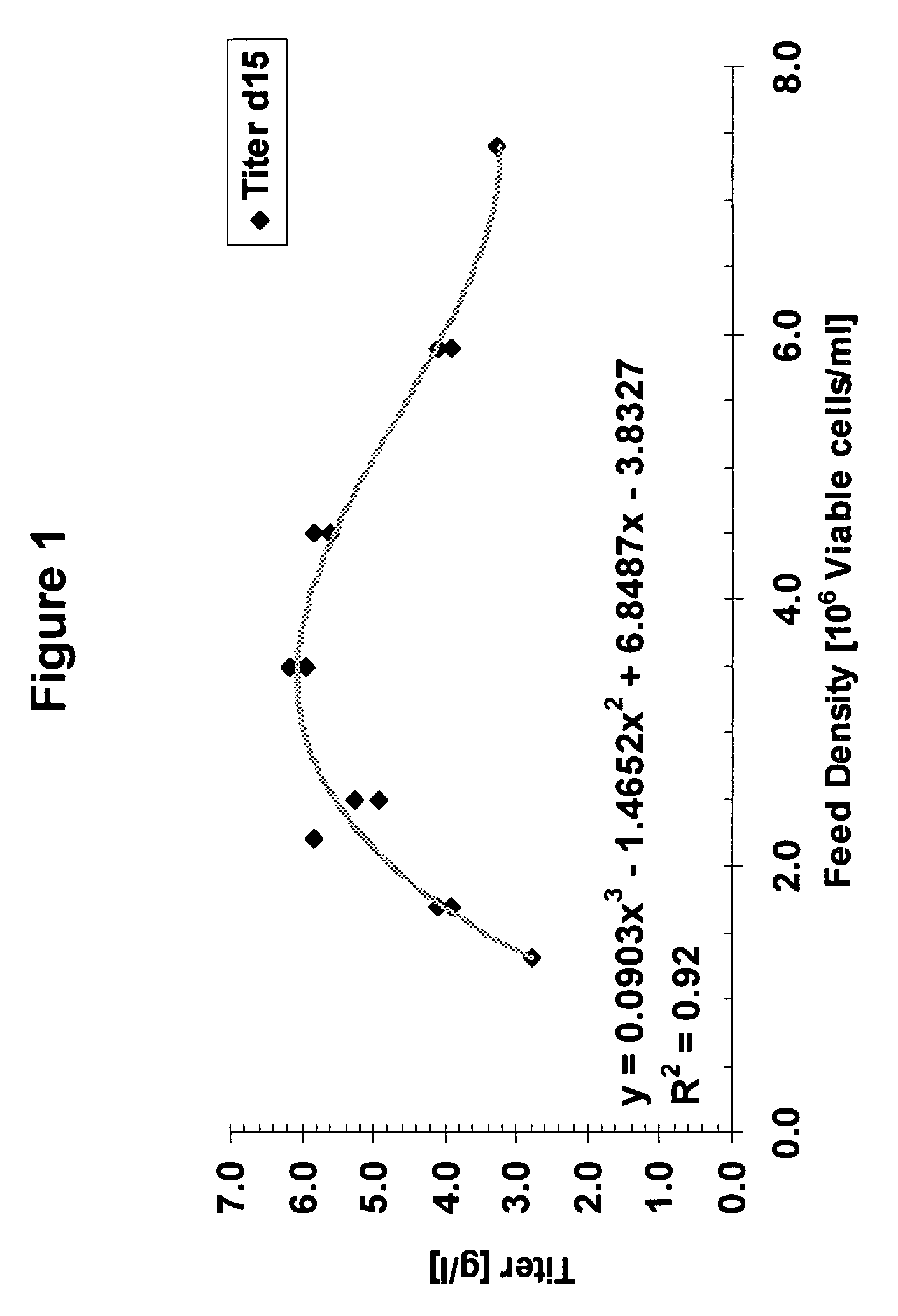
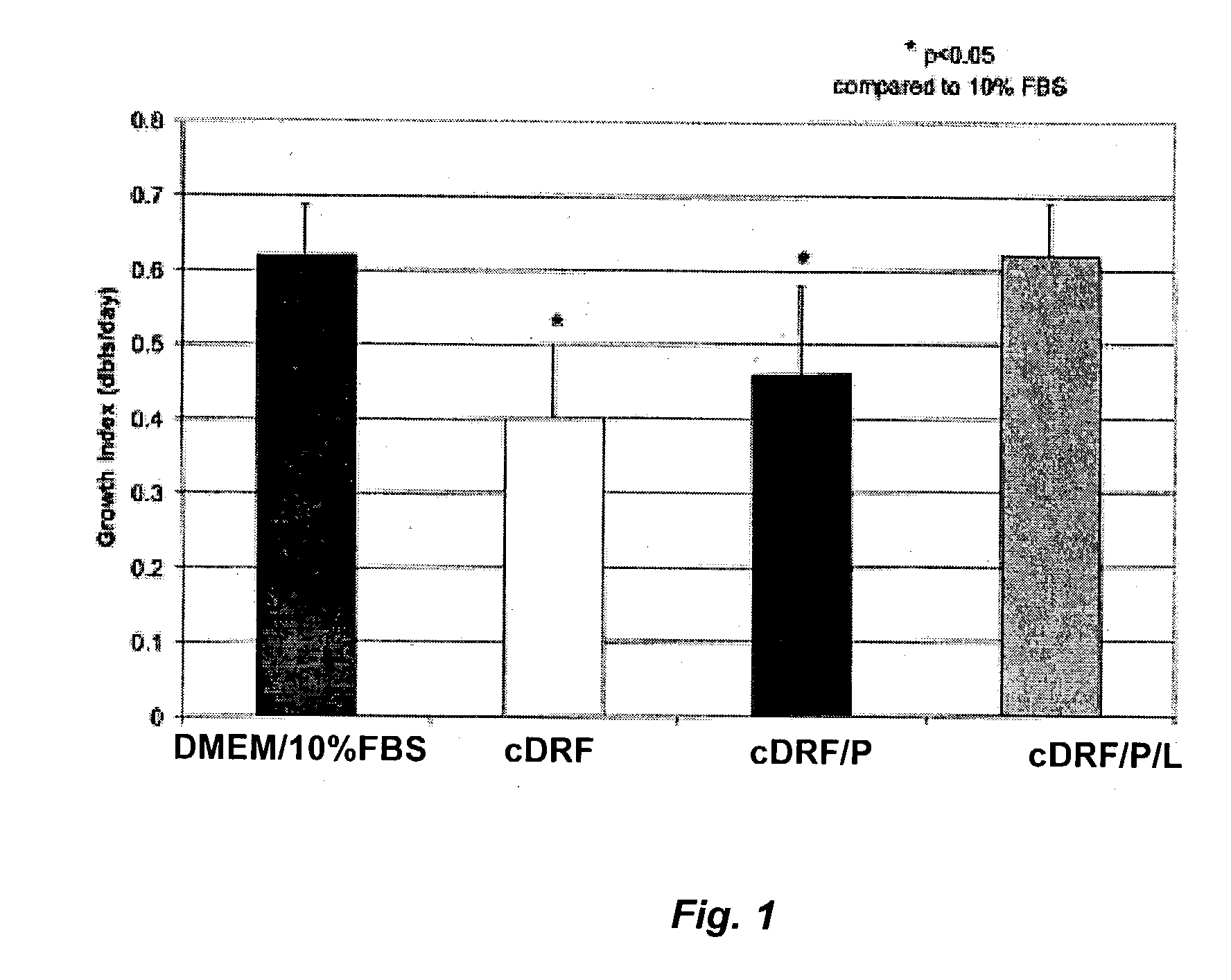
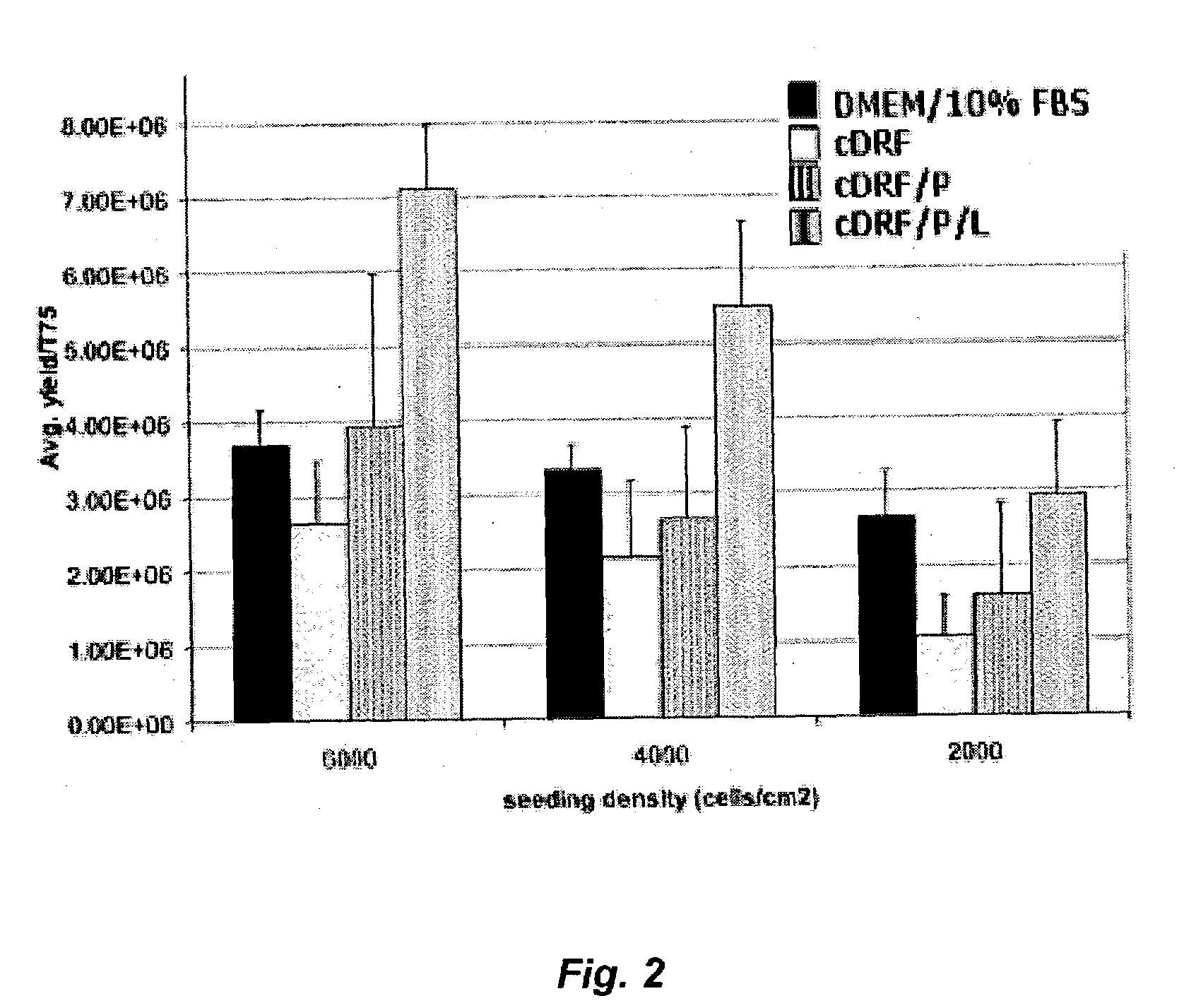
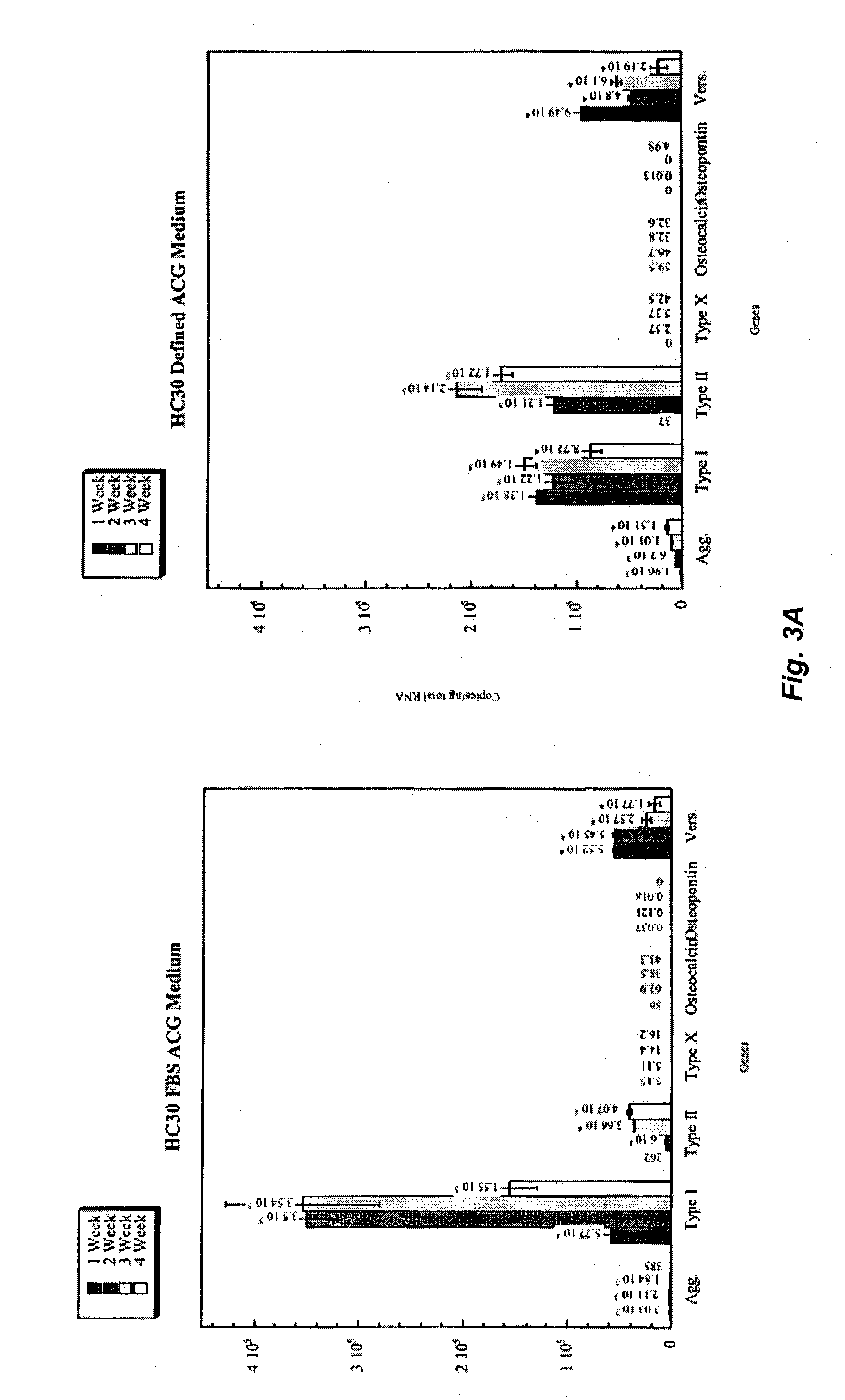
Patents
Literature
2593 results about "Cell culture media" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
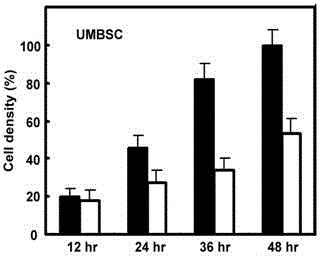
The difference between growth media used for cell culture and those used for microbiological culture is that cells derived from whole organisms and grown in culture often cannot grow without the addition of, for instance, hormones or growth factors which usually occur in vivo.
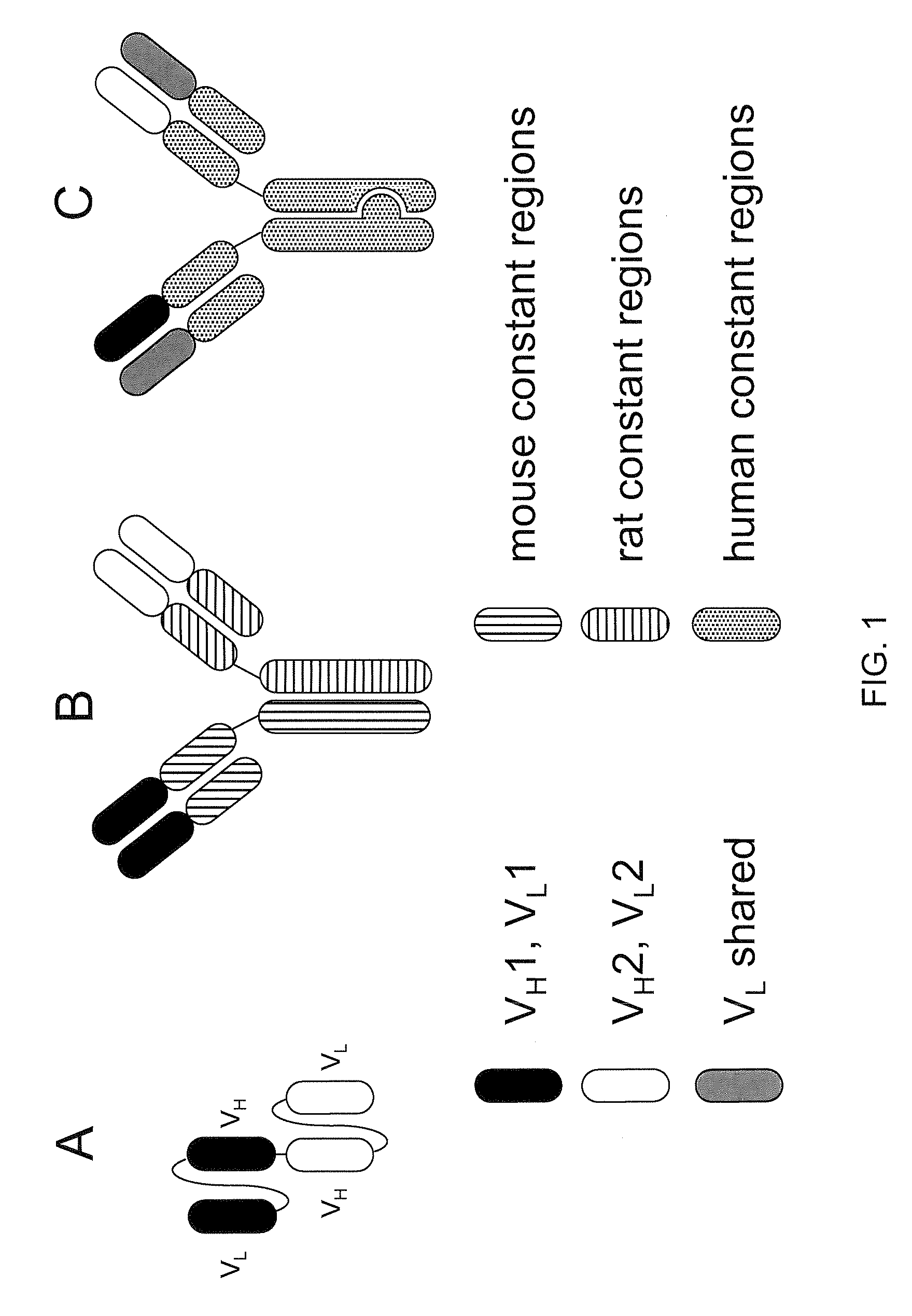
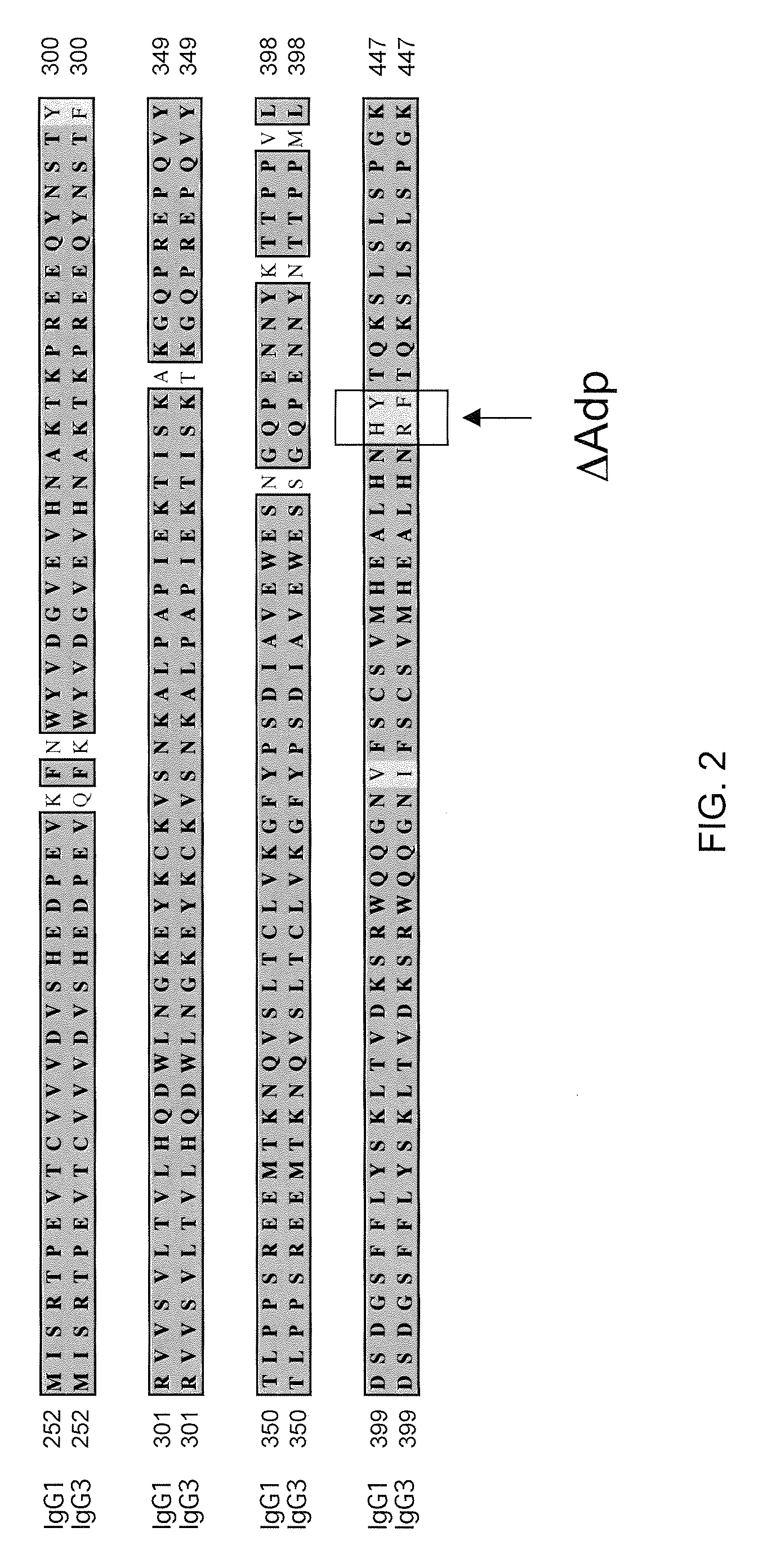
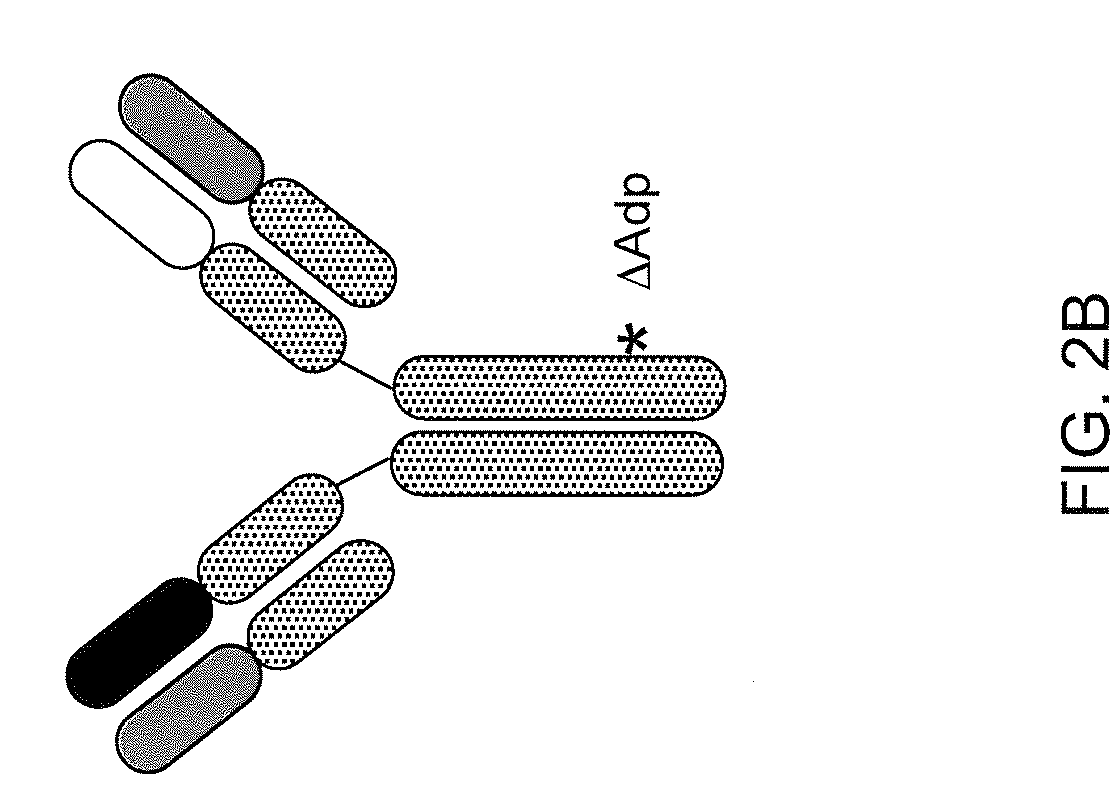
Readily Isolated Bispecific Antibodies with Native Immunoglobulin Format
ActiveUS20100331527A1Improve abilitiesReduces and eliminates bindingHybrid immunoglobulinsSerum immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulin heavy chainHeavy chain
A bispecific antibody format providing ease of isolation is provided, comprising immunoglobulin heavy chain variable domains that are differentially modified in the CH3 domain, wherein the differential modifications are non-immunogenic or substantially non-immunogenic with respect to the CH3 modifications, and at least one of the modifications results in a differential affinity for the bispecific antibody for an affinity reagent such as Protein A, and the bispecific antibody is isolable from a disrupted cell, from medium, or from a mixture of antibodies based on its affinity for Protein A.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Methods of making conditioned cell culture medium compositions
InactiveUS6372494B1Eliminate wrinklesEliminate frown lineCosmetic preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsReserve CellCell culture media
Novel products comprising conditioned cell culture medium compositions and methods of use are described. The conditioned cell medium compositions of the invention may be comprised of any known defined or undefined medium and may be conditioned using any eukaryotic cell type. The medium may be conditioned by stromal cells, parenchymal cells, mesenchymal stem cells, liver reserve cells, neural stem cells, pancreatic stem cells and / or embryonic stem cells. Additionally, the cells may be genetically modified. A three-dimensional tissue construct is preferred. Once the cell medium of the invention is conditioned, it may be used in any state. Physical embodiments of the conditioned medium include, but are not limited to, liquid or solid, frozen, lyophilized or dried into a powder. Additionally, the medium is formulated with a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier as a vehicle for internal administration, applied directly to a food item or product, formulated with a salve or ointment for topical applications, or, for example, made into or added to surgical glue to accelerate healing of sutures following invasive procedures. Also, the medium may be further processed to concentrate or reduce one or more factors or components contained within the medium.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Methods and materials for the growth of primate-derived primordial stem cells in feeder-free culture
Methods and materials for culturing primate-derived primordial stem cells are described. In one embodiment, a cell culture medium for growing primate-derived primordial stem cells in a substantially undifferentiated state is provided which includes a low osmotic pressure, low endotoxin basic medium that is effective to support the growth of primate-derived primordial stem cells. The basic medium is combined with a nutrient serum effective to support the growth of primate-derived primordial stem cells and a substrate selected from the group consisting of feeder cells and an extracellular matrix component derived from feeder cells. The medium further includes non-essential amino acids, an anti-oxidant, and a first growth factor selected from the group consisting of nucleosides and a pyruvate salt.
Owner:ASTERIAS BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
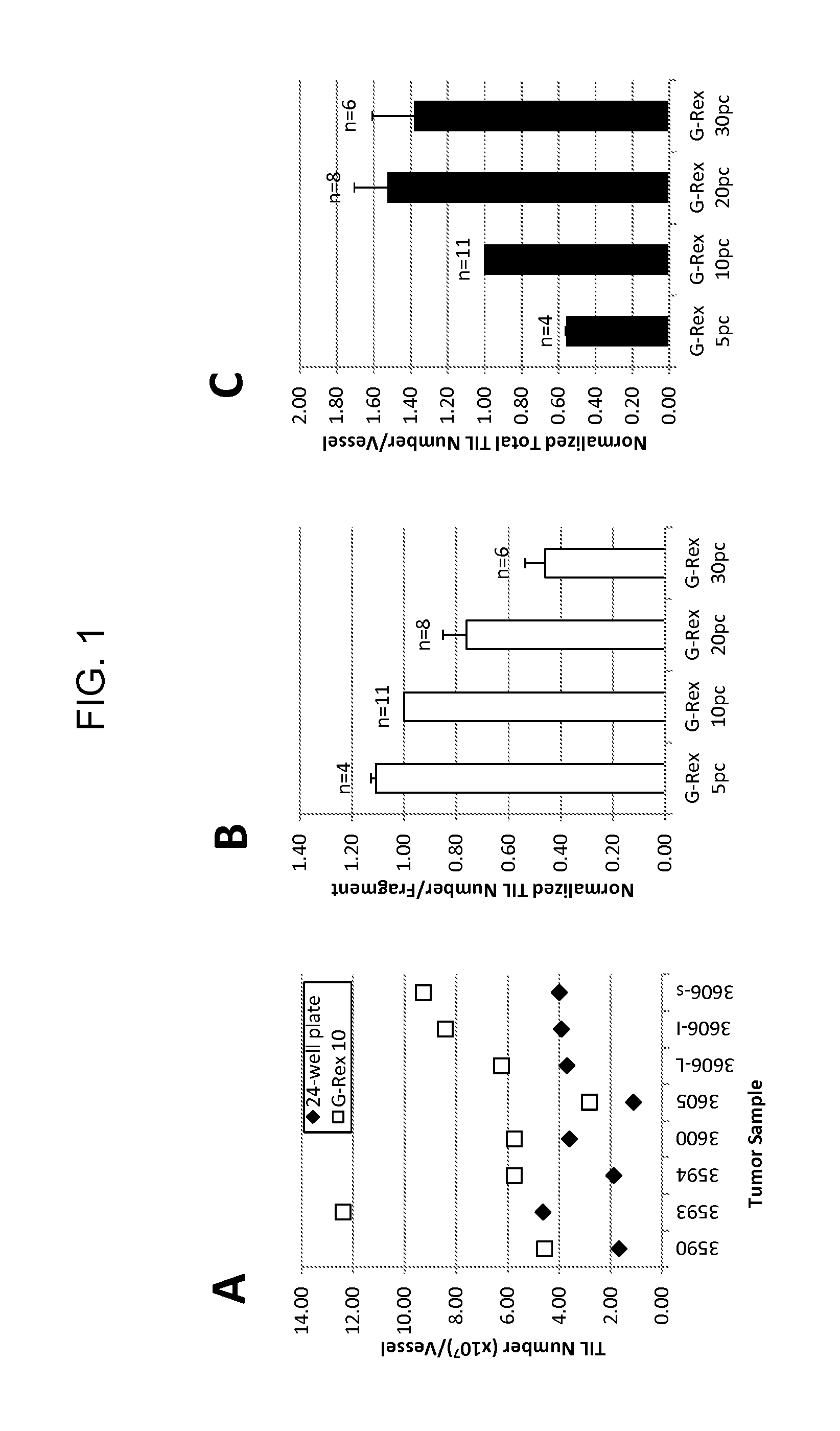
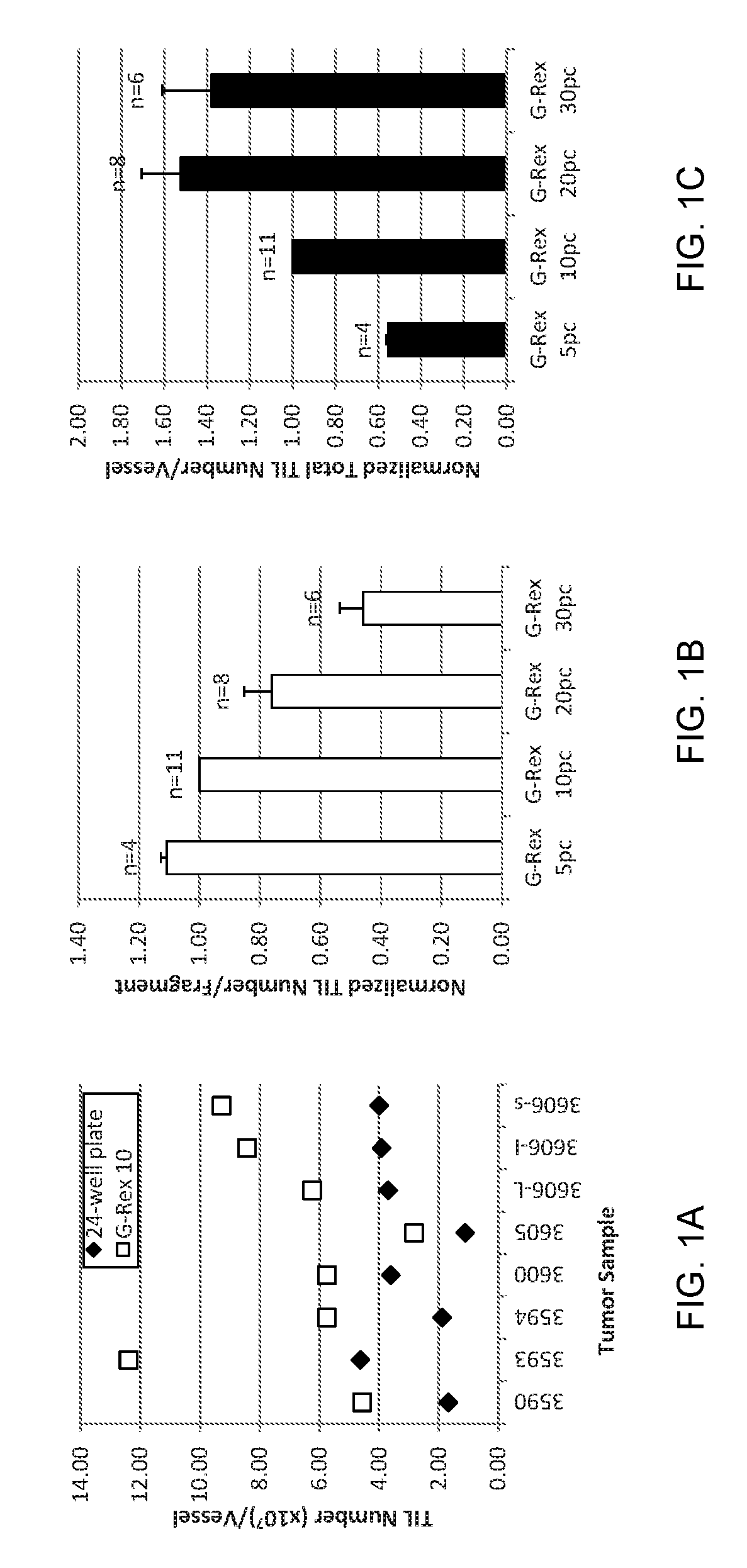
Methods of growing tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in gas-permeable containers
InactiveUS20120244133A1Increase the number ofBiocideArtificial cell constructsTumour tissueCell culture media
An embodiment of the invention provides a method of promoting regression of cancer in a mammal comprising obtaining a tumor tissue sample from the mammal; culturing the tumor tissue sample in a first gas permeable container containing cell medium therein; obtaining tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL) from the tumor tissue sample; expanding the number of TIL in a second gas permeable container containing cell medium therein using irradiated allogeneic feeder cells and / or irradiated autologous feeder cells; and administering the expanded number of TIL to the mammal. Methods of obtaining an expanded number of TIL from a mammal for adoptive cell immunotherapy are also provided.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
Method for expansion of stem cells
InactiveUS20060182724A1Increase oxygen contentAvoid clotsBiocideCosmetic preparationsCell culture mediaCell growth
A method of increasing the growth of stem cells by mixing the stem cells with a growth medium that has been conditioned by an incubation with placental tissue. The method increases the expansion of the stem cell population.
Owner:RIORDAN NEIL H
Oligopeptide-free cell culture media
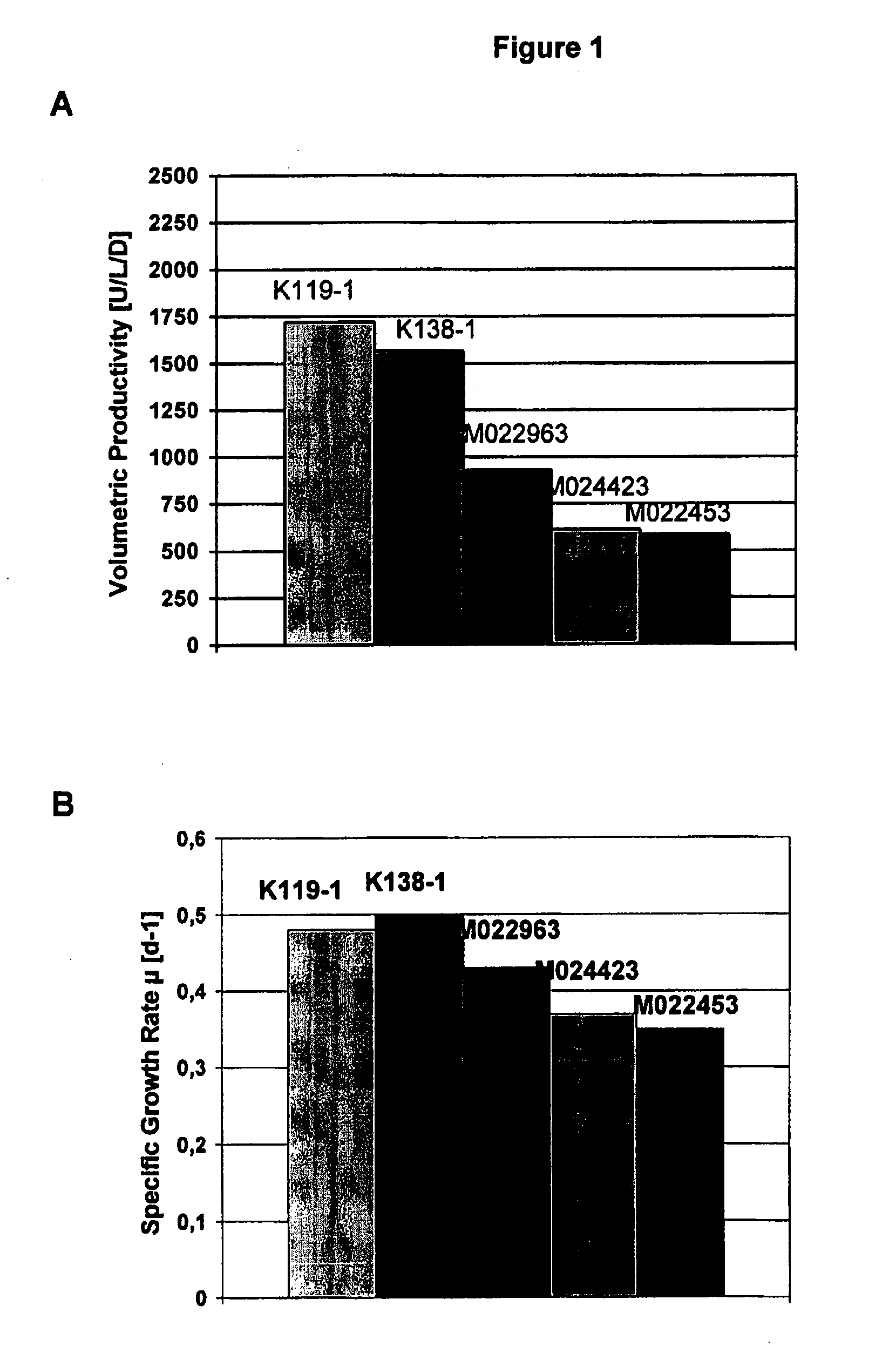
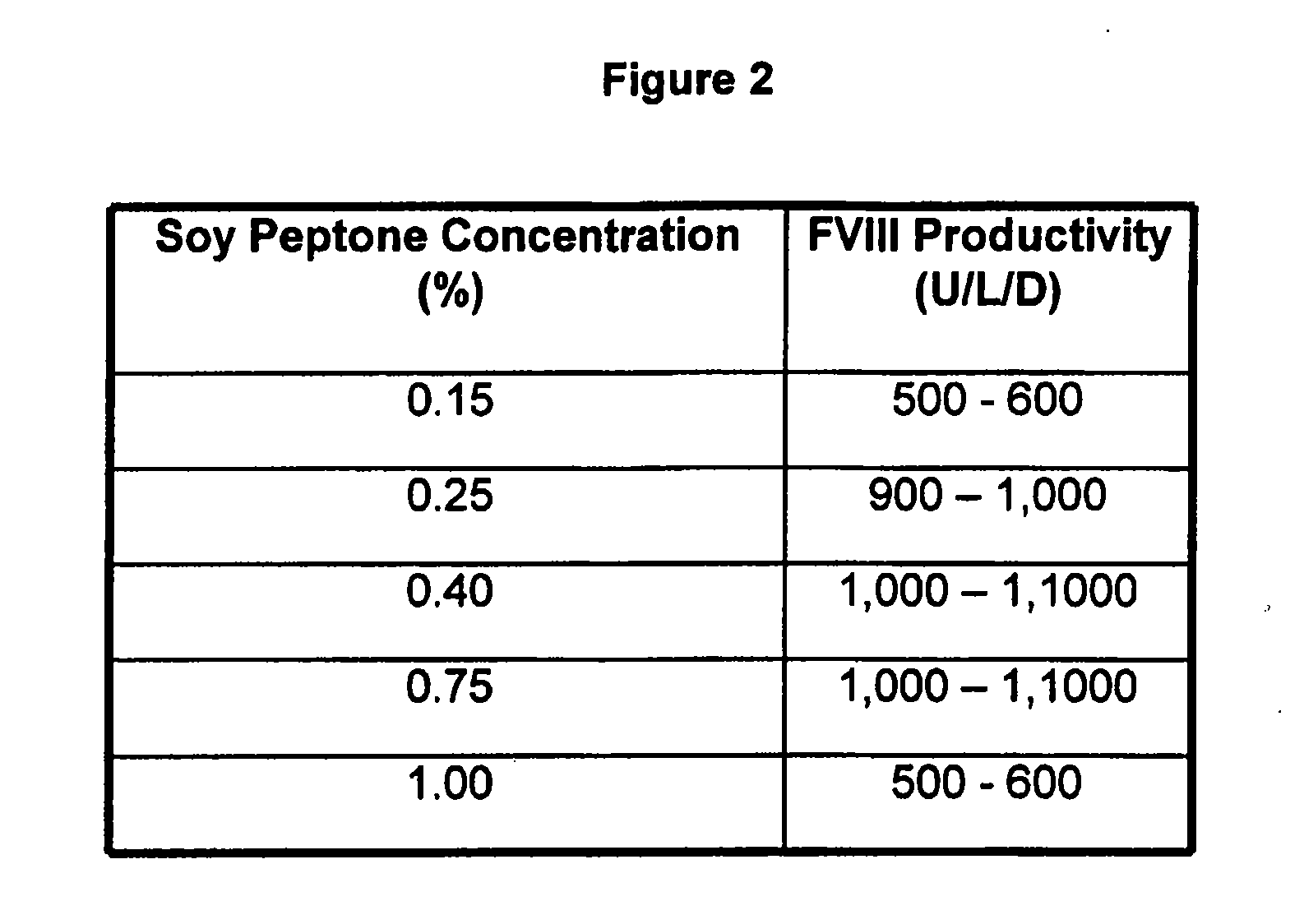
InactiveUS20070212770A1Efficient expression of recombinantEfficient productionFactor VIIBacteriaCulture cellCell culture media
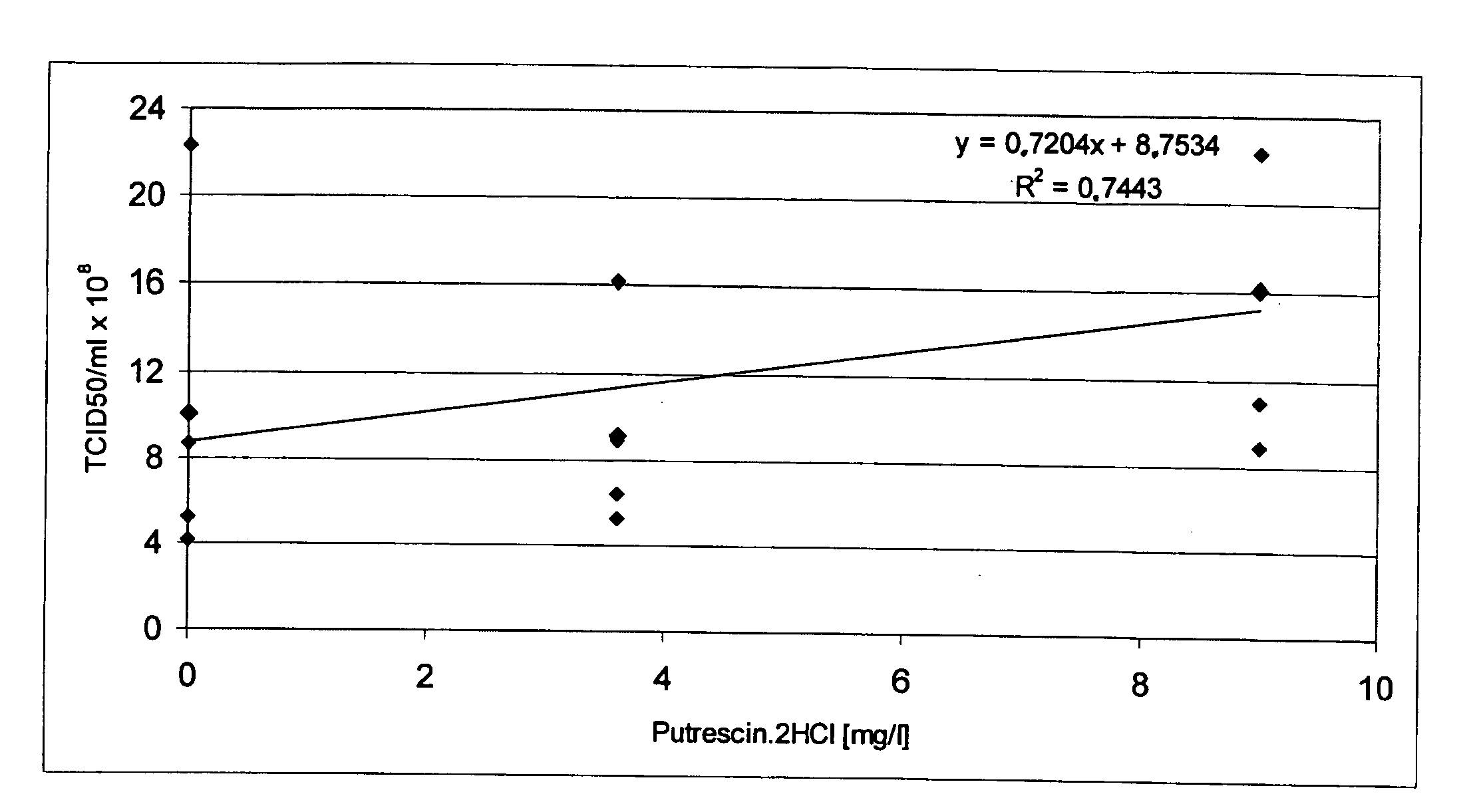
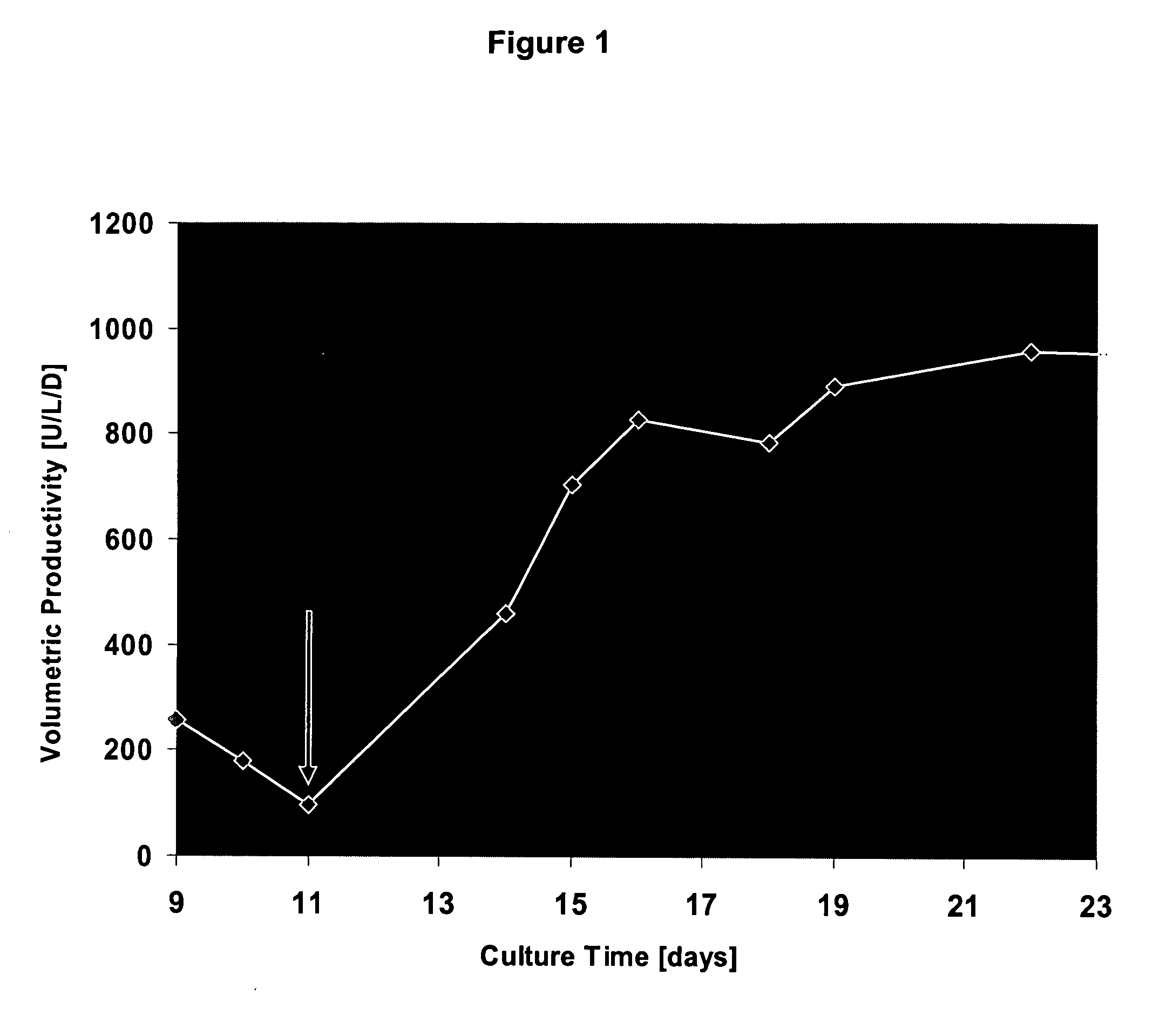
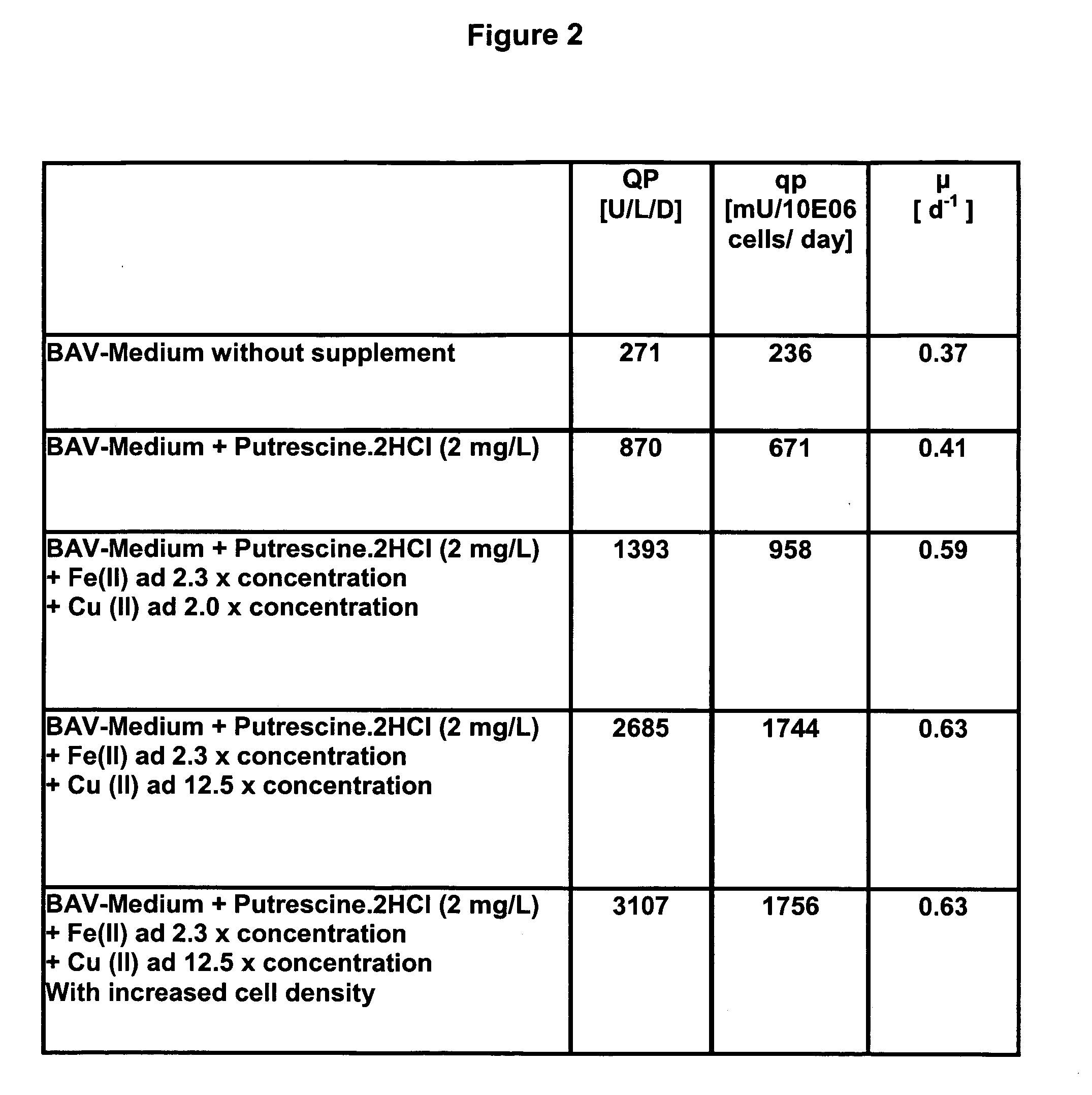
The present invention relates to oligopeptide-free cell culture media comprising at least 0.5 mg / L of a polyamine and to methods for cultivating cells in said oligopeptide-free cell culture media comprising at least 0.5 mg / L of a polyamine. The invention also relates to methods for expressing at least one protein in a medium comprising at least 0.5 mg / L of a polyamine and to methods for producing at least one virus in a medium comprising at least 0.5 mg / L of a polyamine.
Owner:BAXTER HEALTHCARE SA +1
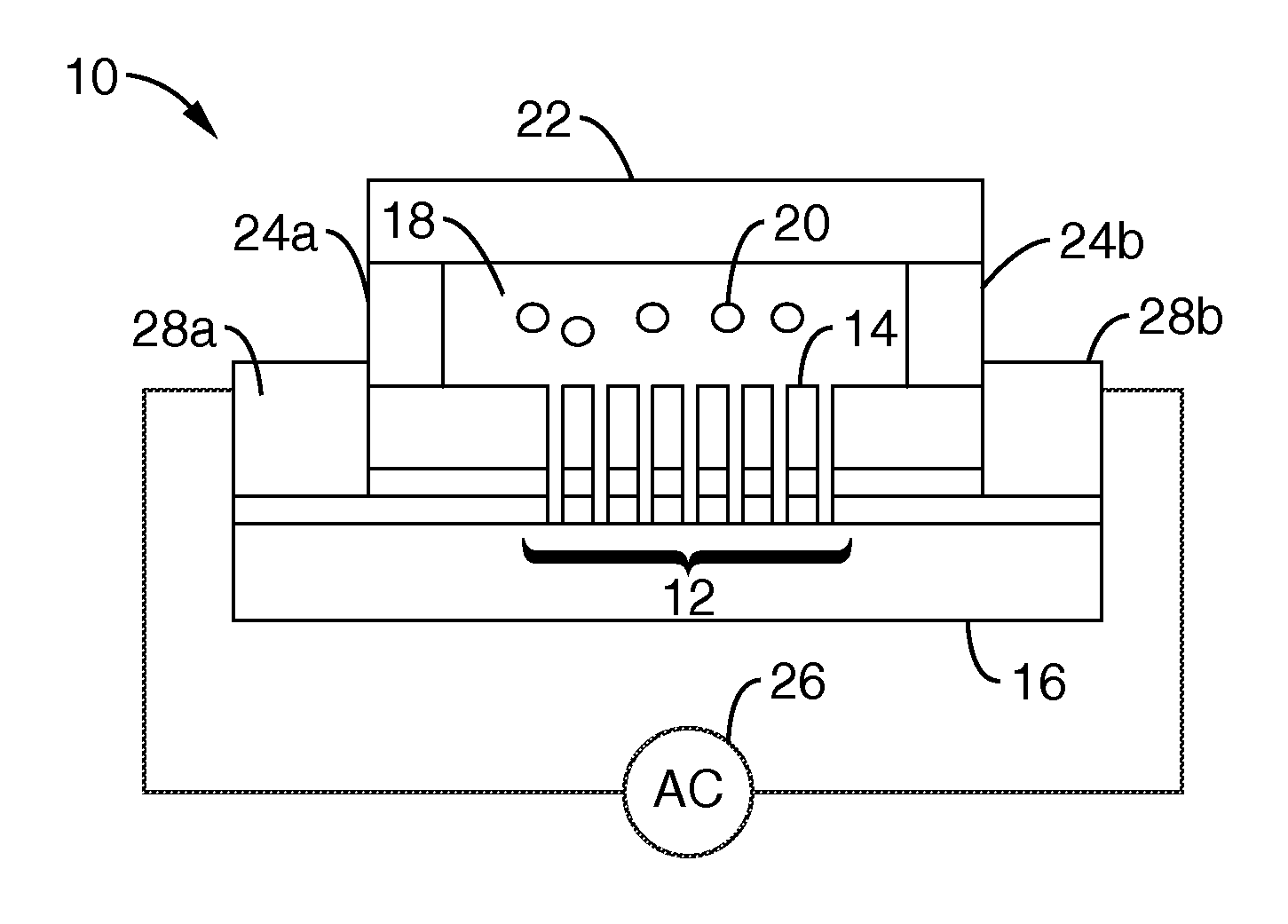
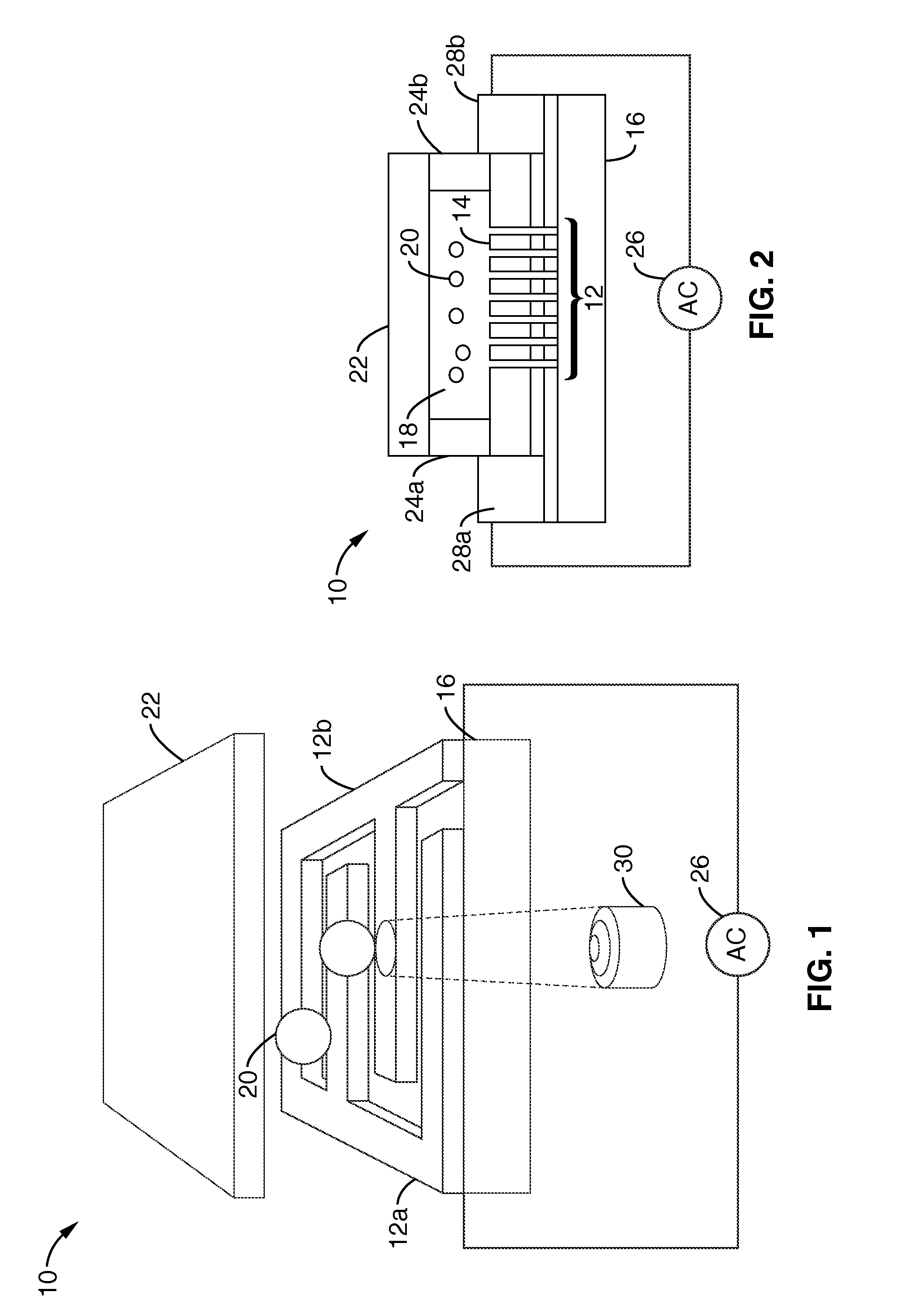
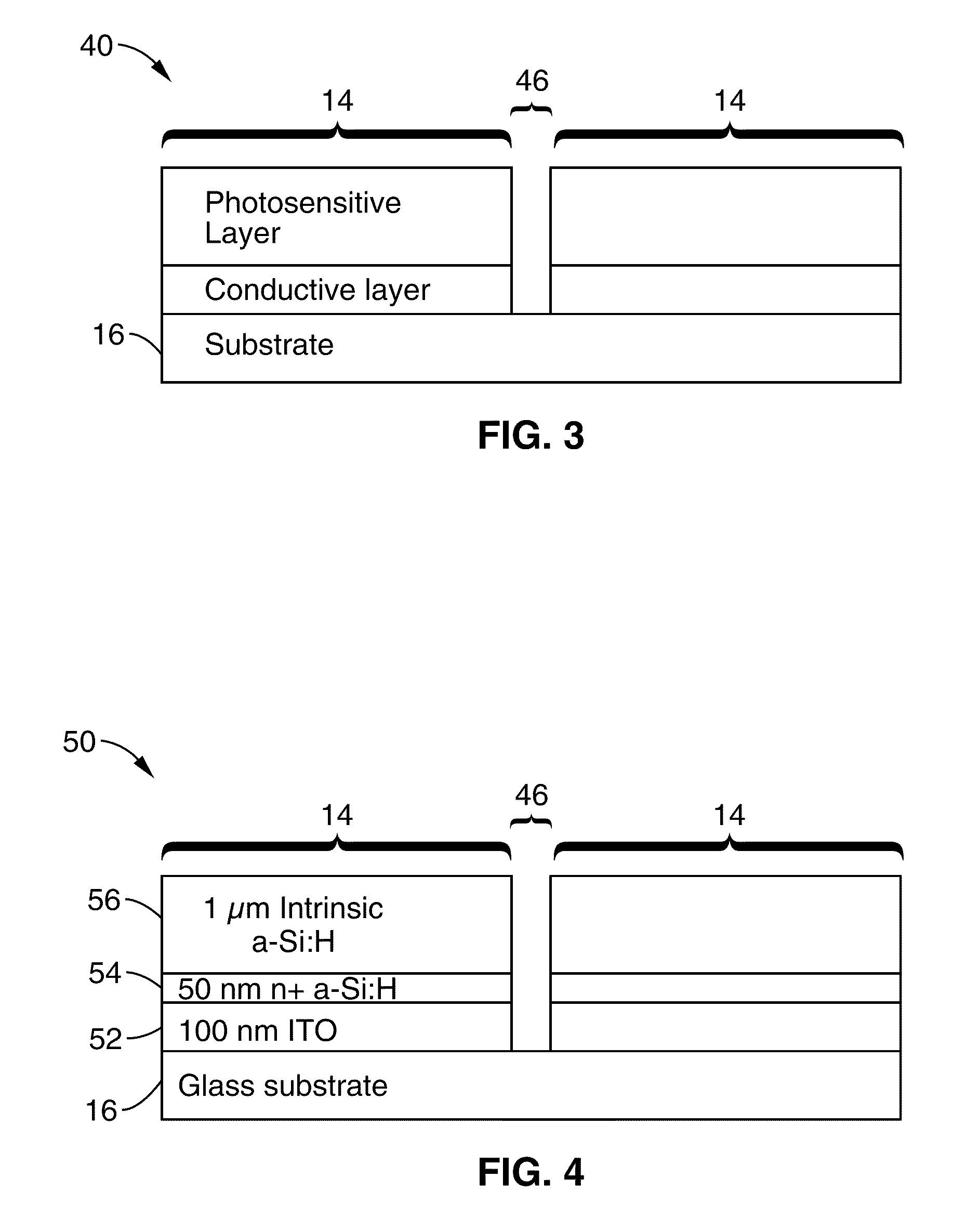
Single-sided lateral-field and phototransistor-based optoelectronic tweezers
ActiveUS7956339B2Good flexibilityElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentDielectrophoretic forceCell culture media
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Cell culture improvements
ActiveUS20080227136A1Improve productivityImproved cell culture longevityGenetically modified cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementCell culture mediaImproved method
The invention describes improved methods and compositions for producing a recombinant protein, e.g., an antibody, in mammalian cell culture. In addition, the invention provides improved cell culture media, including improved production media, feed solutions, and combination feeds, which may be used to improve protein productivity in mammalian cell culture.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
Articles comprising large-surface-area bio-compatible materials and methods for making and using them
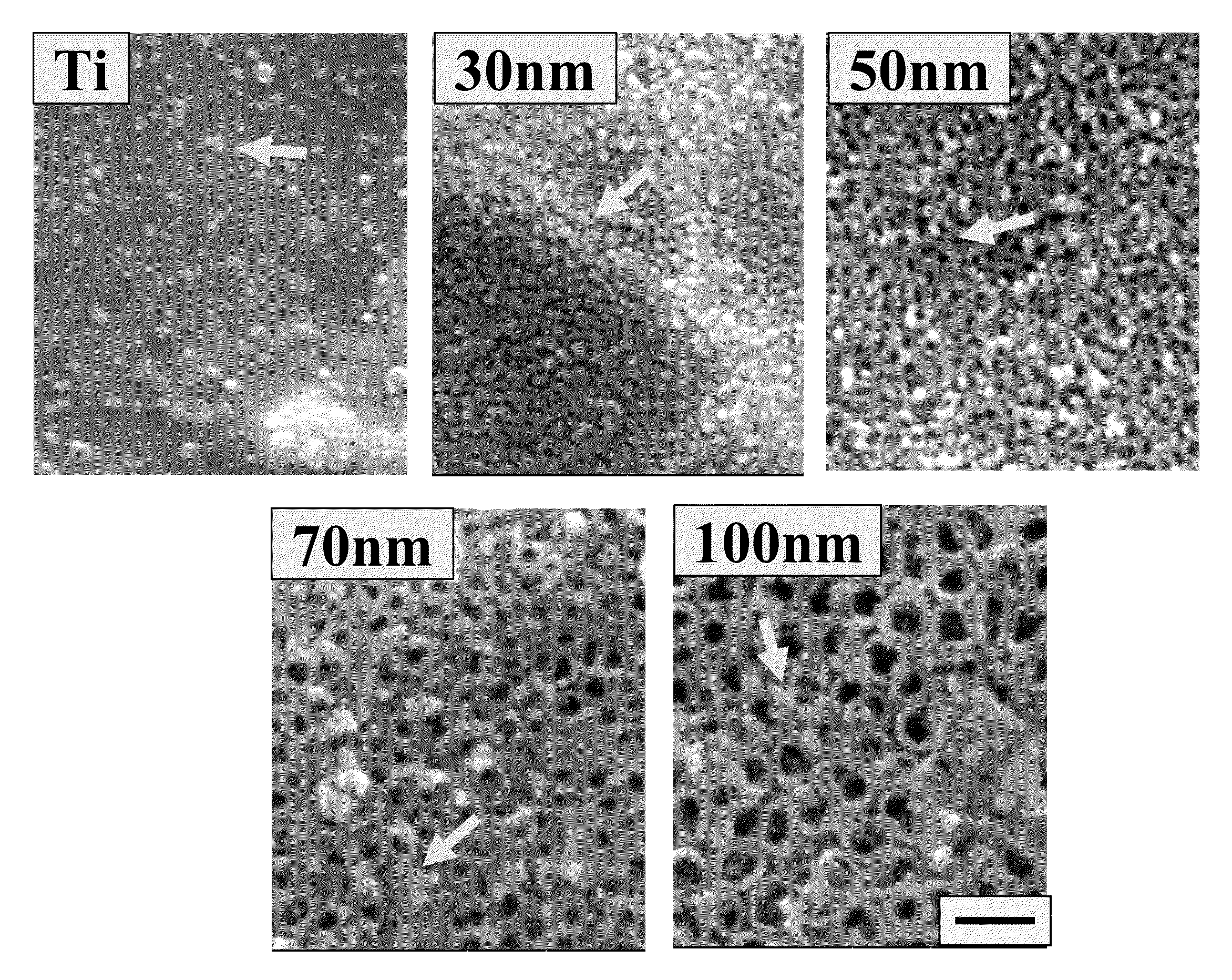
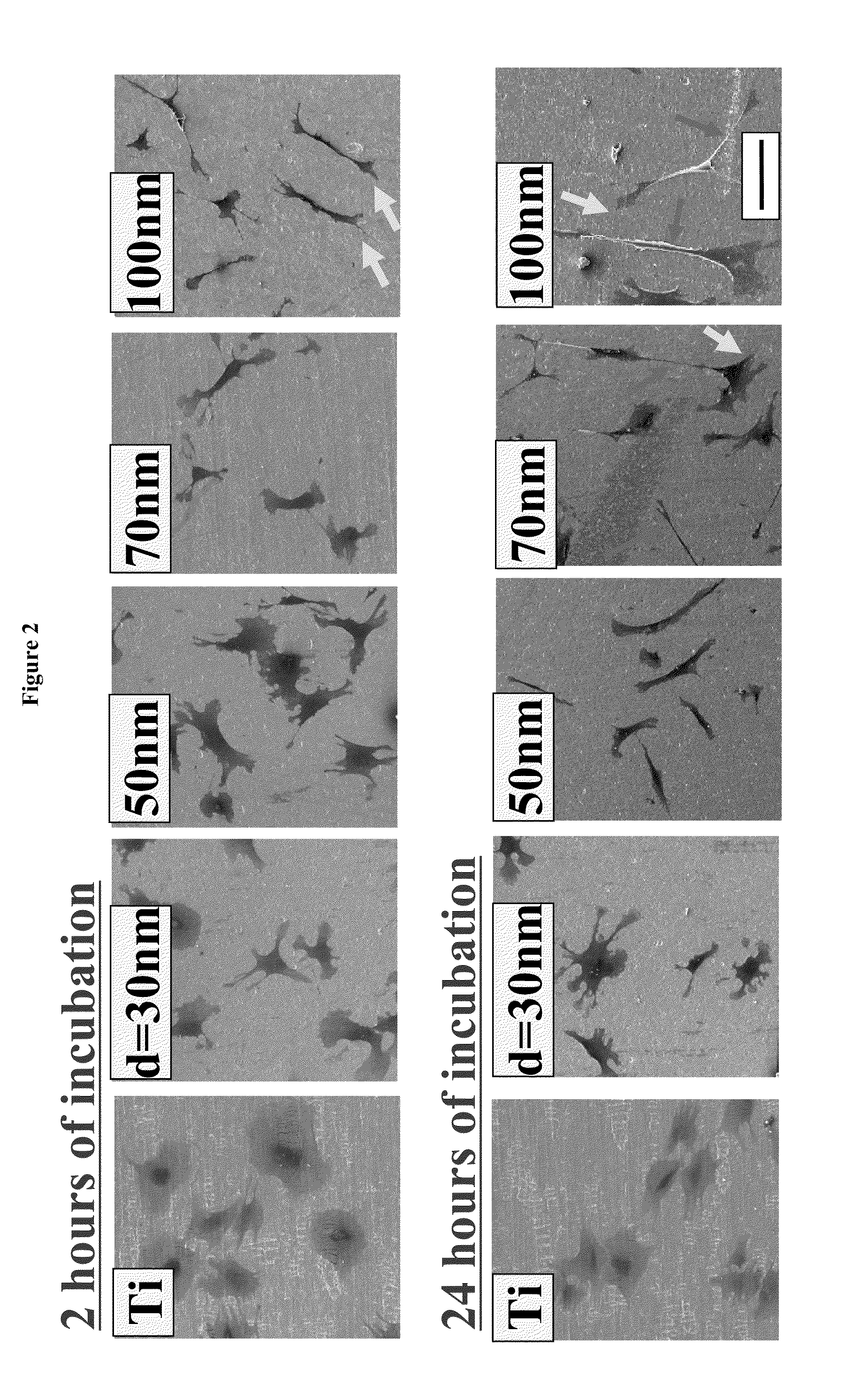
ActiveUS20100303722A1Improve cell adhesionAccelerated cell growth characteristicImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCell culture mediaBone growth
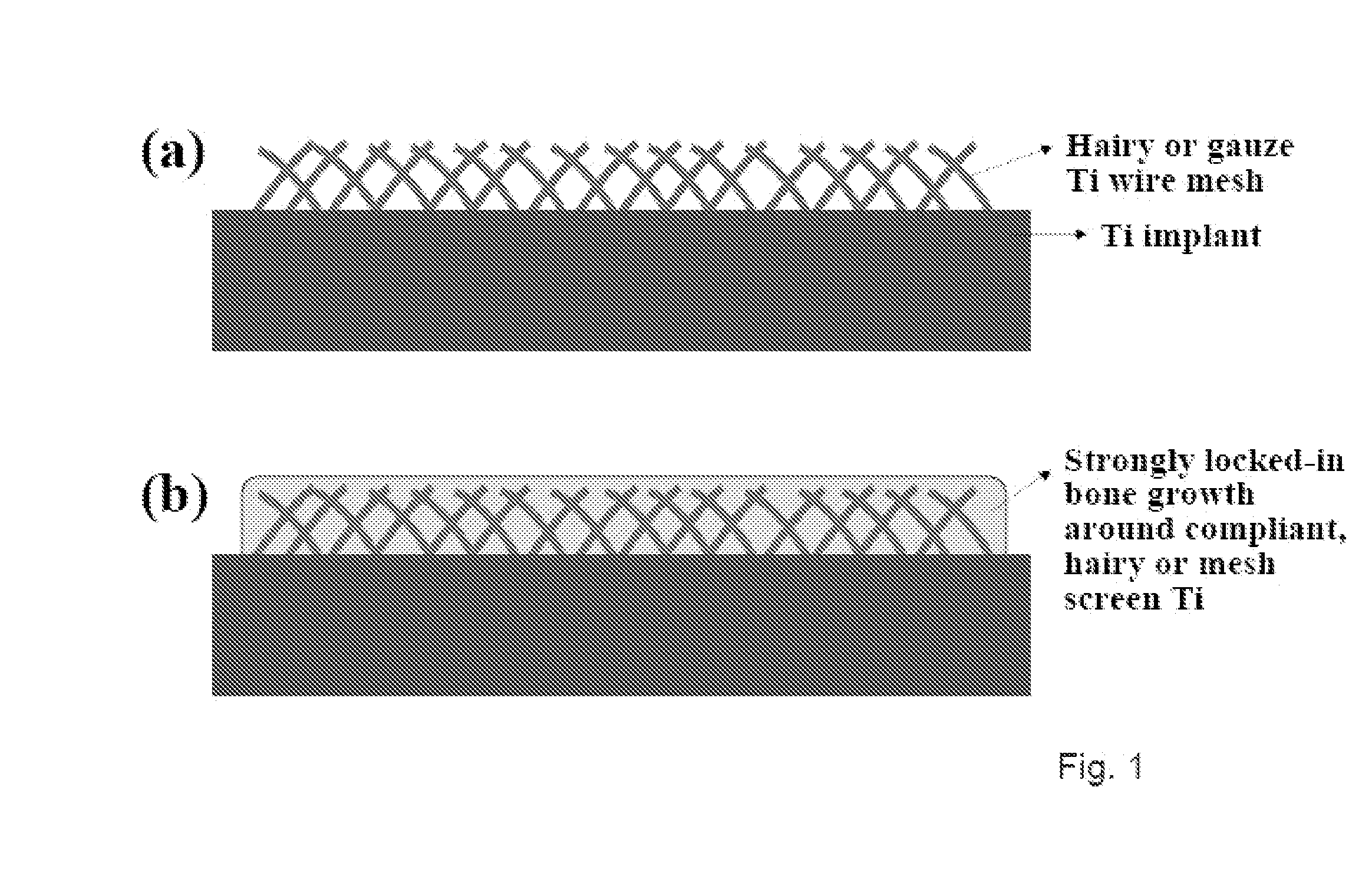
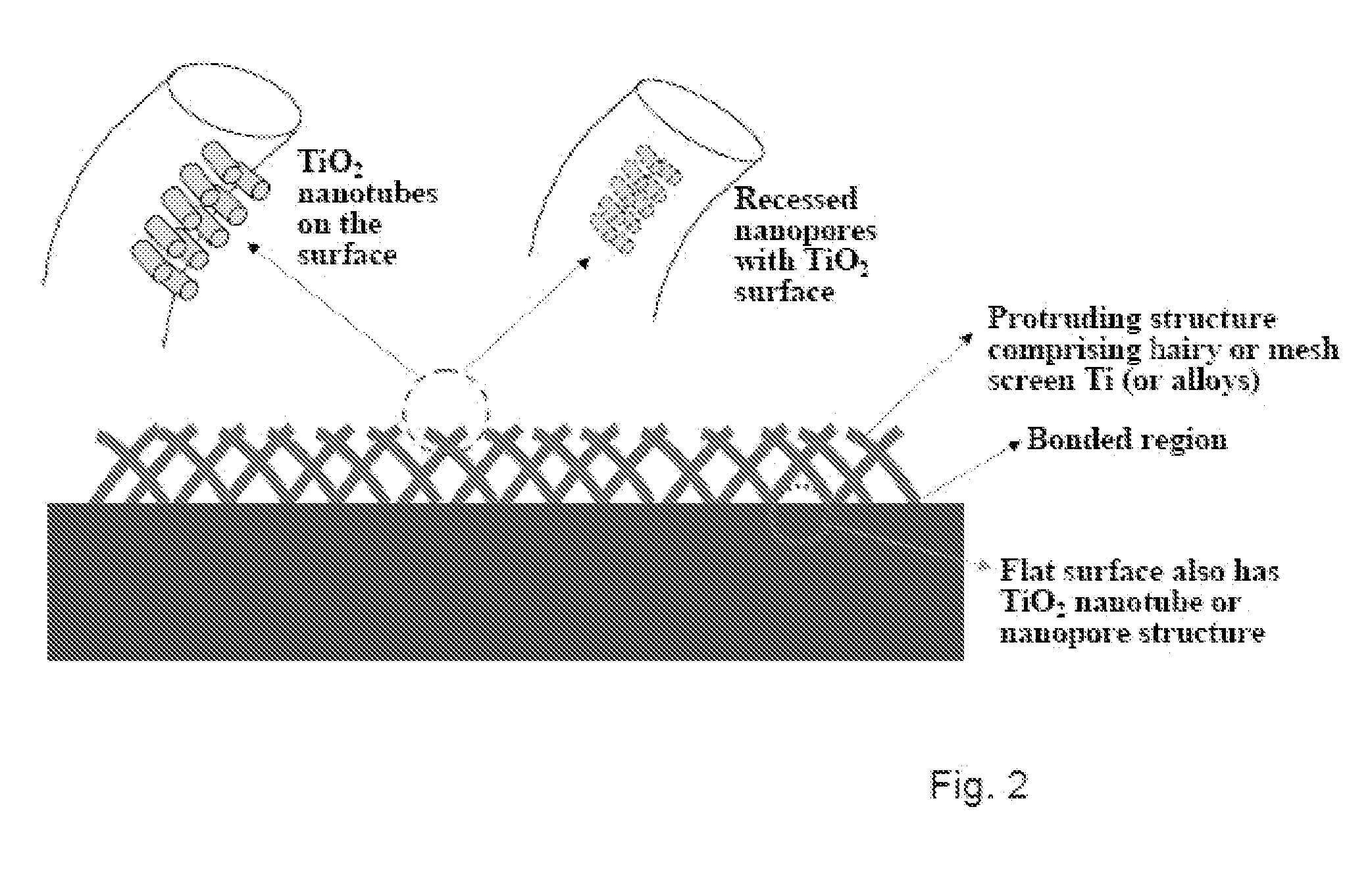
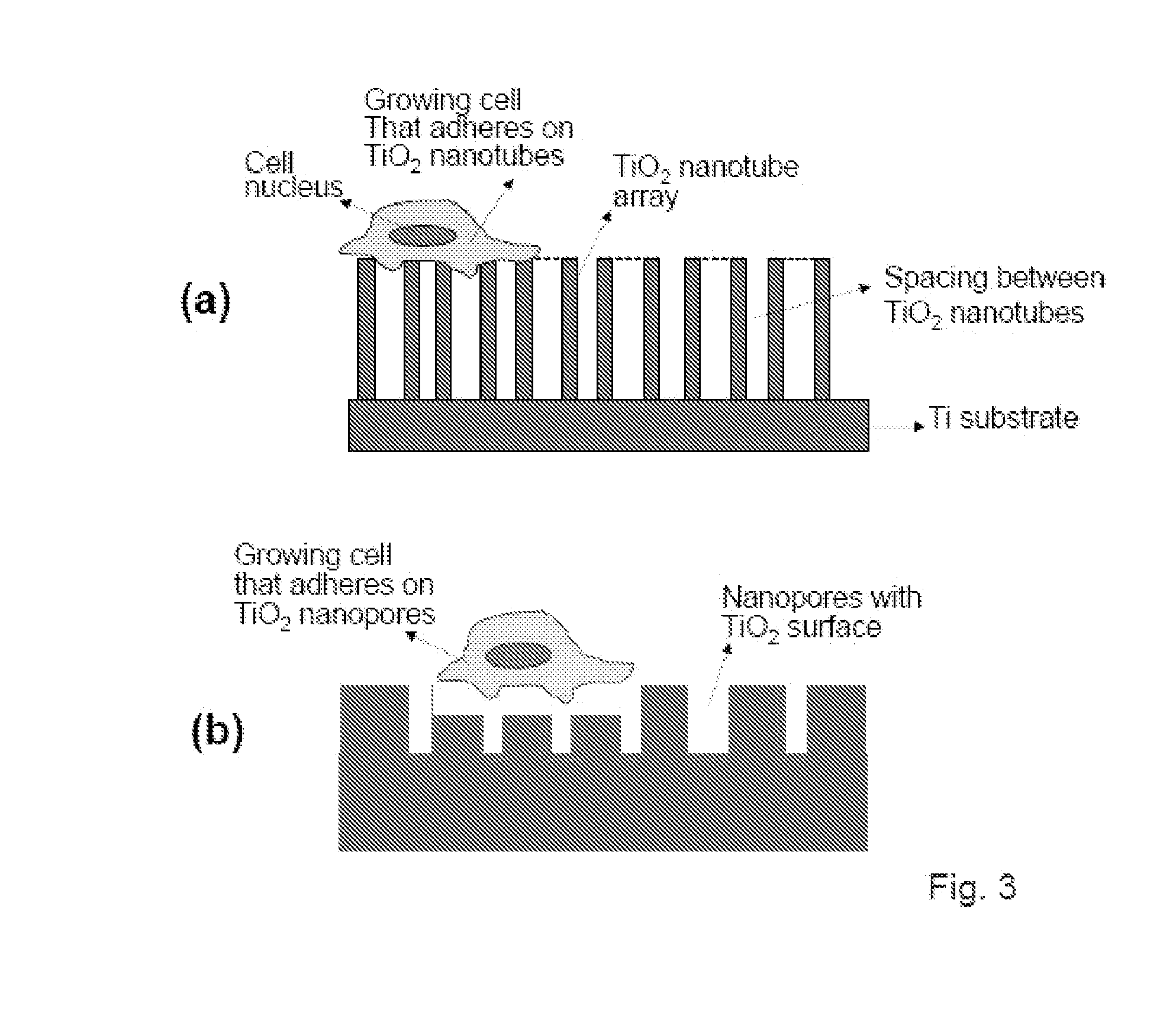
The present invention provides articles of manufacture comprising biocompatible nanostructures comprising significantly increased surface area for, e.g., organ, tissue and / or cell growth, e.g., for bone, tooth, kidney or liver growth, and uses thereof, e.g., for in vitro testing of drugs, chemicals or toxins, or as in vivo implants, including their use in making and using artificial tissues and organs, and related, diagnostic, screening, research and development and therapeutic uses, e.g., as drug delivery devices. The present invention provides biocompatible nanostructures with significantly increased surface area, such as with nanotube and nanopore array on the surface of metallic, ceramic, or polymer materials for enhanced cell and bone growth, for in vitro and in vivo testing, cleansing reaction, implants and therapeutics. The present invention provides optically transparent or translucent cell-culturing substrates. The present invention provides biocompatible and cell-growth-enhancing culture substrates comprising elastically compliant protruding nanostructure substrates coated with Ti, TiO2 or related metal and metal oxide films.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Animal protein-free media for cultivation of cells
InactiveUS20080009040A1Efficient expressionGuaranteed efficient growthMicroorganismsCulture processHydrolysateCell culture media
The present invention relates to animal protein-free cell culture media comprising polyamines and a plant- and / or yeast-derived hydrolysate. The invention also relates to animal protein-free culturing processes, wherein cells can be cultivated, propagated and passaged without adding supplementary animal proteins in the culture medium. These processes are useful in cultivating cells, such as recombinant cells or cells infected with a virus, and for producing biological products by cell culture processes.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
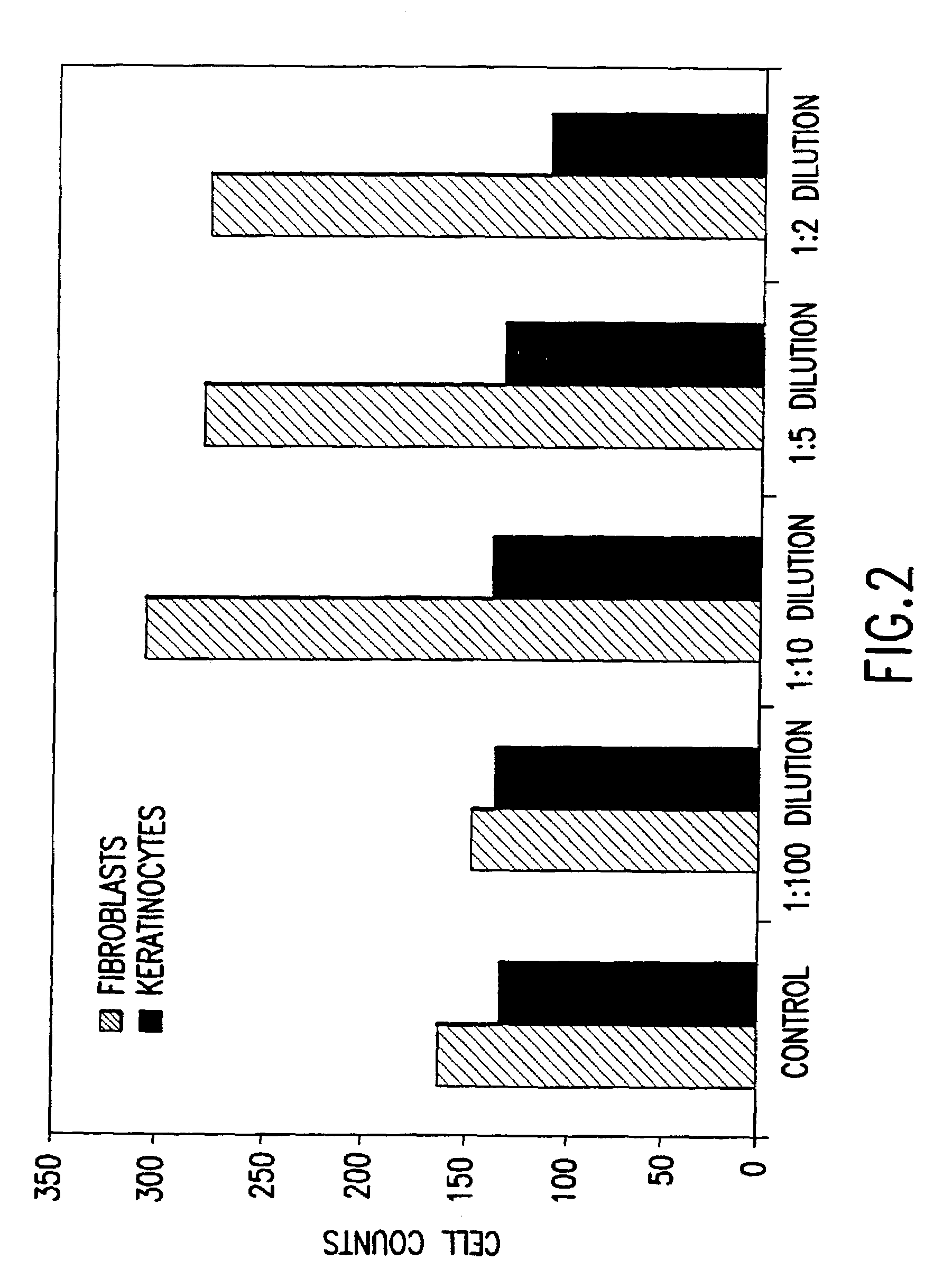
Methods for the culture of human embryonic stem cells on human feeder cells
InactiveUS7432104B2Artificial cell constructsMammal material medical ingredientsBone Marrow Stromal CellCell culture media
Methods and cell culture medium for the generation of human pluripotent embryonic stem cells are disclosed. Human embryonic stem cells are cultured with human granulosa feeder cells, muscle cells, Fallopian ductal epithelial cells, bone marrow stromal cells, and skin fibroblasts and the embryonic stem cells maintain their pluripotent phenotype. The human pluripotent embryonic stem cells can be cultured without feeder cells, and in the presence of supplemental growth factors. The human pluripotent embryonic stem cells can be alternatively cultured with conditioned medium obtained from a cell culture capable of maintaining human embryonic stem cells in a pluripotent state, wherein the cell culture is a human granulosa cell culture.
Owner:VIACYTE INC
Adult stem cells and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050260748A1High expressionHigh activityHepatocytesGenetically modified cellsAdult liverCell culture media
Disclosed are compositions and methods for isolating, immortalizing and differentiating adult stem cells, for example, particular human clonal adult liver stem cells or adipose stem cells, including specialized cell culture media for the isolation and propagation of such stem cells. Also disclosed are methods of screening for toxicity, carcinogenicity and therapeutic activity using such stem cells and immortalized or differentiated derivatives thereof. In addition, methods of treatment using such stem cells and their differentiated or immortalized derivatives thereof are disclosed.
Owner:MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Alternative compositions and methods for the culture of stem cells
InactiveUS20050037488A1Artificial cell constructsMammal material medical ingredientsBone Marrow Stromal CellCell culture media
Methods and cell culture medium for the generation of human pluripotent embryonic stem cells are disclosed. Human embryonic stem cells are cultured with human granulosa feeder cells, muscle cells, Fallopian ductal epithelial cells, bone marrow stromal cells, and skin fibroblasts and the embryonic stem cells maintain their pluripotent phenotype. The human pluripotent embryonic stem cells can be cultured without feeder cells, and in the presence of supplemental growth factors. The human pluripotent embryonic stem cells can be alternatively cultured with conditioned medium obtained from a cell culture capable of maintaining human embryonic stem cells in a pluripotent state, wherein the cell culture is a human granulosa cell culture.
Owner:VIACYTE INC
Devices and methods for growing plants
InactiveUS20080222949A1Suppress soundIncrease oxygen contentSaving energy measuresAgriculture gas emission reductionCell culture mediaEngineering
A gardening system includes a modular seed cartridge including a rigid, cup-shaped receptacle including an upper portion having an outer rim, a soilless growth medium located in the rigid, cup-shaped receptacle, and at least one seed in contact with the soilless growth medium. The gardening system also includes an aeroponic or hydroponic garden including a chamber including a lower portion for storing a liquid nutrient solution, a cover located above the chamber, the cover including a plant opening adapted to removably support the modular seed cartridge by the outer rim, and a pump located in the chamber and adapted to circulate the liquid nutrient solution from the lower portion of the chamber to the modular seed cartridge supported by the plant opening.
Owner:AEROGROW INT
Method and system for the production of cells and cell products and applications thereof
ActiveUS20090269841A1Minimization requirementsAvoid possibilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell culture mediaComputer module
Owner:BIOVEST INT
Buoyant wetland system
InactiveUS7810279B2Low costEasy constructionPlanting bedsAgriculture gas emission reductionCell culture mediaBiology
Owner:FOUNTAINHEAD
Stem cell culture medium and application thereof and stem cell cultivation method
ActiveCN103060264AHigh speedRapid expansionCulture processCell culture mediaMesenchymeCell culture media
The invention discloses a stem cell culture medium, an application of the stem cell culture medium and a stem cell cultivation method. Blood serum does not exist in the stem cell culture medium. The stem cell culture medium comprises amino acid, vitamin, salt, lipoid, cytokines and egg white polypeptide. The stem cell culture medium is suitable for fast cultivating stem cells which are tissue sources of human and mammal, and comprises but not is limited by fat mesenchyme stem cells, mesenchymal stem cells and umbilical cord blood stem cells. The culture medium enables increasing speed of the cells to be improved by 3-5 times, and differential potentials of the cells can not be affected. Compared with an ordinary stem cell culture medium, stem cells from different sources can be fast expanded, passage number is prolonged, and proficiency properties of the stem cells can be well kept.
Owner:苏州博棠再生医学科技有限公司
Methods of growing tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in gas-permeable containers
InactiveUS20170152478A1Mammal material medical ingredientsCancer antigen ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthTumour tissue
An embodiment of the invention provides a method of promoting regression of cancer in a mammal comprising obtaining a tumor tissue sample from the mammal; culturing the tumor tissue sample in a first gas permeable container containing cell medium therein; obtaining tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL) from the tumor tissue sample; expanding the number of TIL in a second gas permeable container containing cell medium therein using irradiated allogeneic feeder cells and / or irradiated autologous feeder cells; and administering the expanded number of TIL to the mammal. Methods of obtaining an expanded number of TIL from a mammal for adoptive cell immunotherapy are also provided.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
Conditioned cell culture medium compositions and methods of use
InactiveUS7118746B1Eliminate wrinkles, frown lines, scarringCondition the skinOrganic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsReserve CellCell culture media
Novel products comprising conditioned cell culture medium compositions and methods of use are described. The conditioned cell medium compositions of the invention may be comprised of any known defined or undefined medium and may be conditioned using any eukaryotic cell type. The medium may be conditioned by stromal cells, parenchymal cells, mesenchymal stem cells, liver reserve cells, neural stem cells, pancreatic stem cells and / or embryonic stem cells. Additionally, the cells may be genetically modified. A three-dimensional tissue construct is preferred. Once the cell medium of the invention is conditioned, it may be used in any state. Physical embodiments of the conditioned medium include, but are not limited to, liquid or solid, frozen, lyophilized or dried into a powder. Additionally, the medium is formulated with a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier as a vehicle for internal administration, applied directly to a food item or product, formulated with a salve or ointment for topical applications, or, for example, made into or added to surgical glue to accelerate healing of sutures following invasive procedures. Also, the medium may be further processed to concentrate or reduce one or more factors or components contained within the medium.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Microfluidic chemostat
InactiveUS20050164376A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiofilmLysis
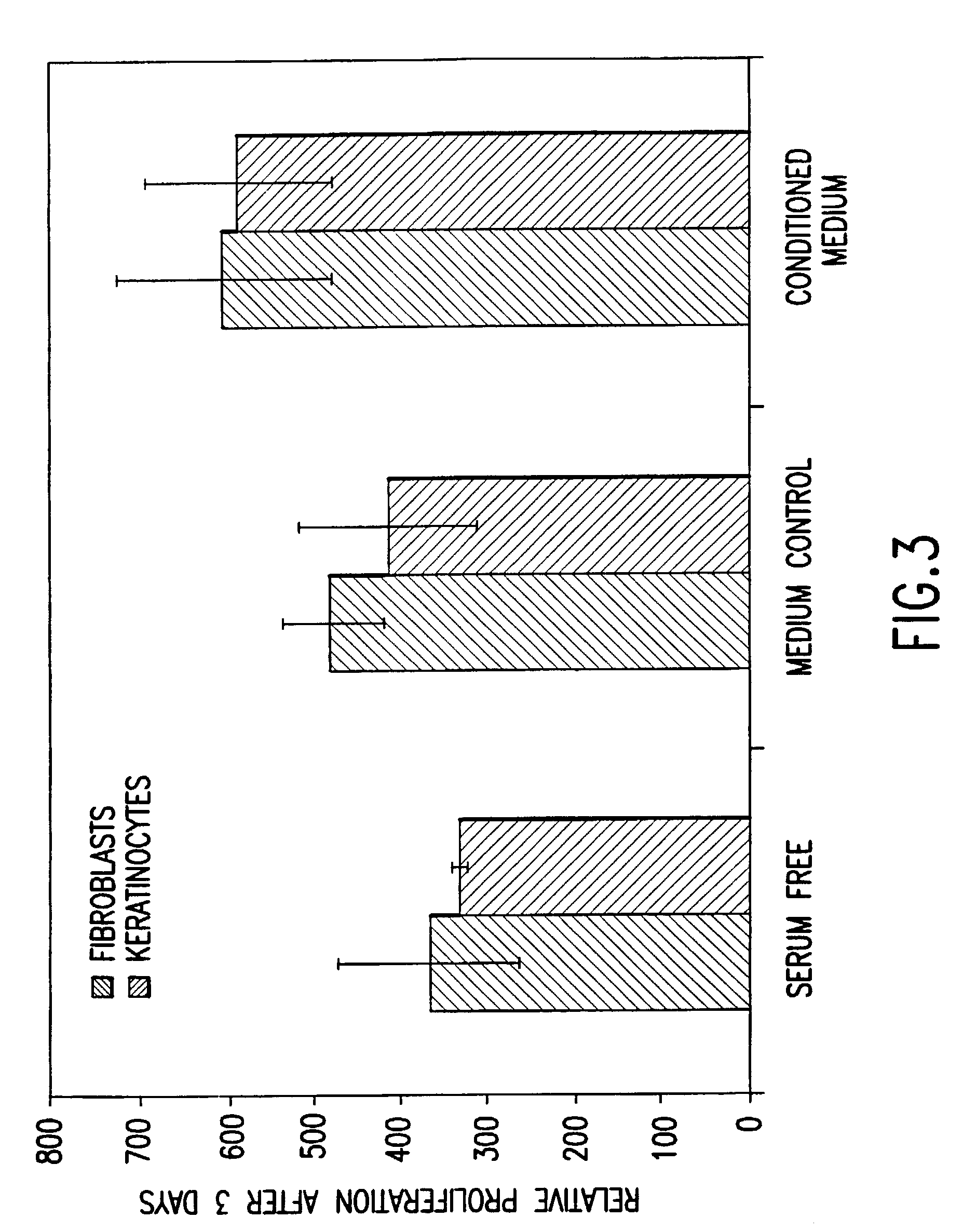
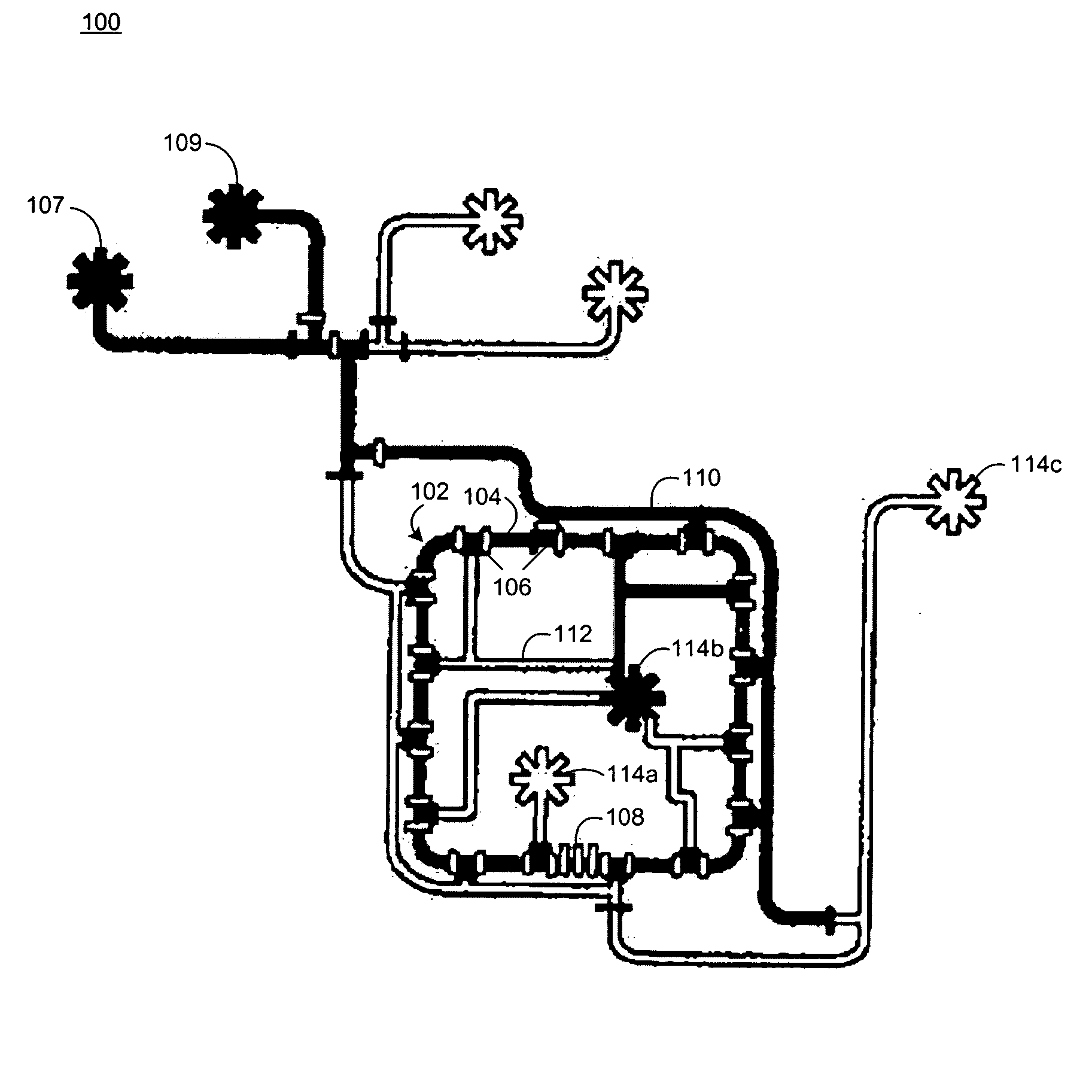
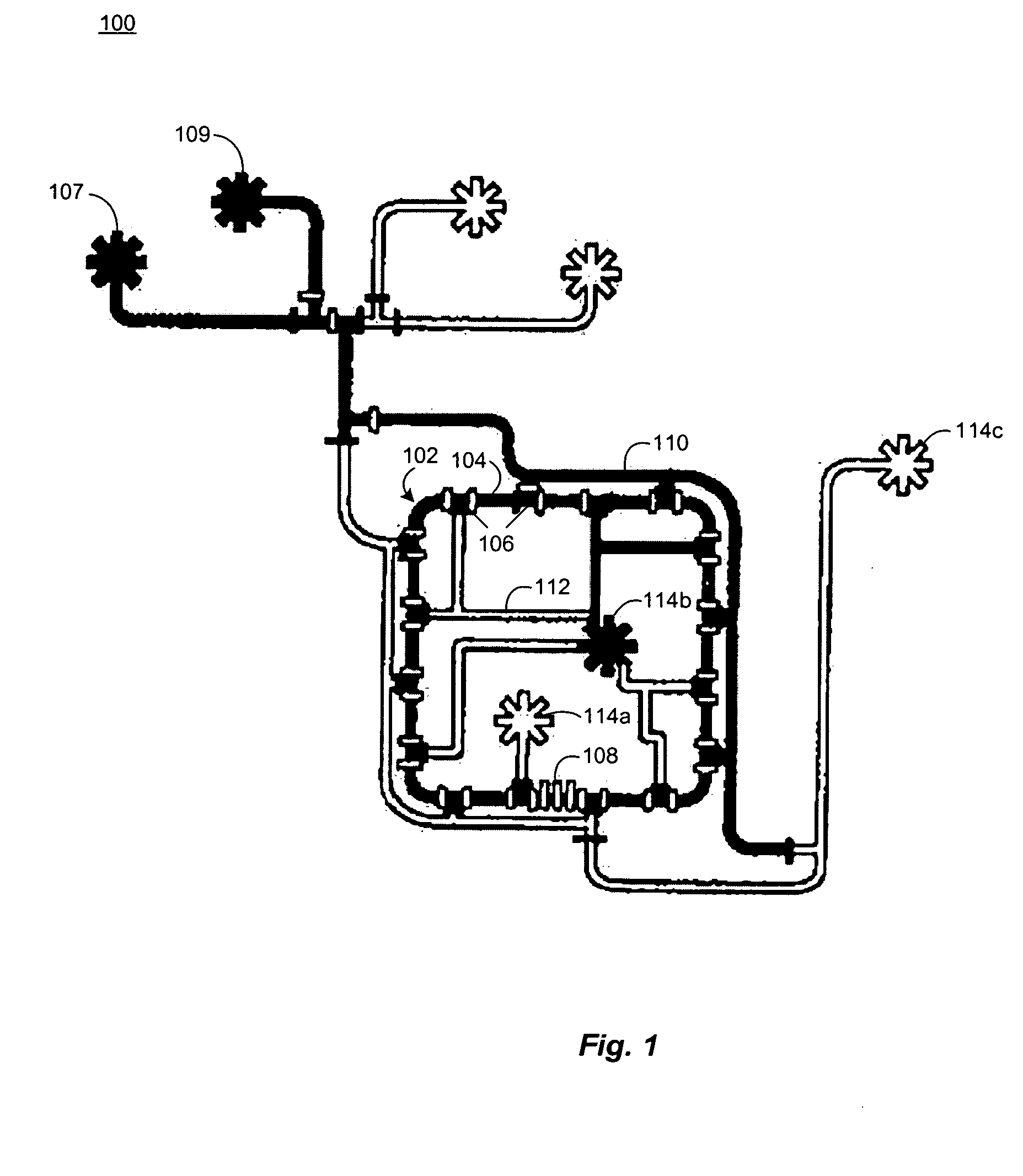
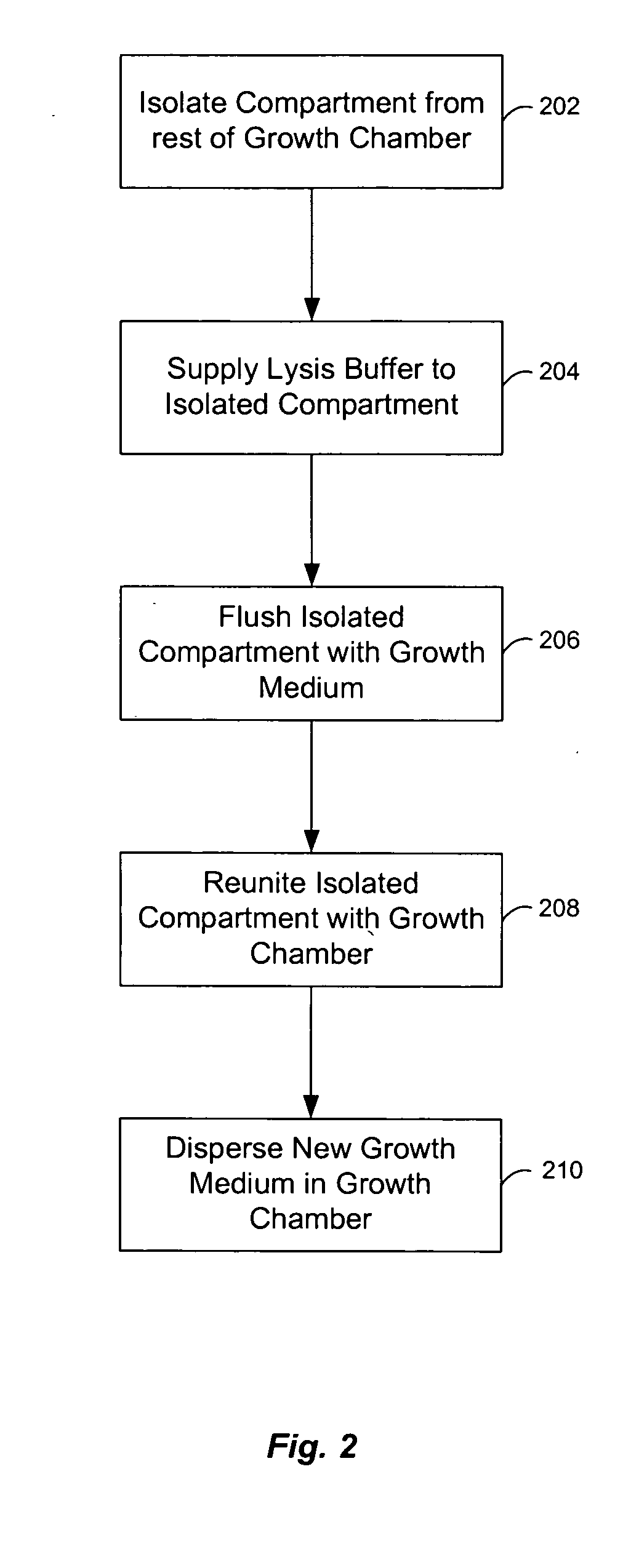
A chemostat that includes a growth chamber having a plurality of compartments, where each of the compartments may be fluidly isolated from the rest of the growth chamber by one or more actuatable valves. The chemostat may also include a nutrient supply-line to supply growth medium to the growth chamber, and an output port to remove fluids from the growth chamber. Also, a method of preventing biofilm formation in a growth chamber of a chemostat. The method may include the steps of adding a lysis agent to a isolated portion of the growth chamber, and reuniting the isolated portion with the rest of the growth chamber.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Fed-batch cell culture methods using non-animal-based hydrolysates
ActiveUS8093045B2Improve productivityHigh potencyGenetically modified cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementHydrolysateCell culture media
The invention describes improved methods and compositions for producing a recombinant protein, e.g., an antibody, in mammalian cell culture. In addition, the invention provides improved cell culture media, including improved production media, feed solutions, and combination feeds, which may be used to improve protein productivity in mammalian cell culture.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
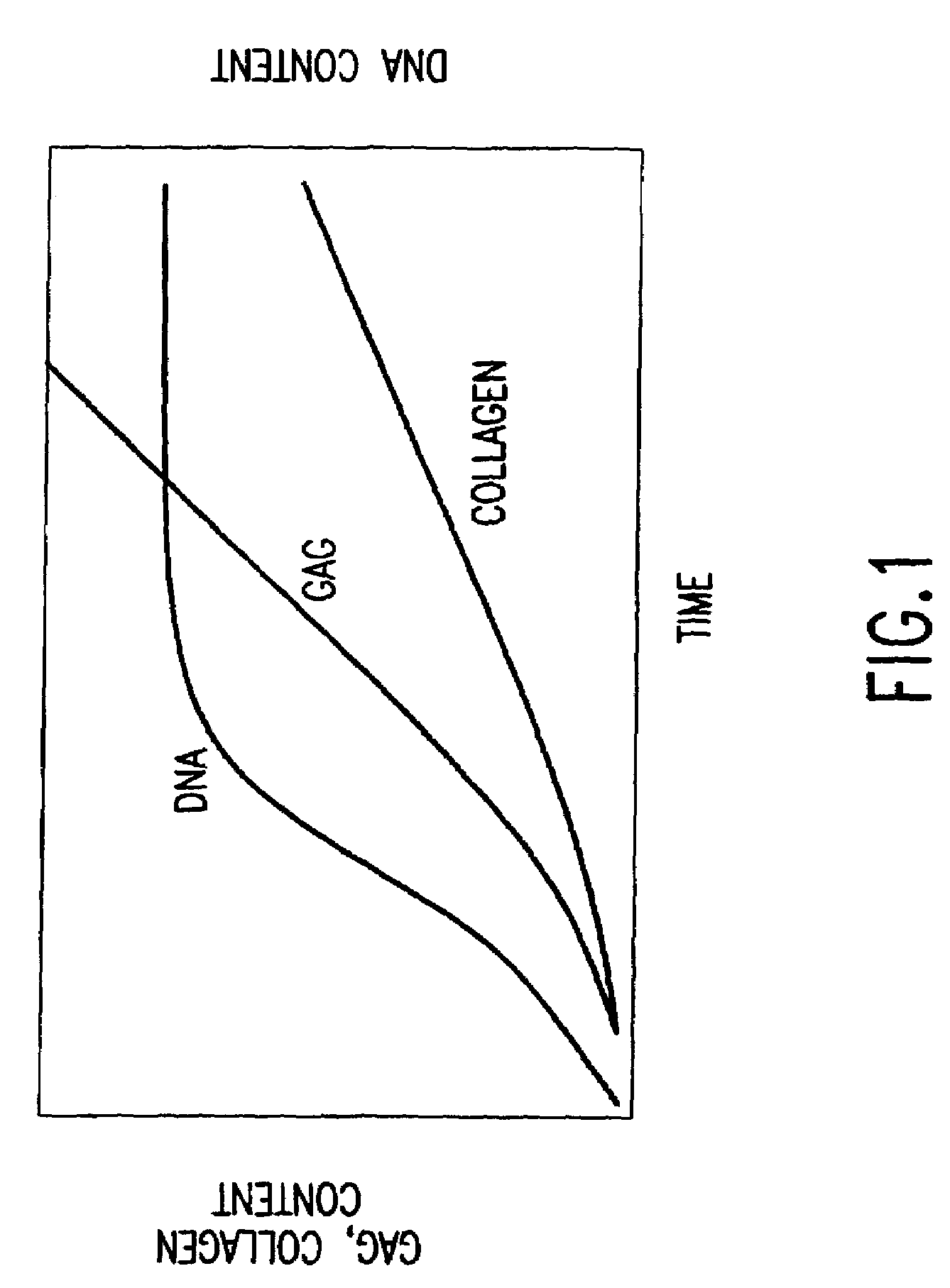
Serum-free media for chondrocytes and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS7169610B2Safe effective inexpensiveSafe and effective and inexpensiveCulture processArtificial cell constructsLipid formationSerum free media
The present invention provides defined serum-free cell culture media useful in culturing fibroblasts, especially articular chondrocytes, that avoids problems inherent in the use of serum-containing media. The defined media comprise platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), and chemically defined lipids, or combinations of these compounds. In another aspect, the present invention also provides tissue culture methods that comprise incubating chondrocytes in the defined serum free media. The methods enhance attachment and proliferative expansion of chondrocytes seeded at low density while maintaining their redifferentiation potential.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
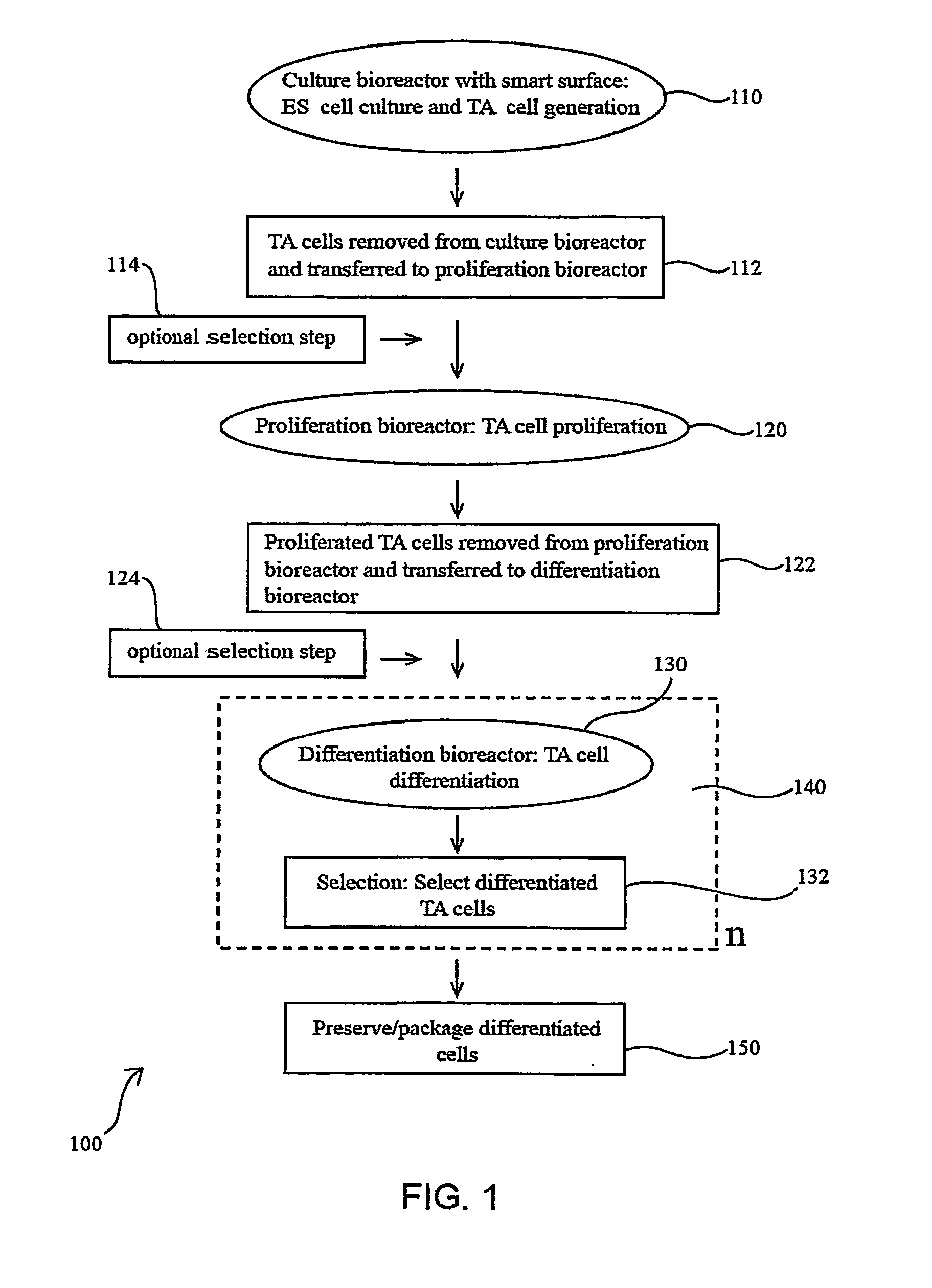
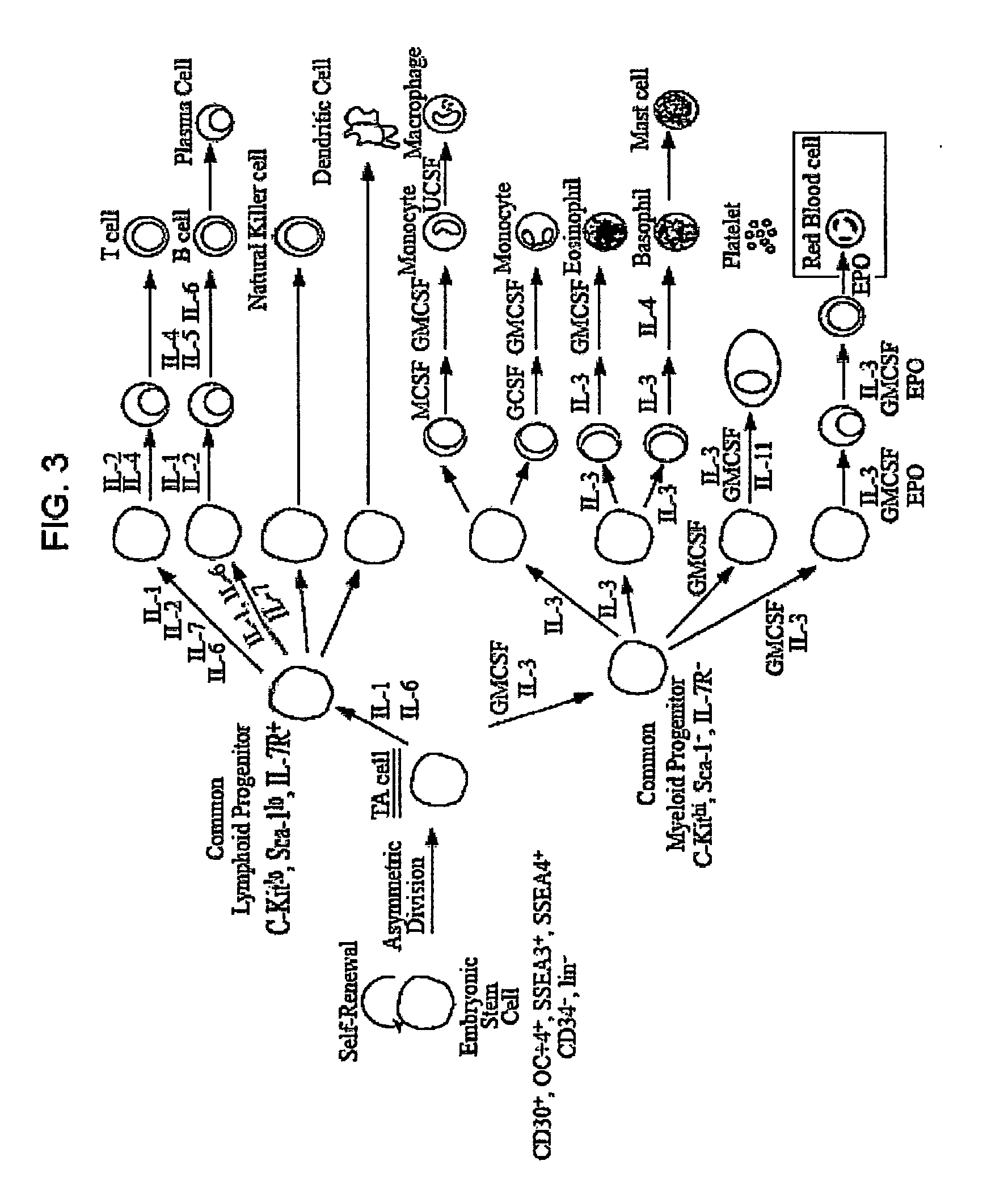
Methods for producing blood products from pluripotent cells in cell culture
The present invention provides methods for in vitro production of clinically useful quantities of differentiated human blood cells. In various embodiments of the present invention, immortal pluripotent cells are used to produce differentiated blood cell populations using a cell production device. In a specific embodiment, the device is a sequential series of bioreactors utilizing growth media containing specific combinations of maintenance-, proliferation- or differentiation-promoting factors that maintain, expand and promote the maturation and differentiation of the desired cell types. The immortal pluripotent cells can optionally be genetically modified so as to remove histcompatibility or blood group antigens.
Owner:AUSTRALIAN STEM CELL CENT
Screening methods
The invention relates to methods for the screening, identification and / or application of microorganisms of use in imparting beneficial properties to plants. In one embodiment, the method involves subjecting one or more plants to a growth medium in the presence of a set of microorganisms, selecting one or more plant, acquiring one or more microorganisms associated with the selected plant(s) and repeating the process one or more times. The method further involves the step of subjecting the one or more microorganisms to a conditioning and / or directed evolution process.
Owner:BIOCONSORTIA
Methods and compositions for the differentiation of stem cells
ActiveUS20100216181A1Overcome limitationsPromote cell differentiationMicrobiological testing/measurementCulture processProgenitorInduced pluripotent stem cell
The present invention provides methods and compositions for the production of hematopoietic progenitor cells or endothelial progenitor cells from human pluripotent stem cells using a defined cell culture medium without the need to utilize feeder cells or serum. In some embodiments, differentiation is accomplished using hypoxic atmospheric conditions. The defined medium of the present invention may contain growth factors and a matrix component. The hematopoietic progenitor cells may be further differentiated into cell lineages including red blood cells, macrophages, granulocytes, and megakaryocytes. The endothelial progenitor cells may be further differentiated into endothelial cells. Also disclosed are screening assays for identification of candidate substances that affect differentiation of pluripotent stem cells into progenitor cells.
Owner:FUJIFILM CELLULAR DYNAMICS INC
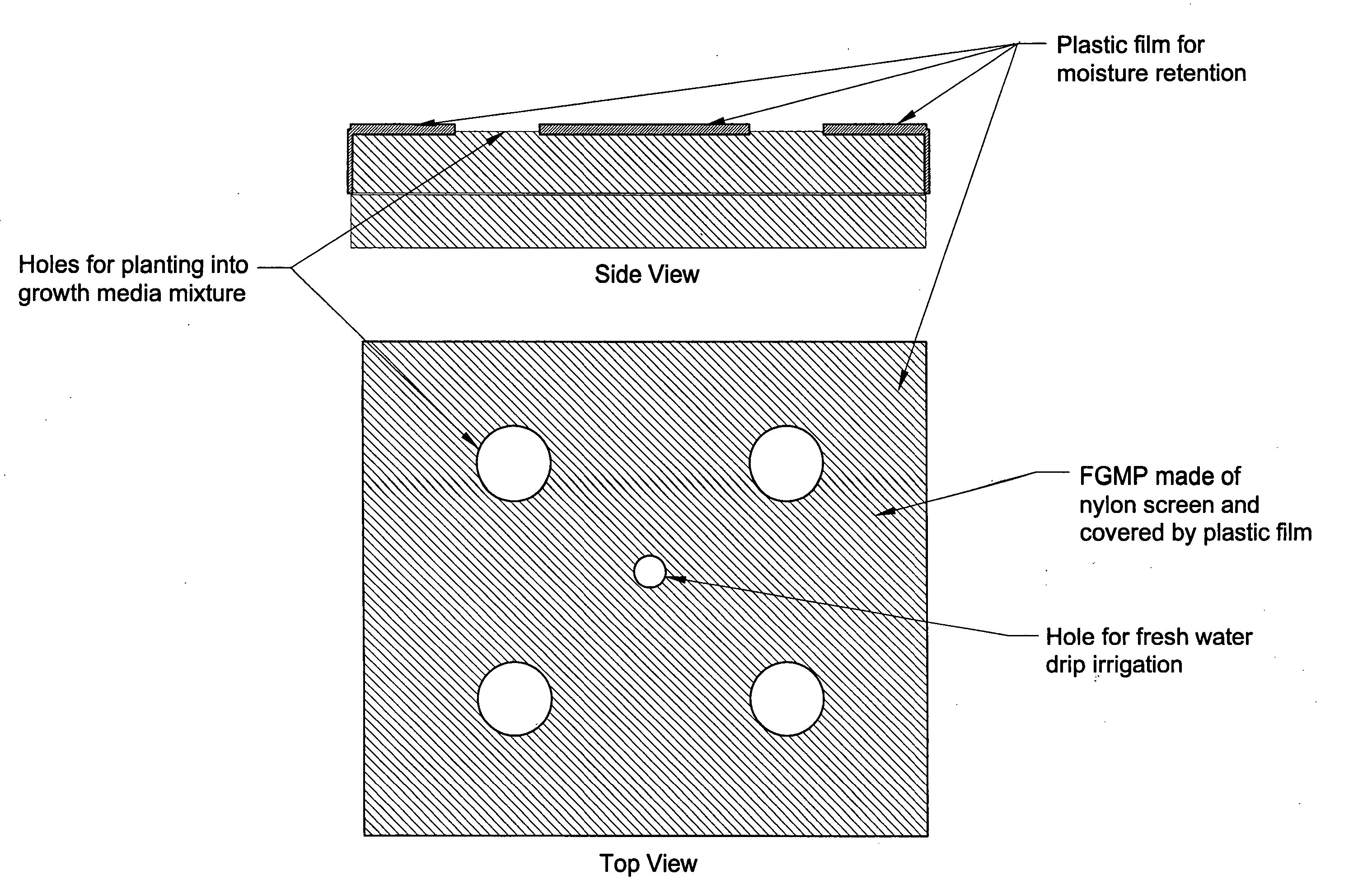
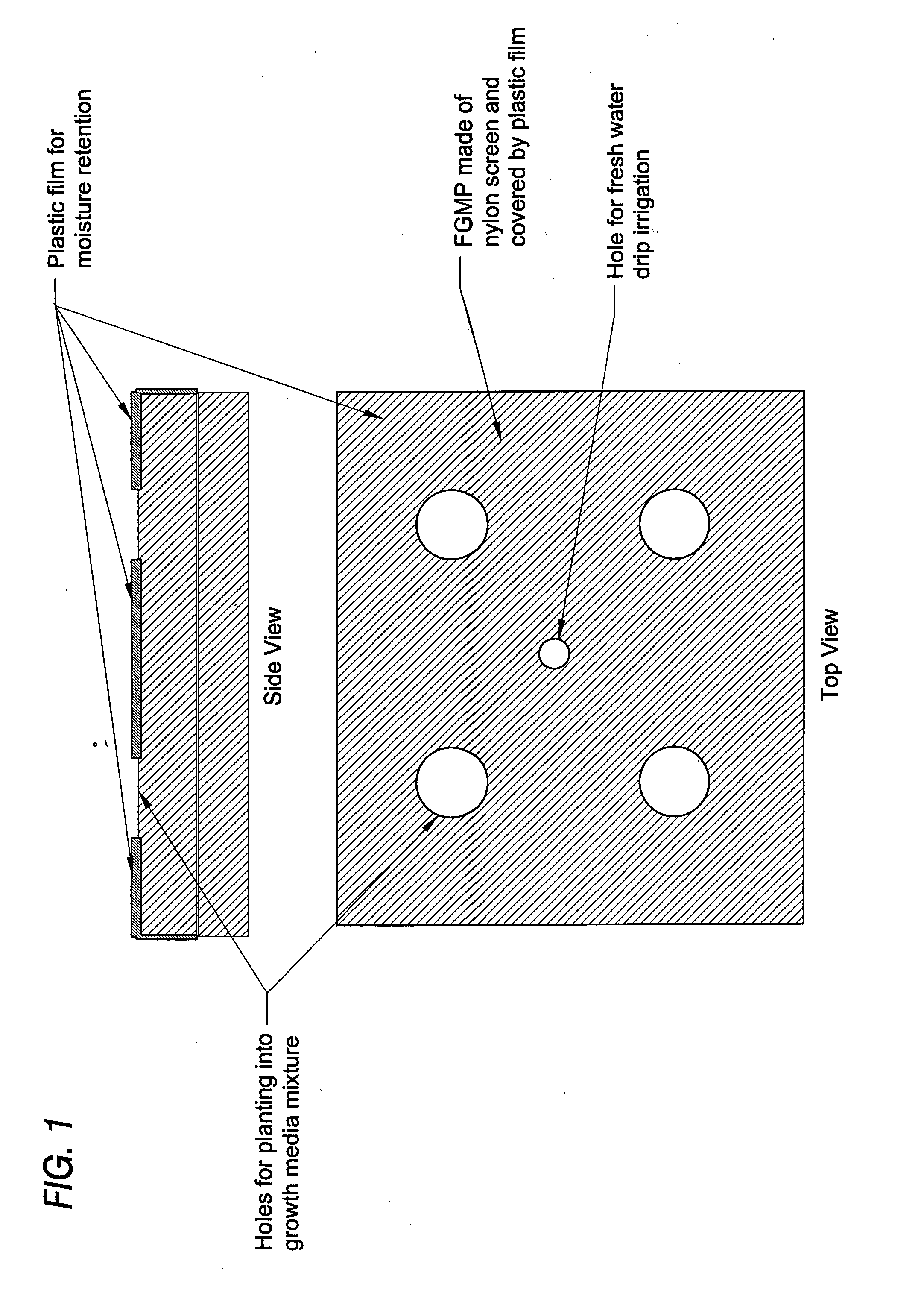
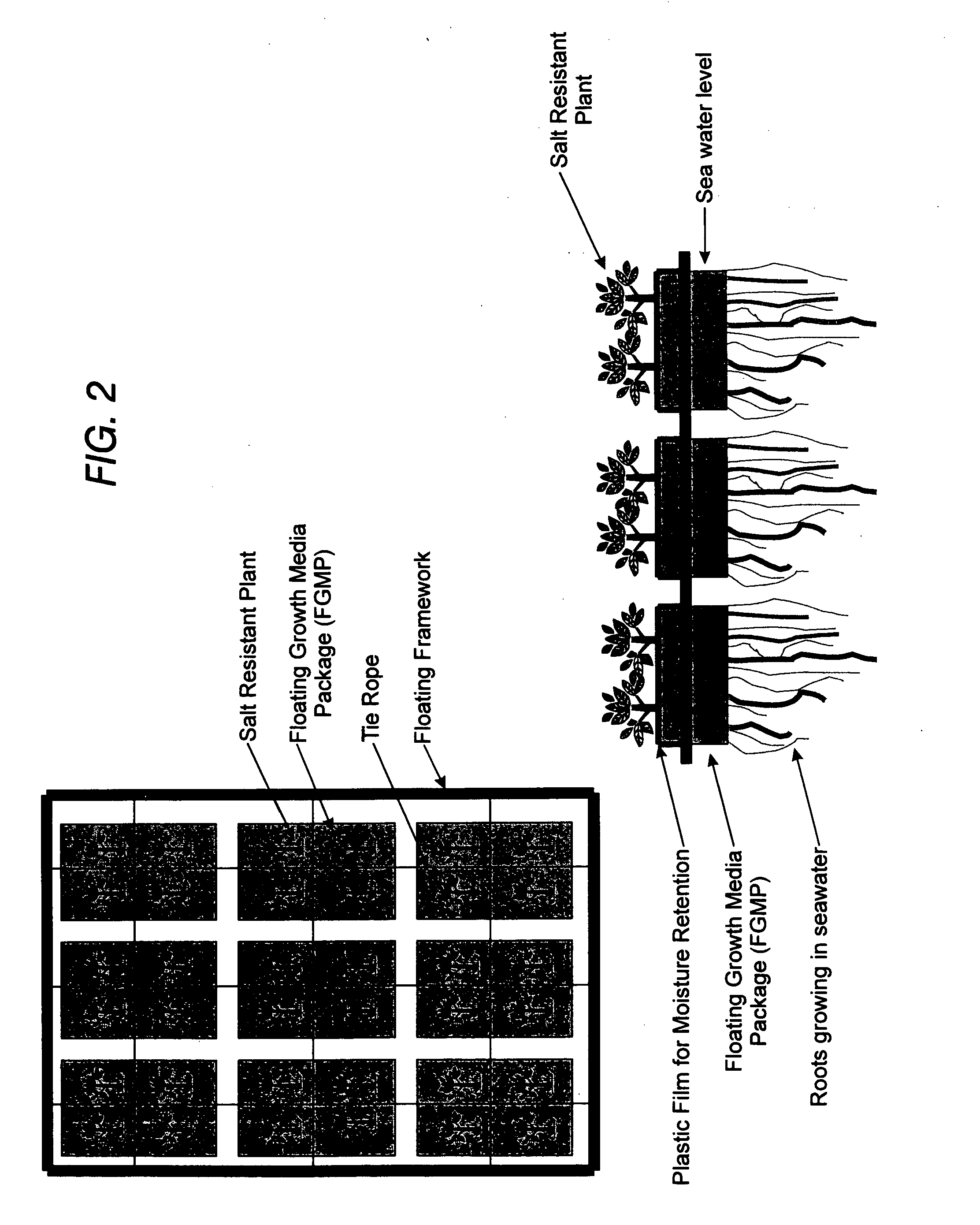
Floating plant cultivation platform and method for growing terrestrial plants in saline water of various salinities for multiple purposes
InactiveUS20050044788A1Efficient managementMinimal requirementSeed and root treatmentClimate change adaptationShootCell culture media
The cultivation of terrestrial plants in brackish water or seawater is carried out with this invention. A light-weight, floating growth medium package (FGMP) or, alternatively, a sheet of suitable material is used to support the growth of terrestrial plants floating on water bodies of various salinity, including 100% seawater in marine environments. The FGMP units can be linked together and confined in a floating, rigid or flexible framework to form a floating seawater cultivation platform (FSCP). Using the method, plants were able to grow and thrive on the FSCP floating on 100% seawater in a sustainable manner. Halophytic akulikuli (Sesuvium portulacastrum L.) can regenerate its shoot and root in seawater. Thus, the discovery will enable us to practice marine agriculture, or agriculture on the sea. The FSCP can be used for wide range of purposes, from environmental protection to landscaping to crop production.
Owner:UNIV OF HAWAII
Polypeptide production in animal cell culture
InactiveUS20050272124A1Promote cell growthHigh protein yieldGenetically modified cellsCulture processBiotechnologyGrowth phase
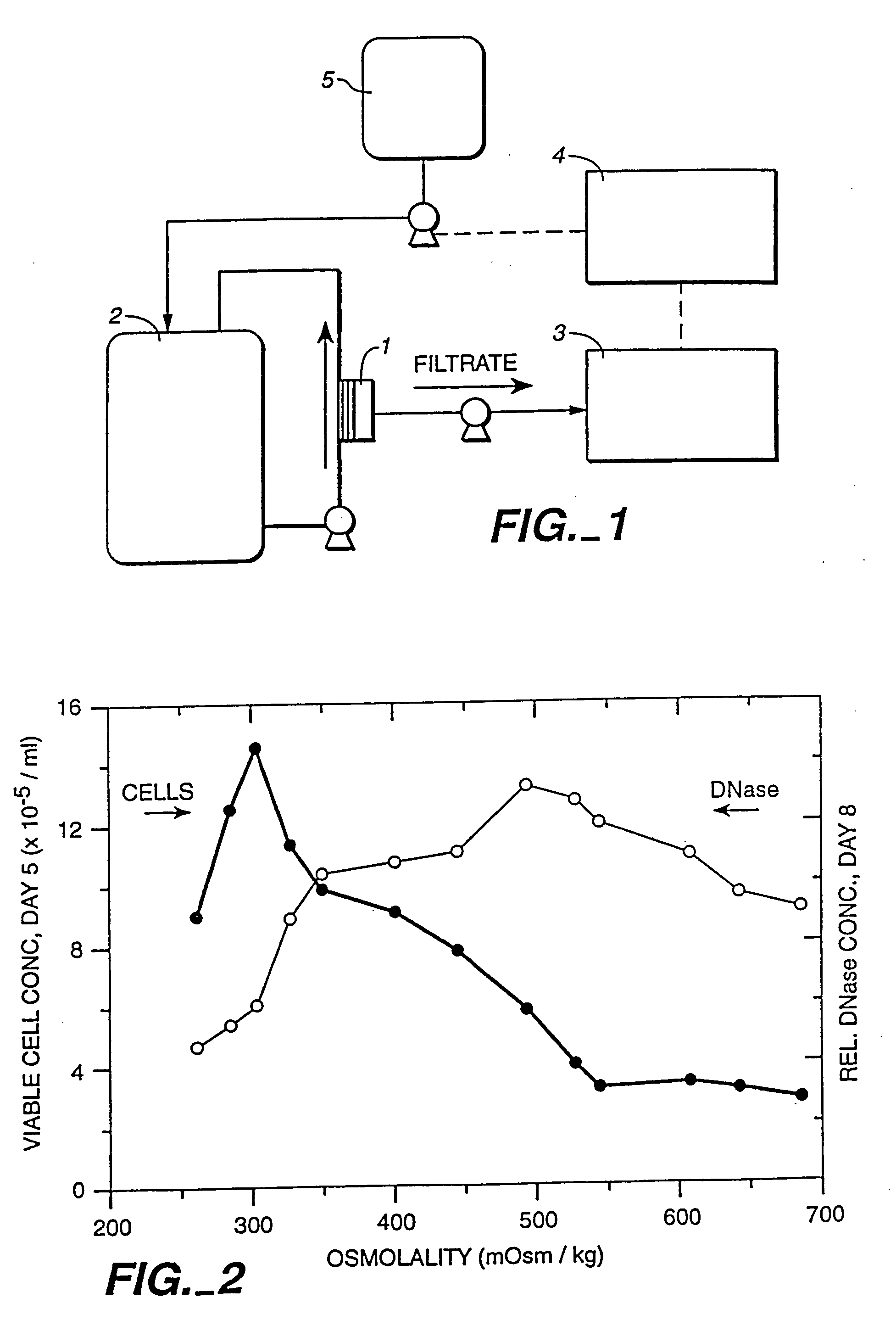
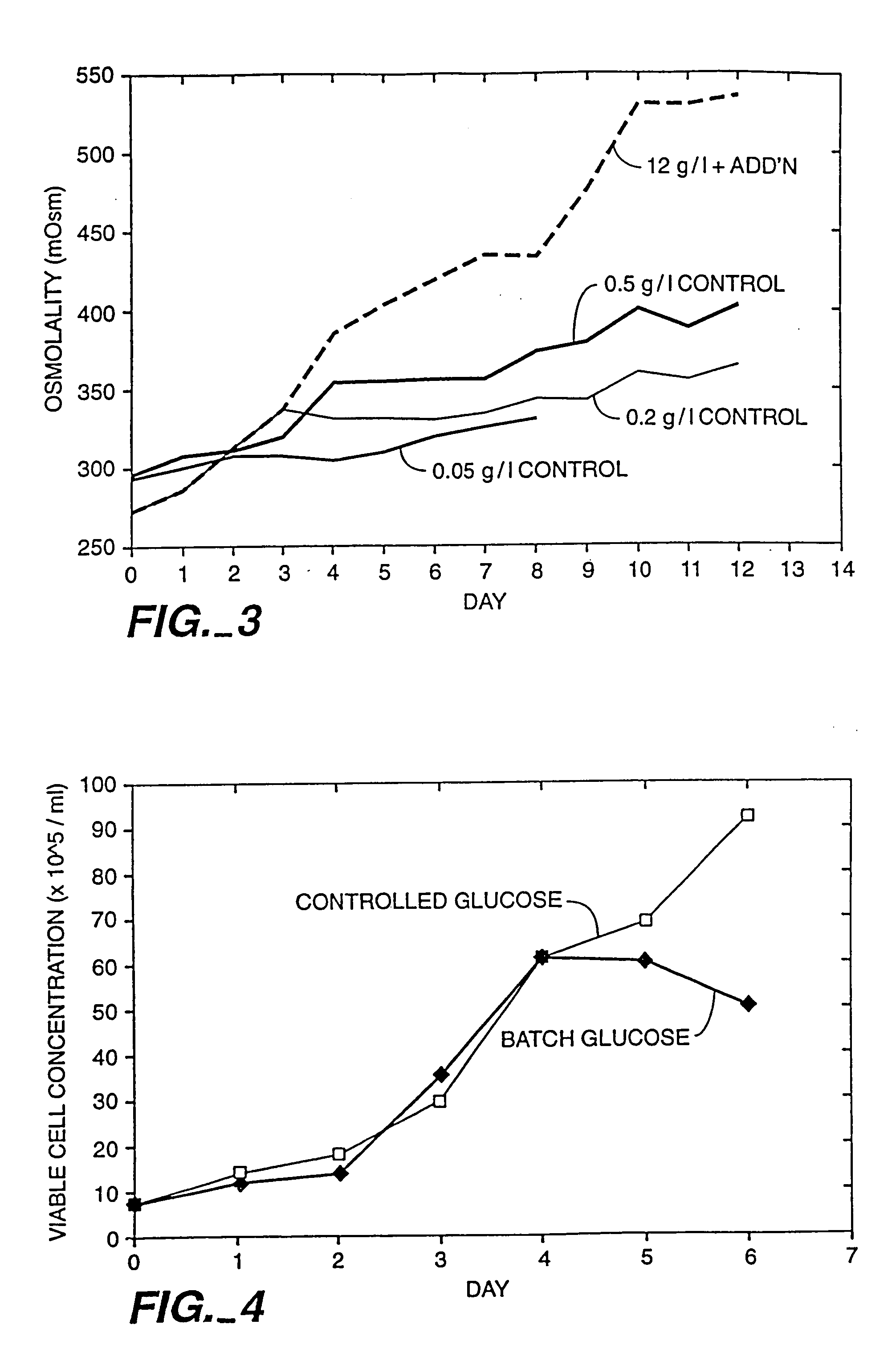
A method of producing a polypeptide in fed batch cell culture is provided which involves an initial cell growth phase and a distinct production phase. In the initial growth stage, animal cells having nucleic acid encoding the polypeptide are cultured at a starting osmolality of about 280-330 mOsm in the presence of a concentration of glucose controlled throughout the culturing to be within a range between about 0.01 and 1 g / L. This is followed by a production phase, where the cultured animal cells of the growth phase are inoculated at a cell seed density of at least 1.0×106 cells / mL and the cells are cultured at a starting osmolarity of about 400-600 mOsm in the presence of a concentration of glucose controlled throughout the culturing to be within a range between about 0.01 and 1 g / L. Preferably, the glutamine concentration in the cell culture medium is simultaneously controlled in order to curtail production of lactic acid and ammonia which result from unnecessarily high glutamine concentrations. During the growth phase, production of potentially detrimental metabolic waste products, such as lactic acid, is controlled thereby curtailing the increase of osmolality due to accumulation and neutralization of waste products. Thus, the cell growth can be improved. In the production phase, the cell culture conditions are modified in order to arrest or reduce cell growth and thereby direct nutrient utilization toward production, as opposed to cell growth. Overall, it is intended that the method results in an improvement in specific productivity, reduction in production run times and / or an increase in final product concentration.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Methods of overexpression and recovery of porcine circovirus type 2 ORF2
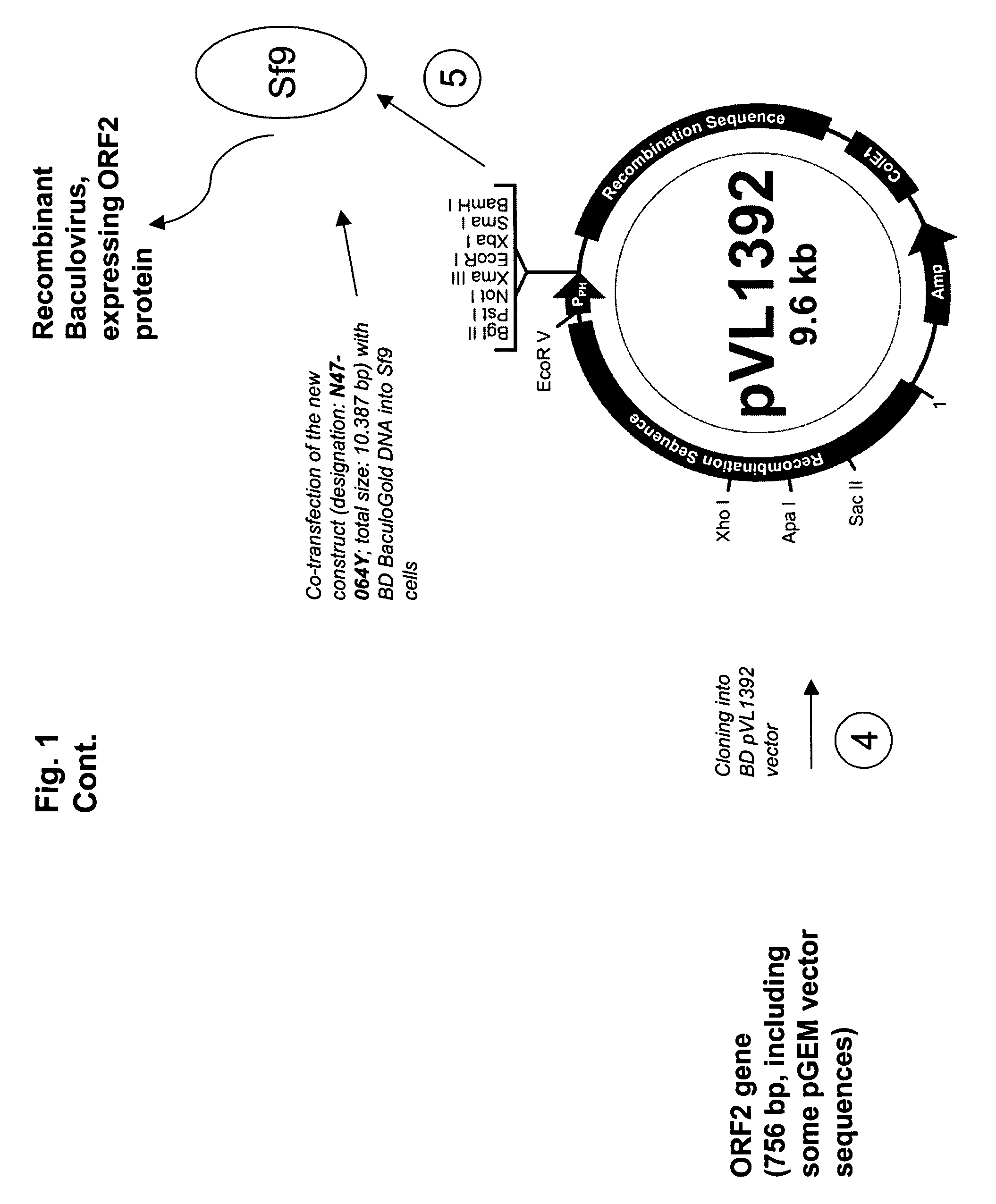
ActiveUS20090042245A1SsRNA viruses positive-senseInorganic active ingredientsOpen reading frameIntracellular
An improved method for recovering the protein expressed by open reading frame 2 from PCV2 is provided. The method generally involves the steps of transfecting recombinant virus containing open reading frame 2 coding sequences into cells contained in growth media, causing the virus to express open reading frame 2, and recovering the expressed protein in the supernate. This recovery should take place beginning approximately 5 days after infection of the cells in order to permit sufficient quantities of recombinant protein to be expressed and secreted from the cell into the growth media. Such methods avoid costly and time consuming extraction procedures required to separate and recover the recombinant protein from within the cells.
Owner:BOEHRINGER LNGELHEIM VETMEDICA GMBH
Articles comprising nano-materials for geometry-guided stem cell differentiation and enhanced bone growth
InactiveUS20110085968A1Improve stabilityGood biocompatibilityBiocideIn-vivo radioactive preparationsCell culture mediaBone growth
The present invention provides articles of manufacture comprising biocompatible nanostructures comprising significantly increased surface area for, e.g., organ, tissue and / or cell growth, e.g., for bone, tooth, kidney or liver growth, and uses thereof, e.g., for in vitro testing of drugs, chemicals or toxins, or as in vivo implants, including their use in making and using artificial tissues and organs, and related, diagnostic, screening, research and development and therapeutic uses, e.g., as drug delivery devices. The present invention provides biocompatible nanostructures with significantly increased surface area, such as with nanotube and nanopore array on the surface of metallic, ceramic, or polymer materials for enhanced cell and bone growth, for in vitro and in vivo testing, cleansing reaction, implants and therapeutics. The present invention provides optically transparent or translucent cell-culturing substrates. The present invention provides biocompatible and cell-growth-enhancing culture substrates comprising elastically compliant protruding nanostructure substrates coated with Ti, TiO2 or related metal and metal oxide films.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods of protein production using Anti-senescence compounds
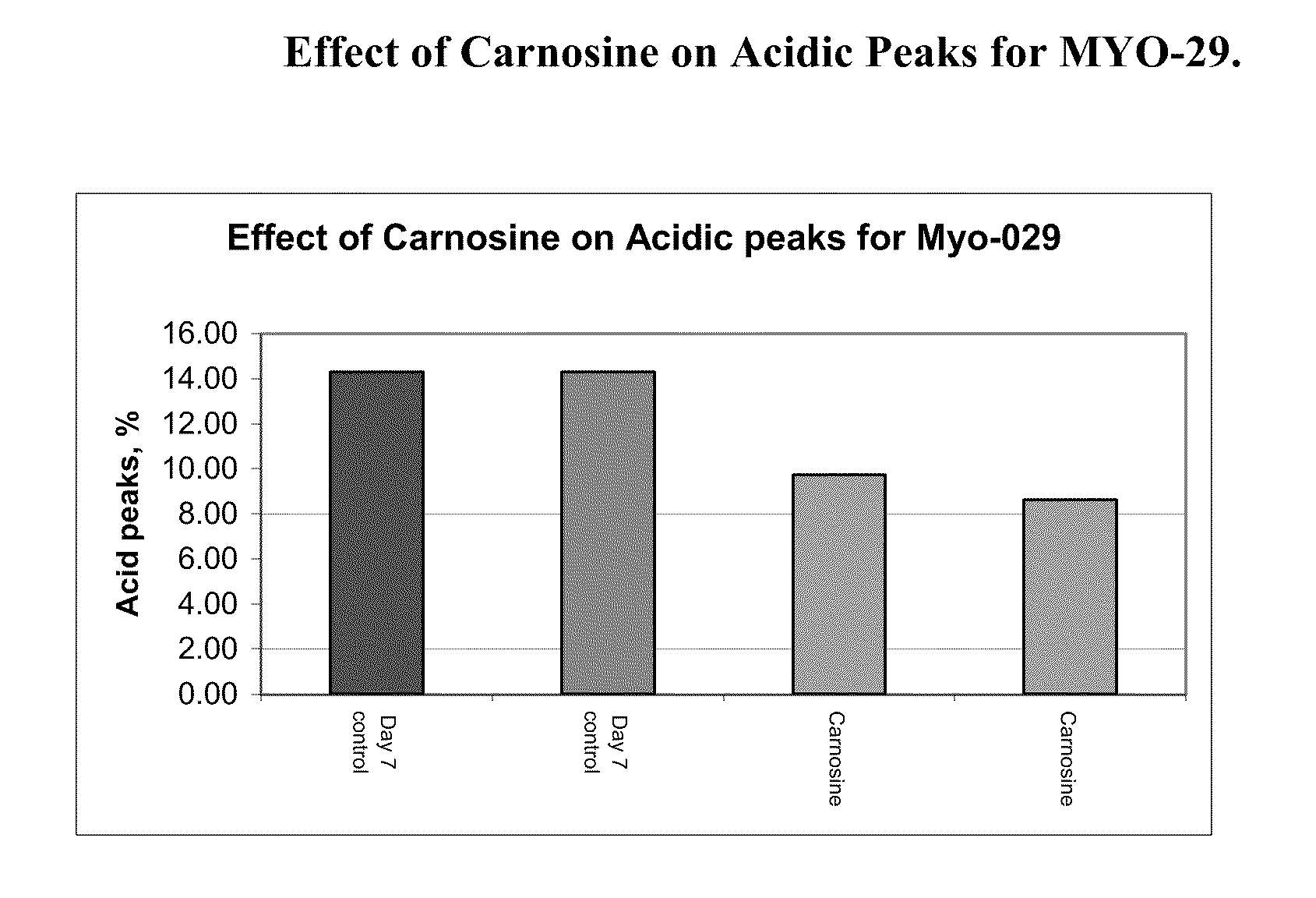
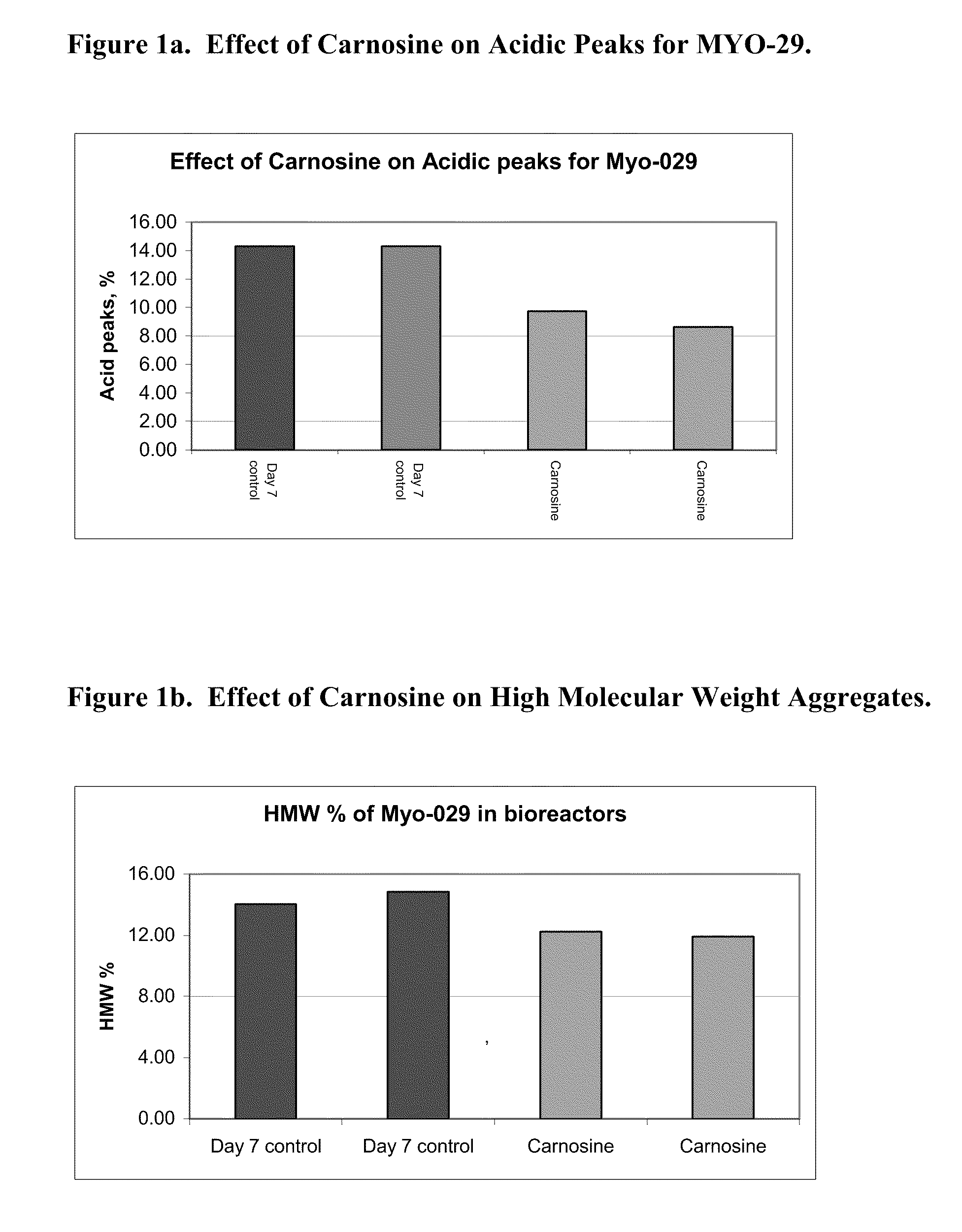
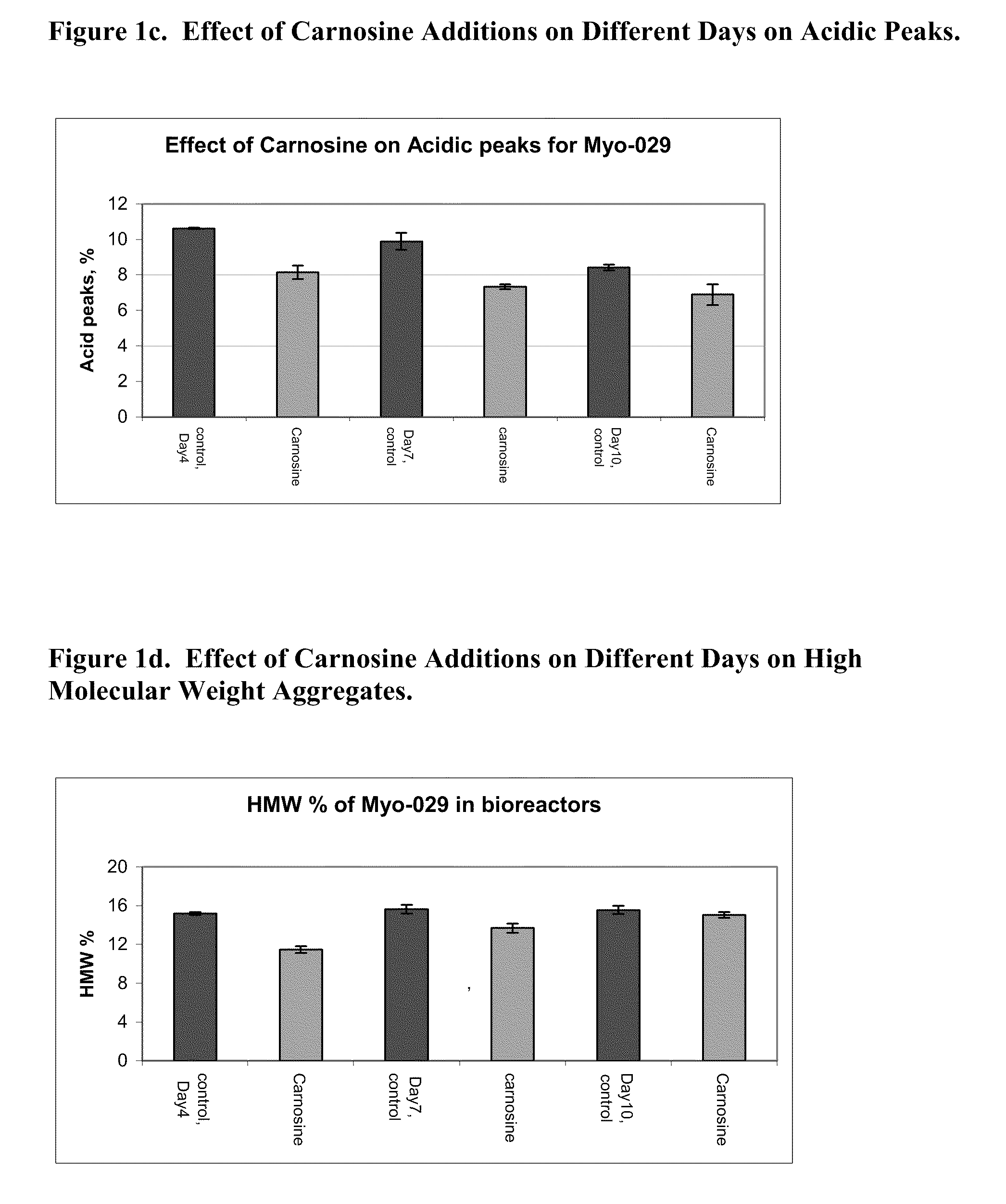
PendingUS20080274507A1High protein yieldIncrease productionGenetically modified cellsCulture processBiotechnologyAntioxidant
Methods of producing a protein in cell culture comprising an anti-senescence compound, such as the antioxidant carnosine, are provided. According to teachings of the present invention, cells grown in a cell culture medium comprising an anti-senescence compound exhibit increased viability and productivity. Furthermore, cell cultures grown in the presence of an anti-senescence compound exhibit decreased levels of high molecular weight aggregates in the cell culture medium.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com