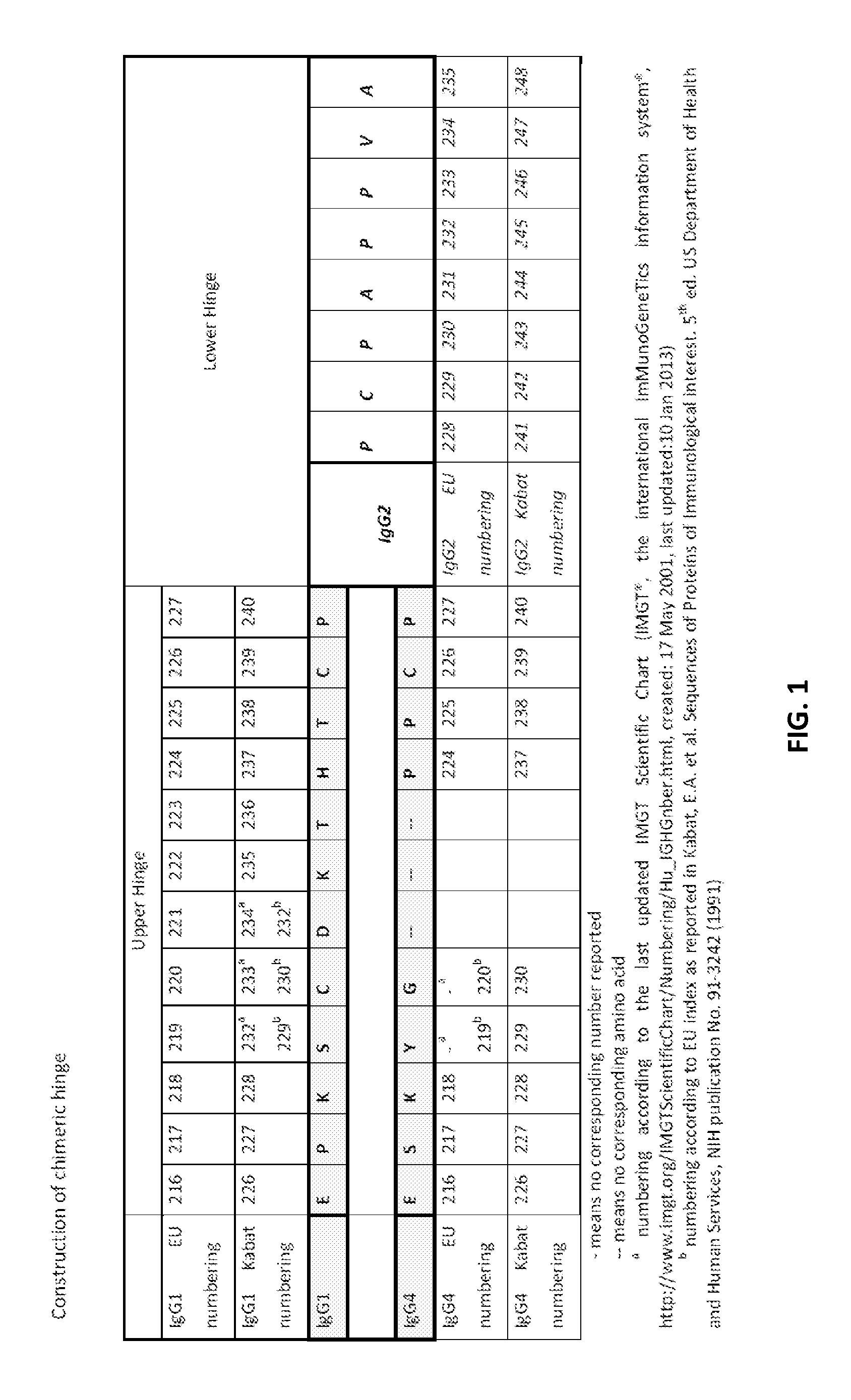
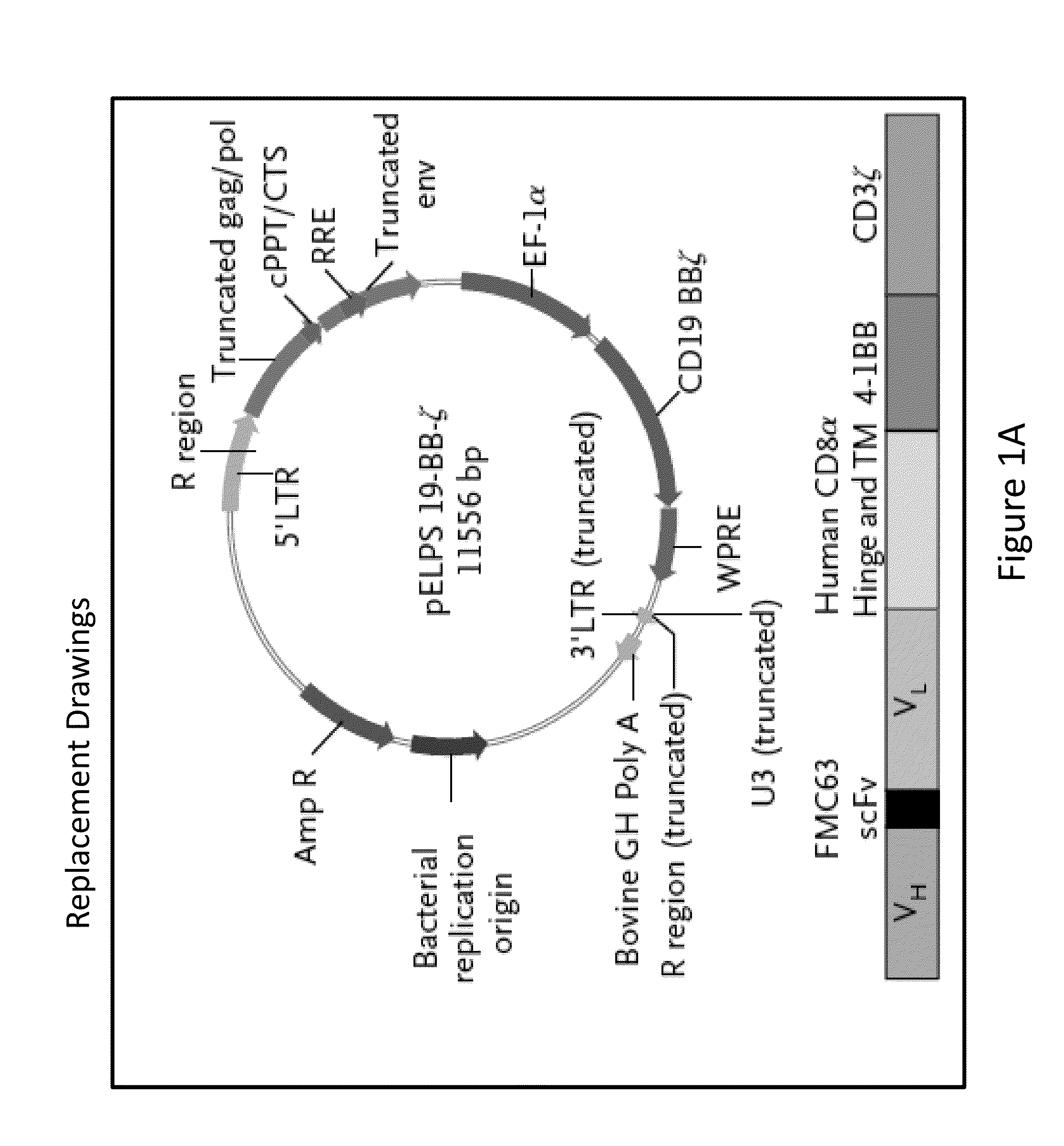
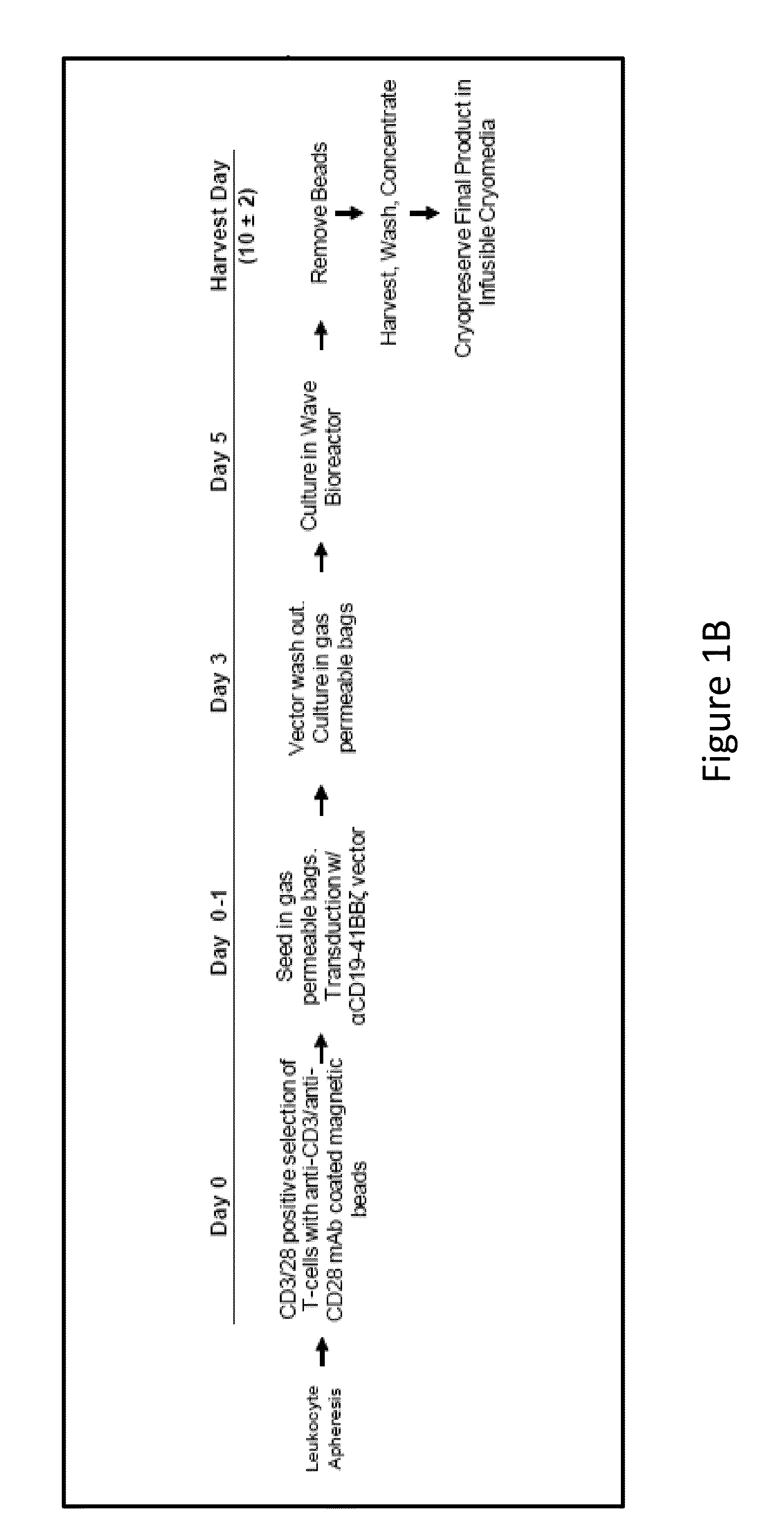
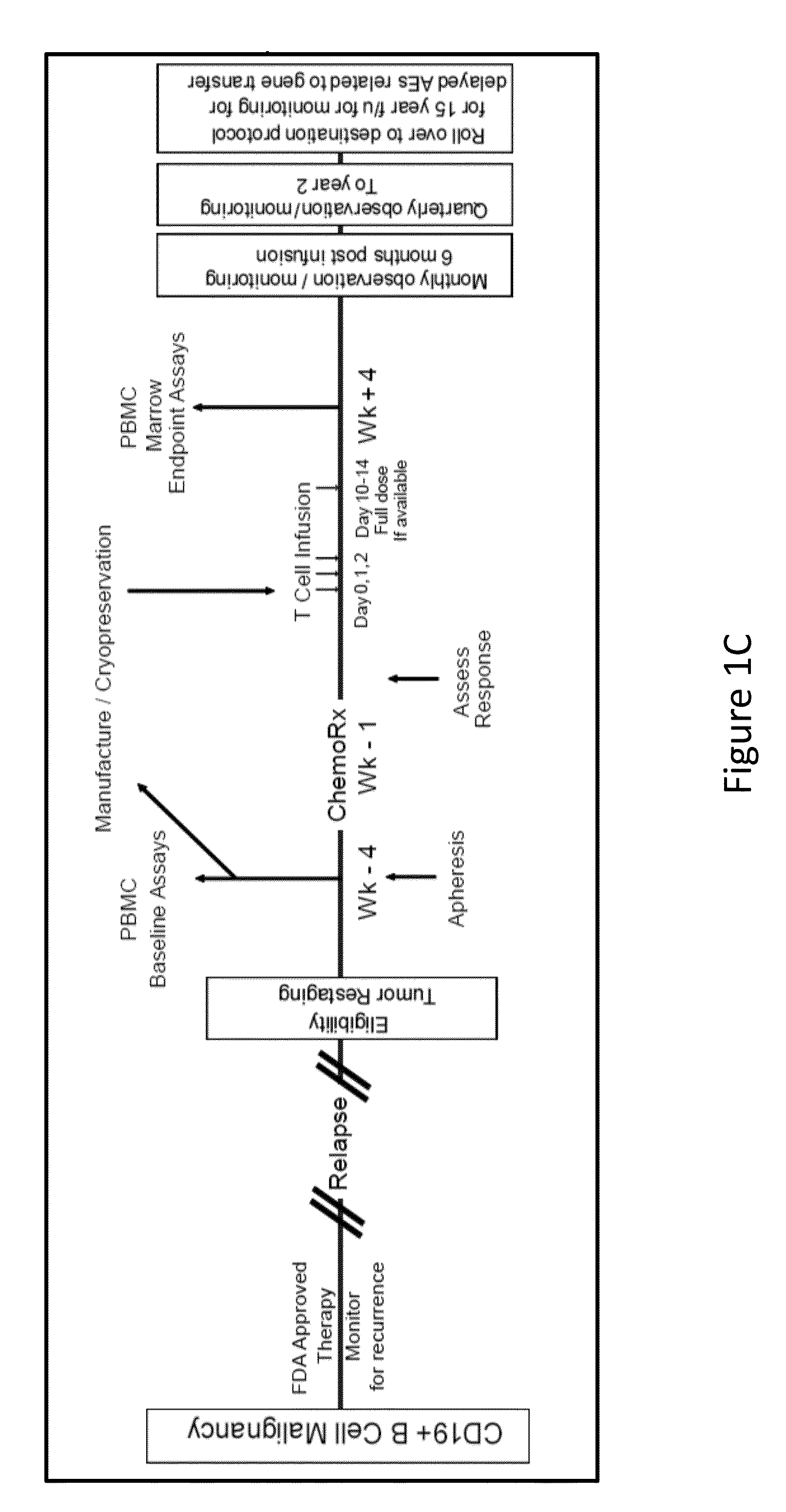
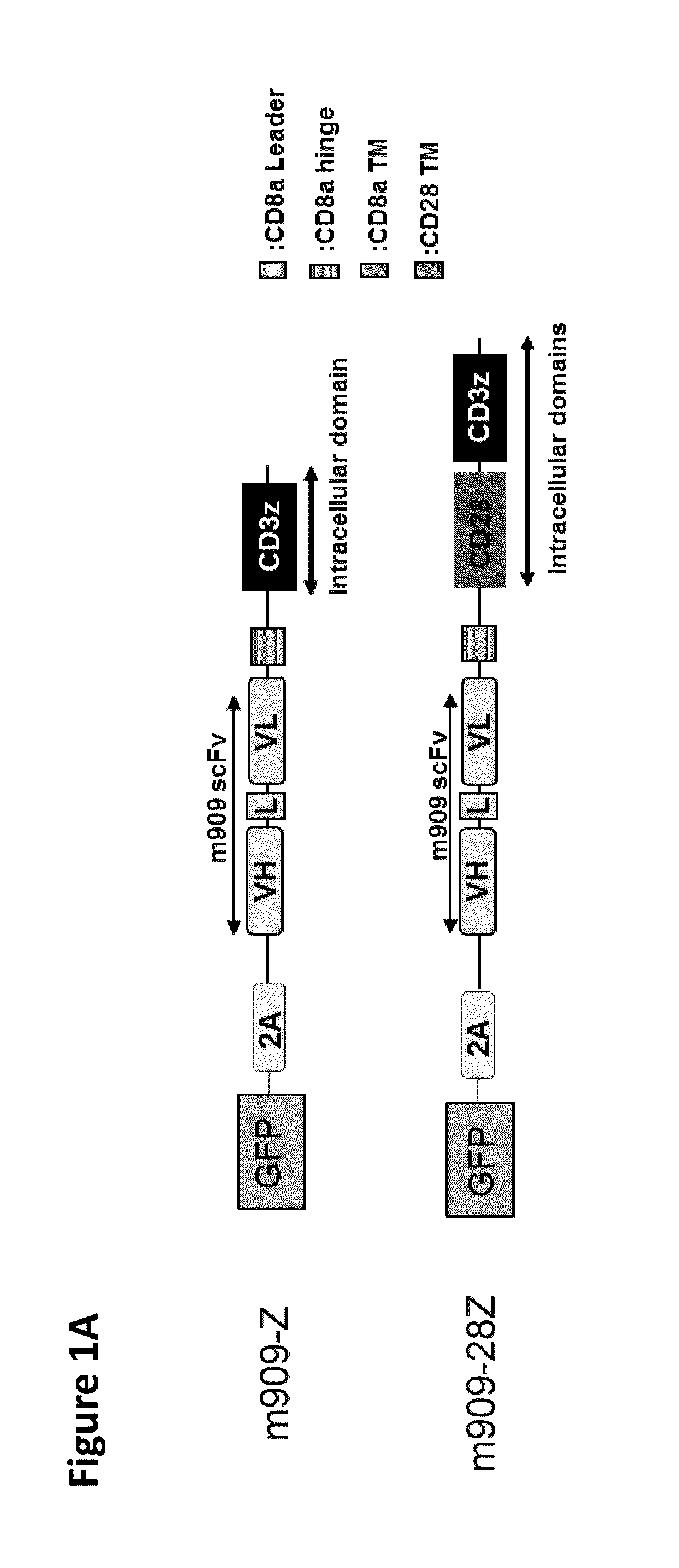
Patents
Literature
1932 results about "Binding domain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
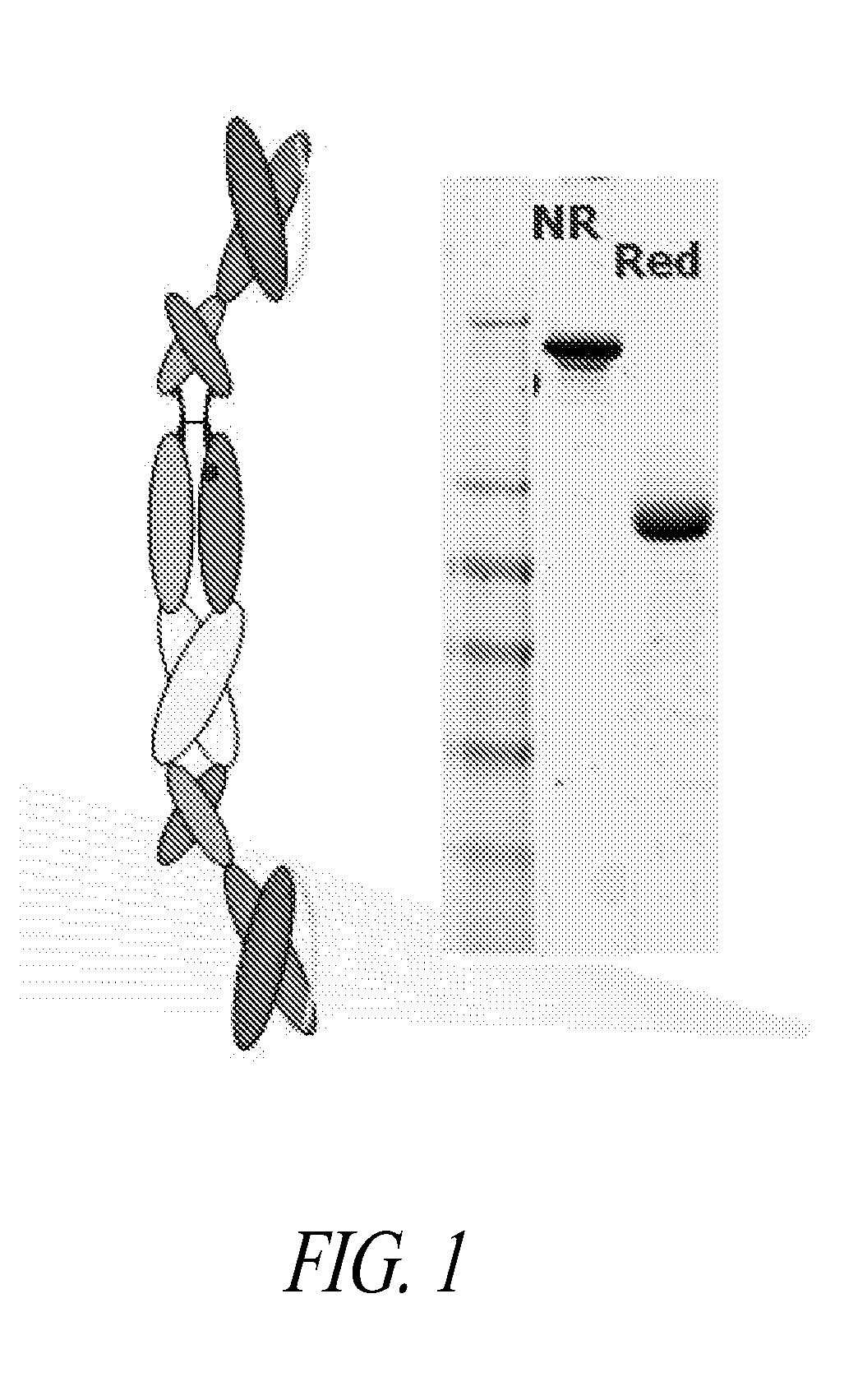
A binding domain is a protein domain which binds to a specific atom or molecule, such as calcium or DNA. Protein Domain is a part of a protein sequence and a tertiary structure that can change, function, and live by itself for the rest of the protein chain. (Phillips 1). Upon binding, proteins may undergo a conformational change. Binding domains are essential for the function of many proteins. They are essential because they help splice, assemble, and translate proteins. (Yong 1).
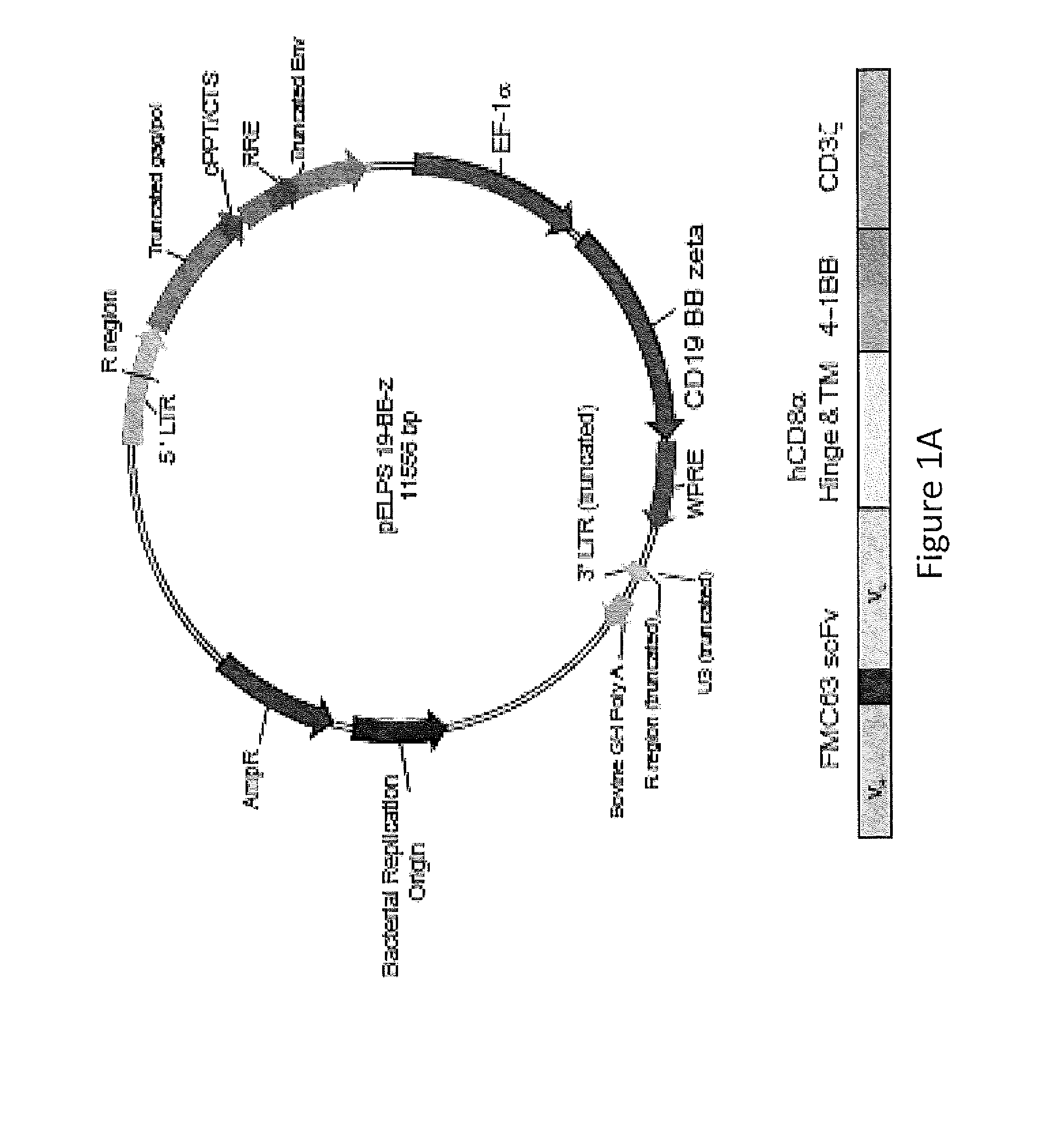
Use of Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Modified T-Cells to Treat Cancer
ActiveUS20130287748A1Stimulate immune responseVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsBinding domainAntigen binding
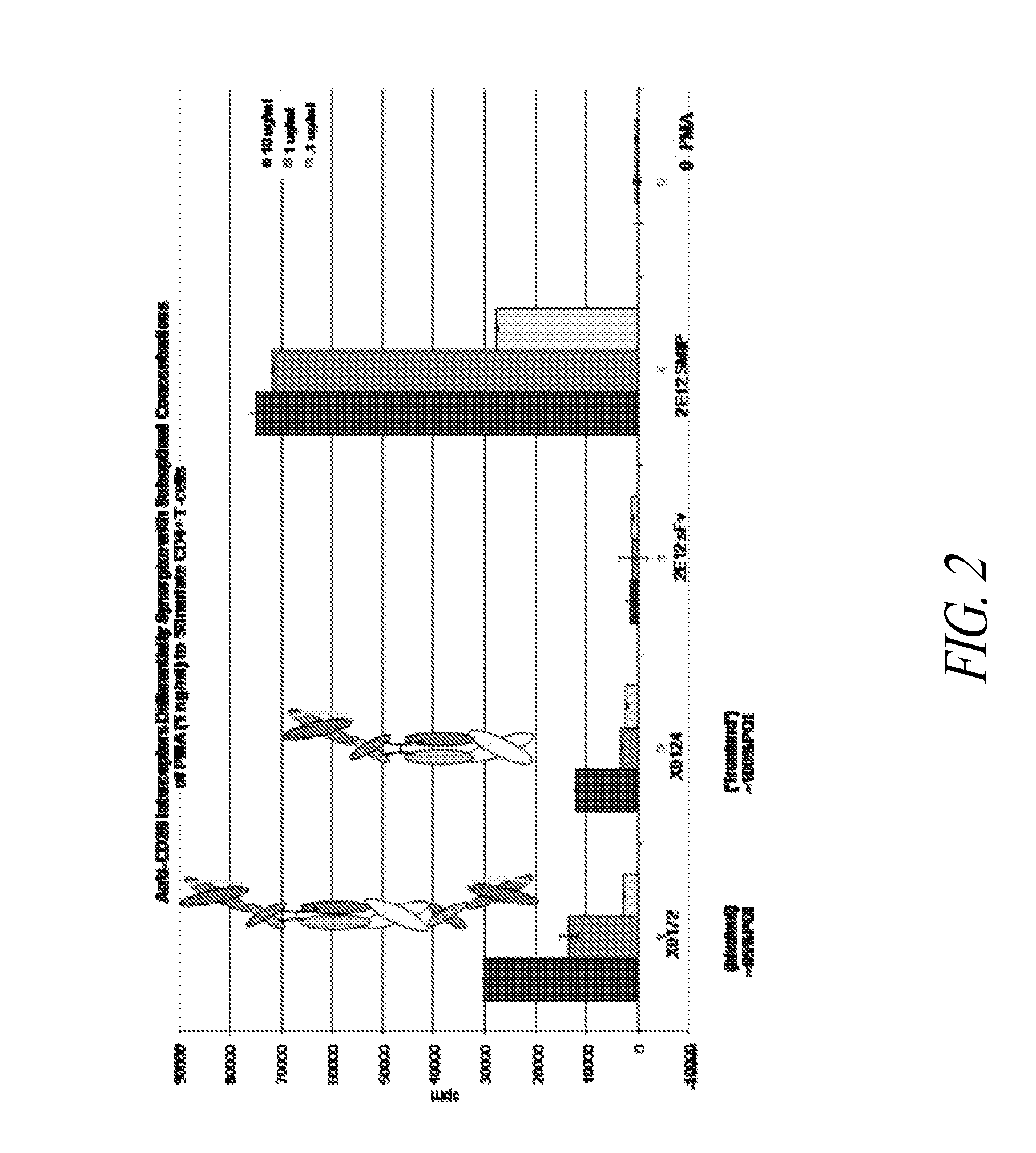
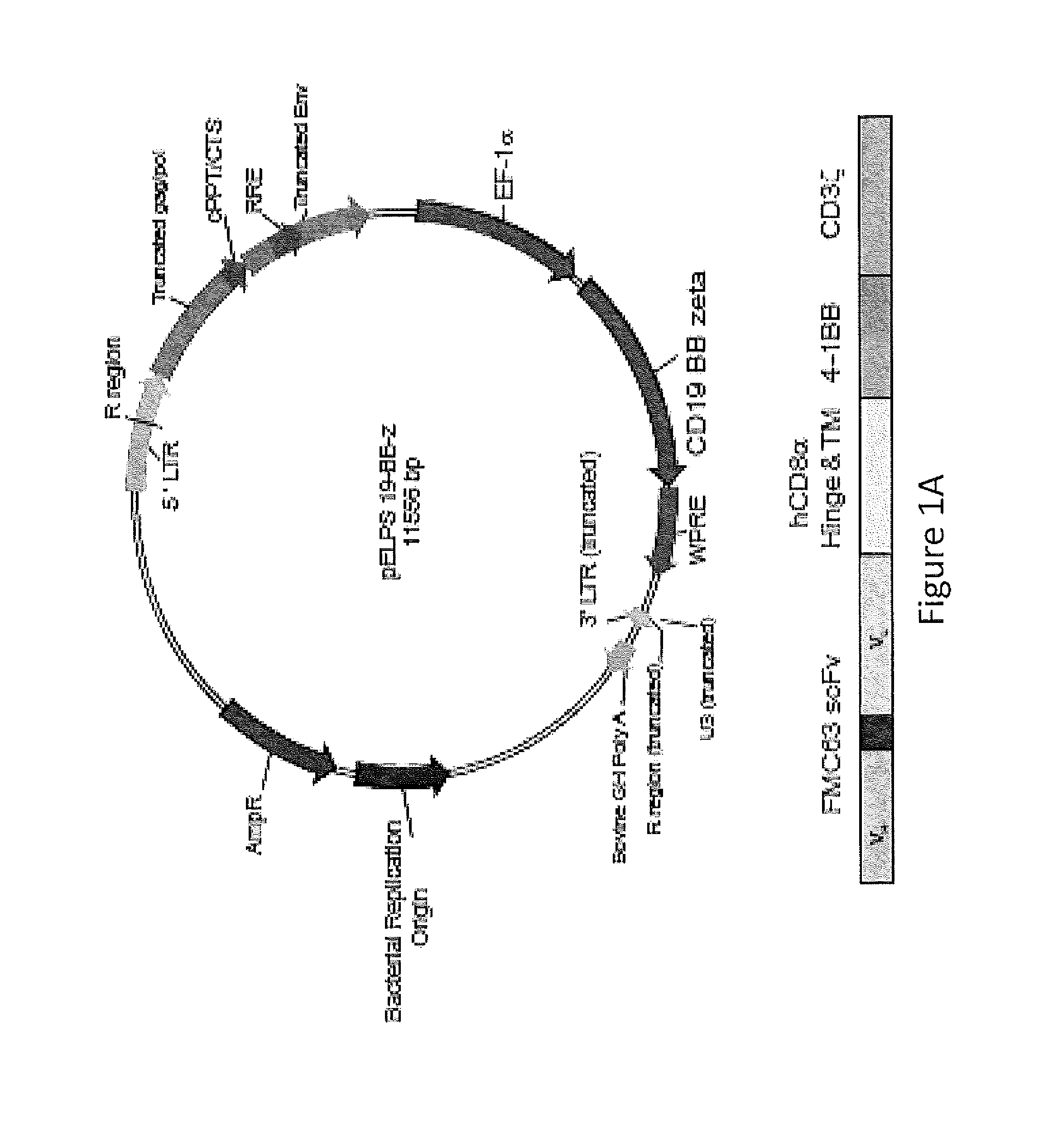
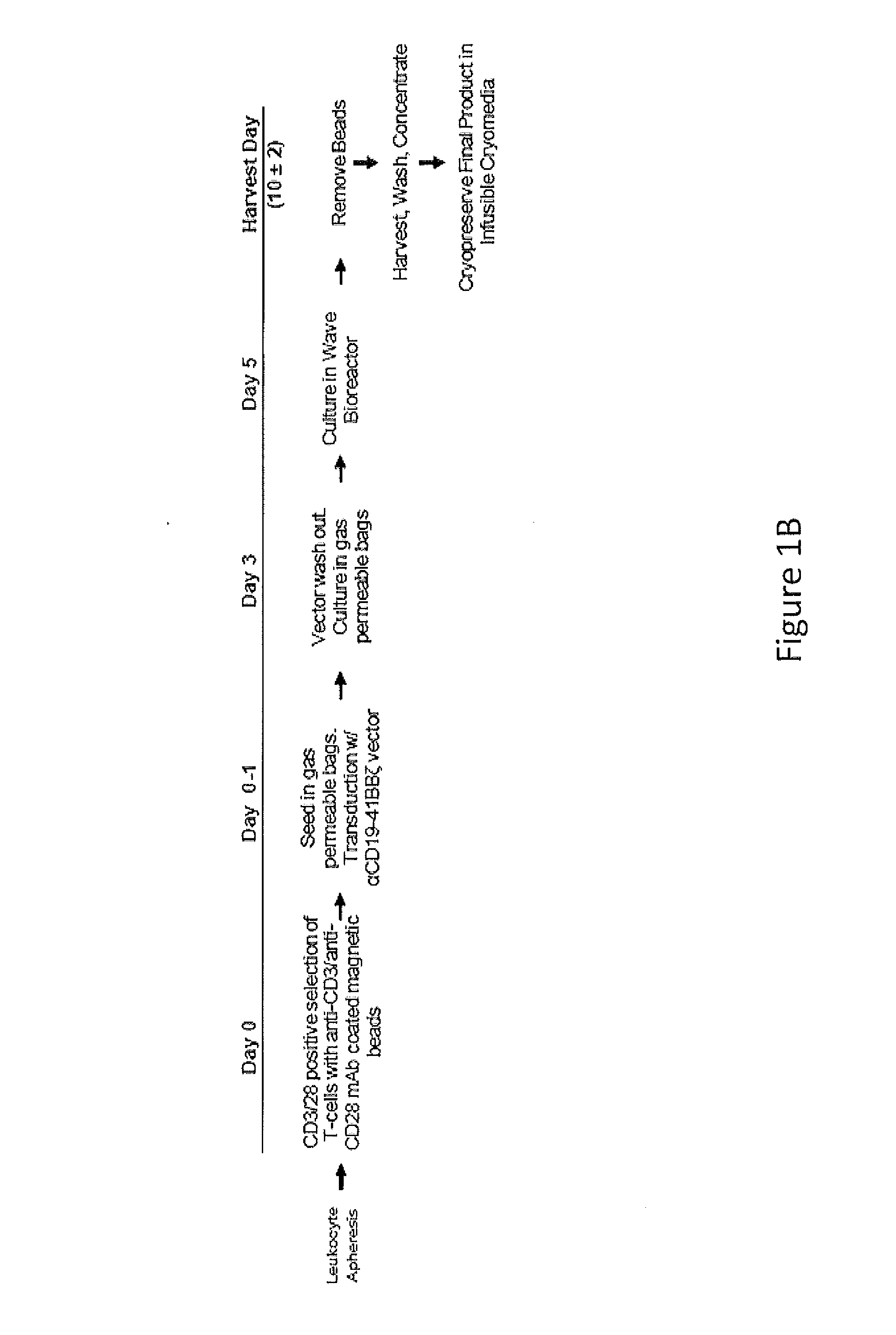
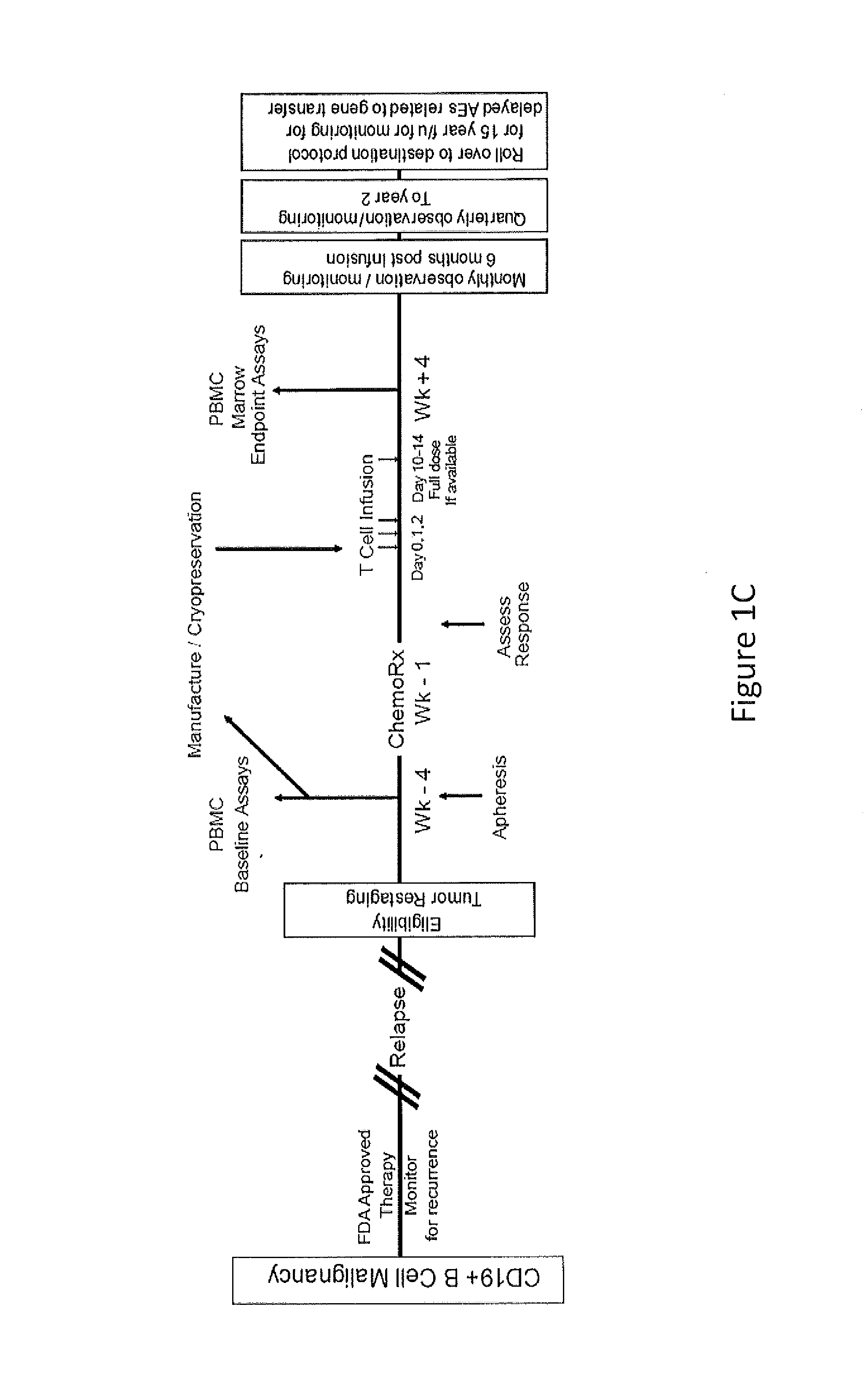
The present invention provides compositions and methods for treating cancer in a human. The invention includes relates to administering a genetically modified T cell to express a CAR wherein the CAR comprises an antigen binding domain, a transmembrane domain, a costimulatory signaling region, and a CD3 zeta signaling domain.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
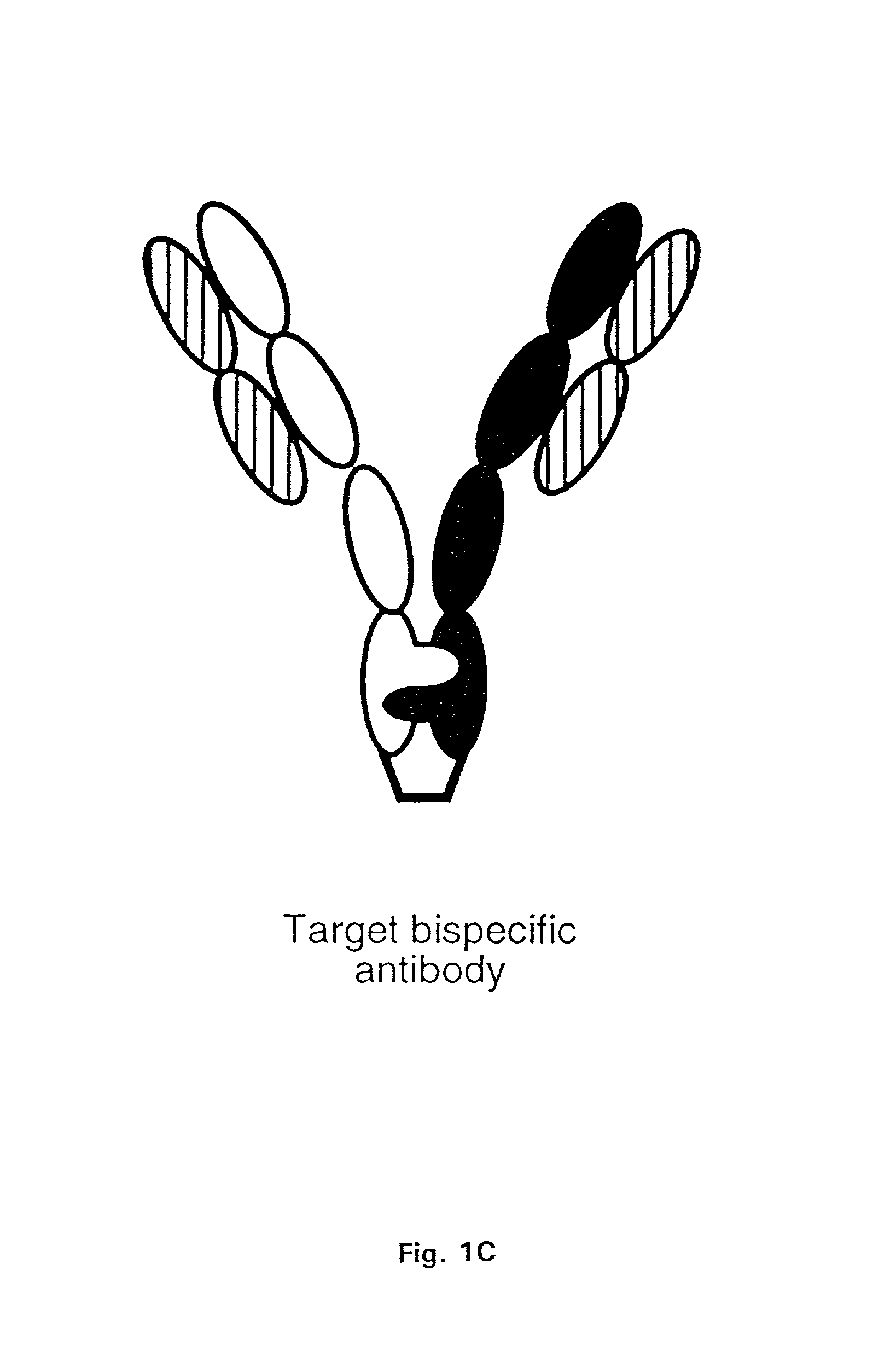
Method for making multispecific antibodies having heteromultimeric and common components
InactiveUS7183076B2Increased formationIncrease productionAnimal cellsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSpecific immunityBispecific antibody
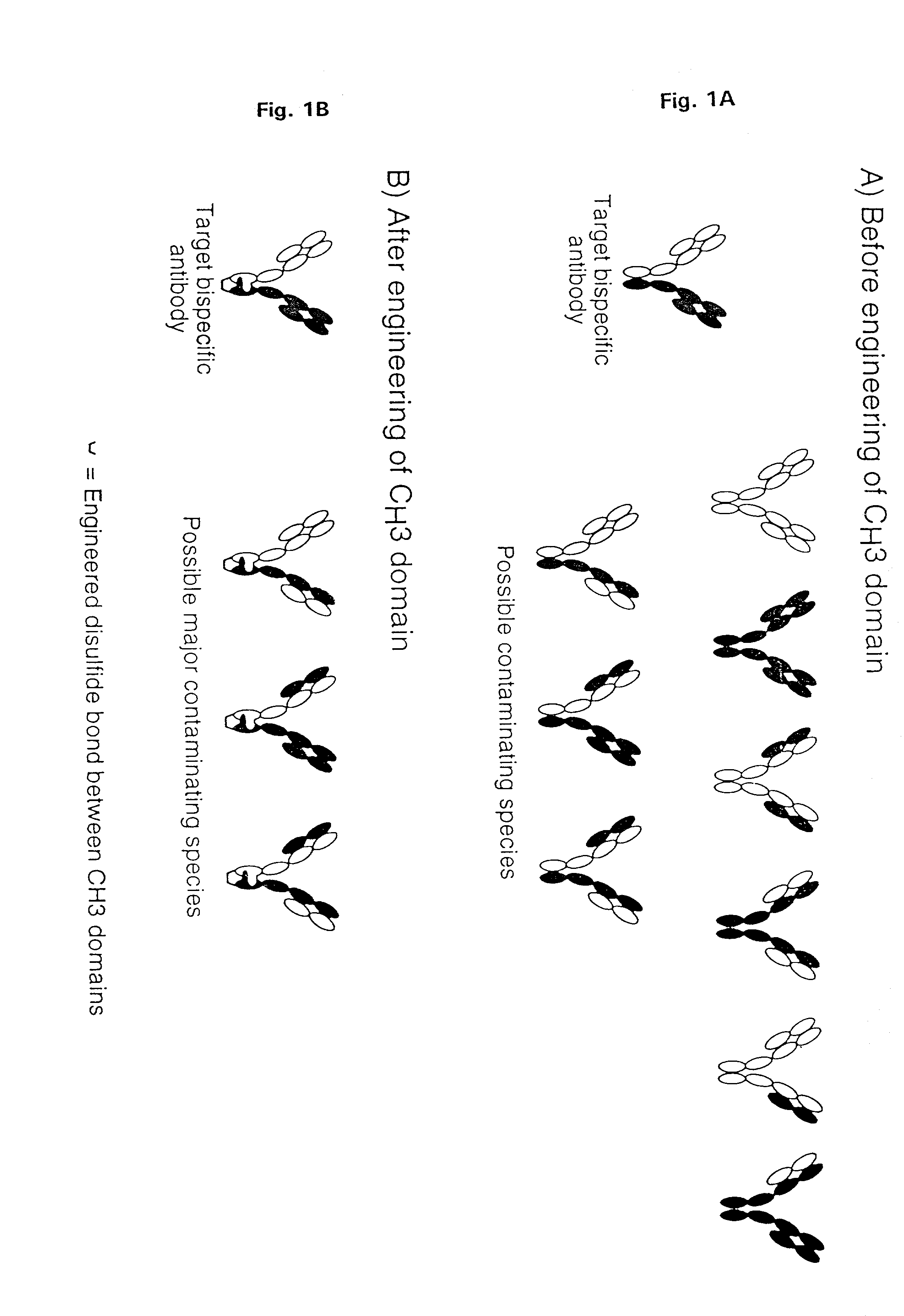
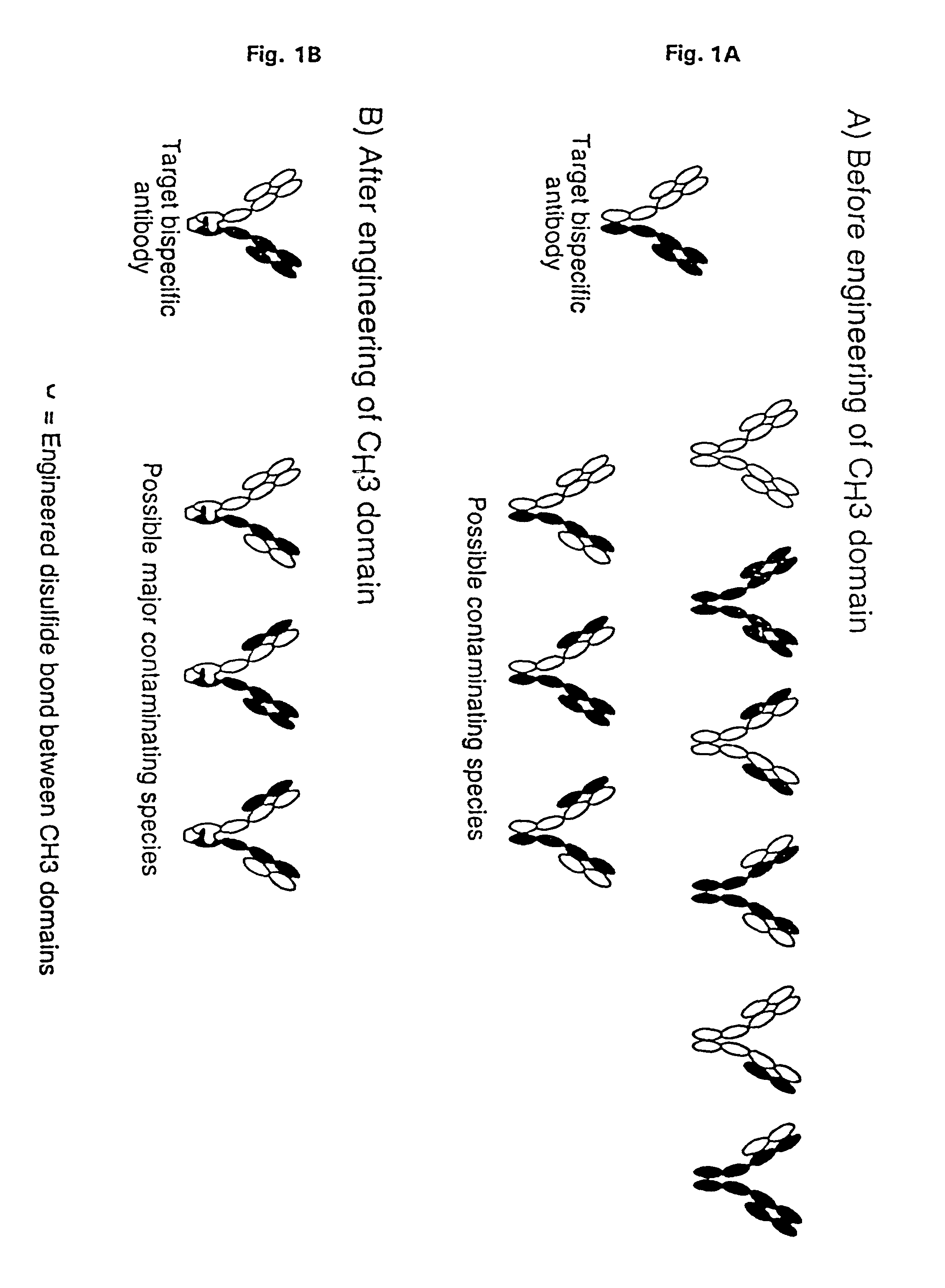
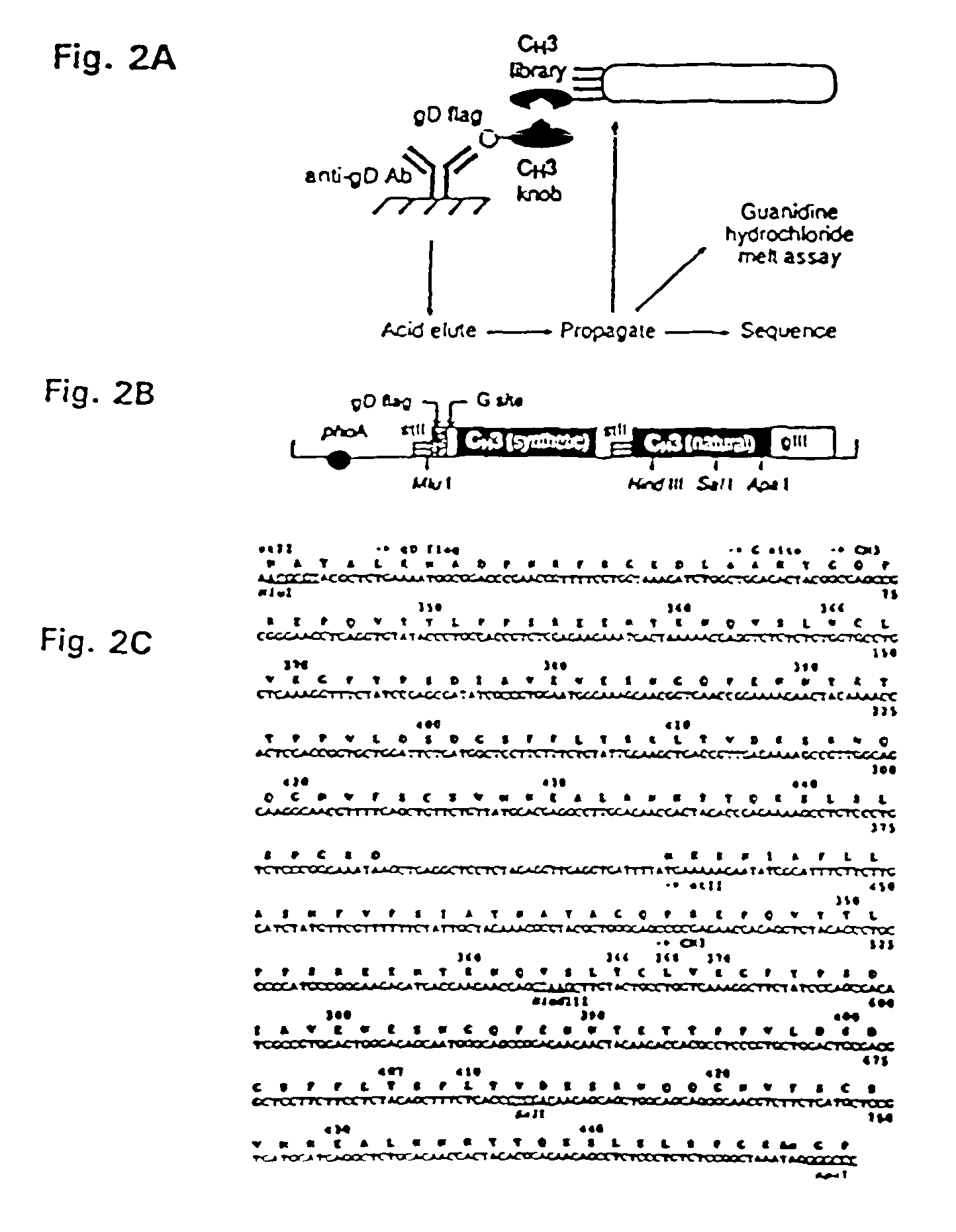
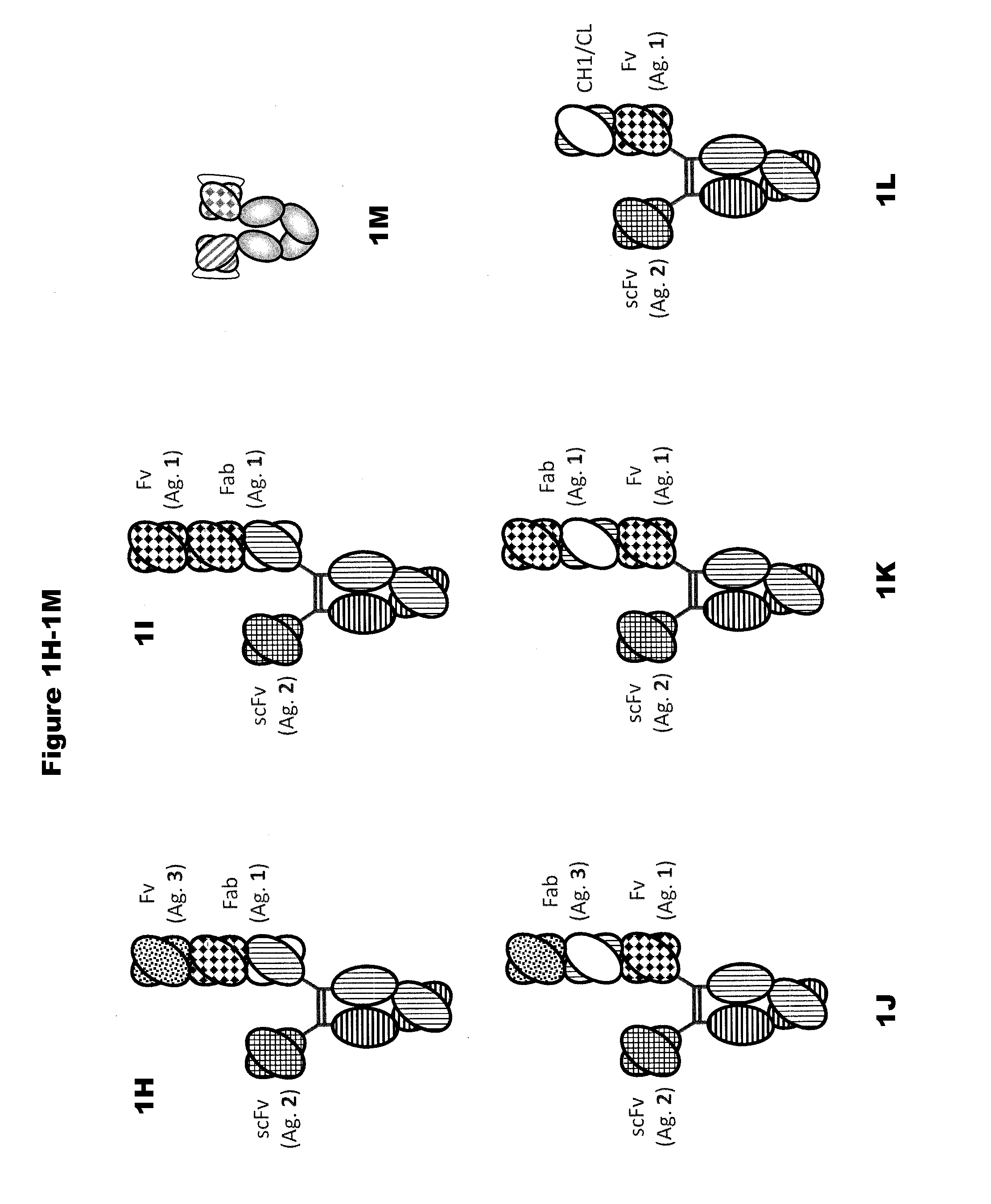
The invention relates to a method of preparing heteromultimeric polypeptides such as bispecific antibodies, bispecific immunoadhesins and antibody-immunoadhesin chimeras. The invention also relates to the heteromultimers prepared using the method. Generally, the method provides a multispecific antibody having a common light chain associated with each heteromeric polypeptide having an antibody binding domain. Additionally the method futher involves introducing into the multispecific antibody a specific and complementary interaction at the interface of a first polypeptide and the interface of a second polypeptide, so as to promote heteromultimer formation and hinder homomultimer formation; and / or a free thiol-containing residue at the interface of a first polypeptide and a corresponding free thiol-containing residue in the interface of a second polypeptide, such that a non-naturally occurring disulfide bond is formed between the first and second polypeptide. The method allows for the enhanced formation of the desired heteromultimer relative to undesired heteromultimers and homomultimers.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Anti-cd3 antibodies, bispecific antigen-binding molecules that bind cd3 and cd20, and uses thereof
ActiveUS20140088295A1Useful in treatmentFacilitates directed killing (cell lysis) of the targetedImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsCD20Disease
The present invention provides antibodies that bind to CD3 and methods of using the same. According to certain embodiments, the antibodies of the invention bind human CD3 with high affinity and induce human T cell proliferation. The invention includes antibodies that bind CD3 and induce T cell-mediated killing of tumor cells. According to certain embodiments, the present invention provides bispecific antigen-binding molecules comprising a first antigen-binding domain that specifically binds human CD3, and a second antigen-binding molecule that specifically binds human CD20. In certain embodiments, the bispecific antigen-binding molecules of the present invention are capable of inhibiting the growth of B-cell tumors expressing CD20. The antibodies and bispecific antigen-binding molecules of the invention are useful for the treatment of diseases and disorders in which an upregulated or induced targeted immune response is desired and / or therapeutically beneficial. For example, the antibodies of the invention are useful for the treatment of various cancers as well as other CD20-related diseases and disorders.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Binding domain-immunoglobulin fusion proteins
InactiveUS20050175614A1Reduced ability to dimerizeHybrid immunoglobulinsAntipyreticCrystallographyAntigen
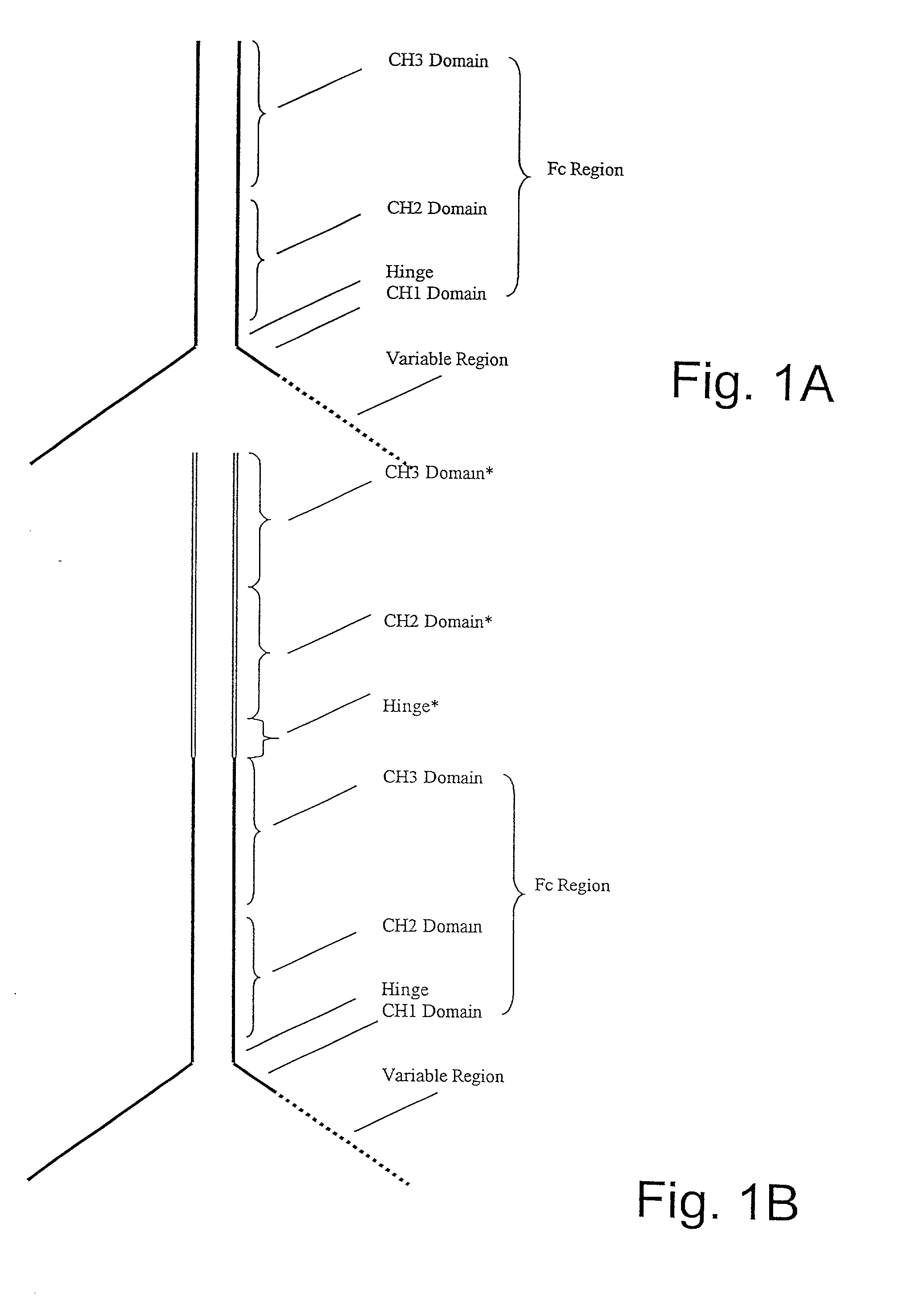
The invention relates to novel binding domain-immunoglobulin fusion proteins that feature a binding domain for a cognate structure such as an antigen, a counterreceptor or the like, a hinge region polypeptide having either zero or one cysteine residue, and immunoglobulin CH2 and CH3 domains, and that are capable of ADCC and / or CDC while occurring predominantly as monomeric polypeptides. The fusion proteins can be recombinantly produced at high expression levels. Also provided are related compositions and methods, including immunotherapeutic applications.
Owner:TRUBION PHARM INC
Non-immunostimulatory antibody and compositions containing the same
ActiveUS20070148167A1Immunoglobulins against animals/humansEnzymologyTherapeutic antibodyFc-Gamma Receptor
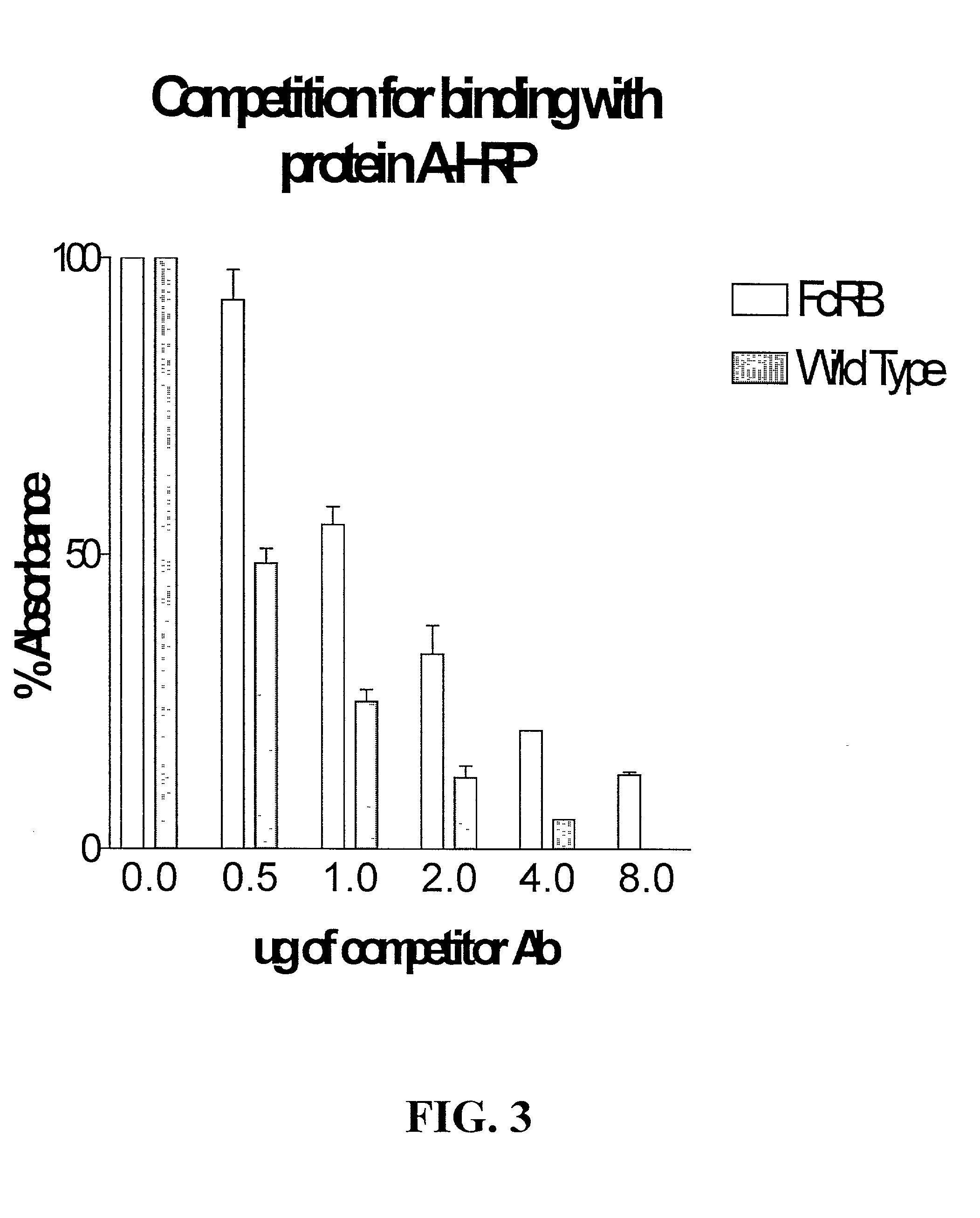
The present invention relates to a non-immunostimulatory antibody which lacks antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity, Fc gamma receptor binding and complement-mediated cytotoxicity. In some embodiments, the antibody contains a modified immunoglobulin G2 (IgG2) Fc region with at least one substitution in the B / C loop, FcRn binding domain, and the F / G loop. The antibody of the invention is useful in the preparation of therapeutic antibodies and pharmaceutical compositions and kits containing the same.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Generation of modified molecules with increased serum half-lives
InactiveUS20020142374A1Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsSerum igeHalf-life
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided methods for the extension of serum half-lives of proteinaceous molecules, particularly antibody molecules, and compositions of molecules modified in accordance with the methods of the invention. In accordance with a first aspect of the present invention, there is provided a method of modifying the half-life of an antibody through providing an antibody containing an FcRn binding domain or the genes encoding such antibody and physically linking the antibody or the antibody as encoded to a second FcRn binding domain. In accordance with a second aspect of the present invention, there is provided a molecule that contains at least two distinct FcRn binding moieties.
Owner:ABQENIX INC
TREATMENT OF CANCER USING HUMANIZED ANTI-EGFRvIII CHIMERIC ANTIGEN RECEPTOR
The invention provides compositions and methods for treating diseases associated with expression of EGFRvIII. The invention also relates to chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) specific to EGFRvIII, vectors encoding the same, and recombinant T cells comprising the anti-EGFRvIII CAR. The invention also includes methods of administering a genetically modified T cell expressing a CAR that comprises an anti-EGFRvIII binding domain.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA +2
Method for making multispecific antibodies having heteromultimeric and common components
InactiveUS7951917B1Increased formationIncrease productionHybrid immunoglobulinsAntibody ingredientsSpecific immunityBispecific antibody
The invention relates to a method of preparing heteromultimeric polypeptides such as bispecific antibodies, bispecific immunoadhesins and antibody-immunoadhesin chimeras. The invention also relates to the heteromultimers prepared using the method. Generally, the method provides a multispecific antibody having a common light chain associated with each heteromeric polypeptide having an antibody binding domain. Additionally the method further involves introducing into the multispecific antibody a specific and complementary interaction at the interface of a first polypeptide and the interface of a second polypeptide, so as to promote heteromultimer formation and hinder homomultimer formation; and / or a free thiol-containing residue at the interface of a first polypeptide and a corresponding free thiol-containing residue in the interface of a second polypeptide, such that a non-naturally occurring disulfide bond is formed between the first and second polypeptide. The method allows for the enhanced formation of the desired heteromultimer relative to undesired heteromultimers and homomultimers.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
System and method for detecting bioanalytes and method for producing a bioanalyte sensor
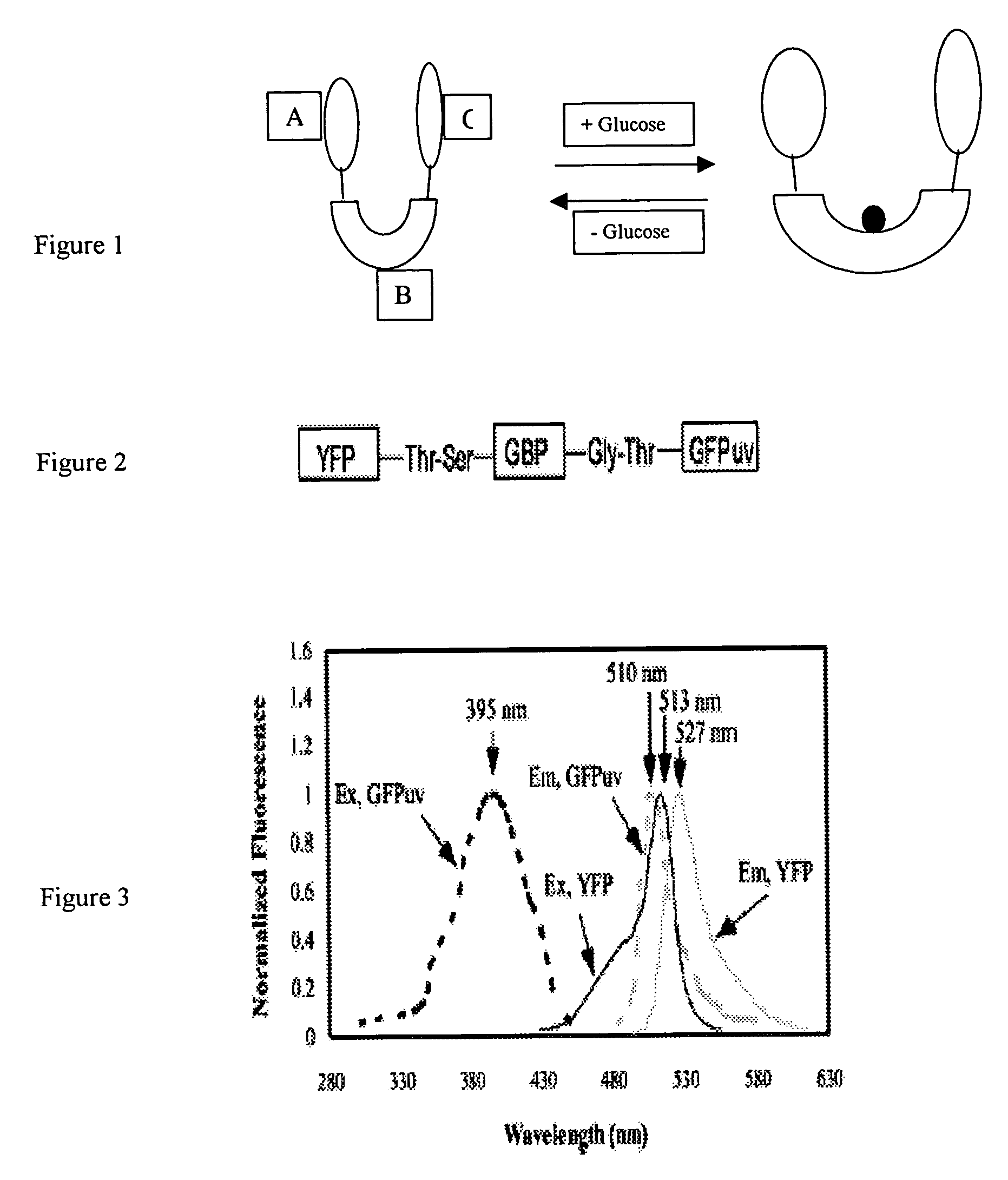
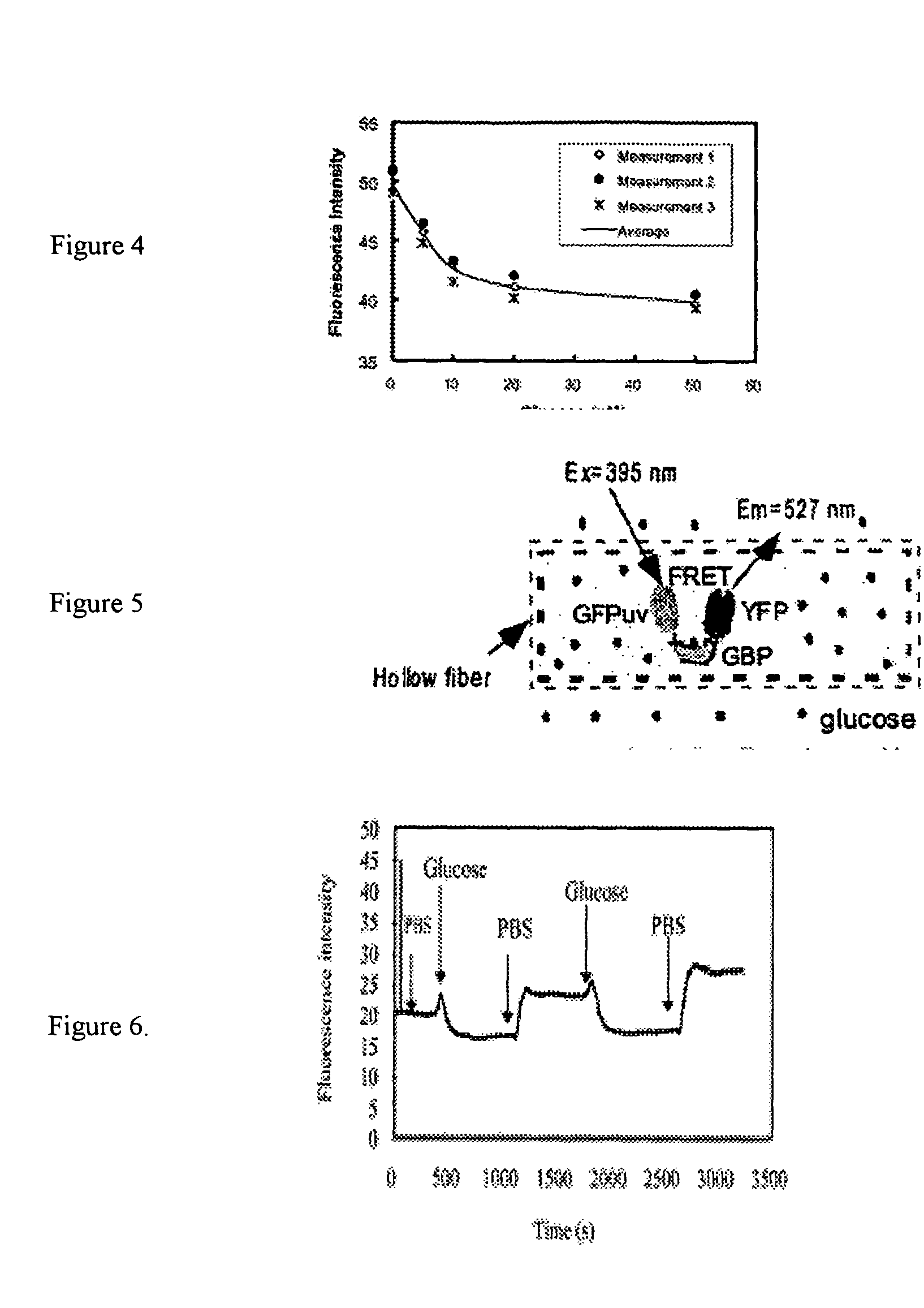
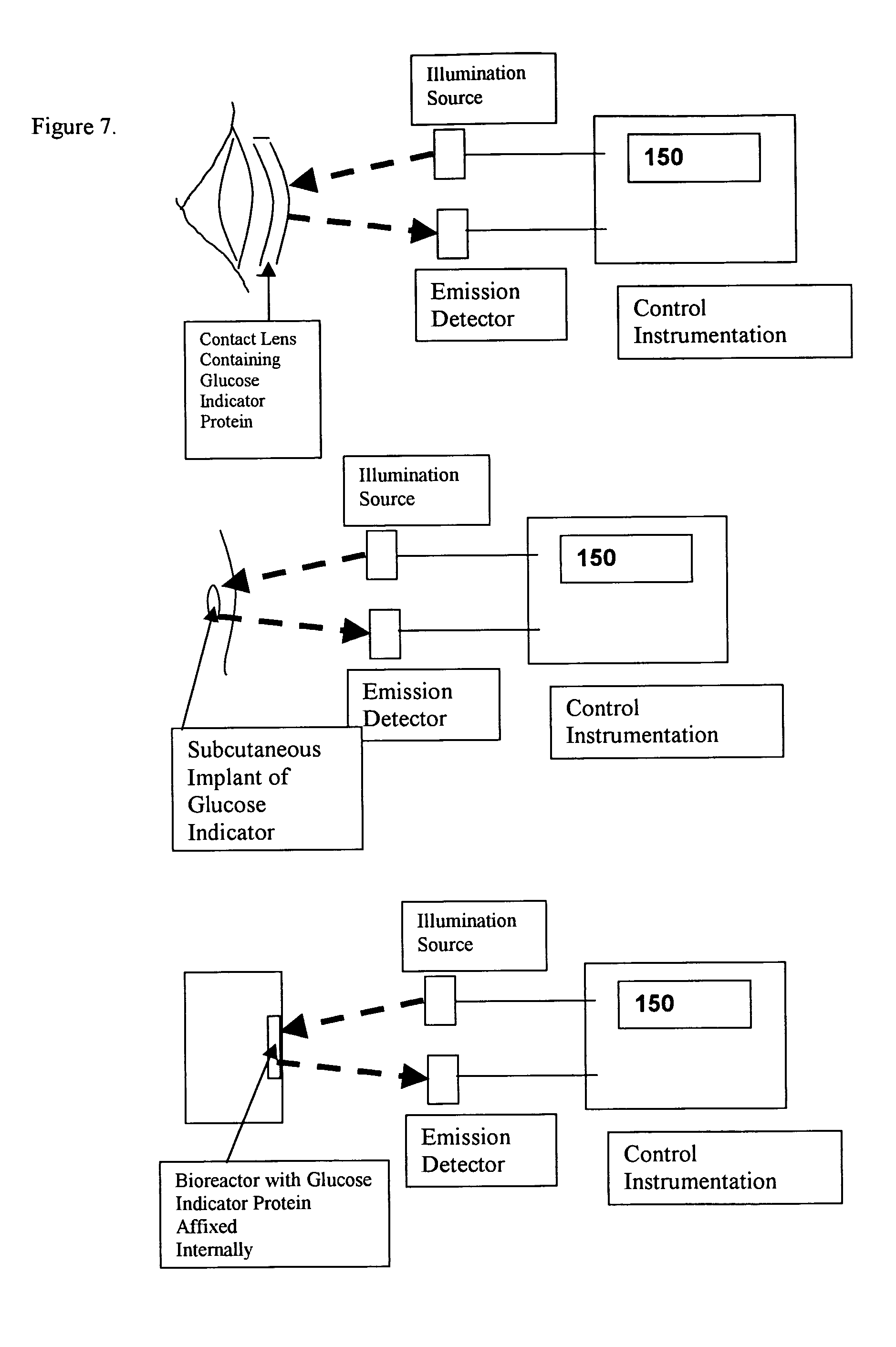
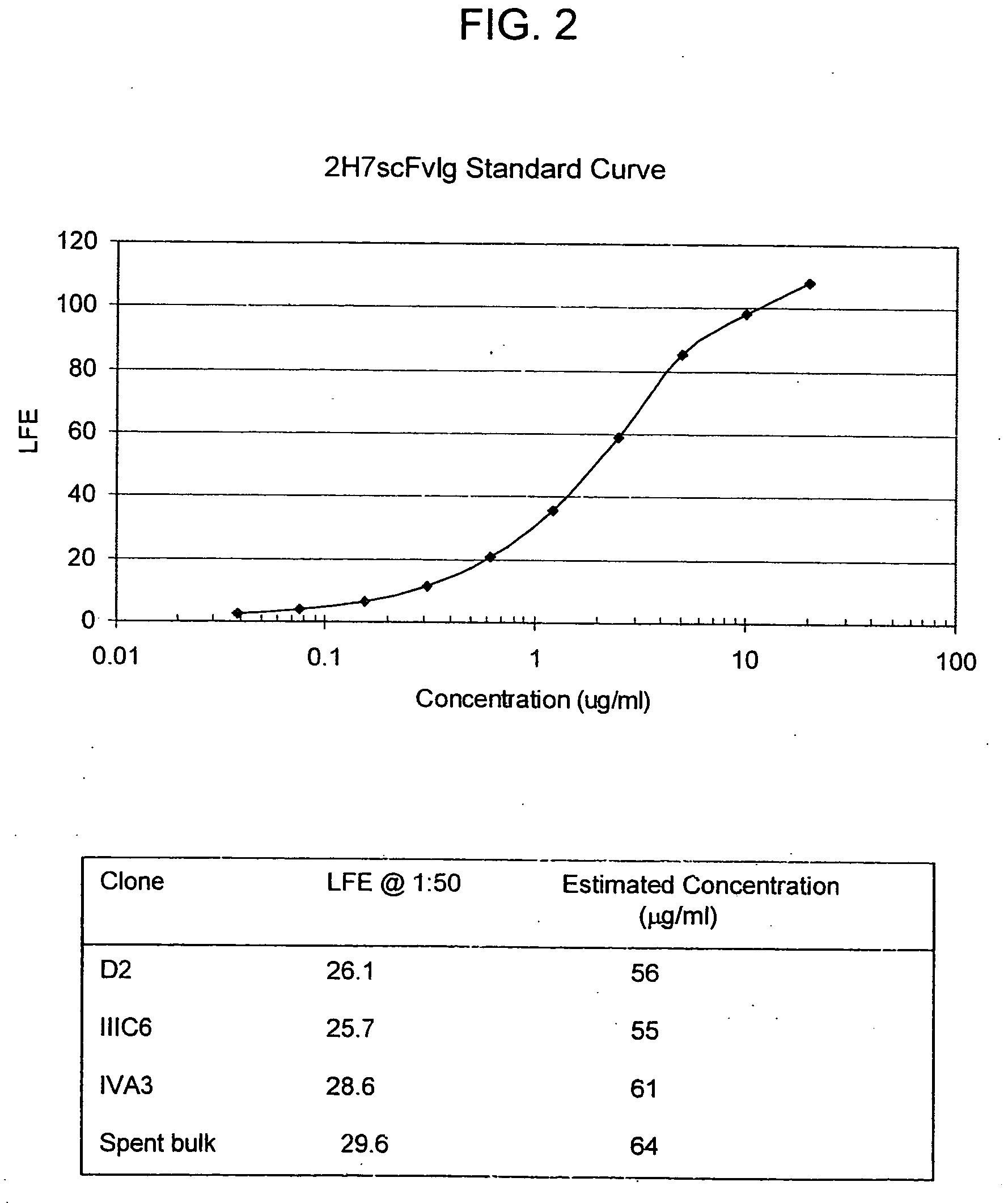
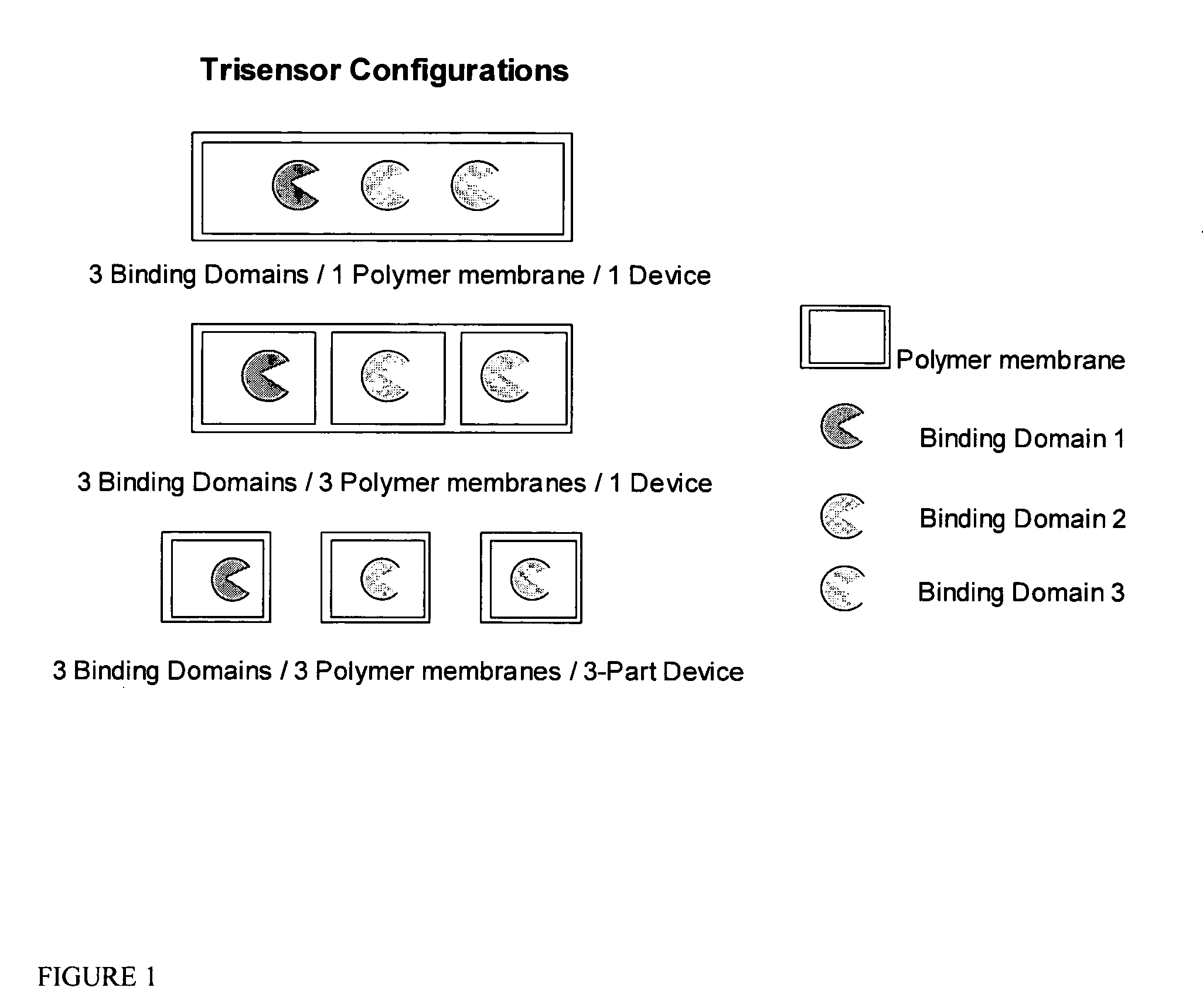
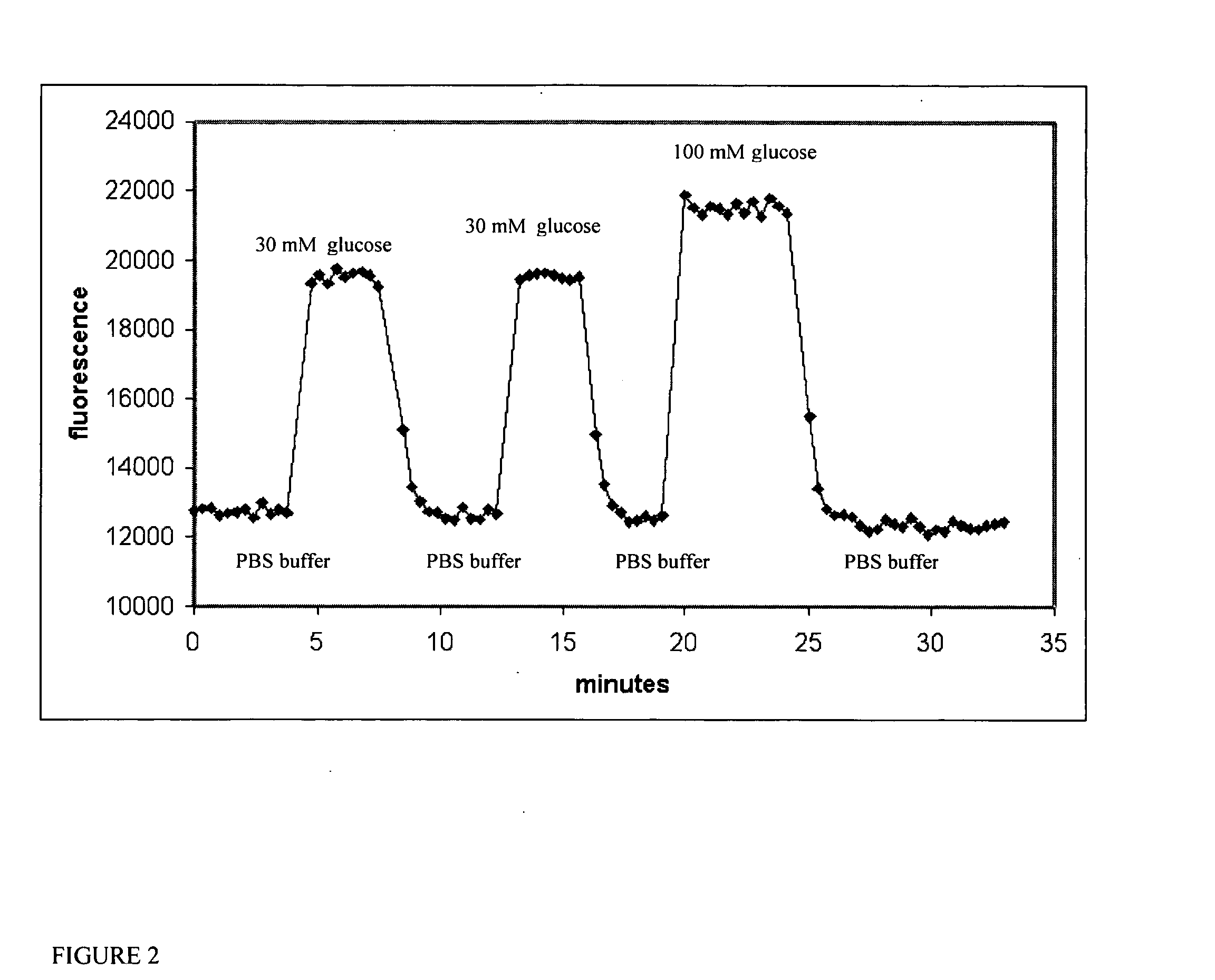
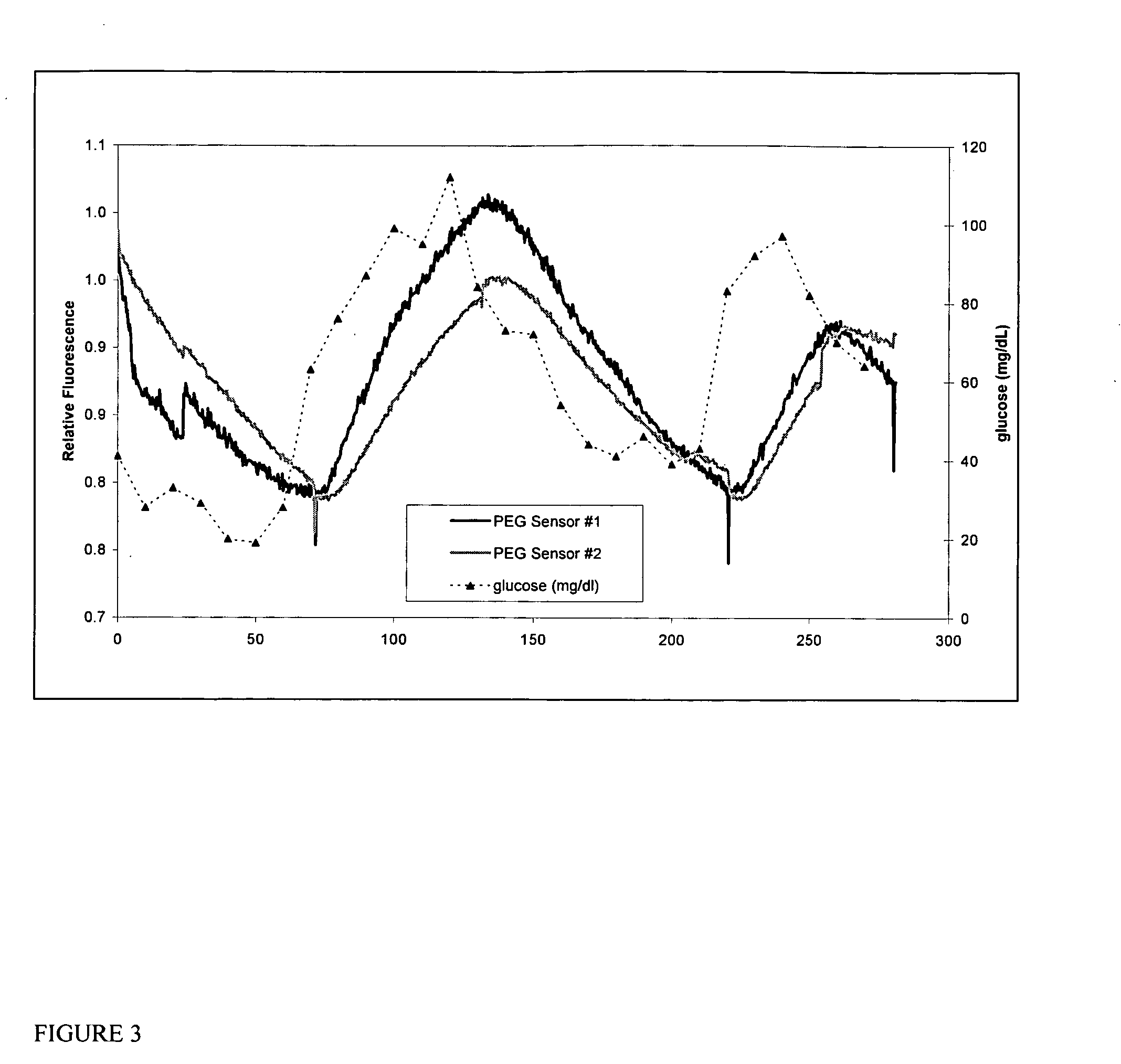
The present invention discloses an indicator protein, and a method for making such a fusion protien, having a first binding moiety having a binding domain specific for a class of analytes that undergoes a reproducible allosteric change in conformation when said analytes are reversibly bound; a second moiety and third moiety that are covalently linked to either side of the first binding moiety such that the second and third moieties undergo a change in relative position when an analyte of interest molecule binds to the binding moiety; and the second and third moieties undergo a change in optical properties when their relative positions change and that change can be monitored remotely by optical means. The present invention also discloses a system and method for detecting glucose that uses such a fusion protein in a variety of formats including a subcutaneously and in a bioreactor.
Owner:SCHULTZ JEROME +1
Binding domain-immunoglobulin fusion proteins
The invention relates to novel binding domain-immunoglobulin fusion proteins that feature a binding domain for a cognate structure such as an antigen, a counterreceptor or the like, a hinge region polypeptide having either zero or one cysteine residue, and immunoglobulin CH2 and CH3 domains, and that are capable of ADCC and / or CDC while occurring predominantly as monomeric polypeptides. The fusion proteins can be recombinantly produced at high expression levels. Also provided are related compositions and methods, including immunotherapeutic applications.
Owner:TRUBION PHARM INC
DNA constructs encoding ligand-binding fusion proteins
Methods for producing secreted receptor analogs and biologically active peptide dimers are disclosed. The methods for producing secreted receptor analogs and biologically active peptide dimers utilize a DNA sequence encoding a receptor analog or a peptide requiring dimerization for biological activity joined to a dimerizing protein. The receptor analog includes a ligand-binding domain. Polypeptides comprising essentially the extracellular domain of a human PDGF receptor fused to dimerizing proteins, the portion being capable of binding human PDGF or an isoform thereof, are also disclosed. The polypeptides may be used within methods for determining the presence of and for purifying human PDGF or isoforms thereof.
Owner:ZYMOGENETICS INC
Parallel polymorphism scoring by amplification and error correction
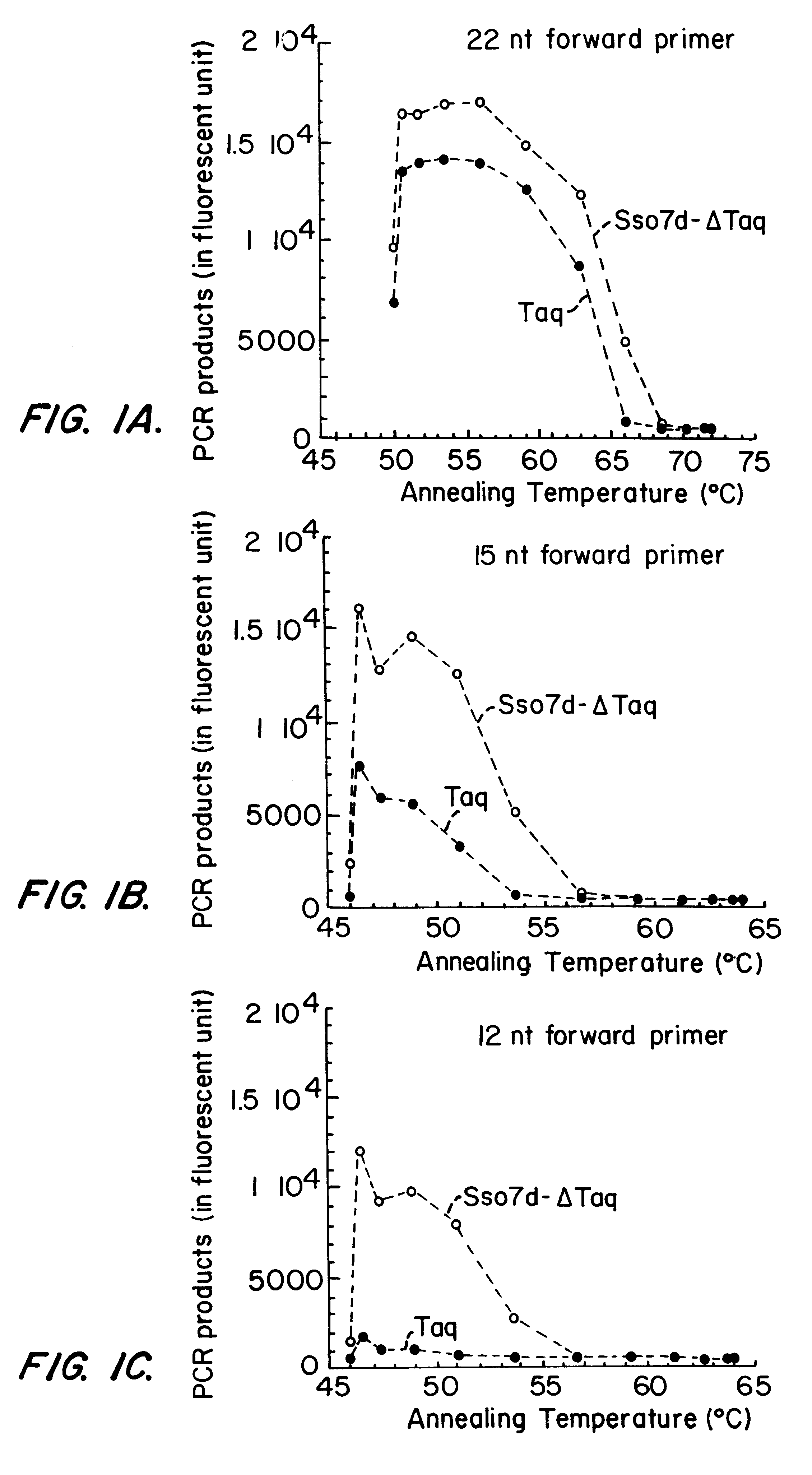
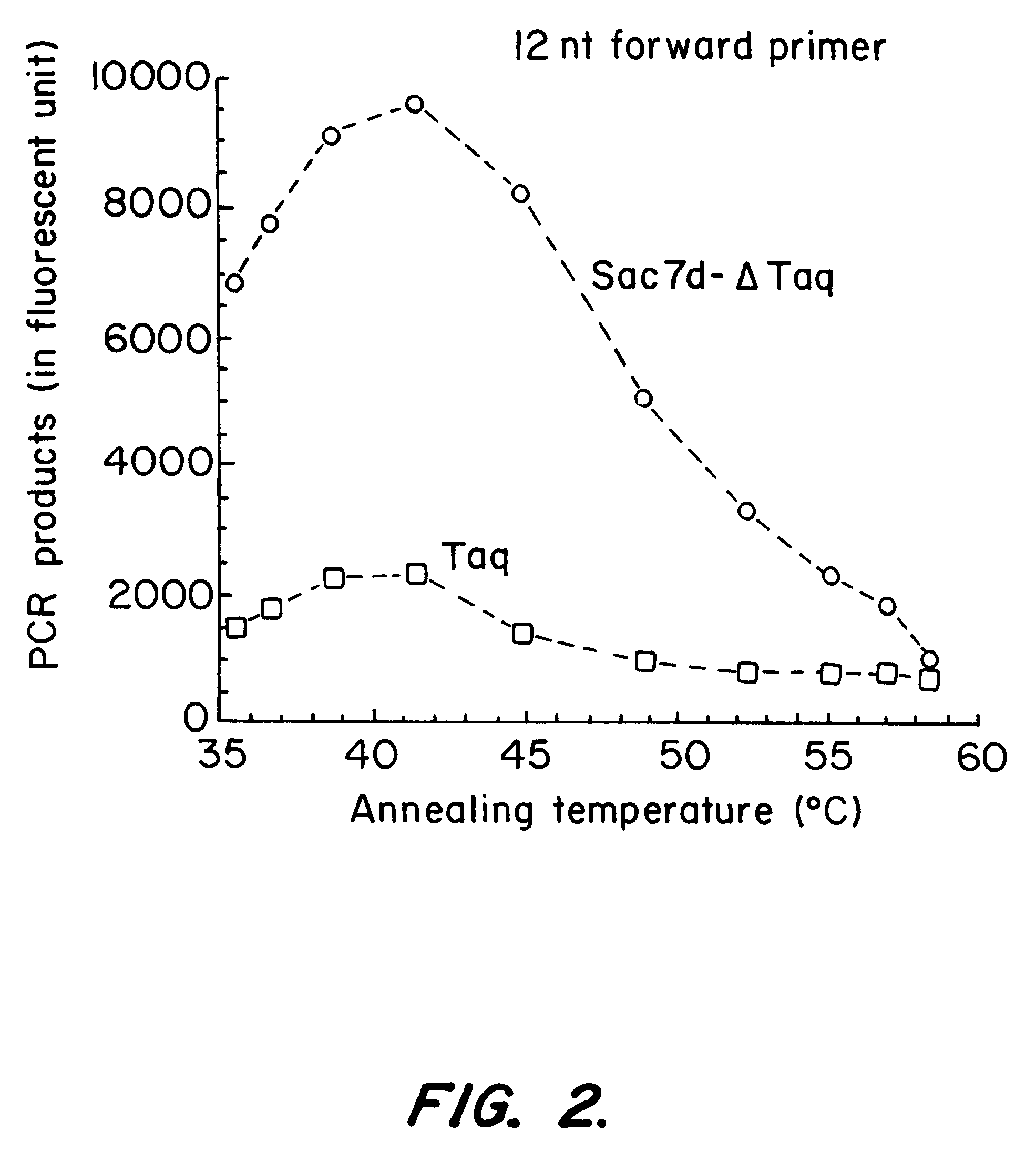
InactiveUS20070009954A1Easy to processFusion with DNA-binding domainSugar derivativesPolymerase LBinding domain
This invention provides a method of detecting polymorphisms, e.g., single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), by amplification and error correction. The invention encompasses methods of performing amplification and error correction using an improved generation of nucleic acid polymerases, and methods of multiplexing the assay. The improvement to the polymerases is the joining of a sequence-non-specific nucleic-acid-binding domain to the enzyme in a manner that enhances the ability of the enzyme to bind and catalytically modify the nucleic acid.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Heterodimeric proteins
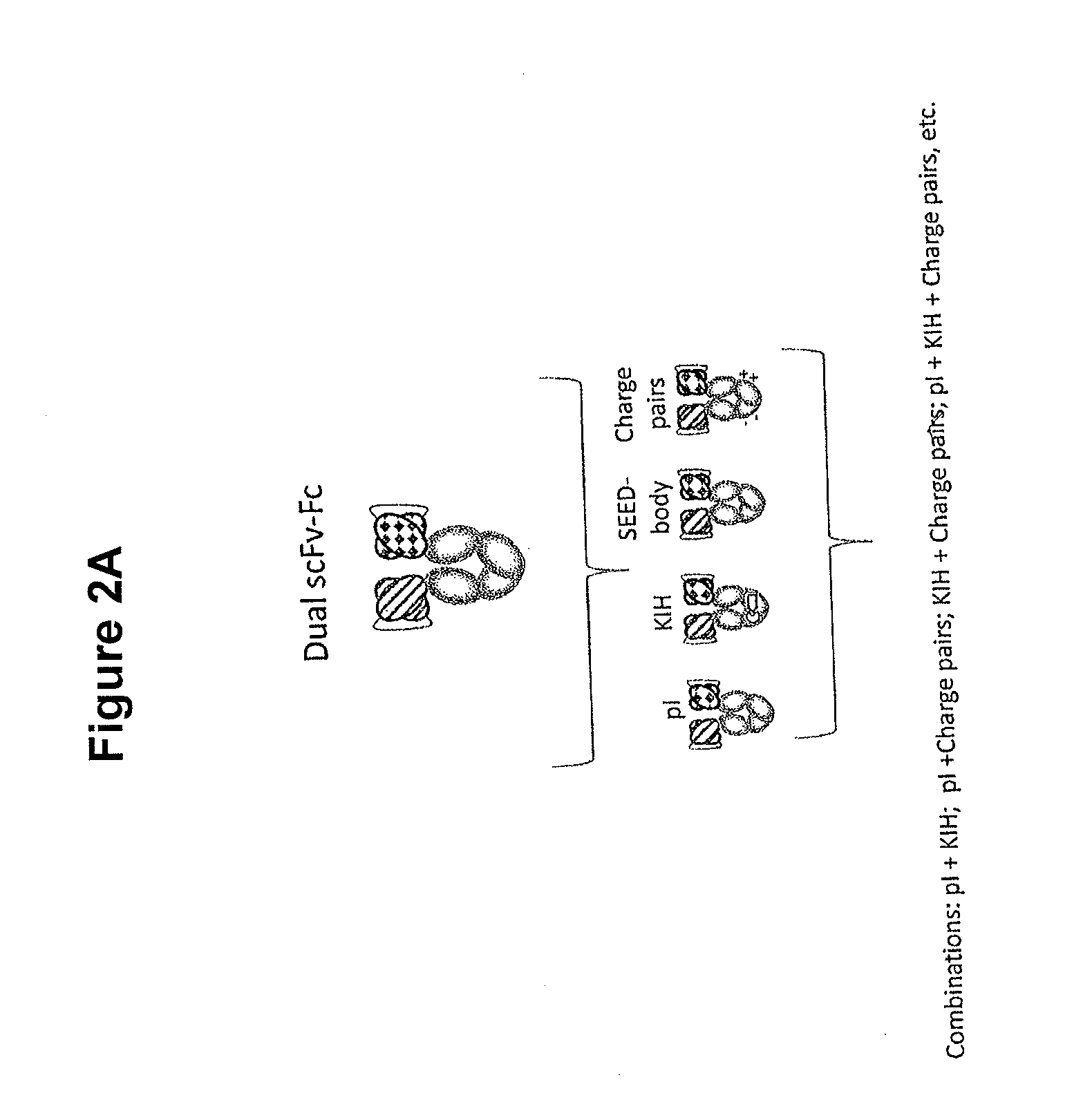
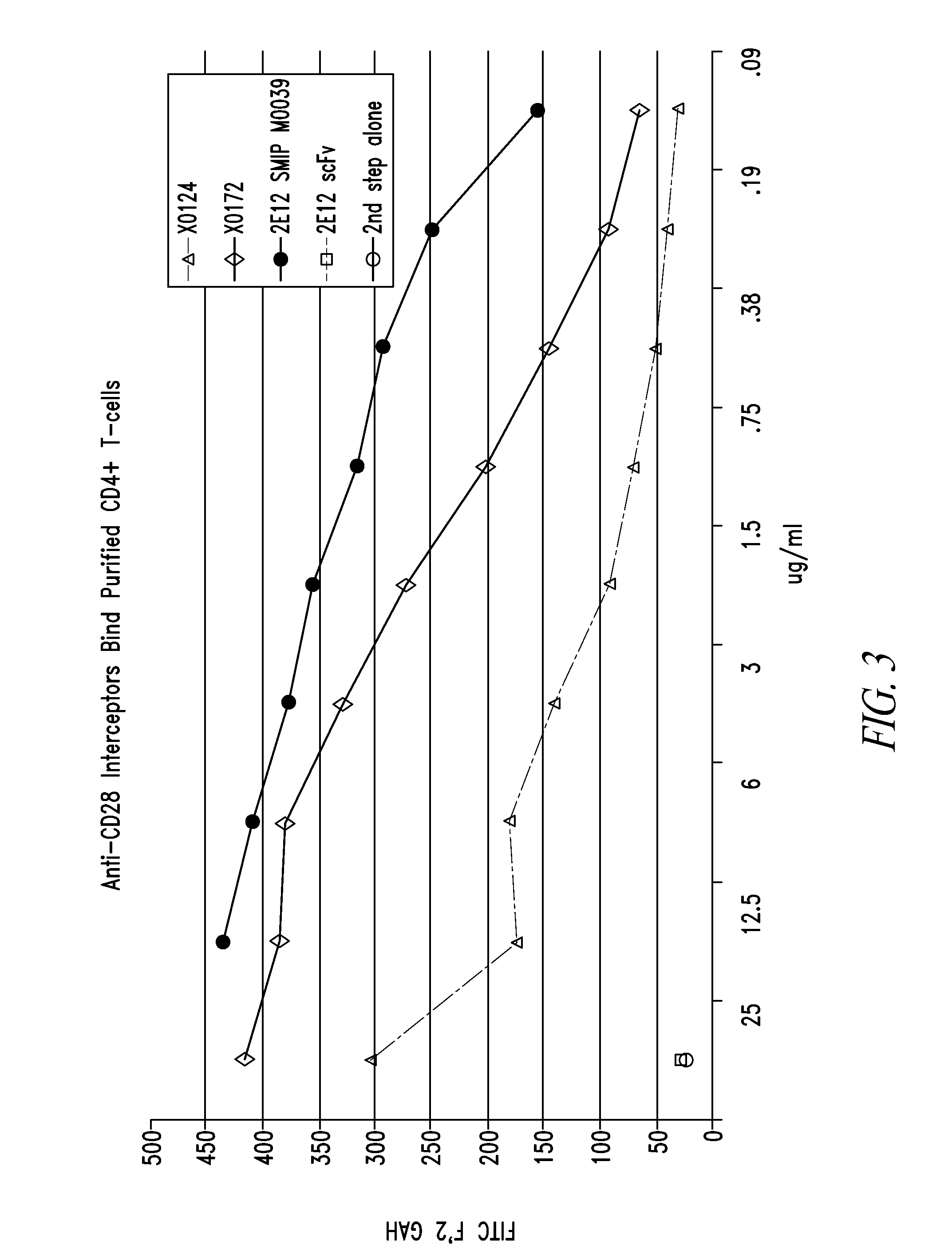
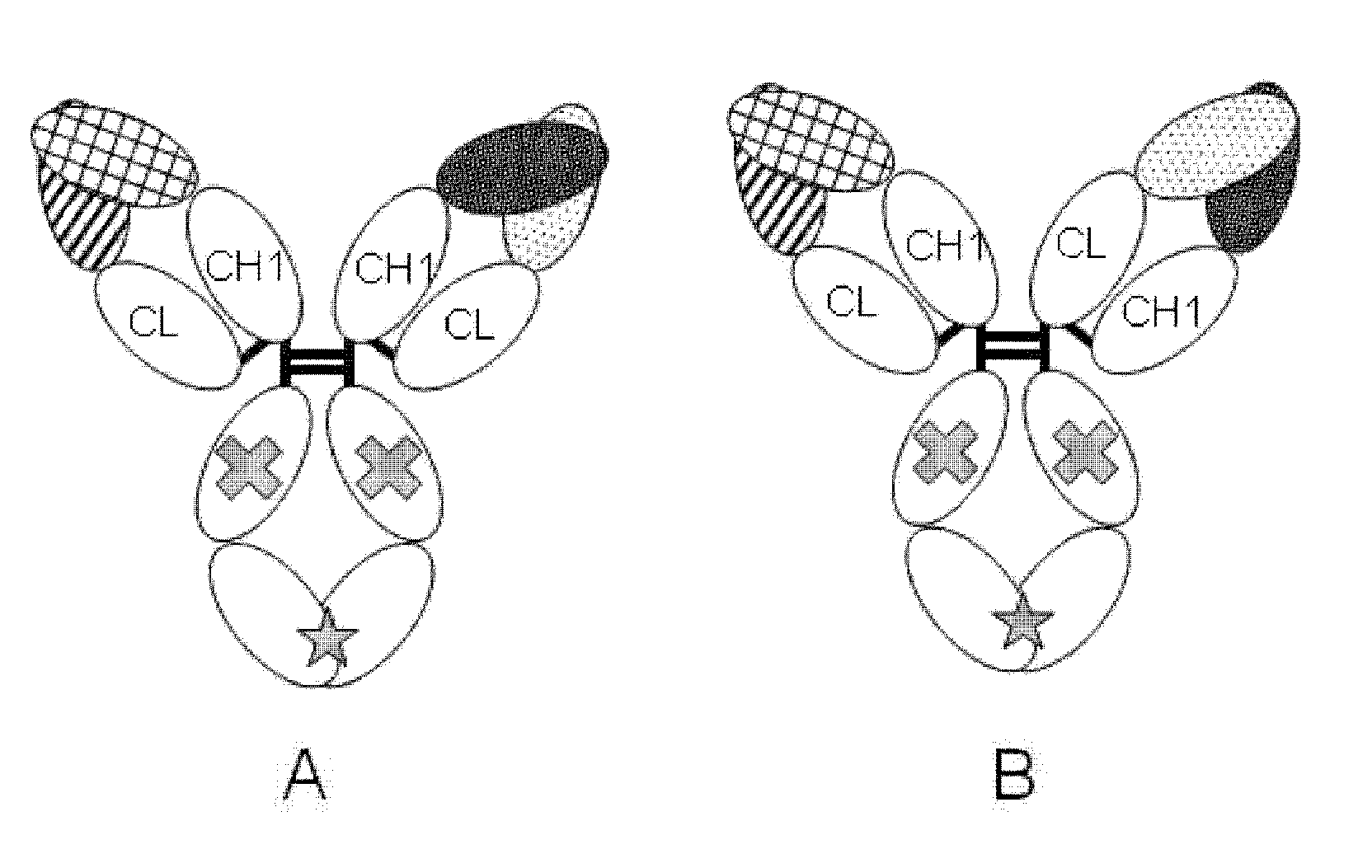
In one aspect, the present invention provides heterodimeric antibodies comprising a first monomer comprising a first heavy chain constant domain comprising a first variant Fc domain and a first antigen binding domain and a second monomer comprising a second heavy chain constant domain comprising a second variant Fc domain and a second antigen binding domain. In an additional aspect the heterodimeric antibody comprises a first monomer comprising a heavy chain comprising a first Fc domain and a single chain Fv region (scFv) that binds a first antigen, wherein the scFv comprises a charged scFv linker. The heterodimeric antibody further comprises a second monomer comprising a first heavy chain comprising a second Fc domain and a first variable heavy chain and a first light chain.
Owner:XENCOR INC
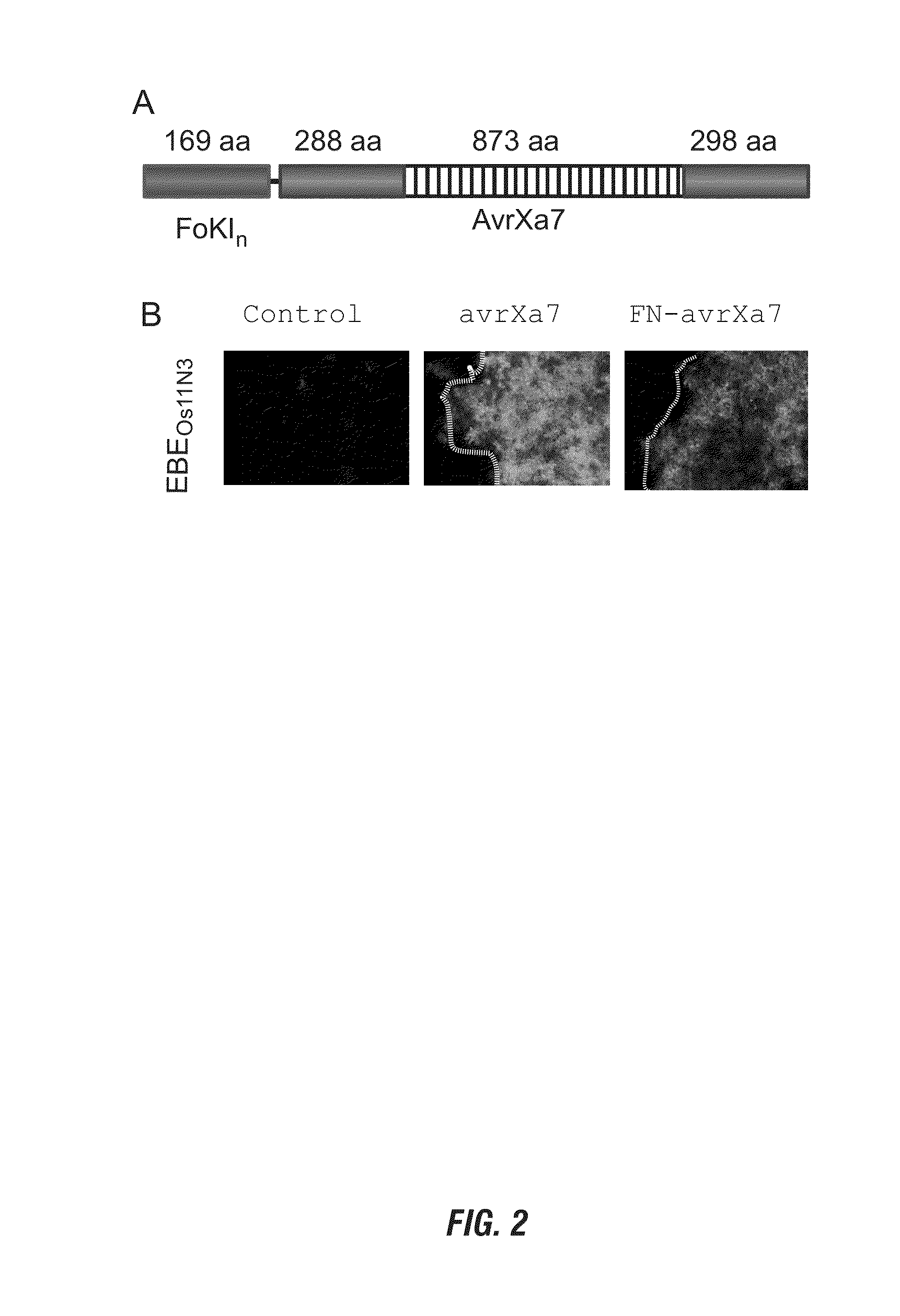
Nuclease activity of tal effector and foki fusion protein
The present invention provides compositions and methods for targeted cleavage of cellular chromatin in a region of interest and / or homologous recombination at a predetermined site in cells. Compositions include fusion polypeptides comprising a TAL effector binding domain and a cleavage domain. The cleavage domain can be from any endonuclease. In certain embodiments, the endonuclease is a Type IIS restriction endonuclease. In further embodiments, the Type IIS restriction endonuclease is FokI.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Nucleic acid modifying enzymes
This invention provides for an improved generation of novel nucleic acid modifying enzymes. The improvement is the fusion of a sequence-non-specific nucleic-acid-binding domain to the enzyme in a manner that enhances the ability of the enzyme to bind and catalytically modify the nucleic acid.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Fully human antibody Fab fragments with human interferon-gamma neutralizing activity
InactiveUS7084257B2Peptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsDNA-binding domainAntigen binding
Selective binding agents of interferon-gamma (IFNγ) are provided by the invention. More particularly, the invention provides for antibodies and antigen binding domains which selectively bind to IFNγ and may be used to prevent or treat conditions relating to autoimmune and inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus and multiple sclerosis. Nucleic acid molecules encoding said antibodies and antigen binding domains, and expression vectors and host cells for the production of same are also provided.
Owner:AMGEN INC
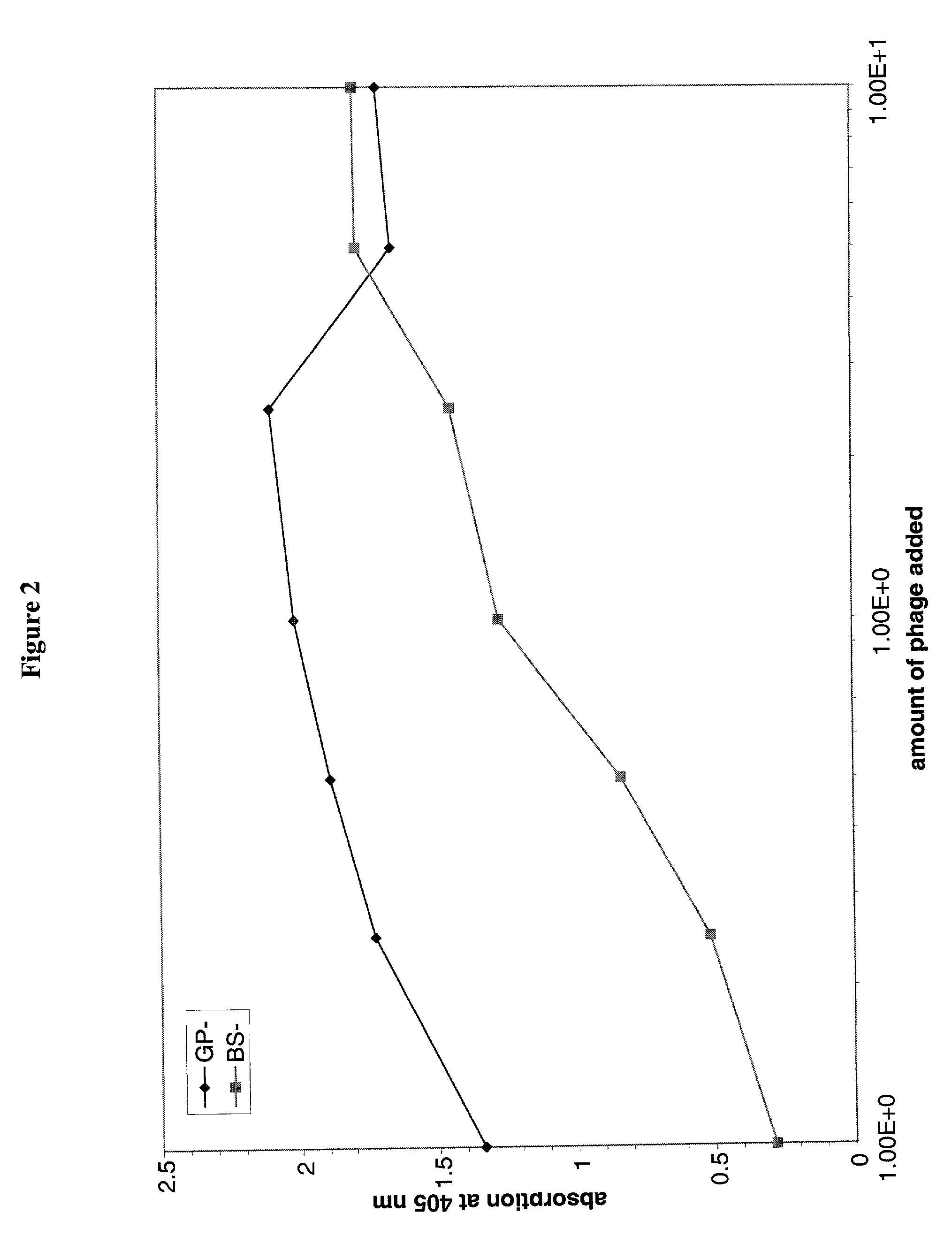
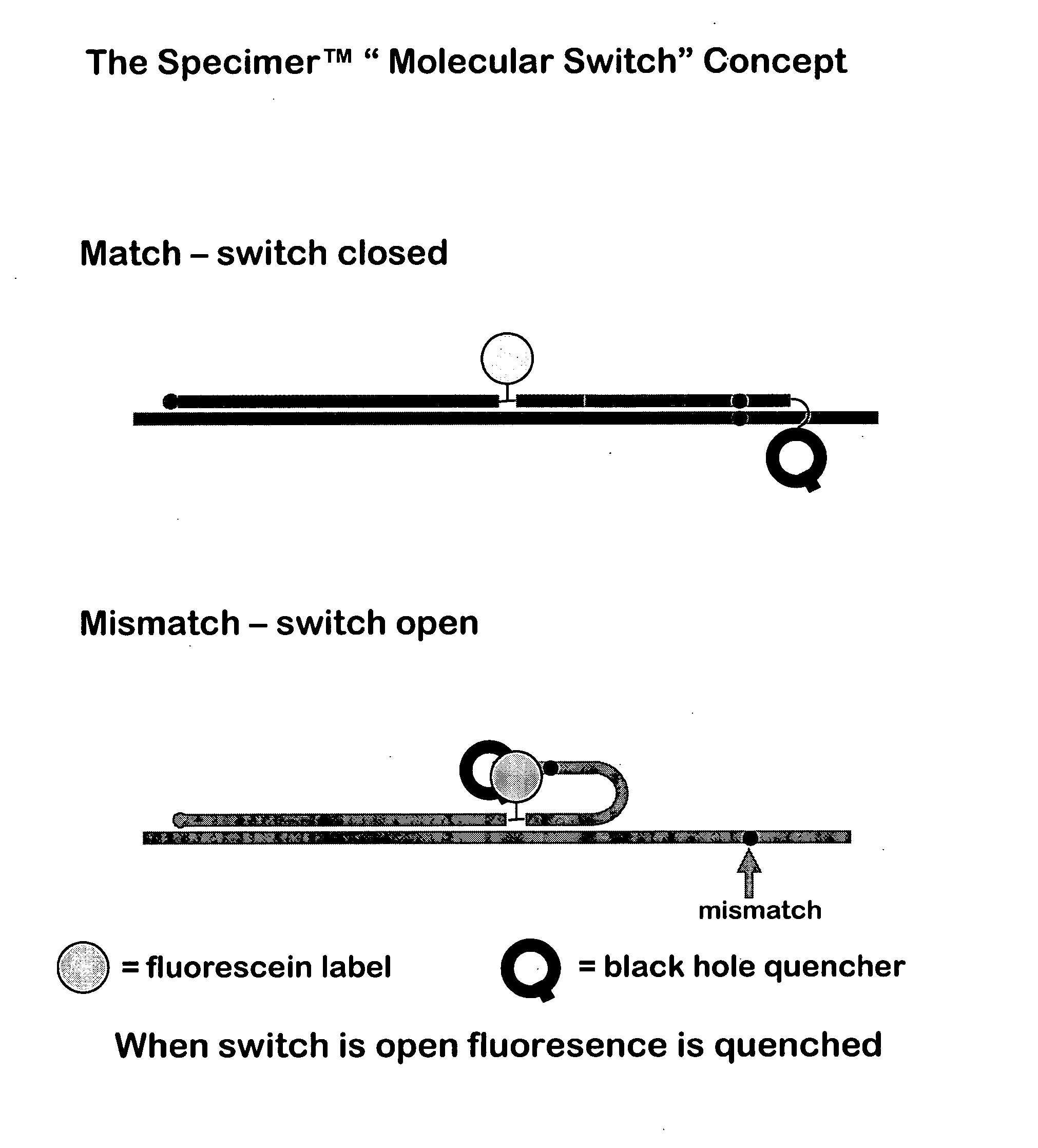
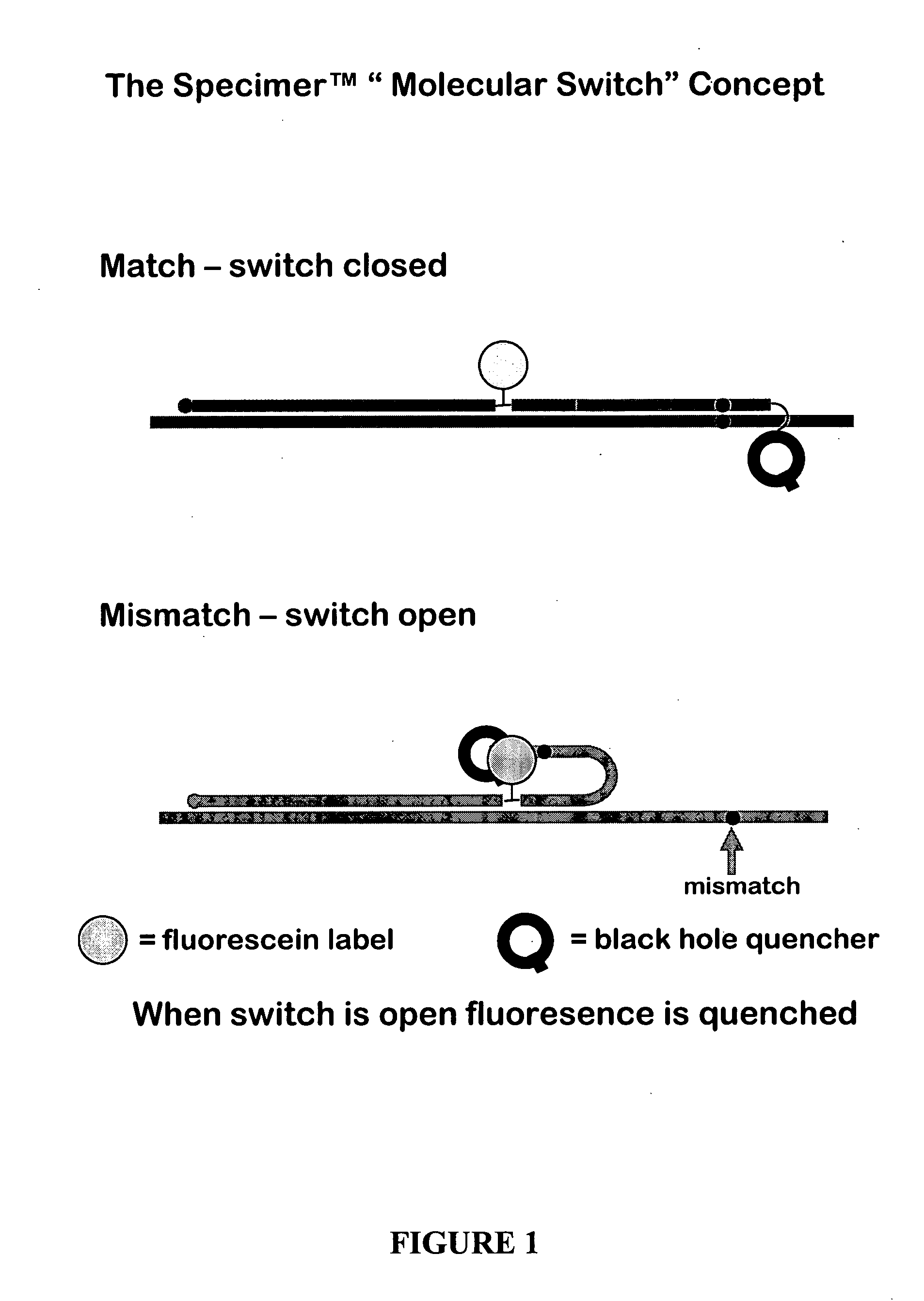
Oligonucleotides comprising a molecular switch
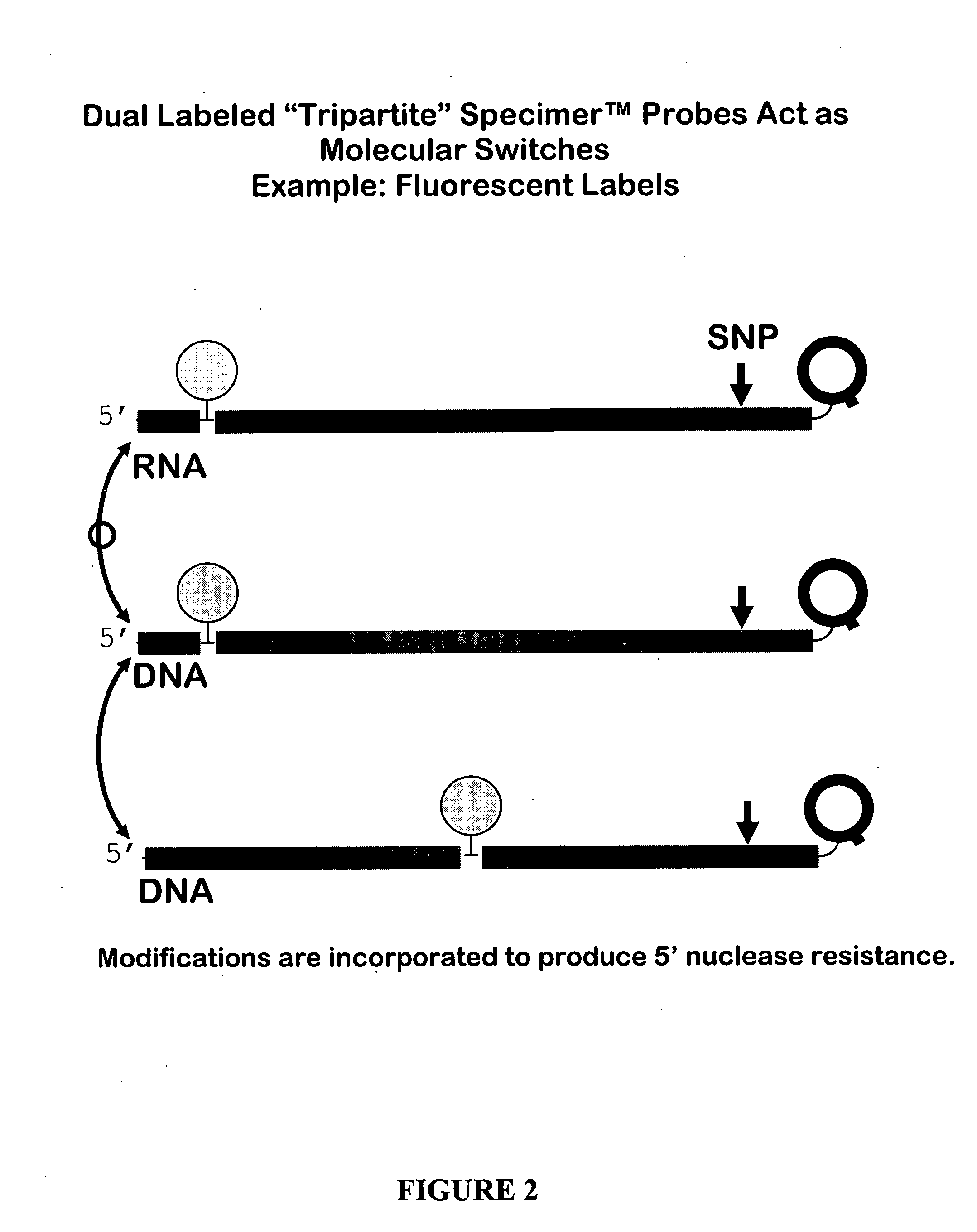
ActiveUS20050042638A1Strong specificityGuaranteed positioningSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBinding domainMolecular switch
This invention relates to oligonucleotides comprising a molecular switch which may exist in an “open” or “closed” position. The molecular switch portion of the probe is particularly sensitive to the identity of sequences complementary to the molecular switch. Oligonucleotides containing a molecular switch are applicable to all kinds of hybridization processes. Due to the sensitivity of the switch domain of the oligonucleotide, probes containing a molecular switch are particularly useful in the identification of single point mismatches. More specifically, a portion, but not all, of the oligonucleotide becomes unbound from a mismatched target. The invention further relates to methods of using said oligonucleotides for research reagents, and clinical diagnostics. An exemplary oligonucleotide comprises a first hybridizable domain, a second bridging block domain, and a third binding domain.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Interfacial biomaterials
InactiveUS20030185870A1Enough timeExtended half-lifePeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementBinding domainBiological organism
An interfacial biomaterial prepared using a plurality of binding agents, each binding agent including a first ligand that specifically binds a non-biological substrate and a second ligand that specifically binds a biological substrate. Also provided is an interfacial biomaterial prepared using a plurality of binding agents, each binding agent including a ligand that specifically binds a non-biological substrate and a non-binding domain that shows substantially no binding to a biological substrate. Also provided are methods for preparing a binding agent, methods for preparing an interfacial biomaterial, and methods for using interfacial biomaterials.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Methods and Antibody Compositions for Tumor Treatment
ActiveUS20150266966A1Decreased killing of T-cellsReduce the burden onImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsDiseaseCD20
The present invention provides bispecific antibodies that bind to CD3 and tumor antigens and methods of using the same. According to certain embodiments, the bispecific antibodies of the invention exhibit reduced effector functions and have a unique binding profile with regard to Fcγ receptors. The bispecific antibodies are engineered to efficiently induce T cell-mediated killing of tumor cells. According to certain embodiments, the present invention provides bispecific antigen-binding molecules comprising a first antigen-binding domain that specifically binds human CD3, a second antigen-binding molecule that specifically binds human CD20, and an Fc domain that binds Fcγ receptors with a specific binding pattern. In certain embodiments, the bispecific antigen-binding molecules of the present invention are capable of inhibiting the growth of B-cell or melanoma tumors expressing CD20. The bispecific antibodies of the invention are useful for the treatment of various cancers as well as other CD20-related diseases and disorders.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Identification and comparison of protein-protein interactions that occur in populations and identification of inhibitors of these interactors
InactiveUS6057101AEfficient screeningLess experimentally significant and specific indicationMaterial nanotechnologyFungiDiseaseBinding site
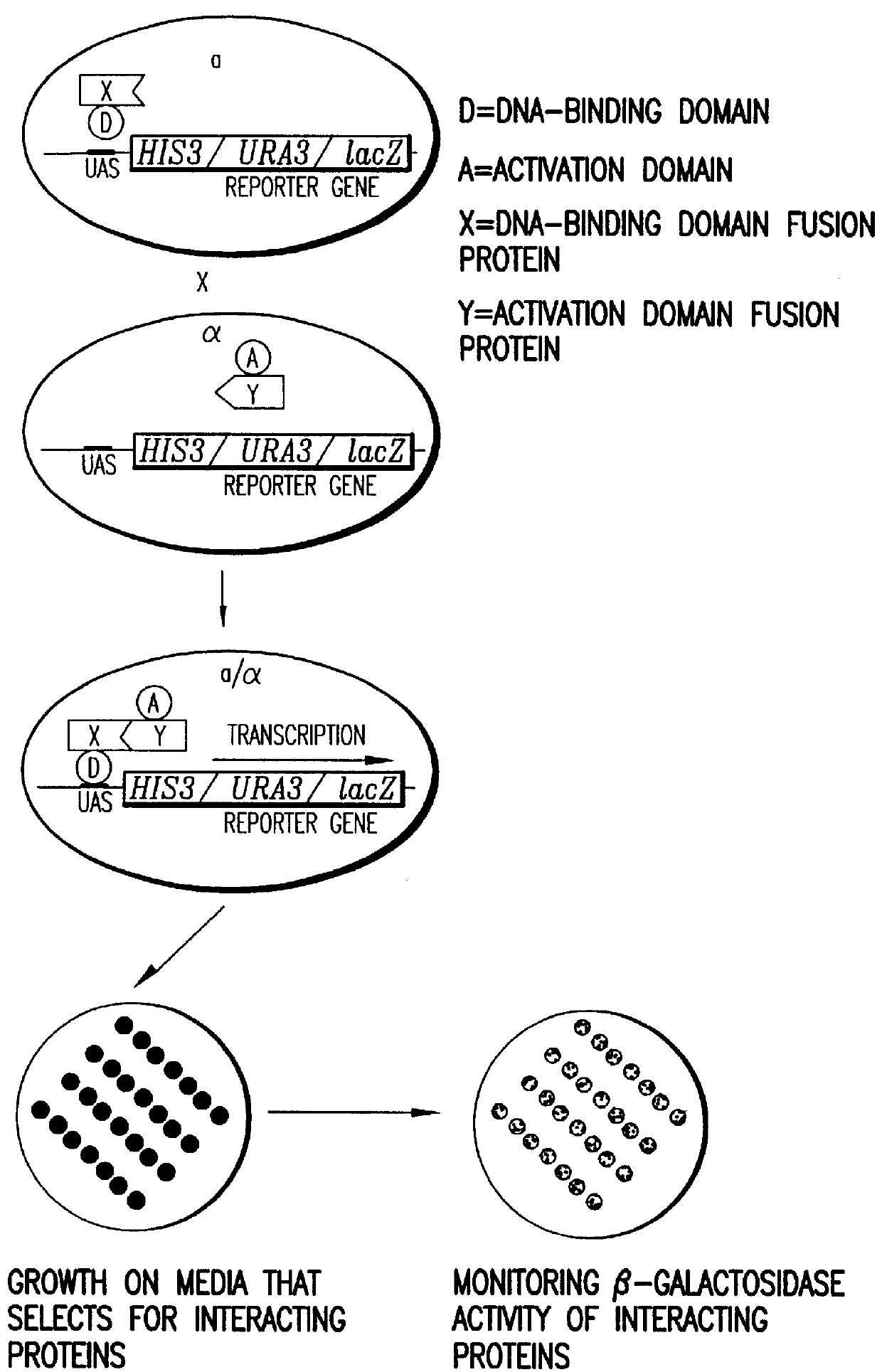
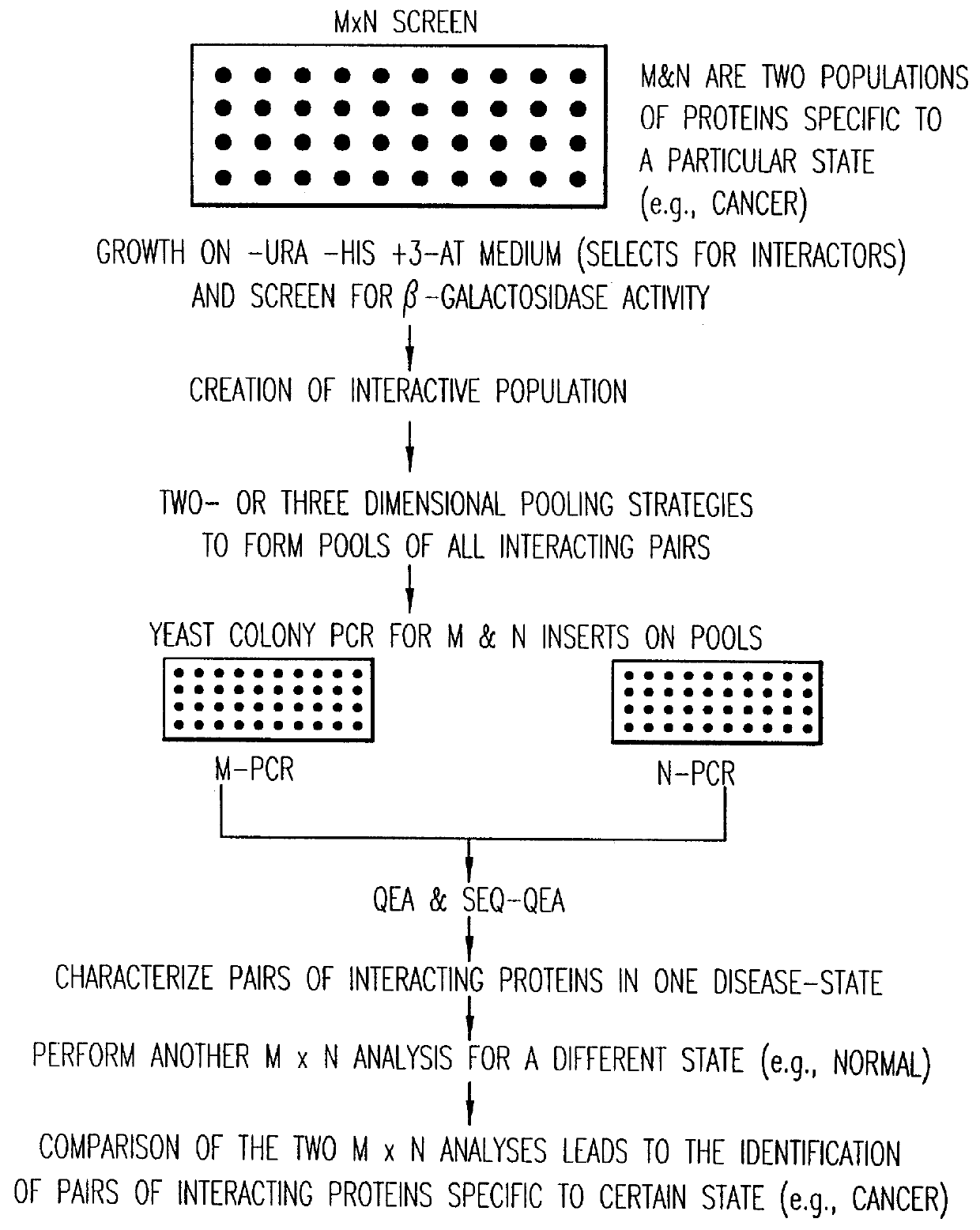
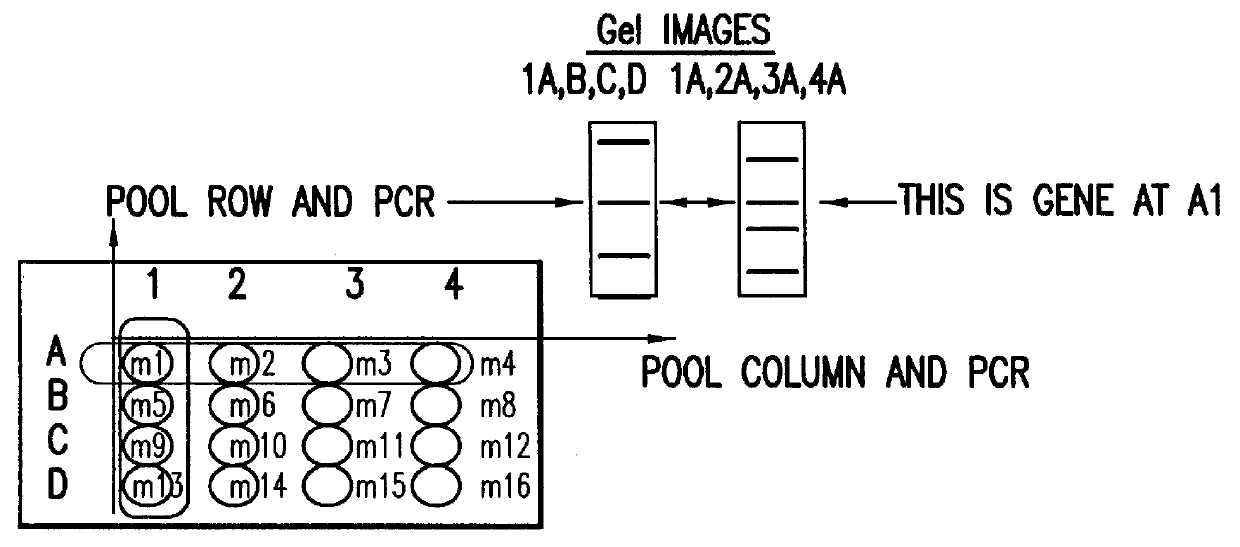
Methods are described for detecting protein-protein interactions, among two populations of proteins, each having a complexity of at least 1,000. For example, proteins are fused either to the DNA-binding domain of a transcriptional activator or to the activation domain of a transcriptional activator. Two yeast strains, of the opposite mating type and carrying one type each of the fusion proteins are mated together. Productive interactions between the two halves due to protein-protein interactions lead to the reconstitution of the transcriptional activator, which in turn leads to the activation of a reporter gene containing a binding site for the DNA-binding domain. This analysis can be carried out for two or more populations of proteins. The differences in the genes encoding the proteins involved in the protein-protein interactions are characterized, thus leading to the identification of specific protein-protein interactions, and the genes encoding the interacting proteins, relevant to a particular tissue, stage or disease. Furthermore, inhibitors that interfere with these protein-protein interactions are identified by their ability to inactivate a reporter gene. The screening for such inhibitors can be in a multiplexed format where a set of inhibitors will be screened against a library of interactors. Further, information-processing methods and systems are described. These methods and systems provide for identification of the genes coding for detected interacting proteins, for assembling a unified database of protein-protein interaction data, and for processing this unified database to obtain protein interaction domain and protein pathway information.
Owner:CURAGEN CORP
Heterodimer Binding Proteins and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20130129723A1Animal cellsFused cellsImmunoglobulin Joining RegionImmunoglobulin light chain
The present disclosure provides polypeptide heterodimers formed between two different single chain fusion polypeptides via natural heterodimerization of an immunoglobulin CH1 region and an immunoglobulin light chain constant region (CL). The polypeptide heterodimer comprises two or more binding domains that specifically bind one or more targets (e.g., a receptor). In addition, both chains of the heterodimer further comprise an Fc region portion. The present disclosure also provides nucleic acids, vectors, host cells and methods for making polypeptide heterodimers as well as methods for using such polypeptide heterodimers, such as in directing T cell activation, inhibiting solid malignancy growth, and treating autoimmune or inflammatory conditions.
Owner:EMERGENT PRODUCTS DEVELOPMENT SEATTLE LLC
Compositions for delivery of therapeutics and other materials
InactiveUS20080015263A1Easy to introduceKind be easilyBiocideIn-vivo radioactive preparationsDiagnostic agentBinding domain
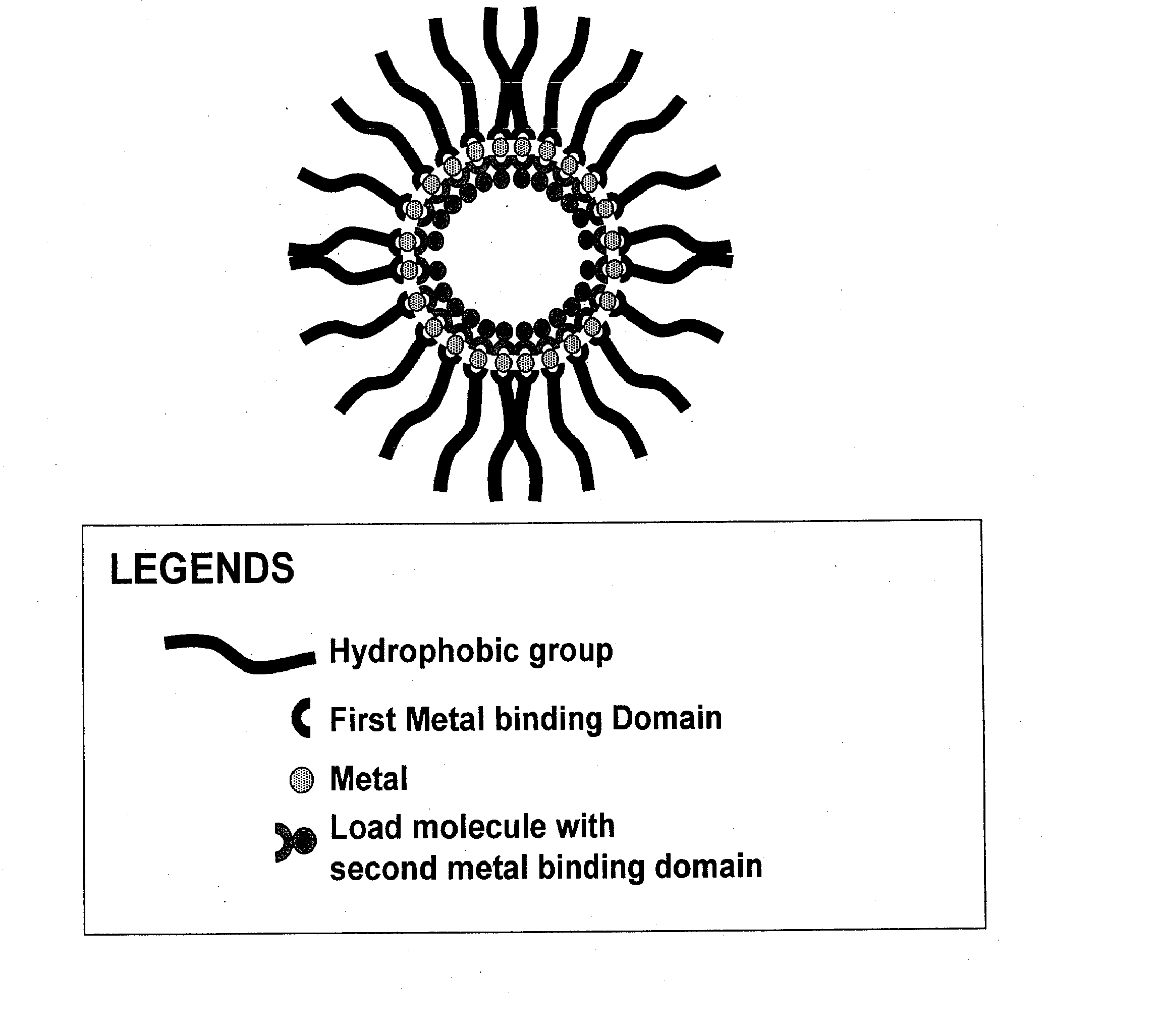
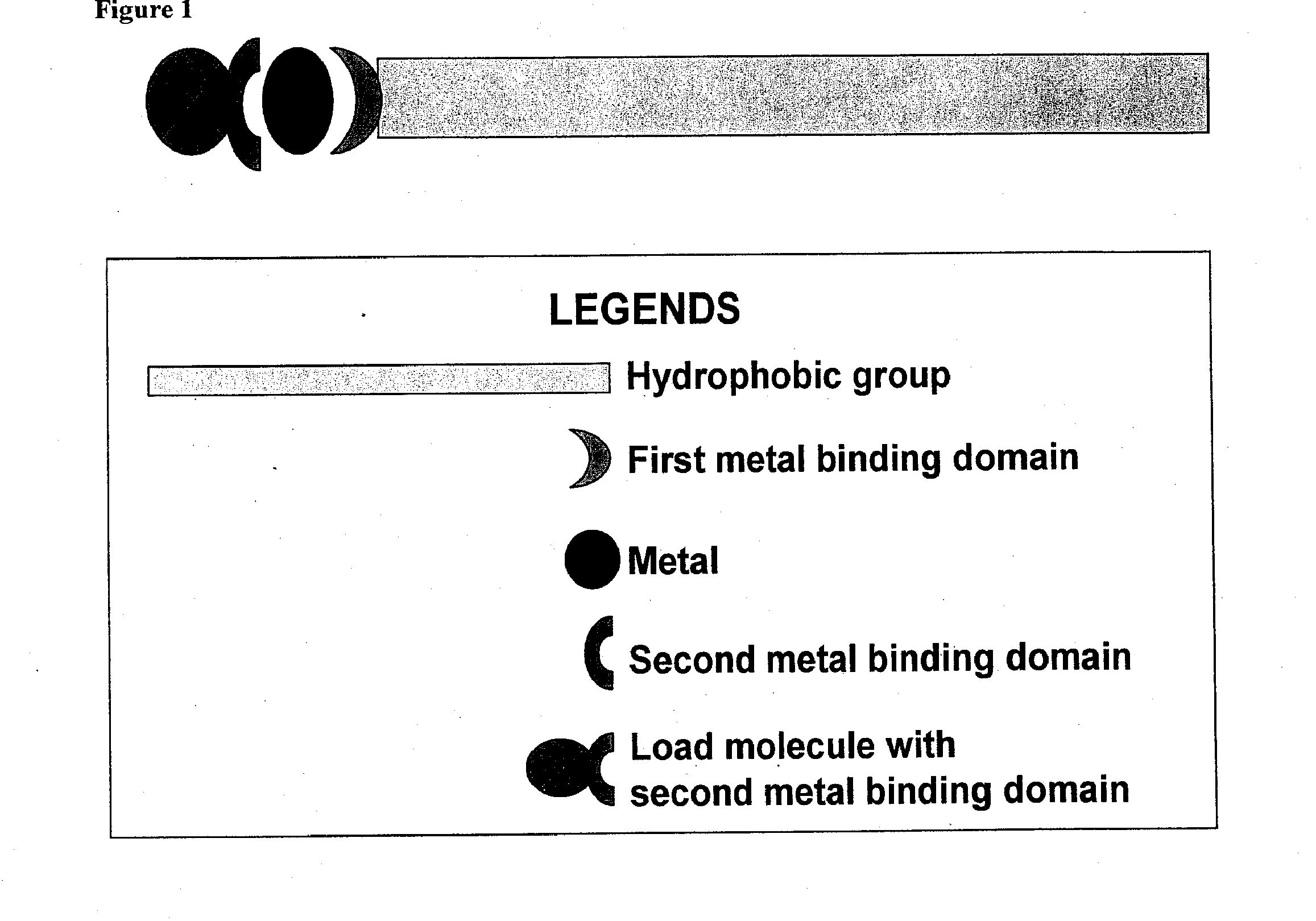
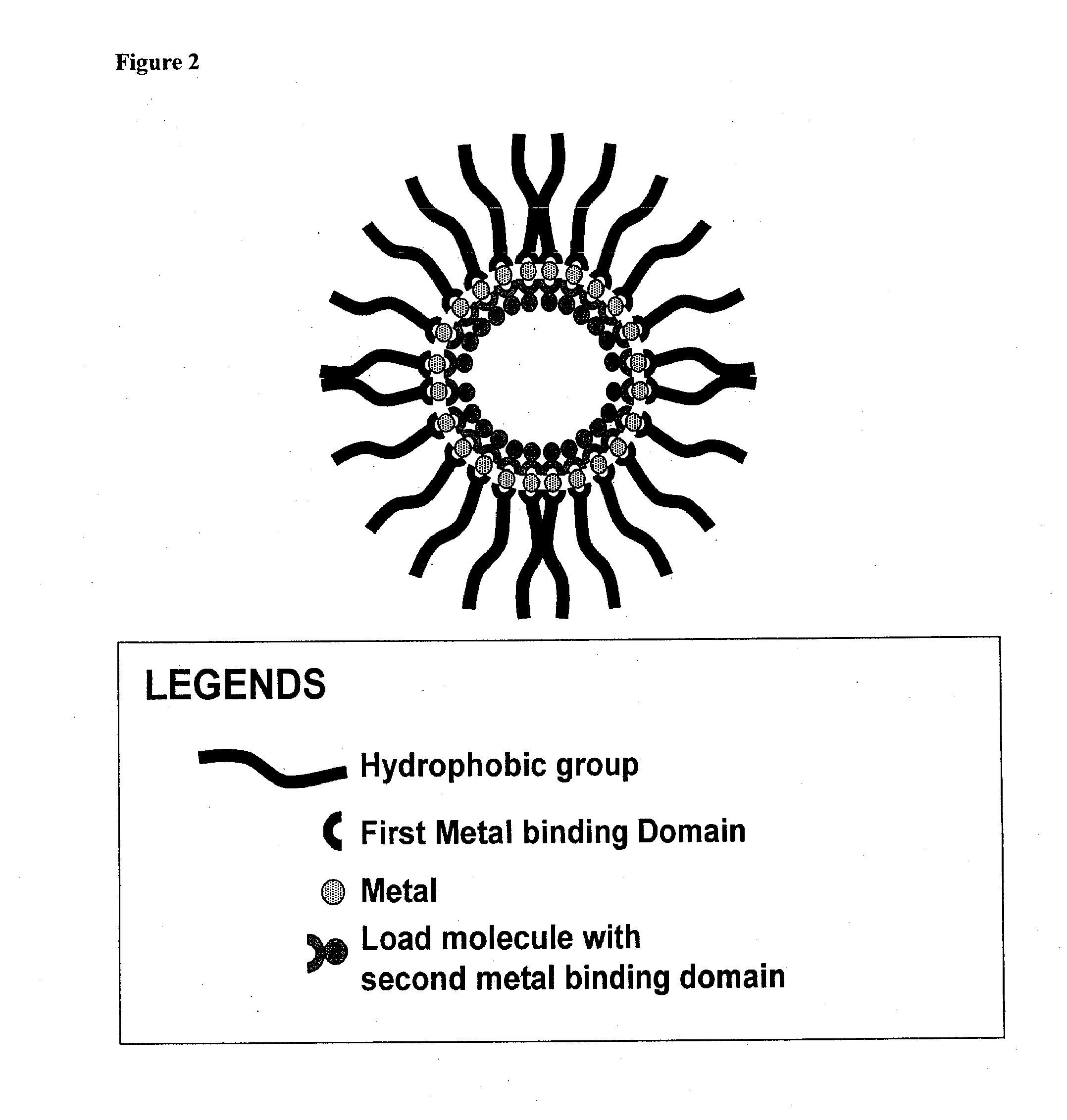
This disclosure relates to compositions for delivering agents to a subject, and in particular, to compositions for delivery of therapeutic agents or diagnostic agents in the presence or absence of targeting moieties. In part, this disclosure relates to compositions comprising a hydrophobic group with a first end and a second end, a first metal binding domain linked to the hydrophobic group, a metal ion capable of being chelated to the first metal binding domain, and an agent linked to a second metal binding domain capable of chelating to the metal ion.
Owner:PHARMAIN CORP
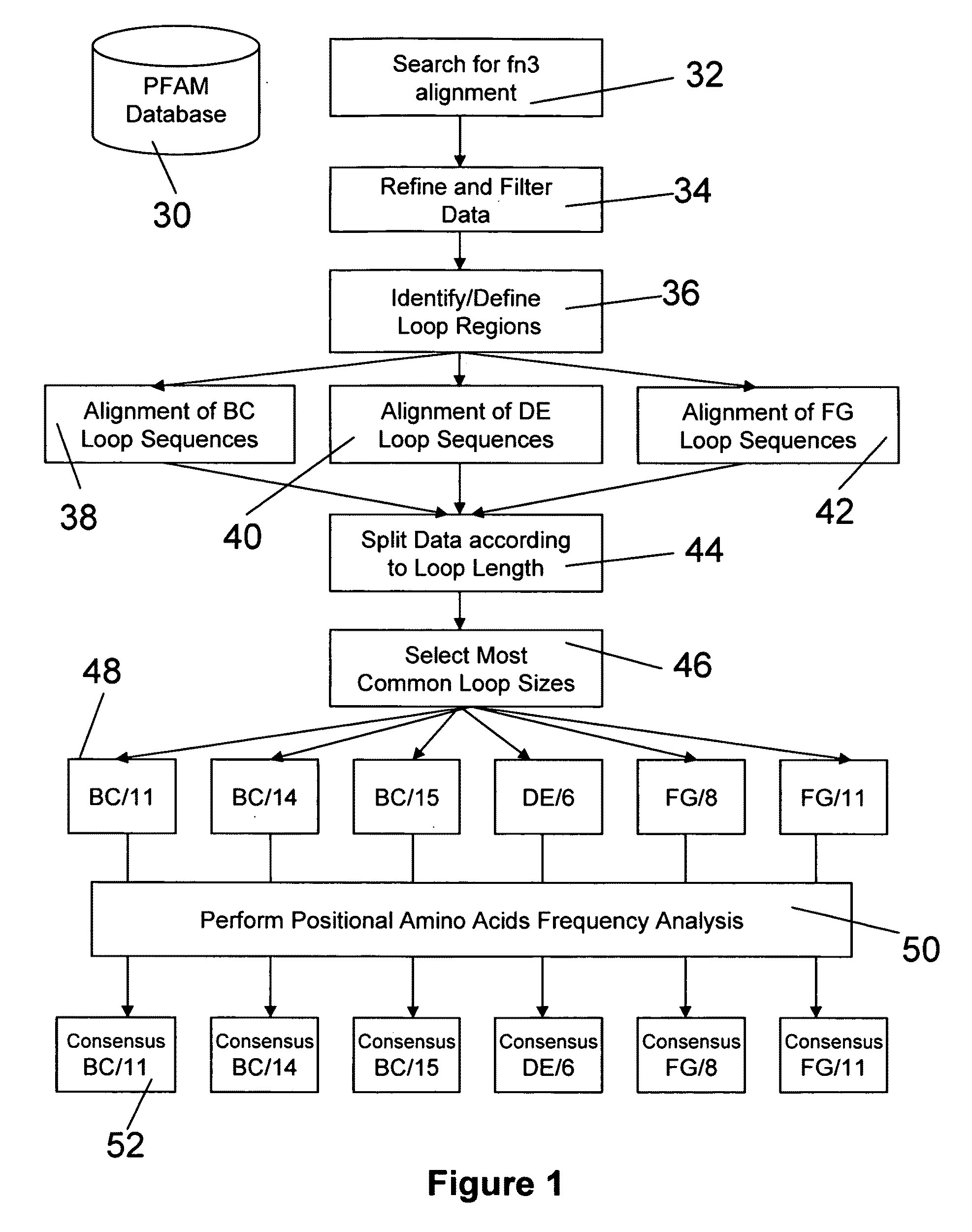
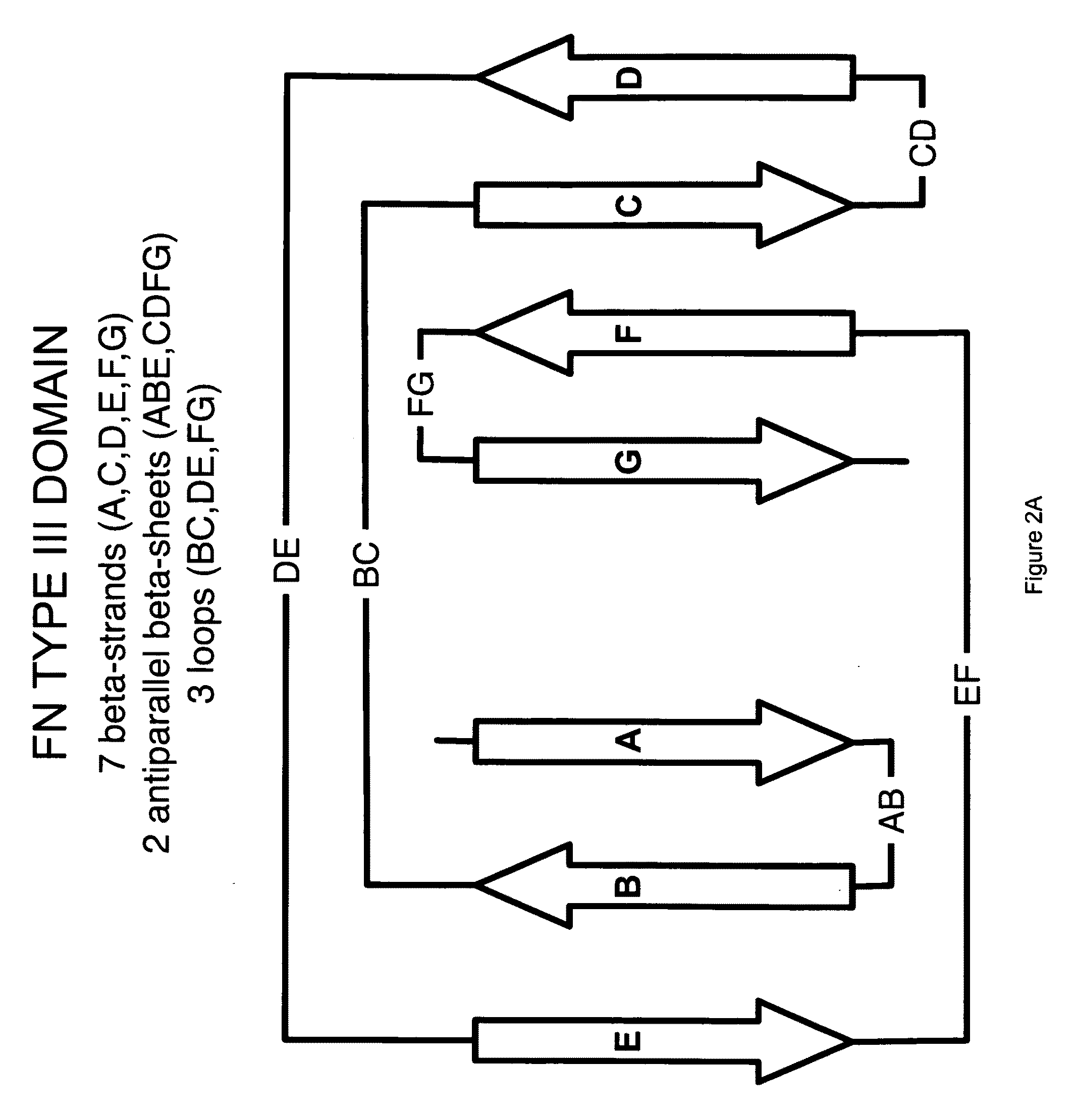
Universal fibronectin type III binding-domain libraries
Walk-through mutagenesis and natural-variant combinatorial fibronectin Type III (FN3) polypeptide libraries are described, along with their method of construction and use. Also disclosed are a number of high binding affinity polypeptides selected by screening the libraries against a variety of selected antigens.
Owner:PROTELIX
Multianalyte sensor
InactiveUS20060078908A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTarget analysisAnalyte
The invention relates to devices for continuously measuring the concentrations of more than one target analyte. Specifically, the devices comprise a plurality of analyte binding domains, with each domain being capable of specifically and reversibly binding to at least one of the target analytes. The devices further comprise a membrane surrounding these binding domains that is permeable to the target analytes. The devices convey binding information to a detector. The invention also relates to methods of using the devices, including monitoring chronic disease states in an individual.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Cytotoxicity-inducing therapeutic agent
ActiveUS20140112914A1Lessen the burden on the bodyHighly convenientBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHalf-lifeCytotoxicity
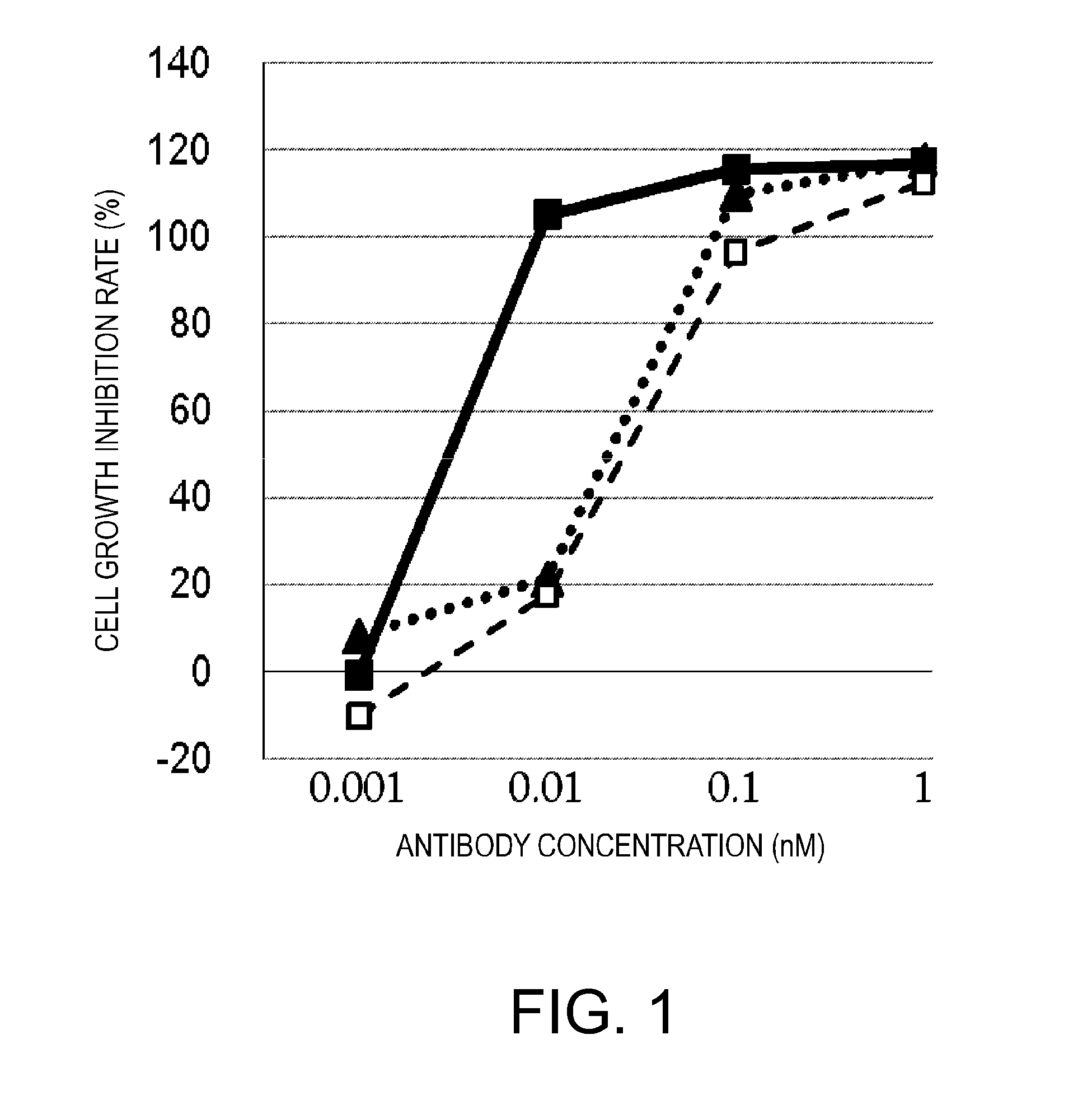
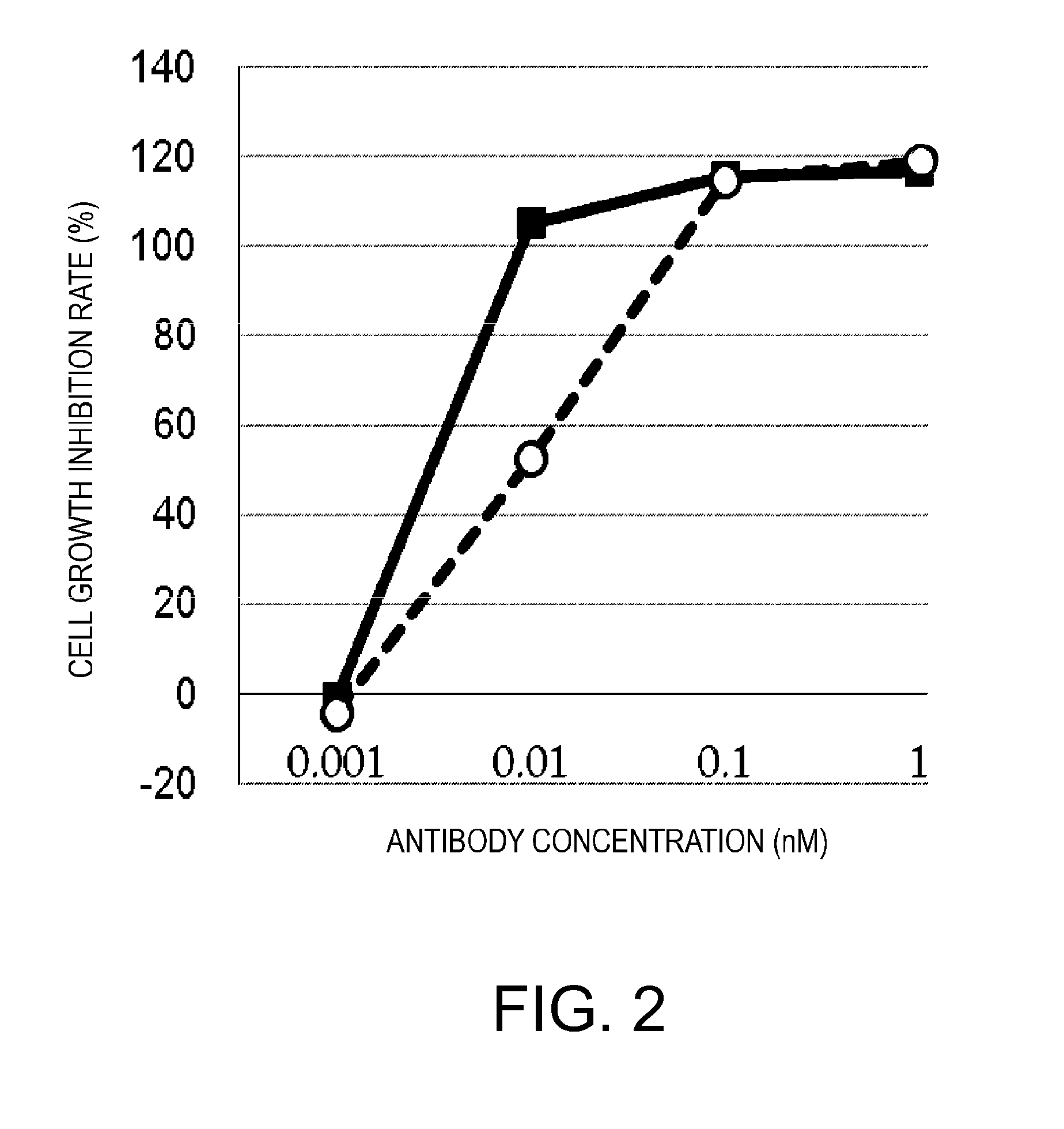
By replacing the antigen-binding domain, the present inventors discovered novel polypeptide complexes that retain BiTE's strong anti-tumor activity and excellent safety properties, as well as have long half-life in blood and can damage various different target cells.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Multi-Chain Chimeric Antigen Receptor and Uses Thereof
ActiveUS20140134142A1Modulate activityStrong specificityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigen receptorReceptor
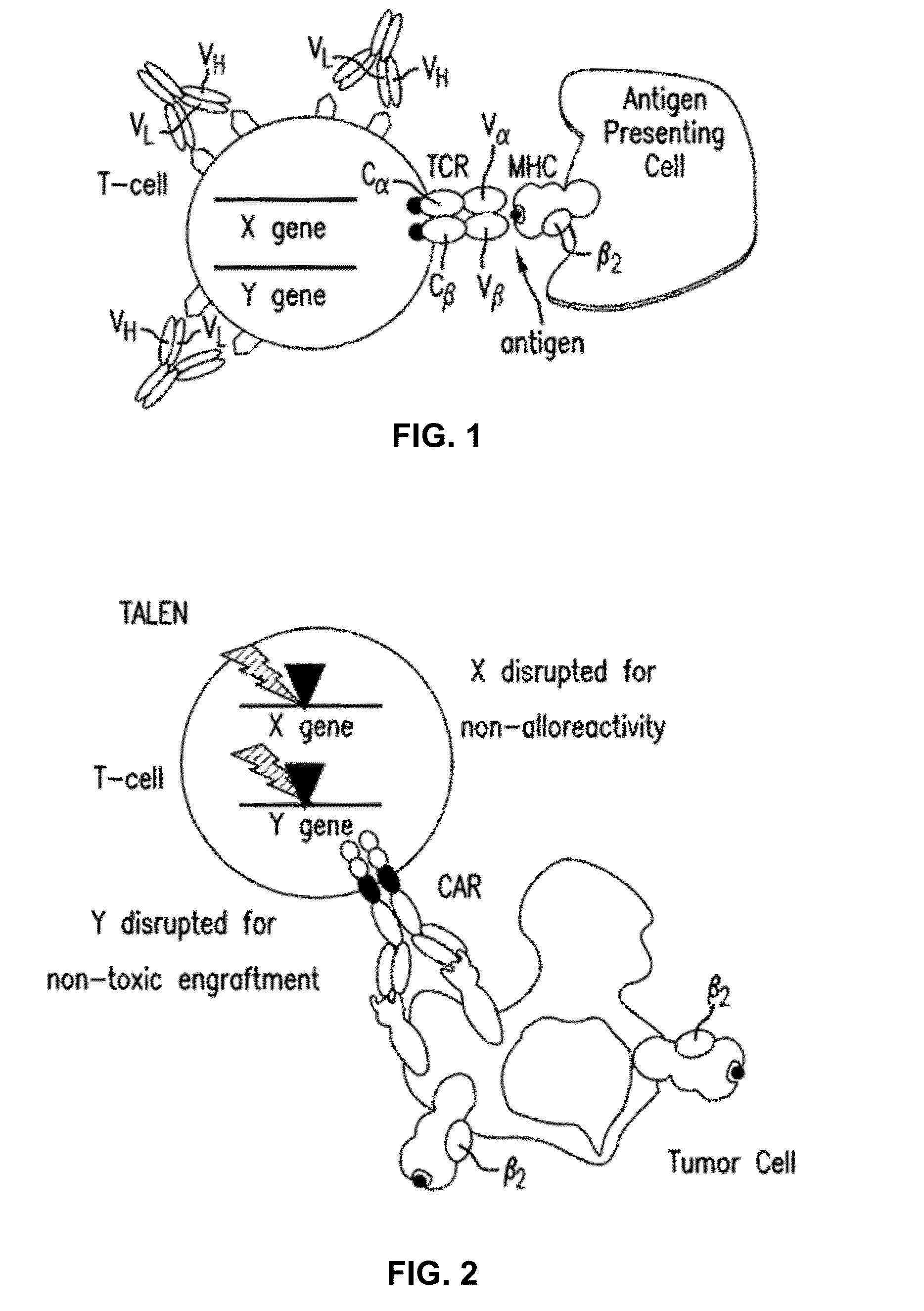
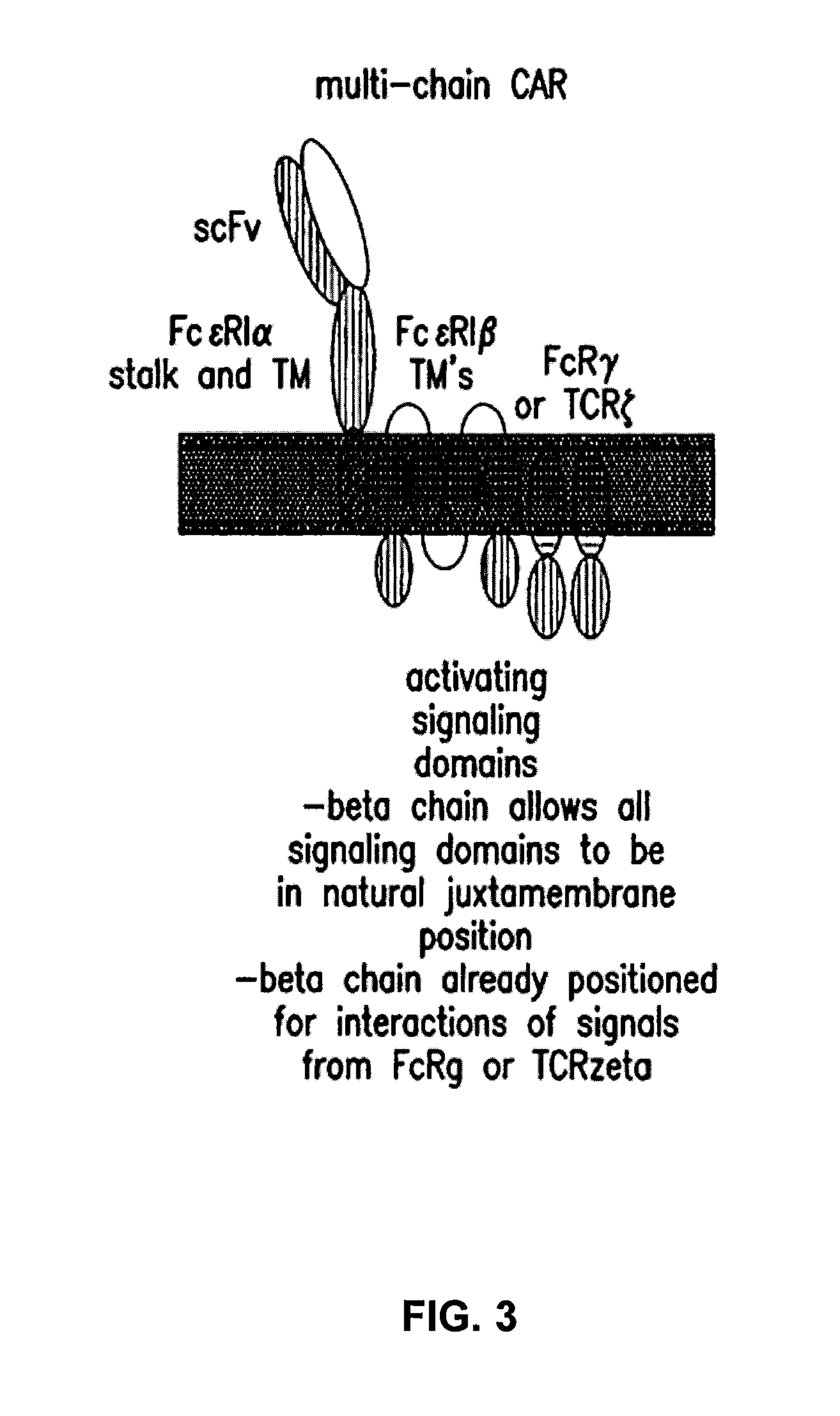
The present invention relates to a new generation of chimeric antigen receptors (CAR) referred to as multi-chain CARs. Such CARs, which aim to redirect immune cell specificity and reactivity toward a selected target exploiting the ligand-binding domain properties, comprise separate extracellular ligand binding and signaling domains in different transmembrane polypeptides. The signaling domains are designed to assemble in juxtamembrane position, which forms flexible architecture closer to natural receptors, that confers optimal signal transduction. The invention encompasses the polynucleotides, vectors encoding said multi-chain CAR and the isolated cells expressing them at their surface, in particularly for their use in immunotherapy. The invention opens the way to efficient adoptive immunotherapy strategies for treating cancer and viral infections.
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
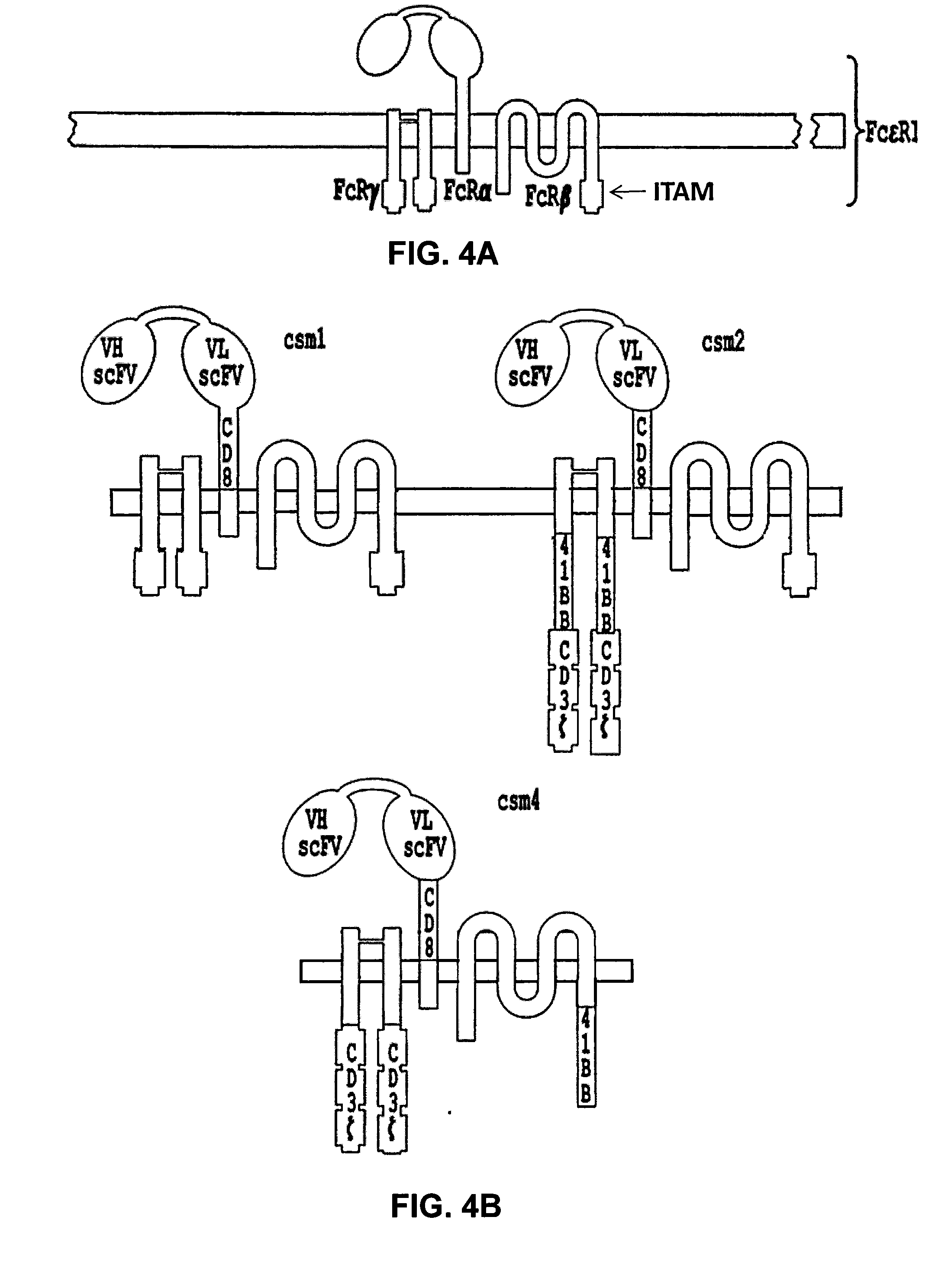
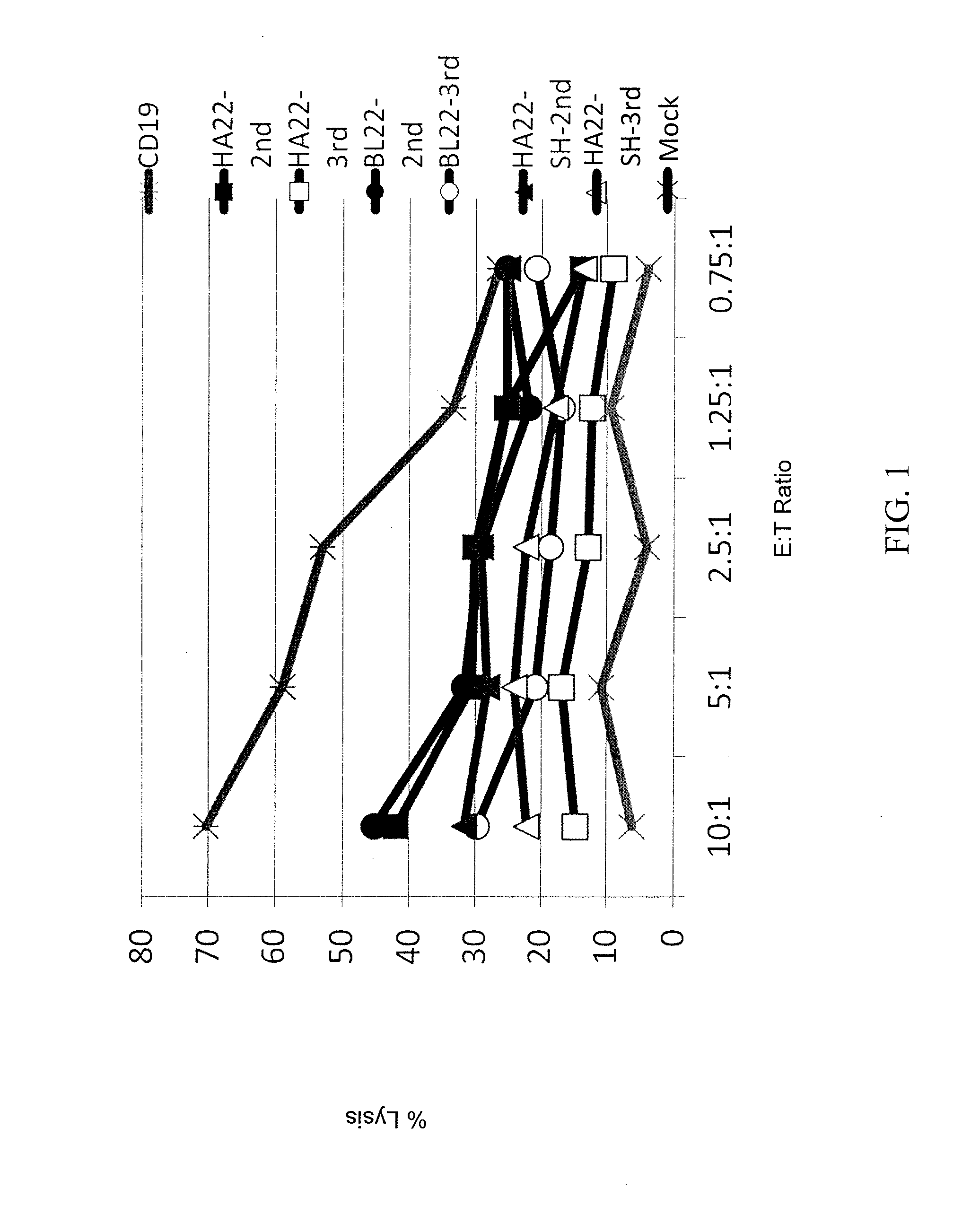
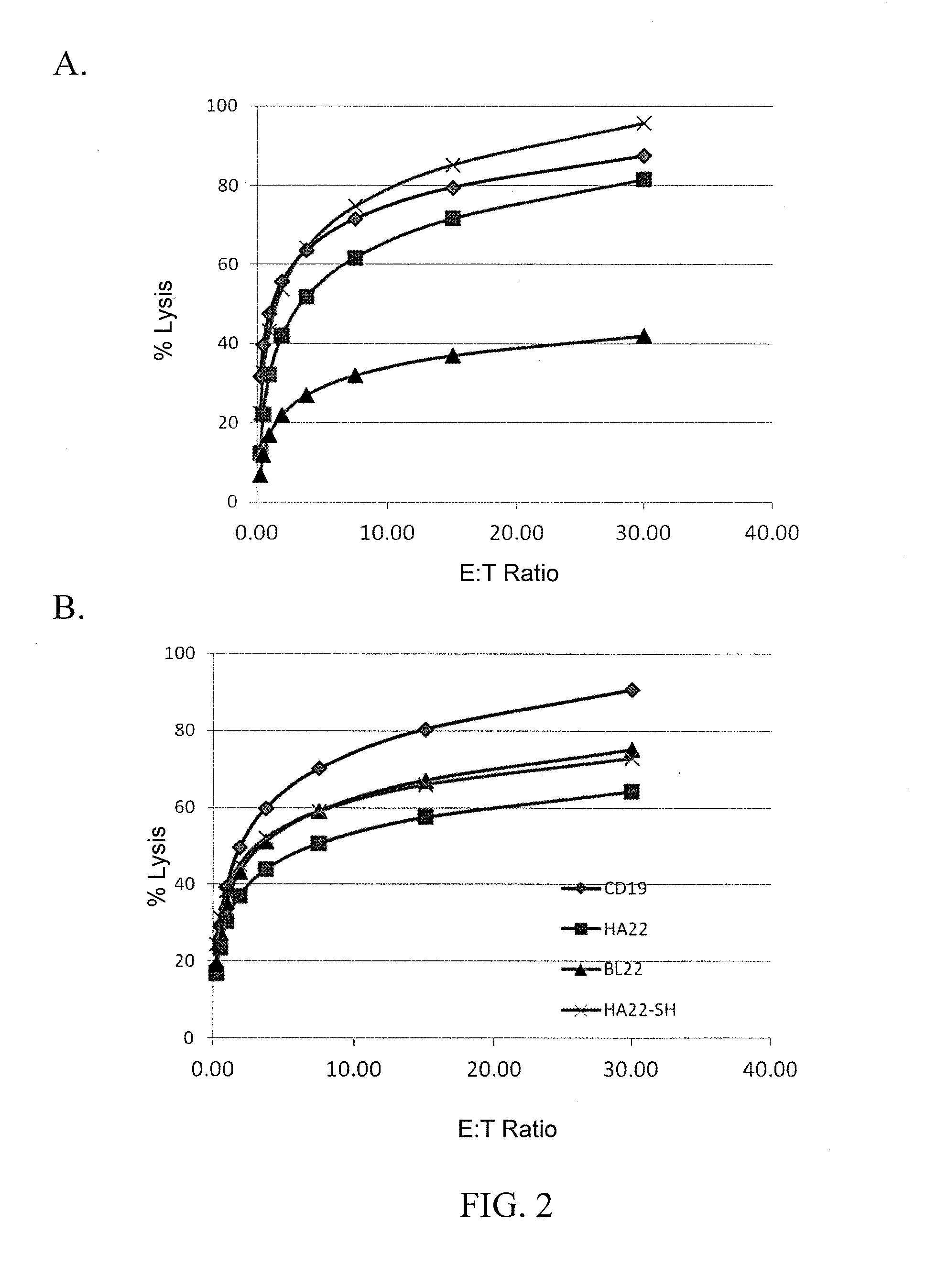
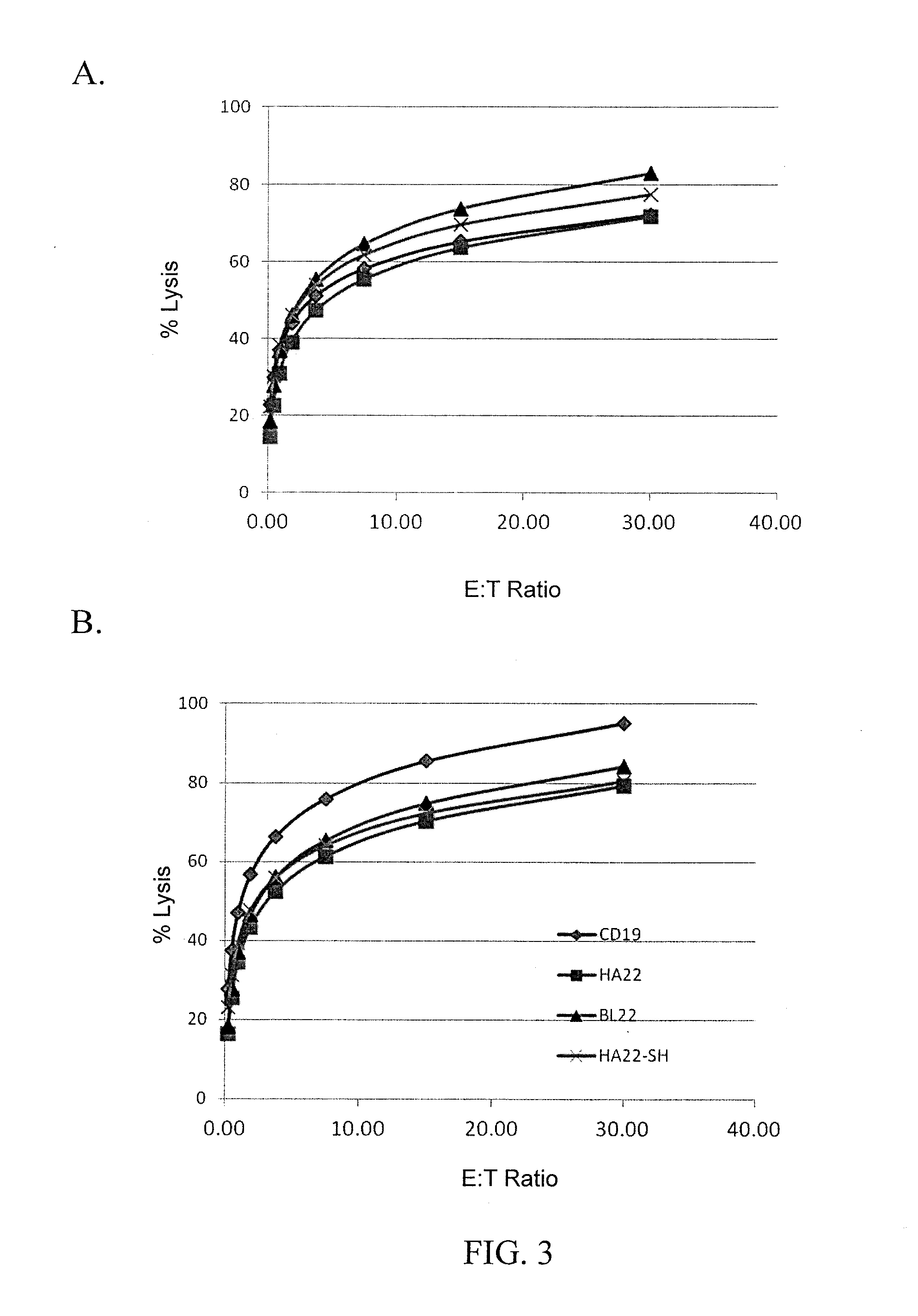
Anti-cd22 chimeric antigen receptors
The disclosure provides a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) comprising a) an antigen binding domain of HA22, a transmembrane domain, and an intracellular T cell signaling domain; or b) an antigen binding domain of BL22, a transmembrane domain, and an intracellular T cell signaling domain comprising CD28 and / or CD137. Nucleic acids, recombinant expression vectors, host cells, populations of cells, antibodies, or antigen binding portions thereof, and pharmaceutical compositions relating to the CARs are disclosed. Methods of detecting the presence of cancer in a mammal and methods of treating or preventing cancer in a mammal are also disclosed.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
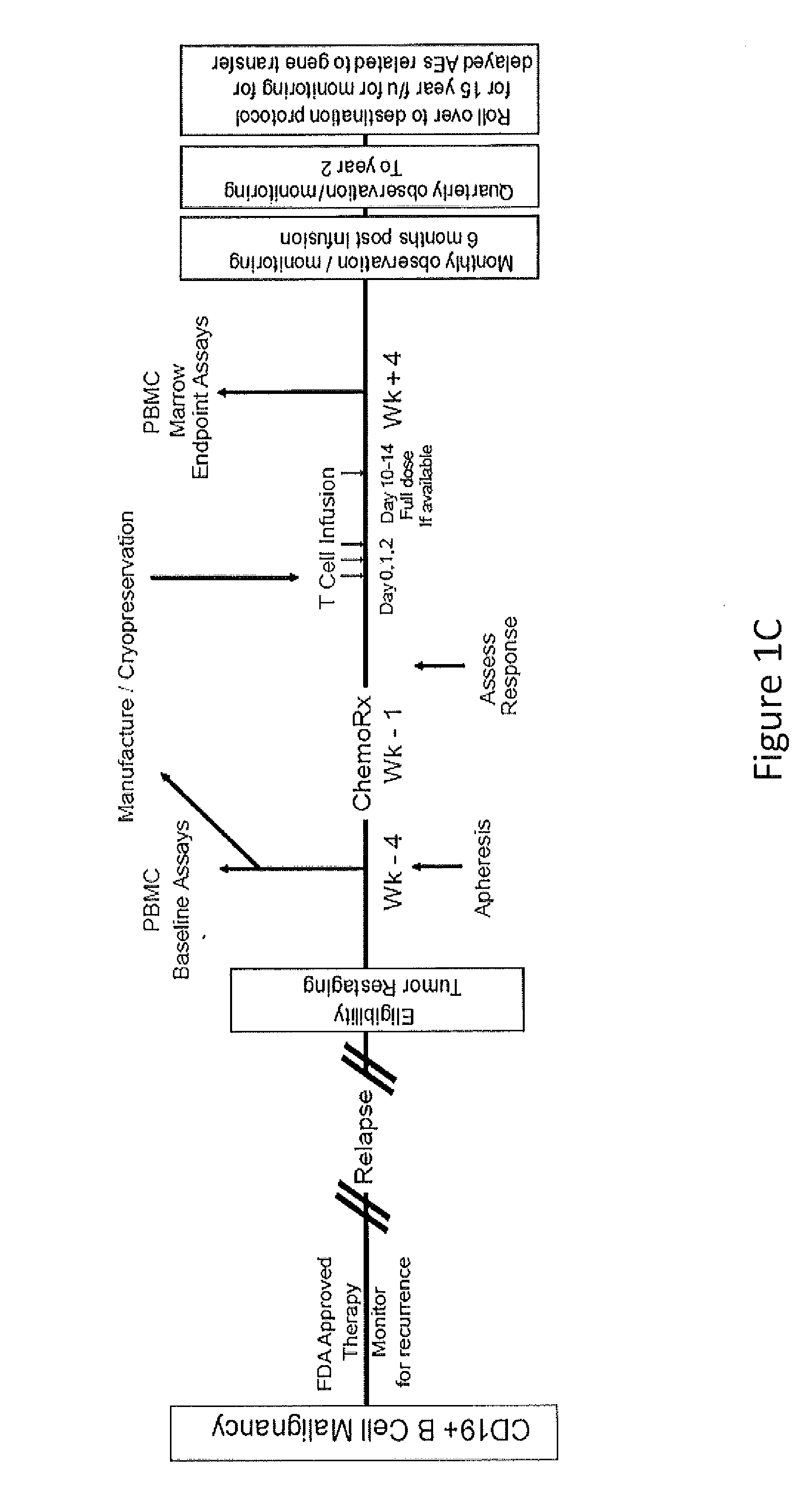
Methods for Treatment of Cancer
The present invention provides compositions and methods for treating cancer in a human. The invention includes relates to administering a genetically modified T cell to express a CAR wherein the CAR comprises an antigen binding domain, a transmembrane domain, a costimulatory signaling region, and a CD3 zeta signaling domain.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
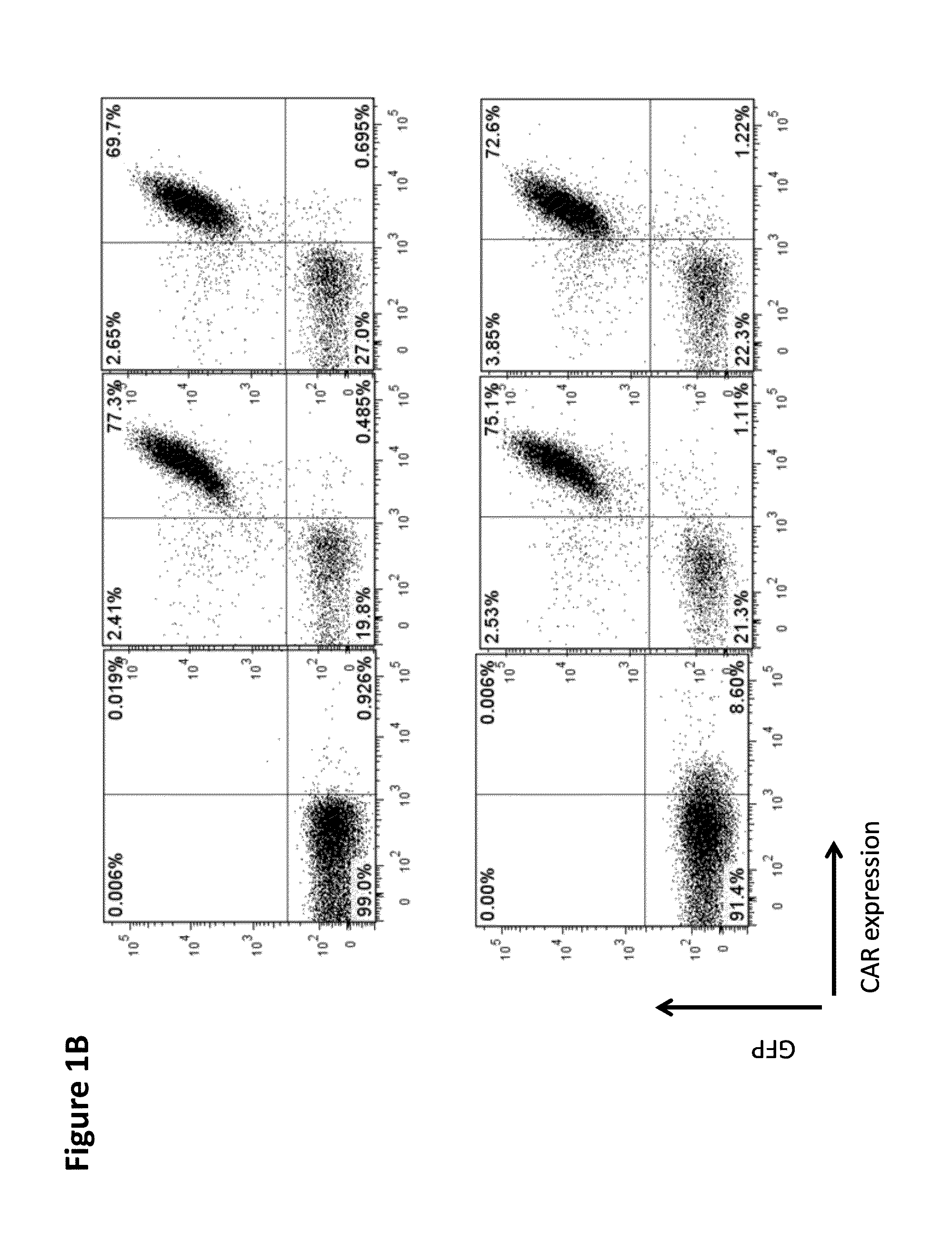
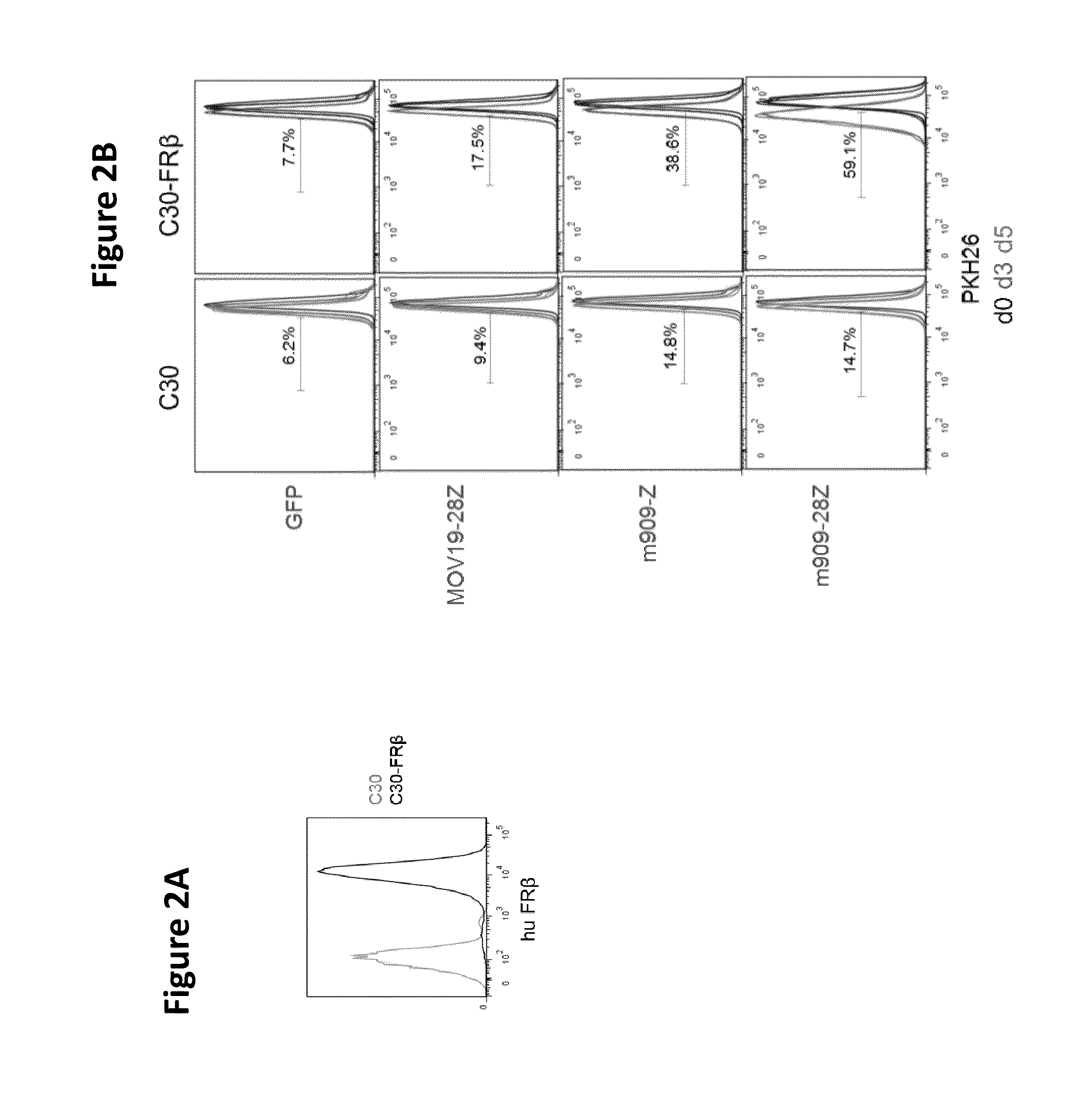
Chimeric antigen receptor specific for folate receptor beta
ActiveUS20140286973A1High affinityLow toxicityBiocideAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAgonistBinding domain
The invention provides compositions and methods for treating leukemia, for example, acute myeloid leukemia (AML). The invention also relates to at least one chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) specific to folate receptor beta (FRβ), vectors comprising the same, and recombinant T cells comprising the FRβ CAR. The invention also includes methods of administering a genetically modified T cell expressing a CAR that comprises a FRβ binding domain in combination with a RXR agonist, such as all-trans retinoic acid.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Compositions for Treatment of Cancer
The present invention provides compositions and methods for treating cancer in a human. The invention includes relates to administering a genetically modified T cell to express a CAR wherein the CAR comprises an antigen binding domain, a transmembrane domain, a costimulatory signaling region, and a CD3 zeta signaling domain.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com