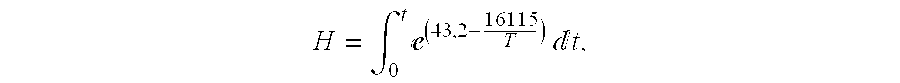Patents
Literature
151results about "Pulping with organic compounds" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
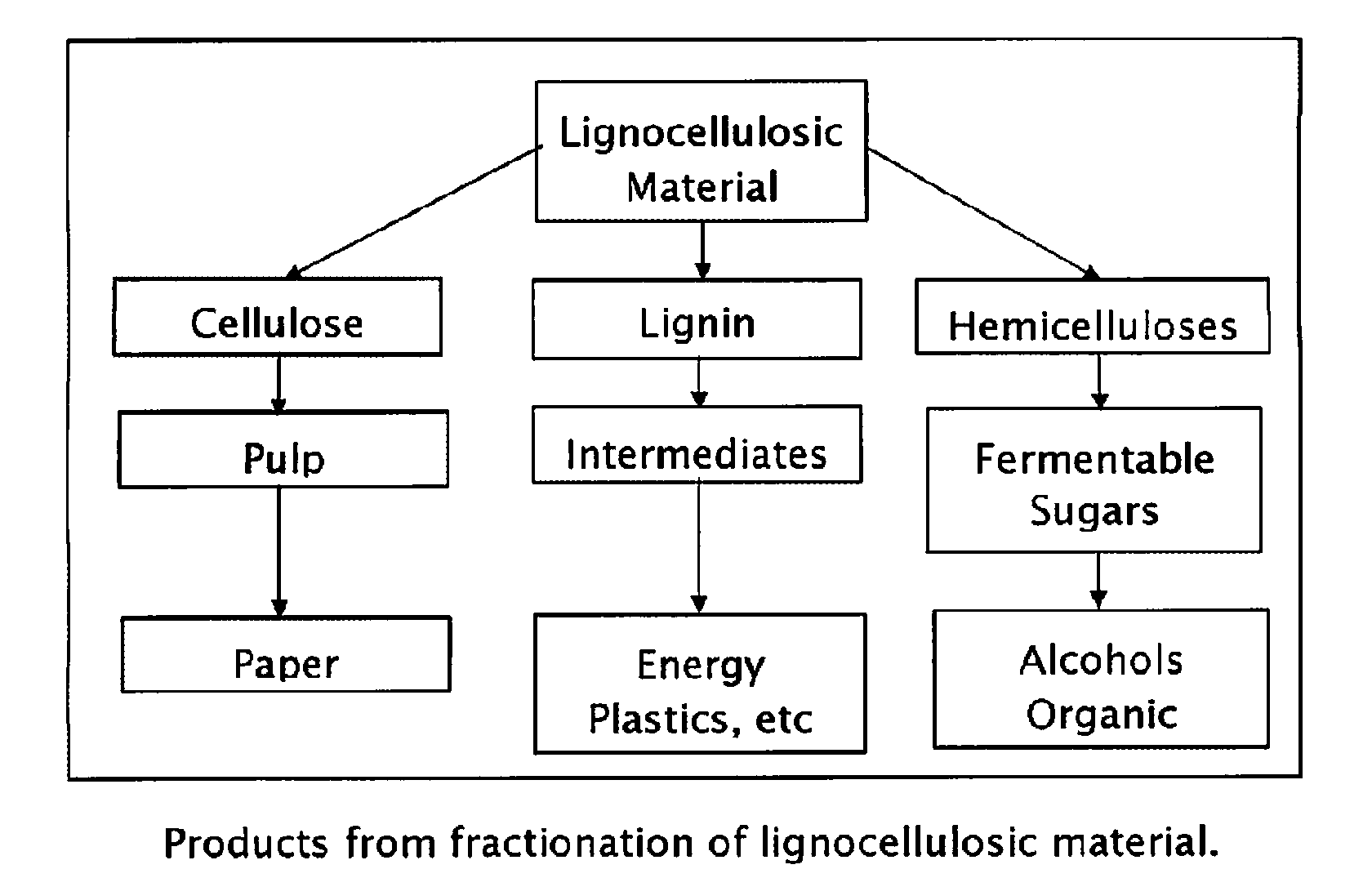
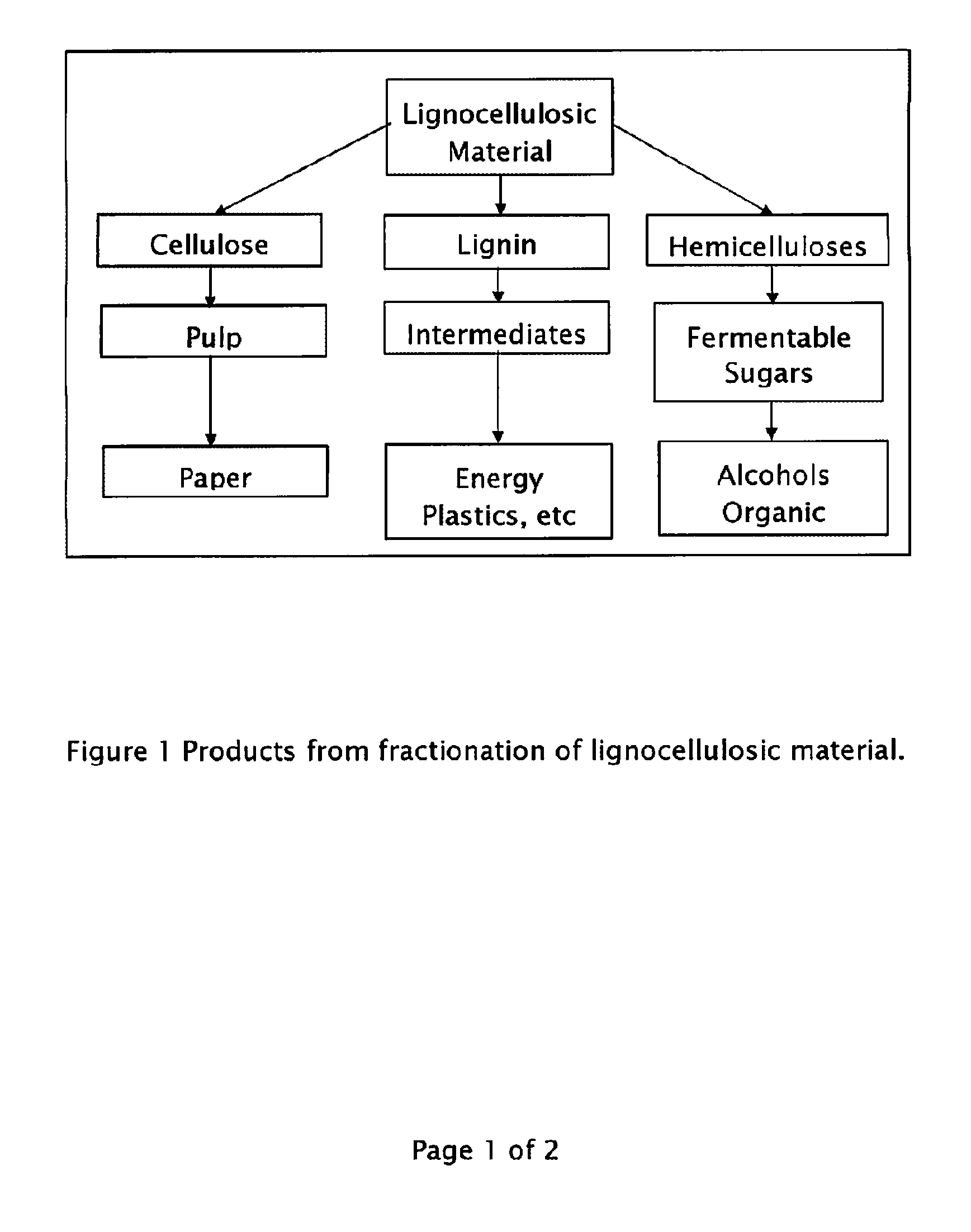
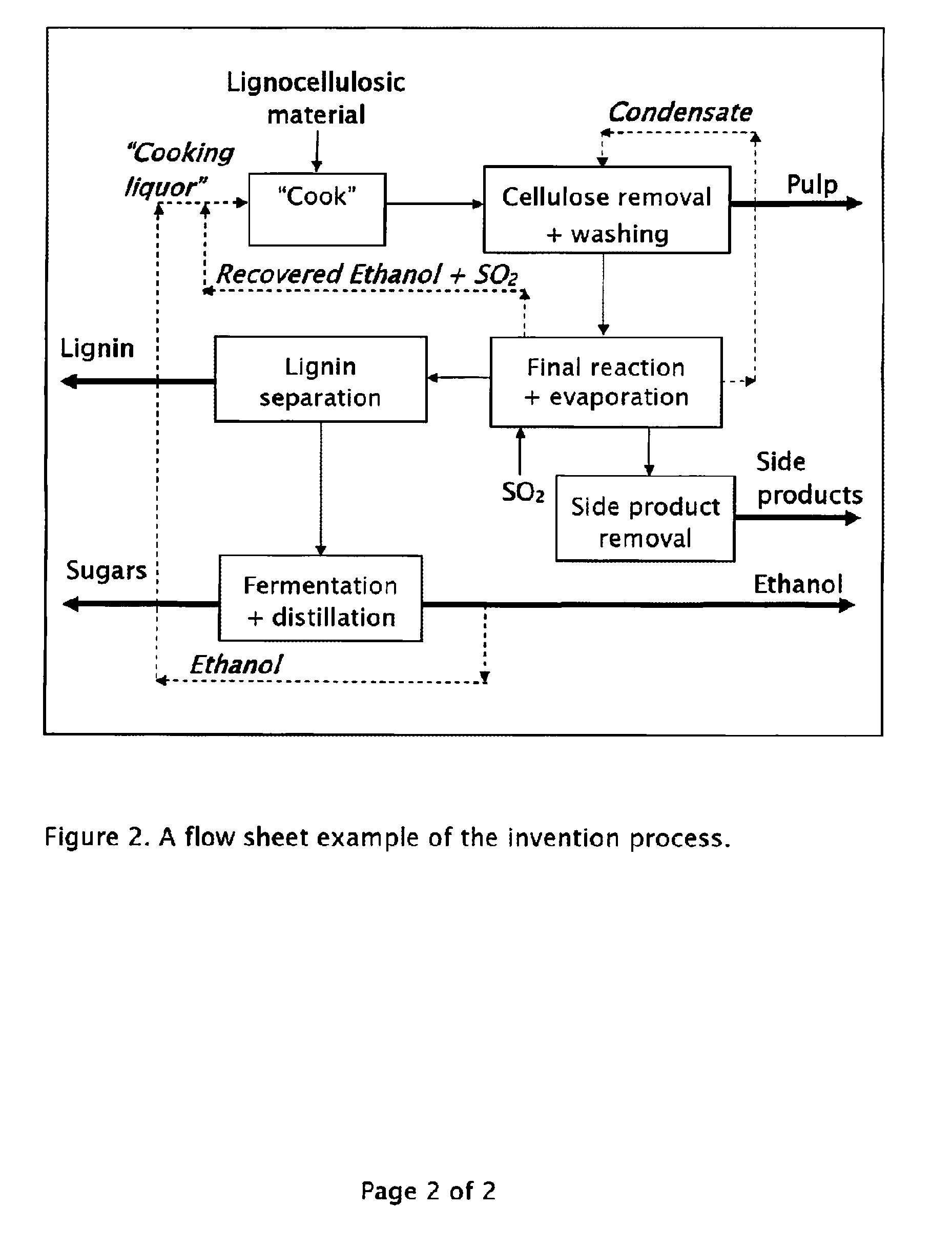
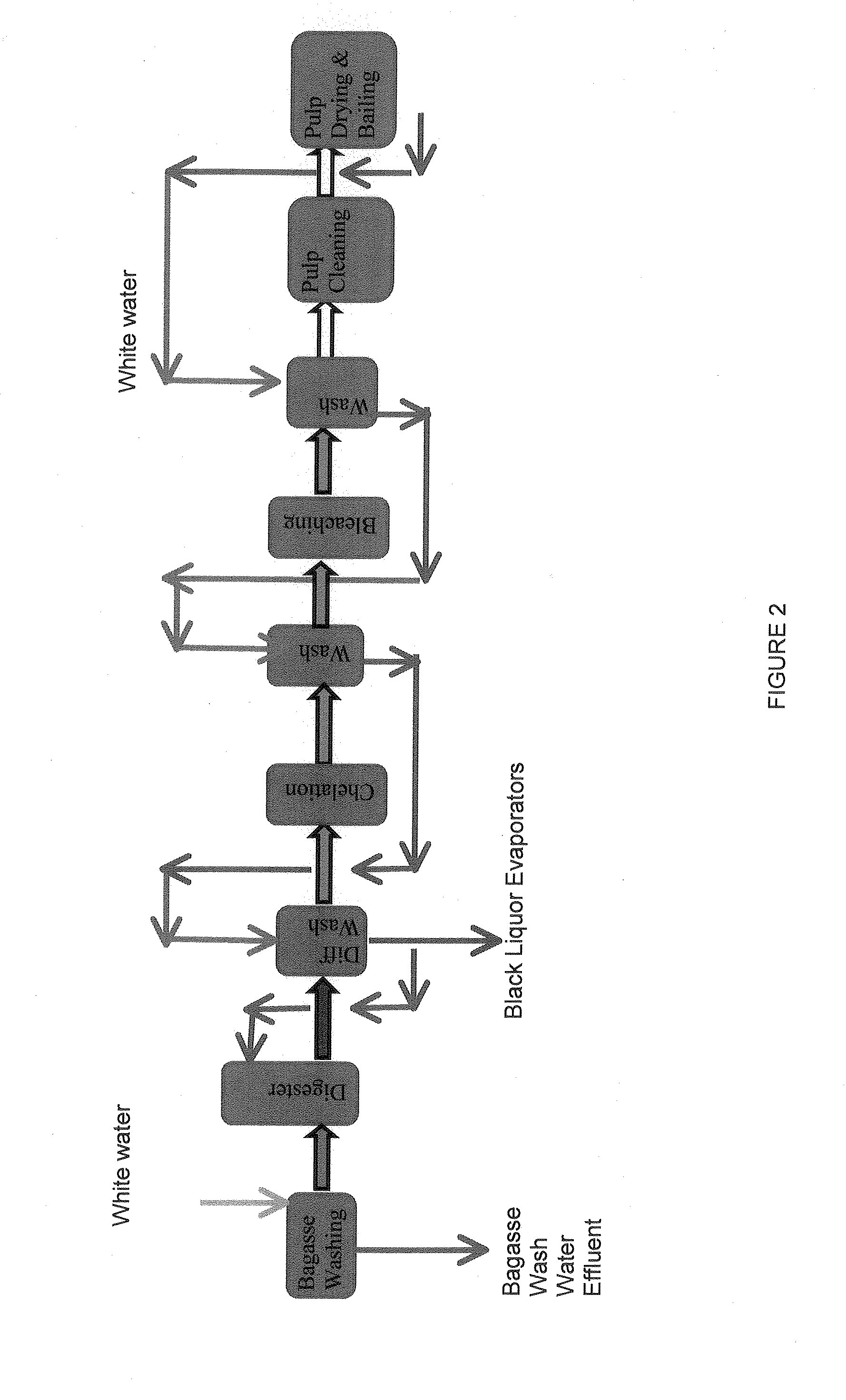
Method for the production of fermentable sugars and cellulose from lignocellulosic material
ActiveUS8030039B1High yieldIncreased ethanol yieldFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpPulping with organic compoundsOrganic acidAlcohol
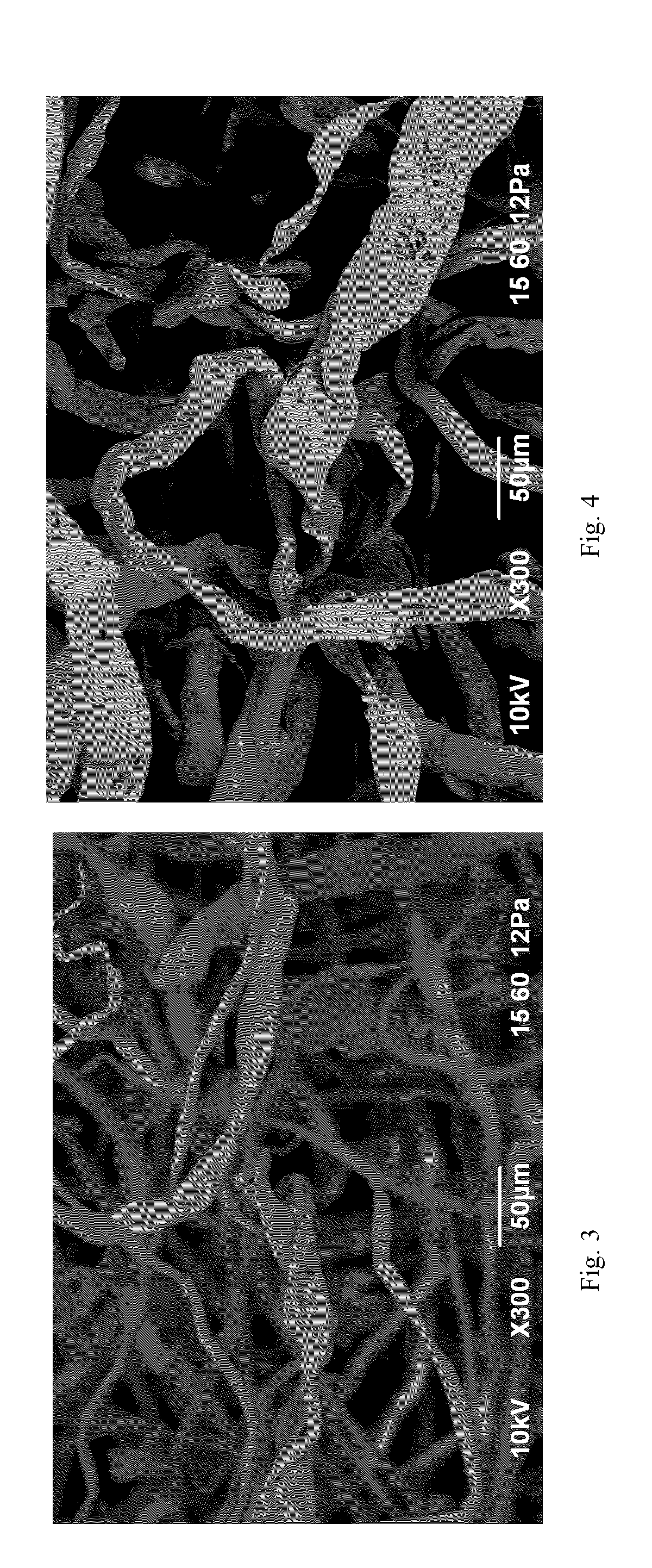
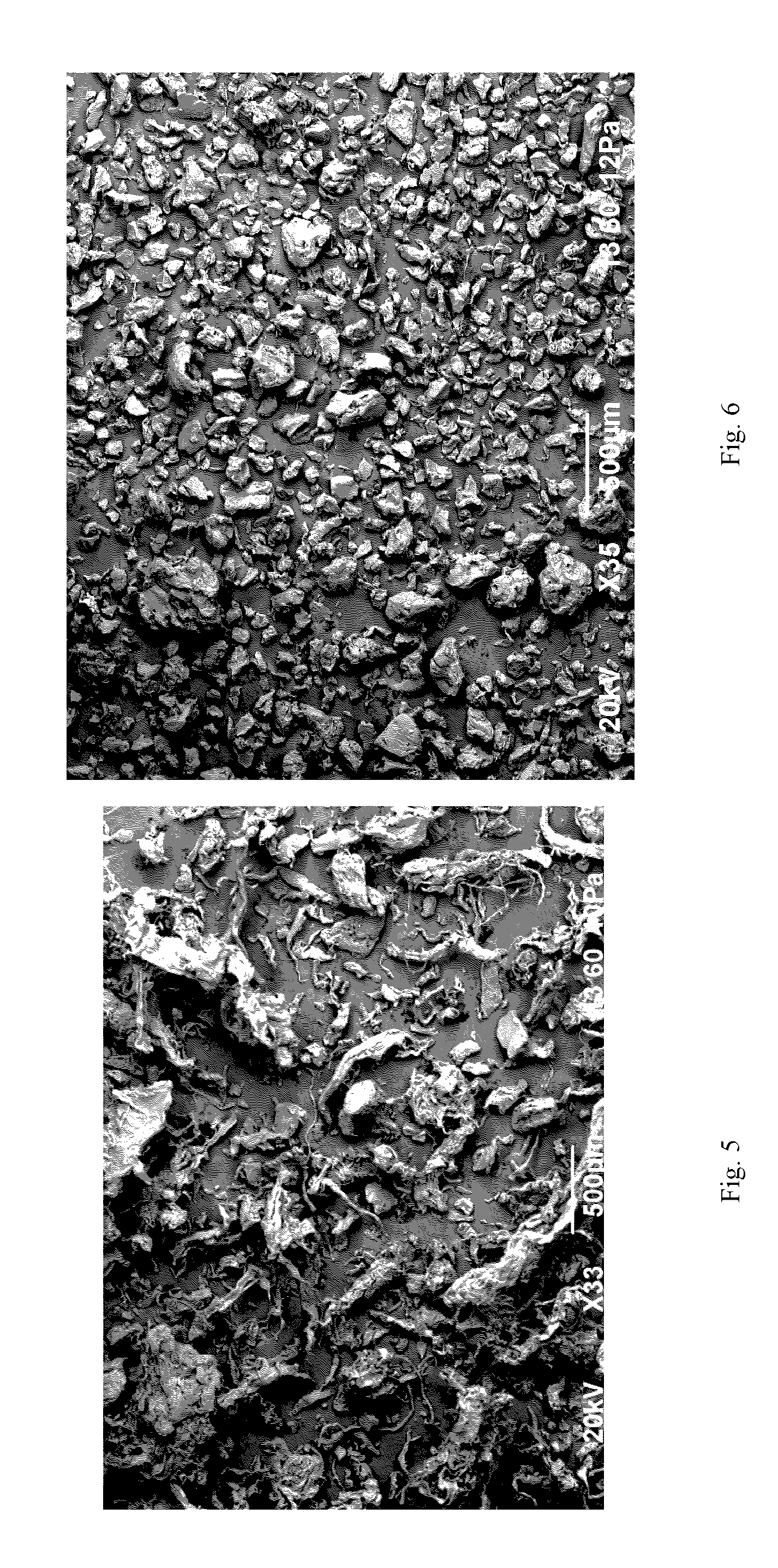
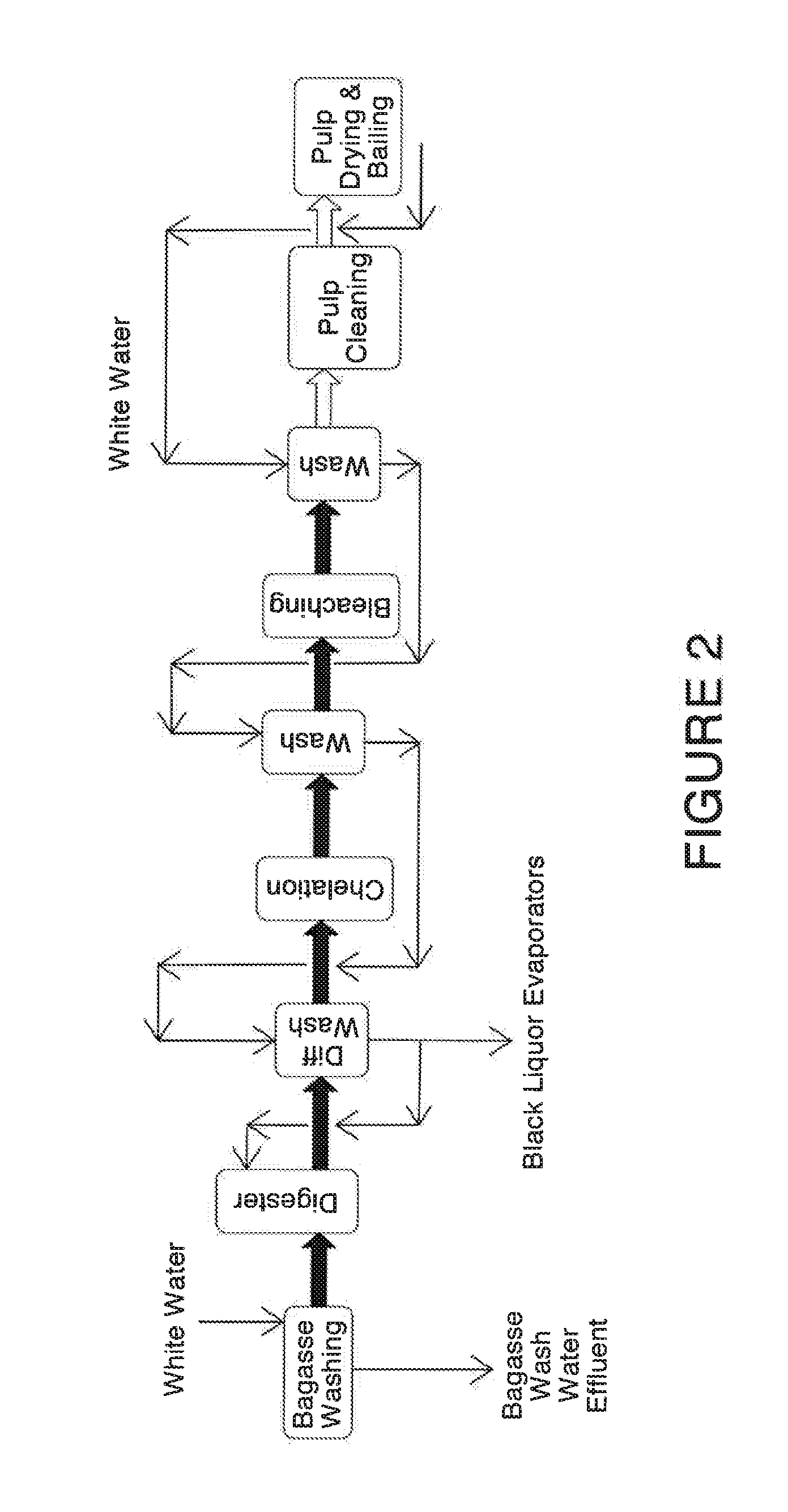
A method for the production of fermentable sugars and high viscosity cellulose from lignocellulosic material in a batch or continuous process is provided. Lignocellulosic material is fractionated in a fashion that cellulose is removed as pulp, cooking chemicals can be reused, lignin is separated for the production of process energy, and hemicelluloses are converted into fermentable sugars, while fermentation inhibitors are removed. High yield production of alcohols or organic acids can be obtained from this method using the final reaction step.
Owner:GRANBIO INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY HOLDINGS LLC
Pulping processes
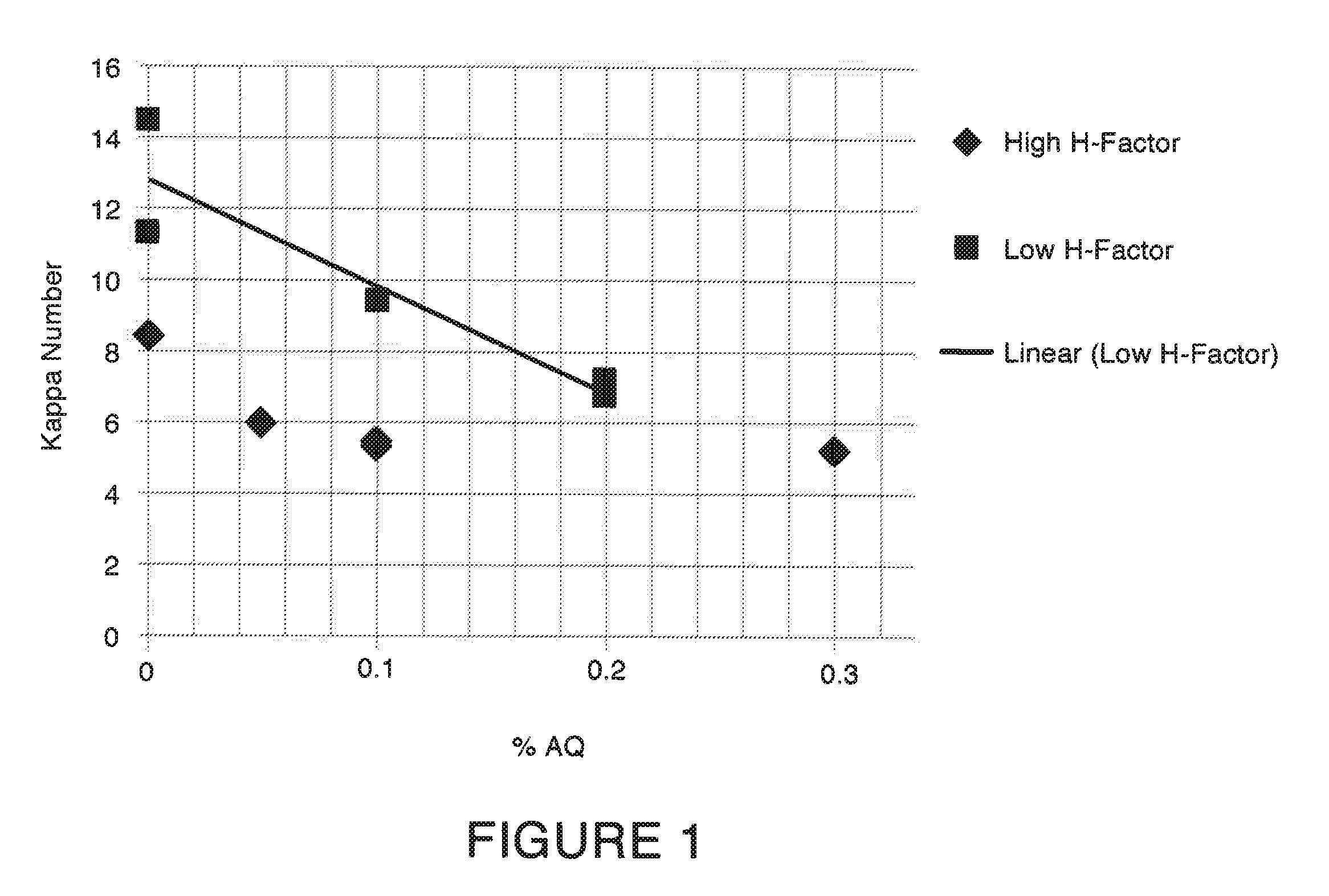
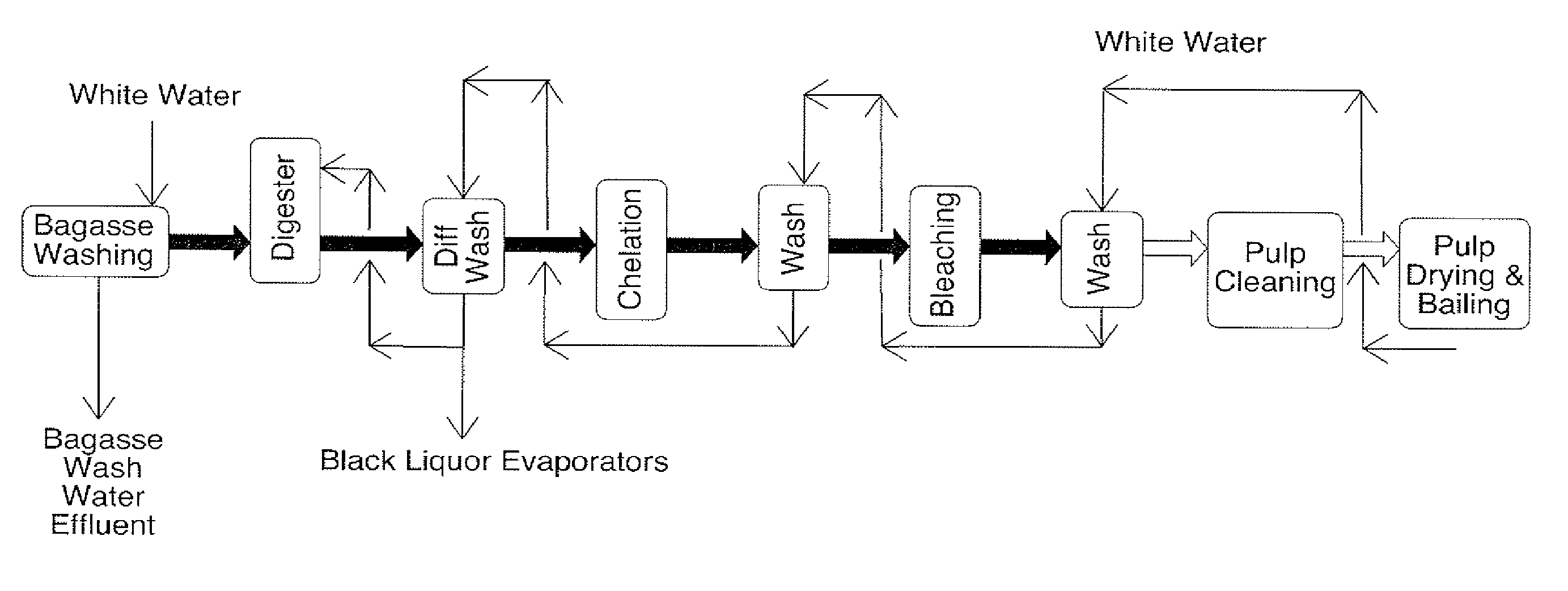
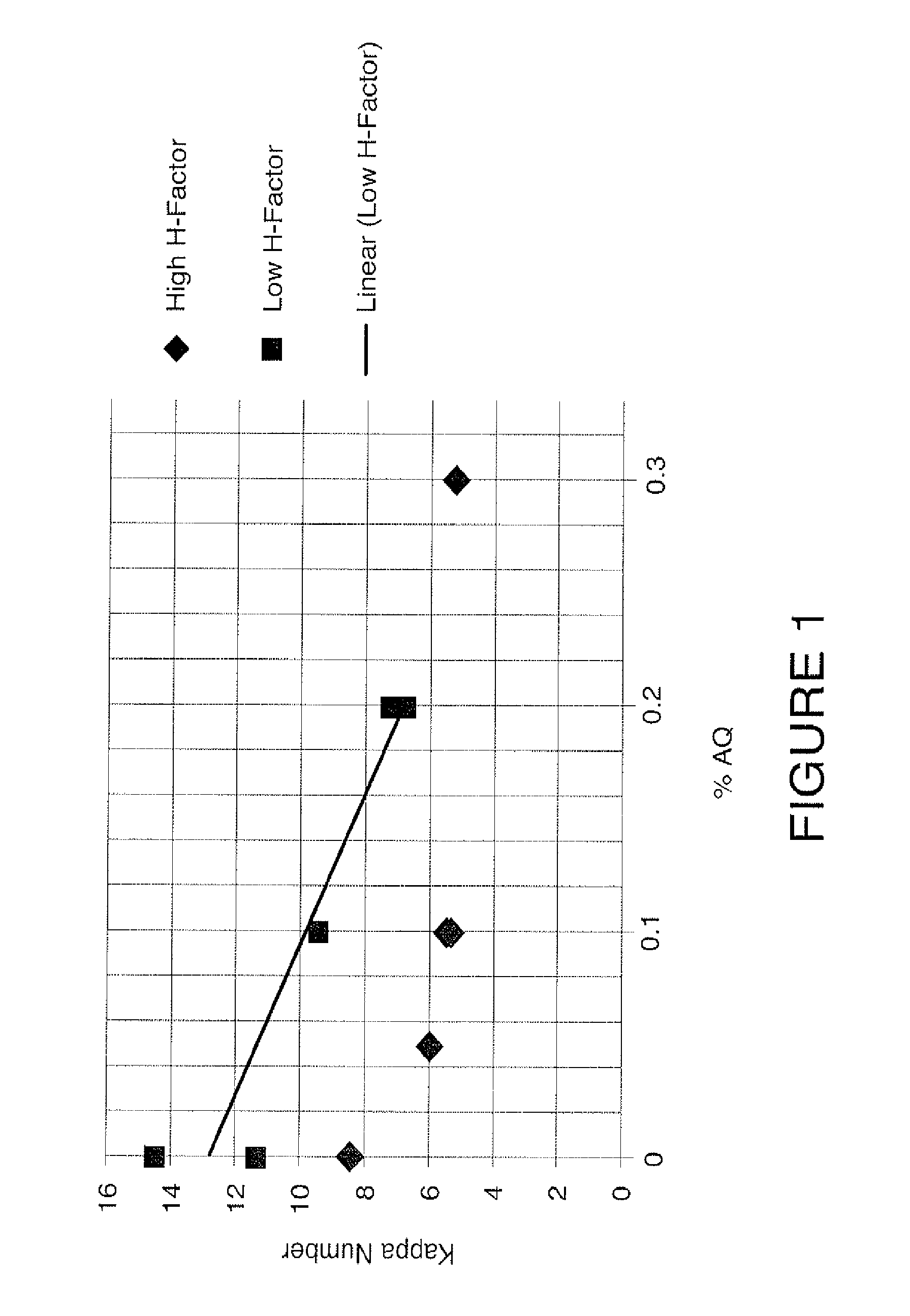
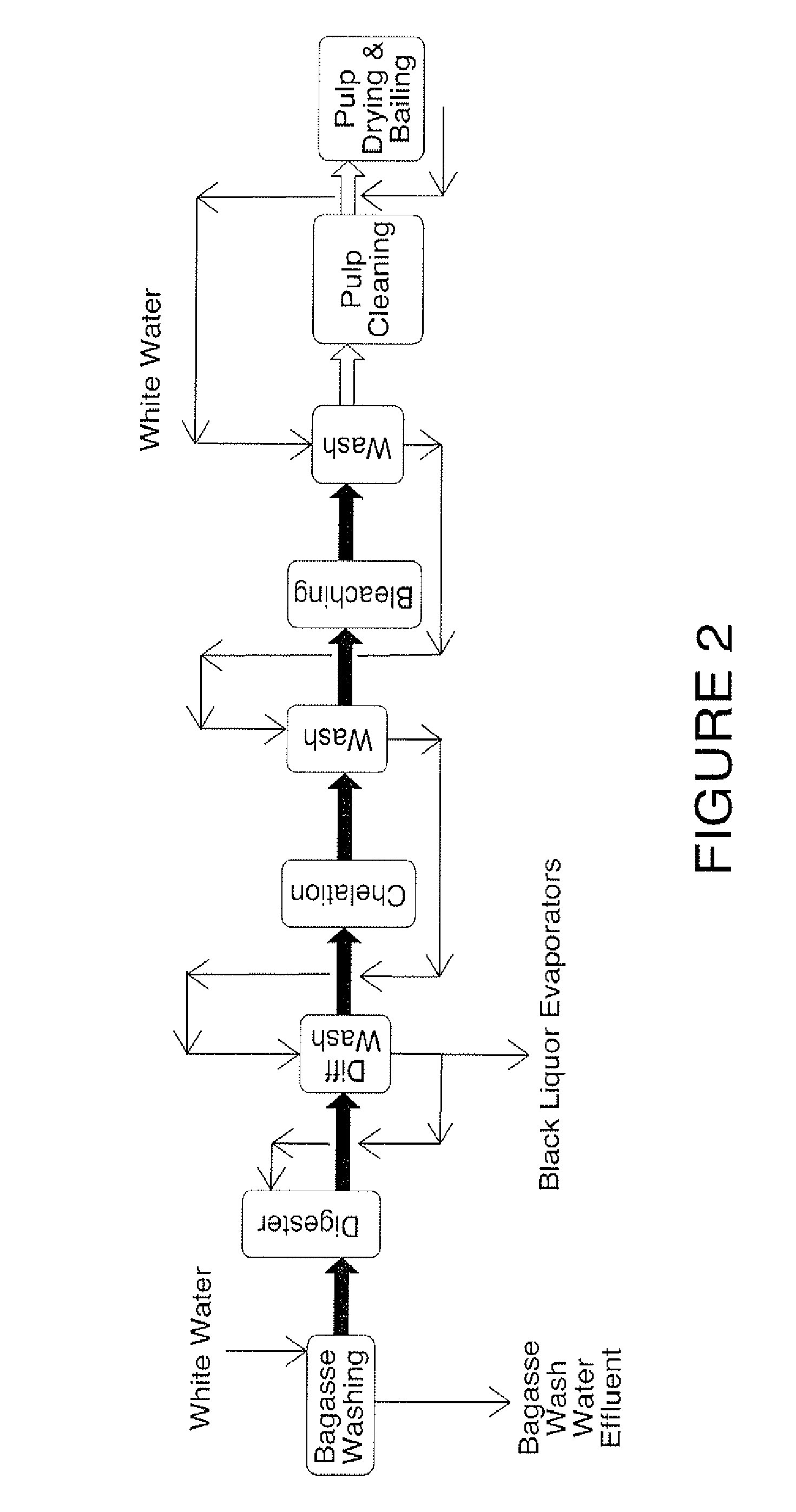
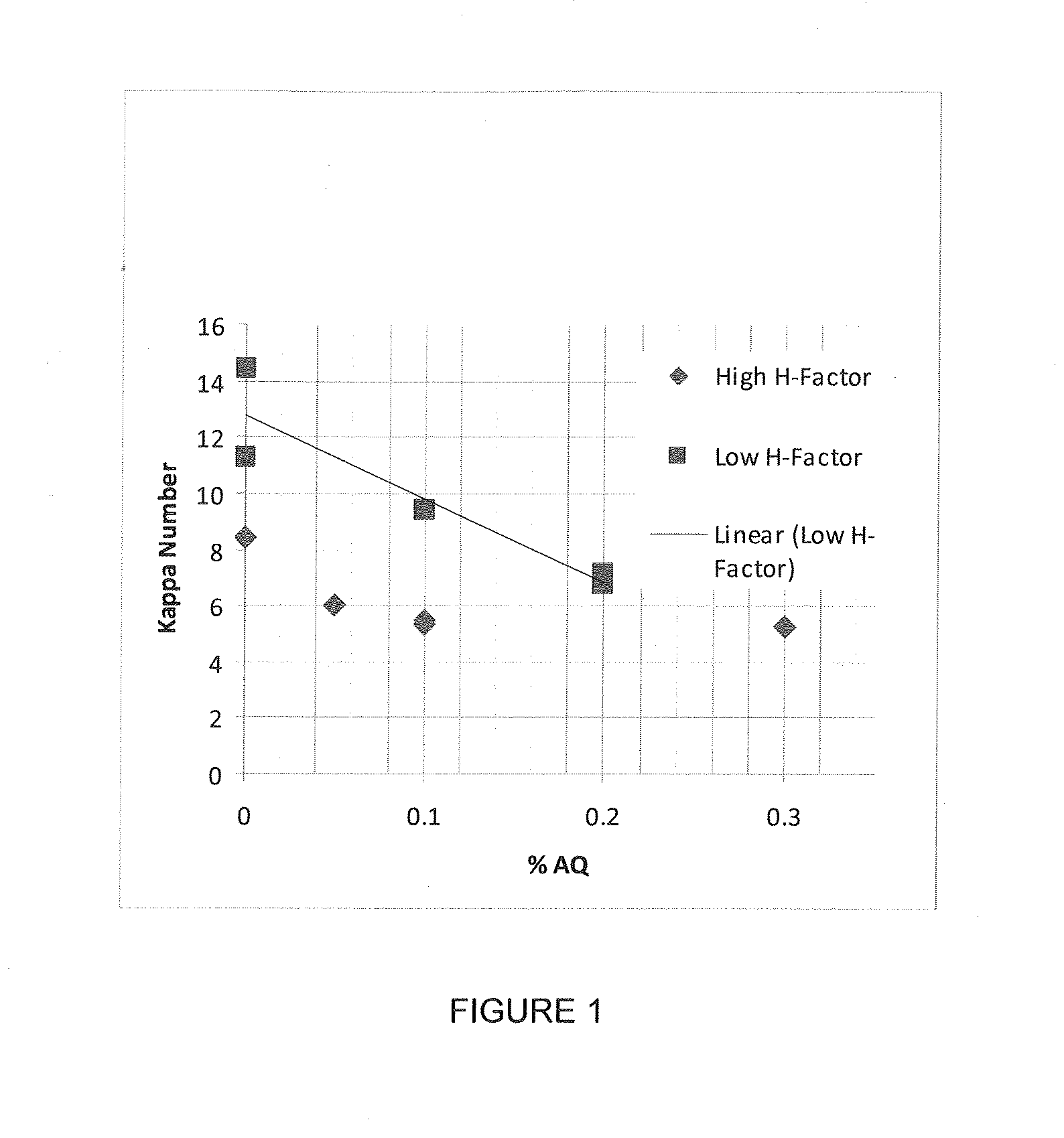
A pulping process comprises using a high concentration of anthraquinone (AQ). The pulping process is capable of providing a pulp having low Kappa number with unexpectedly high strength. The pulping process can use wood or non-wood fibers (e.g., bagasse and corn stover) to provide pulp having good papermaking quality. The method for pulping a fiber comprising cooking a first mixture comprising the fibers, water, an alkali, and a delignification selectivity enhancing chemical for a cooking time and at a cooking condition sufficient to form a first pulp having a desired Kappa number of about 15 or less, and strength parameters that are sufficient for papermaking, where the starting material prior to cooking has a Kappa number of 60 or greater.
Owner:CARGILL INC
Process for producing pulp with a mixture of formic acid and acetic acid as cooking chemical
InactiveCN1170031CPulping with organic compoundsPulping with acid salts/anhydridesAcetic acidHemicellulose
The invention relates to a process based on formic acid cooking for producing pulp from herbaceous plants and deciduous trees by using acetic acid as an additional cooking chemical. The obtained pulp can be used in fine paper and board production as short-fibred material, for instance. The invention also relates to a process for adjusting the hemicellulose content of the pulp in connection with the formic acid cooking by using acetic acid as an additional cooking chemical.
Owner:CHEMPOLIS OY
Method of producing a pulp from cellulosic material using formic acid and hydrogen peroxide
InactiveUS6183597B1Facilitate lignin breakdownIncrease brightnessPulp liquor regenerationPulping with organic compoundsCardboardCellulose
A process for producing a pulp from cellulose-containing material, wherein the material is reacted with formic acid as the solvent, and cooked at approximately the boiling temperature of the solvent, whereby return condensation is used. Annual plants, deciduous or coniferous wood can be used as the cellulose-containing material. In one variant of the process, the cellulose-containing material is only slightly warmed, whereby backflow cooling is used, and then a precisely predetermined quantity of hydrogen peroxide is slowly added to the liquid at a constant rate. This process variant can be repeated at a lower cooking temperature. The pulp thus obtained is preferably utilized in the production of cellulose, and in particular in the production of paper or cardboard. It is proposed that the lignin, which is isolated from the cellulose-containing material, have further applications, whereby such lignin is, after the pulp has been separated from the solvent, itself precipitated out in water. The lignin thus obtained can be used as a new building material, as a filler material or as an output substance to be used in the manufacture of aromatic products.
Owner:NATURAL PULPING
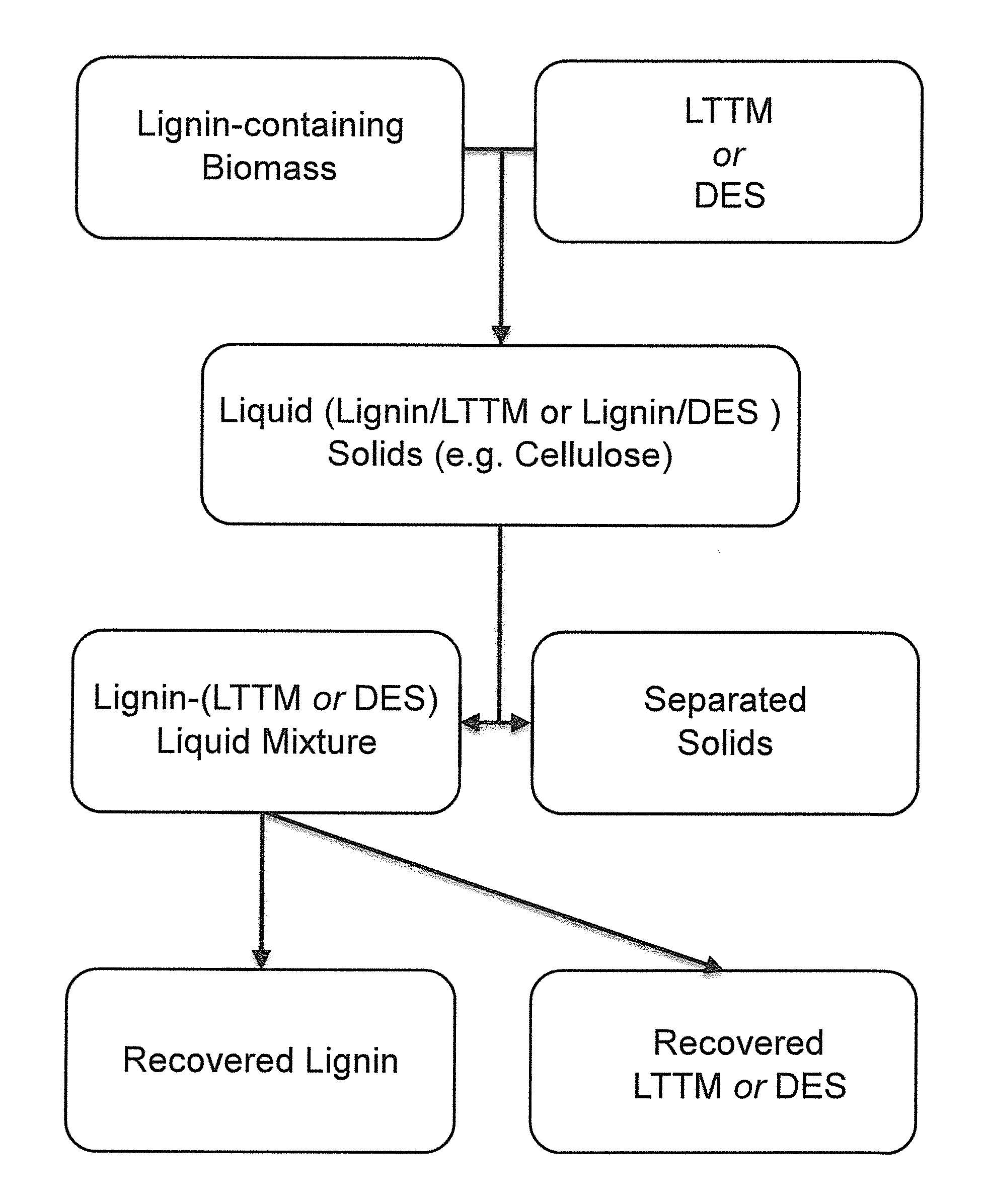
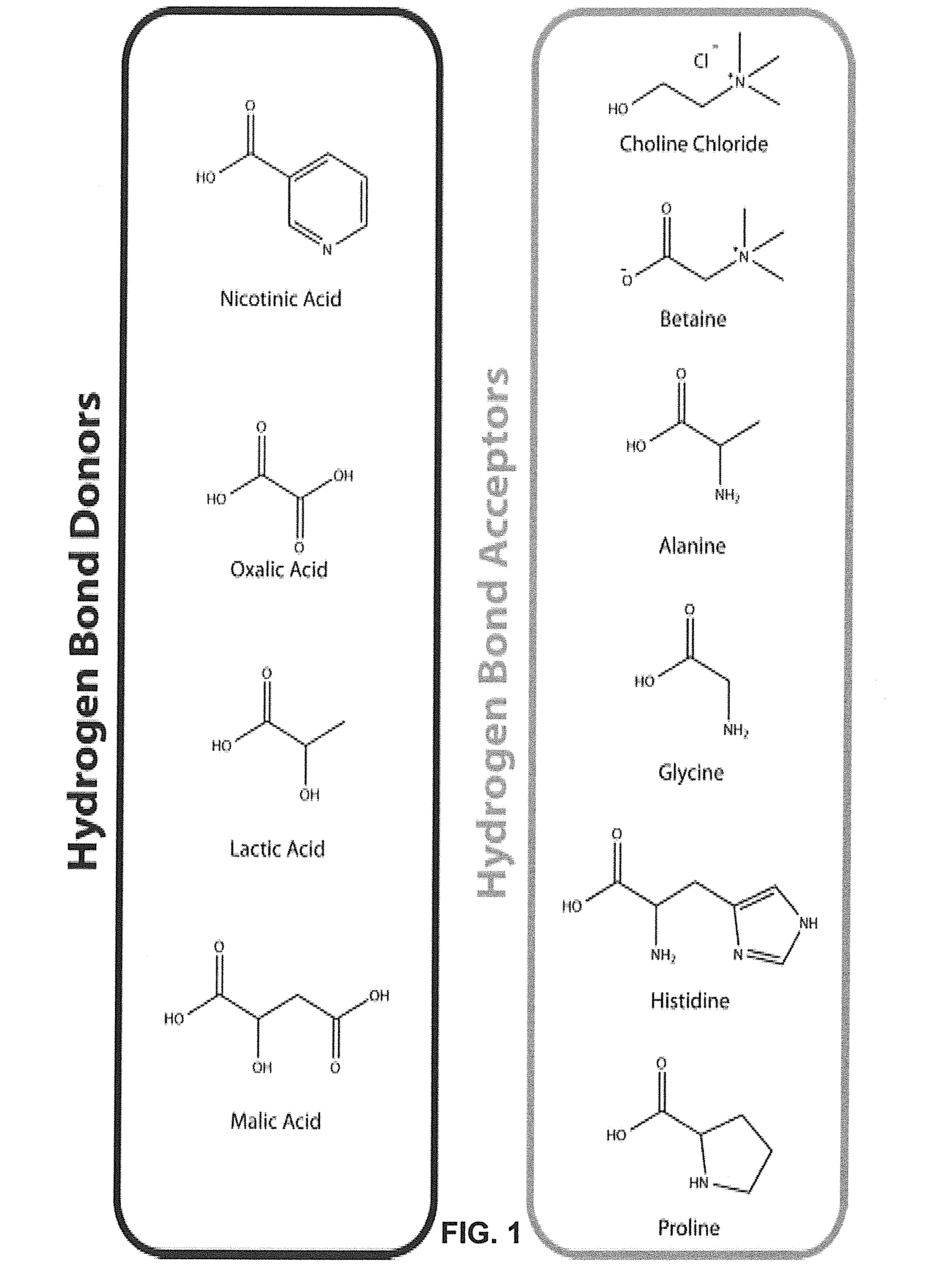
Pretreatment of Lignocellulosic Biomass and Recovery of Substituents using Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents/Compound Mixtures with Low Transition Temperatures
InactiveUS20150094459A1Reduce solubilityPrevent degradationPulping with organic compoundsLignin derivativesCelluloseLignocellulosic biomass
Low transition temperature mixtures (LTTMs) or solvents are provided that can be used in methods and systems to dissolve and bydrolyze certain components from lignin-containing biomass (e.g., lignin) at mild conditions so that further degradation is prevented. The solvents, methods and systems according to the invention have various advantages over prior technology or approaches. For example, LTTMs are cheap solvents, renewable and / or non-toxic food ingredients. LTTMs dissolve lignin selectively from a lignin-containing biomass. A highly efficient (up to 90%) lignin recovery can be achieved. The recovered lignin is of higher quality. The remaining cellulose is also of higher. Much less water is needed, which means a tremendous reduction of the energy requirement in the recovery process, i.e. less energy needed for evaporating large quantities of water.
Owner:TECH UNIV EINDHOVEN
Method for pretreating lignocellulose by adopting alkaline eutectic solvent
ActiveCN108441530AImprove enzymatic hydrolysis efficiencyEasy to recyclePulping with organic compoundsBiofuelsSugarSolvent
The invention relates to a method for pretreating lignocellulose by adopting an alkaline eutectic solvent. With the method, the enzymolysis efficiency of lignocellulose can be effectively enhanced, particularly, the recycling for the hemicellulose sugar monomer is improved, and the yield of total sugar is improved. The method has the advantages that the cost is low, the operability is strong, theenergy consumption is small, the environment protection is realized, etc.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Process for producing pulp with a mixture of formic acid and acetic acid as cooking chemical
InactiveCN1299424AReduce hydrolysisImprove propertiesPulping with organic compoundsPulping with acid salts/anhydridesAcetic acidHemicellulose
The invention relates to a process based on formic acid cooking for producing pulp from herbaceous plants and deciduous trees by using acetic acid as an additional cooking chemical. The obtained pulp can be used in fine paper and board production as short-fibred material, for instance. The invention also relates to a process for adjusting the hemicellulose content of the pulp in connection with the formic acid cooking by using acetic acid as an additional cooking chemical.
Owner:CHEMPOLIS OY
Process for producing pulp
InactiveCN1527896AIncrease productionImprove performancePulping with organic compoundsPulping with acid salts/anhydridesOrganic acidSolvent
The invention relates to a process for producing pulp from a fibre-based raw material using, as the cooking reagent, a solvent mixture which is based on organic acids and also contains furfural. The method is applicable to herbaceous plants, in particular.
Owner:CHEMPOLIS OY
Process for isolating cellulose from cellulosic biomass, isolated cellulose of type i and composite materials comprising same
InactiveUS20150361616A1Simpler and cheap and efficientLess waterPulp properties modificationWashing/displacing pulp-treating liquorsExternal energyCellulose pulp
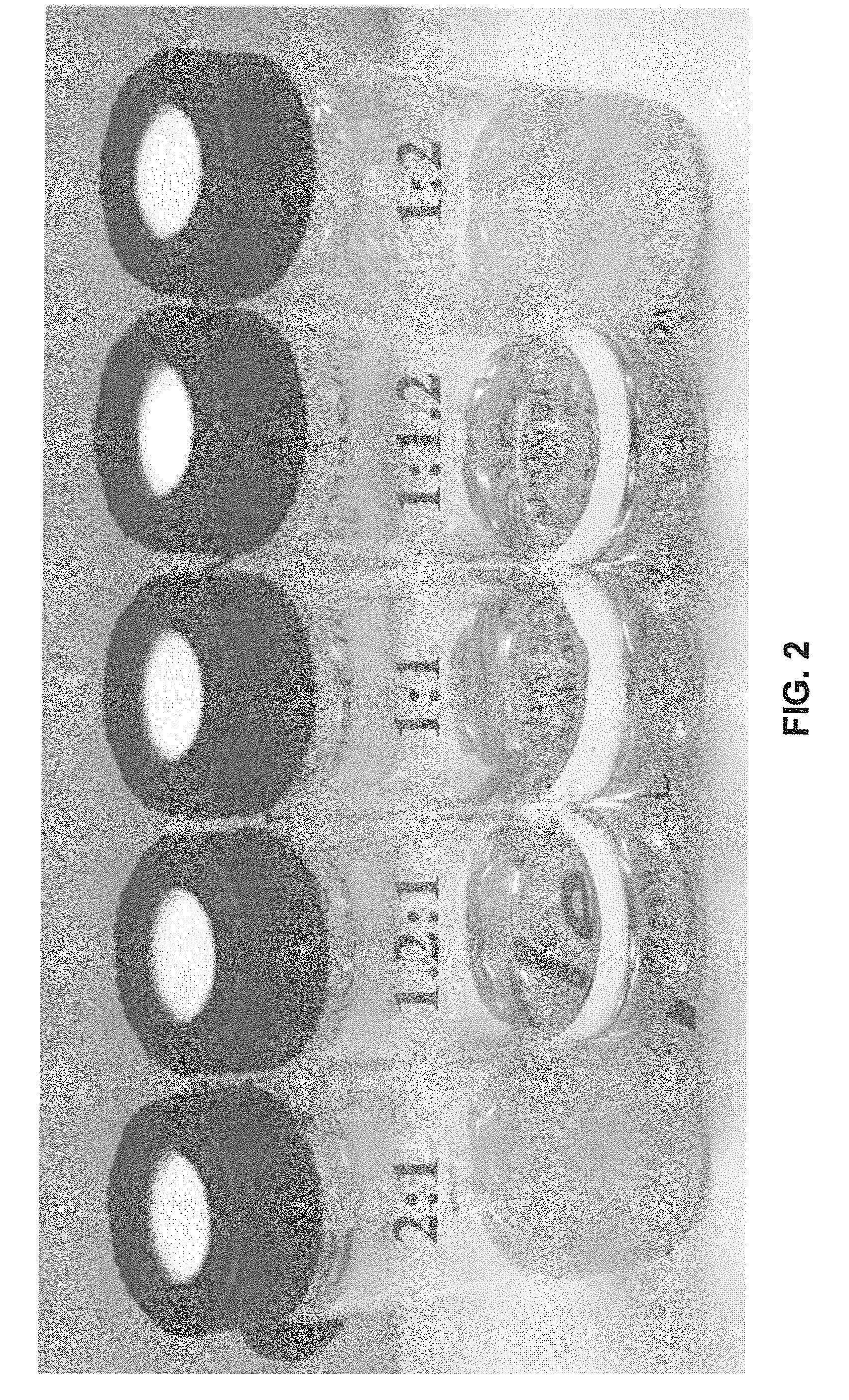
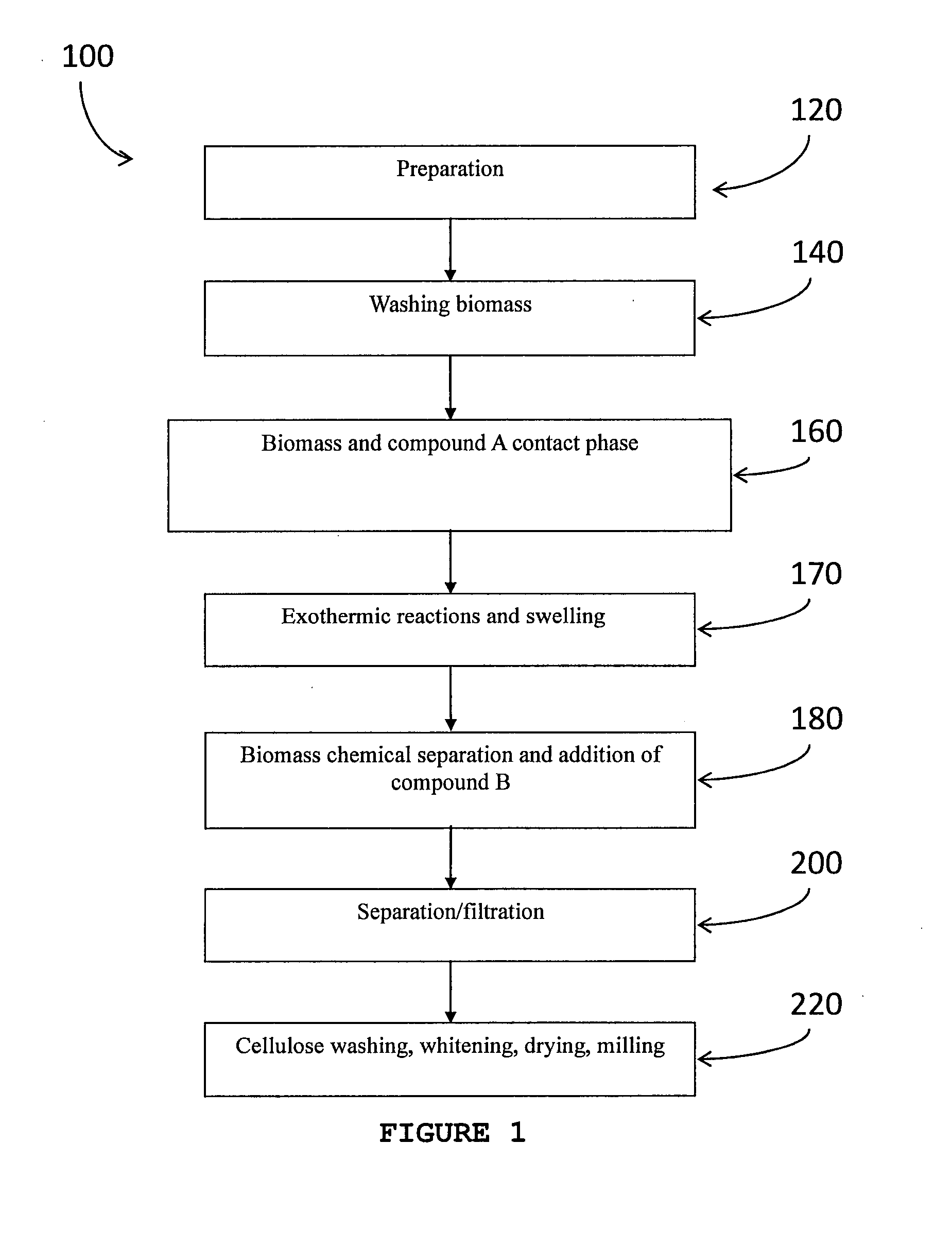
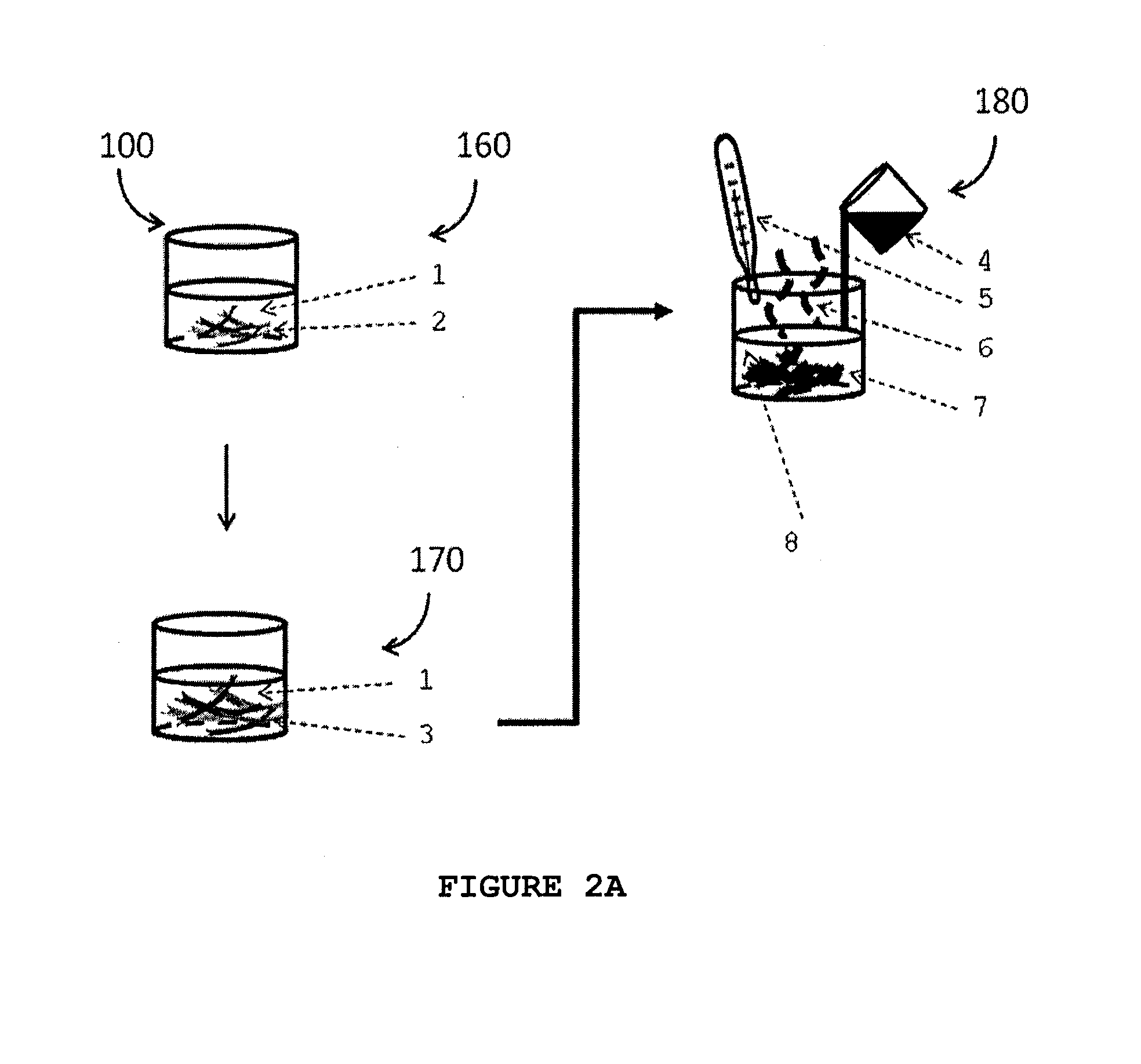
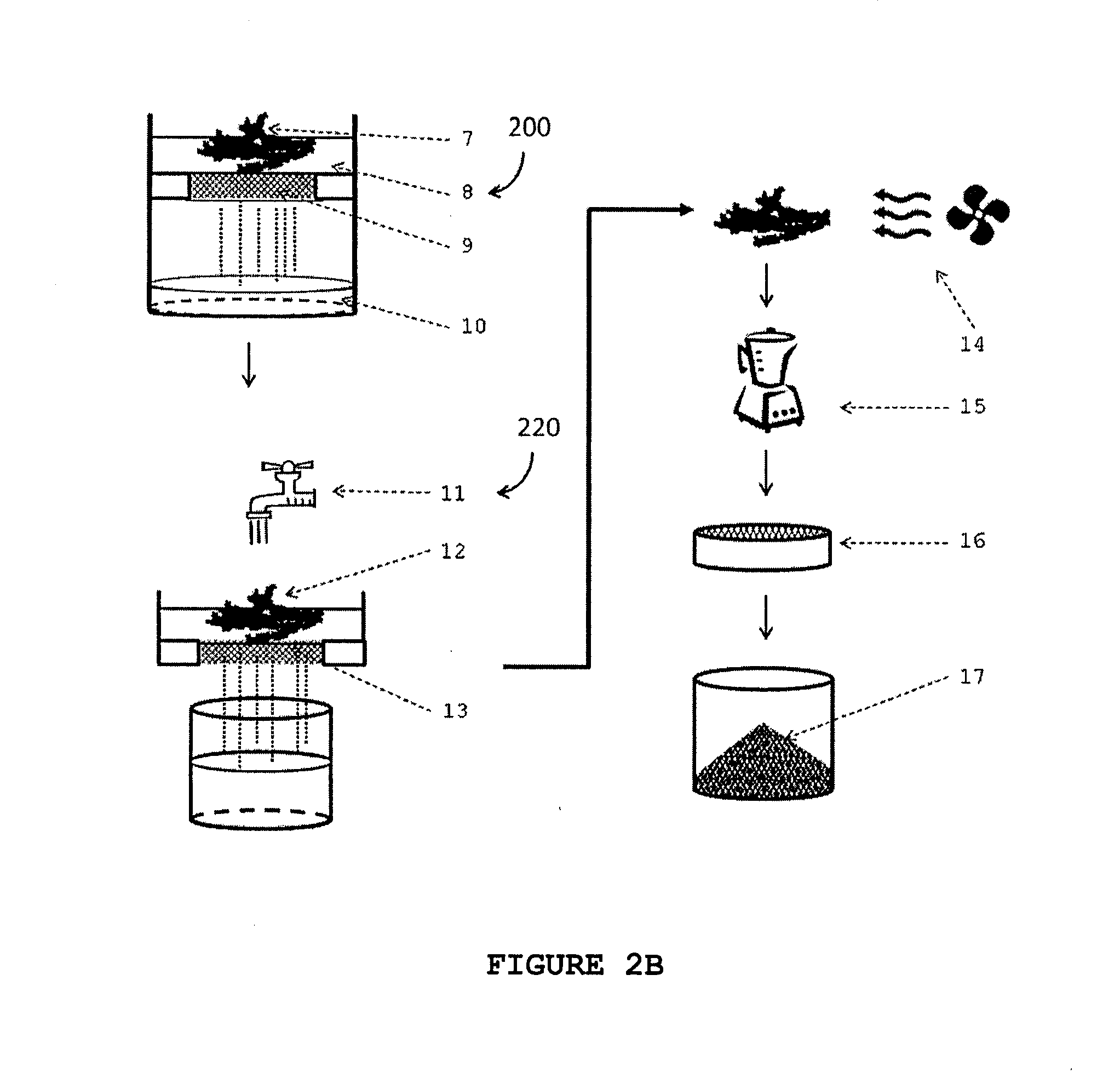
Described herein are processes for the production of a cellulose pulp and processes for isolating cellulose from cellulose-containing biomass. The processes of the invention comprises contacting the biomass with a source of anions and a source of cations, the source of anions and the source of cations being selected to react exothermically with the biomass and with each other. The processes of the invention have the particularity of generating exothermic reactions through enthalpies of reaction and mixture. Accordingly, the processes of the invention do not require any supply of external energy since the required energy is provided by chemical reagents that are already present in the biomass or added as needed. The invention also relates to isolated cellulose obtained from these processes and the use of same in various materials.
Owner:VENTIX ENVIRONNEMENT
Method for preparation of cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibrils
A method for producing nanocellulose is described herein. The method includes contacting a cellulosic material with an oxidizing agent, and a compound selected from the group consisting of an alkali metal bromide, an alkali metal iodide, an alkali metal fluoride, an alkali metal chloride, or a combination thereof, in an aqueous solution to provide an oxidized cellulose mixture. The nanocellulose prepared according to the method is also described.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Method for preparing cellulose nano filaments with pretreatment of low-eutectic solvent
ActiveCN109235102AImprove qualityHigh yieldPulping with organic compoundsPulp de-wateringCelluloseFiber
The invention discloses a method for preparing cellulose nano filaments with the pretreatment of a low-eutectic solvent. The method comprises the following steps: S1, performing the pretreatment withthe low-eutectic solvent: adding chemical slurry into the low-eutectic solvent, and obtaining a mixed solution; S2, separating treated paper pulp fibers: adding water into a reaction system of step S1to terminate the reaction, and separating the paper pulp fibers from the mixed solution; and S3: performing high-pressure homogenization micro-jet treatment: preparing the paper pulp fibers separatedin step S2 into a pulp solution of a given pulp concentration, then performing the high-pressure homogenization micro-jet treatment, spray drying, and obtaining a cellulose nano filament product. Themethod is mild in preparation conditions, simple in operation, low in cost and small in pollution; and the used low-eutectic solvent can be recovered by virtue of a rotary evaporation method so as tobe continuously circularly used, so that the method is environmentally friendly, capable of meeting a green chemical production standard, and good in practical application value.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Processes for producing nanocellulose, and nanocellulose compositions produced therefrom
InactiveUS20170210826A1Pretreatment with water/steamPulping with organic compoundsWater basedFracturing fluid
Various processes are disclosed for producing nanocellulose materials following steam extraction or hot-water digestion of biomass. Processes are also disclosed for producing nanocellulose materials from a wide variety of starting pulps or pretreated biomass feedstocks. The nanocellulose materials may be used as rheology modifiers in many applications. Water-based and oil-based drilling fluid formulations and additives are provided. Also, water-based and oil-based hydraulic fracturing fluid formulations and additives are provided. In other embodiments, polymer-nanocellulose composites are provided.
Owner:GRANBIO INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY HOLDINGS LLC
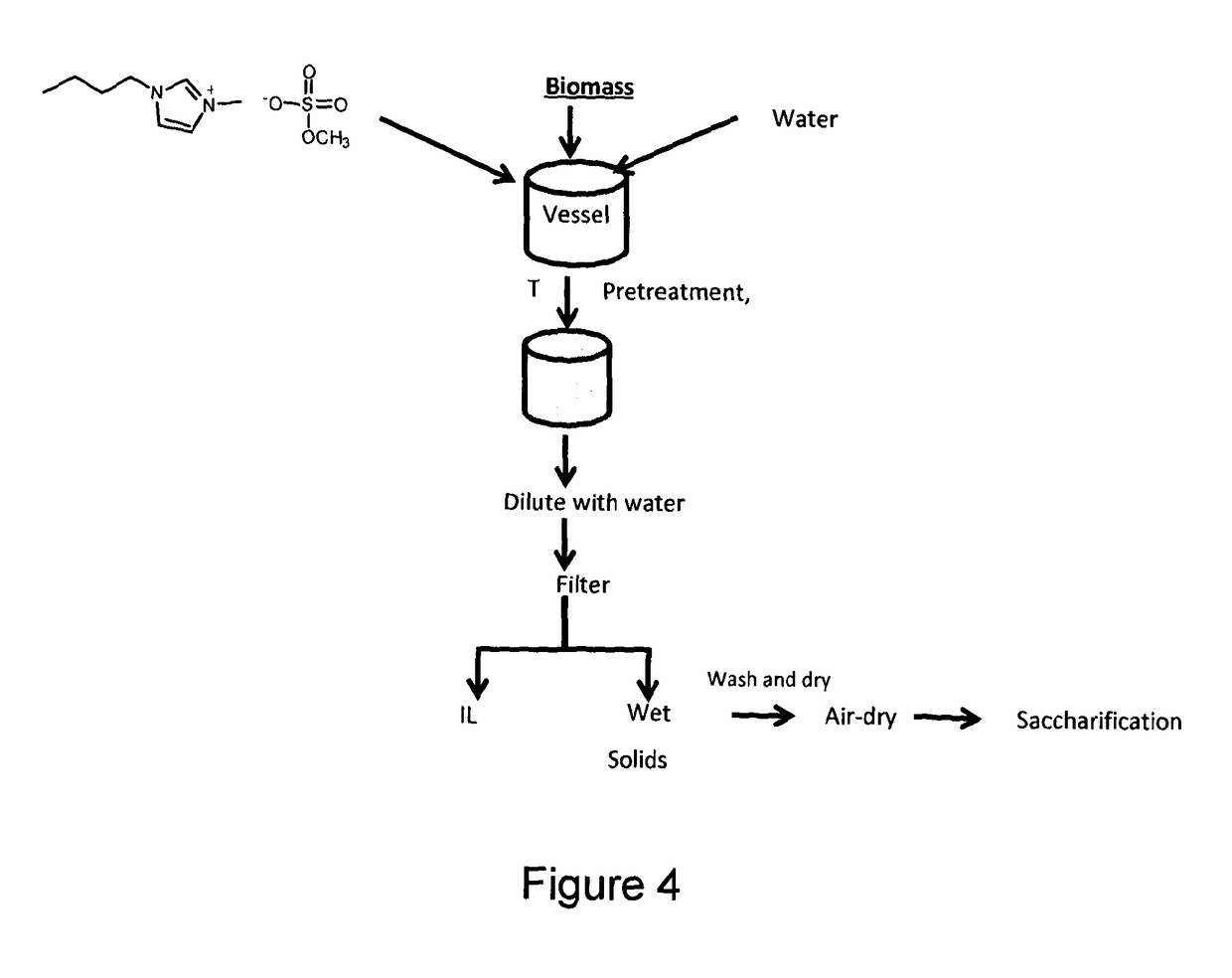
Treatment of biomass to dissolve lignin with ionic liquid composition
ActiveUS9765478B2Increase processing costLower saccharification yieldPulping with organic compoundsBiofuelsChemical industryLignocellulosic biomass
The present invention relates to a method for treating a lignocellulose biomass in order to dissolve the lignin therein, while the cellulose does not dissolve. The cellulose pulp obtained can be used to produce glucose. In addition the lignin can be isolated for subsequent use in the renewable chemical industry as a source for aromatic platform chemicals.
Owner:IP2IPO INNOVATIONS LTD
Organic solvent pretreatment of biomass to enhance enzymatic saccharification
ActiveUS20100159516A1Cost-effectiveHigh yieldSugar derivativesPulping with organic compoundsOrganic solventFermentable sugar
Biomass is pretreated using an organic solvent solution under alkaline conditions in the presence of one or more alkylamine and optionally one or more additional nucleophile to fragment and extract lignin. Pretreated biomass is further hydrolyzed with a saccharification enzyme consortium. Fermentable sugars released by saccharification may be utilized for the production of target chemicals by fermentation.
Owner:SUSTAINABLE TECH CORP
Pulp composition
One aspect of the invention relates to a pulp composition made from agricultural renewable fibers (ARF) having low Kappa number with unexpected quality sufficient for papermaking (e.g., high strength parameters and high freeness). Another aspect of the invention relates to an ARF pulp having ISO brightness of 60% or higher, and unexpected quality sufficient for papermaking (e.g. high strength parameters and high freeness). Another aspect of the invention relates to a pulp composition made from a pulping process comprising using a high concentration of anthraquinone (AQ). The pulping process can use wood or nonwood fibers (e.g., bagasse and corn stover) to provide pulp having good paper-making quality.
Owner:CARGILL INC
Methods for removing hemicellulose
A method for treating a cellulosic material comprising extracting the cellulosic material with an extractant to selectively extract hemicellulose therein and separating the extracted hemicellulose to form a cellulosic product comprising less hemicellulose than the cellulosic material. The extractant comprises an amine oxide and a non-solvent. The cellulosic product retains the cellulosic fiber morphology.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Simplified Method for Digestion of Cellulosic Biomass
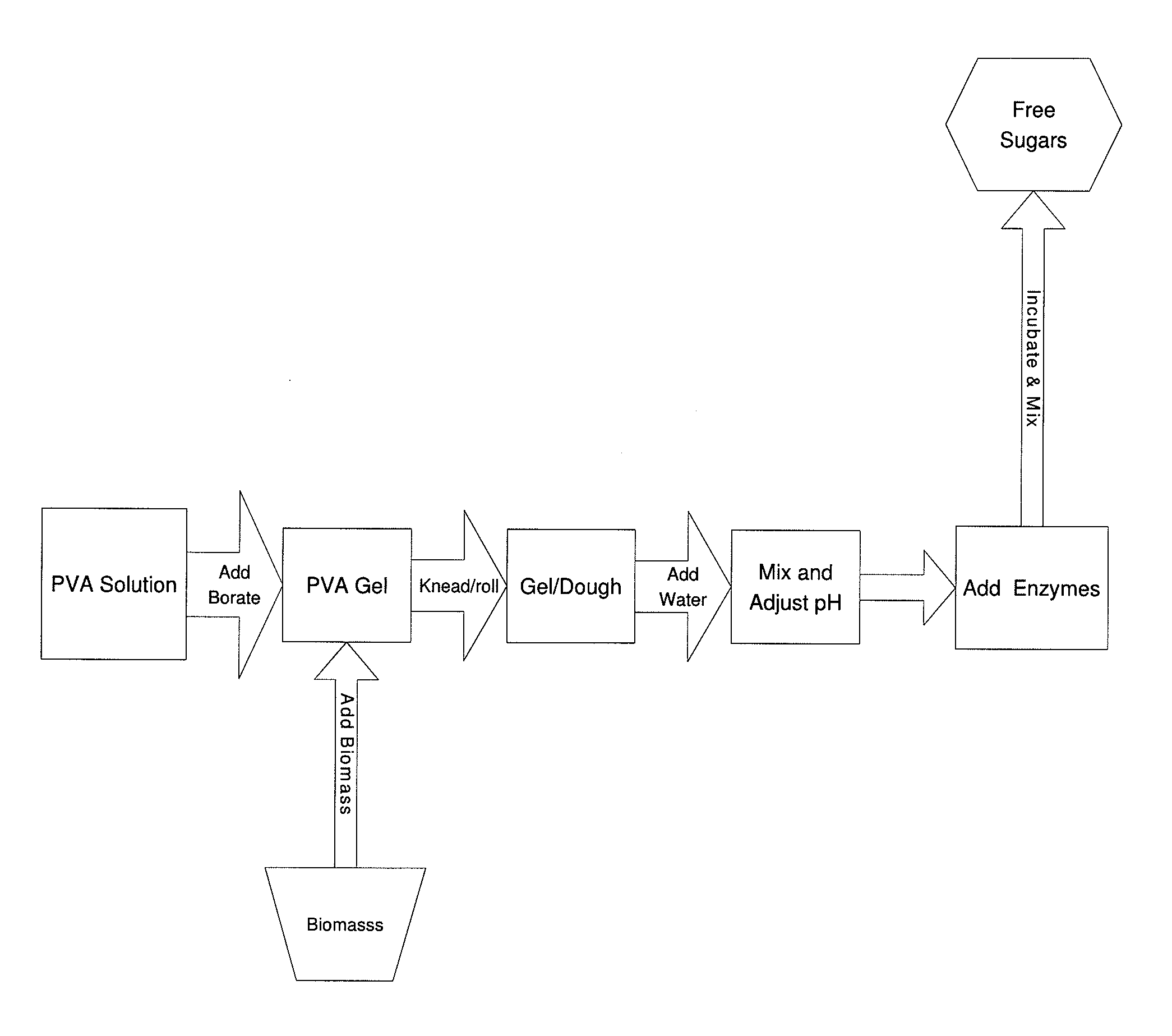
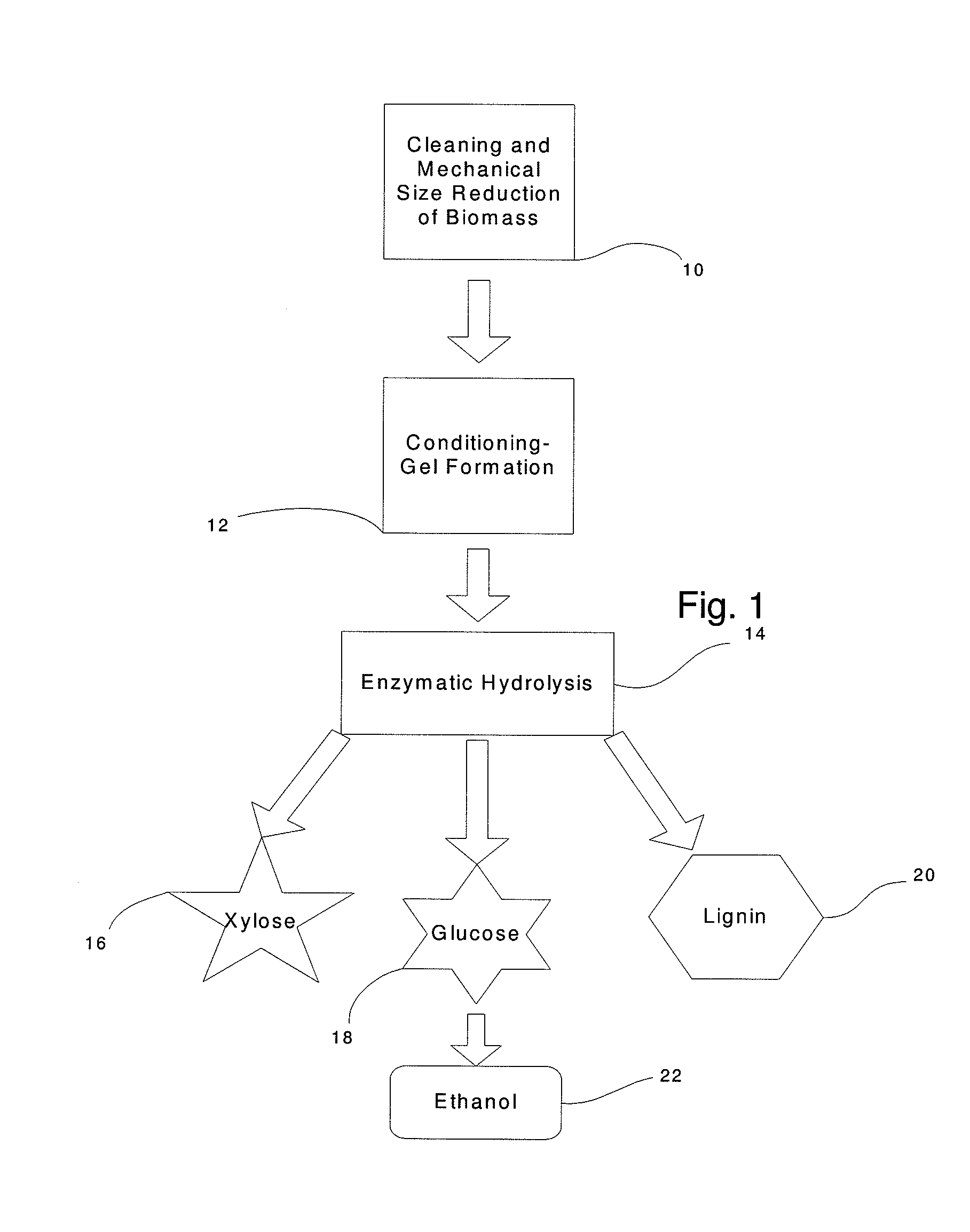
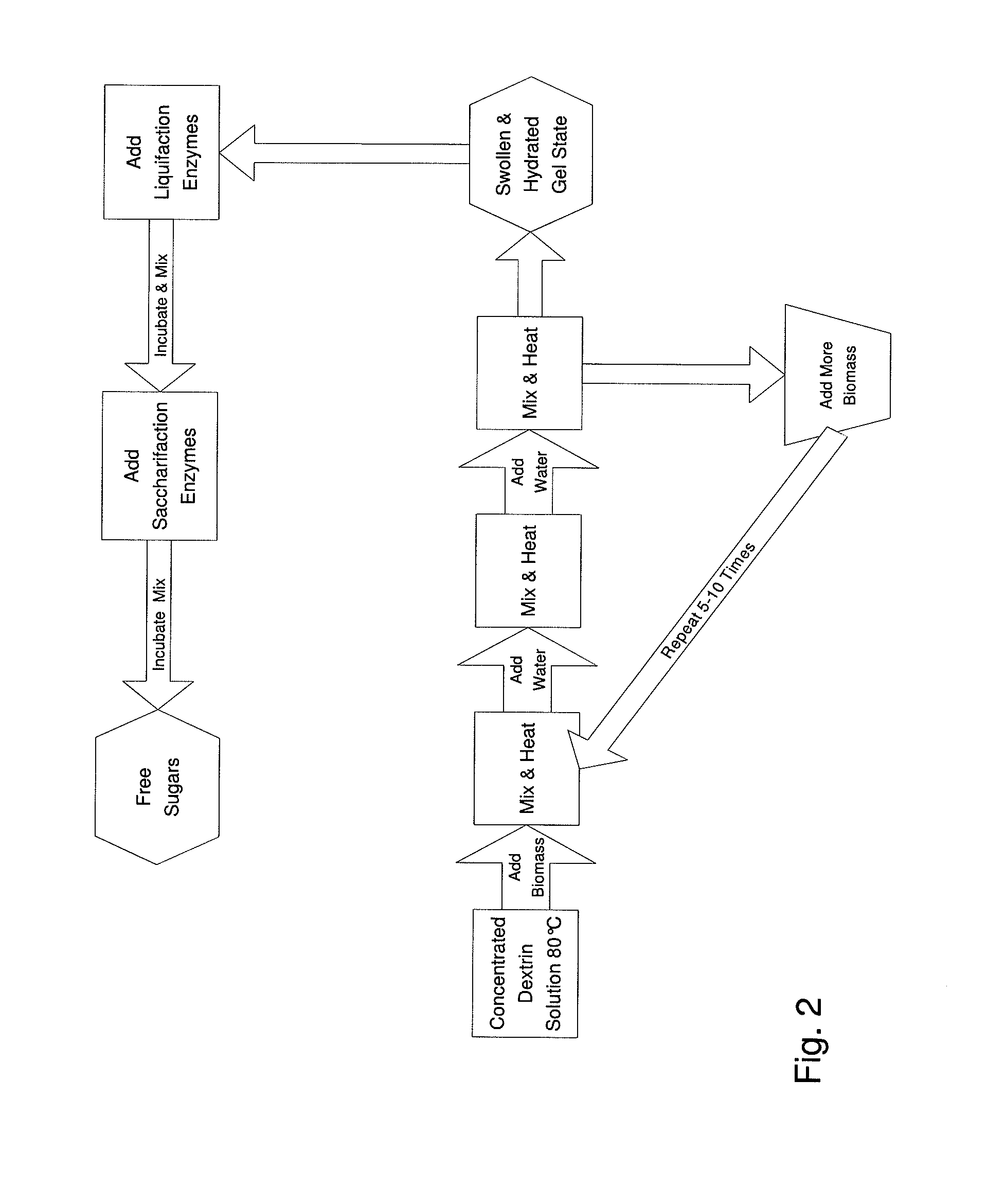
InactiveUS20110020874A1Speed up the processLow viscosityCellulosic pulp after-treatmentPulping with organic compoundsHydrophilic polymersBorate ion
The inventive process converts cellulosic biomass into a gel-like state that is readily hydrolyzed by appropriate enzymes. First the biomass is mechanically reduced in size. The biomass is then mixed and kneaded with an aqueous solution of a hydrophilic polymer that acts as a conditioning agent or as a co-solvent. During mixing the cellulose (and hemicellulose) in the biomass swells and becomes hydrated forming a viscous gel-like material. The processed material can then be thinned through the addition of water whereupon hydrolytic enzymes are mixed into the material and rapid hydrolysis into free sugars takes place. Dextrins are effective hydrophilic polymers for conditioning biomass. Polyvinyl alcohol is a particularly effective conditioning agent for use with biomass when converted into a viscous gel by adding borate ions.
Owner:BIOMASS CONVERSIONS LLC
Methods for extracting hemicellulose from a cellulosic material
InactiveUS20140048221A1Less hemicelluloseWashing/displacing pulp-treating liquorsPulping with organic compoundsNon solventAcetic acid
A method for treating a cellulosic material comprises extracting the cellulosic material with an extractant to selectively extract hemicellulose therein and separating the extracted hemicellulose to form a cellulosic product comprising less hemicellulose than the cellulose-containing material. The extractant comprises an ionic liquid and a non-solvent comprising acetic acid. The cellulosic product retains the cellulosic fiber morphology.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Method for removing straw lignin and hemicellulose by using protic ionic liquid
ActiveCN106702800AEasy to synthesizeLow pricePulping with organic compoundsCrystal structureHemicellulose
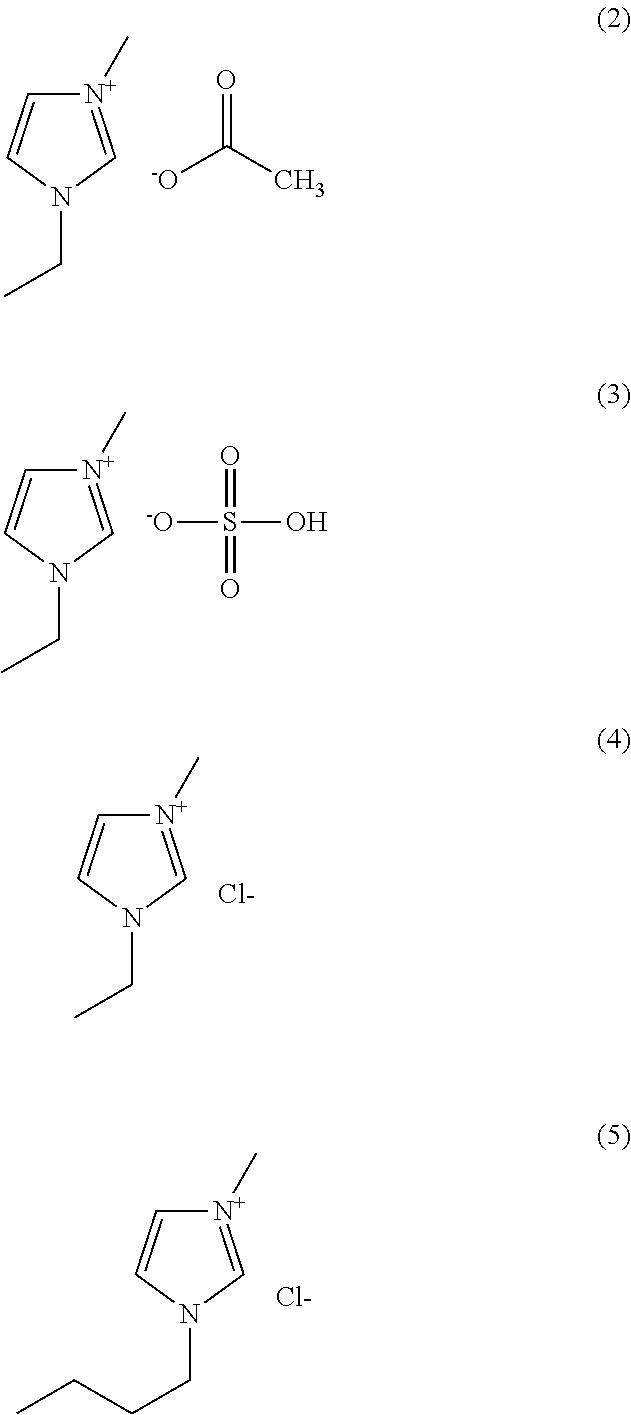
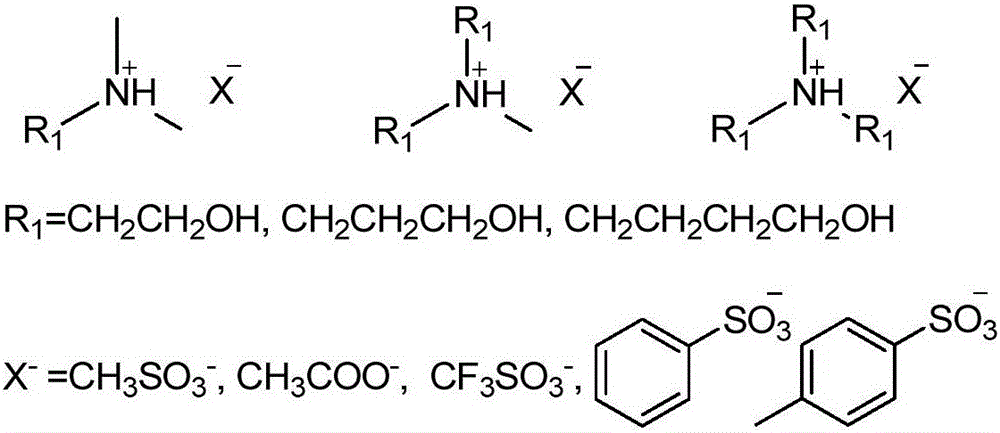
The invention discloses a method for removing straw lignin and hemicellulose by using single ionic liquid and by a one-step method. The ionic liquid in the method is polyhydroxyl protic ammonium salt ionic liquid. The method is characterized in that three components of a lignocellulose material are dissolved and separated under the conditions that the temperature is 80 to 160 DEG C, the time is 0.25 to 24 hours and the mass percentage of the lignocellulose material is 5 to 10 percent, so that the lignin content and the hemicellulose content can be reduced by 50 to 95 percent simultaneously. The ionic liquid is characterized in that the used synthetic raw materials are cheap and simple in synthesis method, and have biodegradability; the lignin and the hemicellulose are dissolved and removed from the biomass component simultaneously by the ionic liquid one-step method, a cellulose I type material with the purity higher than 70 percent is obtained, and the crystal structure of the cellulose in the raw material biomass component is maintained. By the method, the problems that the conventional ionic liquid is expensive and has poor separation effect are solved, possibility is provided for industrialization of pretreating biomass by the ionic liquid, and the ionic liquid belongs to a novel biomass pretreatment solvent.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods for removing hemicellulose
InactiveUS20140048223A1Suitable characteristicWashing/displacing pulp-treating liquorsPulping with organic compoundsNon solventCellulose fiber
A method for treating a cellulosic material comprising extracting the cellulosic material with an extractant to selectively extract hemicellulose therein and separating the extracted hemicellulose to form a cellulosic product comprising less hemicellulose than the cellulosic material. The extractant comprises an amine oxide and a non-solvent. The cellulosic product retains the cellulosic fiber morphology.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Method for catalytic oxidation of cellulose and method for making a cellulose product
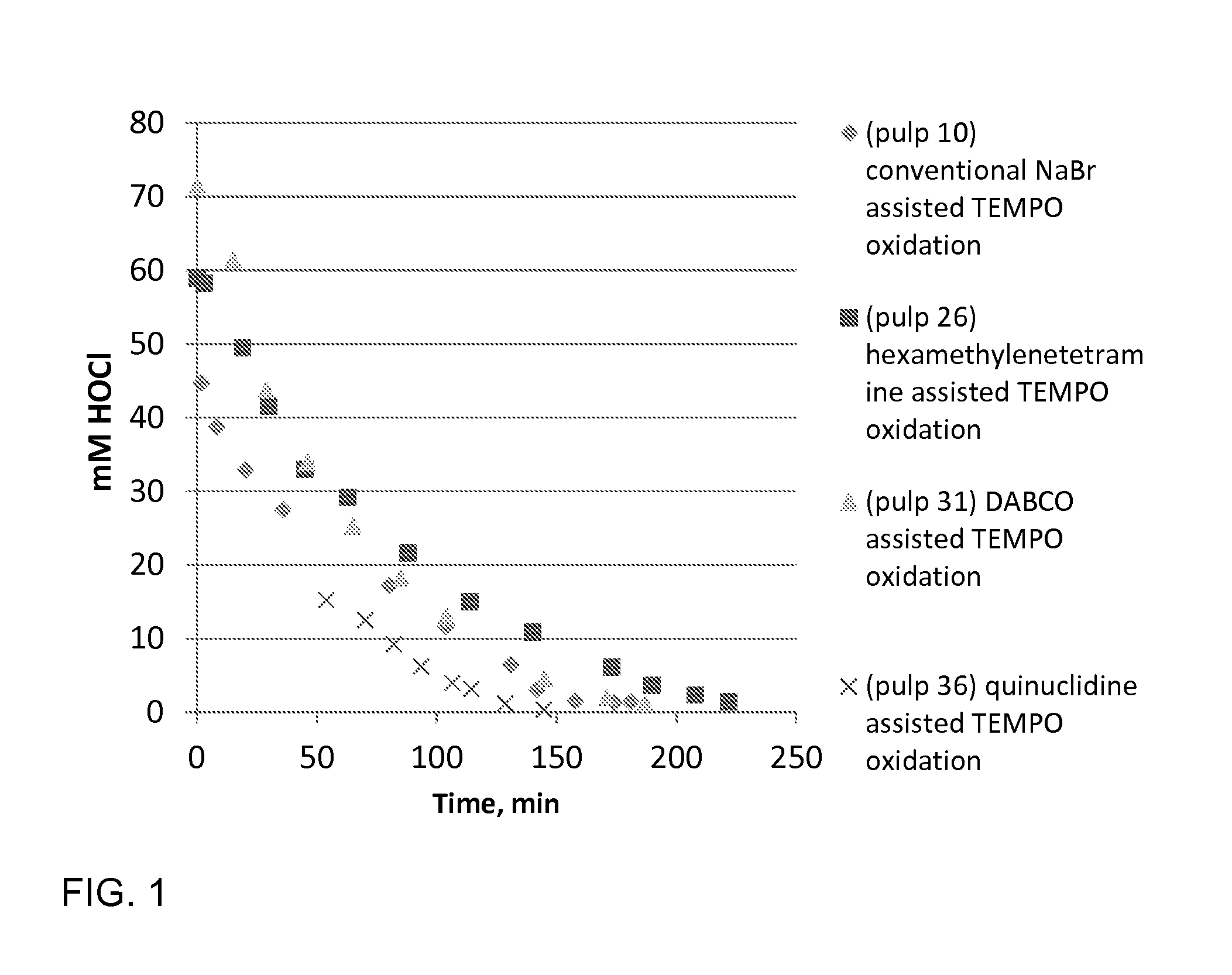
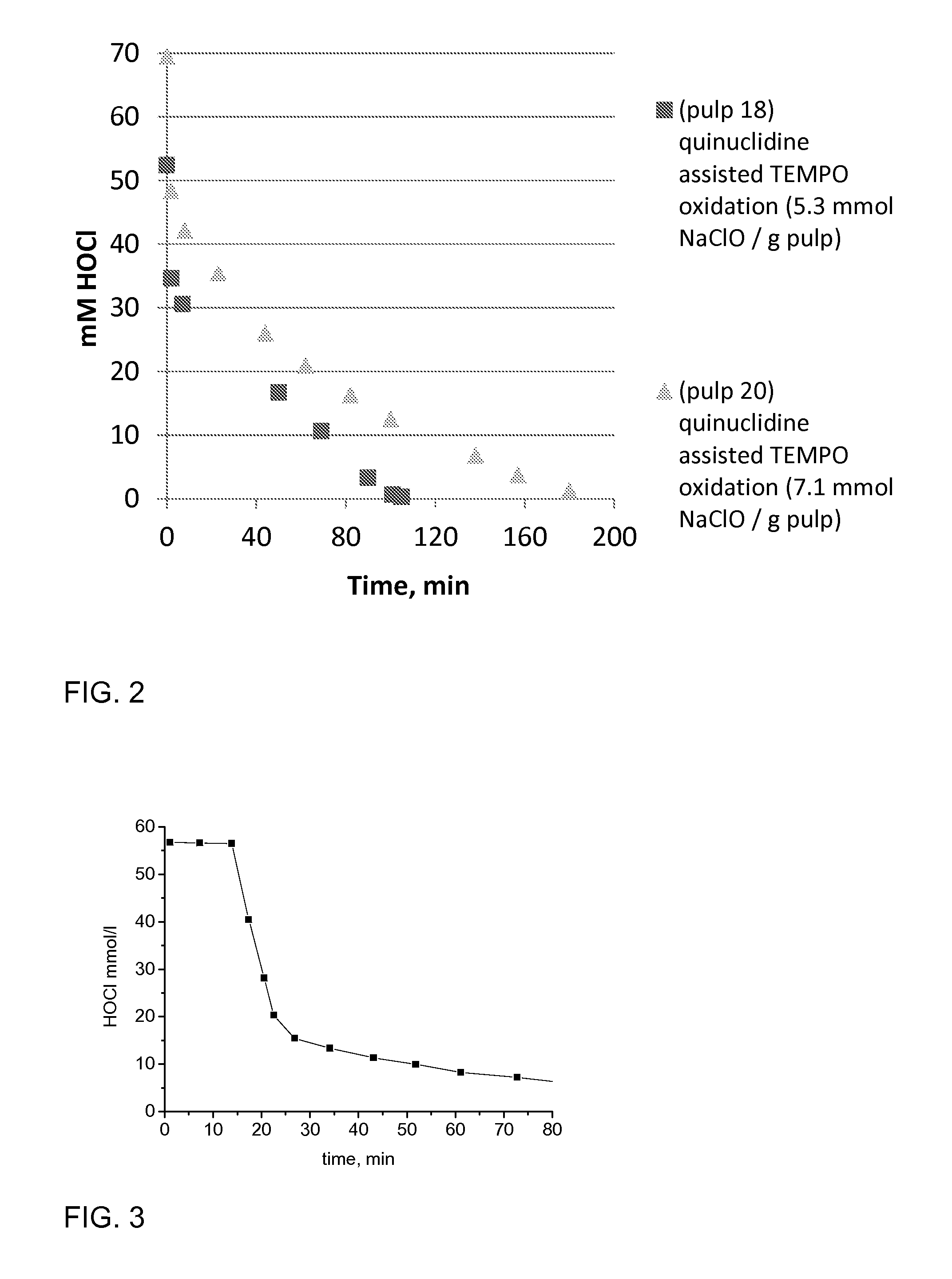
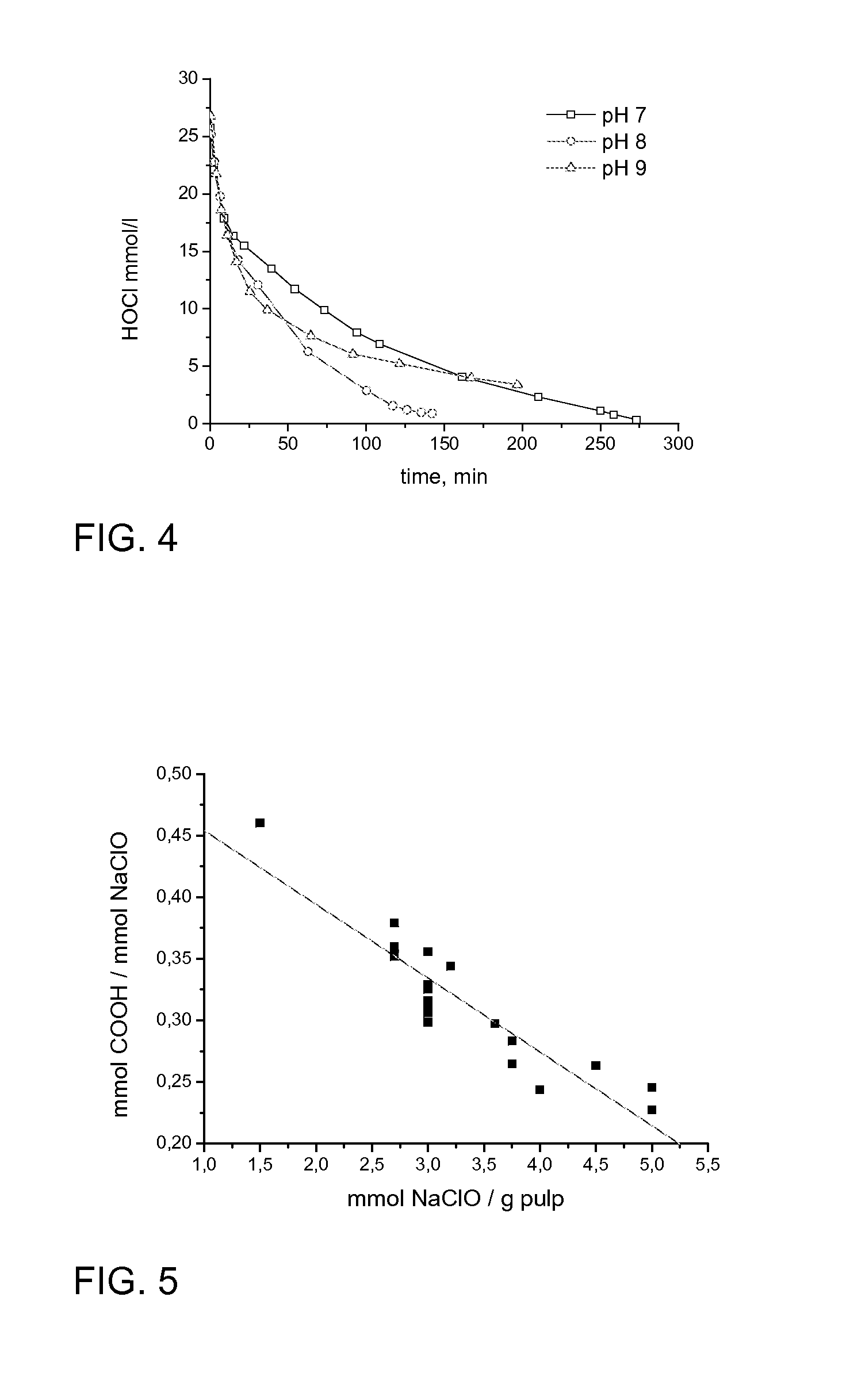
ActiveUS20140110070A1Effectively and selectively oxidizing C-Reduce usageNon-fibrous pulp additionSpecial paperCelluloseHypochlorite
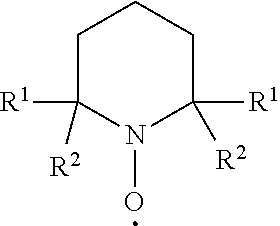
In a method for catalytic oxidation of cellulose a heterocyclic nitroxyl radical is used as catalyst, hypochlorite is used as main oxidant acting as oxygen source, and a tertiary amine or chlorine dioxide as an activator of the heterocyclic nitroxyl radical.
Owner:UPM-KYMMENE OYJ
Nanolignocellulose compositions and processes to produce these compositions
Some variations provide a new nanolignocellulose composition comprising, on a bone-dry, ash-free, and acetyl-free basis, from 35 wt % to 80 wt % cellulose nanofibrils, cellulose microfibrils, or a combination thereof, from 15 wt % to 45 wt % lignin, and from 5 wt % to 20 wt % hemicelluloses. The hemicelluloses may contain xylan or mannan as the major component. Novel properties arise from the hemicellulose content that is intermediate between high hemicellulose content of raw biomass and low hemicellulose content of conventional nanocellulose. The nanolignocellulose composition is hydrophobic due to the presence of lignin. Processes for making and using the nanolignocellulose compositions are also described.
Owner:GRANBIO INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY HOLDINGS LLC
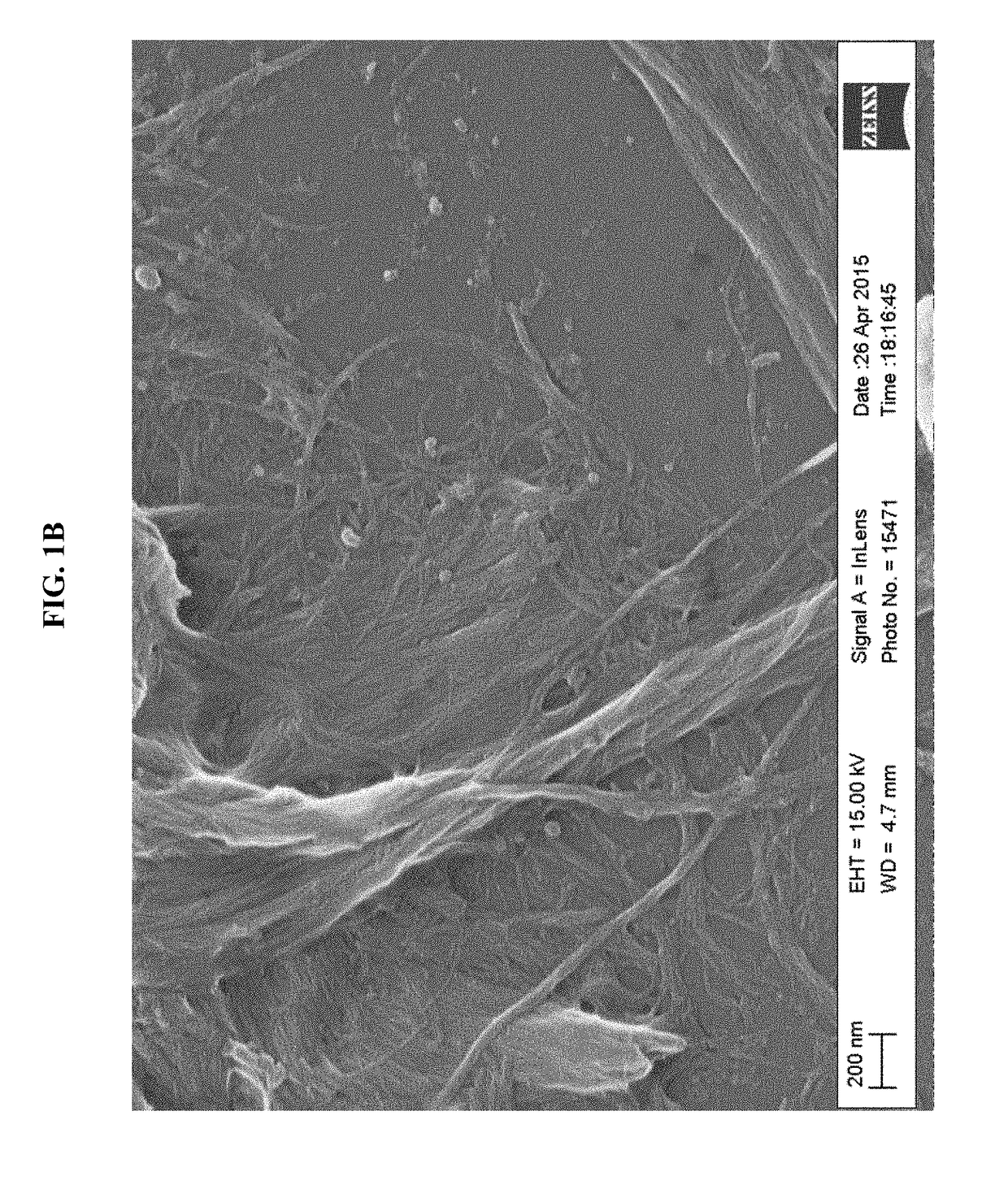
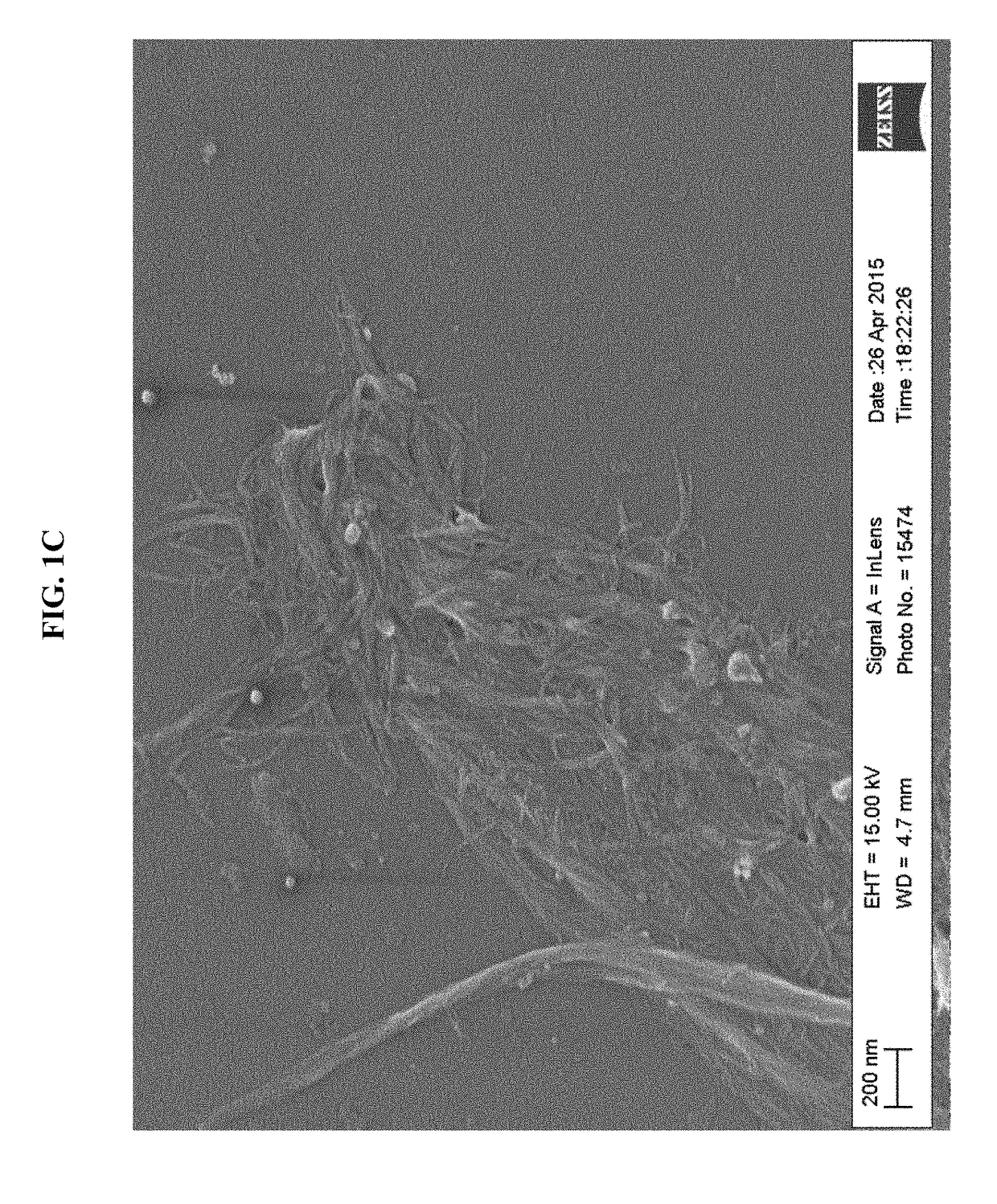
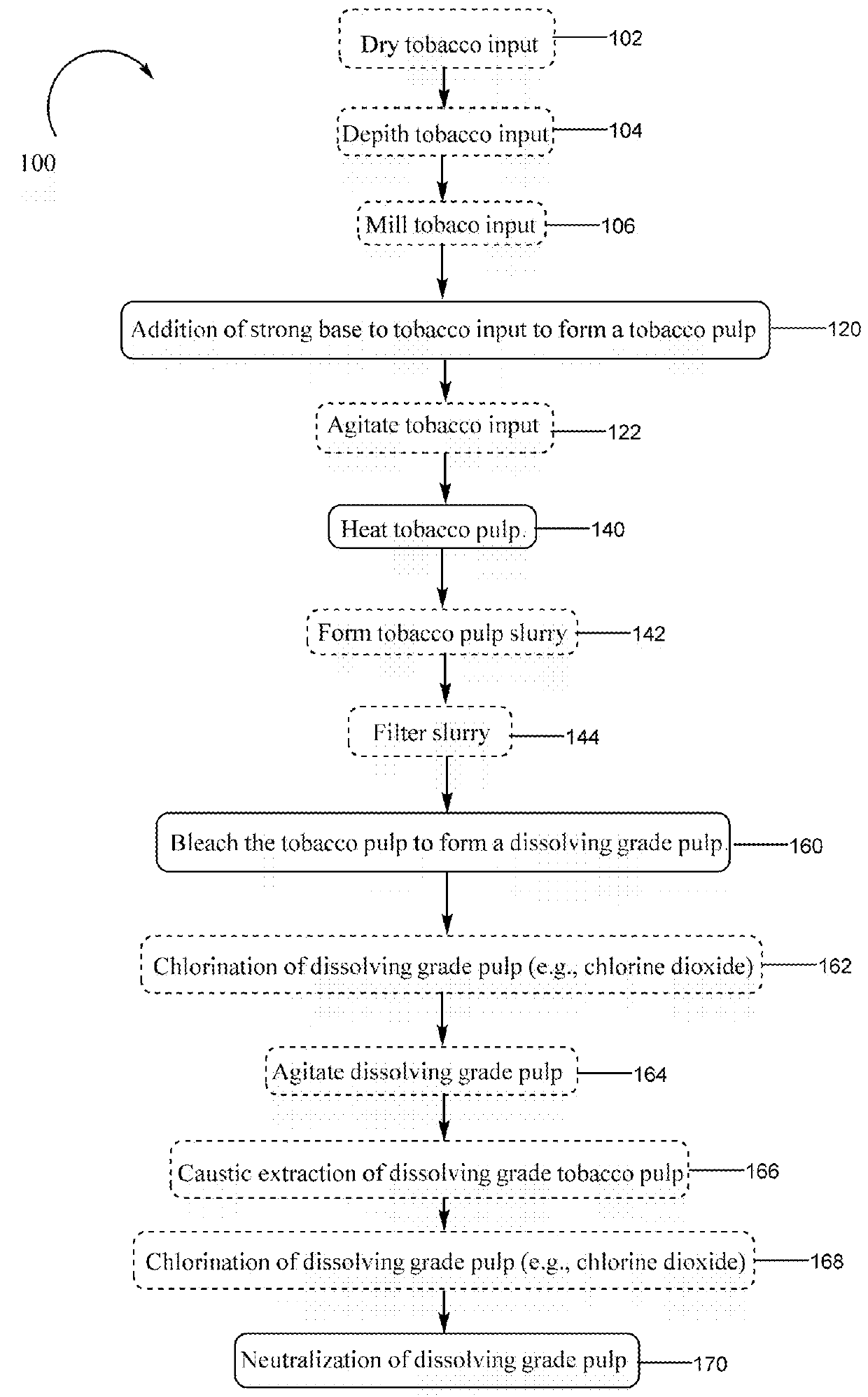
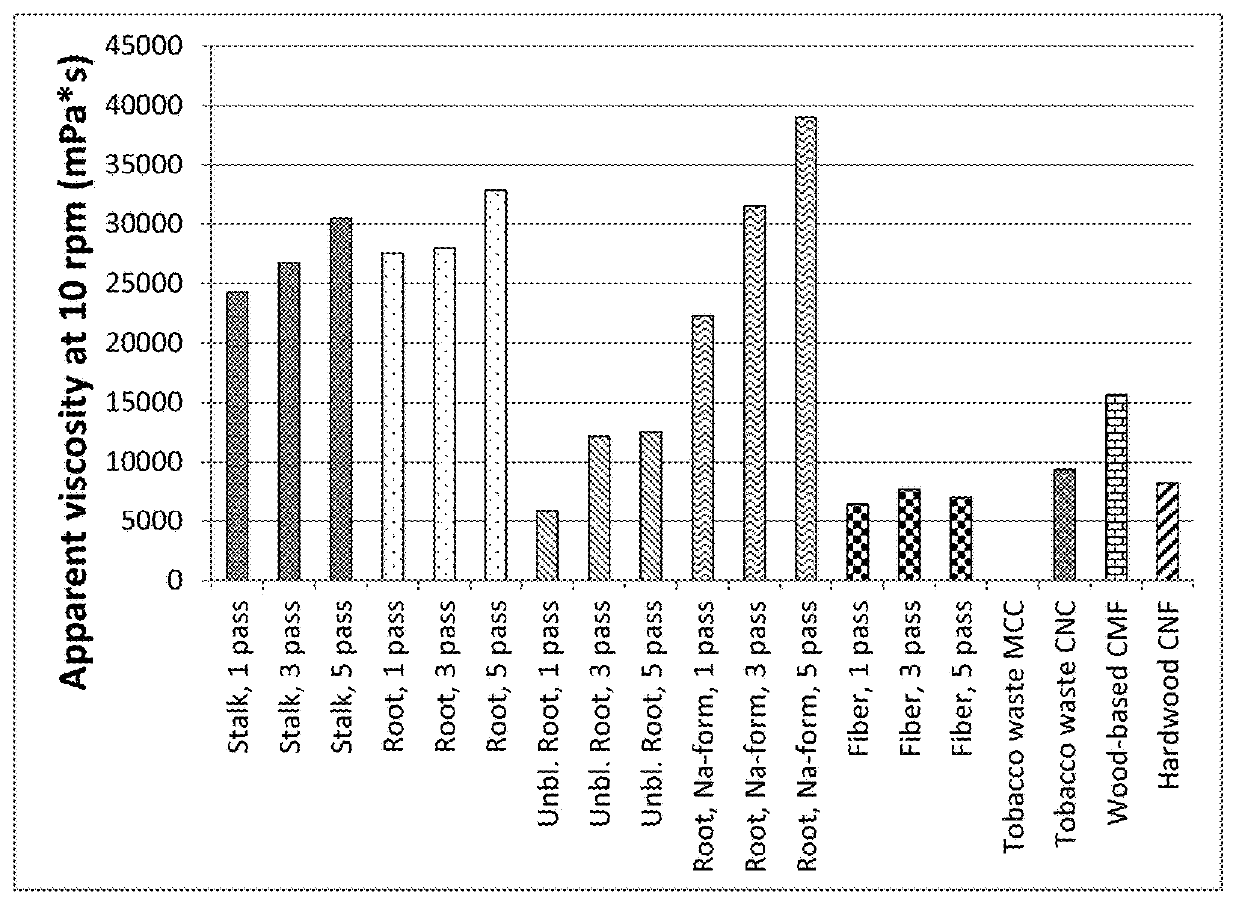
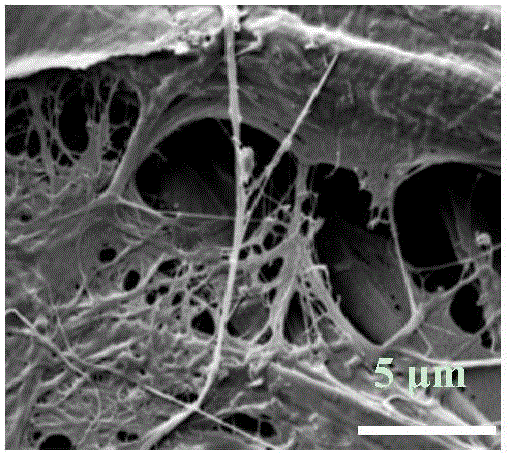
Tobacco-derived nanocellulose material
The present disclosure relates to cellulose nanomaterials made or derived from tobacco and methods for the production thereof. The tobacco-derived cellulose nanomaterials can be employed in various industrial applications such as film forming applications and solution thickening technologies. In particular, the disclosure is directed to methods for preparing tobacco-derived cellulose nanomaterials using less fibrillation cycles than in the production of wood pulp. The invention includes a method for preparing tobacco derived nanocellulose material comprising receiving a tobacco pulp in a dilute form such that the tobacco pulp is a tobacco pulp suspension with a consistency of less than about 5%; and mechanically fibrillating the tobacco pulp suspension to generate a tobacco derived nanocellulose material having at least one average particle size dimension in the range of about 1 nm to about 100 nm.
Owner:R J REYNOLDS TOBACCO COMPANY
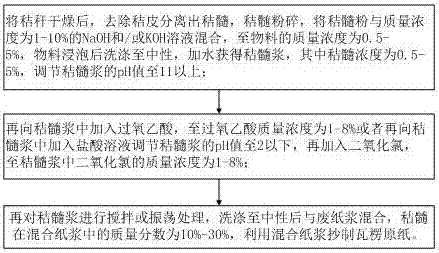
Method for utilizing straw and waste paper pulp to prepare high strength corrugated base paper
ActiveCN107881842ALow costHigh strengthPretreatment with alkaline reacting compoundsPulping with organic compoundsCelluloseChlorine dioxide
The invention discloses a method for utilizing straw and waste paper pulp to prepare high strength corrugated base paper, and relates to the field of utilizing cellulose to make paper. After the strawis dried, straw husk is removed to separate out straw medulla, the straw medulla is pulverized, the straw medulla powder is mixed with a NaOH and / or KOH solution of which the mass concentration is 1-10% till the mass concentration of the material is 0.5-5%, after being soaked, the material is washed to be neutral, and water is added to obtain straw medulla pulp, wherein the concentration of the straw medulla is 0.5-5%; then peroxyacetic acid is added into the straw medulla pulp till the mass concentration of peroxyacetic acid is 1-8%, or a hydrochloric acid solution is added into the straw medulla pulp to adjust the pH value of the straw medulla pulp to be 2 or below, then chlorine dioxide is added till the mass concentration of chlorine dioxide in the straw medulla pulp is 1-8%; then thestraw medulla pulp is stirred or oscillated, after being washed to be neutral, the straw medulla pulp is mixed with the waste paper pulp, the mass percentage of the straw medulla in mixed paper pulpis 10-30%, and the mixed paper pulp is utilized to make the corrugated base paper.
Owner:山东科迈生物制浆有限公司
Pulping processes
A pulping process comprises using a high concentration of anthraquinone (AQ). The pulping process is capable of providing a pulp having low Kappa number with unexpectedly high strength. The pulping process can use wood or non-wood fibers (e.g., bagasse and corn stover) to provide pulp having good papermaking quality. The method for pulping a fiber comprising cooking a first mixture comprising the fibers, water, an alkali, and a delignification selectivity enhancing chemical for a cooking time and at a cooking condition sufficient to form a first pulp having a desired Kappa number of about 15 or less, and strength parameters that are sufficient for papermaking, where the starting material prior to cooking has a Kappa number of 60 or greater.
Owner:CARGILL INC
Making method of hemp root bast filter paper for anti-fog and anti-haze mask
InactiveCN106087503AIncreasing the thicknessEasy to quantifyPulp beating methodsPulping with organic compoundsPorosityMicrometer
The invention discloses a making method of hemp root bast filter paper for an anti-fog and anti-haze mask. The making method comprises the steps that hemp root bast is sequentially subjected to cutting, steaming, bleaching, defibering, pulping, papermaking, squeezing and drying. The thick and hard hemp root bast is made into the hemp root bast filter paper with large thickness, high quantitation, large hole diameter and high porosity, and reutilization of waste textiles is achieved. The filter efficiency of the made hemp root bast filter paper on NaCl aerosol particles with the size of 0.26 micrometer, the density of 15.6 mg / m<3> and the concentration of 2% reaches up to 99.94%-100%, and therefore the hemp root bast filter paper has the high air particle filter efficiency, can be applied to the anti-fog and anti-haze mask and has an efficient filter effect and a wide market application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Method for preparing dissolved pulp by using straw or energy plants
ActiveCN109653012AReduce management costsReduce processing difficultyPulping with organic compoundsPulp bleachingAlpha-CellulosePolymerization
The invention discloses a method for preparing dissolved pulp by utilizing straw and energy plants, and the method comprises the following steps: 1) raw material pretreatment, 2) pre-impregnation treatment, 3) hydro-thermal treatment, 4) mild alkali treatment; 5) refining treatment and the like. According to the method, a whole set of novel dissolved pulp preparation process is designed to aim atthe raw material characteristics of crop straw raw materials and energy plants, and more choices are provided for the high-value utilization of the raw materials; the method is simple in process steps, the equipment and the factory management cost are low; the treatment conditions are relatively mild, the use amount of chemical reagents is small, the production energy consumption is reduced, the chemical reagent cost and the waste liquid treatment difficulty are low; a simple treatment process and a mild reaction condition are adopted, and excessive degradation of cellulose is reduced, so thatthe alpha-cellulose content, cellulose polymerization degree, purity and product yield are improved or stabilized.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +2
Tobacco-derived nanocellulose material
The present disclosure relates to cellulose nanomaterials made or derived from tobacco and methods for the production thereof. The tobacco-derived cellulose nanomaterials can be employed in various industrial applications such as film forming applications and solution thickening technologies. In particular, the disclosure is directed to methods for preparing tobacco-derived cellulose nanomaterials using less fibrillation cycles than in the production of wood pulp. The invention includes a method for preparing tobacco derived nanocellulose material comprising receiving a tobacco pulp in a dilute form such that the tobacco pulp is a tobacco pulp suspension with a consistency of less than about 5%; and mechanically fibrillating the tobacco pulp suspension to generate a tobacco derived nanocellulose material having at least one average particle size dimension in the range of about 1 nm to about 100 nm.
Owner:R J REYNOLDS TOBACCO COMPANY
Separation and comprehensive utilization method of all components of crop straw
ActiveCN110241644AAffect the extraction ratePrevents hydrolytic breakagePulping with organic compoundsPulping with acid salts/anhydridesOrganic acidDistillation
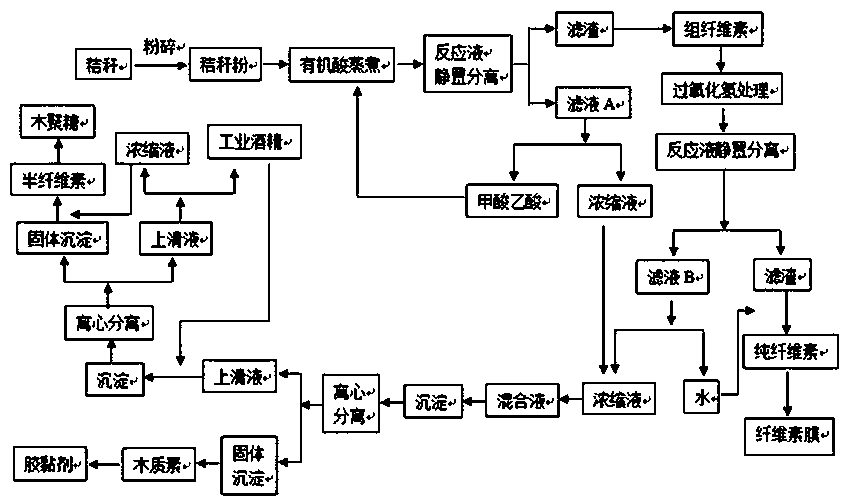
The invention provides a separation and comprehensive utilization method of all components of crop straw. The separation and comprehensive utilization method of all the components of the crop straw comprises the steps of cooking crushed crop straw under the catalytic action of diluted hydrochloric acid by means of organic acid liquid, then conducting solid-liquid separation to obtain filter liquor, namely A liquid, washing filter residues with water until the filter residues are neutral, and then conducting drying to obtain crude cellulose; after the crude cellulose is treated by hydrogen peroxide, conducting solid-liquid separation to obtain filter liquor, namely B liquid, washing filter residues with water until the filter residues are neutral, and then conducting drying to obtain cellulose; conducting reduced pressure distillation on the A liquid and the B liquid separately, mixing obtained distilled products, after a pH is adjusted, conducting solid-liquid separation to obtain filter liquor, namely C liquid, washing sediment with water until the sediment is neutral, and then conducting drying to obtain lignin; adjusting a pH of the C liquid, then adding industrial alcohol, and then conducting solid-liquid separation; and washing sediment with water until the sediment is neutral, and then conducting drying to obtain hemicellulose. By means of the separation and comprehensive utilization method of all the components of the crop straw, the three components of the cellulose, the hemicellulose and the lignin in the straw can be successfully separated, and the recovery rates of the three components are high, so that comprehensive utilization of the straw is truly achieved.
Owner:河南省高新技术实业有限公司
Organic solvent pretreatment of biomass to enhance enzymatic saccharification
ActiveUS8241880B2High yieldCost-effectiveSugar derivativesPulping with organic compoundsOrganic solventFermentable sugar
Biomass is pretreated using an organic solvent solution under alkaline conditions in the presence of one or more alkylamine and optionally one or more additional nucleophile to fragment and extract lignin. Pretreated biomass is further hydrolyzed with a saccharification enzyme consortium. Fermentable sugars released by saccharification may be utilized for the production of target chemicals by fermentation.
Owner:SUSTAINABLE TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com