Patents
Literature
41results about "Sugar juice extraction using extracting agents" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method of processing lignocellulosic feedstock for enhanced xylose and ethanol production
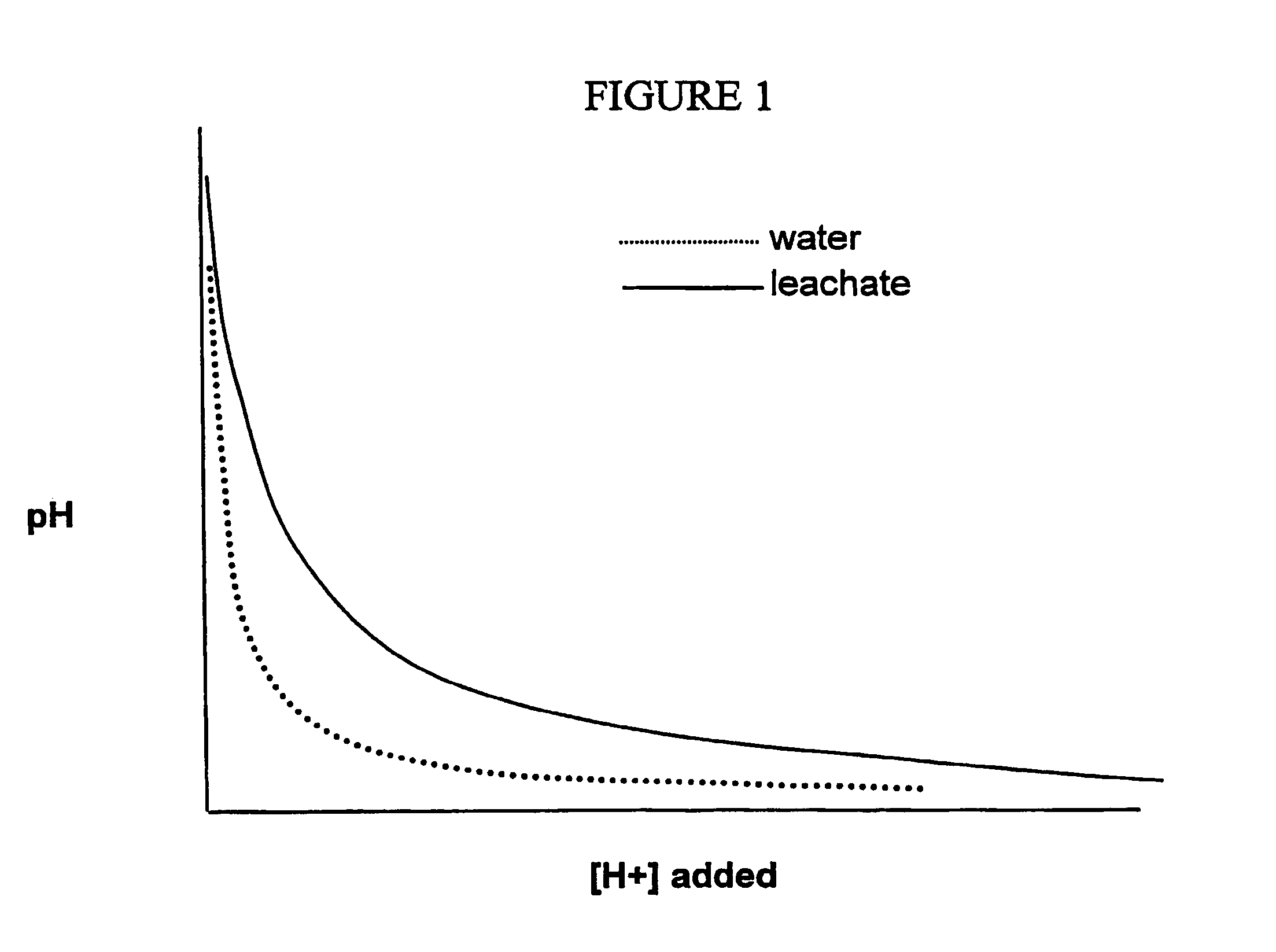
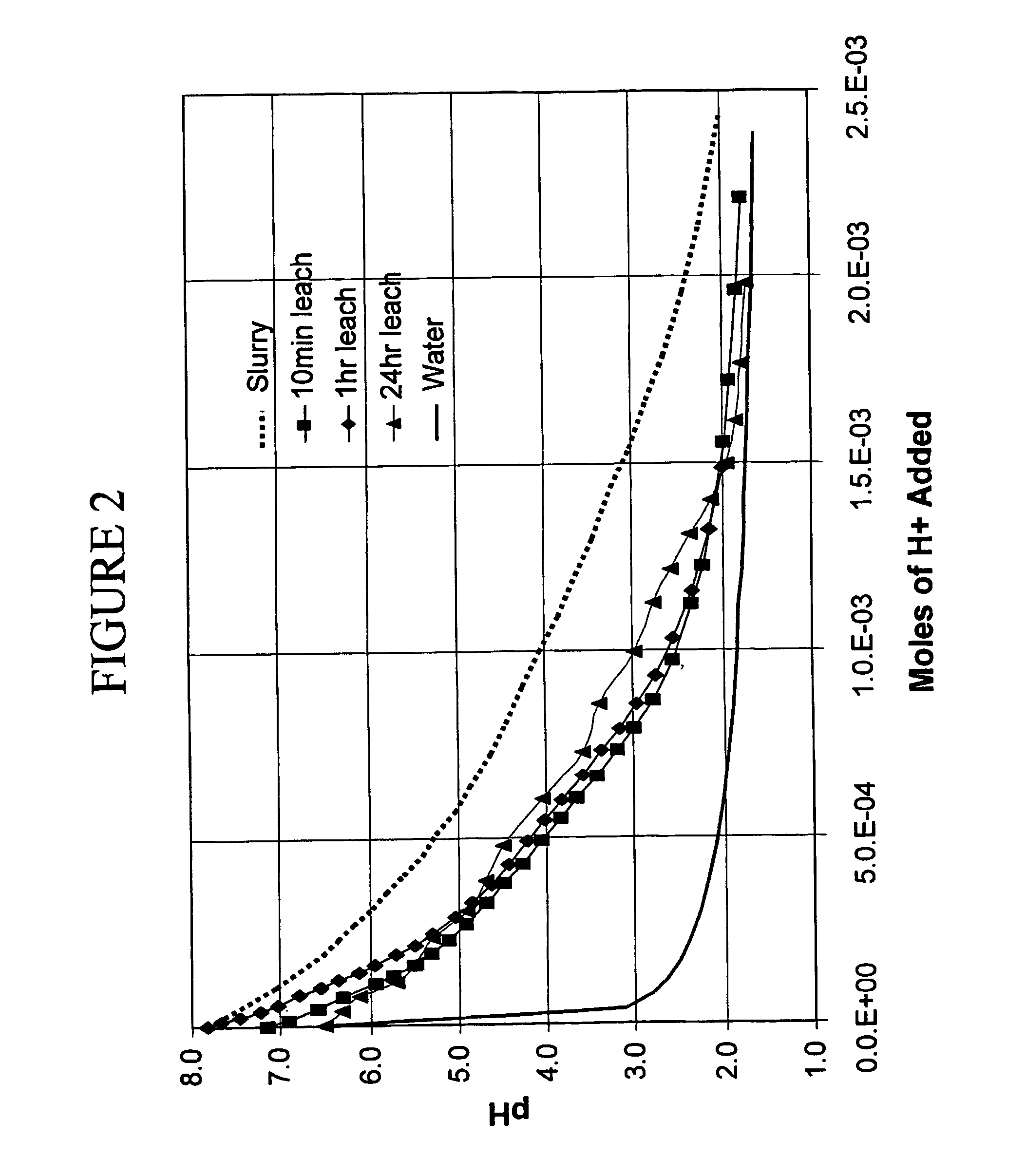
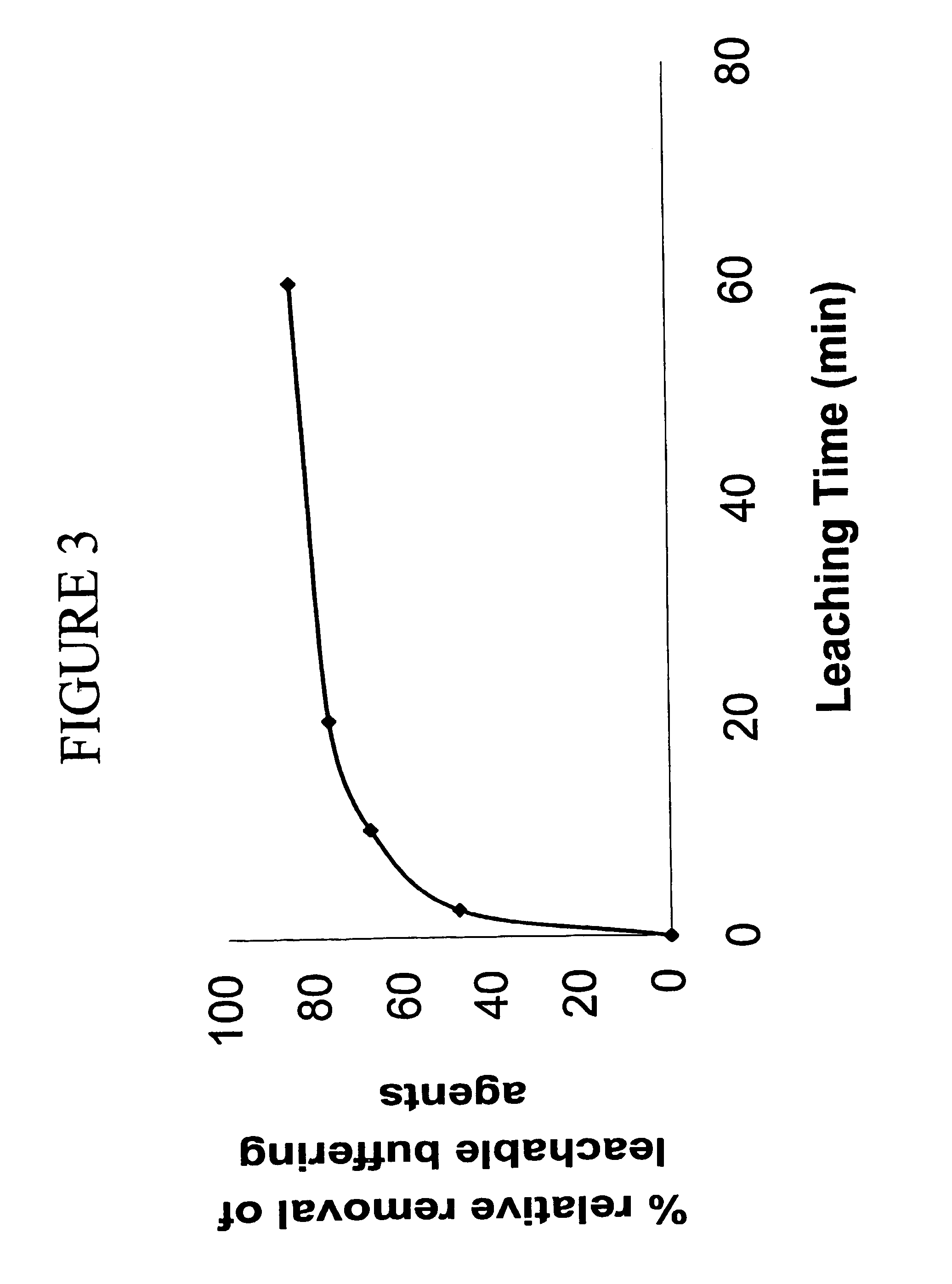
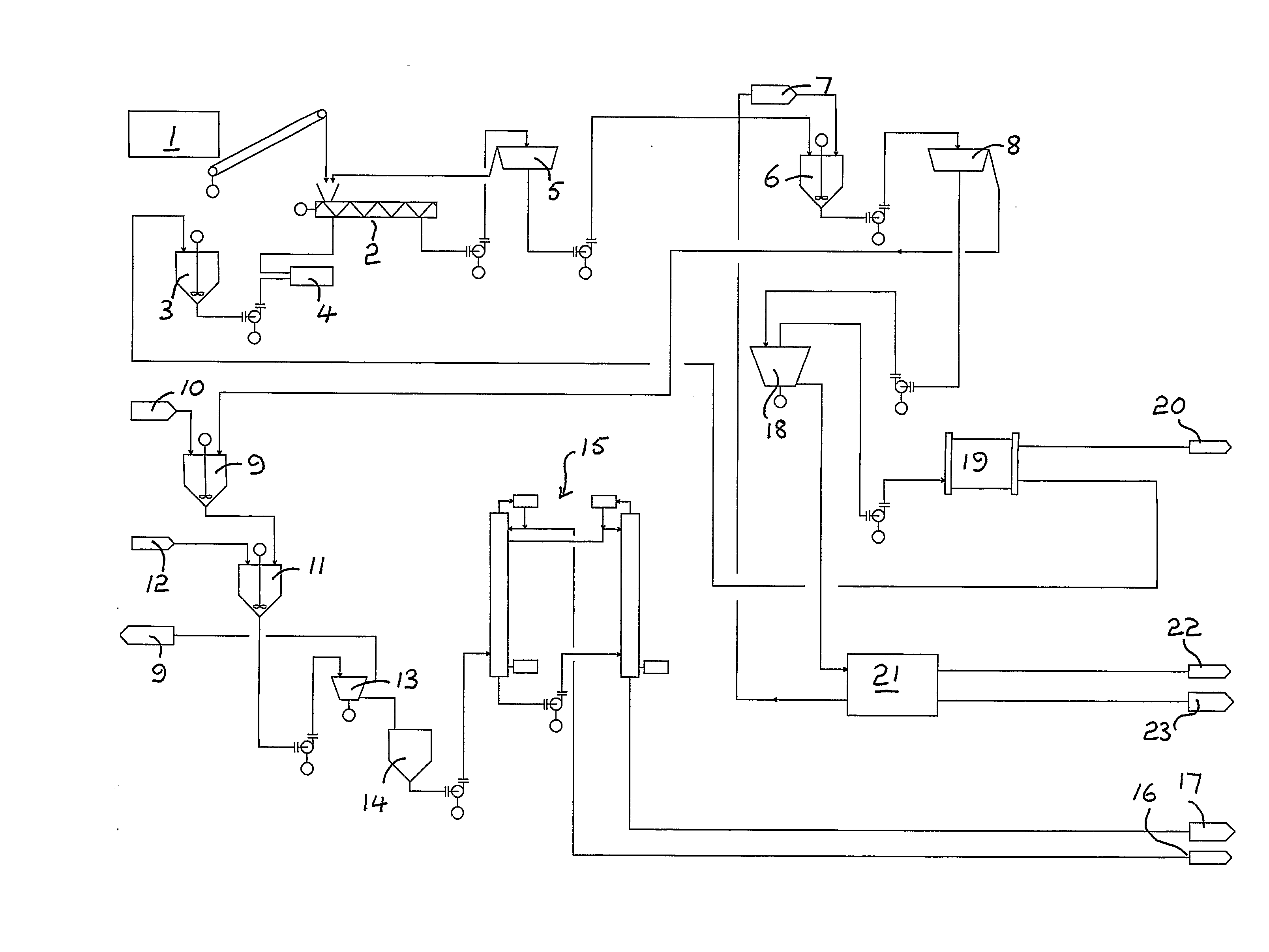
The present invention provides a method of producing xylose from lignocellulosic feedstock. The method comprises disrupting lignocellulosic feedstock; leaching the lignocellulosic feedstock by contacting the feedstock with at least one aqueous solution for a period greater than about 2 minutes to produce a leached feedstock and a leachate; removing the leachate from the leached feedstock; acidifying the leached feedstock to a pH between about 0.5 and about 3 to produce an acidified feedstock, and; reacting the acidified feedstock under conditions which disrupt fiber structure and hydrolyze a portion of hemicellulose and cellulose of the acidified feedstock, to produce a composition comprising xylose and a pretreated feedstock. The xylose may be purified from the pretreated feedstock or it may be converted to ethanol with the pretreated feedstock.
Owner:IOGEN ENERGY CORP
Fractionation of a lignocellulosic material
InactiveUS20100196967A1Lower Level RequirementsImprove permeabilityBiofuelsLignin derivativesCelluloseNon solvent
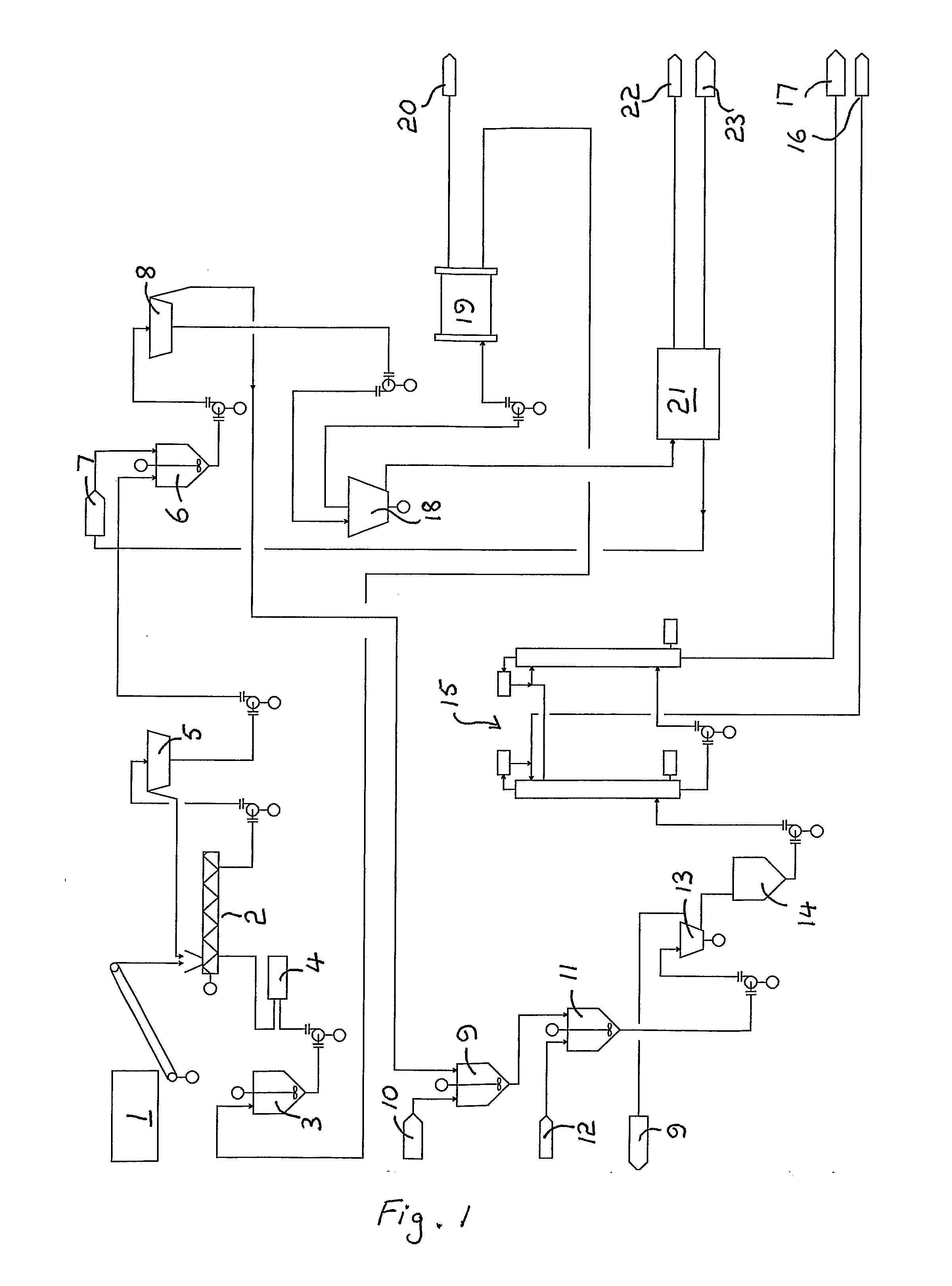
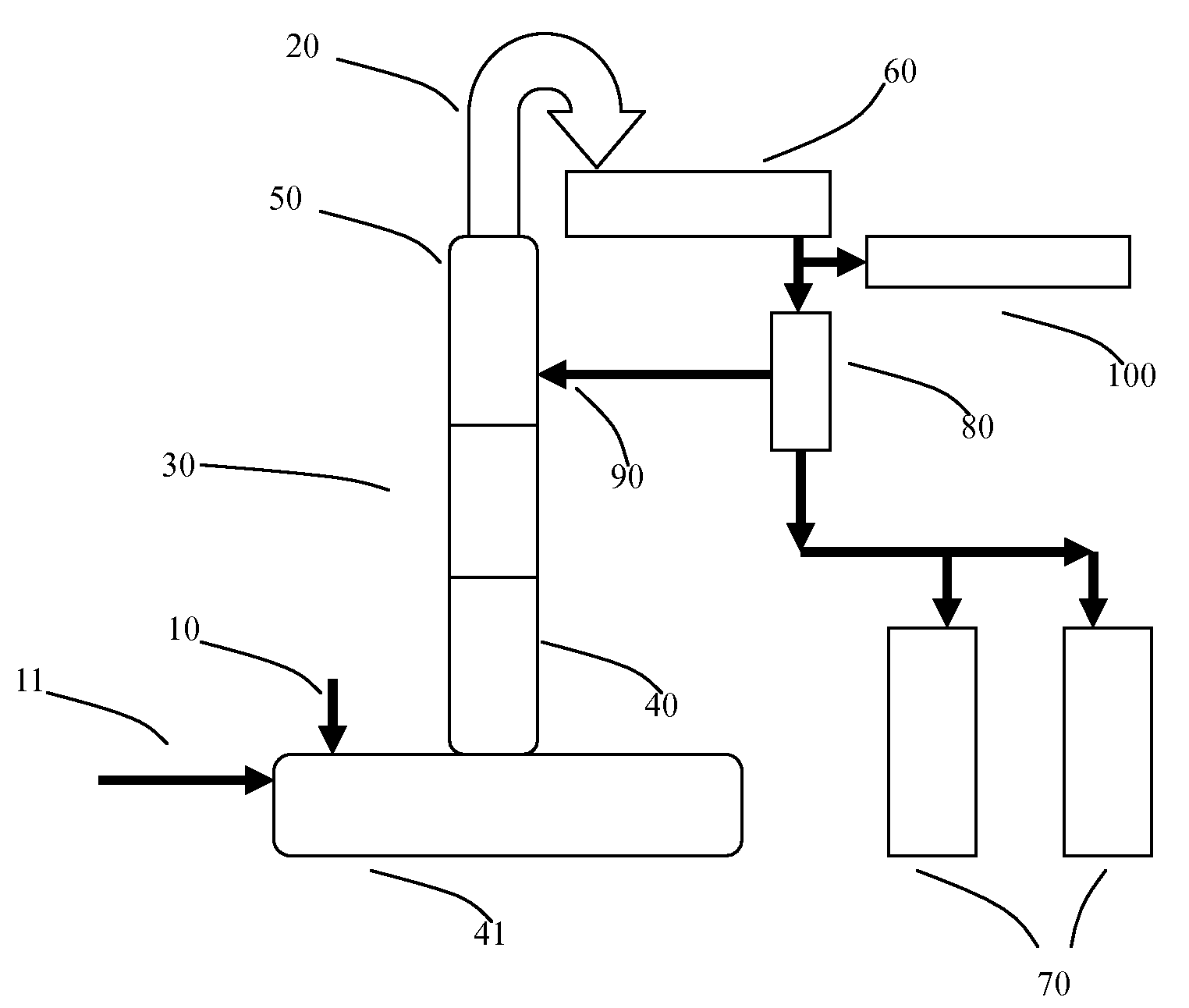
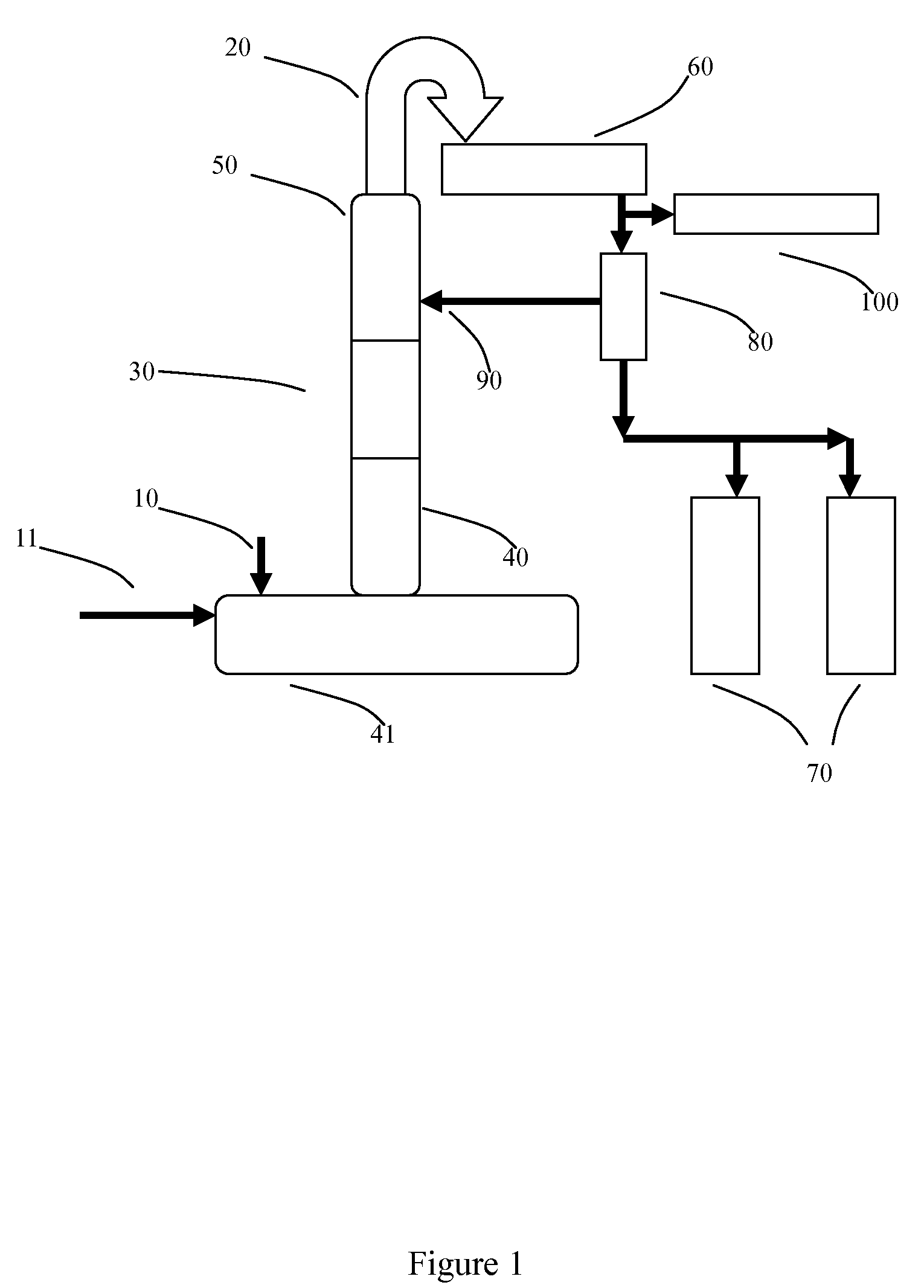
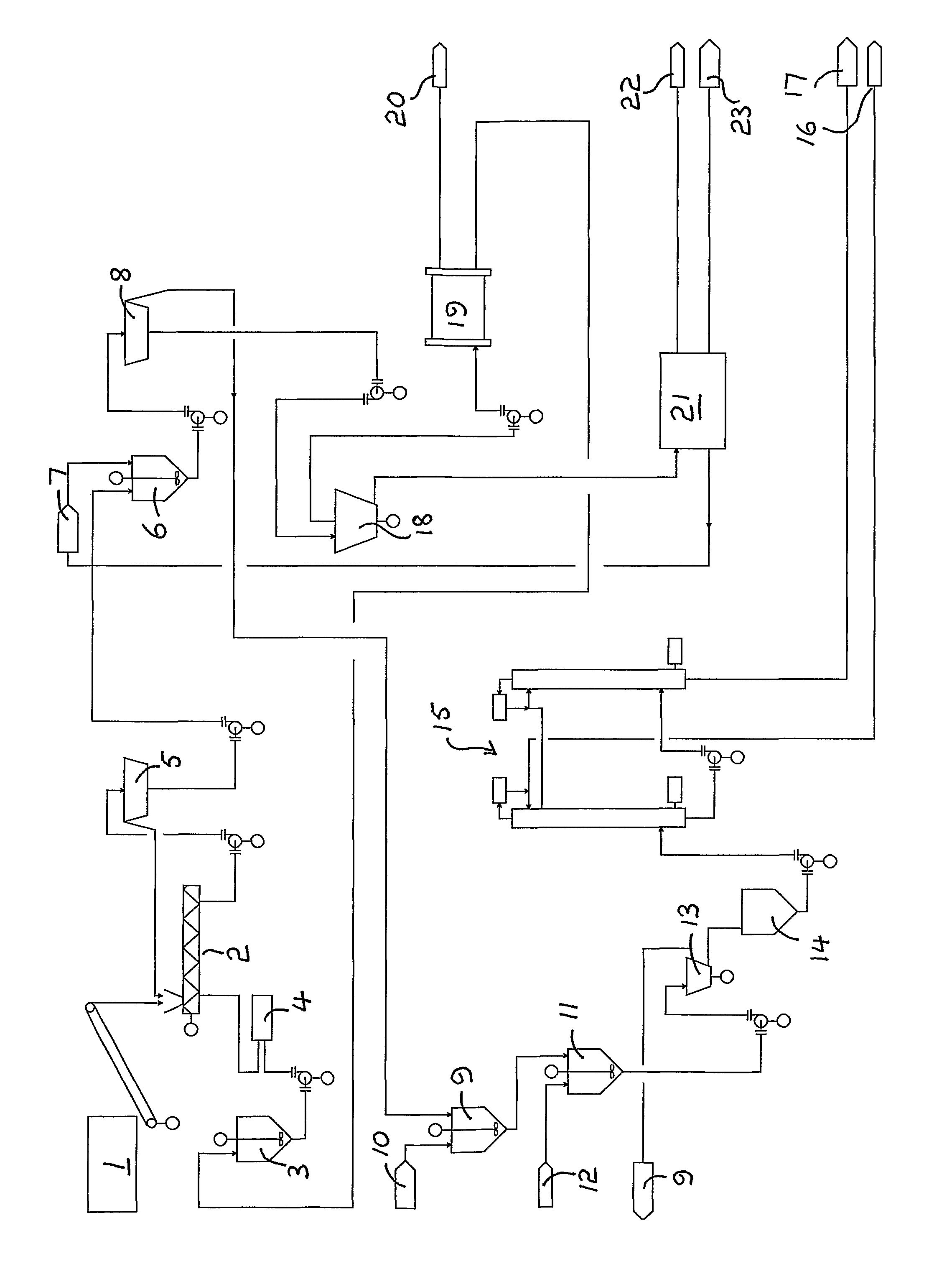
A method for fractionating a lignocellulosic material, the method comprising; contacting (2) the lignocellulosic material with an ionic liquid (3) and dissolving the lignocellulosic material therein, providing a second liquid (7) which is immiscible with the ionic liquid and is also a non-solvent for cellulose, adding the second liquid to the ionic liquid so as to form a biphasic system (6) which comprises an ionic liquid phase essentially free of lignocellulose and a second liquid phase comprising lignin in solution and cellulose as a precipitate, separating the two phases and recovering (8) the precipitated cellulose from the separated second liquid phase.
Owner:QUEENSLAND UNIVERSITY OF TECH
Conversion of natural products including cellulose to hydrocarbons, hydrogen and/or other related compounds
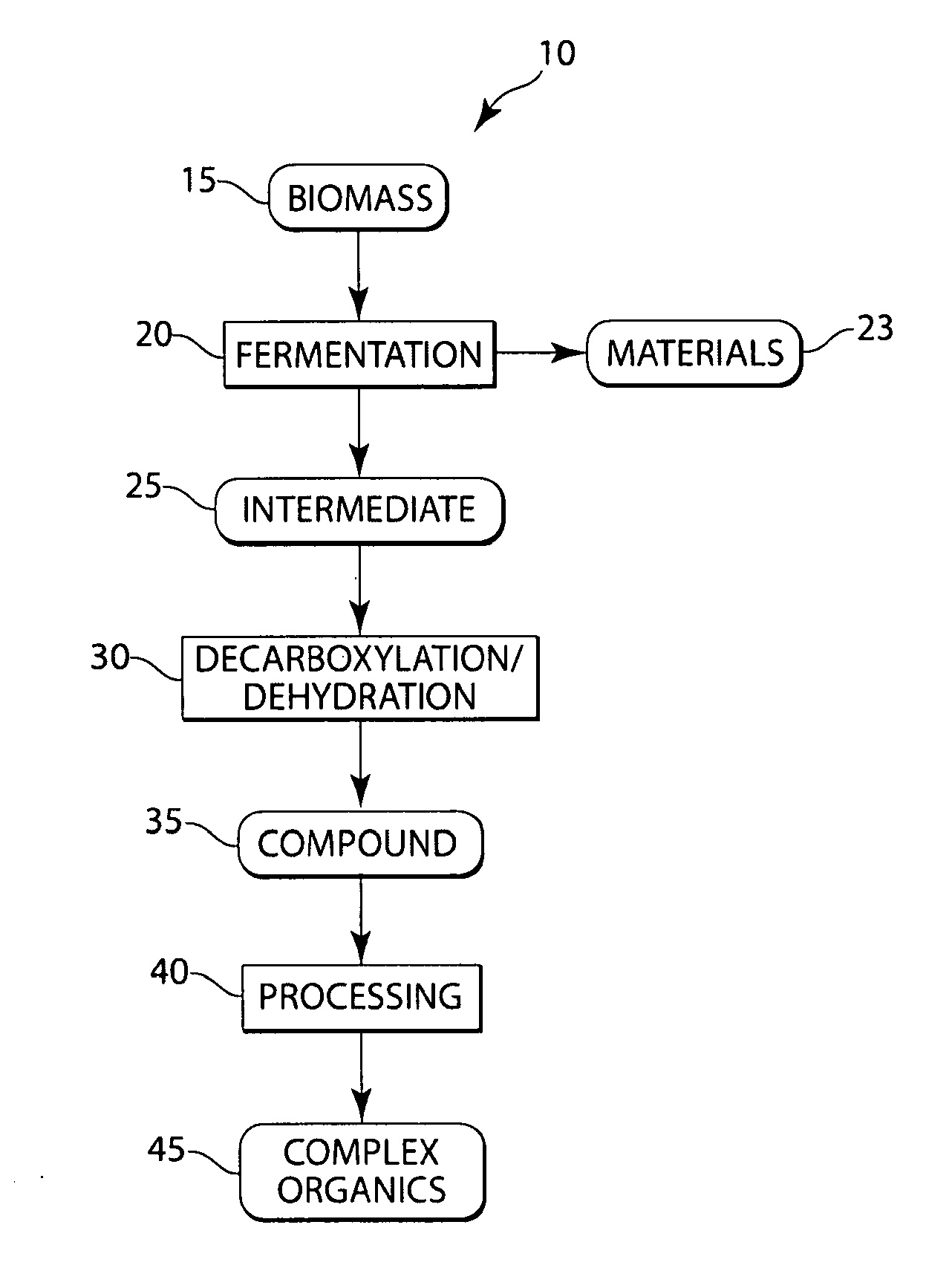
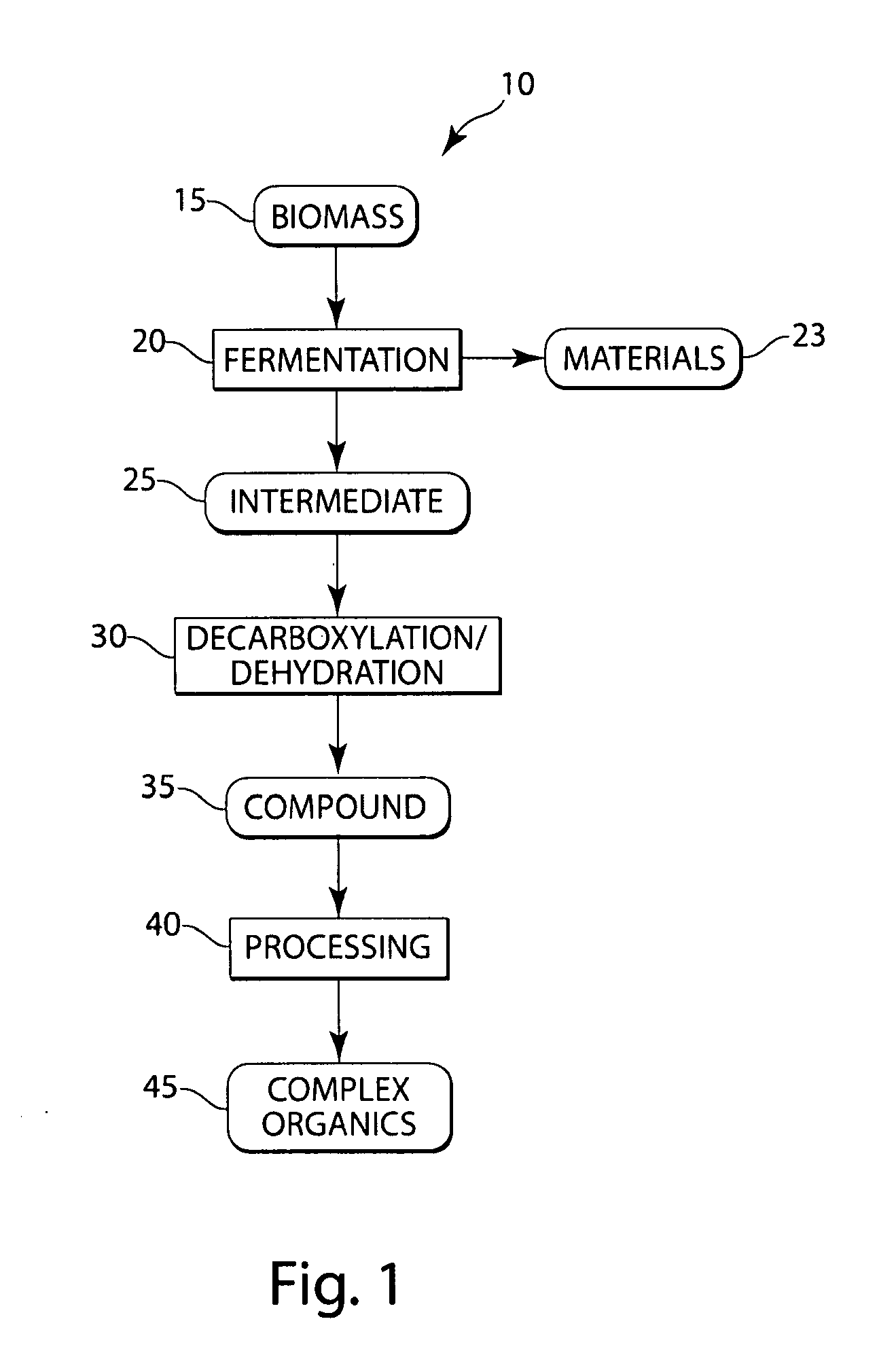
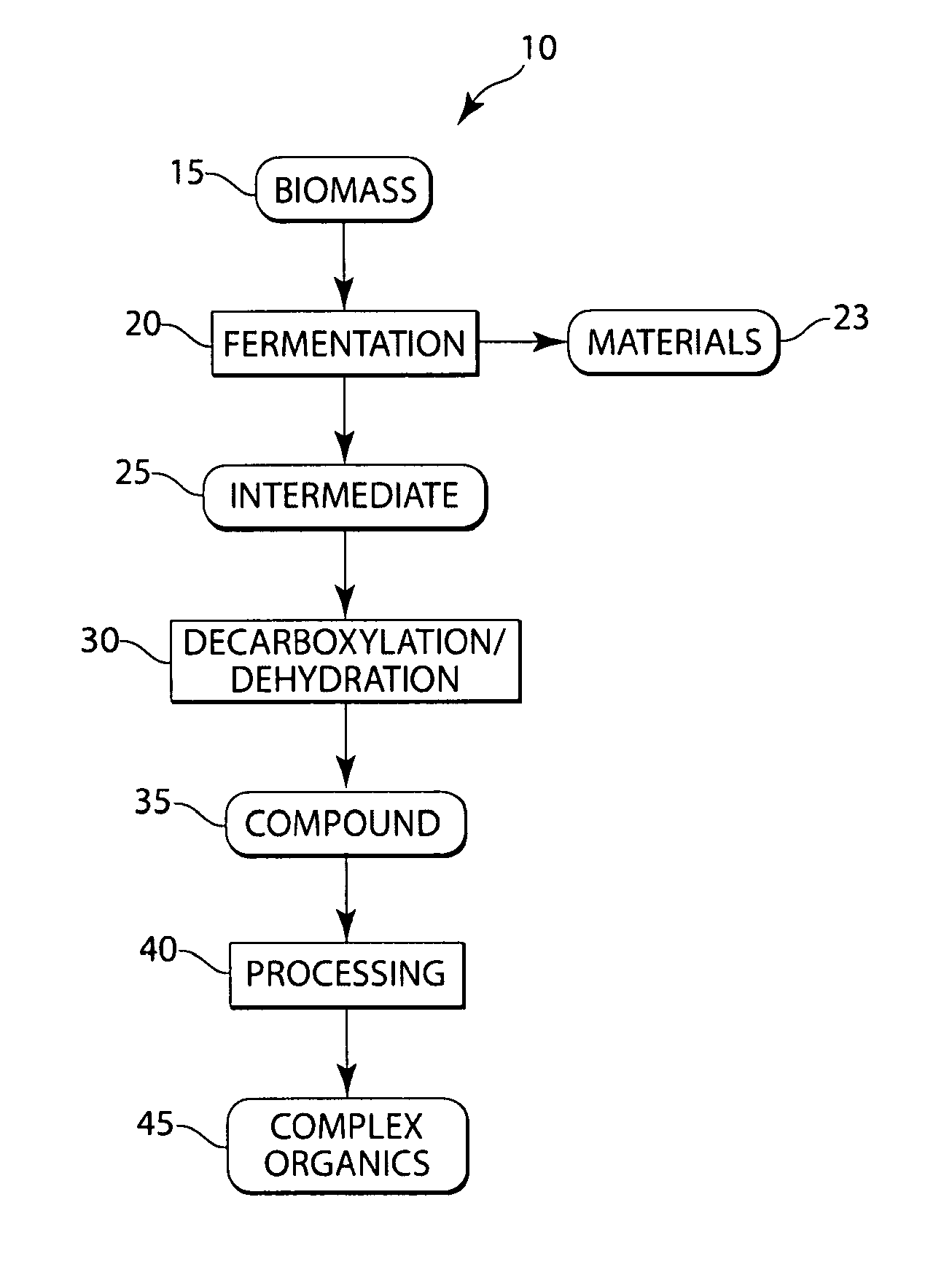
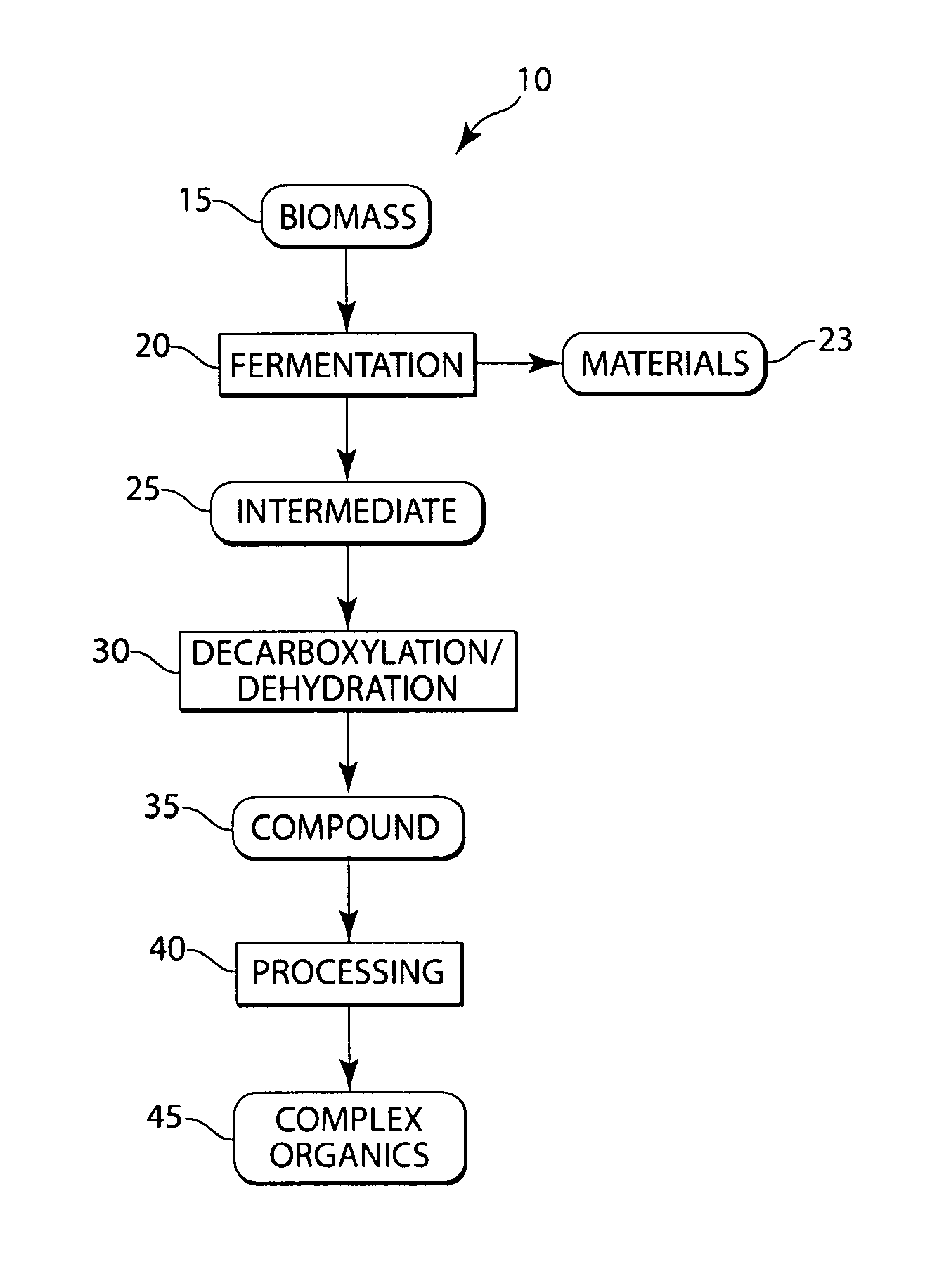
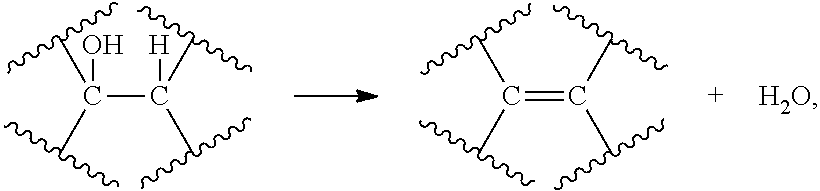
The present invention generally relates to the conversion of sugars and / or other biomass to produce hydrocarbons, hydrogen, and / or other related compounds. In one aspect, the invention includes fermenting biomass to produce one or more organic intermediates, for example, a carboxylic acid, and optionally, hydrogen. The carboxylic acid may then be decarboxylated to produce CO2 and one or more hydrocarbon compounds, for example, an alkane or an alkene, such as propane or ethylene. Such reactions can occur, in some cases, under hydrothermal conditions, and in some instances, without the use of or need for electrolysis of the reactants. In some cases, for example, if the carboxylic acid (or other organic intermediate) includes a hydroxide moiety, the carboxylic acid may be dehydrated, i.e., reacted such that the hydroxide moiety is removed from the molecule as H2O. In certain embodiments, a hydrocarbon compound may then be further reacted to produce other compounds, for example, hydrocarbons having at least 4 carbon atoms (e.g., gasoline), polymers such as polypropylene or polyethylene, or the like. Other aspects of the invention relate to devices for performing such reactions, methods of promoting the making or use of such reactions, or the like.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
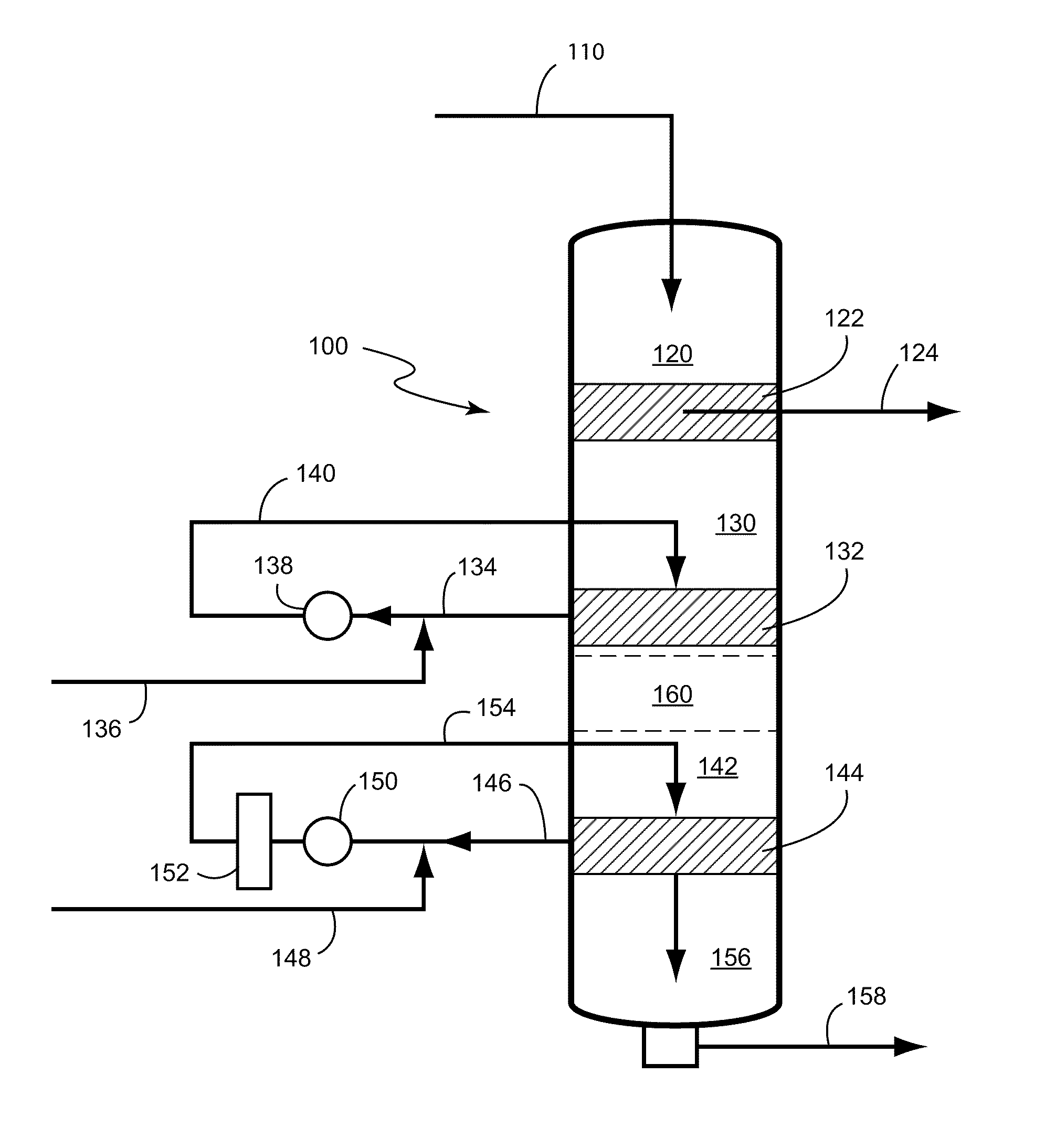
Apparatus and method for hydrolysis of cellulosic material in a multi-step process to produce c5 and c6 sugars using a single vessel
InactiveUS20090308383A1Undesirable effectFructose productionSugar juice extraction using extracting agentsCelluloseSingle vessel
Owner:ANDRITZ INC
Production of Fermentable Sugars and Lignin from Biomass Using Supercritical Fluids
ActiveUS20120291774A1Improve the level ofBiofuelsPulp by-products recoveryFermentable sugarSupercritical fluid
Methods are disclosed for the continuous treatment of biomass comprising a pretreatment step, wherein said biomass is contacted with a first supercritical, near-critical, or sub-critical fluid to form a solid matrix and a first liquid fraction; and a hydrolysis step, wherein said solid matrix formed in said pretreatment step is contacted with a second supercritical or near-supercritical fluid to produce a second liquid fraction and a insoluble lignin-containing fraction. Also disclosed are apparatuses for the continuous conversion of biomass comprising a pretreatment reactor and a hydrolysis reactor associated with said pretreatment reactor.
Owner:RENMATIX INC
Methods to Improve the Compatibility and Efficiency of Powdered Versions of Microfibrous Cellulose
InactiveUS20110059883A1Improve performanceOrganic detergent compounding agentsNon-surface-active detergent compositionsCellulose fiberPolymer degradation
Owner:CP KELCO U S INC
Method for processing vegetable biomass
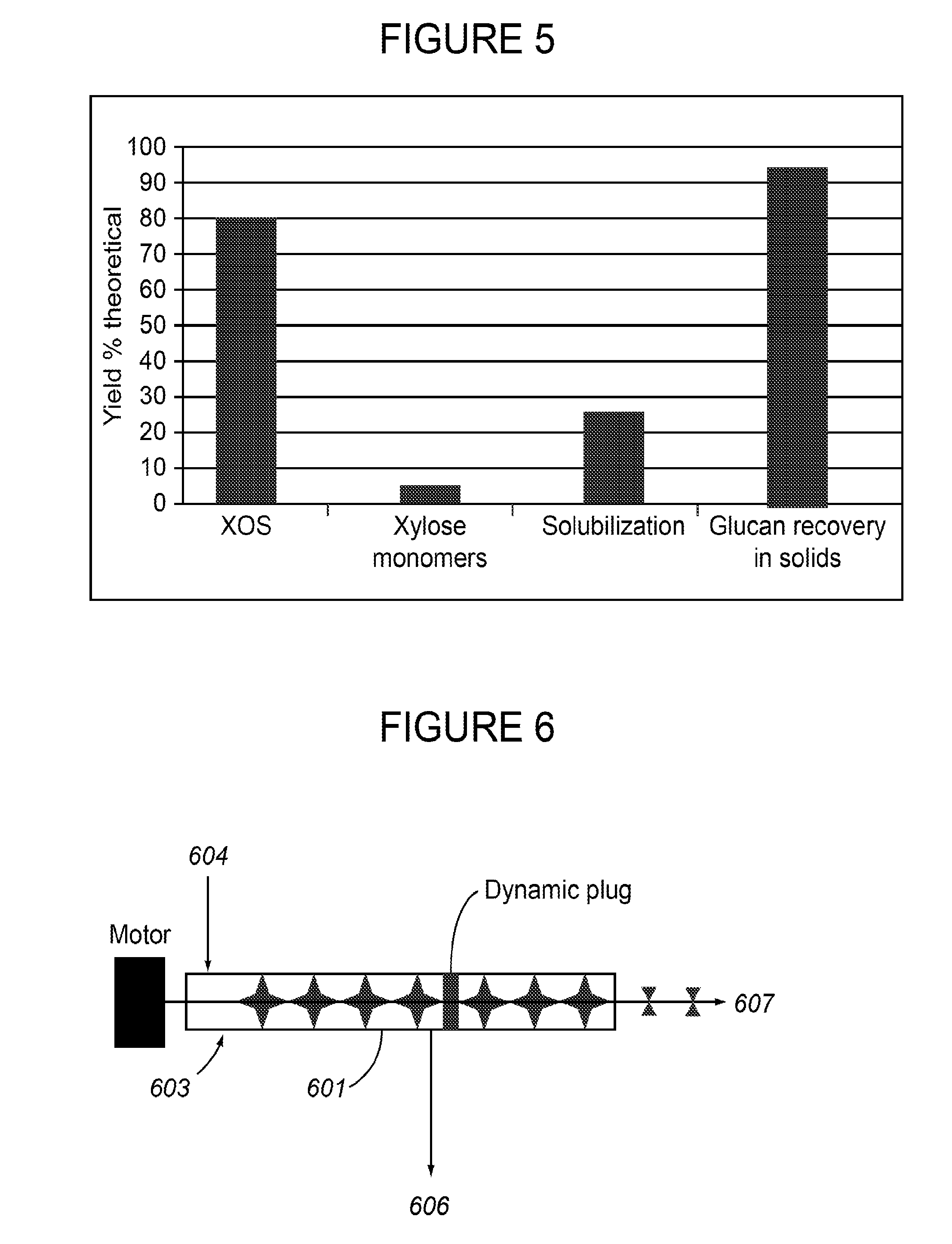
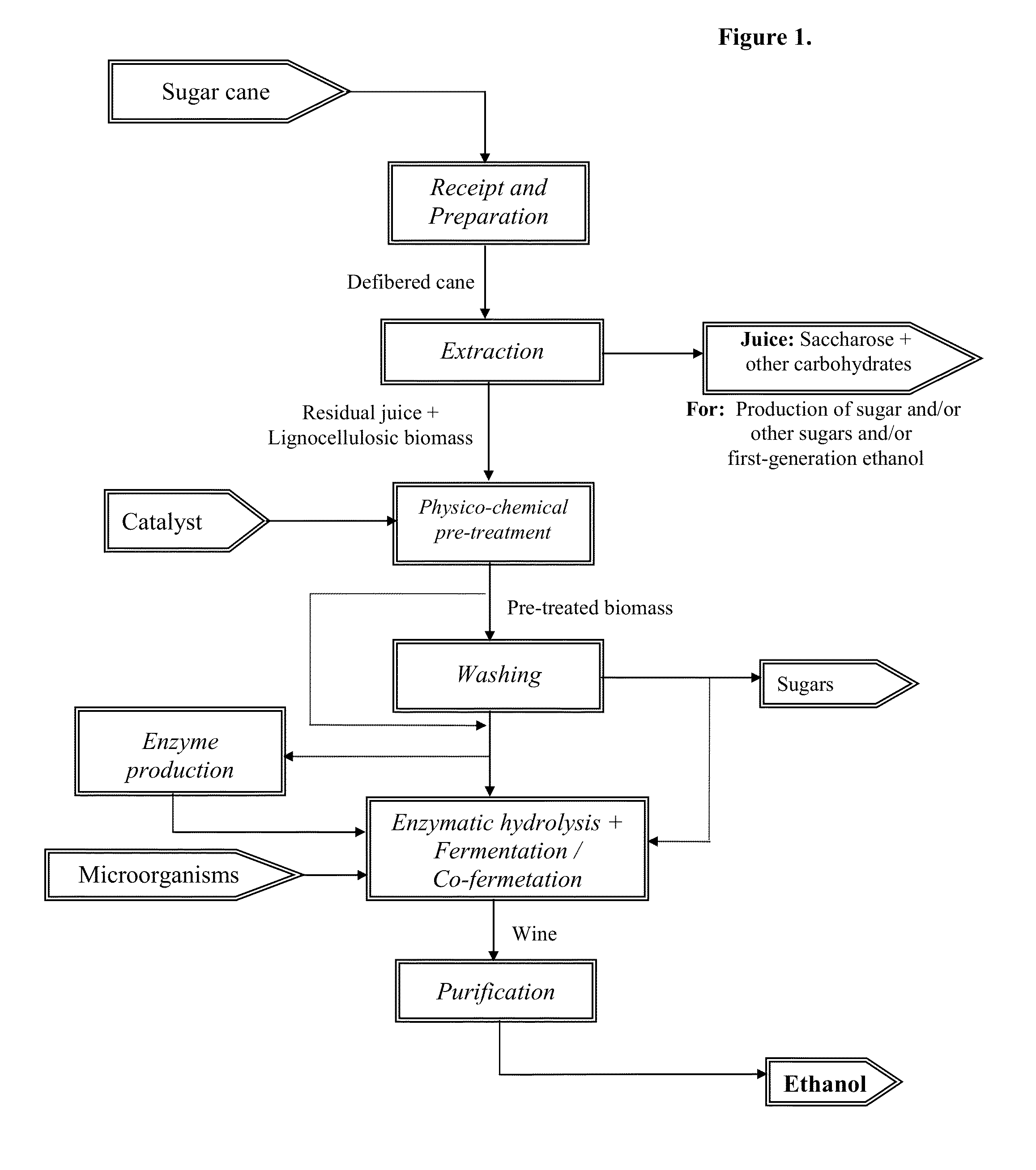
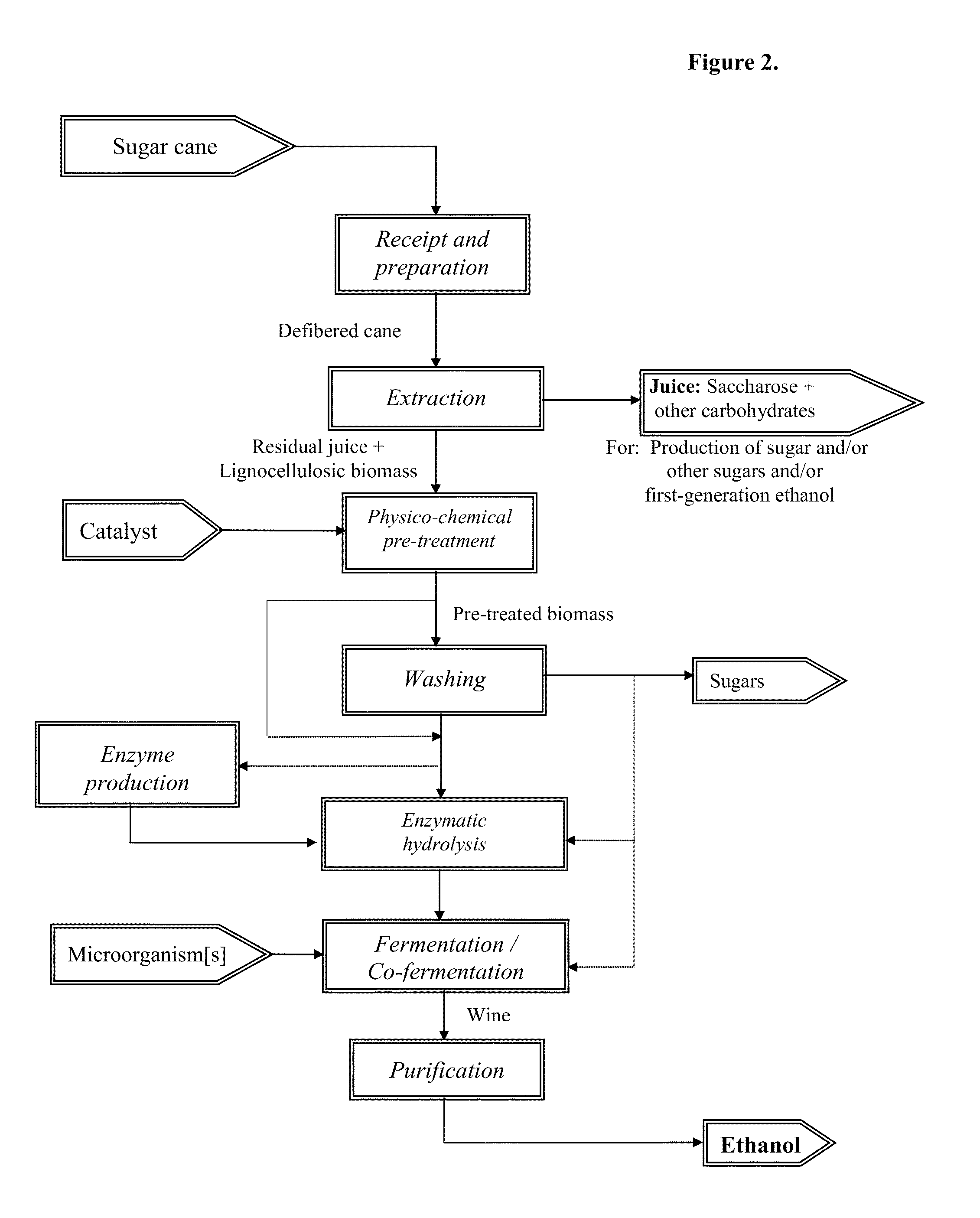
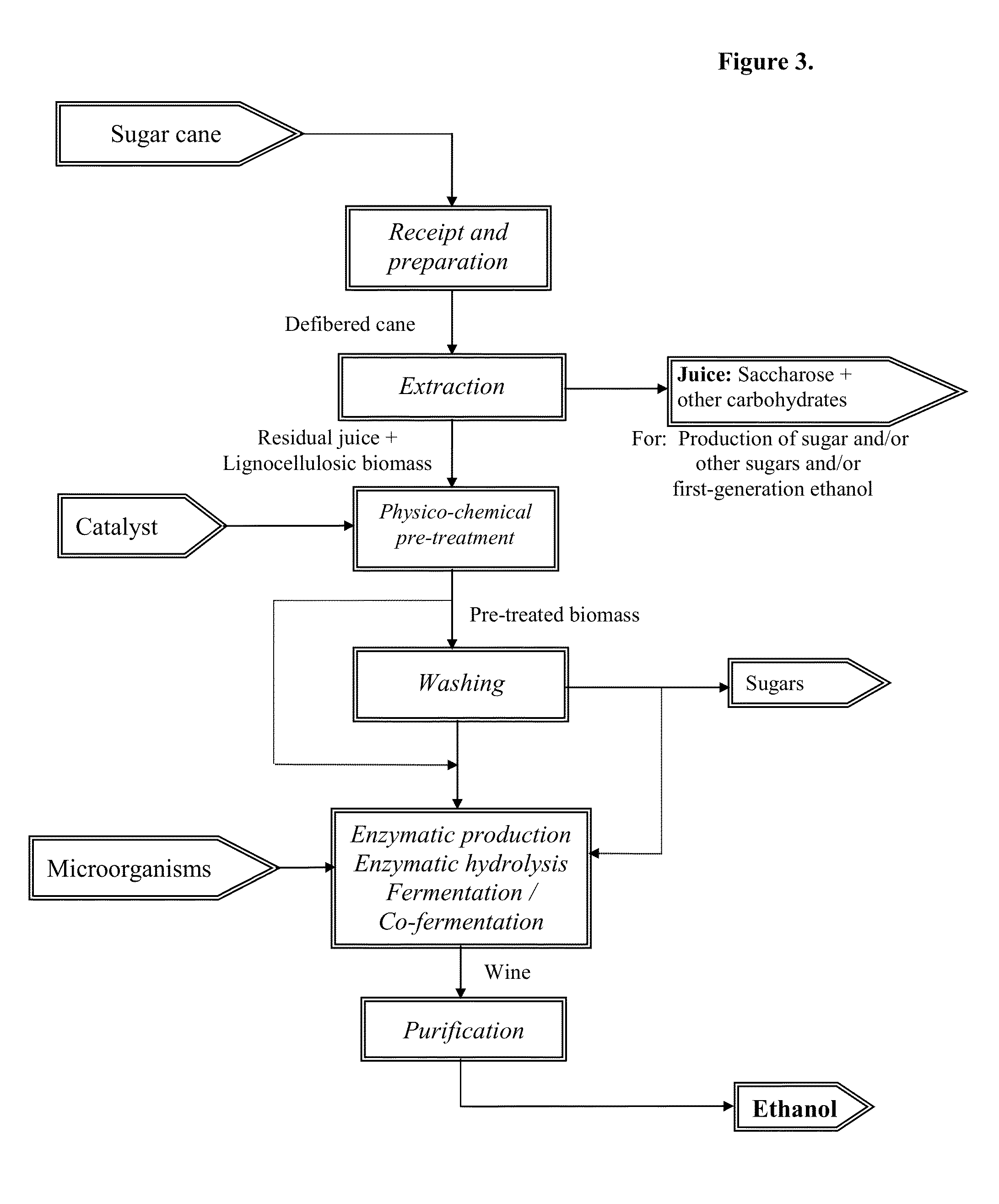
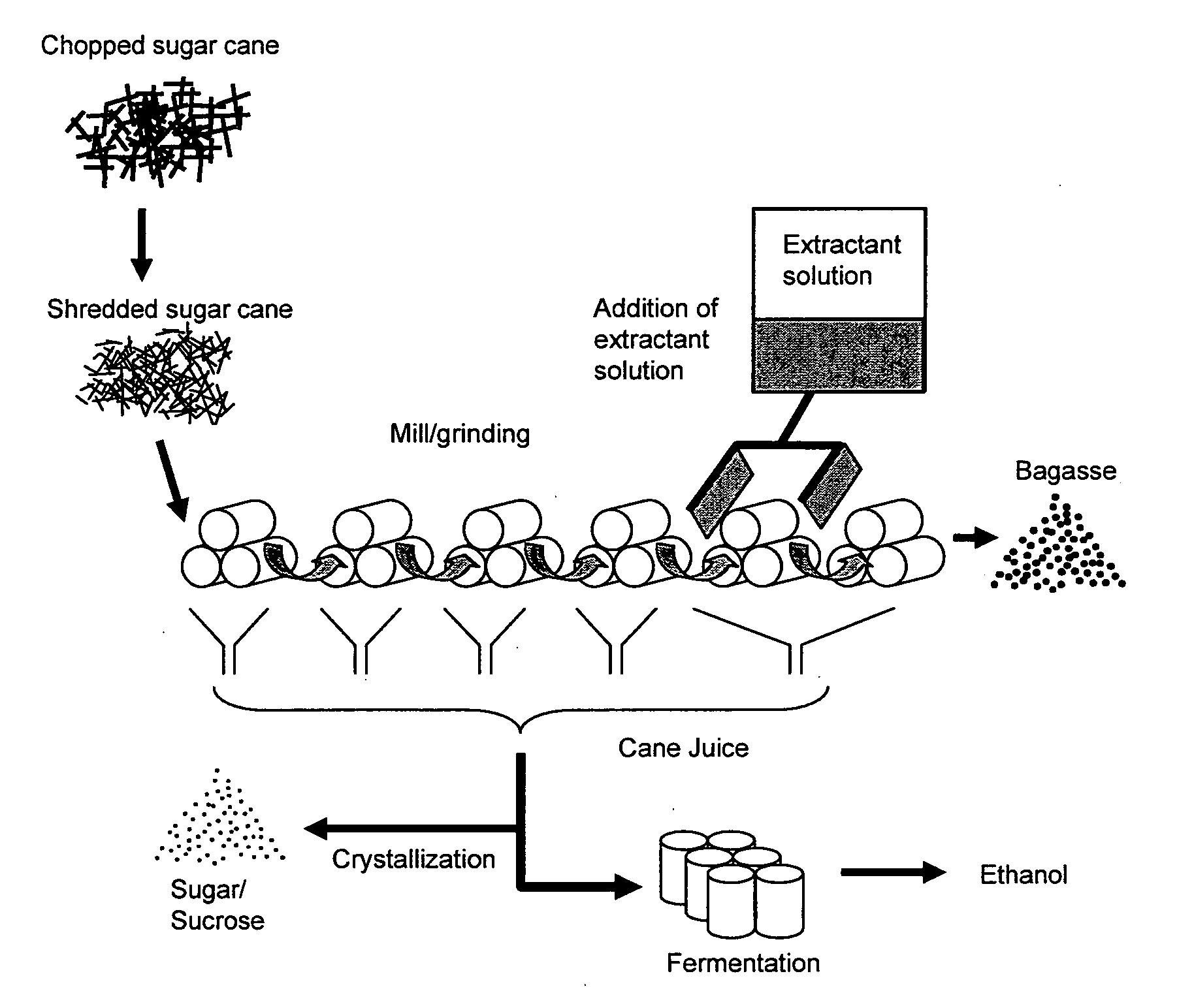
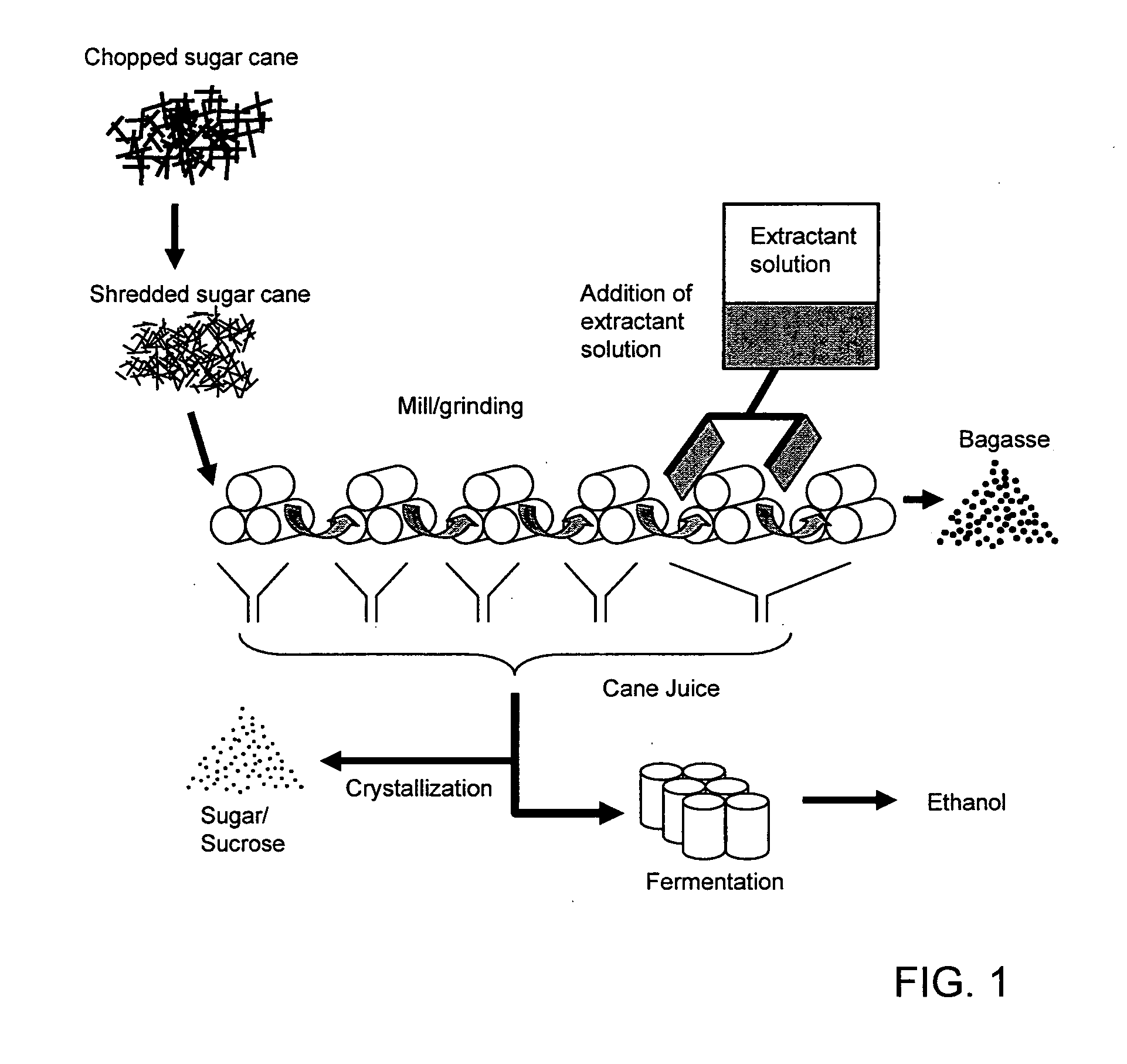
The present invention relates to an energy-efficient process for the treatment of plant biomass, particularly sugar cane, for the production of carbohydrates and ethanol, using physico-chemical and extraction techniques, as well as very simple milling configurations, thereby minimizing energy consumption during extraction of the cane juice.The biomass treated and obtained through this process, when subjected to a fermentation process for the production of ethanol, increases the yield of the process in comparison with that of traditional sugar cane. It can also be used for the production of enzymes, animal feedstuffs, and other useful products.
Owner:CTC CENT DE TECHA CANAVIEIRA
Deep eutectic solvent and preparation method thereof and application thereof in process of preparing glucose by hydrolyzing celluloses
ActiveCN108950091ARaw material environmental protectionDifficult to volatilize and less pollutionSugar juice extraction using extracting agentsGlucose productionCelluloseSolvent
The invention discloses a deep eutectic solvent. A hydrogen bond donor of the deep eutectic solvent is a protonic acid; a hydrogen bond acceptor of the deep eutectic solvent is an ammonium salt containing a specific functional group; and the specific functional group is alkylene, a sulfonic acid group, a carboxyl group, an ether group, an amino group or a sulfhydryl group. The deep eutectic solvent can efficiently hydrolyze celluloses to glucose. The invention also discloses a method of preparing the glucose by using the deep eutectic solvent to hydrolyze cellulose biomasses. The method comprises the following steps of: adding the cellulose biomass and the deep eutectic solvent to a reactor, and reacting at the temperature of 80-120 DEG C for 0.5-10h to obtain the hydrolysate glucose. Themethod has the characteristics of high reduction selectivity and high yield of glucose products in the process of using the cellulose biomass to prepare the glucose, can ensure that the glucose product meets the production quality requirements, and has very good economic, environmental and social benefits.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method of converting lignin and uses thereof
InactiveCN105518157AOrganic compound preparationOxygen compounds preparation by reductionCelluloseLignocellulosic biomass
Owner:SUGANIT SYSTEMS INC
Cellulose-solvent-based lignocellulose fractionation with modest reaction conditions and reagent cycling
ActiveUS20140190471A1Readily converted into glucoseLow costPressurized chemical processBiofuelsAcetic acidSugar
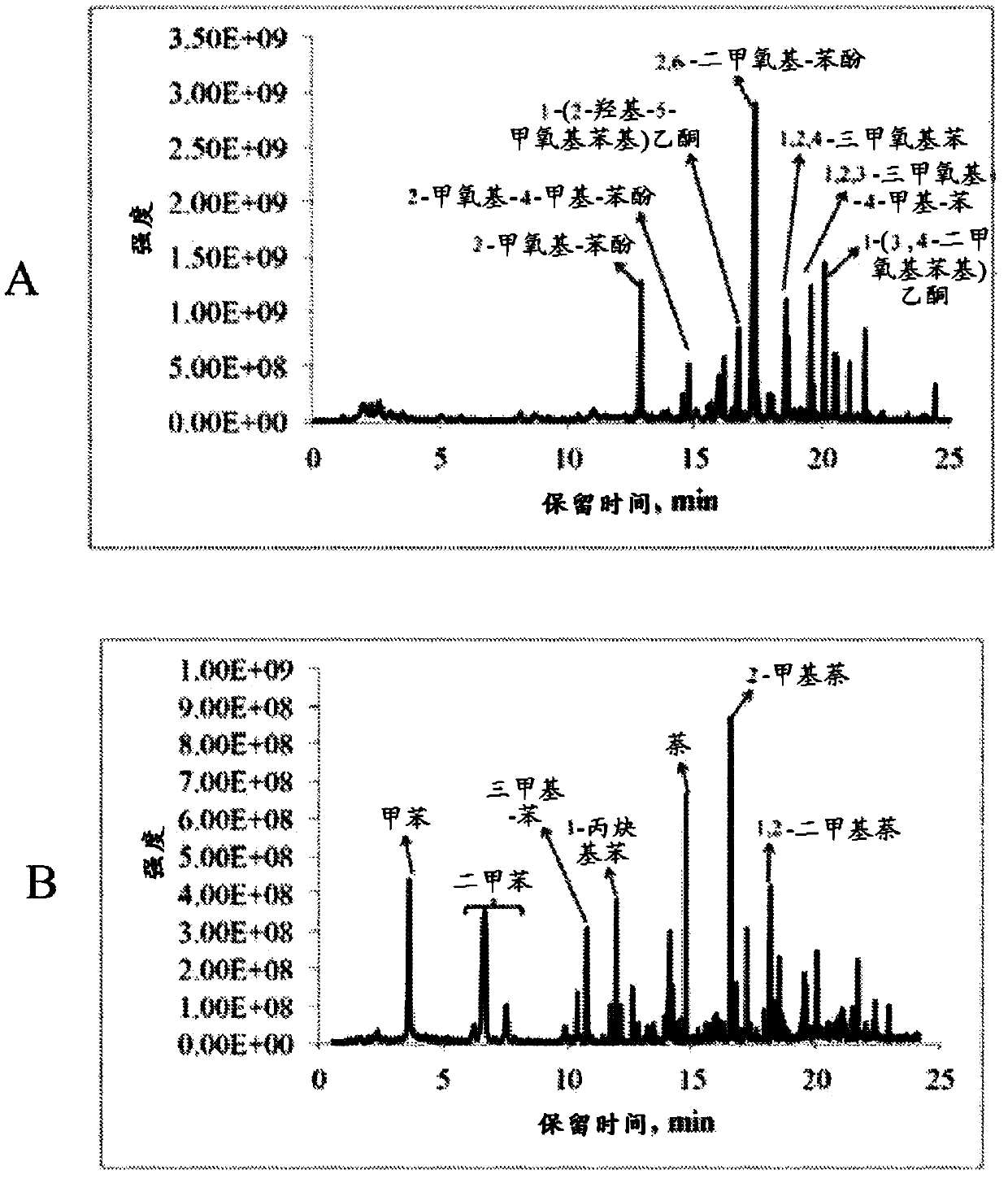
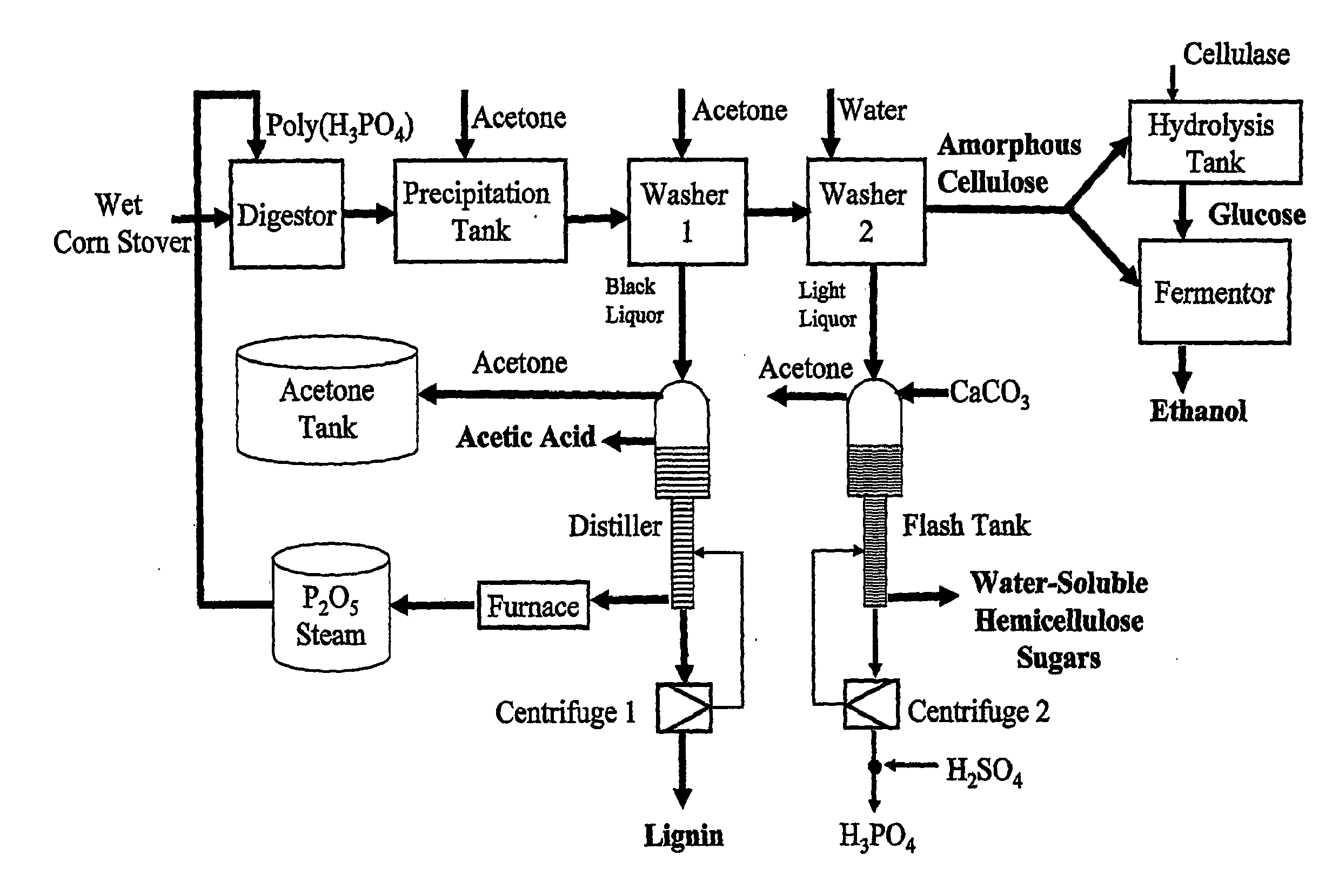
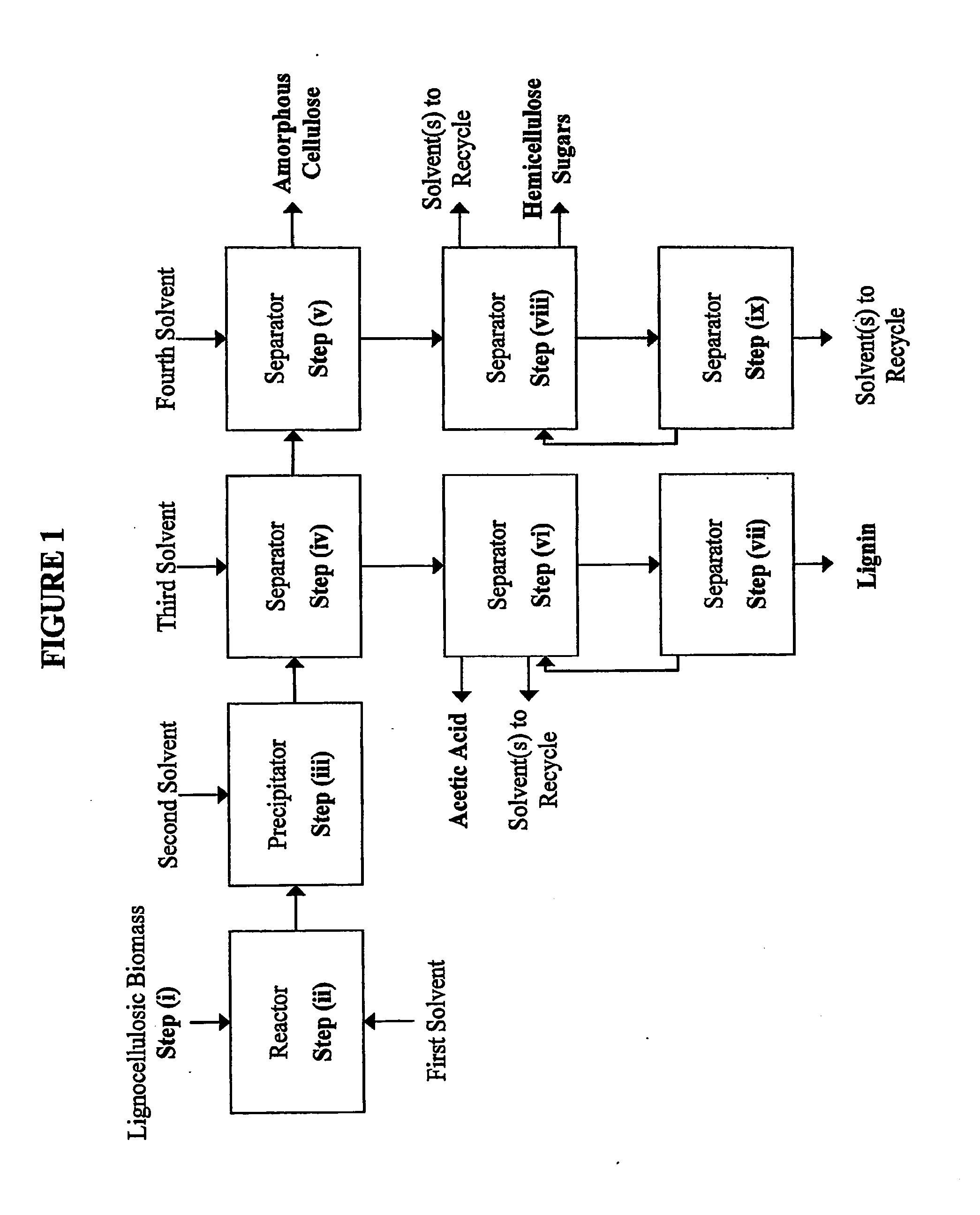
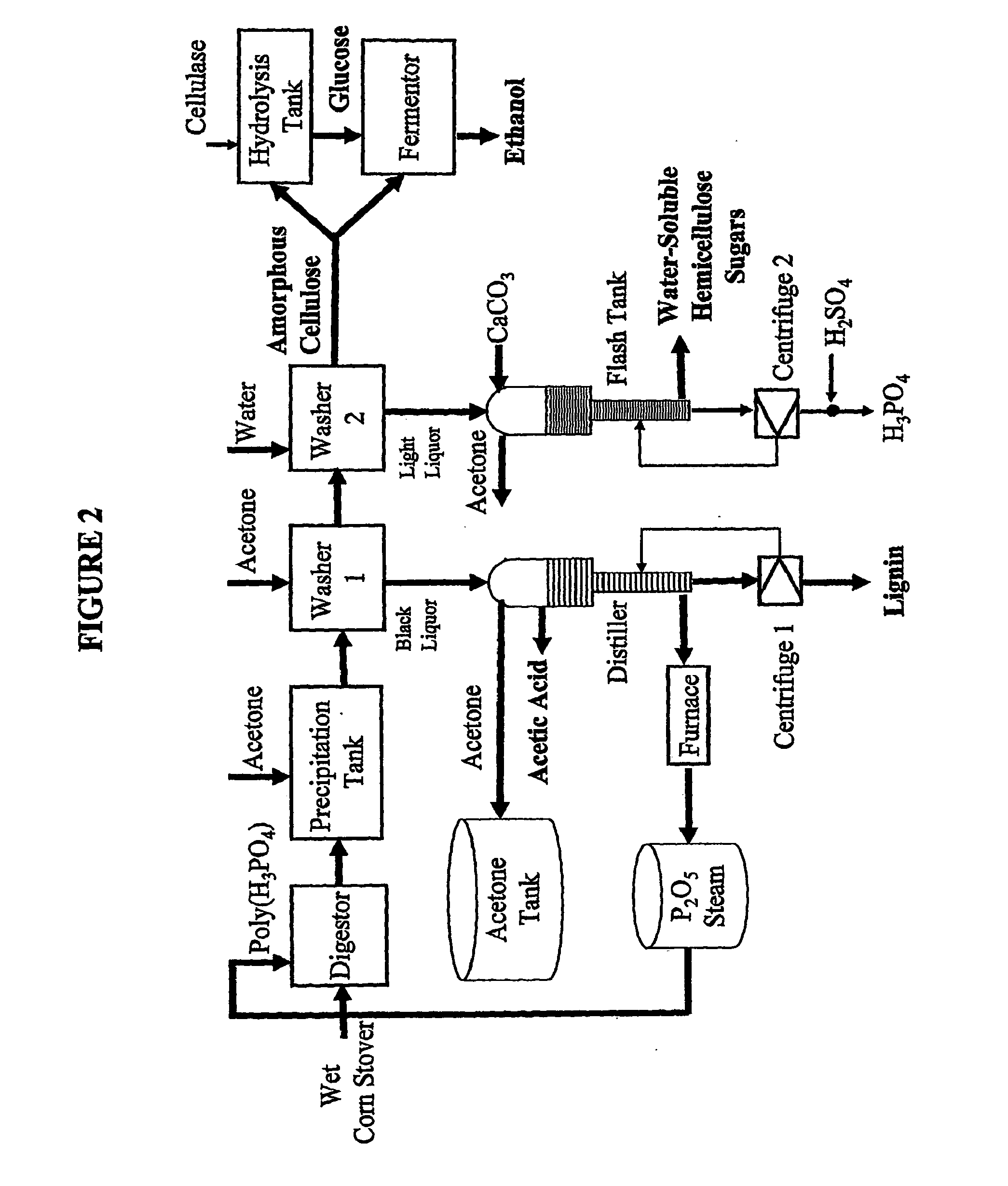
Embodiments of the present invention overcome the well-known recalcitrance of lignocellulosic biomass in an economically viable manner. A process and system are provided for the efficient fractionation of lignocellulosic biomass into cellulose, hemicellulose sugars, lignin, and acetic acid. The cellulose thus obtained is highly amorphous and can be readily converted into glucose using known methods. Fermentable hemicellulose sugars, low-molecular-weight lignin, and purified acetic acid are also major products of the process and system. The modest process conditions and low solvent / solid ratios of some embodiments of the invention imply relatively low capital and processing costs.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Methods and systems for preparing materials for sucralose production
InactiveUS20100019195A1Reduce pressureCarboxylic acid amide separation/purificationSedimentation separationSucroseFiltration
The present invention provides a method for preparing DMF for sucralose production, including, e.g., isolating DMF from a composition comprising DMF, water, and methanol, using a single-tower rectification system. In various embodiments of the present invention, the composition, after the removal of water and methanol, may be further dried / dehydrated, such as, by using a dehydration agent and / or filtration. The resulting substantially pure DMF may comprise at least about 98-99% DMF. The present invention further provides a method of preparing a composition comprising anhydrous sucrose for sucralose production, which may comprise mixing regular sucrose with a water-containing DMF composition, and drying the resulting sucrose-DMF composition. Also provided is a single-tower separation system for isolating DMF from a composition comprising DMF, water, and methanol.
Owner:MAMTEK INT
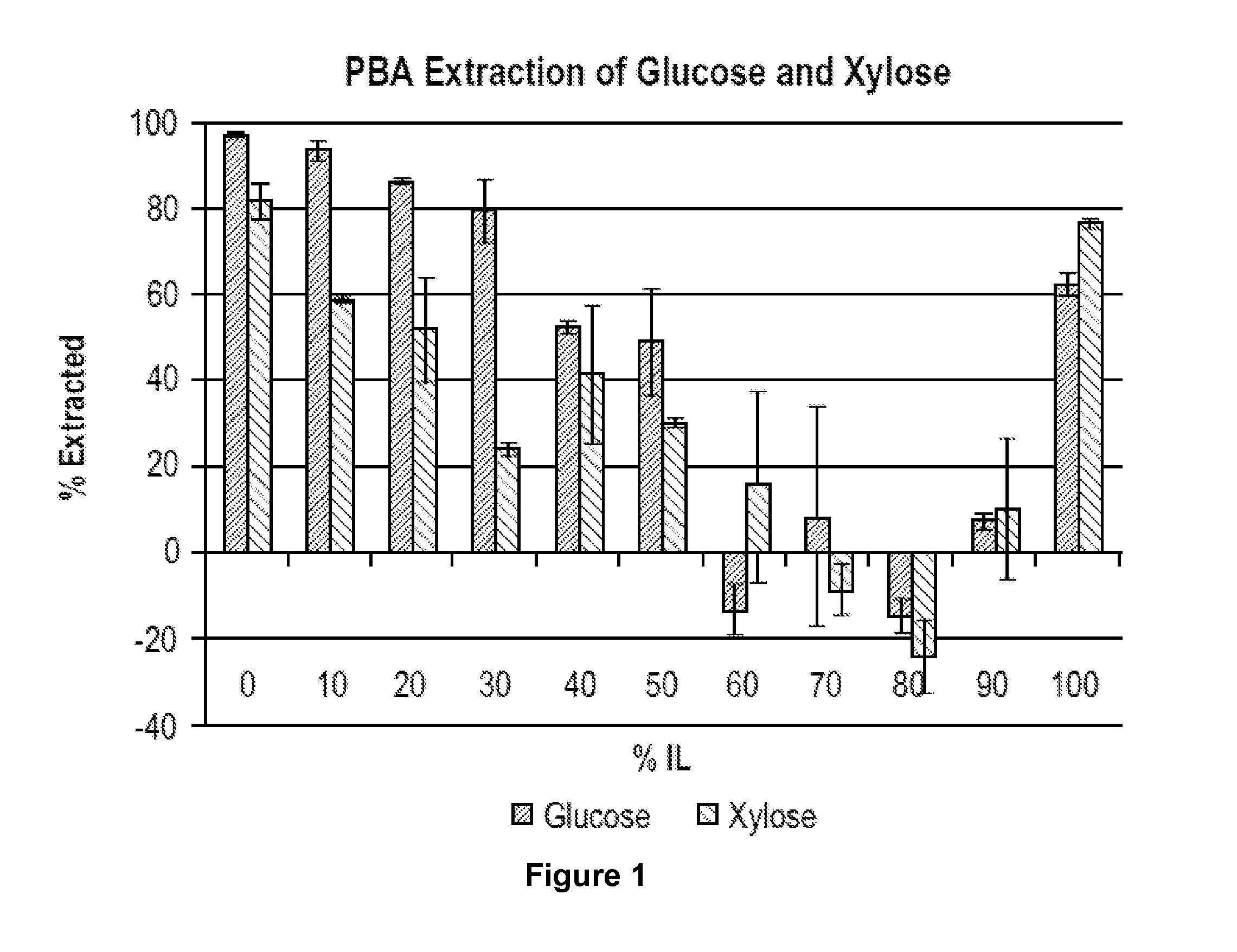
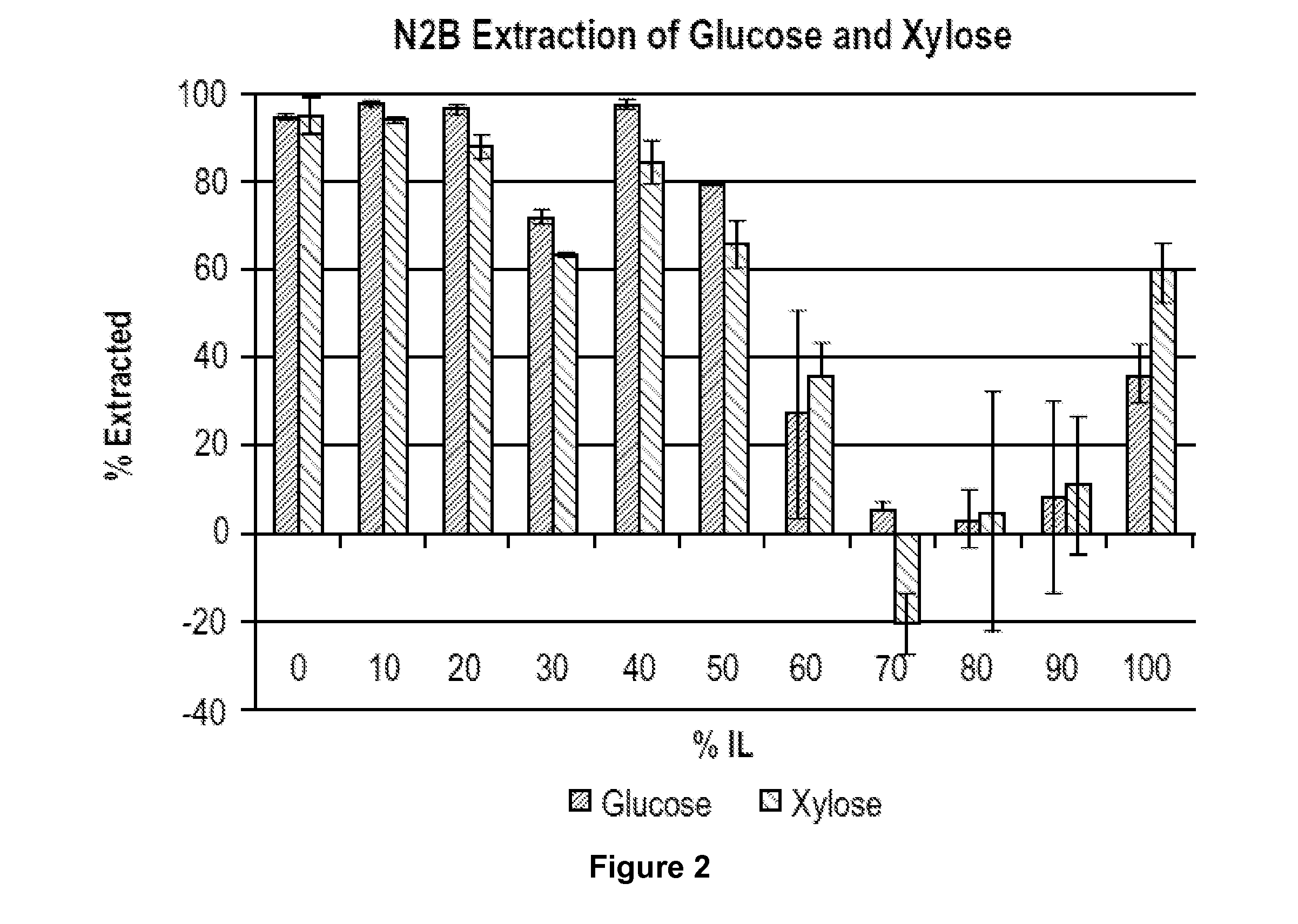
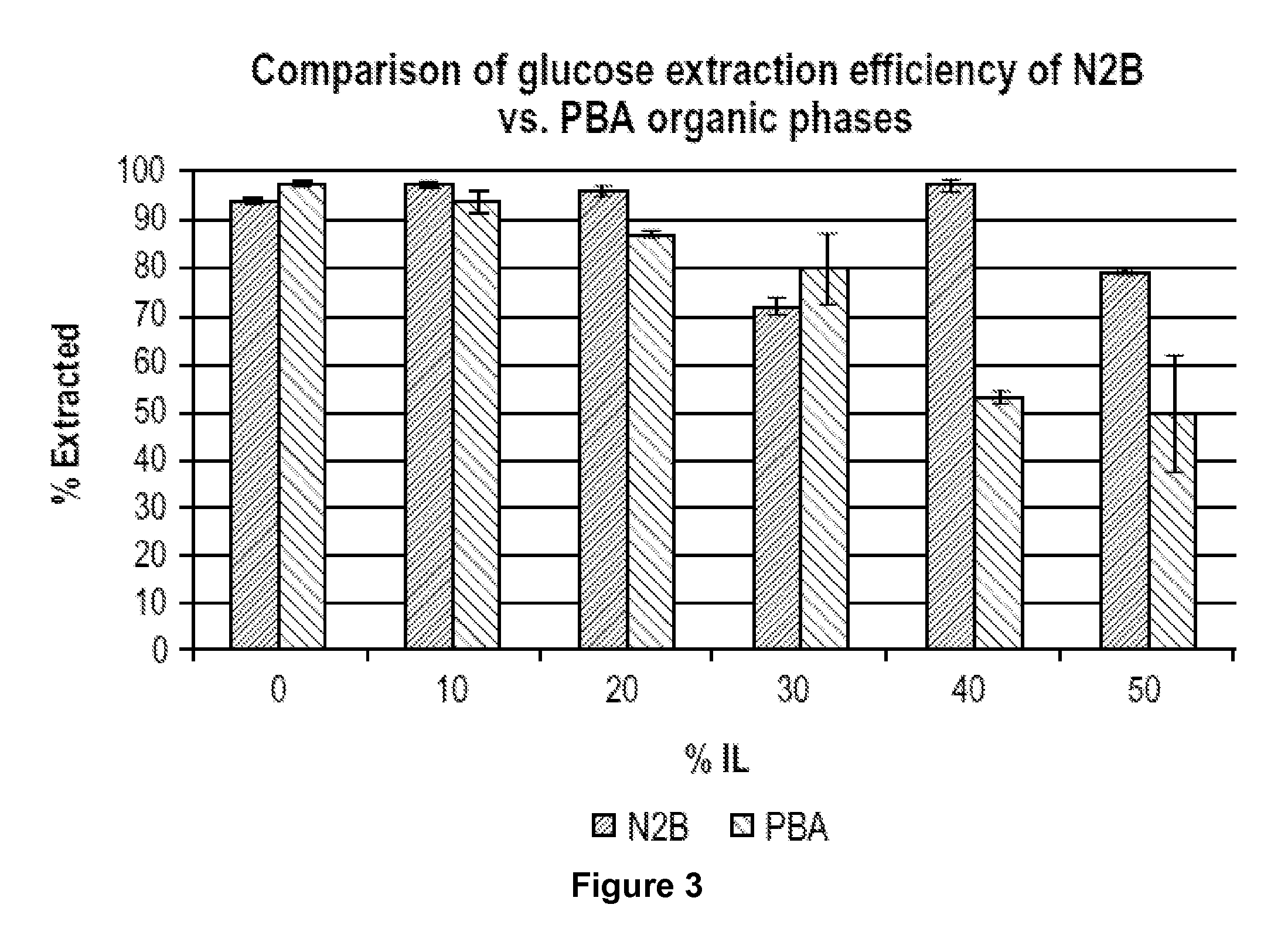
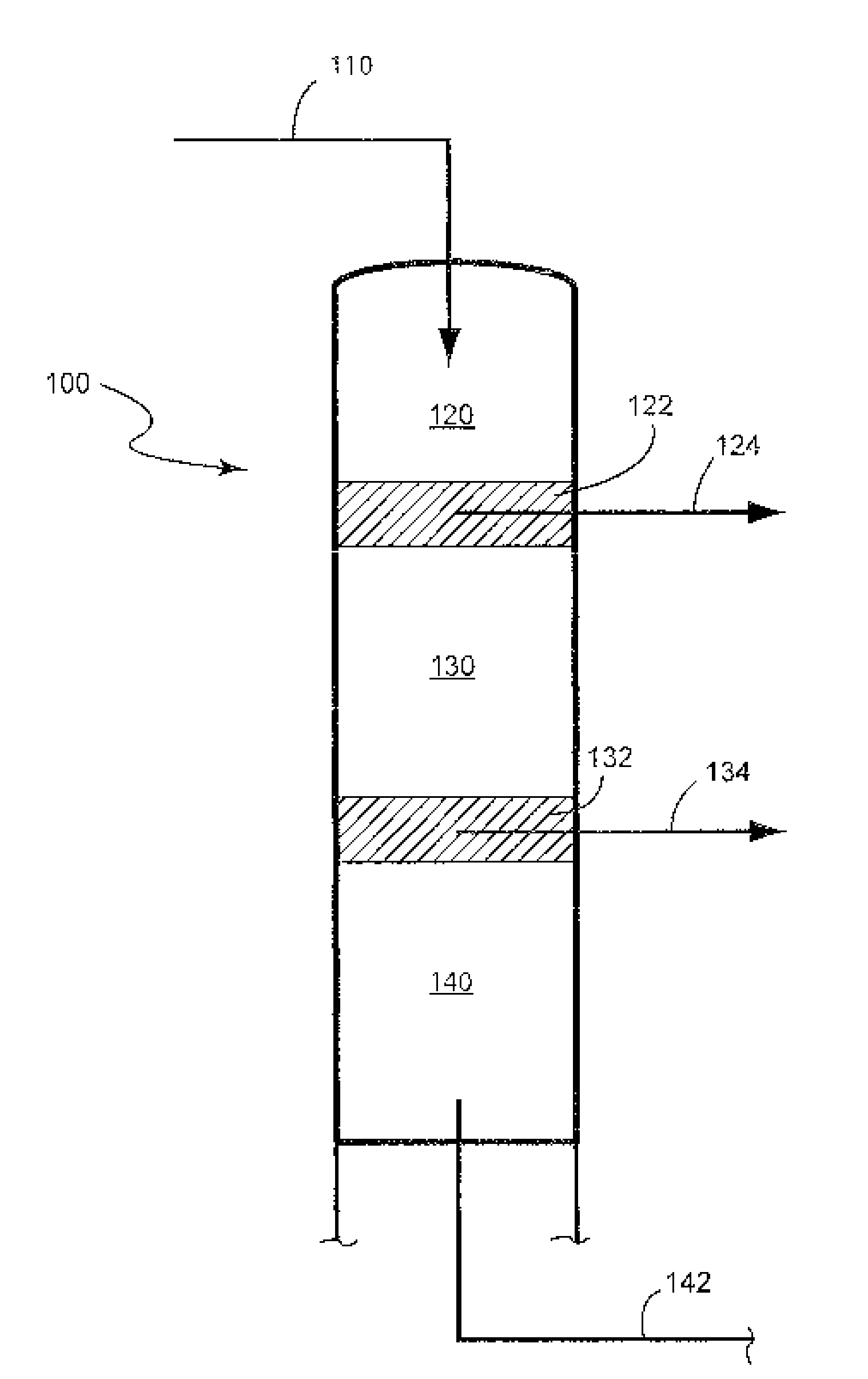
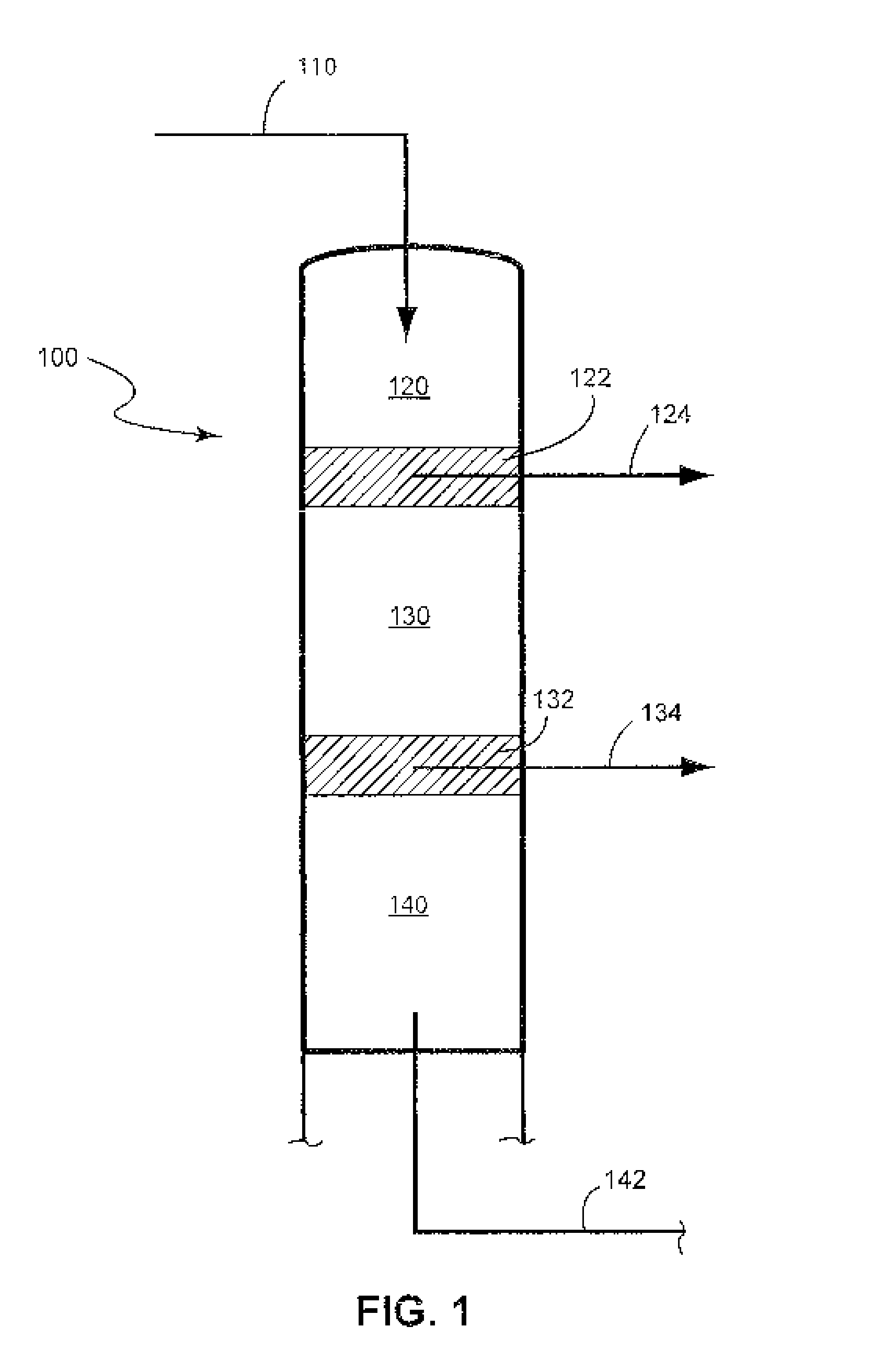
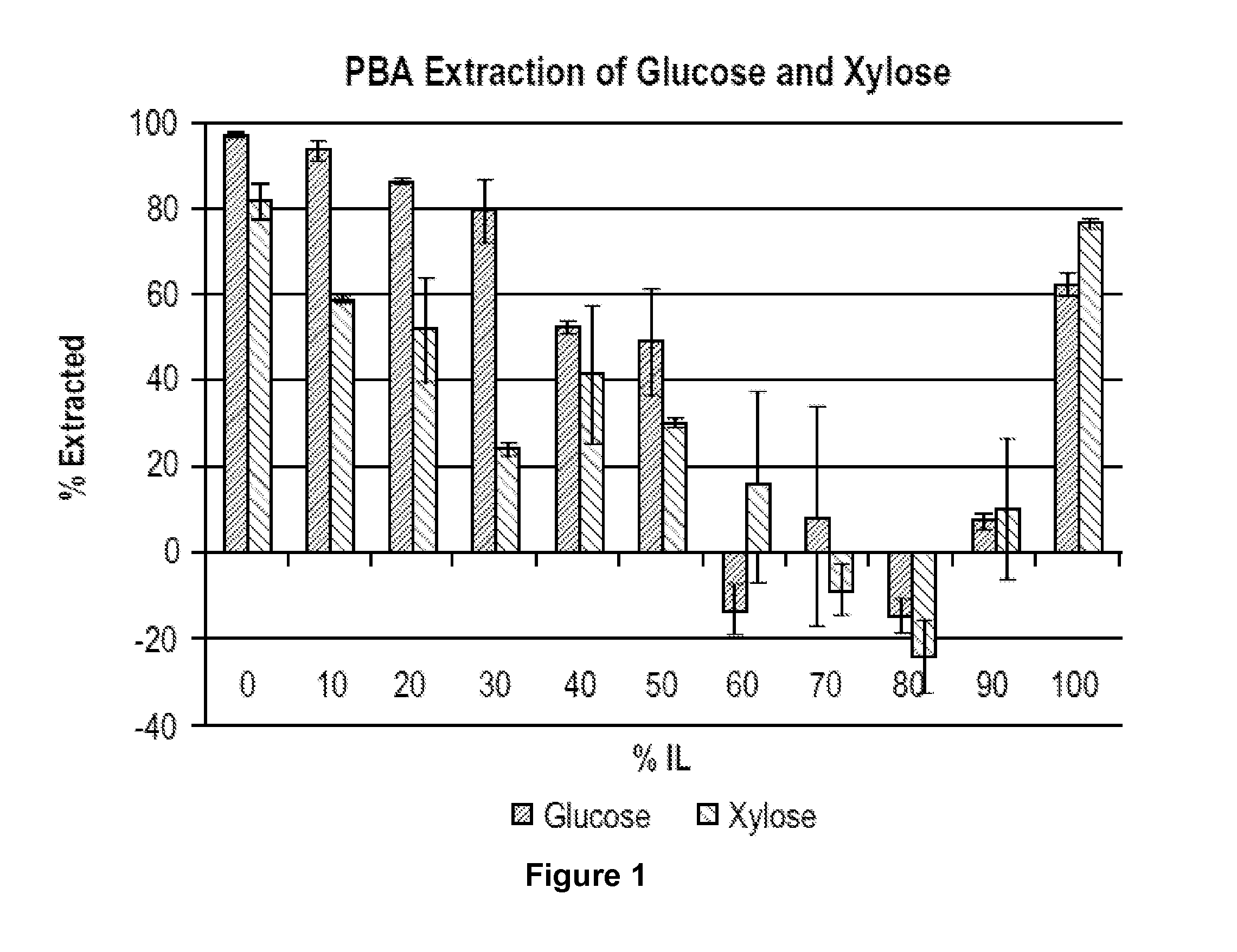
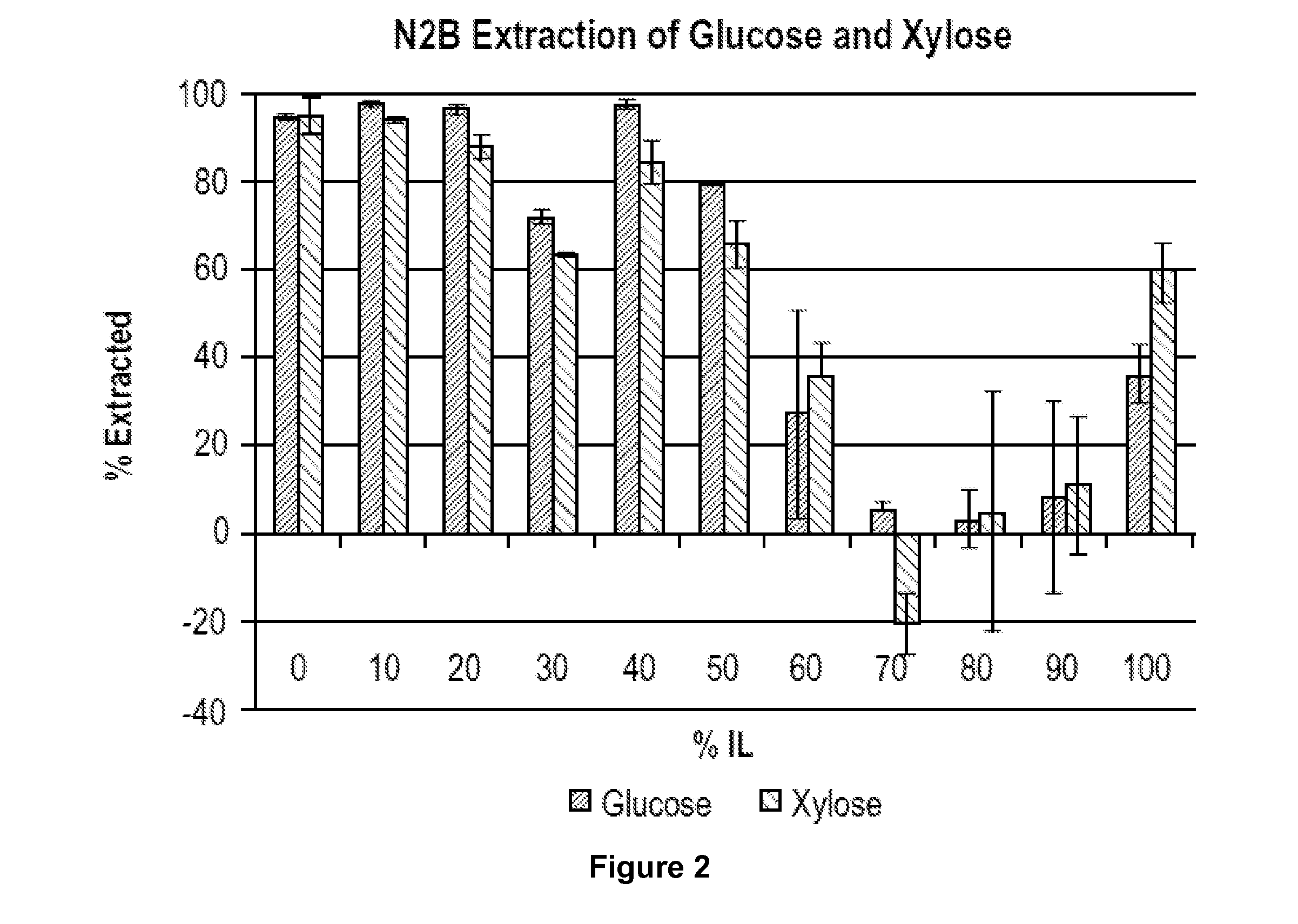
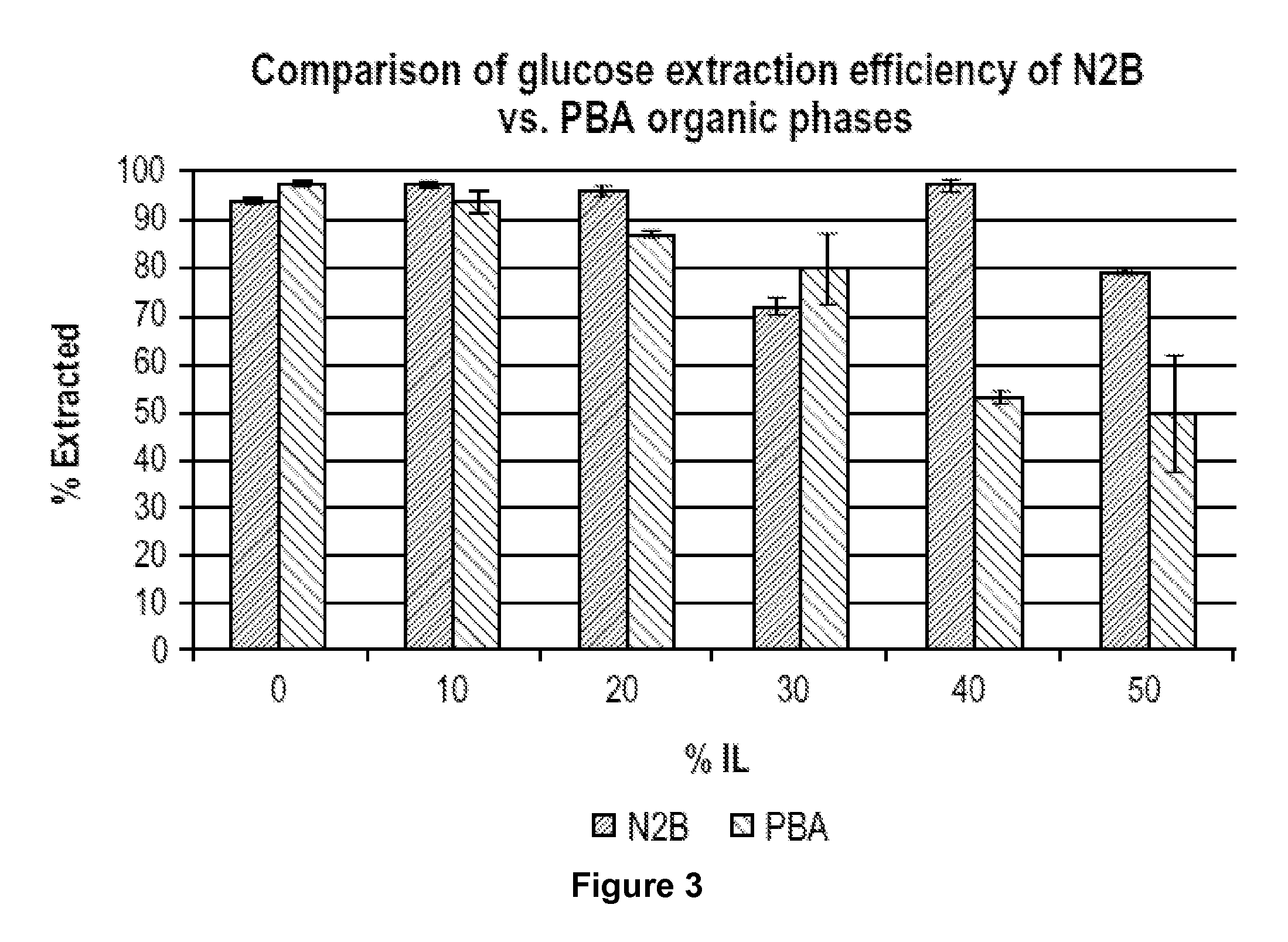
Recovery of sugars from ionic liquid biomass liquor by solvent extraction
The present invention provides for a composition comprising a solution comprising (a) an ionic liquid (IL) or ionic liquid-aqueous (ILA) phase and (b) an organic phase, wherein the solution comprises a sugar and a boronic acid. The present invention also provides for a method of removing a sugar from a solution, comprising: (a) providing a solution comprising (i) an IL or ILA phase and (ii) an organic phase, wherein the solution comprises an IL, a sugar and a boronic acid; (b) contacting the sugar with the boronic acid to form a sugar-boronic acid complex, (c) separating the organic phase and the aqueous phase, wherein the organic phase contains the sugar-boronic acid complex, and optionally (d) separating the sugar from the organic phase.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Apparatus and method for hydrolysis of cellulosic material in a two-step process
InactiveUS20090318679A1Undesirable effectSugar derivativesSucrose extraction by chemical meansCelluloseSlurry
Owner:ANDRITZ INC
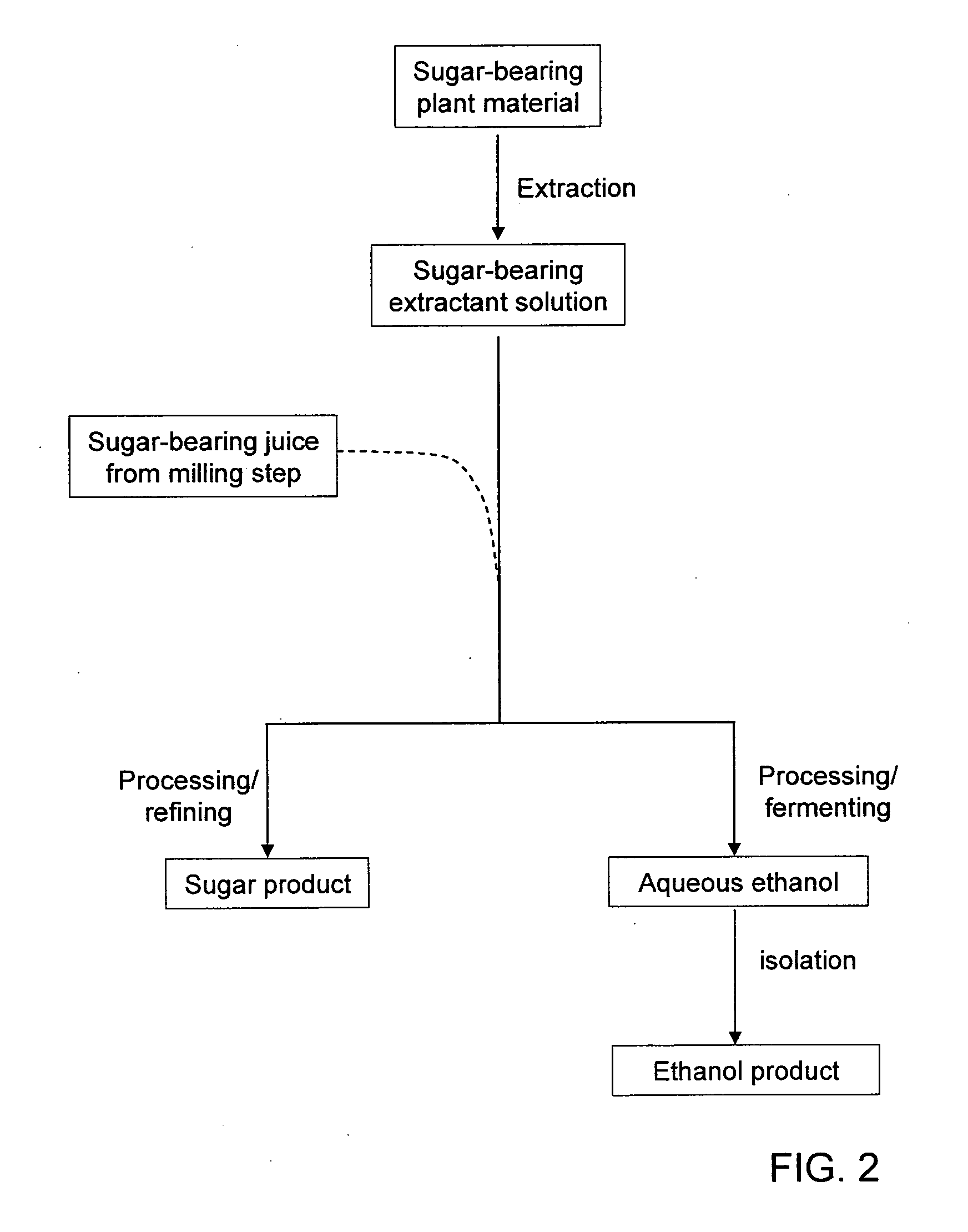
Processes for Extraction of Sugar From Sugar-Bearing Plant Material
The invention provides processes for the extraction of sugar from sugar-bearing plant material such as sugar cane. Accordingly, in one aspect of the invention, a process for extracting sugar from sugar-bearing plant material comprises contacting the sugar-bearing plant material with an extractant solution comprising water and a surfactant; and separating the extractant solution from the sugar-bearing plant material. One example of a suitable surfactant is a poly(alkylene oxide) polymer such as a poly(propylene oxide) polymer, a poly(ethylene oxide) polymer, or a poly(propylene oxide) / (ethylene oxide) copolymer.
Owner:DOW BRASIL SUDESTE IND
Conversion of natural products including cellulose to hydrocarbons, hydrogen and/or other related compounds
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method for extracting zeaxanthin dipalmitate from liquid fructus lycii material
InactiveCN107868028AReduce extraction costsHigh solid contentAlkaloids chemistryOrganic compound preparationDietary fiberZeaxanthin dipalmitate
The invention discloses a method for extracting zeaxanthin dipalmitate from a liquid fructus lycii material. Fresh fructus lycii and rehydrated fructus lycii are pulped, fructus lycii pulp is obtained, enzymolysis, liquid extraction and vacuum desolution are performed, a zeaxanthin dipalmitate extract is obtained, and different content of zeaxanthin dipalmitate micro-capsule powder is prepared andprocessed from the zeaxanthin dipalmitate extract. Dietary fiber, protein and syrup of fructus lycii are obtained from residues obtained after extraction of zeaxanthin dipalmitate respectively, and other fructus lycii functional ingredients such as flavone, polysaccharide, alkaloid and the like of fructus lycii are obtained through extraction. The extraction cost of fructus lycii functional ingredients is reduced, the raw material utilization rate of fructus lycii is increased, raw materials are utilized to the greatest extent, and the additional value of the raw materials is increased.
Owner:周学义
Recovery of sugars from ionic liquid biomass liquor by solvent extraction
The present invention provides for a composition comprising a solution comprising (a) an ionic liquid (IL) or ionic liquid-aqueous (ILA) phase and (b) an organic phase, wherein the solution comprises a sugar and a boronic acid. The present invention also provides for a method of removing a sugar from a solution, comprising: (a) providing a solution comprising (i) an IL or ILA phase and (ii) an organic phase, wherein the solution comprises an IL, a sugar and a boronic acid; (b) contacting the sugar with the boronic acid to form a sugar-boronic acid complex, (c) separating the organic phase and the aqueous phase, wherein the organic phase contains the sugar-boronic acid complex, and optionally (d) separating the sugar from the organic phase.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Cane sugar manufacturing method capable of reducing pigment generation
InactiveCN109530290AImprove cleaning efficiencyImprove cleanlinessSugar dryingPurification using alkaline earth metal compoundsPhosphoric acidEvaporation
The invention provides a cane sugar manufacturing method capable of reducing pigment generation. The cane sugar manufacturing method capable of reducing the pigment generation comprises the followingsteps of 1) introducing ozone into sugarcane juice, and filtering to obtain sugarcane dregs and sugarcane filtered juice; 2) spraying ethanol solution to the surface of the mixture of the sugarcane dregs and sugarcane residues, and squeezing and filtering again to obtain ethanol extract; 3) dropping an acetic acid-chitosan solution into the ethanol extract, adjusting the pH value to 7.0, and filtering to obtain filtrate; 4) introducing nitrogen into the sugarcane filtered juice, heating, adding phosphoric acid while stirring, uniformly mixing, adding lime milk to adjust the pH value to 6.5, and obtaining supernatant liquid after separation and sedimentation; 5) dropping the acetic acid-chitosan solution into mixed solution of the supernatant liquid and the filtrate, adjusting the pH value,adding nano ferroferric oxide powder, carrying out magnetic field separation, introducing nitrogen into clear juice until the clear juice is saturated and carrying out negative pressure evaporation and concentration to obtain fine syrup; and 6) carrying out sugar boiling, honey separation and drying on the fine syrup to obtain finished sugar. According to the cane sugar manufacturing method capable of reducing the pigment generation, the product has the characteristics of low sugar color value, high quality and the like.
Owner:合浦县工业和信息化局
Extraction Method
InactiveUS20150201660A1Affecting palatabilityAffecting colourBiocideAntipyreticDiseaseDietary supplement
The present invention relates to a process for producing an extract derived from sugar cane, the process comprising: i) mixing a sugar cane derived product with ethanol to produce an extraction mixture comprising at least about 50% v / v ethanol; ii) allowing a precipitate to form in the extraction mixture; iii) removing the precipitate from the extraction mixture to obtain a supernatant; and iv) removing ethanol from the supernatant to produce the extract derived from sugar cane. The present invention further relates to extracts produced according to the process of the invention. The invention also relates to the use of such extracts in a method of lowering the available calorific value of a food or beverage, in treating or preventing disease, and as a nutritional supplement, dietary supplement, sports nutrition product, food coating or pharmaceutical product.
Owner:THE PROD MAKERS (AUSTRALIA) PTY LTD
Brown sugar boiling technology with higher sugar production efficiency
InactiveCN110512032AImprove sugar production efficiencyAvoid wastingPurification using adsorption agentsSugar productsHigh sugarSugar white
The invention relates to the technical field of food processing, and discloses a brown sugar boiling technology with higher sugar production efficiency. The brown sugar boiling technology comprises following steps: step one, preparing a plurality of fresh sugarcanes, removing leaves and shells from the sugarcanes, removing bitter tips of sugarcanes, and juicing processed sugarcanes by a juice extractor to obtain sugar juice; step two, filtering extracted sugar juice, filling filtered sugar juice into a precipitation container, and adding a flocculating agent to precipitate the sugar juice; step three, filtering the flocculated and precipitated sugar juice by a membrane machine; and step four, adding ion exchange resin into filter sugar juice to remove the impurities in the sugar juice through adsorption, and filtering the sugar juice again by a filter screen. The provided brown sugar boiling technology has the advantages that brown sugar can be boiled in bathes in a short time, the production period is short, the production efficiency is high, the production technology is simple and easy to perform, sugar waste is avoided, and the brown sugar is convenient to use.
Owner:贵州省好之味精品农业开发有限公司
Apparatus and method for hydrolysis of cellulosic material in a multi-step process to produce C5 and C6 sugars using a single vessel
Owner:ANDRITZ INC
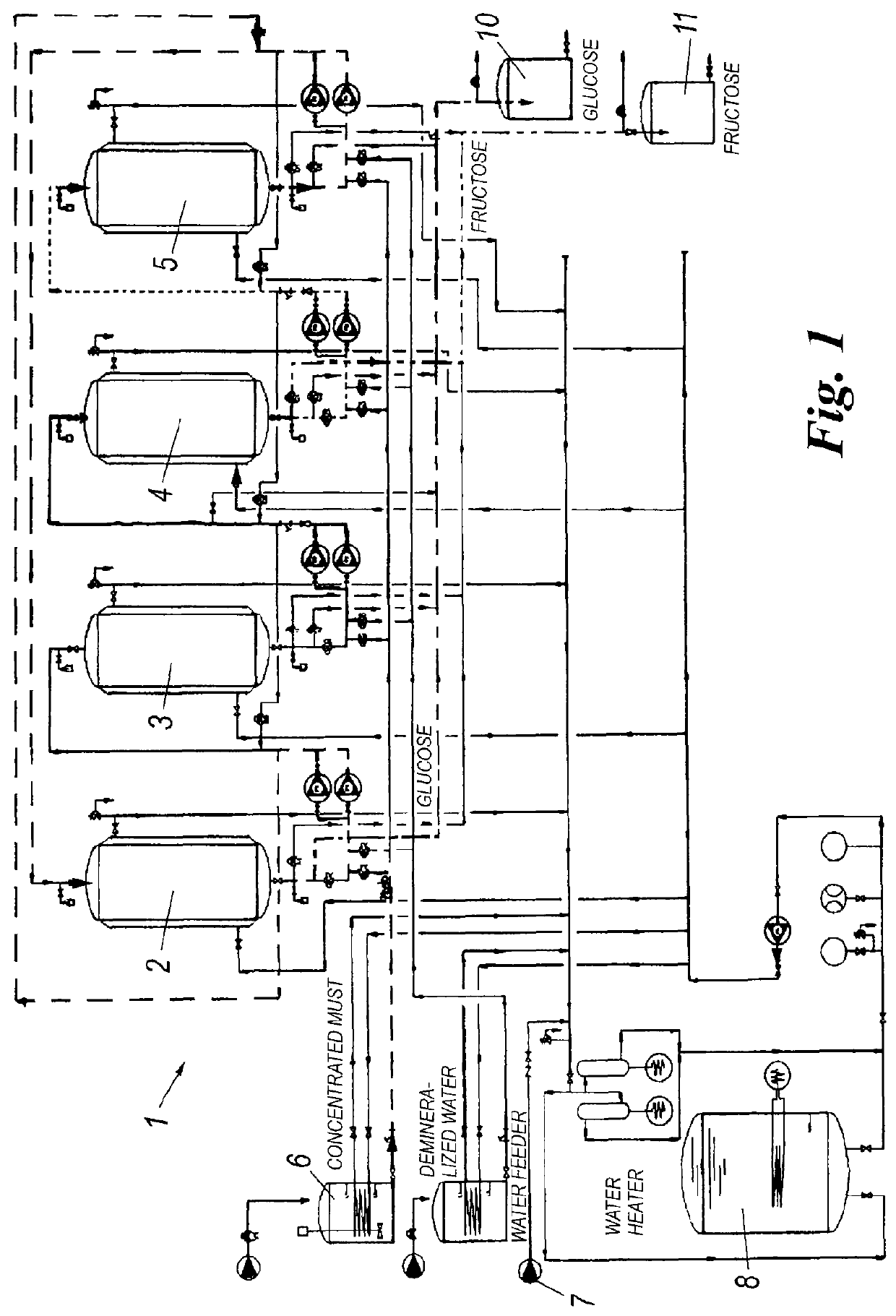
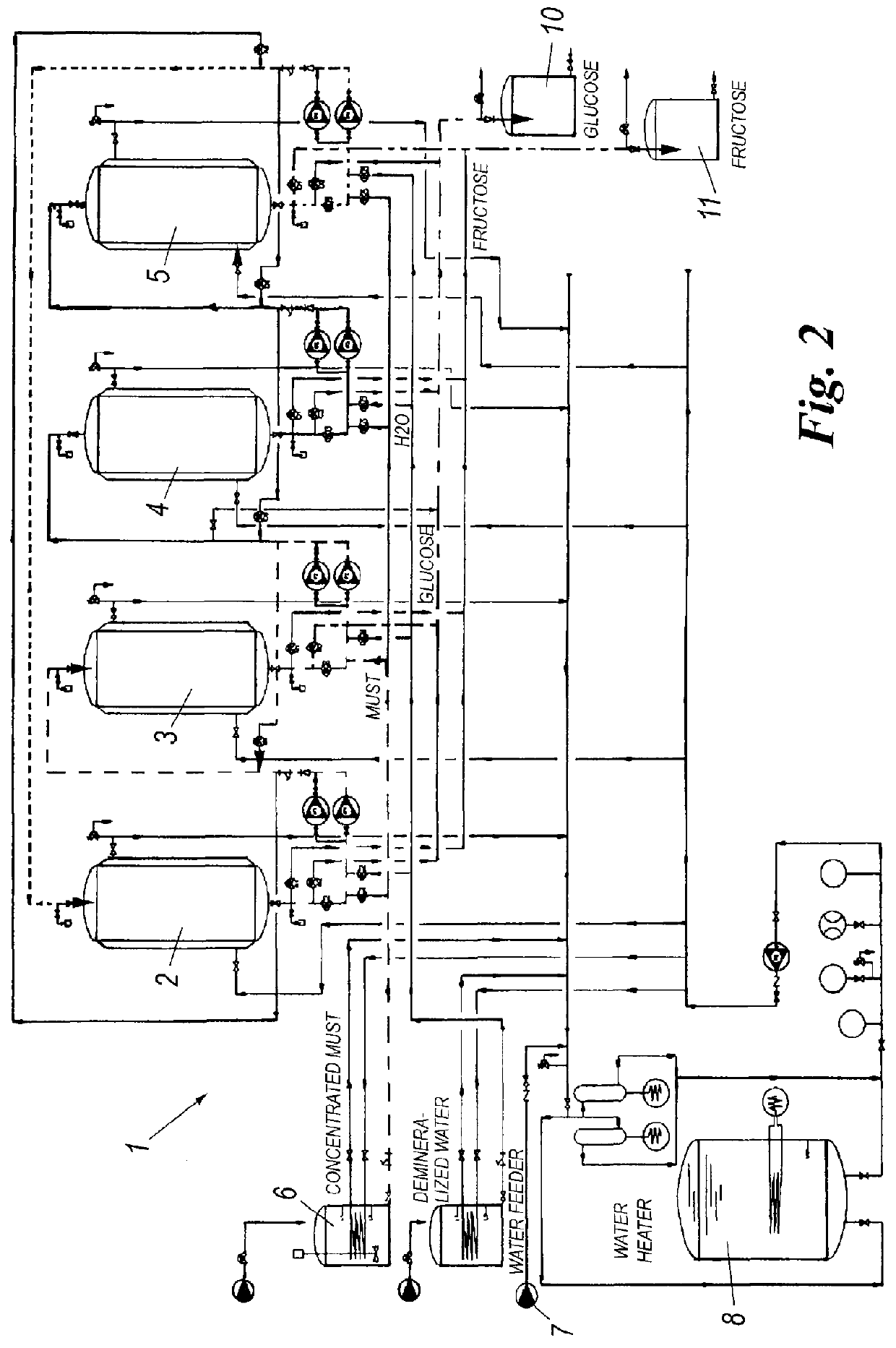
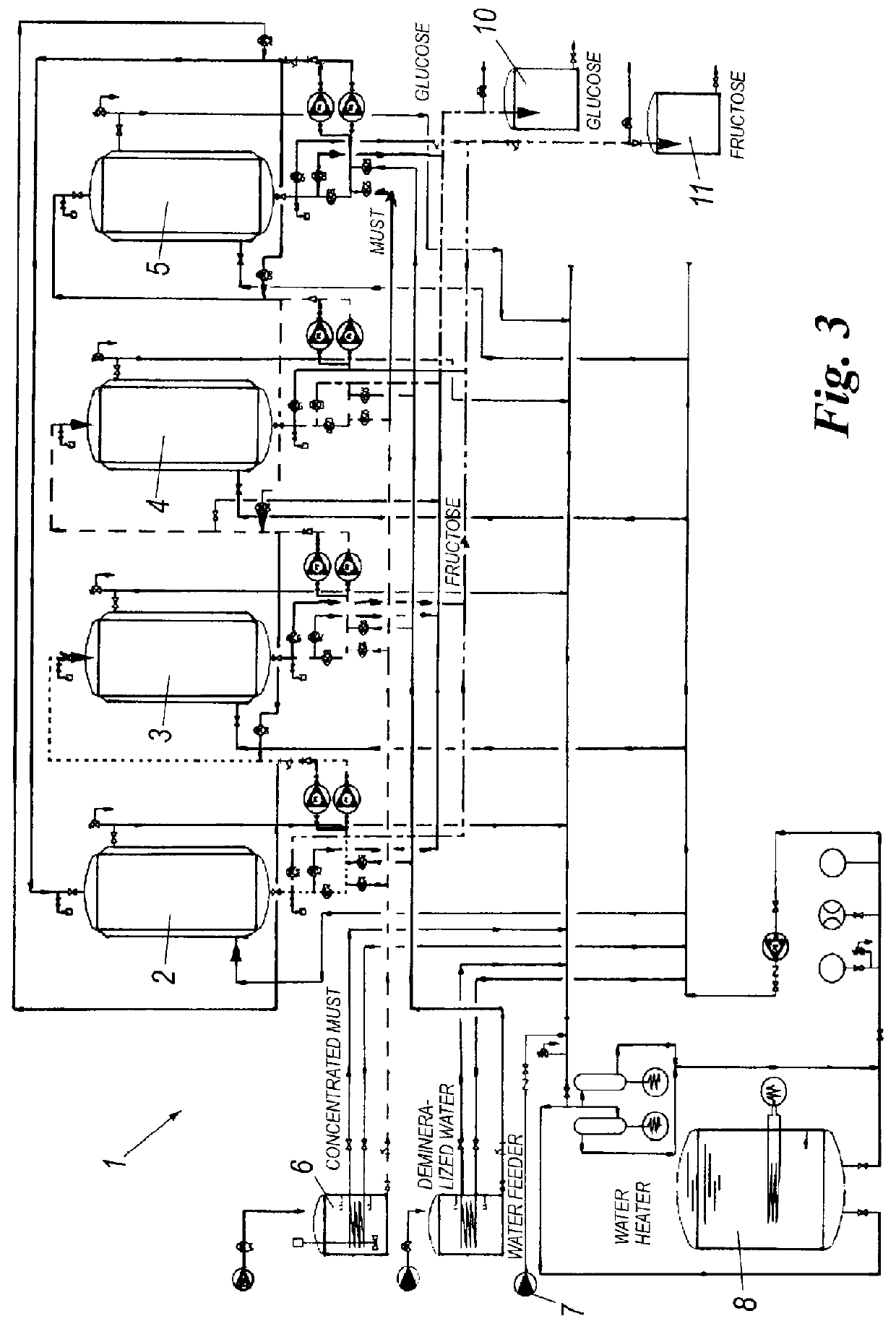
Process and plant for producing sugar products from grapes
The process according to the invention, for producing sugar products from fruits, comprising the steps of:i) demineralizing and decolorizing a fruit juice so as to bring its solid content to comprise from 99% wt to 99.99% wt of a mixture of saccharides, alcohols and flavonoids;iii) separating by chromatography the demineralized and decolorized fruit juice so as to obtain a glucose-enriched fraction or a fructose-enriched fraction from the fruit juice.The solid content of the glucose-enriched fraction comprises at least from 70% wt to 99.99% wt of glucose; the solid content of the fructose-enriched fraction comprises from 70% wt to 99.99% wt of fructose.The low content of anions and cations of the fruit juice to be is treated by chromatography greatly increase the yield of the chromatographic treatment and the purity of the glucose- and fructose-enriched fractions obtained through it.
Owner:NATURALIA INGREDIENTS
Fractionation of a lignocellulosic material
InactiveUS8999067B2Improve permeabilityMaterial is facilitatedBiofuelsLignin derivativesNon solventCellulose
A method for fractionating a lignocellulosic material, the method comprising; contacting (2) the lignocellulosic material with an ionic liquid (3) and dissolving the lignocellulosic material therein, providing a second liquid (7) which is immiscible with the ionic liquid and is also a non-solvent for cellulose, adding the second liquid to the ionic liquid so as to form a biphasic system (6) which comprises an ionic liquid phase essentially free of lignocellulose and a second liquid phase comprising lignin in solution and cellulose as a precipitate, separating the two phases and recovering (8) the precipitated cellulose from the separated second liquid phase.
Owner:QUEENSLAND UNIVERSITY OF TECH
Systems and methods comprising permanganate for improved preservation and yield of crops and related goods
ActiveUS20210062278A1Reduce turbidityReduction of exopolysaccharidesFruit and vegetables preservationSugarcane cuttingFruit juicePermanganate salt
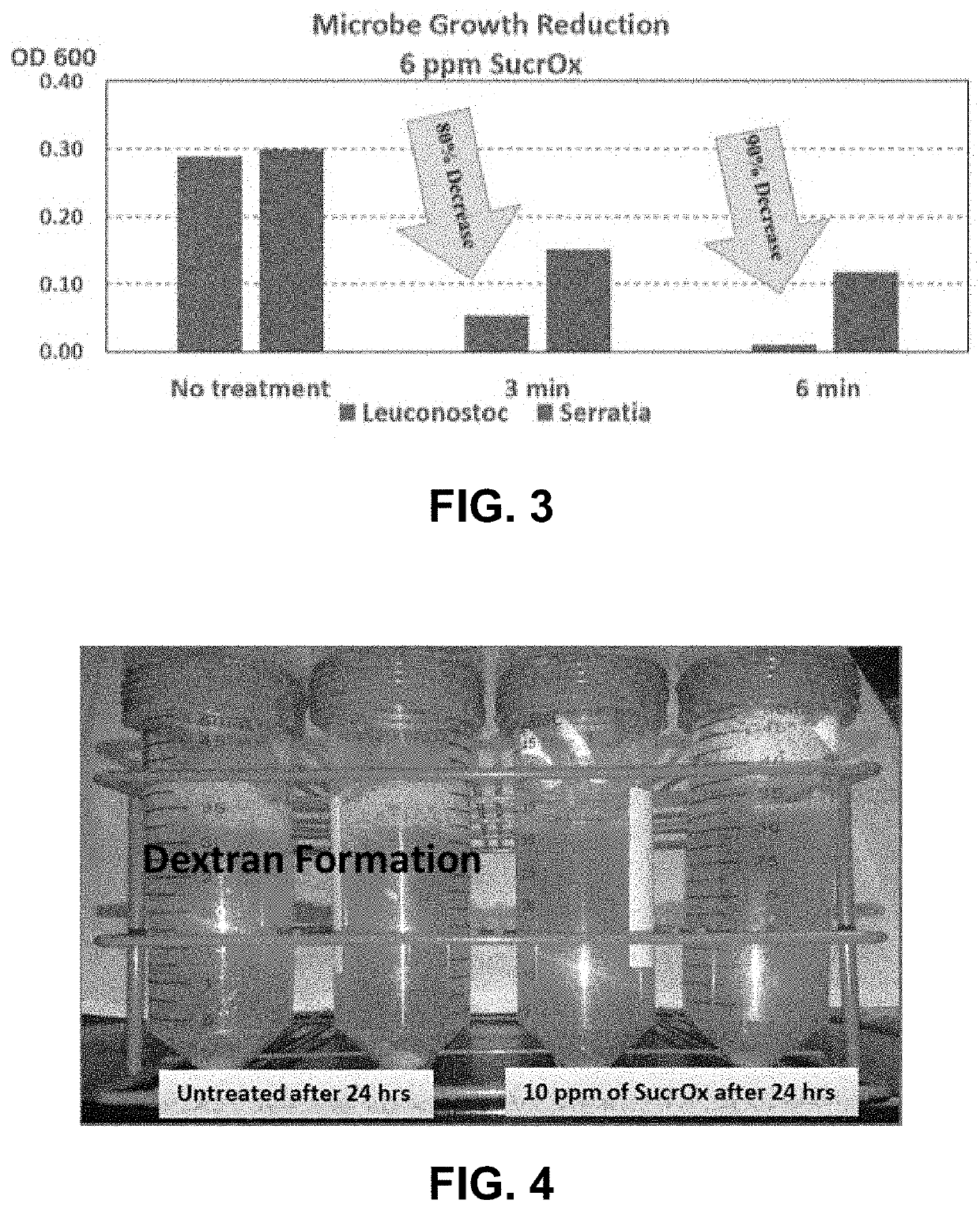
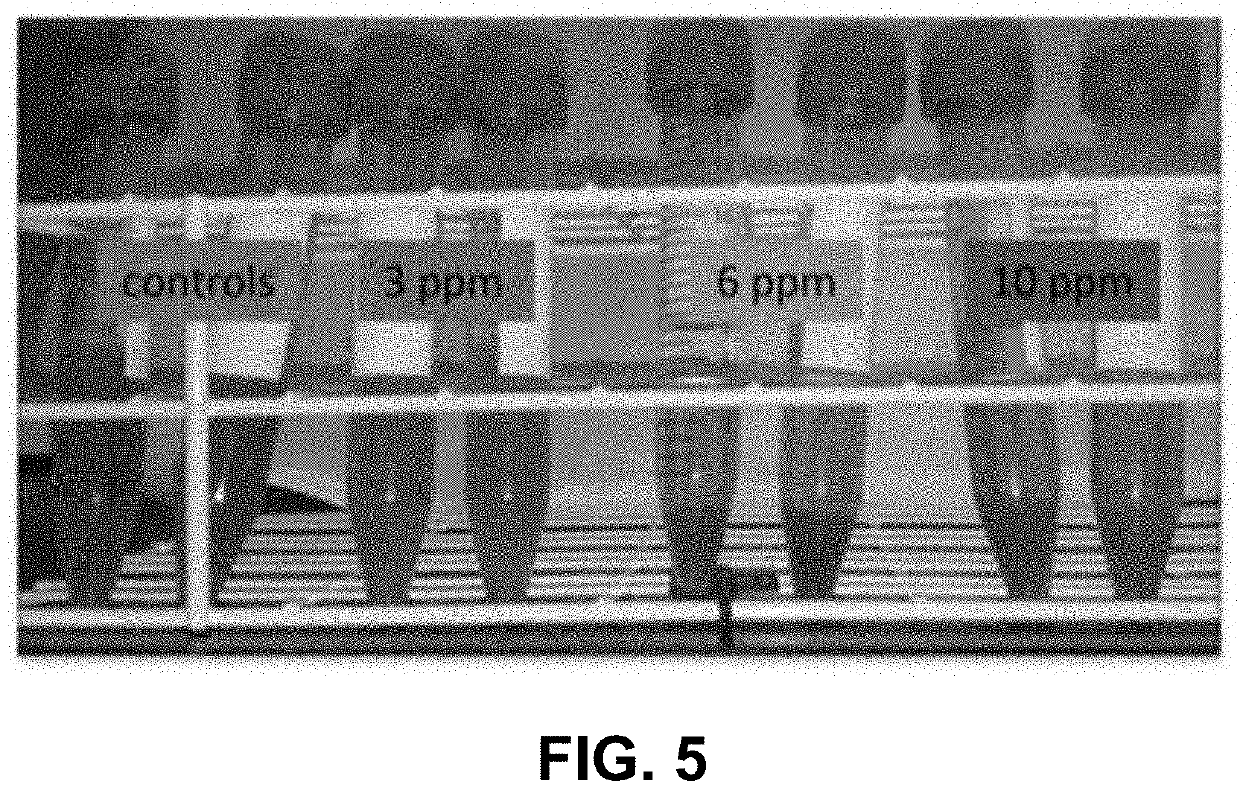
Preferred embodiments of the present invention comprise the optional application of concentrations of an aqueous permanganate solution, such as an approximately 0.01% to approximately 50% liquid permanganate solution and preferably comprising approximately 20% sodium permanganate dosed at approximately 1 ppm to approximately 100 ppm to harvested sugar crops, such as sugarcane, sugar beets, and sweet sorghum, at one or more of the sugar processing steps for the crops. The steps where the liquid sodium permanganate may optionally be applied include at a sugar crop cutting step, a sugar crop conveying step, a sugar juice extraction step, a sugar juice clarifying step, and a clarifier muds filtration step. The application of liquid sodium permanganate in the processing of sugar from sugar crops results in reduced equipment fouling, reduced loss in juice purity, reduced scale formation, decreased turbidity in clarified juices, increased sugarcane processing rates, reduced sugar crop production costs, increased sugar product yield, and increased production capacity.
Owner:CARUS CORP
Systems and methods for acid recycle
Methods and systems for pretreating lignocellulosic biomass are disclosed. An acid solution between 1% to 1.6% sulfuric acid is applied to the biomass. The biomass is subjected to an elevated temperature to cause the production of xylose, glucose, and furfural. Adjustments to temperature, acid concentration, and time can generate at least 80% or 90% of theoretical xylose, 45% or 50% of the theoretical glucose, and less than 4000 ppm of furfural in the xylose liquor. A portion of the resulting xylose liquor may be separated from the glucan solids. The xylose liquor, still highly acidic, can be recycled to reduce subsequent acid loading requirements. Makeup acid solution is added to the xylose liquor and subsequent biomass to ensure a proper solids to liquids ratio. The biomass is again treated to higher temperatures to yield sugars. The process may be repeated for each subsequent cycle.
Owner:POET RES INC
Methods and systems for preparing materials for sucralose production
InactiveUS7862744B2Reduce pressureCarboxylic acid amide separation/purificationSedimentation separationSucroseFiltration
The present invention provides a method for preparing DMF for sucralose production, including, e.g., isolating DMF from a composition comprising DMF, water, and methanol, using a single-tower rectification system. In various embodiments of the present invention, the composition, after the removal of water and methanol, may be further dried / dehydrated, such as, by using a dehydration agent and / or filtration. The resulting substantially pure DMF may comprise at least about 98-99% DMF. The present invention further provides a method of preparing a composition comprising anhydrous sucrose for sucralose production, which may comprise mixing regular sucrose with a water-containing DMF composition, and drying the resulting sucrose-DMF composition. Also provided is a single-tower separation system for isolating DMF from a composition comprising DMF, water, and methanol.
Owner:MAMTEK INT
Brown sugar decocting process
InactiveCN109338018AImprove sugar production efficiencyQuality improvementSugar productsSugar juice boiling/evaporationSaccharumSucrose
The invention belongs to the technical field of food processing and specifically relates to a brown sugar decocting process. By using a mode of adding a mixed enzyme solution to carry out enzymolysisand ethanol extraction on sugarcane crushed substances, sugar in sugarcane bagasse can be furthest extracted so that the sugar manufacturing efficiency is higher; gelatin and bentonite are added to asucrose liquor before being decocted to carry out flocculation on the sucrose liquor so that the sugarcane bagasse mixed in the sucrose liquor can be removed and the sucrose liquor can be clarified; and therefore, the quality of the decocted sucrose is better, and the gelatin and the bentonite also have foam removing effects; as lime does not need to be added during decocting, the obtained brown sugar is more healthy; and 5-6 hours are needed to decoct one pot of brown sugar by using an ancient decocting method. The brown sugar decocting process provided by the invention has the advantages that one pot of brown sugar can be decocted in 40 min on average, the water content of the decocted brown sugar is 3-5%, and the brown sugar freely falls to hard wood ground or ground without being broken from a position with the height of 1 m after being released from a mold.
Owner:贵州大山小农电子商务有限公司
Extraction method
InactiveUS20190183149A1Affecting palatabilityAffecting colourIon-exchange process apparatusAntipyreticDiseaseDietary supplement
The present invention relates to a process for producing an extract derived from sugar cane, the process comprising: i) mixing a sugar cane derived product with ethanol to produce an extraction mixture comprising at least about 50% v / v ethanol; ii) allowing a precipitate to form in the extraction mixture; iii) removing the precipitate from the extraction mixture to obtain a super-natant; and iv) removing ethanol from the supernatant to produce the extract derived from sugar cane. The present invention further relates to extracts produced according to the process of the invention. The invention also relates to the use of such extracts in a method of lowering the available calorific value of a food or beverage, in treating or preventing disease, and as a nutritional supplement, dietary supplement, sports nutrition product, food coating or pharmaceutical product.
Owner:THE PROD MAKERS (AUSTRALIA) PTY LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com