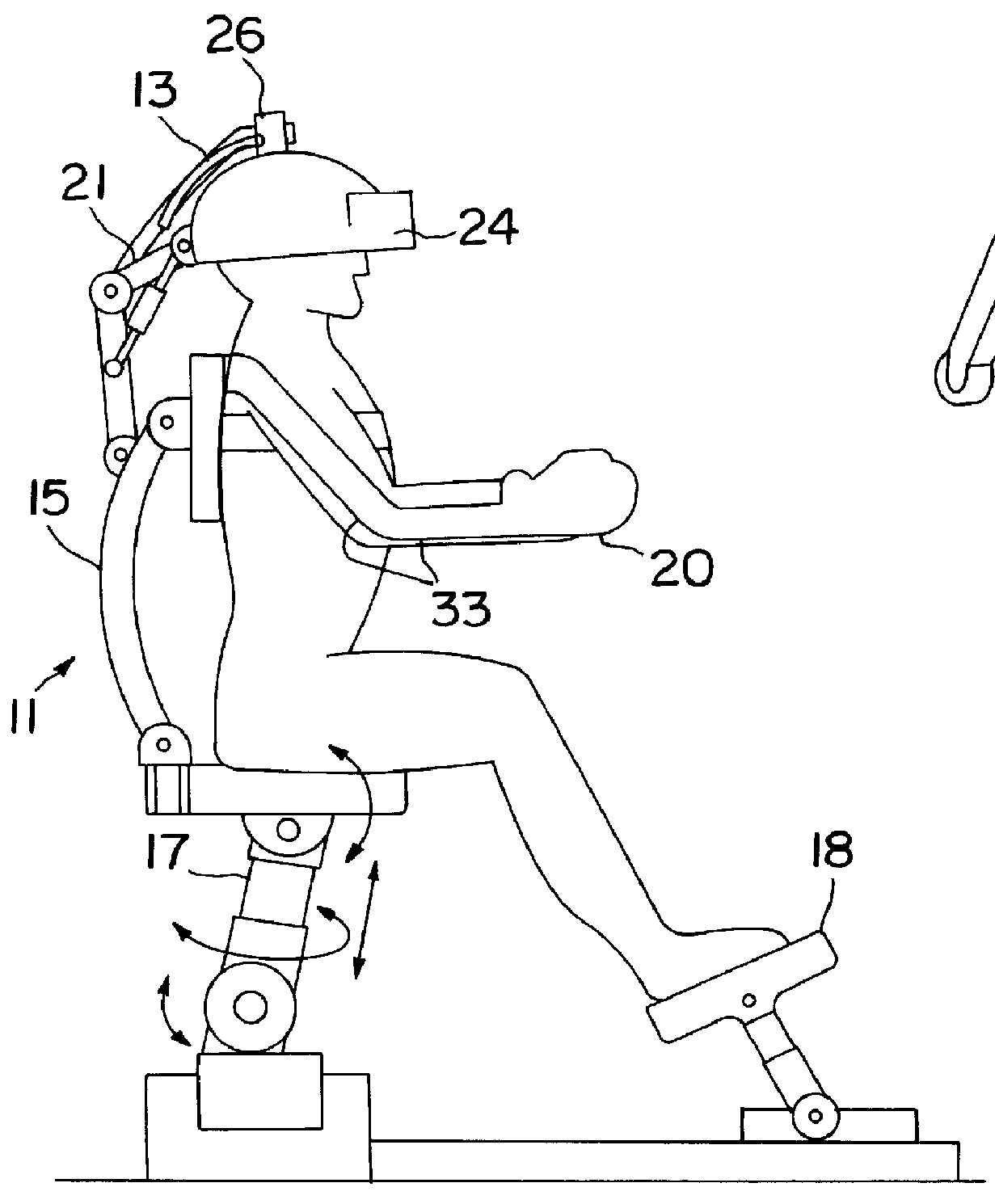
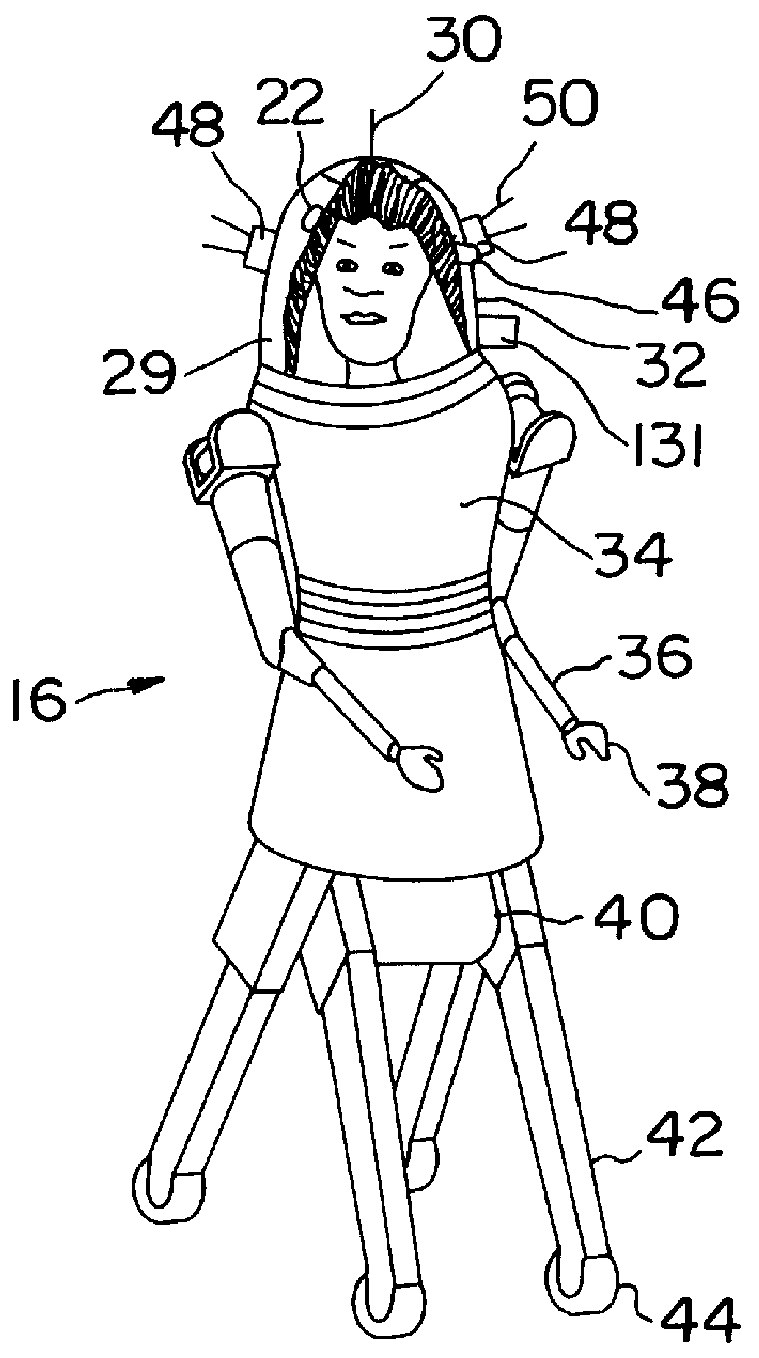
Real time remotely controlled robot
InactiveUS6016385AEffectively and more quicklyInput/output for user-computer interactionProgramme controlRobotic systemsCommunications system
A robot system including a robot, an operator control center and having a communication system connecting the robot and control center wherein an operator in the control center responds with natural movements to stimulus signals from the robot environment by issuing commands that control the robot. In one embodiment, the operator occupies a command chair with an exoskeletal arm that is secured to the "shoulder" (backrest) of the chair. The operator slides his hand into a glove of the invention attached to the end of the exoskeletal arm. He views the robot environment through a video screen and exerts control in response to views presented on the screen. The communication system sends signals to the operator glove in response to conditions at the robot site prompting the operator to take appropriate action.
Owner:FANU AMERICA CORP
Device and method for composition based on small quad-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle
InactiveCN103941750AAchieve positioningImplement navigationPosition/course control in three dimensionsRobot environmentRadar
The invention relates to a device and method for composition based on a small quad-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle and belongs to the technical field of mobile robot positioning and navigation. The small quad-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle can rapidly enter a complex environment which a mobile robot cannot enter, carried laser radar is utilized to construct a two-dimensional map in real time according to an SLAM method, self localization and navigation of the unmanned aerial vehicle can be achieved by combining an IMU device and the like, and efficient exploration of a true complex area is achieved; the height of the small quad-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle can be conveniently adjusted to obtain two-dimensional maps on horizontal planes of different heights; the small quad-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle is rapid in movement speed and more flexible, movement and mapping of the small quad-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle are not subject to disturbance of obstacles on the ground, the range limitation of a detecting robot is broken through, the small quad-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle is extremely high in practical value, and accurate and rapid map construction can be achieved; compared with robot environment composition, the rotor wing robot can perform environment scouting more rapidly and more flexibly, and three-dimensional spatial images can be obtained.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Three-dimensional environment perception method for mobile robot
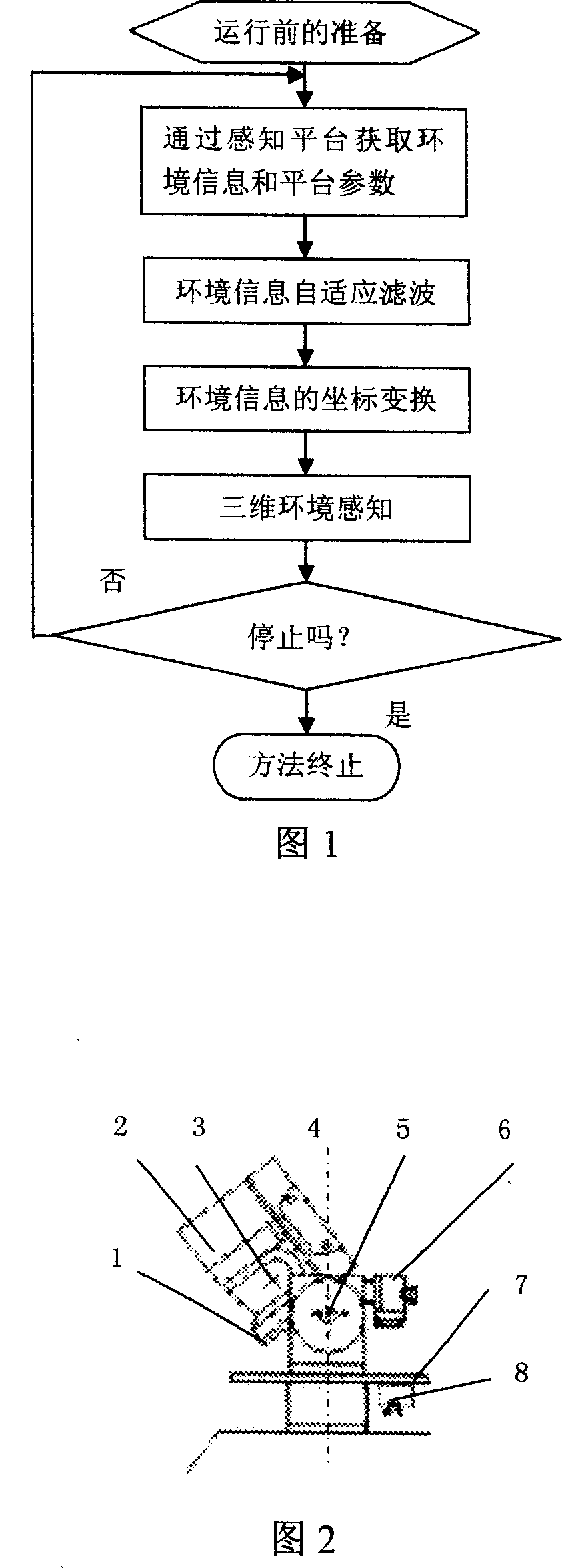
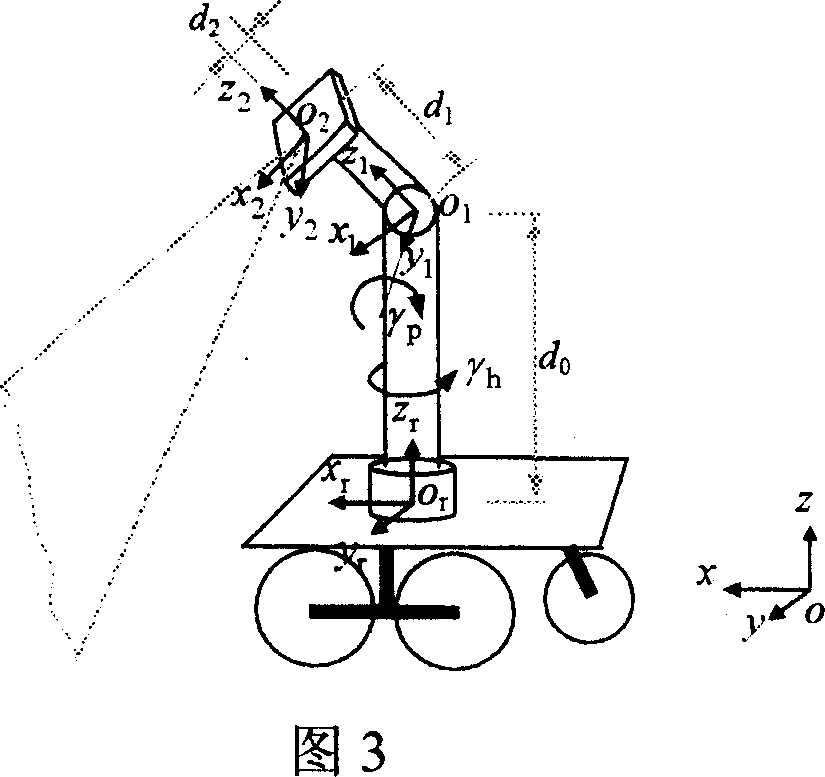
InactiveCN101008571AIncrease flexibilityEasy to detectInstruments for road network navigationImage analysis3d sensorAdaptive filter
This invention relates to one mobile robot 3D sensor method, which comprises steps of environment information acquiring, environment information self adapting filter, environment coordinate exchanging and 3D sensing. This invention gets robot environment information through one sense platform composed of 2D laser radar, rotation bench and step motor. This invention also provides one dynamic self-adaptive filter to realize dynamic filter noise removing aim for environment information interference.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
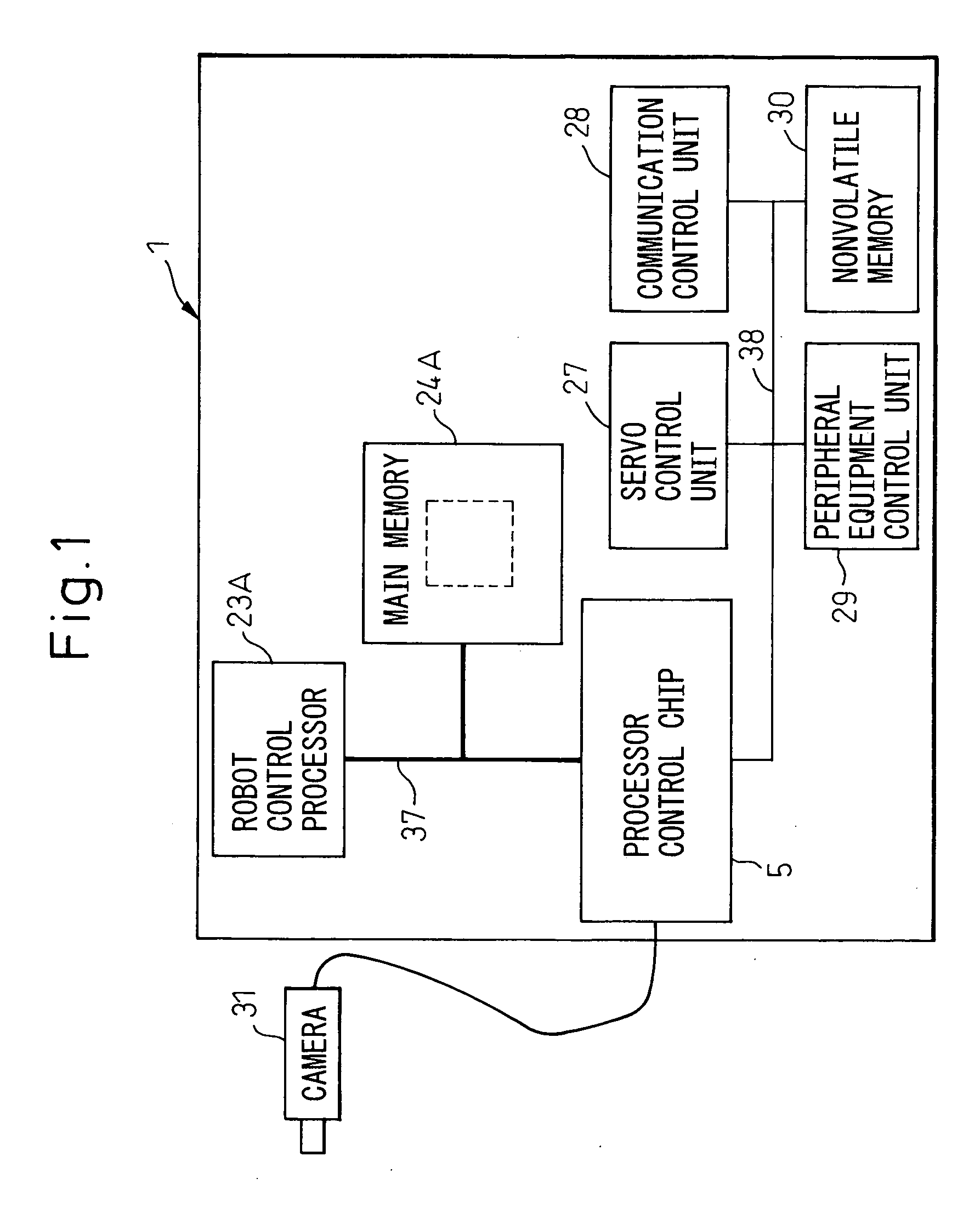
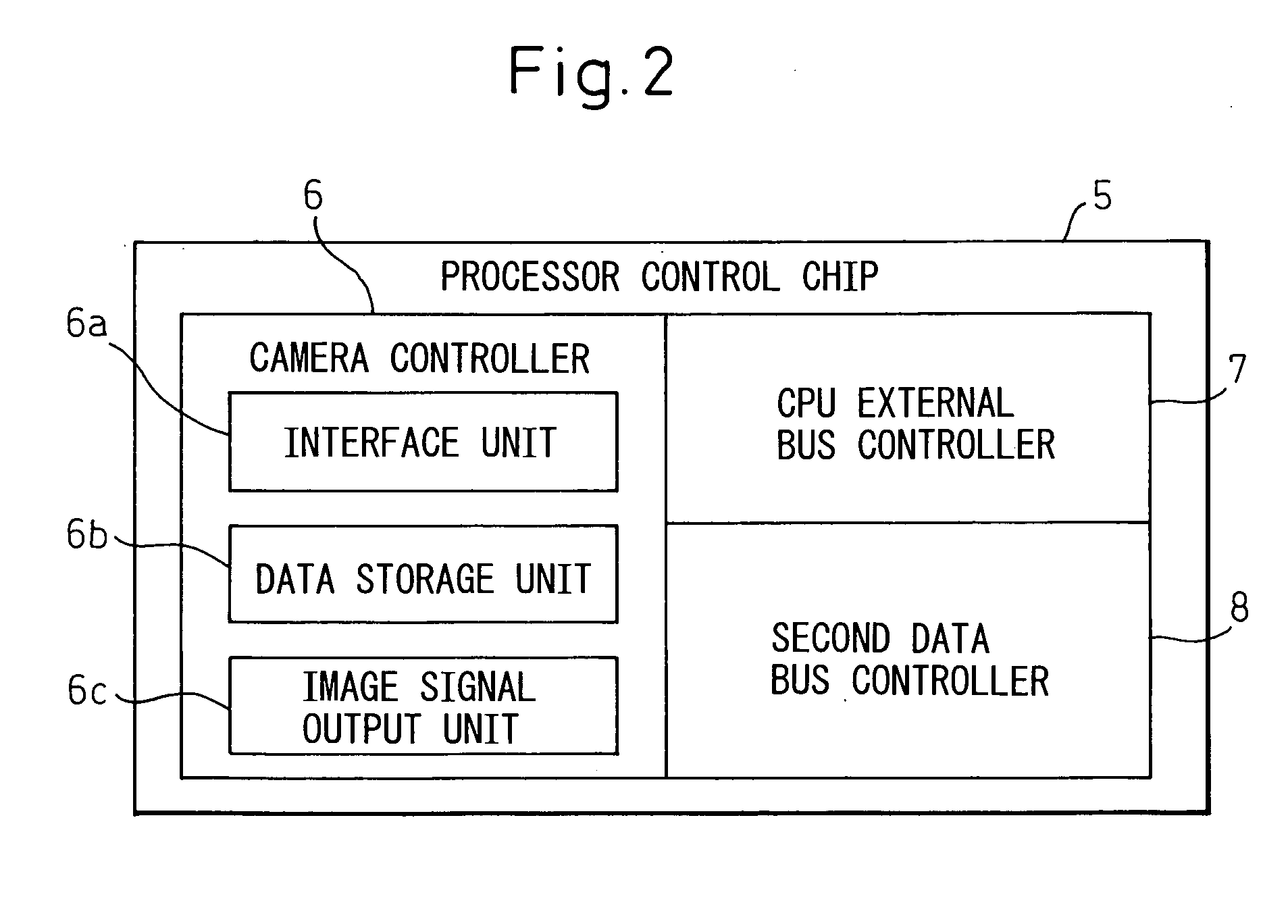
Robot controller
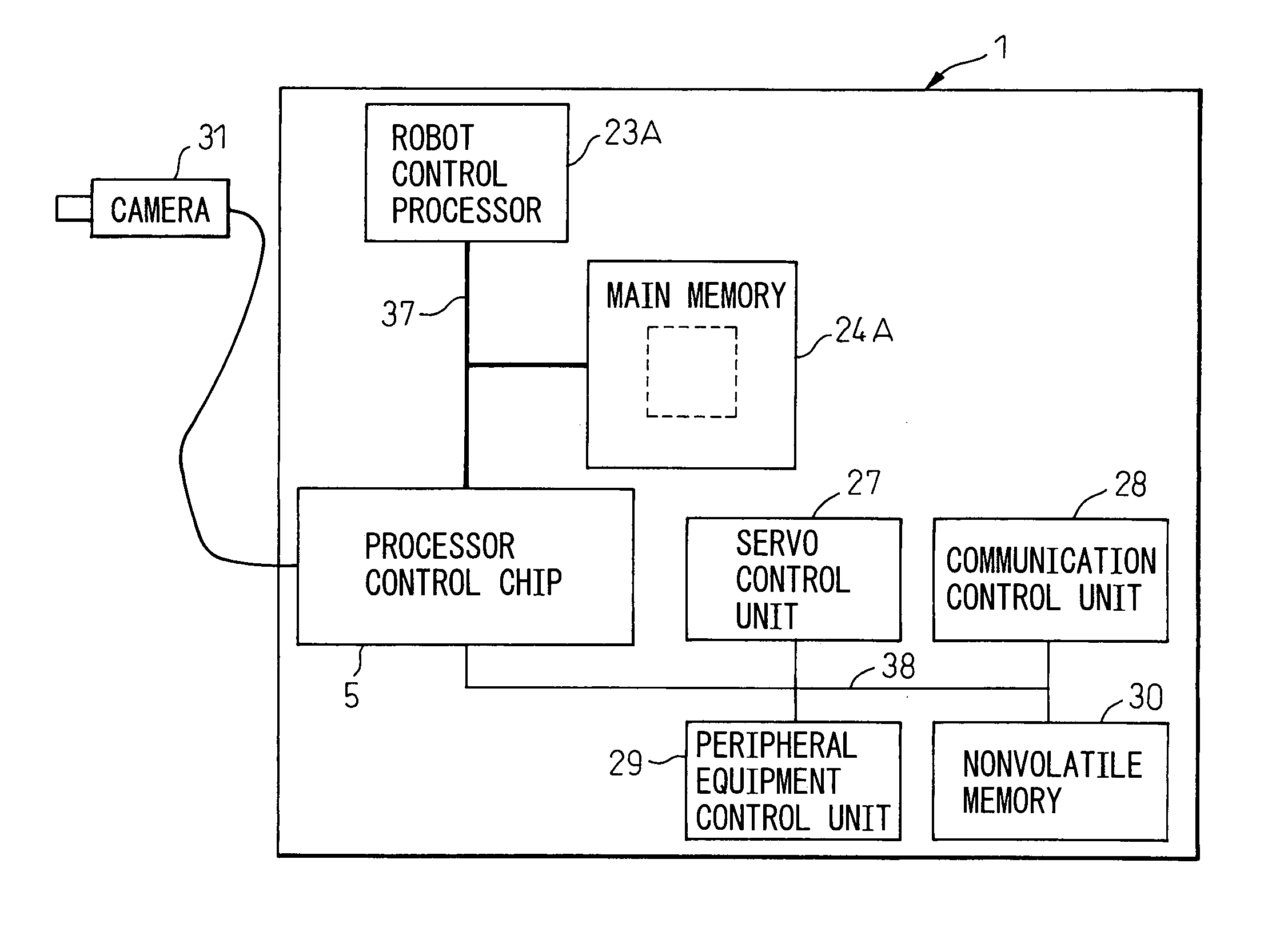
InactiveUS20060279246A1Hindering operationIncrease speedProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorRobot environmentControl data
A robot controller having a function for controlling the motion of a robot, comprising a processor for controlling the robot and for processing the environmental condition data representing the environmental conditions for the robot, a memory accessible by the processor, a writing unit for executing a function of writing the environmental condition into the memory, a first data bus connected to the memory, and a second data bus having a transfer rate lower than that of the first data bus and for transferring the control data used for controlling the robot, wherein the writing unit writes the environmental condition data into the memory through the first data bus, not through the second data bus. The writing unit can be a processor control chip which is connected to the processor through the first data bus.
Owner:FANUC LTD
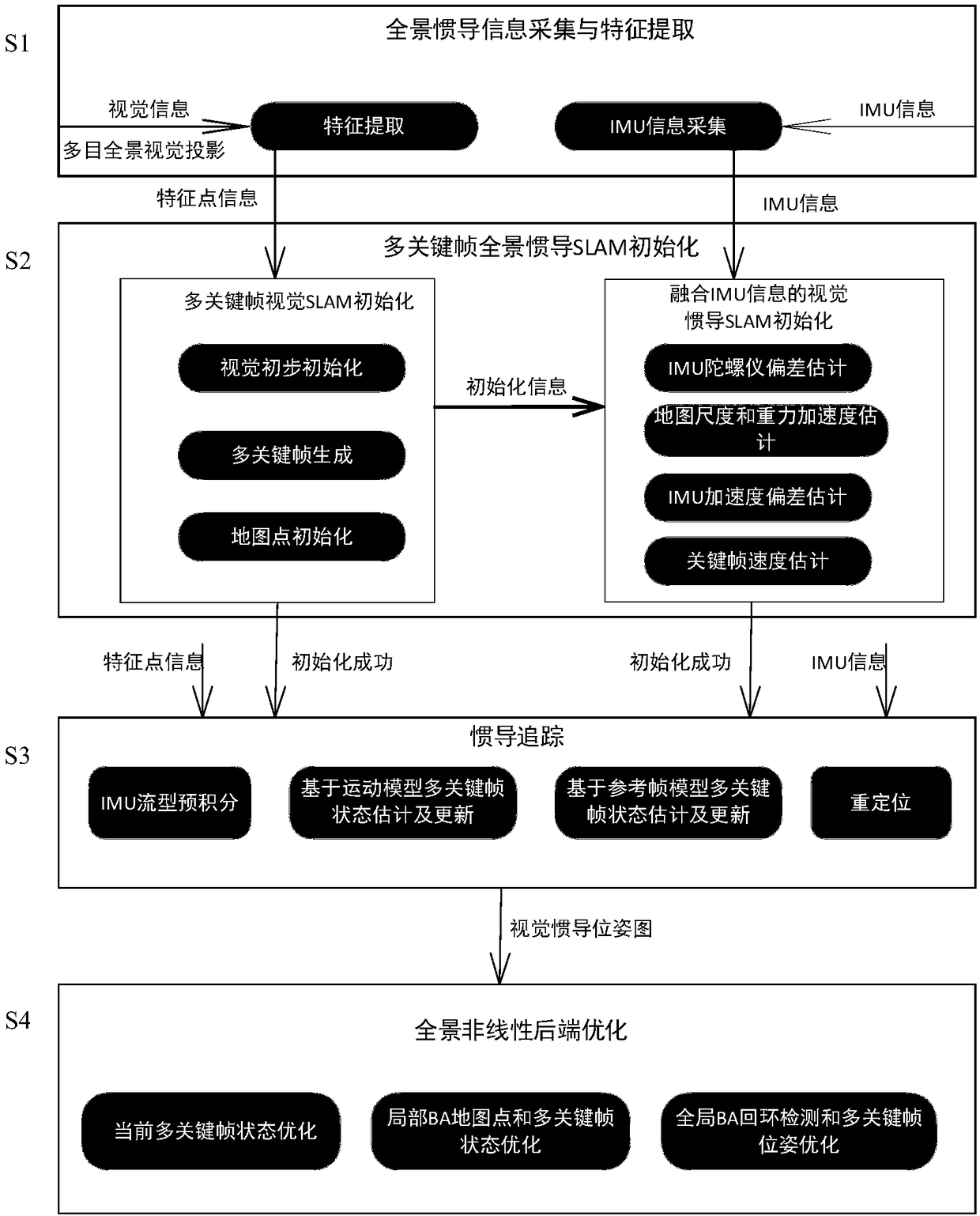
Panoramic inertial navigation SLAM method based on multiple key frames
ActiveCN109307508ALarge field of viewSolve the problem of limited field of viewNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsPicture taking arrangementsKey frameVisual degradation
The invention discloses a panoramic inertial navigation SLAM method based on multiple key frames. The method comprises the following steps of: building a multi-target panoramic visual model, combiningan inertial navigation unit and tightly coupling a fusion visual feature, and realizing a high-precision positioning and a scene map through multiple key frames nonlinear optimization. The method isused for solving the problems in the prior art of the insufficient information acquisition by environment-aware methods and the uncertainty of fast rotation, and limited view limitation, illuminationinfluence and visual degradation of an existing visual SLAM method, providing an effective automation method for a robot environment modeling and positioning navigation in a complex environment such as strong light / weak texture / motion blur, improving the accuracy and the robustness of the method, so that ensuring the sufficiency of autonomous navigation of the robot, and considering the calculation efficiency, can achieve the real-time performance of the visual SLAM method.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Characterising robot environments
A method for characterizing the environment of a robot, the robot having a flexible arm having a plurality of joints, a datum carried by the arm, a plurality of drivers arranged to drive the joints to move and a plurality of position sensors for sensing the position of each of the joints, the method comprising: contacting the datum carried by the arm with a first datum on a second robot in the environment of the first robot, wherein the second robot has a flexible arm having a plurality of joints, and a plurality of drivers arranged to drive those joints to move; calculating in dependence on the outputs of the position sensors a distance between a reference location defined in a frame of reference local to the robot and the first datum; and controlling the drivers to reconfigure the first arm in dependence on at least the calculated distance.
Owner:CMR SURGICAL LTD
Infrastructure for robots in human-centric environments
InactiveUS20150205297A1Beacon systems using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesBeacon systems using electromagnetic wavesSelf maintenanceRobot environment
To improve efficient use of robots in human-centric environments, robots have to overcome a number of challenges, including mobility challenges, physical interface challenges, self-maintenance challenges, security challenges, and safety challenges. These challenges can be overcome either by adding technology to a robot or by adding infrastructure to a robot's environment.
Owner:ROBOTEX
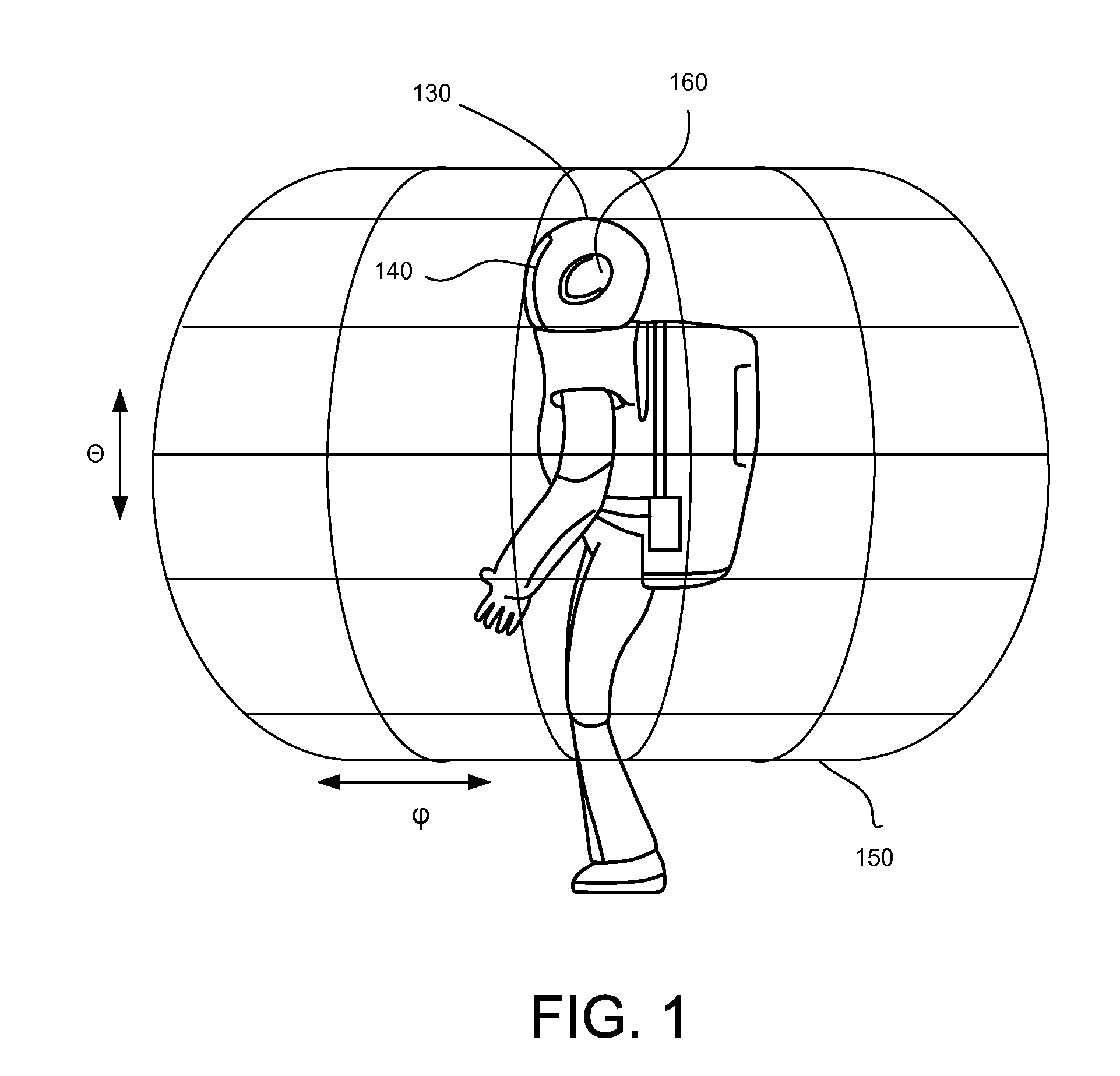
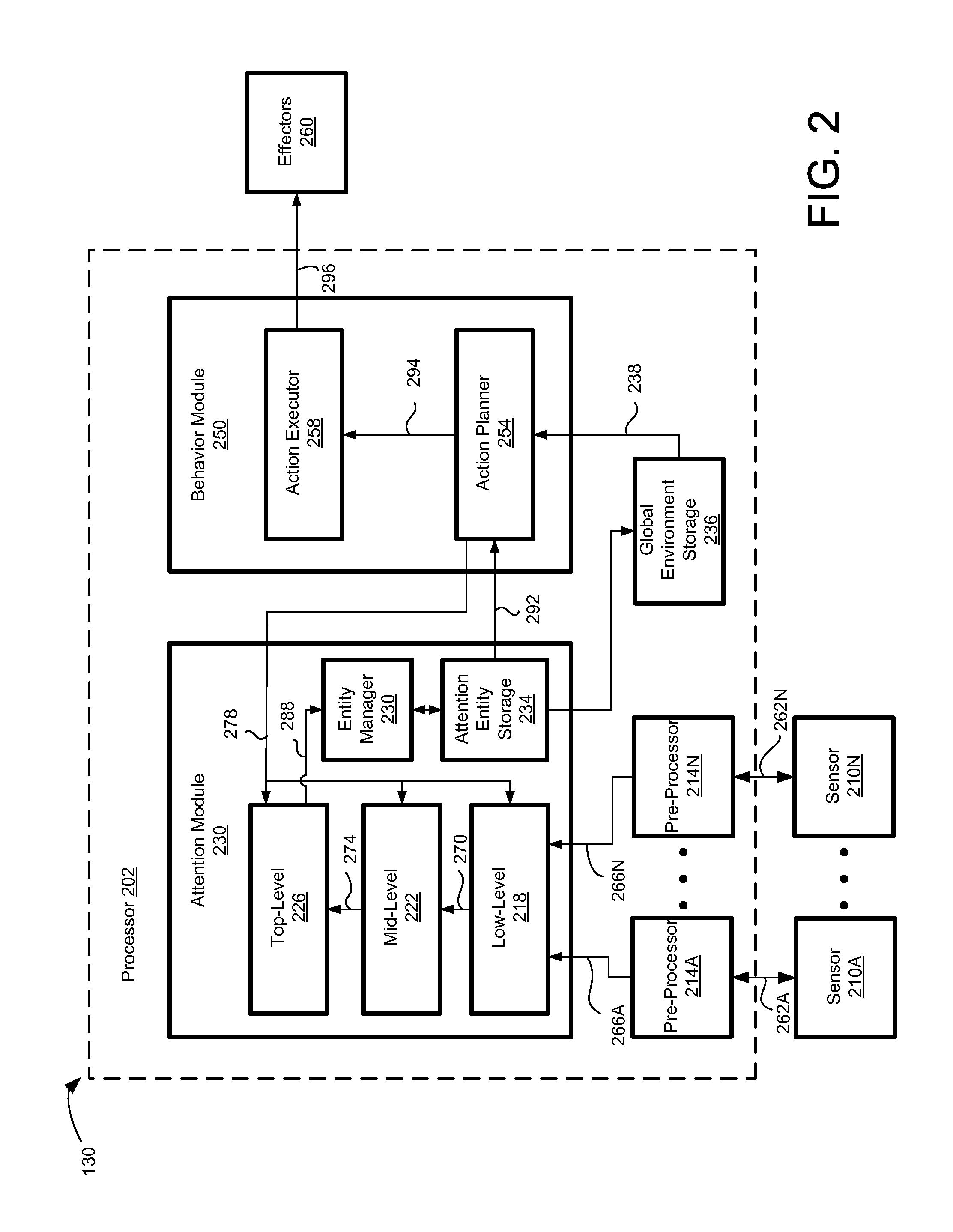
Panoramic Attention For Humanoid Robots
ActiveUS20110004341A1Reduce signalingProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlPanoramaComputer graphics (images)
A robot using less storage and computational resources to embody panoramic attention. The robot includes a panoramic attention module with multiple levels that are hierarchically structured to process different levels of information. The top-level of the panoramic attention module receives information about entities detected from the environment of the robot and maps the entities to a panoramic map maintained by the robot. By mapping and storing high-level entity information instead of low-level sensory information in the panoramic map, the amount of storage and computation resources for panoramic attention can be reduced significantly. Further, the mapping and storing of high-level entity information in the panoramic map also facilitates consistent and logical processing of different conceptual levels of information.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
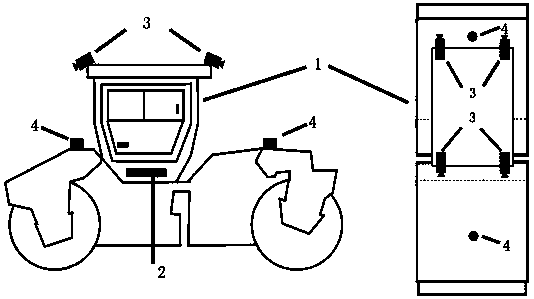
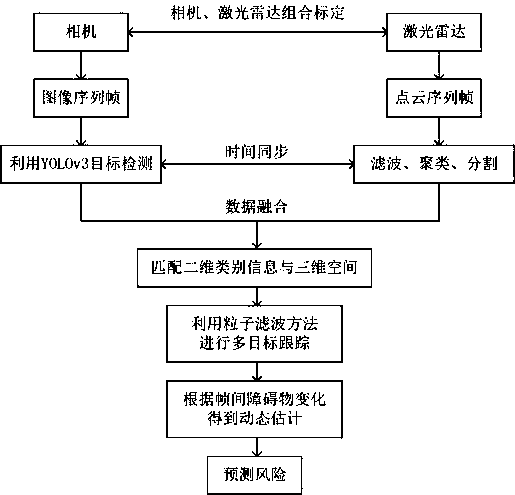
Road surface construction robot environment perception system and method based on multi-source sensor
ActiveCN110244322AImprove target detection accuracyImprove ranging accuracyInternal combustion piston enginesElectromagnetic wave reradiationRoad surfaceTrack algorithm
The invention discloses a road surface construction robot environment perception system and method based on a multi-source sensor. A camera and a laser radar are arranged on a robot body; an embedded industrial control computer is arranged in the robot body; the embedded industrial control computer is used for obtaining and fusing class information of picture data and distance information of the laser radar based on a data fusion multi-target detection ranging algorithm, then, tracking a target by adopting a particle filter algorithm in the two directions of an image and point cloud, obtaining dynamic estimation change of an obstacle target in continuous time, and finally, obtaining the advancing speed and the motion direction of an obstacle in a construction area through the dynamic estimation change; road surface environment perception on the construction area is realized by drawing a risk graph; therefore, the adaptive capacity of the system for different environments is obviously improved; furthermore, the shielding condition between obstacles has some improvements on multi-target detection and a tracking algorithm; therefore, the effective operation of the construction robot is ensured; and thus, the system and the method have good application prospect.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
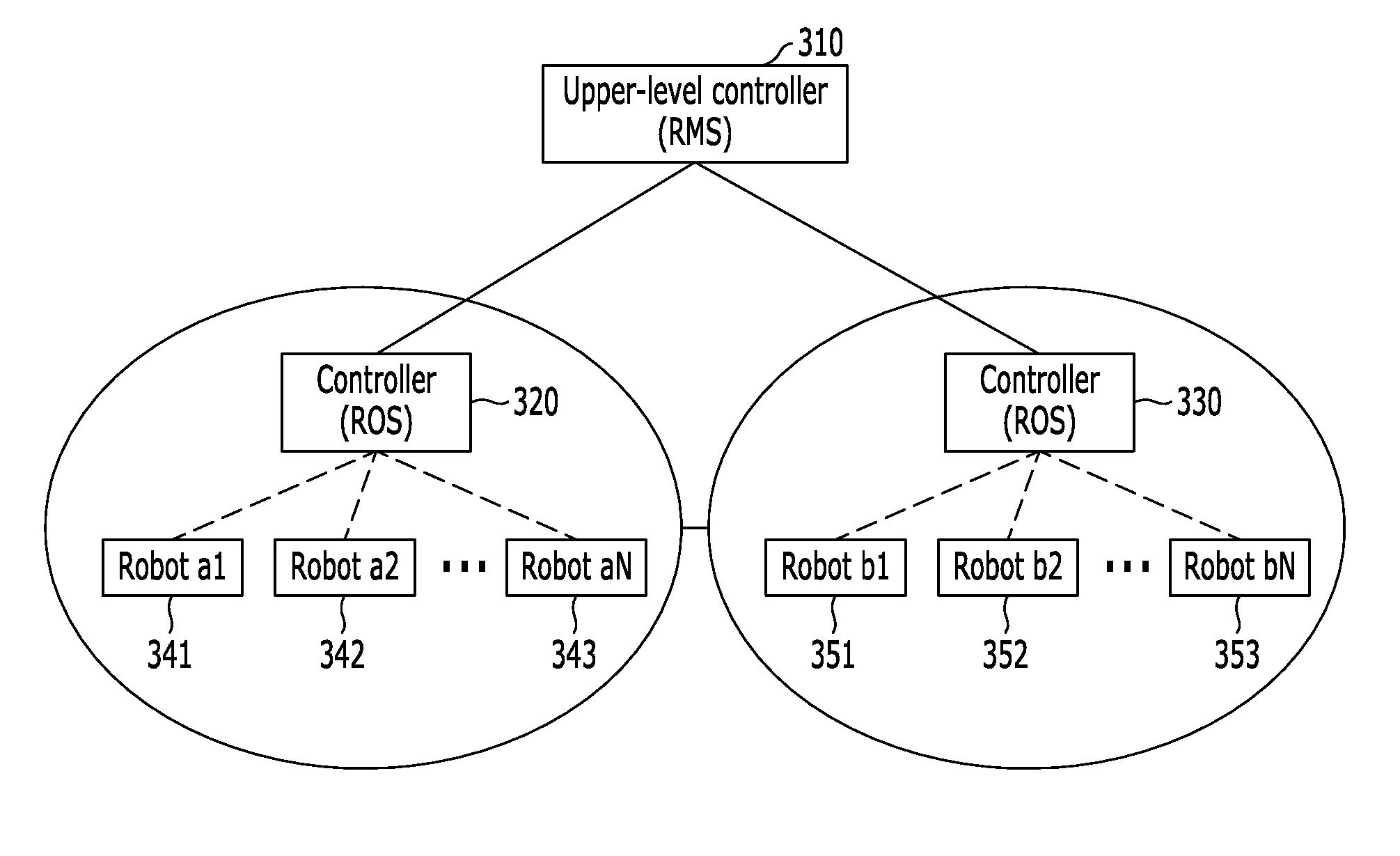
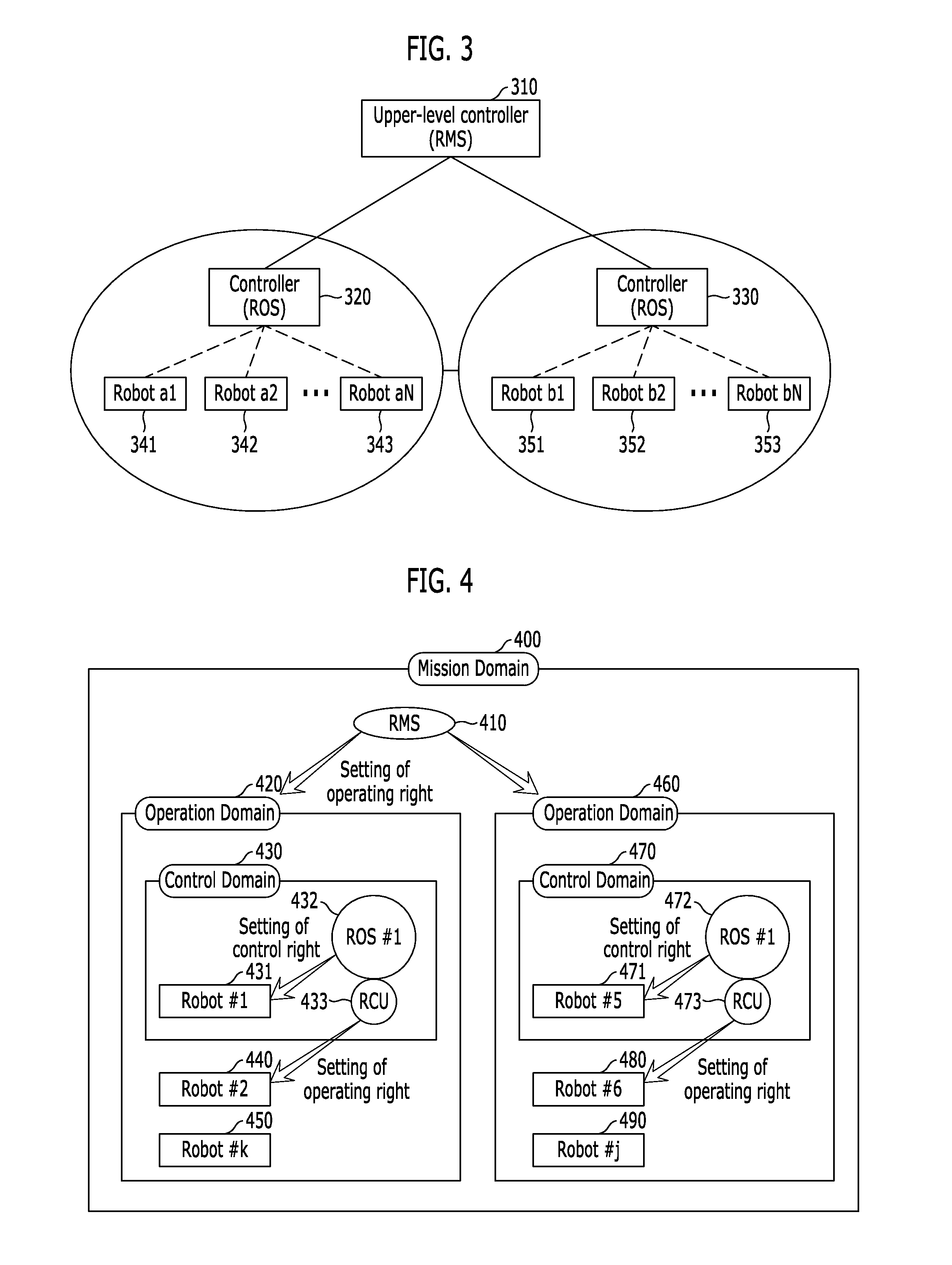
Method and system for transferring/acquiring operation right of moving robot in multi-operator multi-robot environment
InactiveUS20110054684A1Achieve mutual compatibilityImprove mutual compatibilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlRobot environmentOperational system
In an operating system having a first controller configured to manage one or more robots included in a first region, and a second controller configured to manage one or more robots included in a second region adjacent to the first region, a method for enabling the second controller to acquire an operation right of N robots (where N is a natural number equal to or greater than 1) operated by the first controller, the method includes: transmitting a control mapping status (CMS) containing an operation right change message to the first controller, upon reception of an operation right request signal from a user of the N robots; and checking a connection status of the N robots, upon reception of the CMS containing the operation right change message from the first controller, and acquiring an operation right by providing CMS acquisition information and control mapping information to the robots included in the second region.
Owner:AGENCY FOR DEFENSE DEV +1
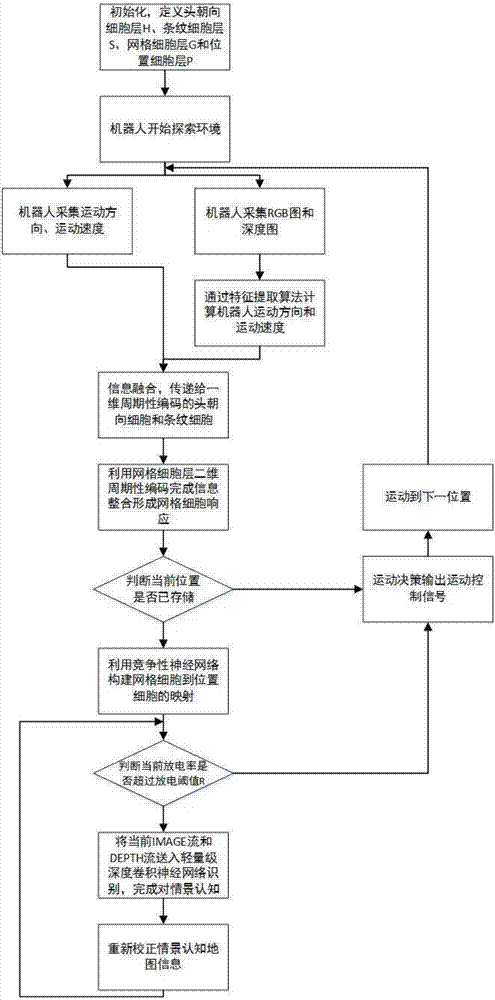
Scene cognition map building and navigation method based on mouse cerebral hippocampal
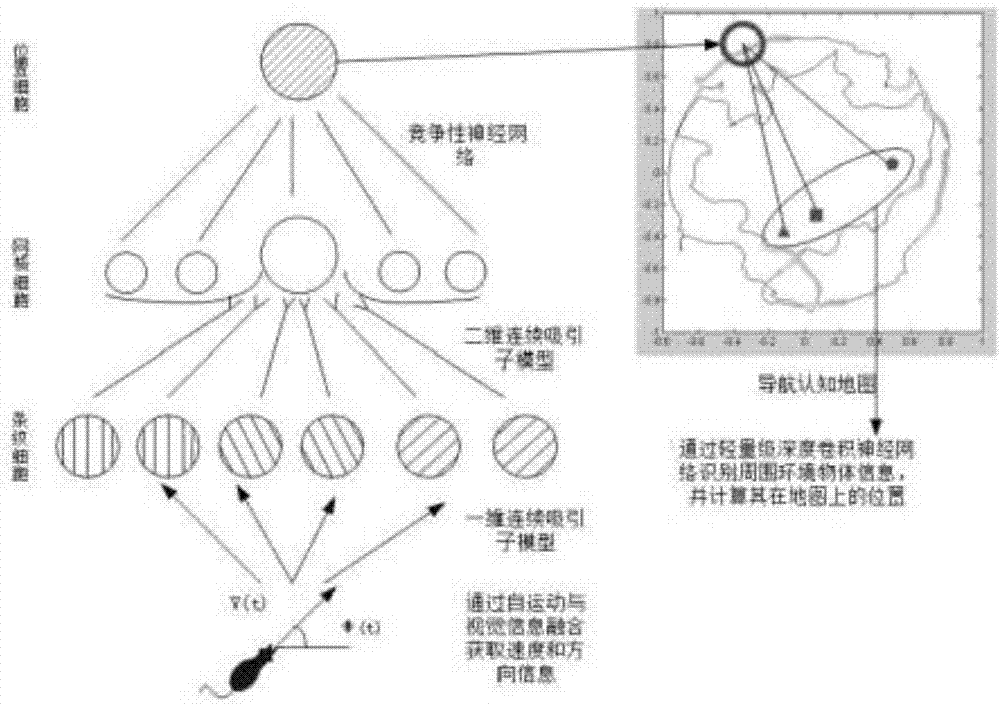
ActiveCN106949896ALow hardware requirementsProactiveNavigational calculation instrumentsRobot environmentDischarge rate
The invention discloses a scene cognition map building and navigation method based on a mouse cerebral hippocampal, and belongs to the technical field of robot environment cognition and motion navigation. When a position discharging rate explored by a robot is larger than a position cell discharging threshold, discharging information Pfire, position Plocation and environment scene information O need to be recorded, and the information is recorded on a scene cognition map. Robot navigation, namely, navigation from an initial position to a specific object position in a specific scene, is finished through space information stored on the scene cognition map. By adopting the scene cognition map building and navigation method, the robot can explore an environment autonomously, environment information is changed into the scene cognition map of the robot, and a corresponding navigation strategy is made according to the cognition map. The whole set of system has a good space cognition effect, and can be applied to scene cognition map building and navigation of indoor environments such as plants, families and laboratories, and outdoor environments such as streets.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
A multiple-mobile-robot-cooperated navigation method and system
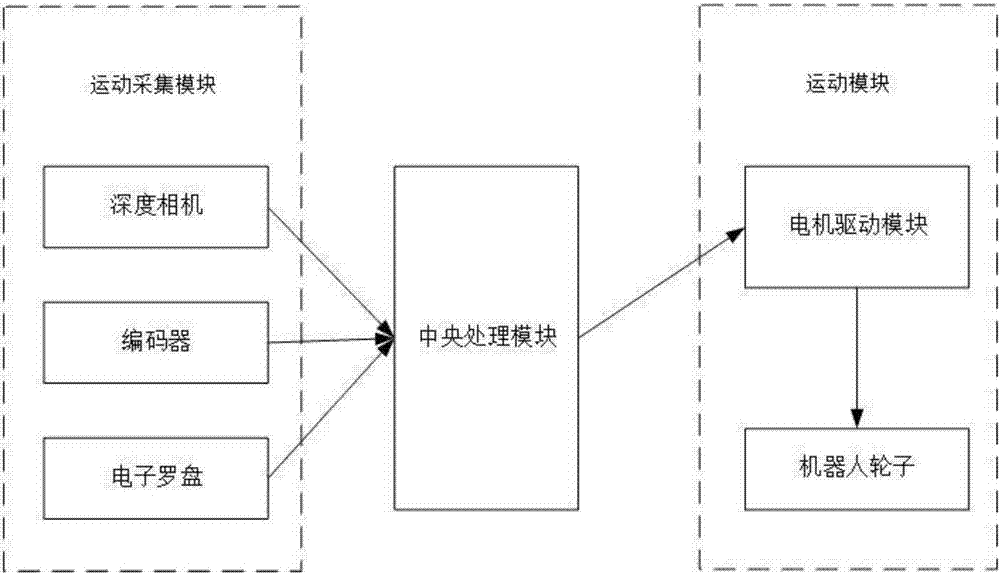
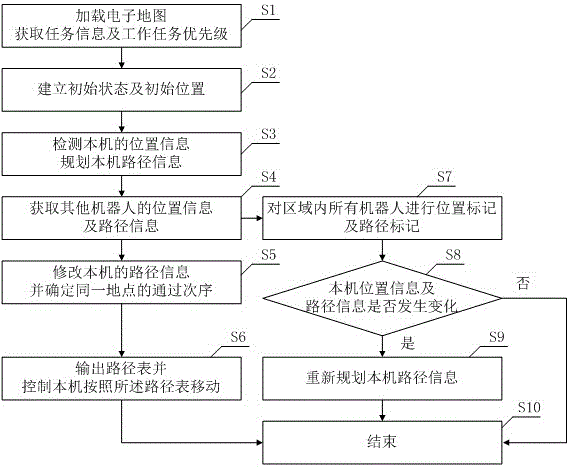
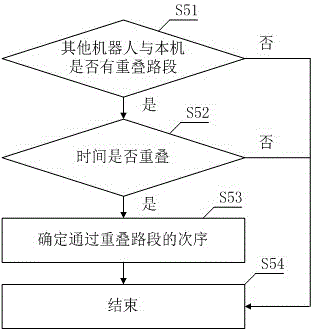
InactiveCN106500700AAutomatic and reliable mobile serviceRealize intelligent navigationNavigational calculation instrumentsTime informationRobot environment
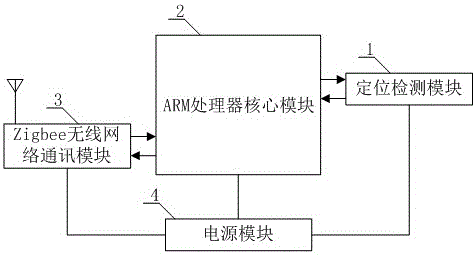
A multiple-mobile-robot-cooperated navigation method is provided. The method includes detecting position information of a local robot, planning path information of the local robot, acquiring position information ad path information of other robots, determining a passing order for a same position, outputting a path table, and controlling the local robot to move along the path table. A multiple-mobile-robot-cooperated navigation system is also provided and includes a positioning detection module, an ARM processor core module and a Zigbee wireless network communication module. Real-time information exchange with other robots in a region is performed through Zigbee wireless communication, the position information and a moving path of the local robot are provided to other robots and the position information and paths of other robots are acquired at the same time. Through cooperated working, intelligent navigation of a multiple-robot environment is achieved, and automatic and reliable moving services and cooperated working of the multiple robots in a same site environment are ensured, thus increasing the navigation precision and the navigation efficiency. The method and the system are simple, practical, and easy in popularization.
Owner:SHENZHEN ZHONGZHOU INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
Implementation method of force telepresence of telerobotics based on integration of virtual strength and real strength
InactiveCN101986219AAchieving force-presence controlReduce the effect of instabilitySimulator controlRobot environmentEngineering
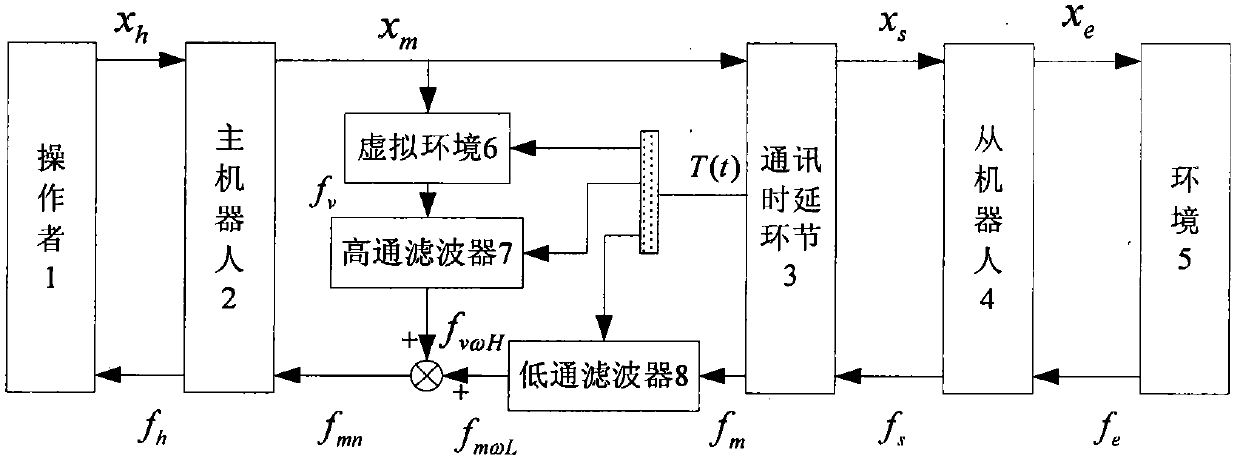
The invention relates to an implementation method of force telepresence of a telerobotics based on integration of virtual strength and real strength, which comprises the following steps: a master side position signal xm is produced by an operator through a master robot, the master side position signal xm enters into a communication time delay environment, a slave side position signal xs is formed after time delay, and the slave side position signal xs further enters into a slave robot as the input of the slave robot. The slave robot outputs an environmental position signal xe to be acted on the environment, the environment simultaneously provides environmental reacting force fe for the slave robot, the slave robot outputs a slave side force signal fs according to the environmental reacting force fe, a master side force signal fm is outputted after entering the communication time delay link for delay, the master side force signal fm further enters into a low-pass filter, and a low-frequency force signal fmwL is outputted. The other line of the master side position signal xm enters into a virtual environment, a model of the virtual environment outputs a virtual force signal fv, the virtual force signal fv further enters into a high-pass filter for processing, and the high-pass filter outputs a high-frequency force signal fv omega H. The high-frequency force signal fv omega H and the low-frequency force signal fmwL are superimposed, a new master side force signal fmn is formed and the signal is acted on the master robot.
Owner:NANTONG MAOYI MACHINE TOOL +1
Workpiece 6D pose estimation method based on deep learning
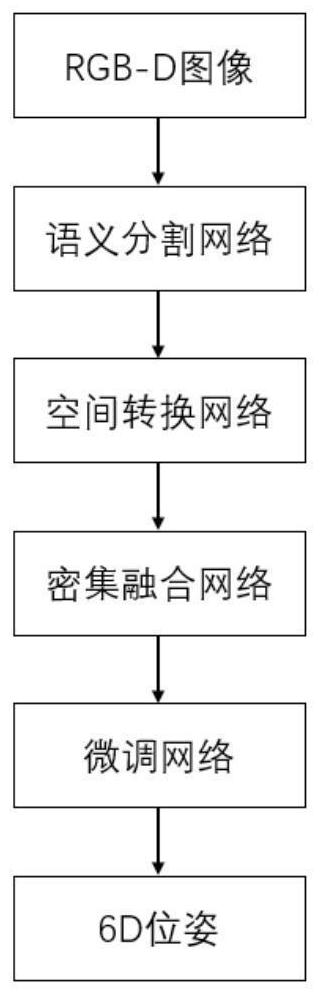
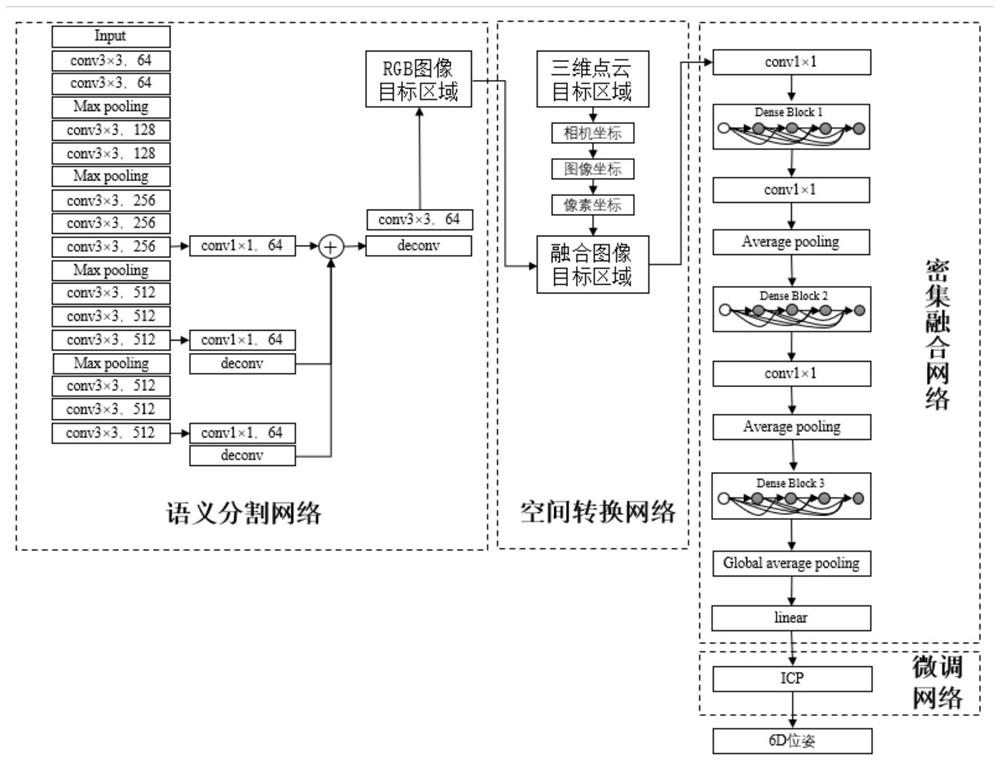
PendingCN111899301AExtract comprehensiveGood for pose estimationImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionRobot environment
The invention discloses a workpiece 6D pose estimation method based on deep learning. The invention relates to the technical field of robot environment perception. The method specifically comprises the following steps: collecting different workpiece images under different backgrounds and illumination conditions; constructing a semantic segmentation model to segment a target object; three-dimensional point cloud coordinates are converted into pixel coordinates for representation through a space conversion network, three-dimensional point cloud data and RGB information are fused, a dense fusionnetwork is constructed to estimate 3D position information and 3D direction information of an object, an ICP algorithm is adopted to iteratively match and finely adjust the pose, and therefore accurate 6D pose information of the object is obtained. Compared with the traditional scheme, the method has the advantages that the end-to-end 6D pose of the target object can be quickly and accurately estimated in real time in complex environments such as occlusion and disorder, and the problems of poor adaptability, low accuracy and limited real-time performance of the traditional pose estimation method in the real complex environment are effectively solved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Mobile robot path planning method
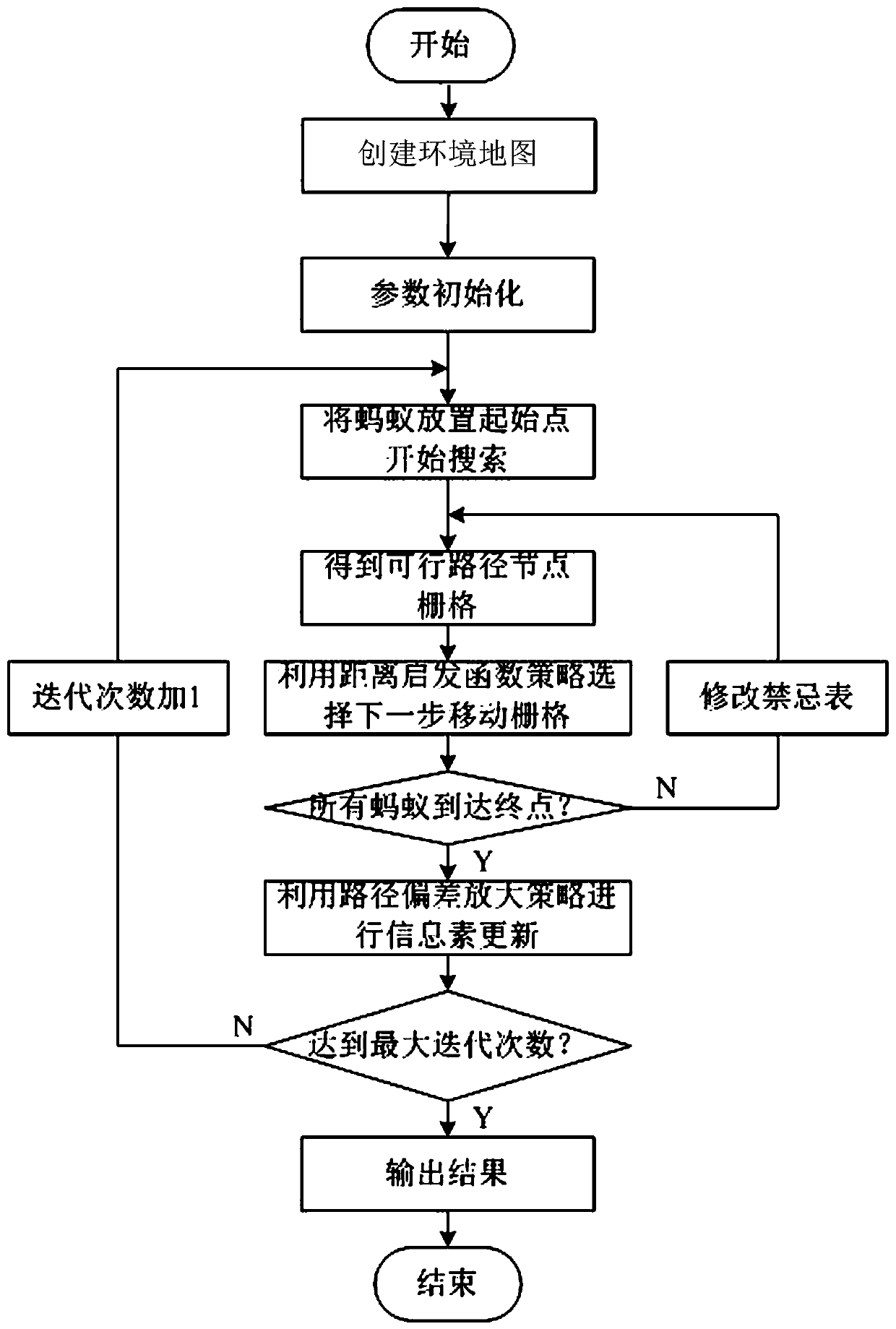
ActiveCN110160546AImprove efficiencyImprove stabilityInstruments for road network navigationRobot environmentGrating
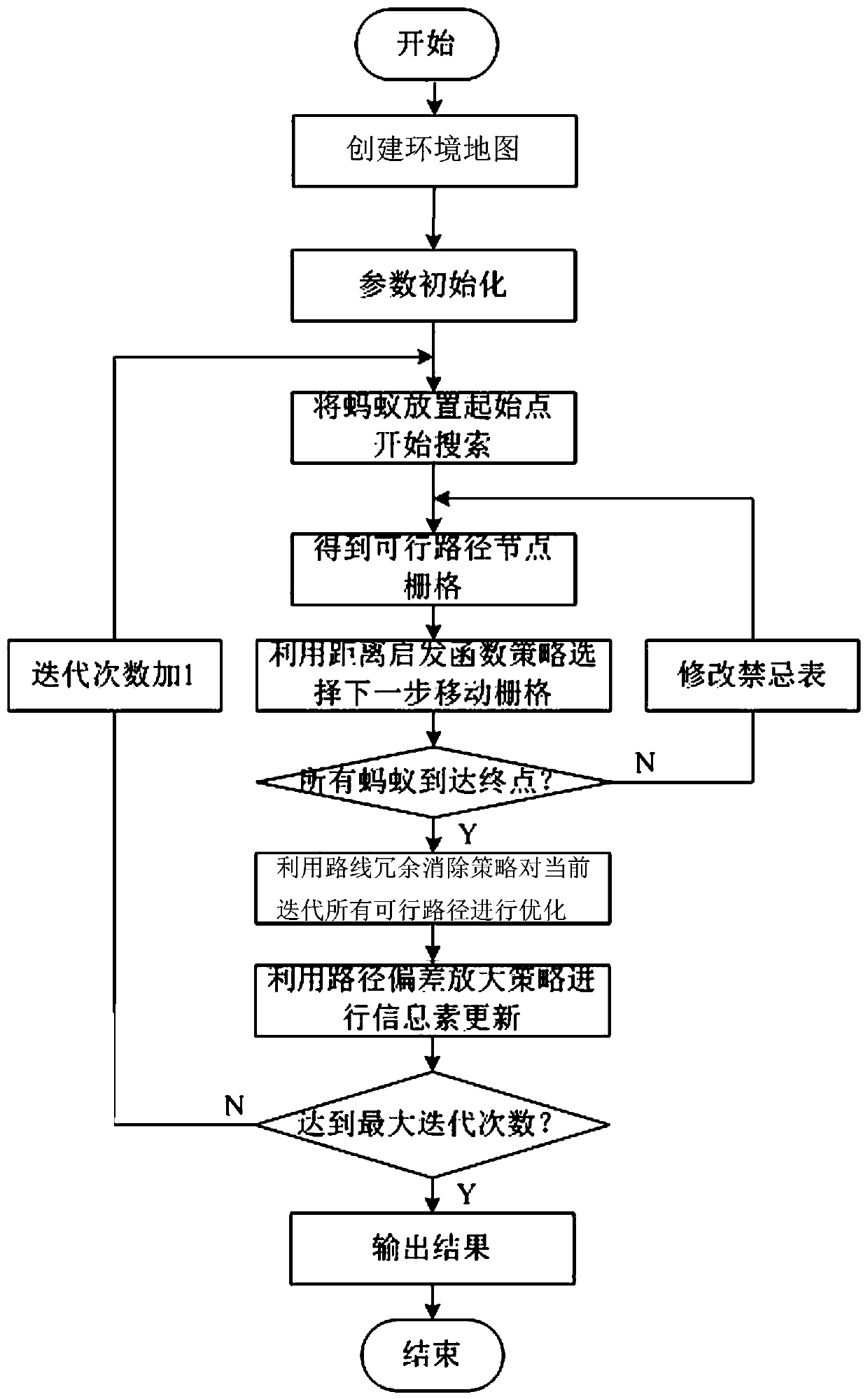
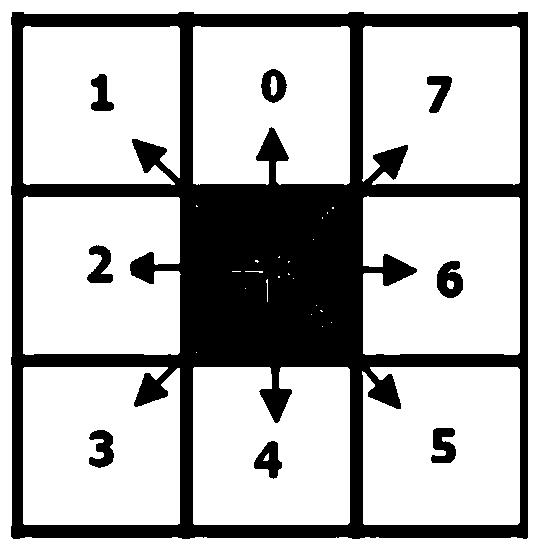
The invention discloses a mobile robot path planning method. The method comprises the following steps: S1, creating a robot environment map by adopting a grid method, and defining a start point and atarget point; S2, searching an environment shortest path by adopting an ant colony, wherein the ant colony algorithm contains the following steps: S21, initializing parameters of the ant colony algorithm; S22, placing m ants at the start point, beginning searching to obtain a feasible path node grating; S23, selecting the next step of moving grid by utilizing a distance heuristic function, and adding the current grid into a tabu table; S24, judging whether all ants reach the target point, if all ants reach the target point, performing the step S25, or returning to step S23; S25, performing pheromone updating by utilizing a path deviation amplifying strategy; and S26, judging whether reaching the maximum number of iterations, ending the ant colony algorithm if reaching the maximum number ofiterations, or adding one on the number of iterations and returning to step S22; and S3, taking the shortest path obtained in the step S2 as the optimal path of the planning. The planning method disclosed by the invention not only improves the global optimal solution, but also improves the convergence speed.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE
Robot behavior control method based on virtual reality
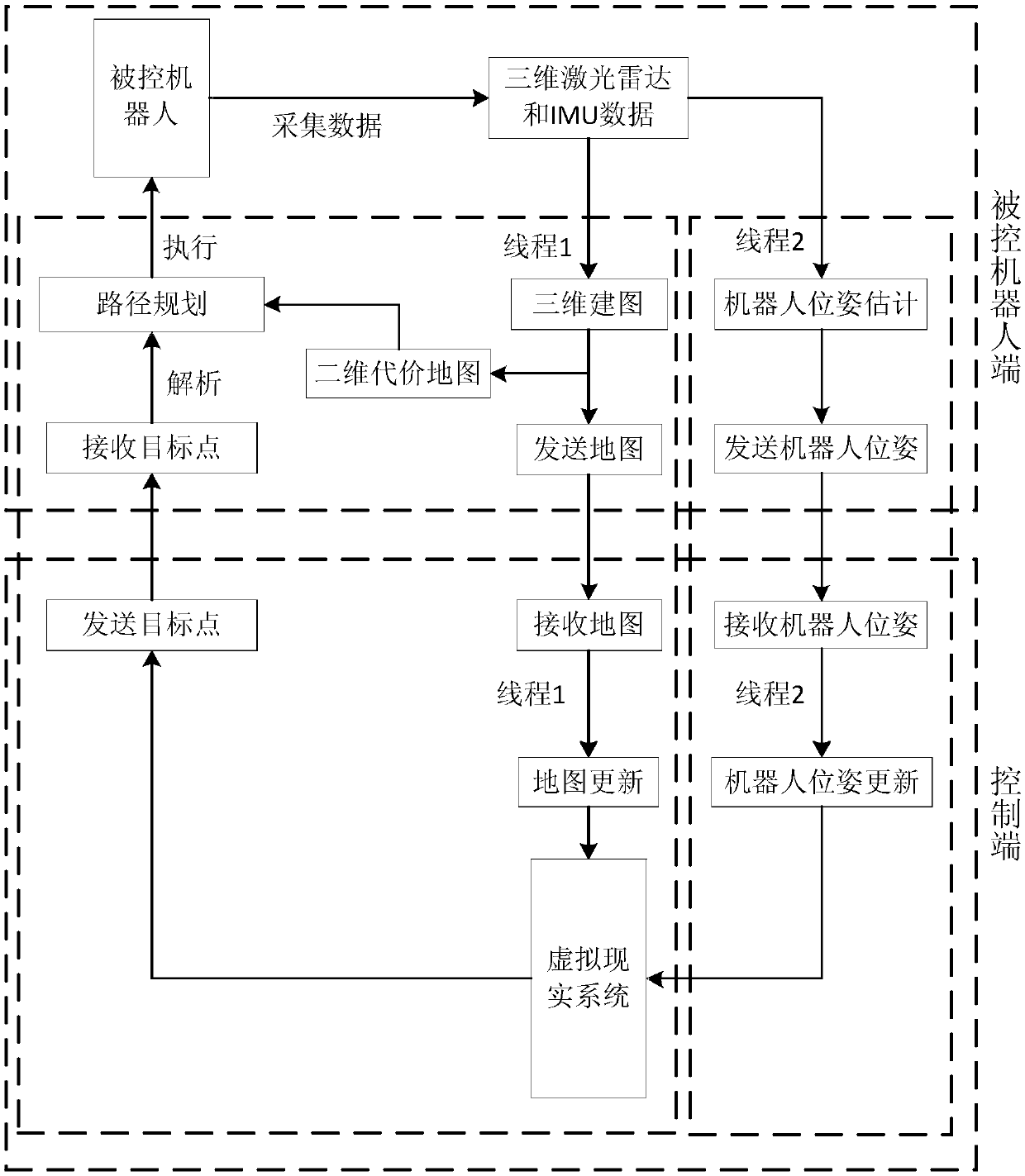
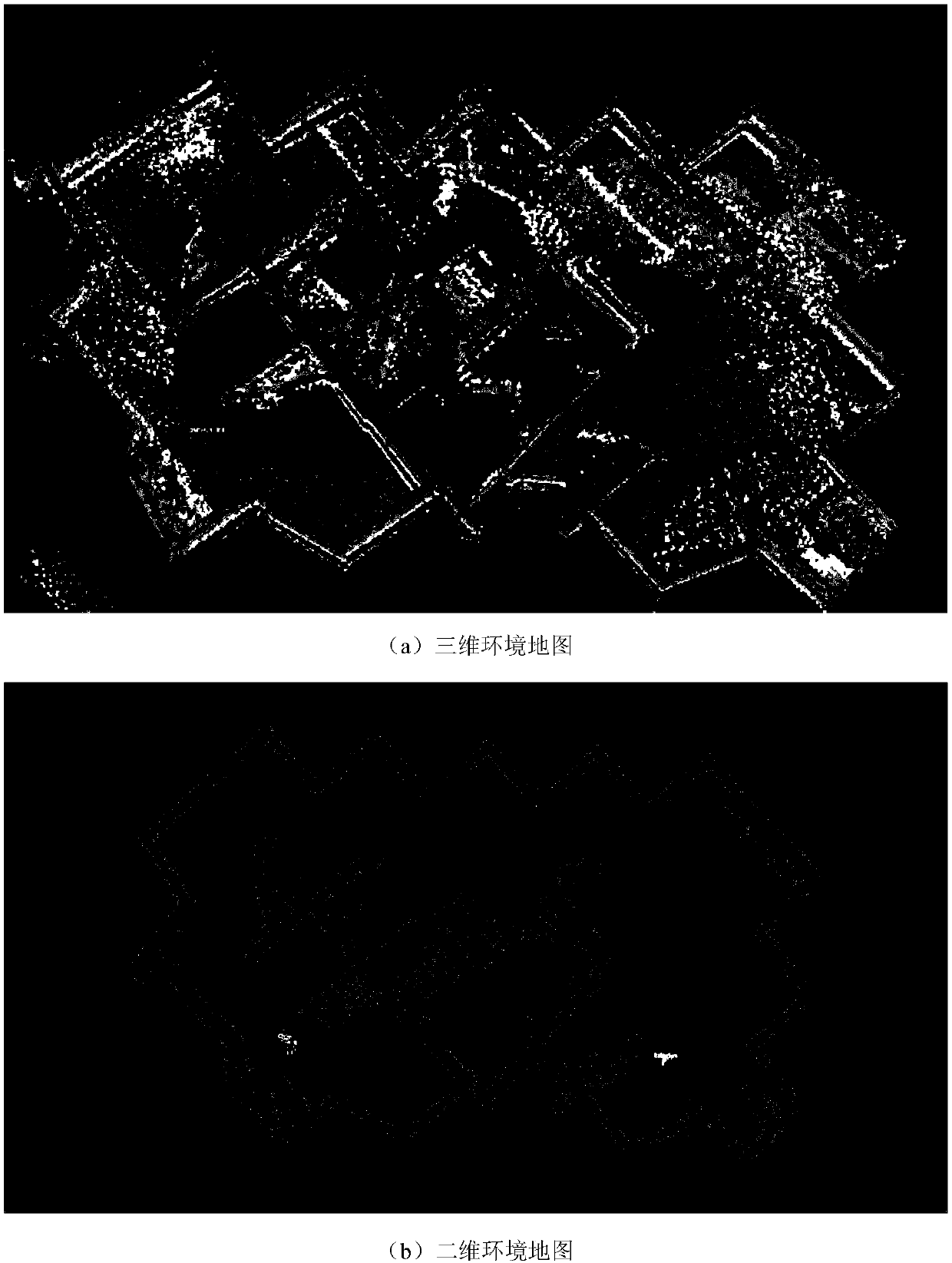
ActiveCN108908330AImprove real-time performanceImprove application flexibilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorRobot environmentSimulation
The invention discloses a robot behavior control method based on virtual reality. The control method includes the steps of S1, after environmental data of a controlled robot is collected in real timeto obtain a robot environment map, constructing an environmental cost map of the robot according to the obtained robot environment map; S2, according to the constructed environmental cost map, planning an optimal path to an assigned target point, controlling the robot to move according to the planned path. The method has the advantages of being easy to control, small in demanded communication bandwidth, high in timeliness, control precision and efficiency, flexible to use and the like.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Robot zero calibration system and method based on laser triangulation ranging
ActiveCN105806309AImprove calibration accuracyImprove versatilityOptical rangefindersRobot environmentEngineering
The invention discloses a robot zero calibration system and method based on laser triangulation ranging. The system comprises calibrators, targets and a controller. The three calibrators are installed on rigid bases at any position in the surroundings of a robot respectively, the three targets are correspondingly pasted on three perpendicular planes, corresponding to the calibrators, of the tail end of a robot body, and the controller is arranged at a certain surrounding position needed by the robot. Each calibrator is composed of two laser triangulation displacement sensors with the absolute displacement measurement function and a shell, wherein read data of the two laser triangulation displacement sensors is directly transmitted to the controller, and the controller achieves zero calibration of the robot through data processing. The robot zero calibration system and method are high in calibration precision, free of influences on the robot body and suitable for design of novel robots and accessory installation of in-service robots and have the highest universality.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
SLAM system based on multi-view panoramic inertia navigation
PendingCN108846867ALarge field of viewSolve the problem of limited field of viewImage analysisGeometric image transformationRobot environmentSimulation
The invention discloses a SLAM system based on multi-view panoramic inertia navigation. A 360 panoramic vision model is constructed, the high-precision vision SLAM and space movement tracking are realized through lightweight-level embedded parallel computation by combining the inertia navigation to closely couple and fuse with the vision feature, the problem that the environment sending method isinsufficient in information acquisition and uncertain in fast rotation in the prior art is solved, and an effective automatic measure is provided for robot environment modeling and positioning navigation in strong light / weak texture / movement fuzzy and like complex environments. The system precision and robustness are improved, the sufficiency of the autonomous navigation of the robot is guaranteed, and the lightweight and the device can be realized through the design way of the embedded system.
Owner:安徽云能天智能科技有限责任公司
Improved ant colony algorithm based mobile robot path planning method
ActiveCN110095122AImprove solution efficiencyImprove stabilityNavigational calculation instrumentsArtificial lifeRobot environmentHeuristic function
The invention discloses an improved ant colony algorithm based mobile robot path planning method. The method comprises the following steps that S1) a grid method is used to create an environment map of a robot; S2) an ant colony algorithm is used to search for a shortest environment path, and the ant colony algorithm comprises the following steps of S21) initializing parameters of the ant colony algorithm, S22) placing m ants in the initial points and starting searching, S23) selecting a next moving grid by using a distance heuristic function, S24) determining whether all ants arrive at a target point, moving to S25) if YES, and otherwise, returning to S23), S25) optimizing all feasible paths of present iteration in a route redundancy elimination strategy; S26) updating pheromones in a path deviation amplification strategy; and S27) determining whether the maximal iteration frequency is reached, ending if YES, and otherwise, adding 1 to the iteration times and returning to the step S22); and S3) the shortest path obtained in the step S2) is used as a planned optimal path. The global optimal solution is improved, and the convergence speed is improved.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE
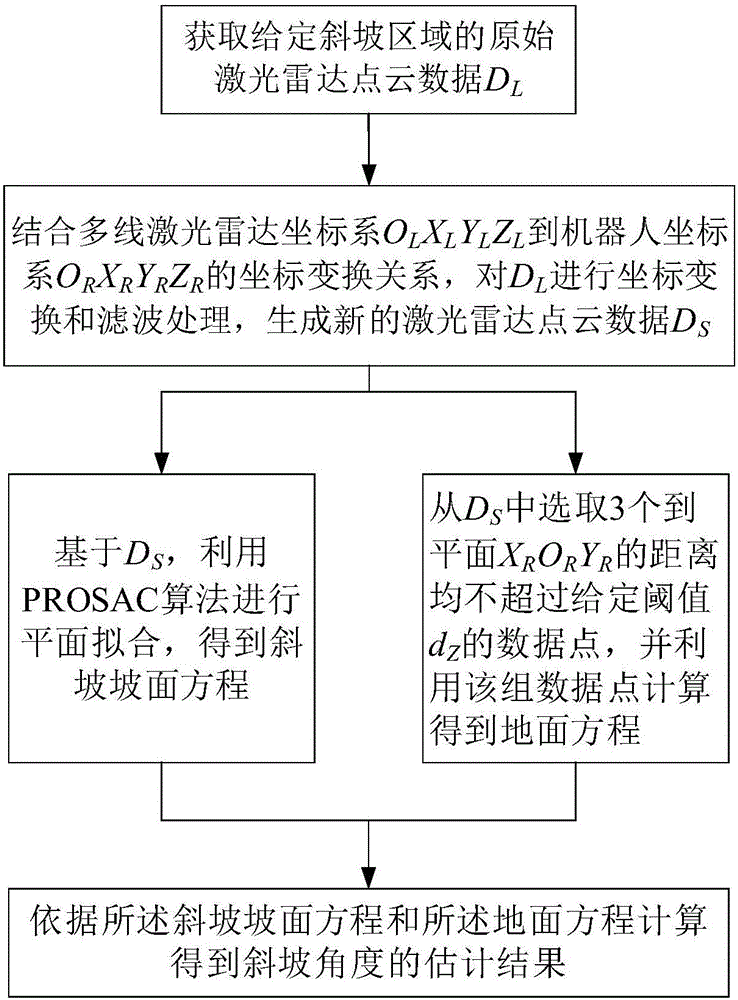
Slope angle estimation method for slope region based on multiline laser radar
ActiveCN106646508AQuality improvementElectromagnetic wave reradiationIncline measurementEuclidean vectorSurface equation
The invention discloses a slope angle estimation method for slope region based on a multiline laser radar, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining original laser radar point cloud data DL of a given slope region; carrying out the coordinate transformation and filtering of the DL through combining with the relation of coordinate transformation from a multiline laser radar coordinate system OLXLYLZL to a robot coordinate system ORXRYRZR, and generating new laser radar point cloud data DS; carrying out the plane fitting through a PROSAC algorithm based on DS, and obtaining a slope surface equation; selecting three data points from the DS, and calculating a ground equation through the data points, wherein the distances between the data points and a plane XRORYR do not exceed a given threshold value dZ; and calculating a slope angle estimation result according to the slope surface equation and the ground equation. The method obtains the distance information of the slope region through the multiline laser radar, achieves the estimation of the slope angle based on a slope surface normal vector, improves the estimation quality of the slope angle, and provides technical support for the application of robot environment understanding.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
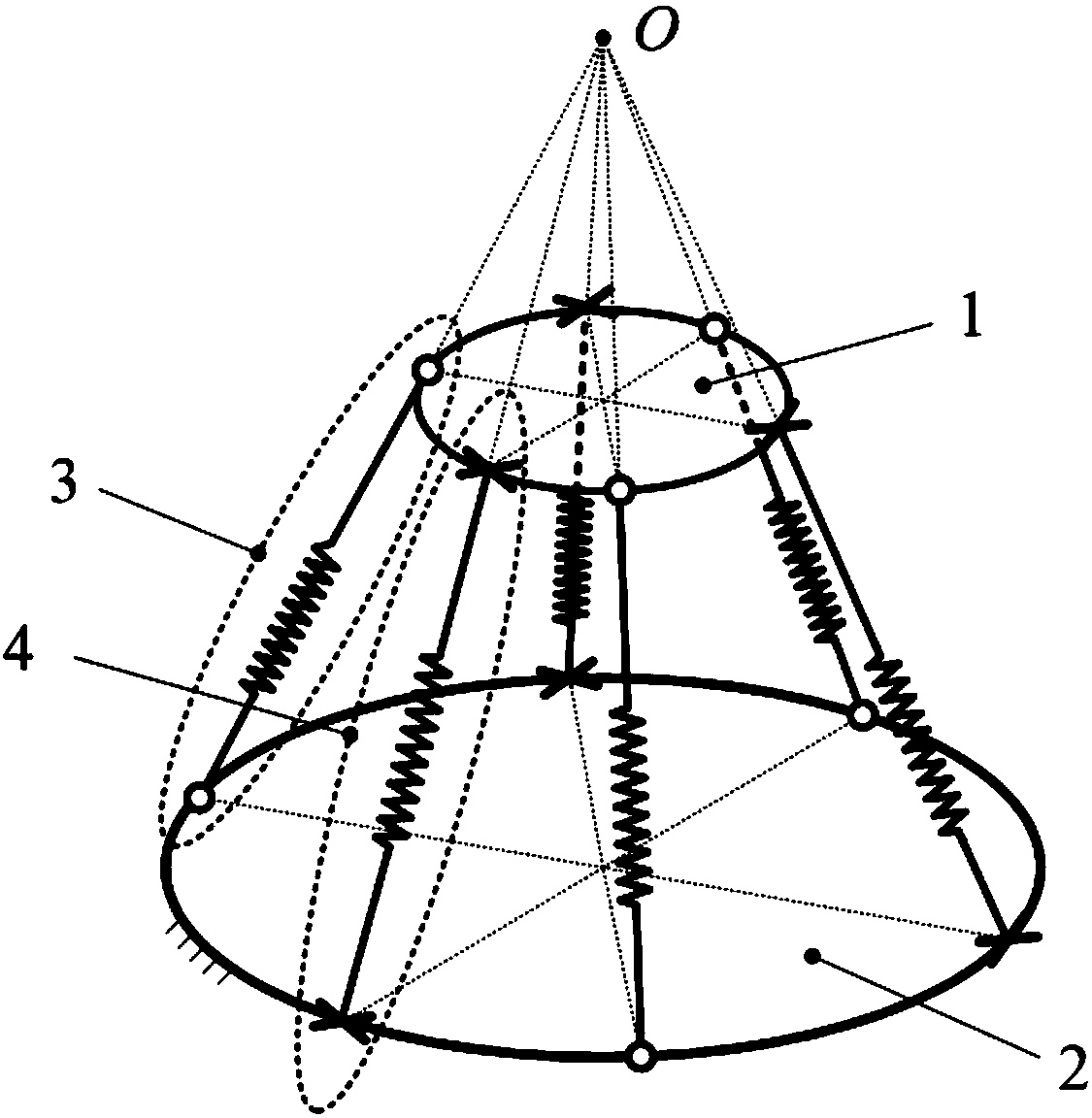
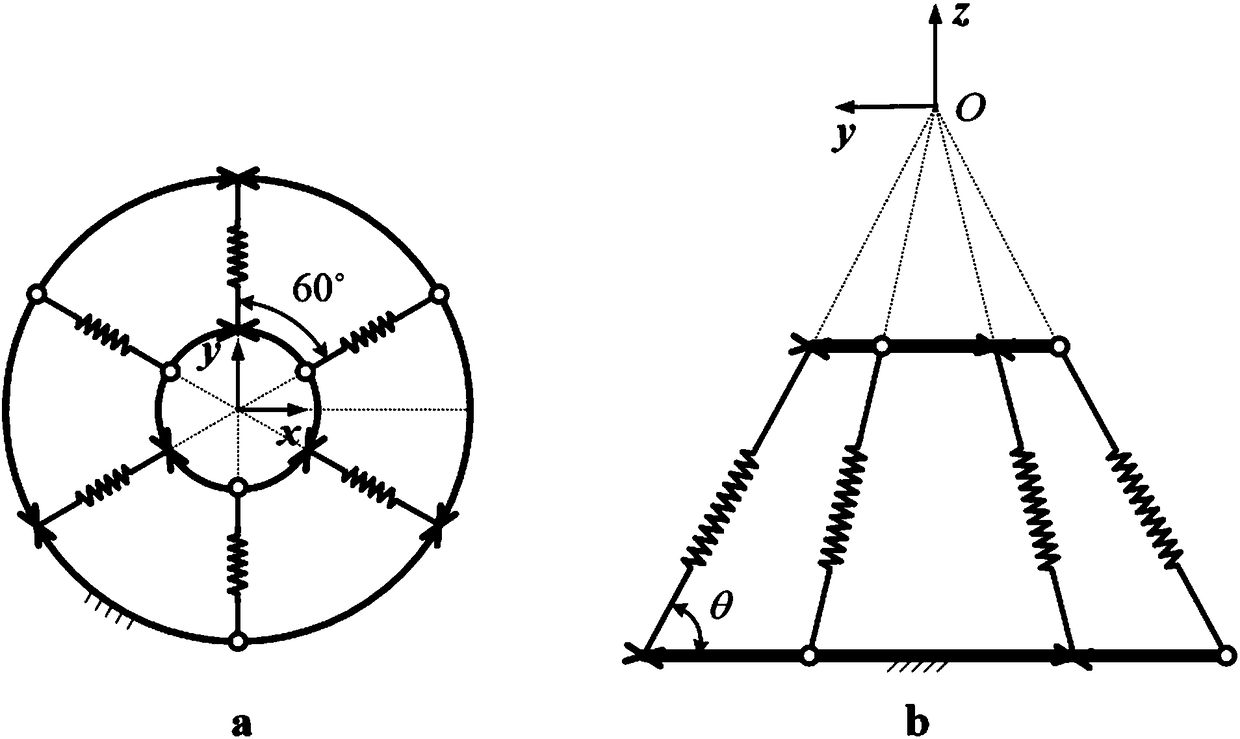
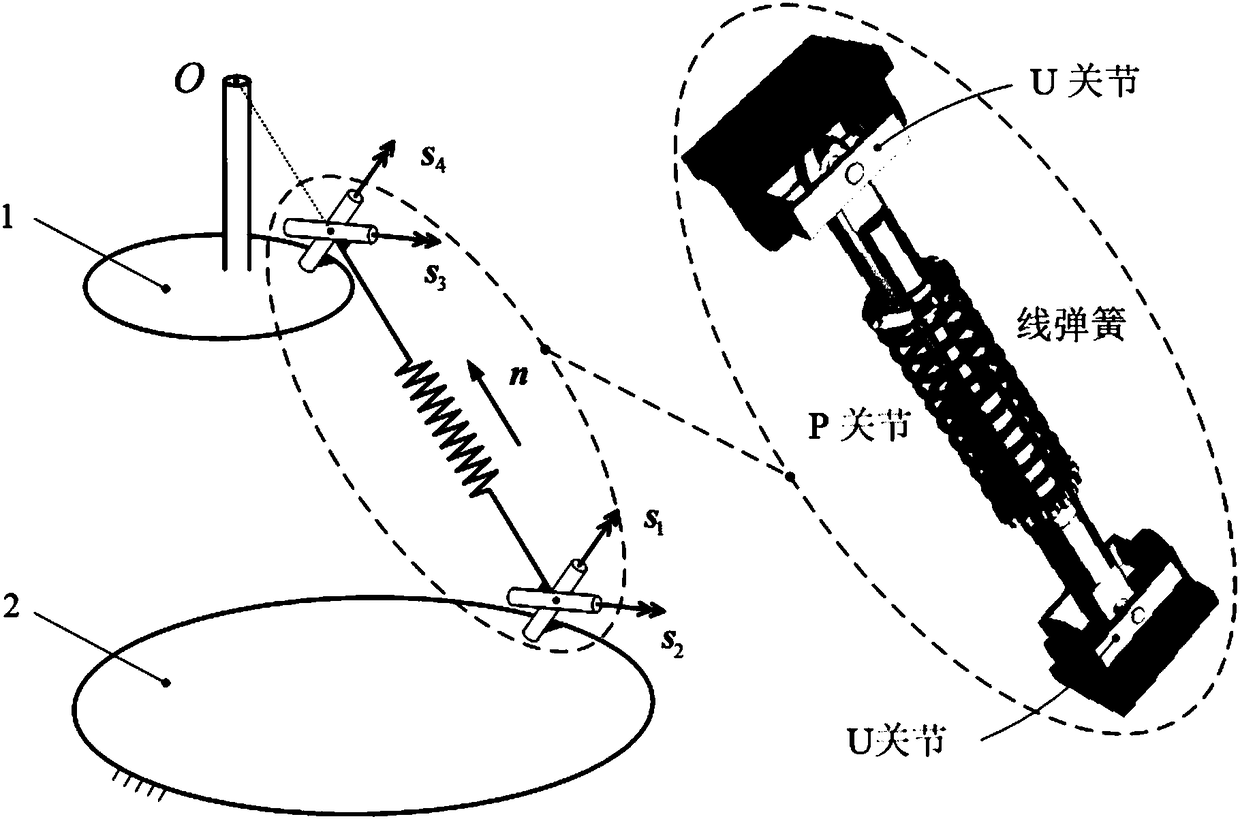
Space multi-degree-of-freedom parallel-connection flexible device
ActiveCN108436887AAvoid damageAvoid injuryProgramme-controlled manipulatorRobot environmentRobotic systems
A space multi-degree-of-freedom parallel-connection flexible device comprises a base, a mobile platform for providing support for a performing mechanism, three UPU-shaped branch chains and at least three SPS-shaped branch chains. The two ends of the UPU-shaped branch chains are connected with the base and the mobile platform correspondingly. The UPU-shaped branch chains and the SPS-shaped branch chains are arranged between the mobile platform and the base alternately. All the branch chains intersect at one point on the space extension line, namely at the tail end operation point of the flexible device, and the flexible device only has the flexible characteristic of space pure translation at the tail end operation point. The space multi-degree-of-freedom parallel-connection flexible devicecan generate natural adaptation to acting force of any direction of the space, safety of a robot system during working in a complex environment can be improved, and smooth implementation of operationtasks with robot-environment physical contact is ensured.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Robot remote control system and method
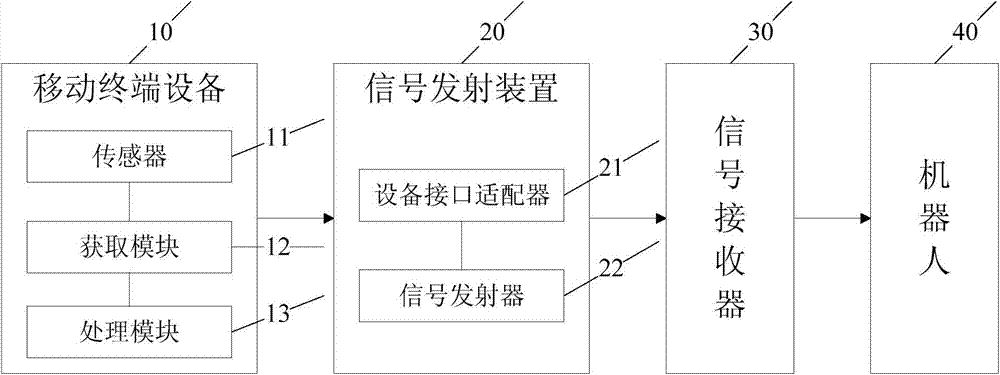
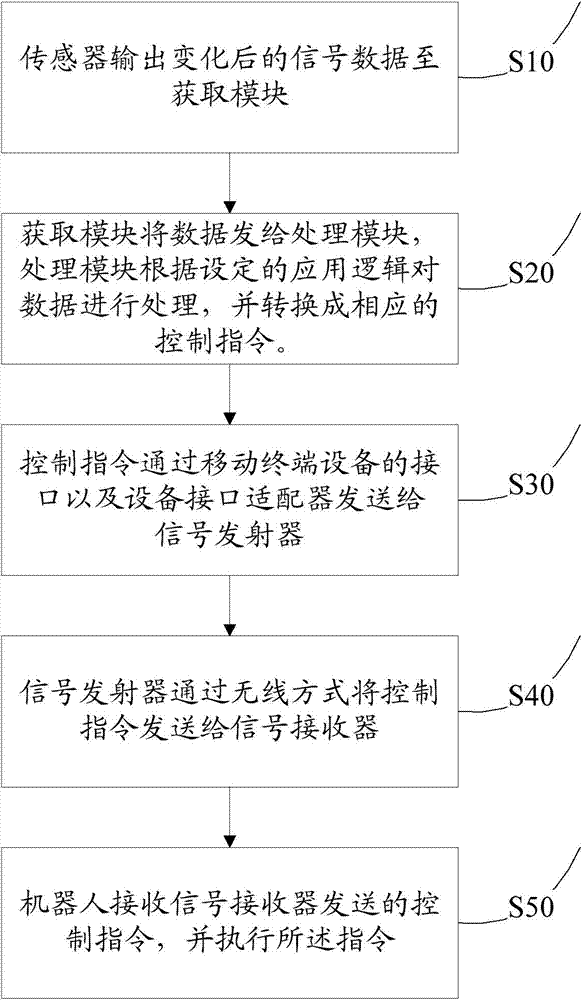
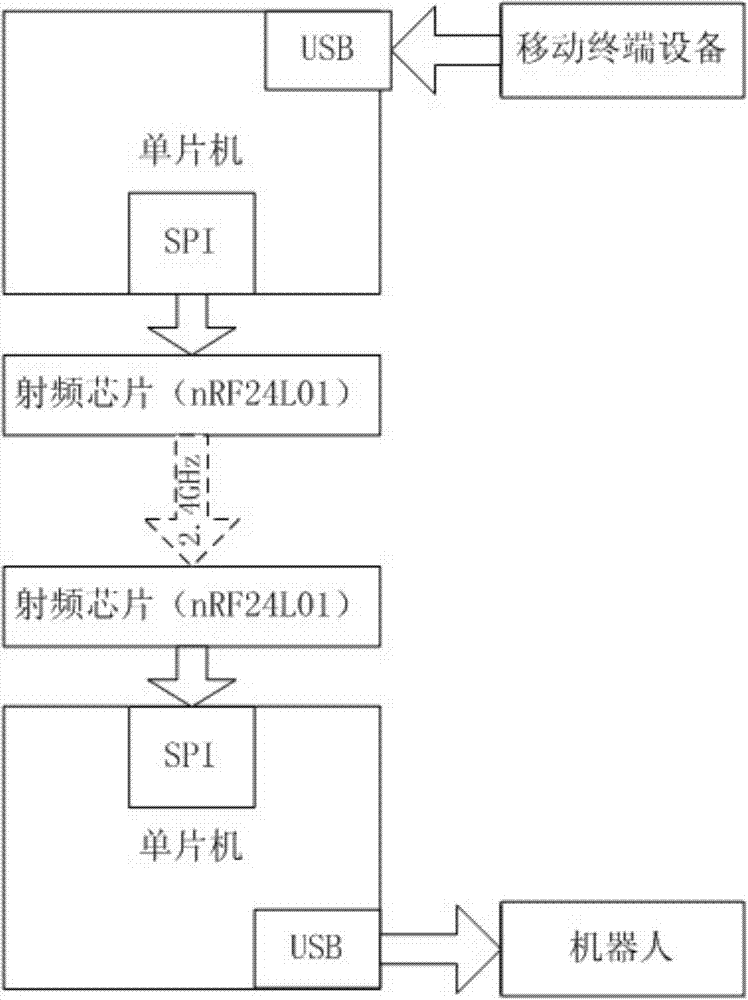
InactiveCN104511903AReduce manufacturing costReduce in quantityManipulatorRobot environmentRemote control
The invention discloses a robot remote control system and a robot remote control method. The robot remote control system comprises an obtaining module, a processing module, a signal emitter, a signal receiver and a robot, wherein the obtaining module is used for monitoring the sensor signal value in real time, and obtaining the signal data if the signal value changes; the processing module is used for receiving the signal data sent by the obtaining module, processing the signal data according to preset application logic and converting the signal data into a corresponding control order; the signal emitter is used for a control order sent by the processing module through an interface of mobile terminal equipment and a equipment interface adapter; the signal receiver is used for receiving the control order sent by the signal emitter; the robot is connected with the signal receiver and used for receiving the control order sent by the signal receiver, and performing the control order. The method can be used for enabling the robot remote control equipment to be standard and unified, can be suitable for various mobile terminal equipment, used for reducing the remote equipment production cost, reducing the quantity of equipment under a multi-robot environment, and improving the operation convenience.
Owner:SHENYANG SIASUN ROBOT & AUTOMATION
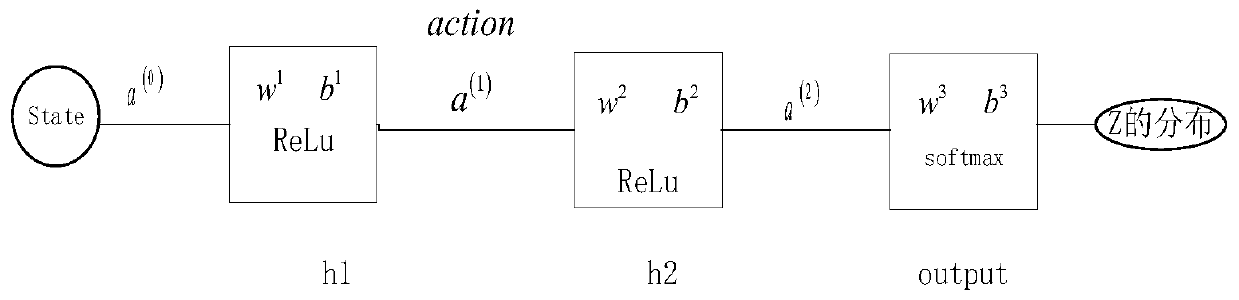
Deep reinforcement learning control method for vertical path following of intelligent underwater robot
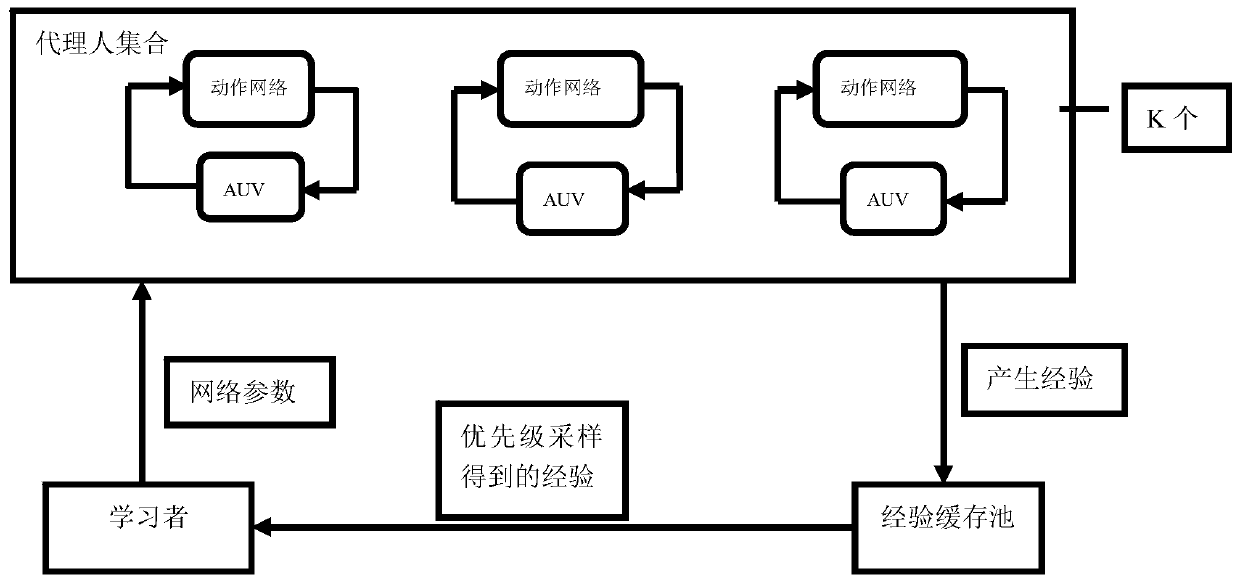
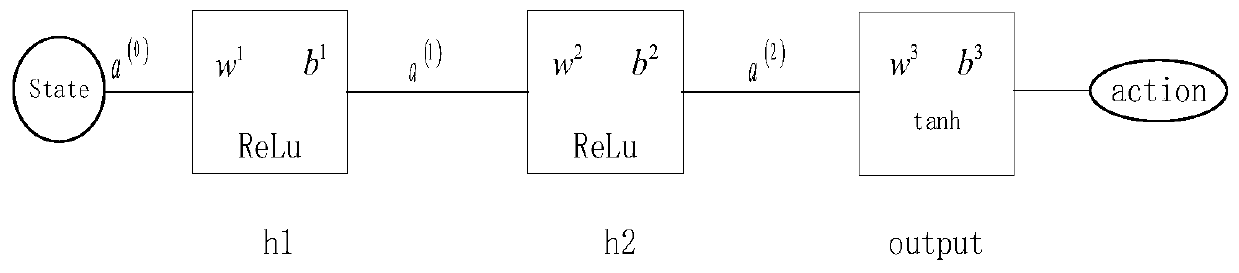
ActiveCN110209152ASelf-learningHigh precisionMathematical modelsAutonomous decision making processRobot environmentArtificial intelligence
The invention provides a deep reinforcement learning control method for vertical path following ofan intelligent underwater robot. The deep reinforcement learning control method comprises the following steps that firstly, according to path following control requirements of the intelligent underwater robot, an intelligent underwater robot environment is established to interact with an agent; secondly, an agent set is established; thirdly, an experience buffer pool is established; fourthly, a learner is established; and fifthly, intelligent underwater robot path following control is conducted byusing a distributed deterministic strategy gradient. According to the deep reinforcement learning control method for the vertical path following ofthe intelligent underwater robot, the deep reinforcement learning control method for the vertical path following ofthe intelligent underwater robot is designed to solve the problem that marine environment in which the intelligent underwater robot is located is complex and variable, thus a traditional control method can not interact with the environment. The path followingand control task of the intelligent underwater robot can be finished in a distribution mode by using a deterministic strategy gradient, and the deep reinforcement learning control method for the vertical path following ofthe intelligent underwater robot has the advantages of self-learning, high precision, good adaptability and stable learning process.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Detecting system and detecting method for air quality based on a robot
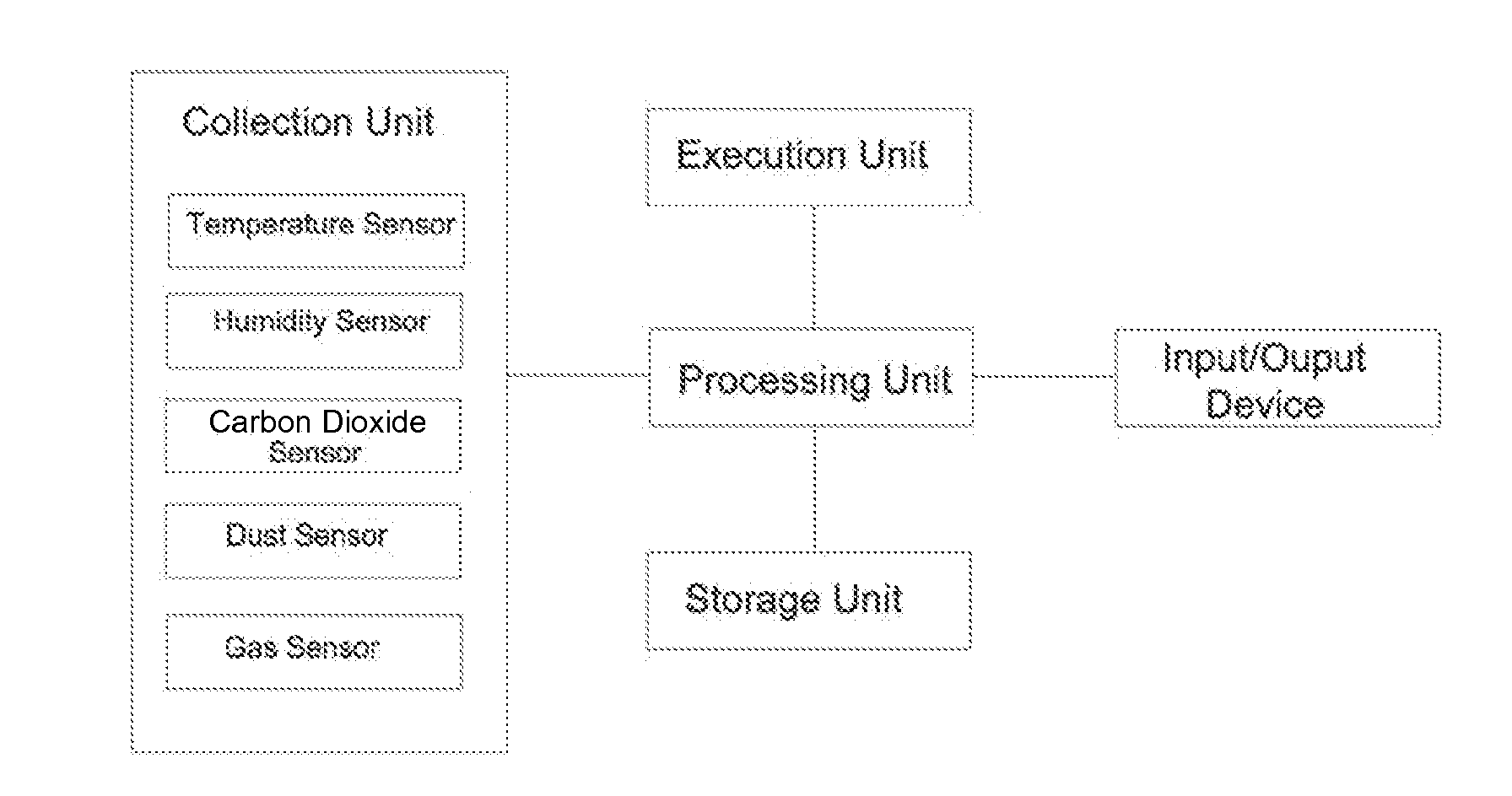
InactiveUS20160238579A1Good for healthSimple processMechanical apparatusSamplingRobot environmentOutput device
A detecting system for air quality based on a robot is described. The system comprises a collection unit, a processing unit, a storage unit, an execution unit, and an input / output device. The detection method comprises: controlling the collection unit to detect the air's status within the environment of the robot, and to form an output of collection data; controlling the processing unit to receive the collection data and receive the storage data output by the storage unit simultaneously, match the storage data to the collection data, and output a processing result formed by the collection data and the storage data; controlling the input / output device to receive the processing result and output a corresponding processing result. The benefit of the present disclosure compared to prior art is that this invention makes it more convenient for the user to see the air quality information of their present environment.
Owner:YUTOU TECH HANGZHOU
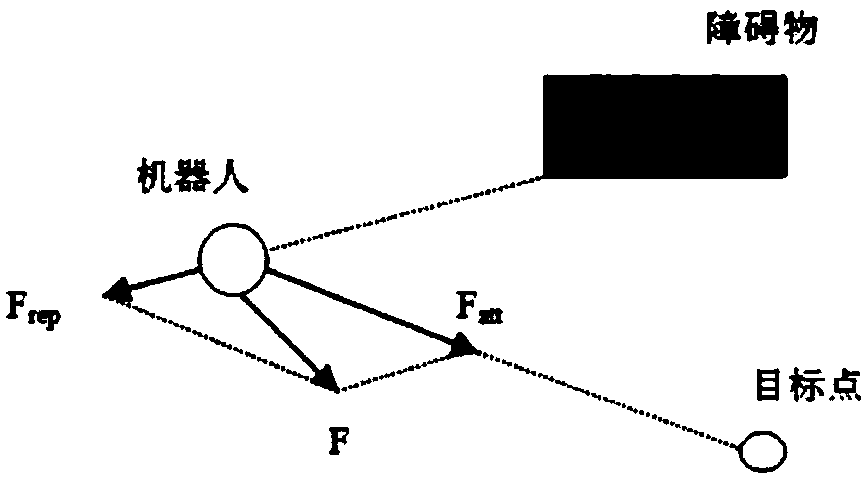
Robot collision avoiding method, device and system
PendingCN108801255AImprove collision avoidance efficiencyNavigational calculation instrumentsPosition/course control in two dimensionsRobot environmentPotential field
The invention provides a robot collision avoiding method, device and system. The method comprises determining one or more target positions on the scheduled path of a first robot to be scheduled and / ora second robot to be scheduled according to the following manner including, based on the current position of the robot to be scheduled which corresponds to a target position to be determined as wellas the corresponding minimum relative distance points on the first robot and the second robot, determining the target position through artificial potential fields, wherein the applied potential fieldsis composed of an attraction potential field of the current position and / or repulsion potential fields corresponding the minimum relative distance points, and when the current position does not coincide with the minimum relative distance points, the applied repulsion potential fields are acquired by transforming the repulsion potential fields of the minimum relative distance points. Therefore, bymeans of the robot collision avoiding method, collision avoiding path scheduling can well conform to a virtual robot environment and further improve the robot collision avoiding efficiency.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH +1
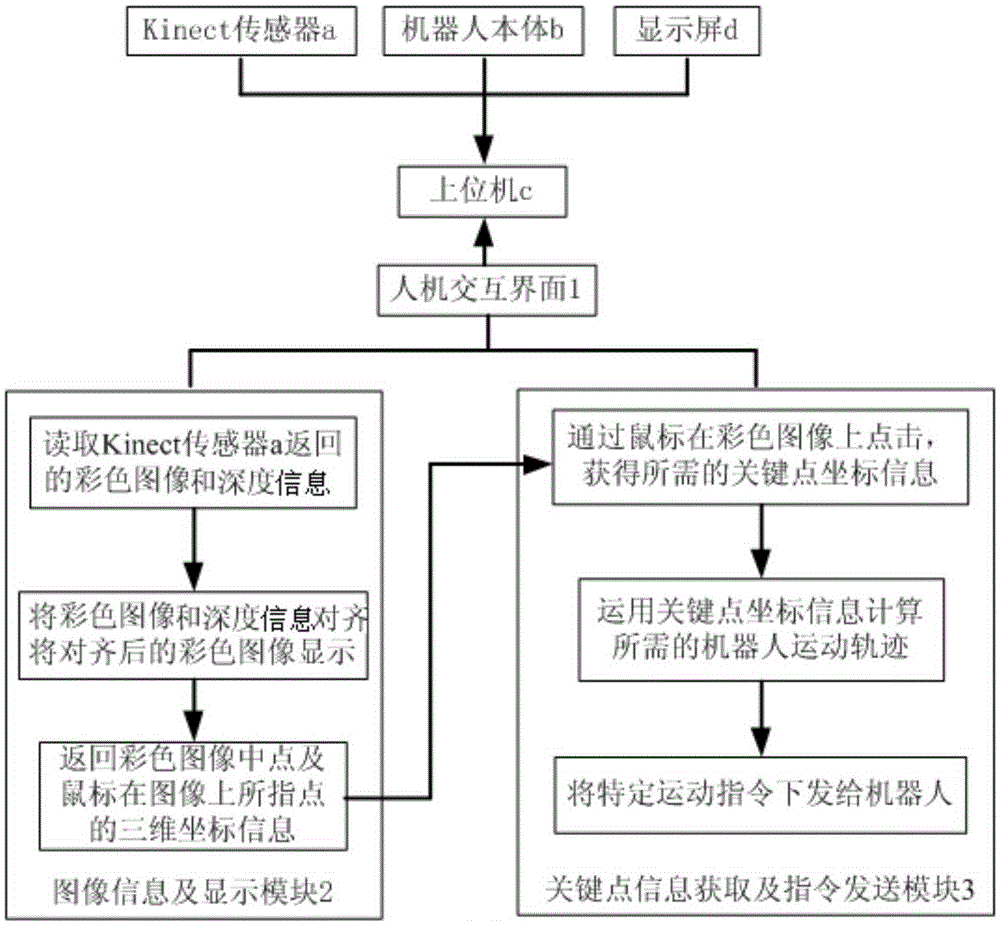
Kinect visual information-based robot environment identification and operation control method
The invention relates to the field of robot operation, and particularly relates to a Kinect visual information-based robot environment identification and operation control method. The invention is aimed to solve the problem of the low stability and the low accuracy of the conventional robot sensing systems and to solve the problems that a preset task is difficult to fulfill due to the instability of operation control or the required time is too long, and an operation process is complicated. The Kinect visual information-based robot environment identification and operation control method includes the following steps: 1 acquiring color images and depth information by a Kinect sensor a; 2 displaying the aligned color images and depth information; 3 acquiring environment information of a robot; 4 acquiring three-dimensional coordinate information of key points; 5 calculating a required motion track of the robot based on the coordinate information of the key points; 6 issuing a specific motion instruction to the robot. The Kinect visual information-based robot environment identification and operation control method is suitable for the field of the robot operation.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Mobile robot environment map construction method and system and storage medium
InactiveCN112033410AImprove balanceBalance costNavigational calculation instrumentsElectromagnetic wave reradiationRobot environmentEngineering
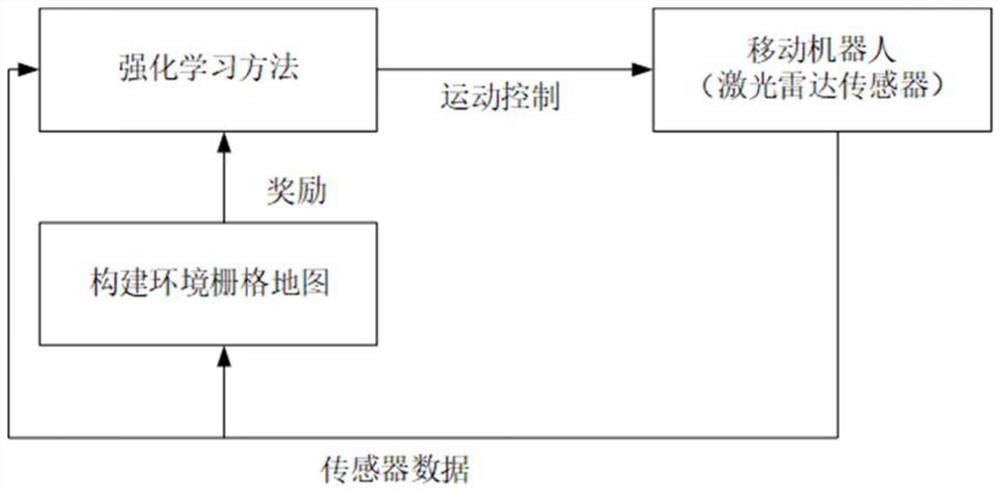
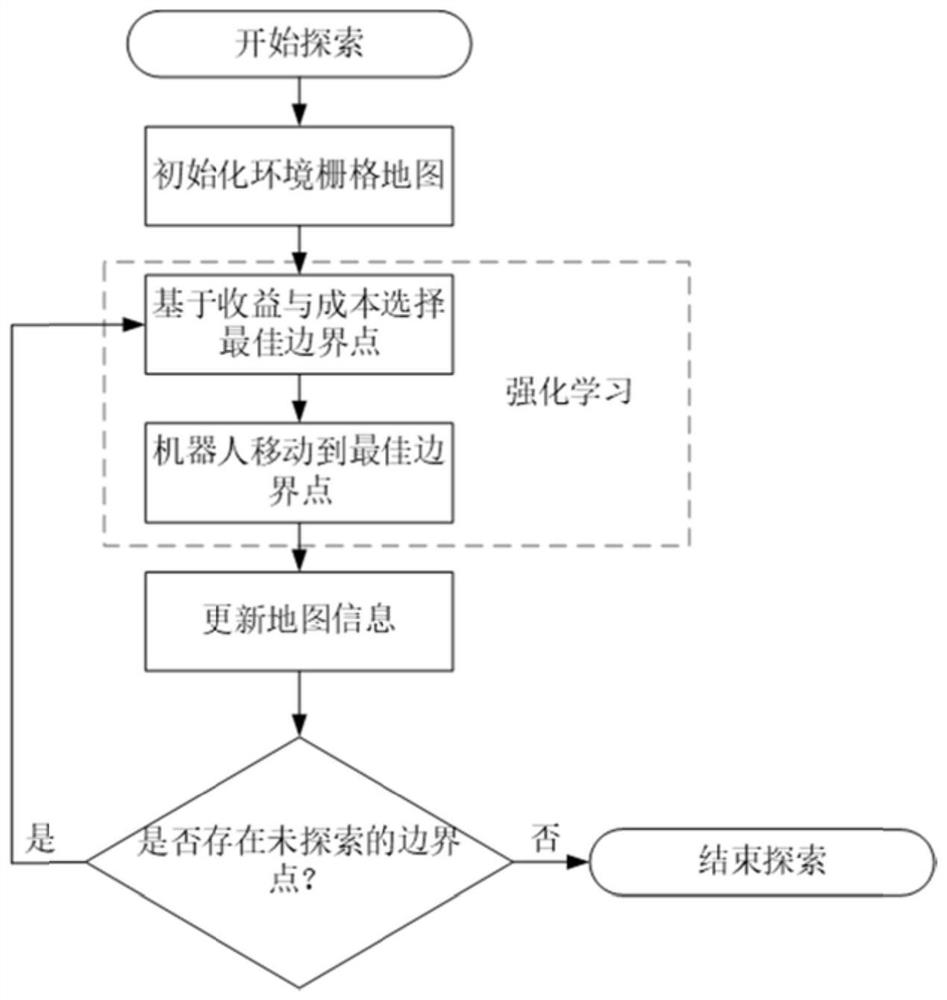
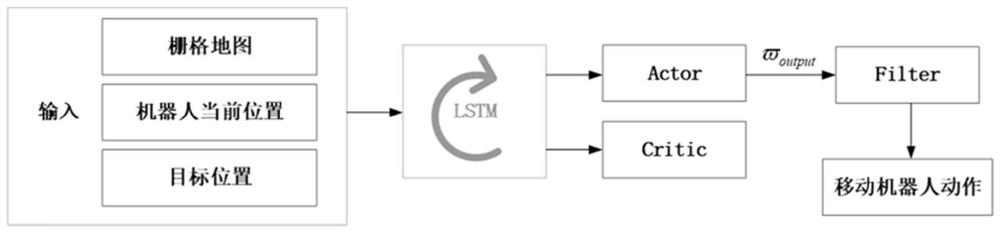
The invention discloses a mobile robot environment map construction method and system and a storage medium, belongs to the technical field of mobile robot autonomous map construction, and relates to the autonomy problem of robot map construction. A mobile robot autonomous mapping method combining a reinforcement learning method and a boundary-based exploration method item is designed, a mobile robot obtains environment information through a laser radar carried by the mobile robot, and then all boundary points in the current environment are found through the boundary-based exploration method. And then an optimal boundary point is selected based on the expected income of the mobile robot at the boundary point and the cost of the robot moving to the boundary point, and the robot moves to theboundary point through obstacle avoidance navigation by using a reinforcement learning method to obtain a reward signal. The autonomous performance of robot map construction enables the robot to adaptto more complex and strange environments.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
P300-based brain-controlled robot system and realization method thereof
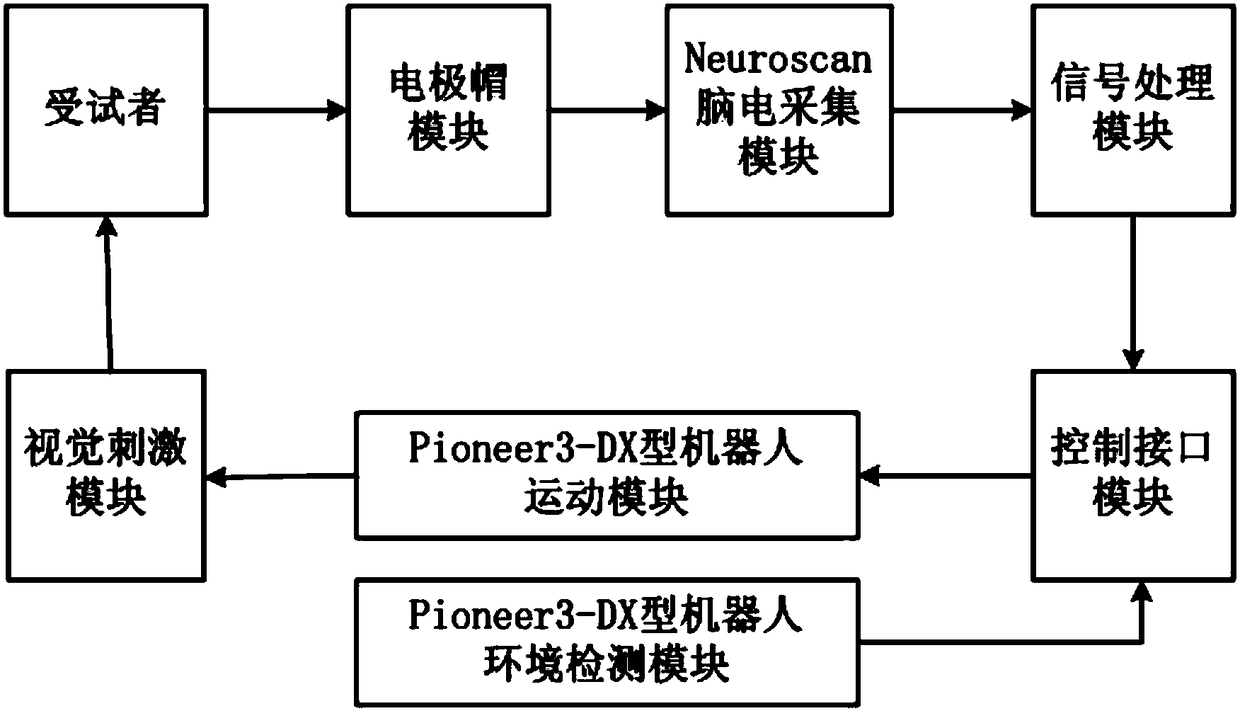
ActiveCN108415554AThe meaning is clearImprove applicabilityInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingBrain computer interfacingAutomatic control
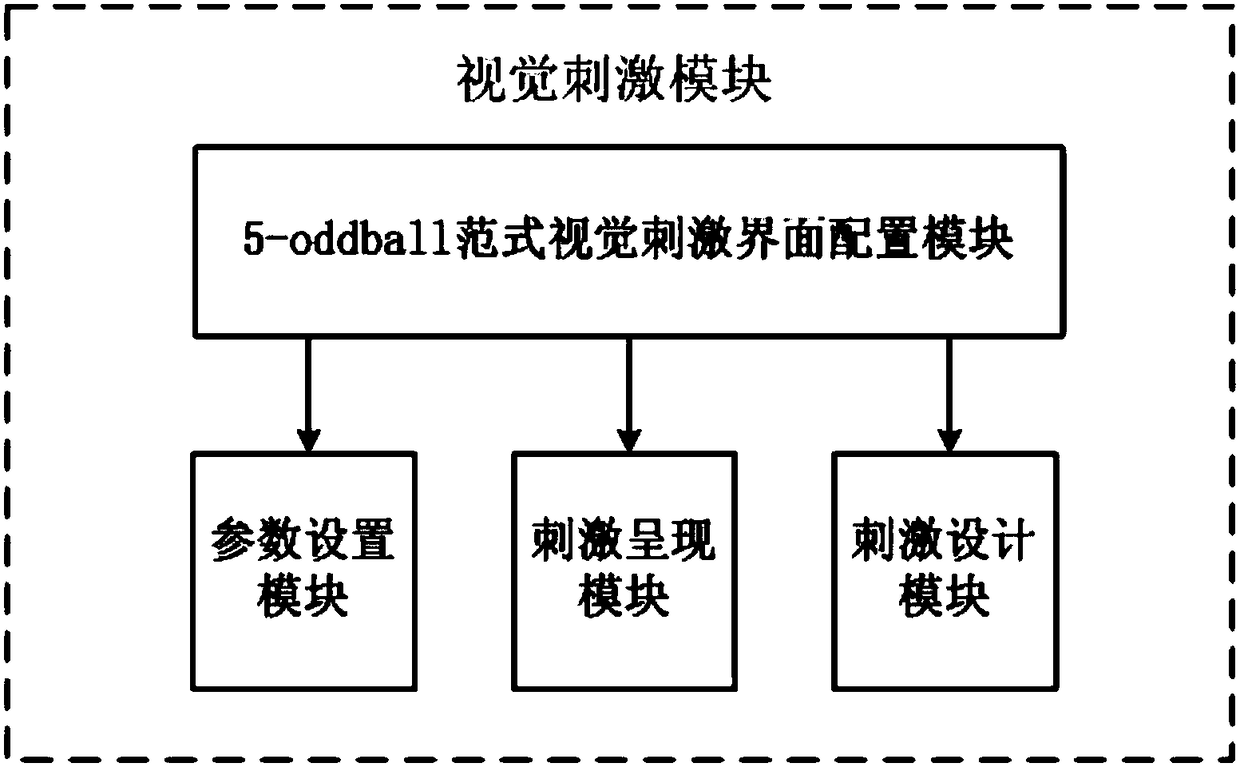
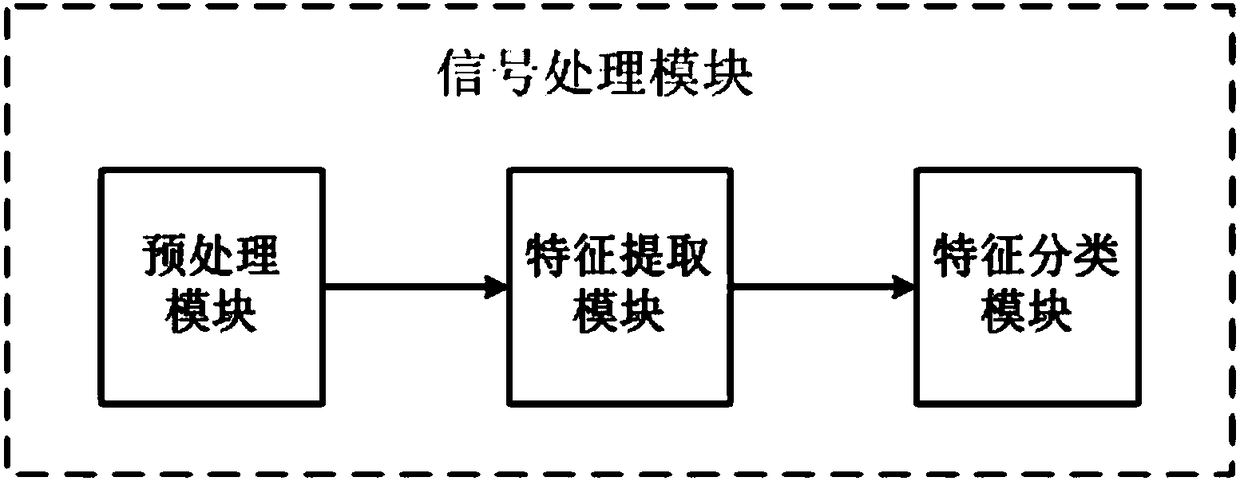
The invention belongs to the technical field of brain-computer interface and robot control, and provides a P300-based brain-controlled robot system and a realization method thereof. The system comprises a visual stimulation module, and a testee, an electrode cap module, a Neuroscan electroencephalogram collection module, a signal processing module, a control interface module, a Pioneer3-DX robot motion module connected with the visual stimulation module in sequence; the Pioneer3-DX robot motion module is further connected with the visual stimulation module; and the control interface is furtherconnected with a Pioneer3-DX robot environment detection module. Graphic symbols are adopted as new stimulation types, and brain-computer interface attributes are combined and improved, so that a higher-amplitude P300 component is induced, and the system transmission rate is increased. Moreover, in combination with a brain-computer interface technology and an automatic control technology, interactive sharing of brain control and robot autonomous control is realized in an asynchronous control mode, and motion behaviors of forward moving, backward moving, left turn, right turn and stillness ofa robot are realized, so that the system is more stable and quicker.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com