Patents
Literature
158 results about "Applied potential" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Applied Potential. Definition - What does Applied Potential mean? The applied potential is the difference of potential measured between two identical metallic leads to two electrodes of an electrochemical cell. In an electrolytic cell, the applied potential drives the chemical reaction that would otherwise not happen in normal conditions.
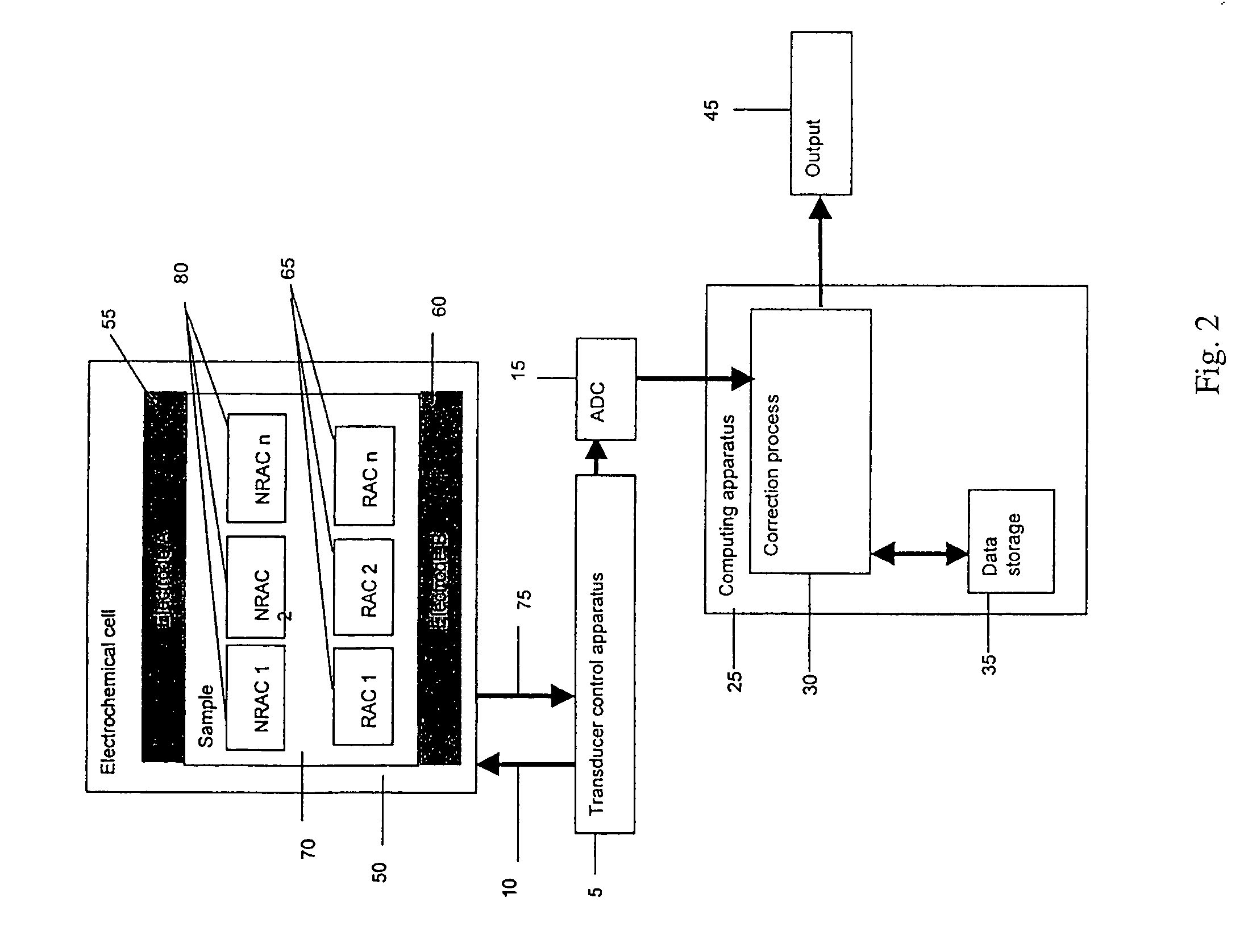
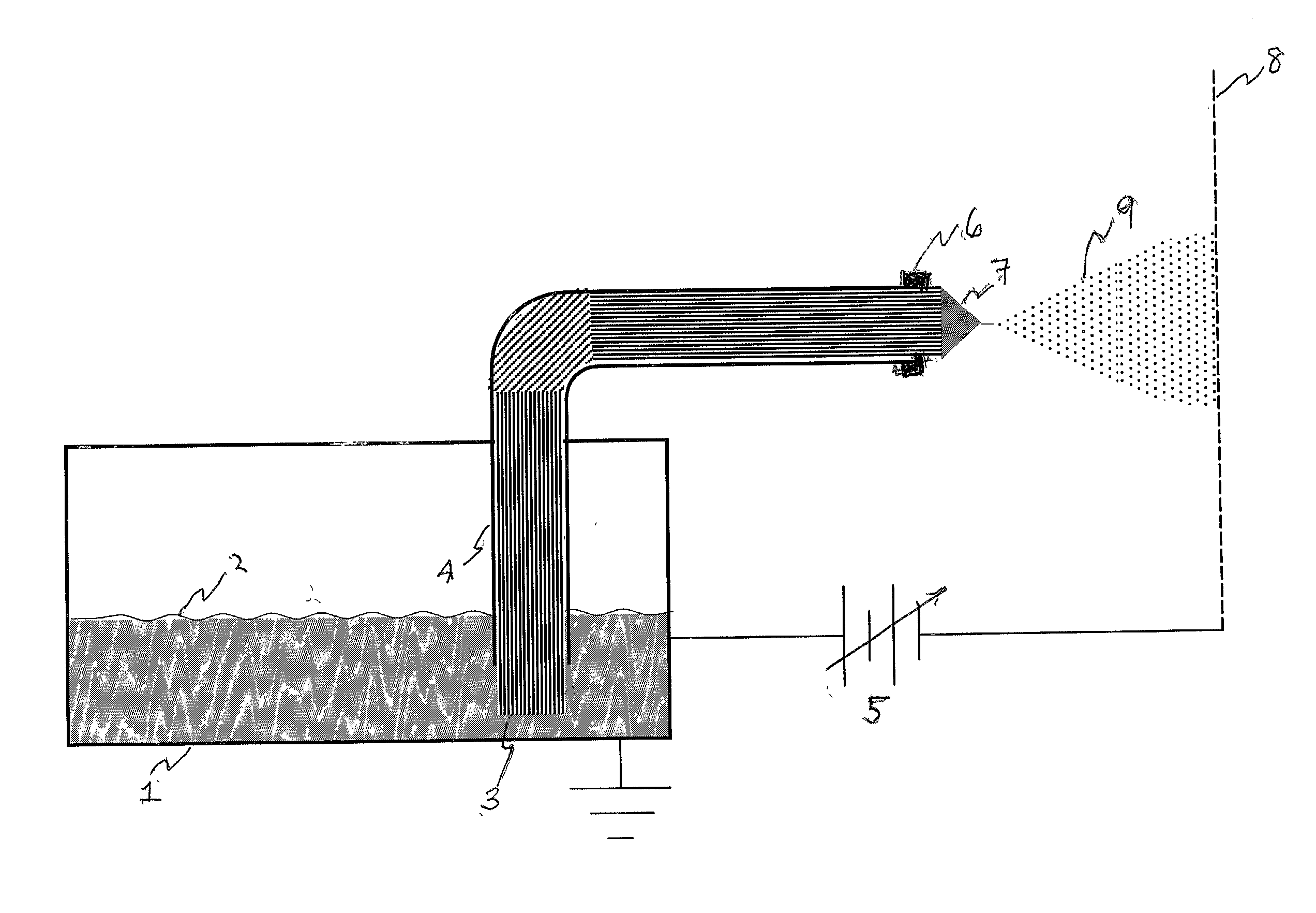
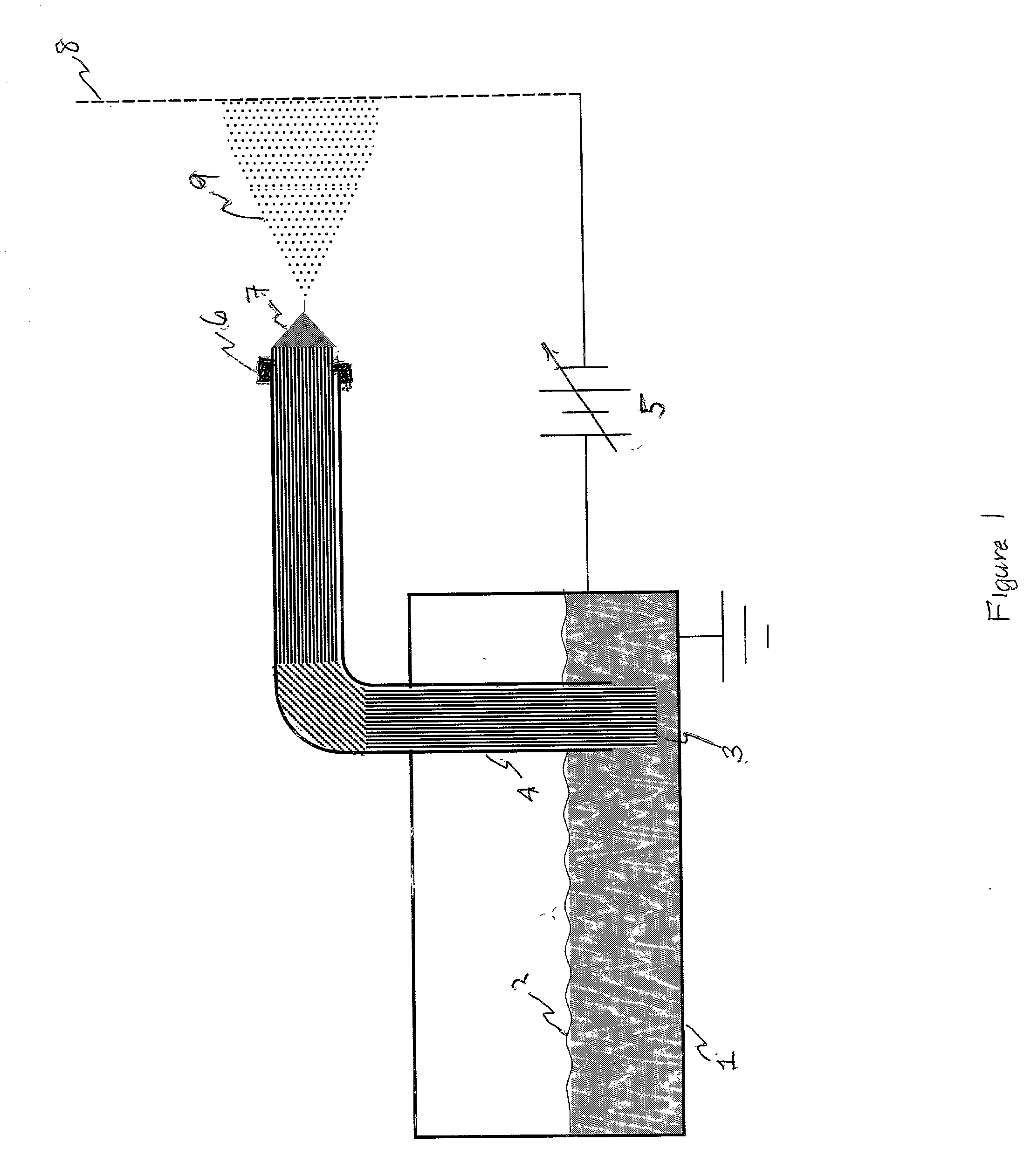
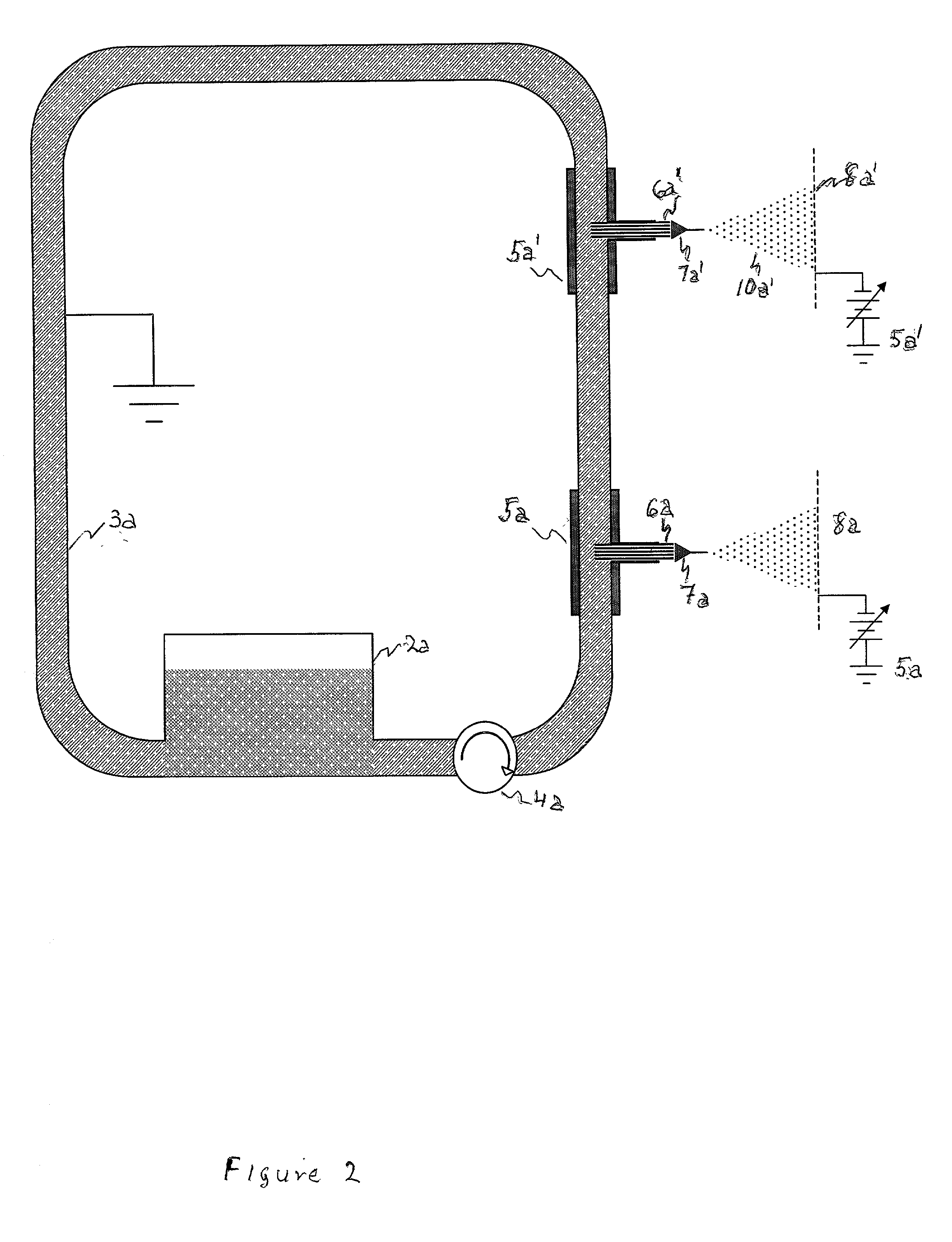
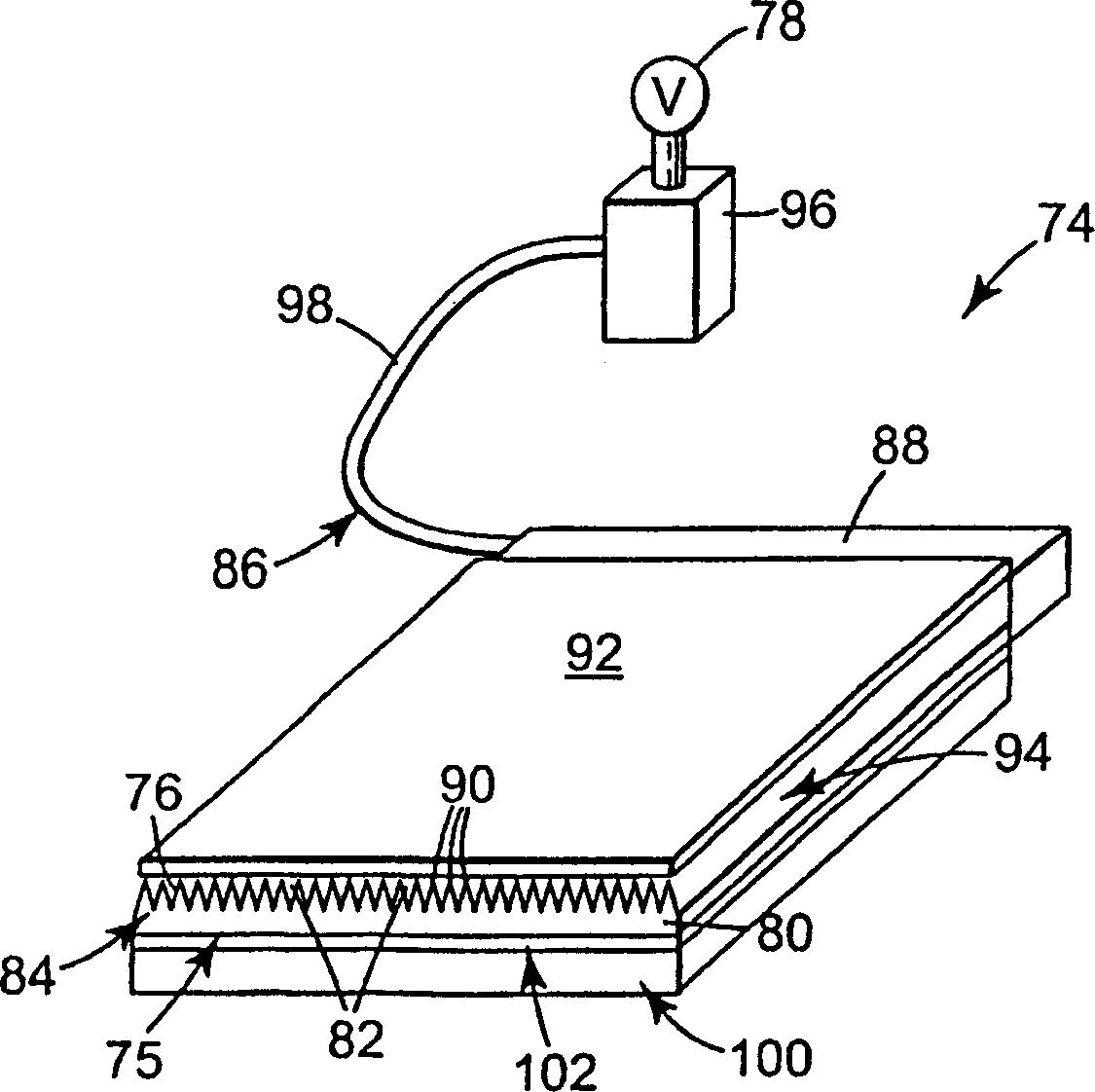
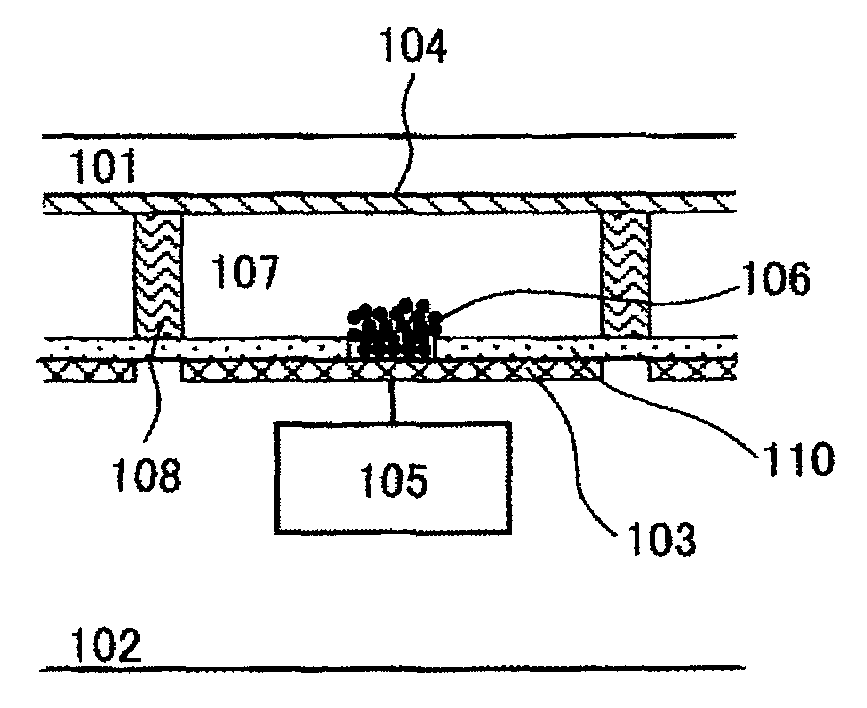
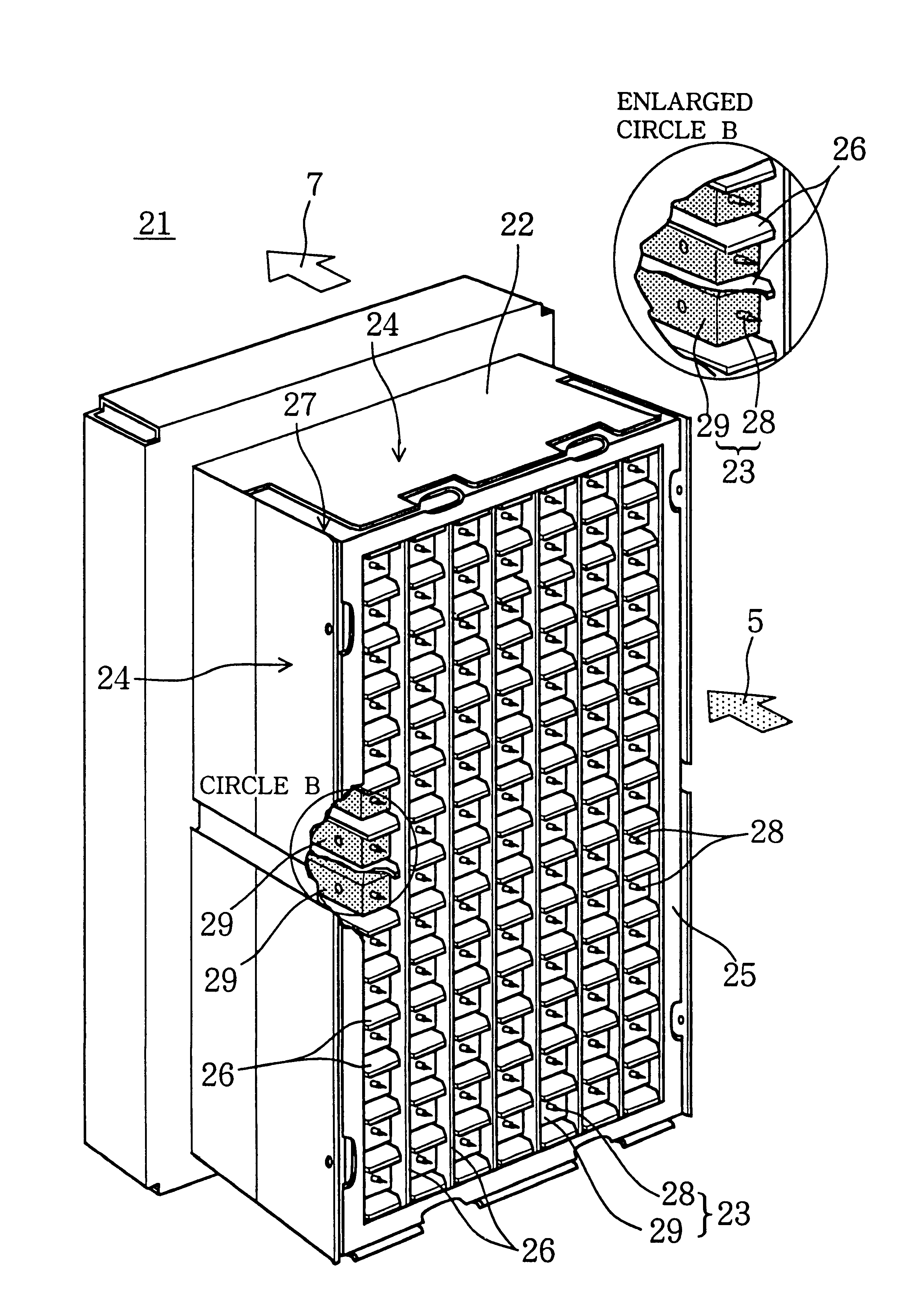
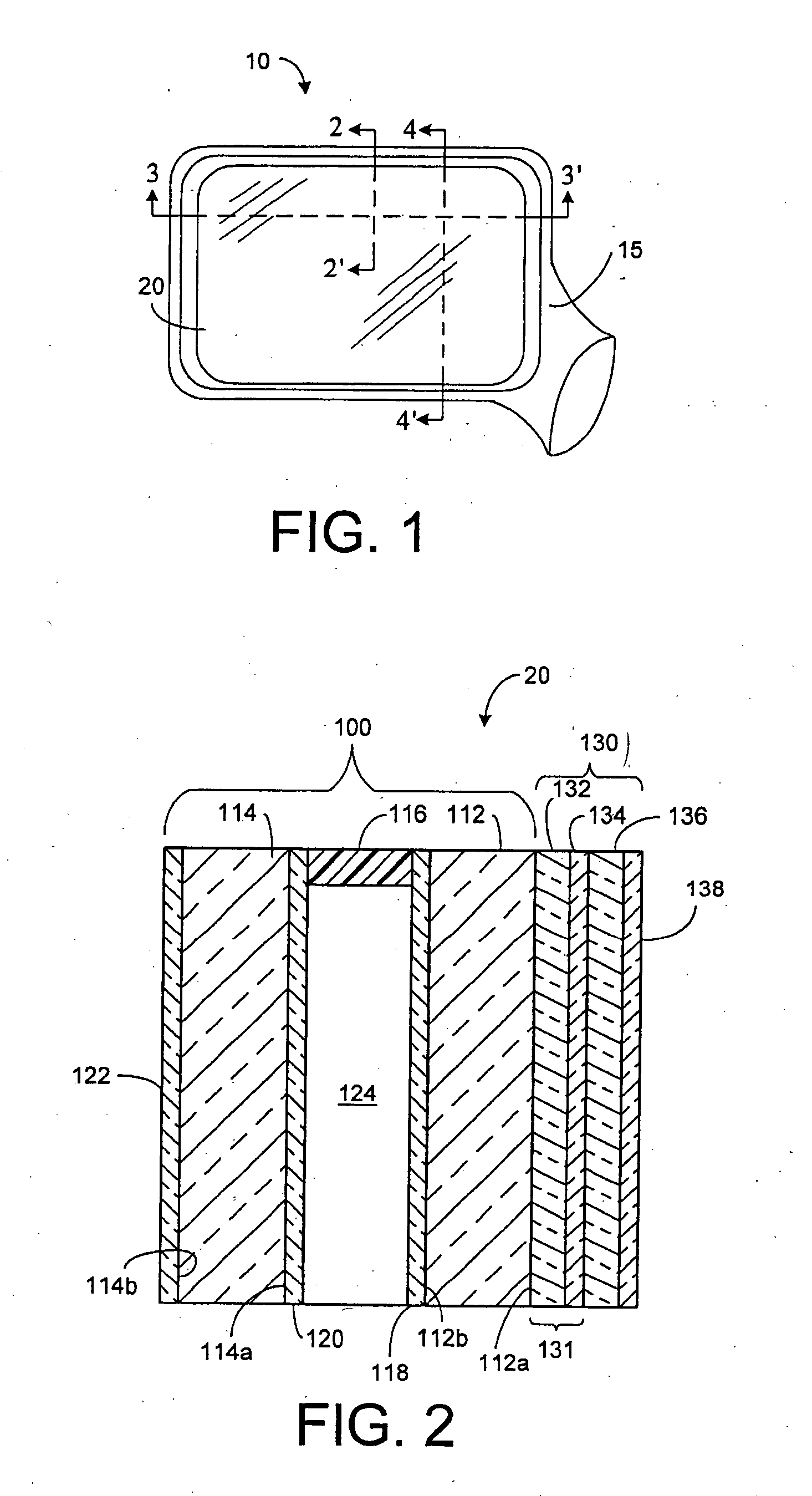
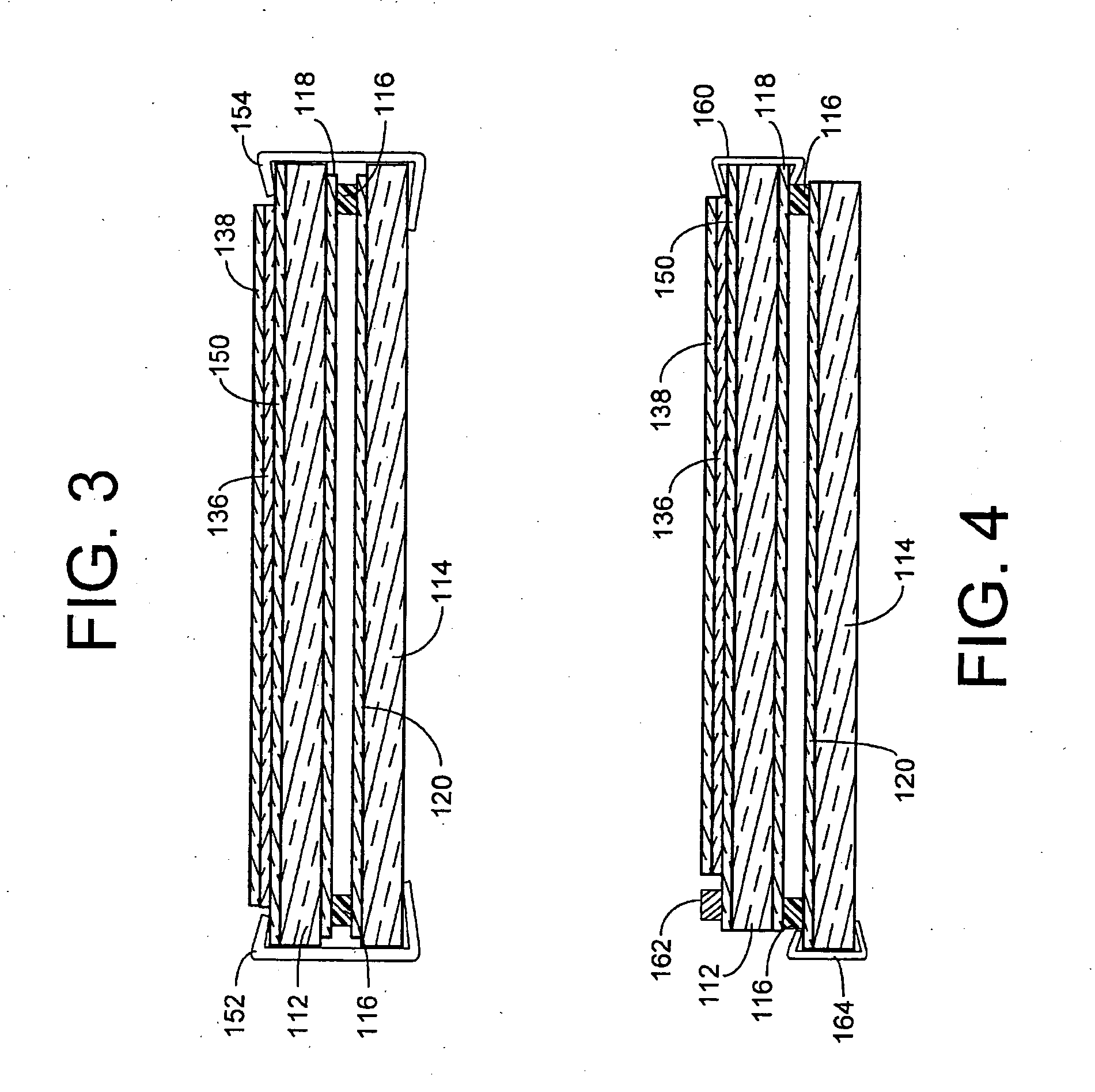
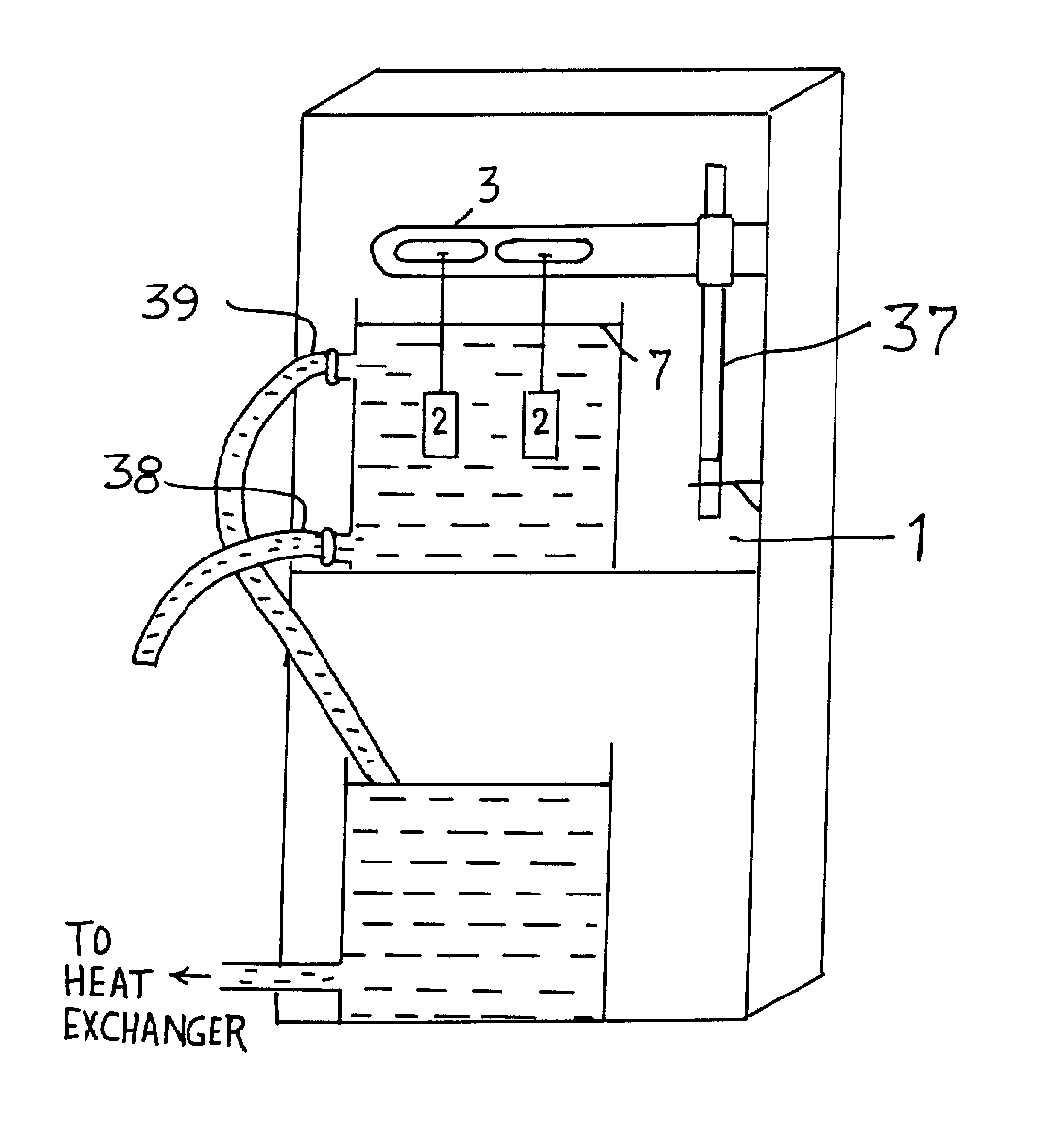
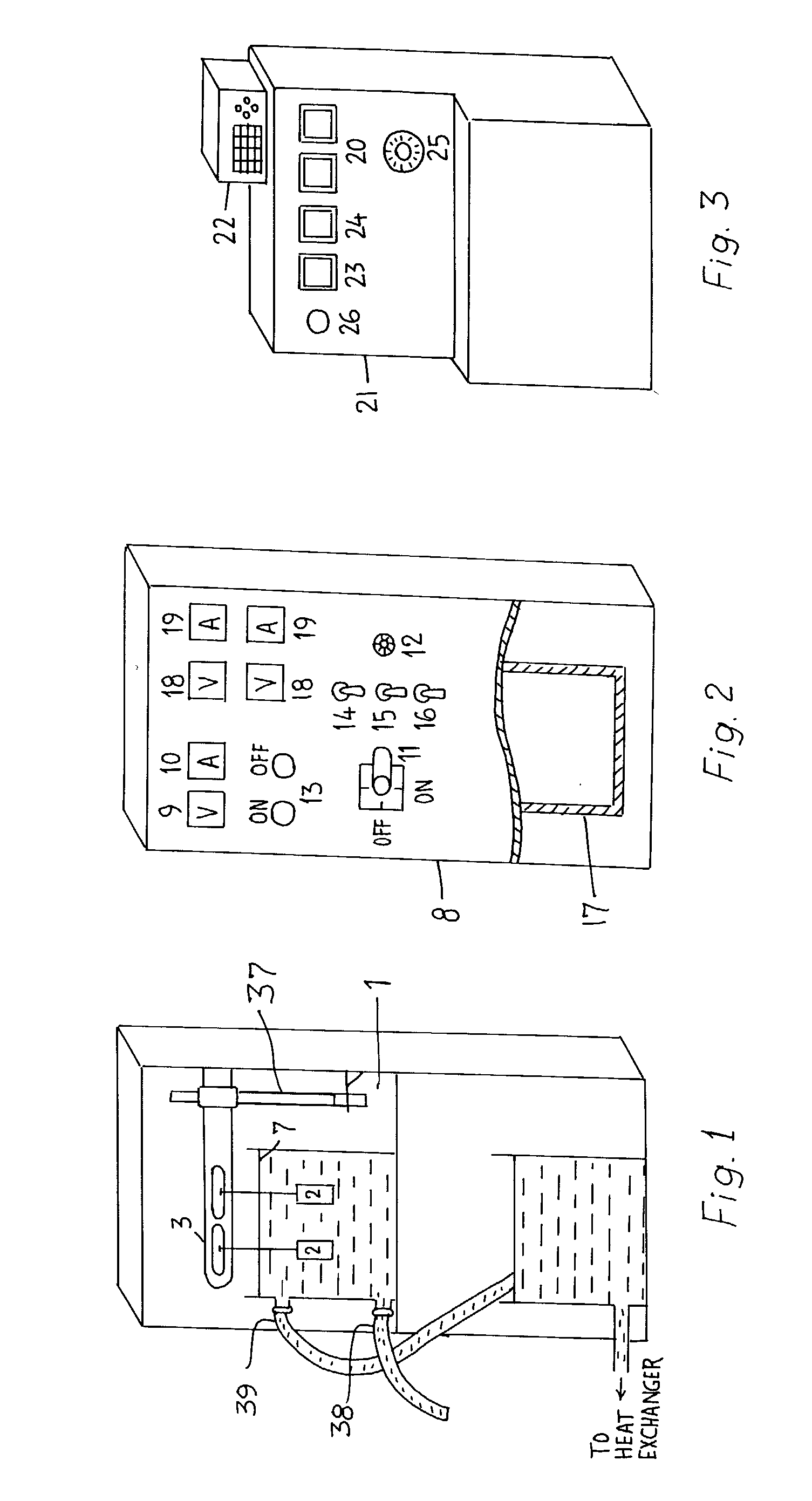
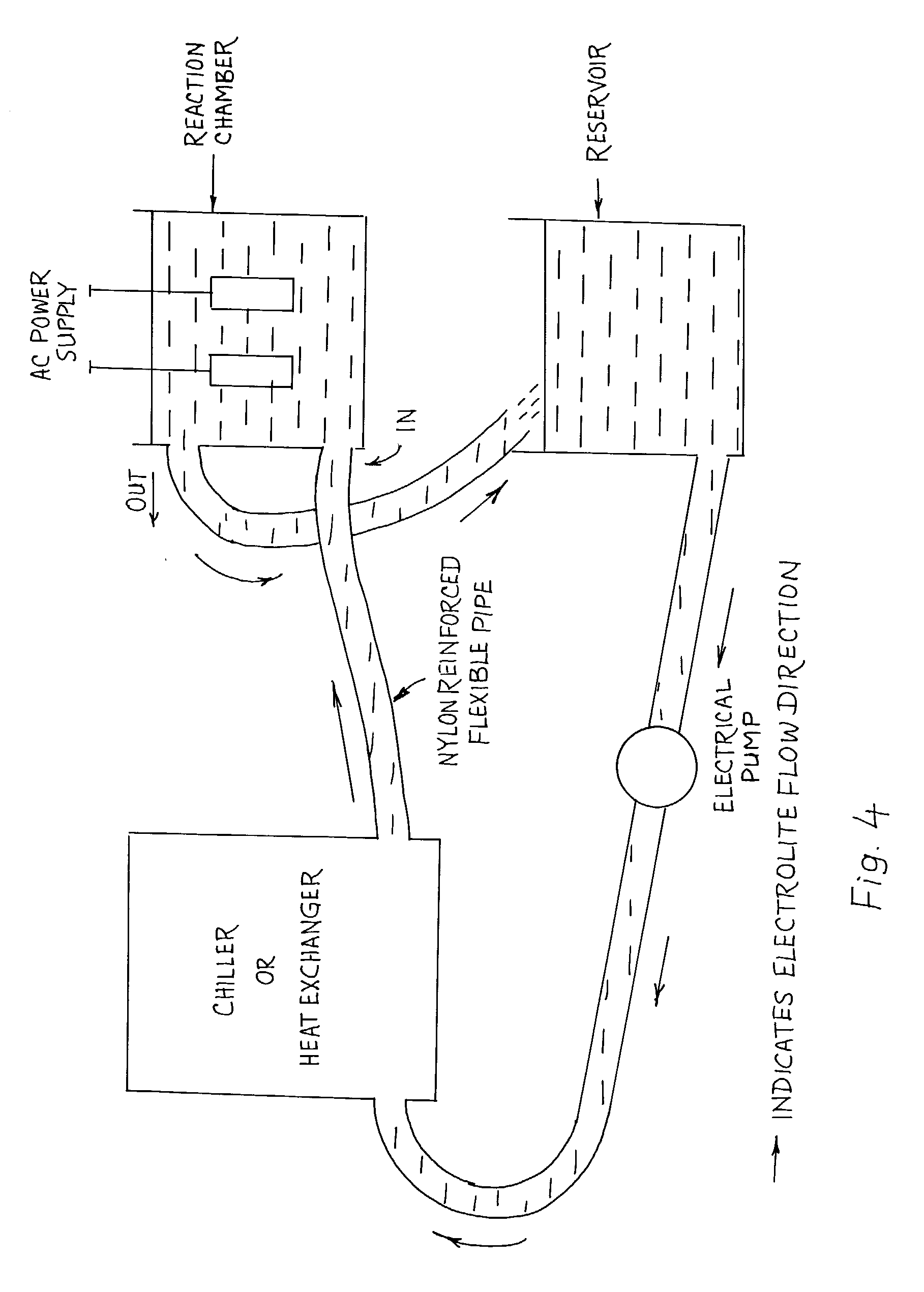
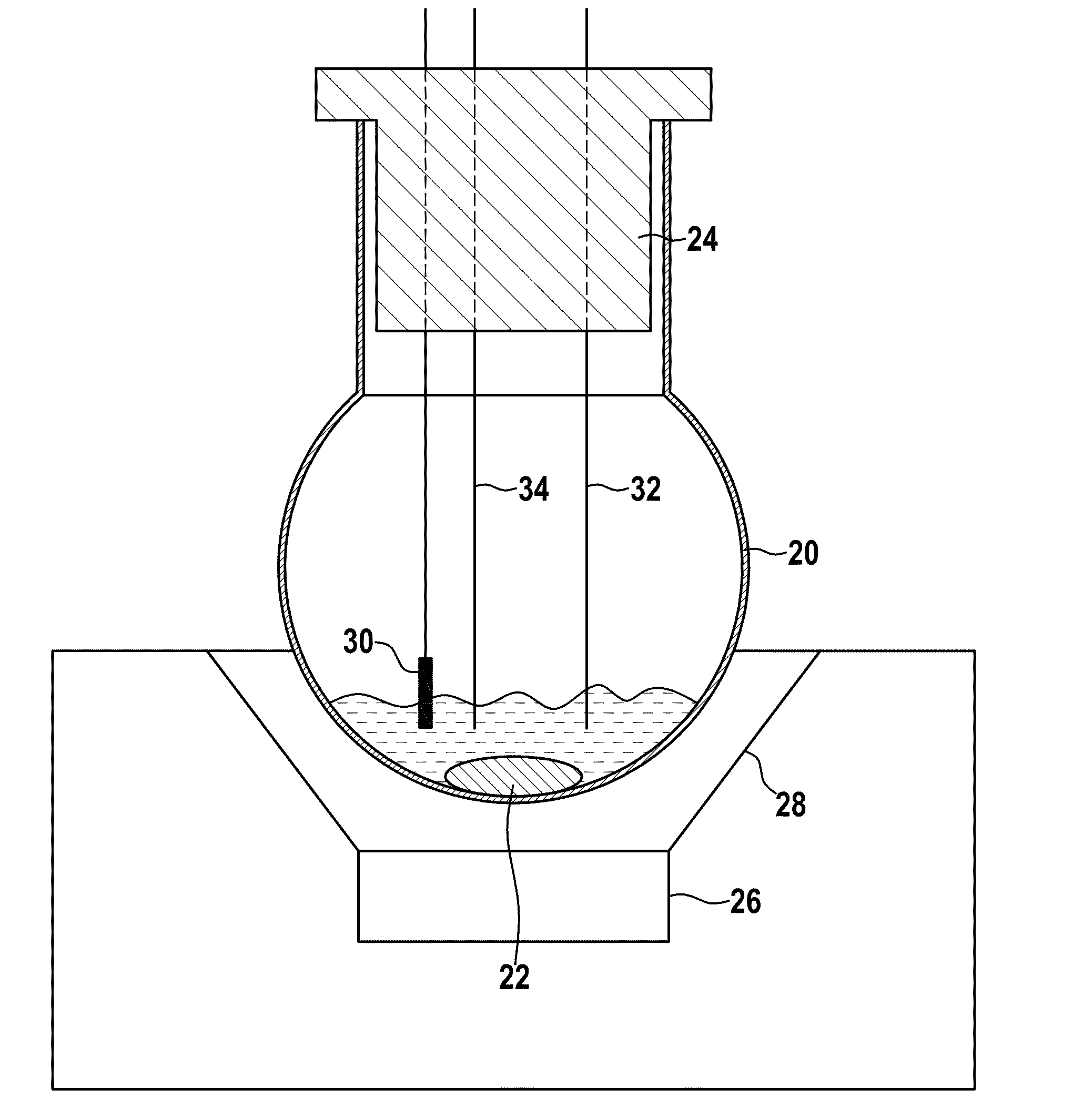
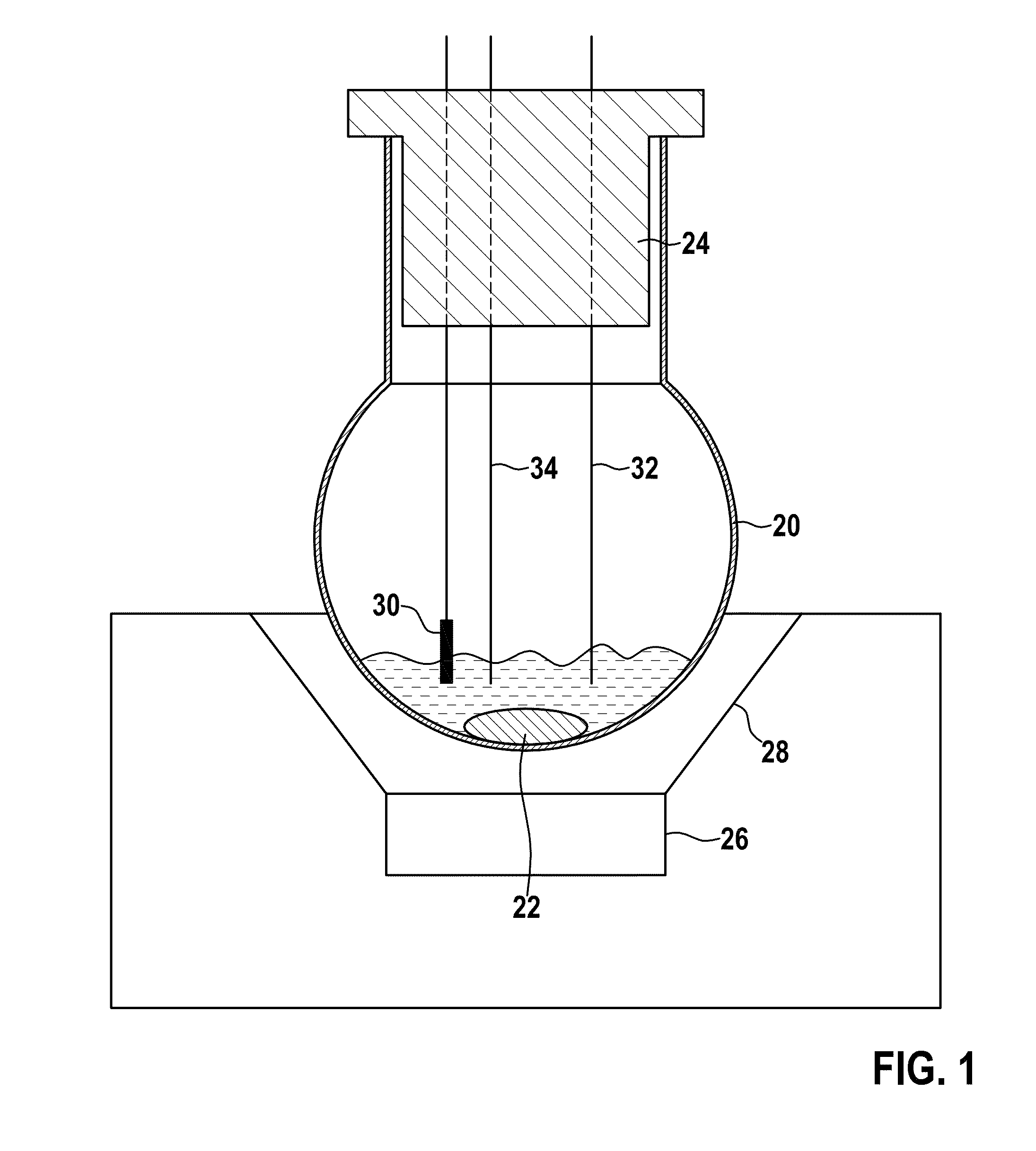
Small volume biosensor for continuous analyte monitoring
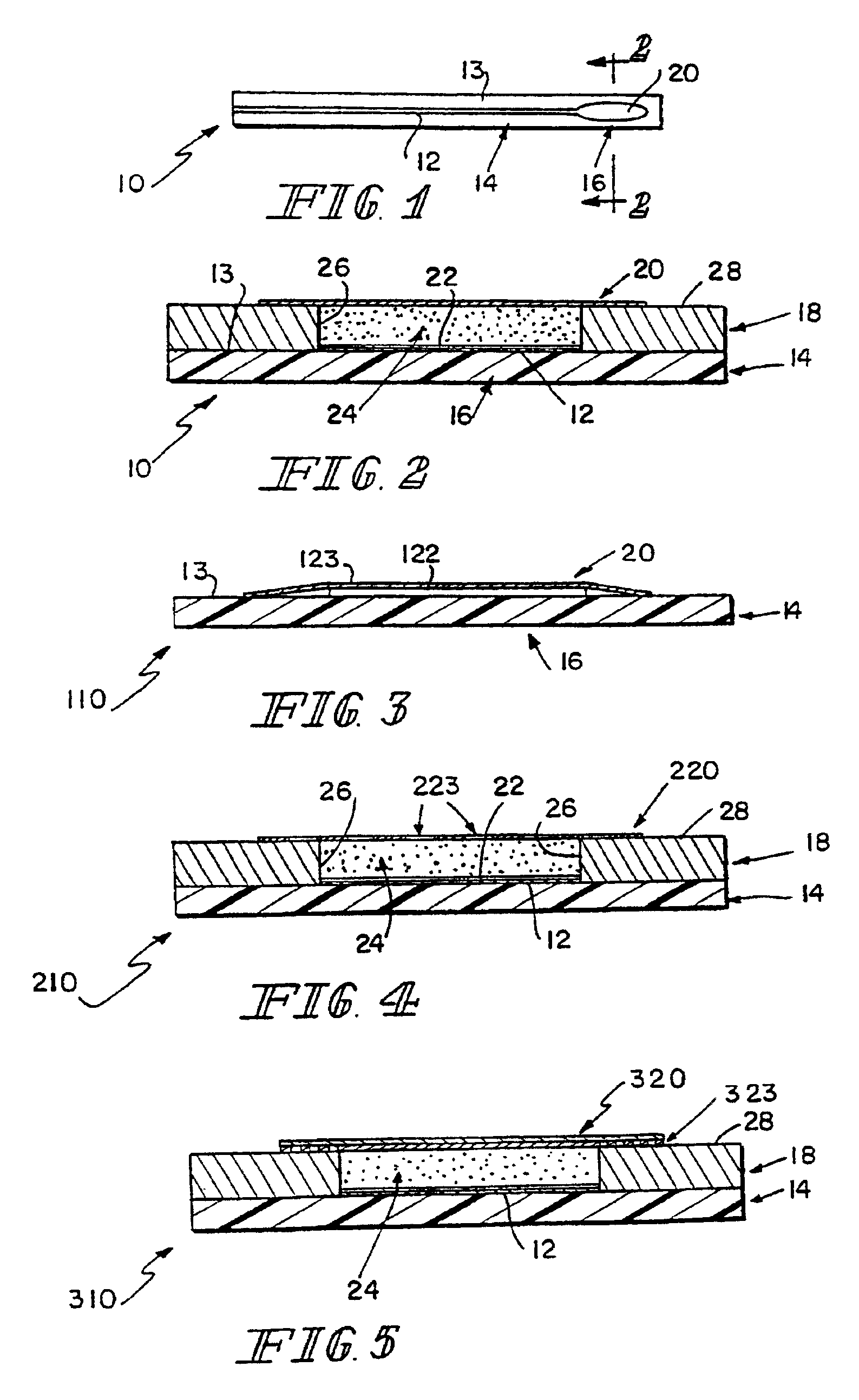
InactiveUS7045054B1Increase ratingsMinimize periodImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsRedox enzymesContinuous analysis
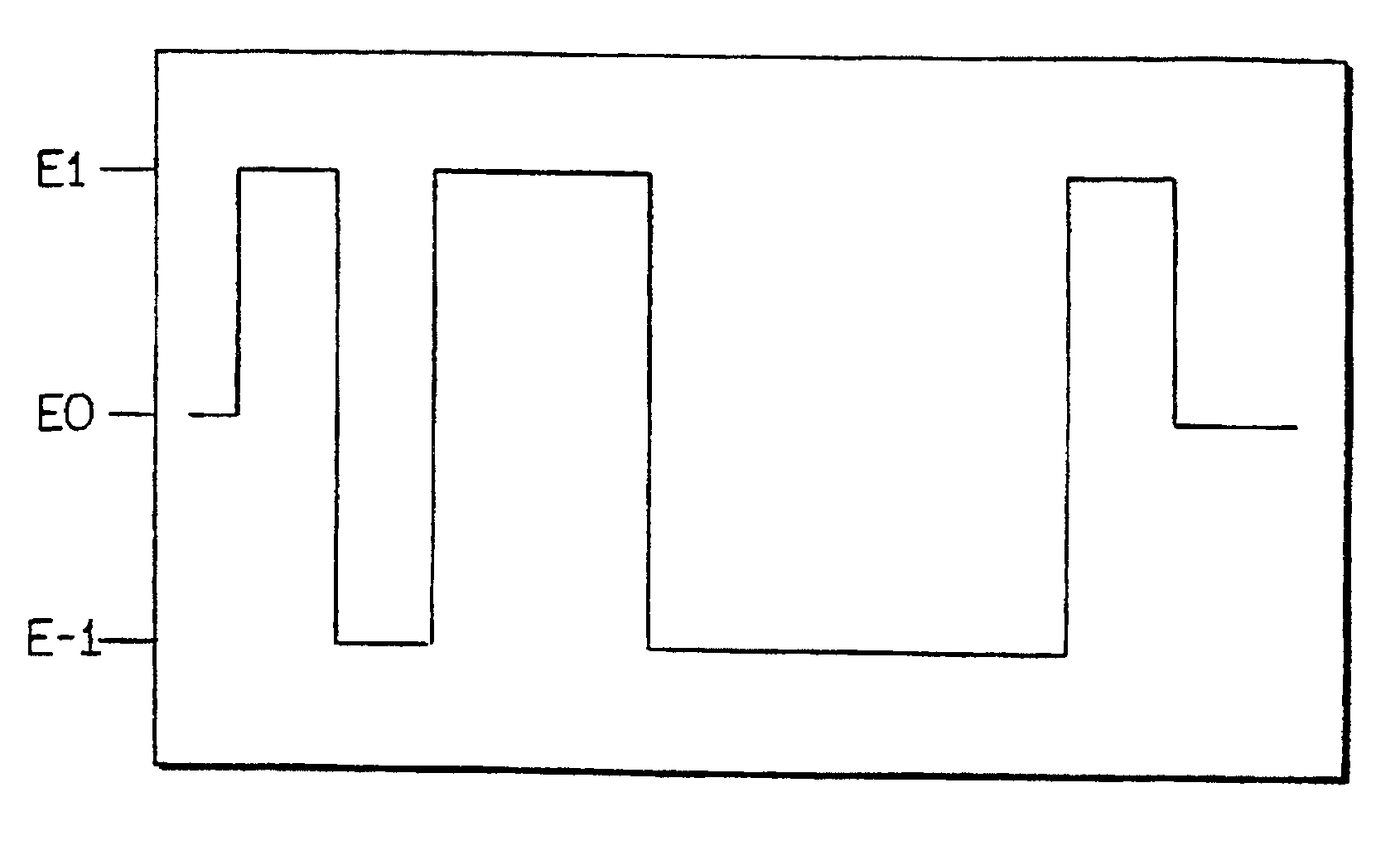
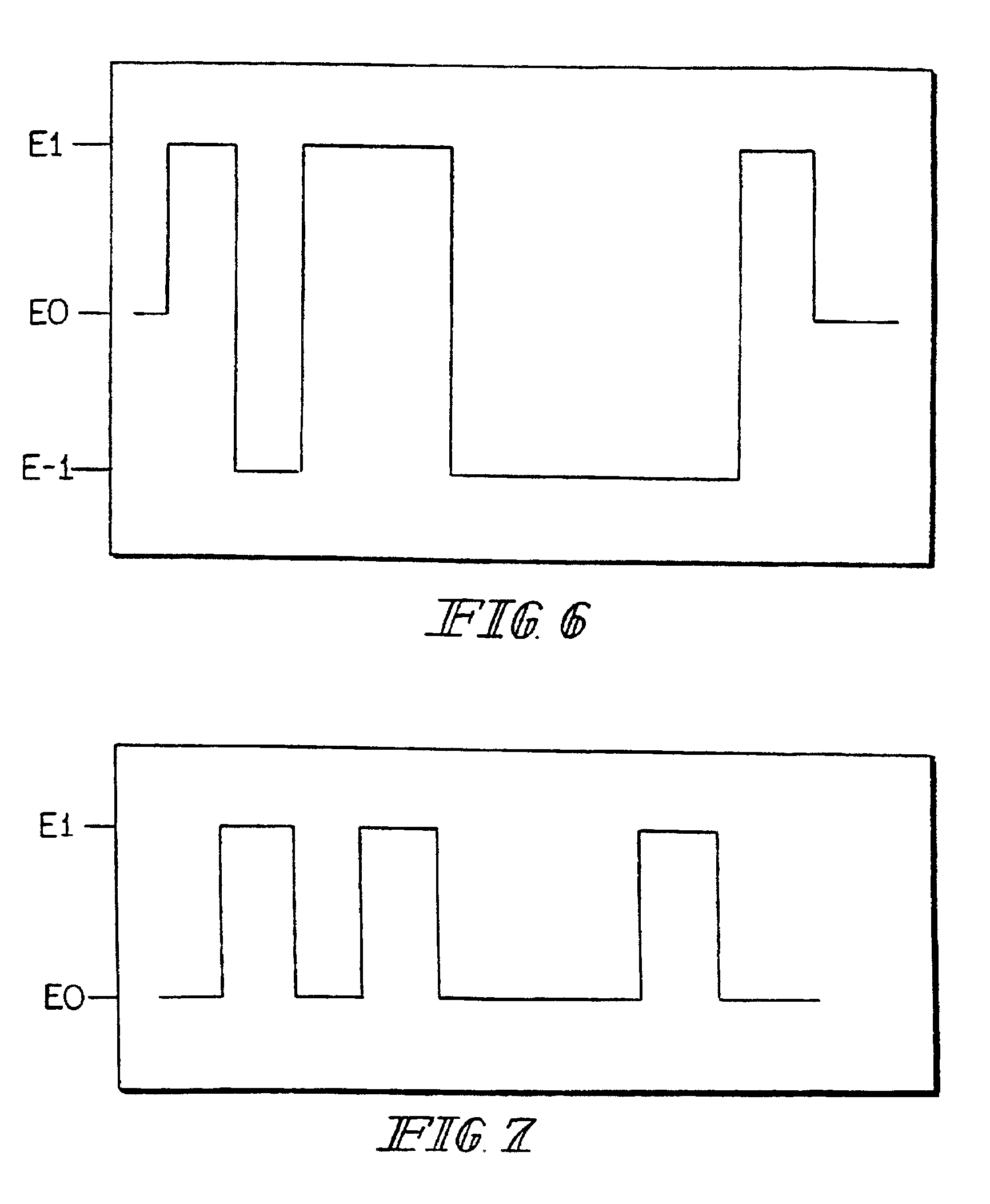
Sensors (10, 110, 210, 310, 410) and a method for detecting an analyte are described. Sensors (10, 110, 210, 310, 410) each have a volume of a hydrophilic medium (24) that retains an amount of analyte proportionate to the concentration of analyte in a biological fluid, electrodes (12) and a redox enzyme in contact with medium (24), and an electron transfer mediator. The fluid contacts sensors (10, 110, 210, 310, 410) and at initially predetermined intervals intermittently applies a potential to electrode (12) sufficient to oxidize the mediator and sensing current through electrode (12) as a function of the duration of the applied potential. The applied mediator oxidizing applied potential is maintained for a period of time sufficient to determine the rate of change of current with time through electrode (12). The current flow is correlated with the current flow for known concentrations of the analyte in medium (24).
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
Method and apparatus for assay of electrochemical properties
ActiveUS20050109637A1Easy to measureImprove accuracyWeather/light/corrosion resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementHand heldApplied potential
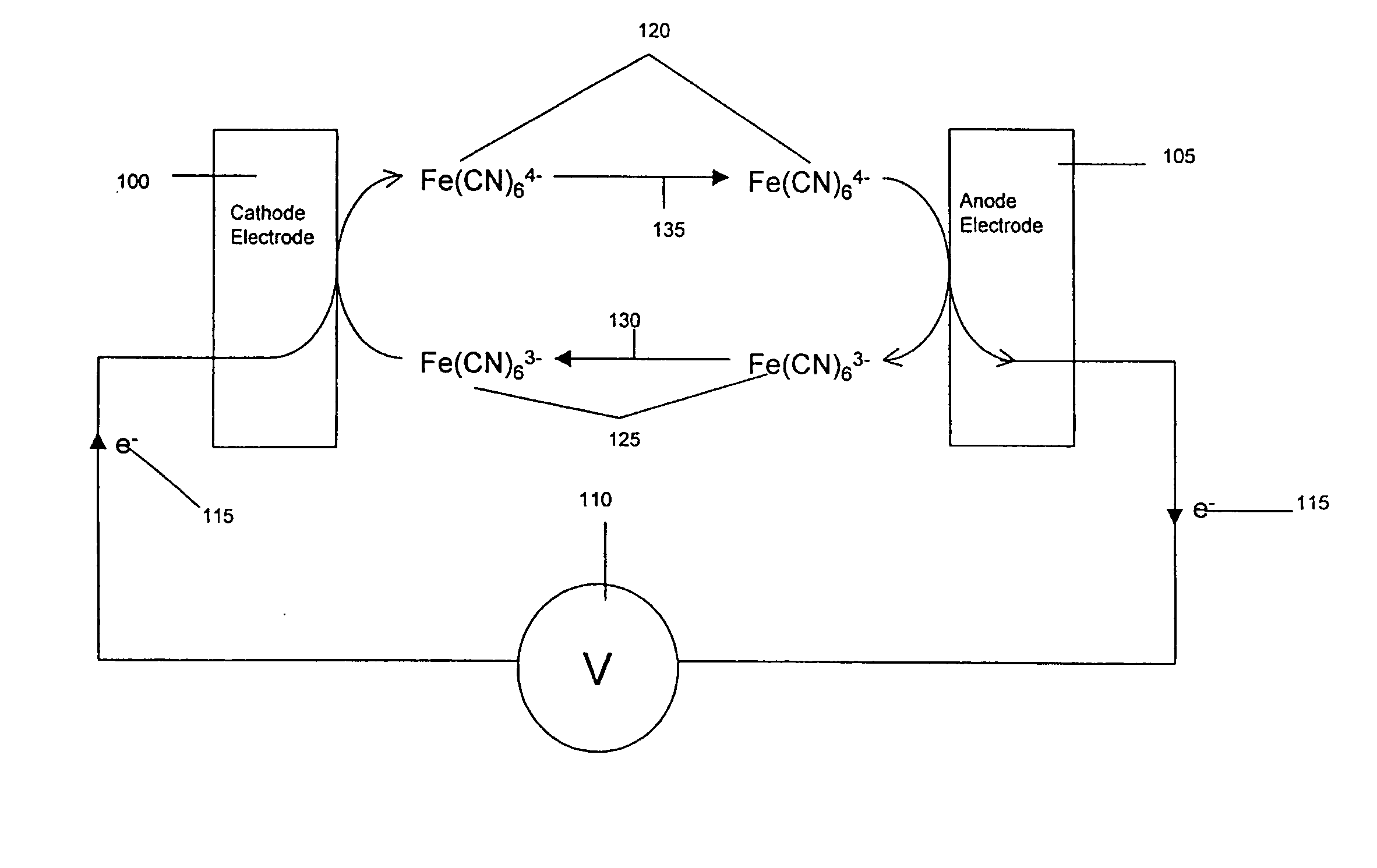
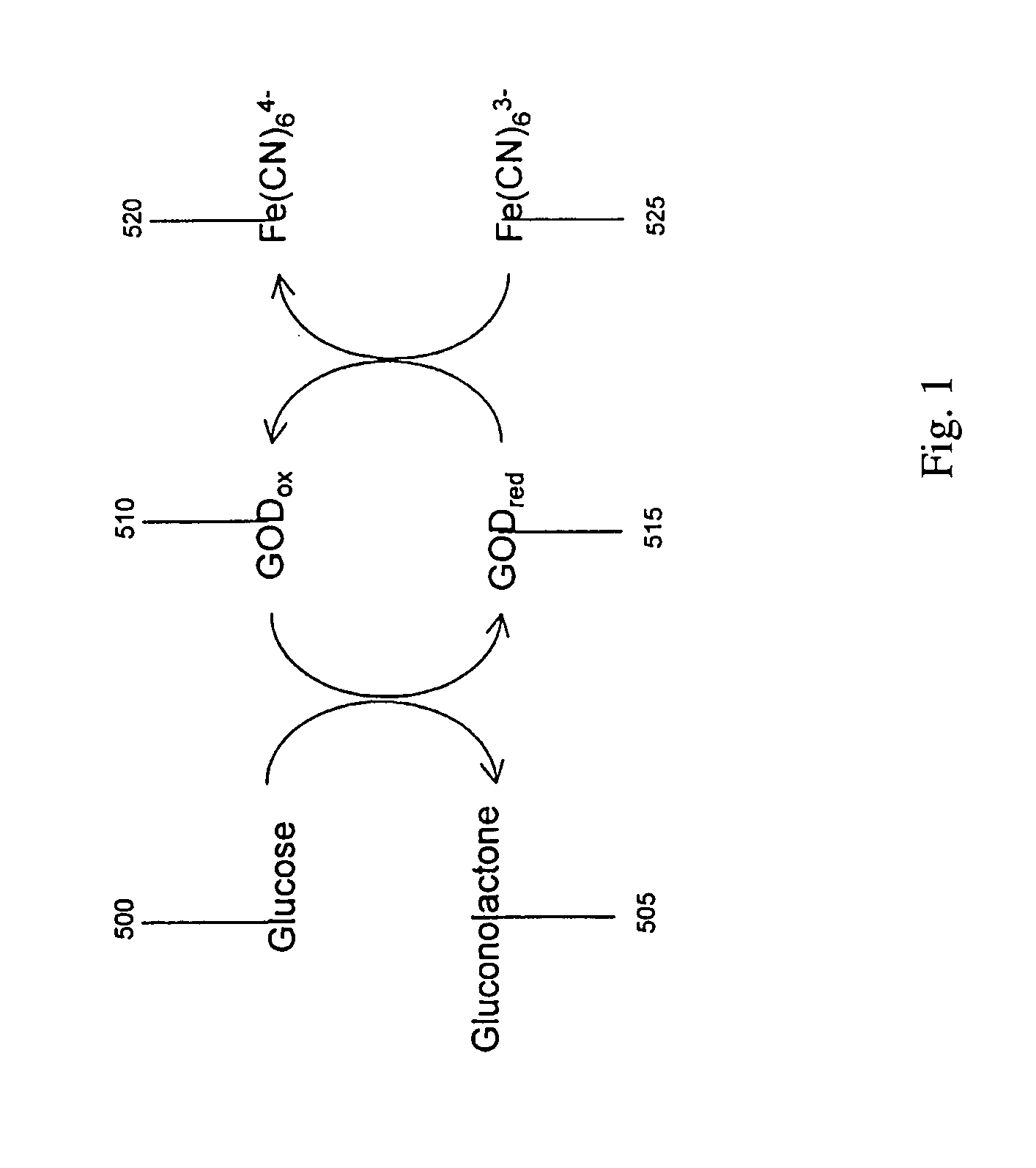
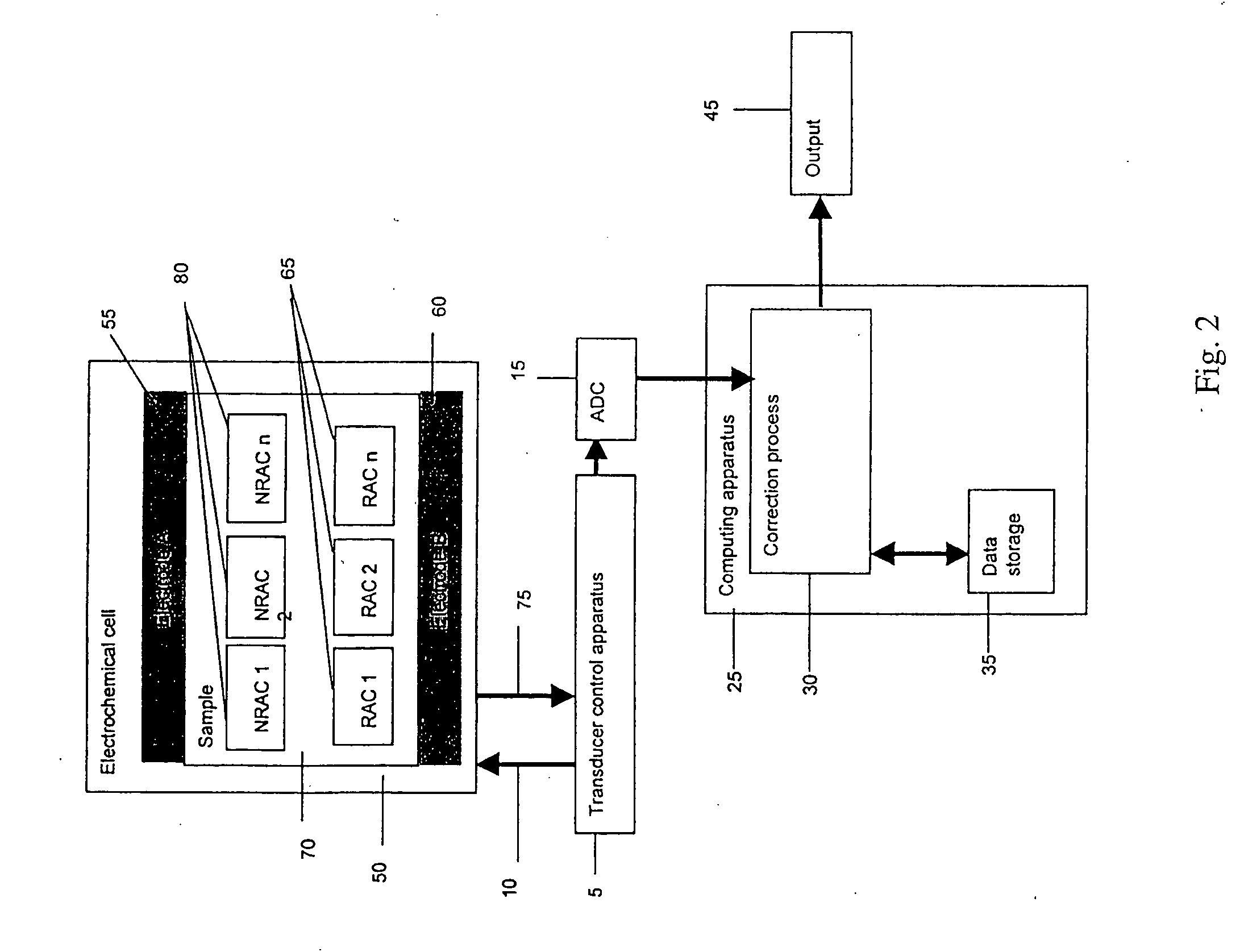
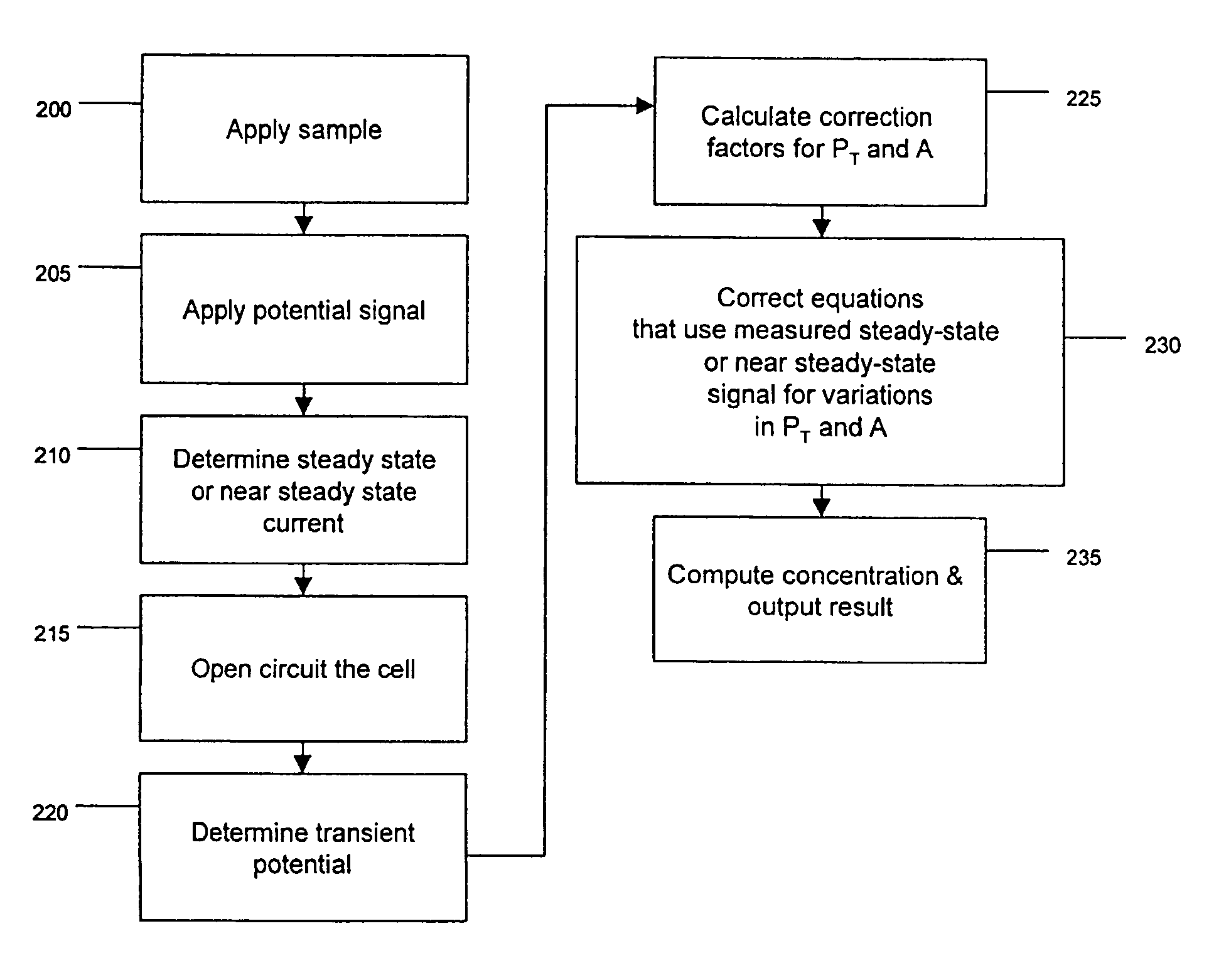
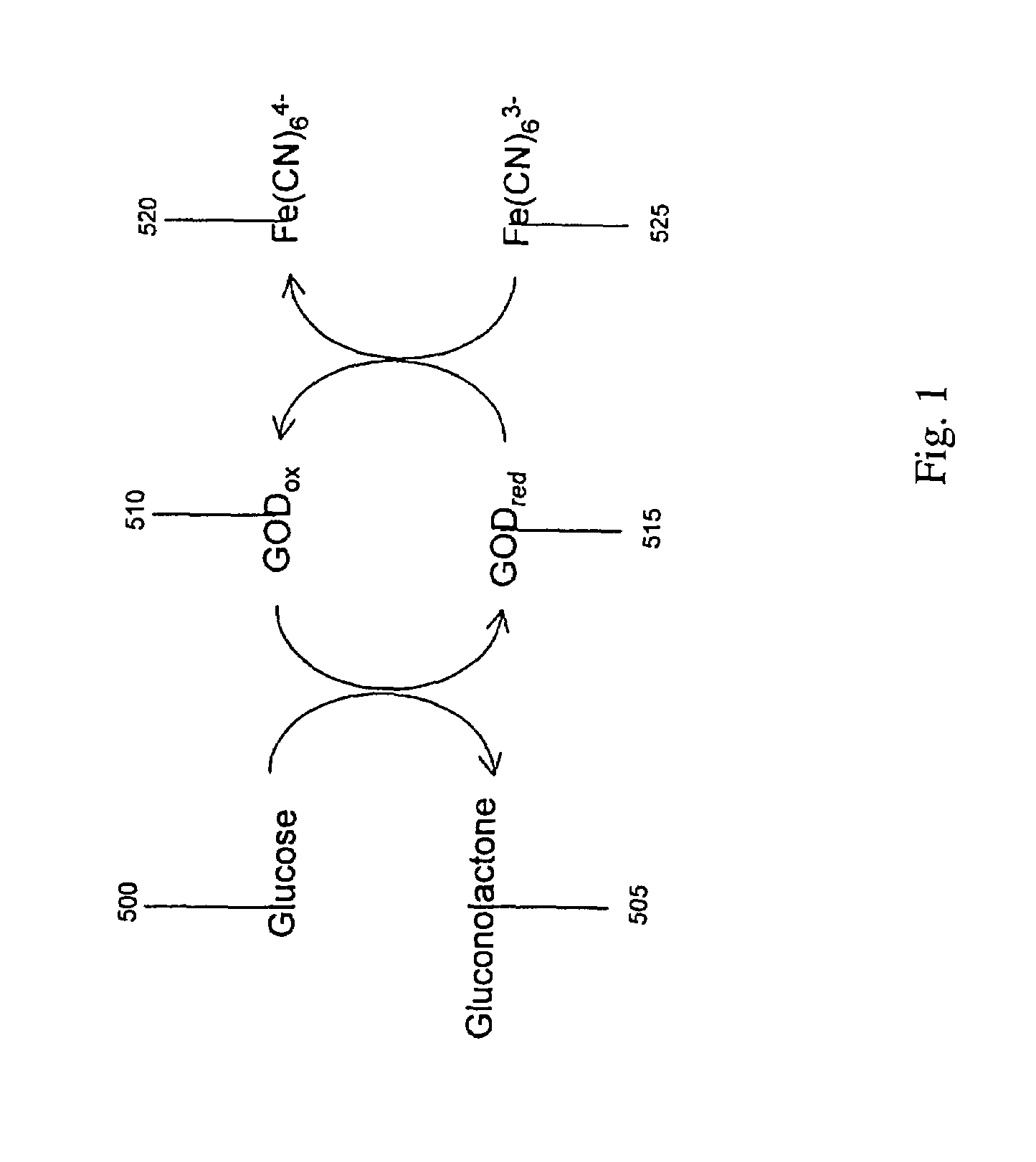
The presence of a select analyte in the sample is evaluated in an an electrochemical system using a conduction cell-type apparatus. A potential or current is generated between the two electrodes of the cell sufficient to bring about oxidation or reduction of the analyte or of a mediator in an analyte-detection redox system, thereby forming a chemical potential gradient of the analyte or mediator between the two electrodes After the gradient is established, the applied potential or current is discontinued and an analyte-independent signal is obtained from the relaxation of the chemical potential gradient. The analyte-independent signal is used to correct the analyte-dependent signal obtained during application of the potential or current. This correction allows an improved measurement of analyte concentration because it corrects for device-specific and test specific factors such as transport (mobility) of analyte and / or mediator, effective electrode area, and electrode spacing (and as a result, sample volume), without need for separate calibration values. The analysis can be performed using disposable test strips in a hand held meter, for example for glucose testing.
Owner:AGAMATRIX INC
Method and apparatus for assay of electrochemical properties
ActiveUS7501052B2Easy to measureImprove accuracy and precisionImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHand heldApplied potential
The presence of a select analyte in the sample is evaluated in an an electrochemical system using a conduction cell-type apparatus. A potential or current is generated between the two electrodes of the cell sufficient to bring about oxidation or reduction of the analyte or of a mediator in an analyte-detection redox system, thereby forming a chemical potential gradient of the analyte or mediator between the two electrodes After the gradient is established, the applied potential or current is discontinued and an analyte-independent signal is obtained from the relaxation of the chemical potential gradient. The analyte-independent signal is used to correct the analyte-dependent signal obtained during application of the potential or current. This correction allows an improved measurement of analyte concentration because it corrects for device-specific and test specific factors such as transport (mobility) of analyte and / or mediator, effective electrode area, and electrode spacing (and as a result, sample volume), without need for separate calibration values. The analysis can be performed using disposable test strips in a hand held meter, for example for glucose testing.
Owner:AGAMATRIX INC
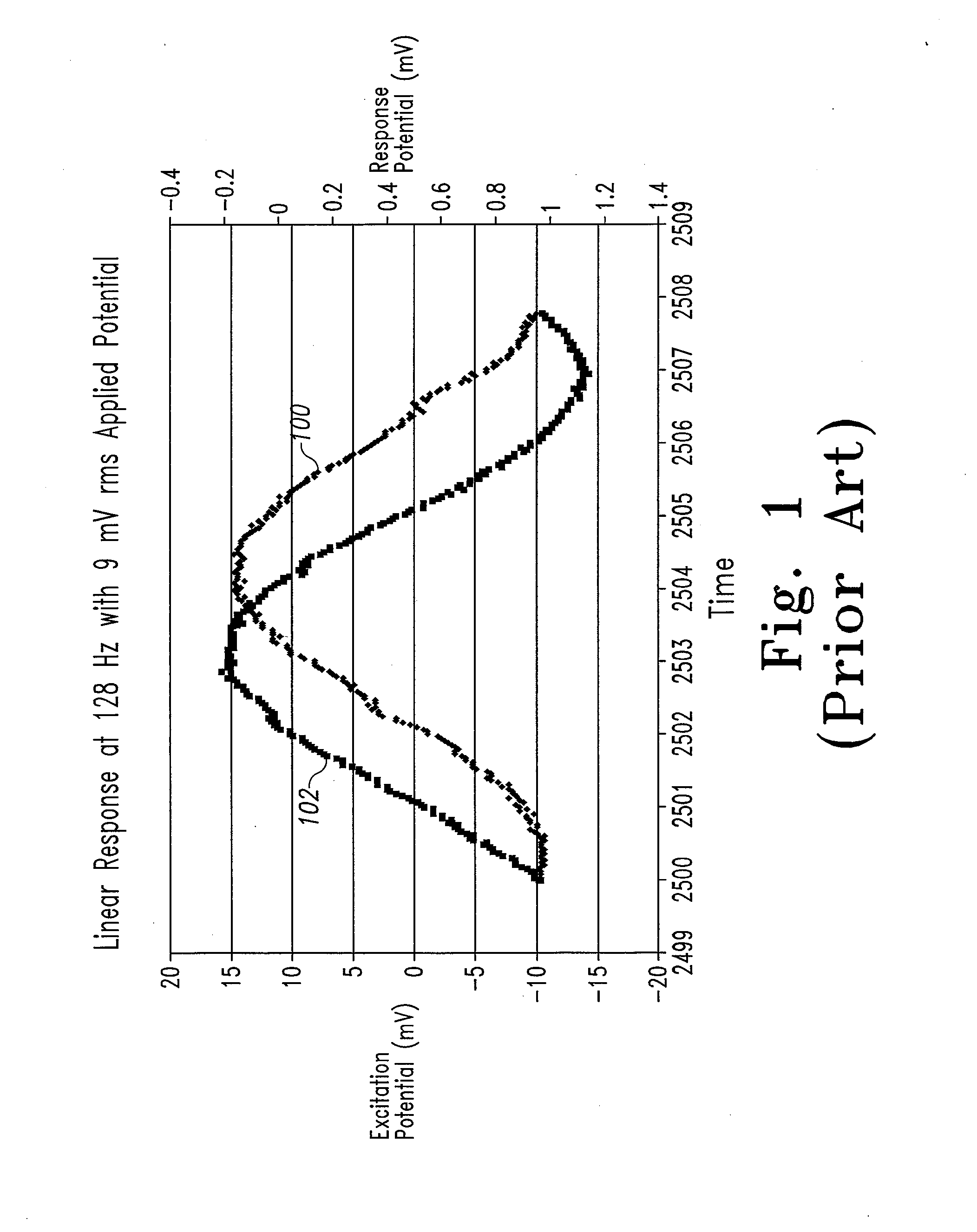
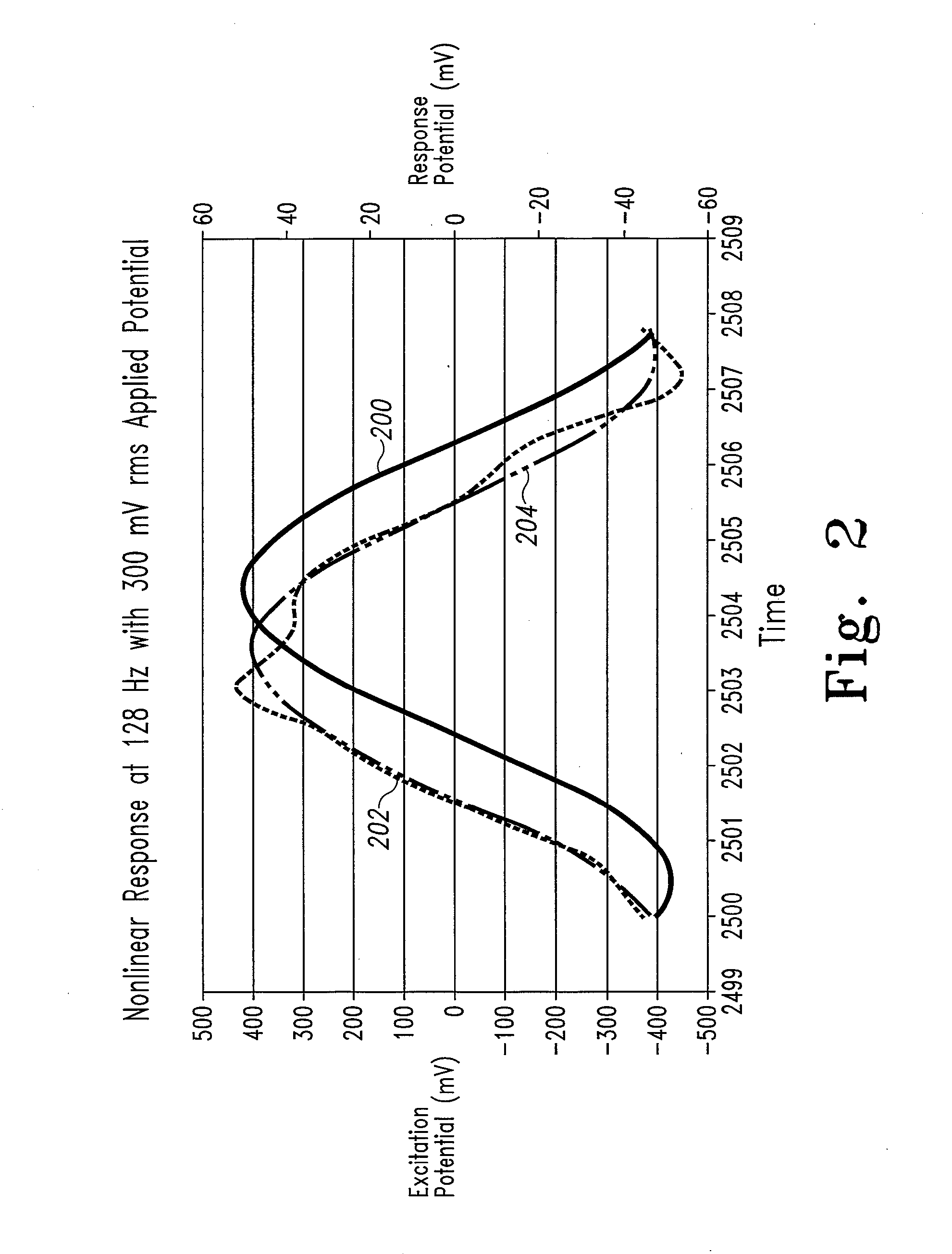
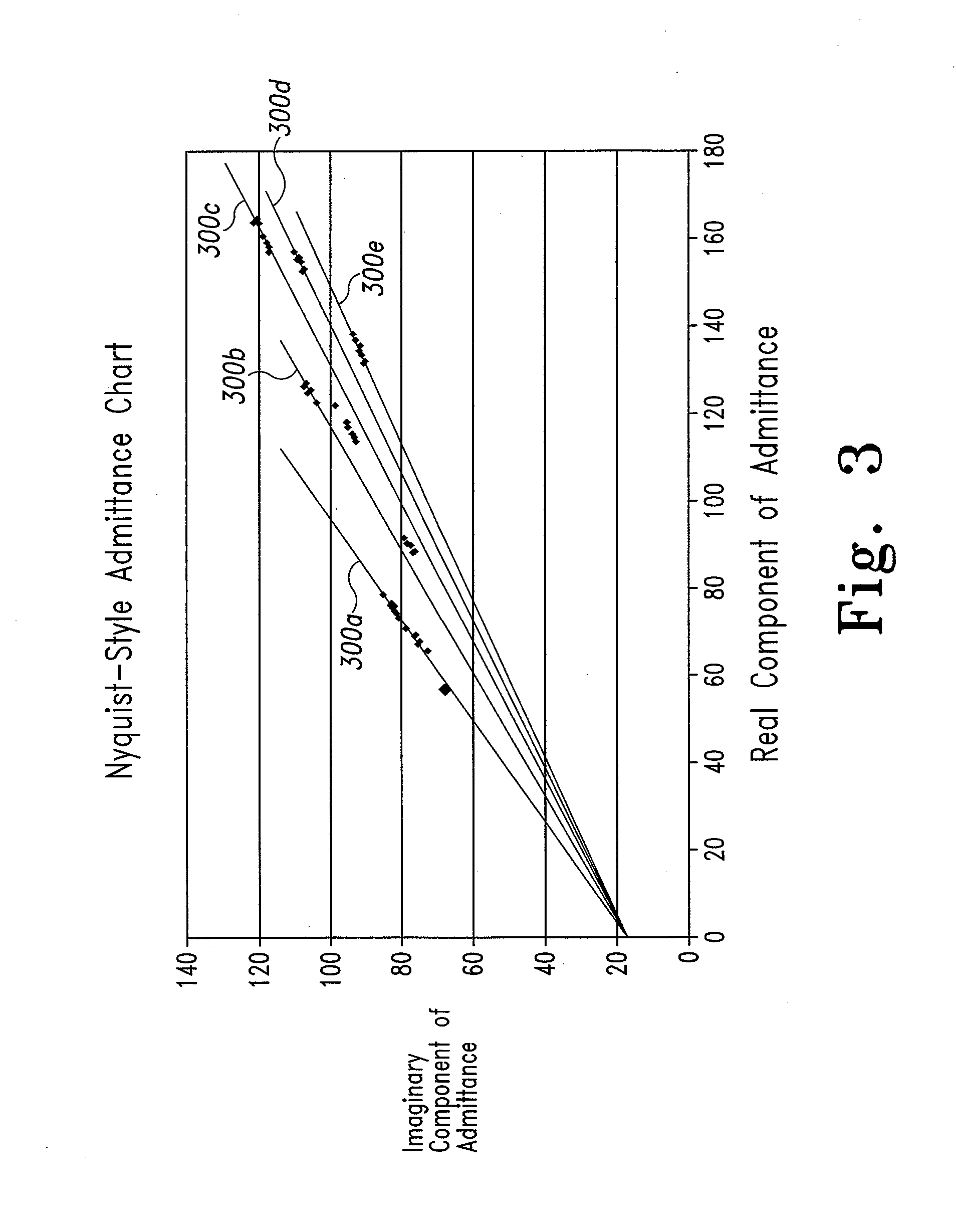
System and method for analyte measurement using a nonlinear sample response
InactiveUS20070264721A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingLinear componentApplied potential
The systems and methods of the present invention utilize a linear component of a non-linear, faradaic current response generated by a biological fluid sample when an AC excitation potential sufficient to produce such a faradaic current response is applied to the sample, in order to calculate the concentration of a medically significant component in the biological fluid sample. The current response is created by the excitation of electrochemical processes within the sample by the applied potential. Typically, the linear component of the current response to an applied AC potential contains phase angle and / or admittance information that may be correlated to the concentration of the medically significant component. Also typically, the fundamental linear component of the current response is utilized in the disclosed systems and methods. Harmonics of the fundamental linear component may also be used. Other methods and devices are disclosed.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
Process and apparatus for switching large-area electrochromic devices
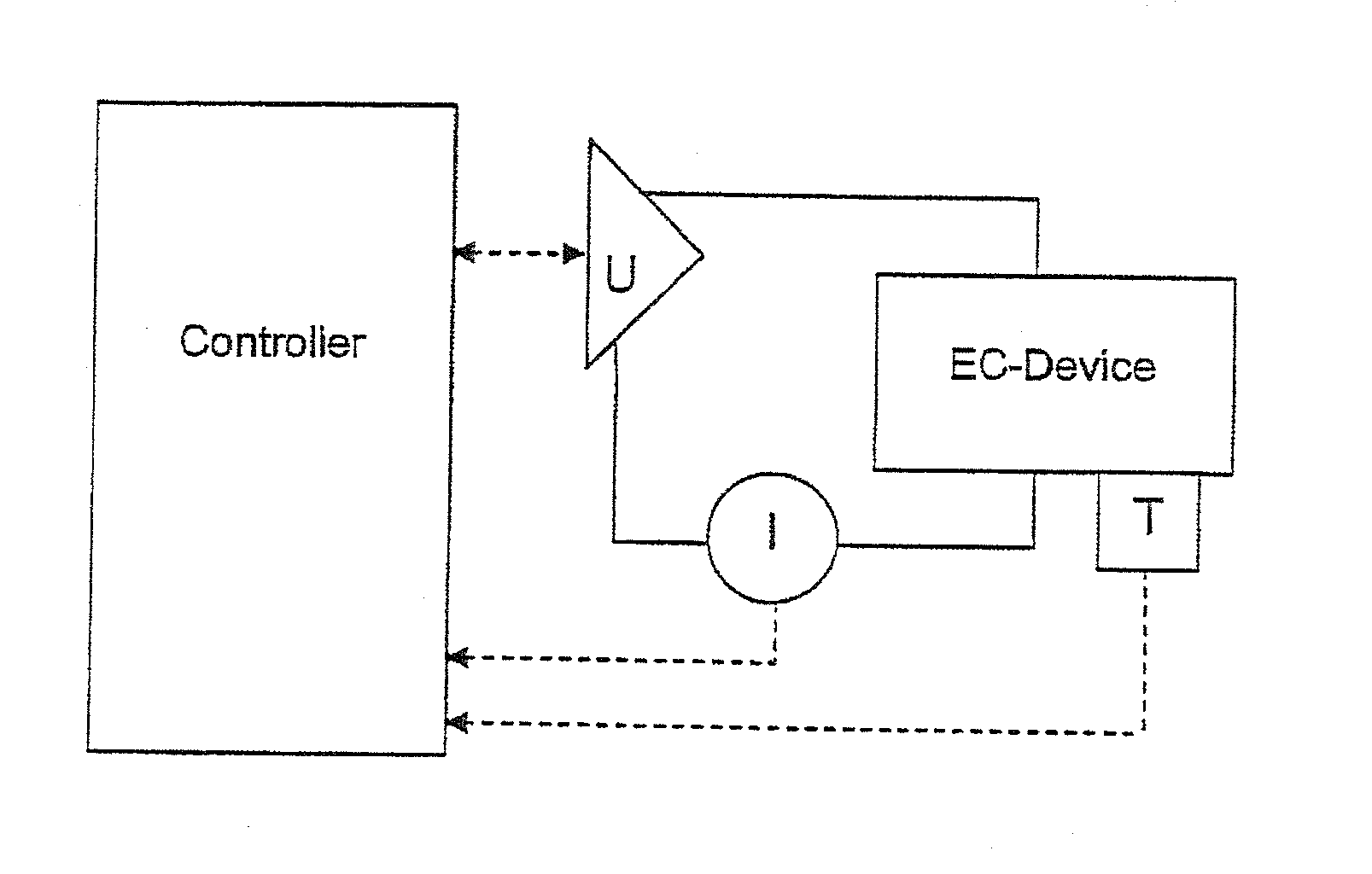
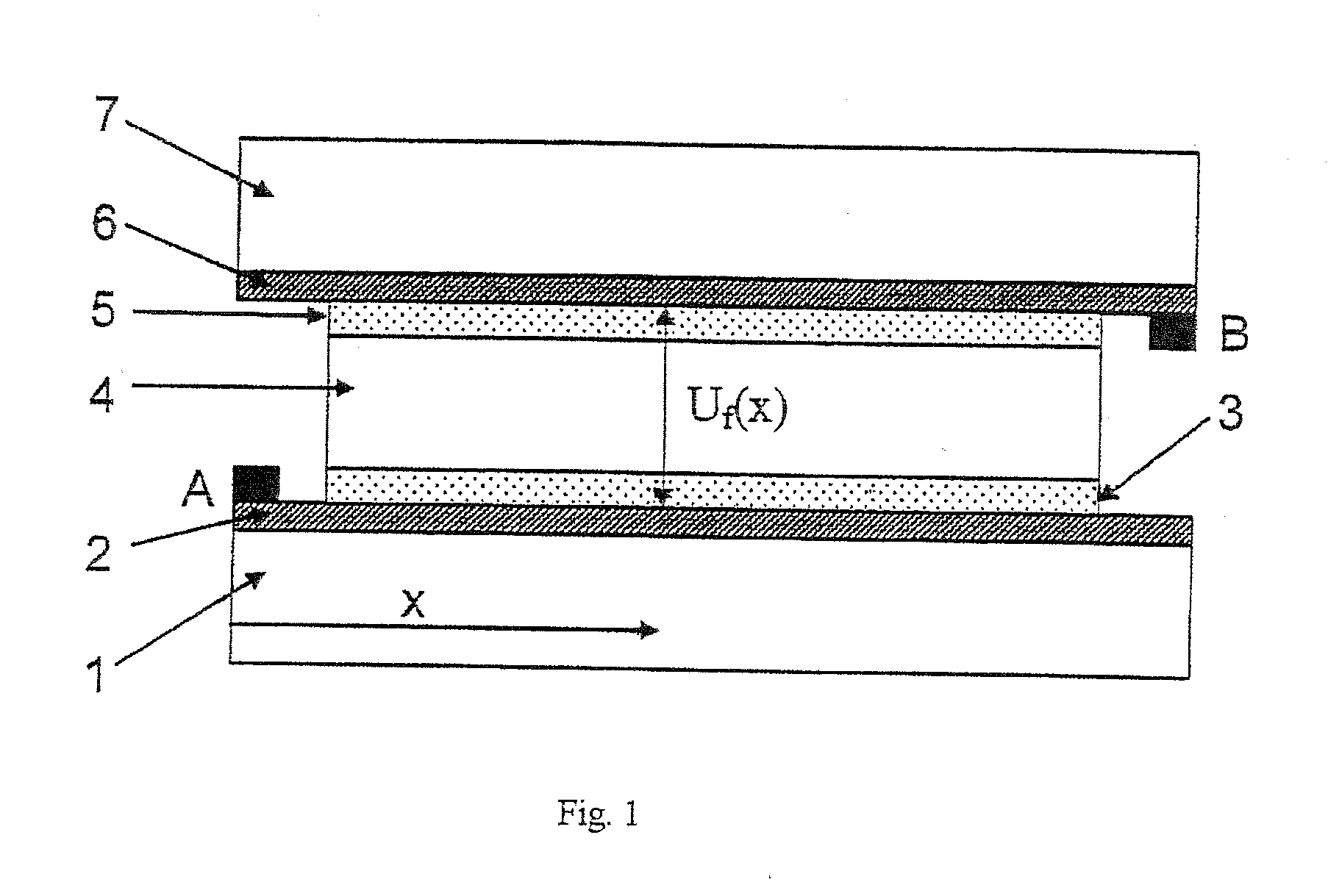
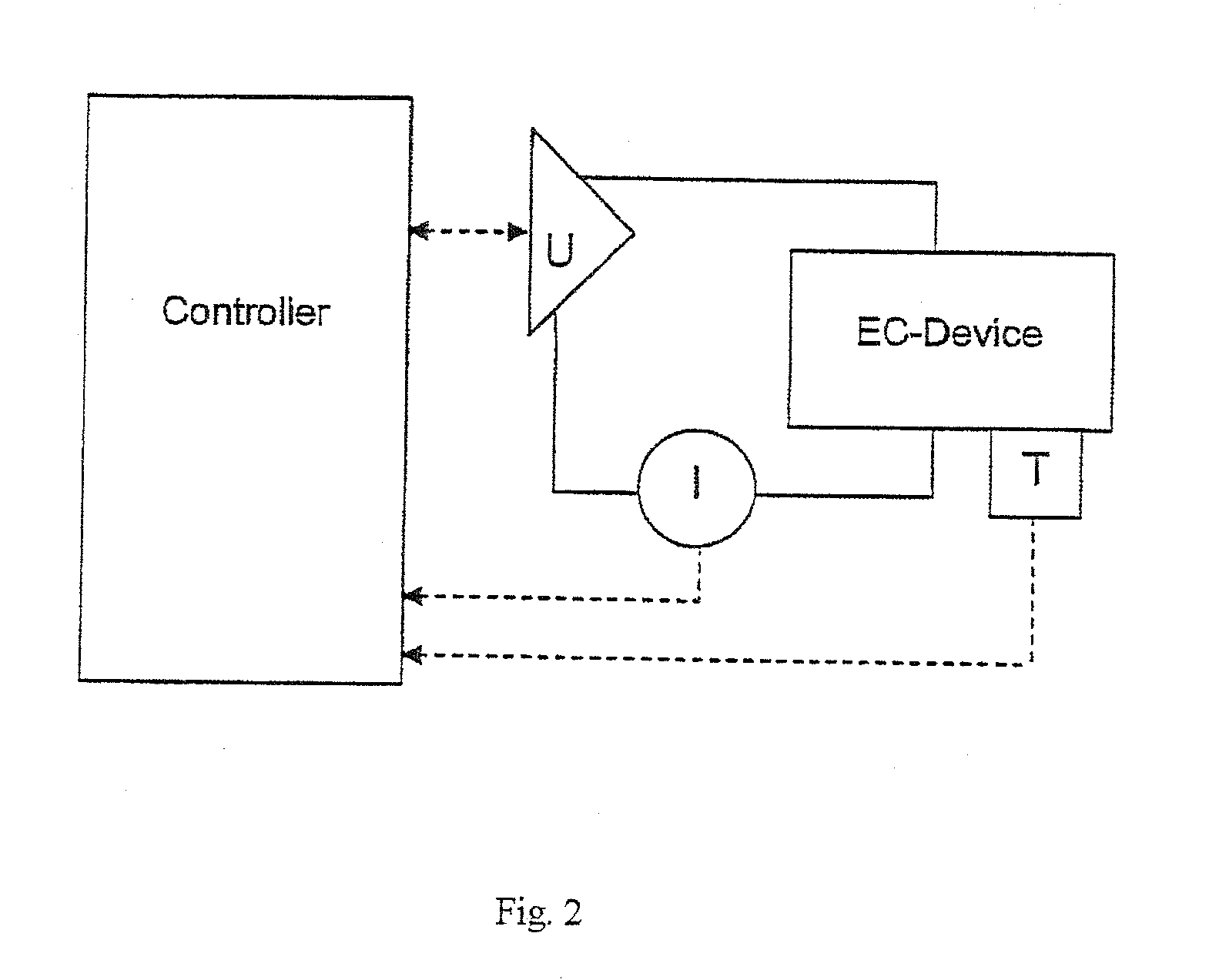
A method is disclosed for controlling switching of an electrochromic device comprising at least the following components: a first and a second electrode layer, a first and a second layer in which ions can be reversibly intercalated, and a transparent ion-conducting layer. At least one of the layers in which ions may be reversibly inserted is electrochromic. The optical properties of the device are modified when a potential is applied between the electrode layers. The potential applied is limited such that the maximum generated potential difference never exceeds the safe redox limits, and that the current does not exceed some predetermined limit. Switching of electrochromic devices in this manner allows for maximum device lifetime, while simultaneously optimising switching speed and transmission homogeneity. The method is characterised in that the potential applied to the electrode layers is varied in the form of a stepped ramp, during which time the current is measured constantly.
Owner:ECONTROL GLAS
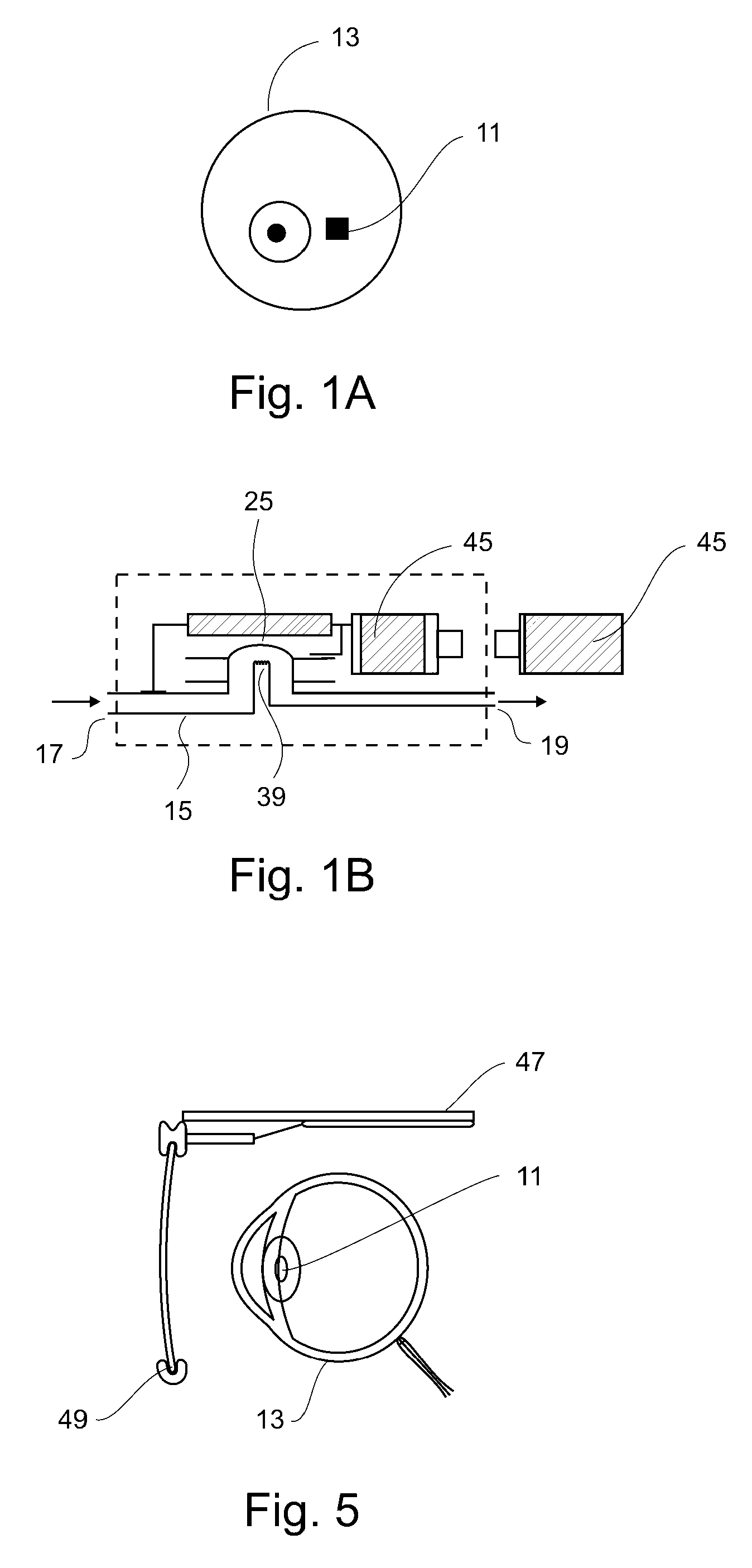
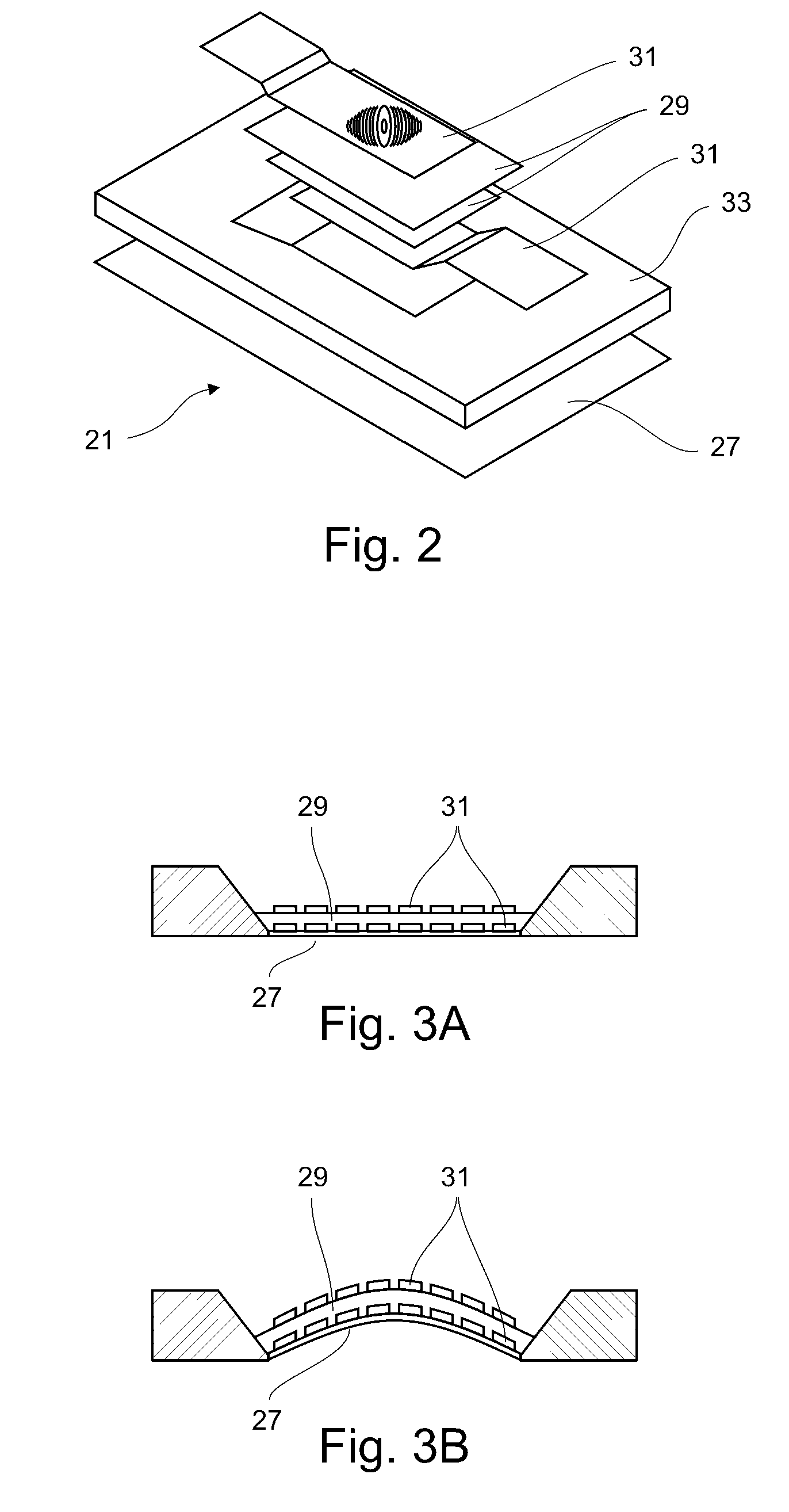
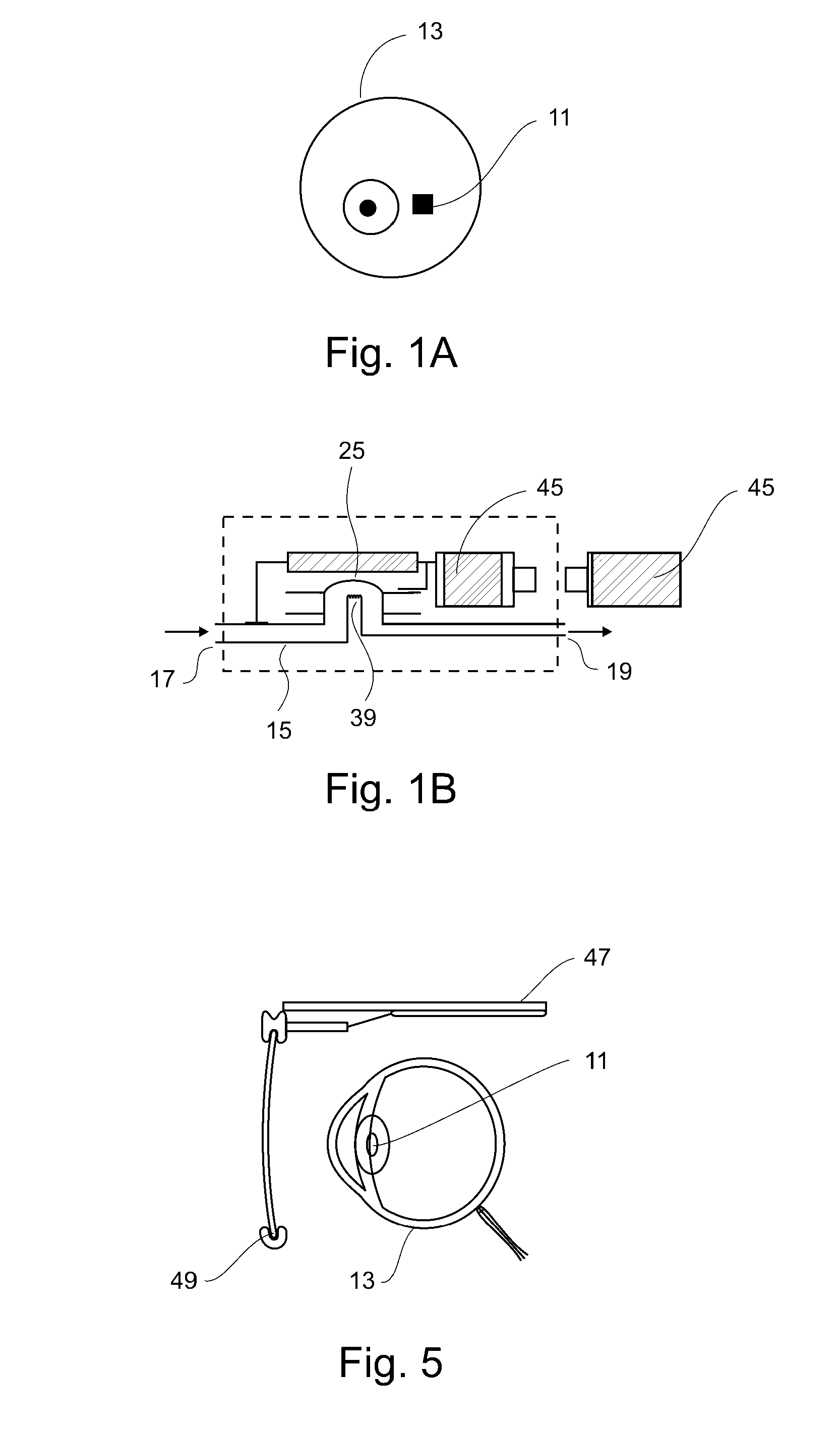
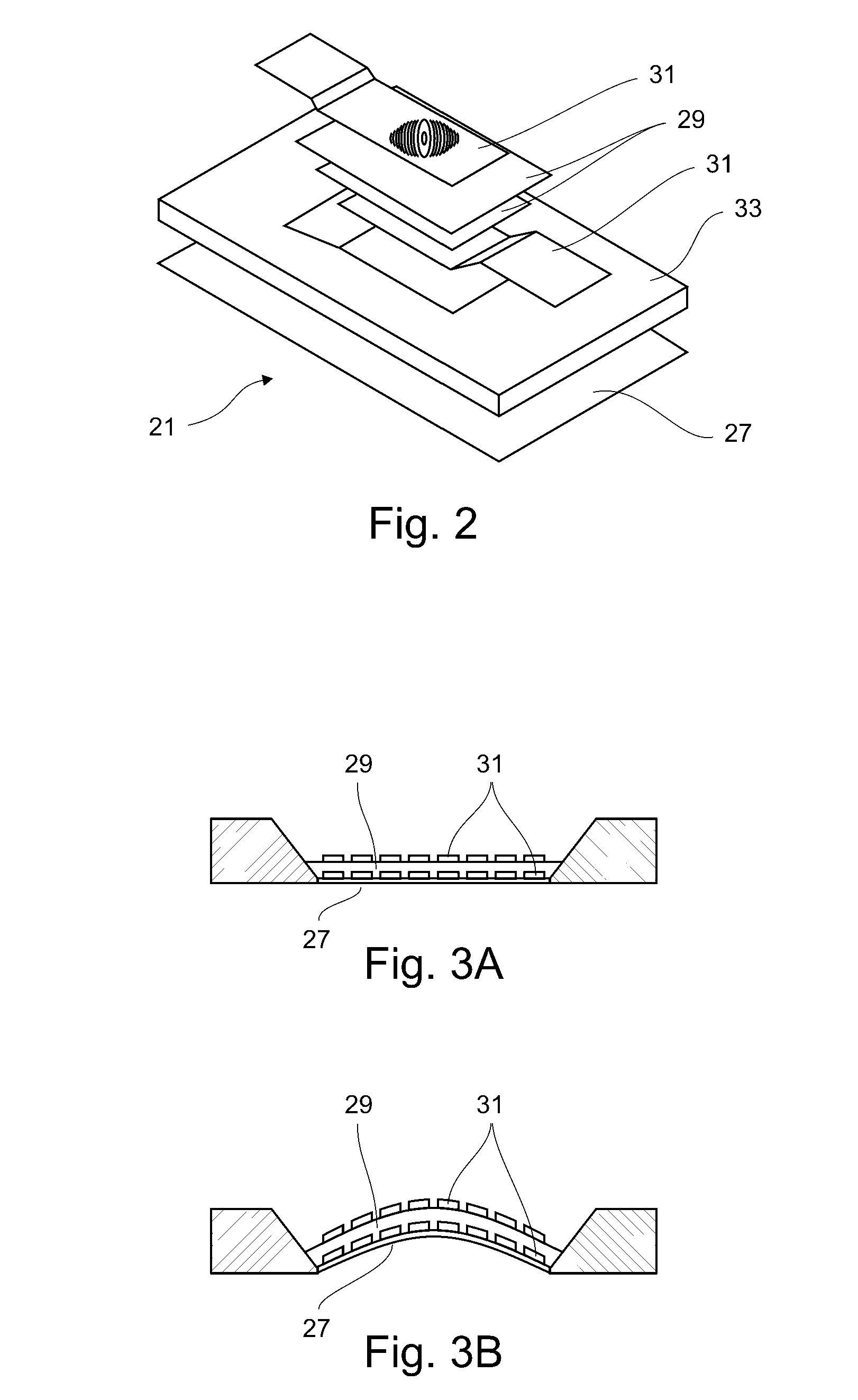
Implantable ocular microapparatus to ameliorate glaucoma or an ocular overpressure causing disease
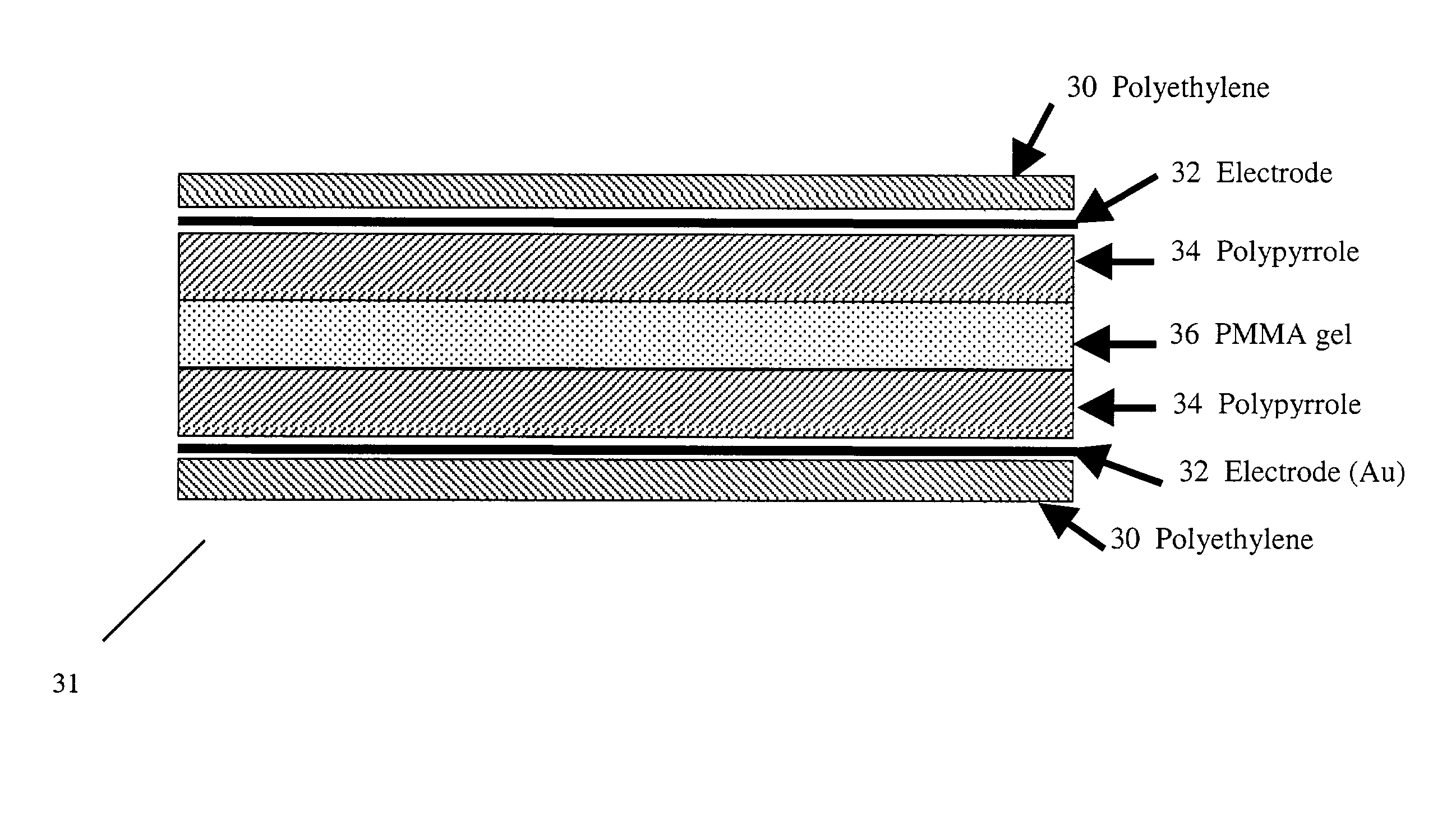
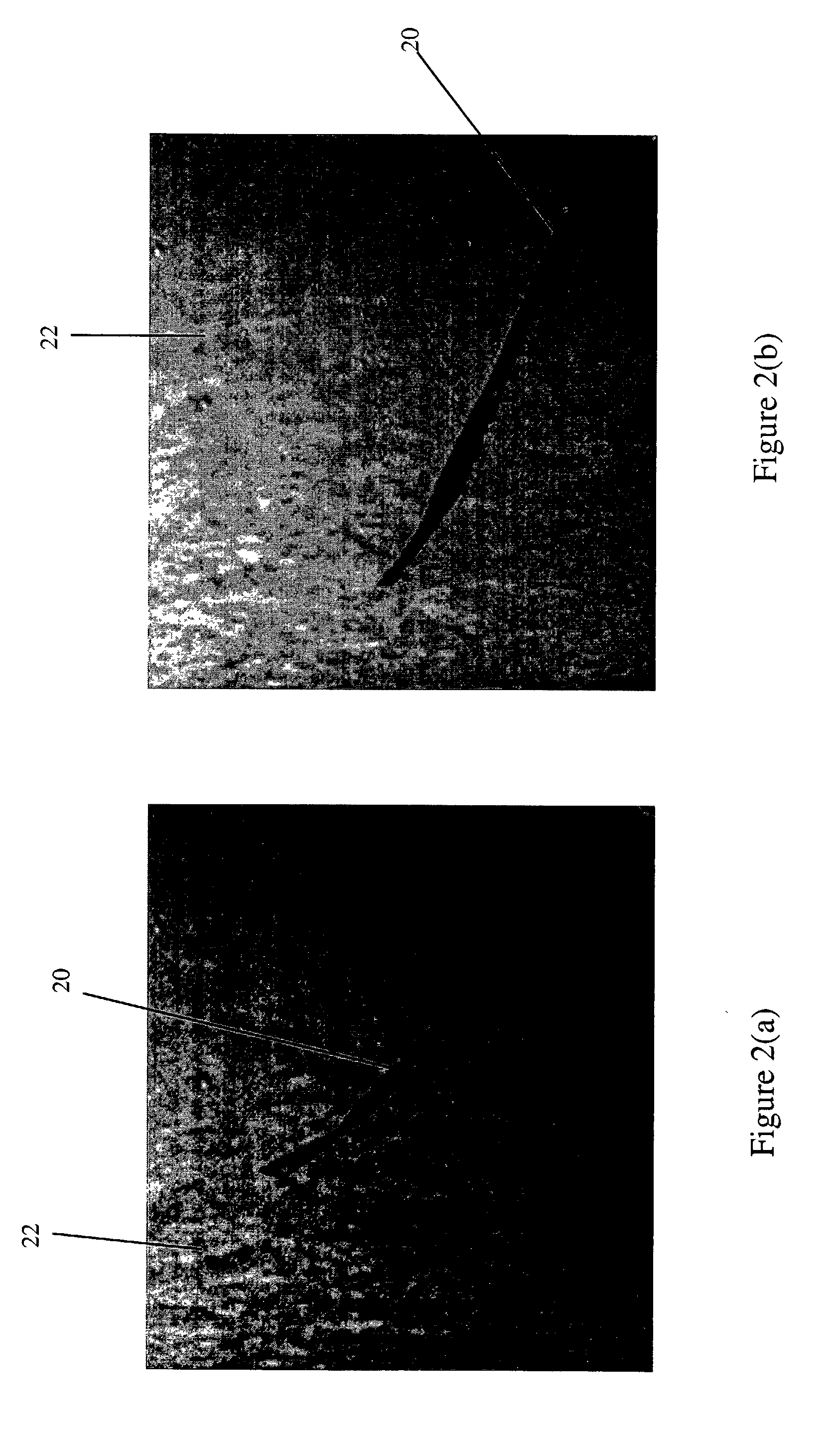
ActiveUS20100042209A1Minimize power consumptionSmall currentEye implantsEye surgeryDiseaseIntraocular pressure
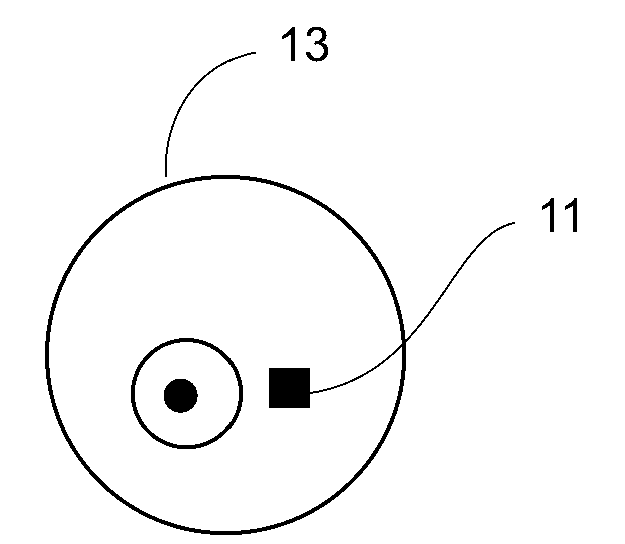
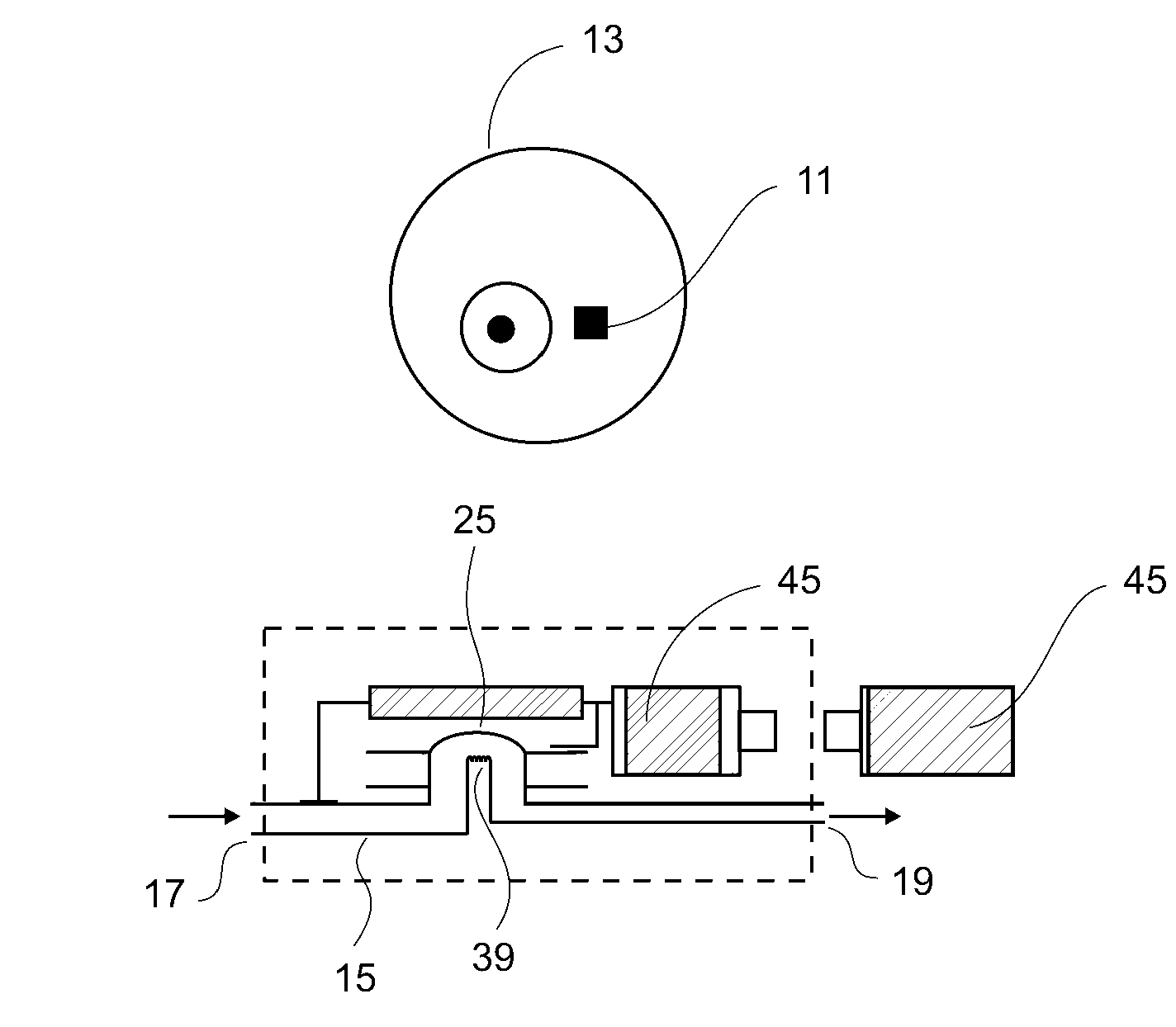
A microapparatus (11) implantable in the eye (13) comprises a cuasi-bistable microvalve (21) commanded by an intraocular pressure sensor (23) in situ. The microvalve mechanism includes a diaphragm (27) made of a conjugated polymer (29) that shows high deformation and biocompatibility capabilities and which volume depends from the electric potential applied by its pair of electrodes (31). The sensor and actuator-valve are coupled to a drainage conduit (15), the first to deform by the pressure in the ocular globe and the second in a position of buckling to normally close the drainage conduit. The sensor us a membrane of conductive polymeric material with the same properties and whose ohmic resistance varies with the mechanical deformation produced by the ocular pressure.
Owner:CONSEJO NAT DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS Y TECH +1
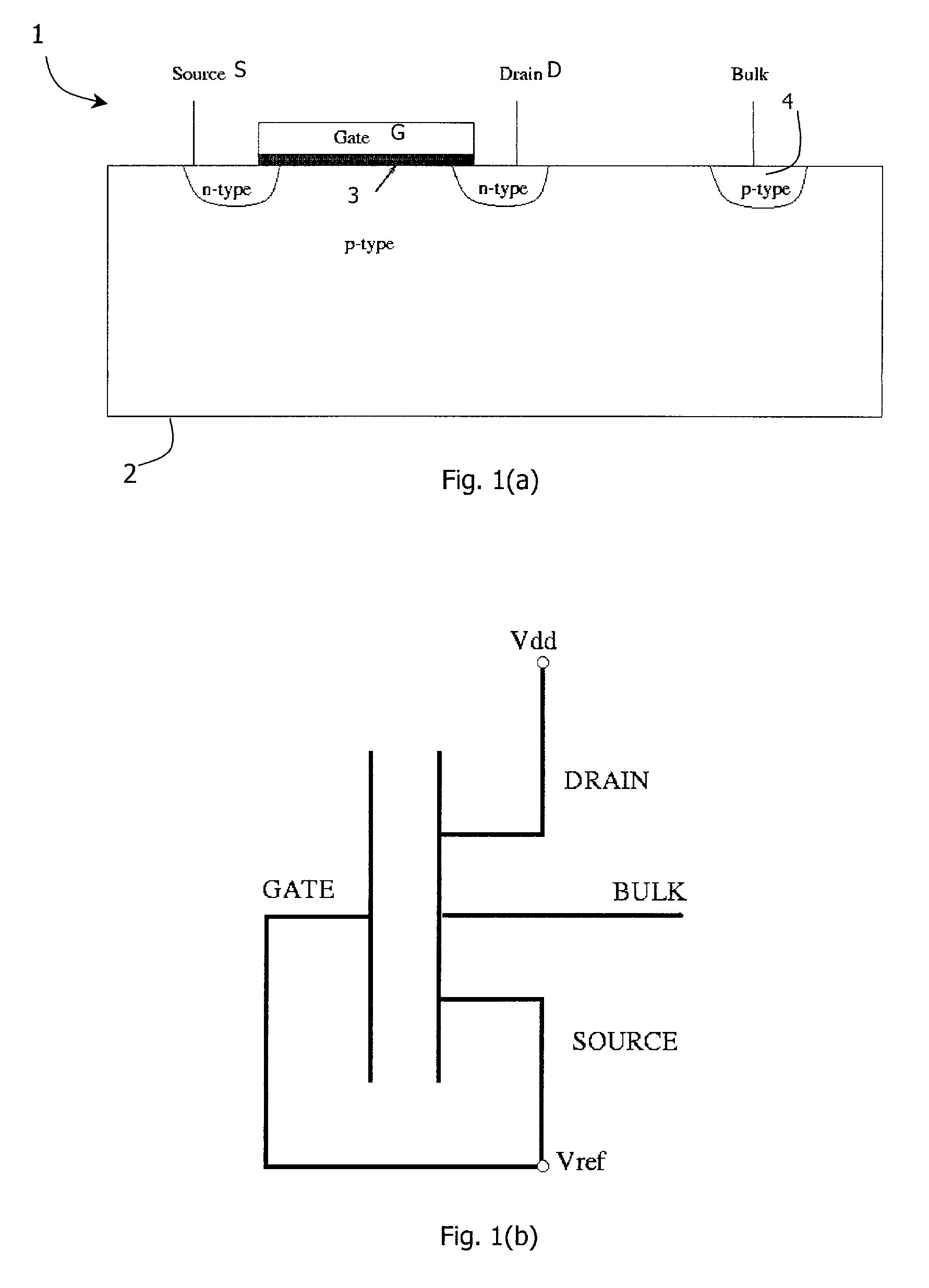
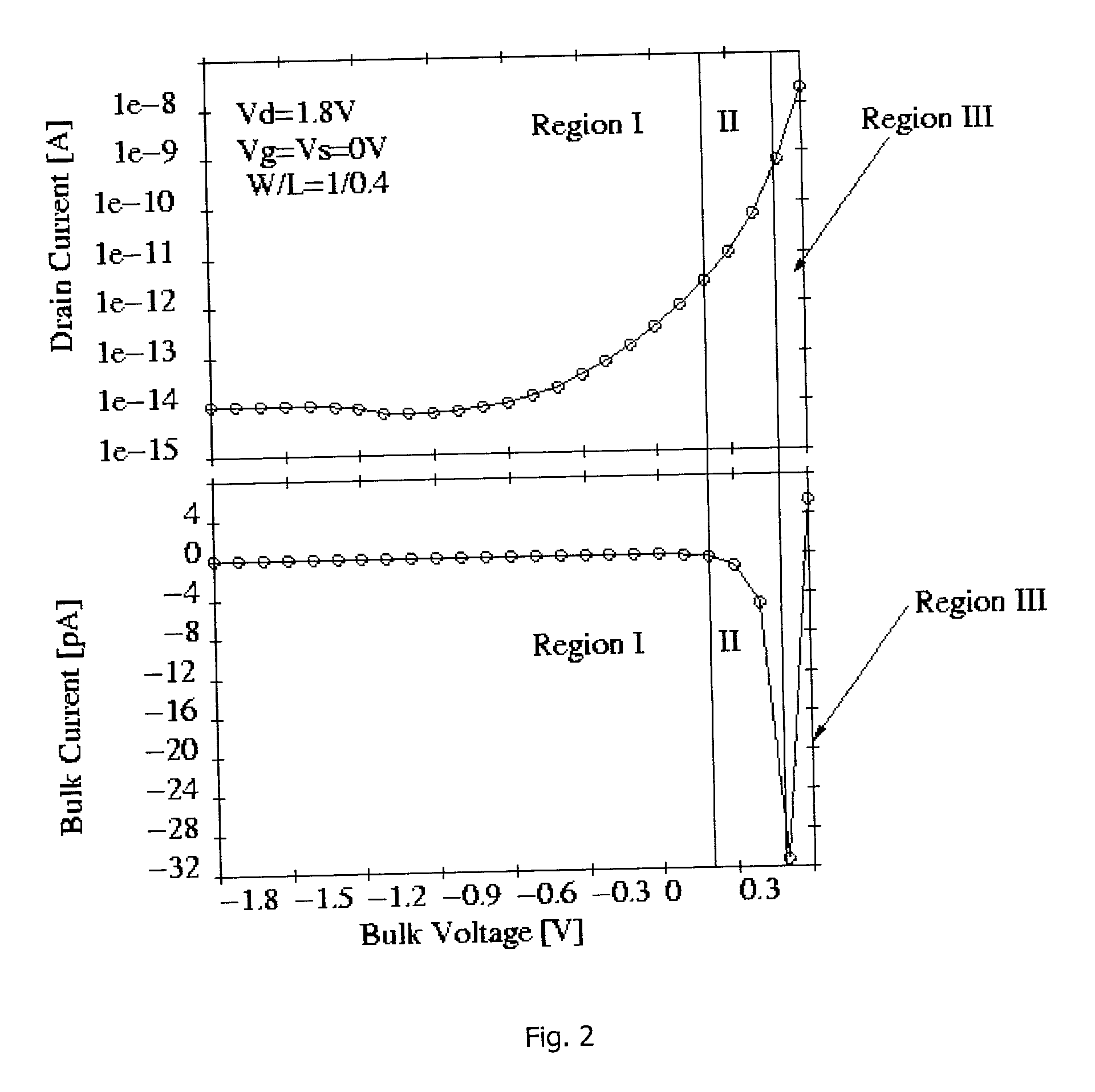
Negative resistance device
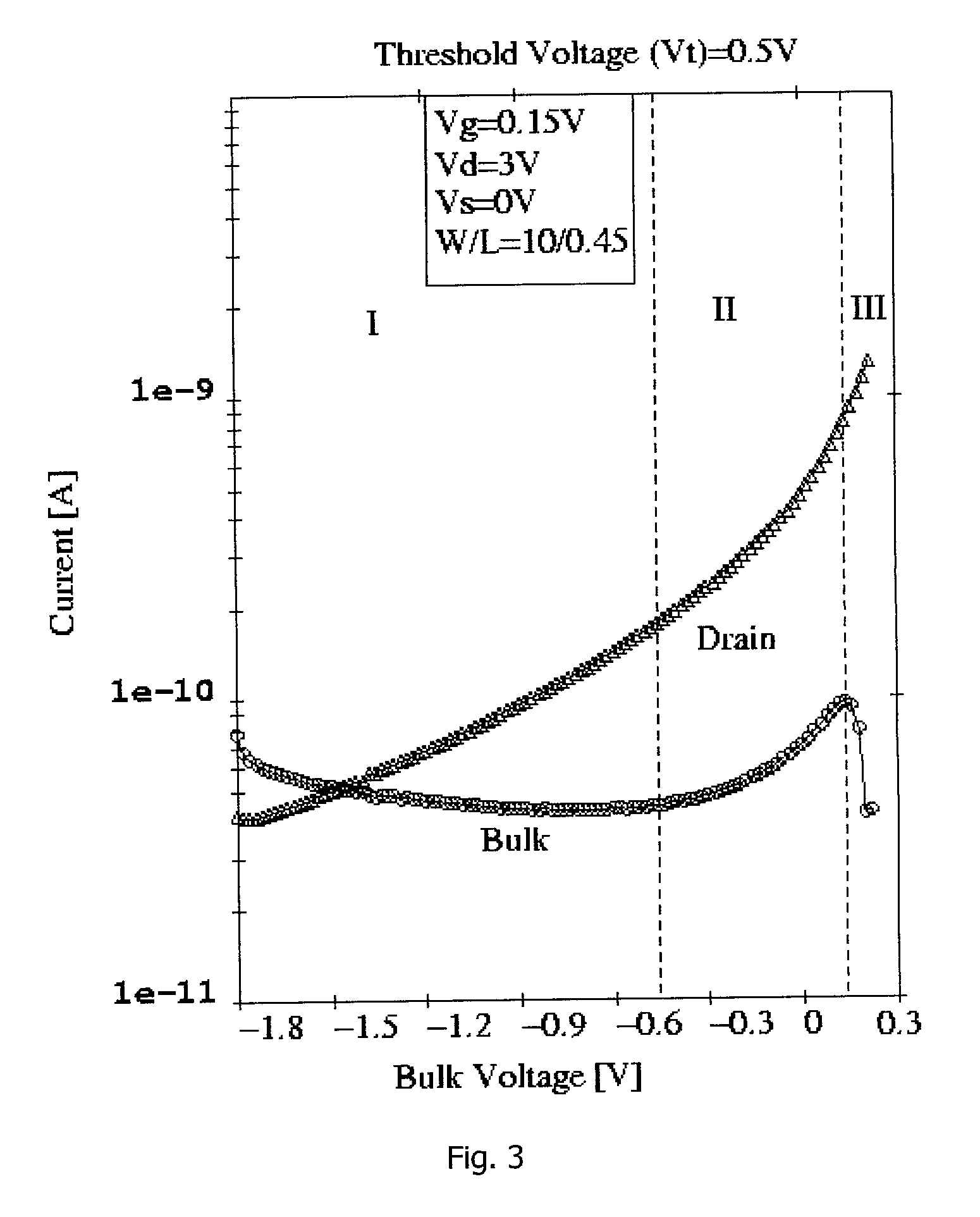
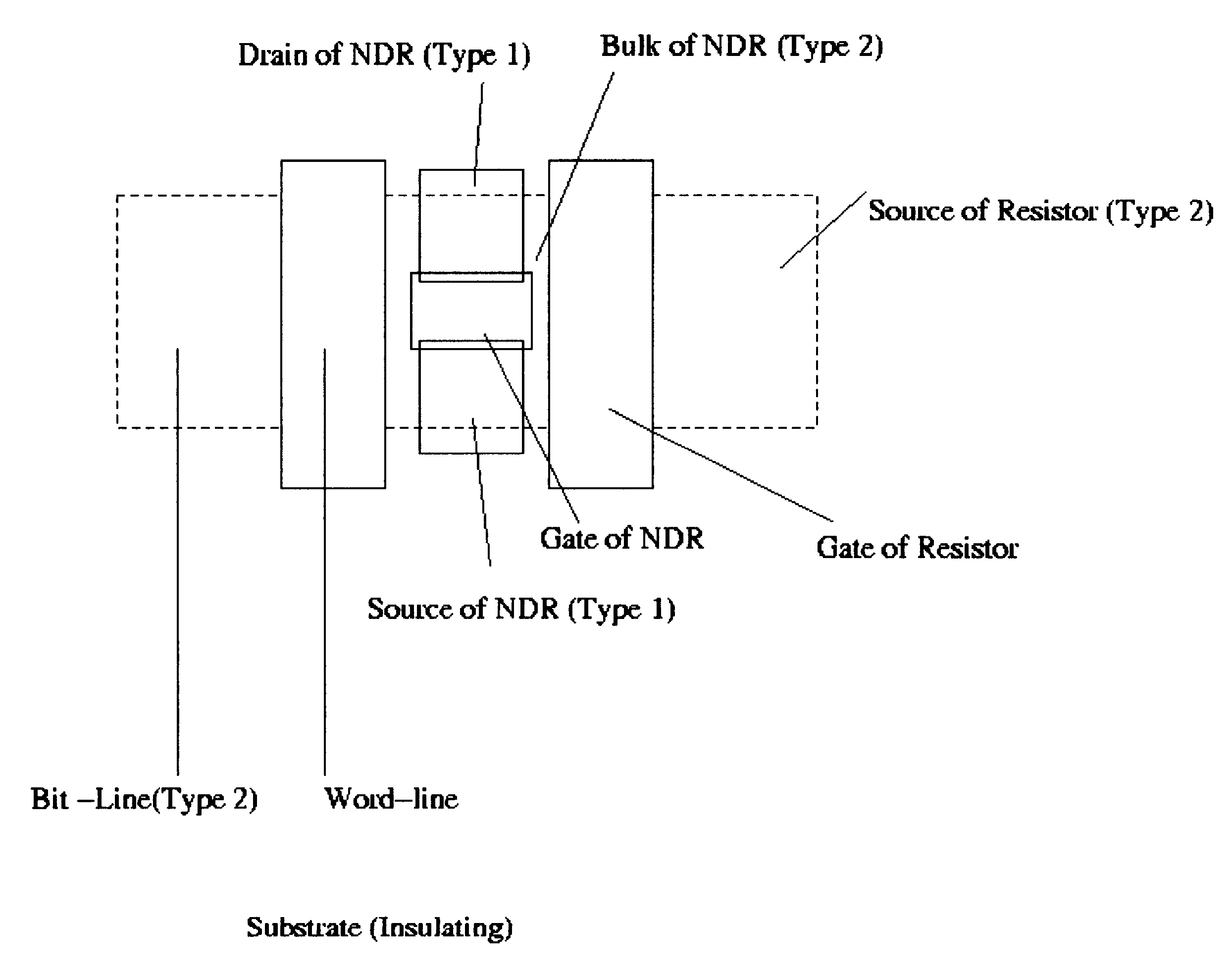
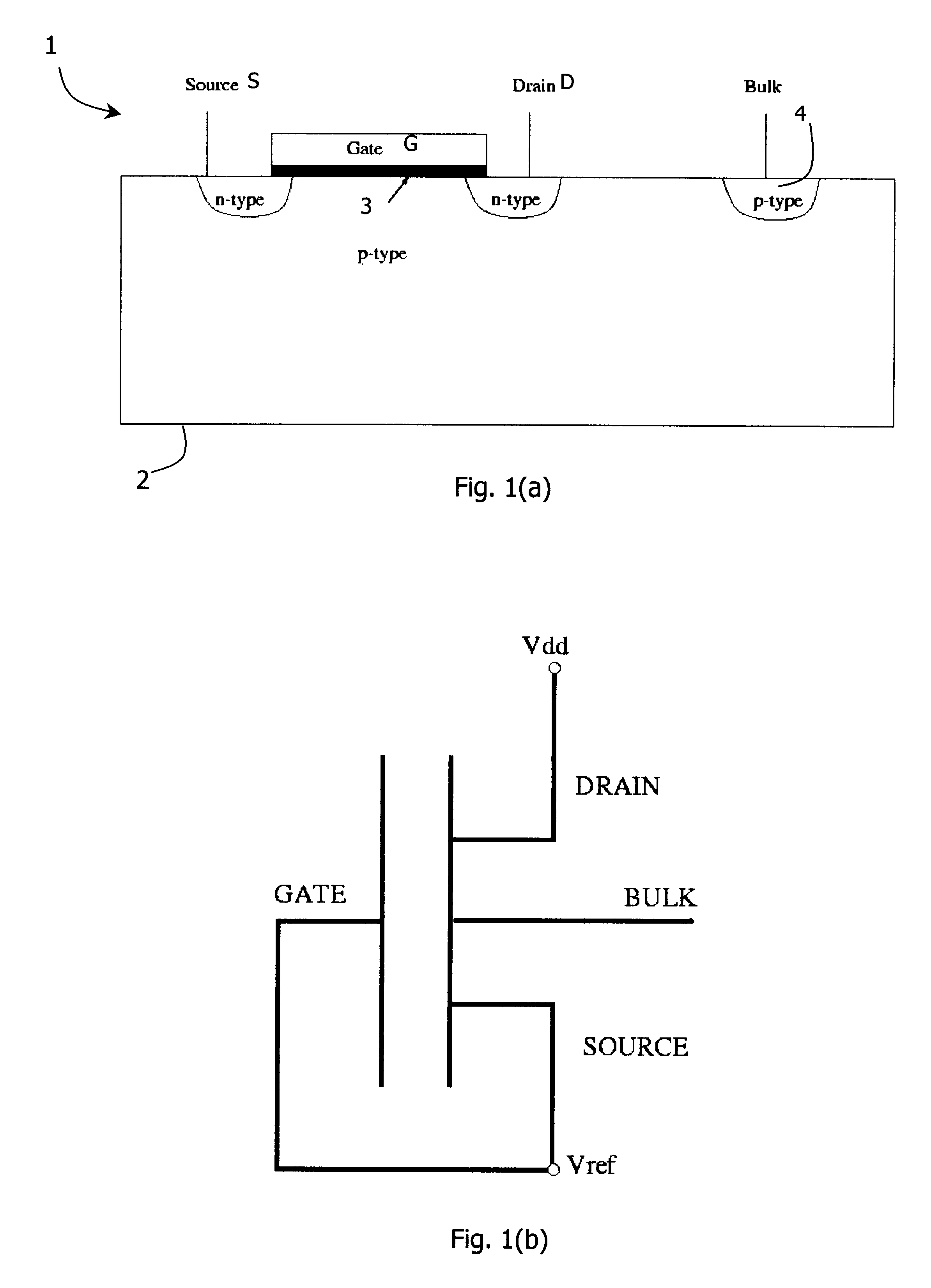
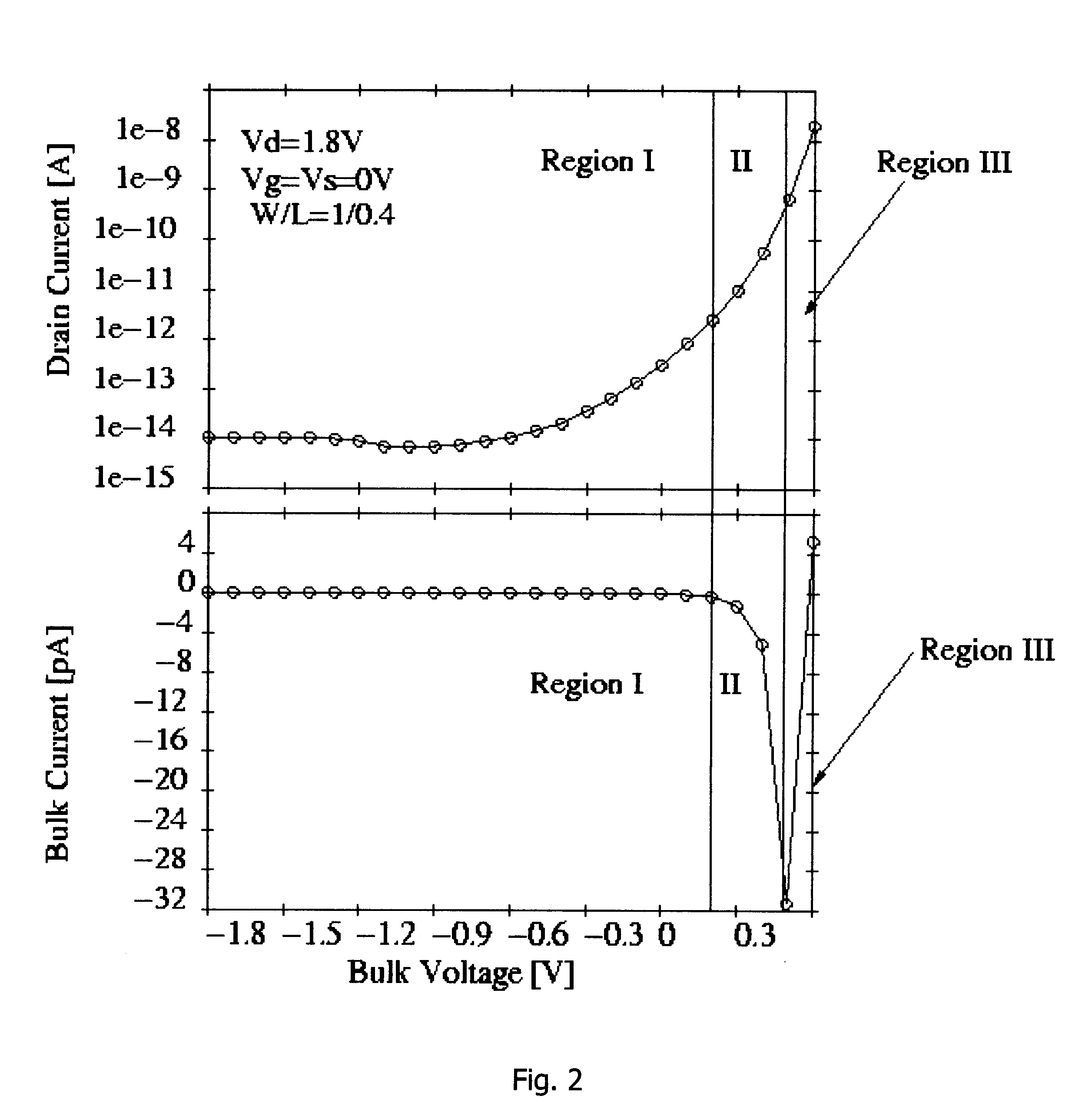
InactiveUS20010005327A1Solid-state devicesDigital storageElectrical resistance and conductanceMOSFET
A negative resistance device (NRD) has a MOSFET-like structure, and is biased by: shorting the gate and source together at a fixed applied potential and applying a different fixed potential to the drain, and sweeping the bulk potential towards the drain potential, causing the bulk current to exhibit a negative resistance characteristic. The NRD may be used in a memory circuit (10) in which a resistor (R) is connected between the bulk (2) and a fixed potential. Two States of the circuit at which the current through the resistor matches that through the bulk of the NRD are stable, providing for bistable memory operation.
Owner:NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF IRELAND
Negative resistance device
A negative resistance device (NRD) has a MOSFET-like structure, and is biased by shorting the gate and source together at a fixed applied potential and applying a different fixed potential to the drain, and sweeping the bulk potential towards the drain potential, causing the bulk current to exhibit a negative resistance characteristic. The NRD may be used in a memory circuit (10) in which a resistor (R) is connected between the bulk (2) and a fixed potential. Two States of the circuit at which the current through the resistor matches that through the bulk of the NRD are stable, providing for bistable memory operation.
Owner:NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF IRELAND
Wick injection of liquids for colloidal propulsion
InactiveUS20030209005A1Cosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusFiberElectric field
Propellant liquid is supplied to a Colloidal Thruster for Micro-Satellite vehicles in Space by capillarity induced flow through a wick element comprising a permeable porous aggregate of fibers or particles of material that is wetted by the propellant liquid. An intense electric field at the tip of the wick element dispersed the arriving liquid into a fine spray of charged droplets. Electrodes having appropriate design, location and potentials accelerate the charge droplets to high velocity, thereby providing reactive thrust to the vehicle. In this method of propellant liquid introduction the flow rate and exhaust velocity, and therefore the thrust level, are determined by the applied potential difference, thereby eliminating the need for pumps or pressurized gas and flow controllers to provide the desired flow-rate for the propellant liquid.
Owner:FENN JOHN BENNETT
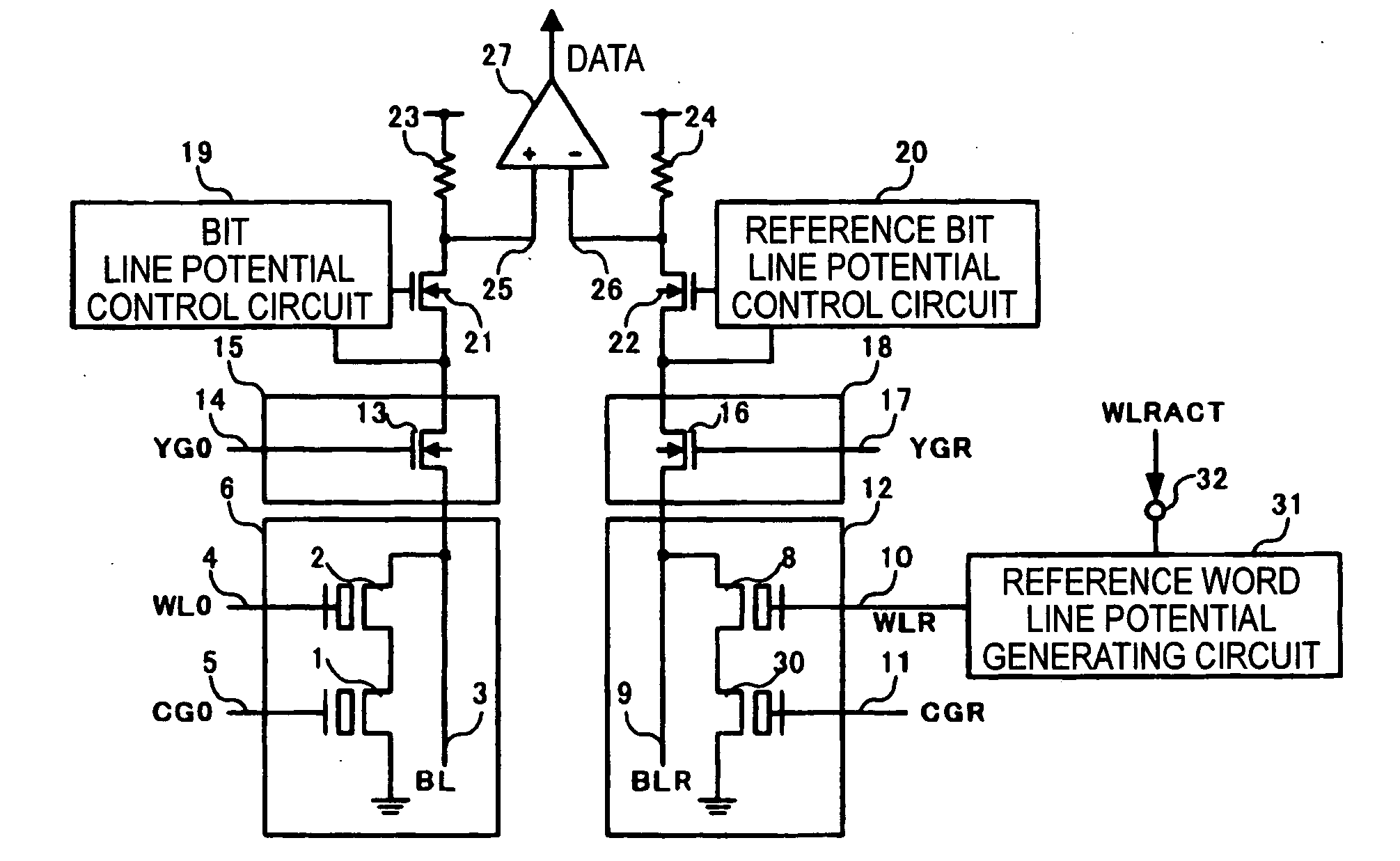
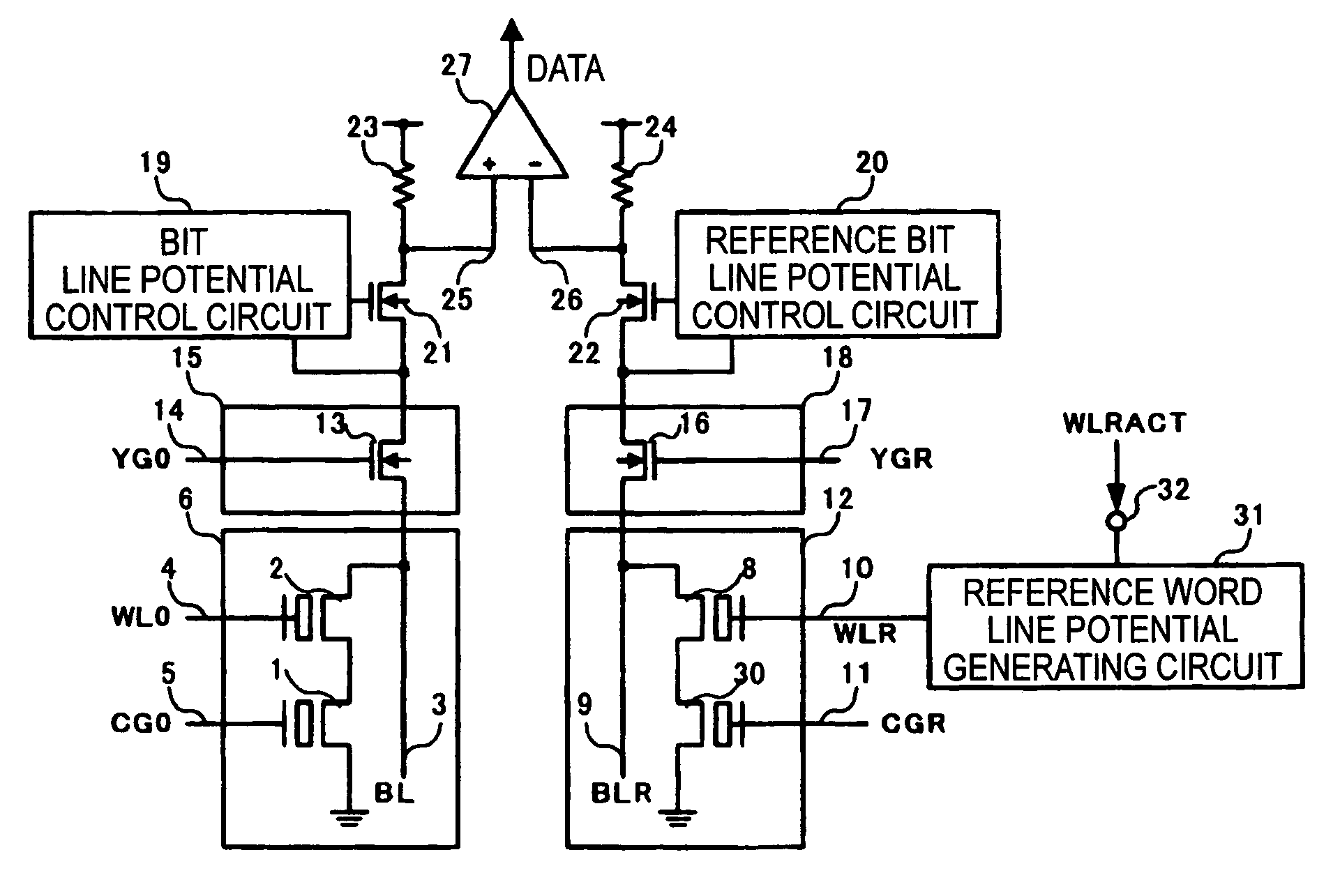
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory
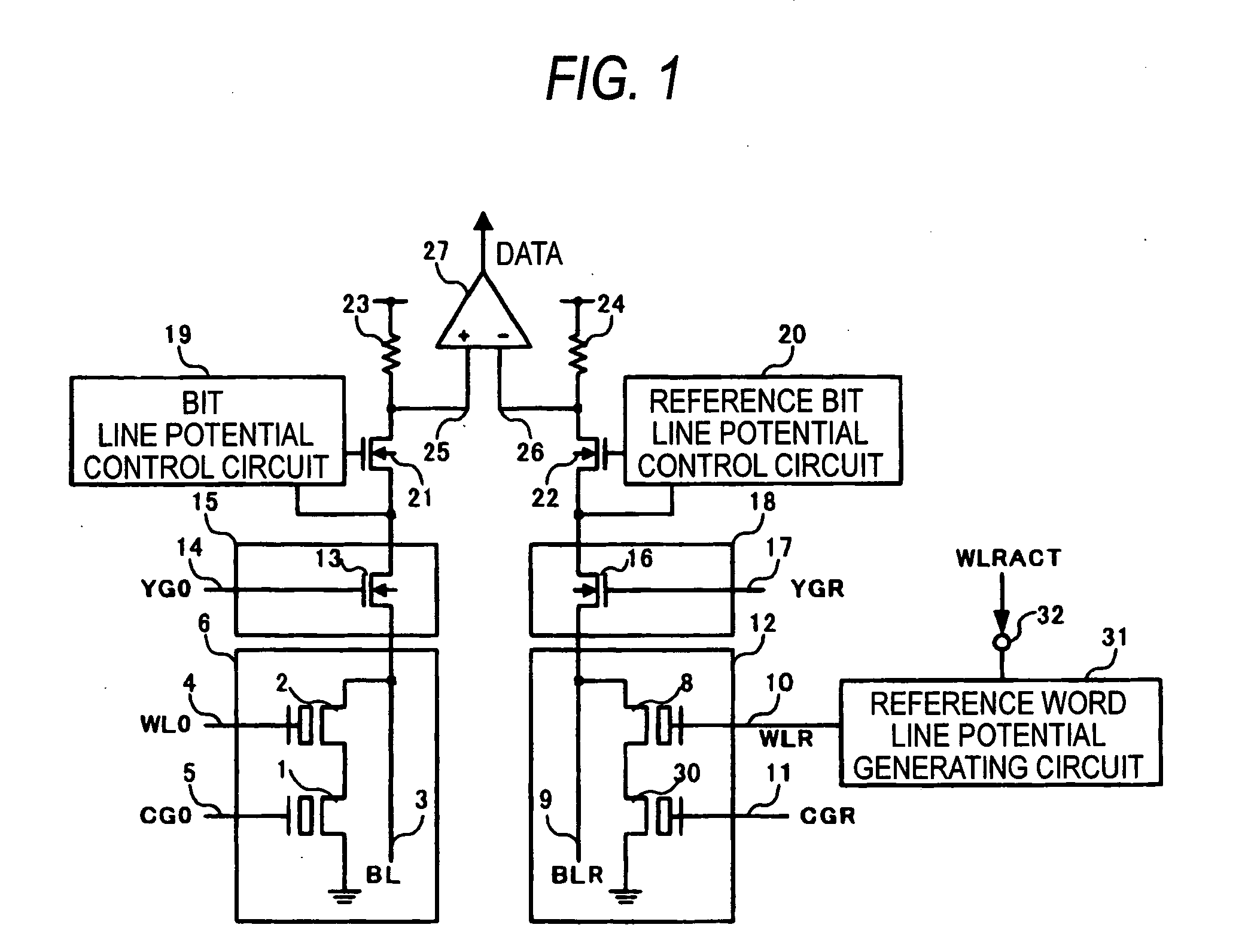
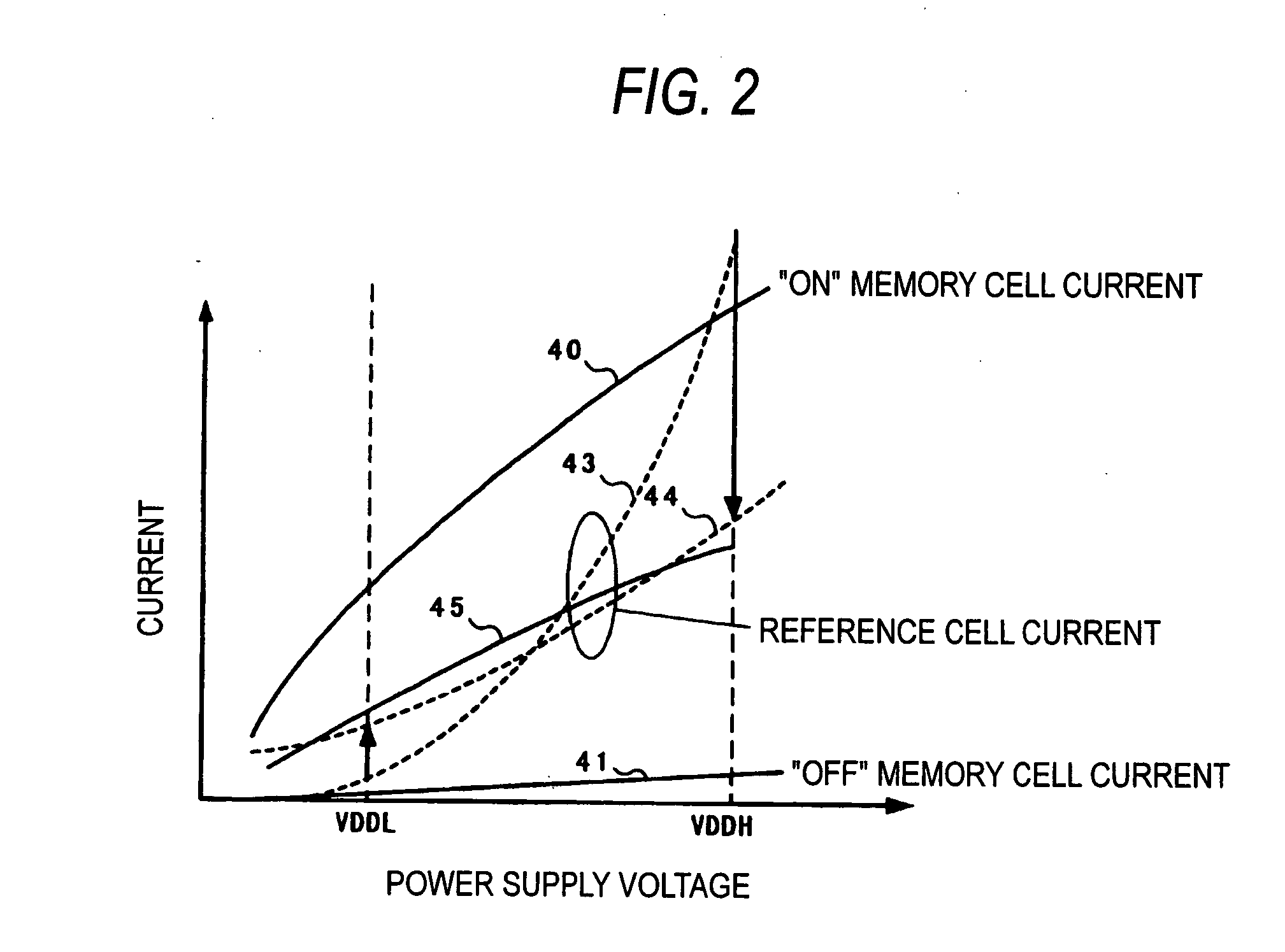
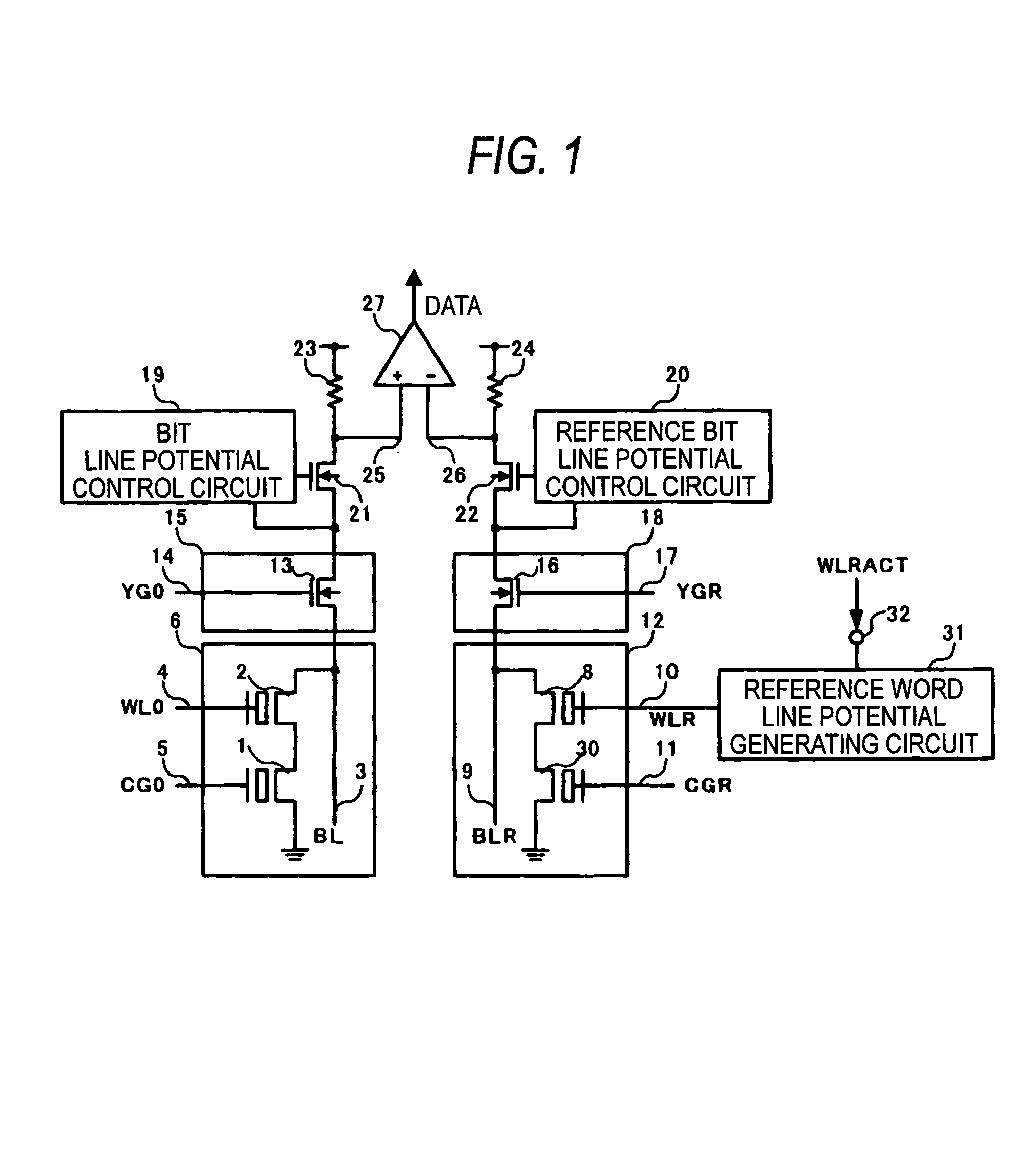
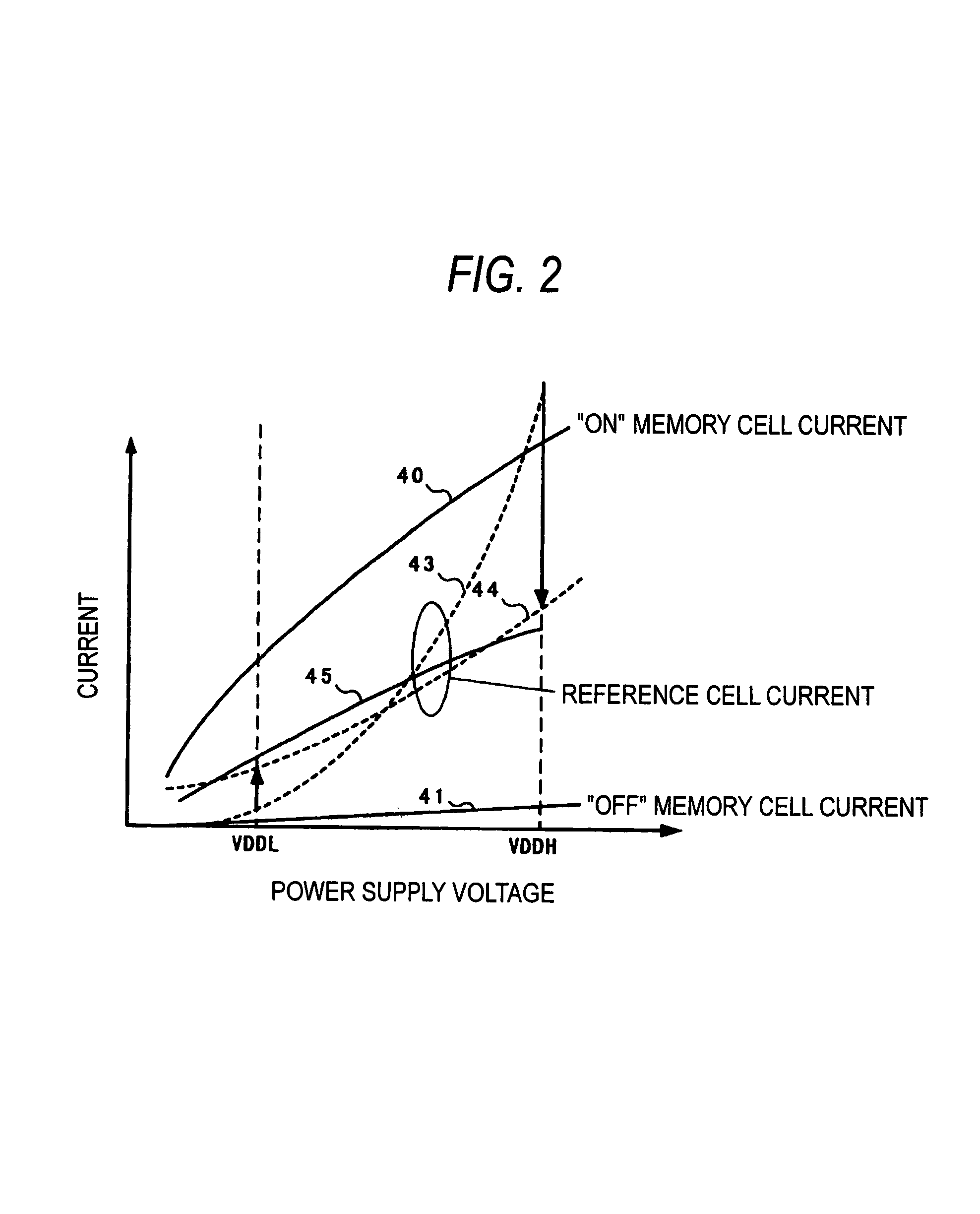
ActiveUS20060083070A1Reduction of production cost increasing factorSuppressing unstable factorsRead-only memoriesDigital storageHemt circuitsApplied potential
A nonvolatile semiconductor memory includes a memory cell 6 composed of a memory cell transistor 1 having a floating gate and a control gate and a memory cell selecting transistor 2, a reference cell 12 composed of a reference cell transistor 30 having the same structure as the memory cell transistor 1 and a reference cell selecting transistor 8, and a reference word line potential generating circuit 31 connected to a gate of the reference cell selecting transistor 8, wherein, in a reading operation, the same power supply voltage is applied between a floating gate and a source node of the reference cell transistor 30, and an intermediate potential between a potential applied when the memory cell selecting transistor 2 is selected and a potential applied when the memory cell selecting transistor 2 is not selected is applied to the gate of the reference cell selecting transistor 8.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
High power-to-mass ratio actuator
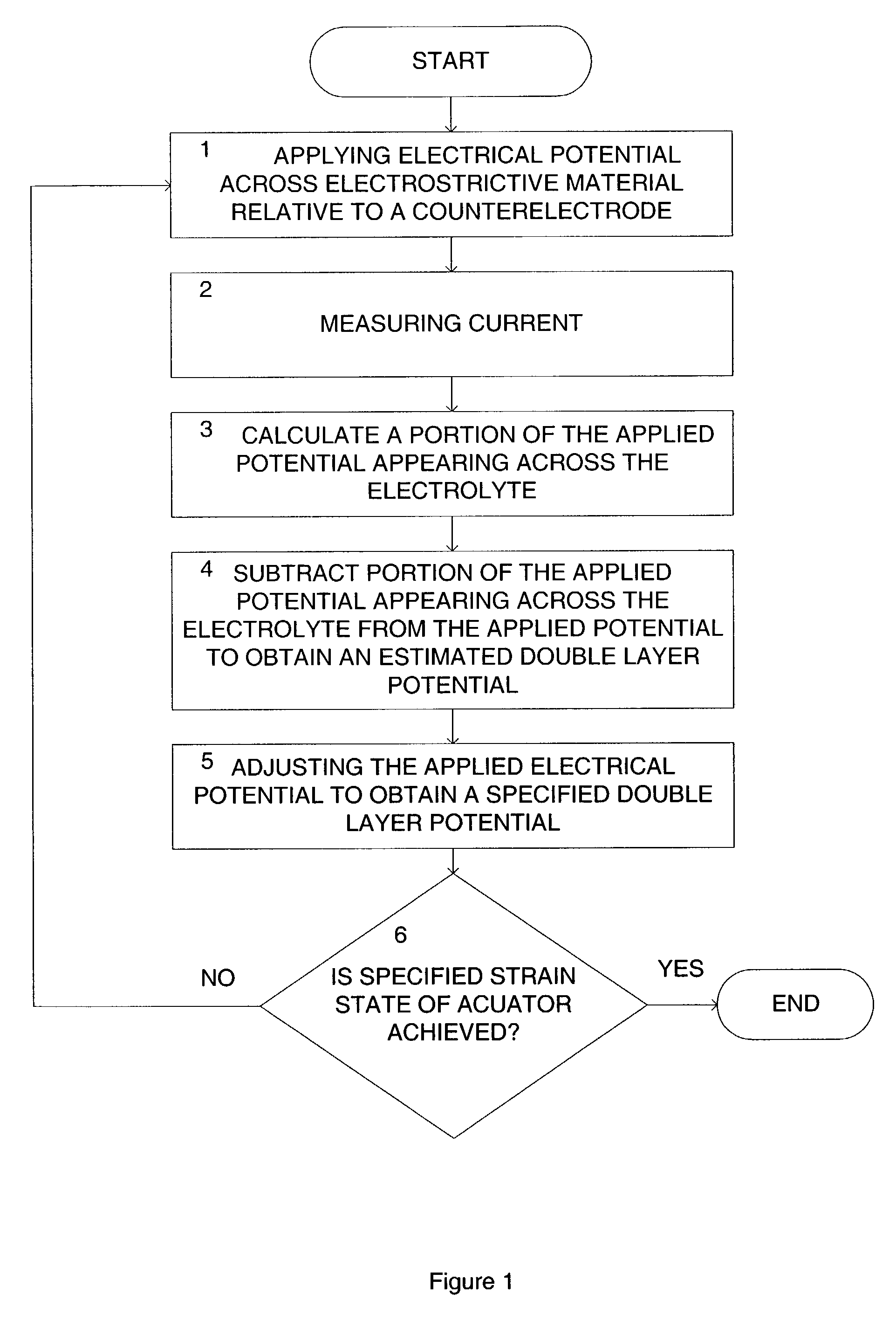
InactiveUS20020195326A1Piezoelectric/electrostrictive device material selectionMachines/enginesElectrolytic agentEngineering
A method for driving an actuator. The method includes applying an electrical potential across an electrostrictive material relative to a counterelectrode disposed within an electrolyte, thereby creating a double layer potential across a region of enhanced ionic concentration. A current flowing between the electorostrictive material and the counterelectrode is measured. A portion of the applied potential appearing across the electrolyte and counterelectrode is calculated and subtracted from the applied potential to obtain an estimated double layer potential. The applied electrical potential is adjusted to obtain a specified double layer potential.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Dual active film electrochromic display device
A dual active electrochromic device is a combination of at least two working electrodes that contain electrochromic materials and at least one counter electrode where the potentials between each working electrode and a counter electrode are independently supplied. No more than one electrode is reflective. The color of the device results from the additive color of the electrochromic materials and varies according to the potentials applied independently. The electrochromic materials can be electrochromic polymers that are deposited as film on substrates to form the working electrodes. The electrochromic device can be used for display or window applications.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Microstructured surface film assembly for liquid acquisition and transprot
InactiveCN1489521AIncrease surface areaEasy to handleMaterial nanotechnologyLayered productsEngineeringAdjacent channel
A film or tape has one of its major surfaces defined by microstructured features including a plurality of channels defined by spaced apart protrusions. The microstructured film is able to acquire liquids and to control the directional transport of such liquids for subsequent removal therefrom. The transport can be passive or active (i.e., caused or enhanced by an applied potential). The inventive microstructured films and tapes have applications in laminate floor assemblies (for spill removal) and industrial articles such as computer keyboards and other devices and assemblies that benefit from fluid removal. The invention also has application in evaporative and condensation applications. In one embodiment, at least one cross-channel is formed on the microstructured surface to join adjacent channels for liquid flow therebetween.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Display
InactiveUS20070211330A1Improve the display effectShort response timeNon-linear opticsOptical elementsPotential differenceDisplay device
A display that has a plurality of charged particles between a pair of substrates and displays images by moving the plurality of charged particles. The display comprises one substrate formed with a pixel electrode; the other substrate that is disposed to face the one surface and is formed with a counter electrode; a plurality of partitions for dividing the gap between the pair of substrates into a plurality of regions; and an insulating layer formed to have an insulating part and openings on the pixel electrode, and displays images by changing the potential difference applied between the pixel electrode and the counter electrode.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Depletion-type NAND flash memory
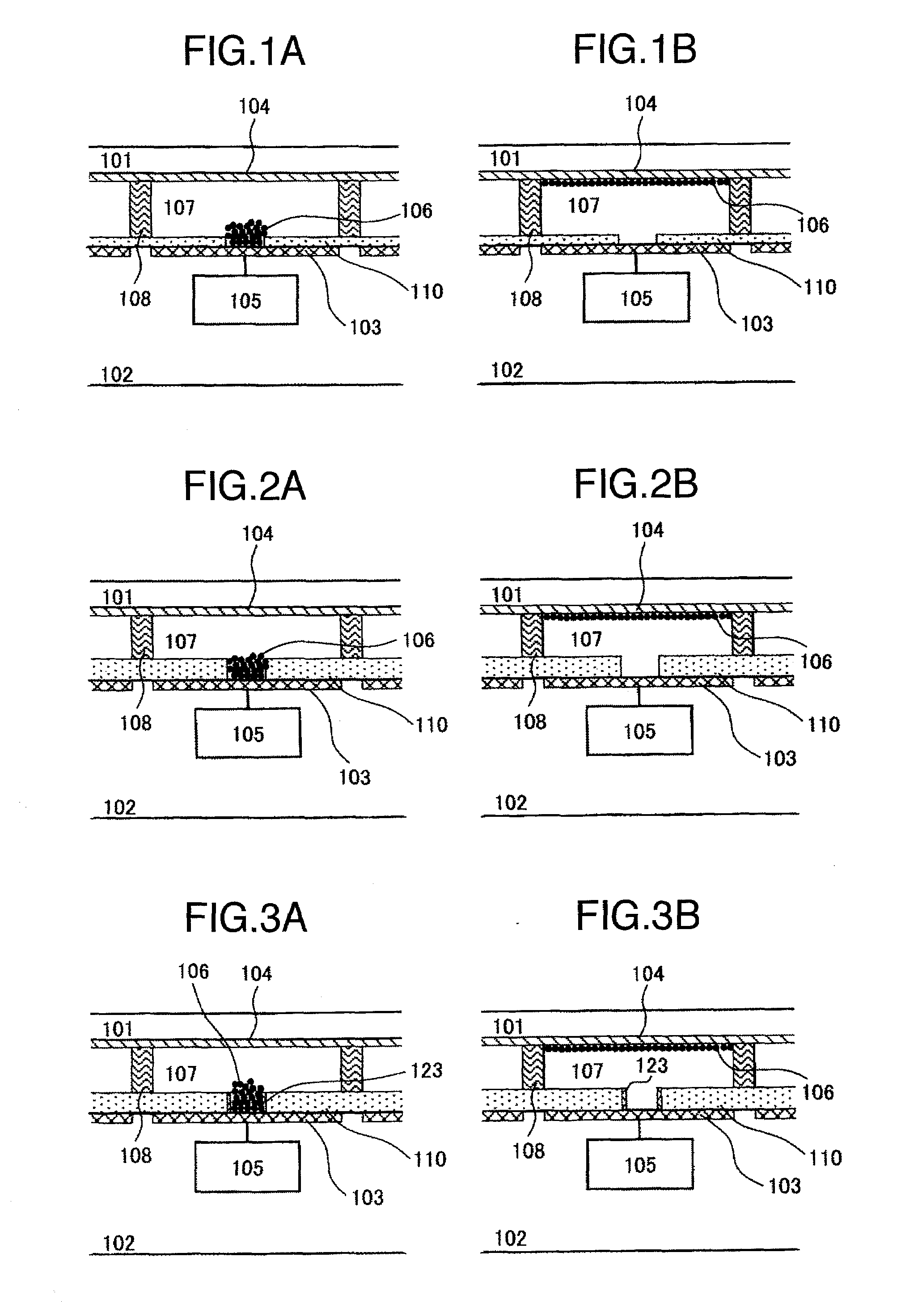
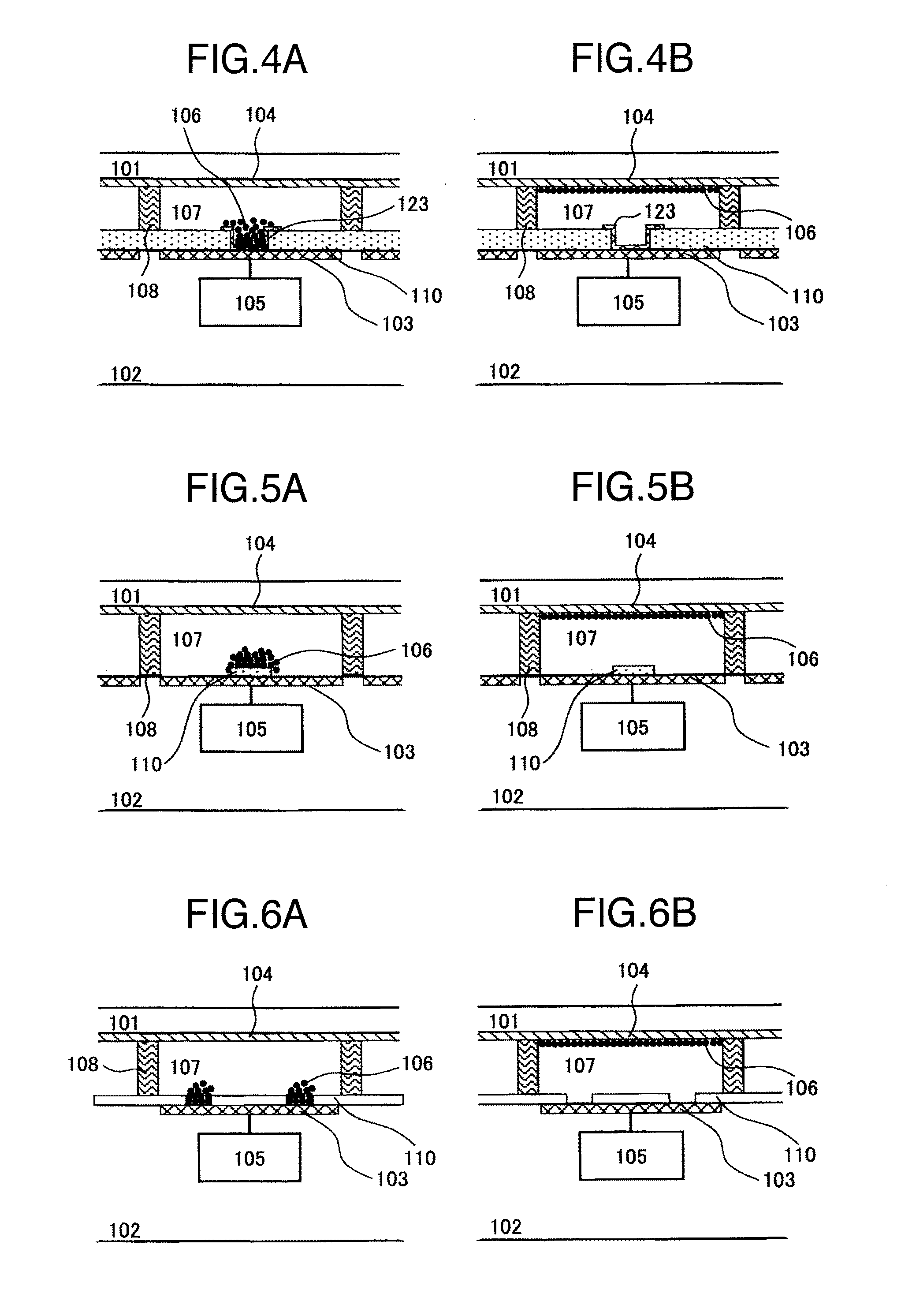
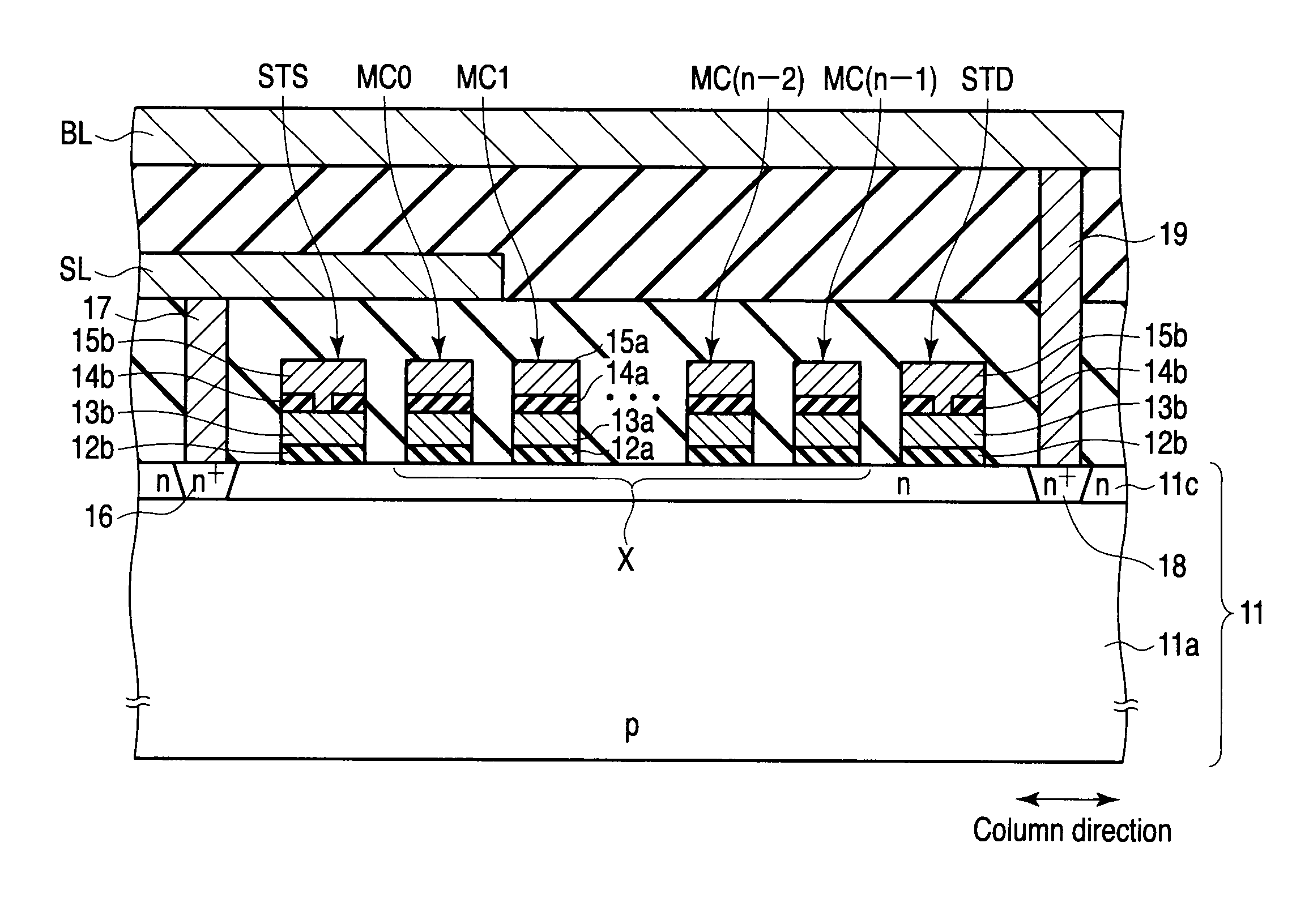
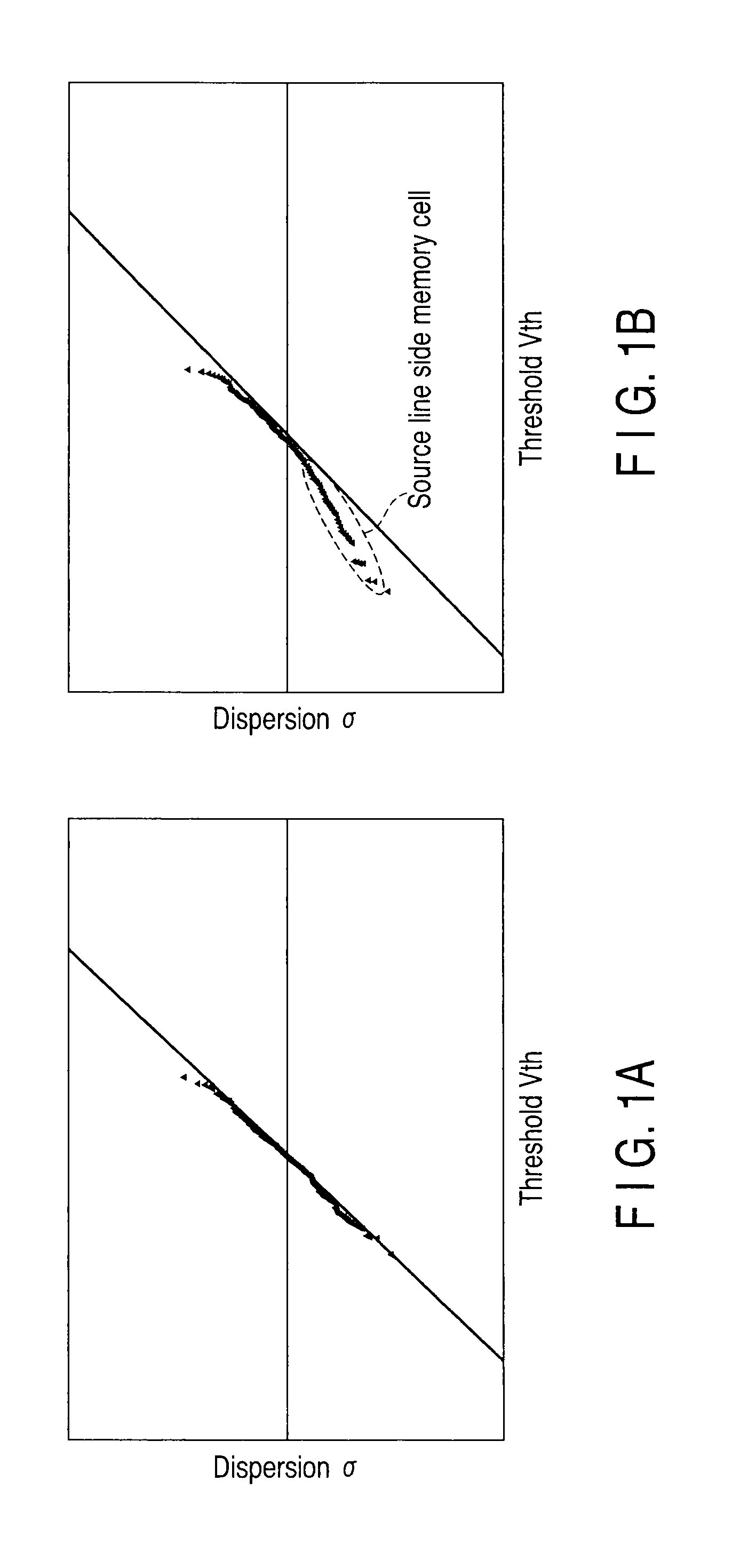
A depletion-type NAND flash memory includes a NAND string composed of a plurality of serially connected FETs, a control circuit which controls gate potentials of the plurality of FETs in a read operation, a particular potential storage, and an adjacent memory cell threshold storage, wherein each of the plurality of FETs is a transistor whose threshold changes in accordance with a charge quantity in a charge accumulation layer, the adjacent memory cell threshold storage stores a threshold of a source line side FET adjacent to a source line side of a selected FET, and the control circuit applies a potential to the gate electrode of the source line side FET in the read operation, the applied potential being obtained by adding a particular potential stored in the particular potential storage to a threshold stored in the adjacent memory cell threshold storage.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Method and apparatus for separating particles by dielectrophoresis
ActiveUS20060290745A1Easy to adjustHigh strengthDielectrophoresisElectrostatic separatorsElectricityPlanar electrode
Methods and apparatus for the micro-scale, dielectrophoretic separation of particles are provided. Fluid suspensions of particles are sorted and separated by dielectrophoretic separation chambers that have at least two consecutive, electrically coupled planar electrodes separated by a gap in a fluid flow channel. The gap distance as well as applied potential can be used to control the dielectrophoretic forces generated. Using consecutive, electrically coupled electrodes rather than electrically coupled opposing electrodes facilitates higher flow volumes and rates. The methods and apparatus can be used, for example, to sort living, damaged, diseased, and / or dead cells and functionalized or ligand-bound polymer beads for subsequent identification and / or analysis.
Owner:CFD RES CORP
Electrochromic material with improved lifetime
ActiveUS20050179012A1High positive charge densityReduce aggregationPhotosensitive materialsDiffusing elementsPotential differenceOxidation-Reduction Agent
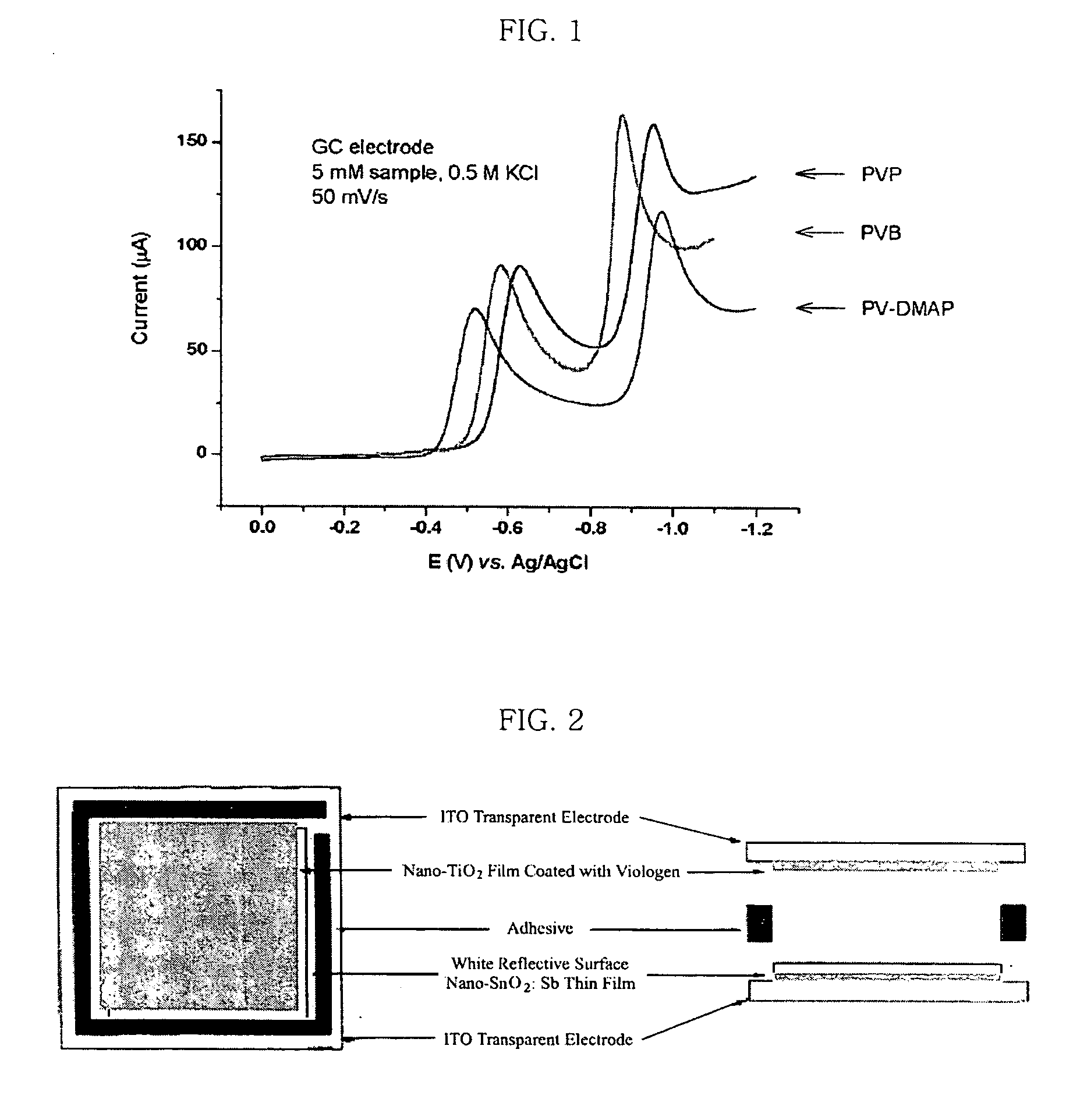
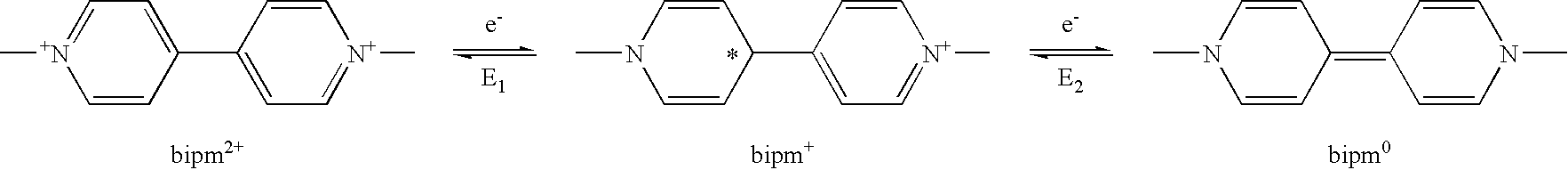
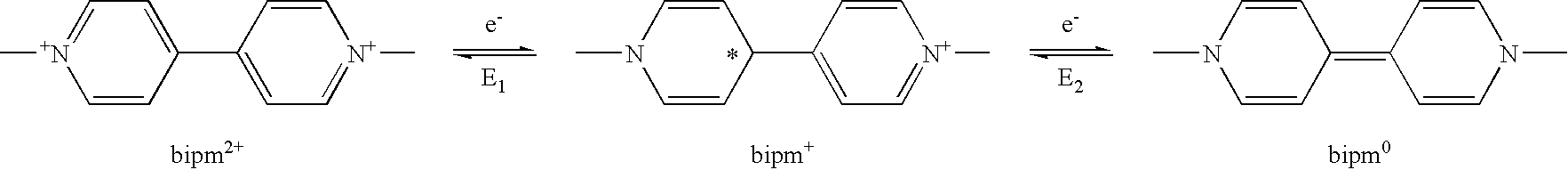
Disclosed are viologen derivatives as an electrochromic material having improved stability and lifetime, a metal oxide electrode including the same, and an electrochromic device using the viologen derivative as an electrochromic material. The viologen derivative includes a suitable regulator group capable of increasing ΔE that is a potential difference between E1 (potential at the first redox reaction) and E2 (potential at the second redox reaction). When ΔE increases, the mole fraction of viologen molecules present in the second reduction state decreases. Therefore, it is possible to lower the mole fraction of viologen molecules present in an irreversibly reduced state at an applied potential, thereby increasing the lifetime of an electrochromic material and an electrochromic device.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Implantable ocular microapparatus to ameliorate glaucoma or an ocular overpressure causing disease
ActiveUS8206440B2Long lastingMinimize power consumptionEye implantsEye surgeryDiseaseIntraocular pressure
A microapparatus (11) implantable in the eye (13) includes a cuasi-bistable microvalve (21) commanded by an intraocular pressure sensor (23) in situ. The microvalve mechanism includes a diaphragm (27) made of a conjugated polymer (29) that shows high deformation and biocompatibility capabilities and which volume depends from the electric potential applied by its pair of electrodes (31). The sensor and actuator-valve are coupled to a drainage conduit (15), the first to deform by the pressure in the ocular globe and the second in a position of buckling to normally close the drainage conduit. The sensor has a membrane of conductive polymeric material with these same properties and whose ohmic resistance varies with the mechanical deformation produced by the ocular pressure.
Owner:CONSEJO NAT DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS Y TECH +1
Method and apparatus for field-emission high-pressure-discharge laser chemical vapor deposition of free-standing structures
InactiveUS20060275537A1Simple structureIncrease ratingsChemical vapor deposition coatingFiberElectricity
A method of growing a free-standing structure, such as a fiber, rod, or tube. A laser beam having is focused on a terminal end of the fiber to heat the terminal end, and at least one gaseous precursor is provided into the beam. At least one electrode is located at a distance from the terminal end. The electrode is in electrical communication with the free-standing structure. A potential is applied between the terminal end and the at least one electrode. The applied potential creates a localized high pressure plasma in the vicinity of the terminal end, and generates reactive species from the gaseous precursor, and accelerates reactive species to the terminal end to grow the free-standing structure at an enhanced rate. An apparatus for growing fibers according to the method is also disclosed.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
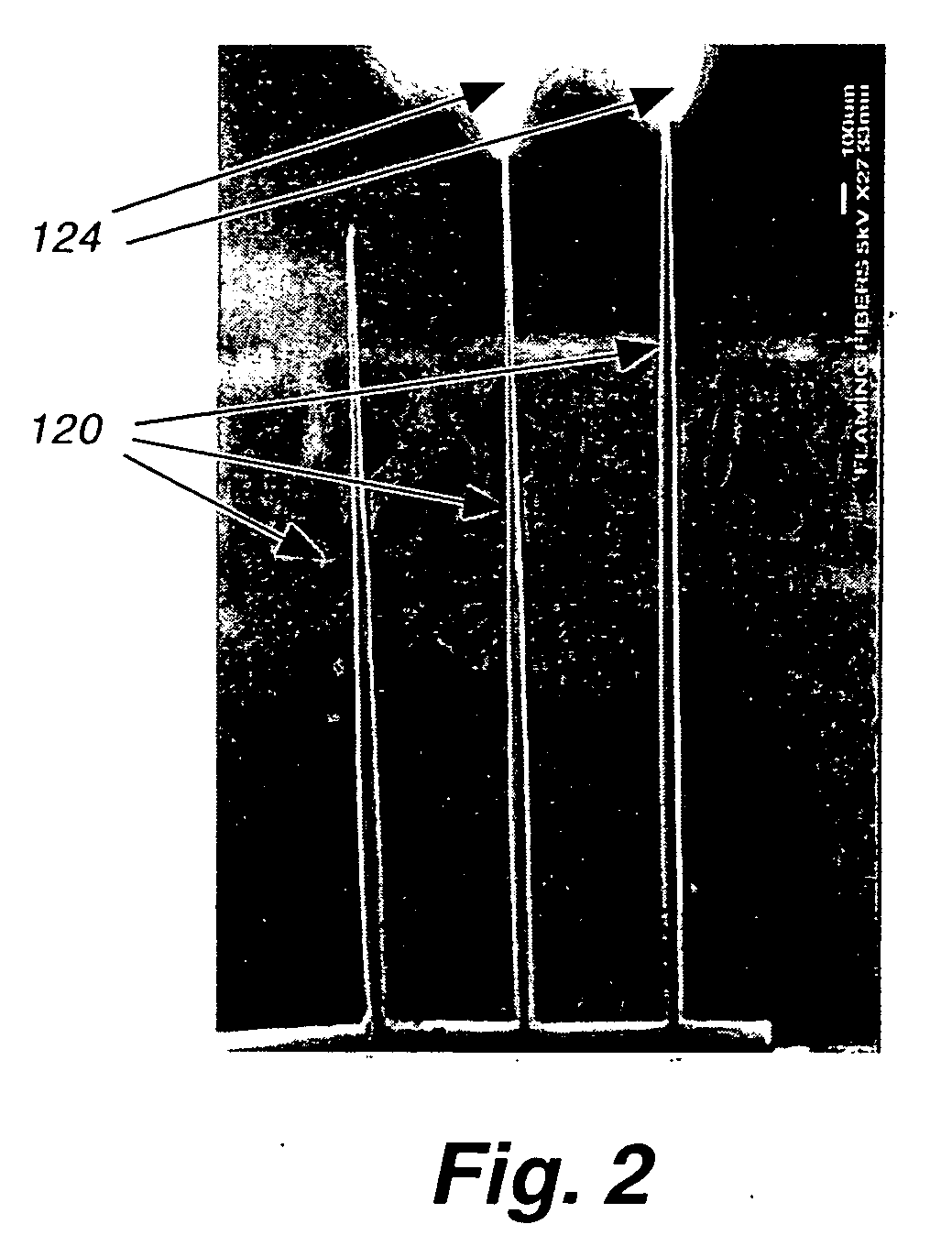
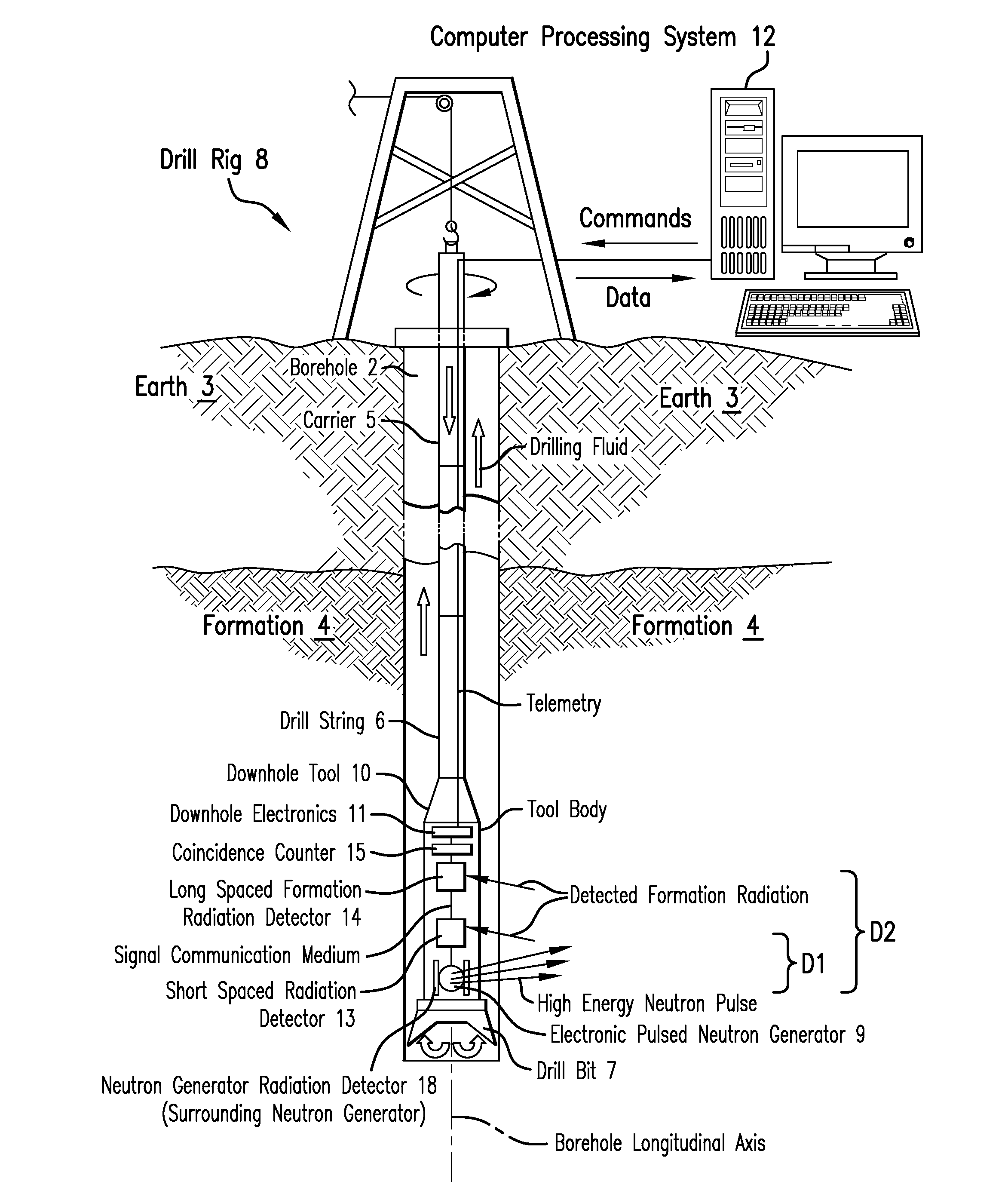
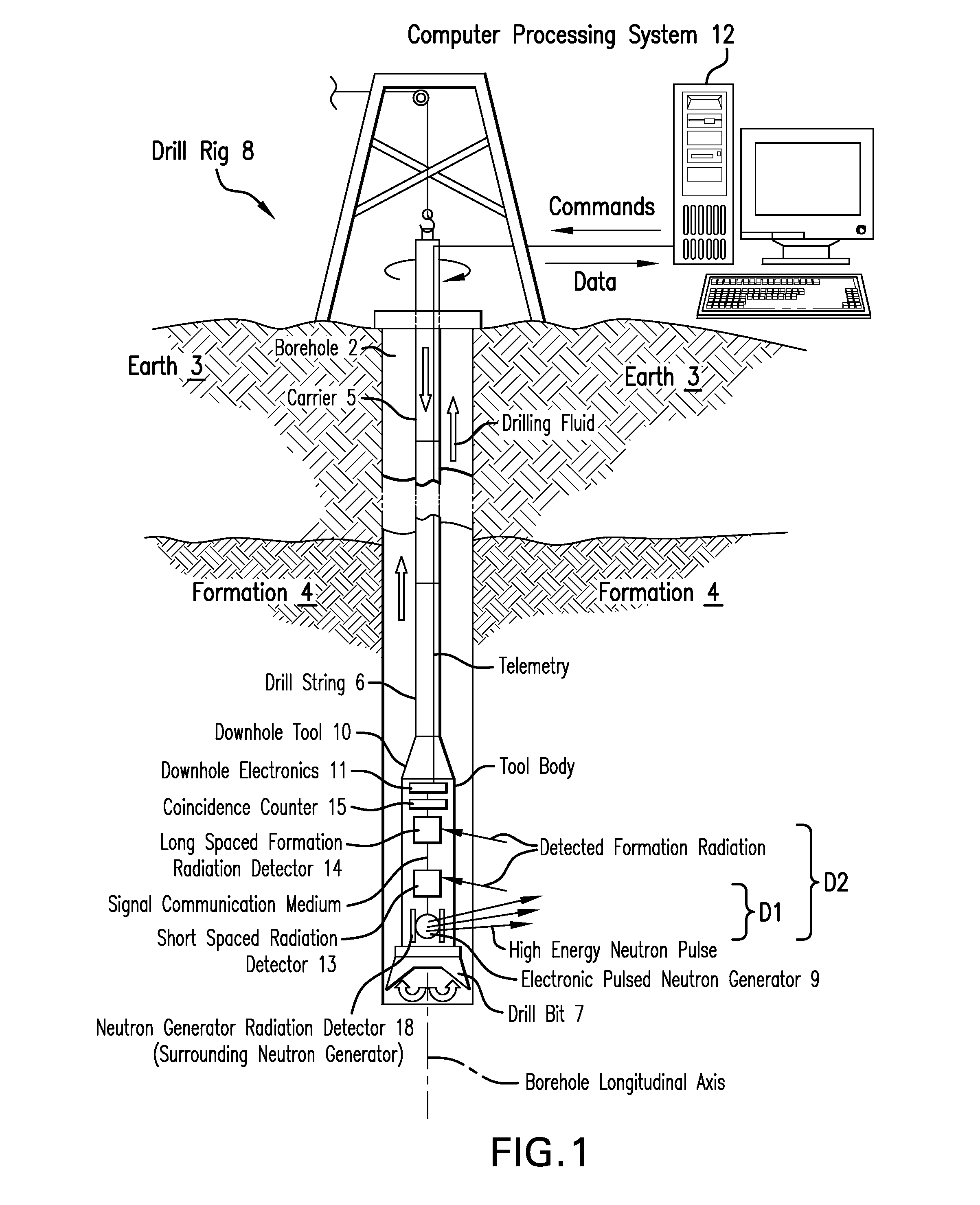
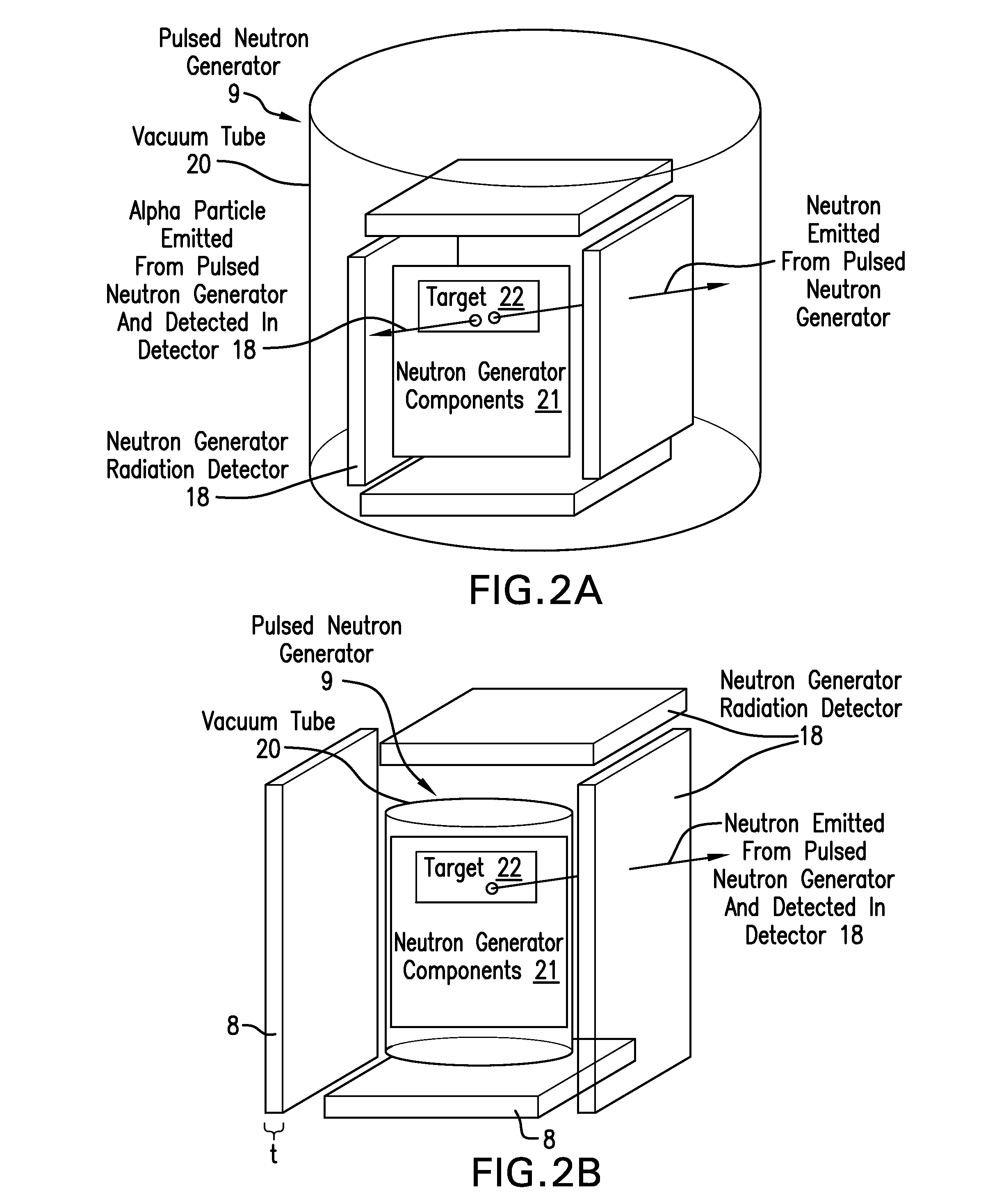
Measurement technique utilizing novel radiation detectors in and near pulsed neutron generator tubes for well logging applications using solid state materials
ActiveUS20150346382A1Measurement with semiconductor devicesNuclear radiation detectionWell loggingCrystal structure
An apparatus for estimating a property of an earth formation includes a pulsed neutron generator configured to emit a pulse of neutrons, a formation radiation detector configured to detect radiation emitted from the formation due to interactions with the pulse of neutrons, and a neutron generator radiation detector having a crystal structure and configured to detect a radiation particle emitted from the pulsed neutron generator and to provide a location within the neutron radiation detector at which the particle was detected. The crystal structure includes a plurality of detection cells, each detection cell having at least two electrically conducting columns with an applied potential difference such that electrons generated in the crystal structure by interaction with the radiation particle are collected by at least one of the electrically conducting columns to provide detection locations. A processor estimates the property using the detected formation radiation and the detection locations.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Electric dust collecting apparatus and manufacturing method of the same
InactiveUS6193788B1Improve workabilityIncrease productivityMetal-working apparatusHeat exchange apparatusElectricityPunch press
An electric dust collecting apparatus includes at least one needle electrode for charging floating particles in air by generating a corona discharge around needle points; at least one collecting electrode provided on cell-liked arrangement corresponding to the needle electrodes, for attracting and collecting the charged floating particles by an electrostatic force; and at least one deflection electrode having a rectangularly hollow longitudinal structure having a front plate portion and side plate portions wherein the needle electrodes are fixed on the front plate portion, for applying a deflection force to the charged floating particles to move toward the collecting electrodes by a potential applied from the side plate portions, and wherein the at least one deflection electrode having the rectangularly hollow longitudinal structure is obtained by bending a profile plate punched up a sheet metal by a predetermined punch press process, accordingly, the plurality of deflection electrodes can be integratedly formed from a profile punched up from a sheet metal by the punching and bending press process, enabling the manufacturing process to have workability and productivity.
Owner:O DEN CORP TOKIO TOKYO
Electrochromic device having a self-cleaning hydrophilic coating with a controlled surface morphology
InactiveUS20050286132A1Reduce manufacturing costEnhances and control characteristicMirrorsOptical viewingHydrophilic coatingOptoelectronics
A variable reflectance rearview mirror for a vehicle, comprising: (a) a variable reflectance mirror element having a reflectivity that varies in response to an applied potential so as to exhibit at least a high reflectance state and a low reflectance state; (b) a self-cleaning, hydrophilic coating applied to a front surface of said mirror element having a controlled surface morphology.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
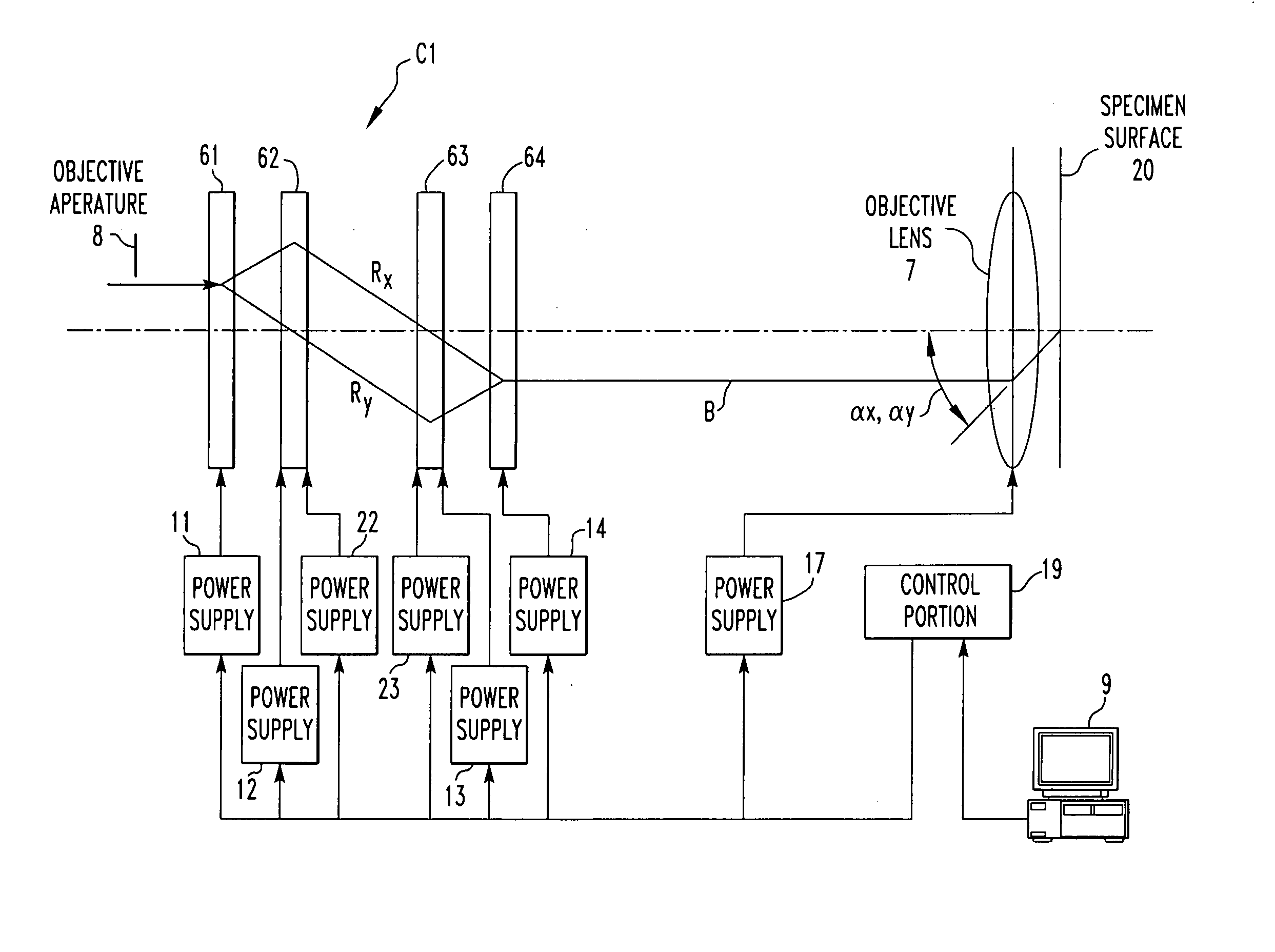
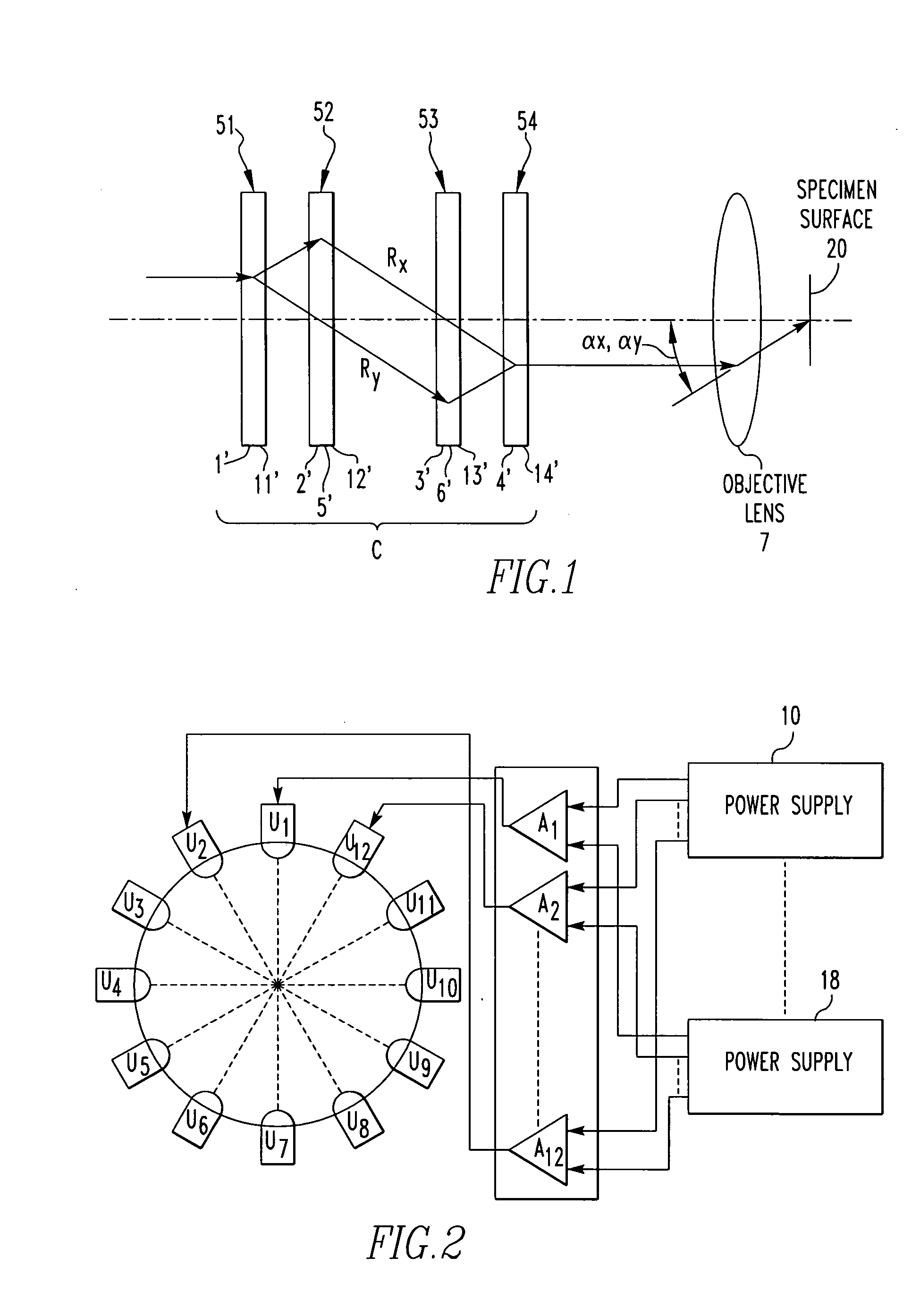
Charged-particle beam instrument and method of correcting aberration therein
ActiveUS20050017194A1Less affected by noiseThermometer detailsStability-of-path spectrometersMagnificationCorrection method
An aberration correction method and charged-particle beam instrument with four stages of multipole units. The two central stages of multipole units function as two stages of magnetic quadrupole components for superimposing a magnetic potential distribution analogous with an applied electric potential distribution on this electric potential distribution. The instrument further includes an objective lens, an objective aperture mounted in the optical path for a beam of charged particles, an operation portion for varying the accelerating voltage or the working distance between the objective lens and a specimen, and a control portion for controlling the multipole units according to an operation of the operation portion. When the accelerating voltage or working distance is varied, the resultant magnification of the four stages of multipole units and objective lens mounted behind the units is adjusted to maintain constant at least one of octupole component-activating potentials for correcting third-order aperture aberrations.
Owner:JEOL LTD
Dual active film electrochromic display device
A dual active electrochromic device is a combination of at least two working electrodes that contain electrochromic materials and at least one counter electrode where the potentials between each working electrode and a counter electrode are independently supplied. No more than one electrode is reflective. The color of the device results from the additive color of the electrochromic materials and varies according to the potentials applied independently. The electrochromic materials can be electrochromic polymers that are deposited as film on substrates to form the working electrodes. The electrochromic device can be used for display or window applications.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
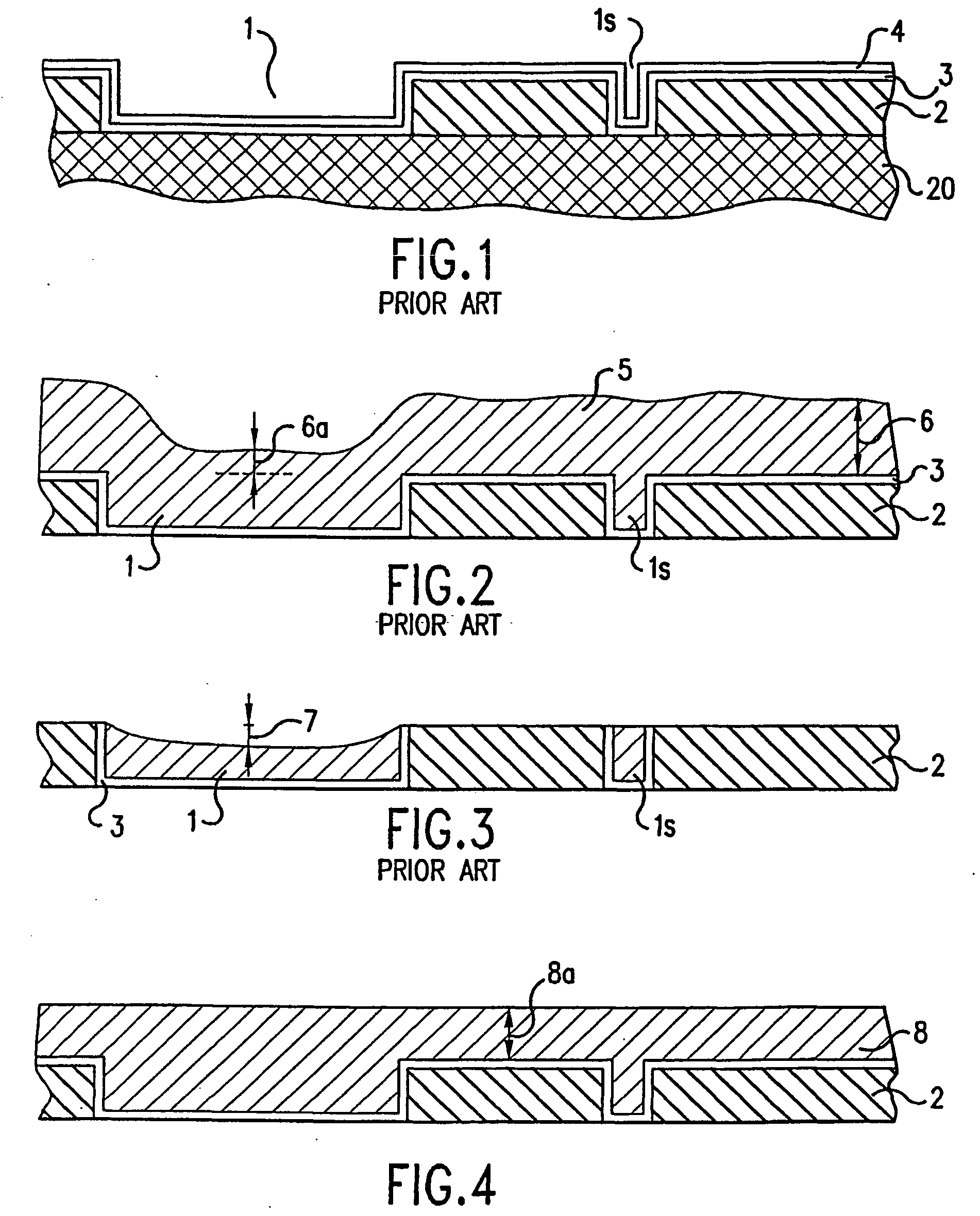
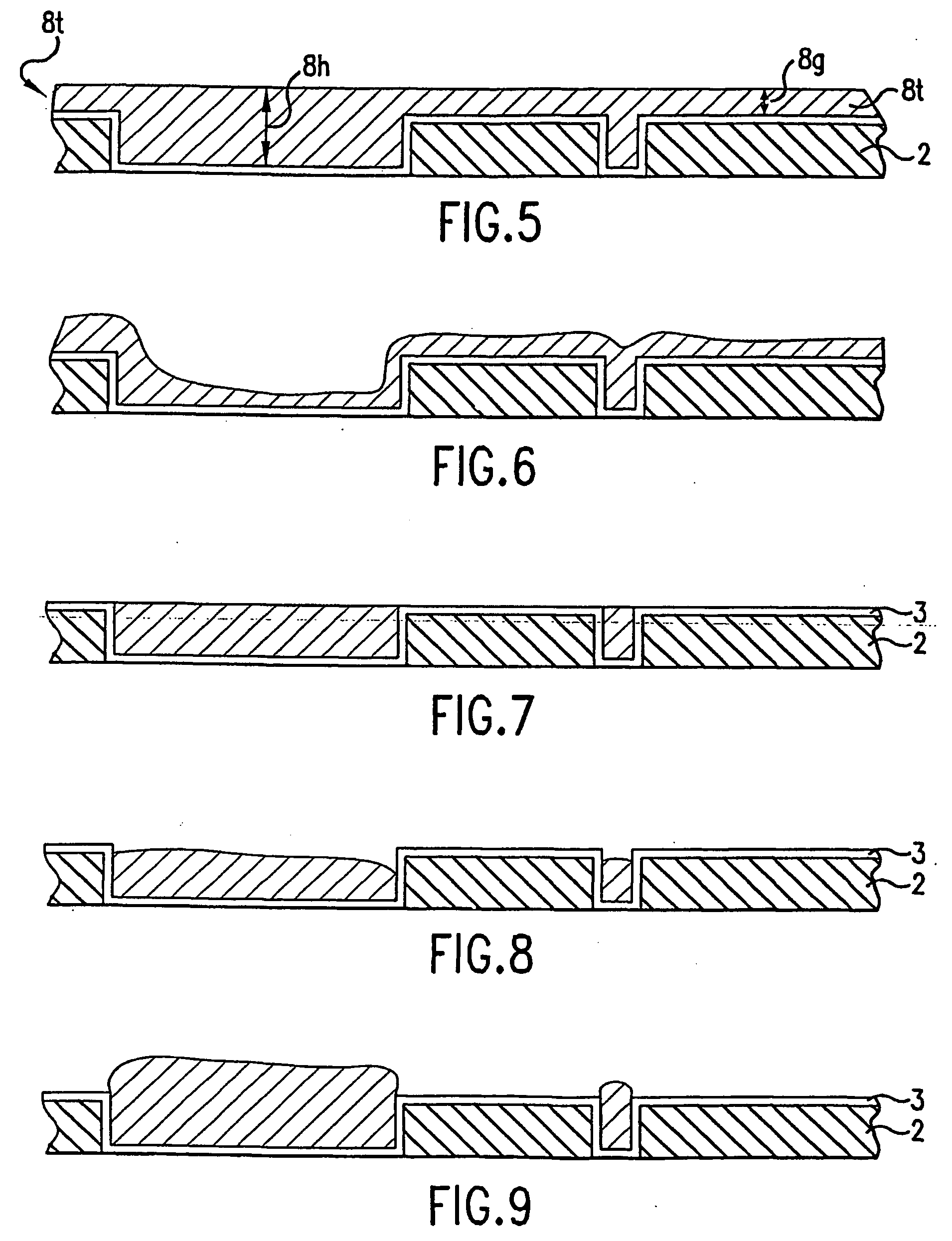
Process to minimize and/or eliminate conductive material coating over the top surface of a patterned substrate
InactiveUS20060118425A1Thickness minimizationEliminate the problemSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPrinted circuit manufactureIntegrated circuitApplied potential
A layer structure usable in manufacturing an integrated circuit is made, in a single apparatus, by a particular process in which a patterned substrate is provided. An electrolyte solution, out of which a conductive material can be plated under an applied potential, is supplied over a surface of the patterned substrate, and a potential is applied so as to deposit a film of the conductive material out of the electrolyte solution and over the surface of the patterned substrate. The film of conductive material is preferably polished as it is deposited. The conductive material is then removed from field regions of the patterned substrate, while deposits of the conductive material are left in features defined in the patterned substrate. The deposits of the conductive material are then electrically isolated, resulting in the layer structure.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory
ActiveUS7164604B2Suppressing unstable factorsLow production costRead-only memoriesDigital storageHemt circuitsApplied potential
A nonvolatile semiconductor memory includes a memory cell 6 composed of a memory cell transistor 1 having a floating gate and a control gate and a memory cell selecting transistor 2, a reference cell 12 composed of a reference cell transistor 30 having the same structure as the memory cell transistor 1 and a reference cell selecting transistor 8, and a reference word line potential generating circuit 31 connected to a gate of the reference cell selecting transistor 8, wherein, in a reading operation, the same power supply voltage is applied between a floating gate and a source node of the reference cell transistor 30, and an intermediate potential between a potential applied when the memory cell selecting transistor 2 is selected and a potential applied when the memory cell selecting transistor 2 is not selected is applied to the gate of the reference cell selecting transistor 8.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
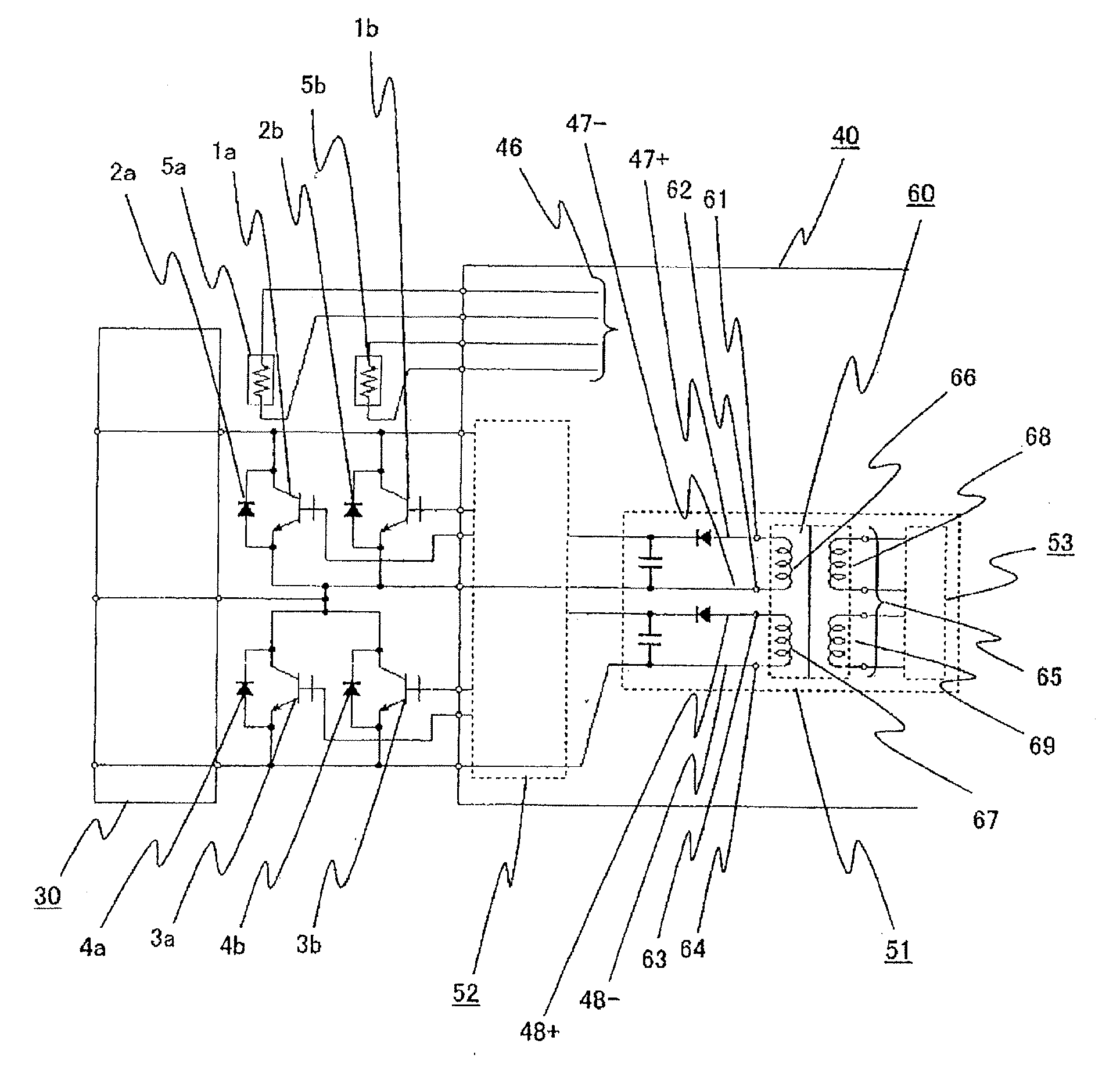
Power Converter
ActiveUS20120320645A1Reduce lossesImprove noise immunityConversion constructional detailsDc-dc conversionElectrical conductorTransformer
A power converter which has a power module allowing supply and cutoff of main current, and a driver module controlling supply and cutoff of the main current allowed by the power module includes: a high potential side semiconductor device which allows supply and cutoff of the main current on the high potential side of the power module; a low potential side semiconductor device which allows supply and cutoff of the main current on the low potential side of the power module, and is connected with the high potential side semiconductor device in series; plural power module side wirings connected with respective electrodes contained in the high potential side semiconductor device and the low potential side semiconductor device, and disposed adjacent to each other substantially on the same plane as the power module in the order of applied potentials with a connection end between the plural power module side wirings and the driver module located along the end of the power module; plural driver module side wirings provided on the driver module as wirings connected with the plural corresponding power module side wirings, and disposed adjacent to each other substantially on the same plane as the driver module in the order corresponding to the positions of the plural power module side wirings in positions along the end of the driver module; a power source transformer as a circuit which converts a signal voltage for controlling the supply and cutoff of the main current by the driver module into voltage applied to a control electrode of the high potential side semiconductor device and a control electrode of the low potential side semiconductor device, plural terminals of the power source transformer in correspondence with the plural driver module side wirings being provided in the order of the positions of the plural corresponding driver module side wirings; and conductors disposed in the vicinity of the plane on which the plural power module side wirings are provided and in the vicinity of the plane on which the plural driver module side wirings are provided, and electrically connected in such positions as to surround magnetic flux generated by current looping at least through the power source transformer, the driver module side wirings, and the power module side wirings.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Remote sensed pre-amplifier for cross-point arrays
ActiveUS20050169034A1Minimize the differenceRead-only memoriesDigital storageElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
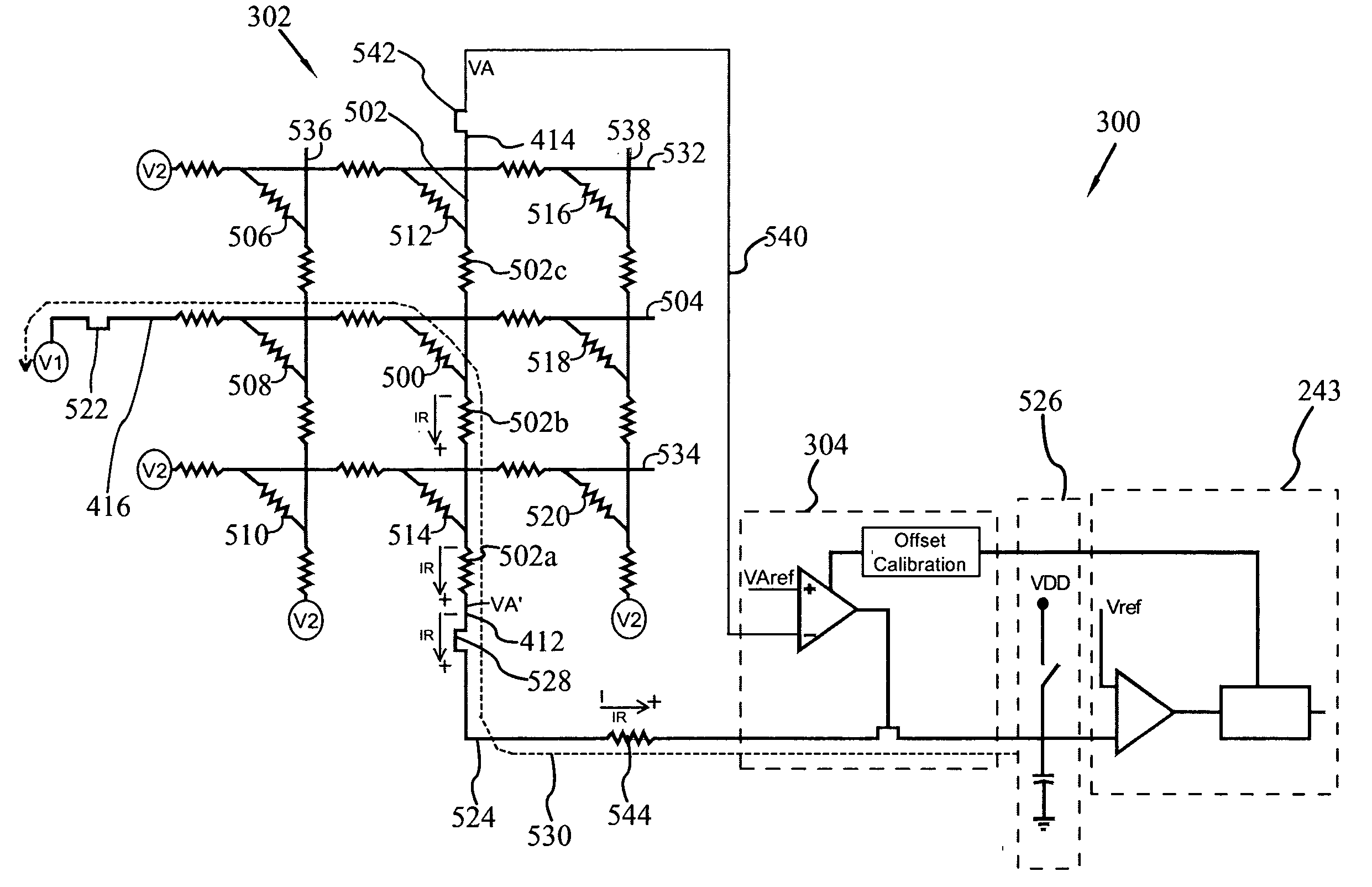
This invention provides a remote sensed pre-amplifier for cross-point arrays. In a particular embodiment, there are a plurality of parallel electrically conductive rows and a plurality of parallel electrically conductive columns crossing the rows, thereby forming a cross-point array with a plurality of intersections. Resistive devices, such as magnetic memory cells, also known as spin valve memory cells, are provided in electrical contact with and located at each intersection. A feedback controlled sense pre-amplifier is also provided to maintain an equi-potential for a given memory cell. A reference voltage is provided to the sense pre-amplifier. As voltage potential, VA′, is provided to the first end of a selected column, contacting a selected memory cell, a feedback voltage VA is provided to the sense pre-amplifier by an independent sense path. The independent sense path connects to the second end of the selected column. The sense pre-amplifier adjusts the applied potential VA to minimize the difference between the feedback and reference voltage. An associated method of use is further provided.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Process for forming coatings on metallic bodies and an apparatus for carrying out the process
InactiveUS20030094377A1Protect the surfaceEconomical and simpleCellsAnodisationCeramic compositeVolumetric Mass Density
This invention disclosed in this application relates to a process for forming oxide based dense ceramic composite coatings on reactive metal and alloy bodies. The process involves suspension of at least two reactive metal or alloy bodies in a non-metallic, non-conducting, non-reactive chamber in such a way that it causes either partial or full immersion of the said bodies in a continuously circulating electrolyte. Thyristor controlled, modified shaped wave multiphase alternating current power supply is applied across the said bodies where in each body is connected to an electrode. Electric current supplied to the said bodies where in each body is connected to an electrode. Electric current supplied to the said bodies is slowly increased to a particular value till the required current density is achieved and the maintained at the same level throughout the process. Visible arcing at the surface of the immersed regions of the said bodies is identified when the applied electric potential crosses 60V. Electric potential is furthr increased gradually to compensate the increasing resistance of the coating. Electrolyte composition is regulated through the changes in pH and conductivity of the electrolytic solution. Thickness of the coating formed on the said bodies is monitored by the time for which the electrical power at constant current density is supplied to the said bodies. The invention also relates to an apparatus for carrying out the above defined process. The coatings obtained according to the present invention are found to exhibit higher density and excellent wear resistance.
Owner:M S INT ADVANCED RES CENT FOR POWDER METALLURGY & NEW METERIALS ARCI
Anode electrode for aluminum electrolytic capacitor and respective production method
ActiveUS20150062782A1Increase the effective surfaceSurface factorLiquid electrolytic capacitorsElectrolytic capacitor manufactureIonic liquidApplied potential
An aluminum electrolytic capacitor including an anode electrode, and a method for producing the anode electrode. The method includes providing an aluminum electrolyte including an ionic liquid and an aluminum salt, galvanically deposing an aluminum on an aluminum foil formed from the aluminum electrolyte, and anodically oxidizing a surface of the aluminum foil. The ionic liquid includes a pyrrolidinium cation and a halogenide. The aluminum electrolyte includes 50-70 mol. % of the aluminum salt based on a total substance amount of the ionic liquid and the aluminum salt. The galvanic deposition includes and is based on a deposition temperature ranging from 20° C. to 100° C., a current density ranging from 1 to 100 mA / cm2, an applied potential ranging from −0.1V to −1.0 V based on a potential of an aluminum reference electrode, and a deposition rate ranging from 1 to 50 μm / h.
Owner:MICRO ENERGY TECHNOLOGIES GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com