Patents
Literature
417 results about "Chromatin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
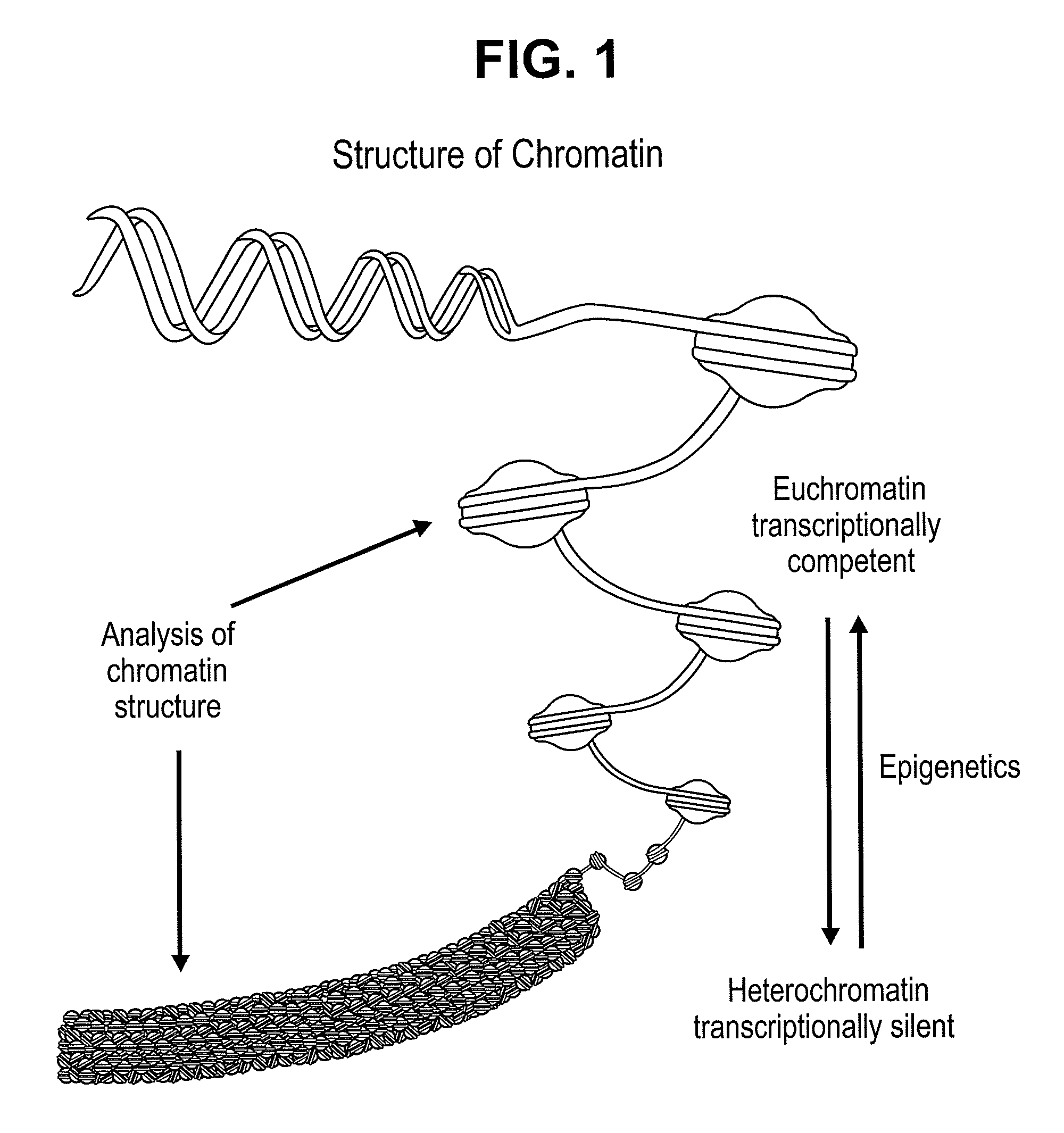
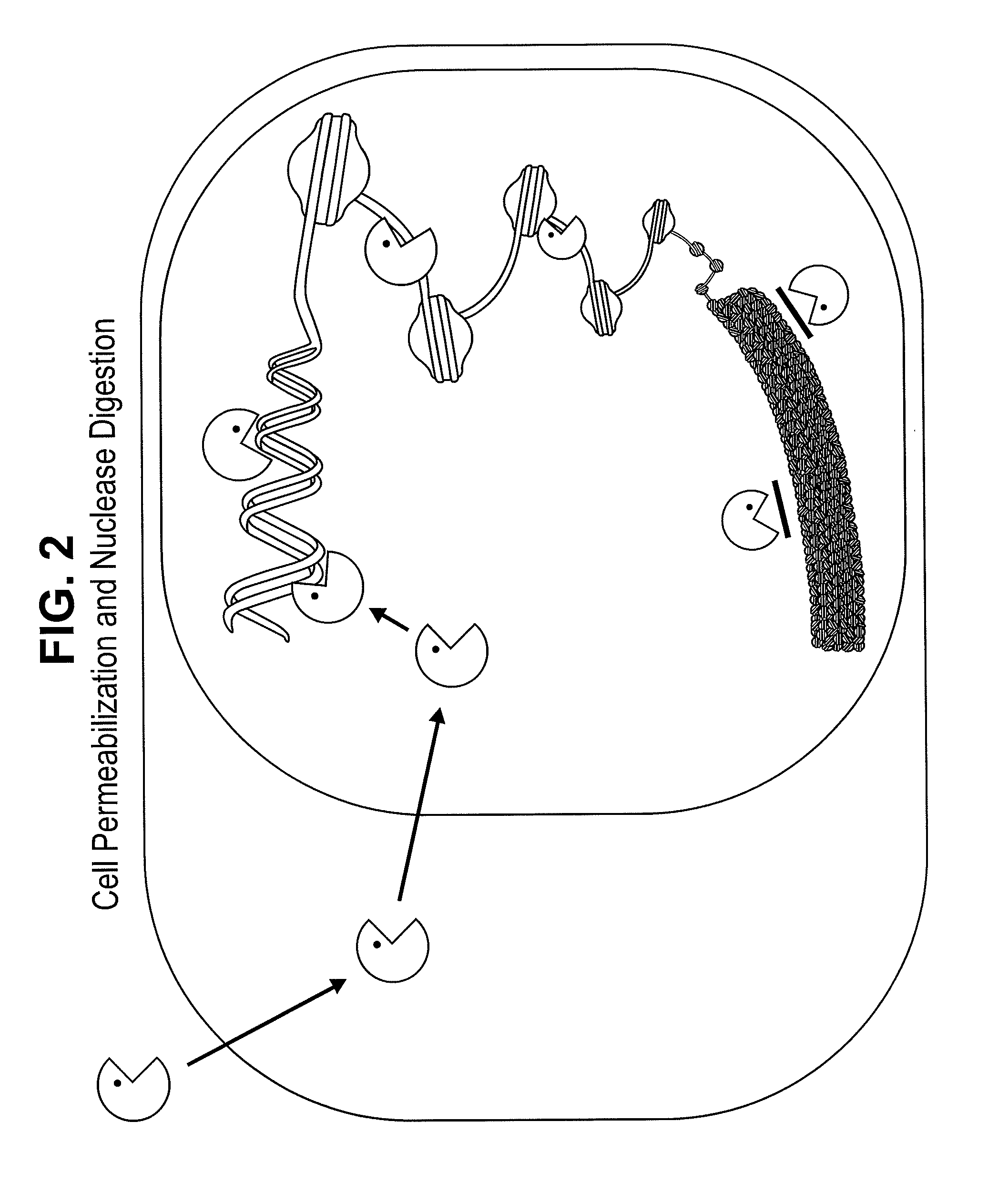
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryotic cells. Its primary function is packaging very long DNA molecules into a more compact, denser shape, which prevents the strands from becoming tangled and plays important roles in reinforcing the DNA during cell division, preventing DNA damage, and regulating gene expression and DNA replication. During mitosis and meiosis, chromatin facilitates proper segregation of the chromosomes in anaphase; the characteristic shapes of chromosomes visible during this stage are the result of DNA being coiled into highly condensed networks of chromatin.
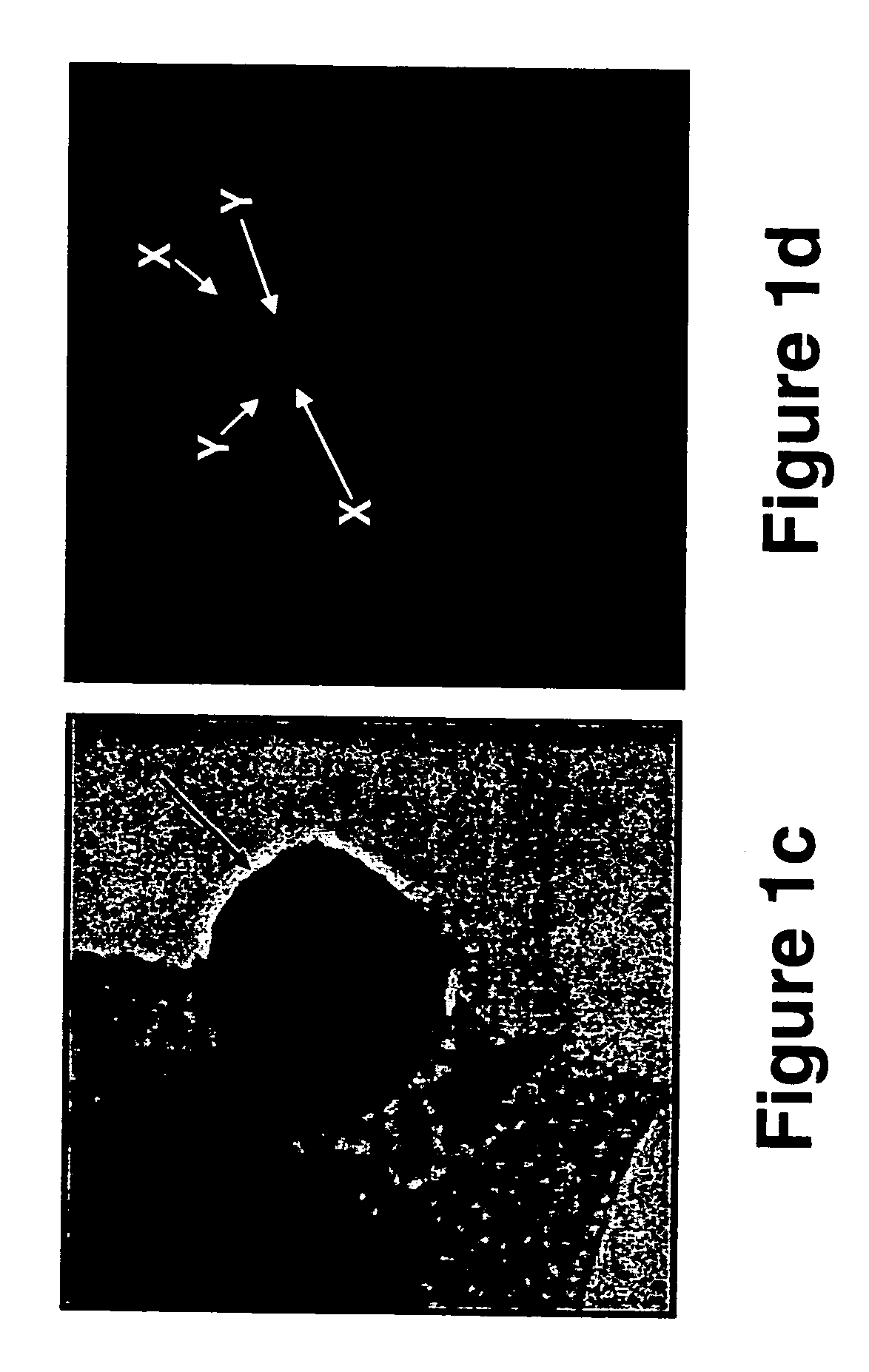
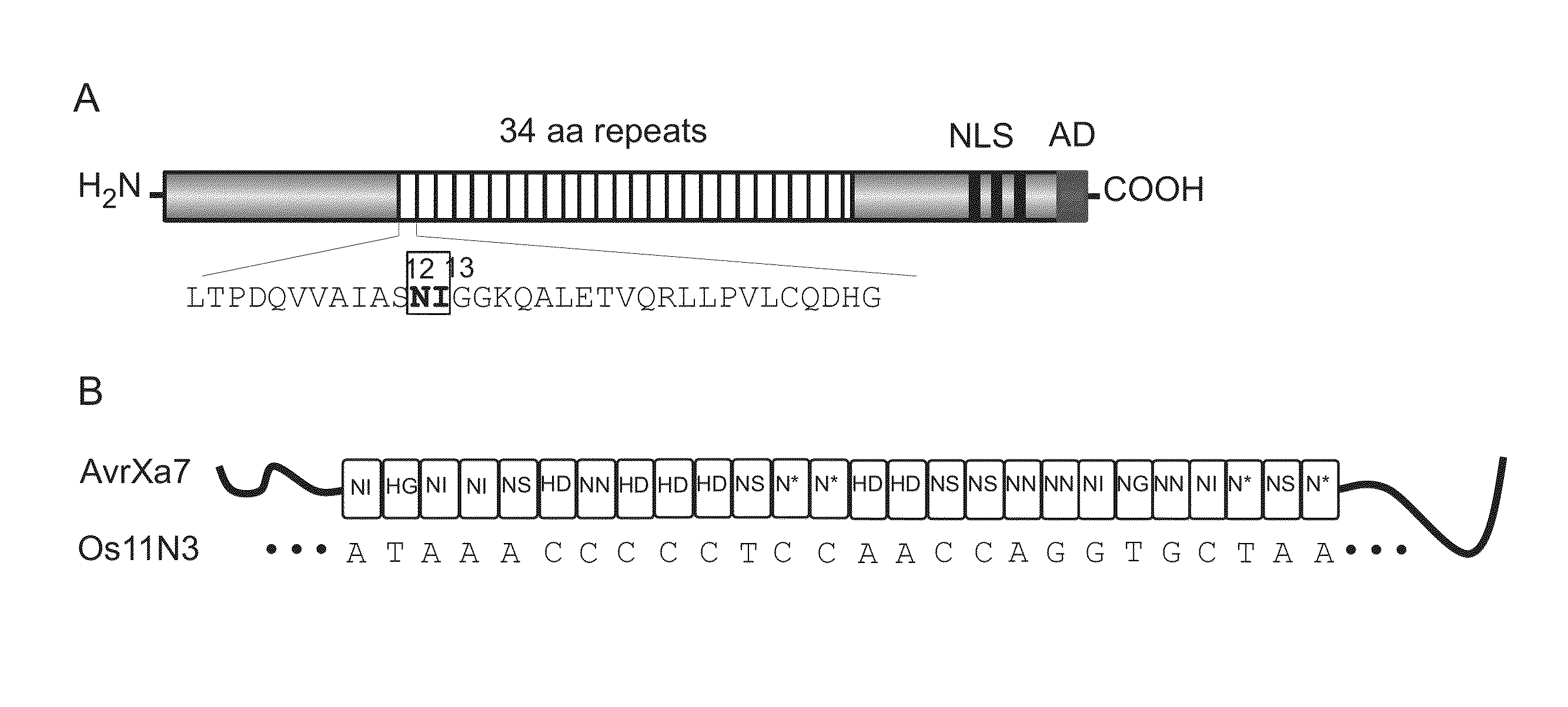
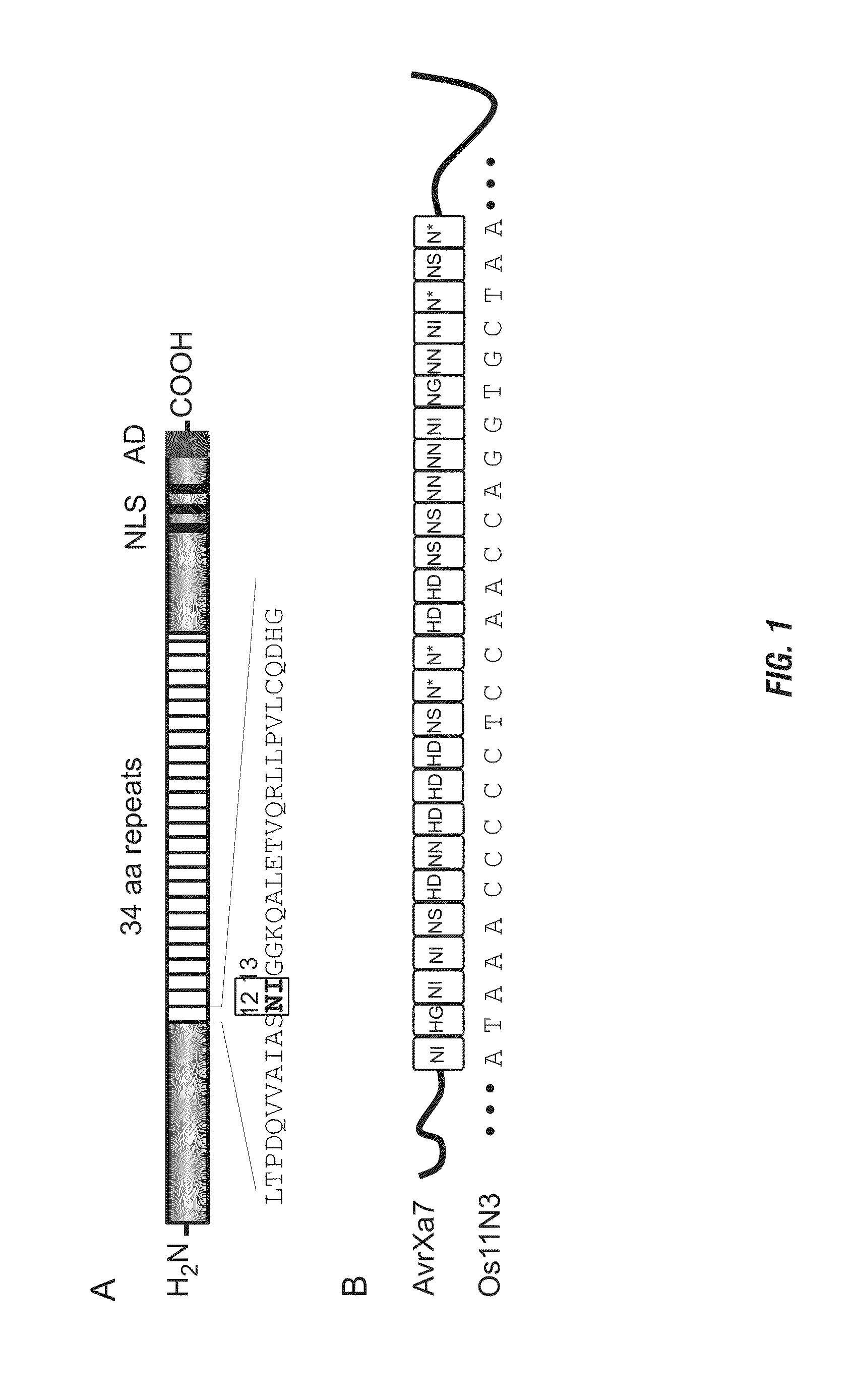
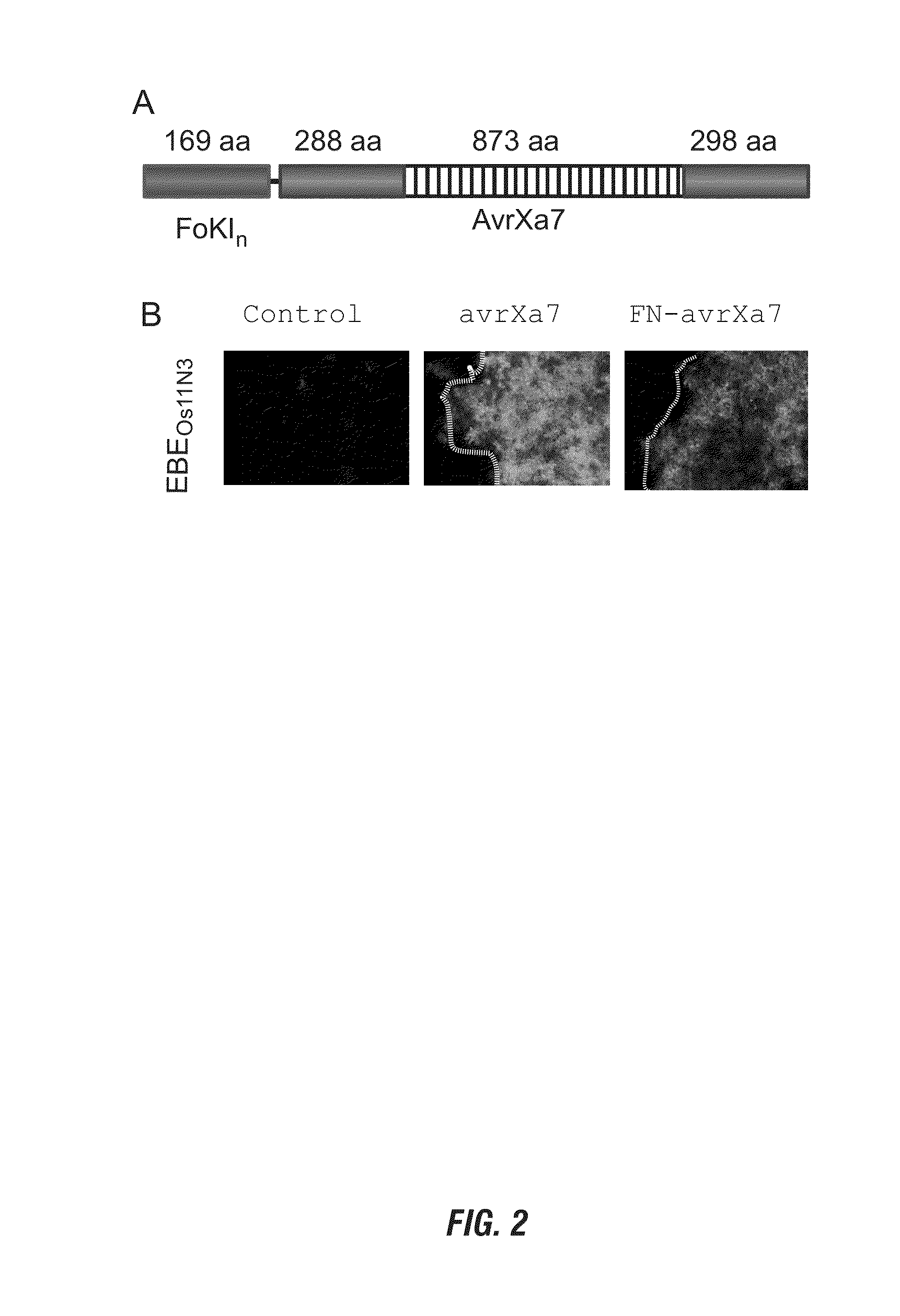
Nuclease activity of tal effector and foki fusion protein
The present invention provides compositions and methods for targeted cleavage of cellular chromatin in a region of interest and / or homologous recombination at a predetermined site in cells. Compositions include fusion polypeptides comprising a TAL effector binding domain and a cleavage domain. The cleavage domain can be from any endonuclease. In certain embodiments, the endonuclease is a Type IIS restriction endonuclease. In further embodiments, the Type IIS restriction endonuclease is FokI.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
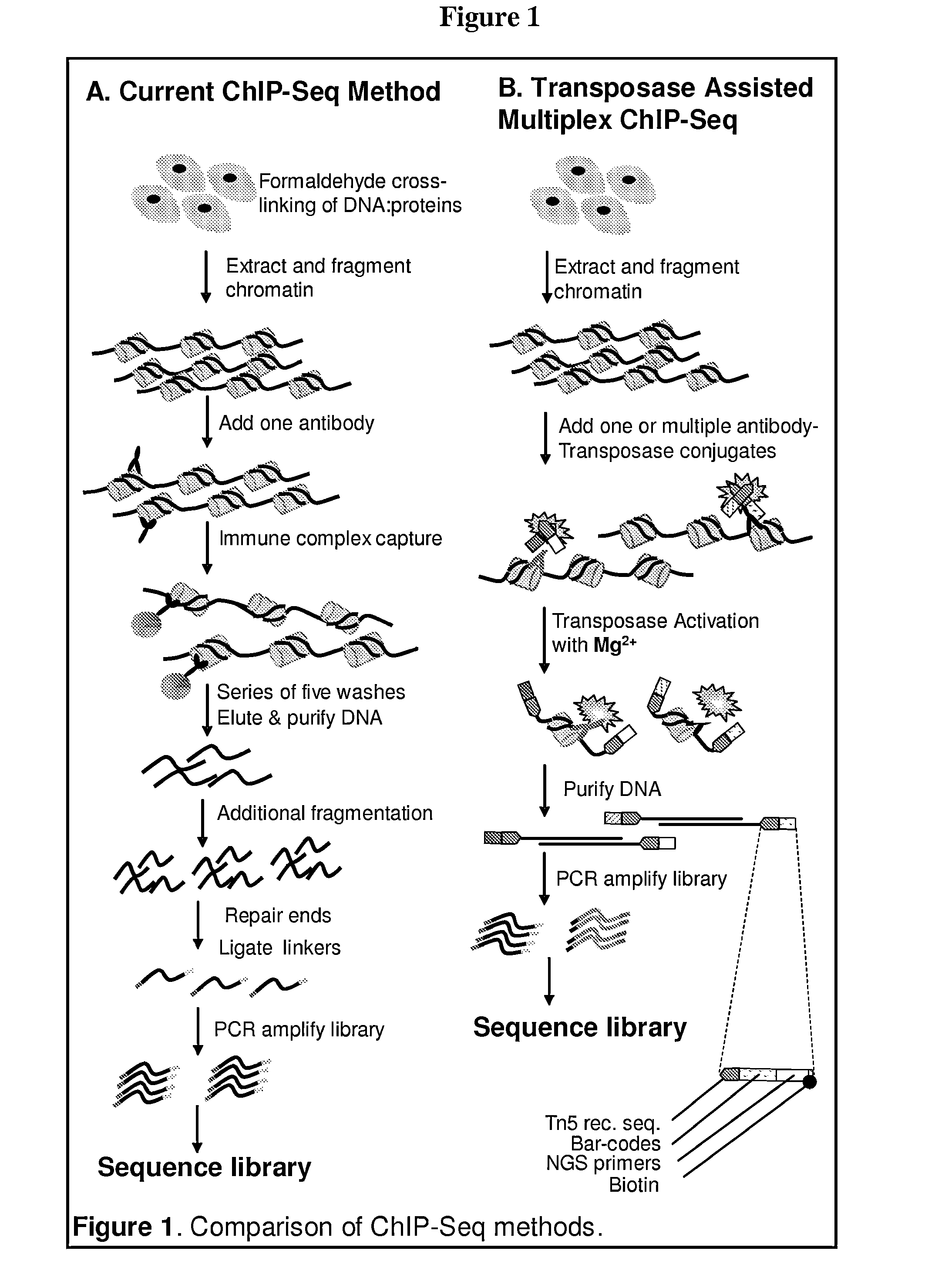
Multiplex isolation of protein-associated nucleic acids
ActiveUS20150111788A1Microbiological testing/measurementEnzyme stabilisationGenomeChromatin immunoprecipitation
The invention provides novel methods and materials for genetic and genomic analysis using single or multiplex isolation of protein-associated nucleic acids, including transposase-assisted chromatin immunoprecipitation (TAM-ChIP) and antibody-oligonucleotide proximity ligation. These methods comprise tagging and isolating chromatin or other protein-associated nucleic acids and using antibody-oligonucleotide complexes that recognize the proteins associated with such nucleic acids.
Owner:ACTIVE MOTIF INC
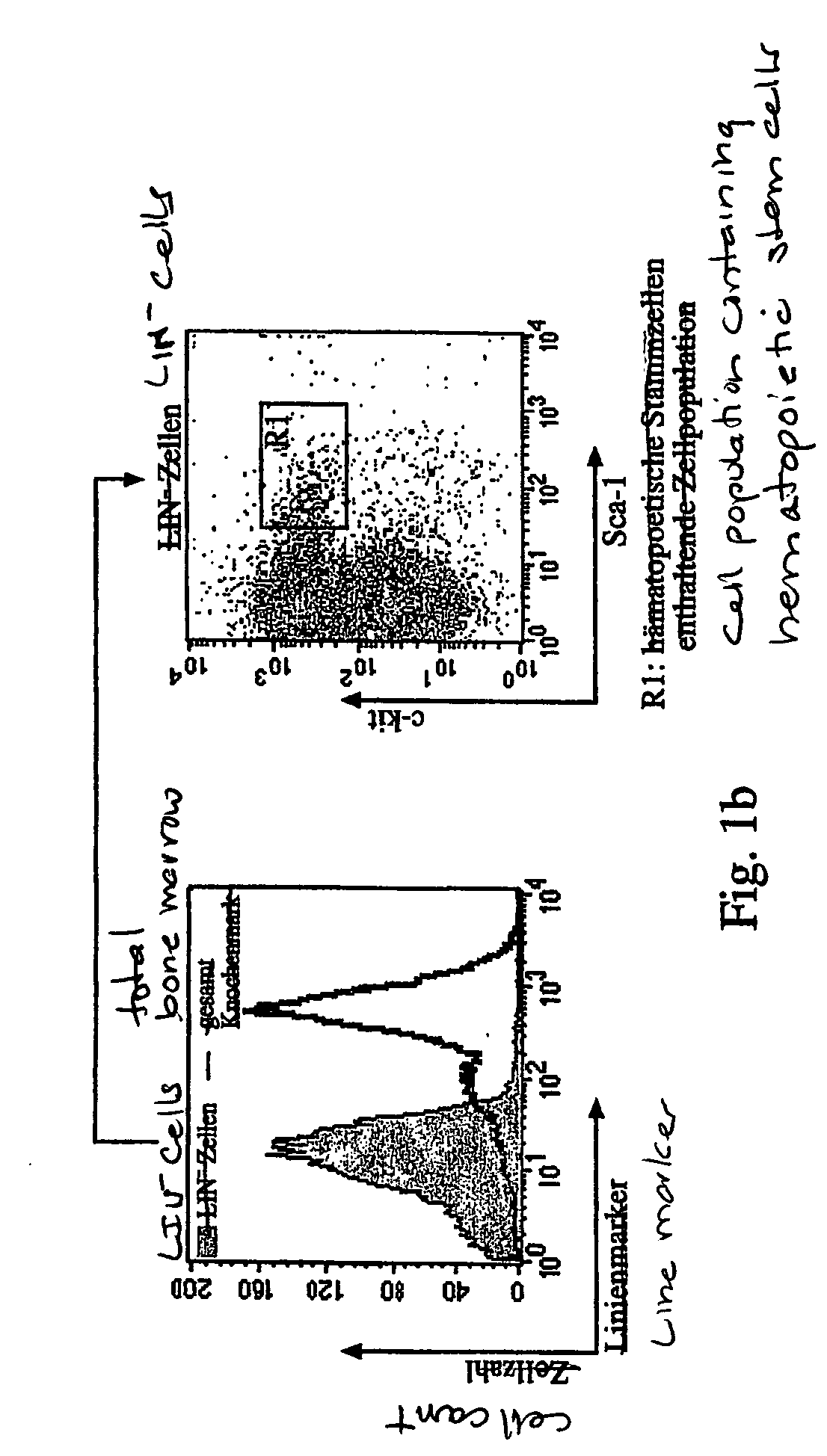
Optimization of determinants for successful genetic correction of diseases, mediated by hematopoietic stem cells
InactiveUS20110294114A1Improve stabilityImprove securityVectorsSugar derivativesNervous systemSickle cell anemia
Methods and compositions disclosed herein generally relates to methods of determining minimum hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) chimerism and gene dosage for correction of a hematopoietic disease; in particular, in in vivo models. The invention also relates to modified lentiviral expression vectors for increase a viral titer and various methods for increasing such titers as well as expression vectors capable of enhancing such titers. The invention also relates to CHS4 chromatin insulator-derived functional insulator sequences. The invention further relates to methods for genetic correction of diseases or reducing symptoms thereof, such as sickle cell anemia, a lysosomal storage disease. The invention further relates to a method of improving and / or correcting one or more central nervous system (CNS) abnormalities caused by one or more lysosomal storage disease. The invention further relates to methods of improving titer in transfection-based bioreactor culture production or transfection-based production systems using eukaryotic cells.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI
Linc rnas in cancer diagnosis and treatment
InactiveUS20120004278A1Increased and decreased expressionEasy to detectOrganic active ingredientsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCancers diagnosisMechanism of action
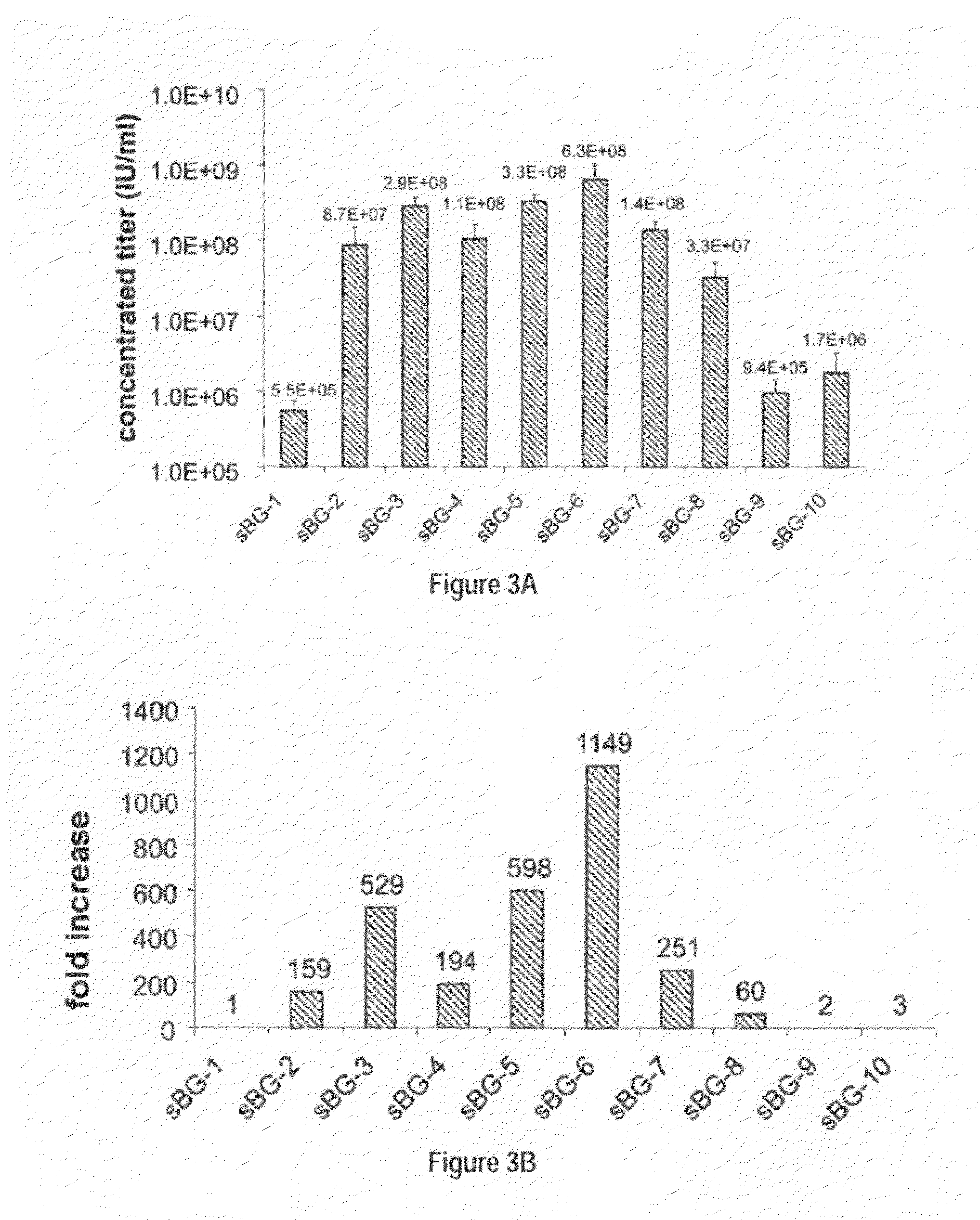
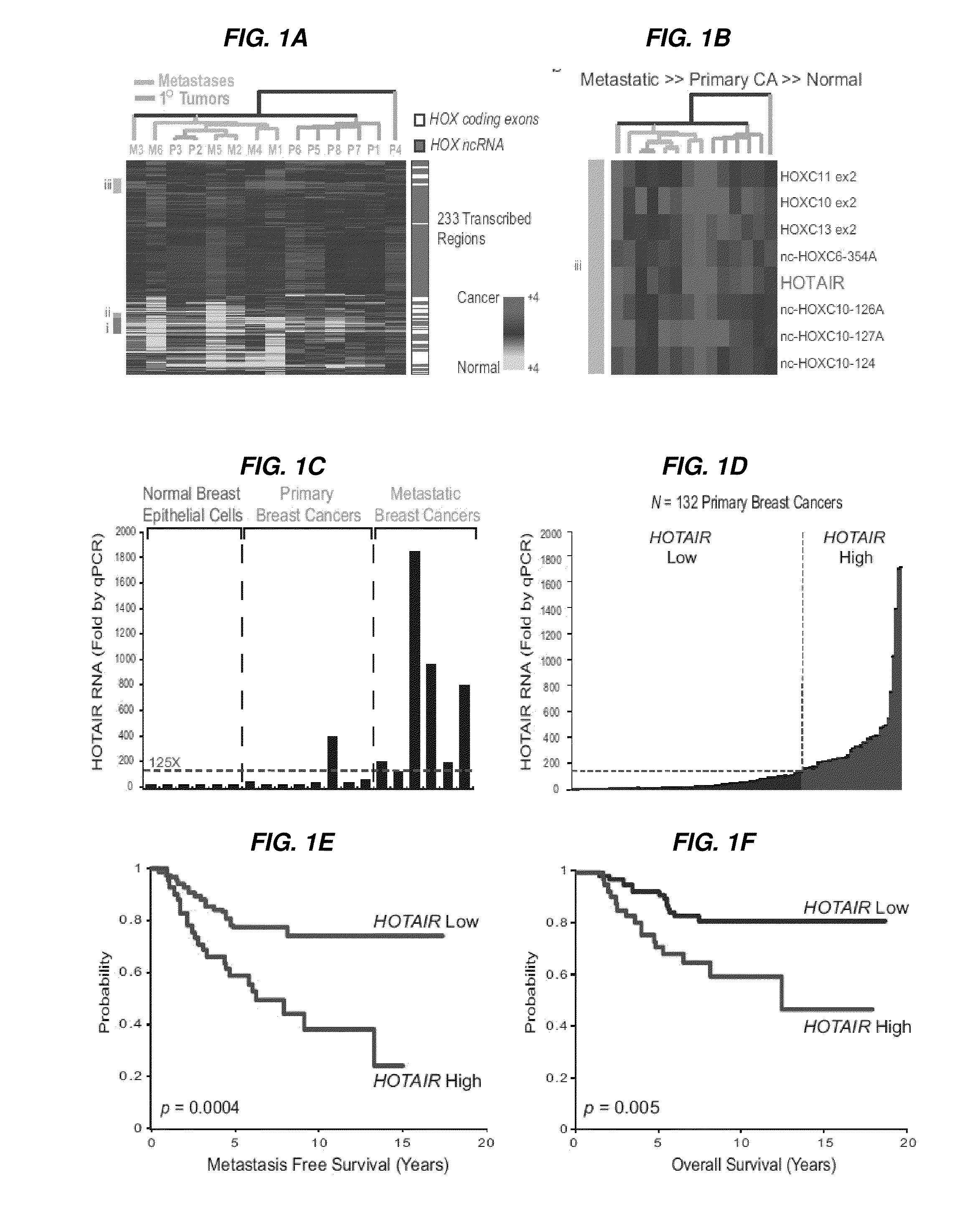
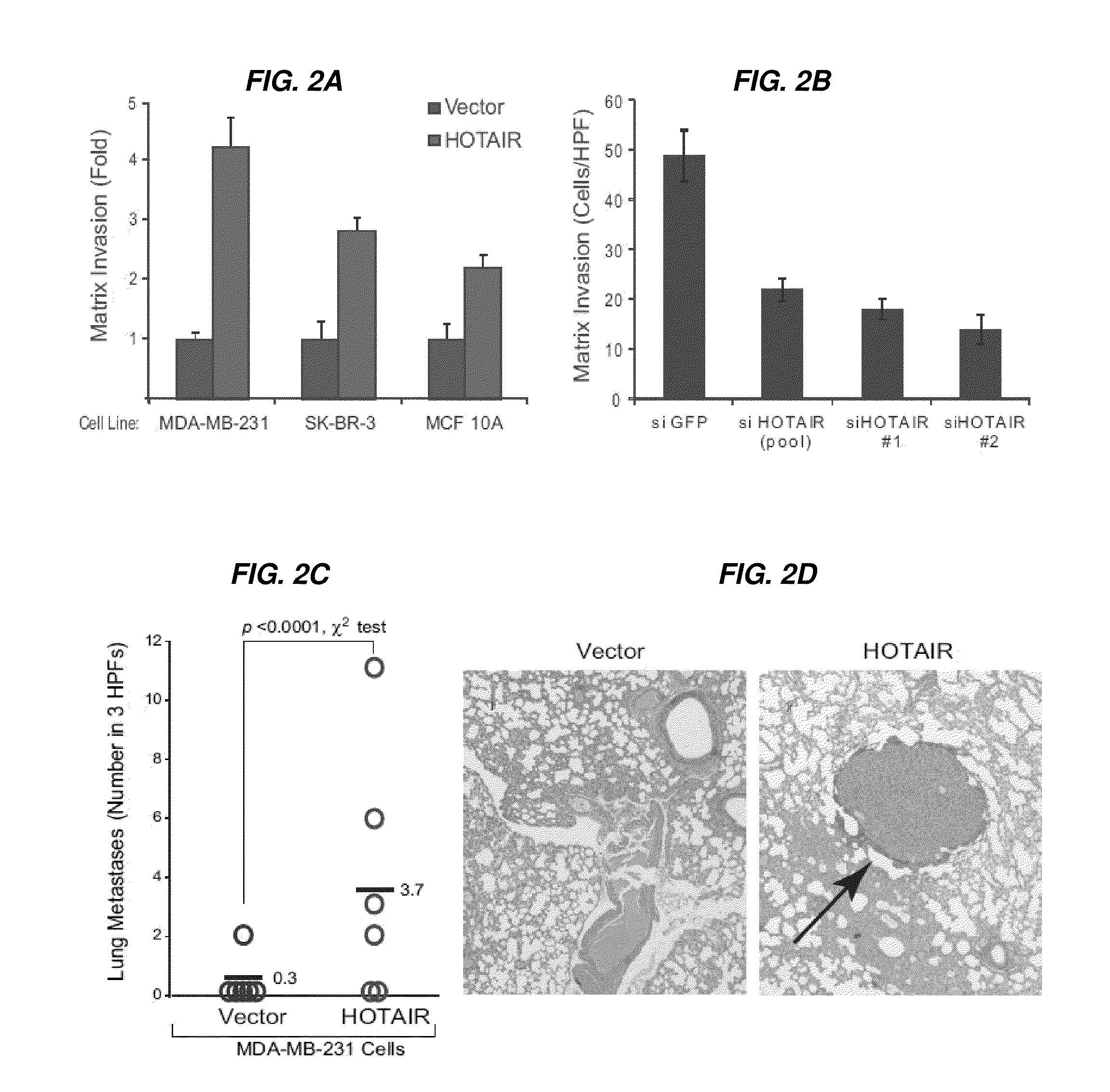
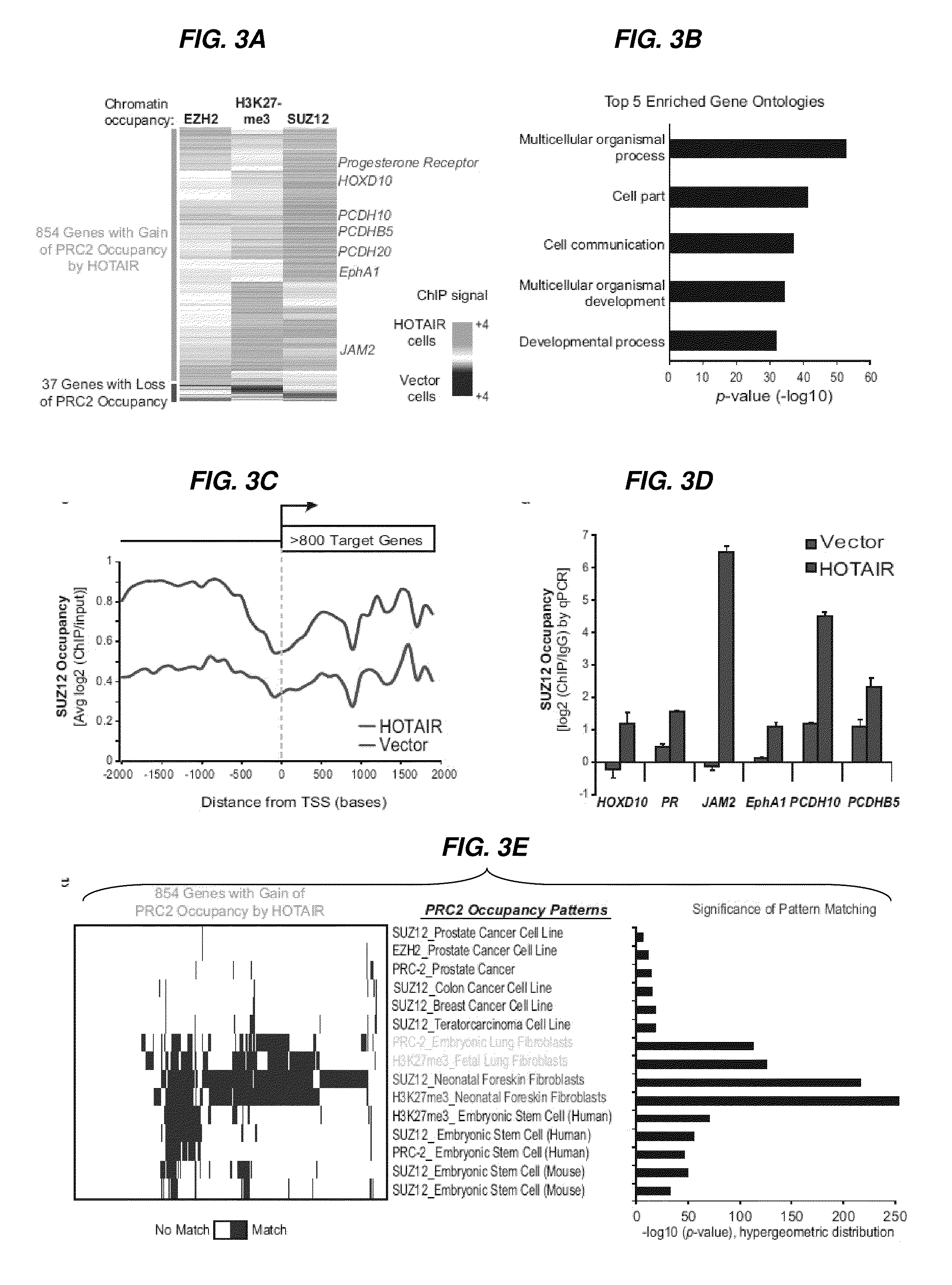
Long non-coding RNAs (lincRNAs), a relatively recently recognized class of widely transcribed genes, are thought to affect chromatin state and epigenetic regulation, but their mechanisms of action and potential roles in human disease are poorly understood. The present invention shows that long non-coding RNAs in the human HOX loci are systematically dysregulated during breast cancer progression, and that expression levels of the lincRNA termed HOTAIR can predict cancer metastasis. Elevated levels of HOTAIR can lead to altered patterns of Polycomb binding to the genome. These findings indicate that lincRNAs have active roles in modulating the cancer epigenome and may be important targets for cancer diagnosis and therapy.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Methods for closed chromatin mapping and DNA methylation analysis for single cells
ActiveUS20150368694A1Reduce and minimize and prevent chanceLess efficiently ligatedMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningDNA methylationGenomic DNA
Methods of identifying DNase I Hyper-Resistant Sites (DHRS), or in board sense, highly compact chromatin and characterizing the DNA methylation status of DMRs such as CpG islands and CpG island shores are provided. The methods are particularly useful for analysis of genomic DNA from low quantities of cells, for example, less than 1,000 cells, less than 100 cells, less than 10 cells, or even one cell, and can be used to generate chromatin and methylation profiles. The downstream analyses include in parallel massive sequencing, microarray, PCR and Sanger sequencing, hybridization and other platforms. These methods can be used to generate chromatin and DNA methylation profiles in drug development, diagnostics, and therapeutic applications are also provided.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Assay for Determining the Type and/or Status of a Cell Based on the Epigenetic Pattern and the Chromatin Structure
The present invention relates to a method for identifying a specific type and / or state of a mammalian cell in a sample obtained from a mammal, comprising a) analyzing the relative amount of accessible chromatin in regions that are specific for a cell-type and / or cellular state in the genome of said cell, b) comparing said relative amount of accessible chromatin said in regions with the relative amount of accessible chromatin in regions in the genome of said cell that are unspecific for a cell-type and / or cellular state, and c) deducing the specific type and / or state of said mammalian cell in said sample based on said comparison. Preferably, said identifying further comprises a relative quantification of said specific cell type and / or state based on said comparison. The method can further comprise a diagnosis of a predisposition to a disease or a disease based on said identification. Kits and certain markers in regions of accessible chromatin in the genome are described, too.
Owner:EPIONTIS GMBH
Method for constructing high-resolution single cell hi-c library with a lot of information
ActiveUS20180305685A1Small initial sample sizeHigh resolutionNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA fragmentationComputer science
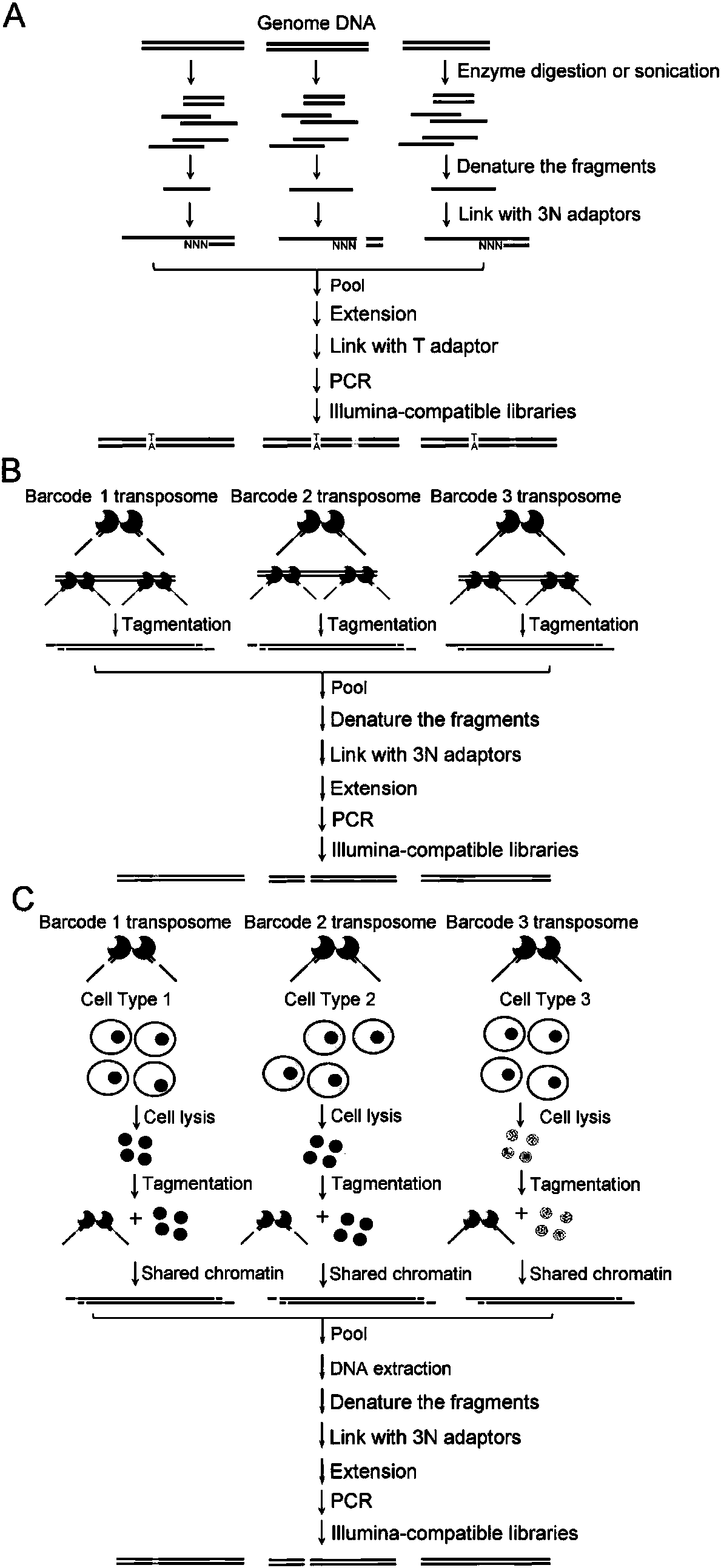
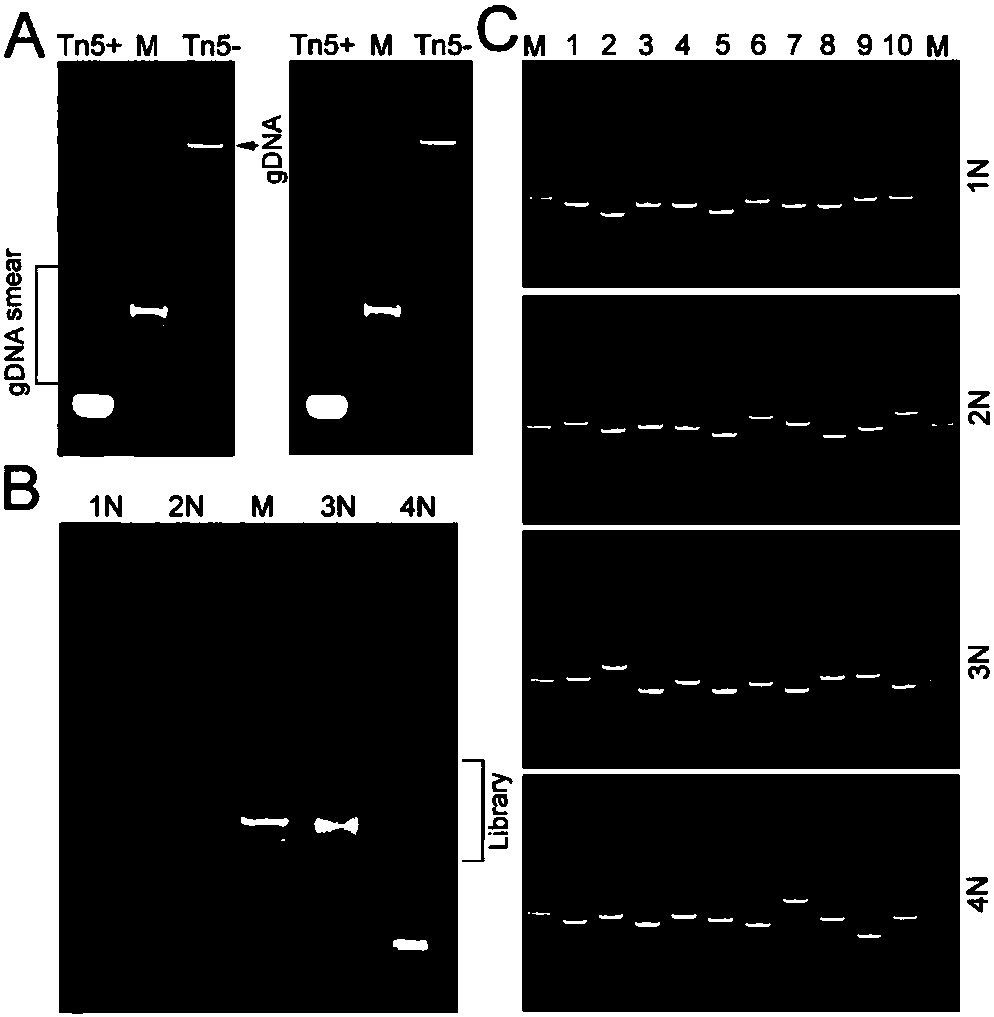
Provided in the present invention is a method for constructing a high-resolution single cell Hi-C library with a large amount of information, comprising the following steps: Step B: obtain a small amount of fixed chromatin; Step C: digest the fixed chromatin in Step B to obtain fragments of the fixed chromatin; Step D: reconnect the fragments of the fixed chromatin in Step C directly to obtain reconnected fragments of the fixed chromatin; Step E: de-fix the reconnected fragments of the fixed chromatin in Step D to release DNA fragments; Step F: amplify the released DNA fragments in Step E to obtain amplified products; and Step H: construct a sequencing DNA library by using the amplified products as the DNA fragments to be sequenced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ANNOROAD BIO TECH CO LTD +1
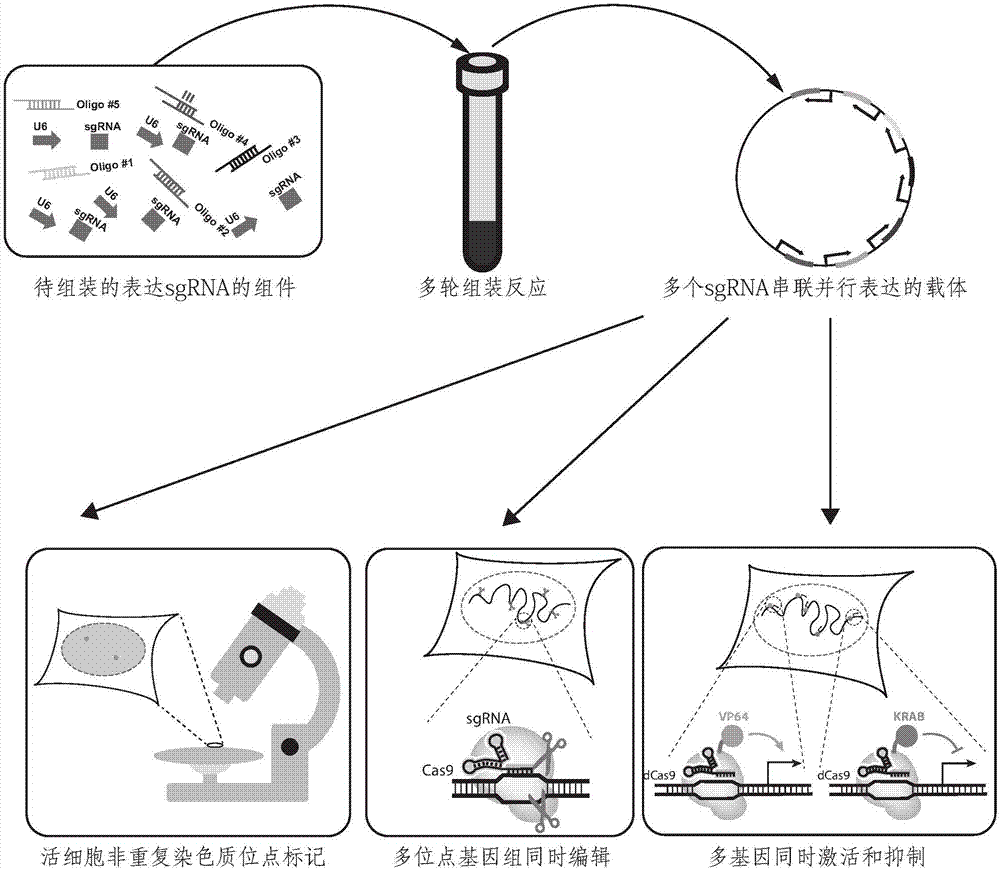
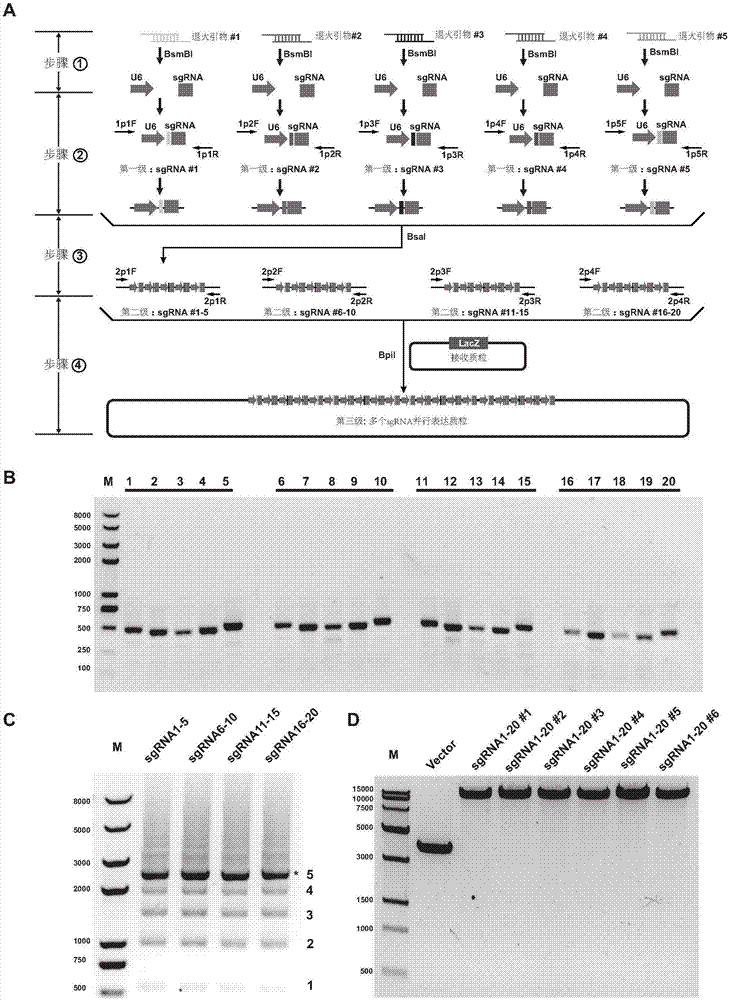
Cloning method for series parallel expression of a plurality of sgRNA based on grading assembling and application
InactiveCN106868031AAvoid lossNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionGolden gateLiving cell
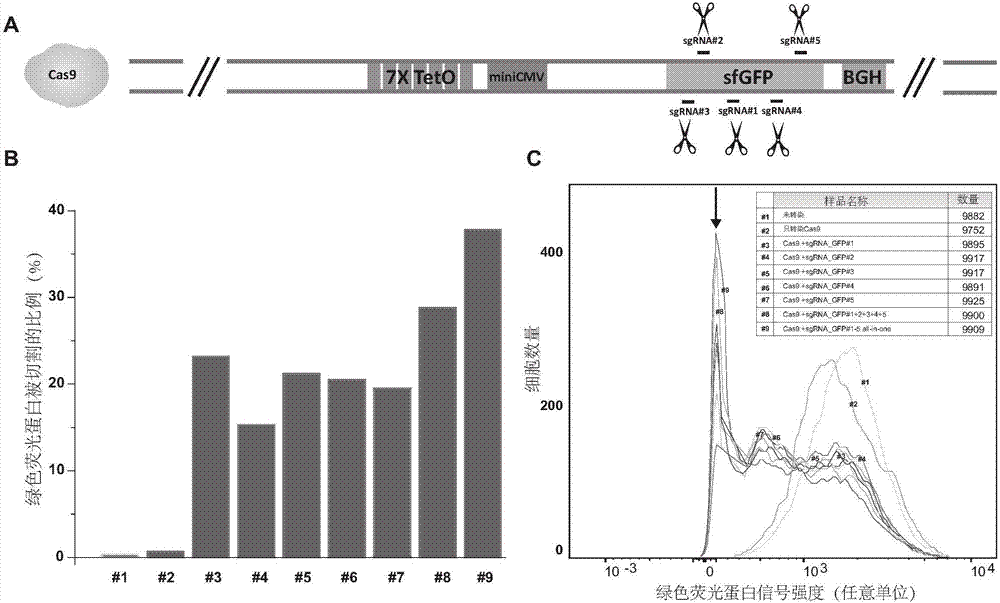
A CRISPR / Cas9 system has an ultrahigh parallel capacity. In order to meet the requirement for expressing a plurality of sgRNA in some cases, the invention provides a quick assembling method for a plurality of parallel expressed sgRNA. The invention utilizes grading Golden Gate reaction to develop a multi-turn amplifying method based on polymerase chain reaction and independent of a carrier, so as to realize the quick connecting assembling for 20 sgRNA within one week. The method for serially assembling a plurality of sgRNA developed by the invention has the advantages of time-saving and labor-saving effect, flexibility, high efficiency and multifunction. The method can be used for quickly assembling 2-20 sgRNA in different quantity onto one carrier. A plurality of parallel expressed sgRNA are utilized to target to a section of DNA, so that the functions of marking and tracking unrepeated sequence chromatin locus in living cells, cooperatively activating or restraining a single gene, simultaneously editing a plurality of genes and simultaneously up-regulating and down-regulating the genes can be achieved. The method can be widely used for editing the gene and understanding the organization structure and dynamic change of chromatin.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Non-invasive prenatal genetic diagnosis using transcervical cells
InactiveUS20050181429A1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisPrenatal diagnosisStaining
A non-invasive, risk-free method of prenatal diagnosis is provided. According to the method of the present invention transcervical specimens are subjected to trophoblast-specific immuno-staining followed by FISH, PRINS, Q-FISH and / or MCB analyses and / or other DNA-based genetic analysis in order to determine fetal gender and / or identify chromosomal and / or DNA abnormalities in a fetus. Also provided is a method of in situ chromosomal, DNA and / or RNA analysis of a prestained specimen by incubating the prestained specimen in ammonium hydroxide. Also provided is a method of identifying embryonic cells according to a nucleus / cytoplasm ratio of at least 1:1 and the presence of at least variably condensed chromatin.
Owner:MONALIZA MEDICAL
Compositions and methods for treating neoplasia, inflammatory disease and other disorders
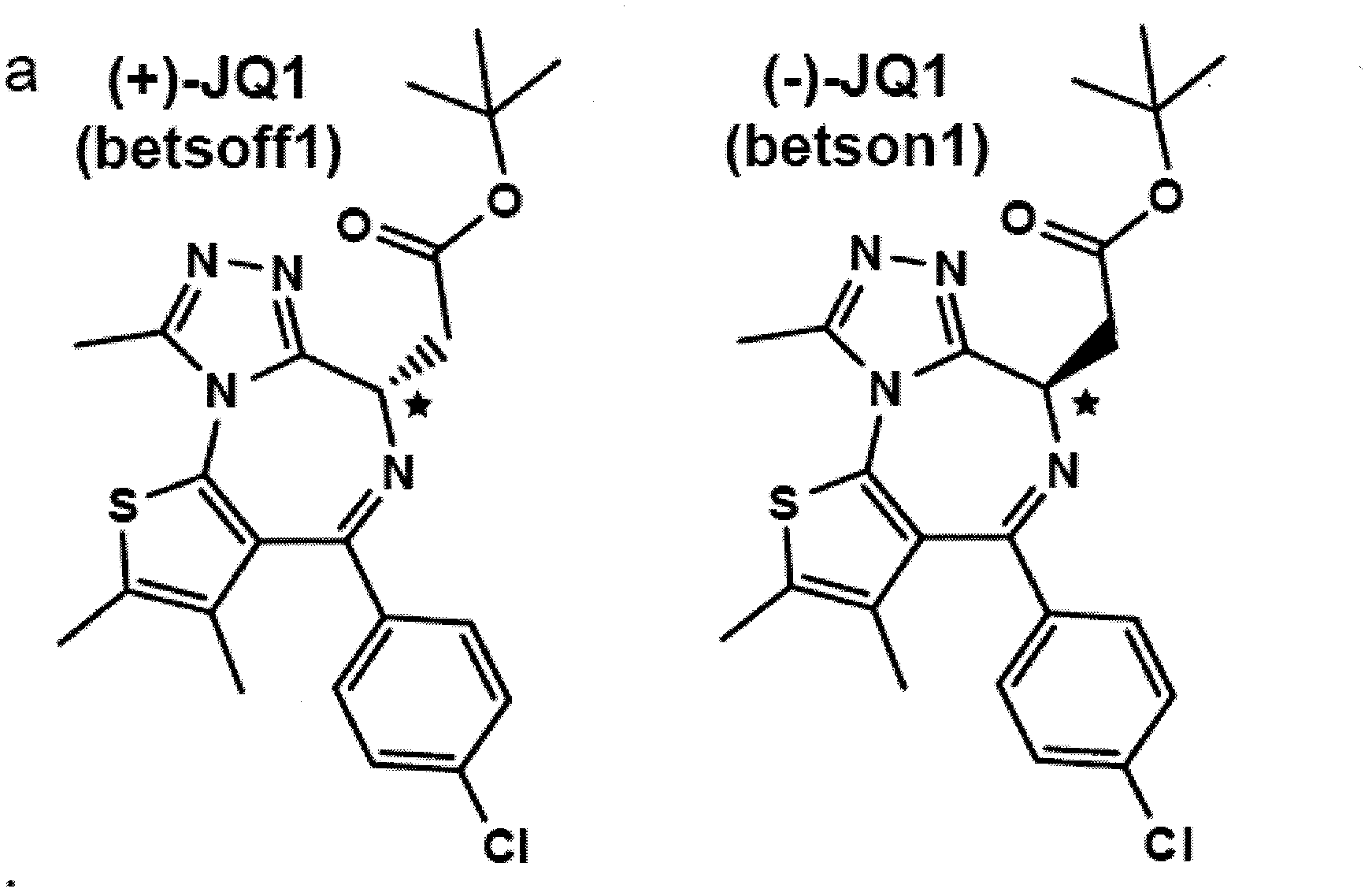
The invention features compositions and methods for treating or preventing a neoplasia. More specifically, the invention provides compositions and methods for disrupting the interaction of a BET family polypeptide comprising a bromodomain with chromatin (e.g., disrupting a bromodomain interaction with an acetyl-lysine modification present on a histone N-terminal tail).
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
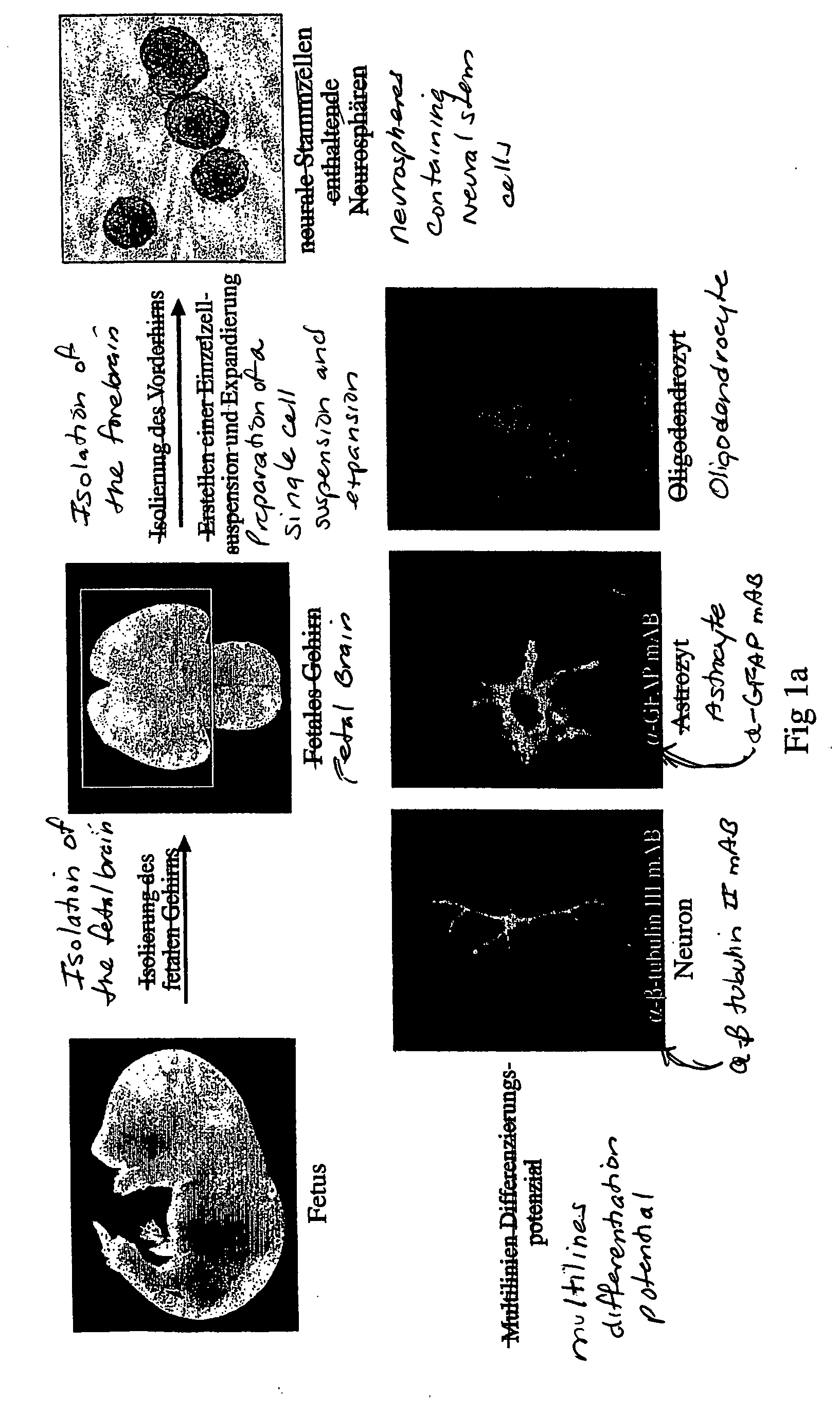
Method for producing stem cells with increased developmental potential
InactiveUS20060084172A1Increased differentiation potentialHigh development potentialGenetic material ingredientsGenetically modified cellsBiological bodyTissue sample
The invention relates to a method for producing stem cells having an increased development potential from somatic stem cells, wherein a tissue sample comprising somatic stem cells or a body fluid sample comprising somatic stem cells is taken from an organism, wherein from this tissue sample or body fluid sample as an option somatic stem cells are isolated and / or cultivated, and wherein the thus obtained somatic stem cells are treated with a substance modulating the methylation of the DNA of the cells or a substance modulating the acetylation of chromatin of the cells.
Owner:JULIUS MAXIMILIANS UNIV WURZBURG
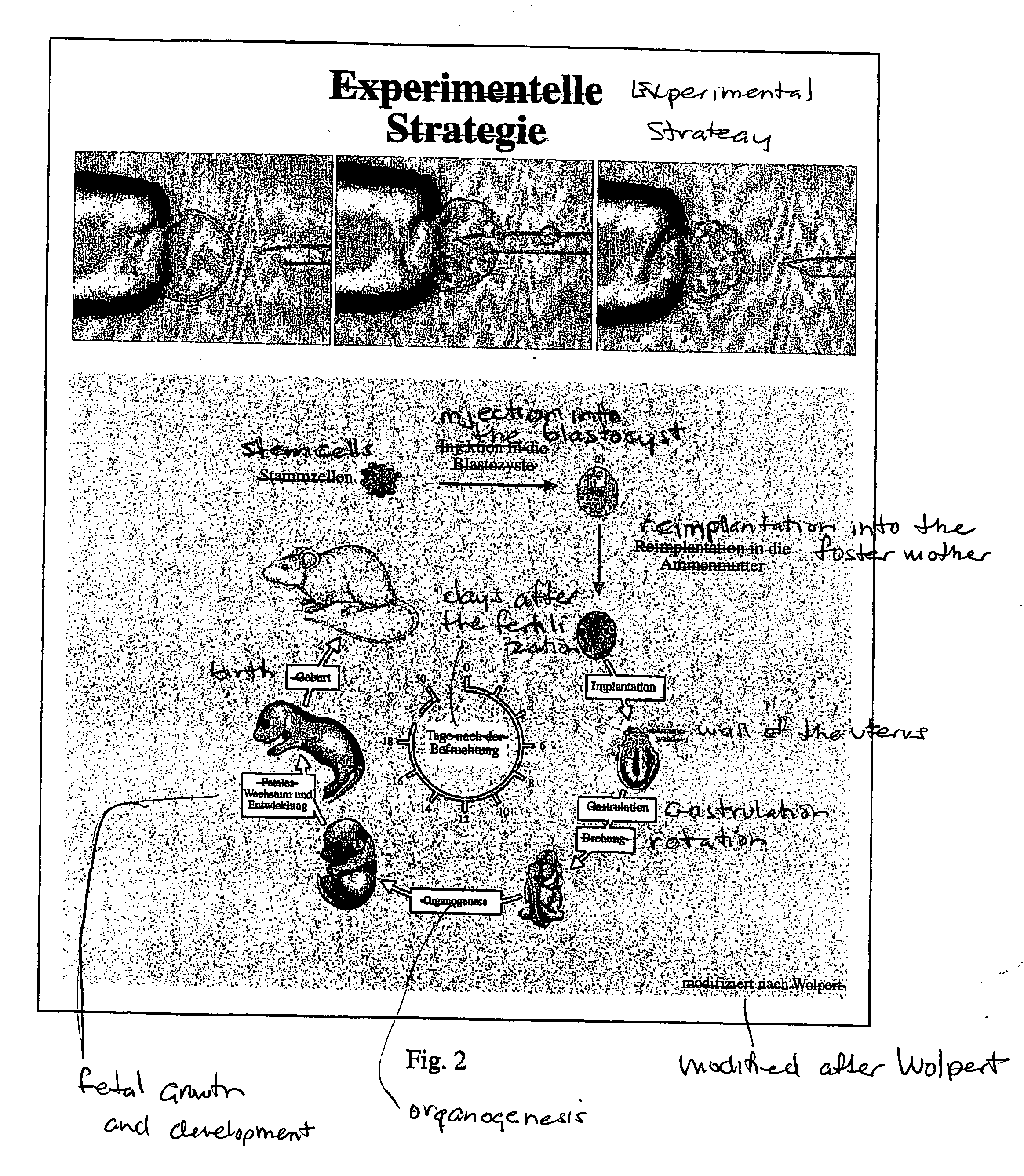
Methods for cloning mammals using reprogrammed donor chromatin or donor cells
InactiveUS20060212952A1Improve completenessImprove survivabilityNew breed animal cellsRecombinant DNA-technologyReprogrammingMammal
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
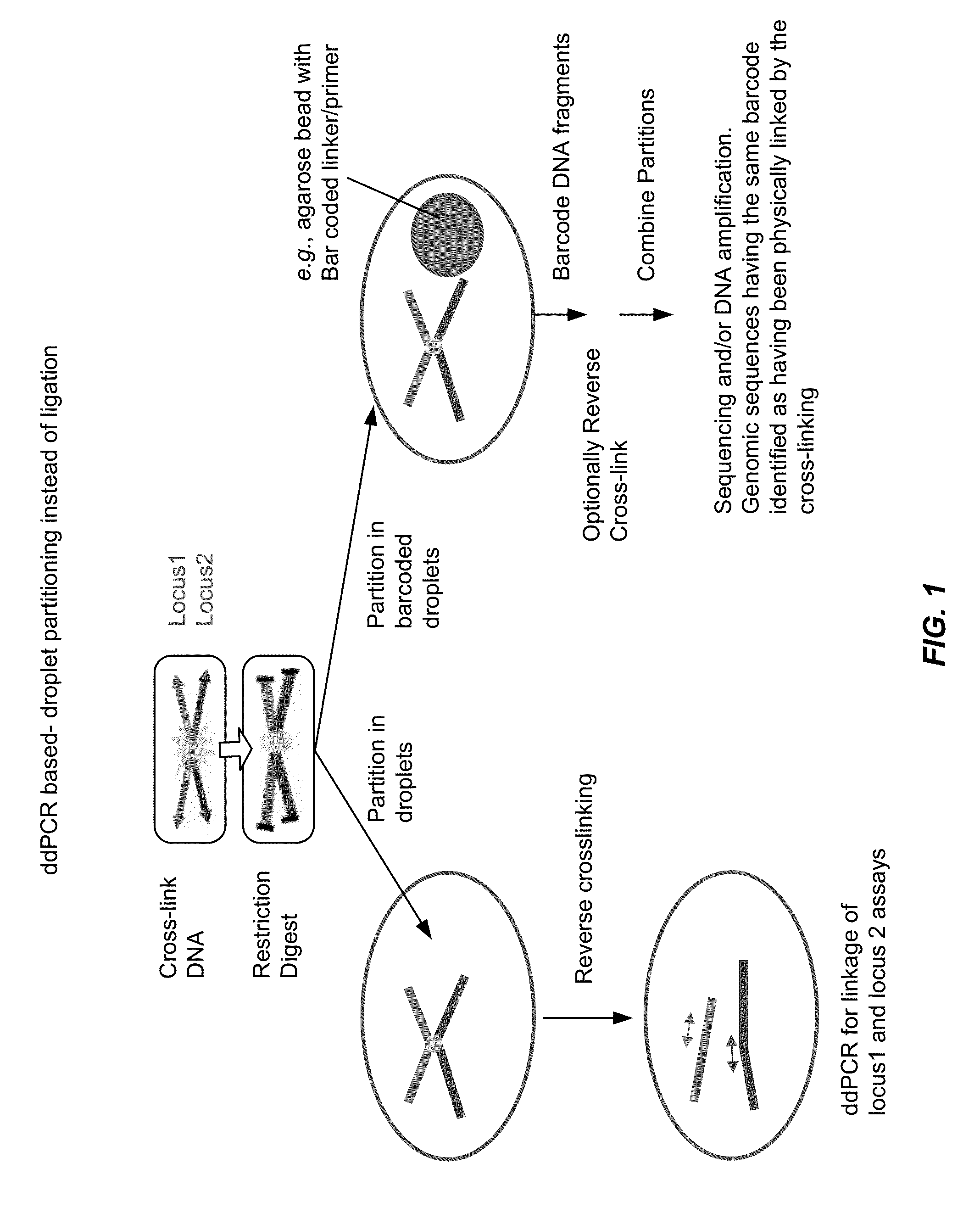
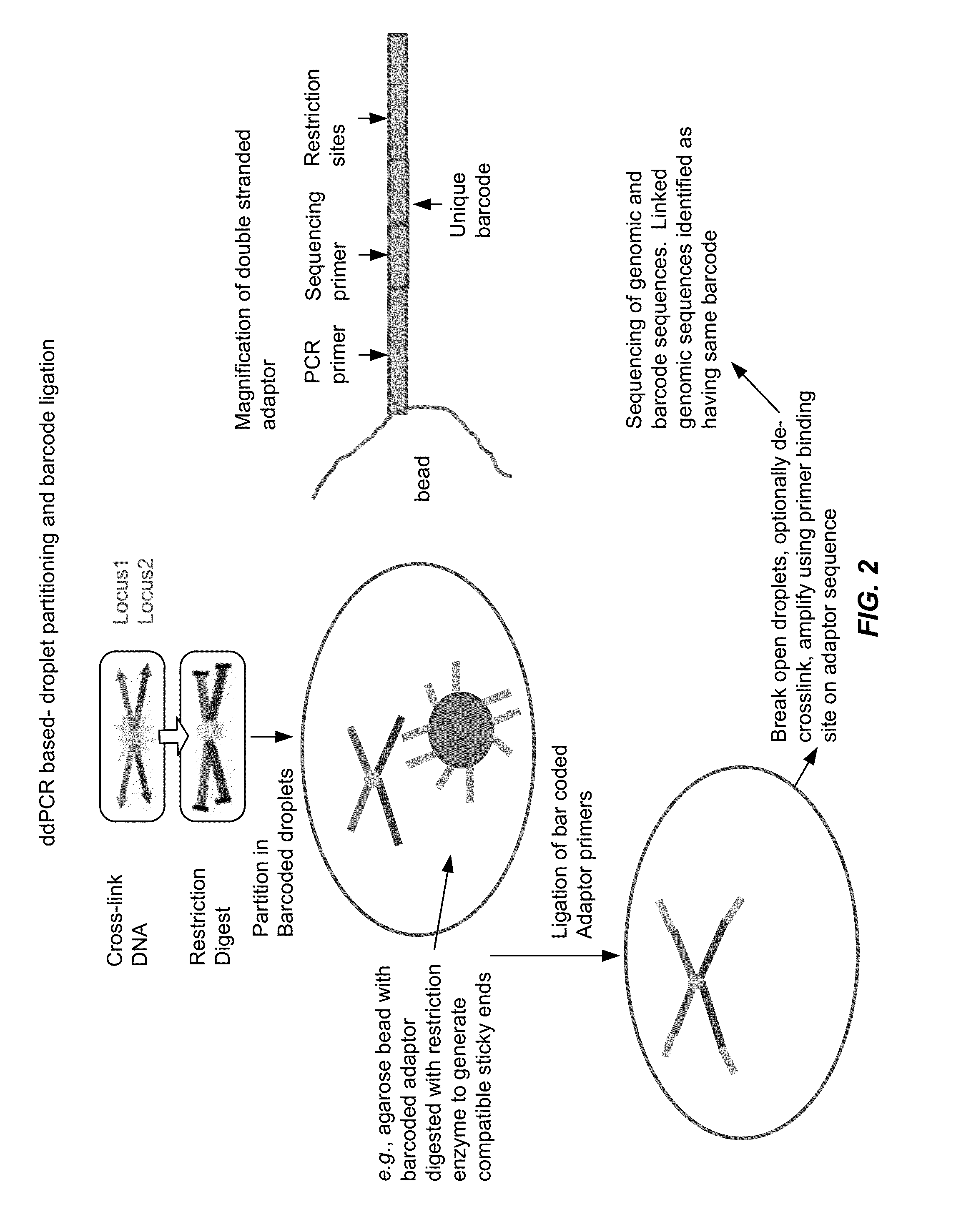
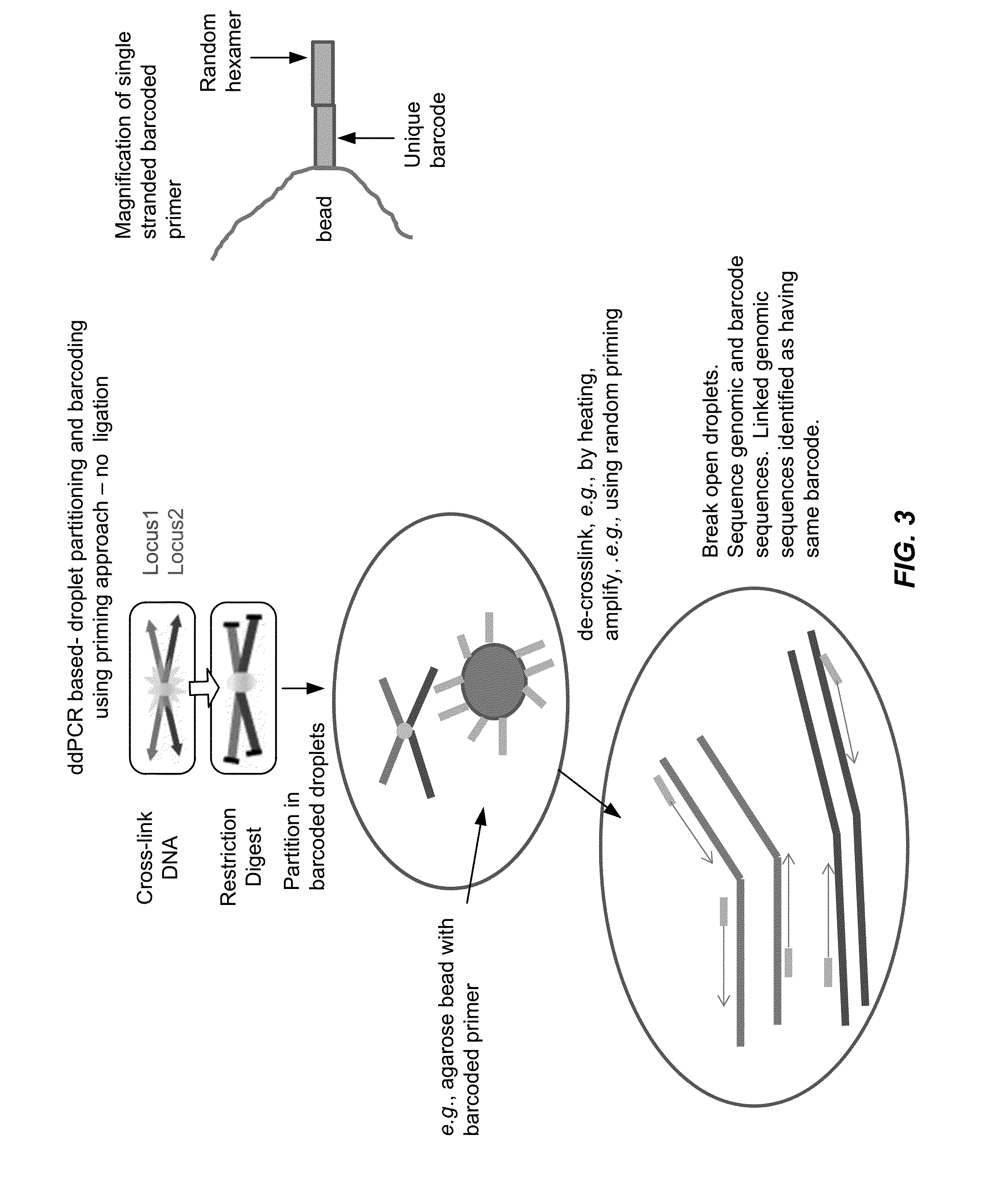
Tethered Conformation Capture
InactiveUS20110287947A1High resolutionReduce noiseMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningCross-linkEnzyme
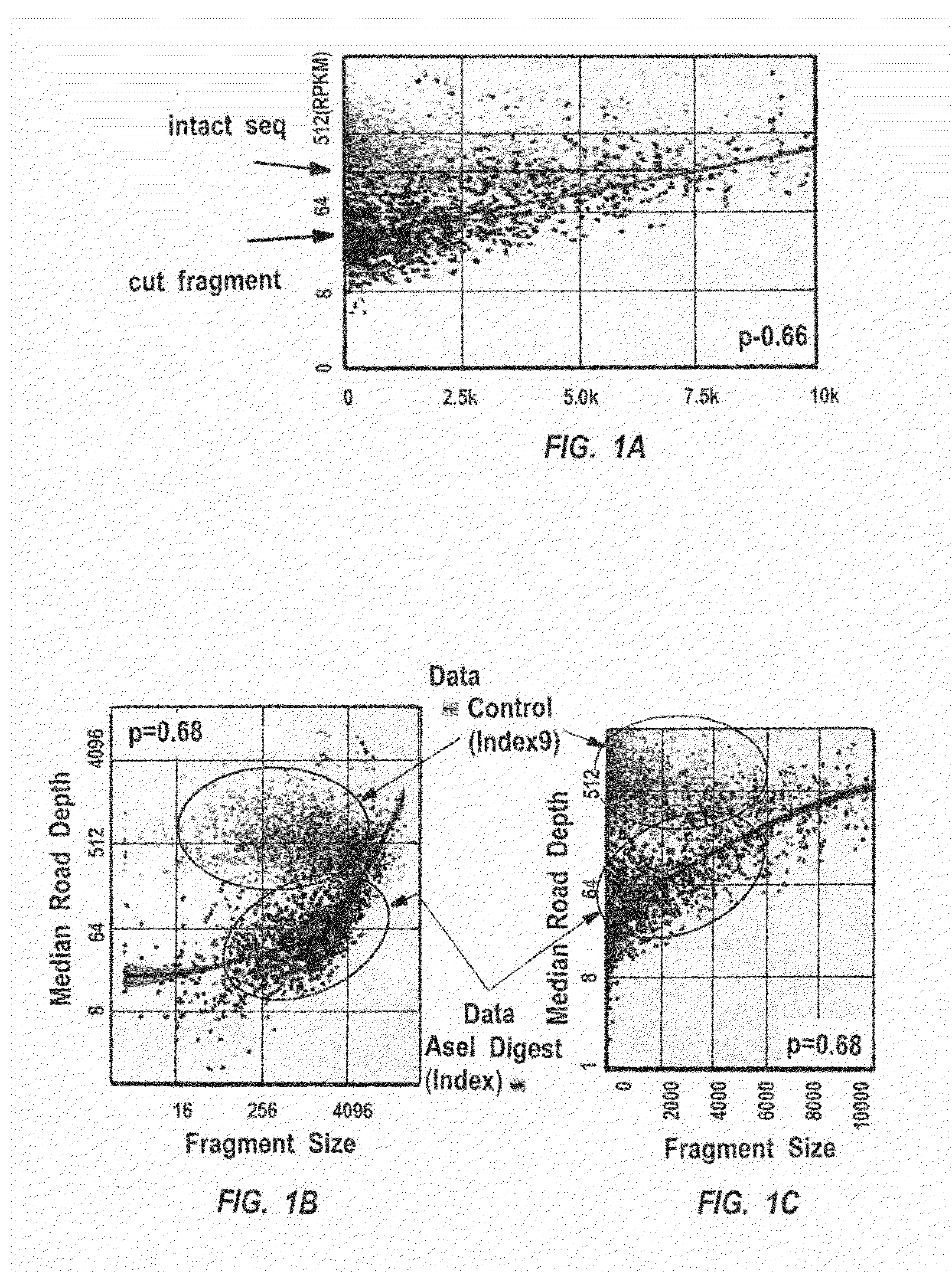
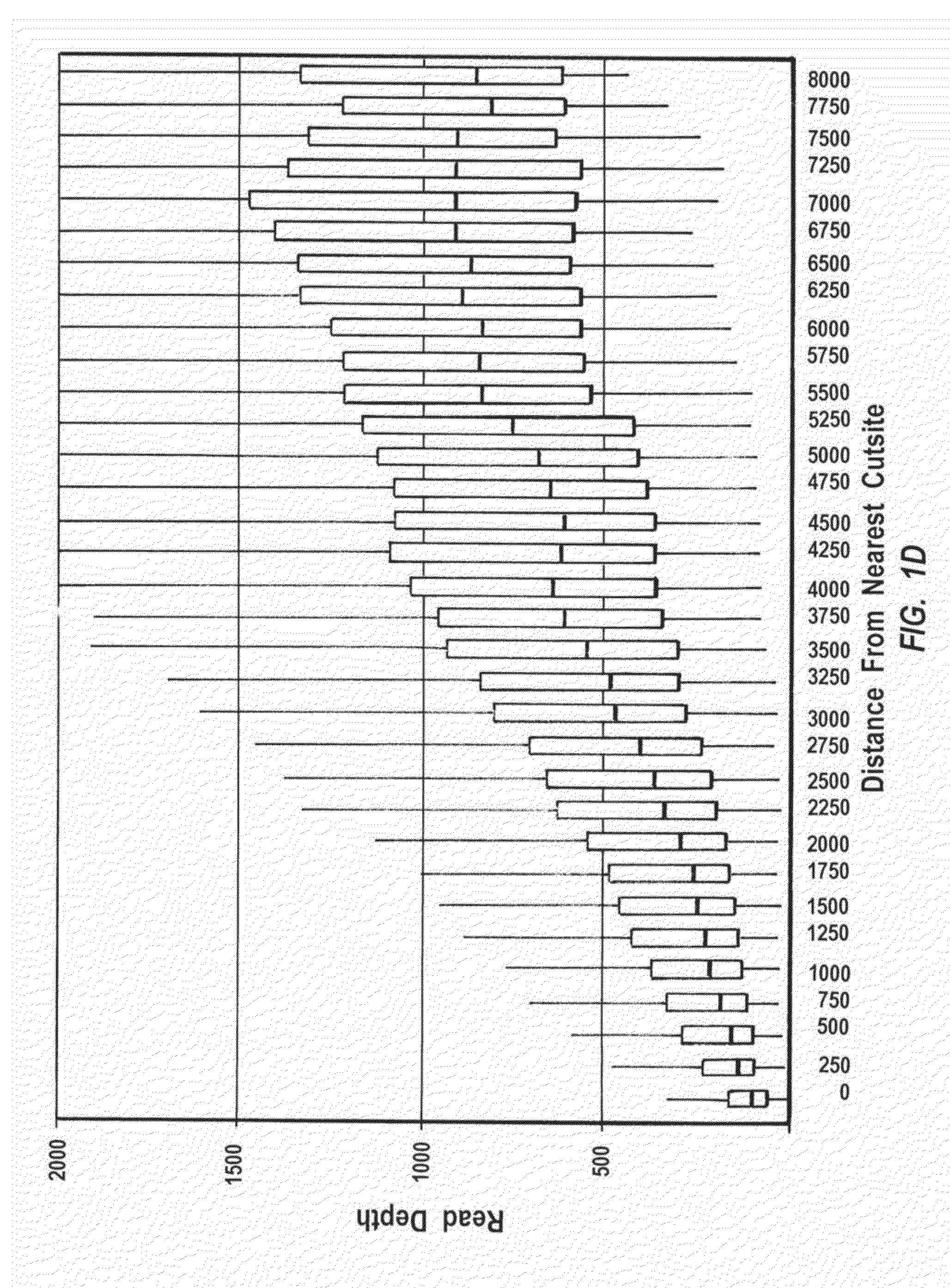
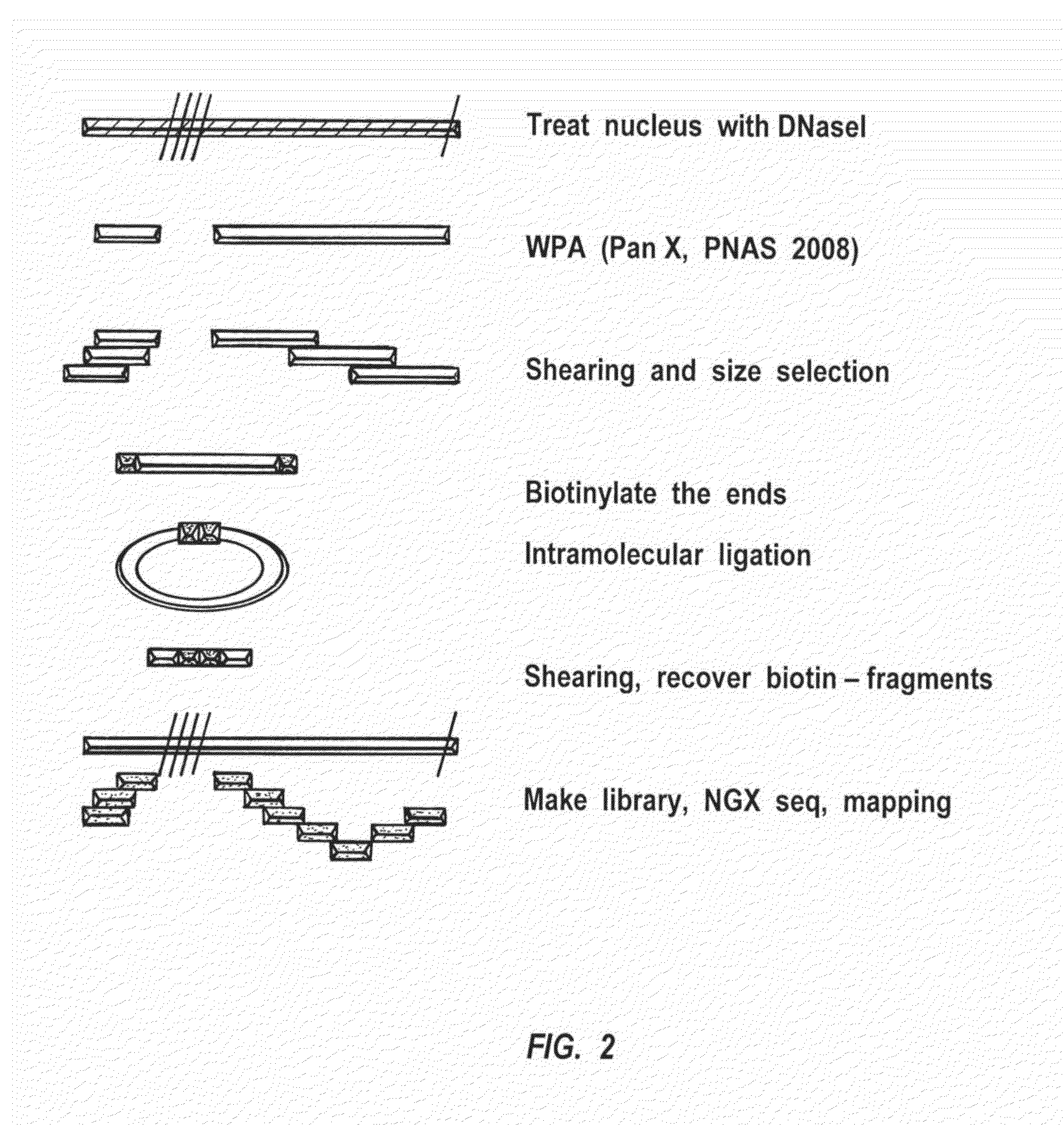
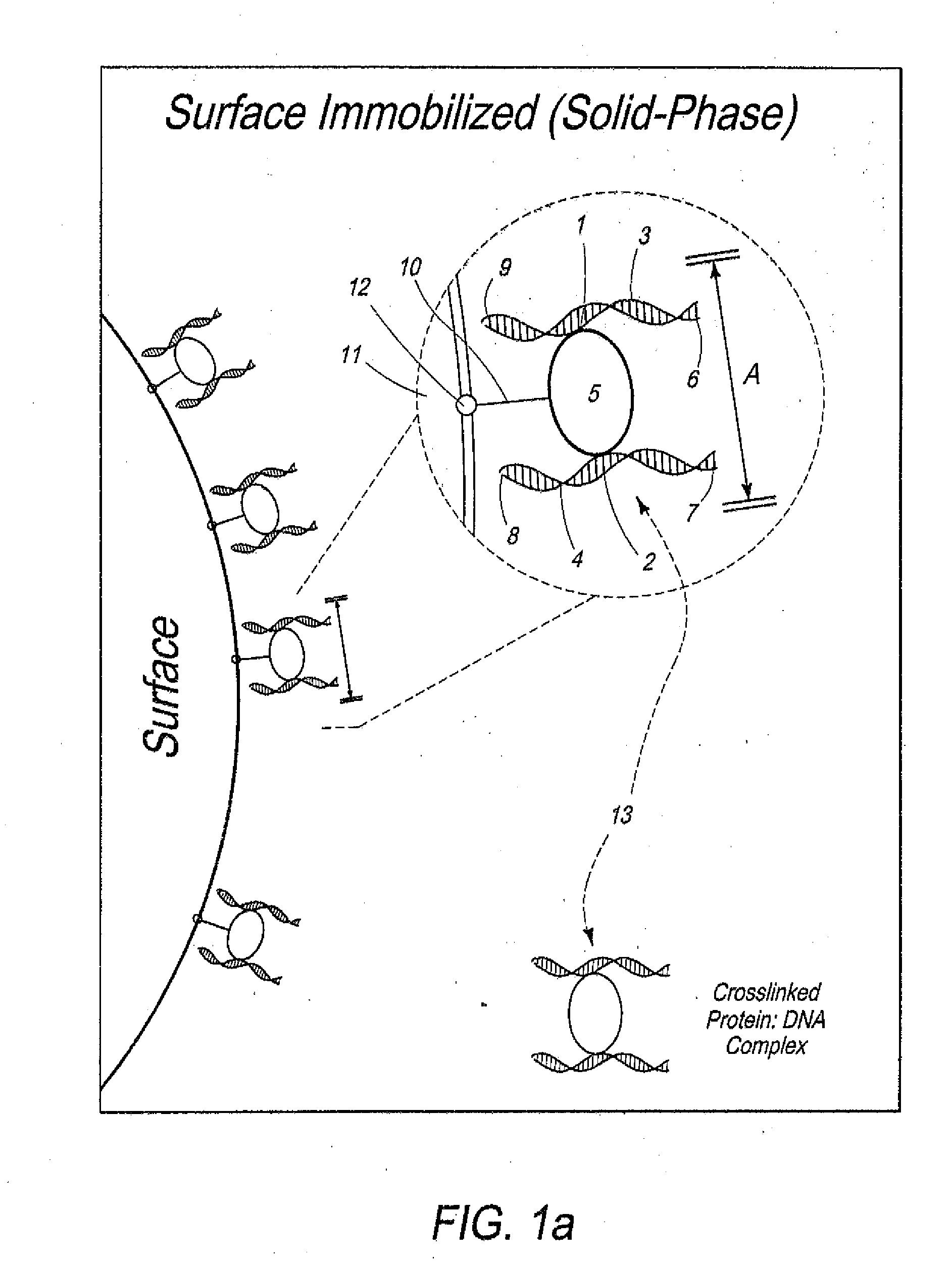
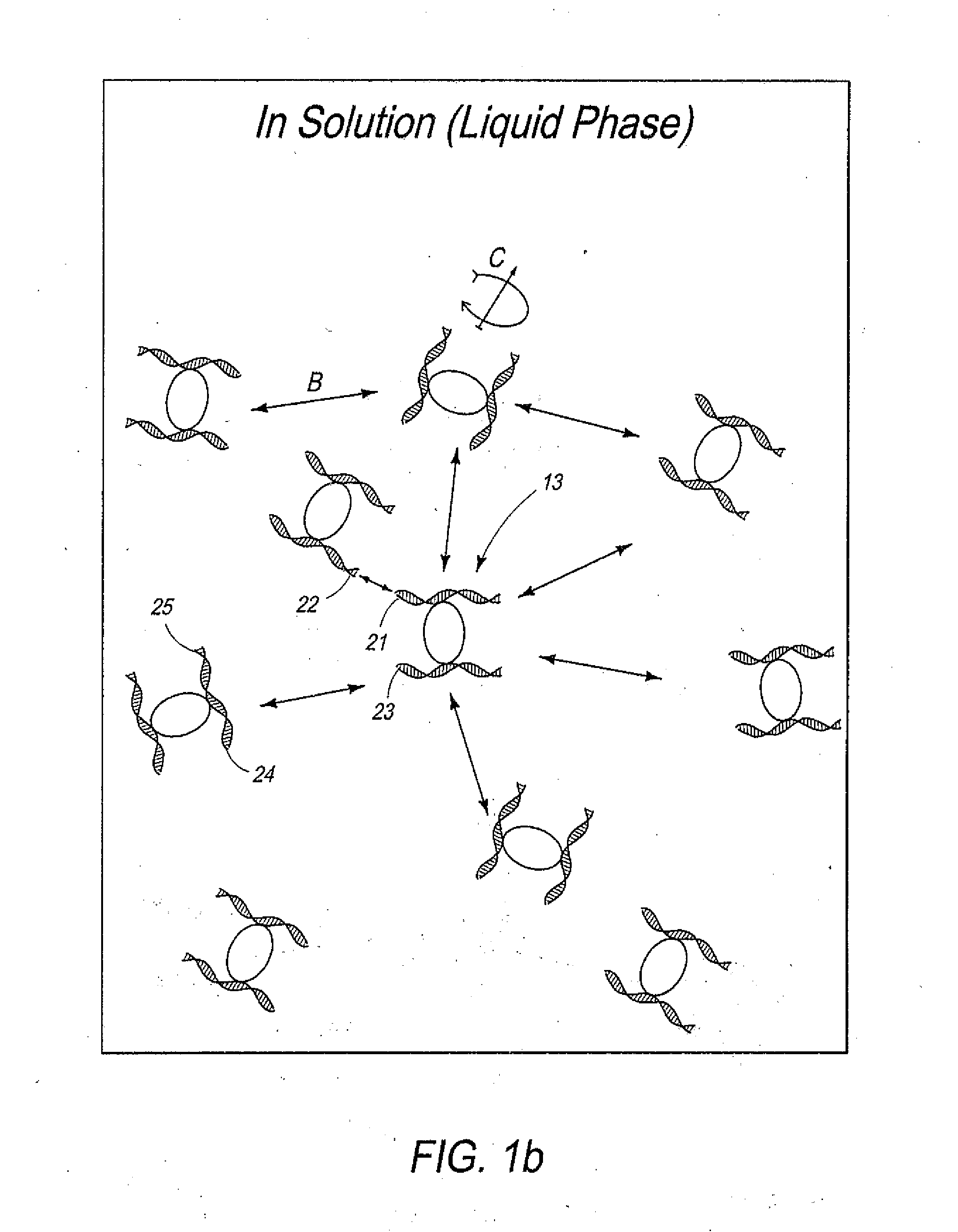
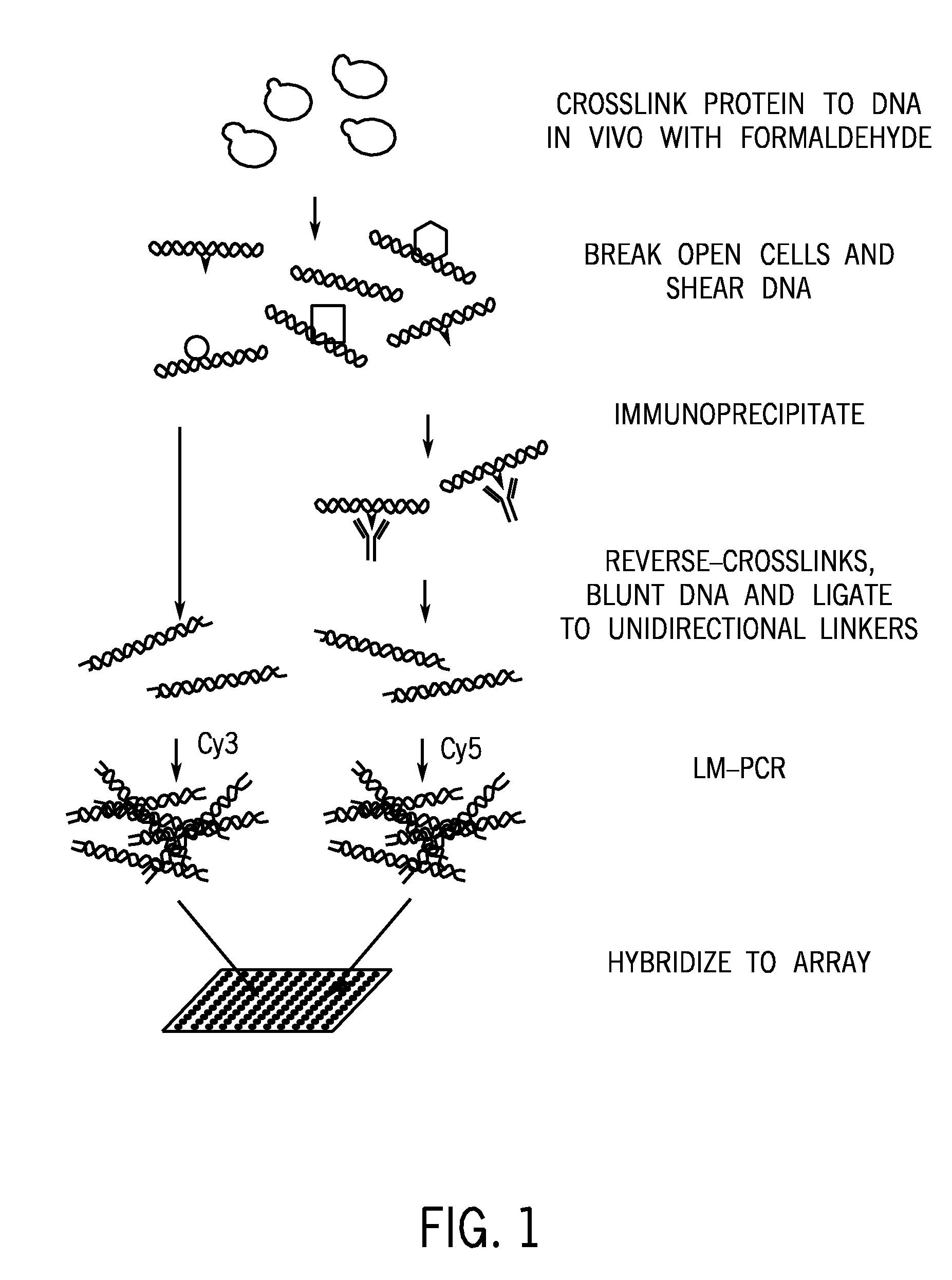
Disclosed are methods and systems for determining the three-dimensional structure of chromatin in eukaryotic cells. More specifically, disclosed are methods and systems for obtaining chromatin structural information by surface immobilization, i.e tethering crosslinked protein:DNA complexes and / or ligated DNA complexes to media such as beads, gels, and or matrices during the conformation capture assay. In general, the method includes contacting a cell with a cross-linking reagent to cross-link DNA and protein in the cell; lysing the cell, producing cross-linked protein:DNA complexes by cutting the chromatin using a chemical, physical or enzymatic method, substantially immobilizing the cross-linked protein:DNA complexes, ligating the cross-linked protein:DNA complexes intramolecularly such that the ligated protein:DNA complexes represent structural organization of the chromatin; characterizing the ligated DNA by sequencing or other methods; and identifying any structural organization of the chromatin. The structural organization preferably includes information relating to interacting loci of the chromatin.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
CRISPR/Cas9 enrichment sequencing method applied in large-scale screening of cancer genes
InactiveCN105400773AHigh infection efficiencyMeet the packaging ratioMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationInfected cellCancer cell
The invention relates to a CRISPR / Cas9 enrichment sequencing method applied in large-scale screening of cancer genes. Firstly, an sgRNA library is established; then the sgRNA library is packaged by lentiviruses, and viruses are collected; the sgRNA library is screened in a cancer cell line, the obtained cells are extracted and screened, and genome DNAs of precancerous cells are screened; finally, enrichment of sgRNAs in the genome DNAs is carried out. When the provided method is compared with the prior art, the screening process of CRISPR / Cas9 cells is improved, the virus infection efficiency is determined and the virus MOI value is determined through a simple method and by utilization of puromycin resistance of infected cells, importantly, the restriction enzyme cutting method and a high flux method are combined, correct chromatin fragments can be obtained effectively, false positive caused by non-specific PCR amplification can be lowered, a DNA template of sgRNAs can be amplified efficiently, and a library establishment efficiency is raised.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Method for ex-vivo separation of apoptotic chromatin fragments from blood or plasma for prevention and treatment of diverse human diseases
InactiveUS20070092509A1Avoid spreadingPrevent initiationGenetic material ingredientsMedical devicesApoptosisInstability
A method of prevention / treatment of pathological consequences of DNA damage triggered by incorporation of circulating apoptotic chromatin fragments into healthy cells of individuals / patients in need therefore, said method comprising ex vivo or extra corporeal treatment of blood / plasma for removal of circulating chromatin fragments released from apoptotic cells which apoptotic chromatin fragments are capable of triggering DNA damage leading to genomic instability, senescence, apoptosis and cancerous transformation of healthy cells on being integrated into their genomes
Owner:TATA MEMORIAL CENT
Chromosome conformation capture in partitions
ActiveUS20150225786A1Increase completionImprove efficiencyNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementChromosome conformation captureChromatin
Methods compositions and kits are provided for performing a chromatin or chromosome conformation capture assay in partitions.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
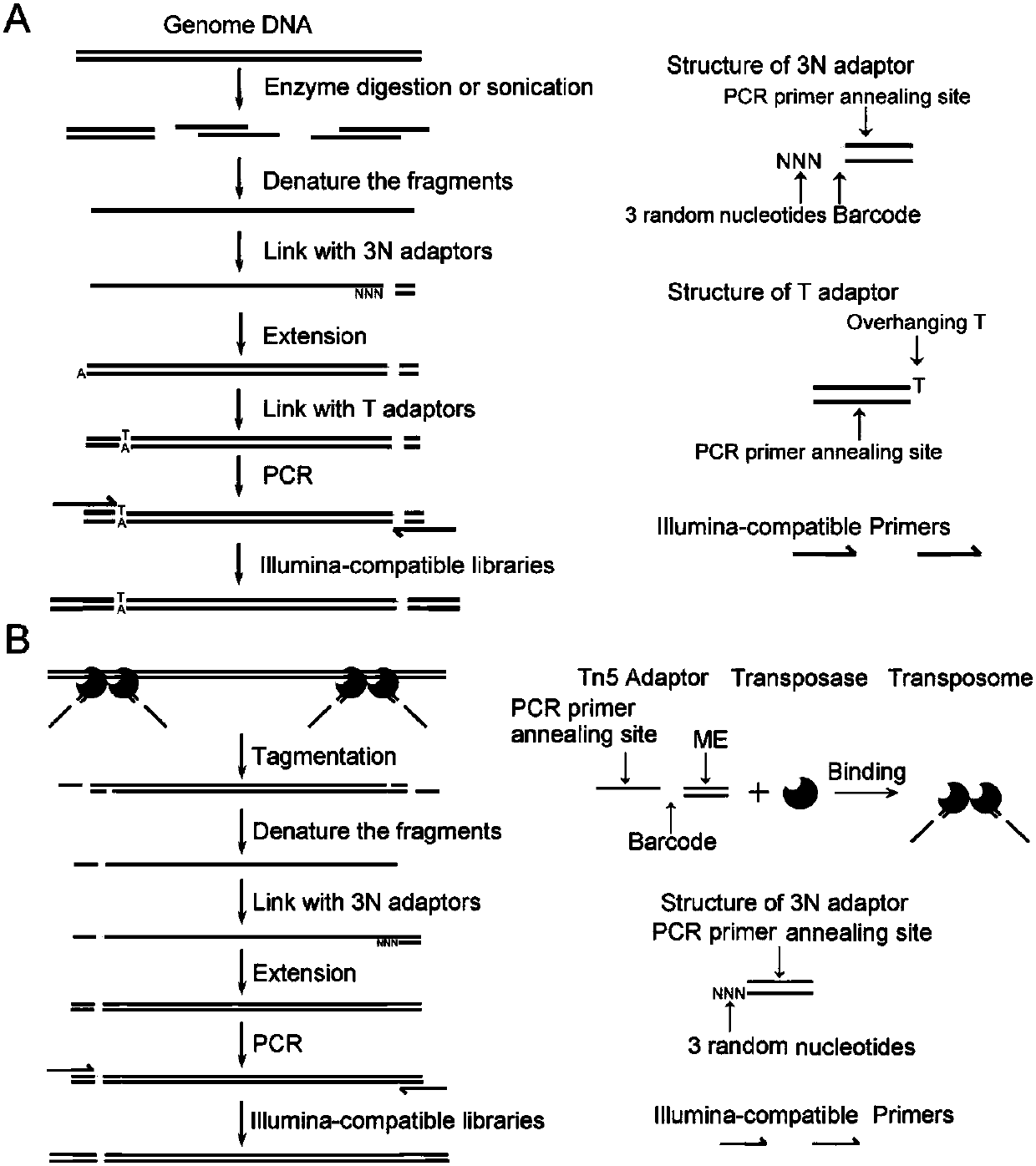
Construction method for next-generation sequencing library based on single-stranded connector and application thereof
ActiveCN107586835AEasy to compare and analyzeSimplify the library building processMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationNucleic acid detectionSingle strand
The invention discloses a construction method for a next-generation sequencing library based on a single-stranded connector and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out denaturation on a double-stranded DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) or RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) / DNA heterozygote segment to generate single-stranded DNA; (2) connecting one single-stranded connector with a 3' end of the single-stranded DNA; (3) extending the single-stranded DNA connected with the single-stranded connector by utilizing DNA polymerase to generate double-stranded DNA; (4) connectingthe other end of the double-stranded DNA with a T connector or a Tn5 label connector; (5) carrying out PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification on the double-stranded DNA with two ends connectedwith the connectors to form a DNA library capable of sequencing of a next-generation sequencing technology. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for constructing the next-generation sequencing library and determining a DNA sequence and also can be used for identifying a chromatin open region, carrying out gene expression detection, carrying out trace nucleic acid amplification and thelike; the method is a novel method which belongs to the field of nucleic acid detection and analysis and has various functions and wide application value.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Minimal dna sequence acting as a chromatin insulator and its use in protein expression
ActiveUS20070134761A1NumberEnhance interestPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsA-DNAChromatin
Owner:MERCK SERONO SA
Chromatin structure detection
InactiveUS20100136559A1Quick buildCumbersome stepsMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic DNAA-DNA
The present application provides methods and compositions for determining accessibility of a DNA modifying agent in genomic DNA.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Method for identification and monitoring of epigenetic modifications
InactiveUS20070196843A1Quick filterMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingGenomeChromatin
The present invention provides novel methods for identifying and monitoring epigenetic modifications, such as imprinted genes, using microarray based technology. Specifically, the invention detects imprinted genes by the presence of overlapping closed and open chromatin markers. The invention also discloses a method for detecting the loss of imprinting on a genome-wide scale, which is indicative of a variety of medical conditions. Diagnostic assays and chromatin structure markers for identifying gene imprinting and loss thereof are also disclosed.
Owner:GREEN ROLAND D +2
Global analysis of transposable elements as molecular markers of cancer
InactiveUS20060115806A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingTransposable elementMethylation
The present invention provides methods of determining expression patterns, methylation patterns and chromatin status patterns for transposable element gene sequences. These methods can be utilized to diagnose, stage and treat cancer.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
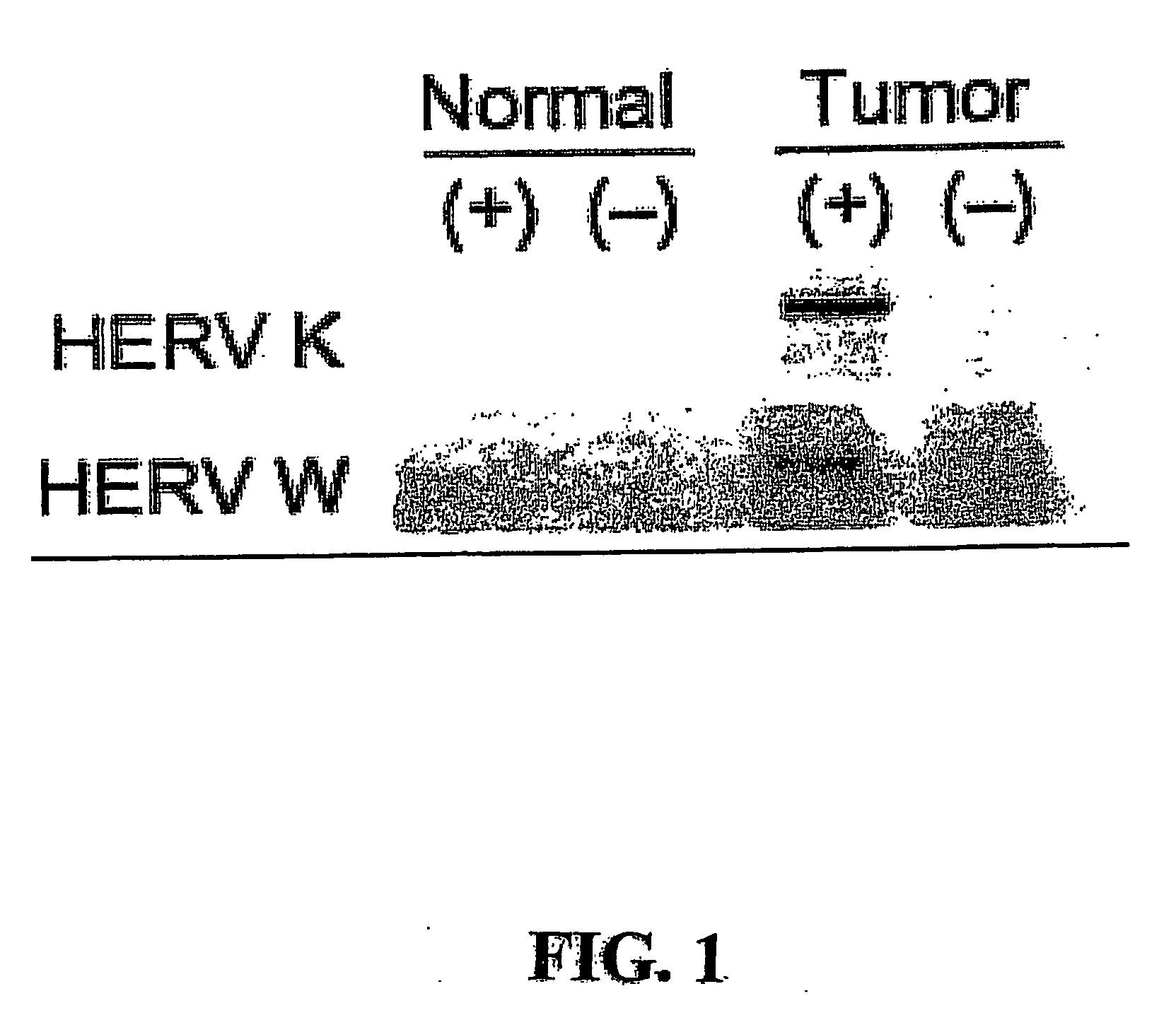
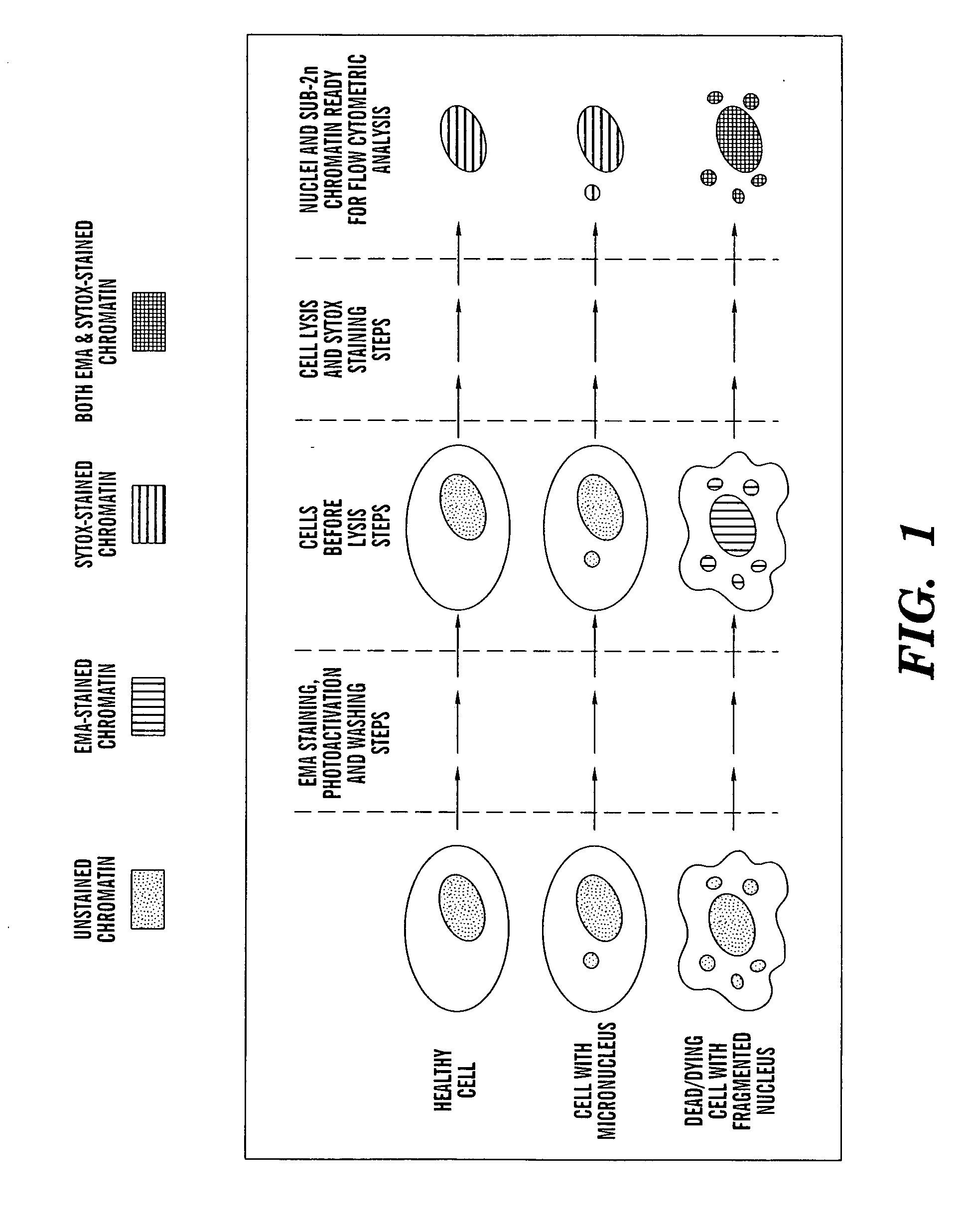
Method for enumerating mammalian cell micronuclei with an emphasis on differentially staining micronuclei and the chromatin of dead and dying cells
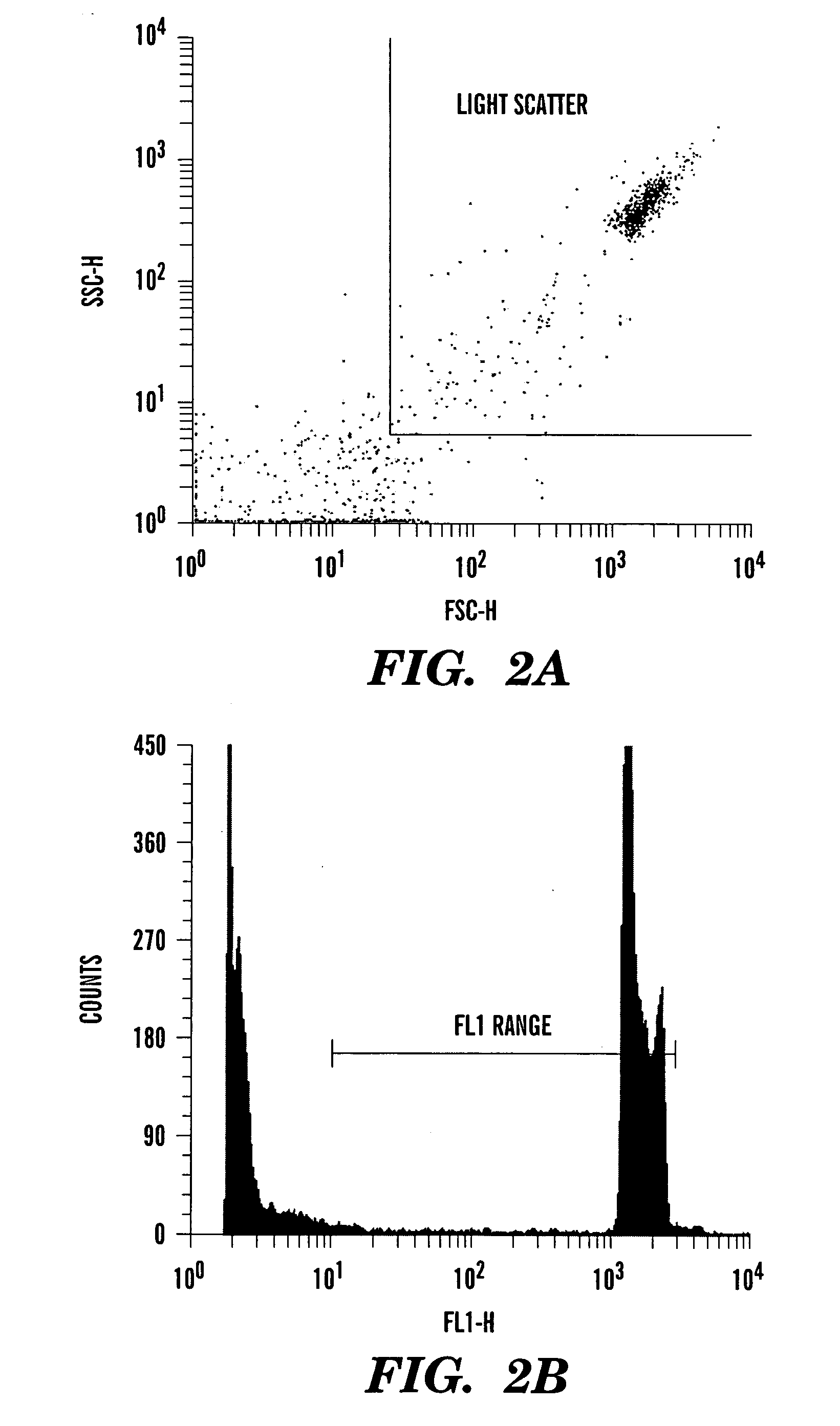
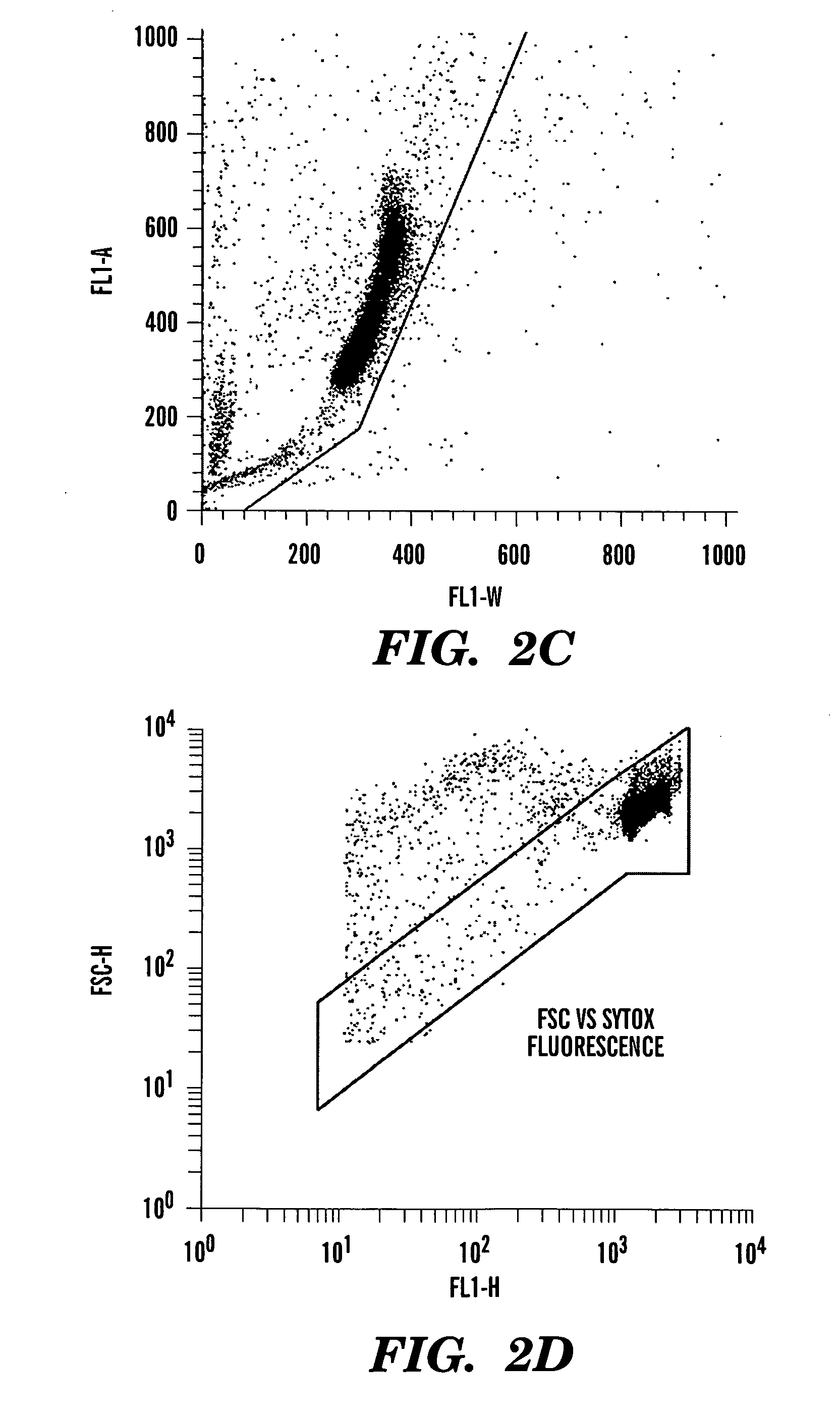
ActiveUS20060040291A1Accurate and reliable micronuclei measurementFast and reliable and accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationMammalPhysical agents
The present invention relates a method for the enumeration of mammalian cell micronuclei, while distinguishing micronuclei from the chromatin of dead and dying cells. The method utilizes differential staining of chromatin from dead and dying cells, to distinguish the chromatin from micronuclei and nuclei that can be detected based upon fluorescent emission and light scatter following exposure to an excitatory light source. Counting of micronuclei events relative to the number of nuclei can be used to assess the DNA-damaging potential of a chemical agent, the DNA-damaging potential of a physical agent, the effects of an agent which can modify endogenously-induced DNA damage, and the effects of an agent which can modify exogenously-induced DNA damage. Kits for practicing the invention are also disclosed.
Owner:LITRON LAB
Device and methods for epigenetic analysis
ActiveUS8735065B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEpigenetic AnalysisGenetic Materials
Provided herein are methods and devices for single object detection. The methods and devices can be used to identify a plurality epigenetic markers on a genetic material, or a chromatin, encompassing fragments thereof. The invention provides for the characterization of the genetic material flowing through a channel in a continuous body of fluid based on detection of one or more properties of the genetic material. The methods and systems provided herein allow genome-wide, high-throughput epigenetic analysis and overcome a variety of limitations common to bulk analysis techniques.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
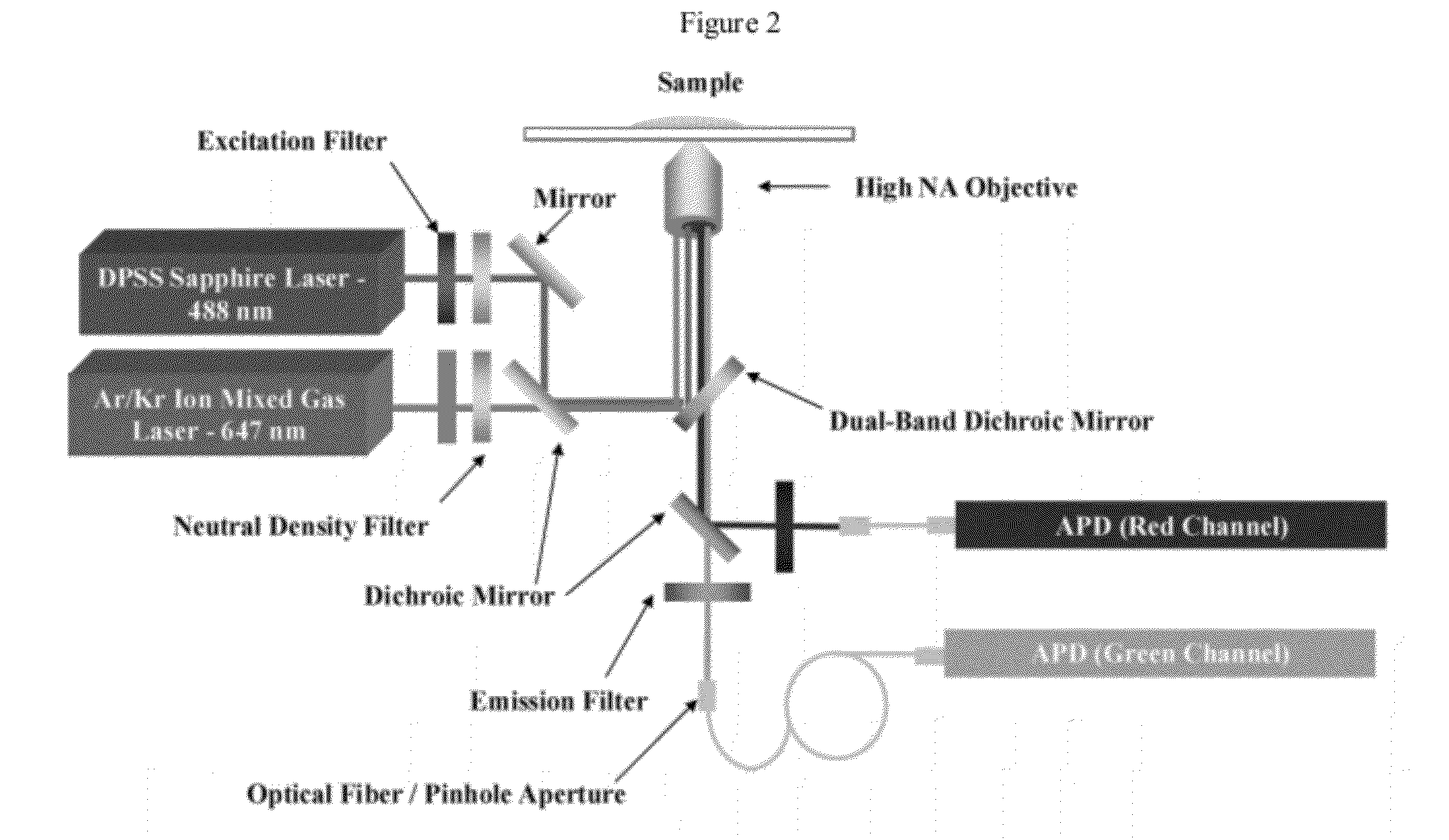
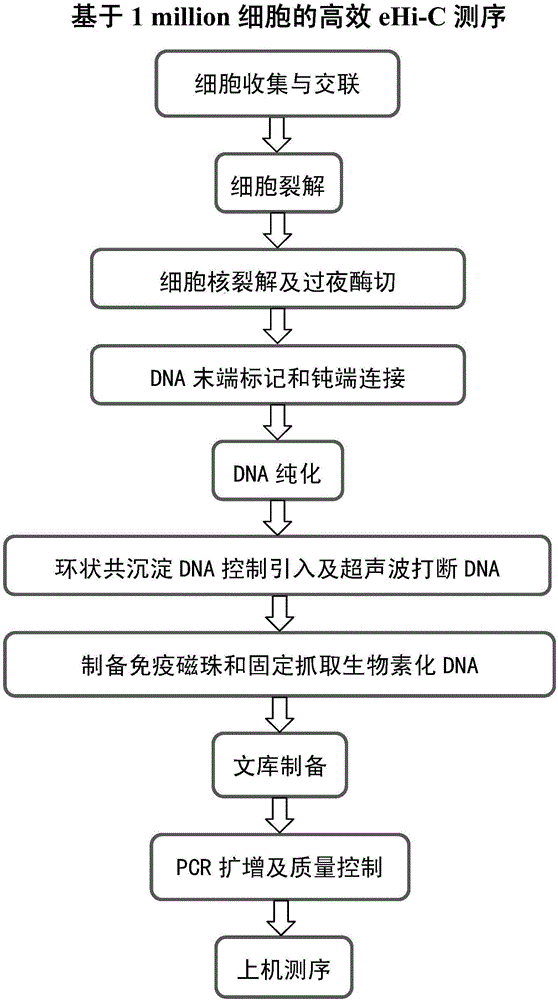
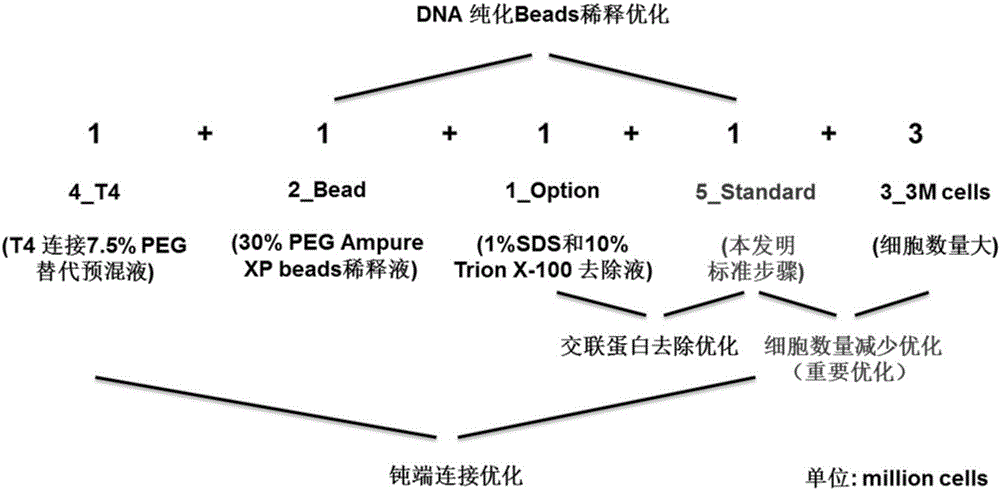
Efficient whole-genome chromosome conformation capture technology (eHi-C)
ActiveCN106566828AReduce demandReduce the cost of trainingMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationEnzyme digestionMagnetic bead
The invention discloses an efficient whole-genome chromosome conformation capture technology (eHi-C). The invention provides an eHi-C sequencing technology for cells. The eHi-C sequencing technology comprises the following steps: 1) subjecting the cells to disintegration so as to obtain chromatin; 2) subjecting the chromatin to enzyme digestion, DNA end labeling, cyclization connection of a blunt end and DNA purification so as to obtain purified circular DNA; 3) introducing a circular co-precipitation DNA molecule used as internal reference; 4) carrying out ultrasonic breaking; 5) capturing all the labeled DNA fragments with immunomagnetic beads; and 6) preparing eHi-C sequencing library from the labeled DNA fragments. The technology provided by invention is low in the amount of needed cells, can easily acquire an experiment material, reduces time in acquisition of the material, greatly lowers cell culture cost and cost for reagent consumables and decreases test errors.
Owner:AGRI GENOMICS INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Inter-simple sequence repeat ISSR-SCAR marker specific to E-group chromosomes of agropyron elongatum
The invention discloses an inter-simple sequence repeat ISSR-SCAR marker specific to E-group chromosomes of agropyron elongatum. The invention provides a kit for detecting the E-group chromosomes of agropyron elongatum. The kit comprises the following primer pair: one primer in the primer pair is nucleotide shown in a sequence 3 of a sequence table, and the other primer in the primer pair is nucleotide shown in a sequence 4 of the sequence table. The E-group chromosomes of thinopyrum elongatum are the basic chromosome group forming the polyploid species of elytrigia and carry the genes beneficial to the genetic breeding of wheat, the detection of exogenous E chromatins in wheat is the key point for identifying recombination lines and introgression lines of the wheat, namely the agropyron elongatum, the work of screening and identifying a large number of filial generations is quite complicated, and tests prove that the ISSR-SCAR marker developed by the invention can lay a foundation for quickly and accurately identifying the E-group chromatins or chromosomes of exogenous agropyron elongatum under the genetic background of wheat.
Owner:HARBIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Device and Methods for Epigenetic Analysis
ActiveUS20120244532A1Easy to implementFast data collectionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEpigenetic AnalysisGenetic Materials
Provided herein are methods and devices for single object detection. The methods and devices can be used to identify a plurality epigenetic markers on a genetic material, or a chromatin, encompassing fragments thereof. The invention provides for the characterization of the genetic material flowing through a channel in a continuous body of fluid based on detection of one or more properties of the genetic material. The methods and systems provided herein allow genome-wide, high-throughput epigenetic analysis and overcome a variety of limitations common to bulk analysis techniques.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
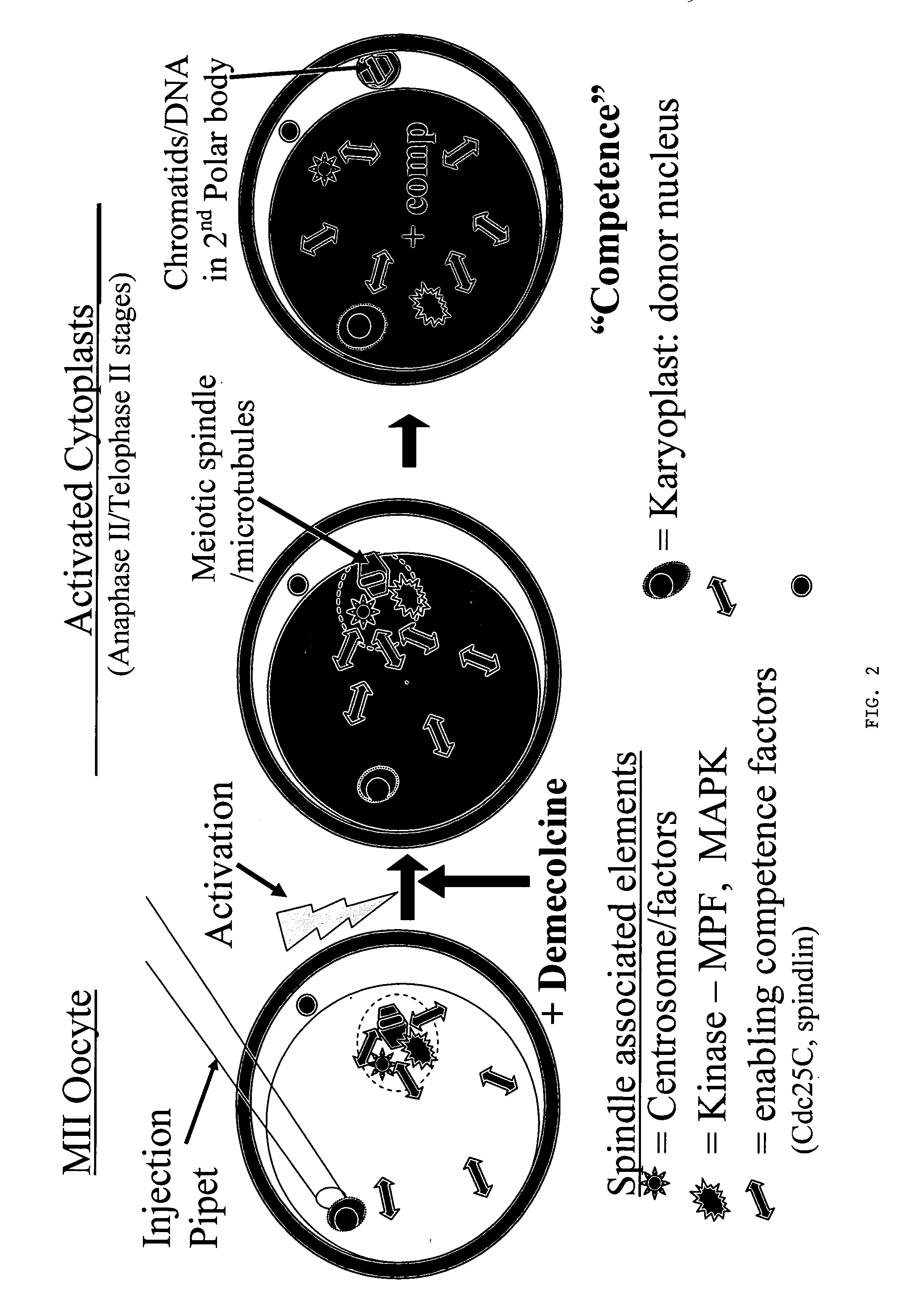
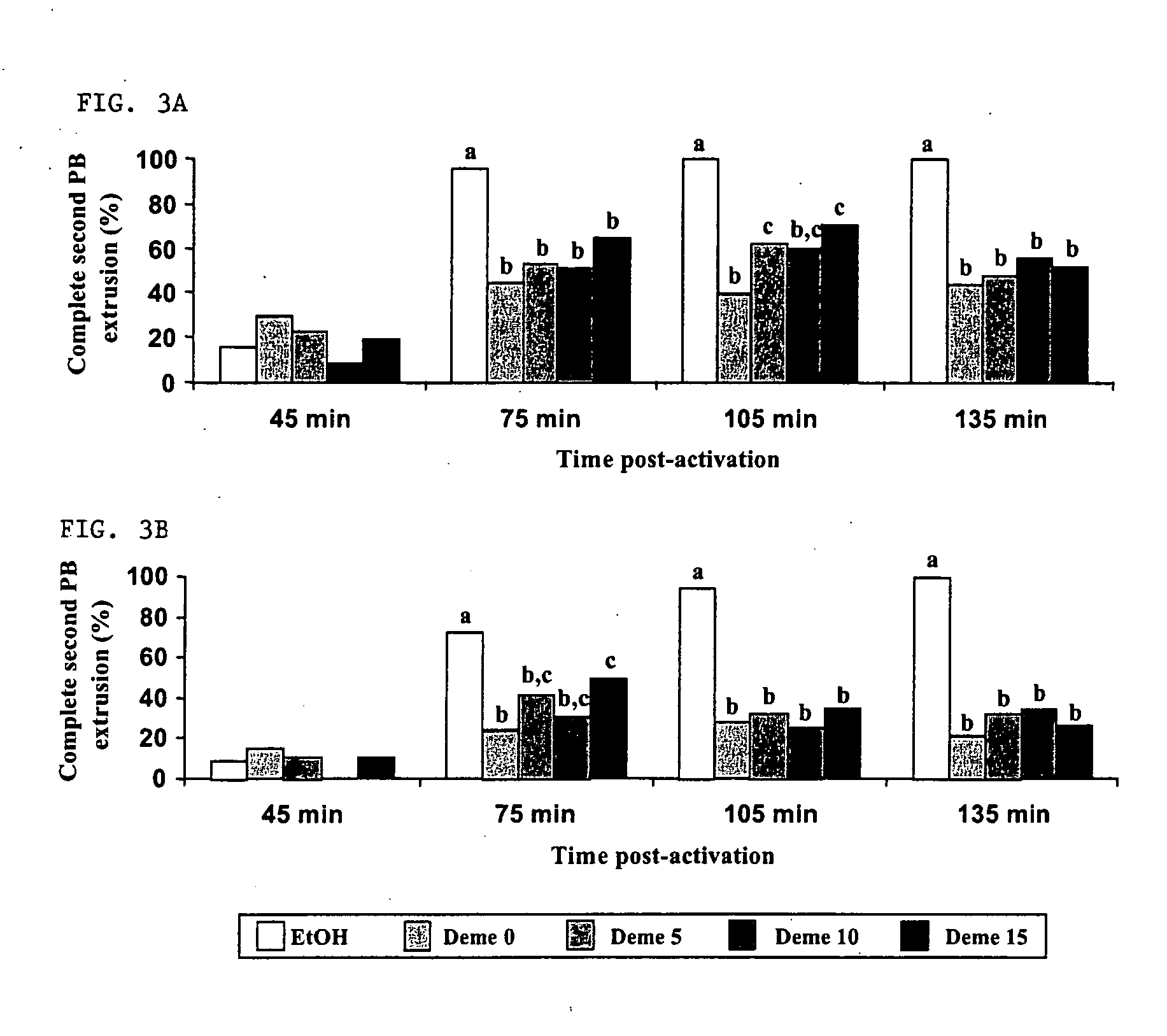
Nuclear transfer embryo formation method
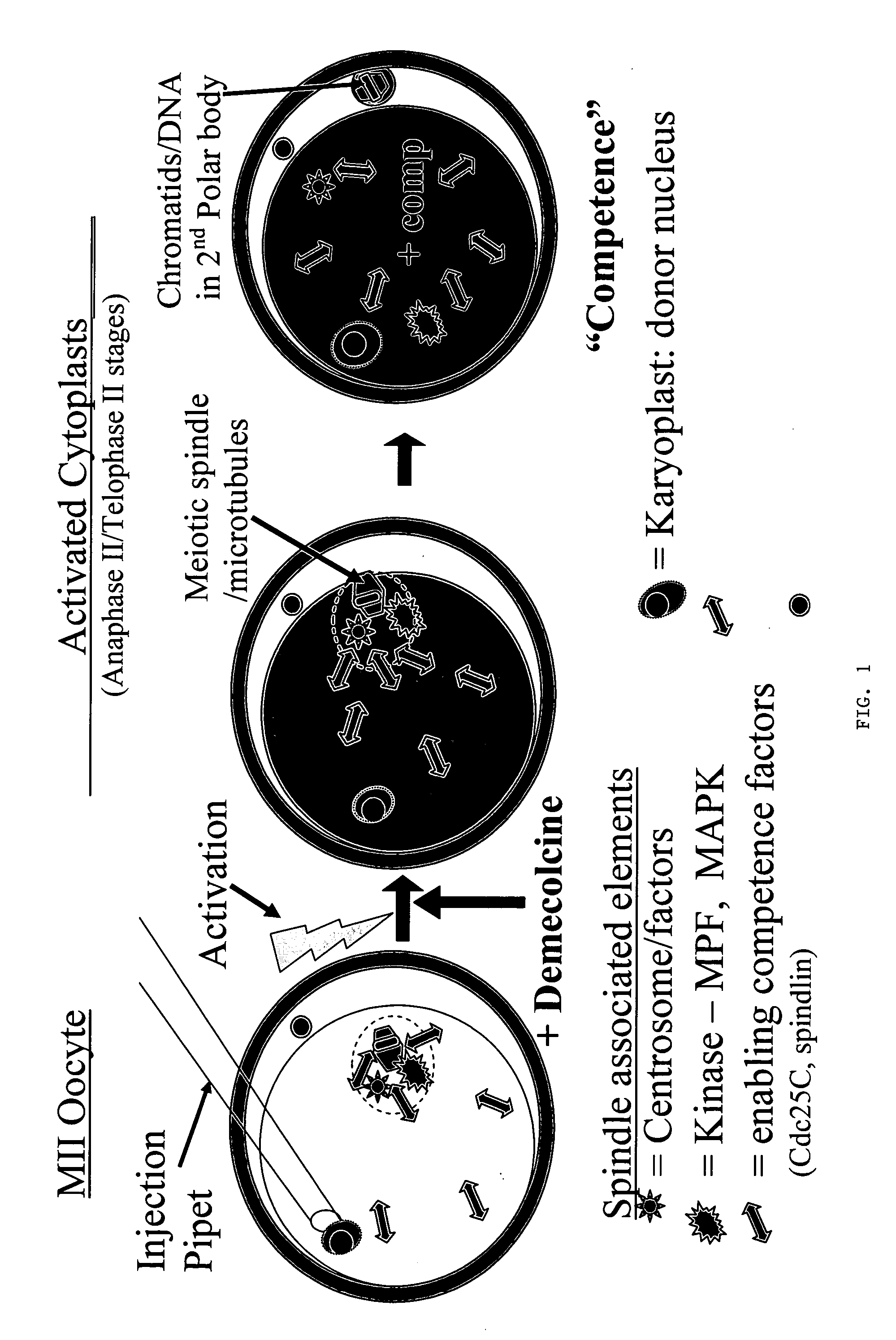
A nuclear transfer embryo is formed by destabilizing microtubules of an oocyte, whereby essentially all endogenous chromatin collects at a second polar body during meiosis of an oocyte. The oocyte is fused with the nucleus of a donor somatic cell of the same species of said oocyte prior to cessation of extrusion of the second polar body from the oocyte, thereby forming the nuclear transfer embryo. In one embodiment, the nuclear transfer embryo is employed to impregnate an animal, such as a mammal. In another embodiment, the donor nucleus is transgenic.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE
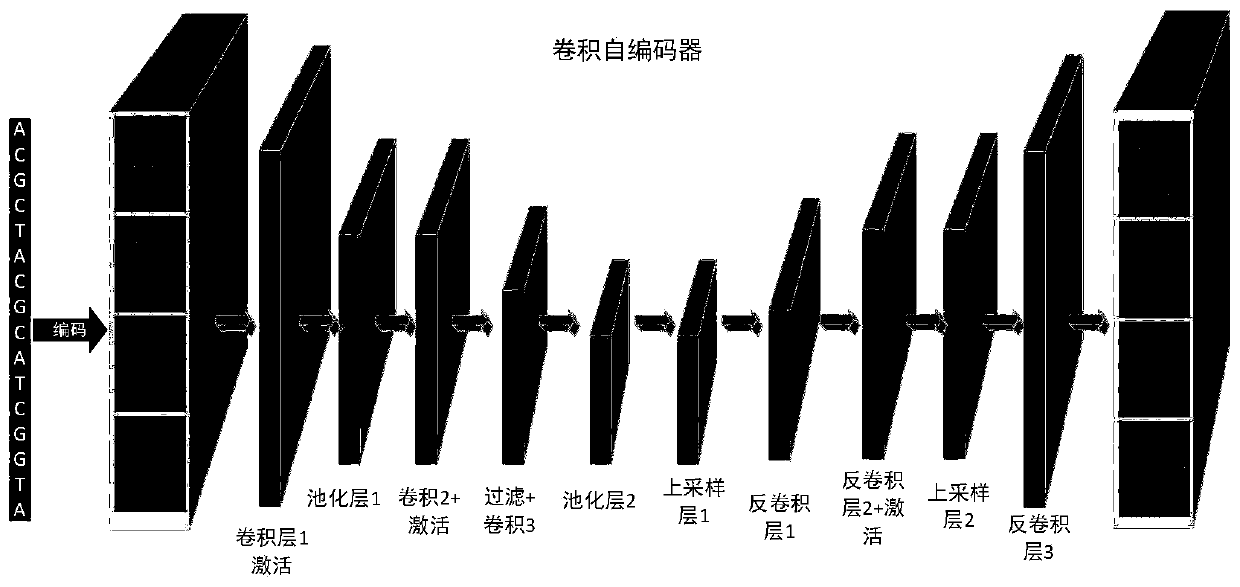
Transcription factor binding site prediction method based on depth convolution automatic encoder
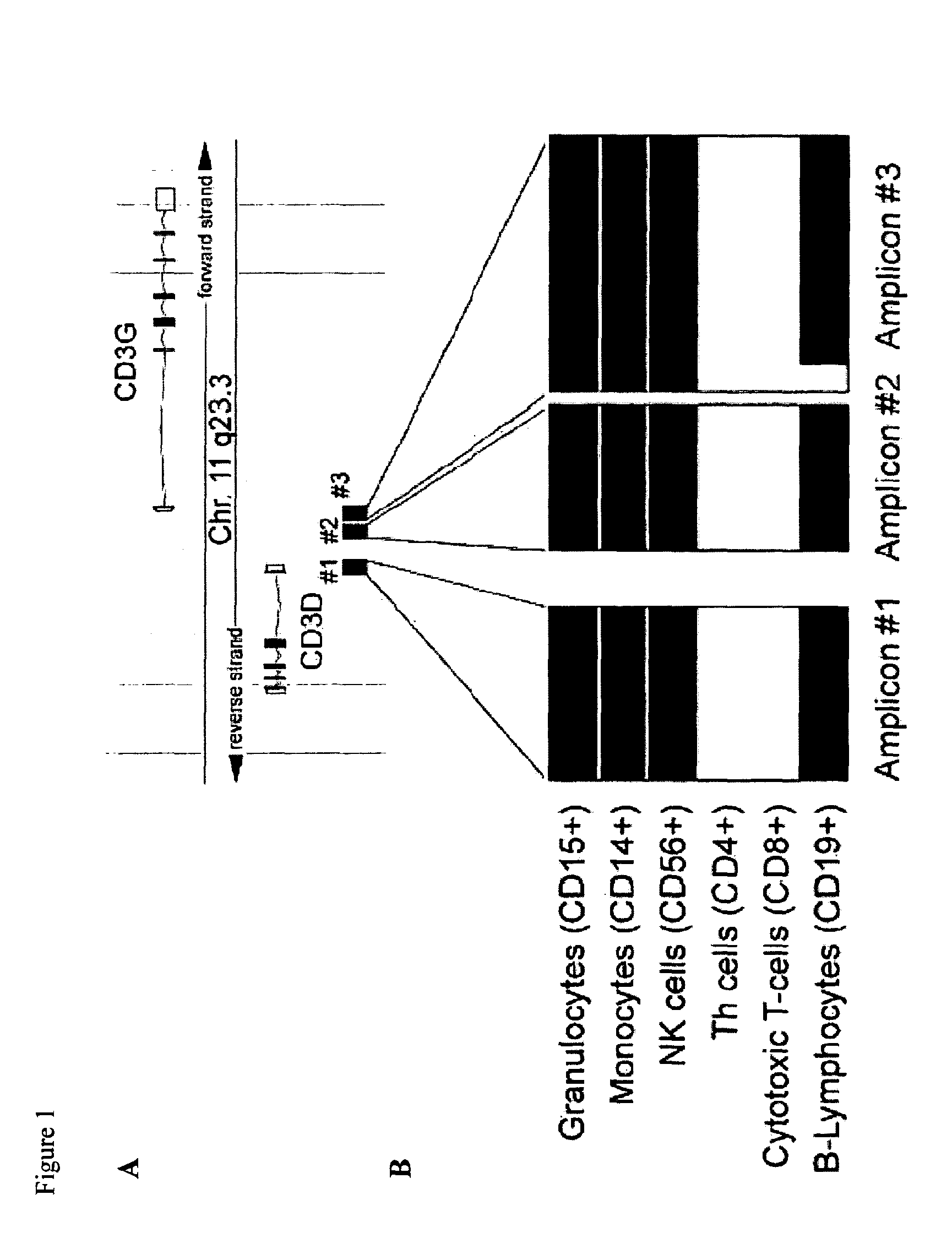
The invention discloses a transcription factor binding site prediction method based on a depth convolution automatic encoder, is applied to the technical field of computer technology and biological information, and aims to improve the generalization ability of a model while solving the dependence of the model on a negative sequence sample without a binding site. The method comprises the followingsteps: firstly, specifically enriching DNA fragments combined with target protein by virtue of a chromatin co-immunoprecipitation technology, so as to obtain an original data set; preprocessing the original data set to obtain a training data set; secondly, inputting the training data set into a convolution automatic encoder for training; and finally, carrying out binding site identification according to the trained convolutional automatic encoder. Experiments prove that the method can predict different transcription factor binding sites of different cell lines, and has a high-accuracy recognition effect.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF INFORMATION TECH
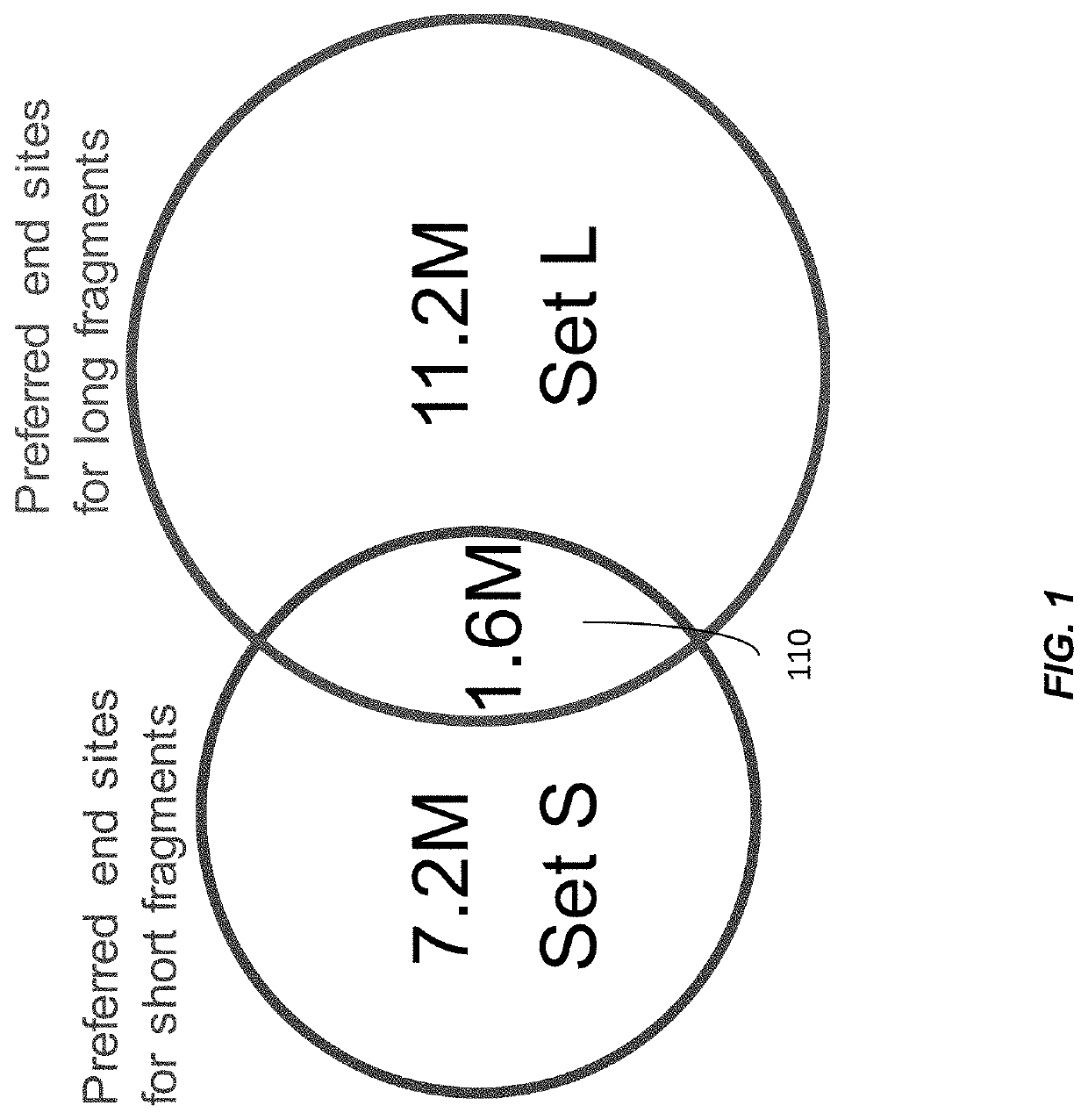
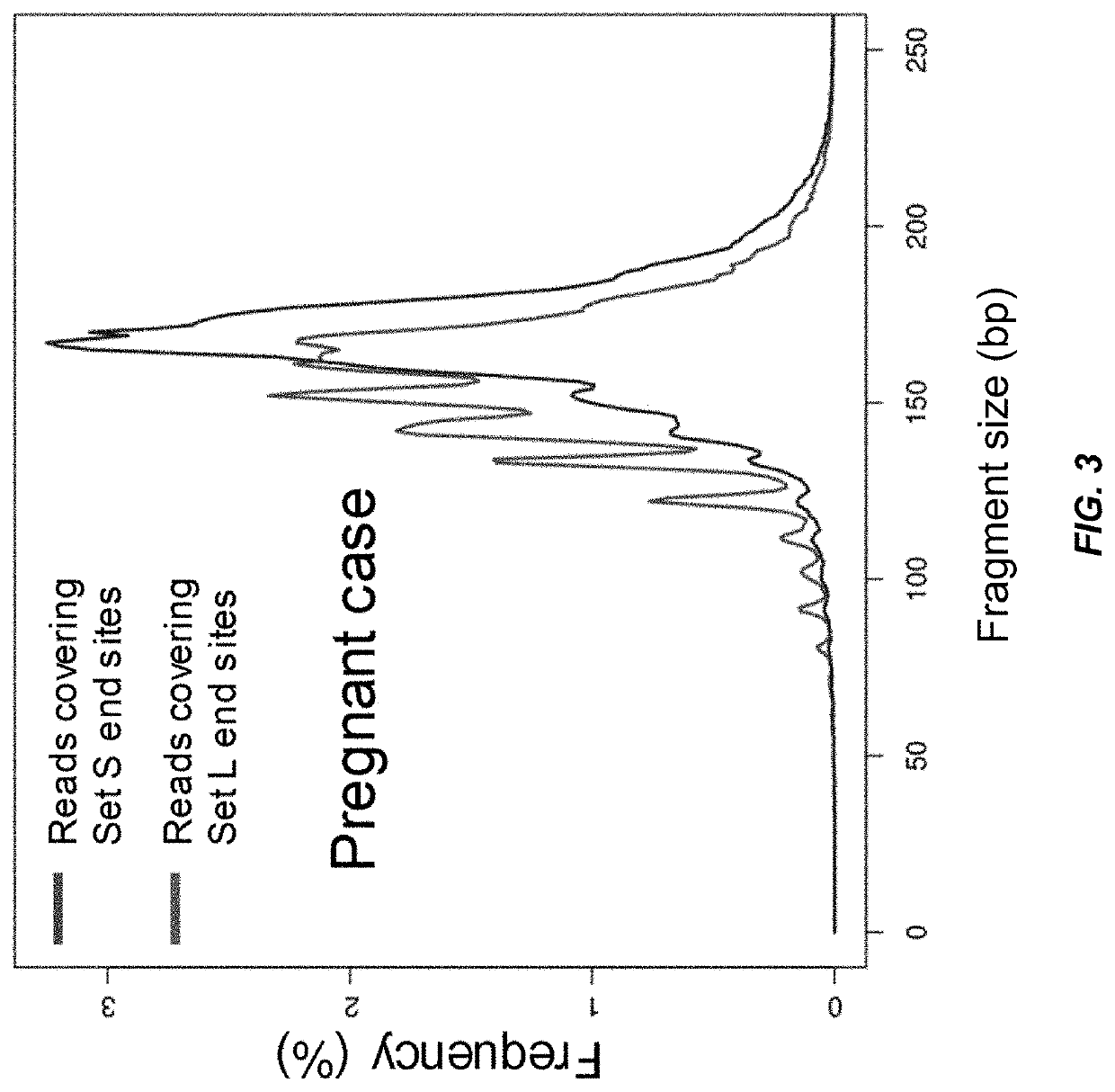
Size-tagged preferred ends and orientation-aware analysis for measuring properties of cell-free mixtures
Various applications can use fragmentation patterns related of cell-free DNA, e.g., plasma DNA and serum DNA. For example, the end positions of DNA fragments can be used for various applications. The fragmentation patterns of short and long DNA molecules can be associated with different preferred DNA end positions, referred to as size-tagged preferred ends. In another example, the fragmentation patterns relating to tissue-specific open chromatin regions were analyzed. A classification of a proportional contribution of a particular tissue type can be determined in a mixture of cell-free DNA from different tissue types. Additionally, a property of a particular tissue type can be determined, e.g., whether a sequence imbalance exists in a particular region for a tissue type or whether a pathology exists for the tissue type.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com