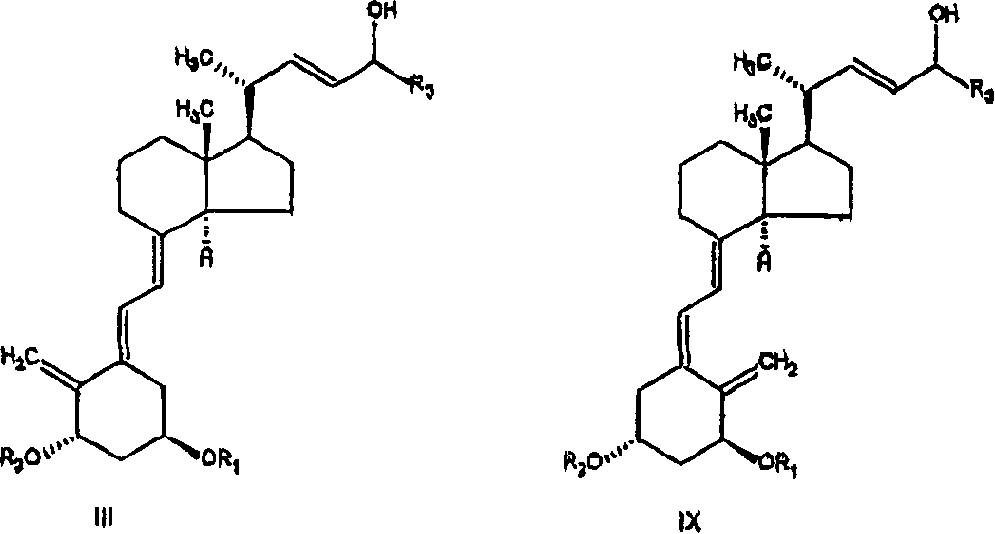
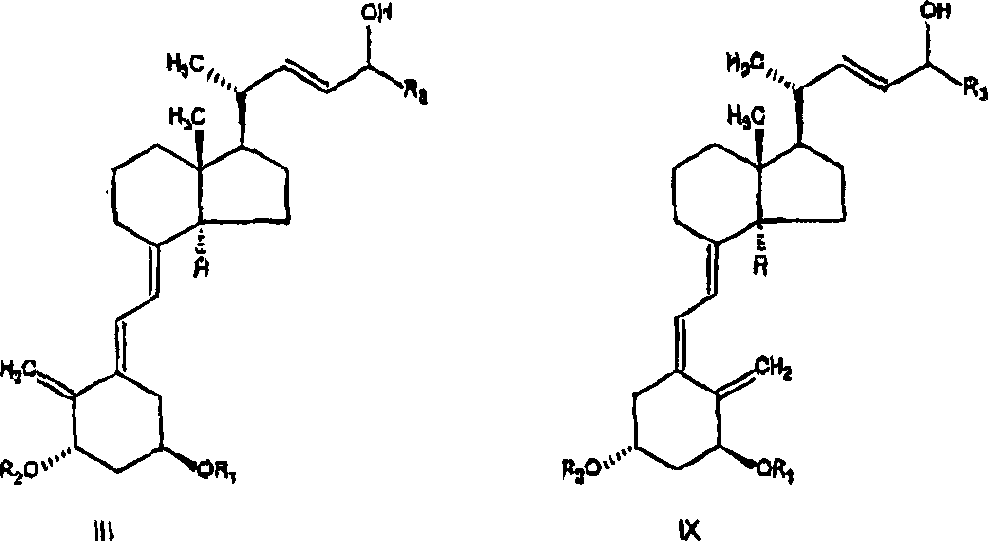
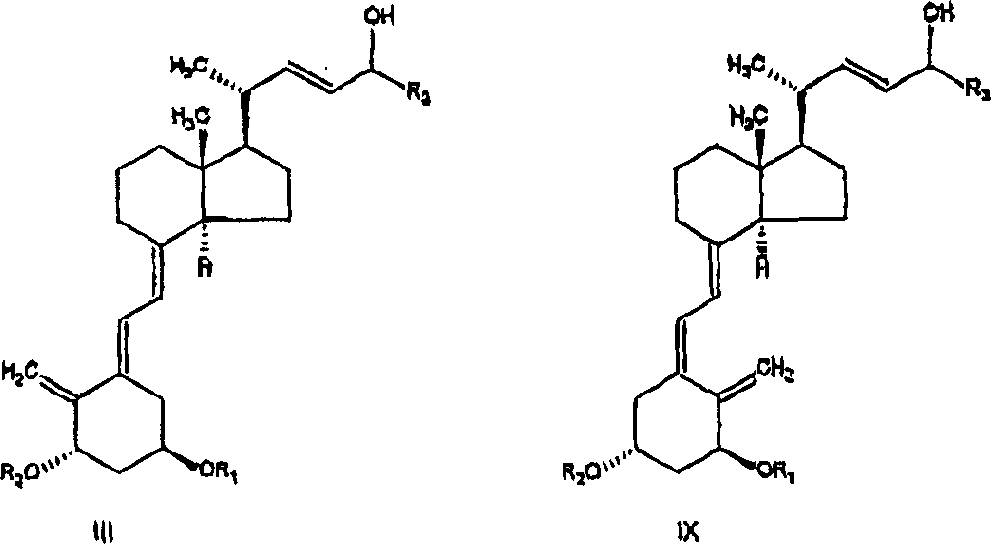
Selective enzymatic esterification and solvolysis of epimeric vitamin D analog and separation of the epimers
A technology for epimers and vitamins, which is applied in the field of separation of mixed epimers of vitamin D analogues, and can solve problems such as difficult effective separation and close retention time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0071] Example 1 - Selective enzymatic esterification
[0072] to the stirred R 1 = R 2 = tert-butyldimethylsilyl and R 3 =C-24 epimer of structure III of the cyclopropyl alcohol mixture (20gr, 31.2mmol) and vinyl acetate (5.8ml, 62.4mmol) in n-hexane (60ml) was added 0.56gr of Alcaligenes Is lipase. The mixture was stirred at 25 ± 3°C for 3 hours, after which HPLC analysis indicated essentially complete conversion of epimer C-24(R) to acetate. Residual unesterified C-24(S) alcohol was >99% diastereomeric excess (HPLC). The solution was filtered and concentrated to dryness. Chromatography of the residue on pretreated silica gel, eluting with 5% ethyl acetate in n-hexane followed by ethyl acetate, gave the C-24 acetate compound IV (11gr) and the C-24 alcohol compound V ( 7.4gr).
[0073] compound
Embodiment 2
[0074] Example 2 - Selective enzymatic esterification
[0075] 0.5 g of Alcaligenes lipase was immobilized on 4 g Eupergit C (Rohm, Germany) according to known methods recommended by the supplier. To the R containing 0.3g (0.47mmol) 1 = R 2 = tert-butyldimethylsilyl and R 3 = cyclopropyl C-24 epimer alcohol mixture III (65:35 isomer ratio), 0.43ml (4.7mmol) vinyl acetate and 3.57ml n-hexane in a round bottom flask was added 400mg of immobilized enzyme. The mixture was stirred at 35°C for 4 hours, after which HPLC analysis indicated the presence of 30% Compound IV, 35% Compound VIII and 35% unreacted Compound V.
Embodiment 3
[0076] Example 3 - Selective enzymatic esterification
[0077] To the R containing 100mg (0.16mmol) 1 = R 2 = tert-butyldimethylsilyl and R 3 = Mixed C-24 epimers (65:35 isomer ratio) of the C-24 alcohol of structure III of cyclopropyl, 0.044 ml (0.47 mmol) of vinyl acetate and 1.5 ml of diisopropyl ether 10 mg of Alcaligenes lipase was added to the vial. The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 2 hours, after which HPLC analysis indicated the presence of 65% compound IV and 35% compound V.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com