System for control of stickies in recovered and virgin paper processing
a technology of stickies and paper processing, applied in the field of paper making processes, can solve the problems of stickies wet end breaks, etc., and achieve the effect of optimizing activity and improving removal and/or control of adhesive materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Comparison of Treatment with Enzyme Alone, Absorbent Alone, and Enzyme in Combination with Absorbent Under Controlled Conditions
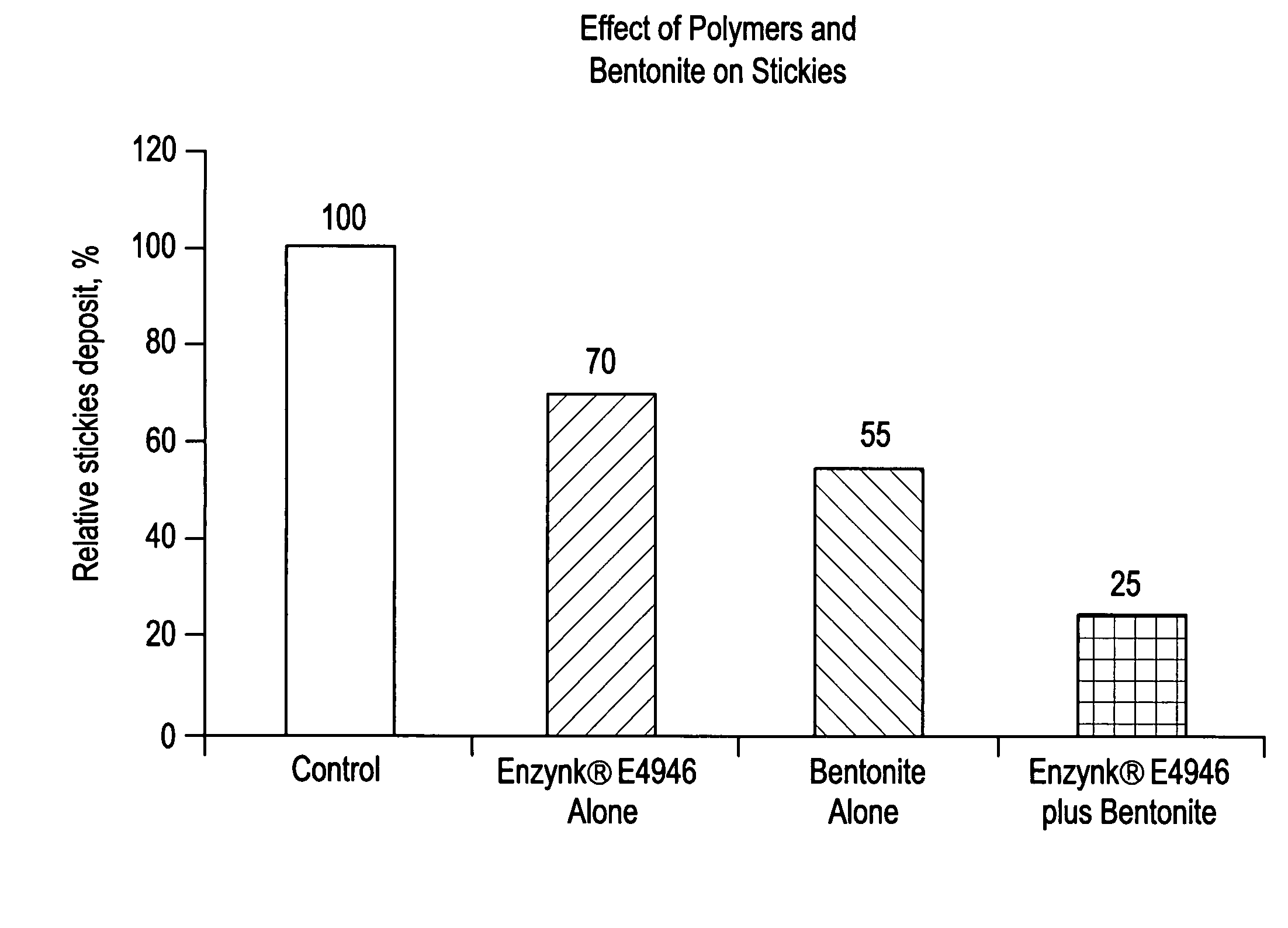
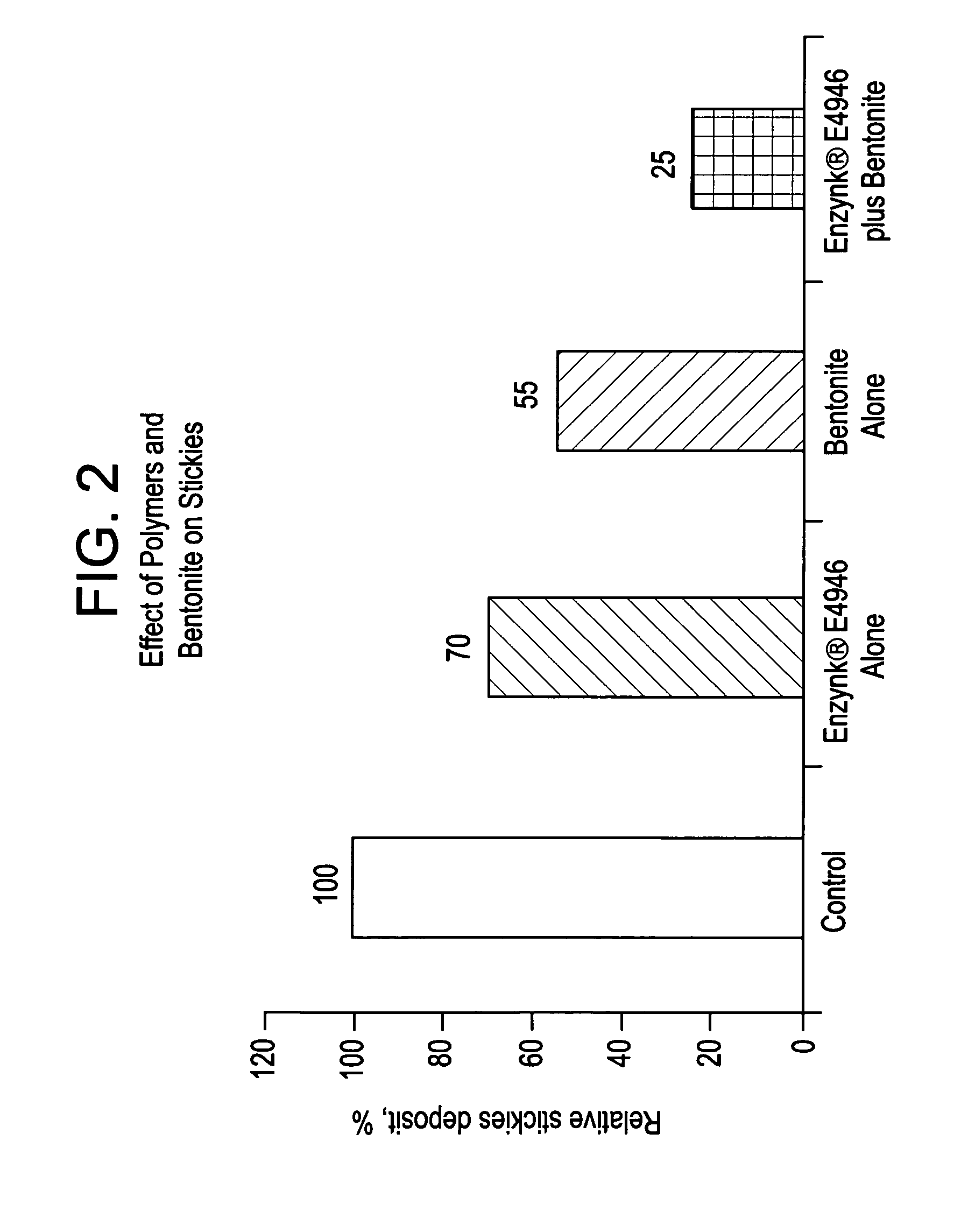
[0044] A comparative study was conducted to look at stickies removal using enzymes (Enzynk® E4946, a mixture of acid and neutral cellulases, amylases, and lipases obtained from Enzymatic Deinking Technologies, LLC, Norcross, Ga. USA) treatment alone, activated bentonite treatment alone, and the combination of enzymes and activated bentonite treatment, in the laboratory in a Kitchen Aid mixer under highly controlled conditions of temperature, time (one hour), dosage, mixing conditions, and stickies.
[0045] The furnish treated was a 60 / 40 blend of US mixed office white ledger waste and office pack. A 1.5 kg quantity of the furnish was pulped in a high consistency pulper. Stickies were contributed from the waste paper plus an additional amount was added to ensure the batch contained a high quantity of stickies. Stickies added were 1 page of Avery Labels (#516...
example 2
Large Scale Study Comparing Enzyme Treatment Alone, Absorbent Alone, and the Combination of Enzyme and Absorbent
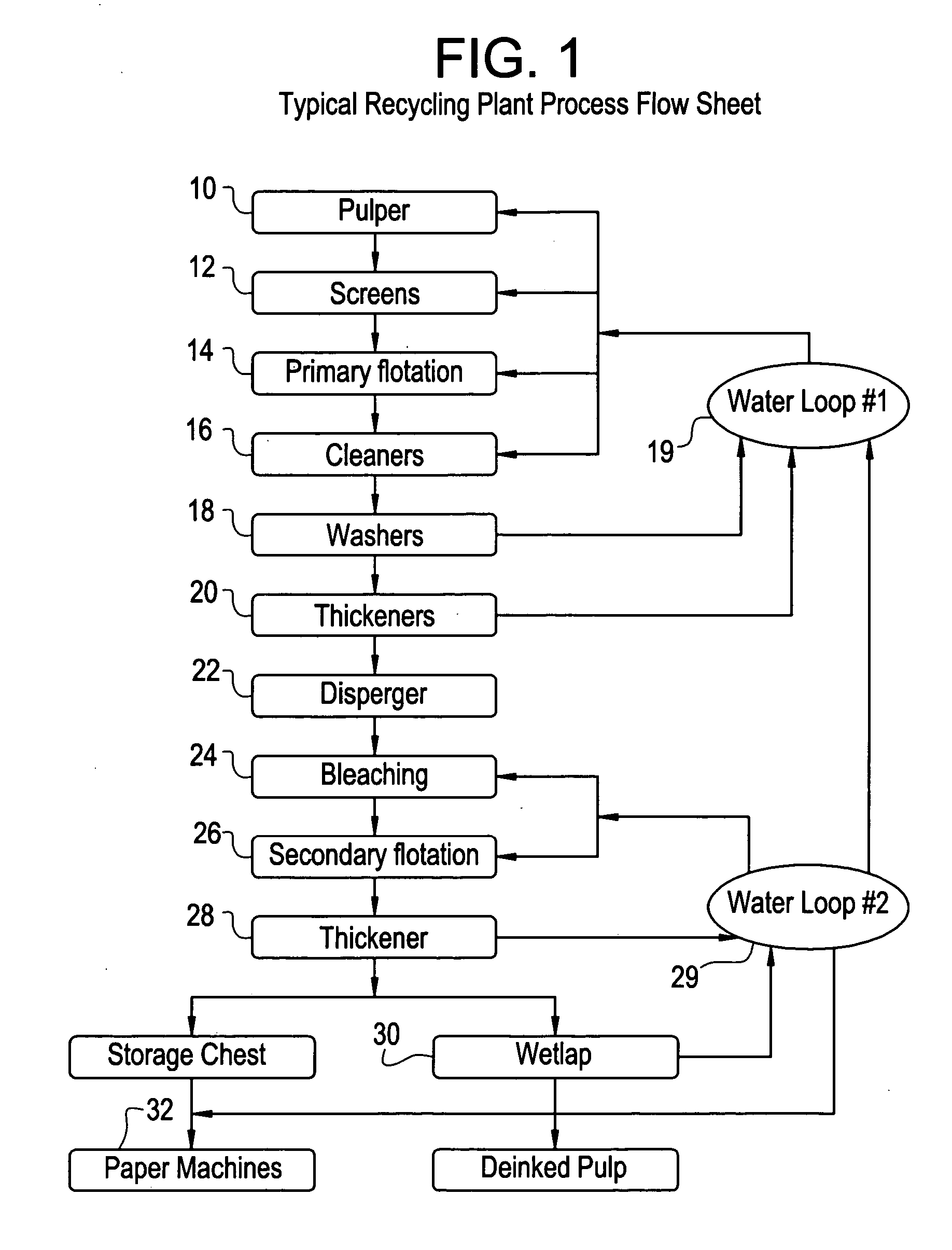
[0047] This study was conducted at a waste paper processing mill under normal processing conditions. Materials were added at the pulper. 1.5 kg Enzynk® E2028 was added per ton wastepaper and 4.0 kg EnzAid® A3300 (activated bentonite) was added per ton mixed office wastepaper. The Enzynk® E2028 is a mixture of acid and neutral cellulases, amylases, and lipases and the EnzAid® A3300 is an activated bentonite treatment. Enzymes and bentonite were added at the pulper. Analyses consisted of light microscope examination of filtrate of machine chest stock after having been passed through a machine fabric.
[0048] As shown in FIG. 3, the stickies count (area, ppm) is significantly reduced by enzyme treatment alone and by bentonite treatment alone, from 3.50 to 2.62 and 2.52, respectively. However, treatment with the combination of enzyme and adsorbent provides an even more strikin...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com