Patents
Literature
58 results about "Terminal protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
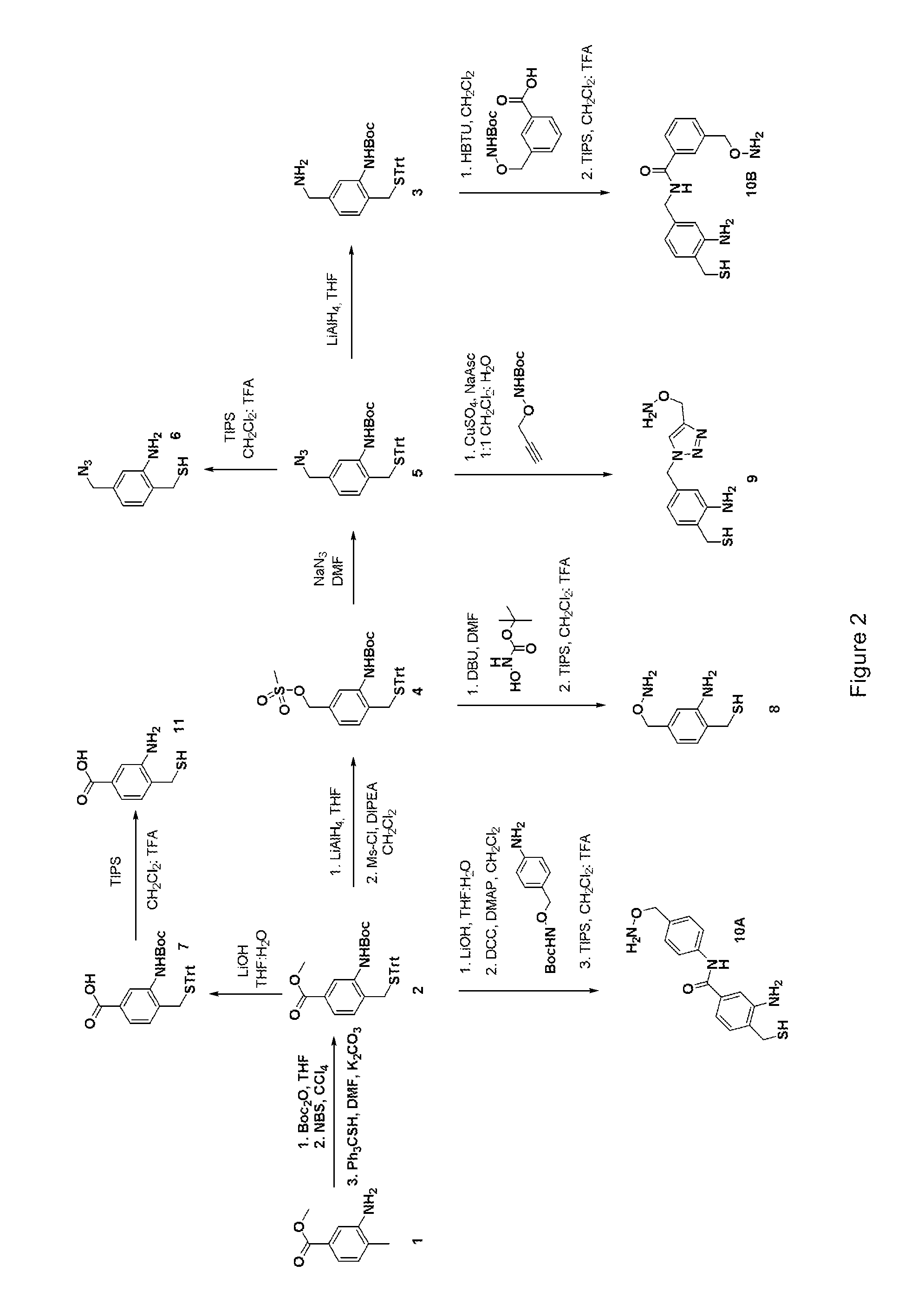
Protein N-terminal is the start point of the expression of a protein. It also influences the subcellular distribution, degradation, and the turnover rate of a protein.
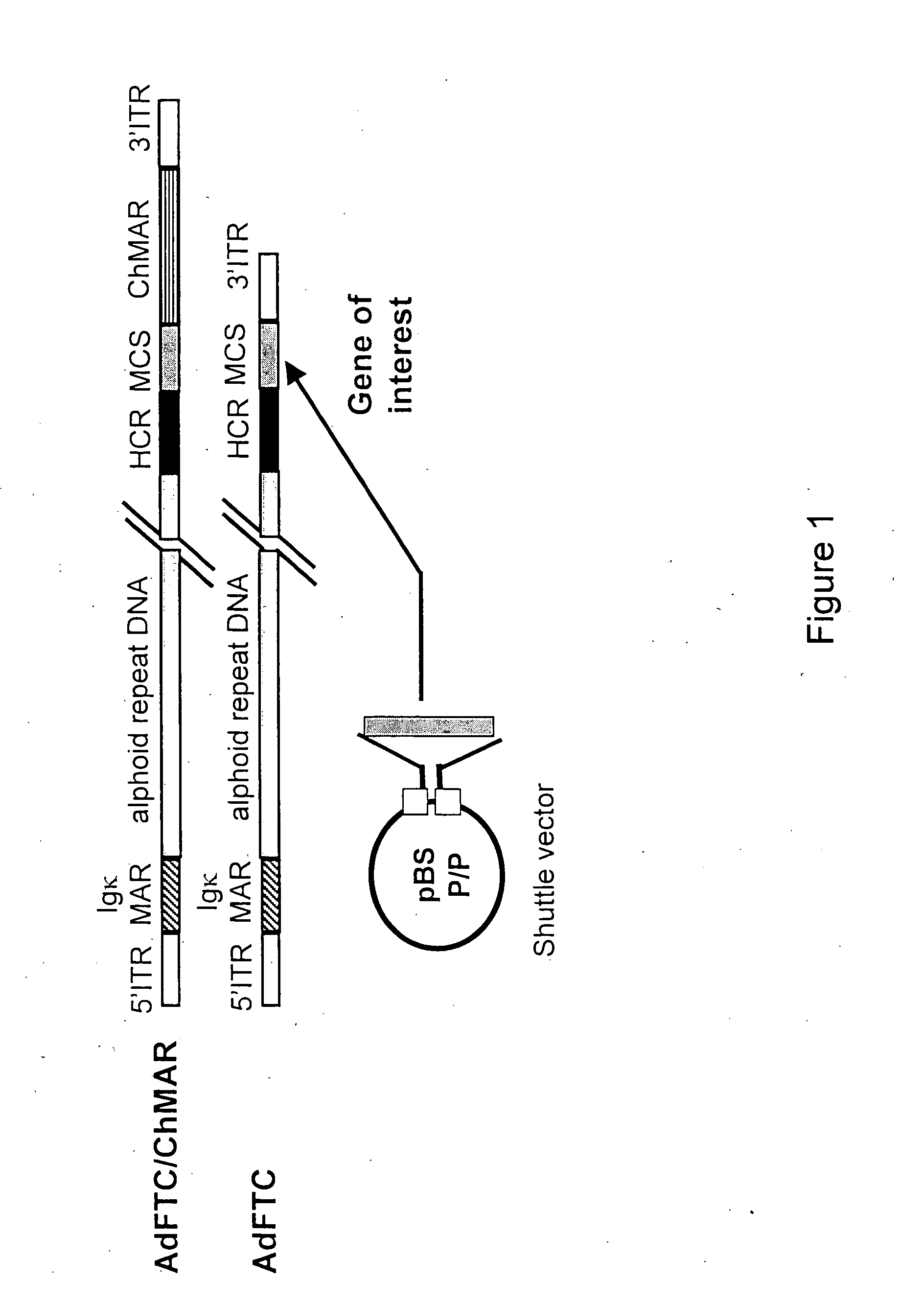
Viral vectors and methods for producing and using the same
InactiveUS20050220766A1Improve AAV production titerReduce and even essentially eliminate contaminationBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsPolymerase LNucleic acid sequencing
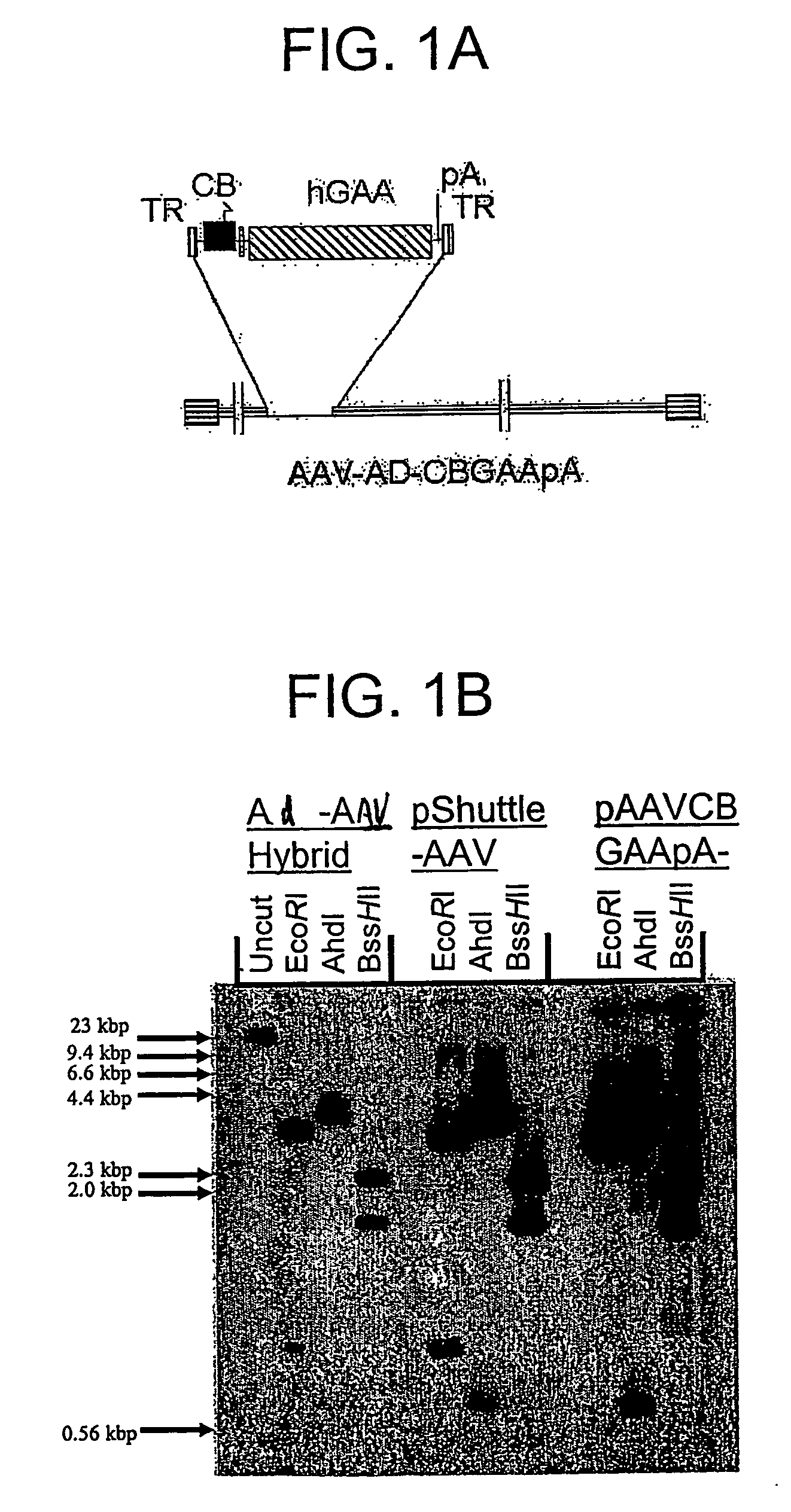
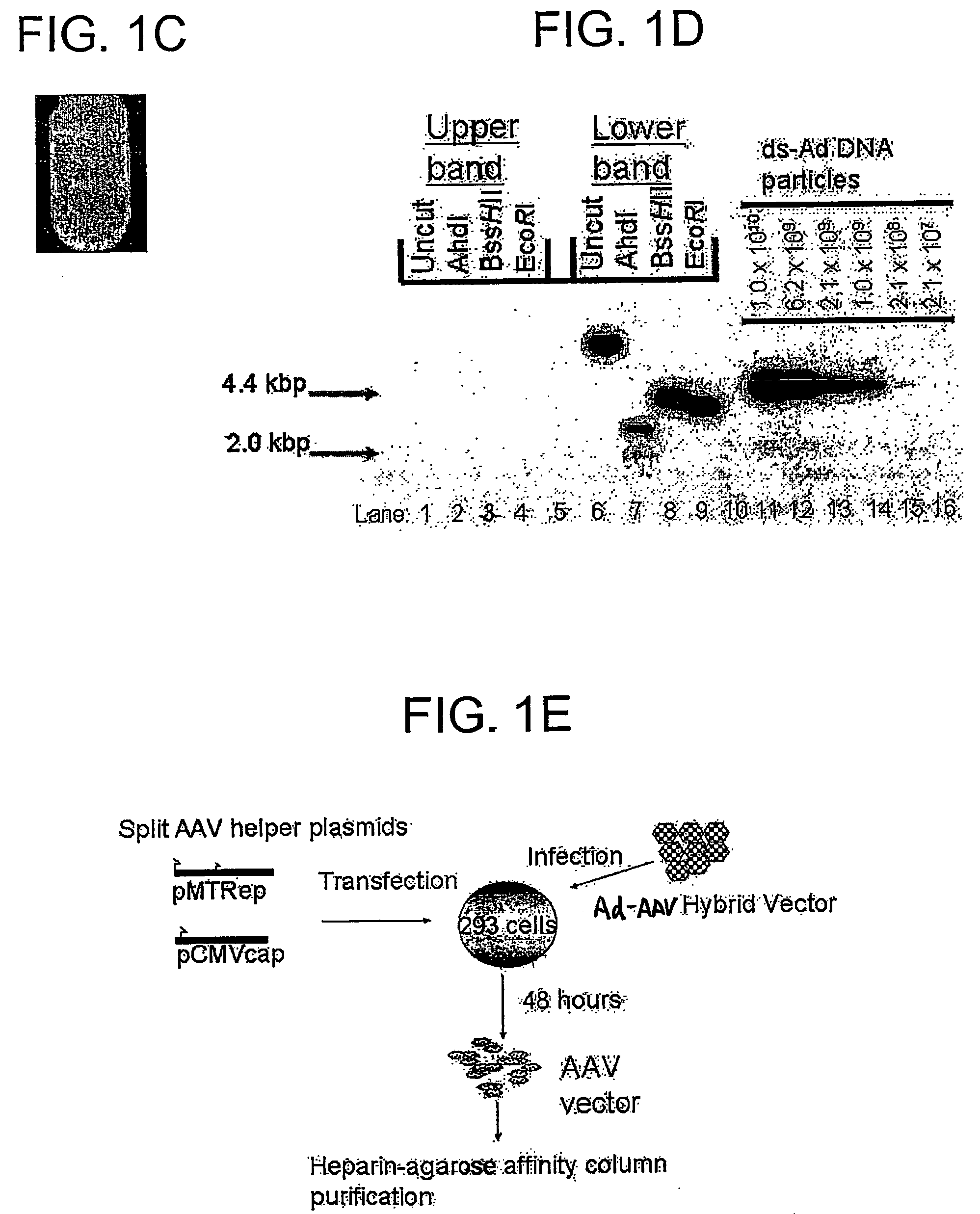
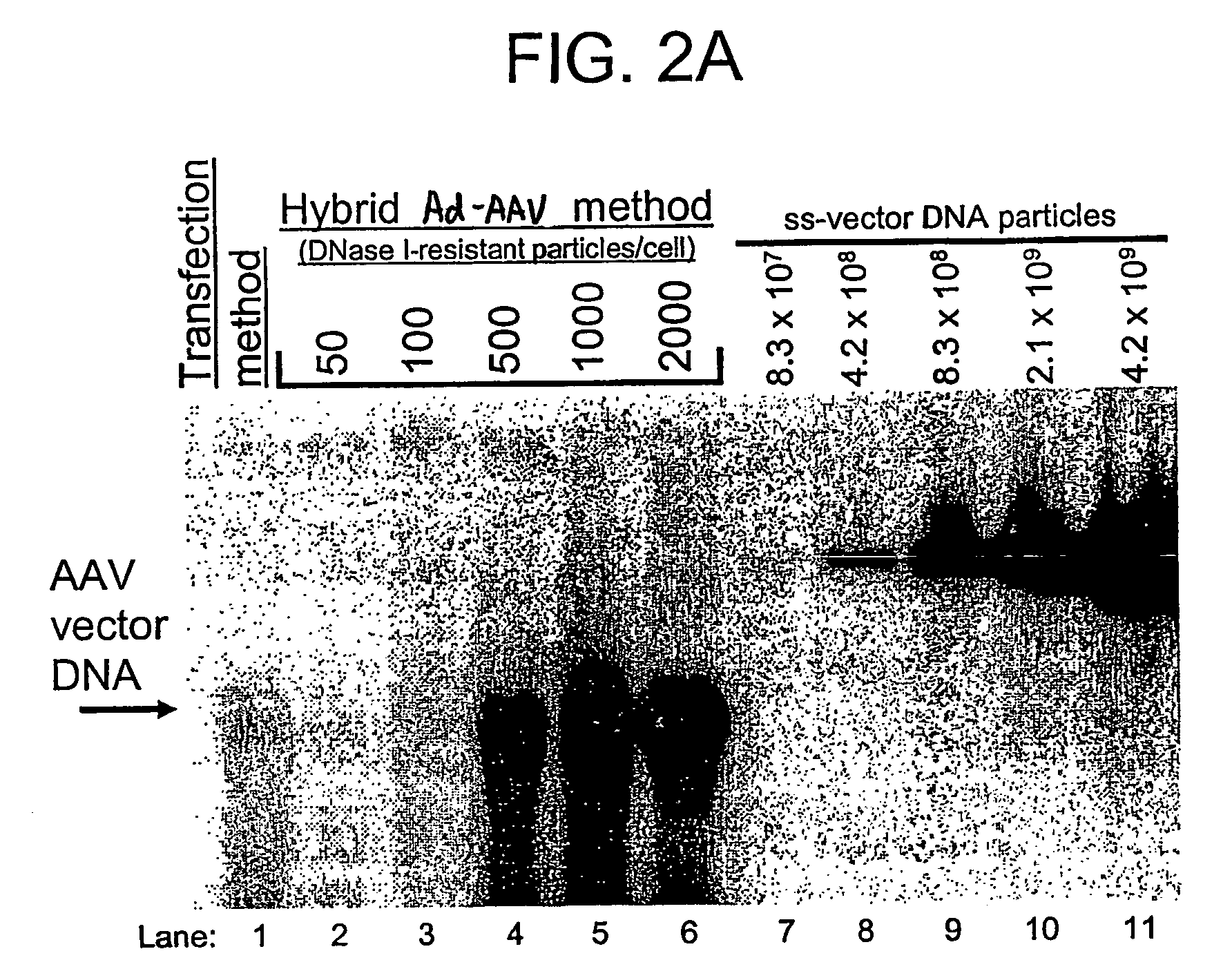
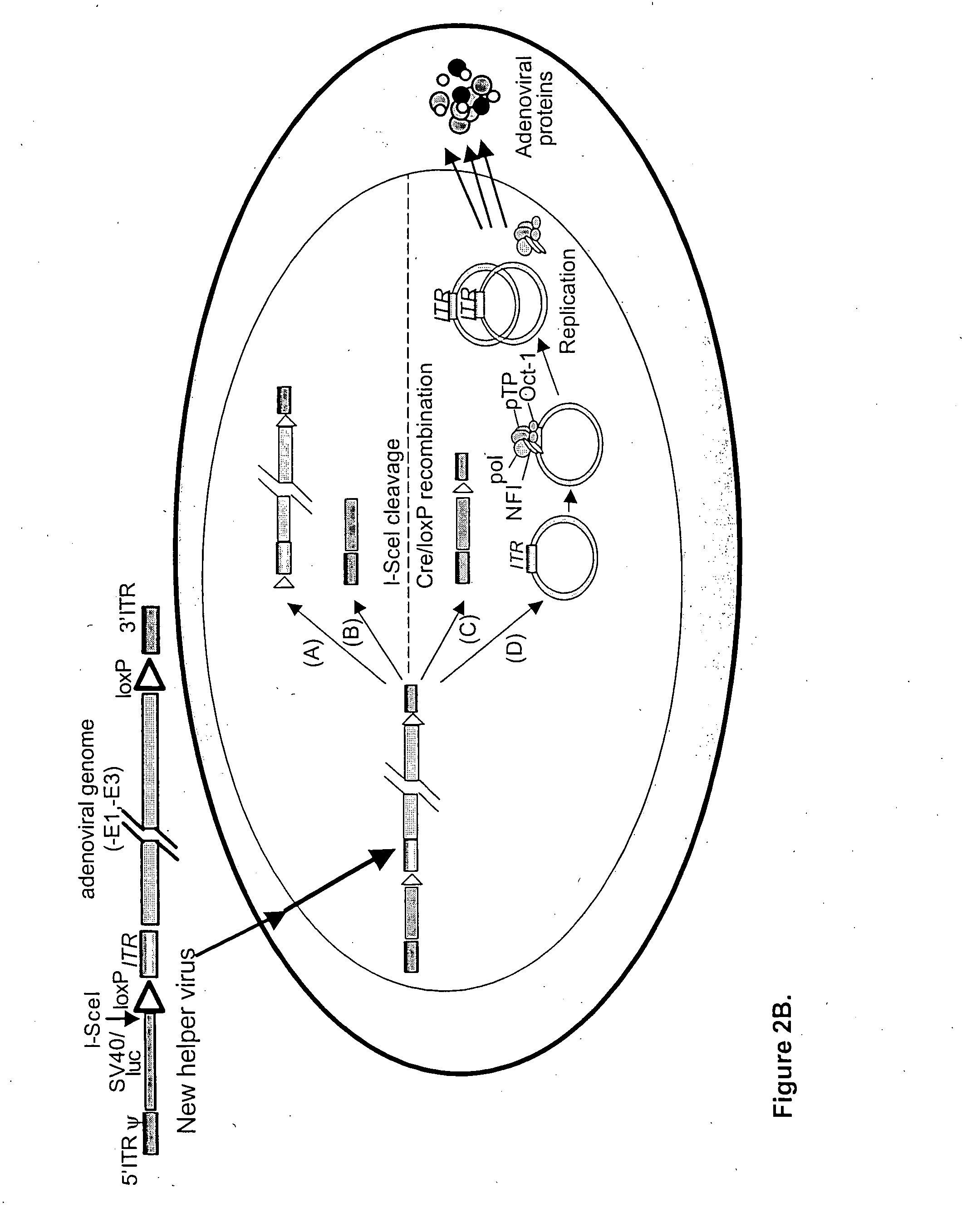
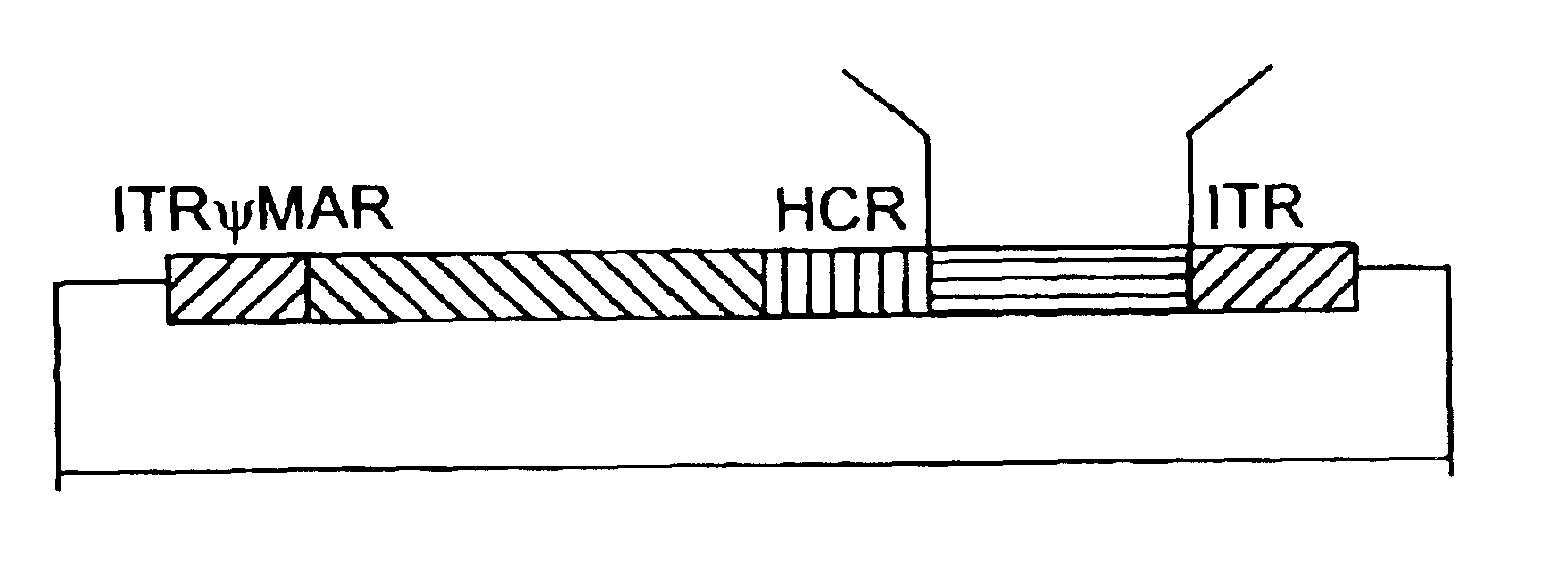
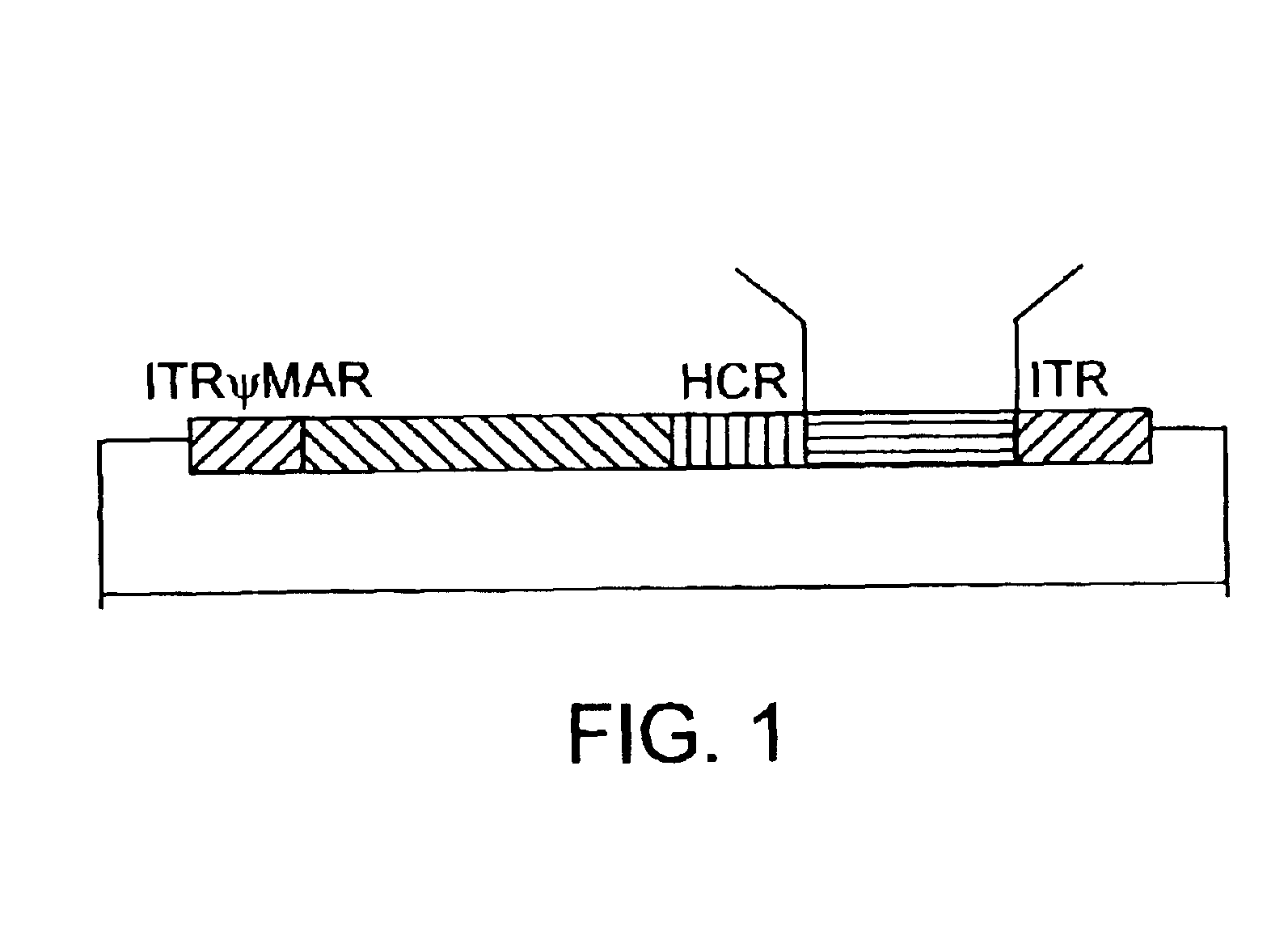
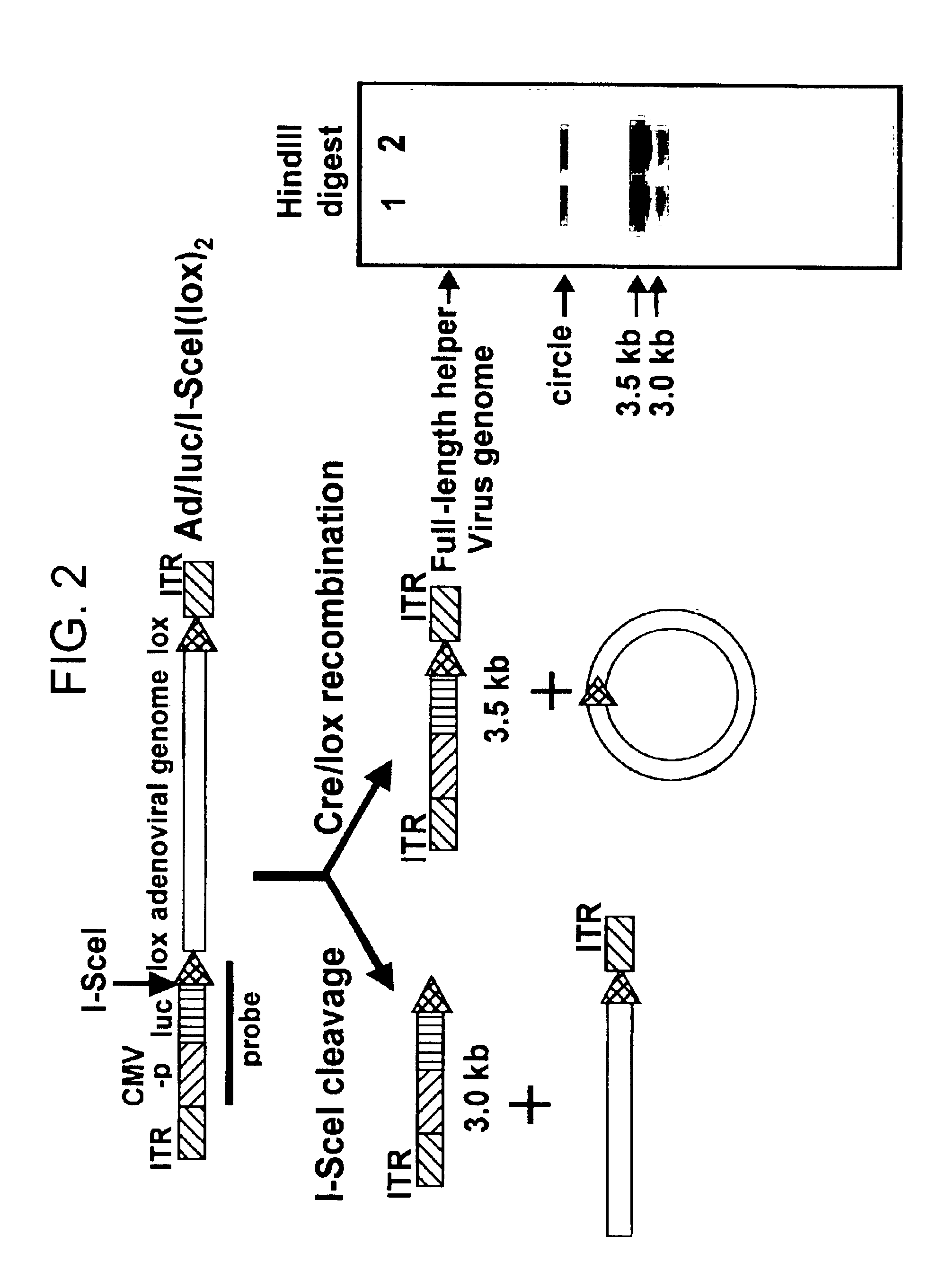
A recombinant hybrid virus, including: (a) a deleted adenovirus vector genome comprising the adenovirus 5′ and 3′ cis-elements for viral replication and encapsidation, and further comprising a deletion in an adenovirus genomic region selected from the group consisting of: (i) the polymerase region, wherein said deletion essentially prevents the expression of a functional polymerase protein from said deleted region and said hybrid virus does not otherwise express a functional polymerase protein, (ii) the preterminal protein region, wherein said deletion essentially prevents the expression of a functional preterminal protein from said deleted region, and said hybrid virus does not otherwise express a functional preterminal protein, and (iii) both the regions of (i) and (ii); and (b) a recombinant adeno-associated virus (AAV) vector genome flanked by the adenovirus vector genome sequences of (a), said recombinant AAV vector genome comprising (i) AAV 5′ and 3′ inverted terminal repeats, (ii) an AAV packaging sequence, and (iii) a heterologous nucleic acid sequence, wherein said heterologous nucleic acid sequence is flanked by the 5′ and the 3′ AAV inverted terminal repeats of (i). Methods of making and using the recombinant hybrid virus are also disclosed.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Monophosphoinositide proteoglycans-3 chemiluminescence immune analysis determination reagent kit and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN101377506AIncrease the effective amountReliable clinical reference valueChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceTreatment effectChemiluminescent immunoassay
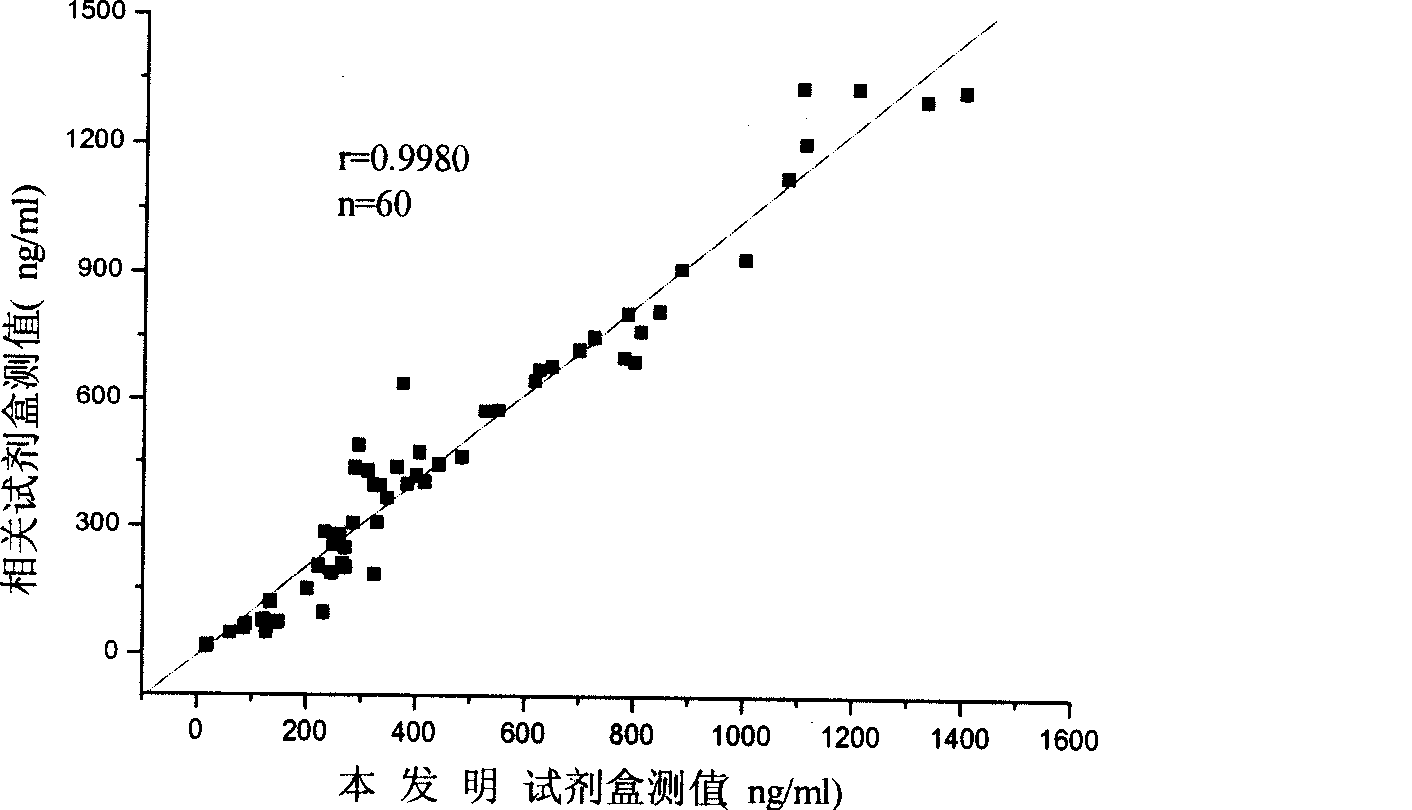
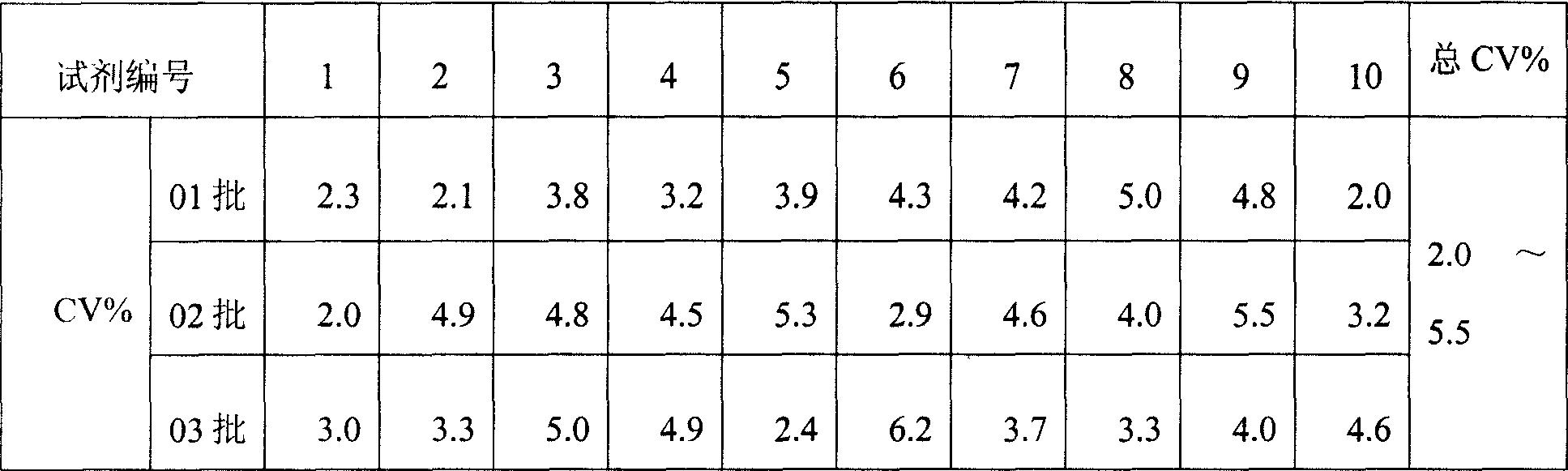
The invention relates to the medical field of immunoassay, more specially, the invention provides a chemiluminescent immunoassay detection kit for phosphatidylinositol proteoglycan-3(GPC-3) and a preparation method thereof, and realizes the simultaneous serological detection of GPC-3 N terminal and C-terminal protein with the chemiluminescent immunoassay method. The kit has the advantages of simple sampling, convenient detection and accurate and specific technical method. The invention adopts a biotin-strapavidin system to coat antibodies and improve the efficiency of antibody coating and the linear range of detection as well as sensitivity, and can be conveniently used for the tracing observation of early diagnosis or treatment effect for primary carcinoma of liver.
Owner:CHEMCLIN DIAGNOSTICS CO LTD
Novel cell-penetrating peptide
InactiveCN103897032AHigh membrane penetration efficiencyReduce the number of AAsFungiBacteriaWild typeGene
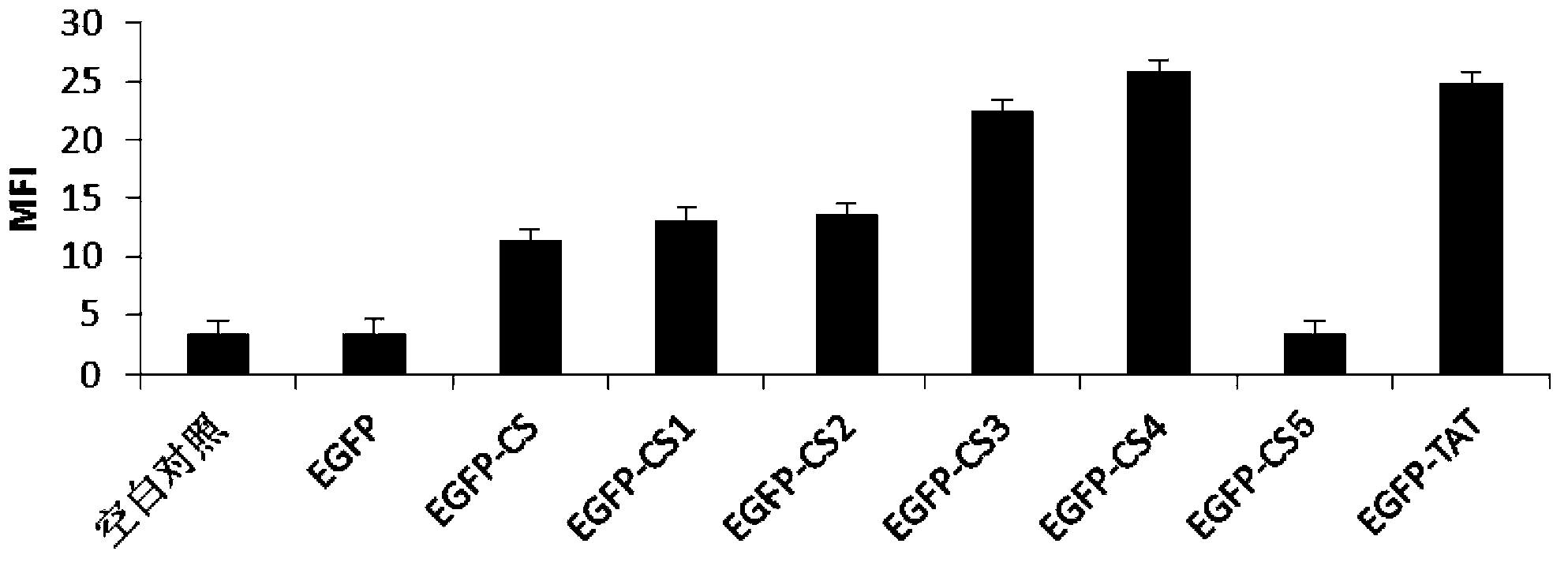
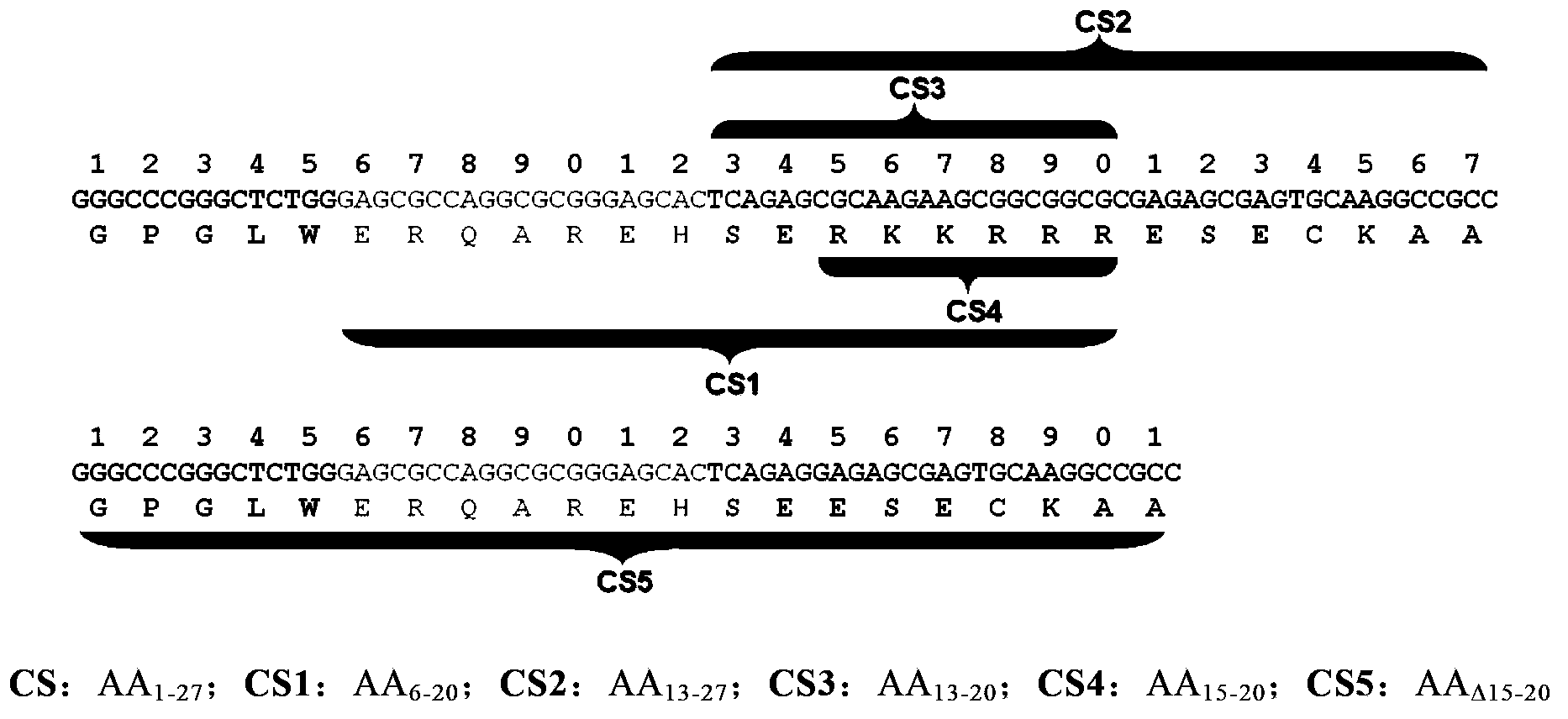
The invention relates to the technical field of biology and specifically relates to a novel cell-penetrating peptide, a gene, a recombinant vector, a transformant, an application thereof and a cell-penetrating drug delivery system. The invention discloses a novel cell-penetrating peptide which is characterized in that the novel cell-penetrating peptide is a polypeptide with the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1, or a polypeptide which contains the amino acid residue as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1 and has the cell-penetrating activity in addition to an EC-SOD carboxyl terminal protein transduction domain as shown in SEQ ID NO. 2. The invention firstly discloses the novel cell-penetrating peptide which can reduce the number of fused AA, reduce the molecular weight, avoid the defect that wild type HBD is easy to form a polymer and improve the cell-penetrating efficiency of the cell-penetrating peptide, wherein the cell-penetrating efficiency is 2 times higher than the wild type HBD. A new idea is provided for developing cell-penetrating drugs.
Owner:ZHEJIANG REACHALL PHARMA
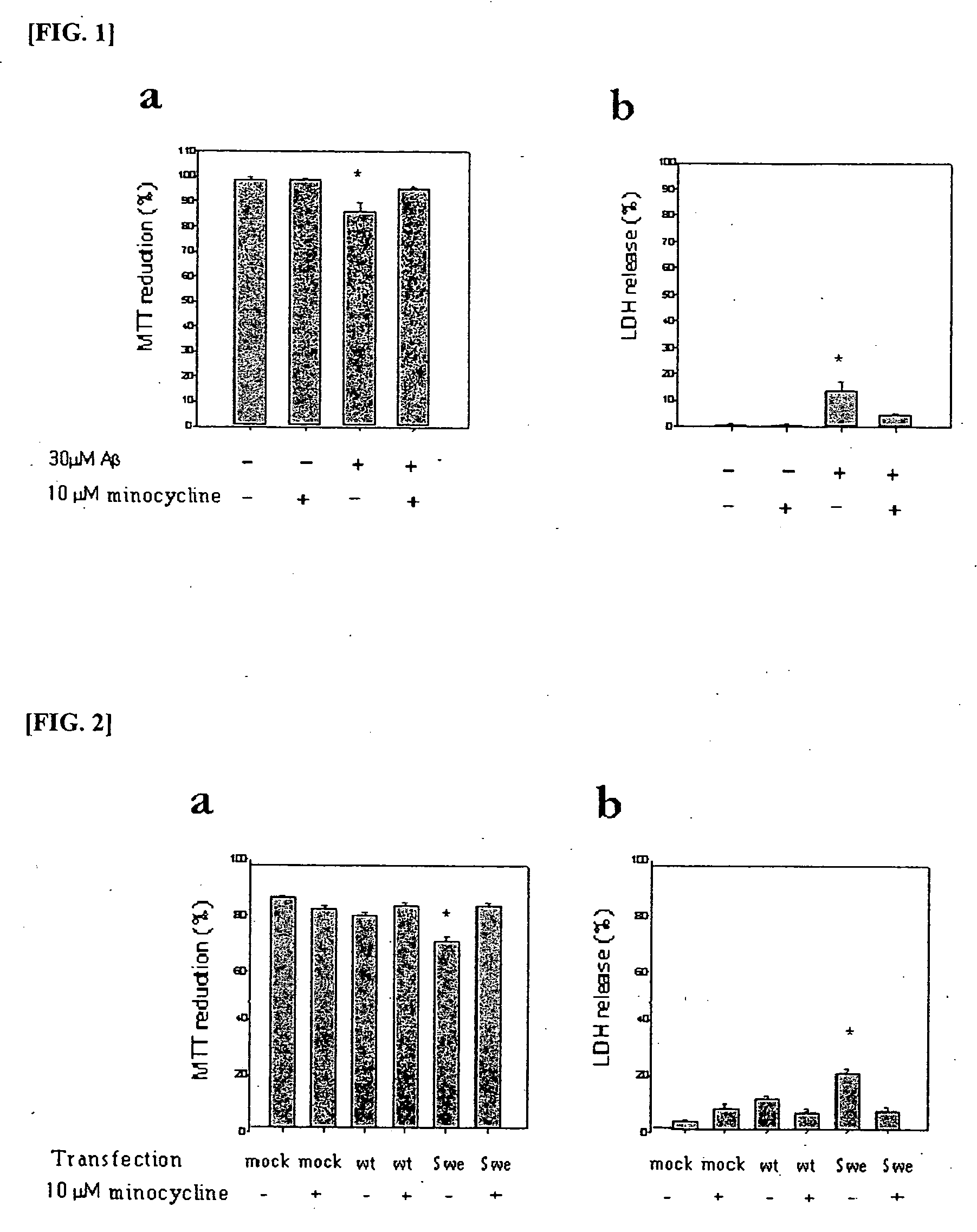
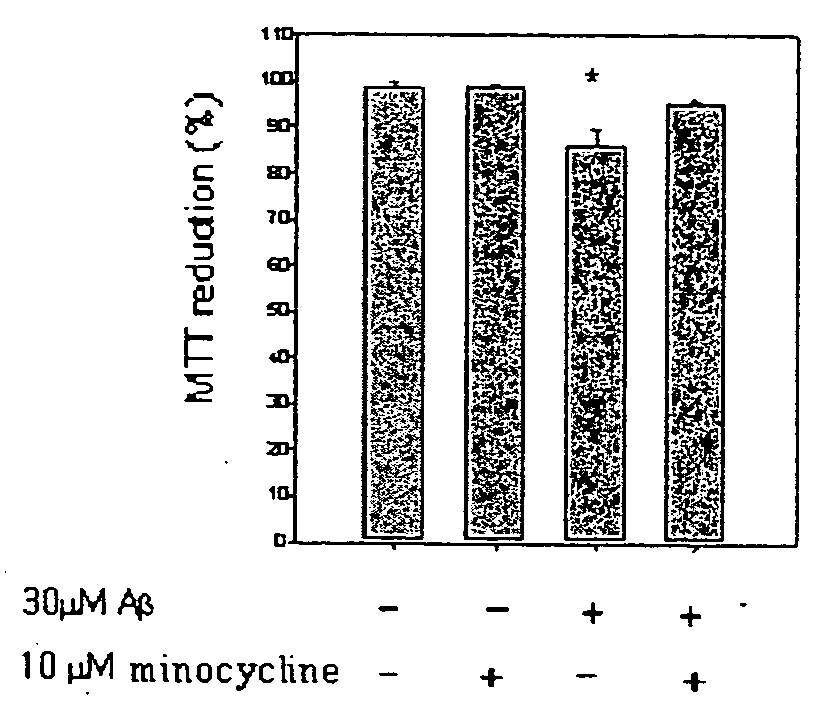
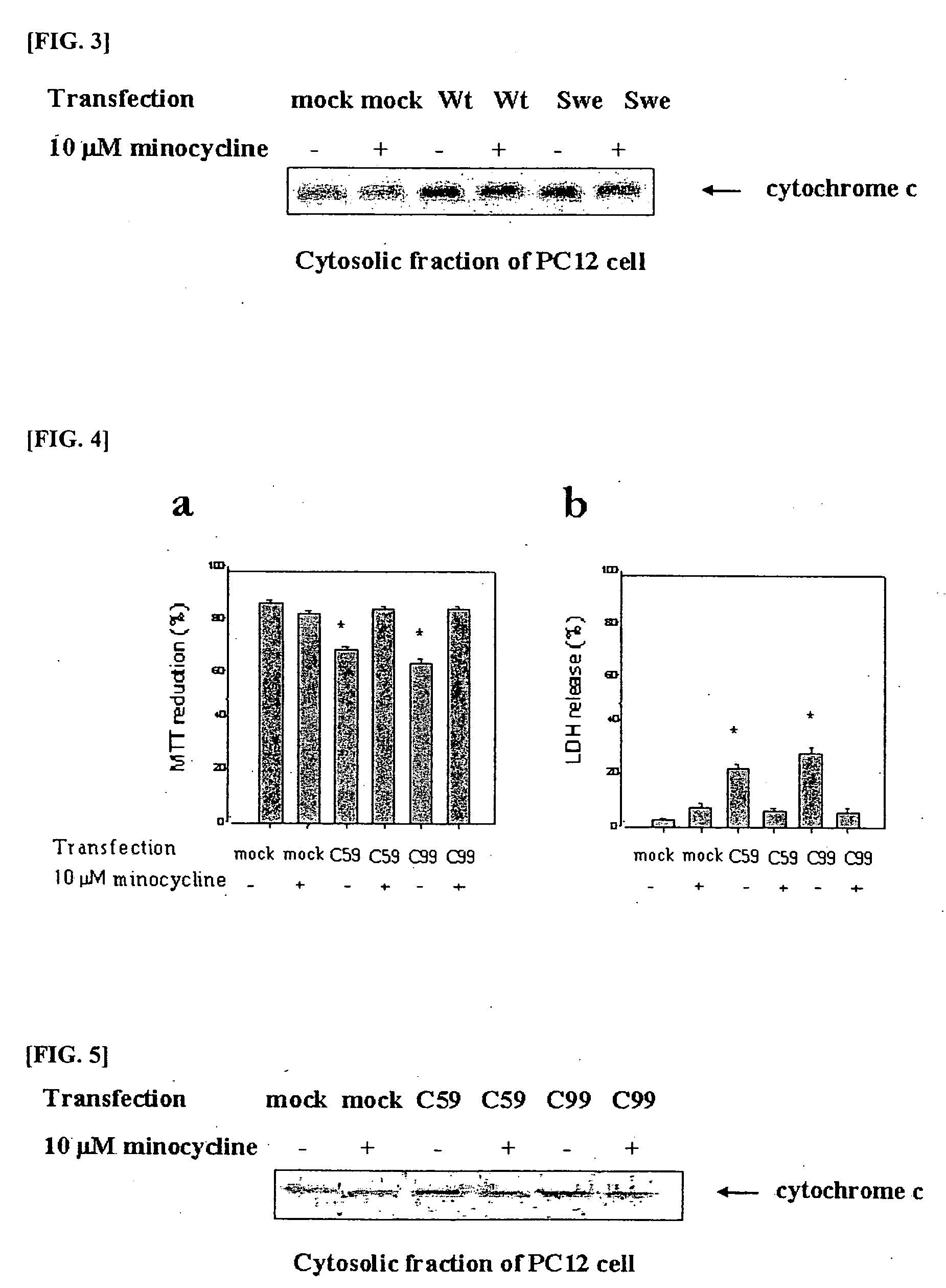
Composition comprising minocycline as an effective component for prevention and treatment of dementia, and learning and memory impairments
InactiveUS20060148766A1Avoid cell deathAvoid cytotoxicityBiocideTetracycline active ingredientsMemory disorderBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The present invention relates to a composition for preventing and treating dementia and memory impairment, which contains minocycline as active ingredient. The composition of the present invention has an effect of inhibiting brain cell death and memory impairment, which are induced by amyloid beta-protein and C-terminal protein. Thus, the composition of the present invention is useful for the prevention and treatment of various dementias, including Alzheimer's disease, and the impairment of learning and memory and cognitive function.
Owner:SUH YOO HUN +4
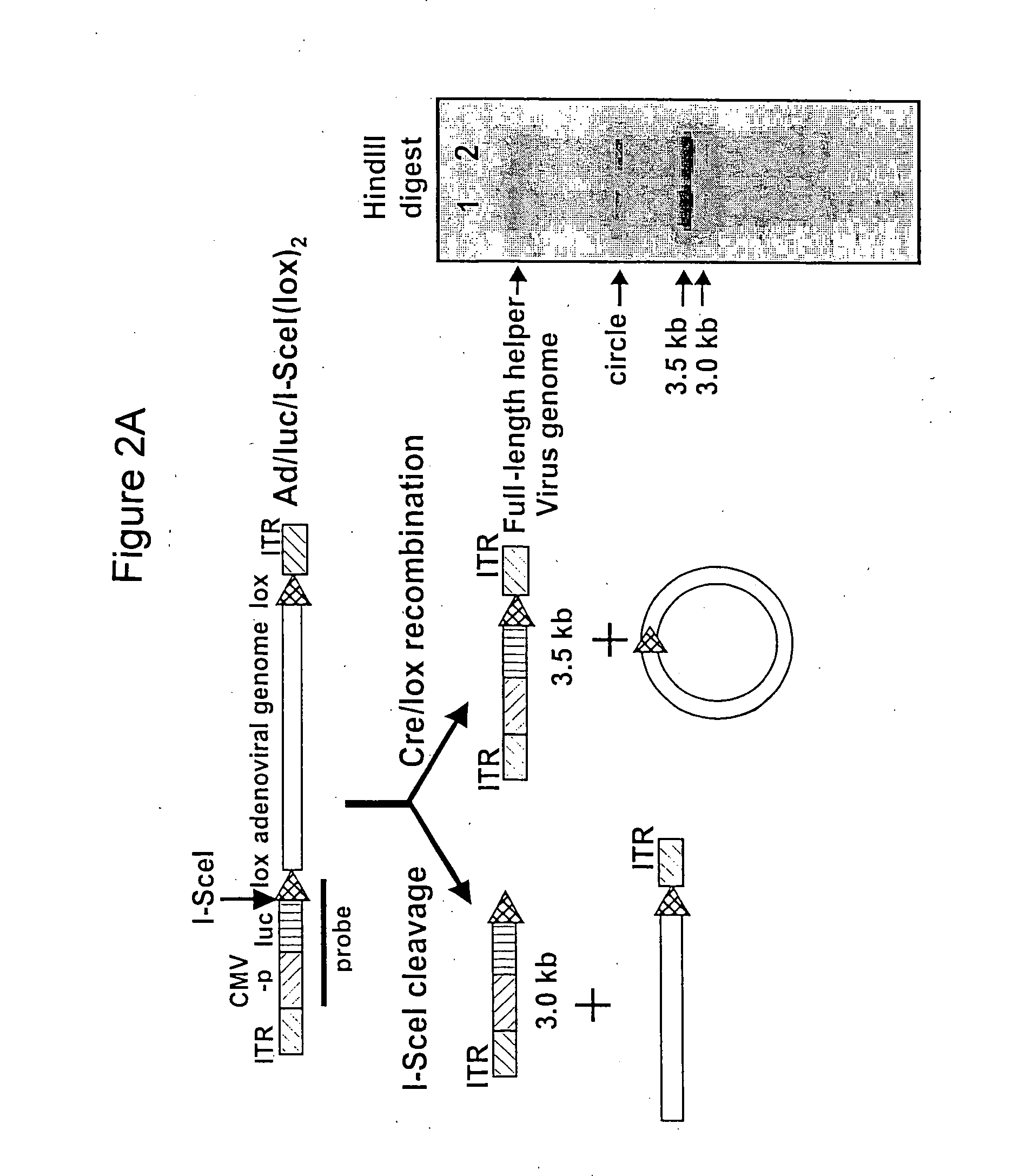
Helper dependent adenoviral vector system and methods for using the same
A helper dependent adenoviral vector system is provided. The subject helper dependent adenoviral vector system is made up of: (1) a "gutless" adenoviral vector, which in certain embodiments includes cis-acting human stuffer DNA that provides for in vivo long term, high level expression of a coding sequence present on the vector, where in certain embodiments the vector includes an integrating domain; (2) an adenoviral helper vector that is characterized by having an adenoviral genome region flanked by recombinase recognition sites, where the helper vectors further include a non-mammalian endonuclease recognition site positioned outside of the adenoviral genome region and in certain embodiments a third adenoviral inverted terminal repeat (ITR) sequence positioned between first and second terminal ITRs; and (3) a mammalian cell that expresses the corresponding recombinase and endonuclease, as well as the adenoviral preterminal and polymerase proteins. Also provided are methods of using the subject systems to produce virions having the subject helper dependent adenoviral vectors encapsulated in an adenoviral capsid. In addition, kits for use in practicing the subject methods are provided.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Deleted adenovirus vectors and methods of making and administering the same
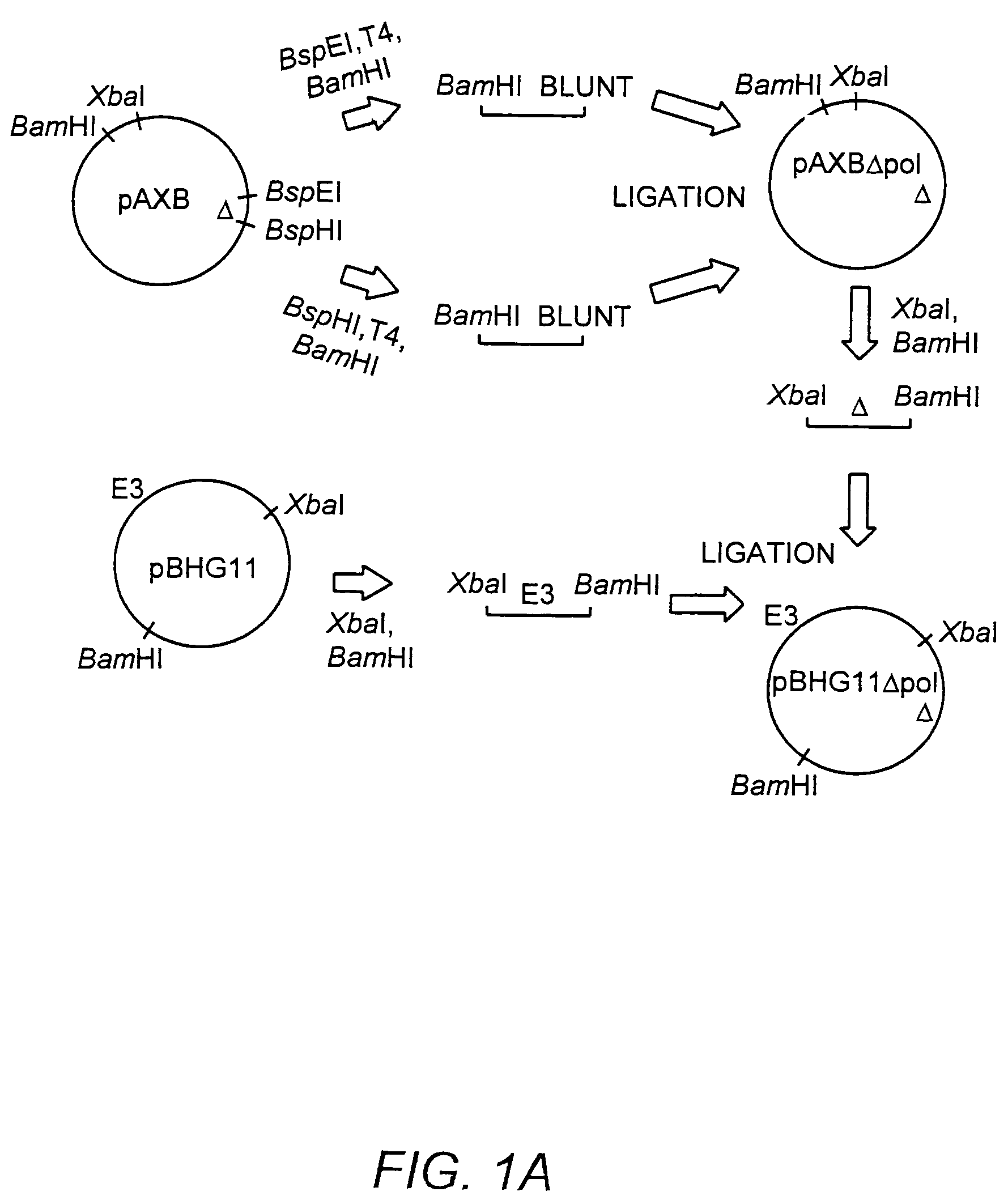
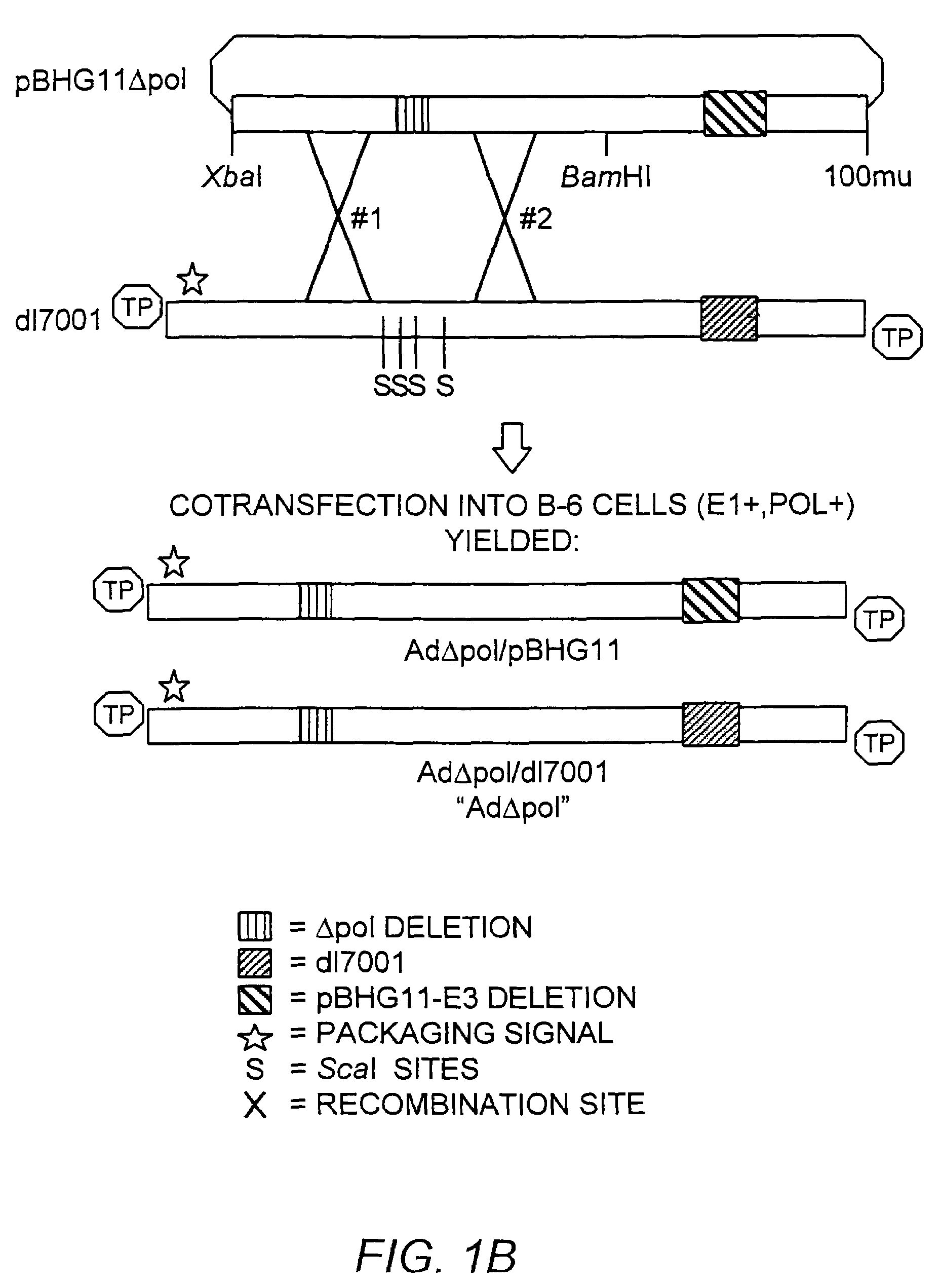
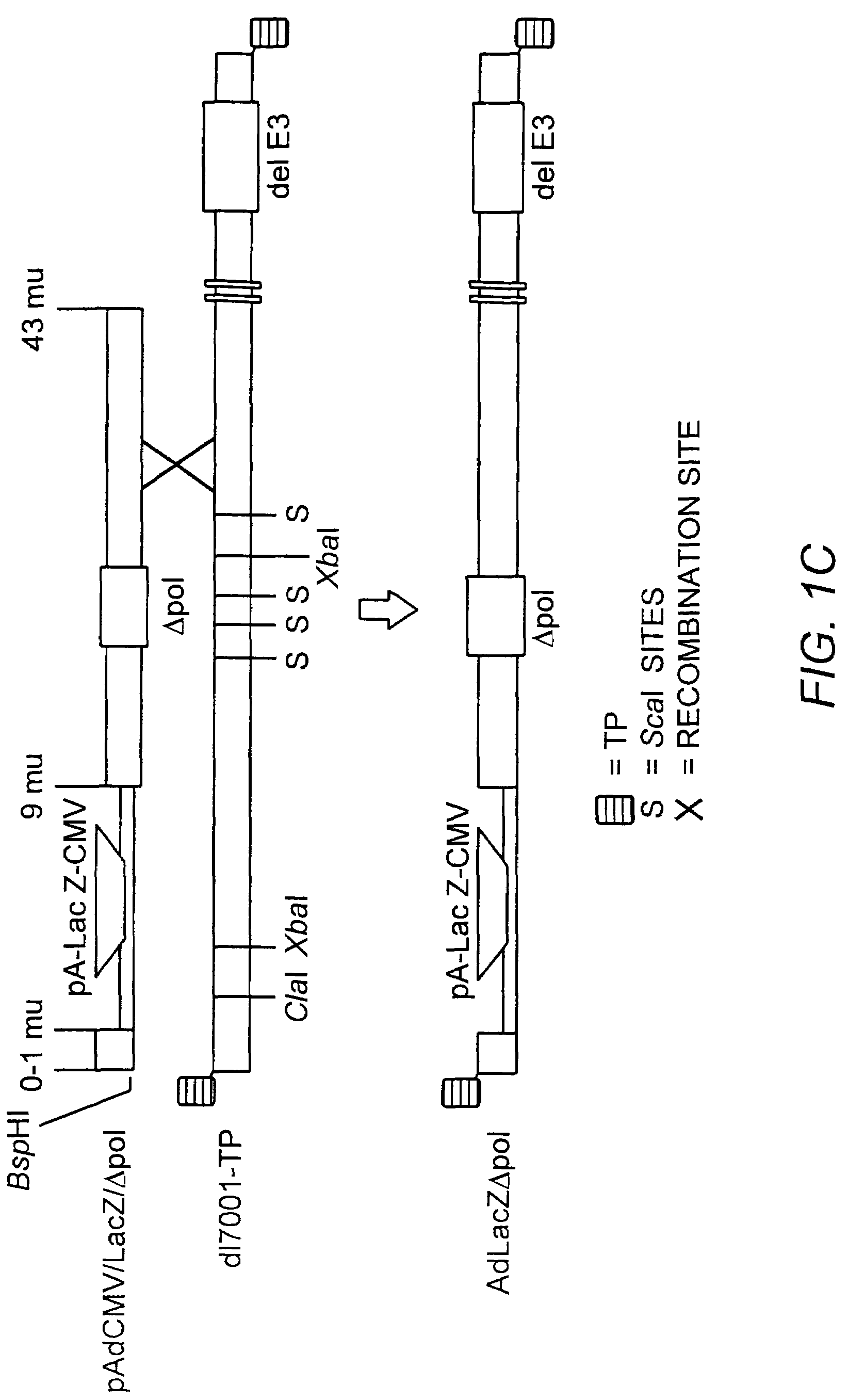
The present invention provides deleted adenovirus vectors. The inventive adenovirus vectors carry one or more deletions in the IVa2, 100K, polymerase and / or preterminal protein sequences of the adenovirus genome. The adenoviruses may additionally contain other deletions, mutations or other modifications as well. In particular preferred embodiments, the adenovirus genome is multiply deleted, i.e., carries two or more deletions therein. The deleted adenoviruses of the invention are “propagation-defective” in that the virus cannot replicate and produce new virions in the absence of complementing function(s). Preferred adenovirus vectors of the invention carry a heterologous nucleotide sequence encoding a protein or peptide associated with a metabolic disorder, more preferably a protein or peptide associated with a lysosomal or glycogen storage disease, most preferably, a lysosomal acid α-glucosidase. Further provided are methods for producing the inventive deleted adenovirus vectors. Further provided are methods of administering the deleted adenovirus vectors to a cell in vitro or in vivo.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Helper dependent adenoviral vector system and methods for using the same
A helper dependent adenoviral vector system is provided. The subject helper dependent adenoviral vector system is made up of: (1) a “gutless” adenoviral vector that include cis-acting human stuffer DNA that provides for in vivo long term, high level expression of a coding sequence present on the vector; (2) an adenoviral helper vector that is characterized by having an adenoviral genome region flanked by recombinase recognition sites, where the helper vectors further include a non-mammalian endonuclease recognition site positioned outside of the adenoviral genome region; and (3) a mammalian cell that expresses the corresponding recombinase and endonuclease, as well as the adenoviral preterminal and polymerase proteins. Also provided are methods of using the subject systems to produce virions having the subject helper dependent adenoviral vectors encapsulated in an adenoviral capsid. In addition, kits for use in practicing the subject methods are provided.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Stichopus japonicas BPI gene, encoded protein, cloning method of stichopus japonicas BPI gene, and method for constructing recombinant stichopus japonicas BPI genetically engineered bacterium
ActiveCN104745595AEfficient killingAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsBPI proteinVibrio parahaemolyticus
The invention discloses a stichopus japonicas BPI gene, an encoded protein, a cloning method of the stichopus japonicas BPI gene, and a method for constructing a recombinant stichopus japonicas BPI genetically engineered bacterium. The stichopus japonicas BPI gene is characterized in that a stichopus japonicas BPI gene sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1; the cloning method comprises the step of designing a nested primer of RACE according to an expressed sequence tag EST sequence which is homologous to the BPI gene; a full-length gene is expanded by employing an RACE technique; a stichopus japonicas BPI protein sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO.2; an N-terminal protein structure domain sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO.3; an N-terminal structure domain of the stichopus japonicas BPI protein is amplified by employing primers which respectively comprise BamH I sites and Not I sites; the cloned target gene is inserted into a vector to obtain recombinant plasmids; and the recombinant plasmids are subjected to induced expression, and purification and renaturation, so as to obtain the genetically engineered bacterium. The stichopus japonicas BPI gene has the advantage of having obvious sterilization effect on vibrio parahaemolyticus, vibrio harveyi and micrococcus luteus.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
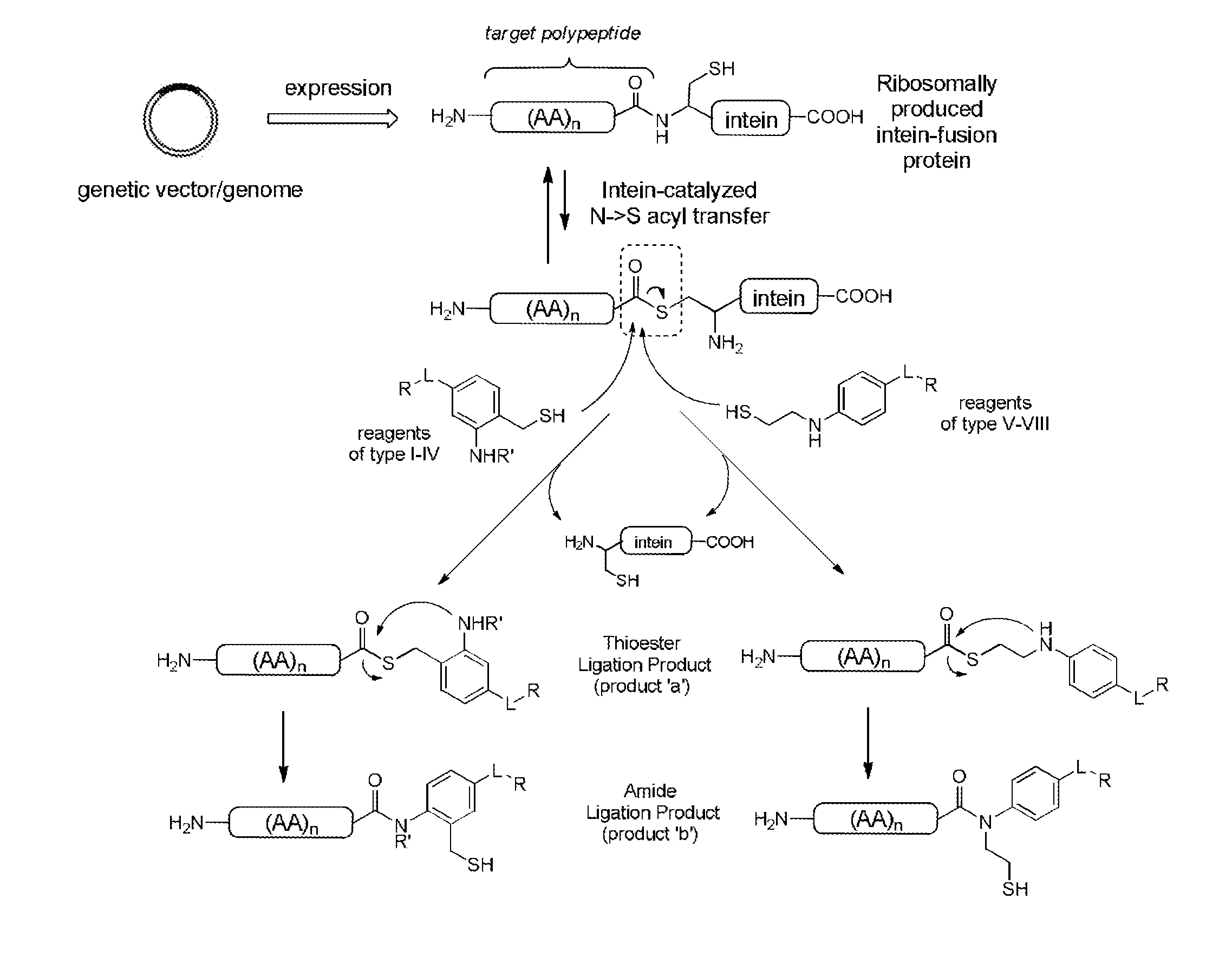
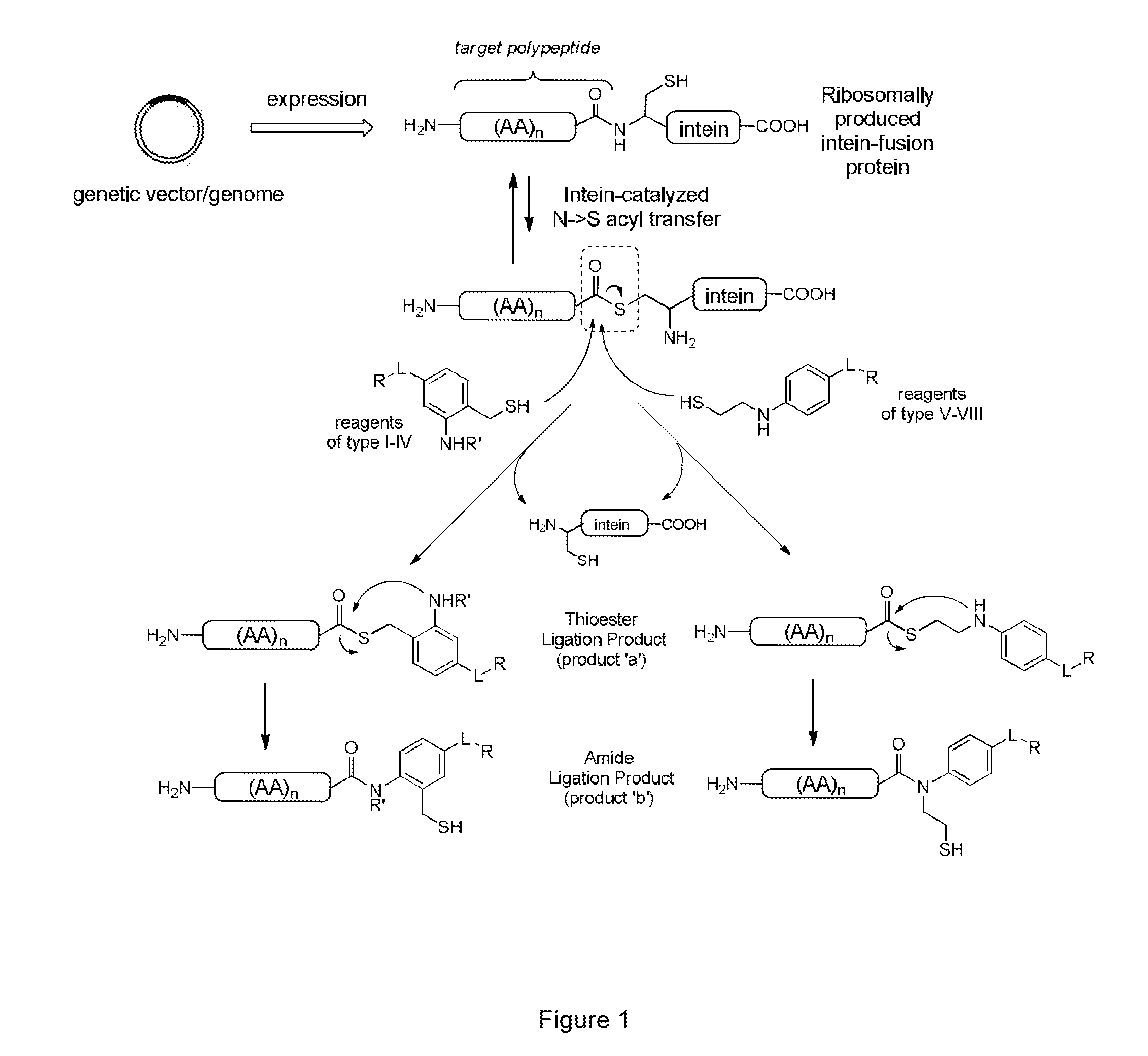
Methods and compositions for site-specific labeling of peptides and proteins
Methods and compositions are provided for covalently linking a chemical species to a recombinant or synthetic polypeptide. The methods involve the reaction of a thioester-comprising polypeptide with a reagent comprising a reactive amino-thiol group connected to the chemical species which is to be covalently linked to the polypeptide, via a linker. Such chemical species can be a functional group, a label or tag molecule, a biological molecule, a ligand, or a solid support. Efficient and catalyst-free methods for C-terminal protein labeling are also provided. The methods expand current capabilities in the area of protein functionalization, providing useful and complementary tools for the isolation, detection, characterization, and analysis of proteins in a variety of in vitro and in vivo applications.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
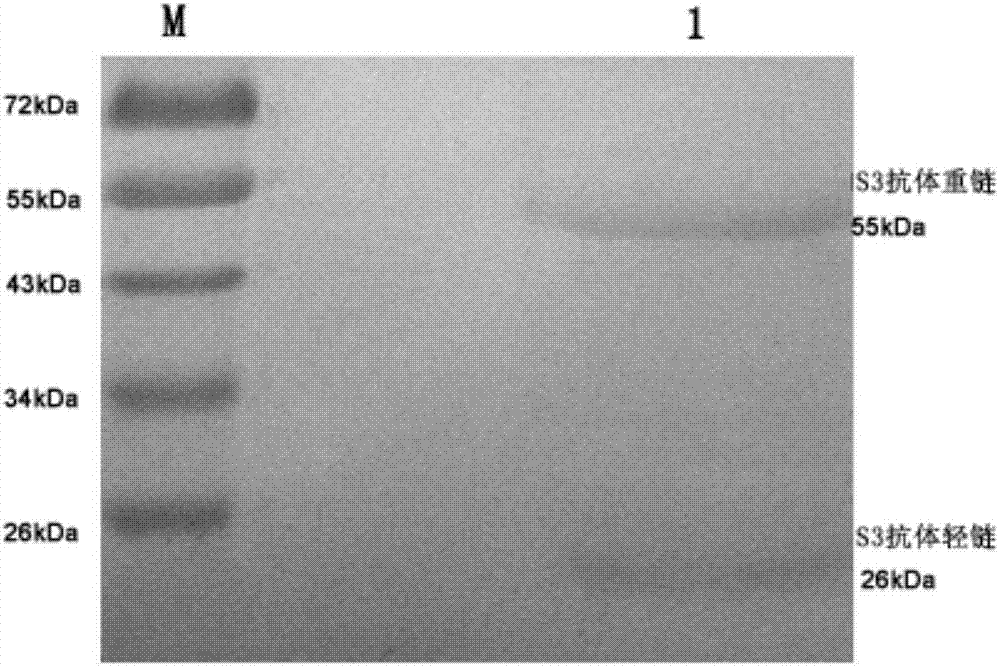
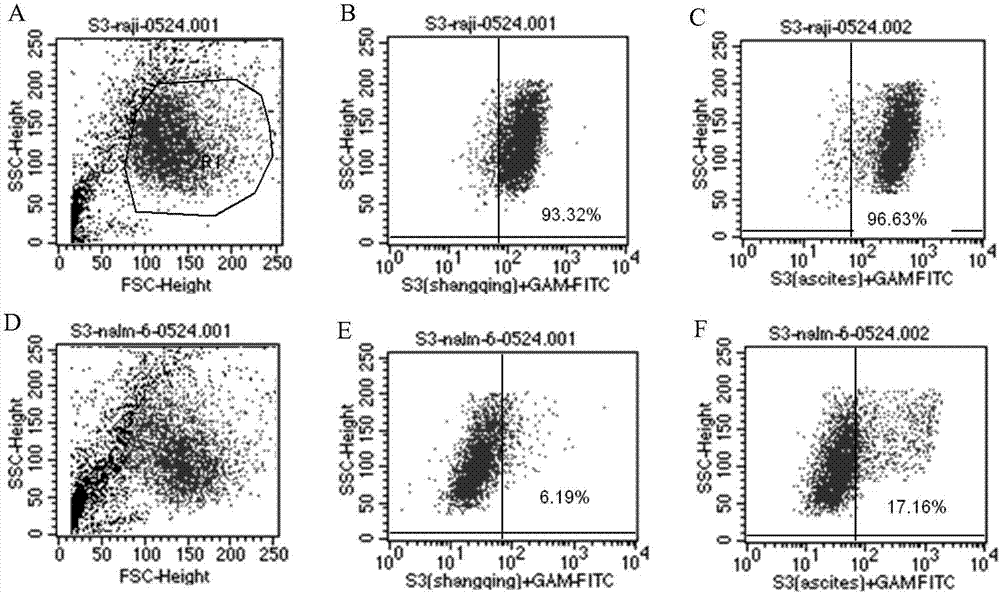
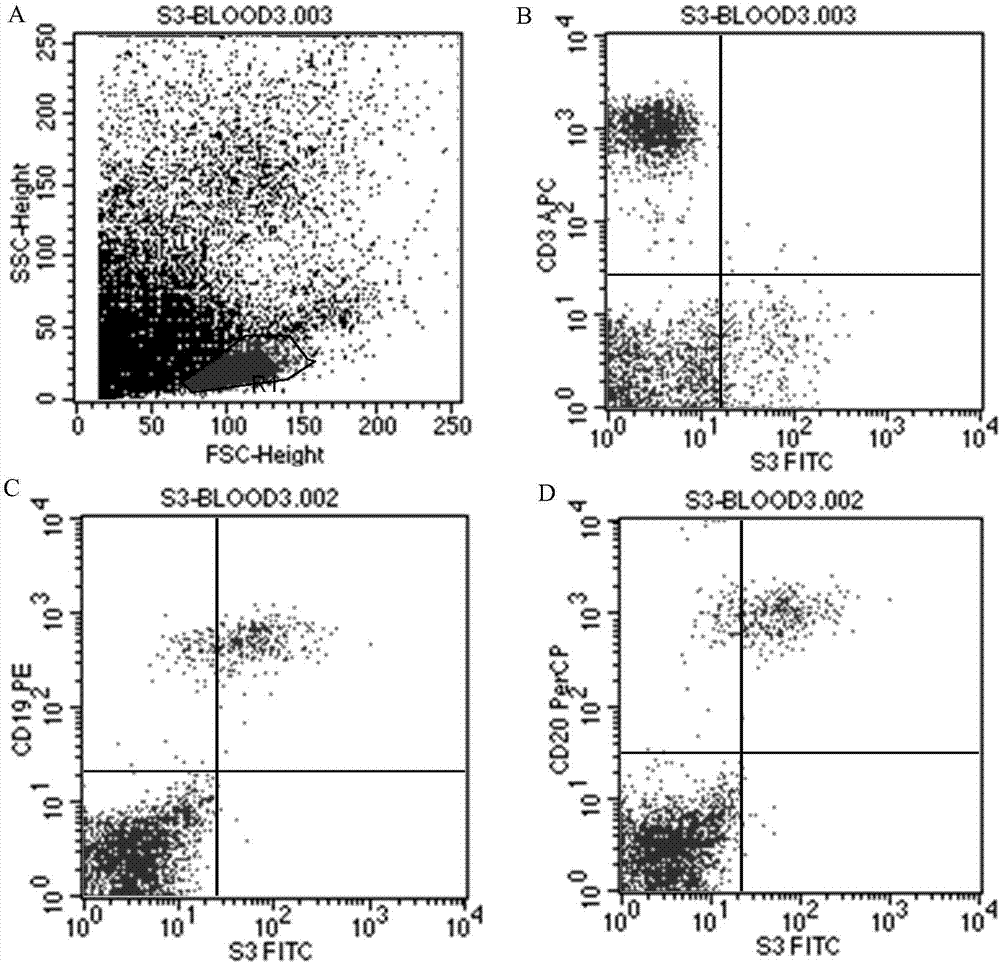
Antibody for resisting human CD79a extracellular terminal protein, coding gene and application
ActiveCN107488230AEfficient identificationHigh internalization rateOrganic active ingredientsTetrapeptide ingredientsDiseaseSequence analysis
The invention discloses an antibody for resisting human CD79a extracellular terminal protein, a coding gene and application. The antibody is characterized in that a human B cell lymphoma Raji cell line is used as an immunogen for immunizing mice; splenocyte is obtained and then is fused with a mouse myeloma cell to obtain a hybridoma cell; a monoclonal antibody for specifically aiming at the human CD79a extracellular terminal protein is obtained via screening; an amino acid sequence of the monoclonal antibody is obtained by sequence analysis; variable region sequence with a heavy chain and a light chain and CDR (Complementarity-Determining Region) sequences with light chains and heavy chains are obtained via analyzing; an chimeric antibody expressed via cloning can be used for effectively and specifically recognizing the human CD79a extracellular terminal protein; in addition, when the antibody acts on human B lymphocyte, the internalization rate is high; the antibody has a good prospect for preparing a targeted drug of targeted B lymphocyte and can be used for treating diseases associated with the B lymphocyte.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Process for preparing target ribonuclease for curing hepatitis B virus infection
The present invention relates to the process of preparing target ribonuclease for curing hepatitis B virus infection. By means of molecular biological measures, it is constituted fusion protein of neurotoxin hEDN and HBV polymerase end protein structural domain DNAPTP or core protein originated from human eosinophil. The fusino protein, that is the said target ribonuclease, may be used in treating huma hepatitis B virus infection via gene therapy or protein medicine mode. Experiment shows that the target ribonuclease can reduce in vitro HBSAg for 46-59 % and inhibit obviously the duplicatino of hepatitis B virus. Available gene therapy or protein medicine mode may be refered to for its specific administratino way or mode.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Isothermal amplification of DNA
InactiveUS8709724B2Improve efficiencyHigh magnificationMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesOligonucleotide primersPolymerase L
A method of amplifying a template DNA molecule comprising incubating the template DNA molecule in a reaction mixture comprising a DNA polymerase and at least one accessory protein at a constant temperature to produce amplified product, wherein production of amplified product does not require exogenously-added oligonucleotide primers and the template DNA molecule does not have have terminal protein covalently bound to either 5′ end.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
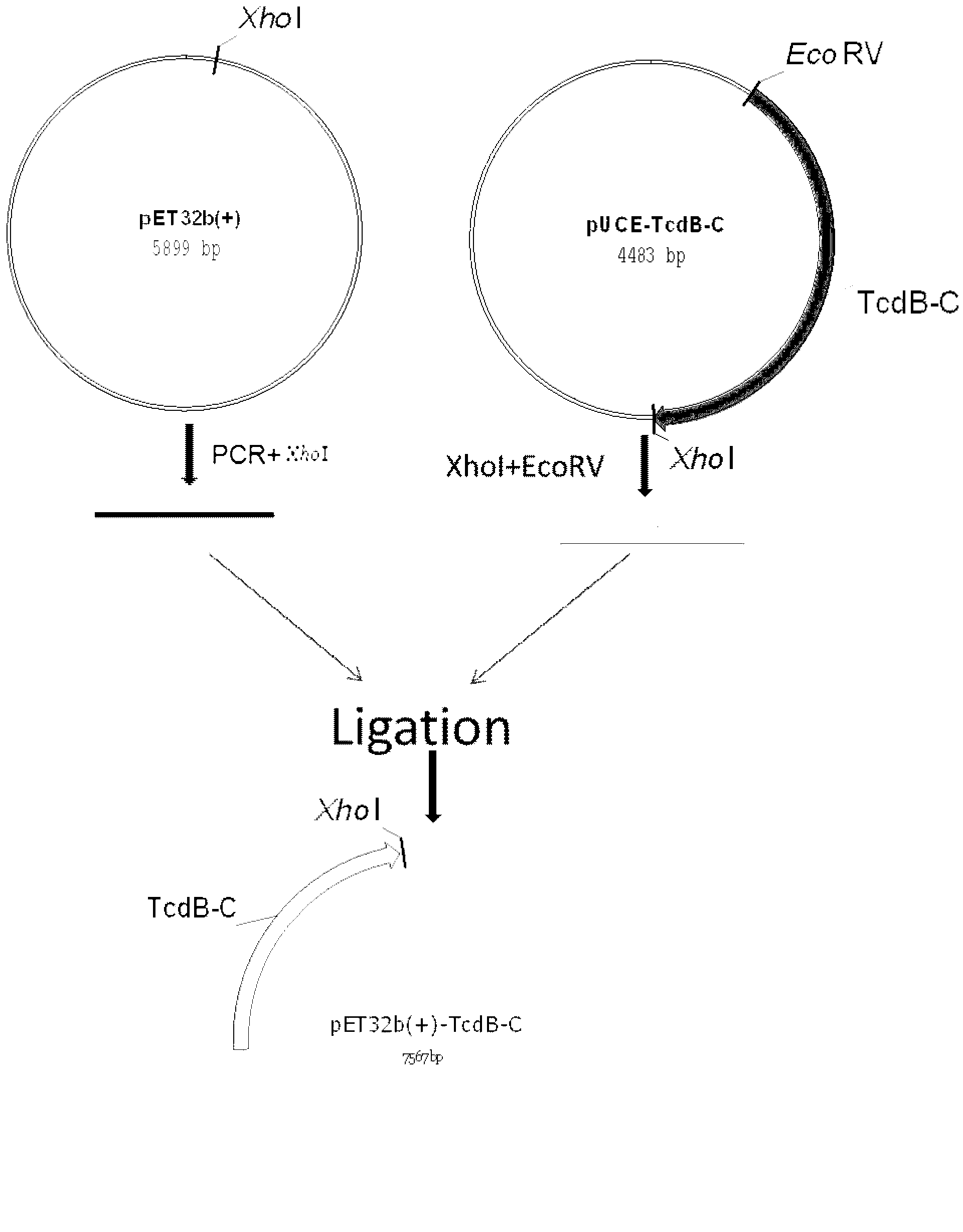
Clostridium difficile exotoxin B carboxyl-terminal protein gene highly expressing in Escherichia coli
ActiveCN103290033AImproved Compositing EffectsLower synthesis costDepsipeptidesFermentationEscherichia coliChemical synthesis
The invention discloses a Clostridium difficile exotoxin B carboxyl-terminal protein gene highly expressing in Escherichia coli, and its high expression method in Escherichia coli. The optimization of the Clostridium difficile exotoxin B carboxyl-terminal protein gene in the invention improves the influences of a plurality of duplicate blocks of an original sequence to the chemical gene synthesis and reduces the synthesis cost, the gene can highly express in Escherichia coli, and the expression level can reach 70% of total mycoproteins, and is far higher than that of present Clostridium difficile exotoxin B carboxyl-terminal protein genes.
Owner:SHANDONG INT BIOTECH PARK DEV
Monoclonal antibody of outer membrane protein of chlamydia abortus and application thereof
ActiveCN102220285AStrong specificityGood fluorescence propertiesImmunoglobulins against bacteriaTissue cultureFluorescenceIMMUNE FLUORESCENCE
The invention relates to monoclonal antibody of N-terminal protein of chlamydia abortus POMP18D as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The monoclonal antibody is secreted by a hybridoma cell strain 1F10D4 with the collection number of CGMCC No.4658. The invention also provides application of the monoclonal antibody in direct fluorescence immune or indirect fluorescence immune detection of chlamydia abortus. The monoclonal antibody of N-terminal protein of chlamydia abortus POMP18D has strong specificity and fluorescent characteristic, and is suitable for being used as a fluorescence antibody to establish a direct fluorescence detection method or indirect immune fluorescence detection method.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
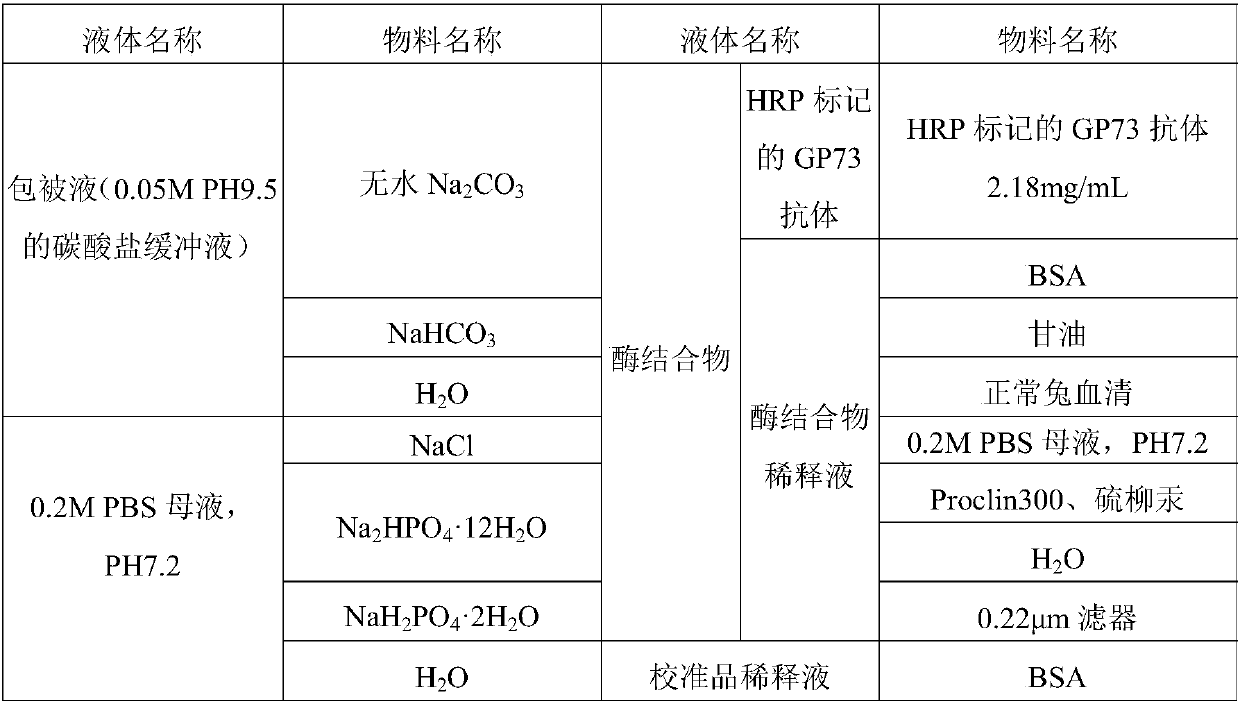
Preparation and application of GP73 C-terminal antigen
ActiveCN107746430APrevention of malignant transformationSimple and fast operationImmunoglobulins against animals/humansDisease diagnosisAntigenMonoclonal antibody
The invention provides a GP73 C-terminal protein and an anti GP73 C-terminal monoclonal antibody prepared thereby; for solving the deficiency of lack of GP73 quantitative detection kits as a liver cirrhosis early diagnosis detection means in clinic currently, another objective of the invention is to provide a test kit having the advantages of being simple in operation, accurate, sensitive, stablein quality and capable of mass production and a determination method thereof, so as to observe the expression content of GP73 at a protein level, take effective integrated treatment schemes as soon aspossible and effectively prevent further malignancy of cirrhosis.
Owner:海南中升健康发展有限公司
Formulations and methods for the treatment of cancers
InactiveUS20190240198A1Growth inhibitionOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsBromodomainAndrogen
The present invention is directed to a formulation for treating cancer comprising an androgen receptor signaling inhibitor and a B-cell-lymphoma-2 inhibitor, which may further comprising a Bromodomain-and-Extra-Terminal protein inhibitor or a phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor.
Owner:STEMIRNA THERAPEUTICS CO LTD
Antifungal protein and usage thereof
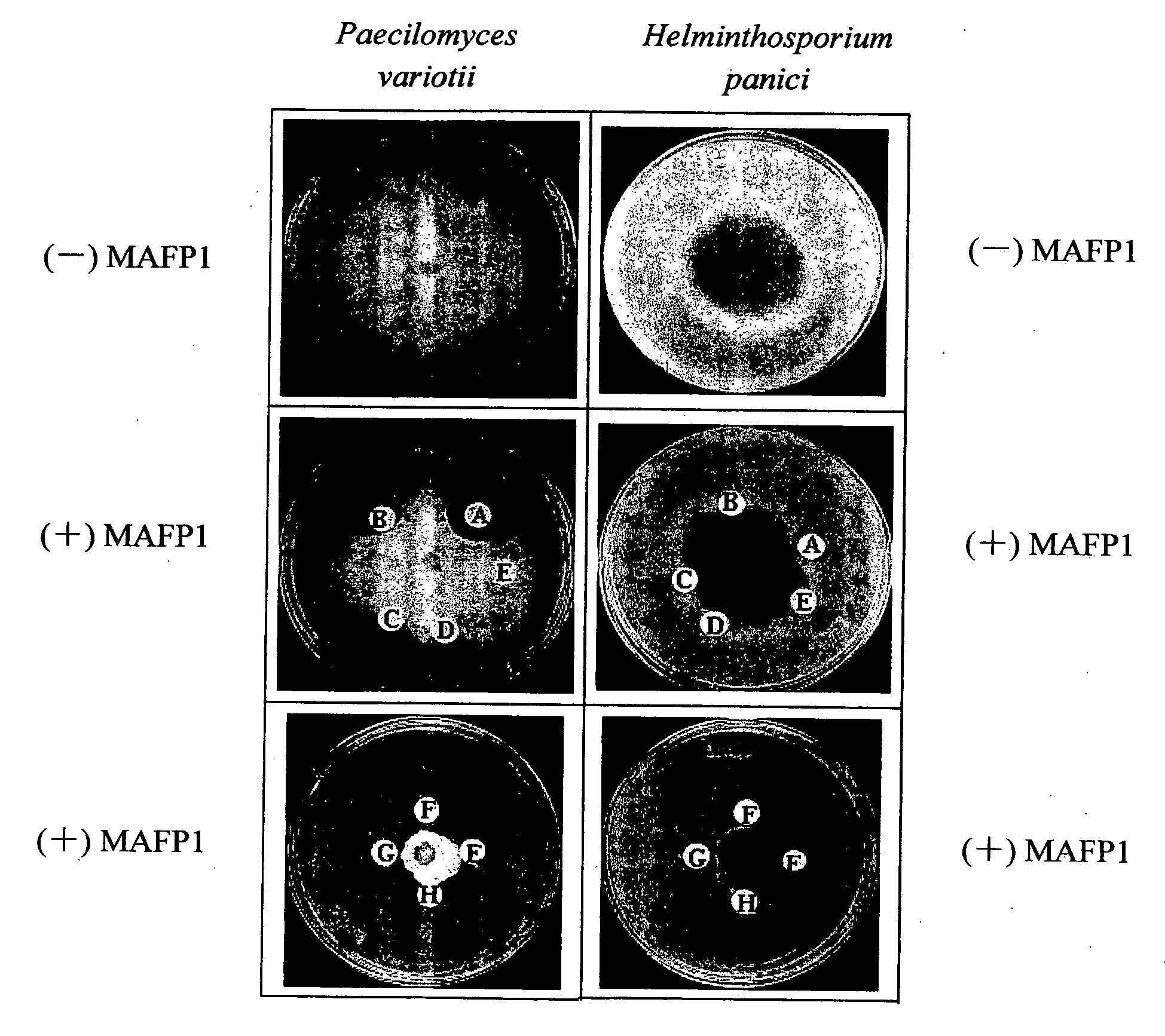
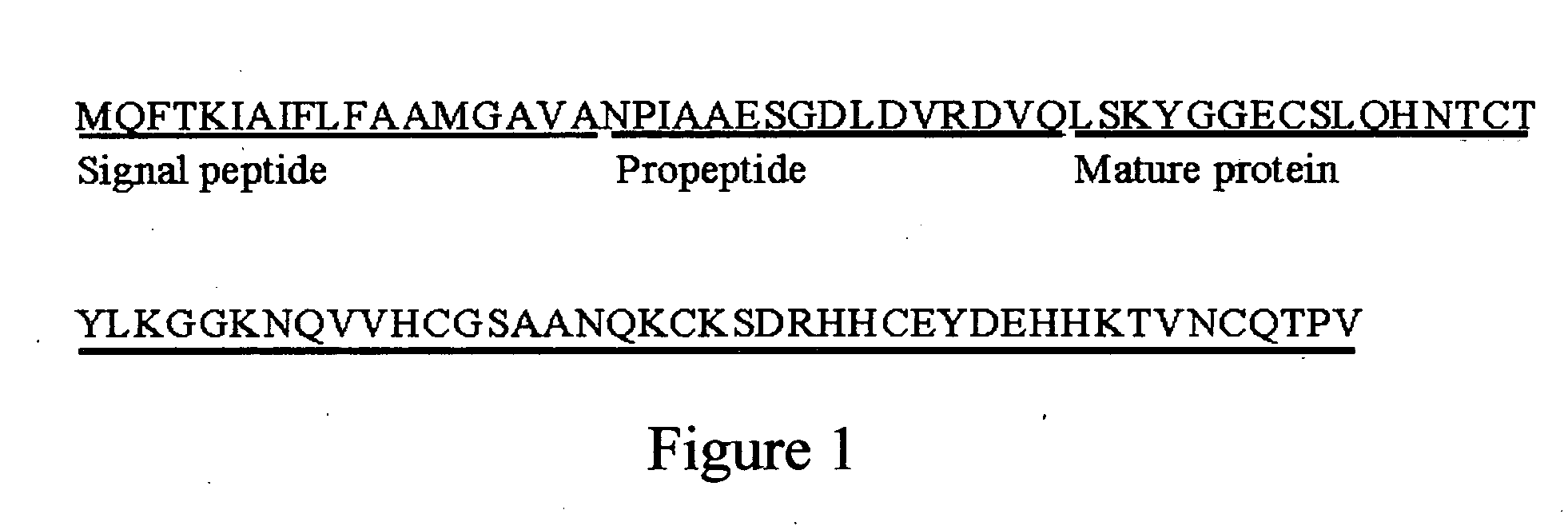
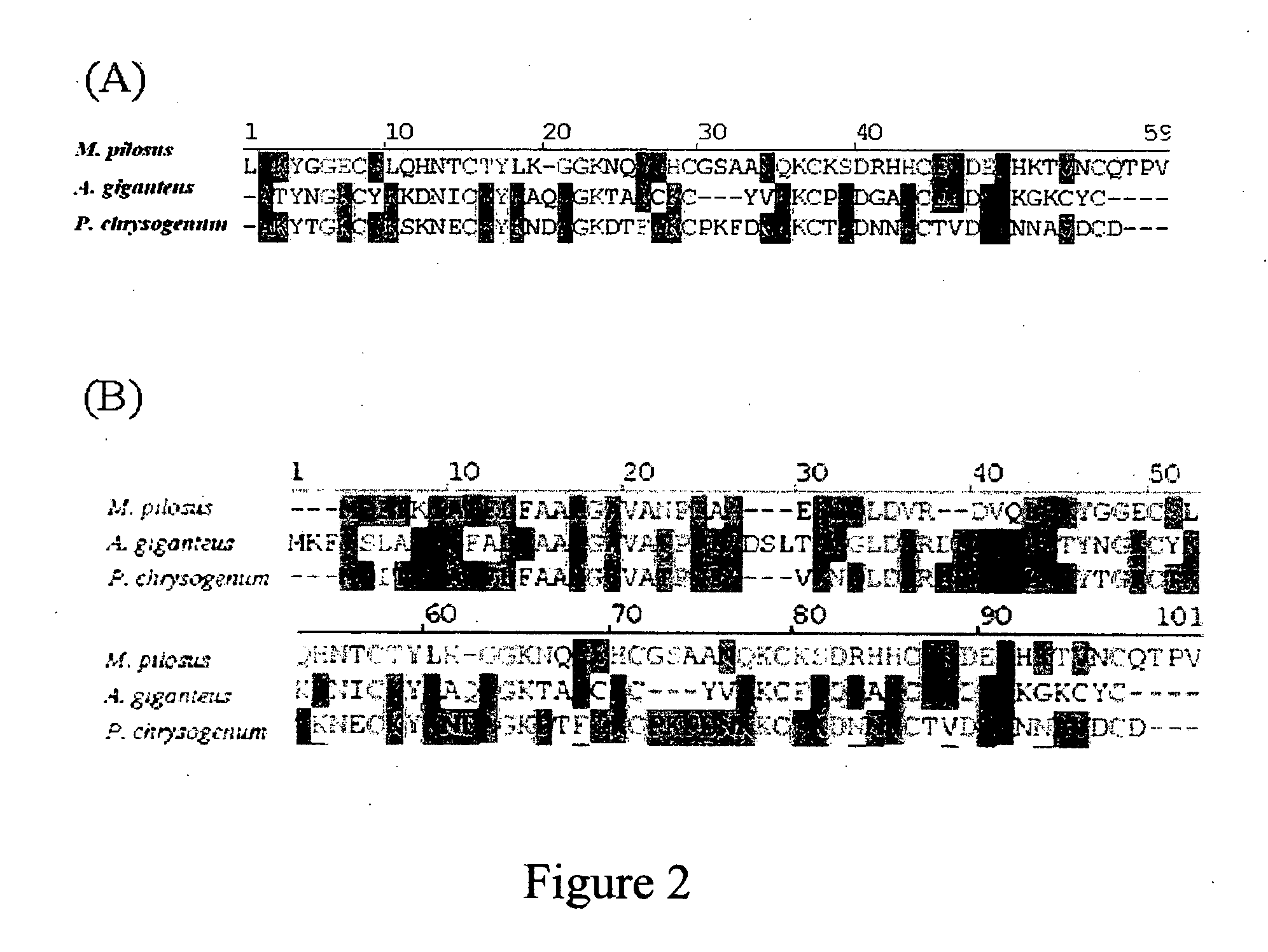
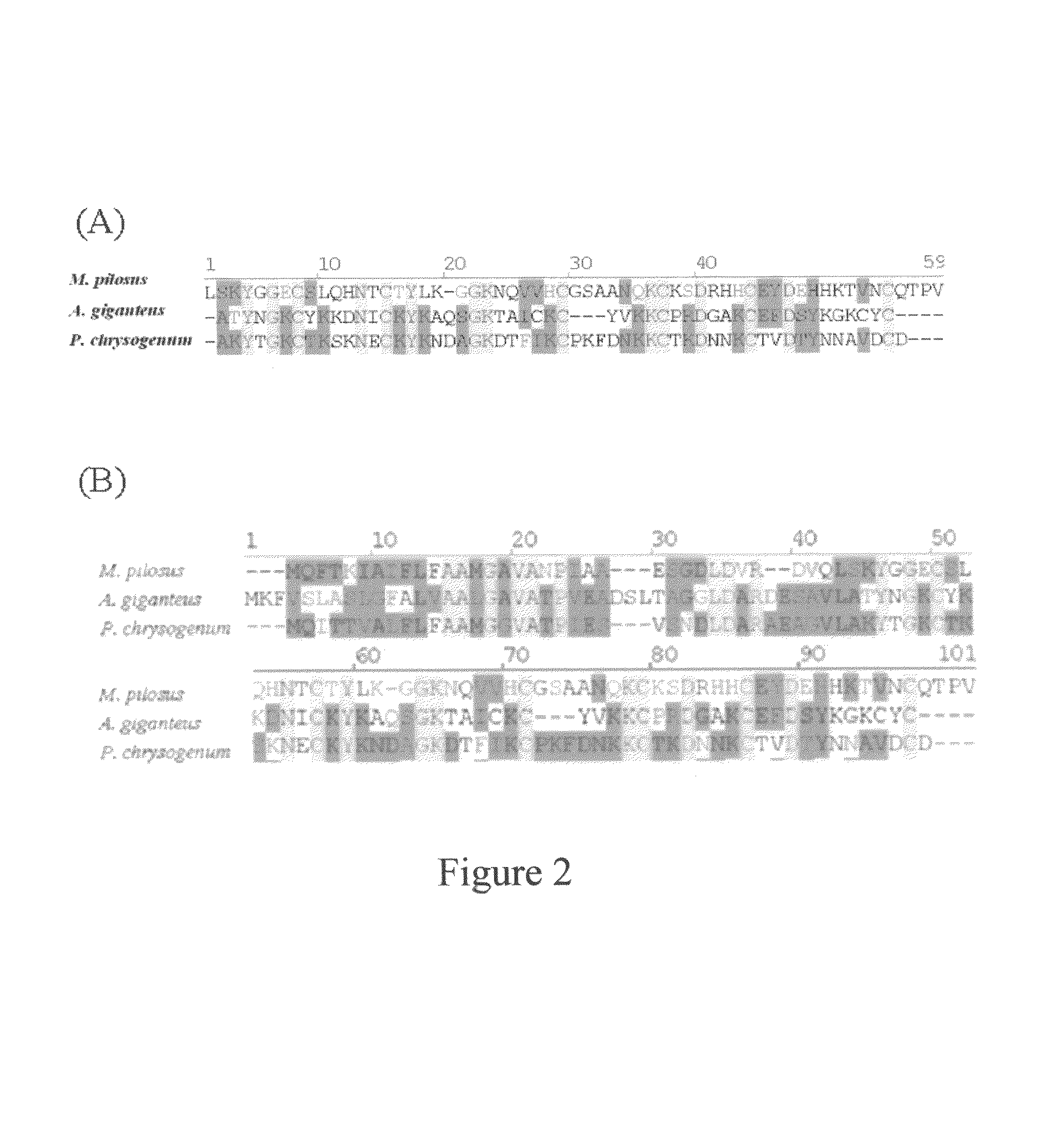
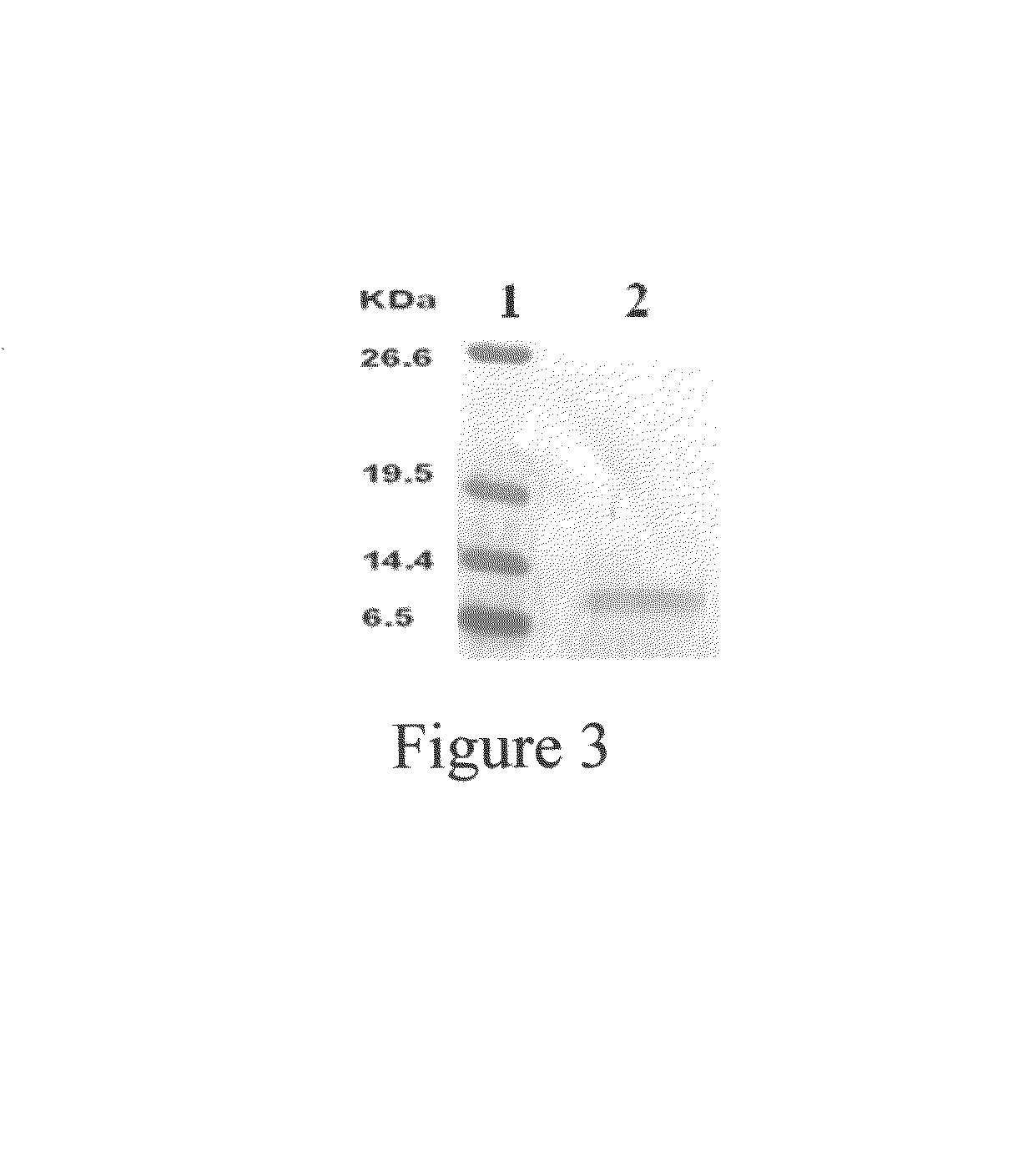
The present invention relates to an antifungal protein gene and cDNA sequence thereof, which is obtained by mining the whole genome sequences of Monascus pilosus BCRC 38072 and the unigene database. The gene can encode an antifungal protein MAFP1. A purified protein obtained from M. pilosus culture broth having molecular weight of about 7 kDa is identified as MAFP1 by N-terminal protein sequencing and comparative analysis. The purified MAFP1 protein can inhibit the growth of pathogens such as Paecilomyces variotii BCRC 33174 and Helminthosporium panici BCRC 35004. In addition, it is found by PCR test that the gene of this antifungal protein exists in other Monascus species such as M. Barkeri, M. floridanus, M. lunisporas, M. pilosus, M. ruber and the like. It is also been proved that the mafp1 gene and cDNA thereof in four Monascus strains, M. pilosus (BCRC 38072, BCRC 38093 and BCRC 31502) and M. ruber BCRC 31533, have the same DNA sequences.
Owner:FOOD IND RES & DEV INST
Production Of Viral Vectors
InactiveUS20110033926A1Faster, higher titer and higher purity productionImprove efficiencyDepsipeptidesNucleic acid vectorAdenovirus DNATiter
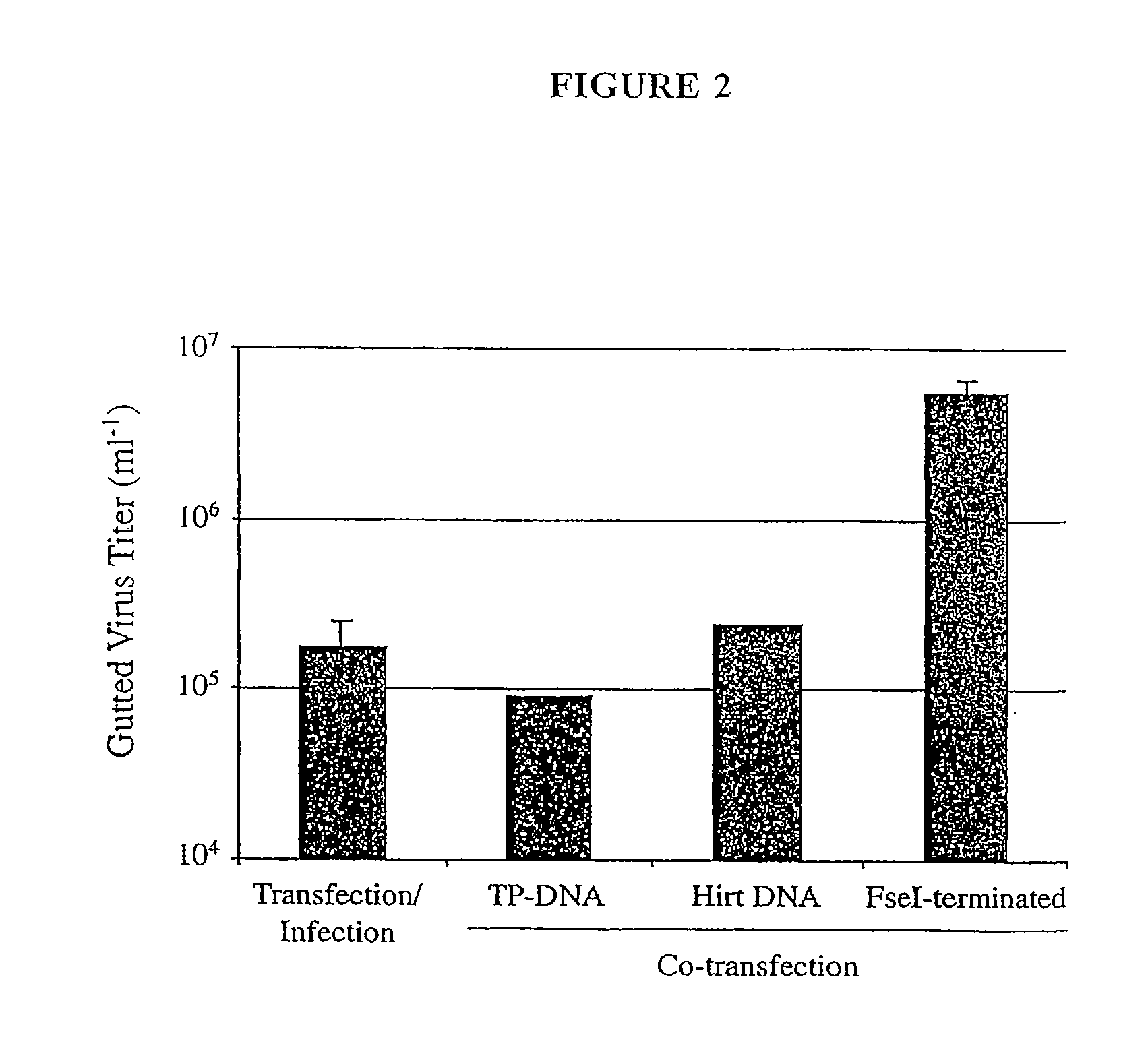
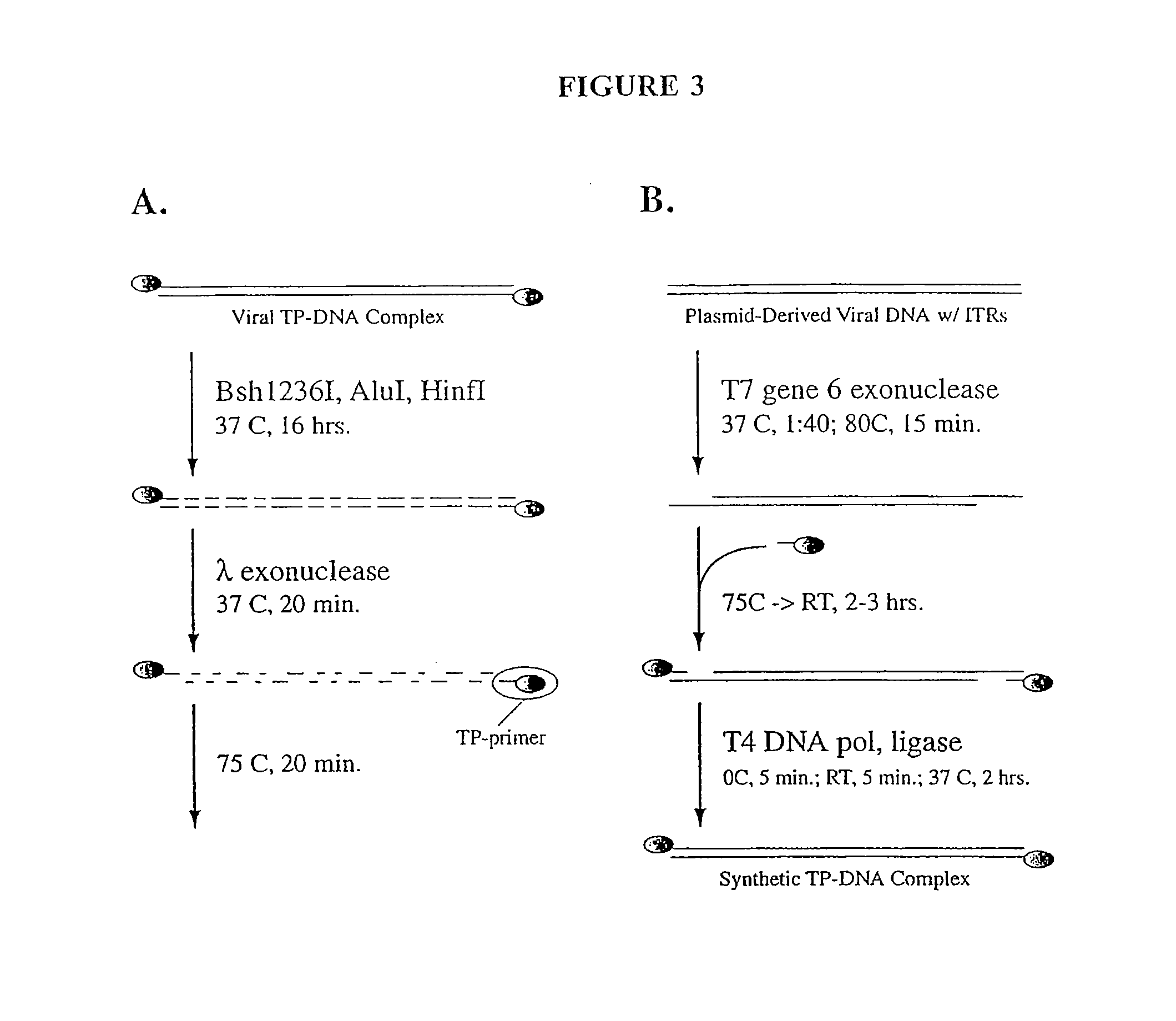
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for the production of viral vectors. In particular, the present invention provides methods and compositions for faster, higher titer and higher purity production of viral vectors (e.g. adenoviral vectors). In some embodiments, the present invention provides gutted and helper viruses with identical or similar termini. In other embodiments, the present invention provides terminal protein linked adenoviral DNA. In certain embodiments, the present invention provides template extended adenoviral DNA.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
PHF14 C-terminal protein, its polyclonal antibody and application thereof
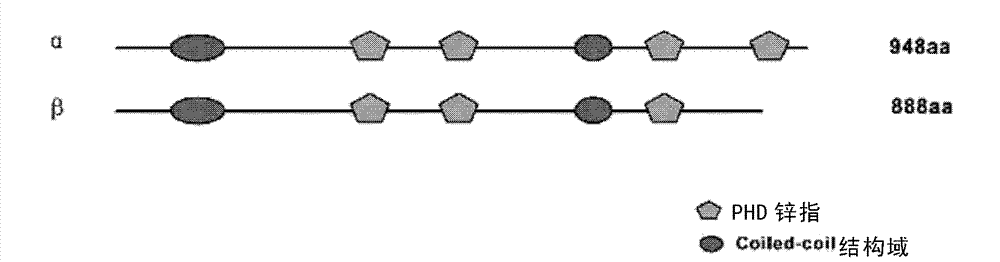
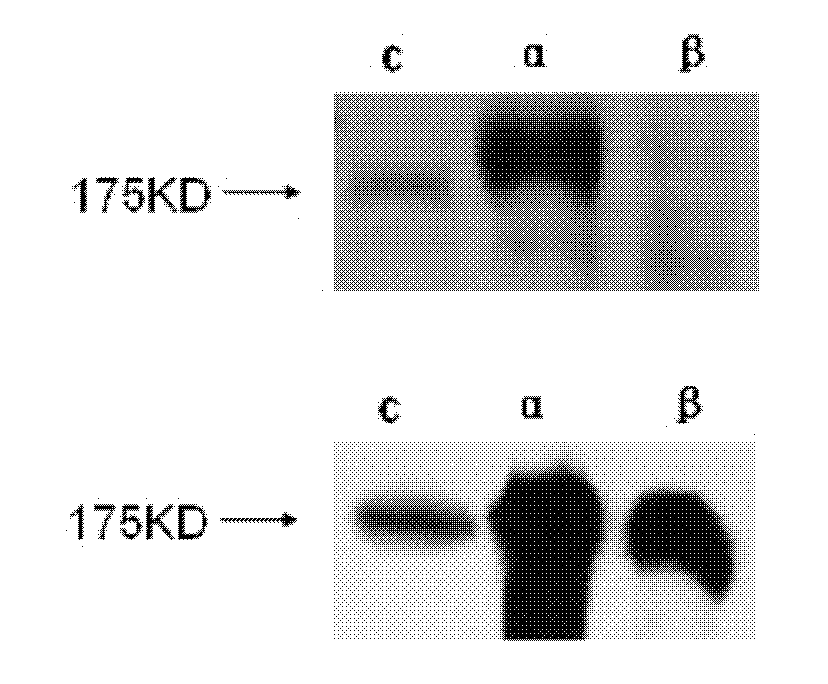
The invention relates to a PHF14 C-terminal protein, its polyclonal antibody and an application thereof. According to the invention, human derived PHF14 C-terminal protein is separated, and it is found by chance that the antigen fragment has good immunogenicity. An antibody obtained from an antigen fragment immune animal can specifically identify PHF14 alpha protein instead of PHF14 beta fragment. The PHF14 C-terminal protein and its polyclonal antibody provided by the invention have advantages of simple preparation method, high titer, strong specificity and high sensitivity.
Owner:CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR CELL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation and application of cryptosporidium protein kinase 660 C-terminal protein
InactiveCN111154792AIncrease productionImprove solubilityTransferasesFermentationEnzyme digestionProtein target
The present invention discloses a preparation method and an application of cryptosporidium protein kinase 660 C-terminal protein. The preparation method comprises the following steps: S1, using amplification primers shown in SEQ ID NO:1-2 to conduct PCR amplification reaction to obtain a Cp 660 C gene segment; S2, carrying out double enzyme digestion on the Cp 660 C gene fragment and a prokaryoticexpression plasmid and conducting connection to obtain a Cp 660 C recombinant plasmid; S3, transferring the Cp 660 C recombinant plasmid into an expression host bacterium and picking a positive clonebacterium; S4, carrying out amplification culture on the positive clone bacterium until a growth logarithmic phase and carrying out induced expression; S5, carrying out refrigerated centrifugation onbacterial liquid after the induced expression, collecting bacterium body, discarding supernatant, washing the bacterium body, carrying out re-suspension, adding a protease inhibitor, carrying out icebath ultrasonic lysis on the bacterium body to obtain a lysate, then carrying out low-temperature centrifugation to obtain supernatant, and conducting filtering with a filter membrane; and S6, takingthe filtered supernatant in the step 5, purifying the supernatant through a Ni column, eluting the supernatant, and collecting a target protein. The method can obtain the recombinant protein with high purity and high antigen specificity, and the purified protein can be further used for analyzing and researching functionality of the cryptosporidium protein.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Preparation of specific antibodies aiming at PCDH10C terminal protein segment molecule
InactiveCN101255193APrevent proliferationPromote apoptosisImmunoglobulins against animals/humansFermentationCultured cellHigh activity
The invention discloses a process for preparing specific antibody for PCDH10 C end albumen fragment molecule and. The method comprises, using polymerase chain reaction, directly cloning PCDH10C 3'end base sequence to the prokaryotic cell expression system from vitro cultured cell strain to purify the PCDH10 C end amalgamation albumen; using purified PCDH10 C end amalgamation albumen as antigen immunity white rabbit, producing anti PCDH10 C end antibody; collecting antiserum to obtain anti PCDH10 C end albumen specific antibody of rabbit with high-purity and high activity after affinity purification. Specific antibody for PCDH10 C end albumen fragment molecule prepared in the invention is one of the main instrumentalities for researching PCD10 mediated signal pathway transduction. The epitope of specific antibody for PCDH10 C end albumen fragment molecule is a potential target of molecular targeted therapy. The specific antibody for PCDH10 C end albumen fragment molecule can be used for clinically estimating the change of tumor gene expression and metastatic potential.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Antifungal protein and usage thereof
Owner:FOOD IND RES & DEV INST
Polypeptide for protein surface immobilization and application thereof
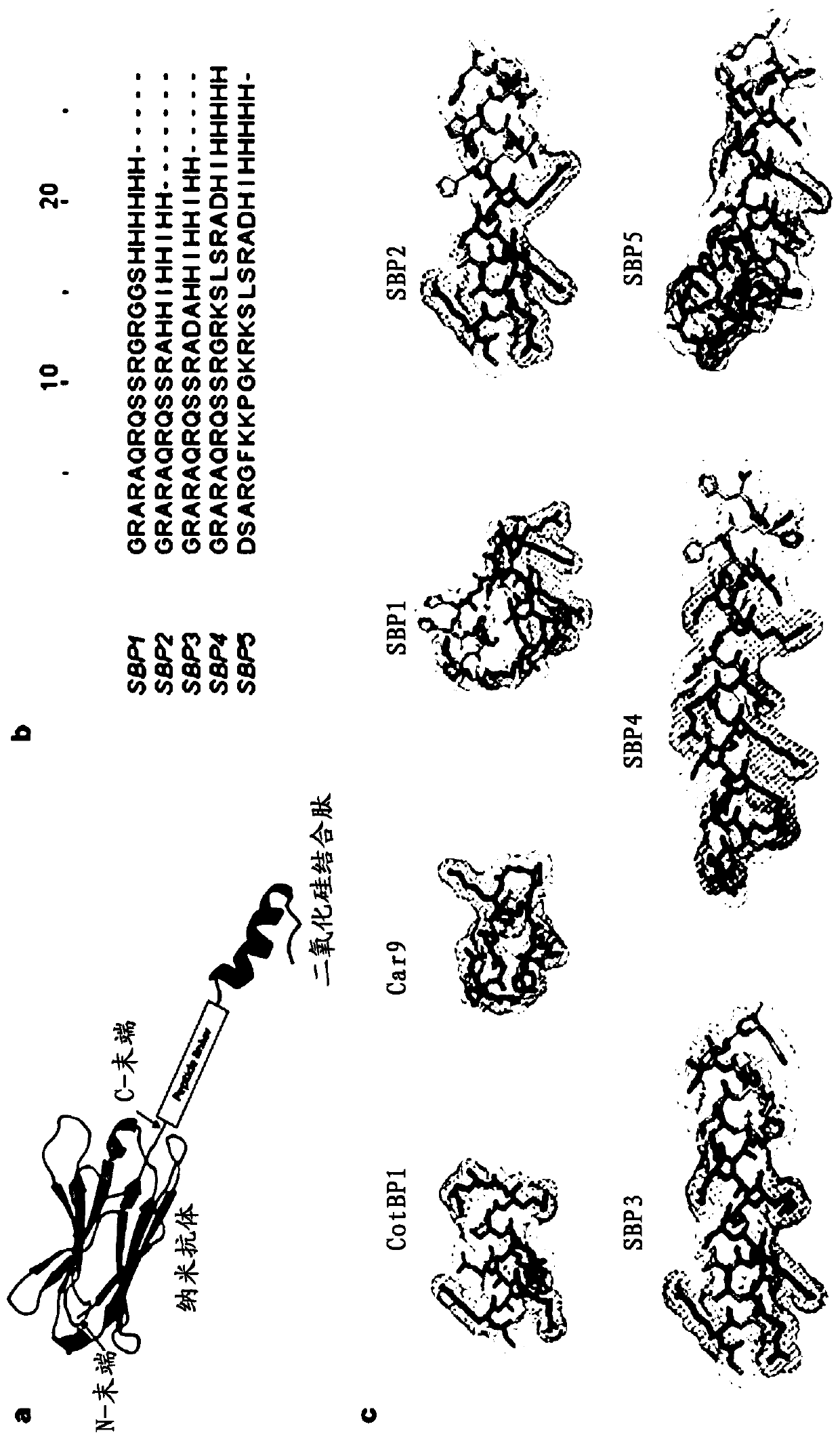
ActiveCN110950963AImprove surface binding propertiesHigh affinityImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsCarrier-bound/immobilised peptidesBinding siteBinding peptide
The invention discloses a polypeptide with silicon dioxide binding activity. The polypeptide contains a silicon dioxide binding unit forming a polypeptide main body part and a hydrogen bond forming unit formed by at least one histidine residue at the N-end or the C-end of the polypeptide. The invention also discloses a fusion protein containing the polypeptide and a functional protein with a biological effect, and a protein immobilization method. The fusion protein provided by the invention is non-covalently combined with directional control, so that related proteins are simply and quickly fixed on the surface of a silicon substrate in one step. Under the conditions of high salt, extreme pH and denaturation, protein binding is kept stable, peptide immobilization does not need surface modification or chemical coupling, and the fusion protein can be prepared at a low cost. Besides, the silicon dioxide binding peptide is fused to a specific tail end of the parent protein, so that the binding site of the protein is controlled, and the steric hindrance of the active site is eliminated.
Owner:深圳市国创纳米抗体技术有限公司
Metastasis suppressor1 protein dimerization fluorescent probes and application thereof
InactiveCN103288930ALower requirementHigh precisionDepsipeptidesBiological testingLymphatic SpreadNucleotide
The invention provides a group of metastasis suppressor1 (Mtss1) protein dimerization fluorescent probe complementary proteins containing amino acid sequences as shown in SEQ ID No: 2 and SEQ ID No: 4 which respectively correspond to a fluorescence probe N-terminal protein and a fluorescence probe C-terminal protein. The invention also provides polynucleotides encoding the group of proteins and recombinant vectors of the polynucleotides. The fluorescence probes provided by the invention can make use of dimerization of an Mtss1 protein, and end-connecting complementation genes of the fluorescence probes are close to each other and interact with each other to form an ability to excite fluorescence. The fluorescence intensity of the probes can indicate the dimerization extent of an I-BAR district of the Mtss1 protein, and shows a linear relationship with activities of Mtss1 protein I-BAR inhibiting drugs. The probe proteins provided by the invention can be used for studying an Mtss1 protein dimerization process, and can also be used for high efficiency screening of Mtss1 protein inhibitors.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Methods and compositions for producing a virus
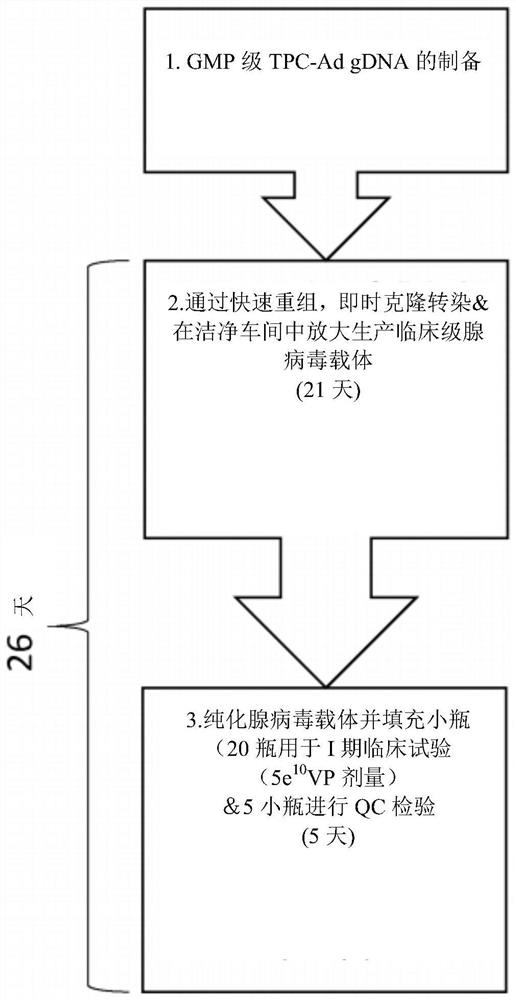
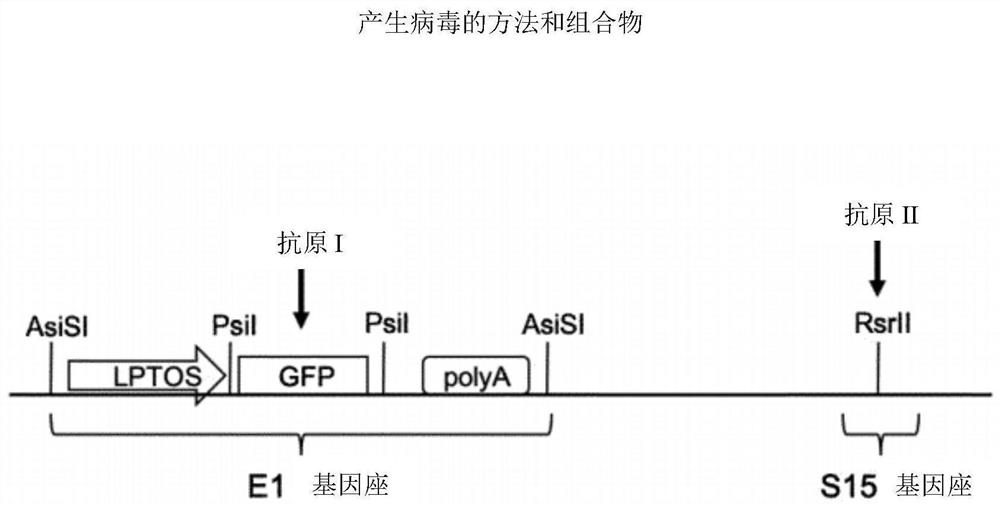
PendingCN112638412AShorten the timeReduce negative impactViral antigen ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementHeterologousNucleotide
The invention relates to methods for generating a recombinant adenovirus comprising a nucleotide sequence encoding a heterologous gene of interest for use as a vaccine comprising the steps of inserting the heterologous gene of interest into the adenovirus genome by recombining terminal protein complexed adenovirus genomic DNA (TPC-Ad gDNA) with a polynucleotide comprising a nucleotide sequence encoding the gene of interest and having 5' and 3' ends that are homologous to the insertion site sequence of the adenovirus genomic DNA in an in vitro recombination reaction, transfecting cells growing in individual vessels with a dilution of the in vitro recombination reaction mixture from (i) such that a number of such individual vessels contain a single cell that is infected by a recombinant adenovirus comprising the nucleotide sequence encoding the heterologous gene of interest, and identifying those individual vessels in which a single cell has been infected by the recombinant adenovirus comprising the nucleotide sequence encoding the heterologous gene of interest. Suitably said TPC-Ad gDNA comprises serotype-matched terminal protein and adenovirus genome, and said gene of interest codes for a single epitope, a string of epitopes, a segment of an antigen or a complete antigen protein. The invention also relates to recombinant adenoviruses and compositions made using these methods.
Owner:OXFORD UNIV INNOVATION LTD
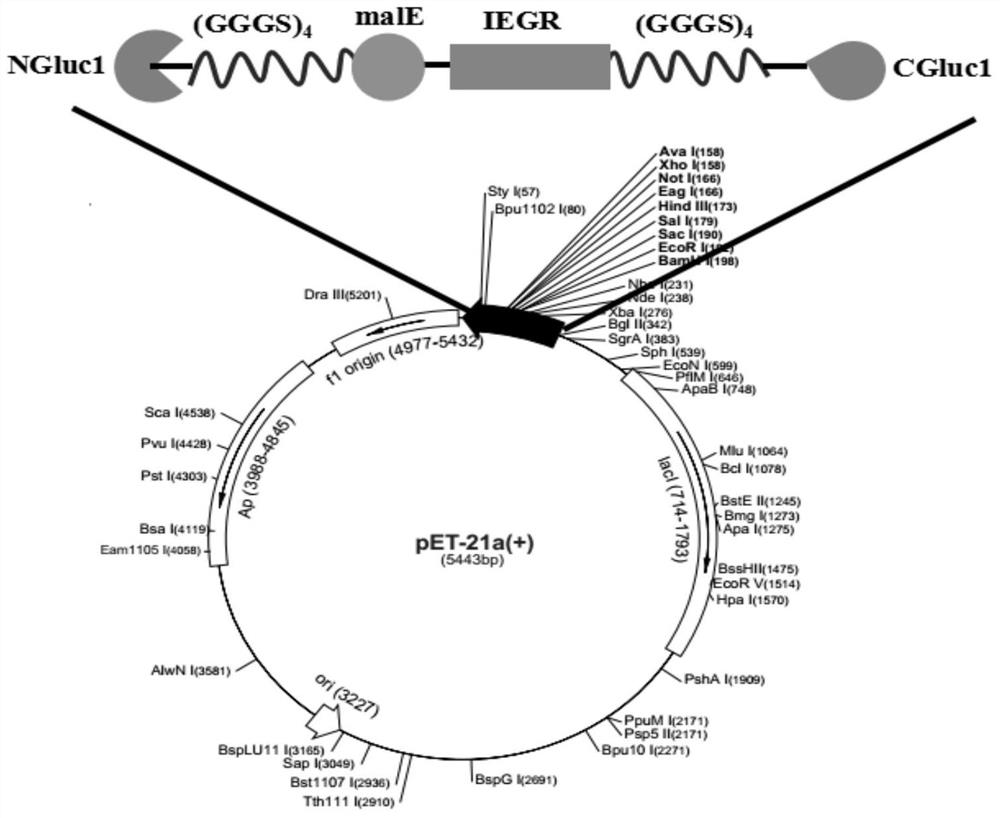
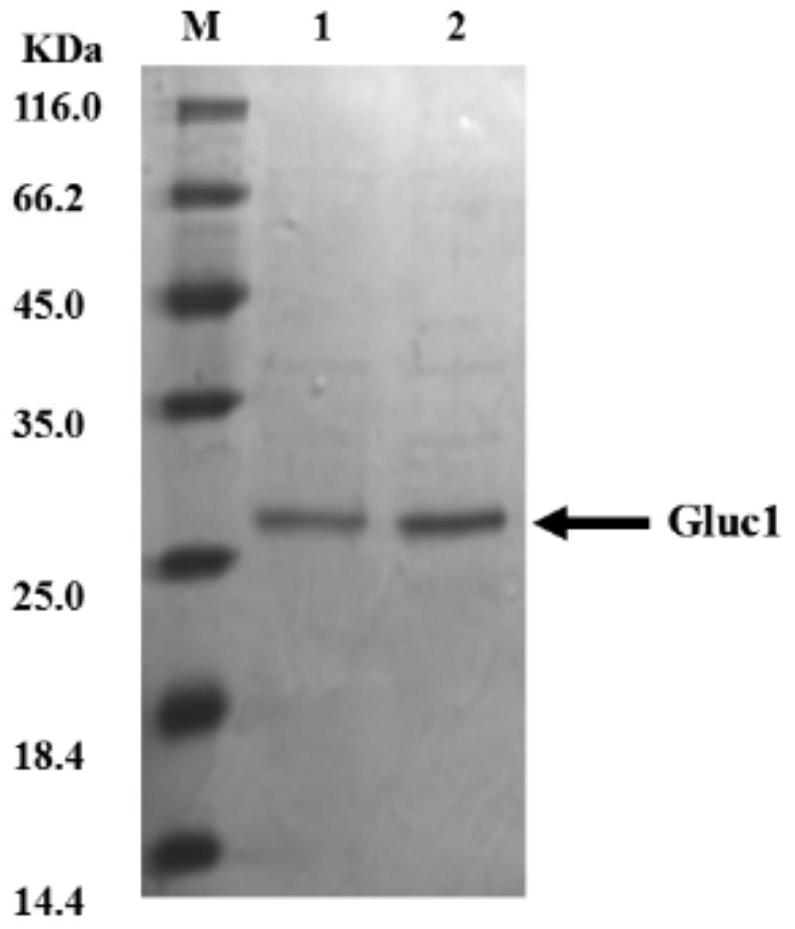
A kind of adjustable luciferase fusion protein, its preparation method and application
ActiveCN106916795BAchieve bioluminescenceHigh fluorescence intensityMicrobiological testing/measurementOxidoreductasesBinding siteAmino acid
The present invention relates to the technical field of molecular biology, in particular to an adjustable luciferase segmented fusion protein, its preparation method and application. The fusion protein includes luciferase N-terminal protein, flexible peptide segment 1, MBP protein, Active valve, flexible peptide segment 2 and luciferase C-terminal protein; wherein, the luciferase N-terminal protein and luciferase C-terminal protein together form luciferase; the active valve is a section of 4-8 hydrophobic short Peptide Amino Acids. Through the short peptide chain amino acid sequence as the "active valve" and the specific cleavage enzyme as the "valve key", a new type of fluorescent complementary protein switching mode is realized, which can be used to evaluate the dynamic interaction of other proteins such as ligands Binding to a substrate, interactions that create new binding sites, protein-protein interactions that deactivate proteins, protein-protein interactions that alter the substrate specificity of a protein.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process for preparing target ribonuclease for curing hepatitis B virus infection
The present invention relates to the process of preparing target ribonuclease for curing hepatitis B virus infection. By means of molecular biological measures, it is constituted fusion protein of neurotoxin hEDN and HBV polymerase end protein structural domain DNAPTP or core protein originated from human eosinophil. The fusino protein, that is the said target ribonuclease, may be used in treating huma hepatitis B virus infection via gene therapy or protein medicine mode. Experiment shows that the target ribonuclease can reduce in vitro HBSAg for 46-59 % and inhibit obviously the duplicatino of hepatitis B virus. Available gene therapy or protein medicine mode may be refered to for its specific administratino way or mode.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Deleted adenovirus vectors and methods of making and administering the same
The present invention provides deleted adenovirus vectors. The inventive adenovirus vectors carry one or more deletions in the IVa2, 100 K, polymerase and / or preterminal protein sequences of the adenovirus genome. The adenoviruses may additionally contain other deletions, mutations or other modifications as well. In particular preferred embodiments, the adenovirus genome is multiply deleted, i.e., carries two or more deletions therein. The deleted adenoviruses of the invention are “propagation-defective” in that the virus cannot replicate and produce new virions in the absence of complementing function(s). Preferred adenovirus vectors of the invention carry a heterologous nucleotide sequence encoding a protein or peptide associated with a metabolic disorder, more preferably a protein or peptide associated with a lysosomal or glycogen storage disease, most preferably, a lysosomal acid α-glucosidase. Further provided are methods for producing the inventive deleted adenovirus vectors. Further provided are methods of administering the deleted adenovirus vectors to a cell in vitro or in vivo.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
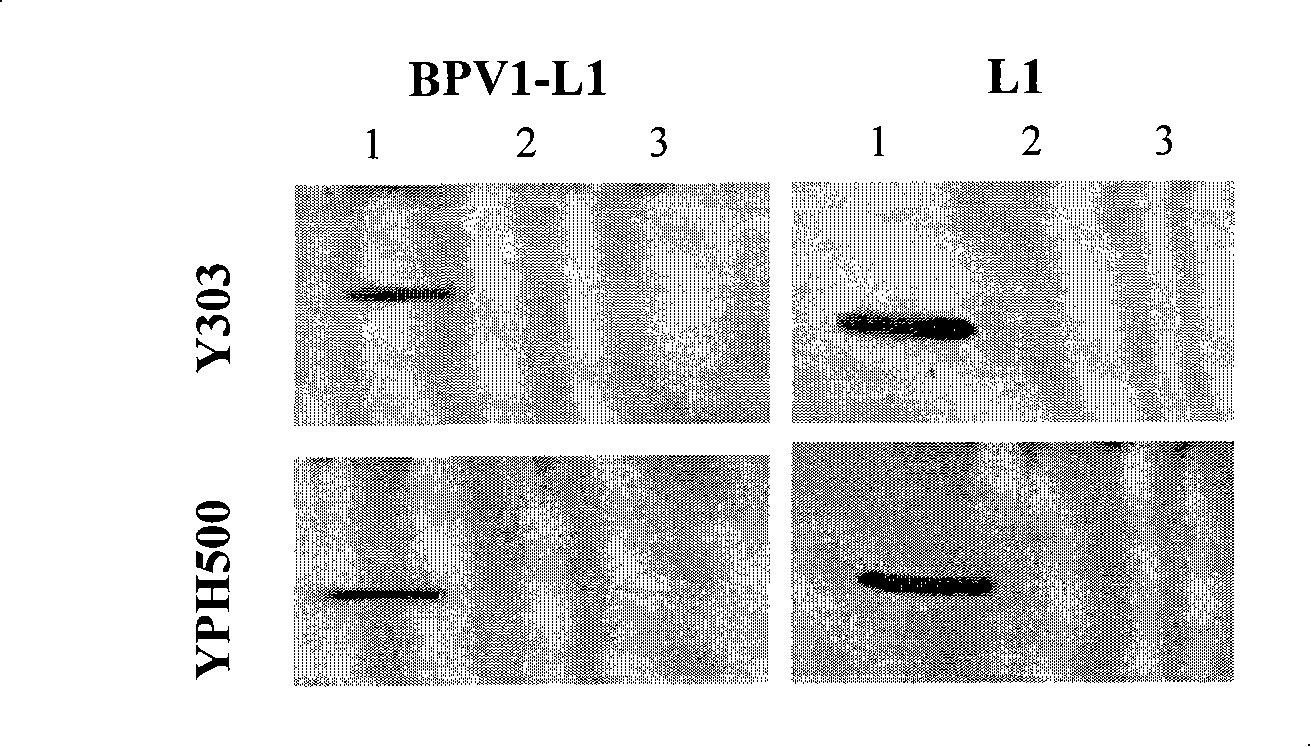
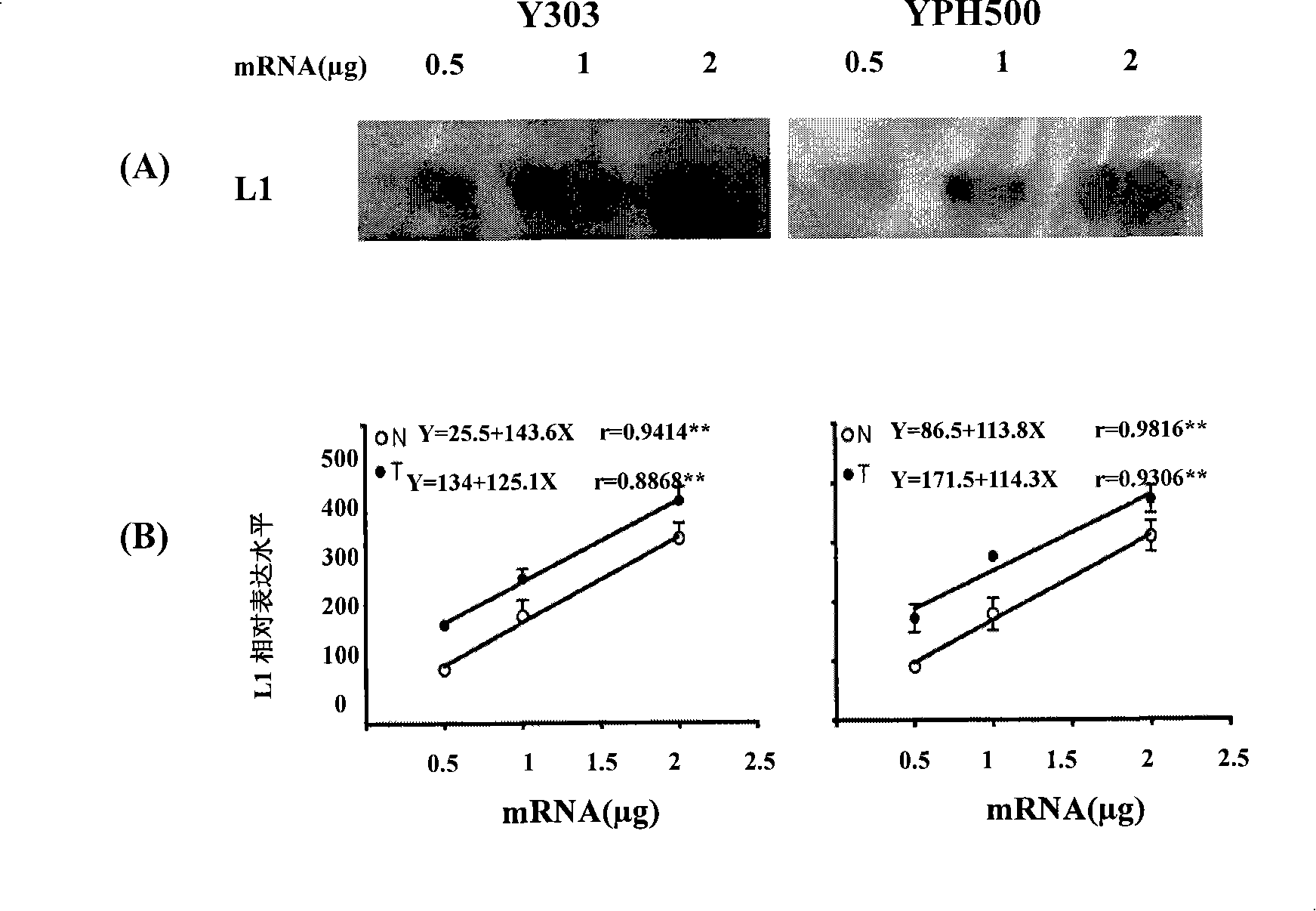
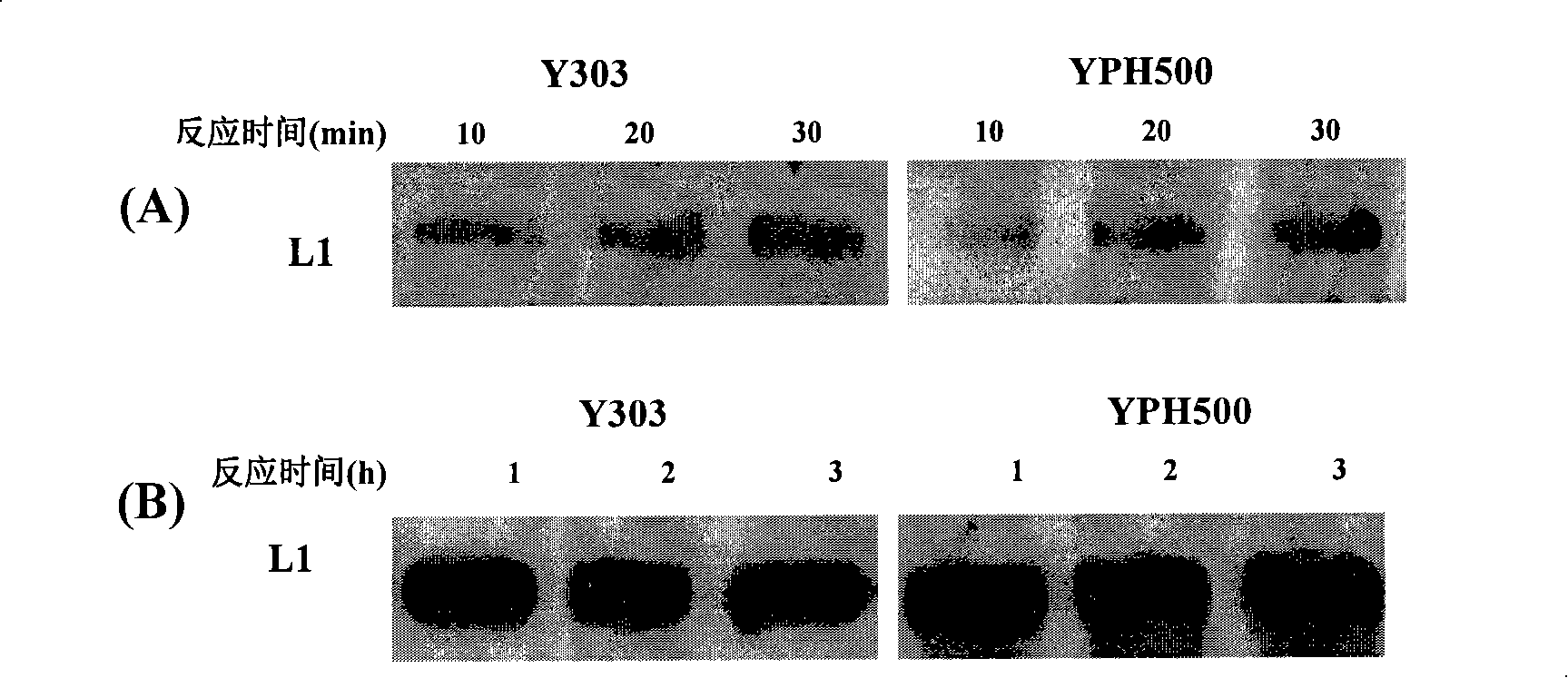
Establishment of HPV gene yeast external translating system
The invention discloses a buildup method of an HPV gene yeast in vitro translating system. The improved yeast in vitro translating system built up by the method of the invention is particularly applicable to in vitro expression of coat protein of human papilloma virus (HPV), providing a convenient and rapid method for researching the coat protein expression system of the HPV. The system is also applicable to in vitro expression of other eukaryotic proteins at the same time. The buildup of the in vitro translating system of the invention provides an effective tool for the research of VLP forming and DNA package after terminal protein expression of the HPV and is hopeful to assist the research of HPV prevention and therapeutic vaccine. The method of the invention can also be used for preparing lysate of various yeast mutants researching the various factors that influence the protein translation after the transcription of eukaryotic mRNA and the reciprocity system of related molecular.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
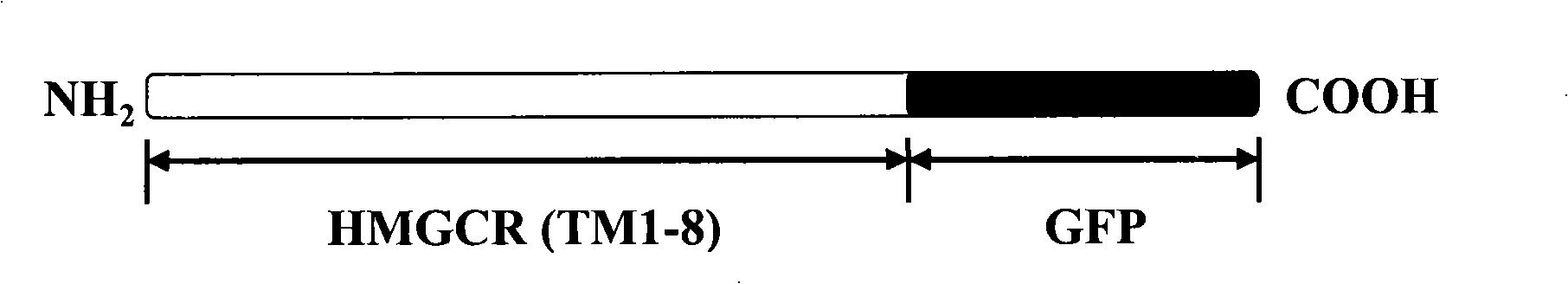
Cholesterol metabolism regulating and controlling medicament sifting motion system and method with hydroxymethyl glutaryl cozymase A reductase as target point
ActiveCN101343326AReserved functionRetain activityBiological testingHybrid peptidesHydroxy methyl glutarylCholesterol metabolism
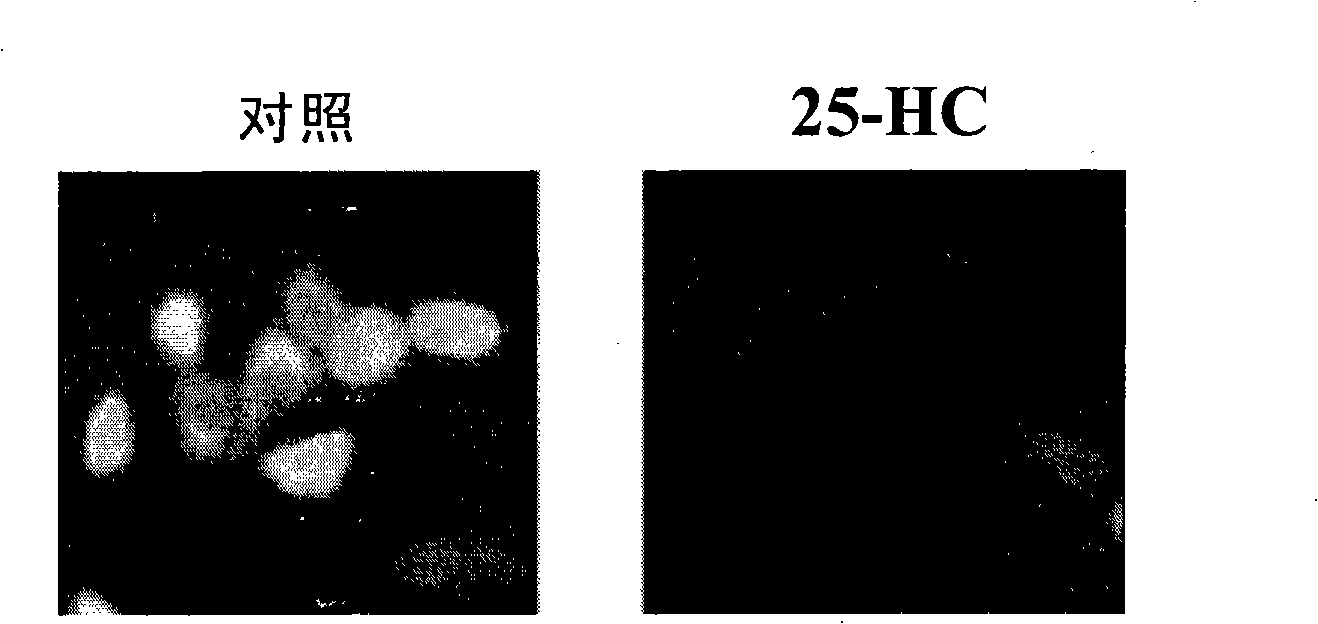
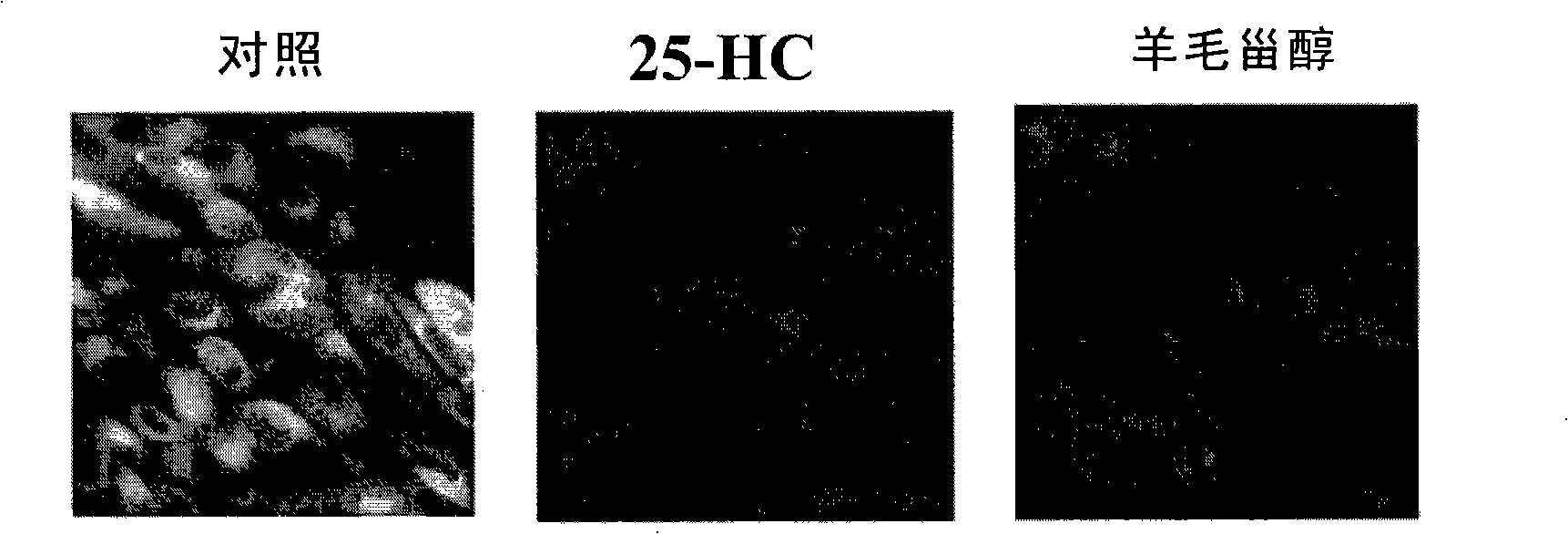
The invention discloses a screening system which takes HMG-CoA reductase A as a target spot to regulate cholesterol drug. The screening system adopts a cell system which is formed through connecting N-terminal protein fragment of HMG-CoA reductase A with a detectable signal element and guiding the N-terminal protein fragment into cells, to ensure cells to express fusion protein. The screening system can be used for screening substances which takes HMG-CoA reductase A as the target spot for regulating cholesterin.
Owner:CHOLESGEN (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com