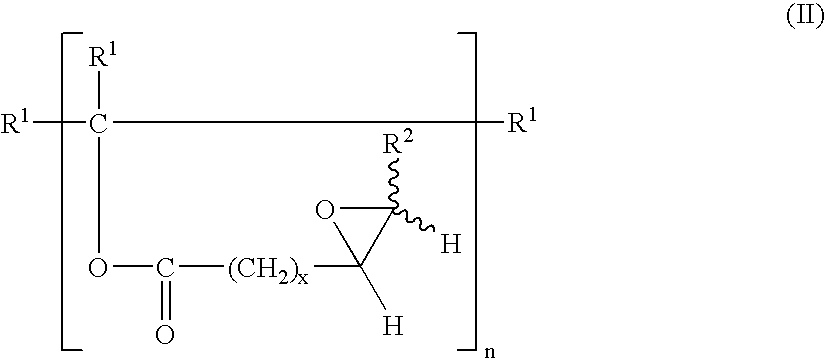
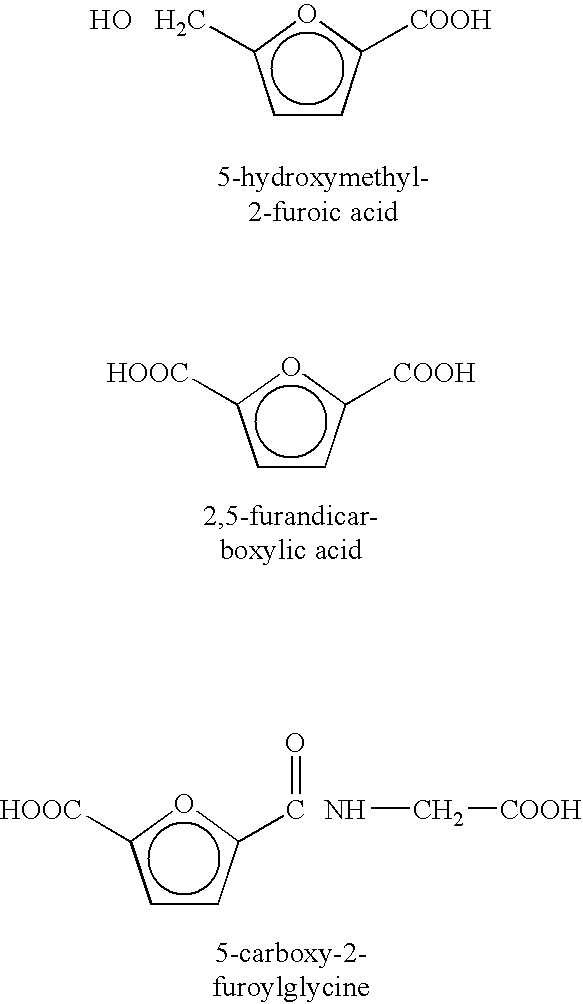
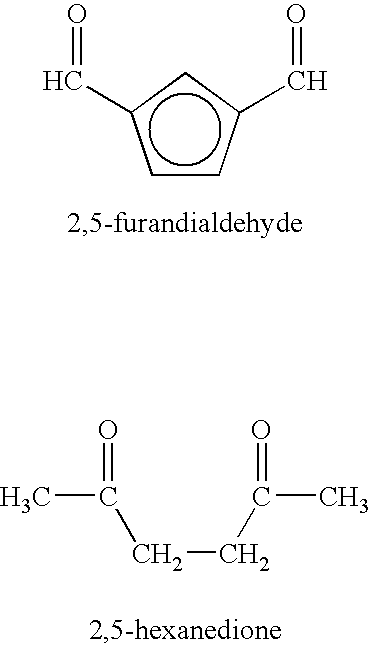
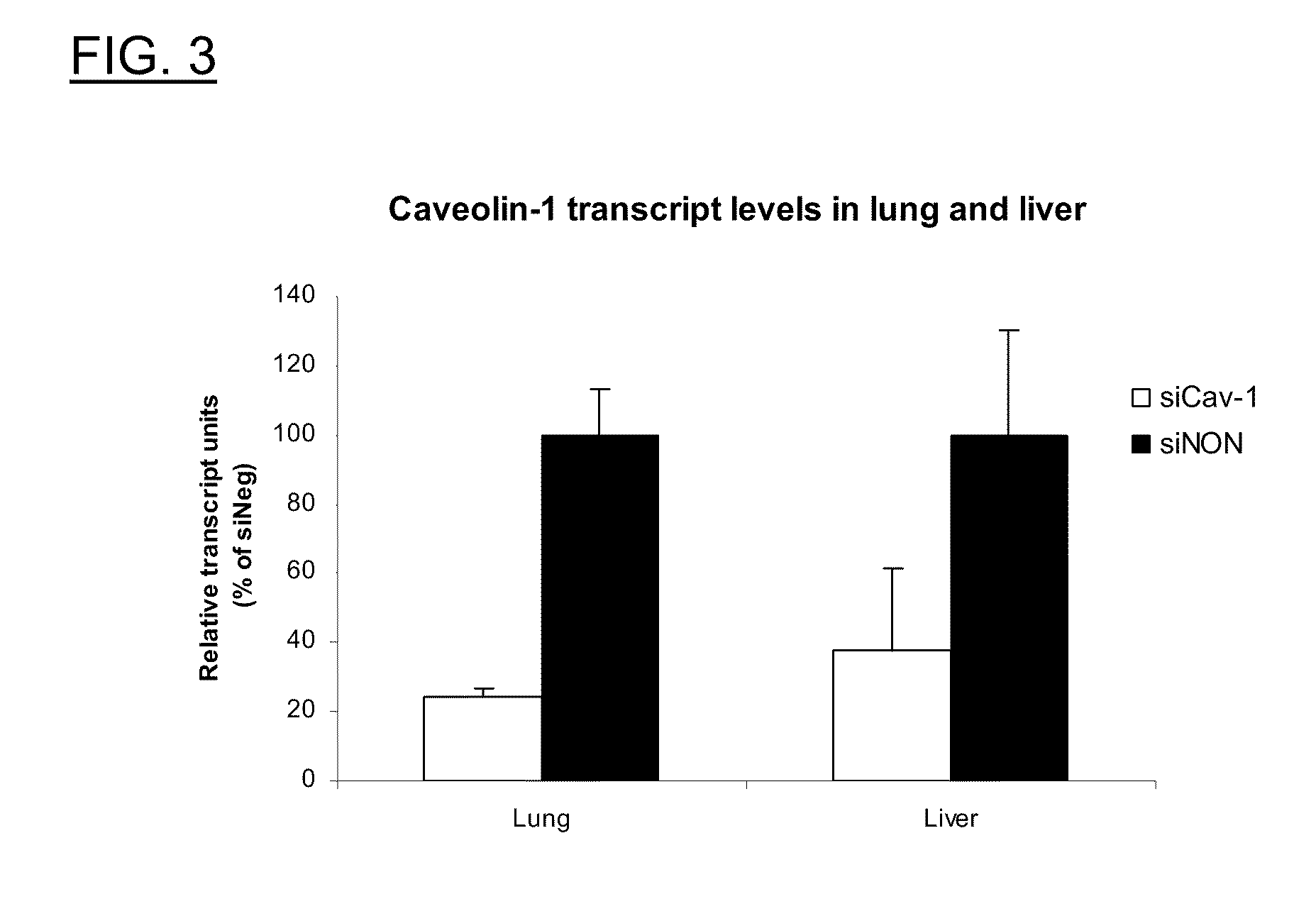
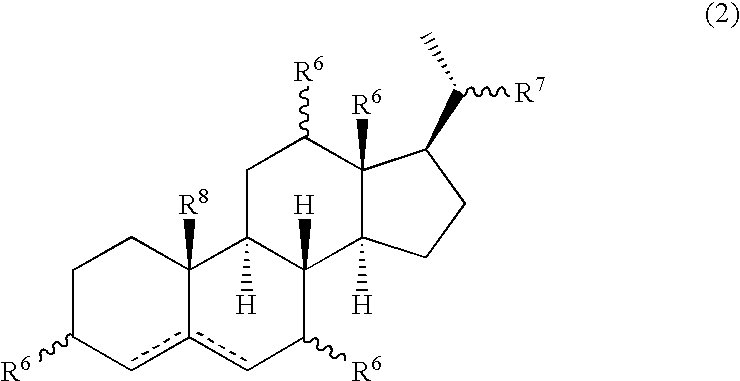
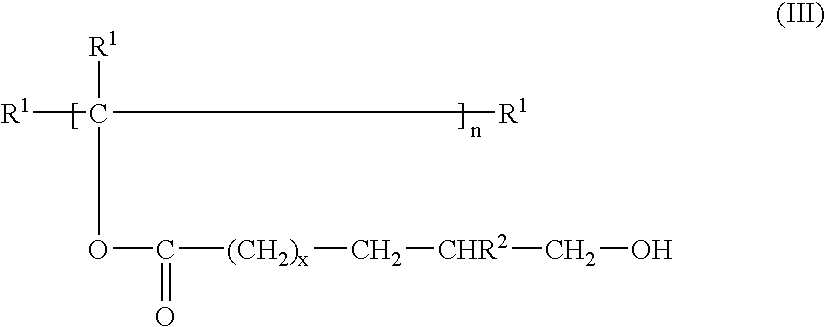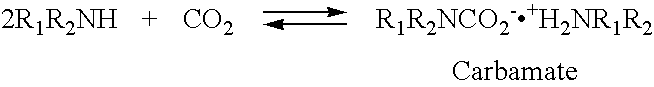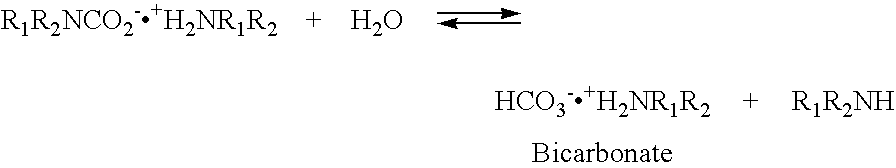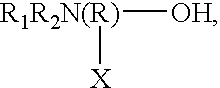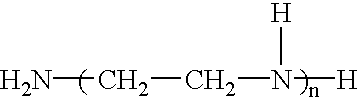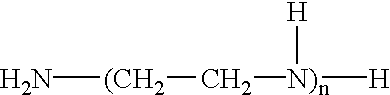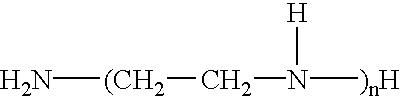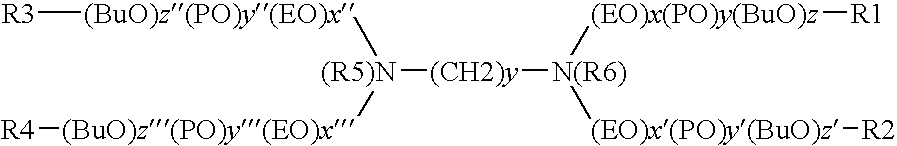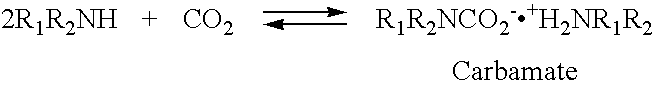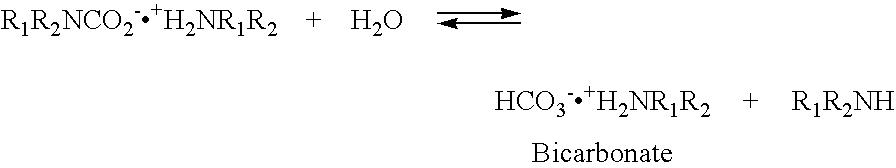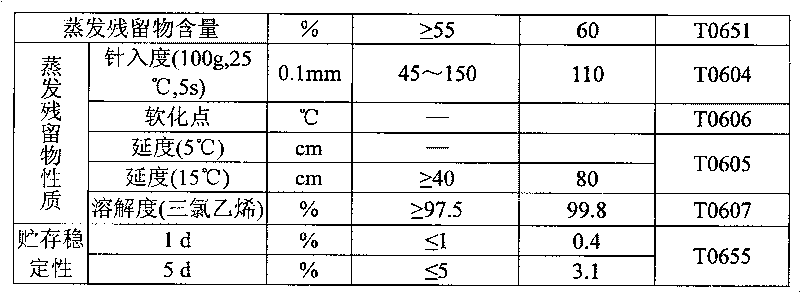Patents
Literature
4094 results about "Polyamine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A polyamine is an organic compound having more than two amino groups. Alkyl polyamines occur naturally but are also synthetic. Alkylpolyamines are colorless, hygroscopic, and water soluble. Near neutral pH, they exist as the ammonium derivatives. Most aromatic polyamines are crystalline solids at room temperature.
Low-chlorine, polyolefin-substituted, with amine reacted, alpha-beta unsaturated carboxylic compounds
A composition of matter comprising an amine acylated with a hydrocarbyl group substituted carboxylic acylating agent containing an average of from 1.3 to 1.6 groups derived from α,β-unsaturated carboxylic compounds per Mn of the hydrocarbyl group, wherein the hydrocarbyl group has Mn determined by GPC ranging from 1500 to 3000, the amine comprises polyamine bottoms and said acylated amine has total base number (TBN) ranging from 17 to 35. A method for preparing the composition, lubricating oils containing the composition and, in another embodiment, lubricating oil compositions of this invention further comprising a metal overbased sulfonate detergent.
Owner:THE LUBRIZOL CORP
Structural modified epoxy adhesive compositions
InactiveUS6572971B2Raise the ratioReduce opening timeSynthetic resin layered productsEpoxy resin adhesivesFirming agentAliphatic amine
The present invention is directed to an adhesive composition, which comprises an epoxy resin, a coupling agent, filler, and an effective amount of an amine-curing agent or curative for said epoxy resin. Advantageously, tri-functional and / or tetrafunctional epoxy resins and / or acrylate monomers will be incorporated into the adhesive composition in order to reduce open time and enhance substrate adhesion. Advantageously, a mixture of amines will be used in the curative including aliphatic amines, which have low viscosities and efficiently wet the substrate for enhancing adhesion; polyamines, which can be used to manipulate open time and allow for improved ratio tolerance of the adhesive system; and amine-terminated rubbers (ATBN), which can improve impact resistance and the toughness of the cured adhesive. Preferred coupling agents are silanes.
Owner:ASHLAND LICENSING & INTPROP LLC
Bioactive Polymers
InactiveUS20080267903A1Strong specificityEnhanced interactionSynthetic polymeric active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsDelivery vehicleActive agent
Various polymers, including cationic polyamine polymers and dendrimeric polymers, are shown to possess anti-proliferative activity, and may therefore be useful for treatment of disorders characterised by undesirable cellular proliferation such as neoplasms and tumours, inflammatory disorders (including autoimmune disorders), psoriasis and atherosclerosis. The polymers may be used alone as active agents, or as delivery vehicles for other therapeutic agents, such as drug molecules or nucleic acids for gene therapy. In such cases, the polymers' own intrinsic anti-tumour activity may complement the activity of the agent to be delivered.
Owner:UNIV COLLEGE OF LONDON
Detection of nucleic acids and nucleic acid units
InactiveUS6127120AReduce riskReducing operator timeSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideBiology
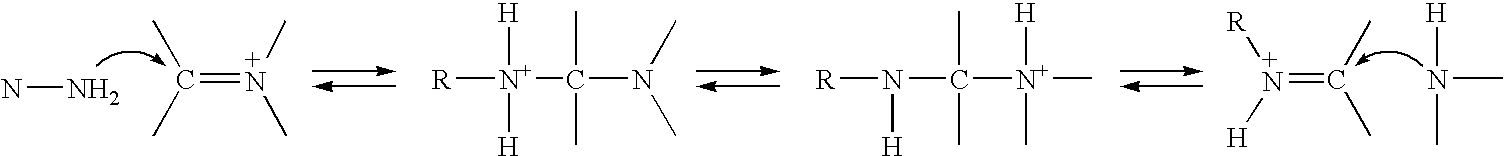
PCT No. PCT / GB96 / 01830 Sec. 371 Date Apr. 21, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Apr. 21, 1998 PCT Filed Jul. 25, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 05280 PCT Pub. Date Feb. 13, 1997The invention relates to the detection of target nucleic acids or nucleic acid units in a sample, by obtaining a SER(R)S spectrum for a SER(R)S-active complex containing, or derived directly from, the target. The complex includes at least a SER(R)S-active label, and optionally a target binding species containing a nucleic acid or nucleic acid unit. In this detection method, the concentration of the target present in the SER(R)S-active complex, or of the nucleic acid or unit contained in the target binding species in the SER(R)S-active complex, is no higher than 10-10 moles per liter. Additionally or alternatively, one or more of the following features may be used with the method: i) the introduction of a polyamine; ii) modification of the target, and / or of the nucleic acid or nucleic acid unit contained in the target binding species, in a manner that promotes or facilitates its chemi-sorption onto a SER(R)S-active surface; iii) inclusion of a chemi-sorptive functional group in the SER(R)S-active label. The invention also provides SER(R)S-active complexes for use in such a method, a kit for use in carrying out the method or preparing the complexes and a method for sequencing a nucleic acid which comprises the use of the detection method to detect at least one target nucleotide or sequence of nucleotides within the acid.
Owner:RENISHAW DIAGNOSTICS
Oligopeptide-free cell culture media
InactiveUS20070212770A1Efficient expression of recombinantEfficient productionFactor VIIBacteriaCulture cellCell culture media
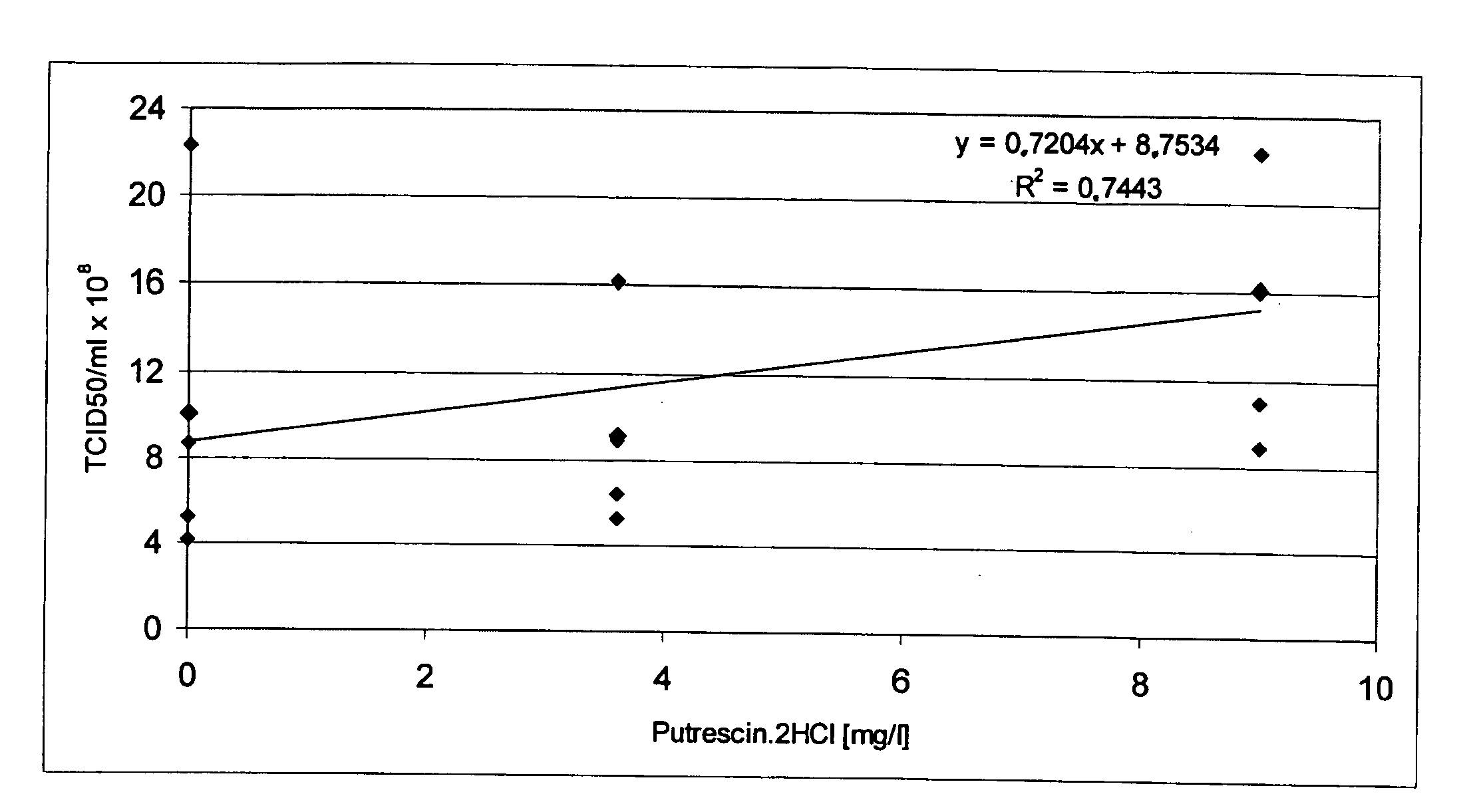
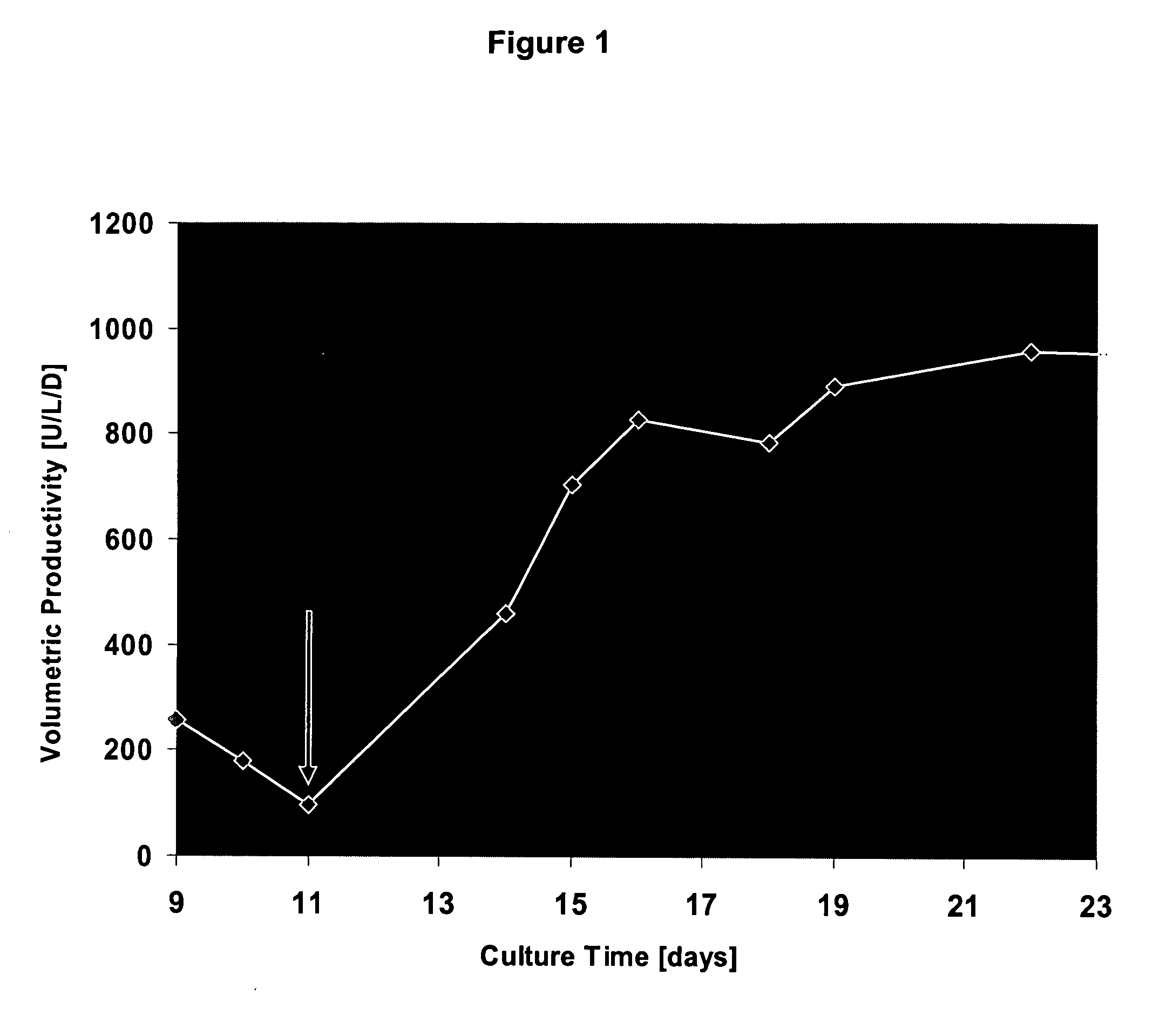
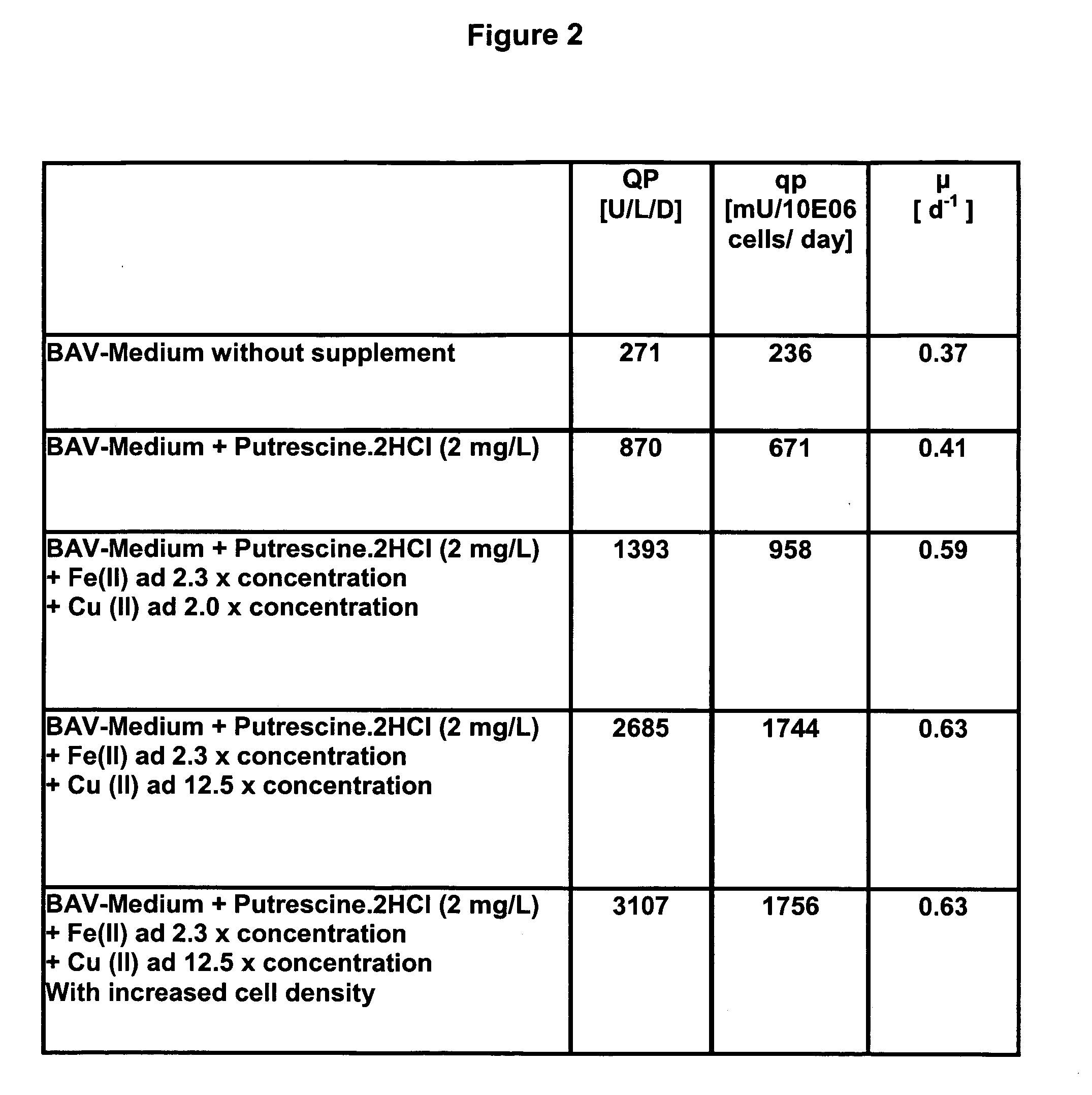
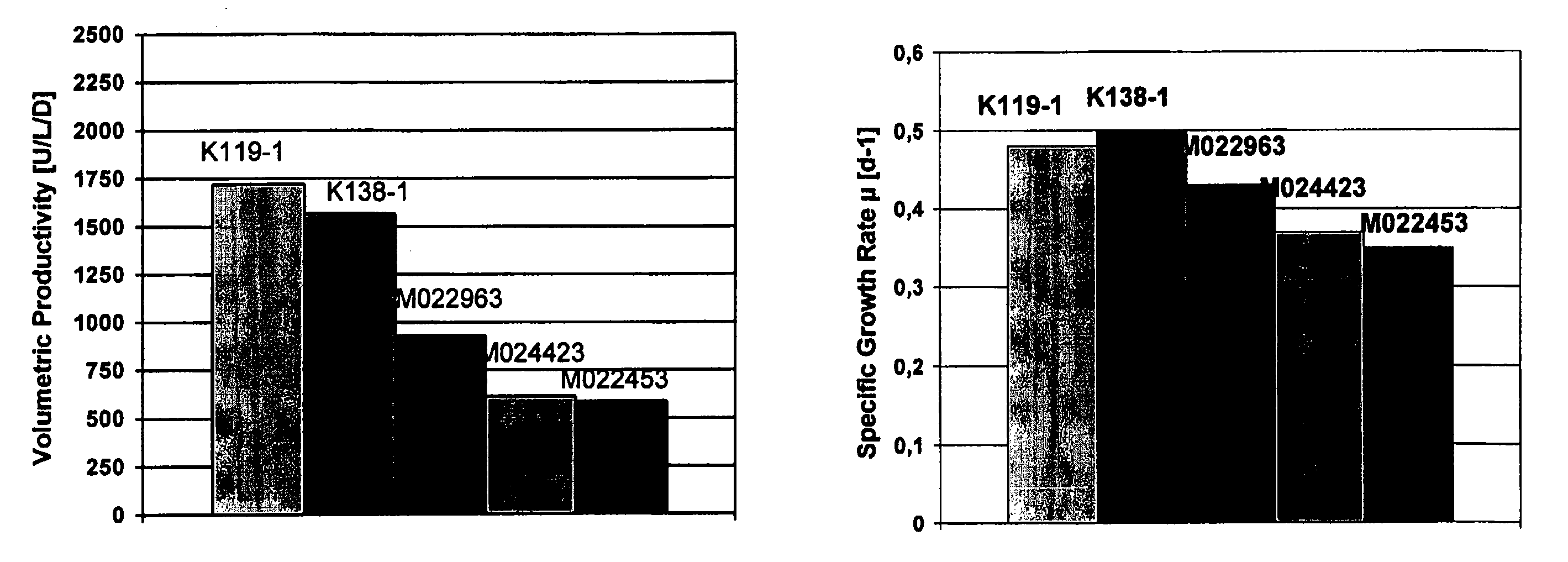
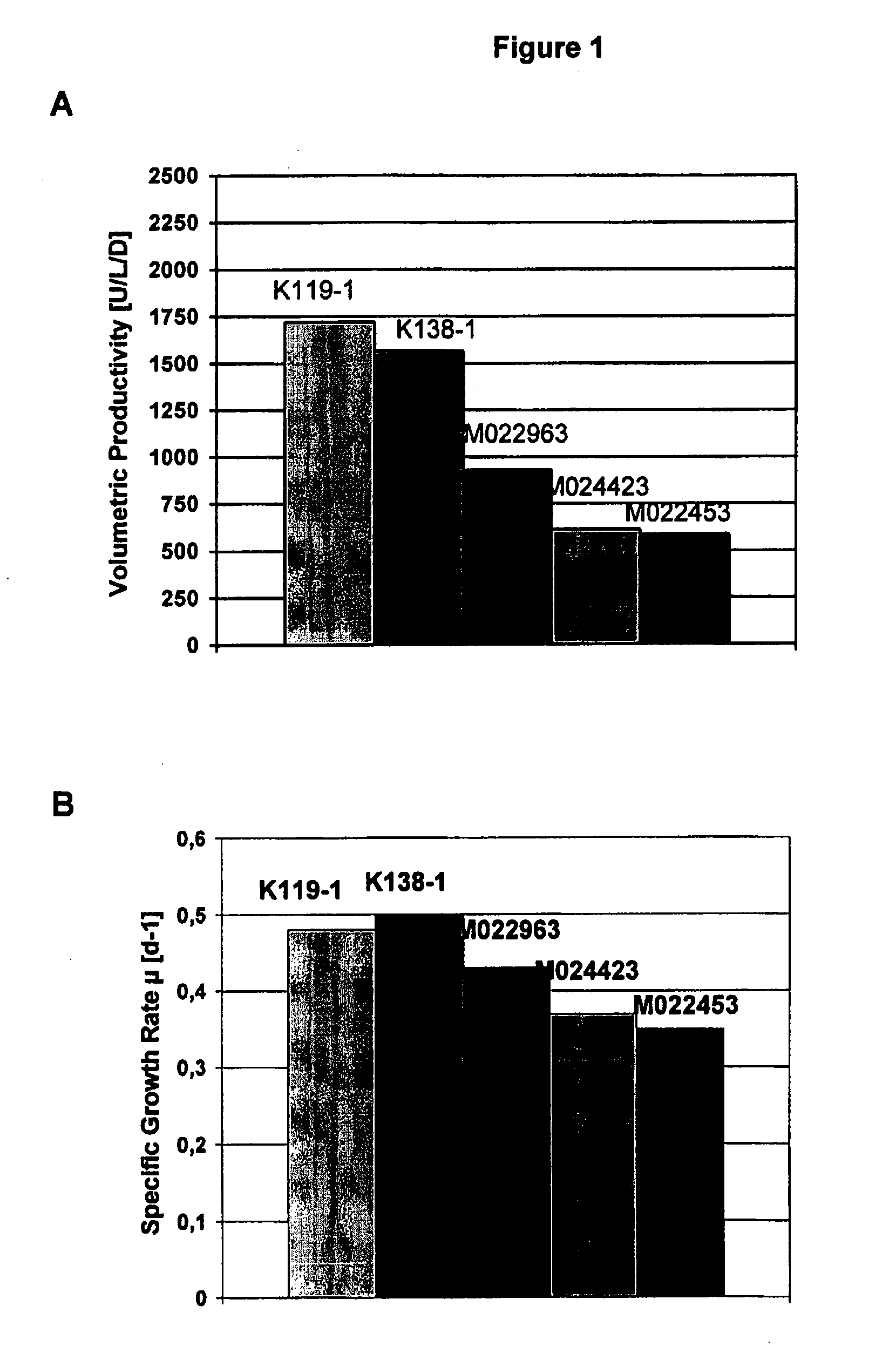
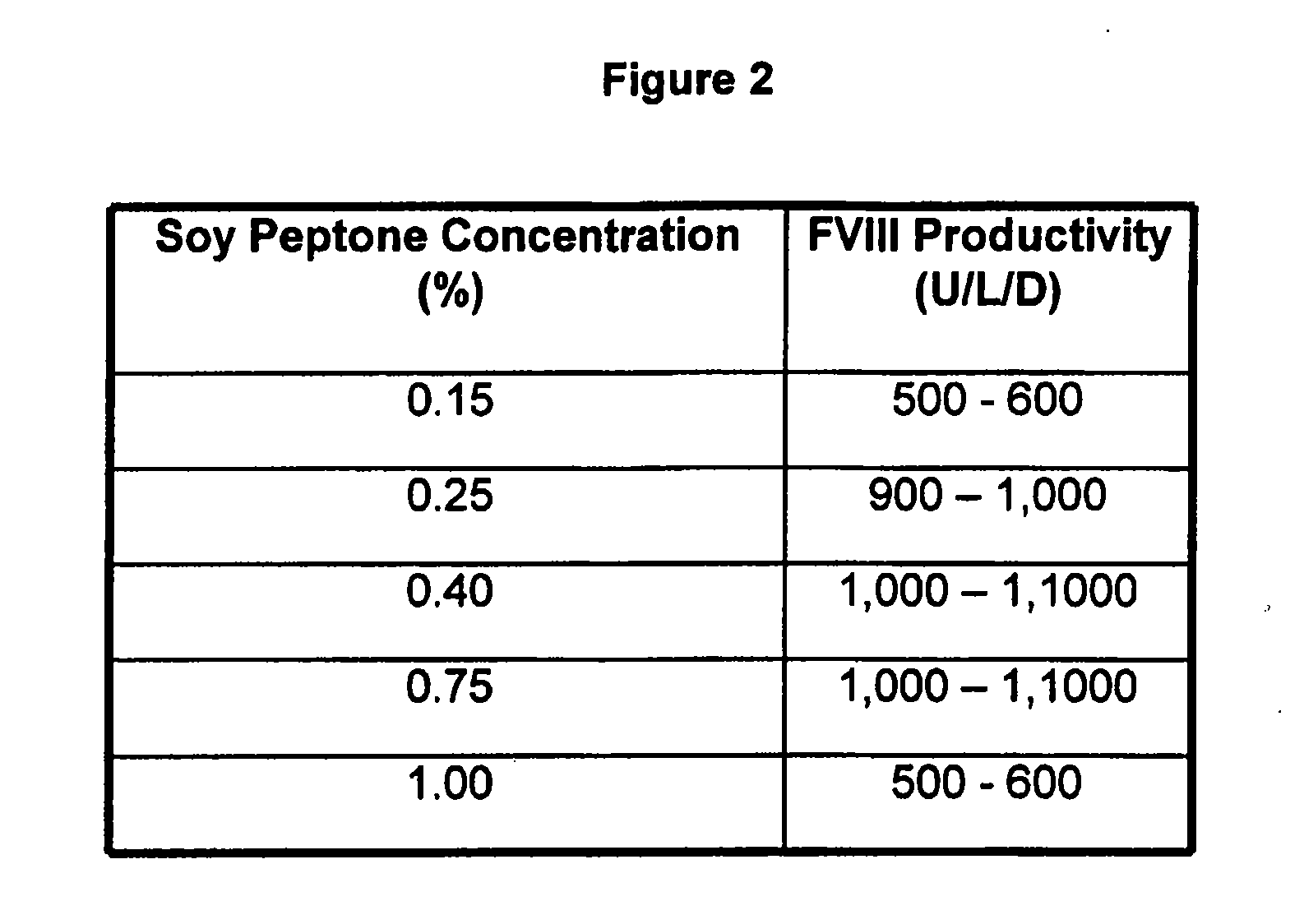
The present invention relates to oligopeptide-free cell culture media comprising at least 0.5 mg / L of a polyamine and to methods for cultivating cells in said oligopeptide-free cell culture media comprising at least 0.5 mg / L of a polyamine. The invention also relates to methods for expressing at least one protein in a medium comprising at least 0.5 mg / L of a polyamine and to methods for producing at least one virus in a medium comprising at least 0.5 mg / L of a polyamine.
Owner:BAXTER HEALTHCARE SA +1
Integrate chemical processes for industrial utilization of seed oils
ActiveUS20050154221A1Easy to operateHigh olefin conversionFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteOxygen-containing compound preparationPolyesterAmino esters
Integrated processes of preparing industrial chemicals starting from seed oil feedstock compositions containing one or more unsaturated fatty acids or unsaturated fatty acid esters, which are essentially free of metathesis catalyst poisons, particularly hydroperoxides; metathesis of the feedstock composition with a lower olefin, such as ethylene, to form a reduced chain olefin, preferably, a reduced chain α-olefin, and a reduced chain unsaturated acid or ester, preferably, a reduced chain α,Ω-unsaturated acid or ester. The reduced chain unsaturated acid or ester may be (trans)esterified to form a polyester polyolefin, which may be epoxidized to form a polyester polyepoxide. The reduced chain unsaturated acid or ester may be hydroformylated with reduction to produce an α,Ω-hydroxy acid or α,Ω-hydroxy ester, which may be (trans)esterified with a polyol to form an α,Ωpolyester polyol. Alternatively, the reduced chain unsaturated acid or ester may be hydroformylated with reductive amination to produce an α,Ω-amino acid or α,Ω-amino ester, which may be (trans)esterified to form an α,Ωpolyester polyamine.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method of treating neurological diseases and etiologically related symptomology using carbonyl trapping agents in combination with medicaments
This invention defines a novel method for treatment of several neurological diseases and pathophysiologically related symptomology, said diseases including peripheral neuropathies, secondary symptomology of diabetes, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, alcoholic polyneuropathy and age-onset symptomology, as well as analogous veterinary disease states. An opportunity exists for pharmacological intervention in some neurological diseases by use of water soluble, small molecular weight primary amine agents and chemical derivatives thereof. Examples of such primary pharmacological agents include 4-aminobenzoic acid and derivatives thereof. The present invention also includes: (1) oral use of optional non-absorbable polyamine polymeric co-agents such as chitosan, (2) oral use of optional known antioxidant co-agents and nutritional factors related thereto, and (3) use of the primary agents and co-agents noted above in optional combination with medicaments recognized as effective for treatment of the diseases addressed herein or symptoms thereof.
Owner:SECANT PHARMA
Animal protein-free media for cultivation of cells
InactiveUS20080009040A1Efficient expressionGuaranteed efficient growthMicroorganismsCulture processHydrolysateCell culture media
The present invention relates to animal protein-free cell culture media comprising polyamines and a plant- and / or yeast-derived hydrolysate. The invention also relates to animal protein-free culturing processes, wherein cells can be cultivated, propagated and passaged without adding supplementary animal proteins in the culture medium. These processes are useful in cultivating cells, such as recombinant cells or cells infected with a virus, and for producing biological products by cell culture processes.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
Polyamine Derivatives
ActiveUS20100260817A1Improve efficiencyImproving of local deliveryOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderWhole bodyMedicinal chemistry
Owner:CLSN LAB
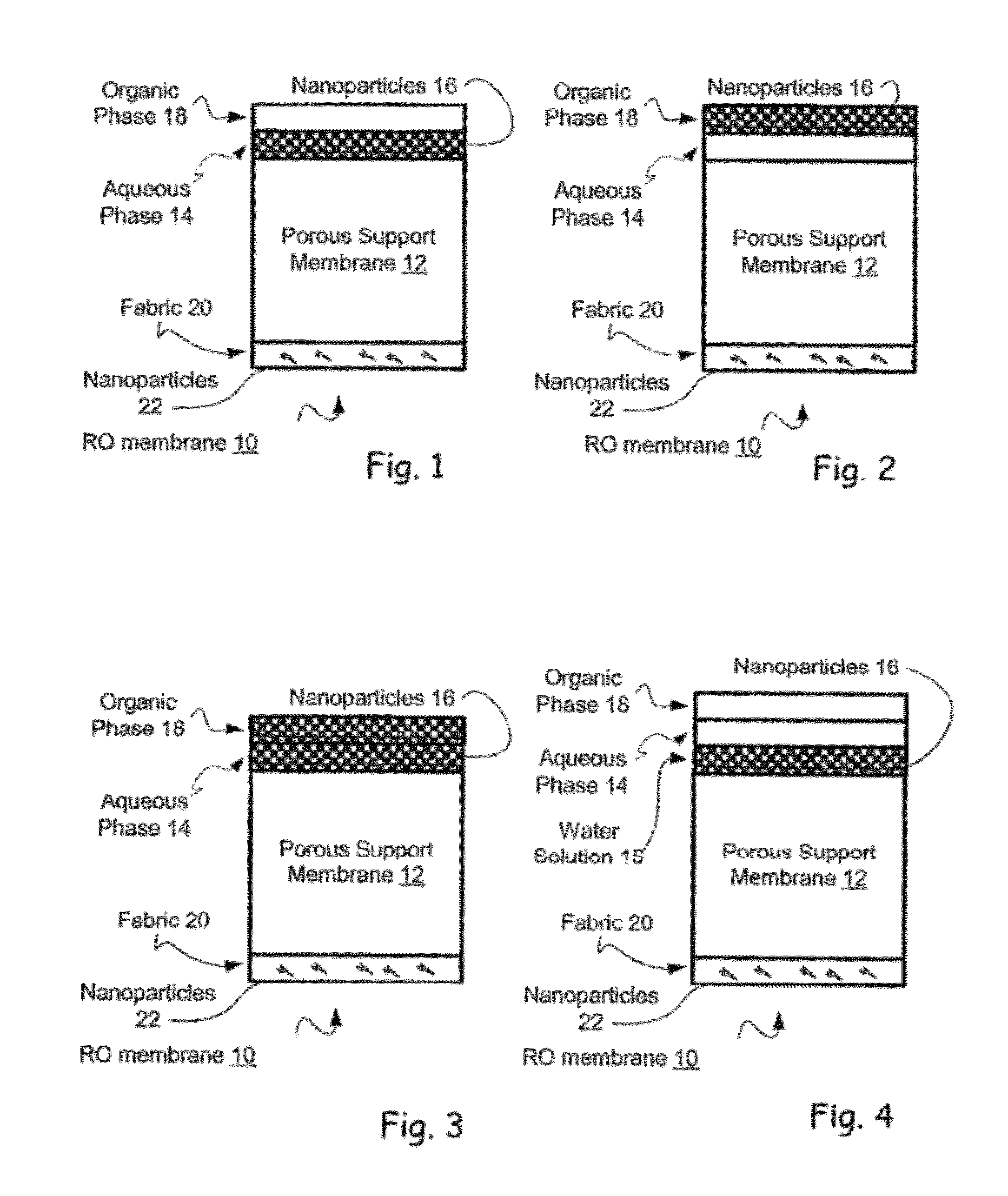
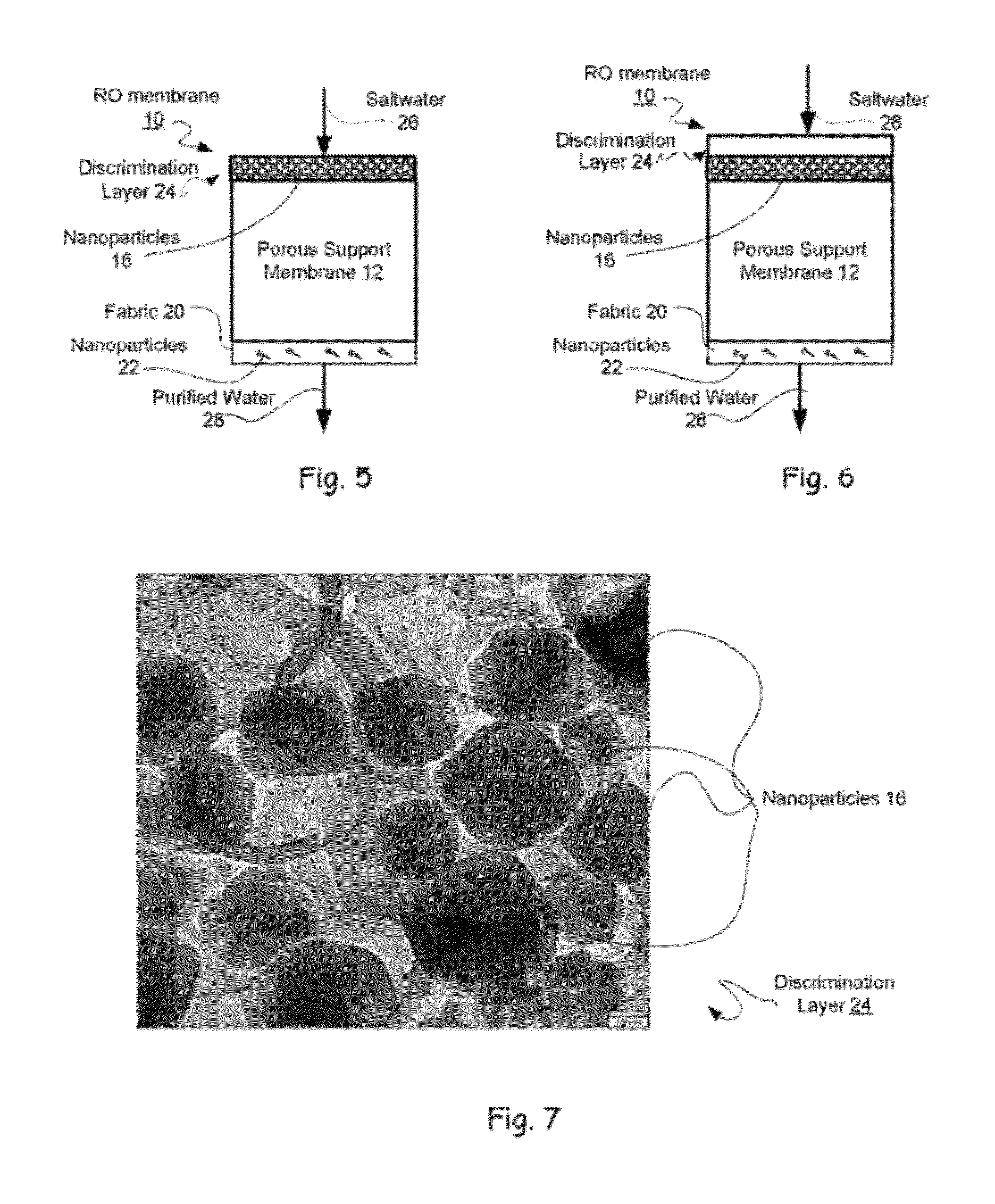
Reverse osmosis membranes
Owner:NANOH2O
Polyamine derivatives
ActiveUS8460696B2Reduce deliveryImprove efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderMedicinal chemistryPolyamine
Owner:CLSN LAB
Nano-structure supported solid regenerative polyamine and polyamine polyol absorbents for the separation of carbon dioxide from gas mixtures including the air
ActiveUS20080293976A1Increased CO absorption capacityIncreased COMaterial nanotechnologyElectrolysis componentsPolyolSorbent
The invention relates to regenerative, supported amine sorbents that includes an amine or an amine / polyol composition deposited on a nano-structured support such as nanosilica. The sorbent provides structural integrity, as well as high selectivity and increased capacity for efficiently capturing carbon dioxide from gas mixtures, including the air. The sorbent is regenerative, and can be used through multiple operations of absorption-desorption cycles.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Multifunctional molecular complexes for gene transfer to cells
A multifunctional molecular complex for the transfer of a nucleic acid composition to a target cell is provided The complex is comprised of A) said nucleic acid composition and B) a transfer moiety comprising 1) one or more cationic polyamines bound to said nucleic acid composition, 2) one or more endosome membrane disrupting components attached to at least one nitrogen of the polyamine and 3) one or more receptor specific binding components.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Ink-jet printing ink compositions having superior smear-fastness
InactiveUS6417249B1Improve printing effectGood printing performanceInksCoatingsPolyesterPolymer science
Specific core-shell binders and additives for use in ink-jet printing ink compositions are provided. One class of specific core / shell binders has the general formula [AmBnC'p]x, where A and B are hydrophobic components in which A exhibits a glass transition temperature Tg between about -150° and +25° C. and B exhibits a glass transition temperature greater than 25° C., C' is a component that forms a hydrophilic or water-soluble component in the polymer chain, and has an ionic or non-ionic structure, m<30 wt %, n>40 wt %, and p<30 wt %, with the total of m+n+p=100 wt %, and x=1 to 100,000. The molecular weight (weight average) of the polymer is between about 1,000 and 2,000,000. The polymers useful in the practice of the invention are prepared by emulsifying the monomers and then conducting a free-radical polymerization in water. The foregoing binder polymer is used in conjunction with additives comprising either (a) amine alcohols having the general formulawhere R1 and R2 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, aryl, and phenoxy, R is alkyl, X is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, aryl, -OH, -COOH, -CHO, and substituted groups or (b) organic acids (water-soluble or water-dispersive), including polymeric acids. Other additives include amines, polyalcohols, polyamines, and polyesters. In the ink compositions of the present invention, the ratio of binder (1) to colorant (pigment) is greater than 1 to 10. The concentration of the additive is within the range of 0.005 to 50 wt %. The general ink formulation comprises: 5 to 50 wt % water-miscible solvent; 0.5 to 10 wt % colorant; 0.005 to 50 wt % additive; and water.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Methods of treating chronic inflammatory diseases using carbonyl trapping agents
InactiveUS6444221B1Improved therapeutic propertyImprove propertiesBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsEtiologyBenzoic acid
Owner:SECANT PHARMA
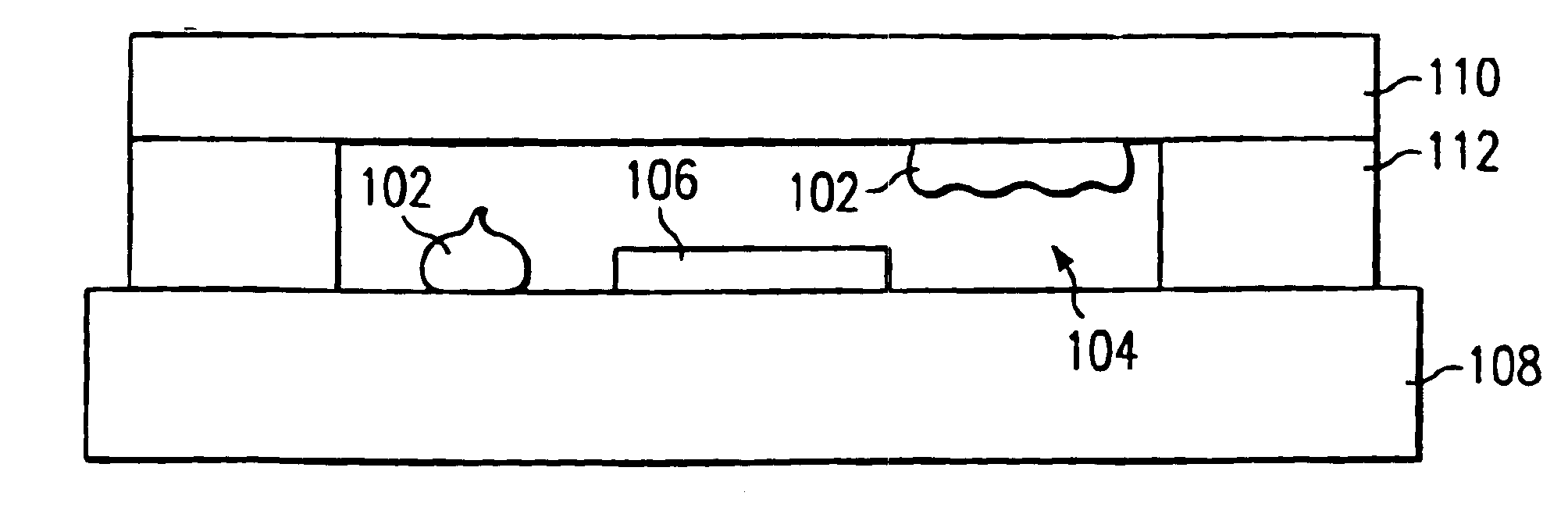
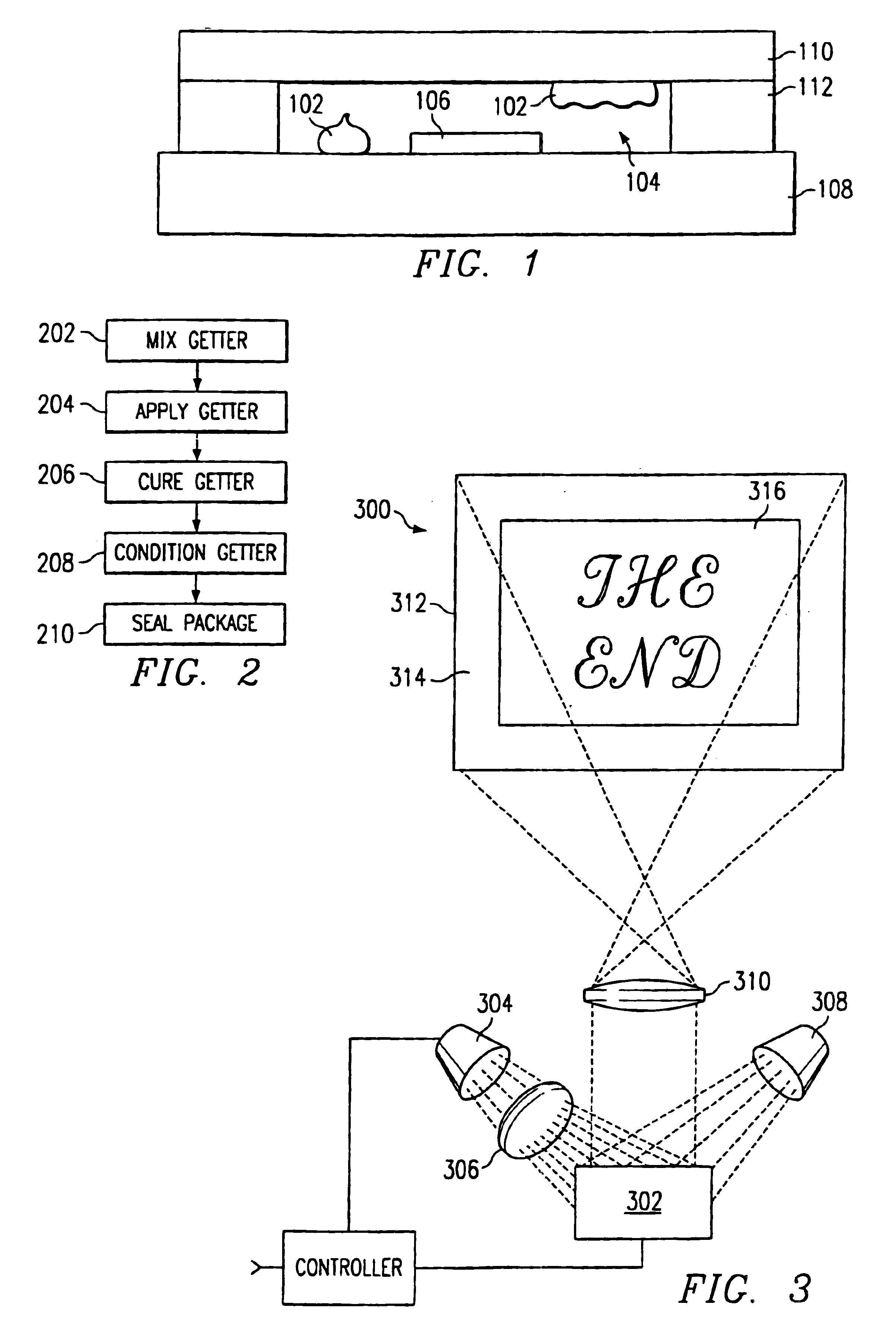
Getter for enhanced micromechanical device performance
A desiccant compound, image projection system using the desiccant compound, and a method for utilizing the desiccant compound. The desiccant compound formed by mixing (202) a polymer binder selected from the group consisting of polysaccharides (including without limitation structural polysaccharides such as cellulose, chitin, and their functionalized derivatives), polyamines, polysulfones, and polyamides with a drying agent, typically a zeolite, at a polymer to drying agent weight ratio of 1:2.1 to 1:100, or 1:4 to 1:10. After the desiccant compound is mixed (202) it is applied (204) to a surface and cured (206), often through the application of heat and vacuum. The cured desiccant compound is conditioned (208) and the it package is sealed (210).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Two component thermosettable compositions useful for producing structural reinforcing adhesives
InactiveUS6451876B1Uniform cell structureExcessive heat dissipationEpoxy resin adhesivesEpoxyPartial system
A two part system for producing structural reinforcing adhesives is provided wherein one component containing epoxy resin is combined with a second component containing a specified curative system. An aliphatic polyamine, an amidoamine, an alcohol and an adduct of a polyamine and an epoxide are present in the curative system. When a thermally activated blowing agent is utilized, the resulting foam is remarkably uniform in cell structure and has improved strength and modulus. Hollow inorganic microspheres are employed to reduce the density of the thermoset produced from the two part system.
Owner:HENKEL KGAA
Encapsulated fragrance chemicals
InactiveUS7125835B2Increase depositionCosmetic preparationsOrganic detergent compounding agentsPersonal careFlavor
A polymeric encapsulated fragrance is disclosed which is suitable for use in personal care and cleaning products. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, the fragrance is encapsulated by a first polymer material to form a fragrance encapsulated polymer, the polymer encapsulated shell is then coated with a mixture of cationic polymers, in a preferred embodiment the coating polymers are a reaction product of polyamines and (chloromethyl) oxirane or (bromomethyl) oxirane.
Owner:INTERNATIONAL FLAVORS & FRAGRANCES
Nano-structure supported solid regenerative polyamine and polyamine polyol absorbents for the separation of carbon dioxide from gas mixtures including the air
The invention relates to regenerative, supported amine sorbents that includes an amine or an amine / polyol composition deposited on a nano-structured support such as nanosilica. The sorbent provides structural integrity, as well as high selectivity and increased capacity for efficiently capturing carbon dioxide from gas mixtures, including the air. The sorbent is regenerative, and can be used through multiple operations of absorption-desorption cycles.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Aqueous polyamine-containing carrier systems for water-insoluble materials
InactiveUS20060286057A1Cosmetic preparationsCationic surface-active compoundsPolyamine CompoundWater insoluble
The present invention is drawn to a carrier composition containing: (a) at least one polyamine compound comprising at least two amino groups; (b) at least one nonionic surfactant; (c) at least one anionic silicone; and (d) at least one water-insoluble material, and wherein the composition, when combined with an aqueous phase, forms an aqueous delivery system which is both stable, and clear to slightly hazy / limpid in appearance.
Owner:LOREAL SA
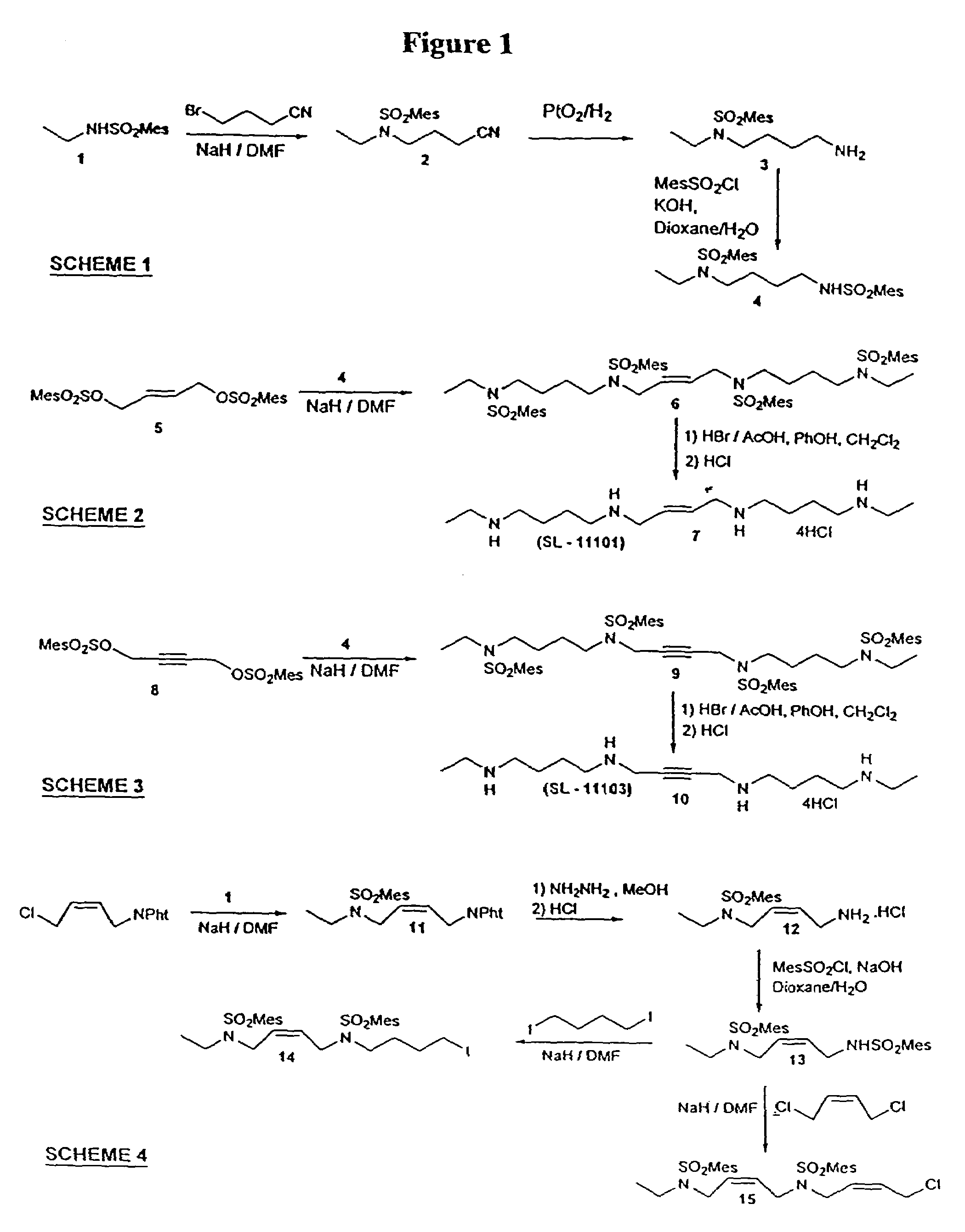
Cycloalkyl substituted polyamines for cancer therapy and methods of synthesis therefor
Conformationally restricted polyamine compounds useful in treatment of cancer and other diseases marked by abnormal cell proliferation are disclosed. Improved methods of synthesizing such compounds are also disclosed. In one method of the invention, a carbene-bearing or carbene equivalent-bearing compound is reacted with the double bond of an alkene compound to form a cyclopropyl ring as the first step in the synthesis.
Owner:CELLGATE
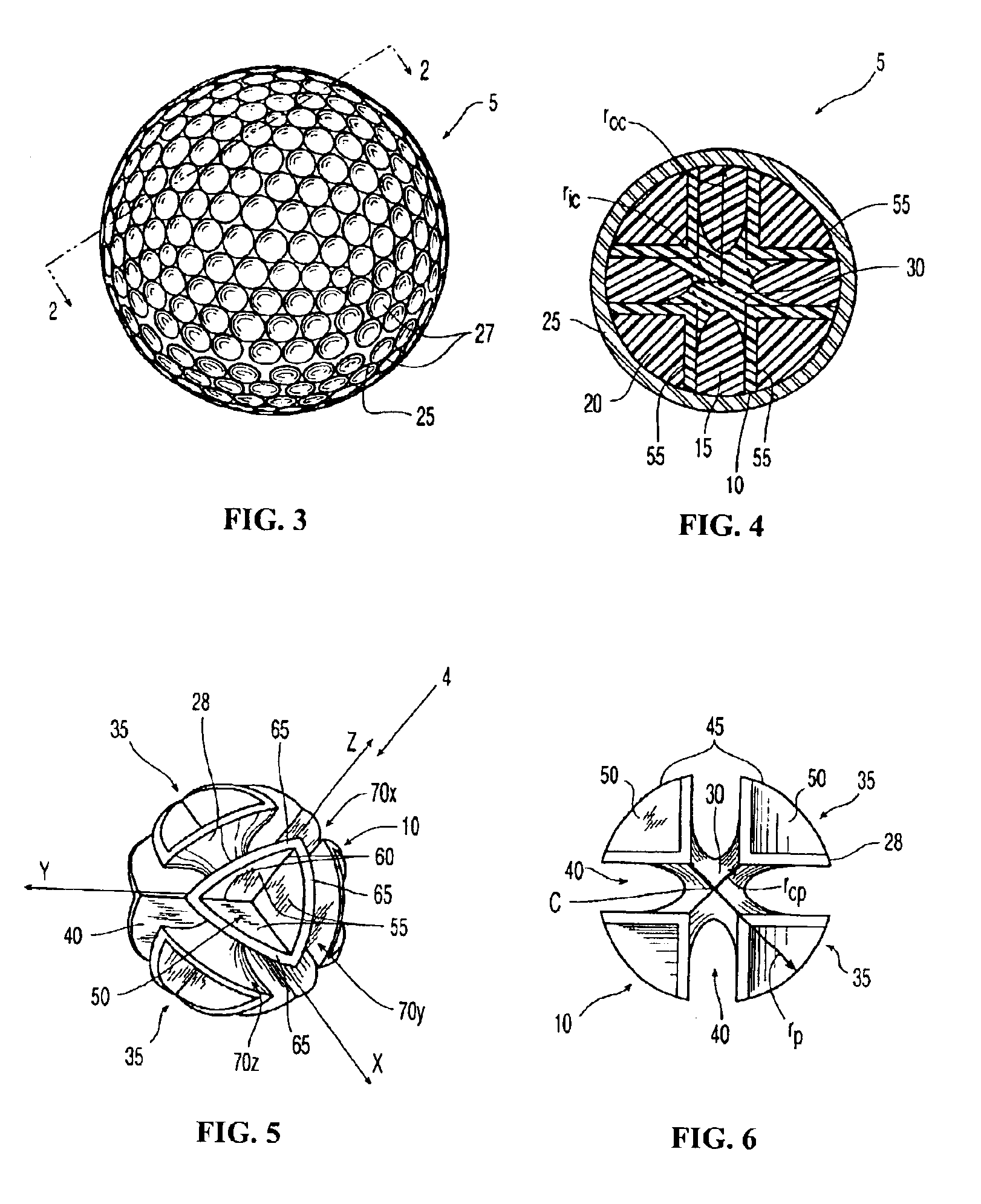
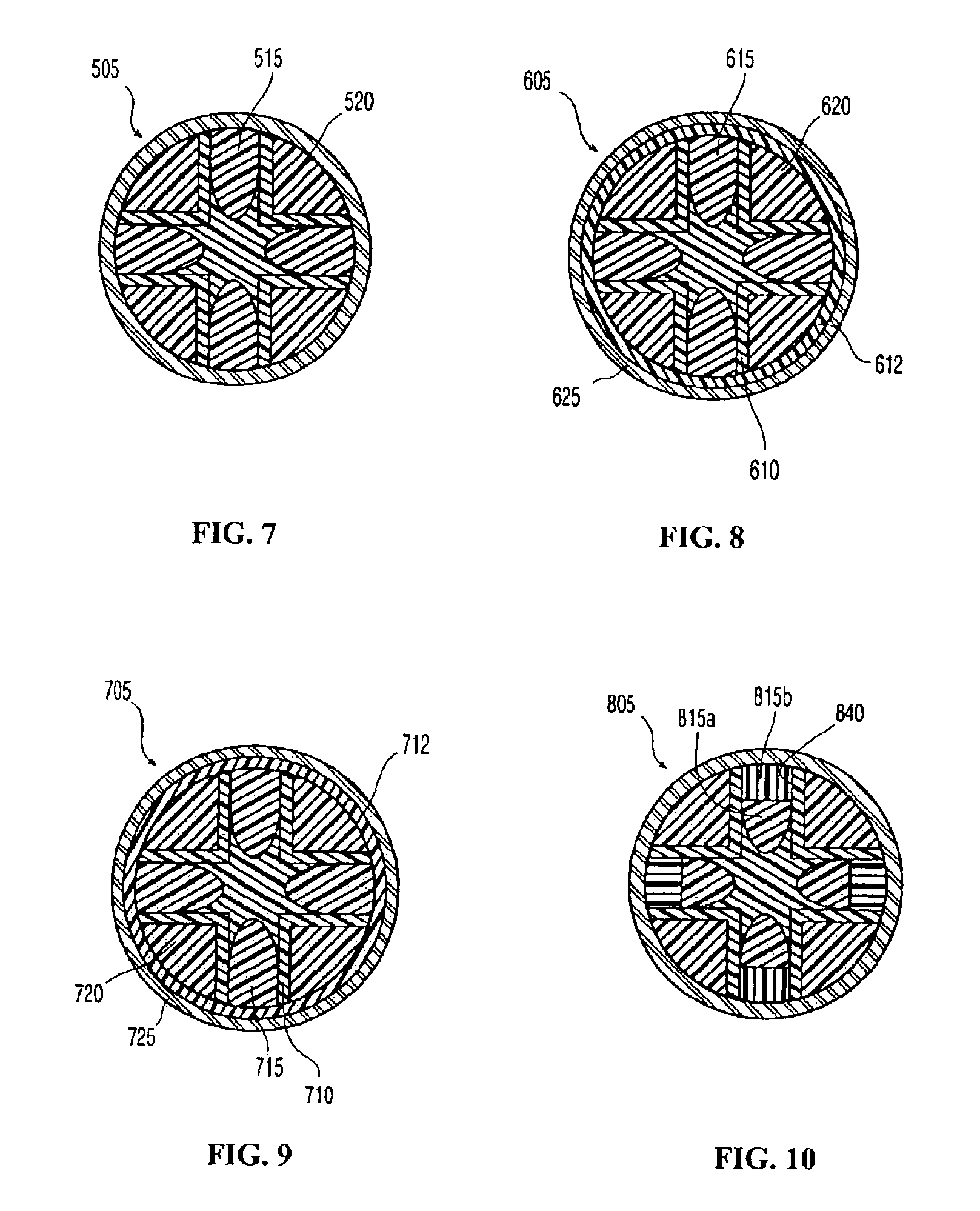
Golf balls comprising highly-neutralized acid polymers
A golf ball comprising a core included of a polymer containing an acid group fully-neutralized by an organic acid or a salt, a cation source, or a suitable base thereof, the core having a first Shore D hardness, a compression of no greater than about 90, and a diameter of between about 1.00 inches and about 1.64 inches; and a cover comprising a polyurea formed from a polyisocyanate, a polyamine, and a curing agent; wherein the ball has a compression of between about 50 and about 120.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
Polyamine analog conjugates and quinone conjugates as therapies for cancers and prostate diseases
Peptide conjugates in which cytocidal and cytostatic agents, such as polyamine analogs or naphthoquinones, are conjugated to a polypeptide recognized and cleaved by enzymes such as prostate-specific antigen (PSA) and cathepsin B are provided, as well as compositions comprising these conjugates. Methods of using these conjugates in the treatment of prostate diseases are also provided.
Owner:CELLGATE
Modified membranes
InactiveUS20050029186A1Reduce dirtEssential mechanical properties of the membranesSemi-permeable membranesMembranesVinyl etherReverse osmosis
A porous polymeric membrane formed from a blend of a polymeric membrane forming material, such as polyvinylidene fluoride or polysulfone and a polymeric reactivity modifying agent adapted to modify the surface active properties of the porous polymeric membrane. The reactivity modifying agent is preferably a linear polymeric anhydride, such as poly(alkyl vinyl ether / maleic anhydride). The surface activity modifications include modification of the hydrophilicity / hydrophobicity balance of the membrane, or hydrolysis followed by reaction with a polyamine to form a crosslinked polyamide layer. Such modified membranes have use as reverse osmosis membranes.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
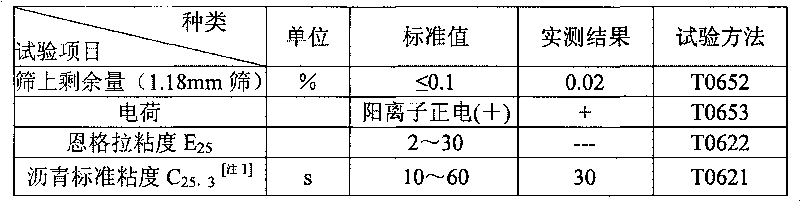
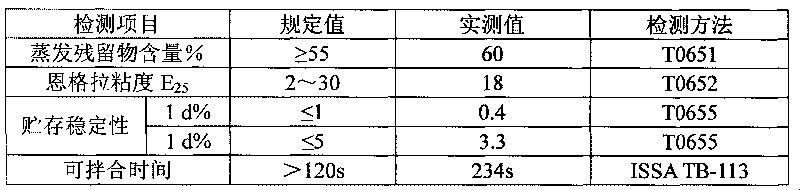
Method for synthesizing amphoteric slow-breaking quick-setting asphalt emulsifier
InactiveCN101712625AWide selectionWide adaptabilityOrganic compound preparationTransportation and packagingChemical synthesisSolubility
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing a novel amphoteric slow-breaking quick-setting asphalt emulsifier, belonging to the technical field of organic chemical synthesis. The method comprises the following steps of: reacting oleic acid with polyamine to generate acid amide polyamine, and then adding chloroactic acid to generate halogenating reaction to prepare the asphalt emulsifier, wherein the polyamine is the mixture of diethylenetriamine and triethylene tetramine. The water solubility of the hydrophilic radical of the emulsifier synthesized by the process is stronger than those of like emulsifiers, thereby obviously lowering the critical micelle concentration (CMC) value, and the particles of the produced asphalt emulsion are finer, smoother and evener. The emulsifier can effectively prevent asphalt from settling, increases the storage stability of the asphalt emulsion, reasonably regulates the charge ratio, widens the selectivity on stone materials in the application of slurry seal construction, enables the mixing time to be sufficient, and has obvious quick-setting effect and improved project quality.
Owner:河南新友公路技术有限公司 +1
Polyamine analog-amino acid conjugates useful as anticancer agents
Conjugates in which polyamine analogs are conjugated to an amino acid are provided, as well as compositions comprising these conjugates. Methods of using these conjugates as anticancer treatments are also provided.
Owner:CELLGATE
Modified membranes
InactiveUS6884350B2Reduce dirtEssential mechanical properties of the membranesMembranesSemi-permeable membranesVinyl etherPolyamide
A porous polymeric membrane formed from a blend of a polymeric membrane forming material, such as polyvinylidene fluoride or polysulfone and a polymeric reactivity modifying agent adapted to modify the surface active properties of the porous polymeric membrane. The reactivity modifying agent is preferably a linear polymeric anhydride, such as poly(alkyl vinyl ether / maleic anhydride). The surface activity modifications include modification of the hydrophilicity / hydrophobicity balance of the membrane, or hydrolysis followed by reaction with a polyamine to form a crosslinked polyamide layer. Such modified membranes have use as reverse osmosis membranes.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
Carrier ampholytes of high pH range
Carboxylic acid-substituted polyalkylene polyamines in which amine nitrogen atoms on the polyamine backbone structure are replaced by guanidine groups provide a pH range extending into high pH values. These substances are useful as carrier ampholytes in isoelectric focusing.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Structural modified epoxy adhesive compositions
InactiveUS20020164485A1Reduce opening timeGood substrate adhesionSynthetic resin layered productsThin material handlingSilanesFirming agent
The present invention is directed to an adhesive composition, which comprises an epoxy resin, a coupling agent, filler, and an effective amount of an amine-curing agent or curative for said epoxy resin. Advantageously, tri-functional and / or tetrafunctional epoxy resins and / or acrylate monomers will be incorporated into the adhesive composition in order to reduce open time and enhance substrate adhesion. Advantageously, a mixture of amines will be used in the curative including aliphatic amines, which have low viscosities and efficiently wet the substrate for enhancing adhesion; polyamines, which can be used to manipulate open time and allow for improved ratio tolerance of the adhesive system; and amine-terminated rubbers (ATBN), which can improve impact resistance and the toughness of the cured adhesive. Preferred coupling agents are silanes.
Owner:ASHLAND LICENSING & INTPROP LLC
Encapsulated fragrance chemicals
InactiveUS7196049B2Increase depositionCosmetic preparationsOrganic detergent compounding agentsPersonal careFlavor
A polymeric encapsulated fragrance is disclosed which is suitable for use in personal care and cleaning products. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, the fragrance is encapsulated by a first polymer material to form a fragrance encapsulated polymer, the polymer encapsulated shell is then coated with a mixture of cationic polymers, in a preferred embodiment the coating polymers are a reaction product of polyamines and (chloromethyl) oxirane or (bromomethyl) oxirane.
Owner:INTERNATIONAL FLAVORS & FRAGRANCES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com