Dual Variable Region Antibody-Like Binding Proteins Having Cross-Over Binding Region Orientation
a technology variable regions, which is applied in the field of antibody-like binding proteins, can solve the problems of reduced avidity, short half-life, and difficult and expensive purification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Design and Engineering of Bispecific Cross-Over Dual Variable Region Antibody-Like Binding Proteins
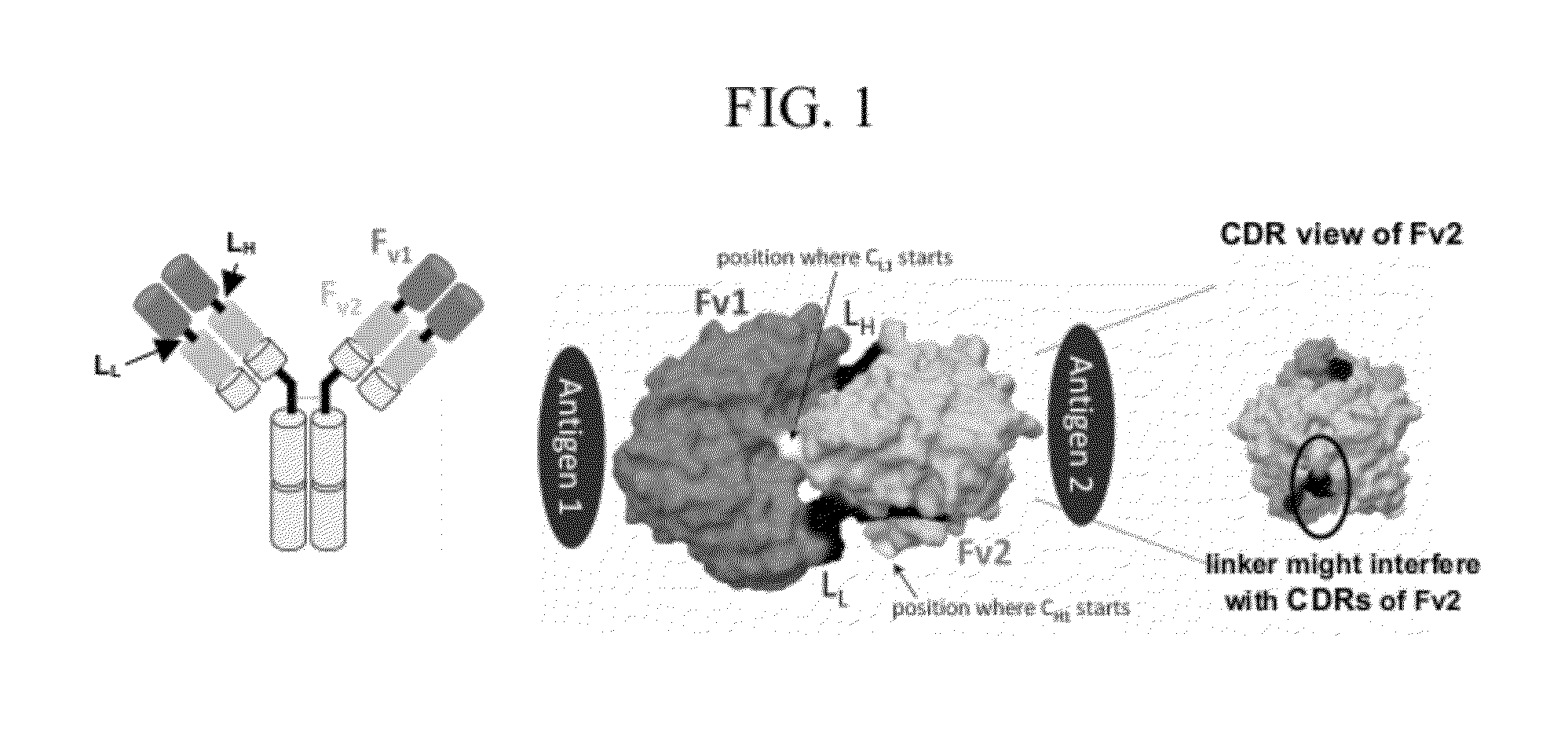
[0228]The cross-over dual variable region in an Fv format was described in U.S. Pat. No. 5,989,830 and was referred to as a cross-over double head (CODH) configuration. Molecular modeling predicted that the cross-over double-head (CODH) design results in a complex with both binding sites facing in opposite directions, without the restraints suggested for the Dual-Fv configuration. The CODH Fv format was examined to determine whether it could be converted into complete antibody-like molecules by adding a CL domain to the light chain and an Fc region to the heavy chain. A similar conversion was successful for the corresponding dual variable domains (DVD-Ig) and TBTI as described in U.S. Pat. No. 7,612,181 and International Publication No. WO 2009 / 052081. The arrangement of the variable regions in the CODH format is shown in the structures below, which indicate the amino to carboxyl orien...
example 2
Design of CODV-Ig Proteins by Molecular Modeling
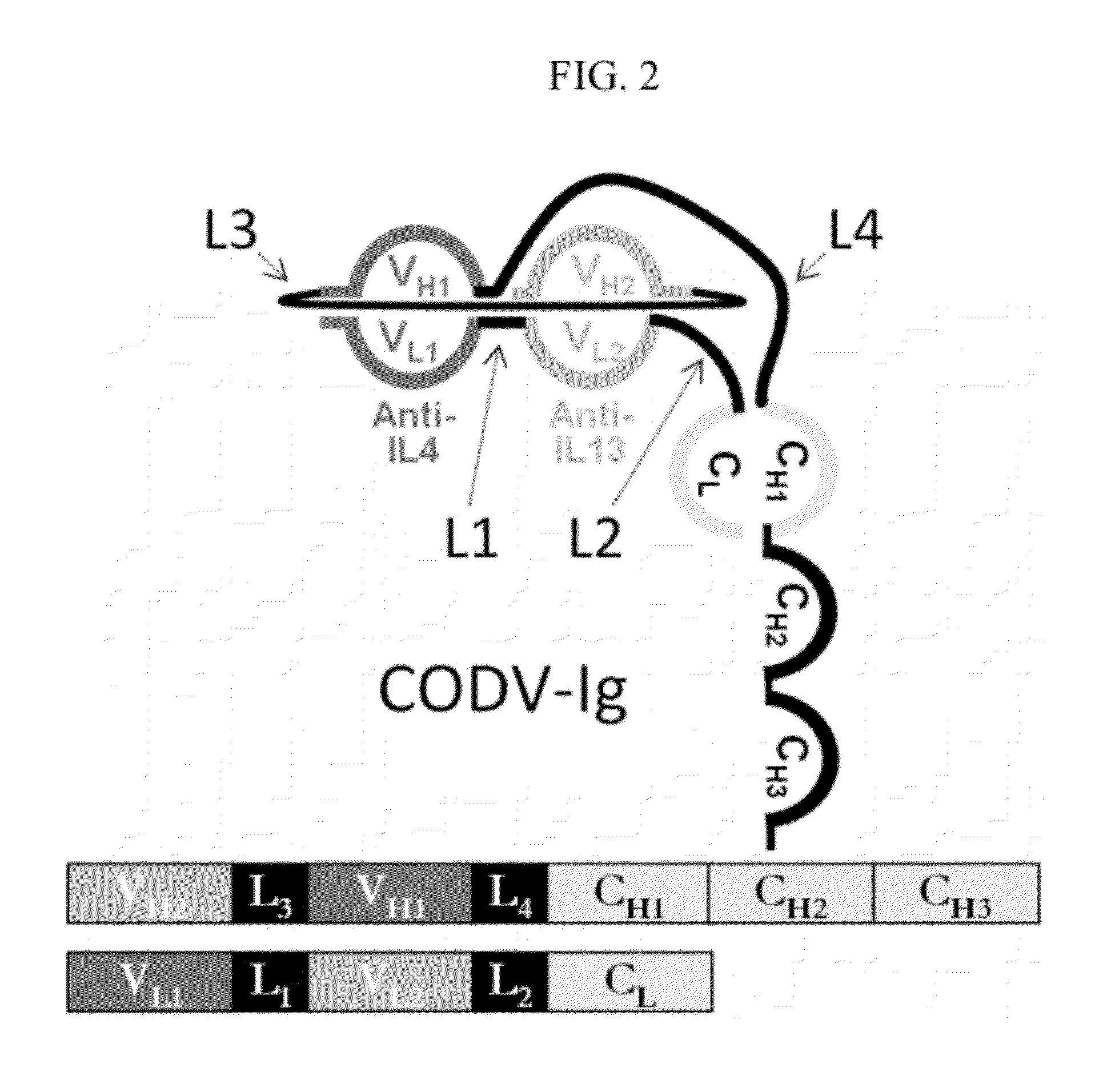
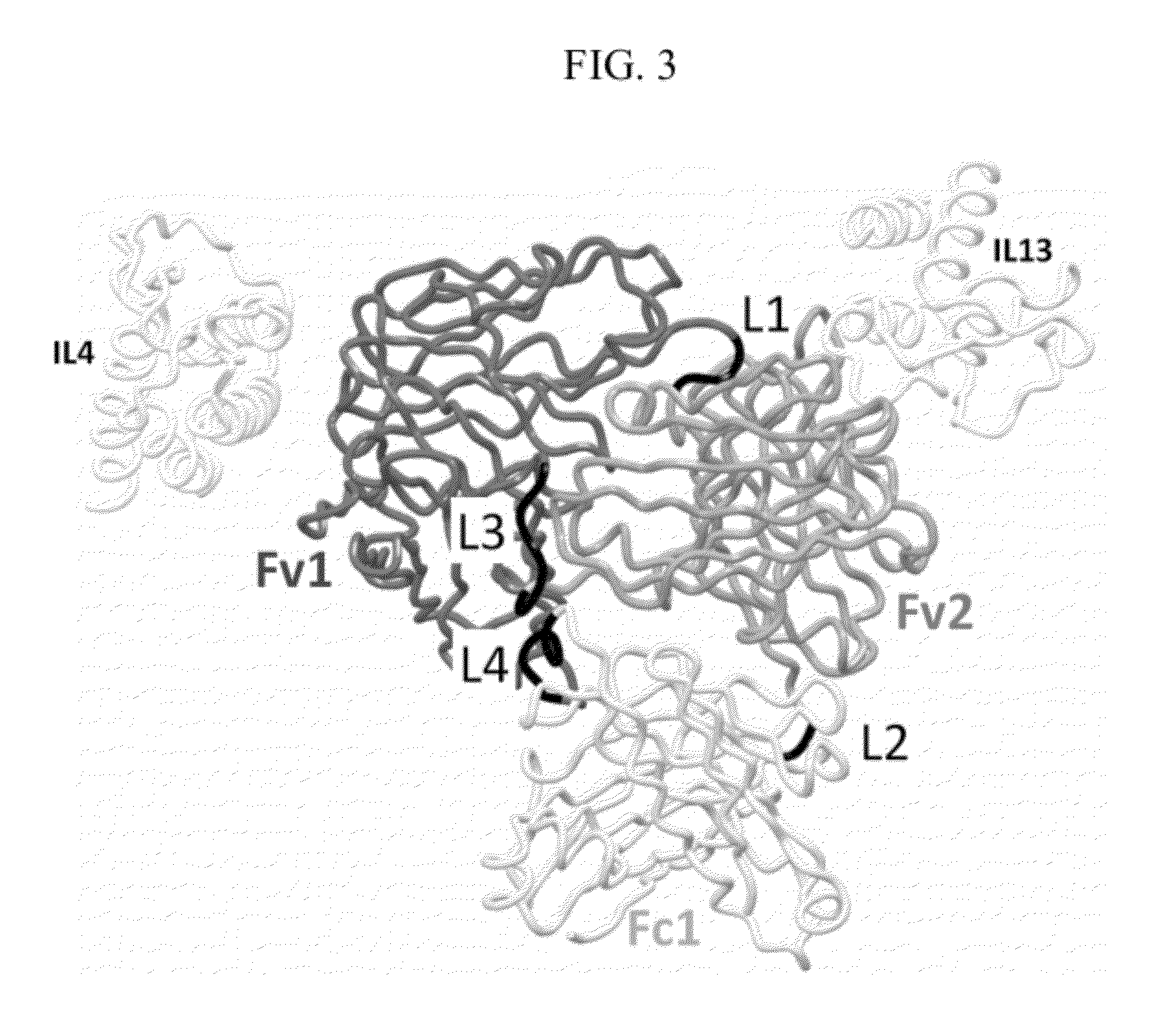
[0241]To obtain fully functional antibody-like proteins utilizing the cross-over double head configuration that are amendable to incorporation of the Fc and CL1 domains, a molecular modeling protocol was developed for the inclusion and evaluation of different linkers between the constant and variable domains and between the dual variable domains on both the heavy and light chains. The question was whether the addition of unique linkers between each constant / variable domain interface and between the two variable / variable domain interfaces on both the heavy and light chains would allow proper protein folding to occur and produce functional antibody-like molecules in the cross-over dual variable region configuration (see FIG. 2). In other words, a total of four independent and unique linkers were evaluated (see FIG. 2). This molecular modeling protocol was based on protein-protein docking of homology models and experimental models of the ...
example 3
Generation of CODV-Ig Expression Plasmids
[0246]Nucleic acid molecules encoding the variable heavy and light chains of the six heavy chains and four light chains described in Table 4 were generated by gene synthesis at Geneart (Regensburg, Germany). The variable light chain domains were fused to the constant light chain (IGKC, GenBank Accession No. Q502W4) by digestion with the restriction endonucleases ApaLI and BsiWI and subsequently ligated into the ApaLI / BsiWI sites of the episomal expression vector pFF, an analogon of the pTT vector described by Durocher et al., (2002, Nucl. Acids Res. 30(2): E9), creating the mammalian expression plasmid for expression of the light chains.
[0247]The variable heavy chain domains were fused to the “Ted” variant of the human constant heavy chain (IGHG1, GenBank Accession No. 569F4), or alternatively, to a 6×His tagged CH1 domain from the human constant IGHG1 in order to create a bispecific Fab. Next, the VH domain was digested with the restriction ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Structure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com