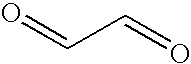Patents
Literature
2546 results about "Binding site" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In biochemistry and molecular biology, a binding site is a region on a macromolecule such as a protein that binds to another molecule with specificity. The binding partner of the macromolecule is often referred to as a ligand. Ligands may include other proteins (resulting in a protein-protein interaction), enzyme substrates, second messengers, hormones, or allosteric modulators. The binding event is often, but not always, accompanied by a conformational change that alters the function of the protein. Binding to protein binding sites is most often reversible (transient and non-covalent), but can also be covalent reversible or irreversible.
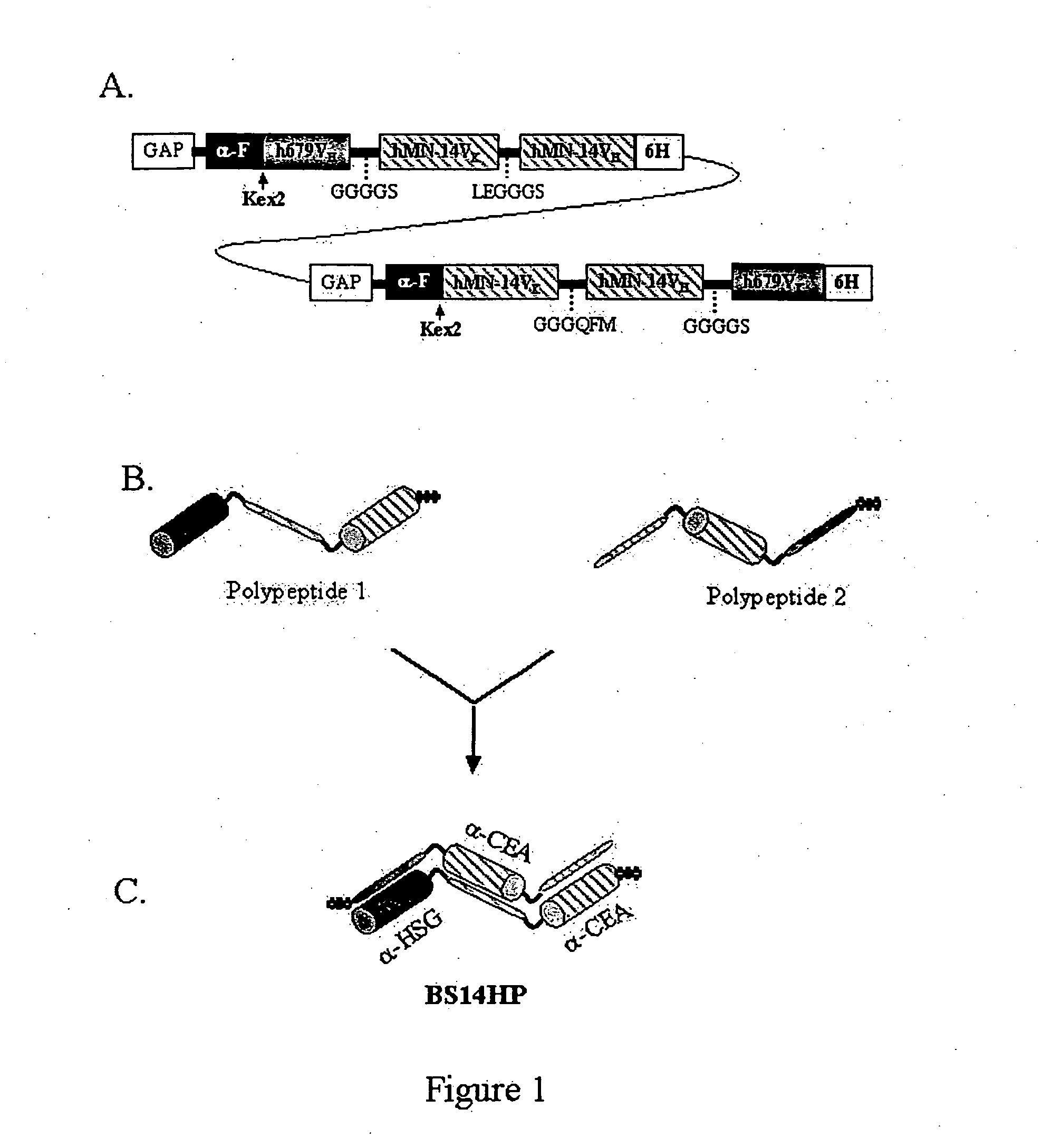
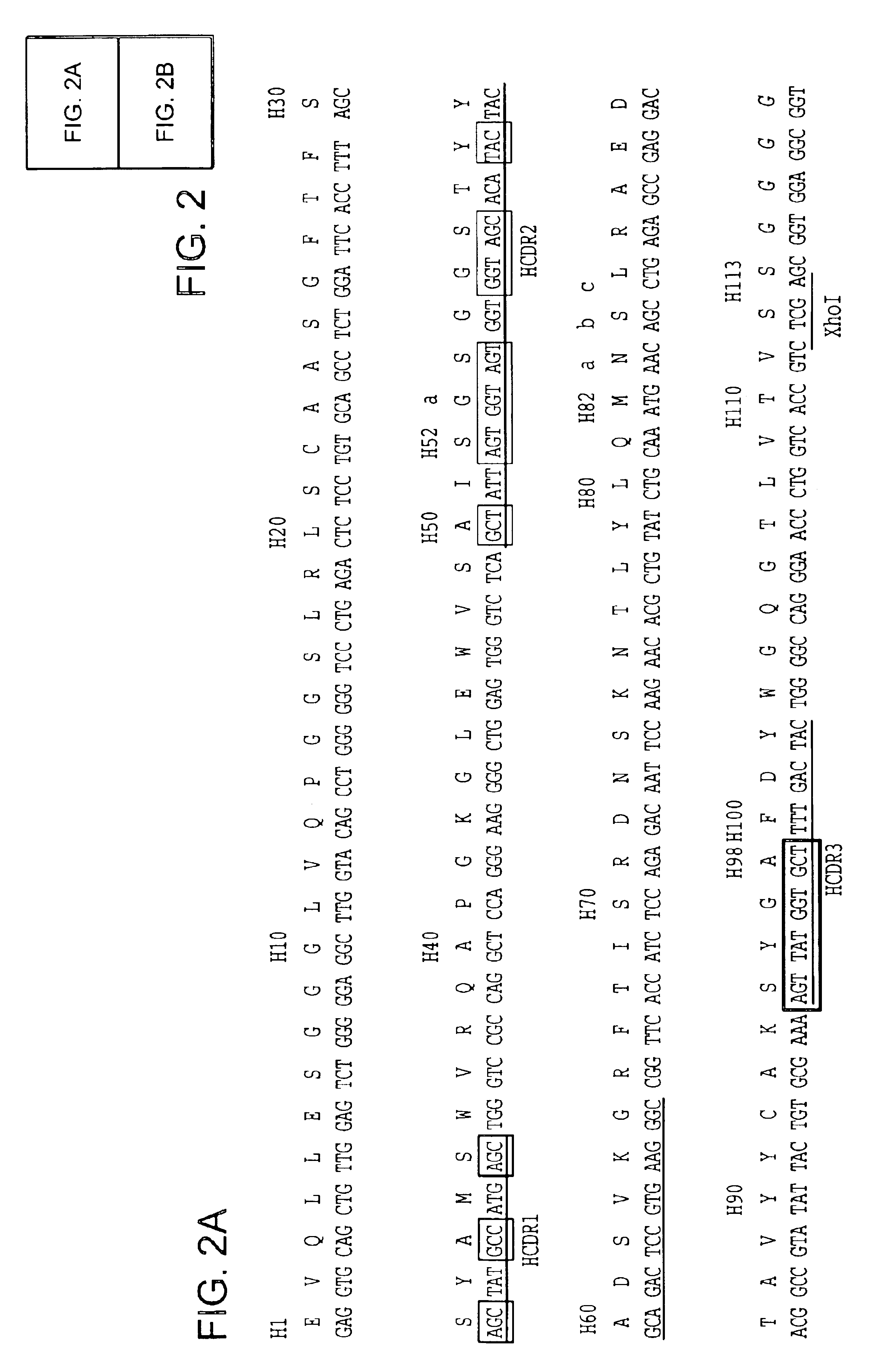
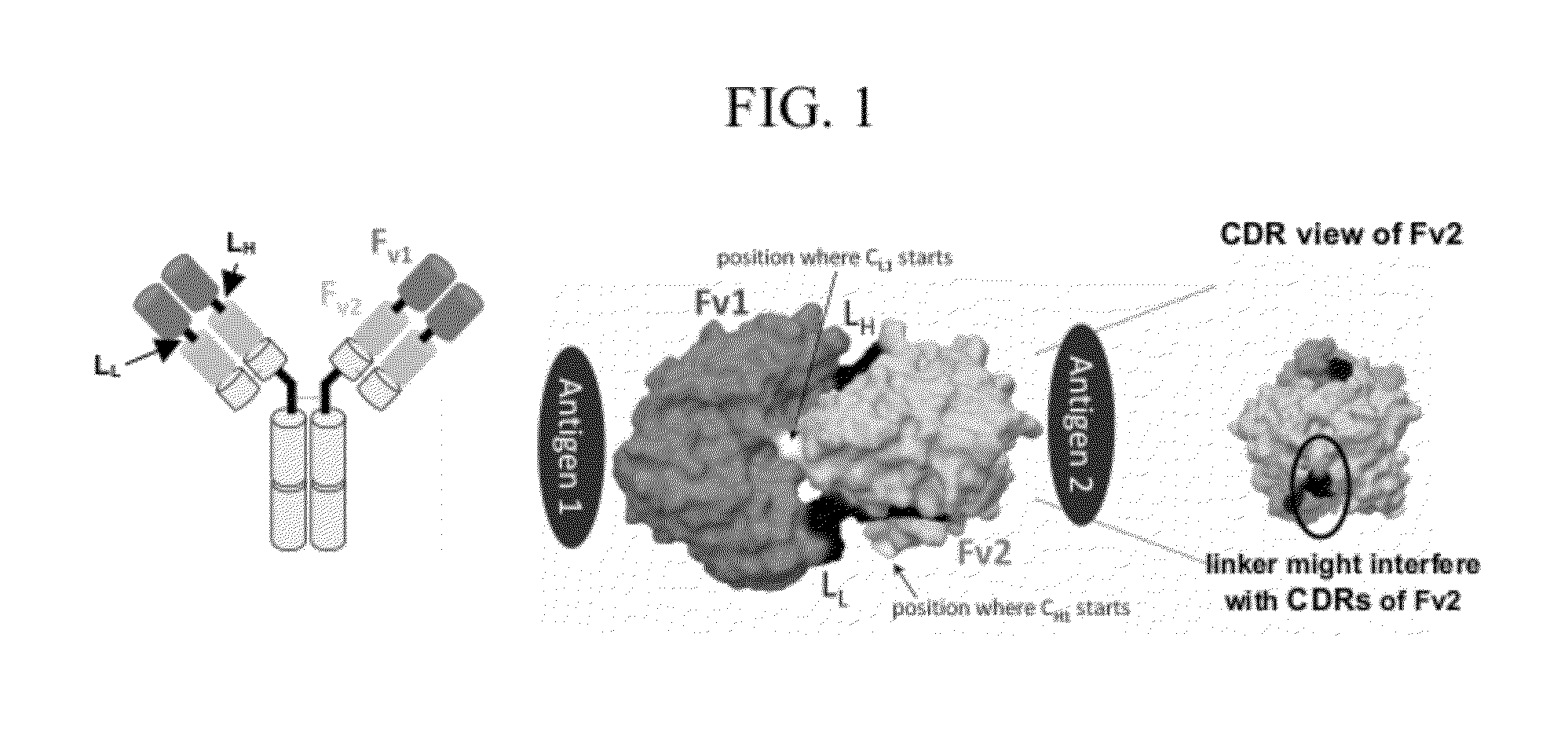
Multivalent antibodies and uses therefor
The present application describes engineered antibodies, with three or more functional antigen binding sites, and uses, such as therapeutic applications, for such engineered antibodies.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
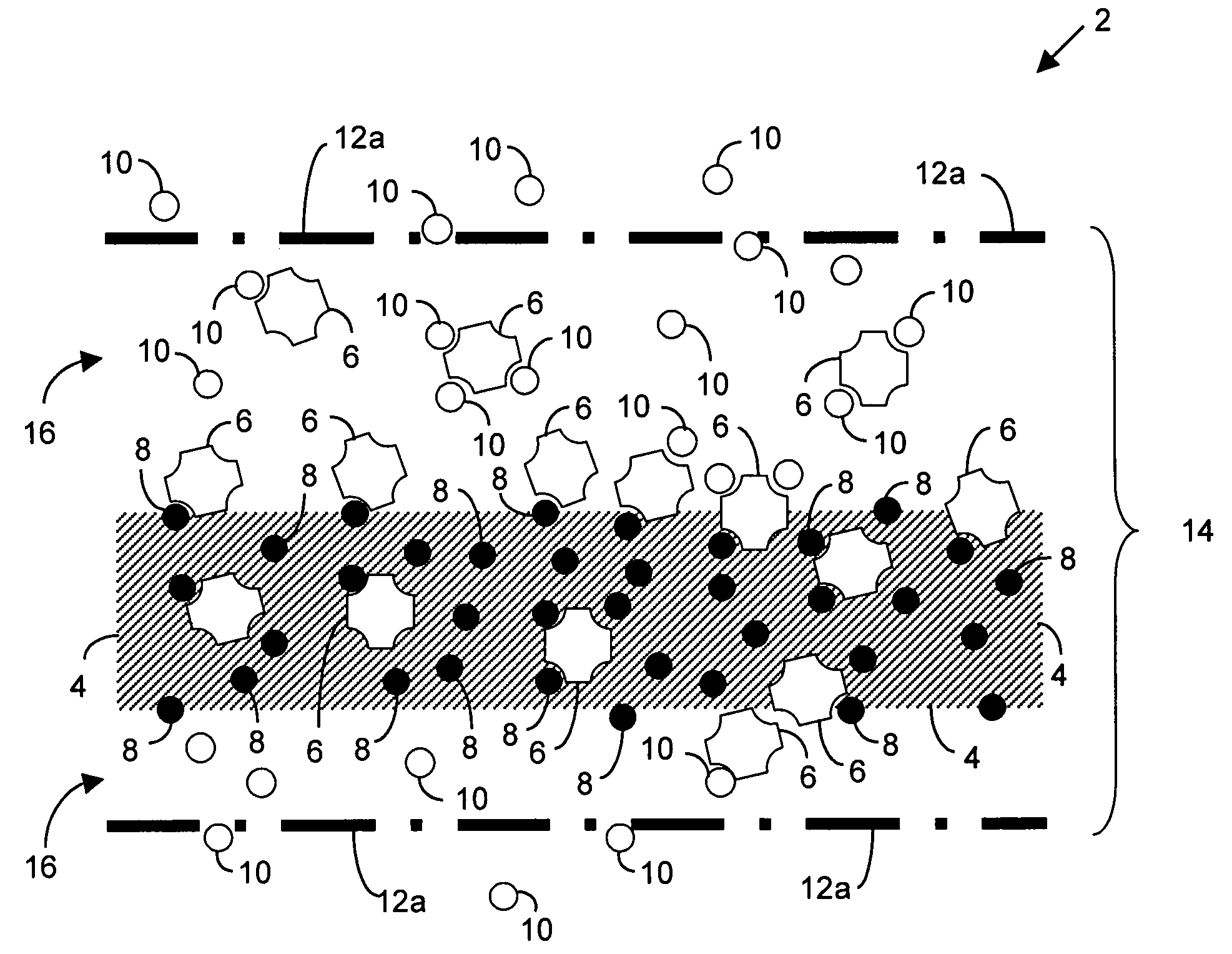
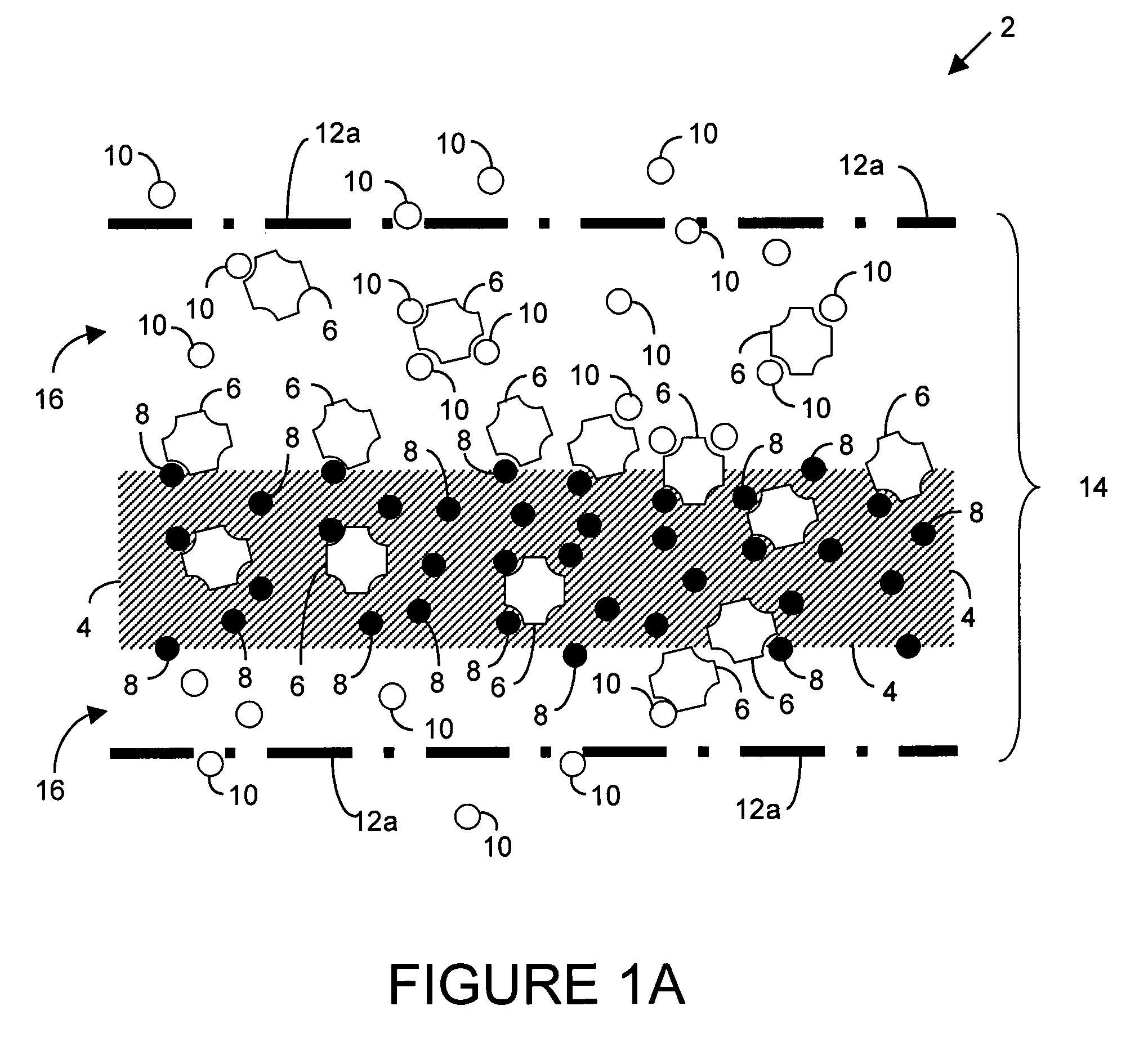
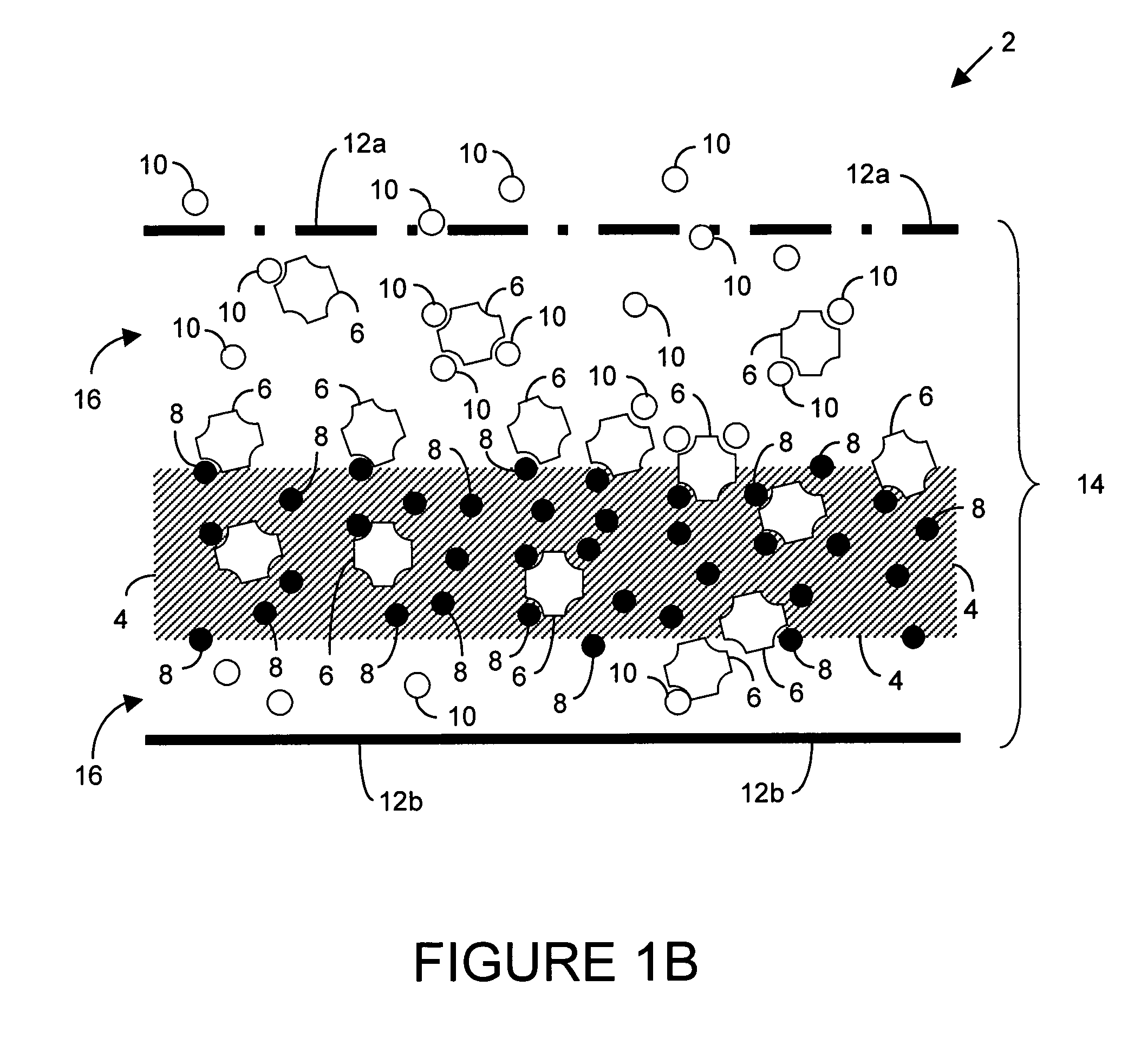
Polyvalent protein complex
The invention provides for a polyvalent protein complex (PPC) comprising two polypeptide chains generally arranged laterally to one another. Each polypeptide chain typically comprises 3 or 4 “v-regions”, which comprise amino acid sequences capable of forming an antigen binding site when matched with a corresponding v-region on the opposite polypeptide chain. Up to about 6 “v-regions” can be used on each polypeptide chain. The v-regions of each polypeptide chain are connected linearly to one another and may be connected by interspersed linking regions. When arranged in the form of the PPC, the v-regions on each polypeptide chain form individual antigen binding sites.
Owner:IBC PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Method to screen phage display libraries with different ligands
InactiveUS6846634B1Overcome inherent biasGuaranteed effective sizePeptide librariesLibrary screeningBinding siteBacteriophage
Owner:DORMANTIS LTD
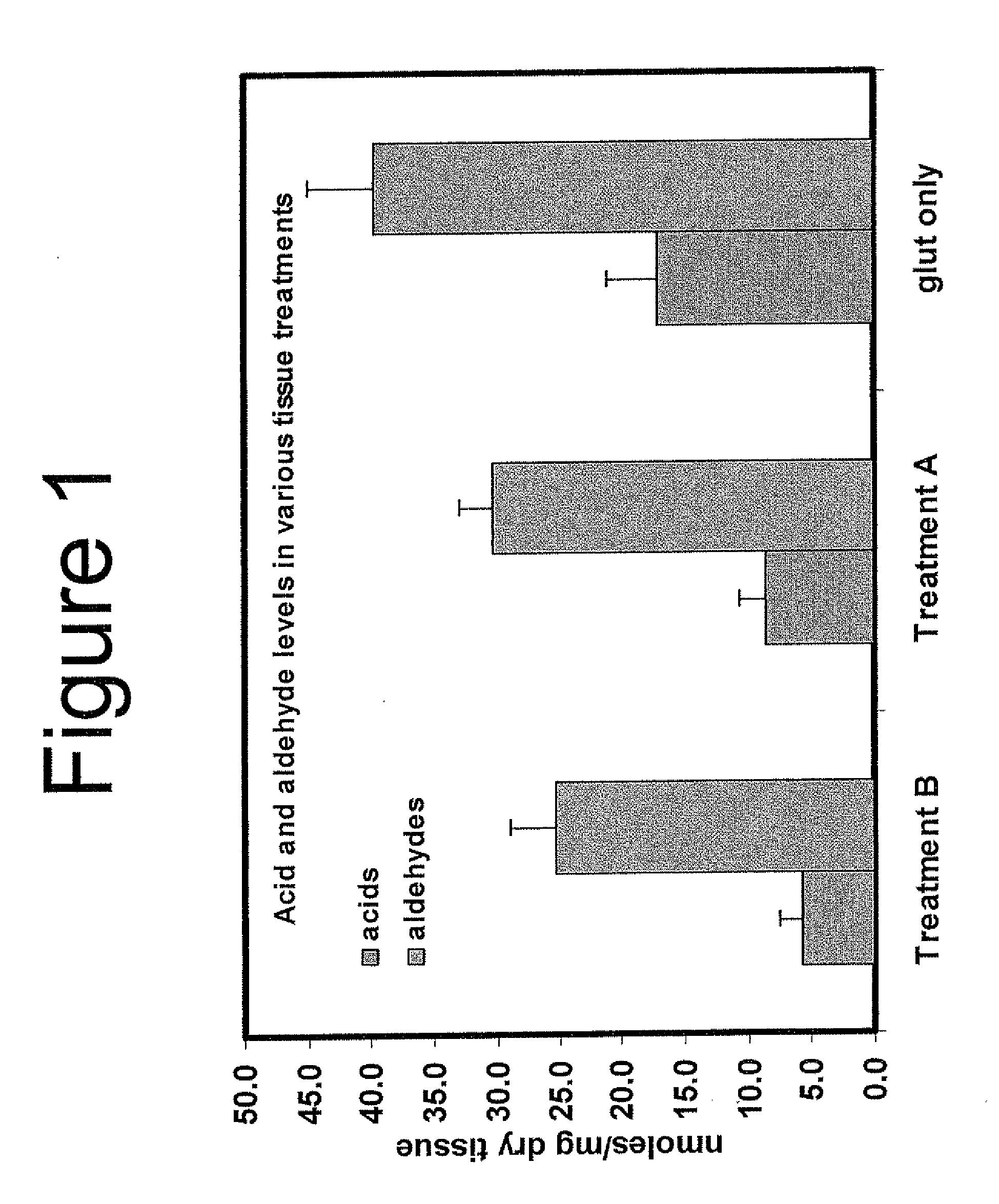
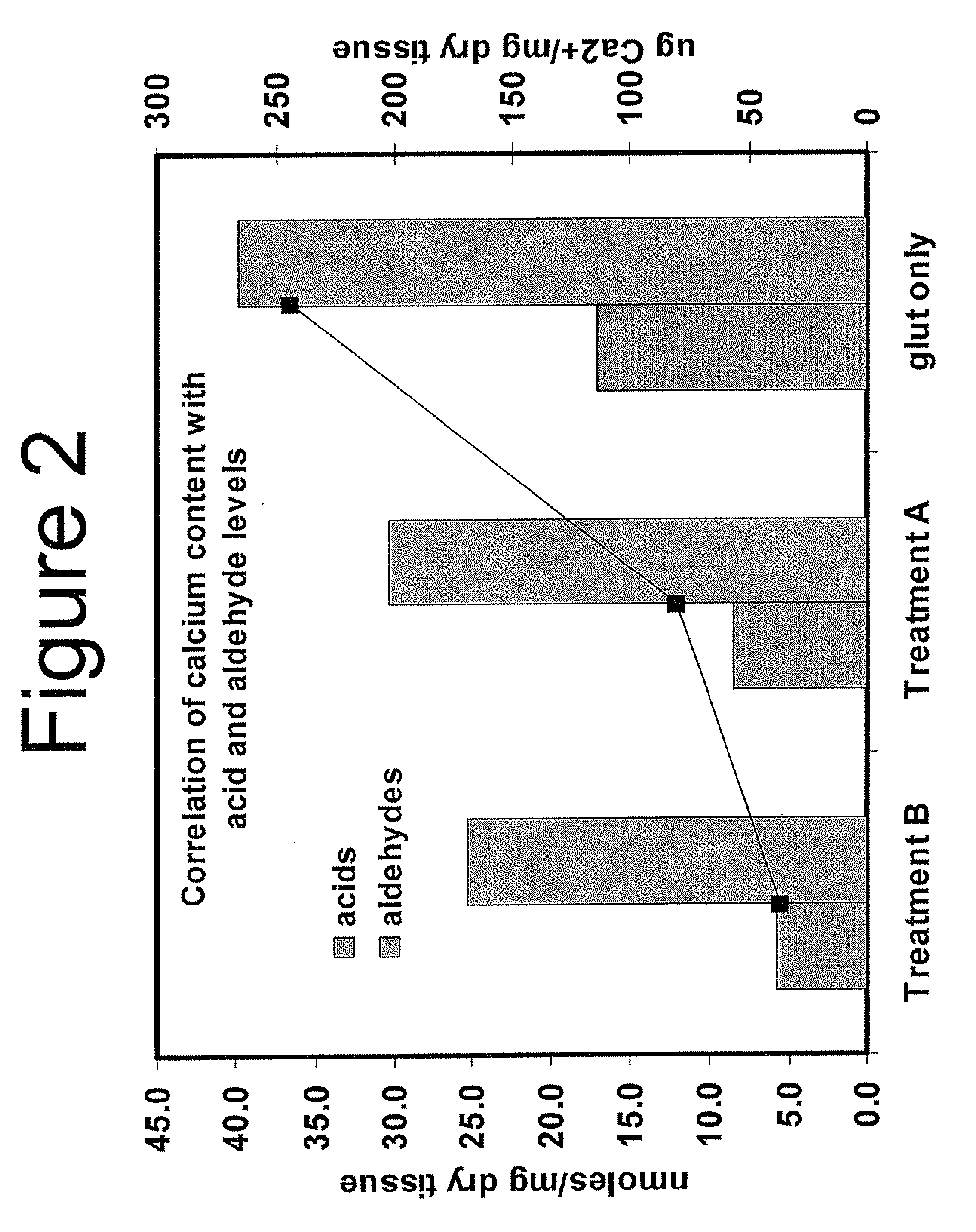
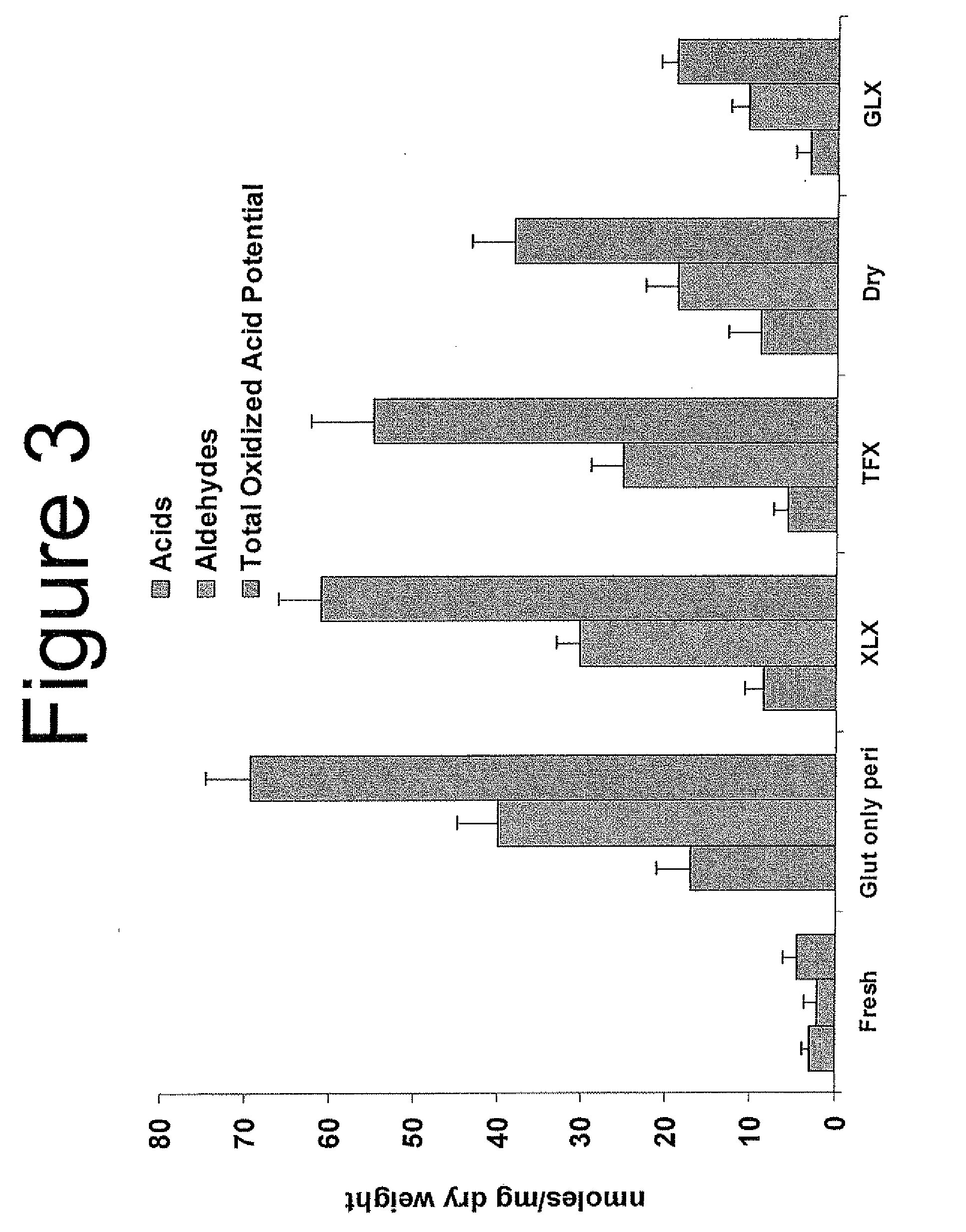
Capping Bioprosthetic Tissue to Reduce Calcification
A treatment for bioprosthetic tissue used in implants or for assembled bioprosthetic heart valves to reduce in vivo calcification. The method includes applying a calcification mitigant such as a capping agent or an antioxidant to the tissue to specifically inhibit oxidation in tissue. Also, the method can be used to inhibit oxidation in dehydrated tissue. The capping agent suppresses the formation of binding sites in the tissue that are exposed or generated by the oxidation and otherwise would, upon implant, attract calcium, phosphate, immunogenic factors, or other precursors to calcification. In one method, tissue leaflets in assembled bioprosthetic heart valves are pretreated with an aldehyde capping agent prior to dehydration and sterilization.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
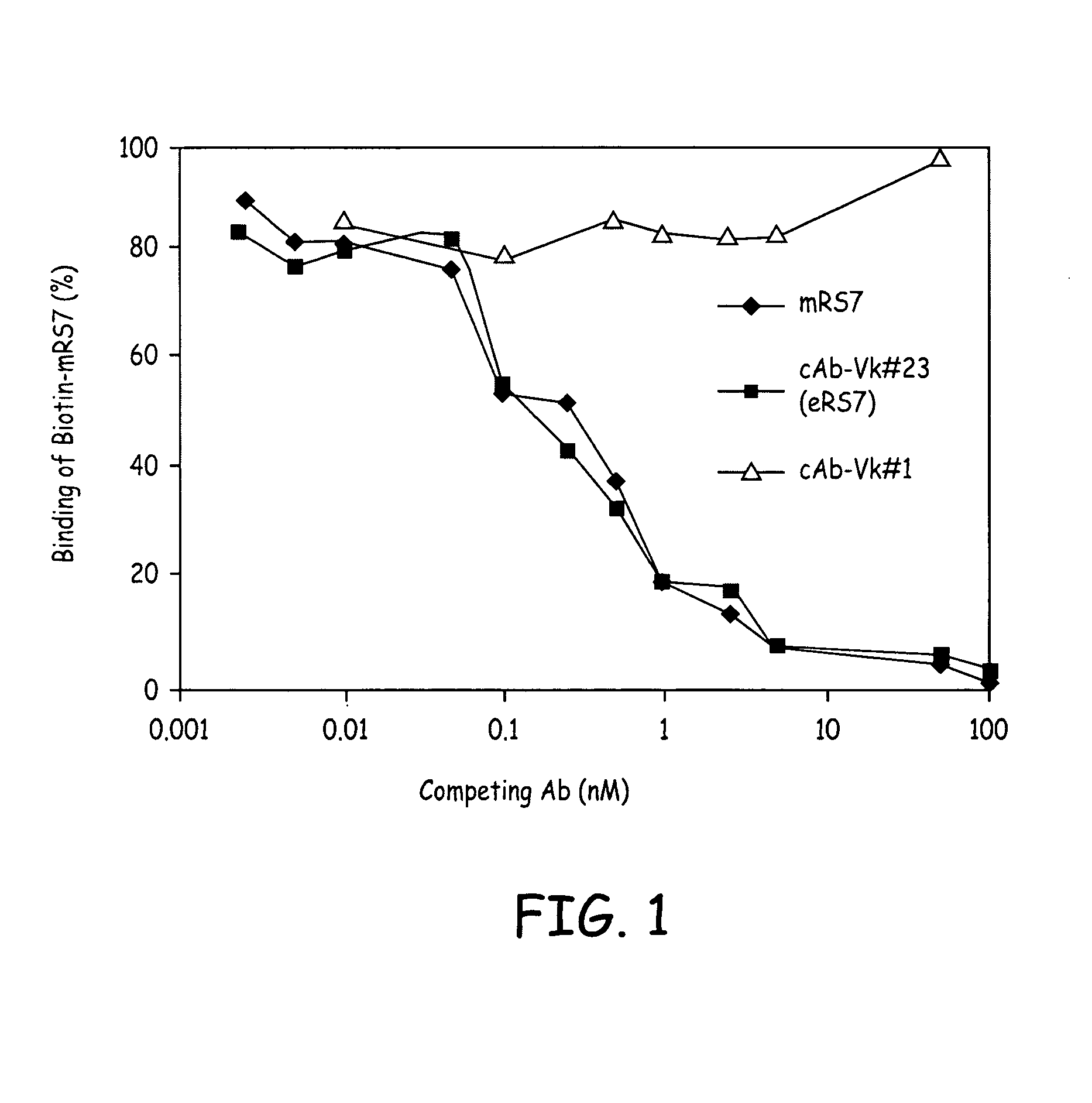
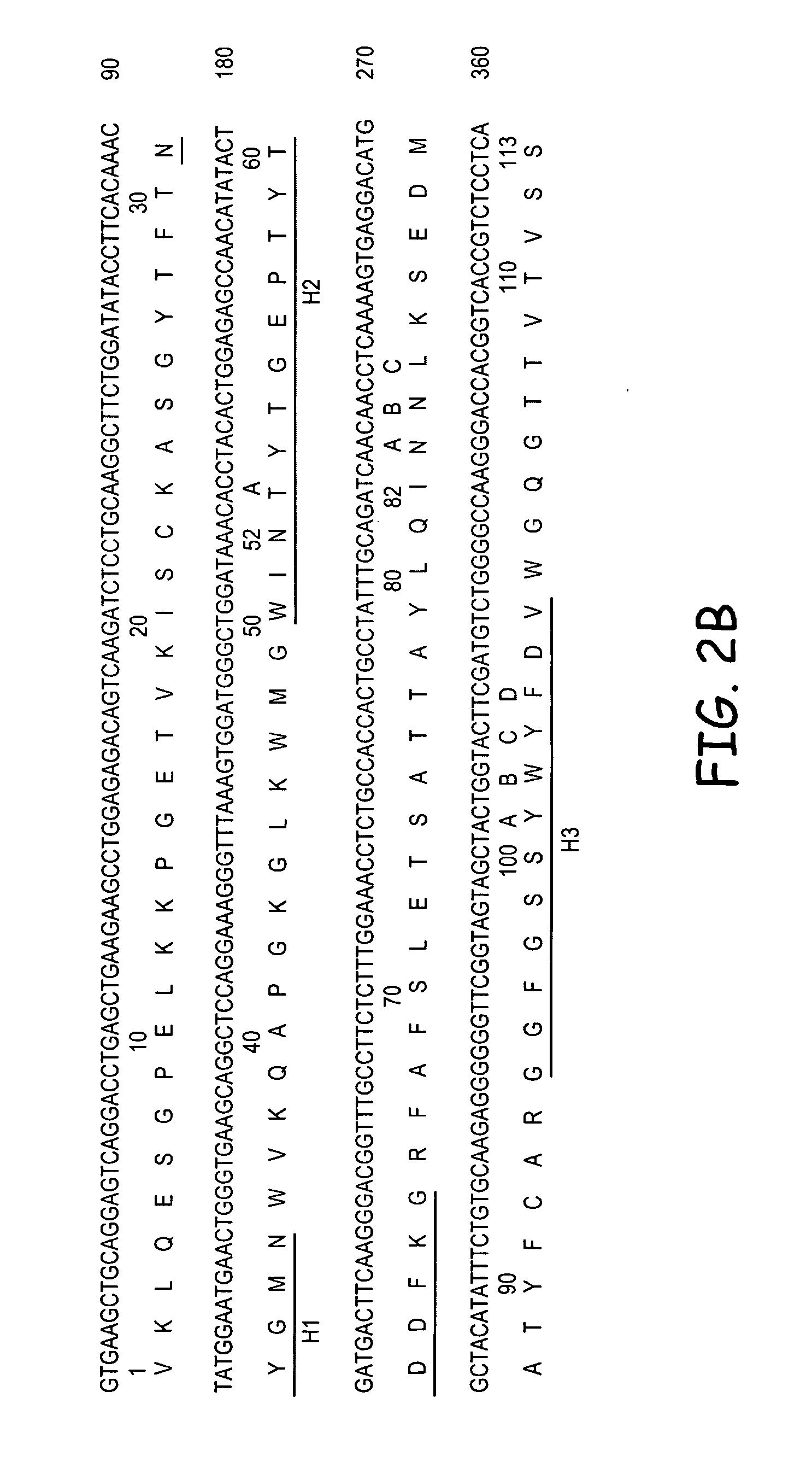
RS7 antibodies
InactiveUS7238785B2Diagnosing and treating malignancyRadioactive preparation carriersImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsEpitopeBinding site
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Methods of modifying antibodies for purification of bispecific antibodies
ActiveUS20090263392A1Efficient purificationFunction increaseSugar derivativesAntibody ingredientsAntiendomysial antibodiesBinding site
The present inventors devised methods for efficiently purifying bispecific antibodies using a chromatography column based on the difference in isoelectric points between the H chains of two types of antibodies, wherein the difference is introduced by modifying the amino acids present on the surface of the antibody variable regions of two types of antibodies that constitute a bispecific antibody. Furthermore, the inventors devised methods for efficiently purifying bispecific antibodies using a chromatography column by linking respective antigen binding sites (heavy chain variable regions) to the antibody constant regions having different isoelectric points, and then coexpressing these antibodies.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
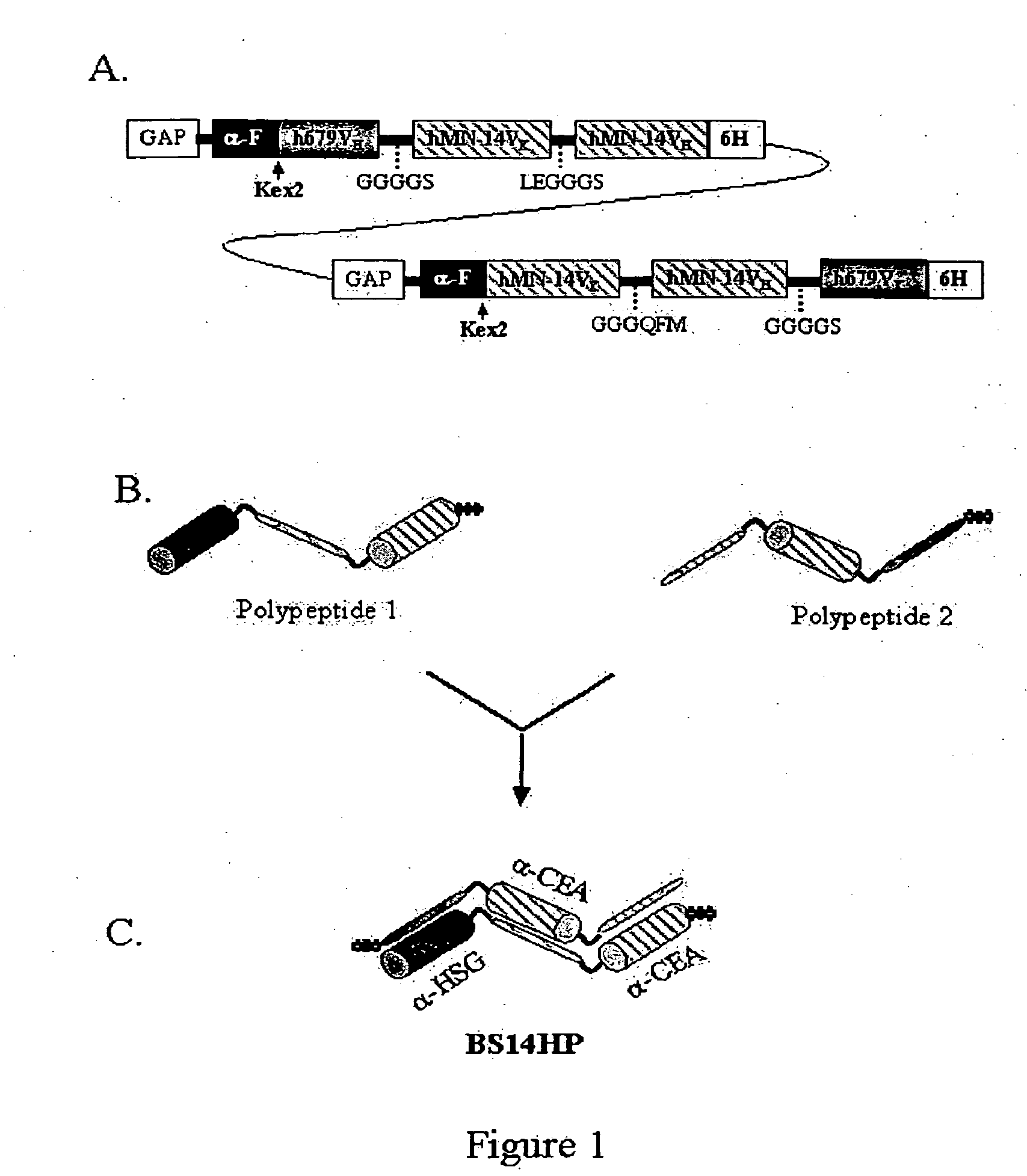
Monoclonal antibody hPAM4
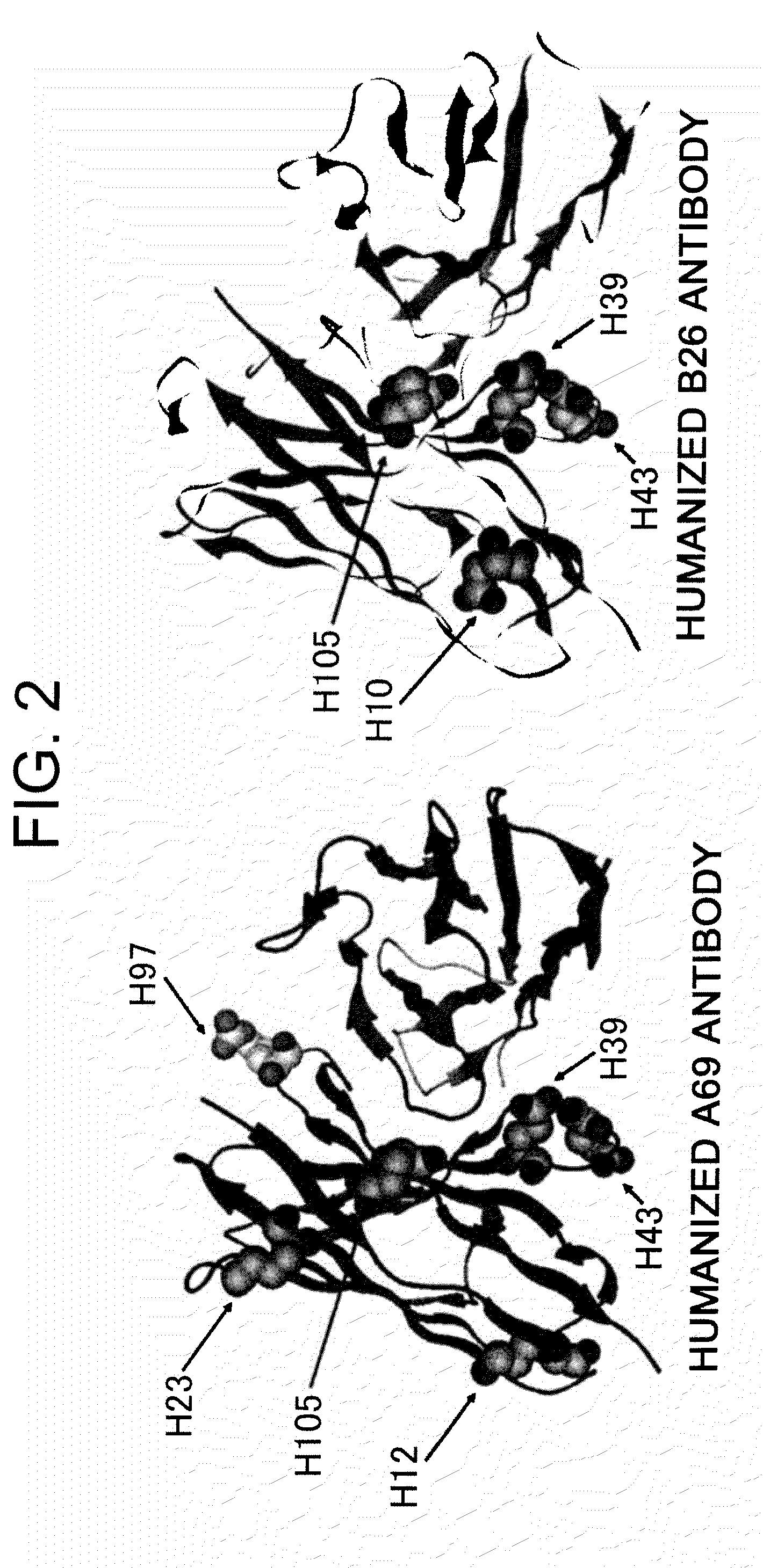
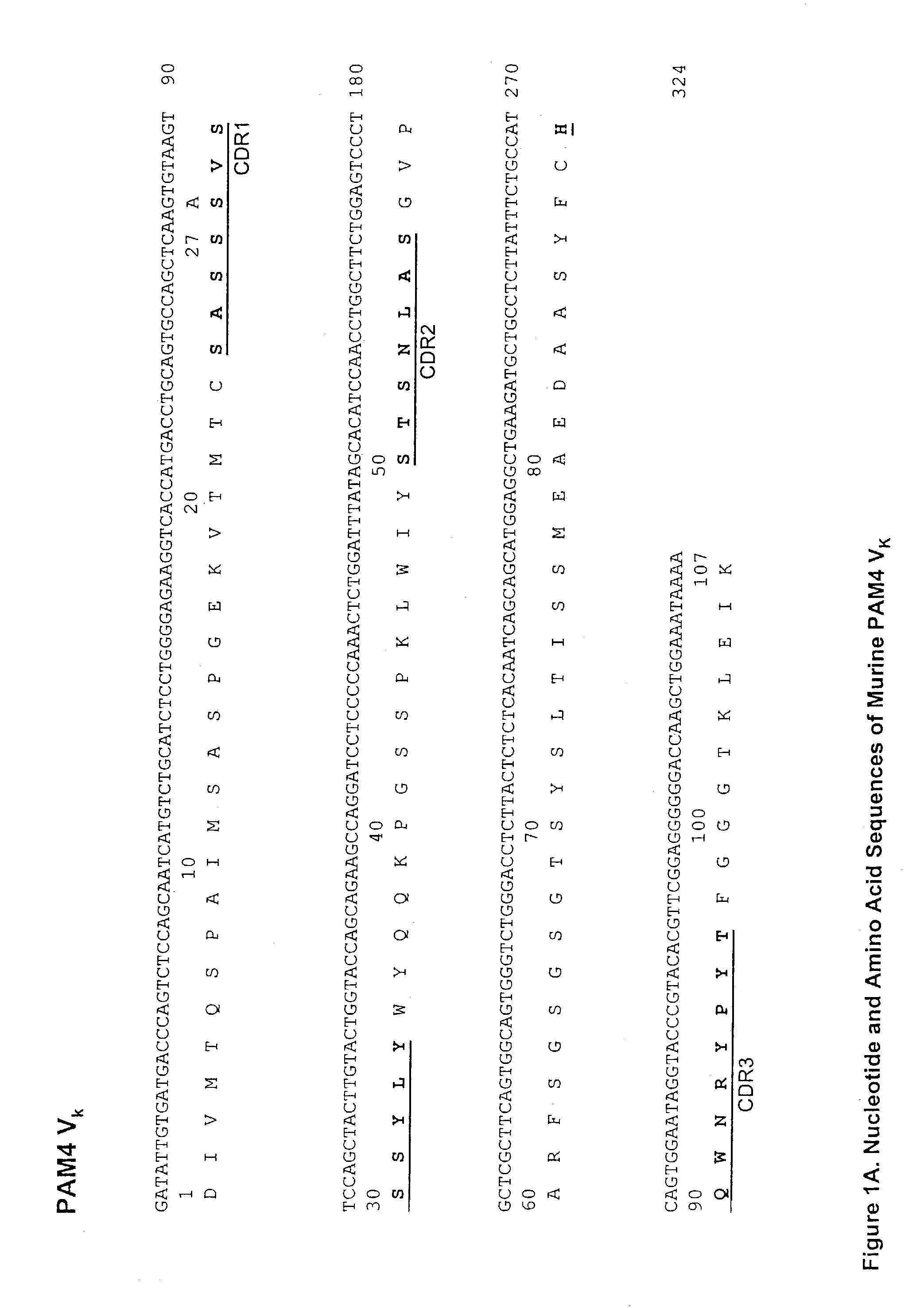
This invention relates to monovalent and multivalent, monospecific antibodies and to multivalent, multispecific antibodies. One embodiment of these antibodies has one or more identical binding sites where each binding site binds with a target antigen or an epitope on a target antigen. Another embodiment of these antibodies has two or more binding sites where these binding sites have affinity towards different epitopes on a target antigen or different target antigens, or have affinity towards a target antigen and a hapten. The present invention further relates to recombinant vectors useful for the expression of these functional antibodies in a host. More specifically, the present invention relates to the tumor-associated antibody designated PAM4. The invention further relates to humanized and human PAM4 antibodies, and the use of such antibodies in diagnosis and therapy.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Biosensor apparatus and methods of use
InactiveUS20060134713A1Increase in the amount of probe boundReduce the amount requiredBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectrochemical responseAnalyte
Disclosed herein are methods and devices for detecting the presence of an analyte of interest. A biosensor device can include a reaction chamber and an electrochemical detection chamber. The reaction chamber can include at least one immobilized binding site and a probe conjugate adapted to bind to at least one of the target analyte and the immobilized binding site, while the detection chamber can include electrodes for detecting an electrochemical reaction. If present, the target analyte in the fluid sample results in a change in the amount of probe conjugate bound in the reaction chamber, which can be detected electrochemically in the detection chamber.
Owner:UNIVERSAL BIOSENSORS
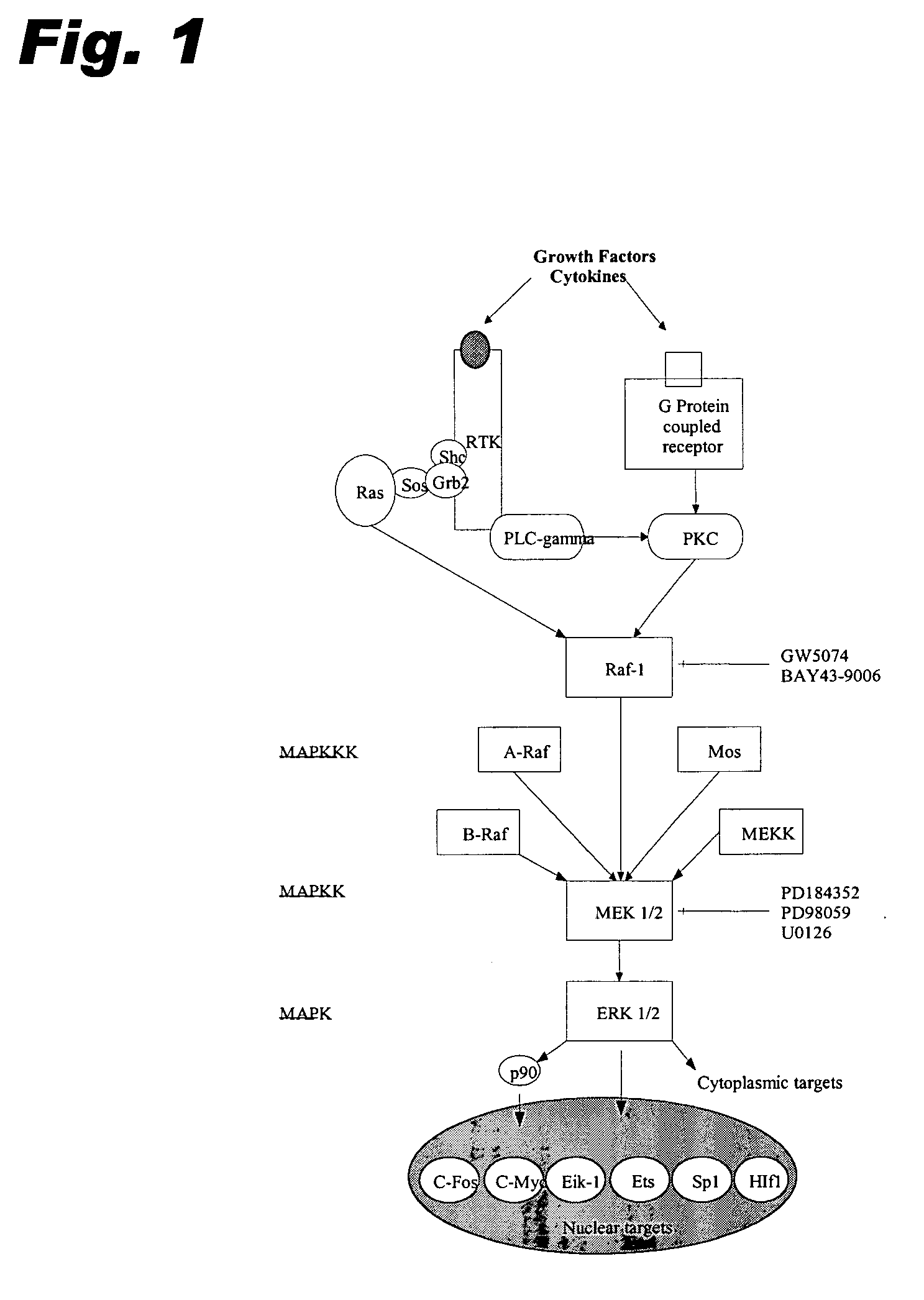
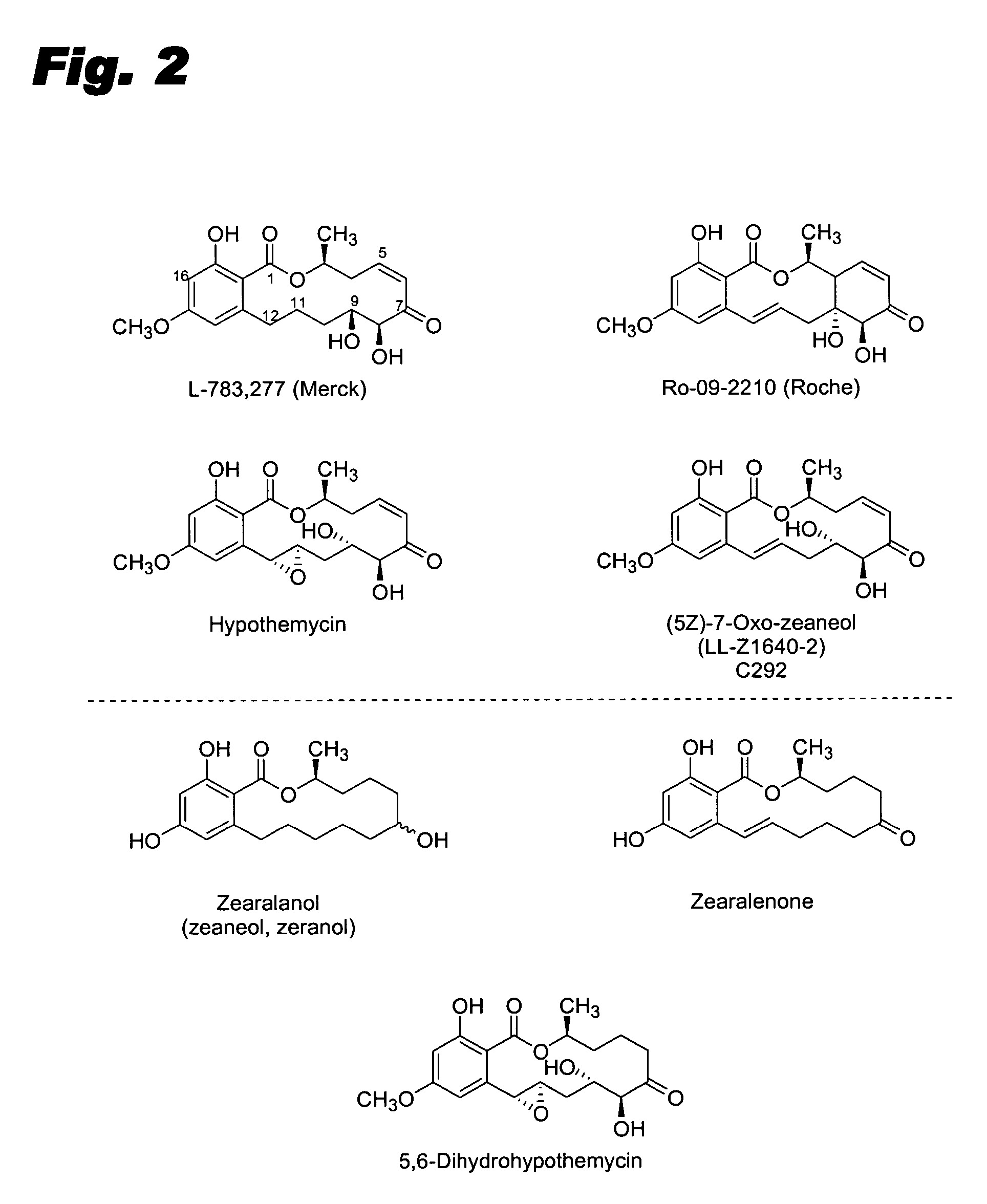
Specific kinase inhibitors
Resorcylic acid lactones having a C5-C6 cis double bond and a ketone at C7 and other compounds capable of Michael adduct formation are potent and stable inhibitors of a subset of protein kinases having a specific cysteine residue in the ATP binding site.
Owner:KOSAN BIOSCI
System, device and method for determining the concentration of an analyte
There are many inventions described and illustrated herein. In one aspect, the present invention is a system, a device and a method for sensing the concentration of an analyte in a fluid (for example, a fluid sample) or matrix. The analyte may be glucose or other chemical of interest. The fluid or matrix may be, for example, the fluid or matrix in the body of an animal (for example, human), or any other suitable fluid or matrix in which it is desired to know the concentration of an analyte. In one embodiment, the invention is a system and / or device that includes one or more layers having a plurality of analyte-equivalents and mobile or fixed receptor molecules with specific binding sites for the analyte-equivalents and analytes under analysis (for example, glucose). The receptor molecules, when exposed to or in the presence of analyte (that resides, for example, in a fluid in an animal), bind with the analyte (or vice versa). As such, some or all (or substantially all) of the receptor molecules within a given layer may bind with the analyte, which results in a change in the optical properties of one or more of the layers. These layer(s) may be examined or interrogated, via optical techniques, whereby the optical response of the layers and / or, in particular, the substance within the layer(s), may be measured, evaluated and / or analyzed.
Owner:BIO TEX LTD INC
Polyvalent protein complex
The invention provides for a polyvalent protein complex (PPC) comprising two polypeptide chains generally arranged laterally to one another. Each polypeptide chain typically comprises 3 or 4 “v-regions”, which comprise amino acid sequences capable of forming an antigen binding site when matched with a corresponding v-region on the opposite polypeptide chain. Up to about 6 “v-regions” can be used on each polypeptide chain. The v-regions of each polypeptide chain are connected linearly to one another and may be connected by interspersed linking regions. When arranged in the form of the PPC, the v-regions on each polypeptide chain form individual antigen binding sites.
Owner:IBC PHARMACEUTICALS INC
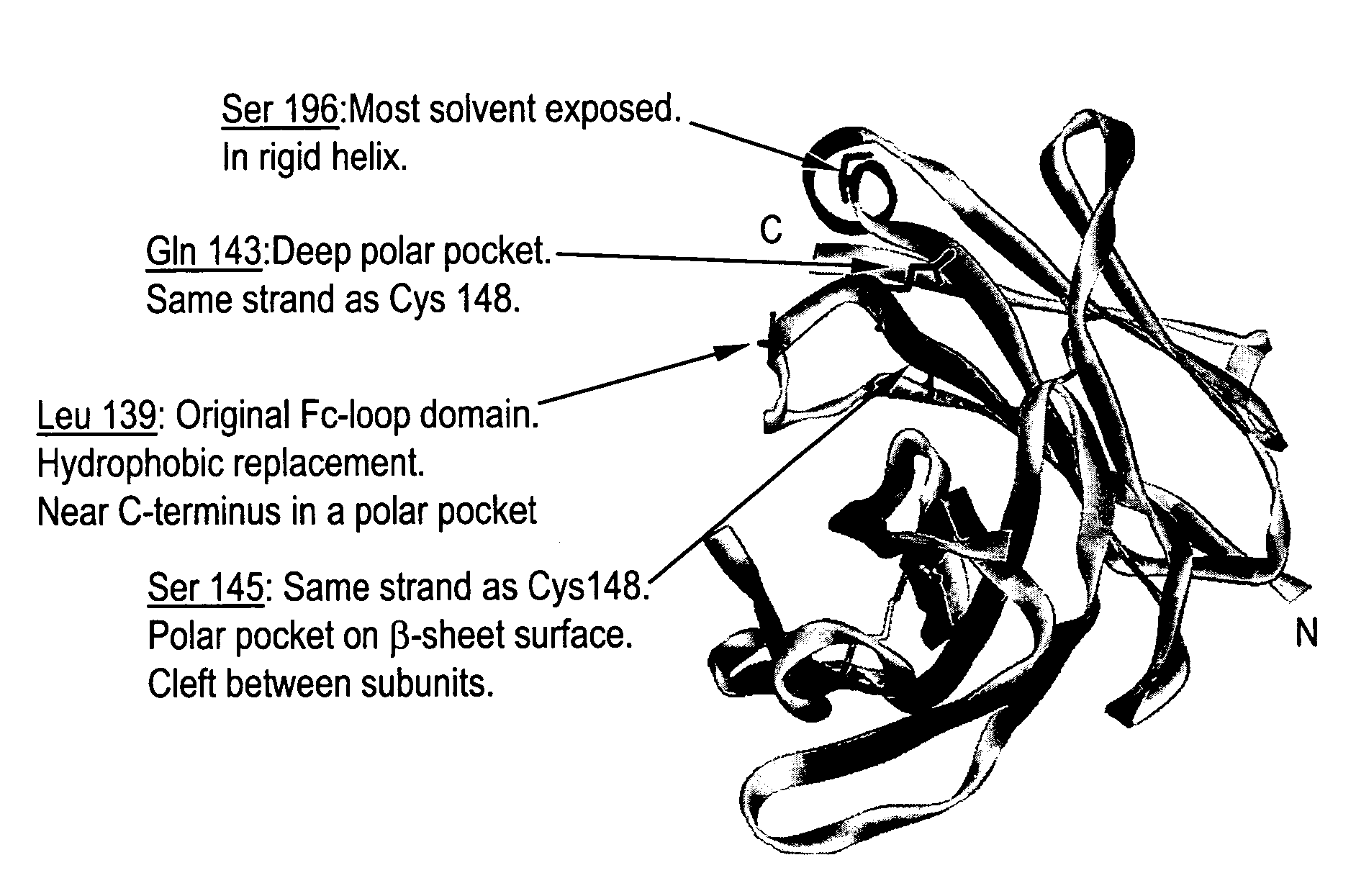
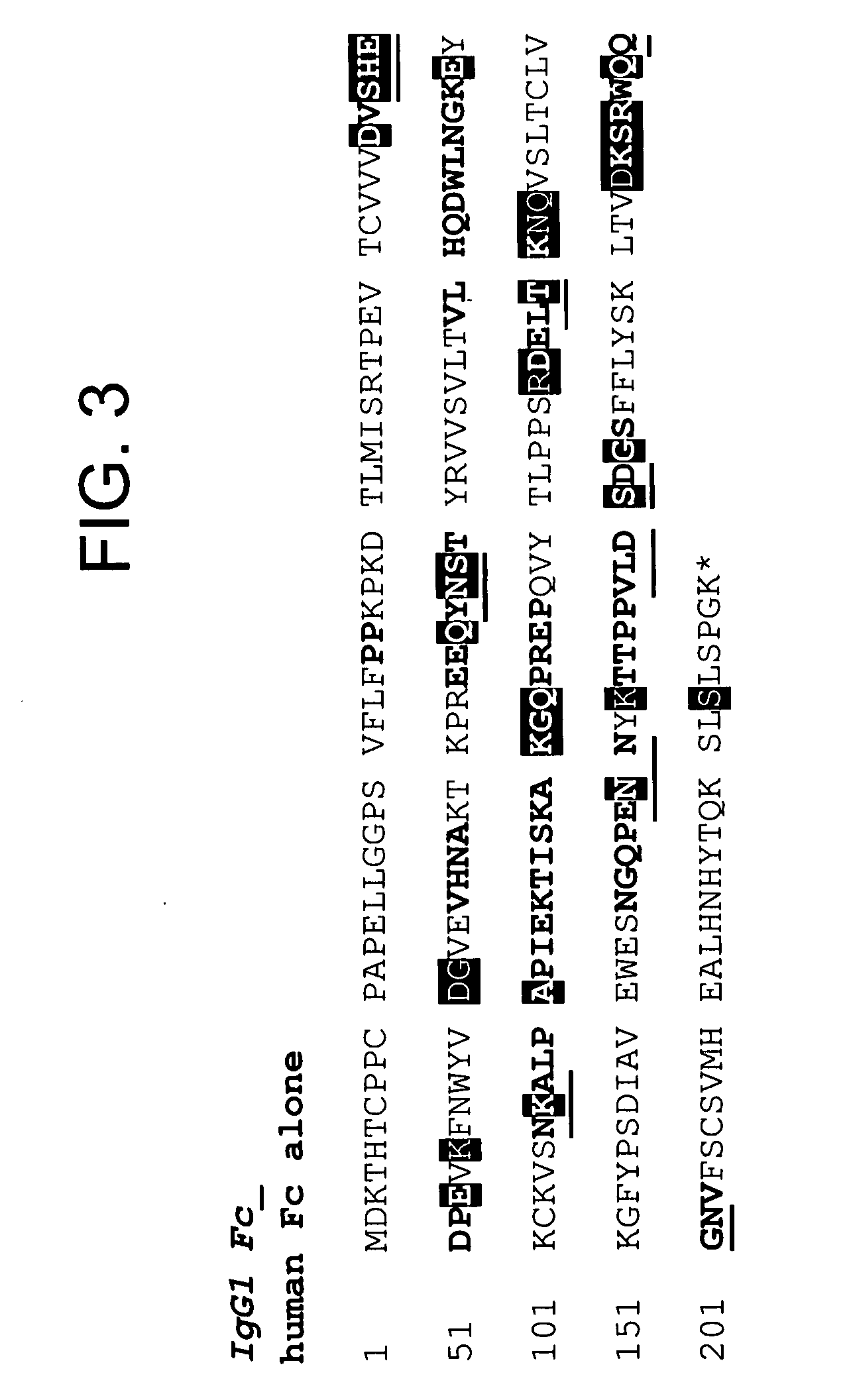
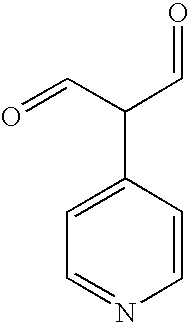
Modified Fc molecules
Disclosed is a process for preparing a pharmacologically active compound, in which at least one internal conjugation site of an Fc domain sequence is selected that is amenable to conjugation of an additional functional moiety by a defined conjugation chemistry through the side chain of an amino acid residue at the conjugation site. An appropriate amino acid residue for conjugation may be present in a native Fc domain at the conjugation site or may be added by insertion (i.e., between amino acids in the native Fc domain) or by replacement (i.e., removing amino acids and substituting different amino acids). In the latter case, the number of amino acids added need not correspond to the number of amino acids removed from the previously existing Fc domain. This technology may be used to produce useful compositions of matter and pharmaceutical compositions containing them. A DNA encoding the inventive composition of matter, an expression vector containing the DNA, and a host cell containing the expression vector are also disclosed.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Insulin and IGF-1 receptor agonists and antagonists
Peptide sequences capable of binding to insulin and / or insulin-like growth factor receptors with either agonist or antagonist activity and identified from various peptide libraries are disclosed. This invention also identifies at least two different binding sites, which are present on insulin and insulin-like growth factor receptors, and which selectively bind the peptides of this invention. As agonists, the peptides of this invention may be useful for development as therapeutics to supplement or replace endogenous peptide hormones. The antagonist peptides may also be developed as therapeutics.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS +1
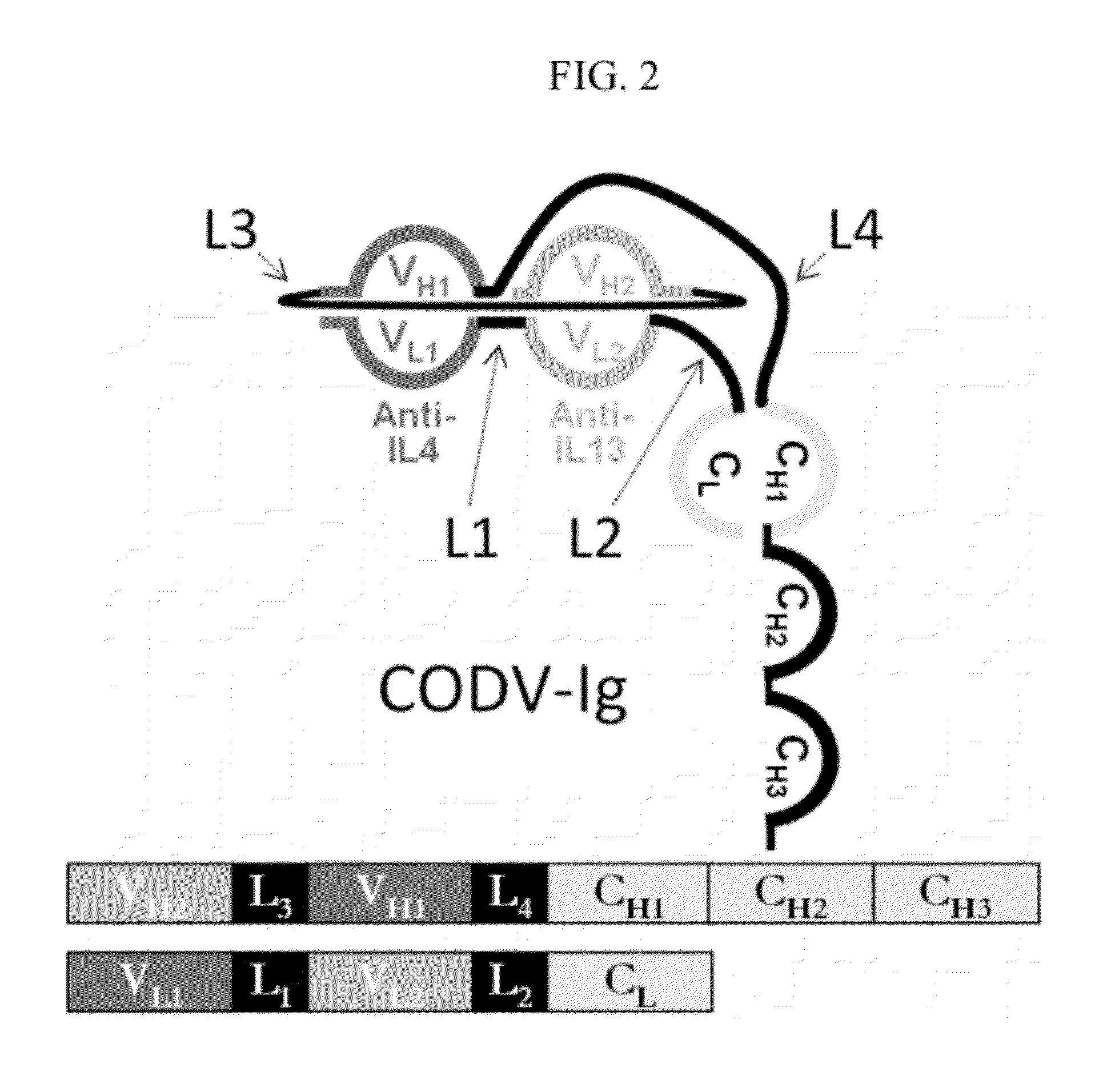
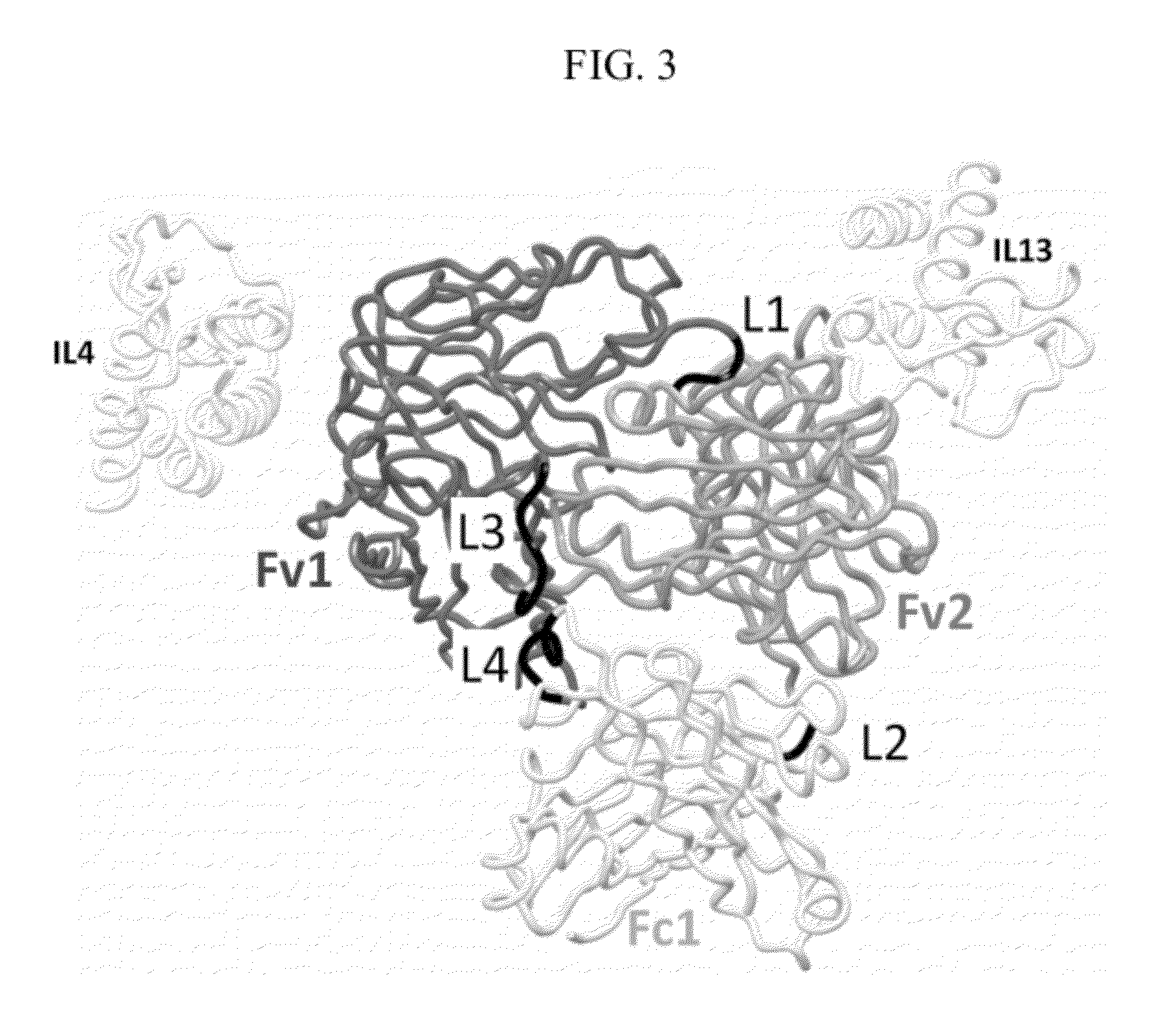
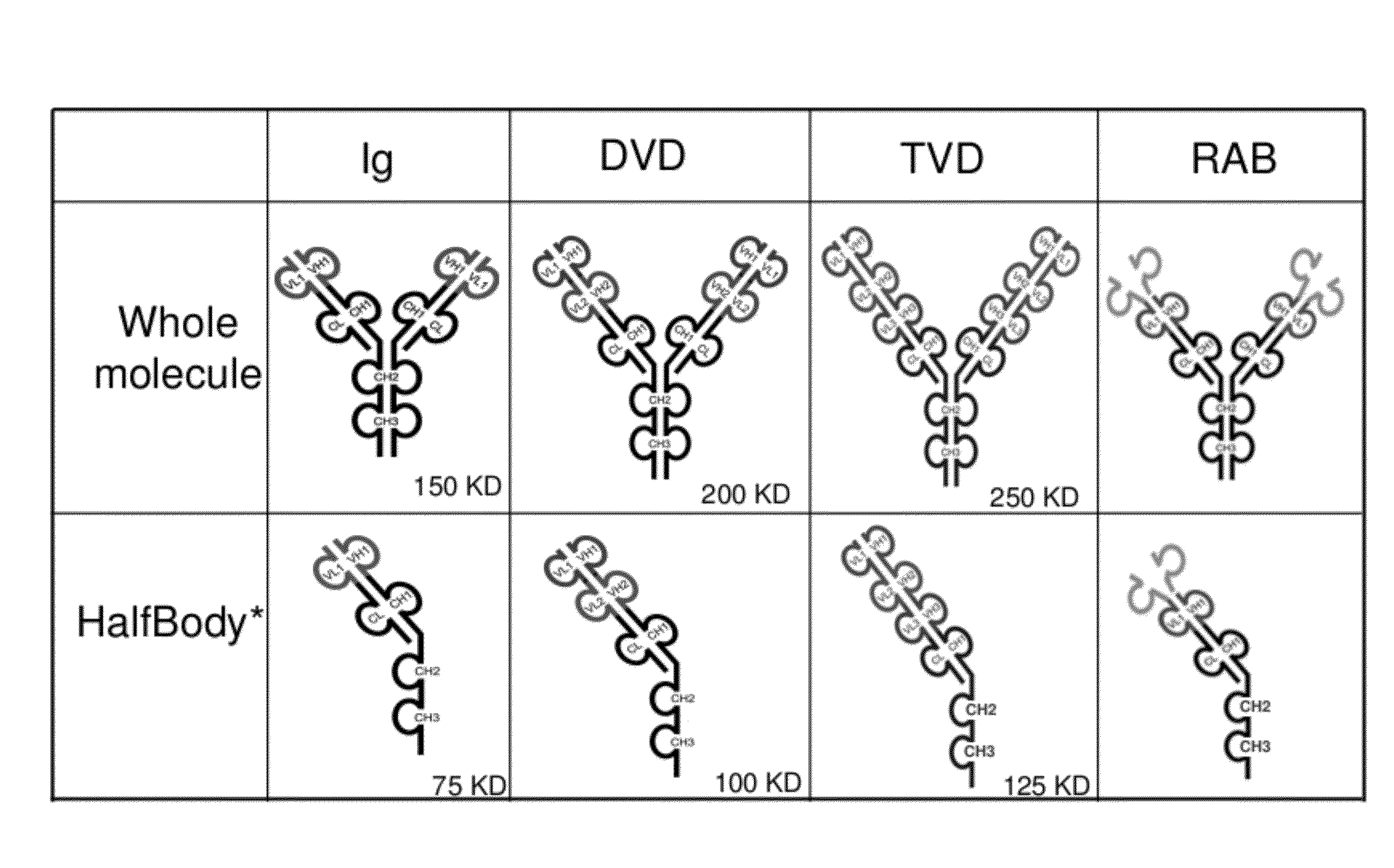
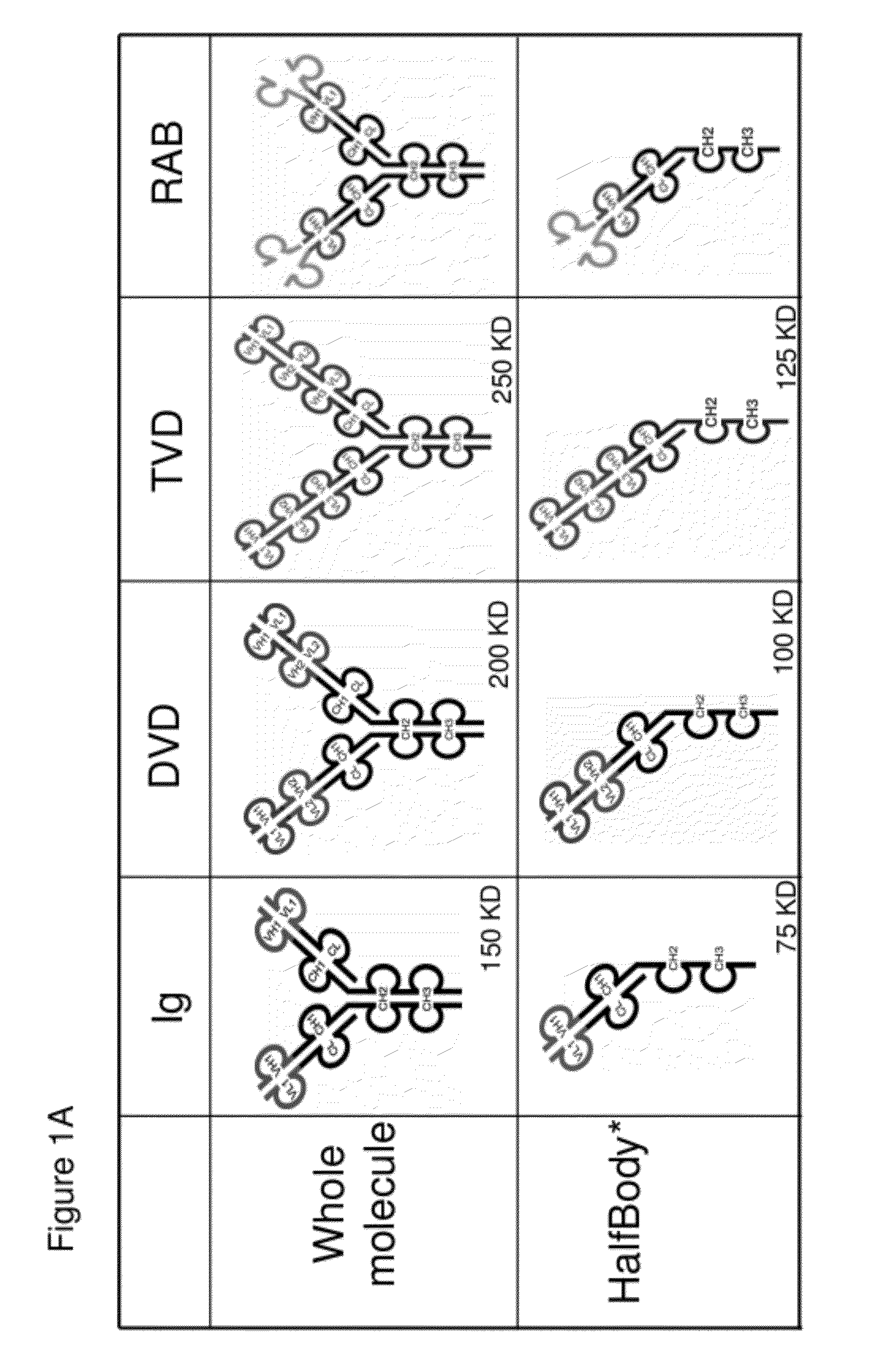
Dual Variable Region Antibody-Like Binding Proteins Having Cross-Over Binding Region Orientation
The invention provides antibody-like binding proteins comprising four polypeptide chains that form four antigen binding sites, wherein each pair of polypeptides forming an antibody-like binding protein possesses dual variable domains having a cross-over orientation. The invention also provides methods for making such antigen-like binding proteins.
Owner:SANOFI SA
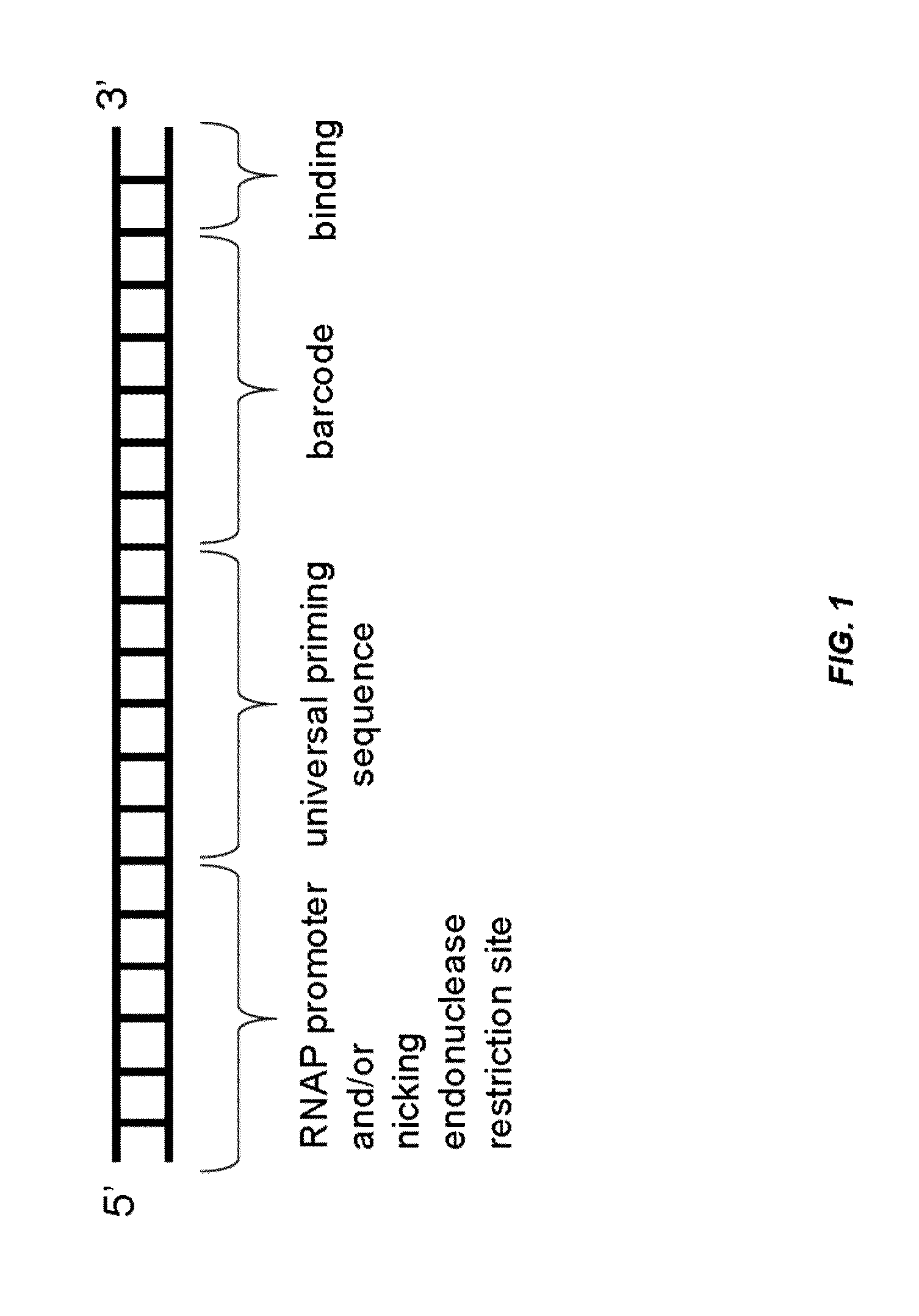
Analysis of nucleic acids associated with single cells using nucleic acid barcodes
ActiveUS20150329891A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSingle sampleBinding site
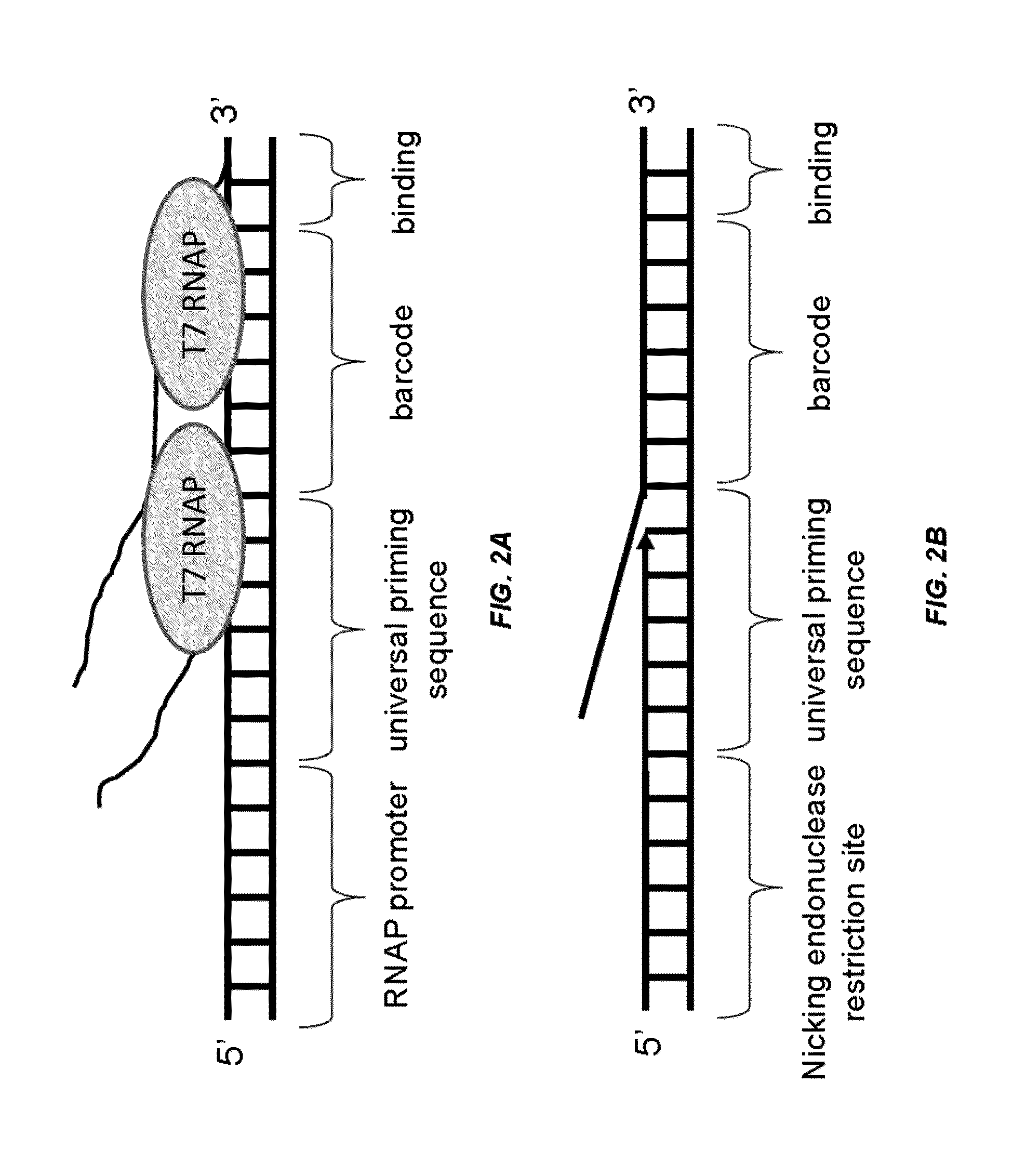
Provided herein are methods and compositions for analyzing nucleic acids associated with single cells using nucleic acid barcodes. According to some embodiments, a method for producing one or more polynucleotides of interest comprises: obtaining a plurality of RNAs associated with one or more samples, wherein the samples are obtained from one or more subjects, each RNA is associated with a single sample, and the RNAs associated with each sample are present in a separate reaction volume; adding an adapter molecule to the RNAs associated with each sample, wherein the adapter molecule is generated using an enzymatic reaction and comprises a universal priming sequence, a barcode sequence, and a binding site; and incorporating the barcode sequence into one or more polynucleotides associated with each sample, thereby producing the one or more polynucleotides of interest.
Owner:ATRECA INC
Methods and compositions for treatment of human immunodeficiency virus infection with conjugated antibodies or antibody fragments
ActiveUS20070264265A1Avoid infectionReduce eliminateOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsDiagnostic agentBinding site
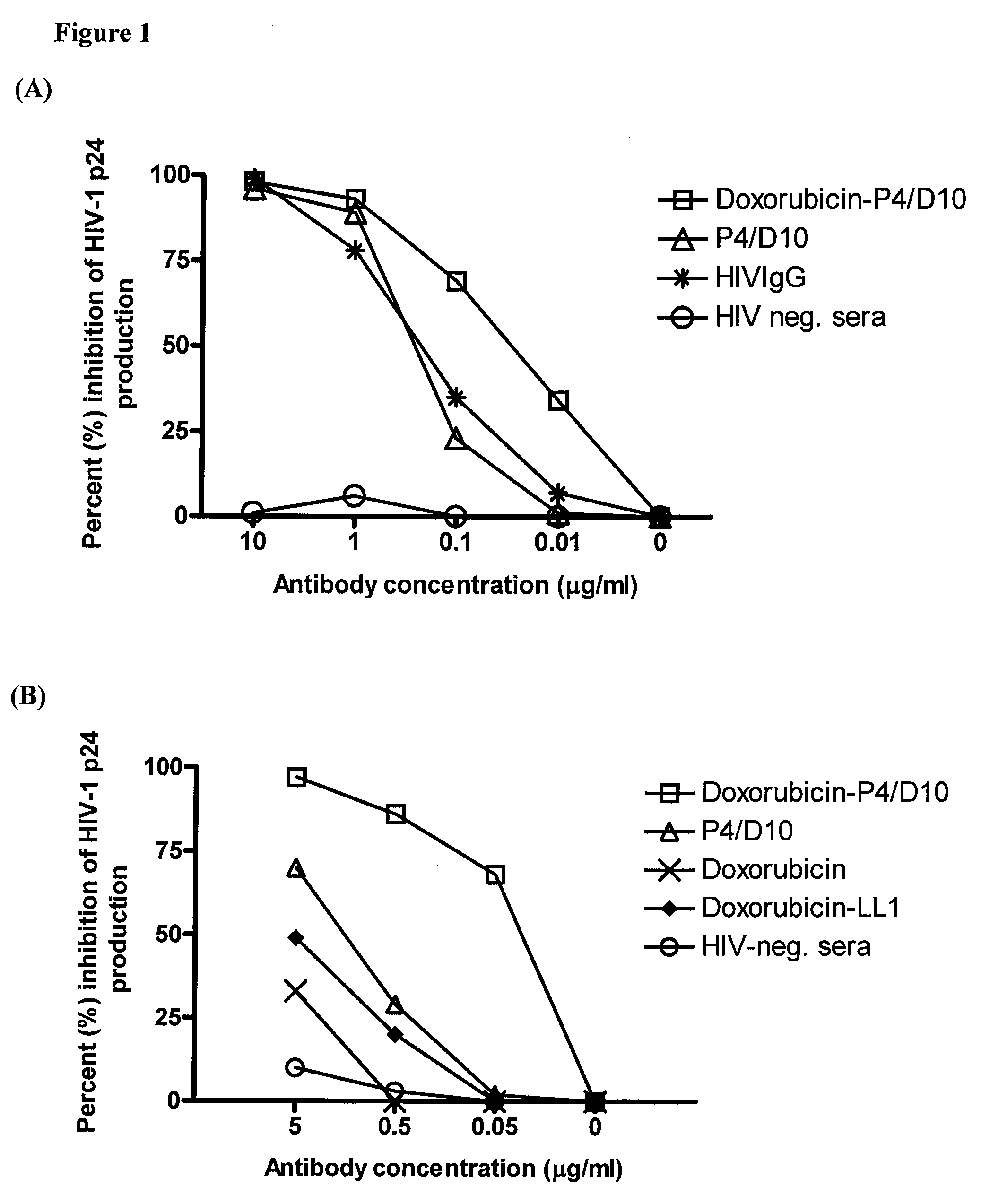
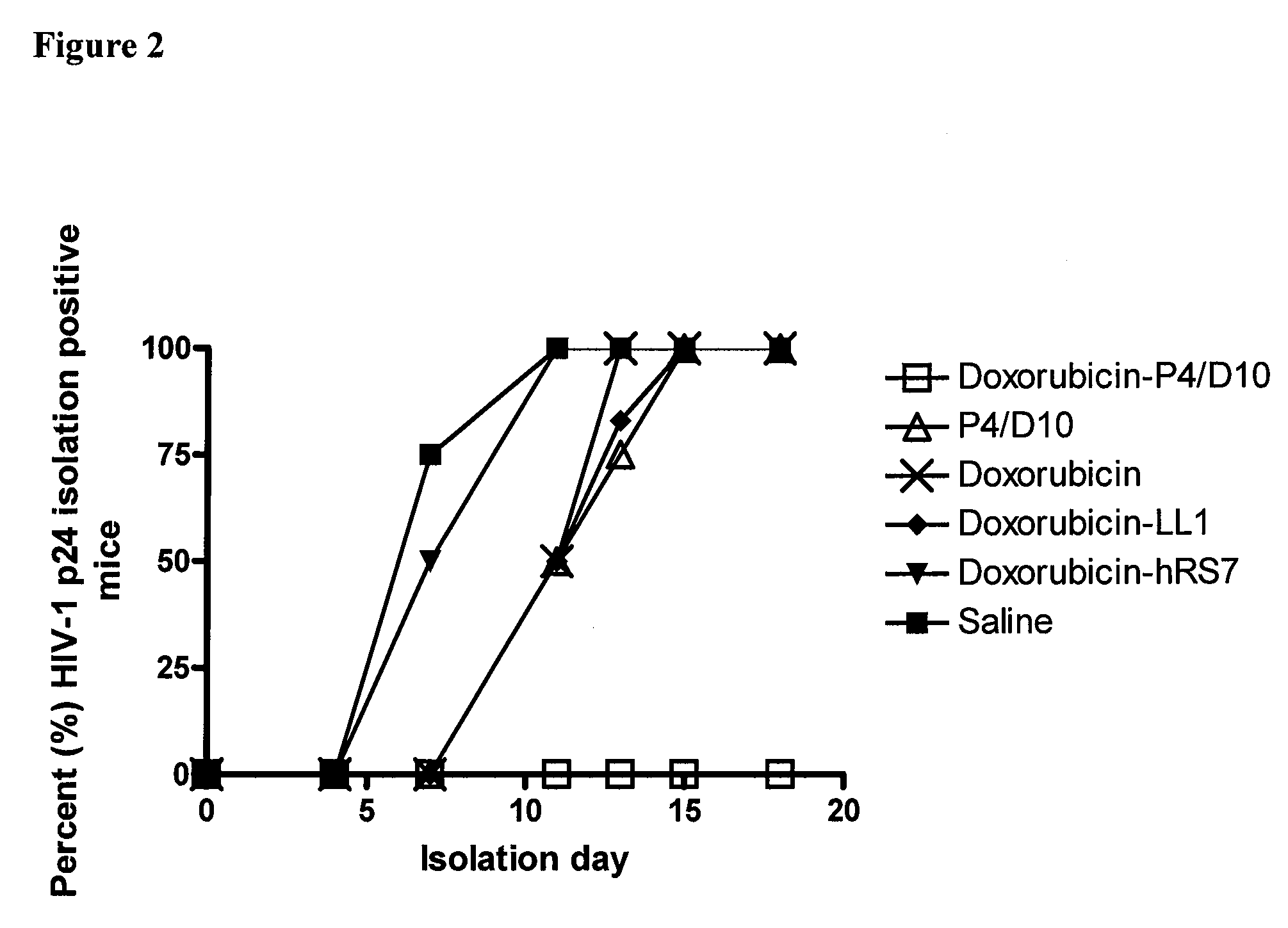
The present invention concerns methods and compositions for treatment of HIV infection in a subject. The compositions may comprise a targeting molecule against an HIV antigen, such as an anti-HIV antibody or antibody fragment. The anti-HIV antibody or fragment may be conjugated to a variety of cytotoxic agents, such as doxorubicin. In a preferred embodiment, the antibody or fragment is P4 / D10. Other embodiments may concern methods of imaging, detection or diagnosis of HIV infection in a subject using an anti-HIV antibody or fragment conjugated to a diagnostic agent. In alternative embodiments, a bispecific antibody with at least one binding site for an HIV antigen and at least one binding site for a carrier molecule may be administered, optionally followed by a clearing agent, followed by administration of a carrier molecule conjugated to a therapeutic agent.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Identification and comparison of protein-protein interactions that occur in populations and identification of inhibitors of these interactors
InactiveUS6057101AEfficient screeningLess experimentally significant and specific indicationMaterial nanotechnologyFungiDiseaseBinding site
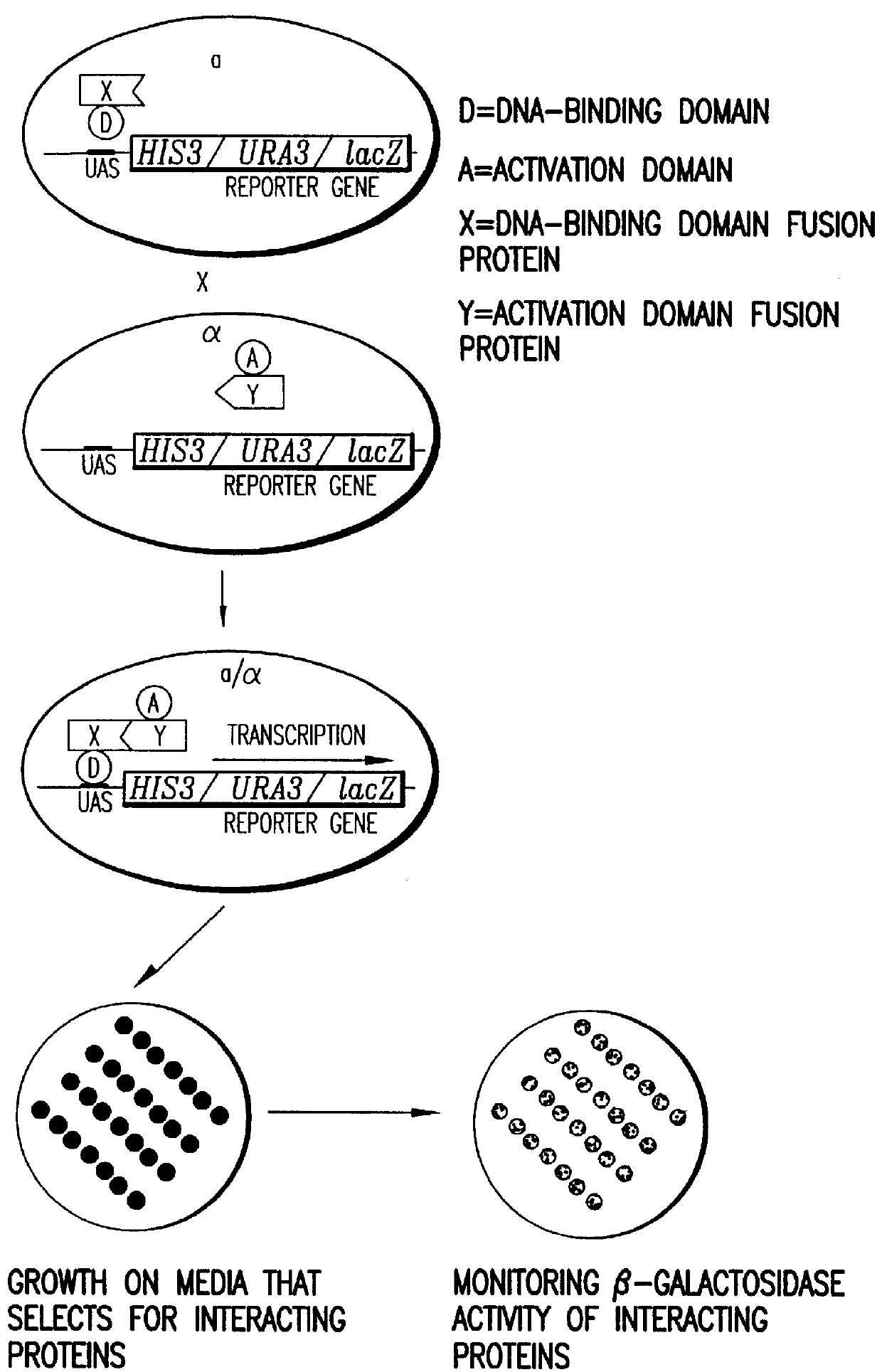
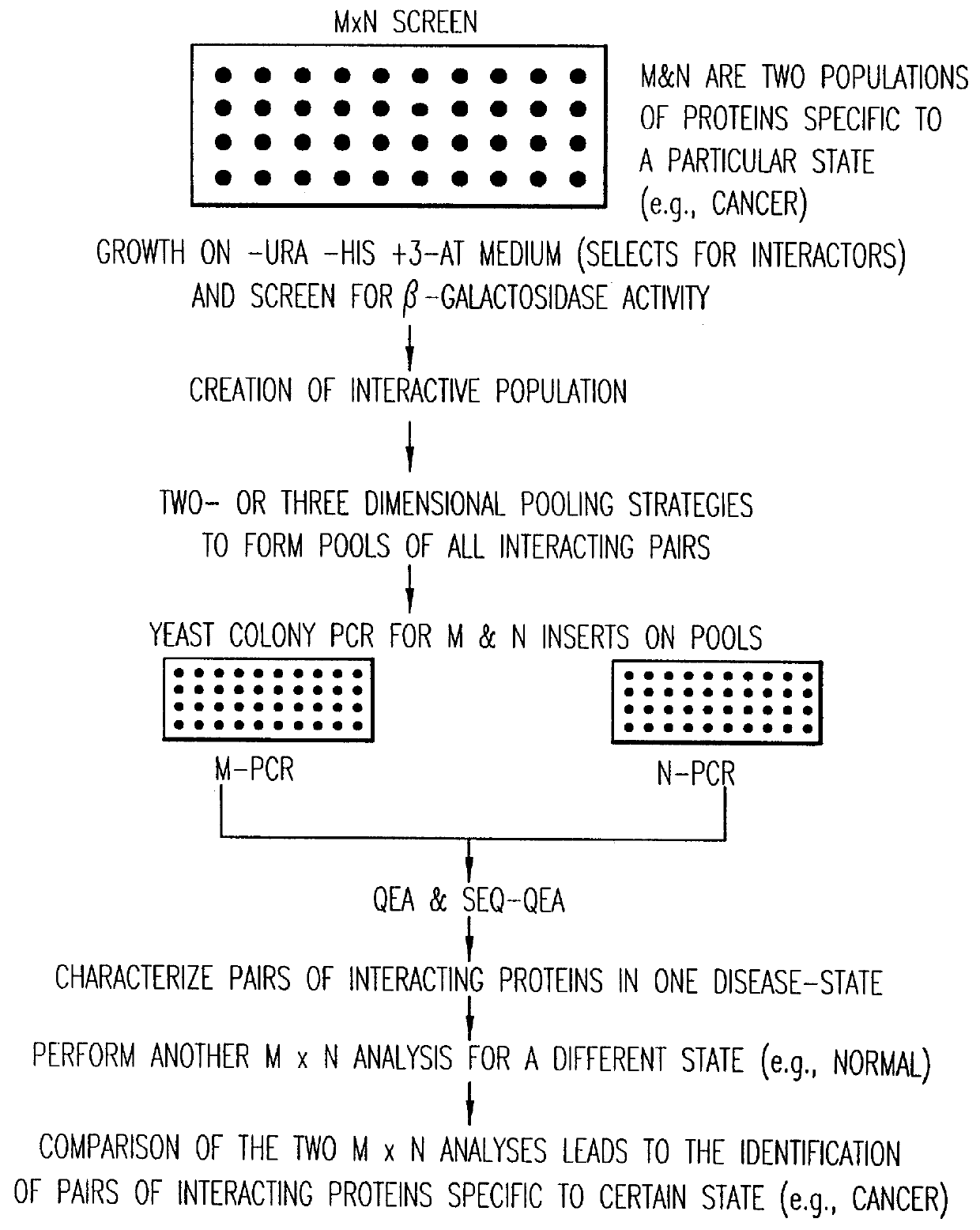
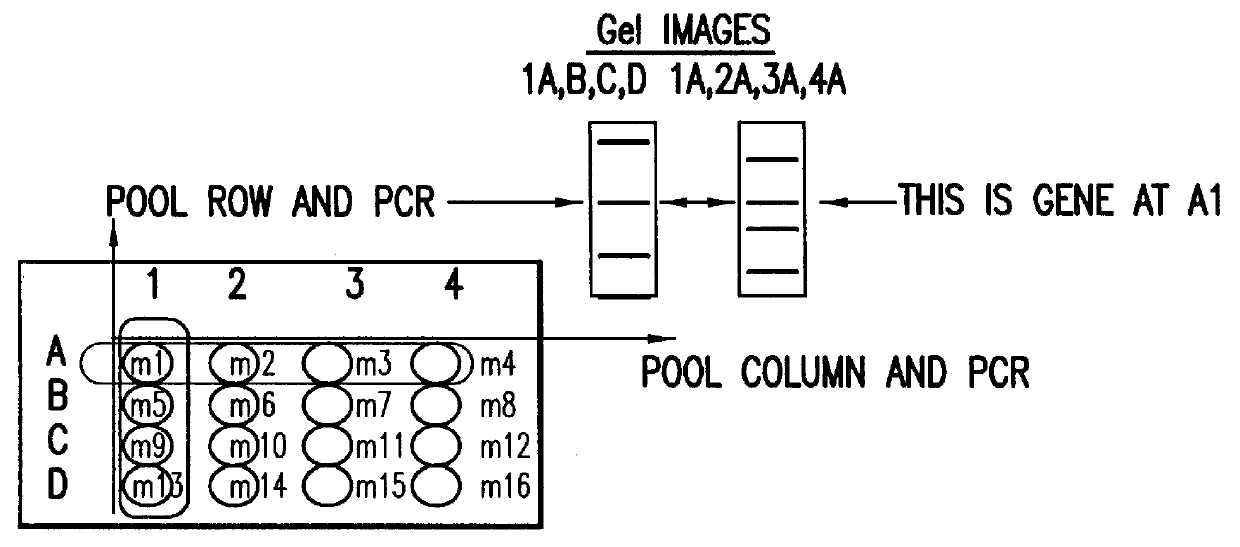
Methods are described for detecting protein-protein interactions, among two populations of proteins, each having a complexity of at least 1,000. For example, proteins are fused either to the DNA-binding domain of a transcriptional activator or to the activation domain of a transcriptional activator. Two yeast strains, of the opposite mating type and carrying one type each of the fusion proteins are mated together. Productive interactions between the two halves due to protein-protein interactions lead to the reconstitution of the transcriptional activator, which in turn leads to the activation of a reporter gene containing a binding site for the DNA-binding domain. This analysis can be carried out for two or more populations of proteins. The differences in the genes encoding the proteins involved in the protein-protein interactions are characterized, thus leading to the identification of specific protein-protein interactions, and the genes encoding the interacting proteins, relevant to a particular tissue, stage or disease. Furthermore, inhibitors that interfere with these protein-protein interactions are identified by their ability to inactivate a reporter gene. The screening for such inhibitors can be in a multiplexed format where a set of inhibitors will be screened against a library of interactors. Further, information-processing methods and systems are described. These methods and systems provide for identification of the genes coding for detected interacting proteins, for assembling a unified database of protein-protein interaction data, and for processing this unified database to obtain protein interaction domain and protein pathway information.
Owner:CURAGEN CORP
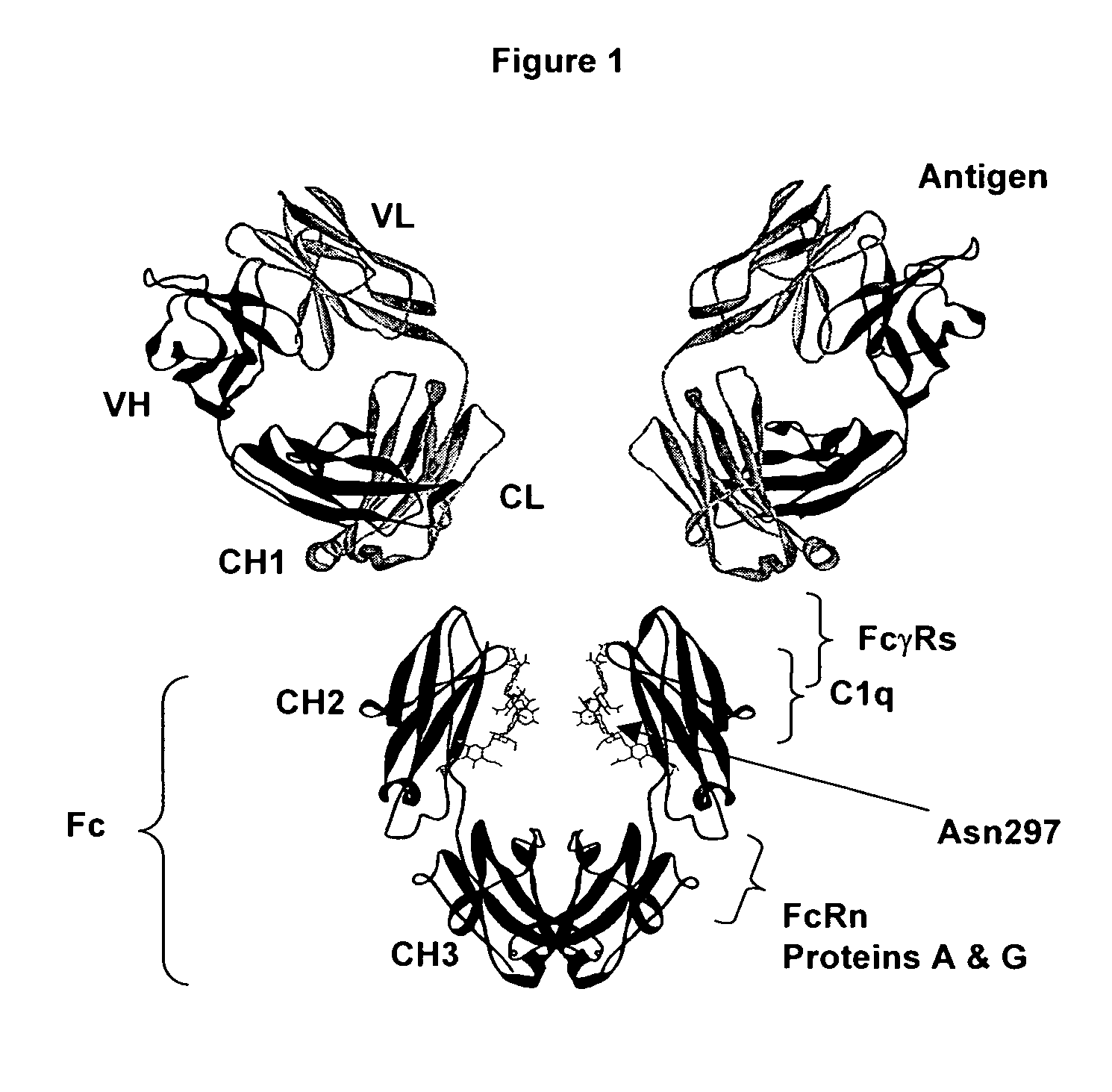
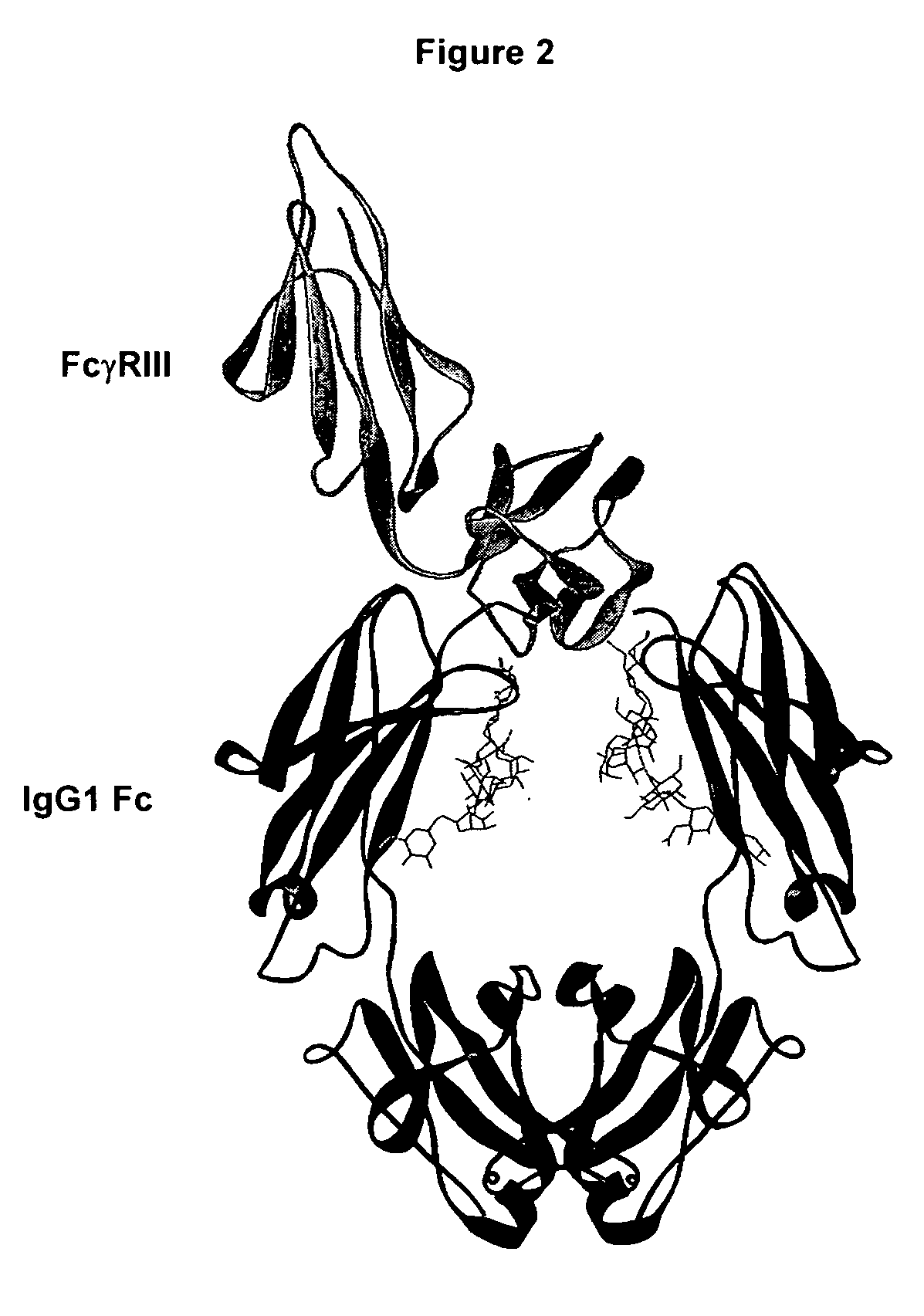
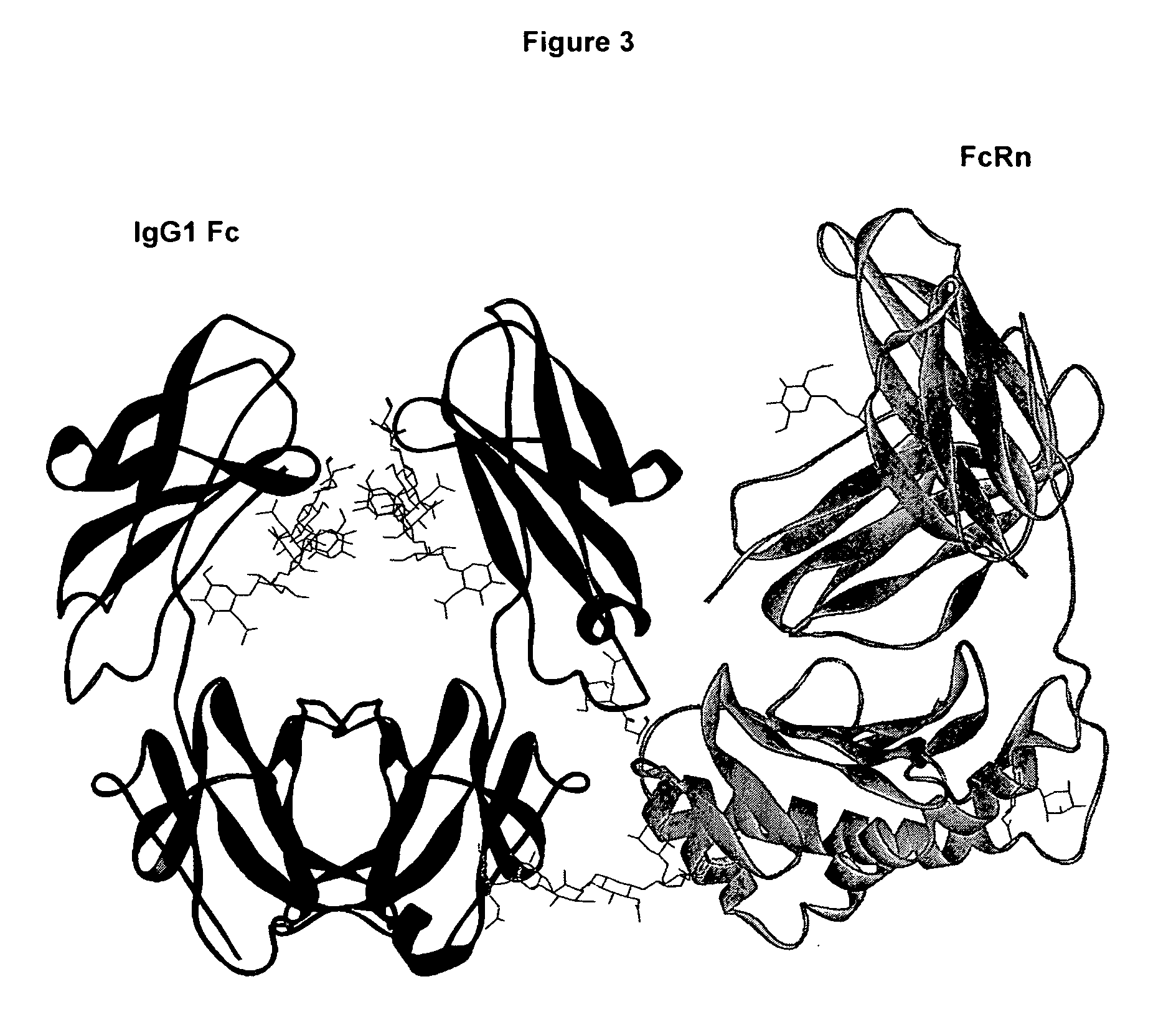
Fc polypeptides with novel Fc ligand binding sites
The present invention relates to Fc polypeptides with novel Fc receptor binding sites, and their application, particularly for therapeutic purposes.
Owner:XENCOR
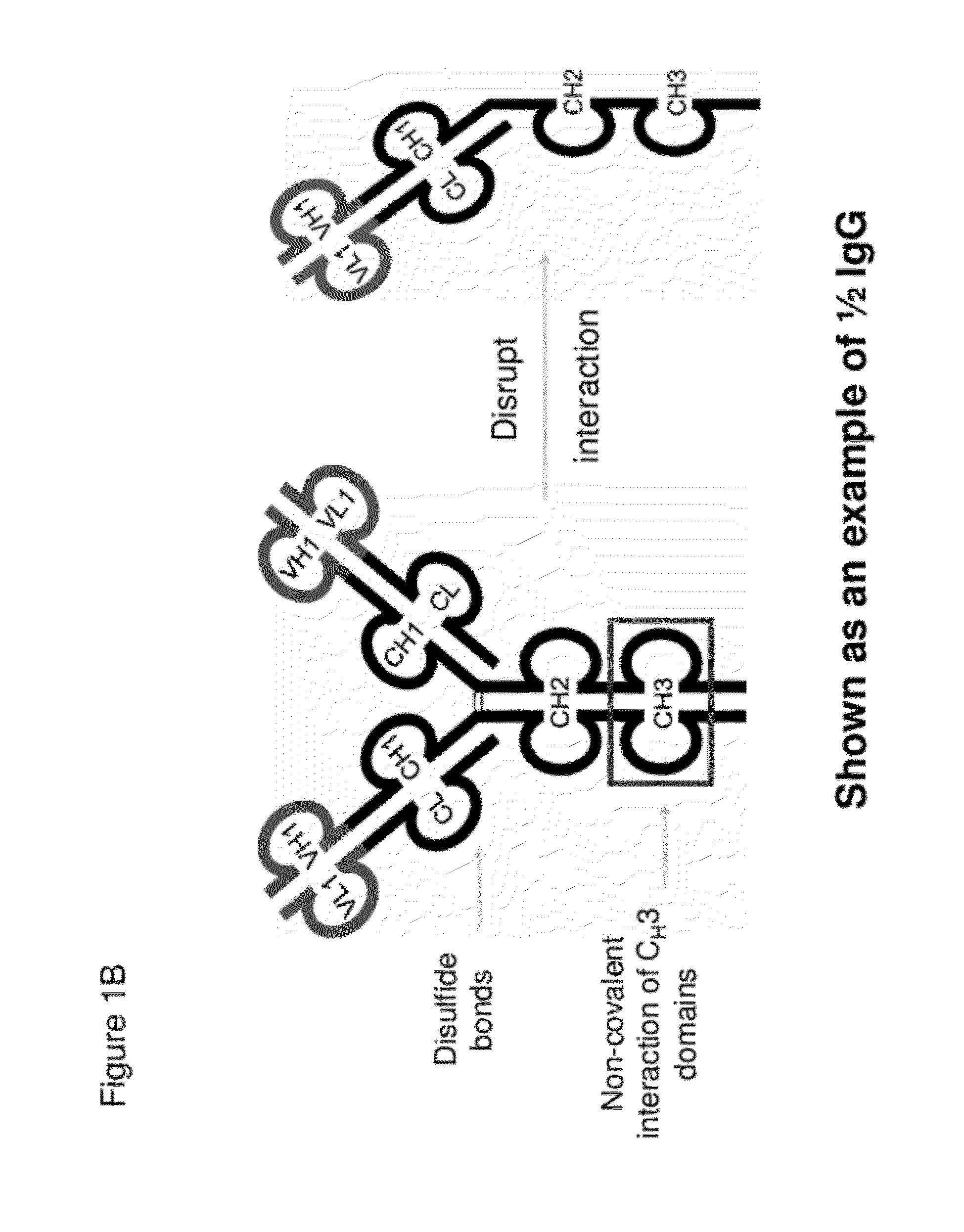
Half immunoglobulin binding proteins and uses thereof
InactiveUS20120201746A1Altered pharmacokineticAltered pharmacodynamic propertyIn-vivo radioactive preparationsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntibody Binding SiteBinding site
The invention provides compositions, methods, and kits related to half-Ig binding proteins that include a functional antibody binding site and a CH3 domain wherein the CH3 domain includes at least one mutation to inhibit CH3-CH3 dimerization.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
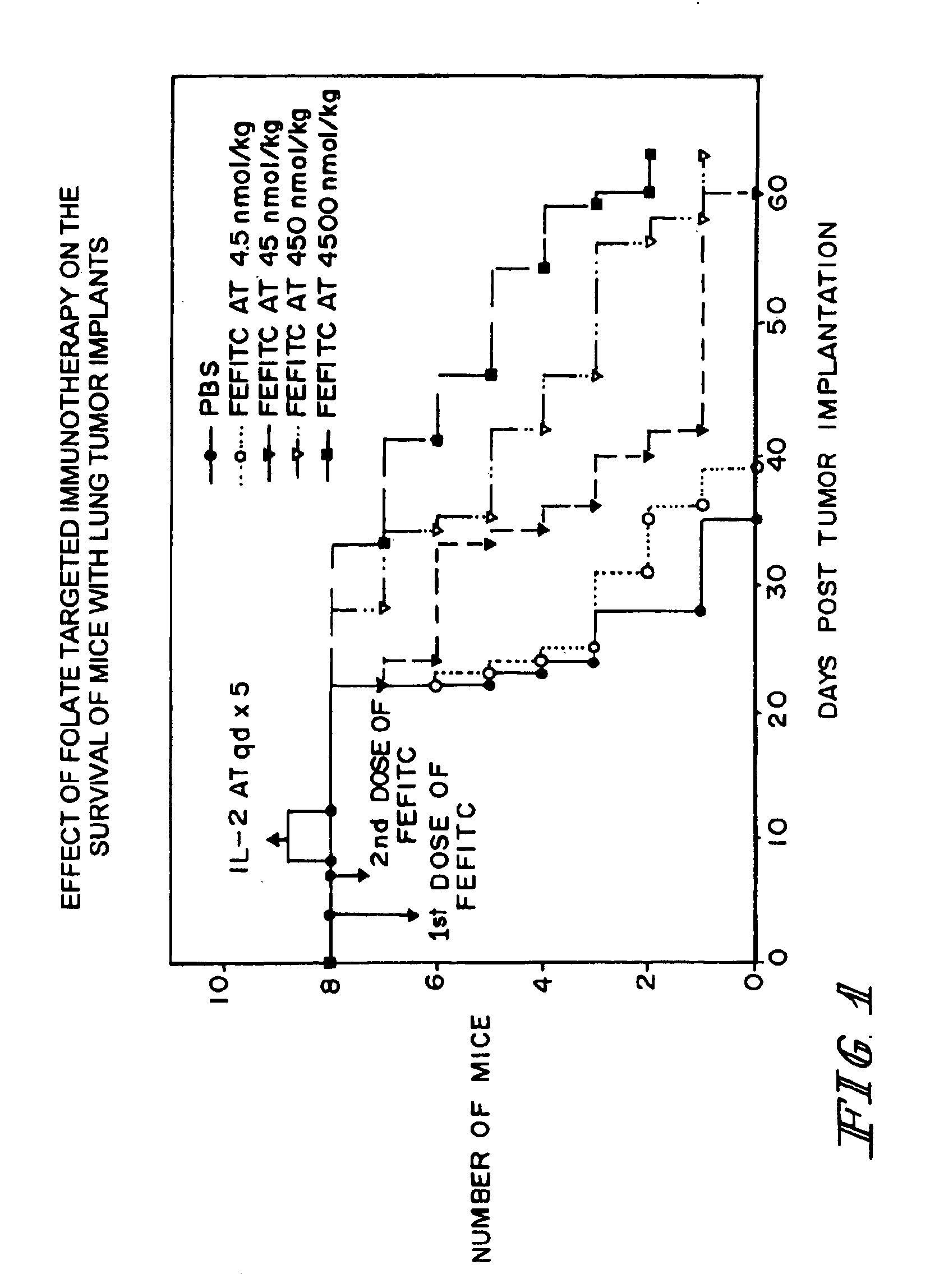
Method of treatment using ligand-immunogen conjugates
InactiveUS7033594B2Improve recognitionEnhance endogenous immune response-mediated eliminationAntibacterial agentsBiocideBinding siteCytotoxicity
A method and pharmaceutical composition are provided for enhancing the endogenous immune response-mediated elimination of a population of pathogenic cells in a host animal wherein the pathogenic cells preferentially express, uniquely express, or overexpress a binding site for a particular ligand. The invention comprises administering the ligand conjugated to an immunogen to a host animal harboring the population of pathogenic cells. Antibodies, preexisting or administered to the host animal to establish a passive immunity, directed against the immunogen bind to the ligand-immunogen conjugate resulting in elimination of the pathogenic cells by the host's immune response. At least one additional therapeutic factor is administered selected from the group consisting of a cell killing agent, a tumor penetration enhancer, a chemotherapeutic agent, antimicrobial agent, a cytotoxic immune cell, and a compound capable of stimulating an endogenous immune response wherein the compound does not bind to the ligand-immunogen conjugate.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Spatial localization of dispersed single walled carbon nanotubes into useful structures
InactiveUS6896864B2Improve structural performanceMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureBinding siteAqueous solution
Methods of aligning single walled carbon nanotube structures into selected orientations for a variety of different applications are achieved by initially dispersing the nanotube structures in aqueous solutions utilizing a suitable dispersal agent. The dispersal agent coats each individual nanotube structure in solution. The dispersal agent may be substituted with a suitable functional group that reacts with a corresponding binding site. Dispersed nanotube structures coated with substituted dispersal agents are exposed to a selected array of binding sites such that the nanotubes align with the binding sites due to the binding of the substituted functional groups with such binding sites. Alternatively, crystalline nanotube material is formed upon deposition of dispersed nanotube structures within solution into channels disposed on the surface of the substrate. Combining dispersal agent chemical modification techniques with deposition of the nanotubes into substrate channels is also utilized to produce useful structures.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Scalable Production Method for AAV
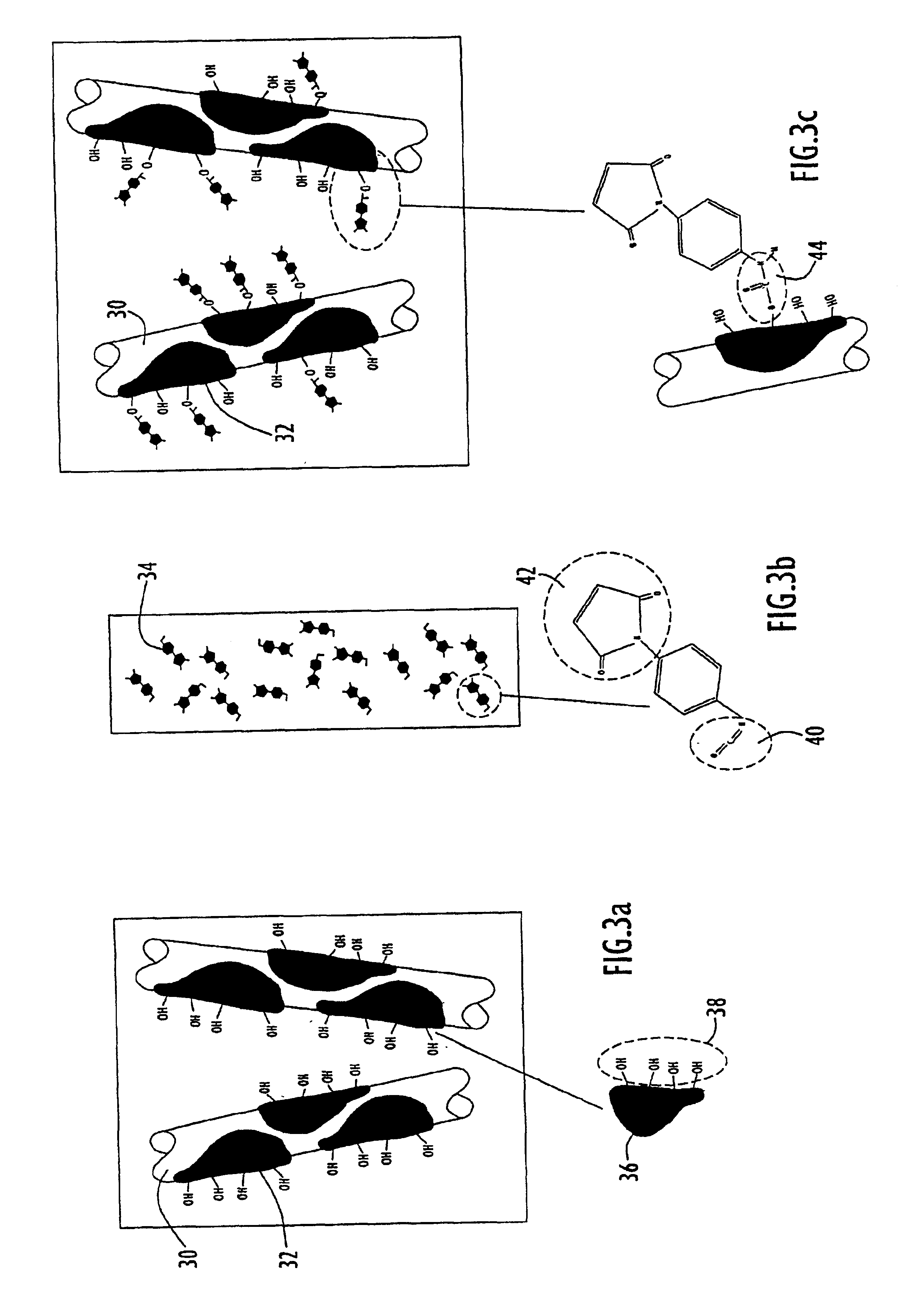
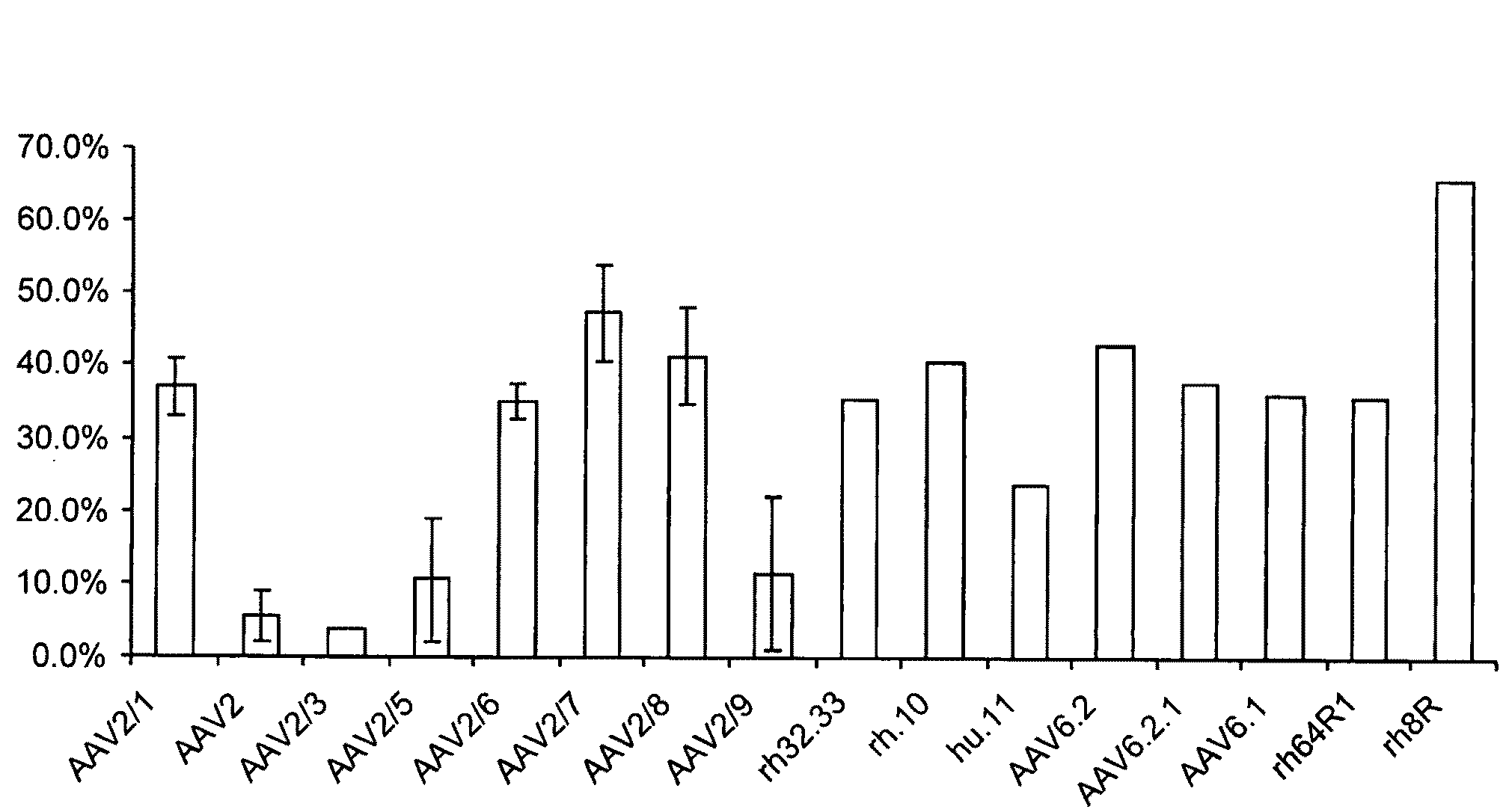
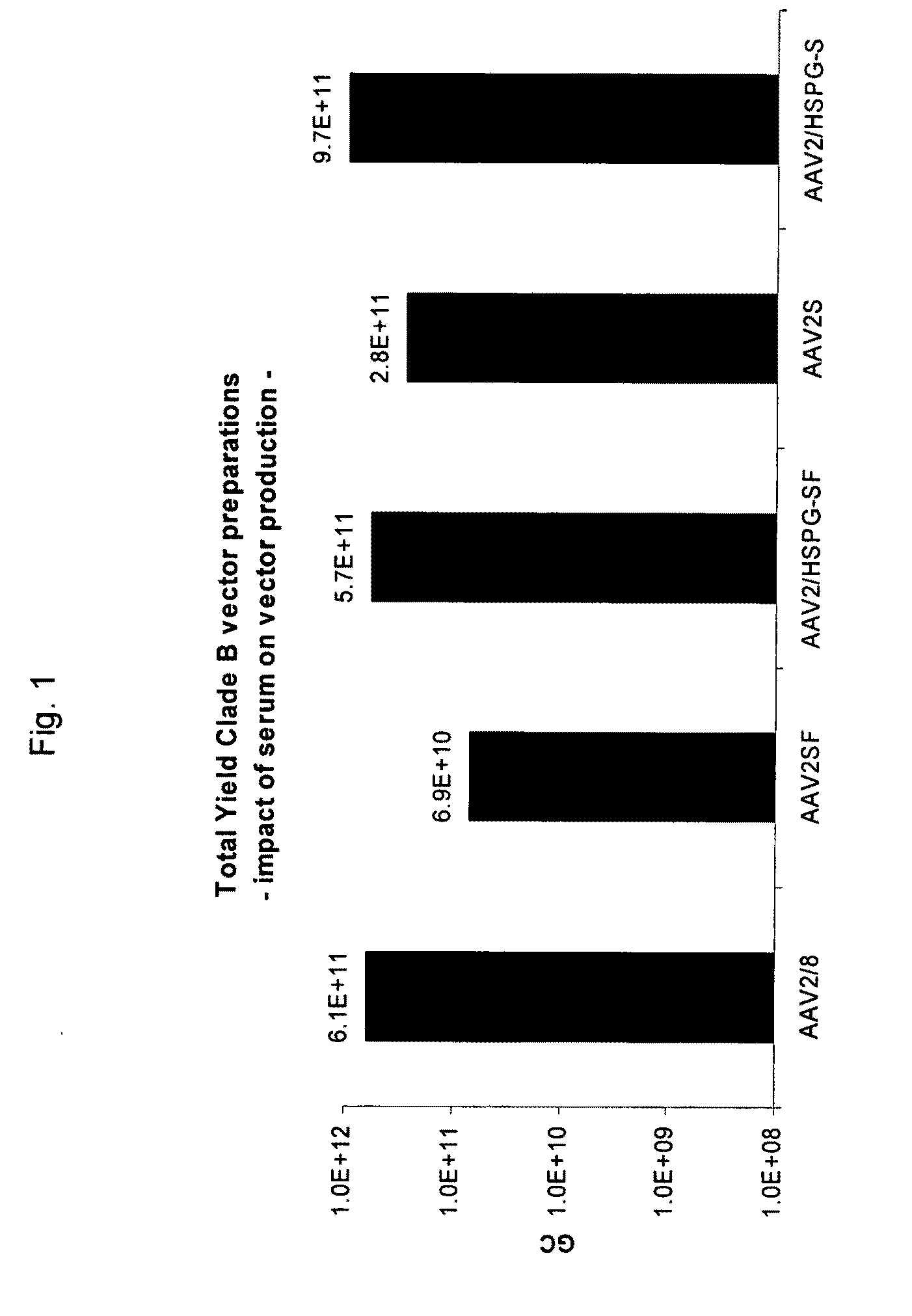
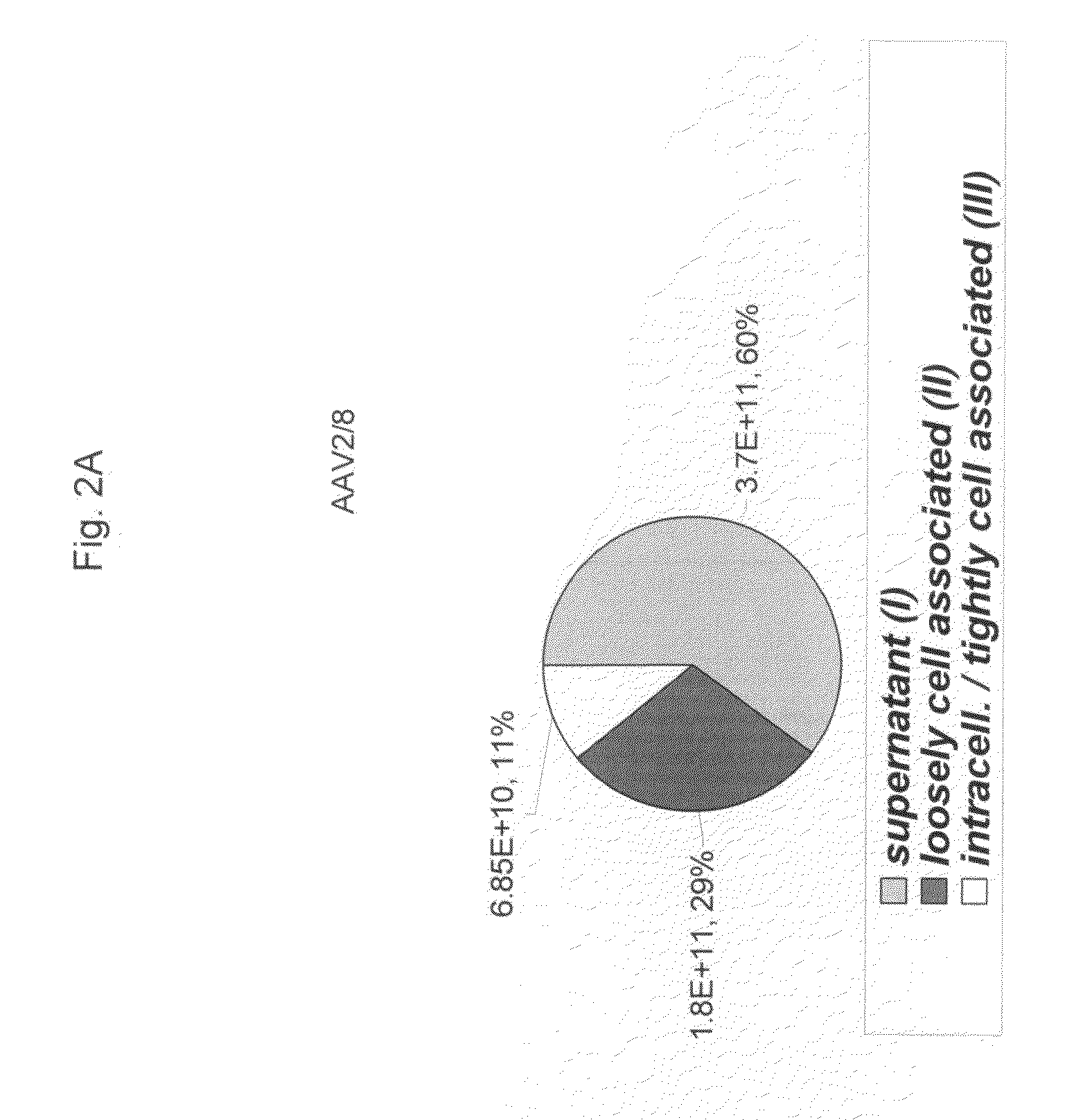
ActiveUS20090275107A1Reduce and eliminate bindingHigh yieldGenetic therapy composition manufactureVirus peptidesLysisBinding site
A method for producing AAV, without requiring cell lysis, is described. The method involves harvesting AAV from the supernatant. For AAV having capsids with a heparin binding site, the method involves modifying the AAV capsids and / or the culture conditions to ablate the binding between the AAV heparin binding site and the cells, thereby allowing the AAV to pass into the supernatant, i.e., media. Thus, the method of the invention provides supernatant containing high yields of AAV which have a higher degree of purity from cell membranes and intracellular materials, as compared to AAV produced using methods using a cell lysis step.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
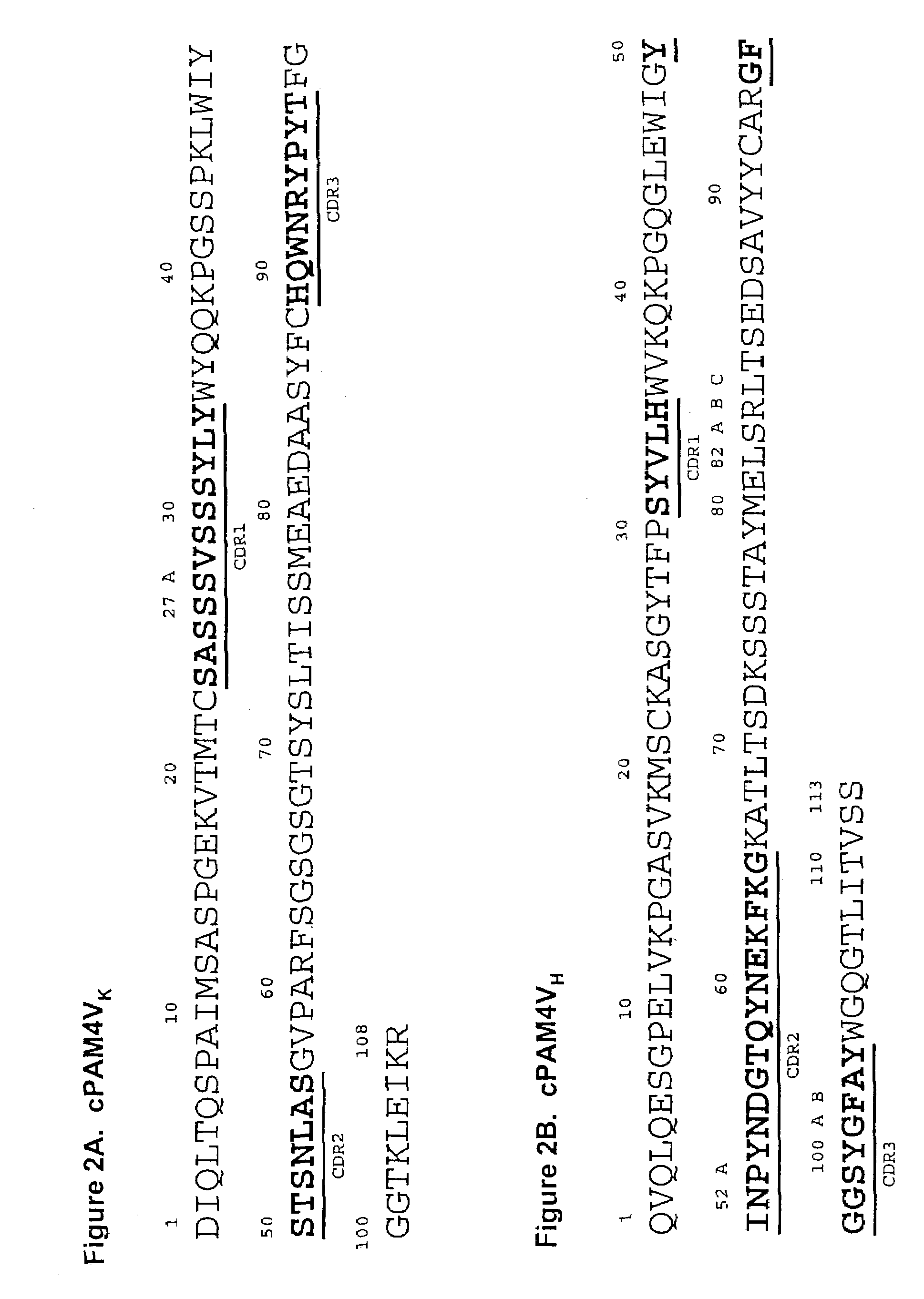
Monoclonal antibody cPAM4
This invention relates to monovalent and multivalent, monospecific antibodies and to monovalent and multivalent, multispecific antibodies. One embodiment of these antibodies has one or more identical binding sites where each binding site binds with a target antigen or an epitope on a target antigen. Another embodiment of these antibodies has two or more binding sites where these binding sites have affinity towards different epitopes on a target antigen or different target antigens, or have affinity towards a target antigen and a hapten. The present invention further relates to recombinant vectors useful for the expression of these functional antibodies in a host. More specifically, the present invention relates to the tumor-associated antibody designated PAM4. The invention further relates to chimeric PAM4 antibodies, and the use of such antibodies in diagnosis and therapy.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Splice choice antagonists as therapeutic agents
The invention relates to methods and reagents for influencing alternative RNA splicing in living cells. More particularly, the invention relates to novel means for influencing RNA splice choice in living cells using polynucleotide-based reagents that compete for binding sites in nucleotide binding proteins, and novel methods for using these reagents as therapeutics.
Owner:NEW YORK MEDICAL COLLEGE
Morpholino imaging and therapy
InactiveUS6899864B2Strong specificityImprove stabilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsOrganic active ingredientsOligomerDiagnostic agent
The present invention provides a kit and a method for targeting of a diagnostic or therapeutic agent to a target site in a mammal having a pathological condition. The kit comprises, in separate containers, (a) a first conjugate comprising a targeting moiety and a Morpholino oligomer, wherein the targeting moiety selectively binds to a primary, target-specific binding site of the target site or to a substance produced by or associated with the target site; (b) optionally, a clearing agent; and (c) a second conjugate comprising a complementary Morpholino oligomer and a diagnostic agent or therapeutic agent. The method comprises administering (a), optionally (b), and (c) to a mammal.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Isulin and IGF-1 receptor agonists and antagonists
Peptide sequences capable of binding to insulin and / or insulin-like growth factor receptors with either agonist or antagonist activity and identified from various peptide libraries are disclosed. This invention also identifies at least two different binding sites, which are present on insulin and insulin-like growth factor receptors, and which selectively bind the peptides of this invention. As agonists, certain of the peptides of this invention may be useful for development as therapeutics to supplement or replace endogenous peptide hormones. The antagonists may also be developed as therapeutics.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS +1
Method for detecting the presence of an analyte in a sample
InactiveUS7097983B2High purityEliminate needBioreactor/fermenter combinationsFatty acid hydrogenationAnalyteBinding site
The invention features a method of determining whether one or more members of an analyte family are present in a sample. The method makes use of a test zone binder, e.g., a receptor that can bind one or a plurality of analytes within an analyte family, the analytes family defined by similar structural binding sites. Members of an analyte family can have different detection level requirements and, therefore, additional analyte binders can be employed to adjust test sensitivity for a subset of the analytes in the analyte family individually, so that each analyte can be detected only if it is present in the sample above a predetermined threshold.
Owner:CHARM SCI
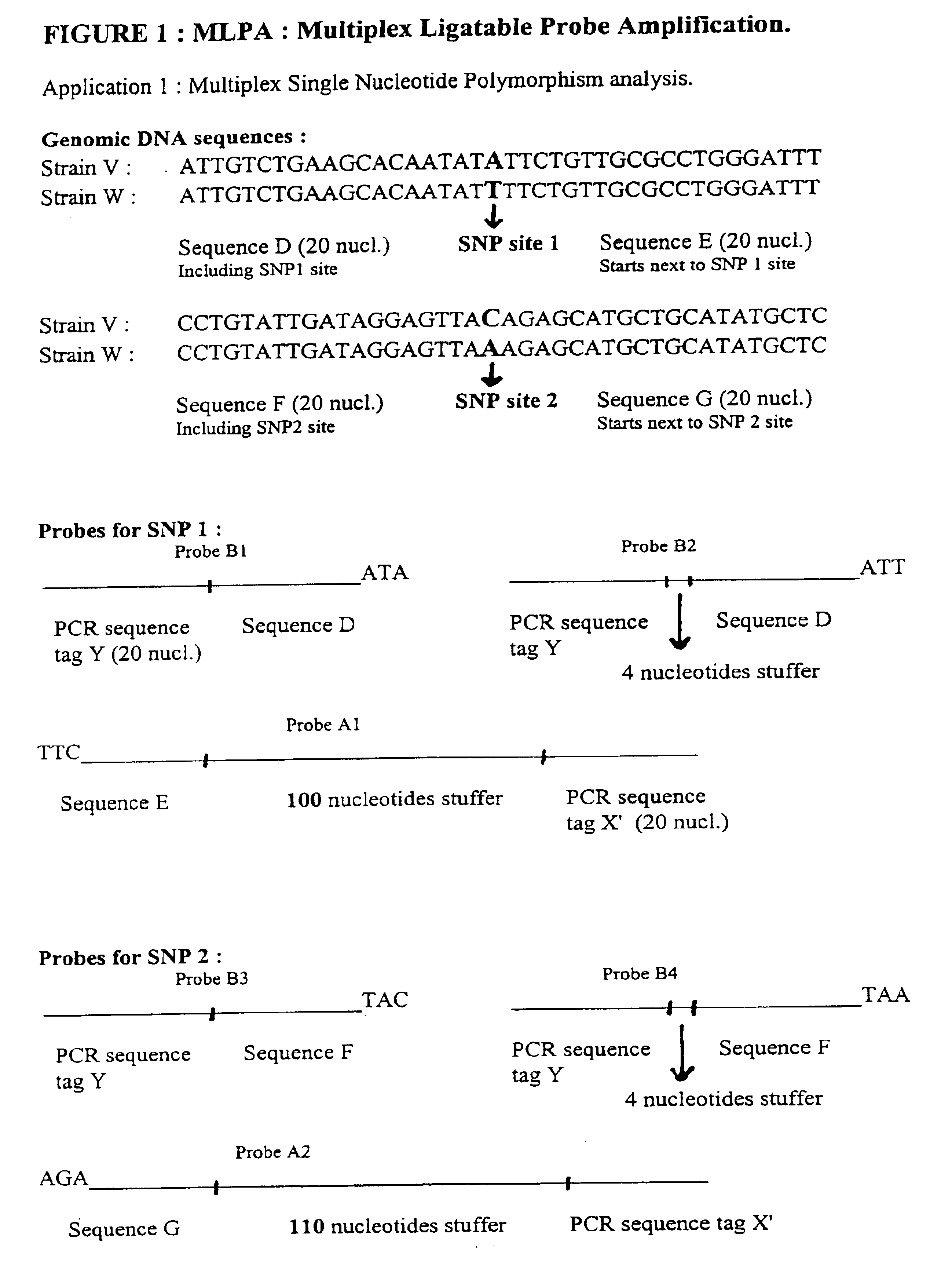
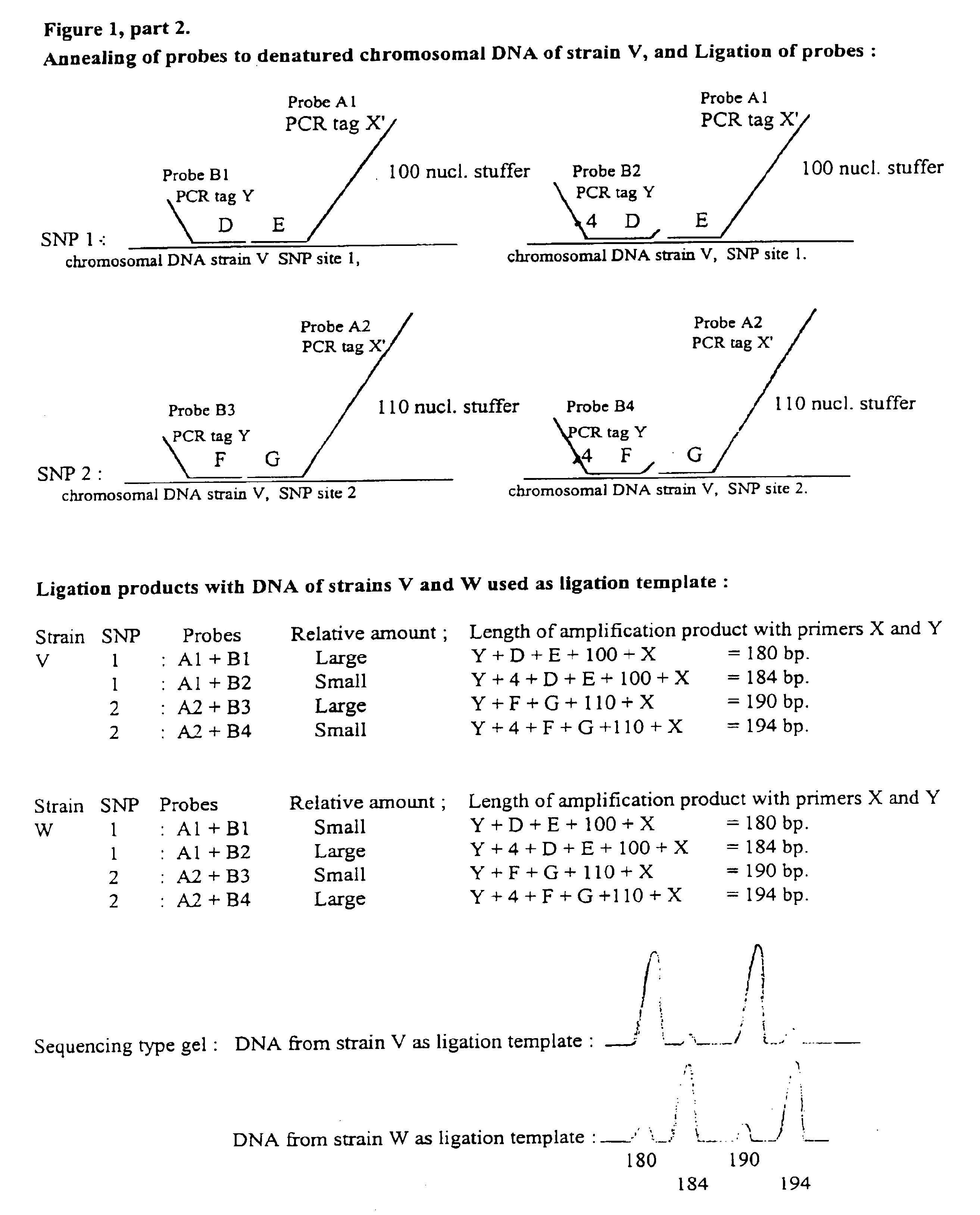
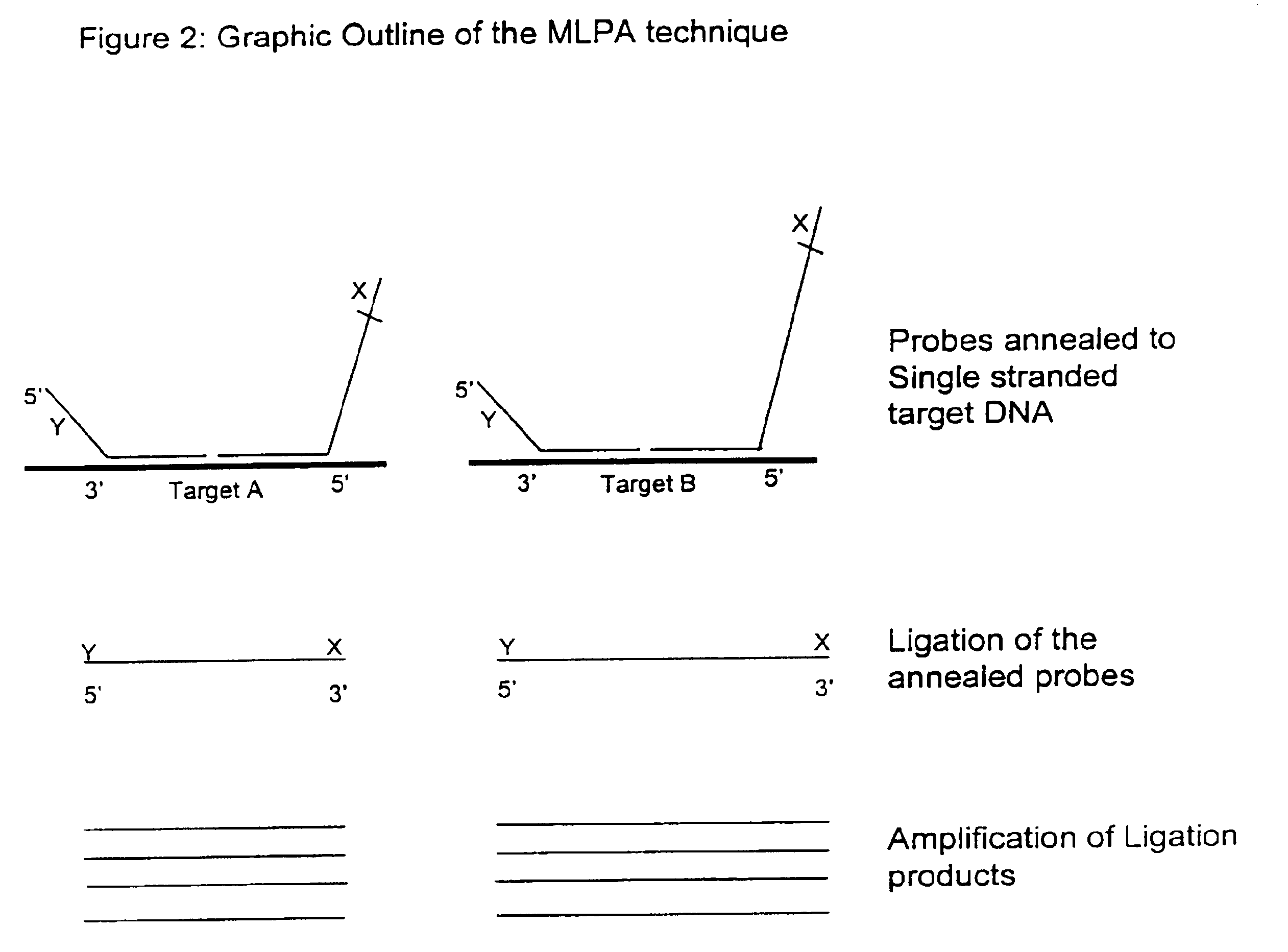
Multiplex ligatable probe amplification
InactiveUS6955901B2Reduce the amount requiredIncrease the molar ratioSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBinding siteNucleic acid sequencing
Described is an improved multiplex ligation-dependent amplification method for detecting the presence and quantification of at least one specific single stranded target nucleic acid sequence in a sample using a plurality of probe sets of at least two probes, each of which includes a target specific region and a non-complementary region comprising a primer binding site. The probes belonging to the same set are ligated together when hybridised to the target nucleic acid sequence and amplified by a suitable primer set. By using a femtomolar amount of the probes a large number of different probe sets can be used to simultaneously detect and quantify a corresponding large number of target sequences with high specificity.
Owner:DE LUWE HOEK OCTROOIEN
Insulin and IGF-1 receptor agonists and antagonists
Peptide sequences capable of binding to insulin and / or insulin-like growth factor receptors with either agonist or antagonist activity and identified from various peptide libraries are disclosed. This invention also identifies at least two different binding sites, which are present on insulin and insulin-like growth factor receptors, and which selectively bind the peptides of this invention. As agonists, certain of the peptides of this invention may be useful for development as therapeutics to supplement or replace endogenous peptide hormones. The antagonists may also be developed as therapeutics.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS +1
Method of identifying inhibitors of DHODH
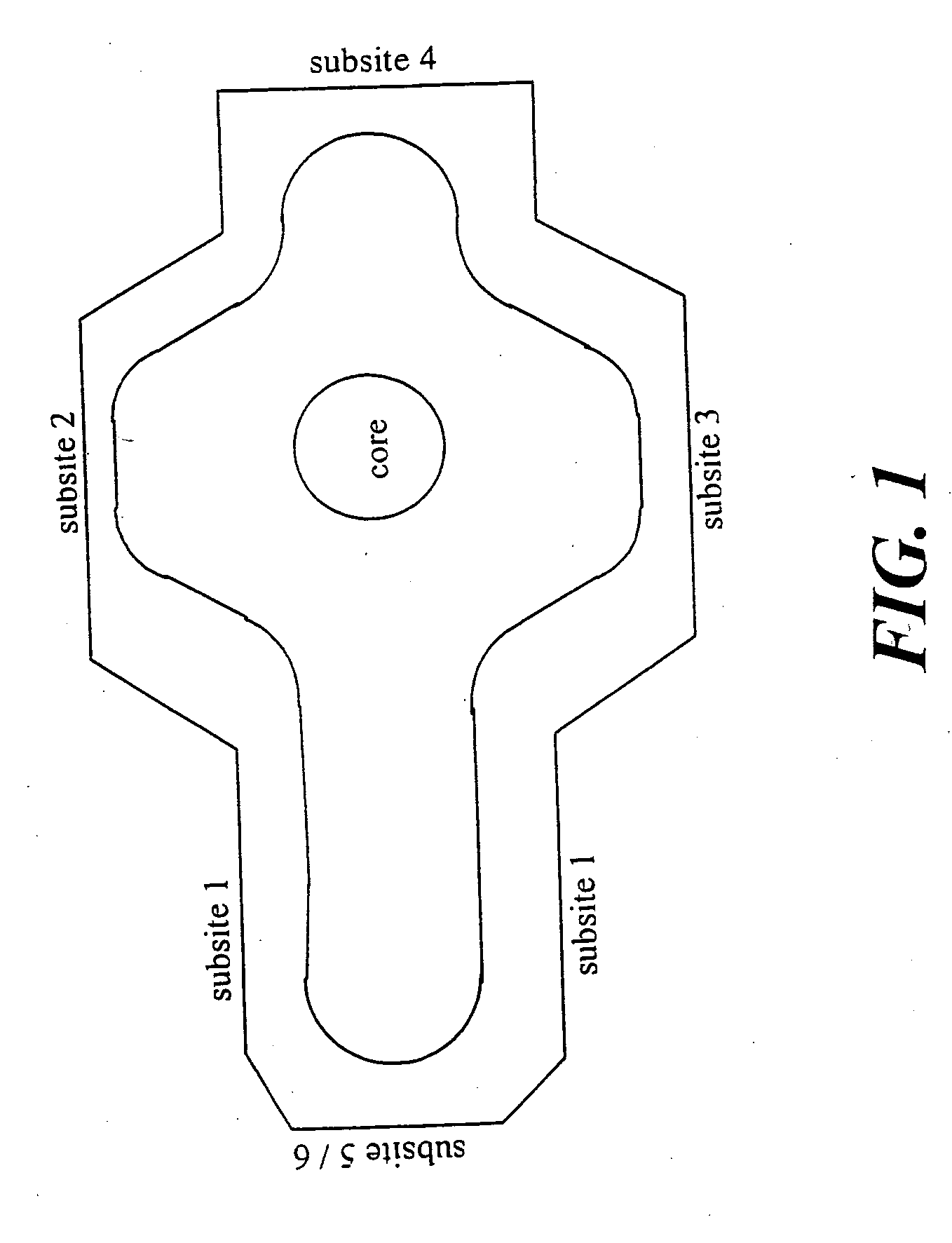
ActiveUS20070027193A1Inhibit biological activityBiocideOrganic compound preparationBinding siteUbiquinone binding
The present invention provides a compound capable of binding to the ubiquinone binding site of DHODH which contains a non-aromatic ring system as a core structure, a group capable of interacting with structural elements of subsite 2 or 3 of the ubiquinone binding site of DHODH and a group capable of interacting hydrophobically with structural elements of subsite 1 of the ubiquinone binding site of DHODH. Furthermore, the present invention provides a compound capable of binding to the ubiquinone binding site of DHODH which contains an aromatic ring system as a core structure, a group capable of interacting with residues His 56 and / or Tyr 356 of subsite 3 of the ubiquinone binding site of DHODH and a group capable of interacting hydrophobically with structural elements of subsite 1 of the ubiquinone binding site of DHODH.
Owner:IMMUNIC AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com