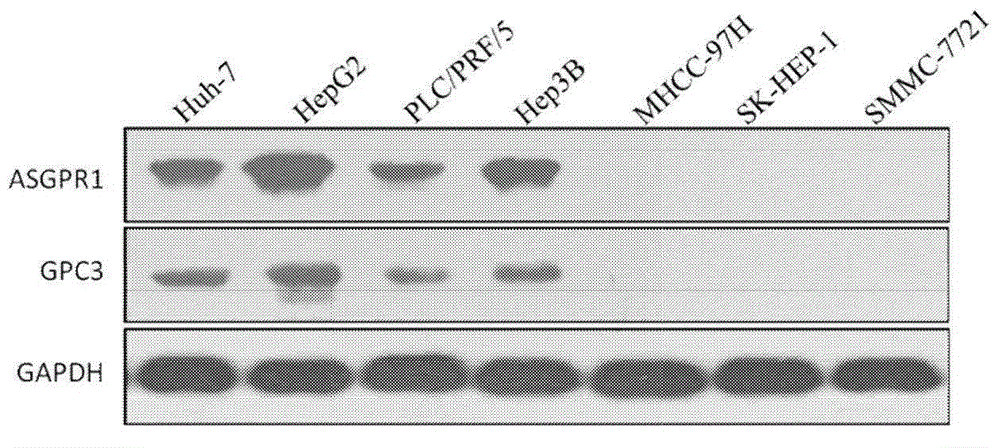
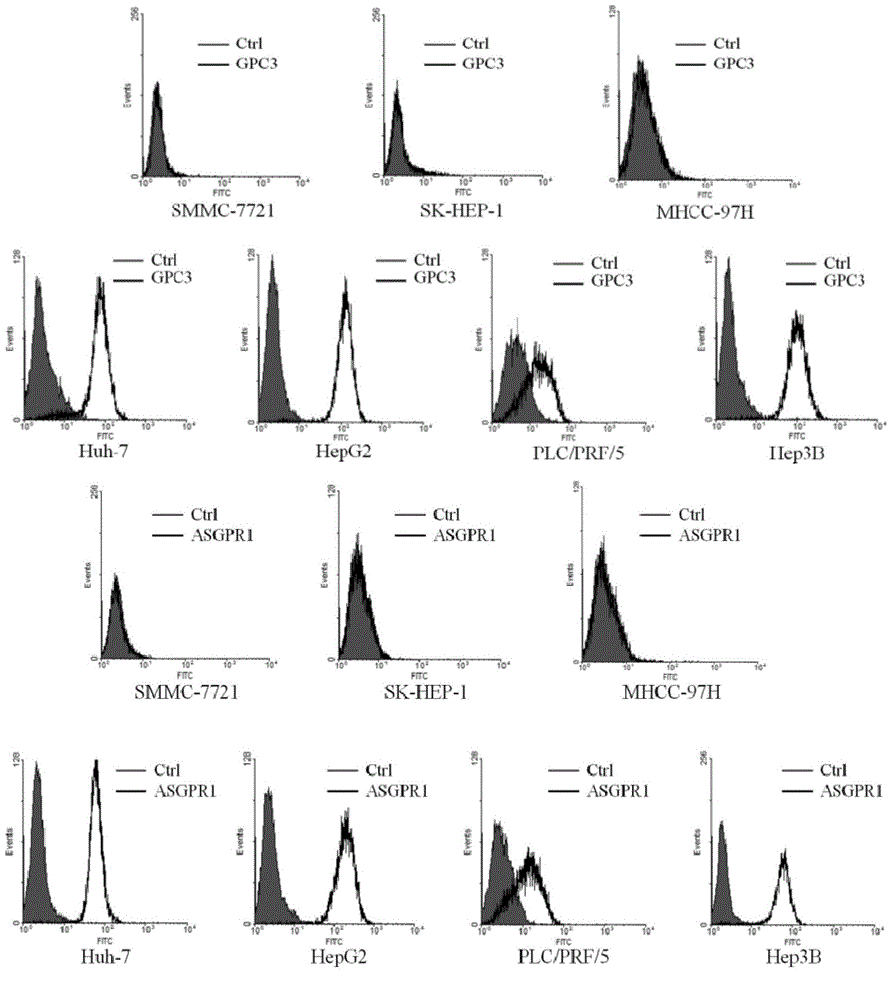
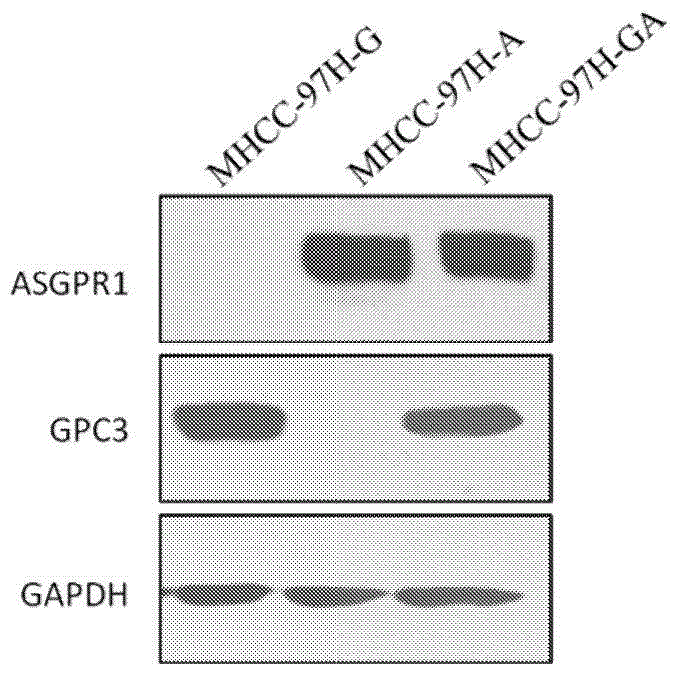
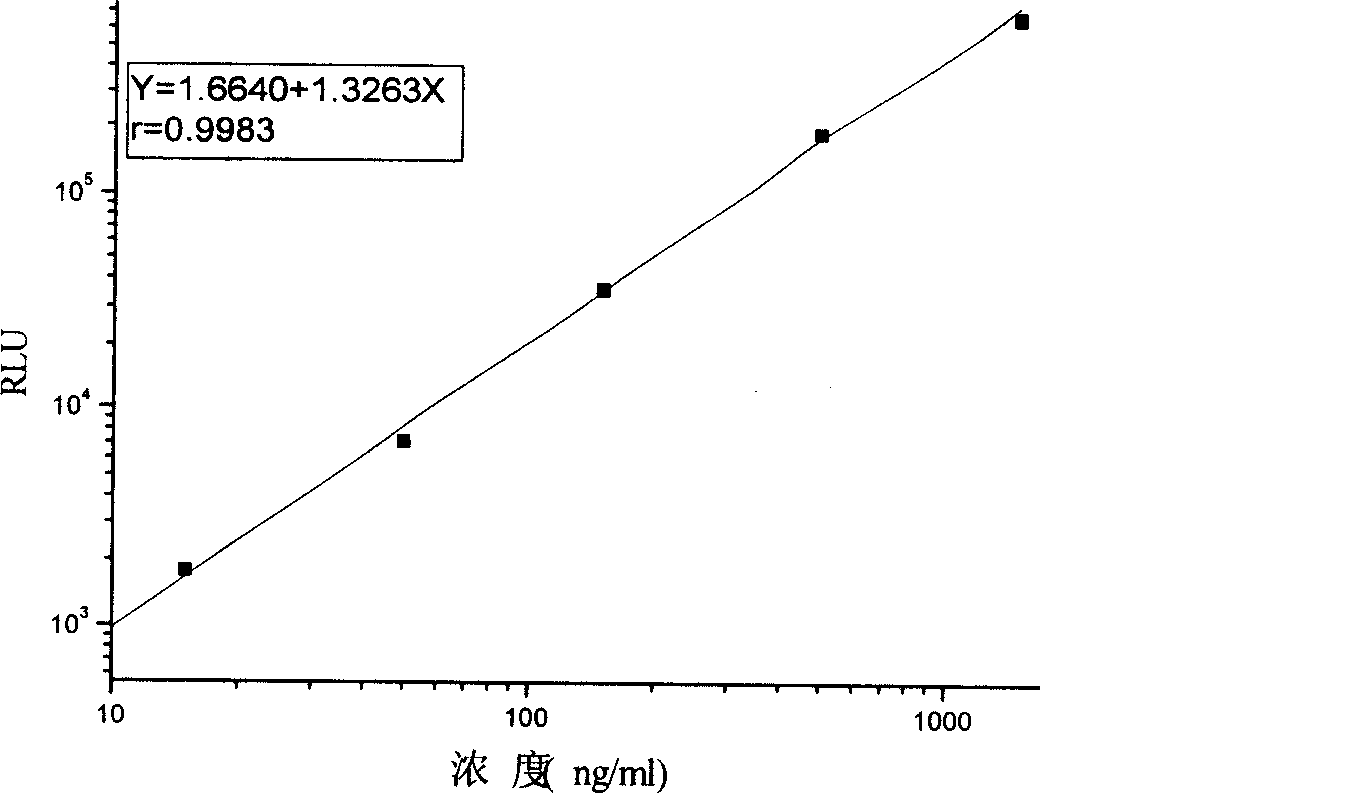
Patents
Literature
70 results about "Glypican" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Glypicans constitute one of the two major families of heparan sulfate proteoglycans, with the other major family being syndecans. Six glypicans have been identified in mammals, and are referred to as GPC1 through GPC6. In Drosophila two glypicans have been identified, and these are referred to as dally (division abnormally delayed) and dally-like. One additional glypican has been identified in C. elegans. Glypicans seem to play a vital role in developmental morphogenesis, and have been suggested as regulators for the Wnt and Hedgehog cell signaling pathways. They have additionally been suggested as regulators for fibroblast growth factor and bone morphogenic protein signaling.
Dual-targeting genetically modified immunologic effector cell aiming at GPC3 (Glypican-3) and ASGPR1 (asialoglycoprotein receptor 1) and applications of dual-targeting genetically modified immunologic effector cell
ActiveCN105713881APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyImmune effector cellEffector cell
The invention relates to a dual-targeting genetically modified immunologic effector cell aiming at GPC3 (glypican-3) and ASGPR1 (asialoglycoprotein receptor 1) and applications of the dual-targeting genetically modified immunologic effector cell. The invention discloses the gene-modified immunologic effector cell capable of simultaneously identifying GPC3 and ASGPR1 for the first time, and the gene-modified immunologic effector cell can be used for the treatment of the GPC3 and ASGPR1 double-positive tumor, such as liver cancer.
Owner:CARSGEN THERAPEUTICS
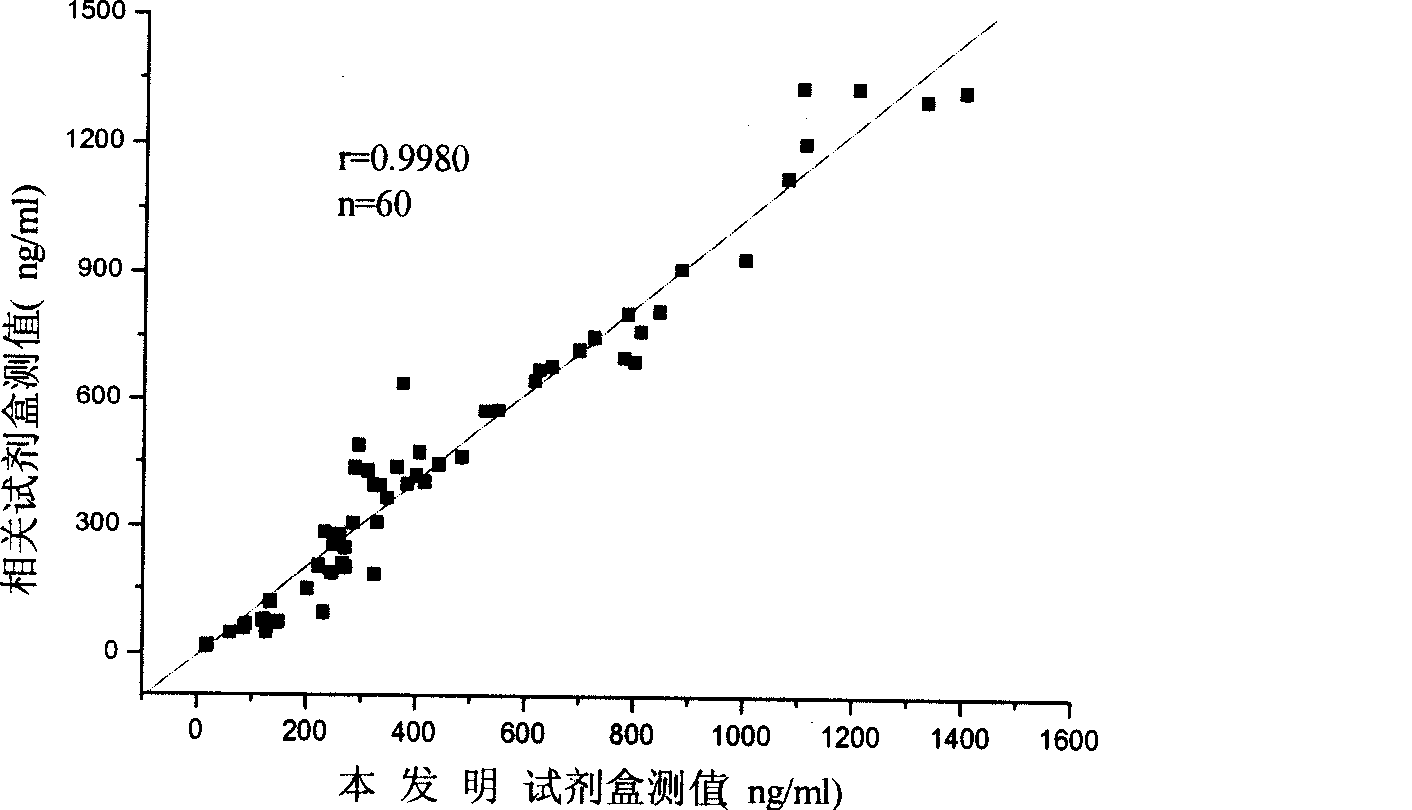
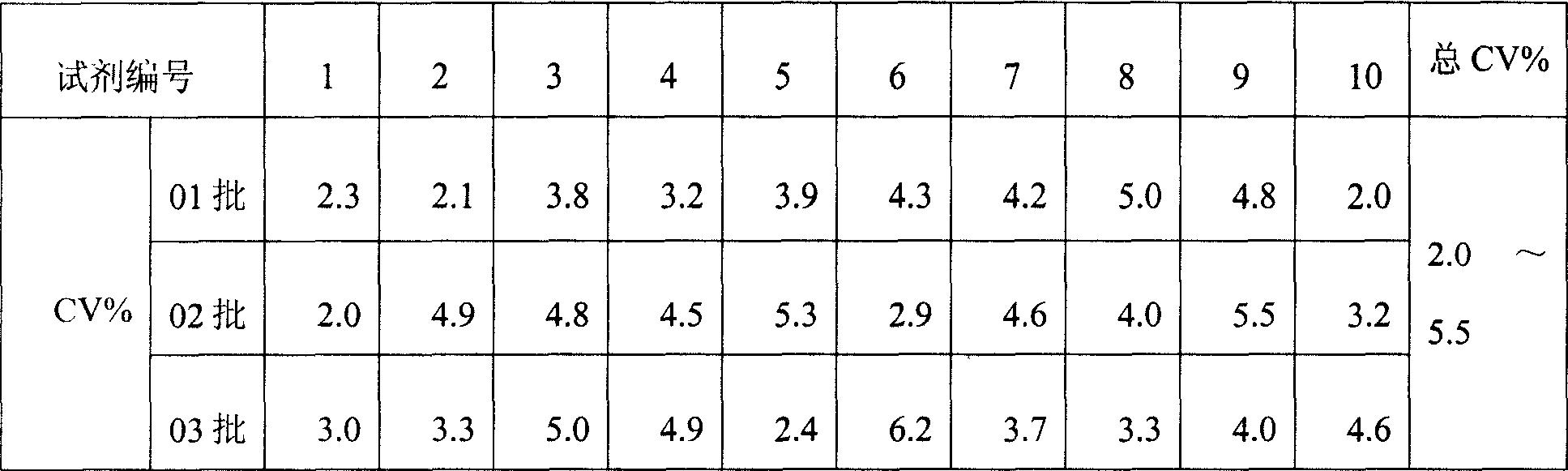
Monophosphoinositide proteoglycans-3 chemiluminescence immune analysis determination reagent kit and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN101377506AIncrease the effective amountReliable clinical reference valueChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceTreatment effectChemiluminescent immunoassay
The invention relates to the medical field of immunoassay, more specially, the invention provides a chemiluminescent immunoassay detection kit for phosphatidylinositol proteoglycan-3(GPC-3) and a preparation method thereof, and realizes the simultaneous serological detection of GPC-3 N terminal and C-terminal protein with the chemiluminescent immunoassay method. The kit has the advantages of simple sampling, convenient detection and accurate and specific technical method. The invention adopts a biotin-strapavidin system to coat antibodies and improve the efficiency of antibody coating and the linear range of detection as well as sensitivity, and can be conveniently used for the tracing observation of early diagnosis or treatment effect for primary carcinoma of liver.
Owner:CHEMCLIN DIAGNOSTICS CO LTD
GPC3 (glypican-3) monoclonal antibody hybridoma cell strain 7D11 and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102634486AReduce manufacturing costConducive to clinical target validationImmunoglobulins against animals/humansMicroorganism based processesMonoclonalSpleen cell
The invention discloses a GPC3 (glypican-3) monoclonal antibody hybridoma cell strain 7D11 and a preparation method and application thereof, which belong to the technical field of bioengineering. The GPC3 monoclonal antibody hybridoma cell strain 7D11 has a preservation code of CGMCC No.5426. The preparation method of the hybridoma cell strain 7D11 includes: using GPC3 protein as an immunogen to immunize a mouse, subjecting spleen cells of the mouse with serum titer more than 1:104 and myeloma cells SP2 / 0 to fusion, using a HATRPMI-1640 medium to screen fused cells, screening by ELISA (enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay) and multiple limiting dilution process, and finally obtaining the hybridoma cell strain 7D11. The GPC3 monoclonal antibody hybridoma cell strain 7D11 is high in yield of secreted antibodies and easy to survive, the secreted monoclonal antibodies are high in titer, flexible in reaction, easy to detect, low in production cost and widely applicable to detection of GPC3 protein expression.
Owner:GUANGZHOU DARUI BIOTECH
Treatment and diagnosis of abnormal bone density with an inhibitor of the glypican-sclerostin interaction
Compositions and methods of treatment for abnormal bone density are disclosed based upon the finding that sclerostin must be bound to glypican in order to inhibit bone deposition. Methods for identifying agents that inhibit the glypican-sclerostin interaction are disclosed for treatment of bone deposition disorders. Diagnostic methods are also disclosed.
Owner:A CHAN HLDG
Glypican-3 (GPC3)-derived tumor rejection antigenic peptides useful for hla-a2-positive patients and pharmaceutical comprising the same
ActiveUS20090239806A1High levelCancer can be prevented and/or treatedTumor rejection antigen precursorsPeptide/protein ingredientsTumor rejectionTumor rejection antigen
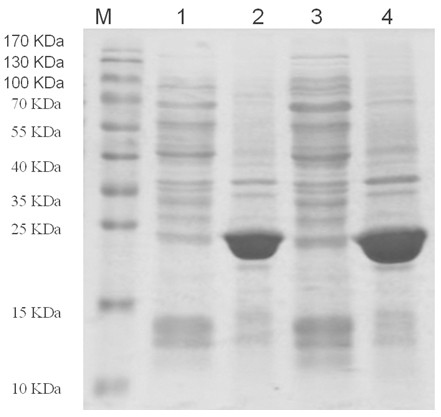
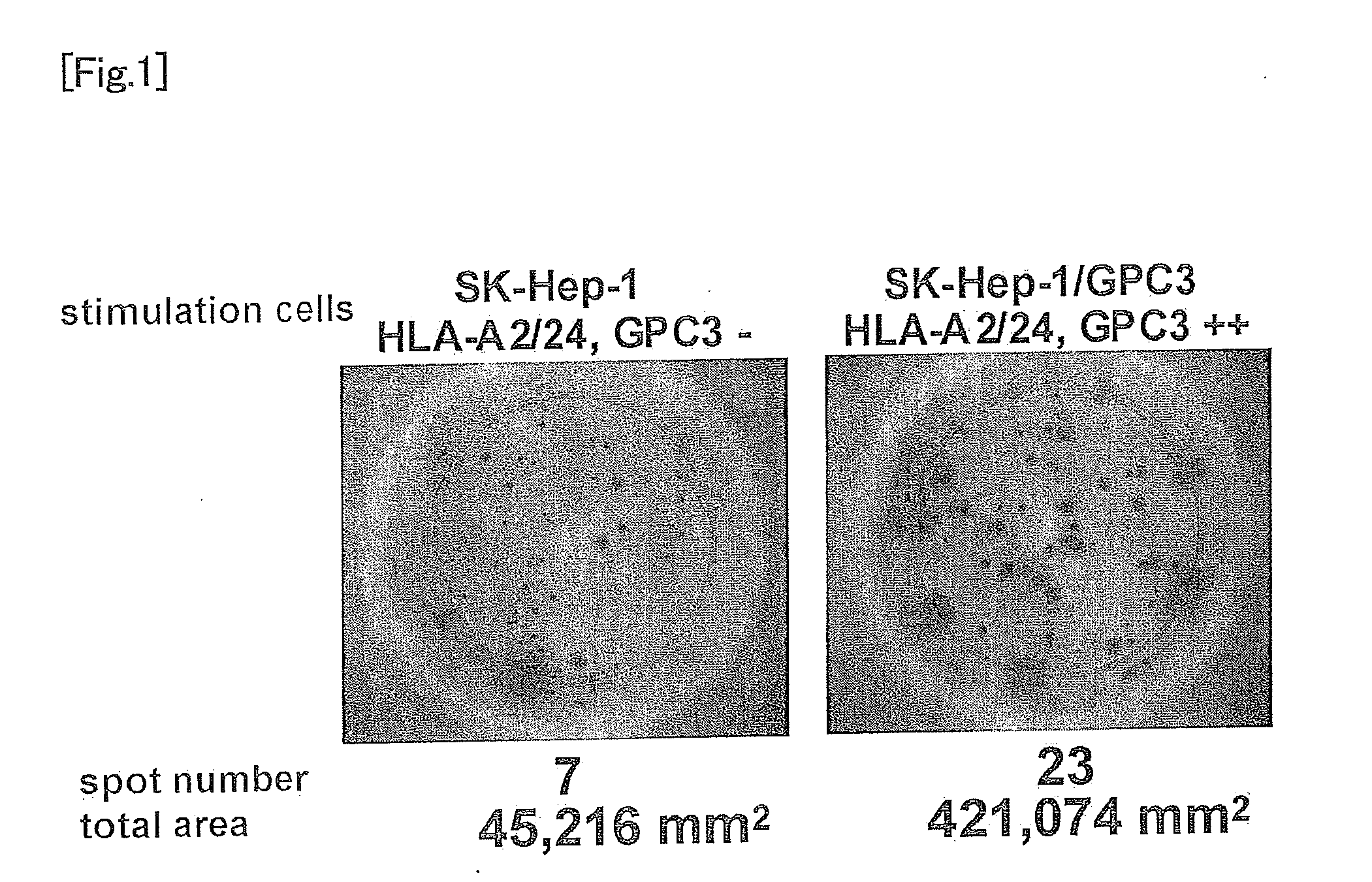
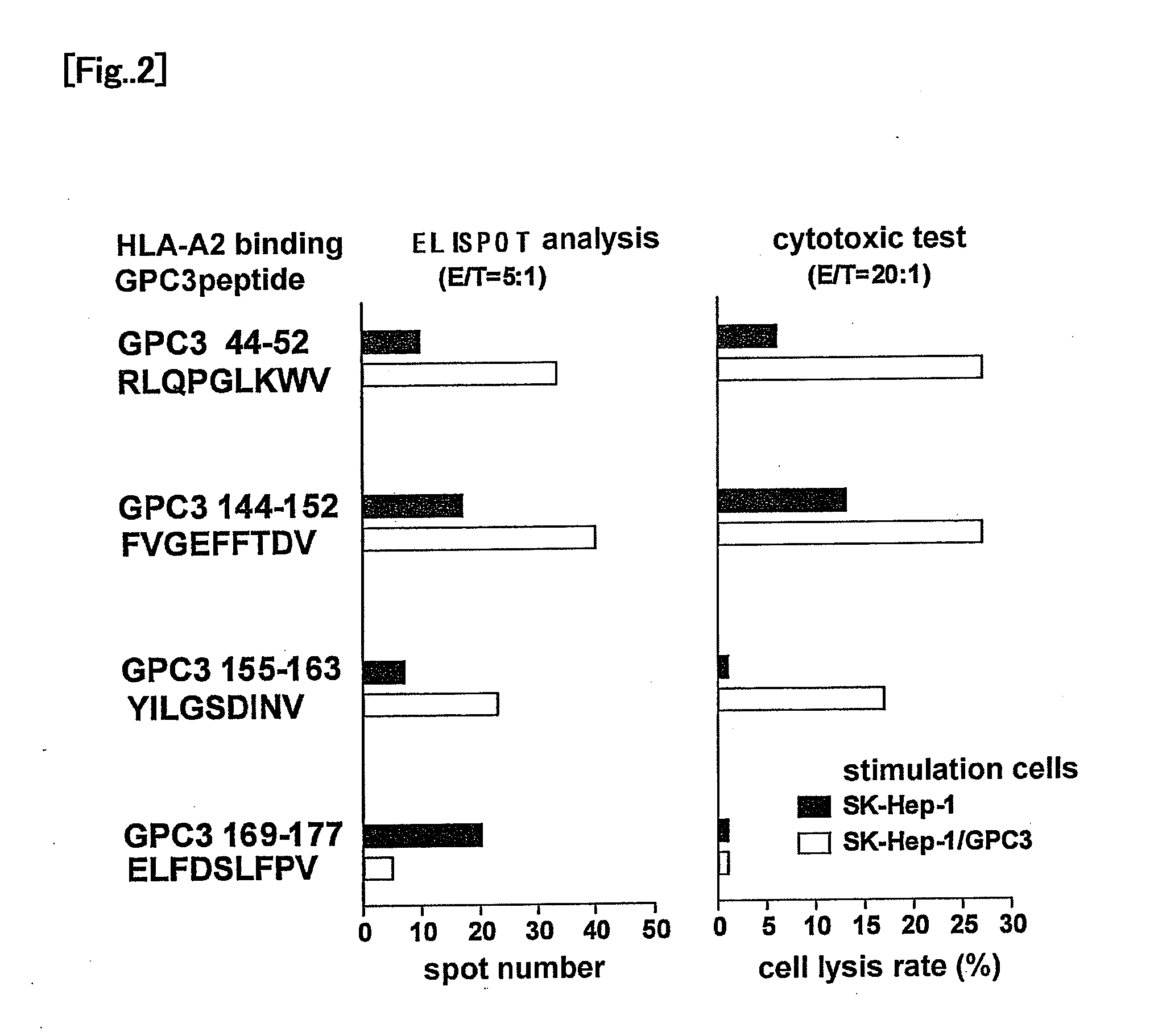
It is an object of the present invention to identify a glypican-3-derived peptide which can bind to HLA-A2 and activate human killer T cells, so as to provide a means for carrying out an immunotherapy which is able to target approximately 40% of Japanese patients suffering from several types of cancers, which express GPC3 at a high level. The present invention provides a peptide of any of the following (A) or (B):(A) a peptide, which has the amino acid sequence as shown in any one of SEQ ID NOS: 1 to 3; or(B) a peptide, which has an amino acid sequence comprising a substitution or addition of one or two amino acids with respect to the amino acid sequence as shown in any one of SEQ ID NOS: 1 to 3, and which has ability to induce killer T cells.
Owner:ONCOTHERAPY SCI INC
Anti-glypican-3 antibody
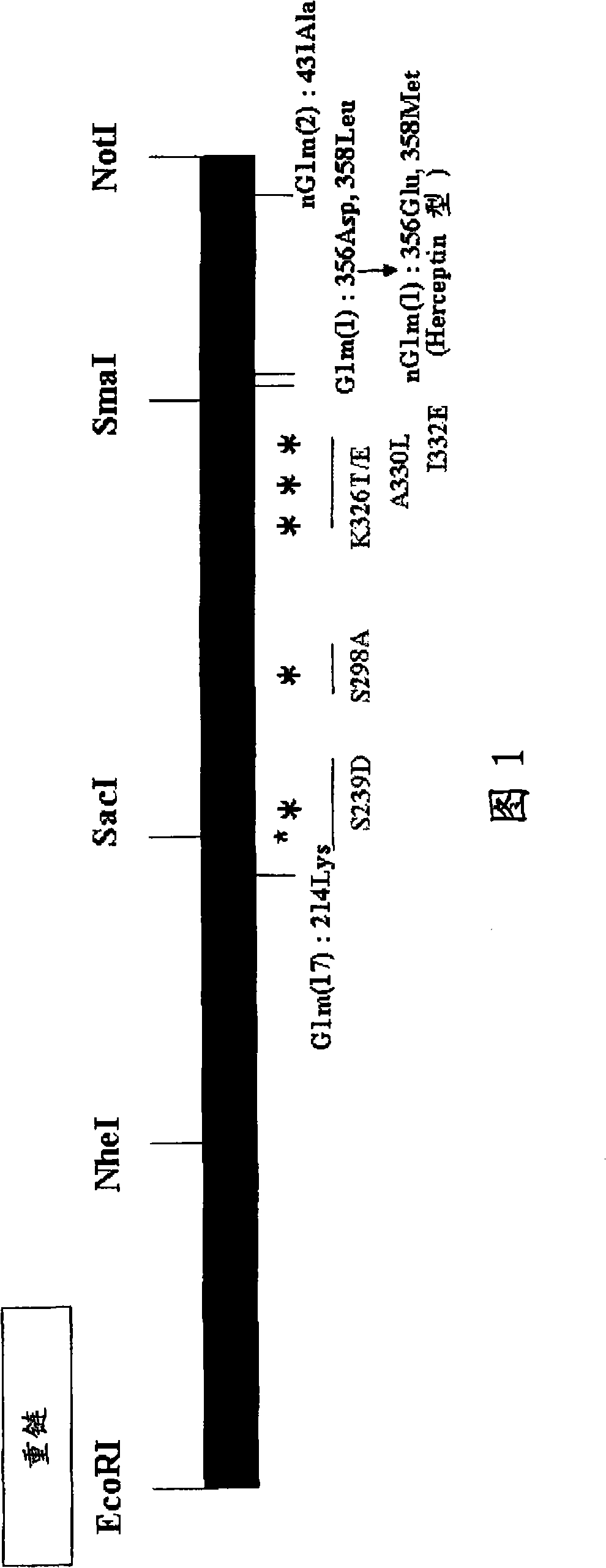
An anti-glypican-3 antibody comprising one or more amino acid substitutions introduced in the Fc region is disclosed. Preferably, in the anti-glypican-3 antibody, one or more of the amino acid residues at the positions 239, 298, 326, 330 and 332 in the Fc region are substituted with other amino acid residues. Since the Fc-modified anti-glypican-3 antibody of the invention exhibit enhanced ADCC activity, it is useful in treating cancers, such as hepatic cancer. Also disclosed are an anticancer agent comprising the anti-glypican-3 antibody of the invention and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, as well as a method of treating a patient with cancer comprising administering to the patient the anticancer agent of the invention.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD +1
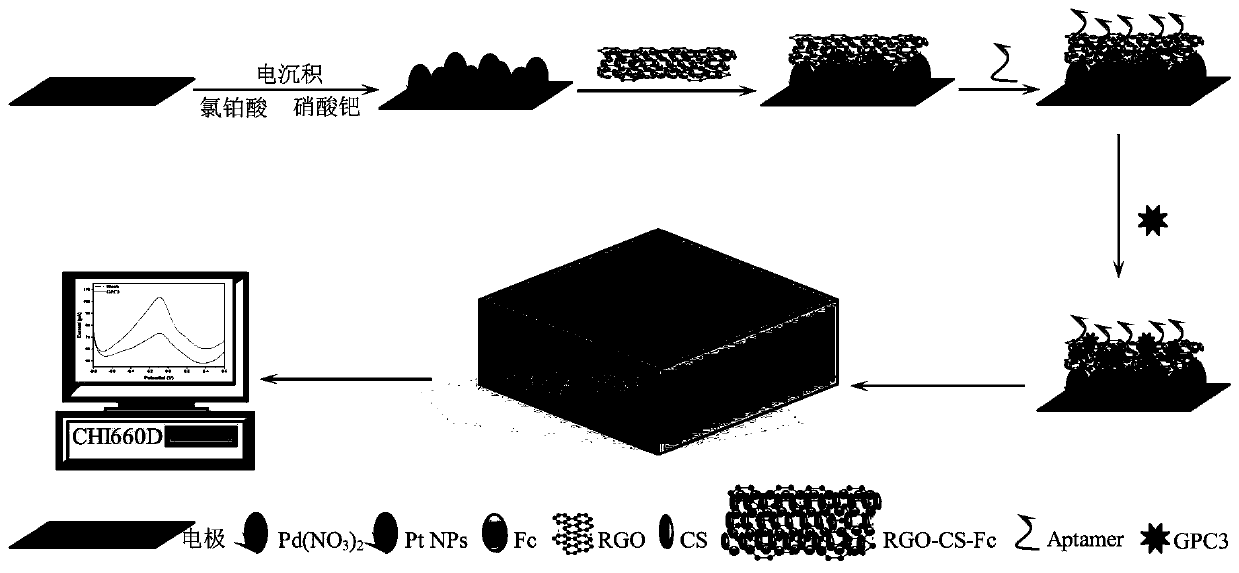
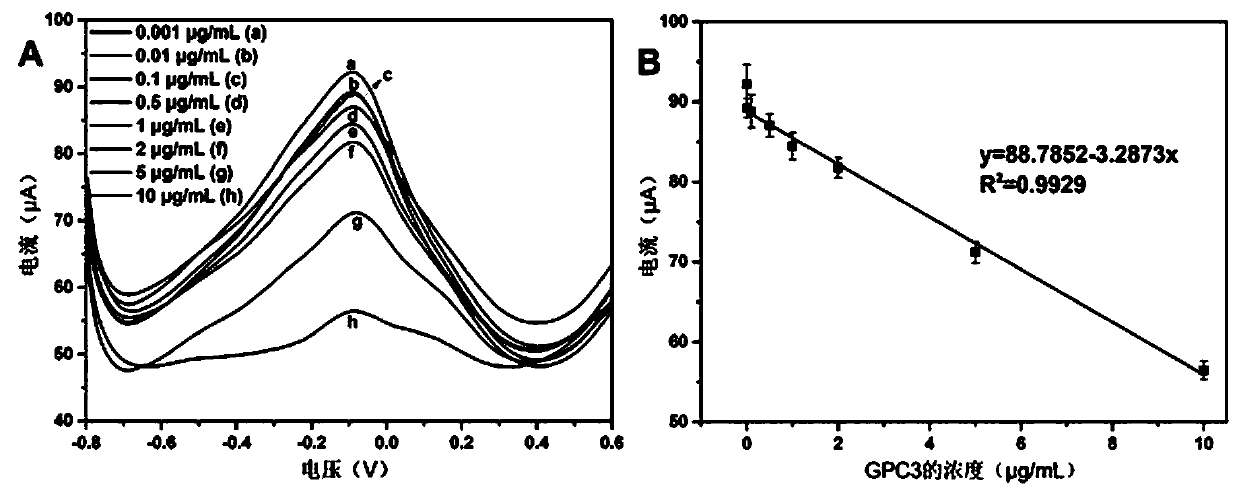
Method for detecting GPC3 based on RGO-CS-Fc/Pt-Pd NPs nano composite material
ActiveCN111413385AEnhanced transfer effectAmplified current signalMaterial electrochemical variablesAptamerNano composites
A liver cancer marker phosphatidylinositol proteoglycan 3 (Glypican-3, GPC3) is used as a research object, a GPC3 aptamer is used as a recognition probe, on the basis of good electron transfer effectand excellent loading capacity of a reductive graphene oxide-chitosan-ferrocene / nano platinum and palladium (Pt-Pd NPs / RGO-CS-Fc) composite material, the GPC3 aptamer can specifically recognize and becombined with GPC3 protein, and a novel aptamer sensor capable of performing specific recognition and quantitative analysis on the GPC3 protein is constructed and used for detecting the content of GPC3 in serum. The method is simple to operate, time-saving, low in cost and relatively low in detection limit.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Primers, probes and detection kit for detecting human HCC (Hepatocellular Carcinoma) marker
ActiveCN103540679AThe detection method is simpleFast detection methodMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSpecific detectionFluorescence
The invention provides primers and probes for specifically detecting human HCC (Hepatocellular Carcinoma) marker, including a primer and a probe (Seq ID No.1-3) for detecting glypican cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) and a primer and a probe (Seq ID No.4-6) used for detecting alpha fetoprotein cDNA. The invention also provides a detection kit containing the primers and the probes and used for detecting the marker of human HCC by multiplex real-time fluorescence quantification PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction). According to the invention, by virtue of the multiplex real-time fluorescence quantification PCR, alpha fetoprotein messenger RNA (AFP mRNA) and glypican messenger RNA (GPC3 mRNA) in human HCC at the mRNA level can be detected; the detection method is simple, quick, high in sensitivity and strong in specificity; the whole detection reaction only lasts for 100min. An important technical support is provided for the specific detection of canceration of human HCC.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF GENOMICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI CHINA NAT CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION
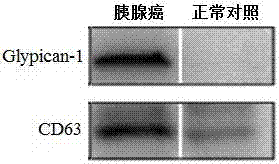
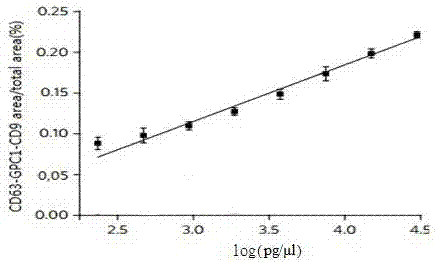
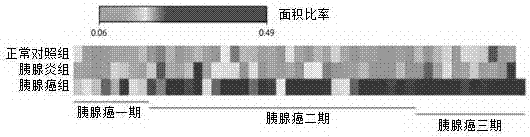
Application of Glypican-1 protein in diagnosis of pancreatic cancer, detection method of positive exosome concentration, and use of detection method
InactiveCN106950374AServe as a diagnosisPlay the role of staging judgment, etc.Raman scatteringBlood plasmaBiology
The invention discloses an application of a Glypican-1 protein in the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer, a detection method of a Glypican-1 positive exosome concentration, and a use of the detection method. A nano-plasma enhanced scattering (nPES) detection technology can be used to quantify exosomes in serum, an exosome extracting process is omitted, the characteristic antigen of the exosomes is used as a target, and the antigen and a corresponding antibody carrying gold nanoparticles form an antigen-antibody complex in order to obtain exosomes, and the amount of the exosomes is reflected by using the light radiation principle of the gold nanoparticles. The Glypican-1 is a pancreatic cancer-derived exosome biomarker, and the content of Glypican-1 positive exosomes in blood plasma has specific specificity even in early pancreatic cancer, so the exosome content index can be used to diagnose the pancreatic cancer, and the exosome level is closely related to the staging and progression of pancreatic cancer patients. Experiments prove that the method using the nPES detection technology to detect the content of the Glypican-1 exosomes in the serum is concise and accurate, and has better sensitivity and specificity than CA19-9 in the diagnosis of the pancreatic cancer.
Owner:AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF NANTONG UNIV
GPC3 (glypican-3) monoclonal antibody hybridoma strain 8G6, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102634487AReduce manufacturing costFunction increaseImmunoglobulins against animals/humansTissue cultureMicrobiological cultureMonoclonal
The invention discloses a GPC3 (glypican-3) monoclonal antibody hybridoma strain 8G6, and a preparation method and application thereof, which belong to the technical field of cell engineering. The preservation code of the GPC3 monoclonal antibody hybridoma strain 8G6 is CGMCC (china general microbiological culture collection center) No.5427. The preparation method of the GPC3 monoclonal antibody hybridoma strain 8G6 includes: using GPC3 protein as immunogen to immunize a mouse; and fusing mouse splenocytes having serum titer more than 1:104 with SP2 / 0 myeloma cells, using an HATRPMI-1640 medium to screen fusion cells, and finally obtaining the hybridoma strain 8G6 by ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) and repeated limiting dilution. The GPC3 monoclonal antibody hybridoma strain 8G6 is high in yield of secretory antibodies, and is easy to survive, and the secreted monoclonal antibodies are high in titer, sensitive in reaction, easy to detect, low in production cost and widely applicable to detection of GPC3 protein expression.
Owner:GUANGZHOU DARUI BIOTECH
Anti-phosphatidylinositol proteoglycan 3 complete humanized antibody
InactiveCN105037540AImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAntibody ingredientsPhage antibodiesAntigen
The invention discloses a complete humanized antibody which is selected from humanized high-capacity phage antibody library and is high-affinity-combined with phosphatidylinositol proteoglycan 3. The invention includes a selection method of the antibody, an antibody coding sequence and corresponding amino acid residue sequence, and especially includes three CDR-zone sequences respectively at a heavy chain and a light chain, combination characters of an antigen and the construction method of the complete antibody. The antibody is a complete humanized antibody, is used for treatment in human body, is low in immunogenicity, is less in toxic and side effects, and has a potential value of treating liver cancer and melanin tumor.
Owner:BEIJING BIYANG BIOTECH
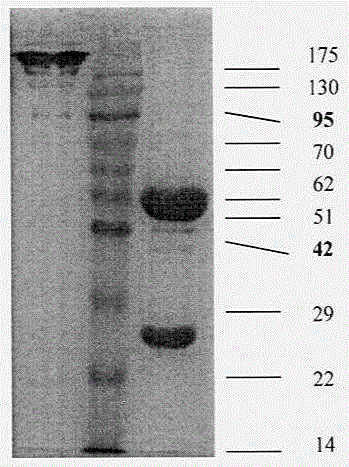
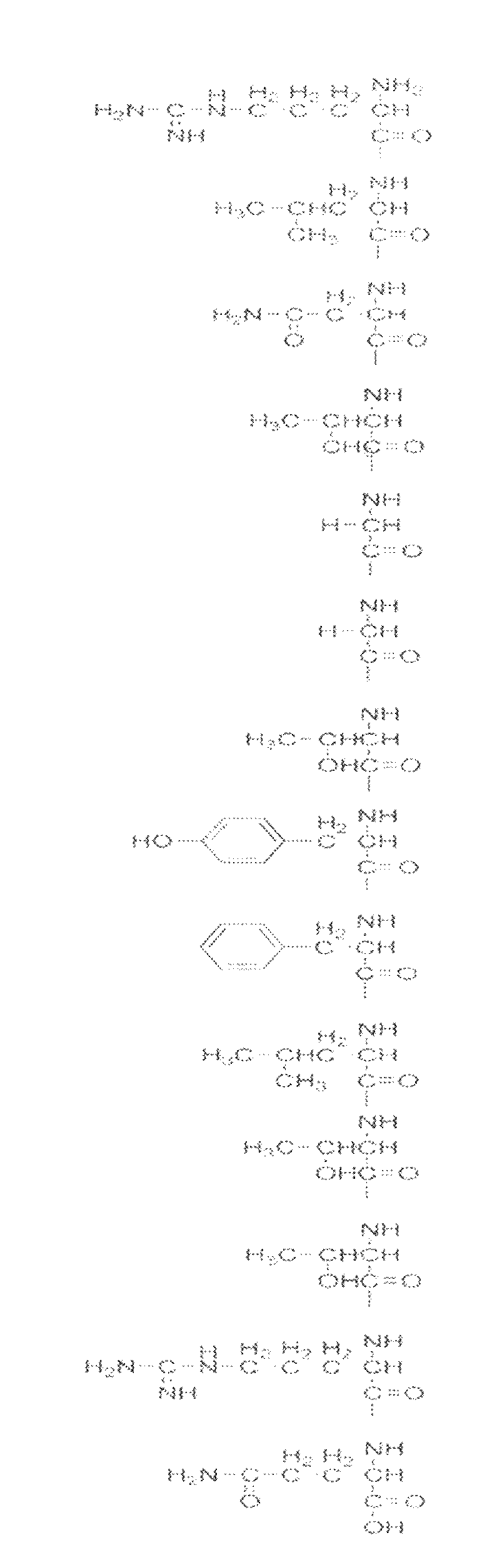
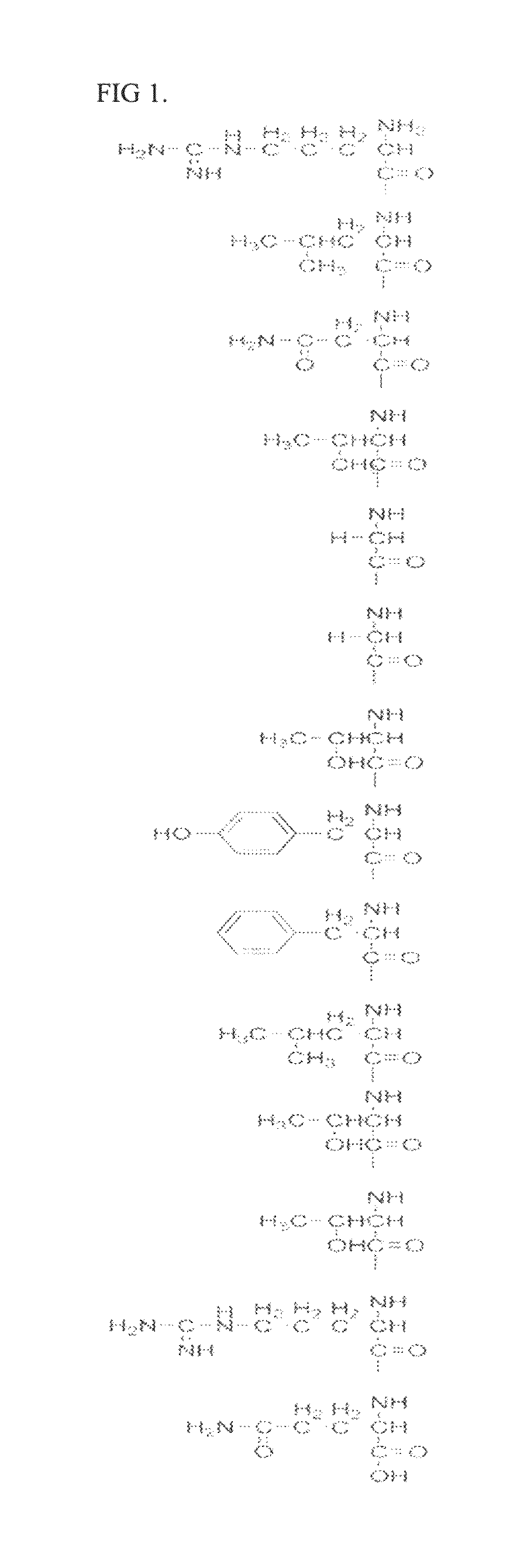
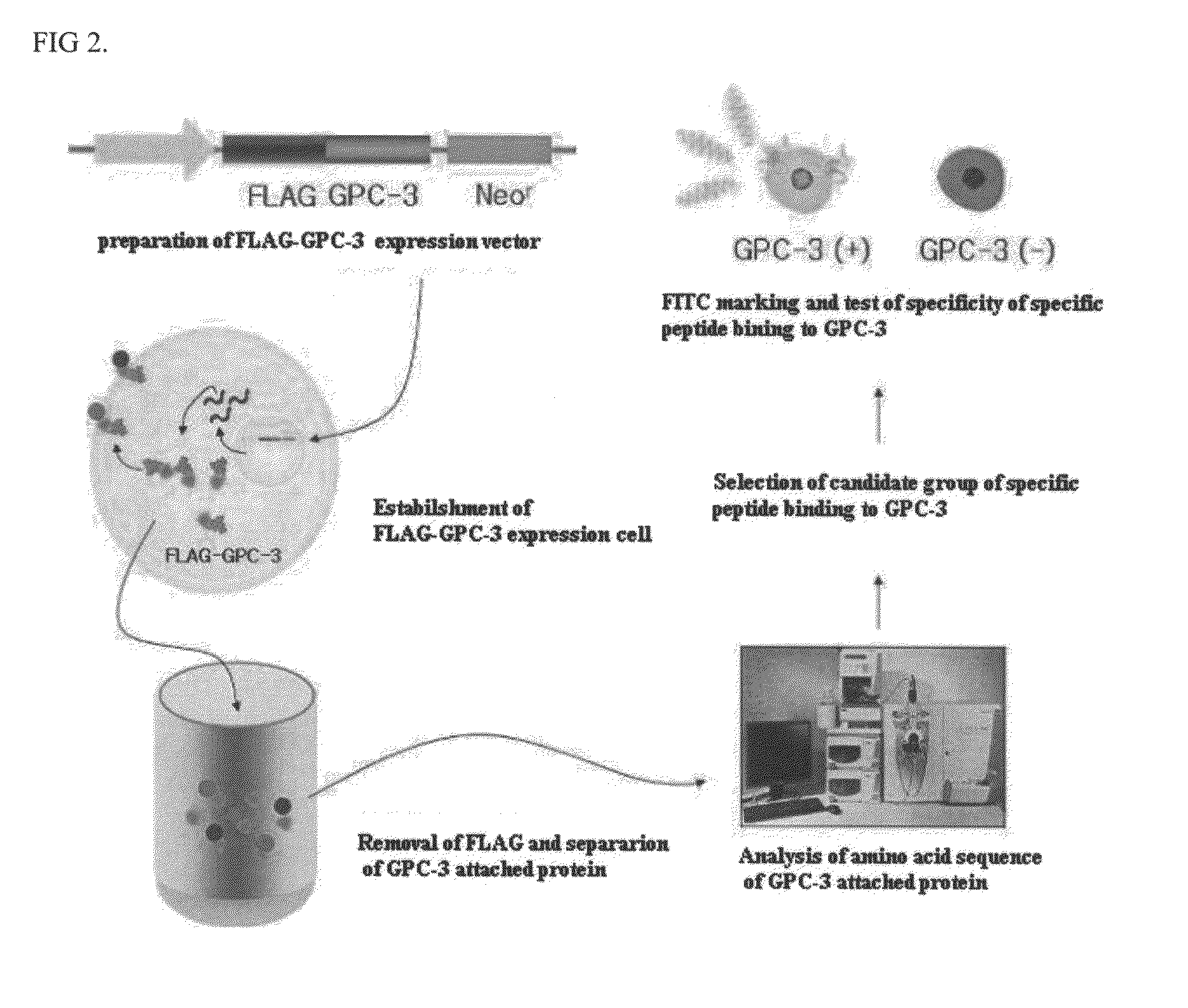
Specific peptide binding to glypican-3
ActiveUS20100203612A1Overcome problemsPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsMelanomaTarget peptide
A specific targeting peptide binding to glypican-3 can specifically binds to glypican-3 overexpressed in carcinoma cells and includes an amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID No. 1 or some thereof. Glypican-3 is overexpressed in malignant tumors including hepatocellular carcinoma, melanoma, germ cell tumor, etc., and may be targeted in diagnosis and treatment of tumors by marking the targeting peptide. A diagnosis using the targeting peptide may detect even small tumors more accurately than conventional methods. A treatment method using the targeting peptide may remove only carcinoma cells without harming other normal tissues.
Owner:KYUNGPOOK NAT UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
GPC3 receptor targeted polypeptide radioactive diagnosis or therapeutic drug
InactiveCN107019807AImprove efficiencyRadioactive preparation carriersPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMedicineTreatment of lung cancer
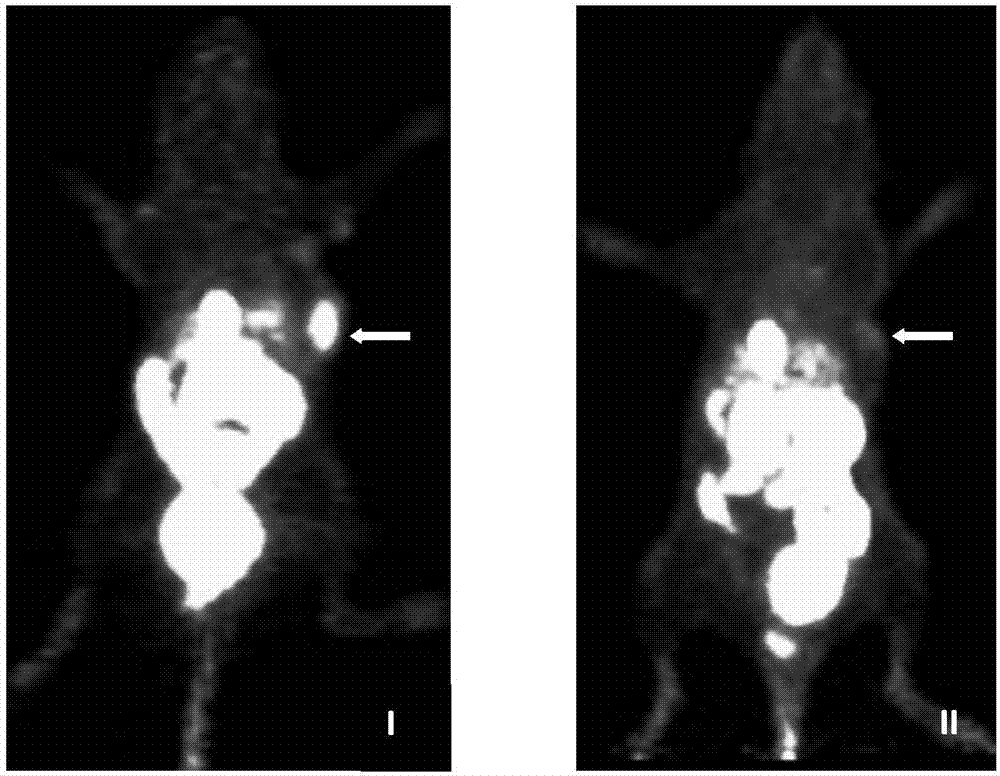
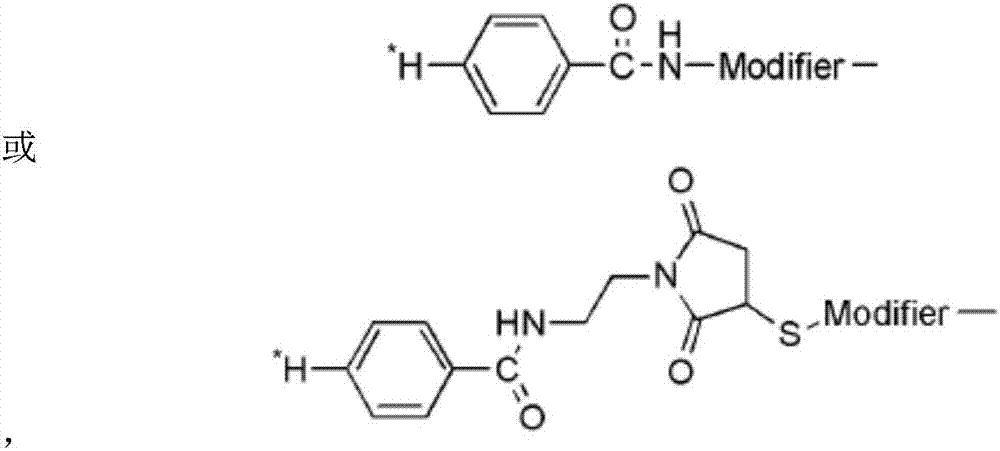
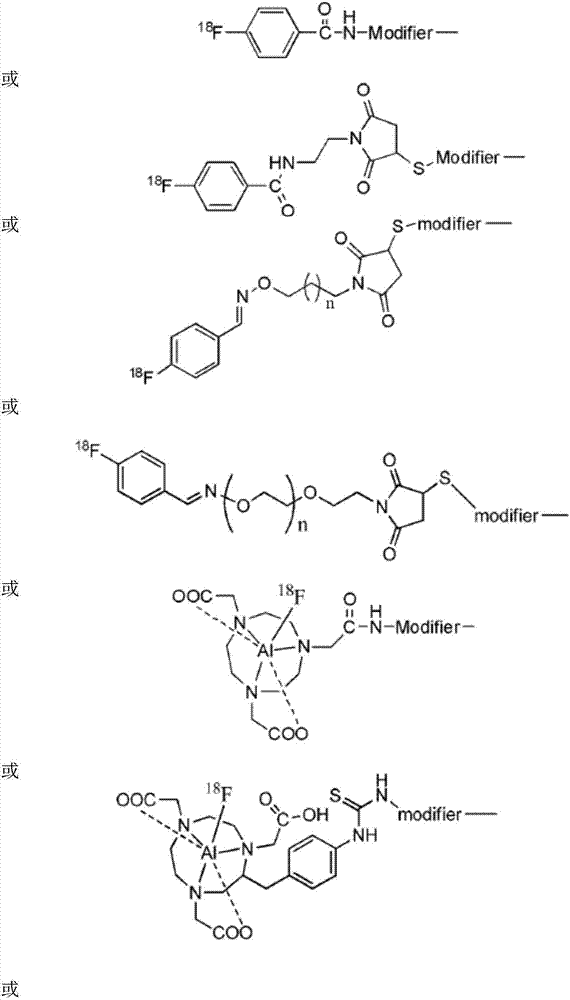
The invention relates to a GPC3 (glypican-3) receptor targeted polypeptide radioactive diagnosis or therapeutic drug. The GPC3 receptor targeted polypeptide radioactive diagnosis or therapeutic drug includes: polypeptide with an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:1; and a radionuclide or positron-emitting nuclide marker coupled to the polypeptide. The invention adopts the radionuclide labeled polypeptide as a hepatocellular carcinoma specific targeting molecular probe to show the expression situation of the GPC3 receptor in hepatocellular carcinoma tumor tissue on a living body level, and improves the effective rate of hepatocellular carcinoma oncotherapy. For lung cancer, melanoma and other GPC3 receptor-positive tumors, the GPC3 receptor targeted polypeptide can also be used for preparation of drugs for diagnosis or treatment of lung cancer and melanoma.
Owner:NANFANG HOSPITAL OF SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
Hepatocellular carcinoma vaccine targeting secondary lymphoid tissues
ActiveCN109422816AOvercoming HLA restrictionChemokinesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHigh risk populationsCell membrane
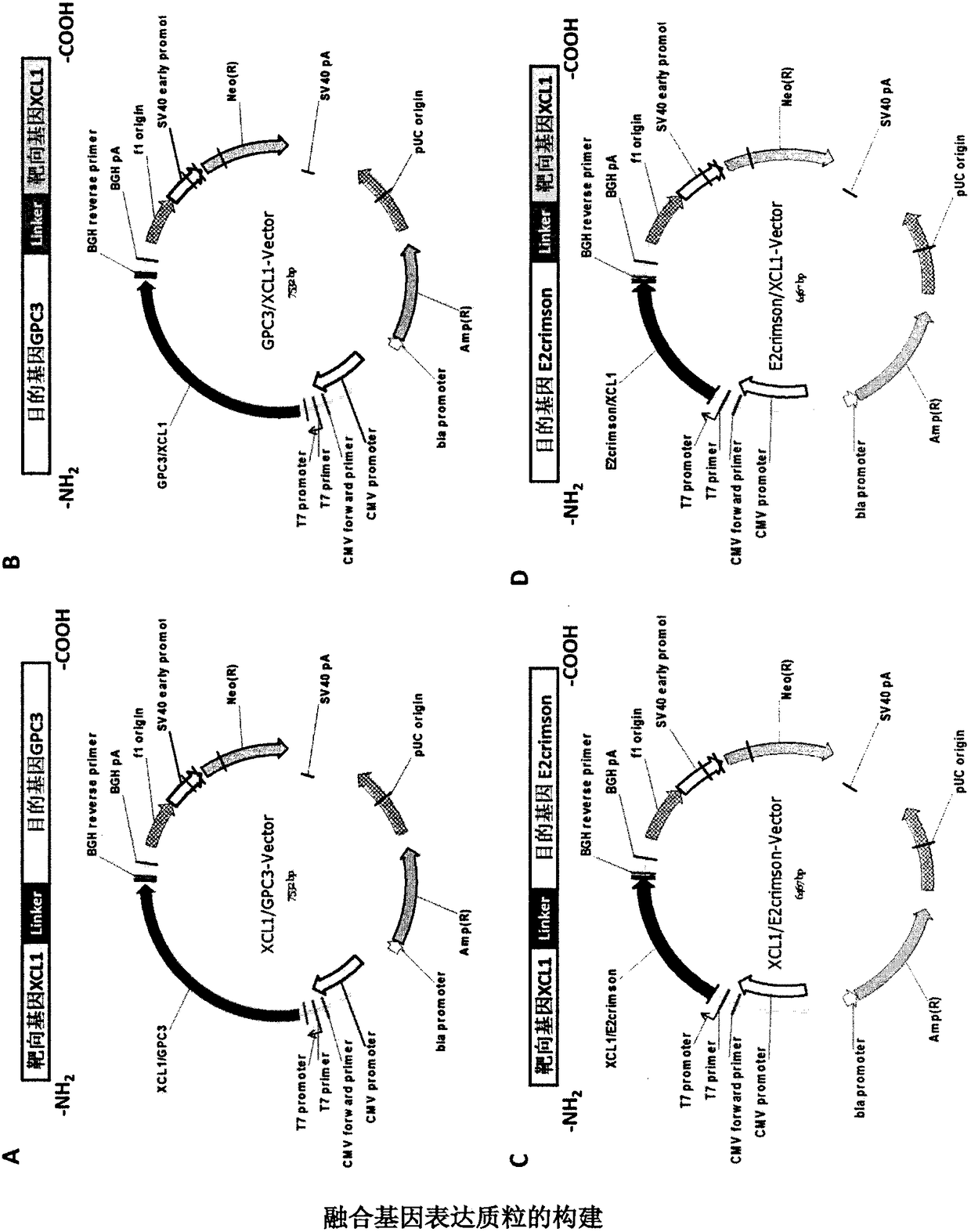
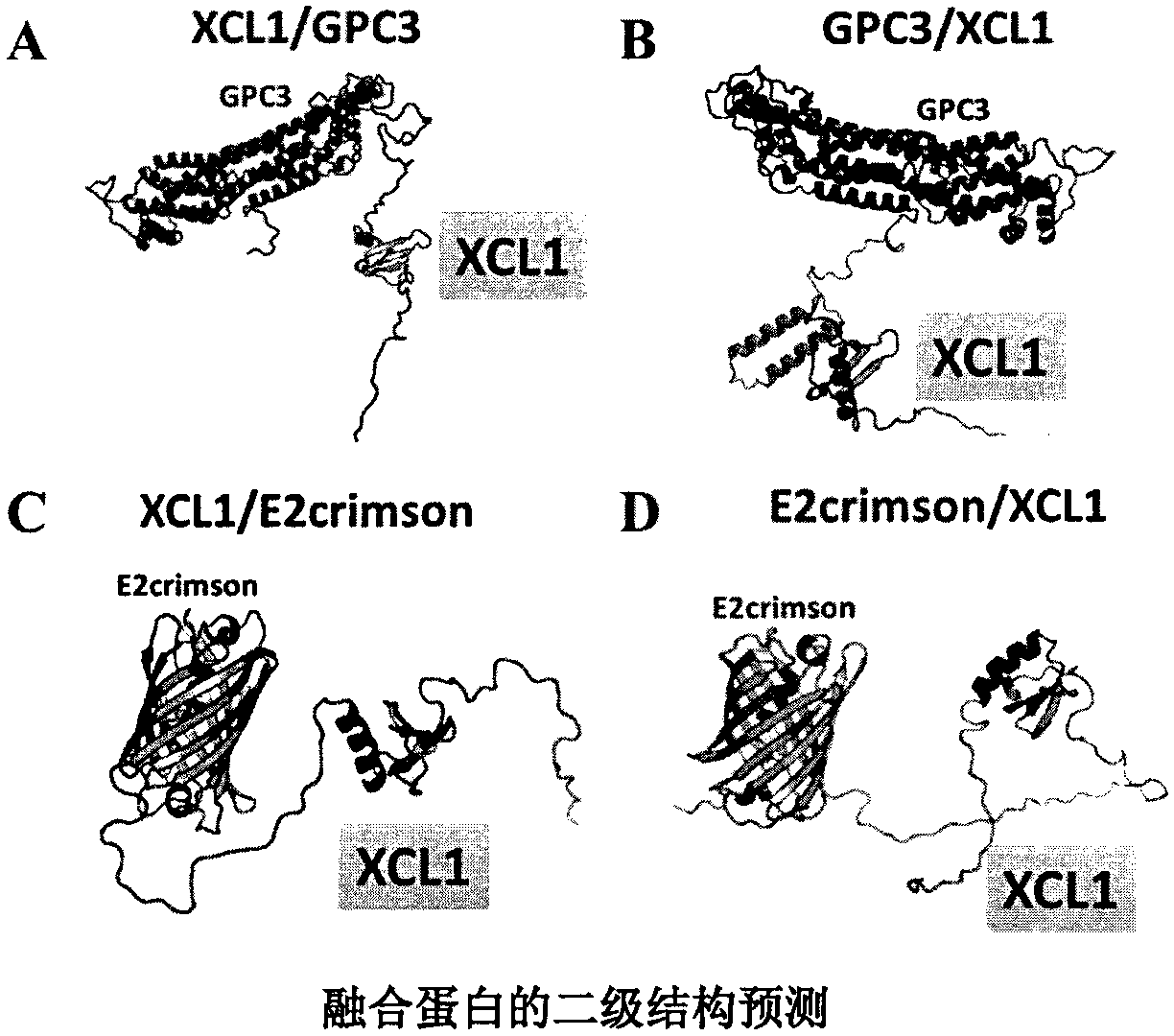
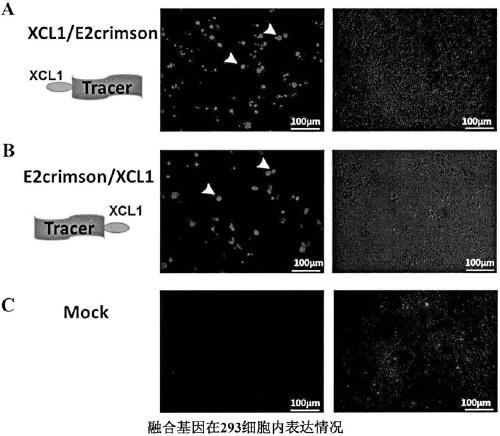
The invention provides a hepatocellular carcinoma vaccine targeting secondary lymphoid tissues. The vaccine comprises fusion protein comprising (a) phosphatidylinositol proteoglycan-3 (GPC3) and (b) lymphocyte chemotactic factor (XCL1) polypeptide of a specifically bonded chemokine receptor 1 (XCR1), nucleic acid encoding the fusion protein and vectors of the nucleic acid, wherein (a) is connectedwith (b) through a linker, and (a) lacks amino acid residues with a cell membrane anchoring effect. The vaccine comprises the fusion protein, the nucleic acid and / or the vectors, and application of the fusion protein, the nucleic acid and / or the expression vectors in prevention and treatment of liver cancers is provided. The vaccine has the effect of intervention of generation and development ofliver cancers, and can be applied to intervention of high-risk population of liver cancer, and for example, the vaccine can be applied to intervention of the generation progress of hepatitis B-relatedpatients to liver cancers.
Owner:NEWISH TECH (BEIJING) CO LTD +1
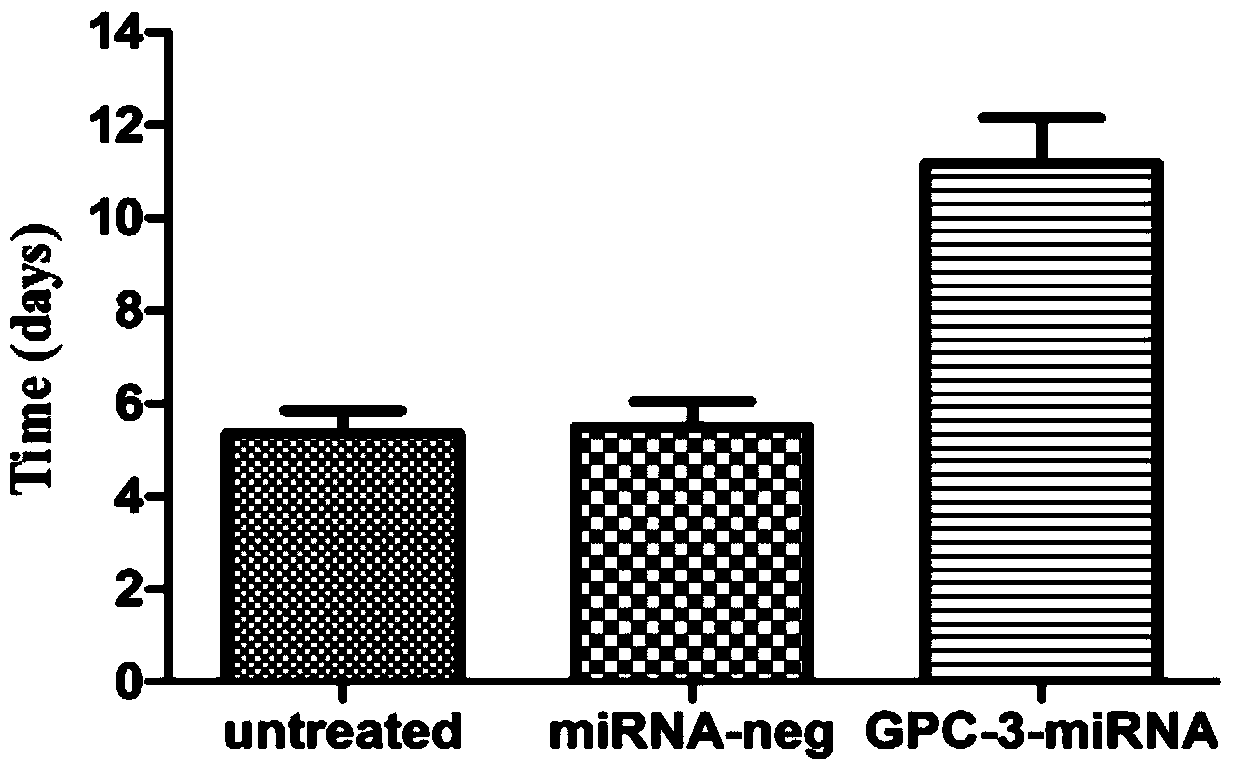
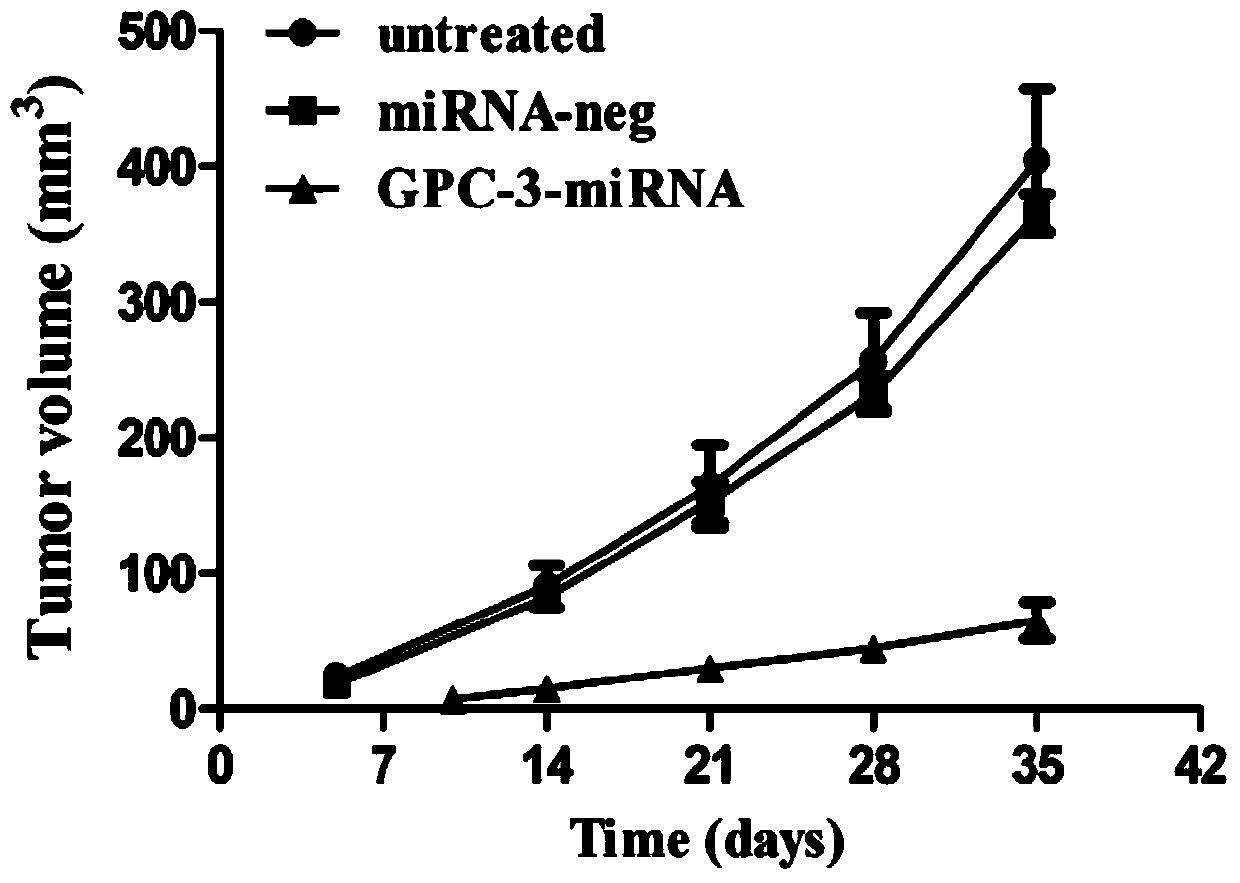
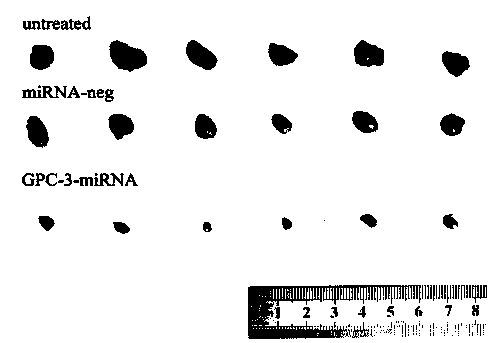
Method for detecting inhibiting ability of silent GPC-3 gene transcription on hepatocellular carcinoma transplanted tumor in nude mouse
InactiveCN103743902ASimple methodVector-based foreign material introductionMaterial analysisFluorescenceHepg2 cells
The invention discloses a method for detecting the inhibiting ability of silent GPC-3 (glypican-3) gene transcription on a hepatocellular carcinoma transplanted tumor in a nude mouse. The method includes: 1) designing and synthesizing 4 pairs of miRNA oligomeric single-strand DNA specific to a target gene consensus sequence, then synthesizing the corresponding dsDNA, inserting the dsDNA into a vector to construct 4 recombinant plasmids, and picking out the recombinant plasmid with the highest interference efficiency through fluorescence quantitative PCR; 2) transfecting the recombinant plasmid with the highest interference efficiency into HepG2 cells to construct transfected HepG2 cells, and performing screening, thus obtaining a stably transfected HepG2 cell; 3) inoculating the stably transfected HepG2 cell to the nude mouse subcutaneously to construct a human hepatocellular carcinoma tumor-bearing nude mouse model; and 4) then determining the growth state of the stably transfected HepG2 cell in the human hepatocellular carcinoma tumor-bearing nude mouse model. The method provided by the invention can be employed to detect the inhibiting ability of silent GPC-3 gene transcription on a hepatocellular carcinoma transplanted tumor in the nude mouse, and can be used for research of GPC-3 on transplanted tumors.
Owner:AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF NANTONG UNIV
Glypican-3 peptide reagents and methods
PendingCN110831634APeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsHepatocellular carcinomaPhospholipid
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
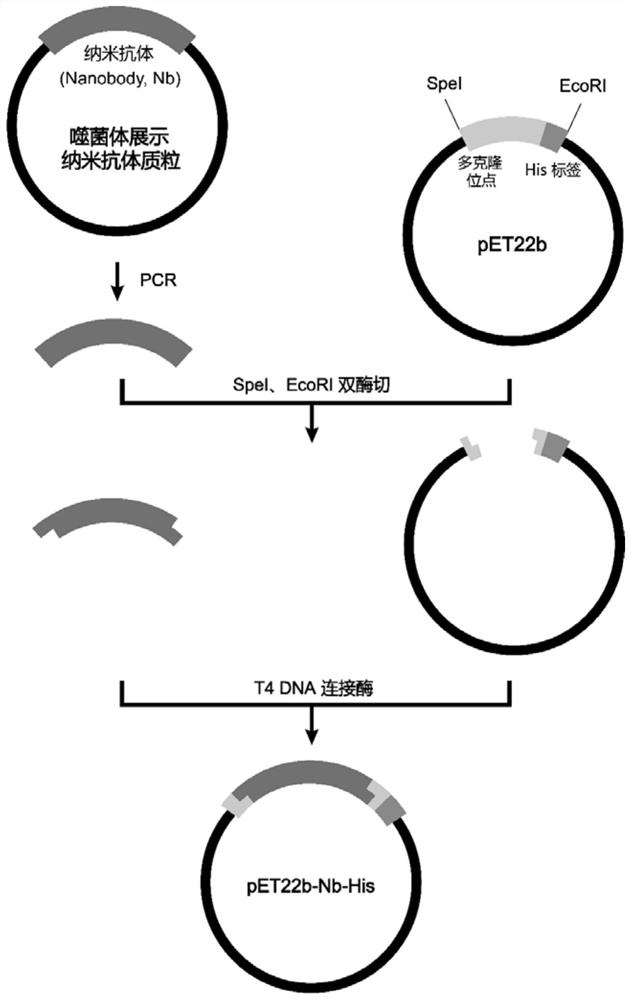
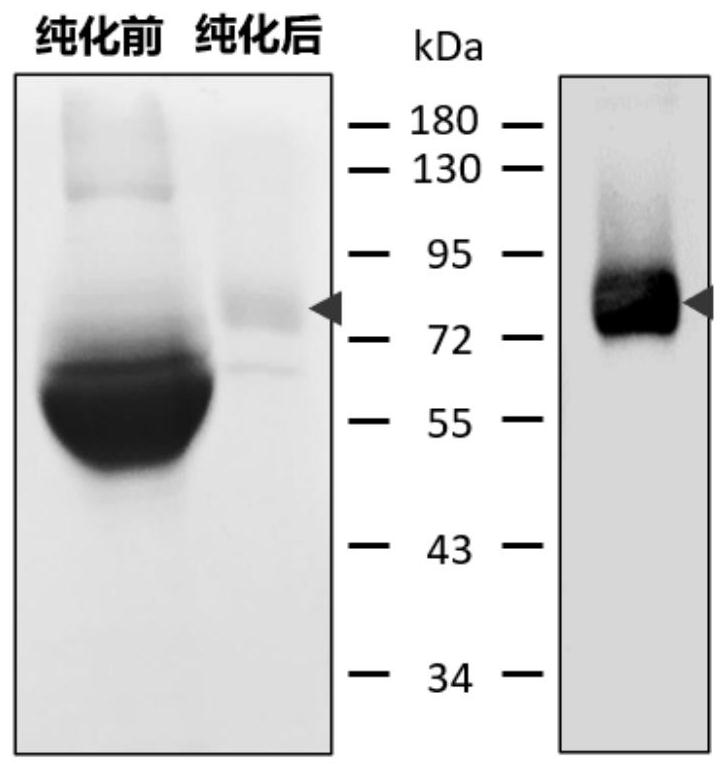
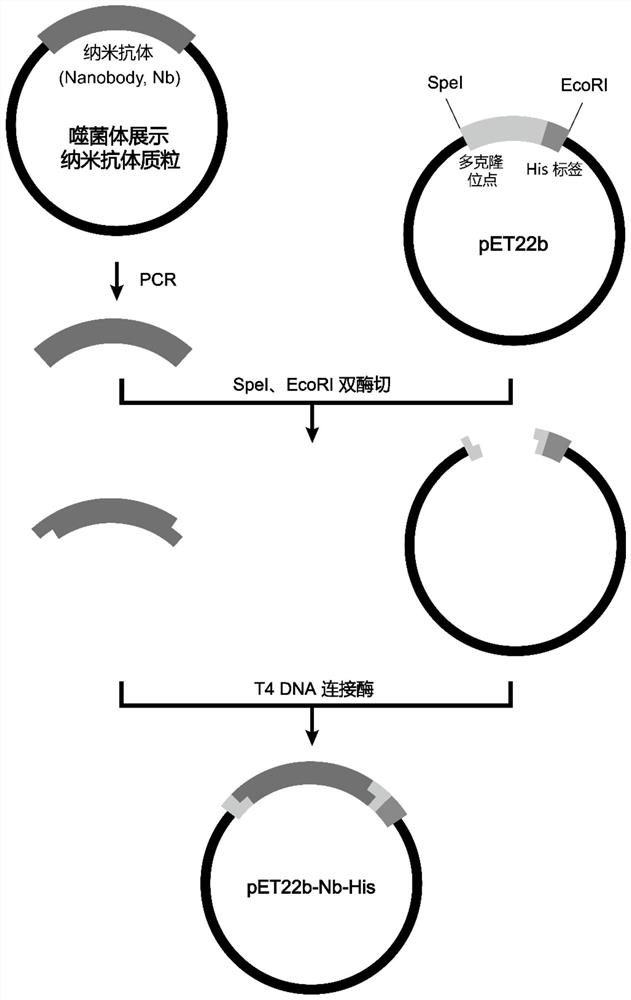
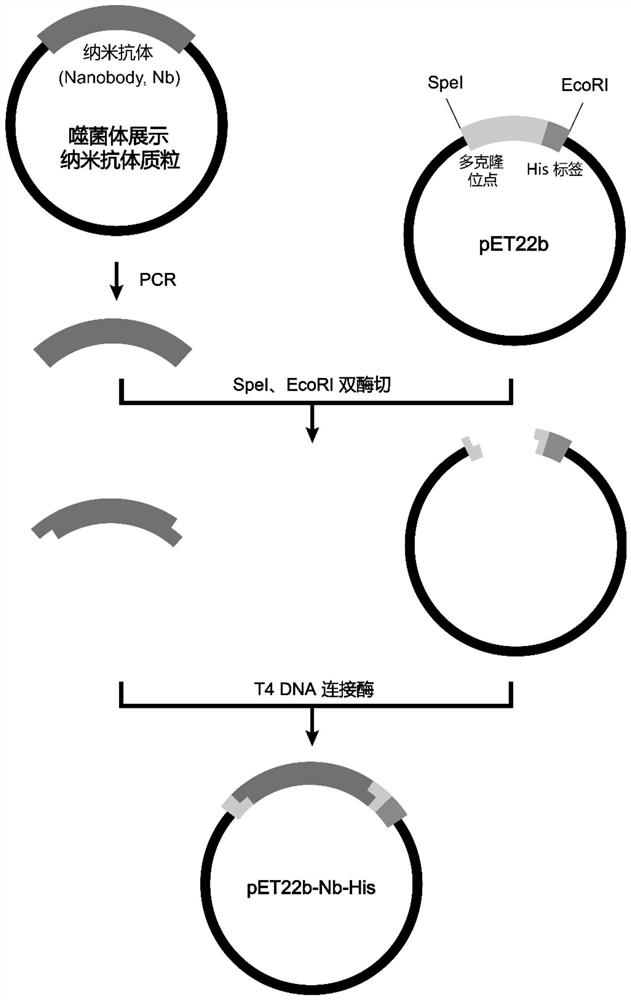
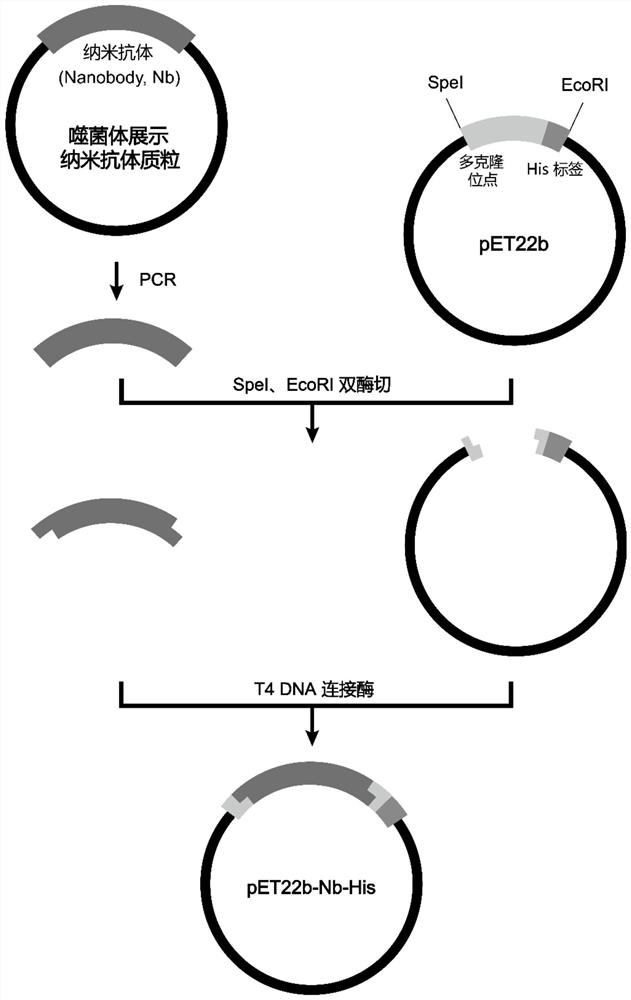
Nano-antibody of glypican 3 with outstanding high stability and preparation method of nano-antibody
ActiveCN111909274AAntibody stability is highEasy to operateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAntiendomysial antibodiesNucleotide
The invention relates to a nano-antibody of glypican 3 with outstanding high stability and a preparation method of the nano-antibody, and also relates to an amino acid sequence of the nano-antibody, agene coding sequence, an expression vector capable of expressing the nano-antibody and a host cell. The amino acid sequence of the nano-antibody of GPC3 is shown as SEQ ID NO: 7, and the nucleotide sequence of the coding gene is shown as SEQ ID NO: 8. The nano-antibody of the GPC3 can specifically identify hepatoma carcinoma cells with high GPC3 expression by binding to the GPC3 expressed by cellmembranes. The antibody has outstanding high stability, can be used for the functional study of the GPC3 and also can be used for the development of the diagnostic reagents and therapeutic drugs of the hepatocellular carcinoma.
Owner:珠海中科先进技术研究院有限公司
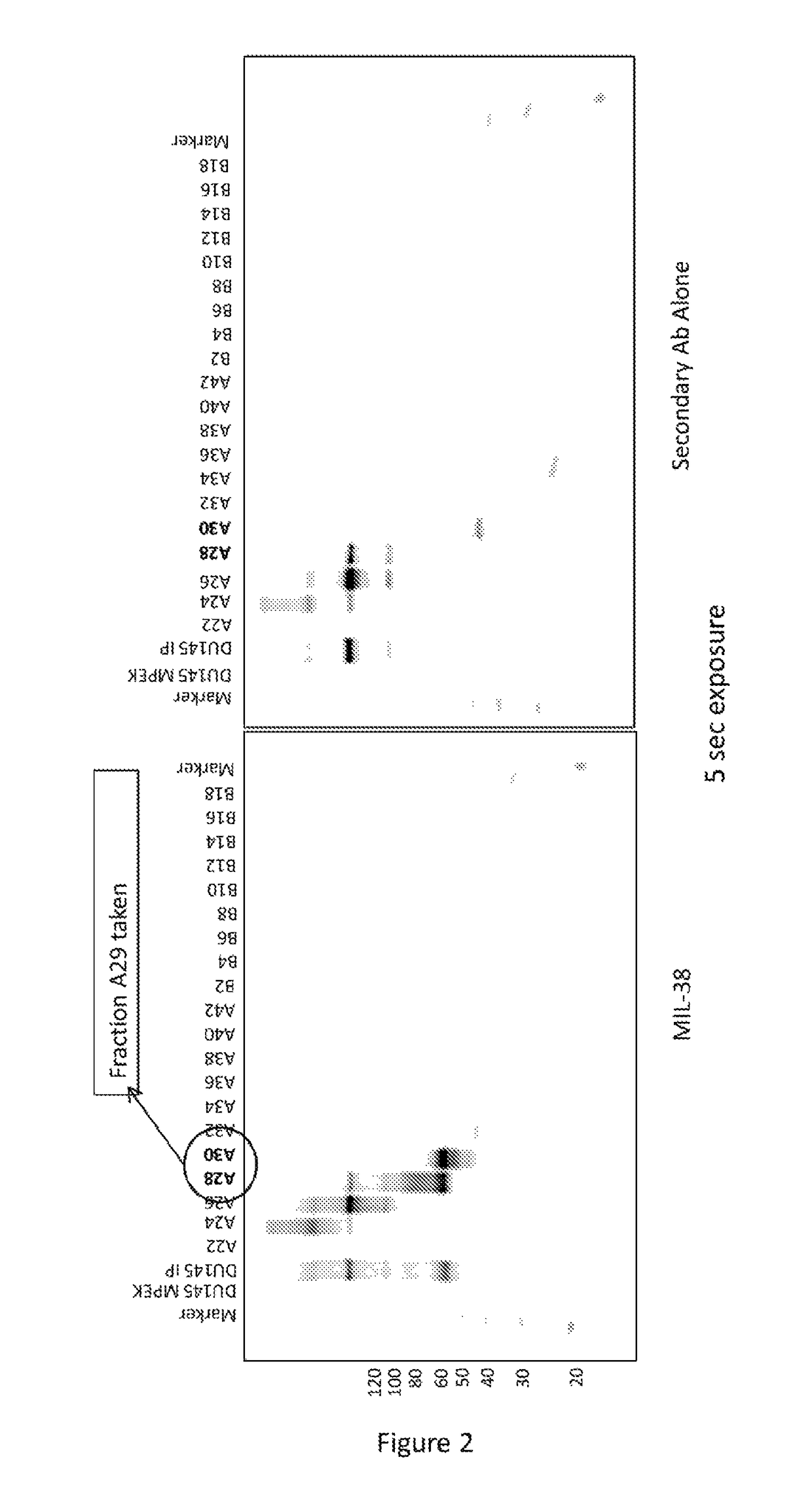
Cell surface prostate cancer antigen for diagnosis
ActiveUS20160349263A1Quick checkBiological material analysisImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntigenProstate cancer
The present invention provides compositions and methods of detecting prostate cancer in the body fluids or tissues of patients. Prostate cancer is detected by measuring the level of glypican-1 in a body fluid sample. In one embodiment prostate cancer is detected by contacting a body fluid sample with an anti-glypican-1 antibody, such as MIL-38. The invention includes kits for detection of prostate cancer in a body fluid sample, comprising an anti-glypican-1 antibody and glypican-1 standards.
Owner:GLYP HLDG PTY LTD
Phenotypic profiling of hepatocellular carcinoma circulating tumor cells for treatment selection
ActiveUS20200182877A1Accurate identificationEfficient captureImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsDisease diagnosisOncologyThelial cell
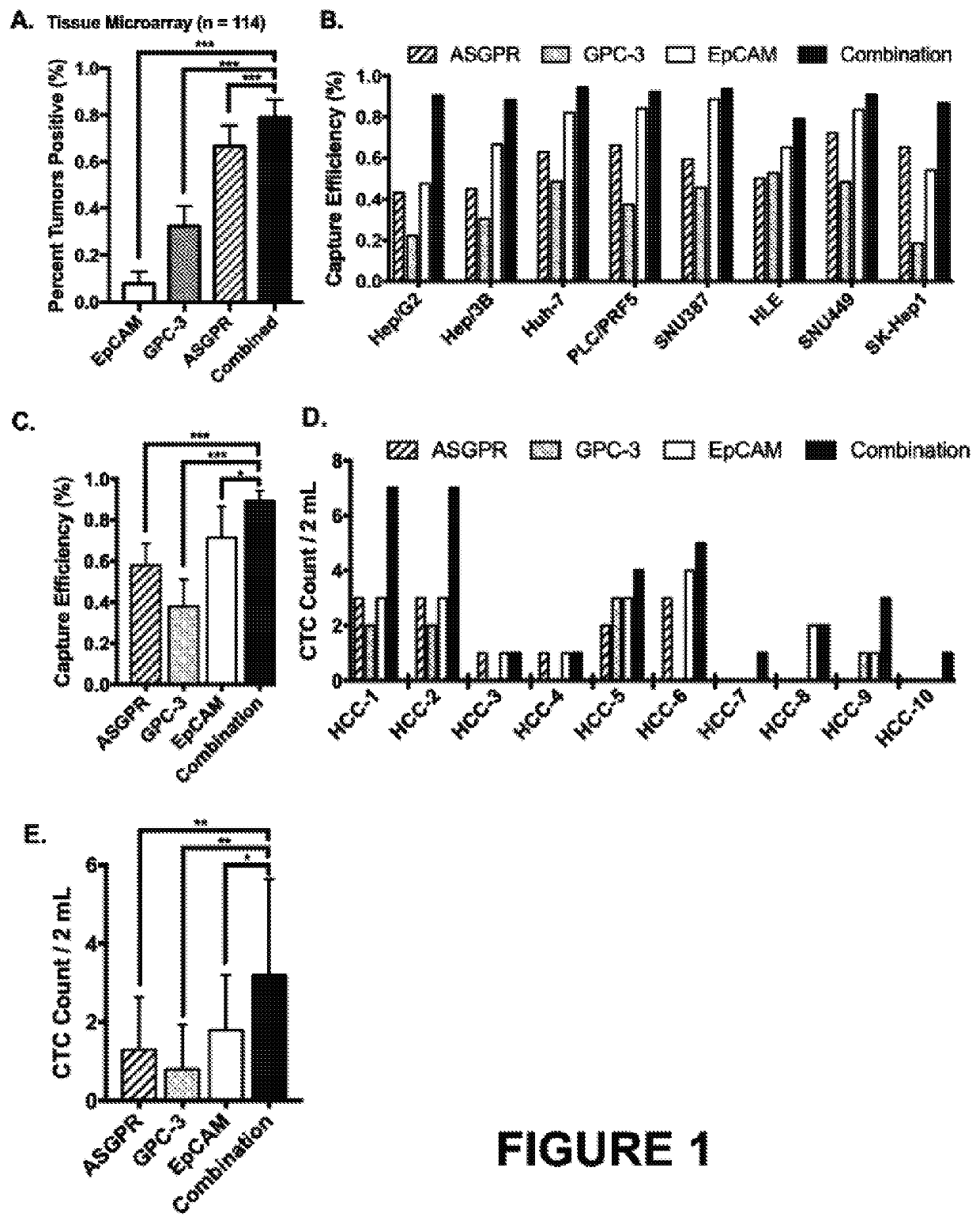
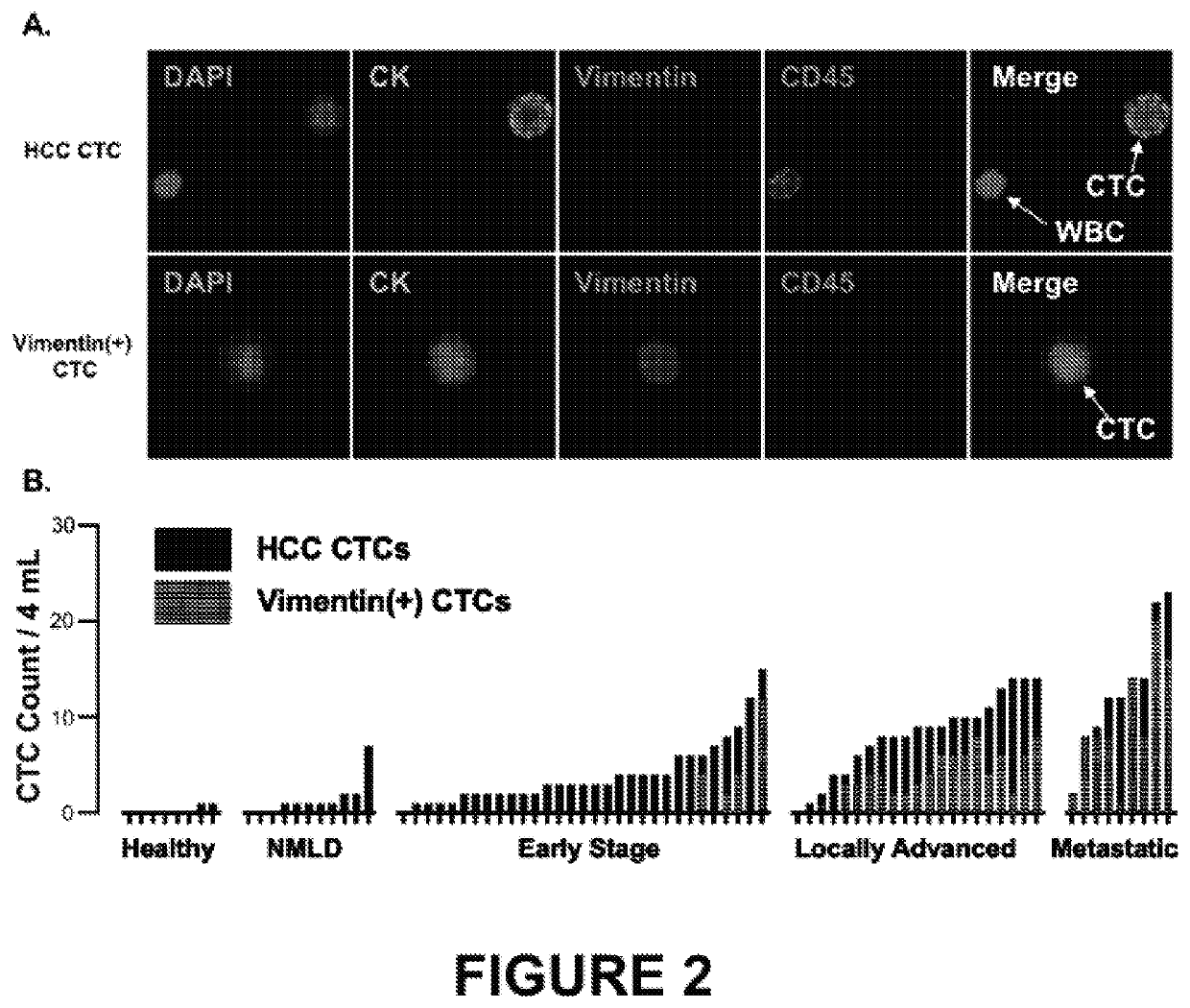
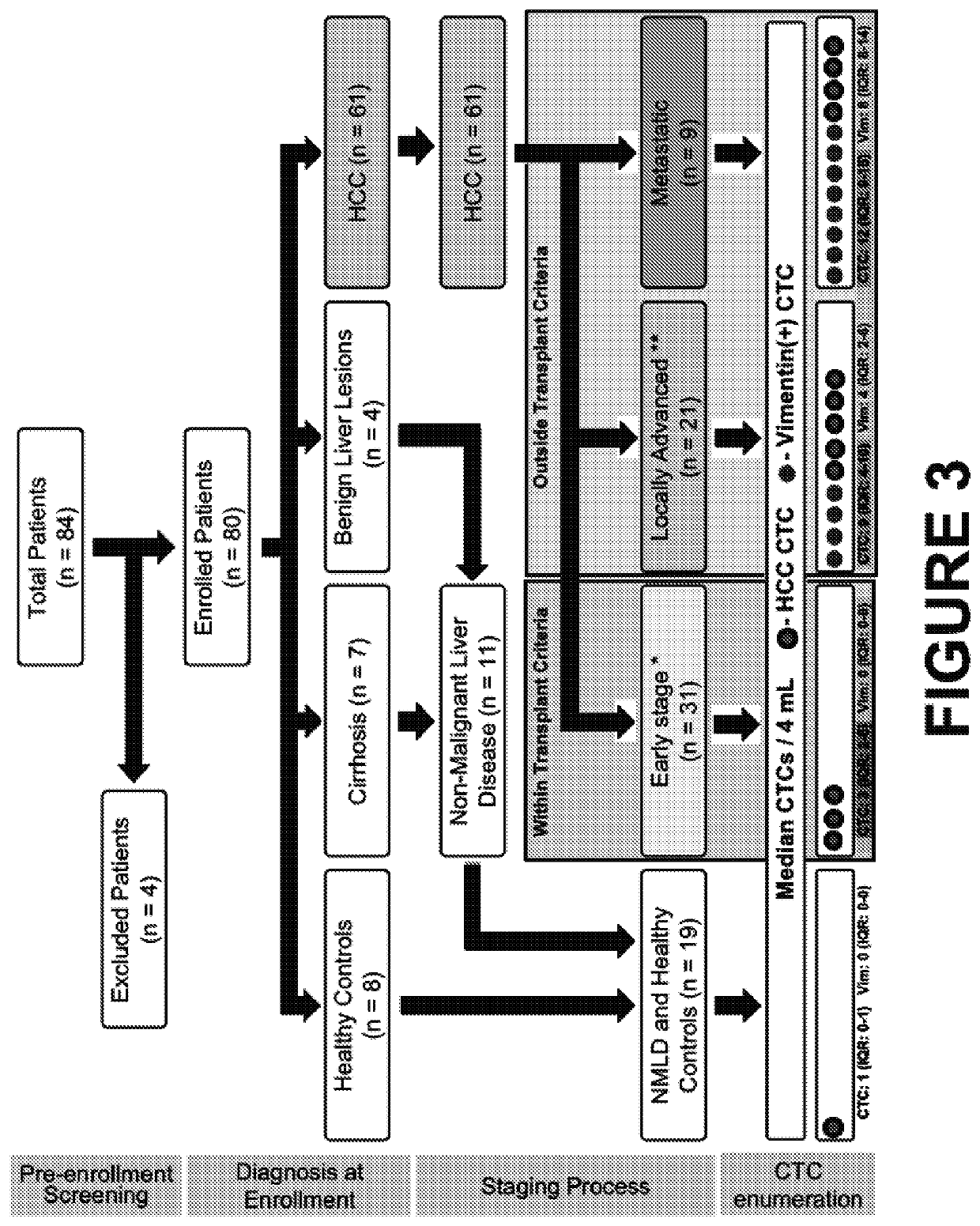
Methods and kits for detecting hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence or metastasis, and of measuring markers of hepatocellular carcinoma, including markers of hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence or metastasis, in a blood sample obtained from a subject by (a) isolating circulating tumor cells (CTCs) by contacting a blood sample obtained from the subject with a set of capture antibodies, wherein the capture antibodies specifically bind asialoglycoprotein receptor (ASGPR), Glypican-3, and epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM); (b) contacting the isolated CTCs with an antibody that specifically binds vimentin; and (c) measuring the number of vimentin-positive CTC.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Glypican-1 in human breast cancer
InactiveUS20070026471A1Good effectConfirming the importance of glypicans in breast cancerImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsInsulin-like growth factorProtein C
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Phosphatidylinositol proteoglycan 3 nanometer antibody as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111732659AImprove stabilityEasy to operateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesComplementarity determining regionAntiendomysial antibodies
The present invention discloses a phosphatidylinositol proteoglycan 3 (Glypican-3, GPC3) nanometer antibody and a preparation method thereof. The nanometer antibody has three complementarity determining regions: CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3, wherein the CDR1 comprises an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and the CDR2 comprises an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.2, and the CDR3 comprises an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.3. The nanometer antibody disclosed by the invention can be used for specifically identifying liver cancer cells with high GPC3 expression by combining with GPC3 expressed by a cell membrane. The antibody has high stability in serum, can be used for function research of the GPC3, and can also be used for development of diagnosis reagents and treatmentdrugs of the hepatocellular carcinoma.
Owner:珠海中科先进技术研究院有限公司
Glypican-1 in human breast cancer
InactiveUS7108986B2Growth stimulatory effectDecrease glypicanSamplingPeptide/protein ingredientsInsulin-like growth factorHigh level expression
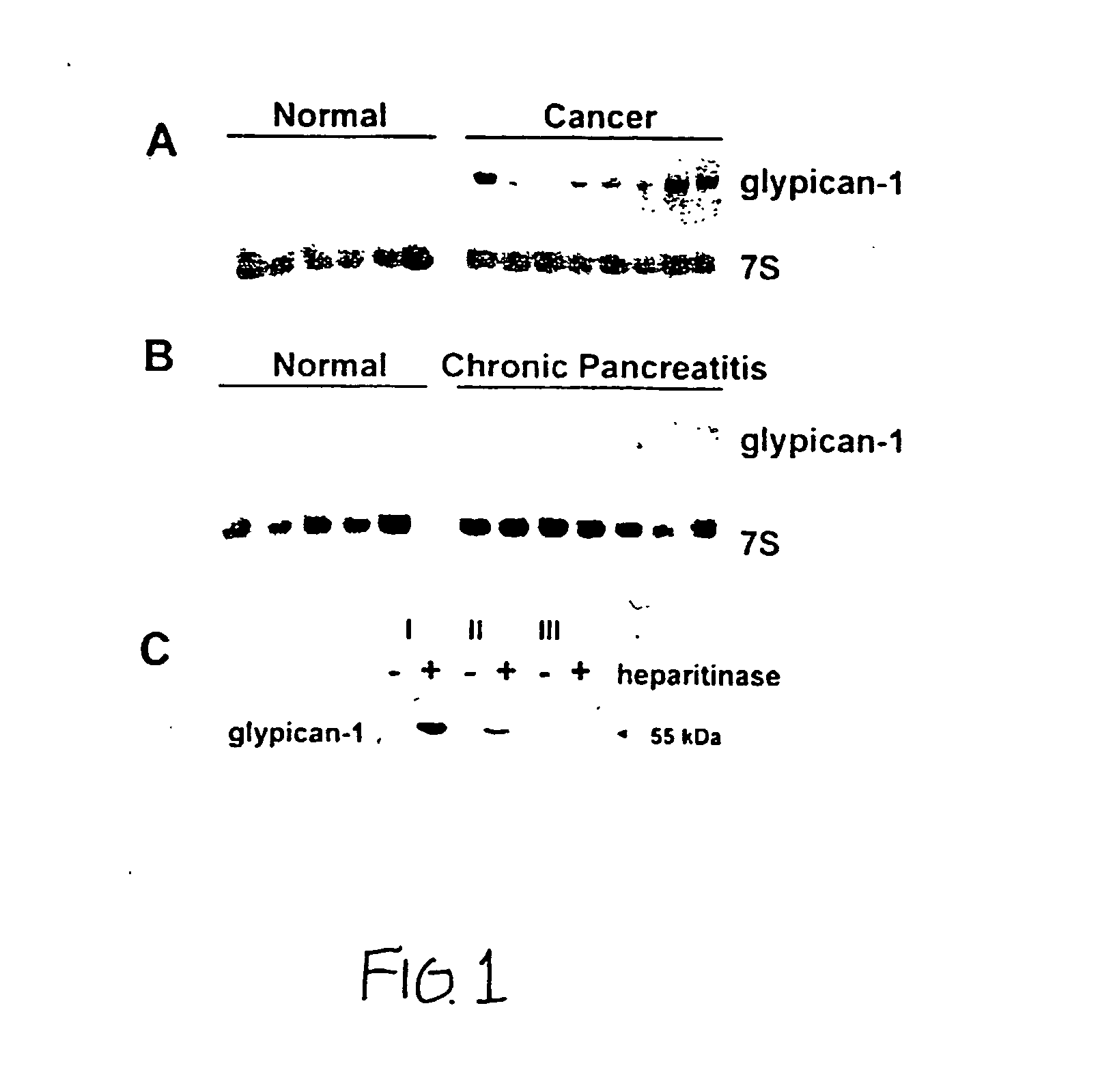
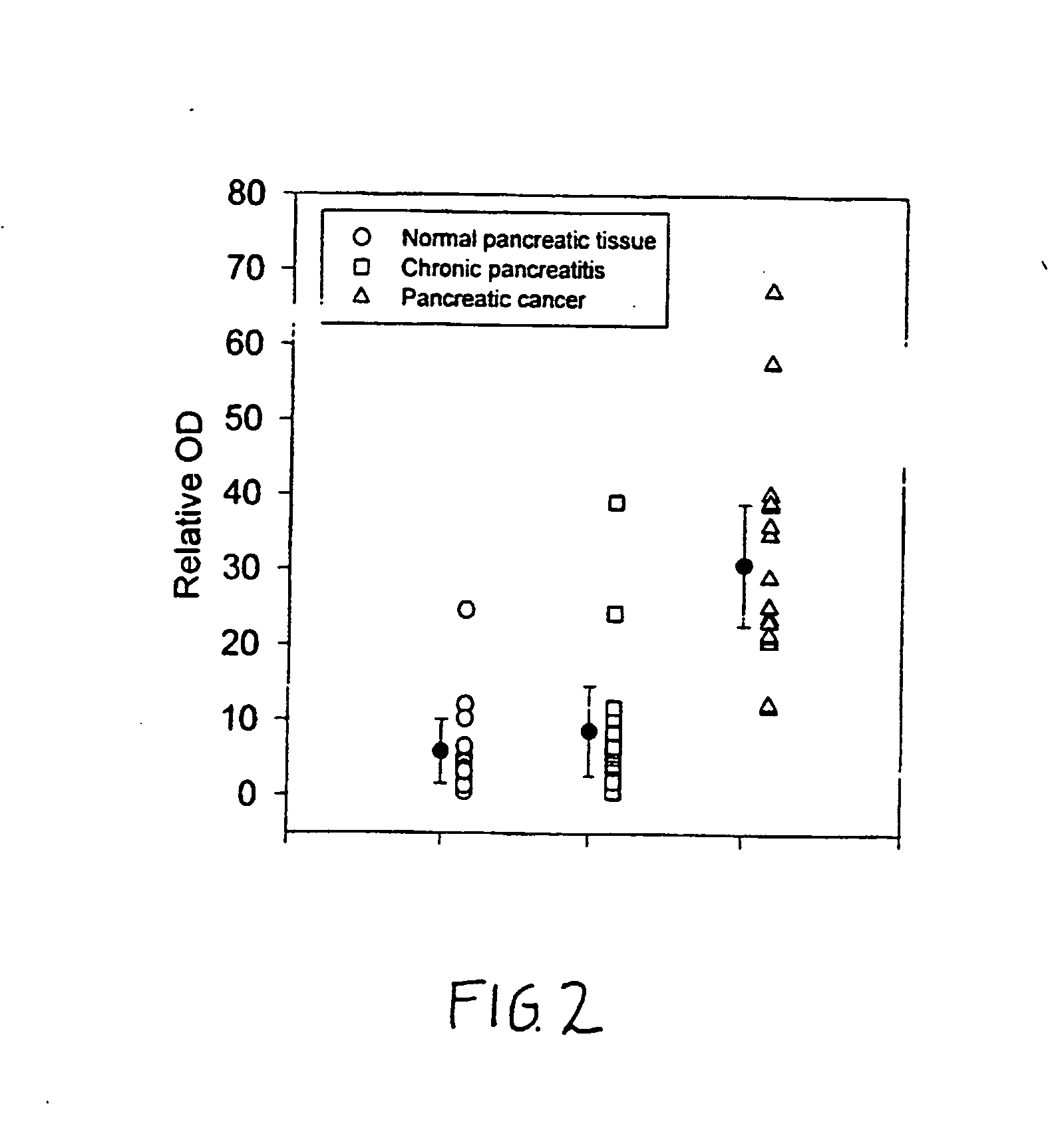
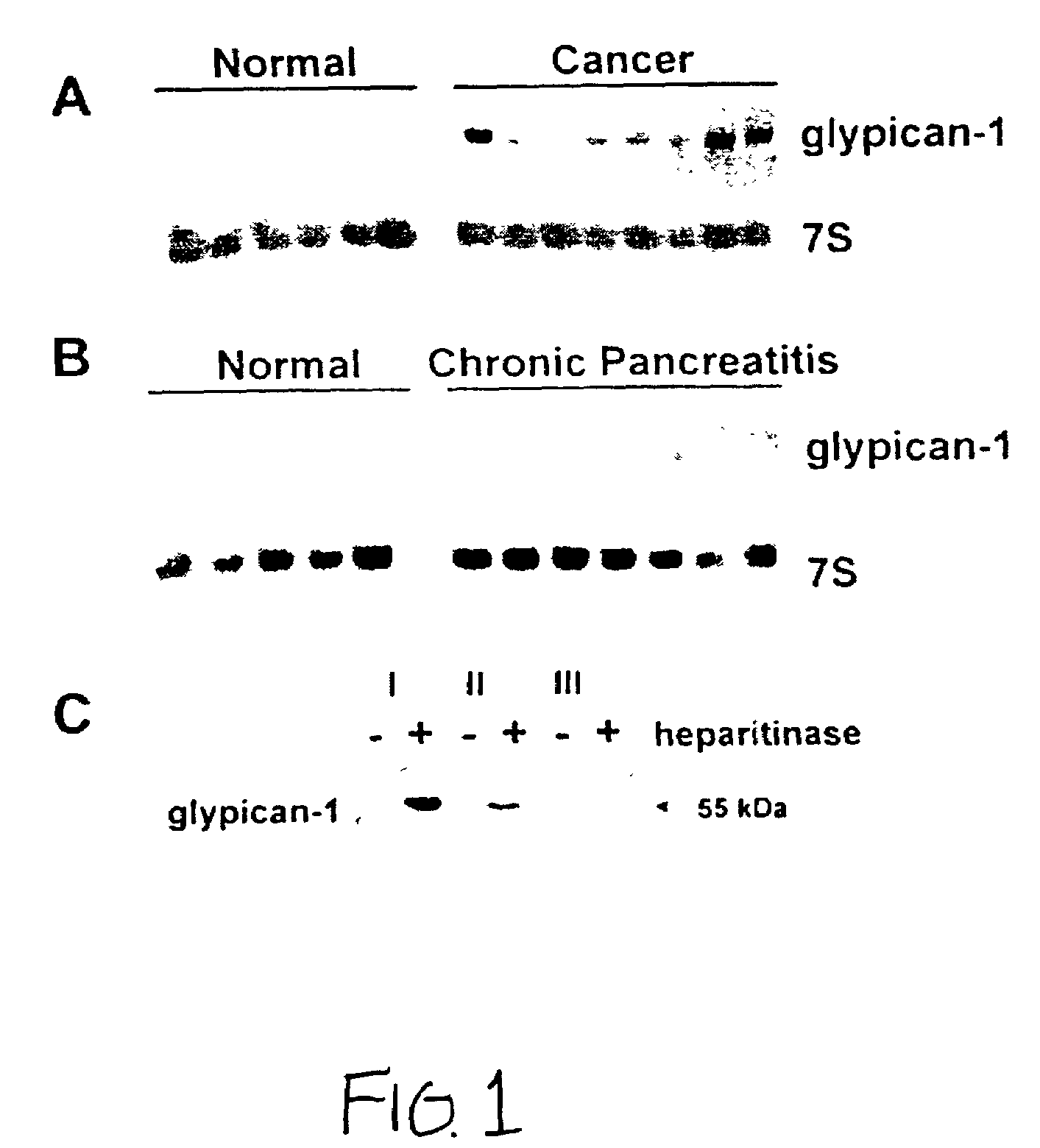
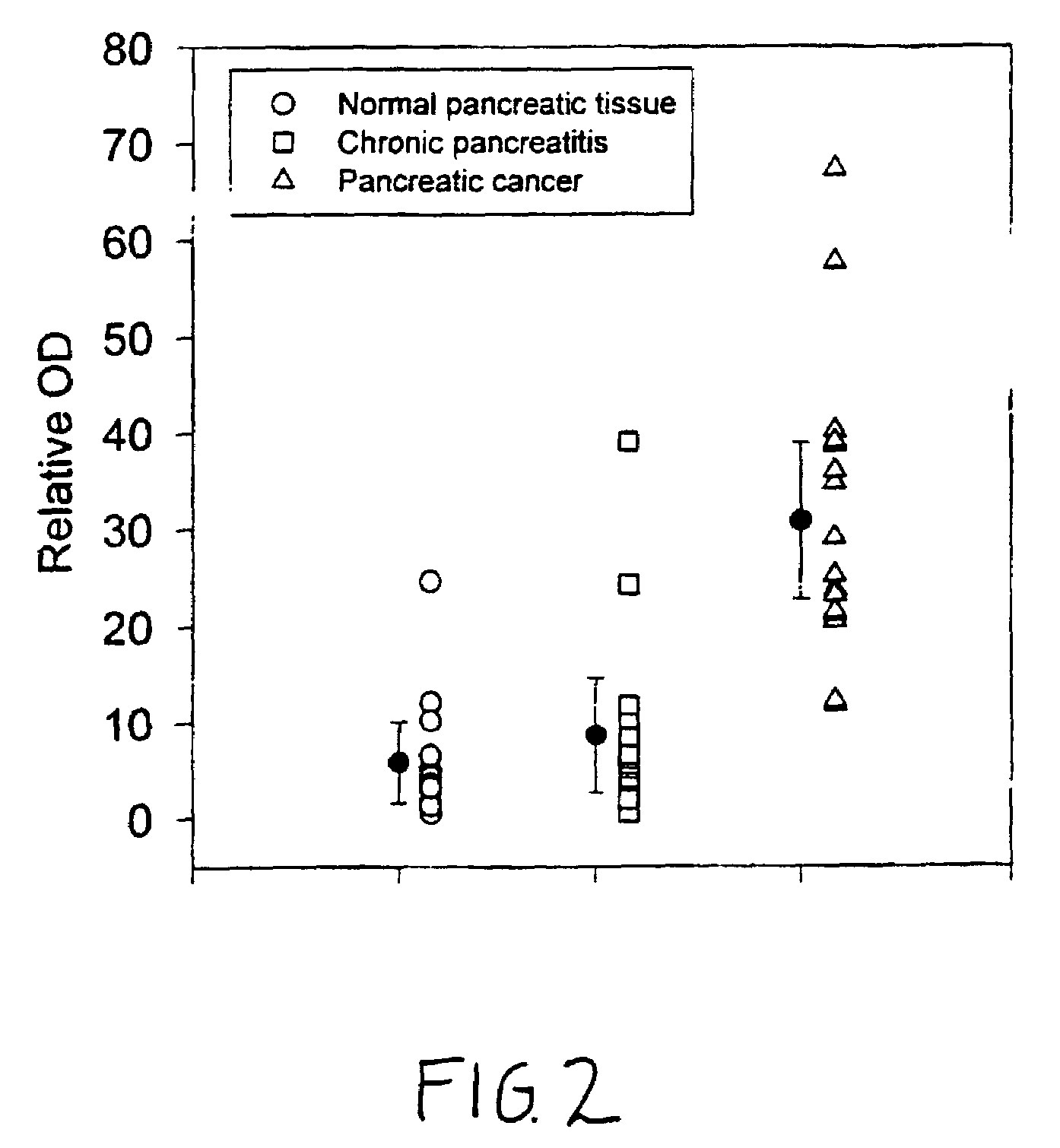
Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-(GPI-) anchored HSPG glypican-1 is strongly expressed in human breast and pancreatic cancer—both by the cancer cells and in the case of pancreatic cancer the adjacent fibroblasts—whereas expression of glypican-1 is low in the normal pancreas and in chronic pancreatitis. Treatment of two pancreatic cancer cell lines, which express glypican-1, with the enzyme phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase-C (PI-PLC) abrogated their mitogenic responses to two heparin-binding growth factors: fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF2) and heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (HB-EGF). Treatment of MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-468 breast cancer cells with PI-PLC abrogates the mitogenic response to two heparin-binding growth factors, heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor (HB-EGF) and fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2). Syndecan-1 is also expressed at high levels in breast cancer tissues as well as breast cancer cells by comparison with breast normal tissues. Temporary or permanent transfection of a glypican-1 antisense construct attenuated glypican-1 protein levels and the mitogenic response to FGF2 and HB-EGF. Glypican can be used to detect the carcinoma in vitro and therapeutics that either bind to (e.g., antibodies or drugs), remove (e.g., enzymes) or prevent the expression (e.g., antisense constructs) of surface of the extracellular domain of glypican-1 are effective in retarding the growth of glypican-responsive carcinomas.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Car t cells with one or more interleukins
PendingUS20210094994A1Enhance cell therapyImproved cancer therapyPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigen receptorWhite blood cell
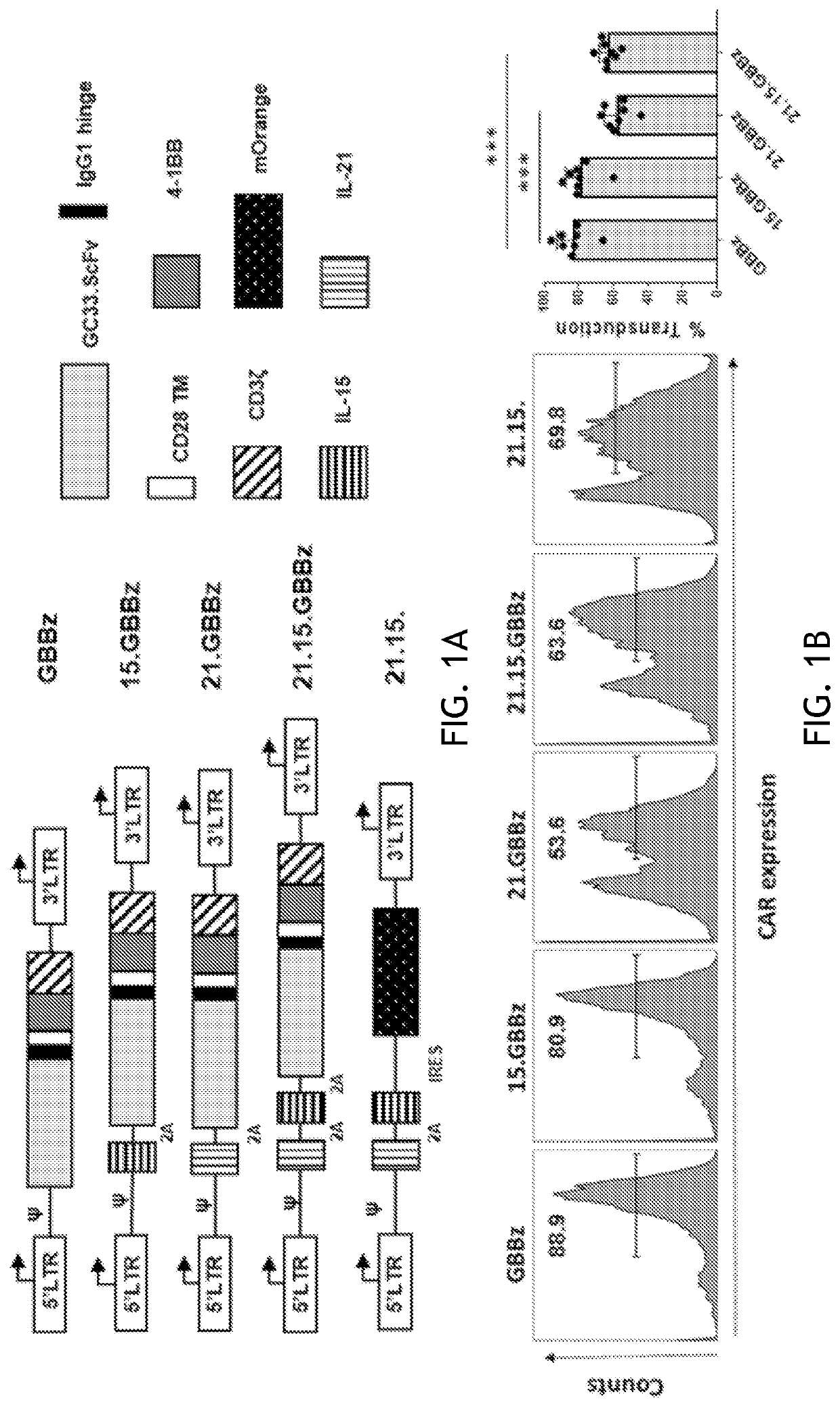
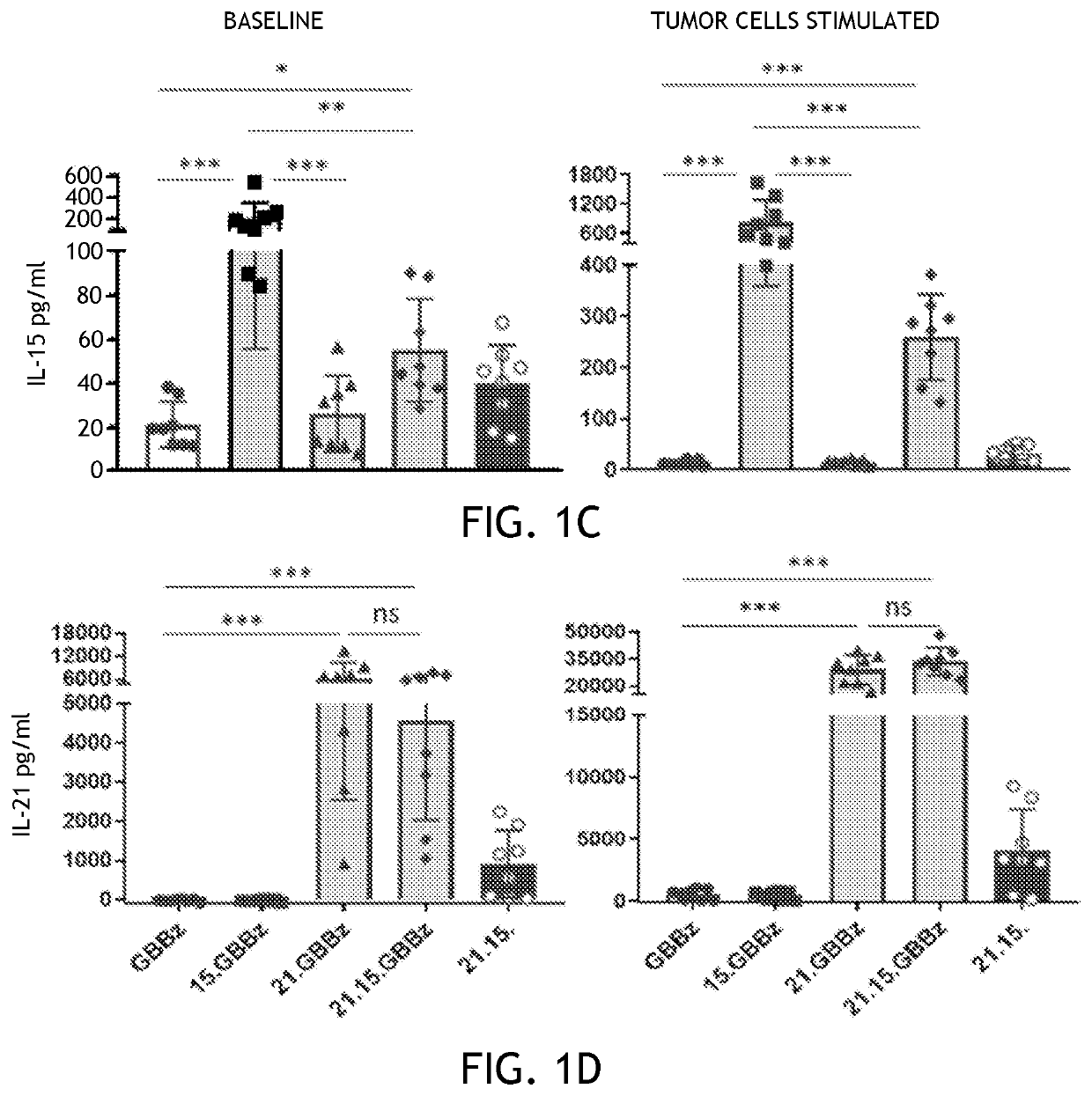
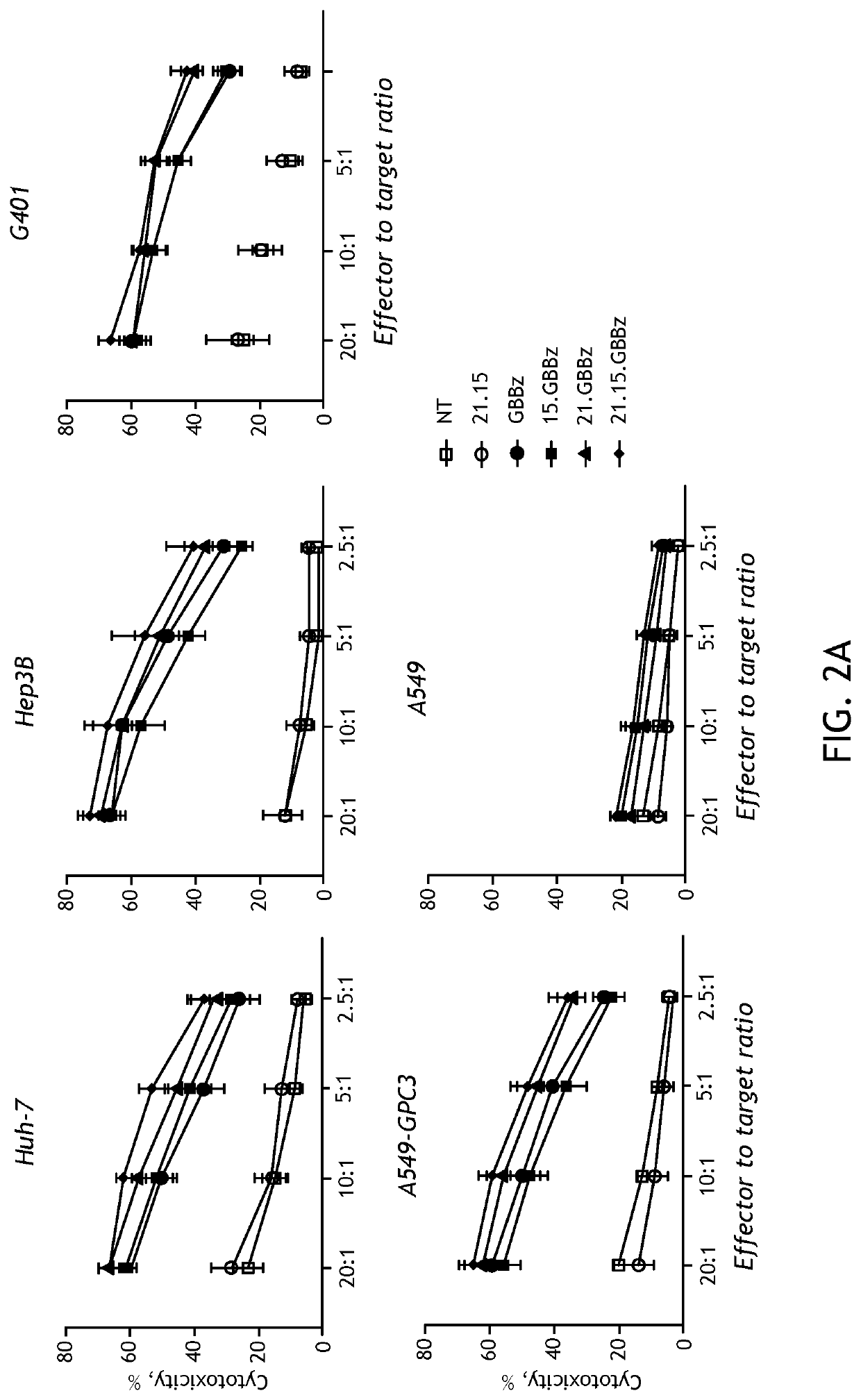
Embodiments of the disclosure encompass methods and compositions related to targeting of tumor antigen-positive cells with therapy using cells that express a chimeric antigen receptor that targets the tumor antigen-positive cells in the presence of None or more interleukins that enhance efficacy of the tumor antigen-specific chimeric antigen receptors. In specific embodiments, the tumor antigen is glypican-3 and the one or more interleukins are EL-15 and EL-21.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
Phosphatidylinositol proteoglycan 3 nano antibody with outstanding acid-base stability and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111848803AAntibody stability is highEasy to operateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAntiendomysial antibodiesNucleotide
The invention relates to a phosphatidylinositol proteoglycan 3 nano antibody with outstanding acid-base stability and a preparation method thereof, and also relates to an amino acid sequence and a gene coding sequence of the nano-antibody, and an expression vector and a host cell capable of expressing the nano-antibody. The amino acid sequence of the GPC3 nano antibody is as shown in SEQ ID NO 7,and the nucleotide sequence of the encoding gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO 8. The GPC3 nano antibody can be combined with GPC3 expressed by a cell membrane to specifically recognize hepatoma carcinomacells highly expressed by GPC3. The antibody has outstanding acid-base stability, can be used for functional research of GPC3, and can also be used for development of diagnostic reagents and therapeutic drugs for hepatocellular carcinoma.
Owner:珠海中科先进技术研究院有限公司
Cell surface prostate cancer antigen for diagnosis
ActiveUS10151754B2Quick checkBiological material analysisImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntiendomysial antibodiesProstate cancer
The present invention provides compositions and methods of detecting prostate cancer in the body fluids or tissues of patients. Prostate cancer is detected by measuring the level of glypican-1 in a body fluid sample. In one embodiment prostate cancer is detected by contacting a body fluid sample with an anti-glypican-1 antibody, such as MIL-38. The invention includes kits for detection of prostate cancer in a body fluid sample, comprising an anti-glypican-1 antibody and glypican-1 standards.
Owner:GLYP HLDG PTY LTD
Quantitative measurement kit for glypican and detection method thereof
The invention discloses a quantitative measurement kit for glypican and a detection method thereof, relates to a kit for measuring or analyzing a material by means of a biologically peculiar combination method and a measurement method thereof, and particularly relates to an immunodetection kit and a detection method thereof. The invention aims at providing a quantitative measurement kit, which is more effective, more sensitive and has higher specificity, for the glypican. The kit provided by the invention comprises a glypican magnetic-separation reagent, an enzyme reactant, a standard substance and a substrate solution. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the kit. The detection method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of sufficiently combining a to-be-detected sample and the standard substance with the glypican magnetic-separation reagent respectively; afterwards, mixing an obtained first mixture with the enzyme reactant, and incubating an obtained second mixture; separating the glypican magnetic-separation reagent; cleaning the glypican magnetic-separation reagent, and then adding the substrate solution into the cleaned glypican magnetic-separation reagent; measuring absorbency. The detection method provided by the invention is good in accuracy, high in precision, high in sensitivity and wide in detection range, and is simple and time-saving to operate.
Owner:北京久峰润达生物技术有限公司
Therapeutic for hepatic cancer
InactiveCN102046200BDigestive systemAntibody ingredientsAntiendomysial antibodiesPharmaceutical drug
A novel pharmaceutical composition for treating or preventing hepatocellular carcinoma and a method of treatment are provided. A pharmaceutical composition for treating or preventing liver cancer is obtained by combining a chemotherapeutic agent with an anti-glypican 3 antibody. Also disclosed is a pharmaceutical composition for treating or preventing liver cancer which comprises as an active ingredient an anti-glypican 3 antibody for use in combination with a chemotherapeutic agent, or which comprises as an active ingredient a chemotherapeutic agent for use in combination with an anti-glypican 3 antibody. Using the chemotherapeutic agent and the anti-glypican 3 antibody in combination yields better therapeutic effects than using the chemotherapeutic agent alone, and mitigates side effects that arise from liver cancer treatment with the chemotherapeutic agent.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Phosphatidylinositol proteoglycan 3 nano antibody with outstanding thermal stability and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111848802AAntibody stability is highEasy to operateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAntiendomysial antibodiesNucleotide
The invention relates to a phosphatidylinositol proteoglycan 3 nano antibody with outstanding thermal stability and a preparation method thereof, and also relates to an amino acid sequence and a genecoding sequence of the nano-antibody, and an expression vector and a host cell capable of expressing the nano-antibody. The amino acid sequence of the GPC3 nano antibody provided by the invention is as shown in SEQ ID NO 7, and the nucleotide sequence of the encoding gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO 8. The GPC3 nano antibody can be combined with GPC3 expressed by a cell membrane to specifically recognize hepatoma carcinoma cells highly expressed by GPC3. The antibody has outstanding thermal stability, can be used for functional research of GPC3, and can also be used for development of diagnosticreagents and therapeutic drugs for hepatocellular carcinoma.
Owner:珠海中科先进技术研究院有限公司
Compositions and methods for inhibiting slit protein and glypican interactions
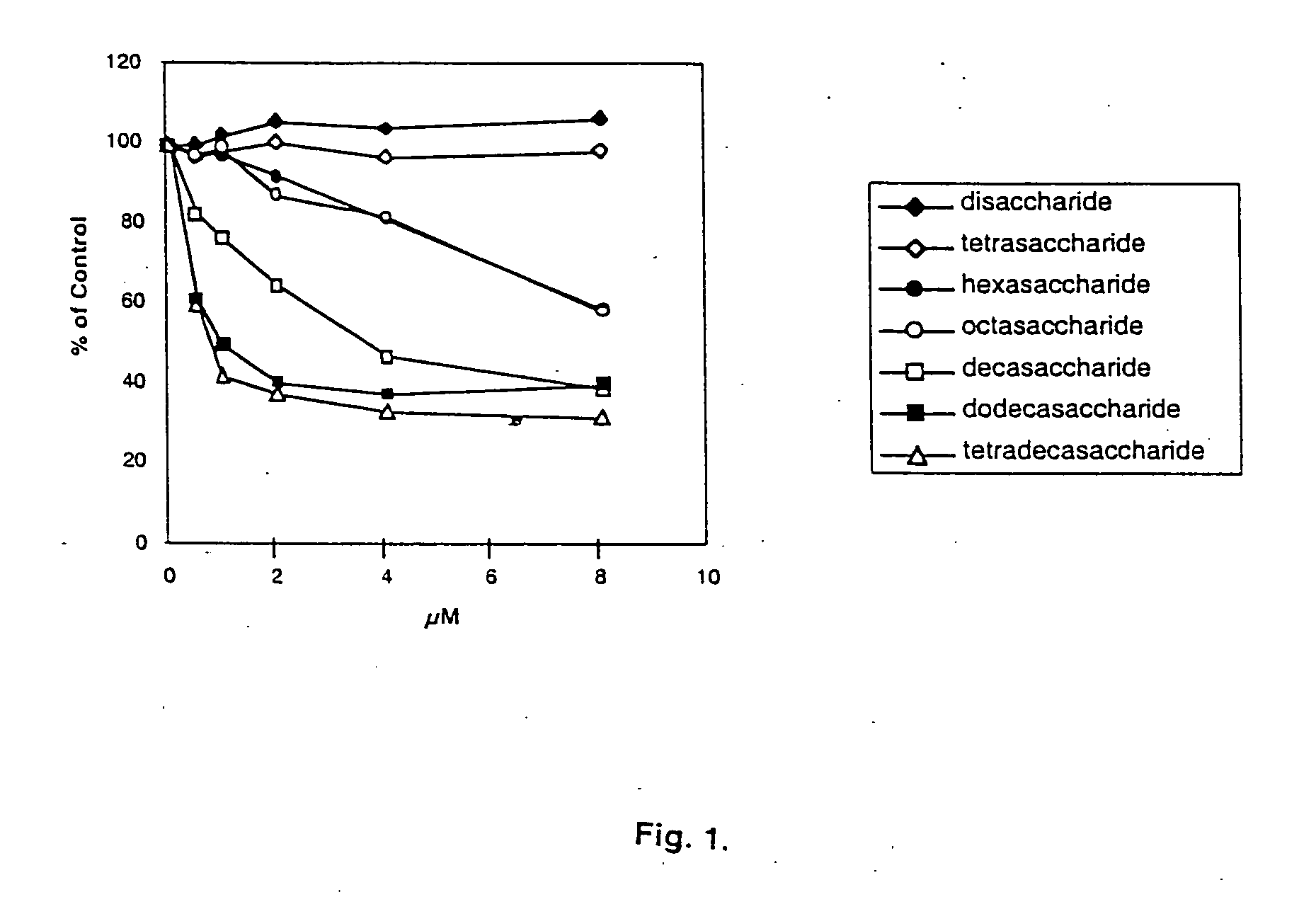
InactiveUS20050043273A1Promoting axonal regenerationPromote regenerationBiocideFibrinogenMedicineDrug carrier
A composition for inhibiting slit protein and glypican interactions including an effective amount of a heparin mimetic. A pharmaceutical composition for inhibiting slit protein and glypican interactions including an effective amount of a heparin mimetic and a pharmaceutical carrier. A composition for promoting axonal regeneration including an effective amount of a heparin mimetic. A therapeutic composition for inhibiting slit protein and glypican interaction or promoting axonal regeneration including an effective amount of a heparin mimetic. Various methods for inhibiting slit protein and glypican interaction, promoting axonal regeneration, and treating spinal cord injury.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
A nanobody of Glypican 3 with outstanding high stability and its preparation method
ActiveCN111909274BAntibody stability is highEasy to operateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAntiendomysial antibodiesNucleotide
Owner:ZHUHAI INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com