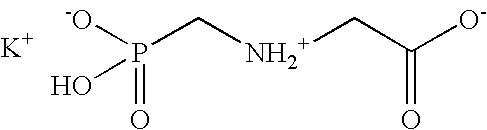Patents
Literature
6818 results about "Glycine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
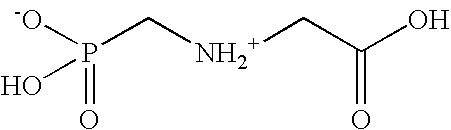
Glycine (symbol Gly or G; /ˈɡlaɪsiːn/) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest amino acid (since carbamic acid is unstable), with the chemical formula NH₂‐CH₂‐COOH. Glycine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. It is encoded by all the codons starting with GG (GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG). Glycine is integral to the formation of alpha-helices in secondary protein structure due to its compact form. For the same reason, it is most abundant amino acid in collagen triple-helices. Glycine is also an inhibitory neurotransmitter - interference with its release within the spinal cord (such as during a Clostridium tetani infection) can cause spastic paralysis due to uninhibited muscle contraction.
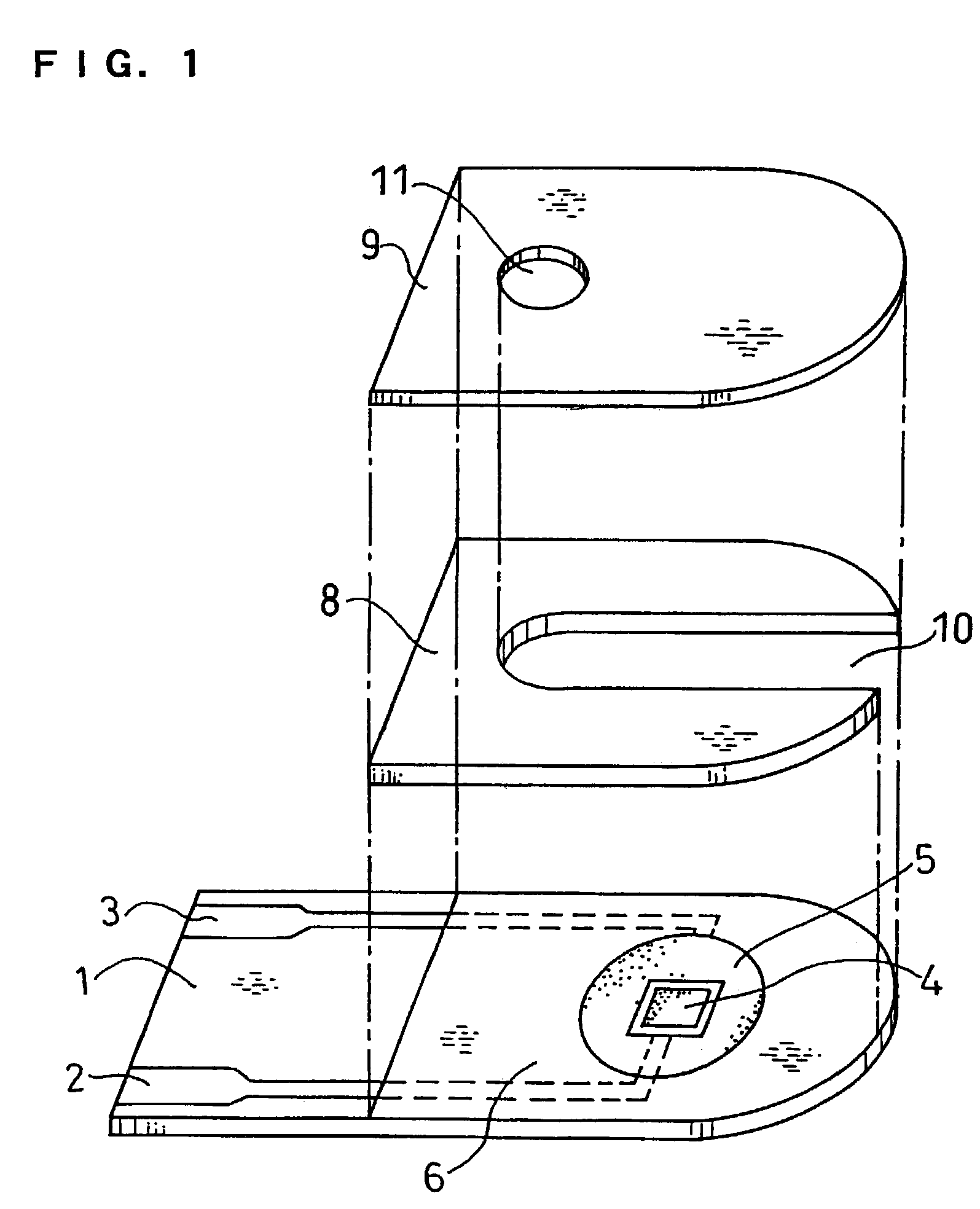
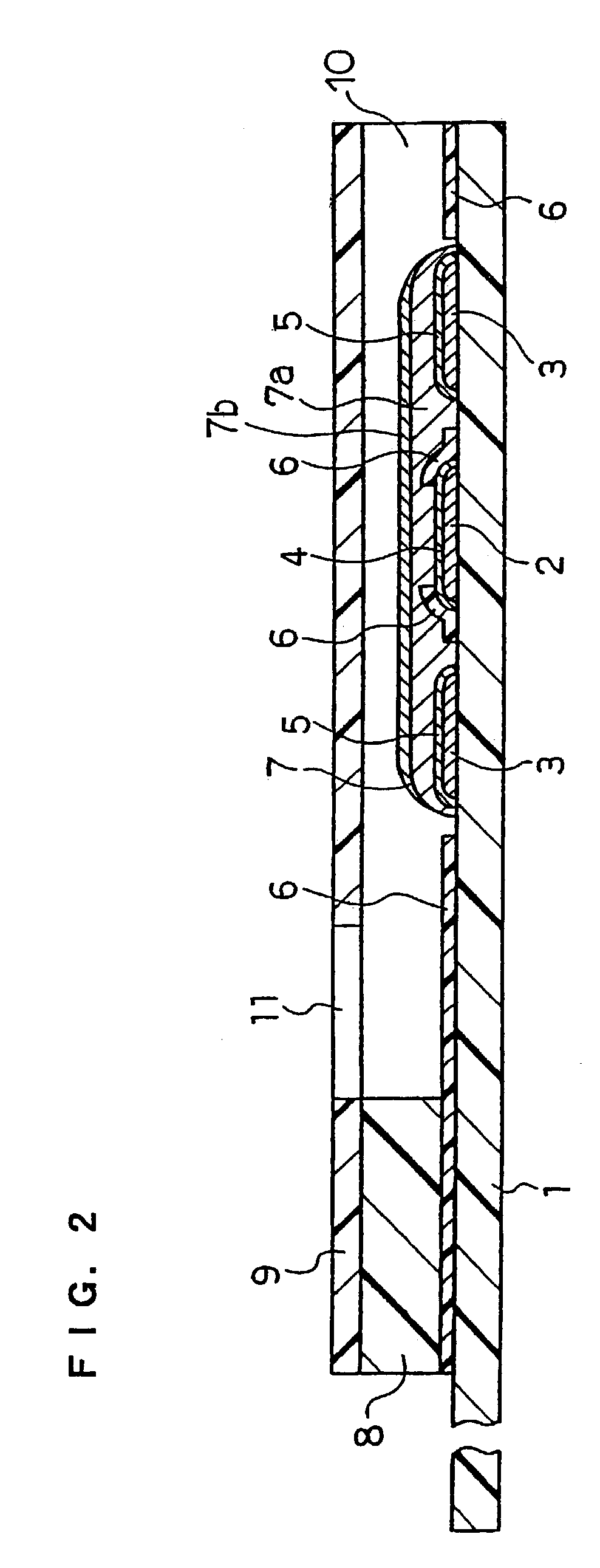
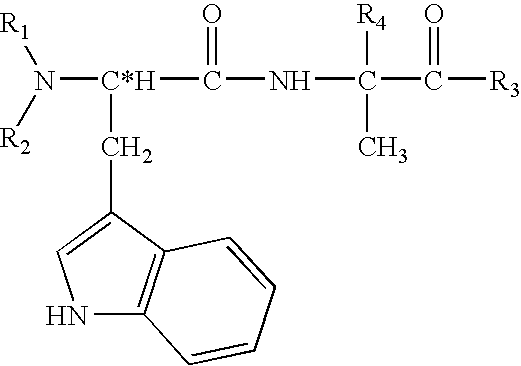
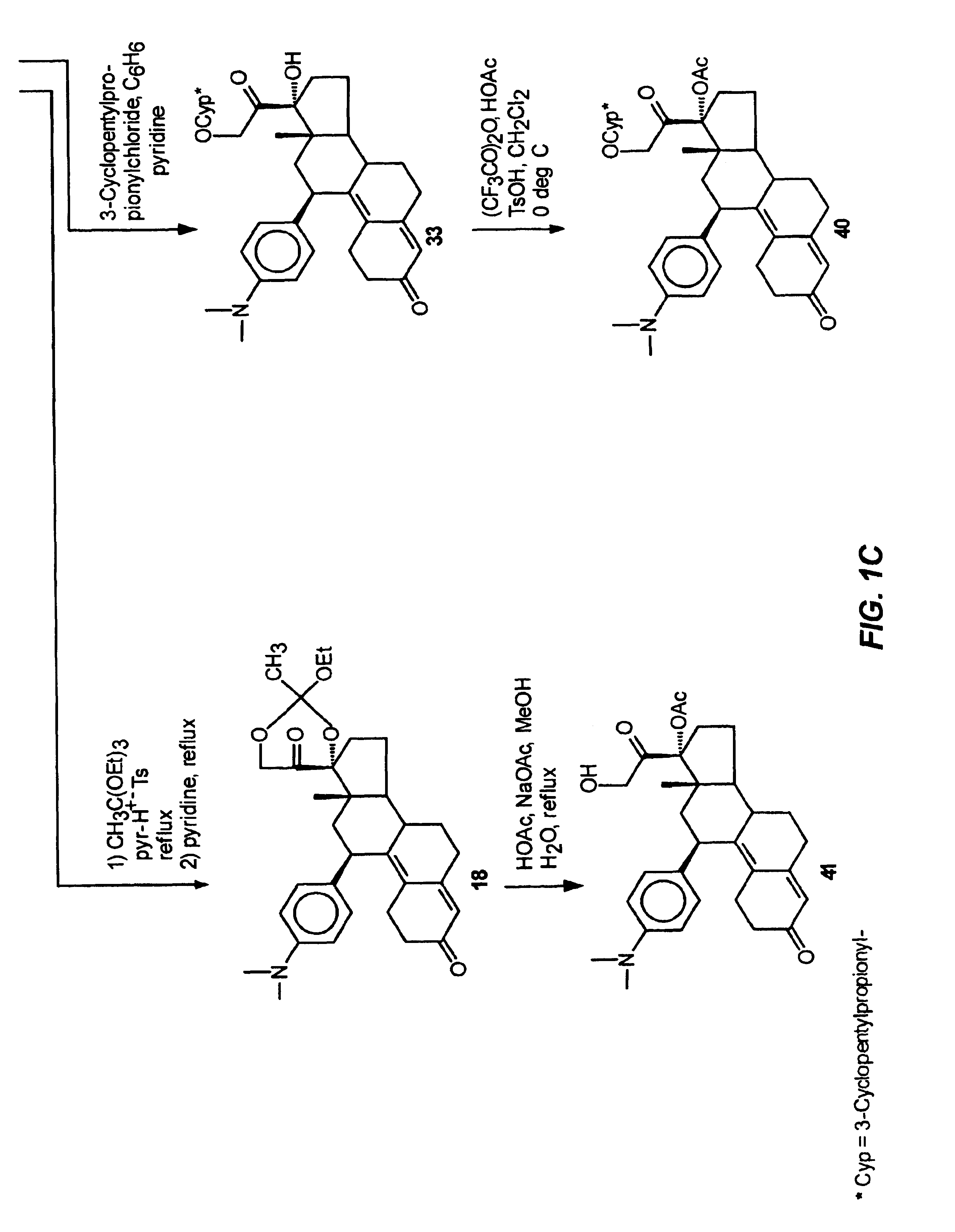
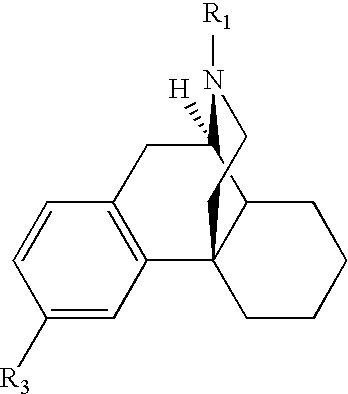
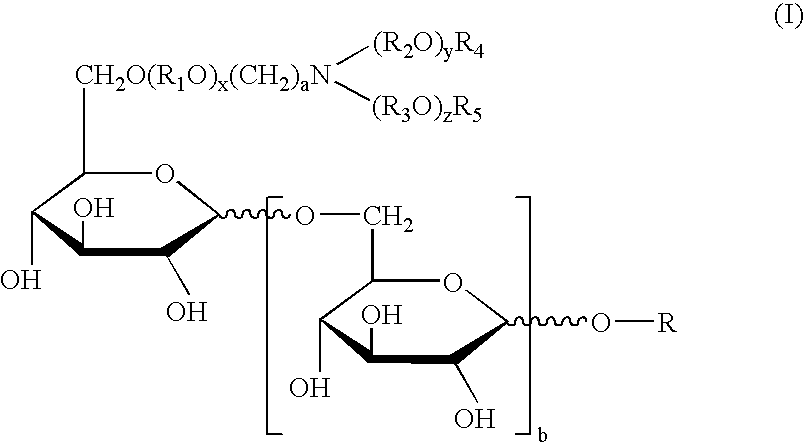
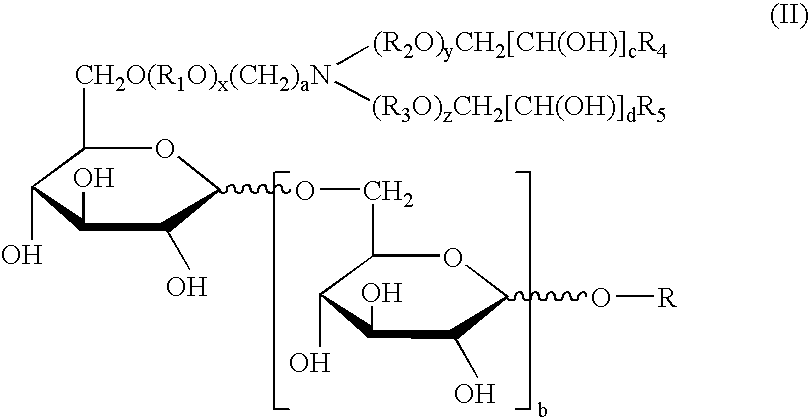
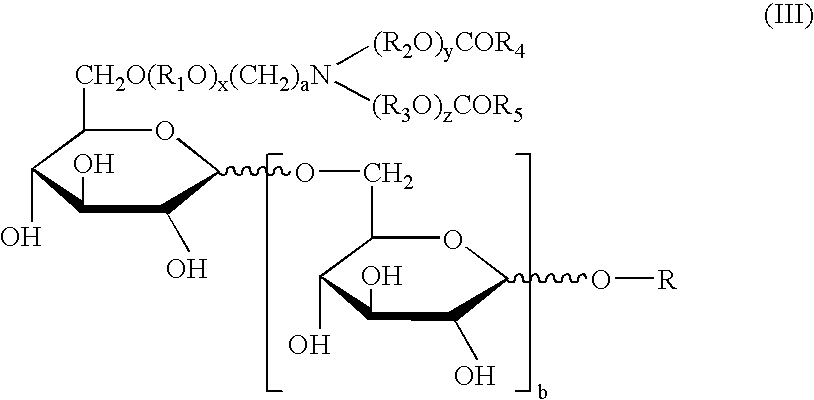
Physiological cooling compositions containing highly purified ethyl ester of N-[[5-methyl-2-(1-methylethyl) cyclohexyl] carbonyl]glycine
The present invention provides, in one aspect, a substantially pure ethyl ester of N-[[5-methyl-2-(1-methylethyl)cyclohexyl]carbonyl]glycine. In another aspect, disclosed is a method for producing substantially pure ethyl ester of N-[[5-methyl-2-(1-methylethyl)cyclohexyl]carbonyl]glycine. In still another aspect, disclosed are various consumer products comprising the substantially pure ethyl ester of N-[[5-methyl-2-(1-methylethyl)cyclohexyl]carbonyl]glycine disclosed herein.
Owner:RENESSENZ
New adjuvant composition
InactiveUS20060009360A1Improve efficiencyImprove area coverageBiocideDead animal preservationGlycineAdjuvant
The present invention is directed to pesticidal formulations utilizing novel alkylpolyglycoside amines as adjuvants. The pesticidal formulation need not, but may, include an additional eye irritation-reducing complex. The adjuvant is particularly useful with glyphosate (N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine) compositions. Methods for using these pesticidal formulations are also disclosed.
Owner:COGNIS IP MANAGEMENT GMBH
Method of coating an intravascular stent with an endothelial cell adhesive five amino acid peptide
InactiveUS6140127APromoting cell attachmentRestore patencyBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsCell specificArginine
Endothelial cell attachment to an intravascular stent is promoted by coating the stent with an endothelial cell specific adhesion peptide. Coating is preferably carried out by activating the intravascular stent using plasma glow discharge, applying on the stent a layer or plurality of layers of a polymer such as poly(2-hydroxyethylmethacrylate), applying a tresylation solution containing pyridine and tresyl chloride, and applying a five amino acid peptide having the sequence glycine-arginine-glutamic acid-aspartic acid-valine.
Owner:CORDIS CORP
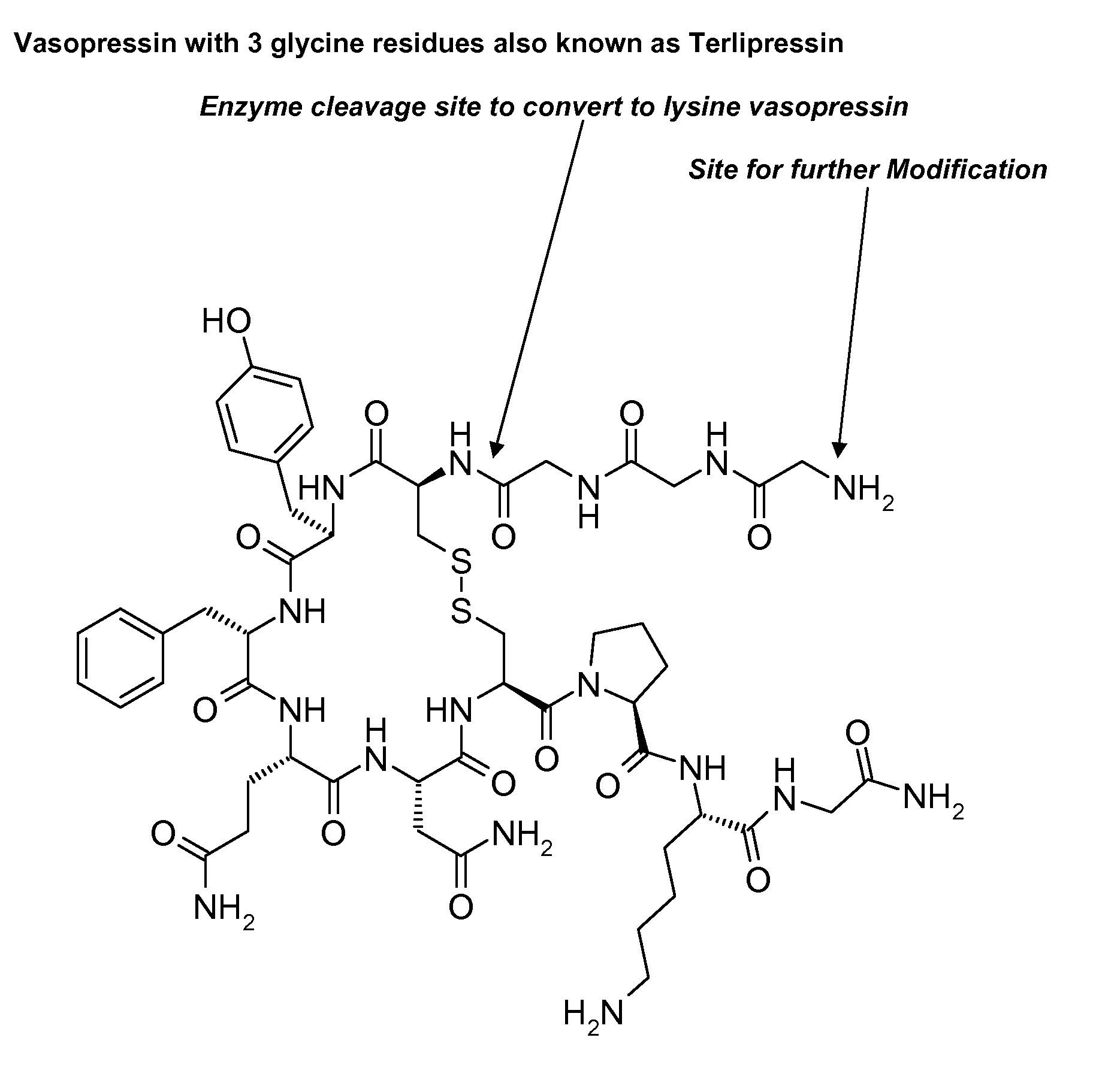
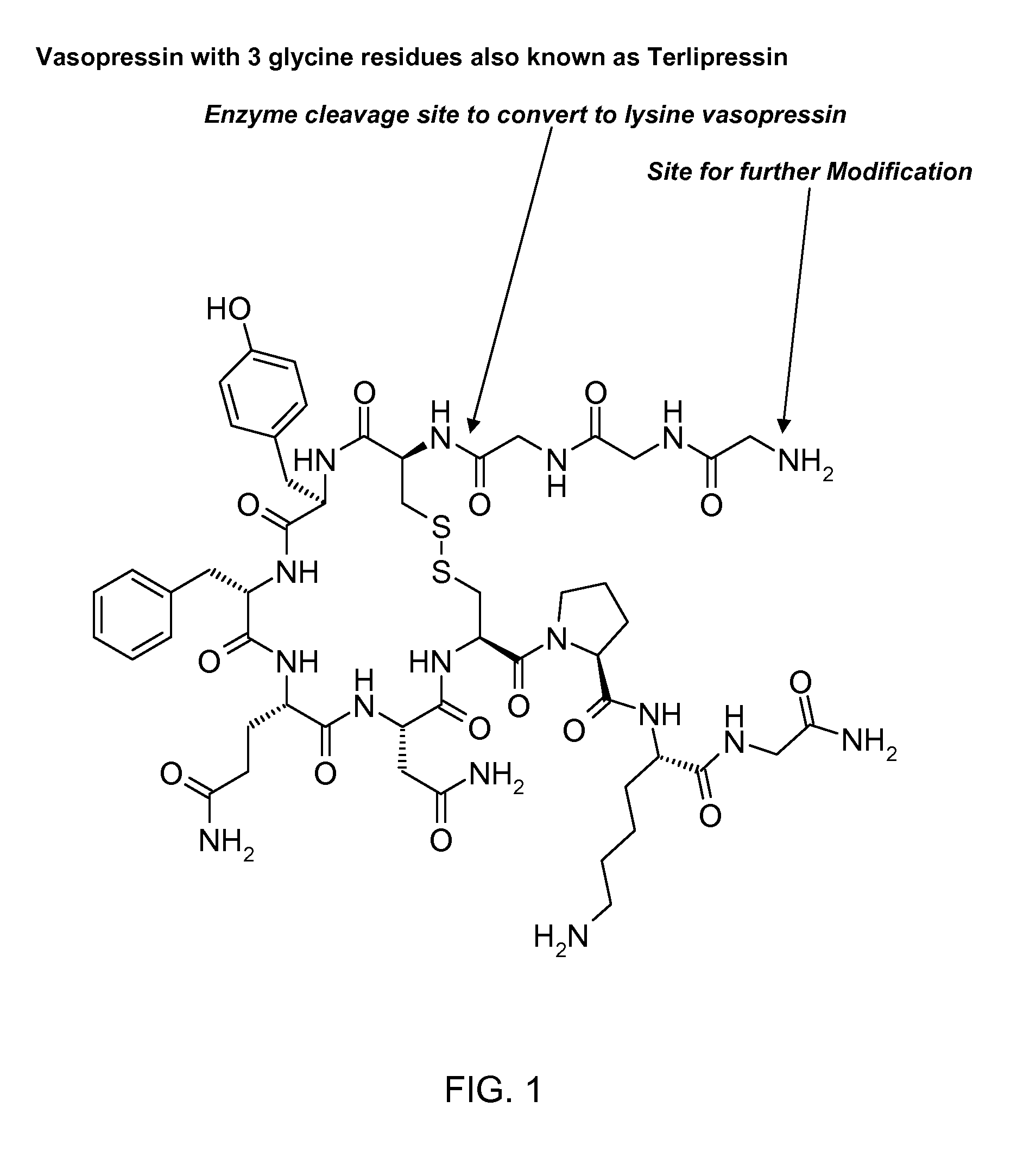
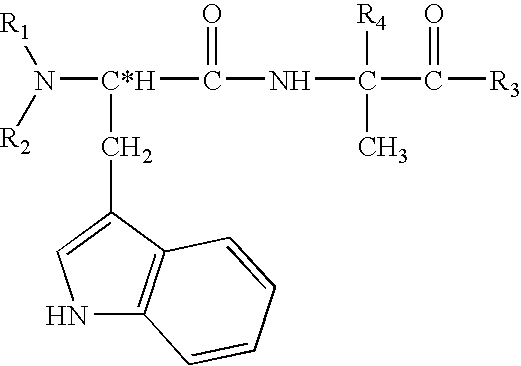
Physiological cooling compositions containing highly purified ethyl ester of N-[[5-methyl-2-(1-methylethyl)cyclohexyl] carbonyl]glycine
ActiveUS20050222256A1Reduce volatilitySuitable for useAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsGlycineEthyl ester
The present invention provides, in one aspect, a substantially pure ethyl ester of N-[[5-methyl-2-(1-methylethyl)cyclohexyl]carbonyl]glycine. In another aspect, disclosed is a method for producing substantially pure ethyl ester of N-[[5-methyl-2-(1-methylethyl)cyclohexyl]carbonyl]glycine. In still another aspect, disclosed are various consumer products comprising the substantially pure ethyl ester of N-[[5-methyl-2-(1-methylethyl)cyclohexyl]carbonyl]glycine disclosed herein.
Owner:RENESSENZ
Proteinic drug delivery system using membrane mimetics
A mixed liposome pharmaceutical formulation with multilamellar vesicles, comprises a proteinic pharmaceutical agent, water, an alkali metal lauryl sulphate in a concentration of from 1 to 10 wt. / wt. %, at least one membrane-mimetic amphiphile and at least one phospholipid. The membrane-mimetic amphiphile is hyaluronic acid, pharmaceutically acceptable salts of hyaluronic acid, lauramidopropyl betain, lauramide monoisopropanolamide, sodium cocoamphopropionate, bishydroxypropyl dihydroxypropyl stearammonium chloride, polyoxyethylene dihydroxypropyl stearammonium chloride, dioctadecyldimethylammonium chloride, sulphosuccinates, stearamide DEA, gamma-linoleic acid, borage oil, evening of primrose oil, monoolein, sodium tauro dihydro fusidate, fusidic acid, alkali metal isostearyl lactylates, alkaline earth metal isostearyl lactylates, panthenyl triacetate, cocamidopropyl phosphatidyl PG-diammonium chloride, stearamidopropyl phosphatidyl PG-diammonium chloride, borage amidopropyl phosphatidyl PG-diammonium chloride, borage amidopropyl phosphatidylcholine, polysiloxy pyrrolidone linoleyl phospholipid, trihydroxy-oxo-cholanylglycine and alkali metal salts thereof, and octylphenoxypolythoxyethanol, polydecanol X-lauryl ether, polydecanol X-oleyl ether, wherein X is from 9 to 20, or combinations thereof. The phospholipid is phospolipid GLA, phosphatidyl serine, phosphatidylethanolamine, inositolphosphatides, dioleoylphosphatidylethanolamine, sphingomyelin, ceramides, cephalin, triolein, lecithin, saturated lecithin and lysolecithin, or a combination thereof. The amount of each membrane mimetic amphiphile and phospholipid is present 1 to 10 wt. / wt. % of the total formulation, and the total concentration of membrane mimetic amphiphiles and phospholipids is less than 50 wt. / wt. % of the formulation.
Owner:GENEREX PHARMA
Thermal treatment process for tobacco materials
ActiveUS20100300463A1Alter natureAlter characterTobacco preparationTobacco treatmentArgininePhenylalanine
A method of thermally processing a tobacco material is provided, the method including the steps of (i) mixing a tobacco material, water, and an additive selected from the group consisting of lysine, glycine, histidine, alanine, methionine, glutamic acid, aspartic acid, proline, phenylalanine, valine, arginine, di- and trivalent cations, asparaginase, saccharides, phenolic compounds, reducing agents, compounds having a free thiol group, oxidizing agents, oxidation catalysts, plant extracts, and combinations thereof, to form a moist tobacco mixture; (ii) heating the moist tobacco mixture at a temperature of at least about 60° C. to form a heat-treated tobacco mixture; and (iii) incorporating the heat-treated tobacco mixture into a tobacco product. Heat-treated tobacco composition prepared according to the method are also provided, such as heat-treated smokeless tobacco composition comprising a tobacco material, water, flavorant, binder, and filler, the heat-treated smokeless tobacco composition having an acrylamide content of less than about 2000 ppb.
Owner:R J REYNOLDS TOBACCO COMPANY
Parvoviral capsid with incorporated gly-ala repeat region
InactiveUS20110171262A1Improve stabilityReduced expression levelBiocideAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNucleic acid sequencingCapsid
Parvoviral capsid with incorporated Gly-Ala repeat region The present invention provides a nucleic acid construct comprising a nucleic acid sequence encoding a parvoviral VP1, VP2 and VP3 capsid proteins comprising an immuno evasion repeat sequence. In addition, the present invention provides a cell comprising such construct, a parvoviral virion comprising a capsid protein that comprises an immune evasion repeat sequence, use of that parvoviral virion in gene therapy and a pharmaceutical composition comprising such parvoviral virion.
Owner:AMSTERDAM MOLECULAR THERAPEUTICS
Method of using hydroxycarboxylic acids or related compounds for treating skin changes associated with intrinsic and extrinsic aging
A composition comprising an amphoteric or pseudo-amphoteric agent and a polyhydroxy alpha hydroxyacid existing as a free acid, lactone, or salt, and isomeric or non-isomeric forms thereof is provided. The amphoteric or pseudo-amphoteric agent can be selected from amino acids, dipeptides, aminoaldonic acid, aminouronic acid, lauryl aminoproplyglycine, aminoaldaric acid, neuraminic acid desulfated heparin, deacetylated hyaluronic acid, hyalobiuronic acid, chondrosine, deacetylated chondroitin, creatine, creatinine, hydroxyproline, homocysteine, homocystine, homoserine, ornithine, citrulline, phosphatidylserine, and sphingomyelin. The composition may contain other additives, including cosmetic or pharmaceutical agents for topical treatment of dermatological disorders.
Owner:TRISTRATA TECH
Stabilized antibody-containing formulations
ActiveUS20090291076A1Good cakingIncrease of the viscosity of the high-concentration antibody-containing solutionAntibody ingredientsImmunoglobulinsArginineThreonine
The present invention relates to antibody-containing lyophilized formulations free from reducing sugars, non-reducing sugars, sugar alcohols or polysaccharides as excipients and including one or more amino acid selected from the group consisting of arginine, histidine, lysine, serine, proline, glycine, alanine and threonine or a salt thereof.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Methods of treating chronic inflammatory diseases using carbonyl trapping agents
InactiveUS6444221B1Improved therapeutic propertyImprove propertiesBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsEtiologyBenzoic acid
Owner:SECANT PHARMA
Biosensor
InactiveUS7235170B2Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsGluconolactonaseOxidoreductase
A biosensor that is highly responsive and capable of rapid and highly sensitive quantification of a specific component contained in a sample is provided. The biosensor of this invention comprises: an electrically insulating base plate; an electrode system comprising a working electrode and a counter electrode disposed on the base plate; and a reagent system comprising an oxidoreductase which catalyzes the oxidation reaction of glucose, gluconolactonase and a buffer. The buffer is selected from the group consisting of phthalic acid and its salts, maleic acid and its salts, succinic acid and its salts, phospholic acid and its salts, acetic acid and its salts, boric acid and its salts, citric acid and its salts, glycine, tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane, piperazine-N,N′-bis(2-ethane sulfonic acid) and the like.
Owner:PHC HLDG CORP
Composition for long-acting peptide analogs
ActiveUS20090088387A1Increase perfusionImprove the level ofAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsHalf-lifeArginine
The invention describes compositions of peptide analogs that are active in blood or cleavable in blood to release an active peptide. The peptide analogs have a general formula: A-(Cm)x-Peptide, wherein A is hydrophobic moiety or a metal binding moiety, e.g., a chemical group or moiety containing 1) an alkyl group having 6 to 36 carbon units, 2) a nitrilotriacetic acid group, 3) an imidodiacetic acid group, or 4) a moiety of formula (ZyHisw)p, wherein Z is any amino acid residue other than histidine, His is histidine, y is an integer from 0-6; w is an integer from 1-6; and p is an integer from 1-6; wherein if A has alkyl group with 6 to 36 carbon units x is greater than 0; and Cm is a cleavable moiety consisting of glycine or alanine or lysine or arginine or N-Arginine or N-lysine, wherein x is an integer between 0-6 and N may be any amino acid or none. The peptide analogs are complexed with polymeric carrier to provide enhanced half-life.
Owner:PHARMAIN CORP
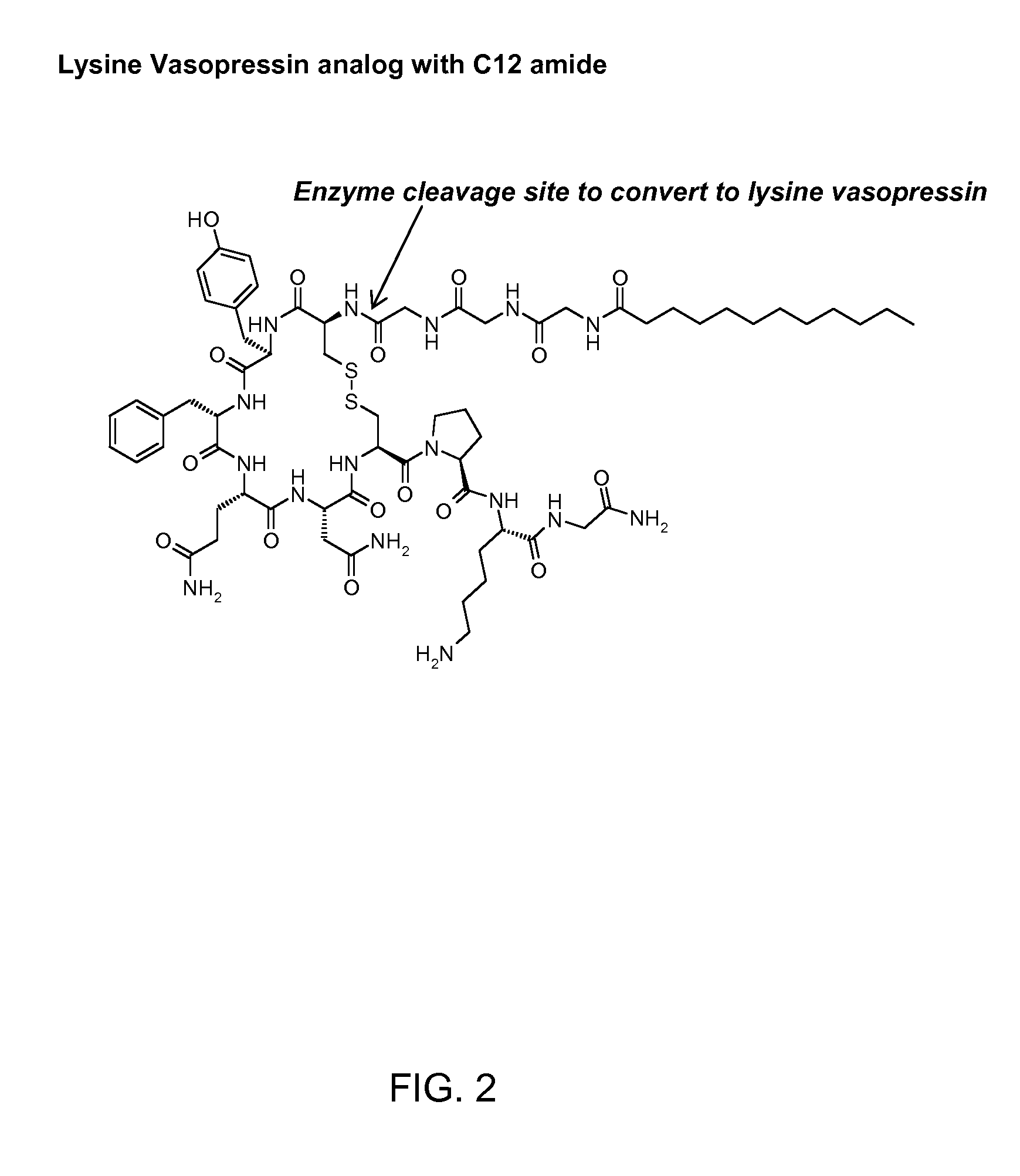
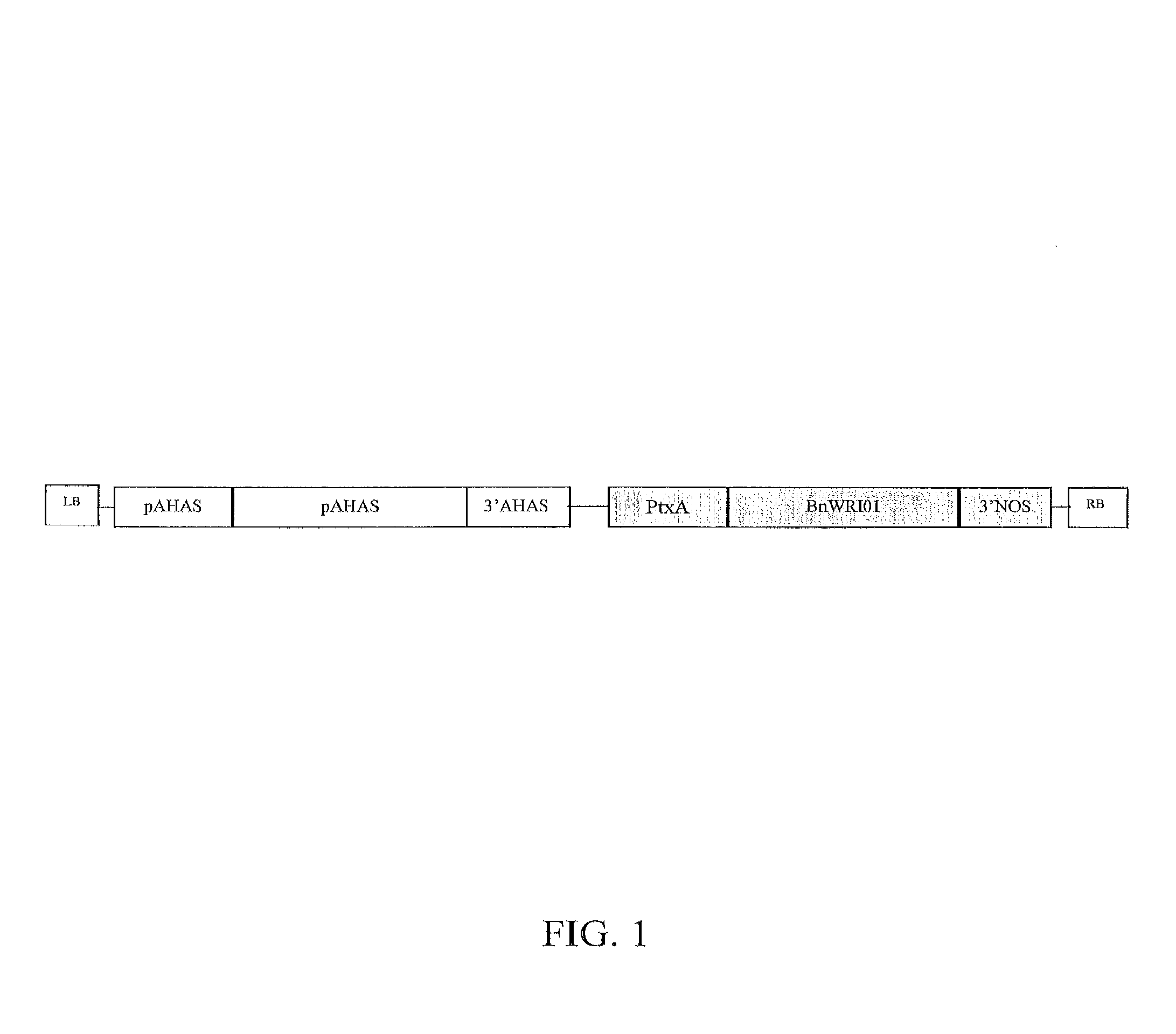
Nucleic acid molecules encoding WRINKLED1-like polypeptides and methods of use in plants
InactiveUS8217223B2High oil contentImprove the level ofBryophytesSugar derivativesBiotechnologyFatty acid
Isolated nucleic acids and proteins associated with lipid and sugar metabolism regulation are provided. In particular, lipid metabolism proteins (LMP) and encoding nucleic acids originating from Arabidopsis thaliana, Brassica napus, Glycine max, Oryza sativa, and Triticum aestivum are provided. The nucleic acids and proteins are used in methods of producing transgenic plants and modulating levels of seed storage compounds. Preferably, the seed storage compounds are lipids, fatty acids, starches, or seed storage proteins. The nucleic acids and proteins also are used in methods of modulating the seed size, seed number, seed weight, root length, and leaf size of plants.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
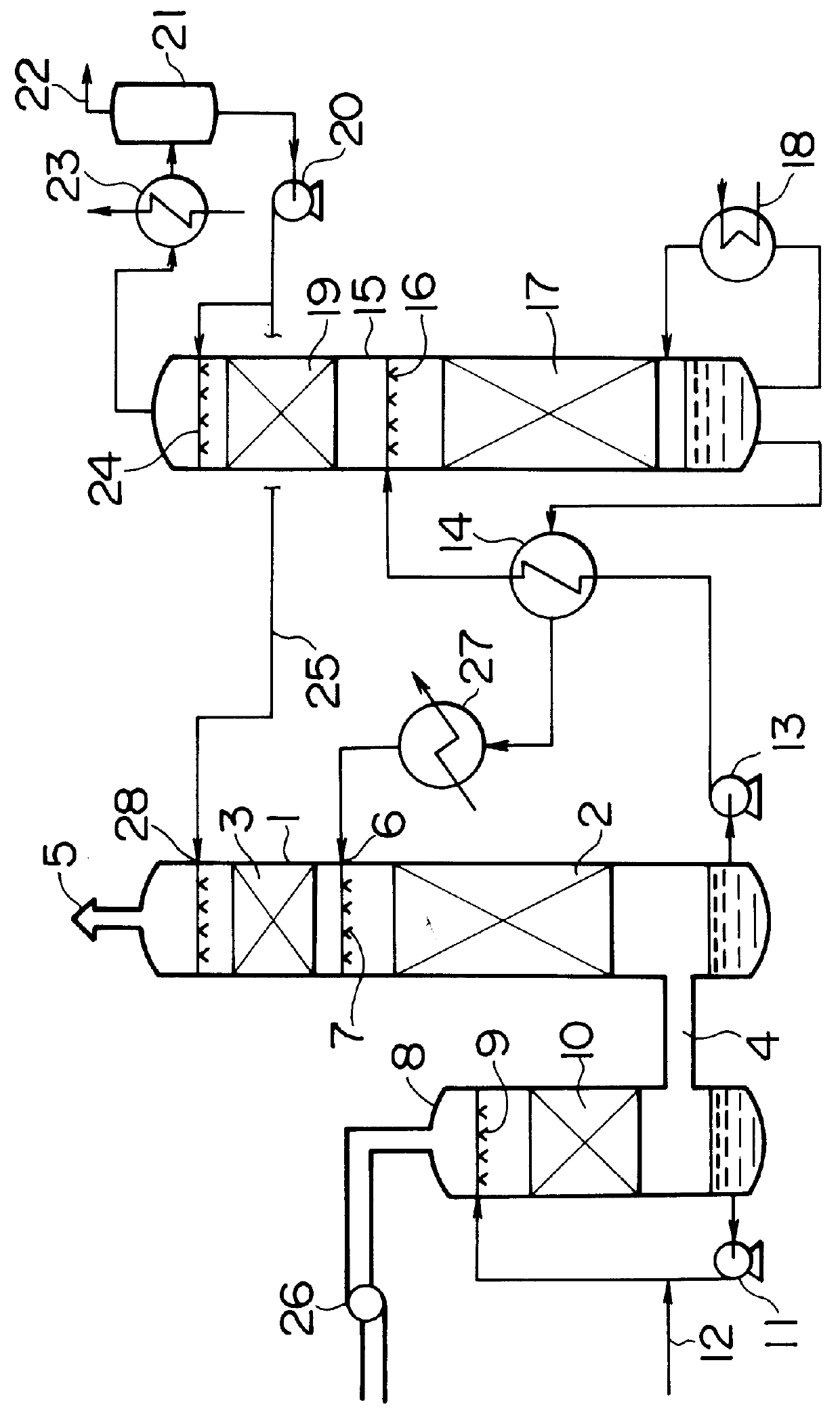
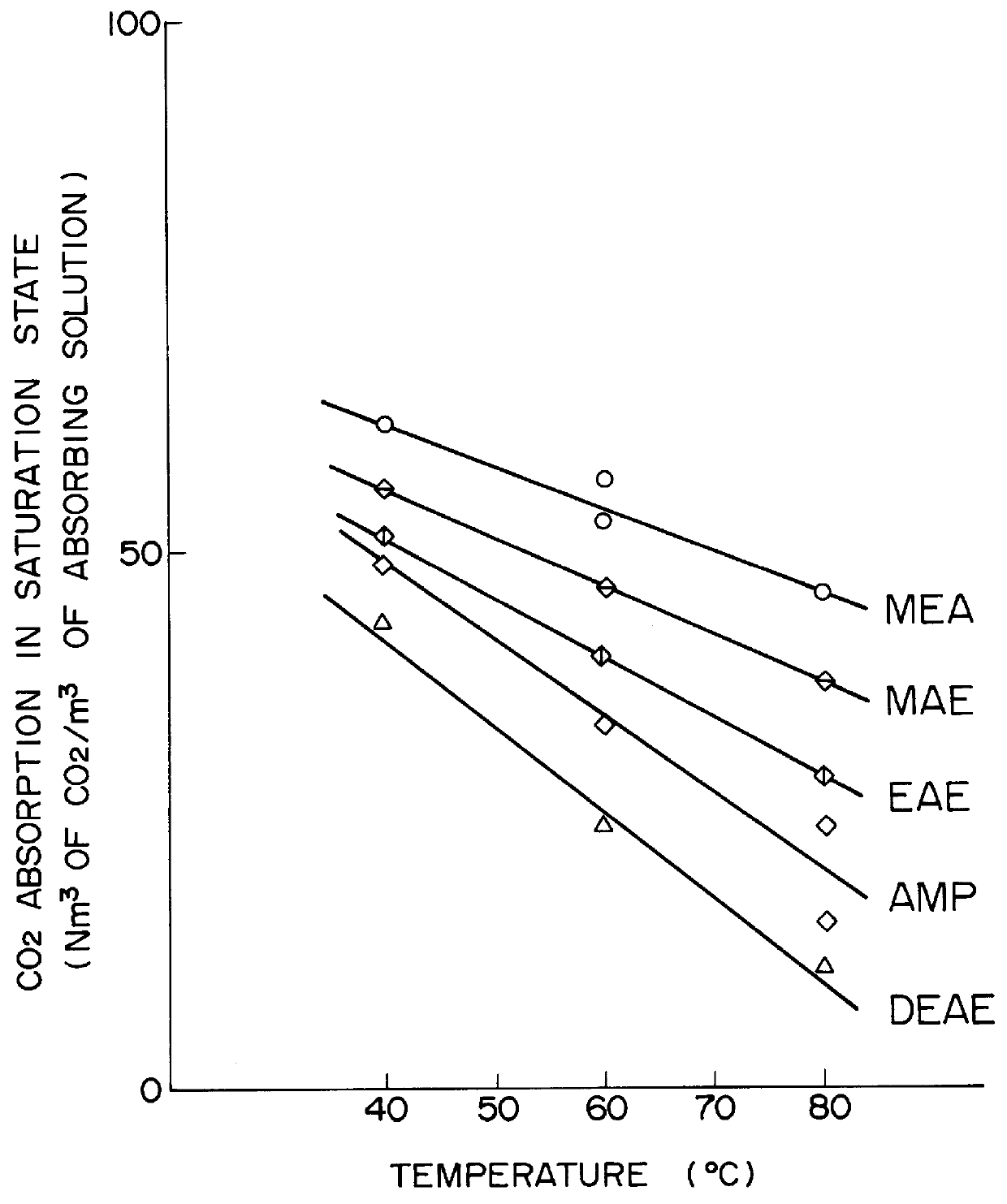
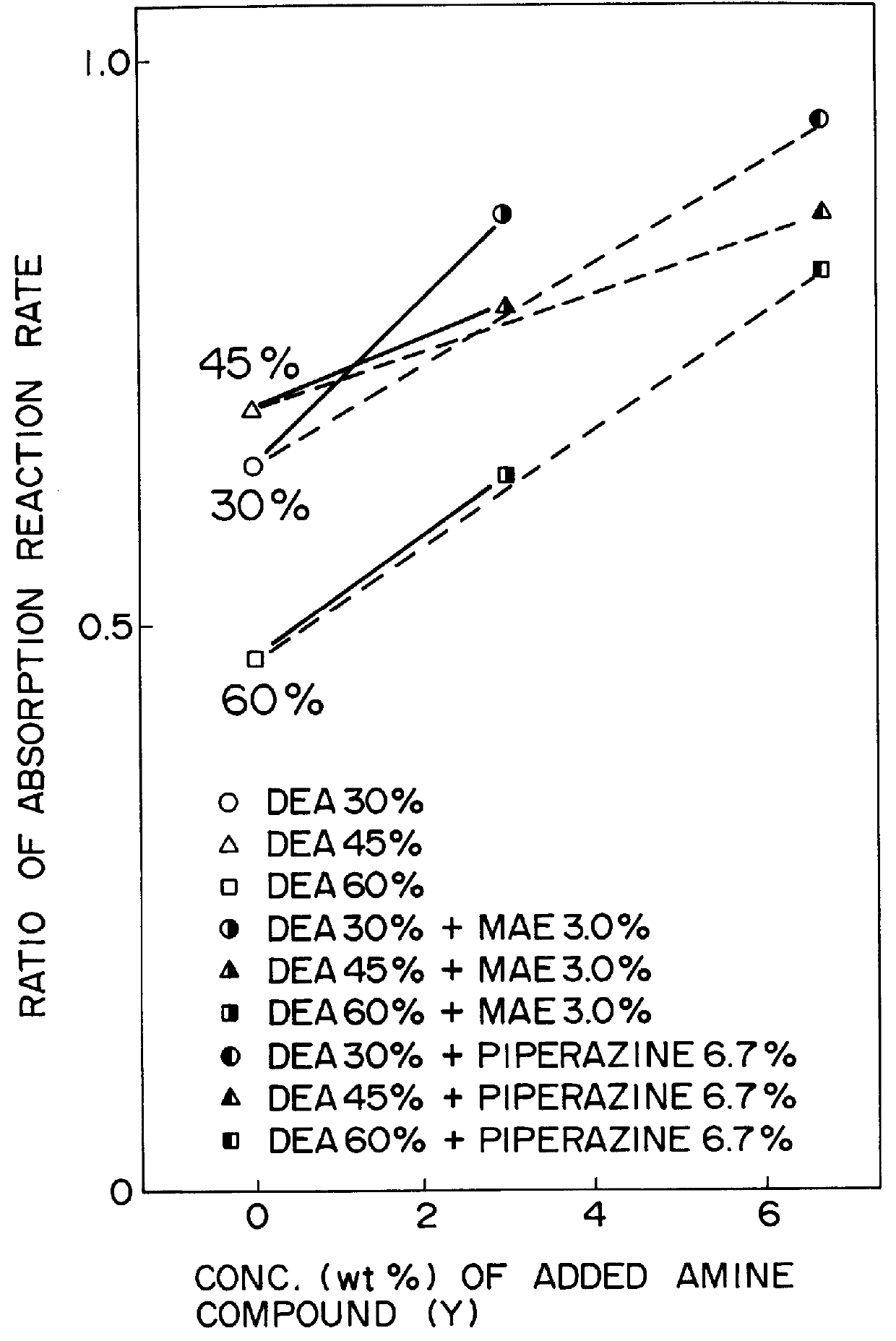
Method for removing carbon dioxide from combustion exhaust gas
InactiveUS6036931AHigh absorption rateImprove absorption rateDispersed particle separationHydrogen sulfides2-methylaminoethanolMorpholine
There are disclosed a method for removing CO2 from a combustion exhaust gas which comprises the step of bringing the combustion exhaust gas under atmospheric pressure into contact with an aqueous solution of a hindered amine selected from the group consisting of 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol, 2-methylaminoethanol, 2-ethylaminoethanol and 2-piperidineethanol; and another method for removing carbon dioxide from a combustion exhaust gas which comprises the step of bringing the combustion exhaust gas under atmospheric pressure into contact with a mixed aqueous solution of 100 parts by weight of an amine compound (X) selected from the group consisting of 2-amino-2-methyl-1,3-propanediol, 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol, 2-amino-2-ethyl-1,3-propanediol, t-butyldiethanolamine and 2-amino-2-hydroxymethyl-1,3-propanediol; and 1-25 parts by weight of an amine compound (Y) selected from the group consisting of piperazine, piperidine, morpholine, glycine, 2-methylaminoethanol, 2-piperidineethanol and 2-ethylaminoethanol.
Owner:THE KANSAI ELECTRIC POWER CO +1
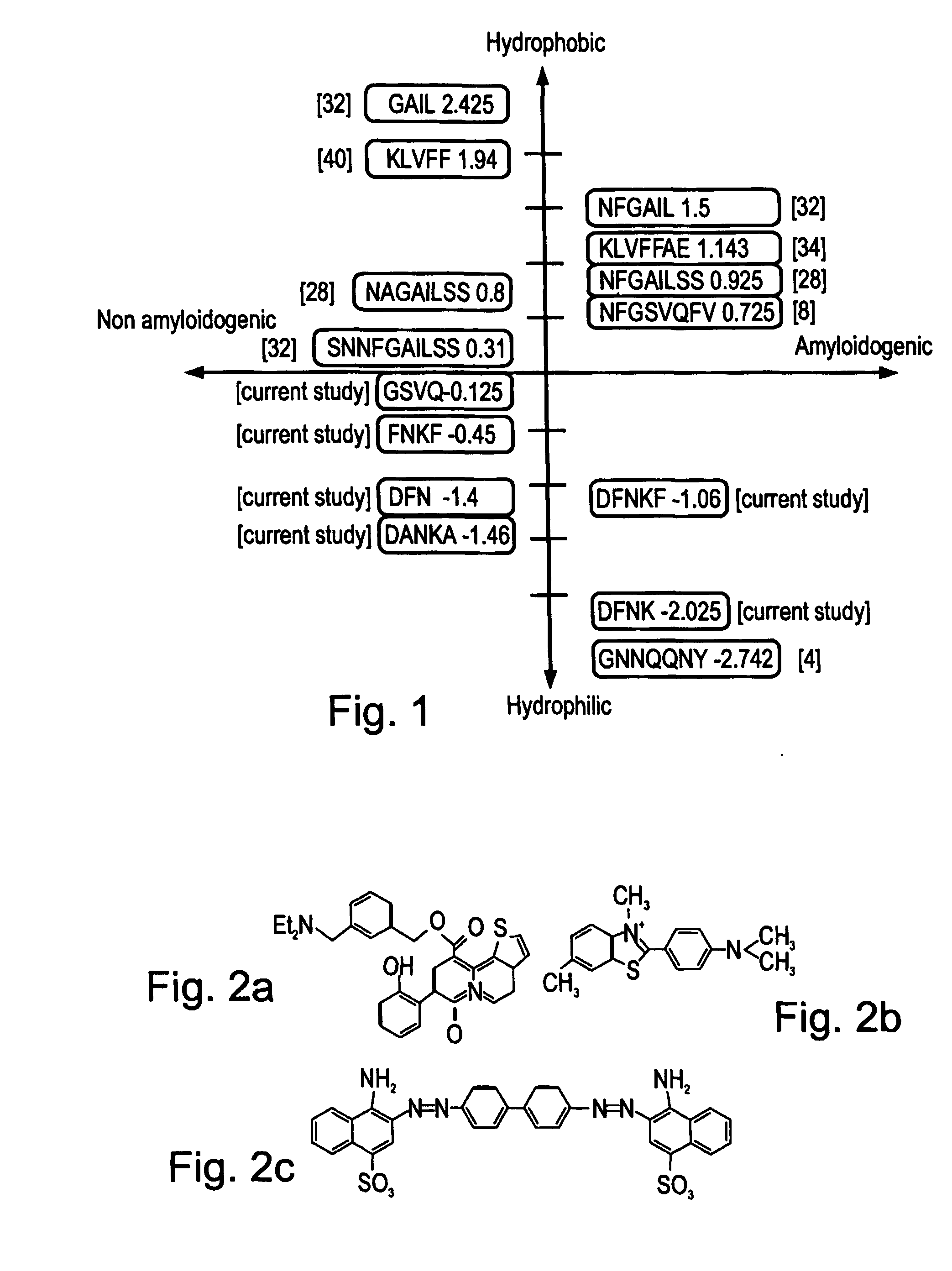
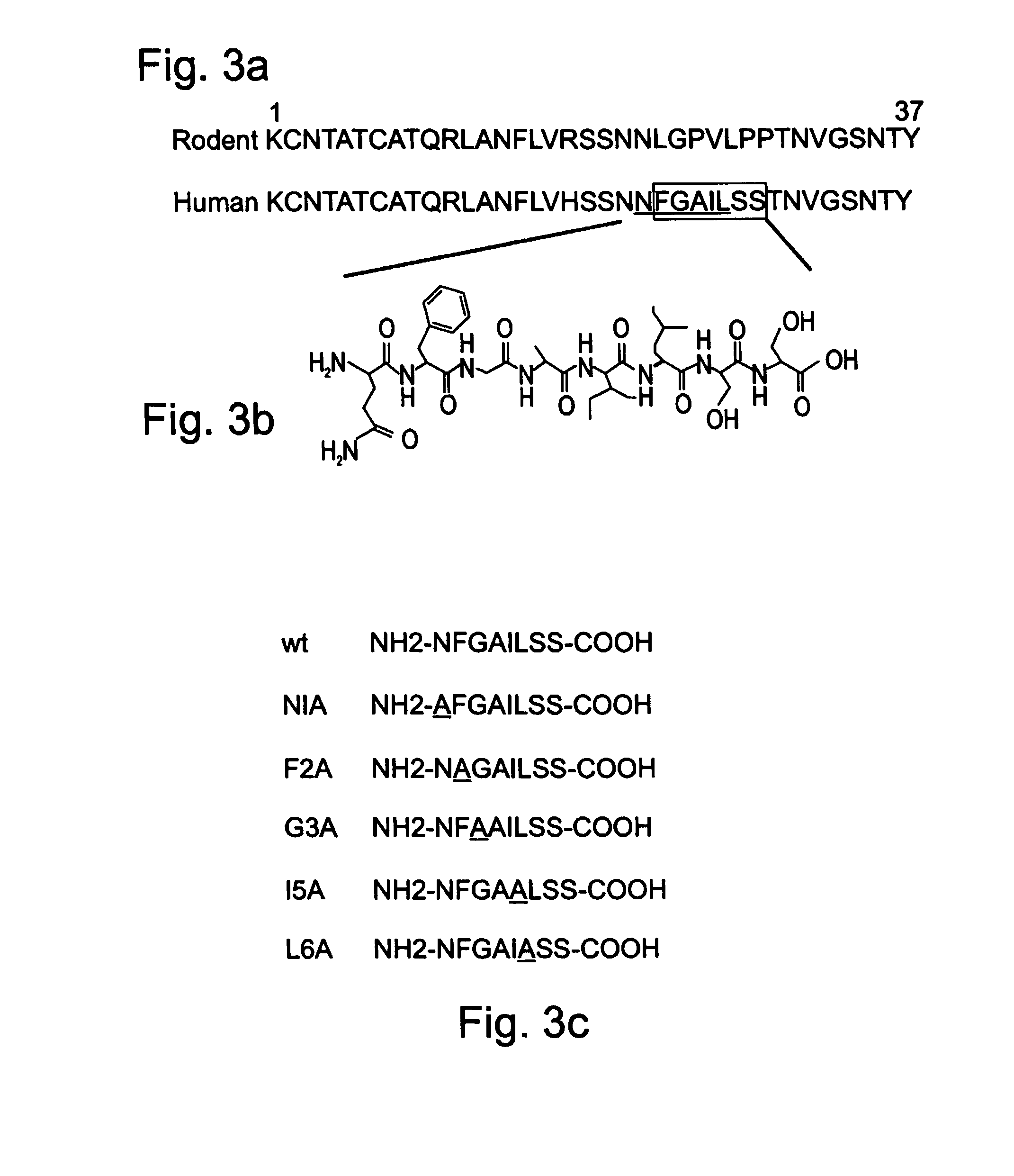
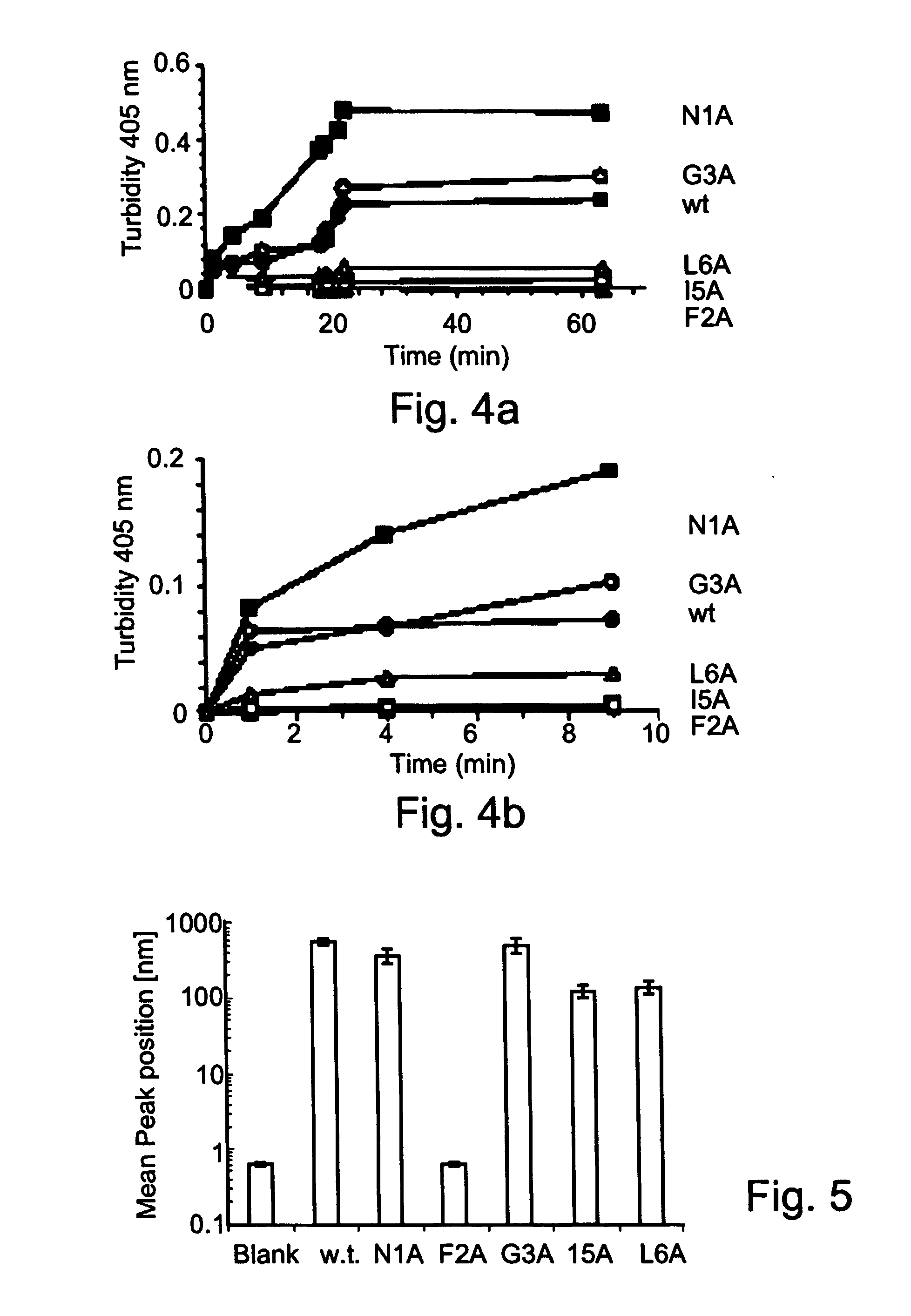
Peptides antibodies directed thereagainst and methods using same for diagnosing and treating amyloid-associated diseases
Peptides having at least 2 amino acids and no more than 15 amino acids are provided. The peptides comprise amino acid sequence X-Y or Y-X, wherein X is an aromatic amino acid and Y is any amino acid other than glycine. Also provided are pharmaceutical compositions and kits including such peptides as well as methods using same for diagnosing and treating amyloid associated diseases.
Owner:TEL AVIV UNIV FUTURE TECH DEVMENT
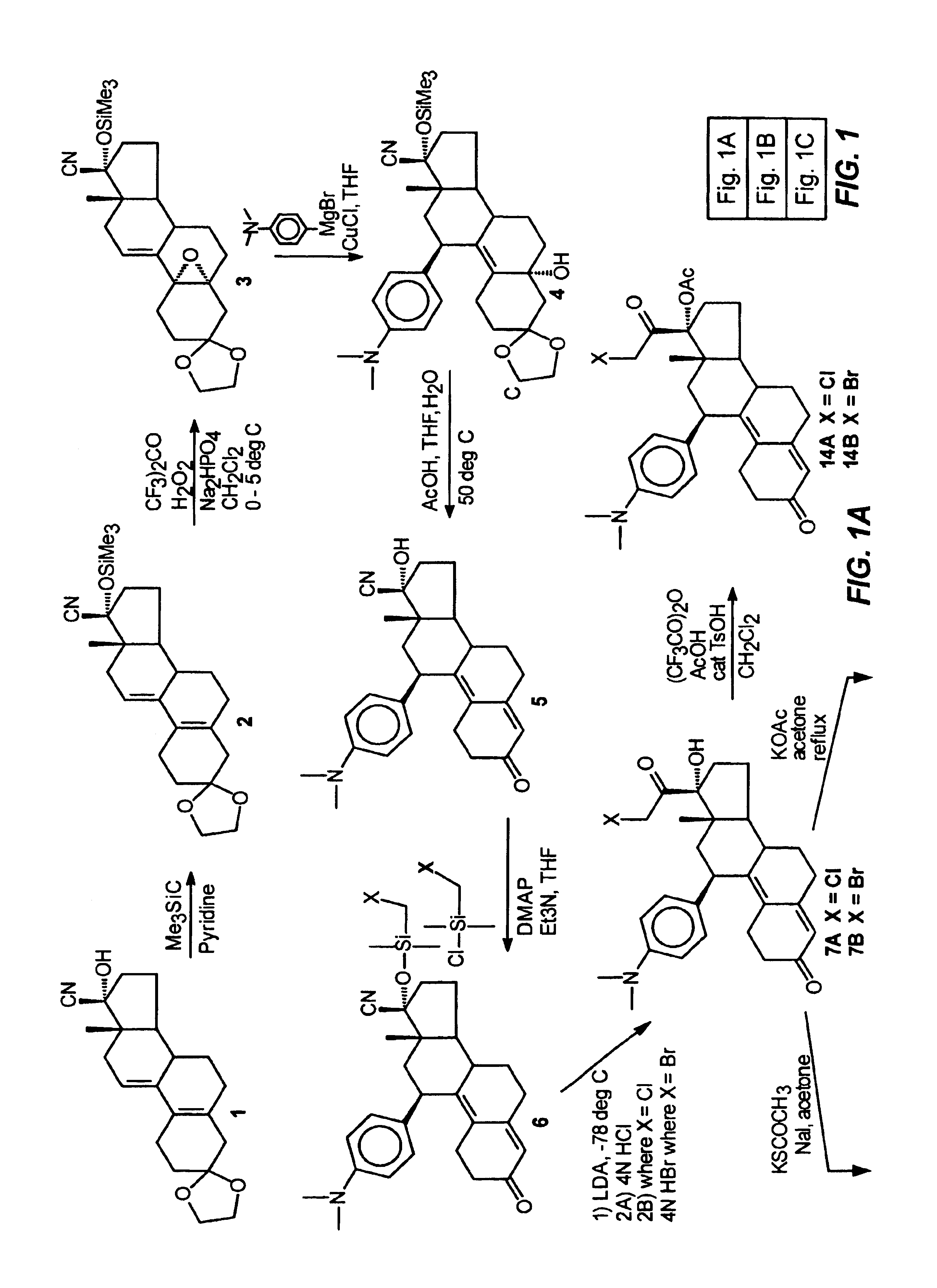
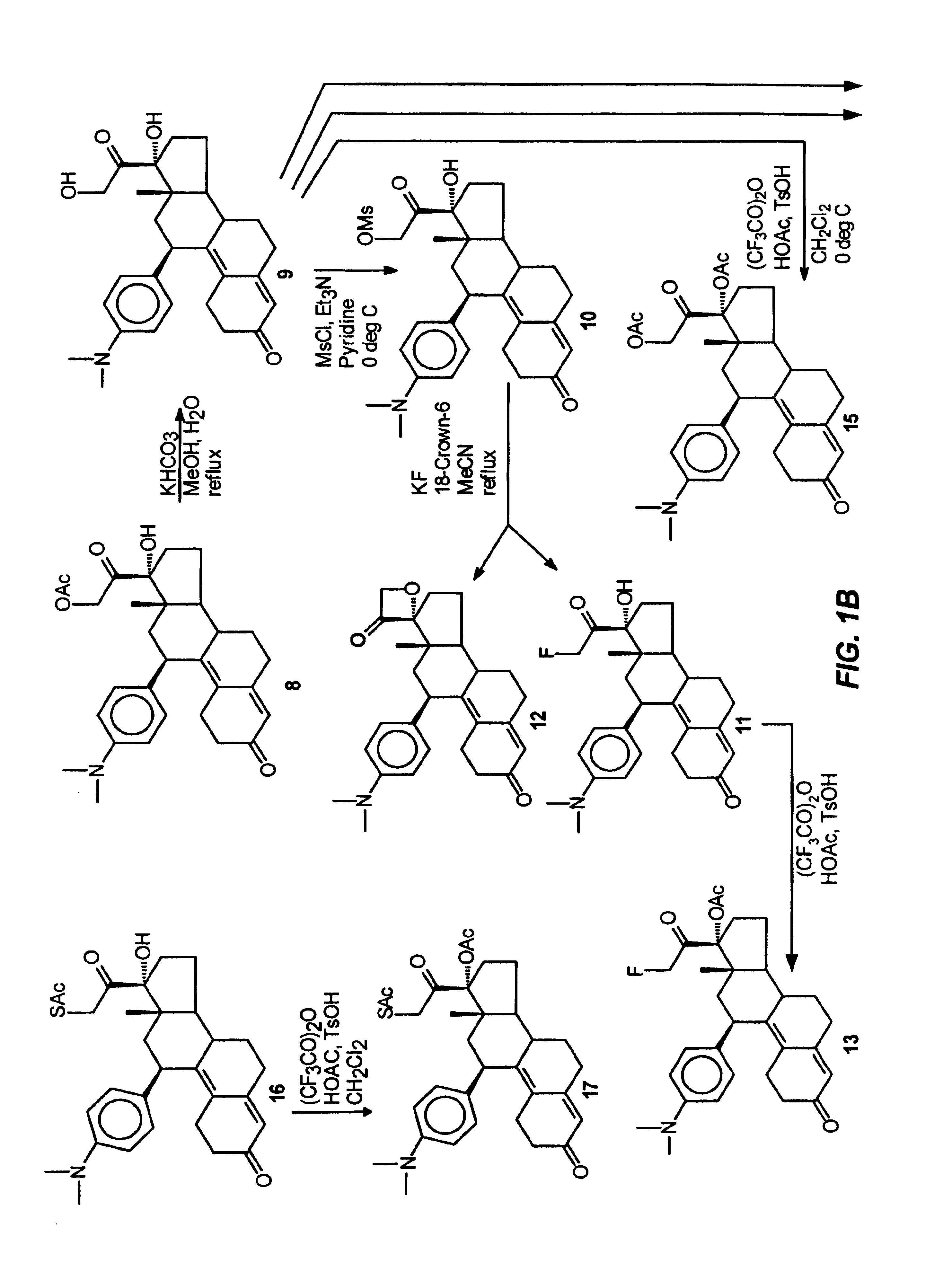
Structural modification of 19-norprogesterone I: 17-α-substituted-11-β-substituted-4-aryl and 21-substituted 19-norpregnadienedione as new antiprogestational agents
The present invention relates, inter alia, to compounds having the general formula: in which: R1 is a member selected from the group consisting of —OCH3, —SCH3, —N(CH3)2, —NHCH3, —NC4H8, —NC5H10, —NC4H8O, —CHO, —CH(OH)CH3, —C(O)CH3, —O(CH2)2N(CH3)2, and —O(CH2)2NC5H10; R2 is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, alkyl, acyl, hydroxy, alkoxy (e.g., methoxy, ethoxy, vinyloxy, ethynyloxy, cyclopropyloxy, etc.), acyloxy (e.g., acetoxy, glycinate, etc.), alkylcarbonate, cypionyloxy, S-alkyl, —SCN, S-acyl and —OC(O)R6, wherein R6 is a functional group including, but not limited to, alkyl (e.g., methyl, ethyl, etc.), alkoxy ester (e.g., —CH2OCH3) and alkoxy (—OCH3); R3 is a member selected from the group consisting of alkyl, hydroxy, alkoxy and acyloxy; R4 is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen and alkyl; and X is a member selected from the group consisting of ═O and ═N—OR5, wherein R5 is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen and alkyl.In addition to providing the compounds of Formula I, the present invention provides methods wherein the compounds of Formula I are advantageously used, inter alia, to antagonize endogenous progesterone; to induce menses; to treat endometriosis; to treat dysmenorrhea; to treat endocrine hormone-dependent tumors; to treat meningiomas; to treat uterine leiomyomas; to treat uterine fibroids; to inhibit uterine endometrial proliferation; to induce cervical ripening; to induce labor; and for contraception.
Owner:HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES THE GOVERNMENT OF THE US SEC THE DEPT OF
Peptides antibodies directed thereagainst and methods using same for diagnosing and treating amyloid-associated diseases
Peptides having at least 2 amino acids and no more than 15 amino acids are provided. The peptides comprise amino acid sequence X-Y or Y-X, wherein X is an aromatic amino acid and Y is any amino acid other than glycine. Also provided are pharmaceutical compositions and kits including such peptides as well as methods using same for diagnosing and treating amyloid associated diseases.
Owner:TEL AVIV UNIV FUTURE TECH DEVMENT
Thermal treatment process for tobacco materials
ActiveUS8434496B2Alter natureAlter characterTobacco preparationTobacco treatmentArgininePhenylalanine
A method of thermally processing a tobacco material is provided, the method including the steps of (i) mixing a tobacco material, water, and an additive selected from the group consisting of lysine, glycine, histidine, alanine, methionine, glutamic acid, aspartic acid, proline, phenylalanine, valine, arginine, di- and trivalent cations, asparaginase, saccharides, phenolic compounds, reducing agents, compounds having a free thiol group, oxidizing agents, oxidation catalysts, plant extracts, and combinations thereof, to form a moist tobacco mixture; (ii) heating the moist tobacco mixture at a temperature of at least about 60° C. to form a heat-treated tobacco mixture; and (iii) incorporating the heat-treated tobacco mixture into a tobacco product. Heat-treated tobacco composition prepared according to the method are also provided, such as heat-treated smokeless tobacco composition comprising a tobacco material, water, flavorant, binder, and filler, the heat-treated smokeless tobacco composition having an acrylamide content of less than about 2000 ppb.
Owner:R J REYNOLDS TOBACCO COMPANY
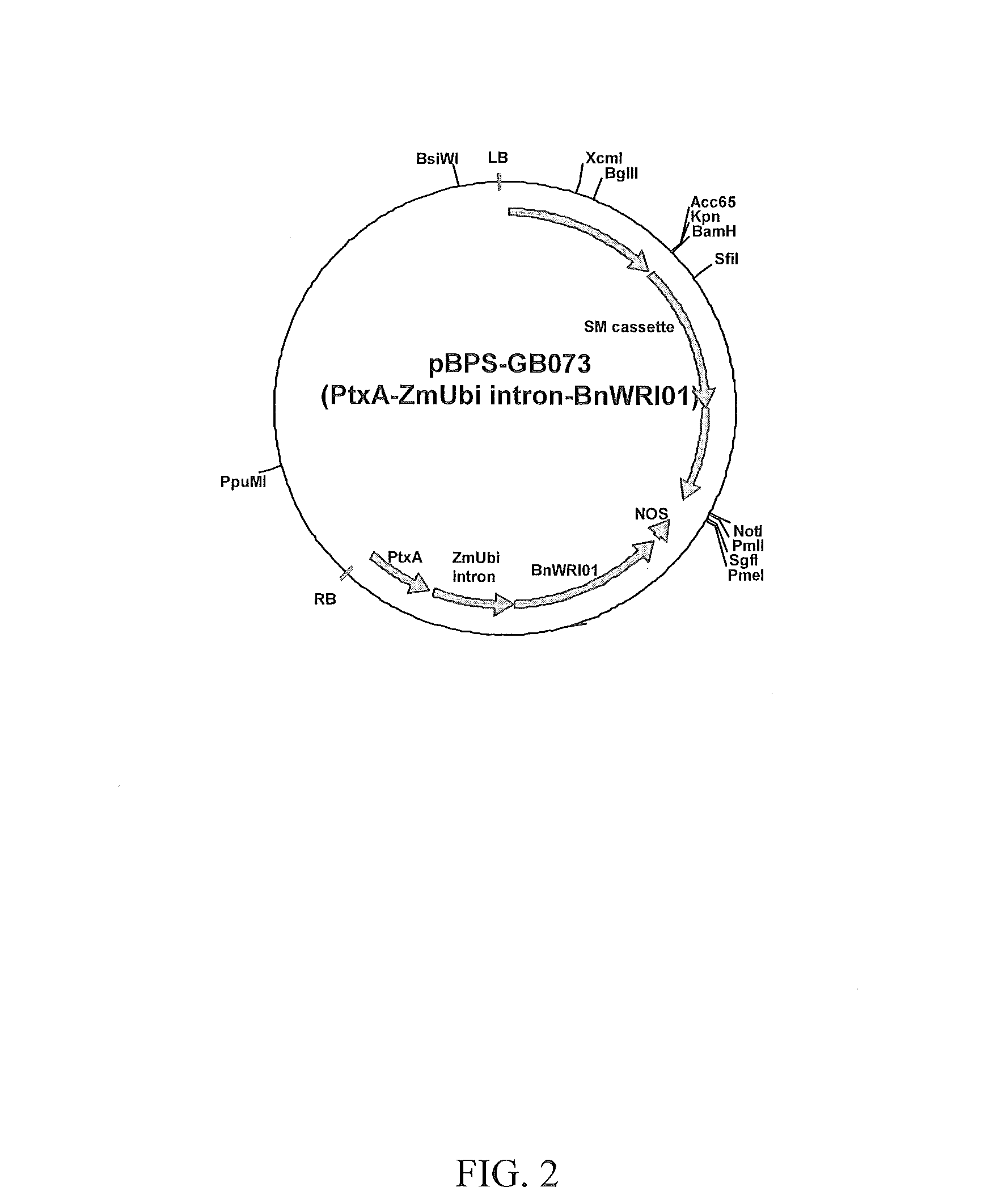
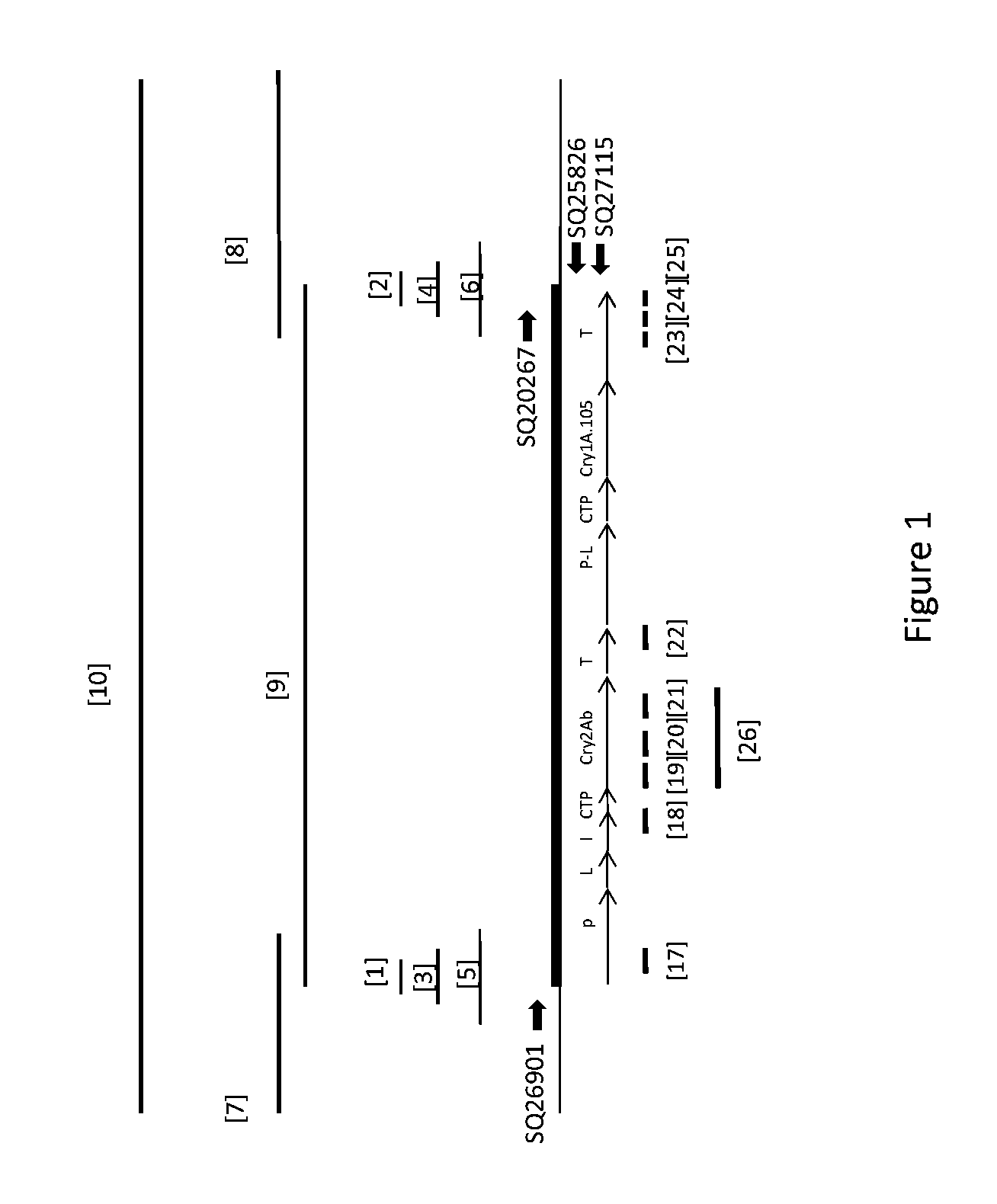
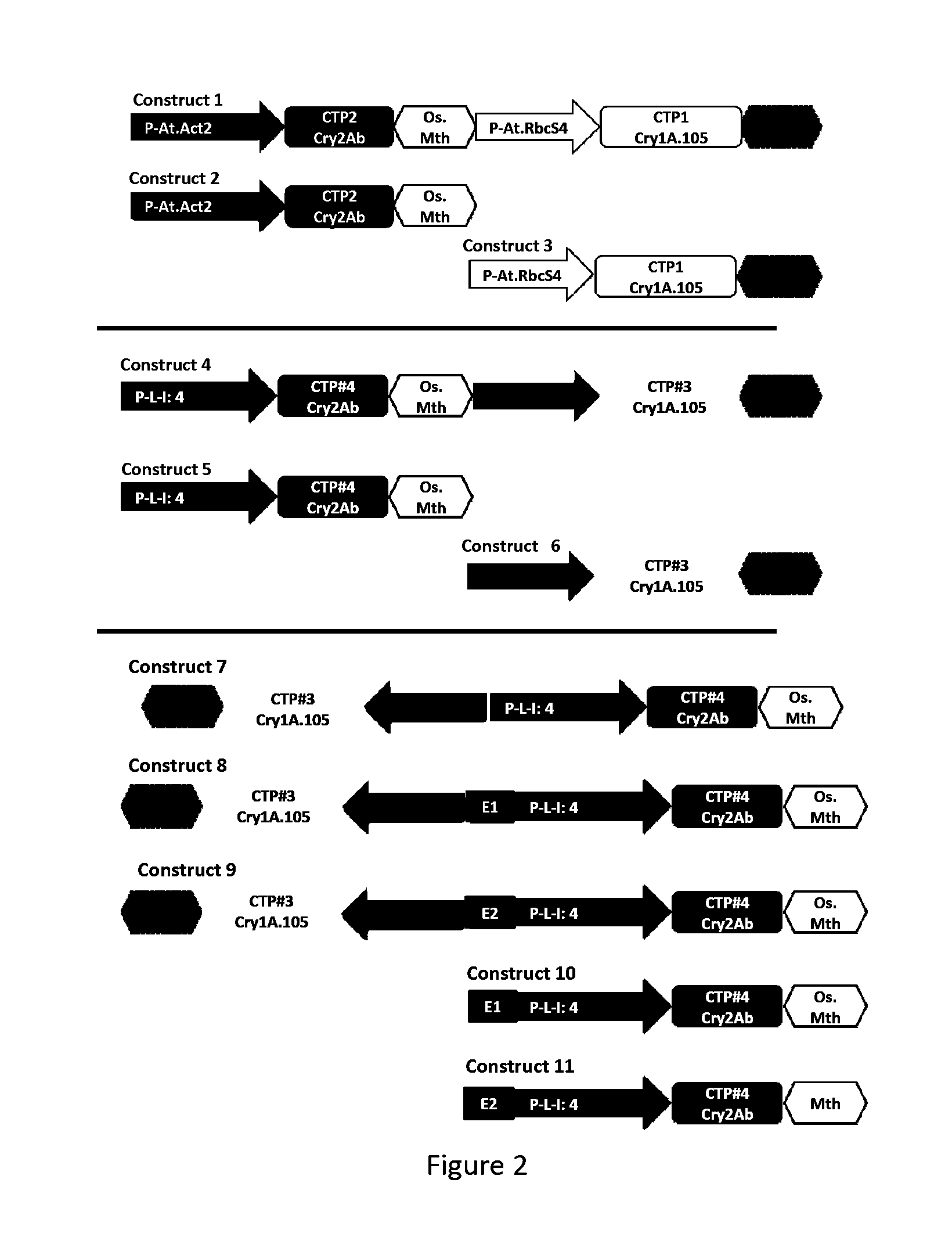
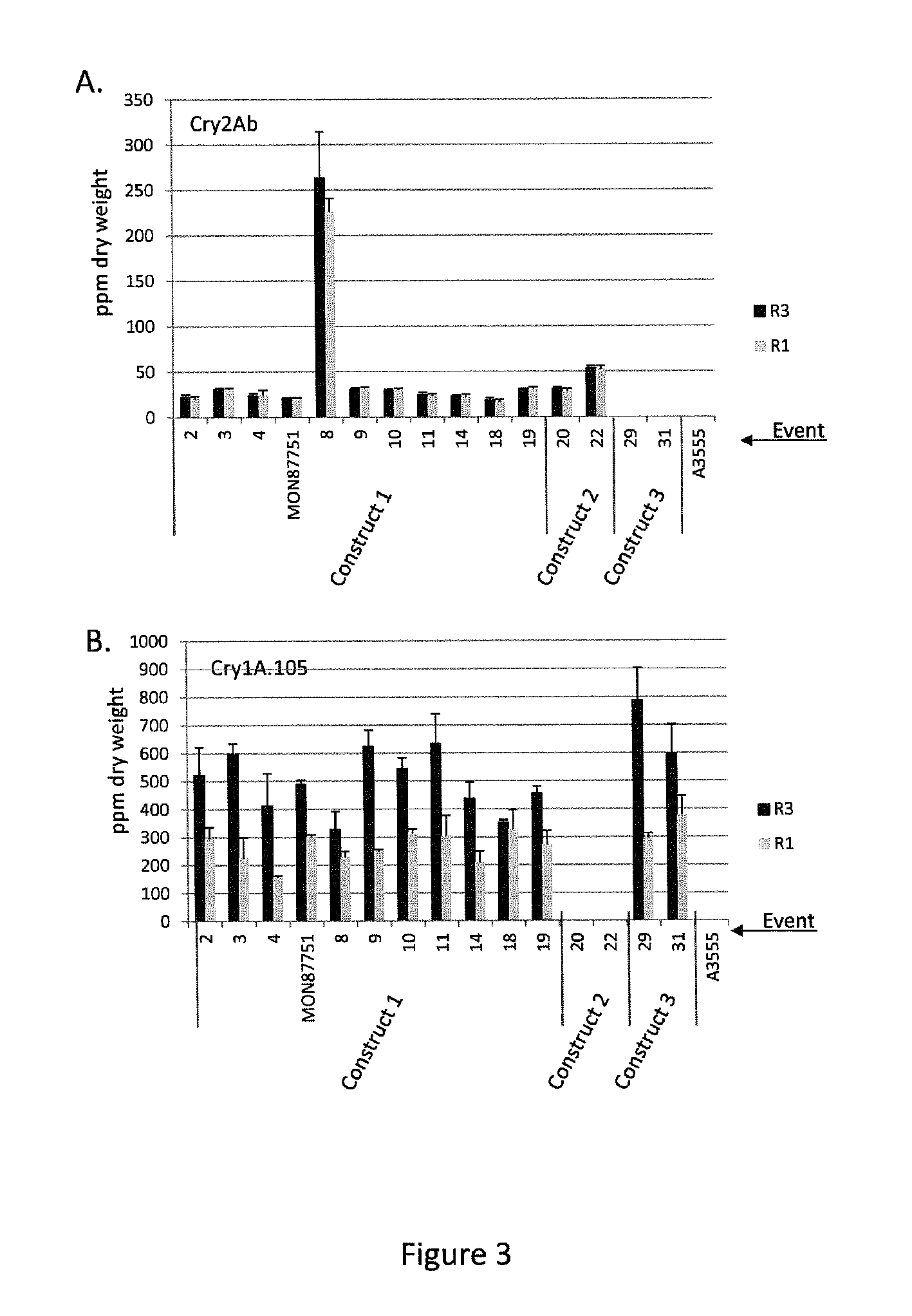
Soybean transgenic event mon87751 and methods for detection and use thereof
ActiveUS20140373191A1Maintain good propertiesImprove performanceCheese manufactureVector-based foreign material introductionGlycinePlant cell
The invention provides a transgenic Glycine max event MON87751, plants, plant cells, seeds, plant parts, progeny plants, and commodity products comprising event MON87751. The invention also provides polynucleotides specific for event MON87751, plants, plant cells, seeds, plant parts, and commodity products comprising polynucleotides for event MON87751. The invention also provides methods related to event MON87751.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Peptides from the E2, E6, and E7 proteins of human papilloma viruses 16 and 18 for detecting and/or diagnosing cervical and other human papillomavirus associated cancers
InactiveUS6933123B2Simple and rapid and and more testMicrobiological testing/measurementVirus peptidesCysteine thiolateTryptophan
Owner:HU YAO XIONG
Herbicidal compositions containing N-phosphonomethyl glycine and an auxin herbicide
InactiveUS20060019828A1Early visual symptomEasy to seeBiocideDead animal preservationGlycineLong term control
Herbicidal compositions are provided which cause rapid symptomology while delivering long term control of regrowth of plants. The herbicidal concentrate compositions comprise N-phosphonomethylglycine or a herbicidal derivative thereof, an auxin herbicide or a herbicidal derivative thereof, and at least one surfactant. Also provided is a method for killing or controlling the growth of certain plants by contacting the foliage of the plants with the diluted concentrate composition.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
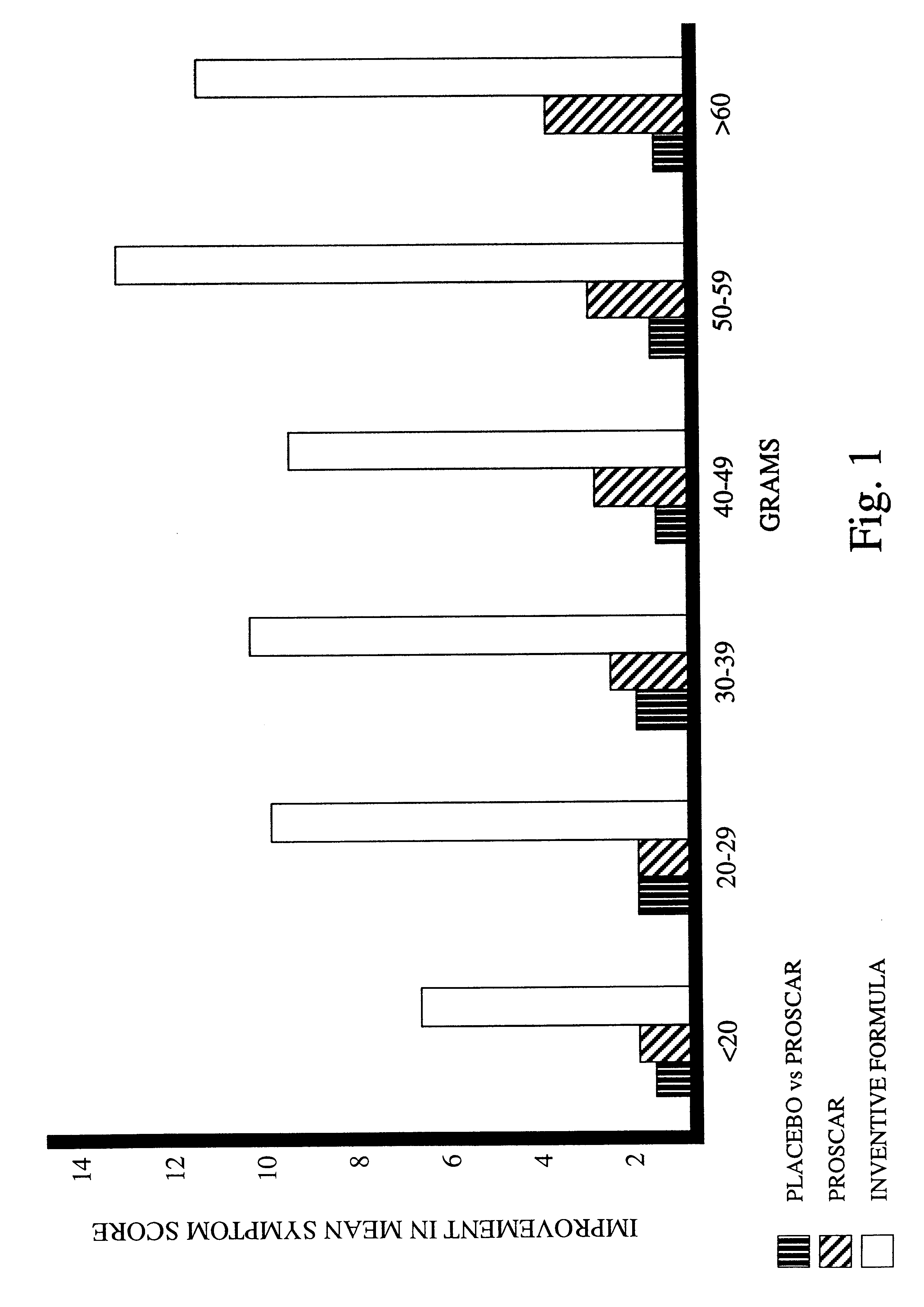
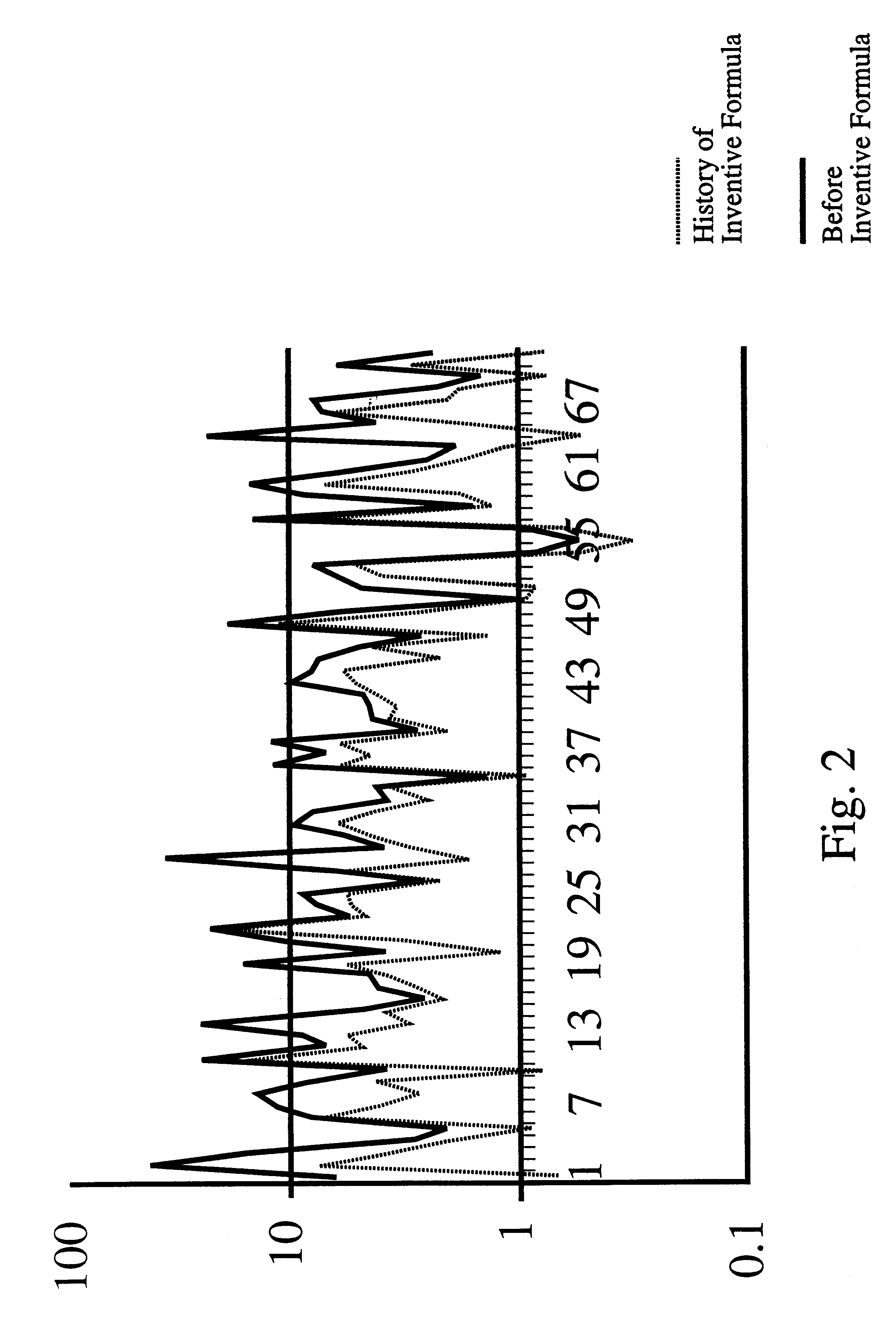
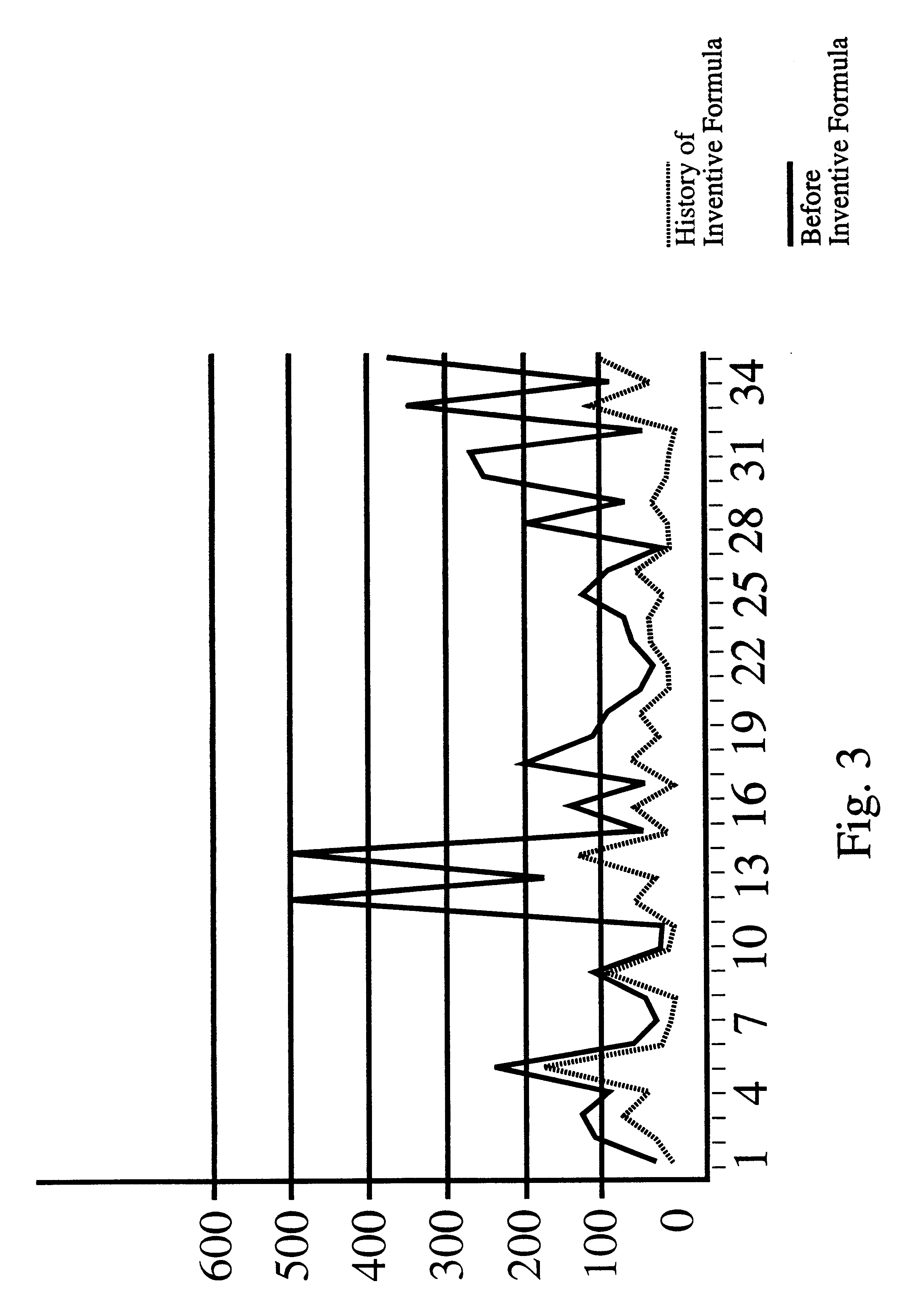
Prostate formula
InactiveUS6197309B1Good effectAlleviates and eliminates symptomHeavy metal active ingredientsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseVitamin C
A composition providing an all-natural, non-surgical preventative of or improvement to disorders of the prostate gland is described. The invention relates to a composition for the prevention of or improvement of prostatitis, and for relieving symptoms and improving objective signs of prostatitis. The formula of the composition preferably includes the following ingredients each in a therapeutically effective amount: Vitamin C, Vitamin B6, Vitamin E, zinc, glycine, L-alanine, Glutamic acid, Saw palmetto, Pygeum extract, Pumpkin seed, Stinging nettle, Echinacea, garlic, Ginkgo leaves, and selenium.
Owner:WHEELER RONALD E
Thermal treatment process for tobacco materials
ActiveUS8991403B2Alter natureAlter characterTobacco preparationTobacco treatmentArginineTobacco product
A method of thermally processing a tobacco material is provided, the method including the steps of (i) mixing a tobacco material, water, and an additive selected from the group consisting of lysine, glycine, histidine, alanine, methionine, glutamic acid, aspartic acid, proline, phenylalanine, valine, arginine, di- and trivalent cations, asparaginase, saccharides, phenolic compounds, reducing agents, compounds having a free thiol group, oxidizing agents, oxidation catalysts, plant extracts, and combinations thereof, to form a moist tobacco mixture; (ii) heating the moist tobacco mixture at a temperature of at least about 60° C. to form a heat-treated tobacco mixture; and (iii) incorporating the heat-treated tobacco mixture into a tobacco product. Heat-treated tobacco composition prepared according to the method are also provided, such as heat-treated smokeless tobacco composition comprising a tobacco material, water, flavorant, binder, and filler, the heat-treated smokeless tobacco composition having an acrylamide content of less than about 2000 ppb.
Owner:R J REYNOLDS TOBACCO COMPANY
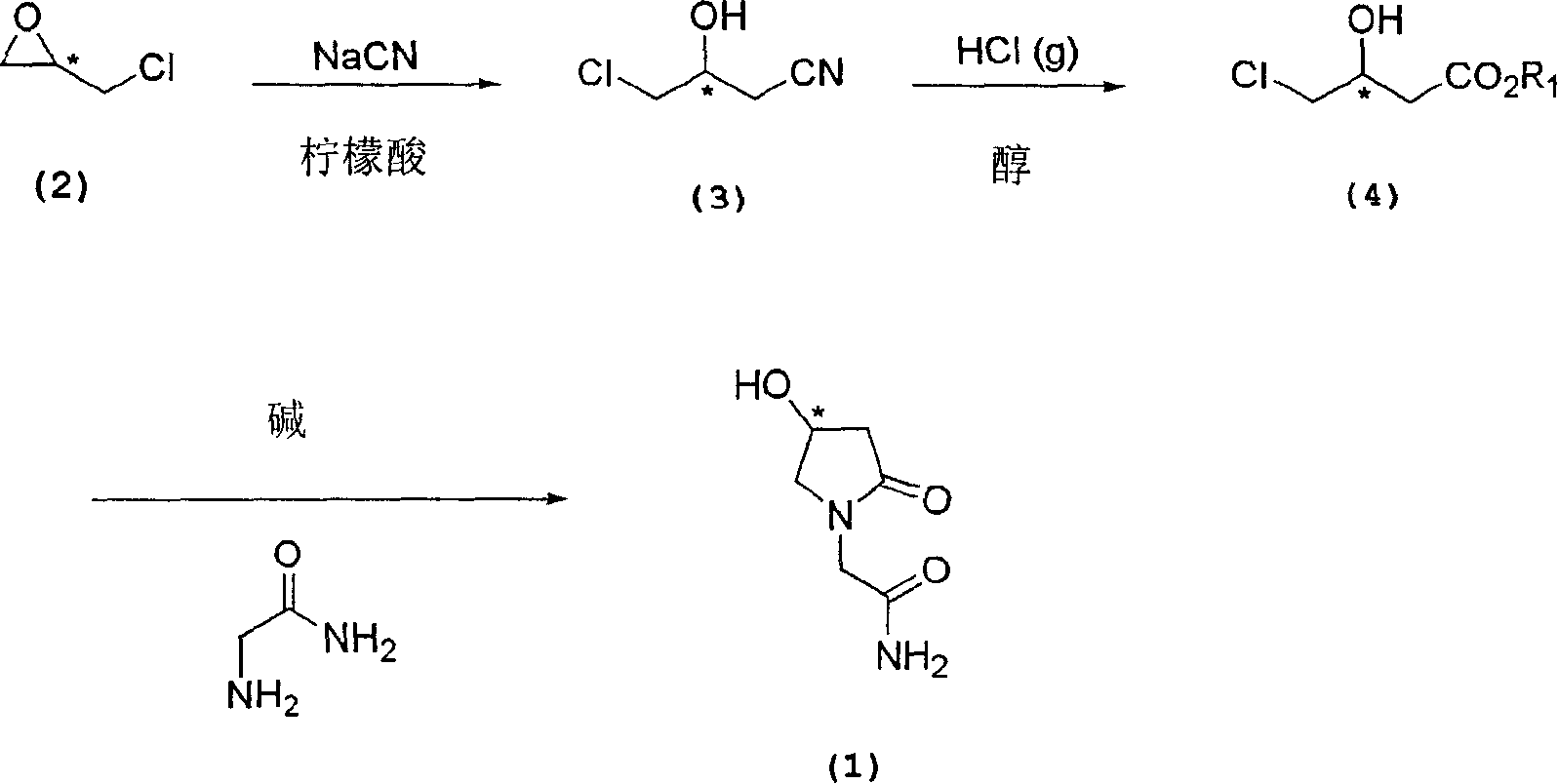
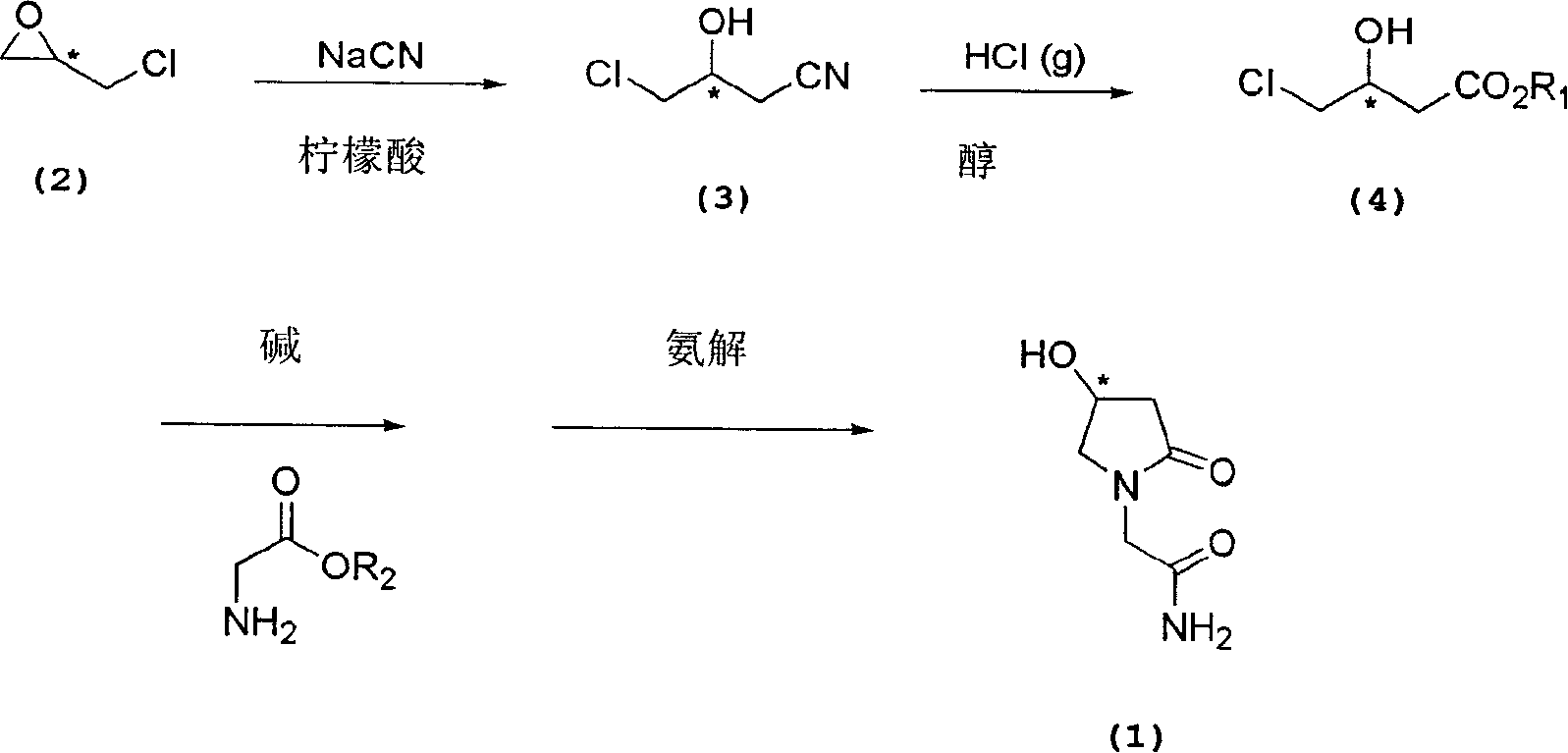
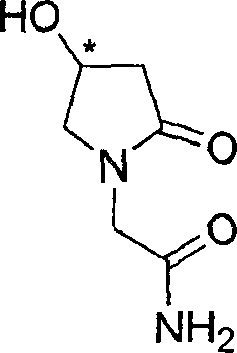
Process for the preparation of optically pure 4-hydroxy-2-oxo-1-pyrrolidine acetamide
The present invention relates to a process for the preparation of chiral 4-hydroxy-2-oxo-1-pyrrolidine acetamide. The process comprises adding sodium cyanide together with citric acid to a solution of chiral epichlorohydrin to obtain chiral 3-chloro-2-hydroxypropionitrile by ring opening reaction of the chiral epichlorohydrin, reacting the obtained product with an alcohol containing hydrochloride gas to obtain chiral 4-chloro-3-hydroxybutyric acid ester, and reacting the obtained product in a presence of a base with glycinamide or with glycine ester accompanied by ammonolysis with ammonia to produce the targeted chiral 4-hydroxy-2-oxo-1-pyrrolidine acetamide. The process according to the present invention provides optically pure 4-hydroxy-2-oxo-1-pyrrolidine acetamide in high yield and in high purity, which is suitable for industrial mass-production.
Owner:AHN GOOK PHARMA CO LTD +1
Betaine with Calcium and/or Strontium Antiperspirants
InactiveUS20070020211A1Good curative effectImprove skinCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsAntiperspirantsBetaine
Aluminum and aluminum-zirconium antiperspirant compositions comprising basic aluminum chlorides that have a particular molecular size distribution defined by having an SEC-HPLC Band III / II ratio of at least 0.5, having SEC-HPLC Band III plus Band II area of at least 70% of the total area and having SEC-HPLC Band I content no more than 5% and containing betaine (trimethylglycine), calcium and / or strontium are disclosed. Also disclosed are the methods of making these compositions and the use thereof in consumer acceptable antiperspirant vehicles such as aerosols, gels, roll-on, sticks and soft solids.
Owner:SUMMIT RES LAB
Method for preparing N-long chain acyl neutral amino acid
InactiveUS6703517B2Efficient conductionLow viscosityCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsNeutral Amino AcidsAlanine
A method for preparing a highly purified N-long chain acyl neutral amino acid for use of a detergent and the like in a simple and convenient manner and in a high yield by reacting a neutral amino acid such as glycine, gamma-aminobutyric acid, and alanine, with a saturated or unsaturated fatty acid halide having 8 to 22 carbon atoms, wherein the reaction is performed in a mixture of water and one or more kinds of hydrophilic organic solvents selected from the group consisting of acetone, acetonitrile, a secondary alcohol having 3 or 4 carbon atoms, and a tertiary alcohol having 4 carbon atoms such as isopropanol, sec-butanol, and tert-butanol in the presence of a base.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Composition and method for reducing the risk or progression of cardiovascular, glaucoma, tardive dyskinesia and other diseases
InactiveUS20040087479A1Reduce riskShorten the progressBiocideOrganic active ingredientsBeta-CaroteneAdditive ingredient
Elevated levels of homocysteine have been implicated as an important risk factor for cardiovascular and other diseases. A composition for decreasing levels of plasma homocysteine and a method for administering the composition are provided, the composition containing dextromethorphan (DM), folic acid and vitamins B6 and B12. The composition provides a synergistic therapeutic effect so that lower amounts of the above ingredients may be employed to minimize any undesirable side effects caused by the use of high levels of a component such as DM. Preferred compositions for cardiovascular diseases further include lecithin, vitamin E, betacarotene, procyanidins / flavonoids, trimethylglycine, garlic oil and minerals. Other compositions for treating glaucoma include bilberry, bioflavonoids and beta-carotene and for treating tardive dyskinesia include an antioxidant such a grape seed extract and pine bark extract, lecithin and oligomeric proanthocyanidins. The compositions may be administered using any suitable means such as orally or intravenous.
Owner:SOSNOWSKI ROBERT E +1
Compositions including iron
Compositions and methods for prevent, stabilize, reverse or treat disorders related to iron deficiency in a human or other animal. In a first embodiment, the composition includes about 10 mg to about 500 mg of one or more forms of iron, wherein at least one form of iron is an aspartic acid-glycine chelate of iron; and about 5 mg to about 500 mg of one or more forms of an organic acid. In another embodiment, the composition includes about 50 to about 150 mg of one or more forms of iron, wherein at least one form of iron is an aspartic acid-glycine chelate of iron; about 50 to about 250 mg of one or more forms of an organic acid; about 150 to about 250 mg of one or more forms of ascorbic acid; about 0.5 mg to about 1.5 mg vitamin B12; about 50 to about 150 mg intrinsic factor; and about 0.5 mg to about 1.5 mg folic acid.
Owner:DRAGTEK CORP
Biosensor
InactiveUS20030175841A1Avoid influenceReduce solubilityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsGluconolactonaseSuccinic acid
A biosensor that is highly responsive and capable of rapid and highly sensitive quantification of a specific component contained in a sample is provided. The biosensor of this invention comprises: an electrically insulating base plate; an electrode system comprising a working electrode and a counter electrode disposed on the base plate; and a reagent system comprising an oxidoreductase which catalyzes the oxidation reaction of glucose, gluconolactonase and a buffer. The buffer is selected from the group consisting of phthalic acid and its salts, maleic acid and its salts, succinic acid and its salts, phospholic acid and its salts, acetic acid and its salts, boric acid and its salts, citric acid and its salts, glycine, tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane, piperazine-N,N'-bis(2-ethane sulfonic acid) and the like.
Owner:PHC HLDG CORP
Aerosol formulations for buccal and pulmonary application
InactiveUS6436367B1Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsChamomile extractOleic Acid Triglyceride
A mixed micellar aerosol pharmaceutical formulation includes a micellar proteinic pharmaceutical agent, an alkali metal lauryl sulphate, at least three micelle forming compounds, a phenol and a propellant. The micelle forming compounds are selected from the group consisting of lecithin, hyaluronic acid, pharmaceutically acceptable salts of hyaluronic acid, glycolic acid, lactic acid, chamomile extract, cucumber extract, oleic acid, linoleic acid, linolenic acid, monoolein, monooleates, monolaurates, borage oil, evening of primrose oil, menthol, trihydroxy oxo cholanyl glycine and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, glycerin, polyglycerin, lysine, polylysine, triolein, polyoxyethylene ethers and analogues thereof, polidocanol alkyl ethers and analogues thereof. The amount of each micelle forming compound is present in a concentration of from 1 to 20 wt. / wt. % of the total formulation, and the total concentration of micelle forming compounds are less than 50 wt. / wt. % of the formulation. The propellant, e.g. a fluorocarbon propellant, provides enhanced absorption of the pharmaceutical agent.
Owner:GENEREX PHARMA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![Physiological cooling compositions containing highly purified ethyl ester of N-[[5-methyl-2-(1-methylethyl) cyclohexyl] carbonyl]glycine Physiological cooling compositions containing highly purified ethyl ester of N-[[5-methyl-2-(1-methylethyl) cyclohexyl] carbonyl]glycine](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/adb4d26a-e9fc-49b3-bec1-672c98d419f4/US07189760-20070313-C00001.png)
![Physiological cooling compositions containing highly purified ethyl ester of N-[[5-methyl-2-(1-methylethyl) cyclohexyl] carbonyl]glycine Physiological cooling compositions containing highly purified ethyl ester of N-[[5-methyl-2-(1-methylethyl) cyclohexyl] carbonyl]glycine](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/adb4d26a-e9fc-49b3-bec1-672c98d419f4/US07189760-20070313-C00002.png)
![Physiological cooling compositions containing highly purified ethyl ester of N-[[5-methyl-2-(1-methylethyl) cyclohexyl] carbonyl]glycine Physiological cooling compositions containing highly purified ethyl ester of N-[[5-methyl-2-(1-methylethyl) cyclohexyl] carbonyl]glycine](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/adb4d26a-e9fc-49b3-bec1-672c98d419f4/US07189760-20070313-C00003.png)
![Physiological cooling compositions containing highly purified ethyl ester of N-[[5-methyl-2-(1-methylethyl)cyclohexyl] carbonyl]glycine Physiological cooling compositions containing highly purified ethyl ester of N-[[5-methyl-2-(1-methylethyl)cyclohexyl] carbonyl]glycine](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/cff1f463-e31a-472e-a9ad-f8d2a848a23c/US20050222256A1-20051006-C00001.png)
![Physiological cooling compositions containing highly purified ethyl ester of N-[[5-methyl-2-(1-methylethyl)cyclohexyl] carbonyl]glycine Physiological cooling compositions containing highly purified ethyl ester of N-[[5-methyl-2-(1-methylethyl)cyclohexyl] carbonyl]glycine](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/cff1f463-e31a-472e-a9ad-f8d2a848a23c/US20050222256A1-20051006-C00002.png)
![Physiological cooling compositions containing highly purified ethyl ester of N-[[5-methyl-2-(1-methylethyl)cyclohexyl] carbonyl]glycine Physiological cooling compositions containing highly purified ethyl ester of N-[[5-methyl-2-(1-methylethyl)cyclohexyl] carbonyl]glycine](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/cff1f463-e31a-472e-a9ad-f8d2a848a23c/US20050222256A1-20051006-C00003.png)