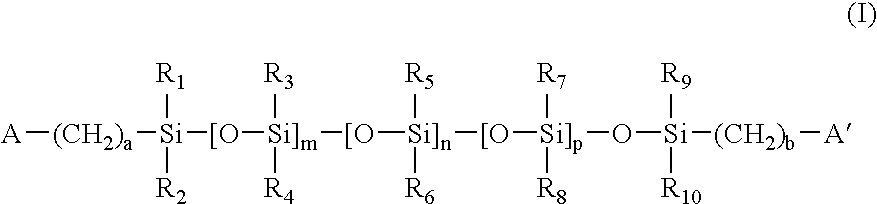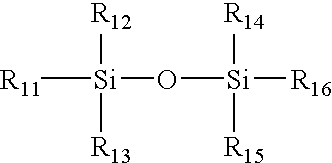Patents
Literature
161 results about "Single vessel" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
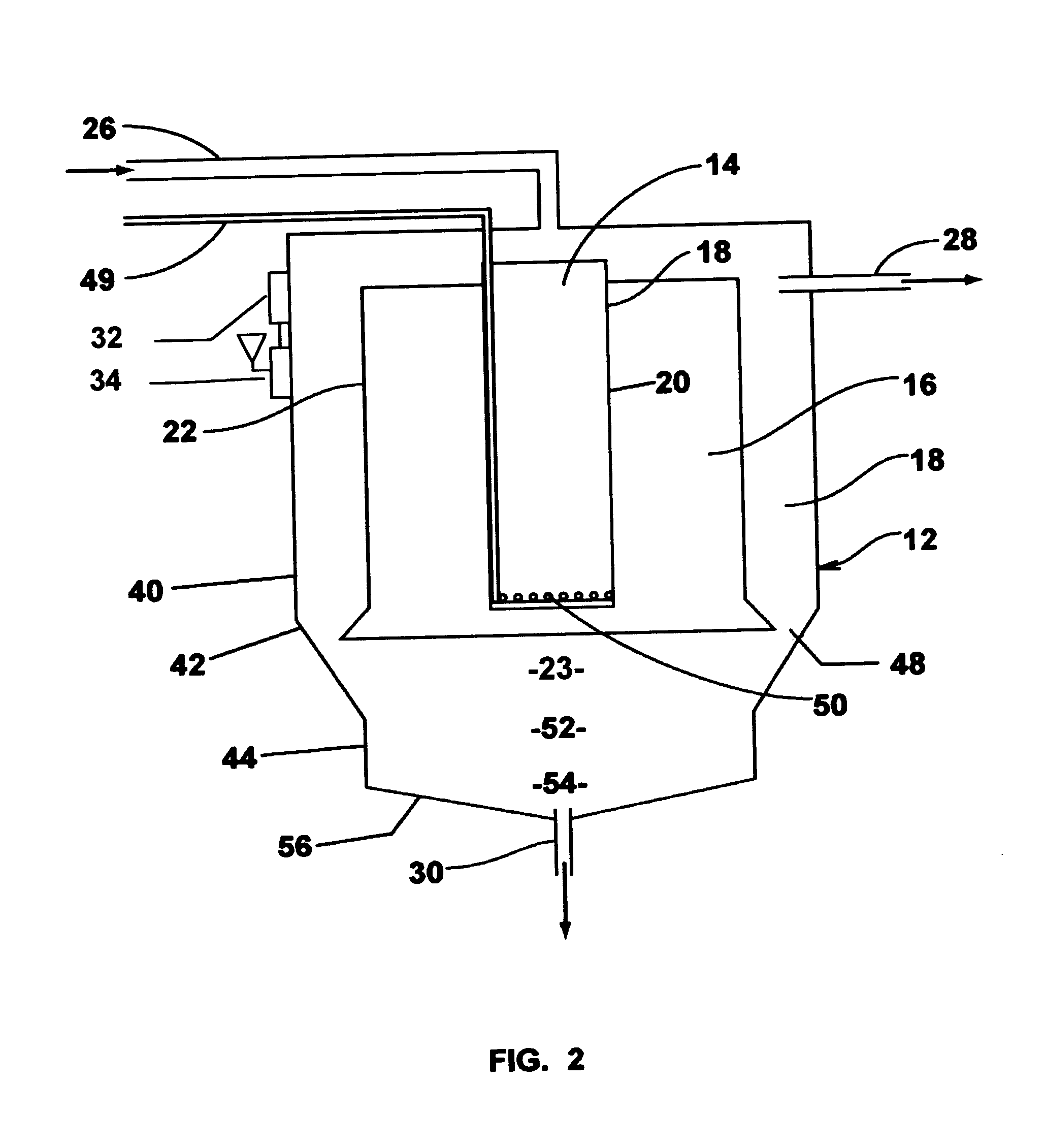
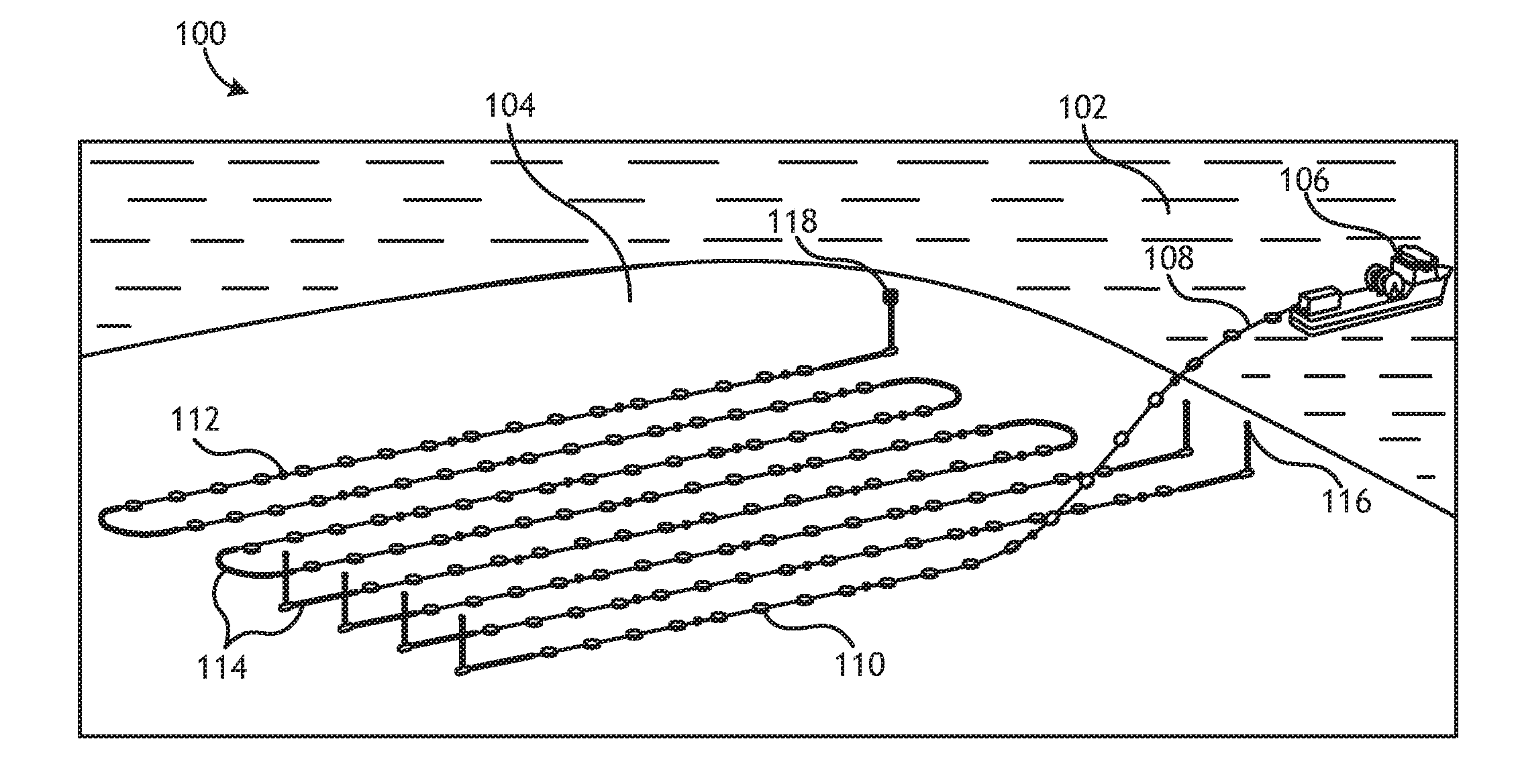
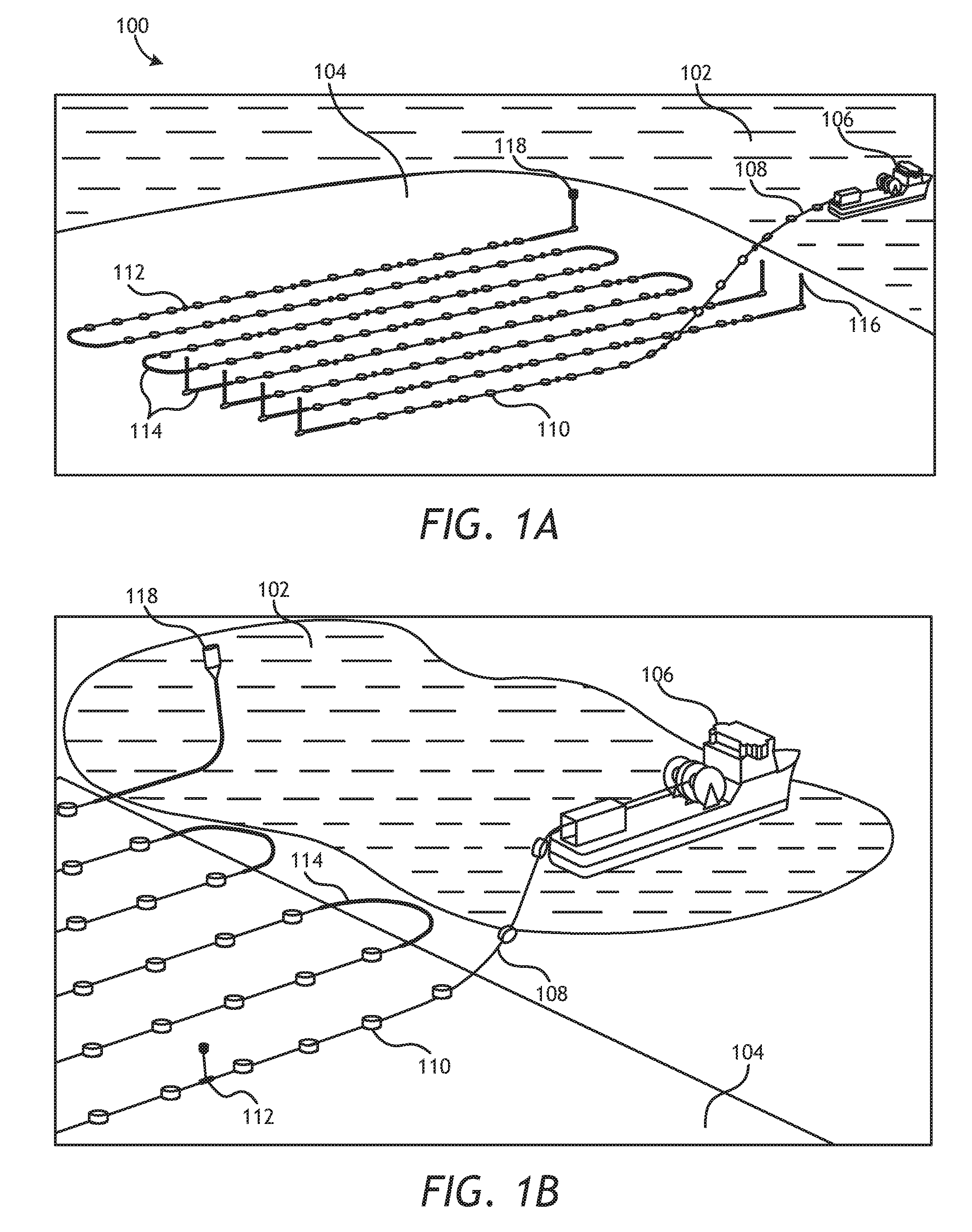
Methods for Efficiently Acquiring Wide-Azimuth Towed Streamer Seismic Data
A technique for use in marine seismic surveying includes a method and an apparatus. In one aspect, the method includes towing a seismic spread including a source multiple streamers on a generally curved advancing path, the streamers being actively steered. The source is fired and data is acquired on the curve. In other aspects, the method is performed with only a single vessel or the generally curved advancing path is a sincurve advancing path. The method may include a dual circular shoot in another aspect. And, in yet another aspect, the invention includes an apparatus comprised of a computing apparatus on board a tow vessel receiving positioning data from the marine seismic streamers. It is also programmed to: sail the tow vessel in a generally curved advancing path and actively steer the marine seismic streamers through the generally curved advancing path.
Owner:REFLECTION MARINE NORGE AS
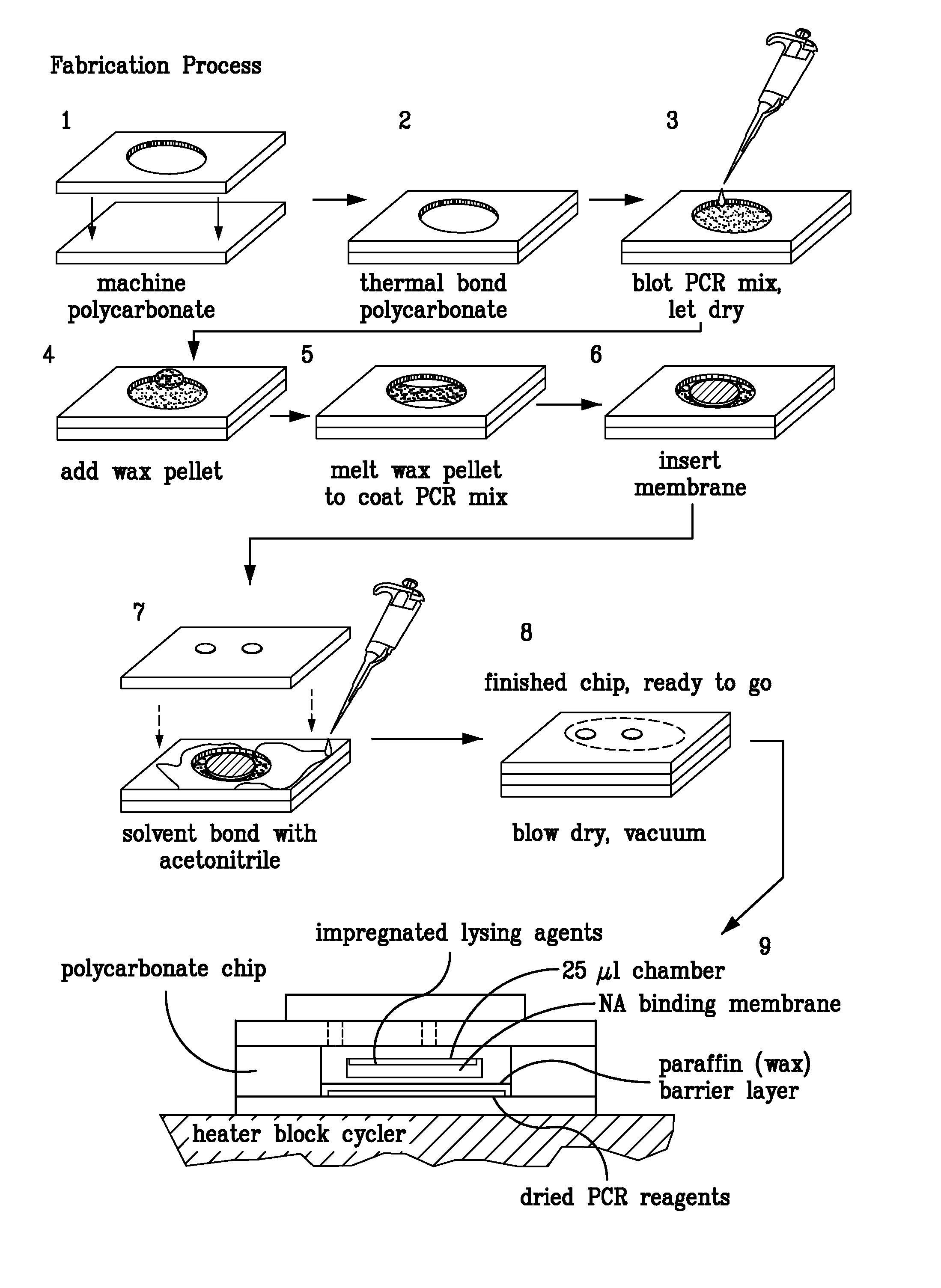
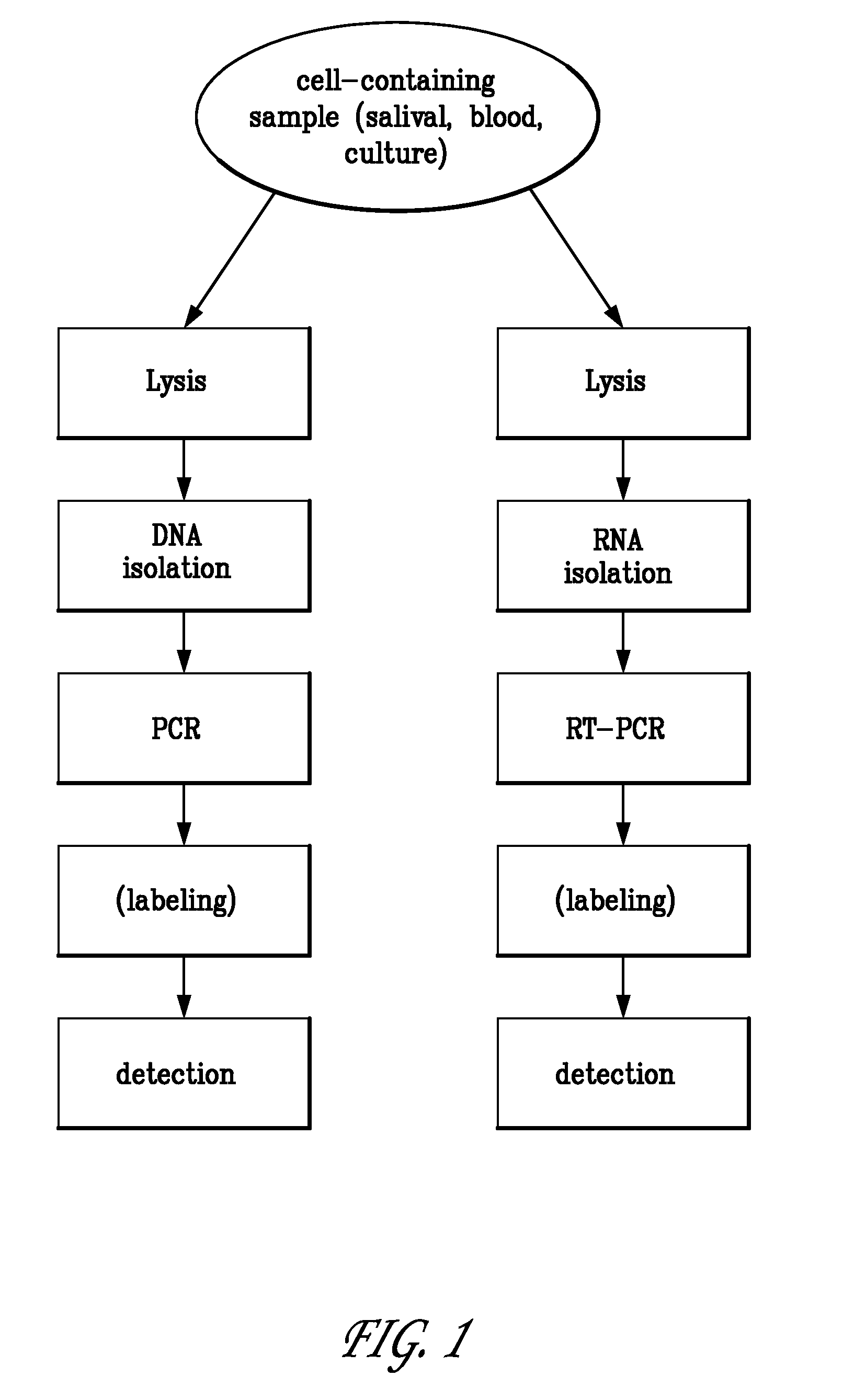
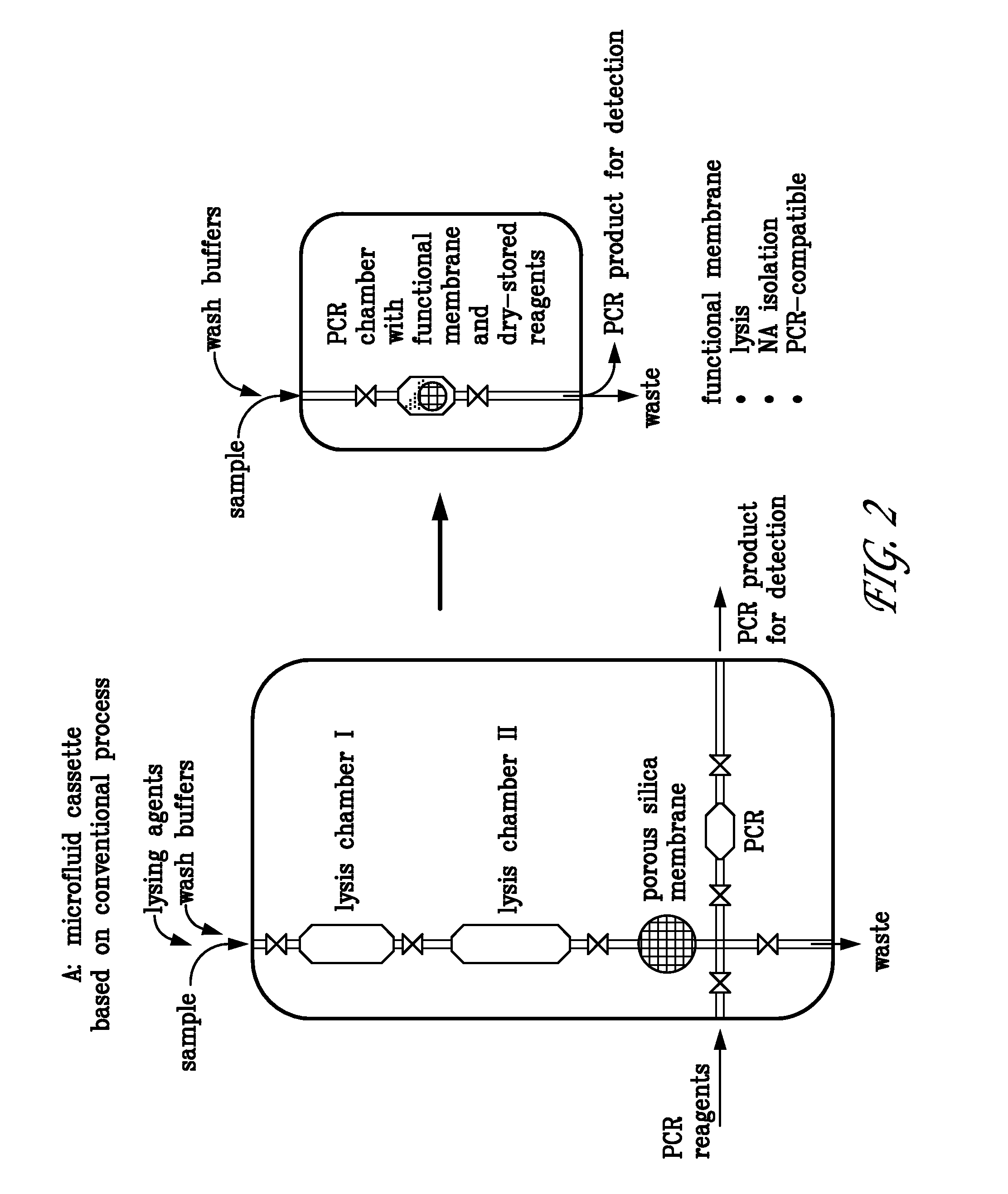
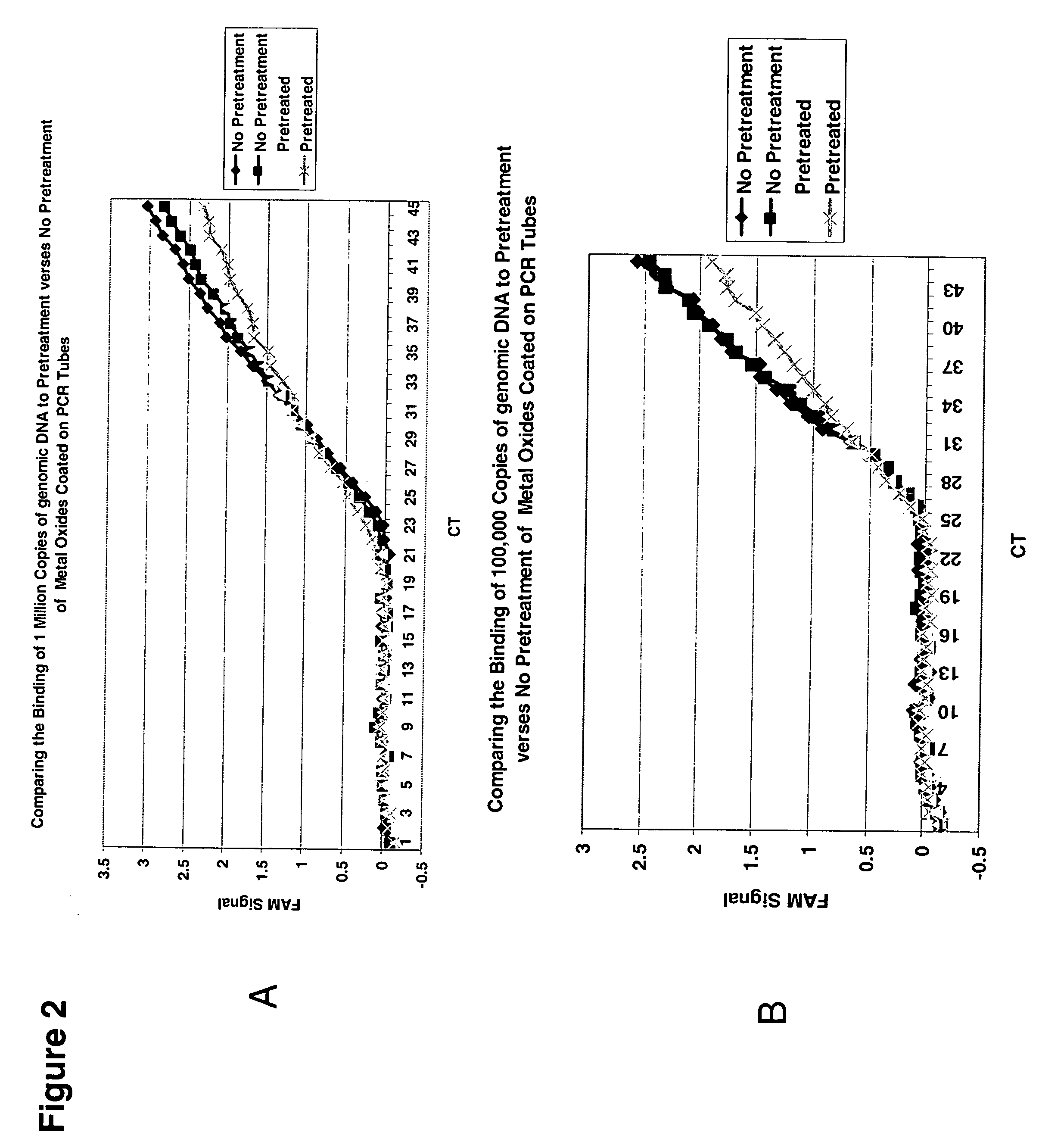
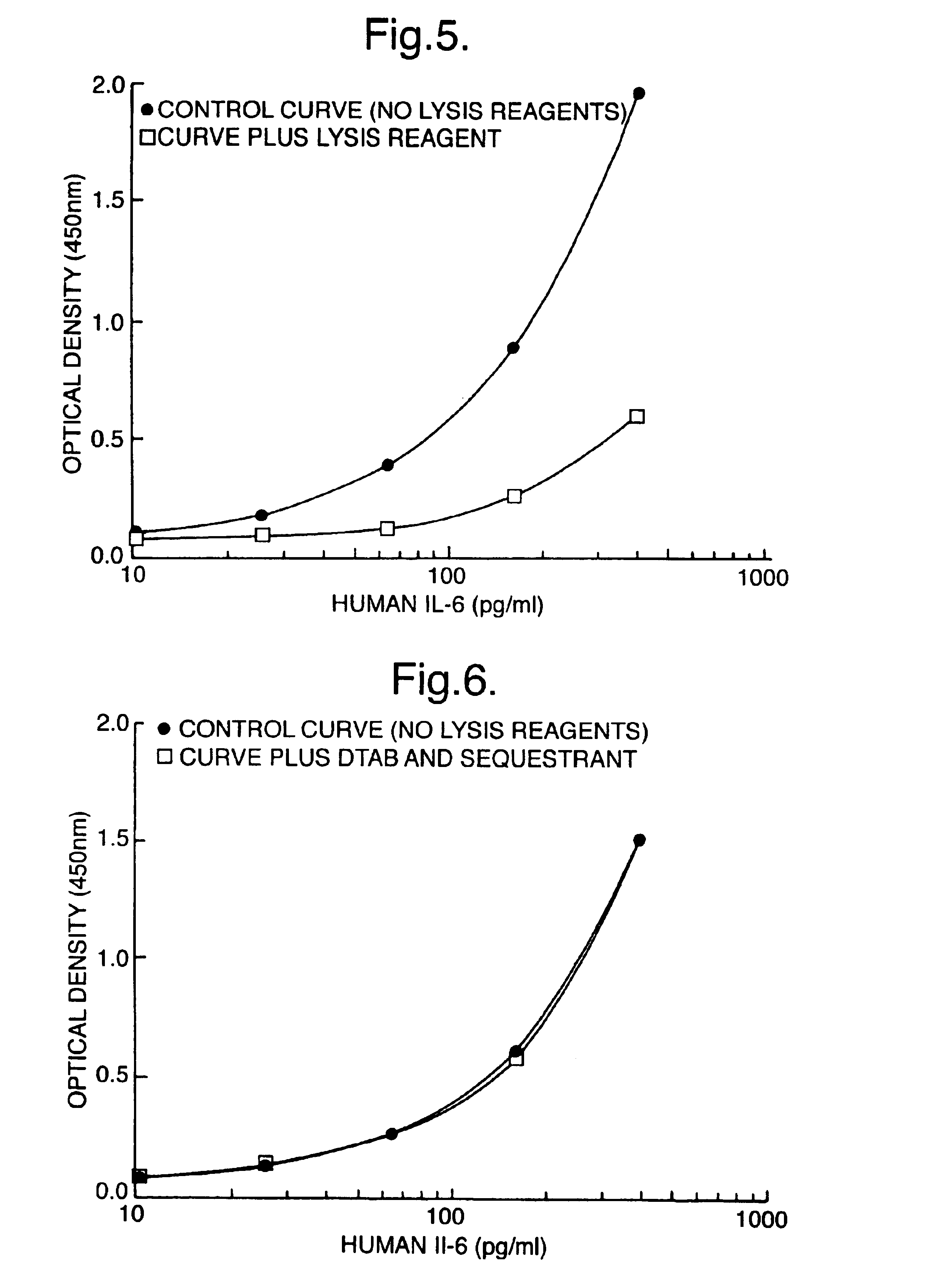
Integrated PCR Reactor for Cell Lysis, Nucleic Acid Isolation and Purification, and Nucleic Acid Amplication Related Applications
ActiveUS20090186357A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSingle vesselLysis
Disclosed are integrated devices capable of performing a polymerase chain reaction within a single vessel. Also disclosed are related methods of sample analysis.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Contact lens materials
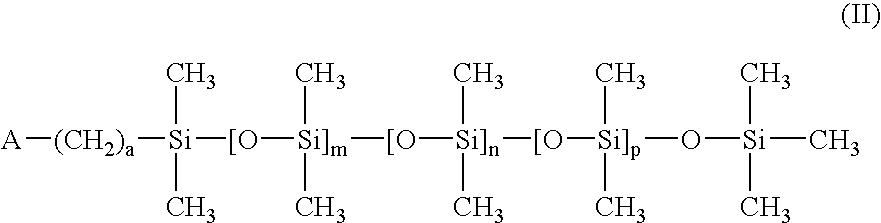
InactiveUS6921802B2High oxygen permeabilityLow densityOptical partsOptical elementsSingle vesselTrimethylsilyl
A method for reducing the modulus of polymer silicone hydrogel compositions by employing monomeric polysiloxanes endcapped with trimethylsilyl to reduce the crosslinking density of the hydrogel. The synthesis consists of a single vessel acid catalyzed ring opening polymerization and may be employed to produce copolymers useful as hydrogel contact lens materials.
Owner:BARCLAYS BANK PLC AS SUCCESSOR AGENT
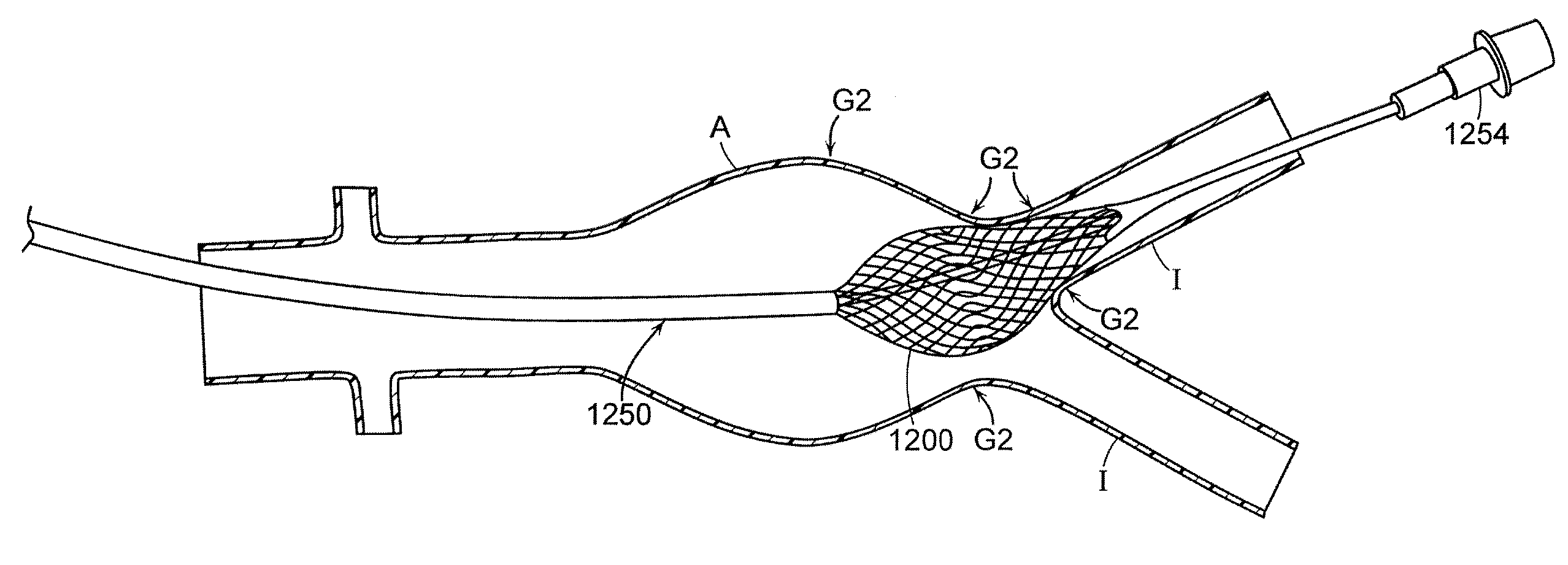
Non-occluding dilation device
An assembly including a device for dilating a vessel or a structure (such as a stent or stent graft) within a vessel wherein the device comprises a plurality of wires that are spaced apart when the device is dilated so as to allow fluid to flow through the device. Thus, when in use the device does not occlude or substantially hinder the flow of blood through a vessel or into side vessels. The device may also be flexible enough to be easily maneuvered through tight bends in a vessel and / or be able to conform to varying diameters within a single vessel or within multiple vessels.
Owner:MERIT MEDICAL IRELAND LTD
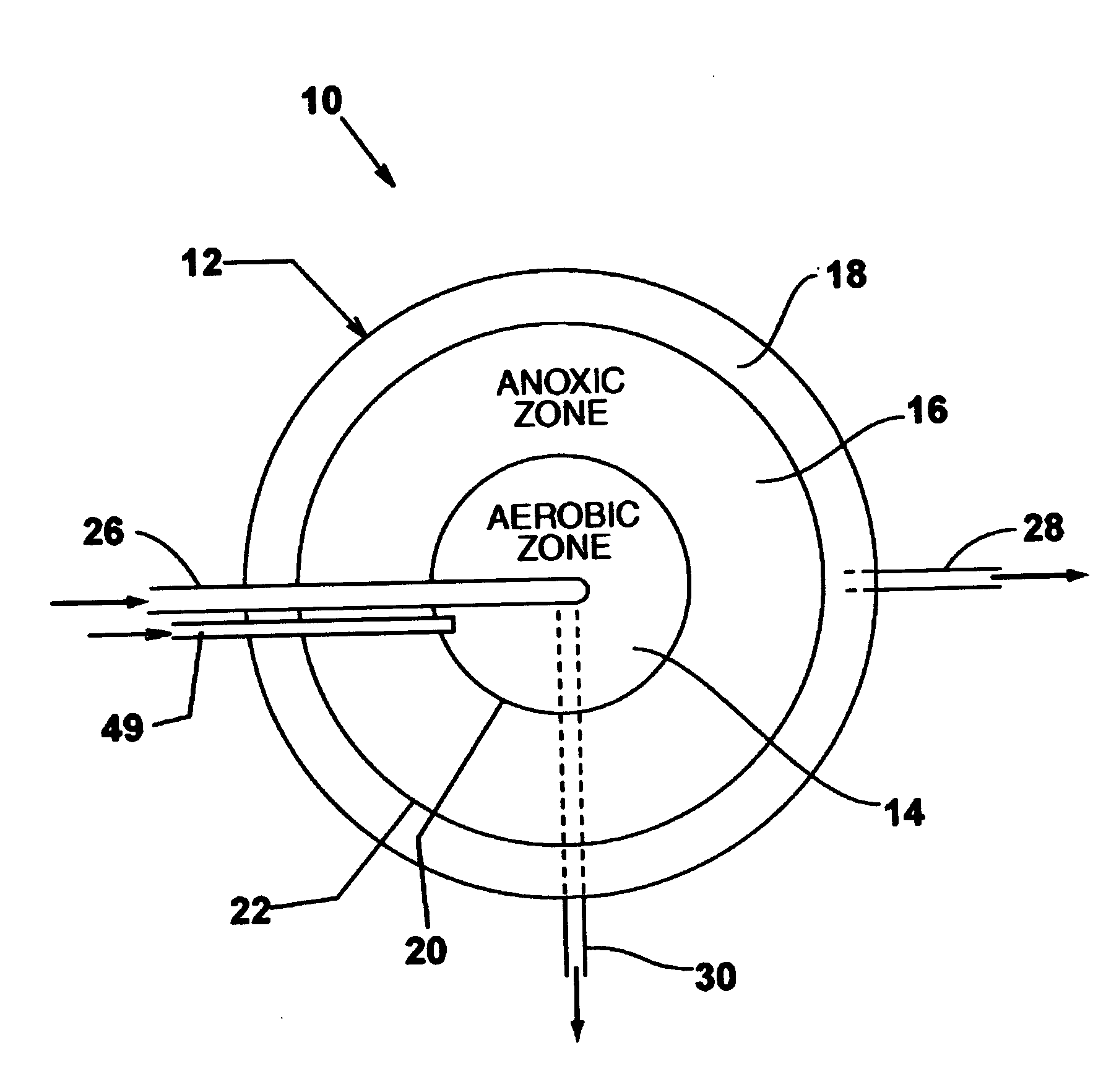
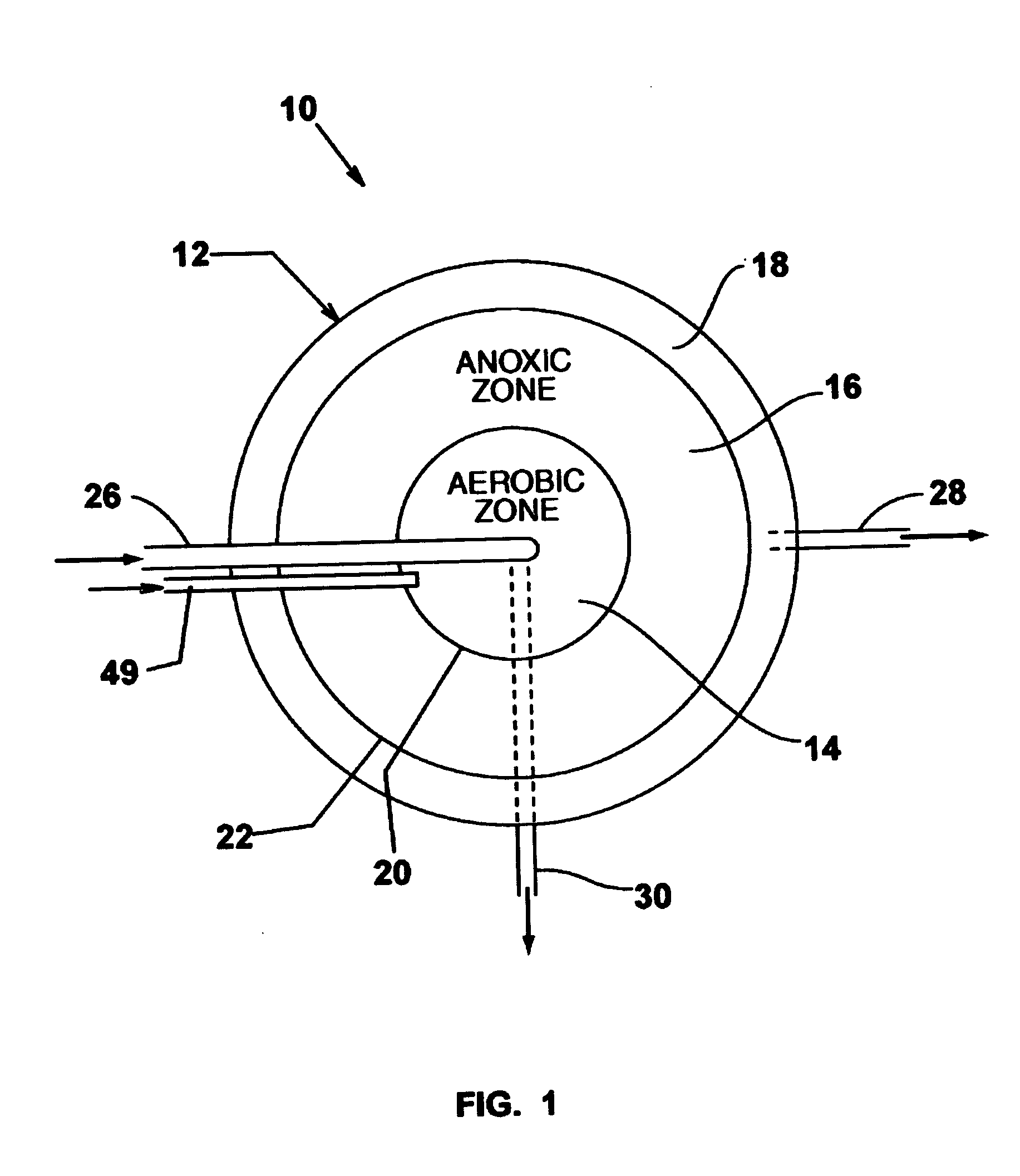
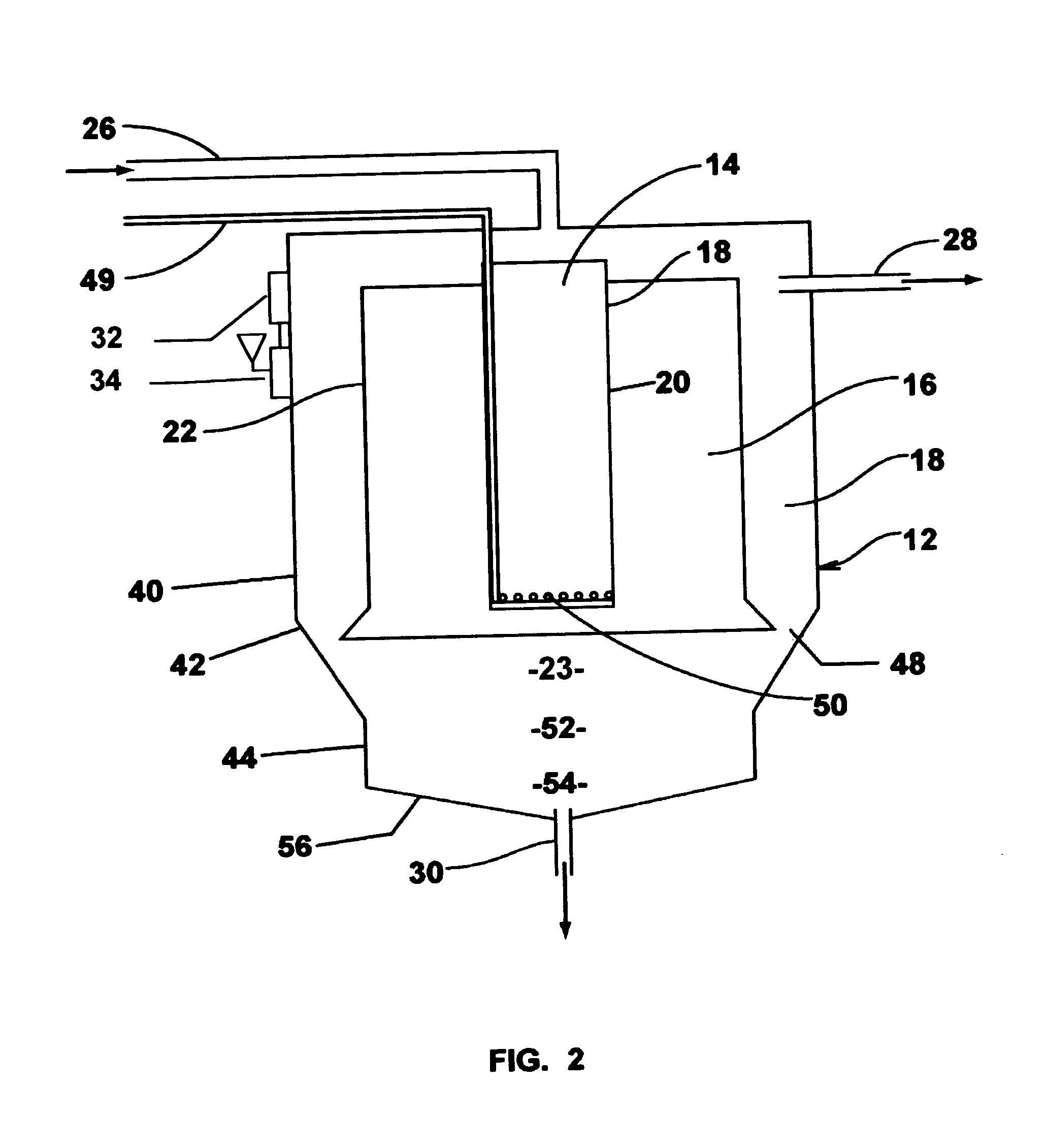
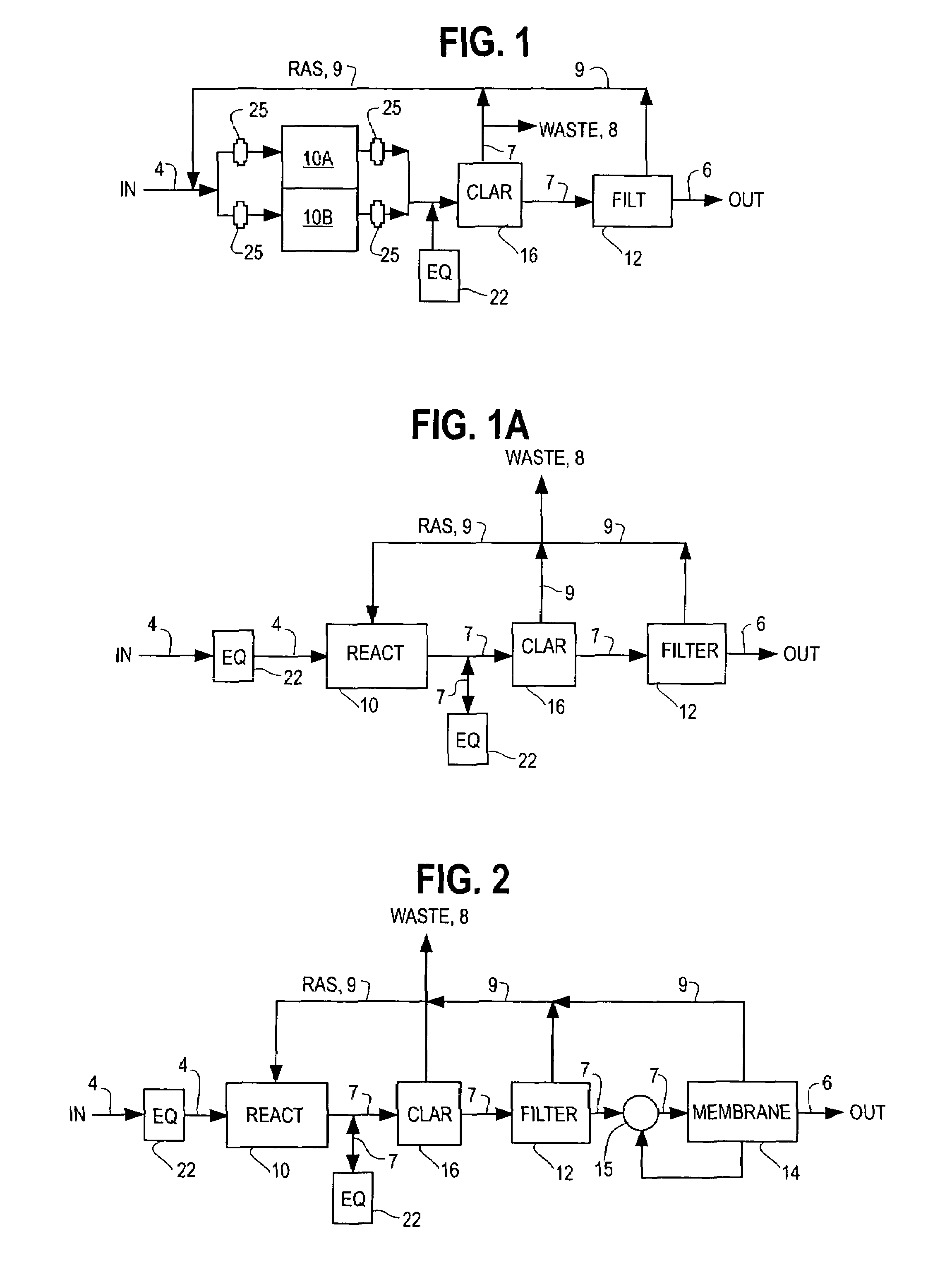
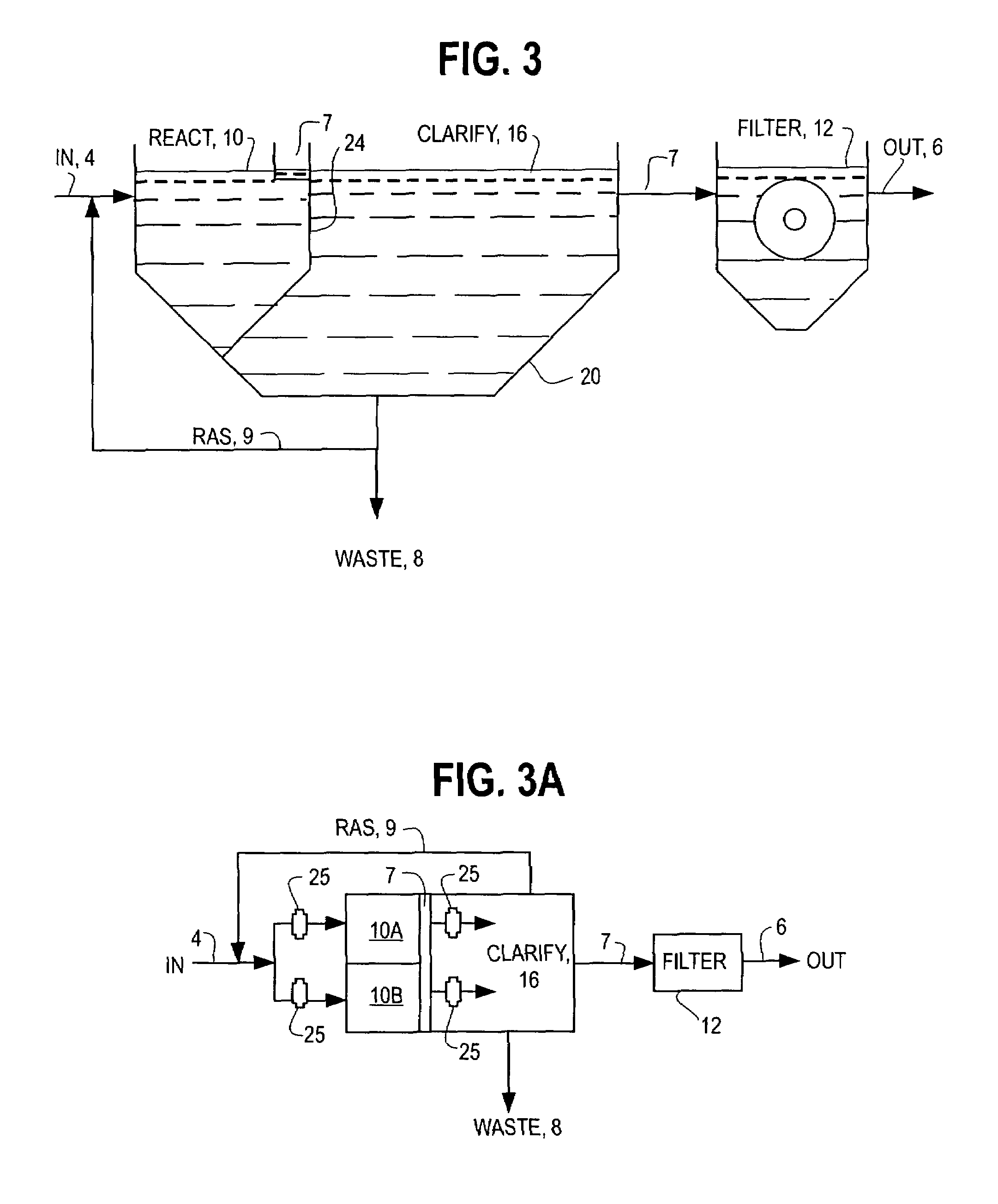
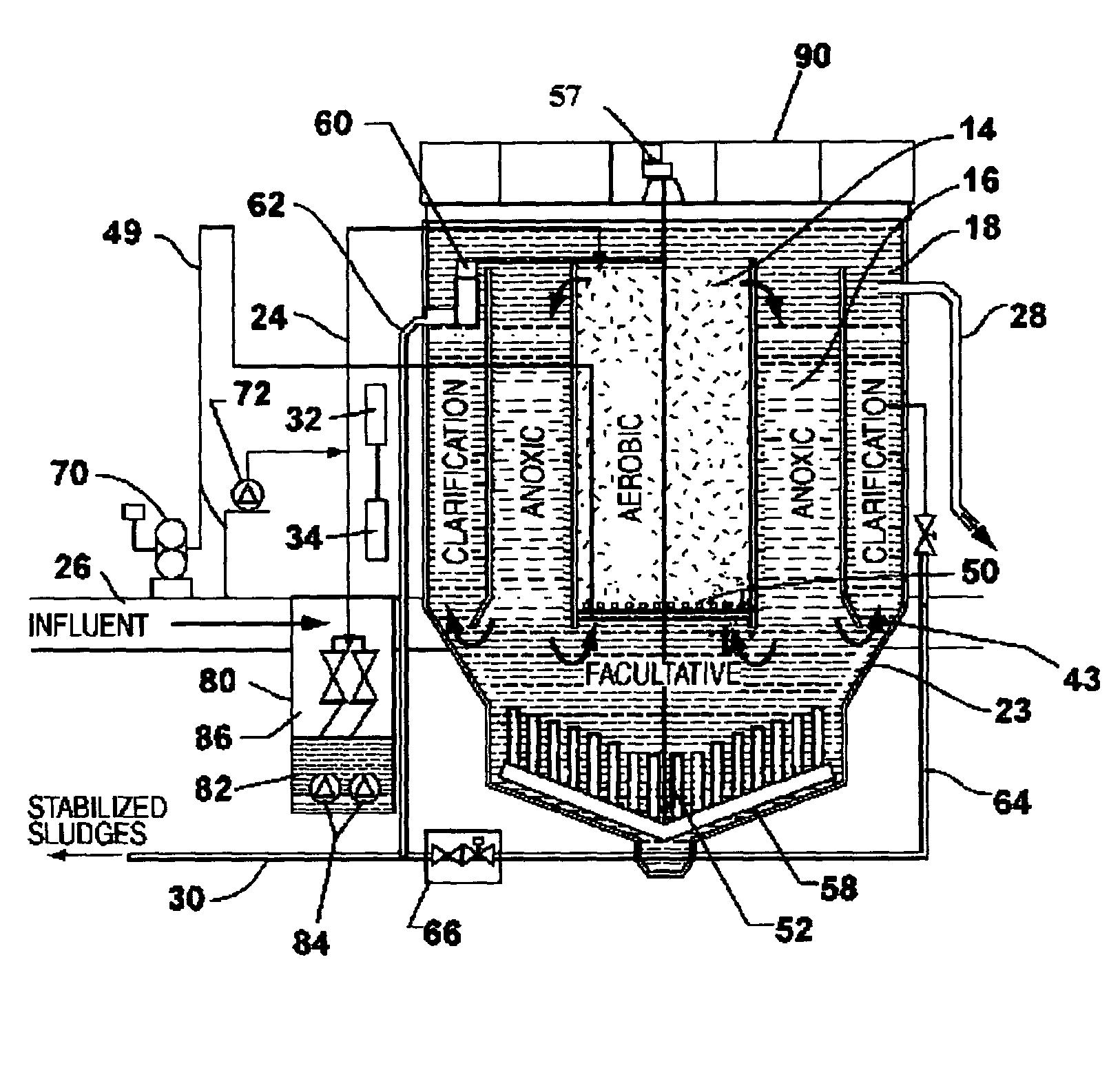
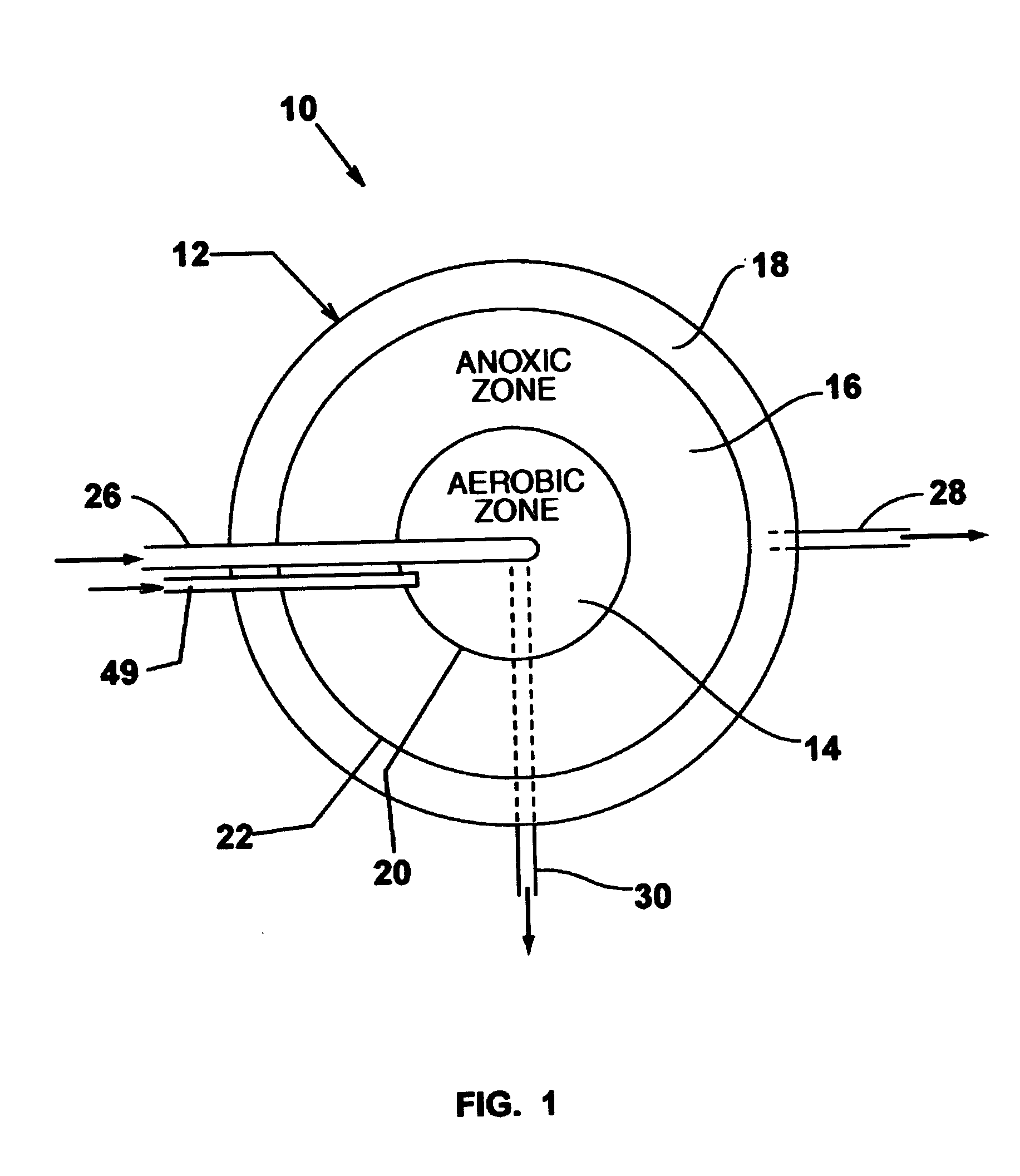
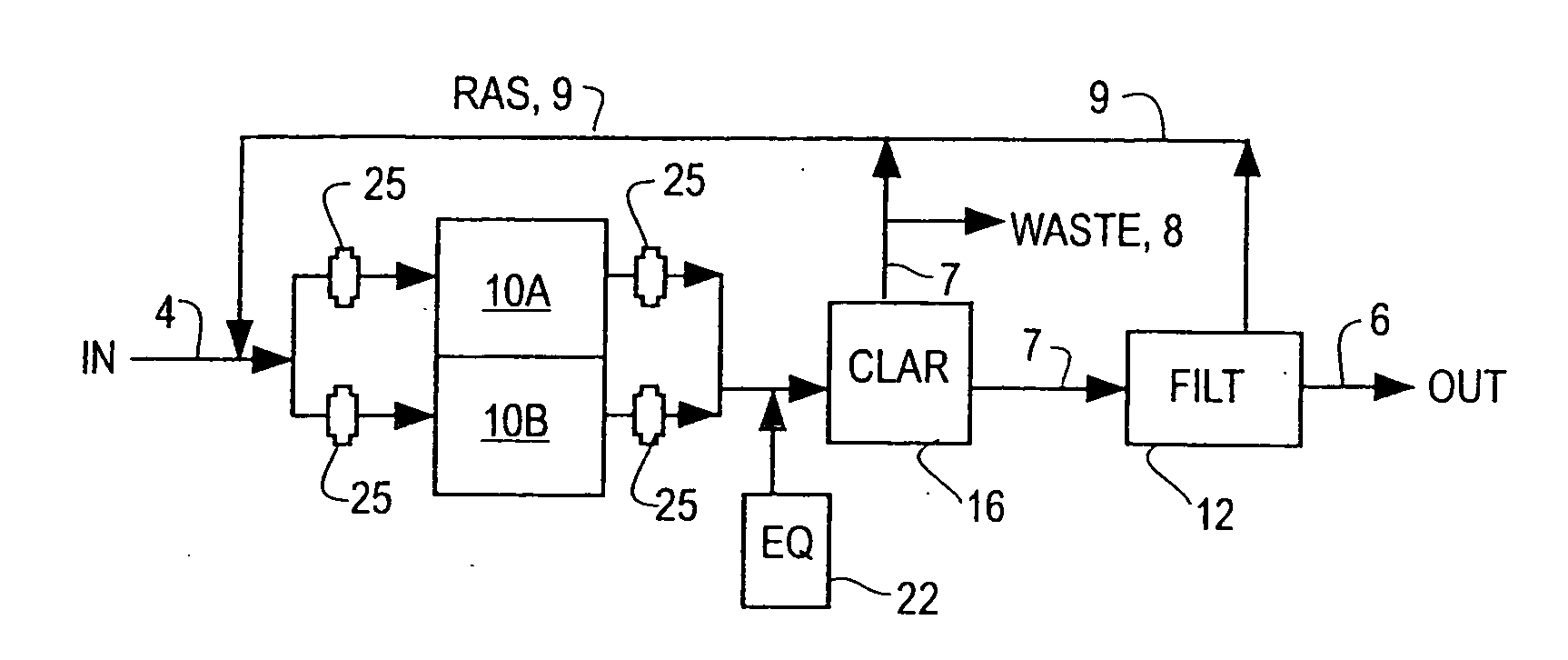
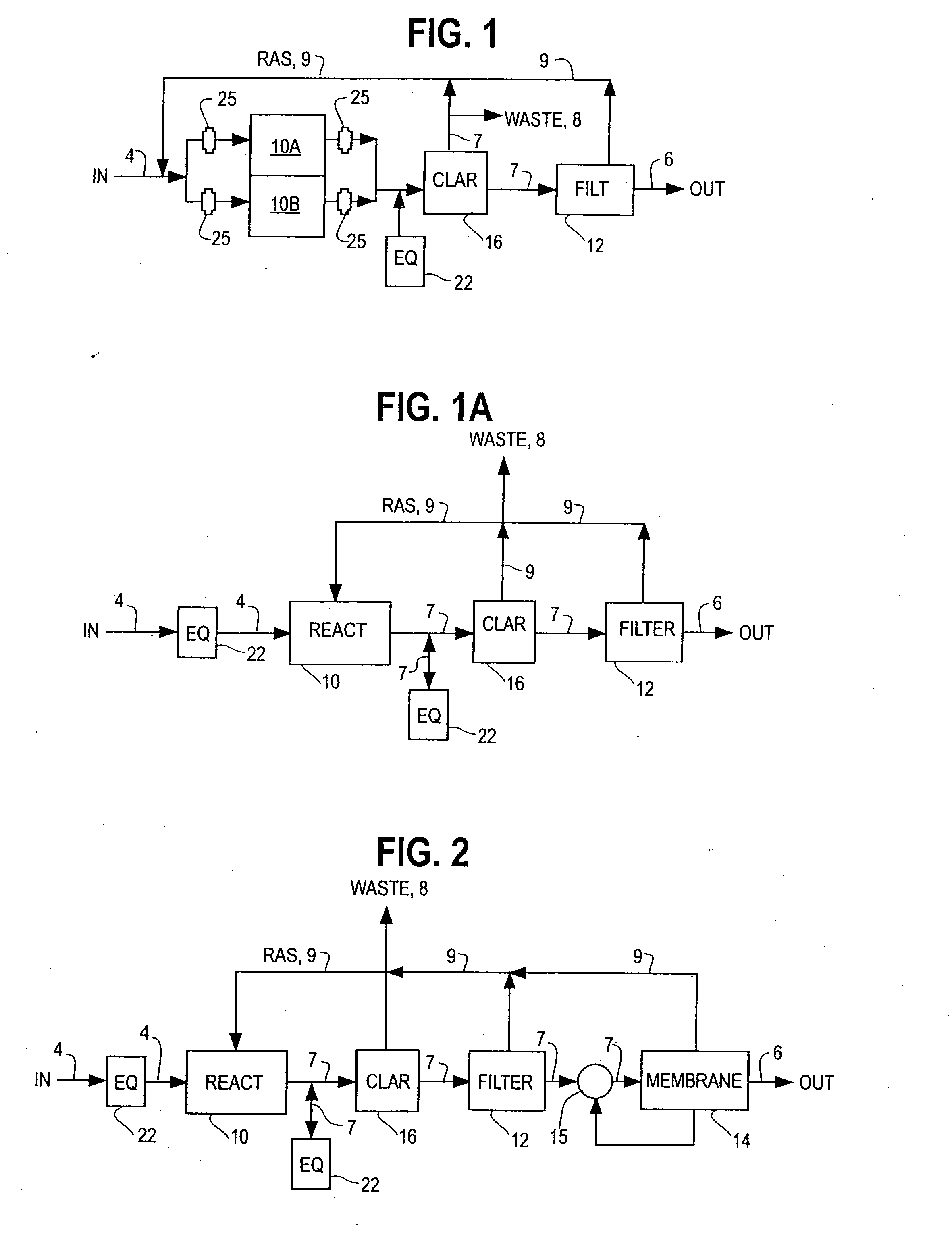
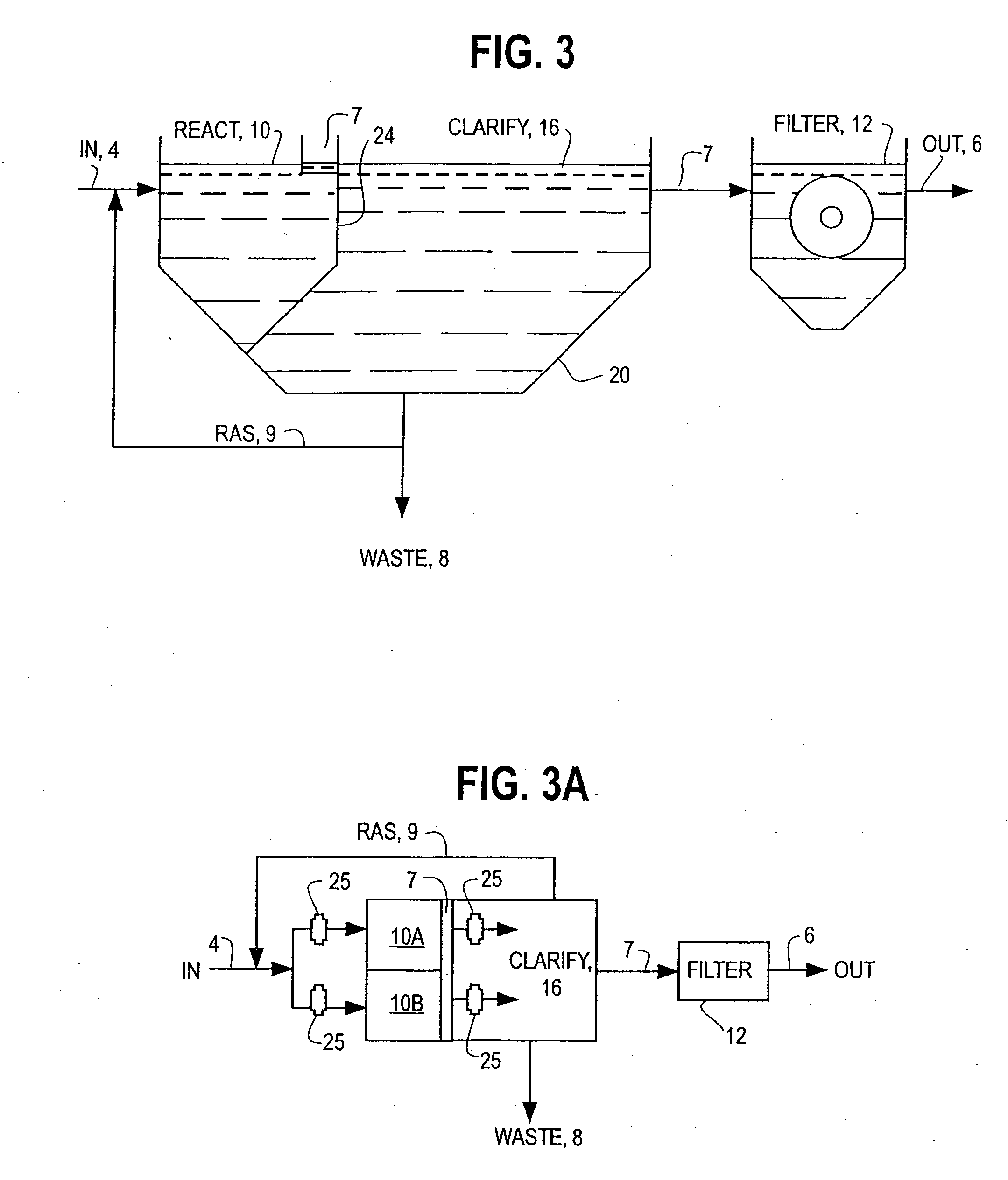
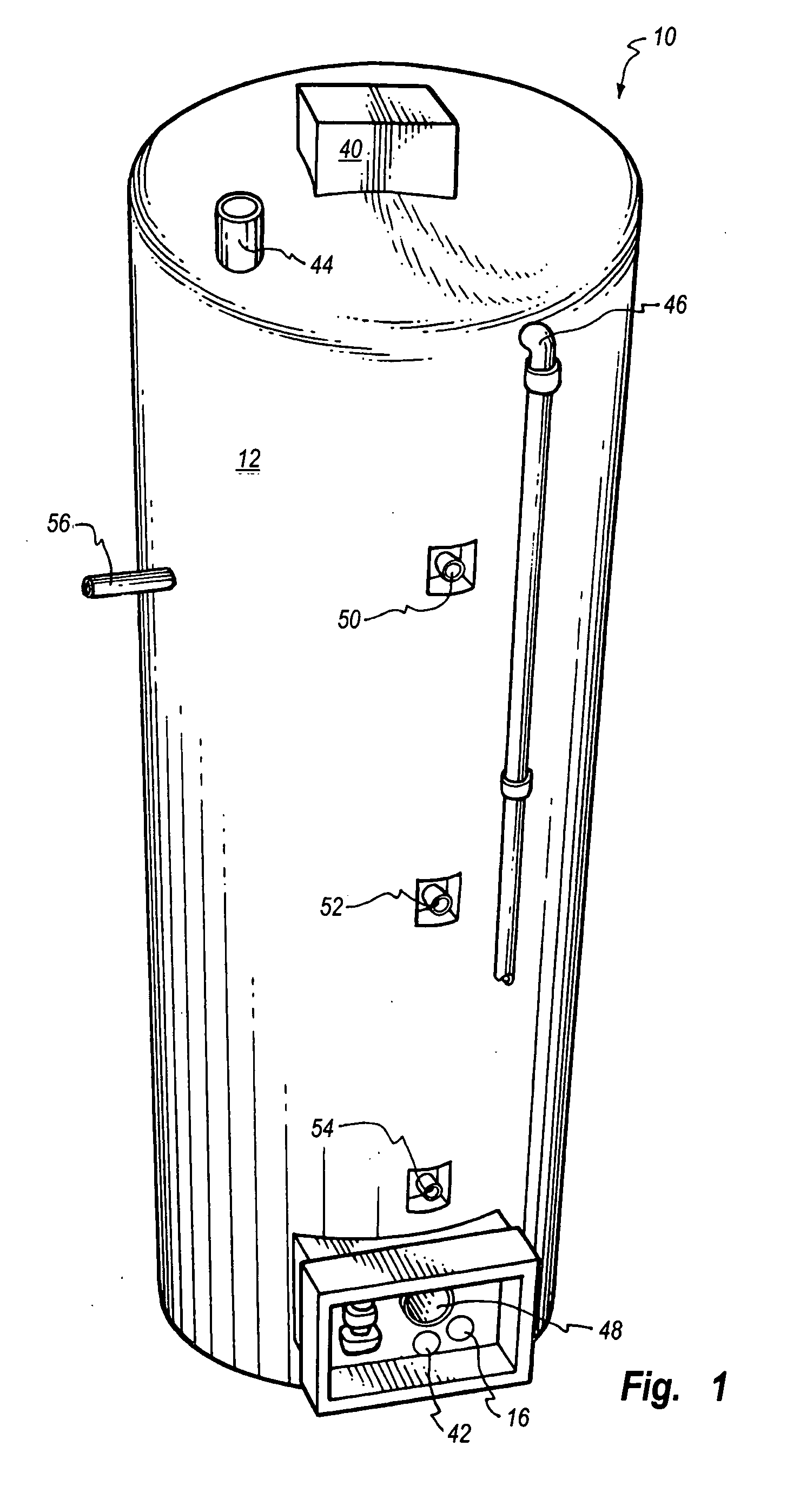
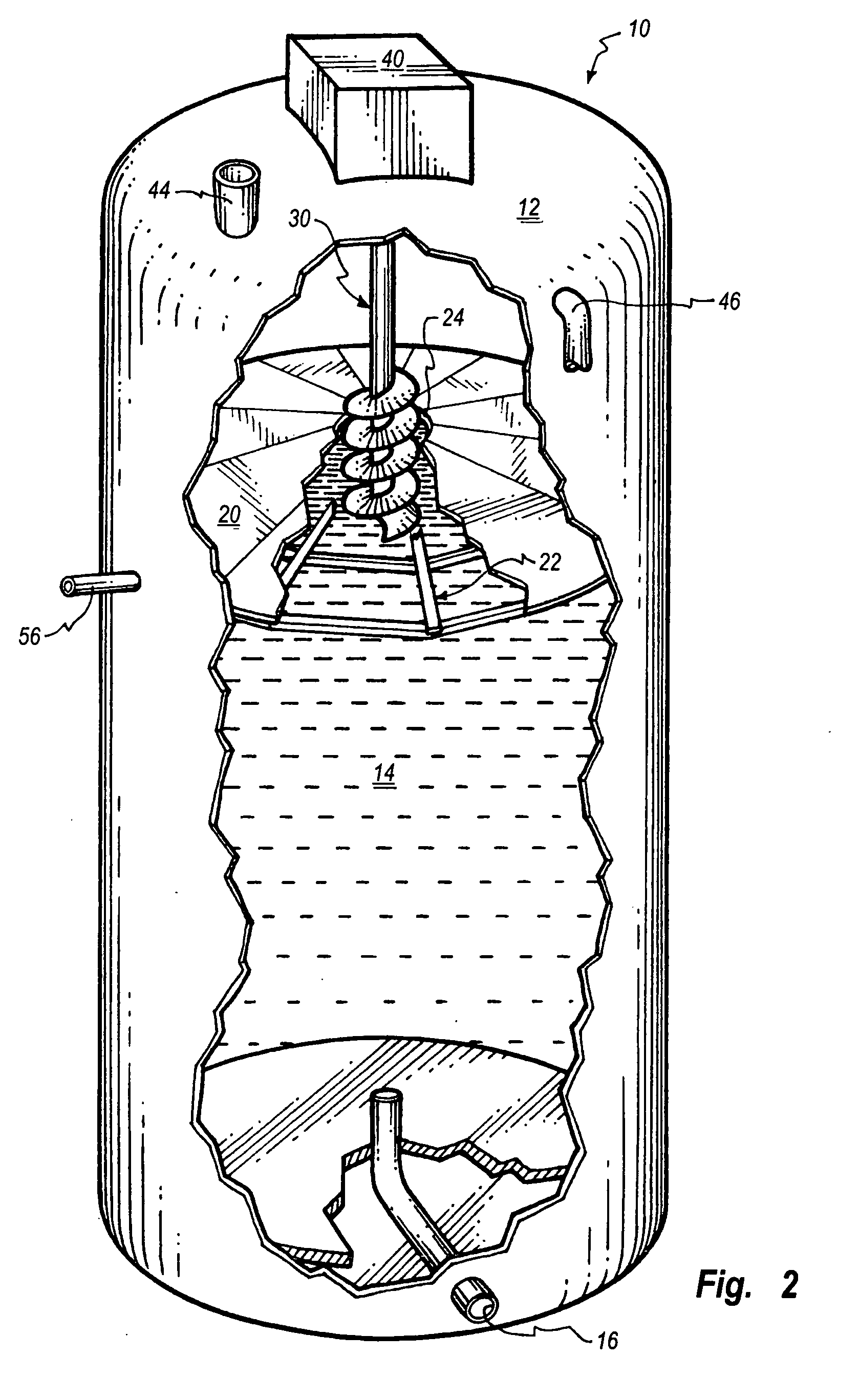
Single vessel multi-zone wastewater bio-treatment system
ActiveUS20050040107A1Suitable for processingSemi-permeable membranesTreatment using aerobic processesSingle vesselNitrate
A process for treating wastewater and a system for practicing the process includes: providing a plurality of zones within a single vessel wastewater treatment system; feeding wastewater into the system; maintaining an aerobic zone in the upper central portion of the vessel; feeding air into the aerobic zone for oxygenation and creating an upflow; maintaining an annularly disposed anoxic zone about said aerobic zone; causing the upflow from the aerobic zone to produce a downflow in the anoxic zone; causing at least a portion of the downflow from the anoxic zone to pass into the upflow of the aerobic zone; maintaining an annularly disposed clarification zone about said anoxic zone for clarified liquid, including an upflow; causing at least a portion of the downflow from the anoxic zone to pass into the upflow of the clarification zone; maintaining a facultative transition zone below the upper aerobic, anoxic and clarification zones; maintaining an anaerobic zone below the facultative zone for absorbing solids settled by gravity and synthesizing volatile fatty acids; withdrawing substantially clarified liquid from the upflow of the clarified liquid zone; withdrawing substantially solids from about the bottom of the anaerobic zone; employing the aerobic zone for breaking down carbon chains and oxidizing volatile fatty acids dispersed from the anaerobic zone; interacting the aerobic and anoxic zones for the removal of nitrates; and interacting the aerobic, anaerobic ananoxic zones for the removal of phosphorus.
Owner:KASPARIAN ANN
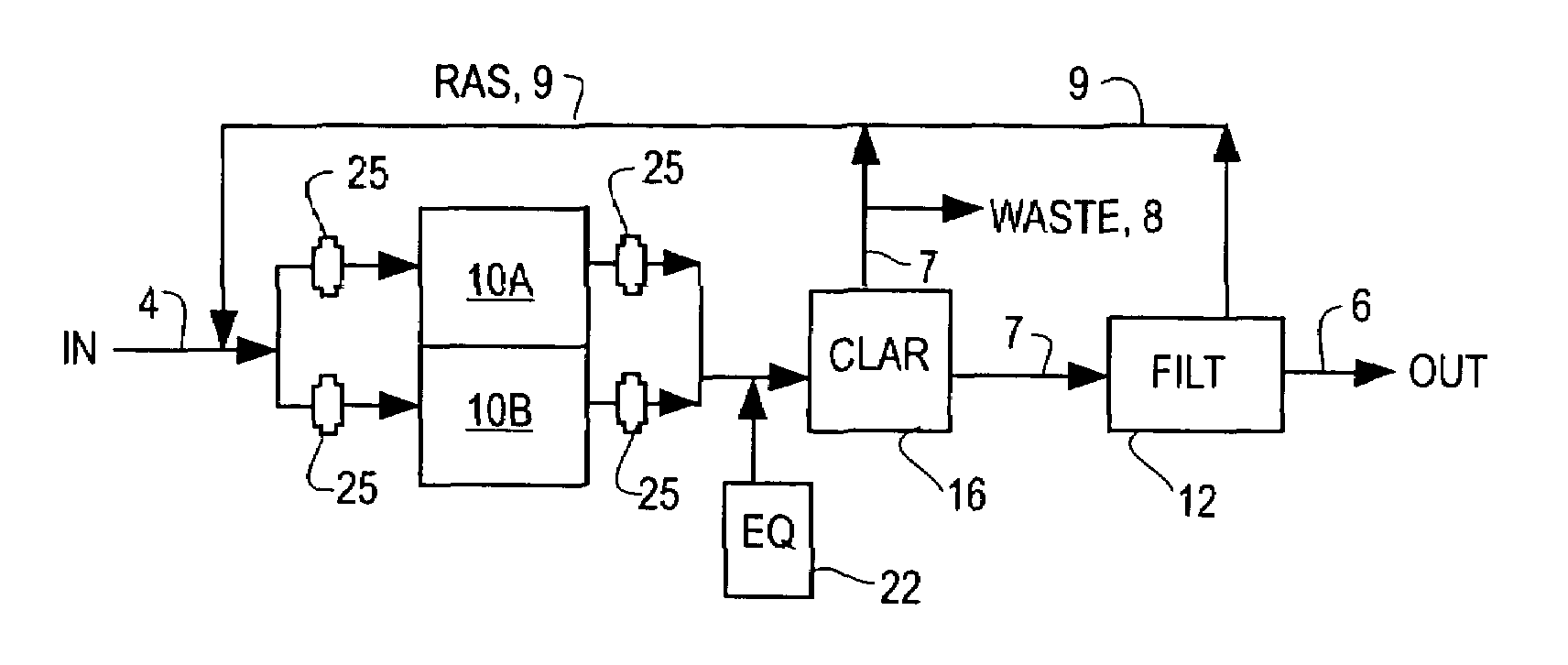
Multiple barrier biological treatment systems
InactiveUS7014763B2Small footprintReduce construction costsTreatment using aerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentSequencing batch reactorSingle vessel
The inventions separate the activated sludge, biochemical reaction stages of the batch treatment process of a sequencing batch reactor from the clarification and sedimentation stages by separating the locations where each process takes place. The separation may be accomplished in a variety of ways including constructing separate basins for each process, installing baffles or other partitions in a single vessel to isolate the areas where each process takes place, or other methods of process separation as are known in the art. In each process, treatment occurs through the performance of a series of operations. The operations are repeated for each batch of wastewater processed by the SBR. In a conventional SBR process, the cycle of operations for clarification and sedimentation are dependent on a preceding biochemical reaction step. However, in the present invention the clarification and sedimentation operations are independent of the biochemical reaction operations. It remains possible to coordinate operations so that the process cycles are coincident, however the benefits of the invention are more readily realized by the practice of independent operation.
Owner:AQUA AEROBIC SYST
Single vessel multi-zone wastewater bio-treatment system
ActiveUS7008538B2Suitable for processingTreatment using aerobic processesMixing methodsSingle vesselNitrate
A process for treating wastewater and a system for practicing the process includes: providing a plurality of zones within a single vessel wastewater treatment system; feeding wastewater into the system; maintaining an aerobic zone in the upper central portion of the vessel; feeding air into the aerobic zone for oxygenation and creating an upflow; maintaining an annularly disposed anoxic zone about said aerobic zone; causing the upflow from the aerobic zone to produce a downflow in the anoxic zone; causing at least a portion of the downflow from the anoxic zone to pass into the upflow of the aerobic zone; maintaining an annularly disposed clarification zone about said anoxic zone for clarified liquid, including an upflow; causing at least a portion of the downflow from the anoxic zone to pass into the upflow of the clarification zone; maintaining a facultative transition zone below the upper aerobic, anoxic and clarification zones; maintaining an anaerobic zone below the facultative zone for absorbing solids settled by gravity and synthesizing volatile fatty acids; withdrawing substantially clarified liquid from the upflow of the clarified liquid zone; withdrawing substantially solids from about the bottom of the anaerobic zone; employing the aerobic zone for breaking down carbon chains and oxidizing volatile fatty acids dispersed from the anaerobic zone; interacting the aerobic and anoxic zones for the removal of nitrates; and interacting the aerobic, anaerobic ananoxic zones for the removal of phosphorus.
Owner:KASPARIAN ANN
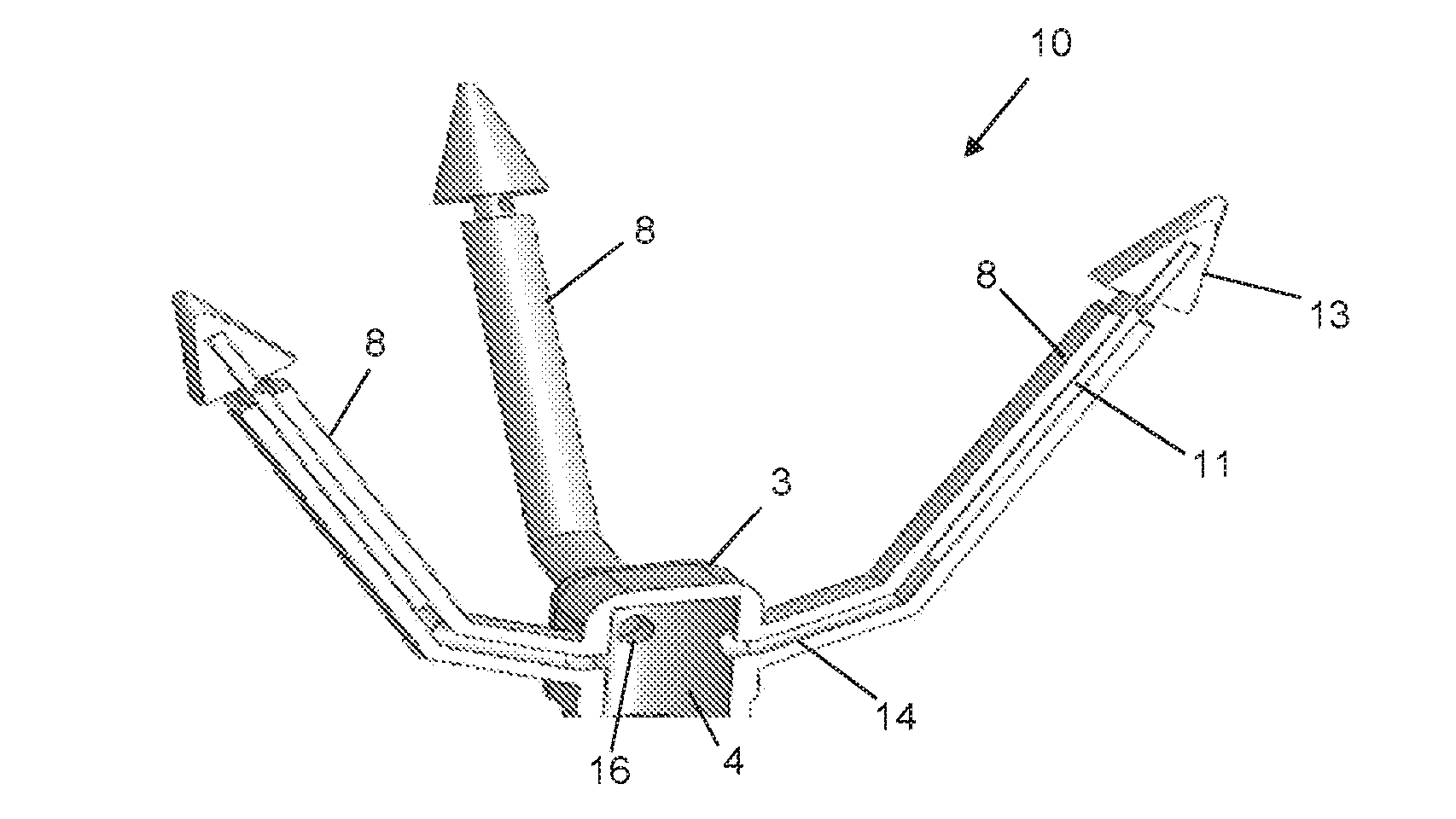
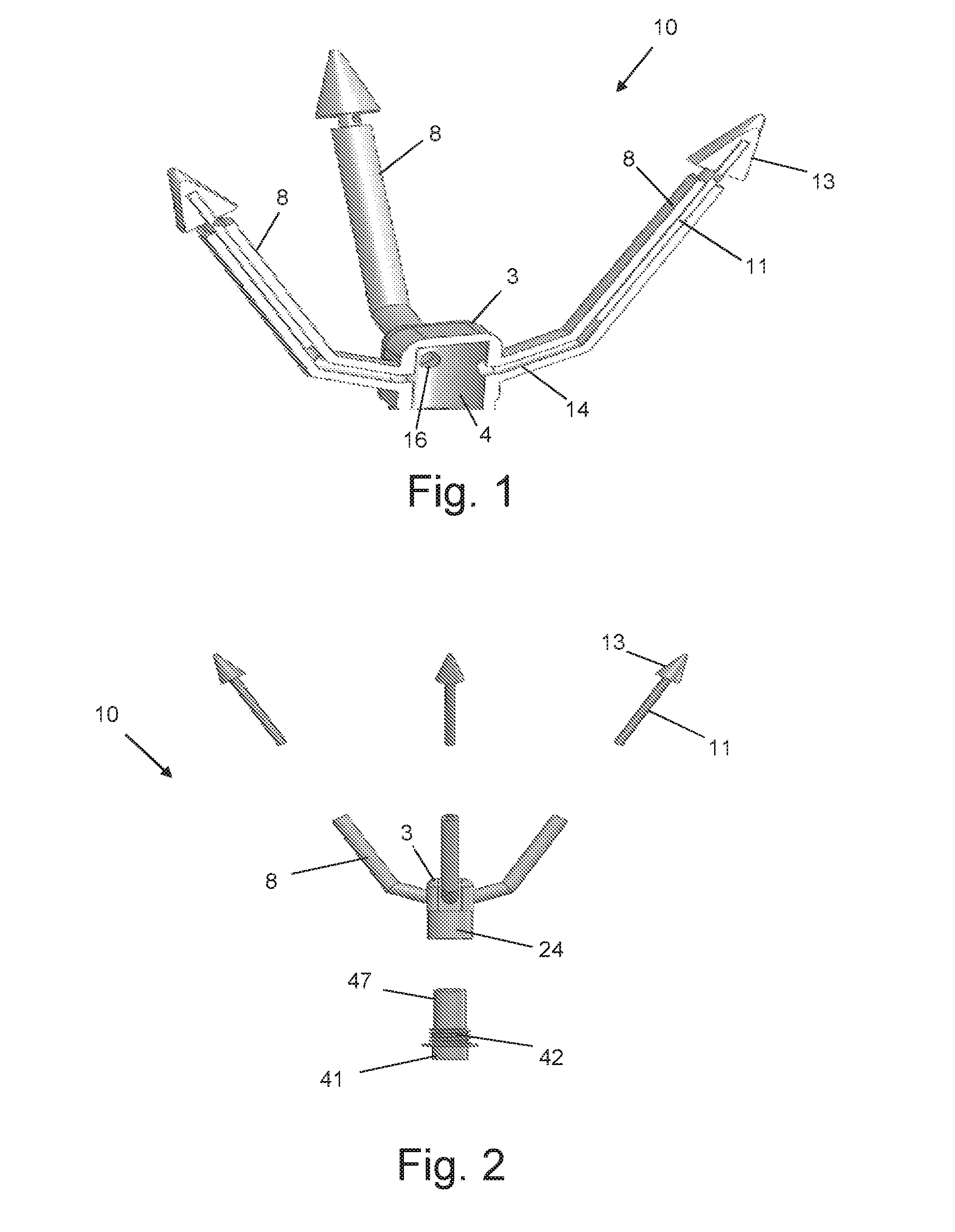
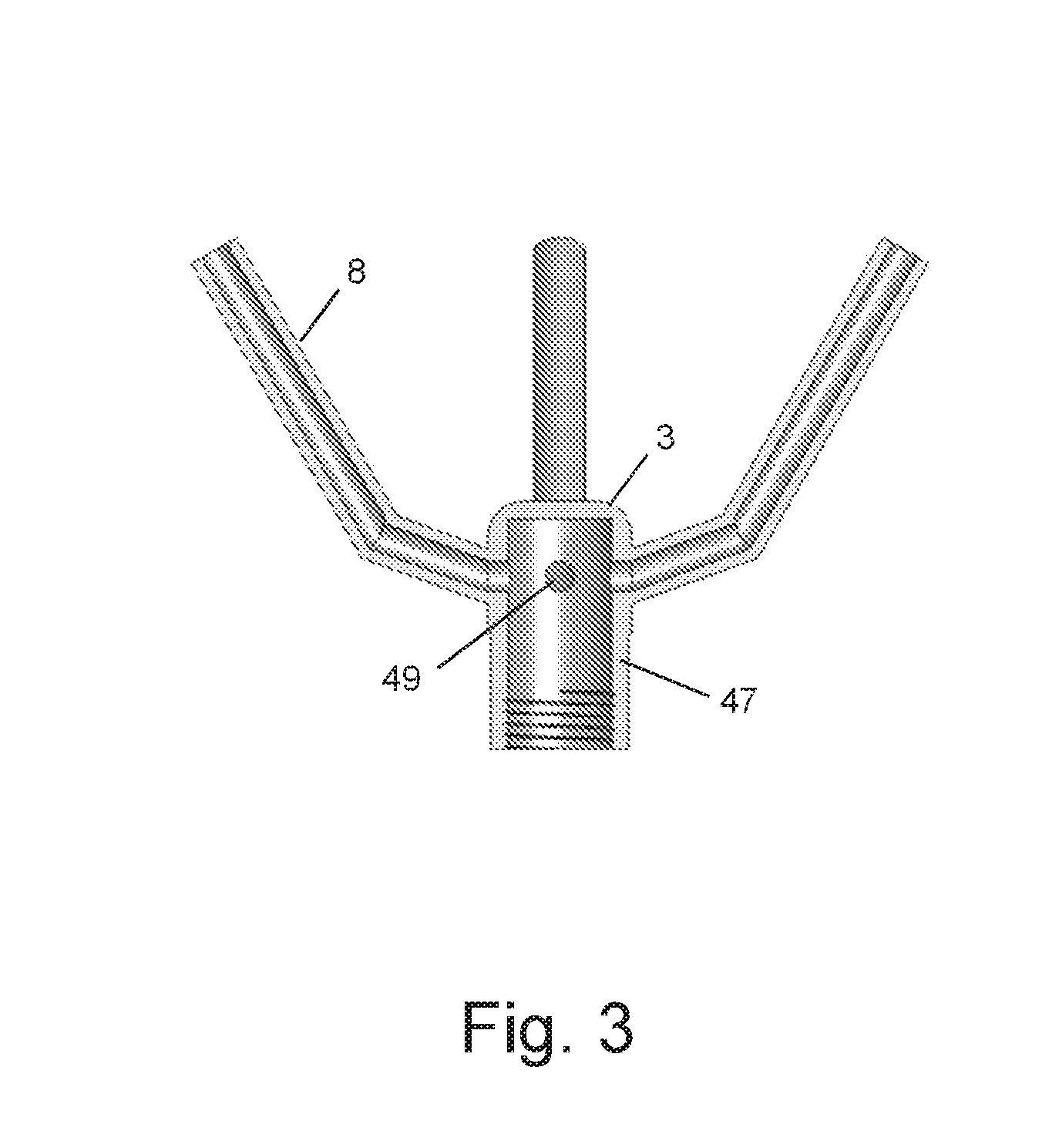
Apparatus and method for rapid deployment of a parachute
The present invention relates to a parachute deploying apparatus, comprising: a) a manifold with which is releasably coupled a single vessel within which pressurized gas is generated; b) a gas generator which cooperates with said vessel; c) a plurality of hollow tubes which extend obliquely and upwardly from, and are in communication with, said manifold; and d) a plurality of projectiles, each of which formed with a rod that is receivable in a corresponding tube and to each of which is connected a cord that is also connected to a corresponding portion of an undeployed parachute, wherein the pressurized gas which is generated upon triggering of said gas generator is flowable through each of said tubes to propel said plurality of projectiles in different directions and to cause said parachute to become deployed.
Owner:PARAZERO LTD
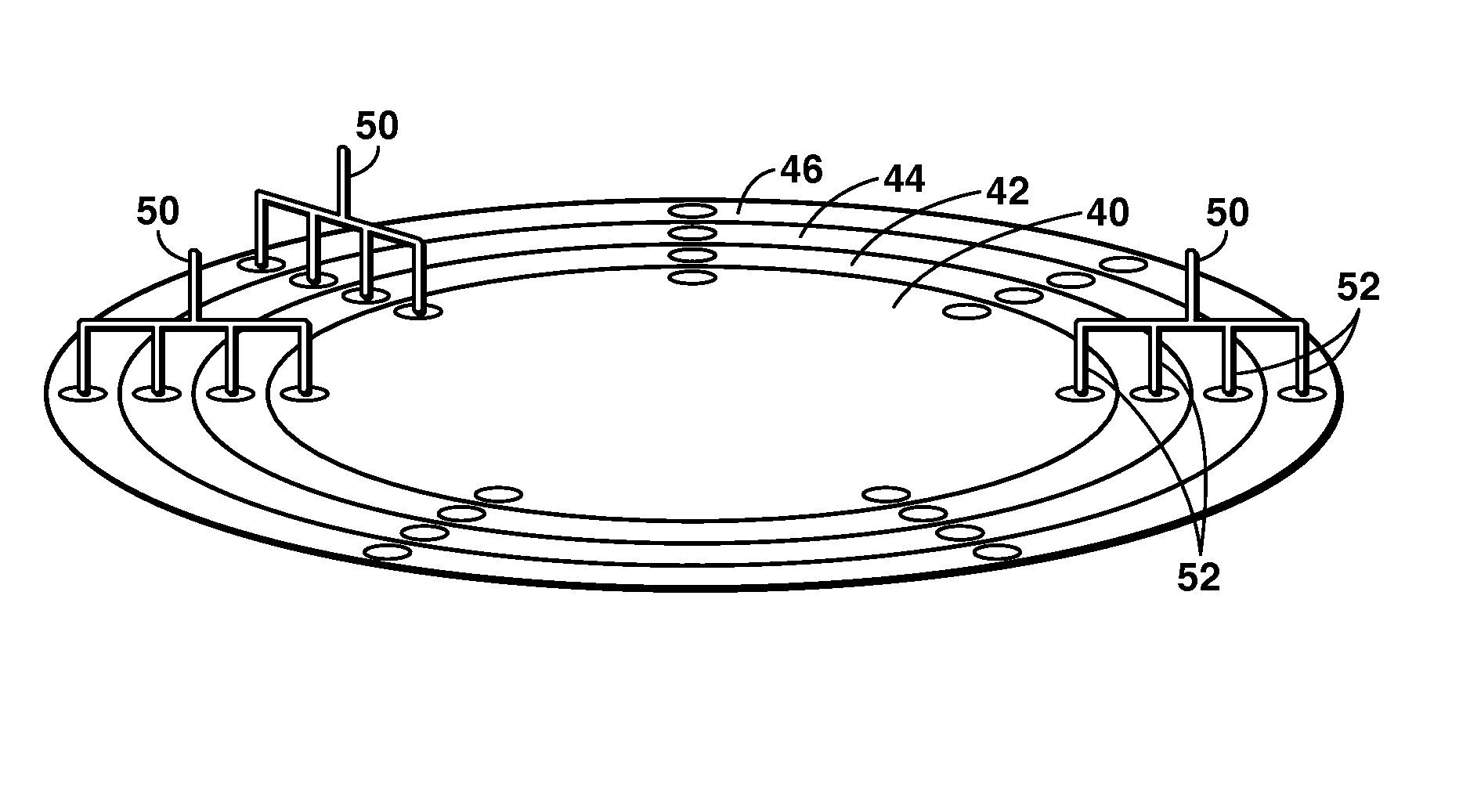
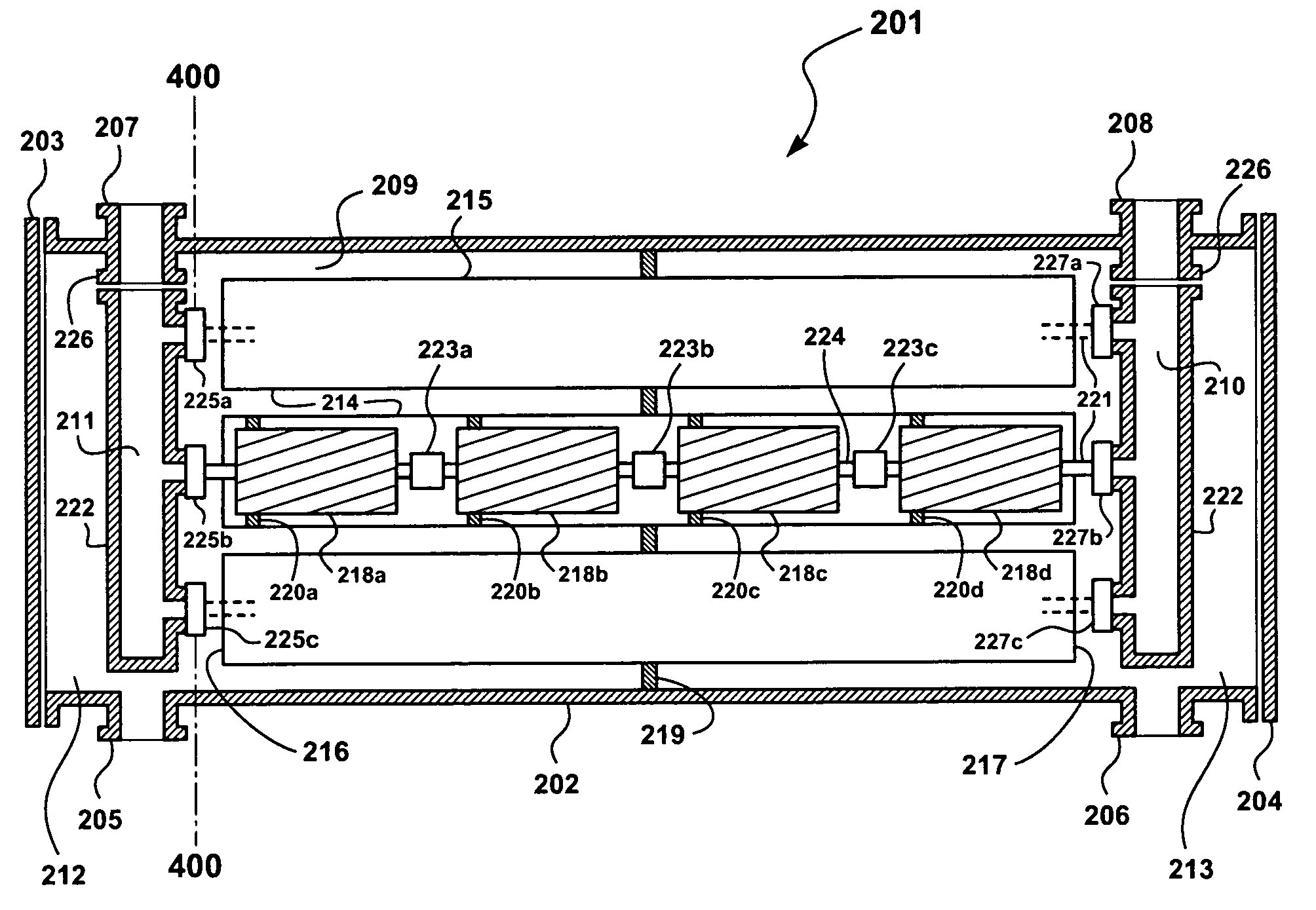
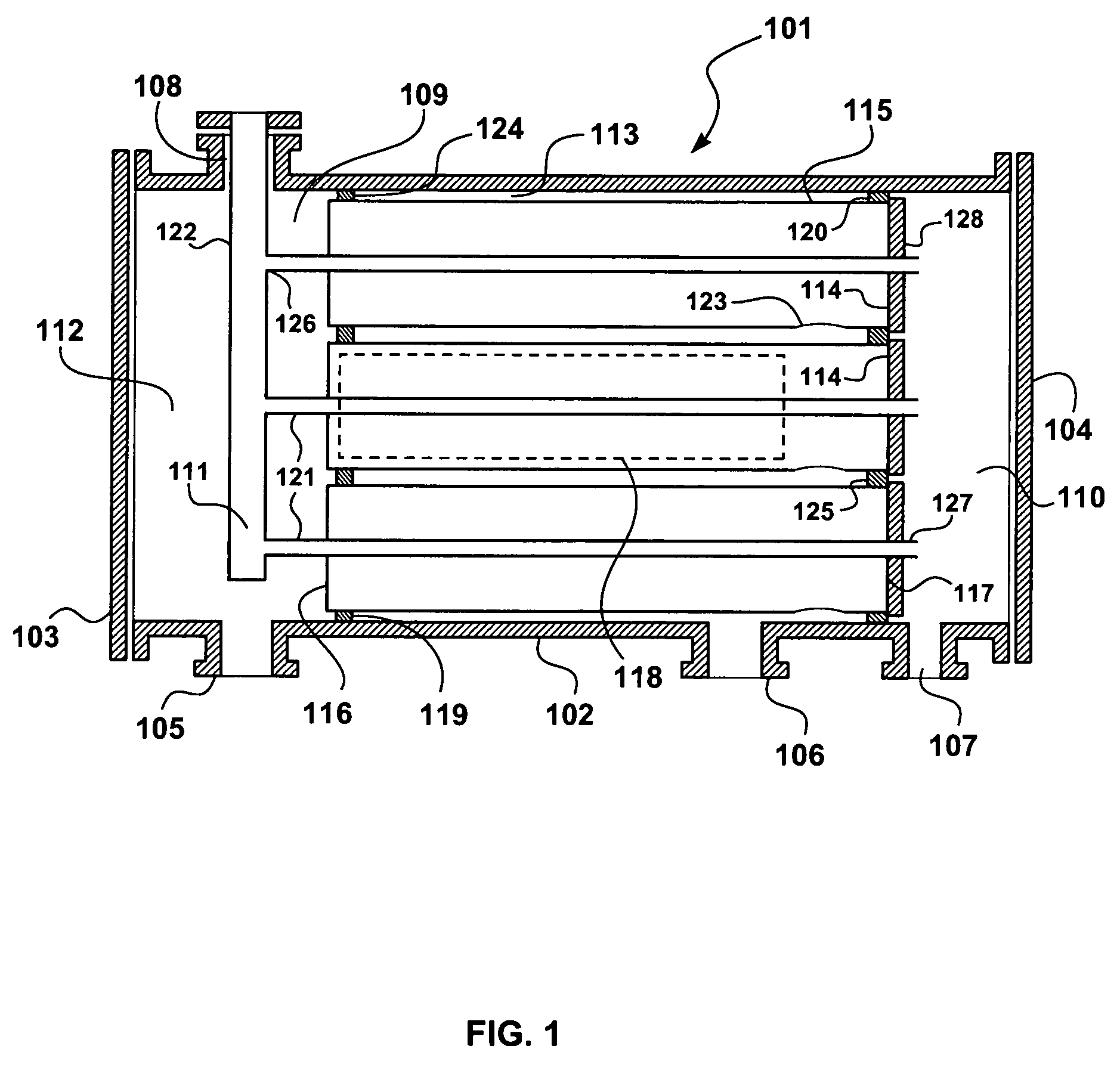
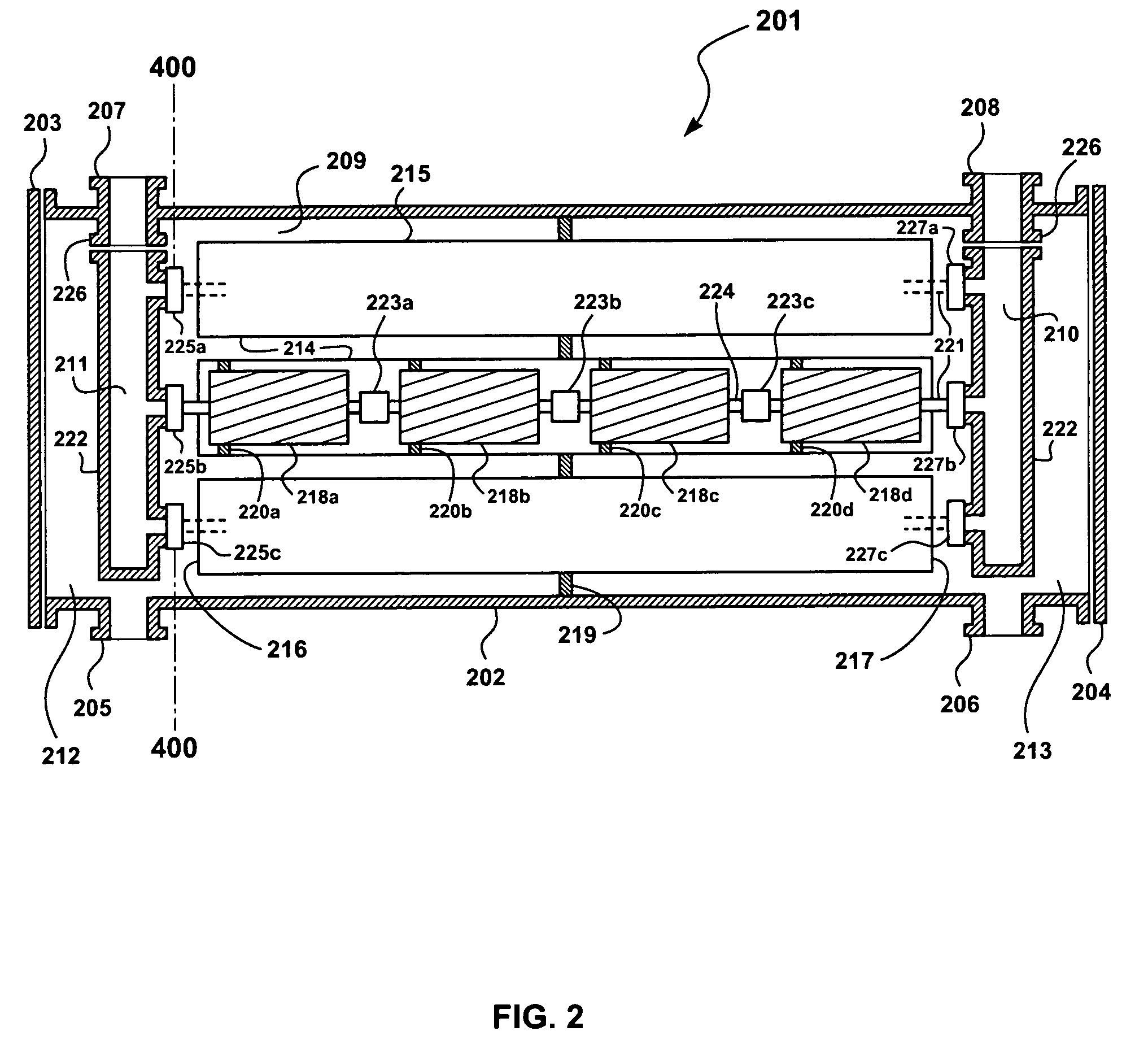
Apparatus and systems having compact configuration multiple swing adsorption beds and methods related thereto
A compact configuration for a plurality of swing adsorption beds. The beds are configured within a single vessel such that one or more beds of adsorbent material are position as successive rings about a first, or core, bed of adsorbent material.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Organic waste material treatment process
InactiveUS7211429B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBio-organic fraction processingSingle vesselPre-condition
An organic waste material treatment process comprising subjecting the organic waste material to conditions under which anaerobic digestion occurs followed by conditions under which aerobic composting occurs. Preferably, the organic waste material is pre-conditioned before anaerobic digestion by subjecting the organic waste material to aerobic composting conditions to facilitate a rise in temperature of the organic waste material. The treatment process is conducted in a single vessel, wherein air and water are evenly distributed to the contents of the vessel. A plurality of vessels may be interconnected, such that water may be extracted from one vessel, whose contents have undergone anaerobic digestion, then recirculated to an interconnected vessel to facilitate conditions for anaerobic digestion of the contents of the interconnected vessel.
Owner:ANAECO
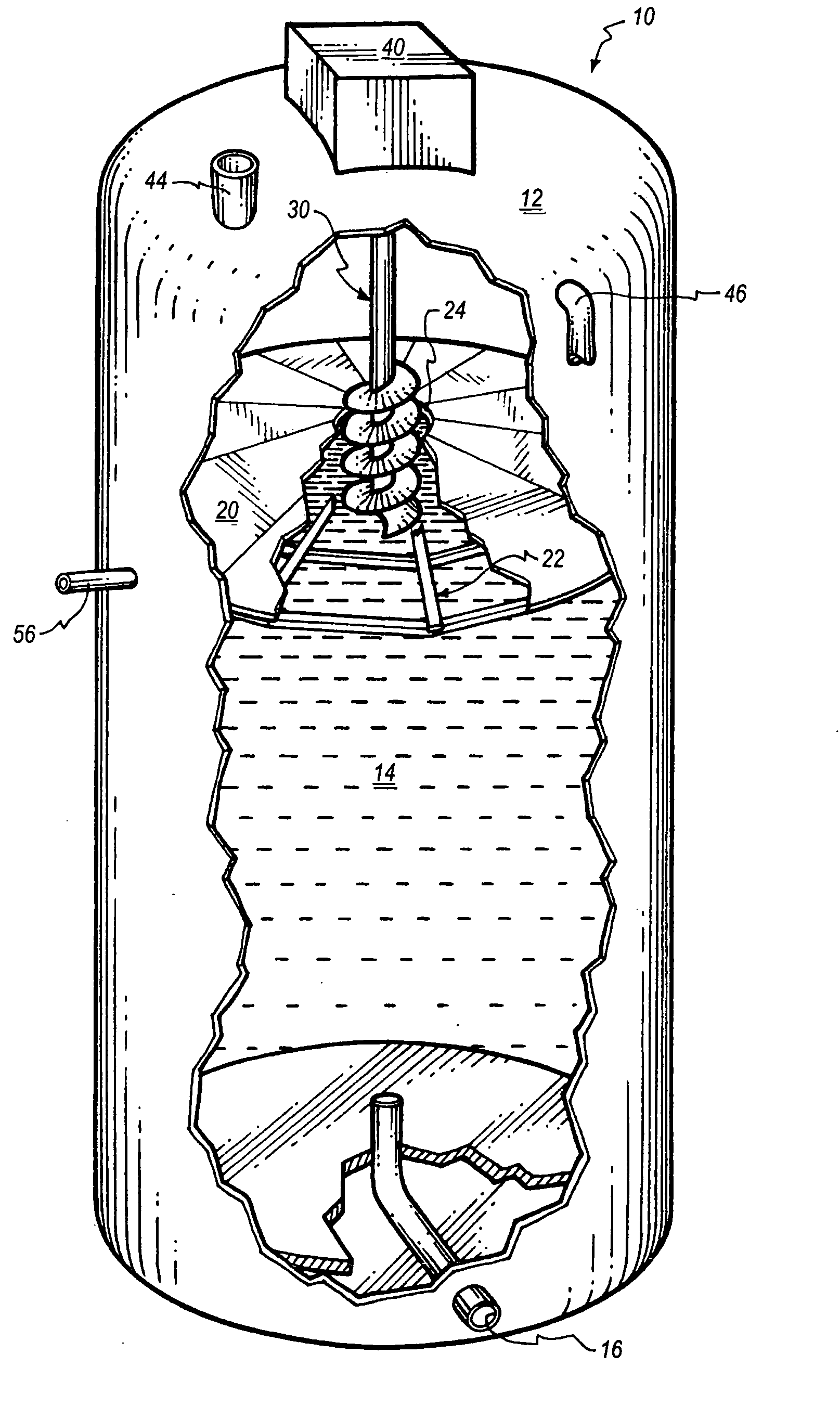
Induced sludge bed anaerobic reactor
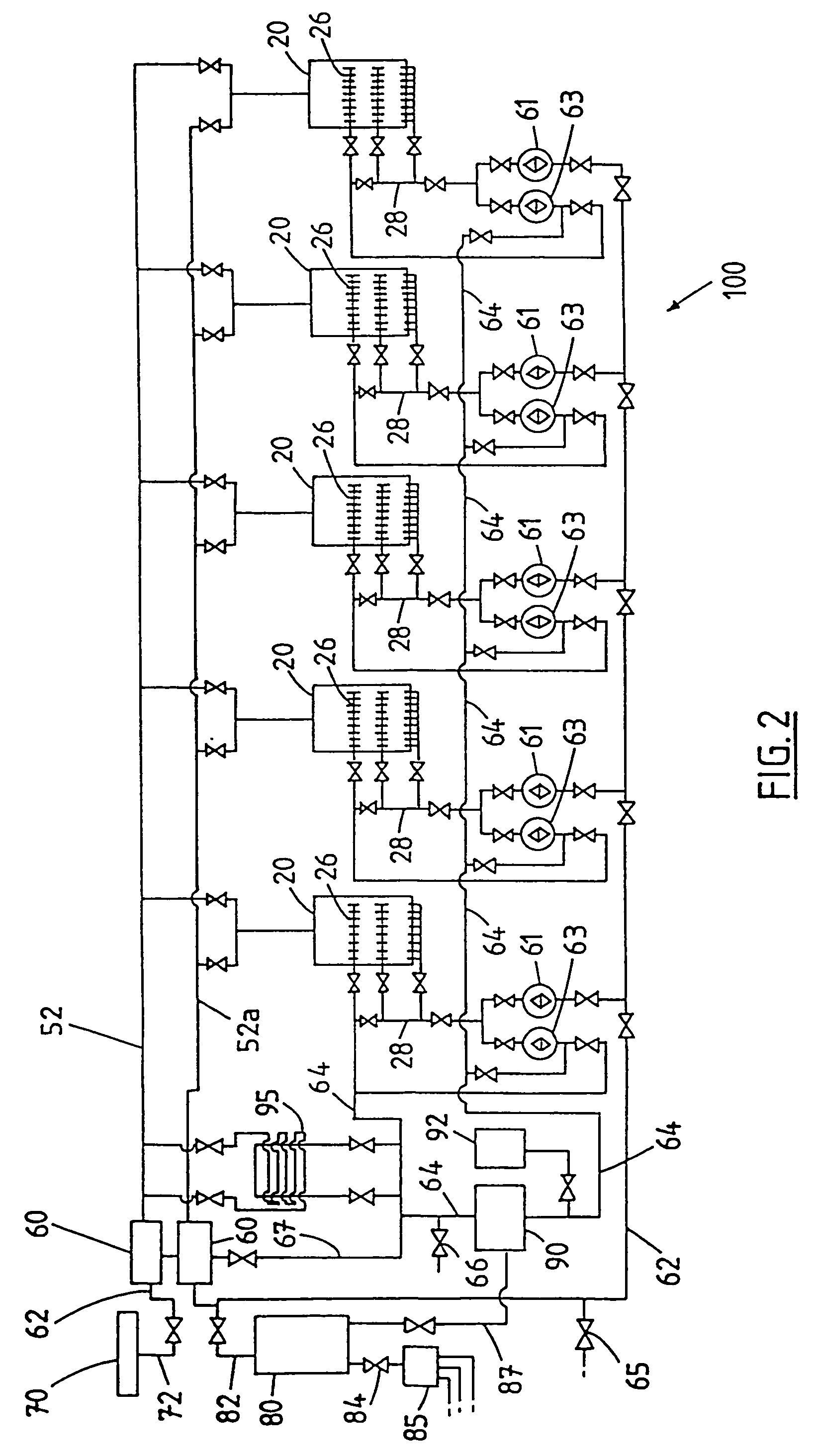
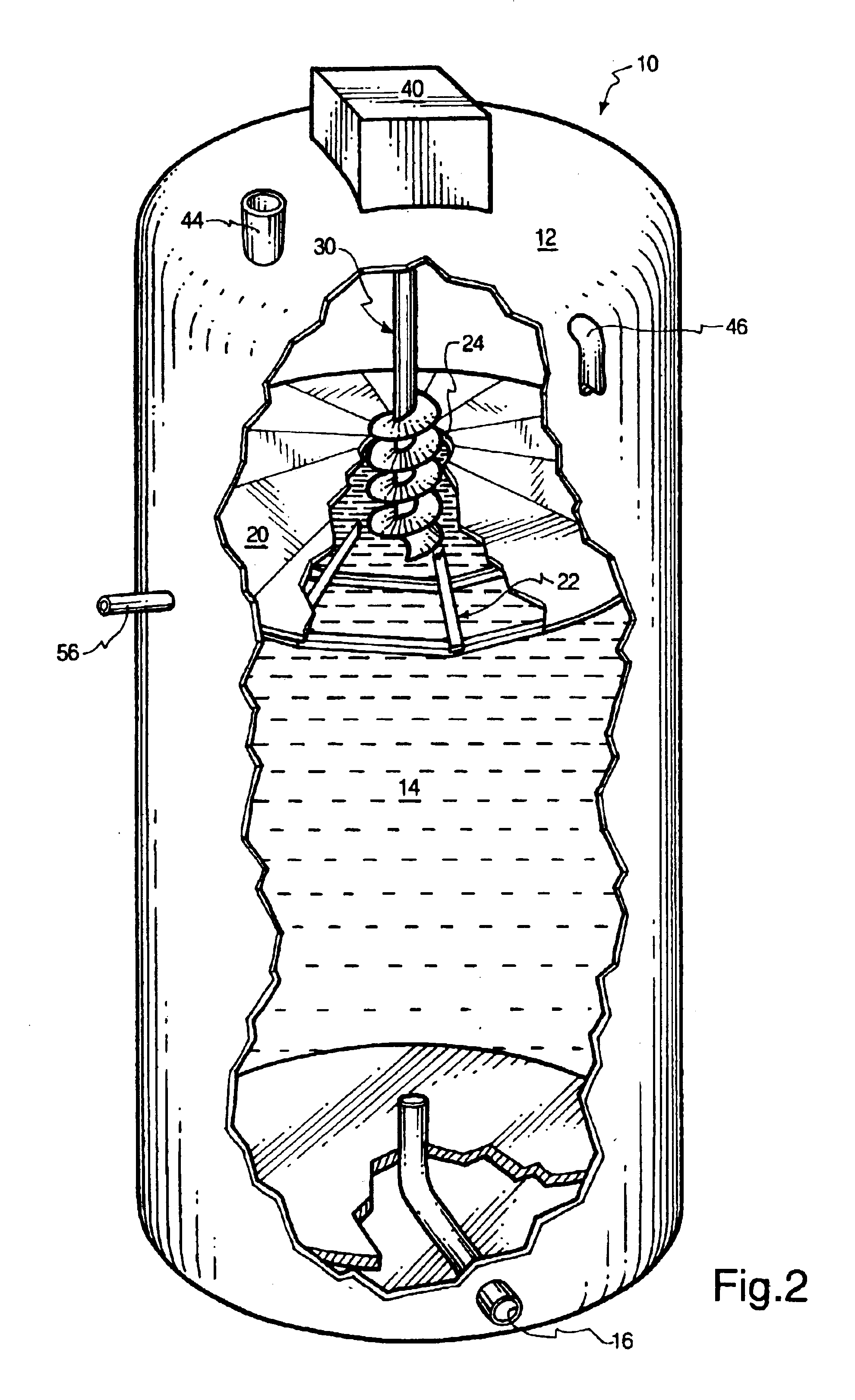
InactiveUS6911149B2Avoid formingWaste based fuelTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesSingle vesselMarine engineering
An induced sludge bed anaerobic reactor includes a vessel in which a septum or other partition is positioned to maintain solids in wastewater being treated toward a lower zone in the reactor. A central aperture is formed in the septum into which a sludge blanket control mechanism, such as an auger, is positioned to force solids to the lower zone of the reactor or, alternatively, pull solids up above the septum so that they can be removed from the vessel, if desired. A mixer may be utilized in connection with the bioreactor to mix the contents and prevent a crust from forming at the top of the bioreactor. Still further, a wall may be positioned to extend above the septum around its perimeter to assist in separating solids from the wastewater. The various types of bacteria used in the anaerobic process may also be separated, according to the present invention, in either a single vessel or multiple vessels so that the conditions of each respective vessel can be altered as desired.
Owner:UTAH STATE UNIVERSITY
Induced sludge bed anaerobic reactor
InactiveUS7452467B2Avoid formingEasy to separateLiquid degasificationGas production bioreactorsSingle vesselAnaerobic reactor
An induced sludge bed anaerobic reactor includes a vessel in which a septum or other partition is positioned to maintain solids in wastewater being treated toward a lower zone in the reactor. A gas trap, which may also comprise an overpressure protection device, may be arranged at an outlet of the vessel. A distribution plate may be located at an inlet. A central aperture is formed in the septum into which a plug control mechanism, such as an auger, may be positioned to force solids to the lower zone of the reactor or, alternatively, pull solids up above the septum so that they can be removed from the vessel, if desired. A mixer may be utilized in connection with the bioreactor to mix the contents and prevent a crust from forming at the top of the bioreactor. Still further, a wall may be positioned to extend above the septum around its perimeter to assist in separating solids from the wastewater. The various types of bacteria used in the anaerobic process may also be separated, according to the present invention, in either a single vessel or multiple vessels so that the conditions of each respective vessel can be altered as desired.
Owner:ANDIGEN +1
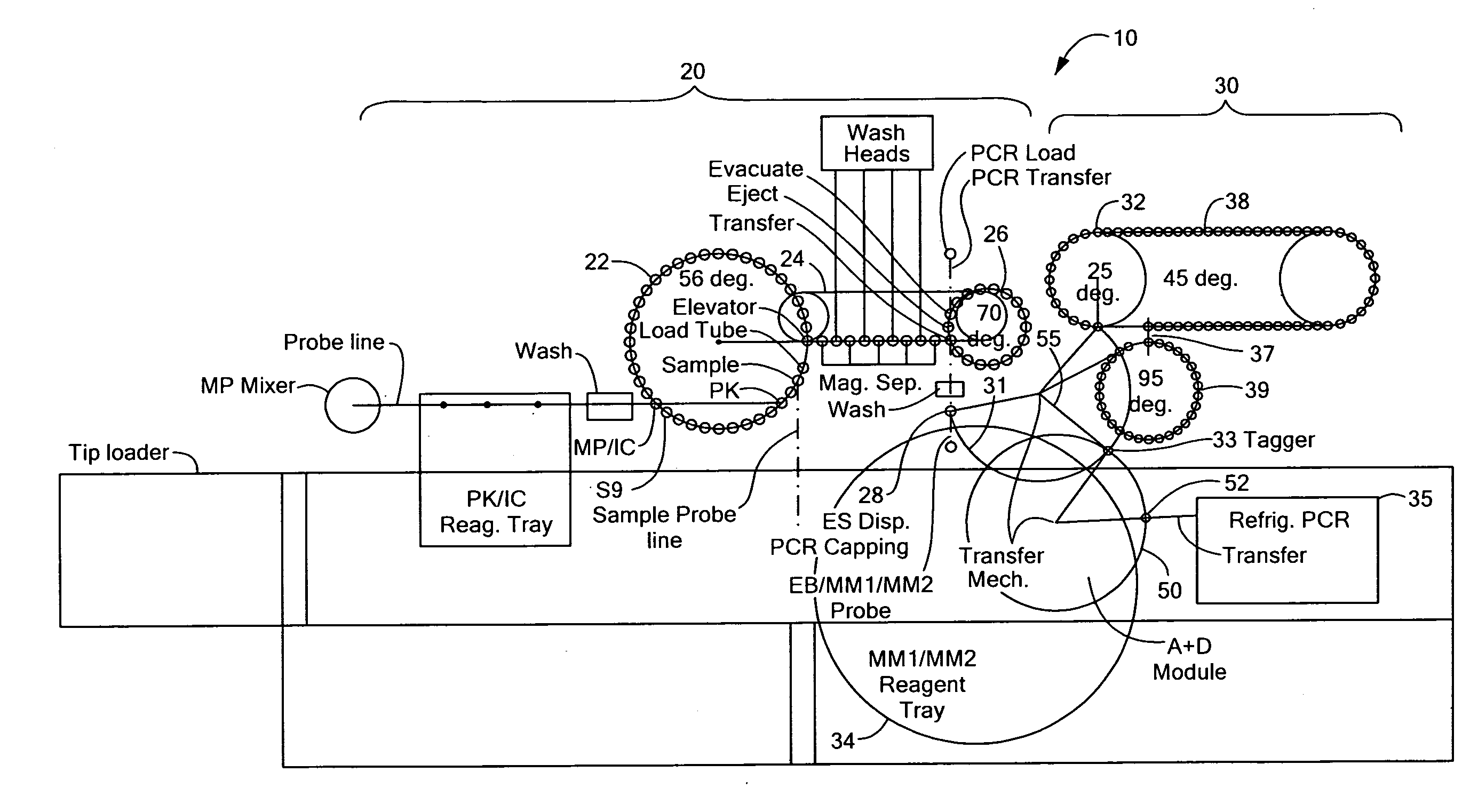
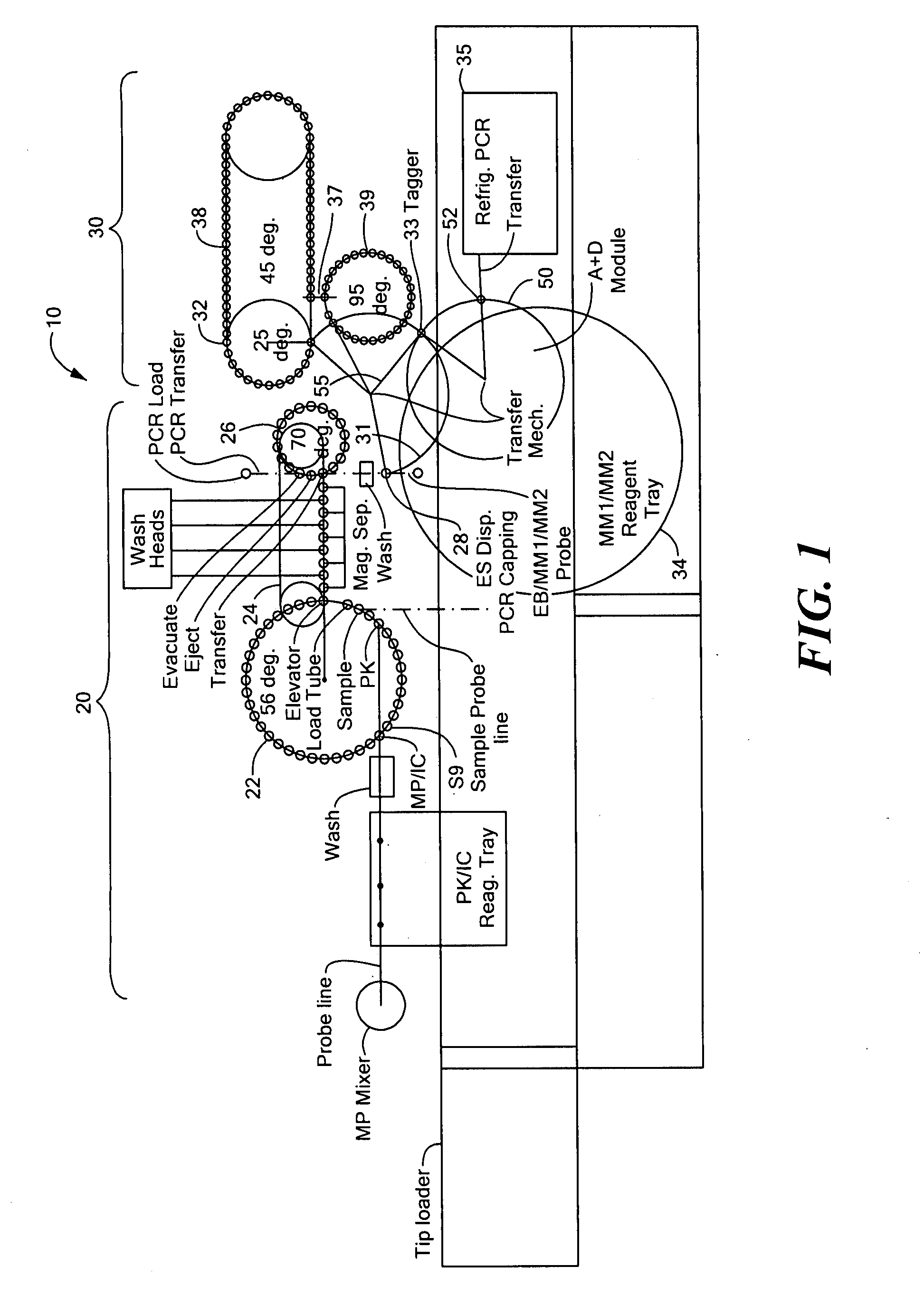
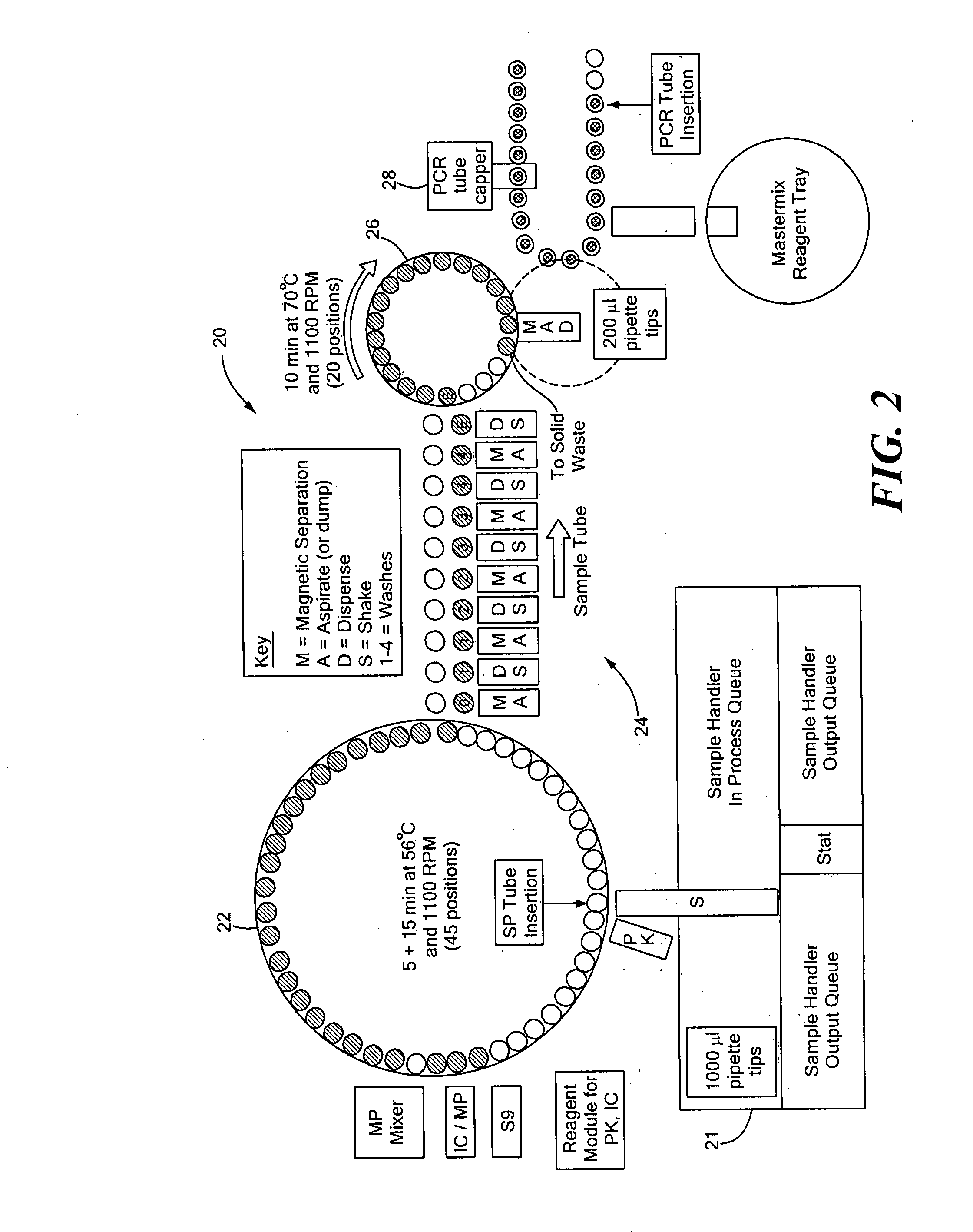
Random access system and method for polymerase chain reaction testing
ActiveUS20100112567A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSingle vesselElution
A random access, high-throughput system and method for preparing a biological sample for polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing are disclosed. The system includes a nucleic acid isolation / purification apparatus and a PCR apparatus. The nucleic acid isolation / purification apparatus magnetically captures nucleic acid (NA) solids from the biological sample and then suspends the NA in elution buffer solution. The PCR testing apparatus provides multiple cycles of the denaturing, annealing, and elongating thermal cycles. More particularly, the PCR testing apparatus includes a multi-vessel thermal cycler array that has a plurality of single-vessel thermal cyclers that is each individually-thermally-controllable so that adjacent single-vessel thermal cyclers can be heated or cooled to different temperatures corresponding to the different thermal cycles of the respective PCR testing process.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
Domestic bar door of refrigerator
InactiveCN1699901AImprove convenienceEasy accessLighting and heating apparatusDomestic refrigeratorsInterior spaceSingle vessel
This invention provides a household taproom door with refrigerator, the structure of which includes the refrigerator door, which is arranged at the front of the refrigerator to open and close and keep the proper temperature inside it; and the household taproom, which forms on the refrigerator door with single vessel box, wherein the refrigerator door has a front opened guiding machine which guides it sliding to open and close the vessel box; and the front part of the household taproom door has a monitor that displays all kinds of information. The effect of this invention is that fetching drink is convenient, and seeing all kinds of information on the monitor at any moment.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS (TIANJIN) APPLIANCES CO LTD
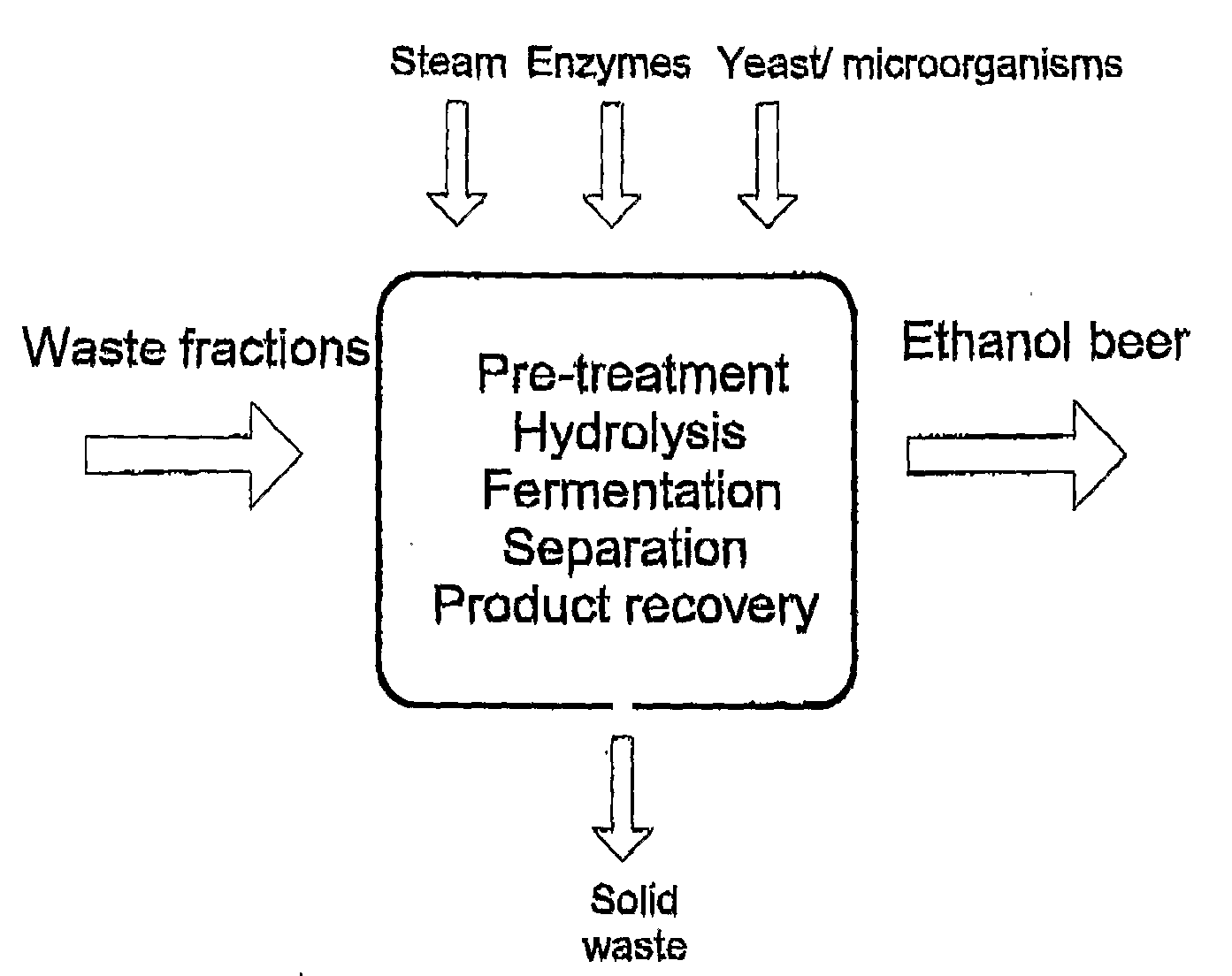
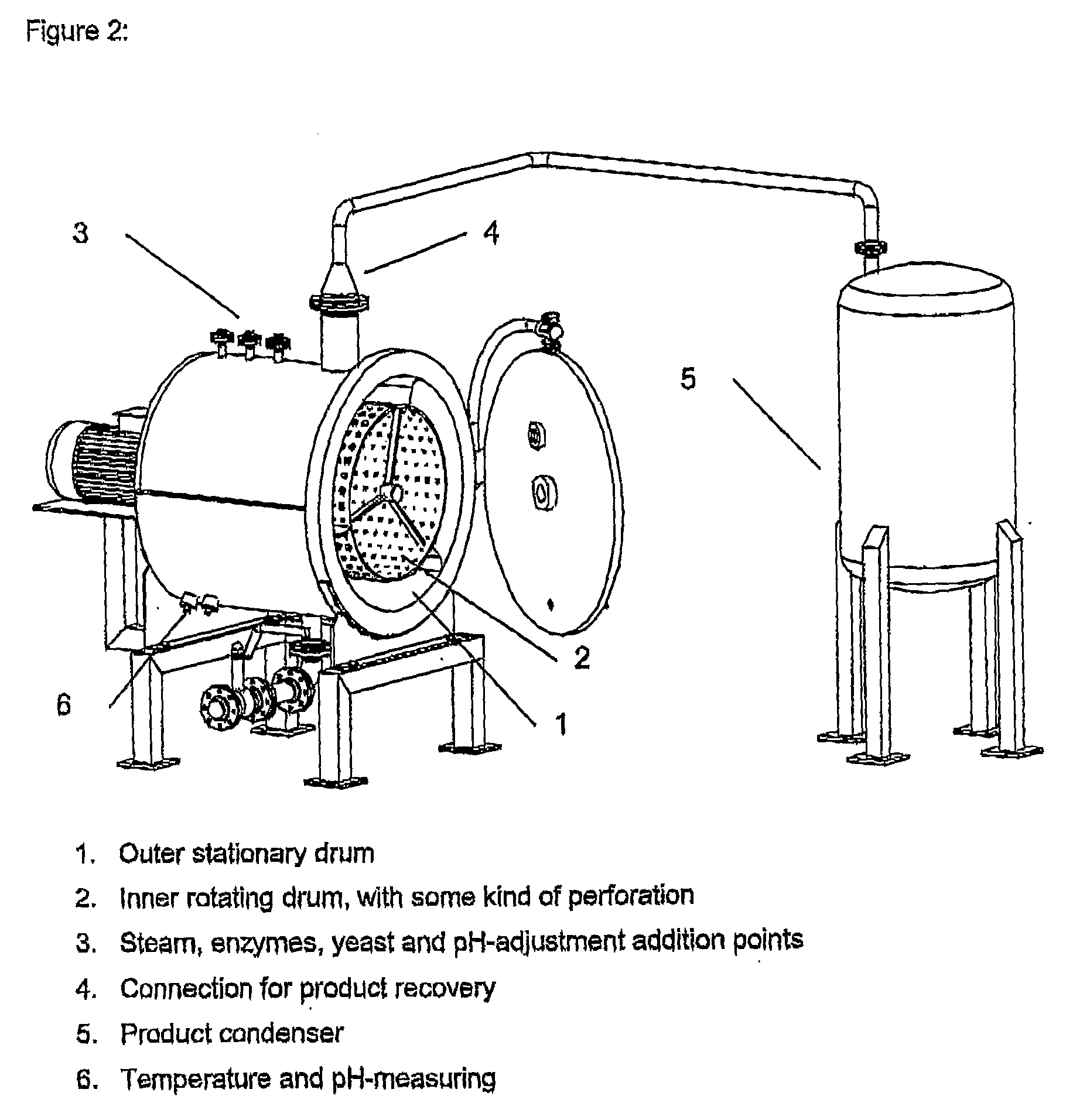
Non-Pressurised Pre-Treatment, Enzymatic Hydrolysis and Frementation of Waste Fractions
ActiveUS20090004714A1Effective treatmentBiological substance pretreatmentsHydrolasesSingle vesselFree falling
The present invention relates to a process for production of fermentation products, including bioethanol by non-pressurised pre-treatment, enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation of waste fractions containing mono- and / or polysaccharides, having a relatively high dry matter content. The process in its entirety, i.e. from non-pressurised pre-treatment over enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation to sorting of fermentable and non-fermentable solids can be processed at a relatively high dry matter content in a single vessel or similar device using free fall mixing for the mechanical processing of the waste fraction.
Owner:DONG ENERGY POWER AS +1
Apparatus and method for hydrolysis of cellulosic material in a multi-step process to produce c5 and c6 sugars using a single vessel
InactiveUS20090308383A1Undesirable effectFructose productionSugar juice extraction using extracting agentsCelluloseSingle vessel
Owner:ANDRITZ INC
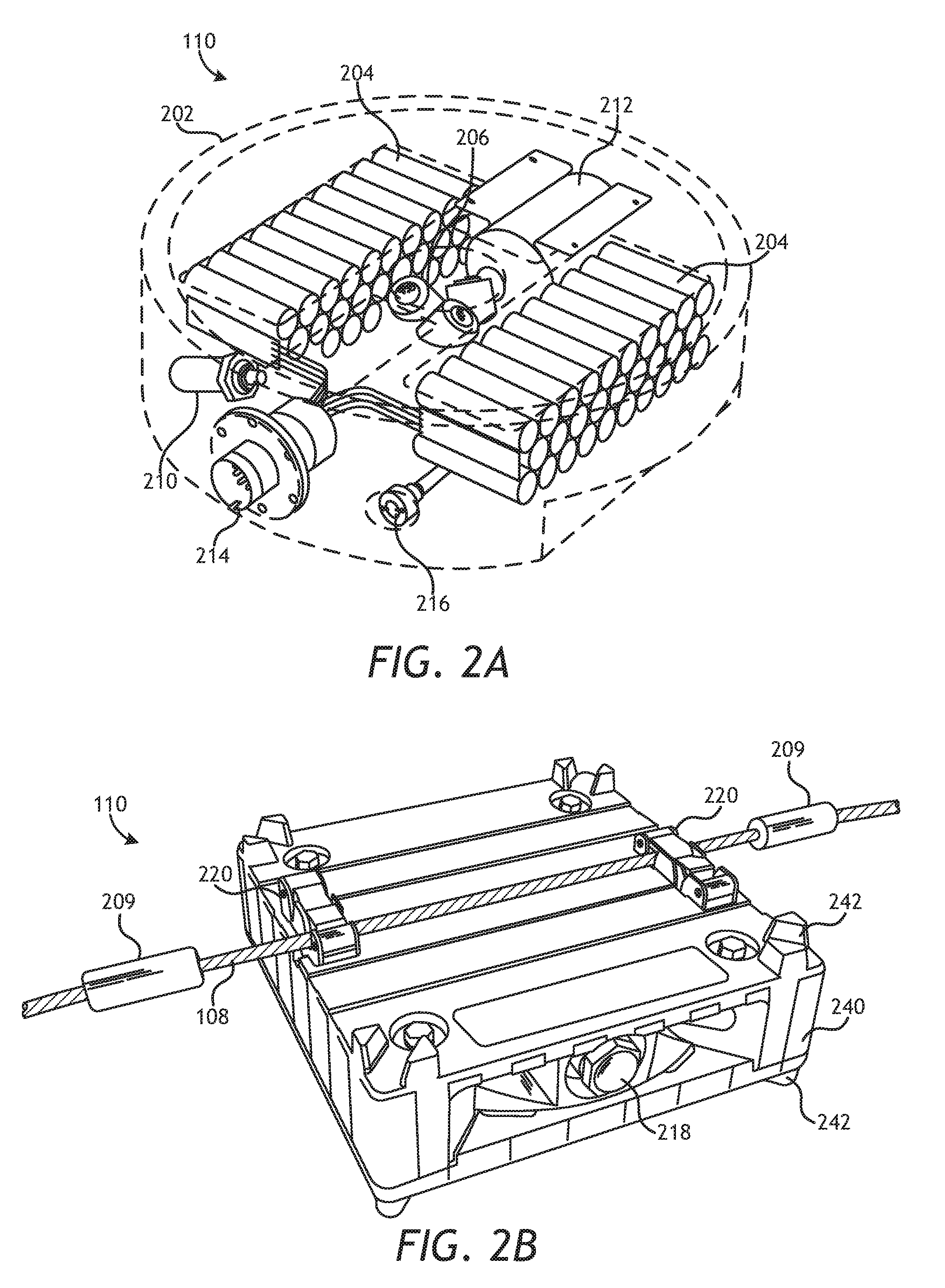
Single vessel range navigation and positioning of an ocean bottom seismic node
Apparatuses, systems, and methods for monitoring, positioning, and / or guiding a plurality of seismic nodes on or near the seabed by a plurality of acoustic pinging devices coupled to a deployment line and at least one surface buoy. The acoustic pinging devices are configured to emit a unique ID that may be detected by a receiver or transceiver located on each of the surface buoys. The acoustic pinging devices may be coupled to each node or only to a portion of the plurality of nodes (such as every two, three, or four nodes). The monitoring system may be configured to identify the ID, position, depth, and height of each seismic node during travel to the seabed and upon node touchdown with the seabed. A guidance system may be configured to guide the deployment of the deployment cable based upon node position data determined by the monitoring system.
Owner:SEABED GEOSOLUTIONS
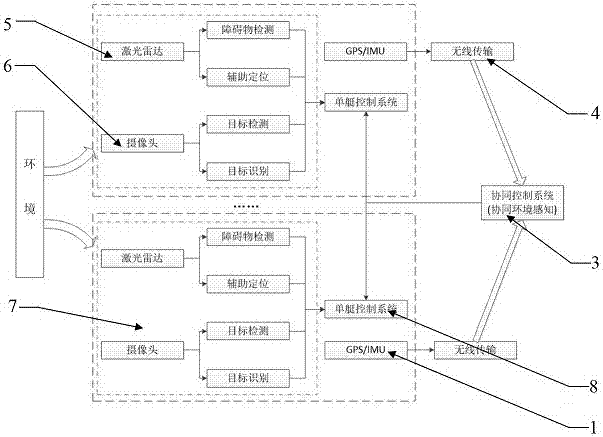
Environment sensing system and method based on coordinated USV (Unmanned Surface Vessel) group
InactiveCN106933232AImprove accuracyIncrease autonomyAutonomous decision making processPosition/course control in two dimensionsSingle vesselSystems design
The invention discloses an environment sensing system and method based on a coordinated USV group. The environment sensing system comprises single-vessel sensing modules, a coordinated control system, wireless communication modules, GPS / IMU modules and single-vessel control modules. Each single-vessel sensing module comprises a camera and a laser radar, the laser radar obtains position and motion information of an object, and the camera identifies the object. The coordinated control system comprises a coordinated control unit and a coordinated sensing unit, the coordinated control unit carries out a coordinated control algorithm to command motion of the USV group, and the coordinated sensing unit coordinates states of the single-vessel sensing modules. The wireless communication modules upload state information and environment sensing information of vessels to the coordinated control system, and also transmits instructions of the coordinated control system. Each GPS / IMU module obtains position and attitude information of the corresponding vessel, and assists in normal operation of other systems. The environment sensing system is reasonable in design, high in system hierarchy, and is easy to realize in the aspects of hardware and software.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
System and method for purifying a gas
The present invention provides for a method for purifying carbon dioxide. Moisture, sulfur species and other impurities are removed from the carbon dioxide by a series of steps which include adsorption means and reaction means. All the steps are preferably carried out in a single vessel.
Owner:BOC GRP INC
Multiple barrier biological treatment systems
InactiveUS20060108283A1Good value for moneySmall footprintTreatment using aerobic processesWater/sewage treatmentActivated sludgeSingle vessel
The inventions separate the activated sludge, biochemical reaction stages of the batch treatment process of a sequencing batch reactor from the clarification and sedimentation stages by separating the locations where each process takes place. The separation may be accomplished in a variety of ways including constructing separate basins for each process, installing baffles or other partitions in a single vessel to isolate the areas where each process takes place, or other methods of process separation as are known in the art. In each process, treatment occurs through the performance of a series of operations. The operations are repeated for each batch of wastewater processed by the SBR. In a conventional SBR process, the cycle of operations for clarification and sedimentation are dependent on a preceding biochemical reaction step. However, in the present invention the clarification and sedimentation operations are independent of the biochemical reaction operations. It remains possible to coordinate operations so that the process cycles are coincident, however the benefits of the invention are more readily realized by the practice of independent operation.
Owner:AQUA AEROBIC SYST
Induced sludge bed anaerobic reactor
InactiveUS20060065593A1Avoid formingEasy to separateLiquid degasificationGas production bioreactorsSingle vesselEngineering
An induced sludge bed anaerobic reactor includes a vessel in which a septum or other partition is positioned to maintain solids in wastewater being treated toward a lower zone in the reactor. A gas trap, which may also comprise an overpressure protection device, may be arranged at an outlet of the vessel. A distribution plate may be located at an inlet. A central aperture is formed in the septum into which a plug control mechanism, such as an auger, may be positioned to force solids to the lower zone of the reactor or, alternatively, pull solids up above the septum so that they can be removed from the vessel, if desired. A mixer may be utilized in connection with the bioreactor to mix the contents and prevent a crust from forming at the top of the bioreactor. Still further, a wall may be positioned to extend above the septum around its perimeter to assist in separating solids from the wastewater. The various types of bacteria used in the anaerobic process may also be separated, according to the present invention, in either a single vessel or multiple vessels so that the conditions of each respective vessel can be altered as desired.
Owner:ANDIGEN +1
Four-port gas separation membrane module assembly
ActiveUS7758670B2Reduce leakageReduce connectionsMembranesSemi-permeable membranesSingle vesselEngineering
A gas-separation membrane assembly, and a gas-separation process using the assembly. The assembly incorporates multiple gas-separation membranes in an array within a single vessel or housing, and is equipped with two permeate ports, enabling permeate gas to be withdrawn from both ends of the membrane module permeate pipes.
Owner:MEMBRANE TECH & RES
Methods for efficiently acquiring wide-azimuth towed streamer seismic data
A technique for use in marine seismic surveying includes a method and an apparatus. In one aspect, the method includes towing a seismic spread including a source multiple streamers on a generally curved advancing path, the streamers being actively steered. The source is fired and data is acquired on the curve. In other aspects, the method is performed with only a single vessel or the generally curved advancing path is a sincurve advancing path. The method may include a dual circular shoot in another aspect. And, in yet another aspect, the invention includes an apparatus comprised of a computing apparatus on board a tow vessel receiving positioning data from the marine seismic streamers. It is also programmed to: sail the tow vessel in a generally curved advancing path and actively steer the marine seismic streamers through the generally curved advancing path.
Owner:REFLECTION MARINE NORGE AS
In-situ cell extraction and assay method
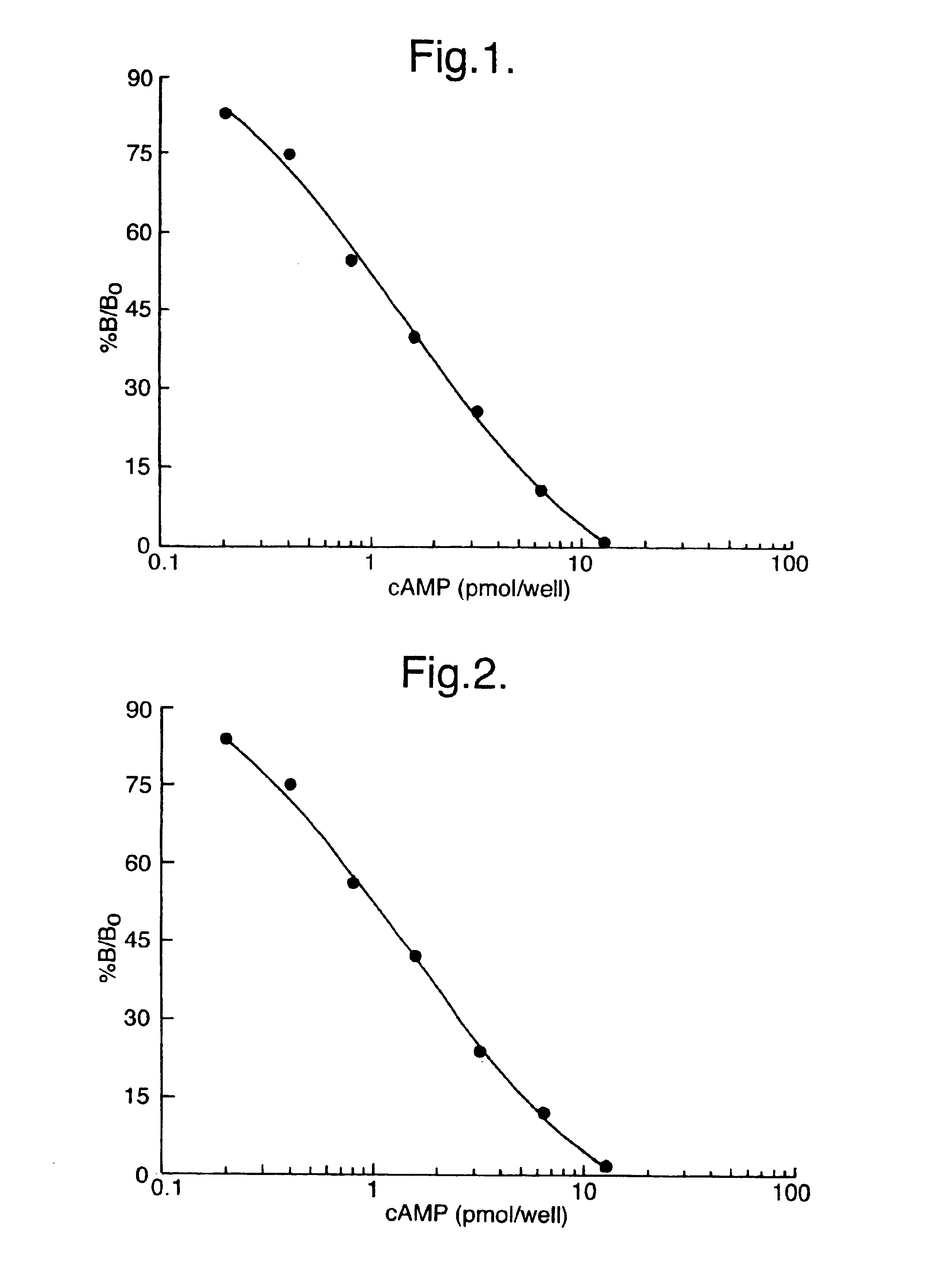
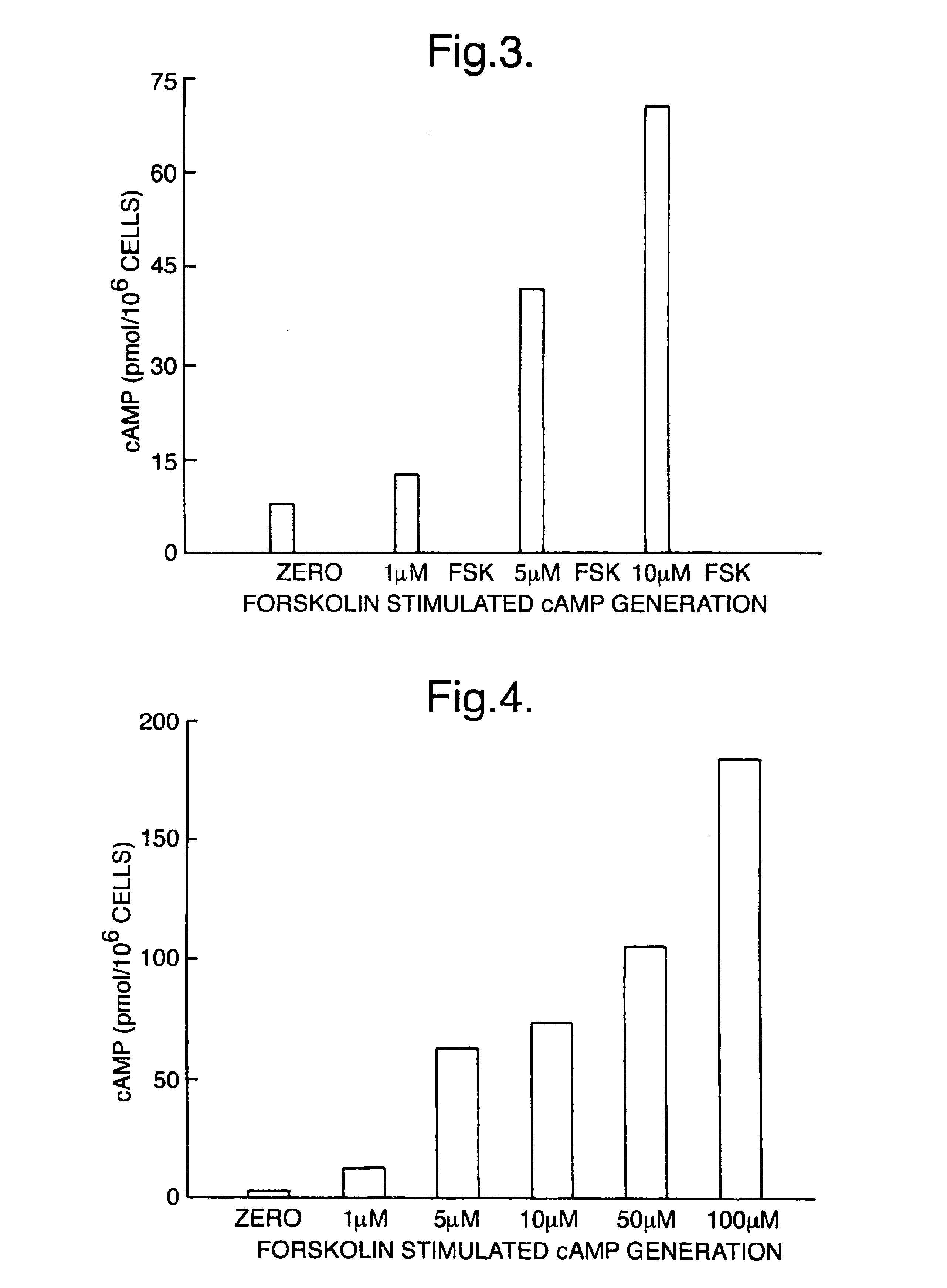
This invention provides a simple and convenient, single stage, single vessel cell extraction and assay method which is suitable for the extraction and measurement of a range of different types of analyte which occur as cellular components. The invention also provides kits of reagents suitable for performing cellular extraction and measurement as a single stage, single vessel process.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE LTD
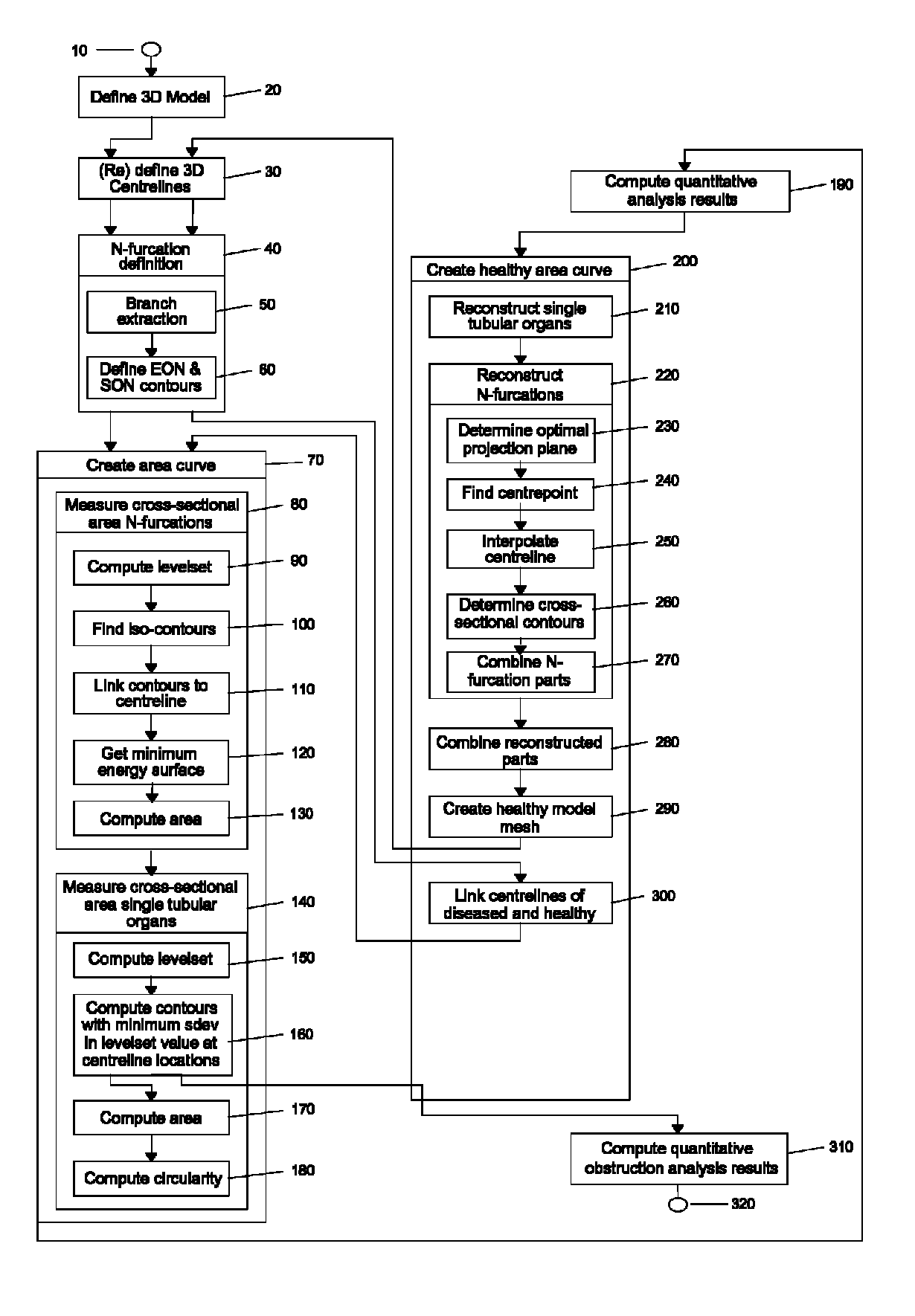
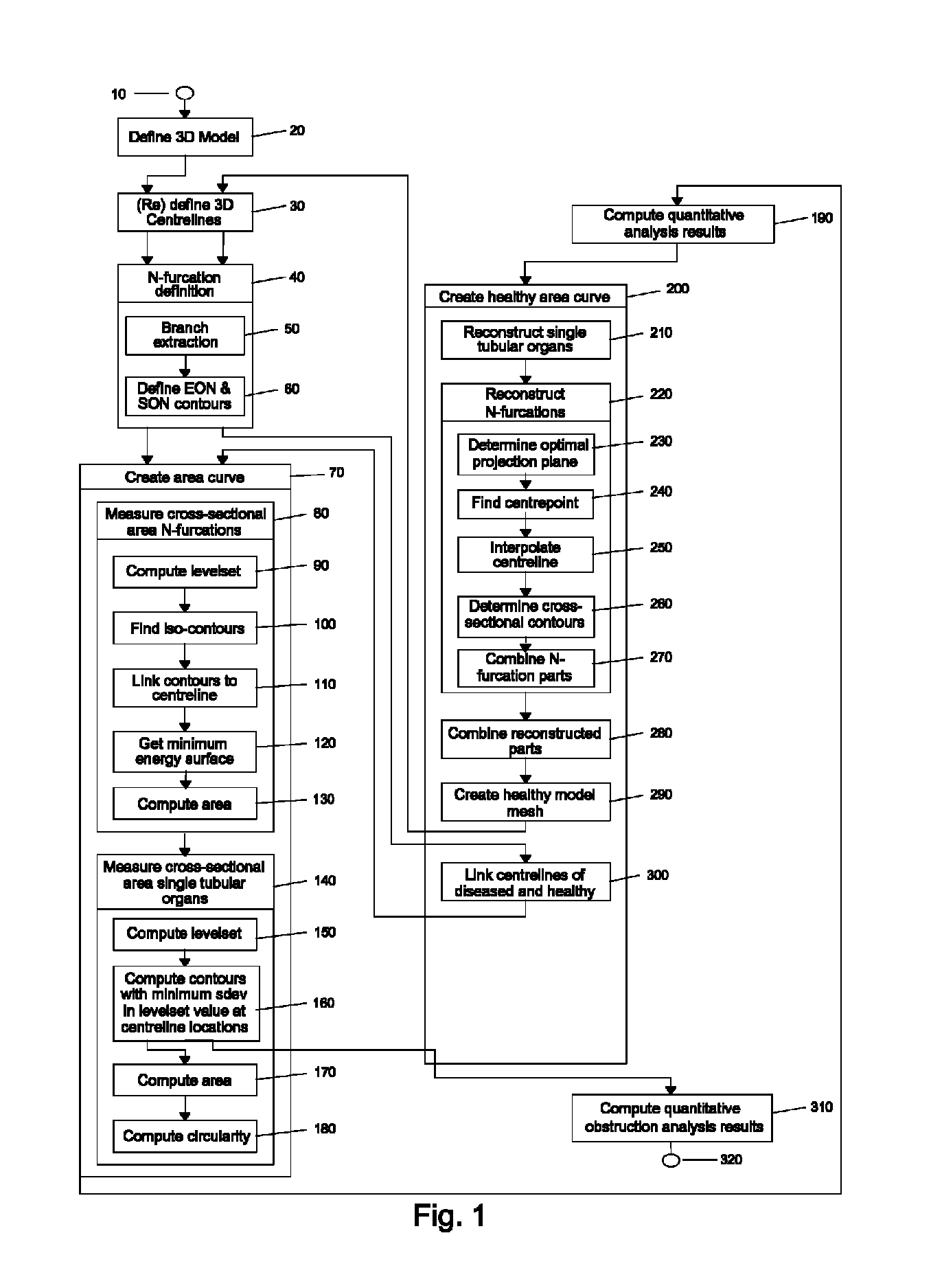
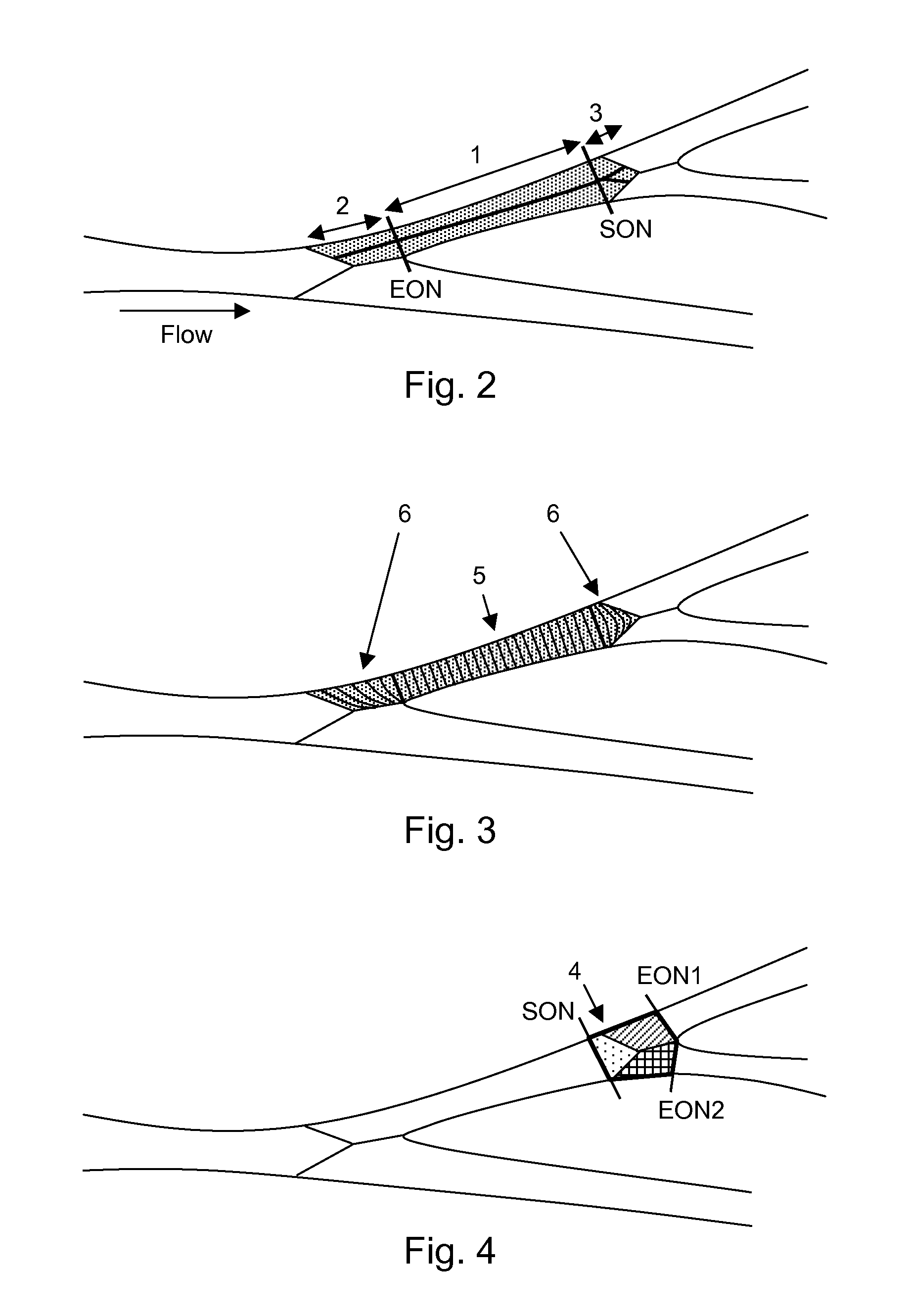
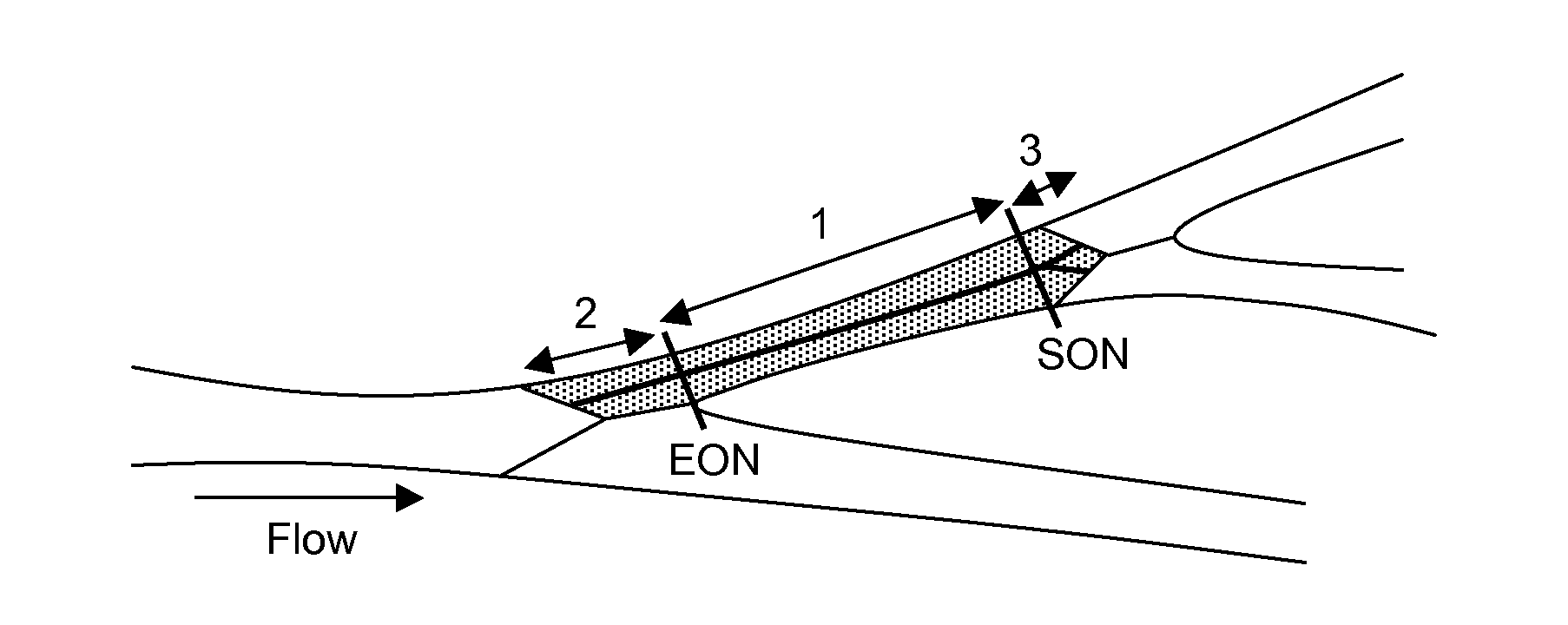
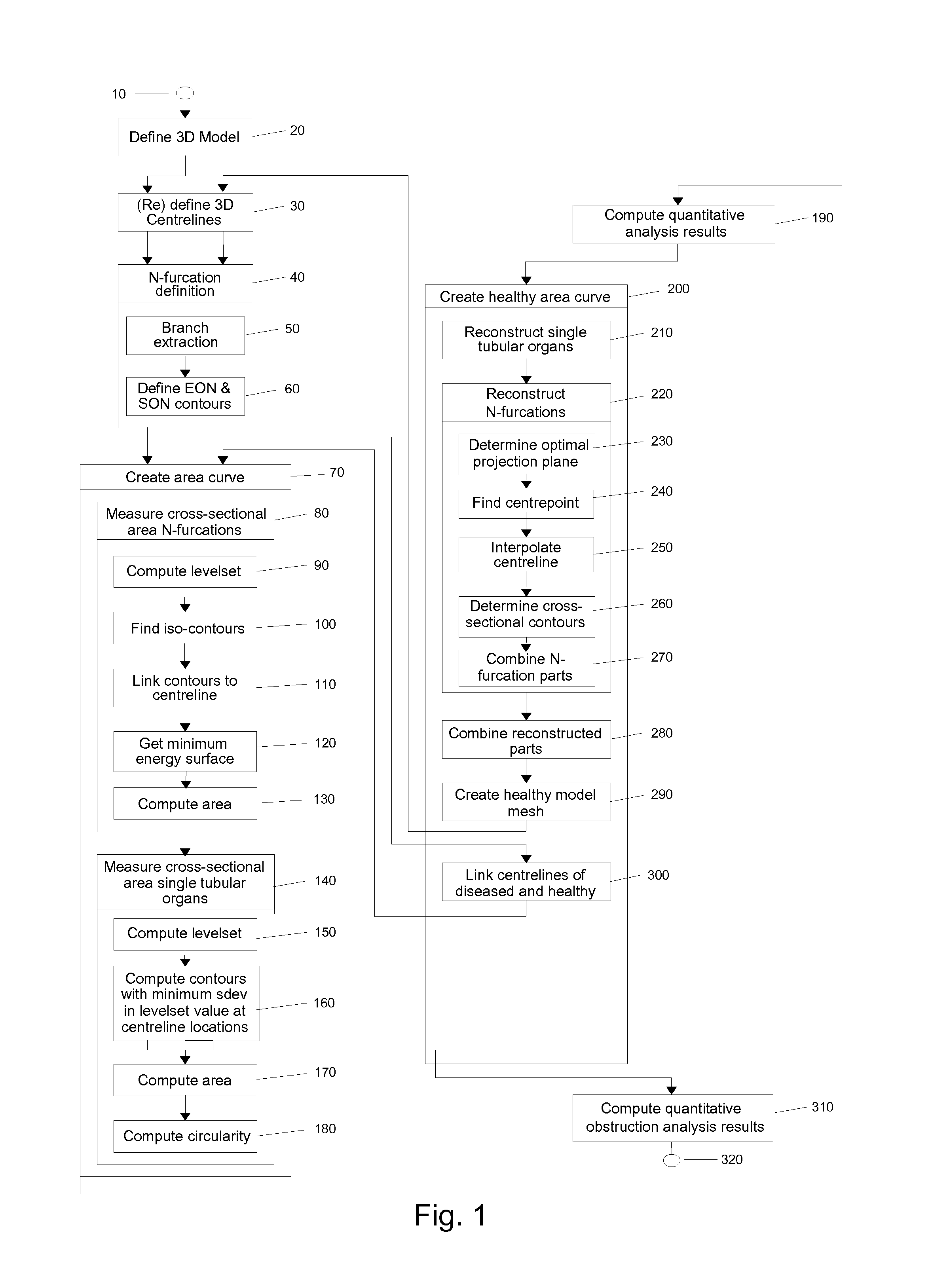
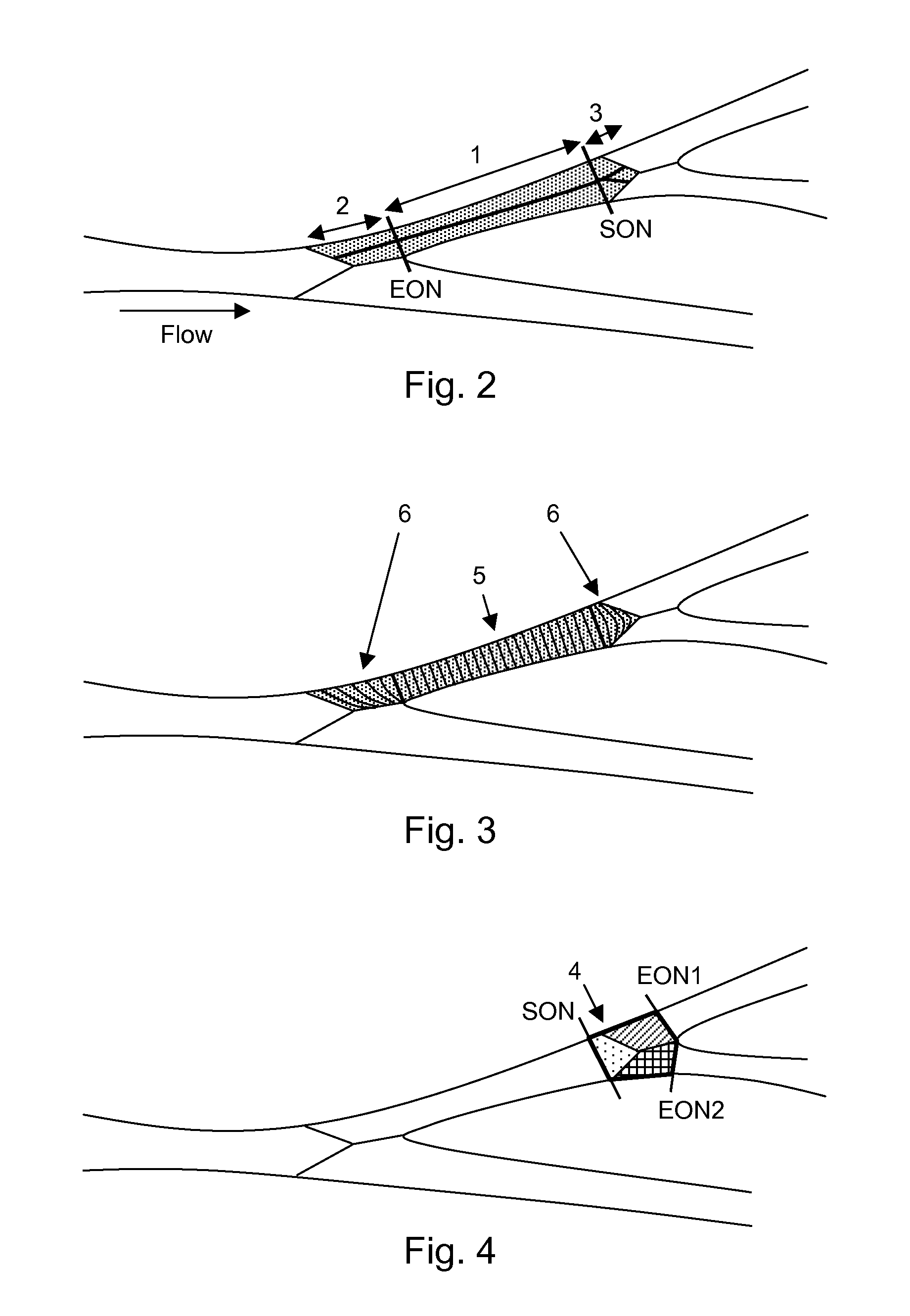
Method and apparatus for quantitative analysis of a tree of recursively splitting tubular organs
ActiveUS8787641B2Fast numerical solutionImproving registration and fusionImage enhancementImage analysisSingle vesselDiagnostic Radiology Modality
Method for quantitative analysis of a tree or part of a tree of recursively splitting tubular organs, the method comprising the following steps: —providing a 3D model of said tree or part of said tree, such 3D model giving a representation of the surface of the lumen wall of the tubular organs forming the tree or part of the tree; —defining the 3D centerlines of said tree or part of the tree; —identifying the branches of the tree; —identifying N-furcations of the tree or part of the tree, an N-furcation being a part of the tree where a proximal tubular organ branches into two or more distal tubular organs, further comprising the step of: —dividing, independently from the modality used for obtaining the 3D model, each branch in one or more regions, such regions being of two different types, named single vessel region and splitting region, different cross-section surfaces being defined in such regions, wherein the splitting regions can exist at the proximal side of a branch as well as at the distal side of said branch and each N-furcation comprises the distal splitting region of a branch and the proximal splitting regions of the N branches directly distal to said branch. A corresponding apparatus and computer program are also disclosed.
Owner:PIE MEDICAL IMAGING
Methods for processing titanium aluminide intermetallic compositions
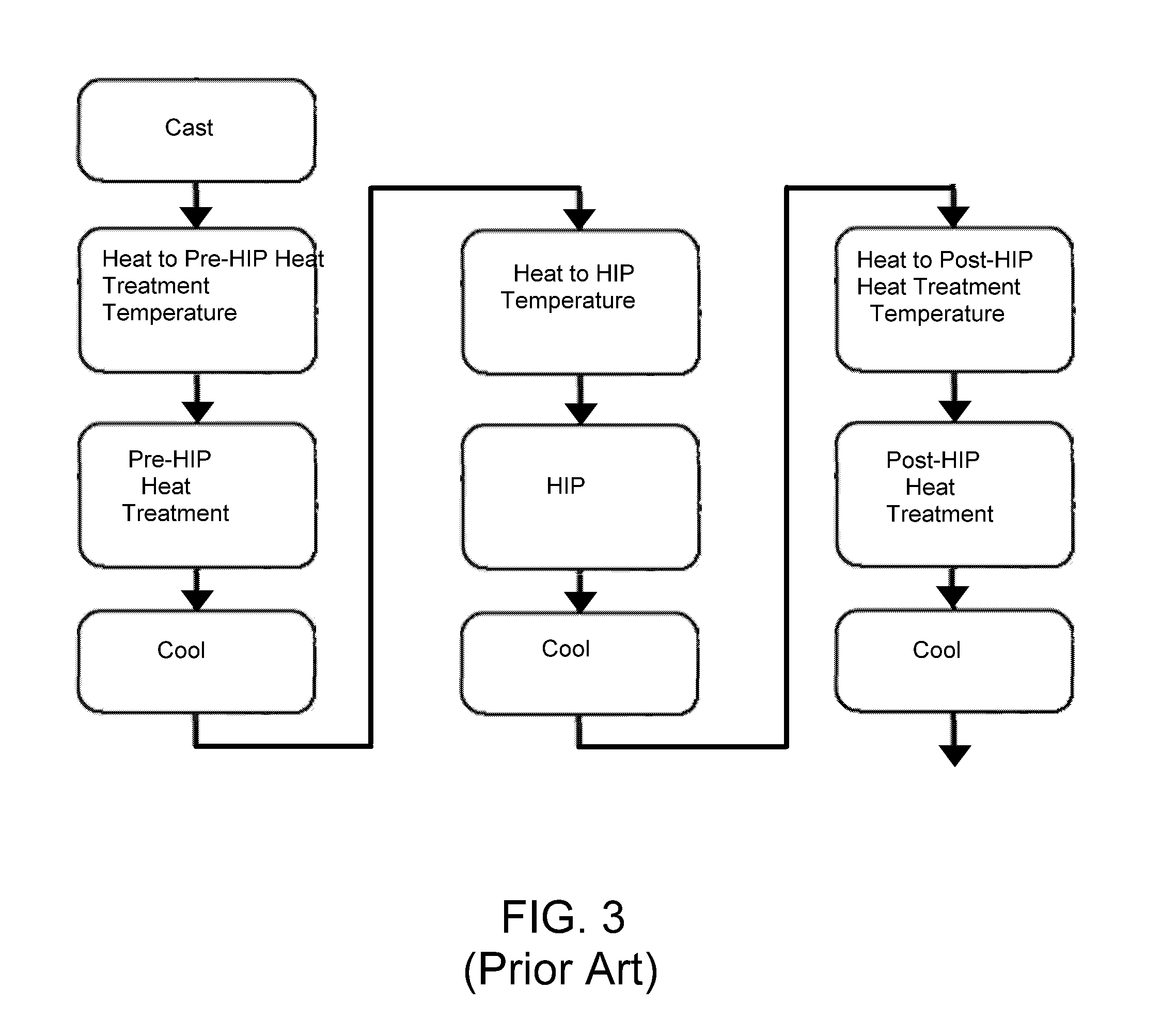
Methods of processing compositions containing titanium and aluminum, especially titanium aluminide intermetallic compositions (TiAl intermetallics) based on the TiAl (gamma) intermetallic compound. The methods entail processing steps that include a hot isostatic pressing (HIP) cycle and a heat treatment cycle that can be performed in a single vessel. TiAl intermetallic compositions processed in this manner preferably exhibit a duplex microstructure containing equiaxed and lamellar morphologies.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Specimen archive
An apparatus for archiving specimens in specimen vessels. The apparatus includes an archive room accessible via a lock for automated feeding of vessels into and out of the room. A storage and restacking system is disposed in the room and includes two side-by-side stacks of trays in a receiving area. Each tray has a receptacle area defining a plurality of receptacles therein, each configured to receive a single vessel. A stacking means forms the stacks of trays. One tray is stacked on another in such a way as to maintain a clearance relative to the receptacle area of the lower tray. A lifting means is provided for vertically lifting trays stacked on a selected tray; and a transfer means is provided for horizontal transfer of a selected tray from one stack to the other, or from one stack to the lock, or from the lock to one of the stacks.
Owner:ABBOTT AUTOMATION SOLUTIONS GMBH
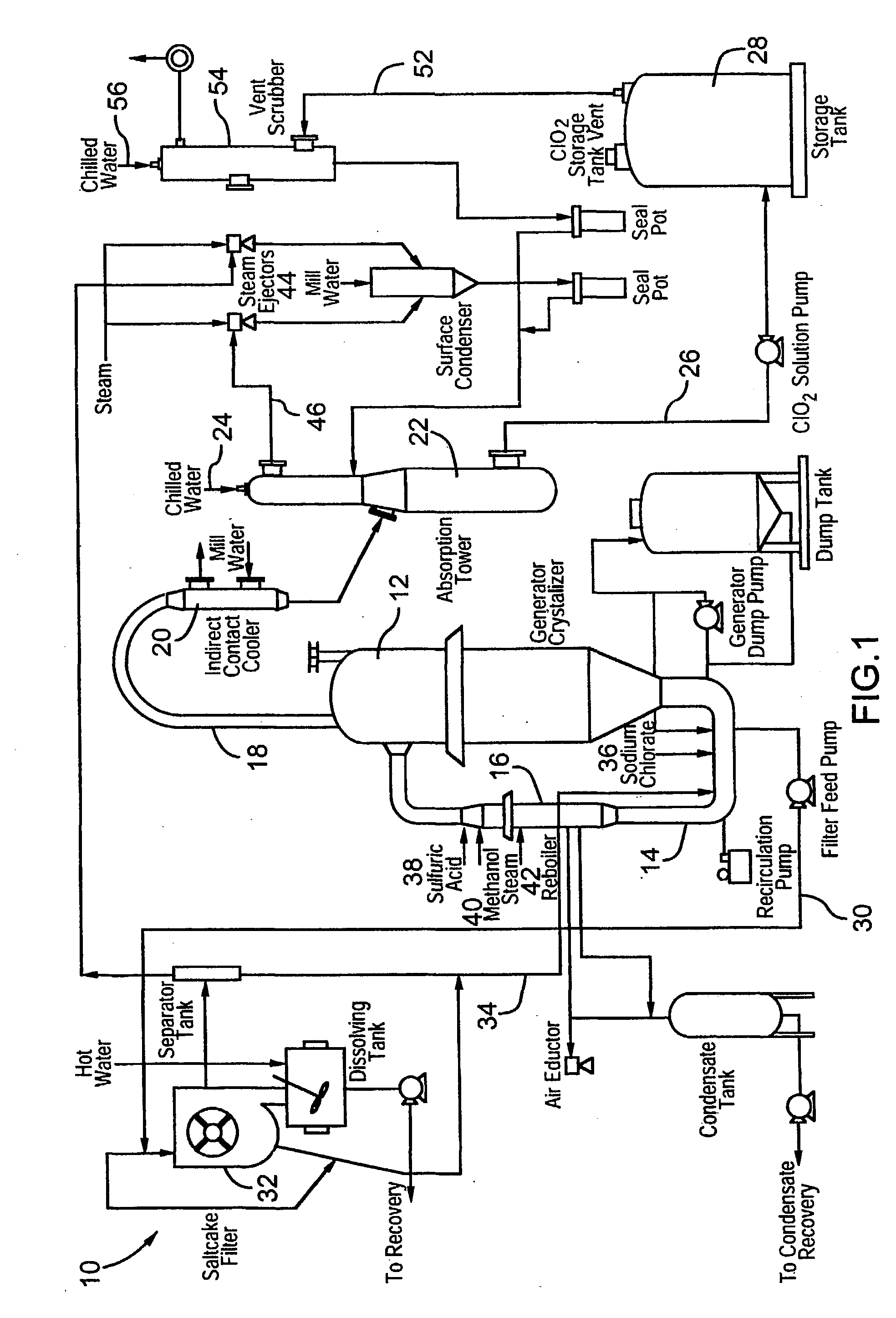
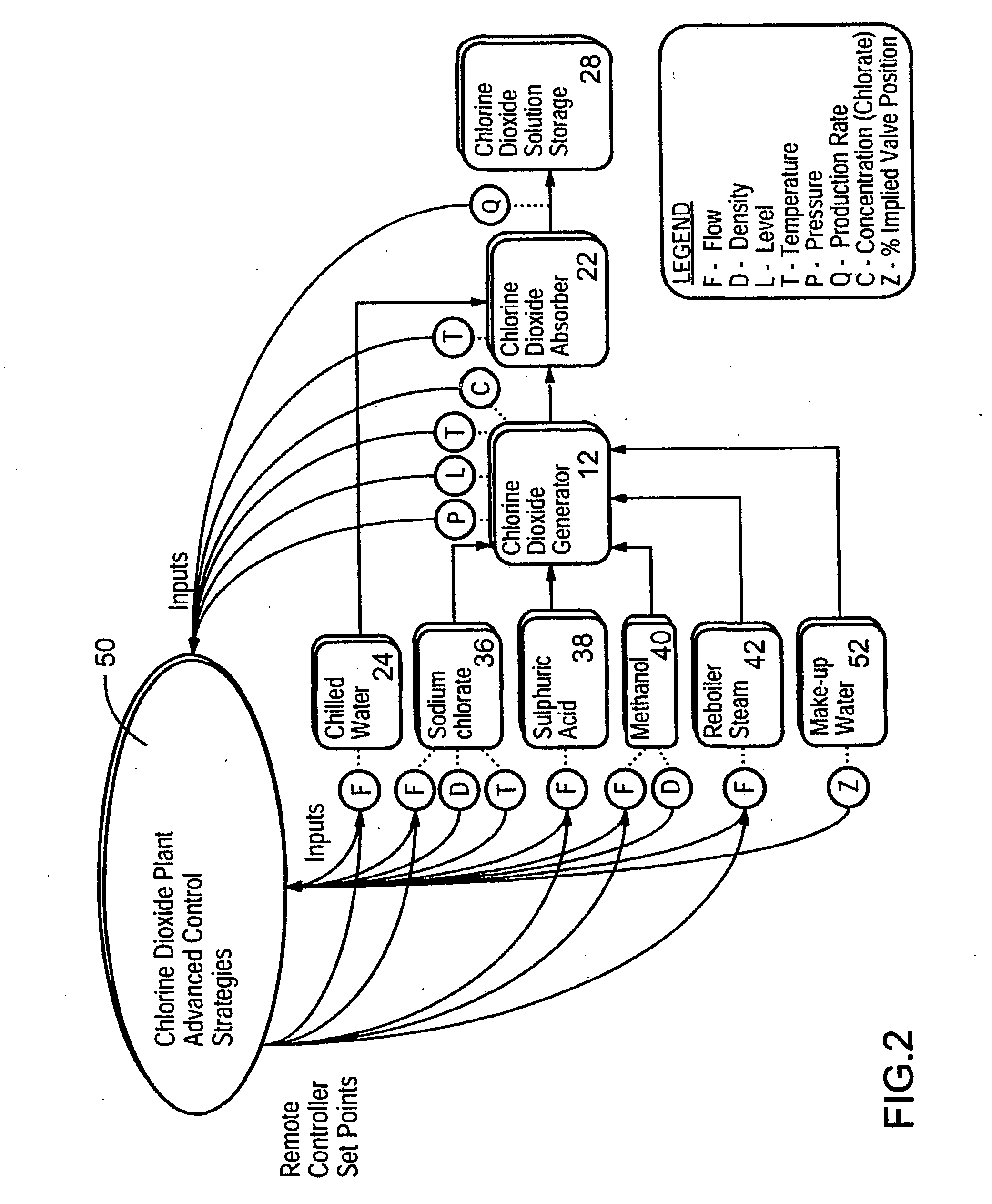
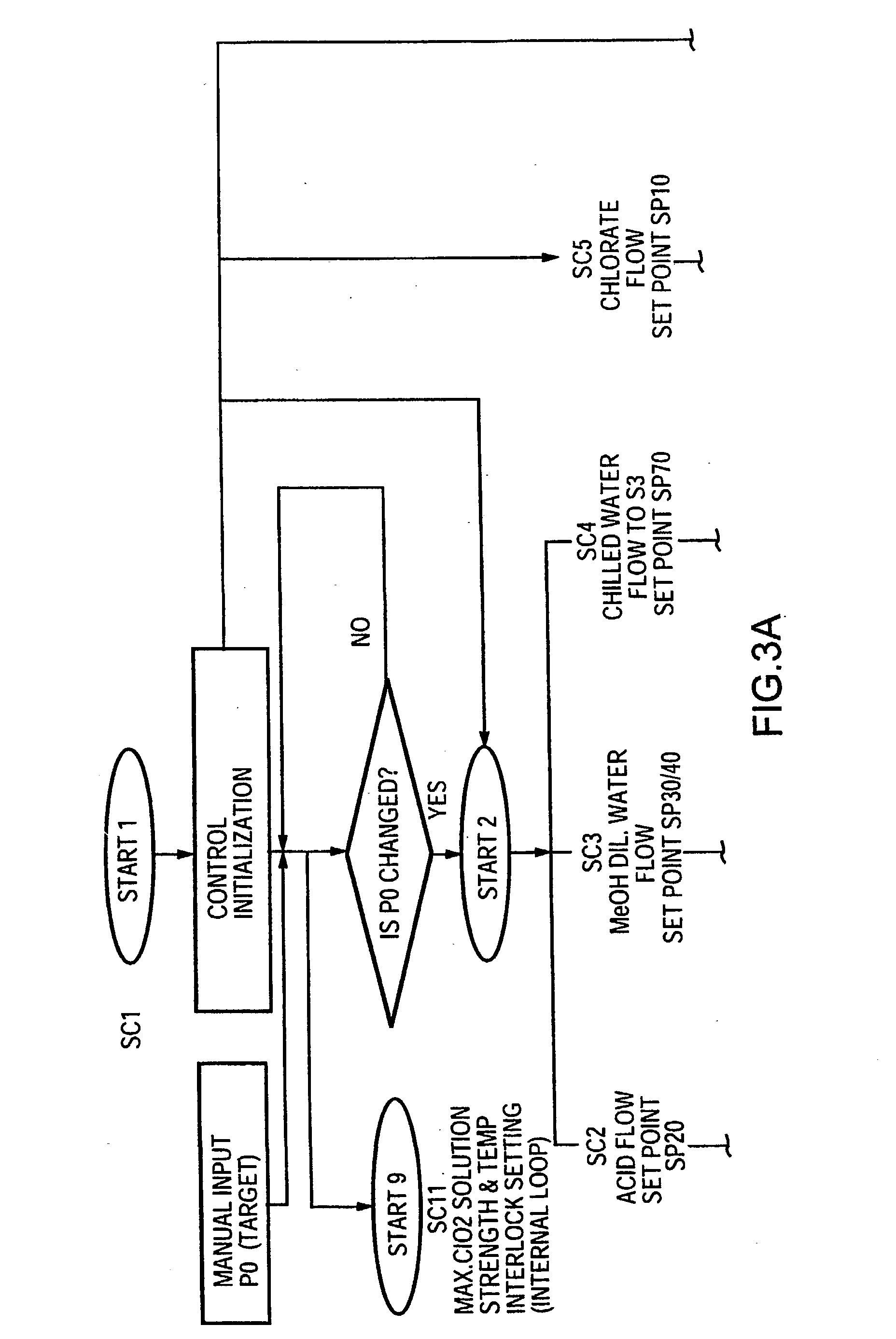
Advanced control strategies for chlorine dioxide generating processes
InactiveUS20030118503A1Saving chemical costReduce loadSampled-variable control systemsComputer controlProduction rateSingle vessel
Chlorine dioxide generating processes of the single vessel type which produce chlorine dioxide of high purity are monitored and controlled by a computer using Advanced Control Strategies for steady, stable operation with optimum chemical usage on the basis of a desired chlorine dioxide production rate as the sole input from an operator to the computer program effecting the computer control.
Owner:SUPERIOR PLUS INCOME FUND +2
Method and Apparatus for Quantitative Analysis of a Tree of Recursively Splitting Tubular Organs
ActiveUS20130158970A1Fast numerical solutionImproving registration and fusionImage enhancementImage analysisSingle vesselDiagnostic Radiology Modality
Method for quantitative analysis of a tree or part of a tree of recursively splitting tubular organs, the method comprising the following steps:—providing a 3D model of said tree or part of said tree, such 3D model giving a representation of the surface of the lumen wall of the tubular organs forming the tree or part of the tree;—defining the 3D centrelines of said tree or part of the tree;—identifying the branches of the tree;—identifying N-furcations of the tree or part of the tree, an N-furcation being a part of the tree where a proximal tubular organ branches into two or more distal tubular organs, further comprising the step of:—dividing, independently from the modality used for obtaining the 3D model, each branch in one or more regions, such regions being of two different types, named single vessel region and splitting region, different cross-section surfaces being defined in such regions, wherein the splitting regions can exist at the proximal side of a branch as well as at the distal side of said branch and each N-furcation comprises the distal splitting region of a branch and the proximal splitting regions of the N branches directly distal to said branch. A corresponding apparatus and computer program are also disclosed.
Owner:PIE MEDICAL IMAGING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com