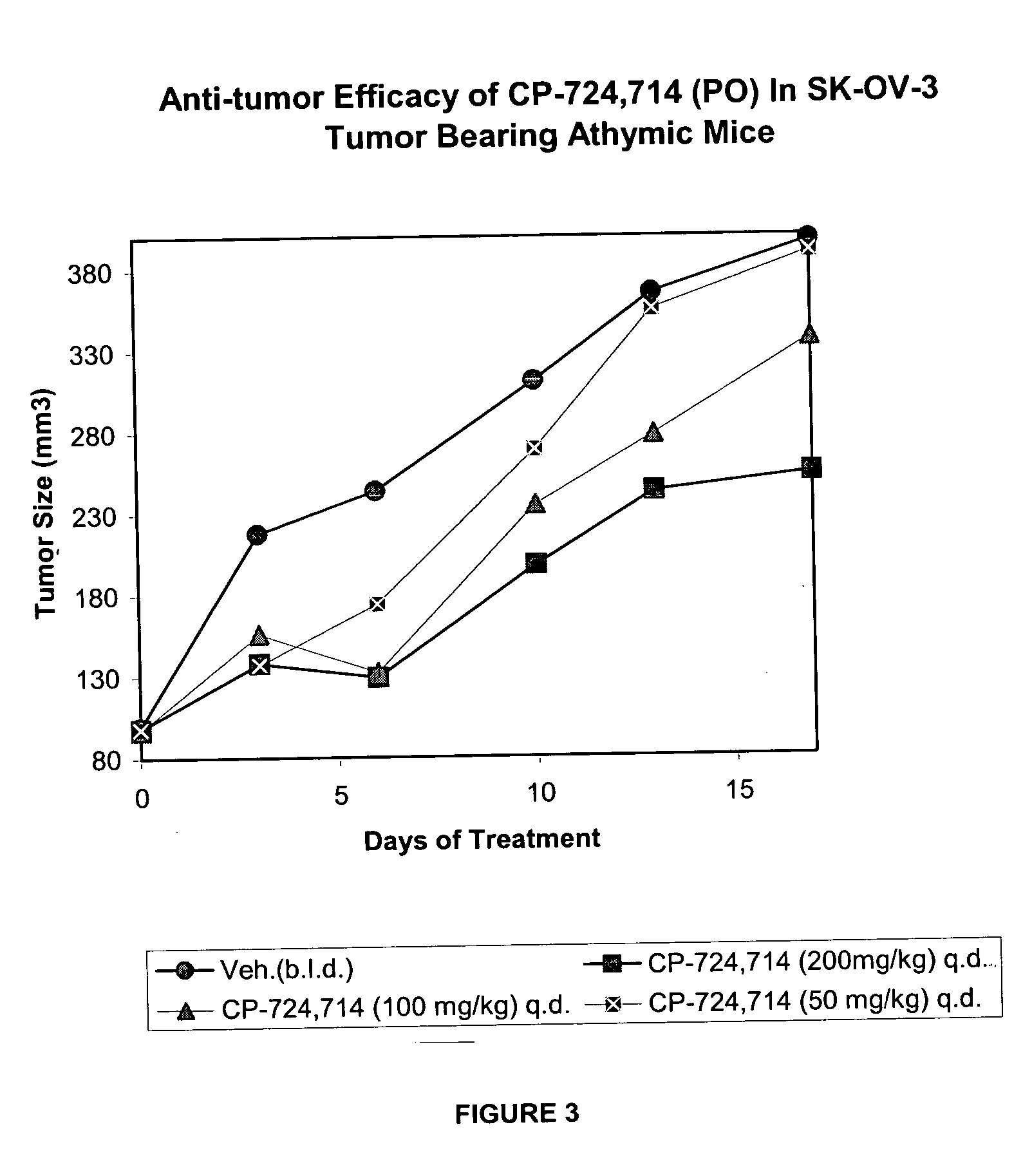
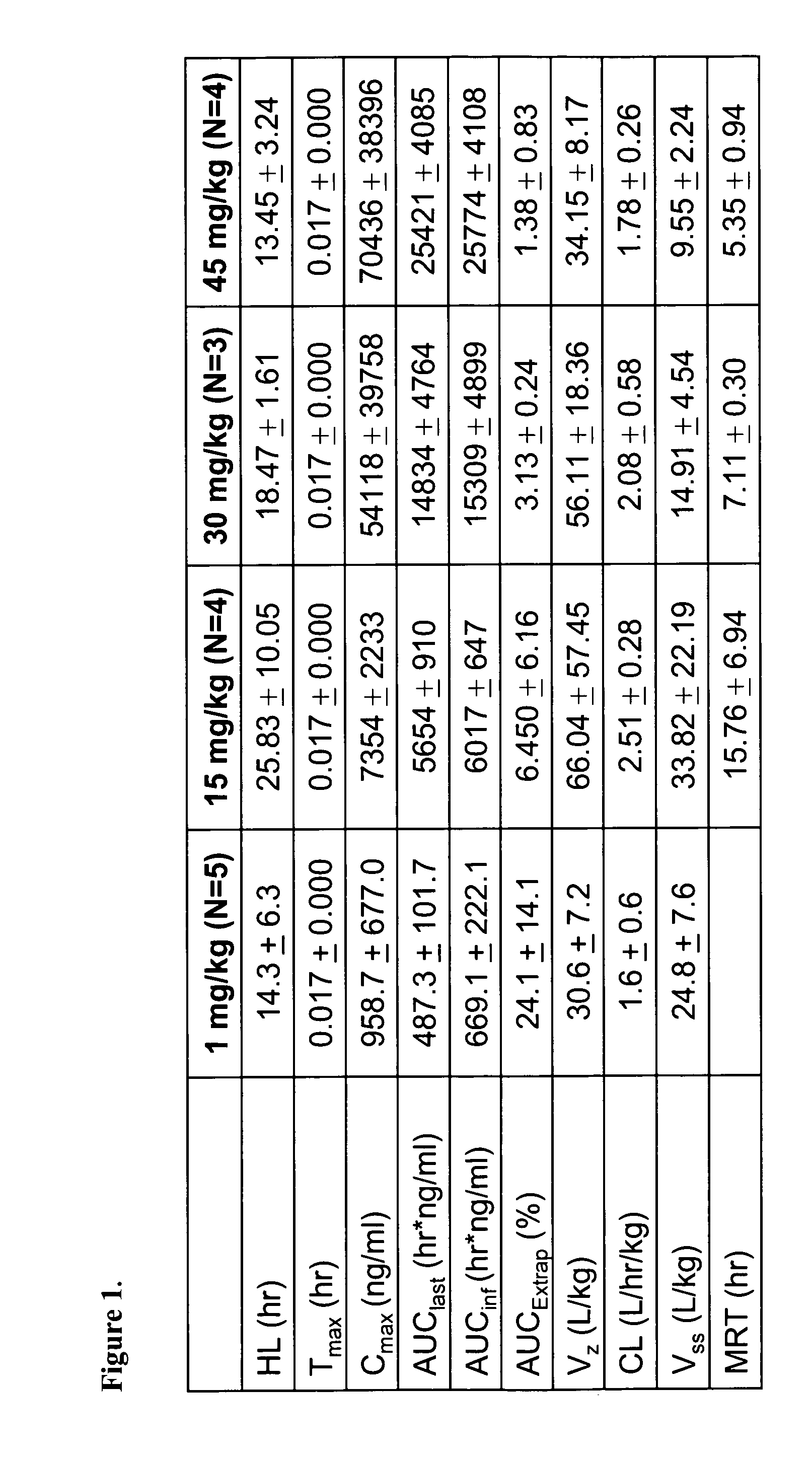
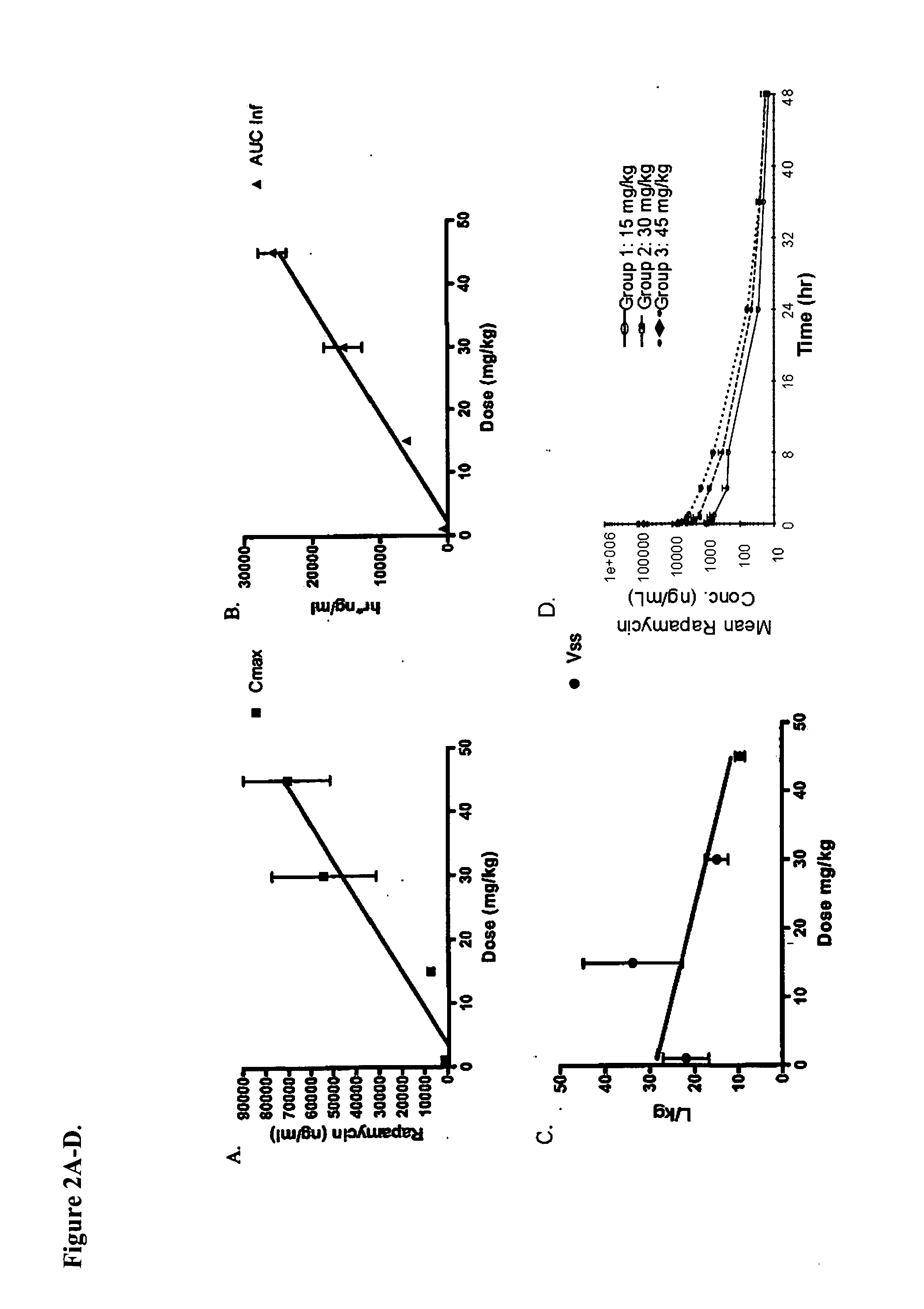
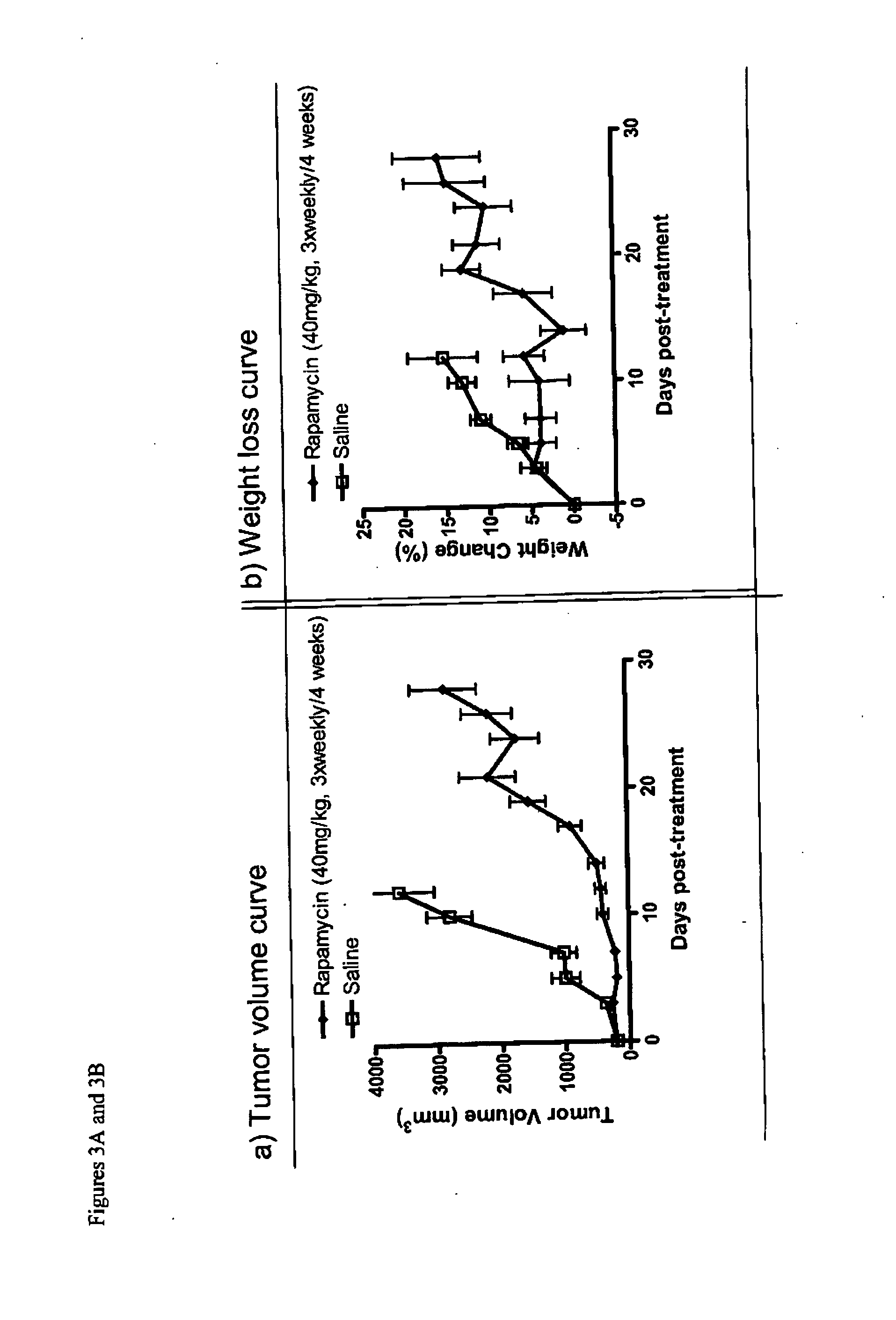
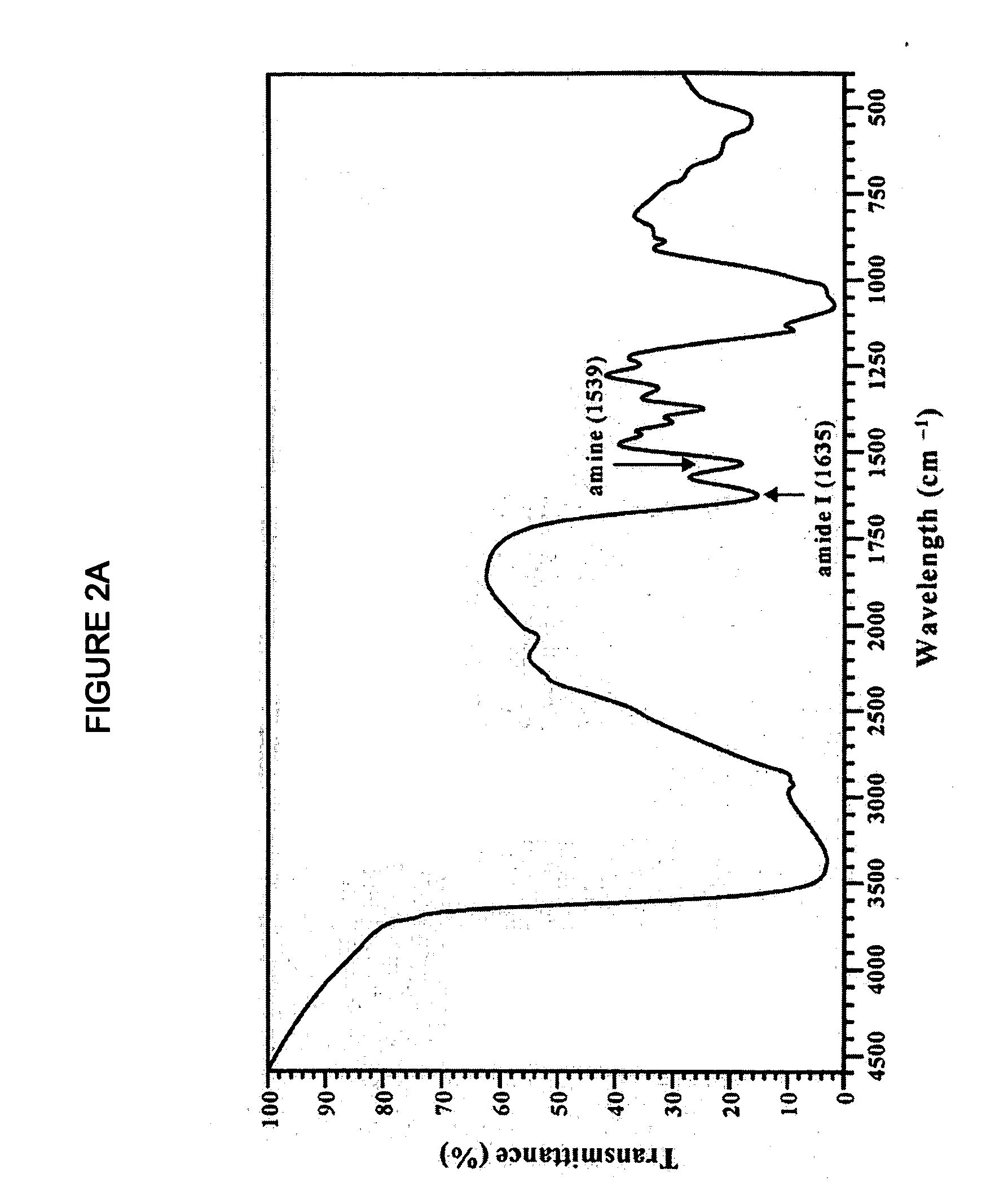
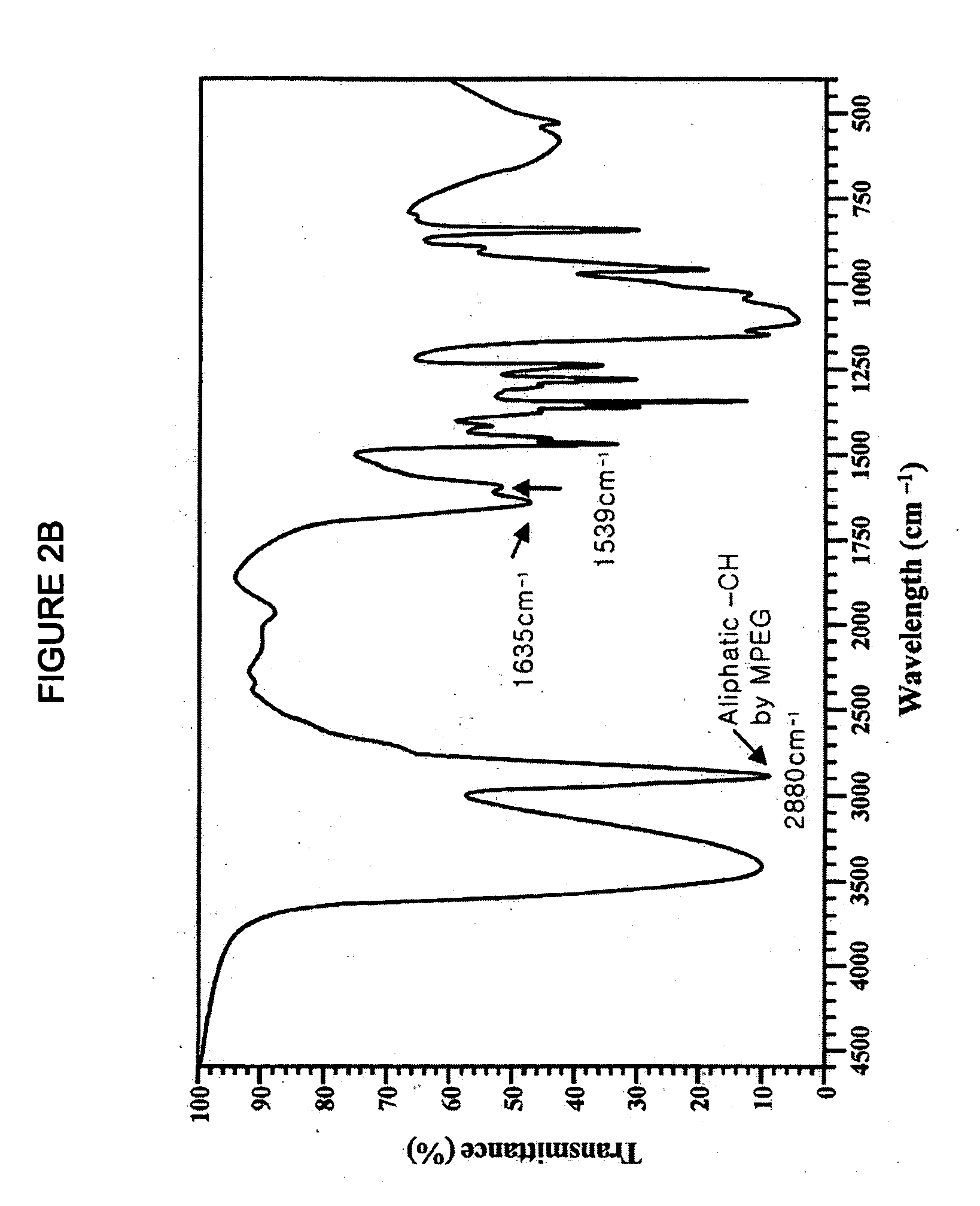
Patents
Literature
1617 results about "Anticarcinogen" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An anticarcinogen (also known as a carcinopreventive agent) is a substance that counteracts the effects of a carcinogen or inhibits the development of cancer. Anticarcinogens are different from anticarcinoma agents (also known as anticancer or anti-neoplastic agents) in that anticarcinoma agents are used to selectively destroy or inhibit cancer cells after cancer has developed. Interest in anticarcinogens is motivated primarily by the principle that it is preferable to prevent disease (preventive medicine) than to have to treat it (rescue medicine).
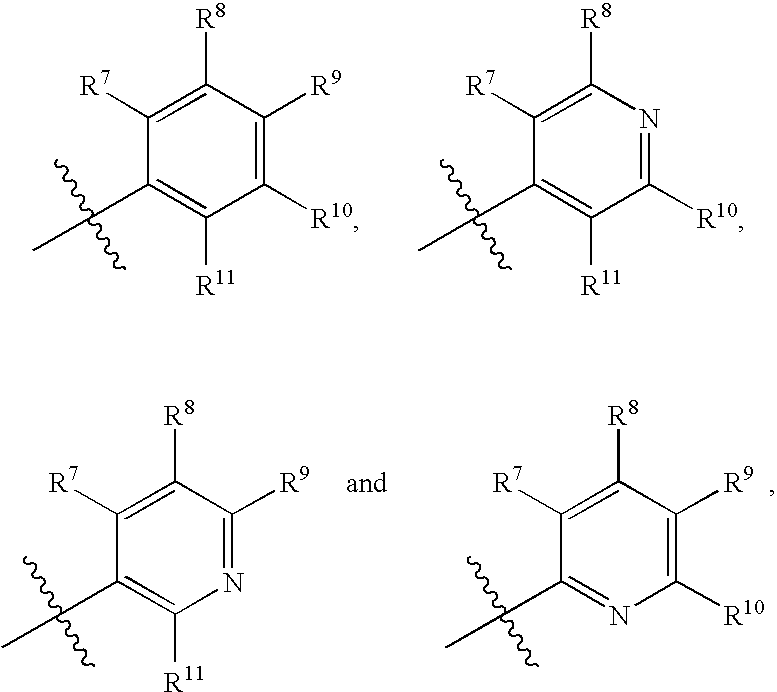
Heterocyclic compounds
InactiveUS6329381B1Excellent interferon biosynthesis inducing activityInhibition thicknessAntibacterial agentsBiocideBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENTInterferon inducer
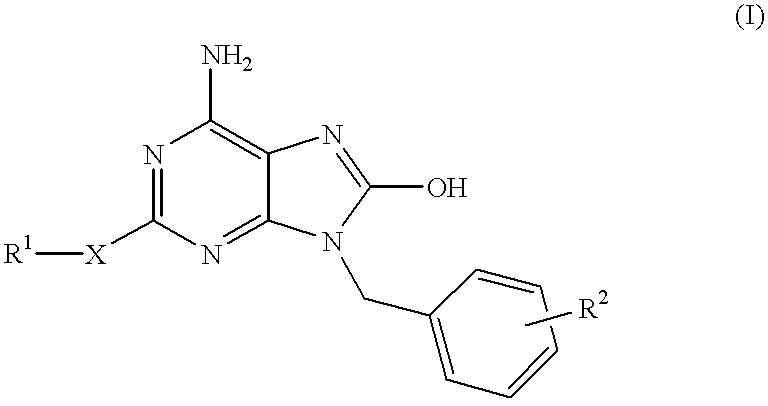
The present invention relates to a heterocyclic compound of the following general formula (I):wherein X is sulfur atom, oxygen atom or -NR3- (R3 may form a heterocyclic ring or a substituted heterocyclic ring with R1 via the nitrogen atom),R1 is alkyl group, substituted alkyl group, aryl group, substituted aryl group, heterocyclic group or substituted heterocyclic group, andR2 is hydrogen atom, halogen atom etc.;or its pharmaceutically acceptable salt and interferon inducers, antiviral agents, anticancer agents and therapeutic agents for immunologic diseases comprising the compound (I) or its pharmaceutically acceptable salt as active ingredients.
Owner:SUMITOMO DAINIPPON PHARMA CO LTD
Application of lipid vehicles and use for drug delivery
InactiveUS7063860B2Reduce and prevent antibody-mediated resistanceIncrease stimulationBiocideAntipyreticAnticarcinogenCapsaicin
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for the administration of lipid-based vehicles to treat various disorders, including bladder inflammation, infection, dysfunction, and cancer. In various aspects, the compositions and methods of the invention are useful for prolonged delivery of drugs, e.g., antibiotics, pain treatments, and anticancer agents, to the bladder, genitourinary tract, gastrointestinal system, pulmonary system, and other organs or body systems. In particular, the present invention relates to liposome-based delivery of vanilloid compounds, such as resiniferatoxin, capsaicin, or tinyatoxin, and toxins, such as botulinum toxin, for the treatment of bladder conditions, including pain, inflammation, incontinence, and voiding dysfunction. Further related are methods of using these vehicles alone or in conjunction with antibodies, e.g., uroplakin antibodies, to improve duration of liposome attachment, and provide a long-term intravesical drug delivery platform. The present invention specifically relates to antibody-coated liposomes that are useful for targeting specific receptors for drug, peptide, polypeptide, or nucleic acid delivery. In one particular aspect, the present invention relates to liposomes coated with antibodies against nerve growth factor (NGF) receptor and containing NGF antisense nucleic acids, which are used as a treatment for neurogenic bladder dysfunction.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Combination of Local and Systemic Immunomodulative Therapies for Enhanced Treatment of Cancer
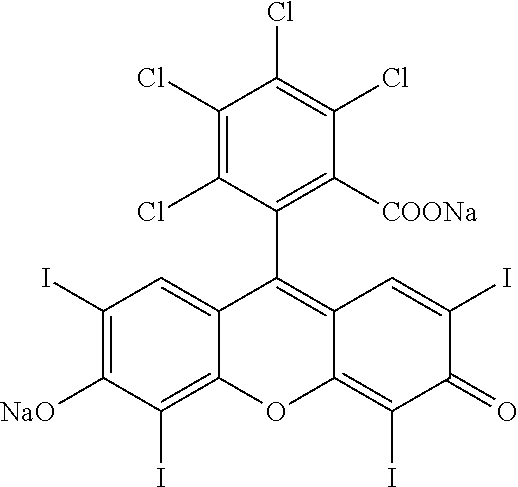
A method for the treatment of cancer comprising administration of a therapeutically effective amount of an intralesional chemoablative pharmaceutical composition, or variant of said composition, in combination with a therapeutically effective amount of a systemic immunomodulatory anticancer agent. A further method for the treatment of cancer comprising administration of a therapeutically effective amount of an intralesional chemoablative pharmaceutical composition, or variant of said composition, in combination with a therapeutically effective amount of a systemic targeted anticancer agent. The present invention is further directed to pharmaceutical compositions for treatment of cancer. The intralesional chemoablative pharmaceutical composition can comprise an IL chemoablative agent comprising primarily a halogenated xanthene.
Owner:PFIZER INC +1
Adipose-derived stromal cells (ASC) as delivery tool for treatment of cancer
InactiveUS20110027239A1Efficient killingSystemic non-specific responses will be minimalBiocideSpecial deliveryAnticarcinogenStromal cell
The present invention generally relates to use of adult Adipose-derived stromal cells (ASC) and genetically engineered ASC for the treatment of cancer. In particular, the present invention generally relates, in part to a method for treating a subject with cancer comprising administering to the subject a composition comprising engineered ASCs which have been modified to express a gene encoding at least one anti-cancer agent. In some embodiments, an anti-cancer agent is a pro-apoptotic agent. In some embodiments an anti-cancer agent is an agent which inhibits the expression of an oncogene.
Owner:TISSUE GENESIS
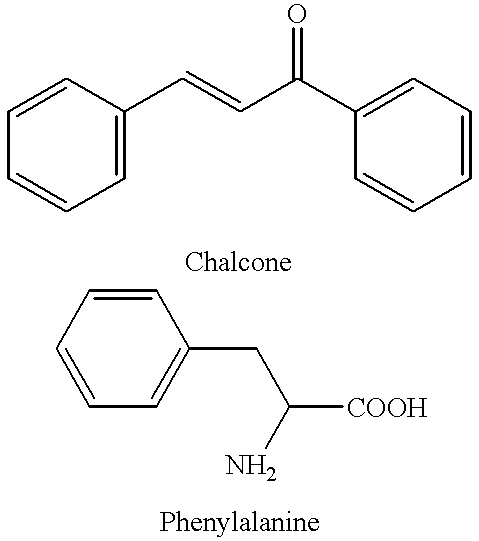
Chalcone and its analogs as agents for the inhibition of angiogensis and related disease states
InactiveUS6462075B1Enhance the beneficial effectEasy to modifyBiocideNervous disorderAnticarcinogenMedicine
The present invention relates to chalcone and chalcone derivatives and analogs which are useful as angiogenesis inhibitors. The present compounds, which are inexpensive to synthesize, exhibit unexpectedly good activity as angiogenesis inhibitors. The present invention also relates to the use of chalcone and its analogs as antitumor / anticancer agents and to treat a number of conditions or disease states in which angiogenesis is a factor, incluidng angiongenic skin diseases such as psoriasis, acne, rosacea, warts, eczema, hemangiomas, lymphangiogenesis, among numerous others, as well as chronic inflammatory disease such as arthritis.
Owner:BOWEN J PHILLIP +3
Anti-cancer agents and uses thereof
InactiveUS20080280891A1Hindering and blocking cell cycle progressionBiocideOrganic chemistryAnticarcinogenProstate cancer
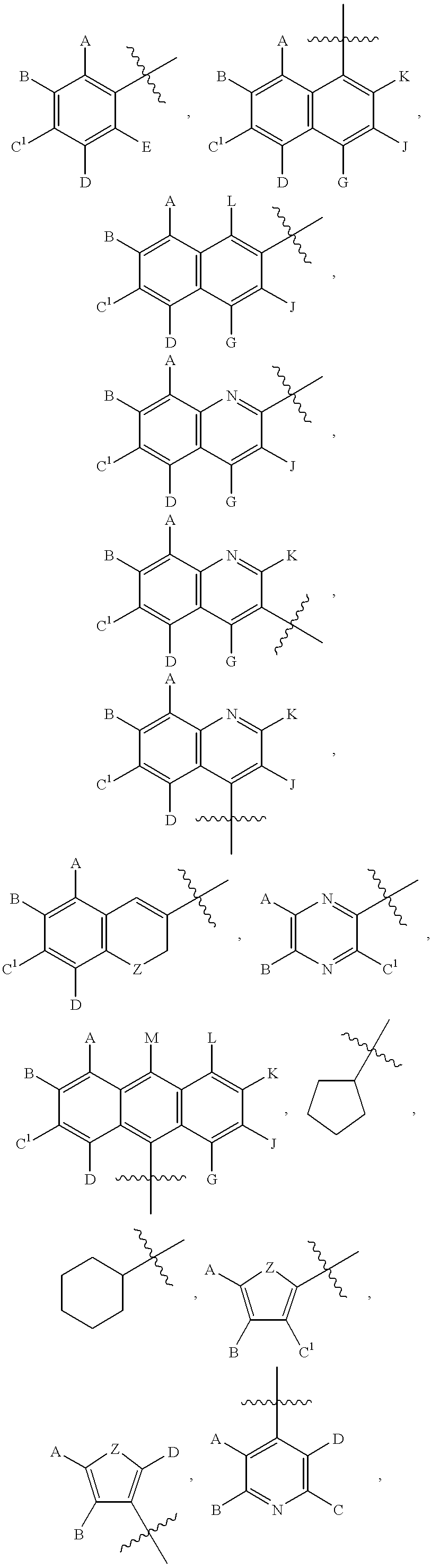
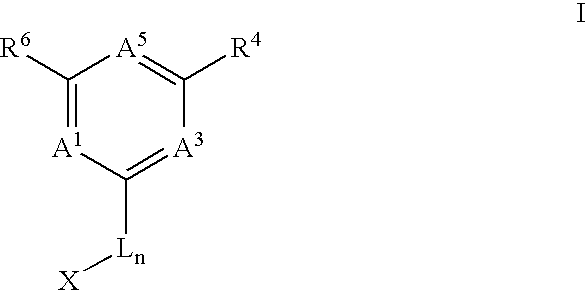
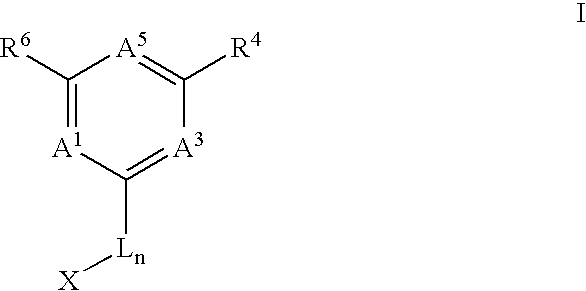
The present invention is in the area of novel compounds and salts thereof, their syntheses, and their use as anti-cancer agents. The compounds include compounds of Formula I:and solvates, hydrates and pharmaceutically-acceptable salts thereof, wherein A1 is N or CR1; A3 is N or CR3; A5 is N or CR5; R1, R3-R6 and L are defined in the specification; n is 0 or 1; and X is an optionally-substituted aryl group having 6-10 carbons in the ring portion, an optionally-substituted 6-membered heteroaryl group having 1-3 nitrogen atoms in the ring portion, an optionally-substituted 5-membered heteroaryl group having 0-4 nitrogen atoms in the ring portion and optionally having 1 sulfur atom or 1 oxygen atom in the ring portion, or an optionally-substituted heteroaryl group in which a 6-membered ring is fused either to a 5-membered ring or to a 6-membered ring, wherein in each case 1, 2, 3 or 4 ring atoms are heteroatoms independently selected from nitrogen, oxygen and sulfur. They are effective against a broad range of cancers, especially leukemia, prostate, non-small cell lung and colon. They are additionally useful in the treatment of proliferative retinopathies such as diabetic neuropathy and macular degeneration.
Owner:LOCUS PHARMA INC
Formulations for cell-schedule dependent anticancer agents
InactiveUS20060121085A1Strong specificityEliminate side effectsPowder deliveryBiocideMetaboliteAnticarcinogen
The present invention provides a flowable composition suitable for use as a controlled release implant. The composition includes: (a) a biodegradable, biocompatible thermoplastic polymer that is at least substantially insoluble in aqueous medium, water or body fluid; (b) a cell-cycle dependent biological agent, a schedule-dependent biological agent, a metabolite thereof, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a prodrug thereof; and (c) a biocompatible organic liquid, at standard temperature and pressure, in which the thermoplastic polymer is soluble. The present invention also provides a method of treating cancer in a mammal. The present invention also provides a method of blocking, impeding, or otherwise interfering with cell cycle progression at the G1-phase, G1 / S interphase, S-phase, G2 / M interface or M-phase of the cell cycle in a mammal. The methods includes administering to a mammal an effective amount of a flowable composition of the present invention.
Owner:QLT USA INC
Combination methods of treating cancer
InactiveUS20070190022A1Dosage of each agent in a combination therapy can be reducedAntitumor effectBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAnticarcinogenOncology
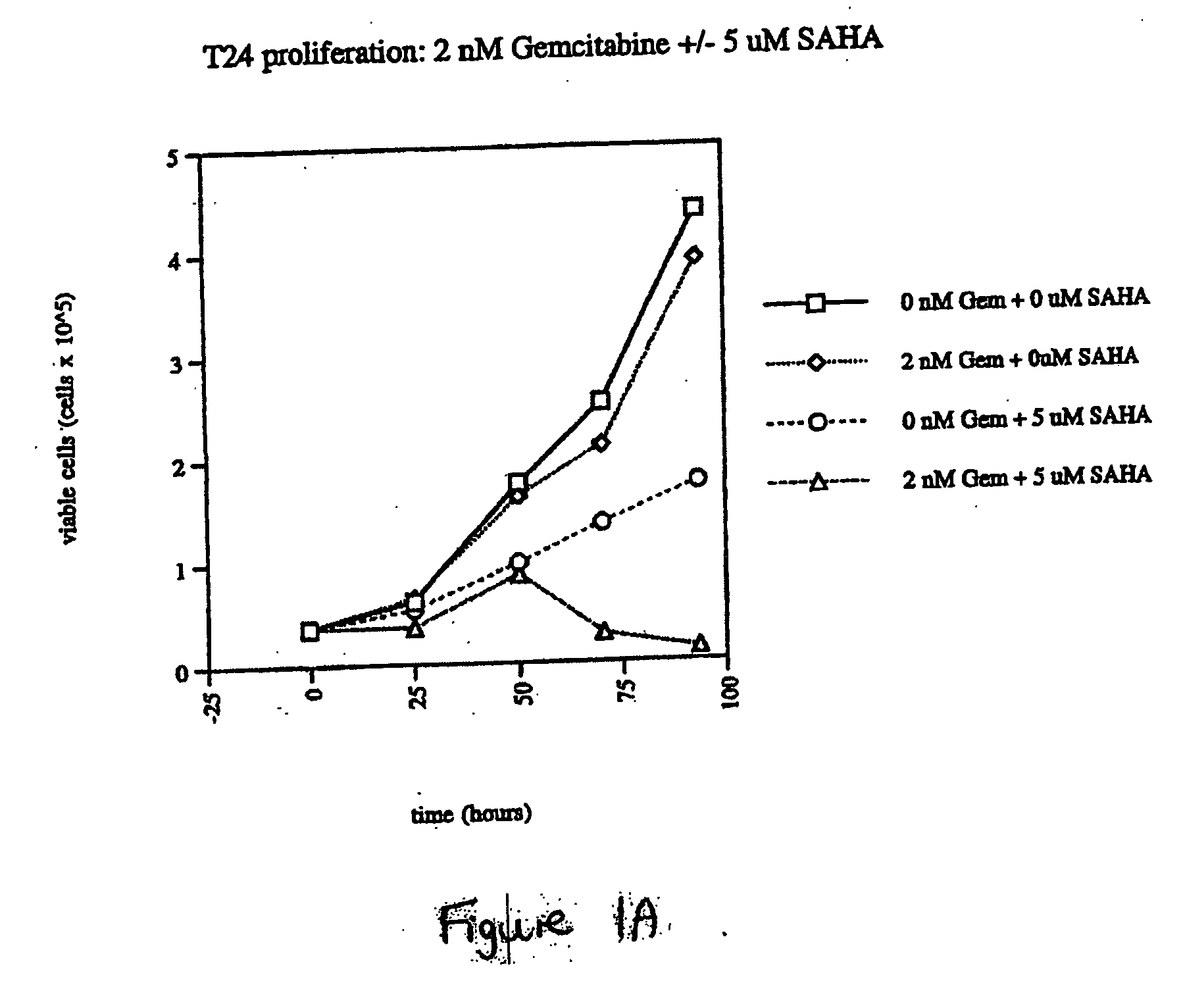
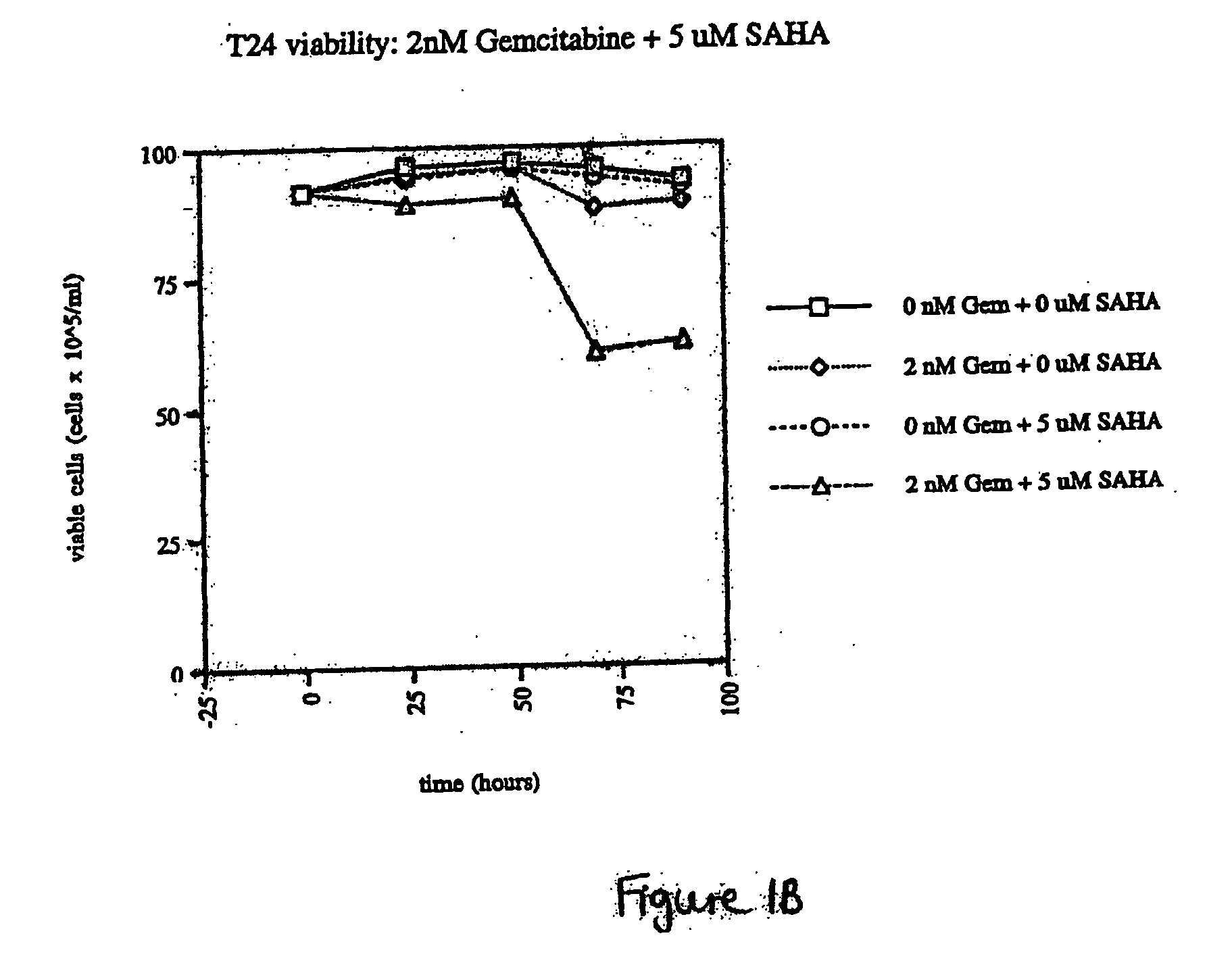
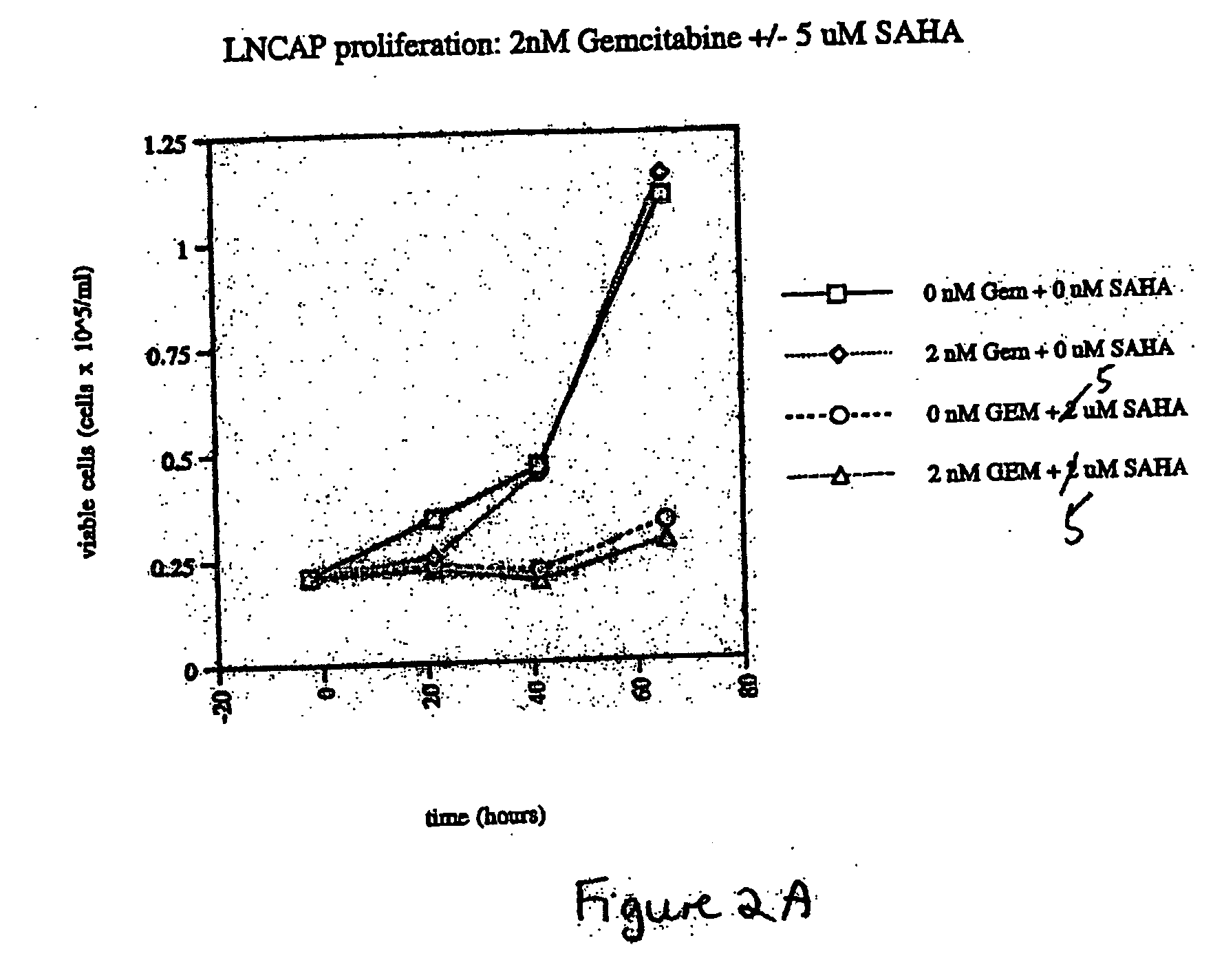
The present invention relates to a method of treating cancer in a subject in need thereof, by administering to a subject in need thereof a first amount of a histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or hydrate thereof, in a first treatment procedure, and a second amount of an anti-cancer agent in a second treatment procedure. The first and second amounts together comprise a therapeutically effective amount. The effect of the HDAC inhibitor and the anti-cancer agent may be additive or synergistic.
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES +1
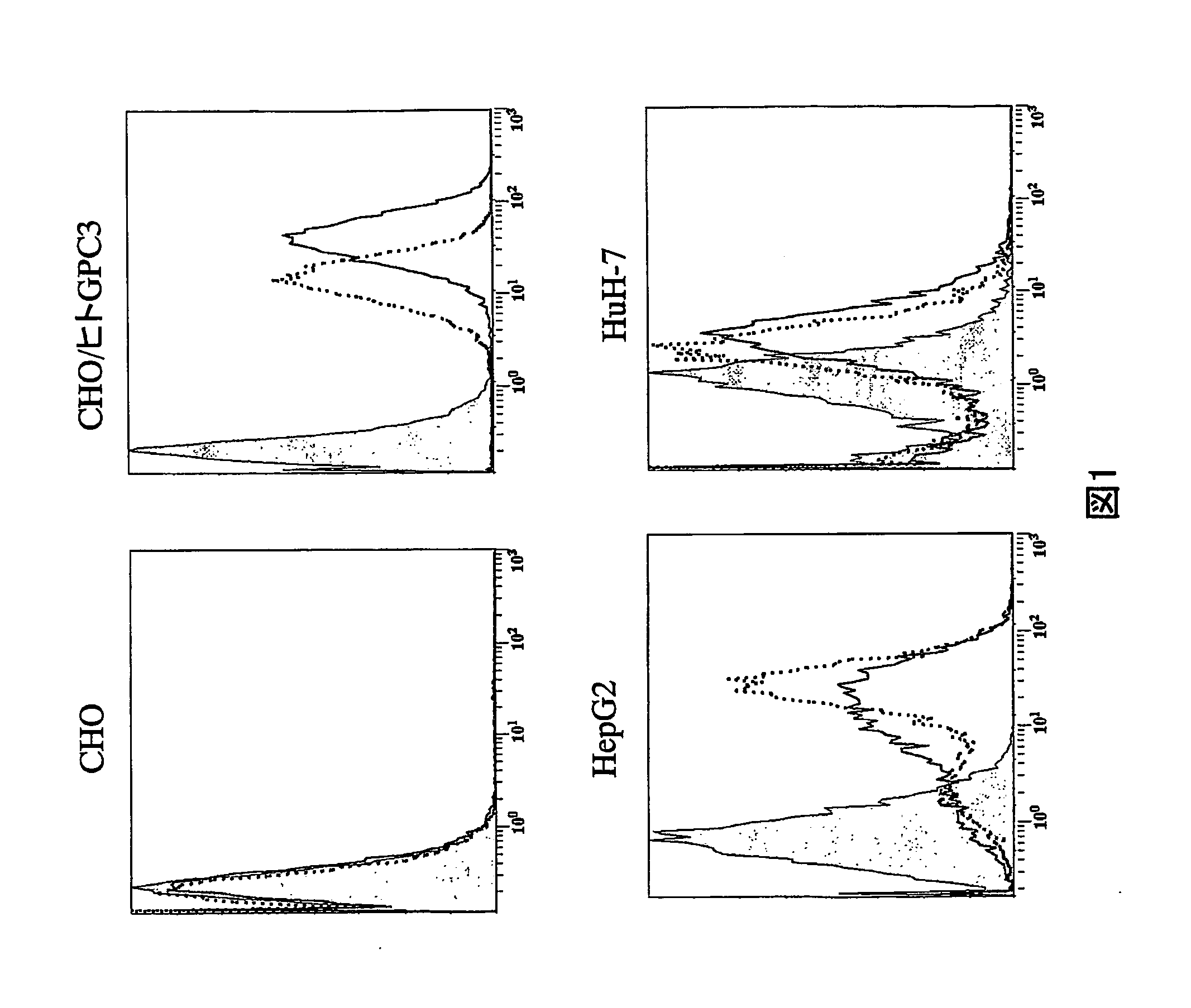
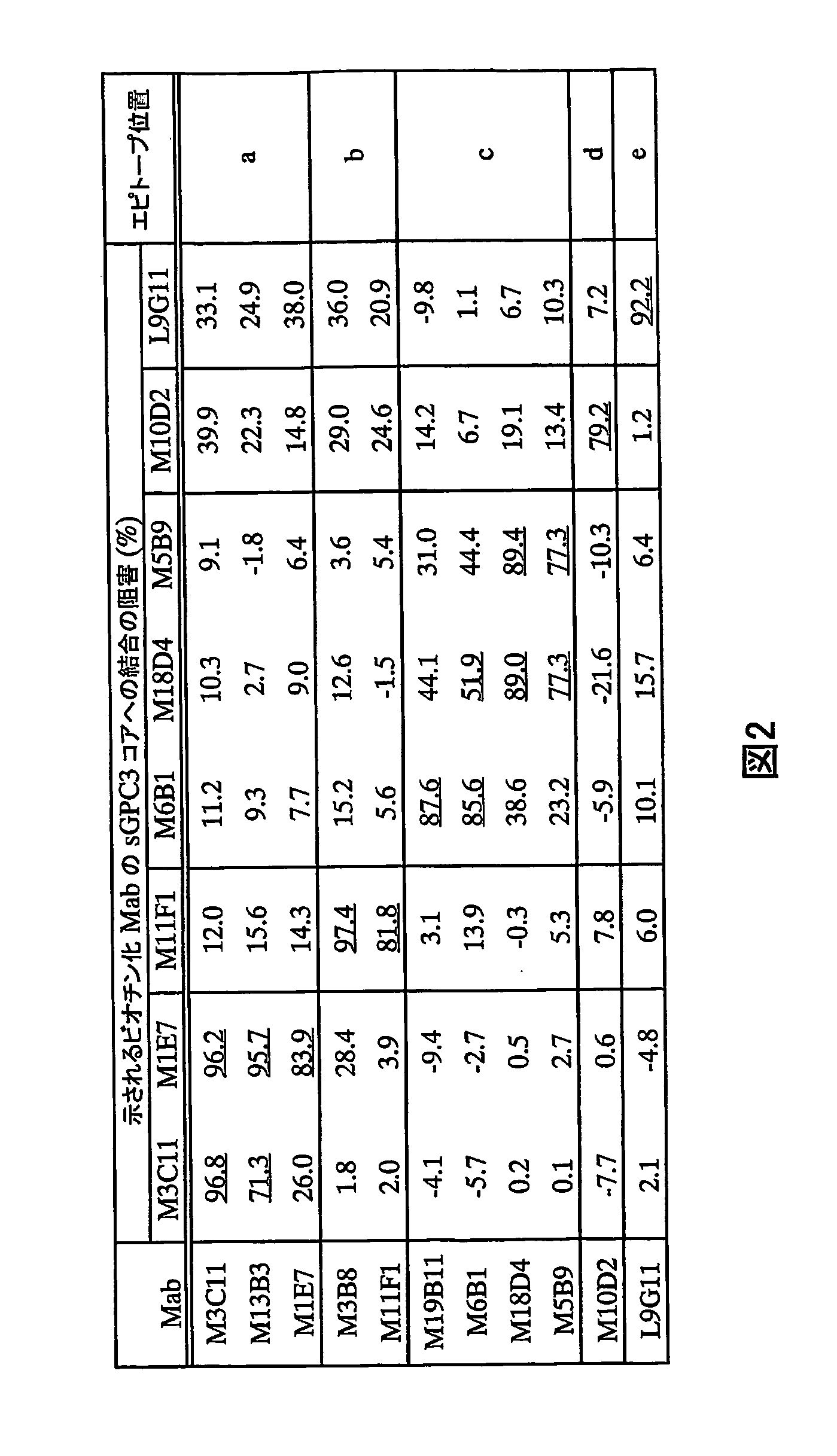
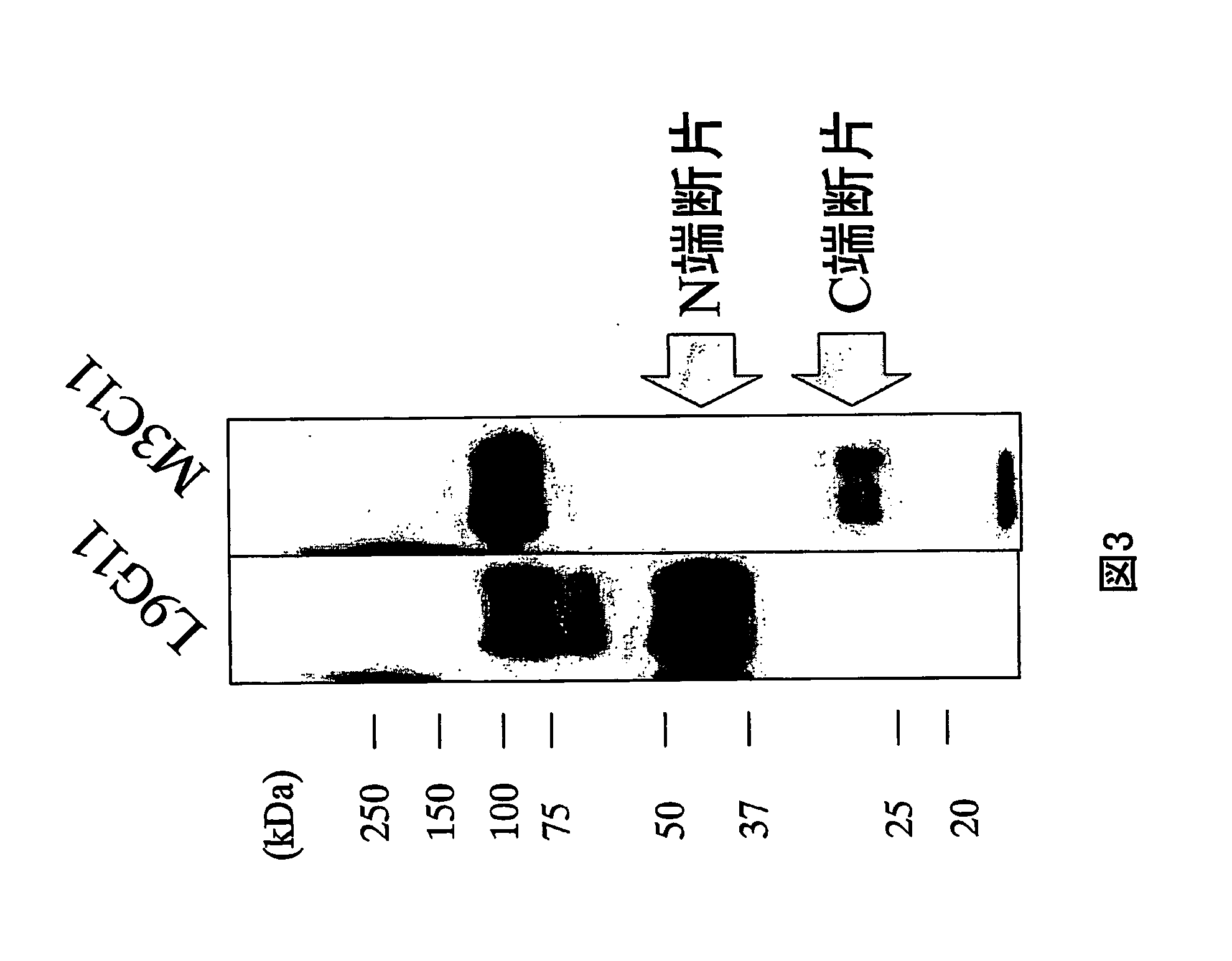
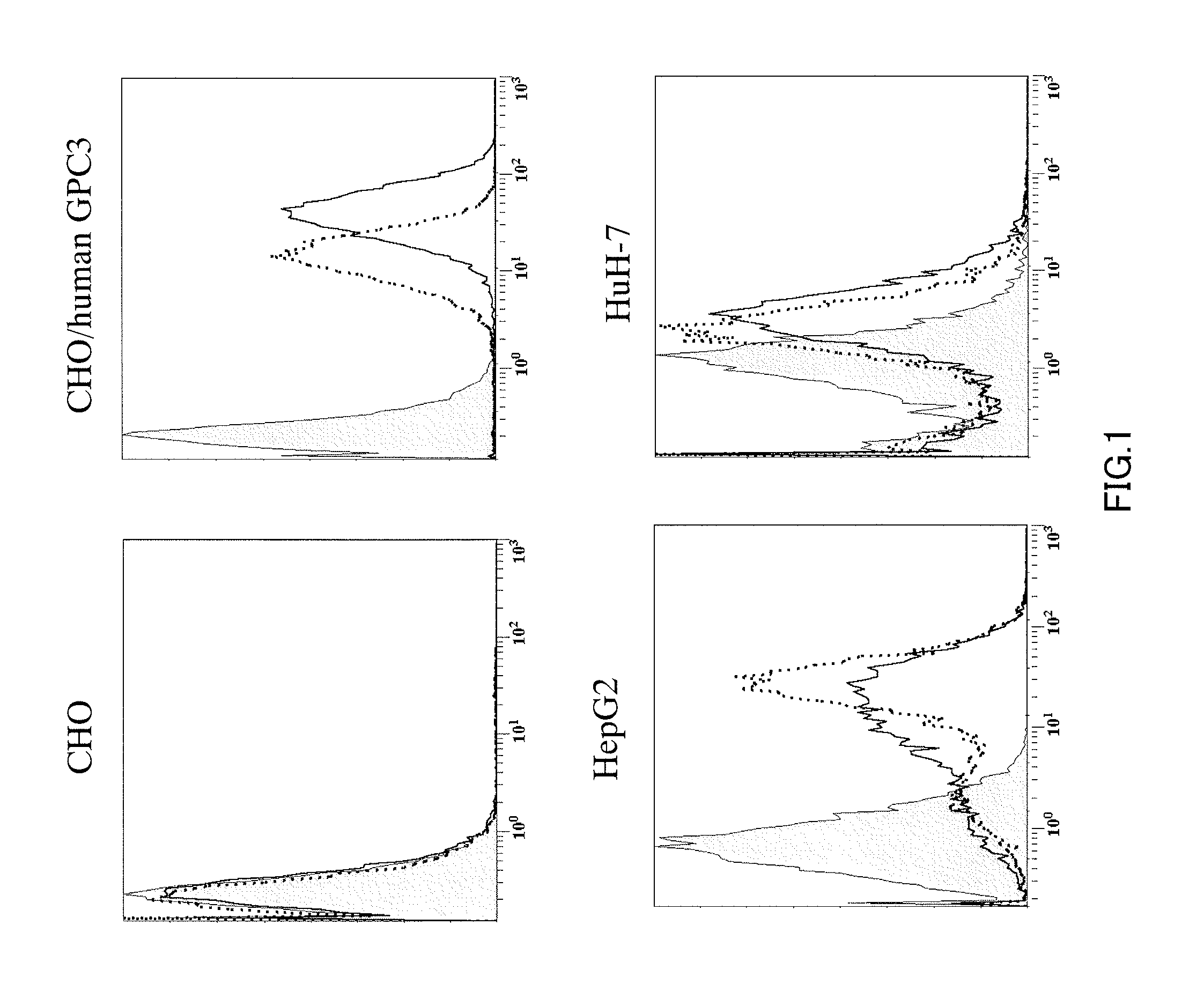
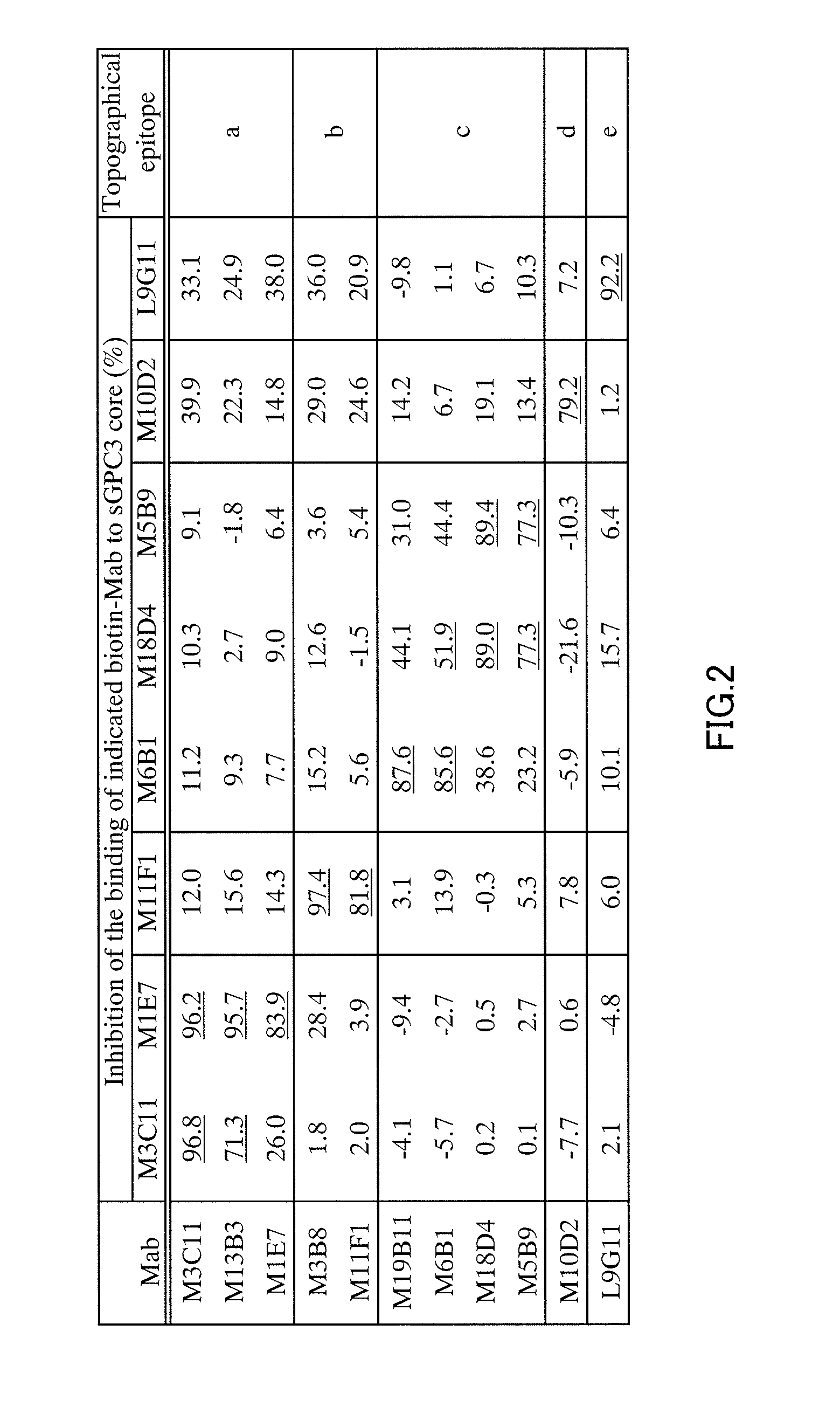
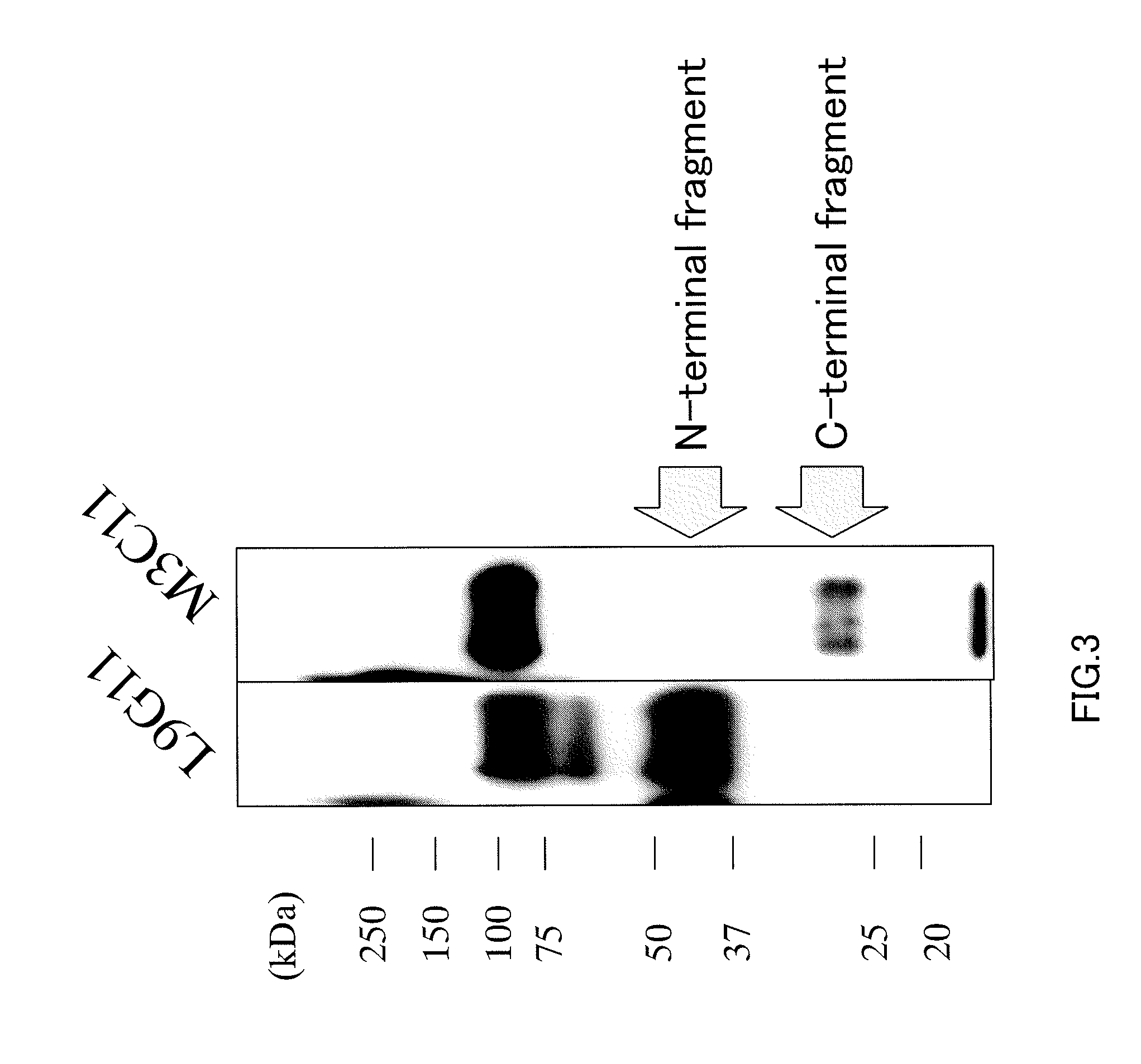
Anti-glypican 3 antibody
ActiveUS20070190599A1High cytotoxic activityAnimal cellsSugar derivativesAnticarcinogenHumanized antibody
An antibody capable of binding to a specific region of glypican 3, as well as a humanized antibody created based on that antibody are disclosed. The anti-GPC3 antibody of the invention has a higher ADCC activity and CDC activity compared with those of a conventional antibody. The antibody of the present invention is useful as a cell growth inhibitor, an anticancer agent and an agent for diagnosis of cancers.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
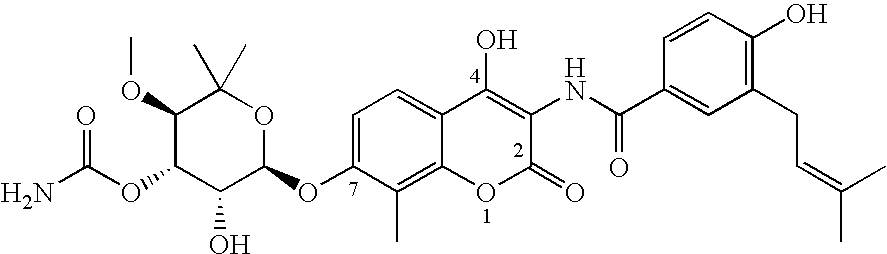
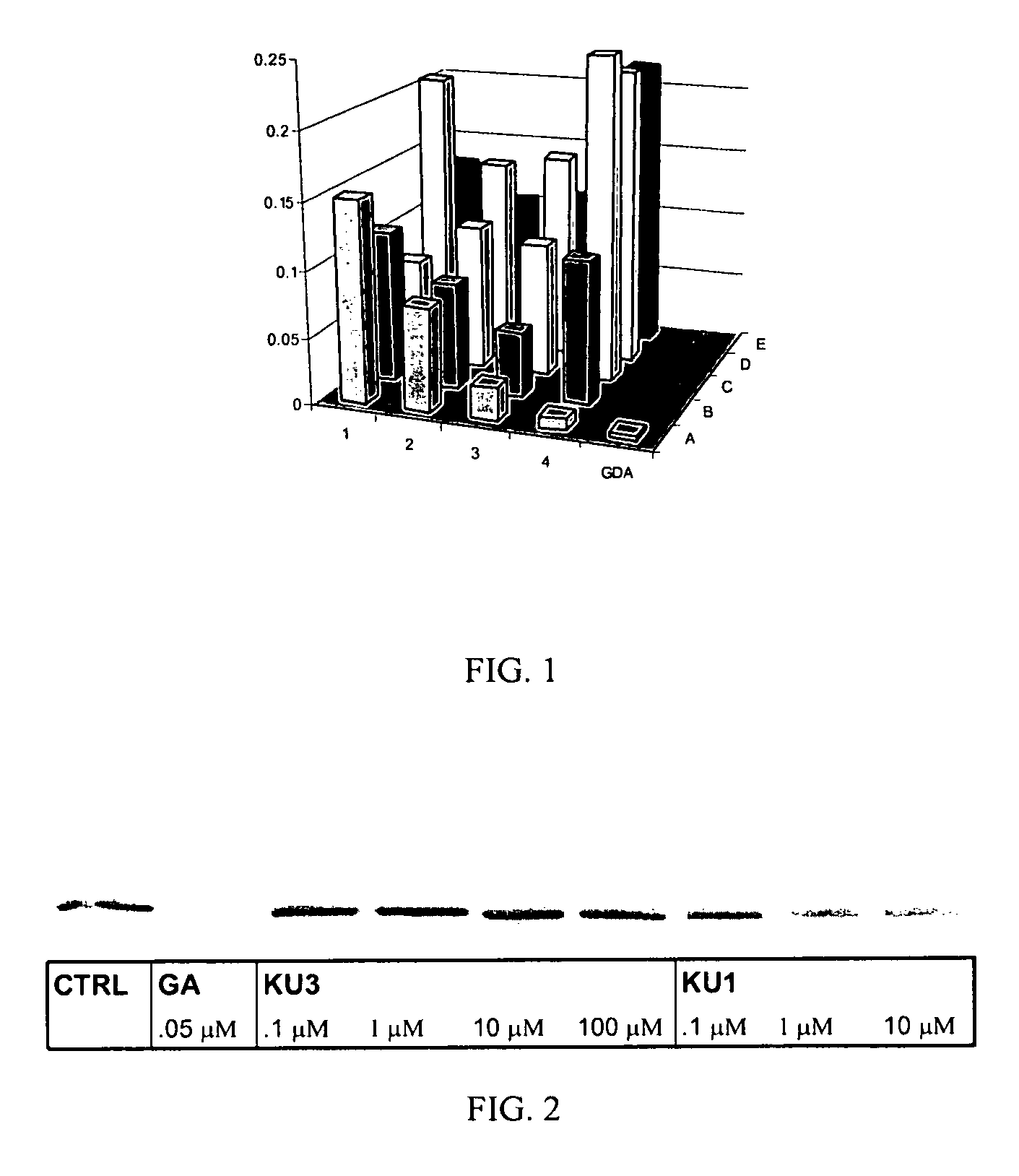
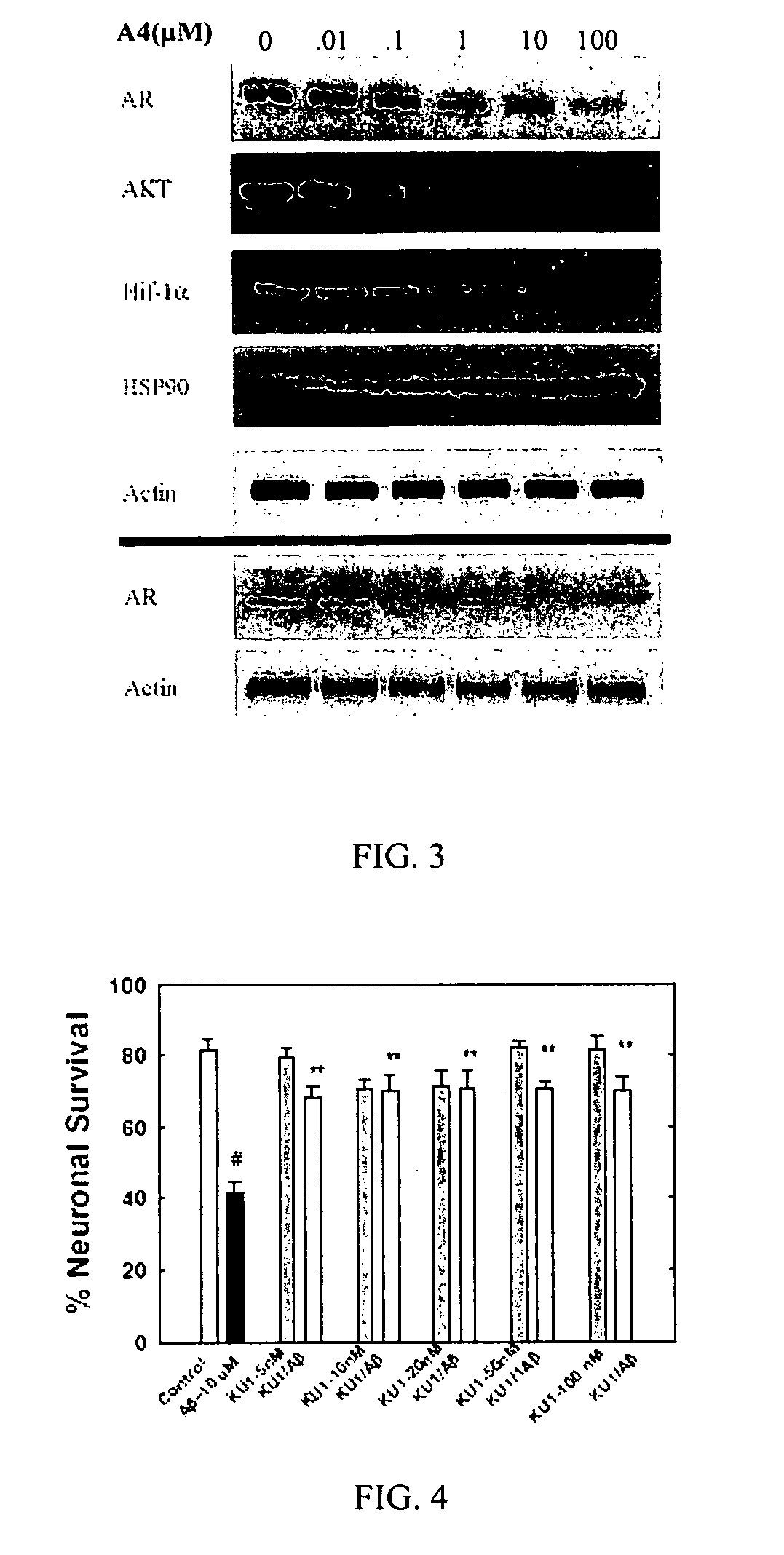
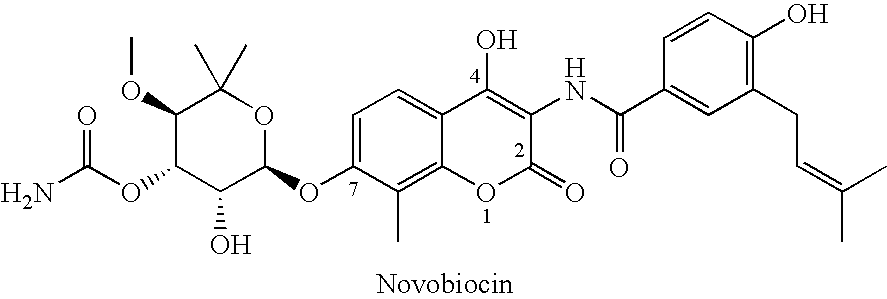
Novobiocin analogues as anticancer agents
Novel analogues and derivatives of novobiocin are provided, including compounds having modifications to the amide side chain, coumarin ring, and sugar moieties. The compounds of the present invention are useful as heat shock protein 90 inhibitors, and may be used as anticancer and neuroprotective agents.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS +1
Novobiocin analogues as anticancer agents
Novel analogues and derivatives of novobiocin are provided, including compounds having modifications to the amide side chain, coumarin ring, and sugar moieties. The compounds of the present invention are useful as heat shock protein 90 inhibitors, and may be used as anticancer and neuroprotective agents.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS +1
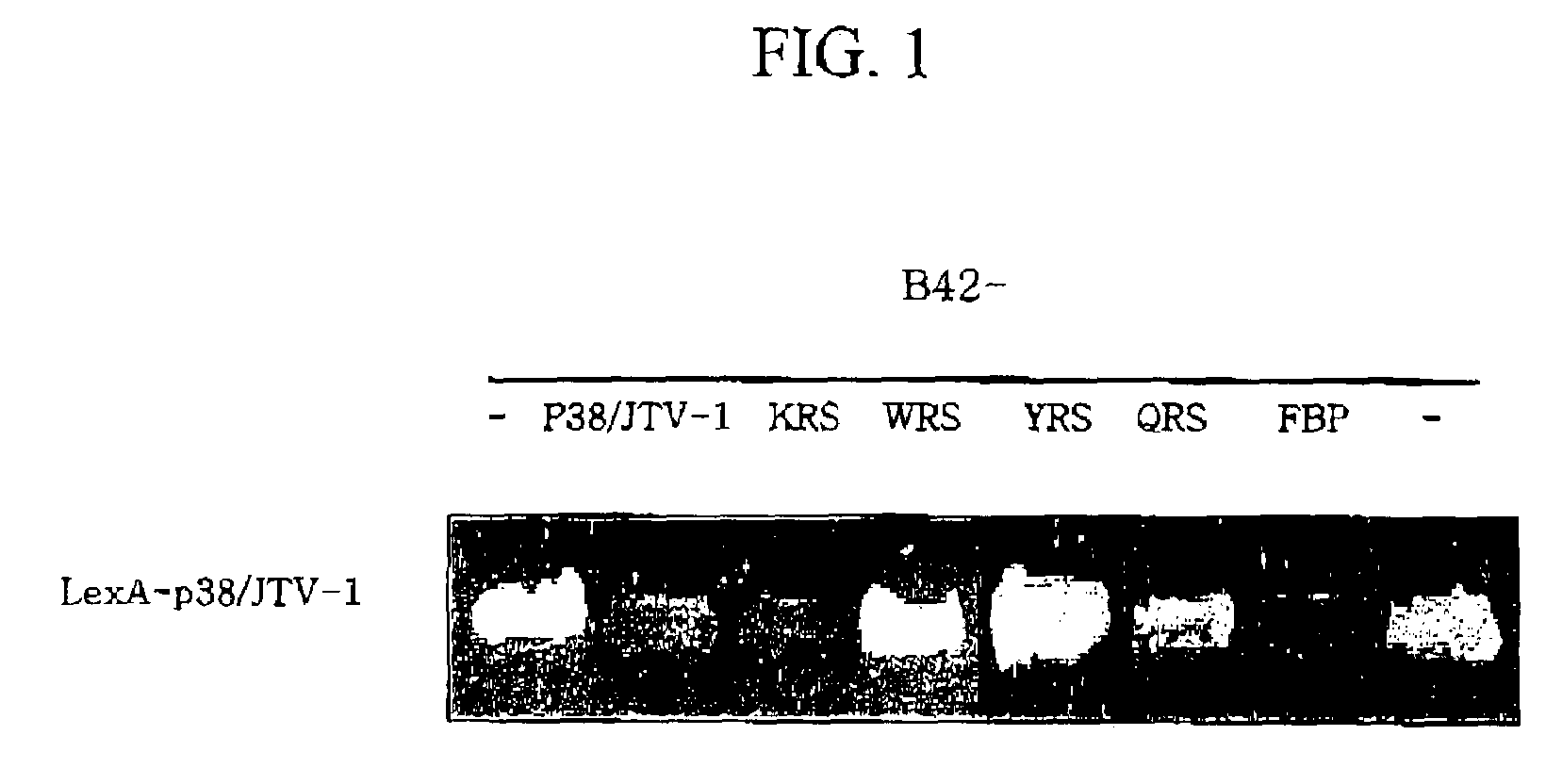
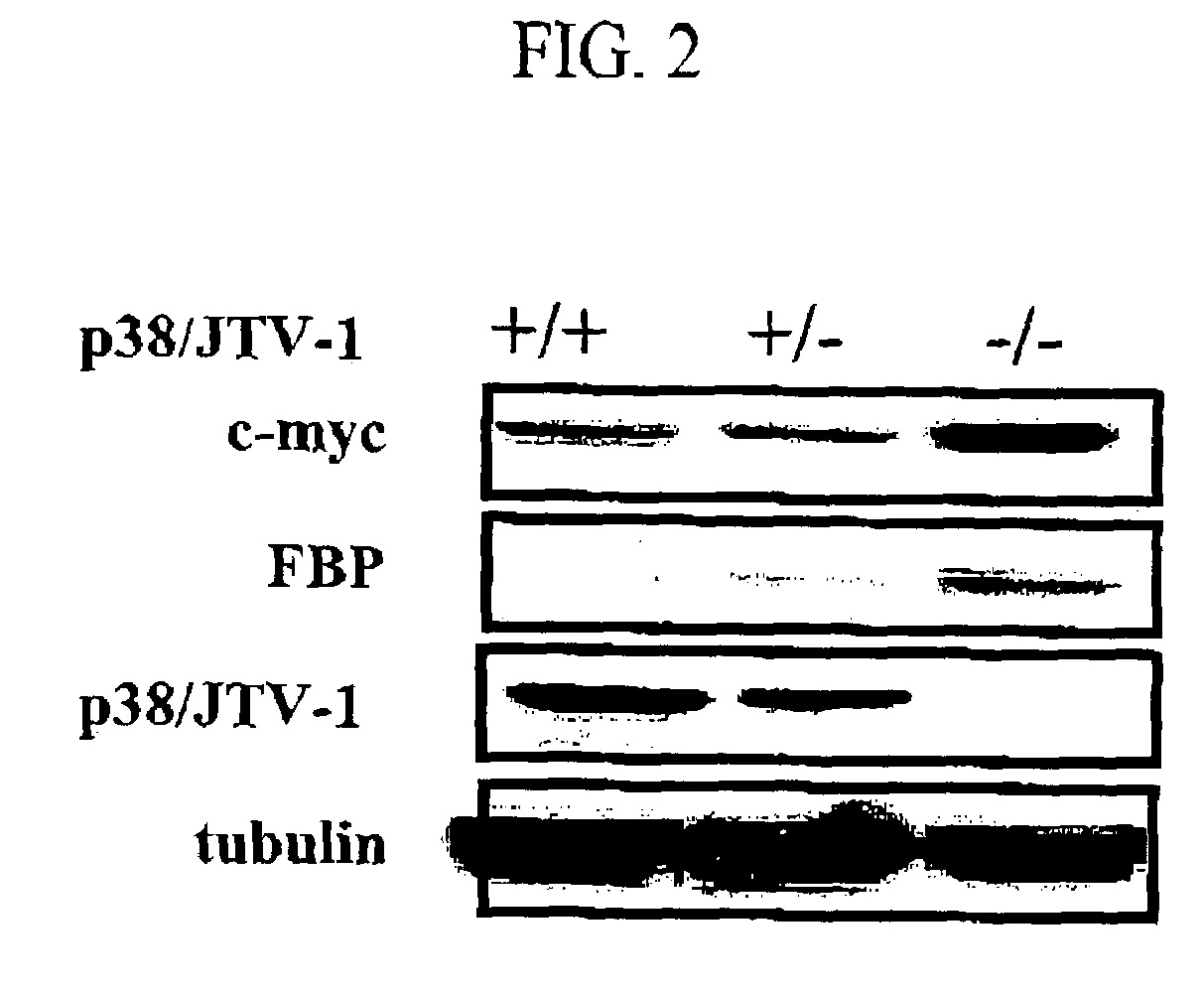
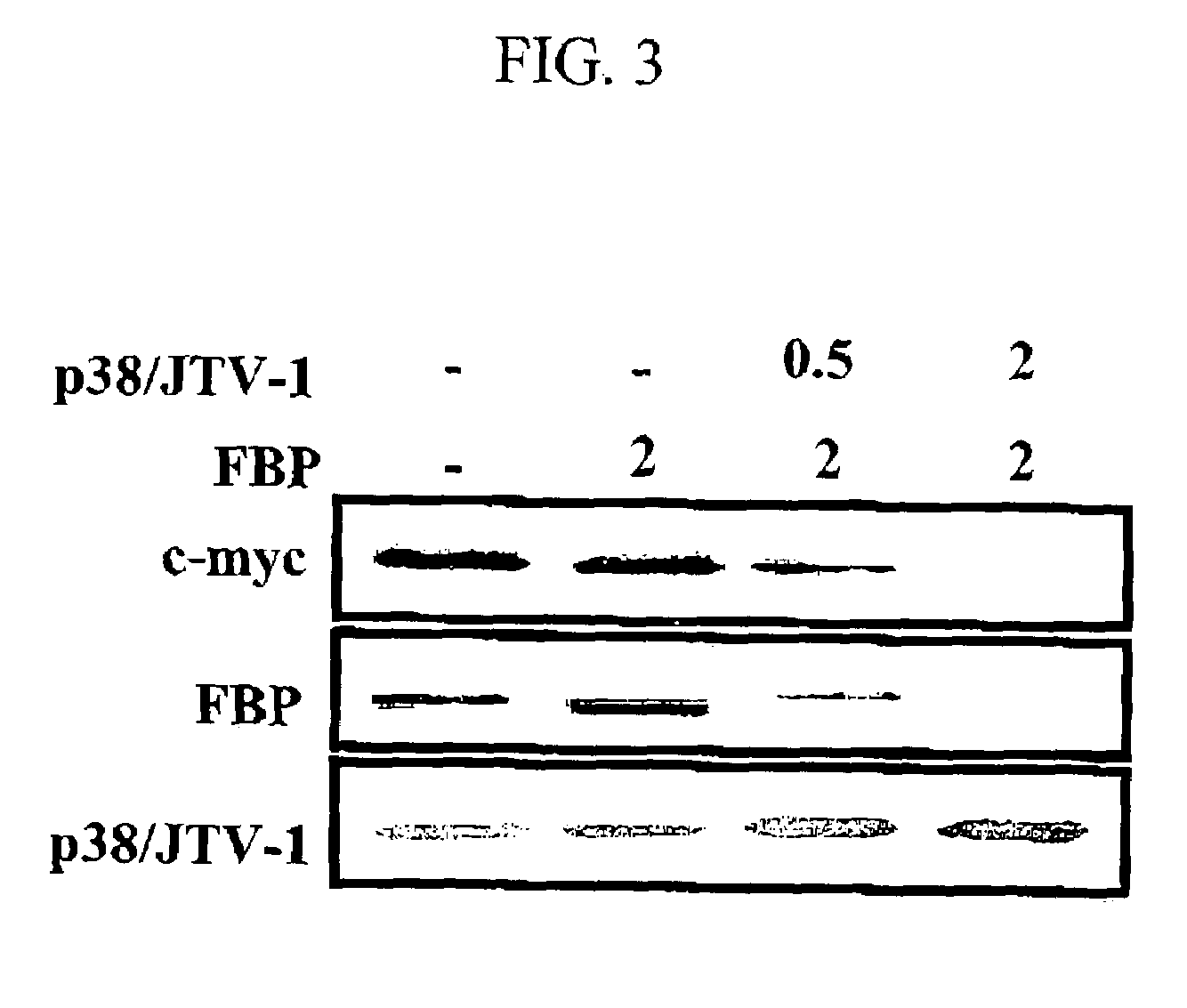
Method for treating cancer using p38/JTV-1 and method for screening pharmaceutical composition for treating cancer
The present invention relates to a method for treating cancer using p38 / JTV-1 and a method for screening pharmaceutical composition for treating cancer. More particularly, this invention relates to the method for treating cancer, which comprises administering the effective amount of p38 / JTV-1 protein or a nucleic acid encoding for said protein to the patient and the method for screening a pharmaceutical composition for treating cancer characterized by selecting a substance having an effect on the increase of the activity of the p38 / JTV-1 protein and the intracellular level thereof.The method according to the invention can be effectively used to treat cancer through the mechanism of suppressing the proliferation of cancer cells by binding to FBP (FUSE-binding protein) and thereby promoting the ubiquitination of FBP to downregulate c-myc gene, which is a proto-oncogene, and the mechanism of promoting the apoptosis of cells by binding to PDK-1 (phosphoinositide-dependent protein) and thereby inhibiting the phosphorylation of AKT (serine / threonine kinase). Also, p38 / JTV-1 can be used as a target for screening of new anticancer agents, by virtue of such regulation mechanisms of p38 / JTV-1.
Owner:MEDICINAL BIOCONVERGENCE RES CENT
Botanical extract compositions and methods of use
A composition having phytoestrogenic and anti-cancer activity is described. The composition comprises wogonin, isoliquiritigenin, coumestrol, their pharmaceutically acceptable salts or esters, their selectively substituted analogs, or combinations thereof. The compositions may also include an anti-cancer agent and / or an immune stimulant. A method for treating or preventing cancer or an estrogen-related disorder includes administering a therapeutically effective amount of the compositions is described. The compositions are particularly useful in the treatment of hormone-related cancers.
Owner:ACTIVEPHYTO TECH LTD
Combinations of signal transduction inhibitors
InactiveUS20050222163A1Promote growthPromote proliferationOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryAnticarcinogenCell Cycle Inhibition
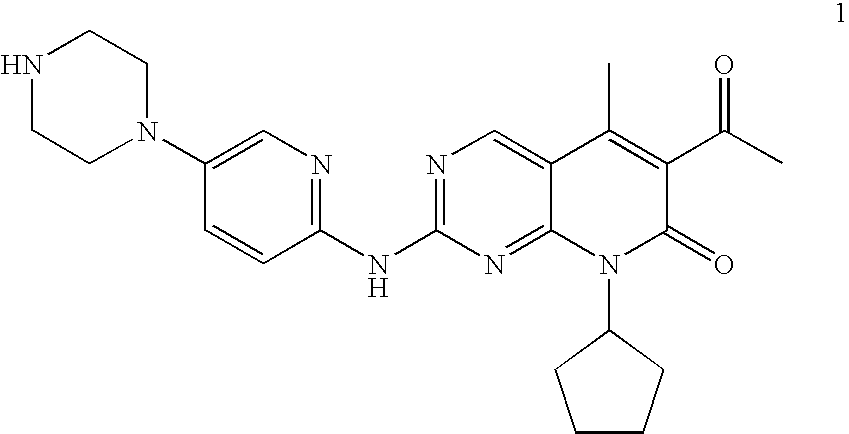
The present invention relates to methods for treating cancer comprising utilizing a combination of signal transduction inhibitors. More specifically, the present invention relates to combinations of so called cell cycle inhibitors with mitogen stimulated kinase signal transduction inhibitors, more specifically combinations of CDK inhibitors with mitogen stimulated kinase signal transduction inhibitors, more preferably MEK inhibitors. Other embodiments of the invention relate to additional combinations of the aforesaid combinations with standard anti-cancer agents such as cytotoxic agents, palliatives and antiangiogenics. Most specifically this invention relates to combinations of 6-acetyl-8-cyclopentyl-5-methyl-2-(5-piperazin-1-yl-pyridin-2-ylamino)-8H-pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7-one including salt forms, which is a selective cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4) inhibitor, in combination with one or more MEK inhibitors, most preferably N-[(R)-2,3-dihydroxy-propoxy]-3,4-difluoro-2-(2-fluoro-4-iodo-phenylamino)-benzamide. The aforementioned combinations are useful for treating inflammation and cell proliferative diseases such as cancer and restenosis.
Owner:PFIZER INC
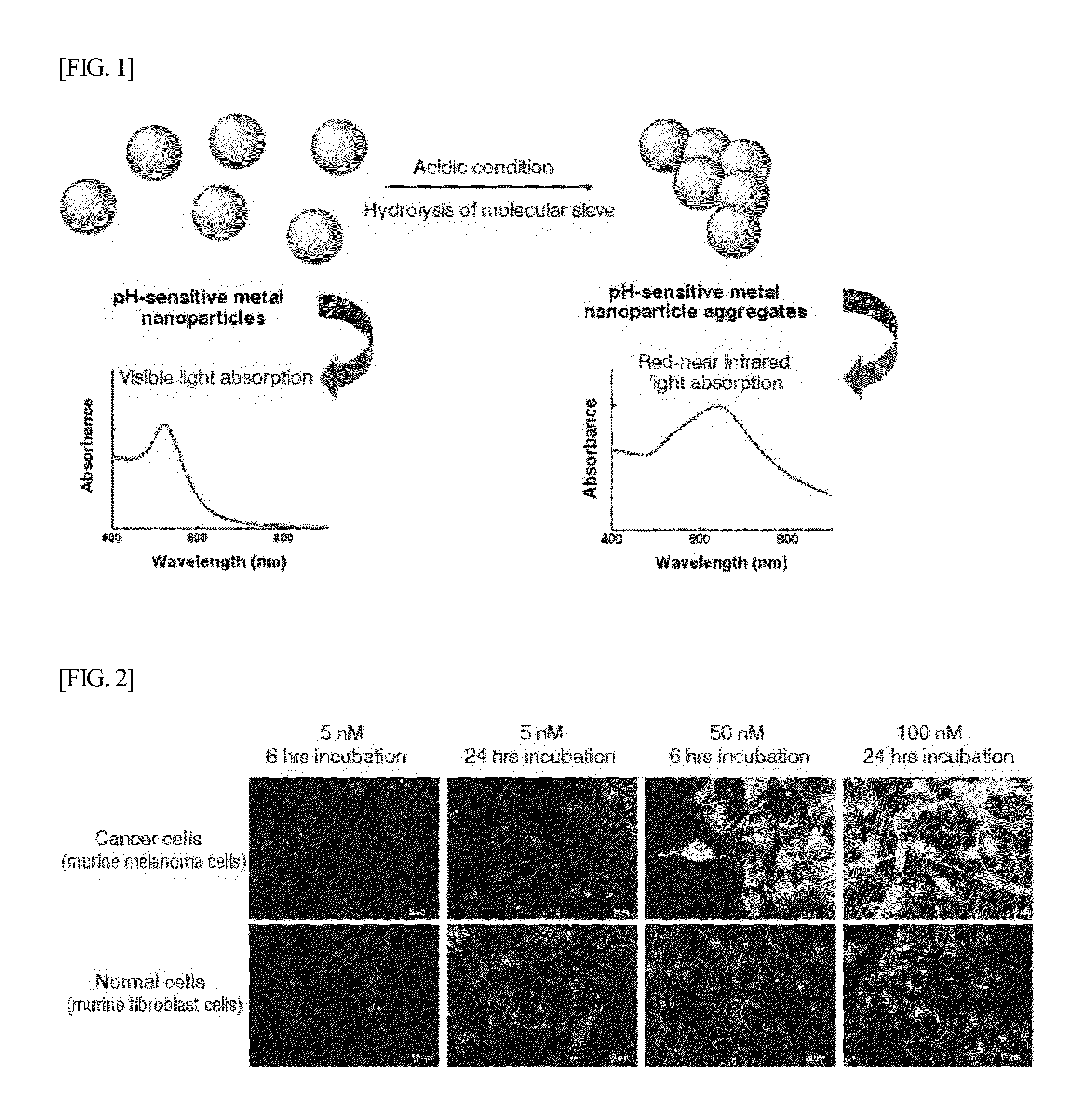
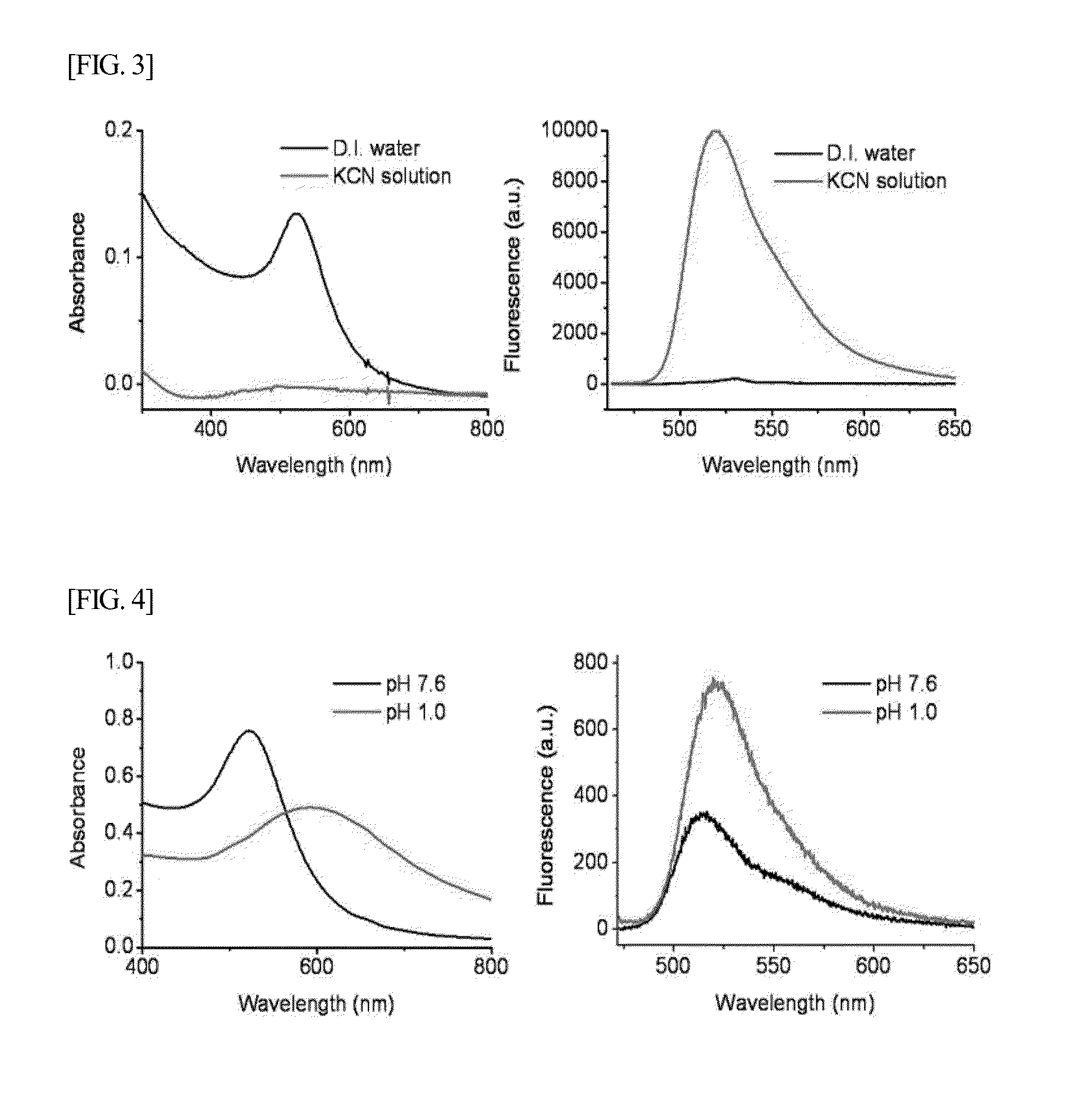
ANTICANCER AGENT DELIVERY SYSTEM USING pH-SENSITIVE METAL NANOPARTICLES
ActiveUS20130138032A1Minimal damageGood curative effectPowder deliveryBiocideAnticarcinogenCancer cell
The present invention relates to a method for effectively delivering an anticancer drug into cancer cells by binding the anticancer drug to pH-sensitive metal nanoparticles so as to be separated from cancer cells. The pH-sensitive metal nanoparticles according to the present invention may be heated by photothermal therapy, thereby effectively killing cancer cells in conjunction with the isolated anticancer drug.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
Methods and compositions for modulating cell proliferation and cell death
InactiveUS6599912B1Enhance in vitroImprove in vivo activityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAnticarcinogenTopoisomerase-II Inhibitor
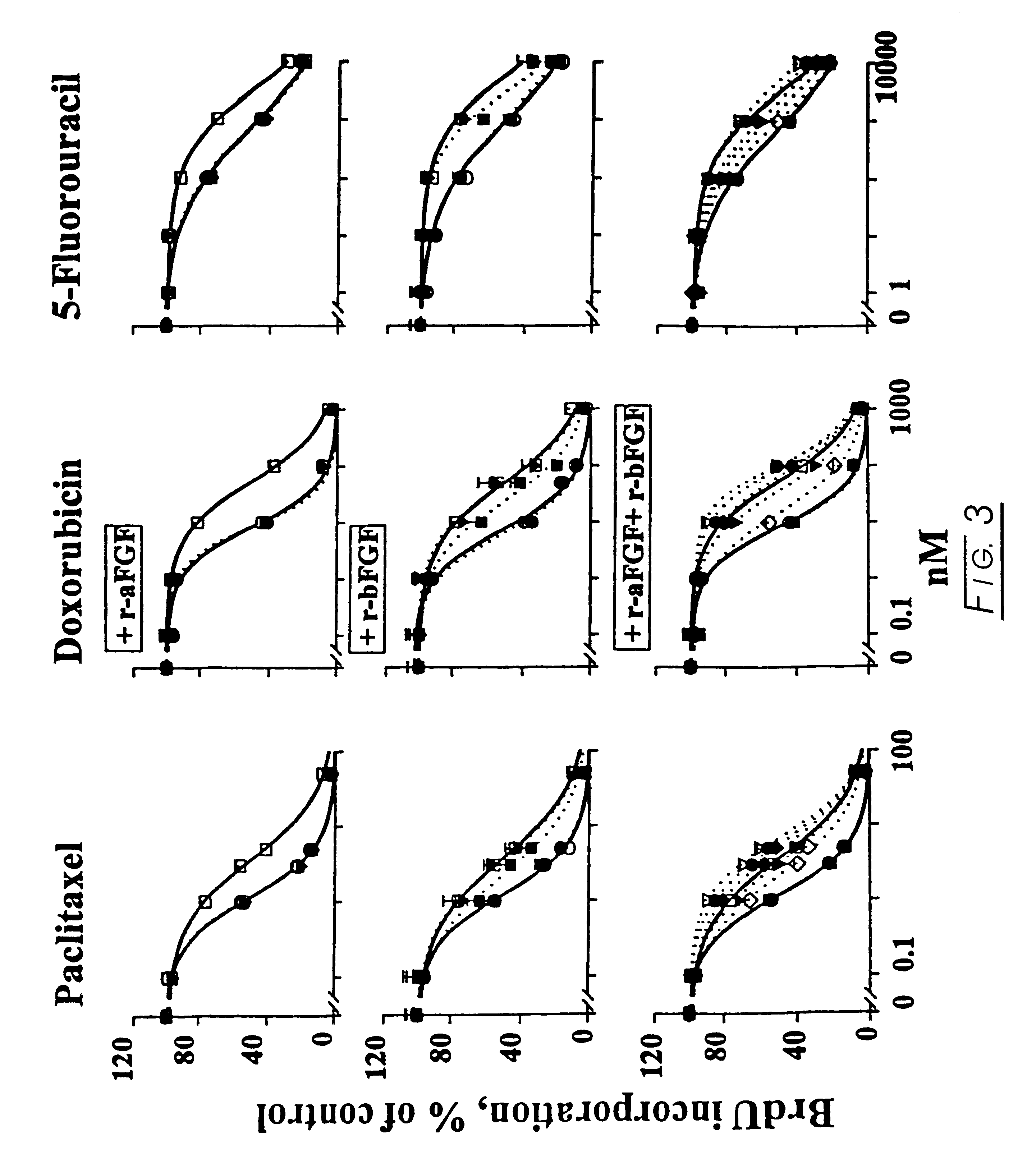
Methods and compositions for modulating the FGF effect on the sensitivity of malignant and normal cells to anticancer agents are provided. In particular, methods and compositions for inhibiting FGF-induced resistance to a broad spectrum of anticancer agents in solid and soft-tissue tumors, metastatic lesions, leukemia and lymphoma are provided. Preferably, the compositions include at least one FGF inhibitor in combination with a cytotoxic agents, e.g., antimicrotubule agents, topoisomerase I inhibitors, topoisomerase II inhibitors, antimetabolites, mitotic inhibitors, alkylating agents, intercalating agents, agents capable of interfering with a signal transduction pathway (e.g., g., a protein kinase C inhibitor, e.g., an anti-hormone, e.g., an antibody against growth factor receptors), an agent that promotes apoptosis and / or necrosis, and interferon, an interleukin, a tumor necrosis factor, and radiation. In other embodiments, methods and composition for protecting a cell in a subject, from one or more of killing, inhibition of growth or division or other damage caused, e.g., by a cytotoxic agent, are provided. Preferably, the method includes: administering, to the subject, an effective amount of at least one FGF agonist, thereby treating the cell, e.g., protecting or reducing the damage to the dividing cell from said cytotoxic agent.
Owner:AU JESSIE L S +1
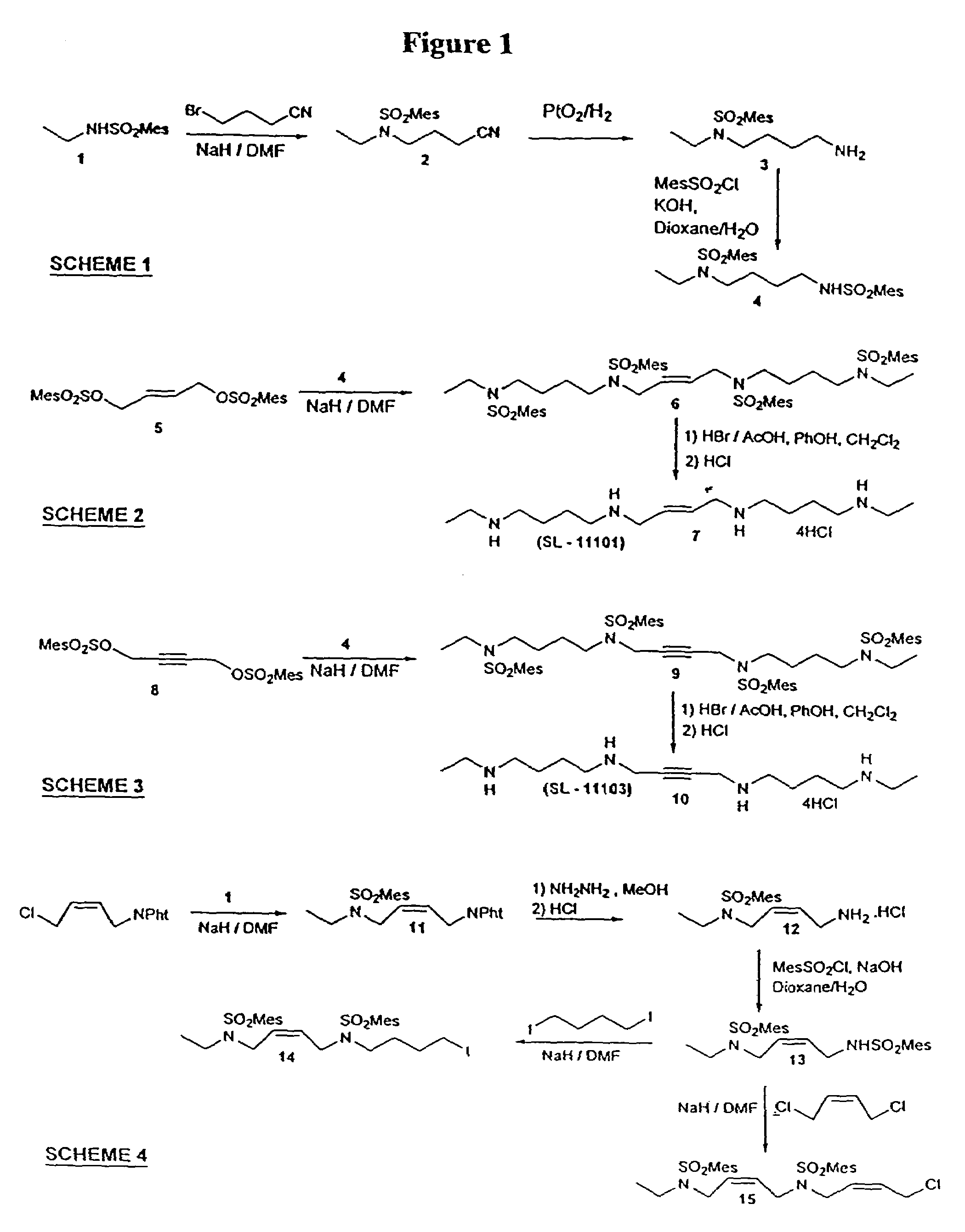
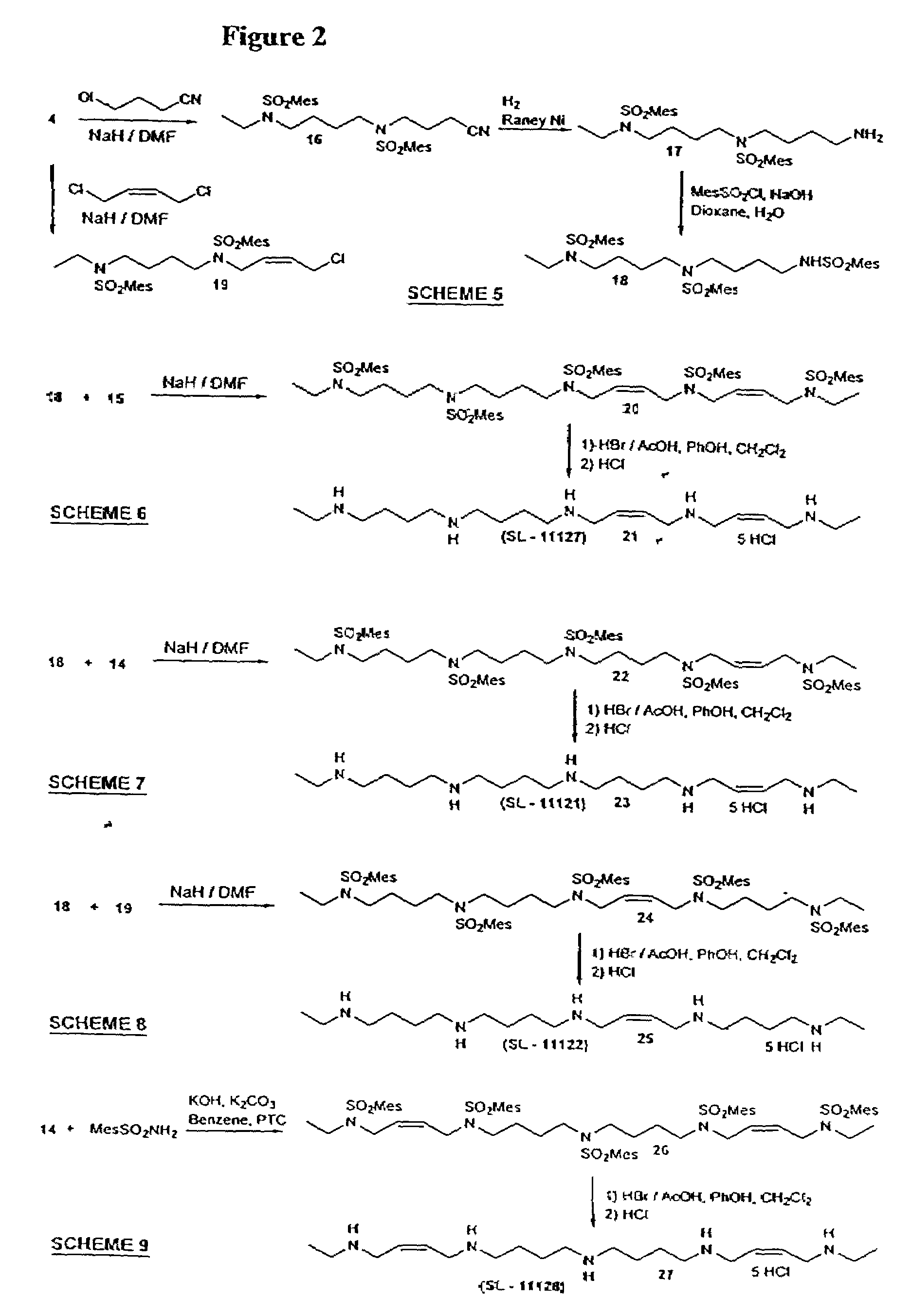
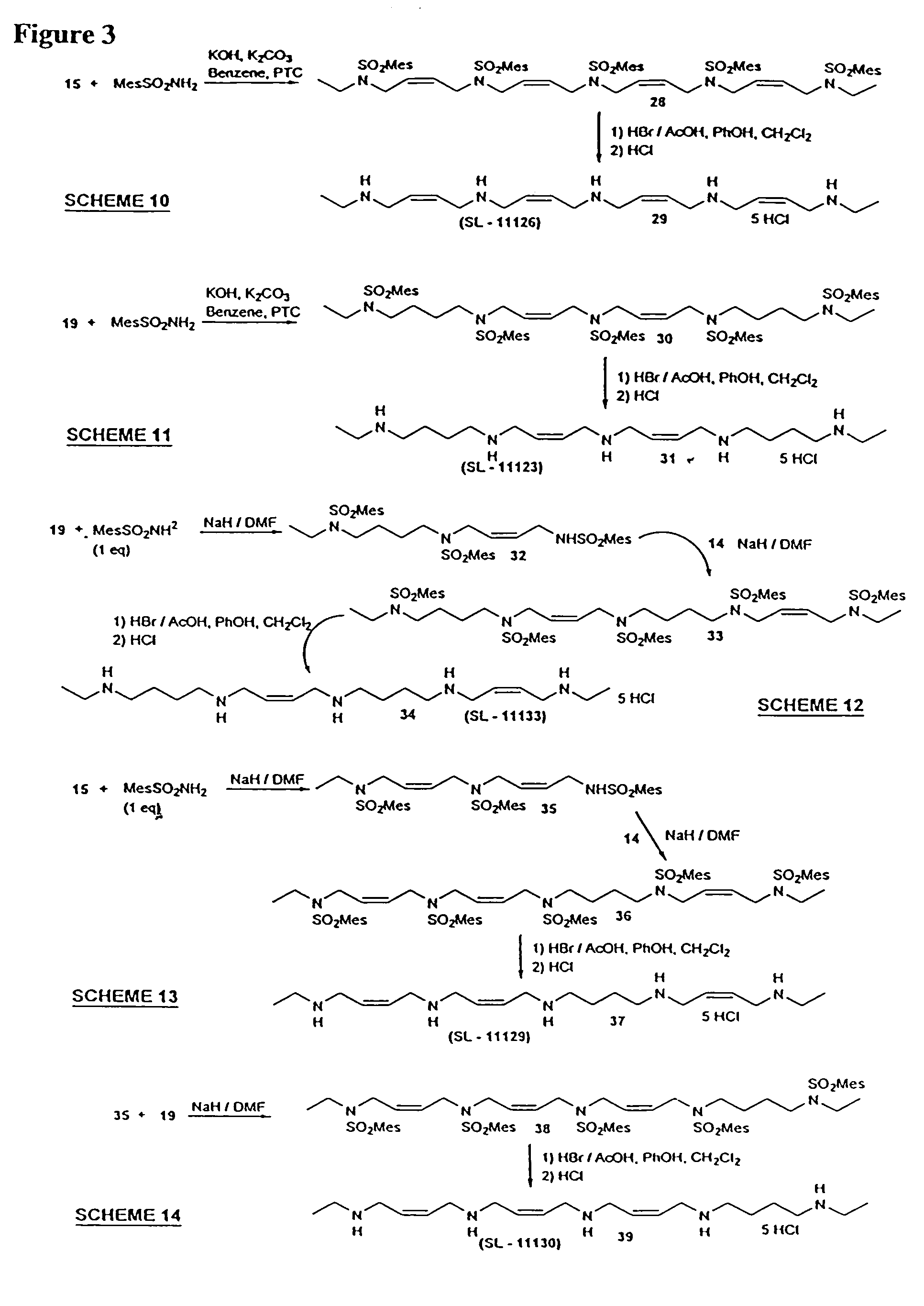
Polyamine analog-amino acid conjugates useful as anticancer agents
Conjugates in which polyamine analogs are conjugated to an amino acid are provided, as well as compositions comprising these conjugates. Methods of using these conjugates as anticancer treatments are also provided.
Owner:CELLGATE
Anticancer Effect Enhancer
InactiveUS20080039521A1Good treatment effectBiocideUrinary disorderAnticarcinogenAdditive ingredient
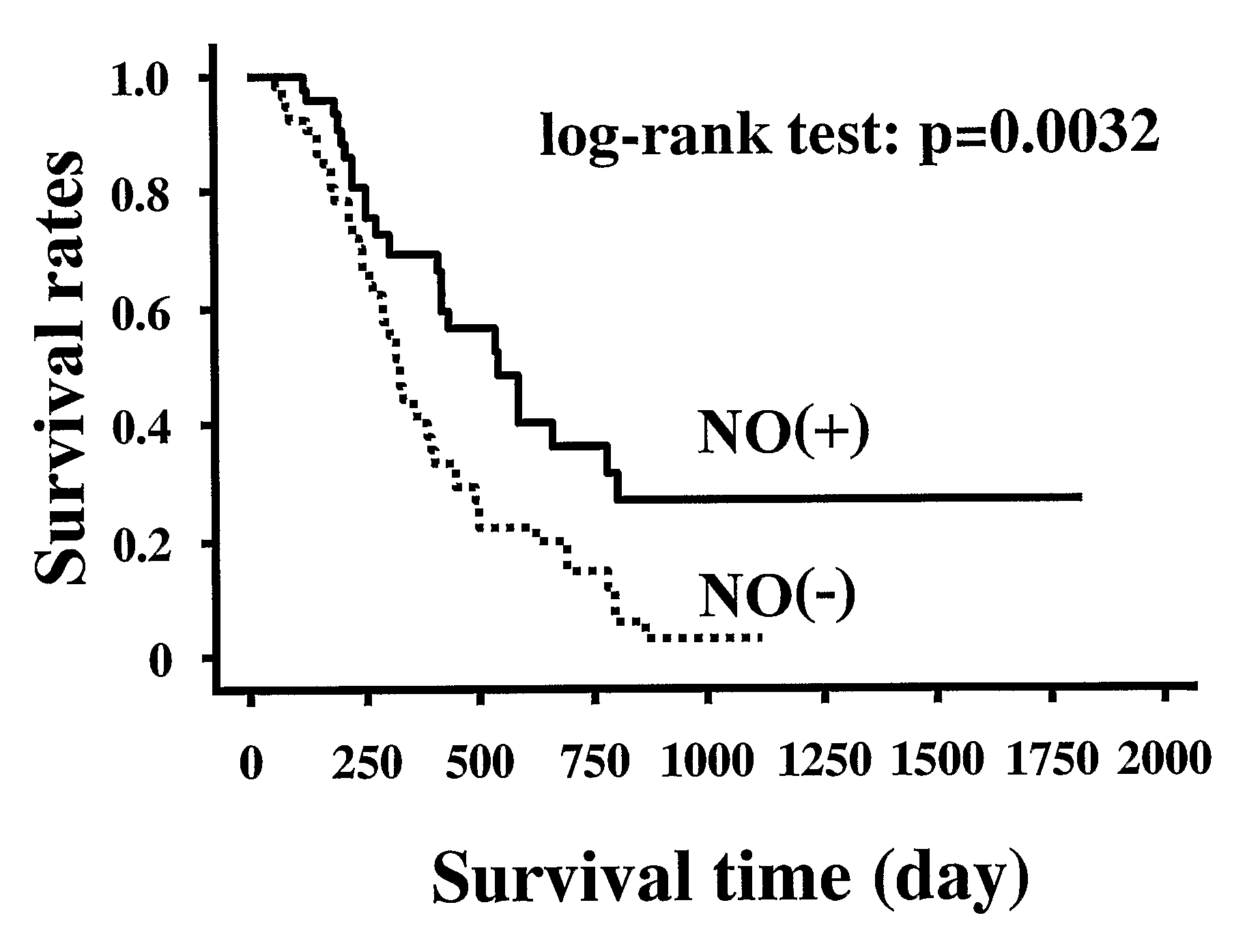
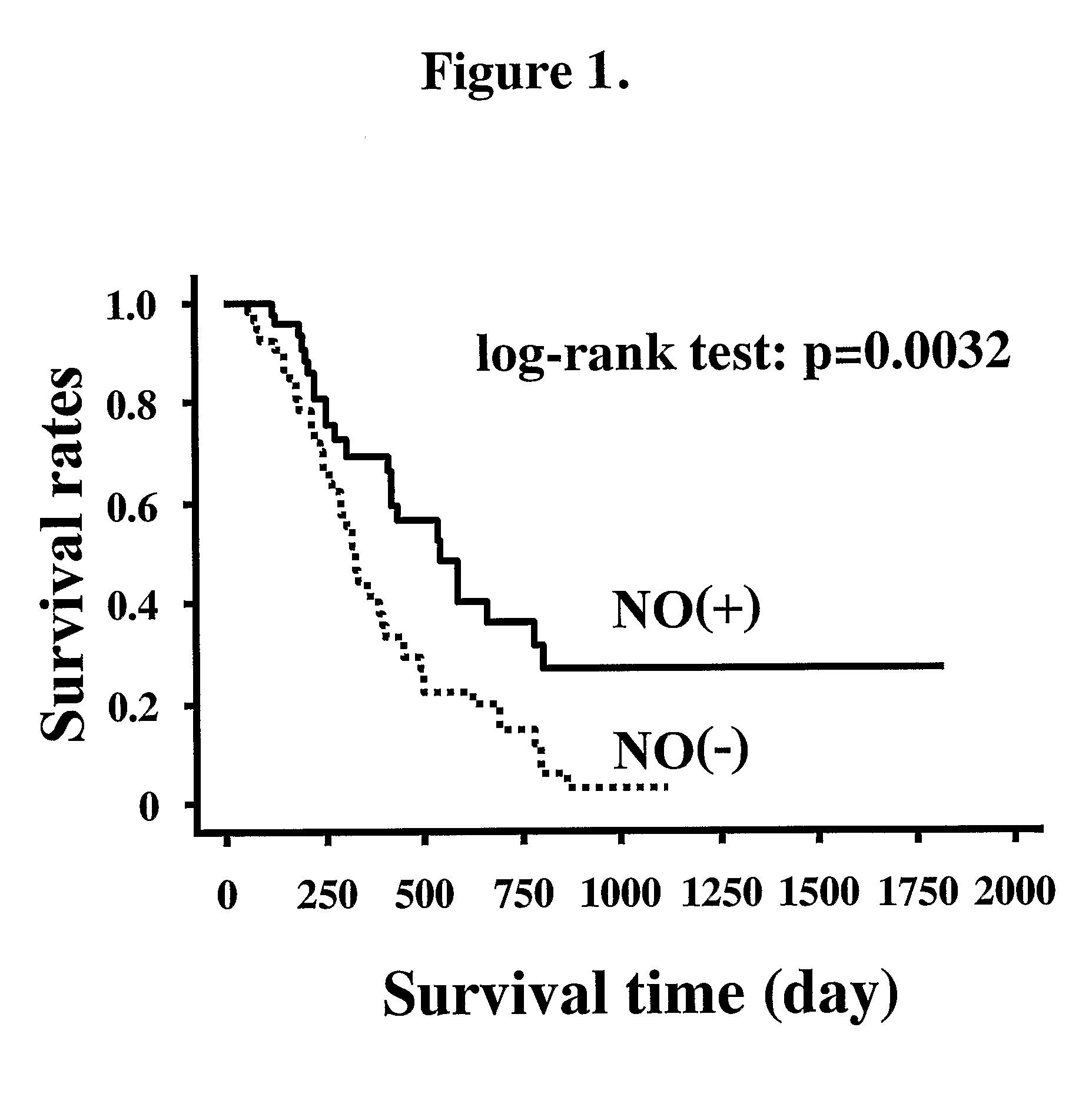
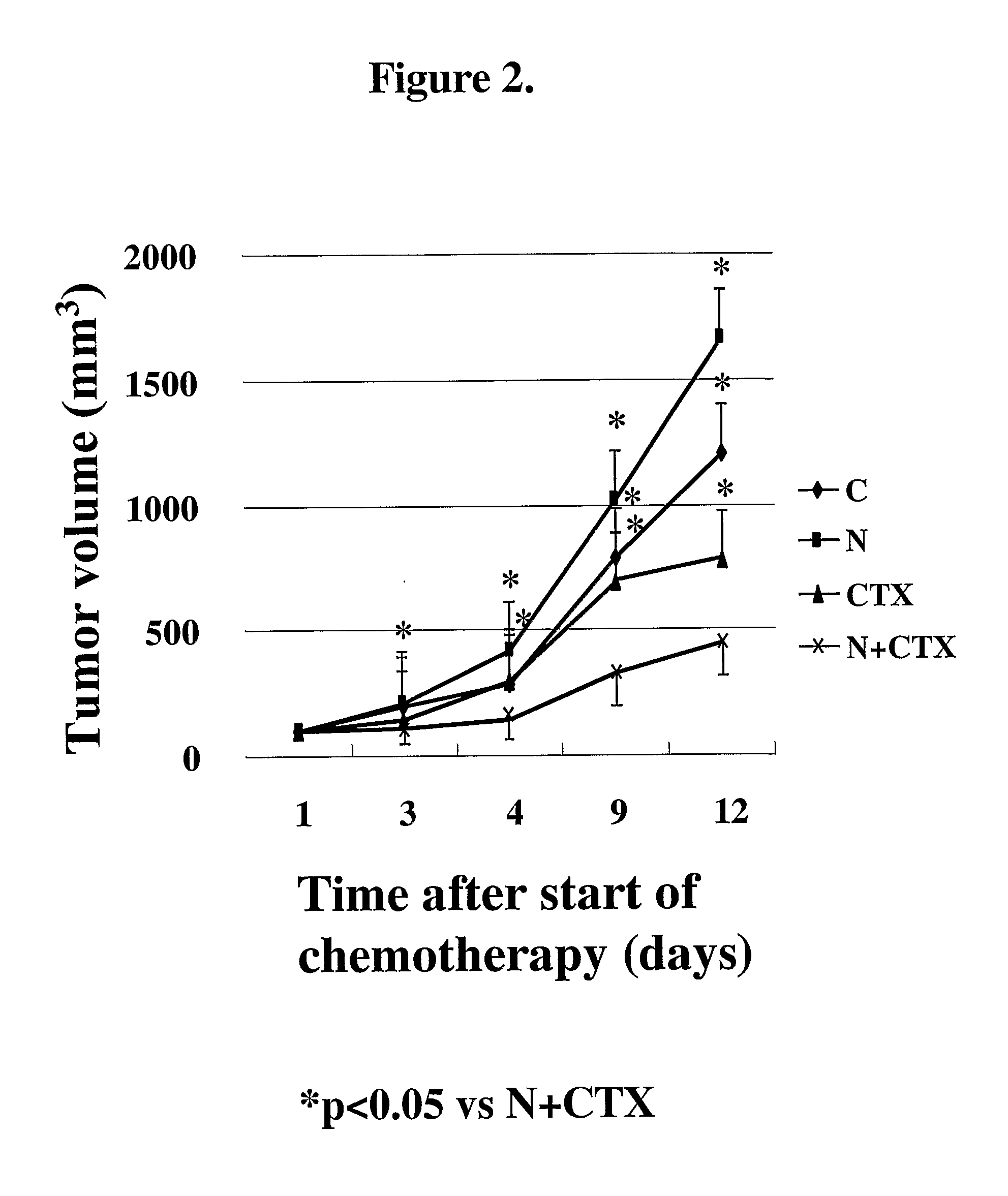
An object of the present invention is to provide an enhancing agent for effect of anticancer agent for achieving an excellent therapeutic effect on cancer. The enhancing agent for effect of anticancer agent according to the present invention which is a solving means therefor is characterized in that a nitric oxide donor is an effective ingredient. In accordance with the present invention, an excellent therapeutic effect is able to be achieved on non-small cell lung cancer which is still in such a state that no effective therapeutic method has been established yet for a progressive cancer which is not operable and is one of cancers where chemotherapy is most difficult to apply.
Owner:NIPPON KAYAKU CO LTD
Anti-glypican 3 antibody
An antibody capable of binding to a specific region of glypican 3, as well as a humanized antibody created based on that antibody are disclosed. The anti-GPC3 antibody of the invention has a higher ADCC activity and CDC activity compared with those of a conventional antibody. The antibody of the present invention is useful as a cell growth inhibitor, an anticancer agent and an agent for diagnosis of cancers.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Medicinal compositions for concomitant use as anticancer agent
InactiveUS20030215523A1Good synergyEliminate side effectsHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideCarboplatinAnticarcinogen
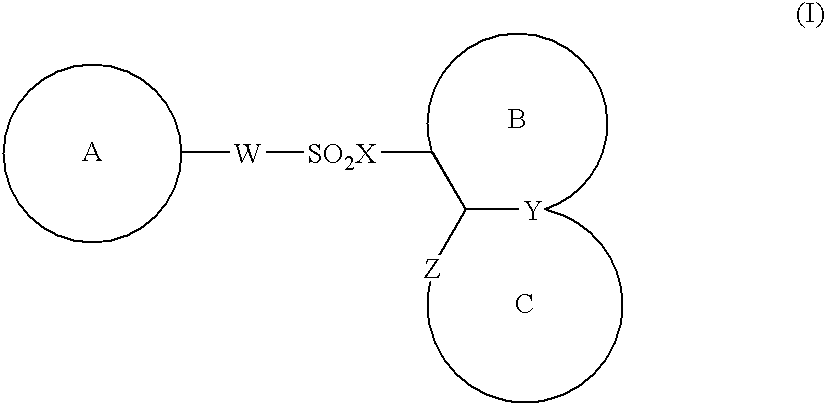
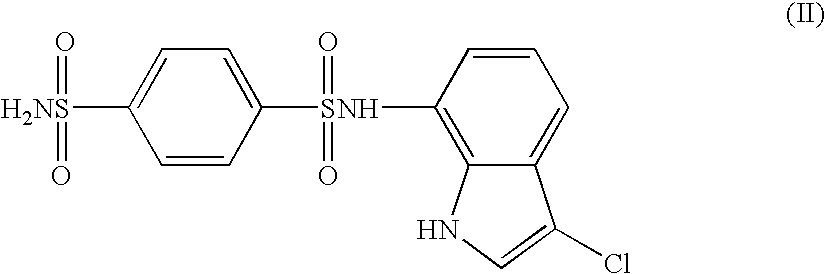
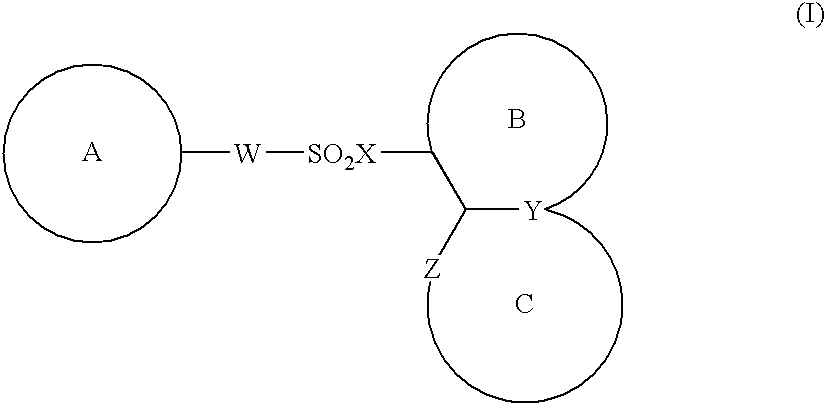
The present invention provides a medicinal composition having an excellent antitumor activity. That is, it provides a medicinal composition comprising a sulfonamide compound, a sulfonate compound or a salt of them, which is represented by the following formula: (wherein ring A represents an aromatic ring which may have a substituent group; ring B represents a 6-membered unsaturated hydrocarbon ring which may have a substituent group etc.; ring C represents a 5-membered hetero-ring containing one or two nitrogen atoms, and the ring C may have a substituent group; W represents a single bond or -CH=CH-; X represents -NH- etc.; and Y represents a carbon atom or a nitrogen atom; and Z represents -NH- etc.), particularly N-(3-chloro-1H-indol-7-yl)-4-sulfamoylbenzenesulfonamide or a salt thereof, combined with at least one substance selected from (1) irinotecan hydrochloride trihydrate; (2) mitomycin C; (3) 5-fluorouracil; (4) cisplatin; (5) gemcitabine hydrochloride; (6) doxorubicin; (7) taxol; (8) carboplatin; (9) oxaliplatin; (10) capecitabine; and (11) a salt of the above-mentioned (1) to (10).
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
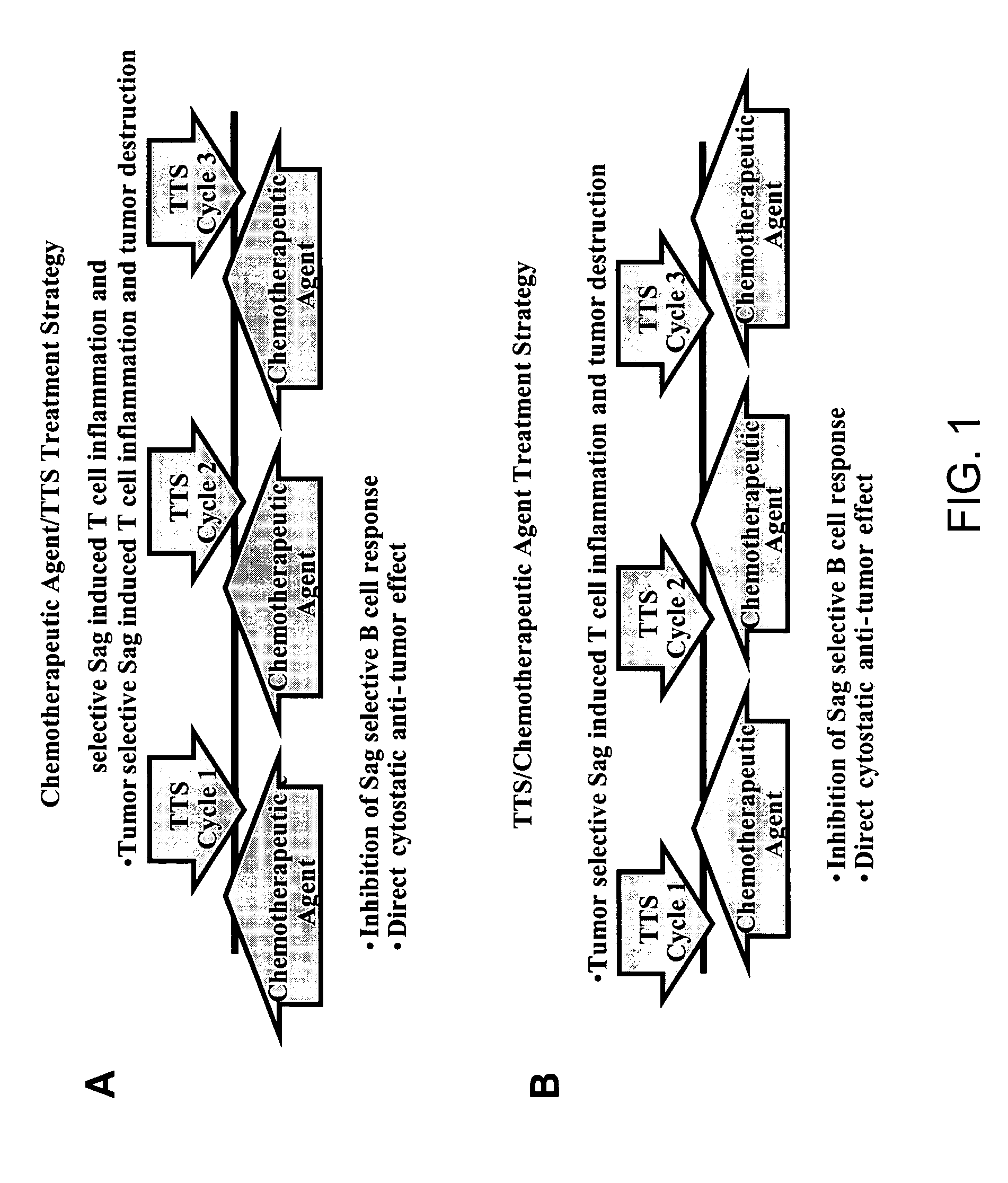
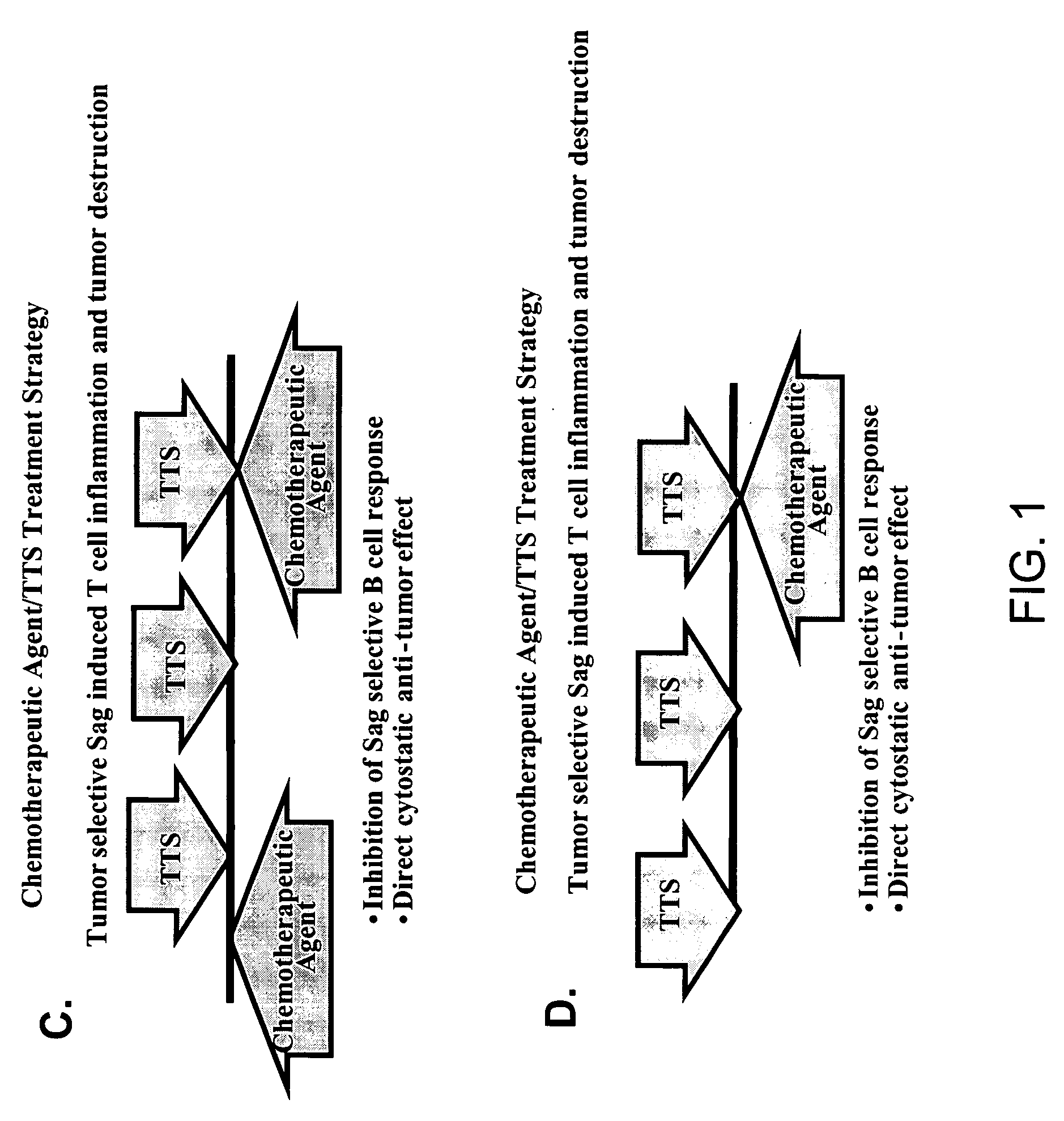
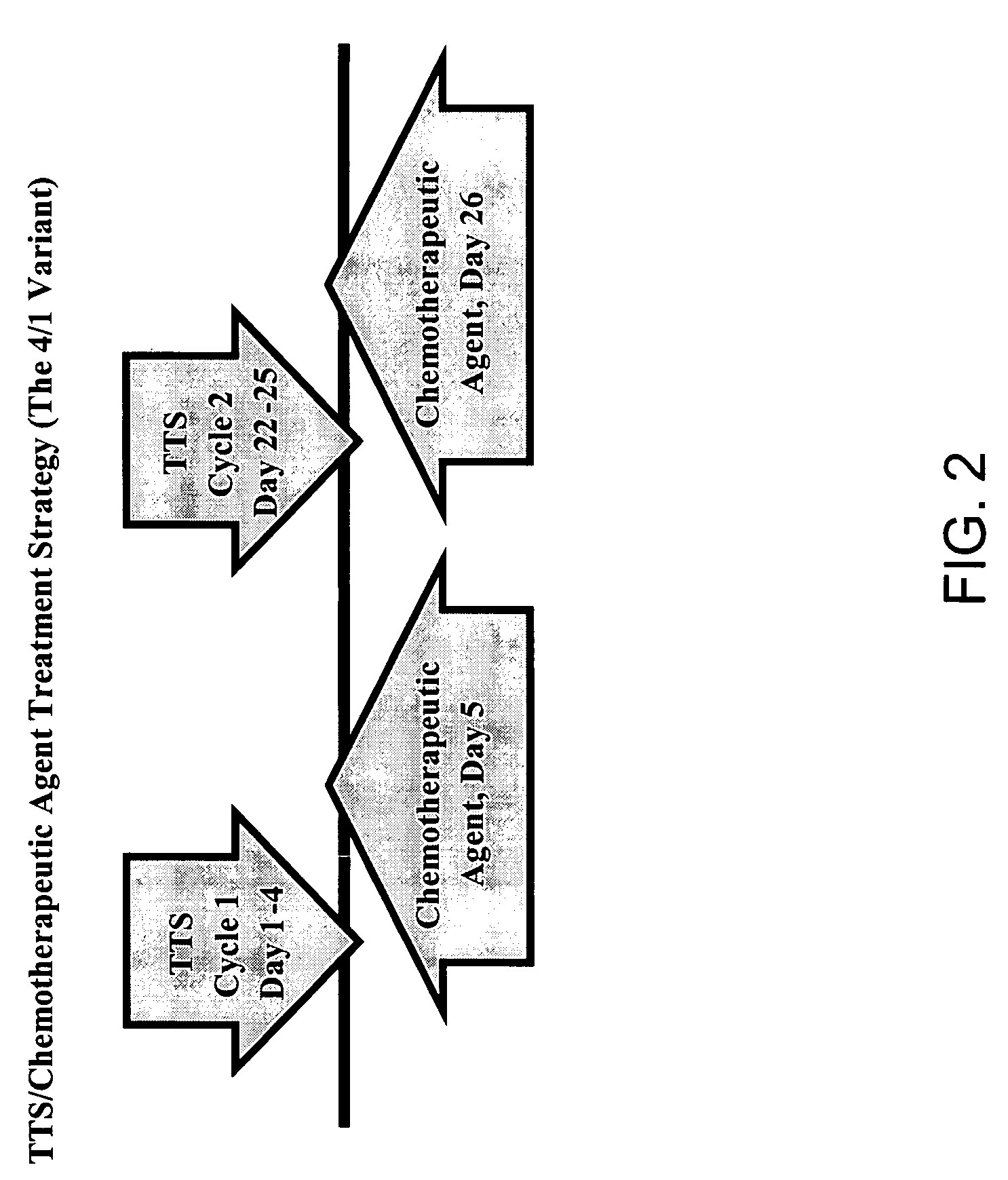
Treatment of hyperproliferative disease with superantigens in combination with another anticancer agent
ActiveUS20060057111A1Reduced antibody productionReduce productionBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsTumor targetDisease
The present invention relates to methods of treating mammals affected by, for example, a hyperproliferative disease such as cancer, by administering a tumor-targeted superantigen and a chemotherapeutic agent, whereby the administration of the tumor-targeted superantigen and chemotherapeutic agent reduce the antibody response and enhance the T cell response. The superantigen, wild-type or modified, is fused to a target-seeking moiety, such as an antibody or an antibody active fragment. The combined administration of a superantigen and a chemotherapeutic agent provides enhanced therapeutic effects in a treated animal.
Owner:ACTIVE BIOTECH AB
Combination anti-cancer therapy
InactiveUS20090263397A1Improve the level ofHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideLymphatic SpreadAnticarcinogen
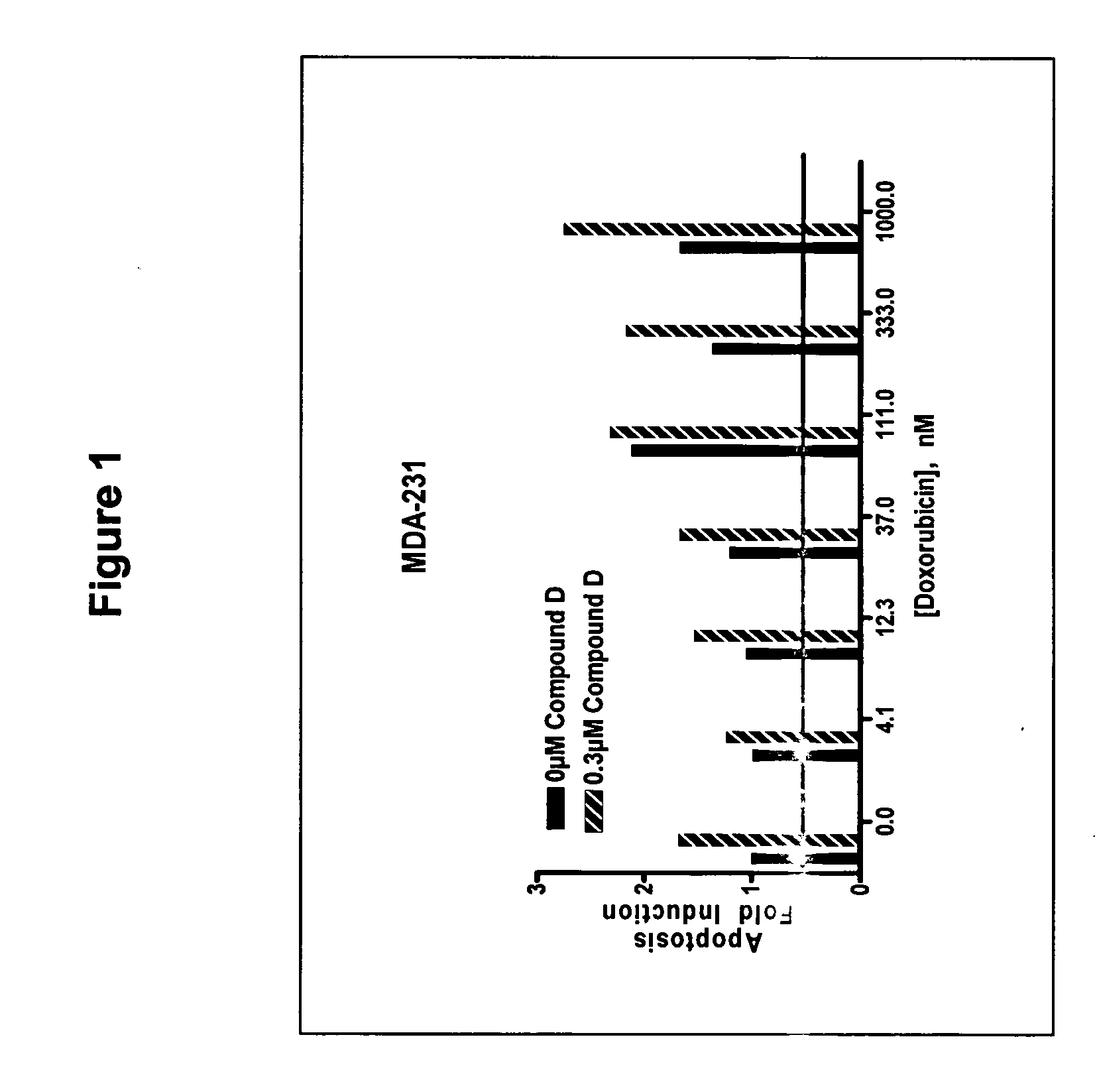
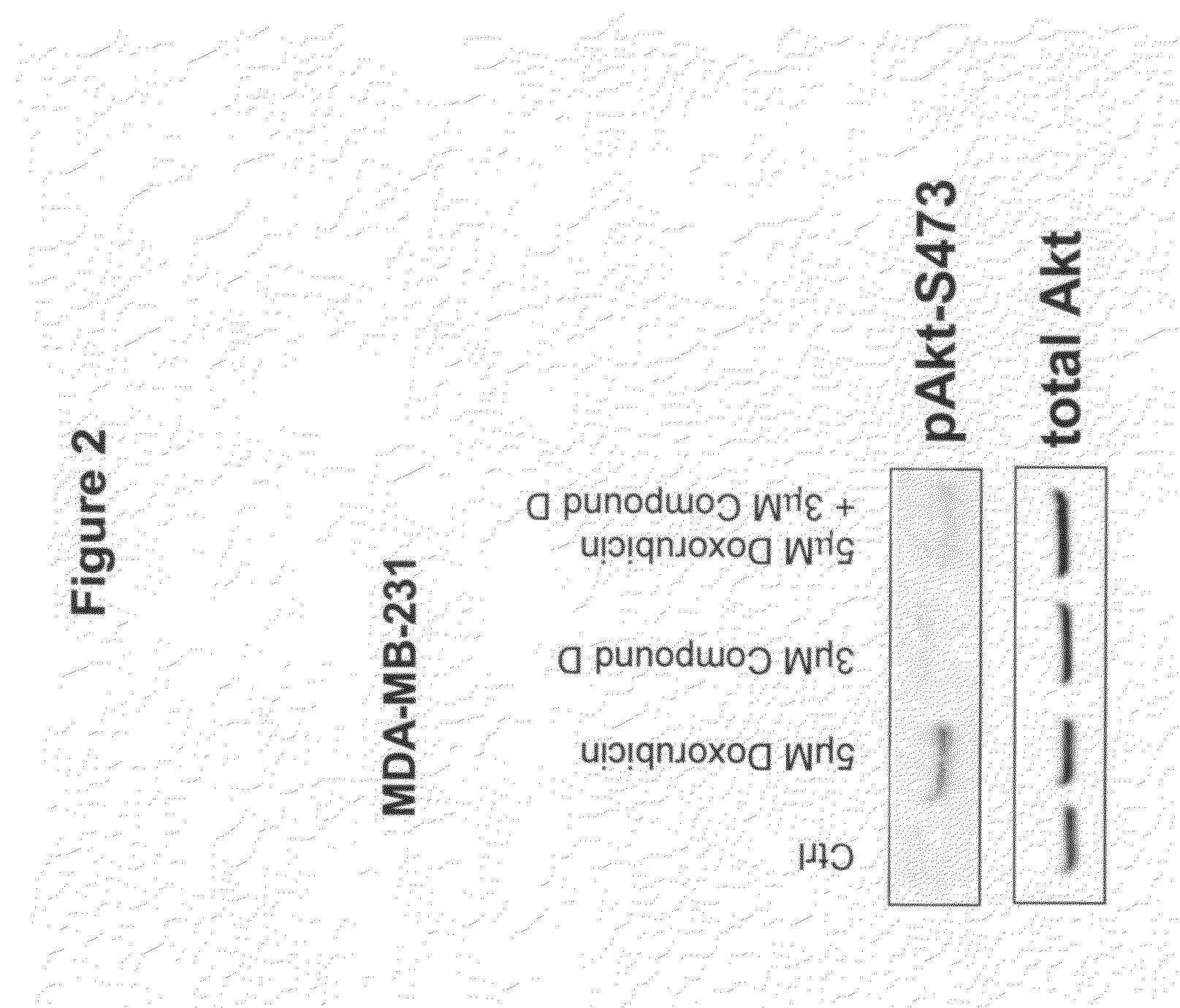
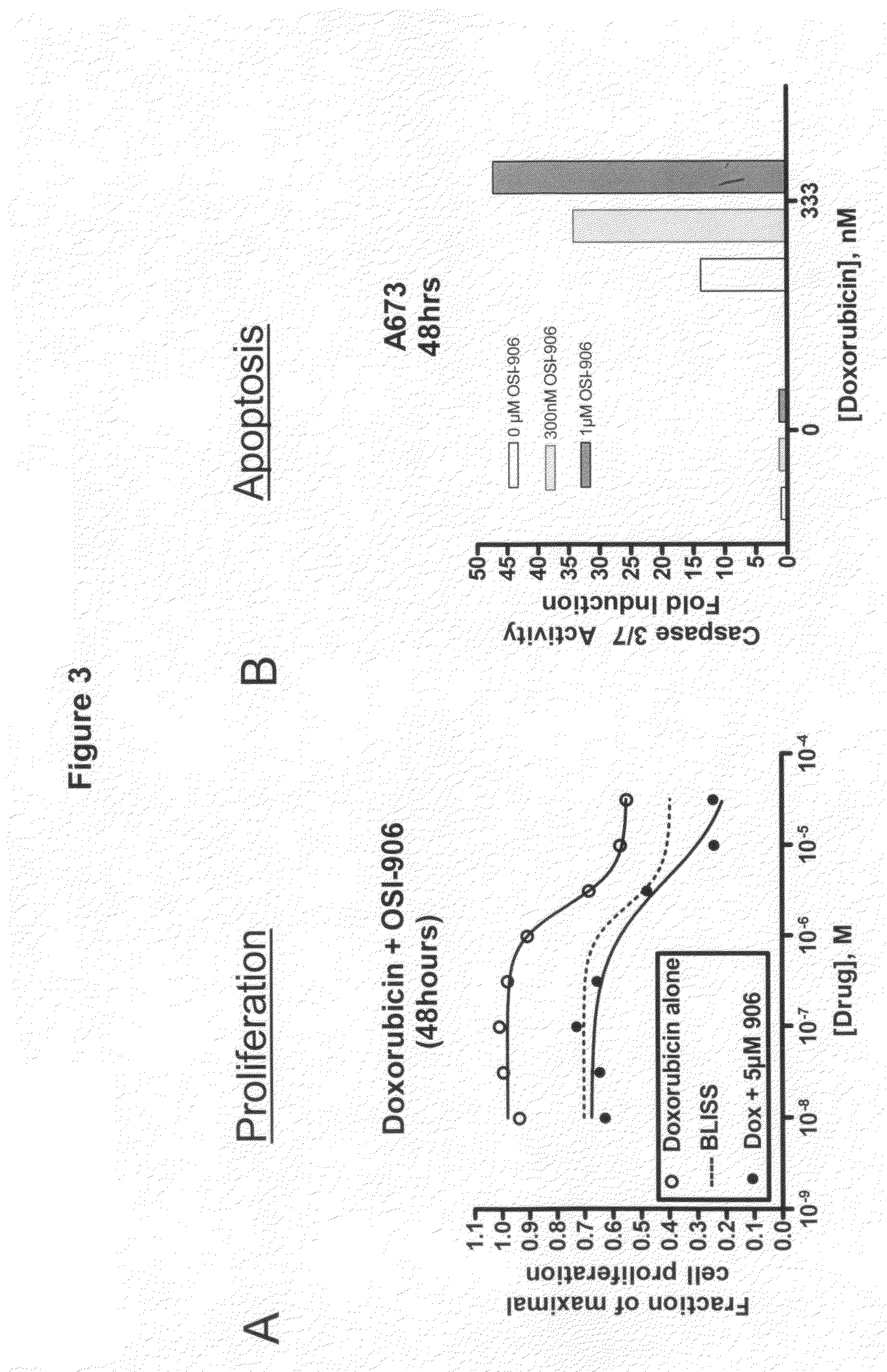
The present invention provides a method for treating tumors or tumor metastases in a patient, comprising administering to said patient simultaneously or sequentially a therapeutically effective amount of a combination of an anti-cancer agent or treatment that elevates pAkt levels in tumor cells and an IGF-1R kinase inhibitor of Formula (I) (e.g. OSI-906). Examples of such anti-cancer agents or treatments include doxorubicin, cisplatin, and ionizing radiation. The present invention also provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising an anti-cancer agent that elevates pAkt levels in tumor cells and an IGF-1R kinase inhibitor of Formula (I), in a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The present invention also provides a method of identifying tumor cells that will respond most favorably to treatment with a combination of an anti-cancer agent or treatment that elevates pAkt levels in tumor cells and an IGF-1R kinase inhibitor.
Owner:OSI PHARMA INC
Treatment of hyperproliferative disease with superantigens in combination with another anticancer agent
ActiveUS7763253B2Reduce productionImprove anti-tumor effectOrganic active ingredientsHeavy metal active ingredientsTumor targetAnticarcinogen
The present invention relates to methods of treating mammals affected by, for example, a hyperproliferative disease such as cancer, by administering a tumor-targeted superantigen and a chemotherapeutic agent, whereby the administration of the tumor-targeted superantigen and chemotherapeutic agent reduce the antibody response and enhance the T cell response. The superantigen, wild-type or modified, is fused to a target-seeking moiety, such as an antibody or an antibody active fragment. The combined administration of a superantigen and a chemotherapeutic agent provides enhanced therapeutic effects in a treated animal.
Owner:ACTIVE BIOTECH AB
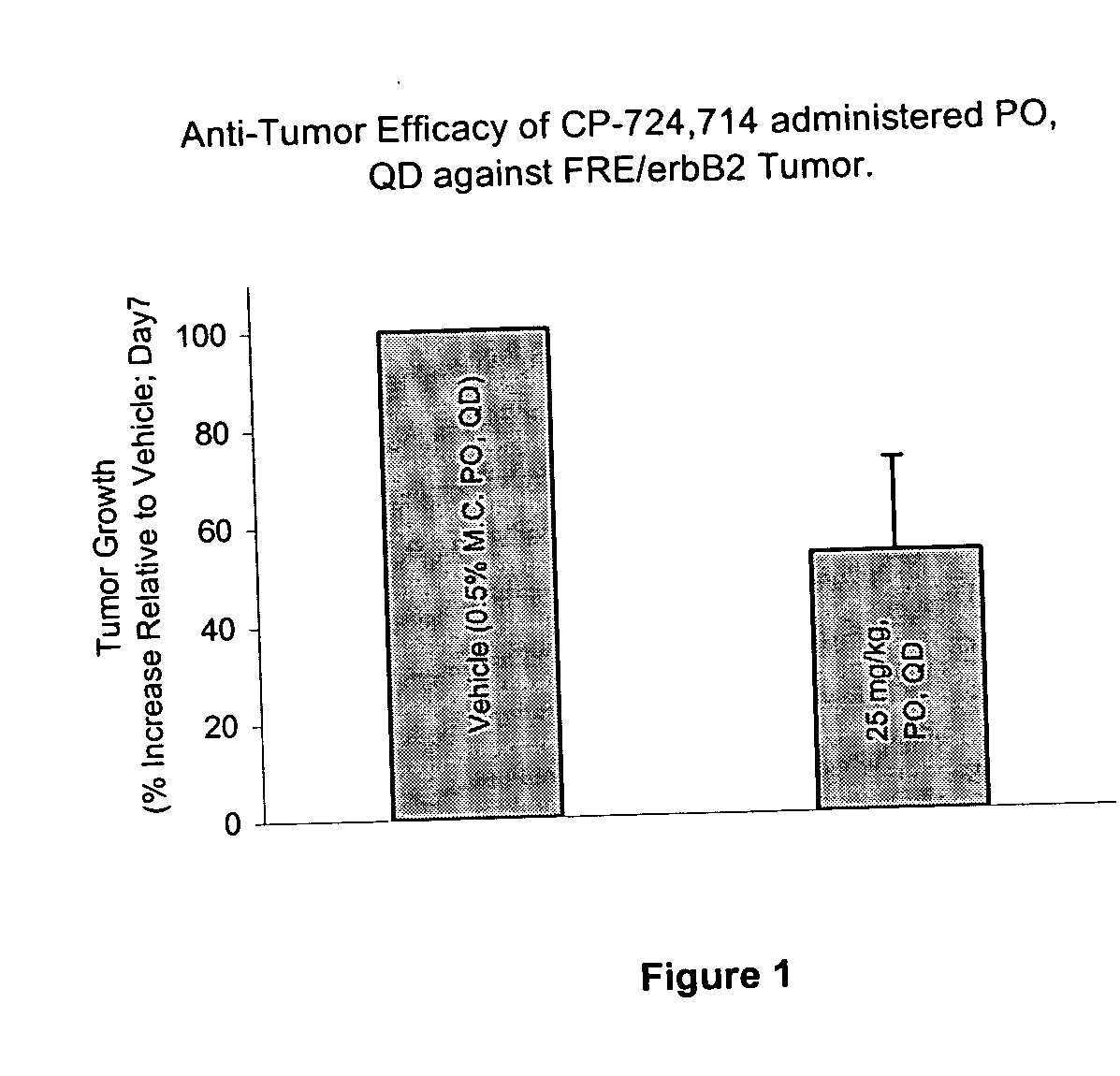
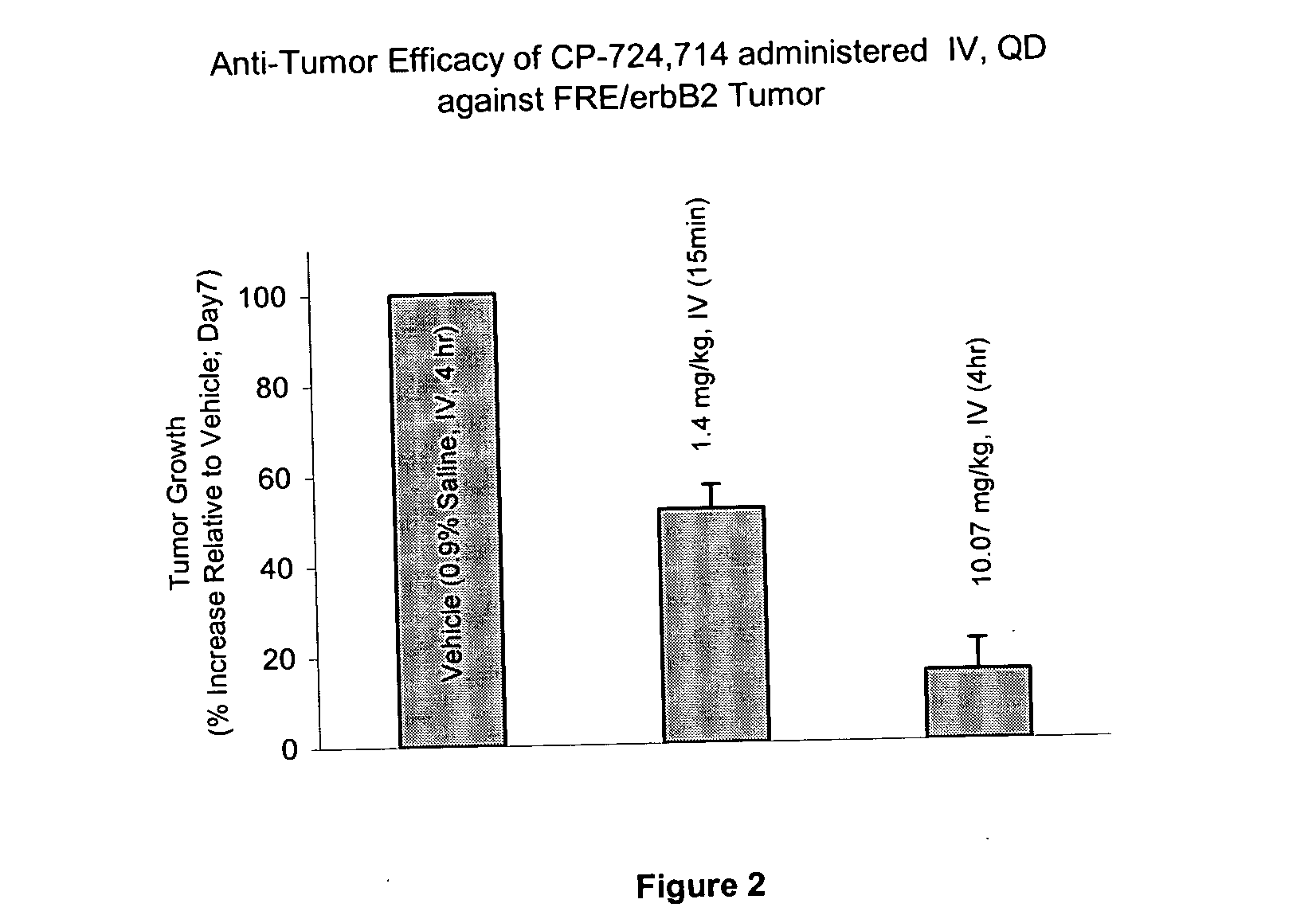
Dosing schedule for a novel anticancer agent
InactiveUS20050119288A1Low affinityMinimize consequencesBiocideOrganic active ingredientsAnticarcinogenMedicine
The invention is directed to methods for the a method for treating overexpression of the erbB2 in a mammal in need of treatment by administering to the mammal a therapeutically effective amount of a first inhibitor of an erbB2 receptor and then, after an interval of less than 24 hours, administering to the mammal from one to six therapeutically effective amounts of the same or different inhibitor of the erbB2 receptor. The invention is also directed to a slow daily infusion of the erbB2 inhibitor. The overexpression of the erbB2 receptor can result in abnormal cell growth and lead to cancer. By the methods of the invention, the efficacy and safety of the inhibitors is increased. The invention is also directed to kits for facilitating the dose administration method of the invention.
Owner:PFIZER INC
Nanoparticle comprising rapamycin and albumin as anticancer agent
The present invention features methods for treating, stabilizing, preventing, and / or delaying cancer by administering nanoparticles that comprise rapamycin or a derivative thereof. The invention also provides compositions (e.g., unit dosage forms) comprising nanoparticles that comprise a carrier protein and rapamycin or a derivative thereof. The invention further provides combination therapy methods of treating cancer comprising administering to an individual an effective amount of nanoparticles that comprise rapamycin or a derivative thereof and a second therapy.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Novel anti-IGF-IR antibodies and uses thereof
InactiveUS20080193445A1Stimulate interestPromote secretionMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against growth factorsDiseaseAnticarcinogen
The present invention relates to novel antibodies capable of binding specifically to the human insulin-like growth factor I receptor IGF-IR and / or capable of specifically inhibiting the tyrosine kinase activity of said IGF-IR receptor, especially monoclonal antibodies of murine, chimeric and humanized origin, as well as the amino acid and nucleic acid sequences coding for these antibodies. The invention likewise comprises the use of these antibodies as a medicament for the prophylactic and / or therapeutic treatment of cancers overexpressing IGF-IR or any pathology connected with the overexpression of said receptor as well as in processes or kits for diagnosis of illnesses connected with the overexpression of the IGF-IR receptor. The invention finally comprises products and / or compositions comprising such antibodies in combination with anti-EGFR antibodies and / or compounds and / or anti-cancer agents or agents conjugated with toxins and their use for the prevention and / or the treatment of certain cancers.
Owner:INST DE RECH PIERRE FABRE +1
Method for preparing cell cultures from biological specimens for chemotherapeutic and other assays
InactiveUS6887680B2Promote growthMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism separationParticulatesAnticarcinogen
An improved system for screening a multiple of candidate therapeutic or chemotherapeutic agents for efficacy as to a specific patient, in which a tissue sample from the patient is harvested, cultured and separately exposed to a plurality of treatments and / or therapeutic agents for the purpose of objectively identifying the best treatment or agent for the particular patient. Specific method innovations such as tissue sample preparation techniques render this method practically as well as theoretically useful. One particularly important tissue sample preparation technique is the initial preparation of cohesive multicellular particulates of the tissue sample, rather than enzymatically dissociated cell suspensions or preparations, for initial tissue culture monolayer preparation. With respect to the culturing of malignant cells, for example, it is believed (without any intention of being bound by the theory) that by maintaining the malignant cells within a multicellular particulate of the originating tissue, growth of the malignant cells themselves is facilitated versus the overgrowth of fibroblasts or other cells which tends to occur when suspended tumor cells are grown in culture. Practical monolayers of cells may thus be formed to enable meaningful screening of a plurality of treatments and / or agents. Growth of cells is monitored to ascertain the time to initiate the assay and to determine the growth rate of the cultured cells; sequence and timing of drug addition is also monitored and optimized. By subjecting uniform samples of cells to a wide variety of active agents (and concentrations thereof), the most promising agent and concentration for treatment of a particular patient can be determined. For assays concerning cancer treatment, a two-stage evaluation is contemplated in which both acute cytotoxic and longer term inhibitory effect of a given anti-cancer agent are investigated.
Owner:PRECISION THERAPEUTICS
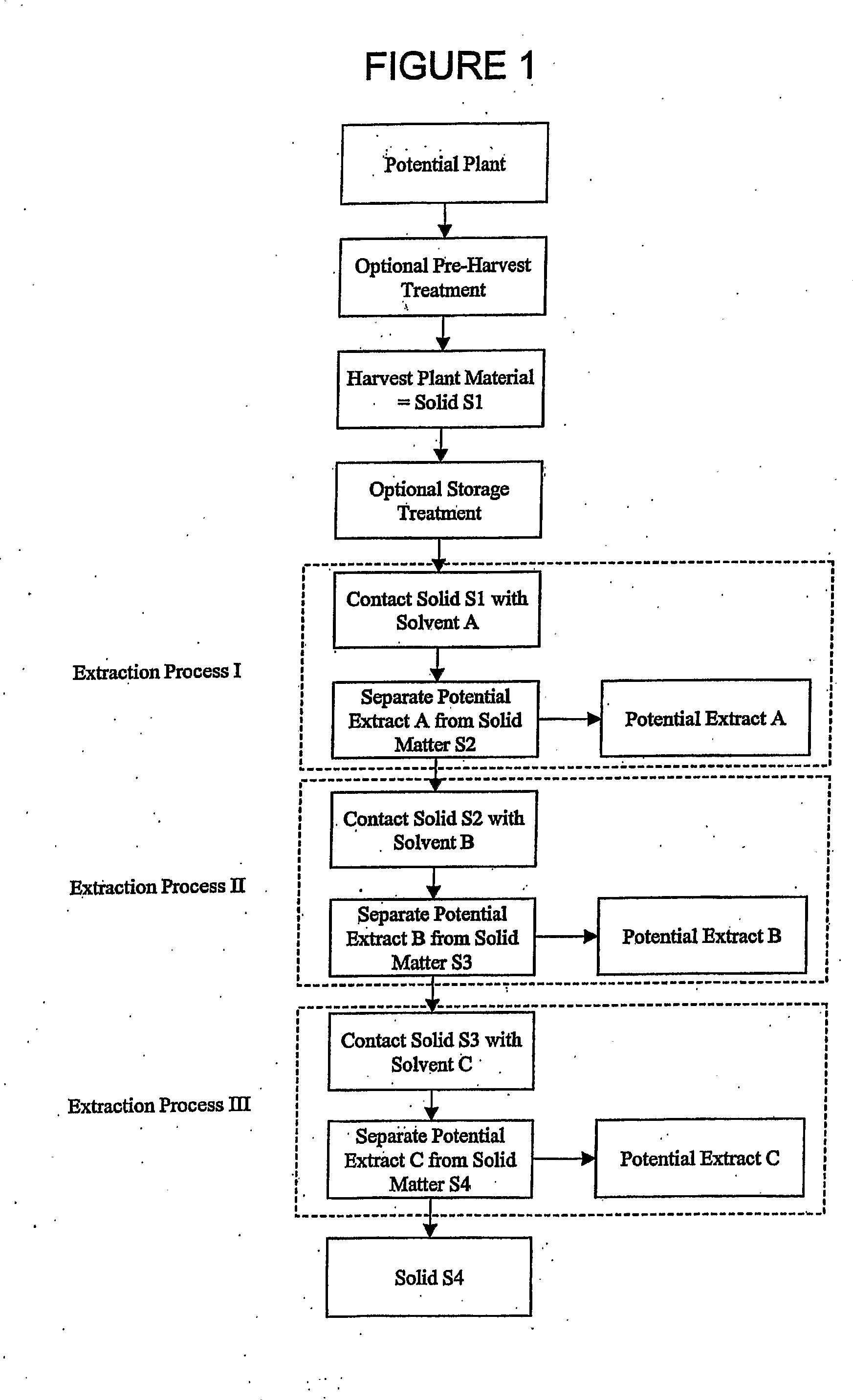
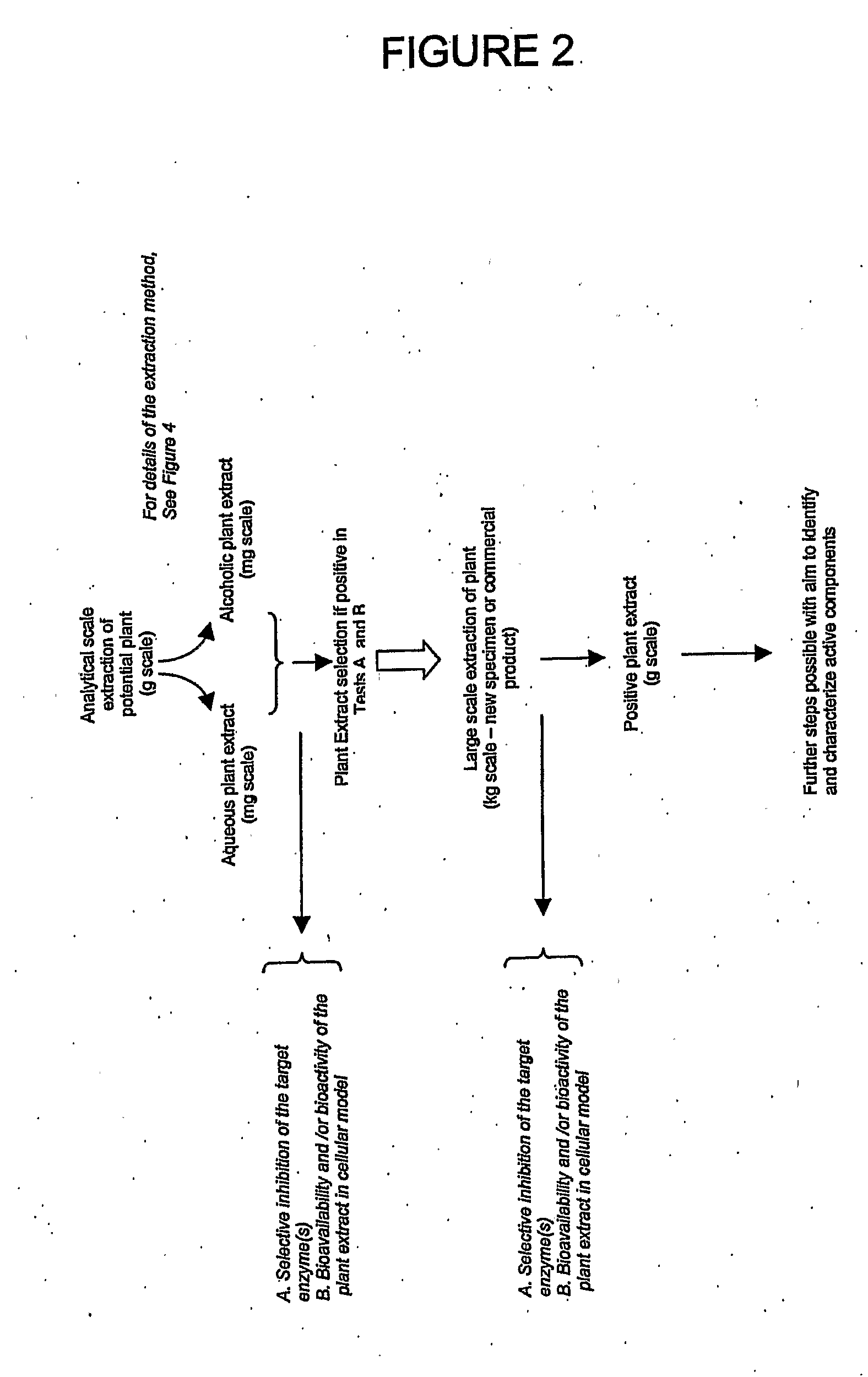
Methods and Therapeutic Compositions Comprising Plant Extracts for the Treatment of Cancer
A method of treating cancer by targeting two proteases, MMP-9 and cathepsin B is provided. Therapeutic compositions comprising one or more plant extracts that inhibit MMP-9 and / or cathepsin B, which are capable of inhibiting neoplastic and / or endothelial cell migration, tumour growth, tumour-induced angiogenesis and / or metastasis are also provided. The therapeutic compositions of the invention can be used in the treatment of cancer, and, methods of inhibiting tumour growth, tumour metastasis, and / or tumour-induced angiogenesis using the therapeutic compositions alone or in combination with an anti-cancer agent are, therefore, also provided.
Owner:BIOPHARMACOPAE DESIGN INT
Method for preparing cell cultures from biological specimens for chemotherapeutic and other assays
InactiveUS6900027B1Promote growthConvenient treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism separationAnticarcinogenActive agent
An improved system for screening a multiple of candidate therapeutic or chemotherapeutic agents for efficacy as to a specific patient, in which a tissue sample from the patient is harvested, cultured and separately exposed to a plurality of treatments and / or therapeutic agents for the purpose of objectively identifying the best treatment or agent for the particular patient. The system includes the initial preparation of cohesive multicellular particulates of the tissue sample, rather than enzymatically dissociated cell suspensions or preparations, for initial tissue culture monolayer preparation. Practical monolayers of cells may thus be formed to enable meaningful screening of a plurality of treatments and / or agents. By subjecting uniform samples of cells to a wide variety of active agents (and concentrations thereof), the most promising agent and concentration for treatment of a particular patient can be determined. For assays concerning cancer treatment, a two-stage evaluation is contemplated in which both acute cytotoxic and longer term inhibitory effect of a given anti-cancer agent are investigated.
Owner:PRECISION THERAPEUTICS
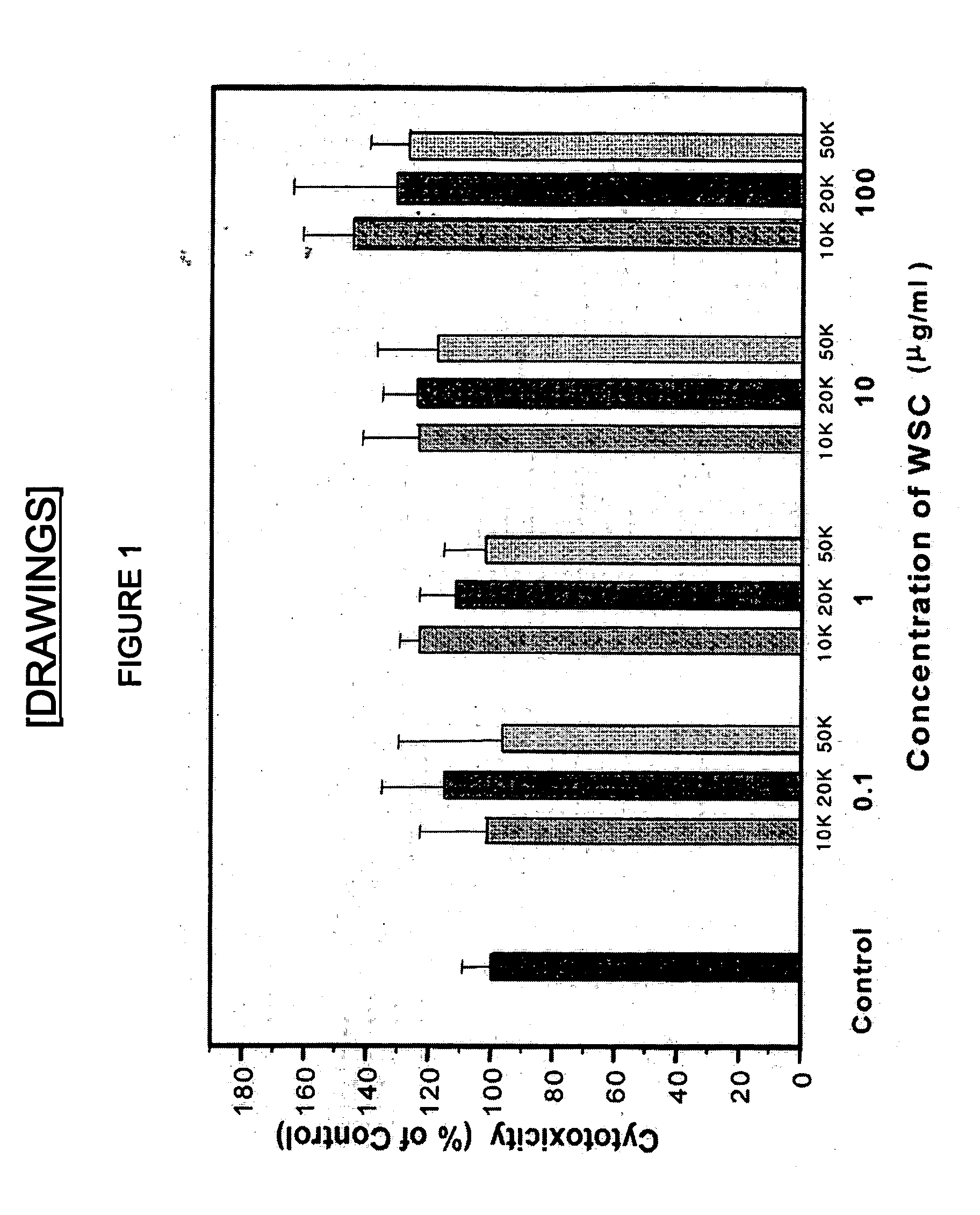
Water soluble chitosan nanoparticle for delivering an anticancer agent and preparing method thereof
The present invention relates to a water soluble chitosan nanoparticle (WSC-NP) for delivering an anticancer agent and a preparing method thereof, more precisely, a water soluble chitosan nanoparticle for delivering an anticancer agent which has function of targeting on a wanted area by introducing a functional group in the location of highly reactive amine group and becomes an excellent gene carrier with the use of water soluble chitosan since the water soluble chitosan itself can combined with DNA having a negative electric charge(−) owing to the very strong positive electric charge(+) of its amine group, and a preparing method thereof. Therefore, a water-soluble chitosan nanoparticle for delivering an anticancer agent of the present invention can effectively envelope paclitaxel by introducing hydrophilic and hydrophobic groups in the position of highly reactive amine group of the water-soluble chitosan. A water soluble chitosan nanopaclitaxel prepared as the above has an excellent re-dispersion force, after freeze-drying, in distilled water and has an outstanding anticancer effect with its accumulation in tumor cells greater than that of the other anticancer agent carriers.
Owner:JEONG TUK RAI +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com