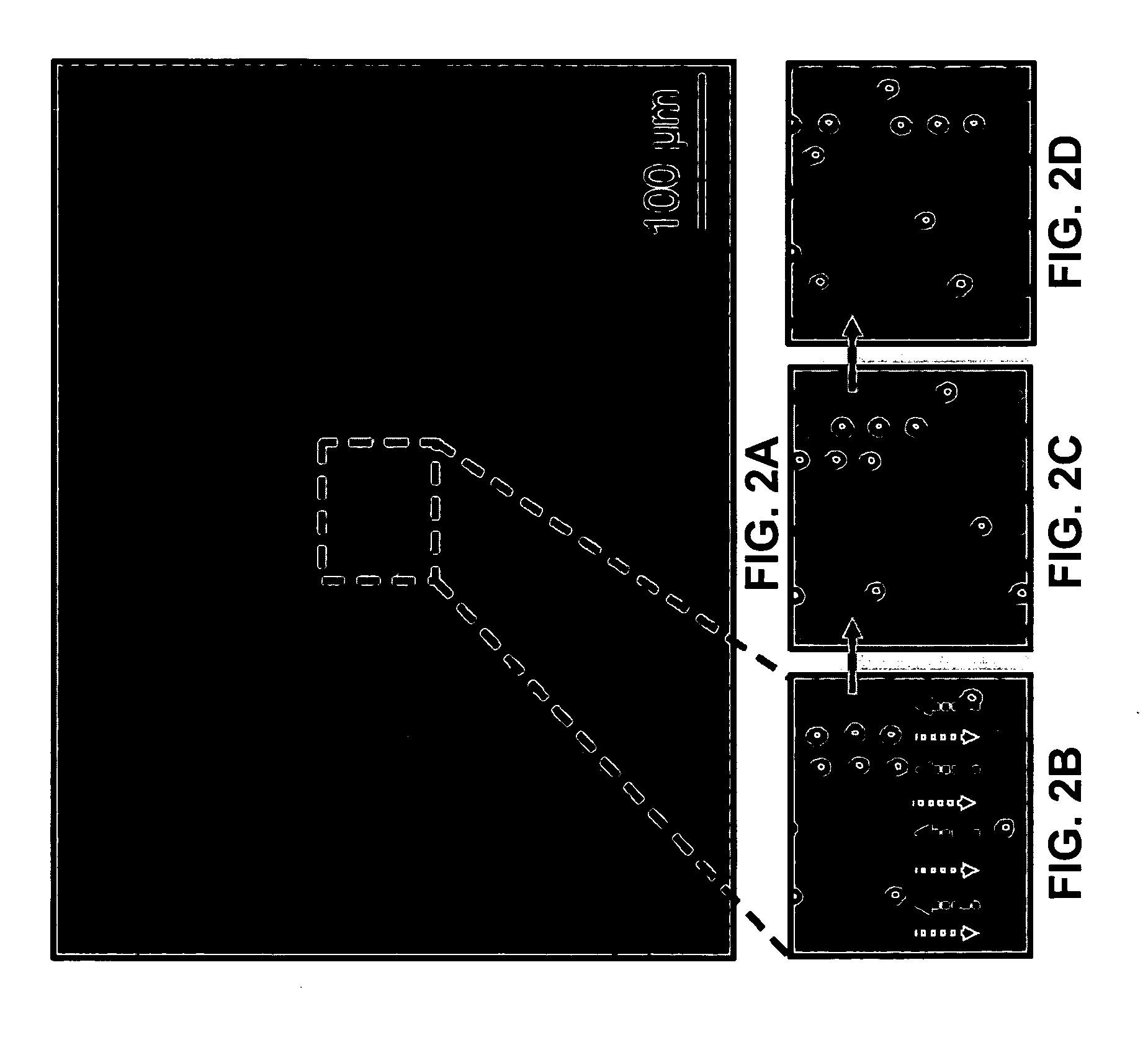
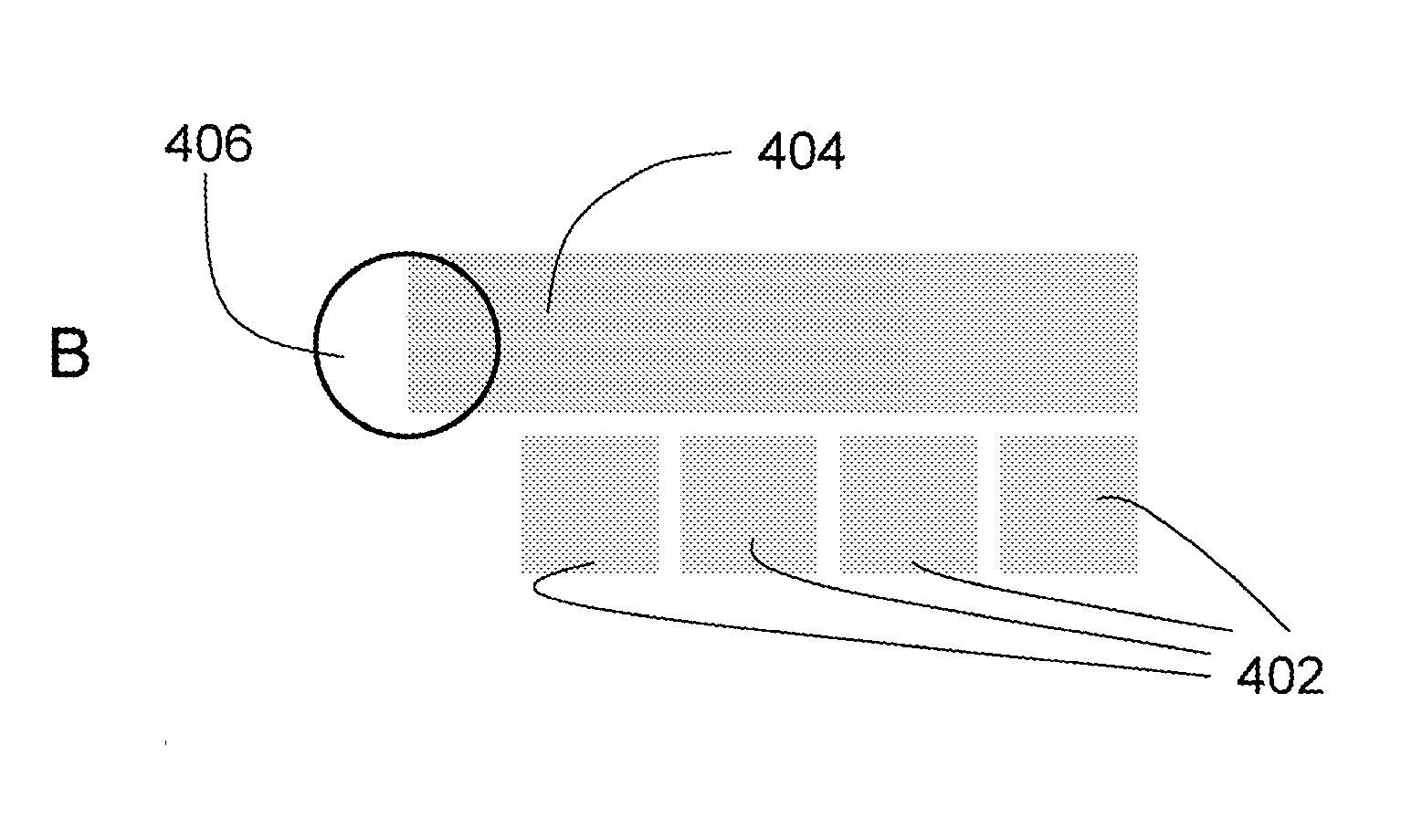
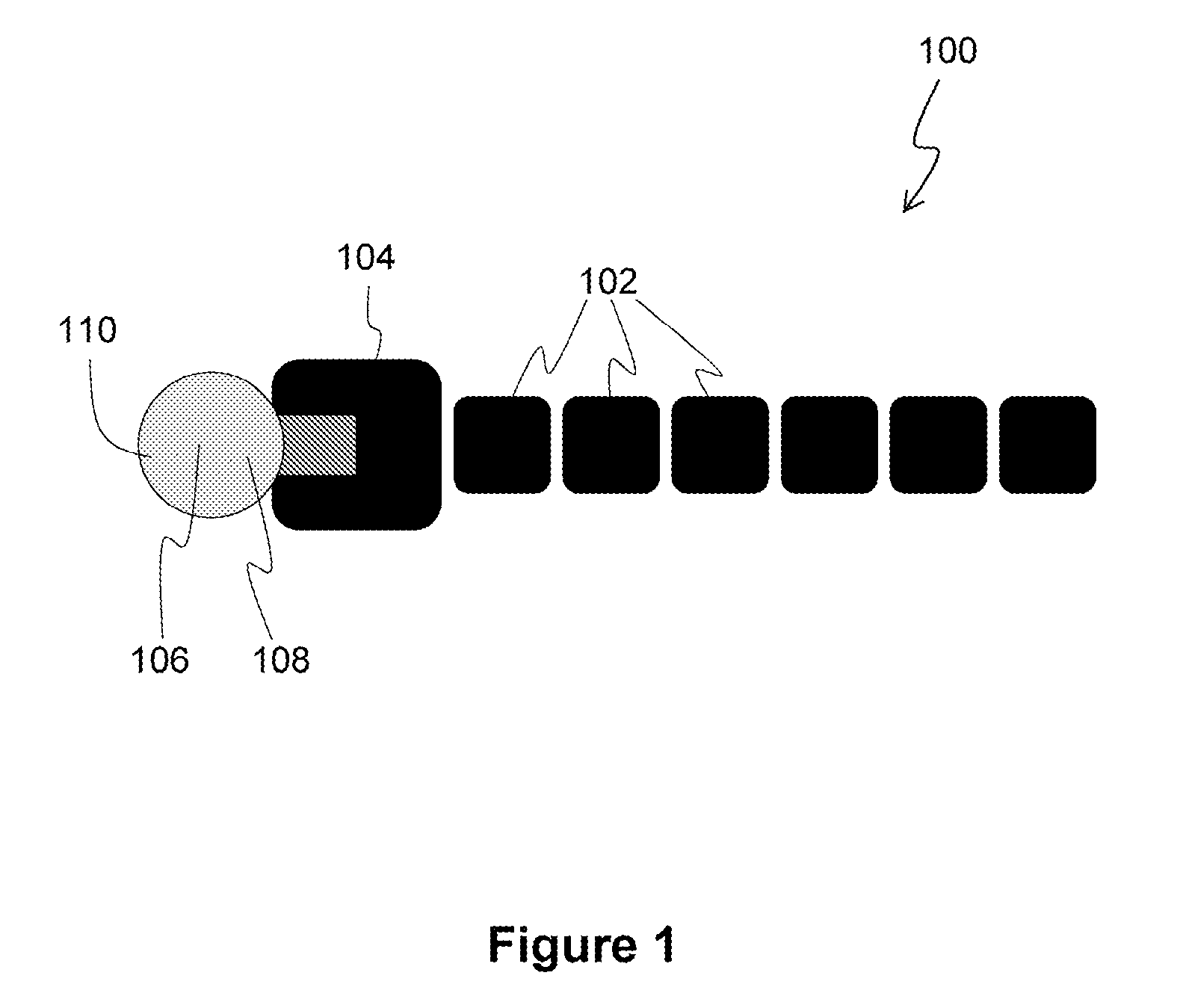
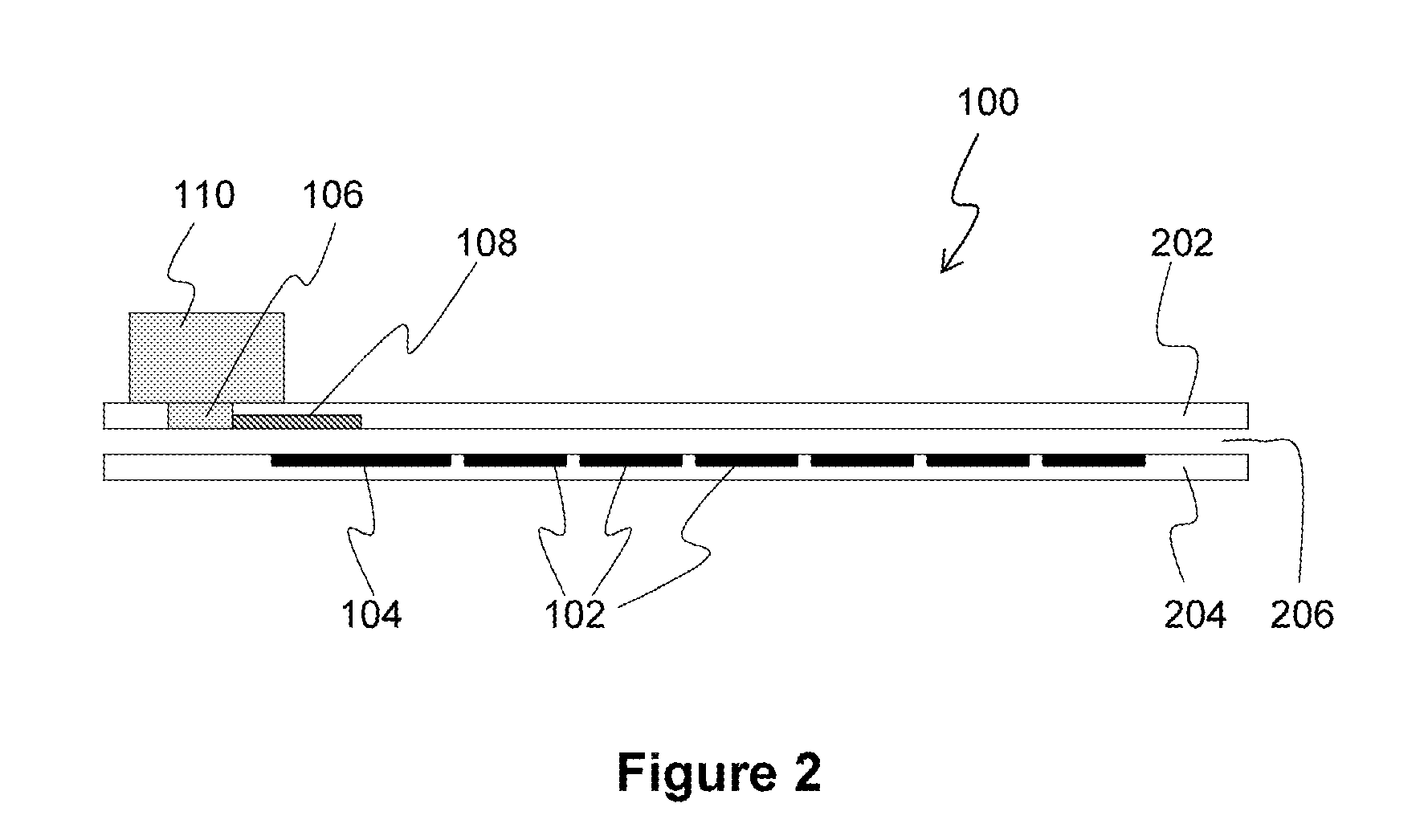
Patents
Literature
1042results about "Electrostatic separators" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
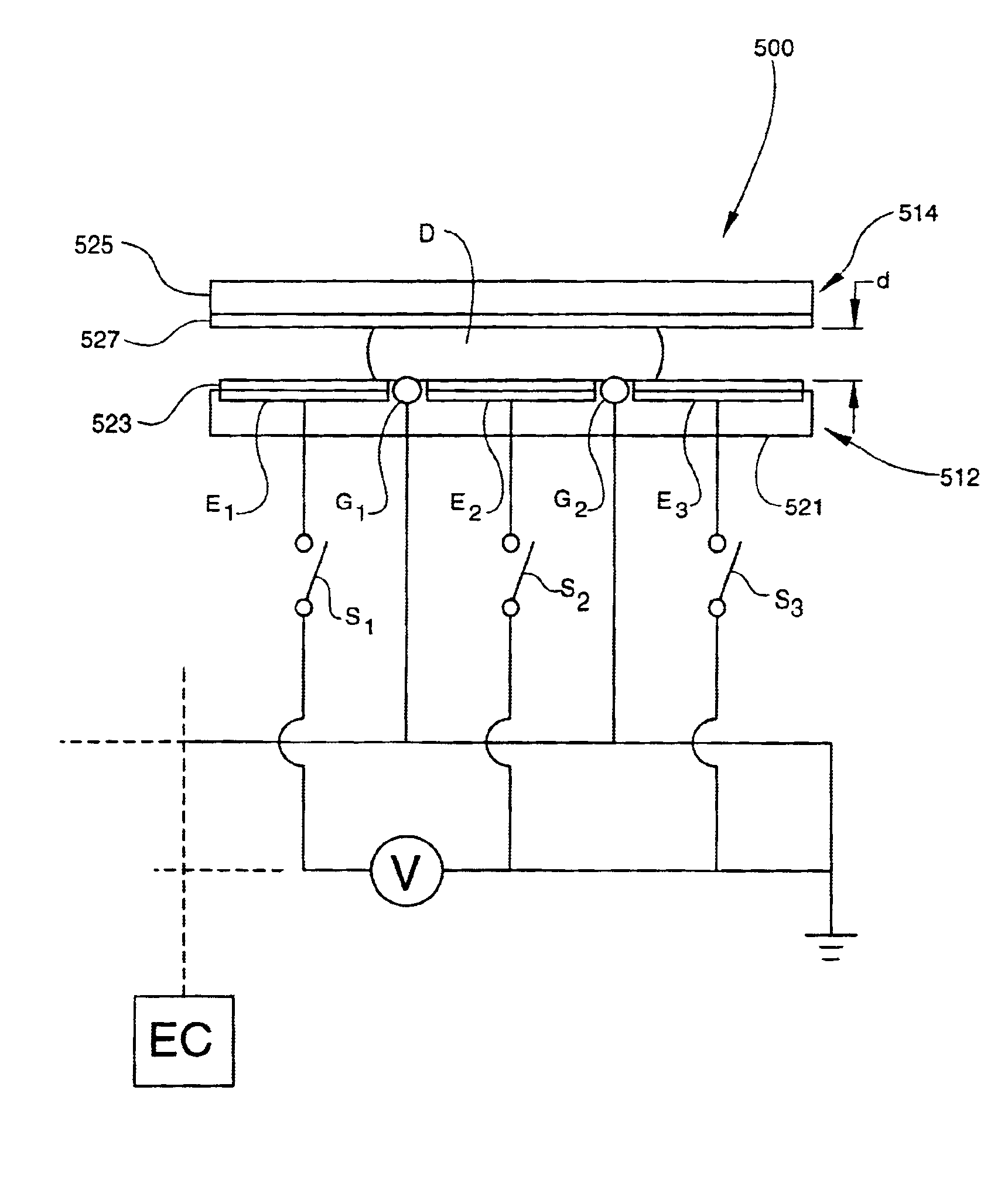
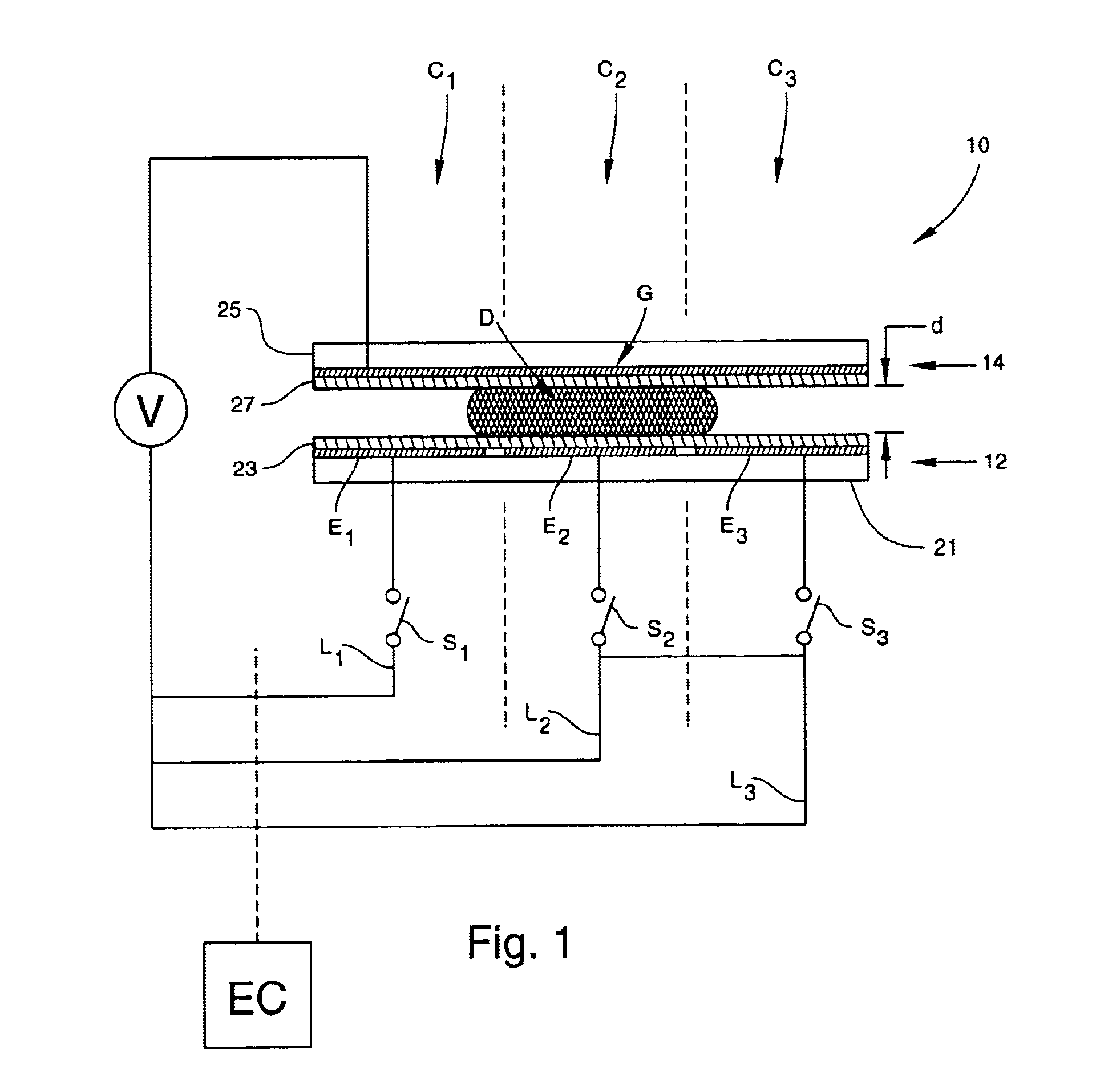
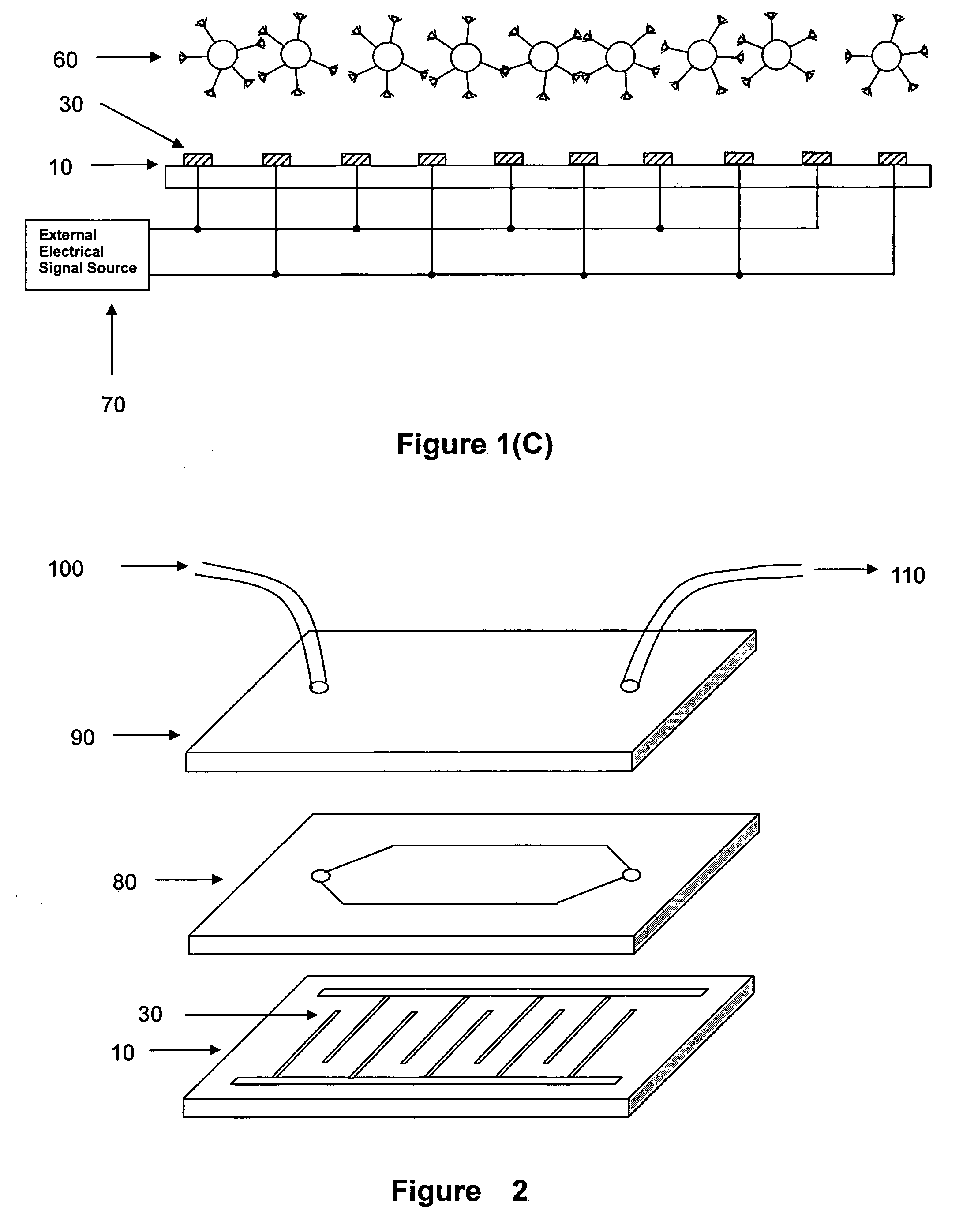
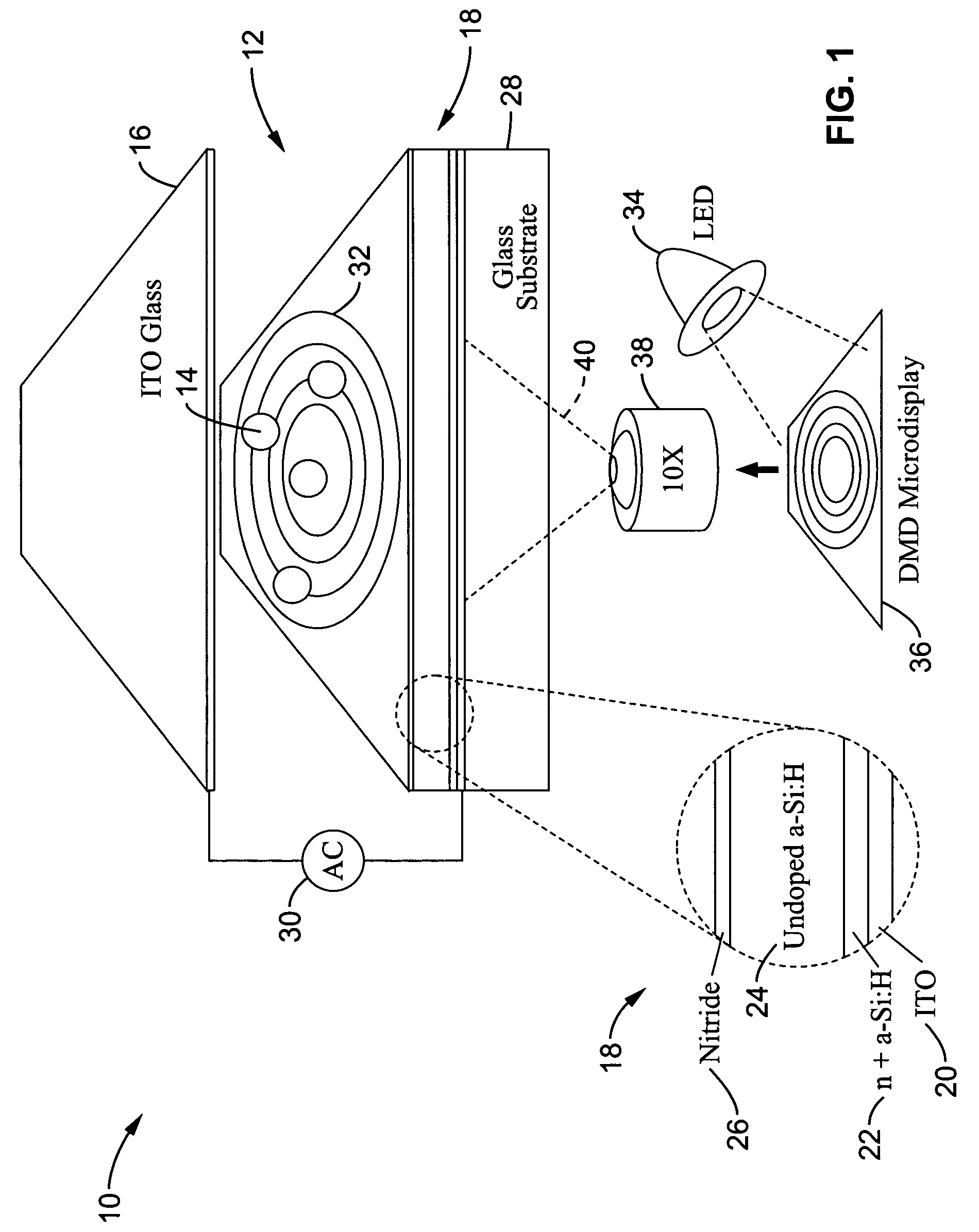
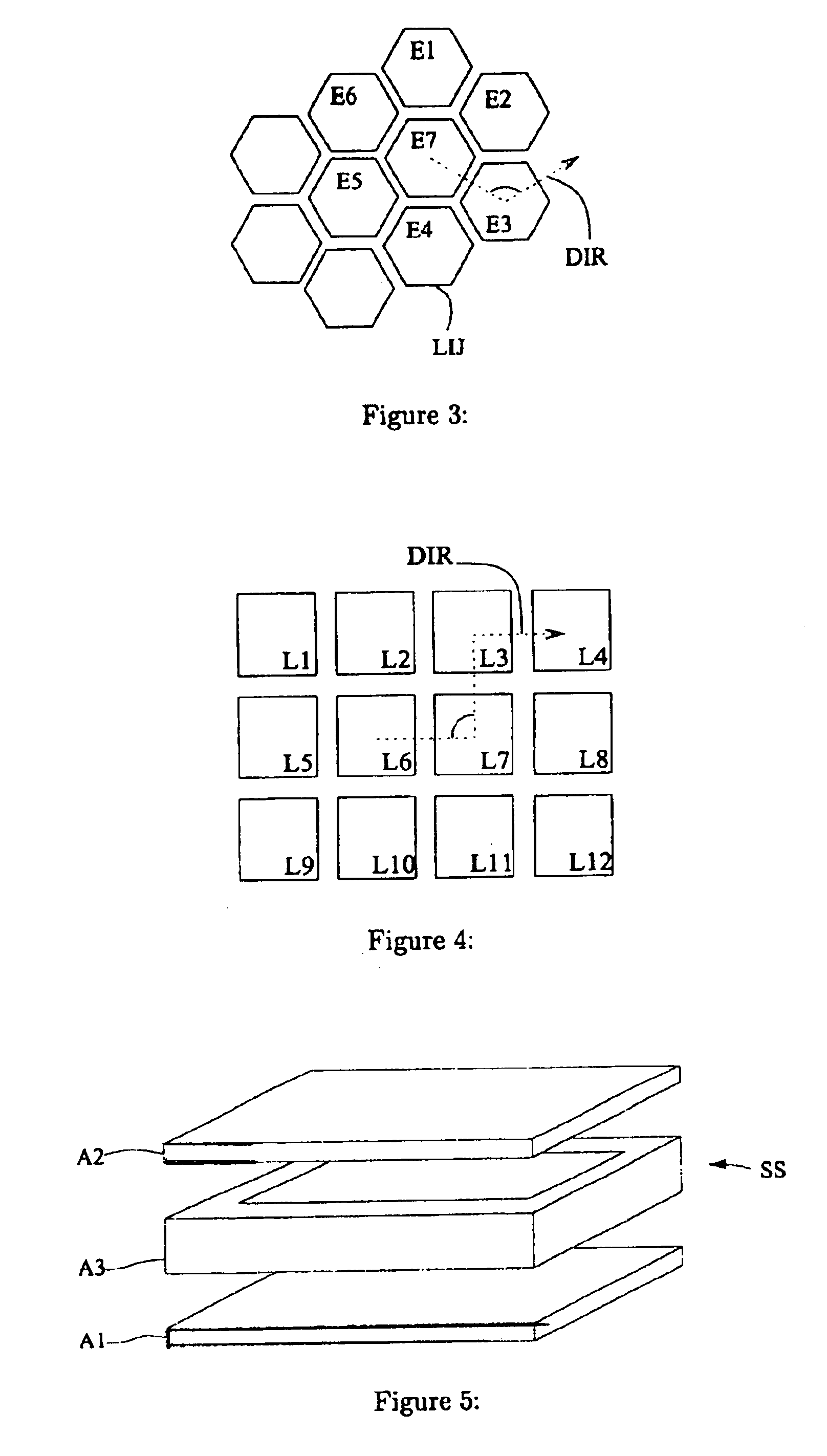
Apparatus for manipulating droplets by electrowetting-based techniques
InactiveUS6911132B2Improve controllabilityImprove accuracyBurnersElectrostatic separatorsElectricityControl manner
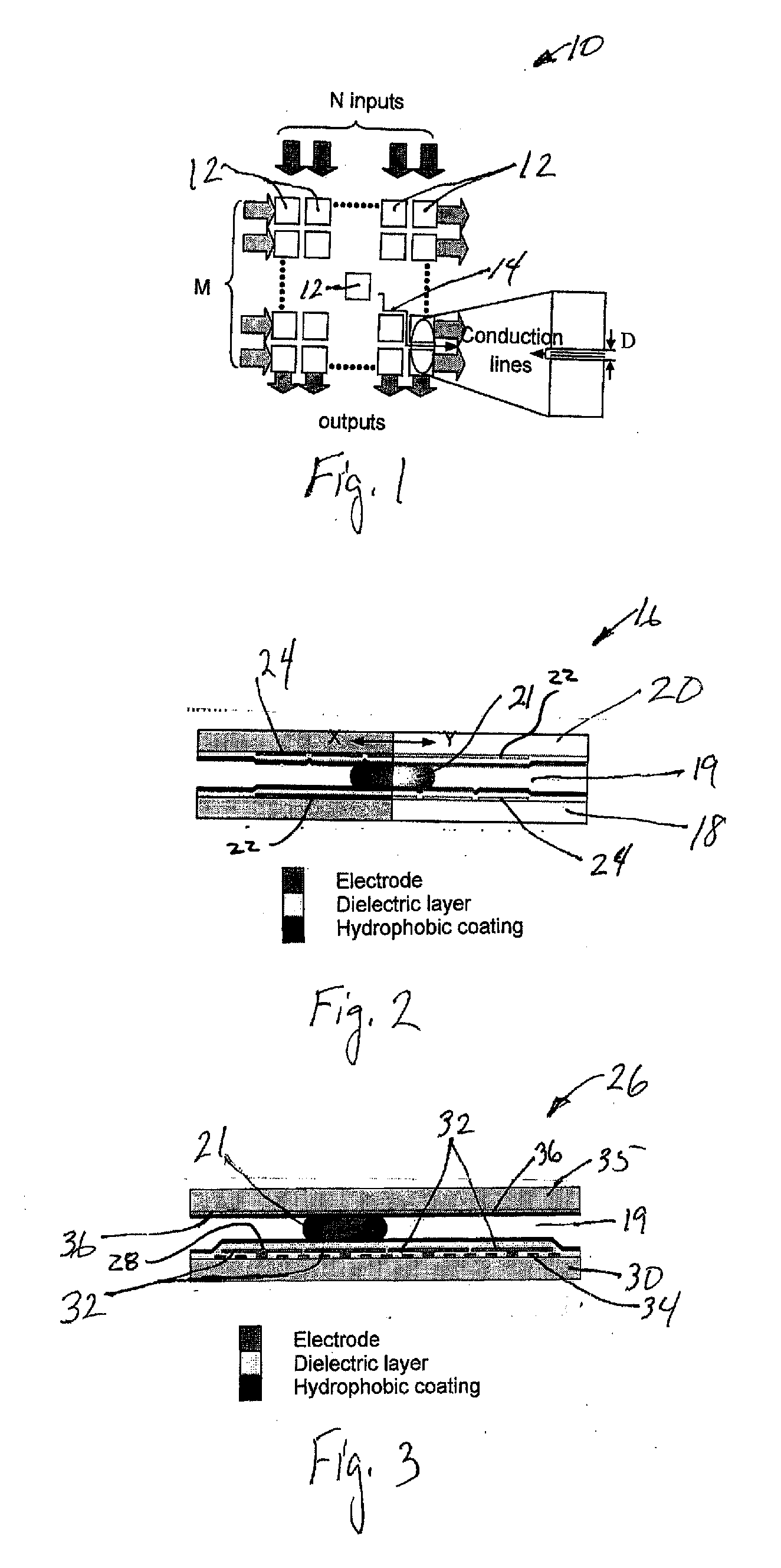
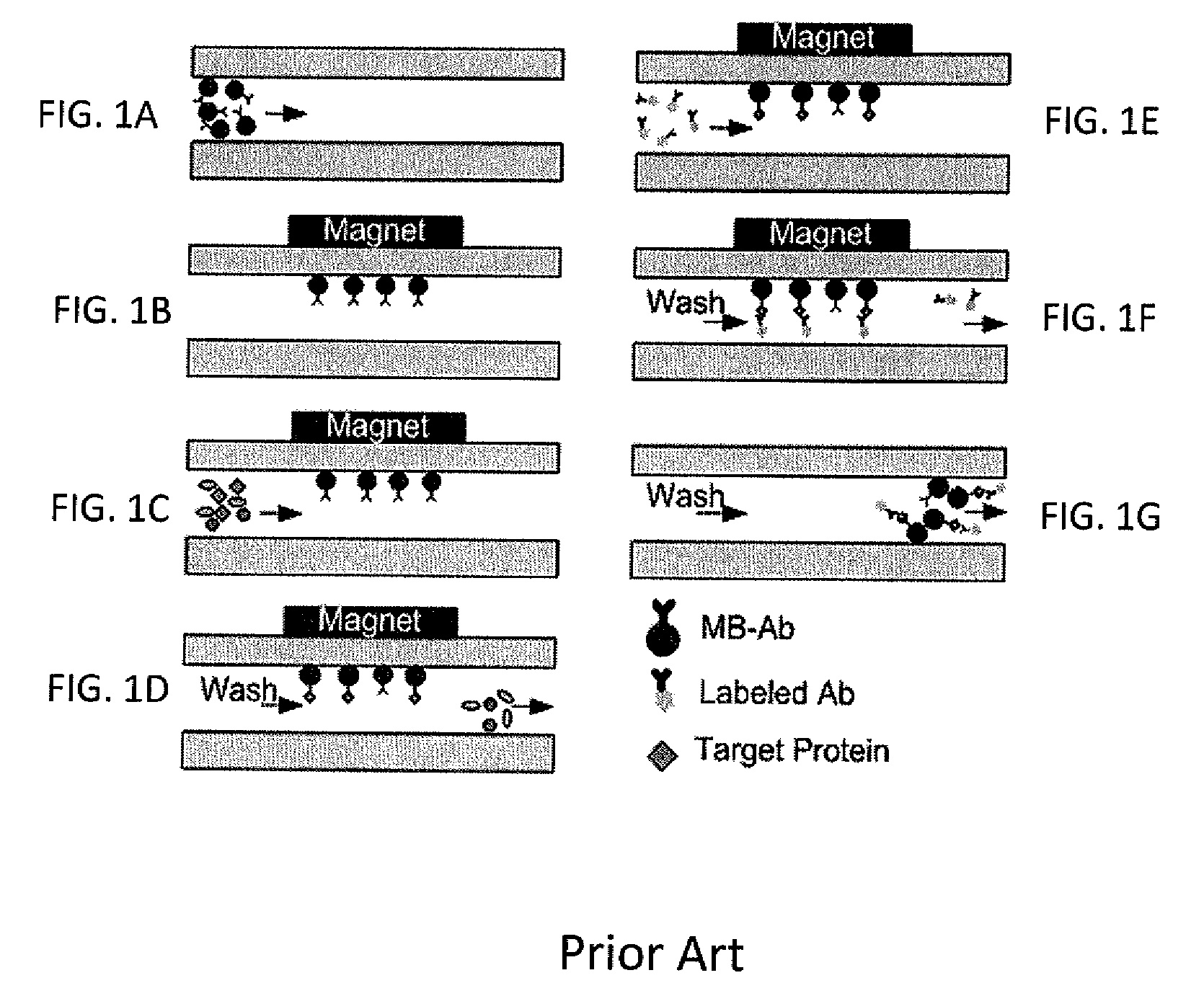
An apparatus is provided for manipulating droplets. The apparatus is a single-sided electrode design in which all conductive elements are contained on one surface on which droplets are manipulated. An additional surface can be provided parallel with the first surface for the purpose of containing the droplets to be manipulated. Droplets are manipulated by performing electrowetting-based techniques in which electrodes contained on or embedded in the first surface are sequentially energized and de-energized in a controlled manner. The apparatus enables a number of droplet manipulation processes, including merging and mixing two droplets together, splitting a droplet into two or more droplets, sampling a continuous liquid flow by forming from the flow individually controllable droplets, and iterative binary or digital mixing of droplets to obtain a desired mixing ratio.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Small object moving on printed circuit board
A printed circuit board based digital or droplet microfluidic system and method for producing such microfluidic system are disclosed. The digital microfluidic device comprises a printed circuit board having a substrate and a plurality of electrode pads disposed on the top surface of the substrate in a rectangular array. A via extends from each electrode pad through the substrate to other locations on the substrate . A dielectric layer is disposed on the electrode pads. Droplets may be manipulated using electrowetting principles and others by applying a voltage to the desired electrodes. Each electrode pad can be controlled directly and independently from the other electrode pads to modify the surface wettability of the dielectric layer in the vicinity of the electrode pad by applying a voltage to the desired electrode pad(s). In this way, droplets may be formed, moved, mixed, and / or divided or other small objects manipulated while in air or immersed in a liquid on the dielectric surface.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods for manipulating moieties in microfluidic systems
InactiveUS7081192B1Simplification and standardization of designExpand and enhance capabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrolysis componentsStereochemistryPHYSICAL FORCES
This invention relates generally to the field of moiety or molecule manipulation in a chip format. In particular, the invention provides a method for manipulating a moiety in a microfluidic application, which method comprises: a) coupling a moiety to be manipulated onto surface of a binding partner of said moiety to form a moiety-binding partner complex; and b) manipulating said moiety-binding partner complex with a physical force in a chip format, wherein said manipulation is effected through a combination of a structure that is external to said chip and a structure that is built-in in said chip, thereby said moiety is manipulated.
Owner:AVIVA BIOSCI
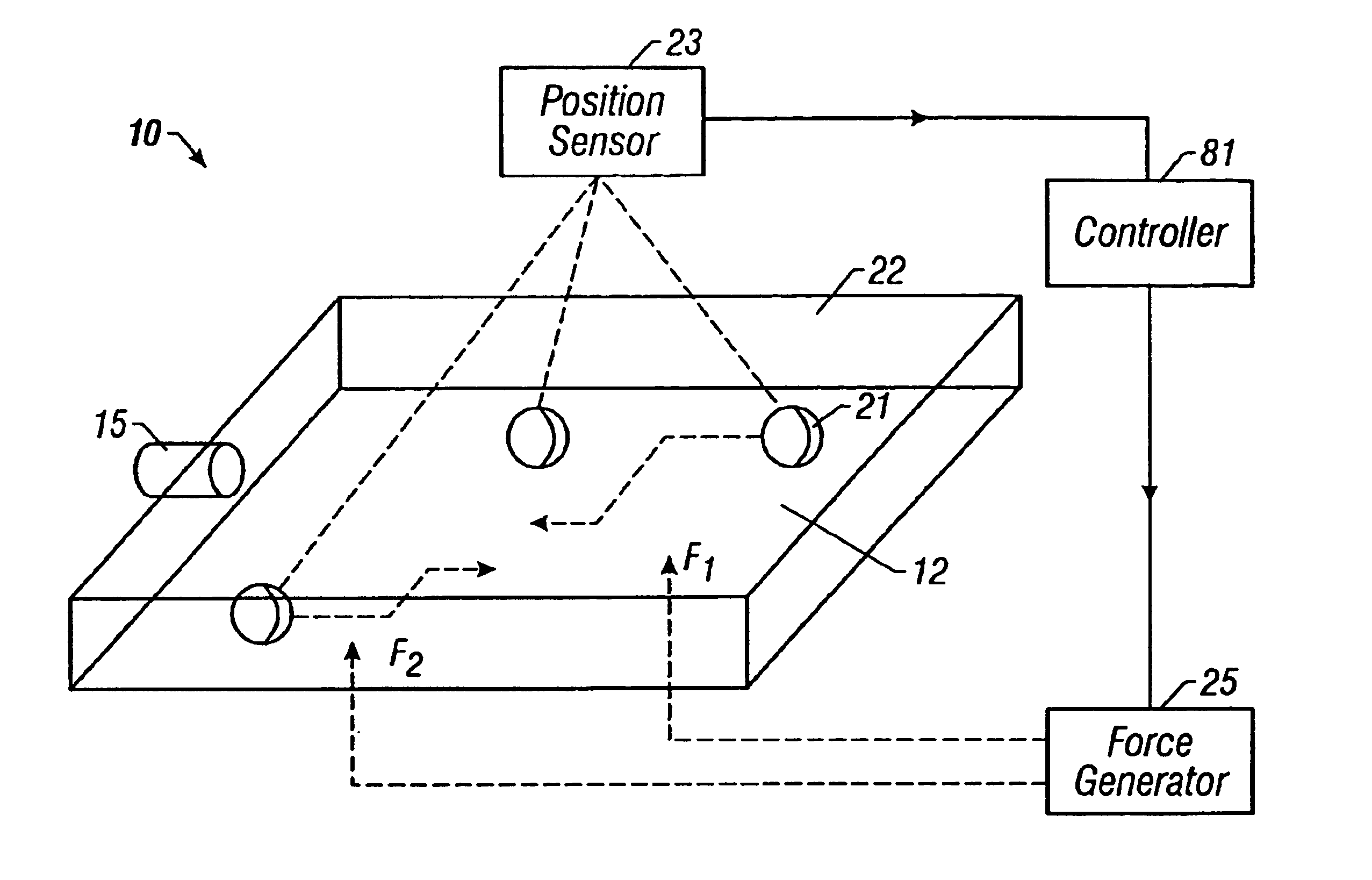
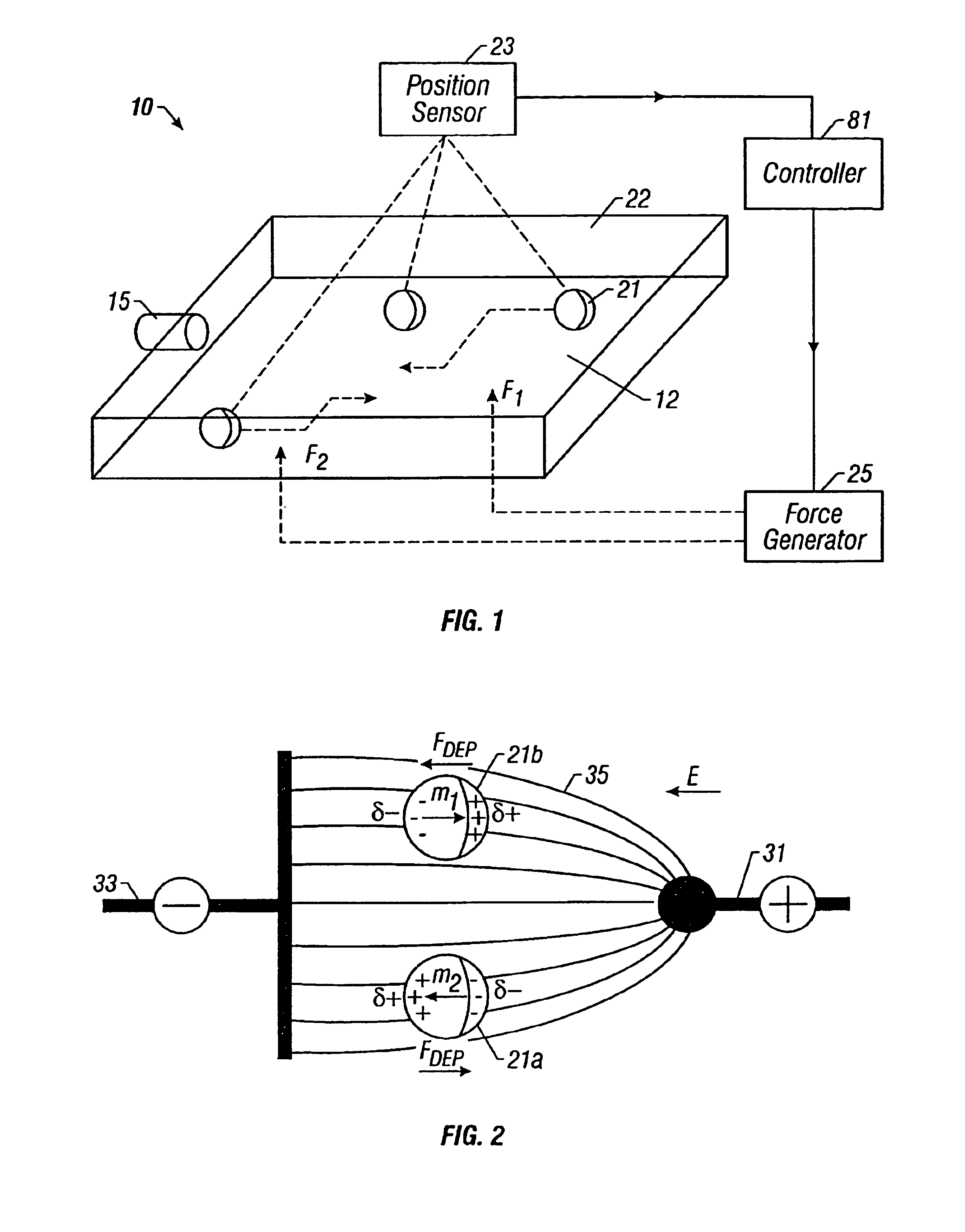
Method and apparatus for programmable fluidic processing
A method and apparatus for microfluidic processing by programmably manipulating a packet. A material is introduced onto a reaction surface and compartmentalized to form a packet. A position of the packet is sensed with a position sensor. A programmable manipulation force is applied to the packet at the position. The programmable manipulation force is adjustable according to packet position by a controller. The packet is programmably moved according to the programmable manipulation force along arbitrarily chosen paths.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Uniform surfaces for hybrid material substrate and methods for making and using same
Devices, systems and methods of using same where hybrid substrate materials are provided with a substantially uniform surface to provide uniformity of properties, including interaction with their environments. Uniform surfaces are applied as coatings over, e.g., hybrid metal / silica, metal / polymer, metal / metal surfaces to mask different chemical properties of differing regions of the surface and to afford a protective surface for the hybrid structure.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
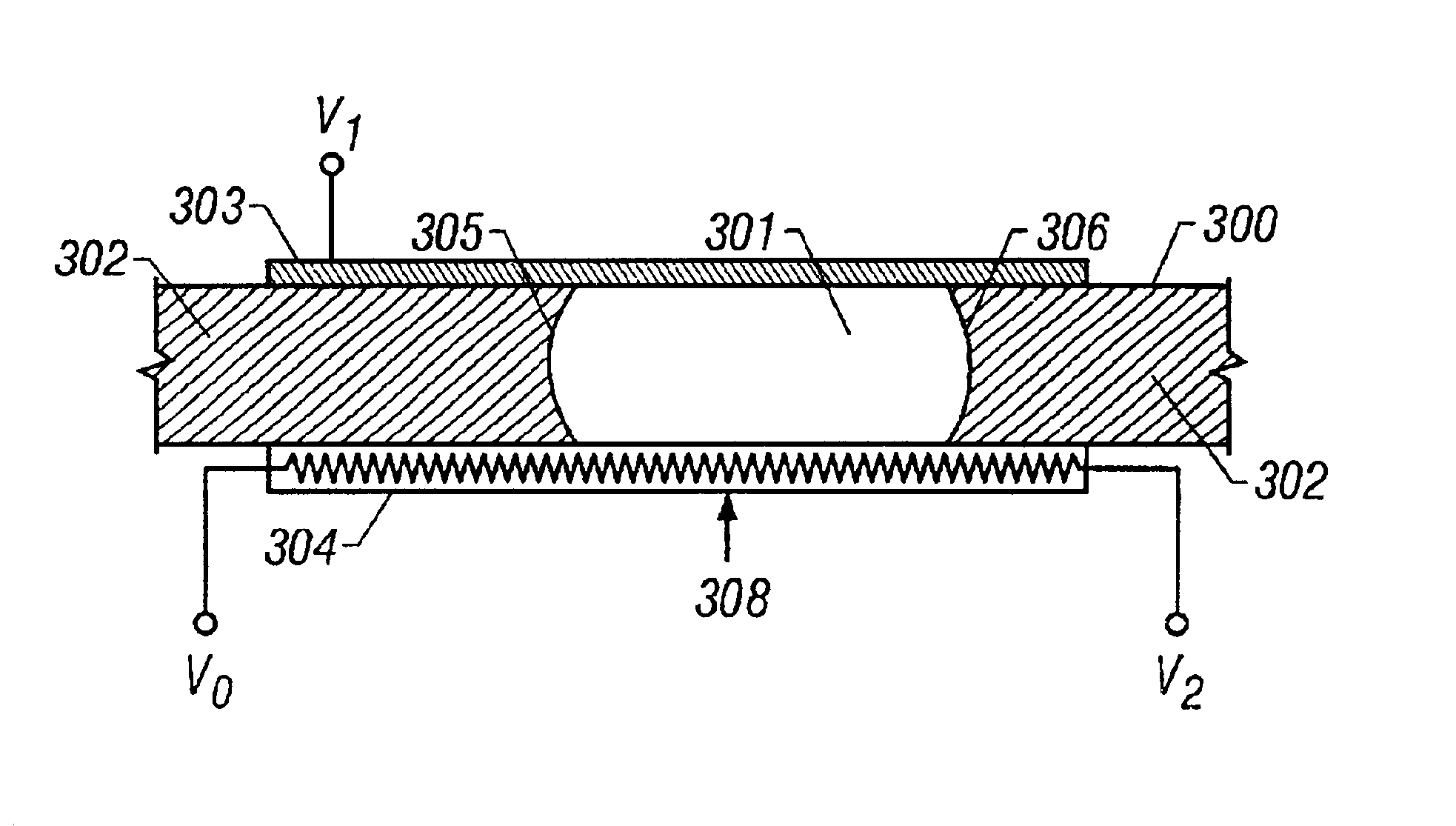
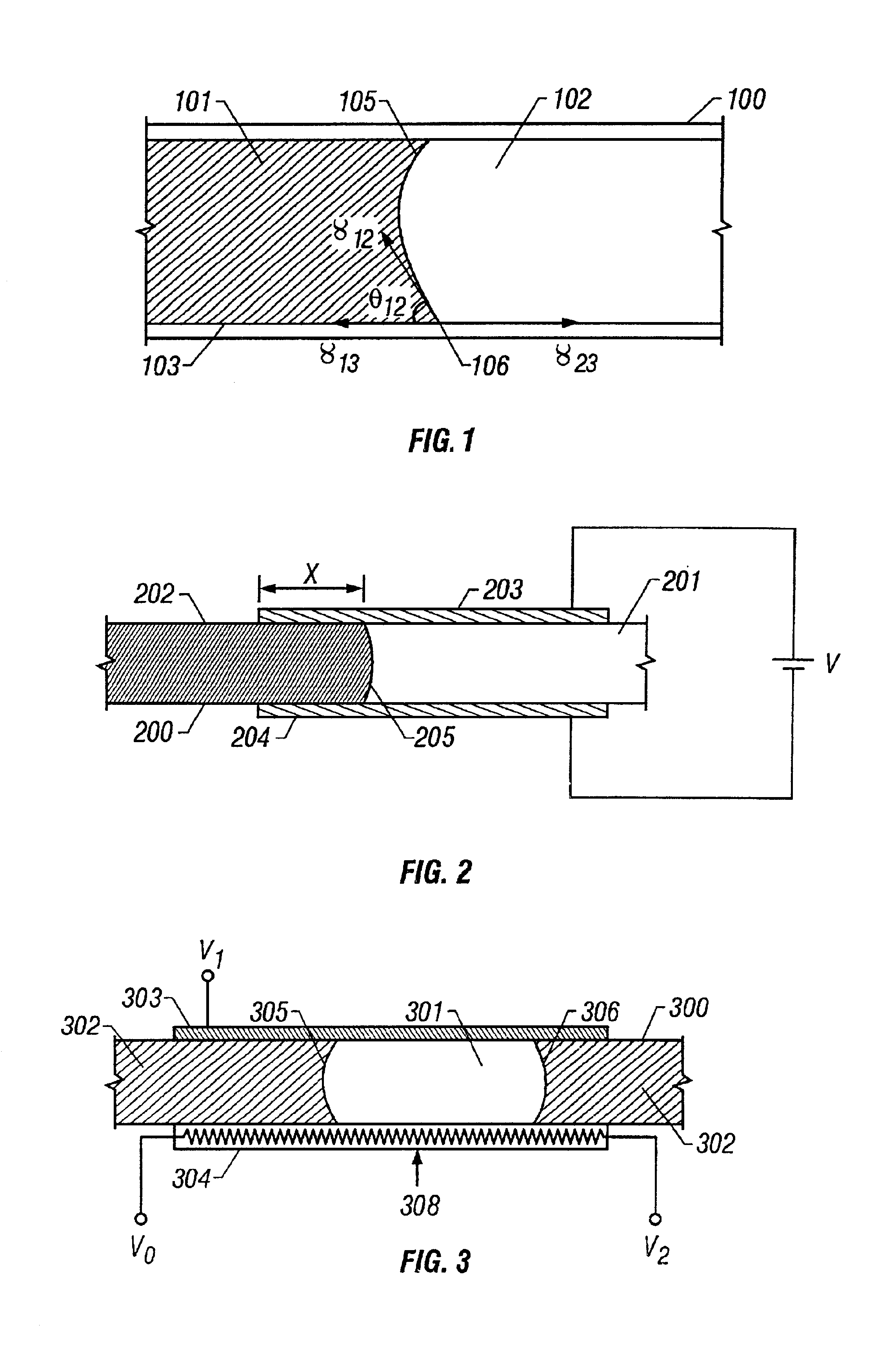
Droplet-based nucleic acid amplification device, system, and method
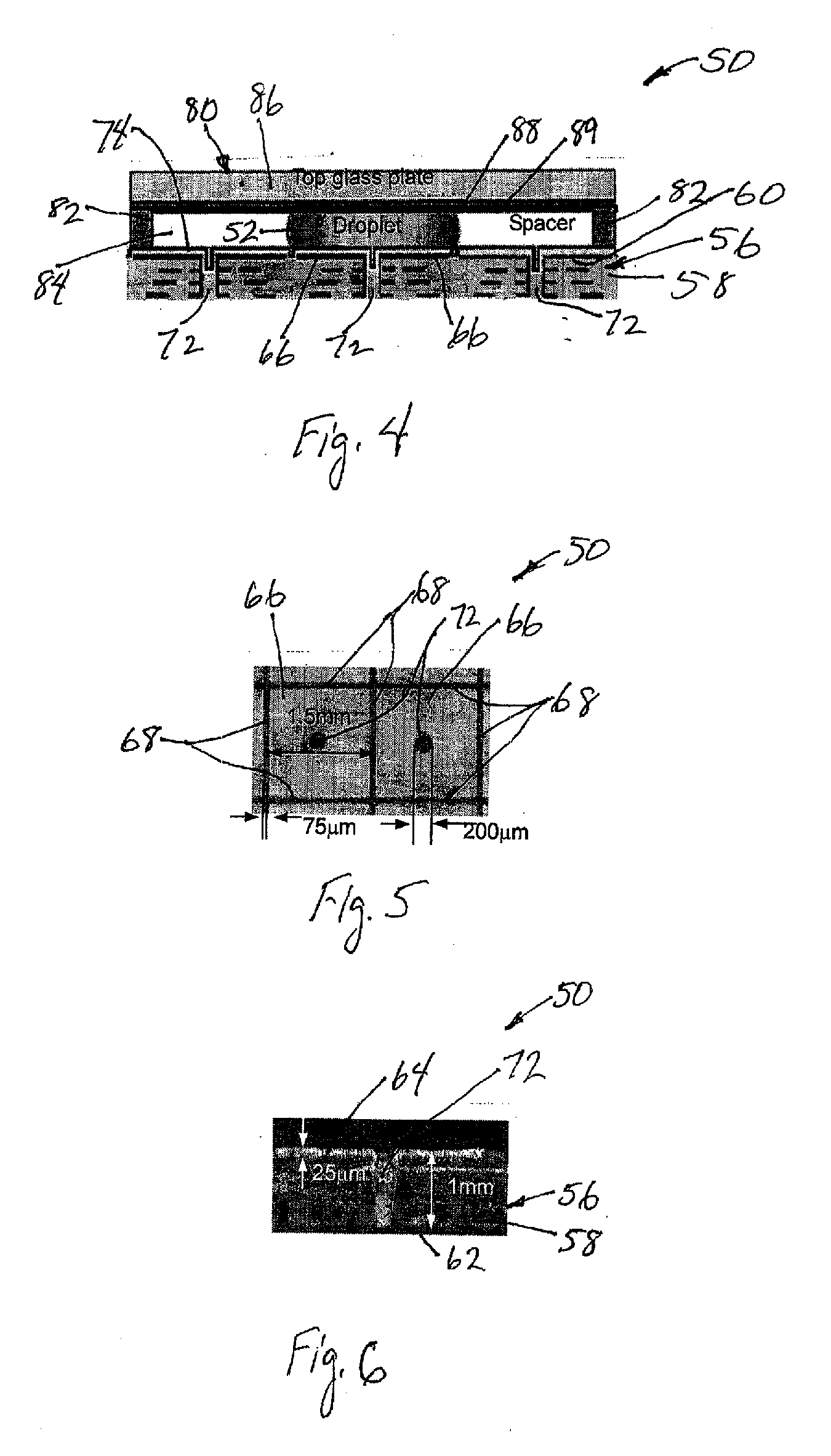
InactiveUS20080038810A1Reduces and eliminates build-upImprove efficiencyElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentTemperature controlBiology
The present invention relates to a droplet-based nucleic acid amplification device, system, and method. According to one embodiment, a droplet microactuator is provided and includes: (a) a substrate comprising electrodes for conducting droplet operations; and (b) one or more temperature control means arranged in proximity with one or more of the electrodes for heating and / or cooling a region of the droplet microactuator and arranged such that a droplet can be transported on the electrodes into the region for heating.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
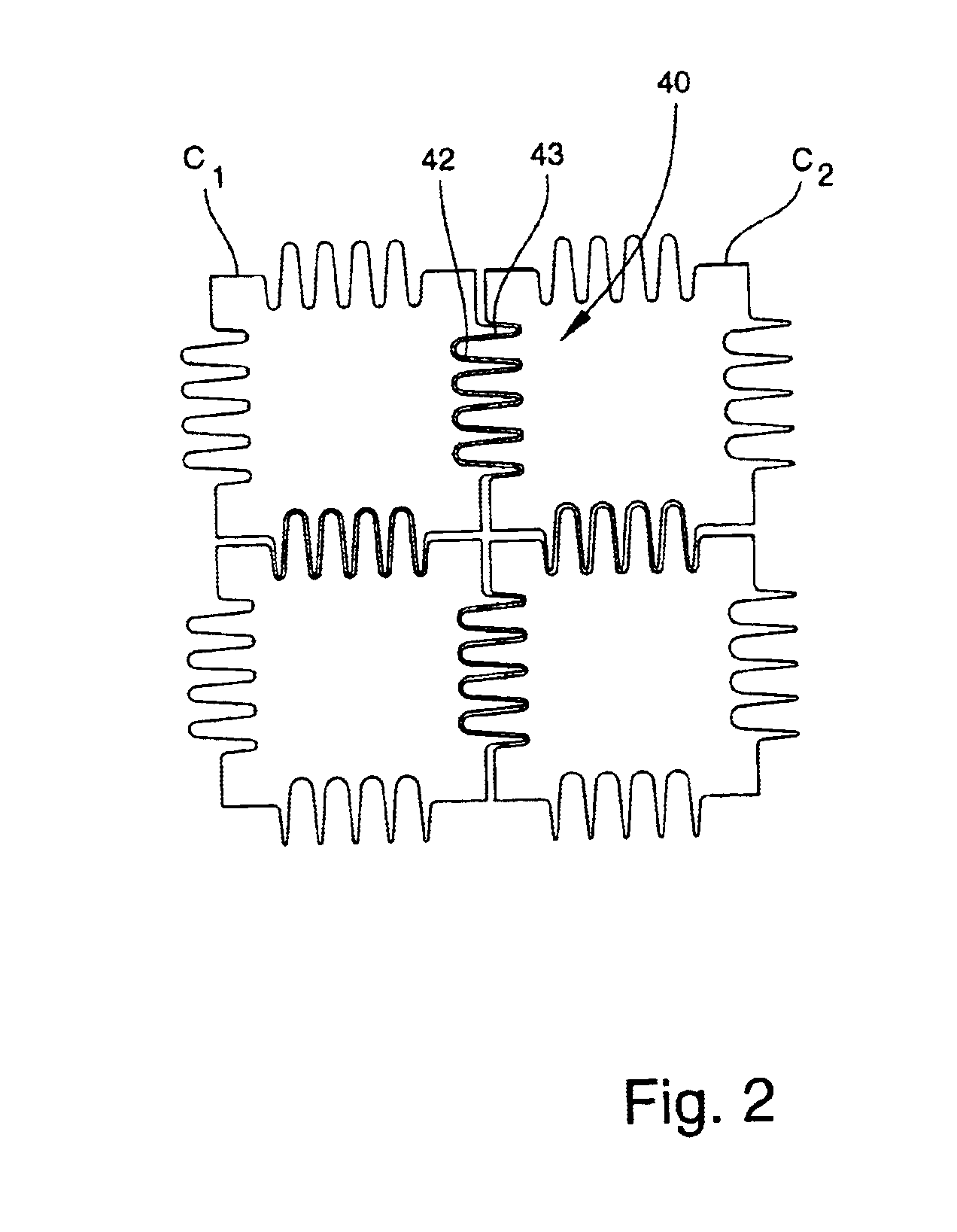
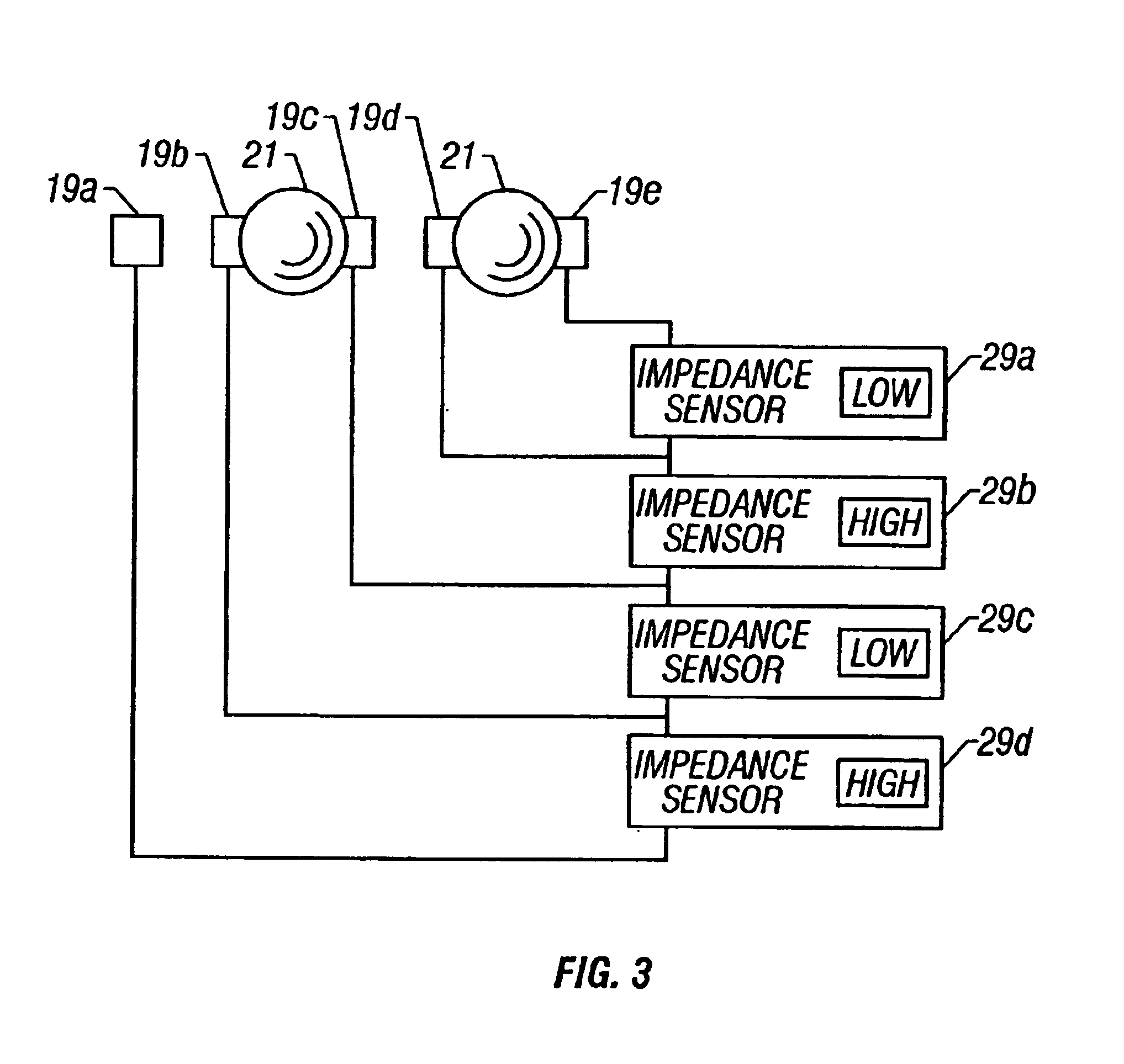
Electrode addressing method
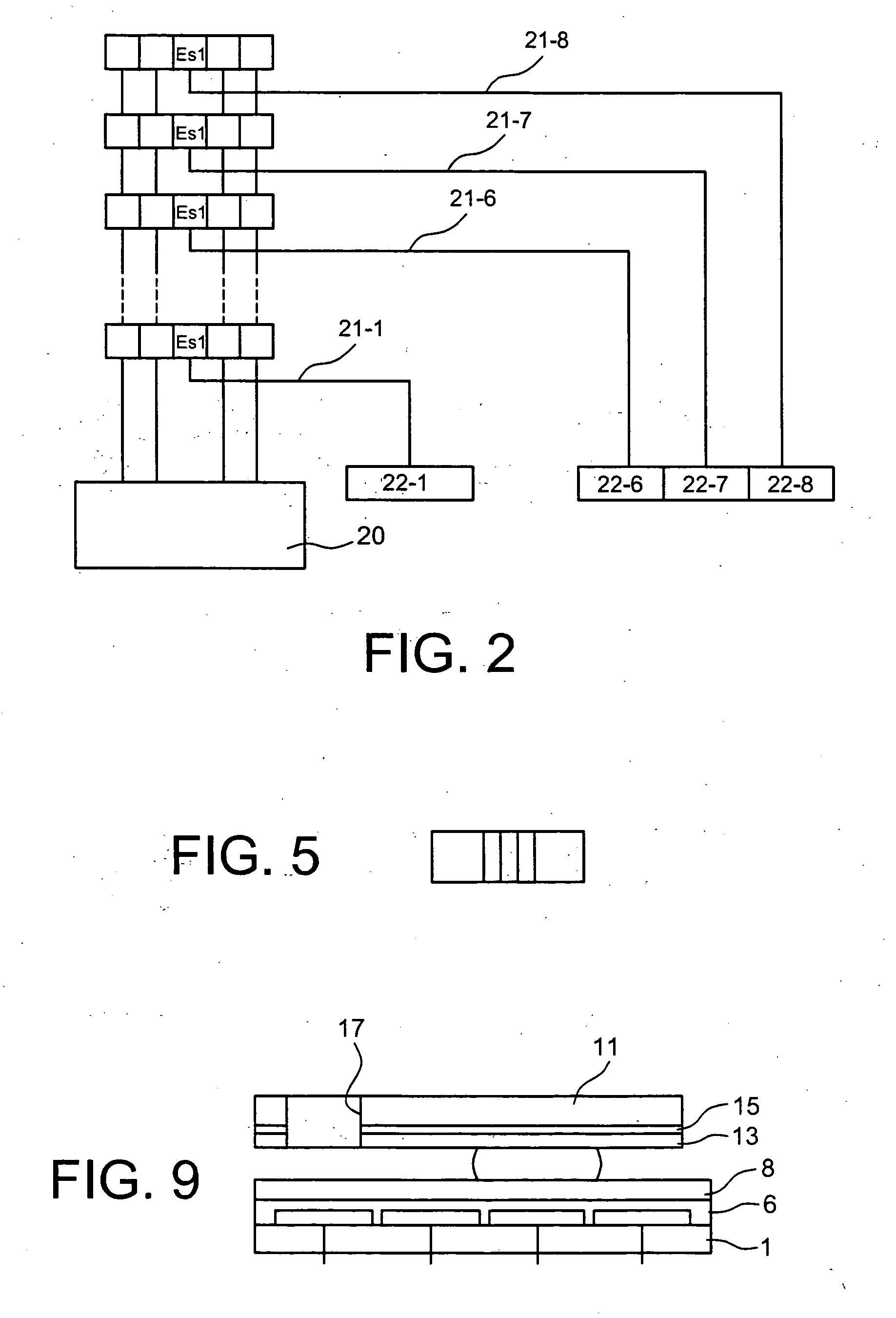
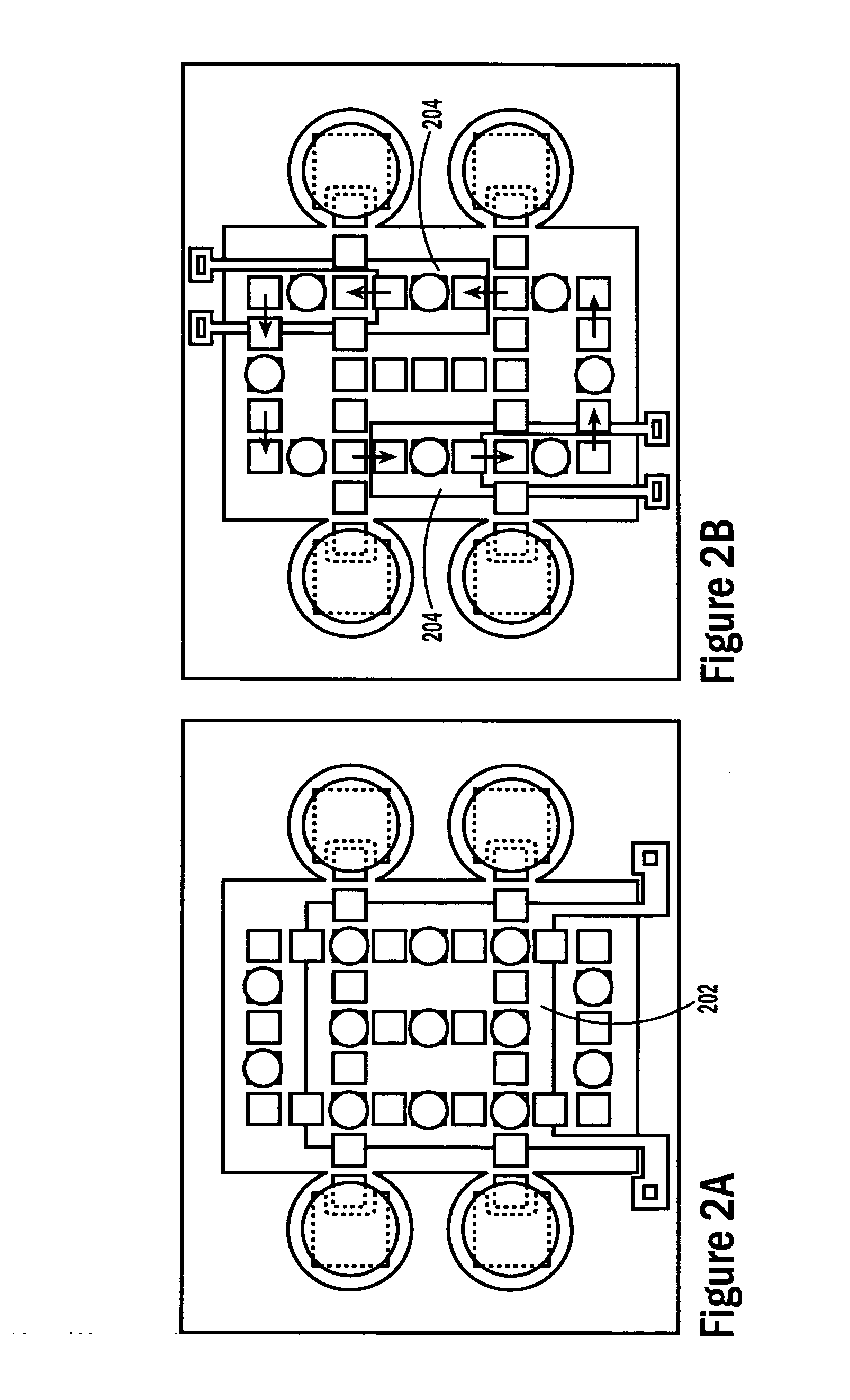
InactiveUS20090192044A1Reduce in quantitySimplify line selection meanElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentElectrode arrayEngineering
A device for addressing an electrode array of 2n lines of an electro-fluidic device, each line having N electrodes (n≦N). The device includes, on each line, n selection electrodes, all of the line selection electrodes being connected to 2n line selection conductors, 2n−1 line selection electrodes of 2n−1 lines being connected to each line selection conductor, and selection devices for selecting one or more line selection conductors.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Method for using magnetic particles in droplet microfluidics
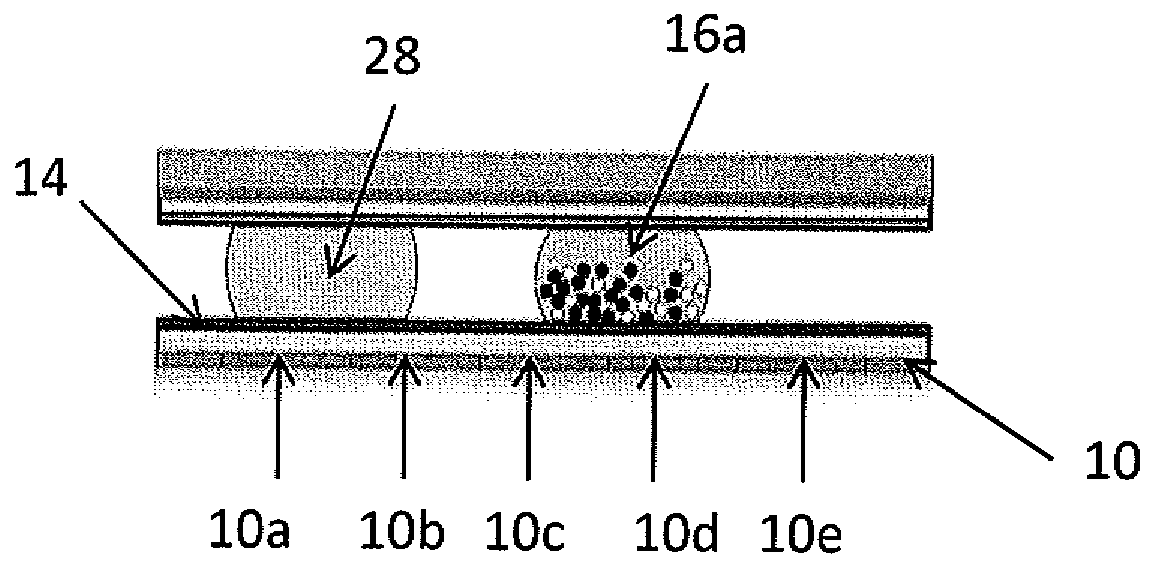
ActiveUS20090283407A1Increasing concentration of targetReduce concentrationElectrostatic separatorsLiquid separation by electricityEngineeringDroplet microfluidics
Methods of utilizing magnetic particles or beads (MBs) in droplet-based (or digital) microfluidics are disclosed. The methods may be used in enrichment or separation processes. A first method employs the droplet meniscus to assist in the magnetic collection and positioning of MBs during droplet microfluidic operations. The sweeping movement of the meniscus lifts the MBs off the solid surface and frees them from various surface forces acting on the MBs. A second method uses chemical additives to reduce the adhesion of MBs to surfaces. Both methods allow the MBs on a solid surface to be effectively moved by magnetic force. Droplets may be driven by various methods or techniques including, for example, electrowetting, electrostatic, electromechanical, electrophoretic, dielectrophoretic, electroosmotic, thermocapillary, surface acoustic, and pressure.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
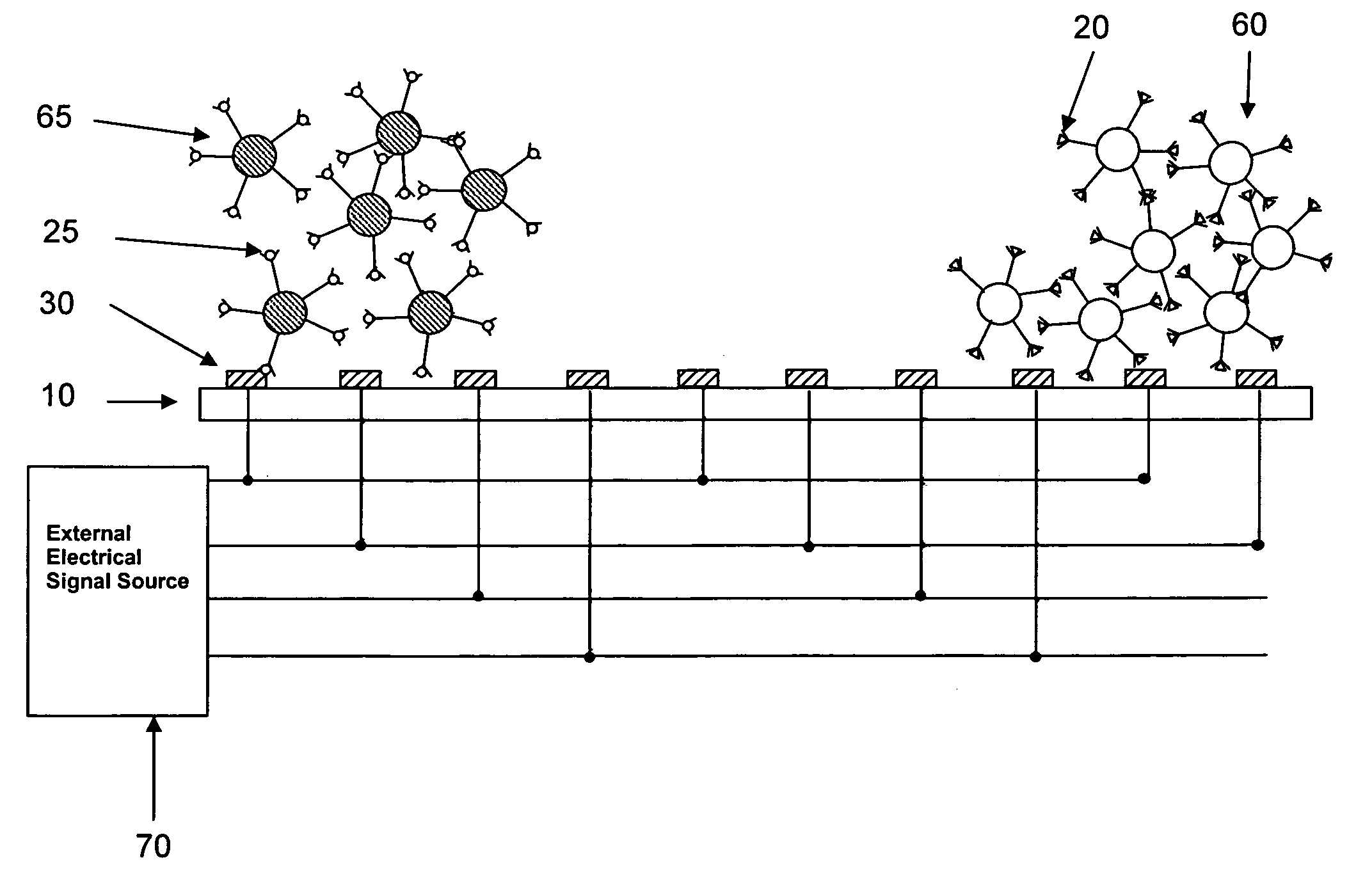
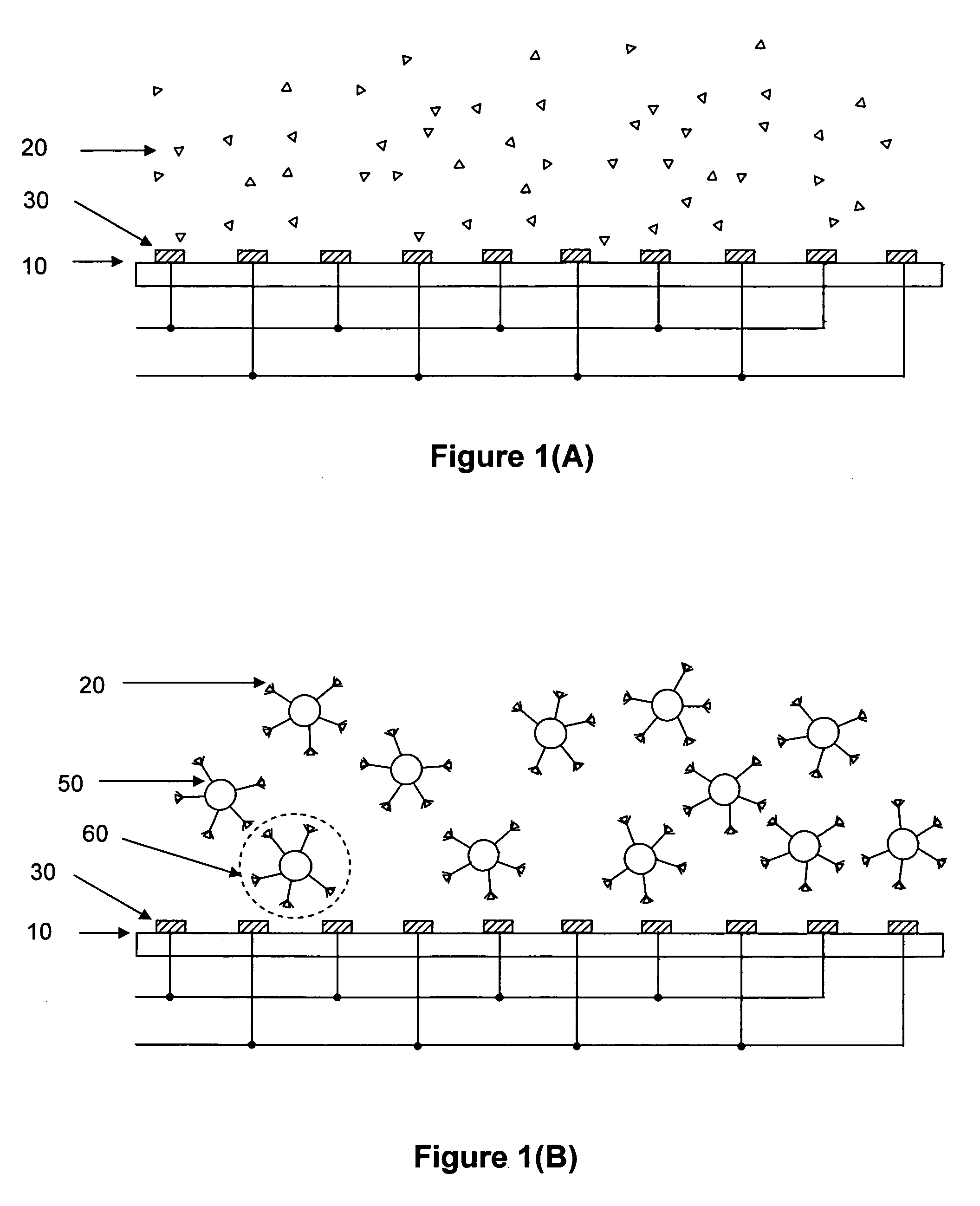
Method and Apparatus Using Electric Field for Improved Biological Assays
ActiveUS20090032401A1Avoid corrosionIncrease electric fieldElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentPresent methodEngineering
Disclosed are a method and apparatus that use an electric field for improved biological assays. The electric field is applied across a device having wells, which receive reactants, which carry a charge. The device thus uses a controllable voltage source between the first and second electrodes, which is controllable to provide a positive charge and a negative charge to a given electrode. By controlled use of the electric field charged species in a fluid in a fluid channel are directed into or out of the well by an electric field between the electrodes. The present method involves the transport of fluids, as in a microfluidic device, and the electric field-induced movement of reactive species according to various assay procedures, such as DNA sequencing, synthesis or the like.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
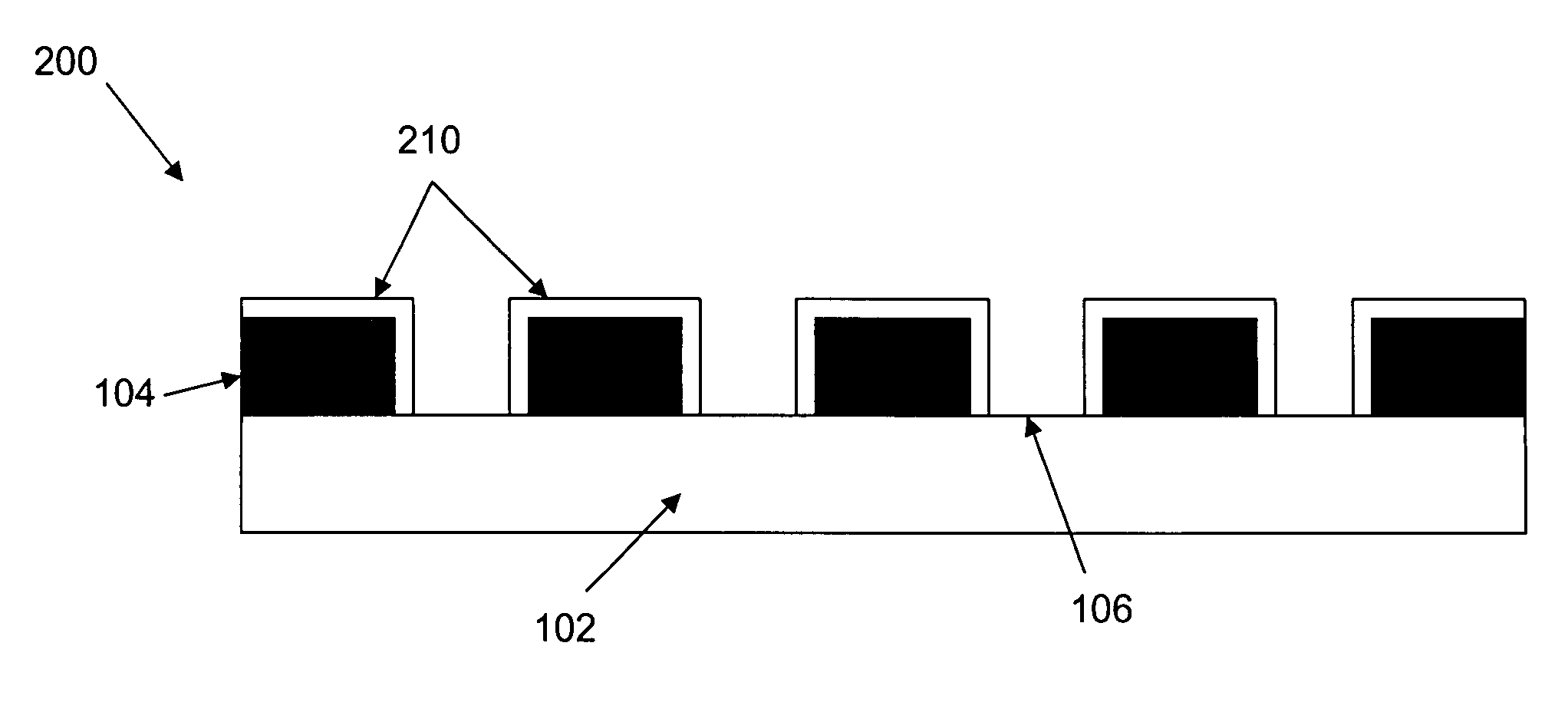
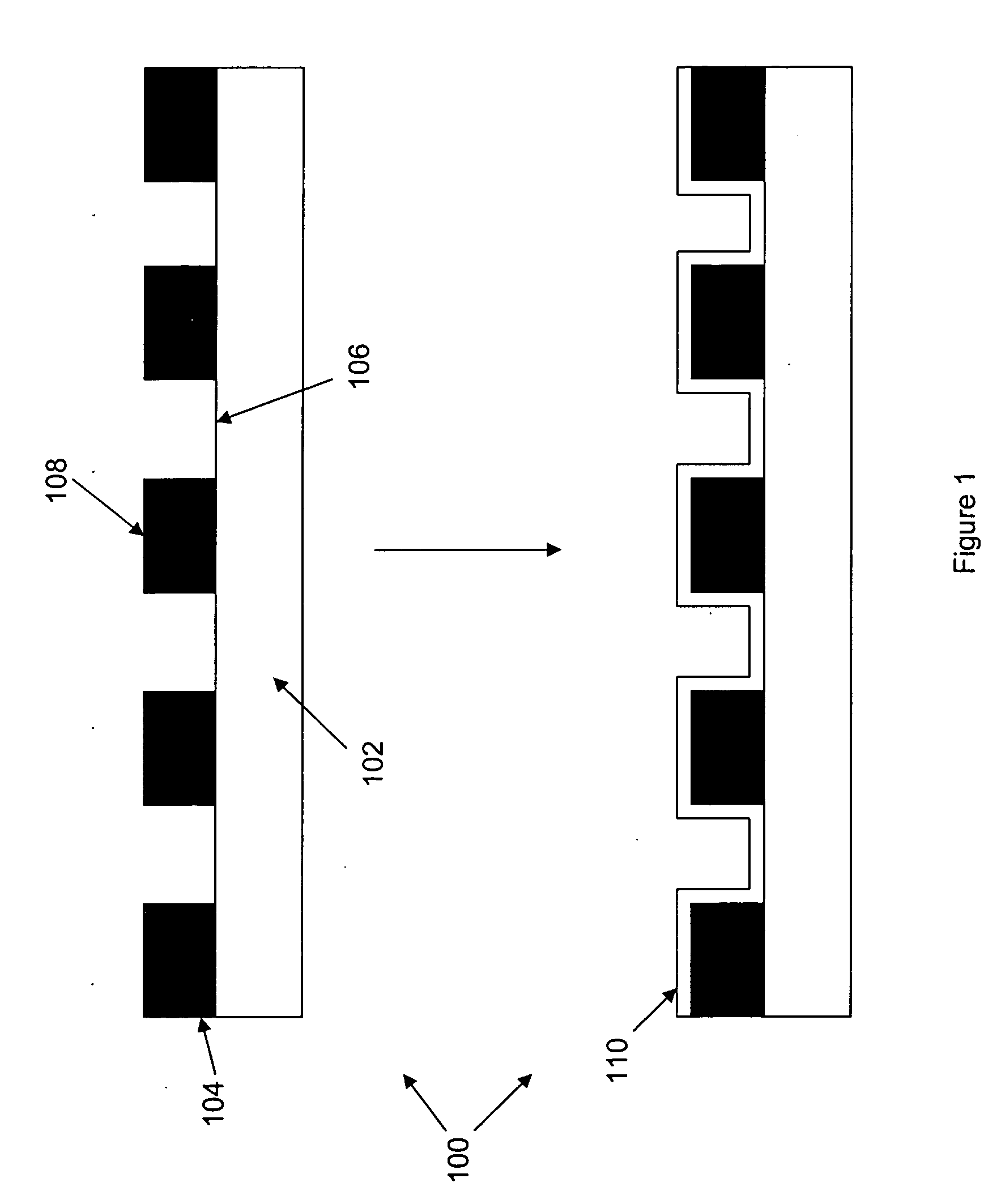
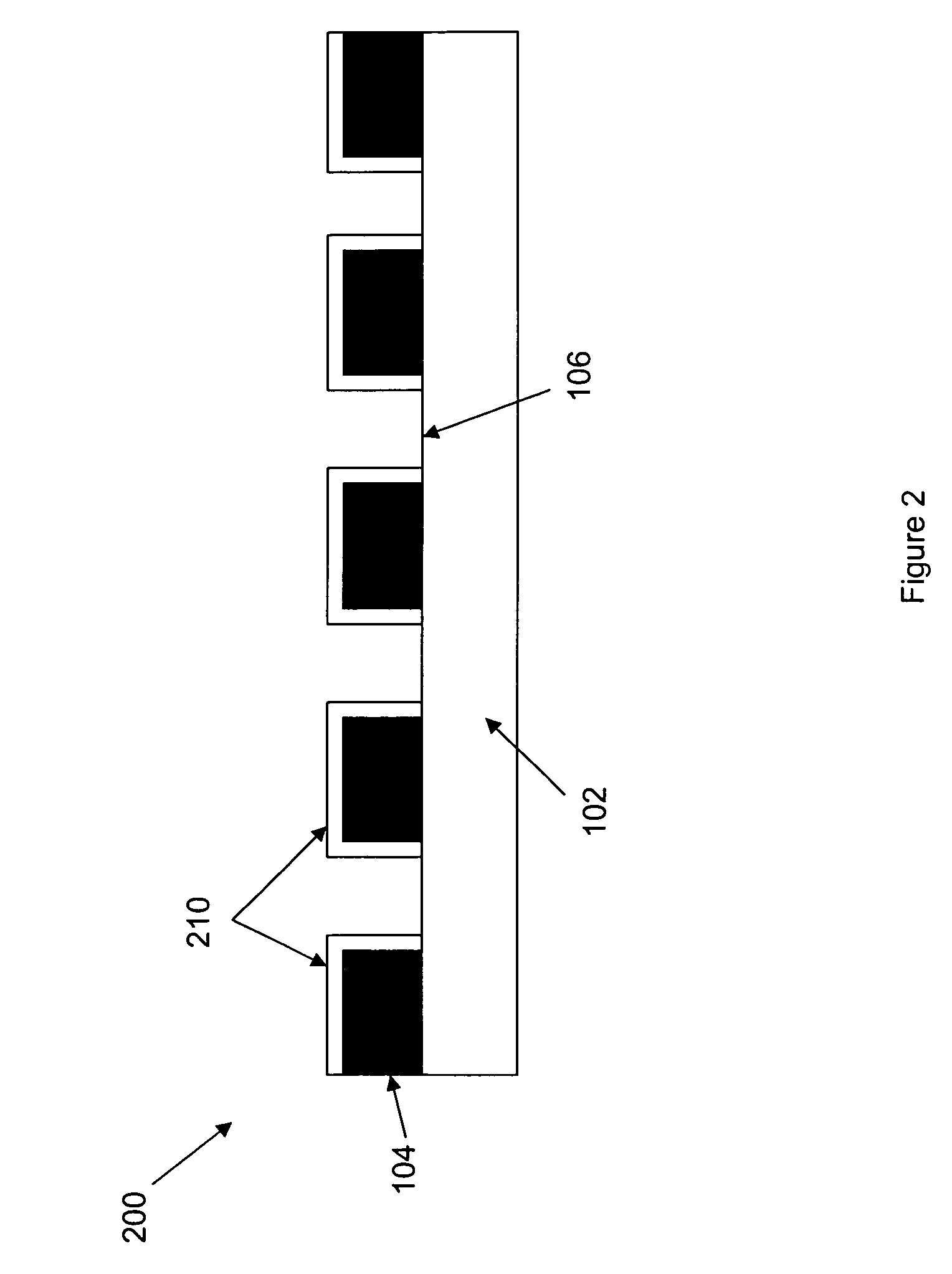
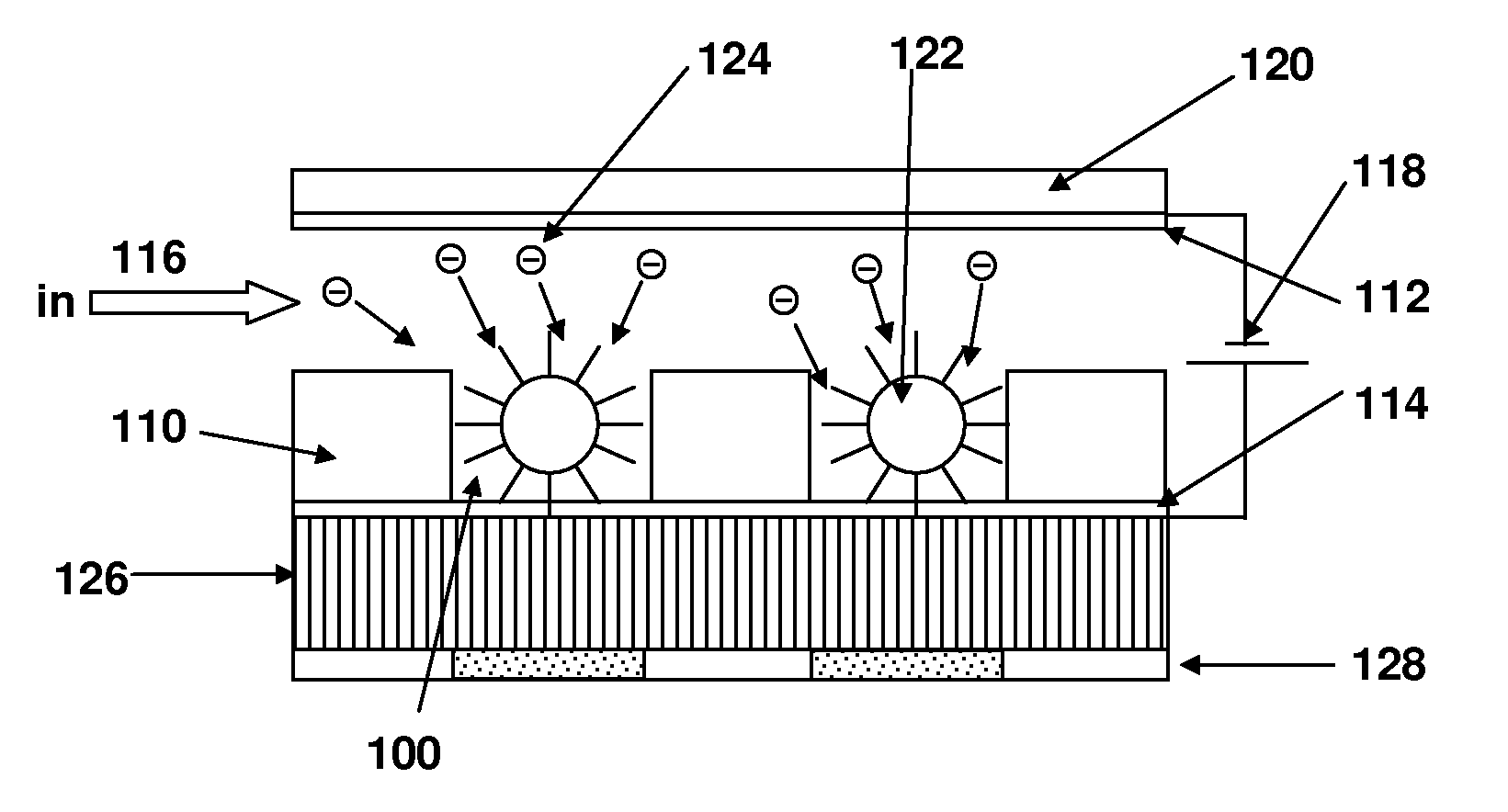
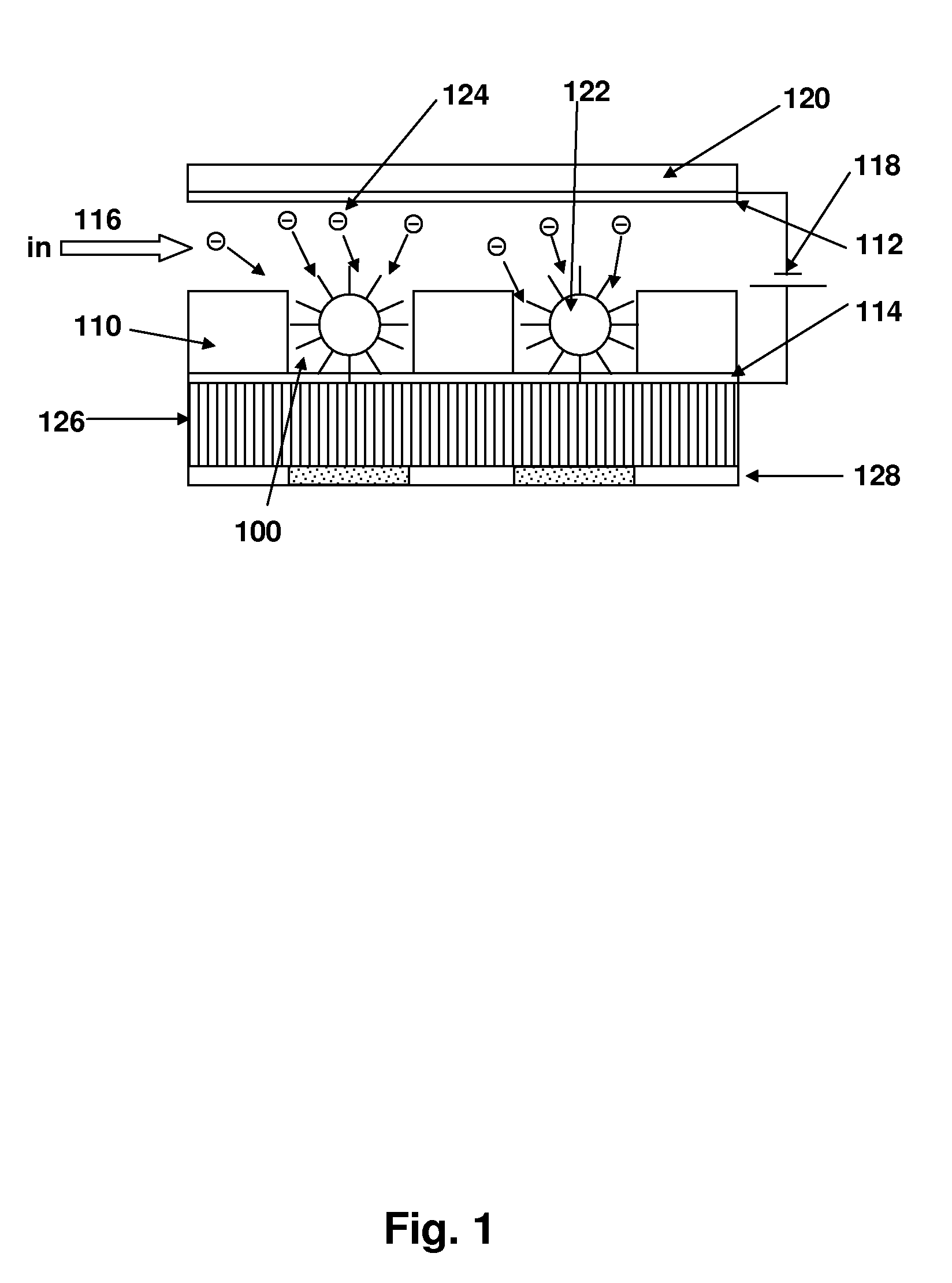
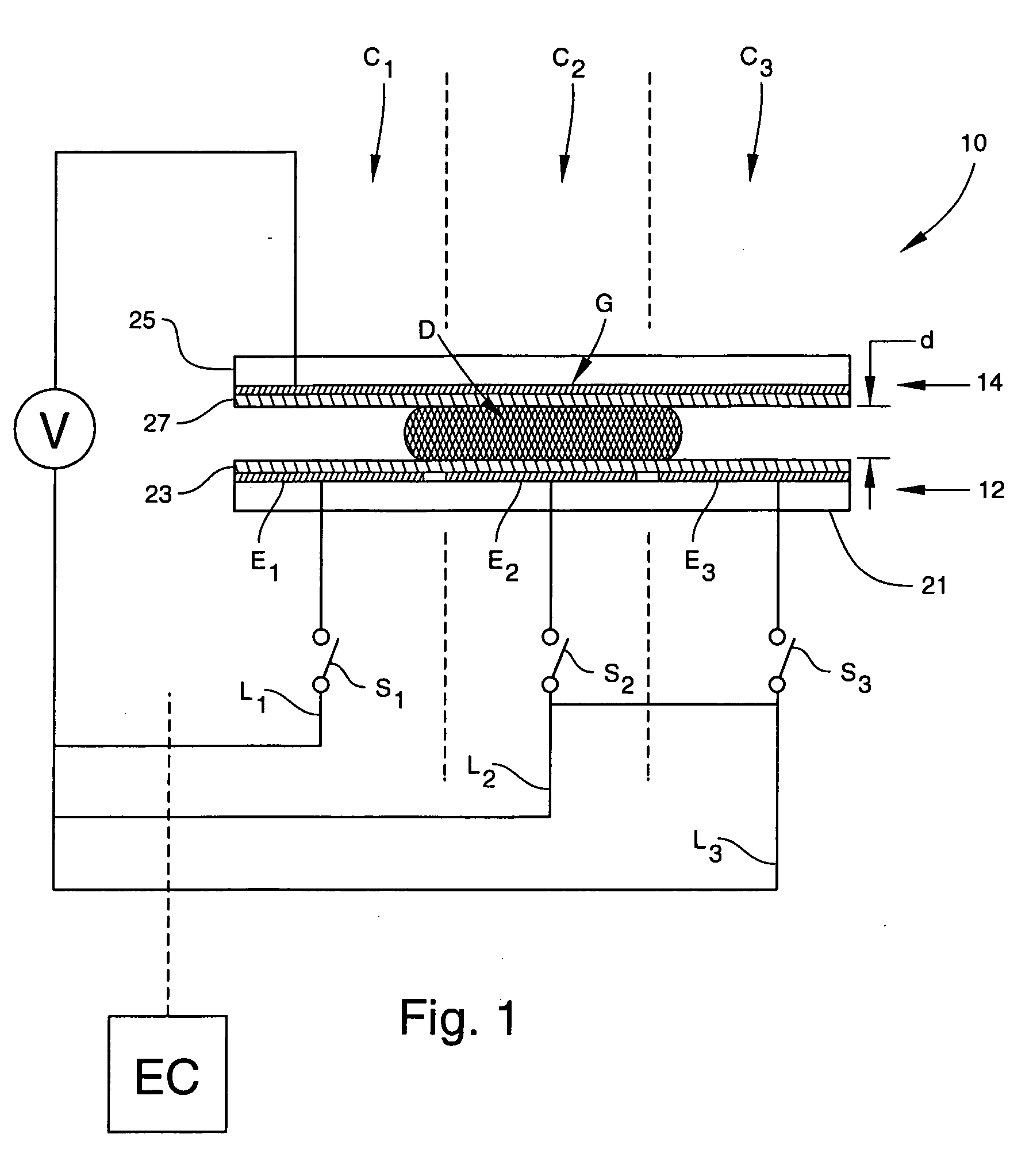
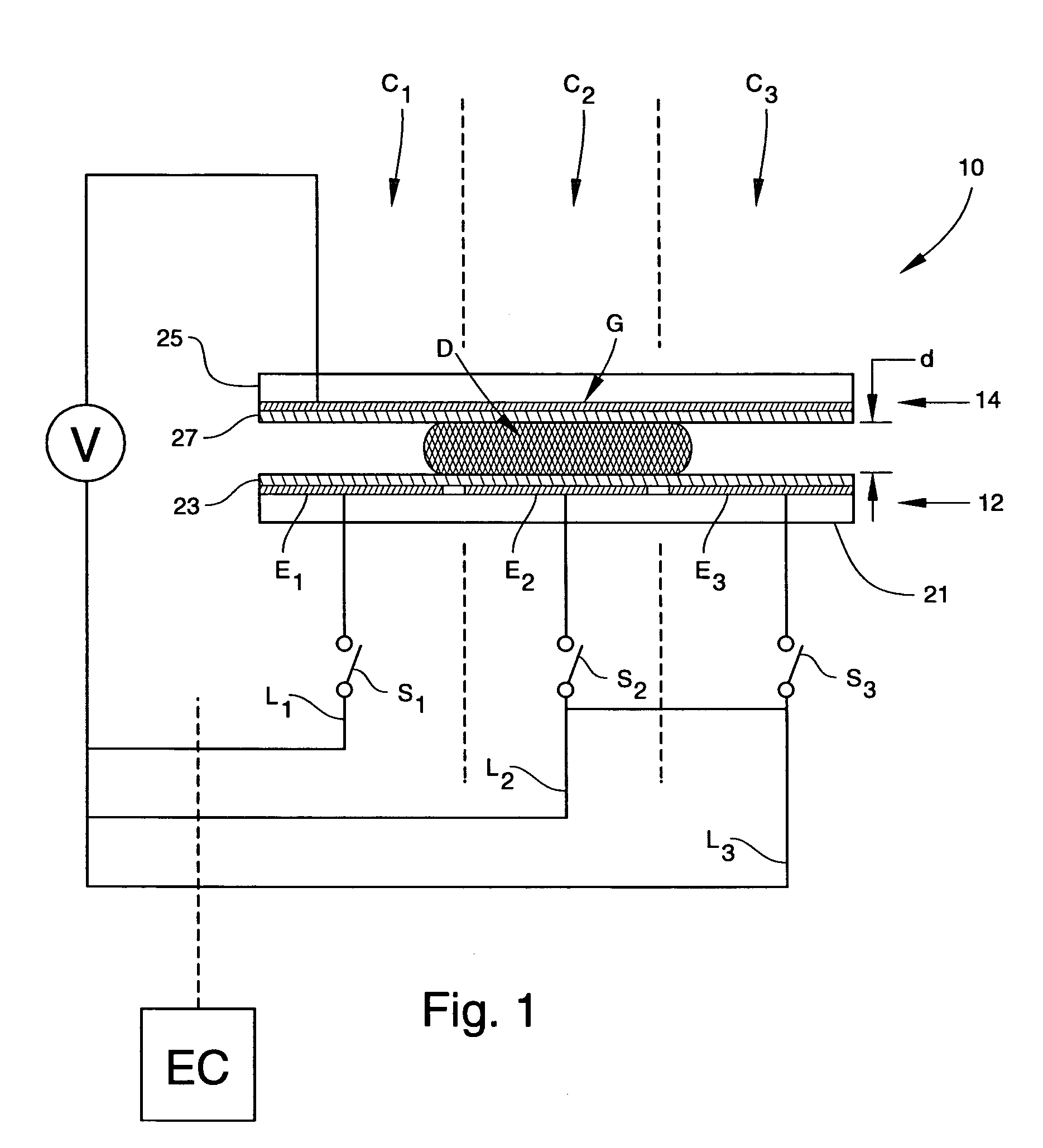
Methods for manipulating droplets by electrowetting-based techniques
InactiveUS20060054503A1Improve controllabilityImprove accuracySludge treatmentShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersElectricityEngineering
Methods are provided for manipulating droplets. The methods include providing the droplet on a surface comprising an array of electrodes and a substantially co-planer array of reference elements, wherein the droplet is disposed on a first one of the electrodes, and the droplet at least partially overlaps a second one of the electrodes and an intervening one of the reference elements disposed between the first and second electrodes. The methods further include activating the first and second electrodes to spread at least a portion of the droplet across the second electrode and deactivating the first electrode to move the droplet from the first electrode to the second electrode.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Filler fluids for droplet operations
ActiveUS20070242105A1Reduces and eliminates build-upImprove efficiencyElectrostatic separatorsFixed microstructural devicesEngineeringLiquid drop
The present invention relates to filler fluids for droplet operations. According to one embodiment of this aspect, a droplet microactuator is provided and includes: (a) a first substrate comprising electrodes configured for conducting droplet operations on a surface of the substrate; (b) a second substrate spaced from the surface of the substrate by a distance sufficient to define an interior volume between the first substrate and second substrate, wherein the distance is sufficient to contain a droplet disposed in the space on the first substrate; and (c) a droplet arranged in the interior volume and arranged with respect to the electrodes in a manner which permits droplet operations to be effected on the droplet using the electrodes.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
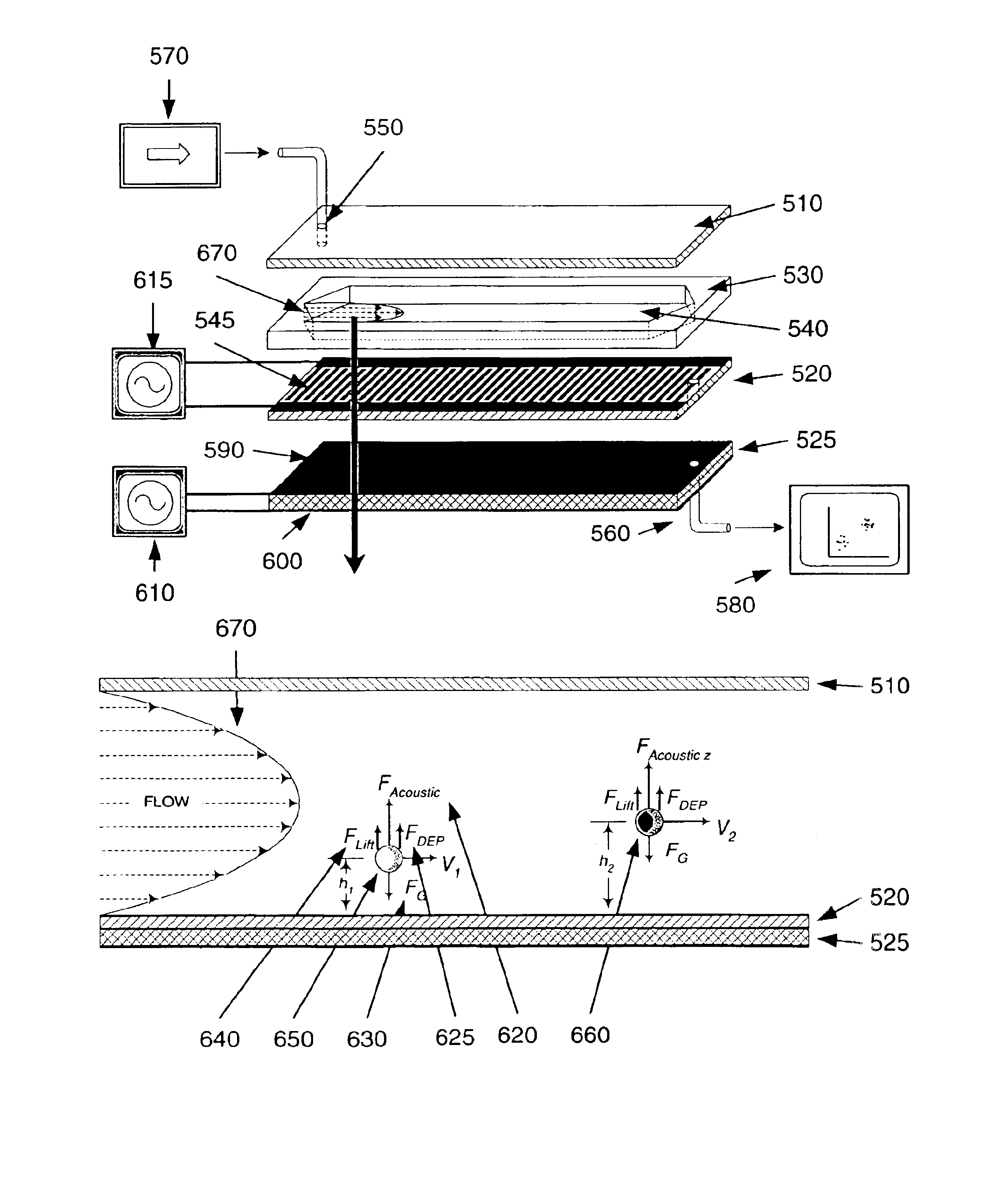
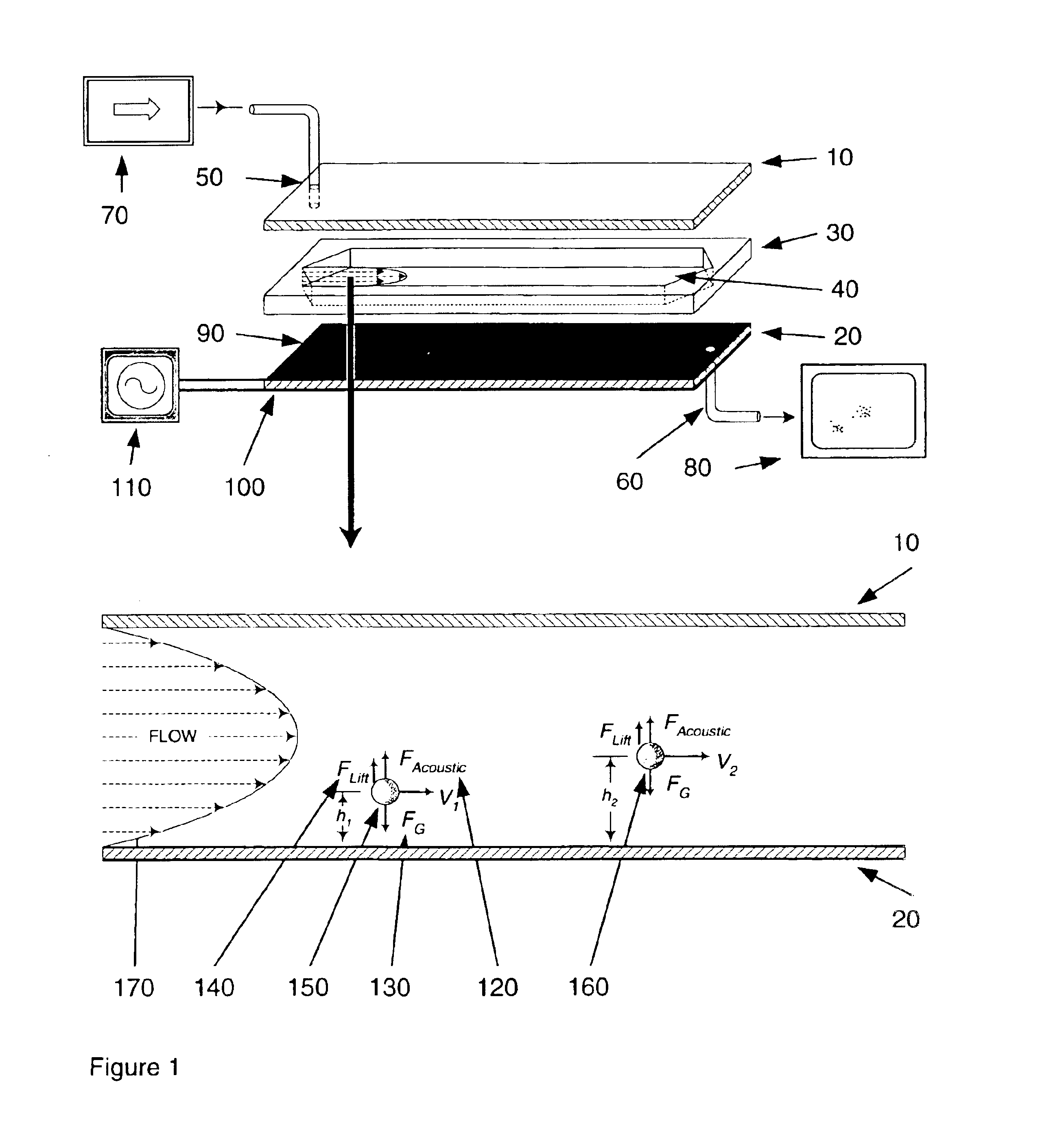
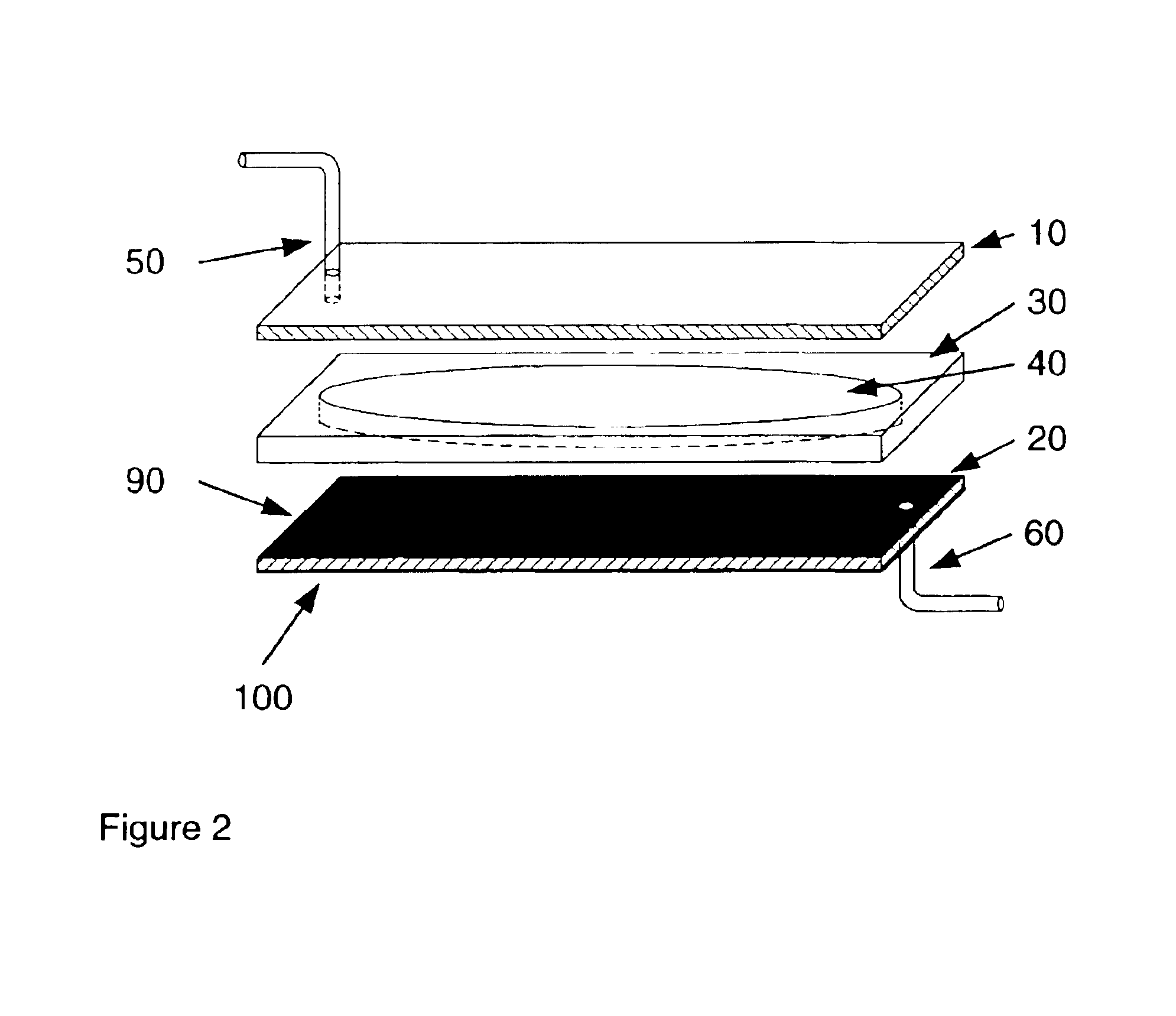
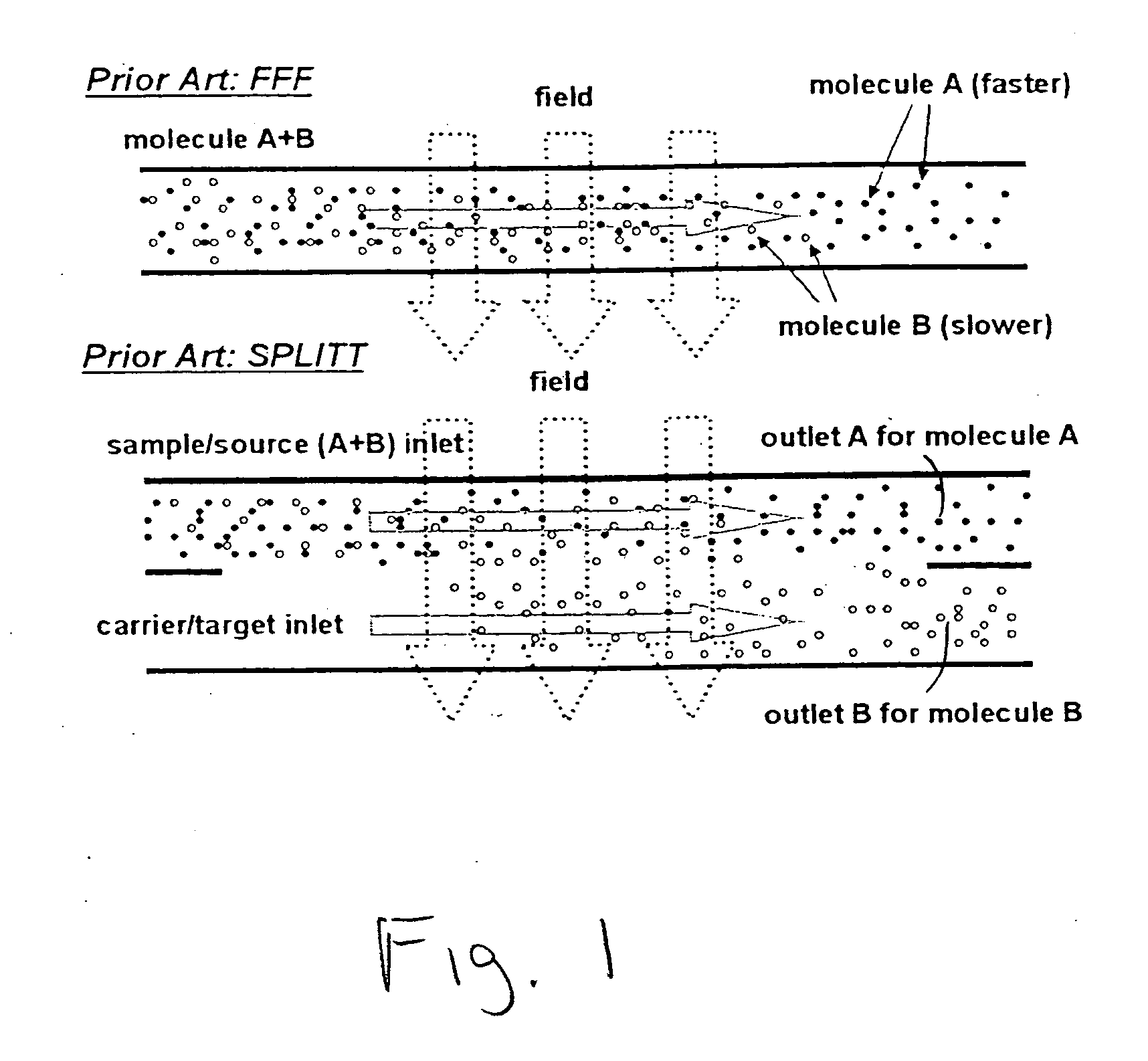
Apparatuses and methods for field flow fractionation of particles using acoustic and other forces
InactiveUS6881314B1Easy to separateEfficient separationDielectrophoresisElectrostatic separatorsElectrophoresisDielectrophoretic force
This invention relates generally to the field of field-flow-fractionation. In particular, the invention provides apparatuses and methods for the discrimination of matters utilizing acoustic force, or utilizing acoustic force with electrophoretic or dielectrophoretic force, in field flow fractionation.
Owner:AVIVA BIOISCI CORP +2
Electrochemical device for moving particles covered with protein
InactiveUS6972080B1Efficient disposalElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentBlood componentElectrolysis
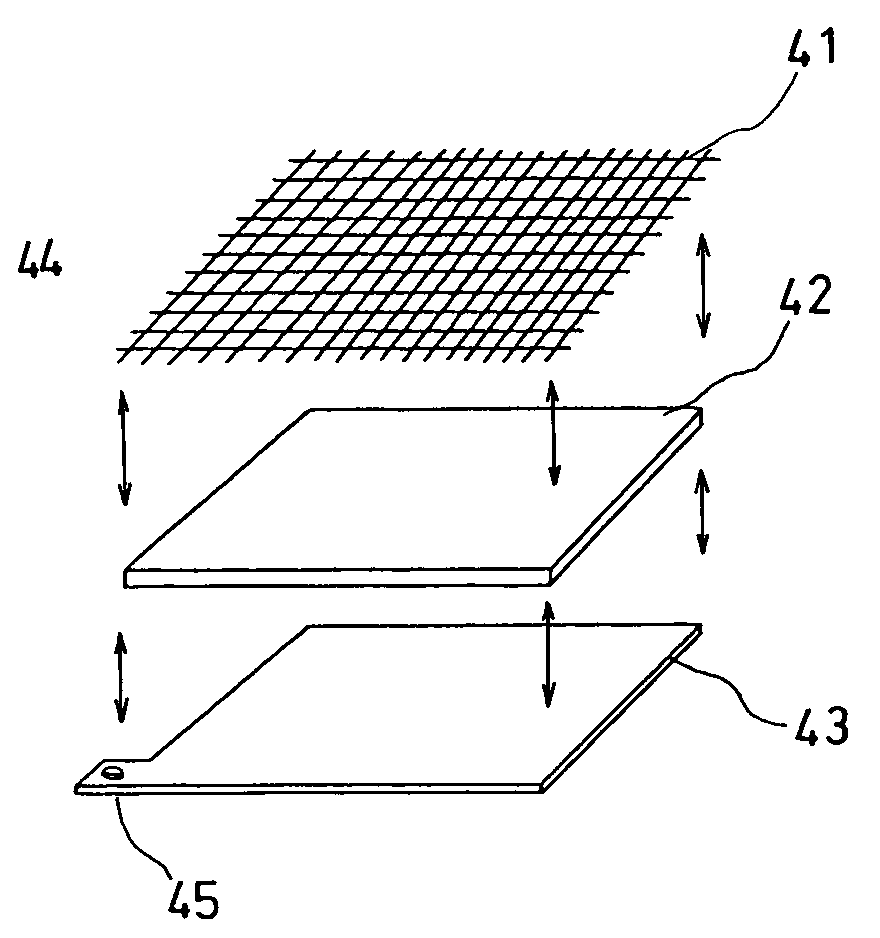
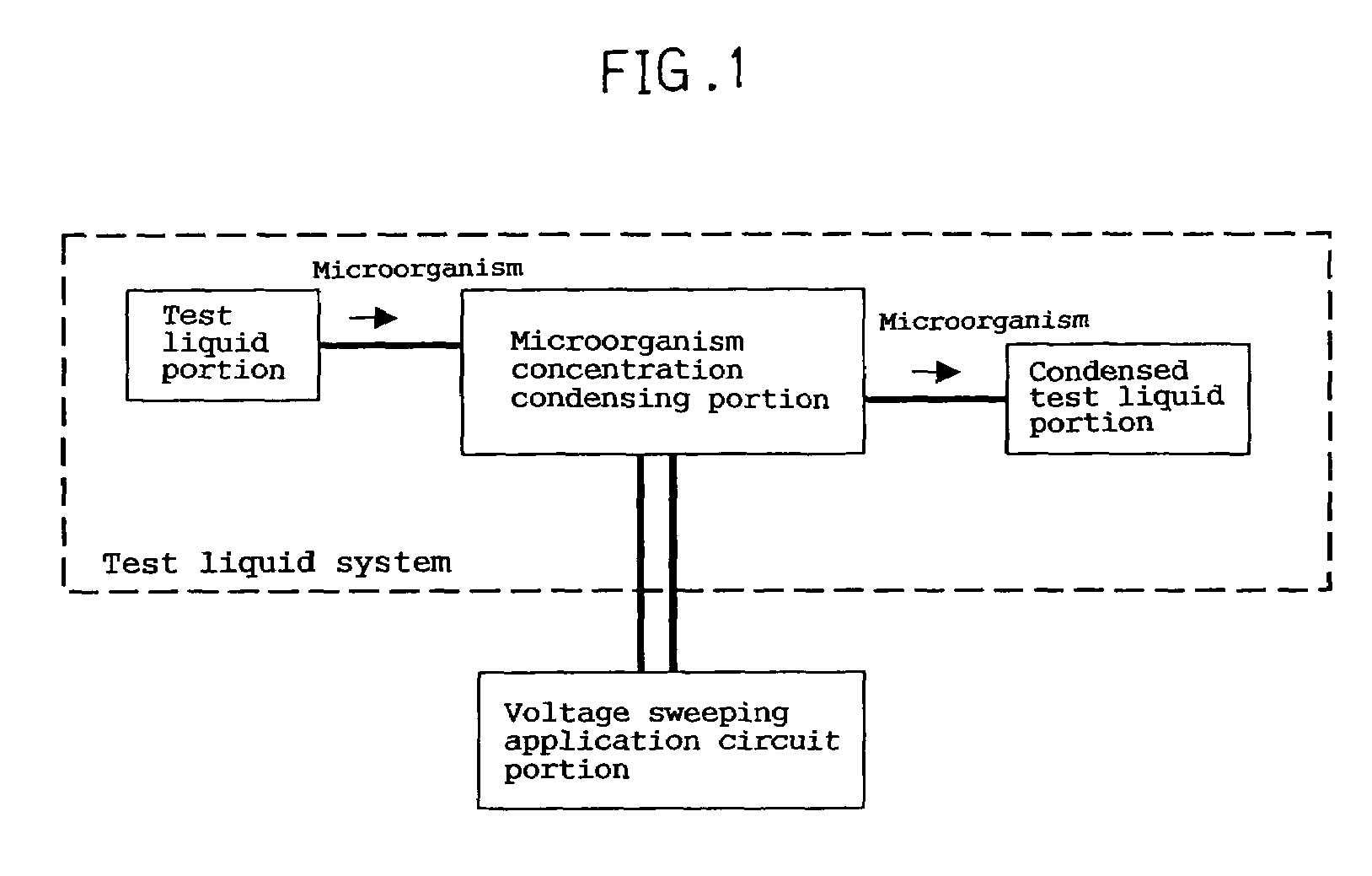
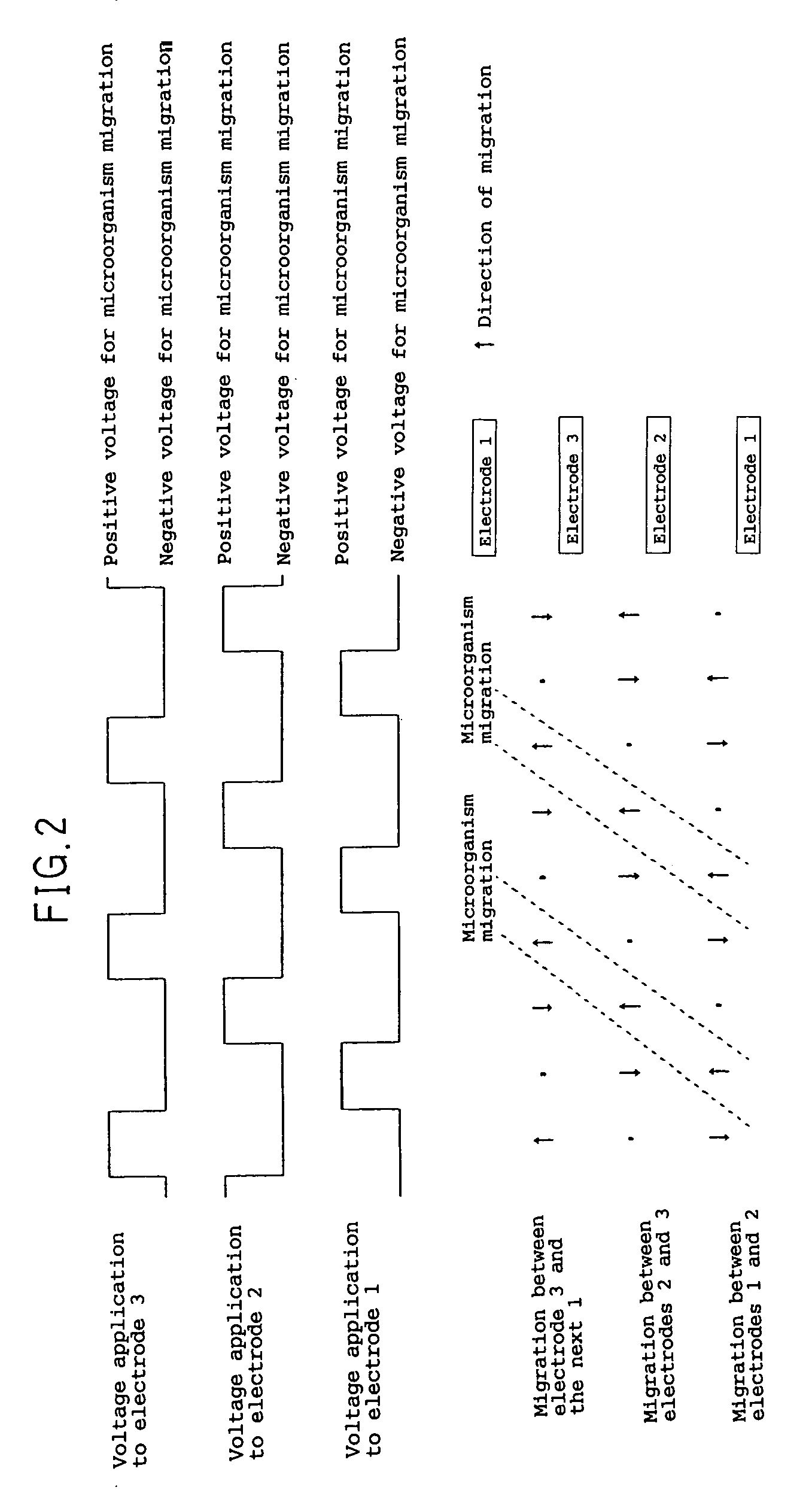
An electrochemical device for moving particles covered with a protein is provided. The device includes at least two electrodes that are in contact with a liquid containing the protein-covered particles and a circuit that generates a potential difference in a range that does not cause electrolysis of the liquid between the electrodes. The particles are moved by electrophoresis in the direction of the arrangement of the electrodes. The invention provided herein has numerous applications, including use in a microorganism concentration condensing device, a blood component induction device, and / or a blood component induction method, and / or an electric appliance that decreases the concentration of microorganisms present on the surface of a heat exchanger.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
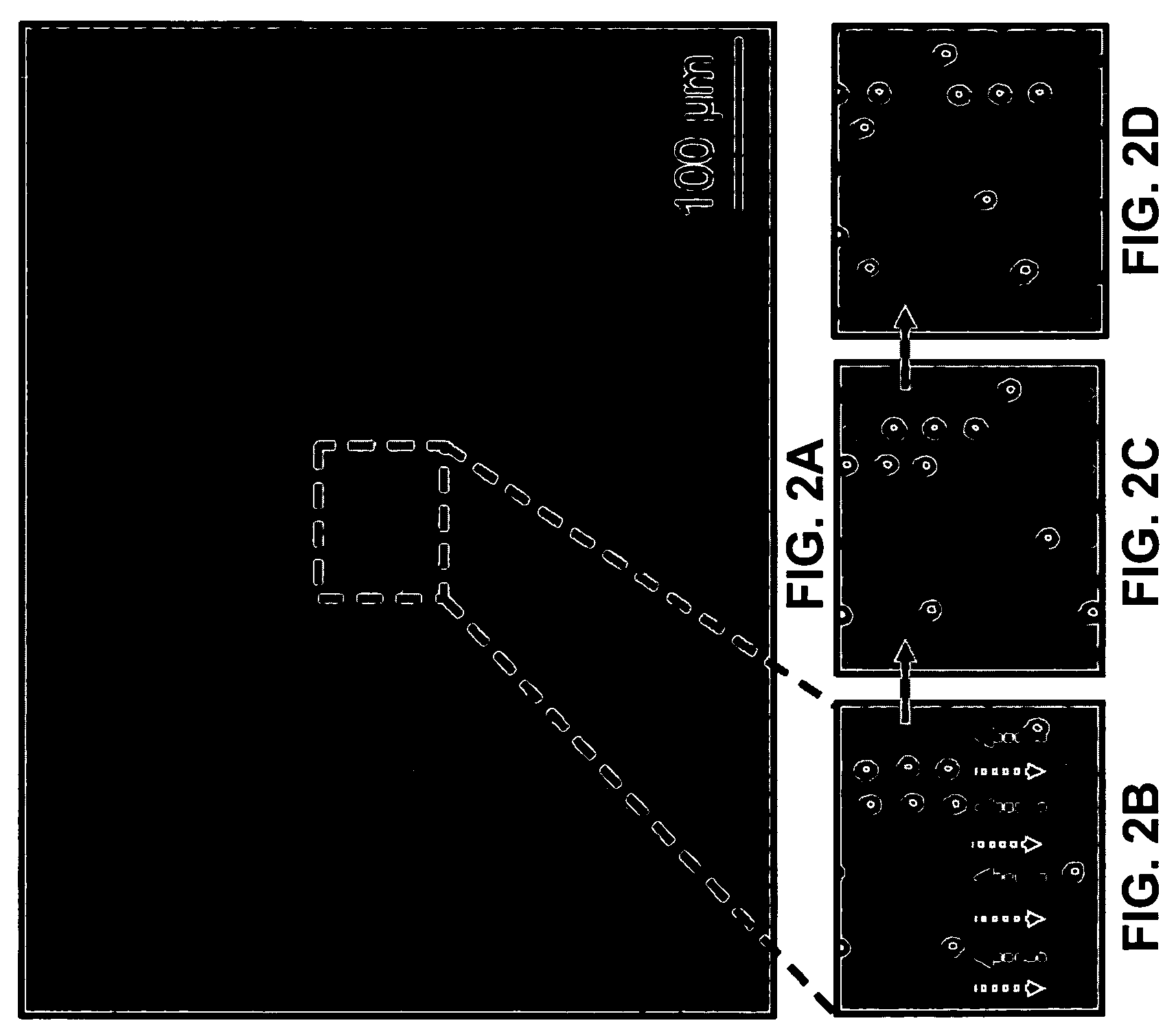
Optoelectronic tweezers for microparticle and cell manipulation
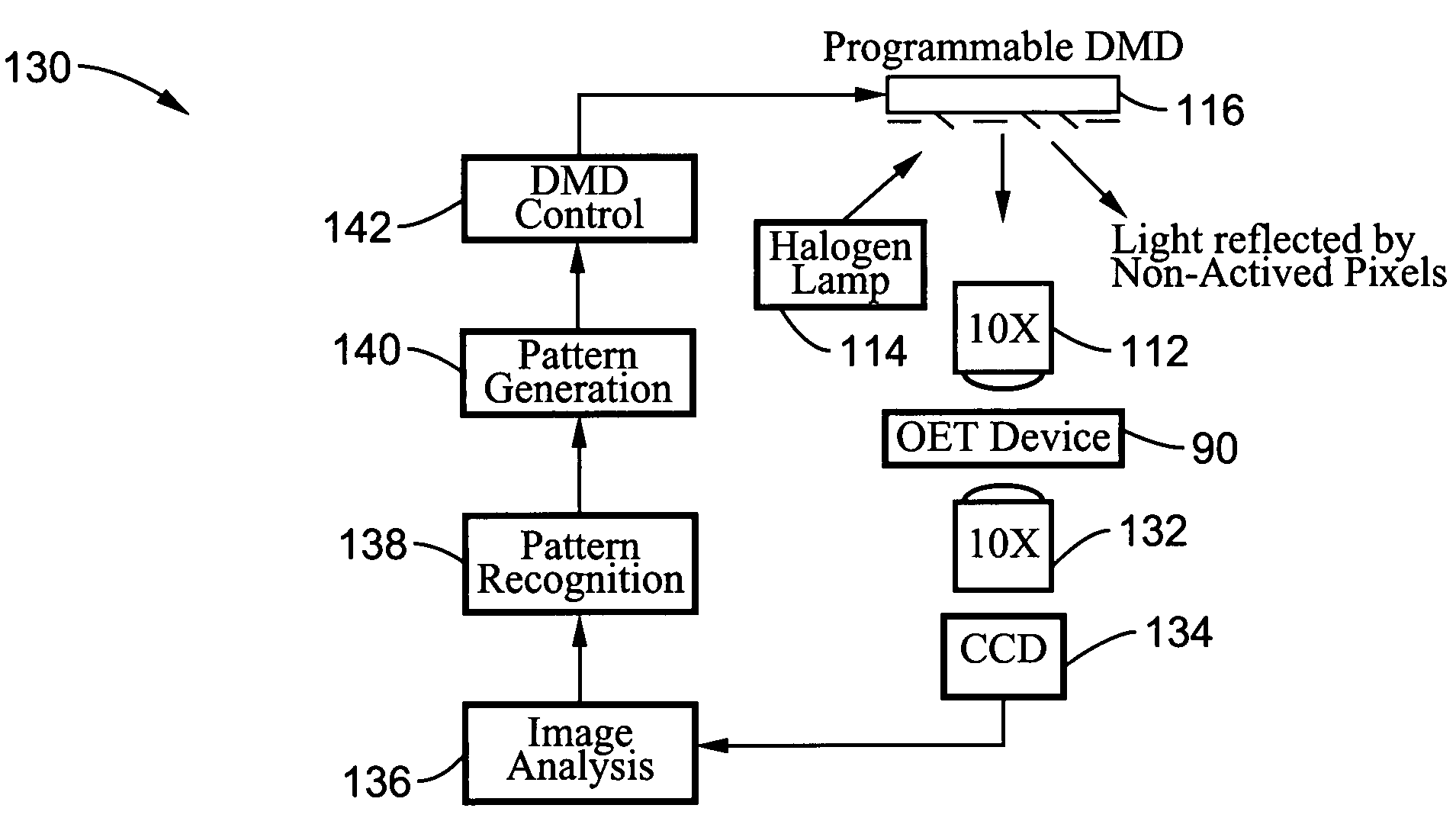
ActiveUS7612355B2Easy to operateEasy to createElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentMicroparticleOpto electronic
An optical image-driven light induced dielectrophoresis (DEP) apparatus and method are described which provide for the manipulation of particles or cells with a diameter on the order of 100 μm or less. The apparatus is referred to as optoelectric tweezers (OET) and provides a number of advantages over conventional optical tweezers, in particular the ability to perform operations in parallel and over a large area without damage to living cells. The OET device generally comprises a planar liquid-filled structure having one or more portions which are photoconductive to convert incoming light to a change in the electric field pattern. The light patterns are dynamically generated to provide a number of manipulation structures that can manipulate single particles and cells or groups of particles / cells. The OET preferably includes a microscopic imaging means to provide feedback for the optical manipulation, such as detecting position and characteristics wherein the light patterns are modulated accordingly.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method and apparatus for the manipulation of particles by means of dielectrophoresis
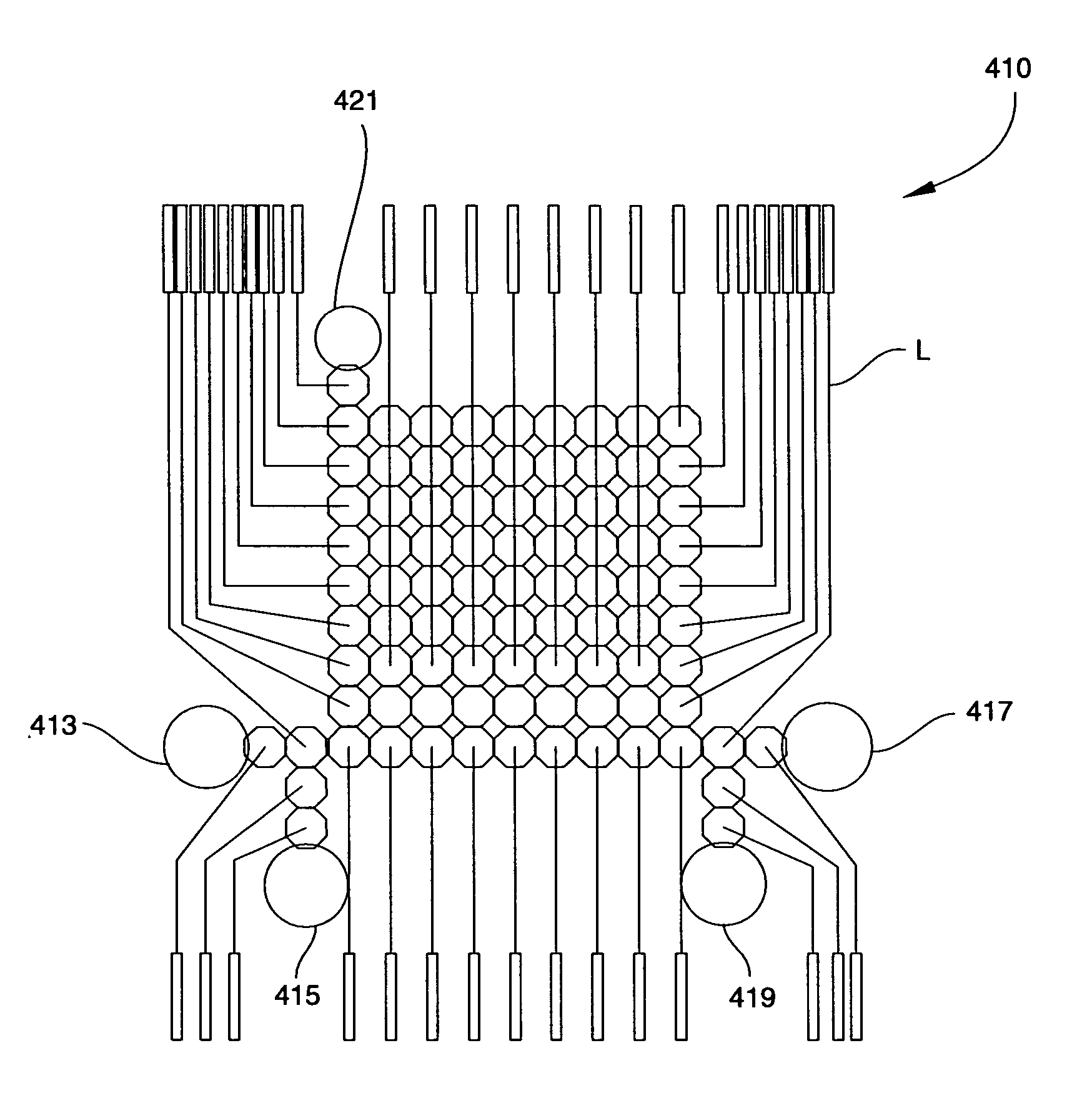
InactiveUS6942776B2Increase rangeAvoid the needElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentPlanar substrateEngineering
An apparatus and method for establishing closed dielectrophoretic potential cages and precise displacement thereof comprising a first array of selectively addressable electrodes, lying on a substantially planar substrate and facing toward a second array comprising one electrode. The arrays define the upper and lower bounds of a micro-chamber where particles are placed in liquid suspension. By applying in-phase and counter-phase periodic signals to electrodes, one or more independent potential cages are established which cause particles to be attracted to or repelled from cages according to signal frequency and the dielectric characteristics of the particles and suspending medium. By properly applying voltage signal patterns into arrays, cages may trap one or more particles, thus permitting them to levitate steadily and / or move. In the preferred embodiment, where one array is integrated on a semiconductor substrate, displacement of particles can be monitored by embedded sensors.
Owner:SILICON BIOSYSTEMS SPA +1
Microfluidic control using dielectric pumping
InactiveUS6949176B2High-performance operationImprove reliabilityElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentMiniaturizationEngineering
Devices and methods utilizing dielectric pumping and variable dielectric pumping to move fluids through microchannels. Two fluids having dissimilar dielectric constants form an interface that is positioned between two electrodes in order to move the interface and therefore the fluids. Dielectric pumping and variable dielectric pumping may be used to move fluids in miniaturized analytical packages containing microchannels in which forces created by surface tension predominate over the gravitational force.
Owner:NEOPHOTONICS CORP
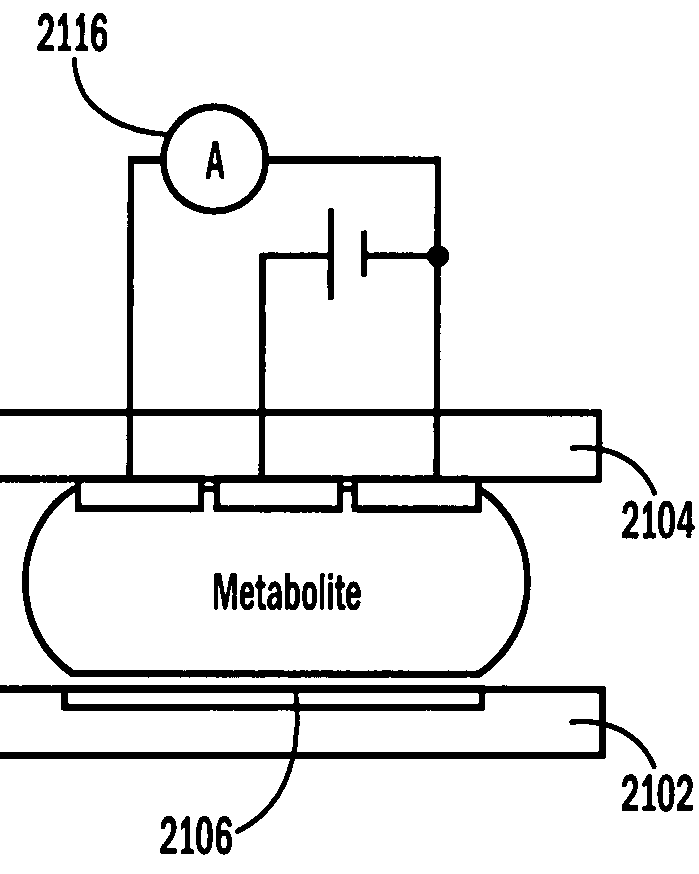
Droplet-based diagnostics
InactiveUS20070242111A1Reduces and eliminates build-upImprove efficiencyElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentEngineeringMicroactuator
The present invention relates to droplet-based diagnostics. According to one embodiment, a droplet microactuator system is provided and includes: (a) a droplet microactuator configured to conduct droplet operations; and (b) a sensor configured in a sensing relationship with the droplet microactuator, such that the sensor is capable of sensing a signal from and / or a property of one or more droplets on the droplet microactuator.
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC
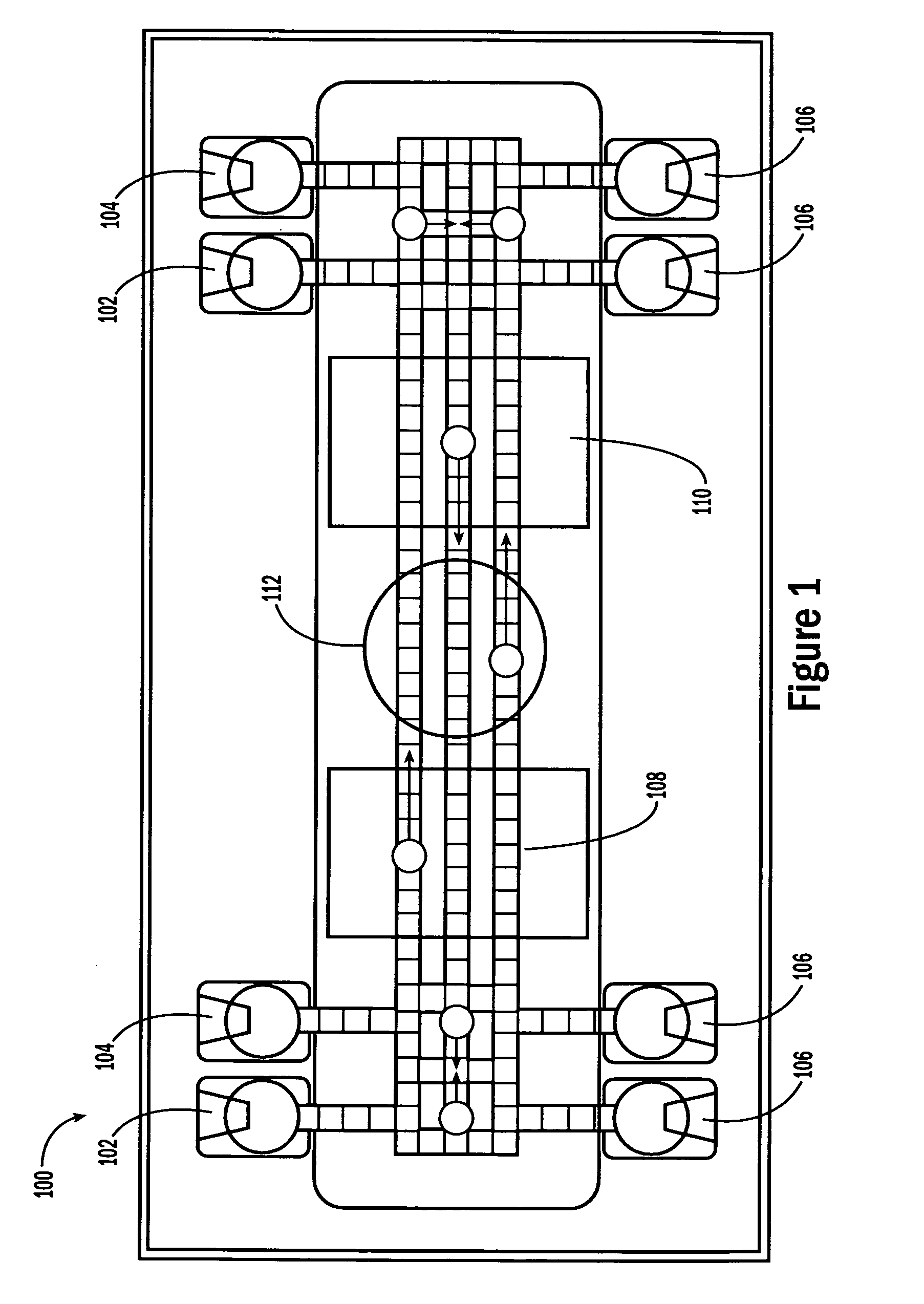
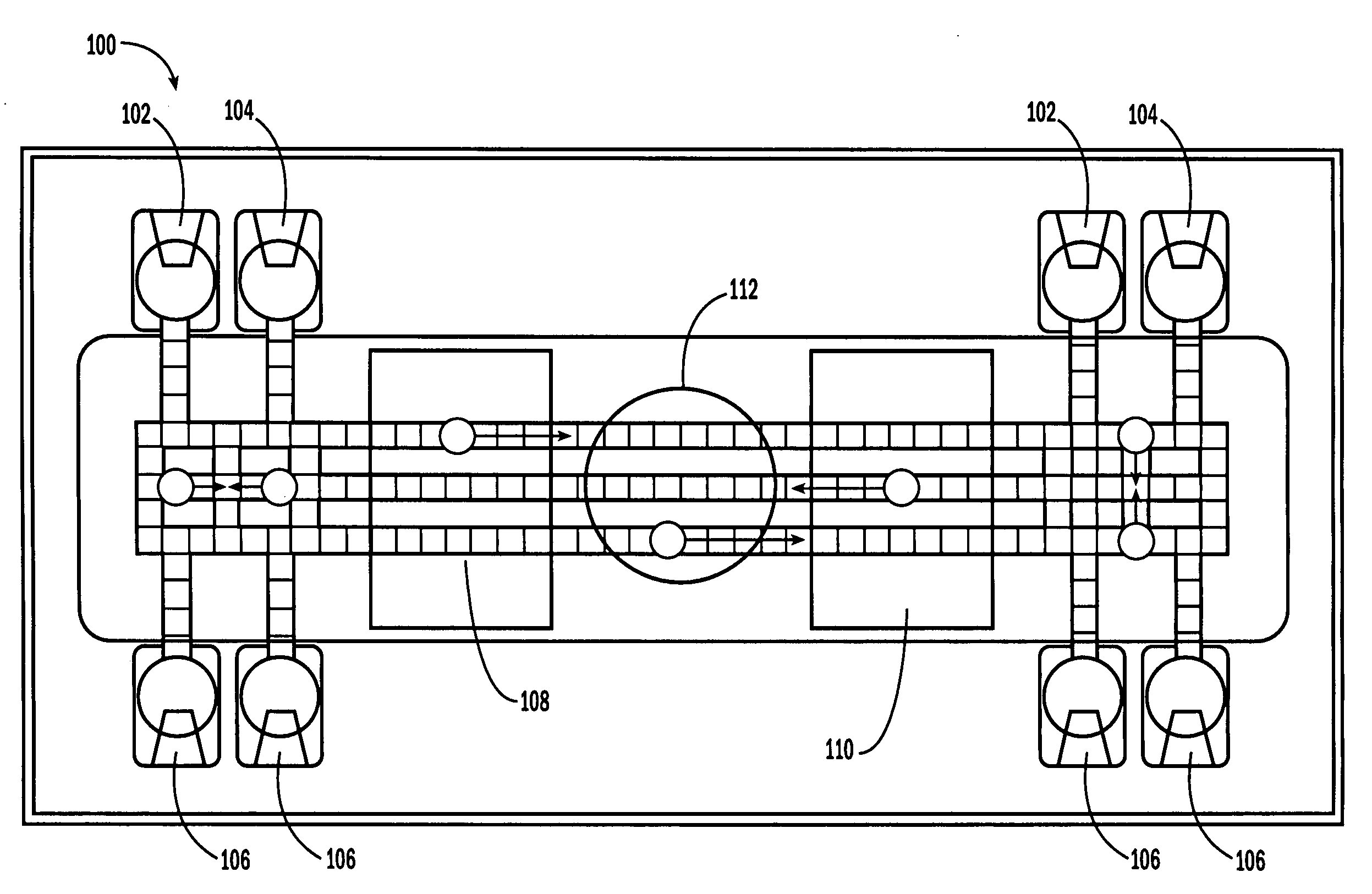
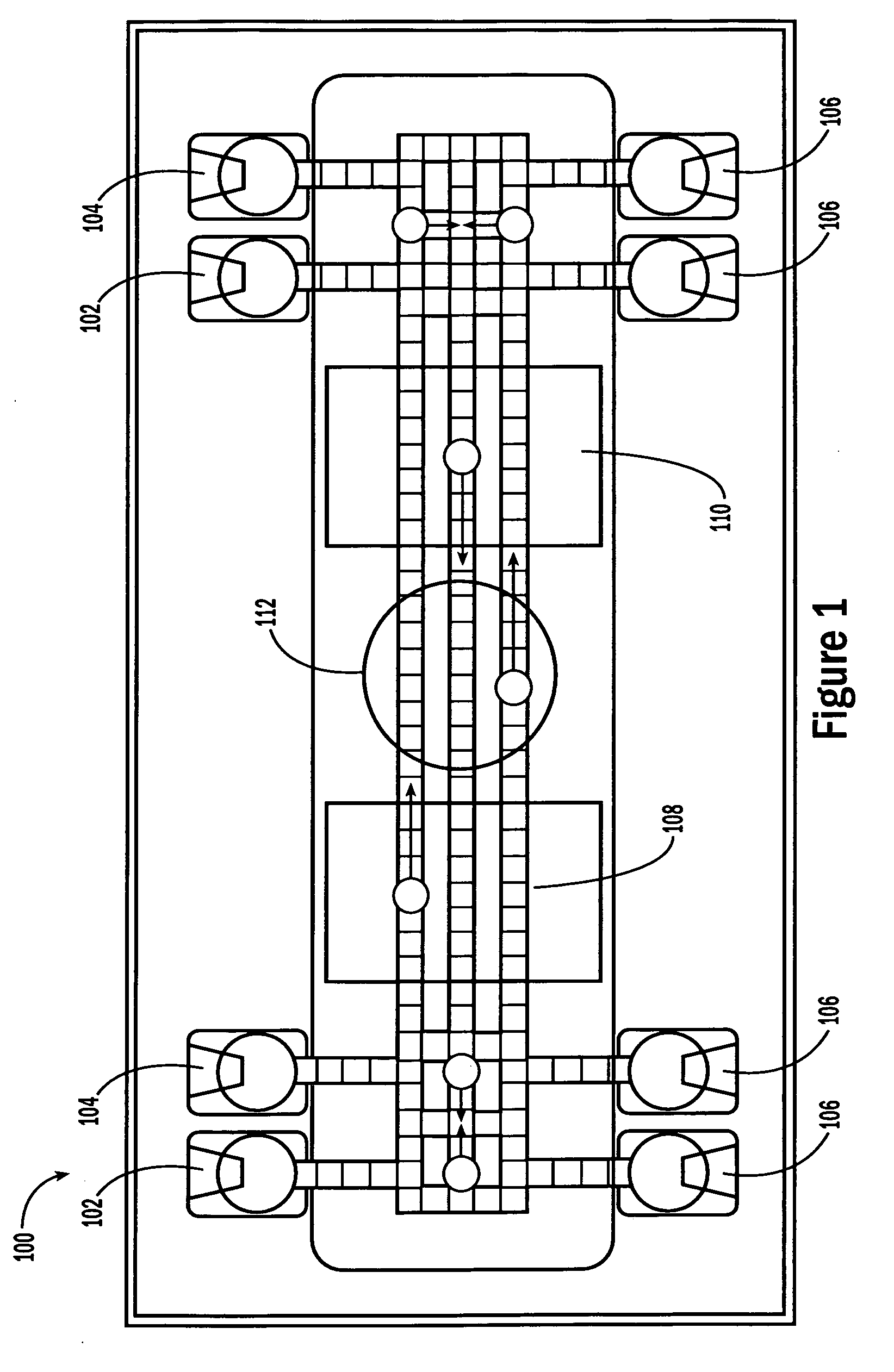
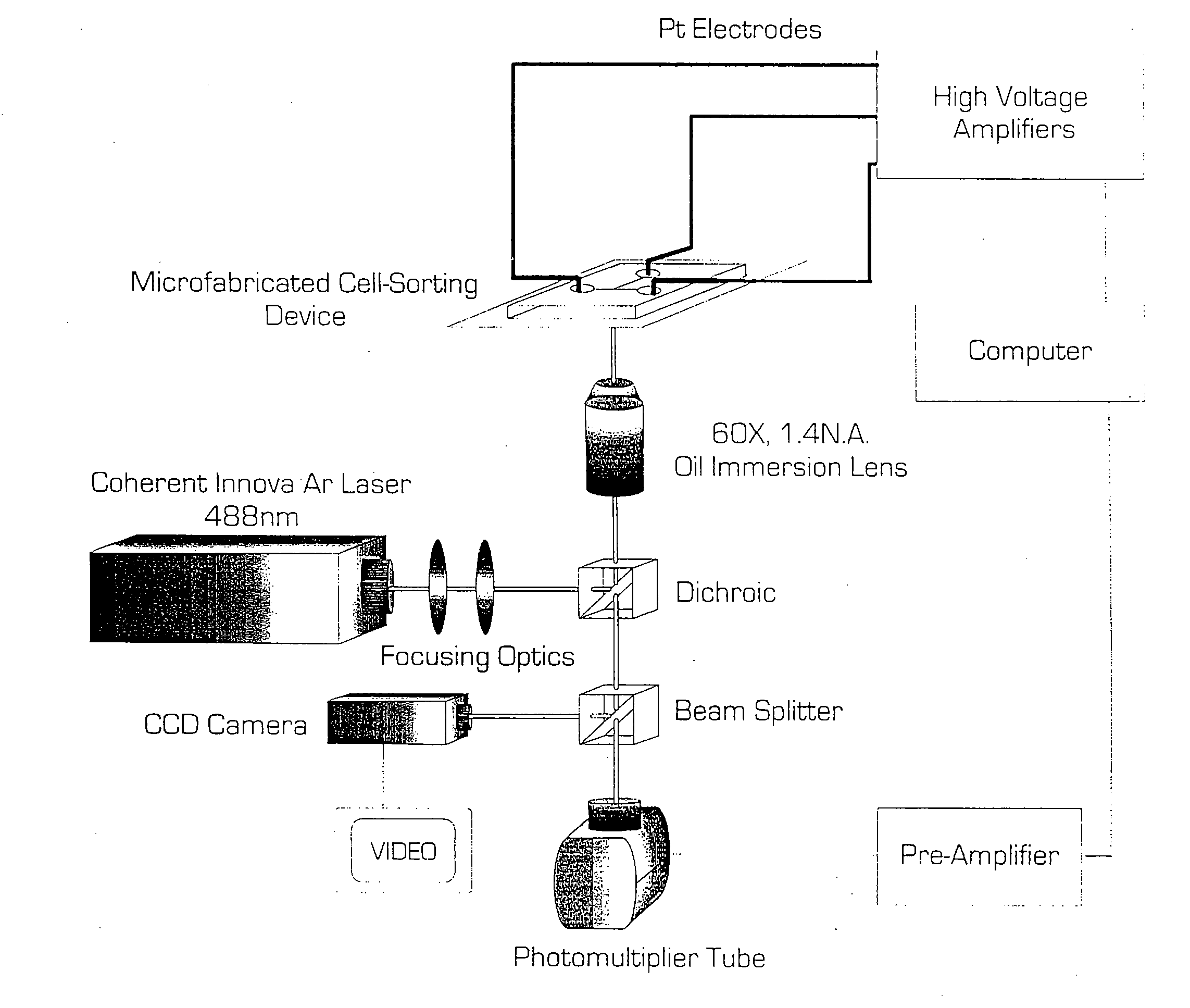
Microfabricated Cell Sorter
InactiveUS20080176211A1Efficient separationIncrease chanceImmobilised enzymesSludge treatmentInlet channelCell sorter
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
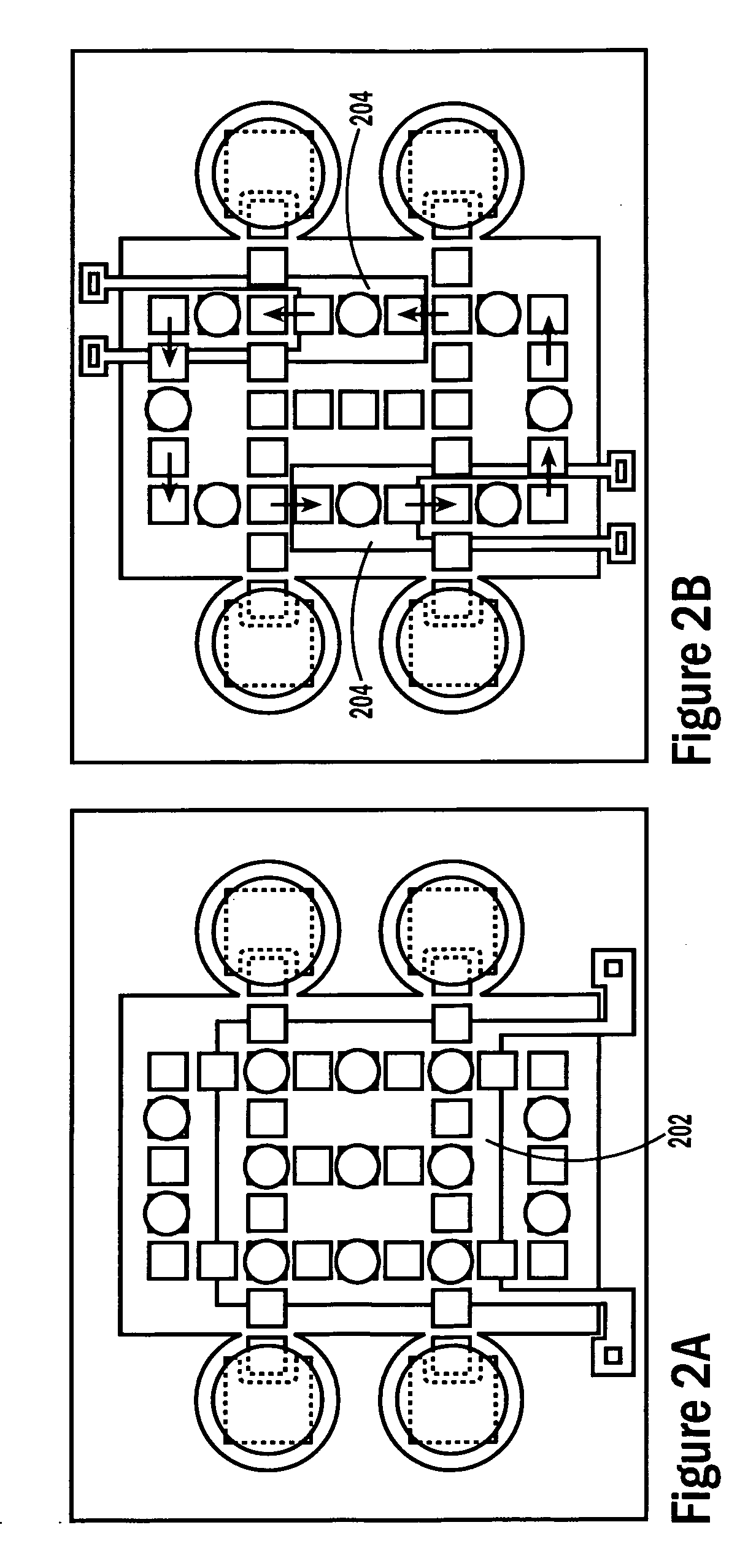
Single-sided lateral-field and phototransistor-based optoelectronic tweezers
ActiveUS7956339B2Good flexibilityElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentDielectrophoretic forceCell culture media
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Droplet microactuator system
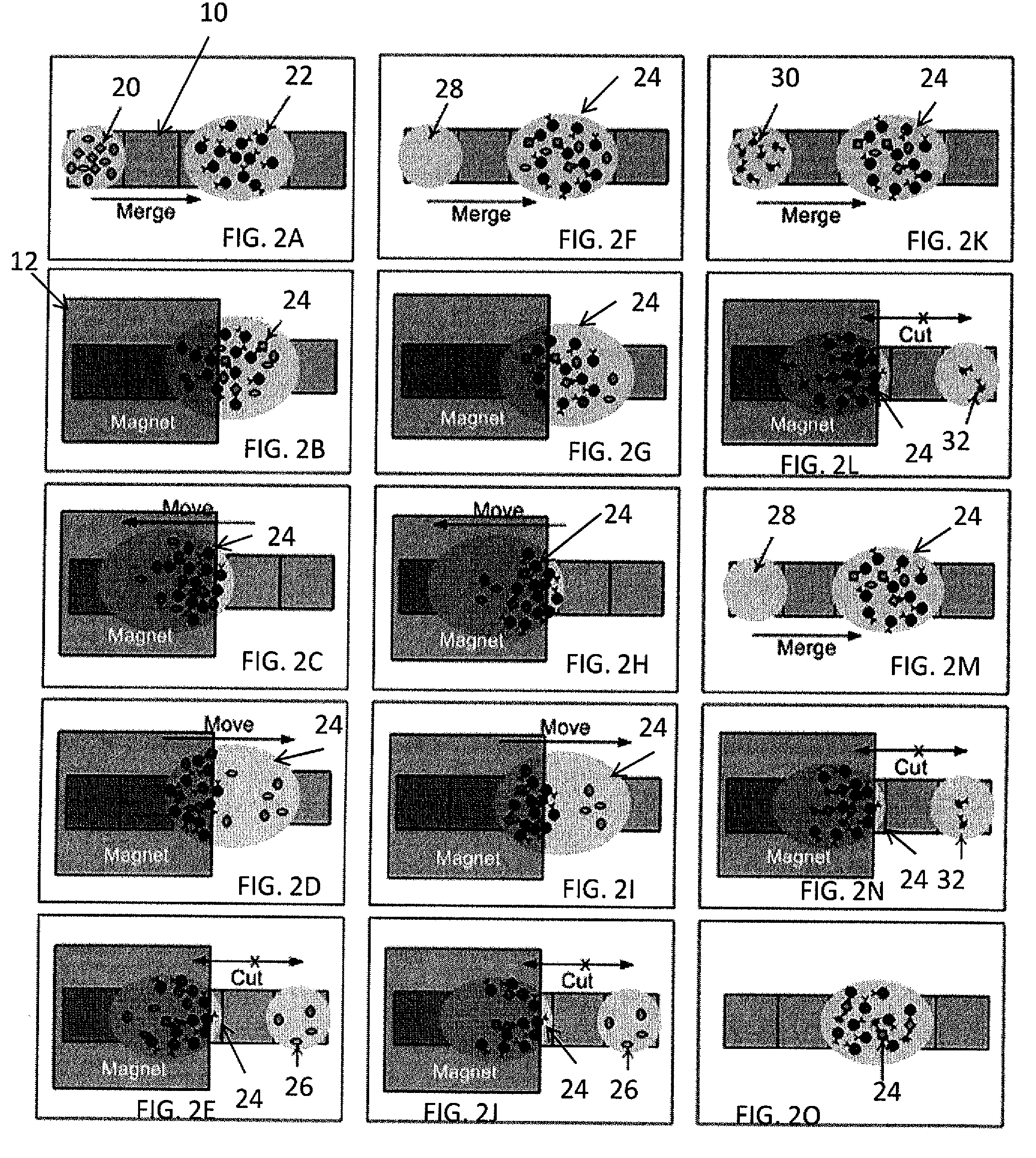
InactiveUS7815871B2Reduces and eliminates build-upImprove efficiencyElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentControl theoryMicroactuator
The present invention relates to a droplet microactuator system. According to one embodiment, the droplet microactuator system includes: (a) a droplet microactuator configured to conduct droplet operations; (b) a magnetic field source arranged to immobilize magnetically responsive beads in a droplet during droplet operations; (c) a sensor configured in a sensing relationship with the droplet microactuator, such that the sensor is capable of sensing a signal from and / or a property of one or more droplets on the droplet microactuator; and (d) one or more processors electronically coupled to the droplet microactuator and programmed to control electrowetting-mediated droplet operations on the droplet actuator and process electronic signals from the sensor.
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC
Universal sample preparation system and use in an integrated analysis system
The invention provides for devices and methods for interfacing microchips to cartridges and pneumatic manifolds. The cartridges, microchips, and pneumatic manifolds can be integrated with downstream preparation devices, such as thermal regulating devices and separation and analysis devices.
Owner:INTEGENX
Method for Controlling a Communication Between Two Areas By Electrowetting, a Device Including Areas Isolatable From Each Other and Method for making Such a Device
InactiveUS20090134027A1Good flexibilityElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentLiquid stateBiomedical engineering
Device for displacing drops of liquid by electrowetting, and a method for isolating two areas delimited by at least one wall including a step for:placing by electrowetting, in an aperture of said wall, a substance capable of reacting to at least one external stimulus in order to pass from a liquid state to a gel or solid state, forming a closure member.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Droplet actuation system and method
InactiveUS7816121B2Reduces and eliminates build-upImprove efficiencyElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentTemperature controlElectrical and Electronics engineering
A droplet actuation system is provided including a droplet actuation device including a substrate that includes electrodes for conducting droplet operations; temperature control means for heating and / or cooling a region of the droplet actuation device and arranged such that a droplet can be transported on the electrodes to a region for heating; and a means for effecting a magnetic field in proximity to one or more of the electrodes sufficient to immobilize magnetically responsive beads in a droplet on the substrate during droplet operations. The system further includes a processor for controlling the electrodes and temperature control means, wherein the processor is programmed, and electrodes and magnetic field are arranged, to cause the electrodes to split a droplet including the magnetically responsive beads yielding a first daughter droplet which includes the magnetically responsive beads and a second daughter droplet without a substantial amount of the magnetically responsive beads.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
Compositions and methods for separation of moieties on chips
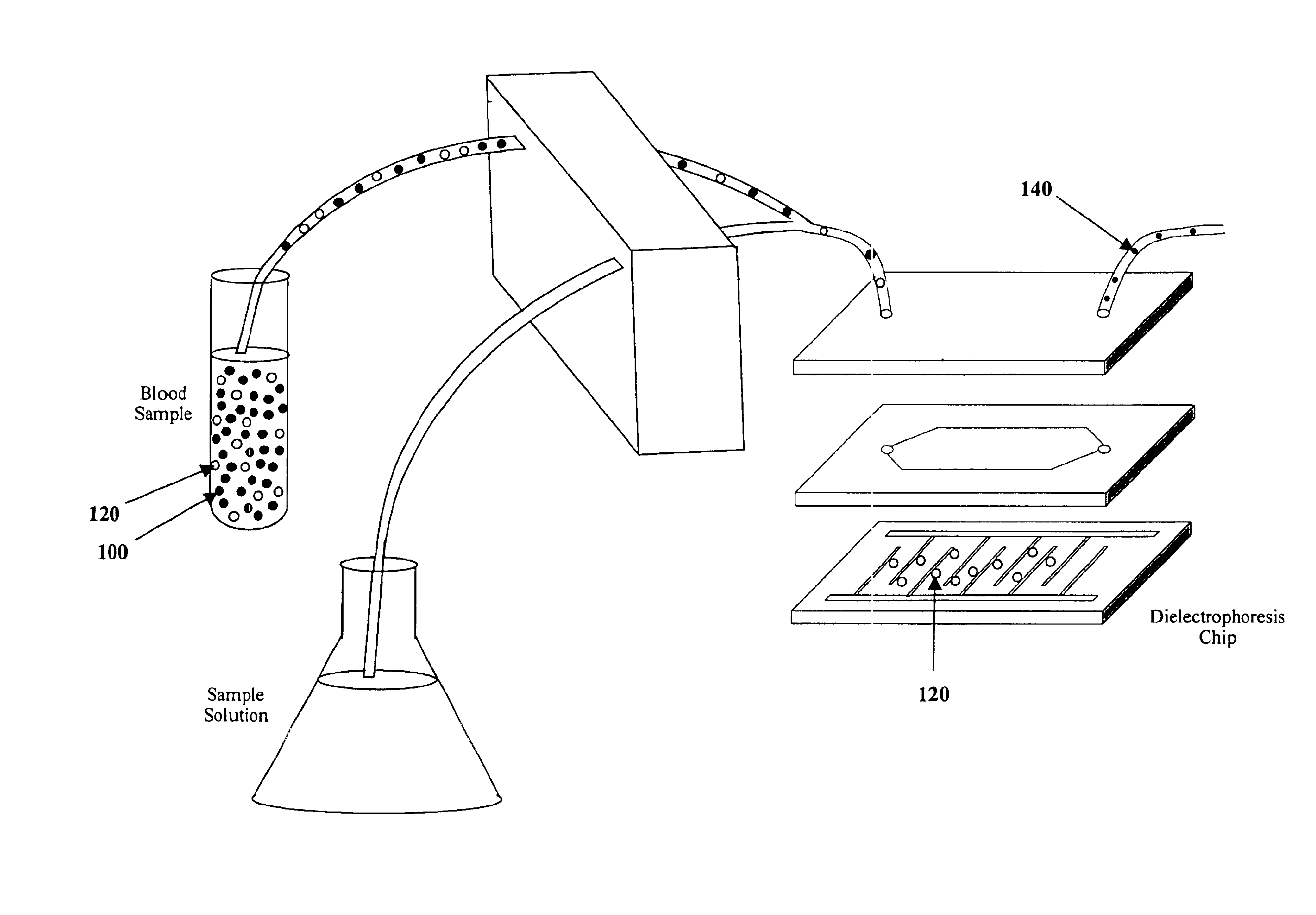
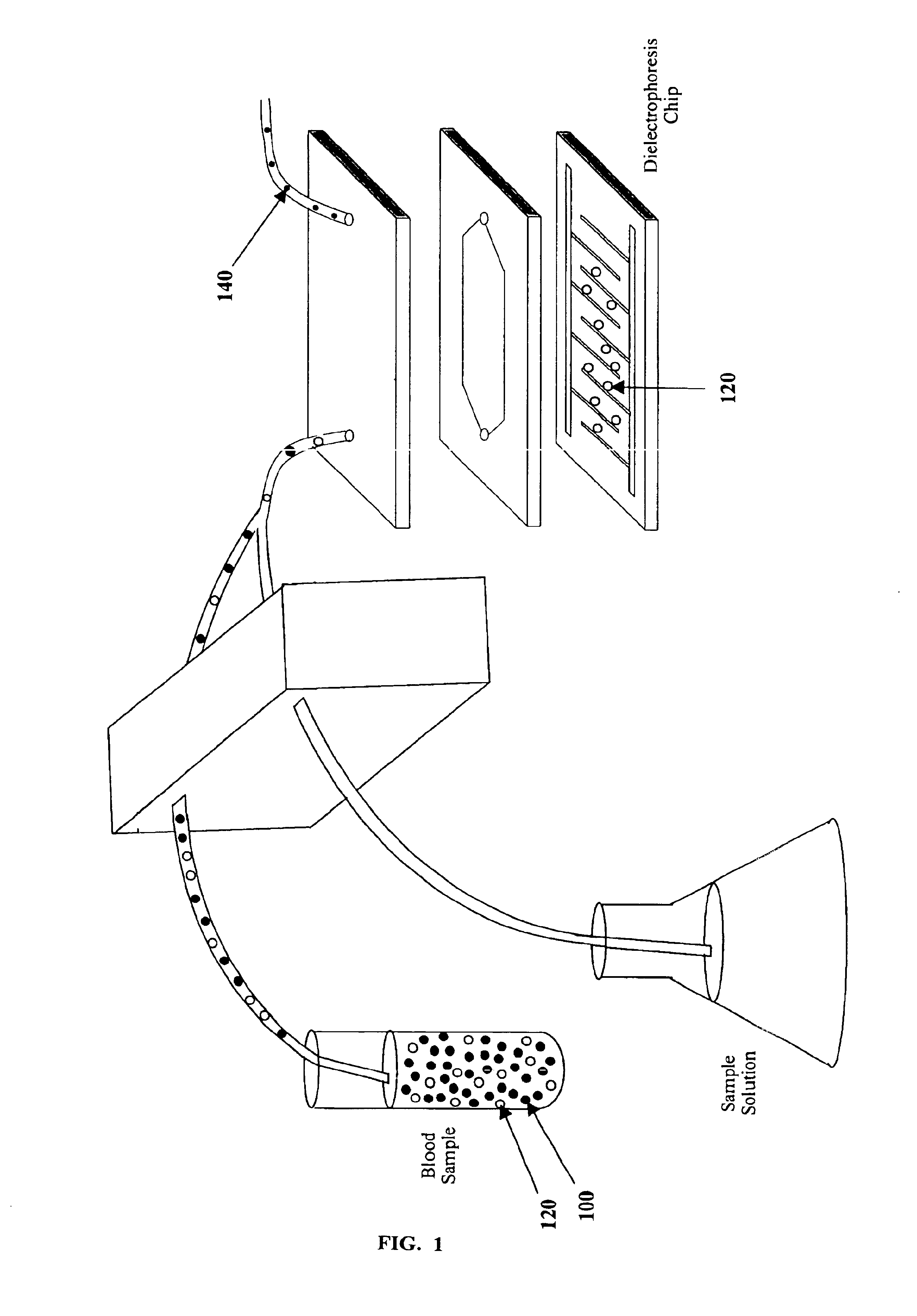
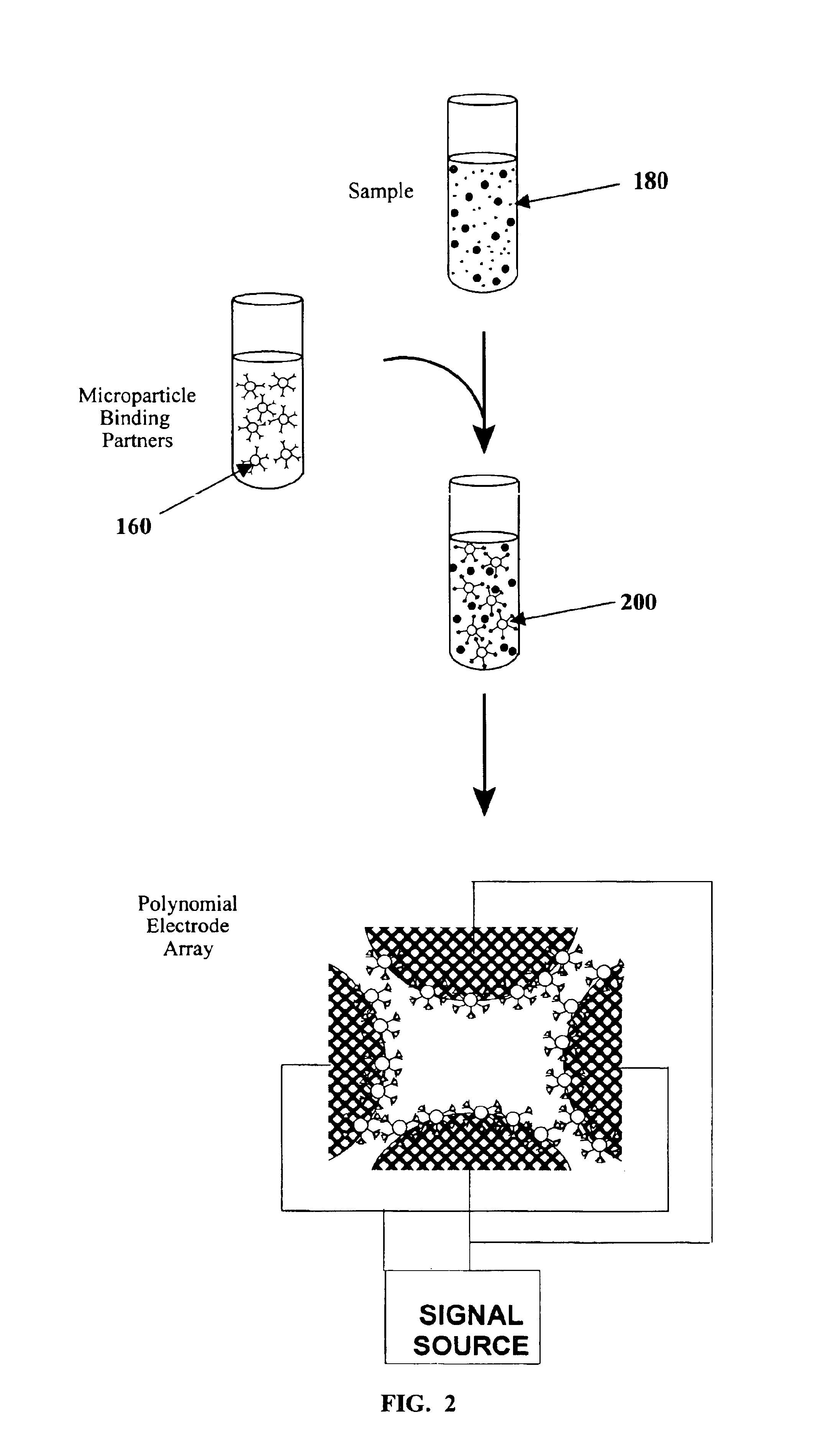
InactiveUS6858439B1Reliable methodMore separatedSequential/parallel process reactionsElectrostatic separatorsChemistryMicroparticle
The present invention recognizes that separation of components of a sample facilitate, and are often necessary for, sample analysis. Dielectrophoretic separation provides an efficient, reliable, nondisruptive, and automatable method for the separation of moieties in a sample based on their dielectric properties. The present invention provides compositions and methods for enhancing the dielectrophoretic separation of one or more moieties in a sample. A first aspect of the present invention is a solution that when mixed with a sample, modifies at least one dielectric property of one or more components of the sample and has a conductivity such that one or more moieties of the sample can be separated using dielectrophoresis. Such solutions can be used in the analysis of samples on chips, and can be used in methods that use binding partners, including microparticles that can be translocated by dielectrophoretic forces, traveling-wave dielectrophoretic forces or magnetic forces.
Owner:AVIVA BIOSCI
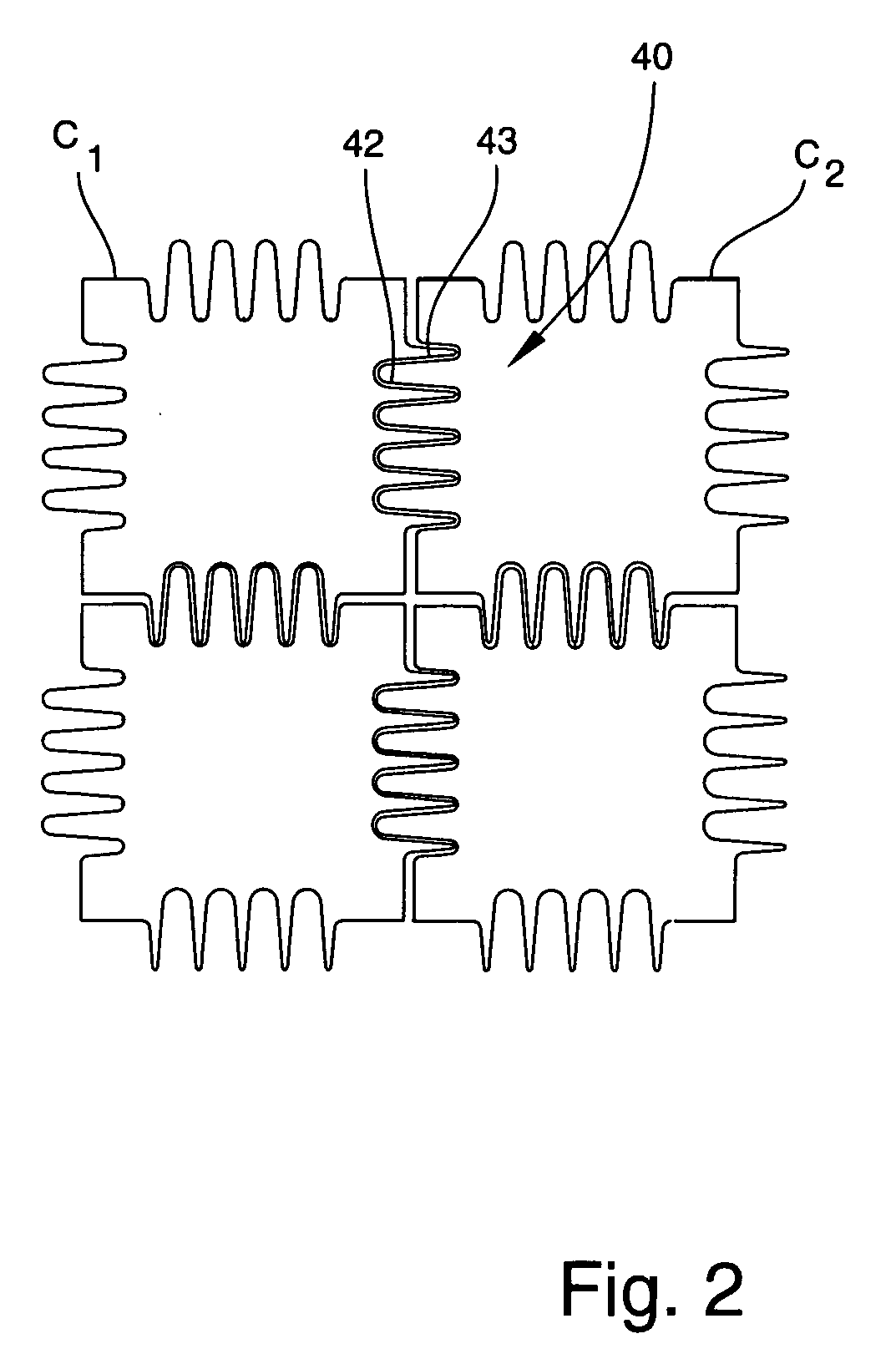
Apparatuses for mixing droplets
ActiveUS20070045117A1Efficiently performing binary mixingHigh precisionElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentElectricityEngineering
Apparatuses for mixing droplets, such as a binary mixing apparatus, are provided. The binary mixing apparatus includes an array of electrodes and a conducting element positioned in relation to at least one of the electrodes to enable a droplet placed in electrical communication with the at least one electrode to electrically communicate with the conducting element. The binary mixing apparatus additionally includes an electrode selector for sequentially biasing one or more selected electrodes of the array to move a droplet disposed on the array into contact with another droplet. The apparatus further includes a first droplet supply area communicating with the array and a second droplet supply area communicating with the array.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Optoelectronic tweezers for microparticle and cell manipulation
ActiveUS20090170186A1Easy to operateEasy to createElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentMicroparticleDielectrophoresis
An optical image-driven light induced dielectrophoresis (DEP) apparatus and method are described which provide for the manipulation of particles or cells with a diameter on the order of 100 μm or less. The apparatus is referred to as optoelectric tweezers (OET) and provides a number of advantages over conventional optical tweezers, in particular the ability to perform operations in parallel and over a large area without damage to living cells. The OET device generally comprises a planar liquid-filled structure having one or more portions which are photoconductive to convert incoming light to a change in the electric field pattern. The light patterns are dynamically generated to provide a number of manipulation structures that can manipulate single particles and cells or groups of particles / cells. The OET preferably includes a microscopic imaging means to provide feedback for the optical manipulation, such as detecting position and characteristics wherein the light patterns are modulated accordingly.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Surface assisted fluid loading and droplet dispensing
InactiveUS8685344B2Easy to useFacilitates of propertyElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentMicro actuatorFluid loading
The present invention relates to surface assisted fluid loading and droplet dispensing on a droplet micro actuator. A droplet actuator is provided and includes one or more electrodes configured for conducting one or more droplet operations on a droplet operations surface of the substrate. The droplet actuator further includes a wettable surface defining a path from a fluid reservoir into a locus which is sufficiently near to one or more of the electrodes that activation of the one or more electrodes results in a droplet operation. Methods and systems are also provided.
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC
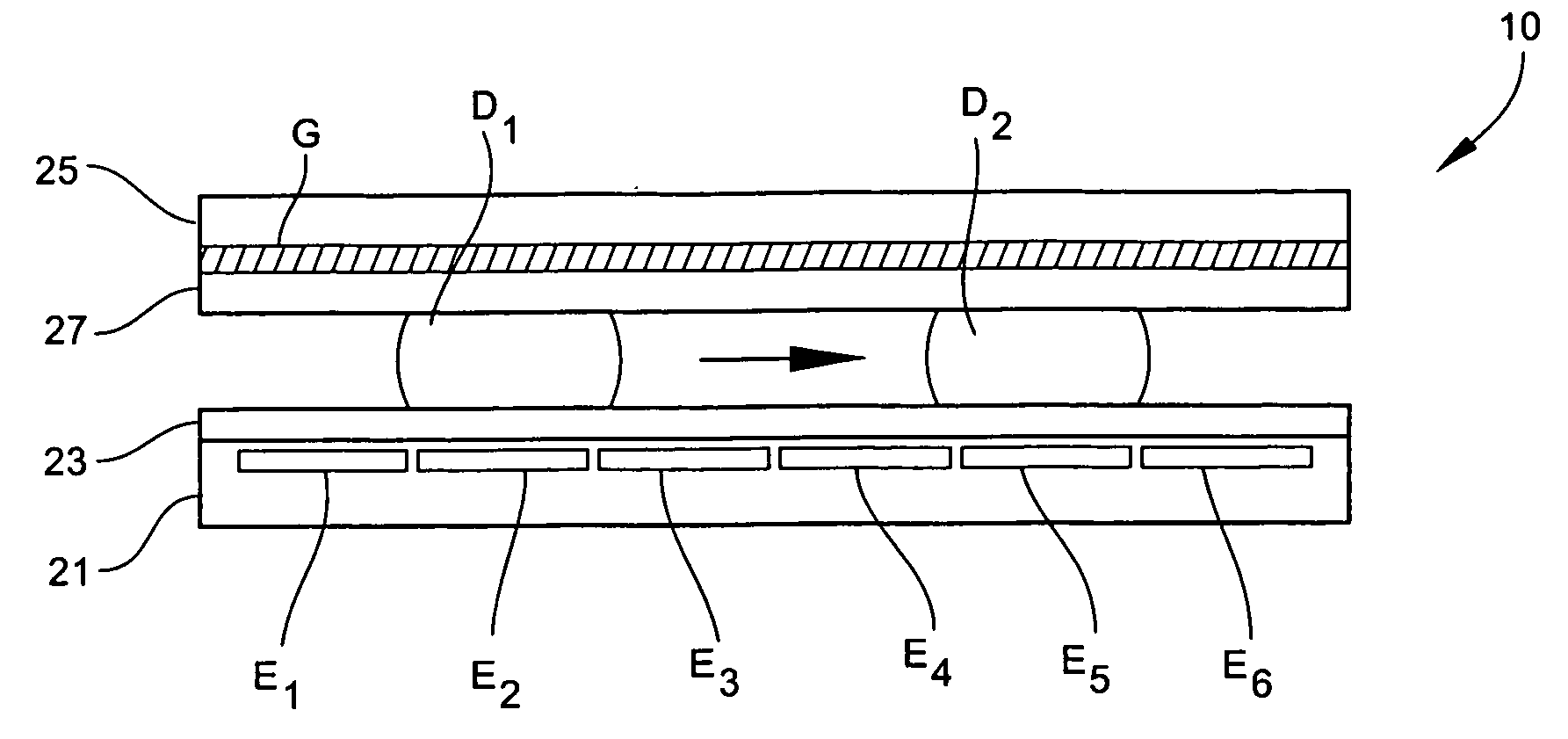
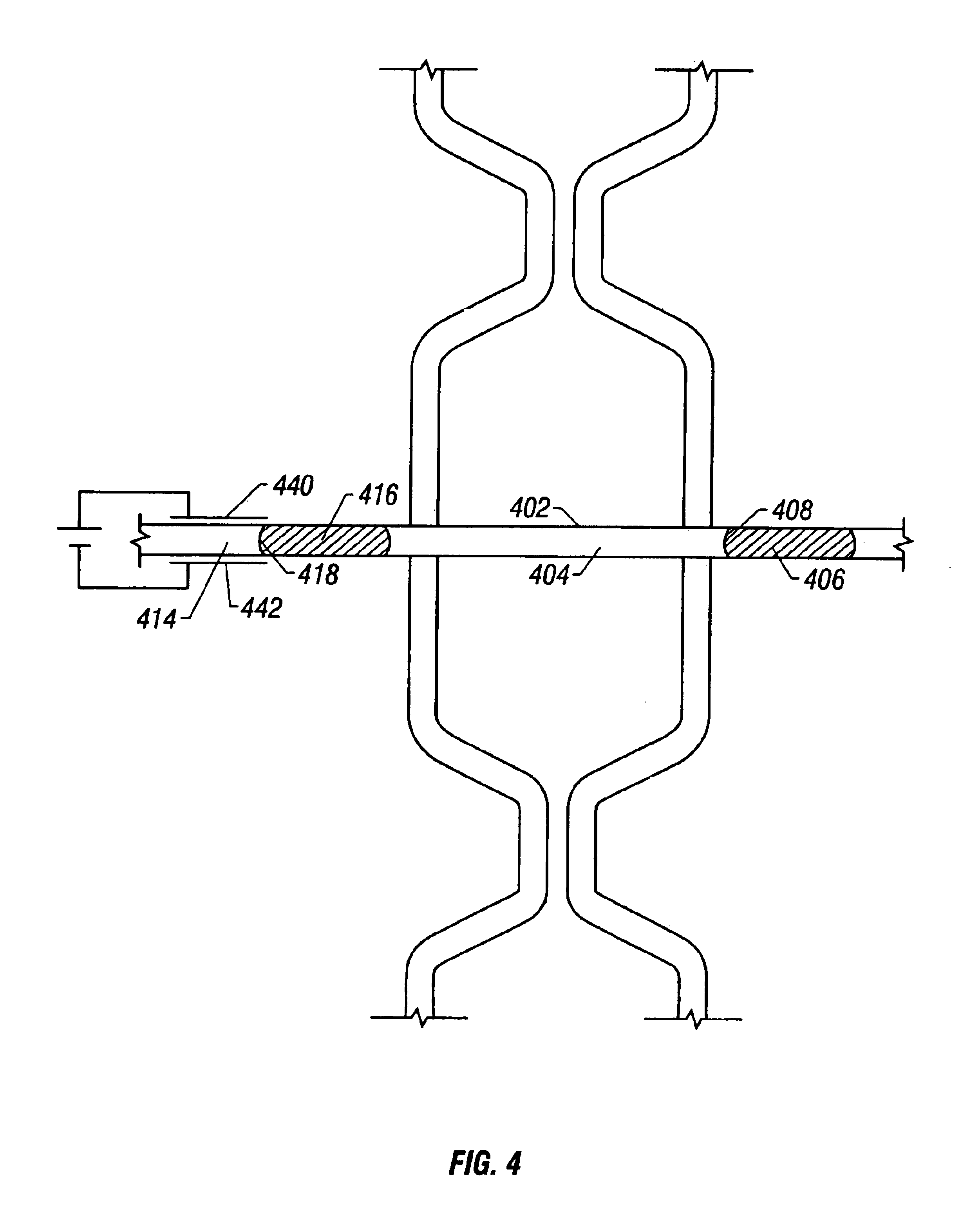
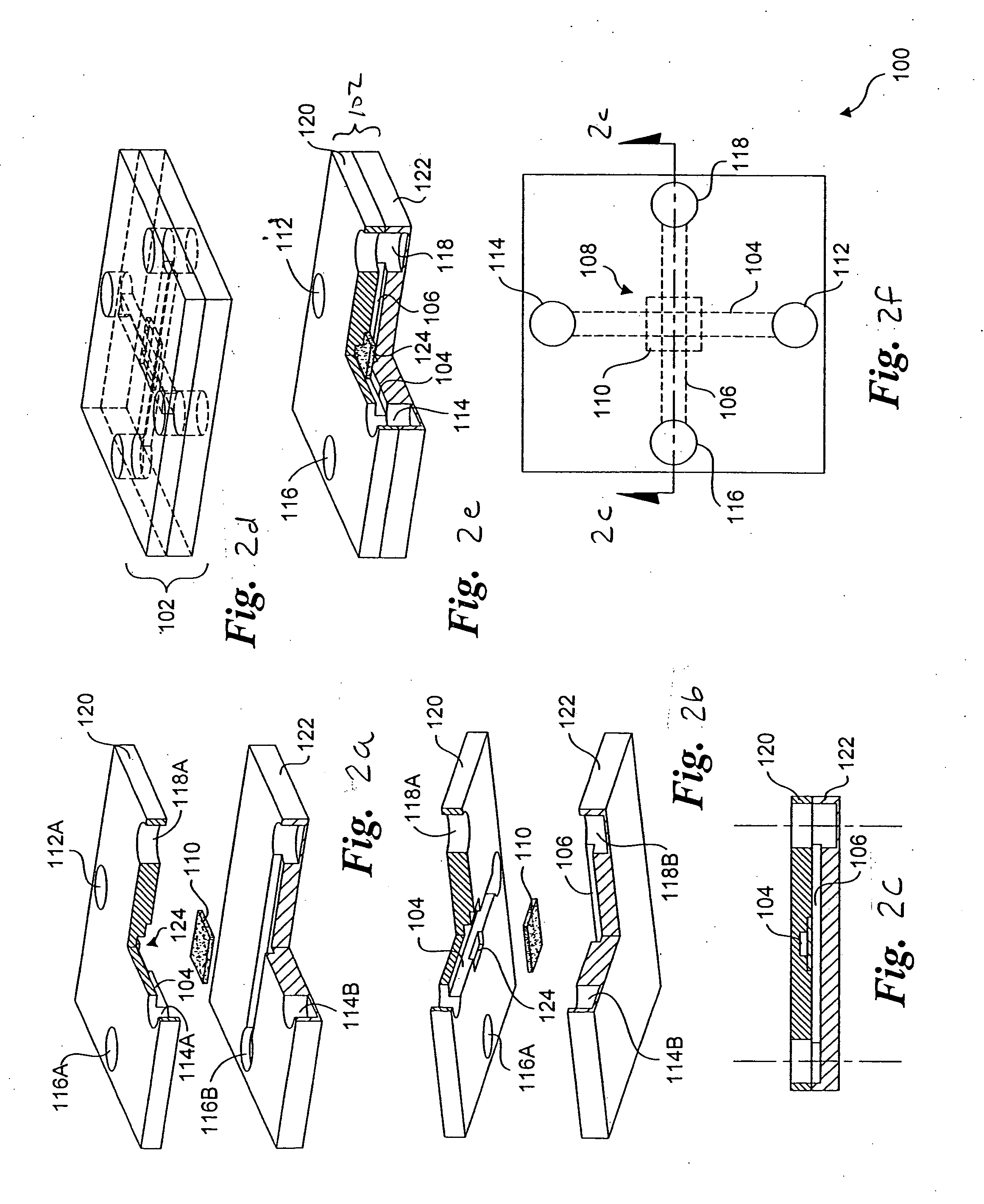
Micromachined electrical field-flow fractionation system
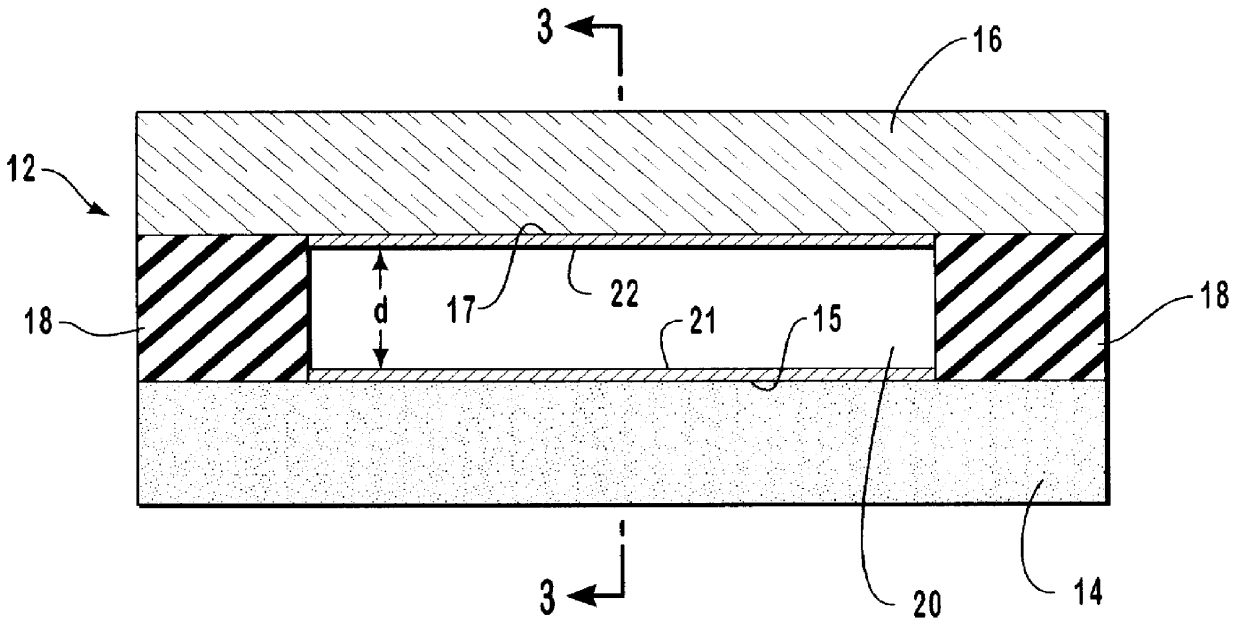
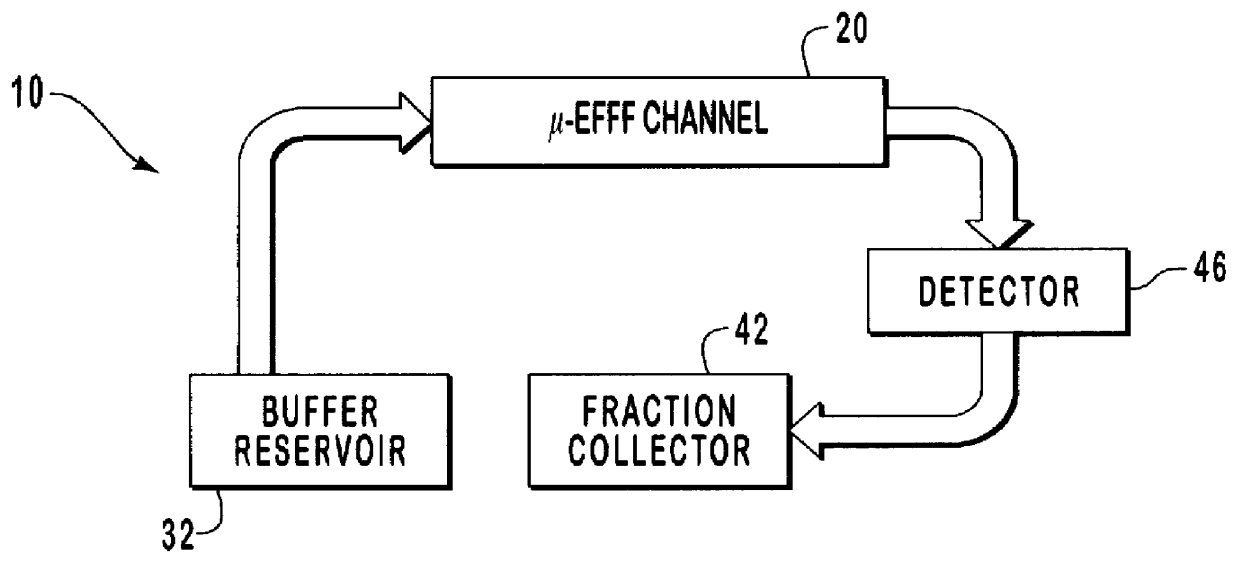
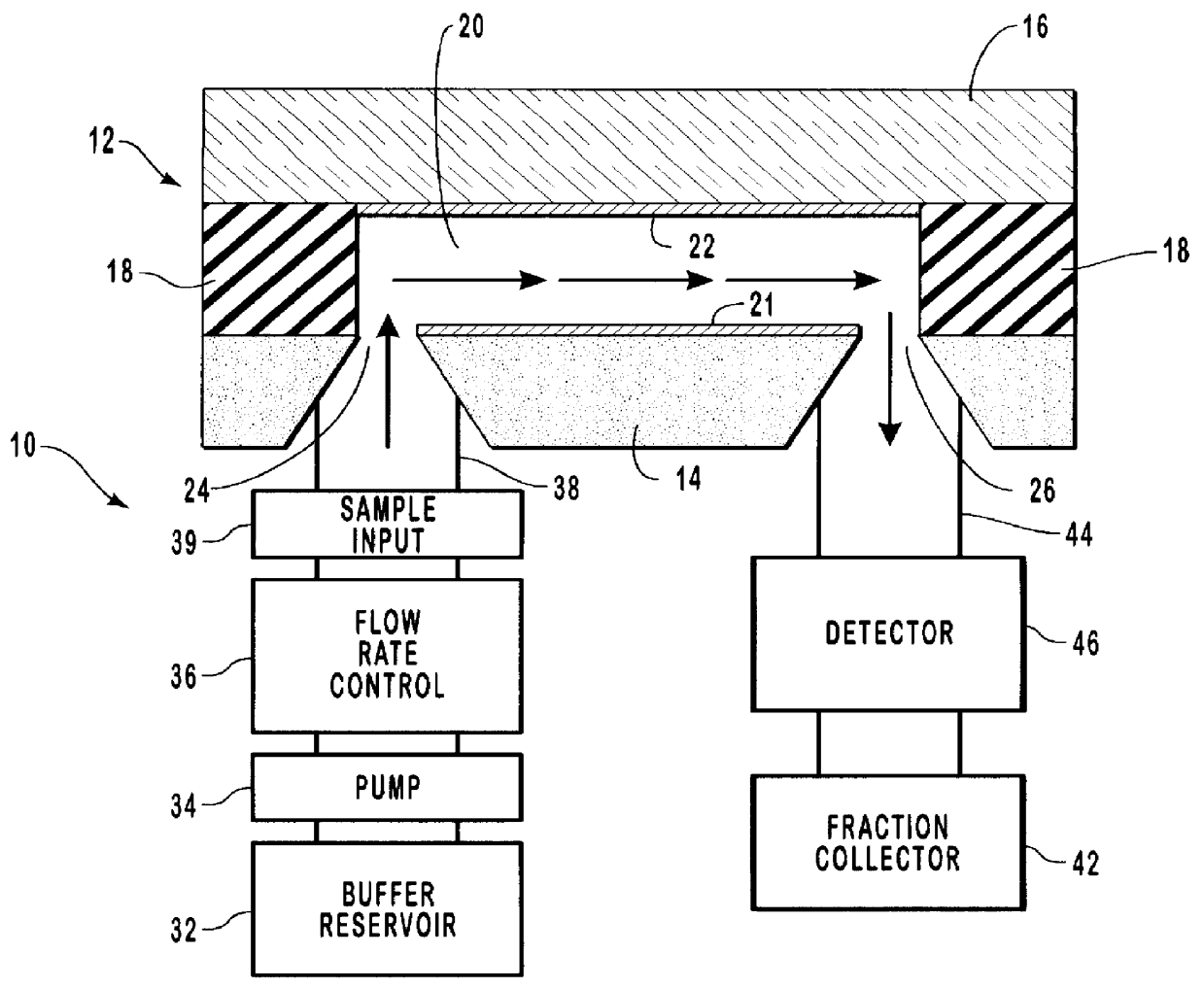
InactiveUS6136171AHigh resolutionSimple and precise constructionElectrostatic separatorsFixed microstructural devicesEngineeringElectrical Field-Flow Fractionation
A micromachined system for electrical field-flow fractionation of small test fluid samples is provided. The system includes a microchannel device comprising a first substrate having a planar inner surface with an electrode formed thereon. A second substrate having a planar inner surface with an electrode formed thereon is positioned over the first substrate so that the respective electrodes face each other. An insulating intermediate layer is interposed between the first and second substrates. The intermediate layer is patterned to form opposing sidewalls of at least one microchannel, with the electrodes on the substrates defining opposing continuous boundaries along the length of the microchannel. Inlet and outlet ports are formed in one or both substrates for allowing fluid flow into and out of the microchannel. The microchannel device can be fabricated with single or multiple microchannels therein for processing single or multiple test fluids. During operation, a voltage differential is applied to the electrodes in order to induce an electric field across the microchannel. This separates particles of different types present in a fluid injected into the microchannel. The separated particles in the fluid can be collected or further processed as desired.
Owner:UTAH RES FOUND UNIV OF THE
Microfluid molecular-flow fractionator and bioreactor with integrated active/passive diffusion barrier
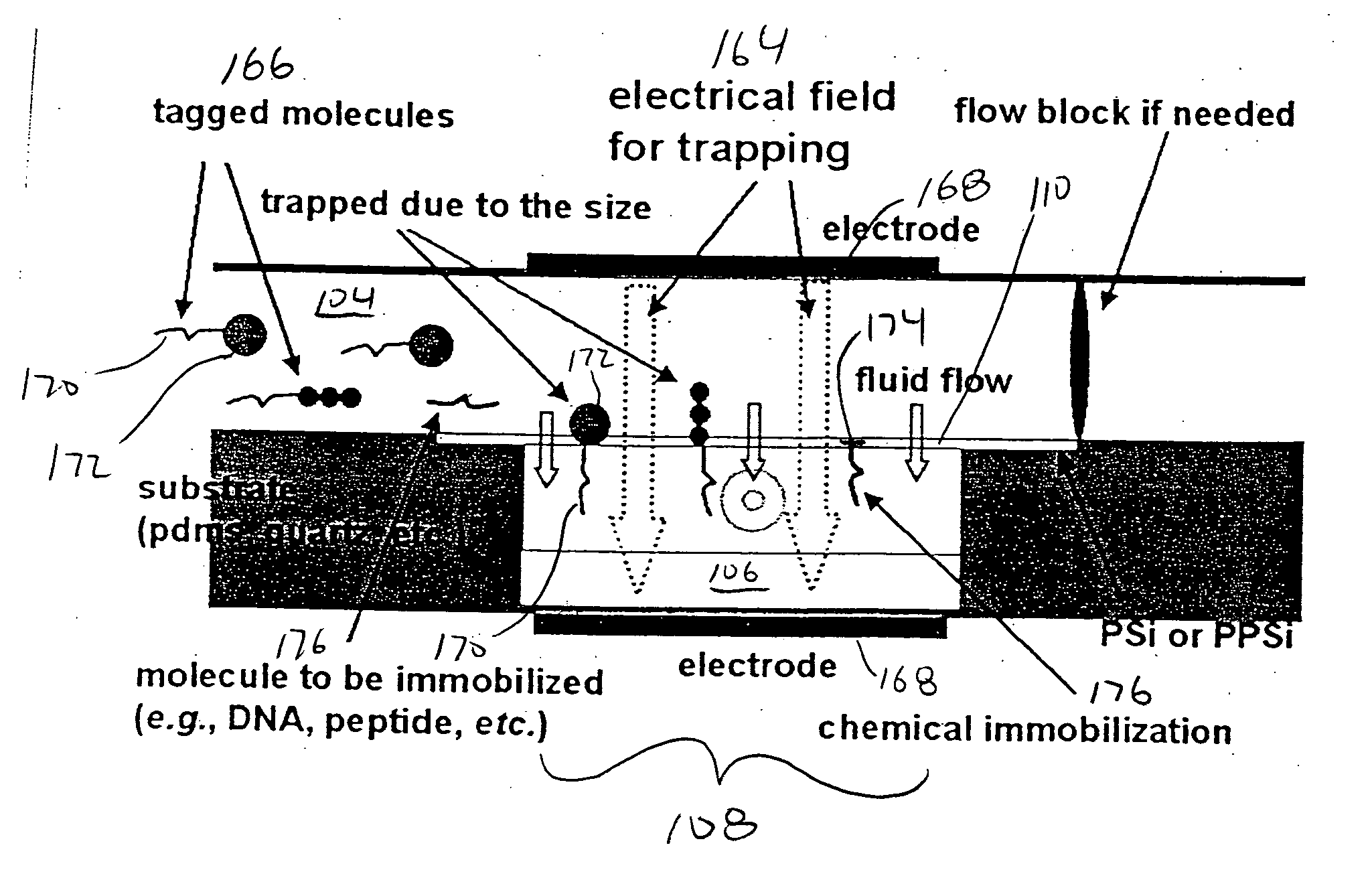
InactiveUS20050148064A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPorous membraneDiffusion barrier
A microfluidic device and method is disclosed for fractionating and / or trapping selected molecules with a diffusion barrier or porous membrane. The device includes a source fluid flow channel and a target fluid flow channel. The target fluid flow channel and the source fluid flow channel meet at cross-channel area and are in fluid communication with each other. A porous membrane separates the source fluid flow channel from the target fluid flow channel in the cross-channel area. A field-force / gradient mechanism may be positioned proximate the porous membrane with or without detection / state monitoring devices.
Owner:INTEL CORP
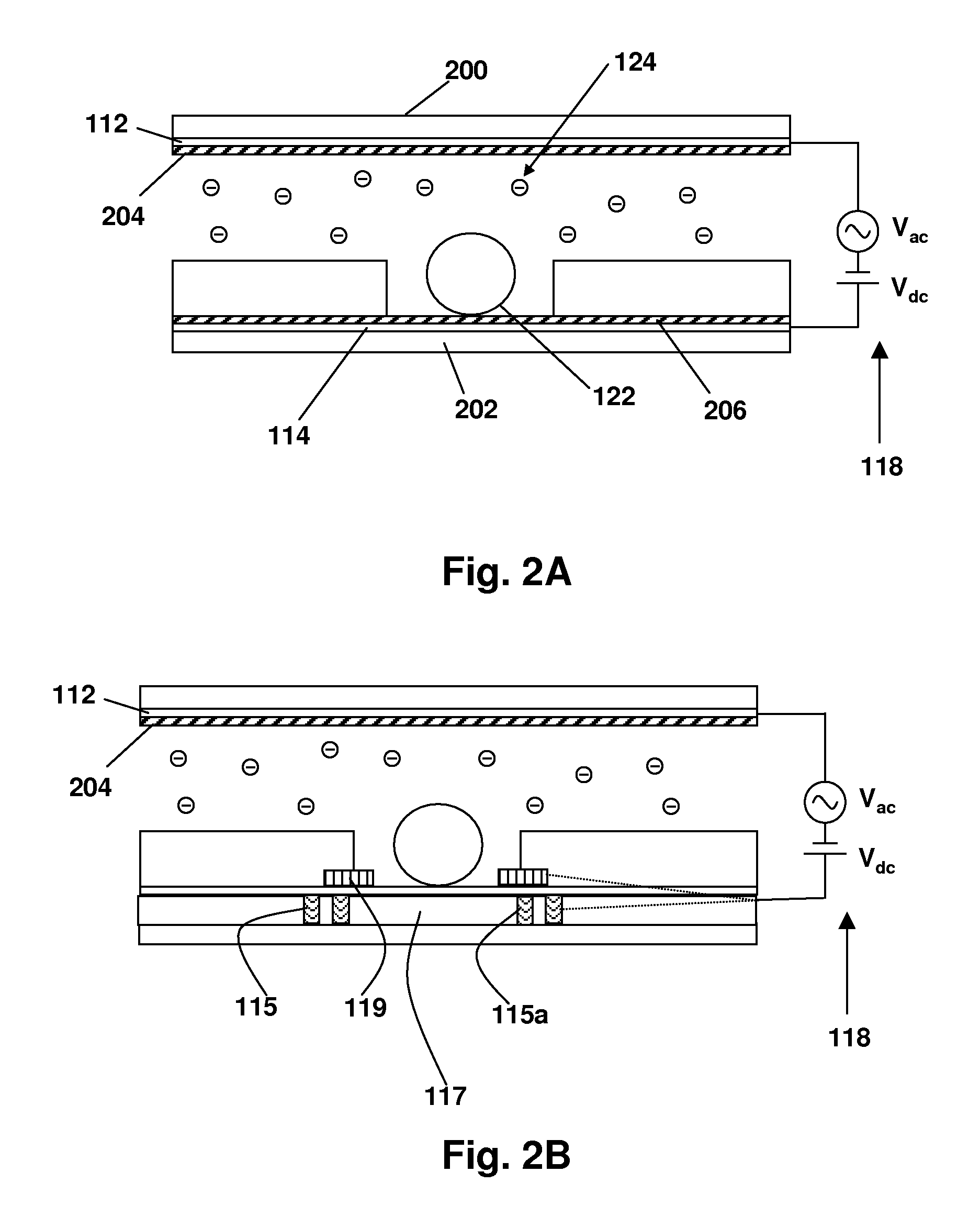
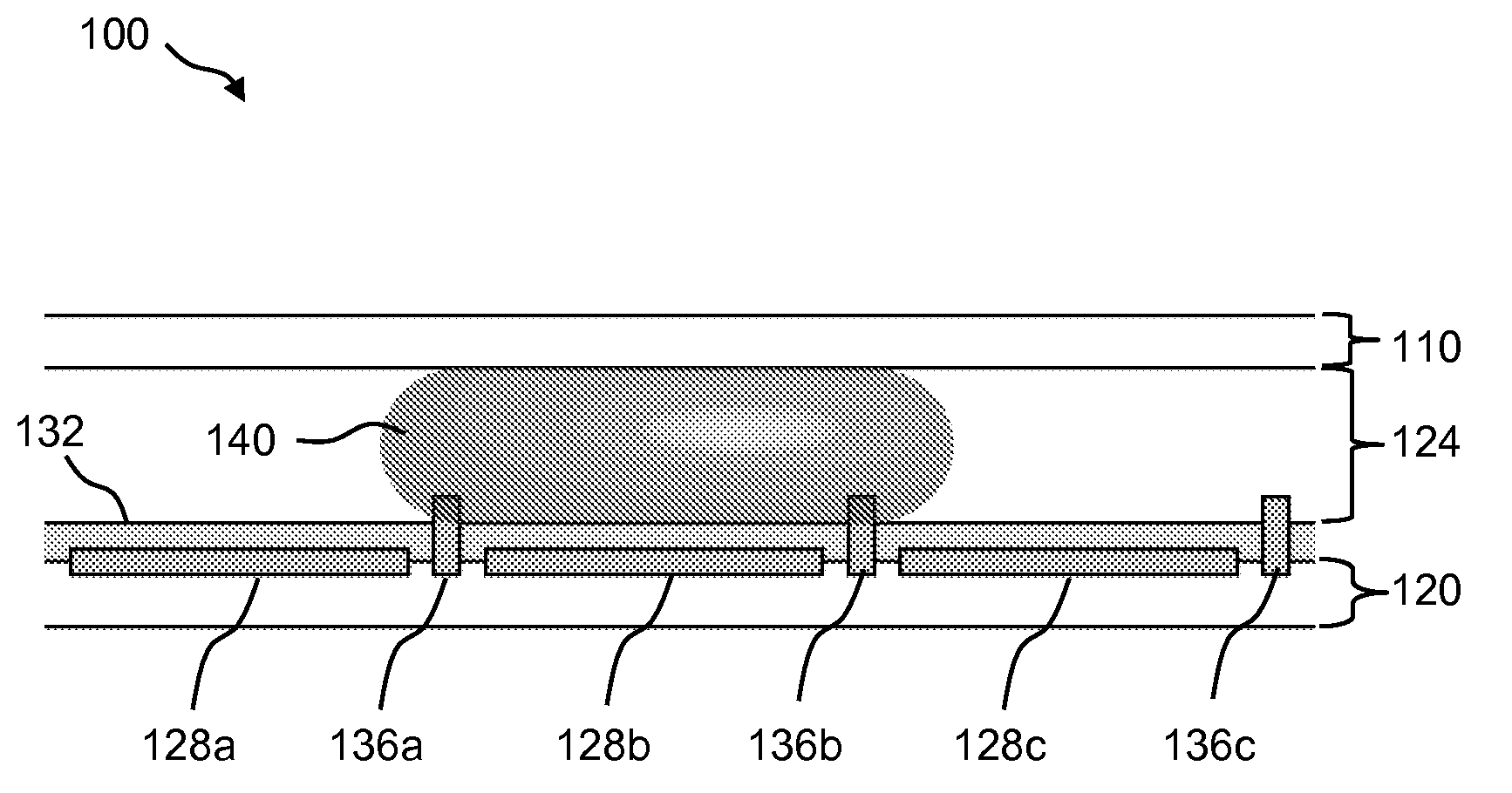
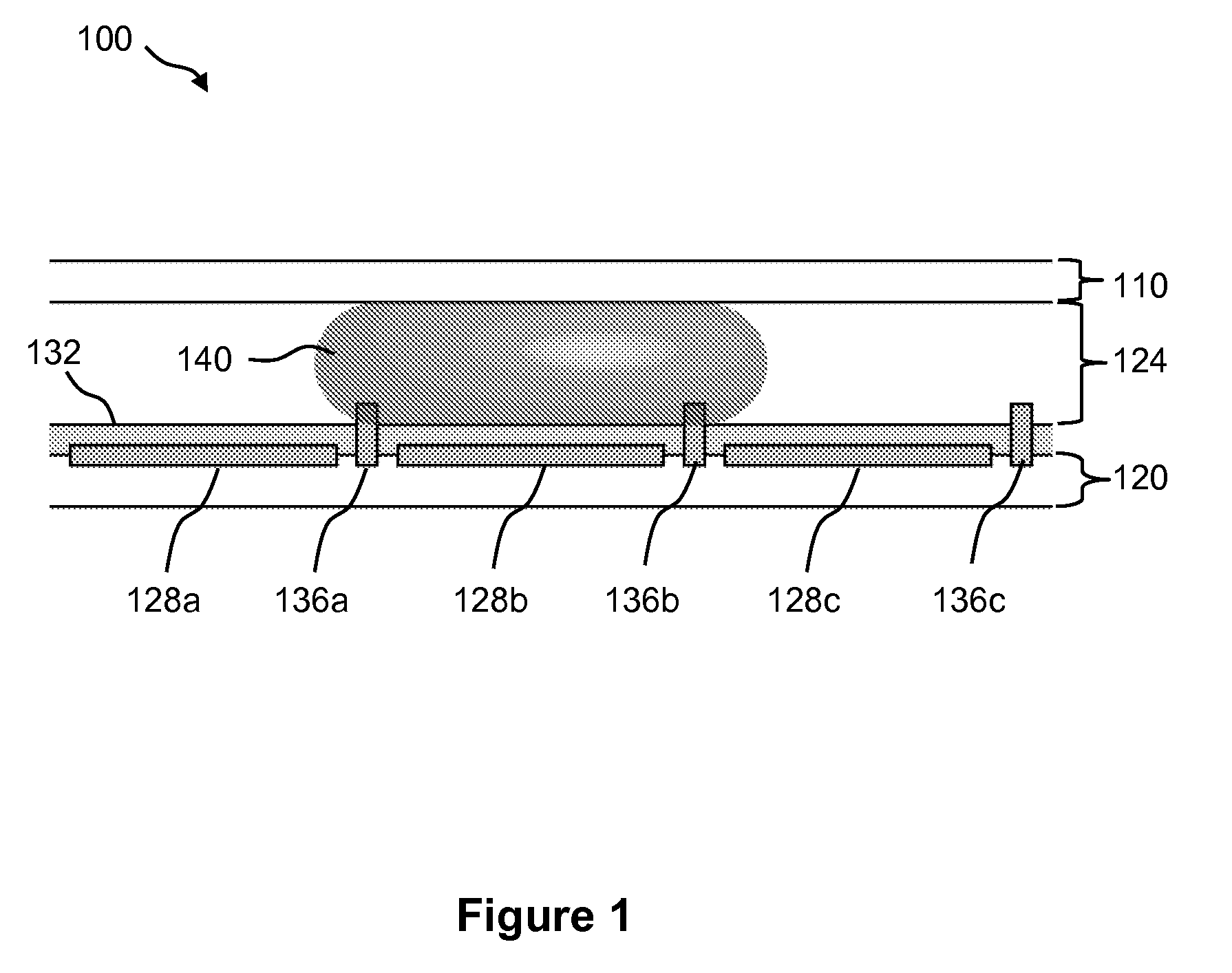
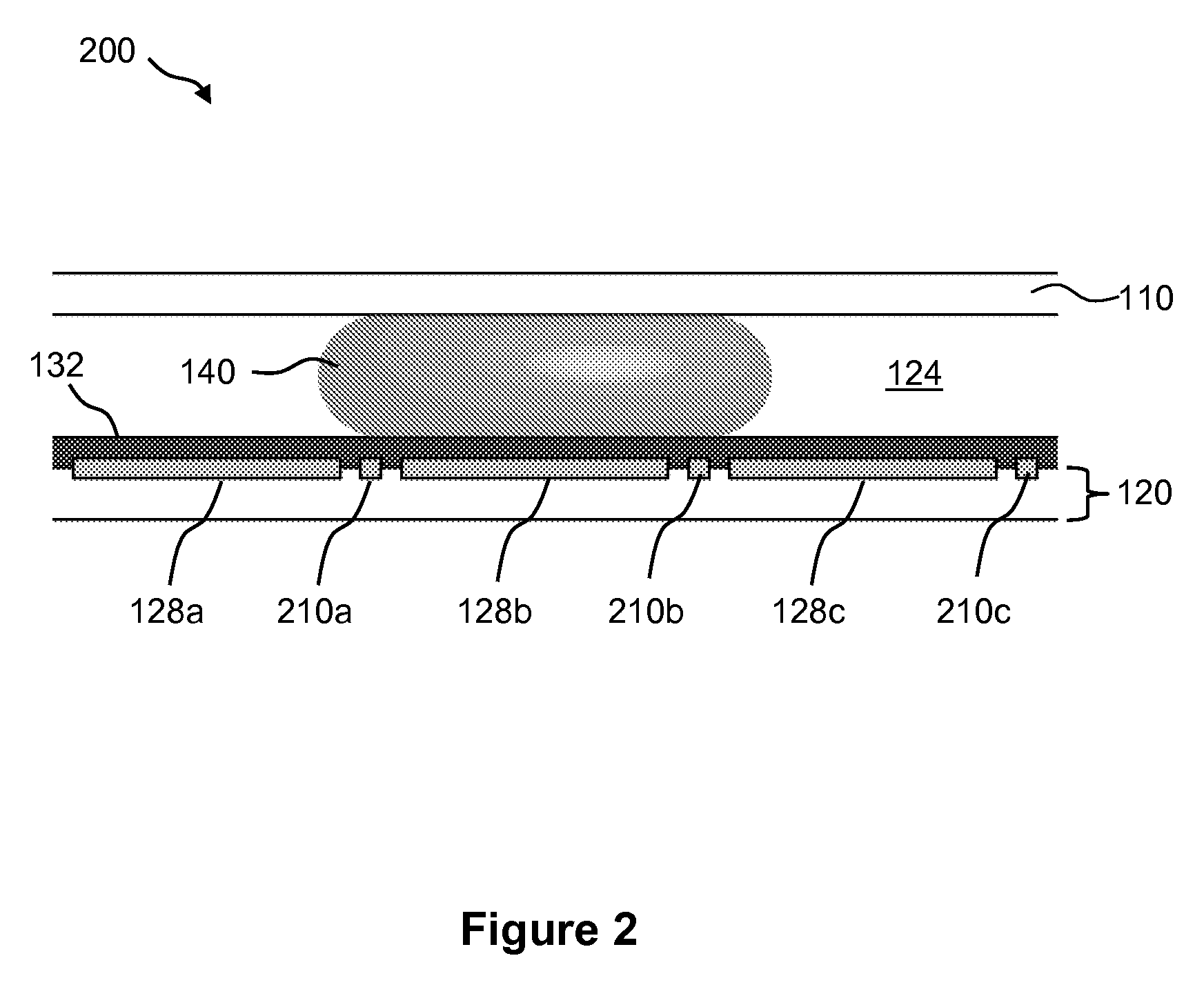
Droplet Actuator Configurations and Methods
InactiveUS20100307917A1Easy to useFacilitates of propertyElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentEngineeringActuator
Droplet actuators for conducting droplet operations, such as droplet transport and droplet dispensing, are provided. In one embodiment, the droplet actuator may include a substrate including, droplet operations electrodes arranged for conducting droplet operations on a surface of the substrate; and reference electrodes associated with the droplet operations electrodes and extending above the surface of the substrate. Other embodiments of droplet actuators and methods of loading and using such droplet actuators are also provided.
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com