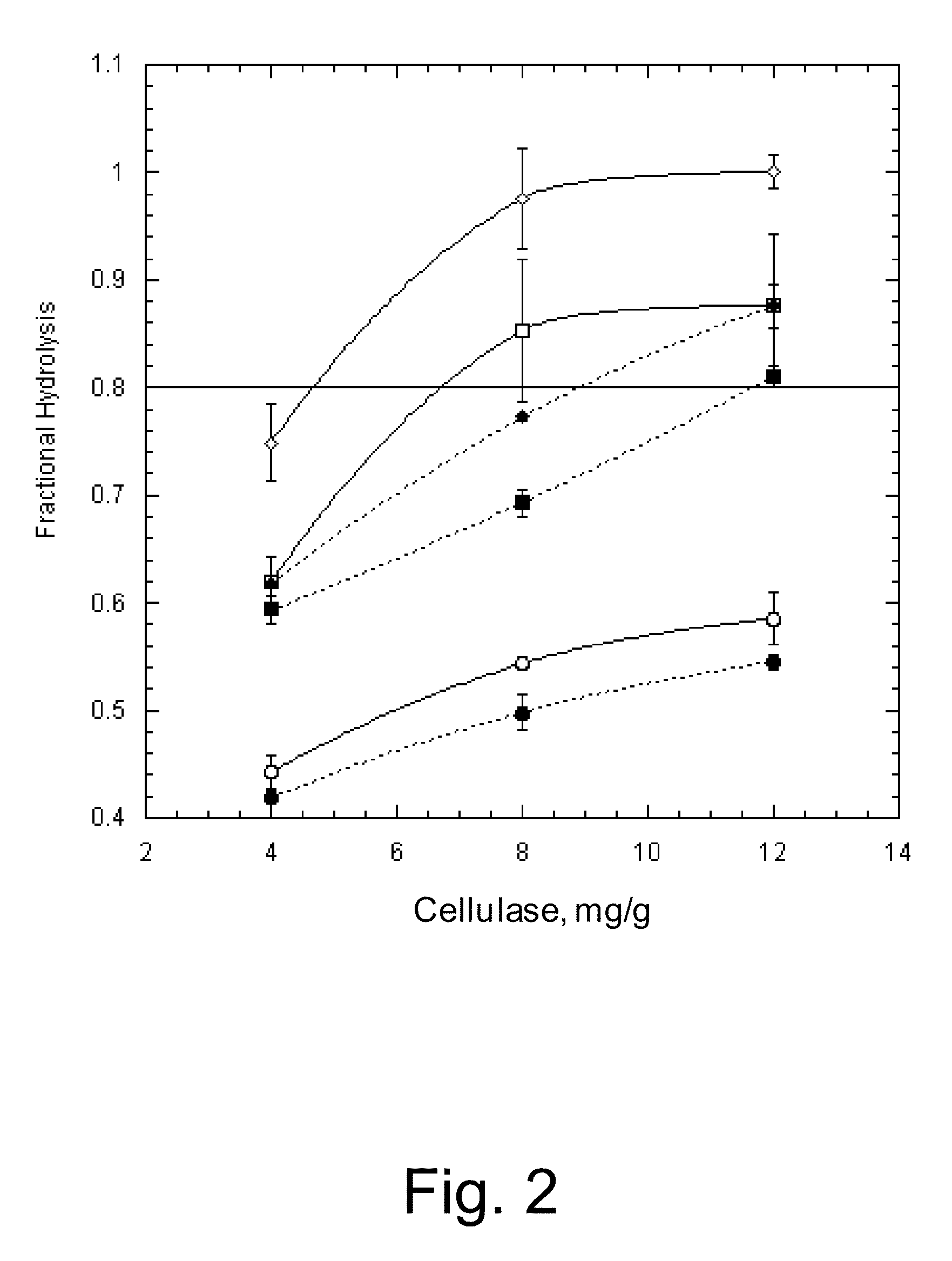
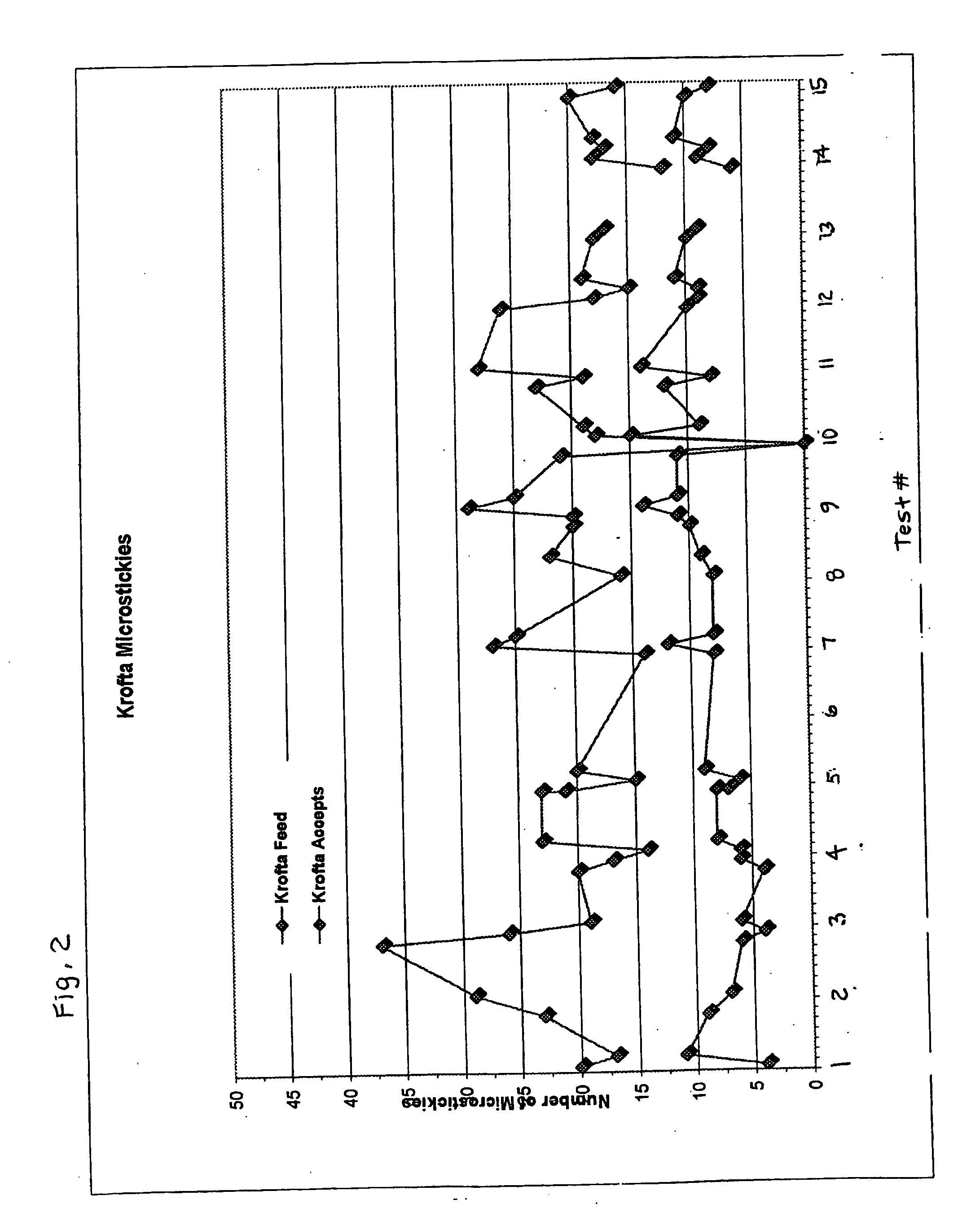
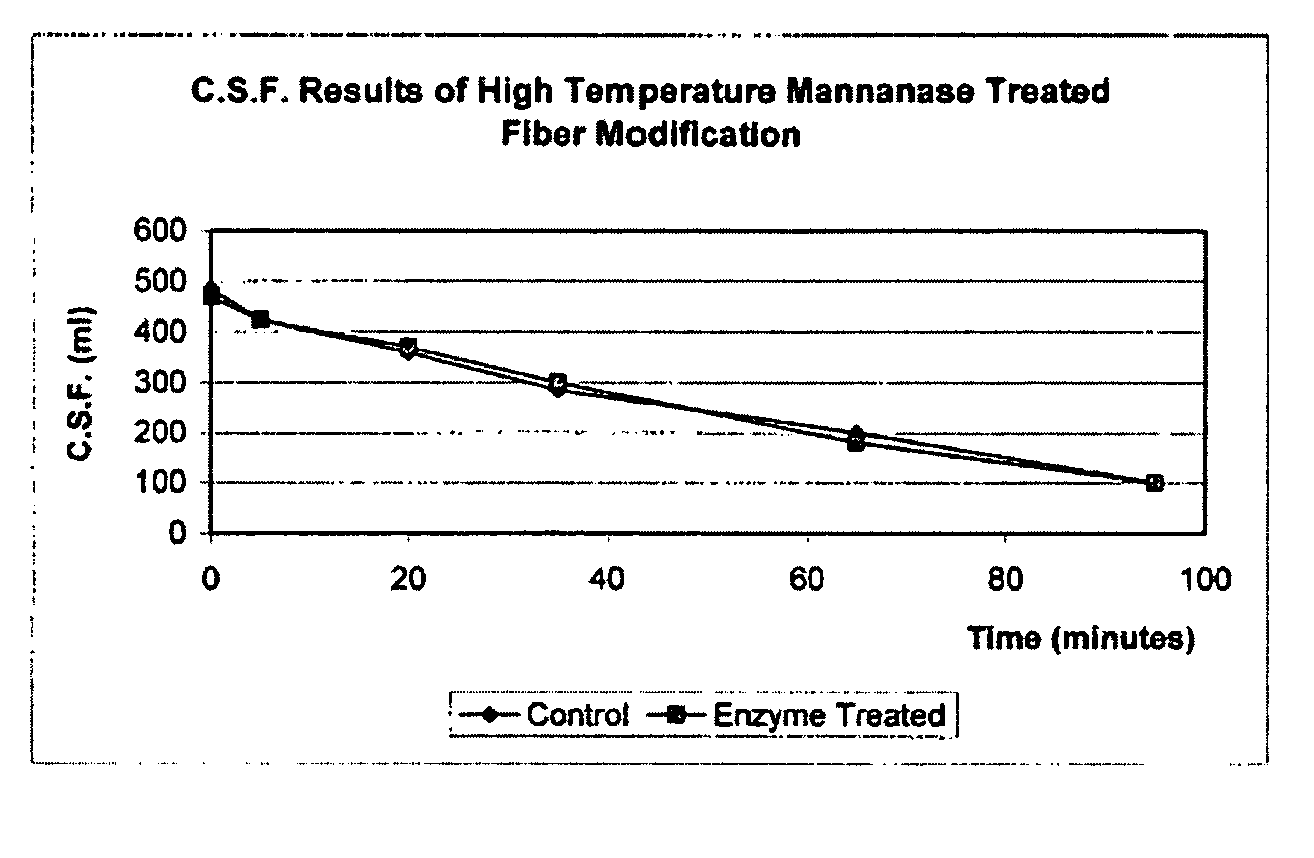
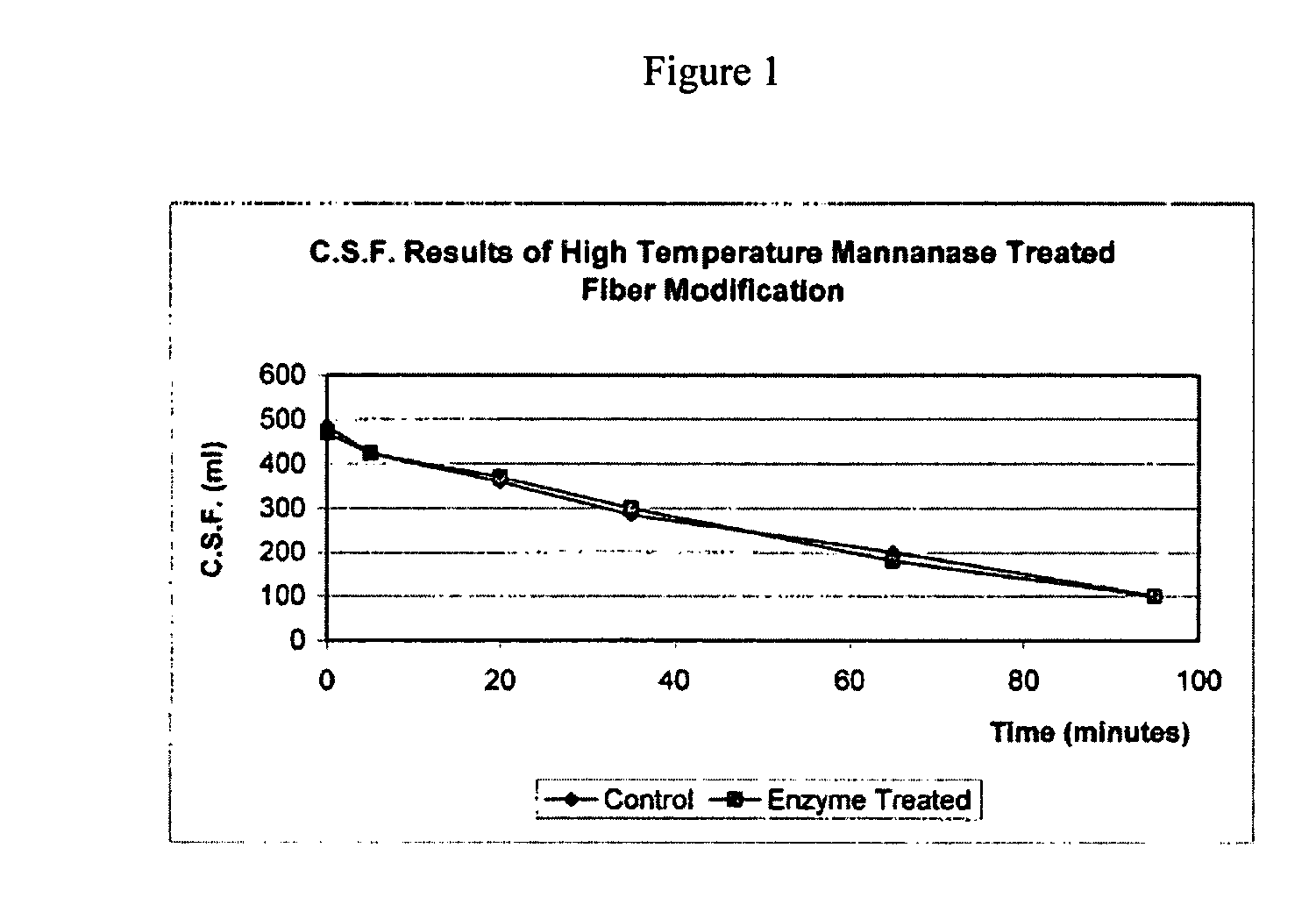
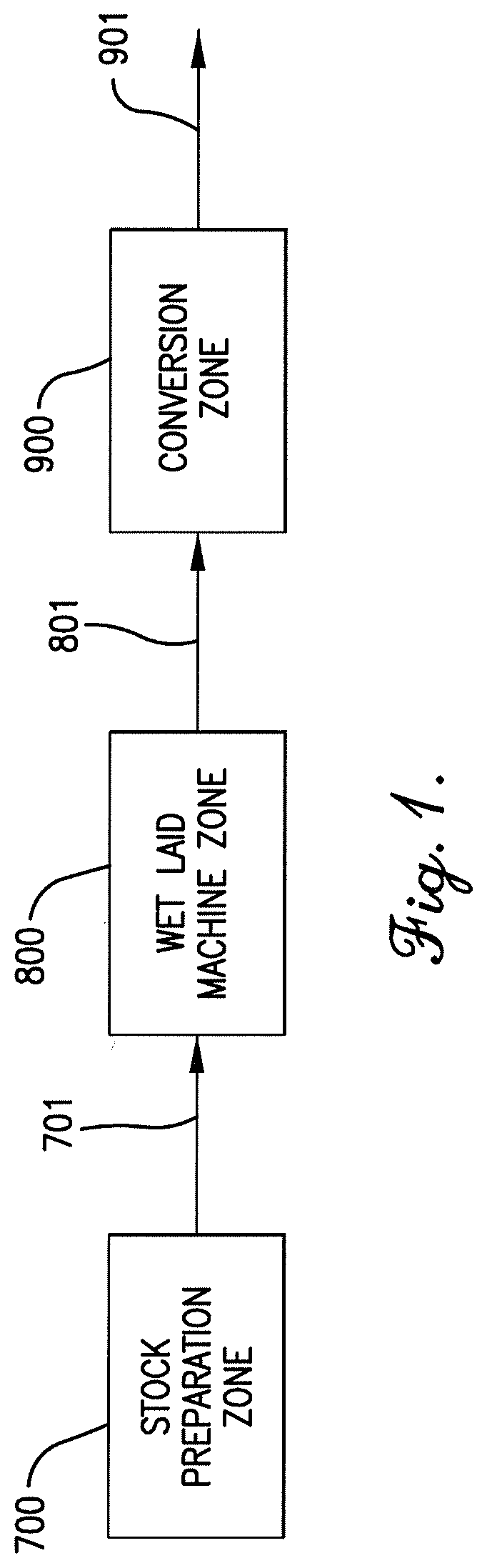
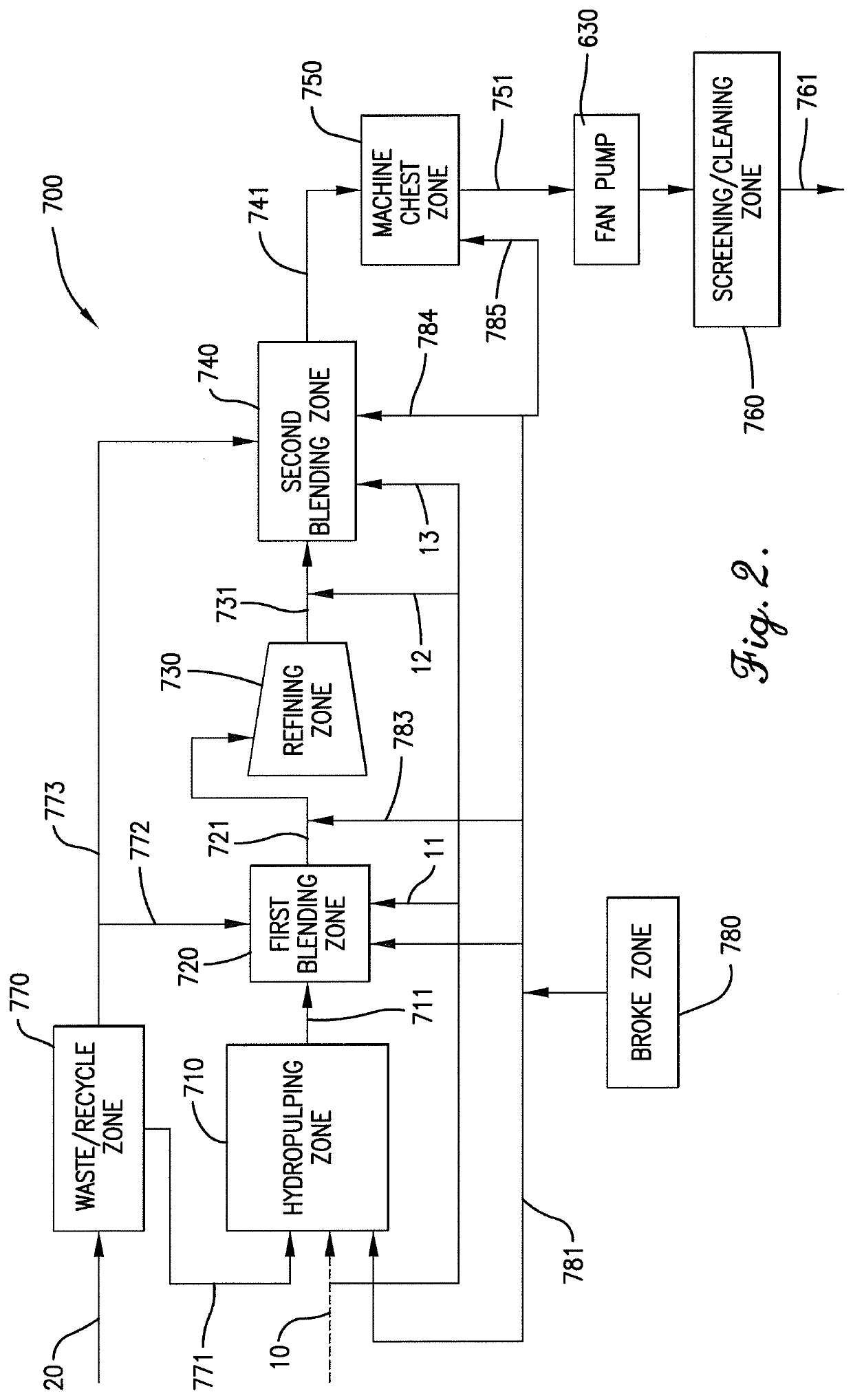
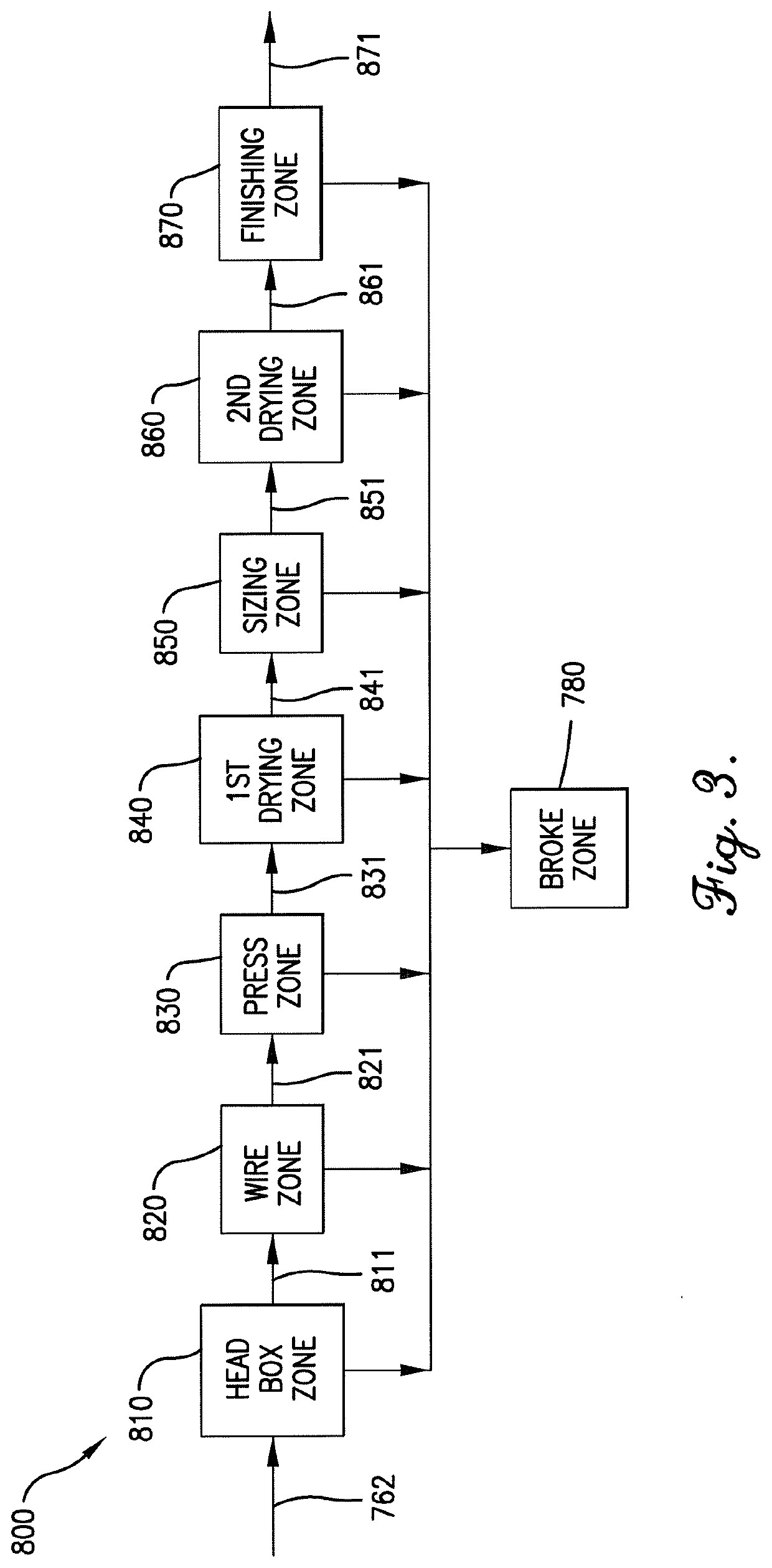
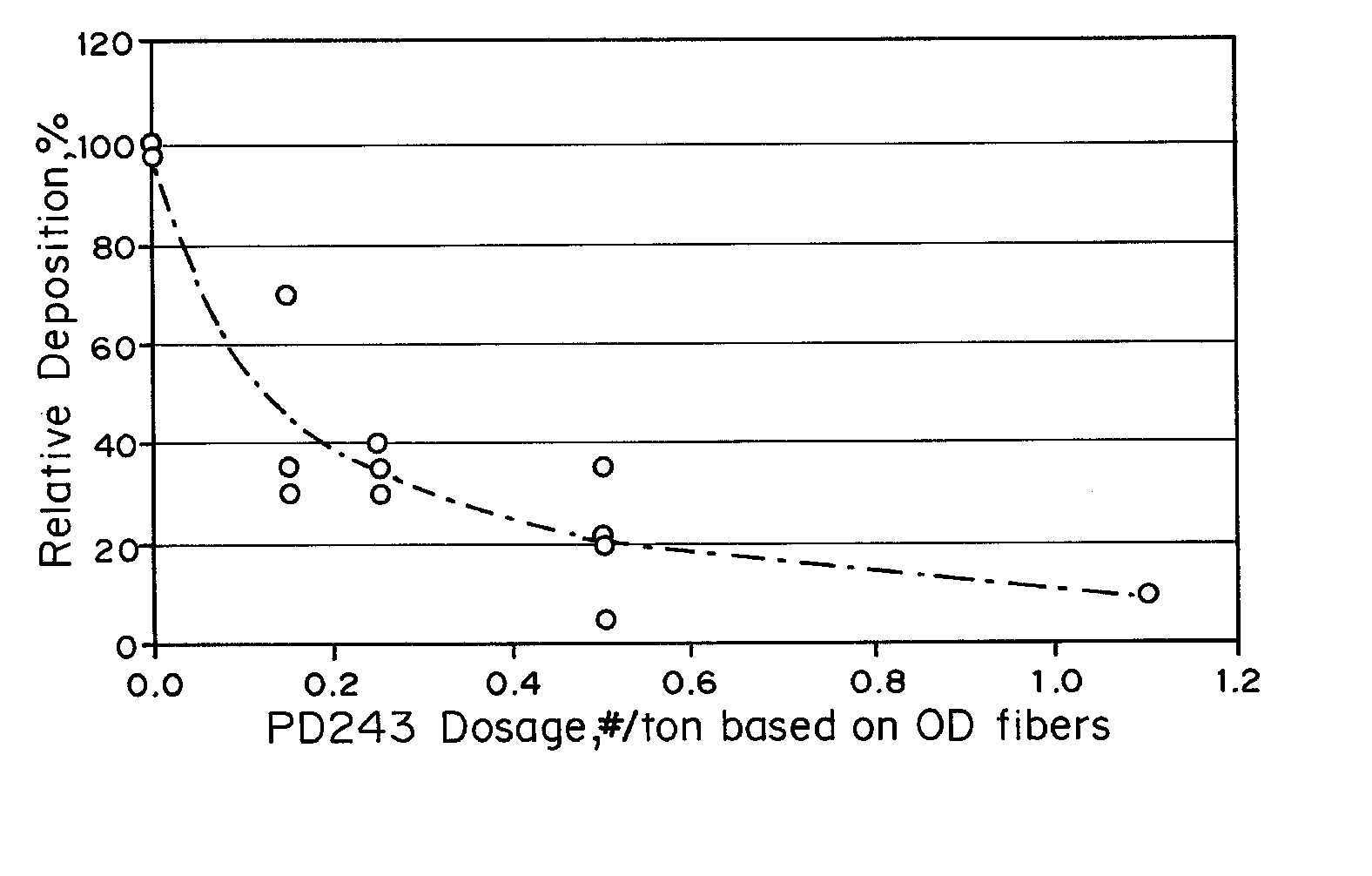
Patents
Literature
414results about "Fats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulp" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Manufacturing process of cellulose nanofibers from renewable feed stocks
InactiveUS20080146701A1High aspect ratioRaise the potentialMaterial nanotechnologyFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpCelluloseNatural fiber
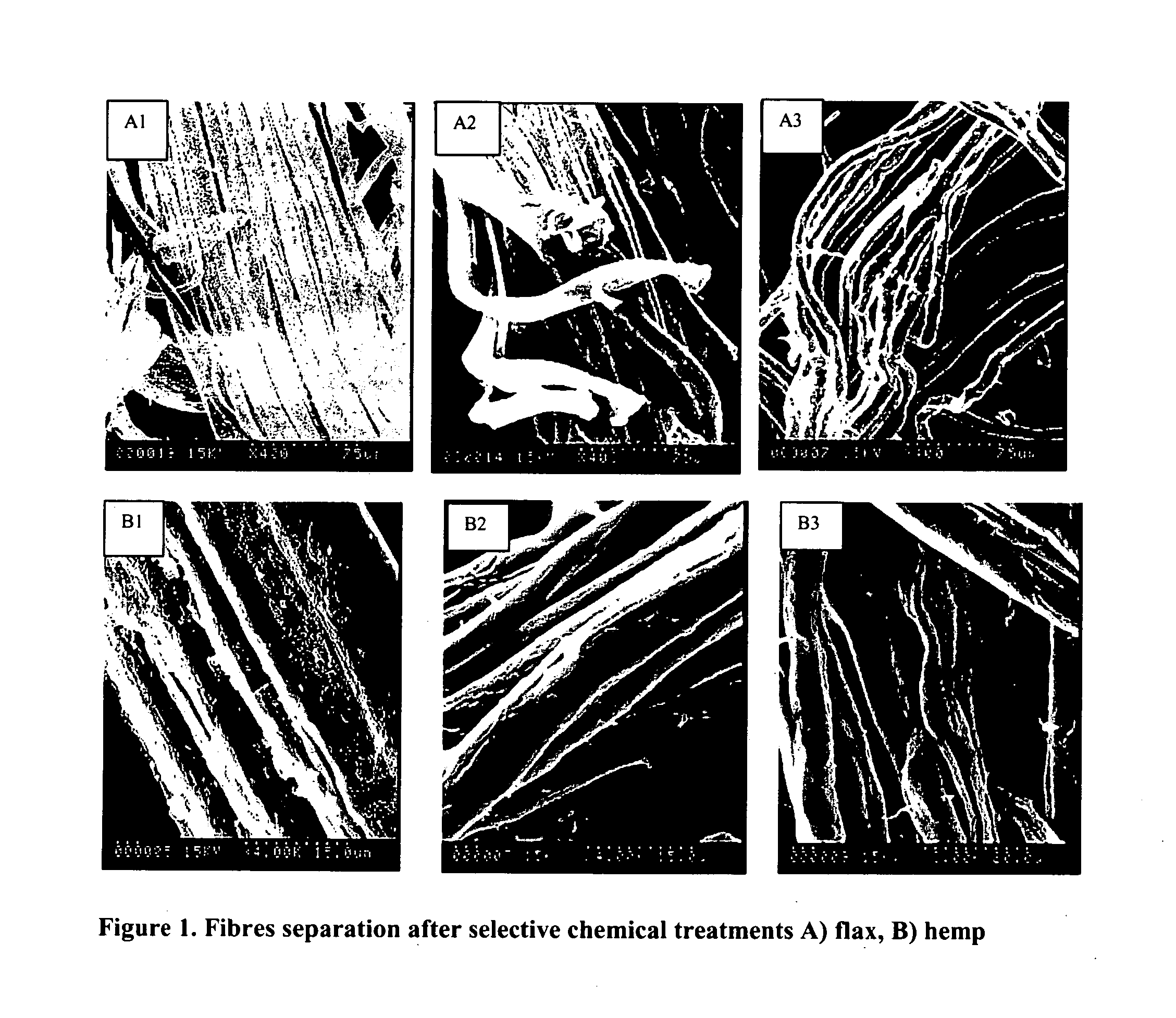
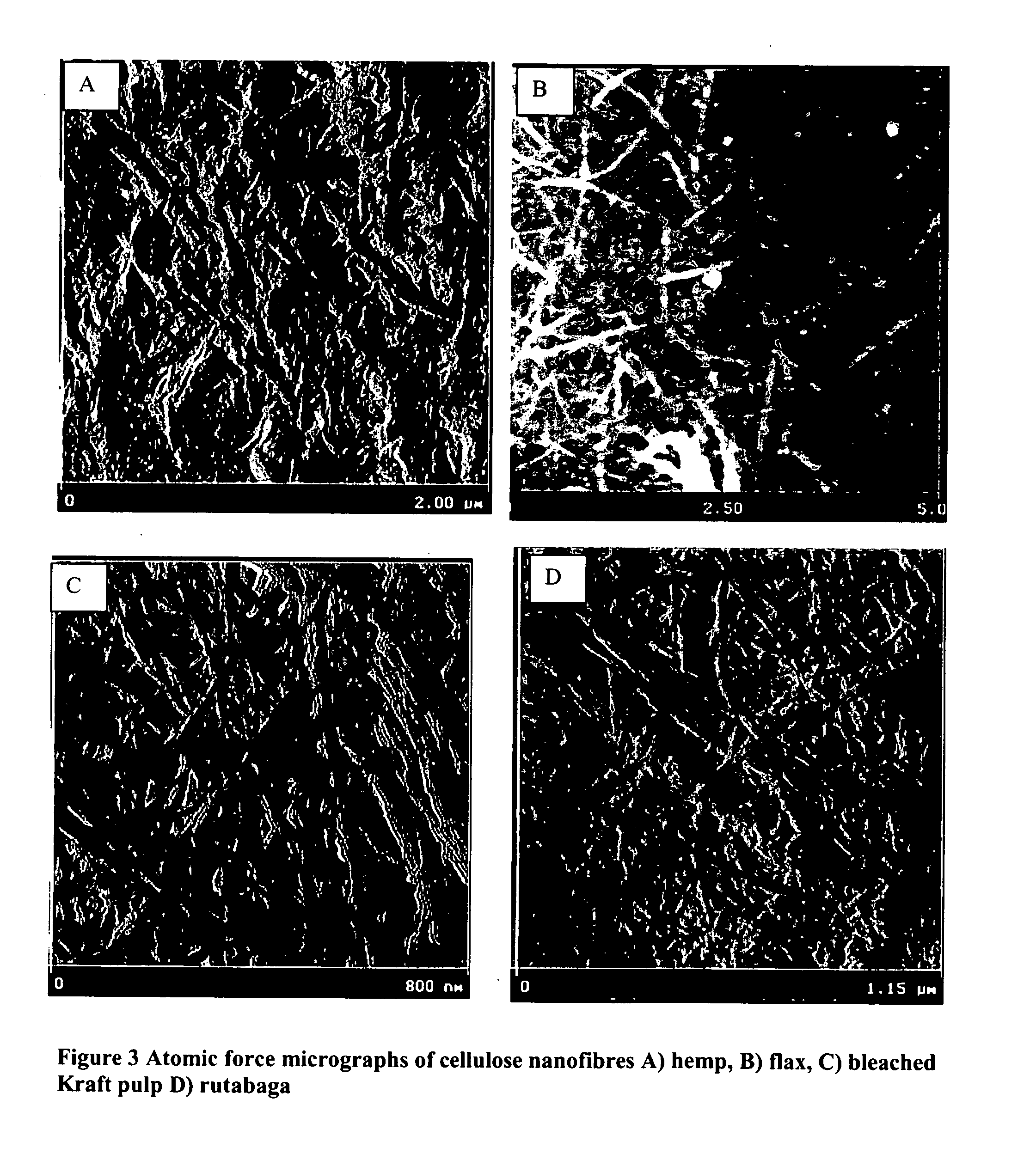
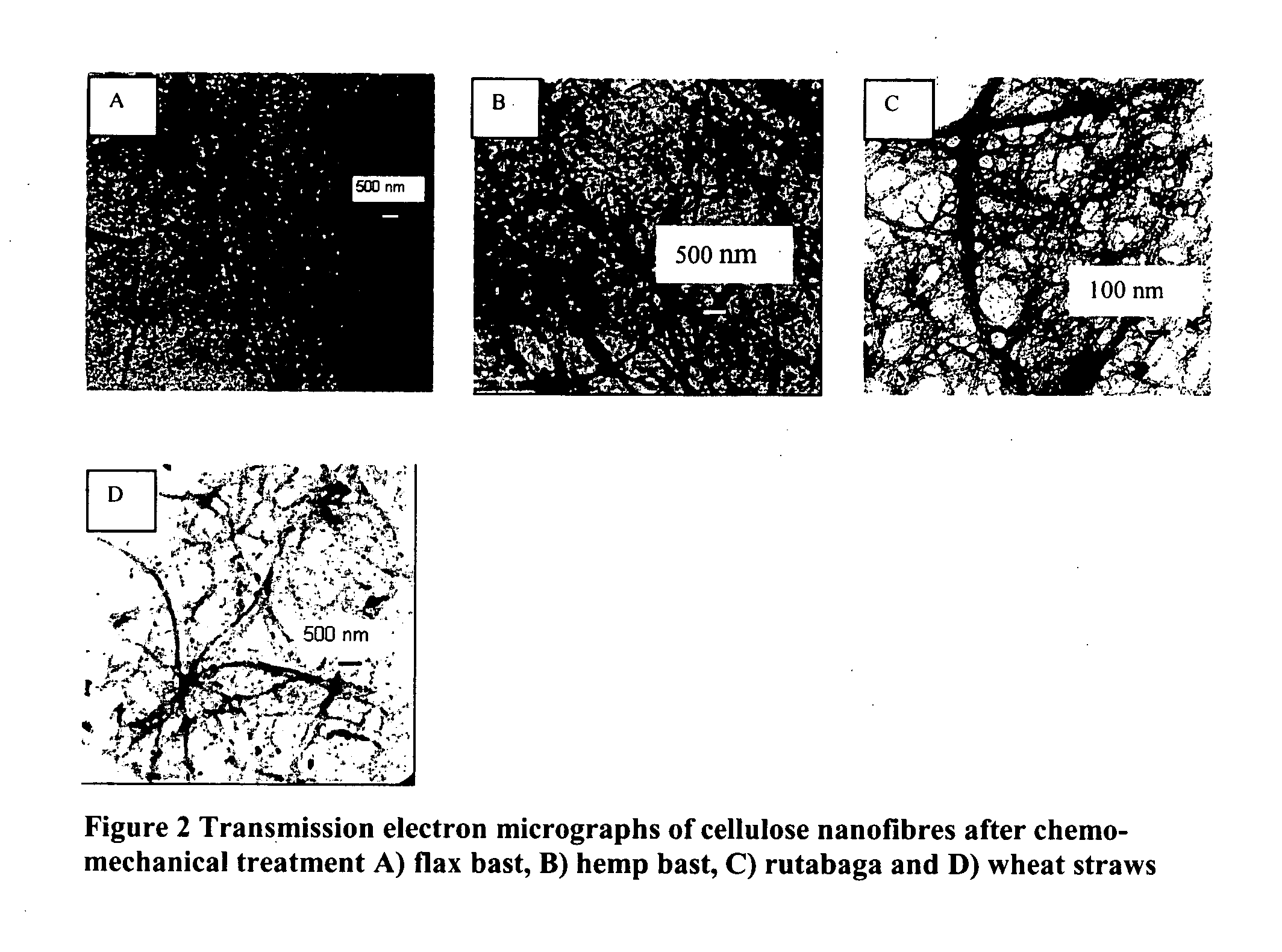
Cellulose nanofibers have been processed from renewable feedstock in particularly from natural fibers, root crops and agro fibers, wherein the pulp was hydrolysed at a moderate temperature of 50 to 90 degree C., one extraction was performed using dilute acid and one extraction using alkali of concentration less than 10%; and residue was cryocrushed using liquid nitrogen, followed by individualization of the cellulose nanofibers using mechanical shear force. The nanofibers manufactured with this technique have diameters in the range of 20-60 nm and much higher aspect ratios than long fibers. Due to its lightweight and high strength its potential applications will be in aerospace industry and due to their biodegradable potential with tremendous stiffness and strength, they find application in the medical field such as blood bags, cardiac devices, valves as a reinforcing biomaterial.
Owner:SAIN MOHINI M +1
Removal of minerals from cellulosic biomass
InactiveUS7503981B2Reduce mineral contentEnhancing cellulosic saccharificationNon-fibrous pulp additionSpecial paperCellulosePre treatment
Disclosed is a method for removing minerals from a cellulosic biomass. For example, the biomass may be prewashed with an acid solution and rinsed with water to remove minerals prior to acid saccharification. The removal of minerals may reduce overall acid requirements, and decrease pretreatment costs.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
System for control of stickies in recovered and virgin paper processing
InactiveUS20060048908A1Good removal effectEasy to controlFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpMachine wet endPectinaseAmylase
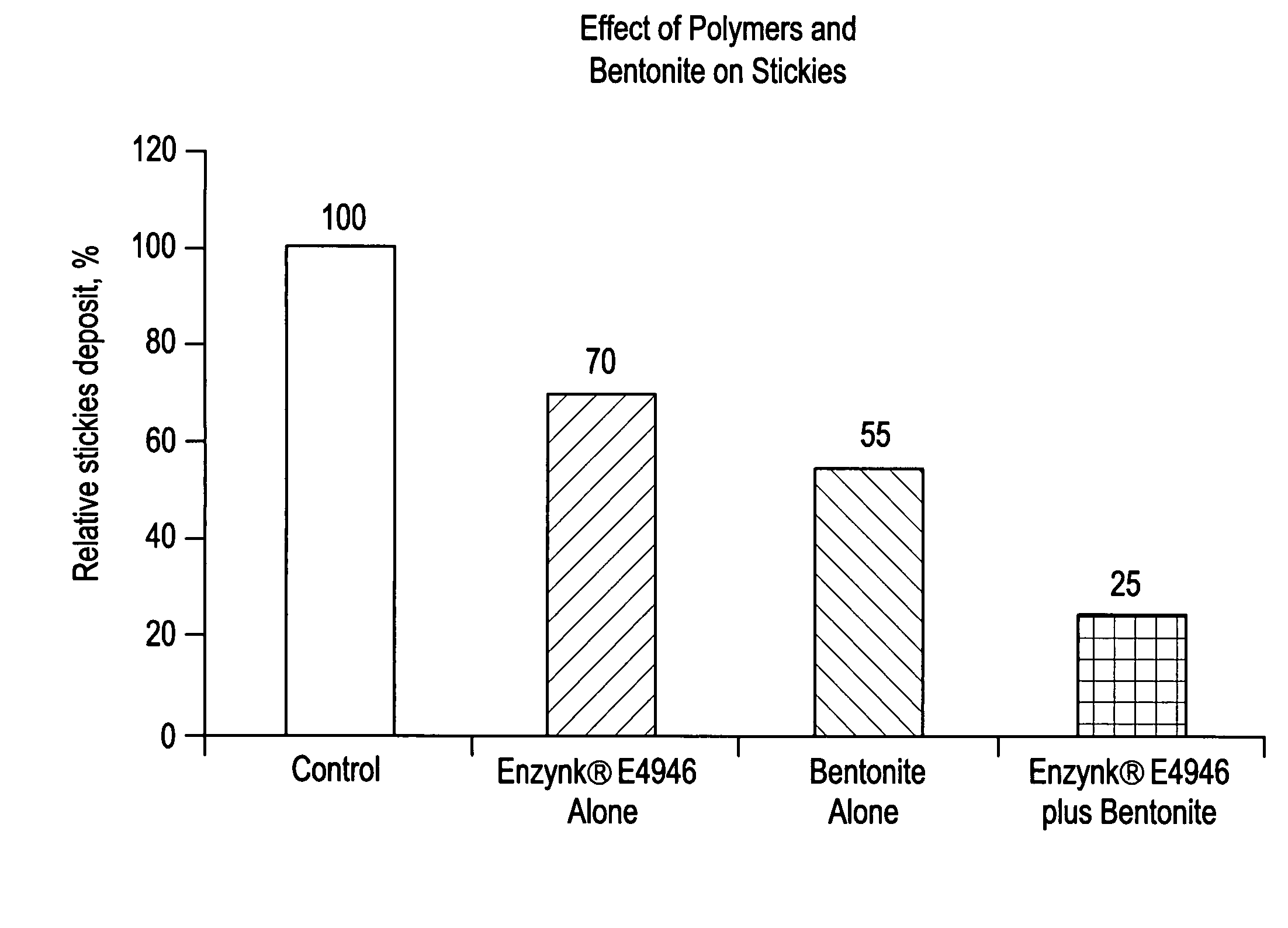
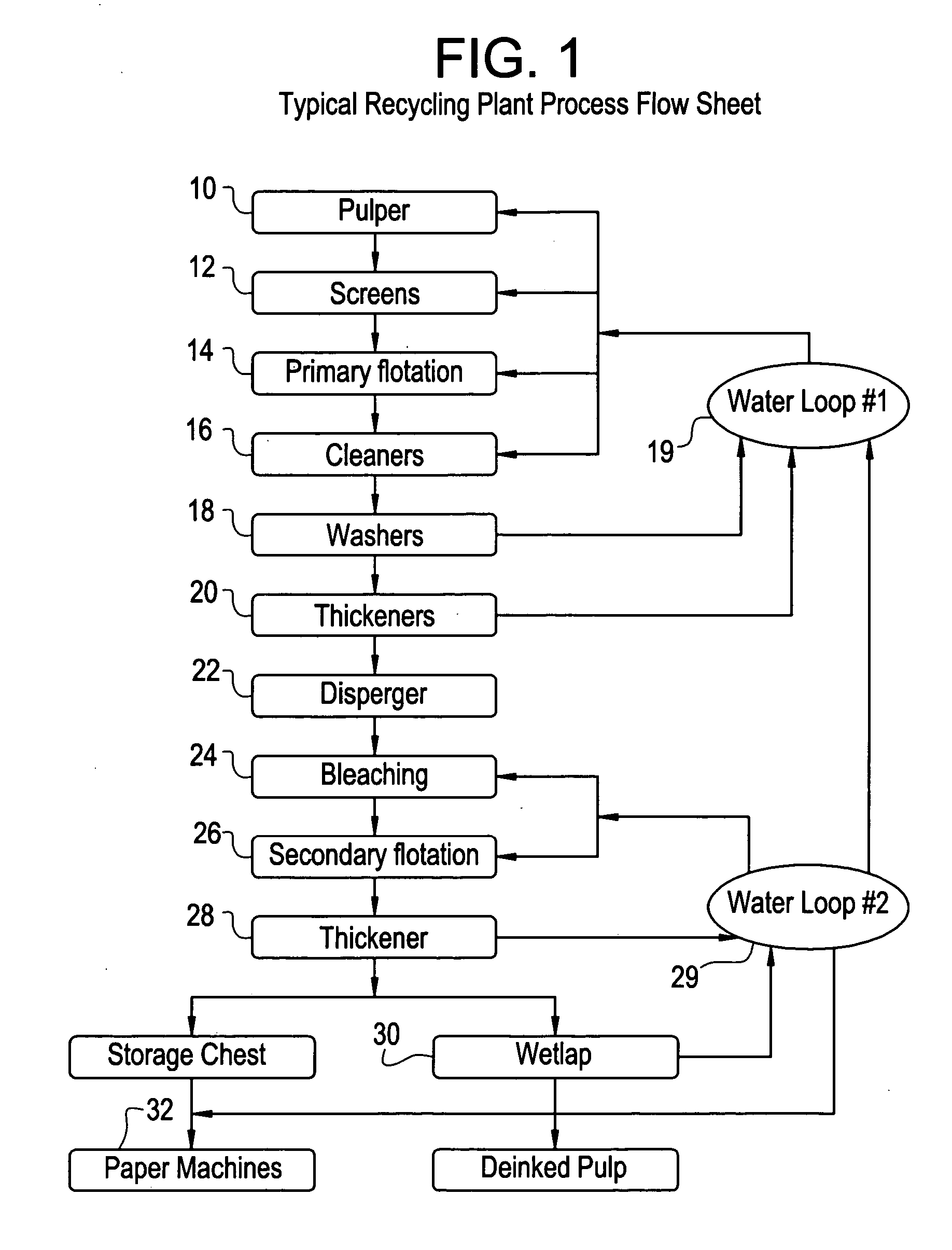
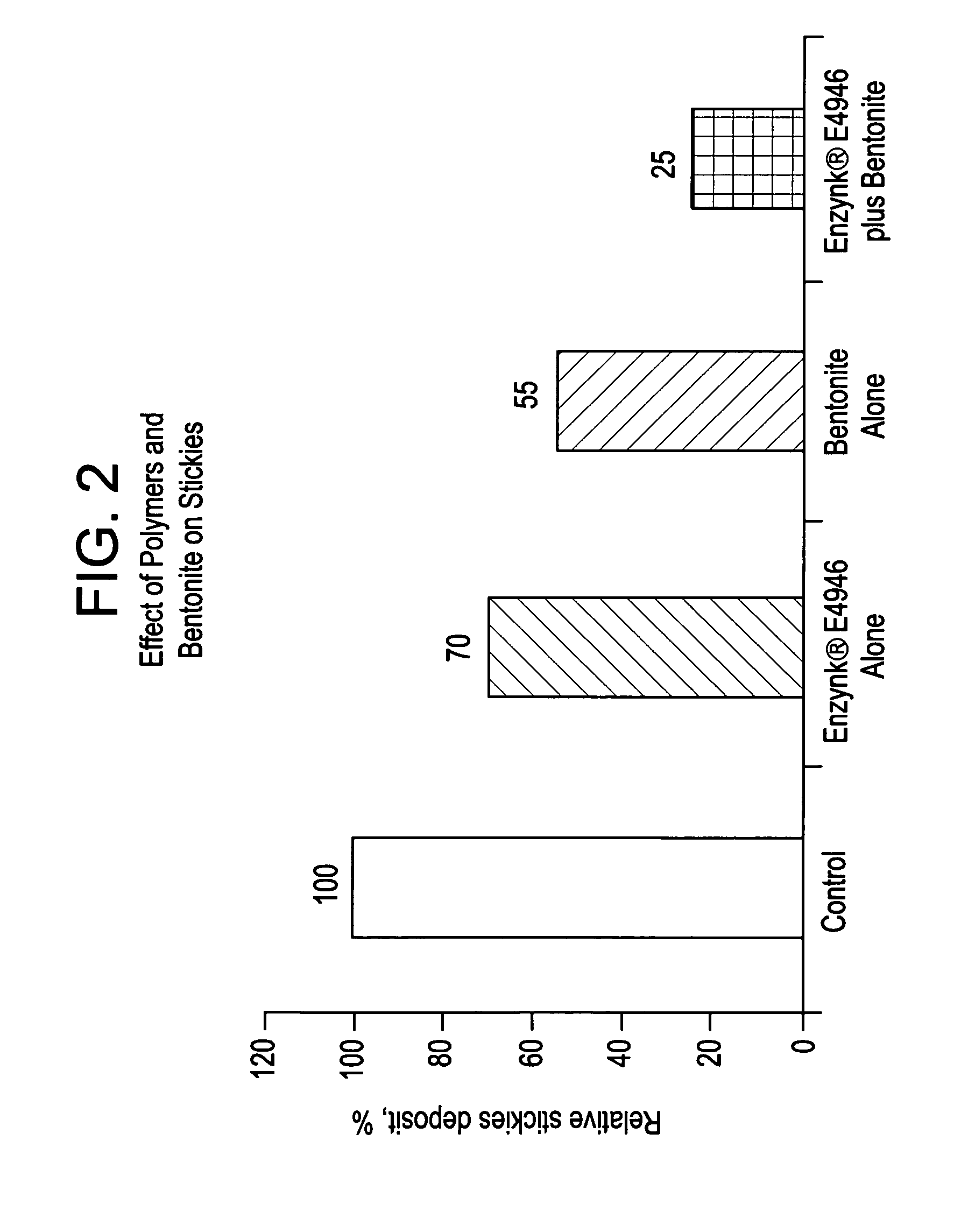
Enhanced removal and / or control of adhesives or sticky materials, “stickies”, from recovered paper stock or virgin pulp fibers is achieved using a combination of enzyme treatment with adsorbents and / or absorbents. Pulp stock to be treated is typically obtained from old magazines, newspapers, household waste, but may include corrugated boxes and office waste. Virgin pulps may include mechanical, chemical, or semi-chemical pulps. Enzymes typically include hydrolases such as cellulases, hemicellulases, pectinases, amylases, and lipases such as esterases, lyases such as pectate lyases, and oxidoreductases. Adsorbents include activated bentonite, microparticles, talc, clay and modified silica. Absorbents typically include water soluble polymers, dispersants, coagulatants and agglomerants.
Owner:ENZYMATIC DEINKING TECH LLC
Product and processes from an integrated forest biorefinery
ActiveUS20070079944A1Easy to optimizePretreatment with water/steamPulping with acid salts/anhydridesPulp and paper industrySugar
An omnibus process of pulping and bleaching lignocellulosic materials in which a charge of a lignocellulosic material is biopulped and / or water extracted prior to pulping and bleaching. The lignocellulosic material may be mechanically pulped and bleached in the presence of an enzyme that breaks lignin-carbohydrate complexes. The aqueous extract in embodiments including a water extract step is separated into acetic acid and hemicellulose sugar aqueous solutions.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Cellulose Nonwoven Fabric
ActiveUS20070207692A1Raw materials are simpleSimple structureFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpPaper/cardboardPorosityCellulose fiber
Disclosed is a cellulose nonwoven fabric containing cellulose fibers having a maximum fiber diameter of not more than 1500 nm and a crystallinity determined by solid state NMR techniques of not less than 60%. The porosity of the cellulose nonwoven fabric is not less than 40% and not more than 99%.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI KK
Method for the production of fermentable sugars and cellulose from lignocellulosic material
ActiveUS8030039B1High yieldIncreased ethanol yieldFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpPulping with organic compoundsOrganic acidAlcohol
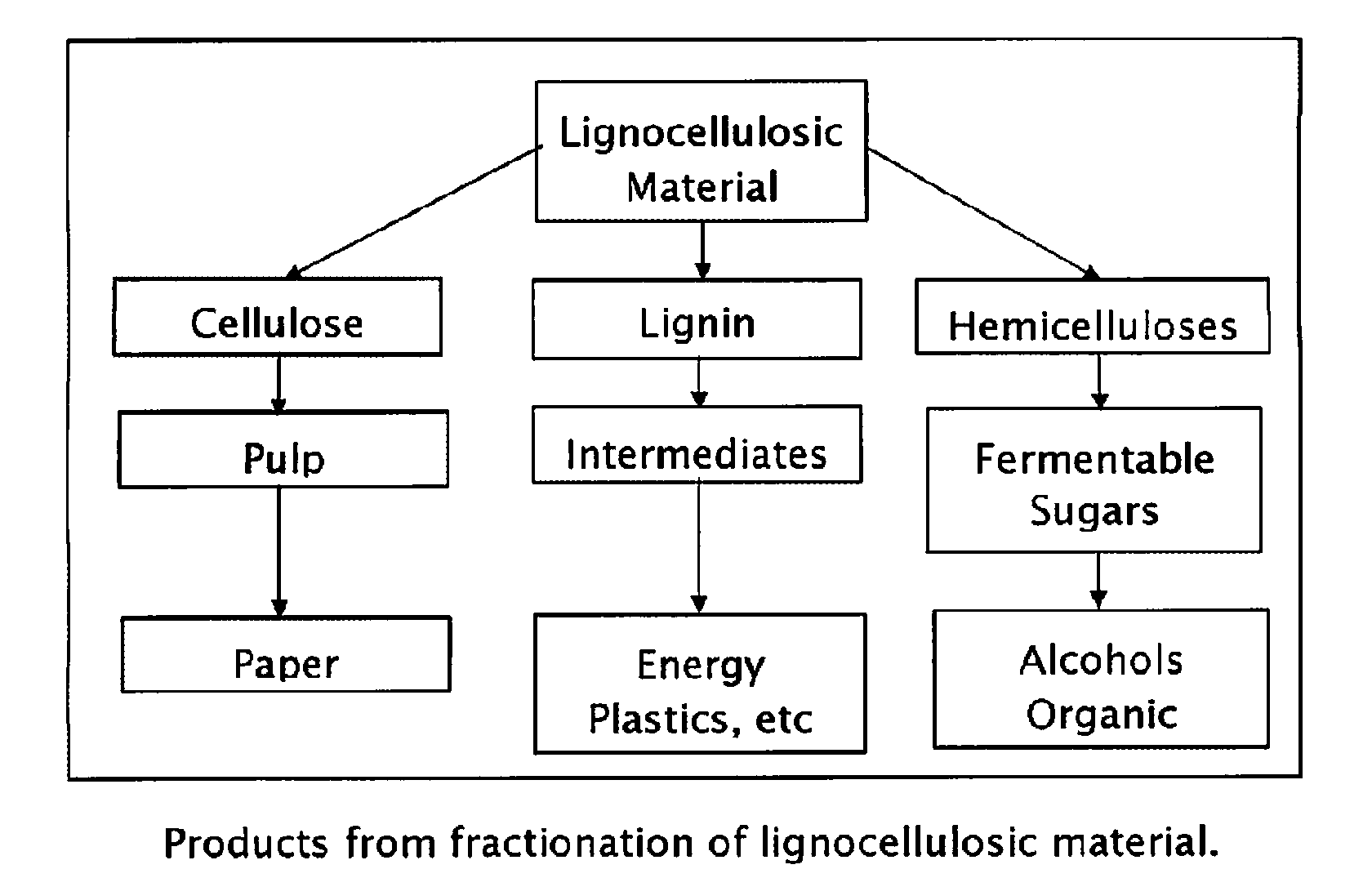
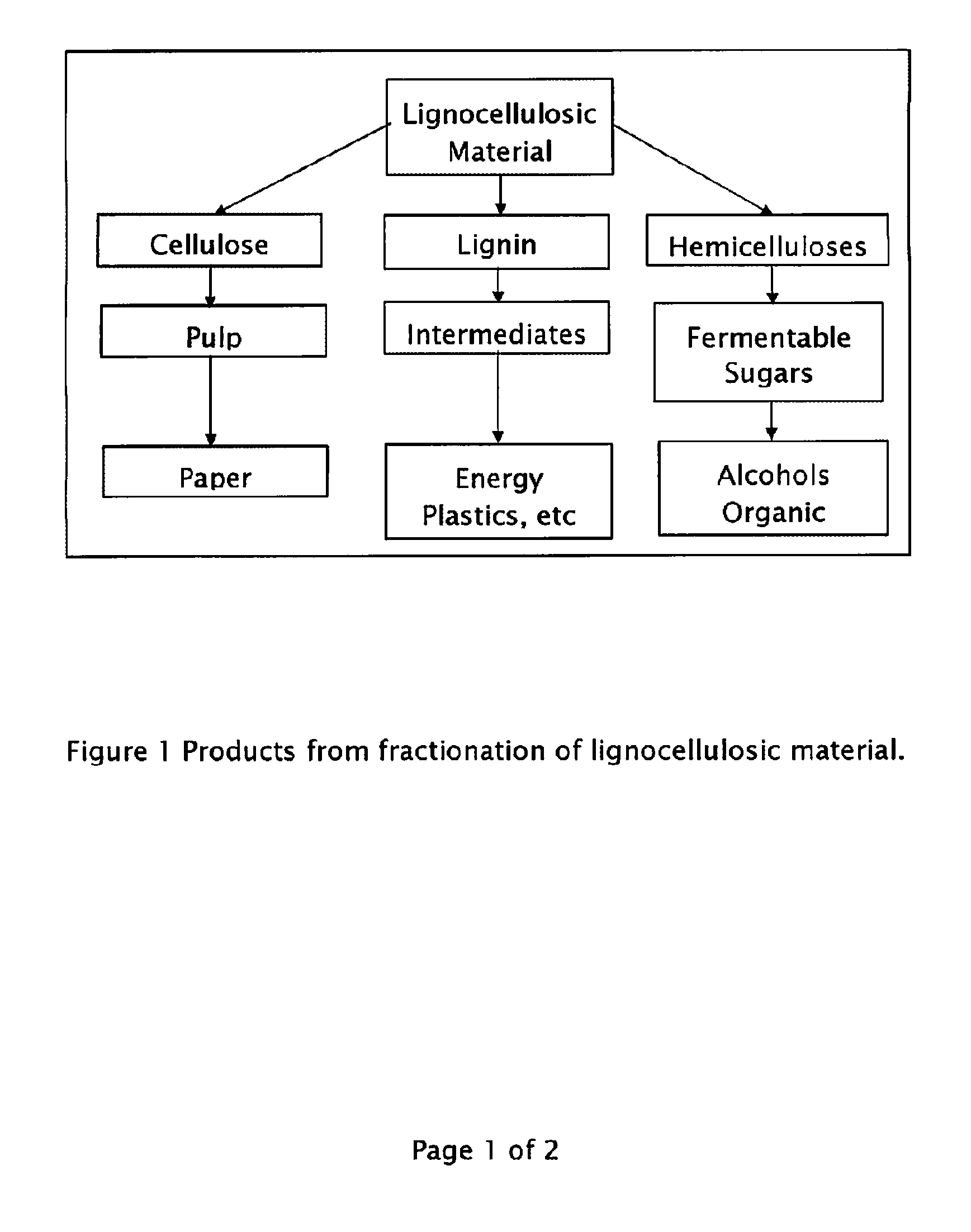
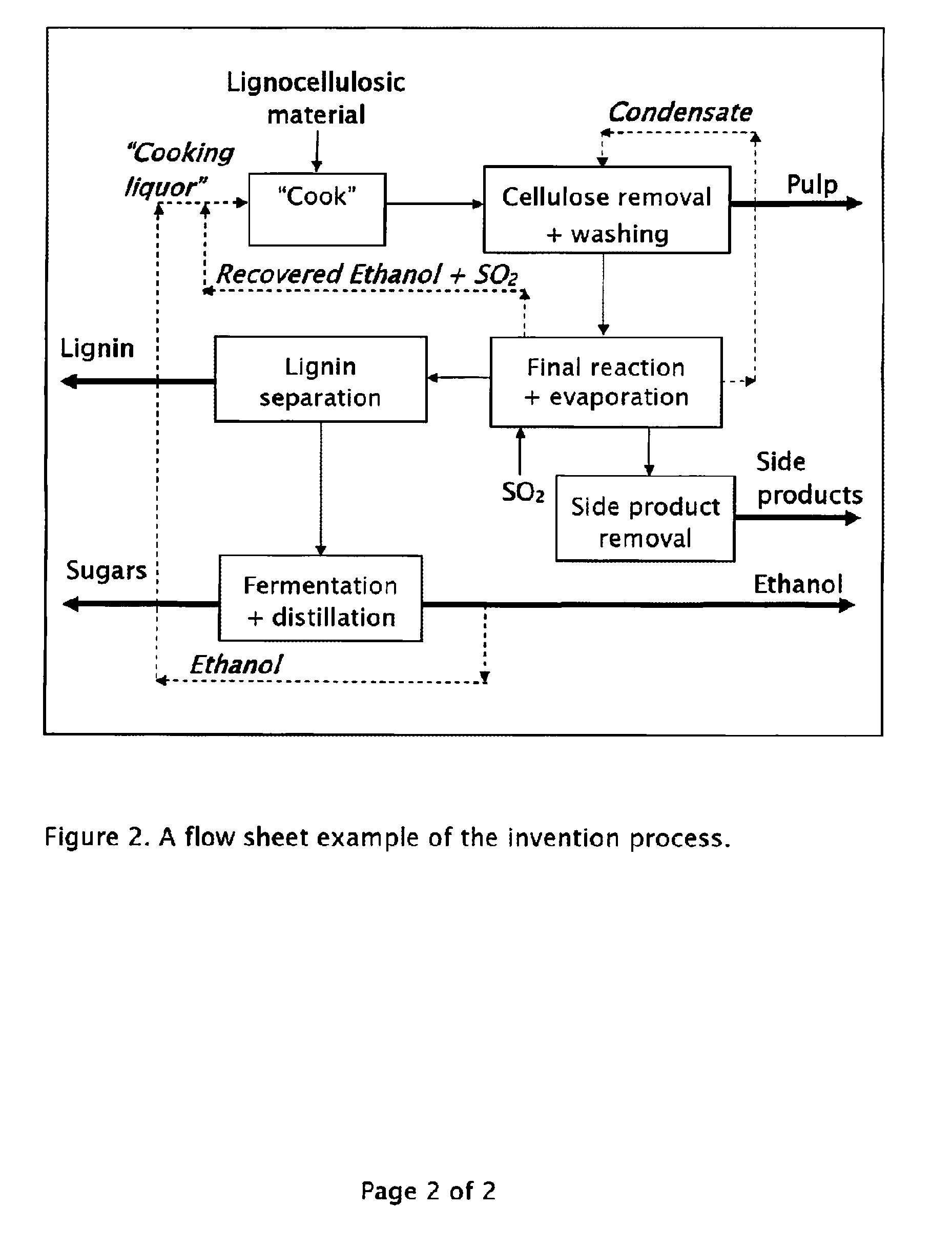
A method for the production of fermentable sugars and high viscosity cellulose from lignocellulosic material in a batch or continuous process is provided. Lignocellulosic material is fractionated in a fashion that cellulose is removed as pulp, cooking chemicals can be reused, lignin is separated for the production of process energy, and hemicelluloses are converted into fermentable sugars, while fermentation inhibitors are removed. High yield production of alcohols or organic acids can be obtained from this method using the final reaction step.
Owner:GRANBIO INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY HOLDINGS LLC
Stabilized absorbent composite material and method for making
InactiveUS20050045296A1Non-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperPersonal careBiomedical engineering
Disclosed herein is a densified stabilized absorbent composite material and a method for making densified stabilized absorbent composite material which may be used in or as an absorbent core material for absorbent products such as personal care absorbent products.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
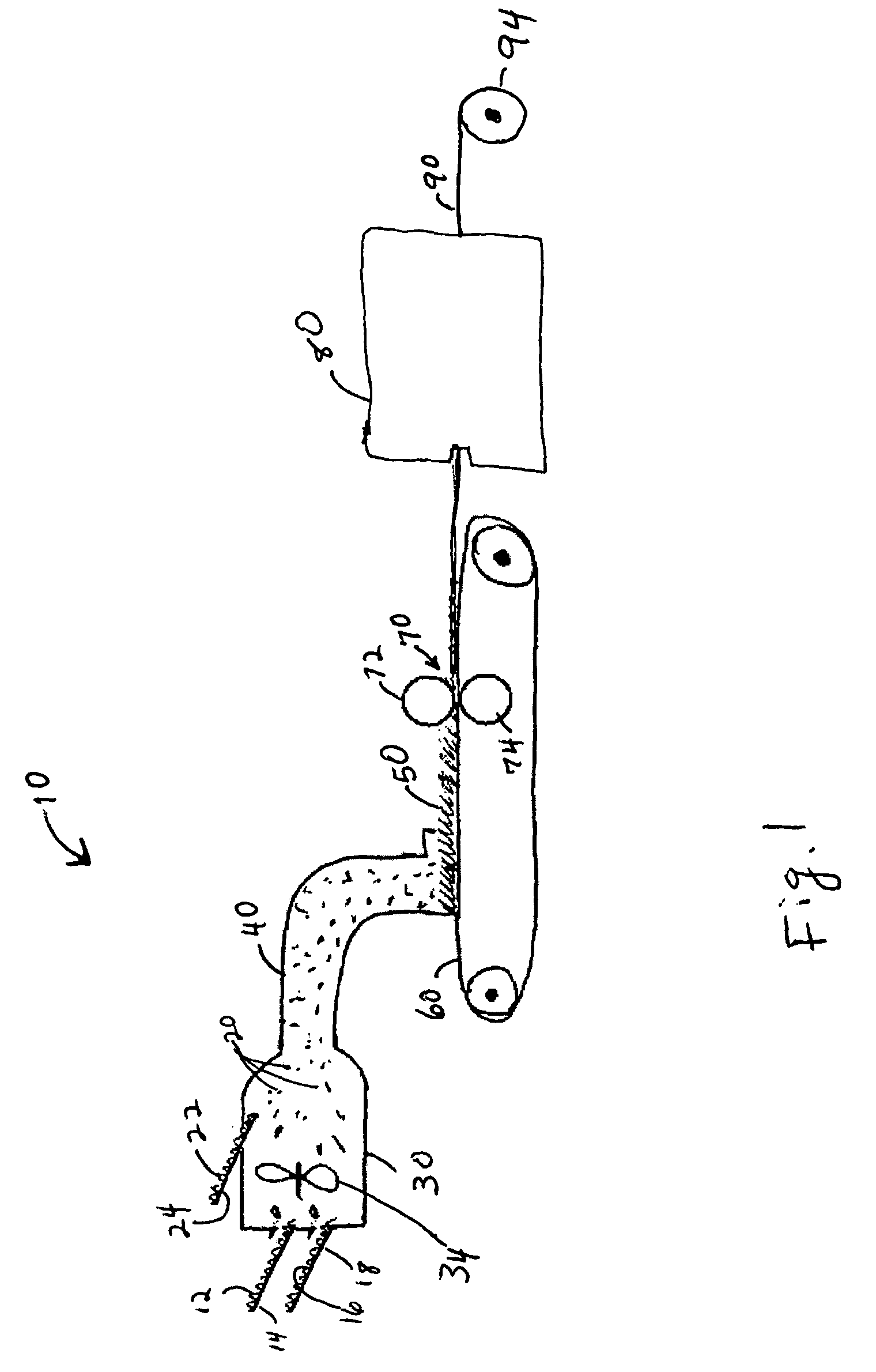
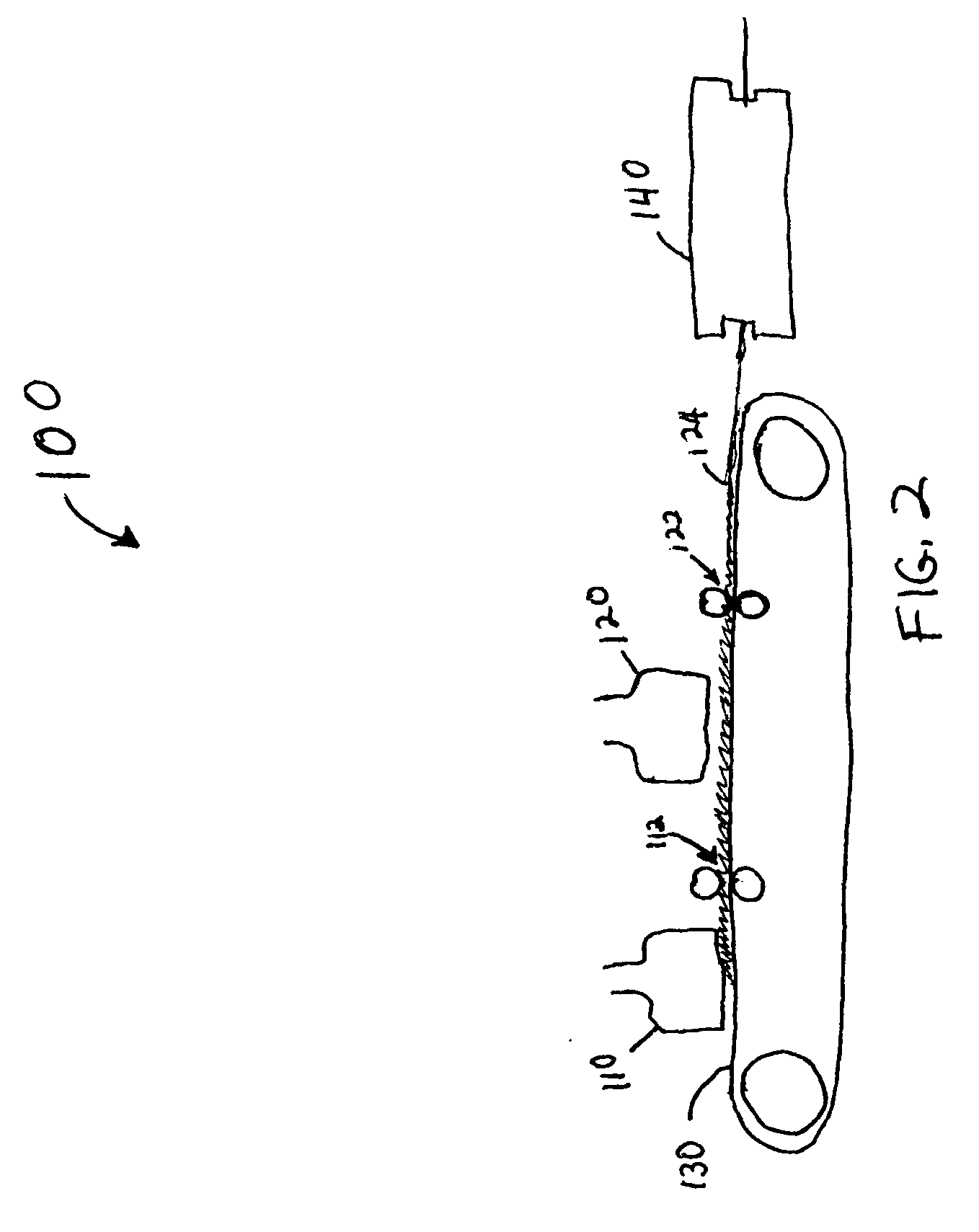
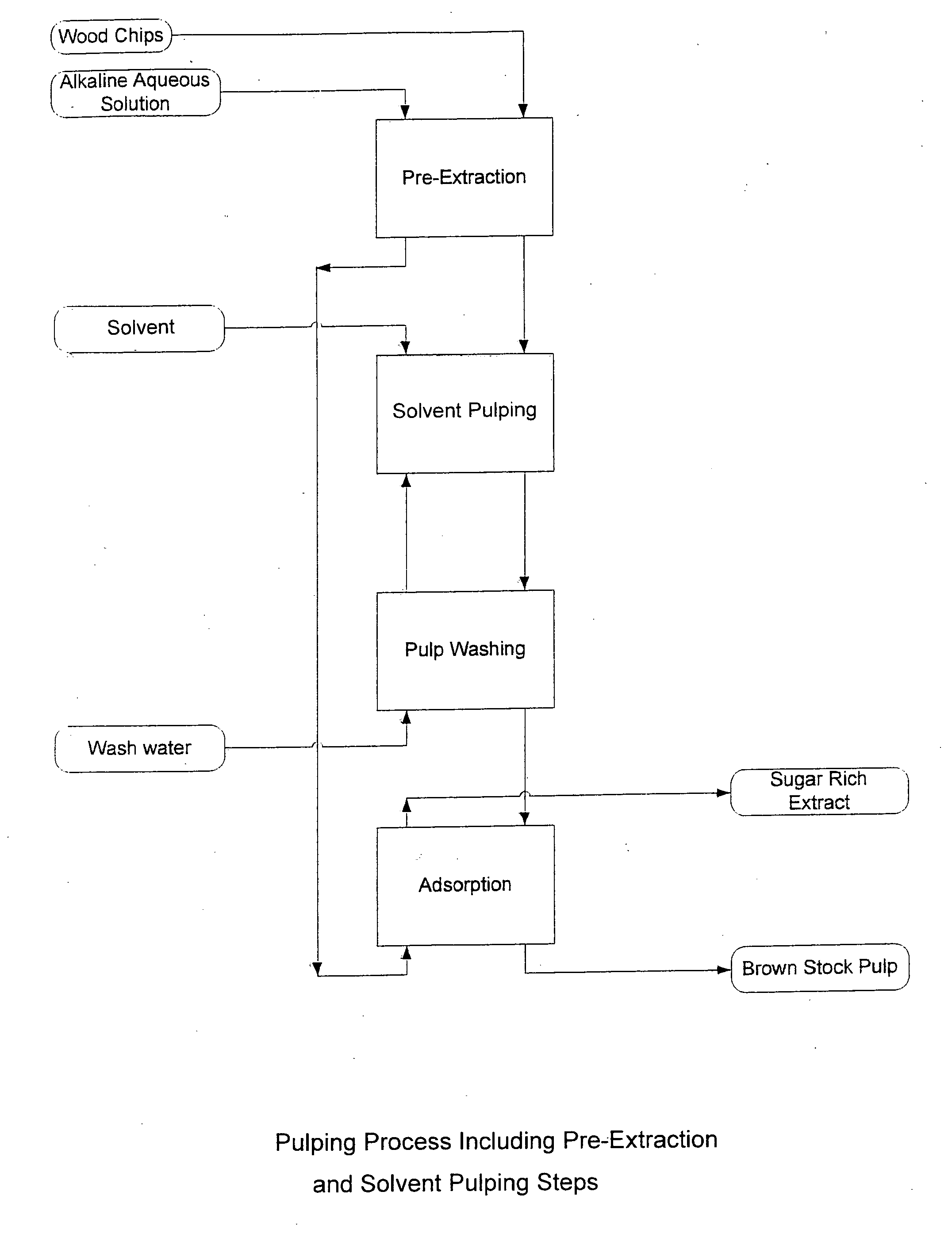
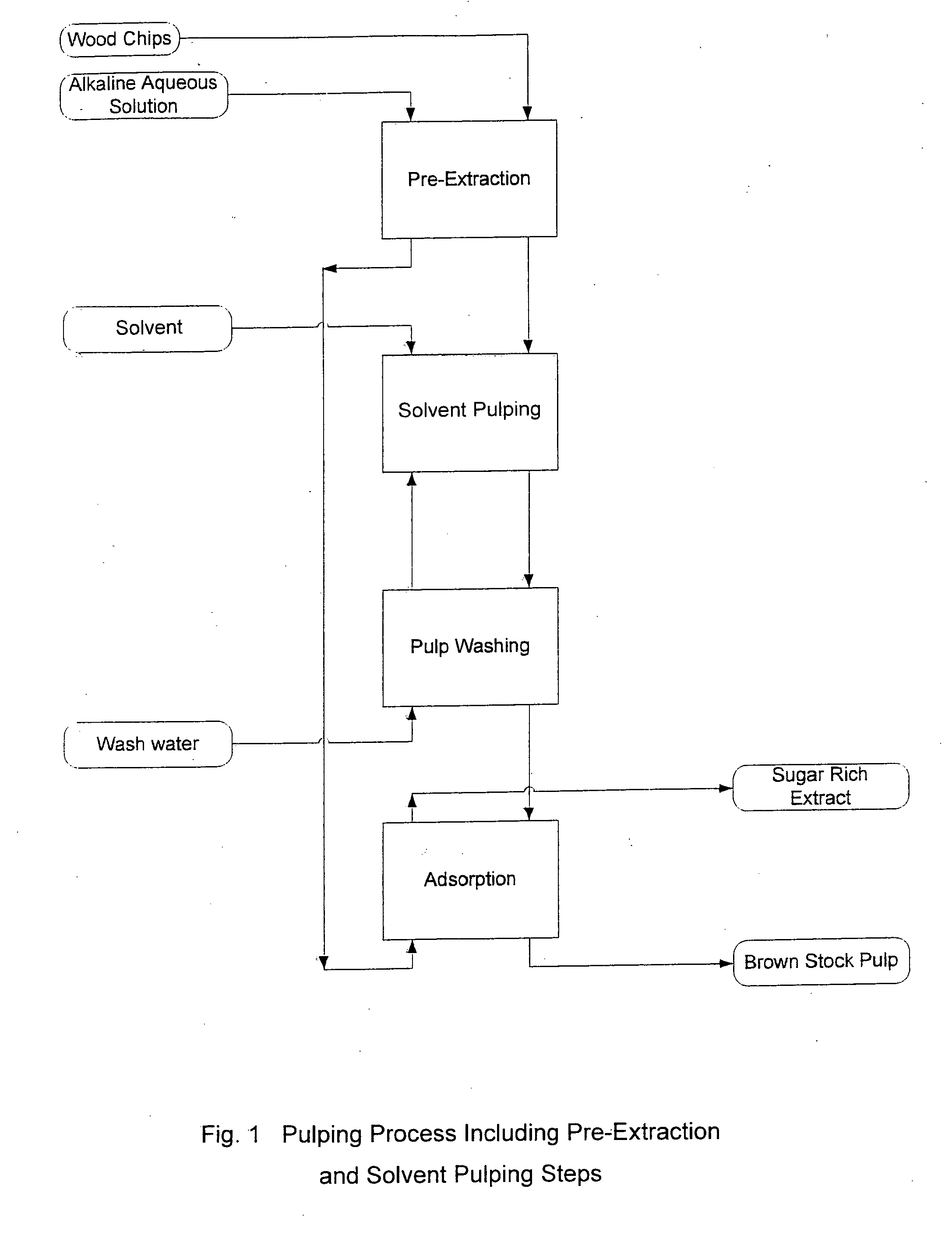
Pre-extraction and solvent pulping of lignocellulosic material
InactiveUS20080196847A1Pretreatment with alkaline reacting compoundsFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpBoiling pointSolvent
A process of treating a lignocellulosic material includes a pre-extraction step in which hemicellulose is extracted from the lignocellulosic material. Then, in a solvent pulping step, the lignocellulosic material is separated into pulp by contacting the lignocellulosic material with a cooking liquor comprising a solvent. In one embodiment, the solvent has a boiling point of at least about 150° C. In another embodiment, the cooking liquor comprises a mixture of solvent and water.
Owner:INT PAPER CO +1
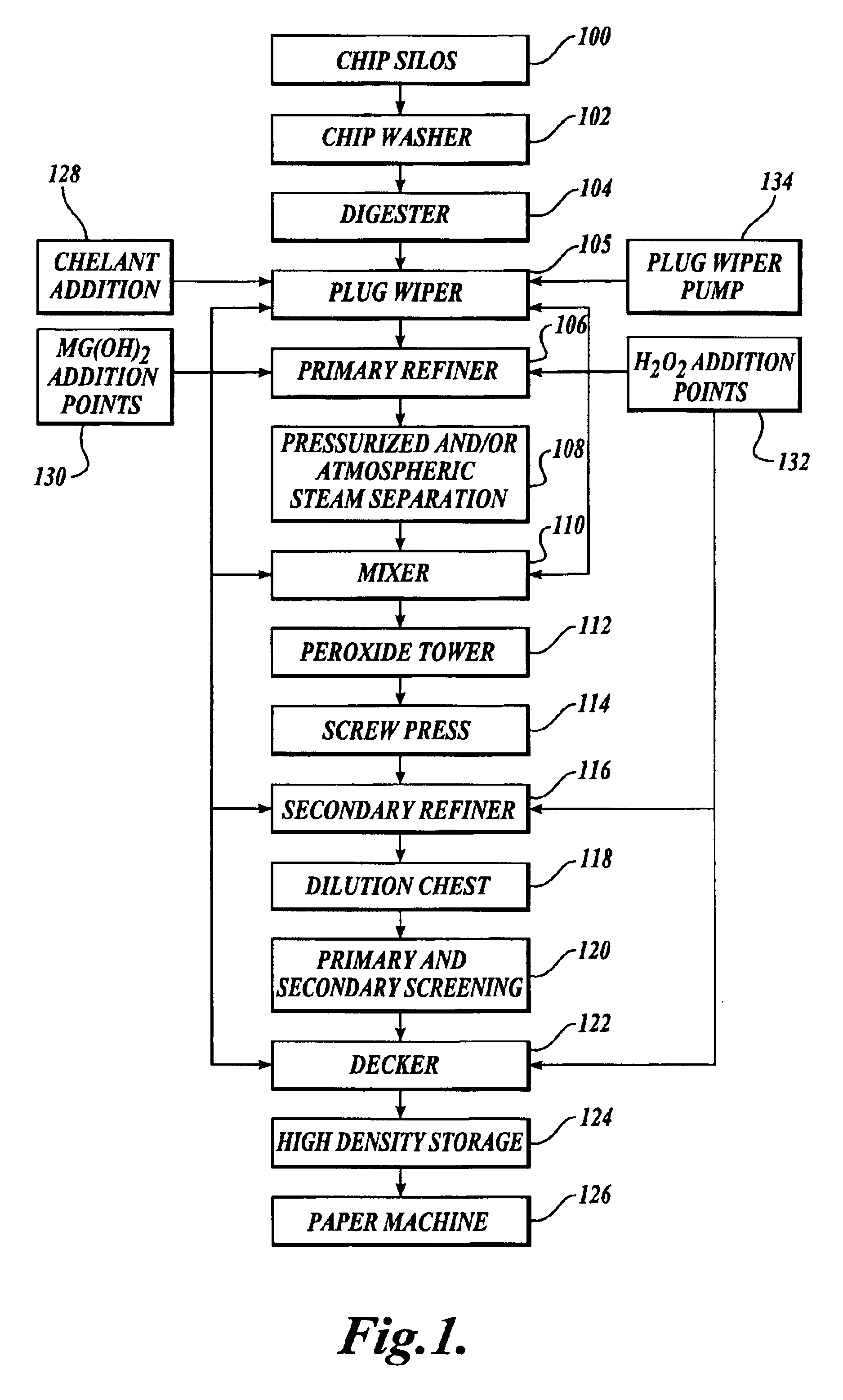
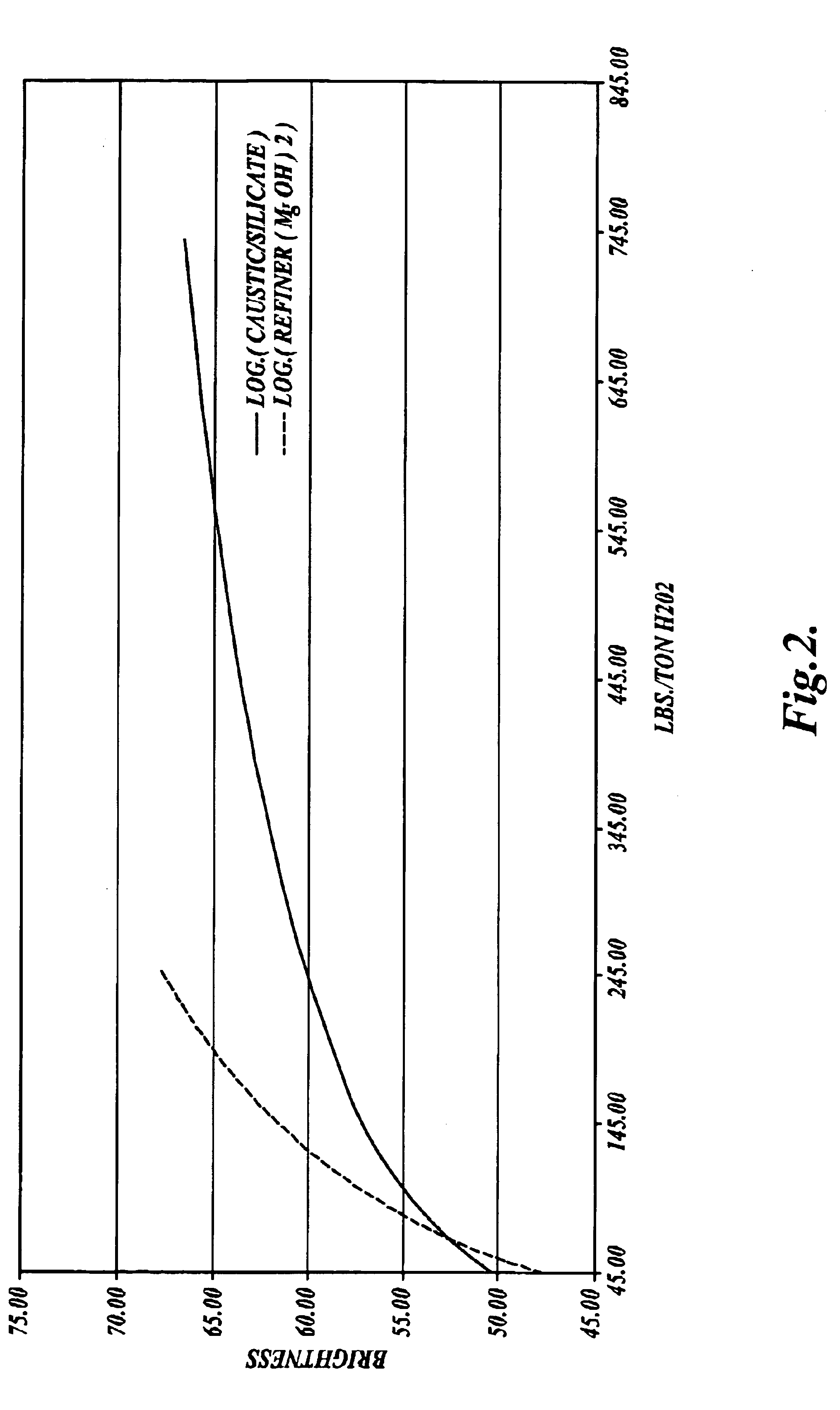
Refiner bleaching with magnesium oxide and hydrogen peroxide
InactiveUS6881299B2Eliminate useHigh retention rateFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpPulp de-wateringParticulatesMagnesium ion
Methods of bleaching mechanical pulp under alkaline conditions with hydrogen peroxide. The methods include introducing a source of magnesium ions and hydroxyl ions to a refiner. The wood particulates are refined into a pulp in the presence of the magnesium ions and hydroxyl ions, and optionally perhydroxyl ions to simultaneously refine and bleach the pulp in a refiner.
Owner:NORTH PACIFIC PAPER
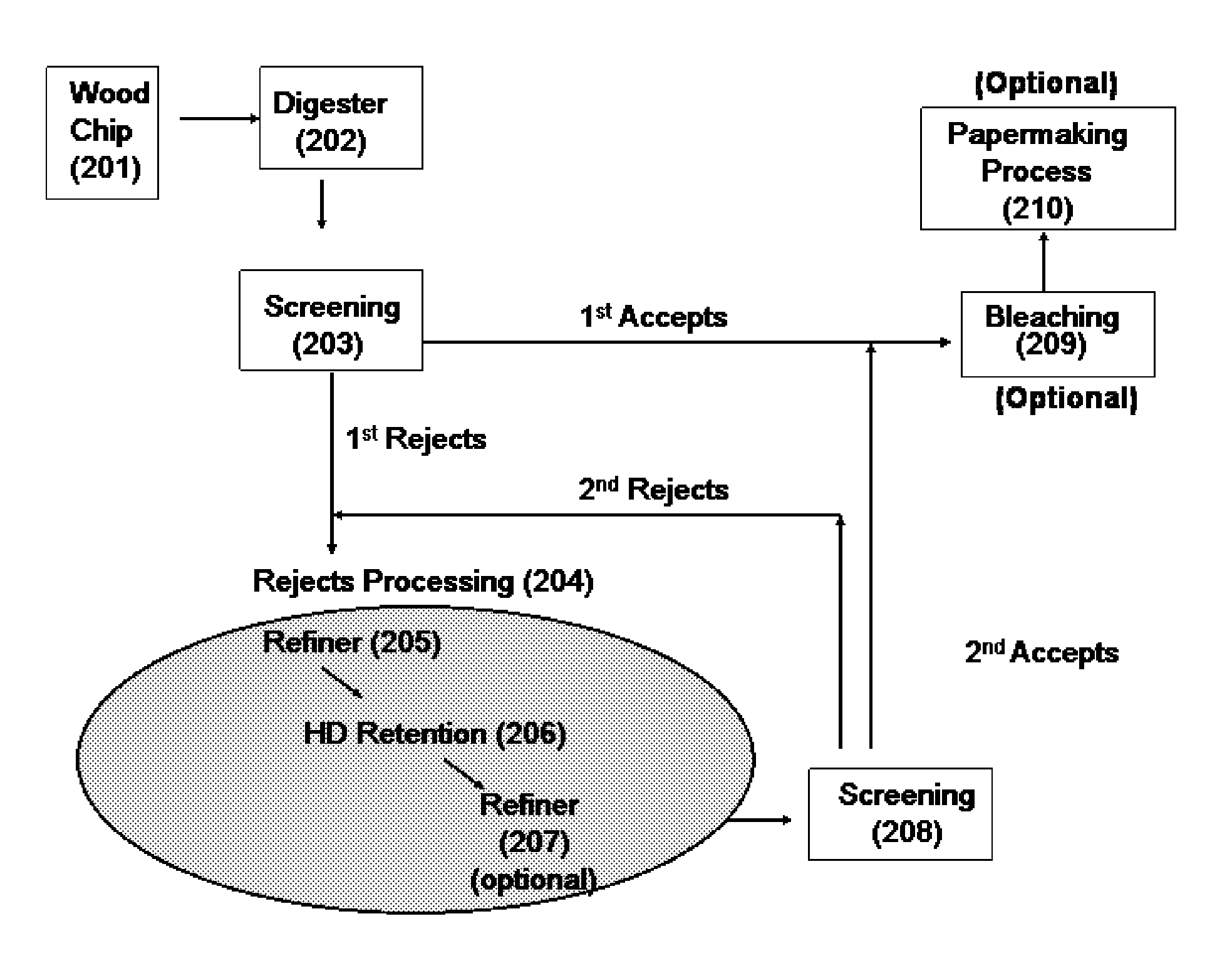
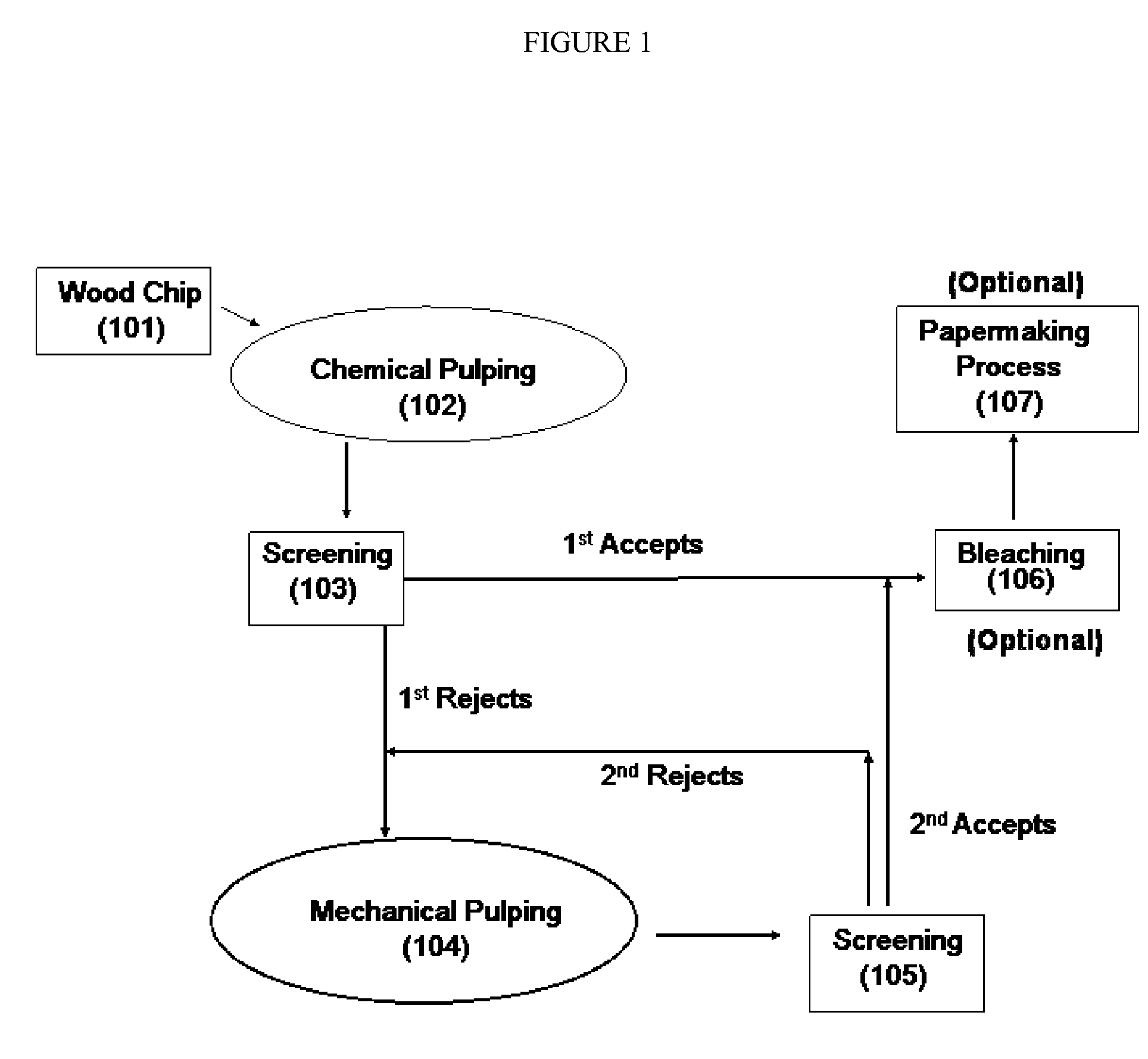
Fiber blend having high yield and enhanced pulp performance and method for making same
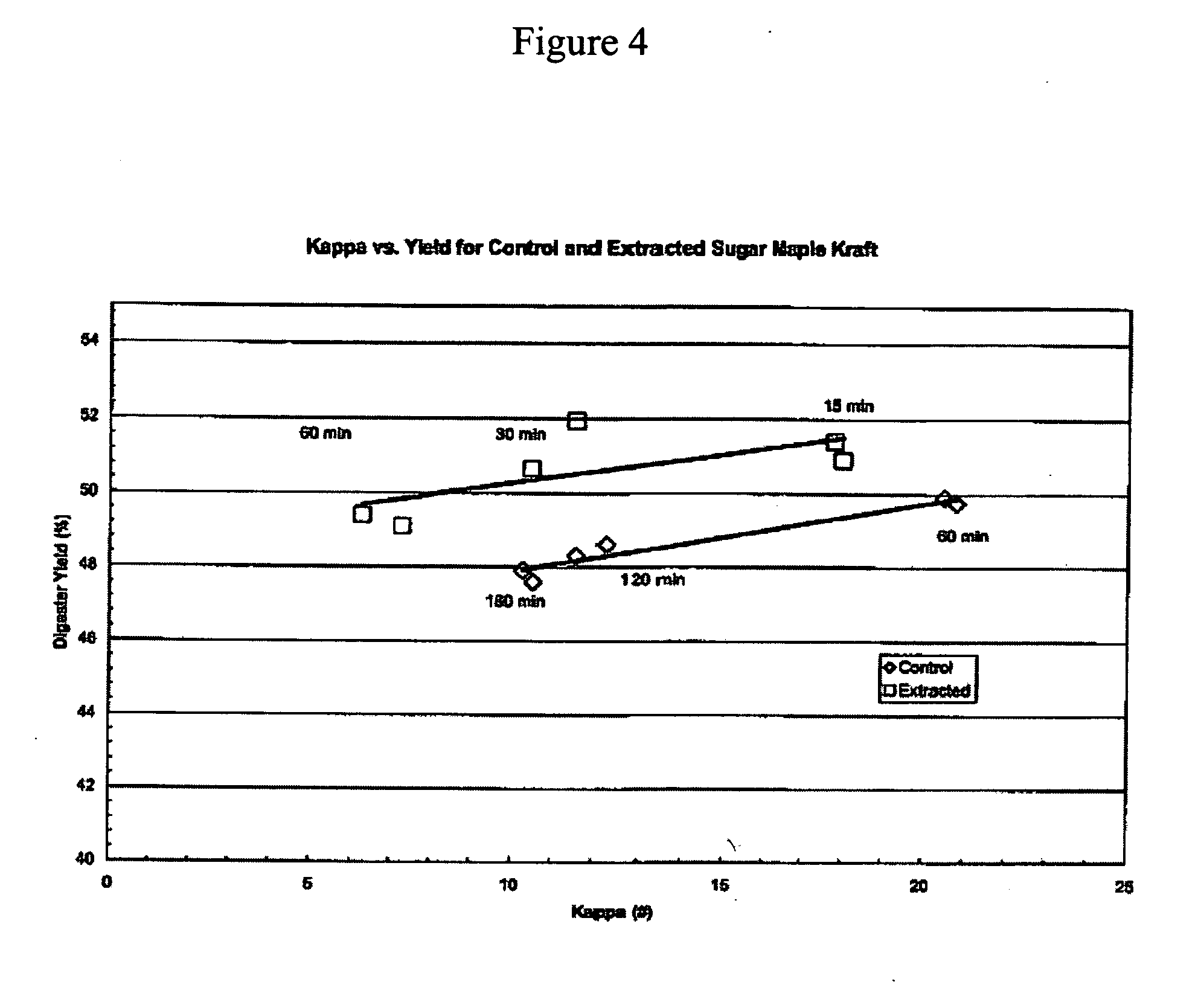
InactiveUS20080308239A1Increase stiffnessHigh strengthFibreboardPulp properties modificationFiberKappa number
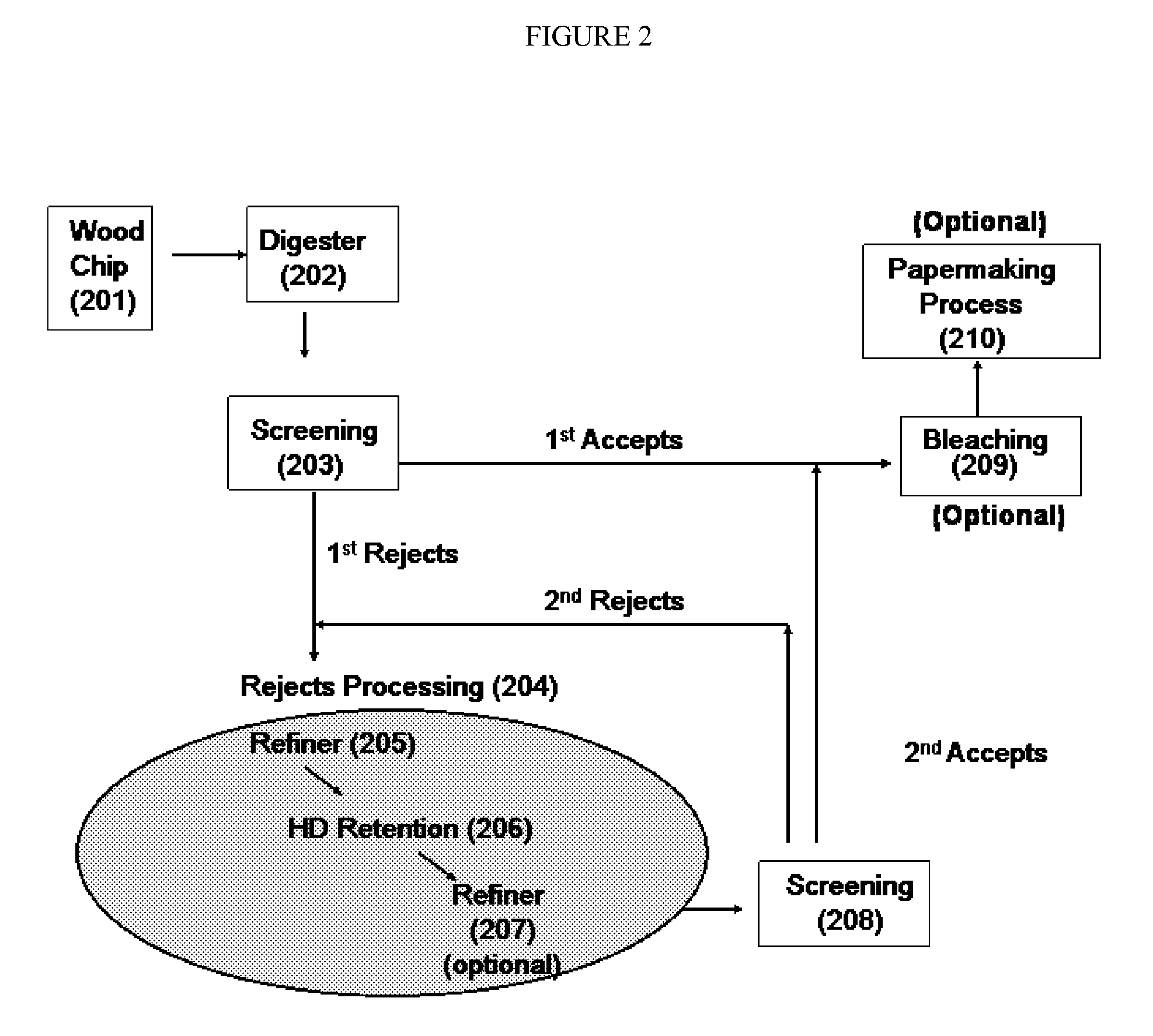
The present disclosure relates to producing paper or paperboard having improved stiffness and strength, compared to the conventional paperboard at the same basis weight. It also discloses a method of wood pulping having a significantly increased yield and providing fiber pulps with enhanced properties such as strength and stiffness. Wood chips are chemically pulped to a high kappa number, providing a rejects component and an accepts component. The rejects component is subjected to a substantially mechanical pulping process, optionally in a presence of bleaching agent, prior to blending back into the accepts component. The resulting fiber blend is washed, optionally bleached, and subjected to a papermaking process to provide paper or paperboard with enhanced strength and stiffness at low basis weight.
Owner:MEADWESTVACO CORP
Printing paper
InactiveUS6923889B2Increase coverageGood printabilityNon-fibrous pulp additionSpecial paperFiberSurface roughness
The invention relates to coated printing paper which contains mechanical pulp and whose opacity is at least 89%, brightness at least 65% and surface roughness not more than 4.5 μm. The printing paper contains mechanical pulp at least 90 weight-% of the total fiber content of the paper.
Owner:UPM-KYMMENE OYJ
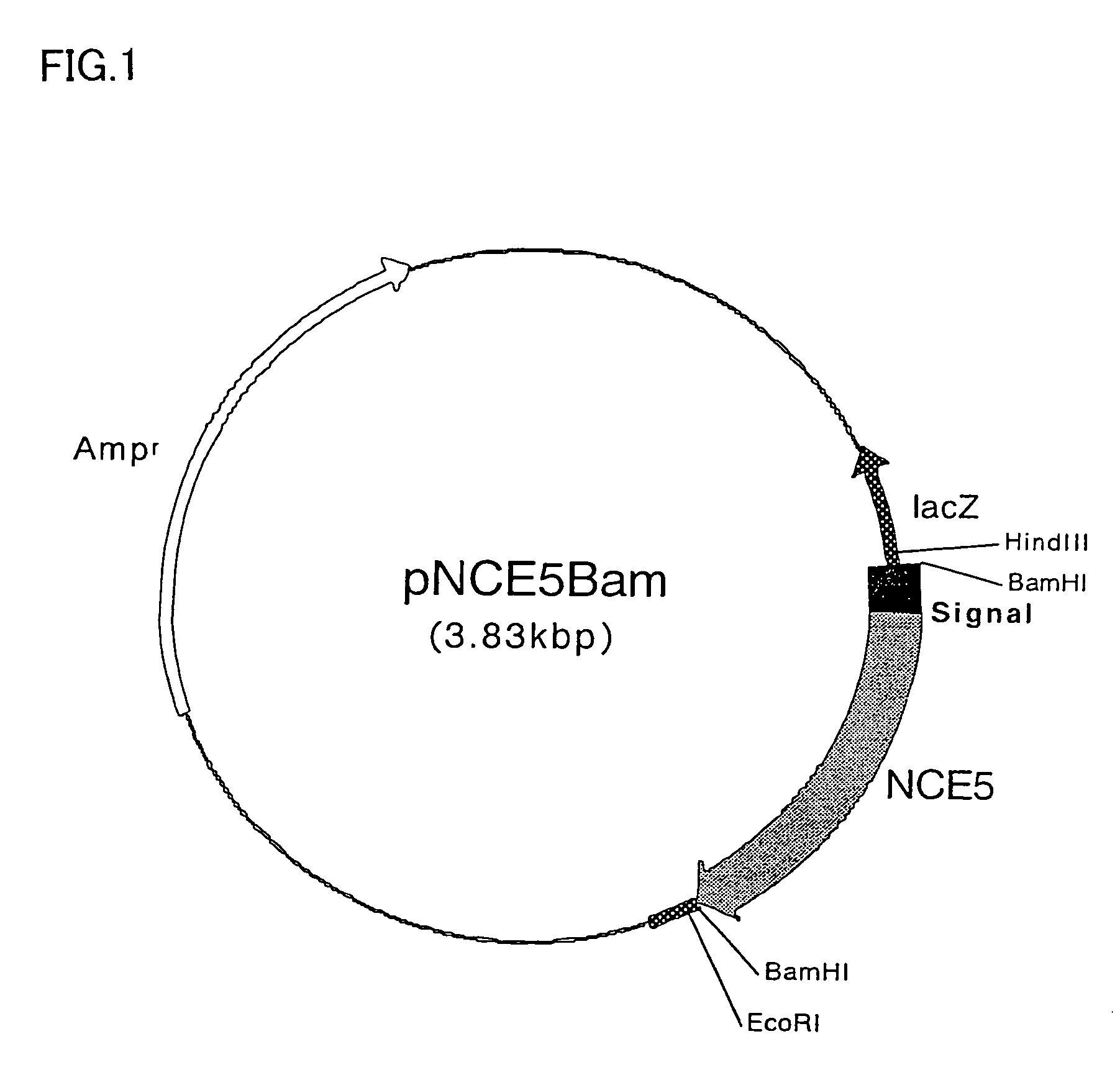
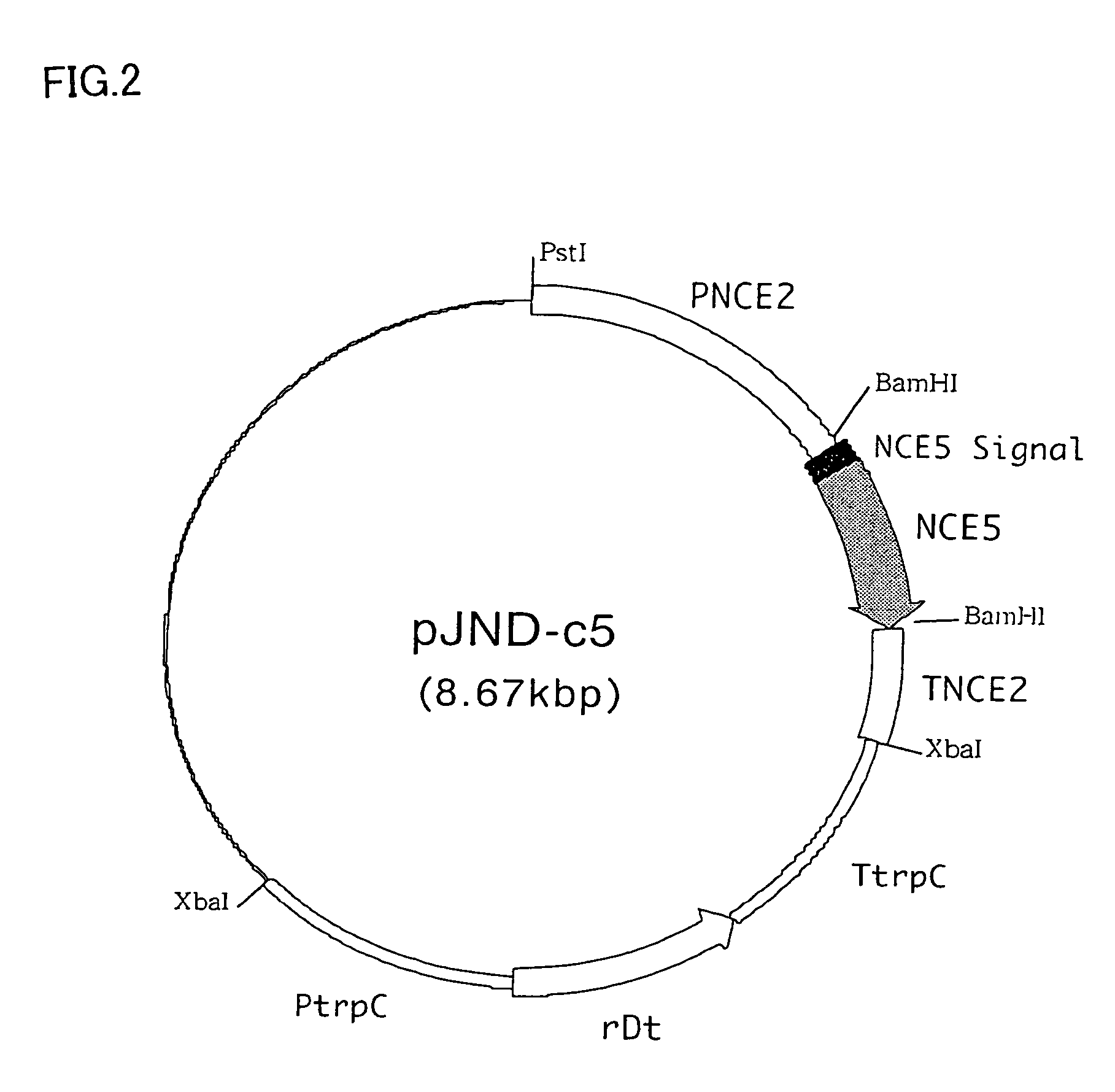
Endoglucanase enzyme NCE5 and cellulase preparations containing the same
InactiveUS7138263B2Efficient and inexpensive treatmentLow degreeFungiOrganic detergent compounding agentsBiotechnologyCellulase
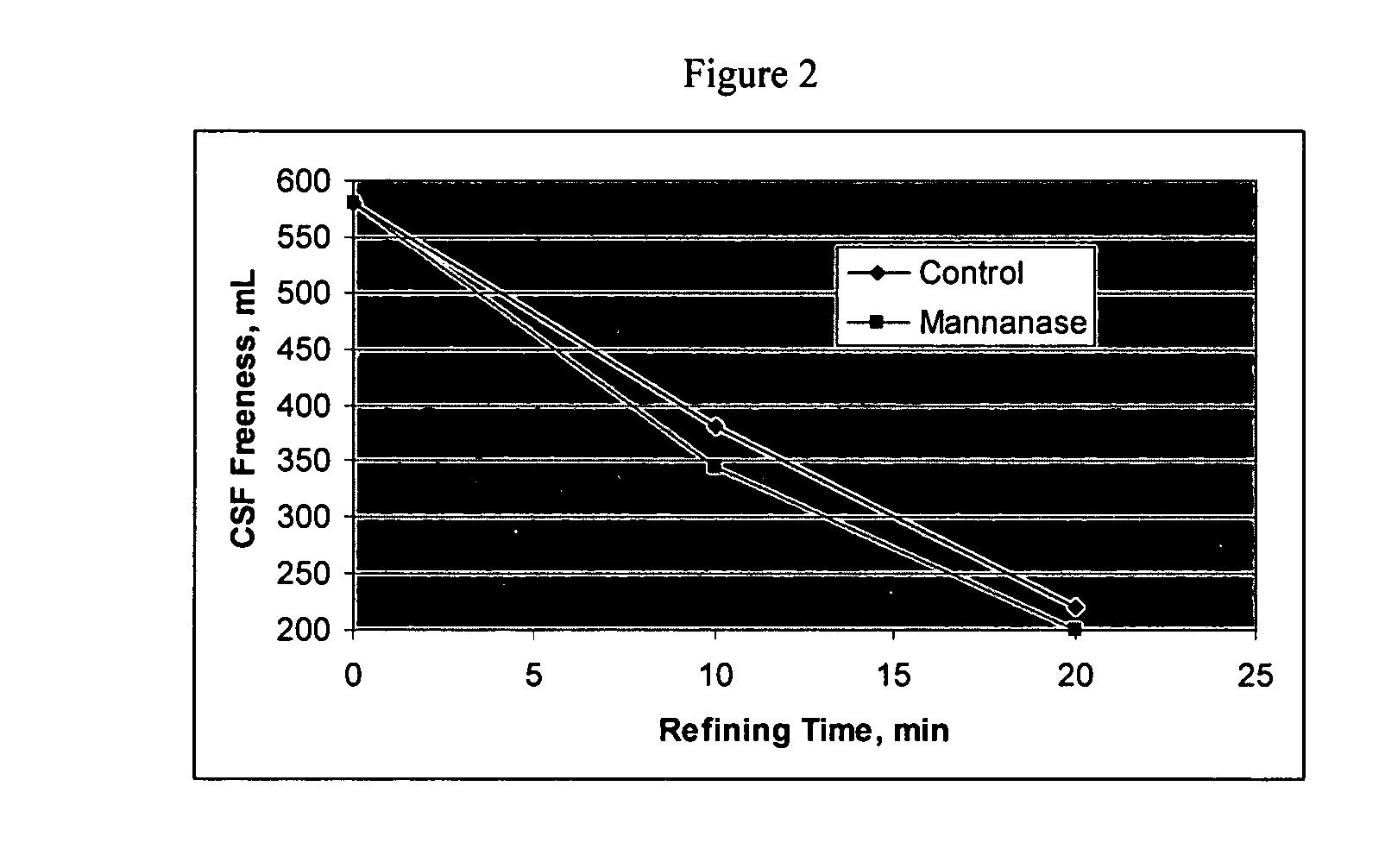
There is provided an endoglucanase enzyme, which is useful for reducing fuzz of regenerated cellulose-containing fabrics, improving the touch and appearance, color clarification, localized variation in color, reducing stiffness and using it as components of a detergent, as well as deinking waste paper and improving freeness of paper pulp. A cDNA coding for the endoglucanase enzyme NCE5 was cloned and its DNA sequence and amino acid sequence derived from it were determined.
Owner:MEIJI SEIKA KAISHA LTD
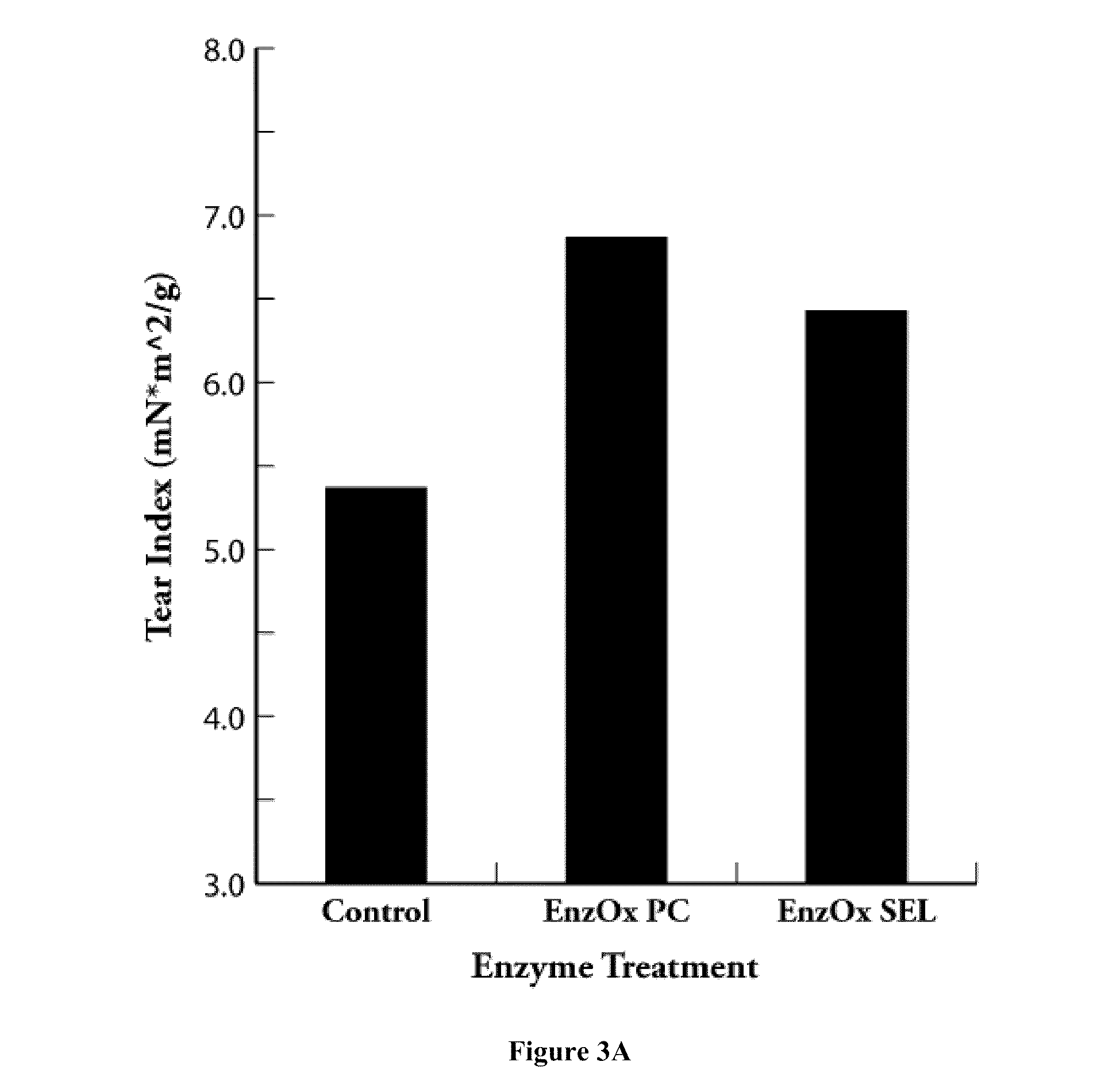
Use of 1,3-selective lipases for pitch control in pulp and paper processes
InactiveUS20100269989A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce concentrationNon-fibrous pulp additionFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpMonoglycerideSorbent
Formulations for pitch control, and methods of making and using thereof, are described herein. The formulations contains one or more 1,3-selective lipases. 1,3-selective lipases catalyze the hydrolysis of the terminal ester groups in triglycerides leaving the internal ester group intact. The enzyme formulations can contain one or more additives, such as dispersants, metal ions, absorbents, adsorbents, cationic polymers, and combinations thereof. The enzyme formulation is typically applied as a solution to the pulp stock. The enzyme formulations can be applied at any of one or more various points during the pulping and paper manufacturing processes. The use of selective lipase(s) decreases the total concentration of fatty acids in the system, and catalyzes the formation of monoglycerides, which are more effective at dispersing fatty acids than glycerol, the product of non-selective lipases, thereby improving pulp and paper machine runnability and pulp and paper quality.
Owner:ENZYMATIC DEINKING TECH LLC
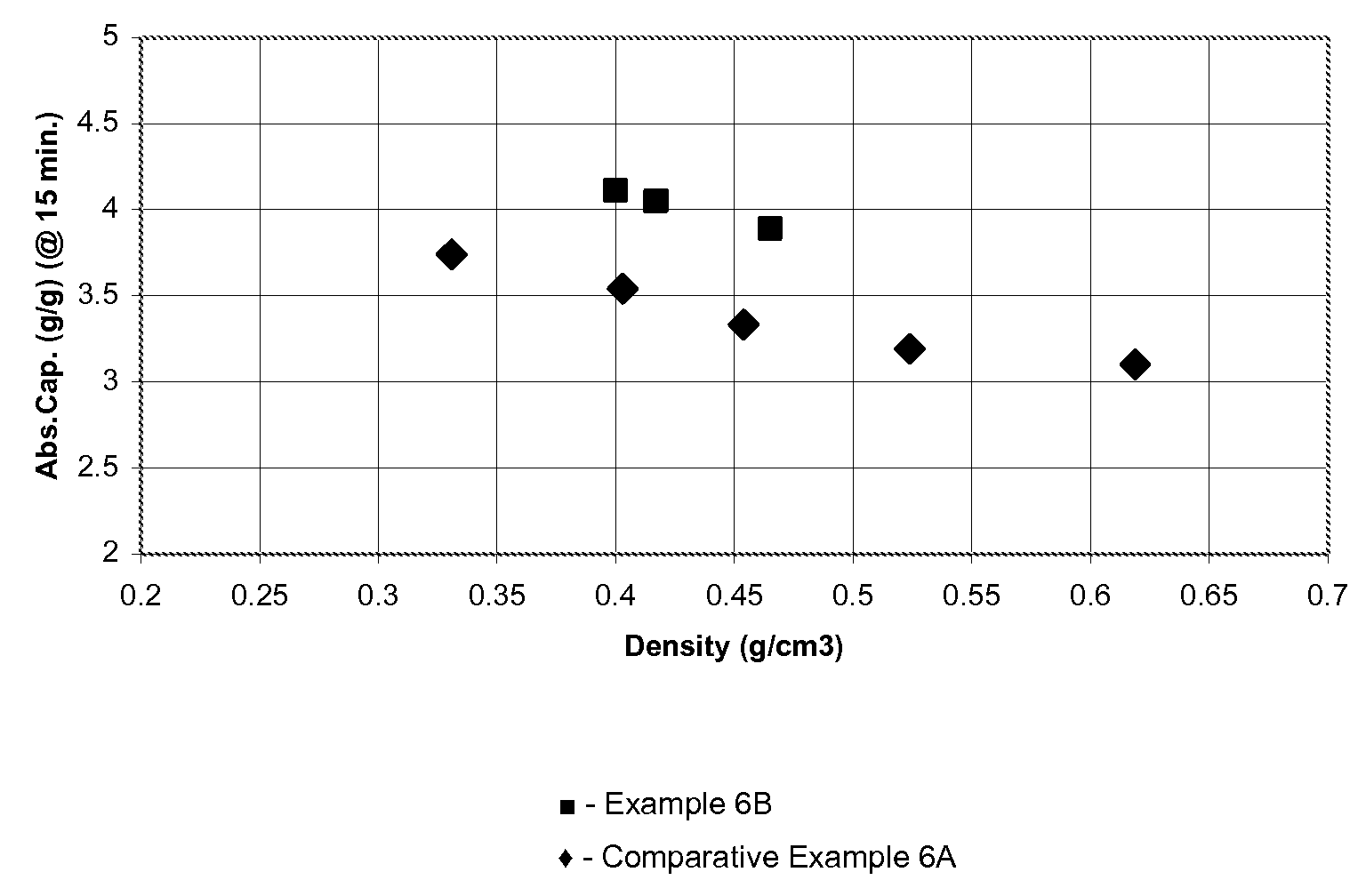
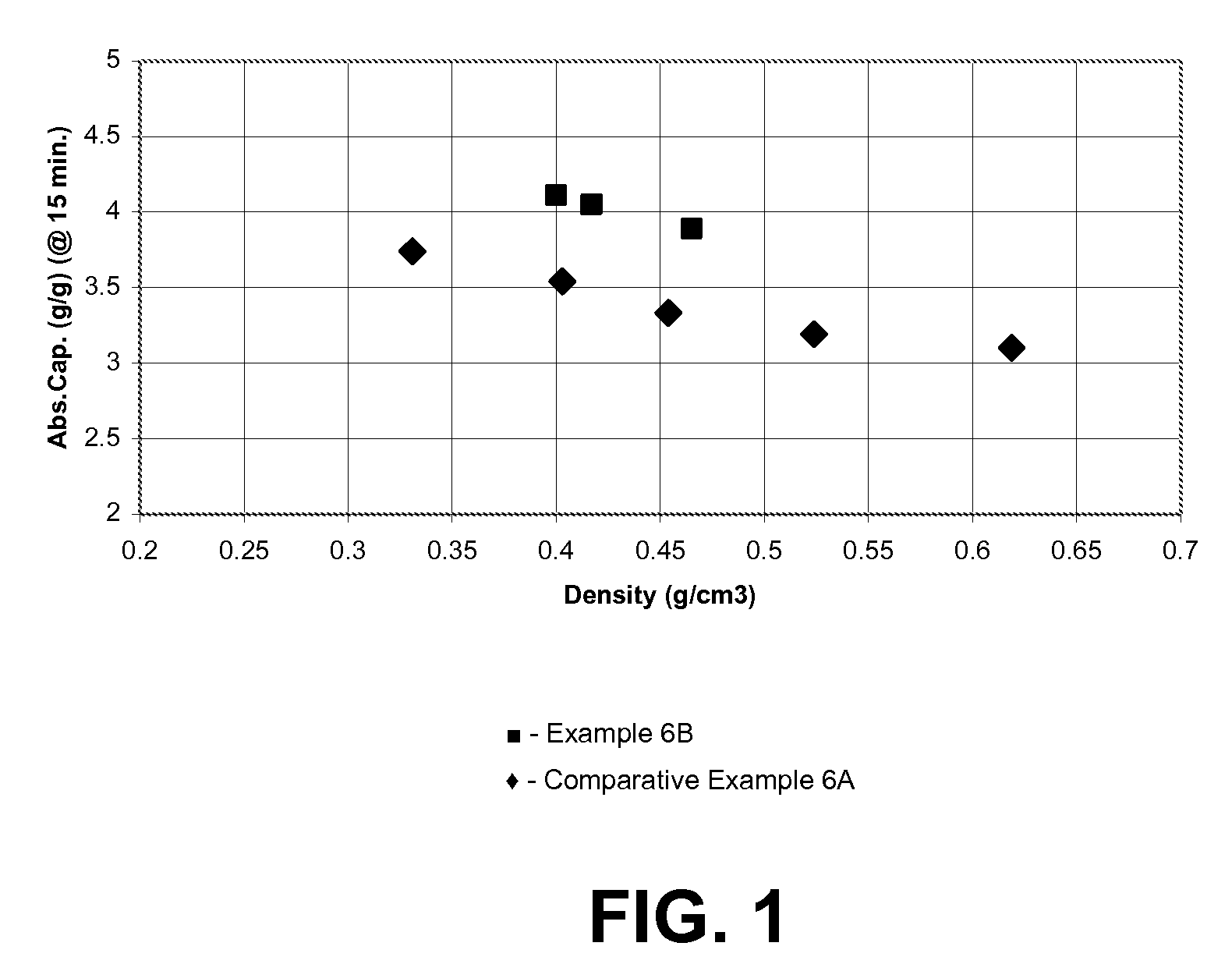
High absorbency lyocell fibers and method for producing same
InactiveUS20090151881A1Promote absorptionFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpMonocomponent cellulose artificial filamentPolymer scienceVolumetric Mass Density
High absorbency lyocell fibers are obtainable by hydrothermal treatment. The fibers can be treated with water at temperatures of at least 60° C. to provide lyocell fibers that can be formed into a random fibrous plug having a mass of 2 g, a density of 0.4 g / cm3, and a diameter of 25 mm which has a GAT Absorbency (at 15 min.) of at least about 3.7 g / g.
Owner:NGUYEN HIEN VU
Nanofiber sheet, process for producing the same, and fiber-reinforced composite material
ActiveUS20090264036A1High cellulose fiber crystallinityReduction factorFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpPrinted circuit aspectsPolymer scienceYoung's modulus
Provided is a nanofiber sheet that sufficiently refined by fibrillation and has high crystallinity of cellulose fiber and can realize a fiber-reinforced composite material exhibiting high transparency, a high elastic modulus, a low coefficient of linear thermal expansion, and high heat resistance and being high in flatness and smoothness. This nanofiber sheet includes crystalline cellulose as the main component and a lignin in an amount of from 10 ppm to 10 wt %. When a fiber / resin composite material obtained by impregnating the nanofiber sheet with tricyclodecane dimethacrylate, subjecting the impregnated product to UV-curing at 20 J / cm2, and heating the cured product in vacuum at 160° C. for two hours includes 60 wt % of the cured tricyclodecane dimethacrylate and 40 wt % of nanofiber, the following physical characteristics (i) to (iii) are satisfied: (i) the parallel light transmittance of light of a wavelength of 600 nm at a sheet thickness of 100 μm is 70% or more; (ii) the Young's modulus is 5.0 GPa or more; and (iii) the coefficient of linear thermal expansion is 20 ppm / K or less.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD +1
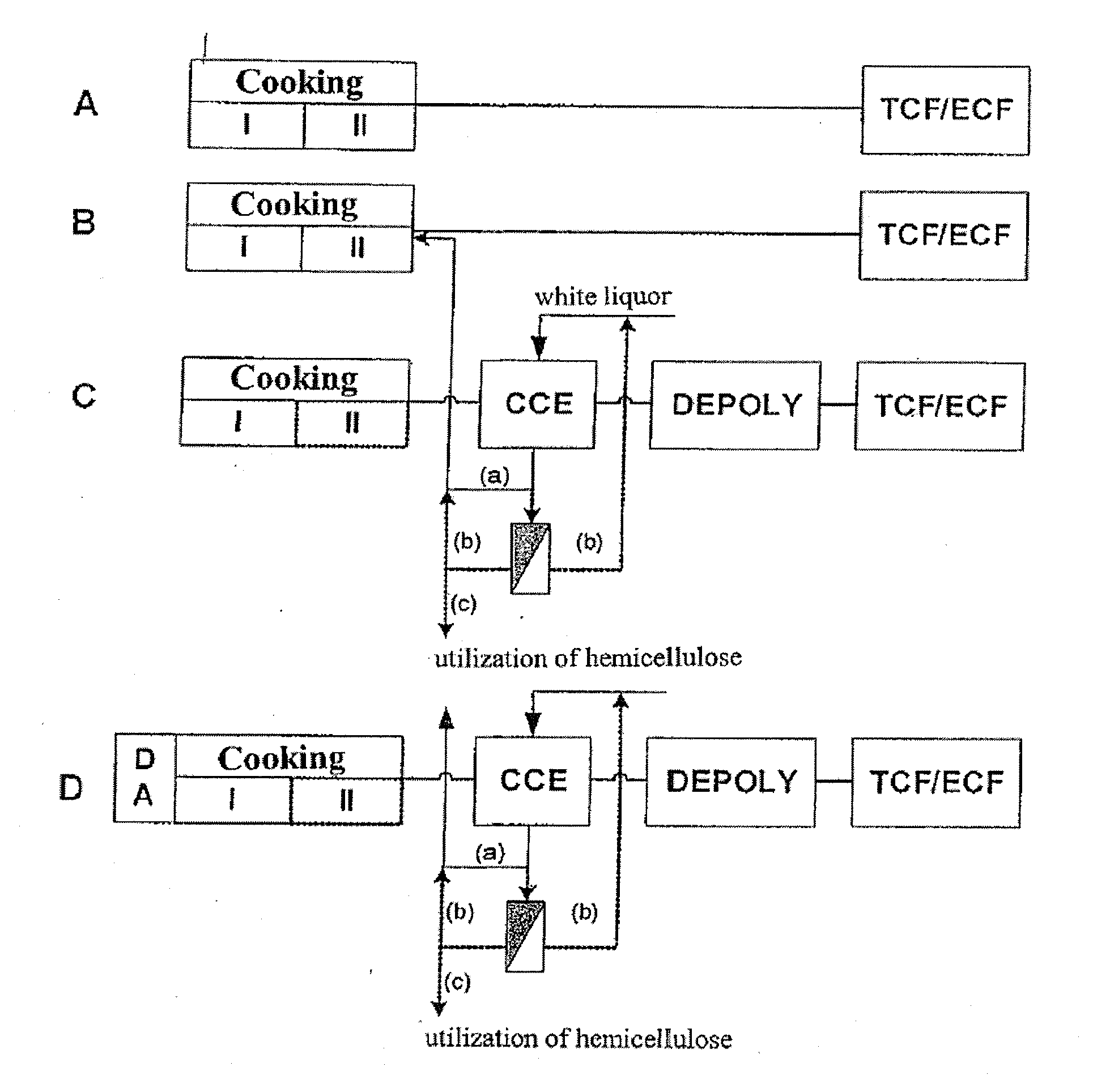
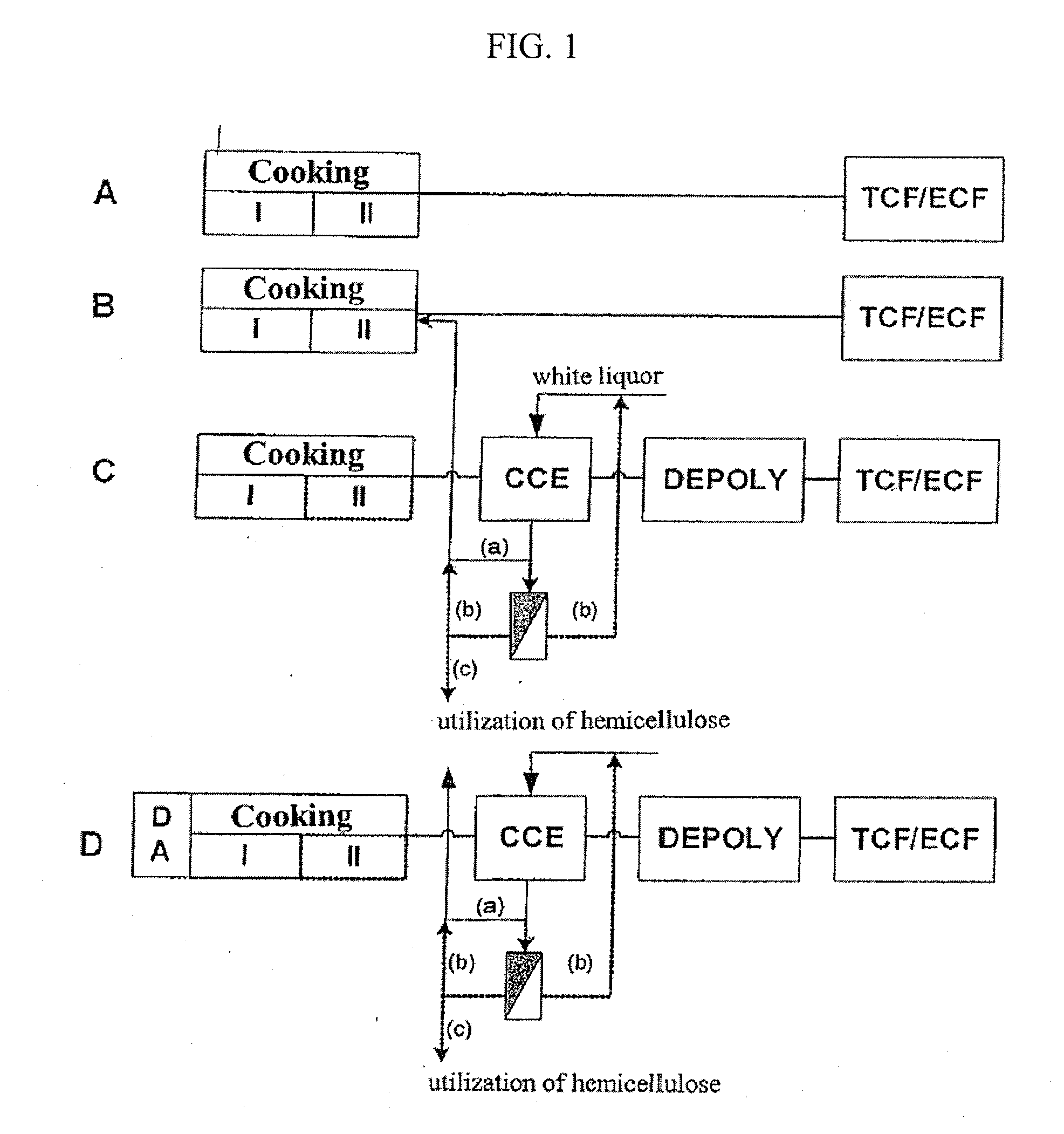
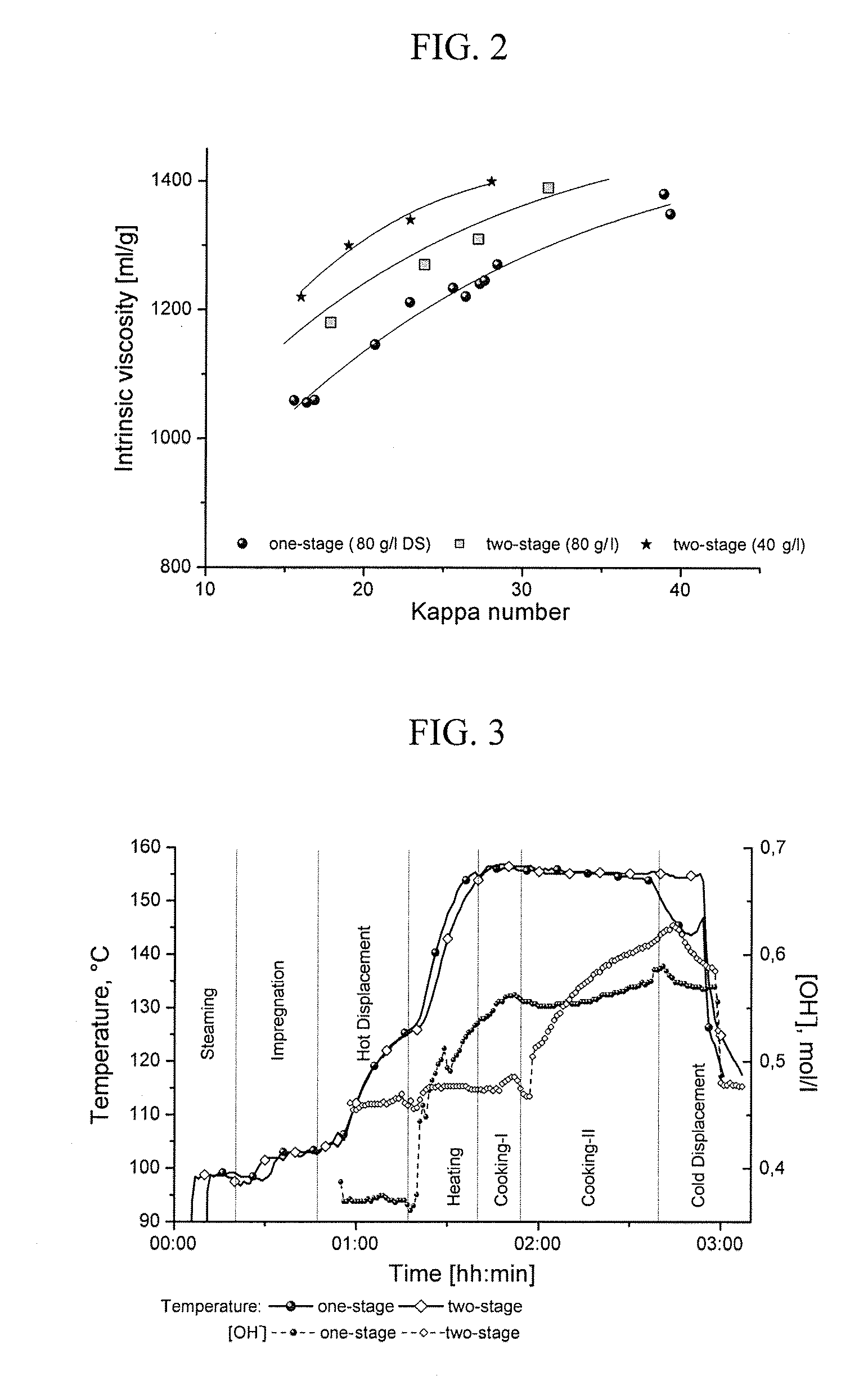
Process For Producing A Pulp
ActiveUS20090312536A1Easy to solvePretreatment with water/steamNon-fibrous pulp additionKraft processPulp and paper industry
The invention relates to a process for producing a dissolving pulp from a cellulosic starting material using the kraft process, comprising the step of cooking the starting material with a cooking liquor. The process according to the invention characterized in that the starting material is exposed to a steam treatment prior to cooking and that the pulp obtained by cooking is subjected to cold caustic extraction (CCE) in the course of further processing.
Owner:LENZING AG
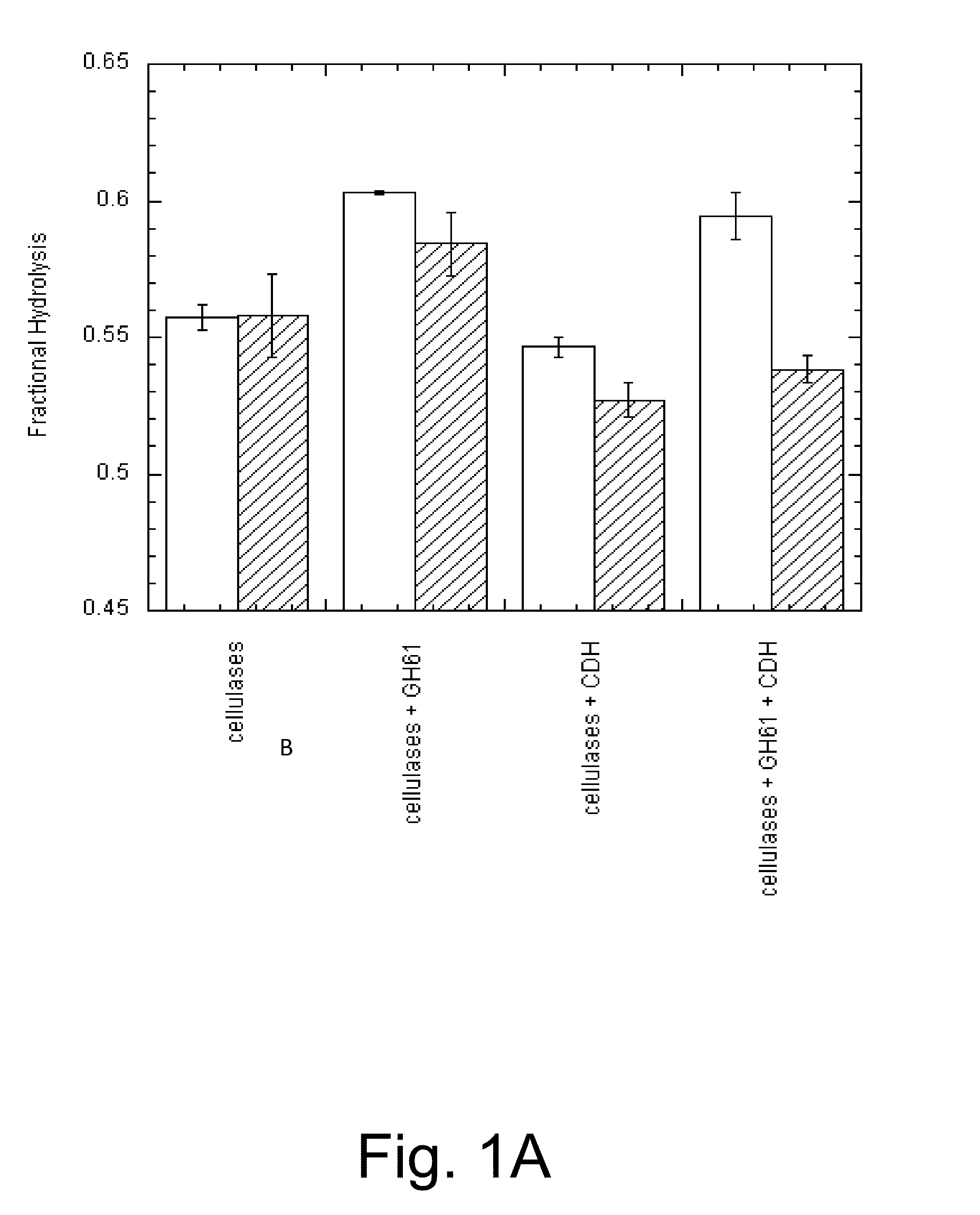
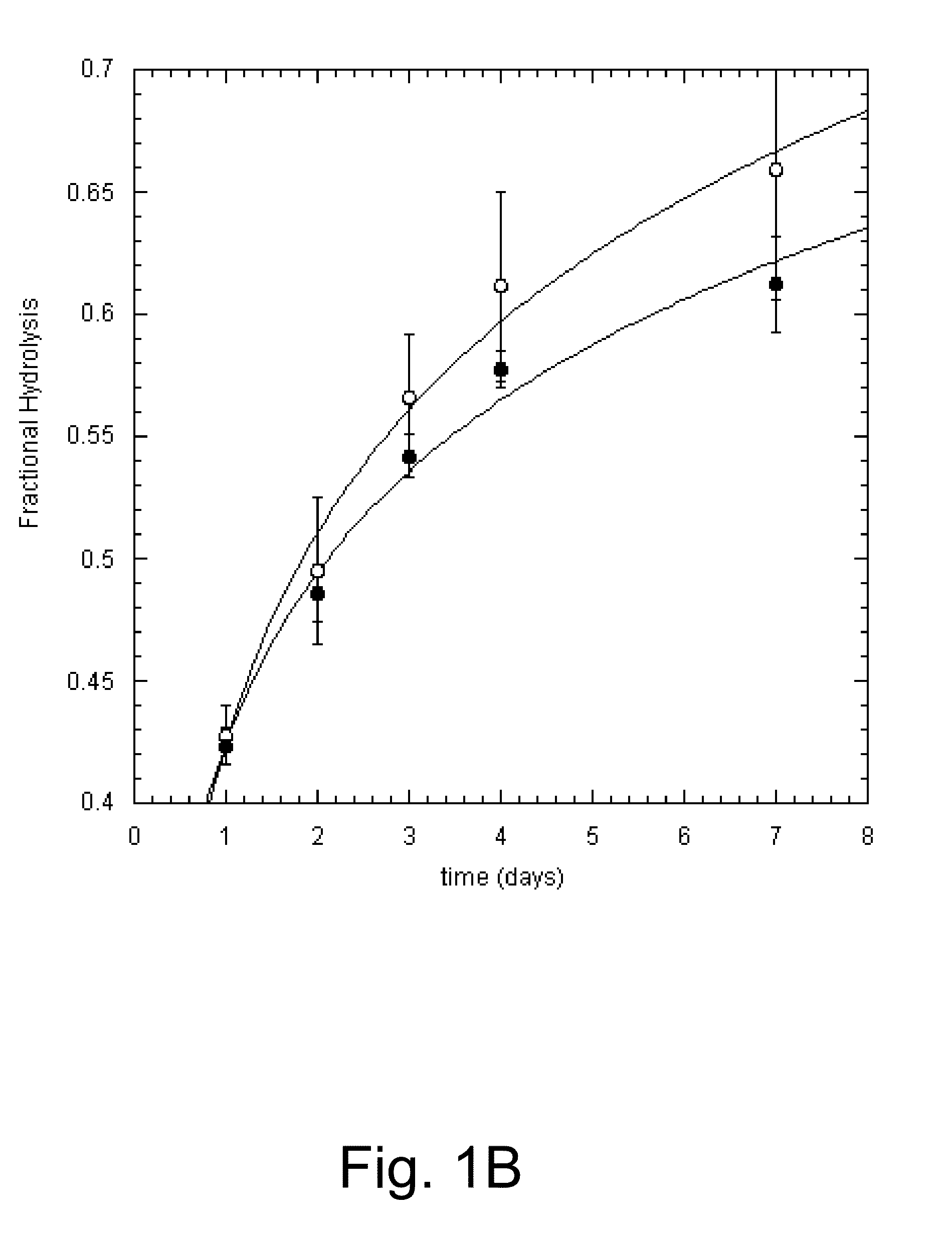
Methods for increasing hydrolysis of cellulosic material
The present invention relates to methods for pretreating a cellulosic material, methods for degrading or converting a cellulosic material, methods for producing a fermentation product, and methods of fermenting a cellulosic material under anaerobic conditions.
Owner:NOVOZYMES INC
Methods To Detect Organic Contaminants In Pulp and Fiber
InactiveUS20090084510A1Accurate readingFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpDigestersFiberFluorescence
A method to detect organic contaminants in pulp and fiber is described which uses hydrophobic dyes, such as fluorescent dyes.
Owner:BUCKMAN LAB INT INC
Mitigation technique in use for producing bleached chemical pulp by using raw material of grass
ActiveCN101092805AFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpChemical/chemomechanical pulpState of artBleach
This invention relates to an easing technology for producing bleach chemical pulp with grasses including: 1, preparing bleach chemical pulp according to the current technology, 2, easing the material pulp to loosen fiber structure in terms of the current technology after steaming grasses materials and before bleaching the pulp so as to loosen leaf structure of the grass fibers, which forms a cubic net structure suitable for exposing lignin in the grasses since the specific surface area is increased.
Owner:SHANDONG FUYIN PAPER & ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Paper-making grade softwood pulp plate modifying production technique
ActiveCN101158125AMeet production requirementsReduce pollutionPretreatment with alkaline reacting compoundsFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpTO-18Cooking methods
The invention provides a denaturizing production technique of paper making needle wood pulp plate, which solves the problems of uneven dipping, slow hemicelluloses stripping, difficult accumulation descending, uneven cooking, single cooking method, single bleaching method and violent conditions existing in denaturizing production technique of wood pulp in the prior art. The invention comprises the following steps: wood pulp plate paging, alkali soaking, pressing, untwining and dispersion, cooking, washing, impurity removal, bleaching, a secondary washing and pulping; wherein, the wood pulp plate paging, alkali soaking, pressing, untwining and dispersion are to send papers into a alkali dipping barrel with concentration of 6 percent to 18 percent after the paper making bleaching wood pulp plates are separated by a paging device. When the wood pulp plates are changed into pulp with concentration of 3 percent to 6 percent, the pulp with concentration of 3 percent to 6 percent is sent to a squeezer to be squeezed and to untwine and disperse fiber. By adopting the invention, the quality of the dissolved viscose fiber wood pulp can be better and more stable; furthermore, the invention provides wider selection range of raw material.
Owner:YIBIN GRACE GROUP CO LTD
Use of hemicellulase composition in mechanical pulp production
InactiveUS20050000666A1High strengthLess energyFibrous raw materialsPulp beating/refining methodsPulp and paper industryHemicellulose
Owner:BUCKMAN LAB INT INC
Method for controlling pitch and stickies deposition
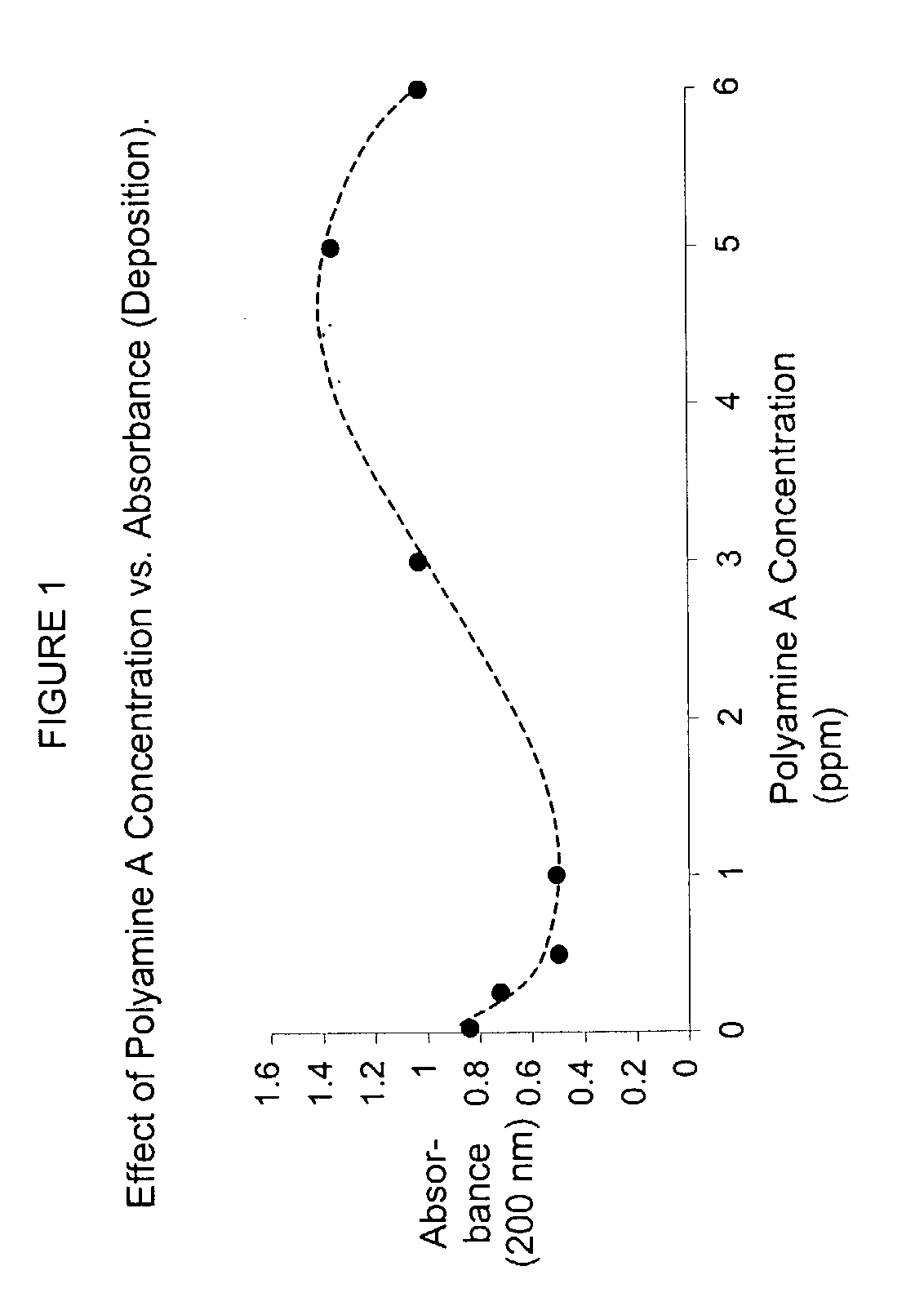
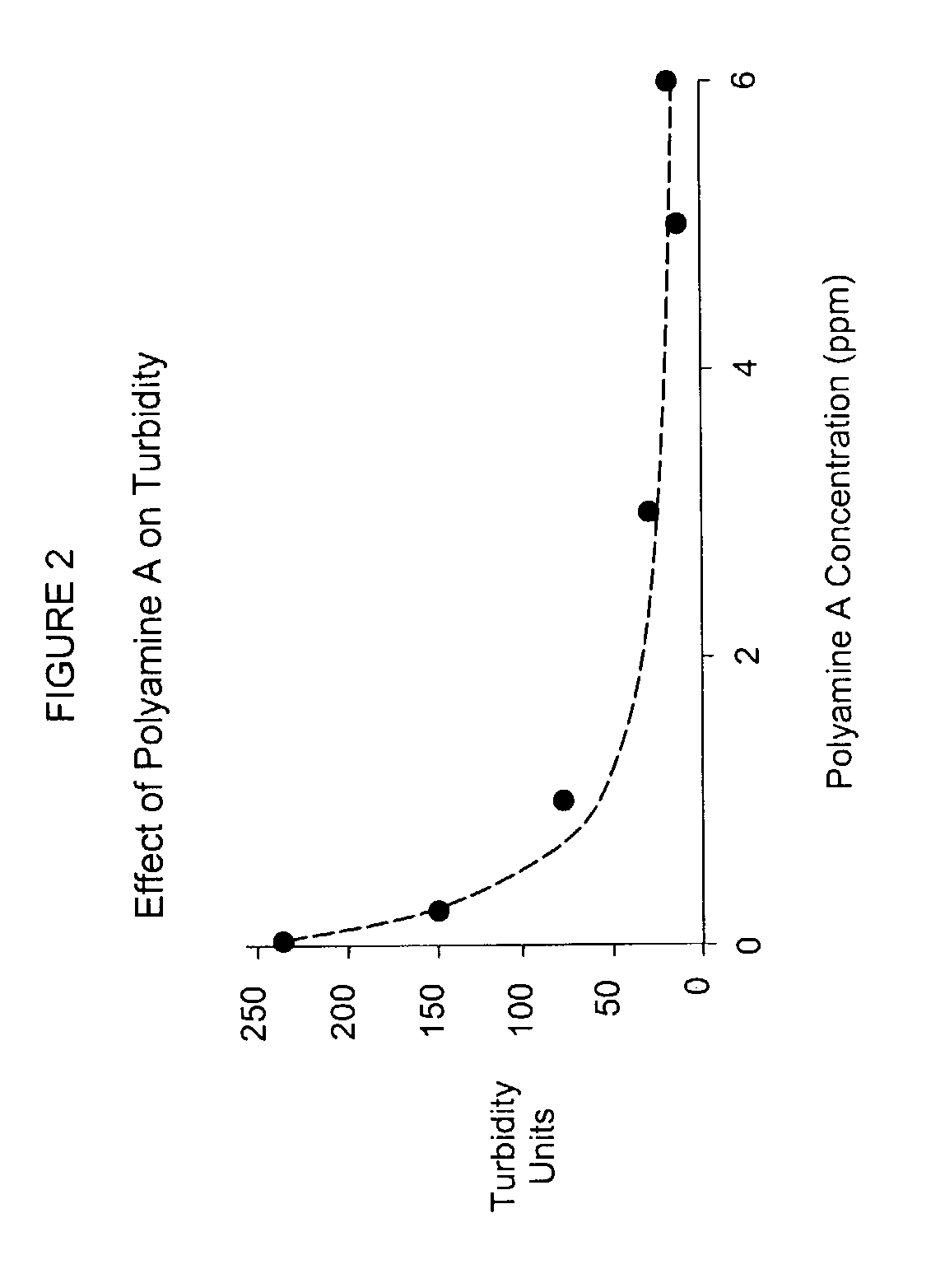
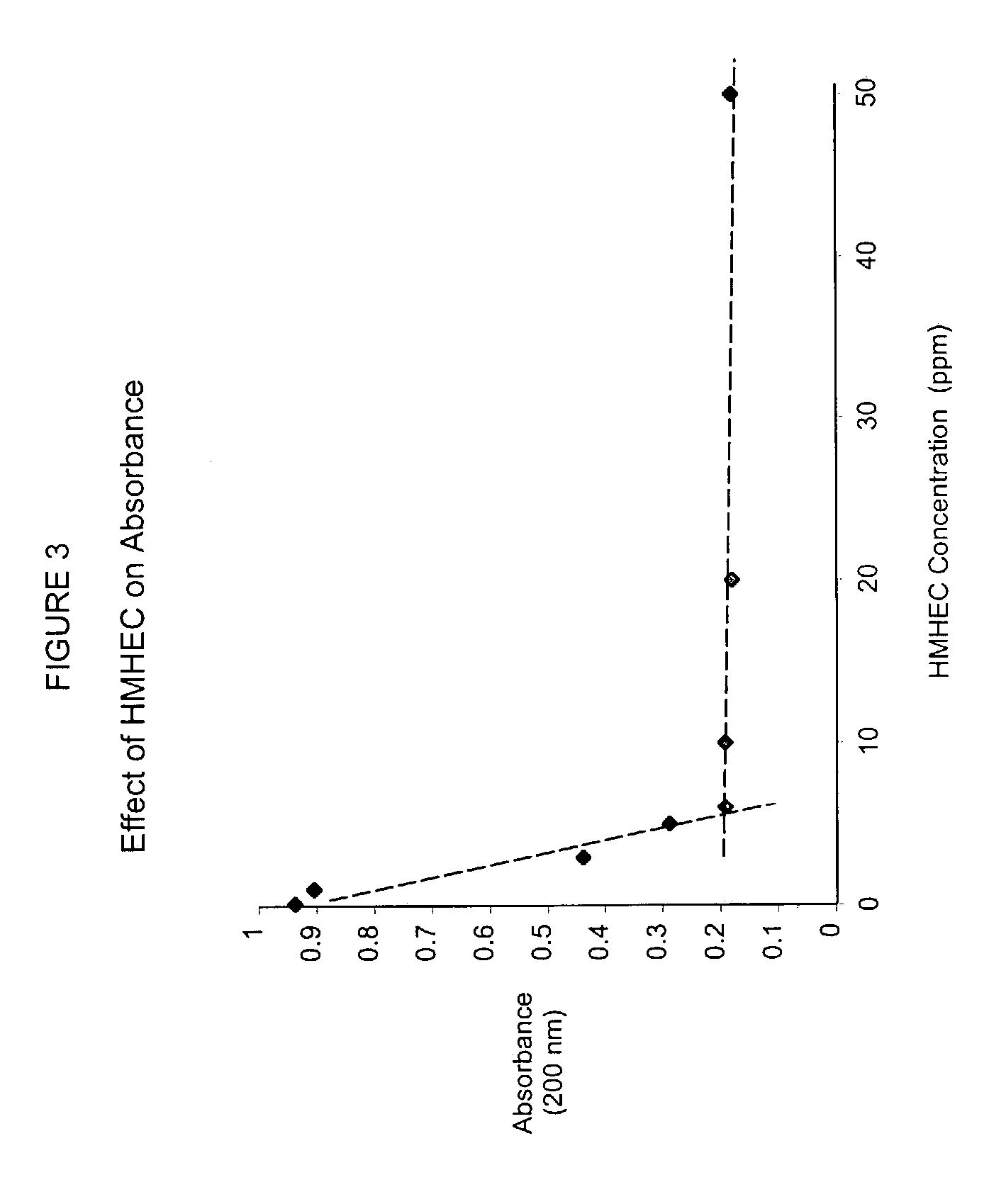
ActiveUS7166192B2Improve retentionImprove usage activityNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperSlurryCellulose fiber
A method for controlling Pitch and Stickies is disclosed. The method comprises adding hydrophobically modified hydroxyethyl cellulose (HMHEC) and cationic polymers to a cellulosic fiber slurry (pulp) or to a paper process or to a paper making system and results in a higher degree of inhibiting organic deposition and retention of pitch on paper fiber as compared to the inhibition of the individual ingredients. The combination of HMHEC and cationic polymers surprising results in a synergistic effect.
Owner:SOLENIS TECH CAYMAN
Use of special screens in the preparation of cellulose powder
InactiveUS20090306364A1Sugar derivativesFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpChemistryCellulose Powders
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Process for producing xylooligosaccharide from lignocellulose pulp
InactiveUS6942754B2Improve efficiencyLow costFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpPulp bleachingCellulose pulpHemicellulose
Xylooligosaccharide is produced from a lignocellulose pulp by enzyme-treating a lignocellulose pulp with hemicellulase, filtering the resultant reaction mixture to separate a liquid fraction from the enzyme-treated pulp, subjecting the separated liquid fraction to a permeation treatment through a separation membrane to separate a non-permeated fraction containing xylooligosaccharide-lignin complex with an increased concentration from a permeated fraction, collecting the non-permeated fraction, and separating and recovering xylooligosaccharide from the collected non-permeated fraction.
Owner:OJI PAPER CO LTD
Pitch and stickies control in pulp and papermaking processes
ActiveCN101548045AFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpMicroorganism/enzyme additionProcess equipmentPapermaking
Owner:SOLENIS TECH CAYMAN
Paper-making-stage bamboo wood pulp plate denaturalization producing technique
ActiveCN101148836ADip evenlyFully impregnatedPretreatment with alkaline reacting compoundsFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpHemicelluloseViscose fiber
The present invention provides denaturating production process of paper-making bamboo pulp sheet pulp superior to available denaturated wood pulp sheet producing process. The denaturating production process includes the following steps: paging paper-making bamboo pulp sheet in a paging device, alkali dipping in 6-18 % concentration alkali solution in a dip vat to form 2.5-5 % concentration pulp, extruding in a extrude, debonding fiber, digesting, washing, depurating, bleaching, washing for the second time, and fishing pulp. The process can obtain high quality wood pulp of soluble viscose fiber stably and has wide material source.
Owner:YIBIN GRACE GROUP CO LTD
Composition of matter effluent from refiner of a wet laid process
ActiveUS20200063339A1Reduce consistencyLow variabilityFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpChemical/chemomechanical pulpPolymer scienceCellulose fiber
A composition and process for making the composition by co-refining: fibrillated virgin cellulose fibers, waste / recycle cellulose fibers, or both; co-refined cellulose ester (CE) staple fibers having a denier per filament (DPF) of less than 3 and the weight percent of CE staple fibers is less than 30 wt. %, based on the weight of CE staple fibers and said cellulose fibers; and water. The composition can be co-refined to obtain lower Canadian standard freeness yet improved drainage and wet laid products having good tensile strength, air permeability, stiffness, burst strength, and bulk.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
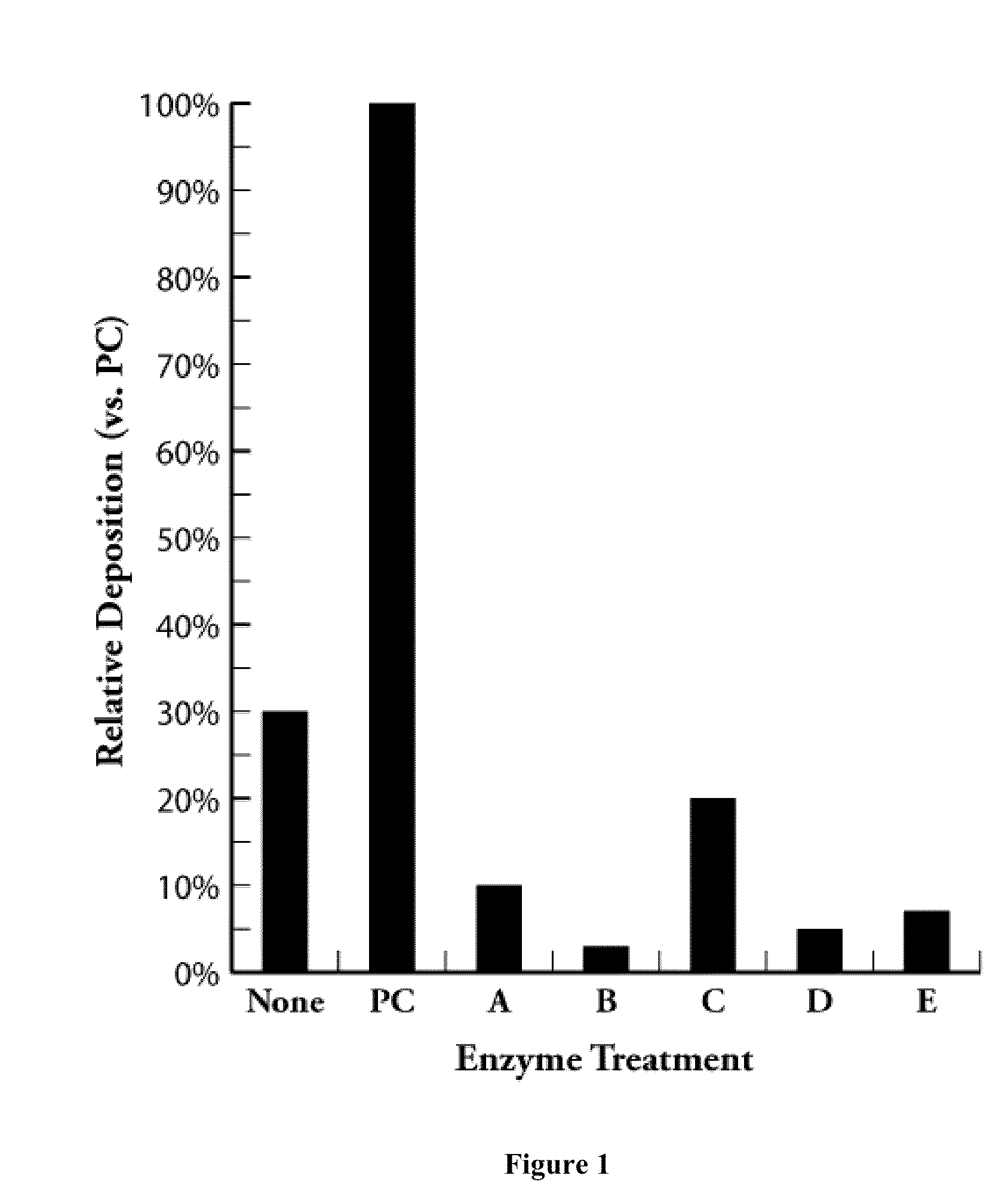
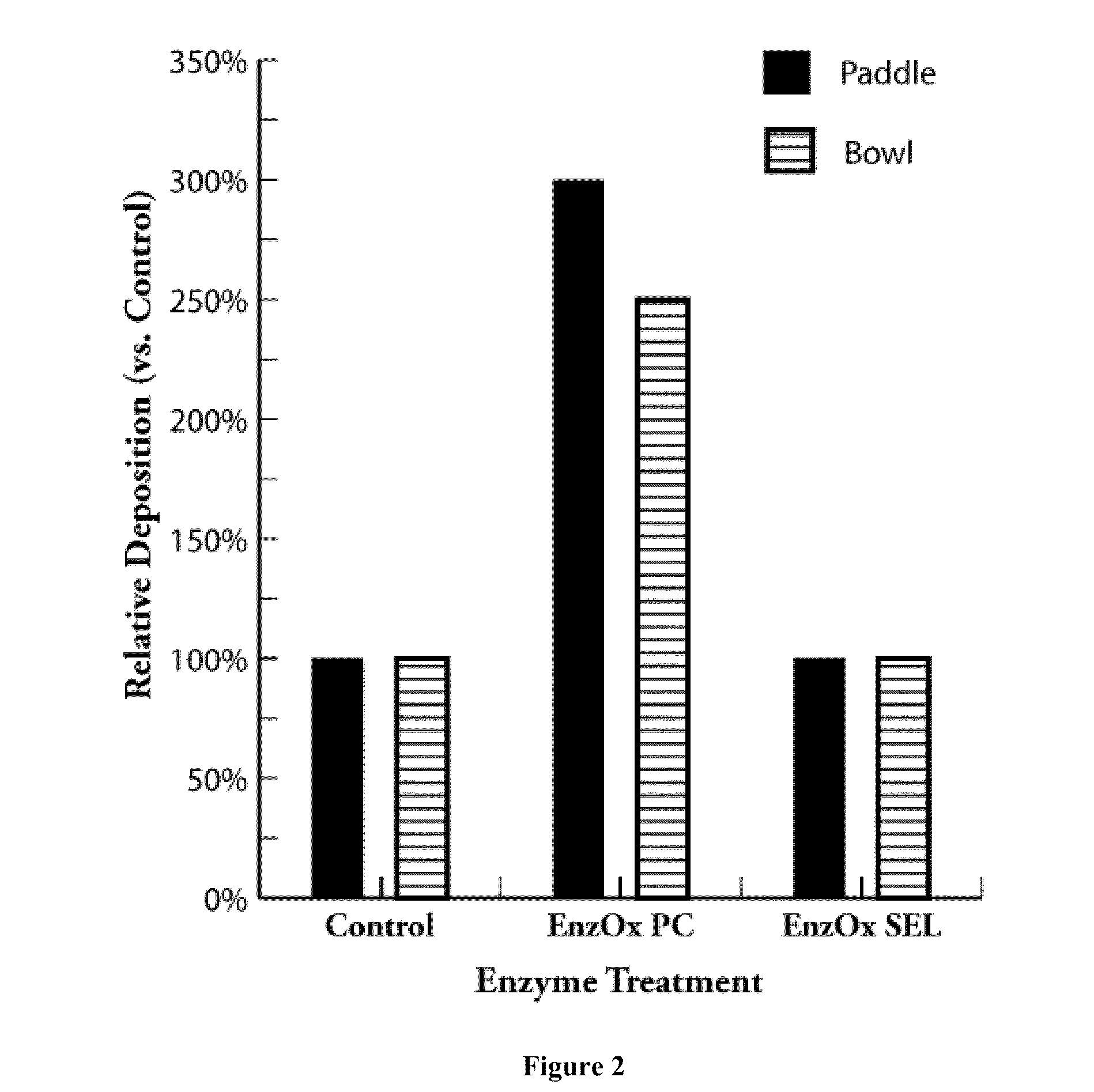
Treatment of Pulp Stocks Using Oxidative Enzymes to Reduce Pitch Deposition
InactiveUS20070261806A1Lower energy requirementsImprove paper strengthPulp liquors combustionFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpTime rangeResin acid
Methods of treating pulp stocks with an enzyme formulation containing one or more oxidative enzymes, to reduce pitch deposition, control pitch related problems, modify the physical and / or chemical properties of tri, di-, and mono-glycerides, fatty acids, resin acids, esters of fatty acids and resin acids, and metal soaps of fatty acids and resin acids, or change the concentration of triglycerides, fatty acids, resin acids, and esters of fatty acids and resin acids, have been developed. The pulp stock is treated with an enzyme formulation containing laccases, peroxidases, esterases, and / or combinations thereof. The enzyme formulations may also contain a laccase mediator and / or a dispersant. The enzyme formulation can be applied at any of several locations during the pulping and / or papermaking process. The enzyme formulation is typically applied as a solution to the pulp stock. The enzyme treatment is effective at a temperature of between about 30° C. to about 95° C., more preferably from about 50° C. to about 80° C. The pH of the pulp stock is from about 4.0 to about 7.0, more preferably from about 4.5 to 5.5. The stock can be treated for a period of time ranging from about 5 minutes to about 10 hours.
Owner:ENZYMATIC DEINKING TECH LLC
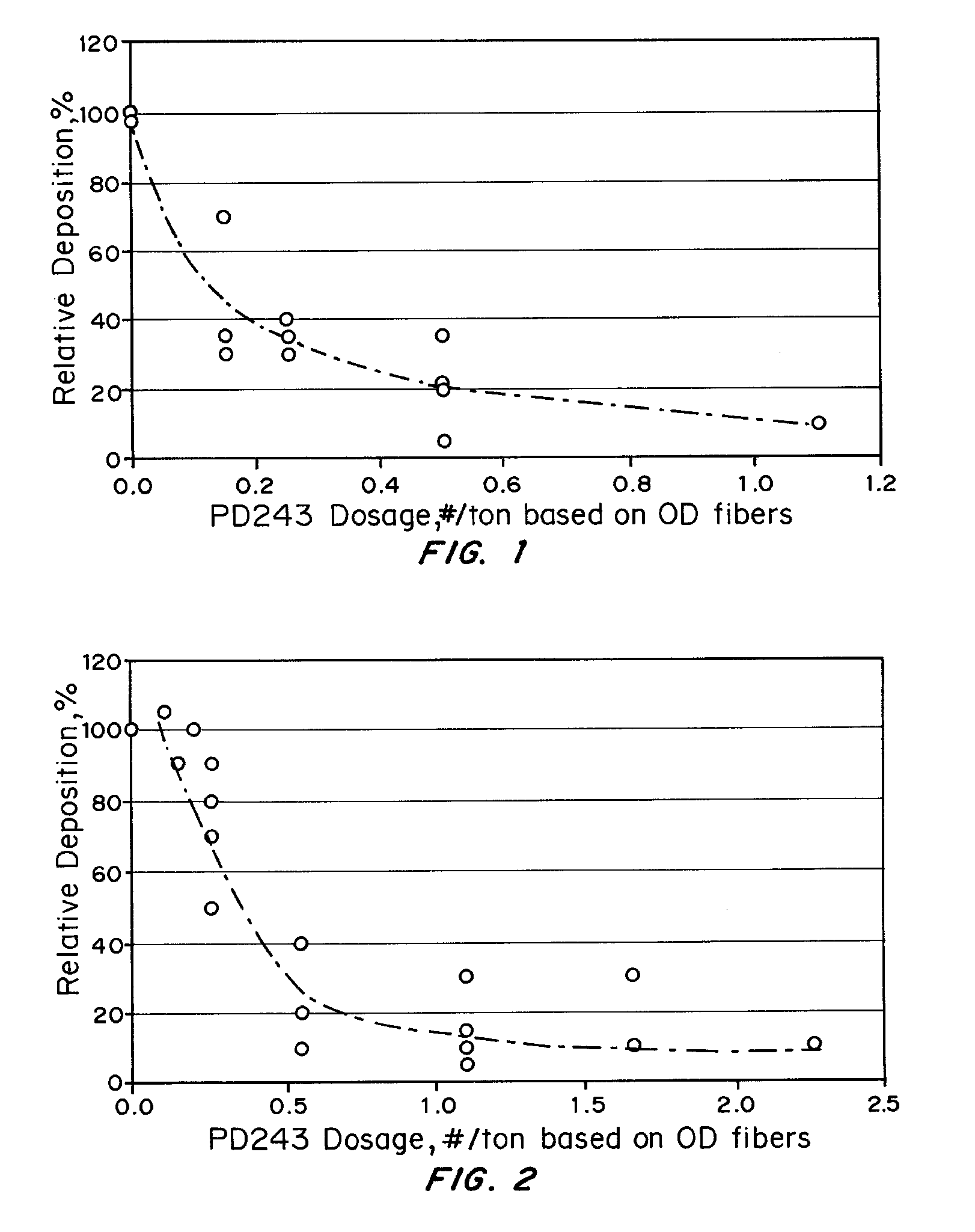
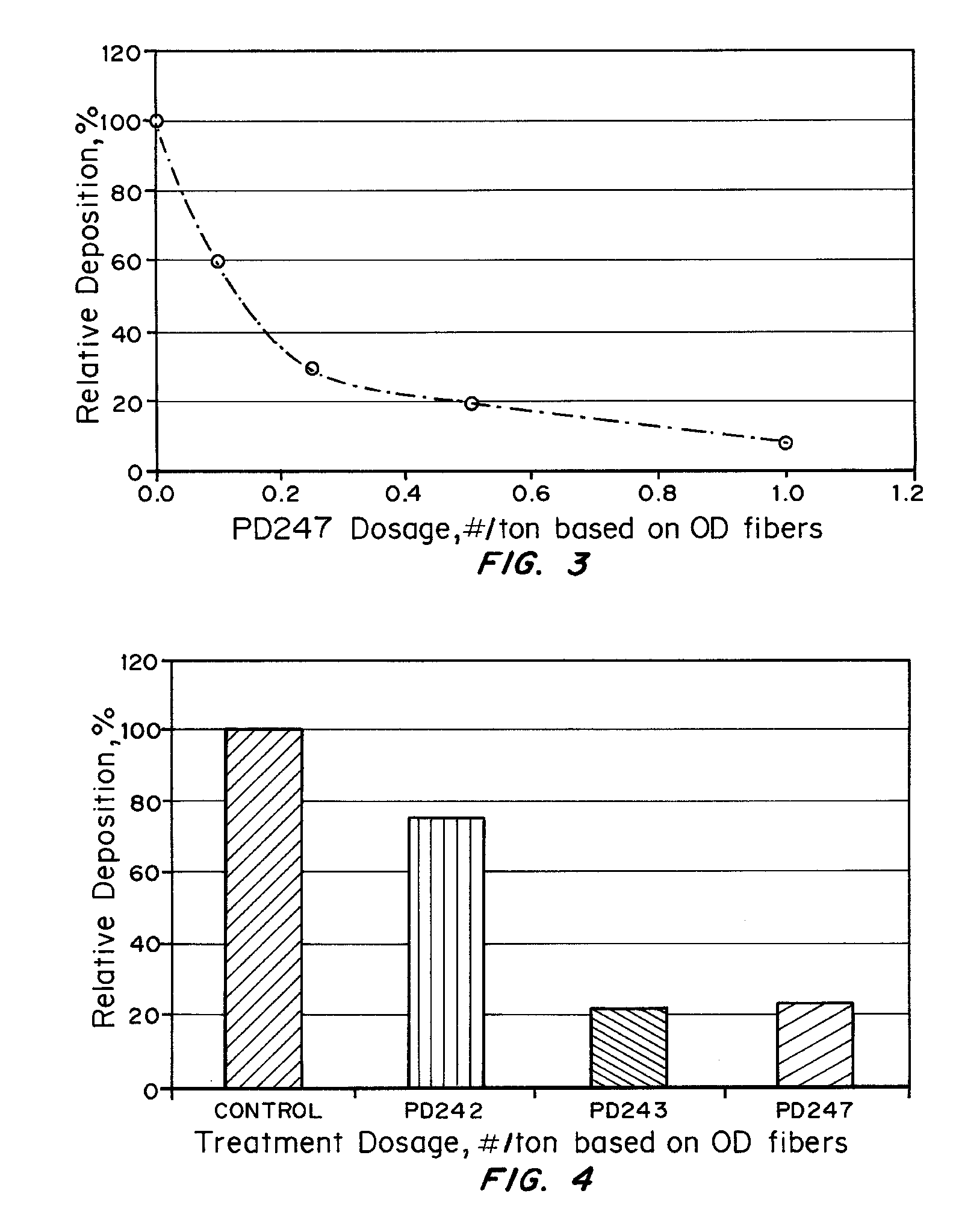
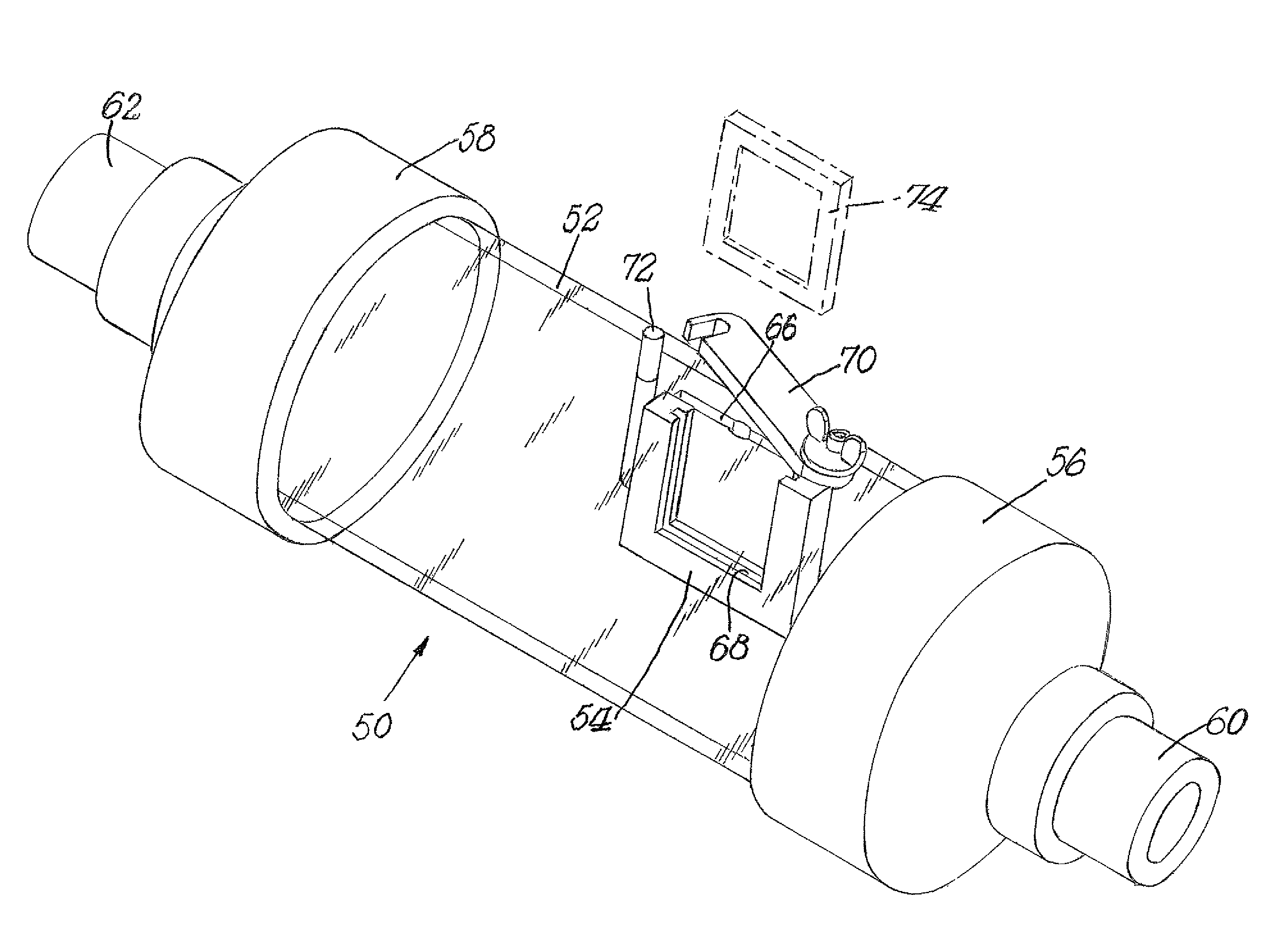
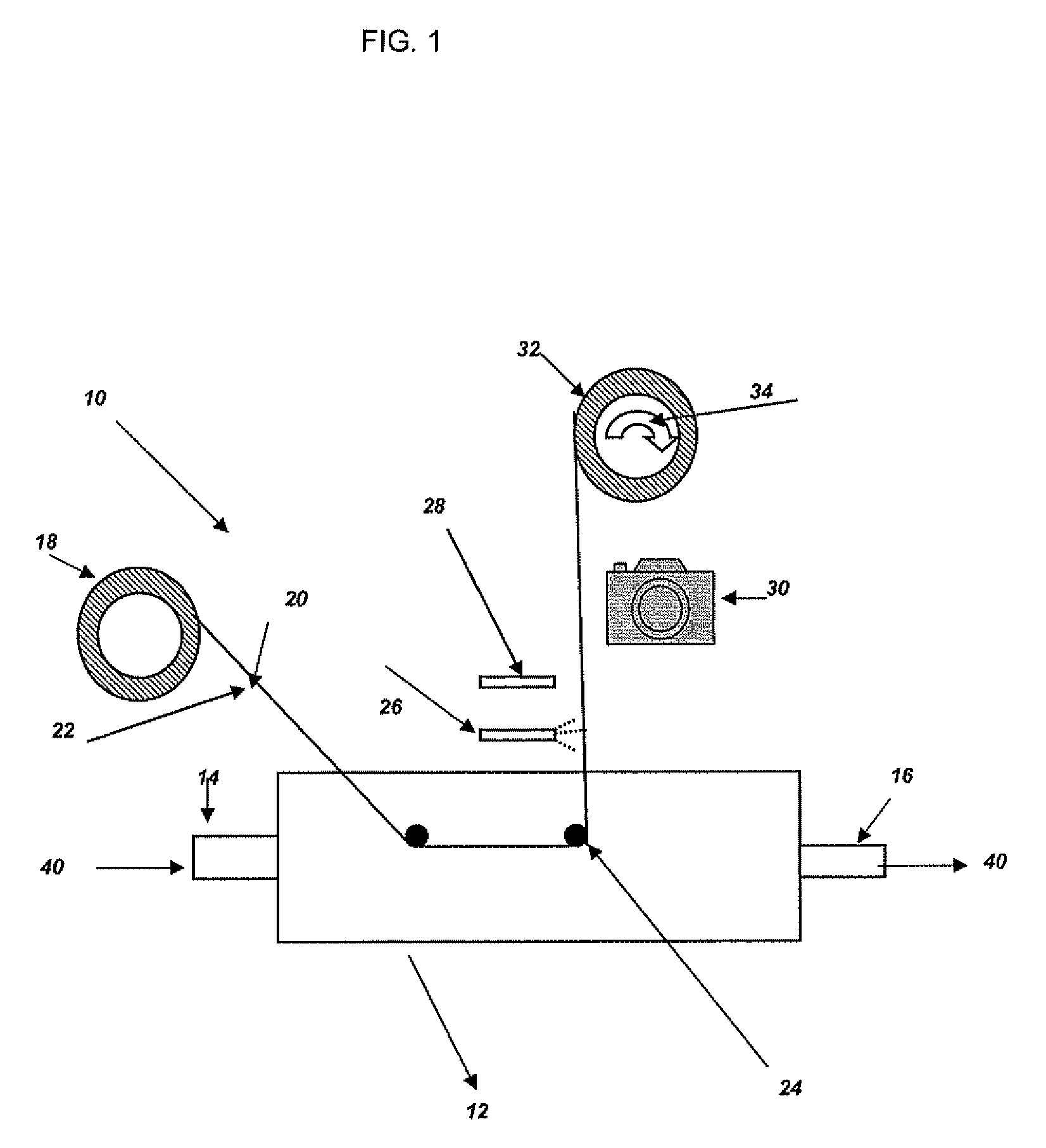
Method and apparatus for measuring deposition of particulate contaminants in pulp and paper slurries
ActiveUS8160305B2Non-fibrous pulp additionFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpParticulatesAdhesive
A method and an apparatus for measuring the depositability of particulate contaminants present in a pulp or paper mill fluid stream and evaluating interactions of such particulate contaminants with other contaminants collects the particulate contaminants on a suitable substrate, such as a plastic film coated with an adhesive or coated with organic contaminate, placed in contact with the pulp or paper mill fluid stream for at least five minutes up to several hours. The amount of contaminants collected on the substrate is quantified and evaluated by taking one or more scanned images of the substrate with a resolution of at least 2,000 dots per inch (DPI) and analyzing the scanned images with image analysis technique.
Owner:SOLENIS TECH CAYMAN
Grass type unbleached paper products and production method thereof
Provided is an unbleached paper product made from grass type pulp, the unbleached paper product has a brightness of 35-60% ISO, the grass type pulp is unbleached. The unbleached paper product includes an unbleached toilet paper, an unbleached hand towel, an unbleached wiping paper, an unbleached duplicating paper, an unbleached meal container, an unbleached food wrapping paper and an unbleached printing paper. The paper products have a high intensity and have no detection of dioxin and absorbable organic halides in the harmful substance detection test.
Owner:SHANDONG FUYIN PAPER & ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com