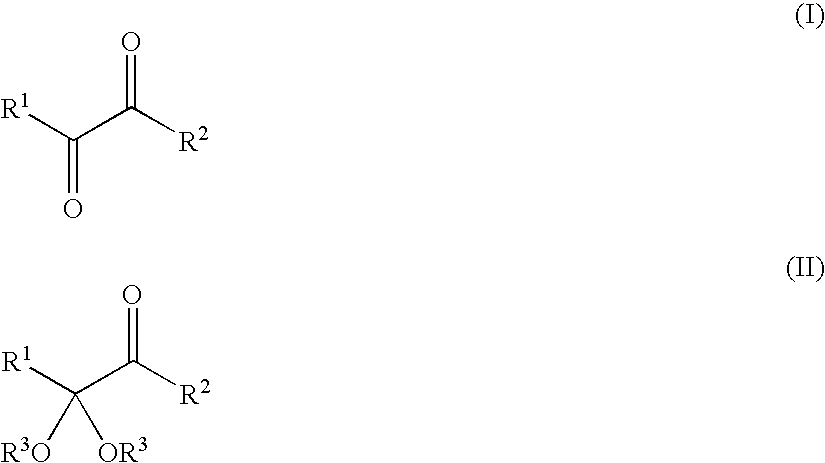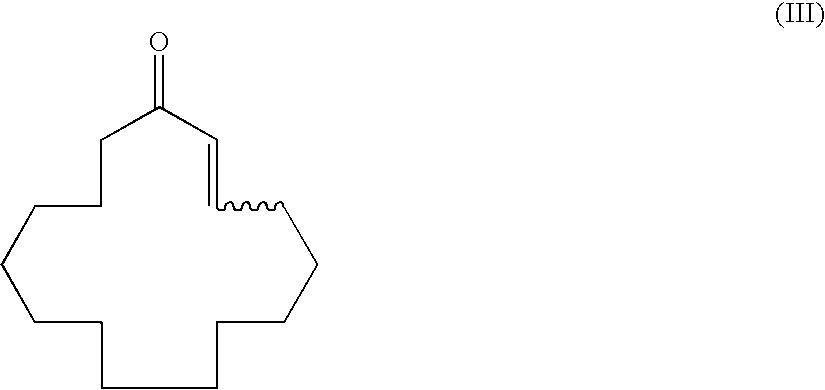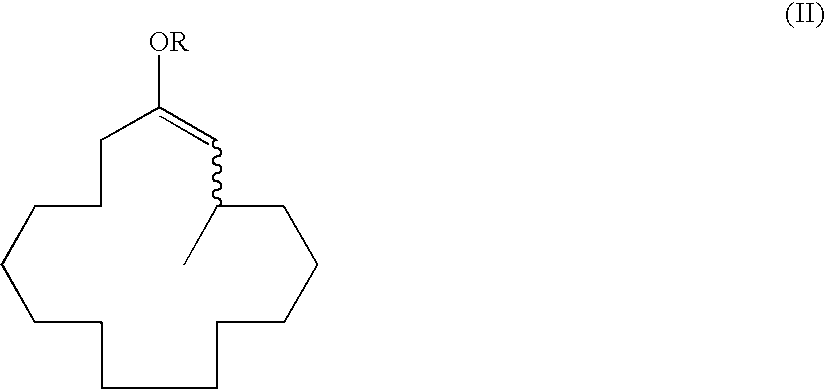Patents
Literature
67 results about "Solvolysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Solvolysis is a type of nucleophilic substitution (SN1) /( SN2) or elimination, where the nucleophile is a solvent molecule. Characteristic of SN1 reactions, solvolysis of a chiral reactant affords the racemate. Sometimes however, the stereochemical course is complicated by intimate ion pairs, whereby the leaving anion remains close to the carbocation, effectively shielding it from an attack by the nucleophile. Particularly fast reactions can occur by neighbour group participation, with nonclassical ions as intermediates or transition states.
Process for treating water-containing natural gas wells and natural gas storage wells
The gas flow in water-containing natural gas wells and natural gas storage wells is improved if a homogeneous phase comprising a water-repellent, solvolysis-resistant active compound is injected into the water-bearing rock.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
Method for producing phenolic compound
InactiveUS7547799B1Organic compound preparationPreparation by ester-hydroxy reactionCompound aWaste stream
A method is provided for producing an ester-substituted phenol product stream from an ester-substituted diaryl carbonate manufacturing waste stream. The method includes the steps of obtaining a waste stream containing an ester-substituted diaryl carbonate from an ester-substituted diaryl carbonate manufacturing facility and creating a reaction mixture by combining the waste stream with a solvent and with a transesterification catalyst. The reaction mixture is maintained at a reaction pressure at or below atmospheric pressure, and at a reaction temperature for a period of time sufficient to produce ester-substituted phenol by solvolysis of the ester-substituted diaryl carbonate. Ester-substituted phenol is removed from the reaction mixtures in an ester-substituted phenol stream. The solvent, the reaction temperature, and the reaction time are selected in combination such that less than 1,000 ppm of acid-substituted phenol is present in the ester-substituted phenol stream.
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
Catalyst Material For Use In Fuel Cell, Catalyst Membrane, Membrane Electrode Assembly and Fuel Cell
InactiveUS20070231671A1Increase profitImprove breathabilityConductive materialActive material electrodesFuel cellsHeat resistance
A catalyst for a fuel cell comprising one or more hydrophilic segments and one or more hydrophobic segments jointly or separately connected to the surface of the carbon material by a single bond or a connection group having a solvolysis resistance and a heat resistance on a surface of a carbon material, wherein the hydrophilic segment has the solvolysis resistance and the heat resistance and has an ionic functional group, and the hydrophobic segment has the solvolysis resistance and the heat resistance and has no ionic functional group.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
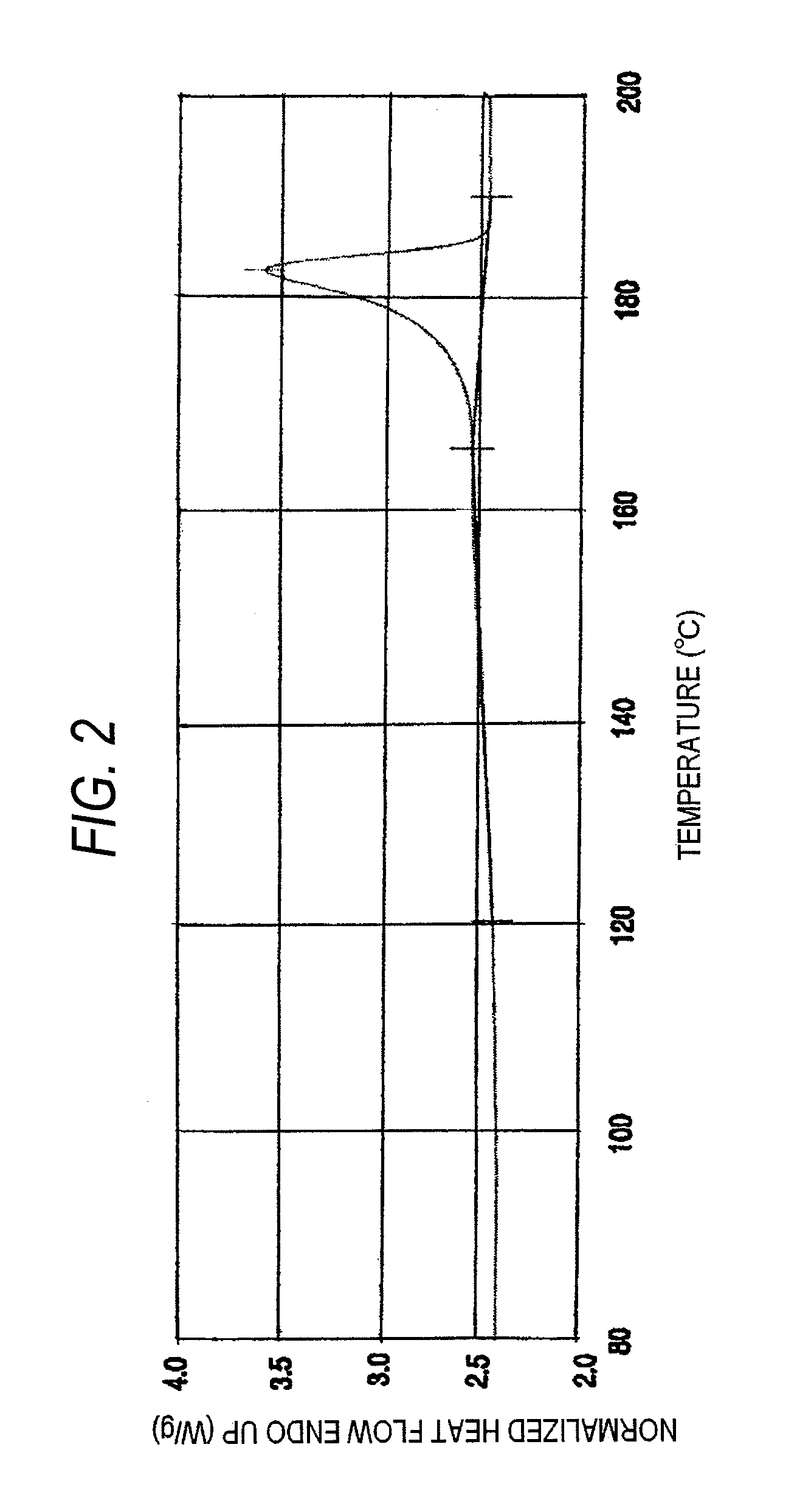
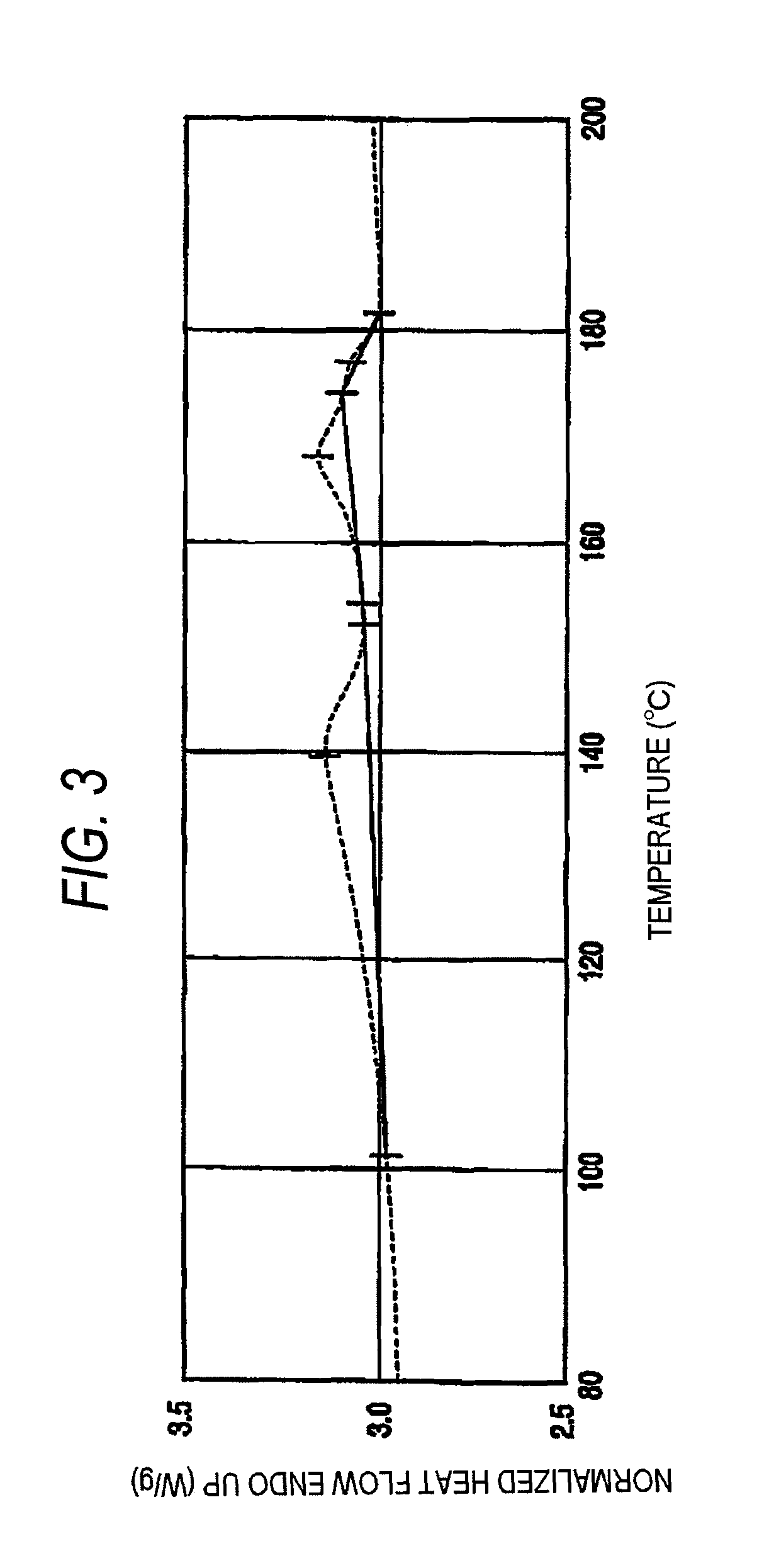
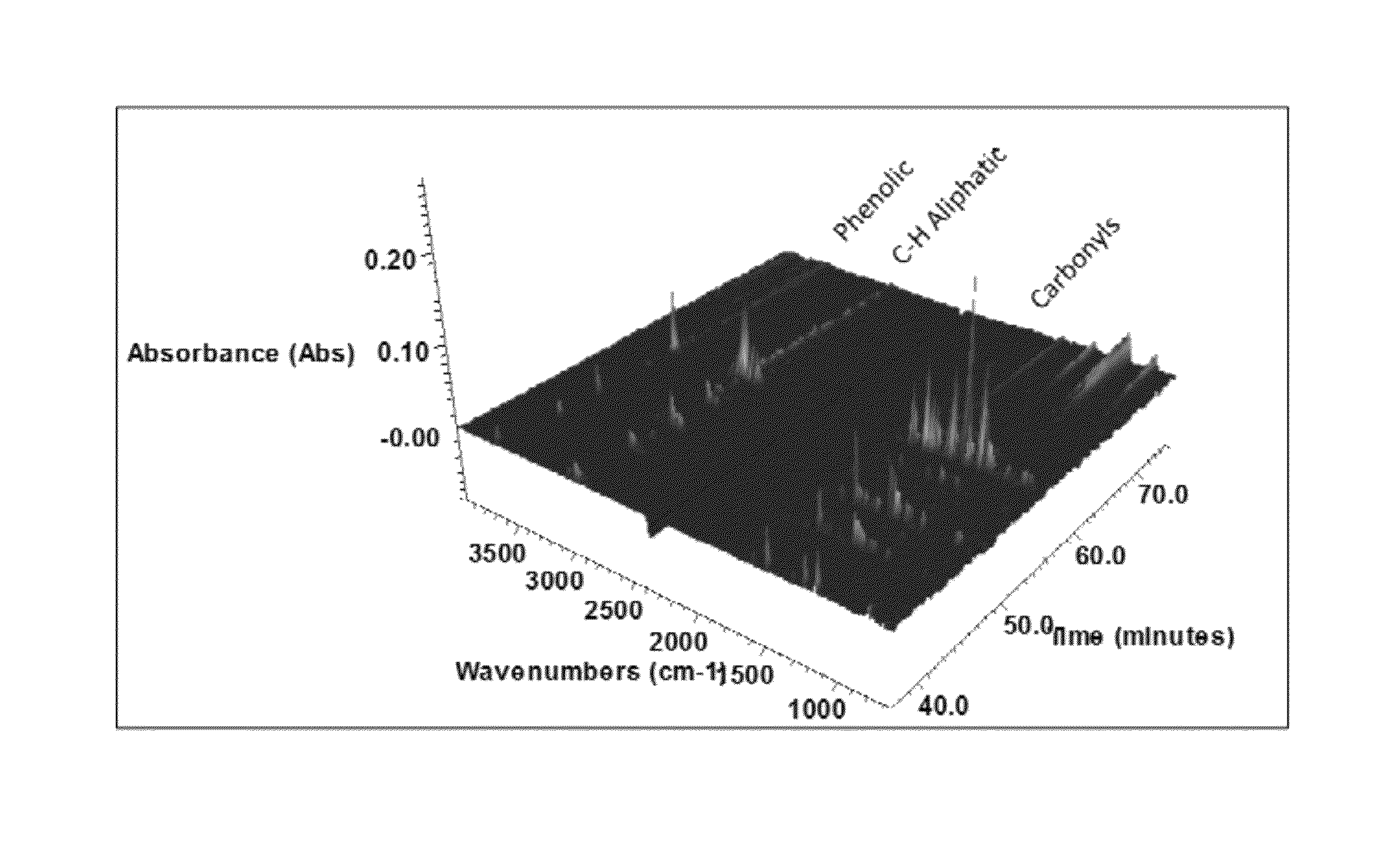
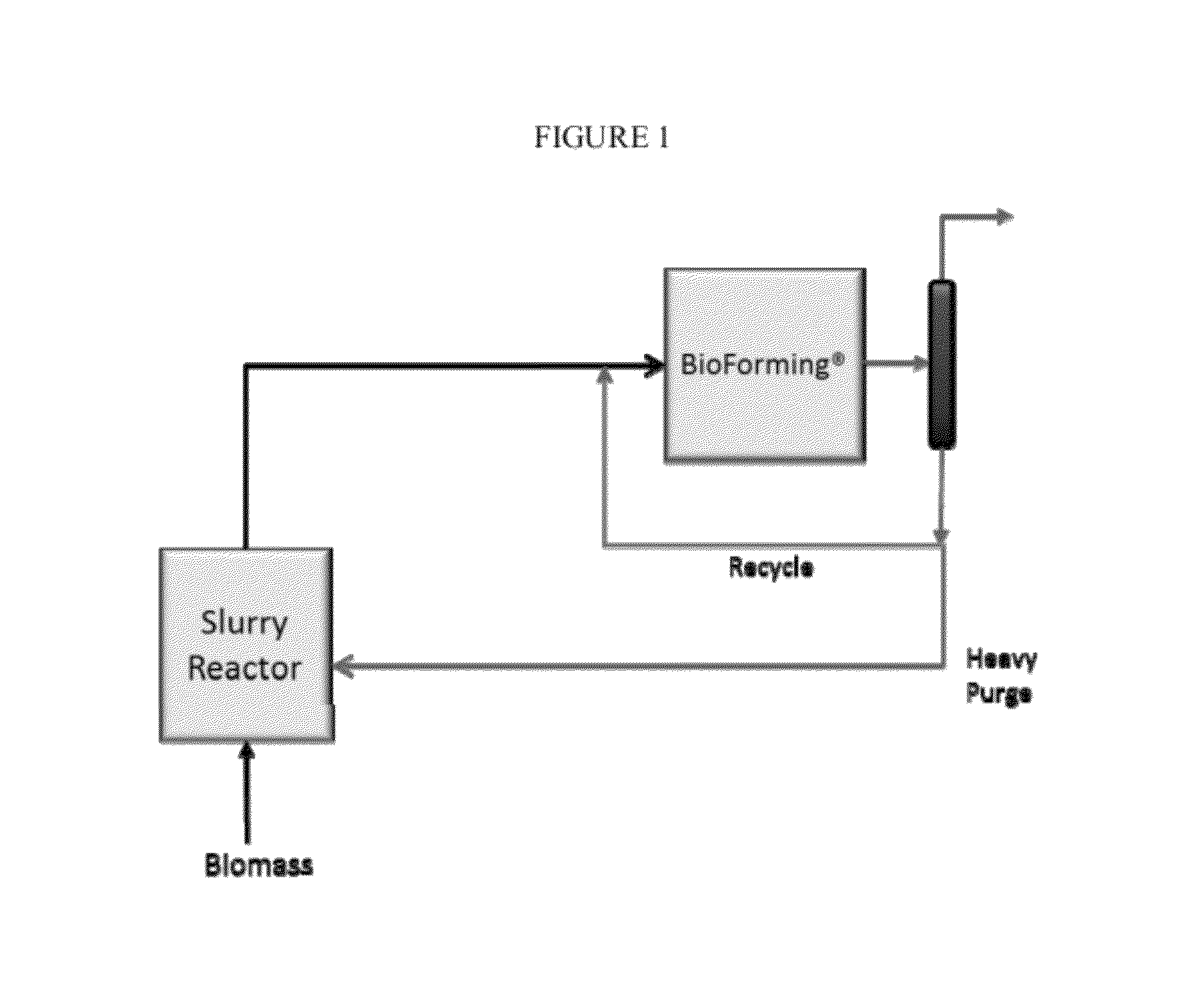
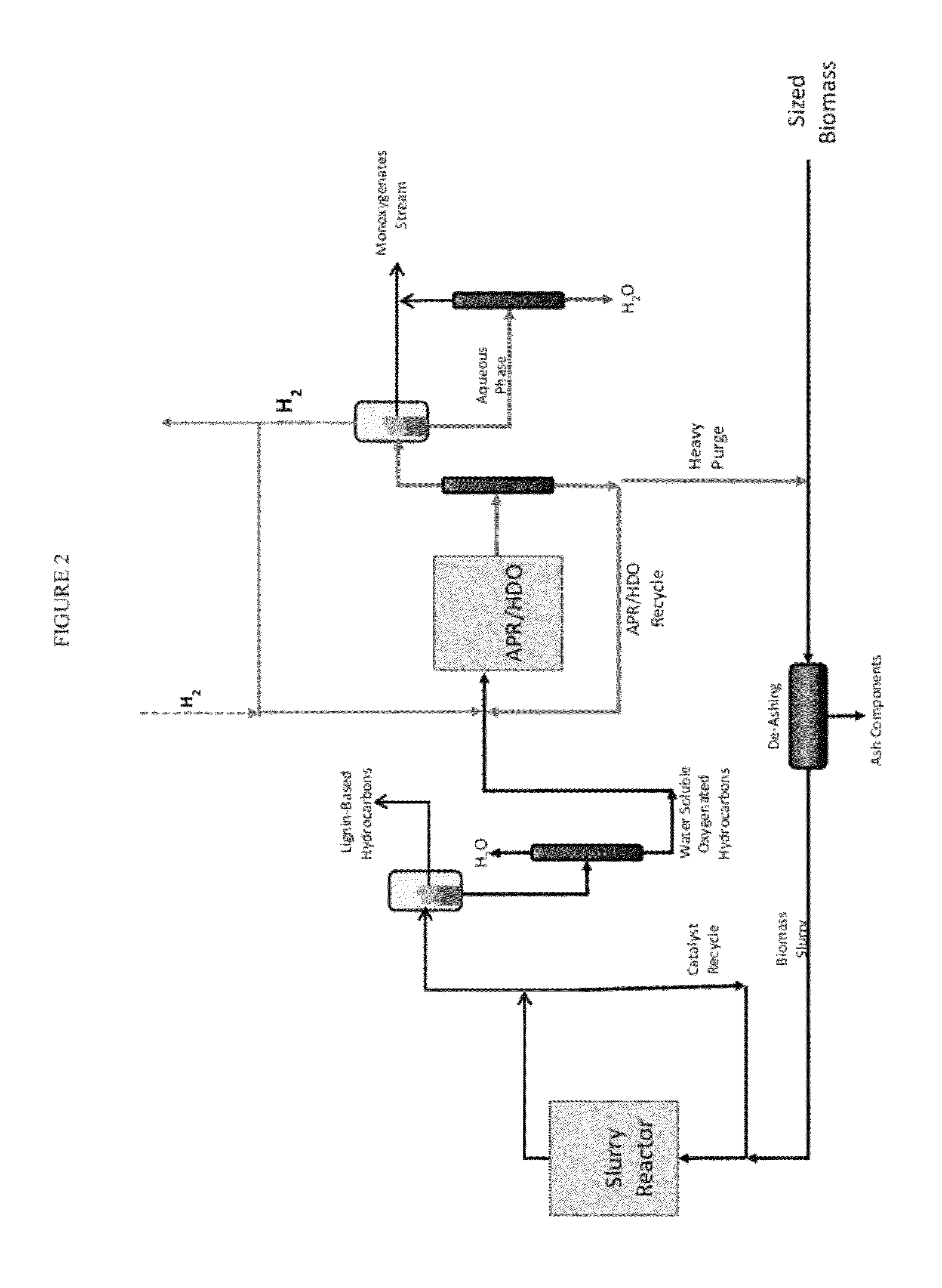
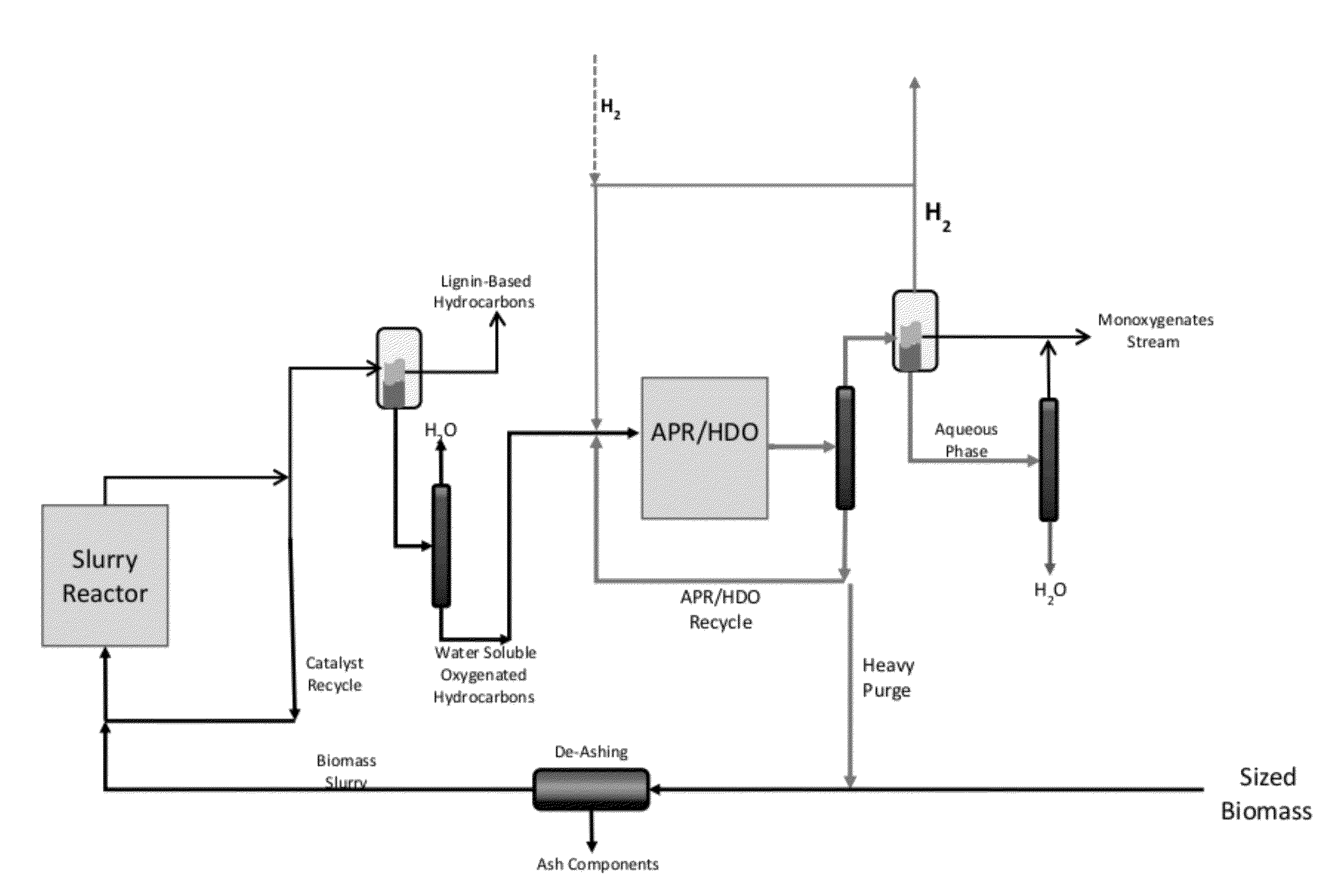
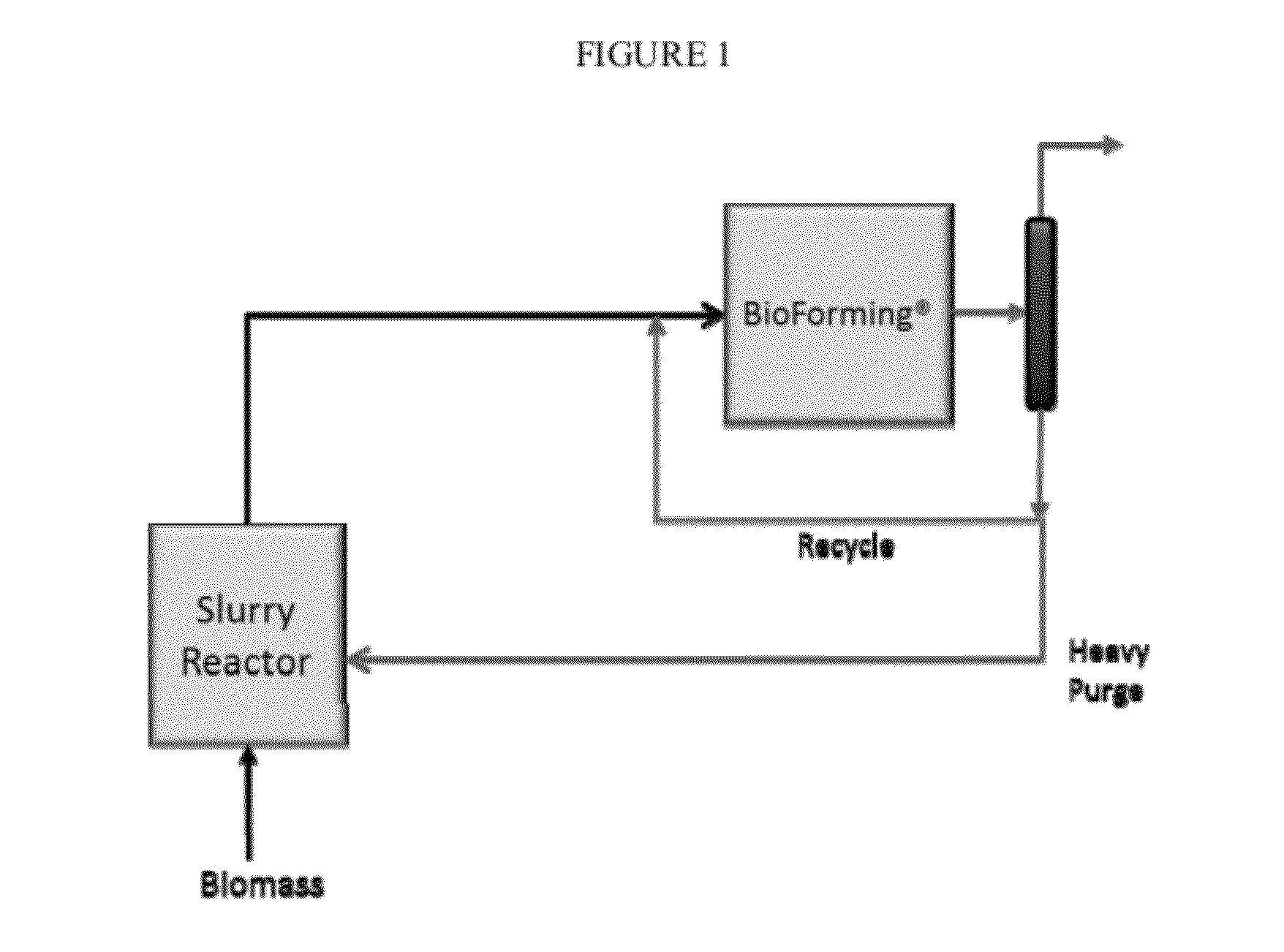
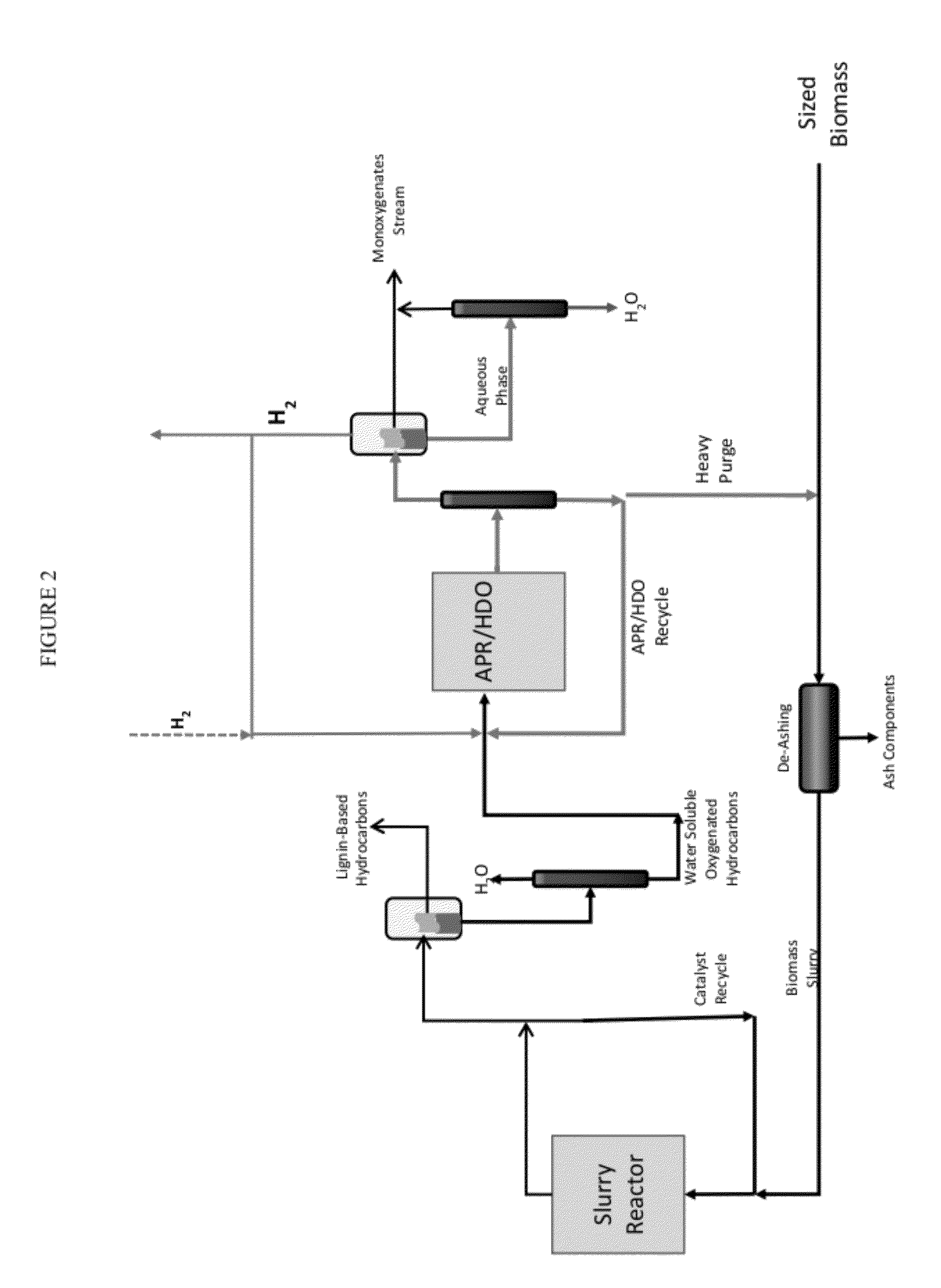
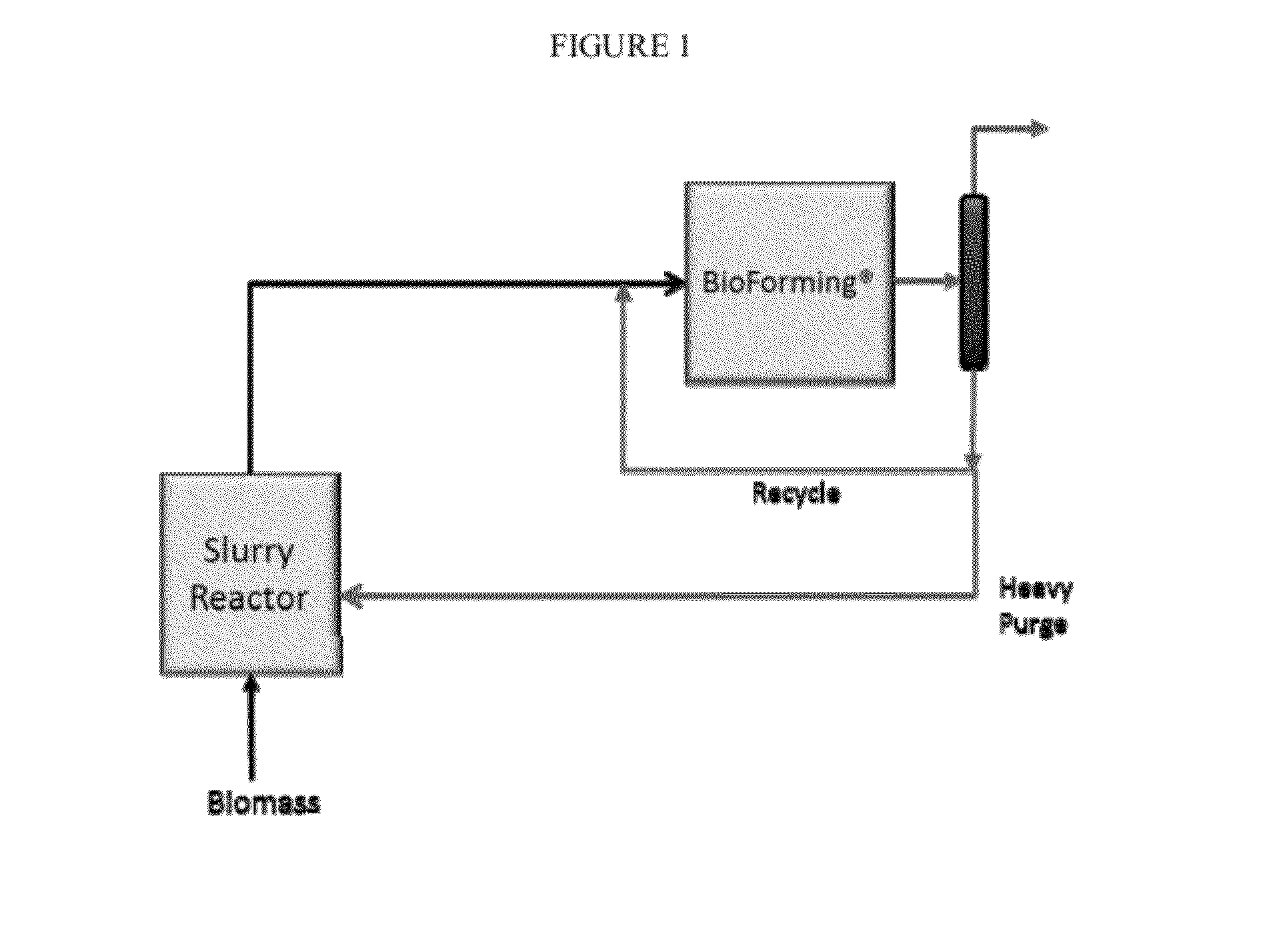
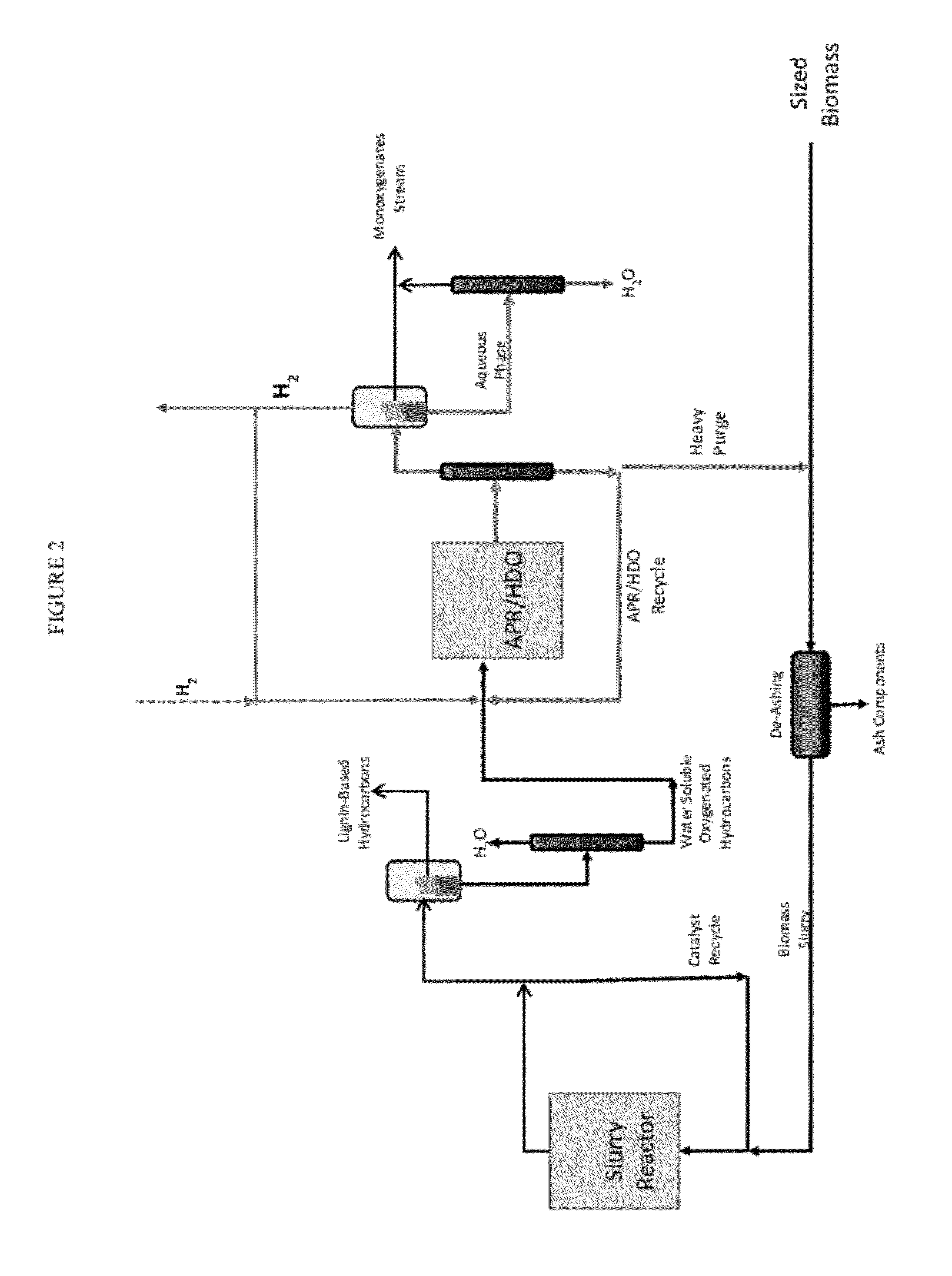
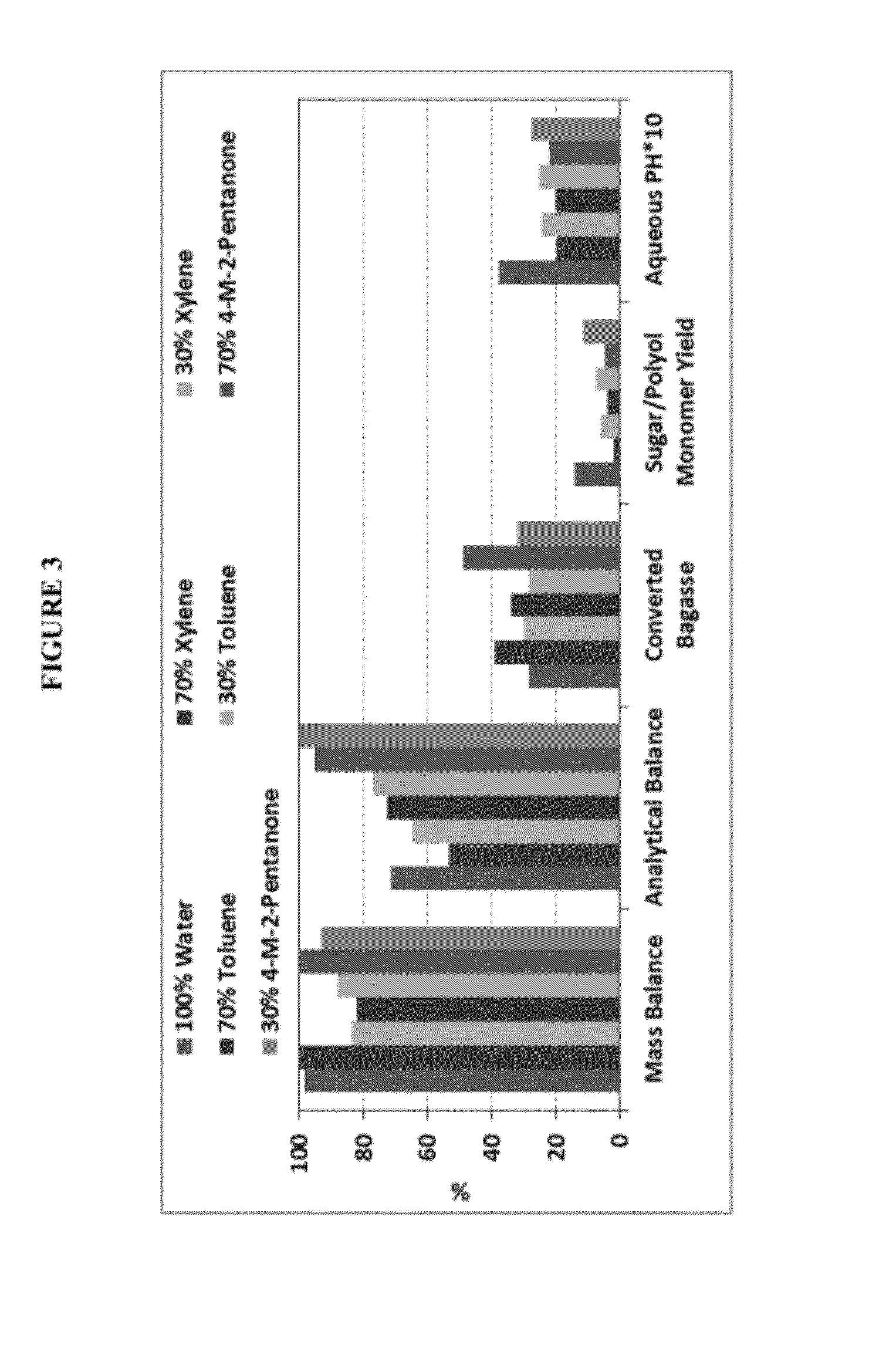
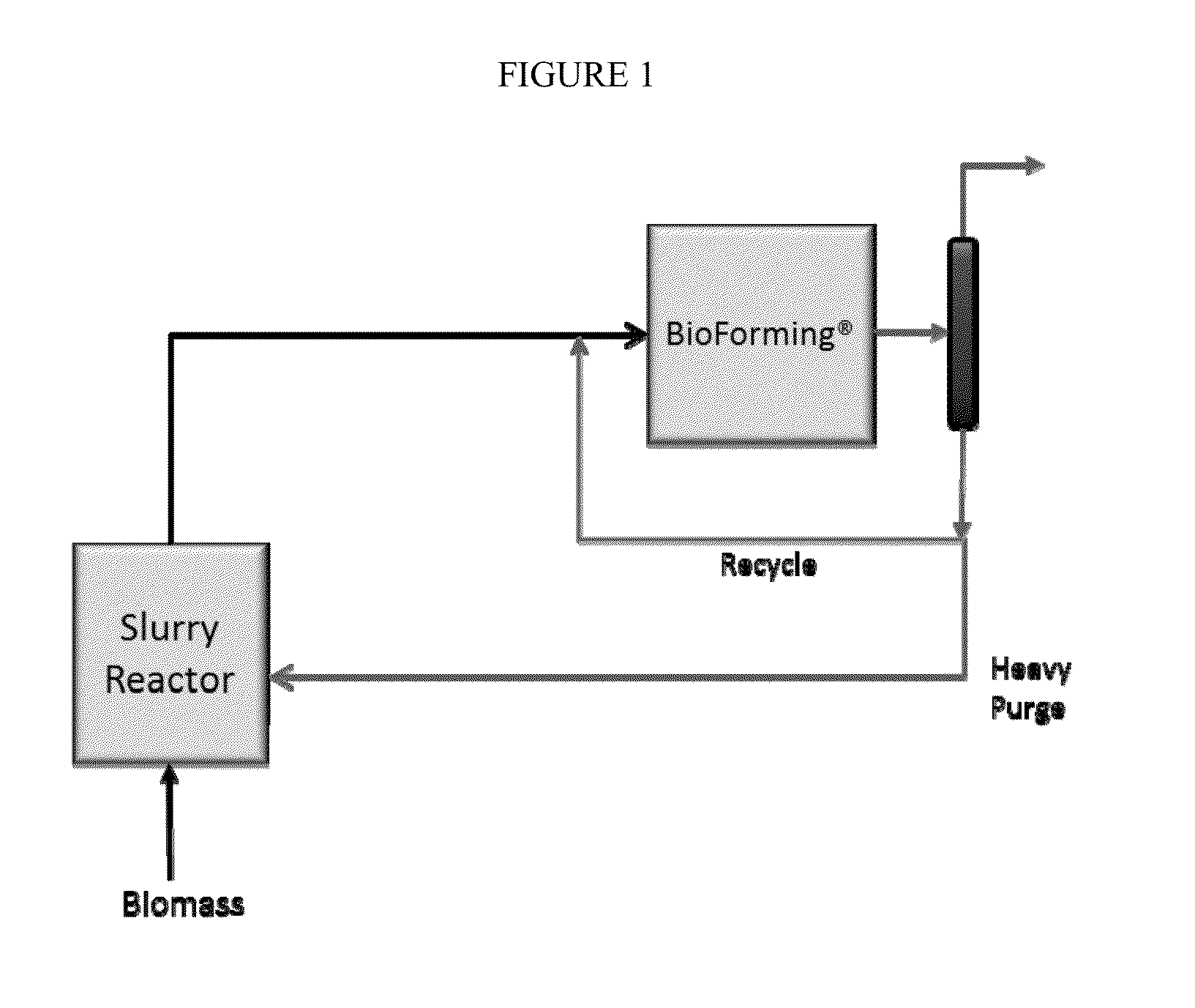
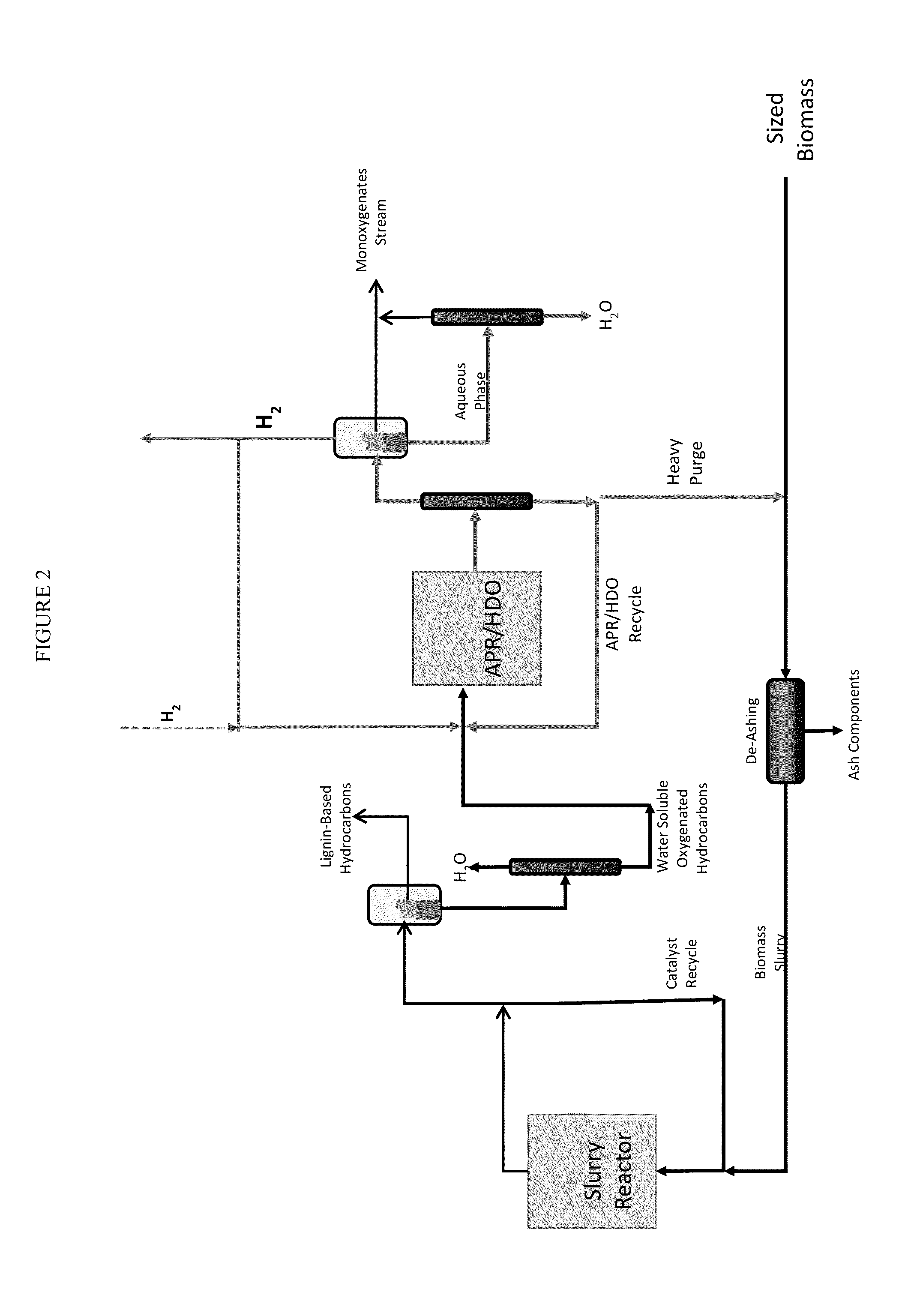
Solvolysis of biomass using solvent from a bioreforming process
ActiveUS20120167875A1Hydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionSolventSolvolysis
Owner:VIRENT
Method for the chemical depolymerization of waste polyethylene terephthalate
InactiveUS20100133088A1Increase chanceEasy to processOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationPolyethylene terephthalate glycolDepolymerization
A method for the chemical depolymerization of waste polyethylene terephthalate by application of microwave radiation and solvolysis in the presence of a catalyst comprising the first stage where the waste polyethylene terephthalate is mixed up with an microwaves absorbing activator, the mixture is melted by its exposing to a microwave radiation on a frequency from 915 to 2450 MHz and with a power output from 0.1 to 0.5 kW per kg of a charge, at a temperature from 230 to 330° C., under atmospheric pressure and the second stage, where the molten mixture is subjected to solvolysis, including acidic or basic hydrolysis, alcoholysis or glycolysis in the presence of a catalyst under continuing microwave radiation and atmospheric pressure yielding terephthalic acid, salts or esters thereof, and ethylene glycol.
Owner:USTAV CHEMCH PROCESU AV CR V V I
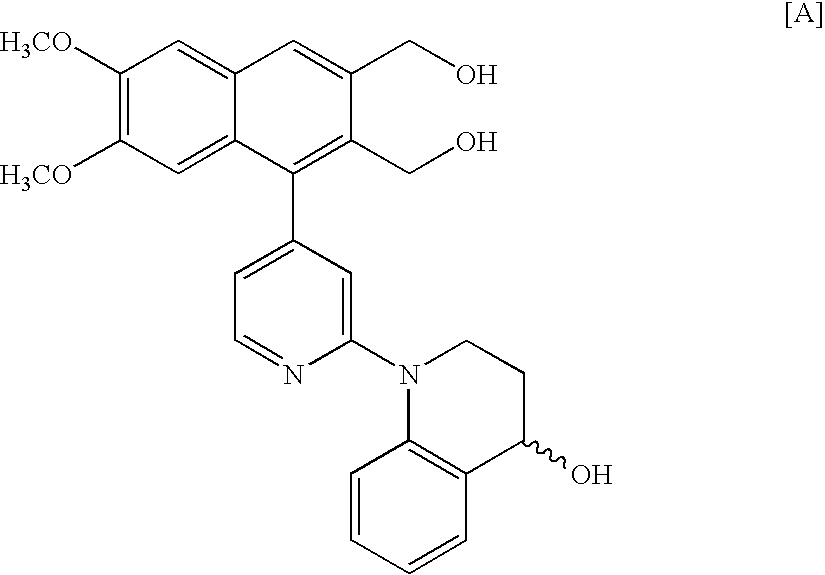
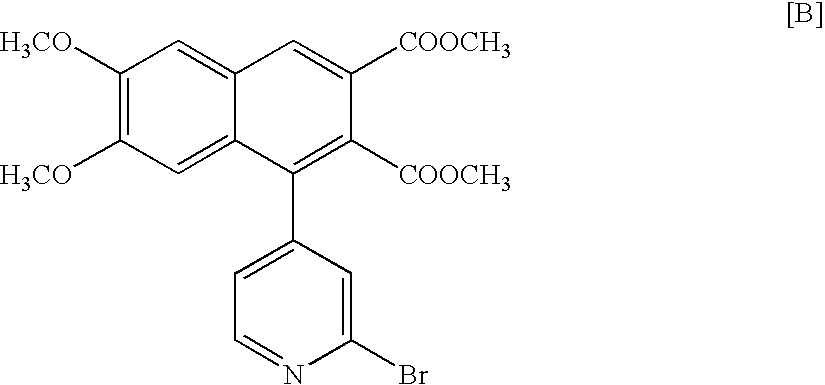
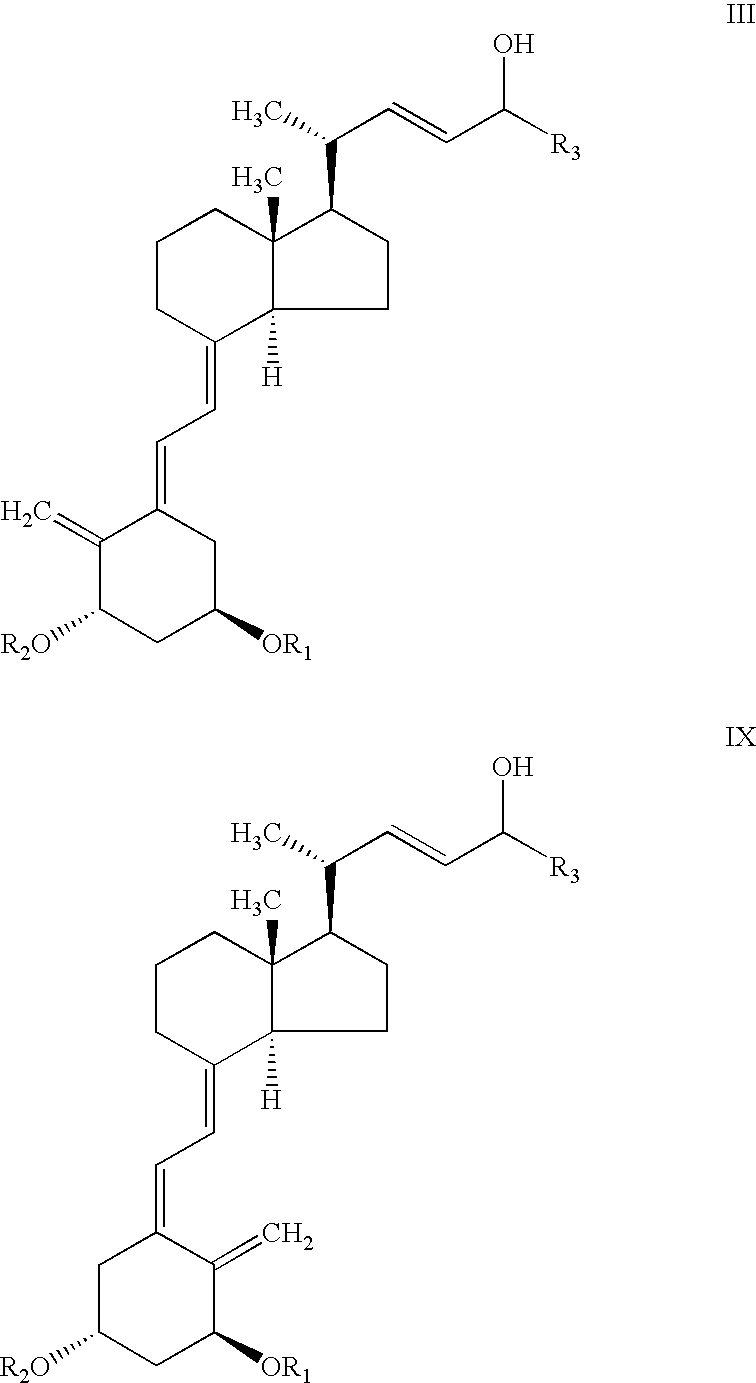
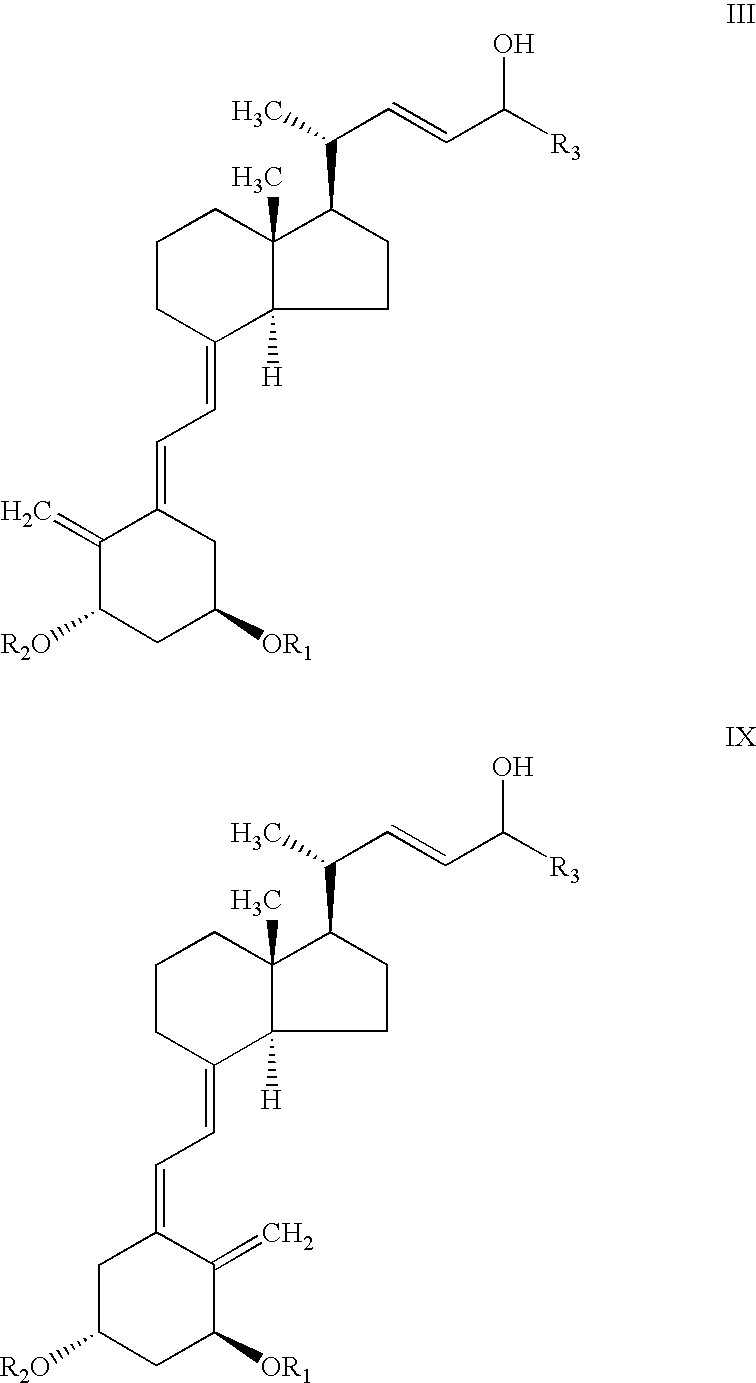
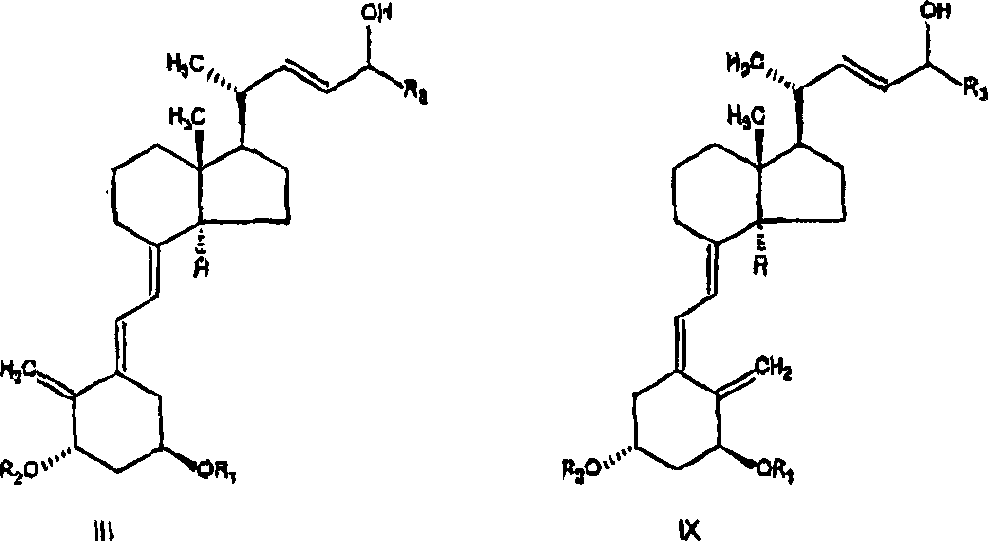
Process for preparing optically active 2-[6-(hydroxy-methyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl] acetic acid derivatives
InactiveUS7094594B2Easy to manufactureImprove efficiencyOrganic chemistryFermentationSolventSolvolysis
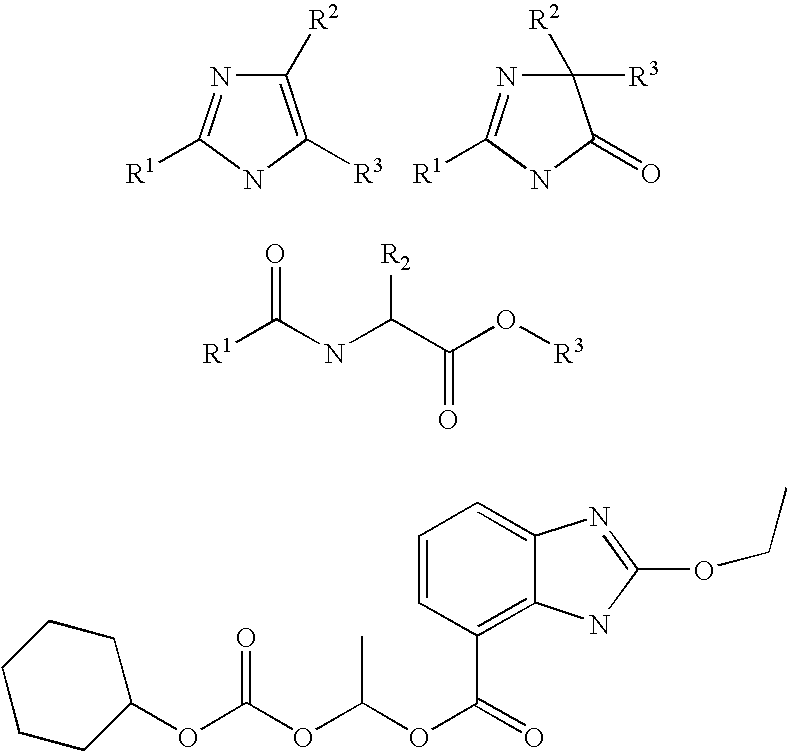
The present invention is to provide a production technology by which an optically active 2-[6-(hydroxymethyl)-1, 3-dioxan-4-yl]acetic acid derivative, which are of value as pharmaceutical intermediates, can be produced from inexpensive and readily available starting materials without using any extraordinary equipment such as an ultra-low-temperature reactor.The present invention is a production process of an optically active 2-[6-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl]acetic acid derivativewhich comprises reacting an enolate, prepared by permitting a base or a 0-valent metal to act on an acetic acid ester derivative with (S)-β-hydroxy-γ-butyrolactone at a temperature not lower than −30° C. to give a dihydroxyoxohexanoic acid derivative,treating the same with an acylating agent in the presence of a base to produce a dihydroxyoxohexanoic acid monoacyl derivative,reducing this compound with a microorganism to produce a trihydroxyhexanoic acid monoacyl derivative,treating this compound with an acetal-forming reagent in the presence of an acid catalyst to produce an acyloxymethyldioxanylacetic acid derivative, andfinally, subjecting this compound to solvolysis in the presence of a base.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Selective enzymatic esterification and solvolysis of epimeric vitamin D analog and separation of the epimers
Provided is a method of selectively enzymatically esterifying or selectively enzymatically solvolyzing epimers of analogs of vitamin D having a stereogenic center at C-24 that has a free or esterified OH group. The metod can be used, for example, for separating mixed epimers of the vitamin D analog.
Owner:TEVA PHARM USA INC
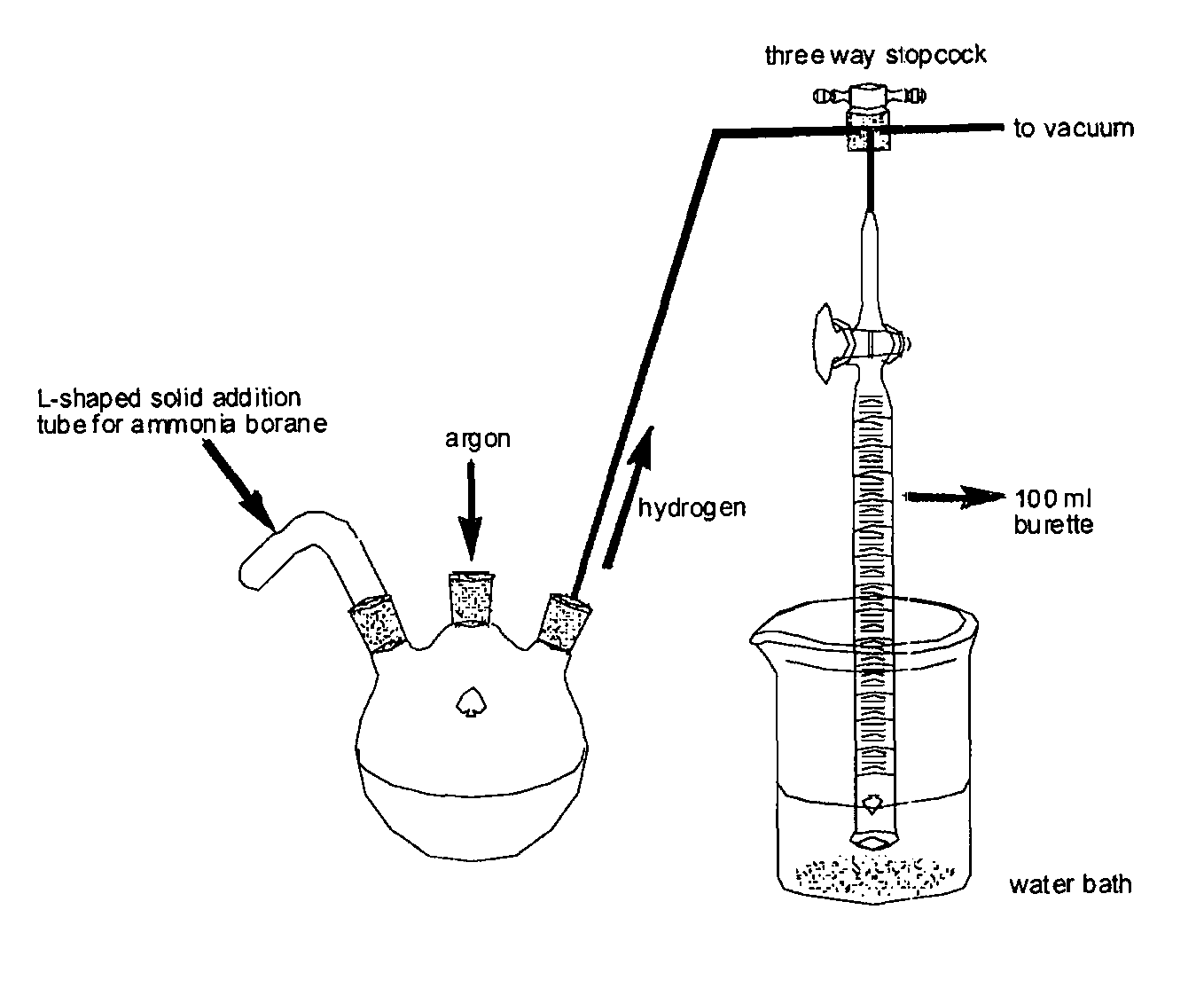
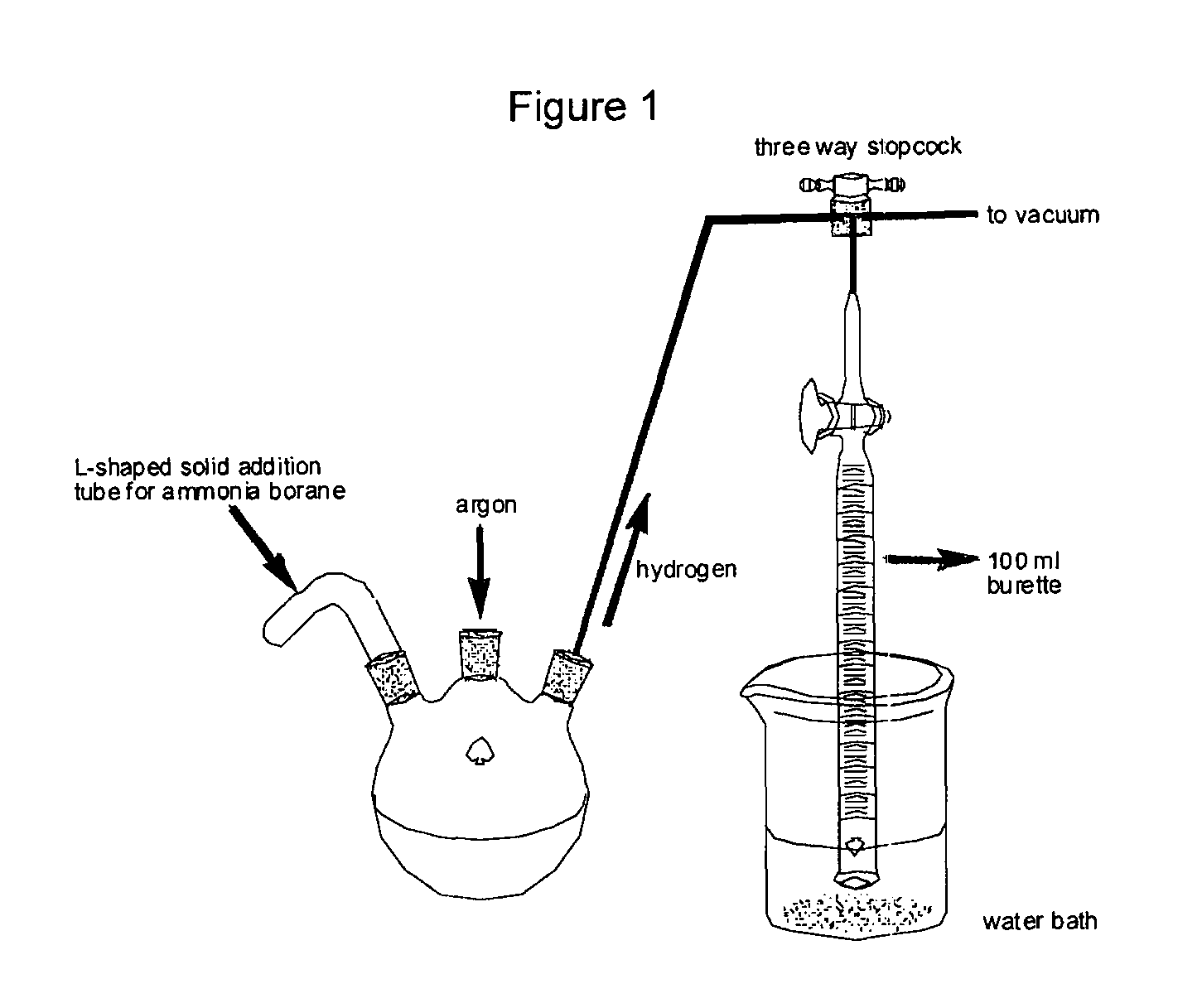
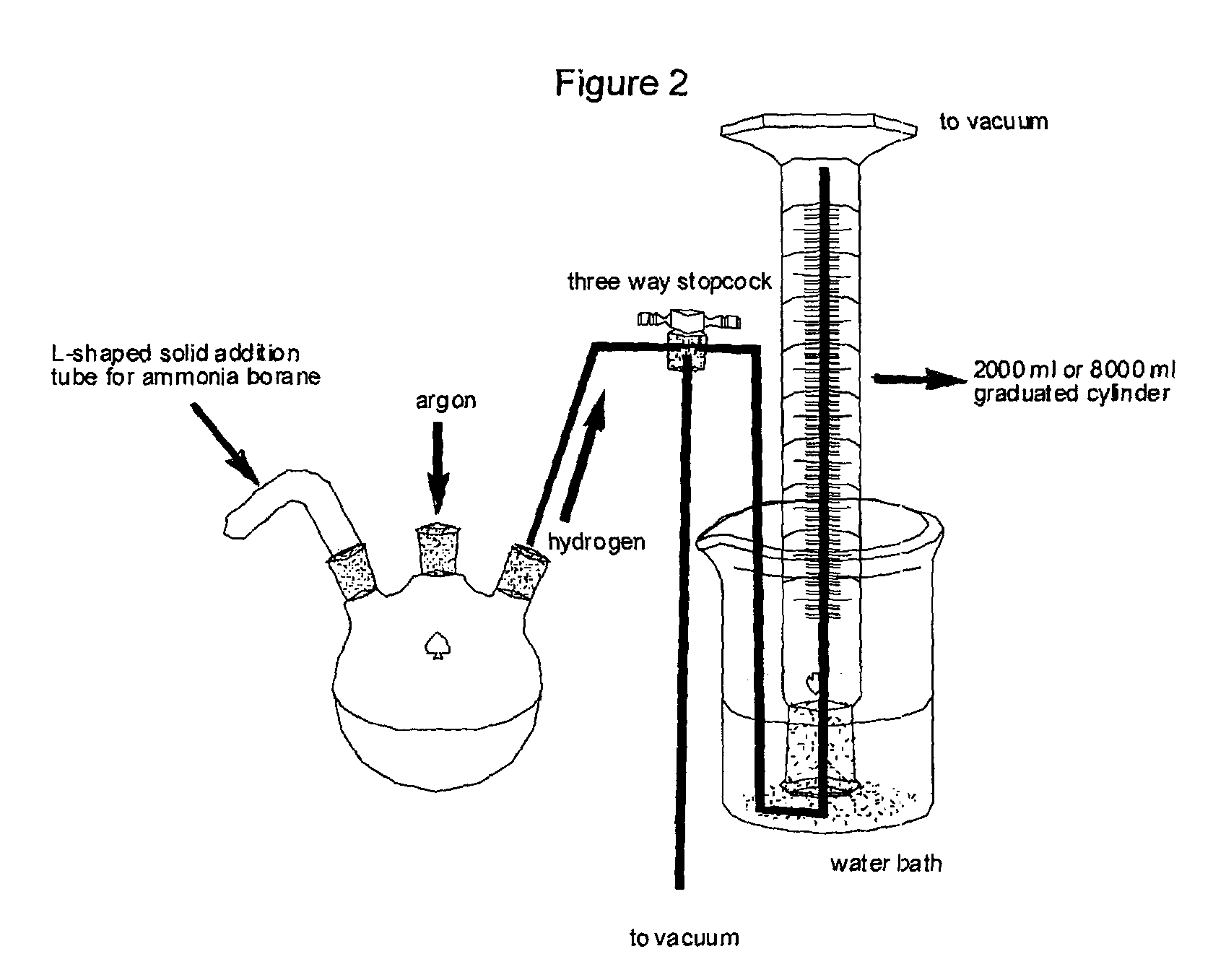
Method for the production of hydrogen from ammonia borane
InactiveUS8518368B2Gaseous chemical processesOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPtru catalystMetal catalyst
The present disclosure relates to processes and methods of generating hydrogen via the hydrolysis or solvolyis of a compound of the formula (I), R1R2HNBHR3R4, using ligand-stabilized homogeneous metal catalysts.
Owner:KANATA CHEM TECH
Method for Preparing Endosseous Implants Anatase Titanium Dioxide Coating
The method includes the following steps: formulation of liquid, non-gelled and stable precursor by solvolysis of Ti(IV) compounds; precursor deposition on endosseous implant surface; thermal treatment to achieve film densification, in the presence of oxygen, of a complex formed by the above mentioned endosseous implant and precursor, to obtain on the implant surface a thin film of nanocrystalline titanium dioxide with good mechanical and chemical stability. The complex above, under a persistent W irradiation modify its surface status conferring a sensible increasing of wettability chemical and biological decontamination.
Owner:GUYA BIOSCI
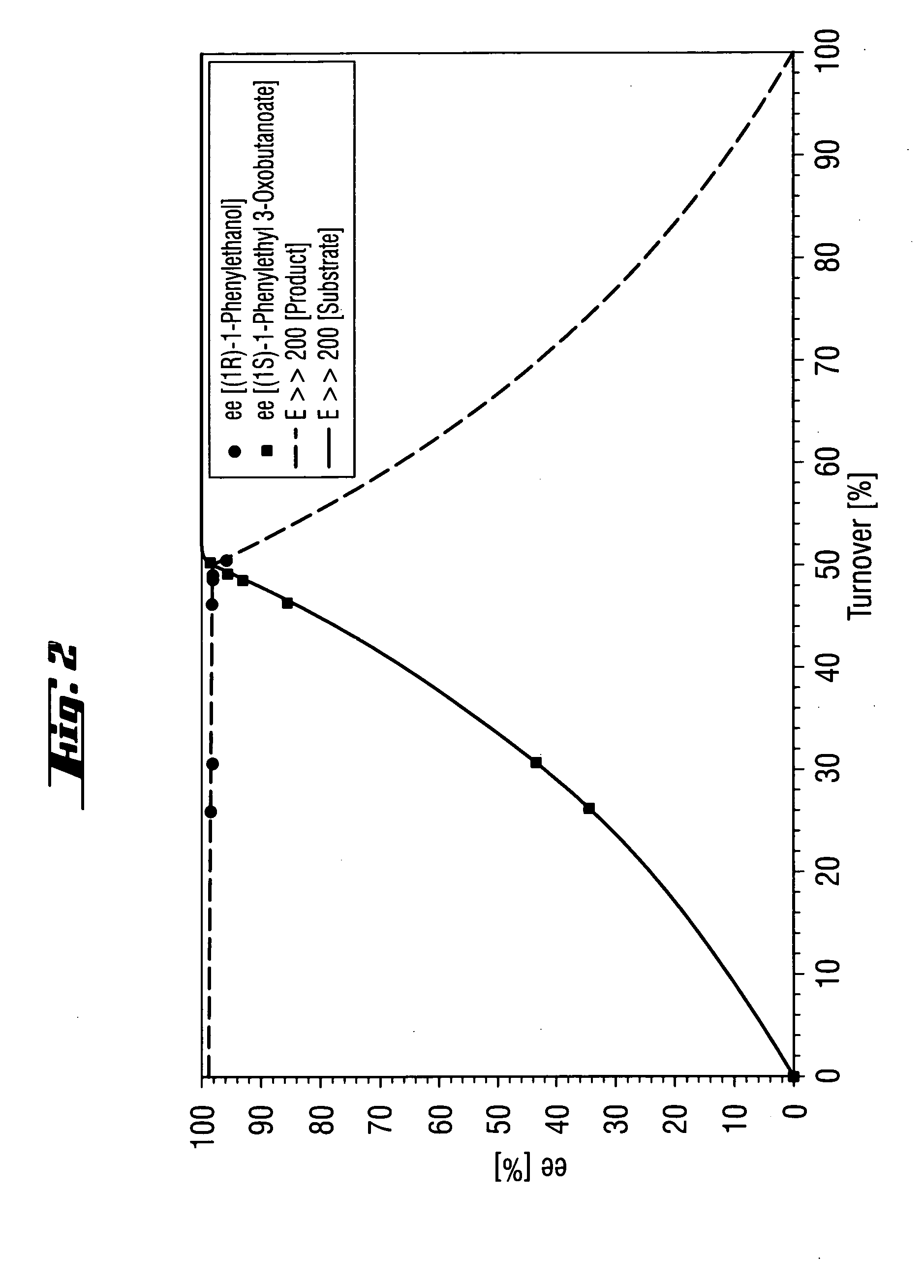
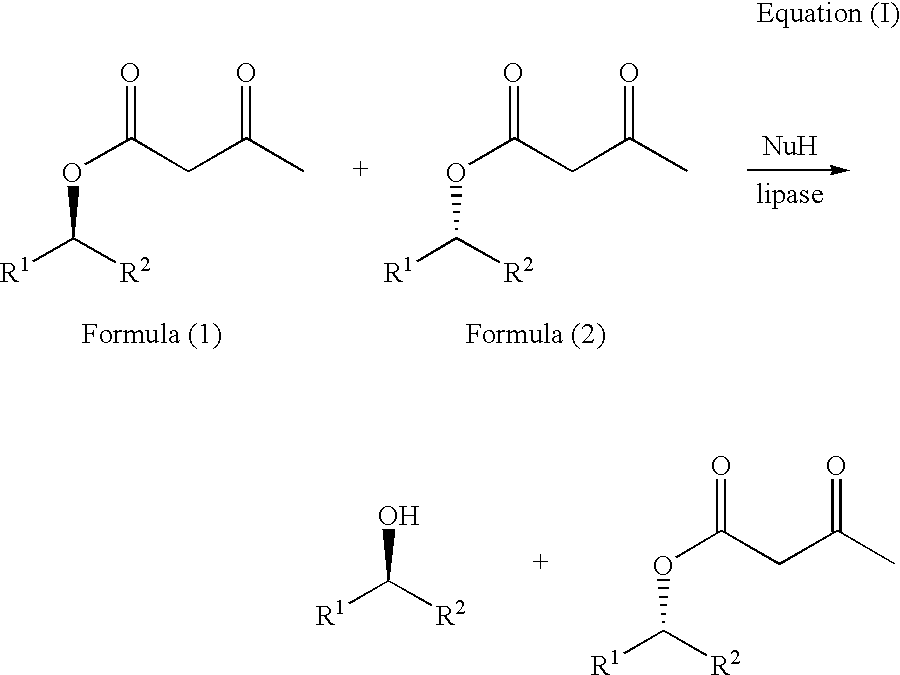
Process for the enantioselective preparation of secondary alcohols by lipase-catalyzed solvolysis of the corresponding acetoacetic esters
InactiveUS20050032182A1Easy to separateHigh enantioselectivityOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationAcetoacetatesAlcohol
Process for the enantioselective preparation of secondary alcohols, wherein a racemic or enantiomerically enriched mixture of acetoacetic esters of chiral secondary alcohols is subjected to enantioselective enzymatic solvolysis in the presence of a nucleophile and a lipase capable of the solvolytic cleavage of an ester group.
Owner:CONSORTIUM FUR ELEKTROCHEM
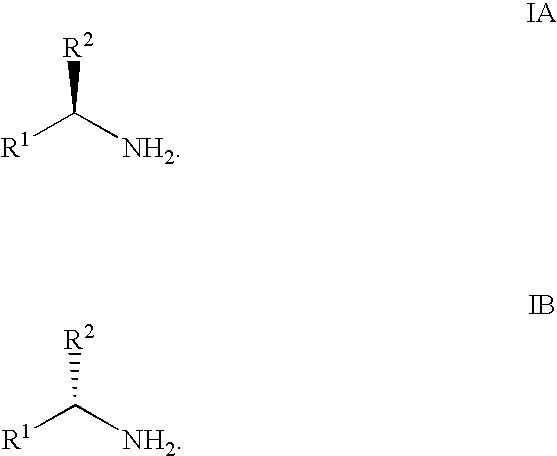
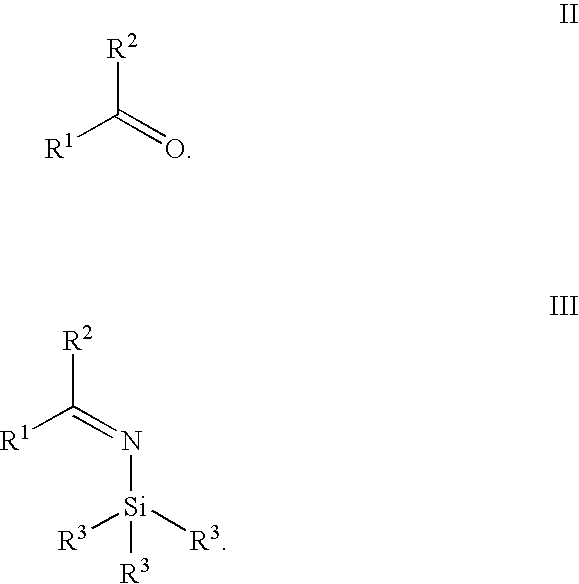
Synthesis of alpha fluoroalkyl amines
This invention describes the reaction of an alpha fluoroalkyl ketone with a bis(trialkylsilyl)amide to give a stable N-trialkylsilyl imine. Treatment of the N-trialkylsilyl imine with an alcohol leads to solvolysis of the trialkylsilyl group and yields a stable mixture of an aminal and an imine in high yield. Catalytic reduction of this mixture, or of the individual components, in the presence of a chiral catalyst leads to a fluoroalkyl amine with high enantioselectivity and high yield.
Owner:MERCK CANADA
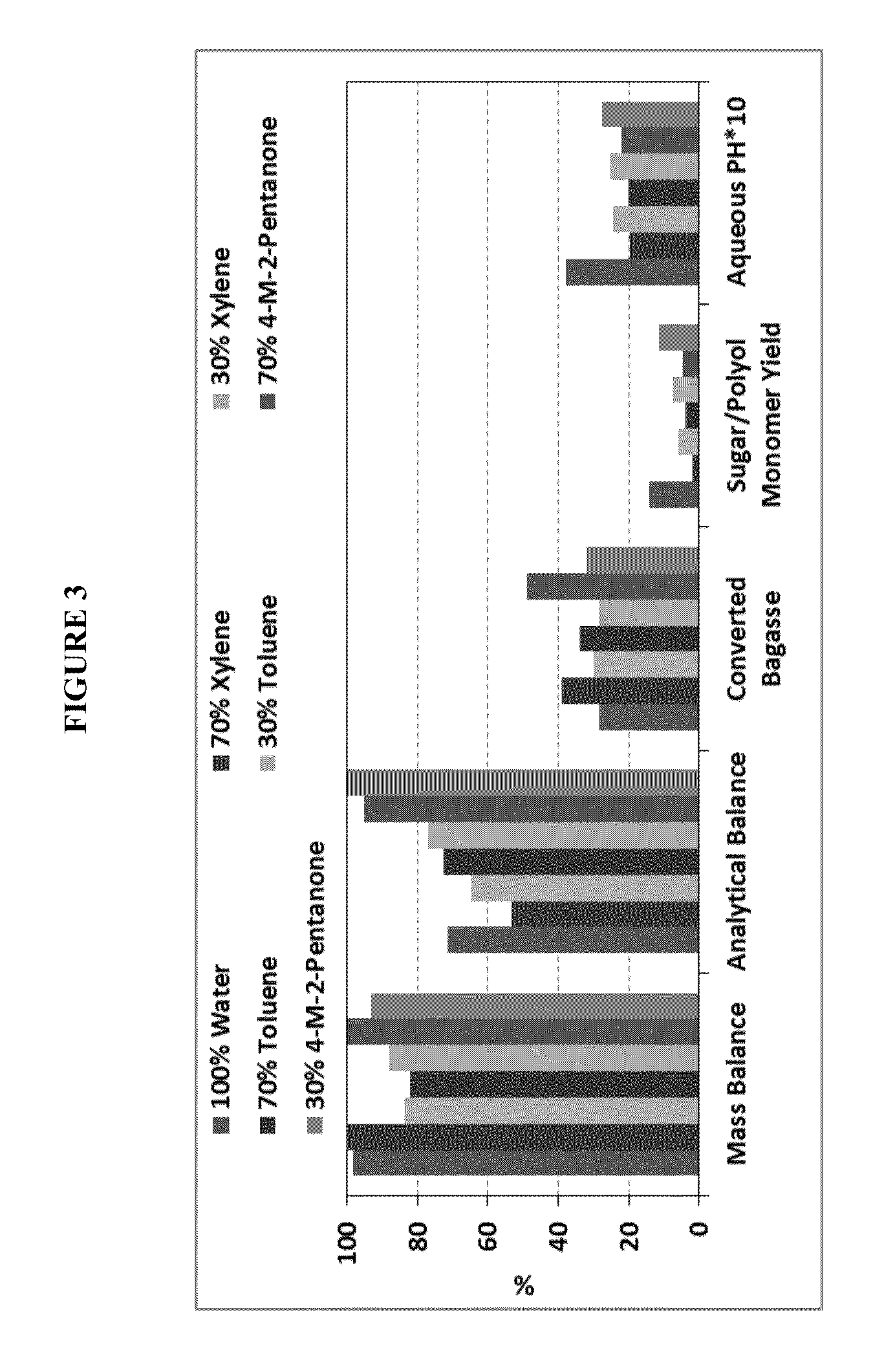
Separation of lignin and sugars from biomass pre-treatment liquors
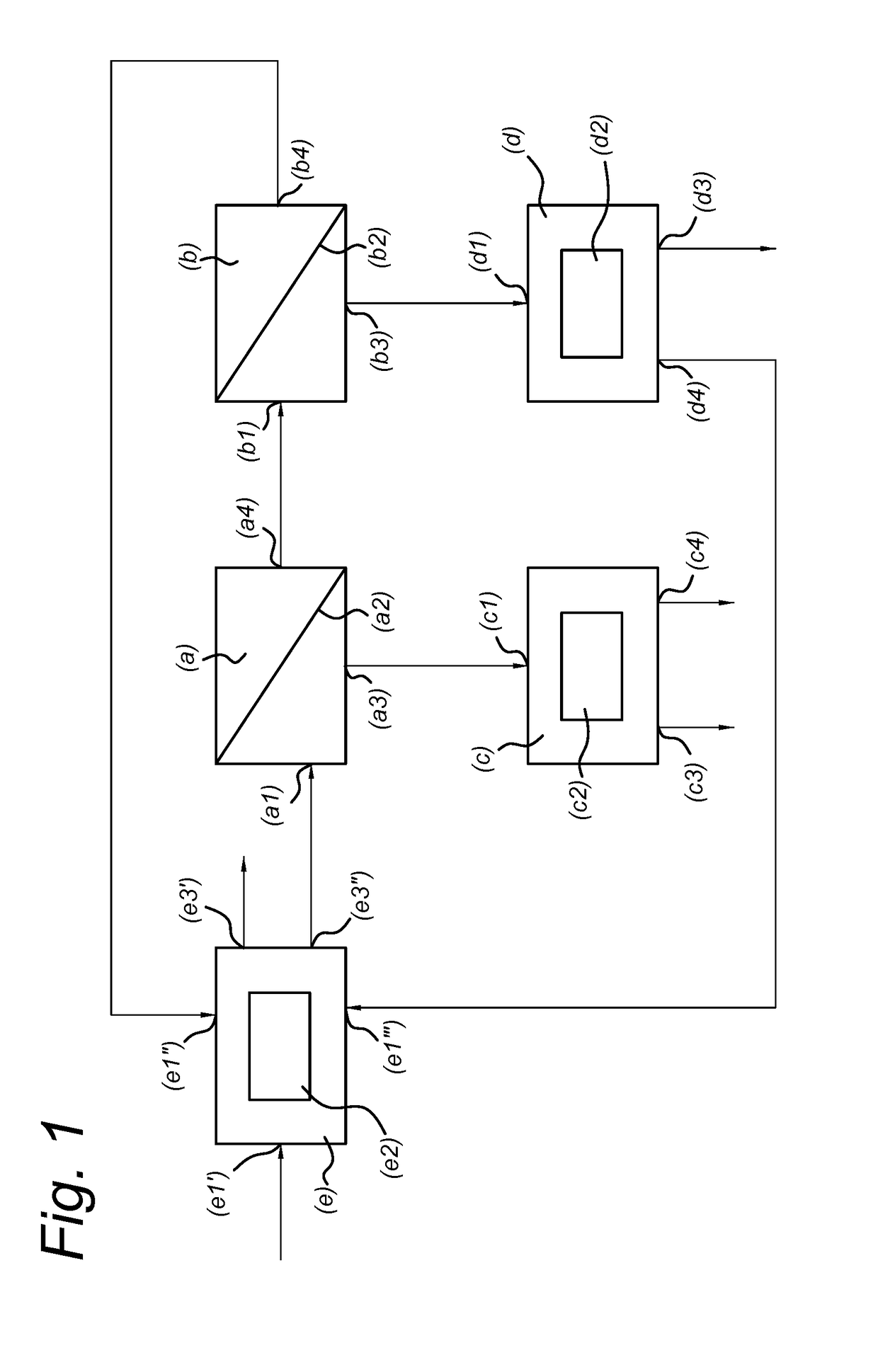
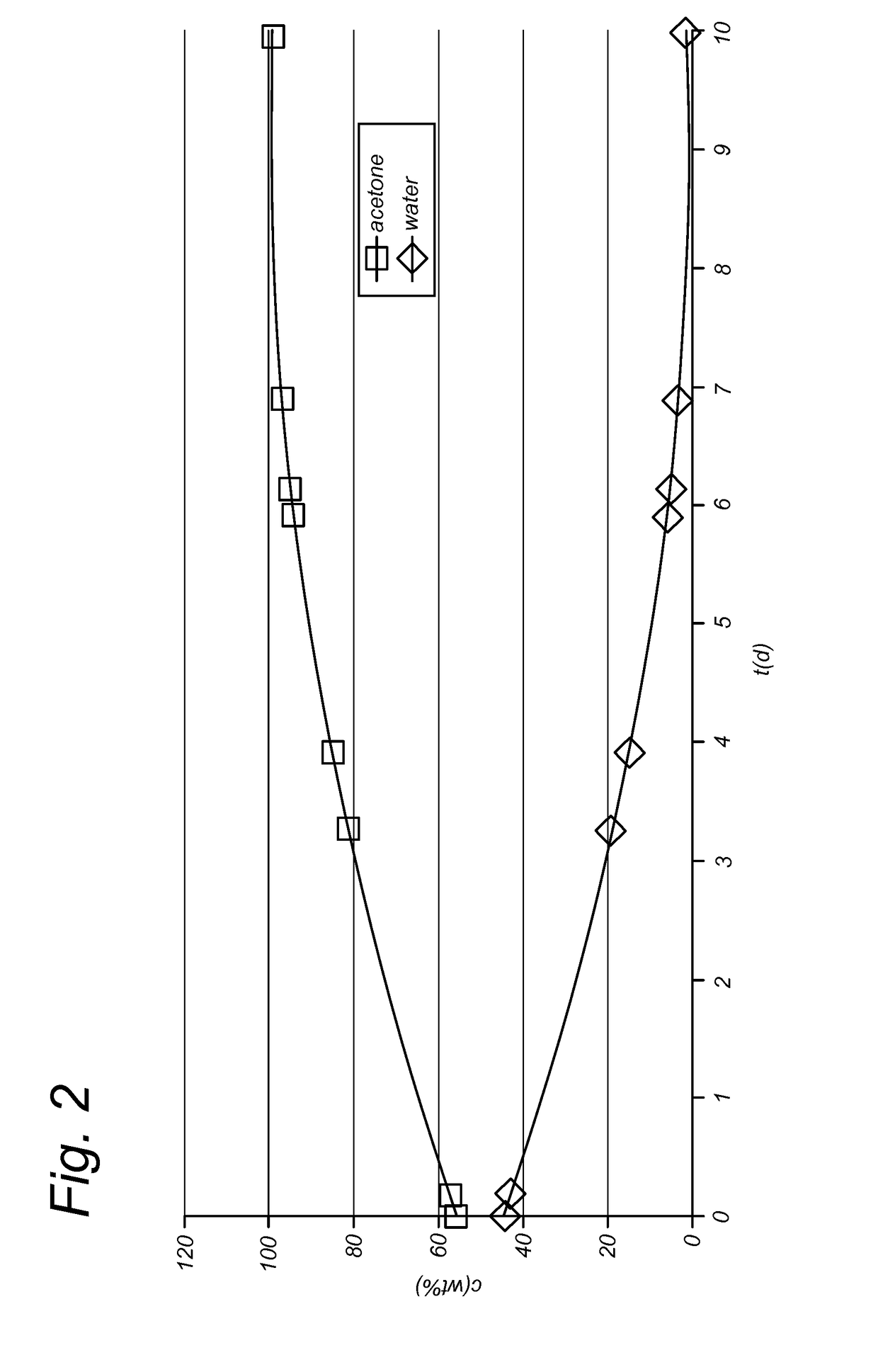
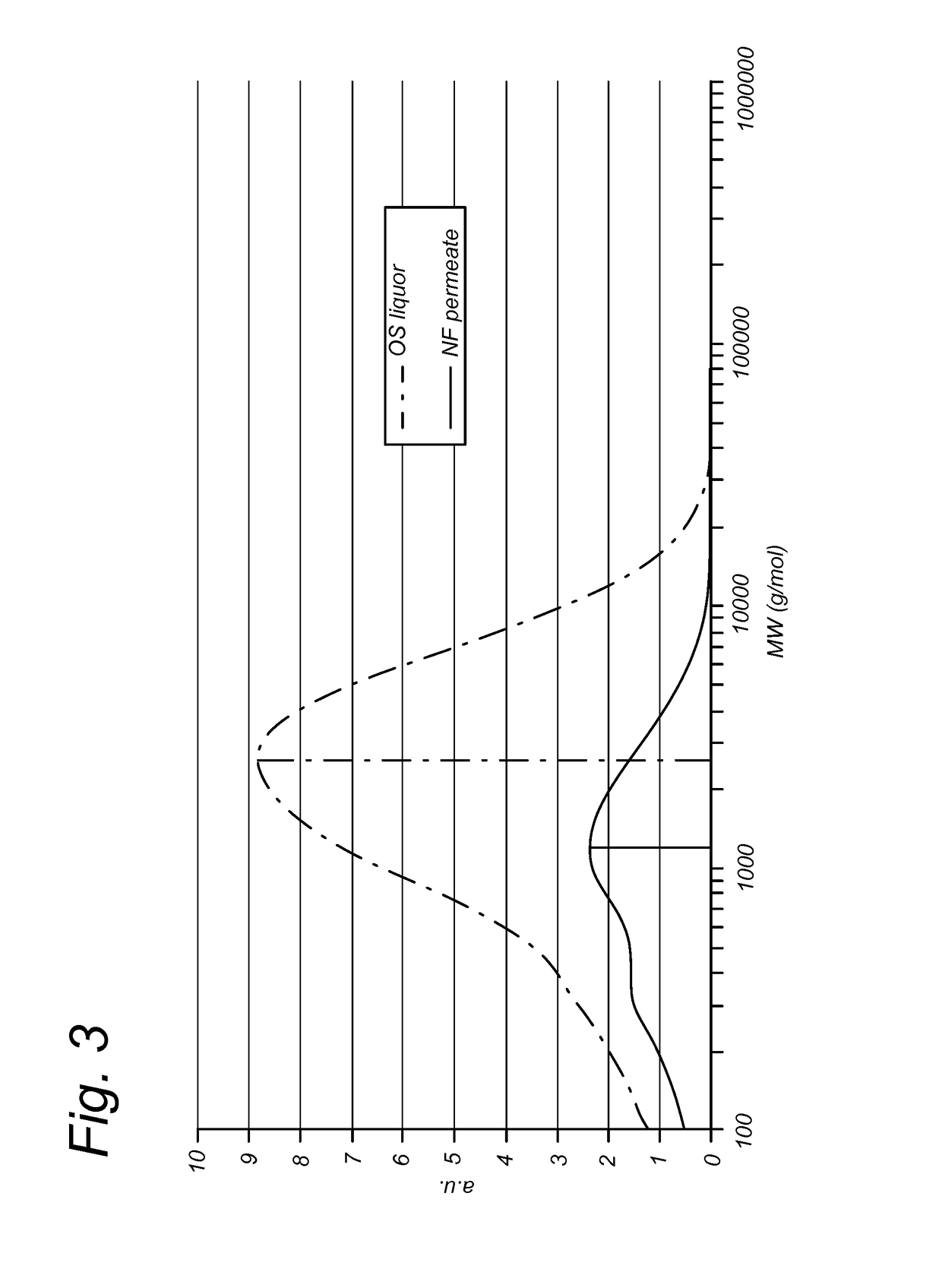
ActiveUS20180030555A1Speed up the processImprove energy efficiencyBiofuelsReverse osmosisCelluloseFractionation
The invention relates to an improved process for separating lignin and monomeric sugars from a liquor comprising lignin and monomeric sugars in a solvent mixture of water and at least one organic solvent, which employs membrane filtration techniques such as nanofiltration and selective water removal, preferably by permeation through a membrane which is selective for water molecules. The invention further relates to a modular system for executing the process according to the invention. The process and system according to the invention are particularly suitable to be incorporated with pre-treatment of lignocellulosic biomass, in particular by organosolv fractionation or solvolysis.
Owner:NEDERLANDSE ORG VOOR TOEGEPAST-NATUURWETENSCHAPPELIJK ONDERZOEK (TNO)
Method of removing the triphenylmethane protecting group
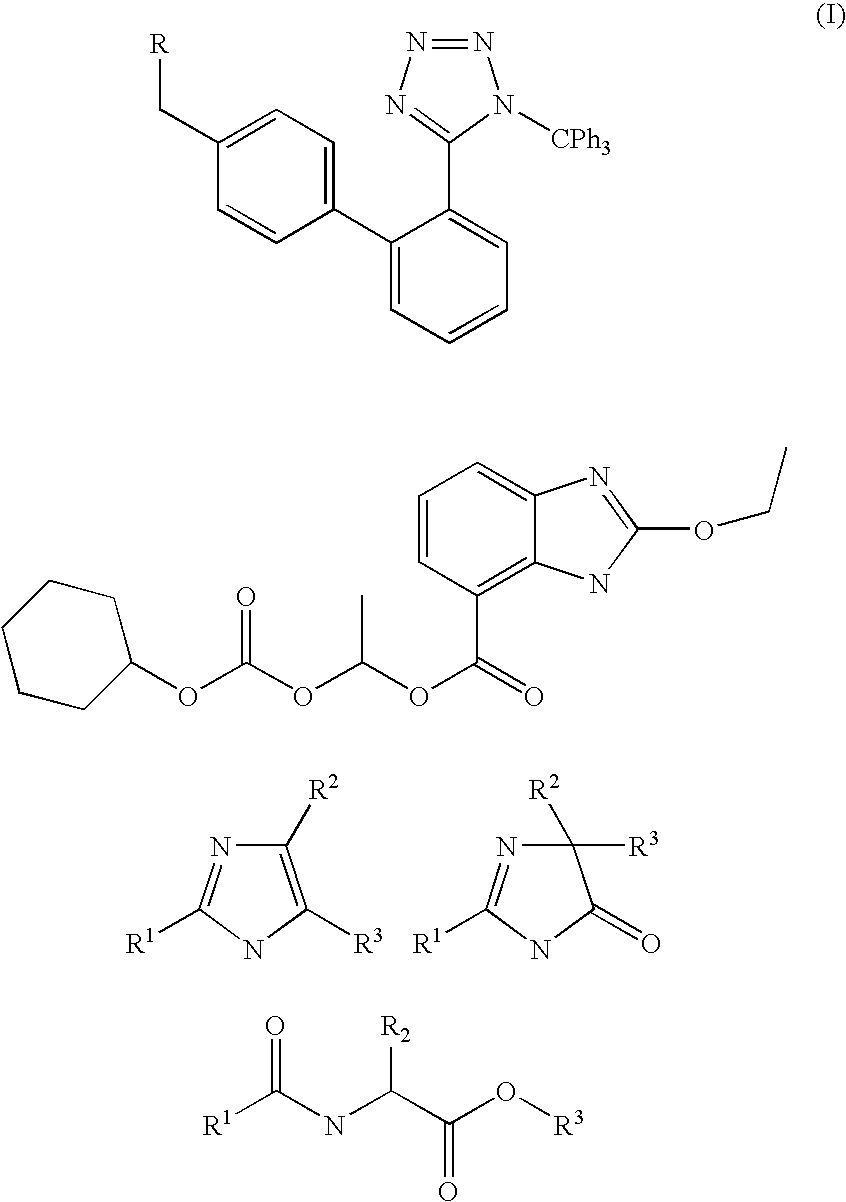
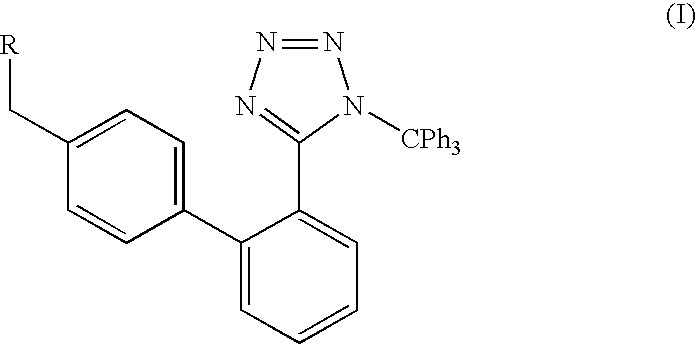
A method of removing the triphenylmethane protecting group from 1-triphenylmethy1-5-(4′-subst. methyl-1,1′-biphenyl-2-yl)-1H-tetrazoles of general formula I wherein R represents the groups of formulae and where R1, R2 and R3 can be H, a halogen, an unbranched or branched C1-C5 alkyl, C1-C5 hydroxyalkyl, C1-C5 alkoxy, C1-C5 alkoxymethyl or benzyl, or wherein R2 and R3 can form together a saturated or unsaturated C5-C7 ring, optionally an unsubstituted or substituted aromatic ring, is carried out by solvolysis in a simple anhydrous C1 to C5 alcohol in a neutral or slightly basic medium. The method is suitable for the preparation of drugs, such as the potassium salts of losartan, irbesartan or valsartan or candesartan cilexetil.
Owner:ZENTIVA AS
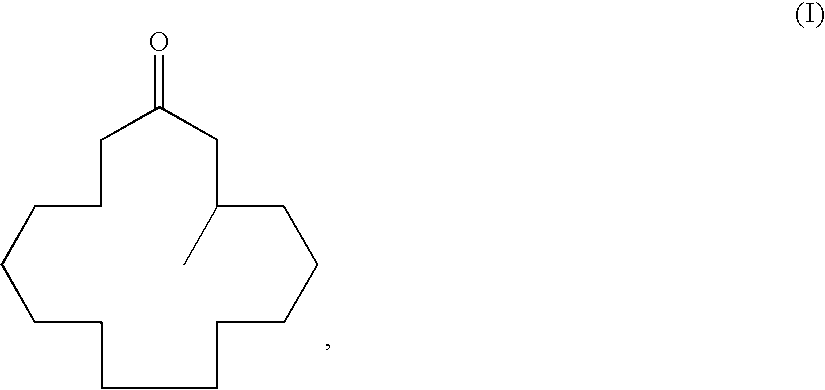
Optically active 3-methylcyclopentadecanone and method for producing intermediate thereof
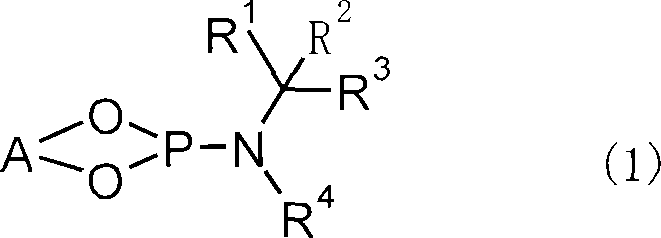
ActiveUS7728177B2High catalytic activityEfficient responseOrganic compound preparationGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsScavengerKetone
Disclosed is a method for producing an optically active 3-methylcyclopentadecan-1-one which is characterized in that 2-cyclopentadecen-1-one is subjected to a 1,4-conjugate addition reaction of a methyl group by using a methylated organic metal in the presence of a copper catalyst, an enol anion scavenger and a specific optically active phosphoramidite for obtaining an optically active 3-methyl-1-cyclopentadecene derivative, and then the thus-obtained 3-methyl-1-cyclopentadecene derivative is subjected to a solvolysis.
Owner:TAKASAGO INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
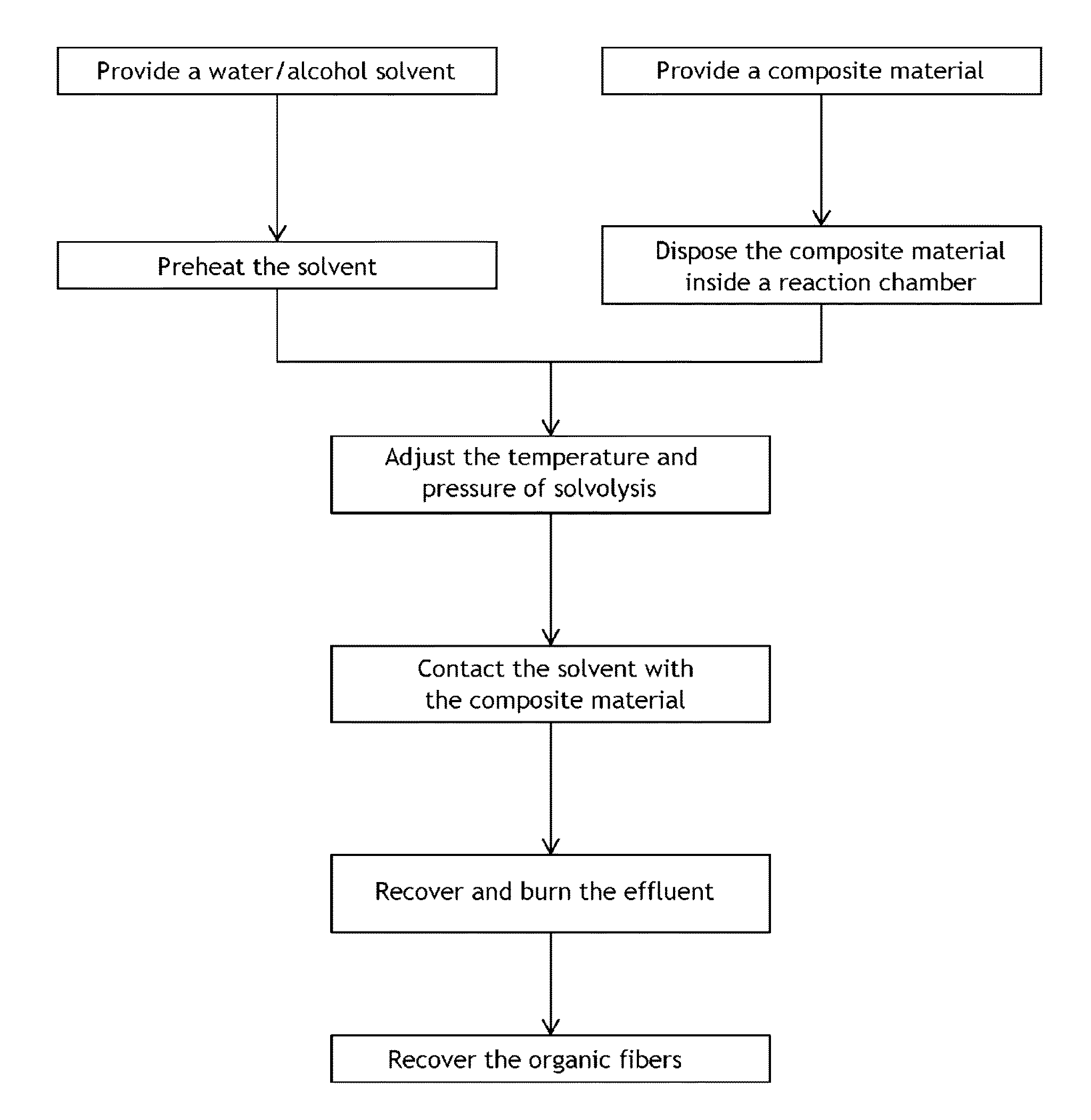
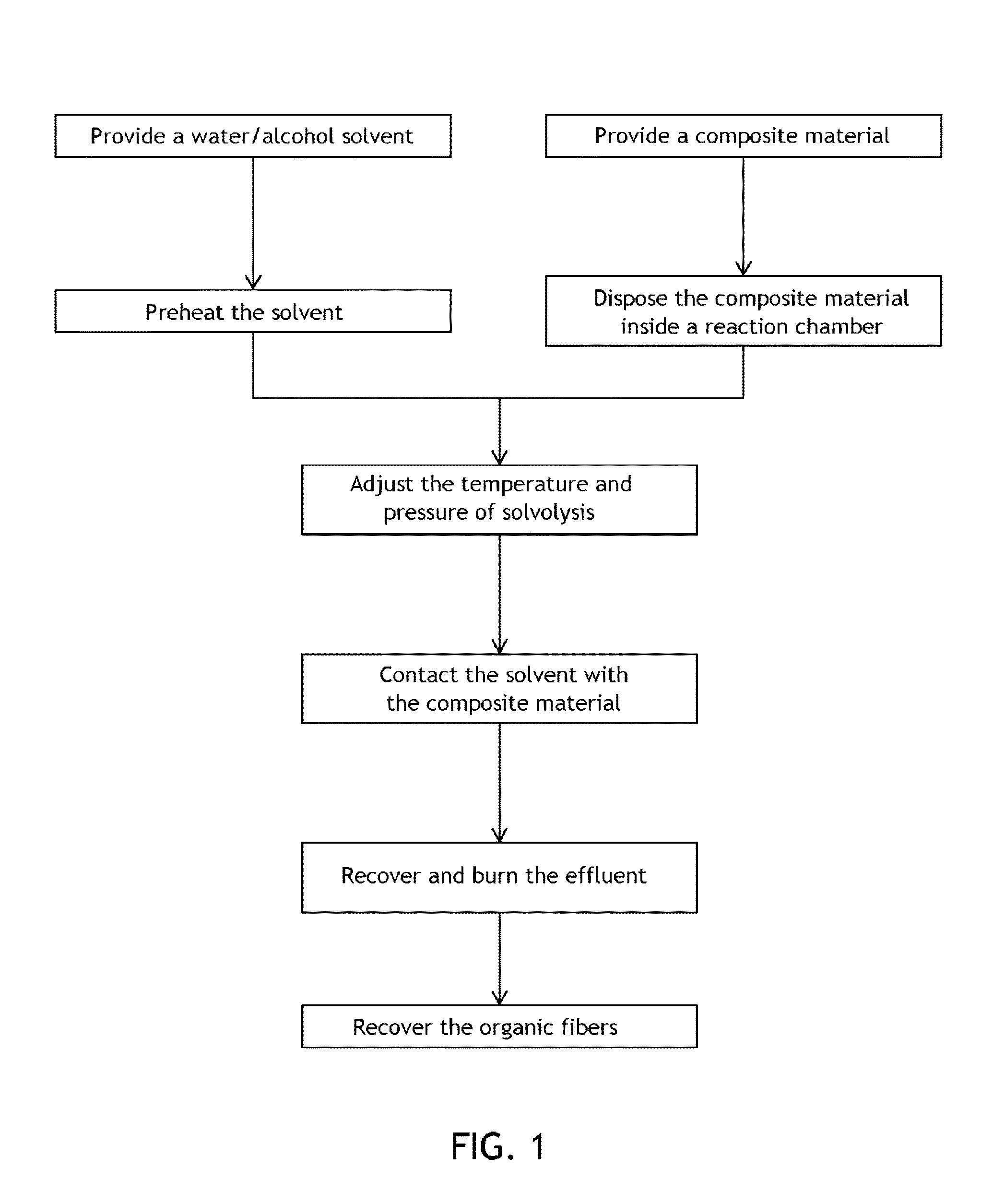
Method for recovering organic fibers from a composite material
The invention relates to a method for recovering organic fibers from a composite material comprising a polymer matrix and organic fibers, wherein the method comprises the following steps: providing a solution comprising a mixture of water and alcohol; placing the composite material inside a reactor; contacting the mixture and the composite material in order to perform a solvolysis reaction of the composite material; and recovering the organic fibers; wherein the pressure and the temperature in the reactor are adjusted such as to fall within the homogeneous sub-critical range of the phase diagram, within the super-critical range or near the critical point; and wherein the temperature is lower than the melting temperature of the organic fibers.
Owner:UNIV DE BORDEAUX +2
Selective enzymatic esterification and solvolysis of epimeric vitamin D analog and separation of the epimers
Provided is a method of selectively enzymatically esterifying or selectively enzymatically solvolyzing epimers of analogs of vitamin D having a stereogenic center at C-24 that has a free or esterified OH group. The metod can be used, for example, for separating mixed epimers of the vitamin D analog.
Owner:TEVA PHARMA IND LTD
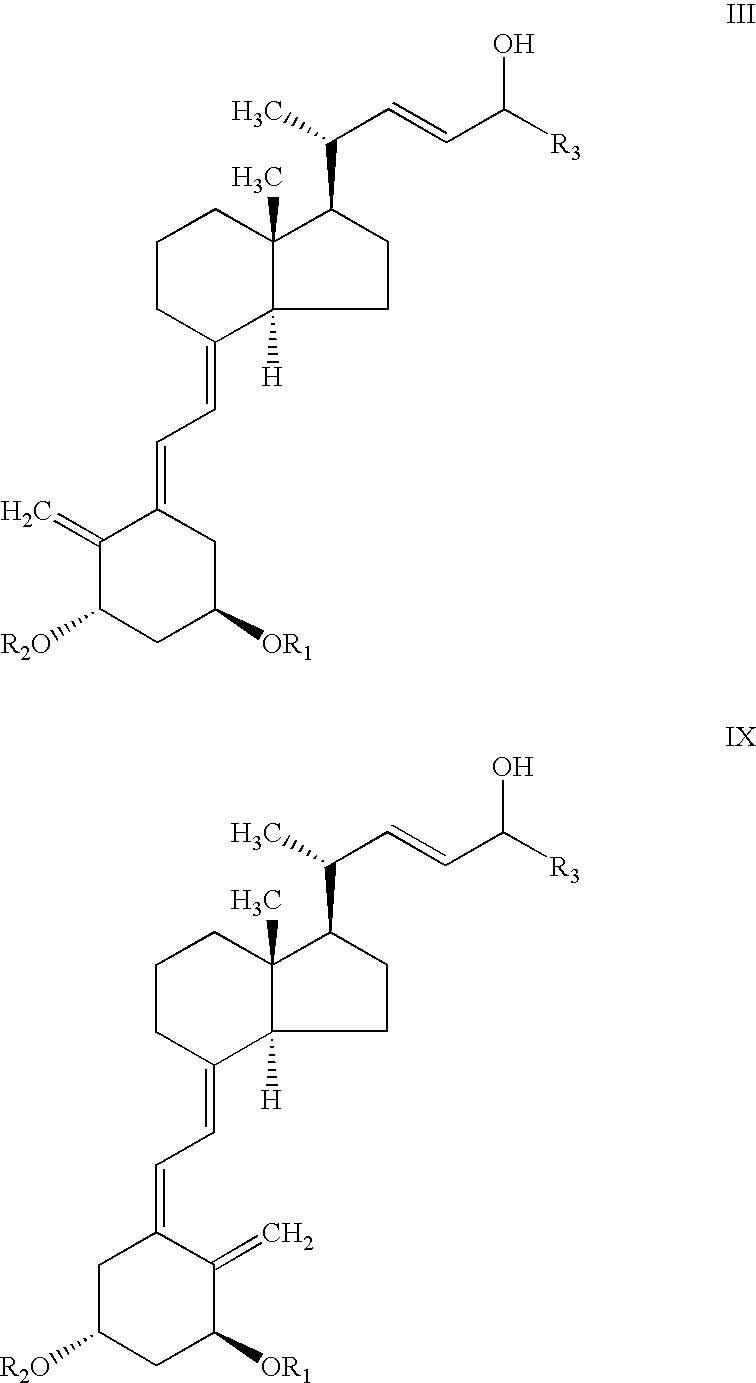
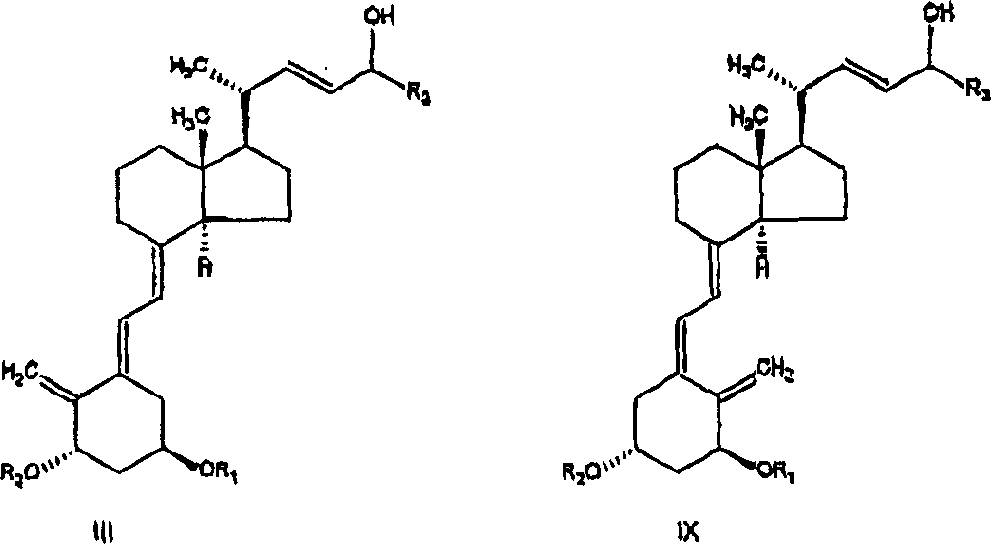
Process for preparing optically active 2-[6-(hydroxy-methyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl] acetic acid derivatives
InactiveUS20050080277A1Easy to manufactureImprove efficiencyOrganic chemistryFermentationAcetic acidAcid derivative
The present invention is to provide a production technology by which an optically active 2-[6-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl]acetic acid derivative, which are of value as pharmaceutical intermediates, can be produced from inexpensive and readily available starting materials without using any extraordinary equipment such as an ultra-low-temperature reactor. The present invention is a production process of an optically active 2-[6-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl]acetic acid derivative which comprises reacting an enolate, prepared by permitting a base or a 0-valent metal to act on an acetic acid ester derivative with (S)-β-hydroxy-γ-butyrolactone at a temperature not lower than −30° C. to give a dihydroxyoxohexanoic acid derivative, treating the same with an acylating agent in the presence of a base to produce a dihydroxyoxohexanoic acid monoacyl derivative, reducing this compound with a microorganism to produce a trihydroxyhexanoic acid monoacyl derivative, treating this compound with an acetal-forming reagent in the presence of an acid catalyst to produce an acyloxymethyldioxanylacetic acid derivative, and finally, subjecting this compound to solvolysis in the presence of a base.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Method of enzymatic optical resolution of racemic 4-hydroxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline
InactiveUS7972836B2High optical purityHigh yieldRespiratory disorderFermentationHydrogen atomEnantiomer
The present invention relates to a method for preparing an optically active 4-hydroxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline compound [I], which comprises the steps of:treating a racemic 4-hydroxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline compound represented by general formula [I]:[wherein R1 represents a hydrogen atom or a protecting group for amino group.]with an enzyme having an ability of selectively or preferentially acylating one enantiomer of the racemic compound [I] in the presence of an acyl donor; andif necessary, subjecting the reaction product to solvolysis.
Owner:MITSUBISHI TANABE PHARMA CORP
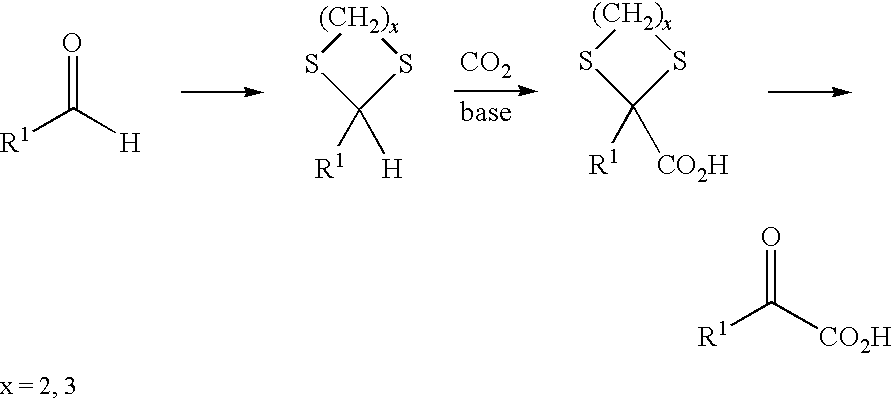
Process for preparing α-keto acids and derivatives thereof
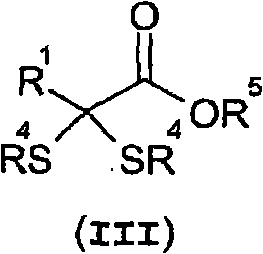
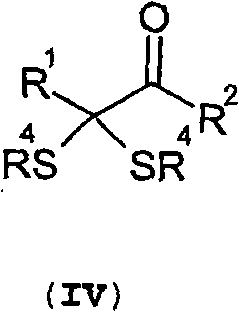
A method for preparing α-keto acids, especially α-ketomethionine, and / or derivatives thereof, whereby an aldehyde is reacted with thiols to give a corresponding dithioacetal, the dithioacetal formed, is reacted with an electrophile in the presence of a strong base, and the resulting α,α-(dithio)carboxylic acid is solvolyzed with acid-catalysis to release thiol and give the α-keto acid or a derivative thereof. Umpolung of aliphatic or aromatic aldehydes is effected by reaction with thiols.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
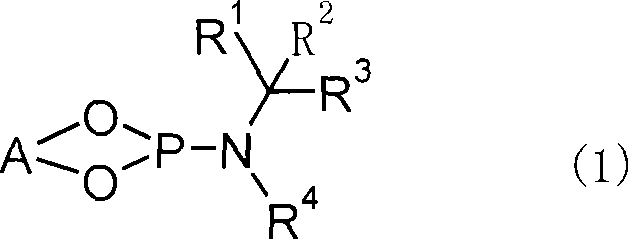
Optically active 3-methylcyclopentadecanone and method for producing intermediate thereof
InactiveCN101166708AEasy to manufactureSimple structureOrganic compound preparationGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsScavengerCopper
Owner:TAKASAGO INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
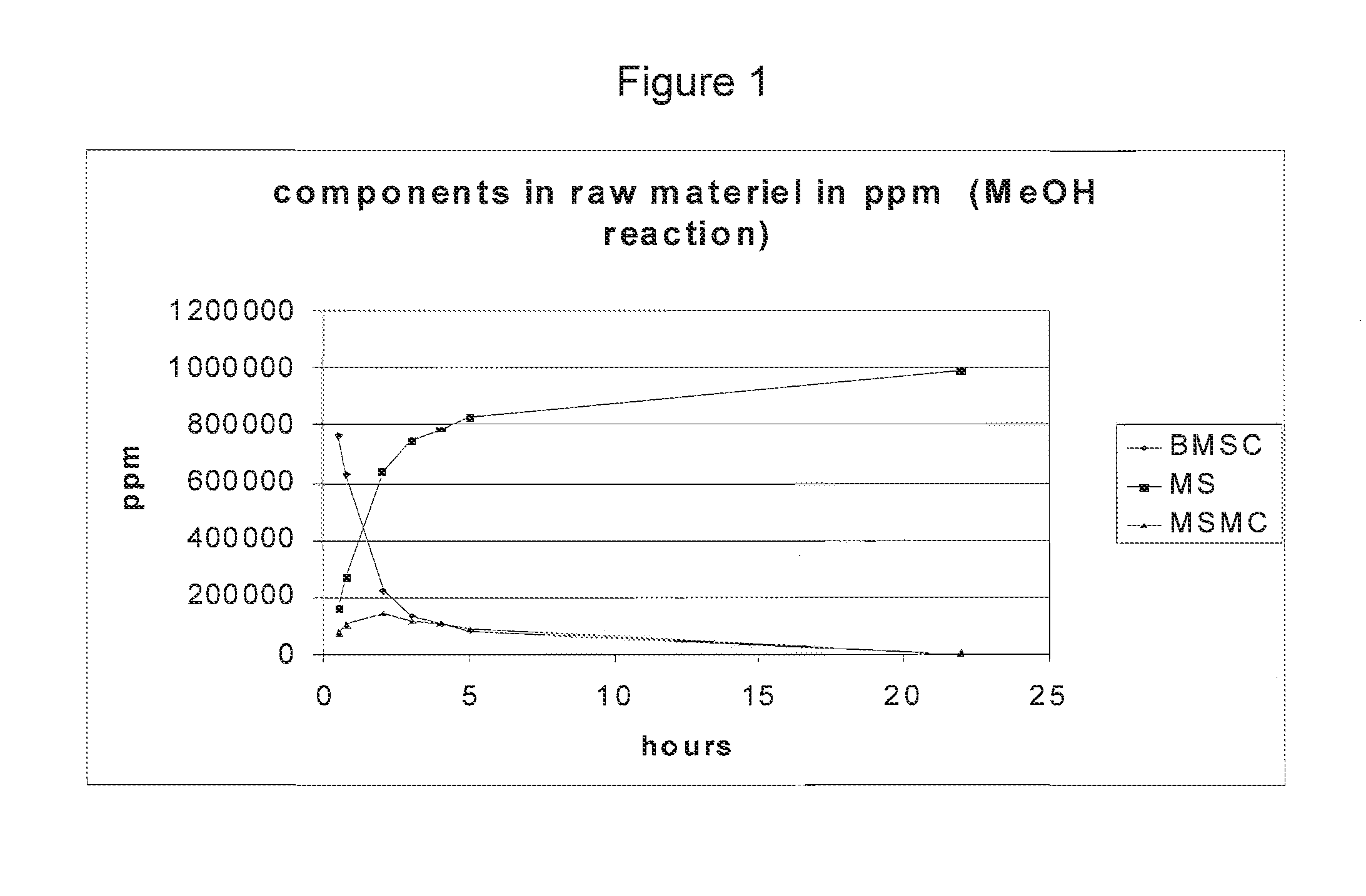
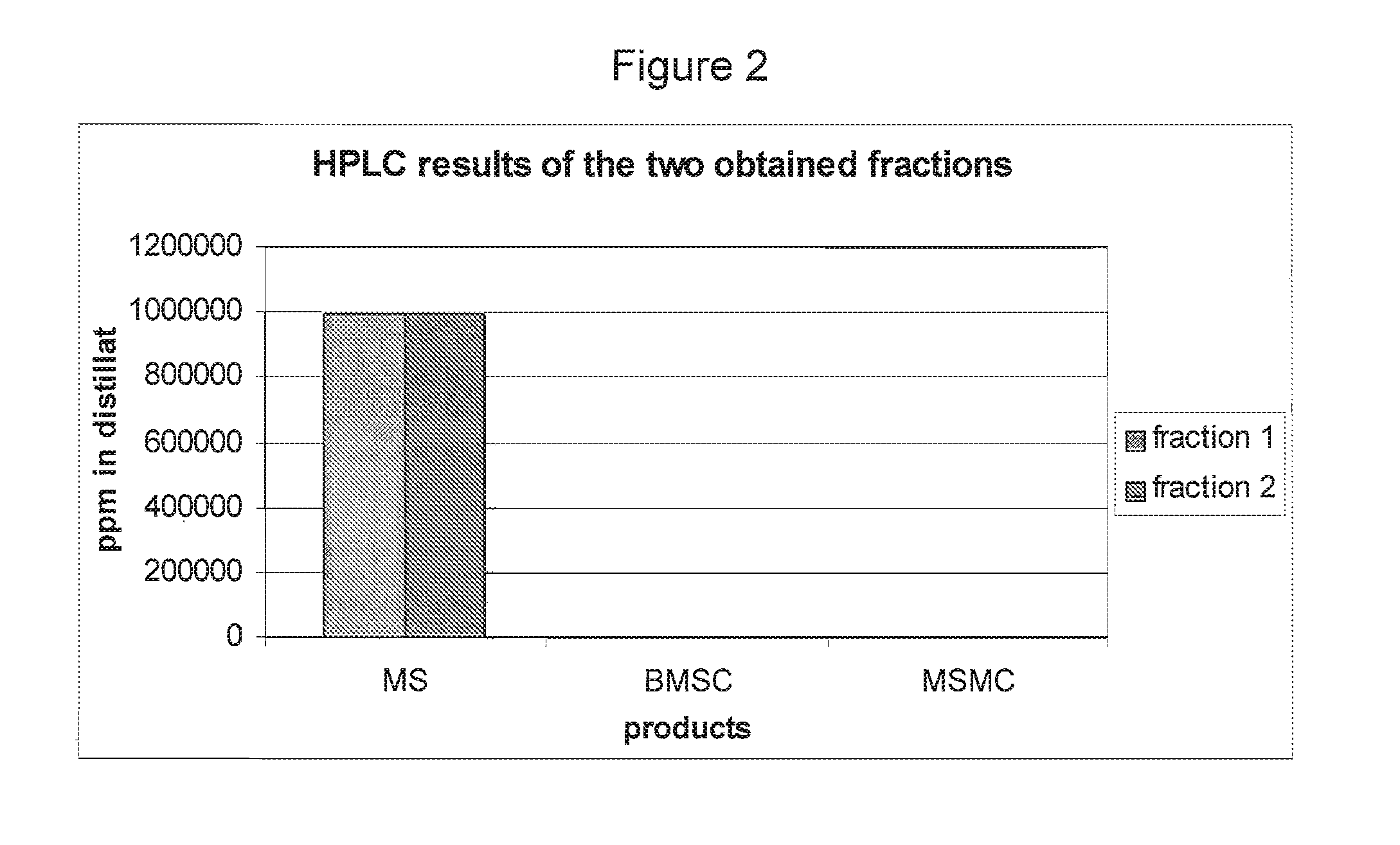
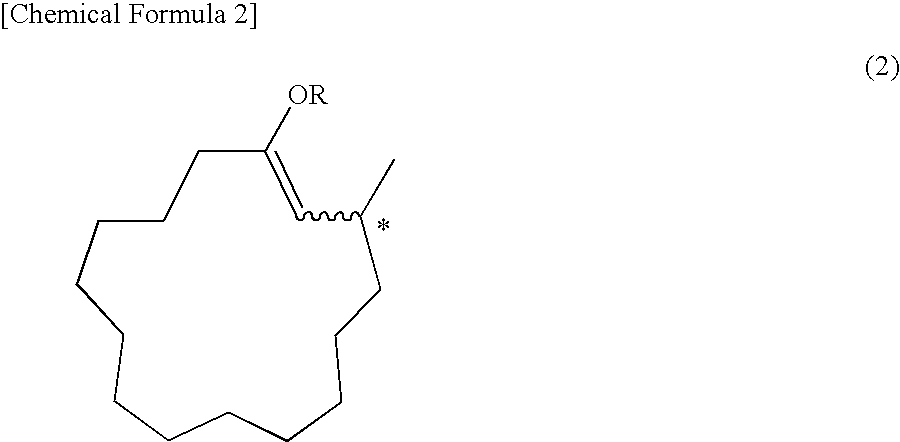
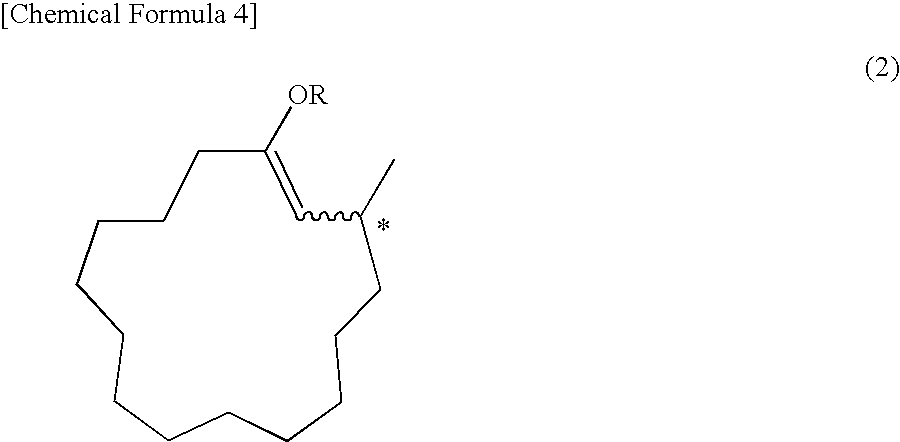
Process for manufacturing composition of solvolysis product of ethylene-vinyl ester copolymer
Processes for manufacturing a composition of a solvolysis product of an ethylene-vinyl ester copolymer, which comprises: conducting solvolysis of an ethylene-vinyl ester copolymer (A′) and a modified ethylene-vinyl ester copolymer (B′) comprising a unit derived from a compound represented by the general formula (2) in one system to manufacture the composition of a solvolysis product of an ethylene-vinyl ester copolymer comprising a solvolysis product (A) of the ethylene-vinyl ester copolymer and a solvolysis product (B) of the modified ethylene-vinyl ester copolymer comprising a unit represented by the general formula (1), wherein a ratio of an ethylene content (B′) / (A′) of copolymer (A′) and copolymer (B′) in conducting solvolysis is 1 or more, and a blending ratio (B′) / (A′) of the ethylene-vinyl ester copolymer (A′) and the modified ethylene-vinyl ester copolymer (B′) is from 50 / 50 to 1 / 99 by weight:
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Pretreated epoxidation catalyst and a process for producing an olefin therewith
InactiveUS8735612B2Low equipment costReduce energy consumptionGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsMolecular sieve catalystsTitaniumSolvent
Owner:BLUE CUBE IP
Process for preparing N-hydroxyalkyl compound and isocynauric acid tri (2-ethoyl) ester composition
InactiveCN1428331APrevent discolorationInhibition formationOrganic chemistryHigh resistanceHeat resistance
The object of the present invention is to provide a process for producing an N-hydroxyalkyl compound which is not only conducive to suppression of the discoloration due to decomposition of the solvent and suppression of formation of impurities originating from the catalyst but also insures a high selectivity of reaction and a tris(2-hydroxyethyl) isocyanurate composition suppressed in discoloration, lean in impurity, with high resistance to heat and, hence, of good quality. The present invention is directed to a process for producing an N-hydroxyalkyl compound comprising the reaction of an amido or imido group-containing compound and an epoxy compound in the presence of a catalyst, wherein the catalyst is a solid ion exchanger.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
Method for the production of ketoacids and their derivatives
InactiveCN101687753AImprove protectionOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationThioenolThiol
A method for the production of a-ketoacids, in particular of a-ketomethionine, and their derivatives is described, as also is the use of thiols for reversing the polarity of aliphatic or aromatic aldehydes. In this method, a) an aldehyde is reacted with thiols to give the corresponding dithioacetal, and b) the resultant dithioacetal then reacts with an electrophile in the presence of a base and after hydrolysis to give an a,a-(dithio)carboxylic acid and c) the a,a-(dithio)carboxylic acid is then reacted via acid-catalysed solvolysis to give the a-ketoacid or its derivatives, with liberation of thiol.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Process for removing titanium oxide or red oxide from ethylene glycol
InactiveUS6645445B1Efficient removalIron oxides/hydroxidesOrganic compound preparationPolyesterDecomposition
A process for efficiently removing titanium oxide or red oxide from an ethylene glycol solvolysis product of a polyester containing titanium oxide or red oxide. The process comprises the steps of:(1) mixing at least one calcium compound selected from the group consisting of calcium oxide, calcium carbonate and calcium hydroxide with a polyester decomposition product containing titanium oxide which is an ethylene glycol solvolysis product of a polyester containing titanium oxide to agglomerate titanium oxide contained in the polyester decomposition product, or mixing titanium oxide with a polyester decomposition product containing red oxide which is an ethylene glycol solvolysis product of a polyester containing red oxide to agglomerate red oxide contained in the polyester decomposition product; and(2) subjecting the agglomerates to solid-liquid separation to remove titanium oxide or red oxide from the polyester decomposition product.
Owner:PET REBIRTH CO LTD
Process for manufacturing composition of solvolysis product of ethylene-vinyl ester copolymer
Processes for manufacturing a composition of a solvolysis product of an ethylene-vinyl ester copolymer, which comprises: conducting solvolysis of an ethylene-vinyl ester copolymer (A′) and a modified ethylene-vinyl ester copolymer (B′) comprising a unit derived from a compound represented by the general formula (2) in one system to manufacture the composition of a solvolysis product of an ethylene-vinyl ester copolymer comprising a solvolysis product (A) of the ethylene-vinyl ester copolymer and a solvolysis product (B) of the modified ethylene-vinyl ester copolymer comprising a unit represented by the general formula (1), wherein a ratio of an ethylene content (B′) / (A′) of copolymer (A′) and copolymer (B′) in conducting solvolysis is 1 or more, and a blending ratio (B′) / (A′) of the ethylene-vinyl ester copolymer (A′) and the modified ethylene-vinyl ester copolymer (B′) is from 50 / 50 to 1 / 99 by weight:
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
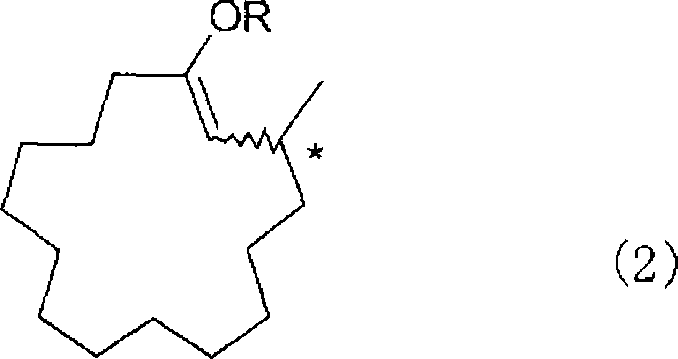
Method of producing macrocyclic ketone, and intermediate thereof
ActiveUS7479574B2Increase concentrationHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsScavengerKetone
A process for producing muscone by methyl addition to the 1,4-conjugation of 2-cyclopentadecenone. By the process, muscone is produced in high yield not under reaction condition including an extremely low temperature and a low concentration but under practical condition. The process comprises subjecting 2-cyclopentadecenone to a 1,4-conjugation addition reaction with an organometallic methylation reagent in the presence of a copper or nickel catalyst and an enol anion scavenger to obtain a 3-methyl-1-cyclopentadecene derivative represented by General Formula (II) and then solvolyzing the enol moiety of the 3-methyl-1-cyclopentadecene derivative to obtain muscone.
Owner:TAKASAGO INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
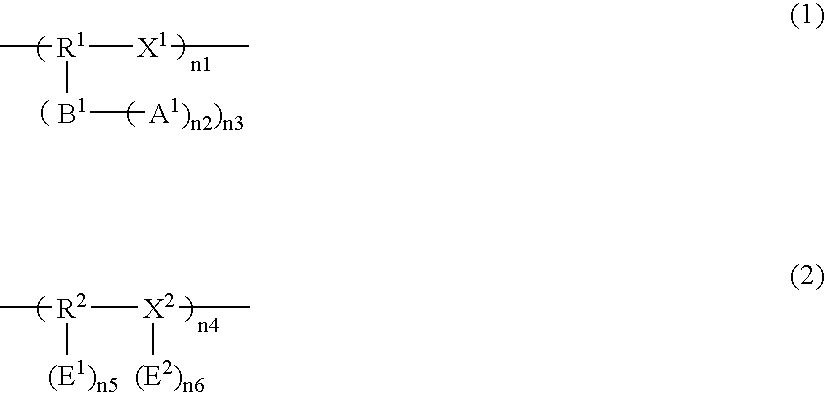
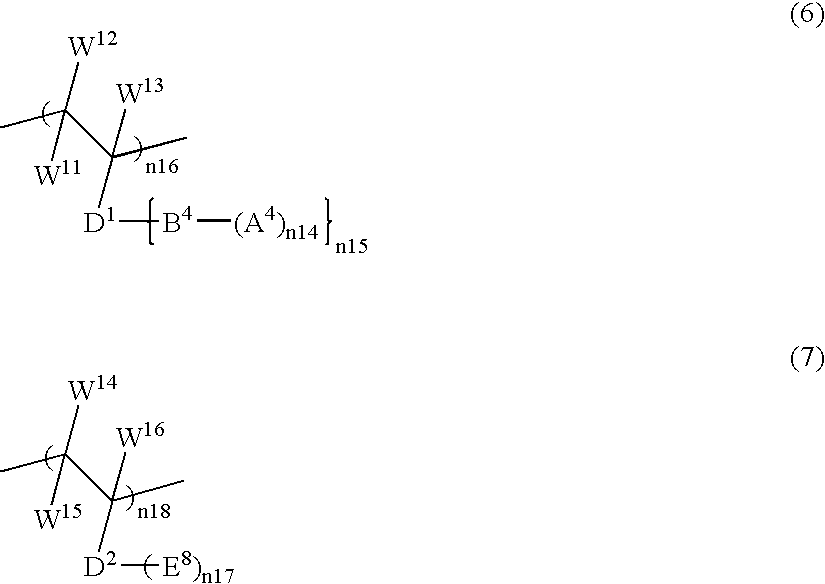
![Process for preparing optically active 2-[6-(hydroxy-methyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl] acetic acid derivatives Process for preparing optically active 2-[6-(hydroxy-methyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl] acetic acid derivatives](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/89ae92db-da16-4ac3-989c-170d79ca11c3/US07094594-20060822-C00001.png)
![Process for preparing optically active 2-[6-(hydroxy-methyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl] acetic acid derivatives Process for preparing optically active 2-[6-(hydroxy-methyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl] acetic acid derivatives](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/89ae92db-da16-4ac3-989c-170d79ca11c3/US07094594-20060822-C00002.png)
![Process for preparing optically active 2-[6-(hydroxy-methyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl] acetic acid derivatives Process for preparing optically active 2-[6-(hydroxy-methyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl] acetic acid derivatives](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/89ae92db-da16-4ac3-989c-170d79ca11c3/US07094594-20060822-C00003.png)
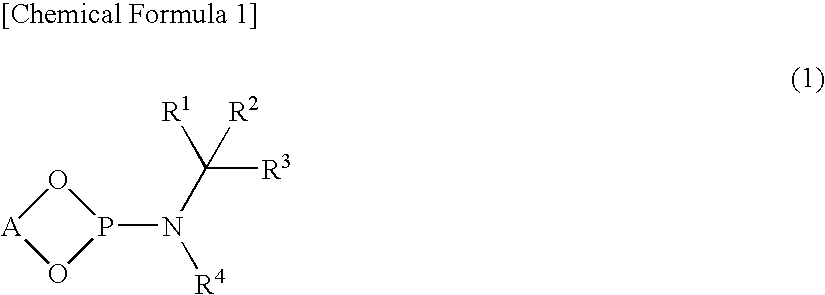
![Process for preparing optically active 2-[6-(hydroxy-methyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl] acetic acid derivatives Process for preparing optically active 2-[6-(hydroxy-methyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl] acetic acid derivatives](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/e1d29781-cd6b-412f-a42a-451e24f40515/US20050080277A1-20050414-C00001.png)
![Process for preparing optically active 2-[6-(hydroxy-methyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl] acetic acid derivatives Process for preparing optically active 2-[6-(hydroxy-methyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl] acetic acid derivatives](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/e1d29781-cd6b-412f-a42a-451e24f40515/US20050080277A1-20050414-C00002.png)
![Process for preparing optically active 2-[6-(hydroxy-methyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl] acetic acid derivatives Process for preparing optically active 2-[6-(hydroxy-methyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl] acetic acid derivatives](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/e1d29781-cd6b-412f-a42a-451e24f40515/US20050080277A1-20050414-C00003.png)