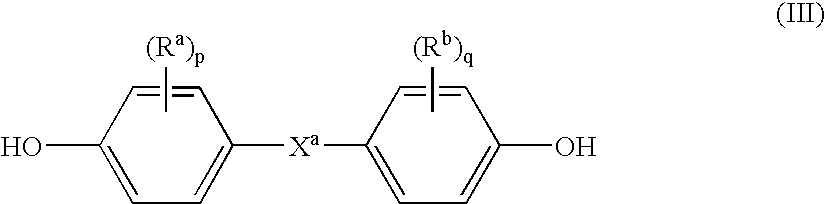
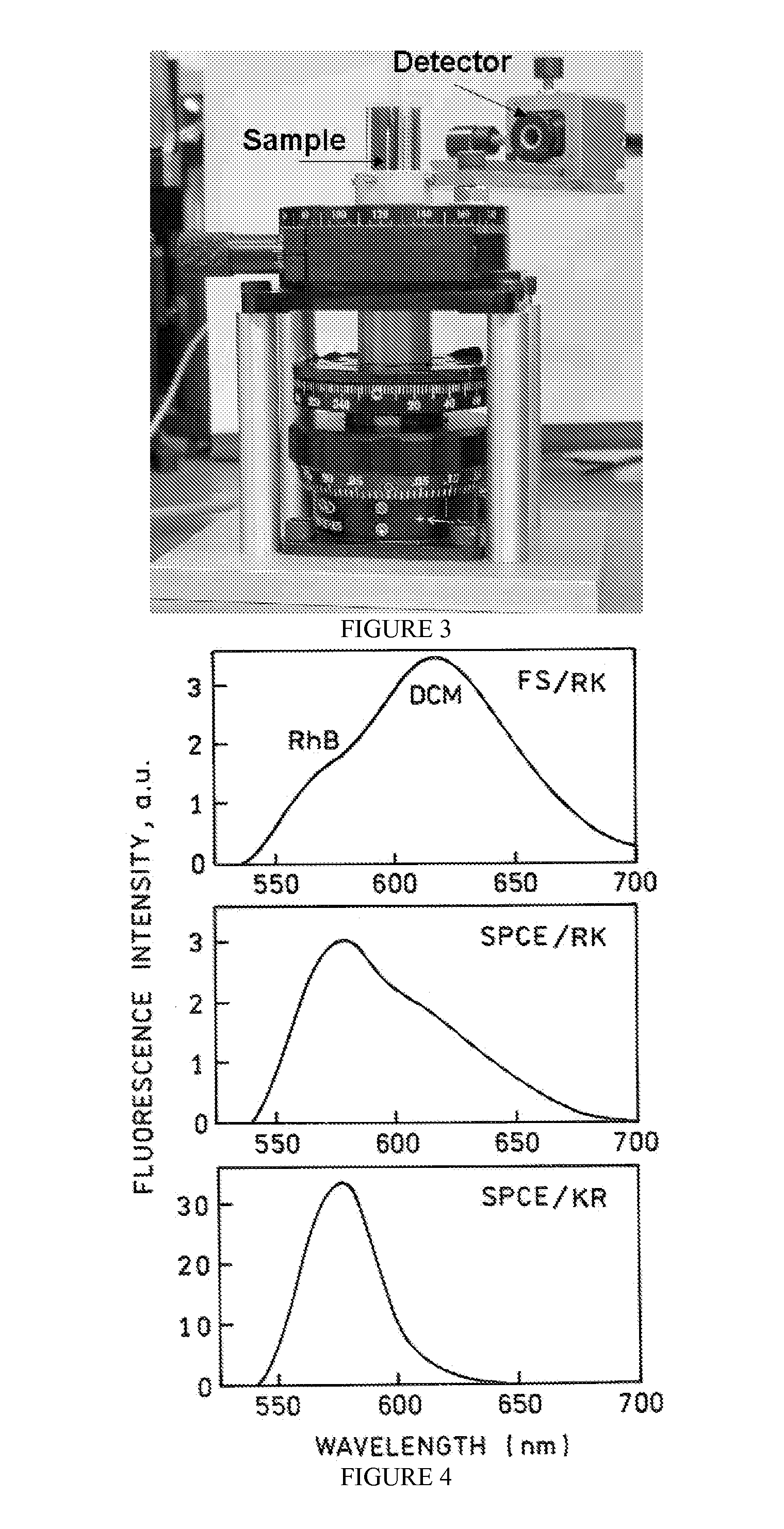
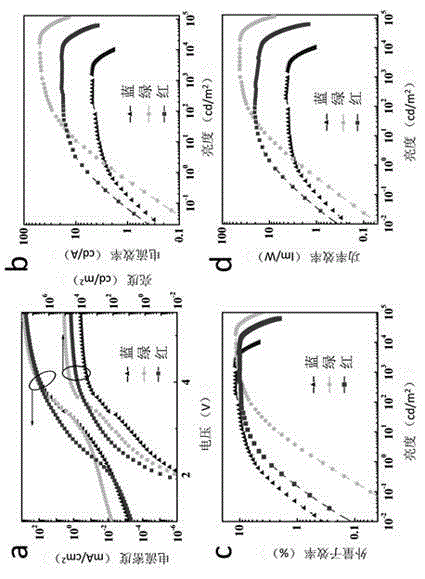
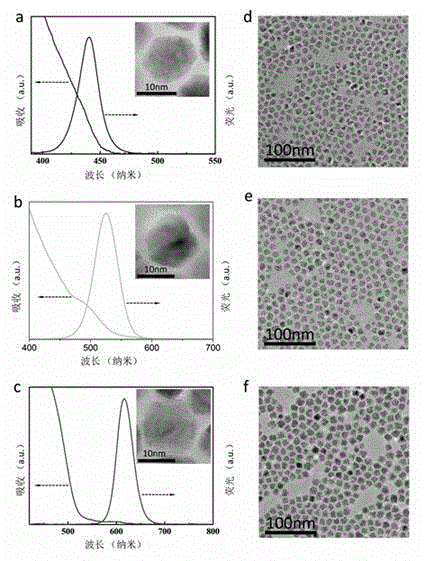
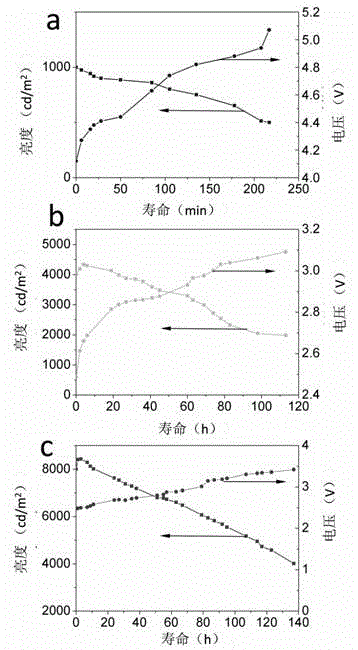
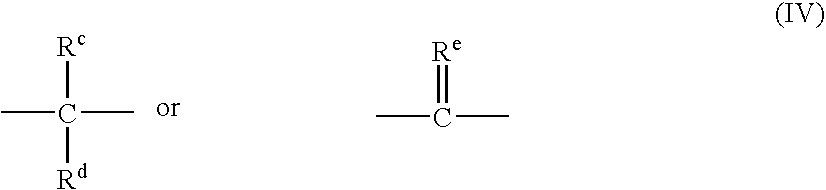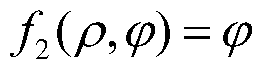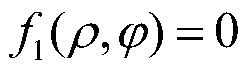Patents
Literature
301 results about "Photobleaching" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
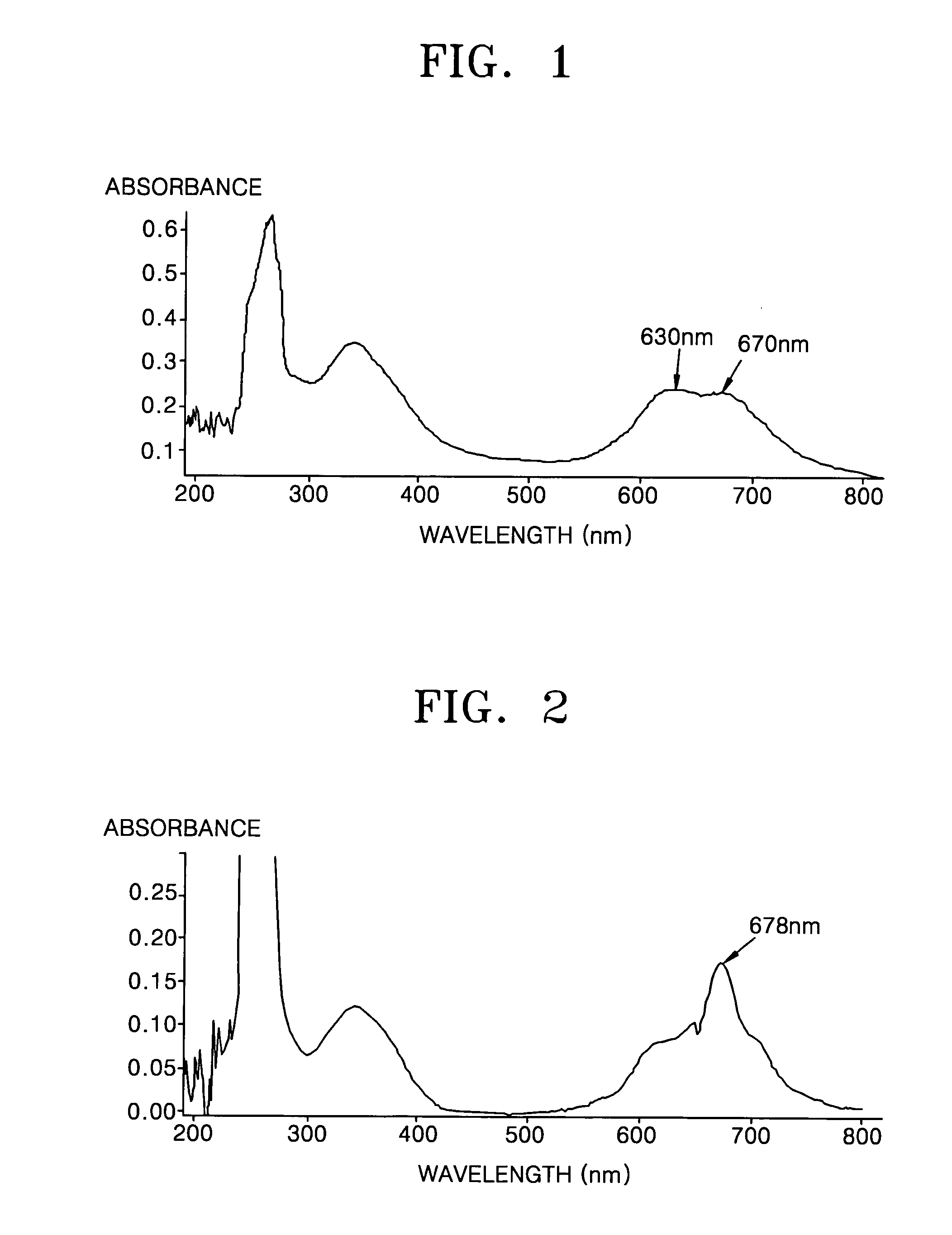
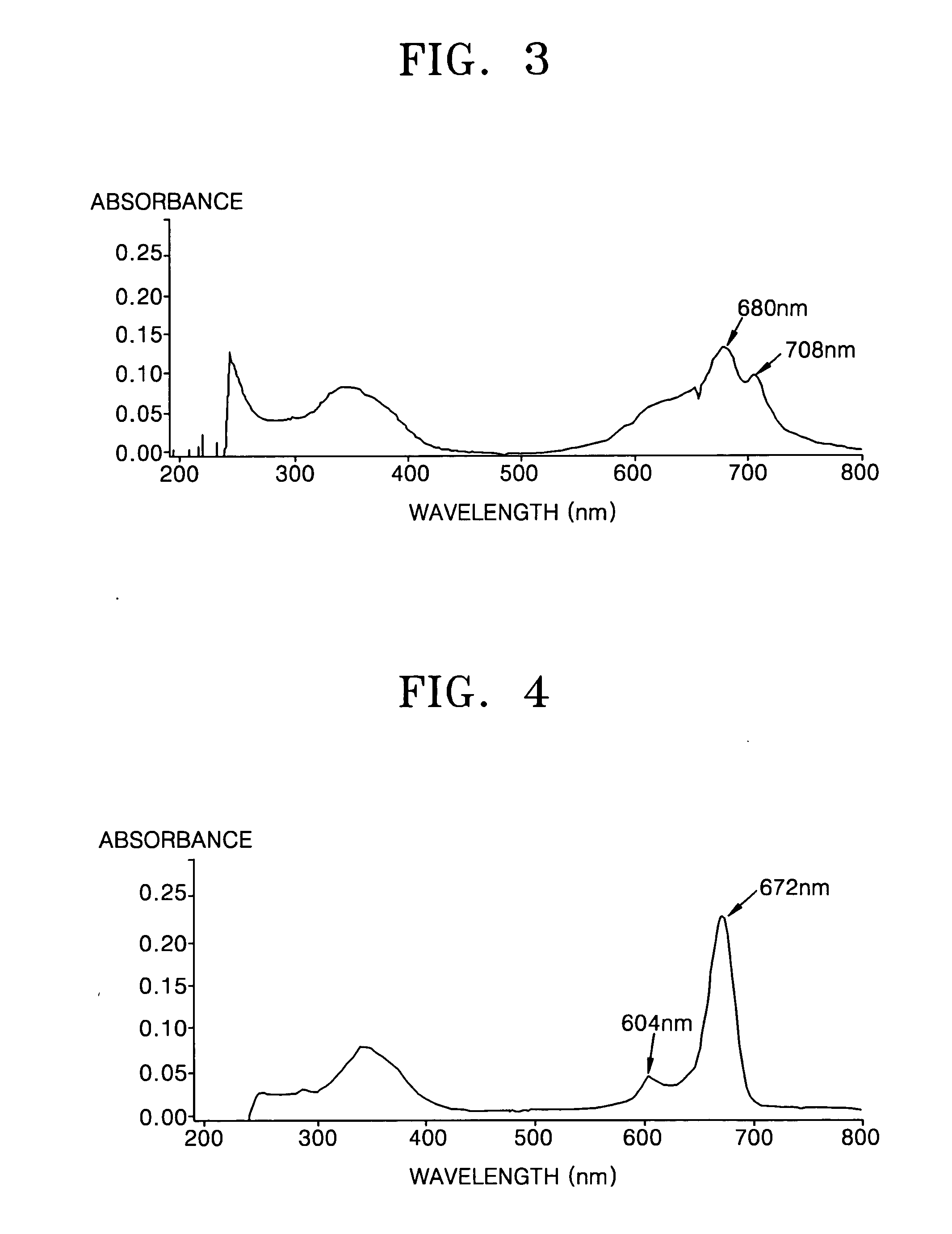
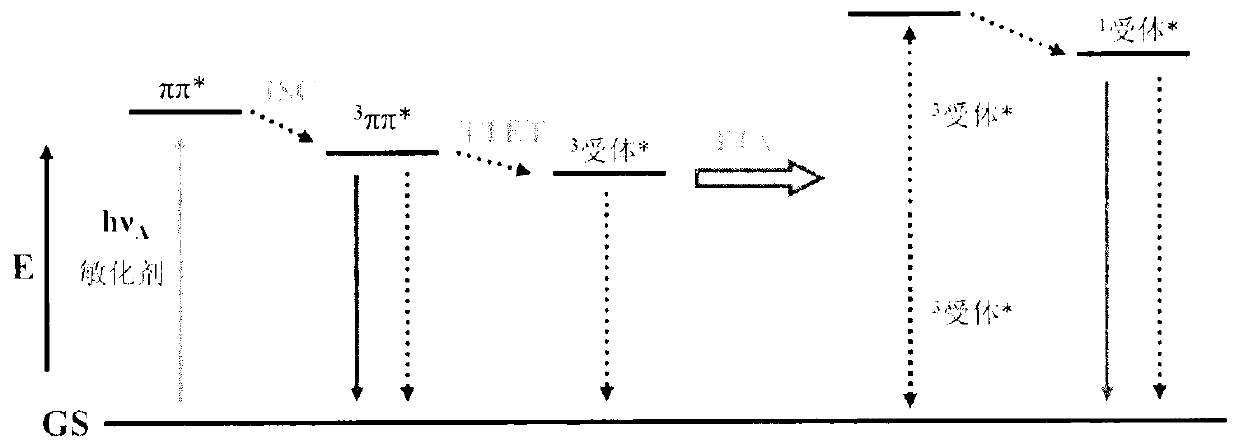
In optics, photobleaching (sometimes termed fading) is the photochemical alteration of a dye or a fluorophore molecule such that it permanently is unable to fluoresce. This is caused by cleaving of covalent bonds or non-specific reactions between the fluorophore and surrounding molecules. Such irreversible modifications in covalent bonds are caused by transition from a singlet state to the triplet state of the fluorophores. The number of excitation cycles to achieve full bleaching varies. In microscopy, photobleaching may complicate the observation of fluorescent molecules, since they will eventually be destroyed by the light exposure necessary to stimulate them into fluorescing. This is especially problematic in time-lapse microscopy.
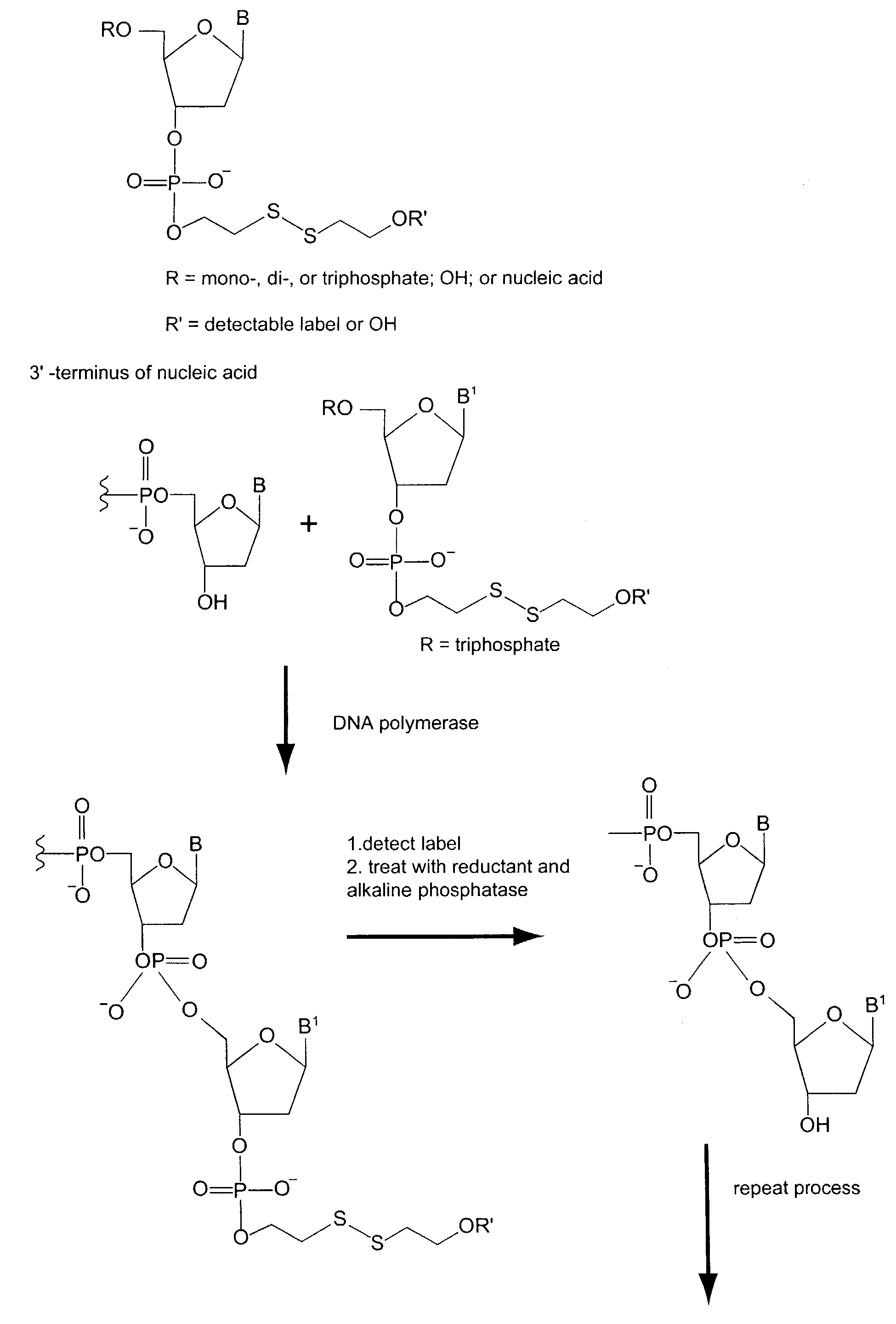
Sequencing by incorporation
Nucleotides and nucleotide analogs are used in various sequencing by incorporation / sequencing by synthesis methods. Nucleotide analogs comprising 3′-blocking groups are used to provide reversible chain-termination for sequencing by synthesis. Typical blocking groups include phosphate groups and carbamate groups. Fluorescent nucleotides are used to perform sequencing by synthesis with detection by incorporation of the fluorescently labeled nucleotide, optionally followed by photobleaching and intercalating dyes are used to detect addition of a non-labeled nucleotide in sequencing by synthesis with detection by intercalation. Microfluidic devices, including particle arrays, are used in the sequencing methods.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
Complex salt for anti-spotting detergents
InactiveUS20050003983A1Avoid chemical reactionsGood photo-bleaching effectCationic surface-active compoundsDetergent dyesActive agentOrganic chemistry
Provided is a method of using a complex salt as anti-spotting detergents, the complex salt being formed by the reaction of a photo-bleaching component having a water-soluble anionic substituent and a cationic surfactant. The complex salt is water insoluble in a stationary state, such as hand washing or pre-soaking for machine washing, so it effectively suppress the spotting of the photo-bleaching component into the interwoven webs of fabric. In addition, the complex salt can uniformly and rapidly dissolve in an agitating state, such as when machine washing, to allow the photo-bleaching component to absorb into fabric for effective bleaching and enhanced detergency.
Owner:KIM DONG GYU +6
Fluorescence polarization assay system and method
An instrument is disclosed for fluorescence assays which is capable of reading many independent samples at the same time. This instrument provides enhanced throughput relative to single-sample instruments, and is well-suited to use in general fluorescence, time-resolved fluorescence, multi-band fluorescence, fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET), and fluorescence polarization. This invention is beneficial in applications such as high-throughput drug screening, and automated clinical testing. Also disclosed are means and methods for a fluorescence polarization measurement which is highly sensitive, inherently self-calibrated, and unaffected by lamp flicker or photobleaching. This fluorescence polarization invention can be practiced on a variety of fluorescence instruments, including prior-art equipment such as microscopes and multi-well plate readers.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE RES & INSTR
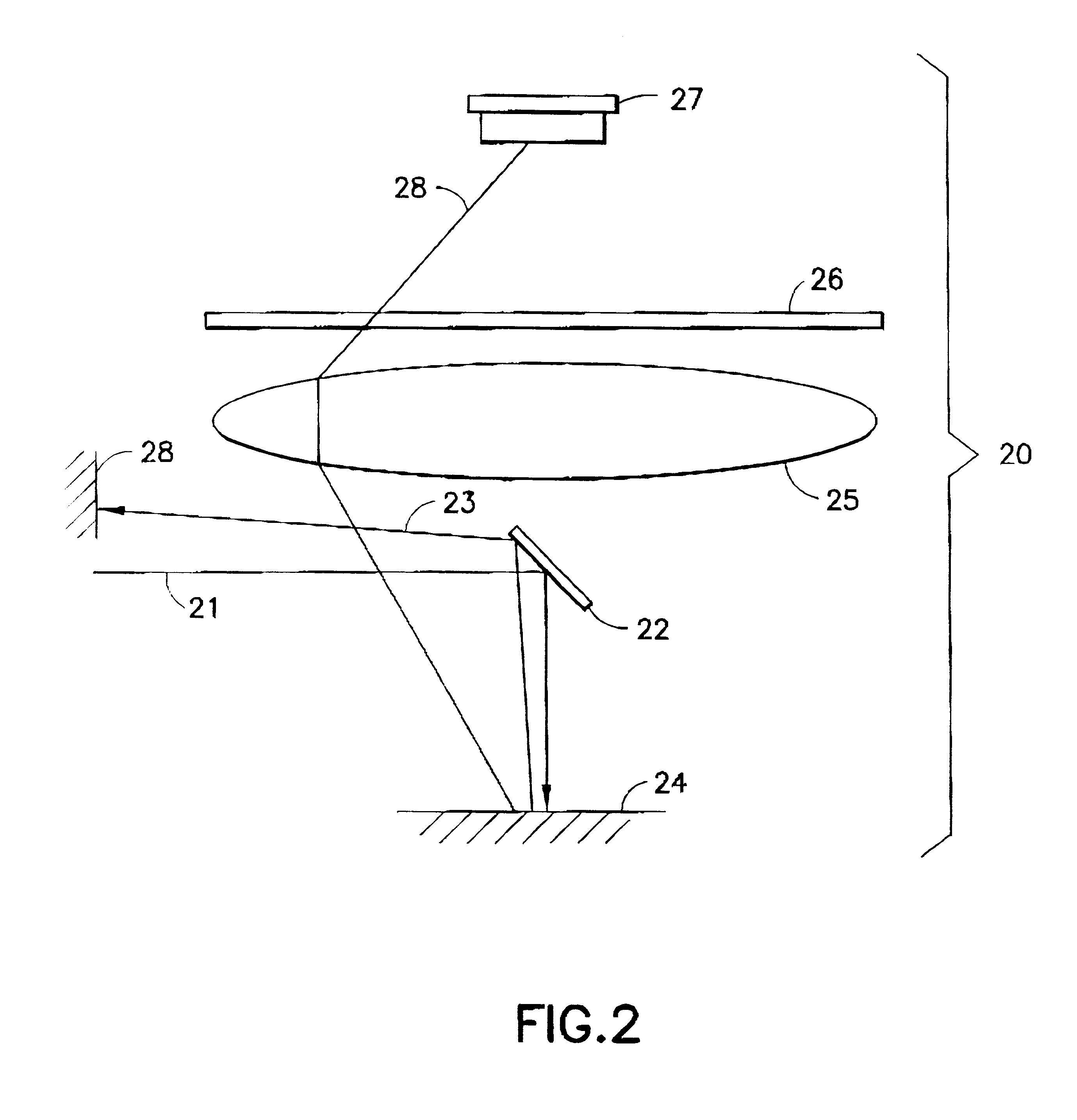
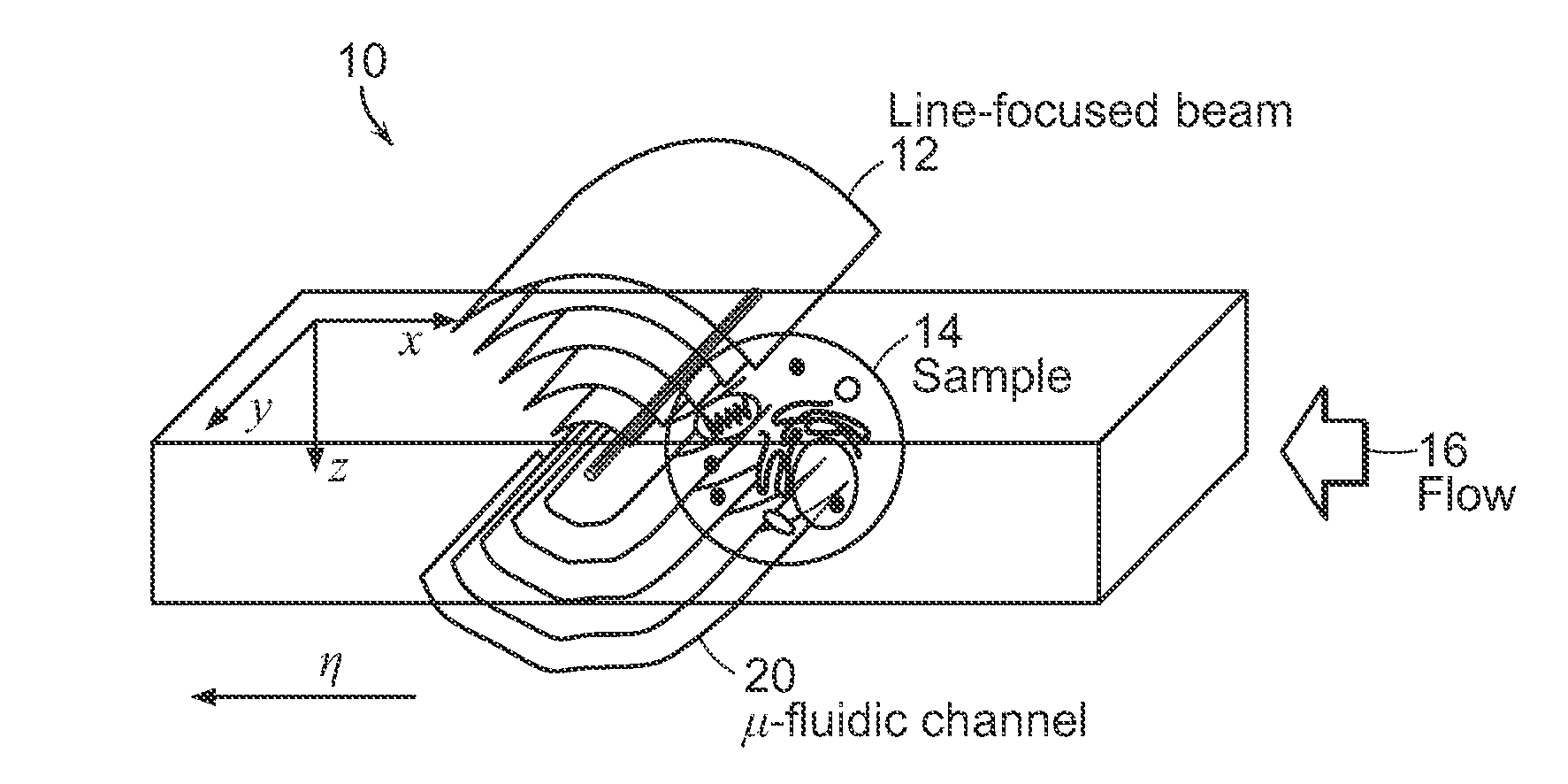
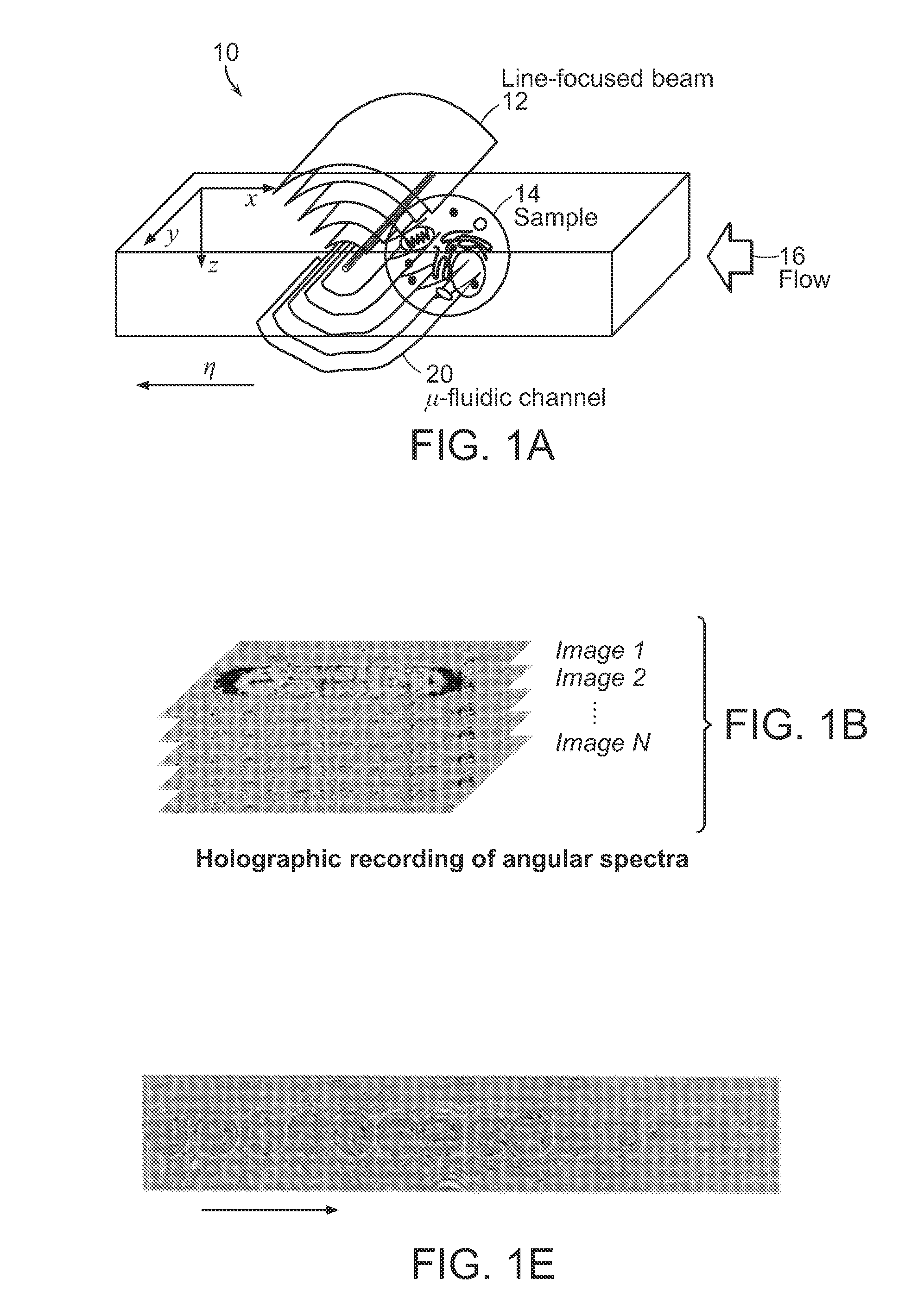
3-d holographic imaging flow cytometry
ActiveUS20140333929A1Limit image throughputReduce artifactScattering properties measurementsHolographic object characteristicsMicro fluidicHolographic imaging
Refractive index of biological specimens is a source of intrinsic contrast that can be explored without any concerns of photobleaching or harmful effects caused by extra contrast agents. This feature also contains rich information that can be related to the metabolism of cells at the cellular and subcellular levels. The present invention relates to systems and methods that can provide, without any moving parts, the 3-D refractive index map of continuously flowing biological samples in a micro-fluidic channel, for example.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Limited play data storage media and coating formulations thereon
The present invention provides a formulation for a reactive dye layer for a limited-play optical storage medium, the reactive formulation including at least one carrier material or curable acrylate monomer, at least one reactive material disposed within the carrier material or acrylate monomer, and at least one photo-bleaching retarder material disposed within the at least one adhesive material. The at least one photo-bleaching retarder material includes at least one polymeric polyhydroxy compound selected from the group consisting of polyhydroxystyrenes, cellulose, and functionalized cellulose derivatives.
Owner:FLEXPLAY TECH INC +1
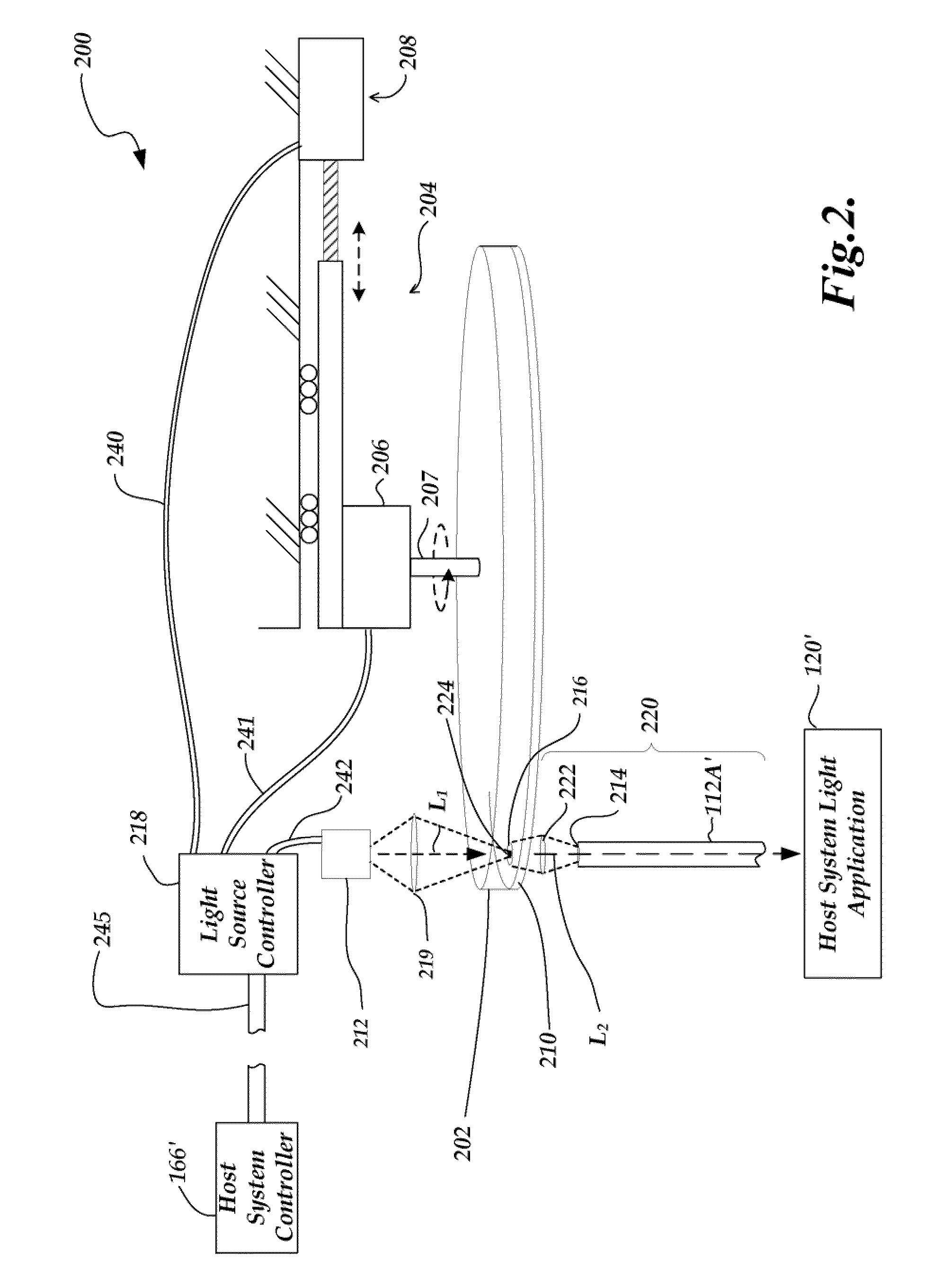
High intensity pulsed light source configurations
InactiveUS20100097779A1High proportionSmall dimensionUsing optical meansSpectral modifiersHigh ratePhosphor
A high-intensity light source configuration has a long lifetime and can be modulated at a high rate. The configuration includes a movable member mounted to an actuator; a light-emitting phosphor region associated with the movable member; an input light source that illuminates the light-emitting phosphor region at a spot that is fixed relative to an emitted light output region; and a light source controller controlling the movable member actuator and the input light source. The input light source (e.g., laser) provides high-intensity input light to the illuminated spot, causing the light-emitting phosphor region to emit high-intensity output light. The light-emitting phosphor region is moved relative to the illuminated spot so as to reduce optical quenching and photobleaching, to thereby extend the life of the light source configuration. The phosphor region may emit broadband light and / or may include respective sub-regions having phosphors that emit respective peak wavelengths.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
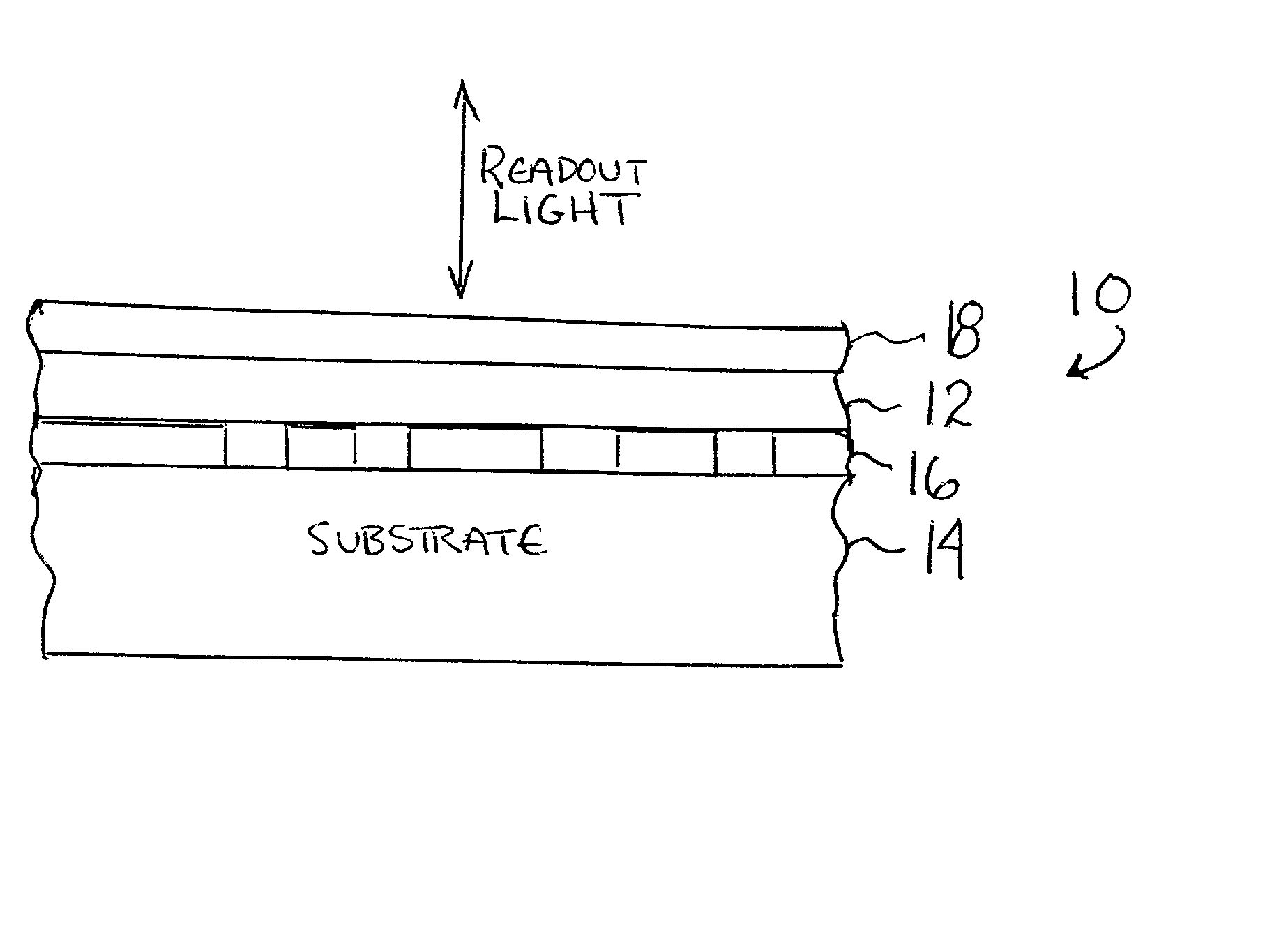
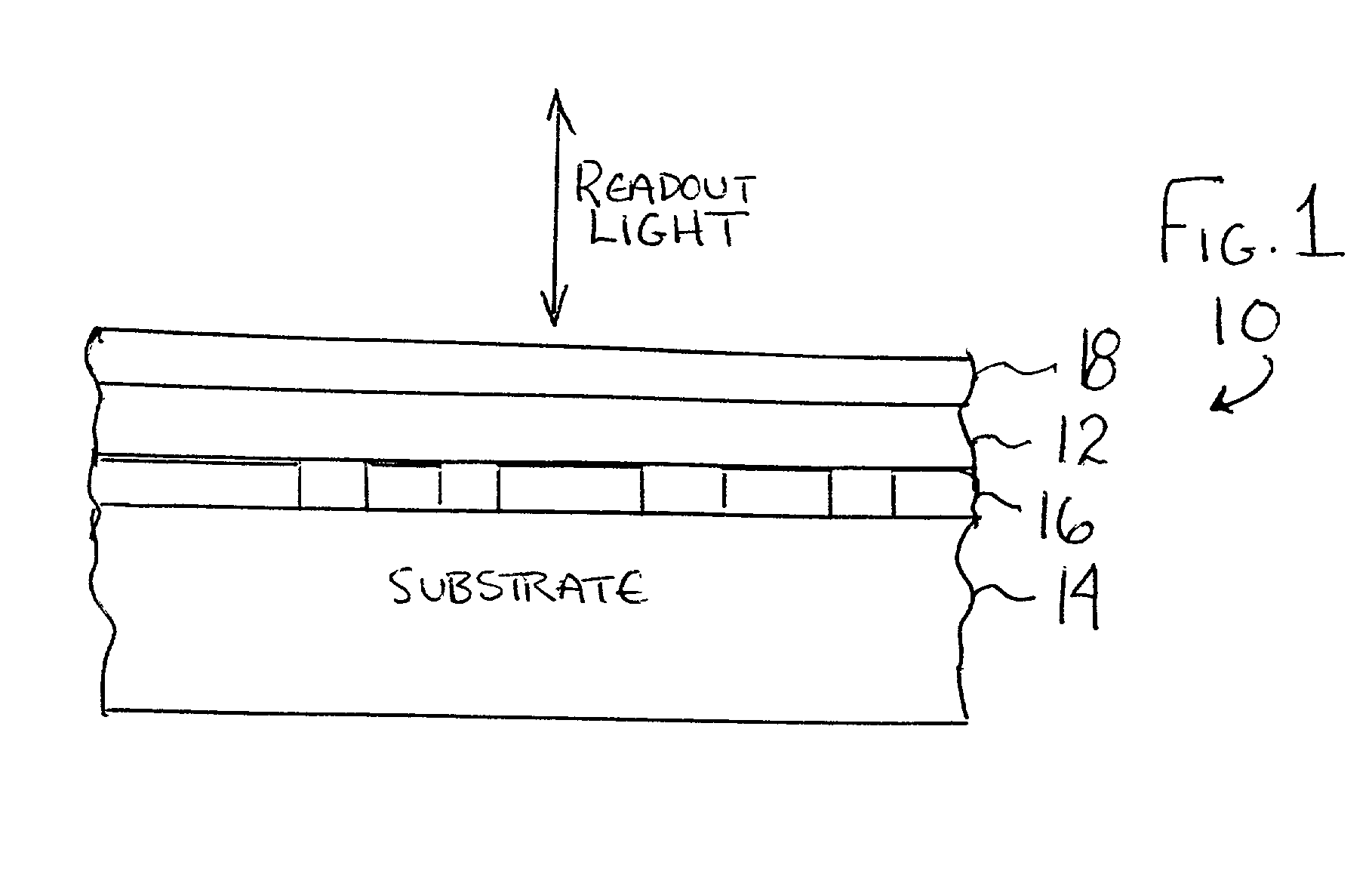
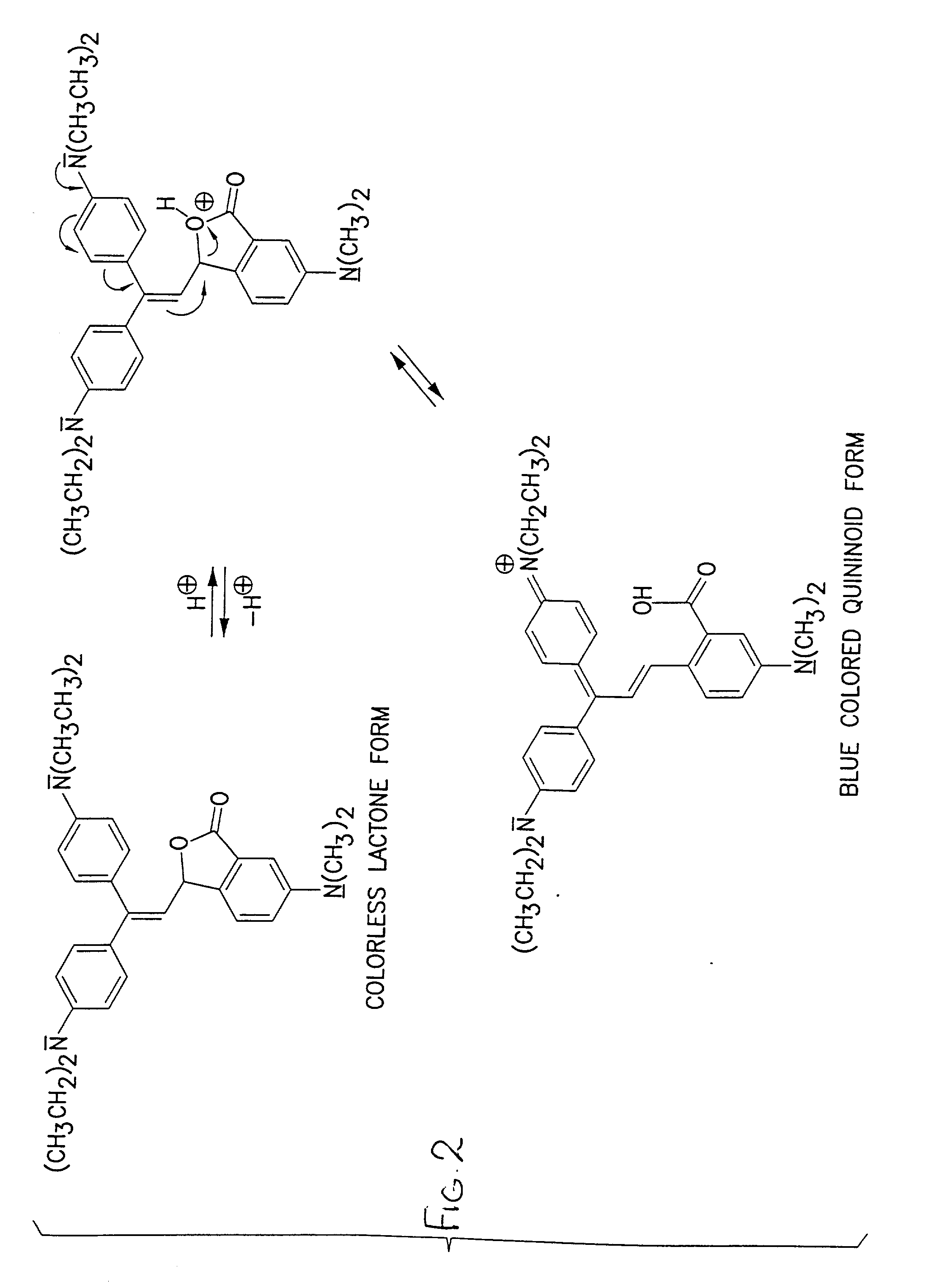
Method for rendering surface layer of limited play disk lightfast
InactiveUS20020102499A1Limit readabilityAvoid readingPhotography auxillary processesLayered productsOptical radiationReadability
An optically readable media (10) has an information-encoding layer (16) and at least one color-forming layer (12) that embodies an optical readout-limiting mechanism. In a first embodiment the at least one color-forming layer contains an additive that does not interfere with the optical readability of the media for a duration of a readout period. The additive, upon exposure to a source of optical radiation that is suitable for reversing the color-forming layer from an optical readout inhibiting state to an optical readout enabling state, undergoes a transformation that maintains the color-forming layer in the optical readout inhibiting state. More specifically, exposure to the source causes the color-forming layer to photobleach and the additive to oxidize, where the oxidation of the additive permanently inhibits the optical readability of the media. The additive may be a leuco dye. In one embodiment the color-forming layer is comprised of 3-[2,2-bis(4-diethylaminophenyl)vinyl]-6-dimethylaminophthalide and the additive is comprised of benzoyl leucomethylene blue. In a further embodiment the additive is placed into a protective layer (18) that overlies the color-forming layer.
Owner:SPECTRADISC
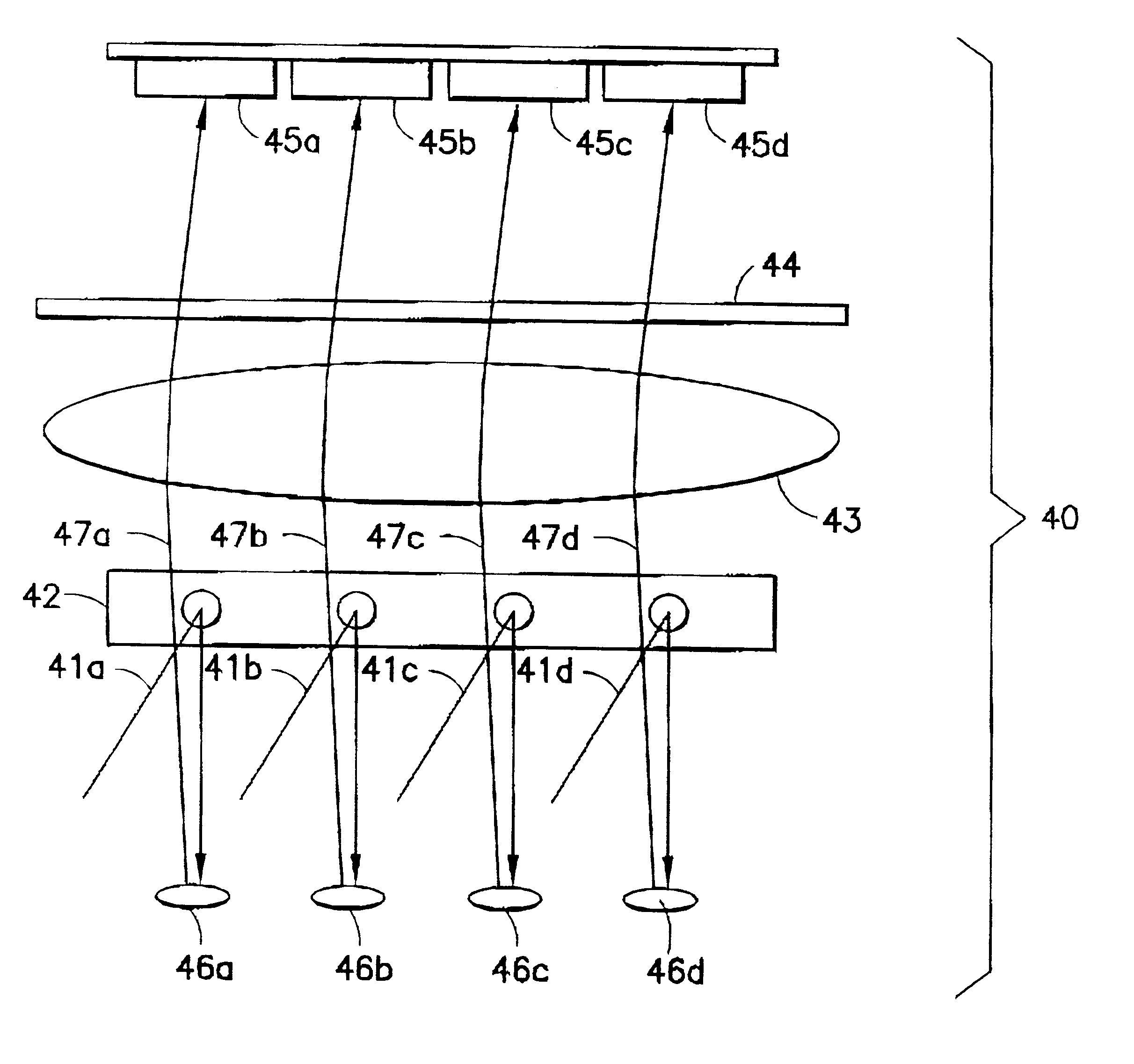
System and method employing photokinetic techniques in cell biology imaging applications
A system and method employing photokinetic techniques in cell biology imaging applications are disclosed. Systems and methods of acquiring image data of an object may comprise: selectively inducing photoactivation of material at a site on the object; performing an optical axis integration scan; simultaneously executing a time delay integration scan sequence; and processing acquired image data in accordance with one or more desired analyses. Various methodologies and applications may include, inter alia, selective photobleaching of a site on the object, diffusion rate, velocity, and wave-front propagation analyses, multi-dimensional analyses of dispersion characteristics, biomolecular binding in cellular organelles, and photoactivation assisted systematic image segmentation for the study of cellular components.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
High intensity pulsed light source configurations
A high-intensity light source configuration has a long lifetime and can be modulated at a high rate. The configuration includes a movable member mounted to an actuator; a light-emitting phosphor region associated with the movable member; an input light source that illuminates the light-emitting phosphor region at a spot that is fixed relative to an emitted light output region; and a light source controller controlling the movable member actuator and the input light source. The input light source (e.g., laser) provides high-intensity input light to the illuminated spot, causing the light-emitting phosphor region to emit high-intensity output light. The light-emitting phosphor region is moved relative to the illuminated spot so as to reduce optical quenching and photobleaching, to thereby extend the life of the light source configuration. The phosphor region may emit broadband light and / or may include respective sub-regions having phosphors that emit respective peak wavelengths.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Method for preparing nitrogen and sulfur-doped fluorescent carbon quantum dots
ActiveCN104449693AEasy to operateThe preparation process equipment is simpleNanoopticsLuminescent compositionsFreeze-dryingCytotoxicity
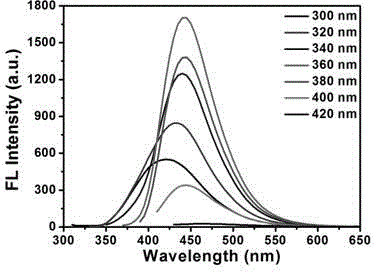
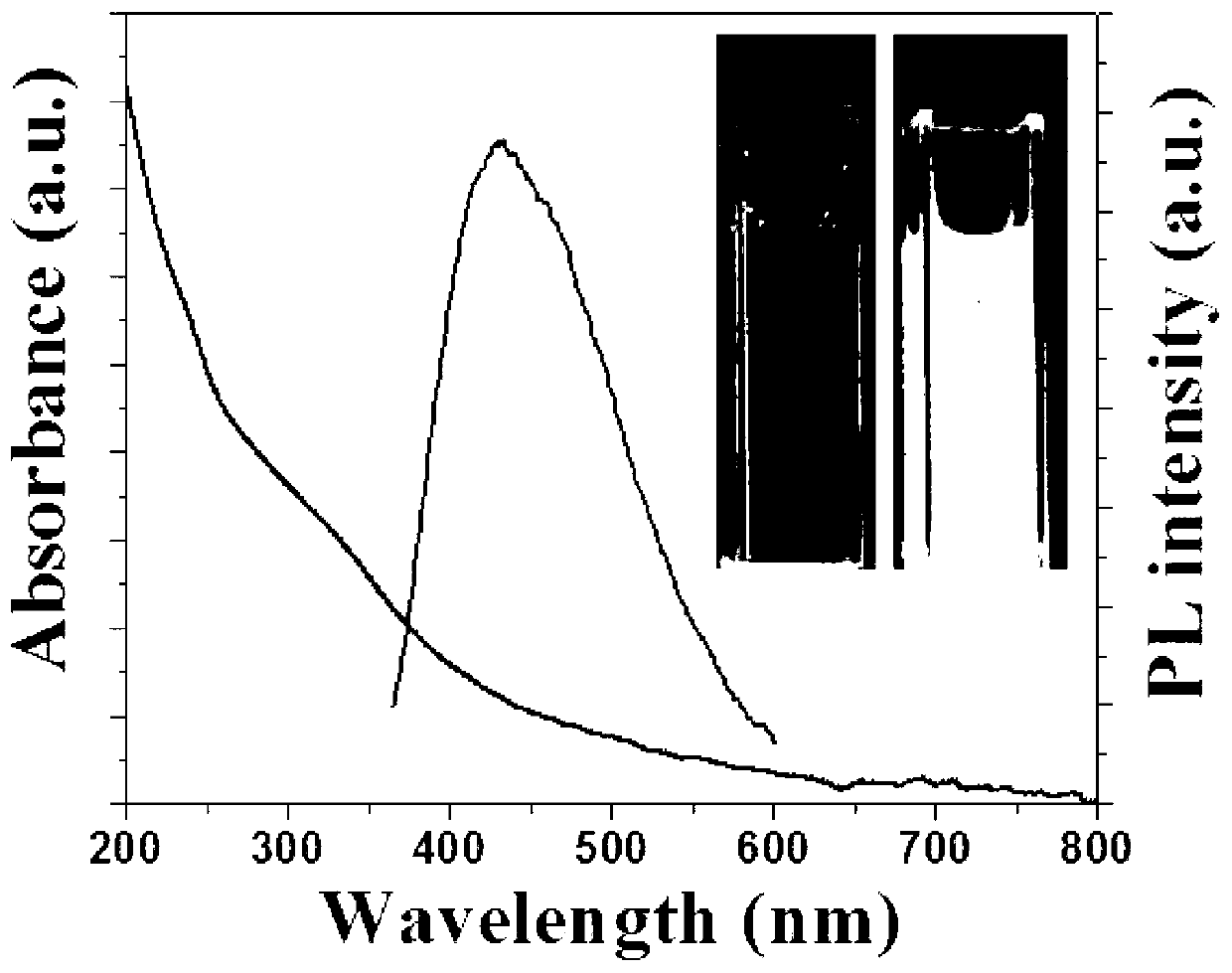
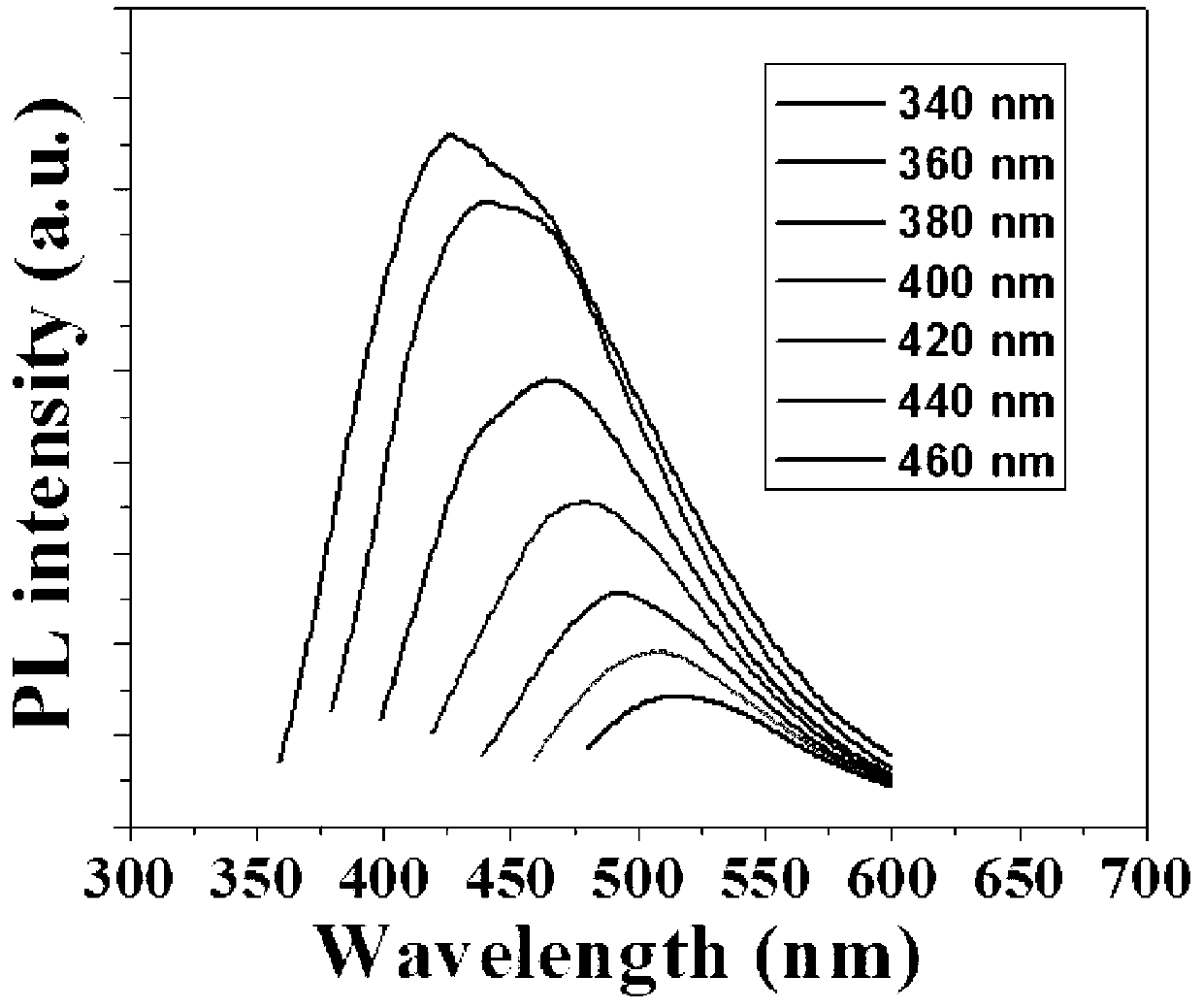
The invention discloses a method for preparing nitrogen and sulfur-doped fluorescent carbon quantum dots. According to the method, citric acid is taken as a carbon source, L-glutathione is taken as a nitrogen-sulfur dopant, a microwave oven is taken as a reaction platform, the carbon quantum dots with fluorescence properties are prepared in a heating manner, the residues and moisture are removed through dialysis and freeze drying, and quantum dot powder is obtained. The nitrogen and sulfur-doped carbon quantum dots are prepared by adopting the method disclosed by the invention; the method is simple in operation, low in cost, high in yield, simple in preparation process and equipment, free of a solvent, and easy to popularize and produce on a large scale, and can be rapidly finished within a short period of time; and the prepared carbon quantum dots have the advantages of good water solubility, high fluorescence properties, photobleaching resistance, adjustable emission spectrum, good biocompatibility, low cytotoxicity and the like, and have a good application prospect in the fields of bioimaging, biosensors and photo-electric devices.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Flourescence polarization assay system and method
An instrument is disclosed for fluorescence assays which is capable of reading many independent samples at the same time. This instrument provides enhanced throughput relative to single-sample instruments, and is well-suited to use in general fluorescence, time-resolved fluorescence, multi-band fluorescence, fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET), and fluorescence polarization. This invention is beneficial in applications such as high-throughput drug screening, and automated clinical testing. Also disclosed are means and methods for a fluorescence polarization measurement which is highly sensitive, inherently self-calibrated, and unaffected by lamp flicker or photobleaching. This fluorescence polarization invention can be practiced on a variety of fluorescence instruments, including prior-art equipment such as microscopes and multi-well plate readers.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE RES & INSTR
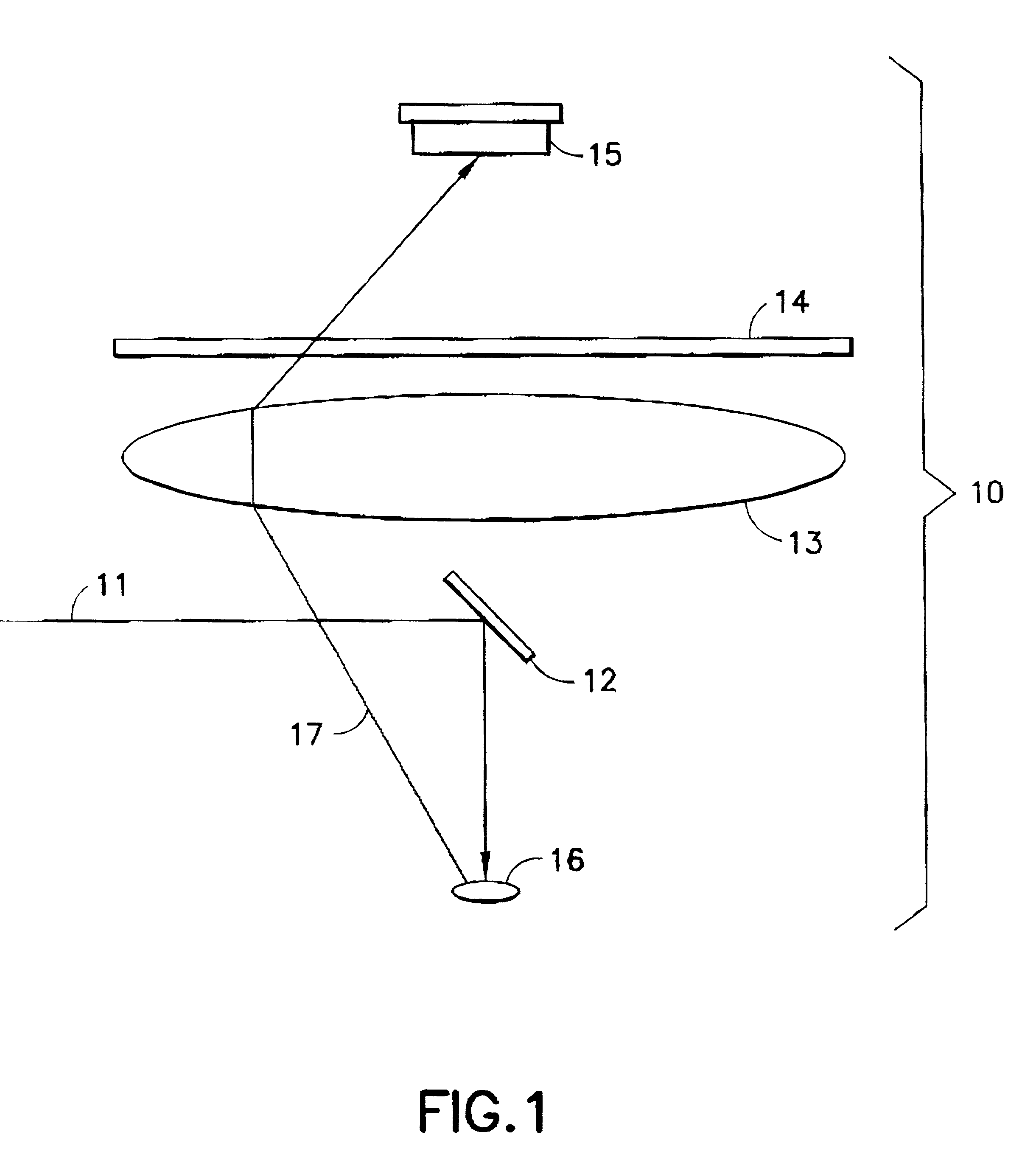
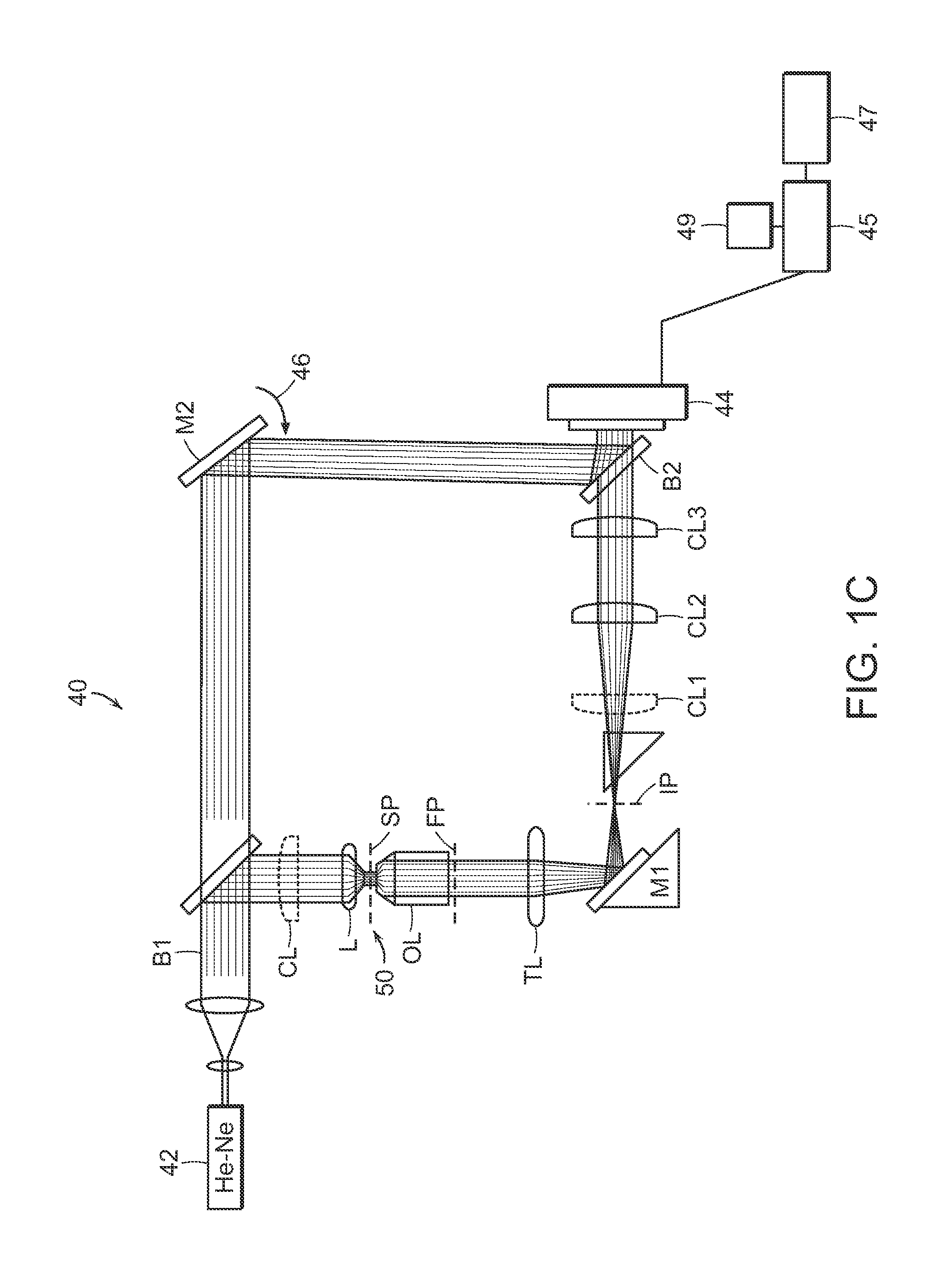
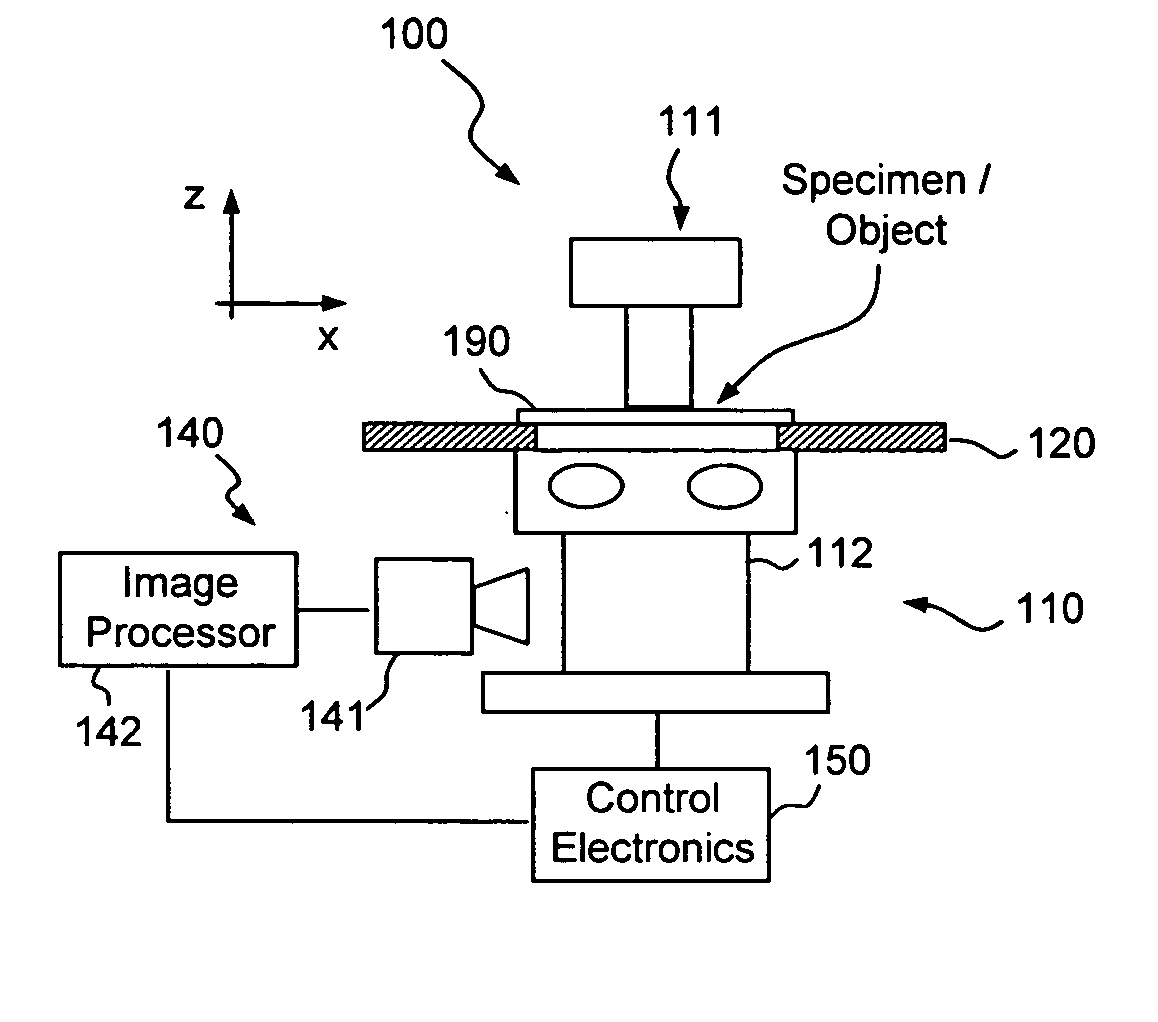
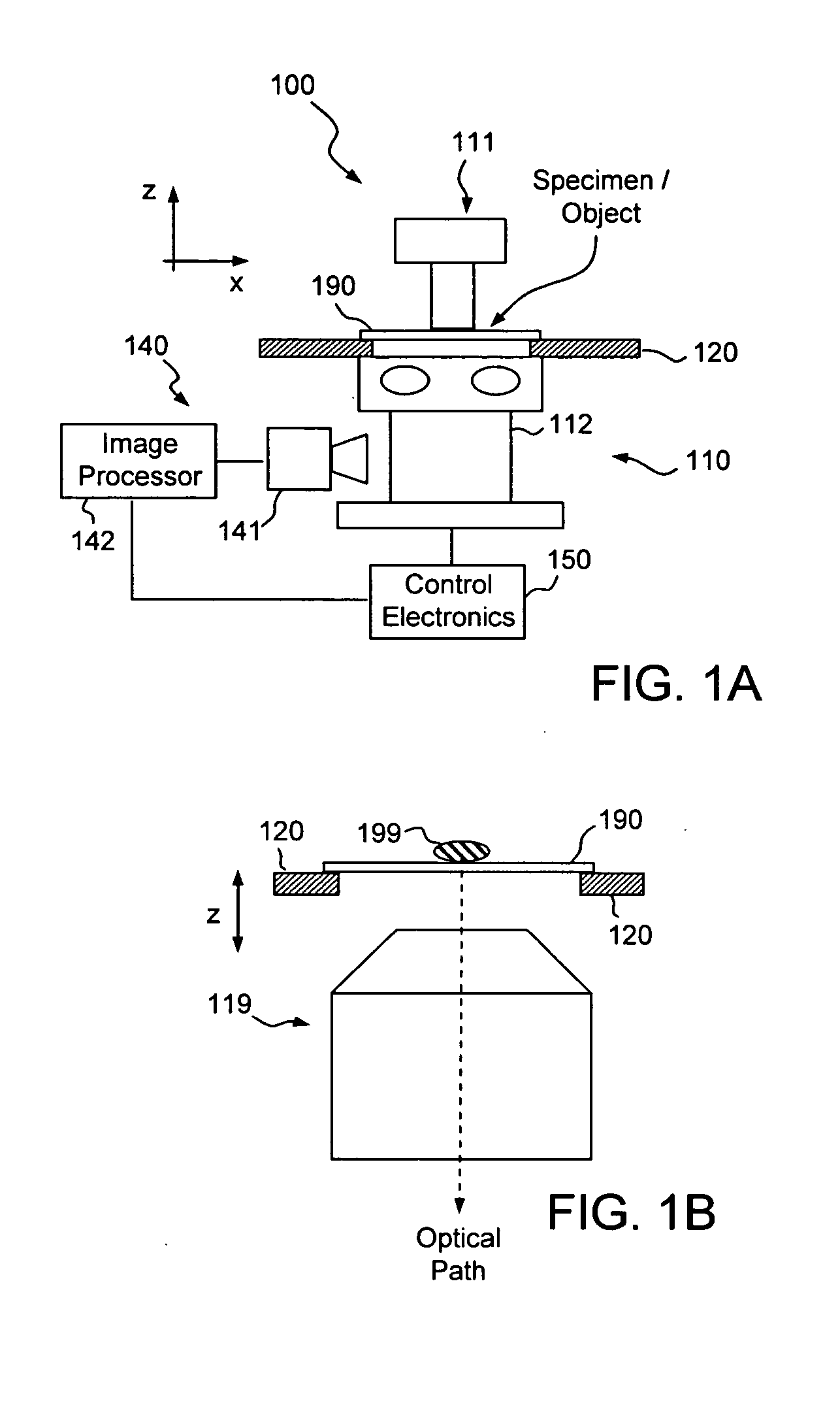
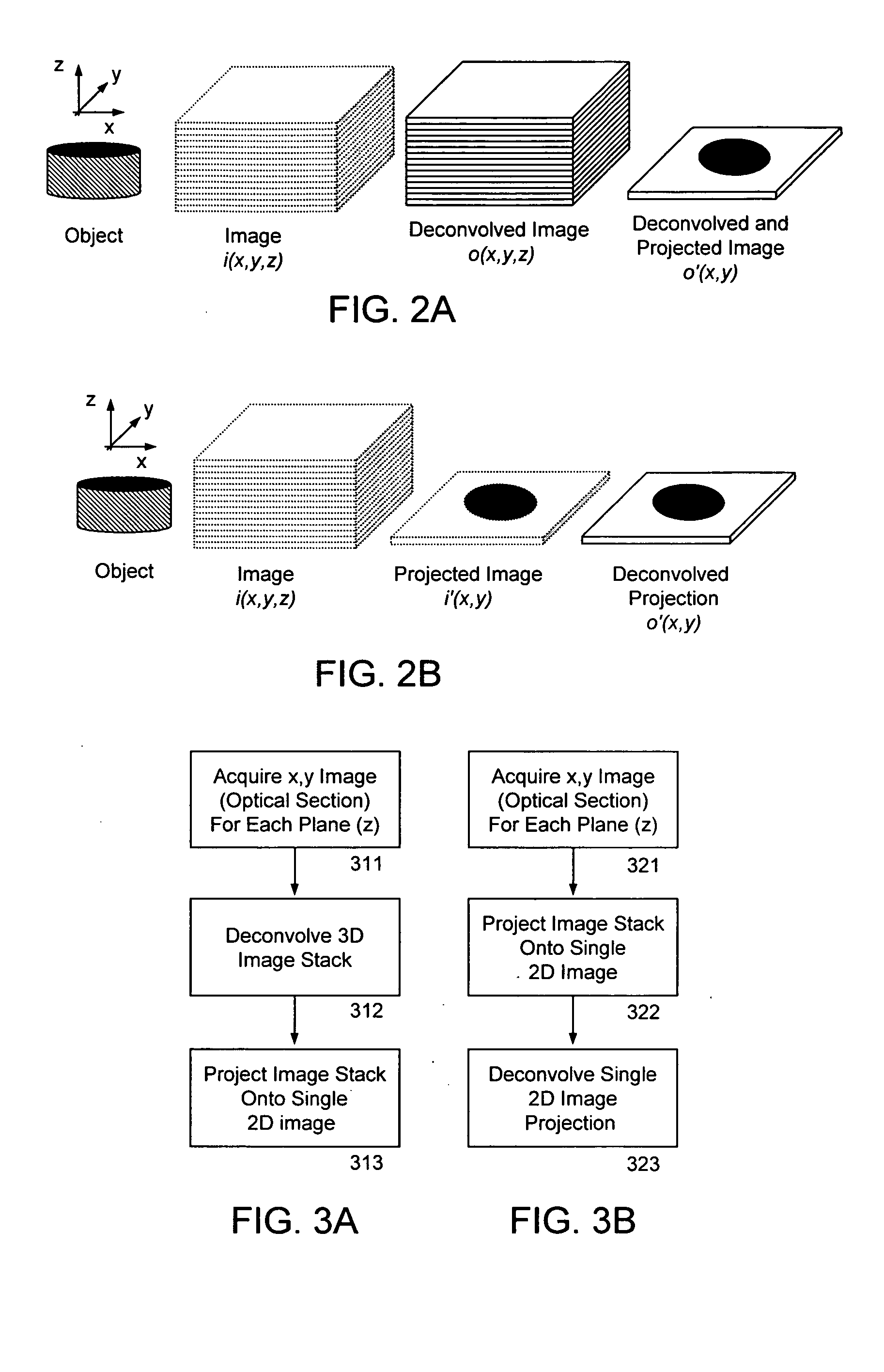
Apparatus and method for three dimensional image reconstruction
InactiveUS7197193B2Improve image acquisition efficiencyEliminate effect caused by motionImage enhancementImage analysisPoint spread functionDiffusion function
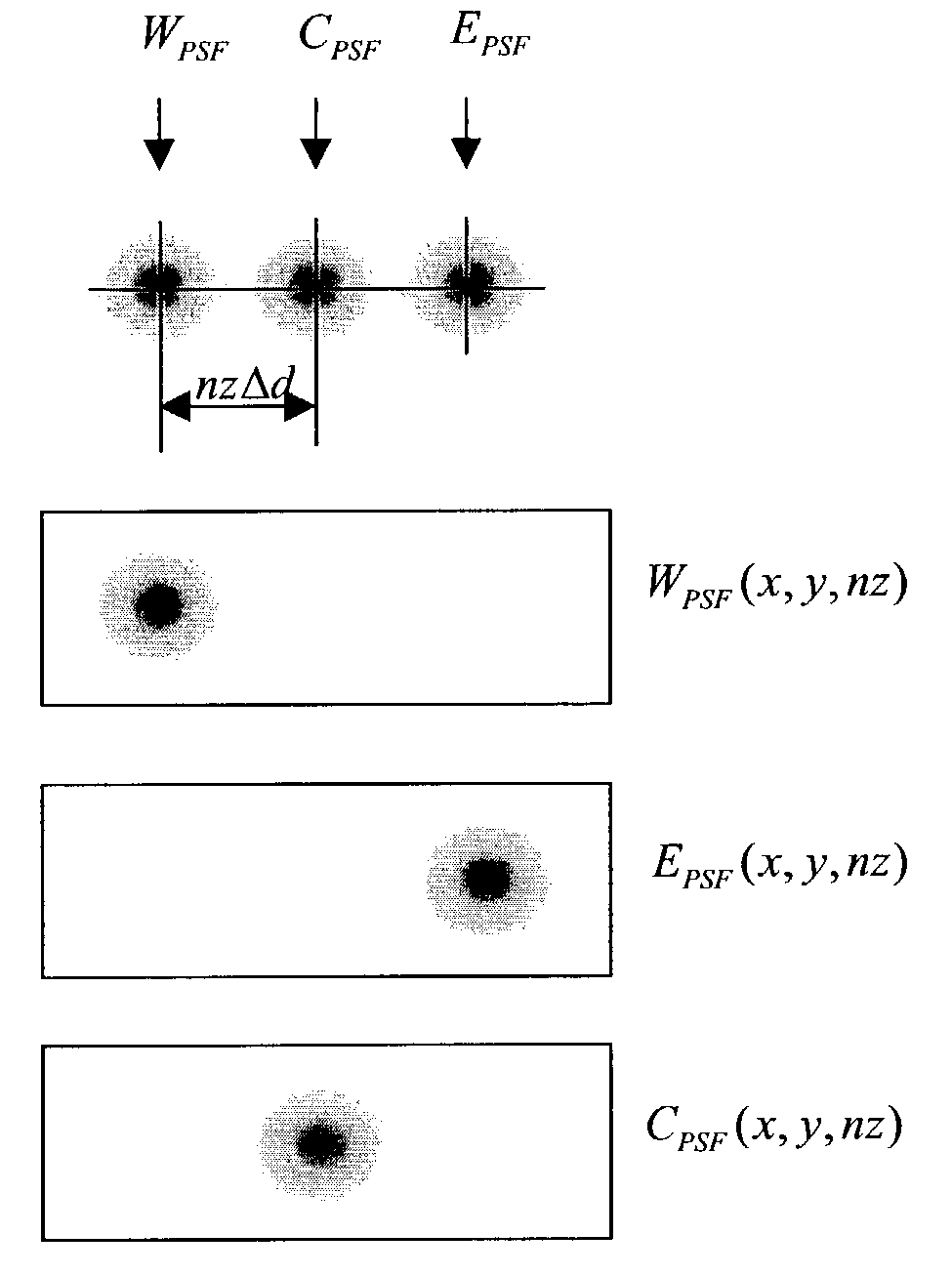
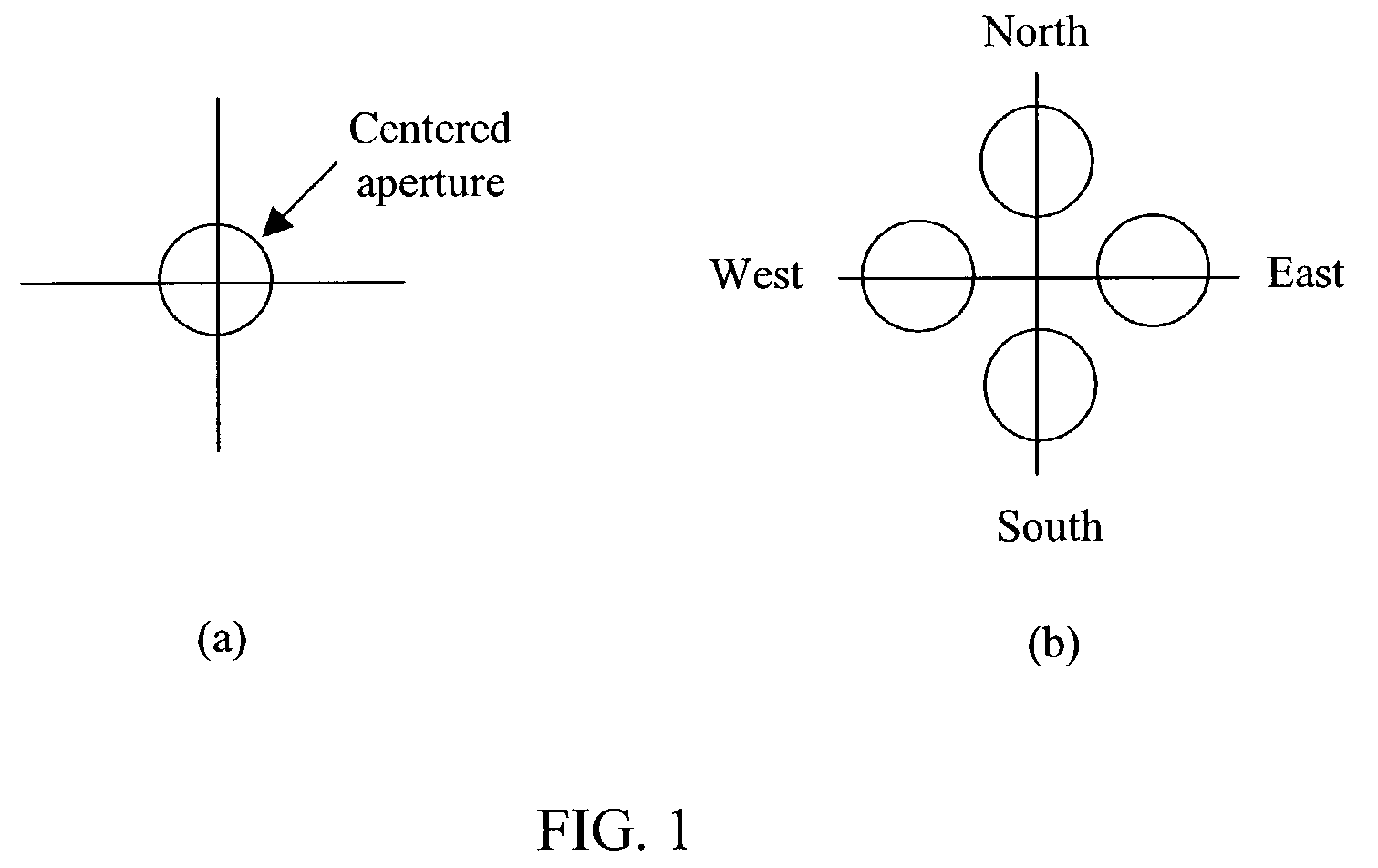
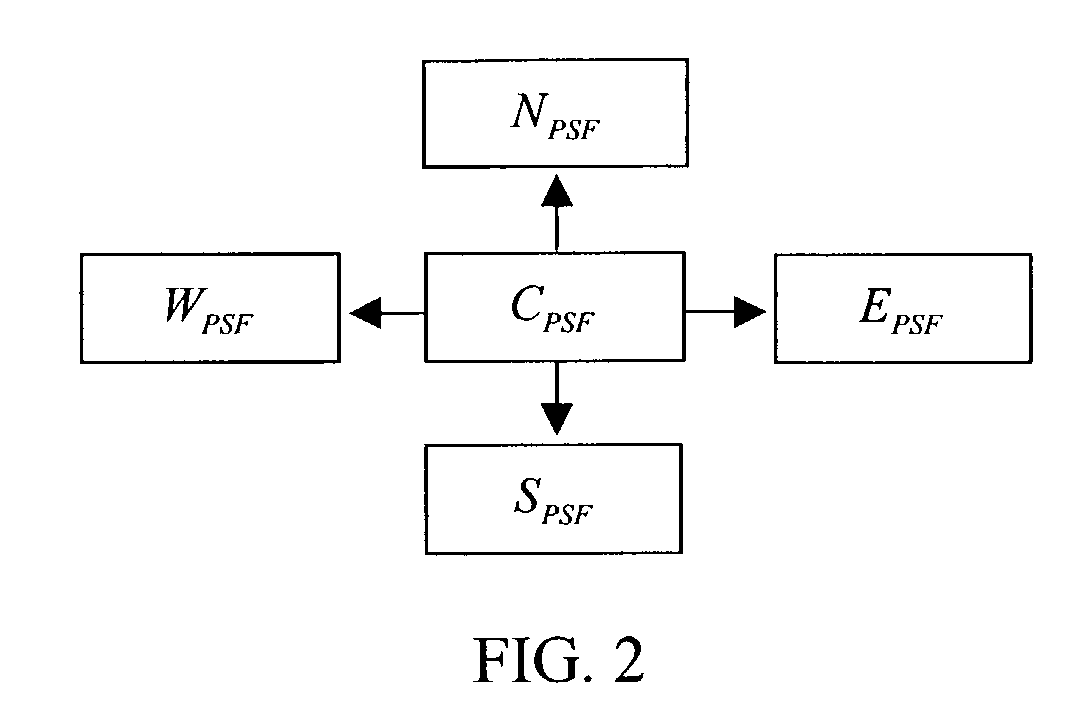
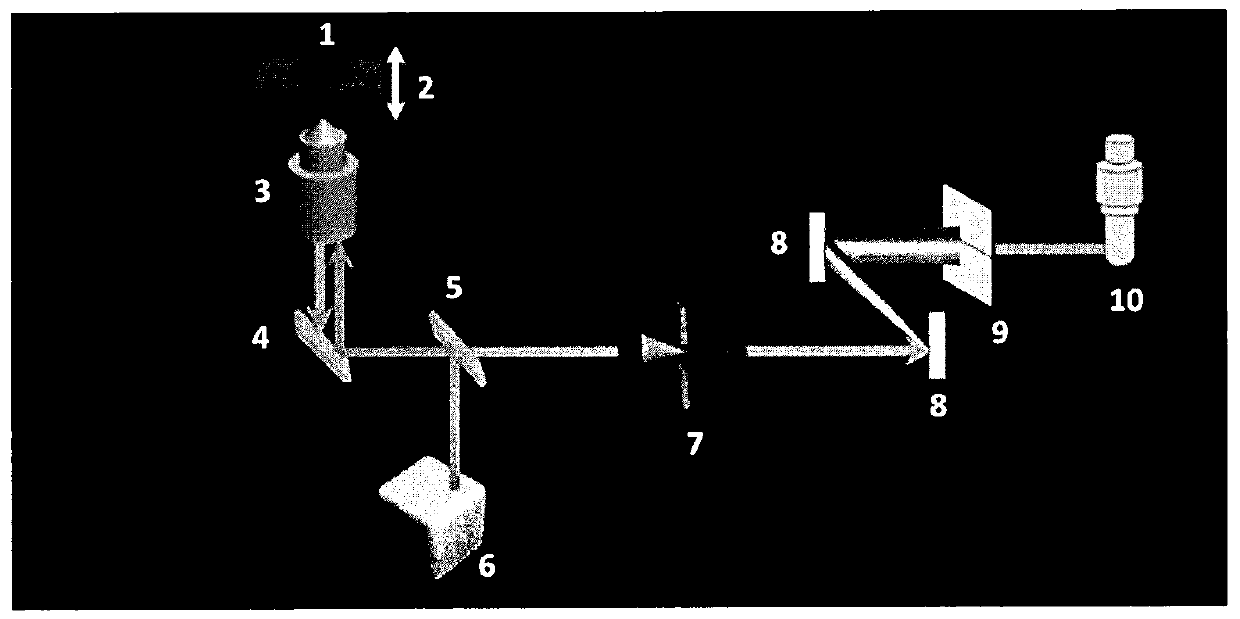
An instrument to acquire and methods to obtain three-dimensional (3D) images from a series of two-dimensional (2D) images which are obtained without moving the relative positions of the target, the detector, or the focusing lens is disclosed. The 2D images consist of one centered image obtained with the aperture at the center of optical system, and at least two directional images obtained with apertures at off-axis locations. The images can be obtained simultaneously or sequentially. The blurred 2D images are sectioned by computational method using point spread function of the optical system resulting in a set of decoupled 2D layers of the 3D object. The layered images are then sharpened by deconvolution using point spread function. The 3D reconstructed image is displayed. This technique provides fast data acquisition and fast image reconstruction and eliminates problems associated with motion, phototoxicity and photobleaching.
Owner:CREATV MICROTECH
Cleaning compositions
InactiveUS6339055B1Organic detergent compounding agentsAnionic surface-active compoundsMethacrylatePorphyrin
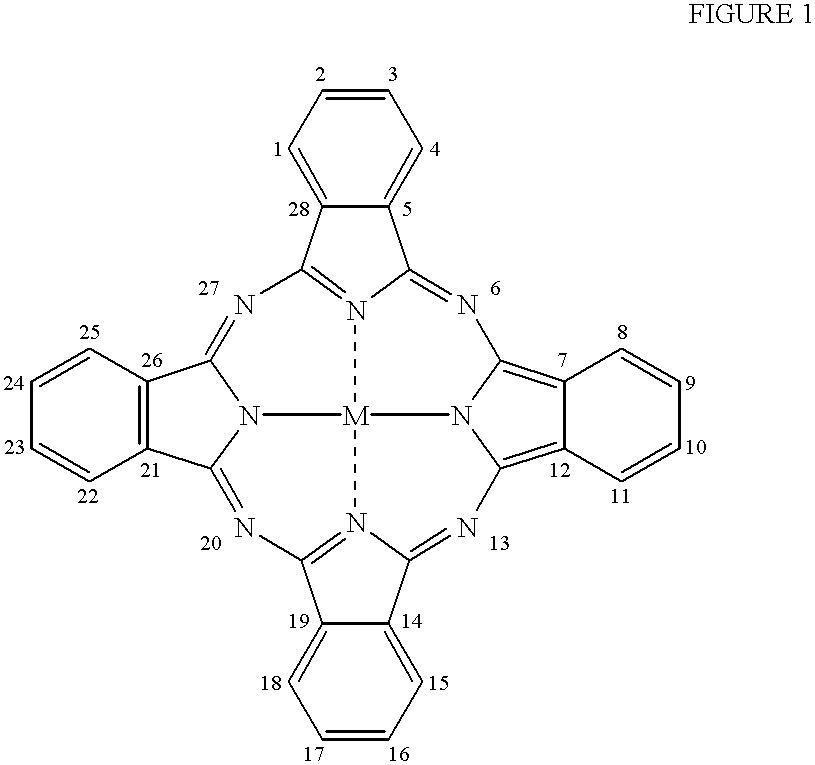
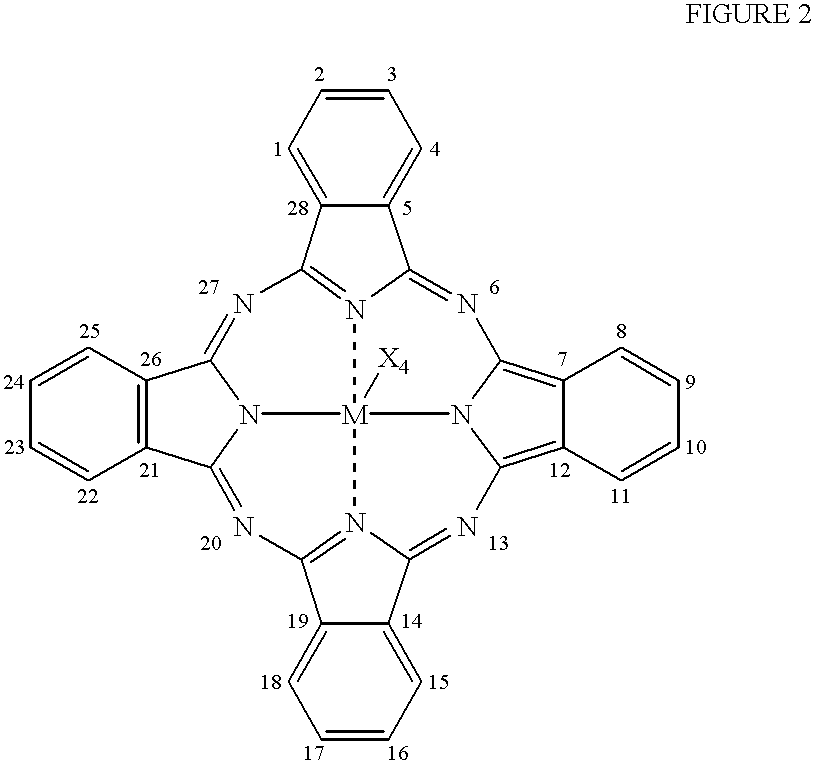
The present invention relates to a photo bleaching compositions comprising:A) from 0.5 ppm by weight, of a photo bleaching agent, said agent comprising:a) a polymeric component, said polymeric component comprising one or more polymeric compounds having an average molecular weight of from 500 to 1,000,000 wherein at least 50% of the monomers which comprise said polymeric compounds comprise one or more di-polar, aprotic groups and have a polymerizable vinyl moiety, the balance comprising monomers selected from the group consisting of acrylic acid, acrylic acid esters, acrylic acid amides, methacrylic acid, methacrylic acid esters, methacrylic acid amides, and mixtures thereof; andb) a photo bleaching component, said photobleaching component comprising a porphyrin or a phthalocyanine ring wherein said phthalocyanine ring can optionally be substituted at one or more ring positions, and said ring comprising a transition metal or cation having an oxidation state of two or greater;wherein said photo bleaching component is integrated with said polymeric component to form said photo bleaching agent and the weight ratio of polymeric component (a) to photobleaching component (b) is from 1:1 to 1000:1;B) from 0.1% by weight, of a peroxy acid bleaching compound precursor; andC) the balance carriers and adjunct ingredients.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Preparation method of carbon quantum dots with high fluorescence property
InactiveCN103342347AThe reaction equipment is simpleSimple and fast operationMaterial nanotechnologyNano-carbonFreeze-dryingBiocompatibility Testing
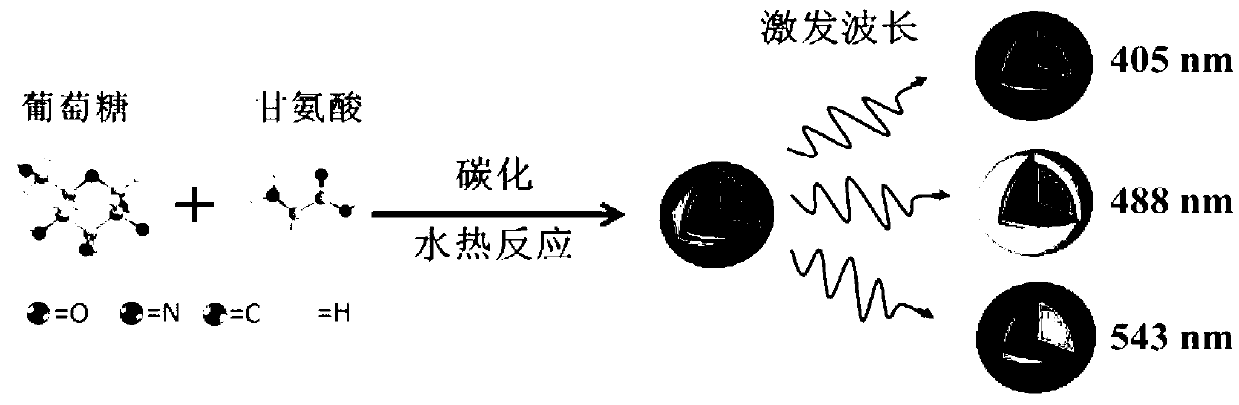
The invention discloses a preparation method of carbon quantum dots with a high fluorescence property by using glycine and glucose as precursors. The method comprises using the glycine as a surface passivating agent, the glucose as a carbon source material and a hydro-thermal reaction vessel as a reaction platform, carrying out a high-temperature and high-pressure hydrothermal reaction, and removing residues and water through dialysis and freeze drying to obtain carbon quantum dot powder. The preparation method of the carbon quantum dots has characteristics of simple operation, low cost and easy mass production. The prepared carbon quantum dots have excellent properties of high fluorescence property, photobleaching resistance, adjustable light emission and good biocompatibility, can be successfully applied in live cell fluorescence imaging and flow cytometry analysis, and is broad in application prospect in biomedical fields.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
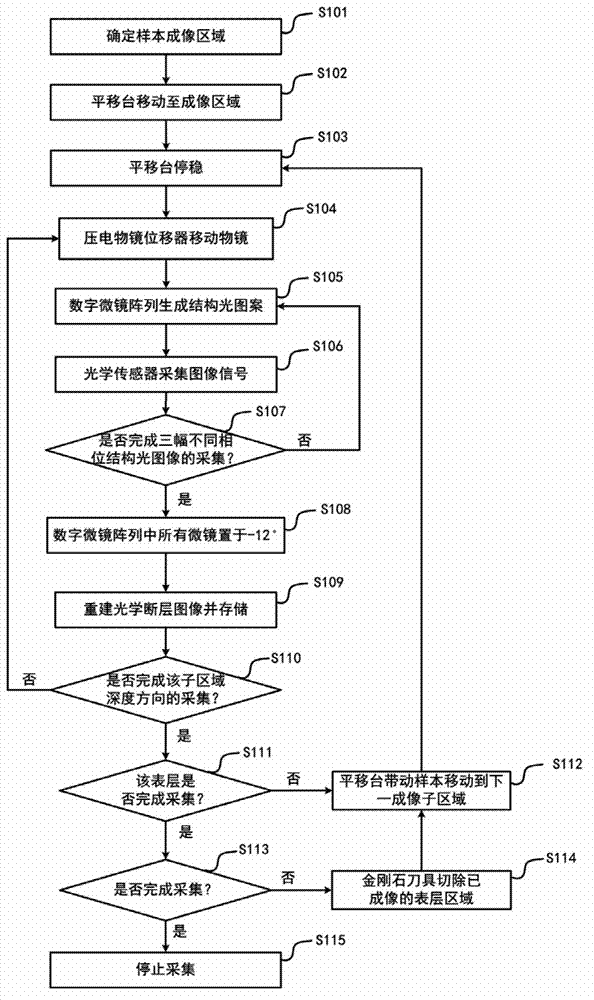
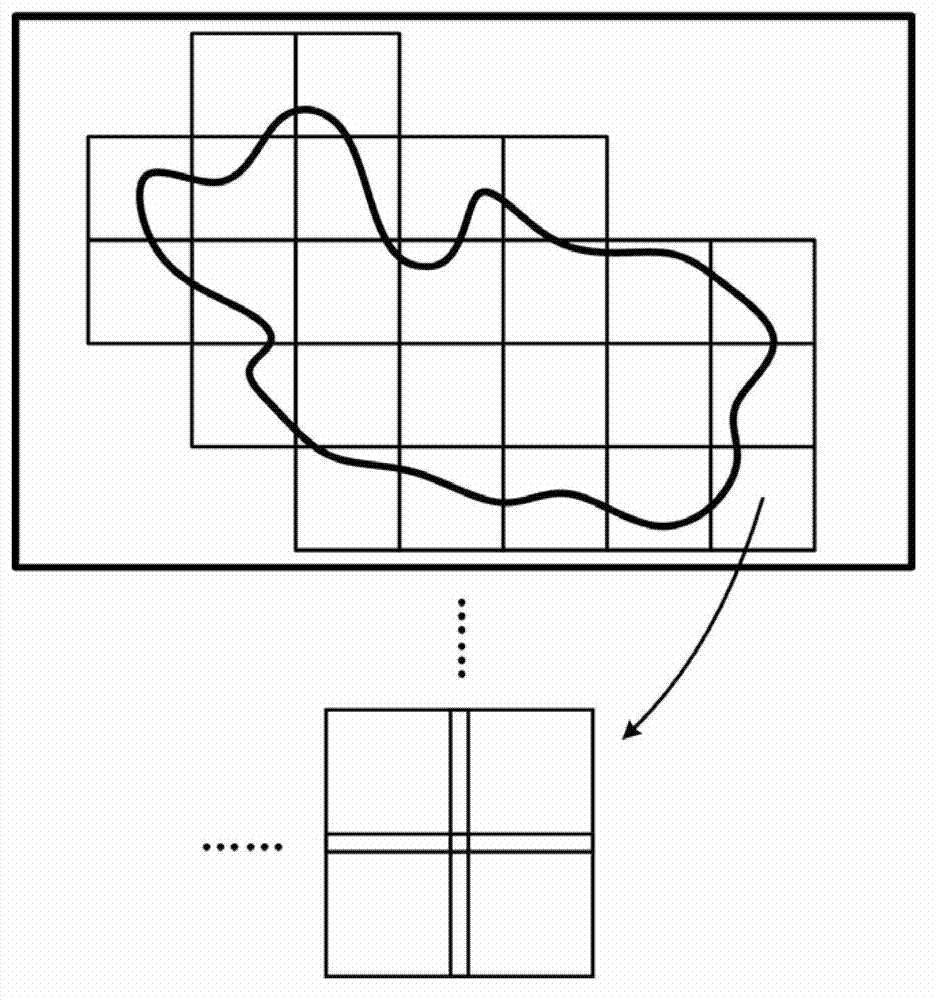
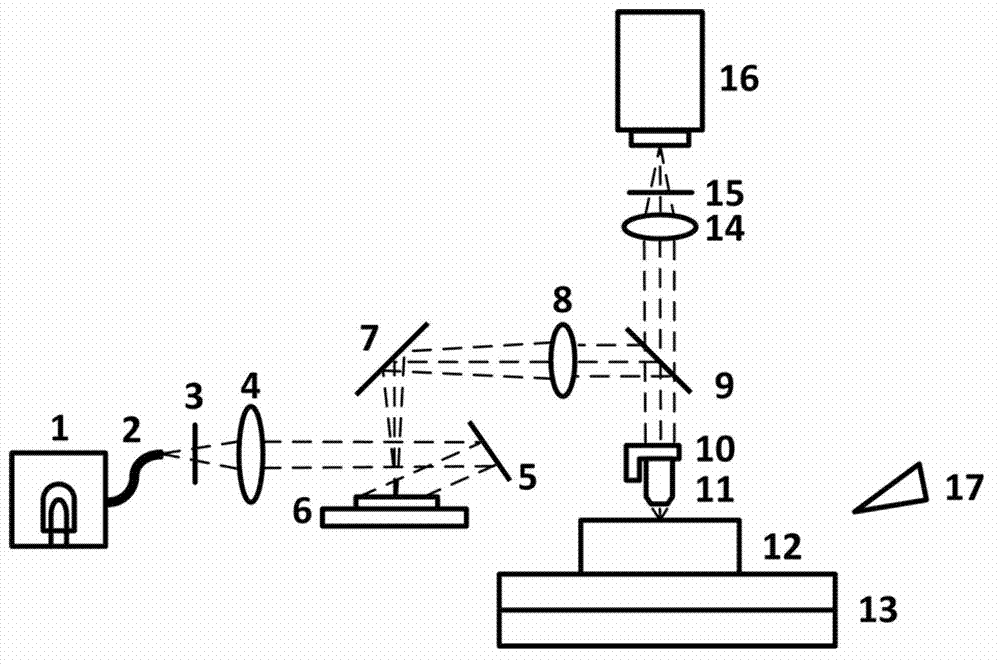
Method and system for rapidly three-dimensionally microimaging large sample
The invention relates to a method and system for rapidly three-dimensionally microimaging a large sample. The method comprises the following steps: 1, a sample is embedded in a sample block and is fixed on a precise three-dimensional electric translation platform; 2, a digital micro mirror array works in a binary modulation mode, and is used for carrying out binary modulation on illuminating light to form structure striations, a structured light microscope collects an image of the surface layer of the sample within a depth of 1-100micrometers; 3, completing the imaging of the inner surface layer of an imaging region, removing an imaged part of the surface layer of the sample block by using a diamond or hard alloy tool; and 4, repeating the steps 2 and 3 until a data acquiring task is completed. According to the invention, the digital micro mirror array works in the binary modulation mode, the imaging speed is effectively increased; and with an exposure synchronization method of the digital micro mirror array and a surface array camera, the sample can be irradiated by exciting light only when a surface array camera is exposed, the exposure quantity of the sample is further reduced, and the negative effects of a light bleaching effect to imaging is avoided.
Owner:WUHAN OE BIO CO LTD
Fluorescent probe and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106833623AStrong forceEasy to pile upOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceSolubilityDouble bond
The invention provides a fluorescent probe represented by the formula (I), wherein R1 and R2 are independently selected from H or an aromatic vinyl group, and at least one of R1 and R2 is the aromatic vinyl group; R3 is selected from H, F, Cl, Br, OH, OCH3, N(CH3)2 or C1-C6 alkyl; and R4 is selected from C1-C6 alkyl. Compared with the prior art, because the fluorescent probe provided by the invention has a relatively large electronic conjugated system and plane, the intensity of the intramolecular charge transfer effect can affect the molecular fluorescence emission intensity; when the fluorescent probe and the G-quadruplex generate a specific action, the flexibility of intramolecular rotatable double bonds is restricted, the intramolecular charge transfer effect is enhanced, and the fluorescence is also enhanced significantly; moreover, the fluorescent probe provided by the invention has the advantages of low biotoxicity, phototoxicity and photobleaching property, good light stability, good water solubility and good cell membrane permeability.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
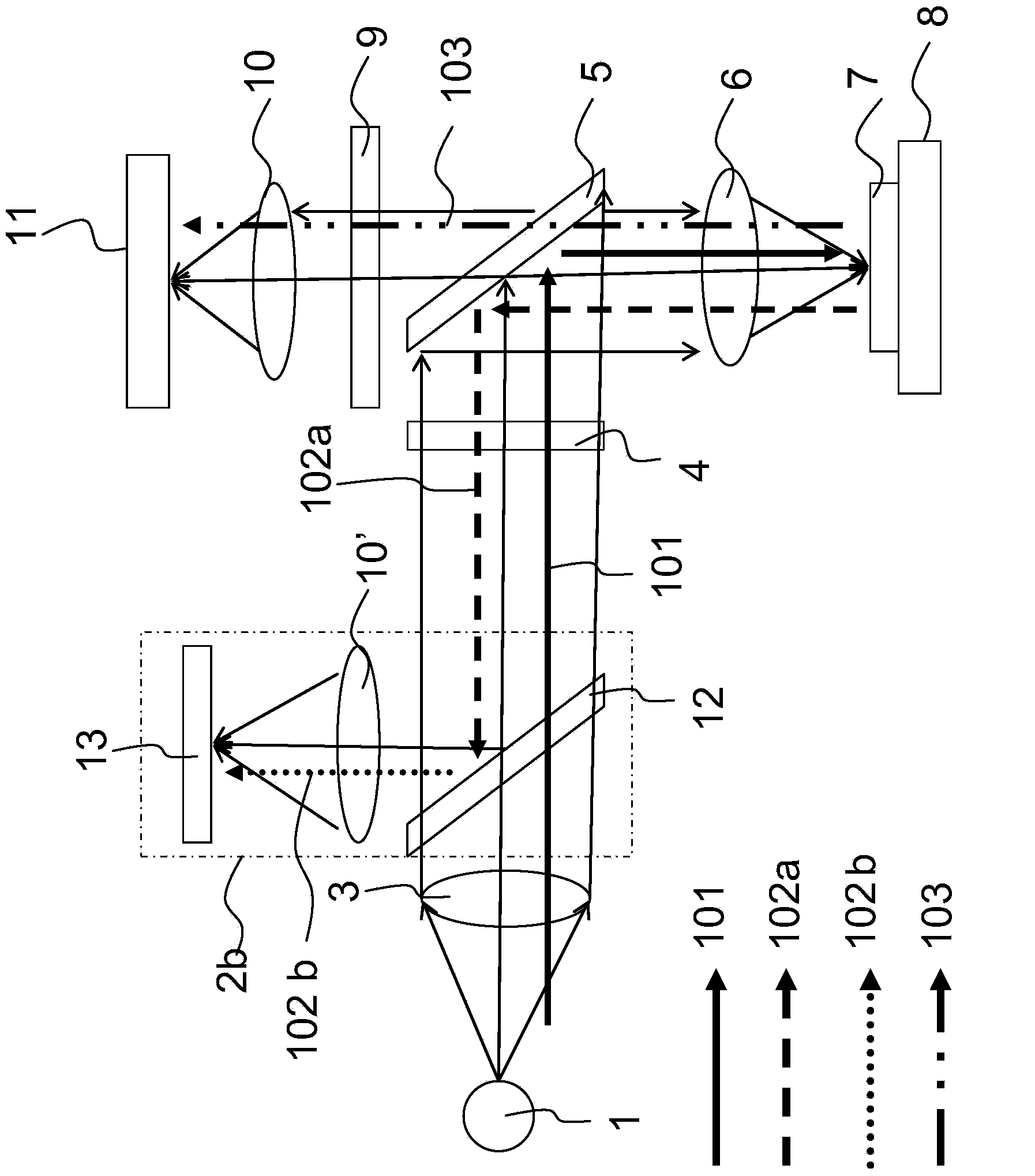
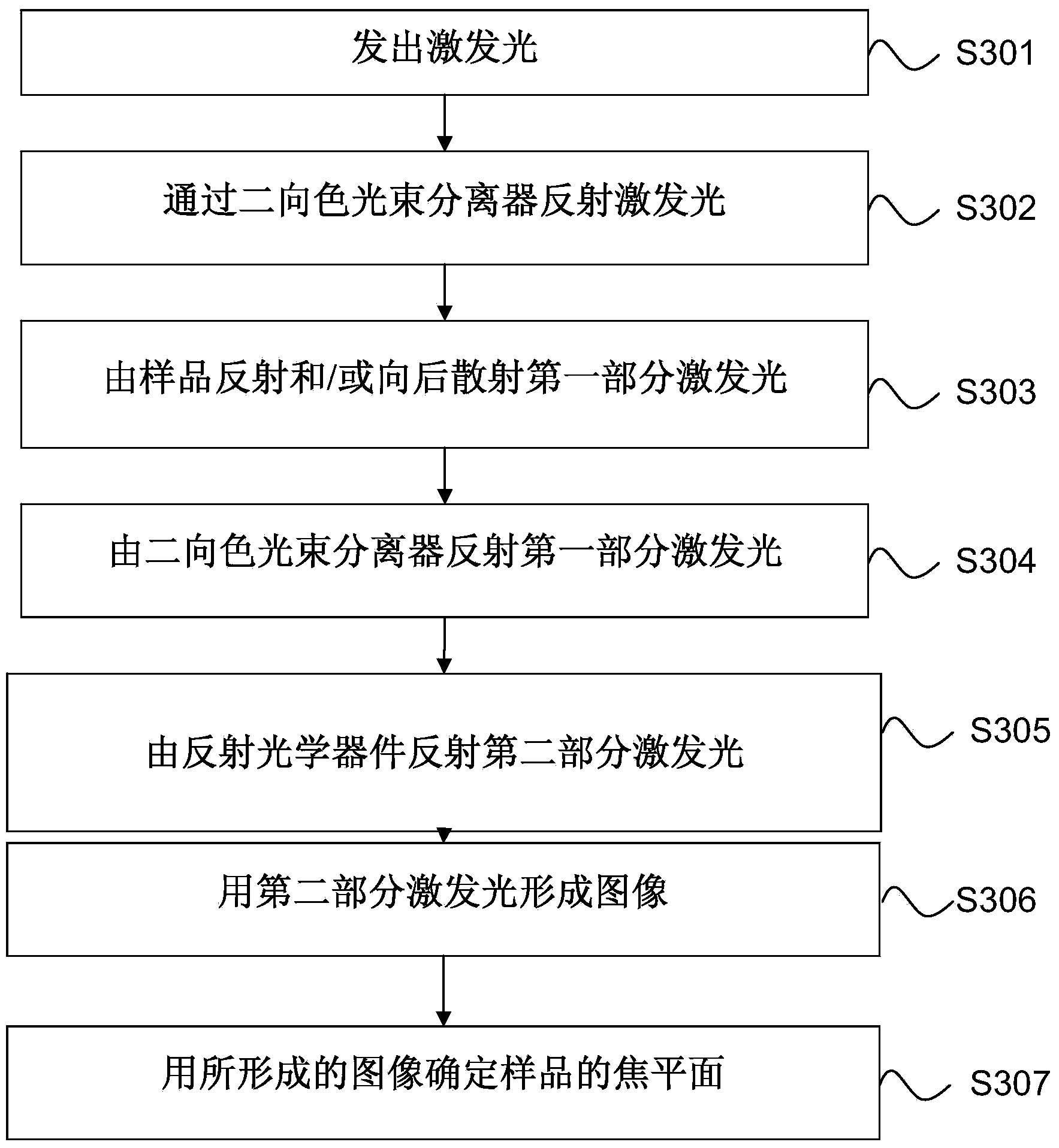
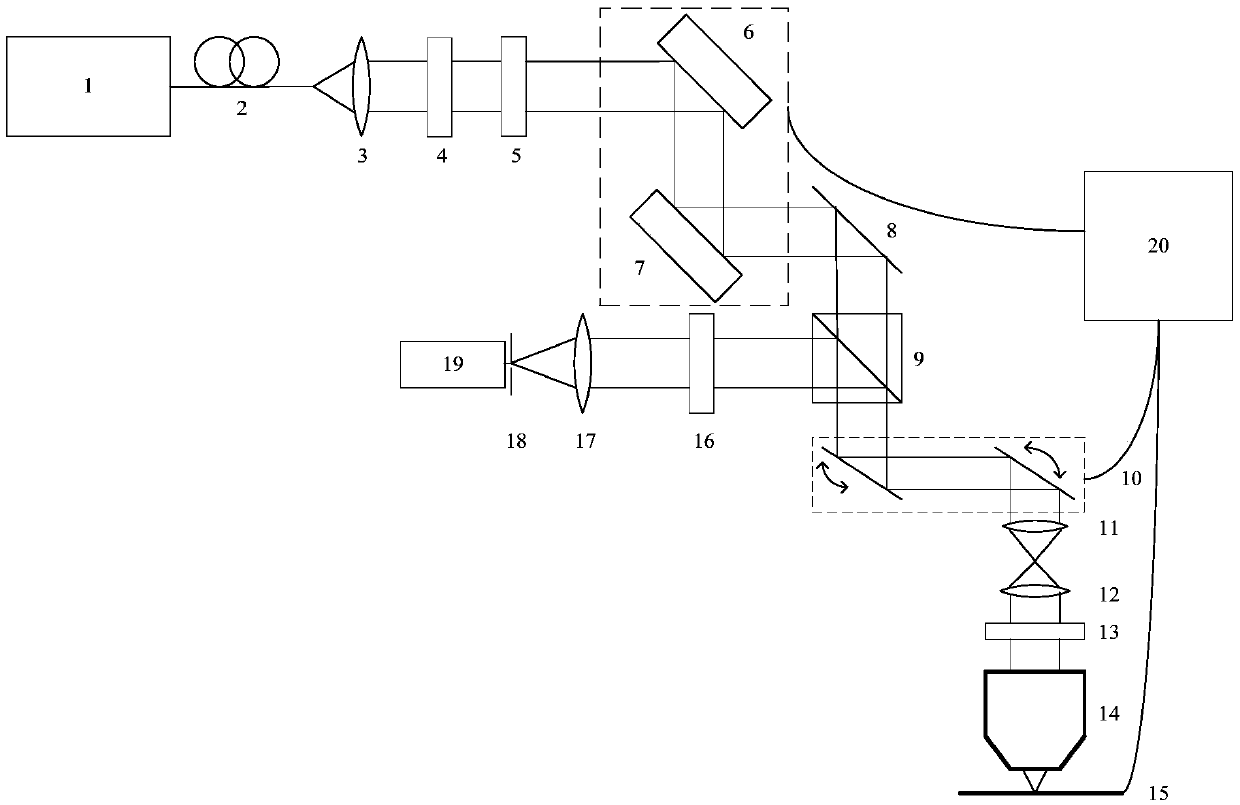
Device and method for focusing in fluorescence microscope
ActiveCN103513411APrevent bleachingAccurate focusMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceImage formationFluorescence microscope
The invention provides a device and method for focusing in a fluorescence microscope. According to the device and method for focusing in the fluorescence microscope, the focusing time can be shortened, the system speed can be increased, and undesired photobleaching can be avoided. According to the fluorescence microscope, part of exciting light is used for forming an image of a sample so that the focal plane of fluorescence imaging can be determined. Due to the fact that the intensity of the part of exciting light is far greater than the intensity of fluorescence, the exposure time for forming a focusing target image is greatly shortened. The fluorescence microscope can conduct prefocusing and multi-path focusing.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
Preparation method and application of carbon dot/gold composite nanoparticles
ActiveCN106141200AHigh quantum yieldSmall sizeLuminescent compositionsQuantum yieldSurface-active agents
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of carbon dot / gold composite nanoparticles. Citric acid and cysteine are taken as raw materials, and N-S codoping carbon dots are synthesized; the carbon dots serve as the heterogeneous nucleation center of the gold nanoparticles, a reducing agent and a stabilizing agent, any other auxiliaries such as a surface active agent or an adsorbent do not need to be added, and the carbon dot / gold composite nanoparticles are prepared by further reducing chloroauric acid. The preparation method of the carbon dot / gold composite nanoparticles is simple, convenient, feasible, mild in reaction condition and environmentally friendly, and the prepared carbon dot / gold composite nanoparticles have the characteristics of being high in quantum yield, small in size, low in biotoxicity, resistant to photobleaching and the like, and can be applied to the fields such as cell imaging or catalytic reaction research.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
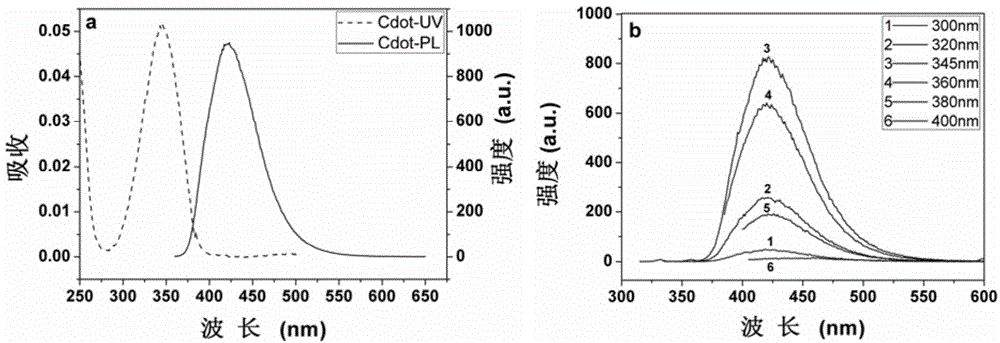
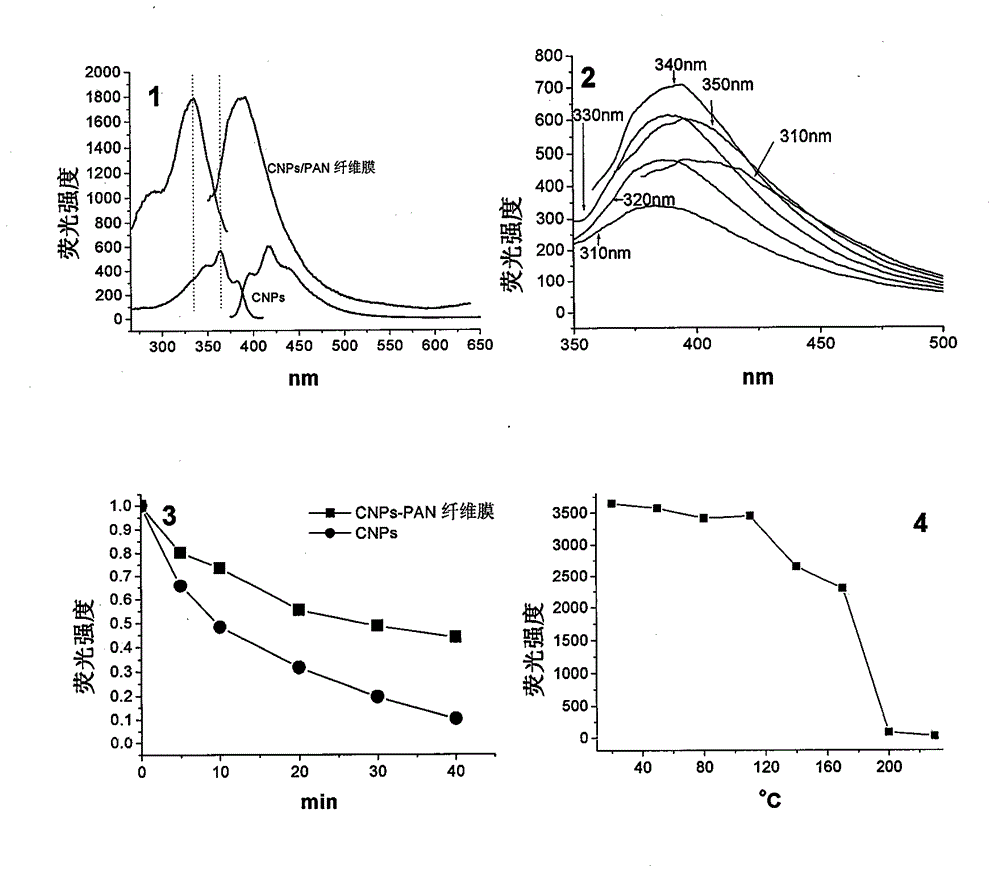
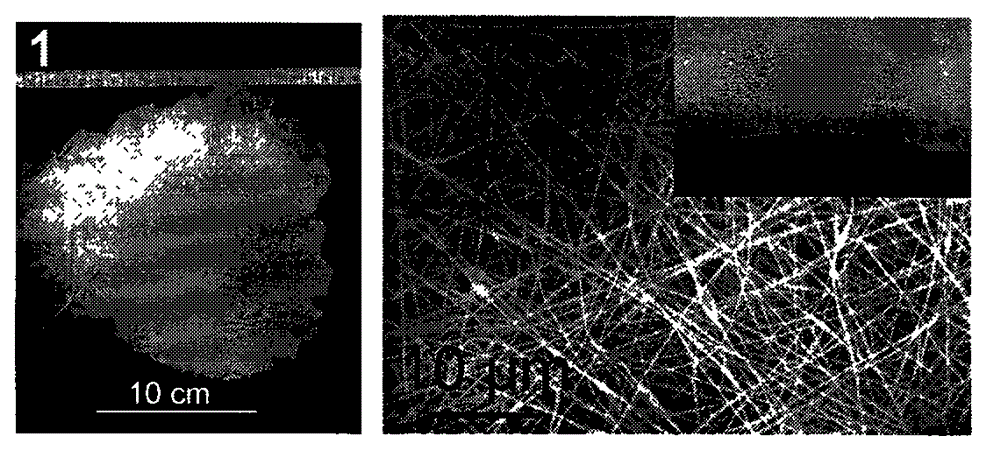
Preparation method and use of fluorescent carbon quantum dot/polyacrylonitrile nanofiber membrane
InactiveCN102944538AImprove photobleaching resistanceImprove thermal stabilityFluorescence/phosphorescenceHeat stabilityNanofiber
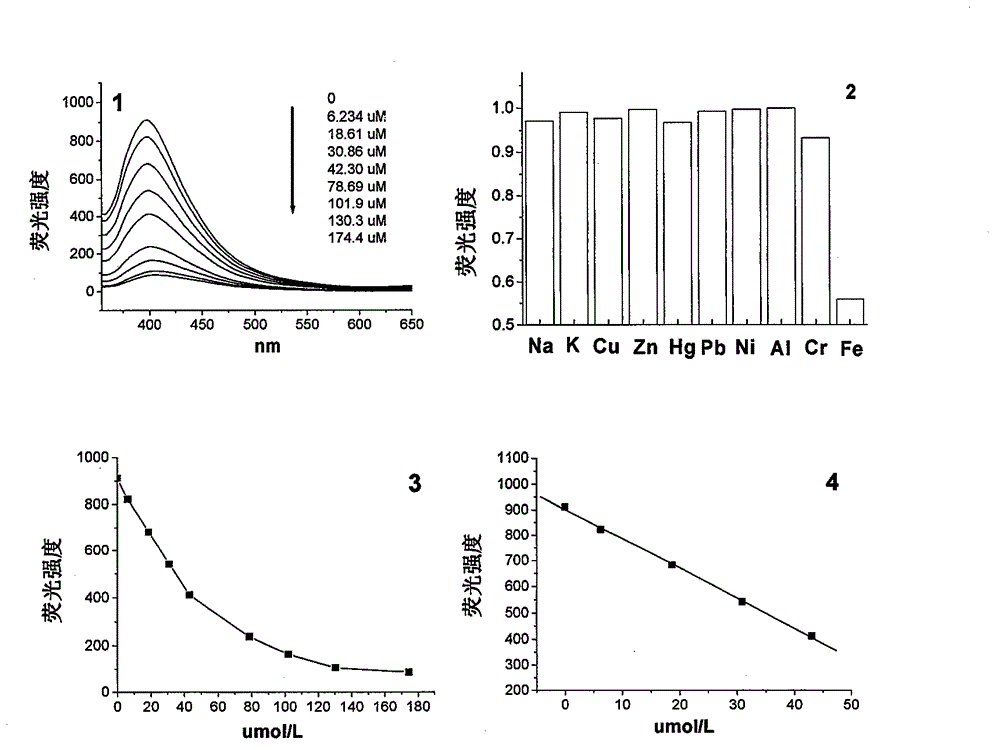
The invention relates to a preparation method and a use of a fluorescent carbon quantum dot / polyacrylonitrile nanofiber membrane. The preparation method comprises that polyacrylonitrile and a fluorescent carbon quantum dot as raw materials are prepared into the fluorescent carbon quantum dot / polyacrylonitrile nanofiber membrane by an electrostatic spinning technology. The fluorescent carbon quantum dot / polyacrylonitrile nanofiber membrane is a nanofiber membrane material loaded with the fluorescent carbon quantum dot. The fluorescent carbon quantum dot / polyacrylonitrile nanofiber membrane can be used for selective fluorescence fast detection of Fe<3+> in water, has good heat stability and strong photobleaching resistance, and is an ideal sensitive material for preparation of a high-sensitivity thin film-type sensing device.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Rapid three-dimensional (3D) super-resolution microscopic method and device
InactiveCN105487214ANo splittingReduce photobleaching effectMicroscopesUsing optical meansSpatial light modulatorOptical power
The invention discloses a rapid three-dimensional super-resolution microscopic method. The method comprises that a laser beam is converted into linearly polarized light after being collimated, phase modulation is carried out on the linearly polarized light, the linearly polarized light is converted into circularly polarized light, the circularly polarized light is projected to a sample to be measured, and pilot light emitted by scanning points of the sample to be measured is collected; and 3D scanning is carried out on the sample. Phase modulation comprises primary phase modulation and secondary phase modulation, a spatial light modulator which modulates the phase of an s light component of the linearly polarized light is used in the primary phase modulation, a spatial light modulator which modulates the phase of a p light component of the linearly polarized light is used in the secondary phase modulation, and a 3D super-resolution image is obtained according to the effective pilot light intensity. The invention also discloses a rapid 3D super-resolution microscopic device. According to the invention, optical power is lower, the photobleaching effect is weakened, 3D imaging is rapid, the device is simple, and light splitting is not needed.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
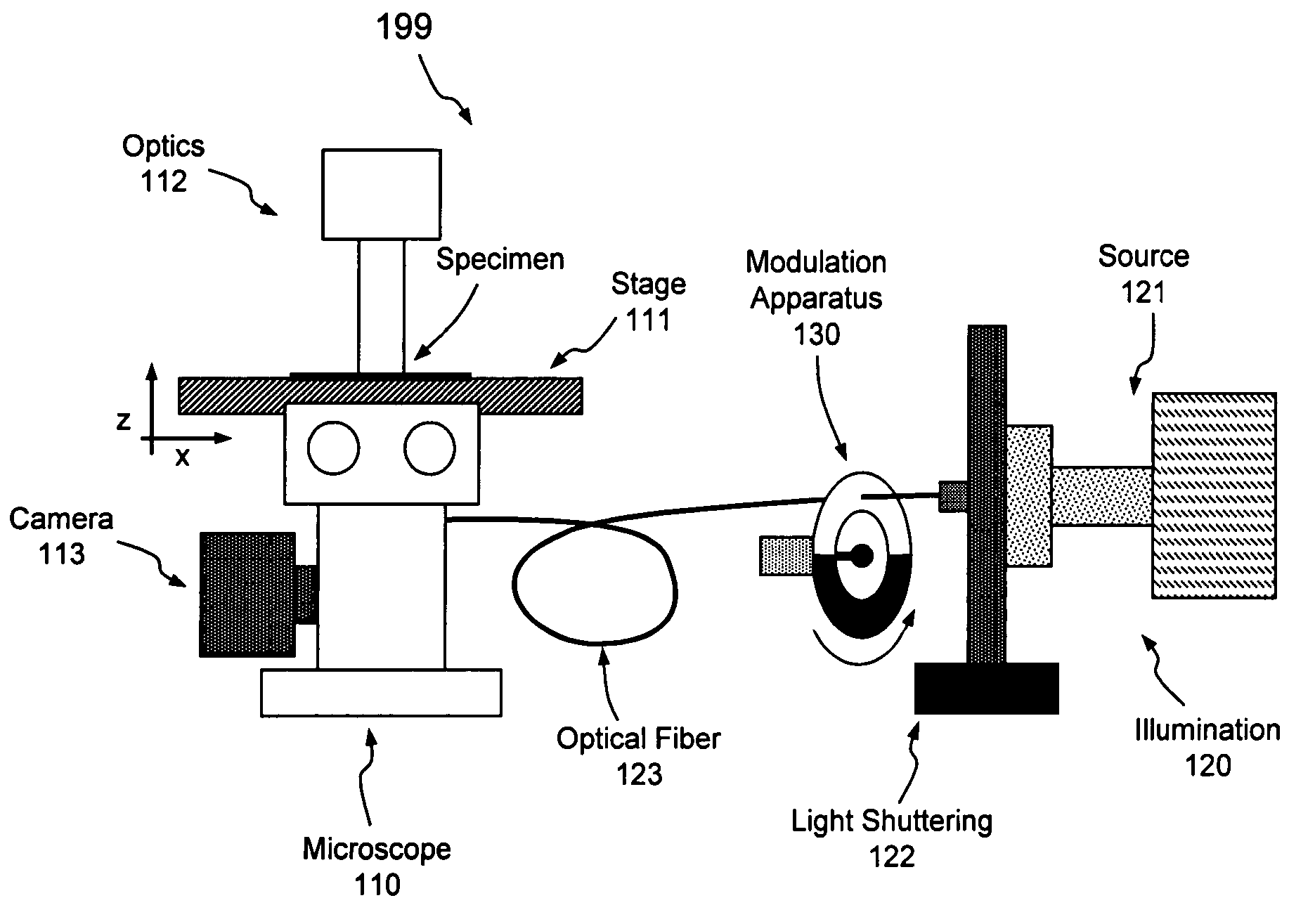
System and method of illuminating living cells for imaging
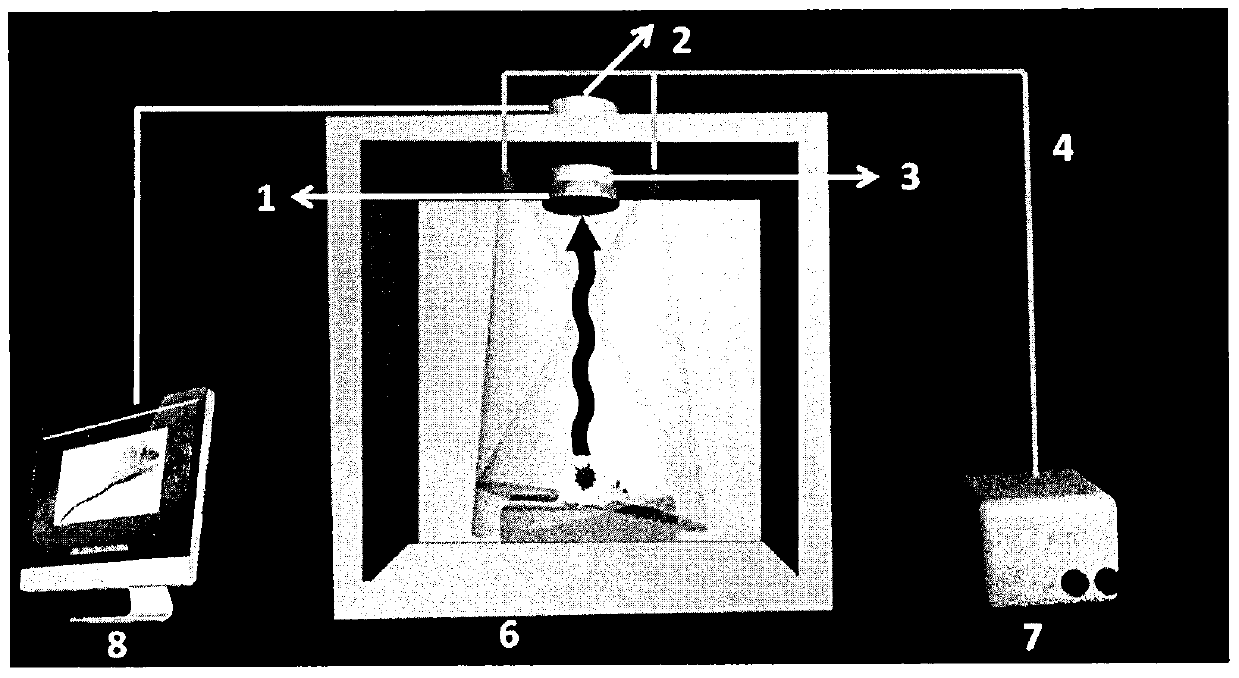
ActiveUS7141801B2Reduce coincidenceMinimizing rateRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationExcited stateLiving cell
A system and method of providing illumination for a cell imaging system delivering modulated light for illumination of a sample. Modulation of illumination intensity may be effectuated by pulsing the output of a light source, for example, or by selectively interrupting light provided by the source. Such modulated illumination may have particular utility in applications where reducing the number of electrons in a super-excited state may minimize the rate of photobleaching and photodamage in the molecules being studied.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
RGB patterning of organic light-emitting devices using photo-bleachable emitters dispersed in a common host
InactiveUS20030186078A1Discharge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesDopantOrganic light emitting device
The present invention provides a method for fabricating an electroluminescent EL display, wherein the individual color pixels are formed by doping a common blue-emitting host with two or more photo-bleachable (or photo-oxidizable) dopants, such as red and green emitting organic materials. The host may also be doped with a blue emitting material that is not photo-bleachable.
Owner:NAVY THE UNTIED STATES OF AMERICAAS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE
Green synthetic method for blue fluorescence carbon quantum dots with high fluorescence quantum yield
InactiveCN104927849AHigh fluorescence quantum yieldEasy to evaporate and separateLuminescent compositionsQuantum yieldWhitening Agents
The invention discloses a green synthetic method for blue fluorescence carbon quantum dots with high fluorescence quantum yield, and belongs to the technical field of fine chemical engineering. The method adopts a mixture of citric acid and glycine as a raw material, the solid mixture is heated directly to a certain temperature for a certain time, so that the solid mixture is dehydrated, after cooling to indoor temperature, the mixture is extracted by a low boiling point organic solvent, and the fluorescence quantum yield of the obtained carbon quantum dots is much higher than the fluorescence quantum yield of carbon quantum dots which are not processed by the organic solvent. The adopted raw material is easy to obtain, cheap and free of poison, three wastes are not generated in the preparing process, the operation is simple and convenient, and the raw material is easy to control. Due to the fact that the higher high fluorescence quantum yield, blue fluorescence emission and good photobleaching resistance are achieved, the carbon quantum dots can serve as a fluorescent whitening agent and be applied to production of paper pulp, scouring agents and washing powder, and the carbon quantum dots can serve as fluorescence markers of biomolecules.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Water-soluble up-conversion luminescence nano material based on triplet state-triplet state annihilation and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103289674AHigh quantum yieldGood up-conversion luminescence performanceFluorescence/phosphorescenceIn-vivo testing preparationsIridiumBiological imaging
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological detection, and particularly relates to an up-conversion luminescence nano material based on triplet state-triplet state annihilation, a preparation method thereof and an application thereof in biological imaging. The invention provides an up-conversion luminescence material based on triplet state-triplet state annihilation, which can be applied to biological imaging. The up-conversion luminescence material based on triplet state-triplet state annihilation for biological imaging comprises a sensitizer and an annihilation agent, wherein the sensitizer is classified into three types; the first type of sensitizer is a porphyrin and phthalocyanine metal complex, and the metals in the complex include palladium, platinum, iridium and zinc; the second type of sensitizer is an iodo- or bromo-boron fluorine compound; and the third type of sensitizer is a complex of ruthenium, iridium and platinum. According to the material provided by the invention, the annihilation agent is a biphenyl and acene compound and a derivative thereof, or a bromo-boron fluorine compound or an imine luminous compound. The material has the advantages of high sensitivity, photobleaching resistance and the like, and has great application values in terms of biological marking and imaging.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Molecular fluorescence sensor for highly sensitive and selective detection of mercury
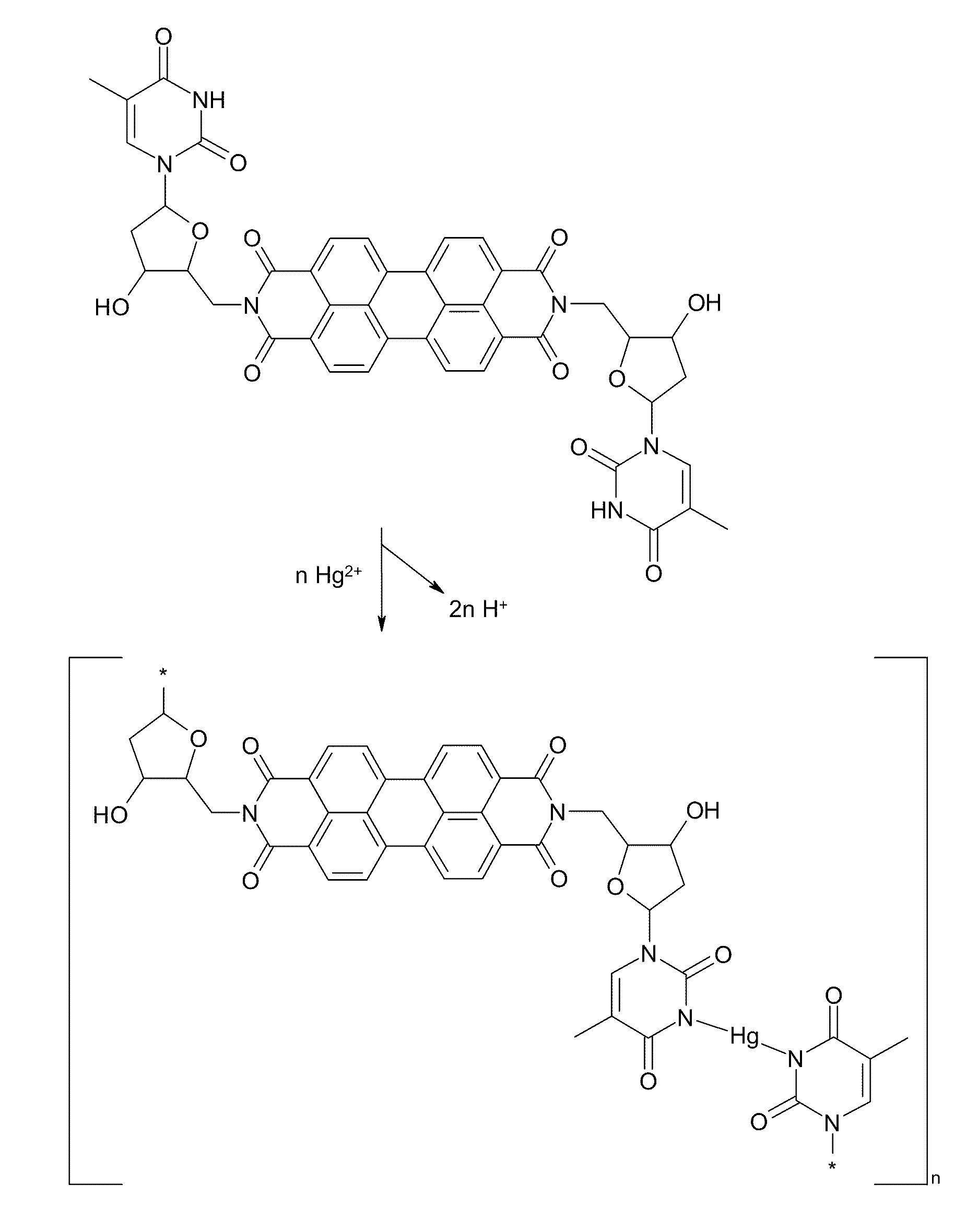
ActiveUS8058075B2Organic chemistryAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionMolecular fluorescenceFluorescence sensor
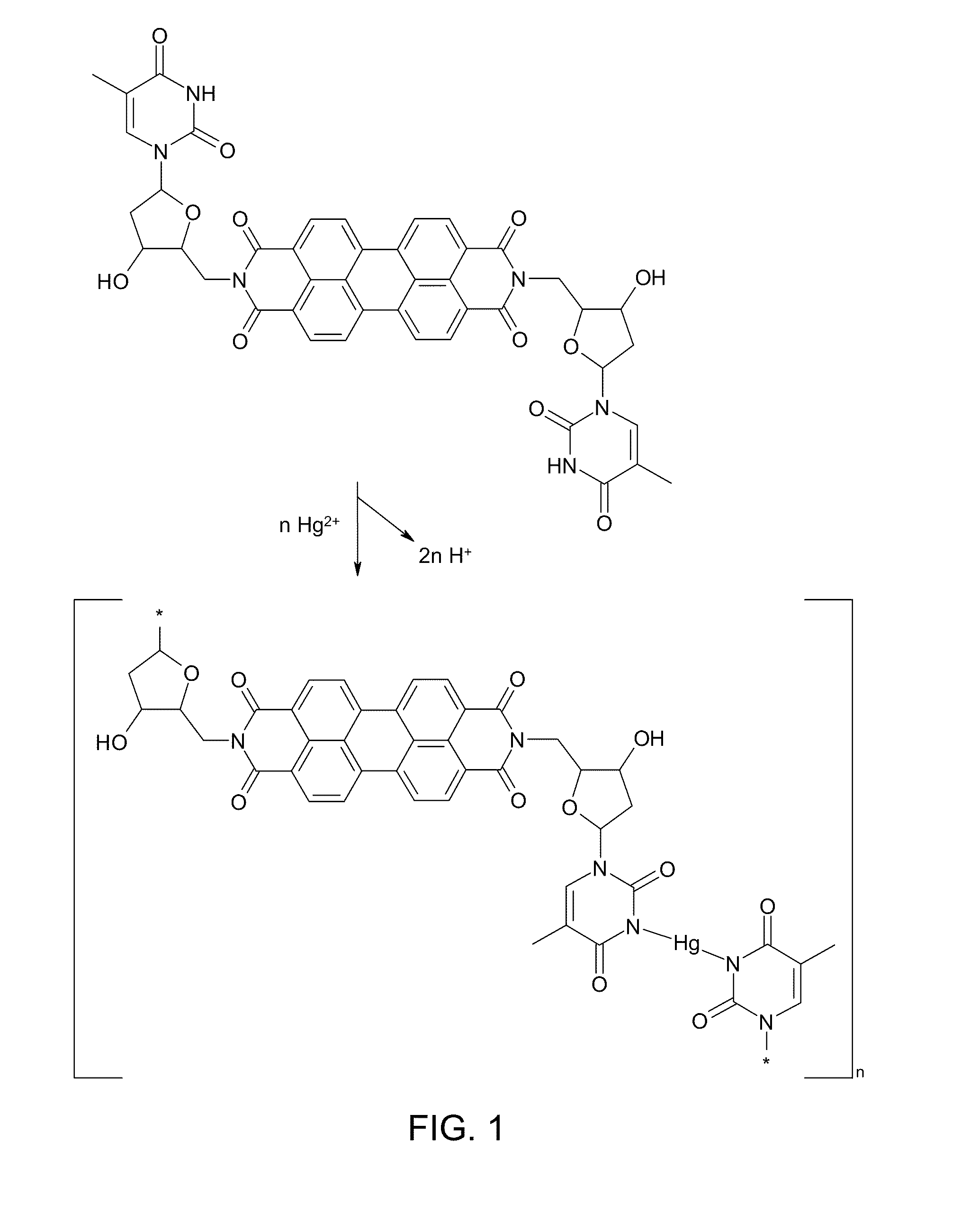
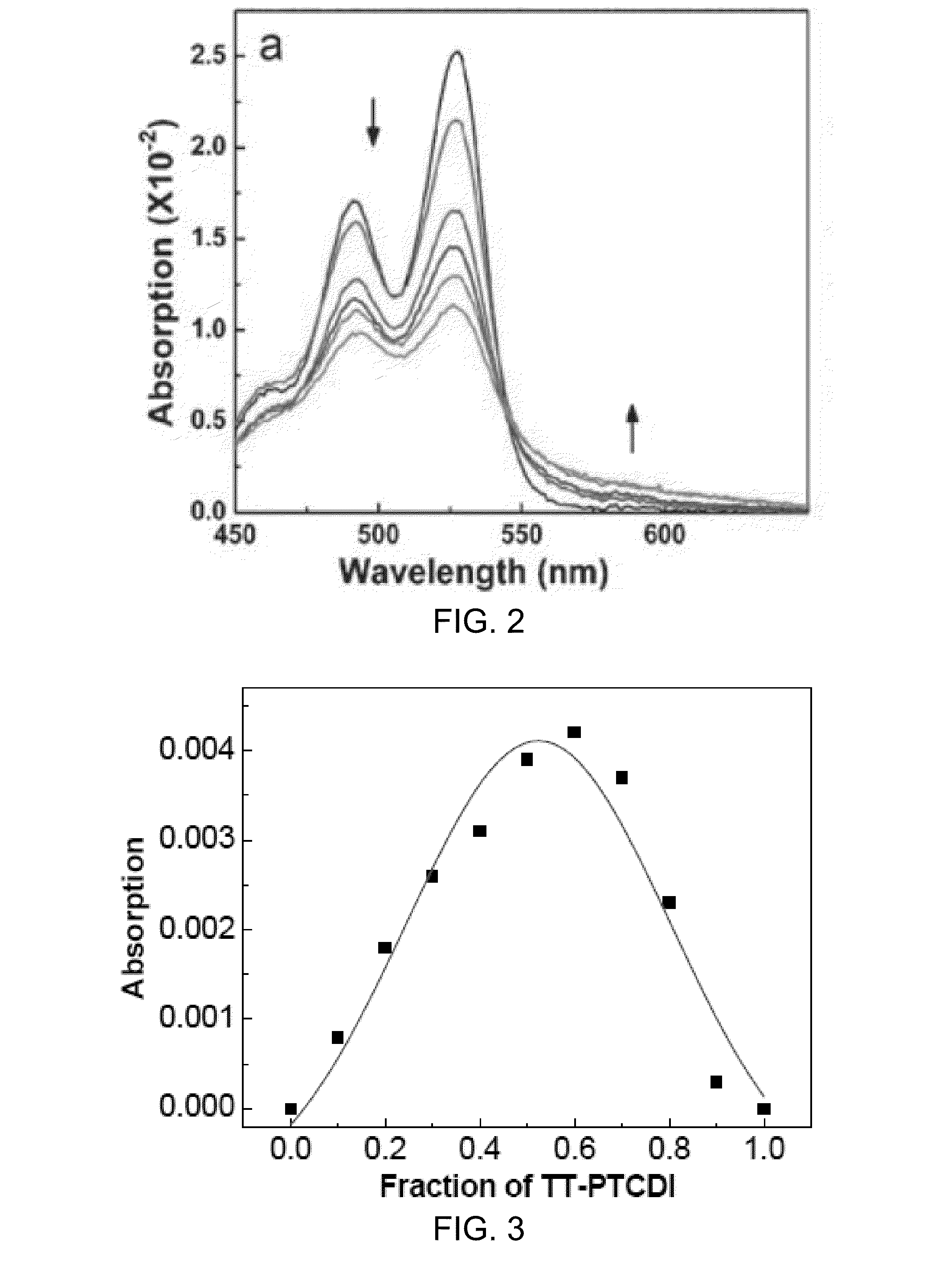
A fluorescent sensor compound based on a perylene core is described and disclosed. The fluorescent sensor compound for detecting mercury can have a structure I:where A and A′ are linking groups, B and B′ are binding ligands which are selective for binding with Hg2+, and R1 through R8 are side groups. These fluorescence sensor materials are robust against photobleaching, while still providing exceptional detection sensitivity and selectivity.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Surface plasmon assisted microscope
InactiveUS20080231834A1Significantly degrading fluorophore emissionAccelerate emissionsSamplingMaterial analysis by optical meansAnalyteSurface plasmon
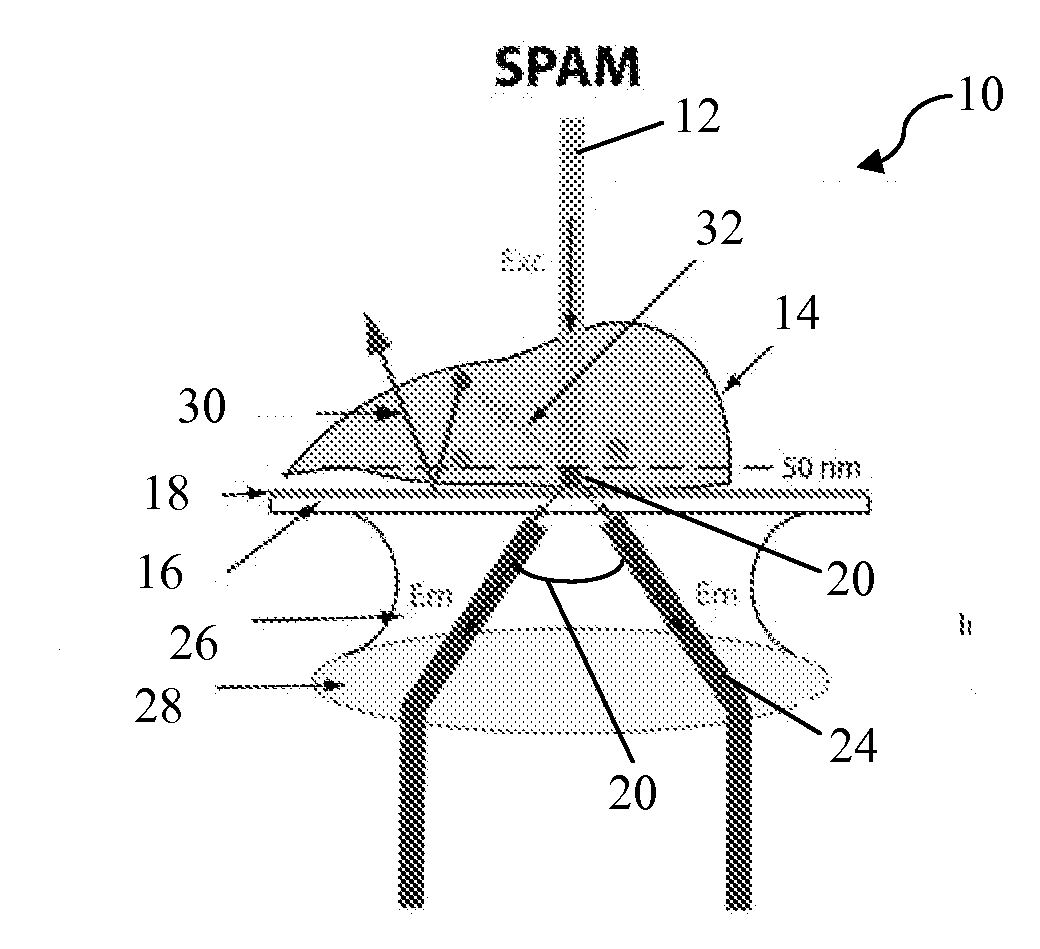
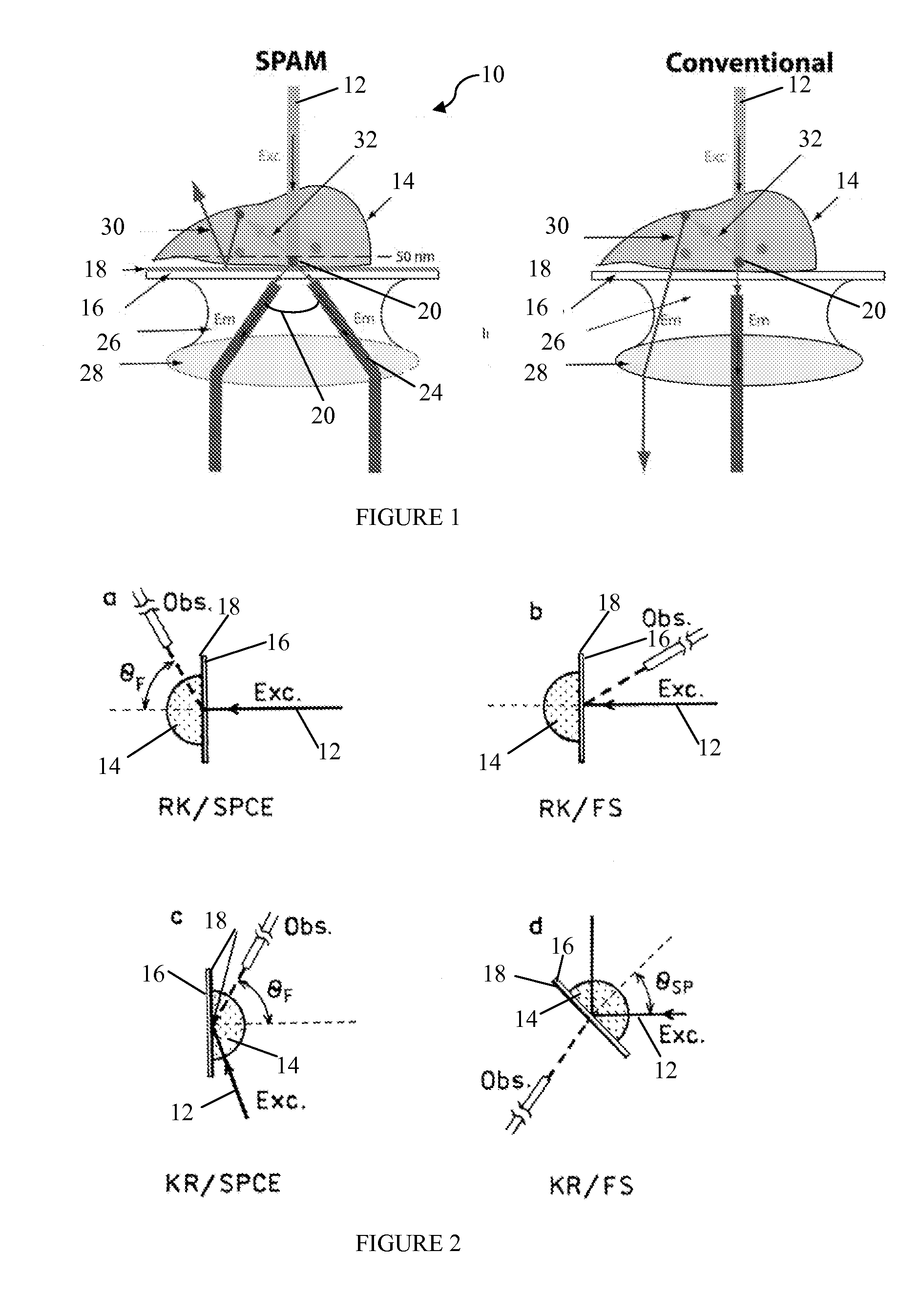
The present invention includes a microscope and a method for using the microscope for single molecule with reduced photobleaching of a fluorophore (20) that includes a light translucent material (16); a metal layer (18) disposed on the light translucent material (16); a medium (15) disposed on the metal layer (18), the medium (15) having one or more fluorophores (20) capable of binding a target analyte (e.g., inside a cell); a microscope positioned to observe the surface plasmon emissions from the one or more fluorophores (20) within 50 nanometers of the surface of the metal layer (18); an excitation source capable of exciting the one or more fluorophores (20), the excitation source positioned to strike the light translucent material (16) at a first angle; and a light detector (38) that selectively detects emitted light generated by excited fluorophores (20) at a second angle (22), wherein light emitted by the one or more fluorophores (20) at the surface plasmon angle is detected through the microscope, such that single molecules may be detected without significantly degrading fluorophore (20) emissions.
Owner:UNIV OF NORTH TEXAS HEALTH SCI CENT
Method for prolonging service life of quantum dot LED
The invention belongs to the field of electroluminescent cells, and relates to a method for prolonging the service life of a quantum dot LED. The method is that the volume ratio of a shell to a kernel of a quantum dot used as a lighting layer is more than 60: 1; the shell and the kernel of the quantum dot selected are both manufactured from materials in the II-VI cluster, and the materials can be CdSe / ZnS, CdSe / ZnCdS / ZnS, CdSe / CdS, ZnCdSe / ZnS or ZnCdSe / ZnSe / ZnS; the shell layer can be formed by compounding ZnCdS and ZnS, or ZnSe and ZnS. According to the method, the quantum dot with huge shell is used as the lighting layer, so that the fluorescent blinking of the quantum dot can be effectively inhibited, and the photobleaching resistance can be improved; the service life of the electroluminescent cell of which the lighting layer is a semiconductor fluorescent quantum dot can be effectively improved.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
Photobleach speckle and laundry detergent compositions containing it
InactiveUS6696400B2Little or no stainingReduce stainsOrganic detergent compounding agentsDetergent dyesParticulatesBleach
A speckle composition for use in particulate laundry detergent compositions comprising a porous granular carrier, and at least 0.01 wt % photobleach, preferably at least 0.05 wt %, more preferably at least 0.1 wt %, based on the active ingredient the composition being layered with a finely divided high carrying capacity particulate material and / or a water-soluble material. The most preferred photobleach is a blend of Zn and Al sulphonated phthalocyanine.
Owner:HENKEL IP & HOLDING GMBH
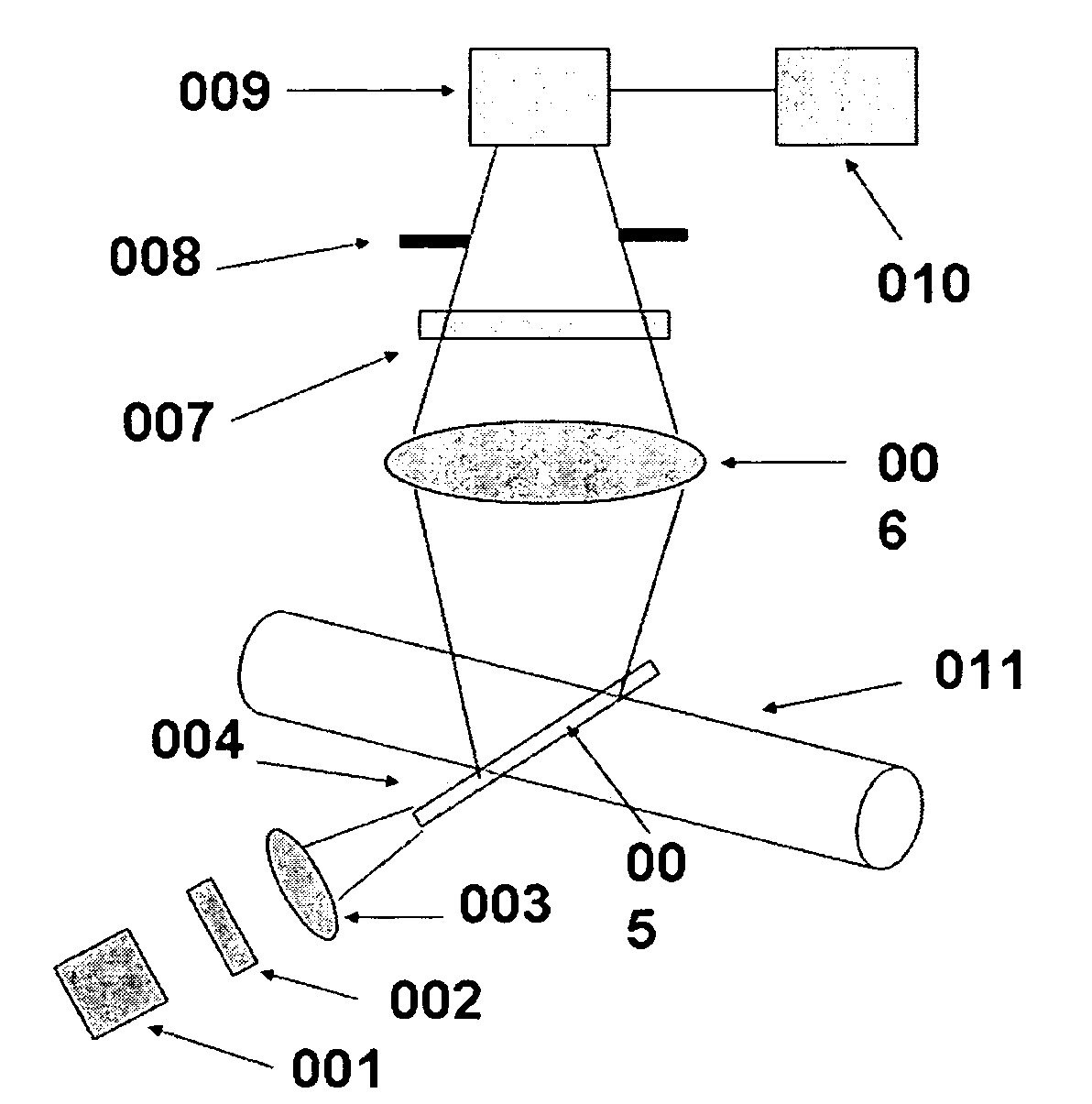
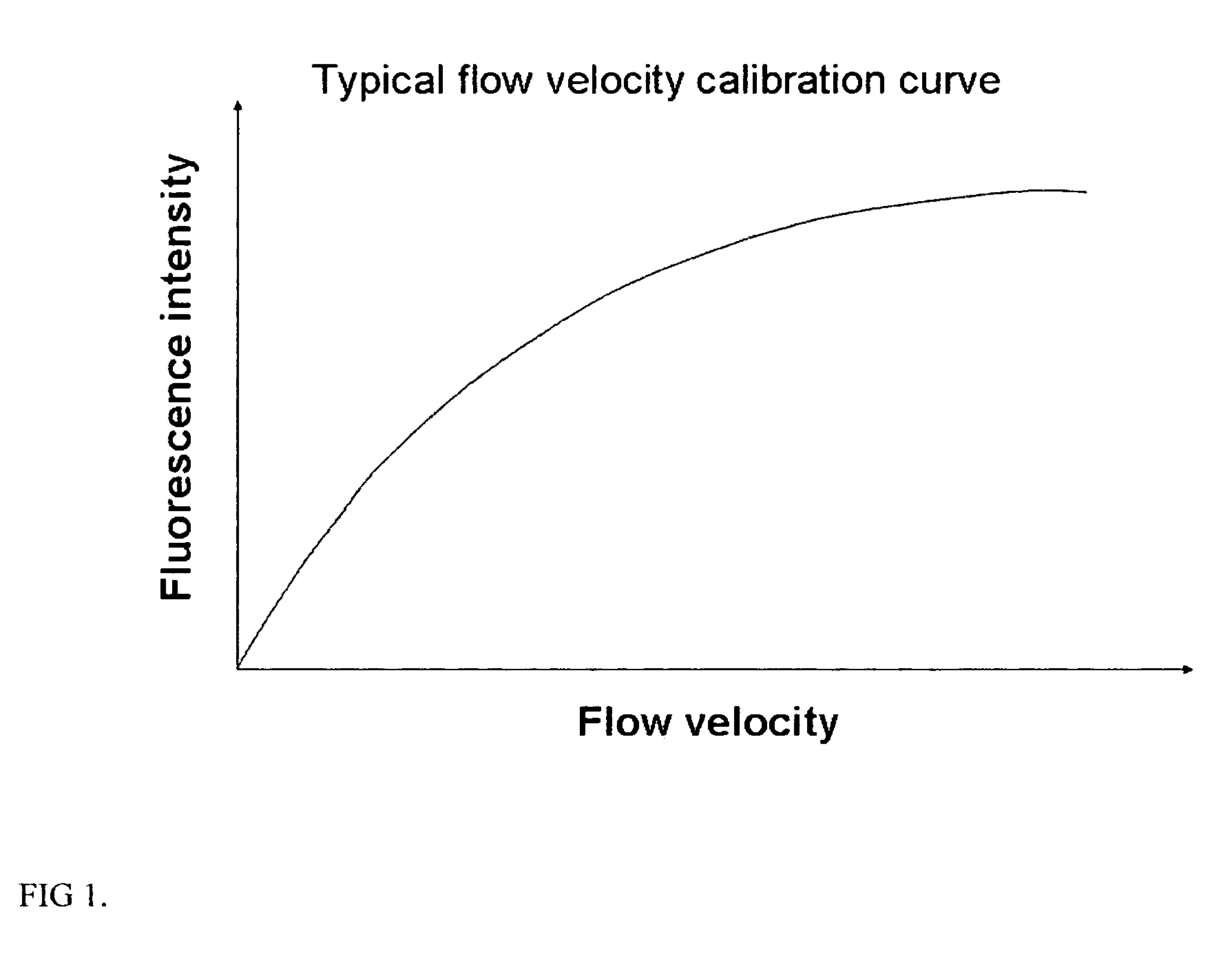
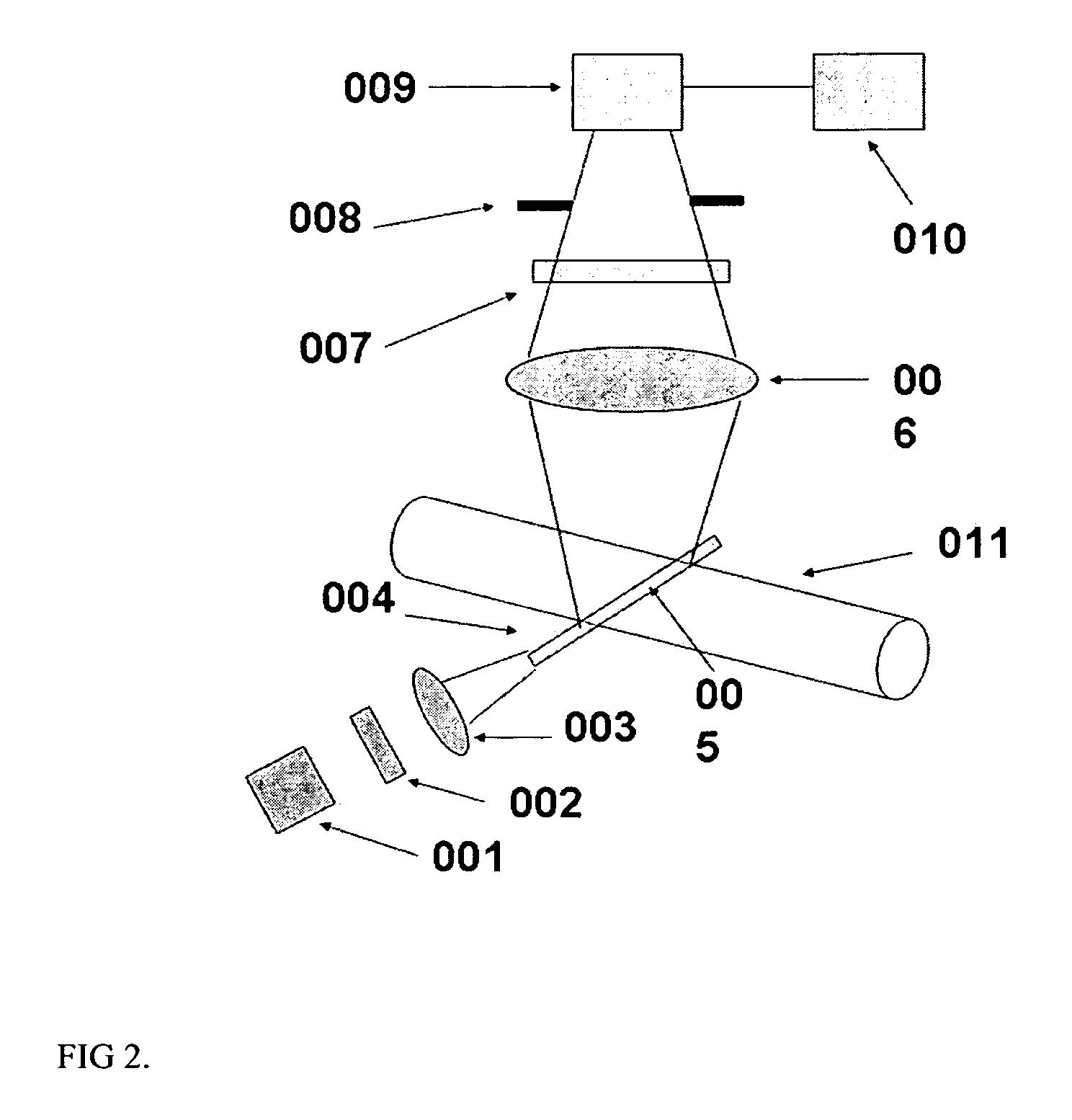
Method and apparatus for fluid velocity measurement based on photobleaching
InactiveUS7283215B2Volume/mass flow measurementFull-field flow measurementTemporal resolutionImage resolution
Methods and apparatus for fluid flow velocity and flow rate measurement are provided. Fluid velocity is measured in optical method based on fluorescence photobleaching of a fluorescent dye. The invented method and apparatus requires a calibration relation between flow velocity and fluorescence signal and is easy to use. The invented method and apparatus can measure bulk flow velocity and flow rate inline, two and three components of flow velocity vector. It can also measure flow velocity in near wall region using evanescent wave. Since the invented method and apparatus uses molecular dye and calibration relation between flow velocity and fluorescence signal, it has ultra high spatial and temporal resolution. The invented method can be used not only to apparatuses and devices in conventional size, but also to that in MEMS and NEMS.
Owner:WANG GUIREN
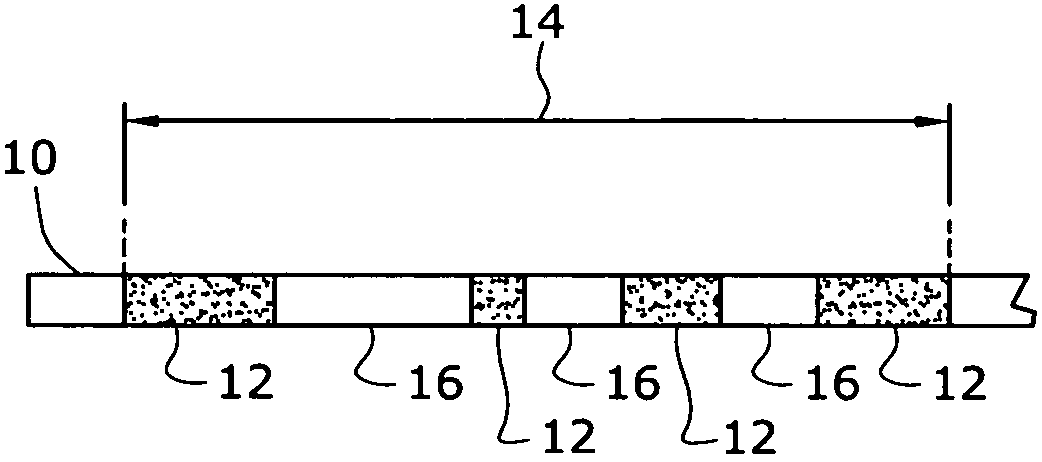
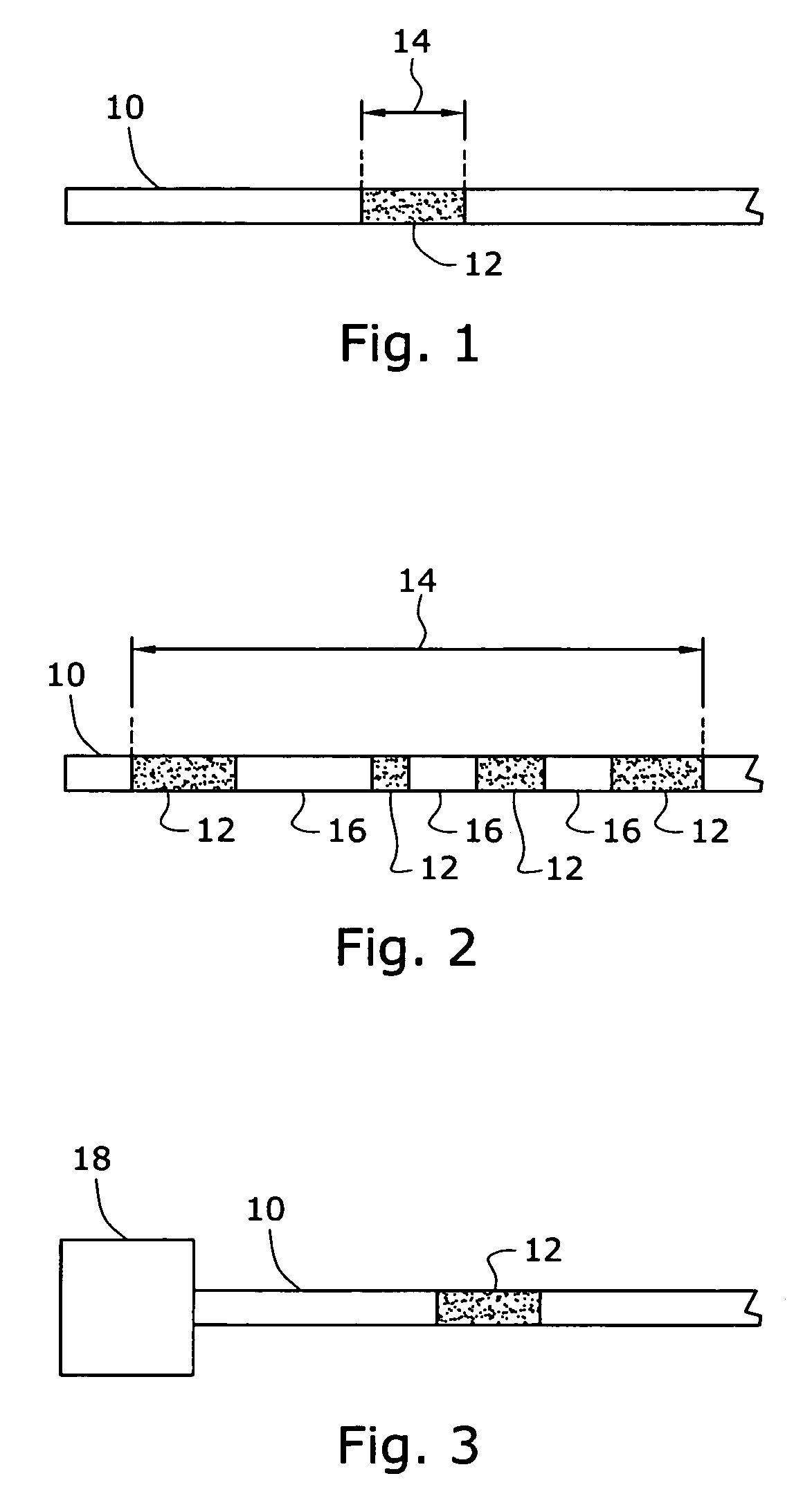
Random refractive index modulated optical fibers
An optical fiber containing one or more random modulations capable of reflecting one or more random wavelengths of light passing through the optical fiber is provided. Each modulation is a section of the optical fiber in which the refractive index has been modified or a section of random refractive index optical fiber that has been spliced into the optical fiber. The optical fiber is produced by modifying the refractive index of at least one portion of the optical fiber through photo-etching, photo-bleaching, ultraviolet radiation exposure or splicing. The optical fiber containing the random modulation is used to measure one or more engineering parameters by locating the section or portion of the optical fiber containing the random modulation in an area where the engineering parameter is to be measured and measuring the engineering parameter using optical frequency domain reflectometry.
Owner:LUNA ENERGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com