Patents
Literature
310 results about "Oxidoreductase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
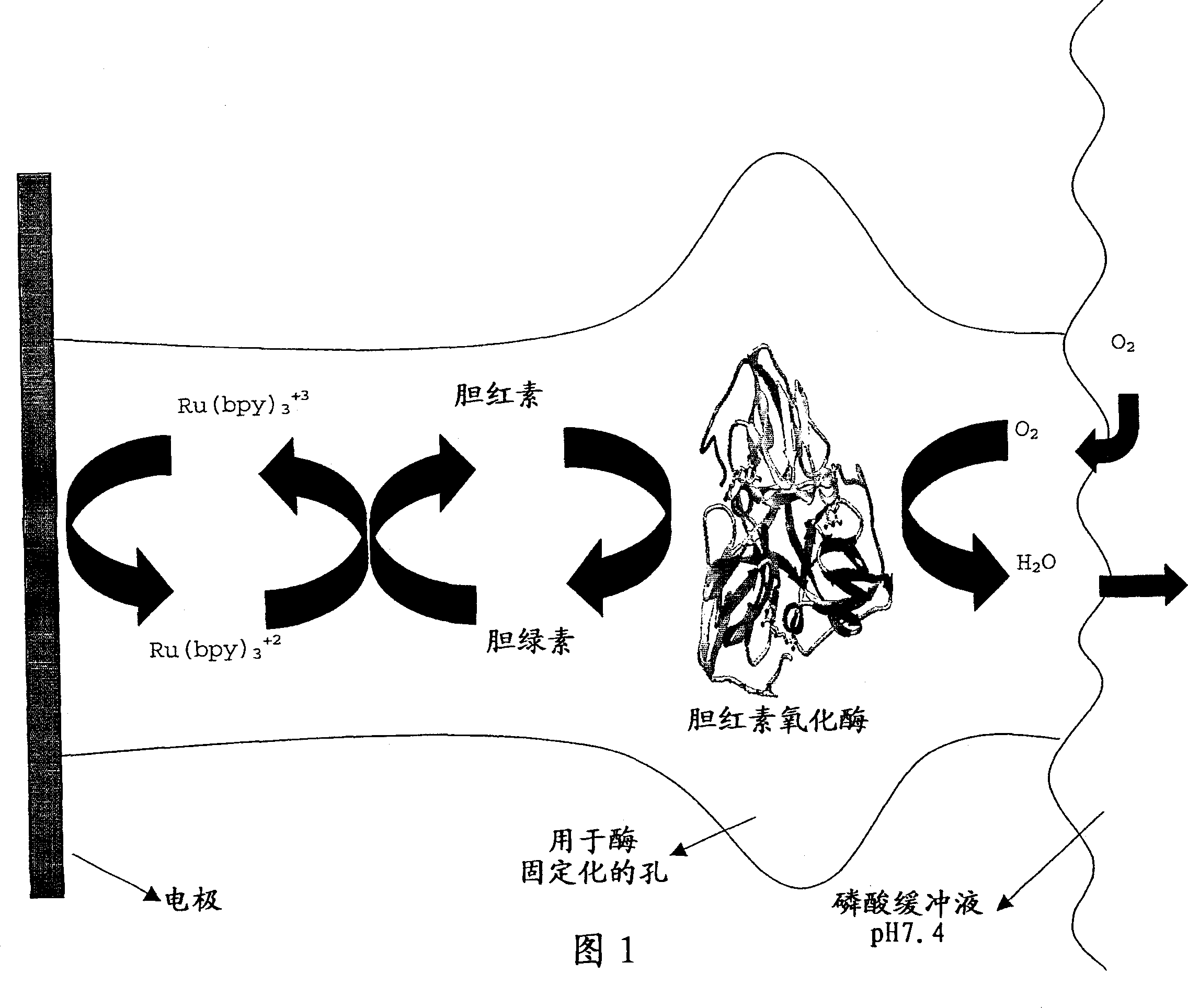
In biochemistry, an oxidoreductase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of electrons from one molecule, the reductant, also called the electron donor, to another, the oxidant, also called the electron acceptor. This group of enzymes usually utilizes NADP or NAD+ as cofactors. Transmembrane oxidoreductases create electron transport chains in bacteria, chloroplasts and mitochondria, including respiratory complexes I, II and III. Some others can associate with biological membranes as peripheral membrane proteins or be anchored to the membranes through a single transmembrane helix.
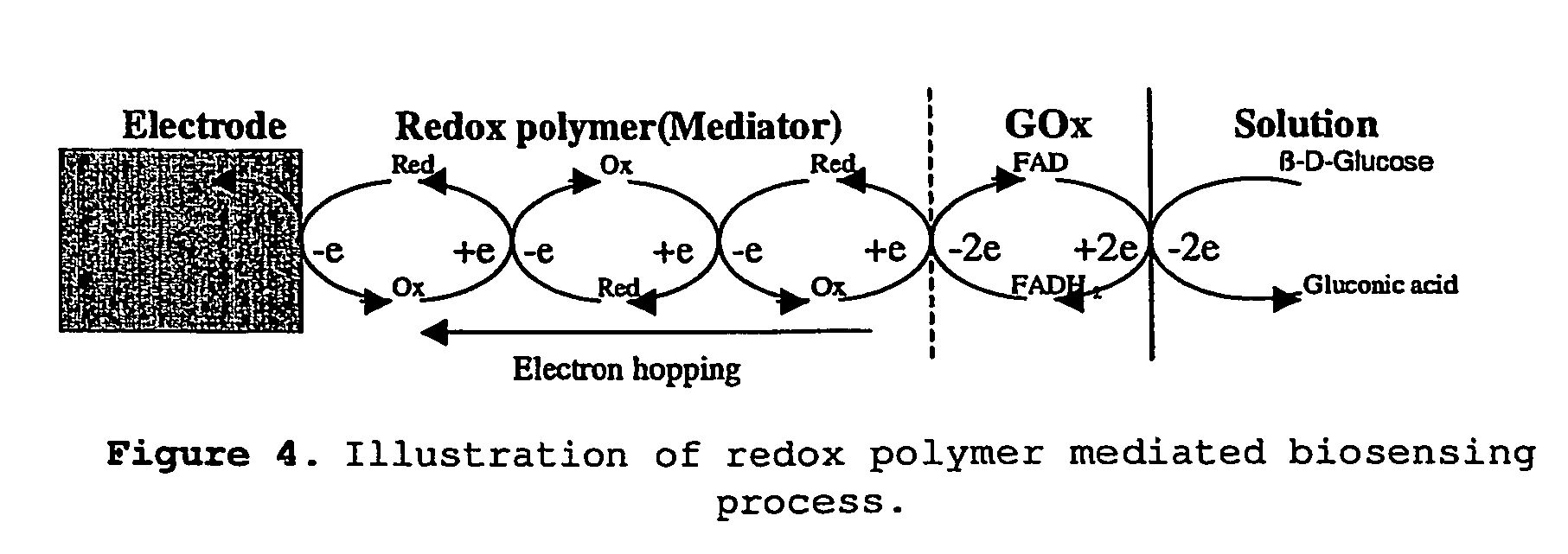
Biosensor
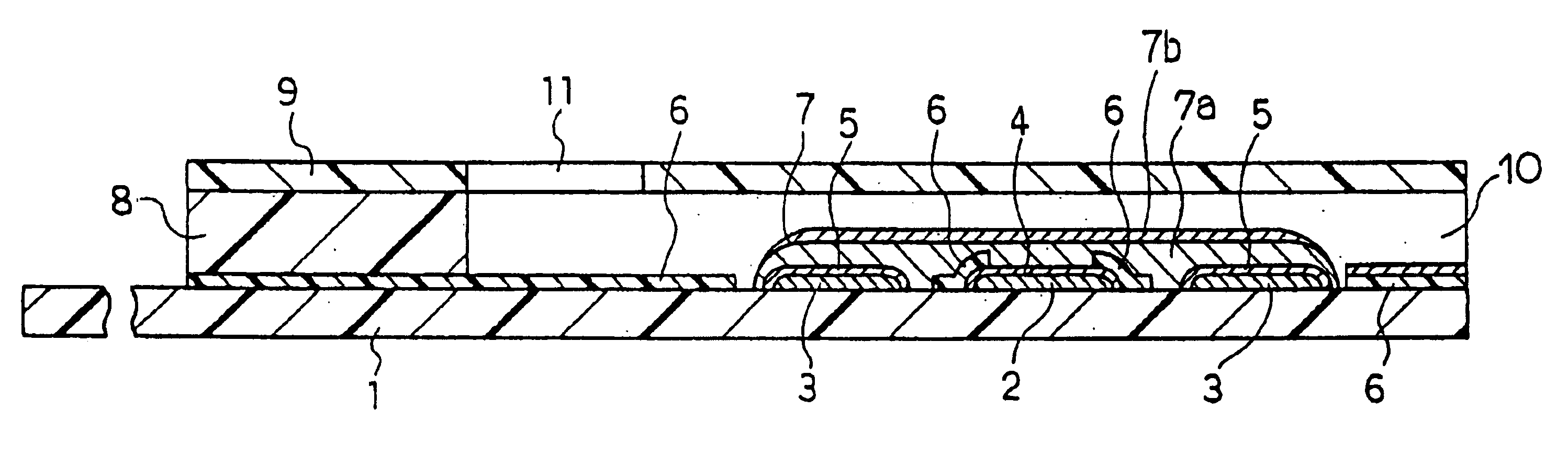
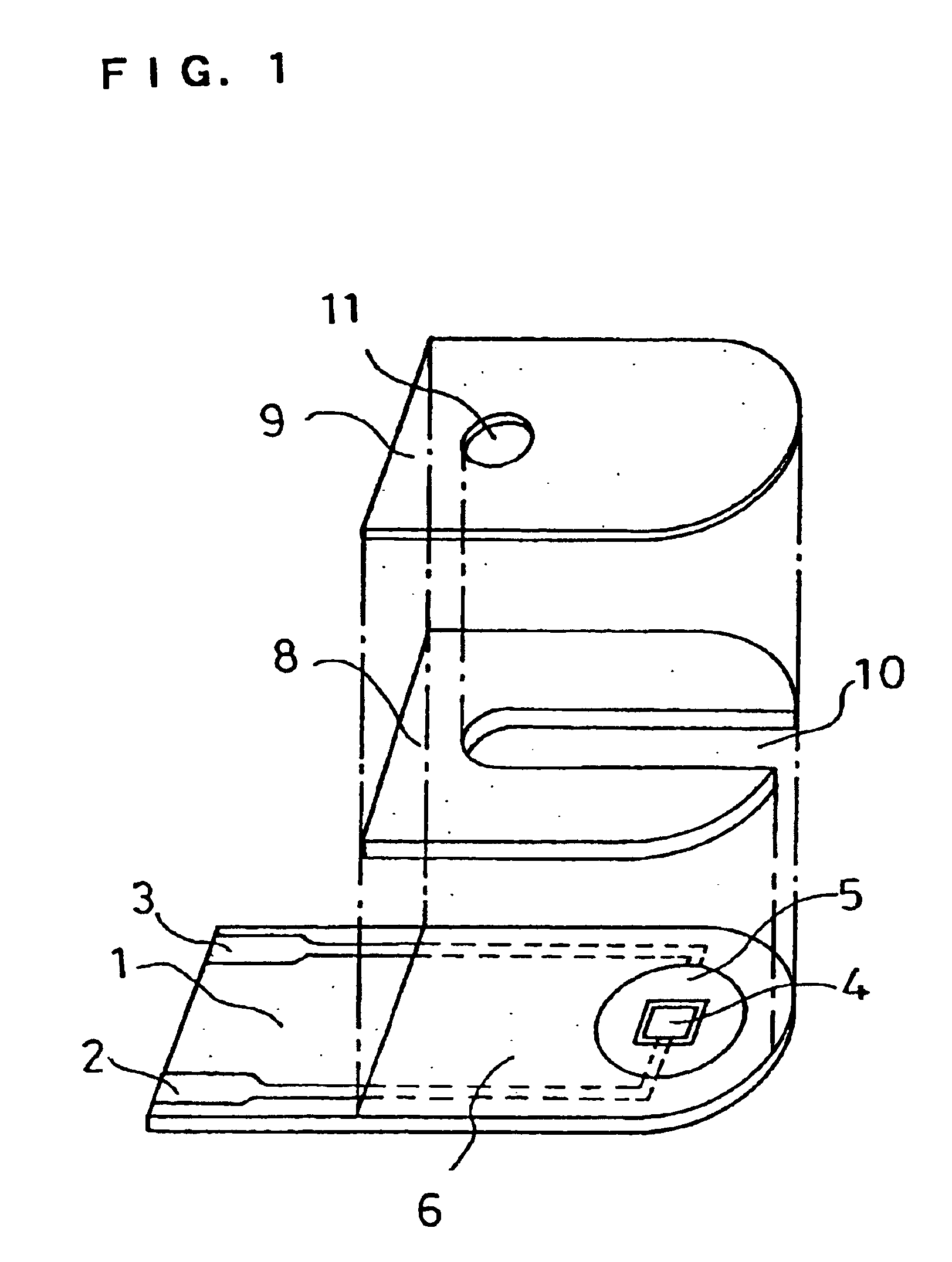
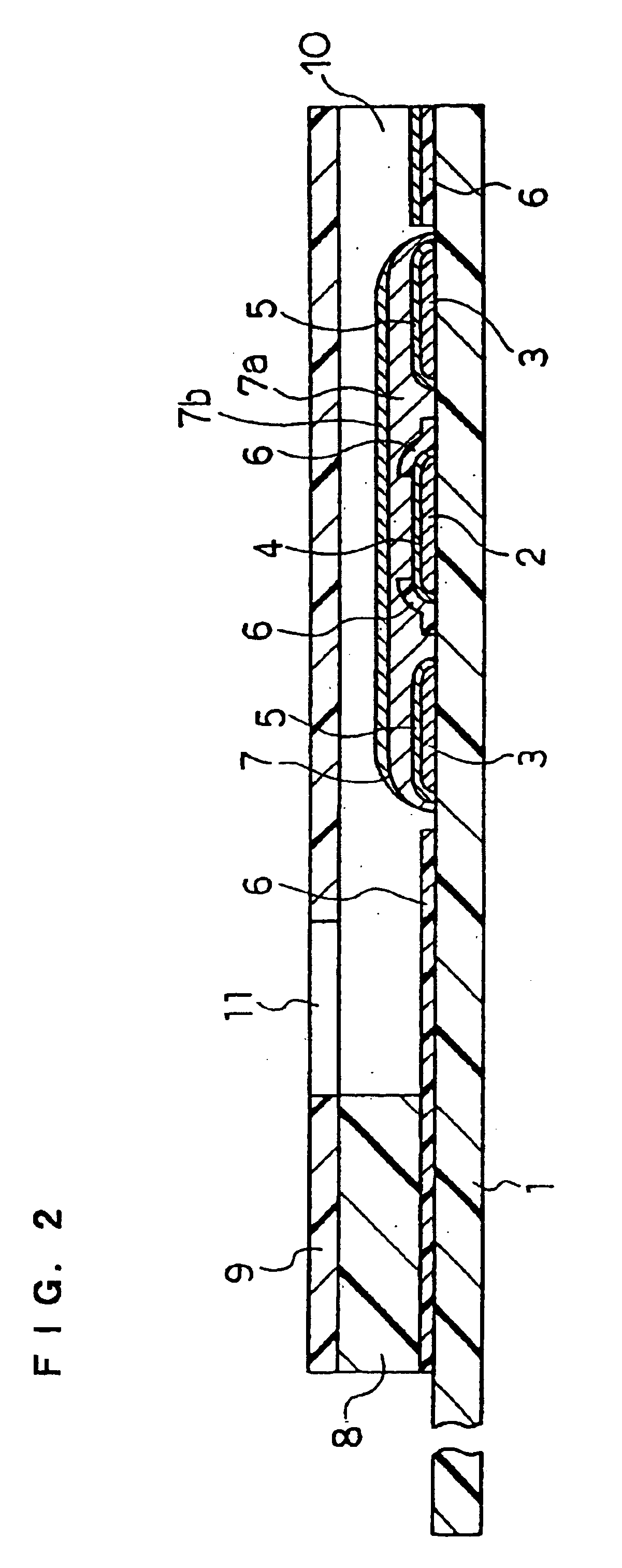
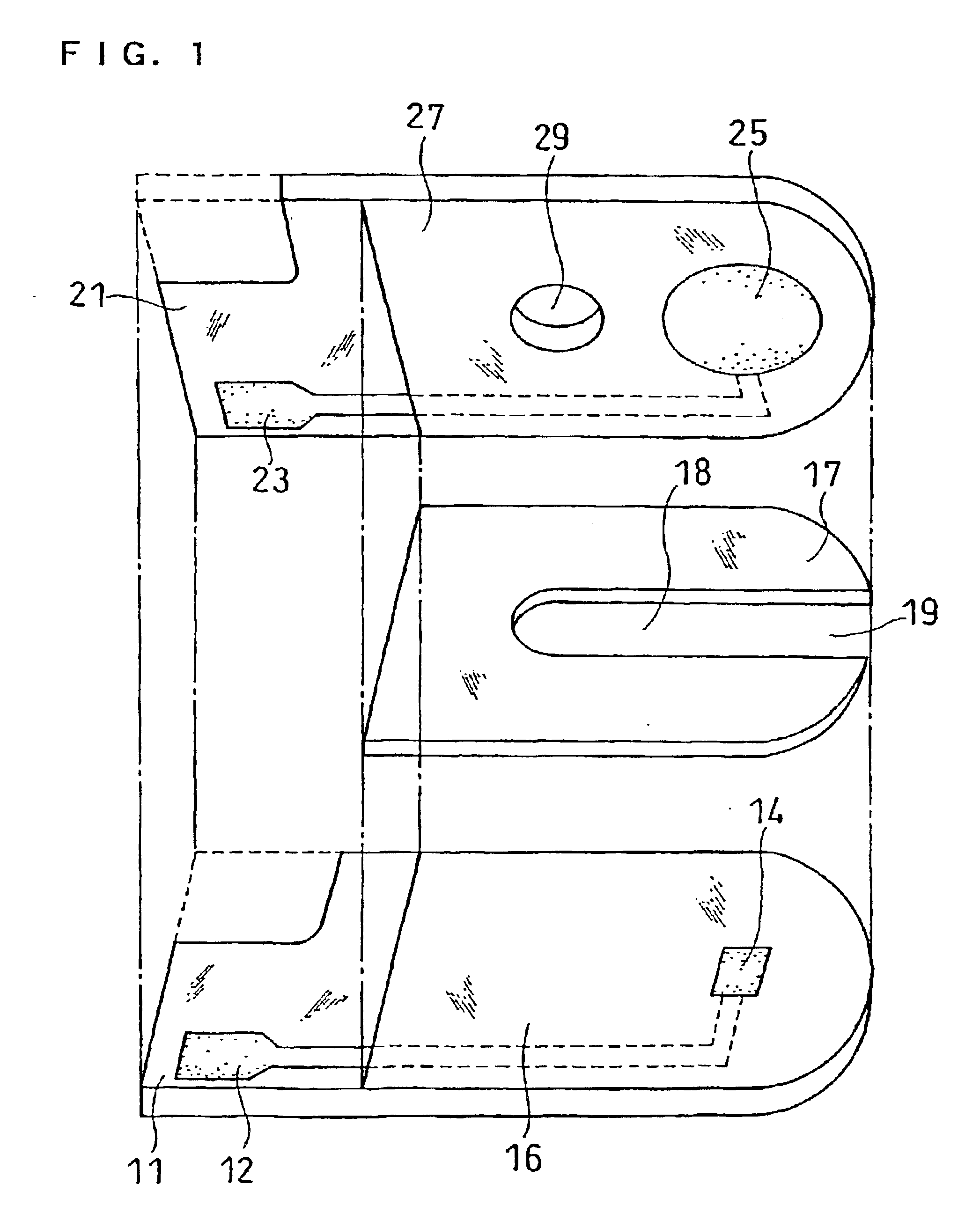
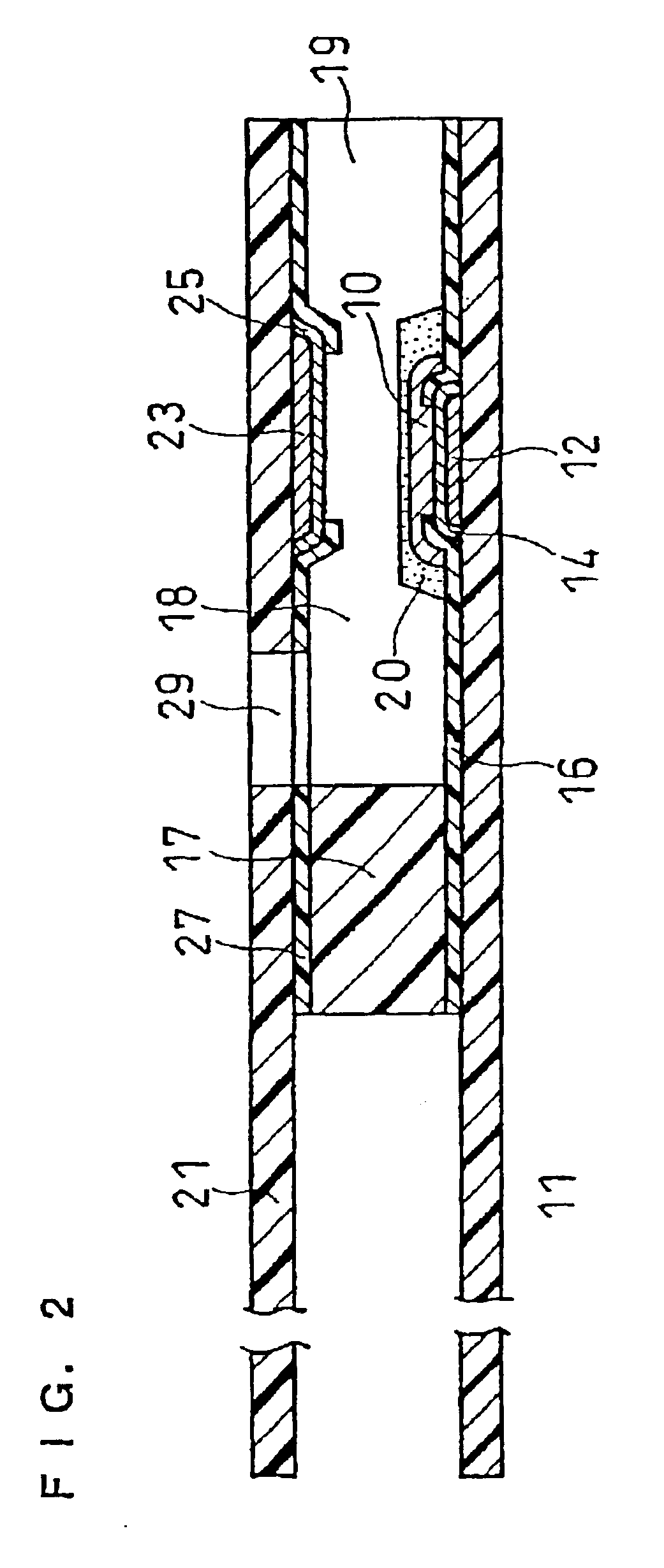
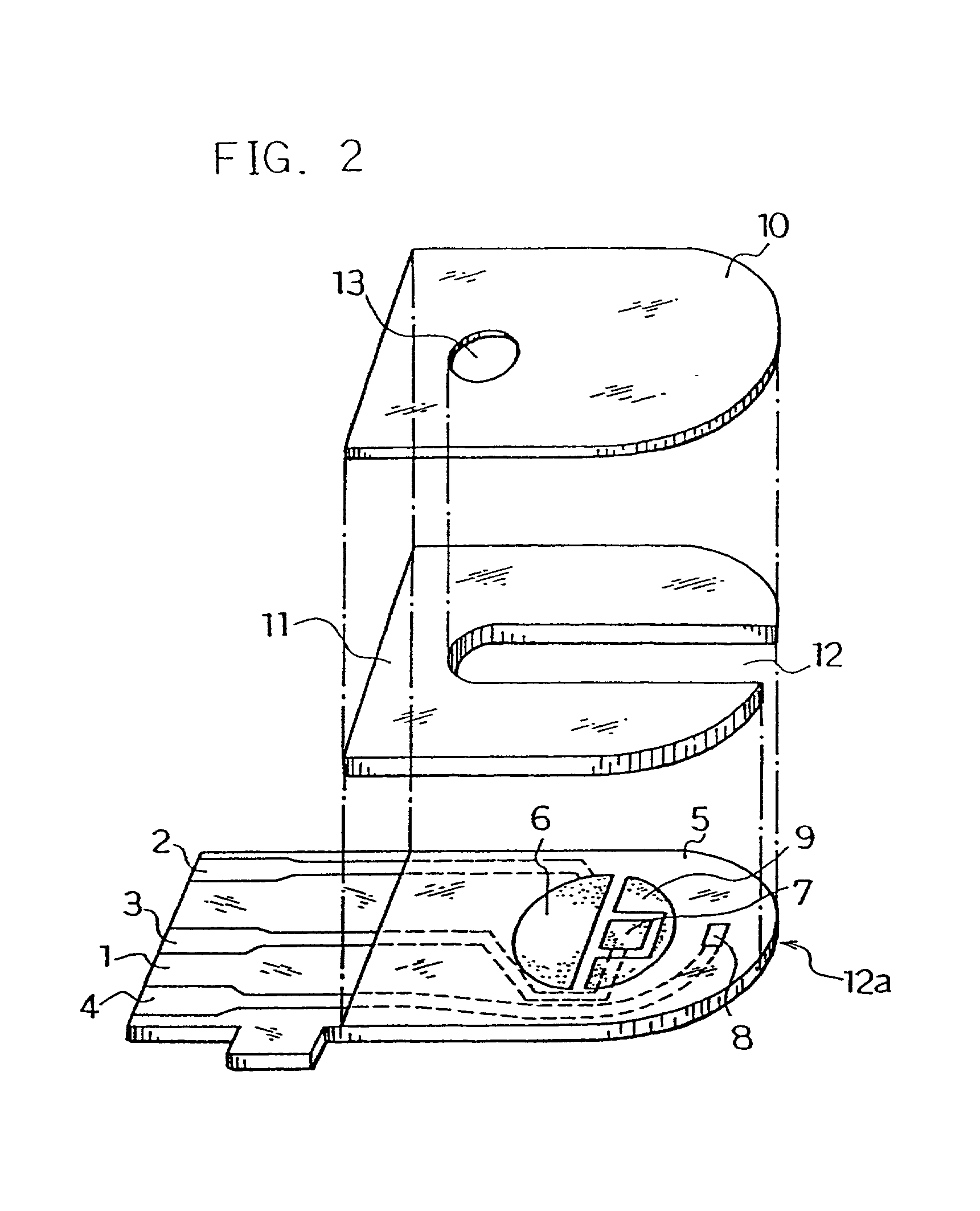
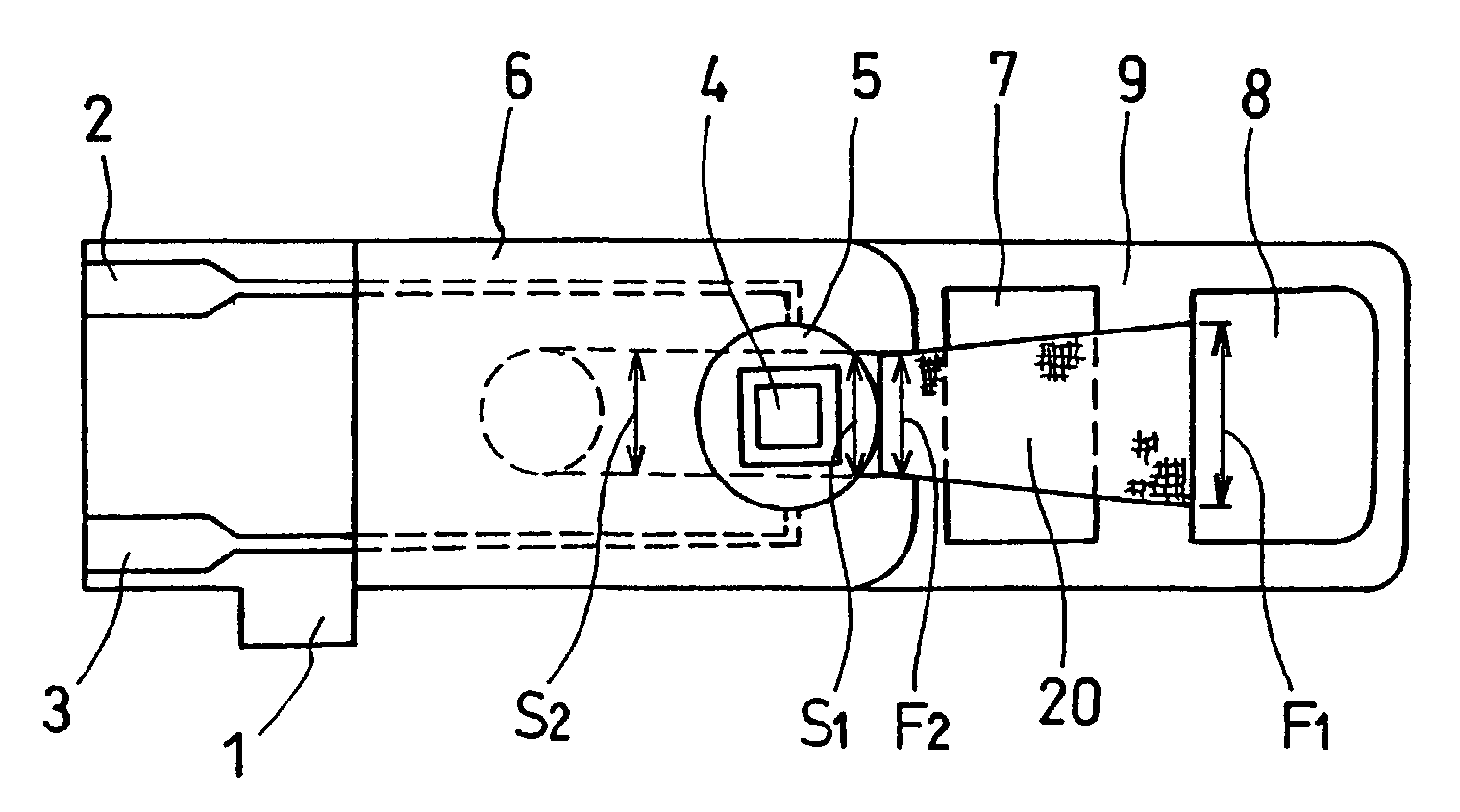
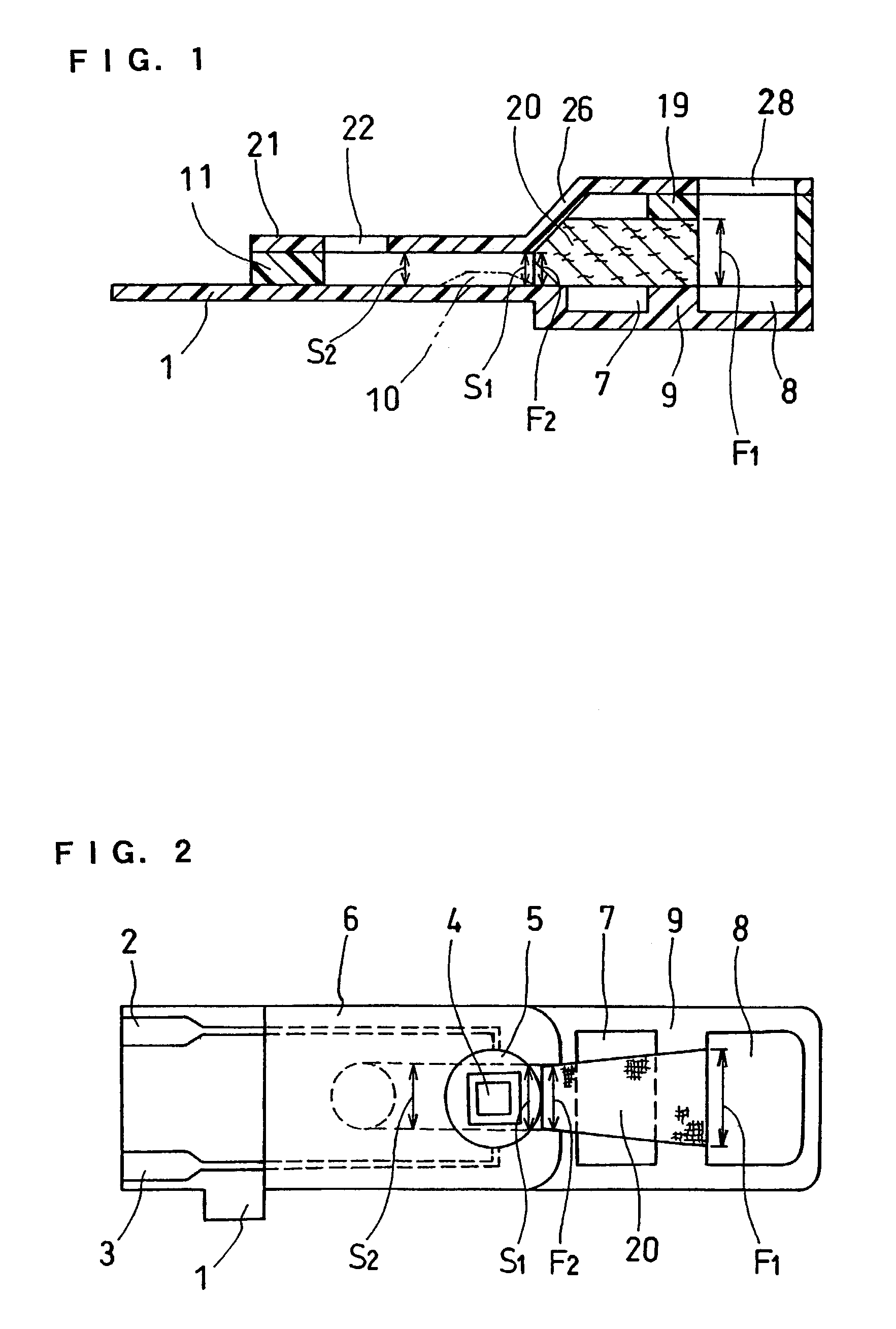
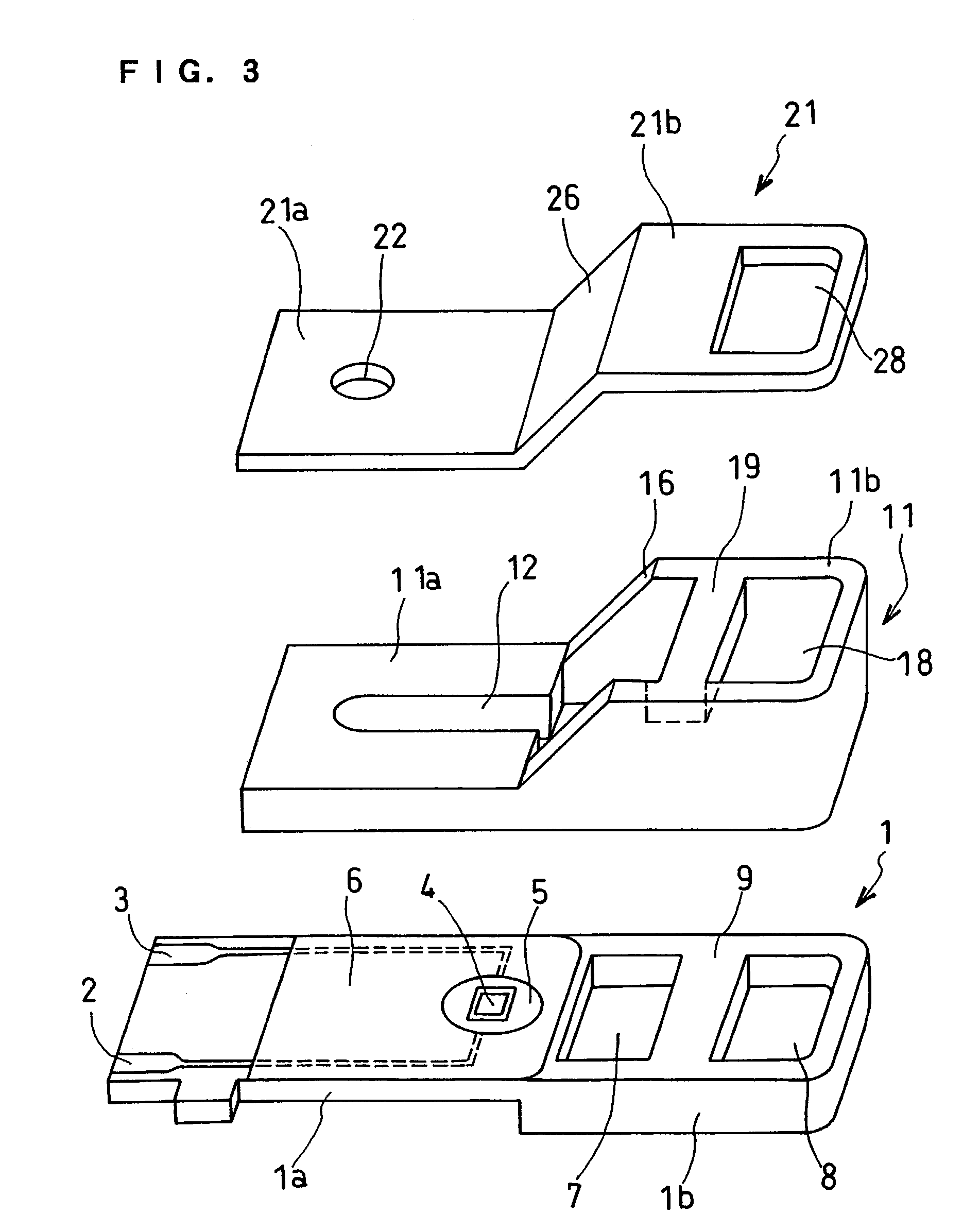
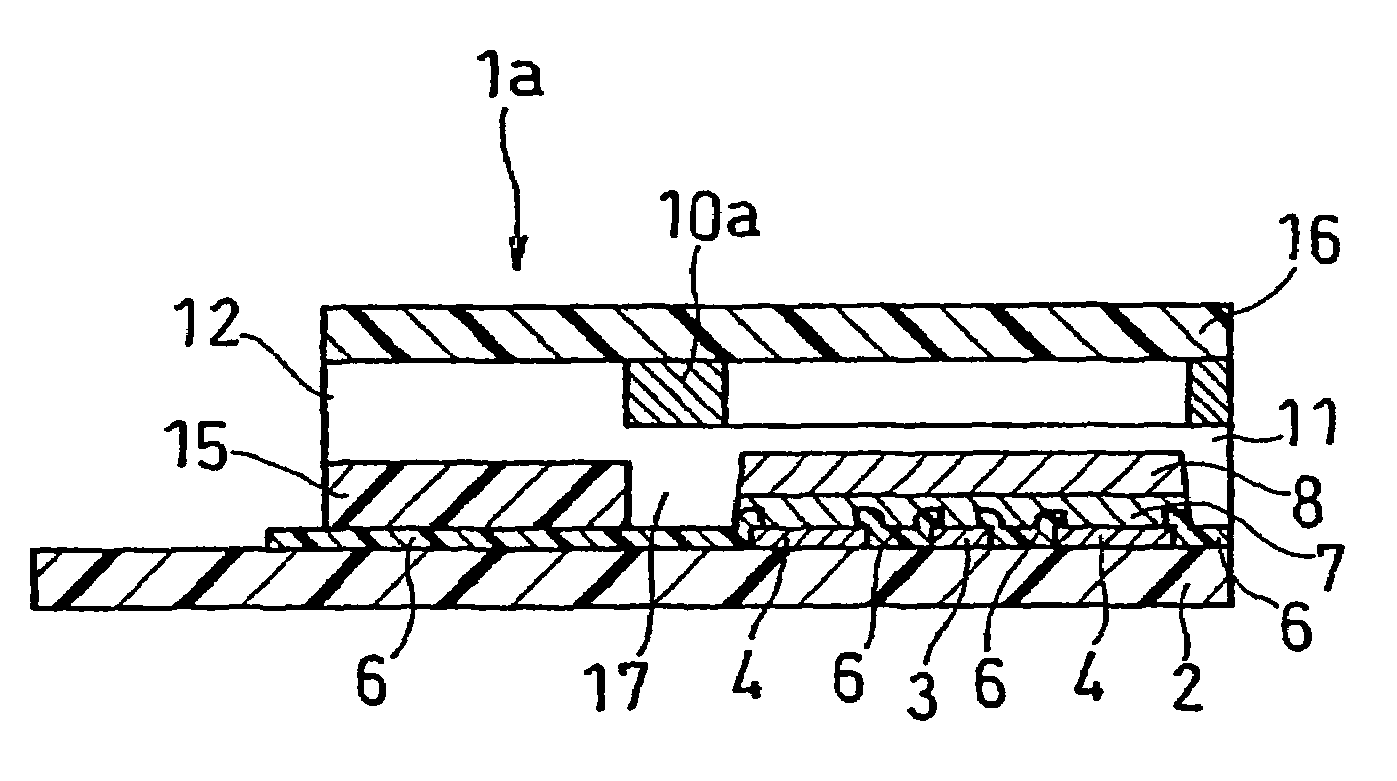
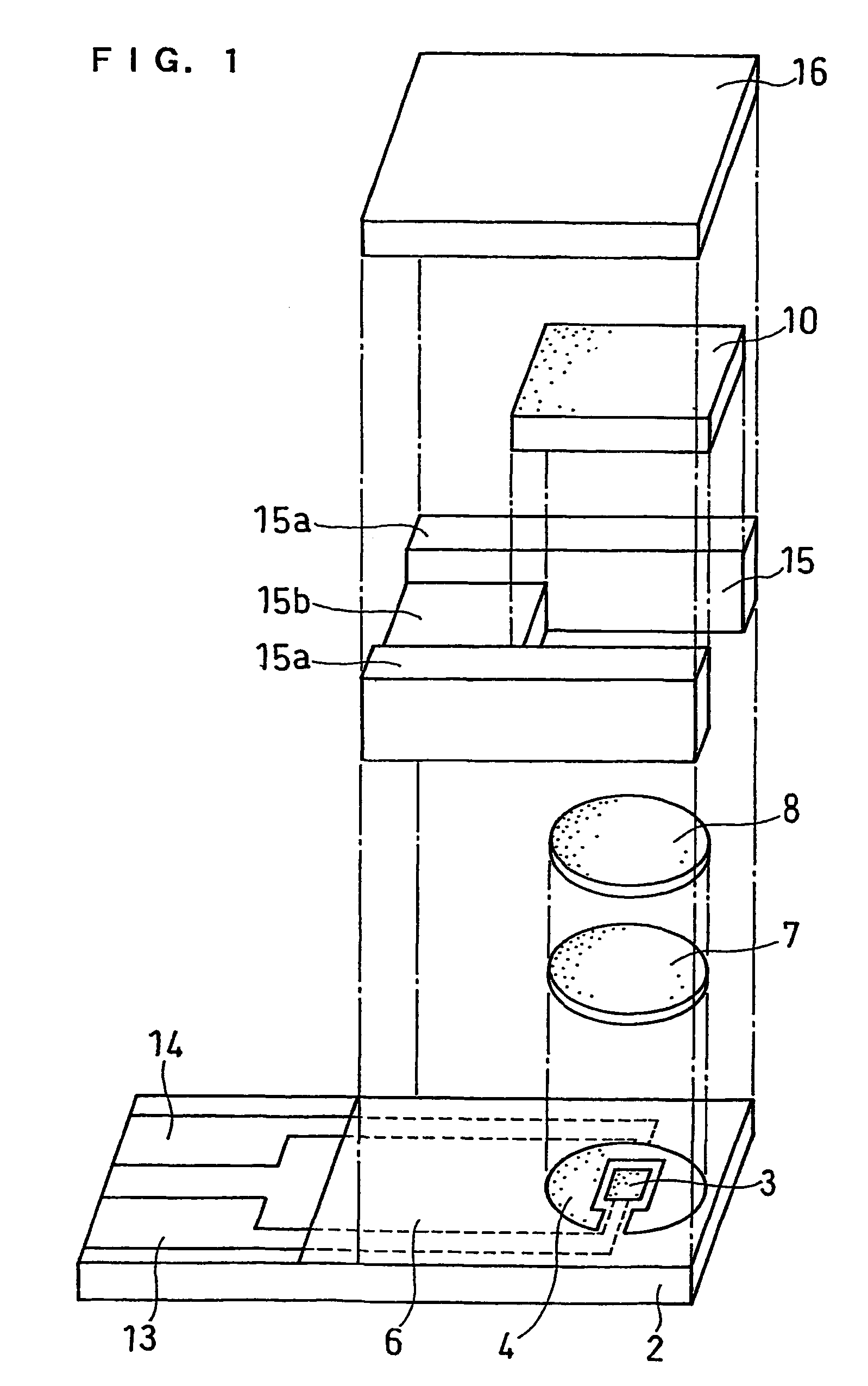
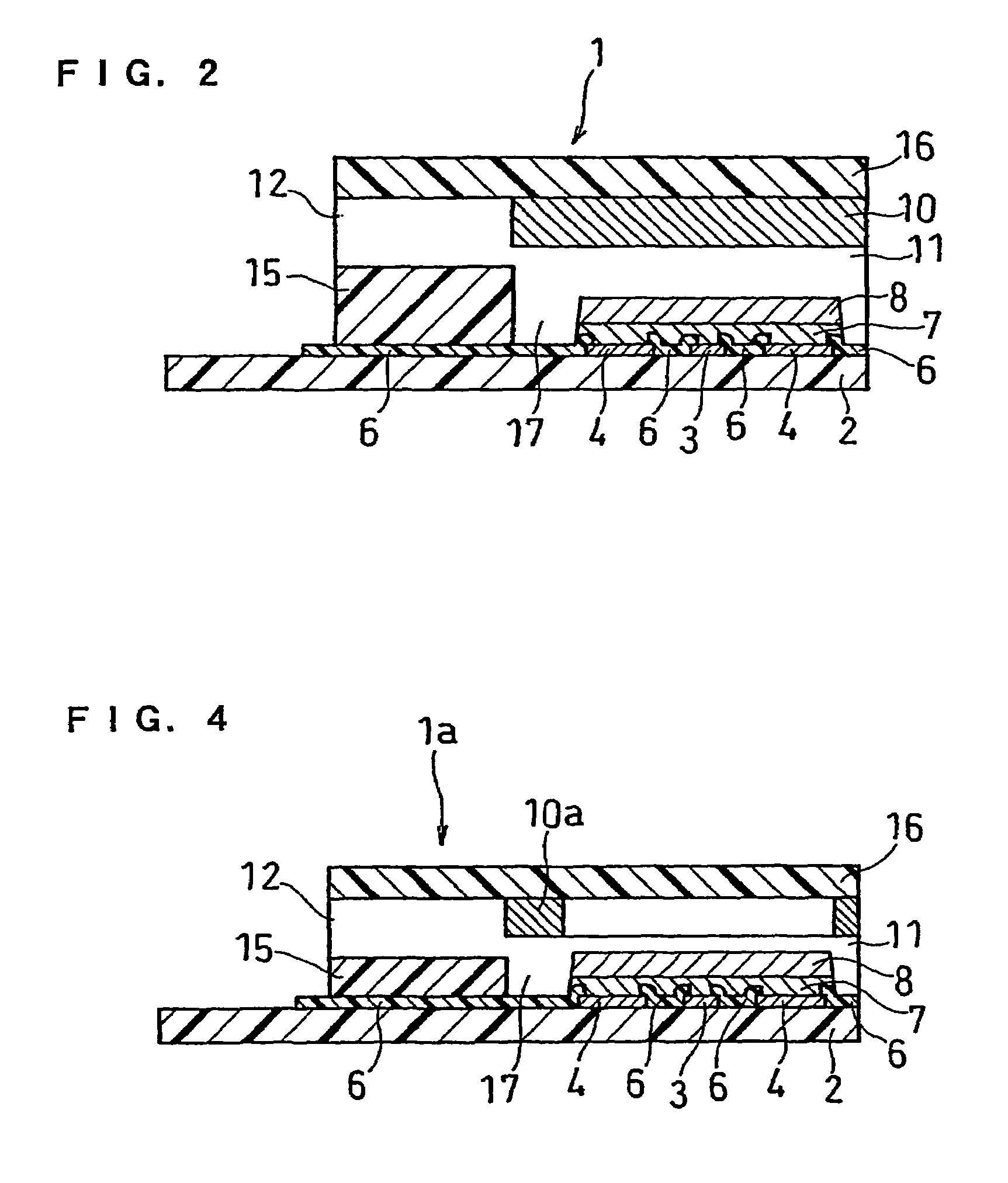
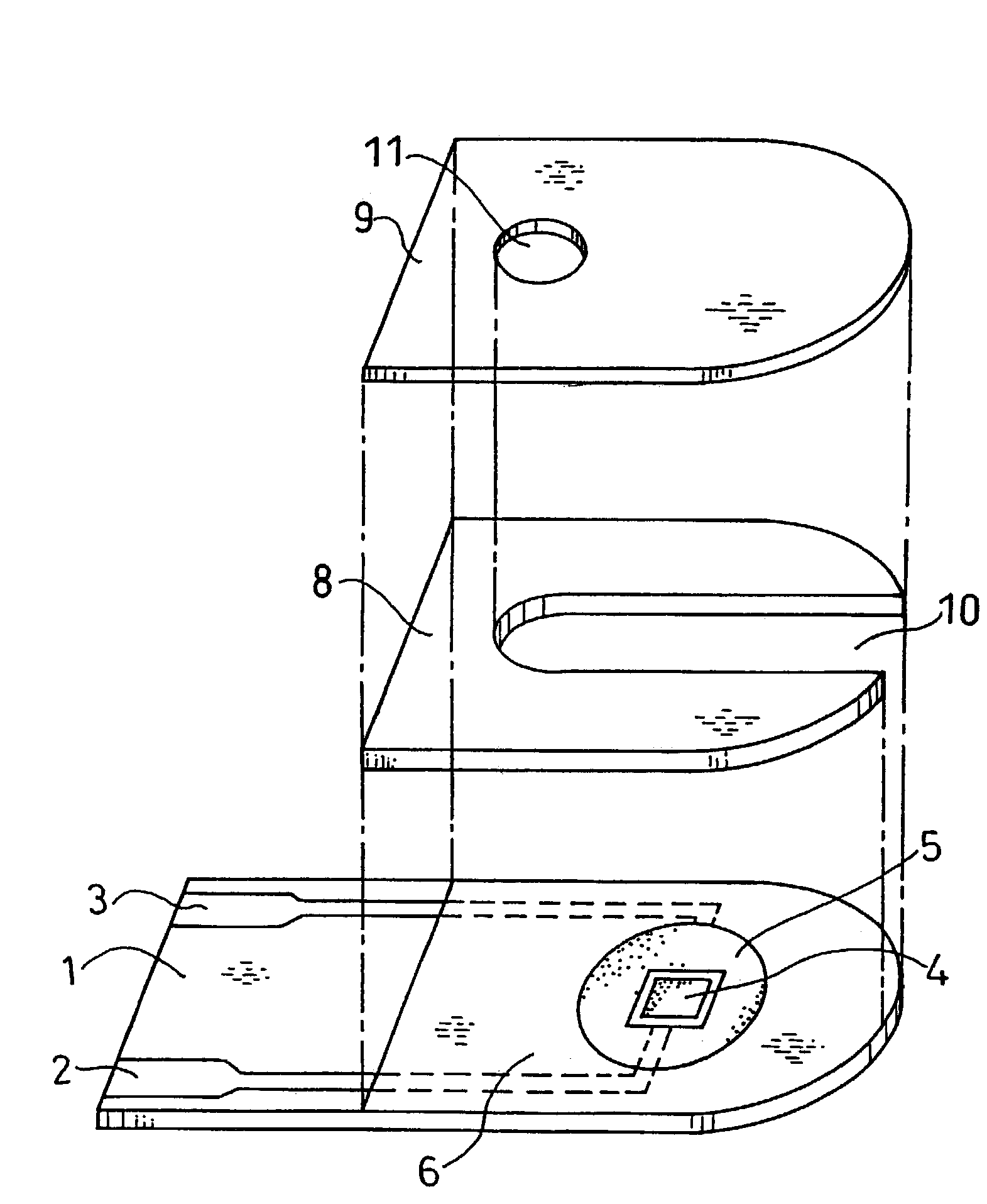
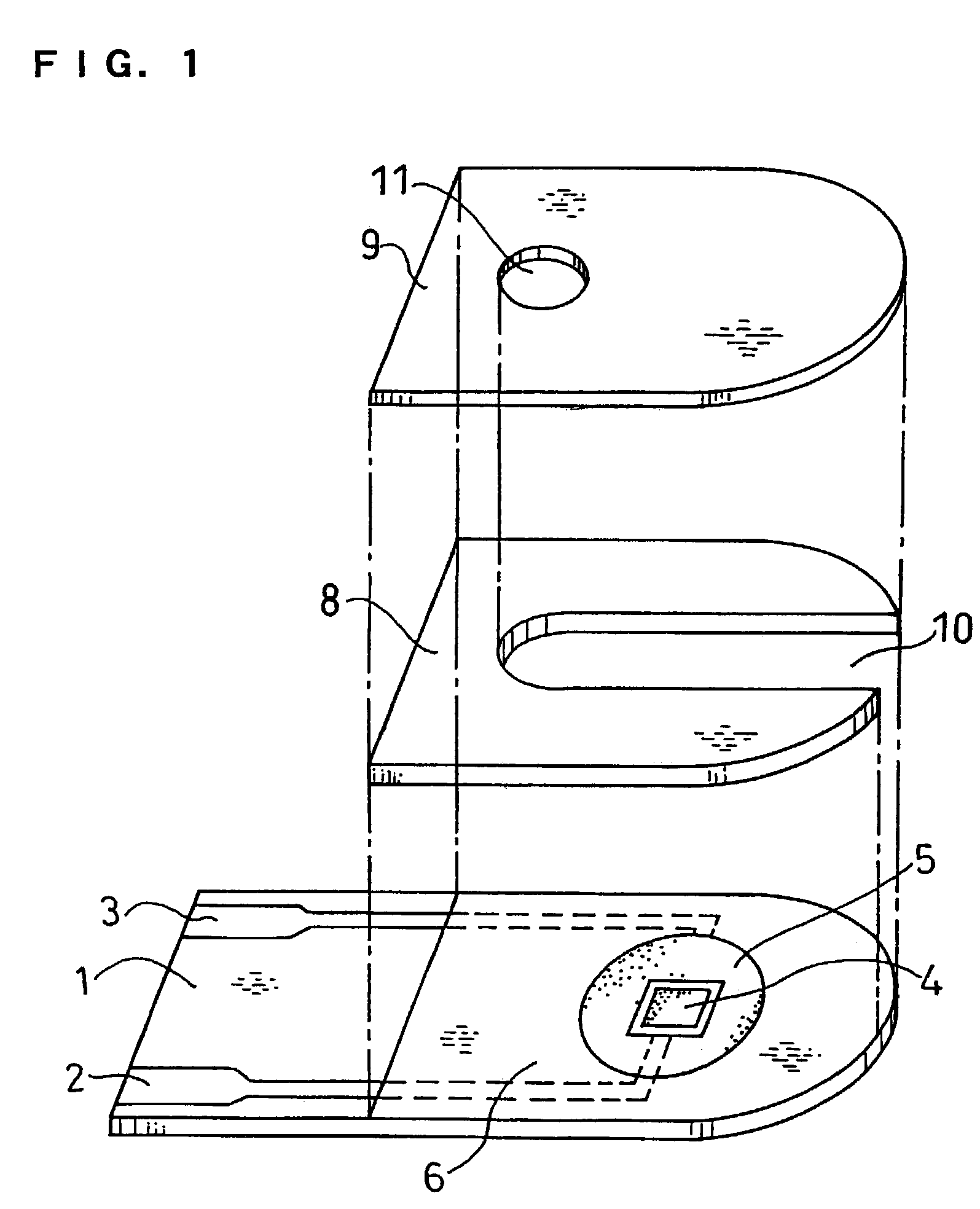
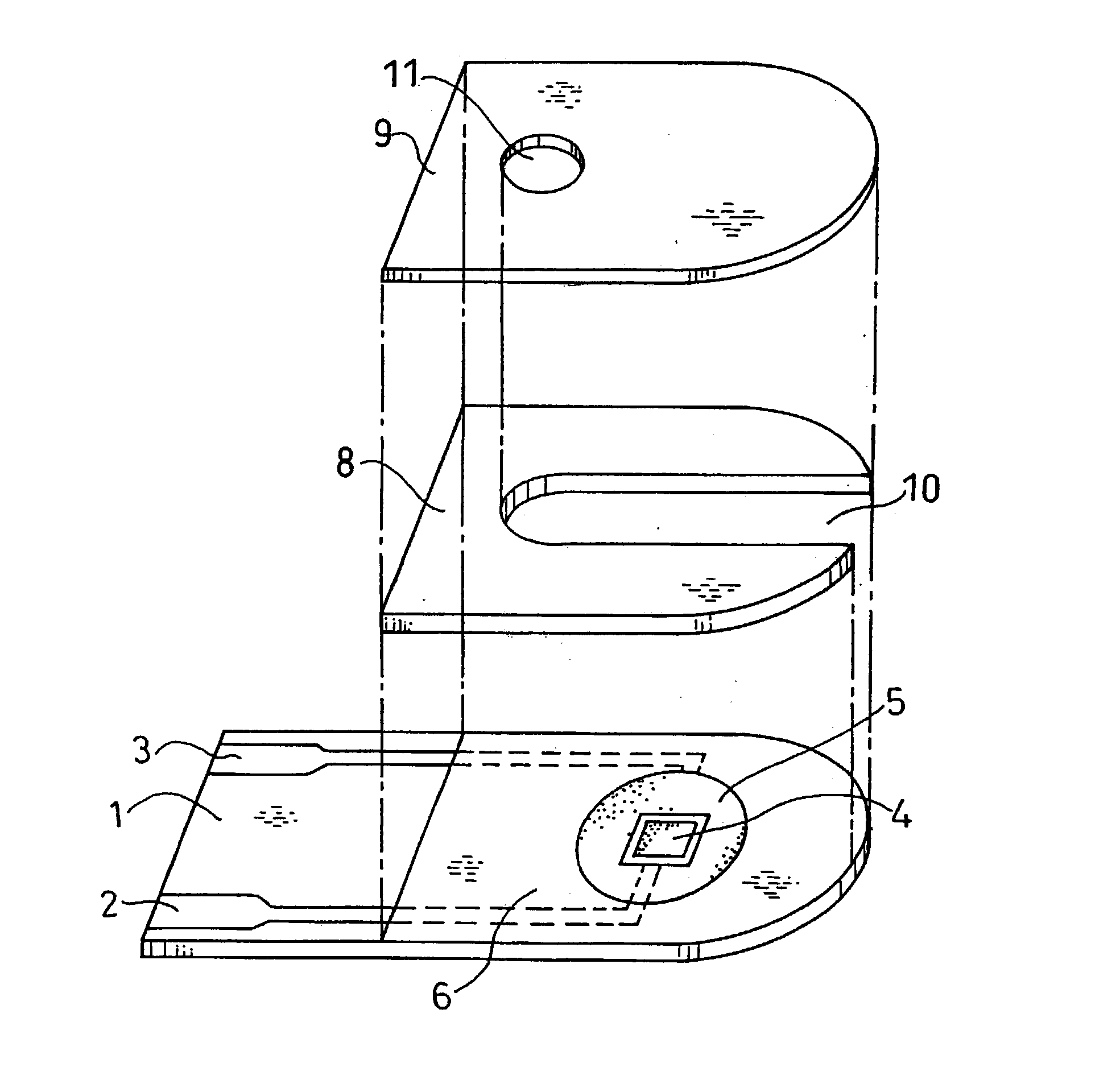
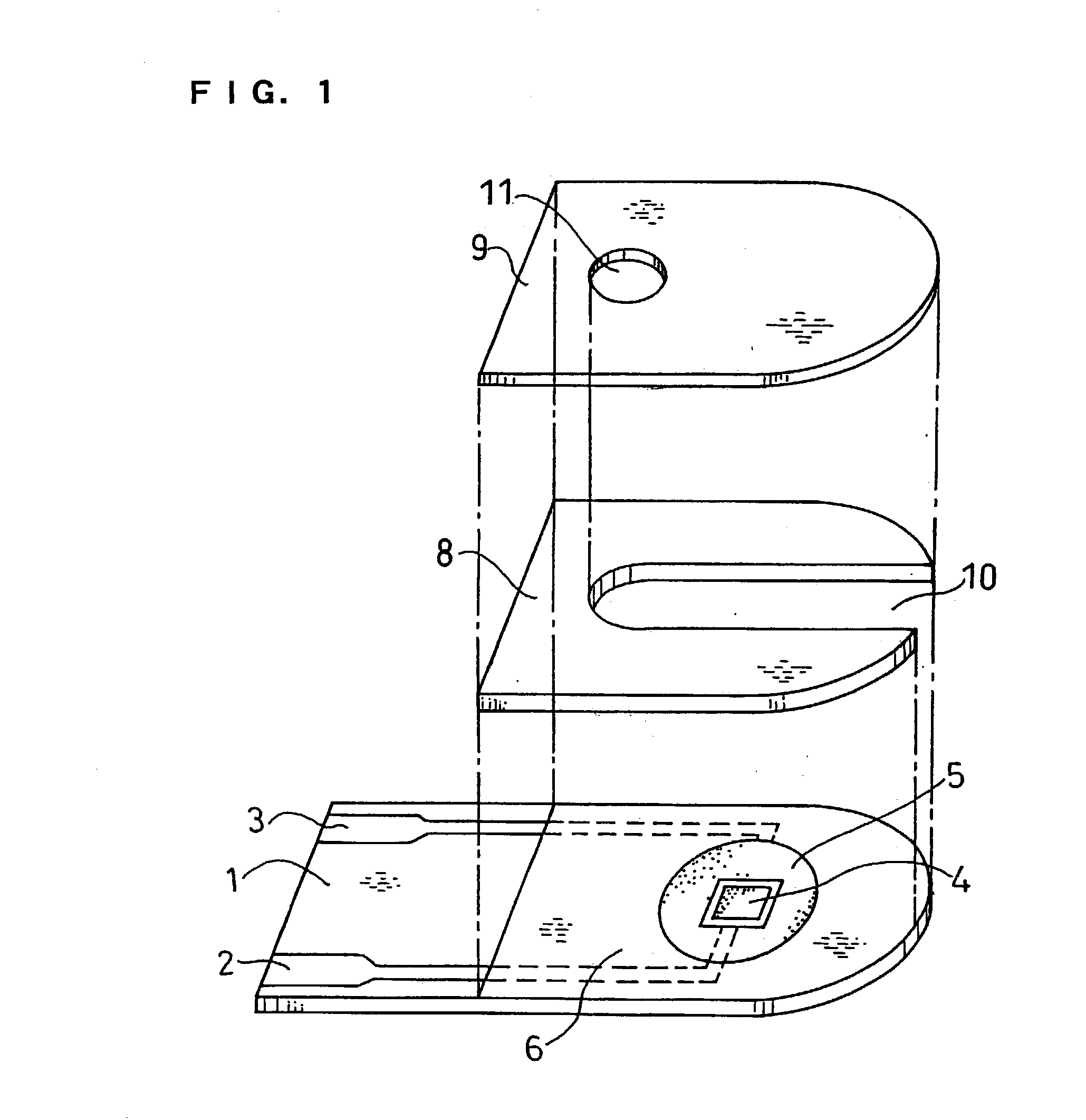
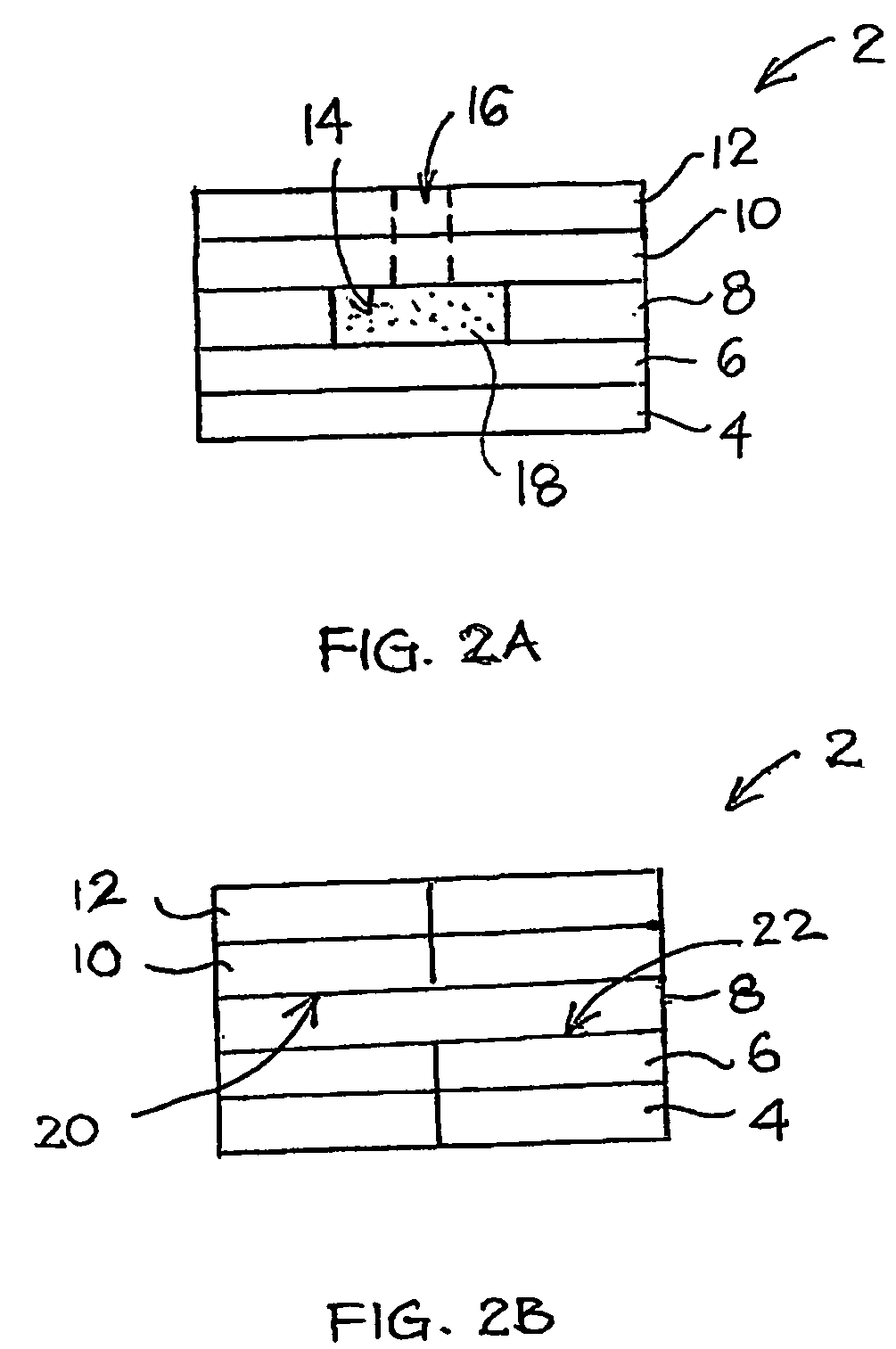
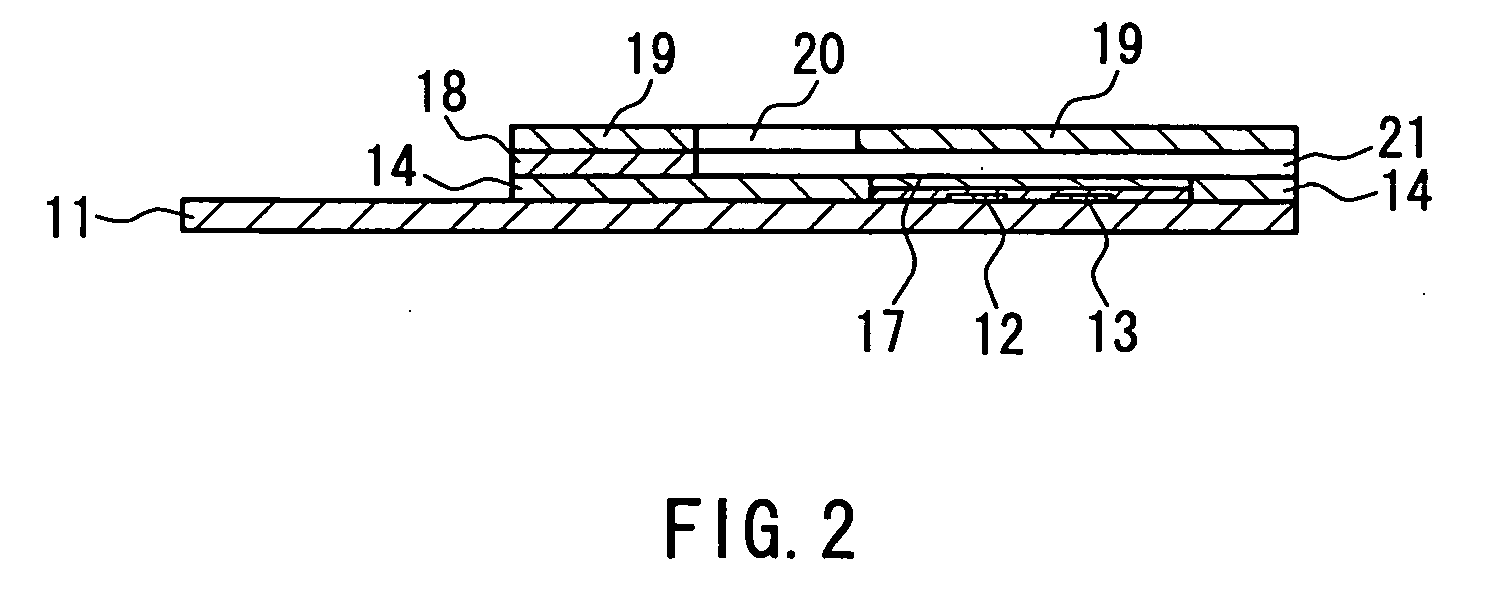
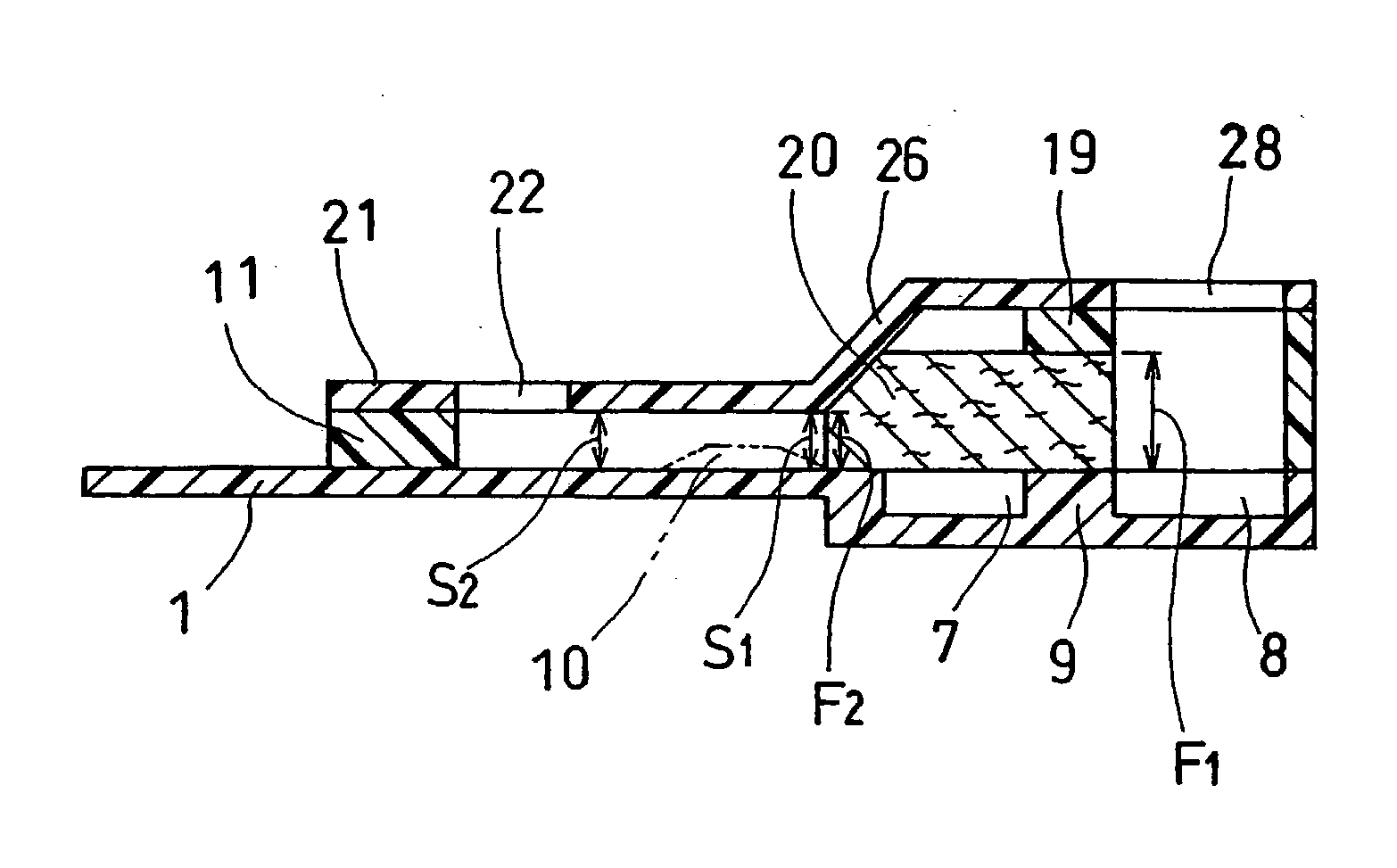
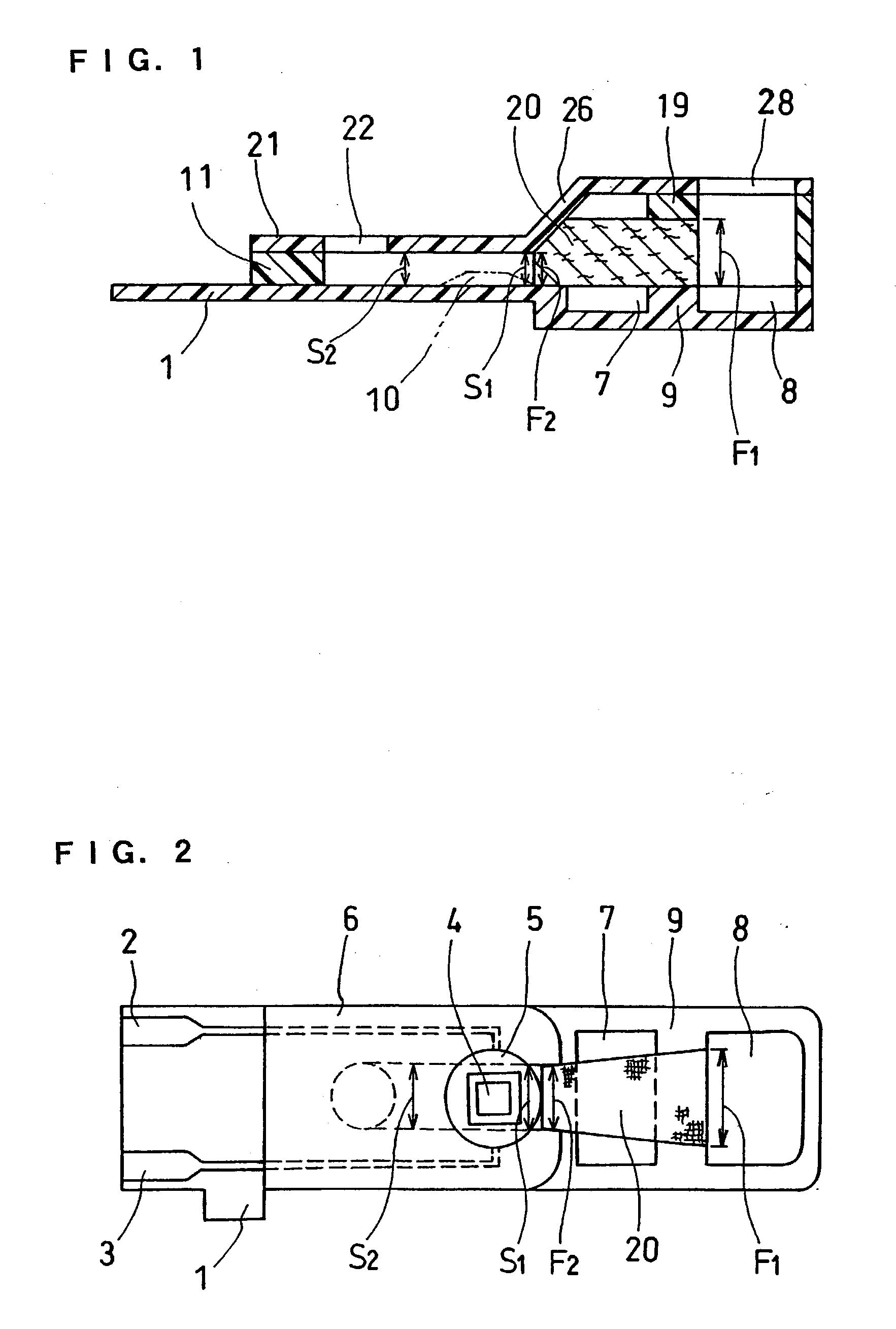
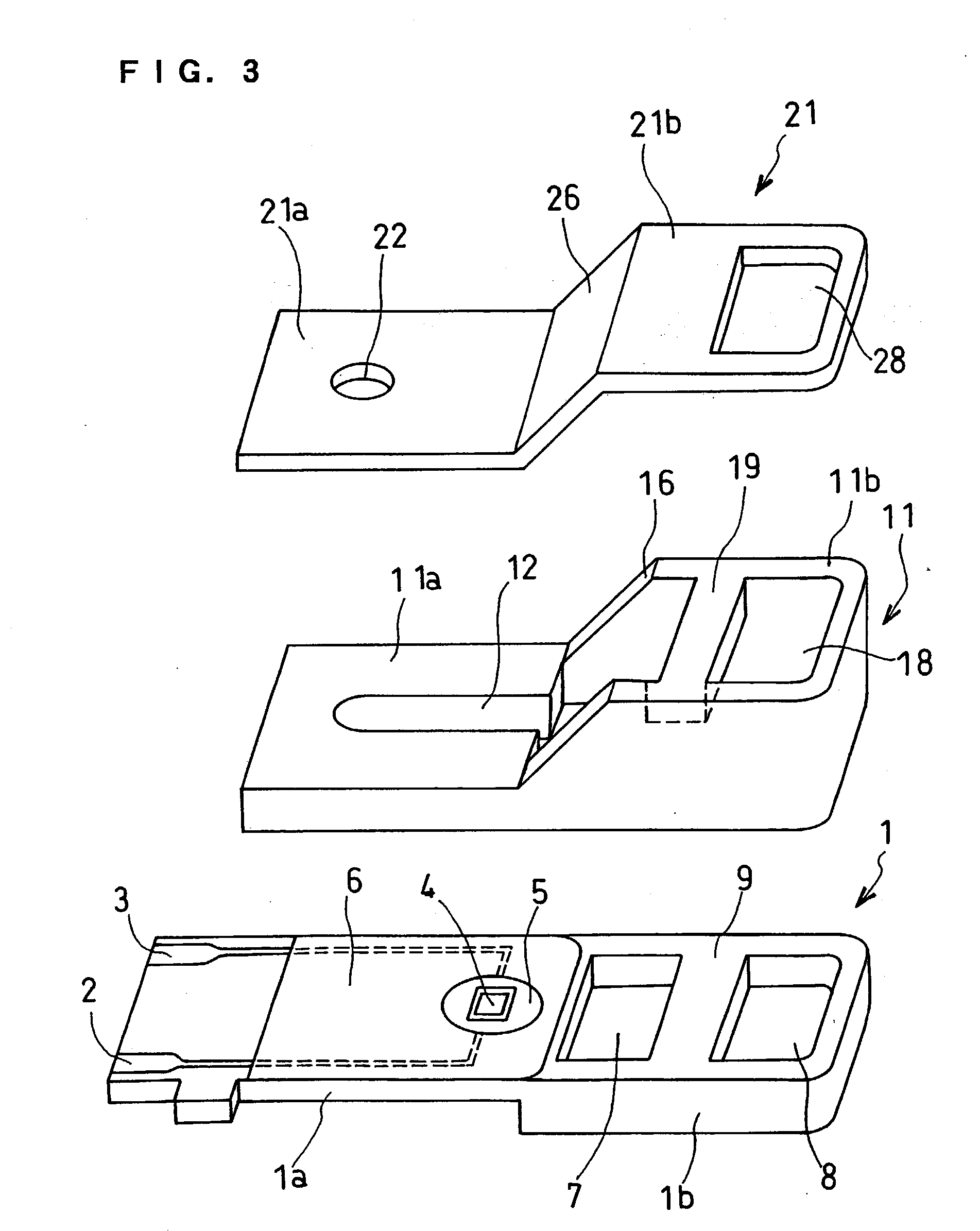
InactiveUS6740215B1Large responseImprove accuracyImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHydrophilic polymersOxidoreductase
A biosensor comprising an electrically insulating base plate, an electrode system containing a working electrode and a counter electrode disposed on the base plate, and a reagent system comprising at least an oxidoreductase, a hydrophilic polymer and an electron mediator, wherein the reagent system further comprises a substance having a function to convert an organic product generated by direct reaction of a substrate to be measured with the oxidoreductase to another compound.
Owner:PANASONIC HEALTHCARE HLDG CO LTD
Biosensor
InactiveUS6885196B2Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsOptoelectronicsOxidoreductase
Owner:PHC HLDG CORP
Device and method for determining the concentration of a substrate
InactiveUS20020043471A1Error in measurement resultExclude influenceImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsReaction layerElectricity
A method for determining the concentration of a substrate in a sample solution using an electrode system comprising a working electrode and a counter electrode, both being formed on an electrically insulating base plate, and a reaction layer which contains at least an oxidoreductase and an electron mediator and is formed on the electrode system to electrochemically measure a reduced amount of the electron mediator resulting from enzyme reaction in the reaction layer, wherein a third electrode is formed as an interfering substance detecting electrode somewhere apart from the reaction layer to detect supply of the sample solution on the basis of an electrical change between the counter electrode and the third electrode. A current flowing between the counter electrode and the third electrode is measured which is taken as a positive error. Subsequently, voltage application between the counter electrode and the third electrode is released and a voltage for oxidizing the reduced form electron mediator is applied between the working electrode and the counter electrode to measure a current flowing between the two electrodes. Influences of any interfering substance such as easy-to-oxidize substance are reduced, whereby a highly reliable value of substrate determination can be obtained.
Owner:PHC HLDG CORP
Method of measuring blood component, sensor used in the method, and measuring device
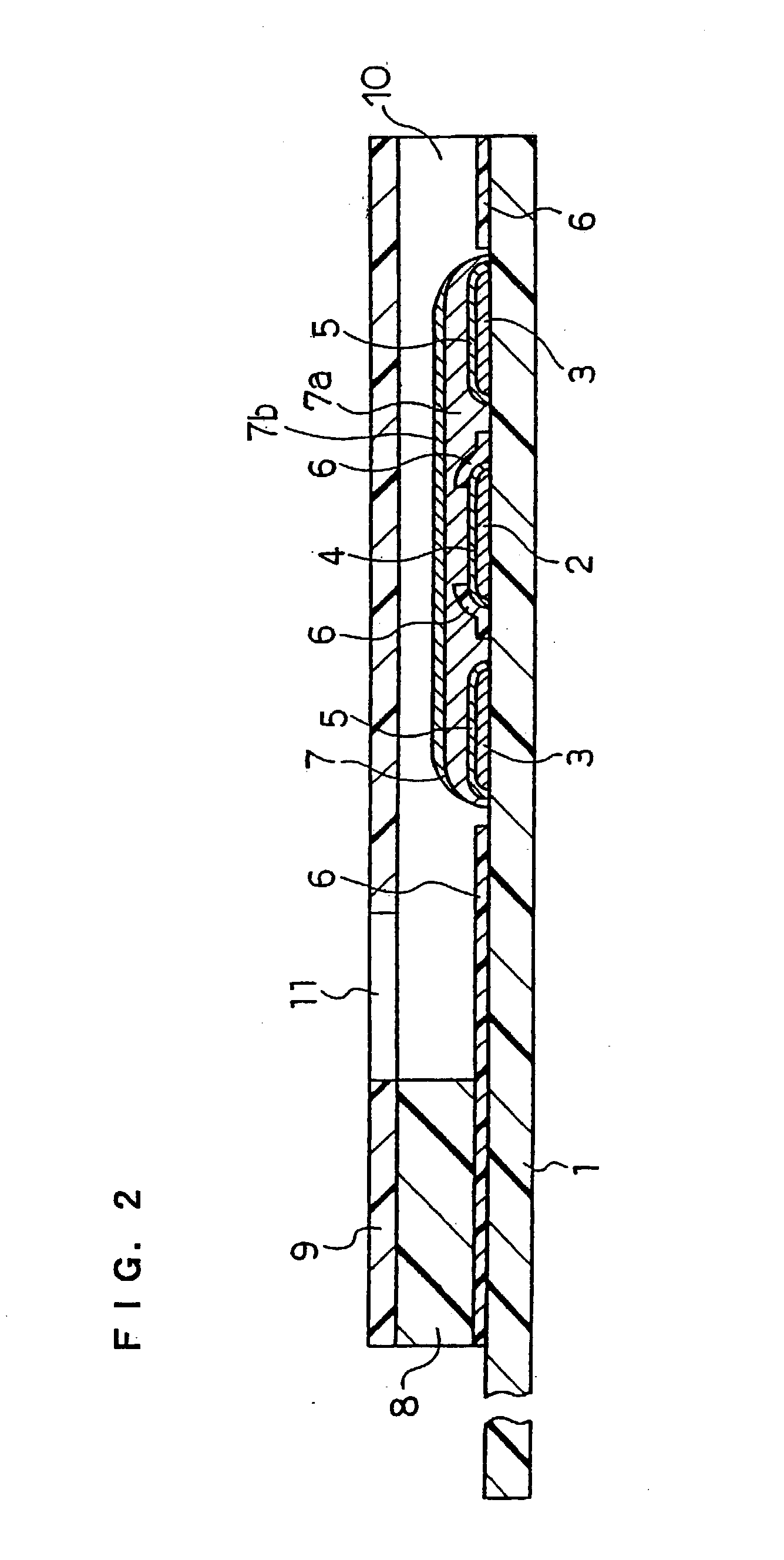
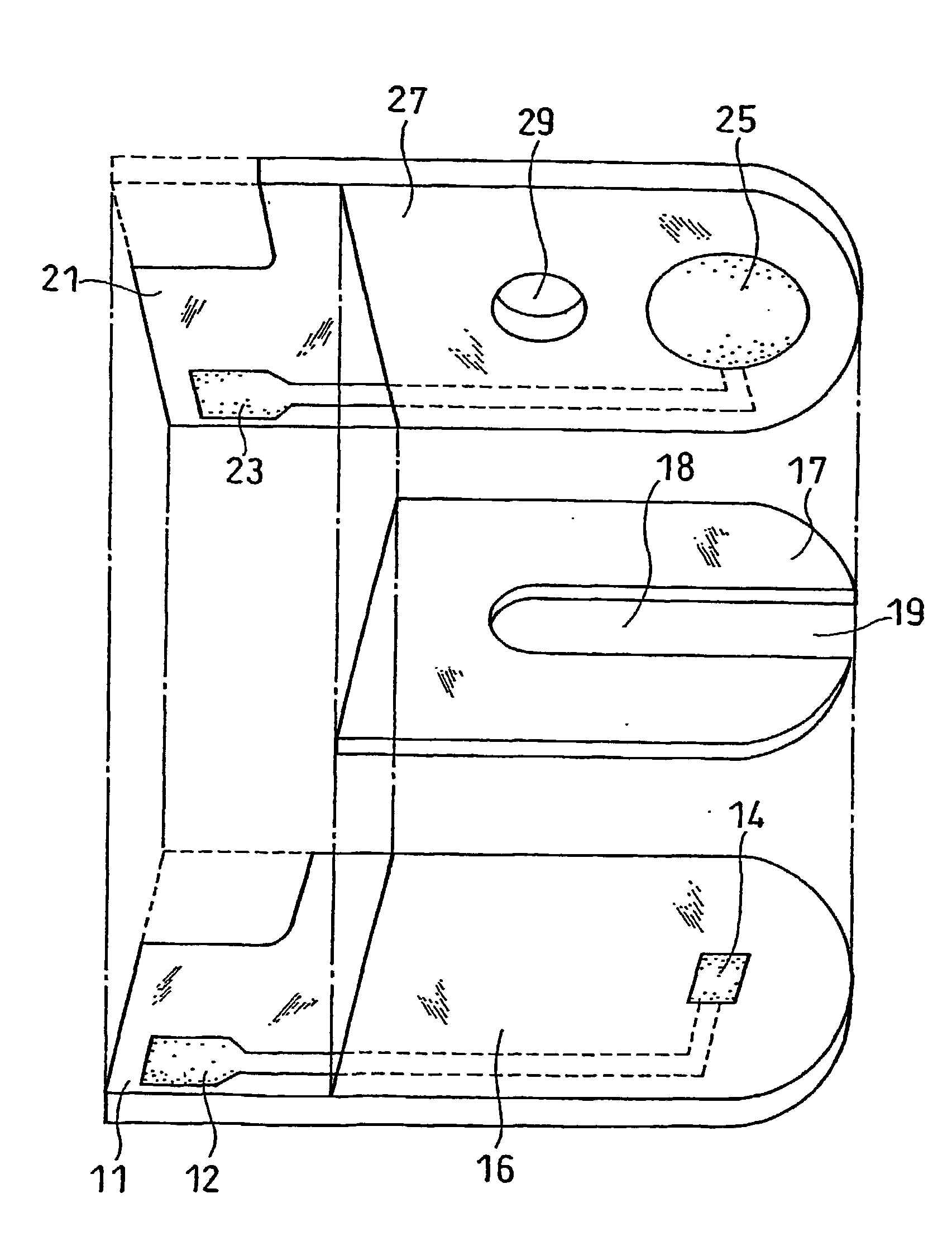
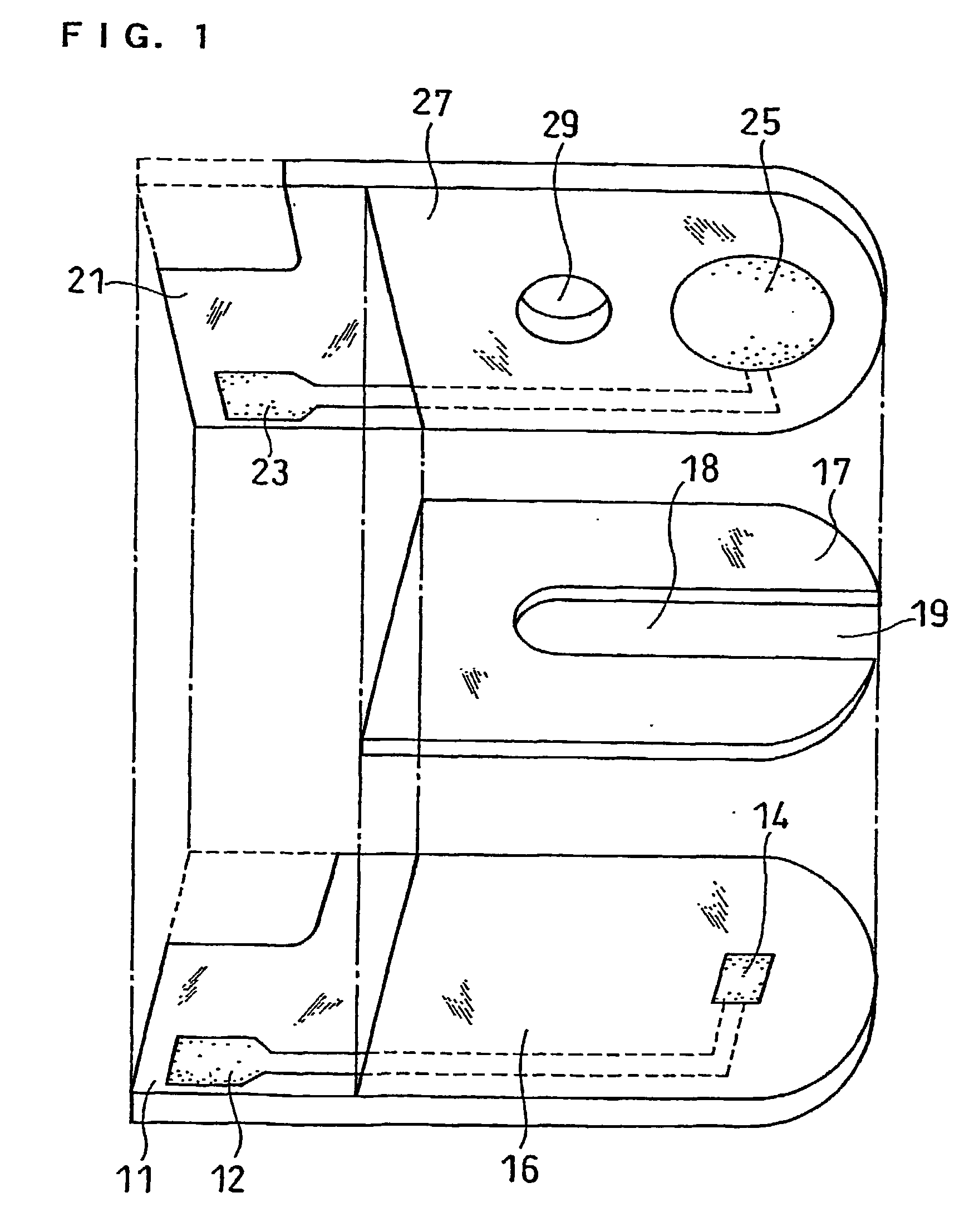
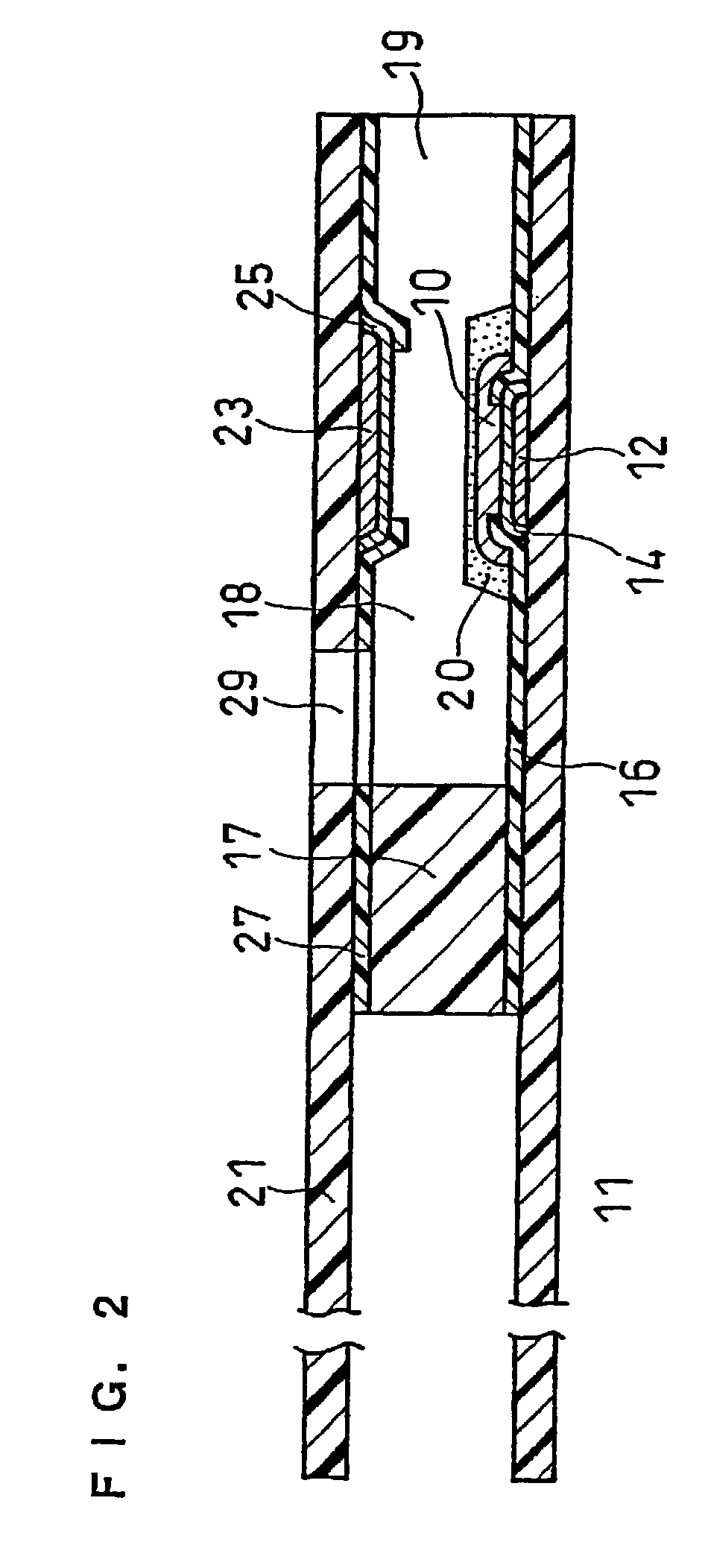
ActiveUS20070131565A1Easy to measureImprove accuracyImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsOxidoreductasePhysics
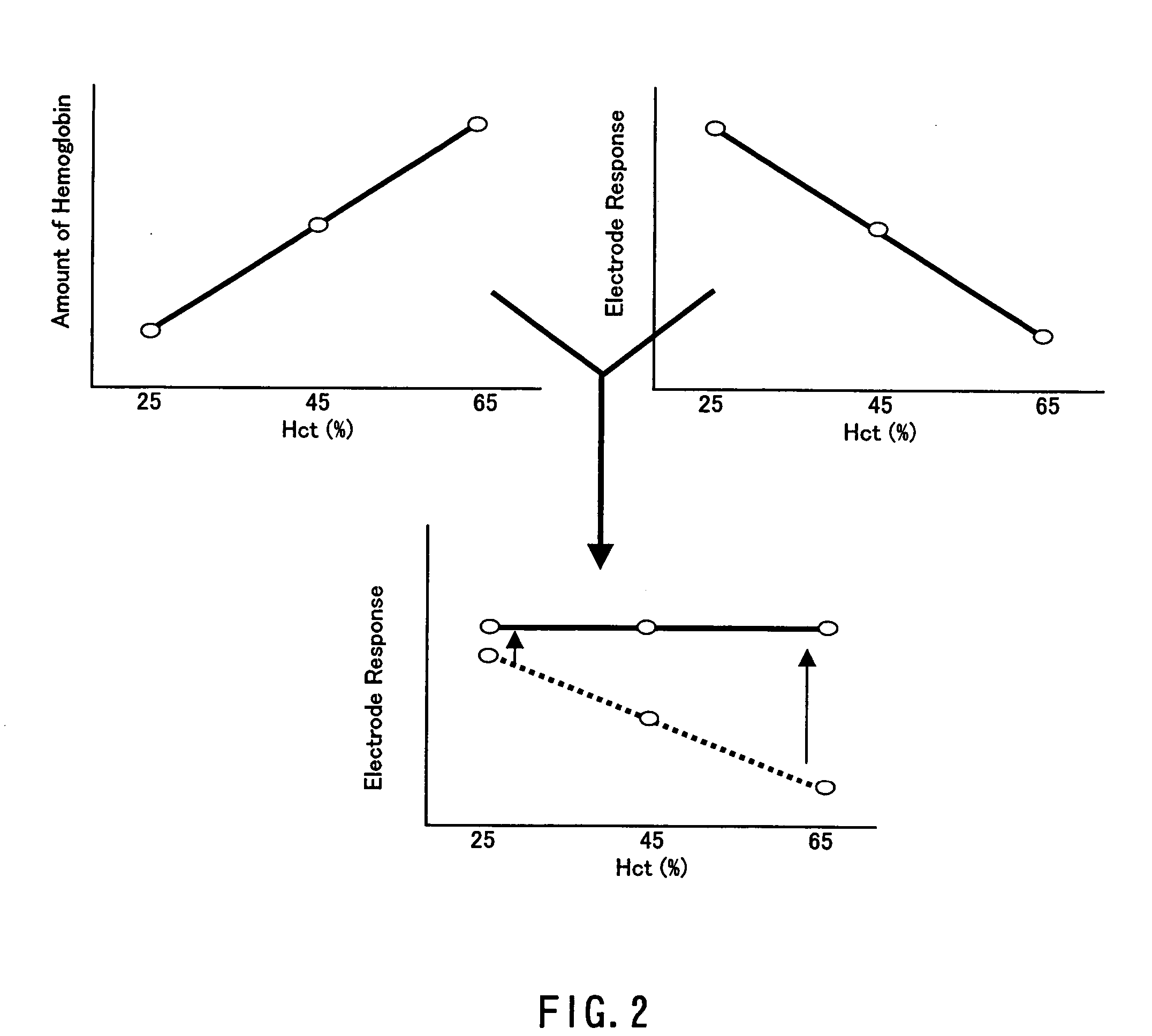
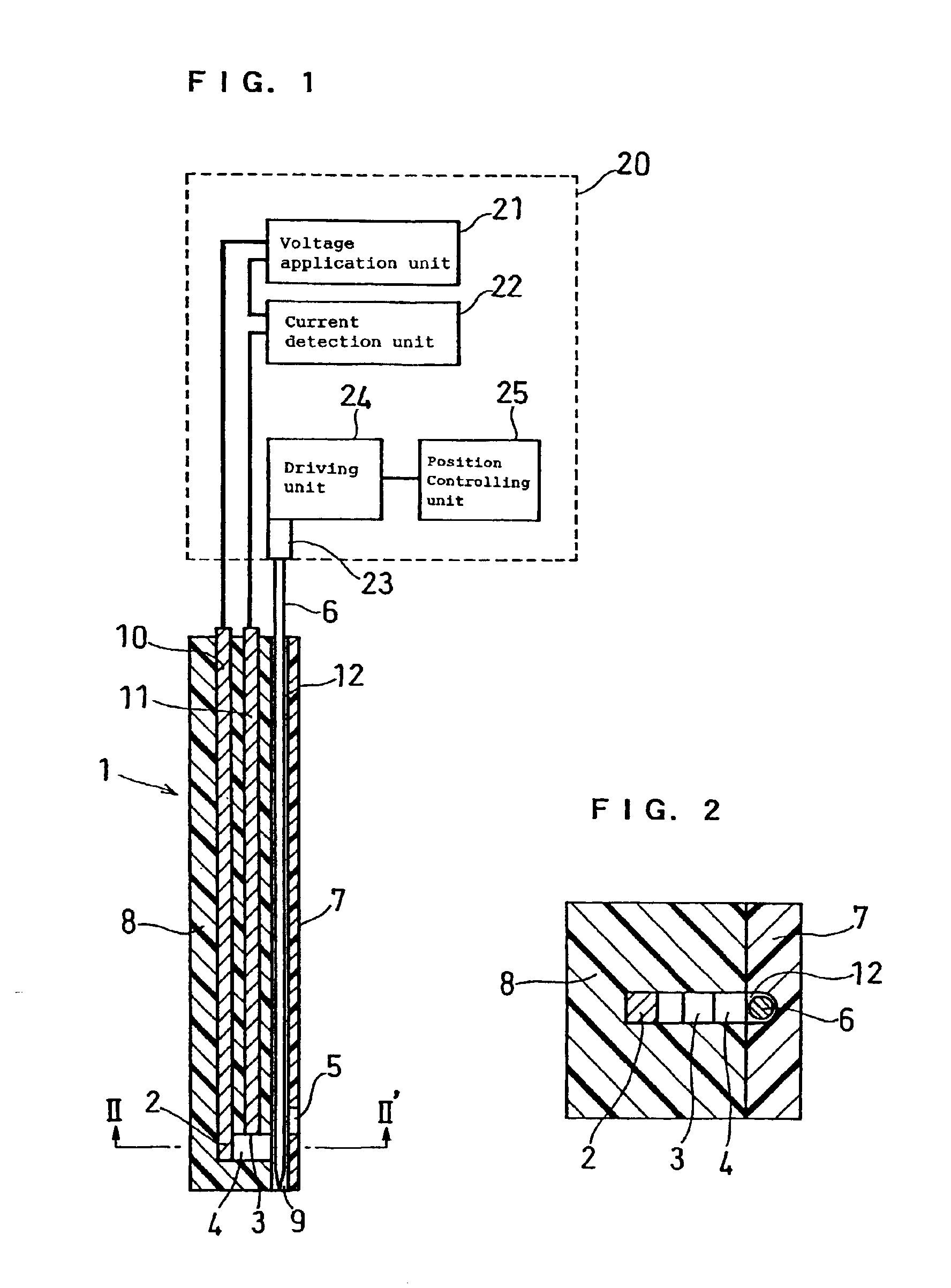
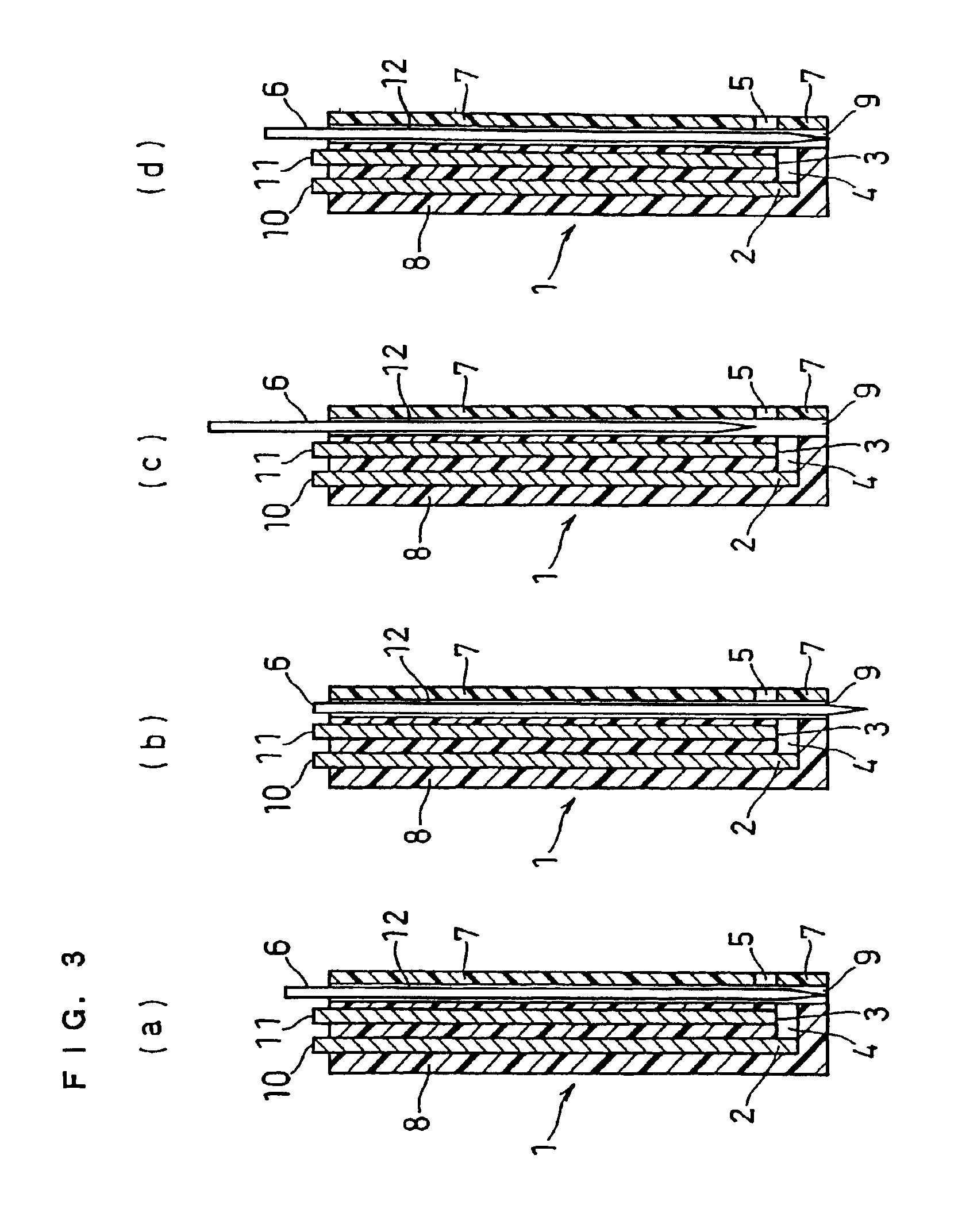
The present invention provides a method of measuring a component in blood, by which an amount of the component can be corrected accurately by measuring a hematocrit (Hct) value of the blood with high accuracy and high reliability and also provides a sensor used in the method. The sensor for measuring a component in blood has a first analysis portion and a second analysis portion. The first analysis portion has a first electrode system (11,12) and a reagent layer (14), and the reagent layer (14) has an oxidoreductase that acts on the component and a mediator. In the first analysis portion, the component in the blood is measured by causing a redox reaction of the component with the oxidoreductase in the presence of the mediator and detecting a redox current caused when a voltage is applied by the first electrode (11,12). The second analysis portion has a working electrode and a counter electrode, and a mediator is provided on the counter electrode but not on the working electrode. In the second analysis portion, a Hct value of the blood is measured by supplying the blood to the electrode system, applying a voltage to cause a current to flow, and detecting a value of the current. Using this Hct value, the amount of the component is corrected.
Owner:PHC HLDG CORP
Biosensor with interdigitated electrodes
InactiveUS7022218B2Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsOxidoreductaseInterdigitated electrode
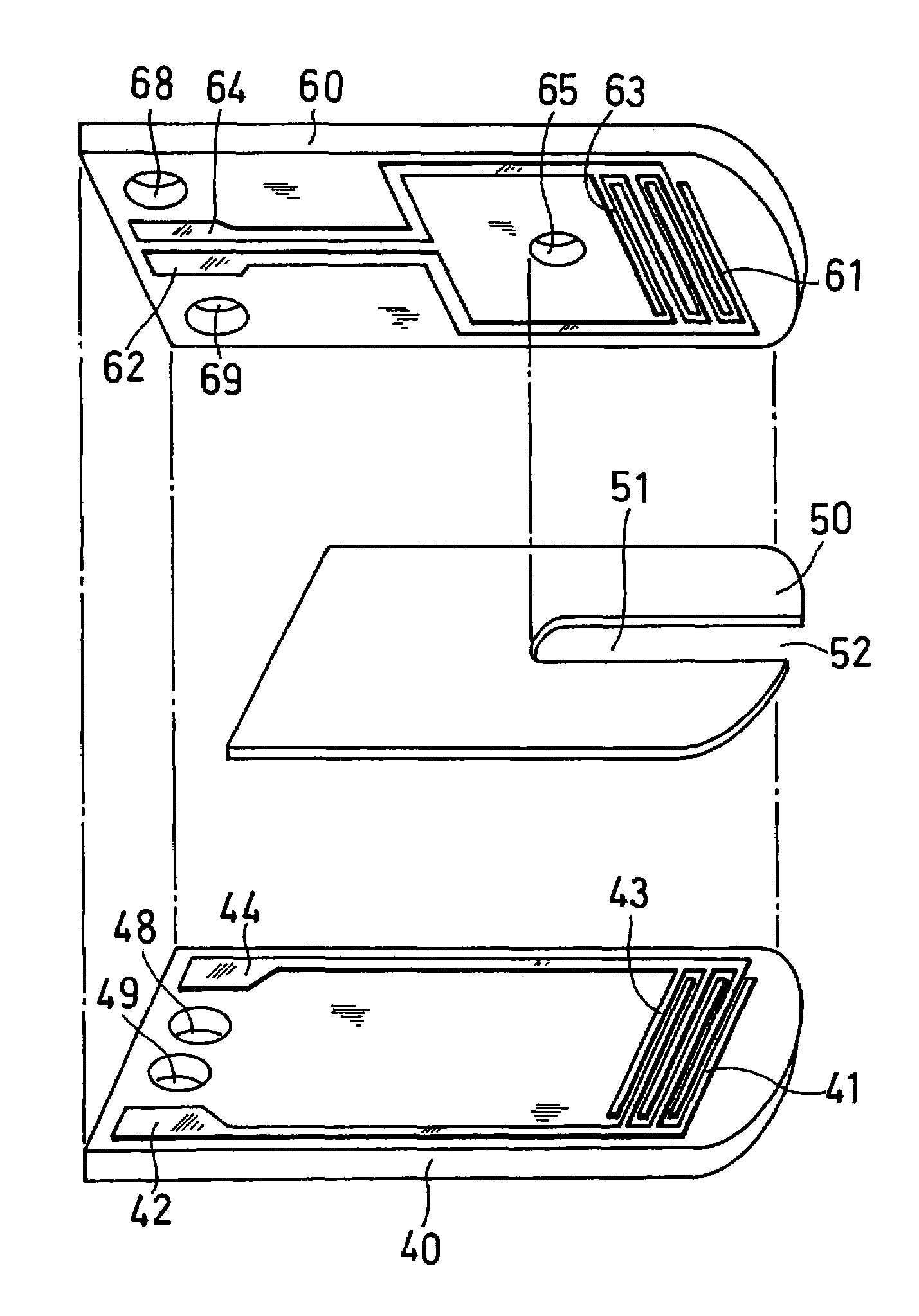
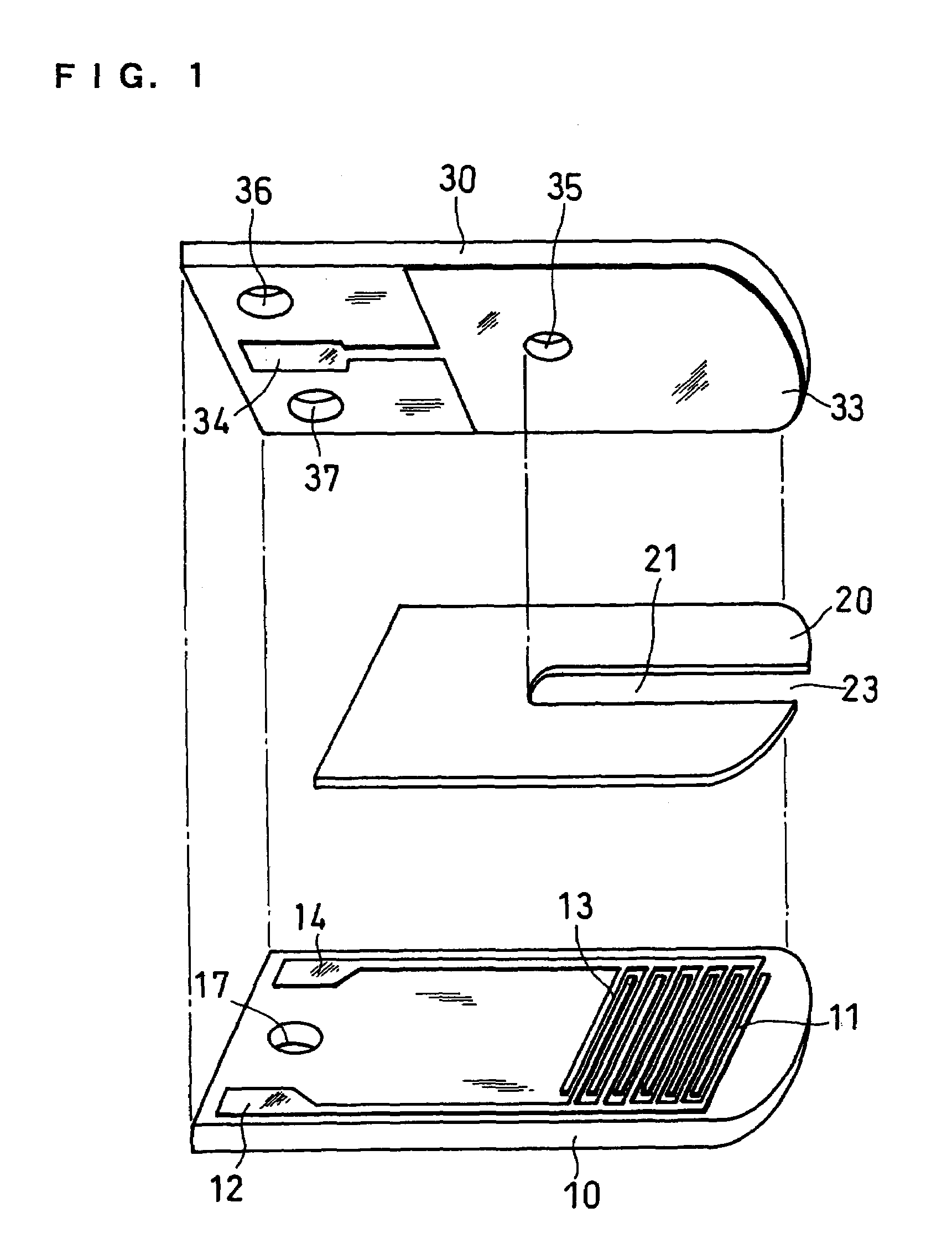
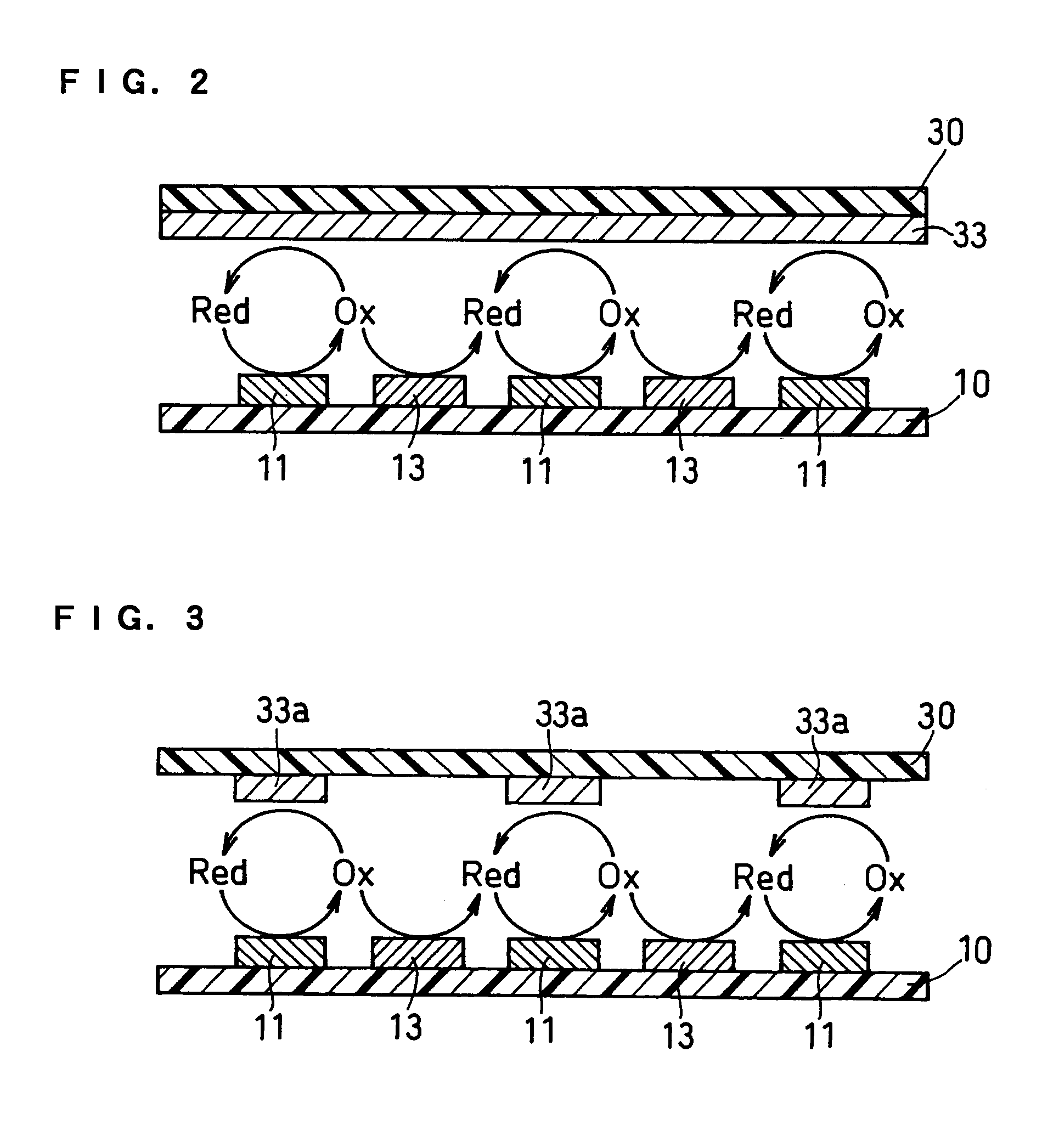
The present invention provides a highly sensitive biosensor capable of yielding good response even when the amount of a sample is extremely small. The biosensor of the present invention includes: a first insulating base plate which has a working electrode comprising a plurality of branches and a first counter electrode comprising a plurality of branches, the branches of the working electrode and the first counter electrode being arranged alternately; a second insulating base plate which has a second counter electrode and which is disposed at a position opposite to the first insulating base plate; a reagent system comprising an oxidoreductase; and a sample supply pathway formed between the first and second insulating base plates, wherein the branches of the working electrode and the first counter electrode that are arranged alternately, the second counter electrode, and the reagent system are exposed in the sample supply pathway.
Owner:PHC HLDG CORP
Biosensor and measuring method using the same
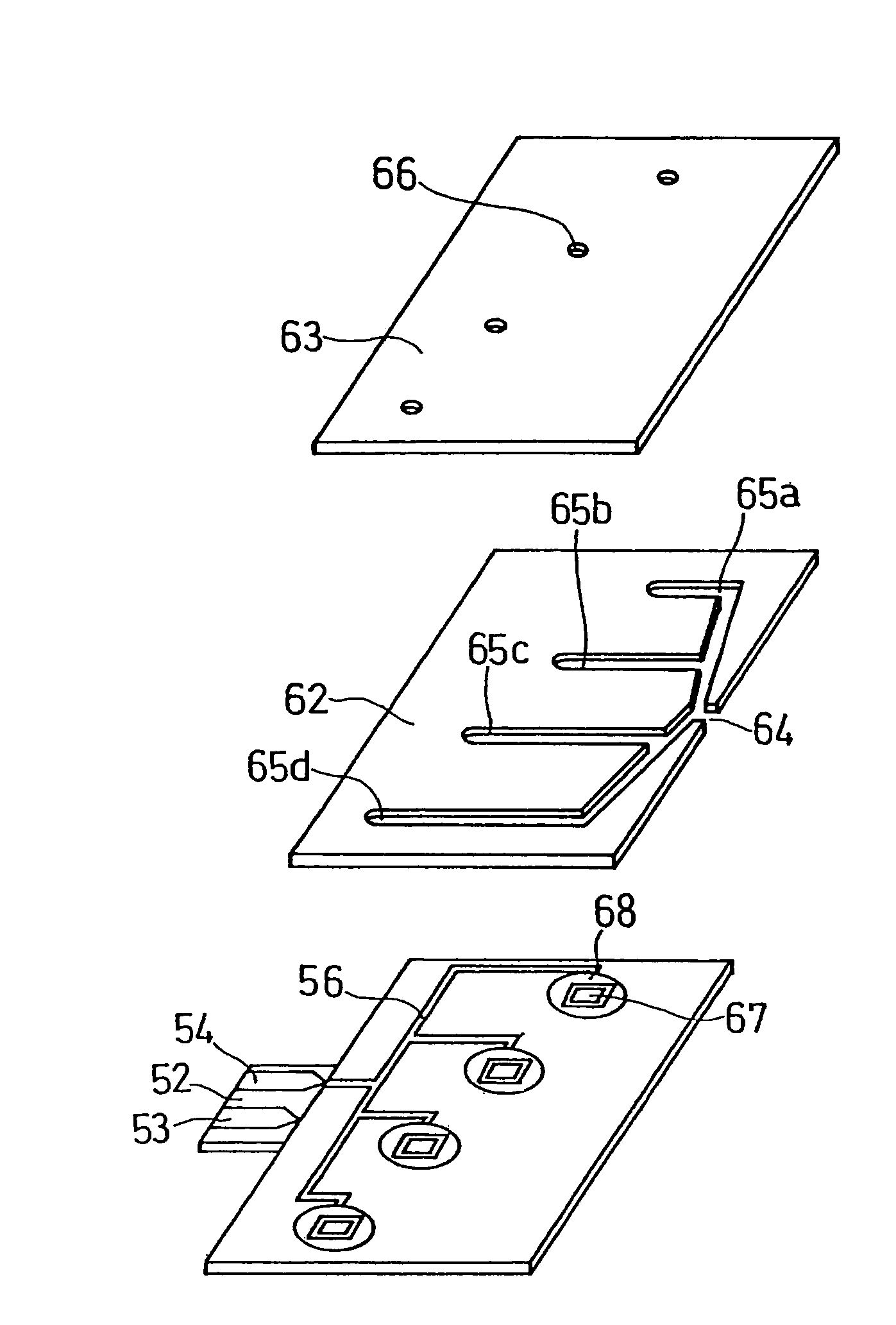
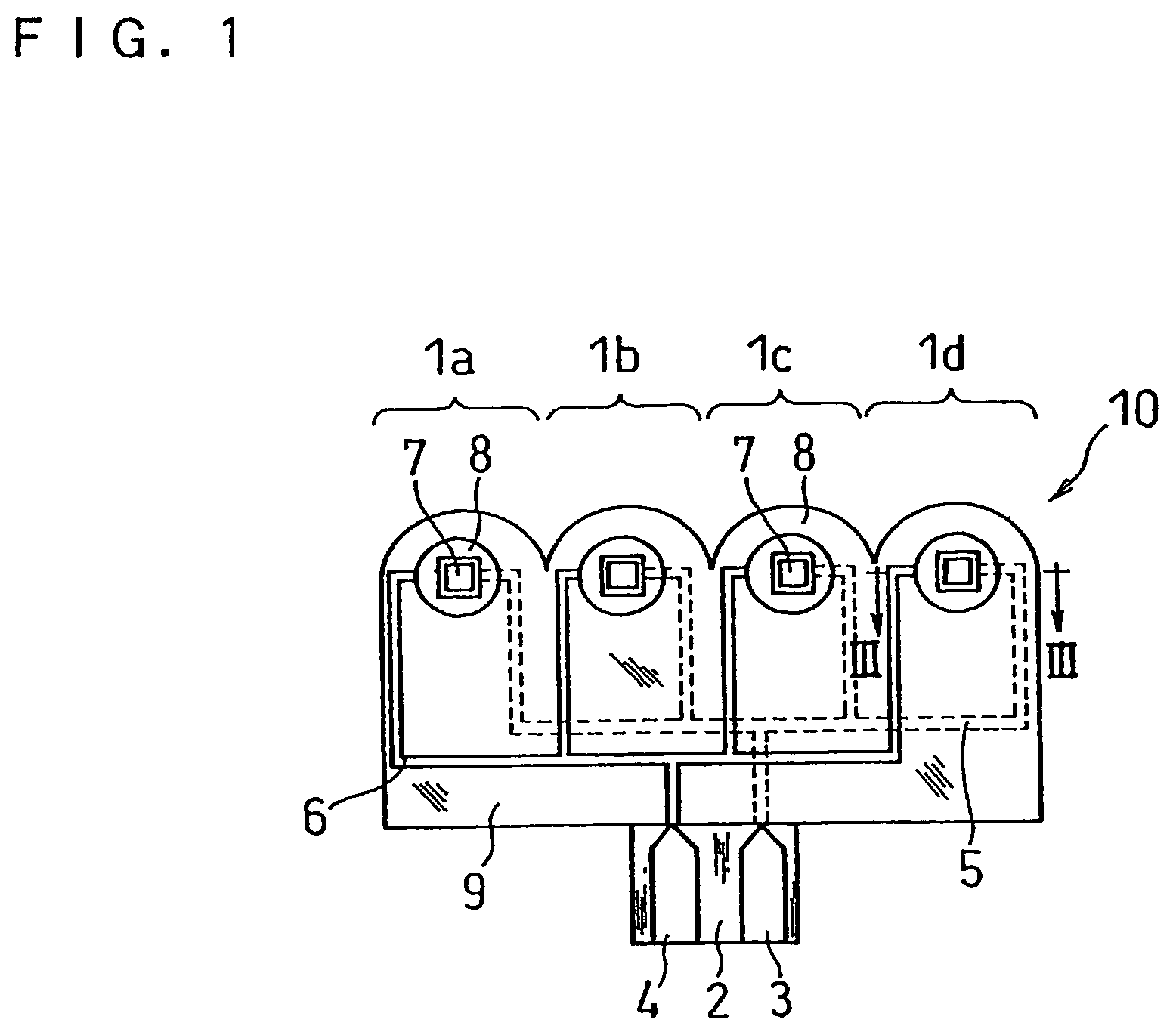
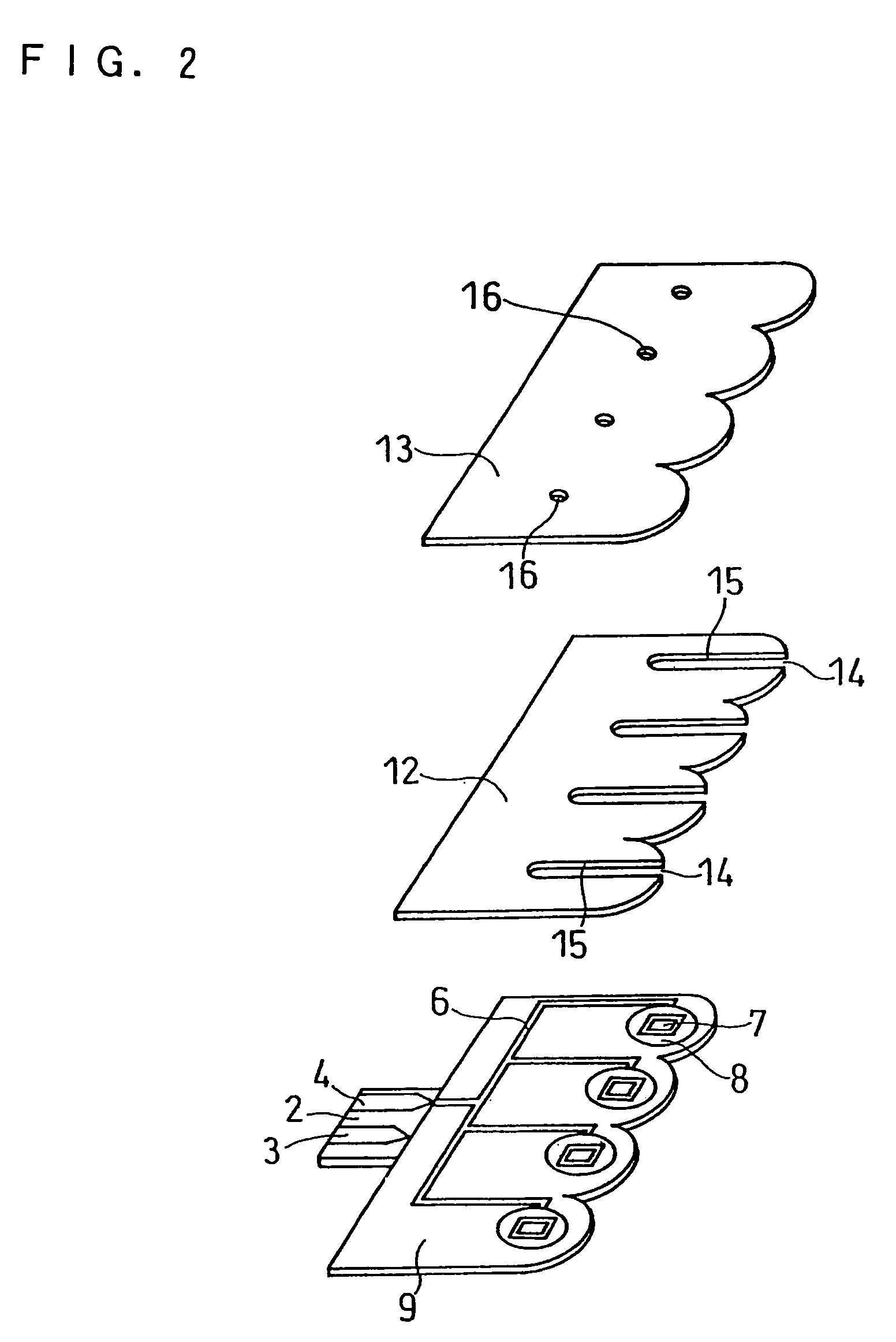
A biosensor capable of measuring the concentration of one or more specific substances in one or more sample solutions almost simultaneously is provided. The biosensor comprises a plurality of sensor units, and each of the sensor units comprises an electrode system including a working electrode and a counter electrode on an insulating base plate and a reagent system including an oxidoreductase and an electron mediator. The biosensor is so configured that sample solutions supplied to the respective sensor units reach the respective reagent systems at different times. Specifically, each of the sensor units has a controlling system between a sample supply inlet and the reagent system, and the controlling system controls the time it takes for the sample solution to reach the reagent system from the sample supply inlet.
Owner:PHC HLDG CORP
Method of measuring blood component and sensor used in the method
ActiveUS20050145490A1Great HctConvenient amountImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsRed blood cellOxidoreductase
A sensor for blood component analysis that can correct the effect of a hematocrit easily is provided. The sensor includes an analysis portion including a working electrode, a counter electrode, and a reagent portion. The reagent portion includes an oxidoreductase that reacts with the blood component and a mediator, and the blood component is measured by causing a redox reaction between the blood component and the oxidoreductase in the presence of the mediator and detecting a redox current generated by the redox reaction by the working electrode and the counter electrode. In this sensor, the reagent portion further includes a hemolyzing agent (e.g., sodium cholate) for hemolyzing an erythrocyte, and when detecting the redox current, the erythrocyte is hemolyzed with the hemolyzing agent so as to cause hemoglobin released to an outside of the erythrocyte to react with the mediator and a current generated by this reaction also is detected to correct an effect of a hematocrit.
Owner:PHC HLDG CORP
Analytical element and measuring device and substrate quantification method using the same
InactiveUS6878262B2Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMeasurement deviceEvaporation
The present invention provides an analytical element which is free from evaporation of a sample during measurement and therefore capable of quantifying a substrate using a very small amount of sample with high accuracy and which is free from scattering of the sample during and after the measurement and therefore hygienically excellent; and a measuring device and a substrate quantification method using the same. The analytical element comprises a cavity for accommodating a sample, a working electrode and a counter electrode exposed to an inside of the cavity, a reagent layer which comprises at least an oxidoreductase and is formed inside or in the vicinity of the cavity, an opening communicating with the cavity and a member covering the opening.
Owner:PHC HLDG CORP
Biosensor
Owner:PANASONIC HEALTHCARE HLDG CO LTD
Biosensor
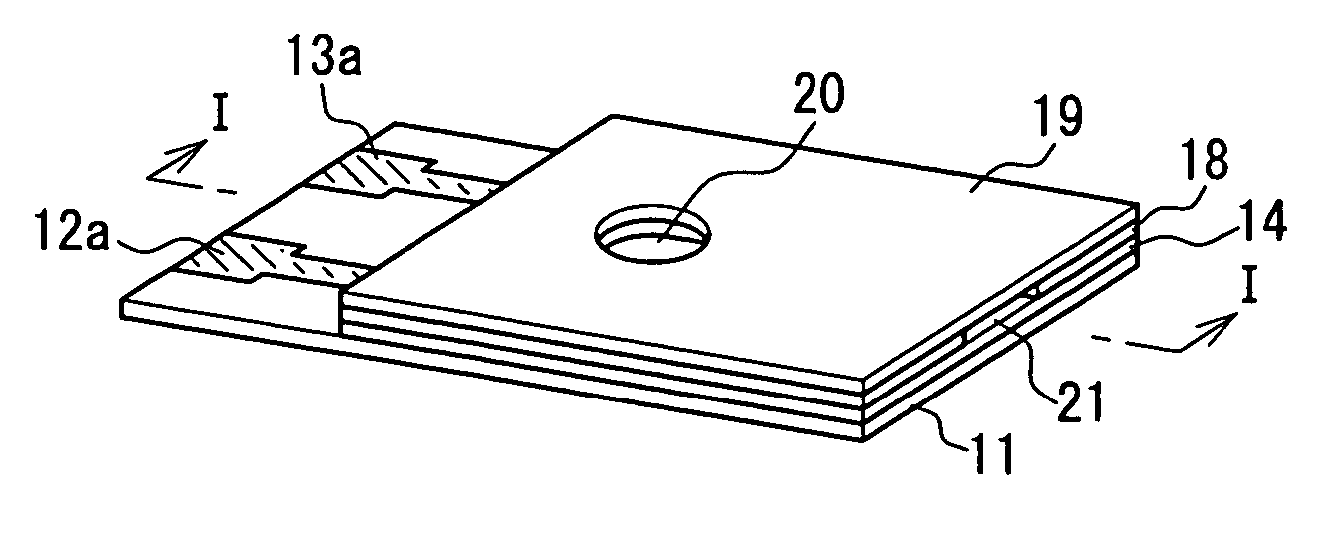
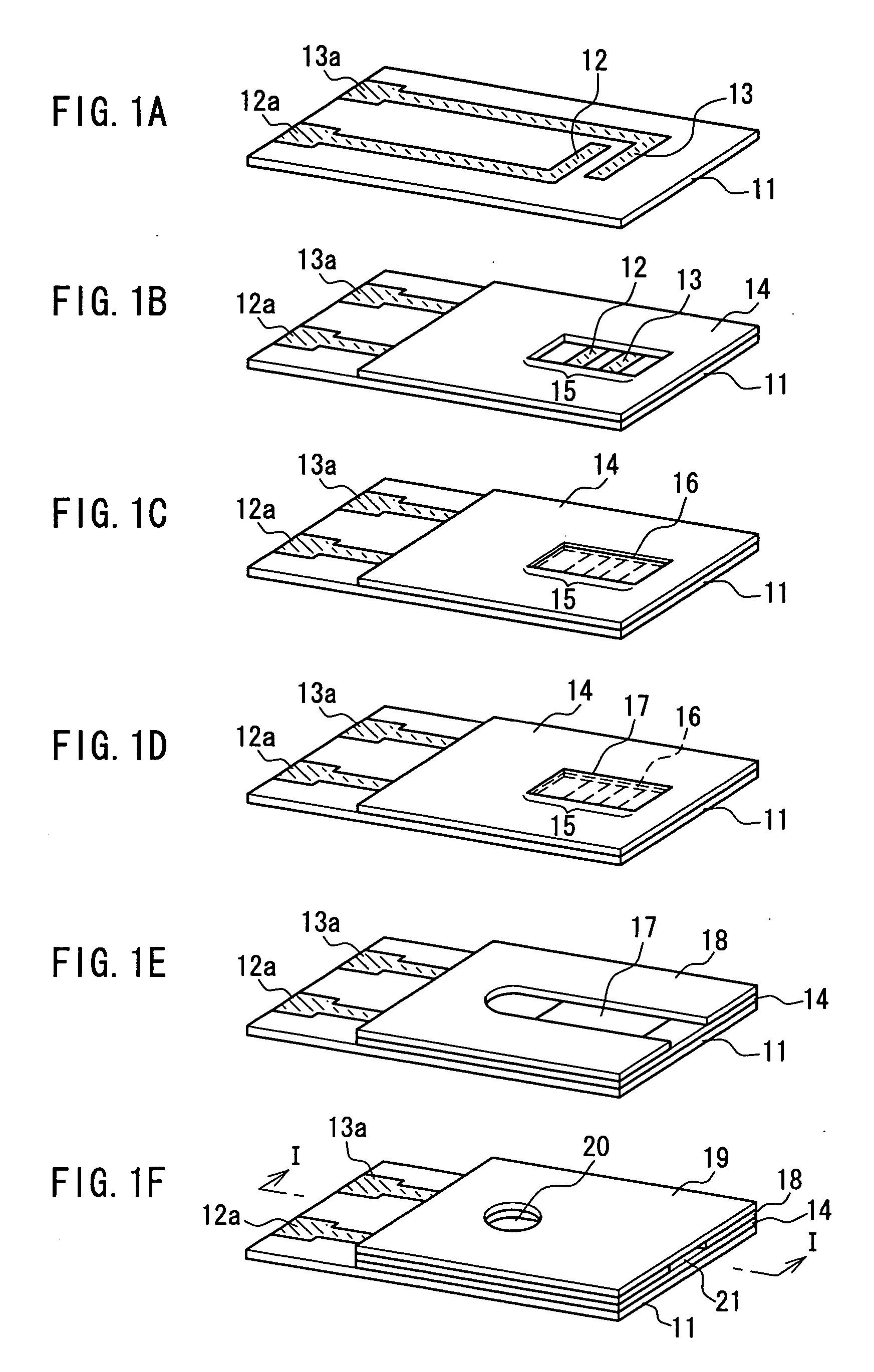
A biosensor comprising: an electrically insulating base plate; an electrode system comprising a working electrode and a counter electrode formed on the base plate; a cover member which is joined to the base plate to form a sample solution supply pathway for supplying a sample solution to the electrode system between the cover member and the base plate; and a reagent system comprising at least an oxidoreductase and an electron mediator disposed in the sample solution supply pathway, wherein the electron mediator is provided on the base plate and the oxidoreductase is provided on the cover member such that the electron mediator and the oxidoreductase are not in contact with each other.
Owner:PHC HLDG CORP
Biosensor
InactiveUS7235170B2Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsGluconolactonaseOxidoreductase
A biosensor that is highly responsive and capable of rapid and highly sensitive quantification of a specific component contained in a sample is provided. The biosensor of this invention comprises: an electrically insulating base plate; an electrode system comprising a working electrode and a counter electrode disposed on the base plate; and a reagent system comprising an oxidoreductase which catalyzes the oxidation reaction of glucose, gluconolactonase and a buffer. The buffer is selected from the group consisting of phthalic acid and its salts, maleic acid and its salts, succinic acid and its salts, phospholic acid and its salts, acetic acid and its salts, boric acid and its salts, citric acid and its salts, glycine, tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane, piperazine-N,N′-bis(2-ethane sulfonic acid) and the like.
Owner:PHC HLDG CORP
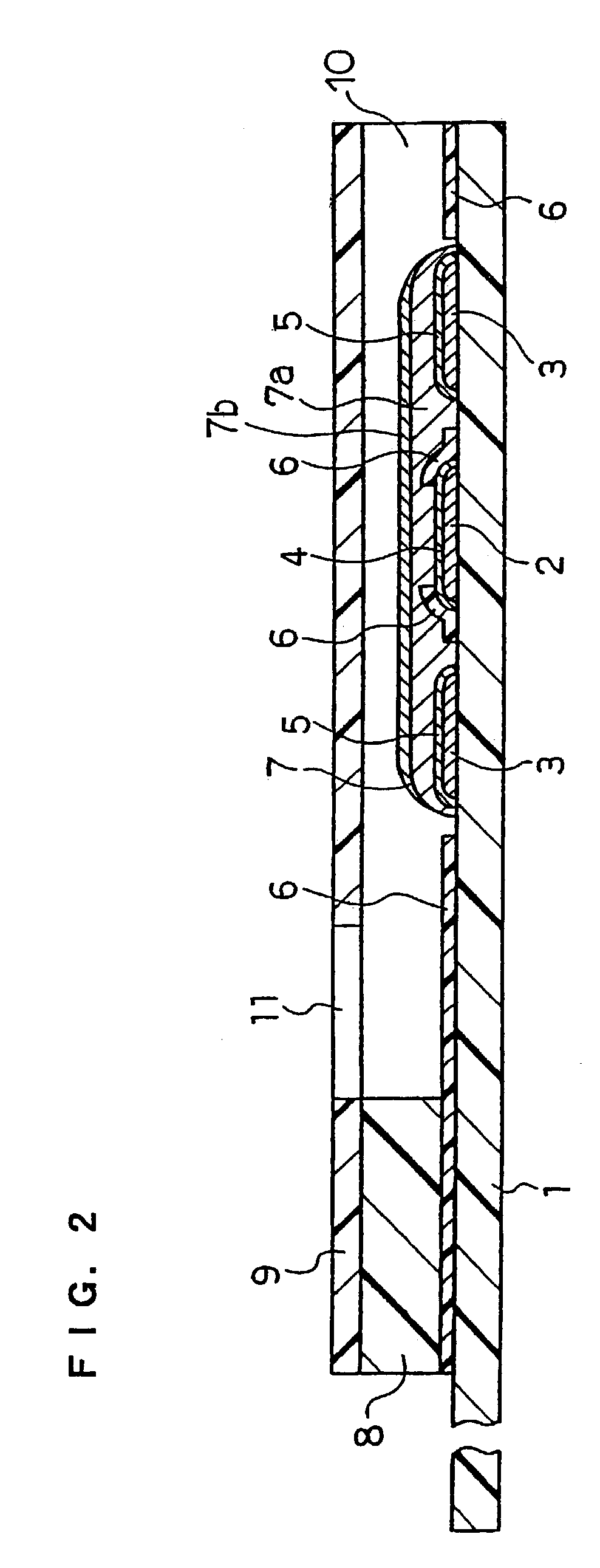
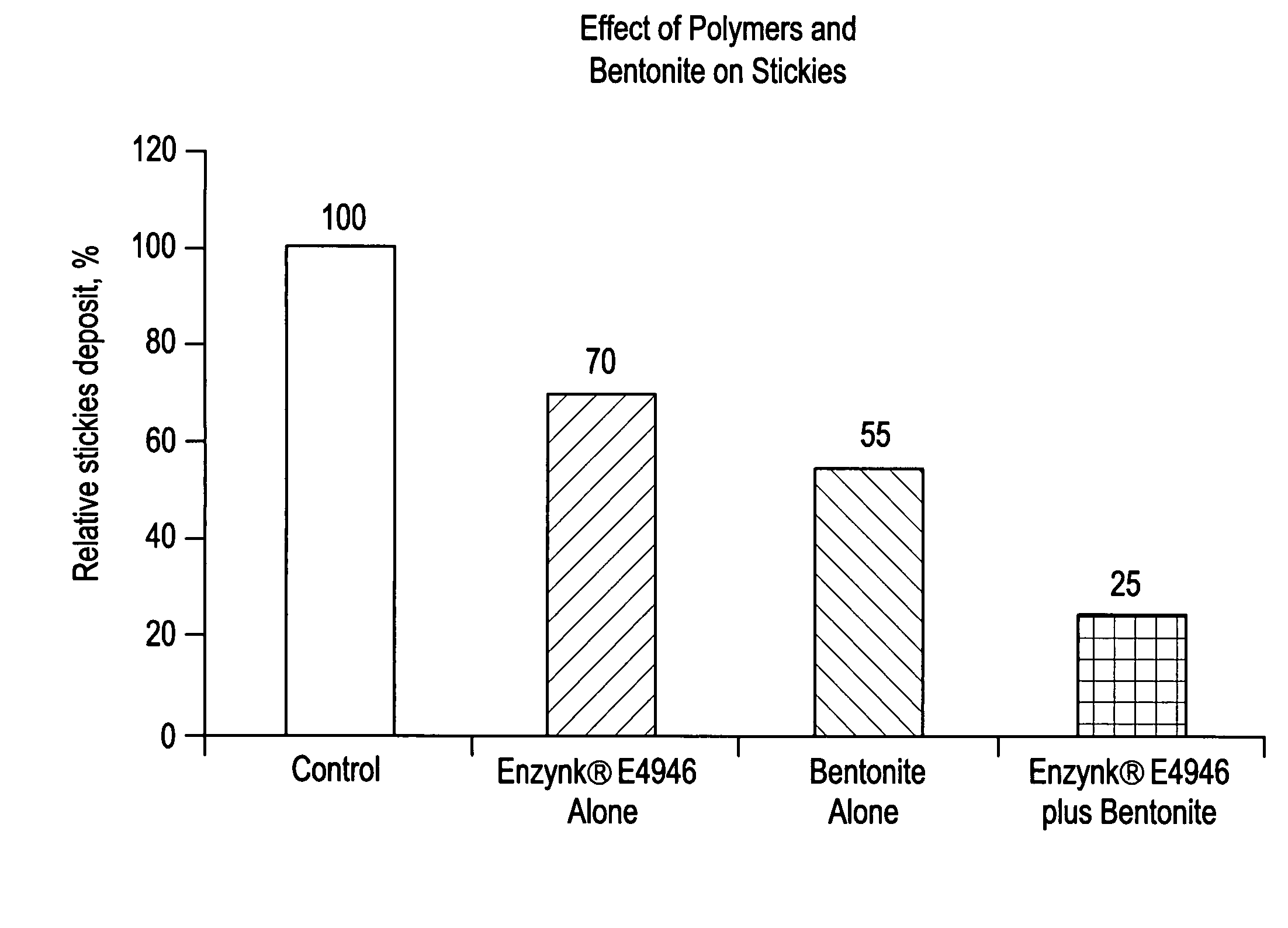
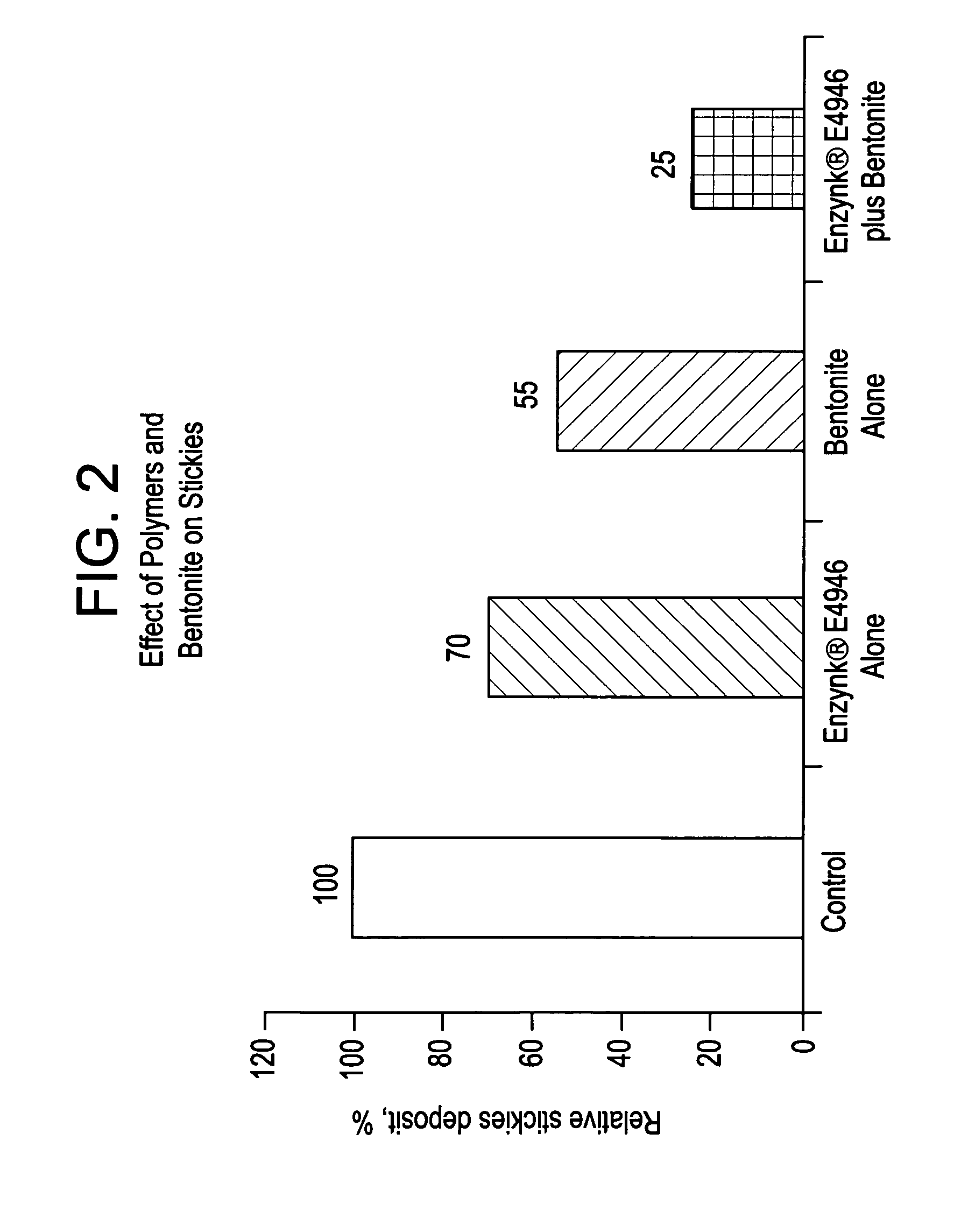
System for control of stickies in recovered and virgin paper processing
InactiveUS20060048908A1Good removal effectEasy to controlFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpMachine wet endPectinaseAmylase
Enhanced removal and / or control of adhesives or sticky materials, “stickies”, from recovered paper stock or virgin pulp fibers is achieved using a combination of enzyme treatment with adsorbents and / or absorbents. Pulp stock to be treated is typically obtained from old magazines, newspapers, household waste, but may include corrugated boxes and office waste. Virgin pulps may include mechanical, chemical, or semi-chemical pulps. Enzymes typically include hydrolases such as cellulases, hemicellulases, pectinases, amylases, and lipases such as esterases, lyases such as pectate lyases, and oxidoreductases. Adsorbents include activated bentonite, microparticles, talc, clay and modified silica. Absorbents typically include water soluble polymers, dispersants, coagulatants and agglomerants.
Owner:ENZYMATIC DEINKING TECH LLC
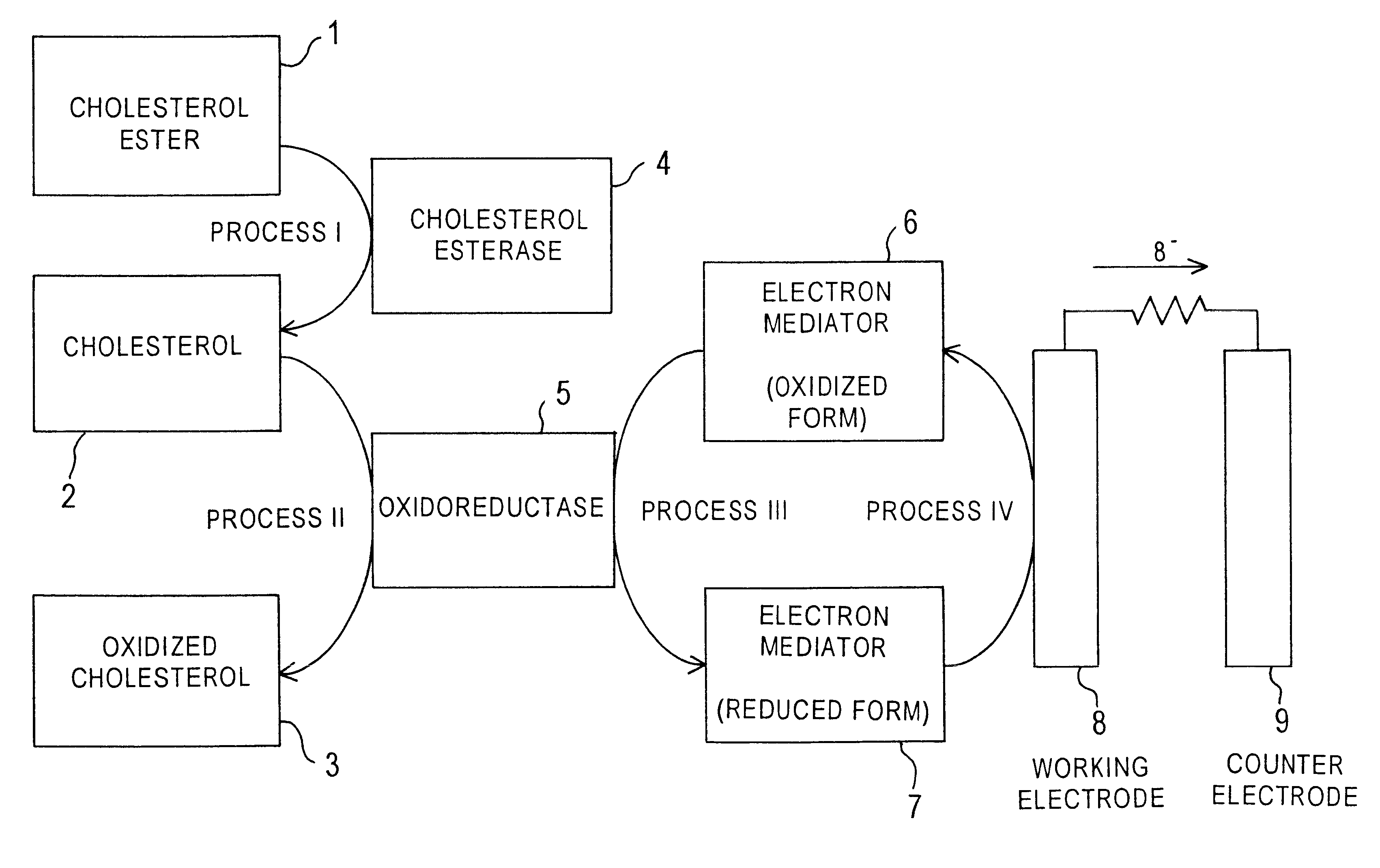
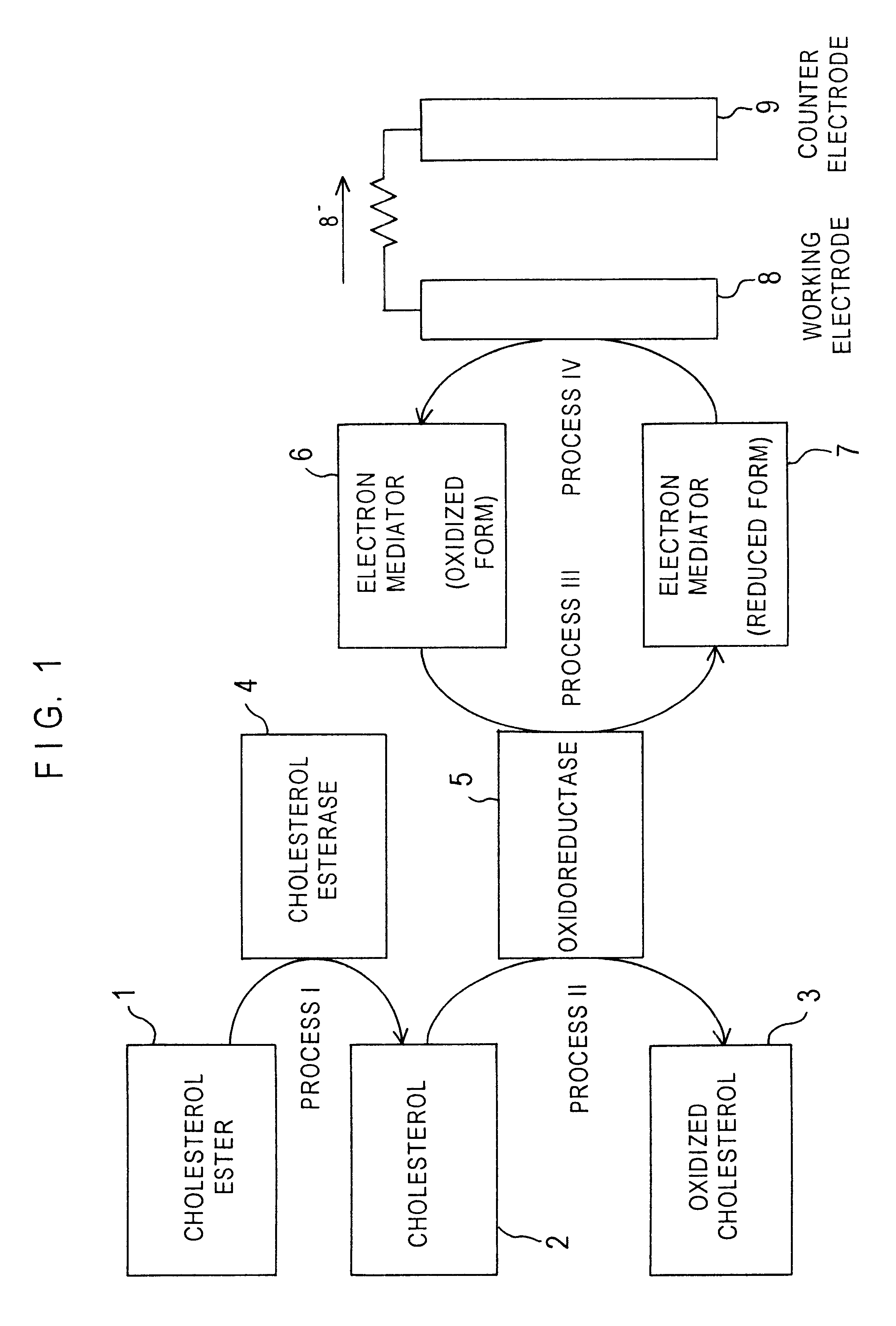
Cholesterol sensor and method of determining cholesterol
InactiveUS6342364B1Good reproducibilityImprove accuracyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsOxidoreductaseWater soluble
The present invention provides a sensor that electrochemically determines cholesterol in low density lipoprotein by only one feed of a sample. The sensor has: an electrode system that is mounted on an electrically insulating base plate and includes at least a working electrode and a counter electrode; an enzyme layer formed on the base plate with the electrode system; and a reagent layer that is arranged before the enzyme layer in a sample solution supply path to the electrode system. The enzyme layer includes at least an oxidoreductase and an electron mediator. The reagent layer includes a reagent that depresses reactivity of cholesterol in lipoproteins other than the low density lipoprotein with the oxidoreductase, for example, a reagent that attaches to lipoproteins other than the low density lipoprotein to form a water-soluble complex.
Owner:PHC HLDG CORP
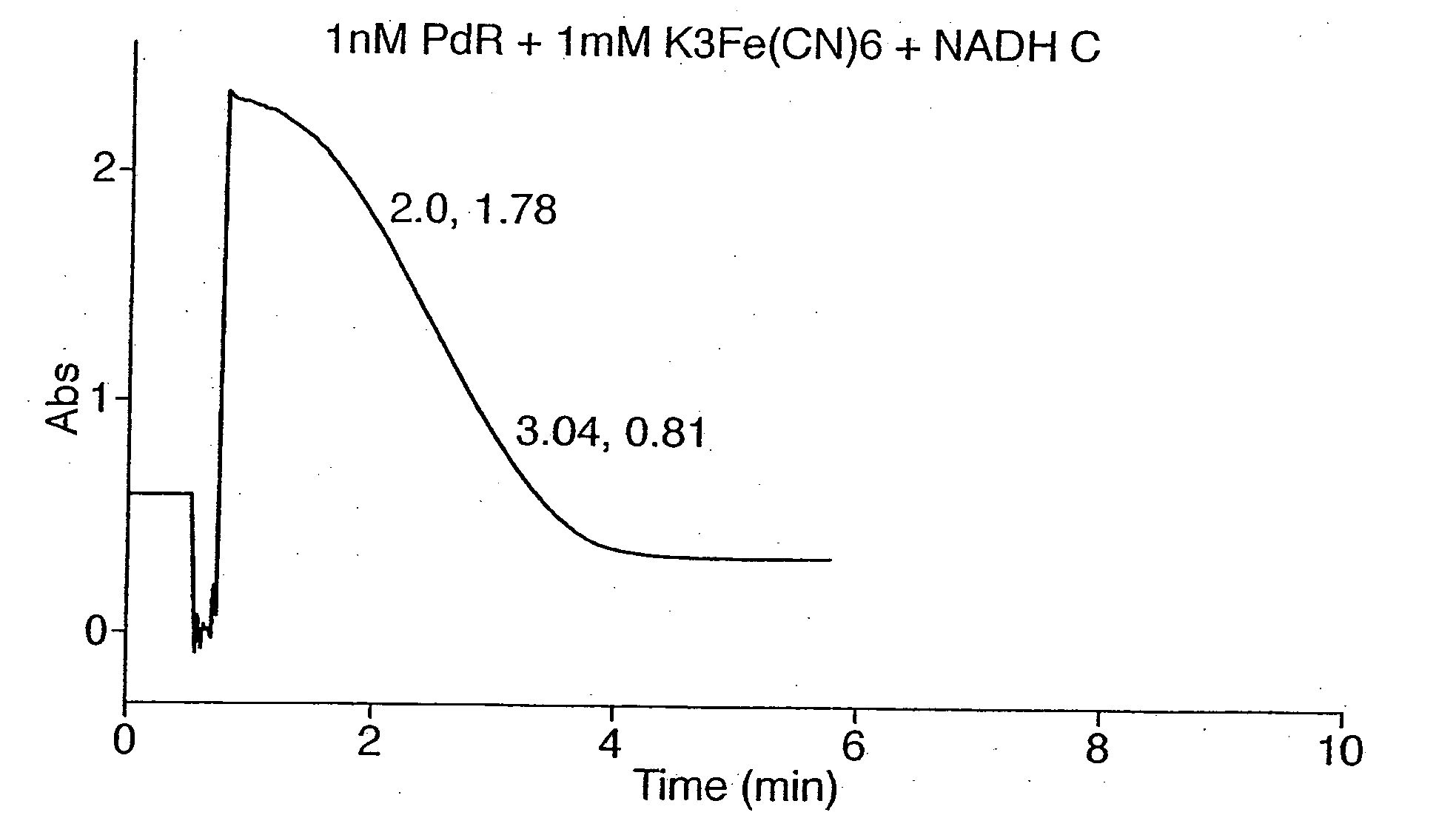
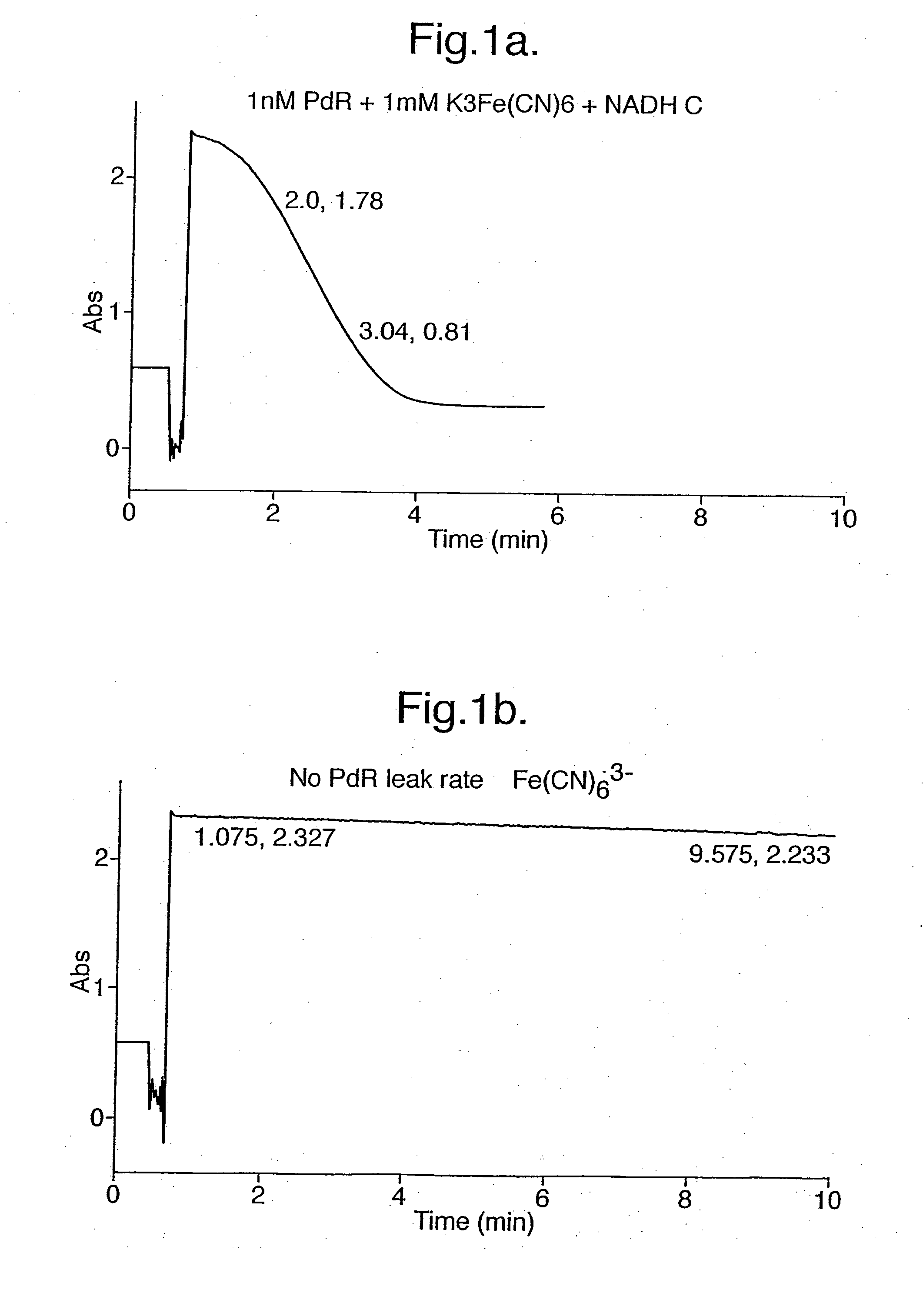
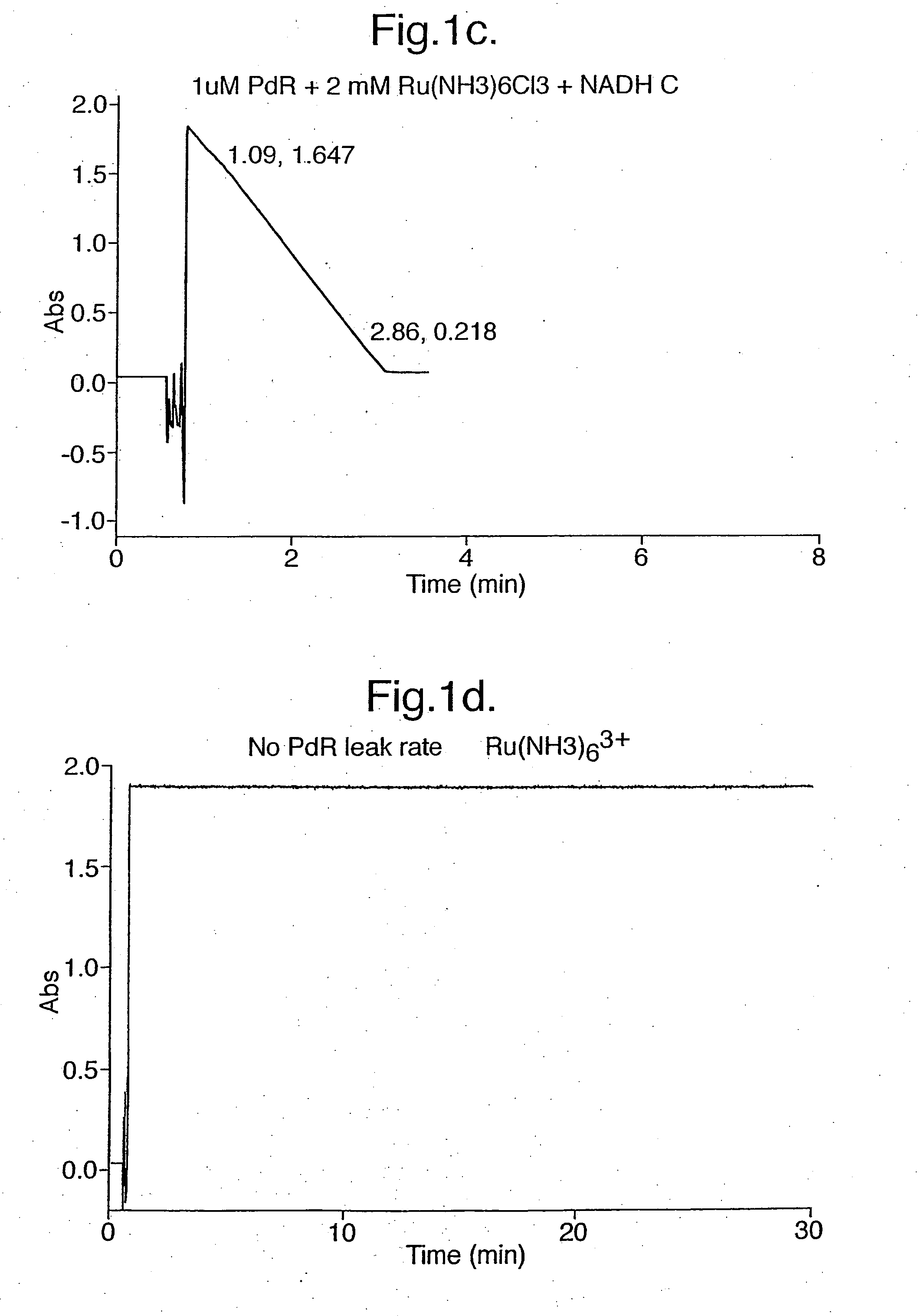
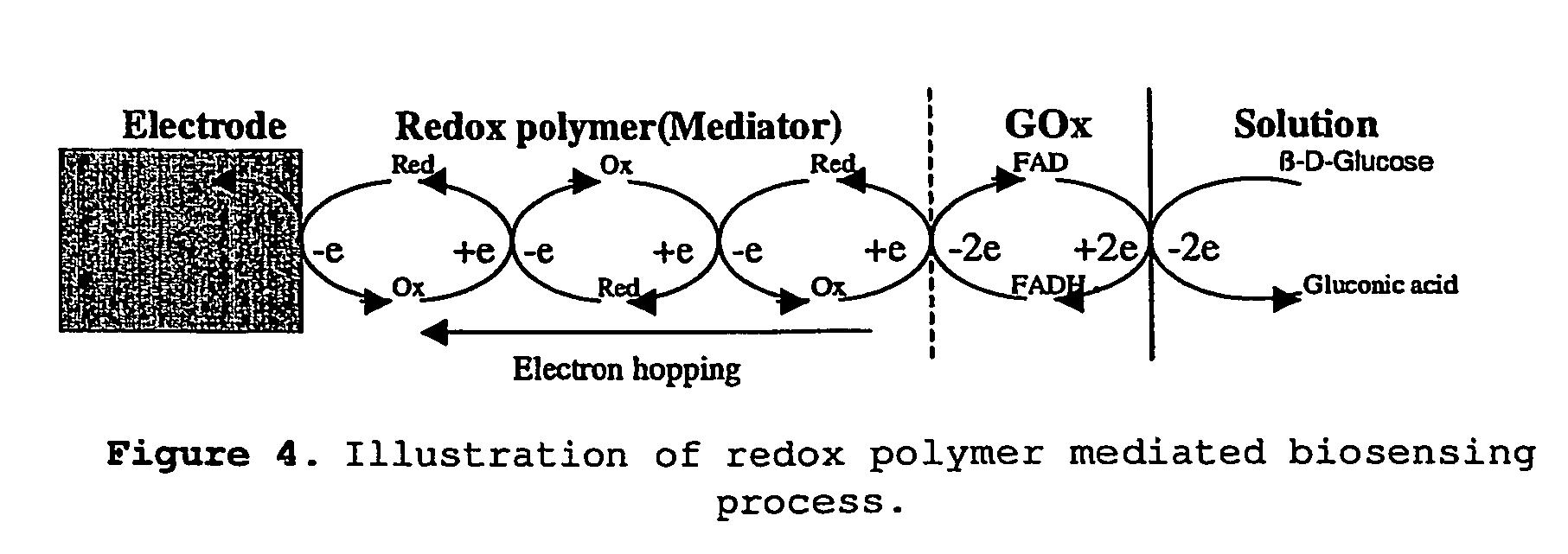
Electrochemical detection of nadh or naph
InactiveUS20050067303A1Easy to carryFast electron transfer rateImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsOxidoreductaseReductase
A method for detecting the presence or absence of, or for determining the concentration of, NADH or NADPH in a sample is provided, wherein the method comprises contacting a reductase and a redox active agent to said sample; and measuring the quantity of reduced redox active agent produced by the reductase, by electrochemical means. The method may be used to quantify the amount or activity of a redox enzyme or its substrate, wherein the redox enzyme uses NAD+, NADP+, NADPH or NADP as a cofactor.
Owner:ISIS INNOVATION LTD
Biosensor
InactiveUS20030175841A1Avoid influenceReduce solubilityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsGluconolactonaseSuccinic acid
A biosensor that is highly responsive and capable of rapid and highly sensitive quantification of a specific component contained in a sample is provided. The biosensor of this invention comprises: an electrically insulating base plate; an electrode system comprising a working electrode and a counter electrode disposed on the base plate; and a reagent system comprising an oxidoreductase which catalyzes the oxidation reaction of glucose, gluconolactonase and a buffer. The buffer is selected from the group consisting of phthalic acid and its salts, maleic acid and its salts, succinic acid and its salts, phospholic acid and its salts, acetic acid and its salts, boric acid and its salts, citric acid and its salts, glycine, tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane, piperazine-N,N'-bis(2-ethane sulfonic acid) and the like.
Owner:PHC HLDG CORP
Biosensor
InactiveUS20030032875A1Reduce sample volumeAmount of sample can be reducedImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsOptoelectronicsOxidoreductase
The present invention provides a highly sensitive biosensor that needs a smaller amount of sample for measurement. The biosensor comprises a first insulating base plate having a working electrode, a second insulating base plate having a counter electrode opposed to the working electrode, a reagent layer comprising at least an oxidoreductase, and a sample supply pathway formed between the first and second insulating base plates, wherein the working electrode, counter electrode and reagent layer are exposed to an inside of the sample supply pathway, and the distance between the working electrode and the counter electrode is 150 mum or less.
Owner:PHC HLDG CORP
Wound dressings comprising hydrated hydrogels and enzymes
InactiveUS20060034816A1Prevents undesired migrationAvoid injuryPeptide/protein ingredientsPlastersWound dressingPeroxidase
A skin dressing, particularly a wound dressing, comprises oxidoreductase enzyme and, optionally, peroxidase enzyme, wherein the enzyme(s) are present in hydrated condition, e.g. being present in one or more hydrated hydrogels. The dressing is used by being located on the skin of a human or animal e.g. over a wound. The oxidoreductase enzyme catalyses a reaction that produces hydrogen peroxide from an appropriate substrate, the substrate either being naturally present in body fluids and / or being supplied separately and / or being incorporated into the dressing. The currently preferred oxidoreductase enzyme is glucose oxidase. The catalyses reaction of β-D-glucose substrate to give hydrogen peroxide and gluconic acid. A mixture of oxidoreductase enzyme can undergo reaction (optionally catalysed by the peroxidase enzyme) to produce a variety of species including reactive oxygen intermediates that have antimicrobial properties and that can therefore assist in promoting wound healing.
Owner:SYSTAGENIX WOUND MANAGEMENT (US) INC
Biosensor
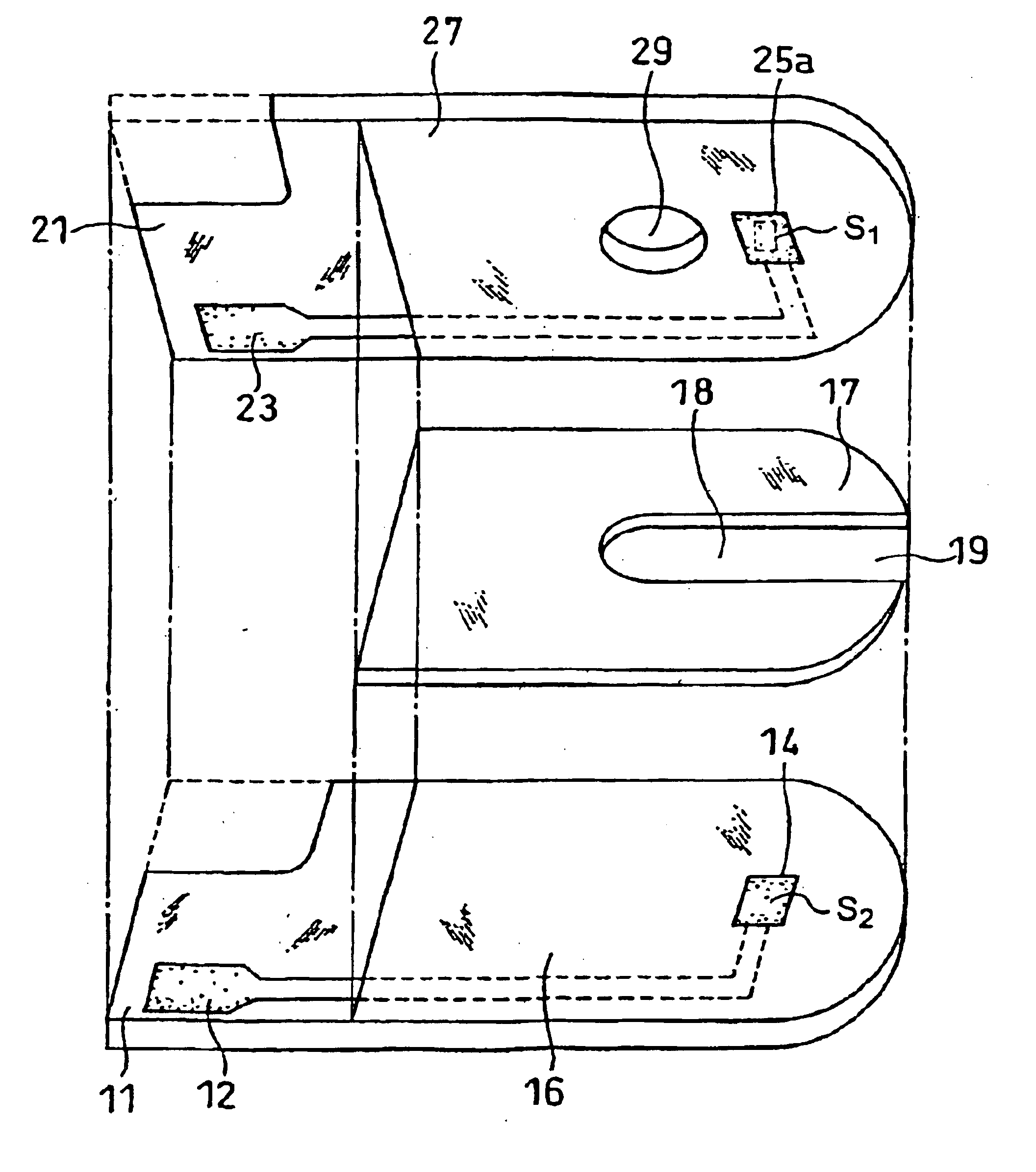
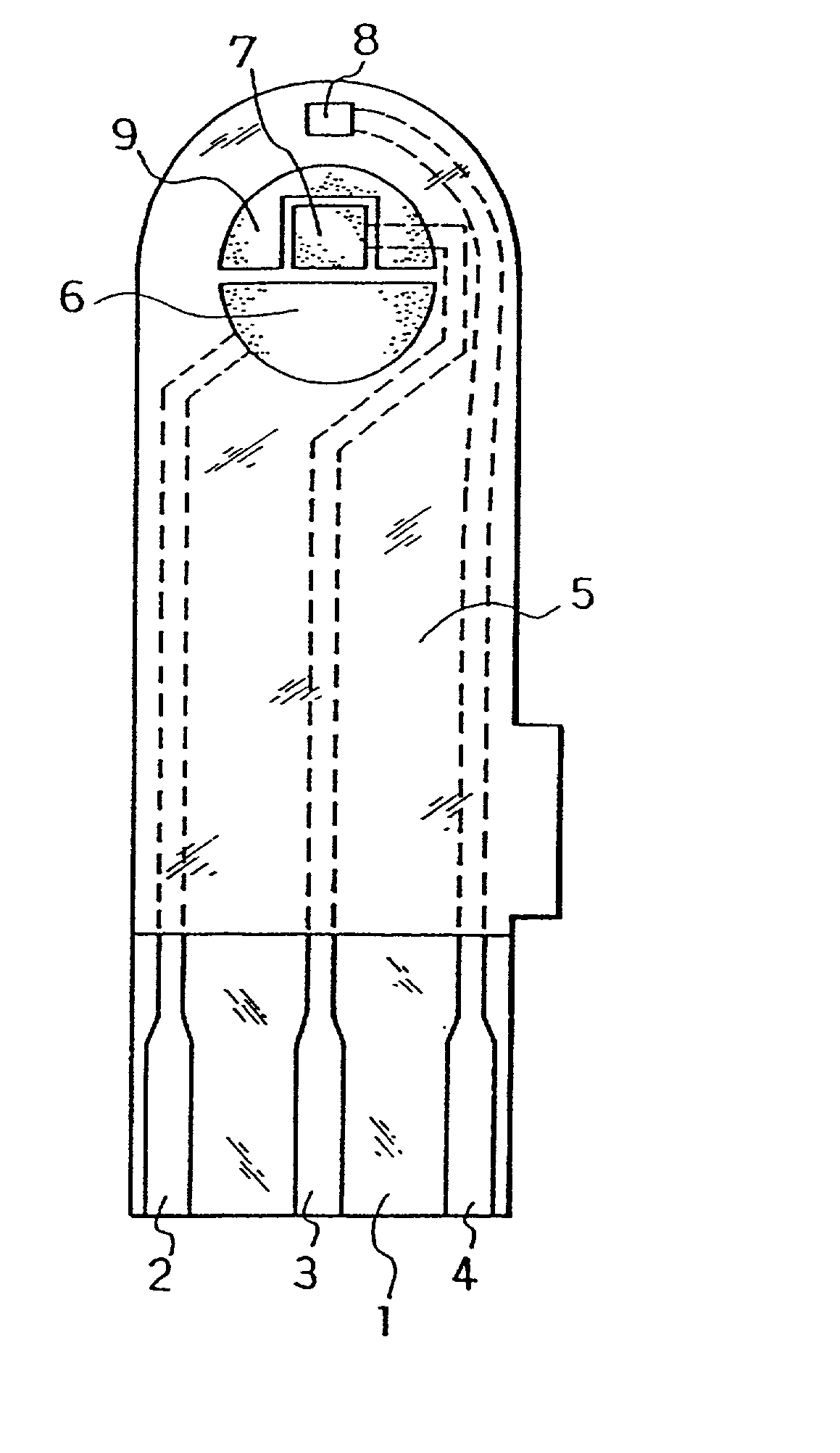
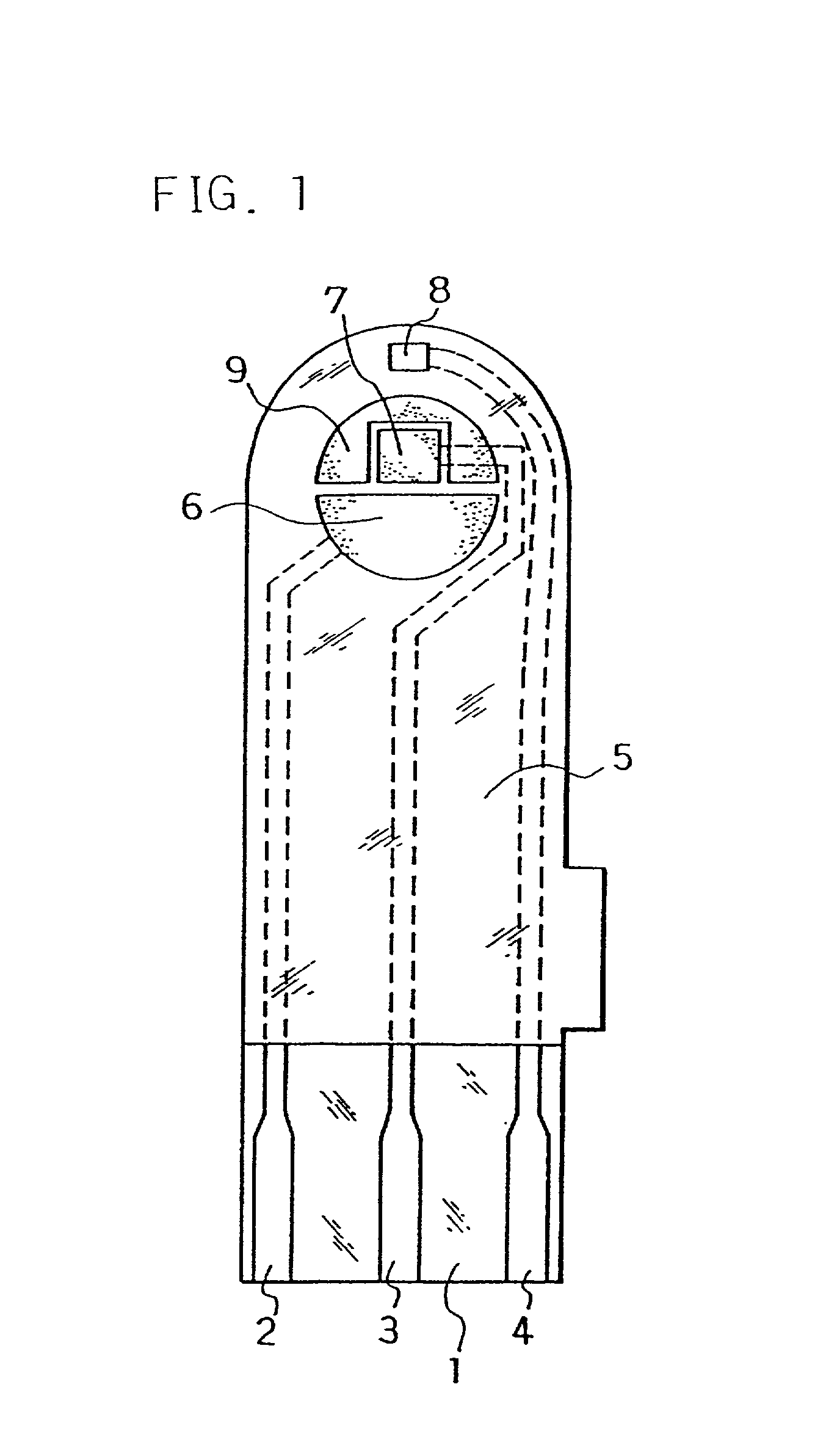
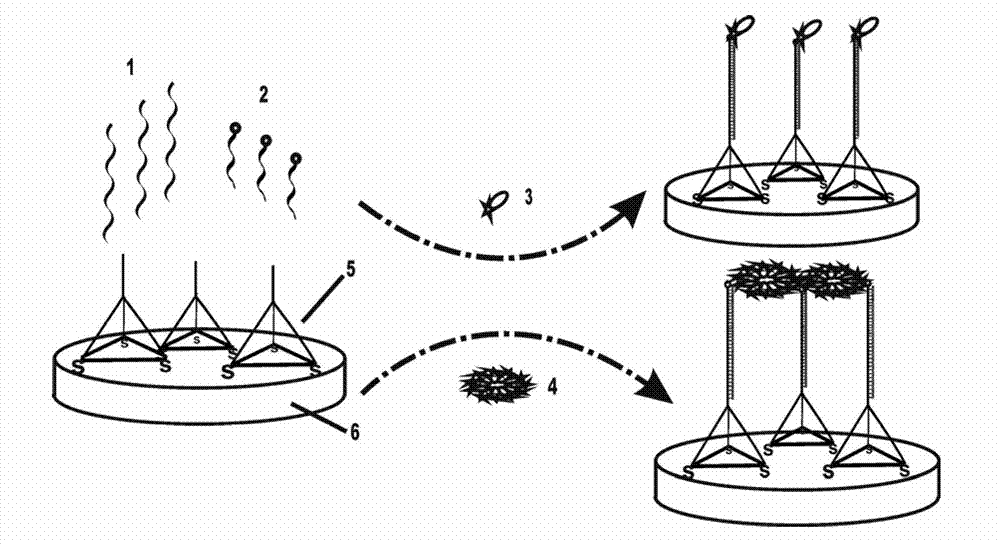
A sensor for determining the presence of an analyte in a test sample, said sensor comprising a nanoparticulate membrane comprising nanoparticles of at least one inorganic oxide of an element selected from Group IA, IIA, IIIA, IVA, IB, IIB, IIIB, IVAB, VB, VIB, VIII3 or VIIII3 of the Periodic Table, and wherein an oxidoreductase and an electrochemical activator are diffusibly dispersed in said nanoparticulate membrane.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Biosensor and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20070034512A1Avoid natural oxidationHigh measurement accuracyImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteInorganic compound
The present invention provides a biosensor that can prevent a mediator from being affected by oxygen, thereby allowing an analyte in a sample solution to be measured rapidly and easily with high accuracy. The biosensor can be produced by providing a substrate having electrodes, applying a solvent containing a mediator, a surfactant, a buffer, and a layered inorganic compound to surfaces of the electrodes to form an inorganic gel layer for preventing natural oxidation of the mediator, and forming an enzyme reagent layer containing an oxidoreductase on the inorganic gel layer. In this biosensor, due to the inorganic gel layer, the mediator having been reduced by the reaction between an analyte and the oxidoreductase can be measured electrochemically, without being reoxidized by dissolved oxygen or the like.
Owner:ARKRAY INC
Biosensor
InactiveUS20030132110A1Flow fastReduce the cross-sectional areaImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsReaction layerOxidoreductase
Owner:PANASONIC HEALTHCARE HLDG CO LTD
Test-Sensor Production Monitoring Using XRF Spectrometry
ActiveUS20090310743A1X-ray spectral distribution measurementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAnalyteTest sample
A sensor for determining the presence of an analyte in a test sample, said sensor comprising a nanoparticulate membrane comprising nanoparticles of at least one inorganic oxide of an element selected from Group IA, IIA, IIIA, IVA, IB, IIB, IIIB, IVAB, VB, VIB, VIII3 or V11113 of the Periodic Table, and wherein an oxidoreductase and an electrochemical activator are diffusibly dispersed in said nanoparticulate membrane.
Owner:ASCENSIA DIABETES CARE HLDG AG
Method and material for site activated complexing of biologic molecules
ActiveUS20100158885A1High affinityCeases the propagation of the pathogenAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMicroorganismBiopolymer
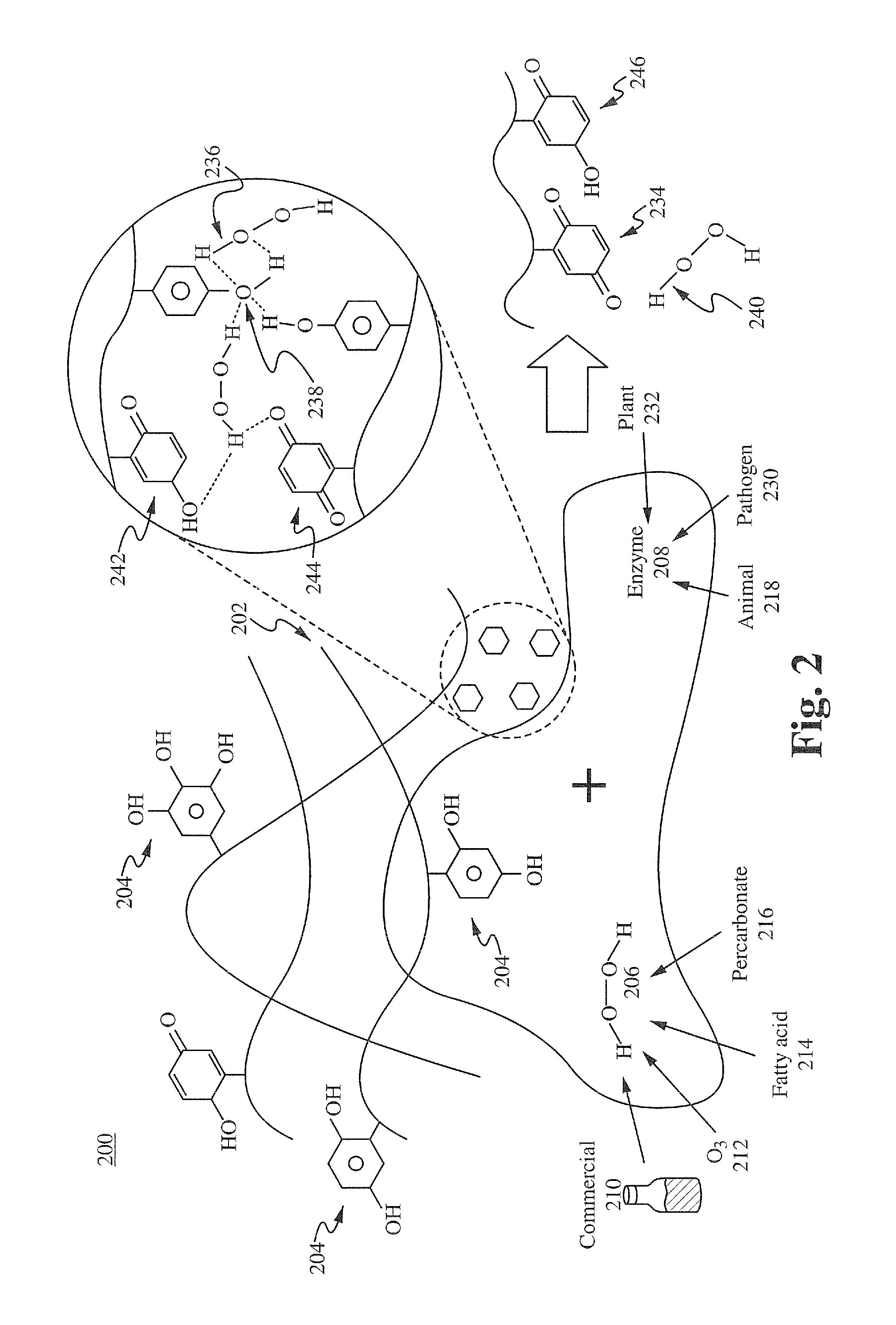
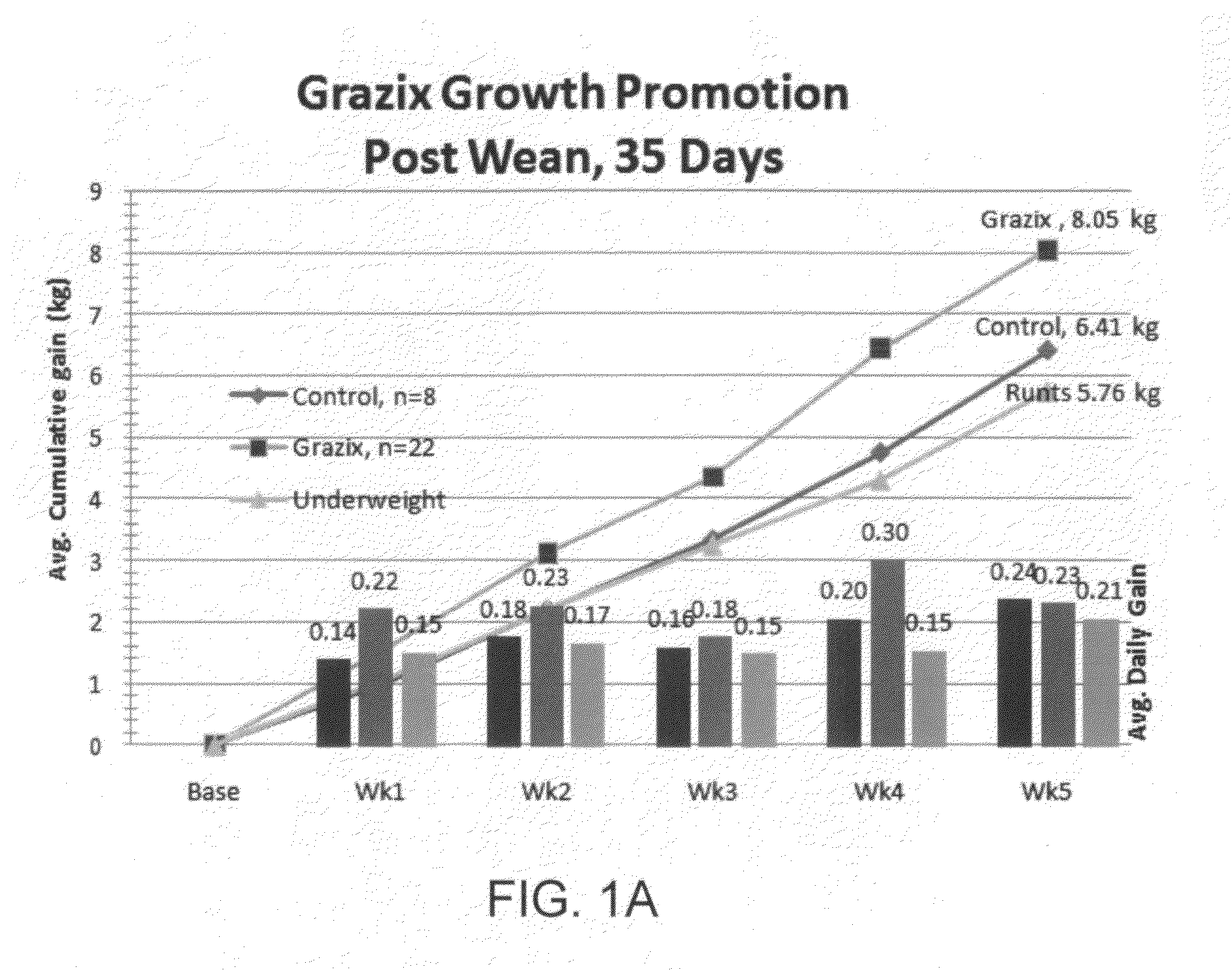
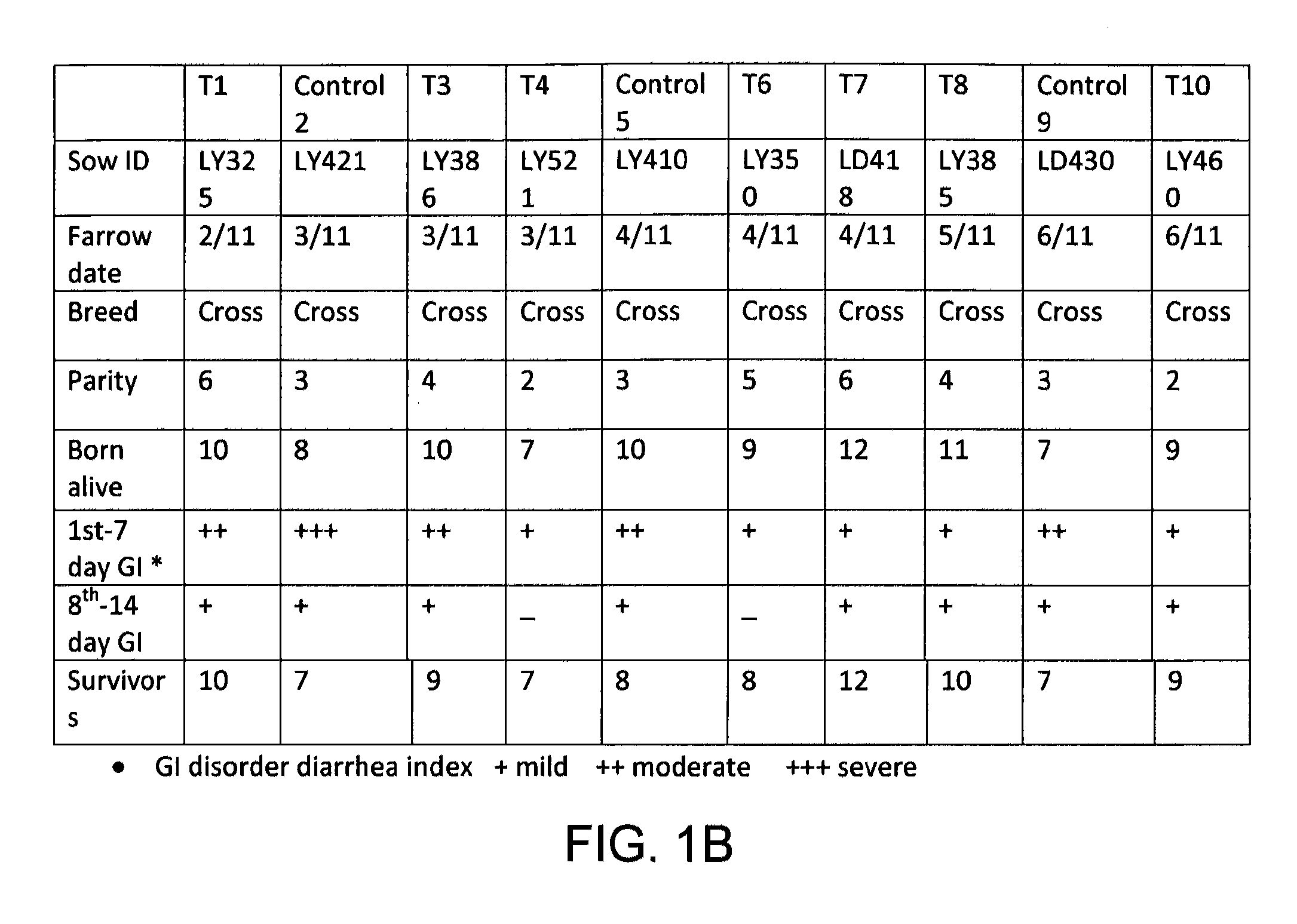
Methods of and compositions for producing and using plant-based materials are provided. The methods include using biopolymers or their synthetic equivalents combined with a stable source of reactive oxygen species that when applied to or combined with a separate source of oxido-reducing enzyme or catalyst will cause the formation of an activated biopolymer with increased protein binding affinity and microbial control activities.
Owner:LIVELEAF HLDG LLC
Site-activated binding systems that selectively increase the bioactivity of phenolic compounds at target sites
ActiveUS20120328593A1Improve biological activityAssists in the healing of the damaged tissueAntibacterial agentsBiocideOxidoreductaseOxygen
The teachings provided herein generally relate to site-activated binding systems that selectively increase the bioactivity of phenolic compounds at target sites. More particularly, the systems taught here include a phenolic compound bound to a reactive oxygen species, wherein the phenolic compound and the reactive oxygen species react at a target area in the presence of an oxidoreductase enzyme.
Owner:LIVELEAF HLDG LLC
Electrically non-conductive, nanoparticulate membrane
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Immobilized enzymes in biocathodes
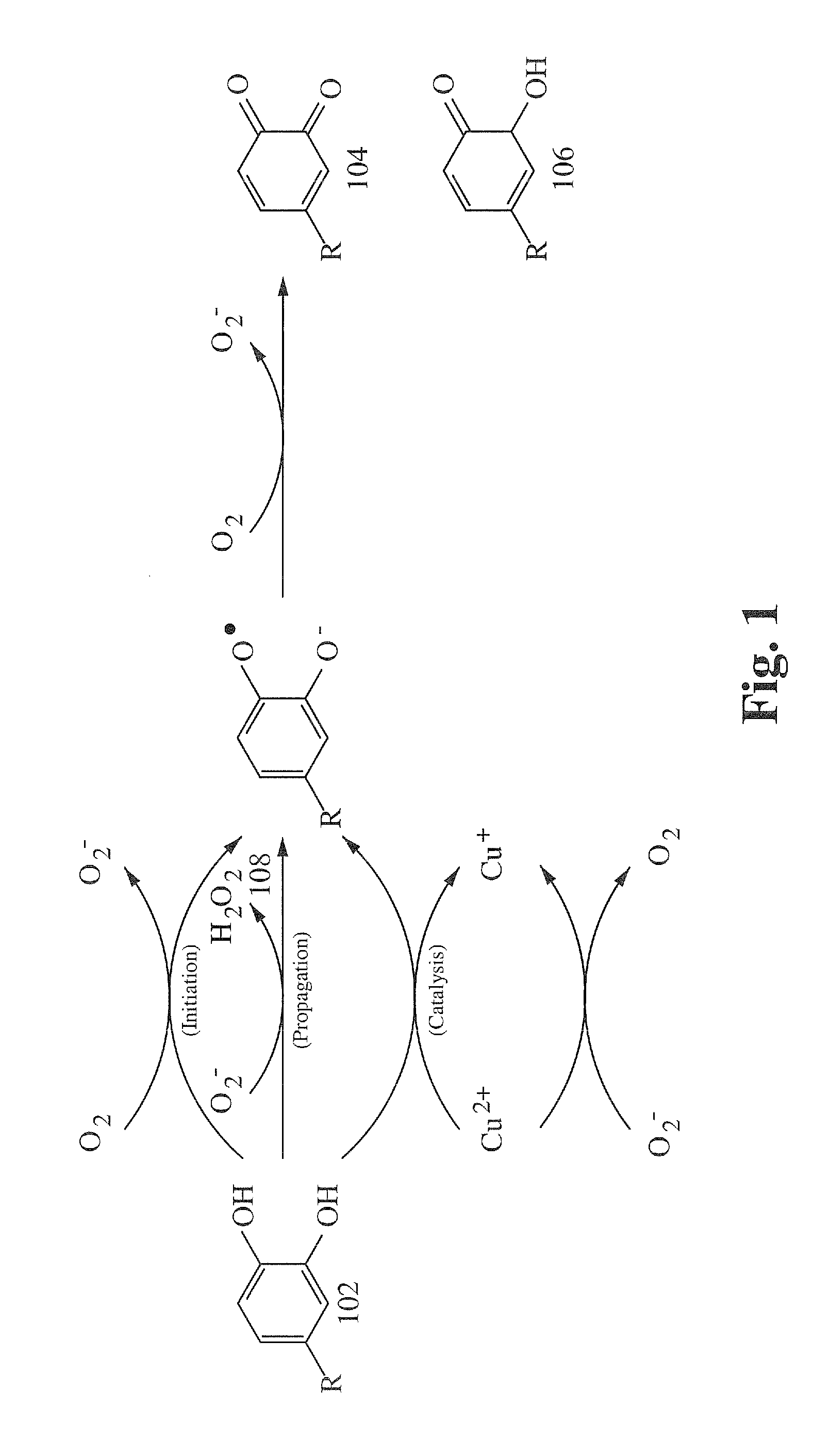
An improved biofuel cell having a cathode comprising a bifunctional membrane containing an oxygen oxidoreductase immobilized within a buffered compartment of the membrane and an electron transport mediator that conducts electrons from The electrodes are transferred to a redox reaction catalyzed by an oxygen oxidoreductase. The improved biofuel cell also has an anode that contains an oxidoreductase that uses an organic fuel, such as an alcohol, as a substrate. Electric current can flow between the anode and cathode.
Owner:SAINT LOUIS UNIVERSITY
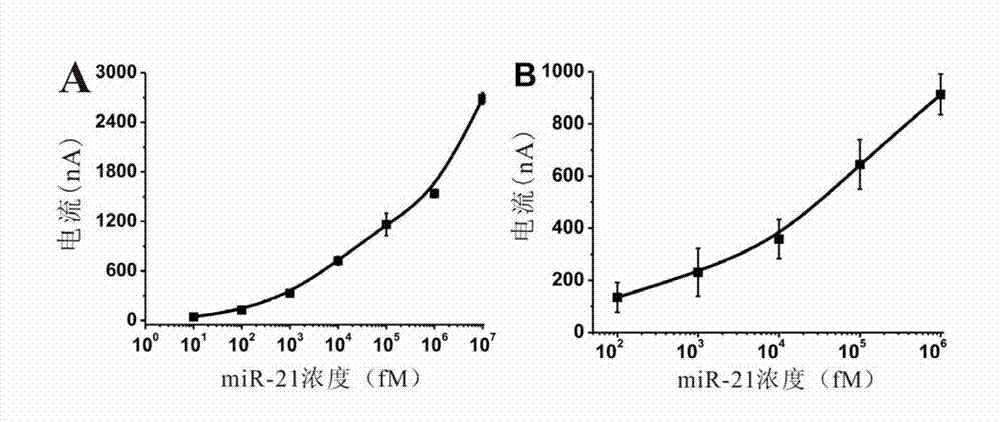
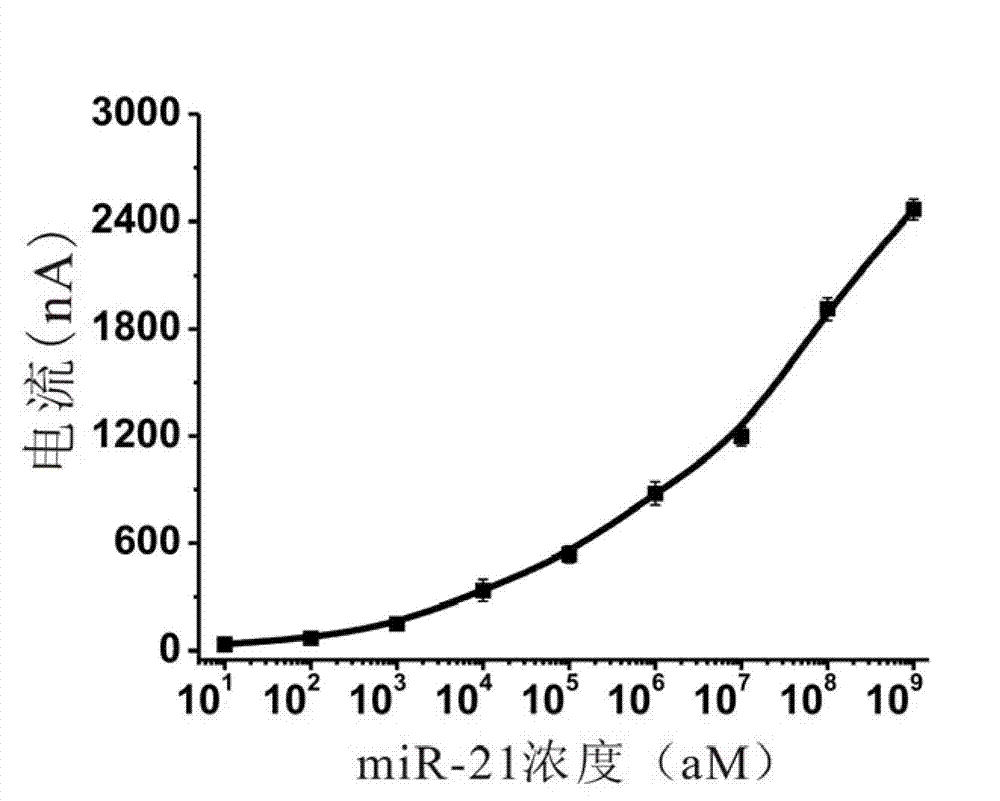
Electrochemical miRNA (micro Ribose Nucleic Acid) detection method based on DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) three-dimensional nano structure probe
The invention provides an electrochemical miRNA (micro Ribose Nucleic Acid) detection method based on a DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) three-dimensional nano structure probe. The electrochemical miRNA detection method comprises the steps of: synthesizing a DNA three-dimensional nano structure probe through a self-assembly method, wherein the DNA three-dimensional nano structure probe comprises one section of extended recognition sequence; assembling the DNA three-dimensional nano structure probe on the surface of a working electrode of an electrochemical device; hybridizing a target miRNA with the DNA three-dimensional nano structure probe on the surface of the working electrode; and adding oxidordeuctase and a corresponding substrate, and carrying out electrochemical detection by using the electrochemical device. The method can be used for detecting the miRNA of 10aM, therefore, the problem of the great demand on test samples in the detection method in the prior art is solved. In addition, the method has strong specificity selection and can be well used for distinguishing base pair mismatching of same family of miRNA. Compared with the method using the single-chain DNA probe, the electrochemical miRNA detection method is higher in stability.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
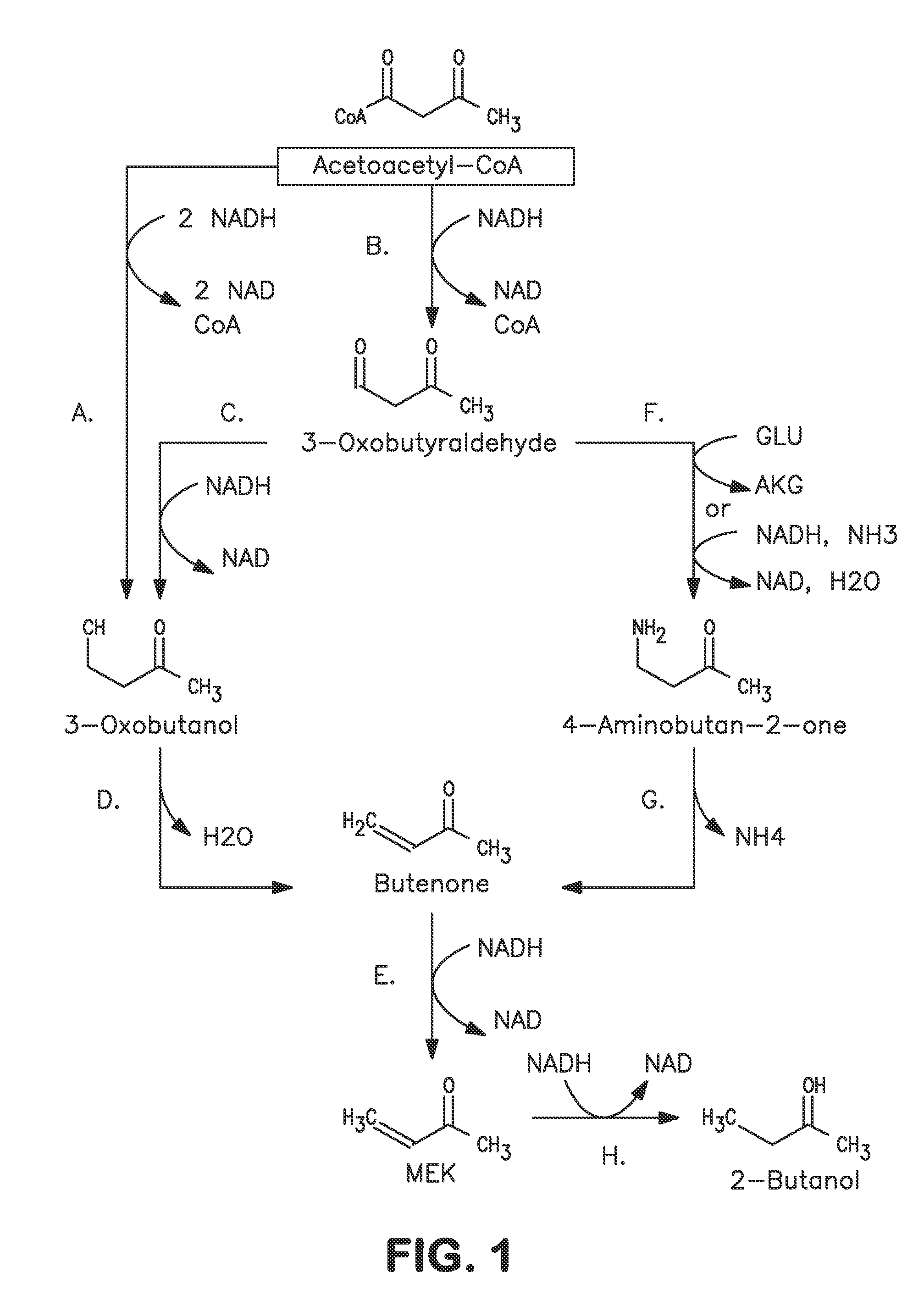
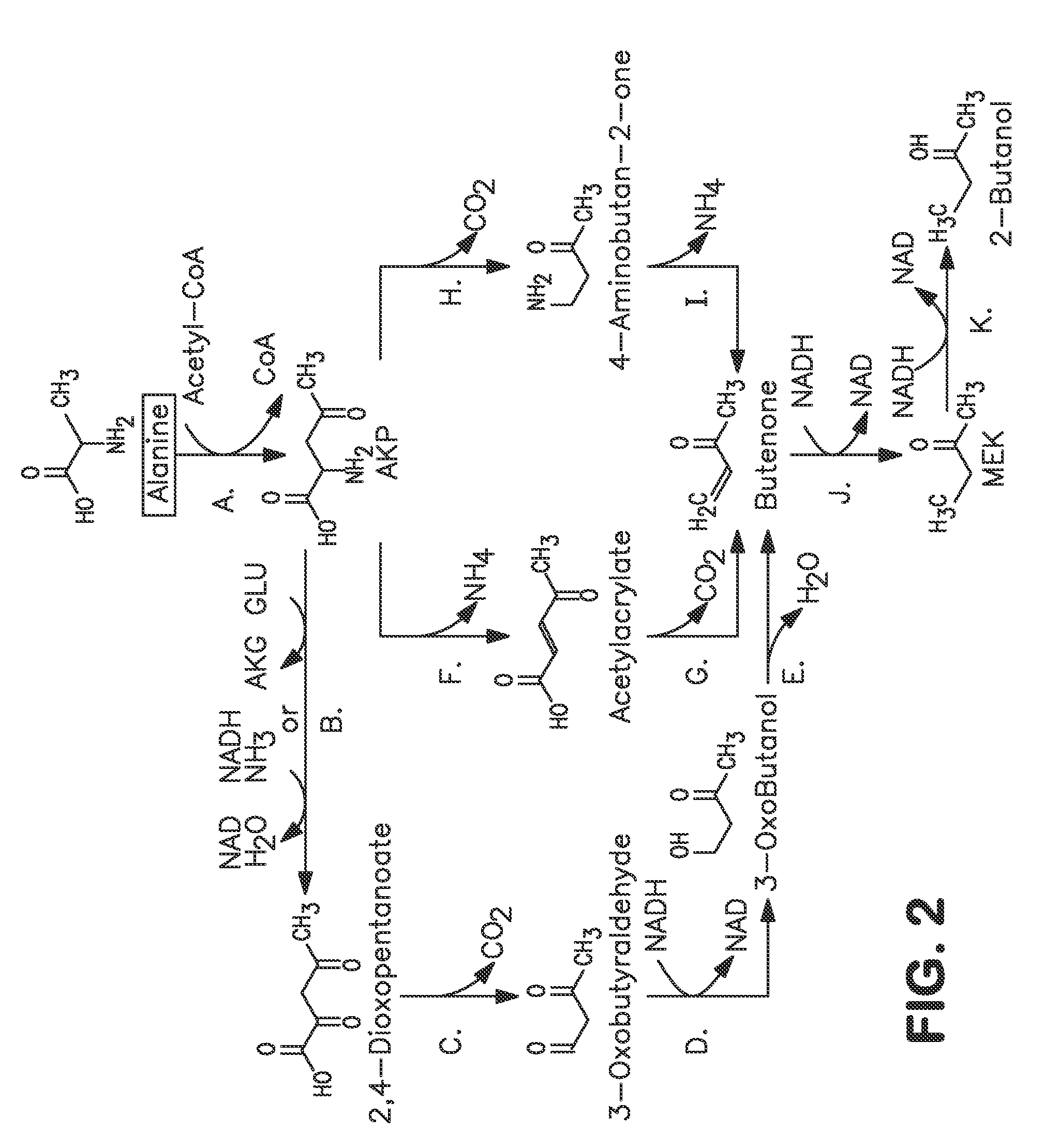
Microorganisms and methods for carbon-efficient biosynthesis of MEK and 2-butanol
A non-naturally occurring microbial organism has at least one exogenous nucleic acid encoding a MEK pathway enzyme expressed in a sufficient amount to produce MEK. The MEK pathway includes an enzyme selected from an acetoacetyl-CoA dehydrogenase (bifunctional), an acetoacetyl-CoA aldehyde dehydrogenase, a 3-oxobutyraldehyde reductase, a 3-oxobutanol dehydratase, an MEK oxidoreductase, a 3-oxobutyraldehyde aminotransferase, a 4-aminobutan-2-one deaminase, a 2-amino-4-ketopentanoate (AKP) thiolase, an AKP aminotransferase, a 2,4-dioxopentanoate decarboxylase, an AKP deaminase, an acetylacrylate decarboxylase, an AKP decarboxylase, a glutamate dehydrogenase, a 3-oxobutyraldehyde oxidoreductase (aminating) and an AKP oxidoreductase (aminating). A 2-butanol pathway further includes an MEK reductase. A method for producing MEK or 2-butanol includes culturing these organisms under conditions and for a sufficient period of time to produce MEK or 2-butanol.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
Wound dressings comprising hydrated hydrogels and enzymes
InactiveUS7731954B2Slow effectDelaying functioningPeptide/protein ingredientsPlastersWound healingWound dressing
A skin dressing, particularly a wound dressing, comprises oxidoreductase enzyme and, optionally, peroxidase enzyme, wherein the enzyme(s) are present in hydrated condition, e.g. being present in one or more hydrated hydrogels. The dressing is used by being located on the skin of a human or animal e.g. over a wound. The oxidoreductase enzyme catalyses a reaction that produces hydrogen peroxide from an appropriate substrate, the substrate either being naturally present in body fluids and / or being supplied separately and / or being incorporated into the dressing. The currently preferred oxidoreductase enzyme is glucose oxidase. The catalyses reaction of β-D-glucose substrate to give hydrogen peroxide and gluconic acid. A mixture of oxidoreductase enzyme can undergo reaction (optionally catalysed by the peroxidase enzyme) to produce a variety of species including reactive oxygen intermediates that have antimicrobial properties and that can therefore assist in promoting wound healing.
Owner:SYSTAGENIX WOUND MANAGEMENT (US) INC
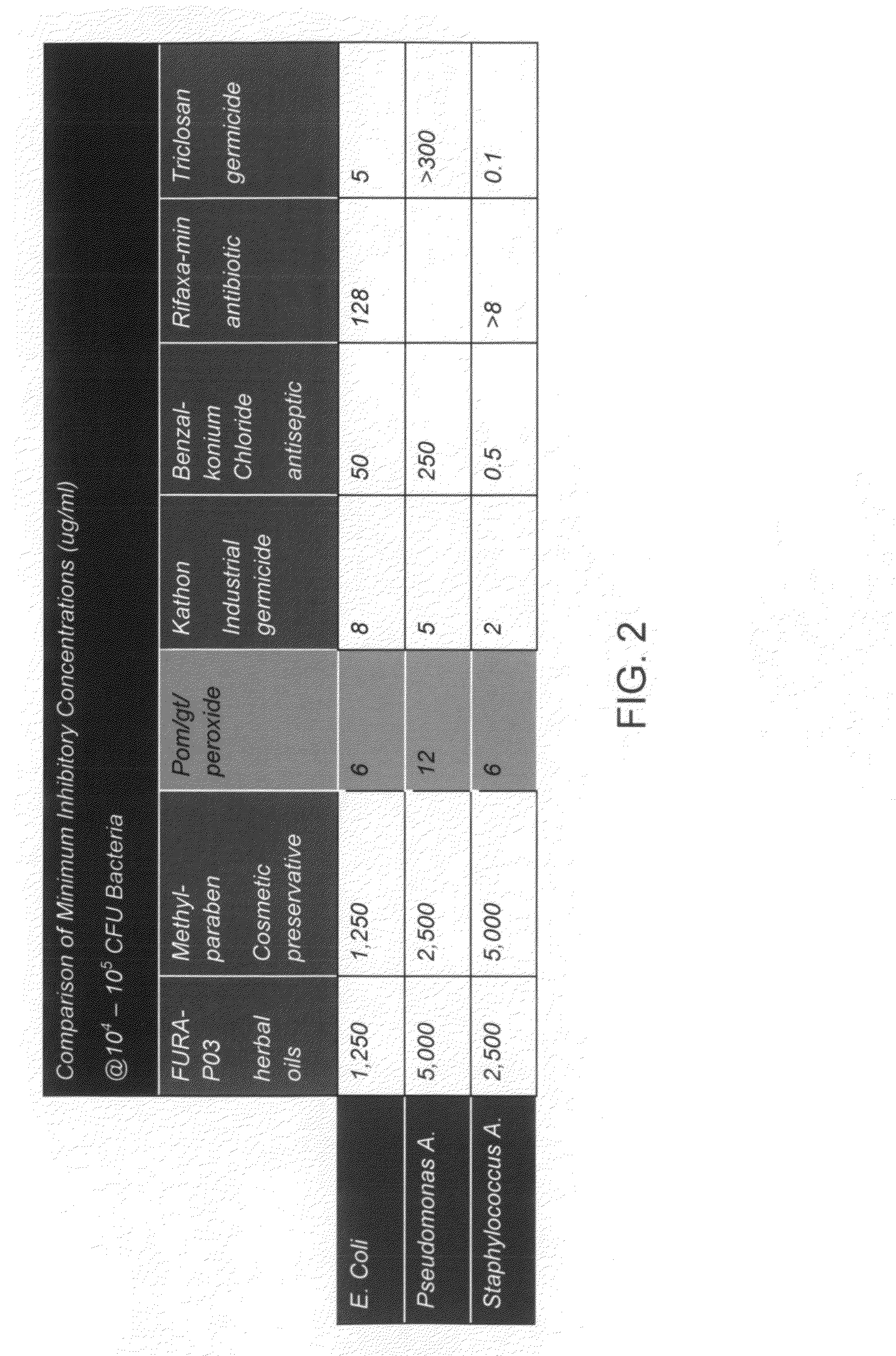
Food ingredients and food products treated with an oxidoreductase and methods for preparing such food ingredients and food products
InactiveUS20060008555A1Prevent excessive browning of the cheese during heatingReduce absorptionMilk preparationOxidoreductasesDairy foodsAdditive ingredient
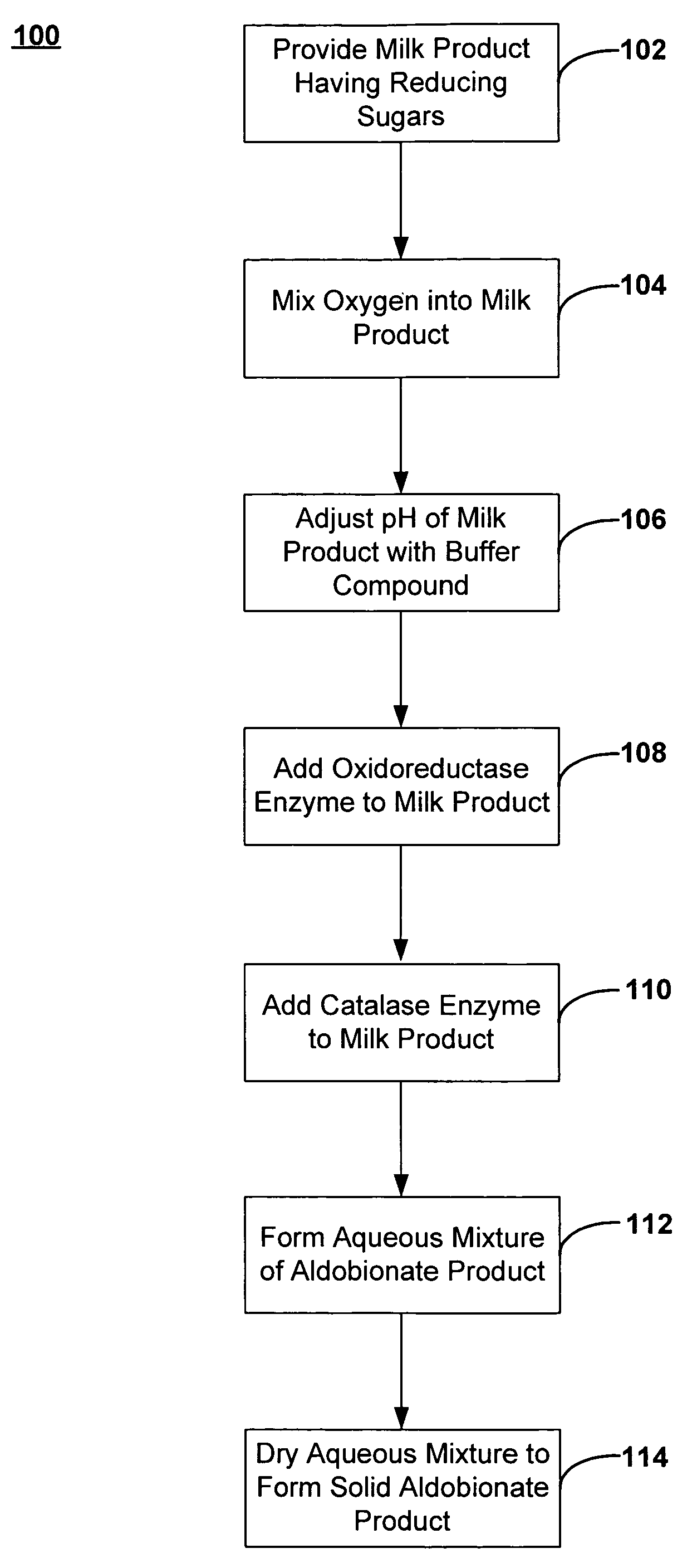
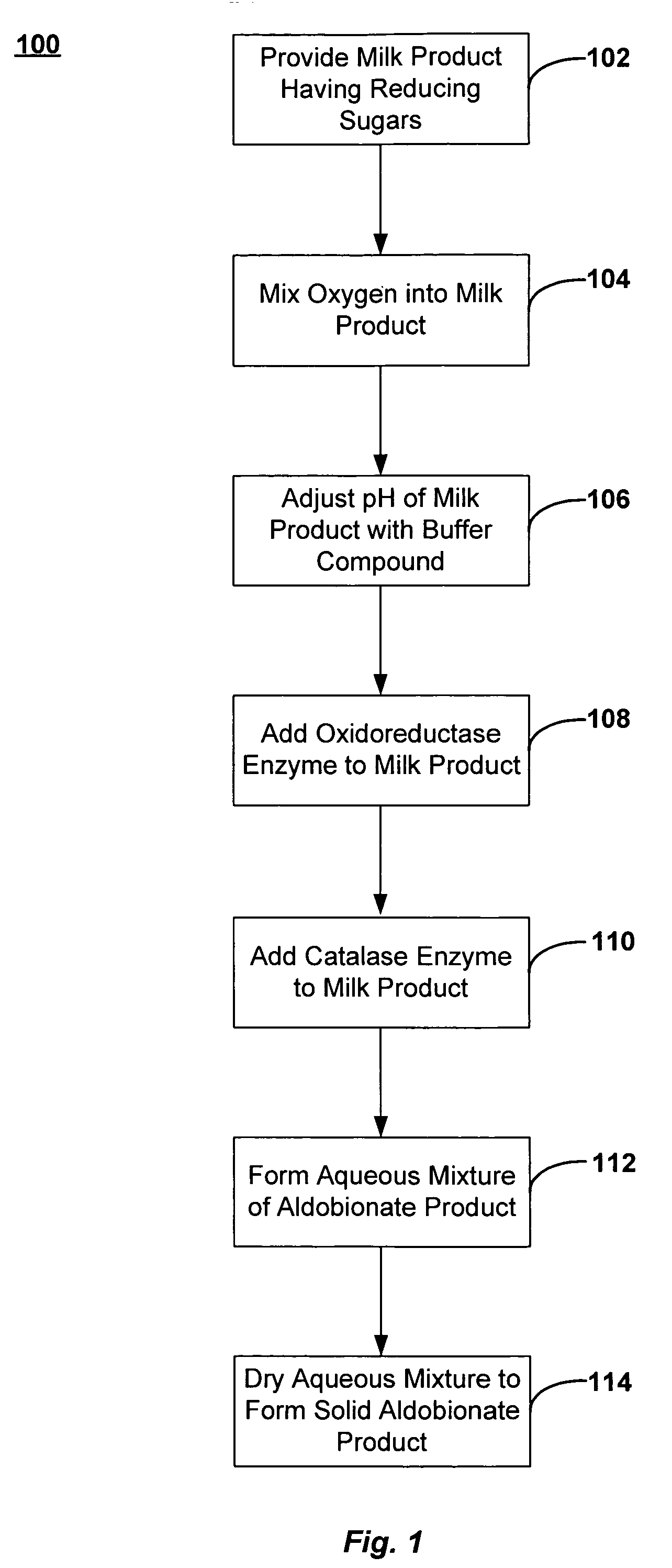
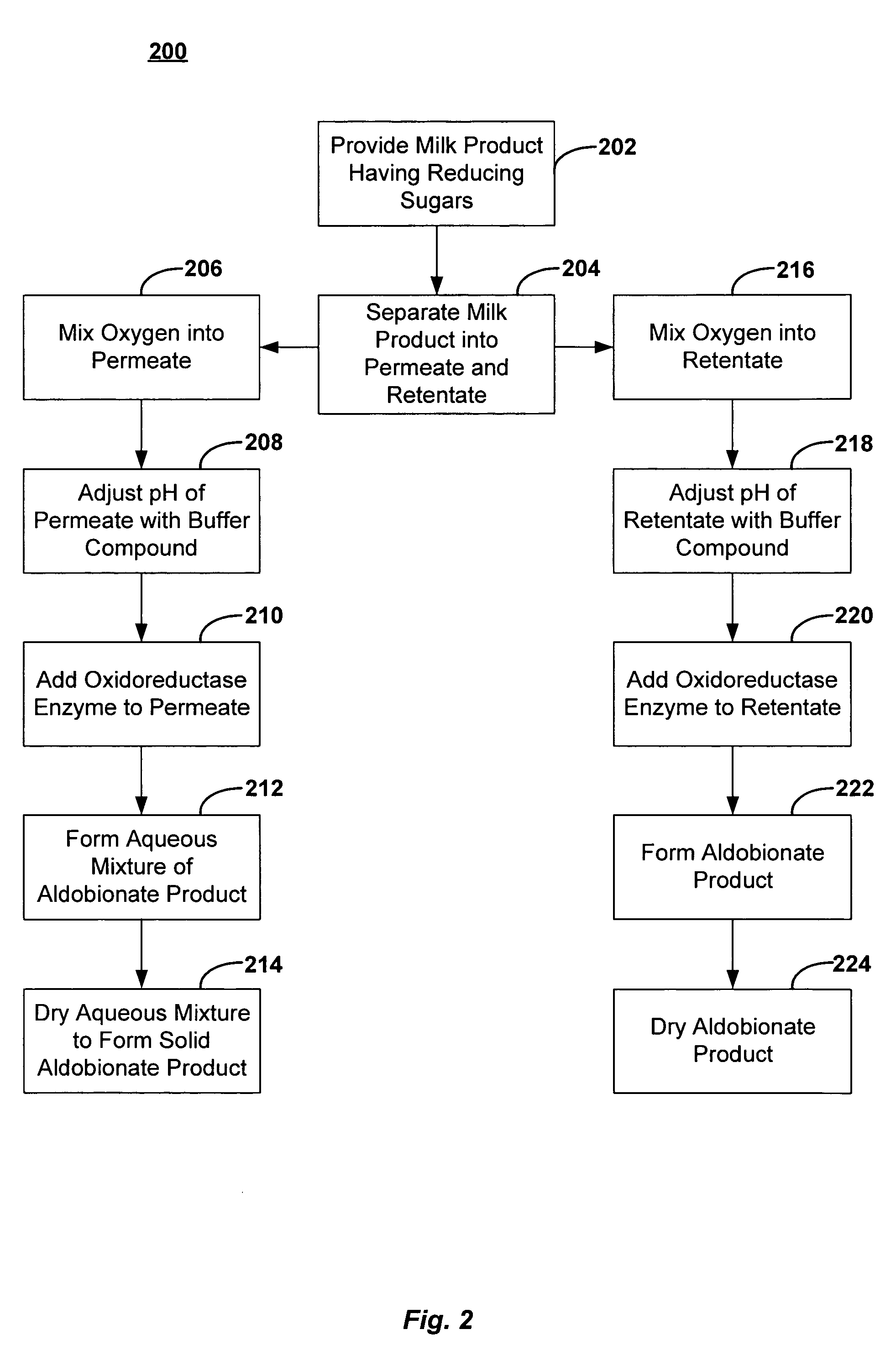
A method of making an aldobionate product is described. The method may include providing a milk product having one or more reducing sugars, and maintaining a pH of the milk product at about 5.5 or more by adding a buffer compound to the milk product. The method may also include adding an oxidoreductase enzyme to the milk product, where at least a portion of the reducing sugar is oxidized into the aldobionate product. In addition, a method of making an aldobionate product is described that includes the steps of providing a milk product comprising a reducing sugar, mixing oxygen into the milk product, and adding an oxidoreductase enzyme to the milk product, where at least a portion of the reducing sugar is oxidized into the aldobionate product.
Owner:LEPRINO FOODS
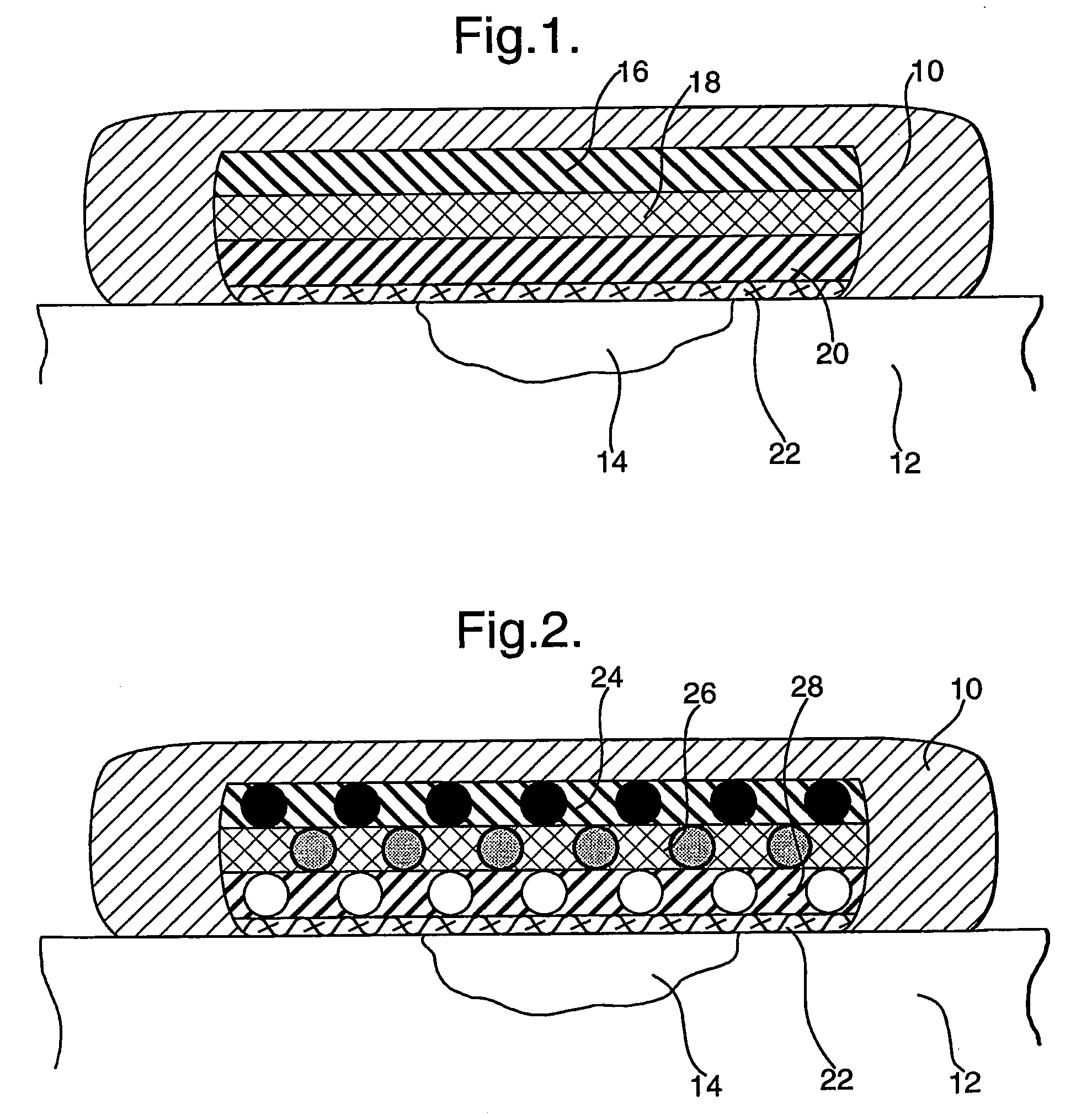
Skin dressings containing oxidoreductase enzyme
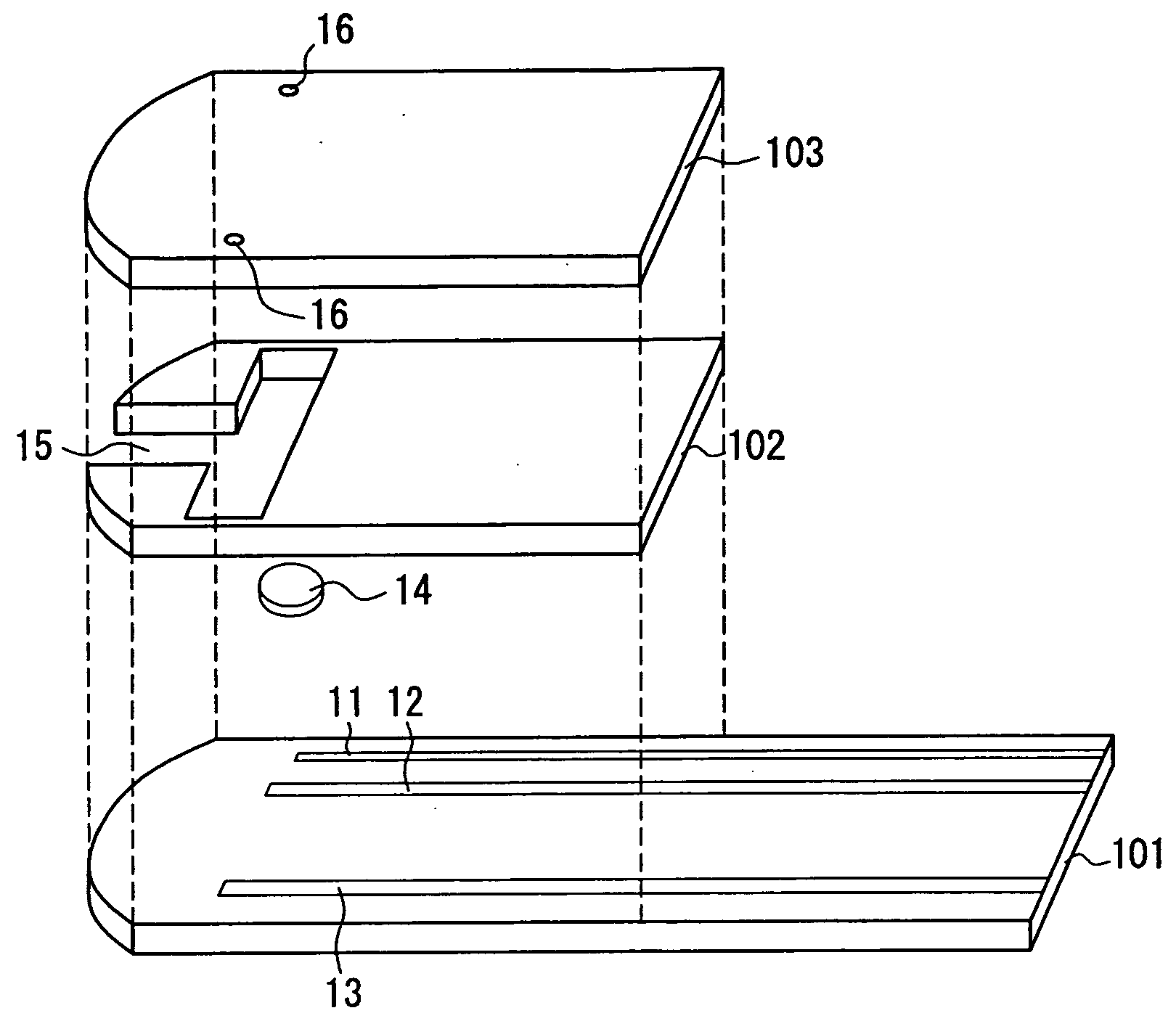
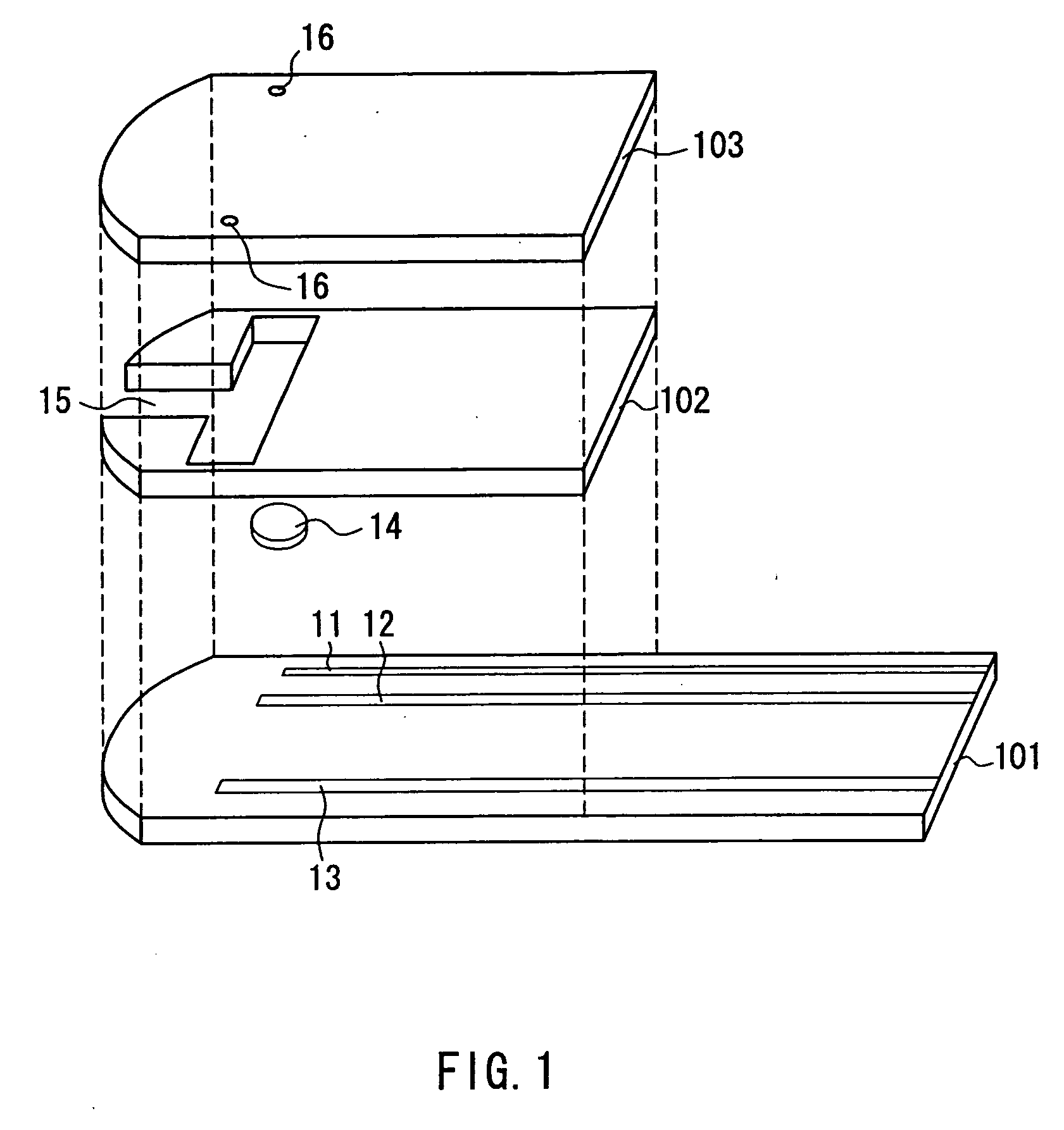
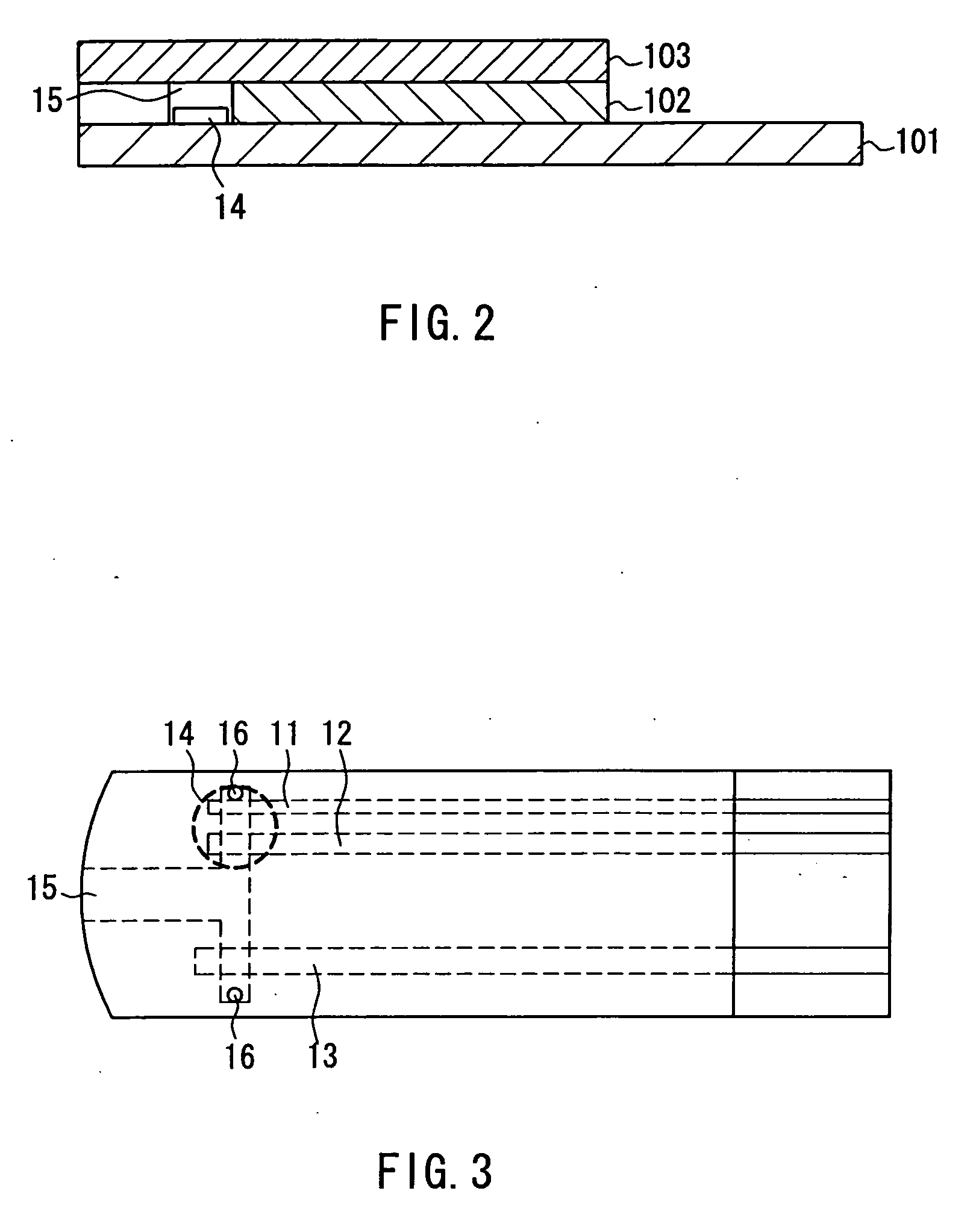
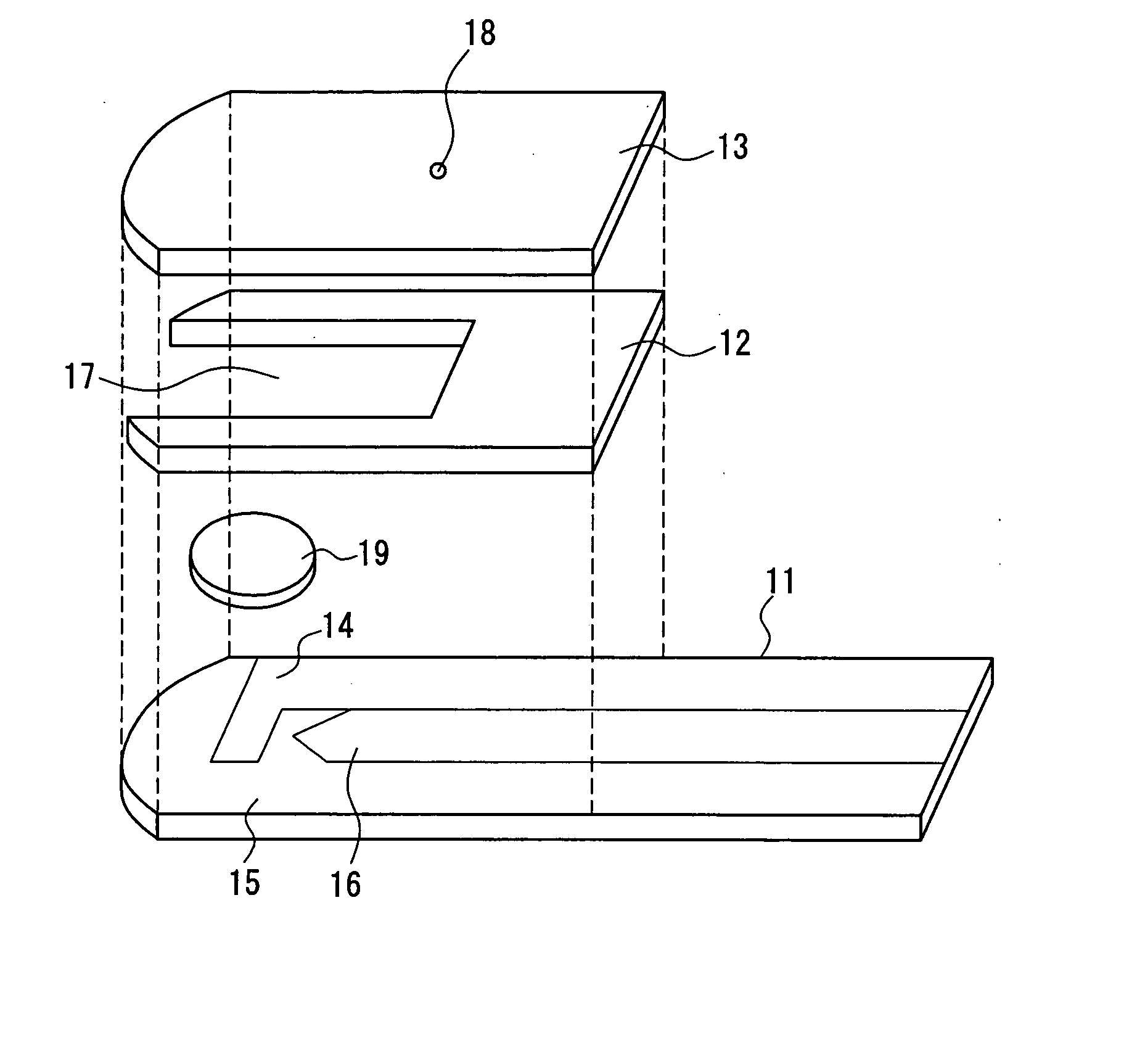
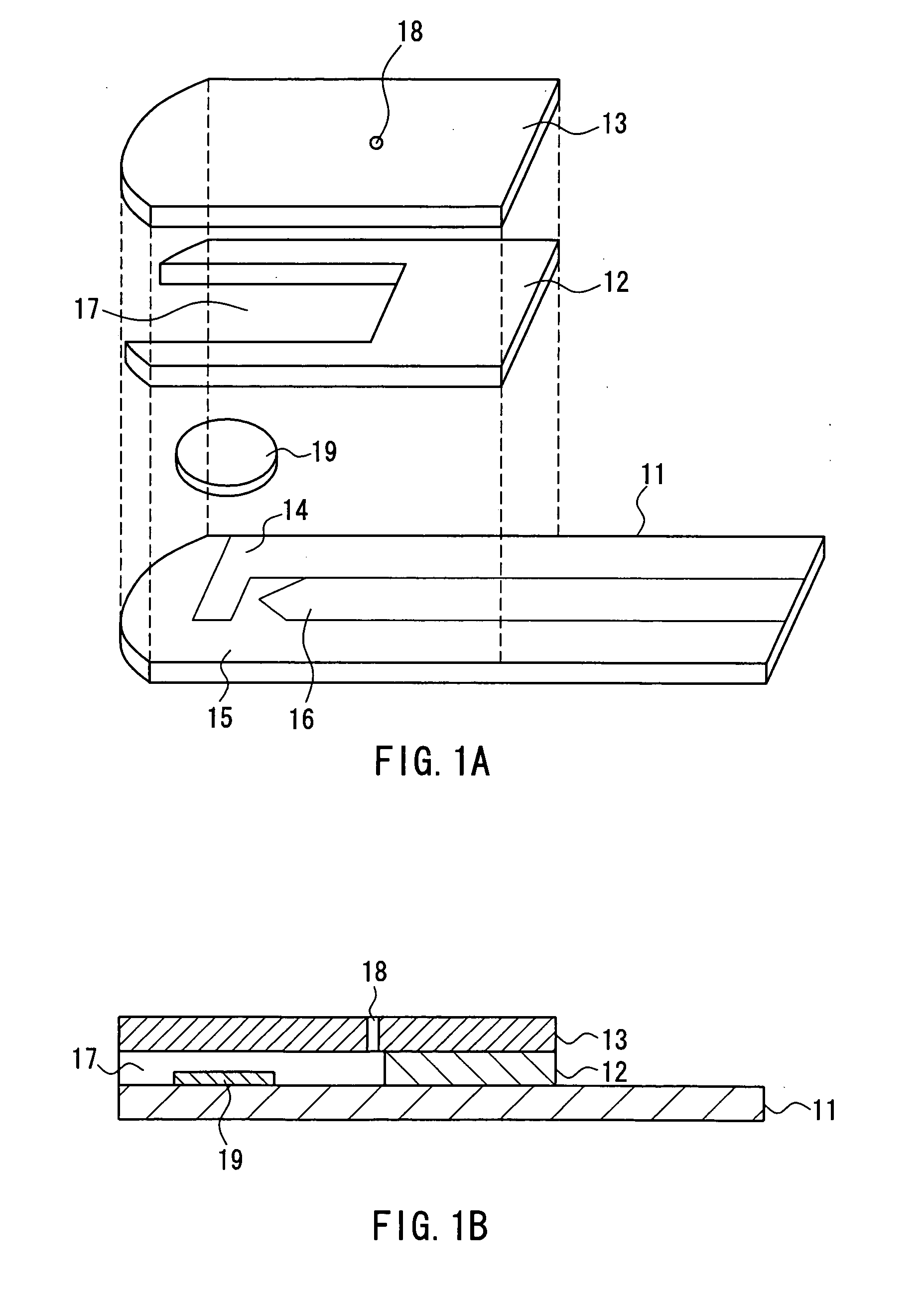
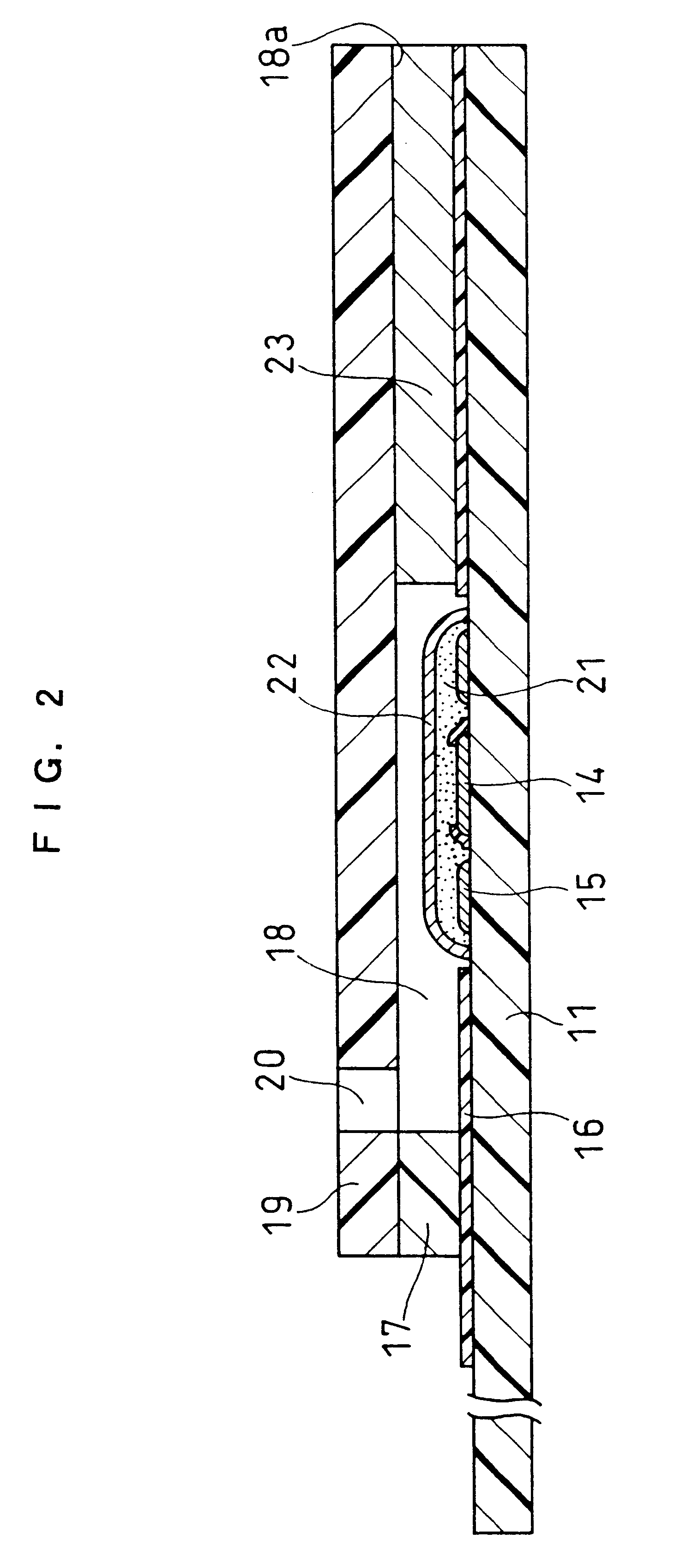
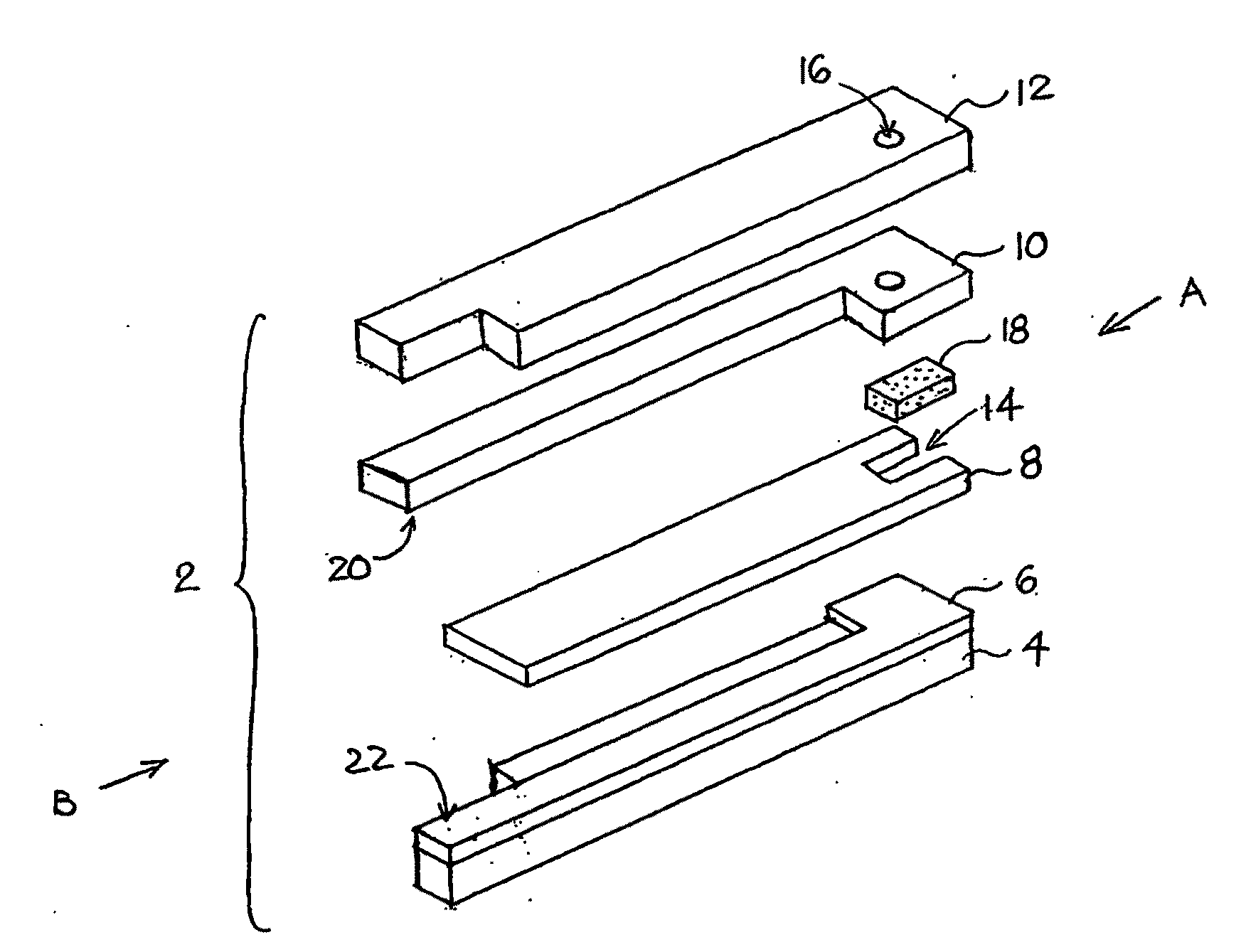
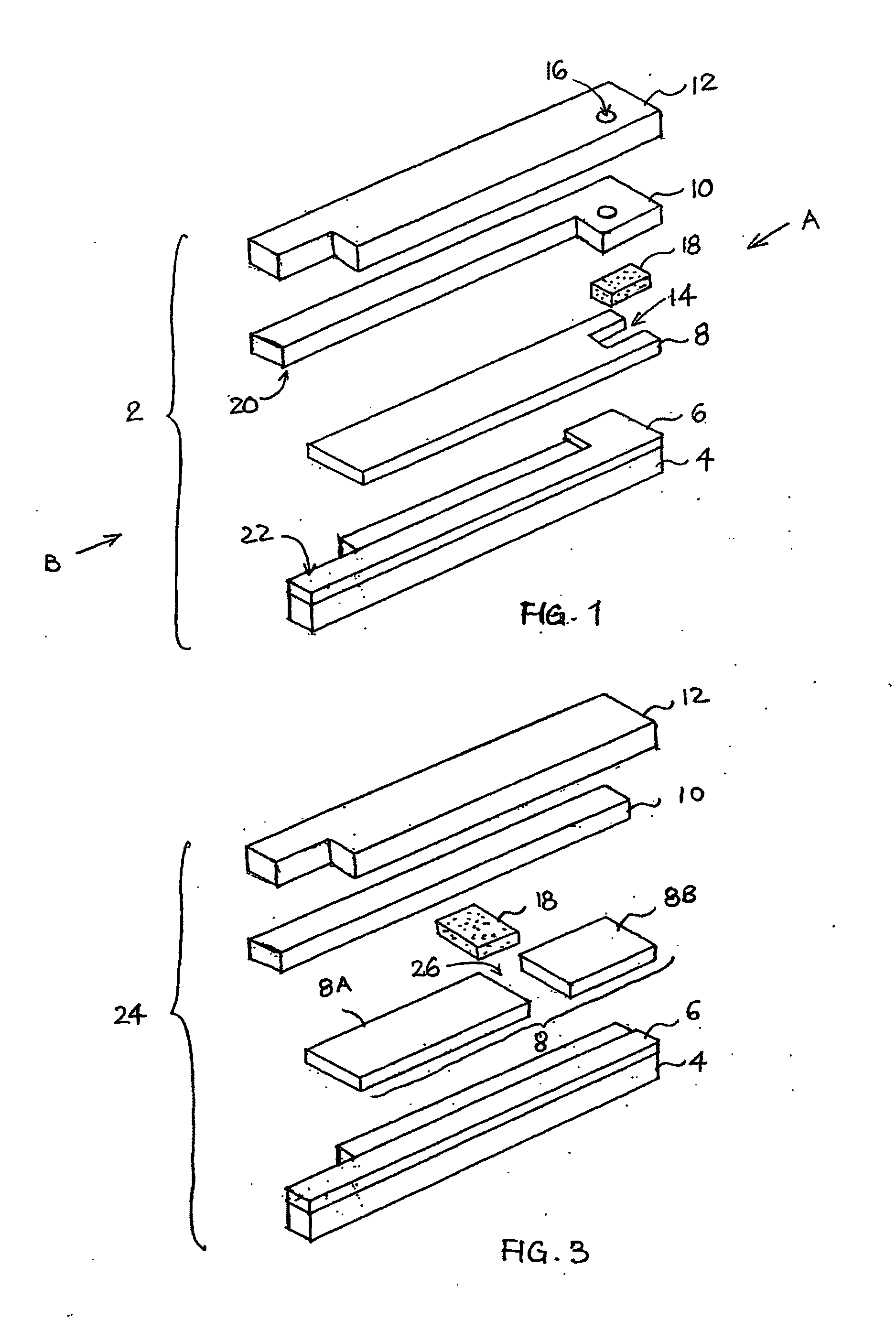
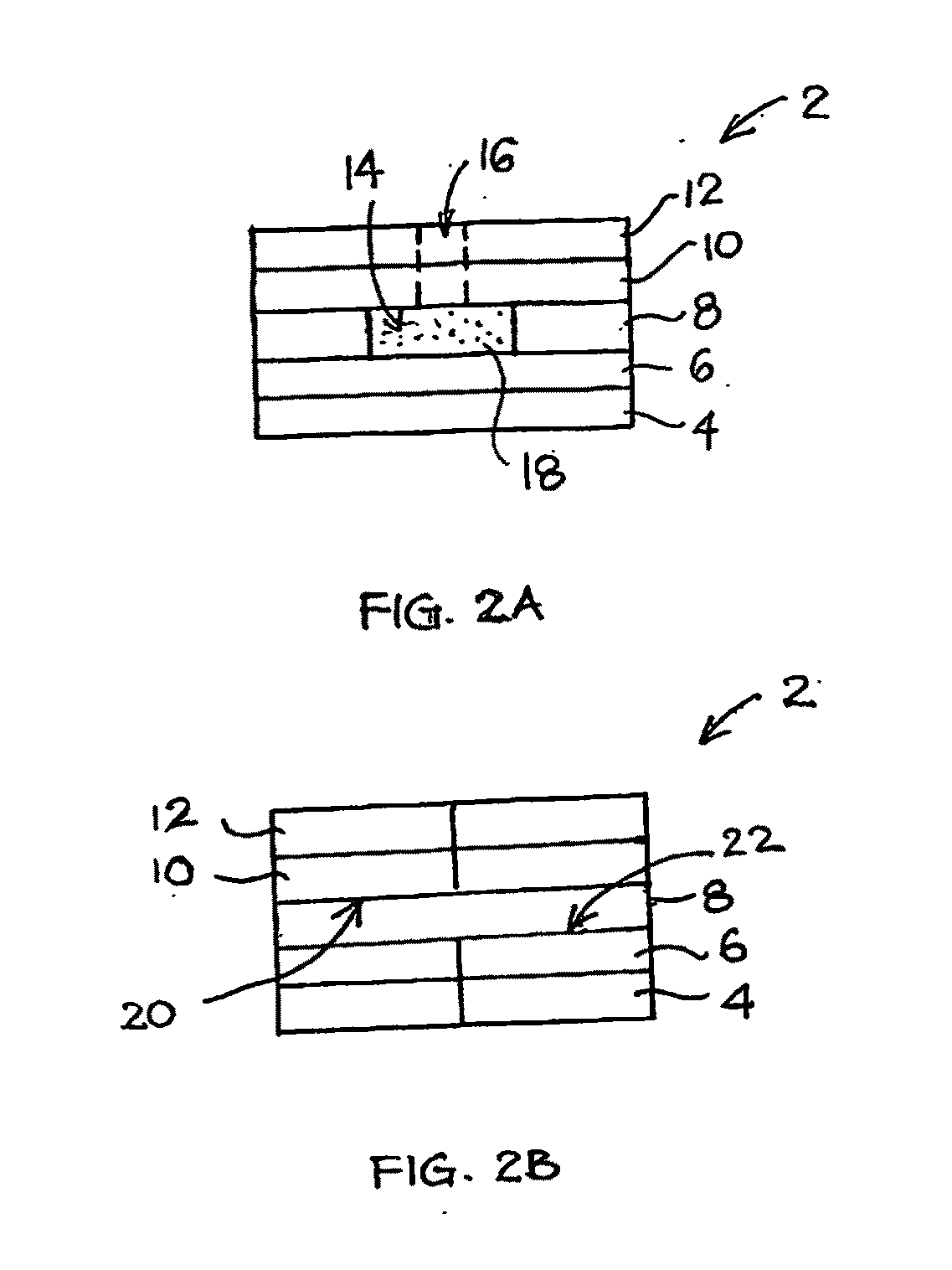
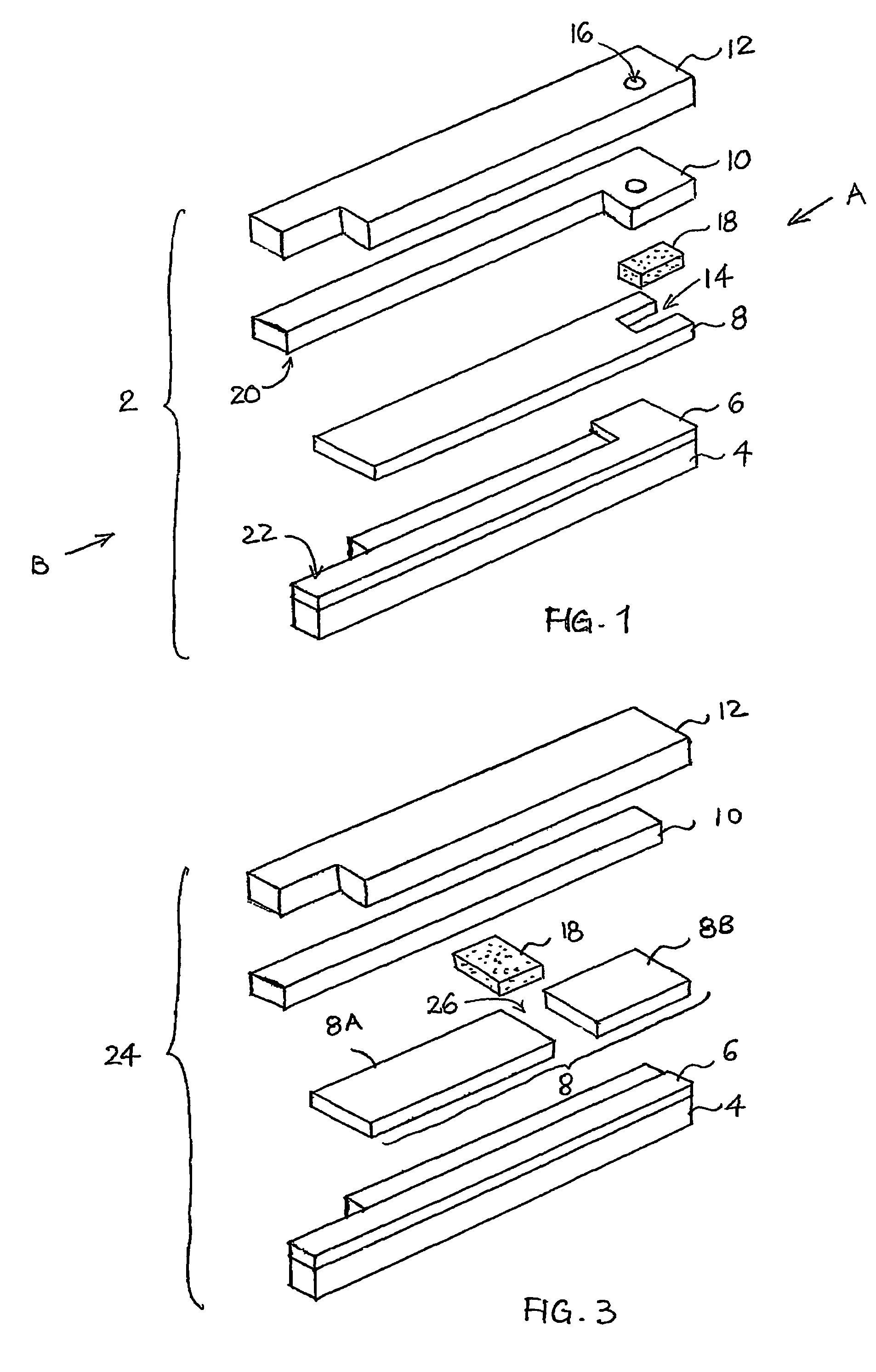
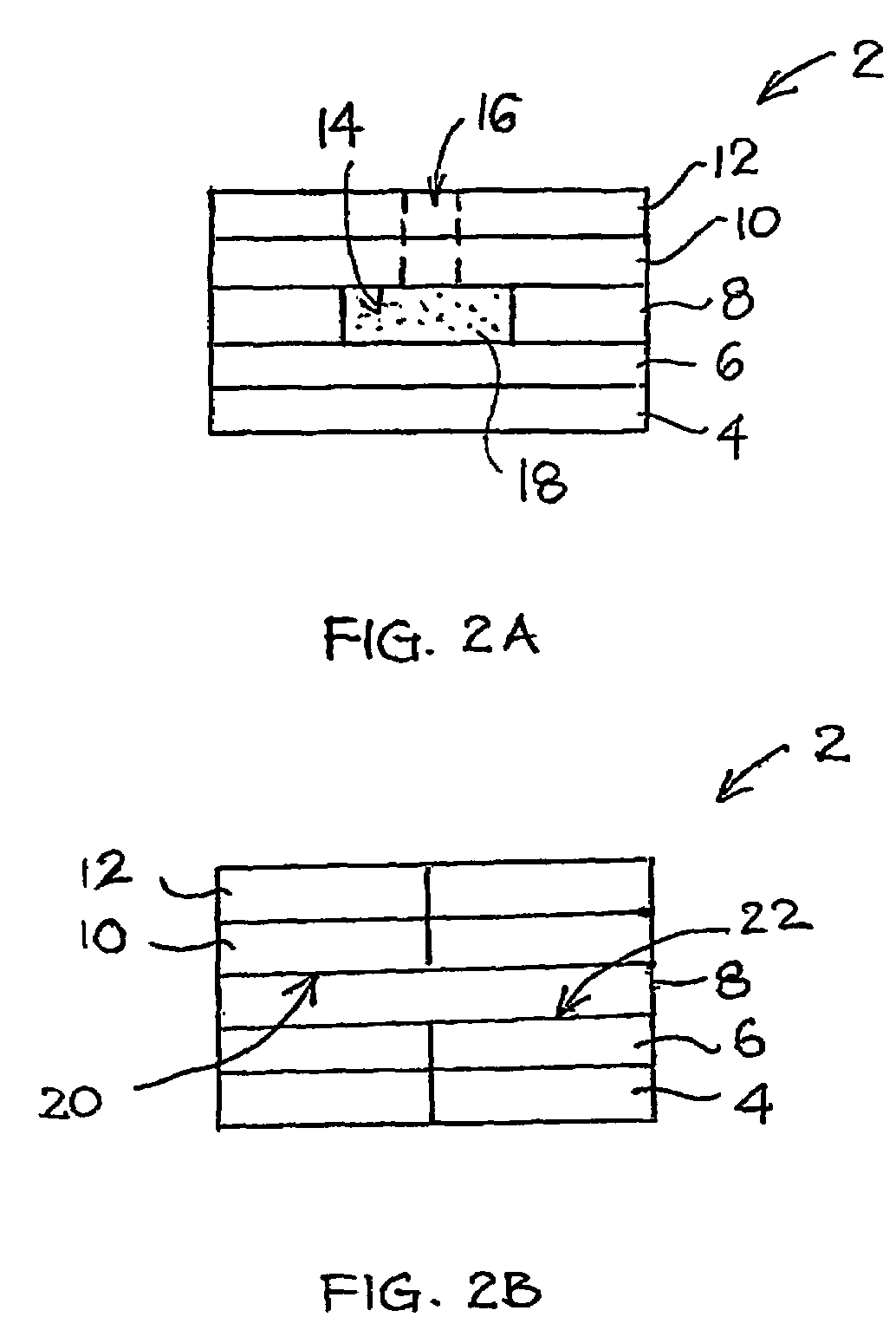
ActiveUS20060275350A1Prevent potentially damaging build-upPromote wound healingPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementOxidoreductaseTissue skin
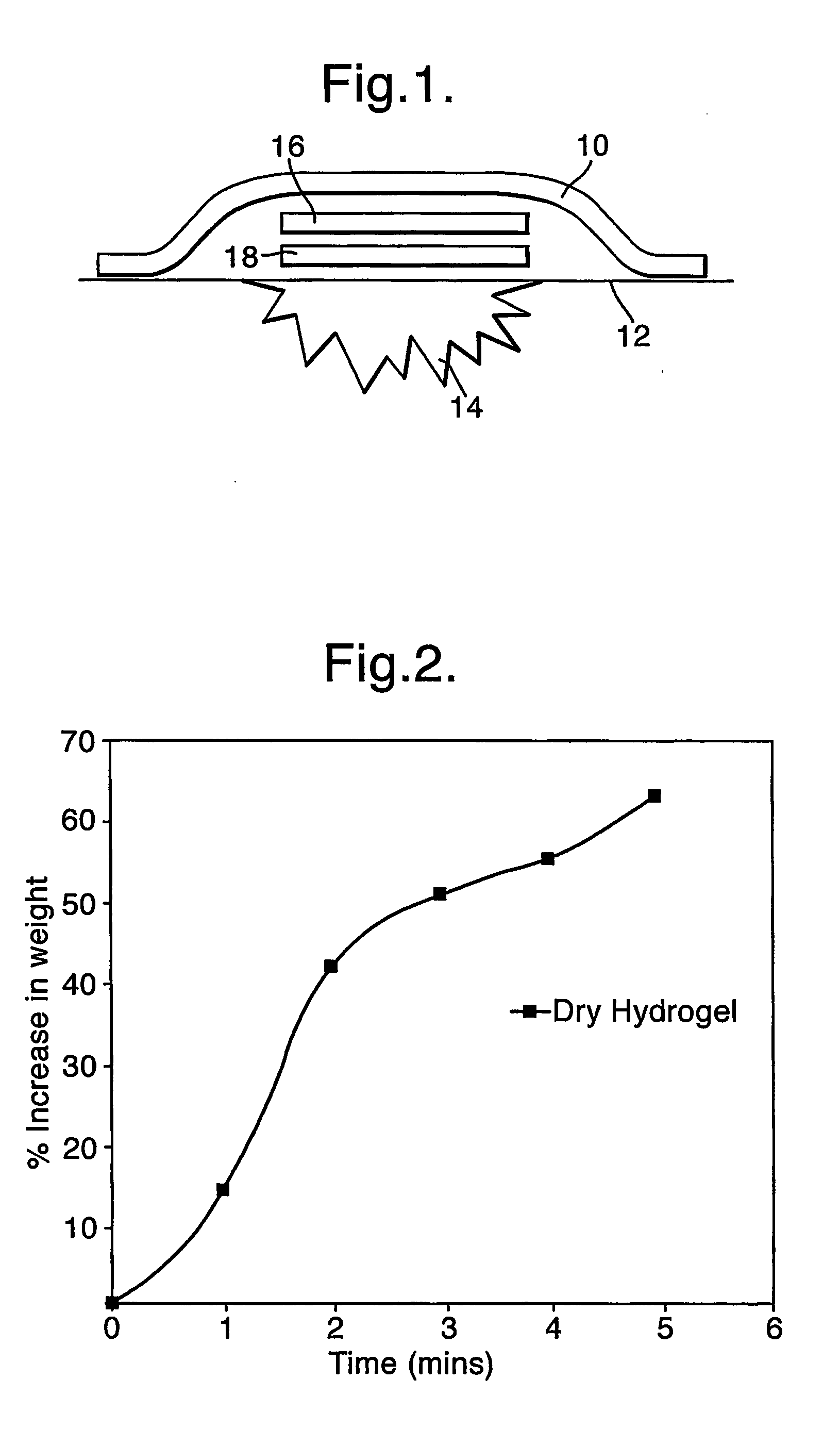
A skin dressing comprises a first dressing component (16) carrying oxidoreductase enzyme in dried condition; and a second dressing component (18) carrying a source of water, such that when the first and second dressing components are placed in fluid communication with each other, water migrates from the second component towards the first comportent and acts to hydrate enzyme carried by the first component, at least at the surface of the first component. The dressing components are kept separate before use, e.g. being sealed in separate sterile, water-impervious packages such as laminated aluminium foil pouches. In use of the dressing, the second dressing component is located on the skin of a human or animal, e.g. over a wound to be treated or on a region of skin to be treated for cosmetic or therapeutic purposes such as for treatment of acne or other skin conditions. The first dressing component is placed on top of the second component in fluid communication therewith. In embodiments comprising only first and second dressing components, the first dressing component is placed in direct contact with the second dressing component. Water from the second component migrates towards the first comportent and acts to hydrate enzyme carried by the first component, at least at points of contact at the interface between the first and second components. Once hydrated, the oxidoreductase enzyme can immediately begin functioning in known manner with beneficial effects.
Owner:SYSTAGENIX WOUND MANAGEMENT (US) INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com