Compositions and methods for treating neoplasia, inflammatory disease and other disorders
A compound, optionally a technology, for use in drug combinations, anti-vector-borne diseases, antineoplastic agents, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
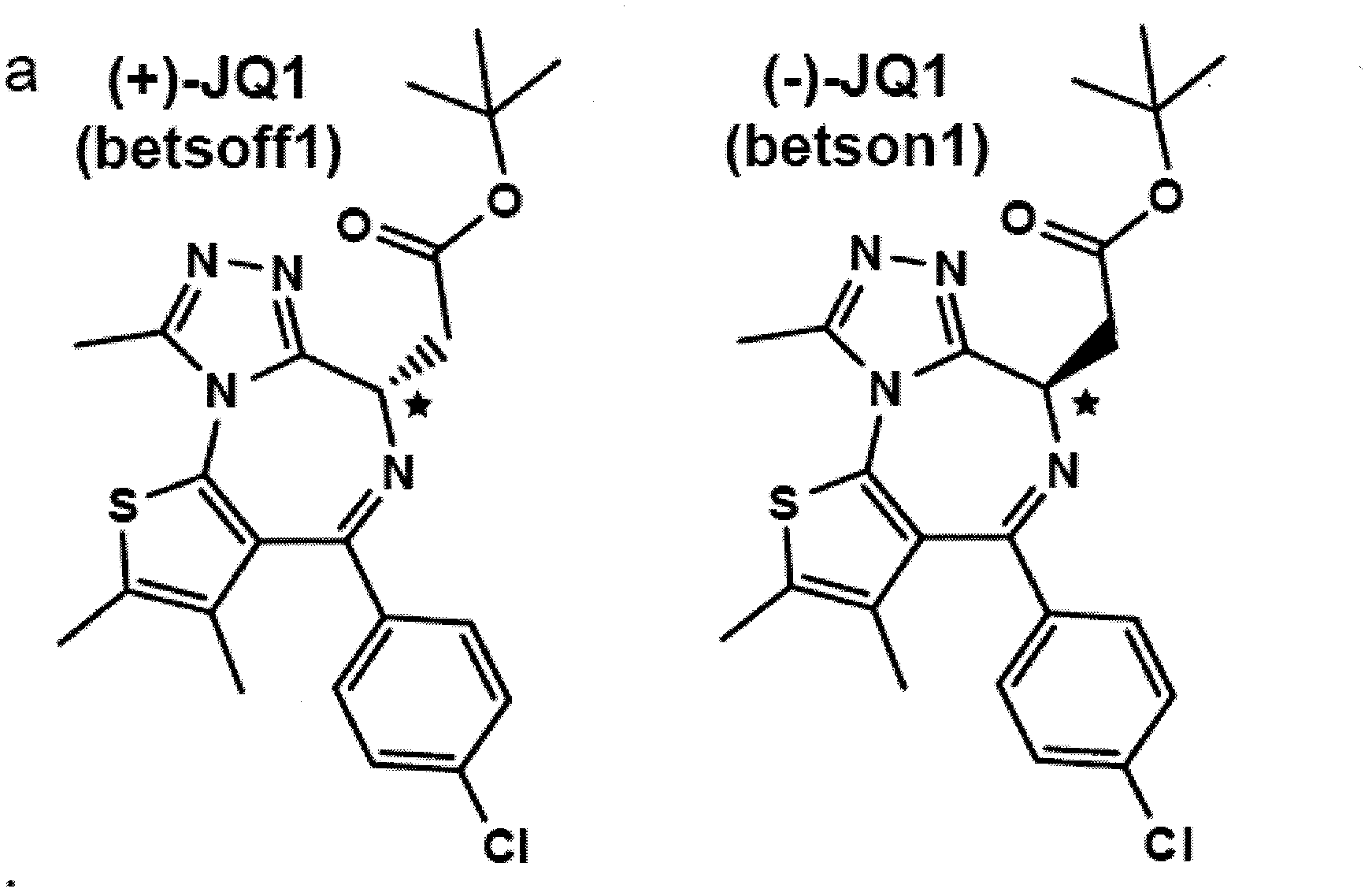
[0746] Example 1: JQ1
[0747] attached figure 1 Various enantiomers of JQ1 are shown.
example 2
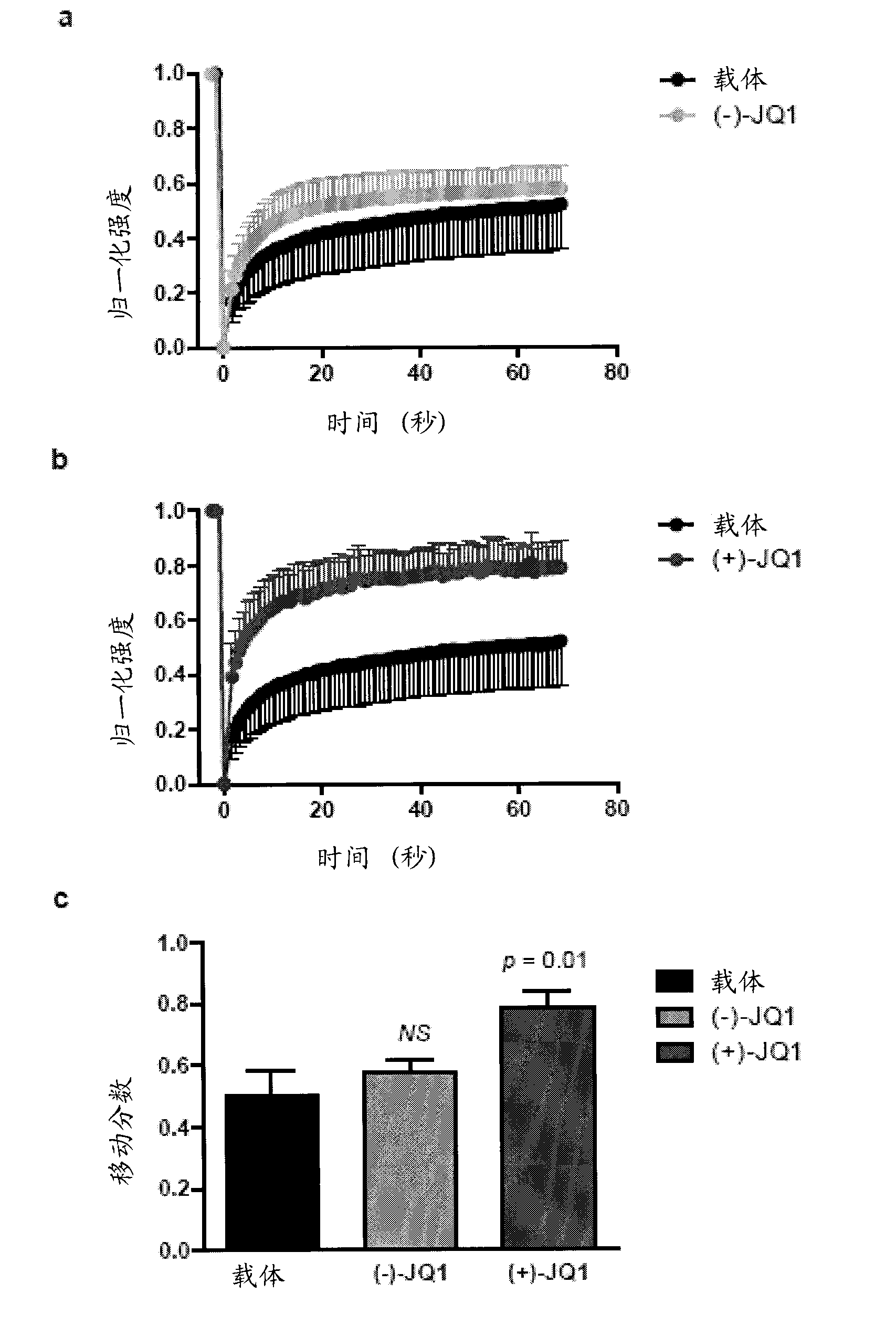
[0748] Example 2: JQ1 displaces BRD4 from nuclear chromatin in cells.
[0749] To determine whether JQ1 could competitively bind to chromatin bromodomains in the cellular context, fluorescence recovery from photobleaching (FRAP) assays were performed on BRD4. Previous studies have demonstrated the utility of FRAP in evaluating the lateral redistribution pace of bromodomain-containing fluorescent chimeras following selective bleaching of discrete regions of nuclear chromatin. Human osteosarcoma cells (U2OS) transfected with GFP-BRD4 showed a time-dependent recovery of fluorescence intensity (attached figure 2 A and 2B). In the presence of JQ1 (500 nM), the observed restoration was directly related to the displaced BRD4 (attached image 3 A and 3B) are consistent. Cellular FRAP studies confirmed that the effect on the mobile fraction of BRD4 is restricted to the biochemically active (+)-JQ1 stereoisomer (attached figure 2 A to 2C).
[0750] Having demonstrated effective s...
example 5
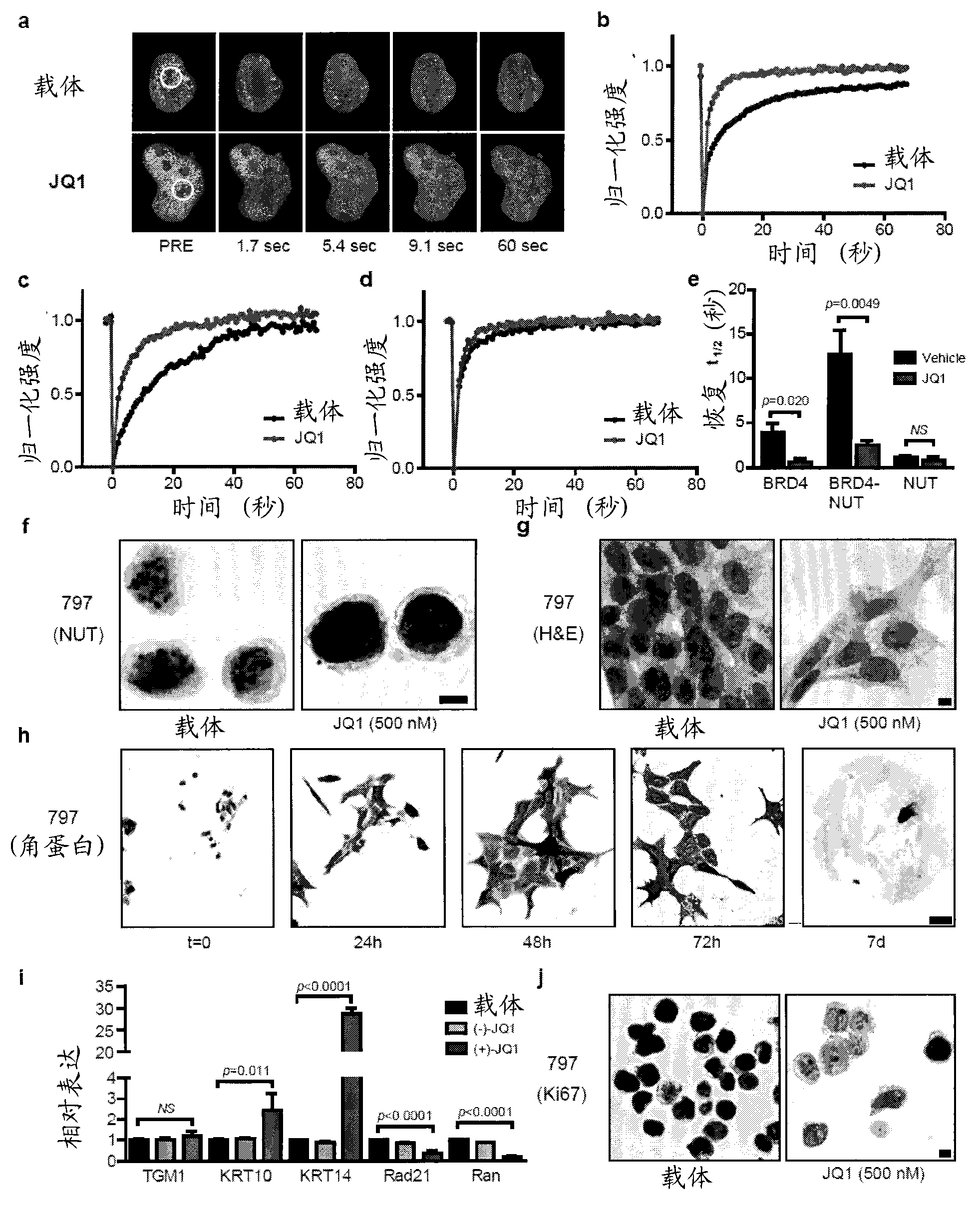
[0751] Example 5: JQ1 induces squamous differentiation and growth inhibition in BRD4-dependent carcinoma.
[0752] Direct inhibition of gene products expressed from recurrent, oncogenic translocations is an effective avenue for cancer therapy. The phenotypic consequences of chemical inhibition of BET-family bromodomains in BRD4-dependent NUT midline carcinomas were explored. The BRD4-NUT chromatin location is mechanistically linked to the protected tandem bromodomain of BRD4 in this fusion protein. A characteristic feature of NMC is the appearance of discrete nuclear dots of the BRD4-NUT oncoprotein as determined by immunocytochemistry (IHC) for NUT. Treatment of this patient-derived 797NMC cell line with JQ1 (500nM) for 48 hours by IHC abolished nuclear foci and produced diffuse nuclear NUT staining (attached image 3 f).
[0753] A marked differentiation phenotype was observed with knock-down of BRD4-NUT in NMC cell lines. JQ1 produces an identical, dose- and time-depend...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com