Method for removing straw lignin and hemicellulose by using protic ionic liquid
A technology of lignocellulose and ionic liquid, applied in the field of biomass, can solve the problems of incompatible with sustainable development and green process engineering, high cost, and many synthesis steps, and achieve excellent dissolution and separation ability, low price, and simple synthesis. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
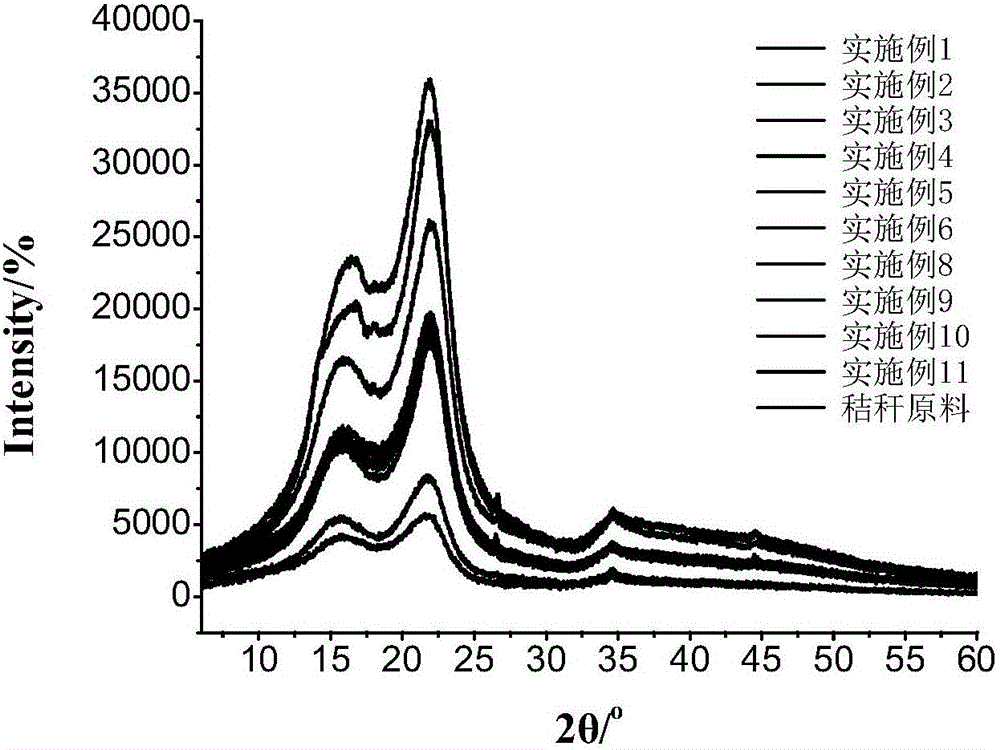
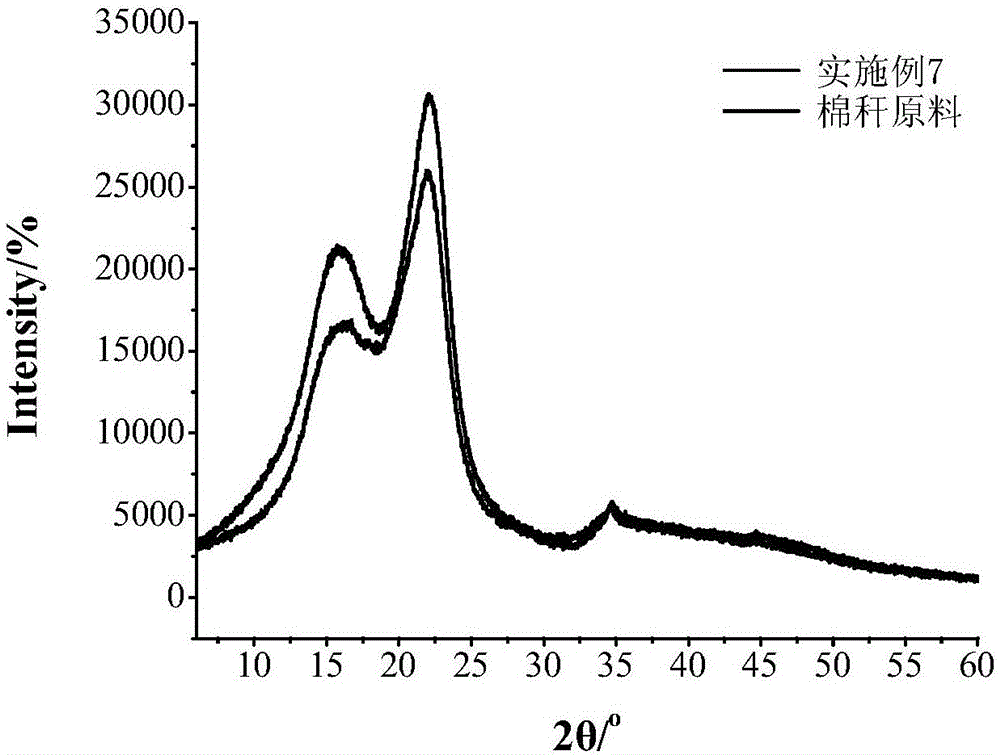
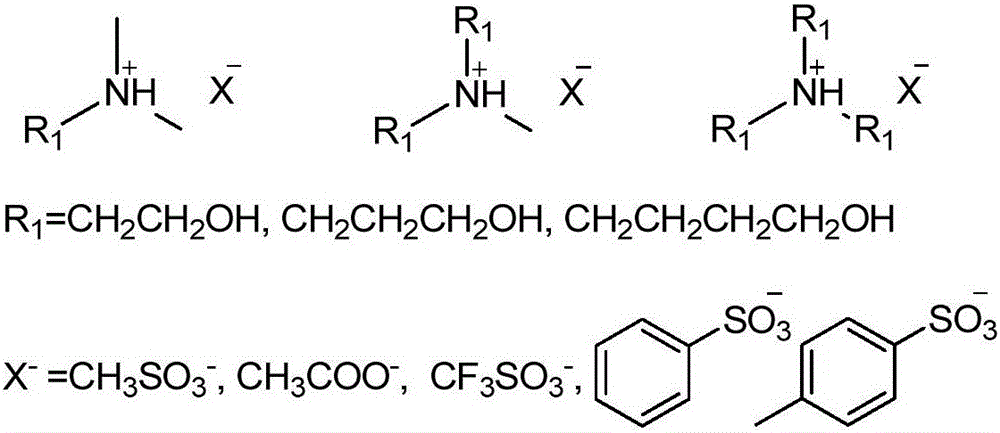
[0024] To the dried 10g protic ionic liquid solvent N-methyldiethanolamine methanesulfonate ([(HOCH 2 CH 2 ) 2 NH(CH 3 )] + CH 3 SO 4 - ) was added 0.5 g of corn stalk powder that had been washed, dried, and sieved (≤0.125 mm), stirred magnetically at 120°C for 24 hours, and 10 mL of deionized water was added to the reacted ionic liquid and straw mixture for dilution and centrifuged. The obtained undissolved product is washed with clear water, dried and weighed, the solubility of the ionic liquid is calculated, and the product is subjected to lignocellulose component analysis. Component analysis results showed that the lignin content in the product decreased from 15.28% to 1.99%, the hemicellulose content decreased from 31.21% to 4.04%, and the cellulose content increased from 50.53% to 91.81%.
Embodiment 2
[0026] To the dried 10g protic ionic liquid solvent N-methyldiethanolamine methanesulfonate ([(HOCH 2 CH 2 ) 2 NH(CH 3 )] + CH 3 SO 4 - ) was added 0.5 g of corn stalk powder that had been washed, dried, and sieved (≤0.125mm), stirred magnetically for 0.25 h at 120°C, and 10 mL of deionized water was added to the reacted ionic liquid and straw mixture to dilute and centrifuged. . The obtained undissolved product is washed with clear water, dried and weighed, the solubility of the ionic liquid is calculated, and the product is subjected to lignocellulose component analysis. Component analysis results showed that the lignin content in the product decreased from 15.28% to 5.30%, the hemicellulose content decreased from 31.21% to 10.08%, and the cellulose content increased from 50.53% to 76.53%.
Embodiment 3
[0028] To the dried 10g protic ionic liquid solvent N-methyldiethanolamine methanesulfonate ([(HOCH 2 CH 2 ) 2 NH(CH 3 )] + CH 3 SO 4 - ) was added 0.5 g of corn stalk powder that had been washed, dried, and sieved (≤0.125 mm), stirred magnetically for 6 h at 80° C., and 10 mL of deionized water was added to the reacted ionic liquid and straw mixture for dilution and centrifuged. The obtained undissolved product is washed with clear water, dried and weighed, the solubility of the ionic liquid is calculated, and the product is subjected to lignocellulose component analysis. Component analysis results showed that the lignin content in the product decreased from 15.28% to 8.14%, the hemicellulose content decreased from 31.21% to 12.60%, and the cellulose content increased from 50.53% to 70.00%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com